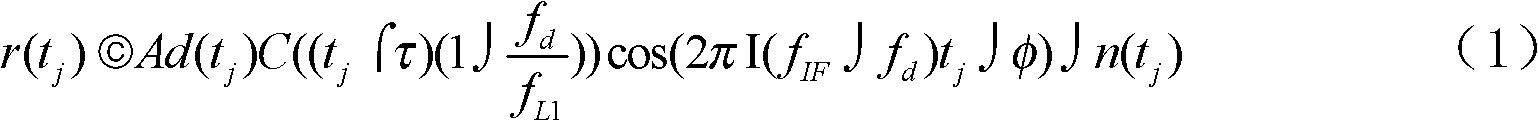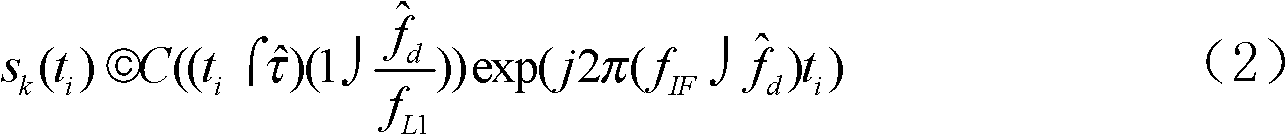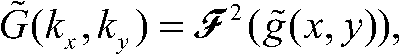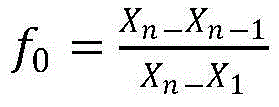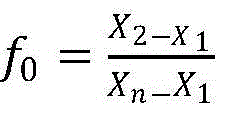Patents
Literature
272 results about "Zero padding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
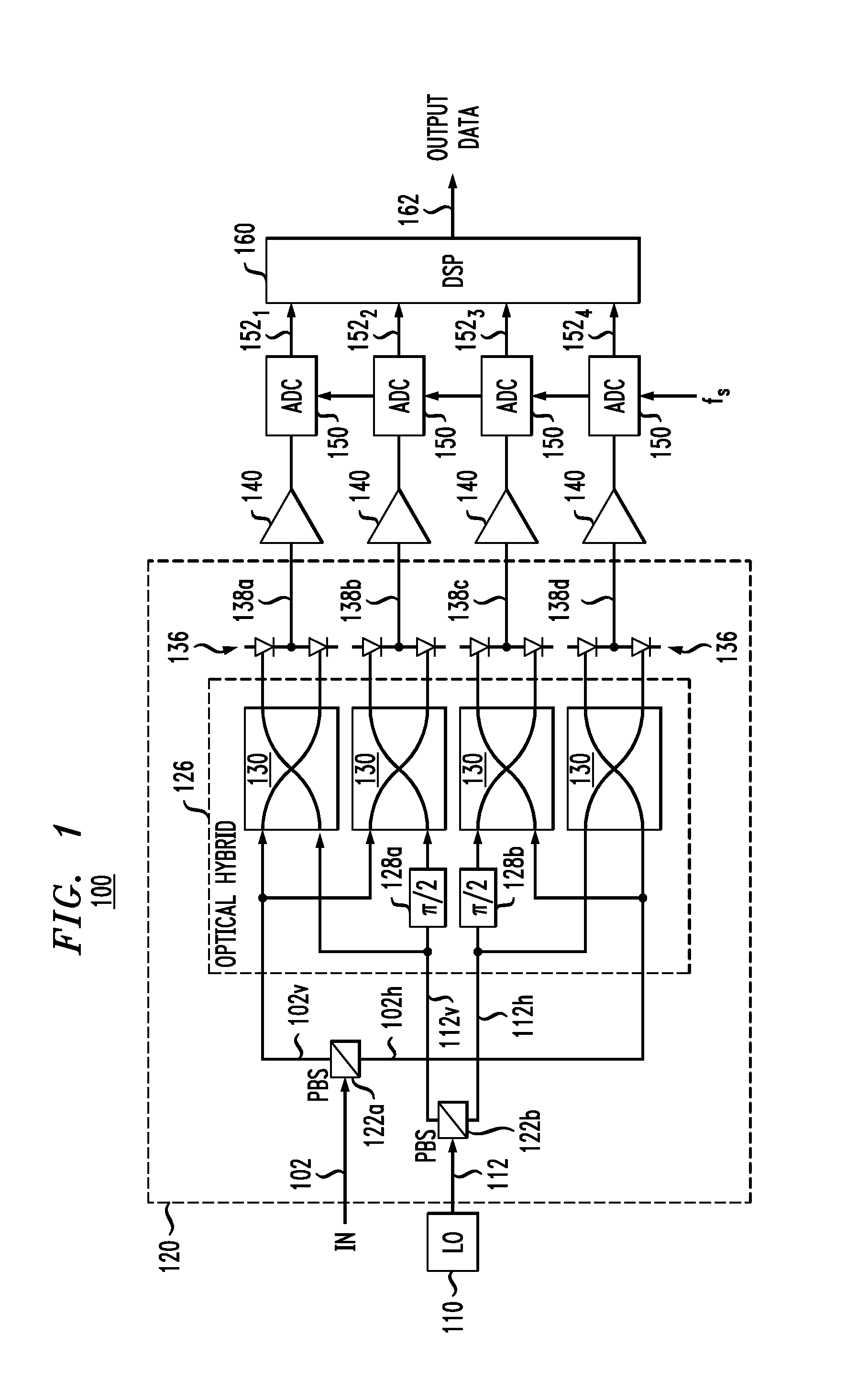
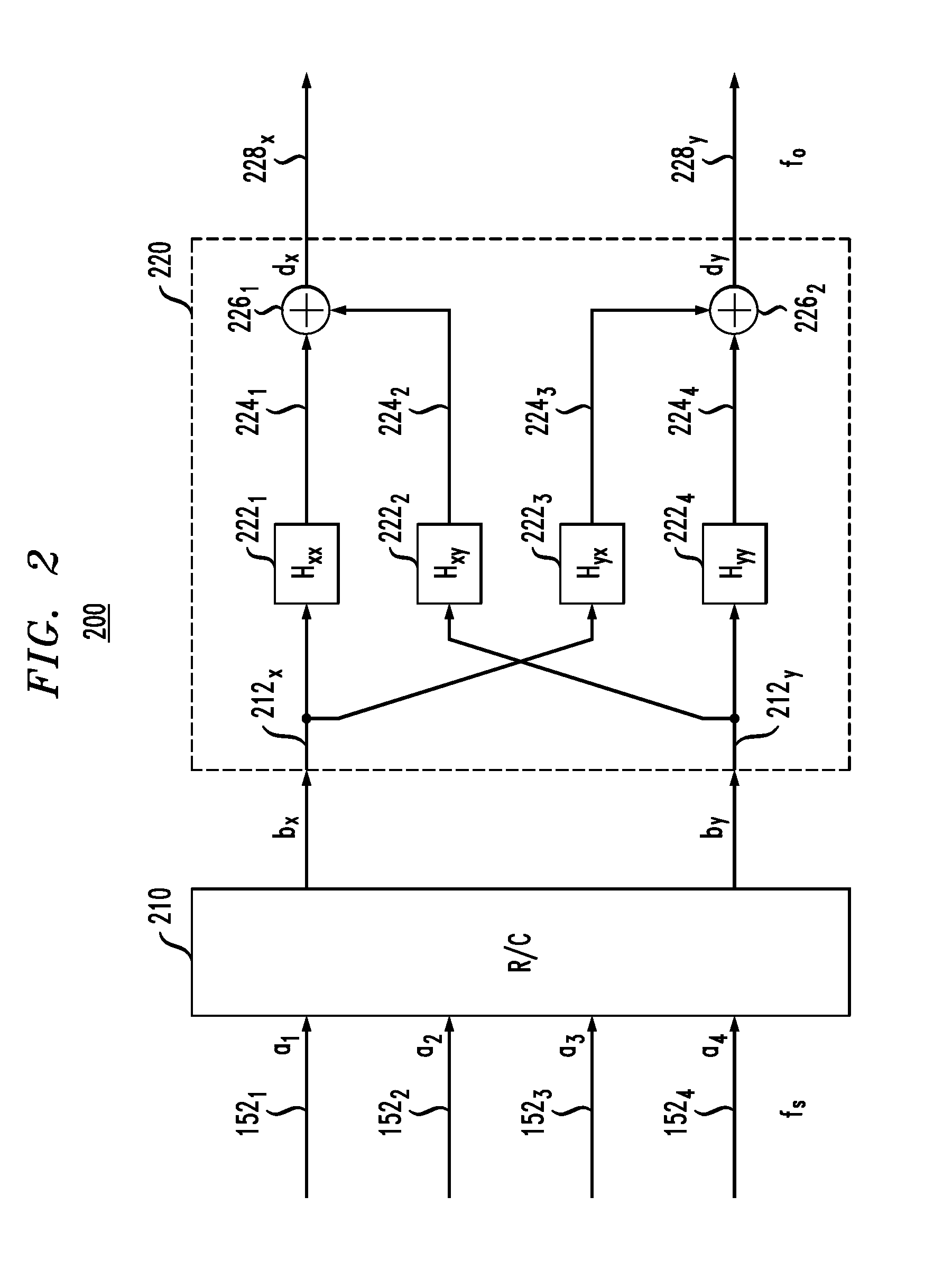
Transmitting apparatus and puncturing method thereof
InactiveUS20150082118A1Improve decoding performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionLow-density parity-check codeLow density
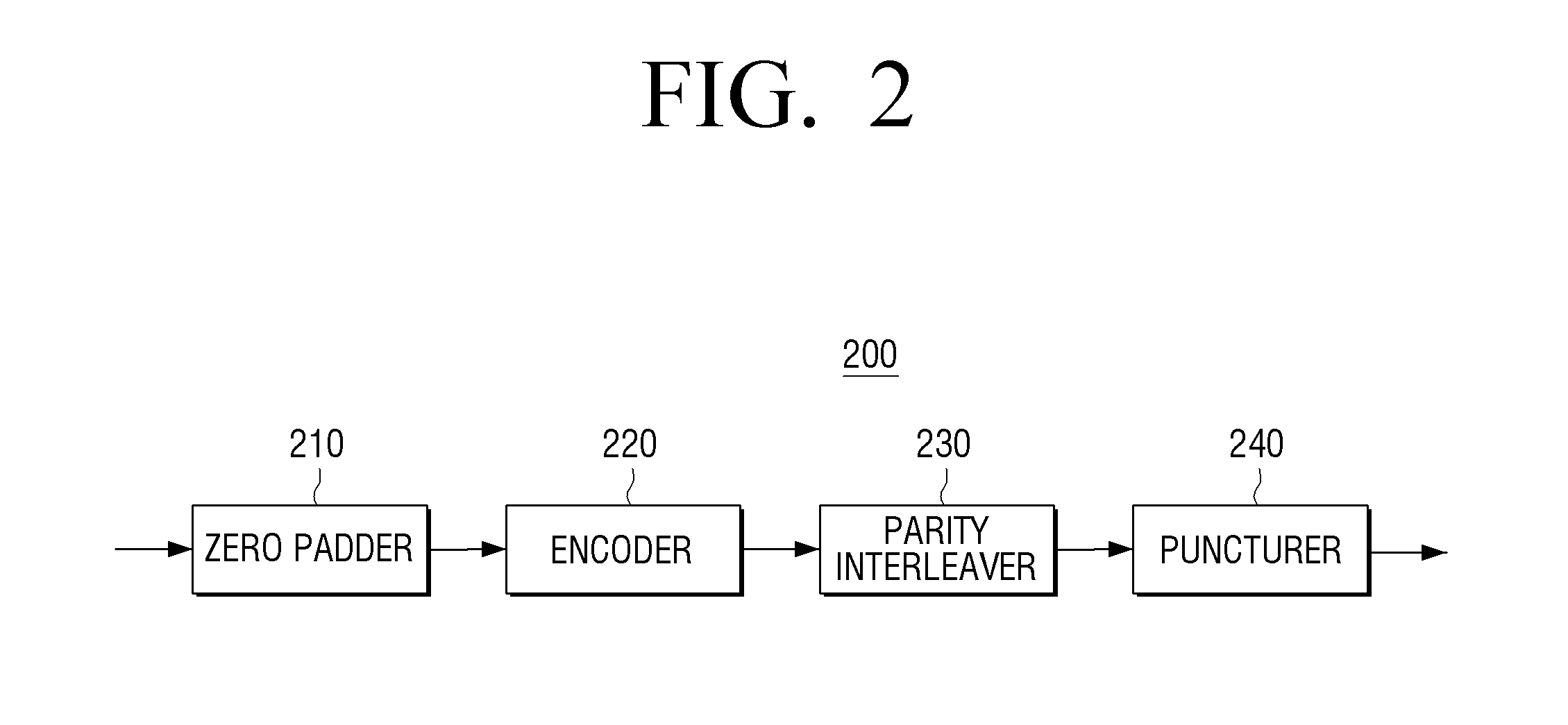
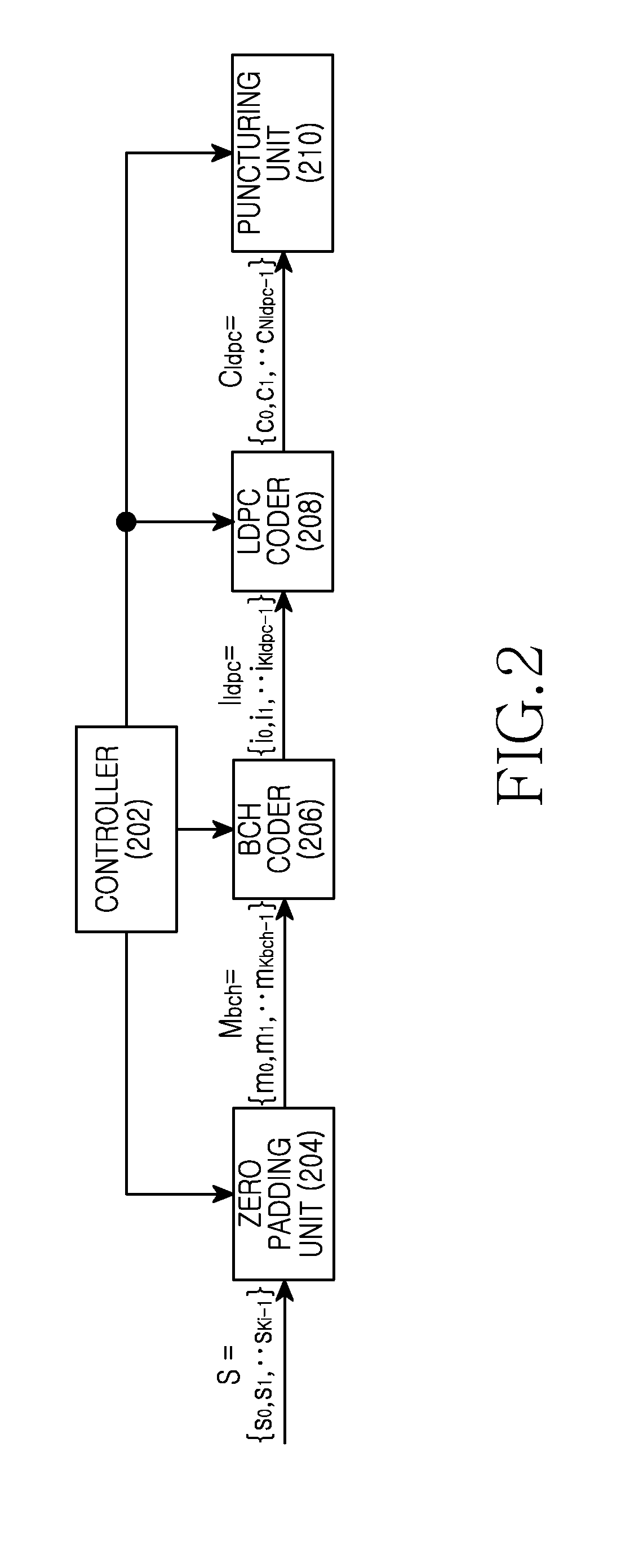
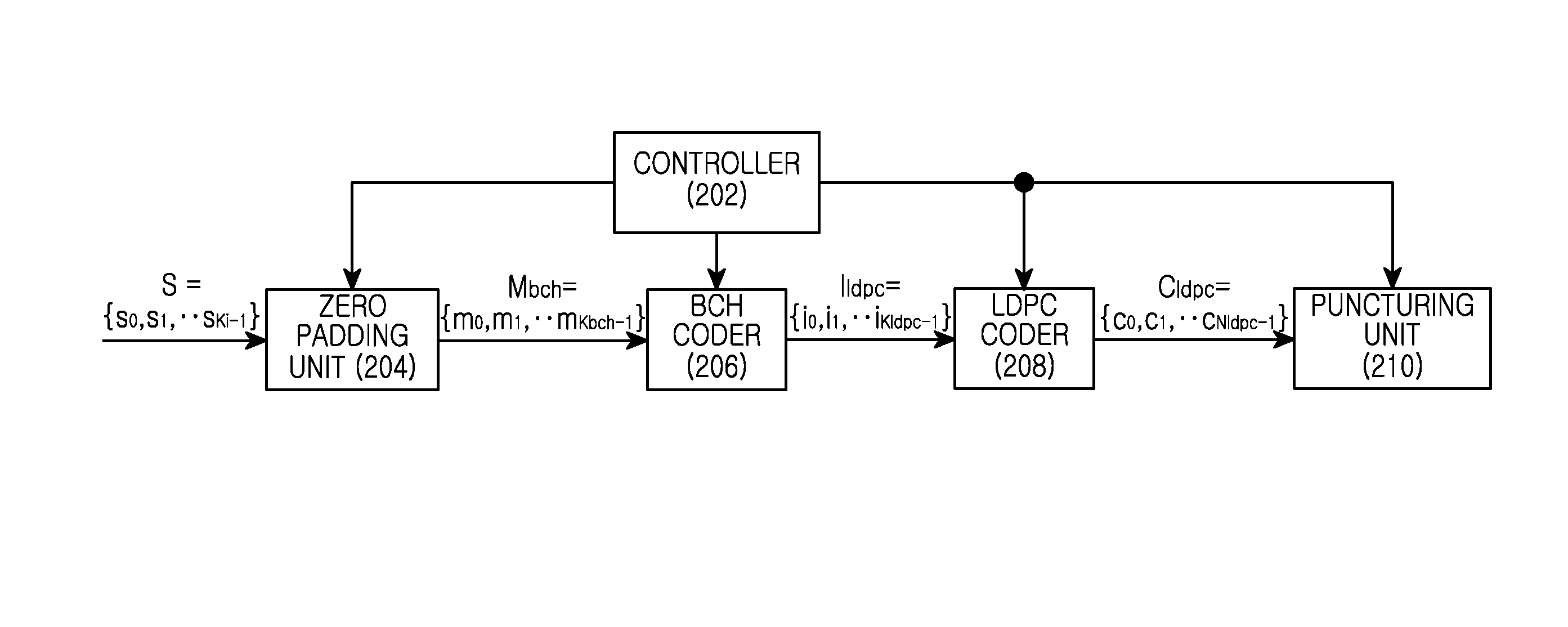
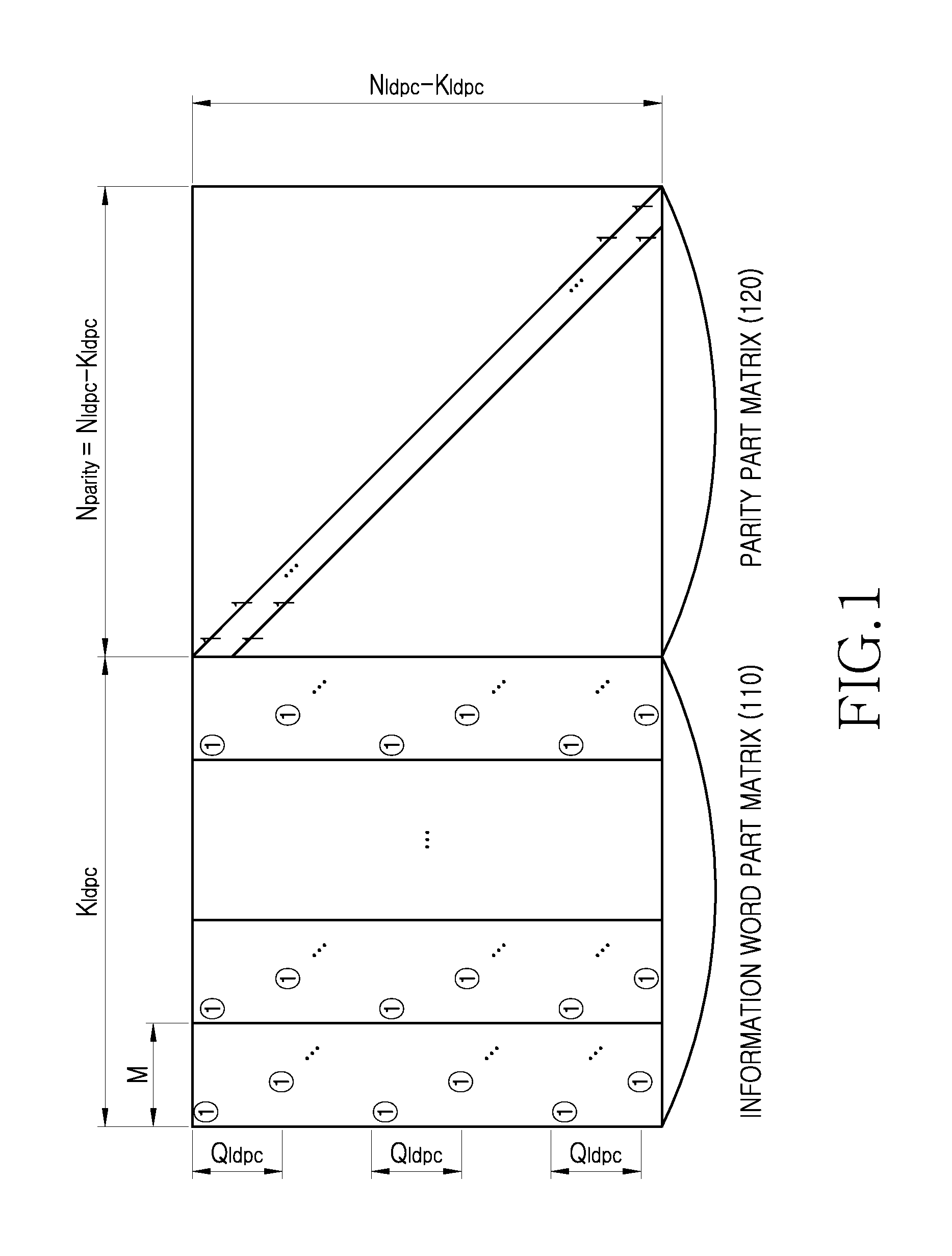
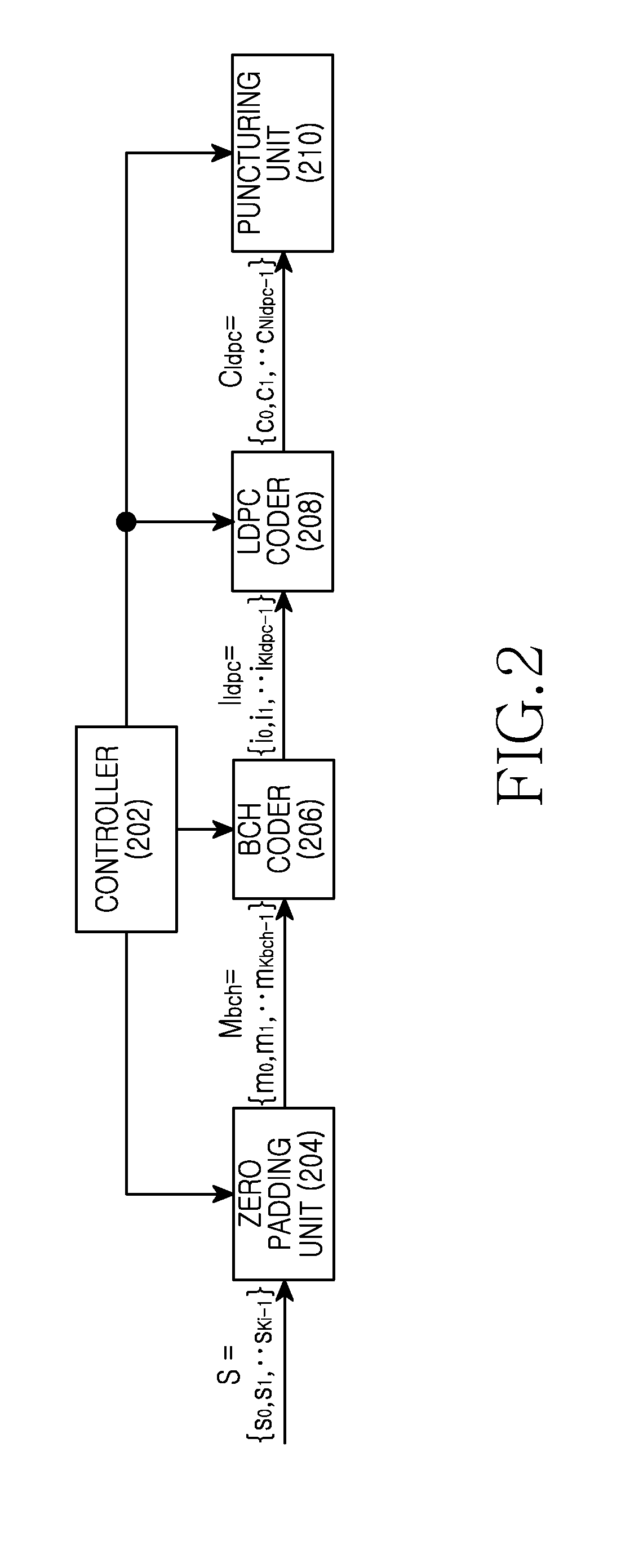
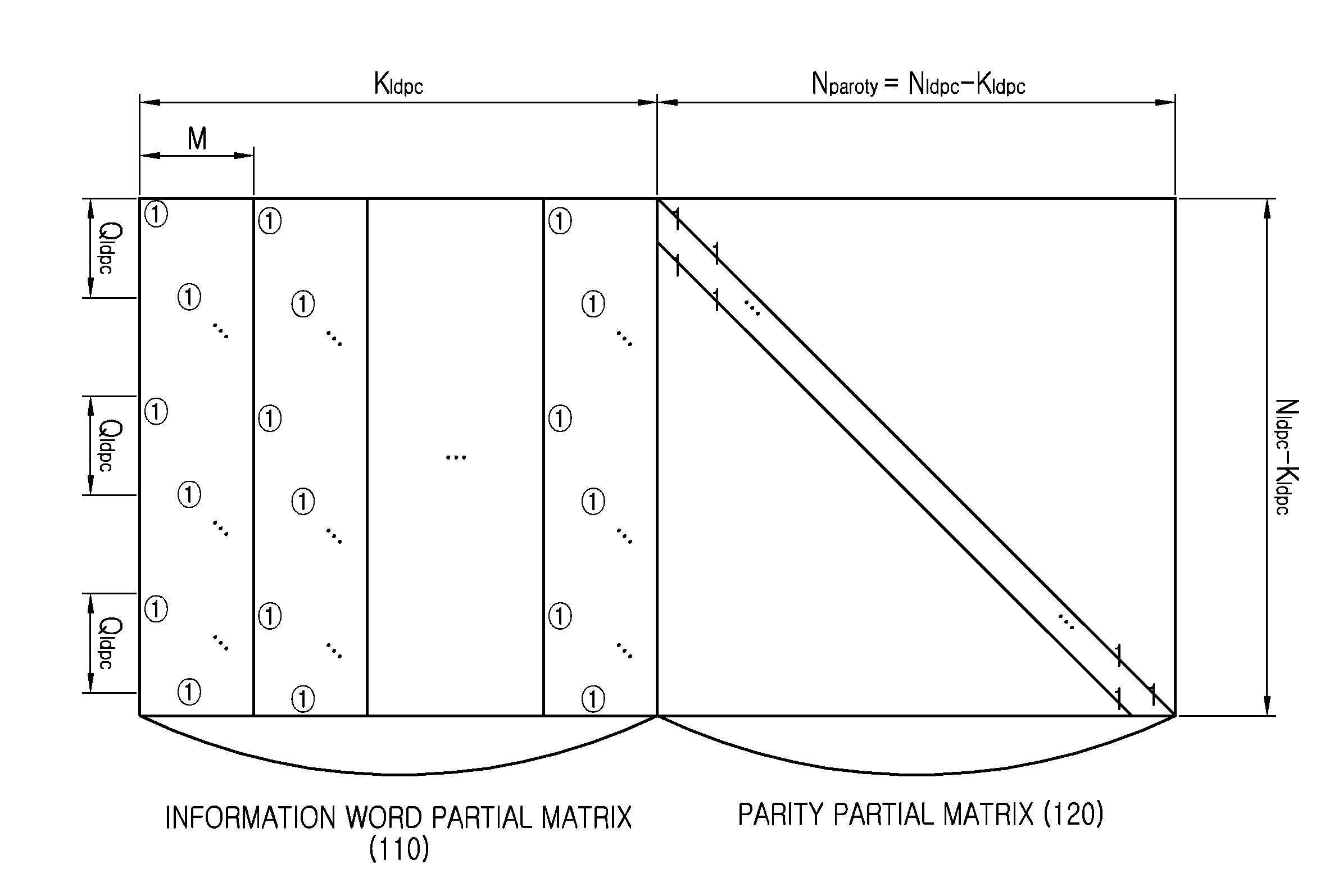
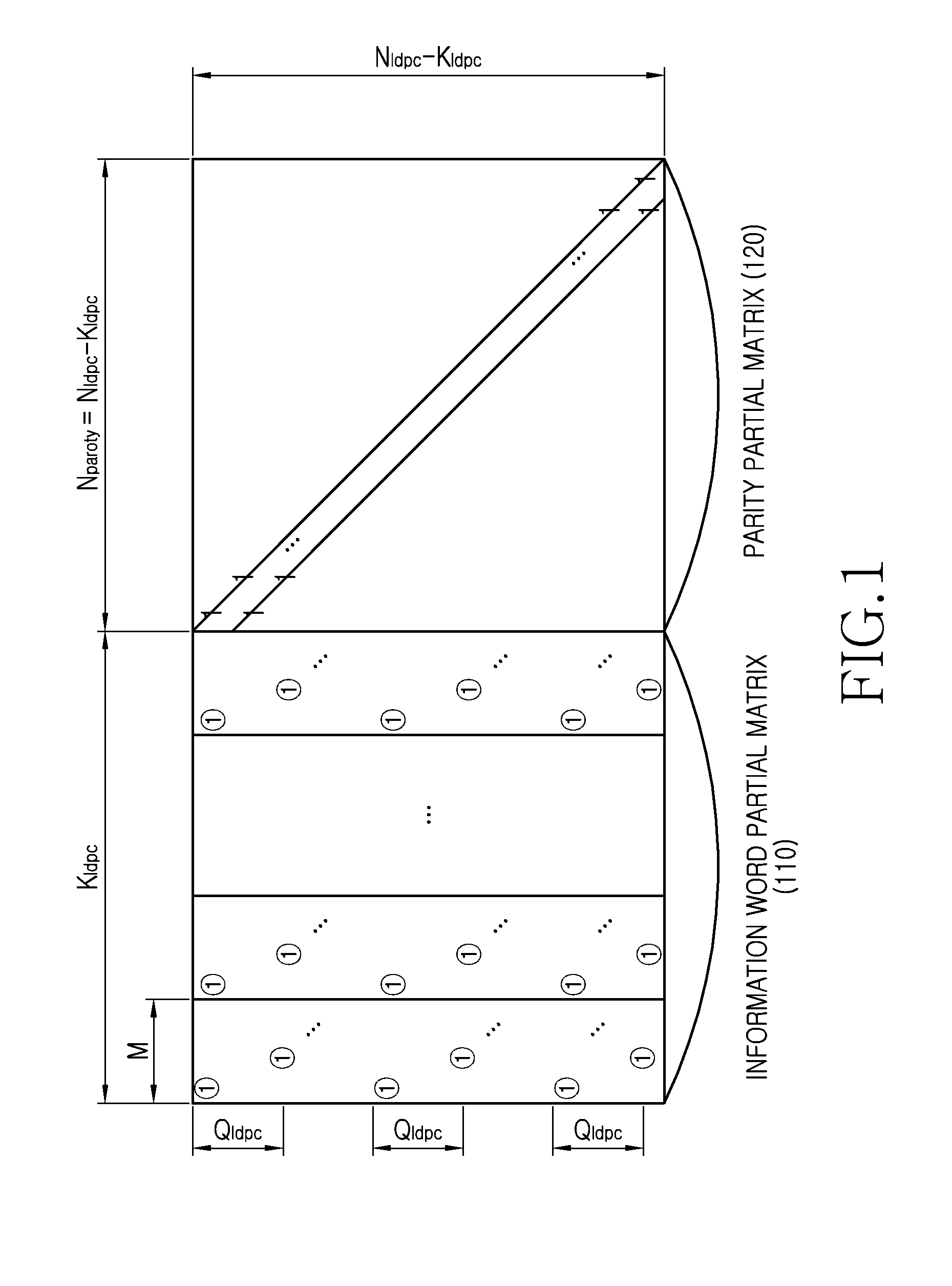
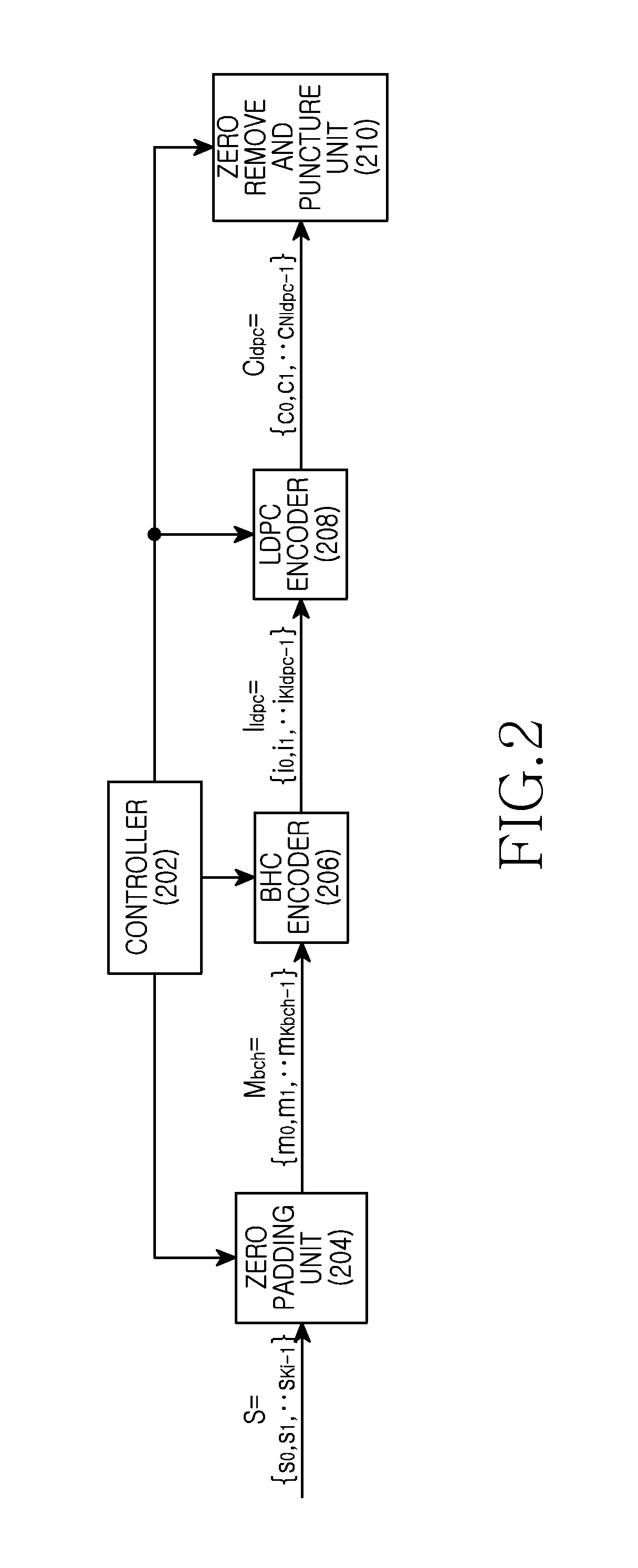
Provided are a transmitting apparatus, a receiving apparatus and methods of puncturing and depuncturing of parity bits. The transmitting apparatus includes: a zero padder configured to pad at least one zero bit to input bits; an encoder configured to generate a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codeword by performing LDPC encoding with respect to the bits to which the at least one zero bit is padded; a parity interleaver configured to interleave LDPC parity bits constituting the LDPC codeword; and a puncturer configured to puncture at least a part of the interleaved LDPC parity bits based on a pre-set puncturing pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Signal diversifying method for OFDM system
InactiveCN101394392AImprove performanceEasy to operateMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsZero paddingData information
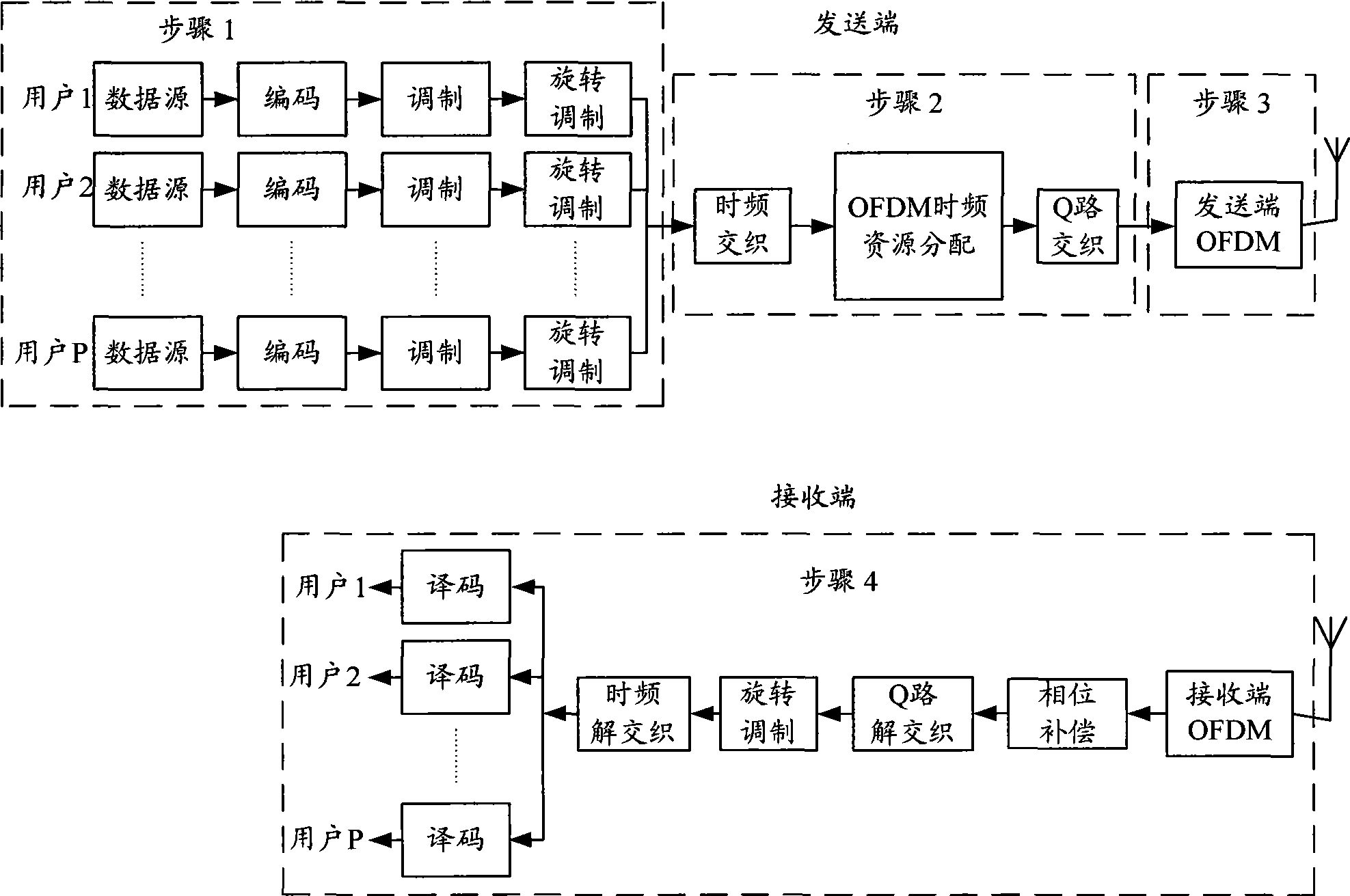
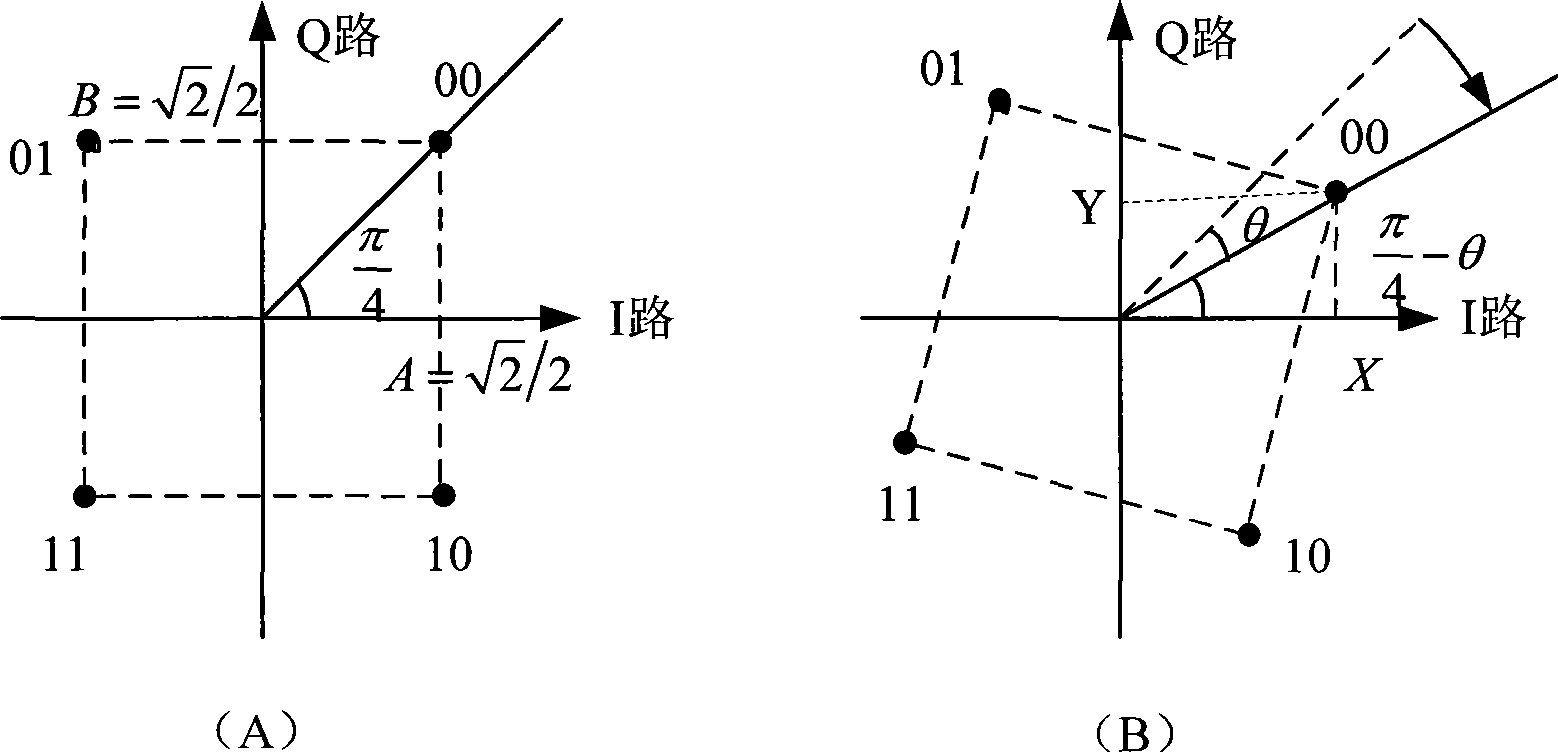
A signal diversity method of an OFDM system comprises the following steps: carrying out data decoding, modulation and rotation-modulation by a transmitting end, and storing the symbols of the processed data blocks; subjecting the symbols of the data blocks of a plurality of users in a memory to grouping and time-frequency interleaving, OFDM time-frequency resource allocation and Q-path interleaving according to the set number of the users, respectively subjecting the symbols of each data block to IFFT operation and CP addition after zero padding according to the OFDM modulation length, then transmitting the data; and subjecting the symbols of the data blocks to de-CP and FFT operations after a receiving end receives the data, carrying out phase compensation and zero removal, and sequentially subjecting the symbols of the obtained data blocks to Q-path de-interleaving, rotation demodulation, time-frequency de-interleaving and coding to obtain the desired data information. By adopting OFDM technique and rotation modulation technique and by selecting an optimal rotation angle, the method can acquire signal diversity gain and maximal performance improvement, thereby improving the system performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on FCFNN
ActiveCN109672464AQuality improvementFully extractedSpatial transmit diversityNeural architecturesMulti inputInformation feedback
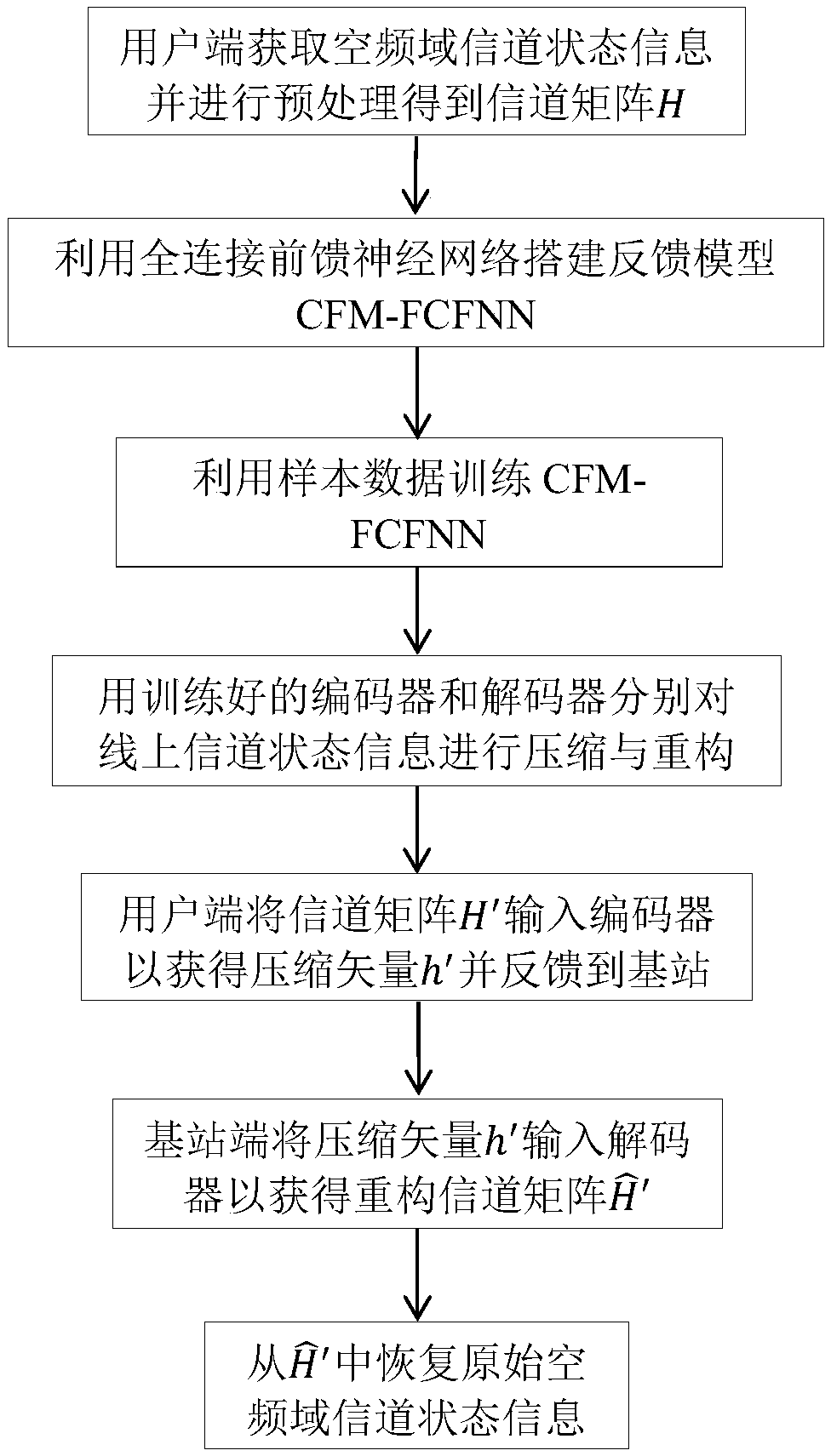
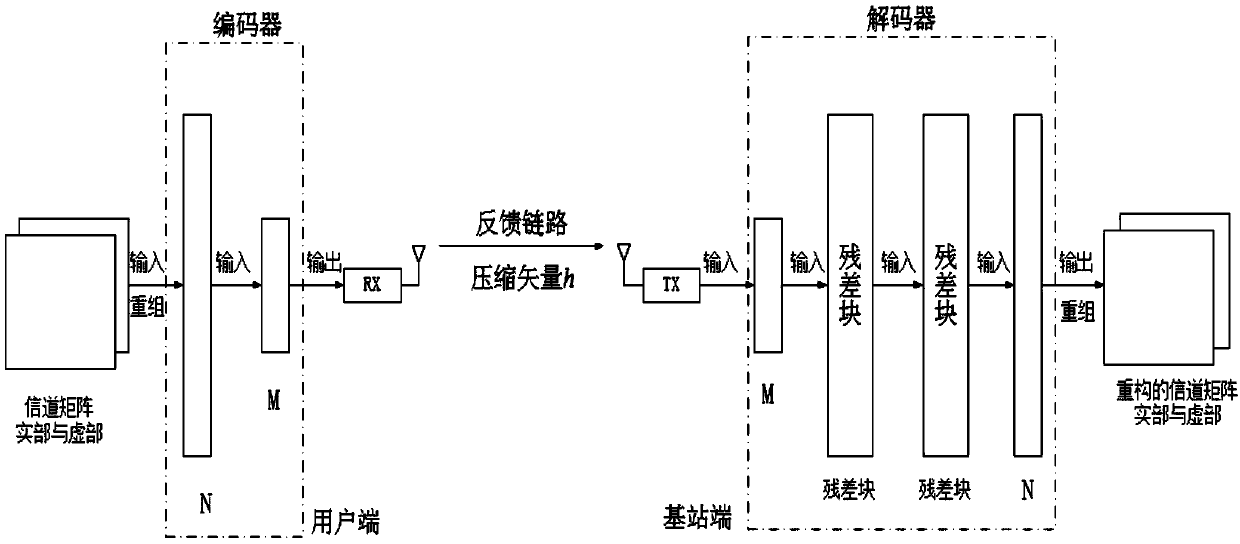
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on FCFNN, and mainly aims to solve the problems of overlarge technical feedback overhead and poor channel feedback quality in the prior art. According to the scheme, the method comprises the following steps: on a user side, performing two-dimensional discrete Fourier transform and truncation processing on adownlink channel matrix of a space-frequency domain to obtain a channel matrix H; building a channel feedback model including an encoder and a decoder, and training the channel feedback model; placingthe trained encoder and decoder on the user side and a base station side respectively; inputting the channel matrix H into the encoder to obtain a compressed vector h on the user side, and feeding back the compressed vector to a base station; inputting the h into the decoder to obtain a rebuilt channel matrix by the base station; and performing zero-padding and two-dimension inverse discrete Fourier transform on the rebuilt channel matrix to obtain an original space-frequency domain channel matrix. Through adoption of the large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method, feedback overhead of the channel state information is lowered, and the channel rebuilding quality is improved remarkably. The large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method can be applied to a large-scale multi-input and multi-output communication system under a frequency division duplex mode.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in communication/broadcasting system
ActiveUS20120185757A1Improve performanceError correction/detection using concatenated codesError correction/detection using LDPC codesZero paddingLow density
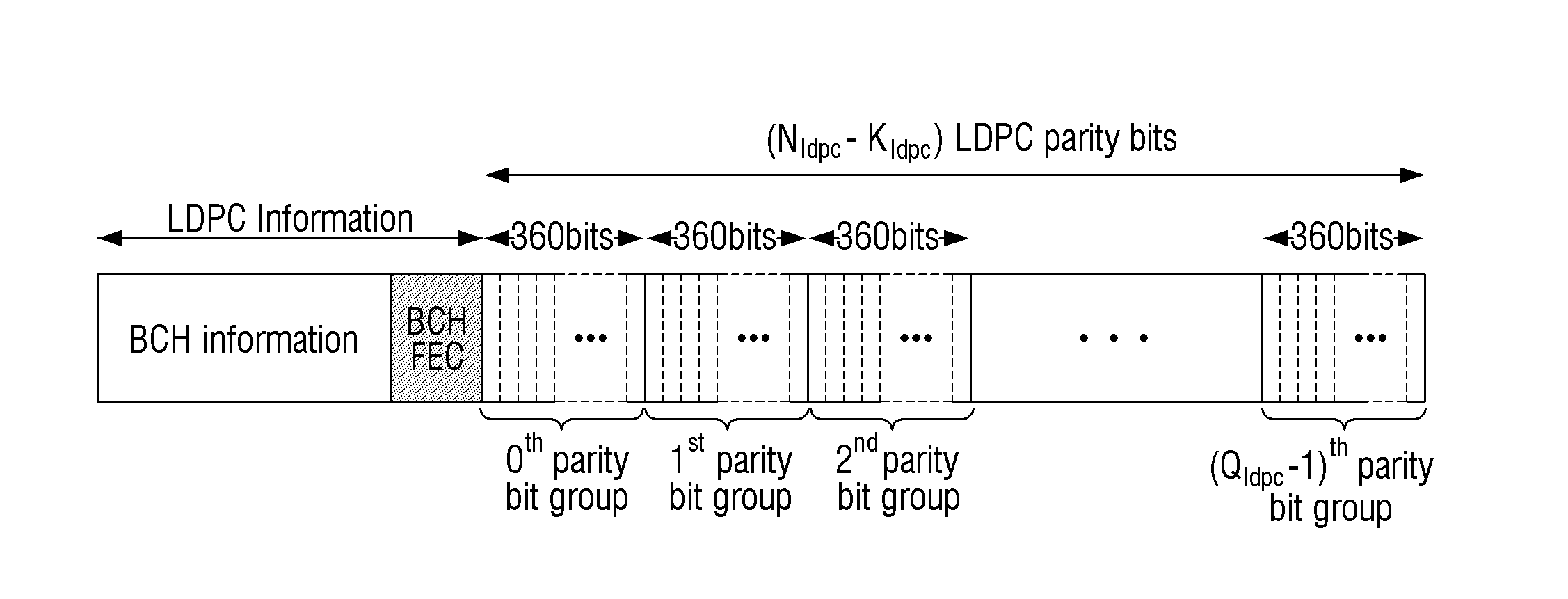
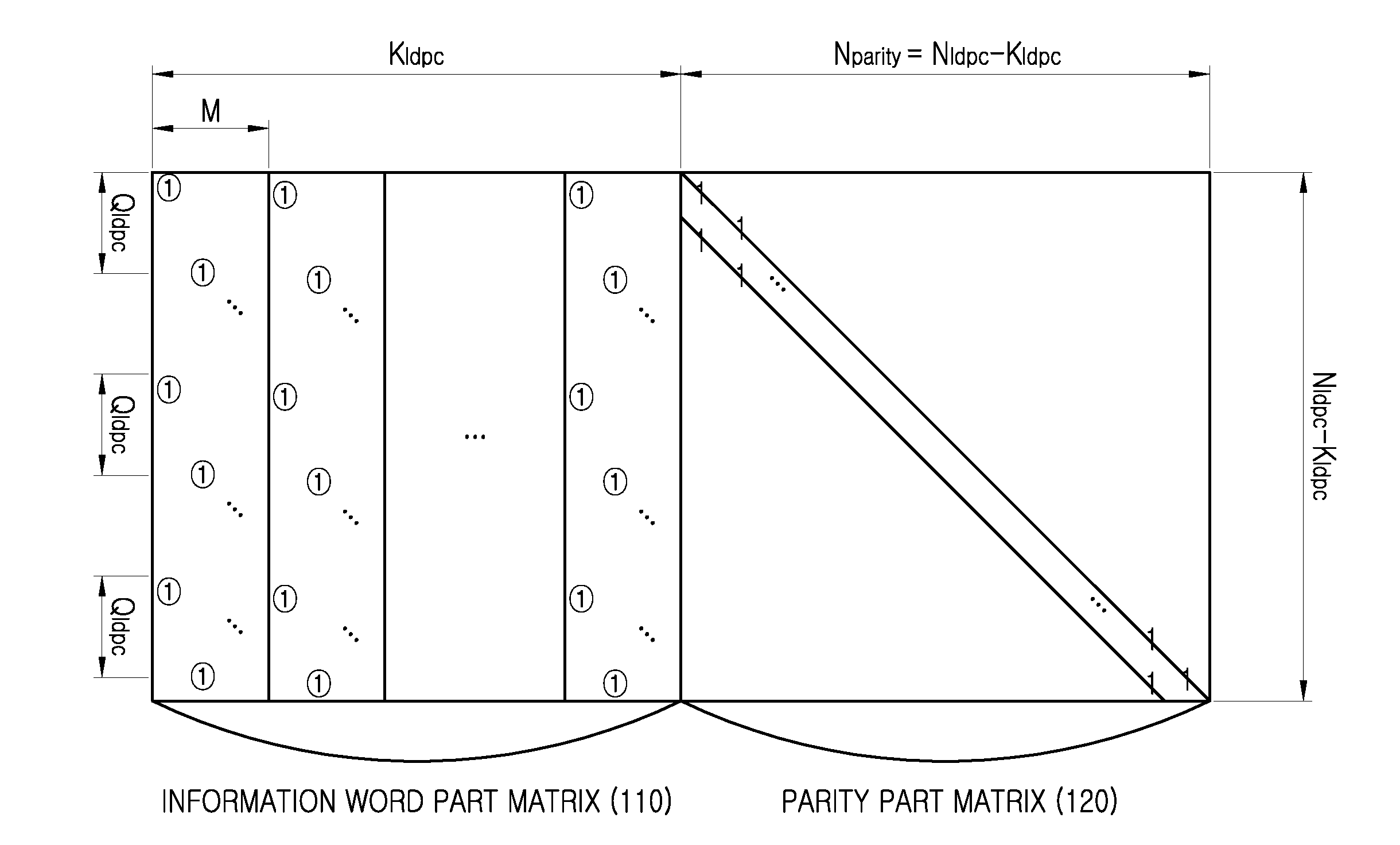
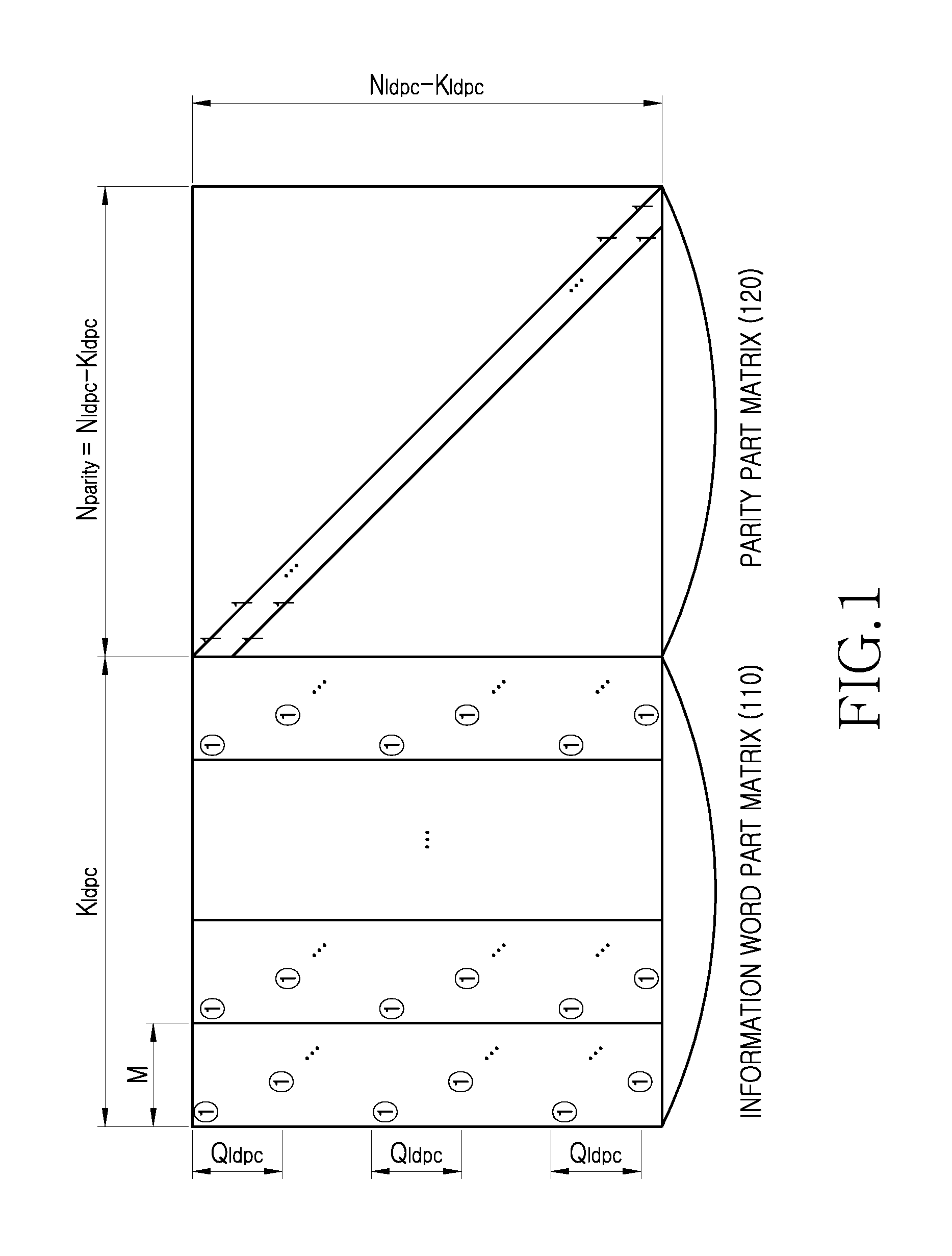
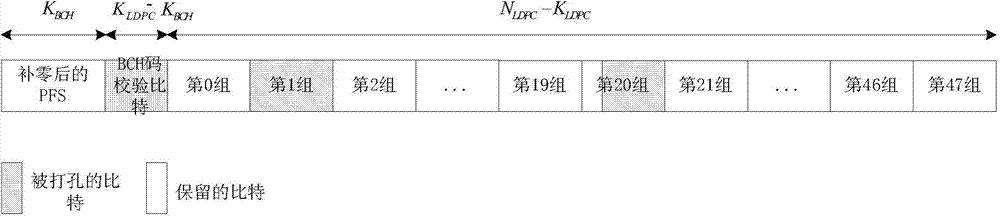
An apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in a wireless communication is provided. The method includes determining a number of zero-padding bits, determining a number (Npad) of bit groups in which all bits are padded with zeros, padding the all bits within 0th to (Npad−1)th bit groups indicated by a shortening pattern with zeros, mapping information bits to bit positions which are not padded in Bose Chaudhuri Hocquenghem (BCH) information bits, BCH encoding the BCH information bits to generate Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) information bits, and LDPC encoding the LDPC information bits to generate a zero-padded codeword, wherein the shortening pattern is defined as an order of bit groups defined as 6, 5, 4, 9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 0, 7, 10 and 11.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
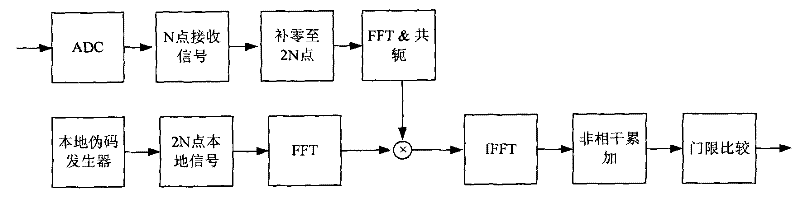
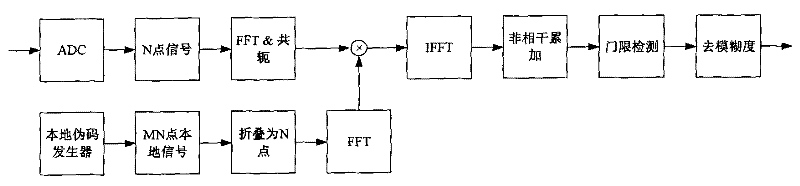
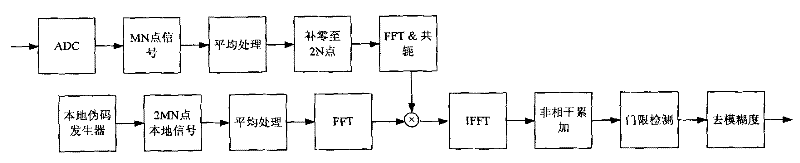
Method and system for capturing weak GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signal under condition of large-scale frequency deviation
ActiveCN102162852AMinimize impact on capture performanceImprove capture sensitivitySatellite radio beaconingFast Fourier transformZero padding
The invention discloses a method and a system for capturing a weak GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signal under the condition of large-scale frequency deviation. The method comprises the following steps of: according to a pre-detection integration time, a carrier frequency and a sampling rate, determining a maximum carrier frequency searching step; dividing the whole frequency range to be searched into a plurality of carrier frequency units according to the maximum frequency searching step to realize rough search of the carrier frequency; mapping a received satellite signal onto each carrier frequency unit and regulating a local pseudo code rate according to the carrier frequency units so as to reduce the influence of code Doppler; calculating correlation in a flexible zero-padding mode through FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) / IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform) so as to realize code phase parallel search; and carrying out FFT operation on different correlation values corresponding to the same code phase so as to fulfill the aim of carrying out fine search on the carrier frequencies in the carrier frequency units. By the method and the system, a capturing speed and a capturing sensitivity of a receiver can be improved, so that the receiver completes the work of capturing a weak navigation signal pseudo code under the condition of the large-scale frequency deviation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
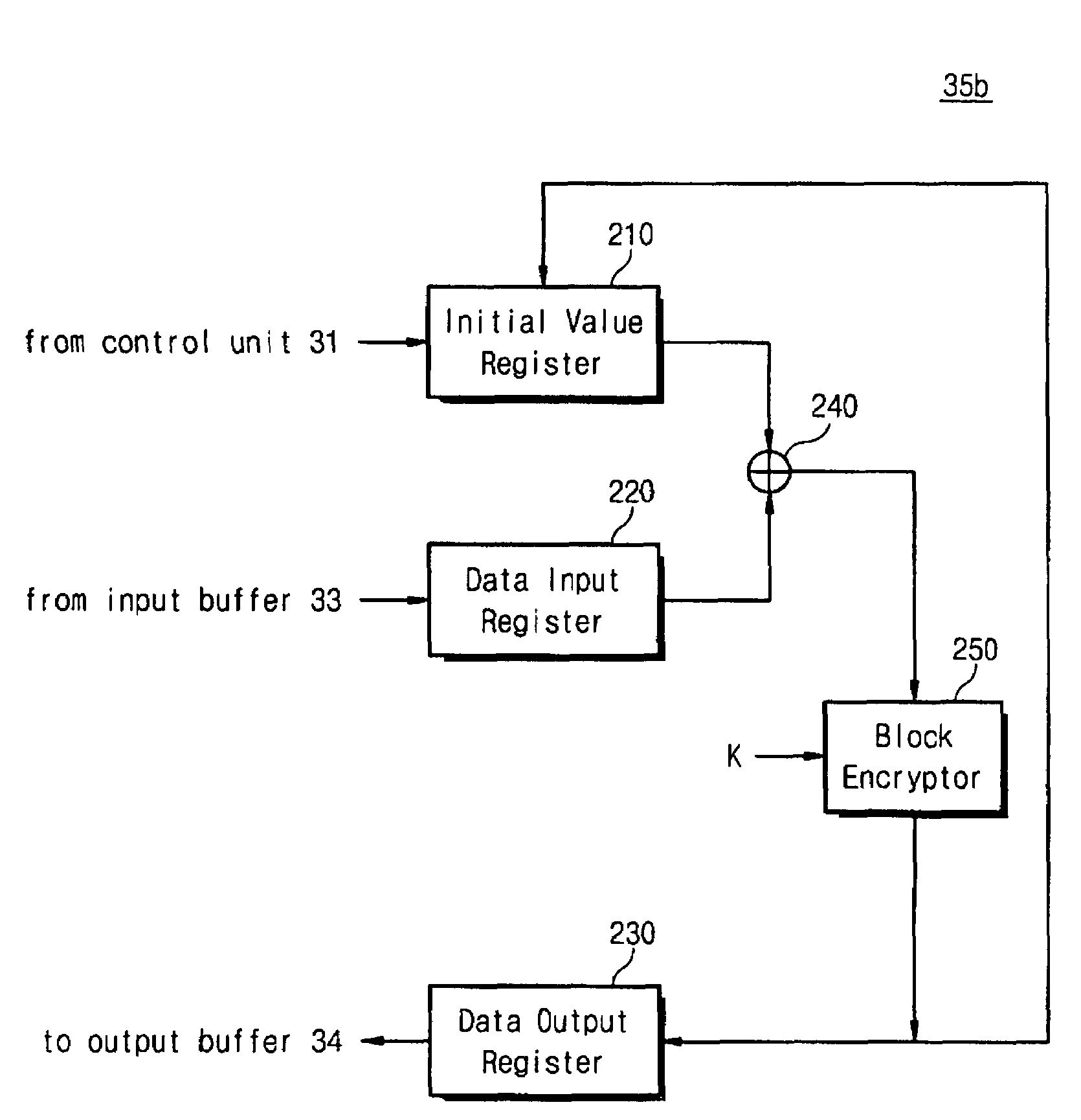
Cryptographic apparatus for supporting multiple modes
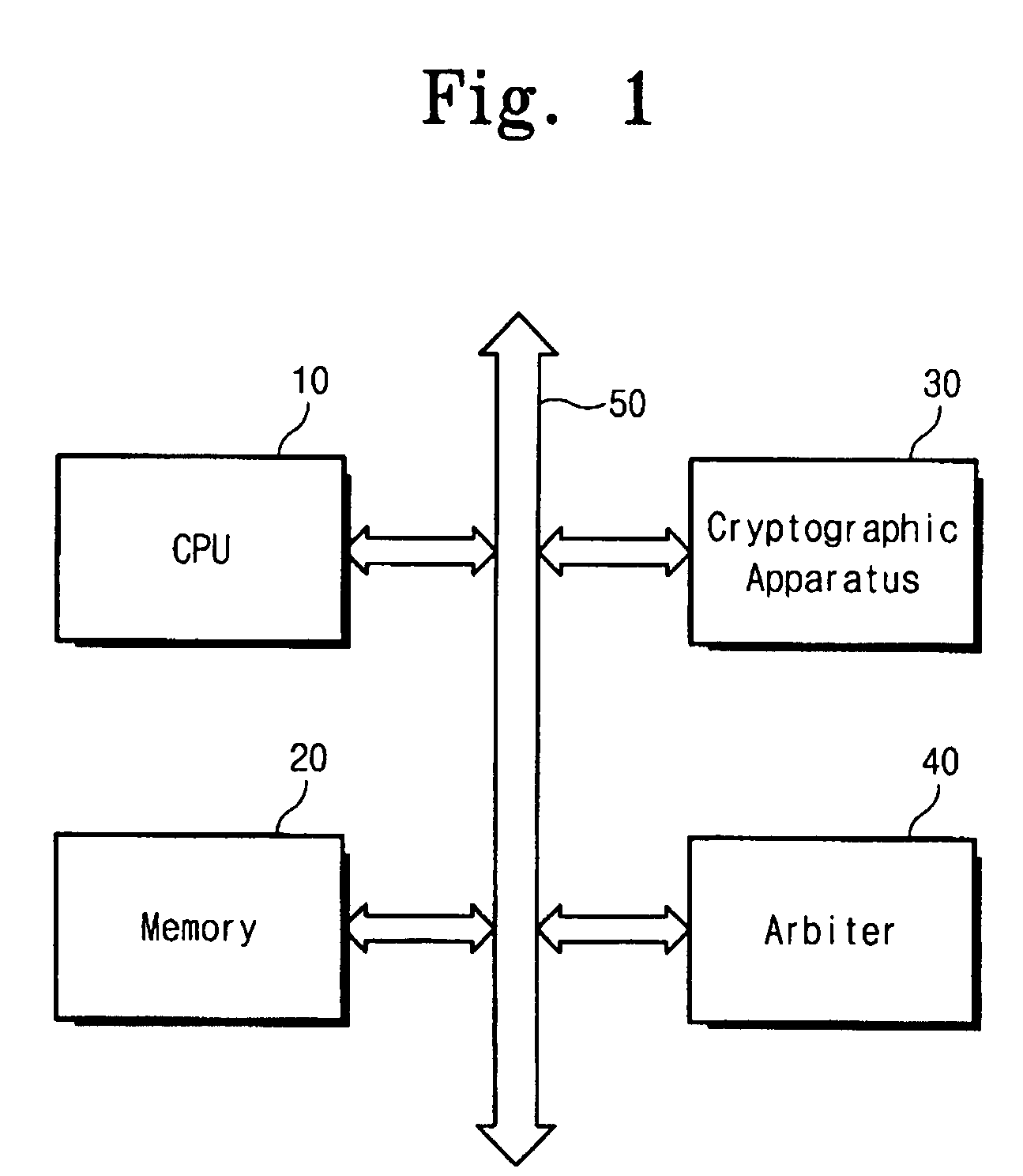
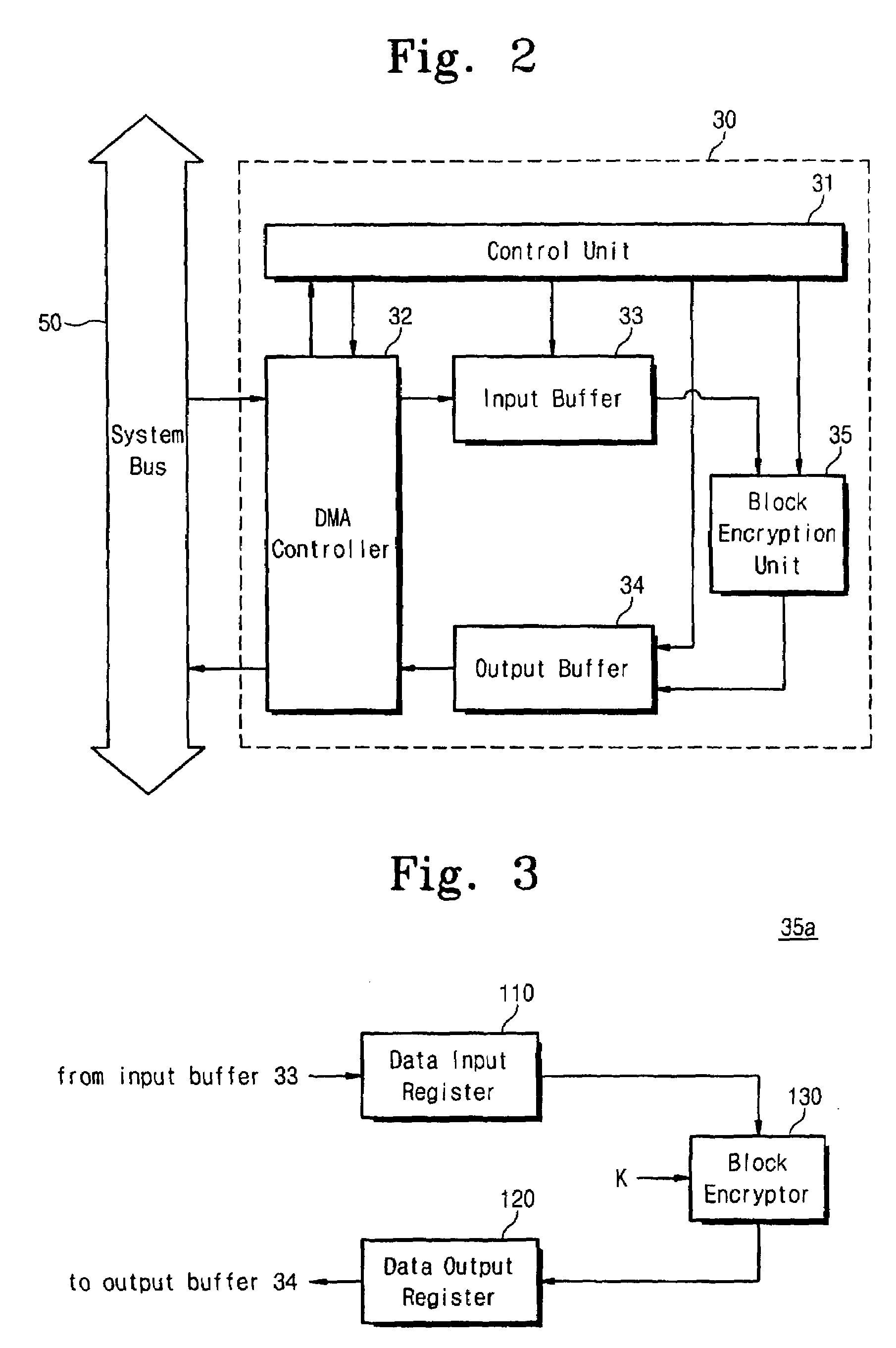
ActiveUS7509501B2Simple circuit configurationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationZero paddingCommunications system
The present invention relates to a cryptographic apparatus for encrypting data stored in a memory. The cryptographic apparatus of the present invention operates in the ECB, CBC, CBC-MAC, counter and OCB modes using small and simple elements. The cryptographic apparatus minimizes data communication between CPU and the cryptographic apparatus to improve the performance of the communication system. On the other hand, the input buffer and output buffer of the cryptographic apparatus are configured to store at least two blocks respectively, so that the performance of the cryptographic apparatus is maximized. Furthermore, the cryptographic apparatus supports zero-padding, so that the process of the CPU is minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transform domain quadratic estimation method uniting weighted threshold de-noising and balanced decision
ActiveCN106789764AChannel estimationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksChannel frequency responseBaseband
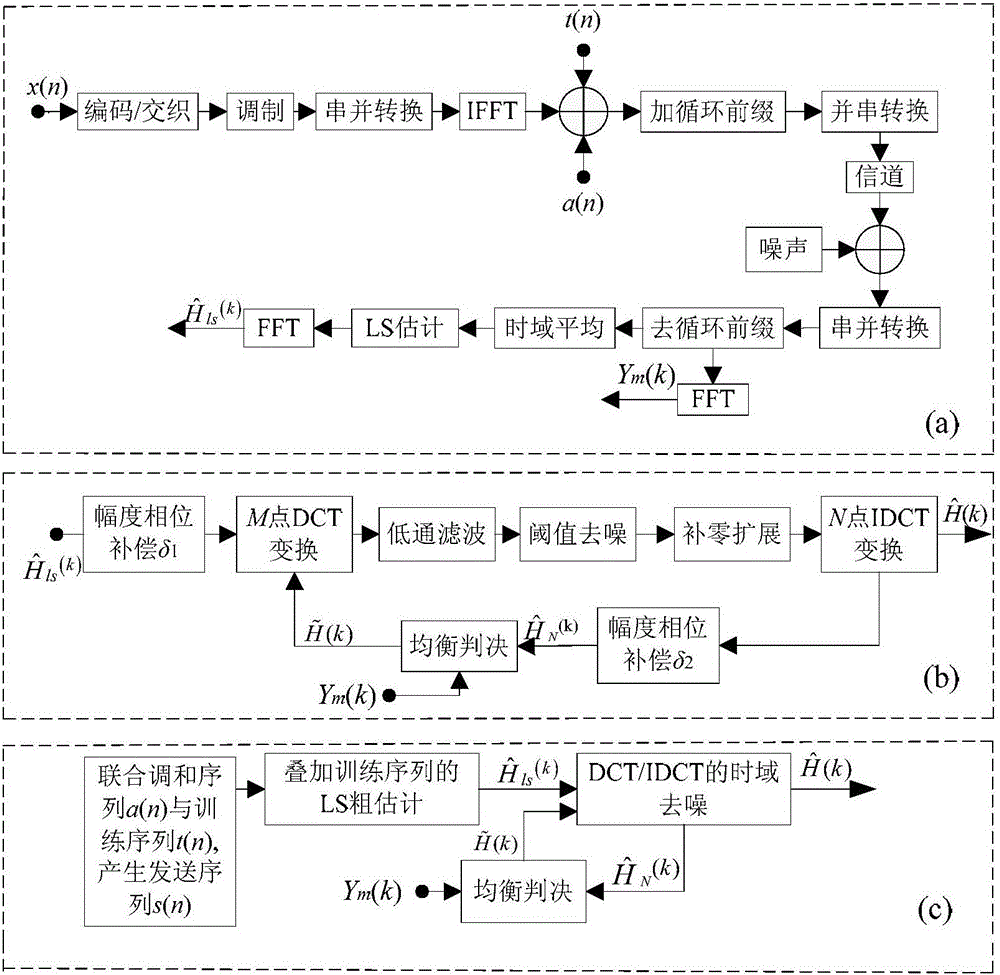
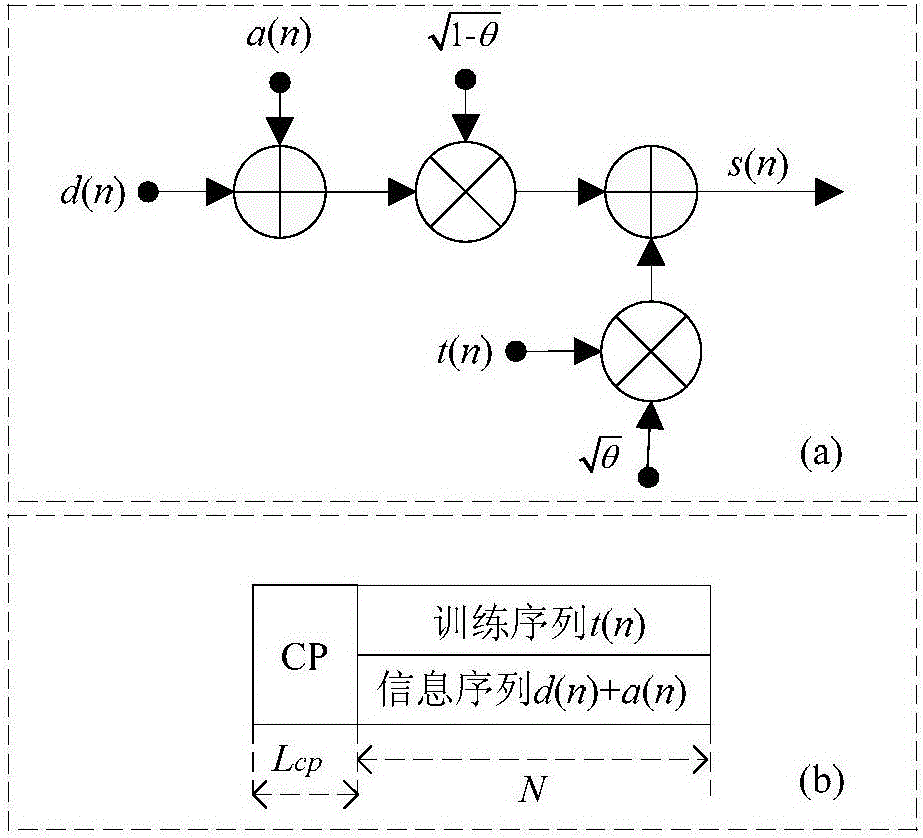
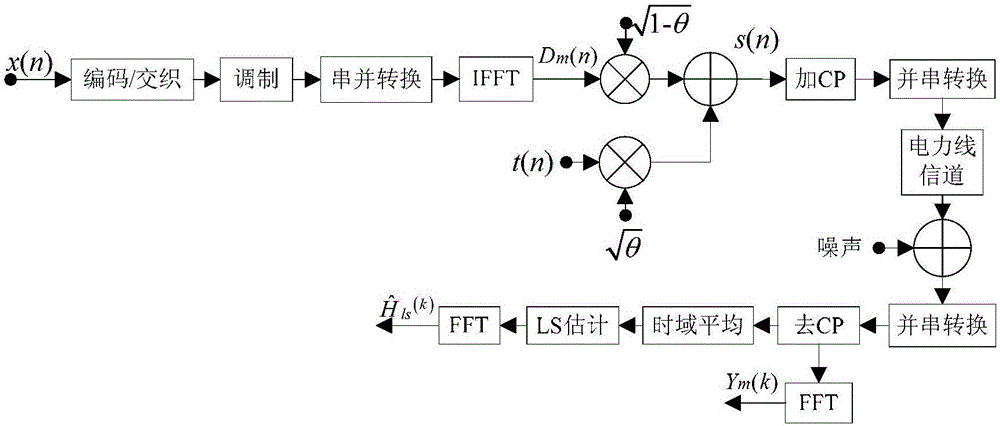
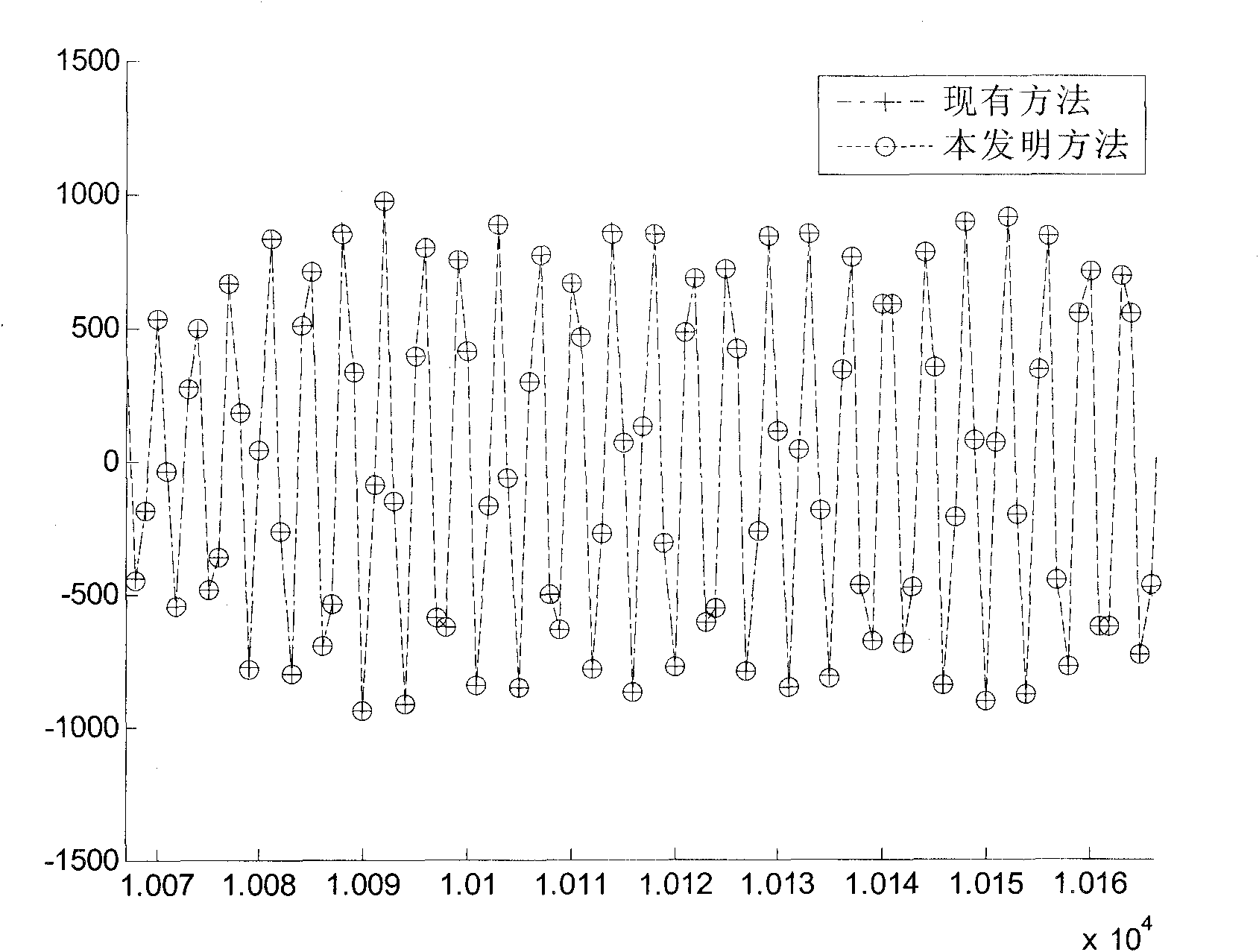
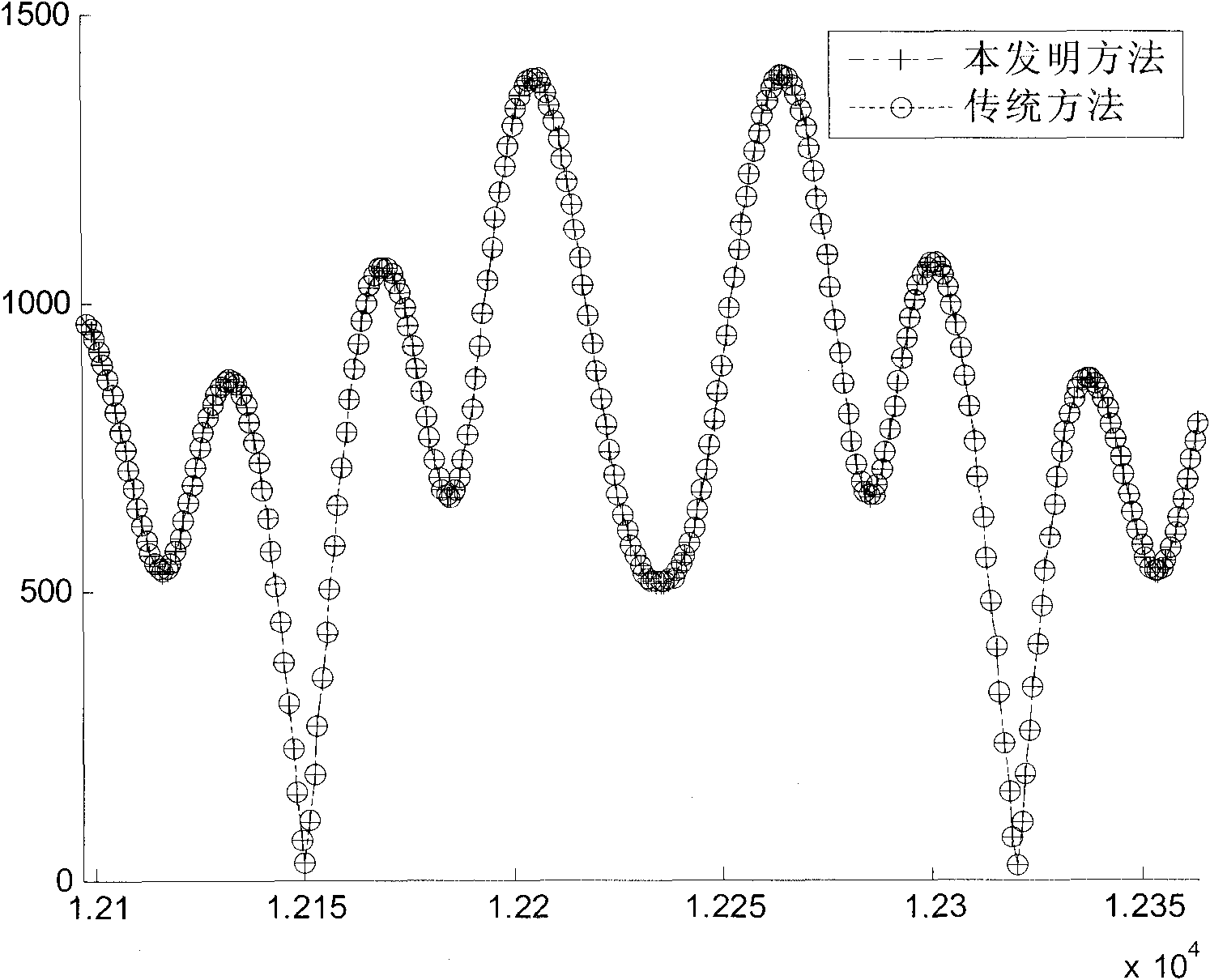
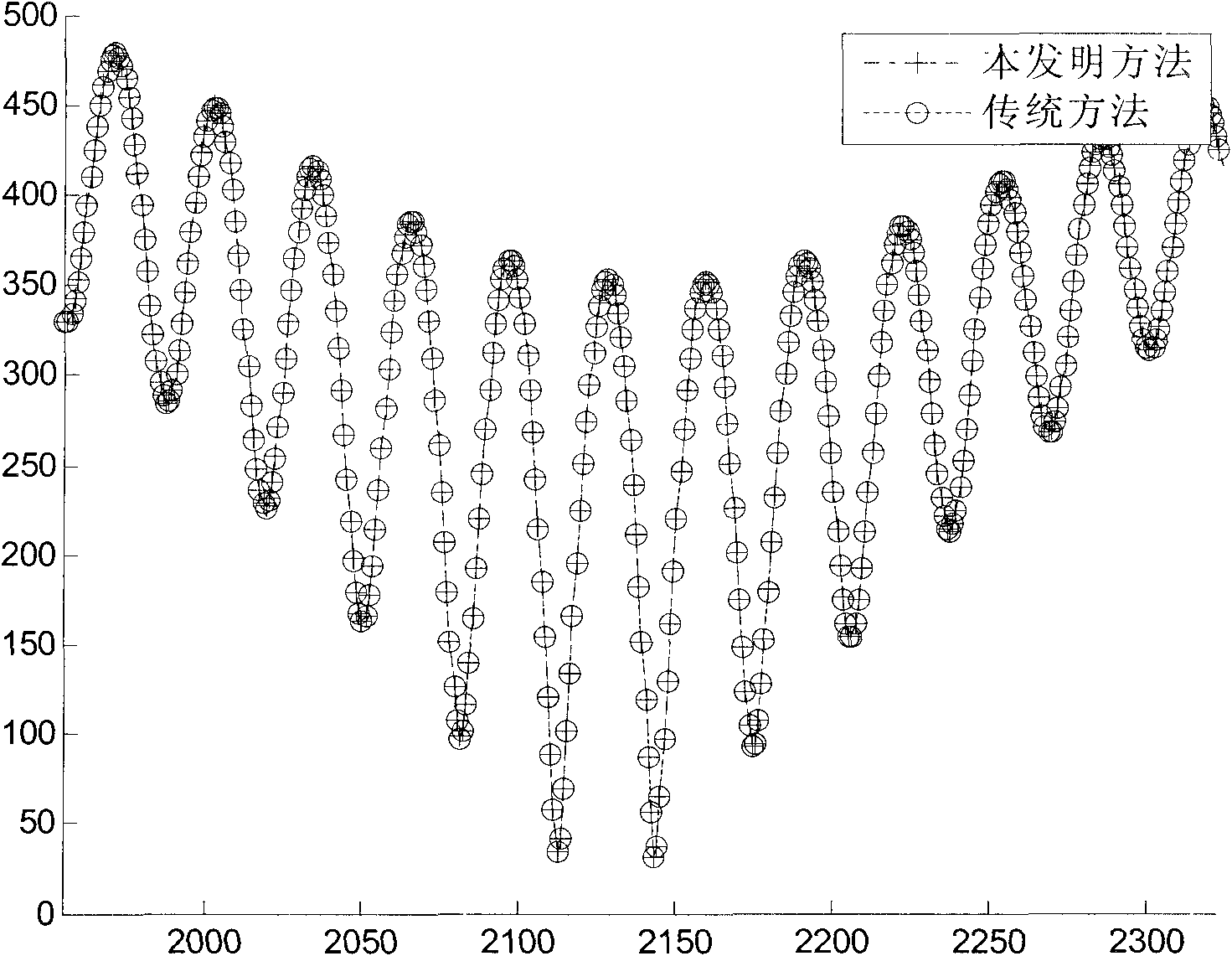
The invention discloses a transform domain quadratic estimation method uniting weighted threshold de-noising and balanced decision. The method comprises the following steps: step 1), uniting a superimposed training sequence and a harmonic sequence and generating a sending sequence; step 2), in an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) baseband system, through an estimation method of an LS channel of the superimposed training sequence, obtaining coarse estimation of a channel frequency response; step 3), performing amplitude phase compensation on the coarse estimation of the channel frequency response, adding a window function with a width of M and performing DCT (Discrete Cosine Transformation) of an M point, performing low-pass filtering, time domain de-noising and sequence zero padding extension processing on the obtained sequence, performing N point IDCT (Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform), window removing and secondary amplitude phase compensation on an extended N point sequence, as the following formula, and obtaining the following formula; step 4), performing balanced decision on the obtained result and obtaining the following formula, repeating M point DCT, low-pass filtering, time domain de-noising, interpolation zero padding and N point IDCT, and obtaining a final estimation of a frequency domain response, as the following formula. The transform domain quadratic estimation method uniting the weighted threshold de-noising and the balanced decision provided by the invention eliminates the influence of a data sequence and the training sequence on the channel estimation performance, improves the performance of the existing LS (Least Squares) channel estimation, and has lower implementation complexity.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method for generating random access pilot in low complexity in long term evolution system
InactiveCN101820301AHeavy calculationSmall amount of calculationModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmission for post communicationZero paddingFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses a method for generating a random access pilot in low complexity in a long term evolution system, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: directly generating a frequency domain sequence with the length of NZC; through frequency offset treatment, performing zero-padding on the frequency domain sequence to a nonequispaced fast Fourier transform NFFT point; through cyclic shift, performing inverse fast Fourier transform, performing K-time oversampling, adding prefix and the suffix and delivering to a filter; and through the frequency offset shift, finally adding a cyclic prefix to generate the random access pilot. Compared with the conventional methods, the method for generating the random access pilot in low complexity in the long term evolution system greatly reduces the complexity; meanwhile, the realized result of the method is consistent with that of the conventional methods, and is more suitable for an actual system.
Owner:新奇点智能科技集团有限公司
Method for estimating OFDM rapid-varying channels in low-density pilot-frequency distribution
InactiveCN101699807AImprove estimation accuracyAchieve estimatesMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputation complexityChannel parameter
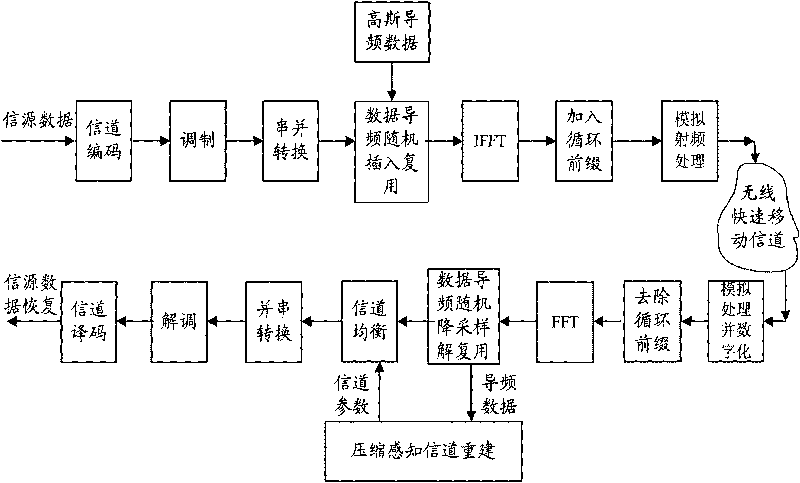
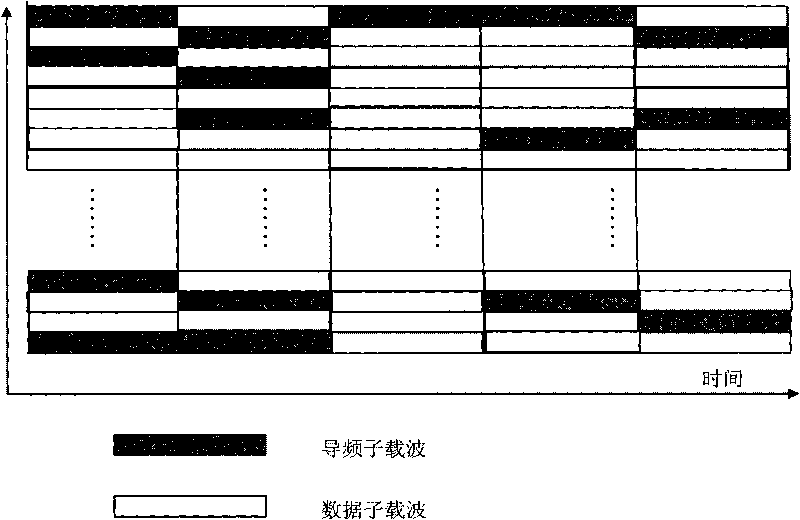
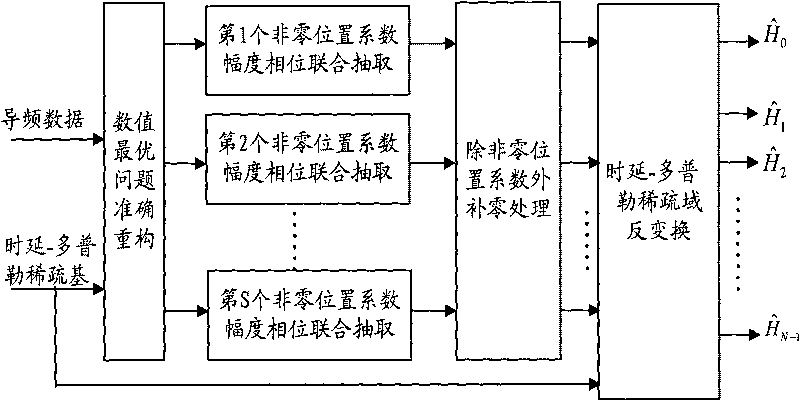
The invention discloses a method for estimating OFDM rapid-varying channels in low-density pilot distribution. The method comprises: multiplexing Gaussian-distribution pilot-frequency data and to-be-transmitted data at a transmitting end according to a time-frequency random insertion mode; performing random down-sampling and multiplexing at a receiving end on a frequency far below Nyquist frequency; transmitting received pilot-frequency data which is obtained through multiplexing and corresponds to a pilot-frequency position to perform compressed sensing channel reconstruction; obtaining S nonzero channel values in a channel delay-Doppler sparse domain; and obtaining the channel parameters of all sub-carriers in a frequency domain through channel coefficient zero padding excepting S nonzero positions, as well as delay-Doppler sparse domain inverse transformation processing. The method has the advantages of performing random down-sampling on the frequency far below Nyquist frequency, utilizing the compressed sensing channel reconstruction to filter noise so as to improve the parameter estimation precision of OFDM rapid-varying channels under pilot-frequency distribution conditions low in signal-to-noise ratio and density and realizing high-precision channel parameter estimation and tracking, along with low estimation-calculation complexity and low bit error rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in communication/broadcasting system
ActiveUS8782499B2Improve performanceTransmission systemsError correction/detection using concatenated codesZero paddingLow density
An apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in a wireless communication is provided. The method includes determining a number of zero-padding bits, determining a number (Npad) of bit groups in which all bits are padded with zeros, padding the all bits within 0th to (Npad−1)th bit groups indicated by a shortening pattern with zeros, mapping information bits to bit positions which are not padded in Bose Chaudhuri Hocquenghem (BCH) information bits, BCH encoding the BCH information bits to generate Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) information bits, and LDPC encoding the LDPC information bits to generate a zero-padded codeword, wherein the shortening pattern is defined as an order of bit groups defined as 6, 5, 4, 9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 0, 7, 10 and 11.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting data with conditional zero padding
An apparatus and method for transmitting data with conditional zero padding is provided. In accordance with an embodiment of the disclosure, a transmitter transmits data to a receiver by transmitting symbols such that each symbol is preceded by a cyclic prefix of a fixed length and the symbol conditionally includes enough zero padding to avoid ISI (Inter-Symbol Interference) between consecutive symbols. In some implementations, if the fixed length for cyclic prefixes is long enough to avoid ISI between consecutive symbols, then the symbols may omit zero padding. Otherwise, the symbols may include enough zero padding to avoid ISI between consecutive symbols. The zero padding may be zero tail or zero head.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and system for global position system (GPS) signal capture
InactiveCN102662183AEfficient captureReduce power lossSatellite radio beaconingFast Fourier transformZero padding
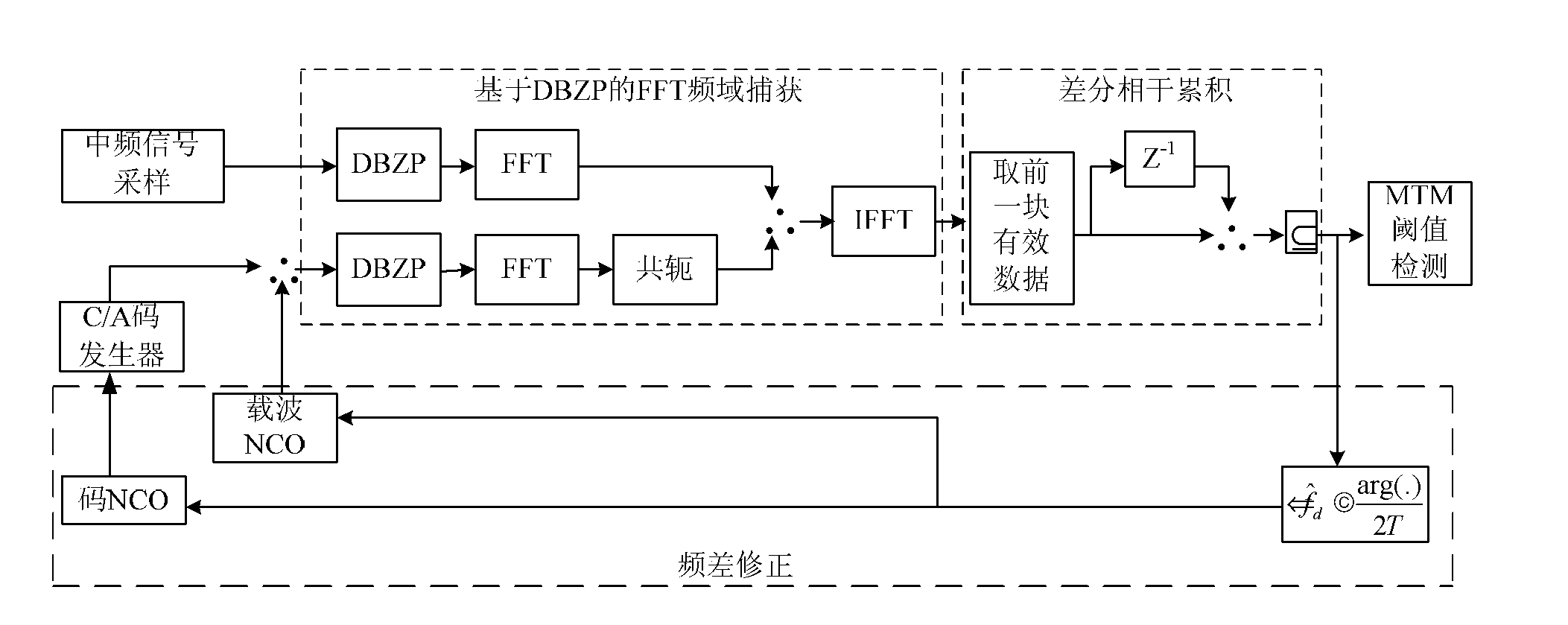
The invention discloses a method and a system for global position system (GPS) signal capture, which organically combine fast Fourier transformation (FFT), double block zero padding (DBZP), differential coherence, frequency difference correction and other techniques, can achieve efficient and fast GPS signal capture and can reduce related power loss caused by chip speed change due to large doppler frequency shift in a fast Fourier transformation calculating process. In addition, power loss caused by residual doppler frequency shift errors can be reduced through the frequency difference correction technique, and efficient and fast capture is achieved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
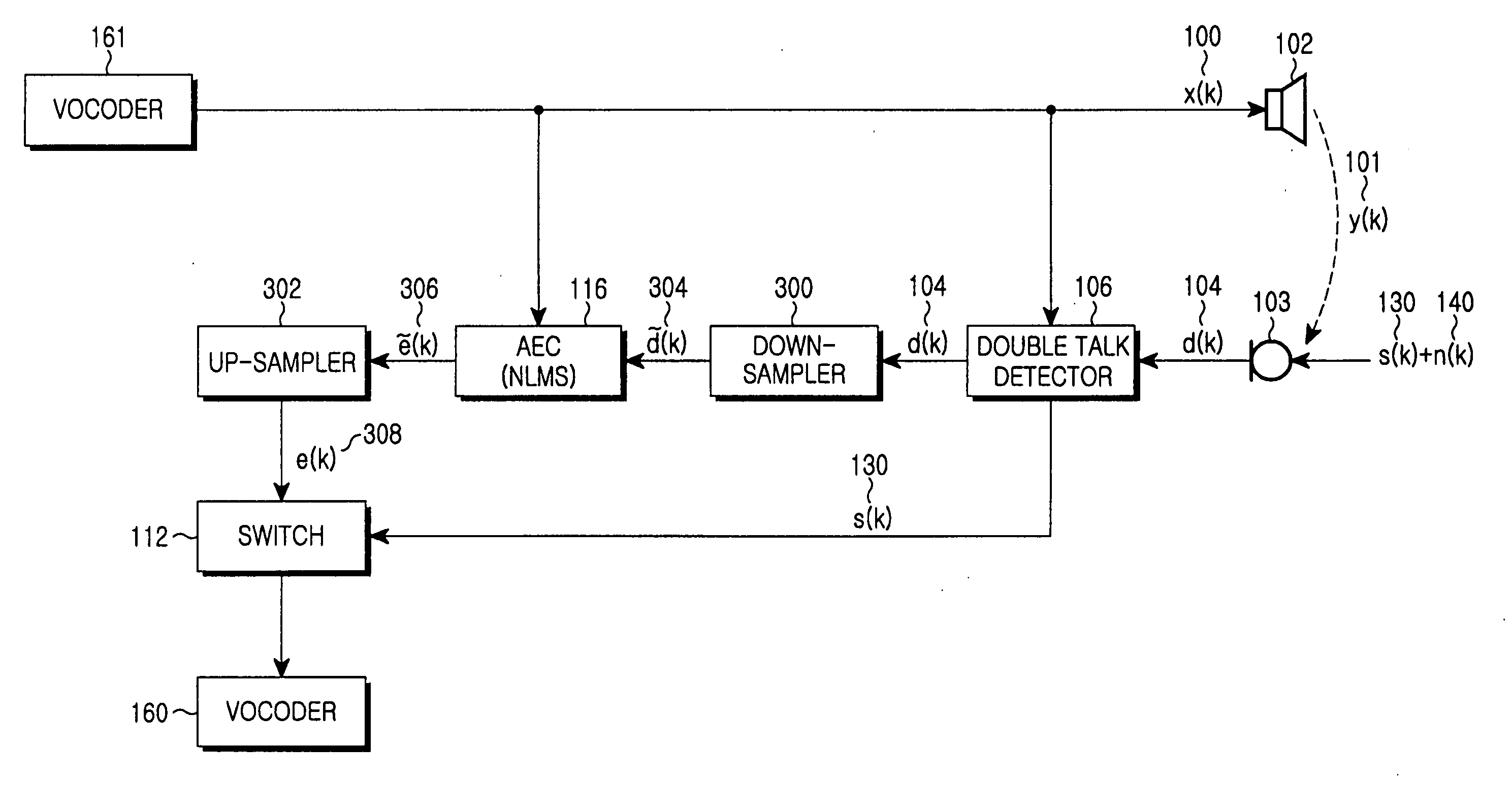
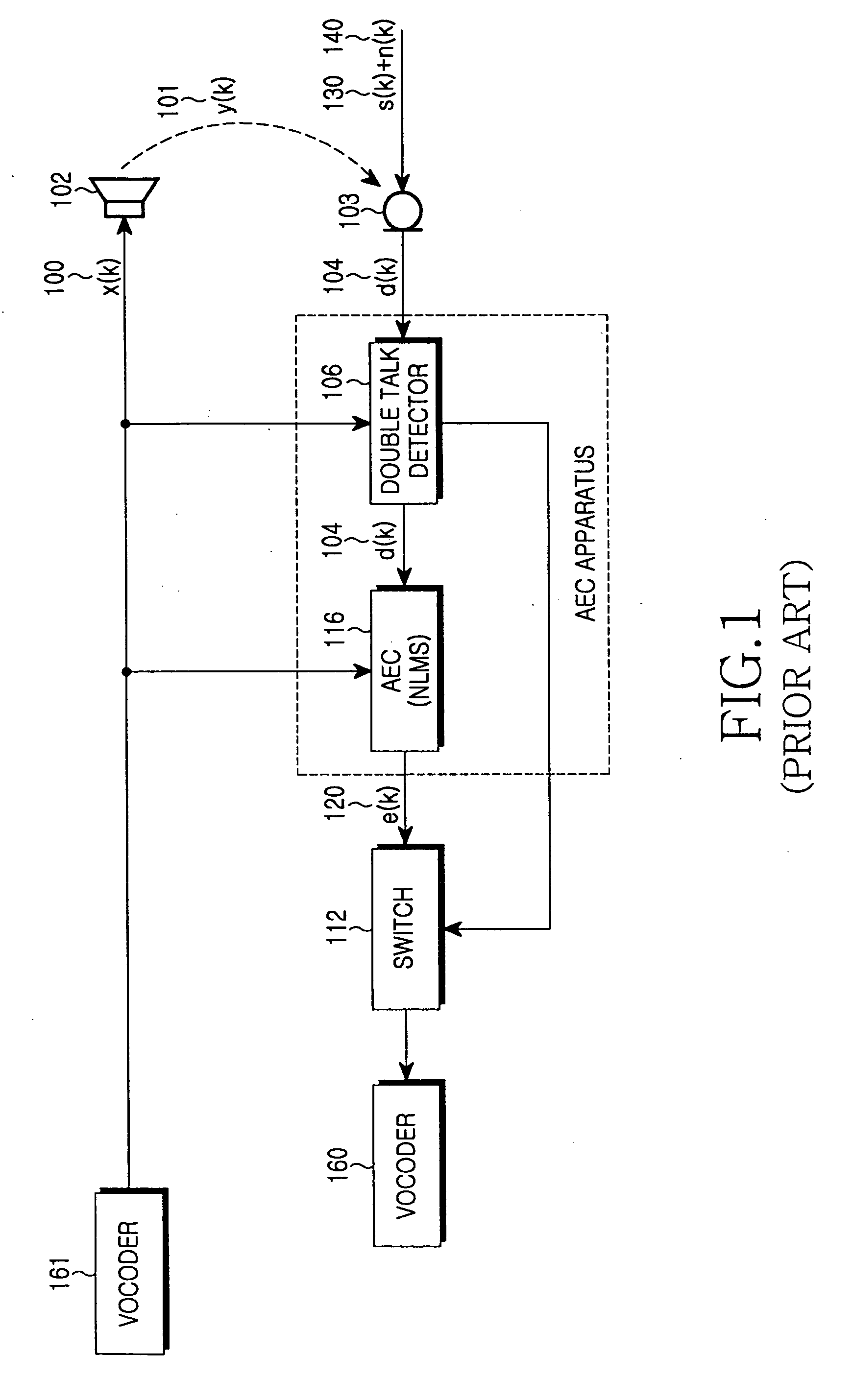
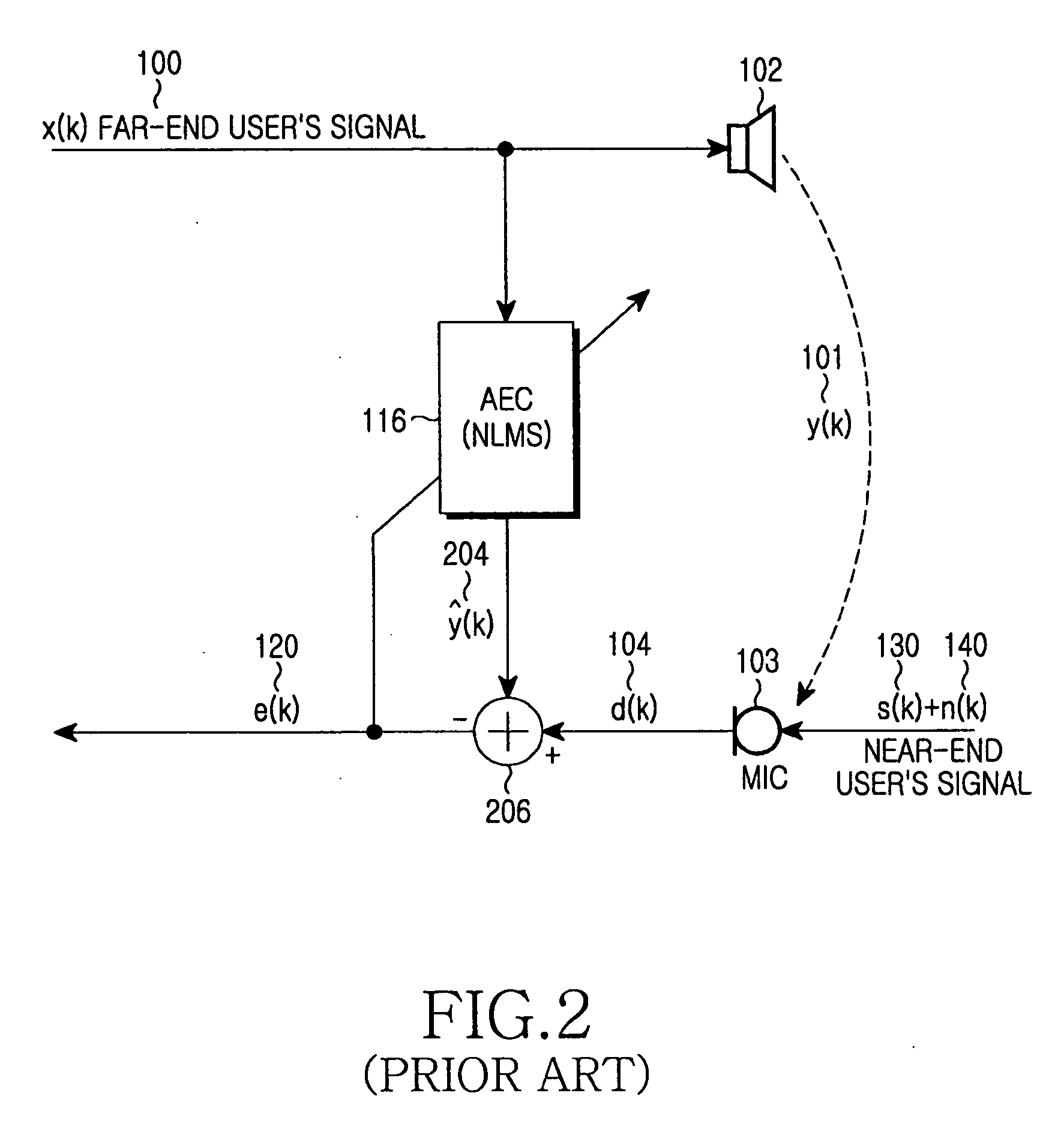
Method and apparatus for canceling acoustic echo in a mobile terminal
InactiveUS20060062380A1Easy to calculateIncrease in calculationTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsTransmissionZero paddingAcoustics
A method and apparatus for canceling an acoustic echo in a mobile terminal involving an acoustic echo canceller (AEC) for canceling an echo signal from a received far-end user's signal. Upon detecting double talk, a down-sampler lowpass-filters an output signal and down-samples the lowpass-filtered signal. The AEC estimates an echo signal using the far-end user's signal, and outputs a residual echo signal by canceling the estimated echo signal from the down-sampled signal. An up-sampler up-samples the residual echo signal by zero padding, and lowpass-filters the up-sampled signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
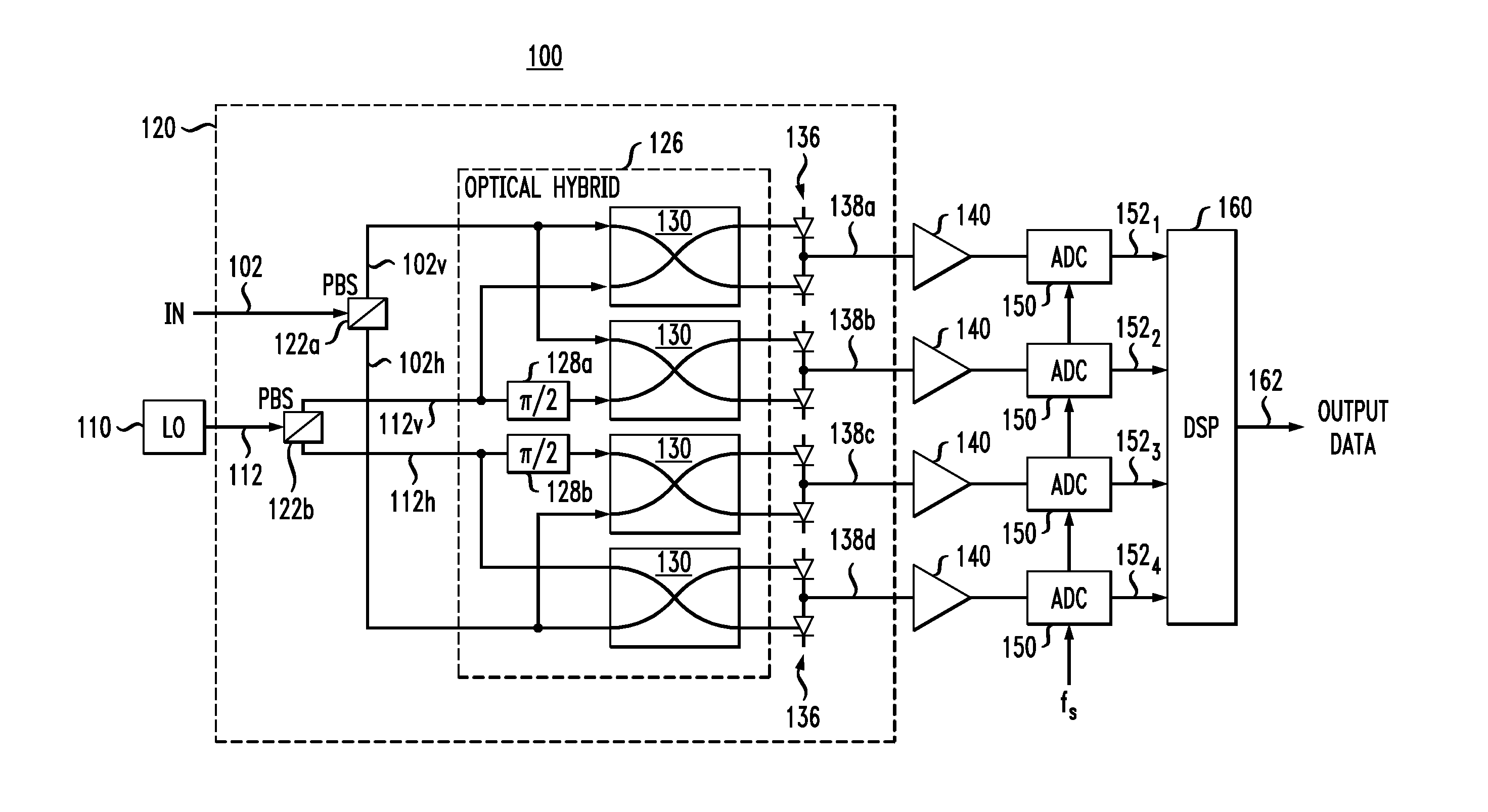
Optical receiver having an equalization filter with an integrated signal re-sampler
We disclose an optical receiver having a digital filter with an integrated signal re-sampler that enables the receiver to both equalize and re-sample the digital signals generated by the receiver's ADCs configured to run at a fractional sampling frequency. In an example embodiment, the digital filter performs both signal equalization and signal interpolation in the frequency domain by applying an appropriate discrete spectral transfer function to a fractionally oversampled signal and then zero-padding the resulting equalized set of spectral samples. The digital filter re-samples the signal by applying an inverse Fourier transform to the zero-padded set of spectral samples and then truncating and decimating the resulting interpolated set of time-domain samples.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Radio terminal, radio base station, channel signal forming method and channel signal receiving method
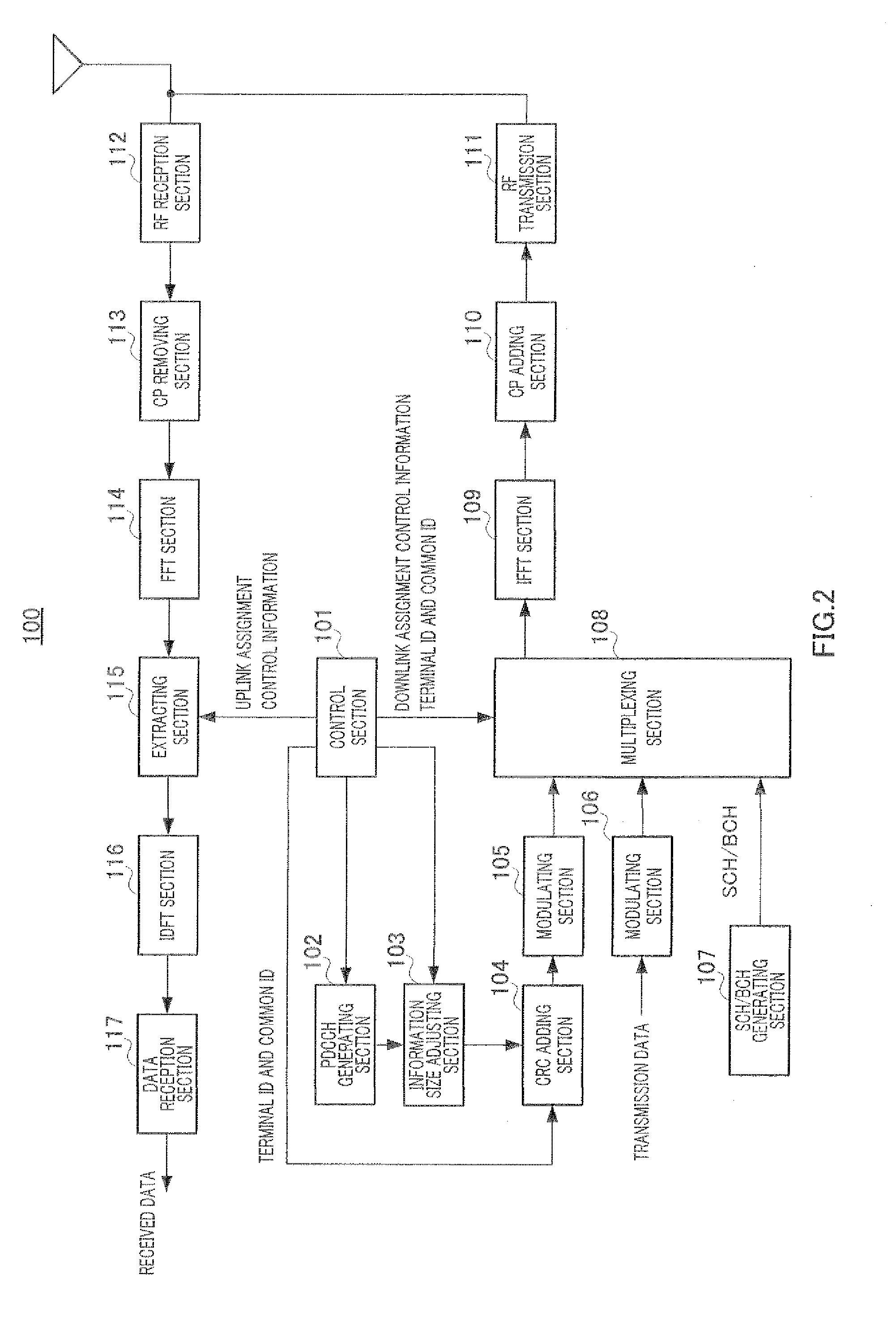
ActiveUS20110223926A1Quality improvementTransmission path divisionReceiver specific arrangementsZero paddingComputer terminal
A radio terminal, radio base station, channel signal forming method and channel signal receiving method wherein when an upstream unit band and a plurality of downstream unit bands associated therewith are used to perform communications, the quality of downstream assignment control information can be prevented from being degraded. In a base station (100), the PDCCH signals including upstream assignment control information are limited to ones that are placed in some of the downstream unit bands. This can reduce the probability of performance of zero padding to downstream assignment control information having greater importance. Also in the base station (100), the PDCCH signals of the downstream unit bands other than the basic unit band include only downstream resource assignment information. For this reason, in the individual regions of the downstream unit bands other than the basic unit band, the bandwidth of the downstream unit bands is always used as a reference of size adjustment and hence requires no information size adjustment. As a result, there is no need of performing zero padding to the downstream assignment control information, so that the quality of downstream assignment control information can be prevented from being degraded.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Systems and Methods for Ofdm Transmission and Reception
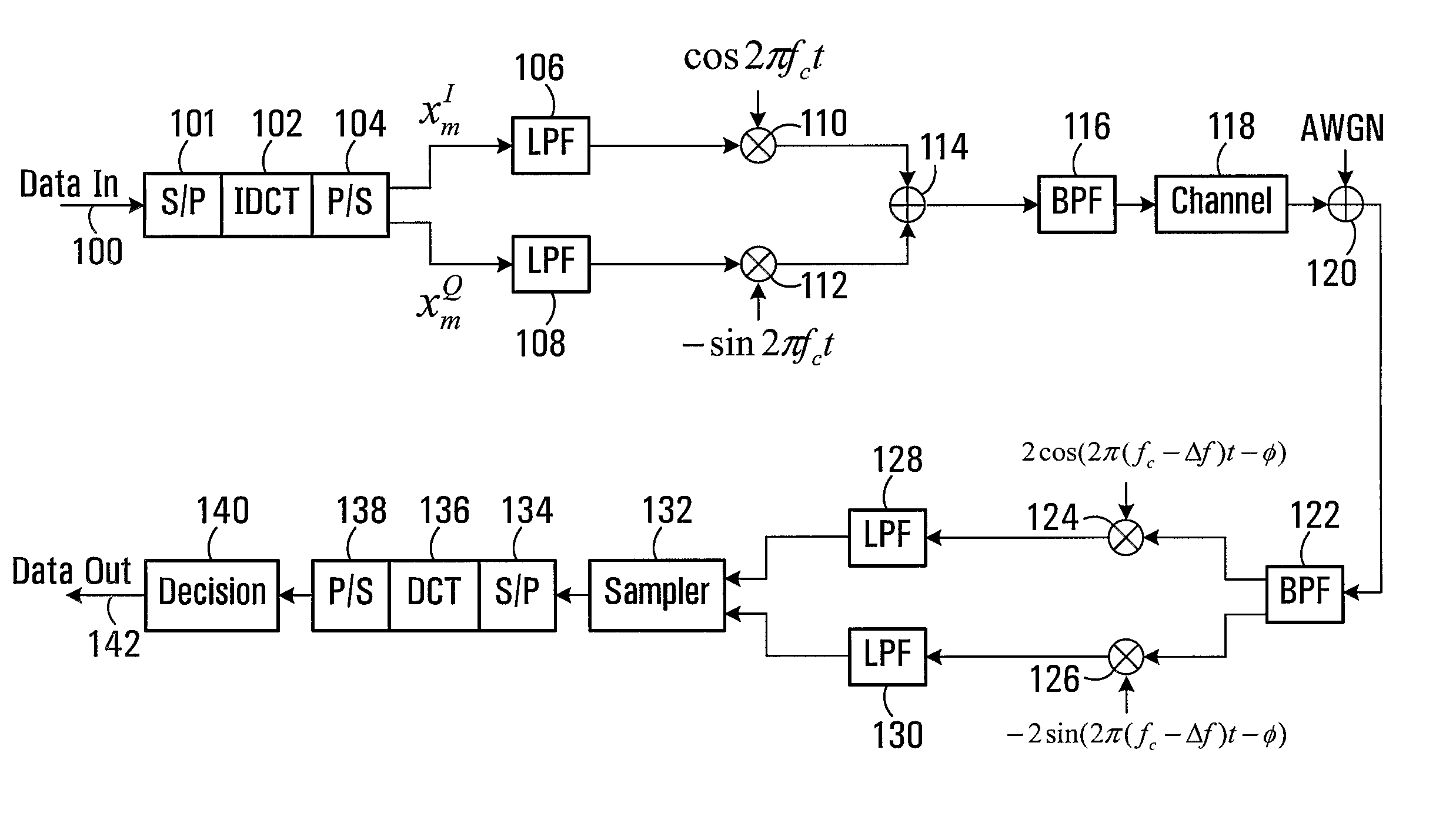
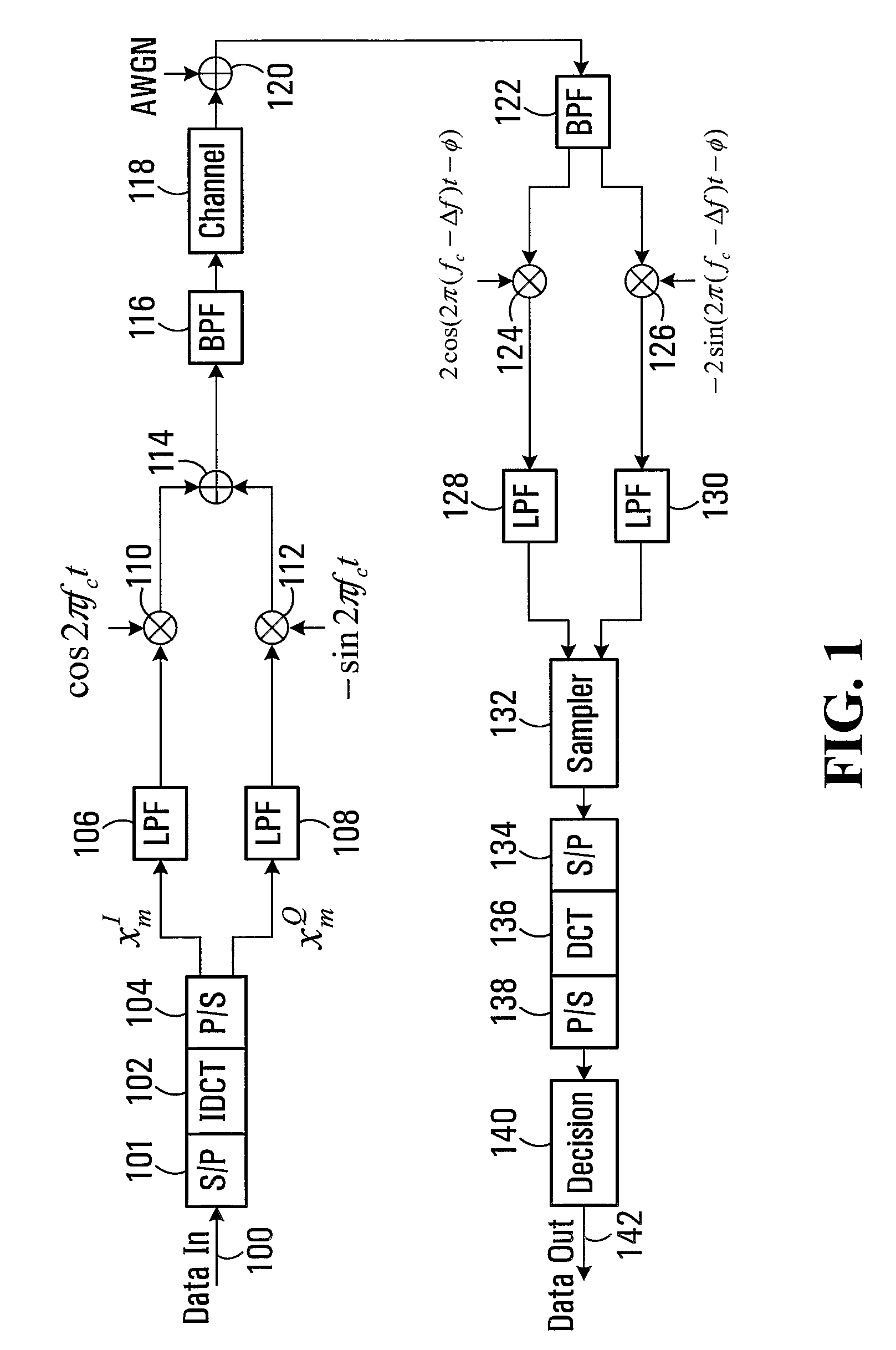
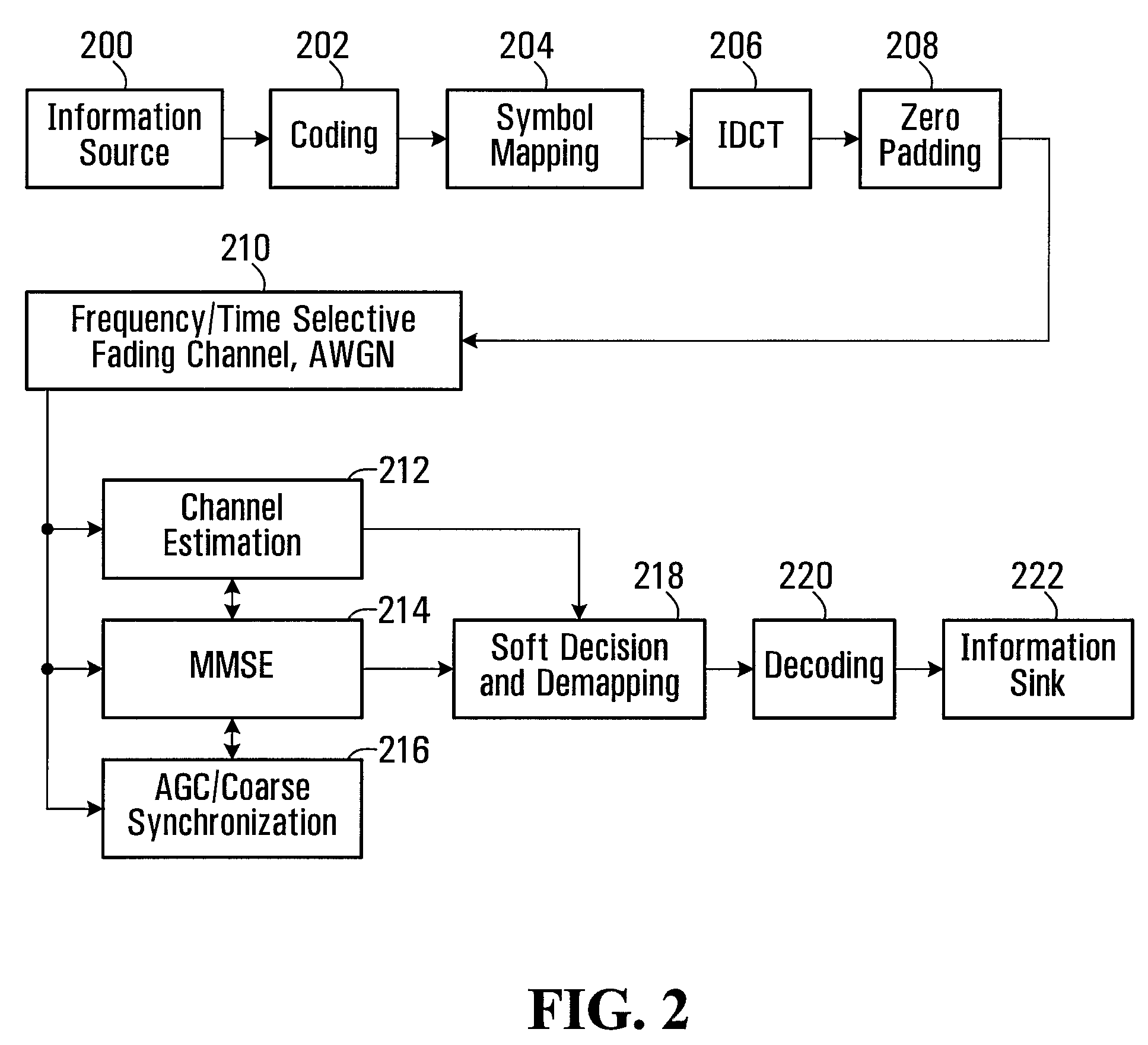
InactiveUS20080095267A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationZero paddingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A discrete cosine transform (DCT)-based orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) system is provided with a zero-padding guard interval and MMSE reception. The performance of the DCT-OFDM system with the zero-padding guard interval scheme and the minimum mean-square error (MMSE) receiver over time-varying multipath Rayleigh fading channels is investigated. The results show that employing the proposed DCT-OFDM system rather than the conventional DFT-OFDM system can provide better bit error rate performance in practical systems, by as much as 6 dB in signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Method for removing truncation artifacts in magnetic resonance images based on missing data reconstruction
InactiveCN101810480AImprove signal-to-noise ratioOvercoming Artifact ProblemsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFrequency spectrumMissing data
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
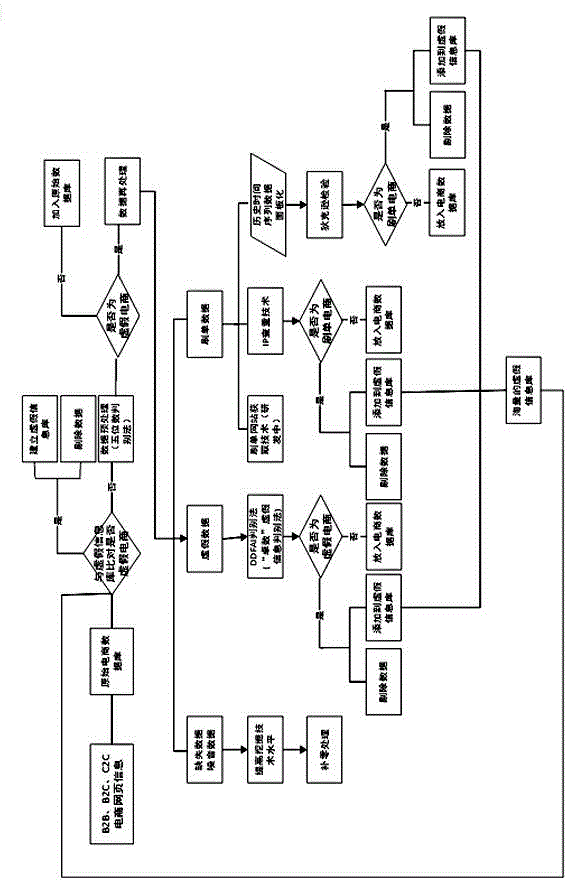
Method for preprocessing abnormal values of e-business sales amounts based on statistical discrimination process
InactiveCN104657503AMaster quicklyShorten the timeResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsZero paddingInformation repository
The invention discloses a method for preprocessing abnormal values of e-business sales amounts based on a statistical discrimination process. The preprocessing method comprises the following steps: improving data mining technologies and tools; performing preliminary verification on basic data; classifying abnormal values; enhancing comparison and elimination with a false information base, reducing missing data and noise data, and performing zero padding processing on real missing data; performing discrimination and verification on false data; performing verification processing on scalping data; comparing an acquired result with an abnormal database in a data acquisition process; and establishing a basic information base after forming a massive database, and performing batch processing on massive data. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has greater pertinence on abnormal e-business data, and ensures that the acquisition cycle can be shortened and the data accuracy can be greatly increased after the abnormal e-business data is checked; and moreover, the method is simple to operate and ensures that the time for customers to look up information can be saved.
Owner:INSPUR GROUP CO LTD
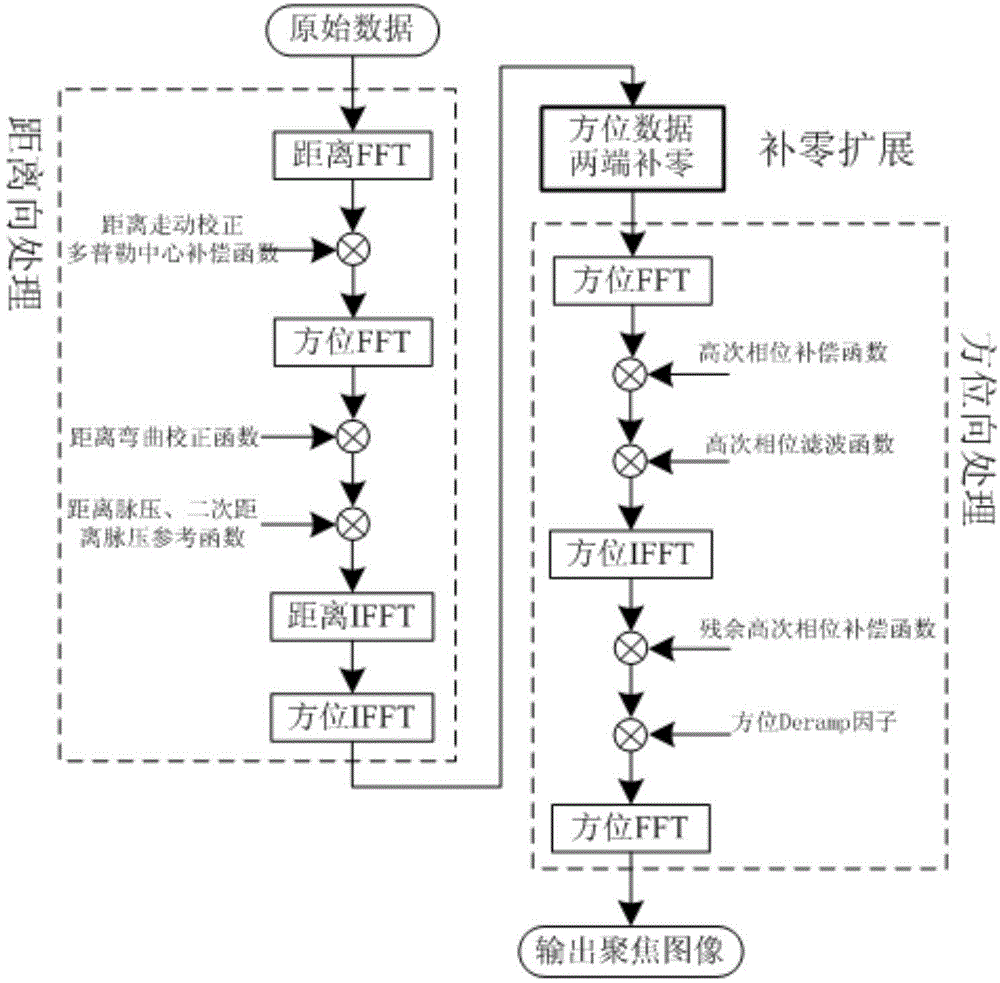
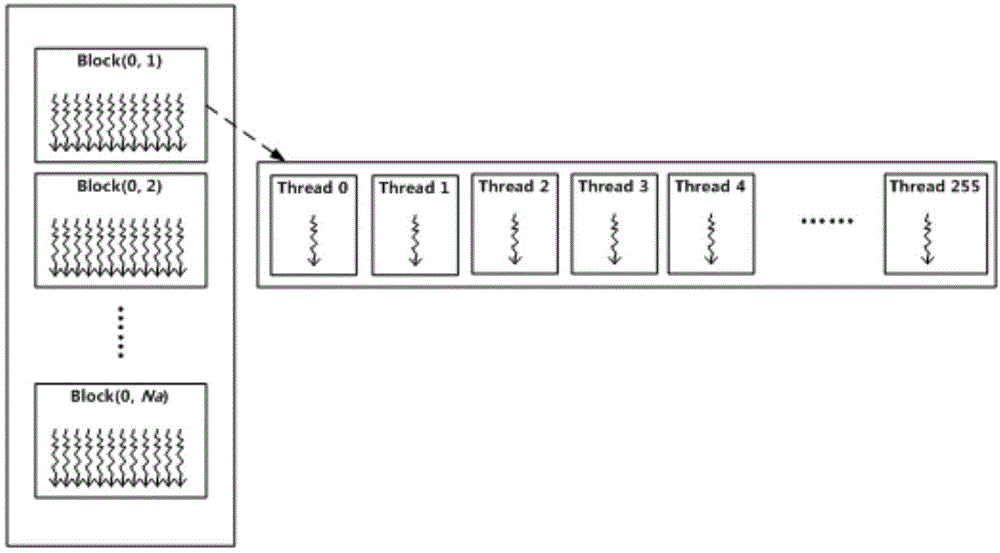
Missile-borne SAR forward-squint imaging method based on GPU
InactiveCN104459693ALow costReduced imaging timeSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionZero paddingTime domain
The invention belongs to the technical field of missile-borne SAR imaging, and particularly relates to a missile-borne SAR forward-squint imaging method based on a GPU. The method comprises the specific steps that the work parameter of a synthetic aperture radar is set on a GPU side, and stored in the GPU, and SAR raw echoed data are stored in the GPU in a matrix mode; on the GPU side, distance direction processing is carried out on an SAR raw echoed data matrix, and distance orientation two-dimensional time domain data are obtained; on the GPU side, zero padding expansion is carried out on a distance orientation two-dimensional time domain data matrix in the azimuth, and a distance orientation two-dimension time domain data matrix of Na'*Nr is obtained after azimuth zero padding expansion; on the GPU side, azimuth processing is sequentially carried out on the distance orientation two-dimension time domain data matrix obtained after azimuth zero padding expansion, and focused SAR image data are obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Coprime MIMO radar arrival direction estimation method based on multi-sample snapshots and set array signal discrete Fourier transform
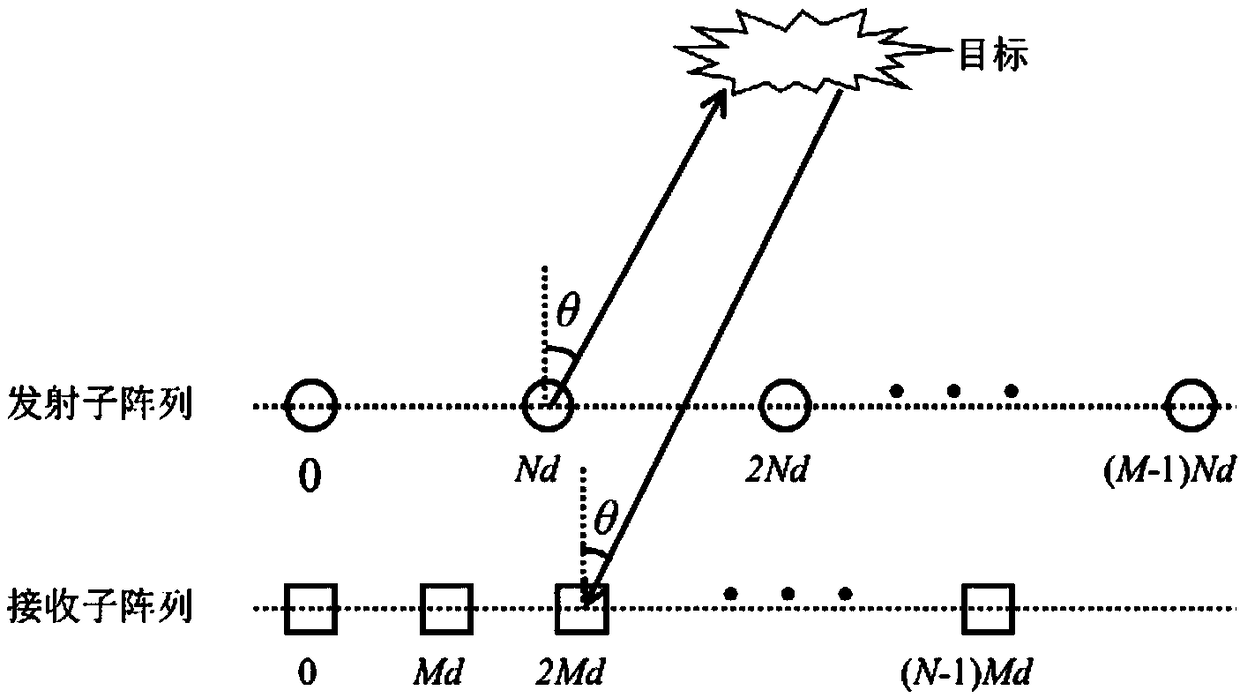
ActiveCN109471086ALarge array apertureHigh resolution performanceWave based measurement systemsZero paddingComputation complexity
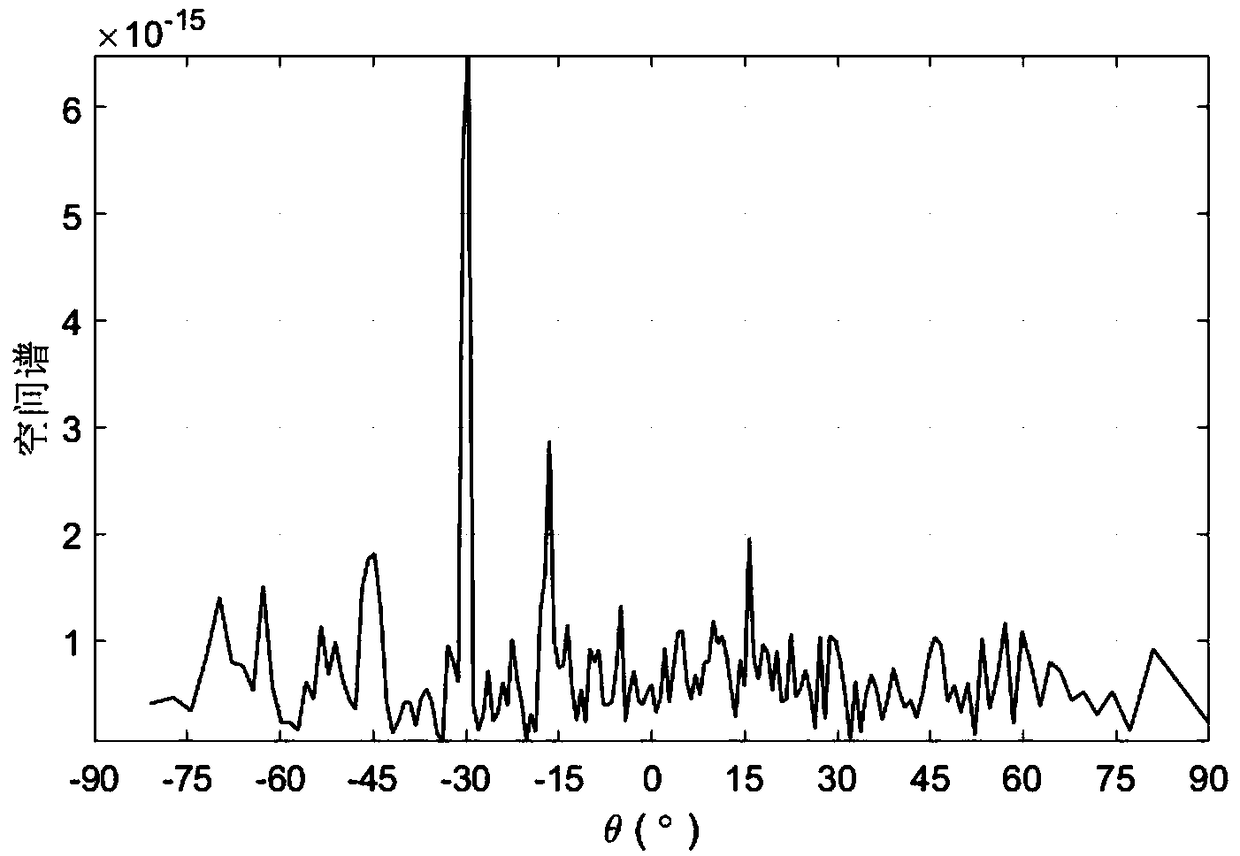
The invention discloses a coprime MIMO radar arrival direction estimation method based on multi-sample snapshots and set array signal discrete Fourier transform. The method mainly solves the problem that the calculation complexity of an existing method is high. The method comprises the steps that a homogeneous MIMO radar structure is established; reflected signals are received through a radar receiving sub-array, and modeling is carried out on radar output signals; the coprimey MIMO radar multi-sample snapshots and set array receiving signals are constructed; zero padding is carried out on themulti-sample snapshots and the set array receiving signals; the multi-sample snapshots and the set array receiving signals obtained after zero padding are subjected to sidelobe suppression; the multi-sample snapshots and the set array receiving signals obtained after filtering are subjected to discrete Fourier transform to construct a spatial spectrum; arrival direction estimation is conducted according to the obtained spatial spectrum. A larger array aperture is obtained under the condition that the number of physical array elements is certain, and the calculation complexity of arrival direction estimation is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
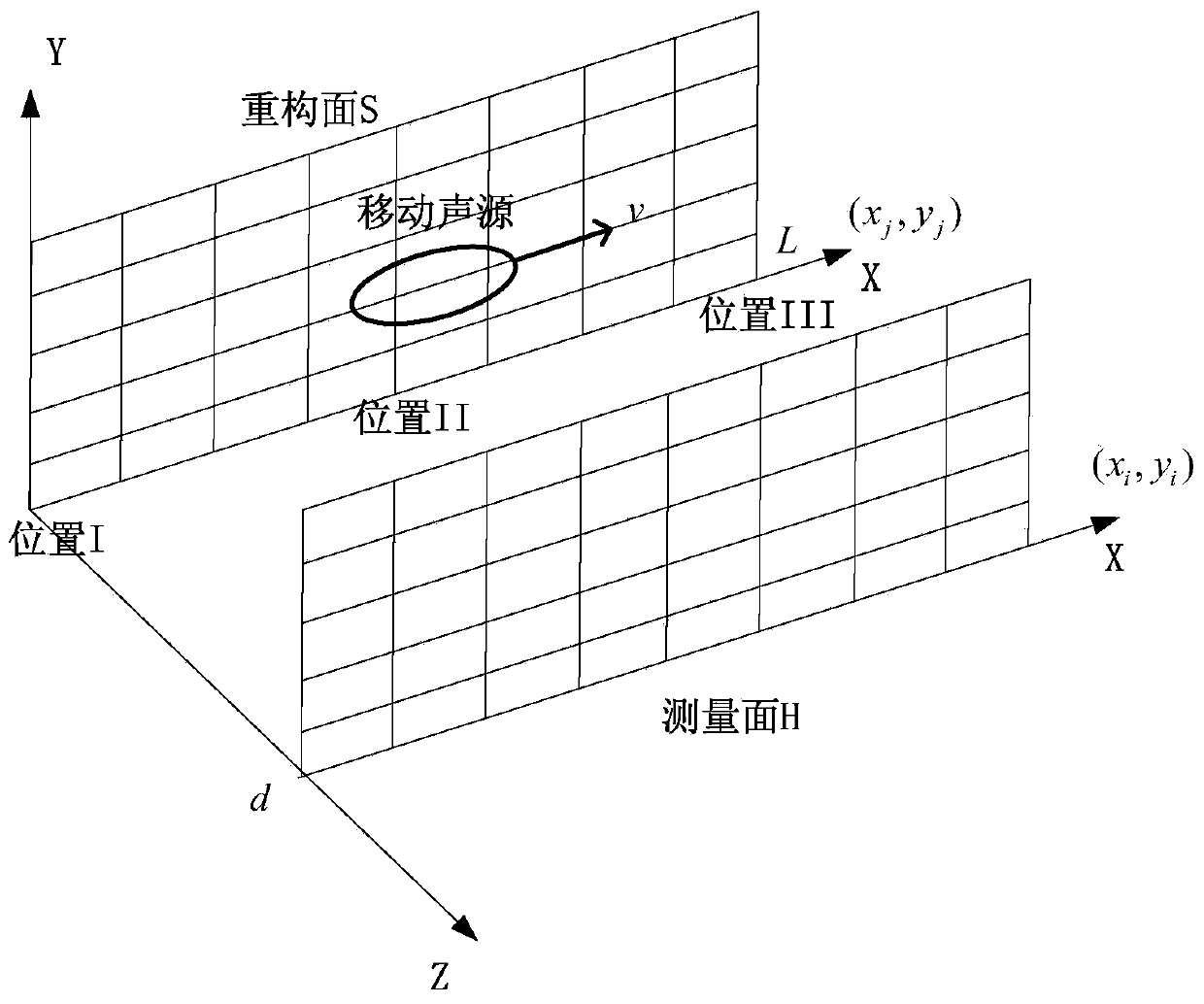
Movable noise source recognizing method based on local near field acoustical holography method
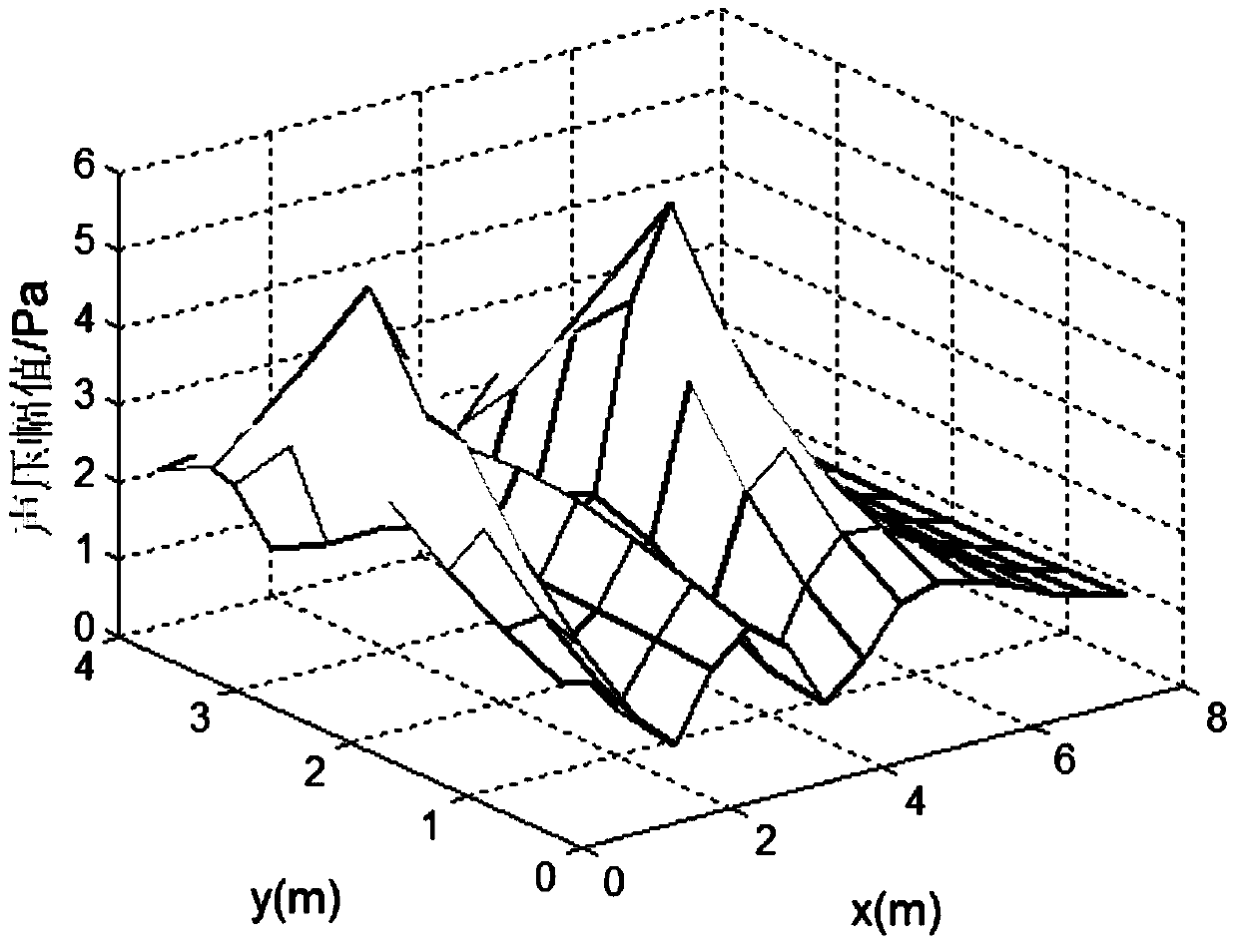
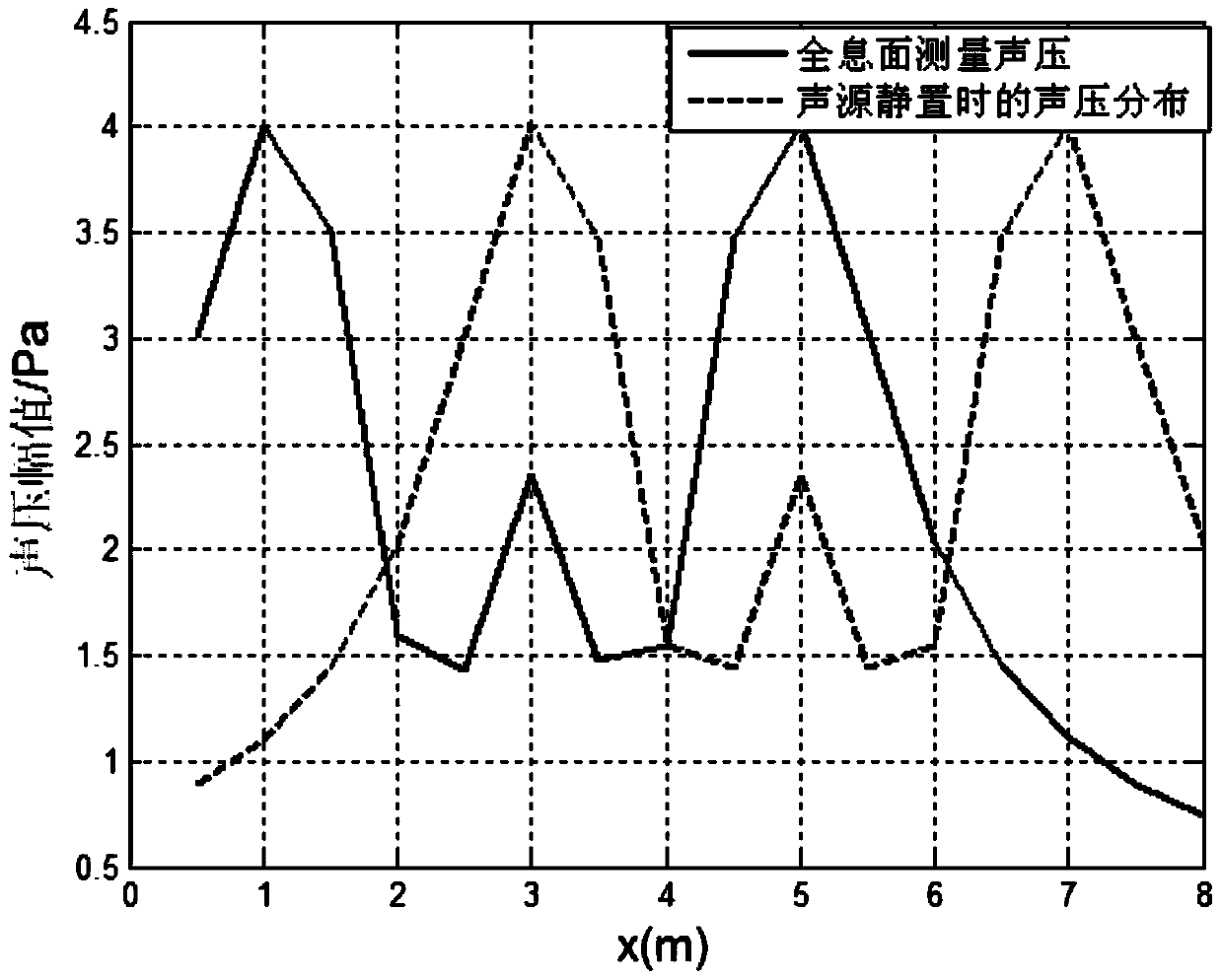
InactiveCN103941229ASimple calculationShort calculation timePosition fixationZero paddingTransmission matrix
The invention belongs to the field of noise like sound field reconstruction and visualization, and particularly relates to a movable noise source recognizing method based on a local near field acoustical holography method. The movable noise source recognizing method includes the steps that sound pressure on a measuring plane H is measured; Doppler effect removal is carried out on the sound pressure obtained through measuring to obtain sound pressure, not containing the Doppler effect, on the measuring plane H; zero padding expansion is performed on the sound pressure on the measuring plane H to obtain sound pressure on a measuring plane H+; a transmission matrix between the sound pressure on the measuring plane H+ and the sound pressure on a reconstruction plane S is calculated; the sound pressure on the reconstruction plane S is solved. Based on the local near field acoustical holography method, the movable noise source recognizing method has the advantages of being simple in calculation, short in calculation time, high in calculation efficiency and the like compared with a traditional method.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multi-pose face recognition method based on face mean and variance energy images
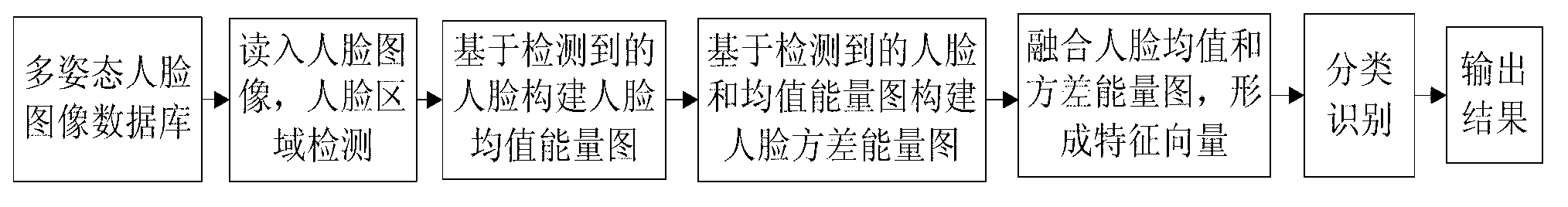
InactiveCN103218606AImprove performanceWeaken noise interferenceCharacter and pattern recognitionZero paddingFeature vector
The invention relates to a biological feature identity recognition technique, in particular to a multi-pose face recognition method based on face mean and variance energy images. The method comprises the following steps of detecting face areas to carry out the size normalizing on the images of the face areas; building a narrow face mean energy image and a generalized face mean energy image; building a narrow face variance energy image and a generalized face variance energy image; combining obtained features, so as to obtain a final feature vector; and classifying and recognizing by a nearest neighbor classifier based on Euclidian distance. The method has the advantages that the storage space is well saved, the calculation complexity is reduced, and the noise interference in the single-frame image is weakened; and the face energy images contain face contour information under multiple poses, and have large advantage for recognizing the faces with large-angle pose change, the zero-padding processing is not needed, and the recognition property of the multi-pose face is improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Image interpolation method and image interpolation device
InactiveCN104574277AAvoid distortionReduce computational complexityImage enhancementImage analysisZero paddingSource image
The invention discloses an image interpolation method and an image interpolation device. The image interpolation method includes: performing interpolation zero padding on source image pixels to form upper sampling images; acquiring benchmark interpolation kernels by the aid of the upper sampling images; performing convolution on the source image pixels, the benchmark interpolation kernels and direction displacement coefficient matrixes and performing benchmark kernel interpolation based on direction displacement. According to the image interpolation method and the image interpolation device, the direction displacement matrixes are introduced on the basis of diagonal double cubic interpolation, so that the benchmark interpolation kernels are invariant, the matrixes are displaced according to the convolution direction, the interpolation images are favorably optimized in all directions, continuity of image content is taken into consideration, and distortion of high-frequency details of image edges and the like is avoided.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
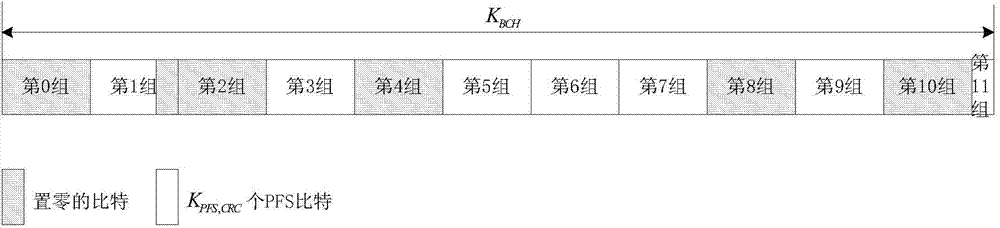
Signaling coding method and signaling coding system based on BCH code and short LDPC code cascading
The invention provides a signaling coding method and a signaling coding system based on BCH code and short LDPC code cascading. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a zero padding group table of the correspondence between the sequences of zero padding groups divided in turn and the positions of the zero padding groups based on a default LDPC code check matrix and establishing a punching group table of the correspondence between the sequences of punching groups divided in turn and the positions of the punching groups based on the default LDPC code check matrix; zero-padding an input signaling after scrambling treatment according to the zero padding group; sequentially calculating the BCH code check bit and the LPDC code check bit corresponding to the signaling after zero padding based on preset BCH code and LPDC code error correction coding parameters; and determining the number of punching bits of the LPDC code check bit based on the preset linear relationship between the code length of the signaling and the number of punching bits, and punching the LDPC code check bit according to the number and according to the punching group table.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Block time domain equalizer for time reversal-space time block code system and method for encoding and equalizing received signal in the block time domain equalizer
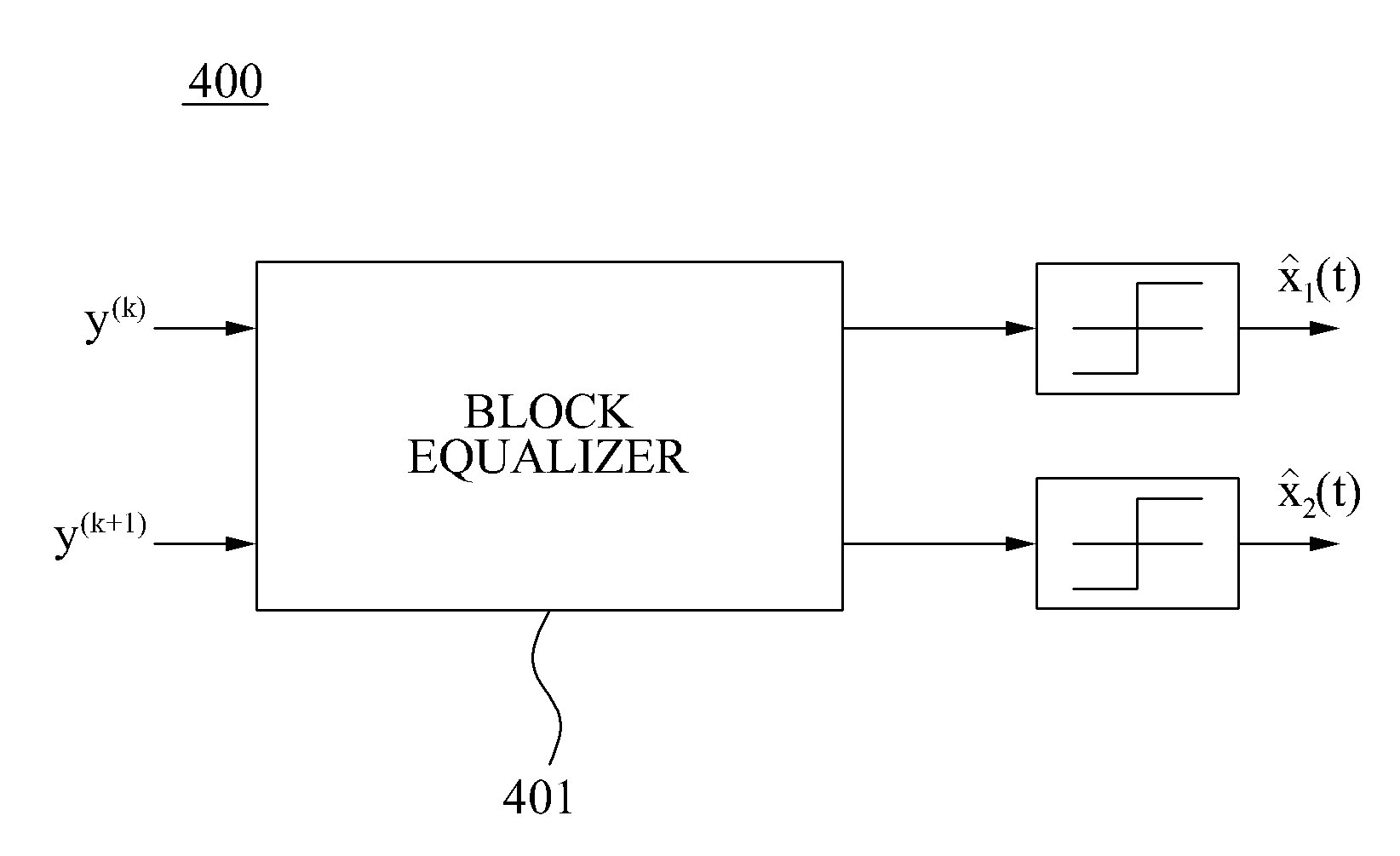
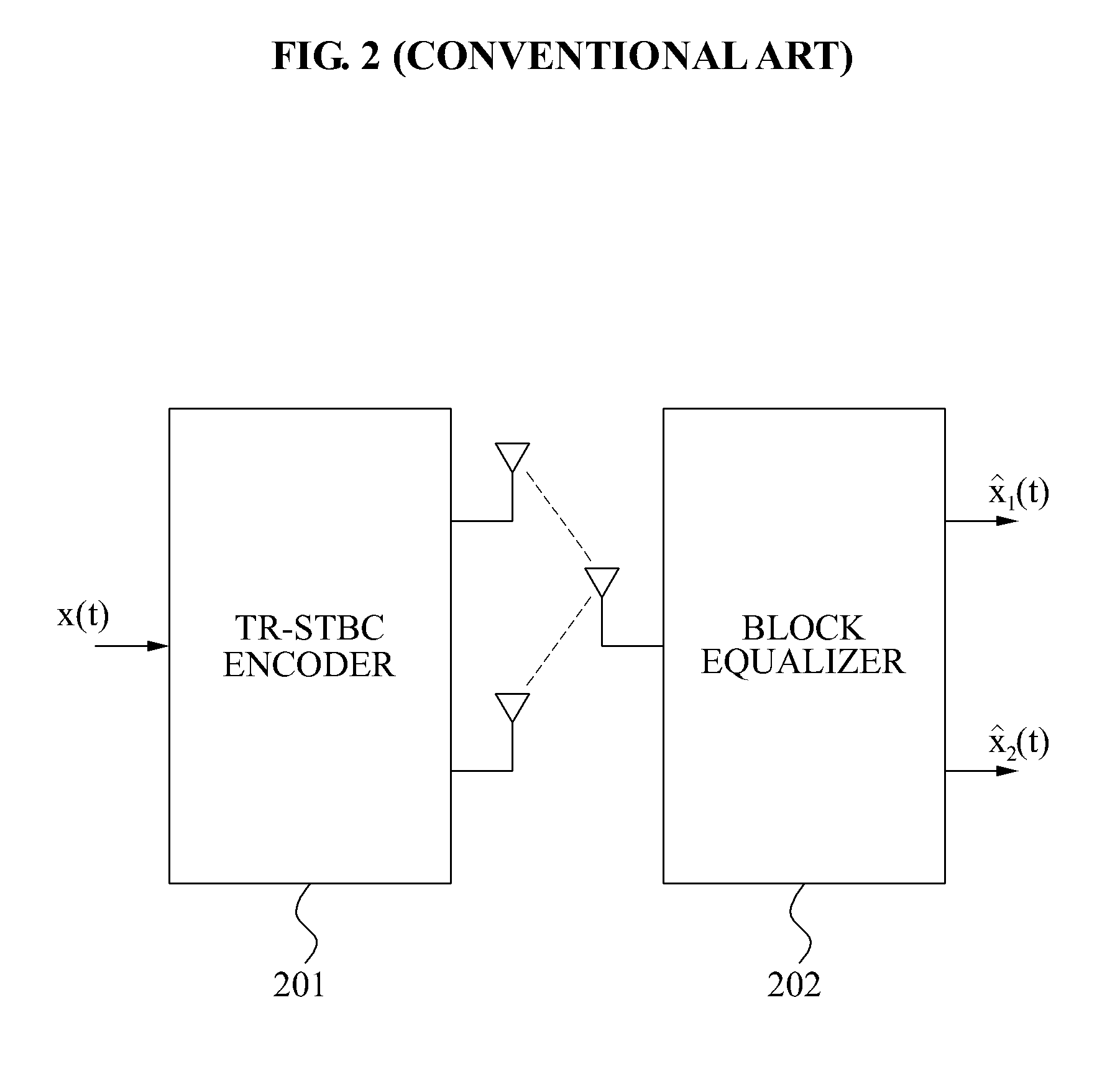
ActiveUS20080080613A1Reduce computational complexityEasy to driveMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainZero padding
Provided is a block Time Domain Equalizer (TDE) for a Time Reversal-Space Time Block Codes (TR-STBC) system. The block TDE comprises a block equalizer which generates an output based on an equalizer tap weight with respect to two consecutively received blocks, an equalizer tap weight updating unit which generates an error vector based on the output and the equalizer tap weight and updates the equalizer tap weight using the error vector, and a signal processing unit which processes the output into a digital signal wherein zero padding is eliminated from the output.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in communication/broadcasting system
ActiveUS20140258815A1Improve performanceError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsZero paddingComputer science
An apparatus and a method for performing shortening and puncturing in case of performing encoding and decoding using a parity test matrix in a communication / broadcasting system are provided. The method includes determining a number of zero-padding bits, determining a number Npad of bit groups in which all bits are padded with zeros, padding the all bits within 0th to (Npad−1)th bit groups with zeros based on a shortening pattern, encoding information bits including the zero-padded bits to generate a codeword. Here, the shortening pattern is defined in a sequence of bit groups defined as 9, 8, 15, 10, 0, 12, 5, 27, 6, 7, 19, 22, 1, 16, 26, 20, 21, 18, 11, 3, 17, 24, 2, 23, 25, 14, 28, 4, 13, 29.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Indoor navigation positioning system based on ultra wide band
InactiveCN103281281AStrong anti-multipath abilityHigh positioning accuracyRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalBand-pass filter
The invention discloses an indoor navigation positioning system based on an ultra wide band. At a fixed transmitting end, a transmitter adopts a PRN (Pseudo-Random Noise) sequence to generate an input signal, after input signal source coding and channel coding, a baseband modulation signal is generated through inverse Fast fourier transform, Zero Padding is added to the baseband modulation signal, the baseband modulation signal is subjected to digital to analog conversion to form a baseband analog signal, the baseband analog signal modulates a carrier with the central frequency of 3.432GHz to form an ultra wide band signal, and the ultra wide band signal is transmitted through a transmitting antenna of the transmitter; and at a mobile receiving end, a receiving antenna of a mobile receiver receives the ultra wide band signal, after passing a band-pass filter and a low-noise amplifier, the ultra wide band signal is subjected to down-conversion and analog to digital conversion to obtain a baseband digital signal, the baseband digital signal is subjected to synchronization and channel equalization, and finally primary information of the transmitting end is obtained through reverse processing programs of the fixed transmitting end.
Owner:HUADONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECHN INST OF ANHUI PROVINCE
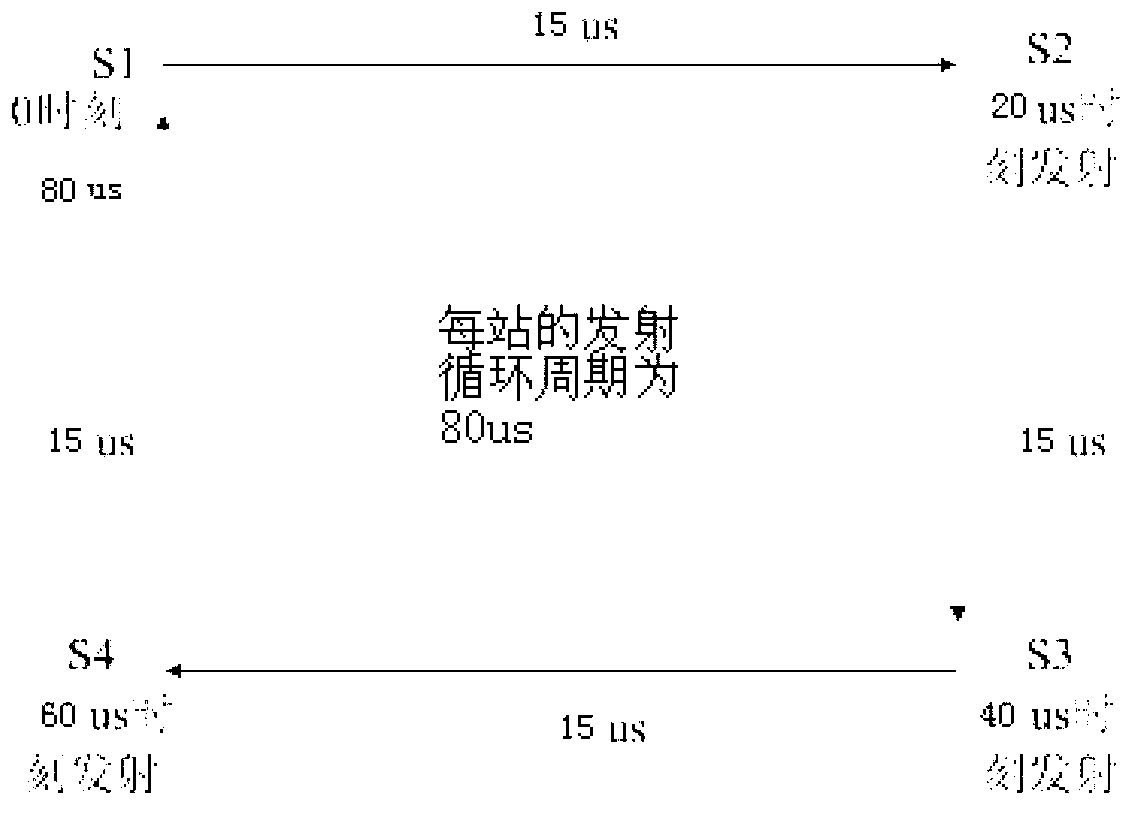
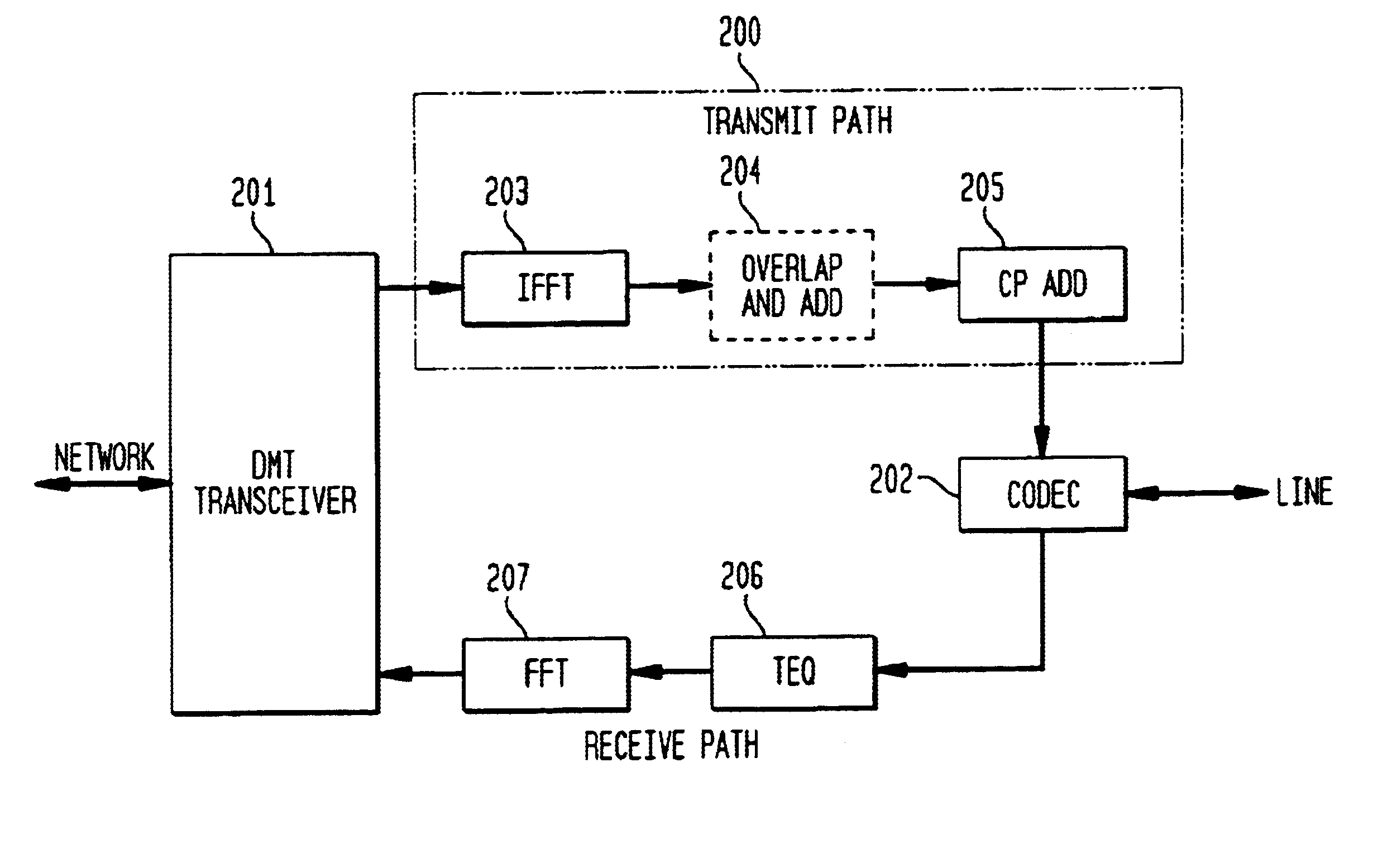
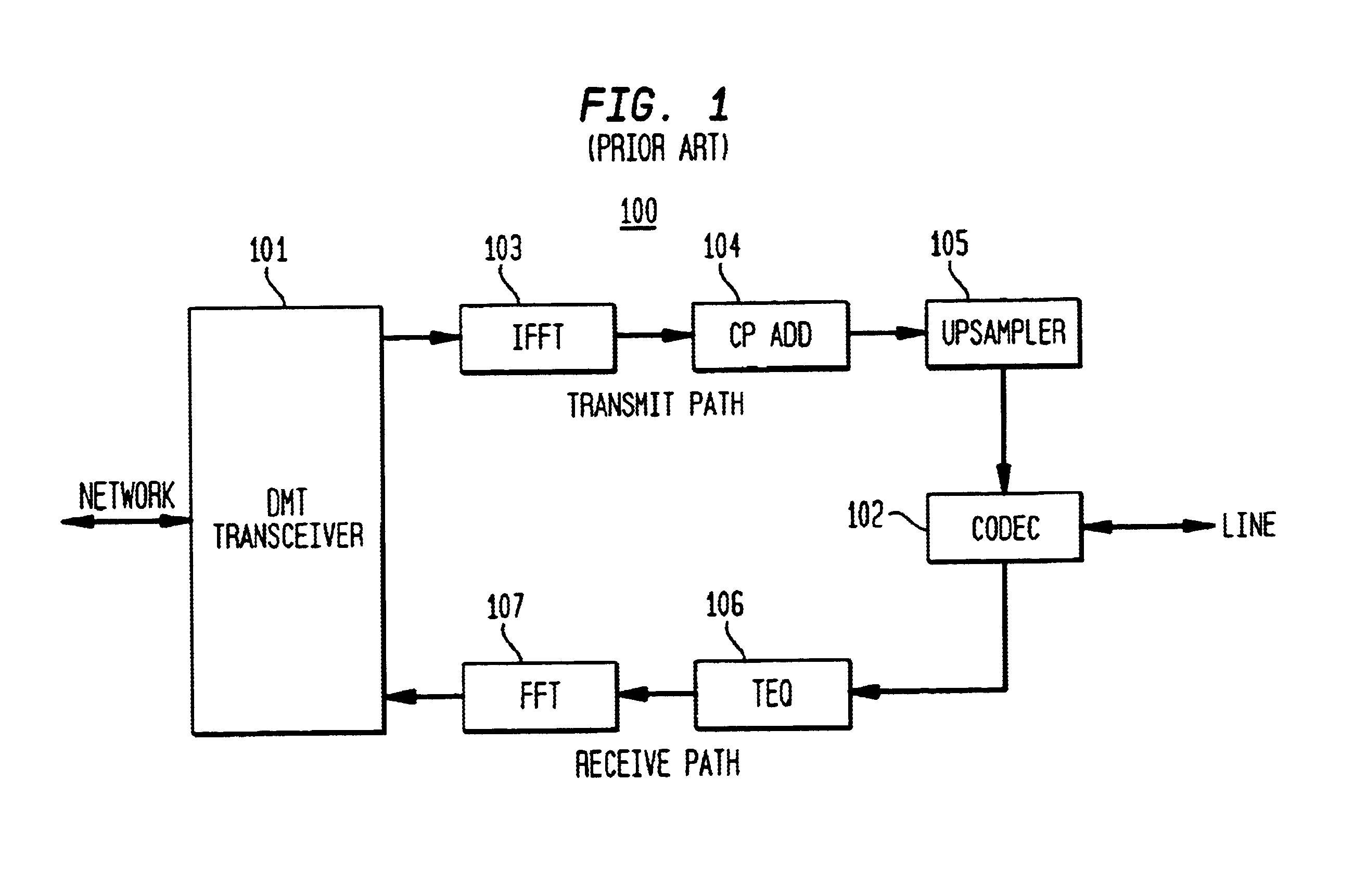
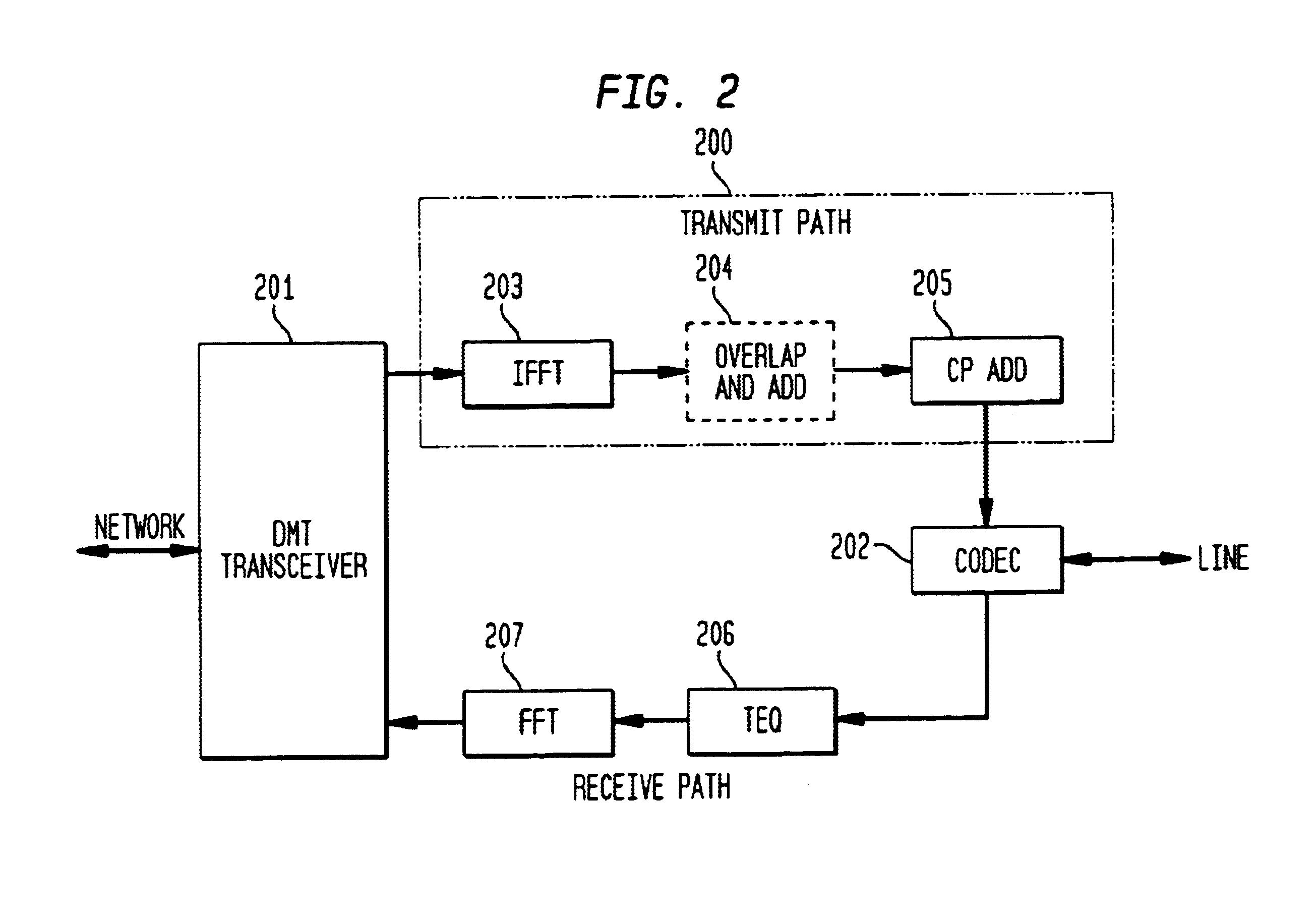
Transmission rate compensation for a digital multi-tone transceiver
InactiveUS6873650B1Difference in transmission rateTime-division multiplexSecret communicationFast Fourier transformZero padding
A circuit compensating for the difference in transmission rate of digital samples generated in transmit and receive paths between a user and a transceiver processing in the frequency domain, such as a digital multi-tone (DMT) transceiver. Compensation of the DMT transmission rate in the receive path in accordance with exemplary embodiments of the present employs zero-padding of the frequency domain coefficients generated by the DMT transceiver prior to applying an inverse transform, such as the inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT). Zero-padding the frequency domain coefficients allows for the compensation of the transmission rate in the receive path by generating digital samples from the frequency domain coefficients with an inverse transform having a rate matched to the frequency domain transform and rate employed in the transmit path.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD +1
Low-complexity large-scale MIMO channel parameter estimation method
ActiveCN108683619AReduce data volumeReduce complexityTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionPeak valuePollution
A low-complexity large-scale MIMO channel parameter estimation method comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing a MIMO system channel model; step 2, after a base station receives data, performing discrete Fourier transform on the received data by using an FFT algorithm; step 3, reconstructing a continuous spatial domain spectrum of received signals for an obtained spatial discrete spectrum of the receive signals through interpolation; and step 4, analyzing the continuous spatial domain spectrum obtained in the step 3 and estimating an angle of arrival and amplitude attenuation of thereceived signals on different physical paths. According to the method provided by the invention, the spatial discrete spectrum of the signals is obtained through the FFT algorithm and then the continuous spatial domain spectrum of the signals is obtained by means of zero-padding and interpolation techniques, so that the spatial continuous spectrum of the received signals can be recovered more accurately. Finally, incident angle parameters and amplitude of the signals when the signals arrive at the base station through physical channels can be estimated according to a peak value of the continuous spatial spectrum. The algorithm is low in complexity and pilot pollution does not exist.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV CITY COLLEGE
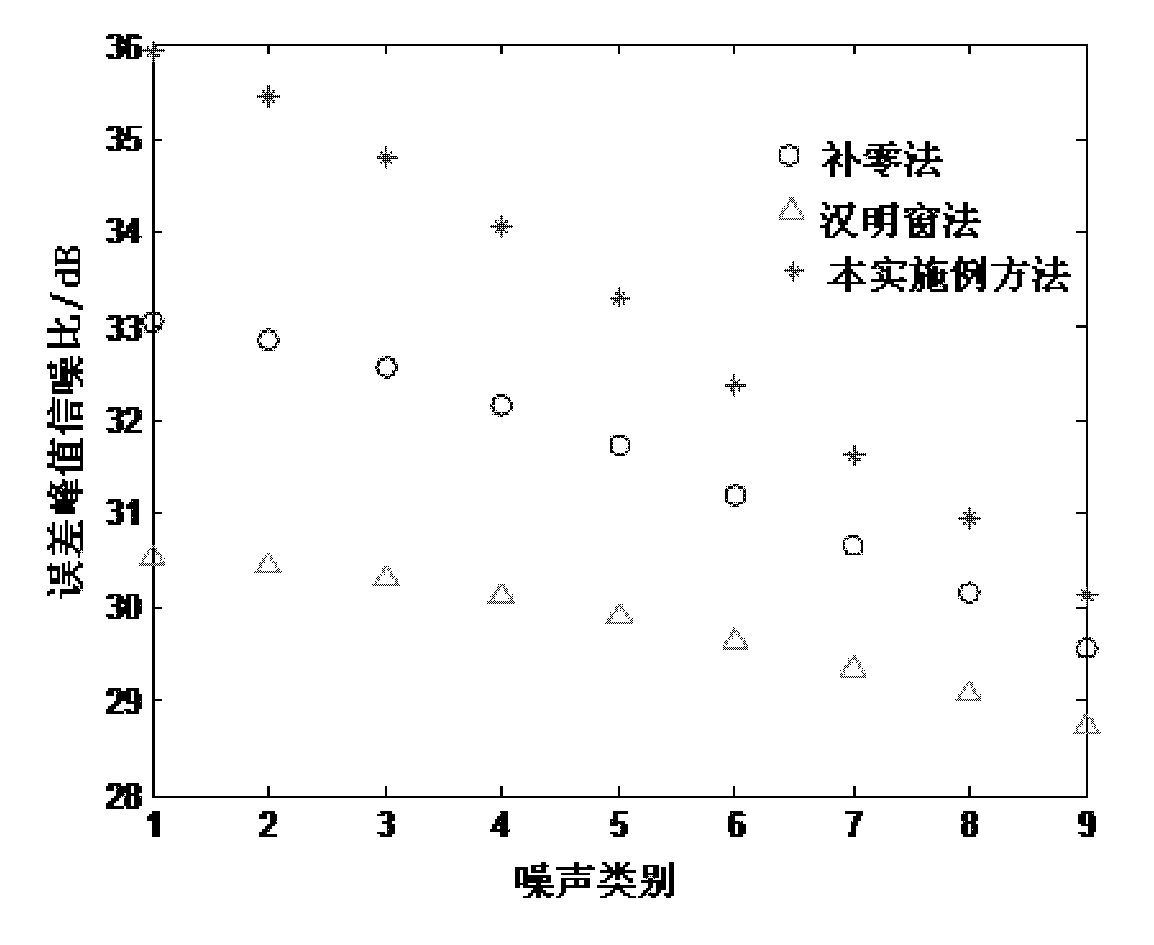
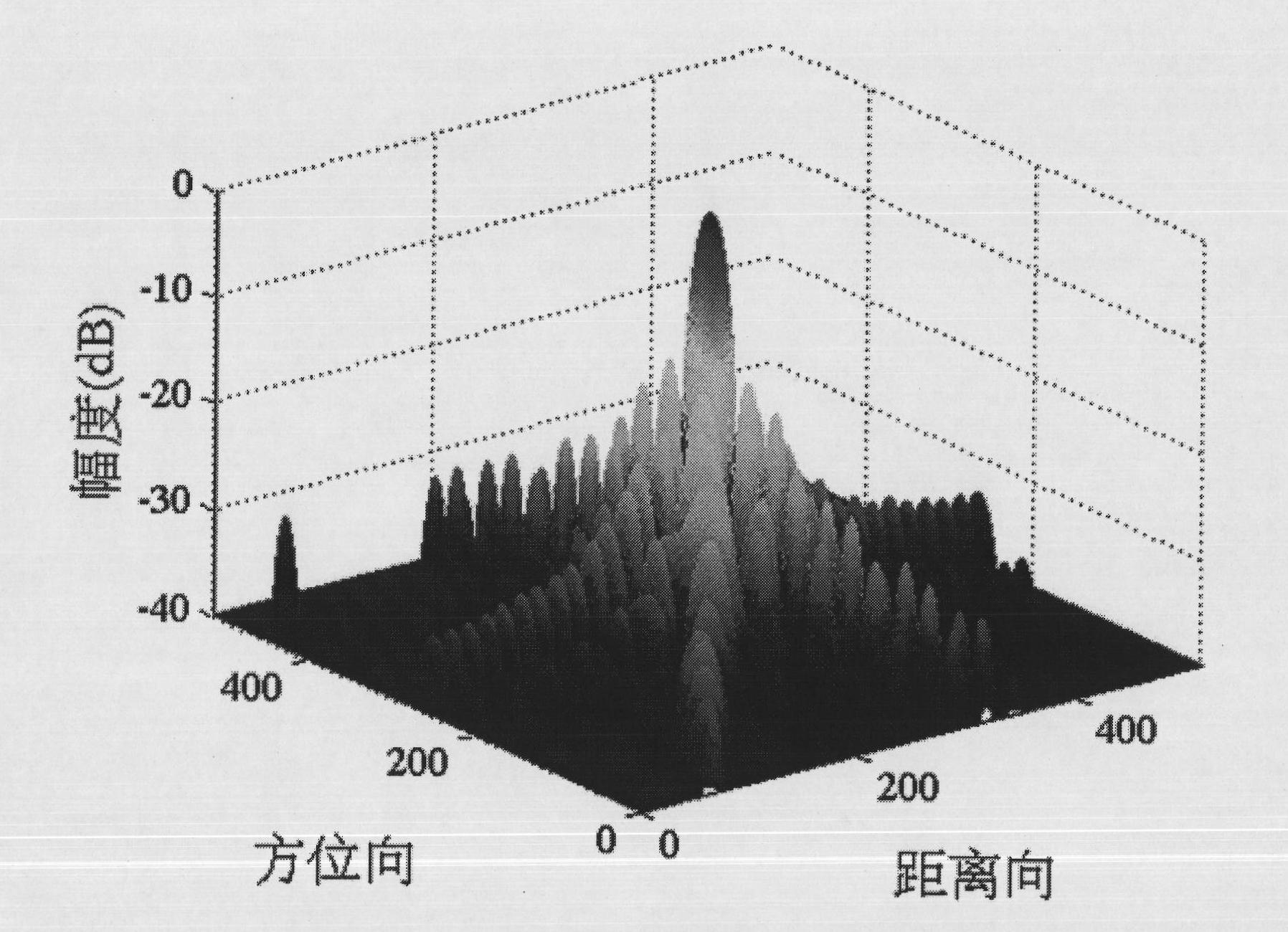
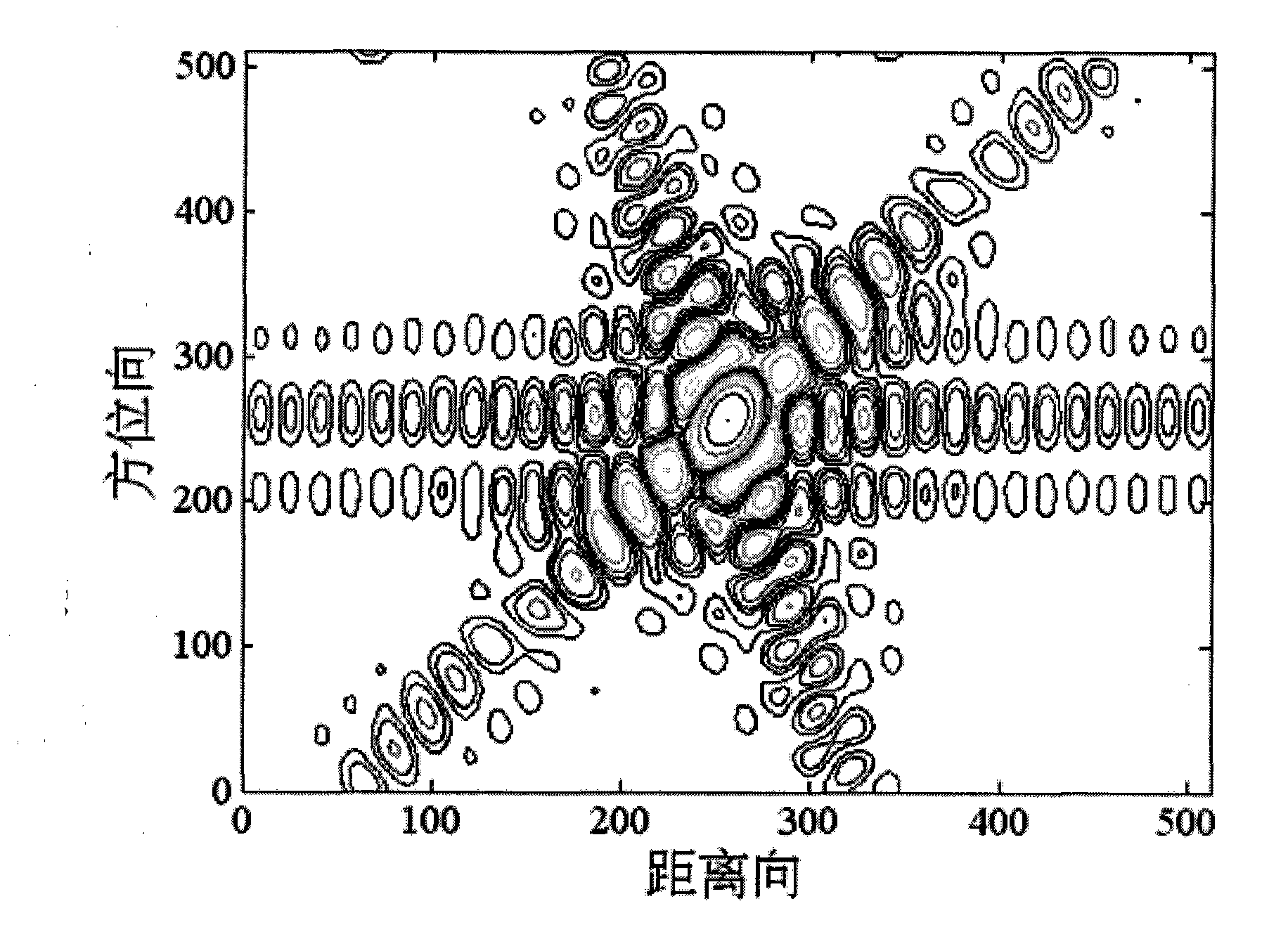
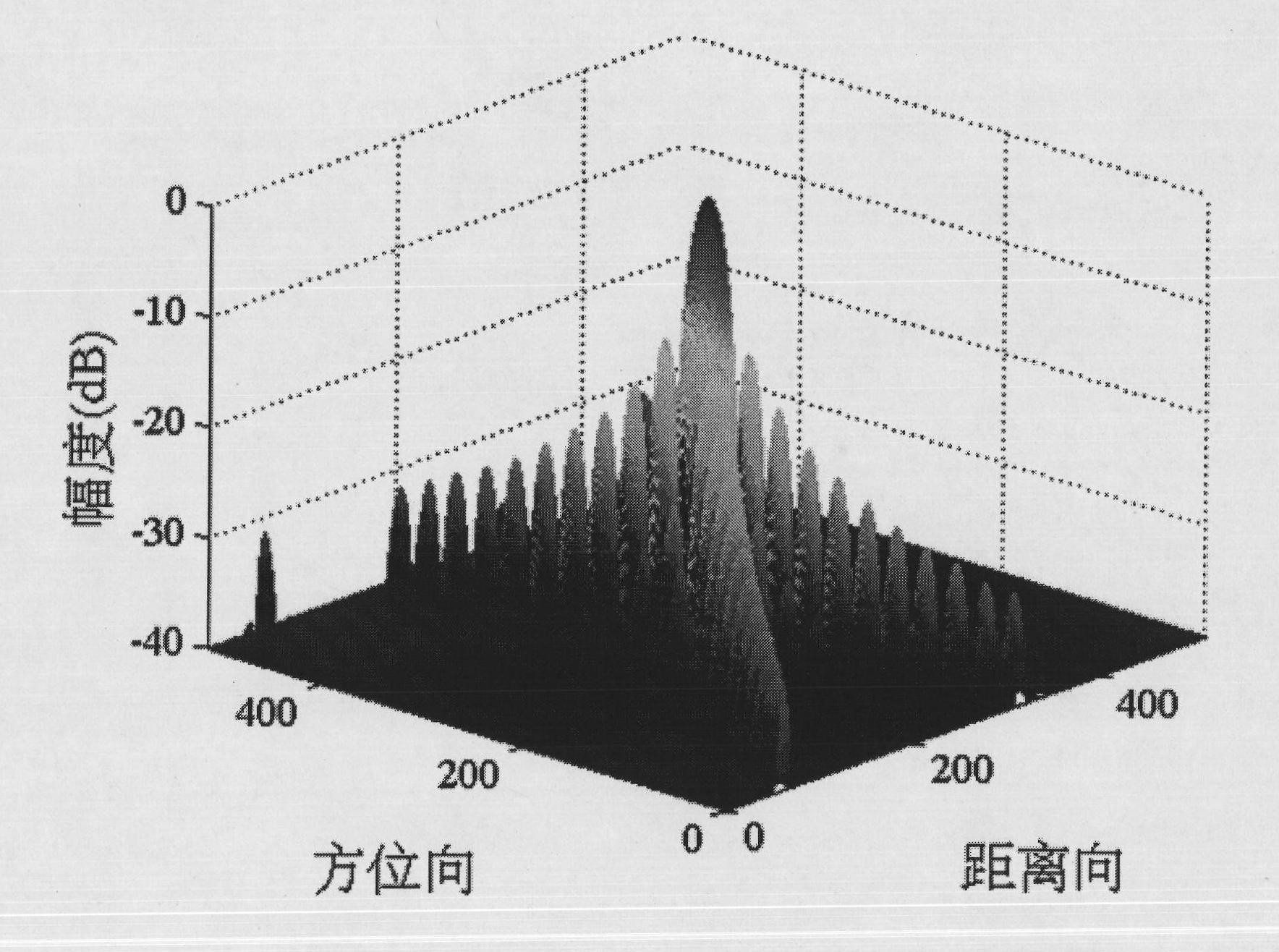
Self-adaption two-dimensional interpolation method for synthetic aperture radar point target imaging quality assessment
InactiveCN101806893ACorrect interpolationPrecisely refine imagesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging qualityPoint target
The invention discloses a self-adaption two-dimensional interpolation method for synthetic aperture radar point target imaging quality assessment, which comprises the following steps: utilizing two-dimensional fast fourier transform to transform a point target imaging result into a two-dimensional frequency domain, adaptively determining interpolation location of each row and each column in a two-dimensional spectrum matrix, and then utilizing two-dimensional fast fourier inverse transform to transform the data after frequency domain zero-padding into a two-dimensional time-domain matrix to obtain an interpolation result. Under the condition that the synthetic aperture radar works at any squint angle, and whether imaging processing compensates the fixed phase introduced by reference distance, the method can correctly carry out interpolation on the point target imaging result, and is helpful to obtain more accurate point target imaging quality assessment.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com