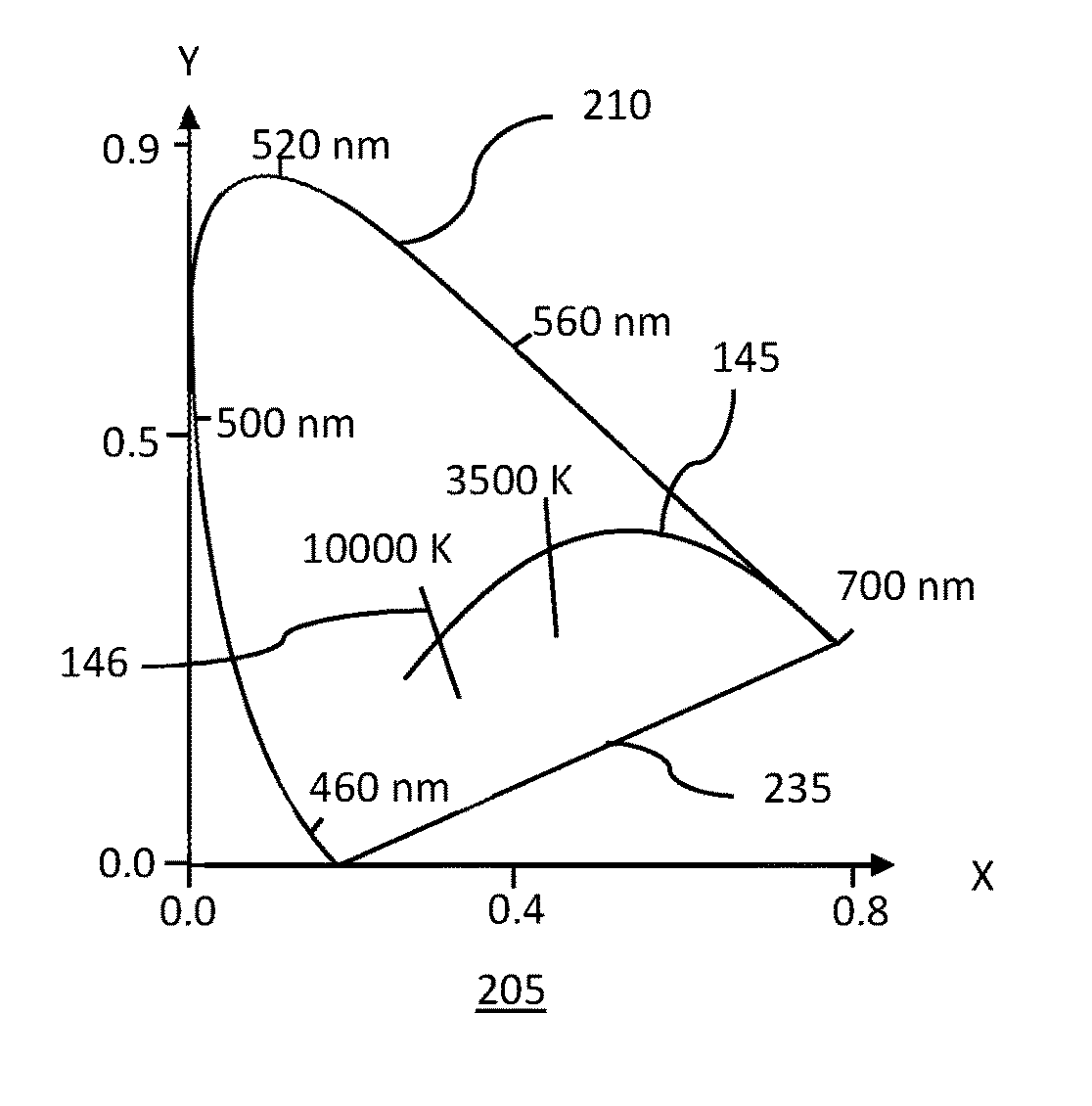
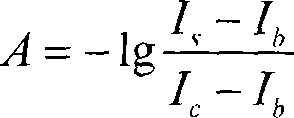Patents
Literature
502 results about "Continuous spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, a continuous spectrum usually means a set of attainable values for some physical quantity (such as energy or wavelength) that is best described as an interval of real numbers, as opposed to a discrete spectrum, a set of attainable values that is discrete in the mathematical sense, where there is a positive gap between each value and the next one.
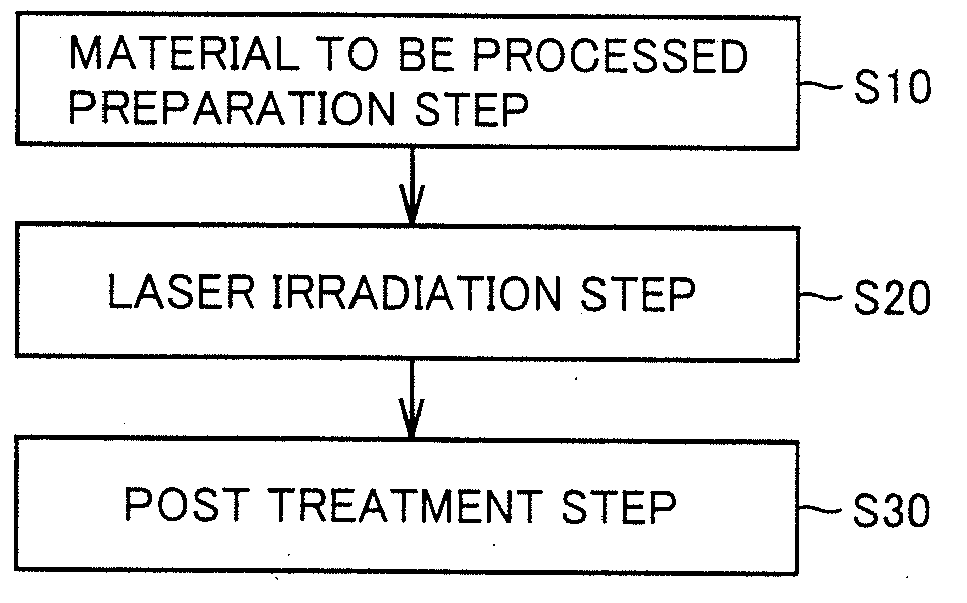
Laser processing method
ActiveUS20120255935A1Good body shapeReduce processing costsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesLaser processingOptoelectronics
There is obtained a laser processing method by which an excellent shape of a cut surface can be achieved and an increase in cost can be suppressed. A laser processing method includes the steps of: preparing a material to be processed; and forming a modified area in the material to be processed, by irradiating the material to be processed with laser beam. In the aforementioned step, pulsed laser beam having a continuous spectrum is focused with a lens, thereby forming a focusing line constituted by a plurality of focuses that are obtained by predetermined bands forming the continuous spectrum of the laser beam, and the material to be processed is irradiated with the laser beam such that at least a part of the focusing line is located on a surface of the material to be processed, thereby forming the modified area on an axis of the focusing line.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
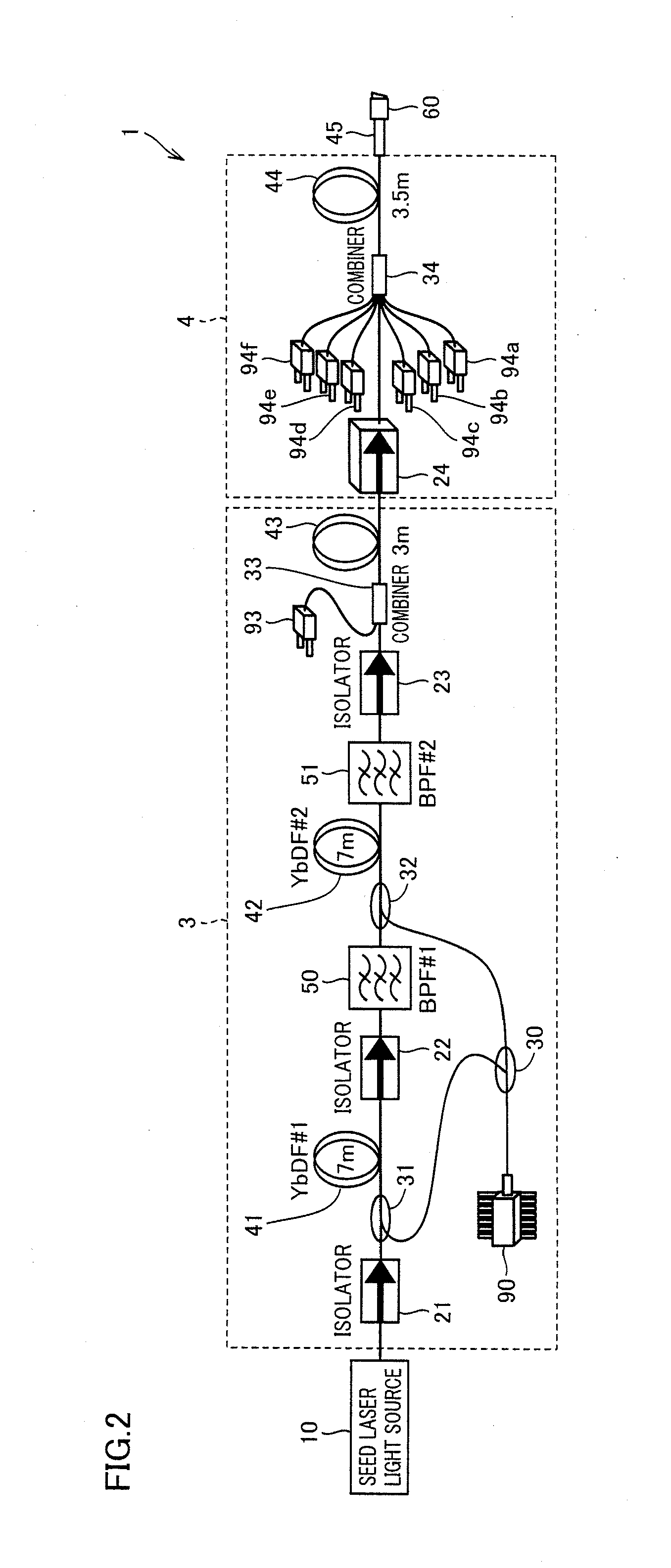
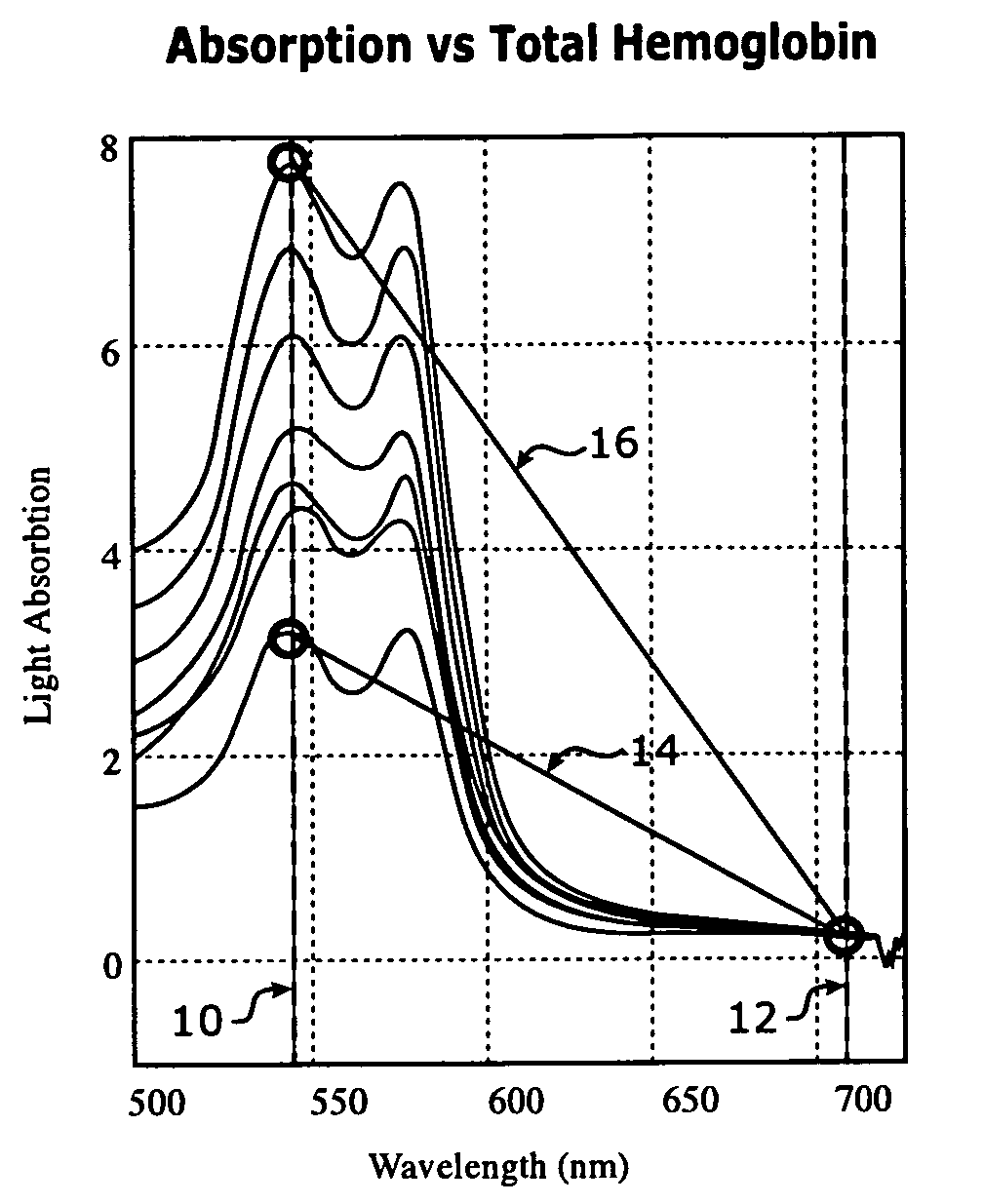
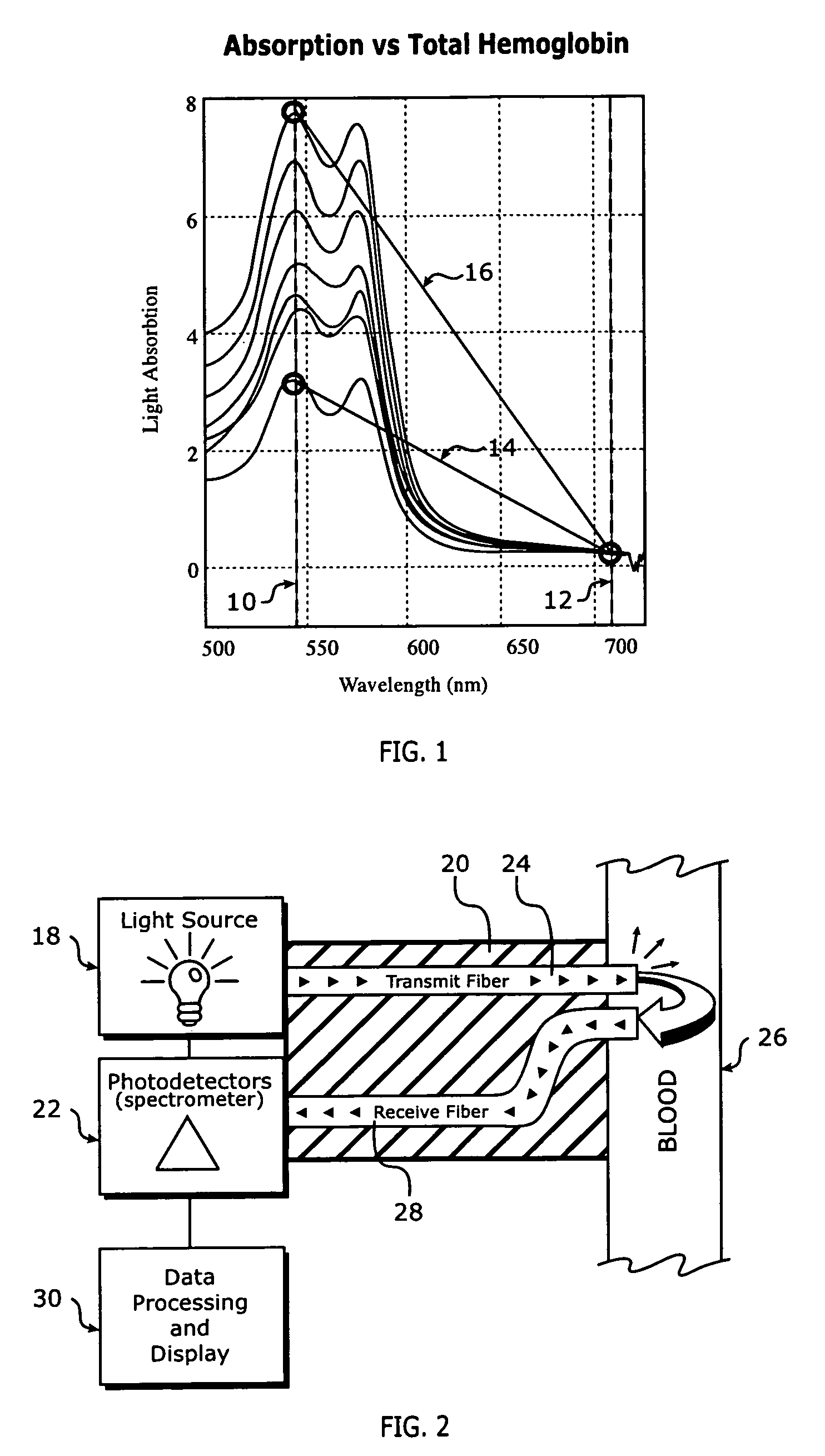
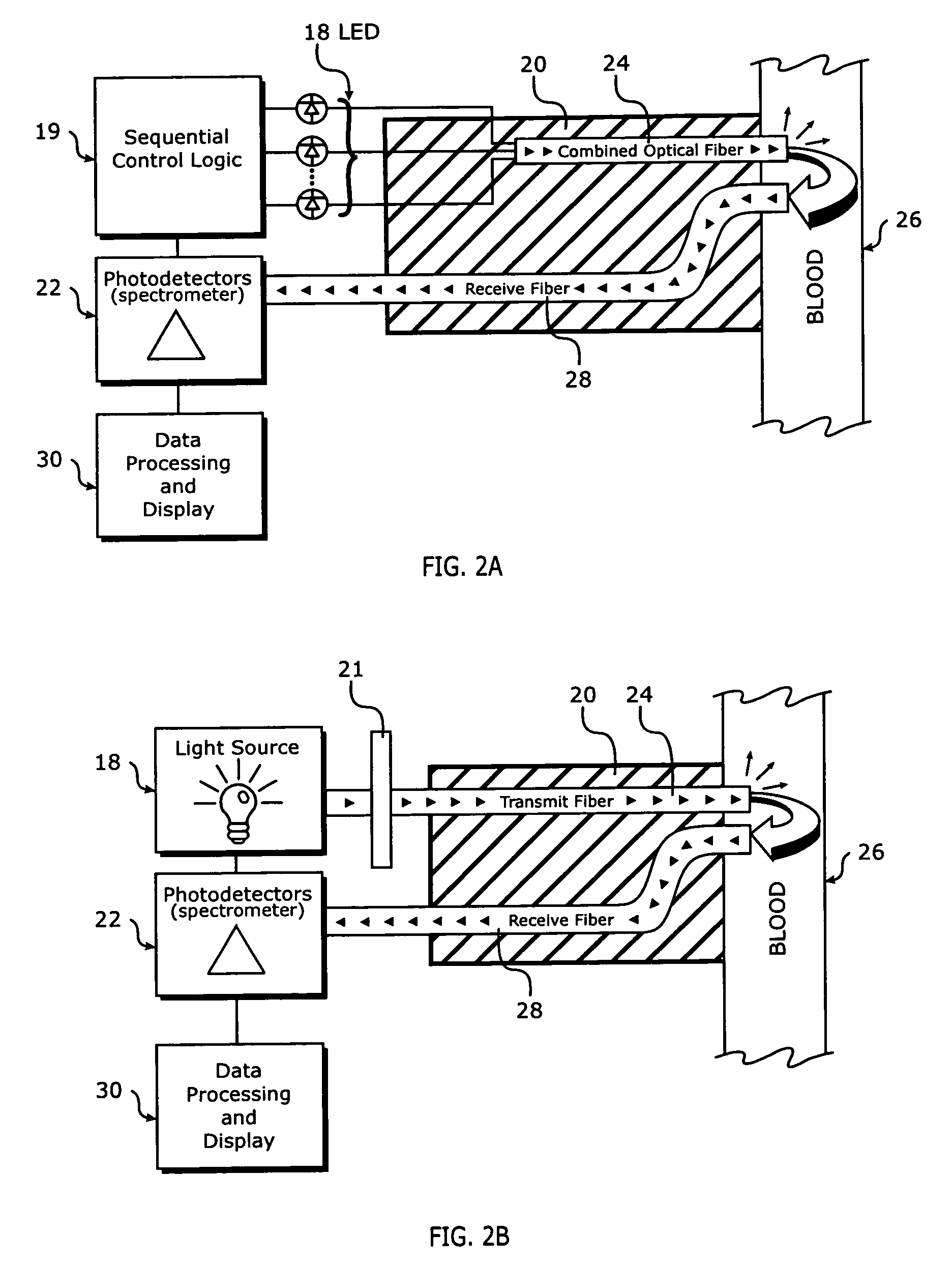
Continuous spectroscopic measurement of total hemoglobin
ActiveUS7319894B2Fast informationEasy to readDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterPhotodetectorTotal hemoglobin
Methods for measuring the total hemoglobin of whole blood include measuring reflective light at multiple wavelengths within the visible spectrum, calculating light absorbance at each of the multiple wavelengths, performing a comparison in a change in like absorbance between the multiple wavelengths, and / or relating the comparison to total hemoglobin. A system for measuring total hemoglobin of whole blood may include at least one light source, a catheter, optical fibers, at least one photodetector, data processing circuitry, and / or a display unit.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Hybrid fet incorporating a finfet and a planar fet
A stack of a vertical fin and a planar semiconductor portion are formed on a buried insulator layer of a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate. A hybrid field effect transistor (FET) is formed which incorporates a finFET located on the vertical fin and a planar FET located on the planar semiconductor portion. The planar FET enables a continuous spectrum of on-current. The surfaces of the vertical fin and the planar semiconductor portion may be set to coincide with crystallographic orientations. Further, different crystallographic orientations may be selected for the surfaces of the vertical fin and the surfaces of the planar semiconductor portion to tailor the characteristics of the hybrid FET.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Novel Karaoke and Multi-Channel Data Recording / Transmission Techniques via Wavefront Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
InactiveUS20110197740A1Quality improvementEnhance security and integrityElectrophonic musical instrumentsTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareFrequency spectrum
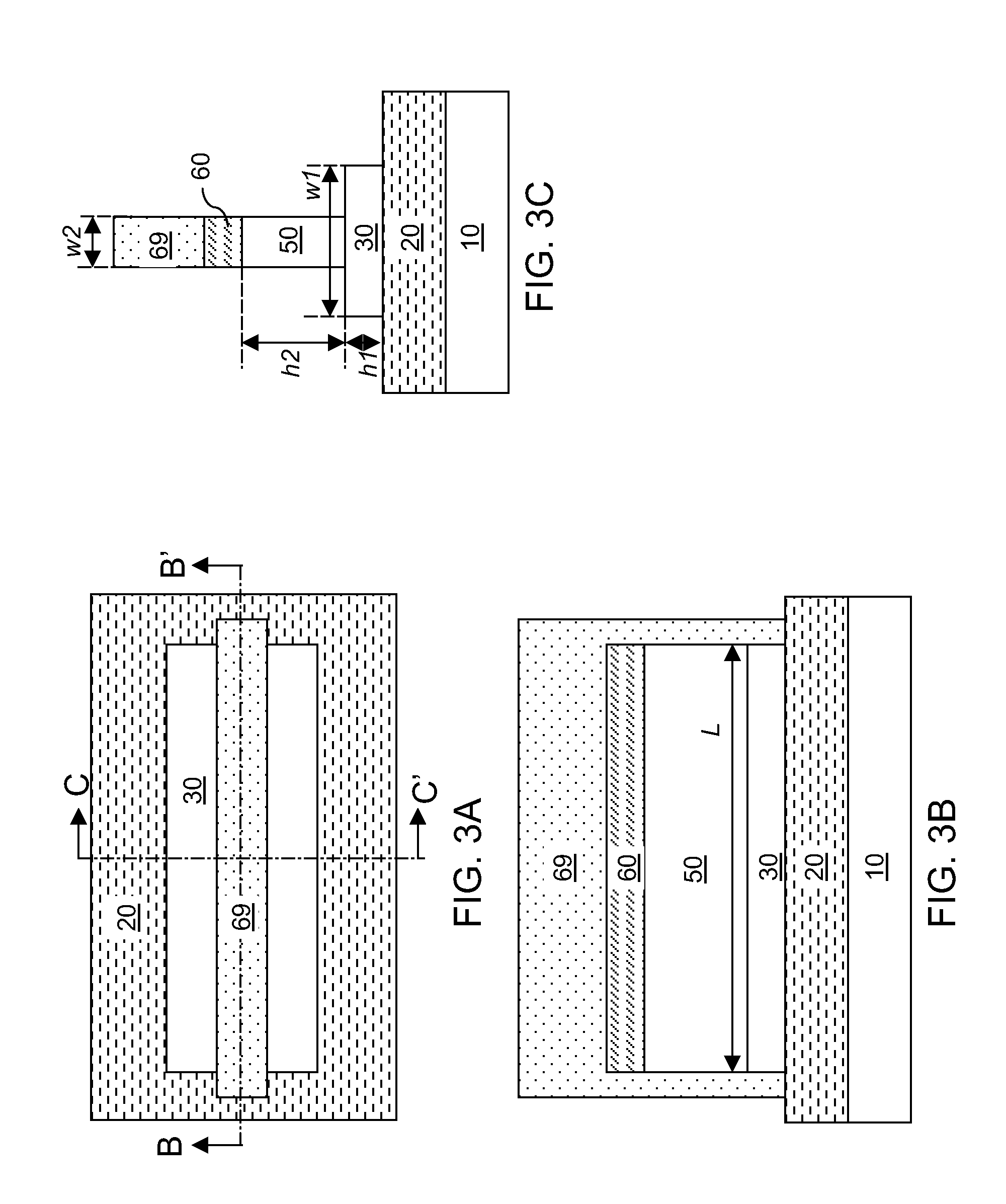
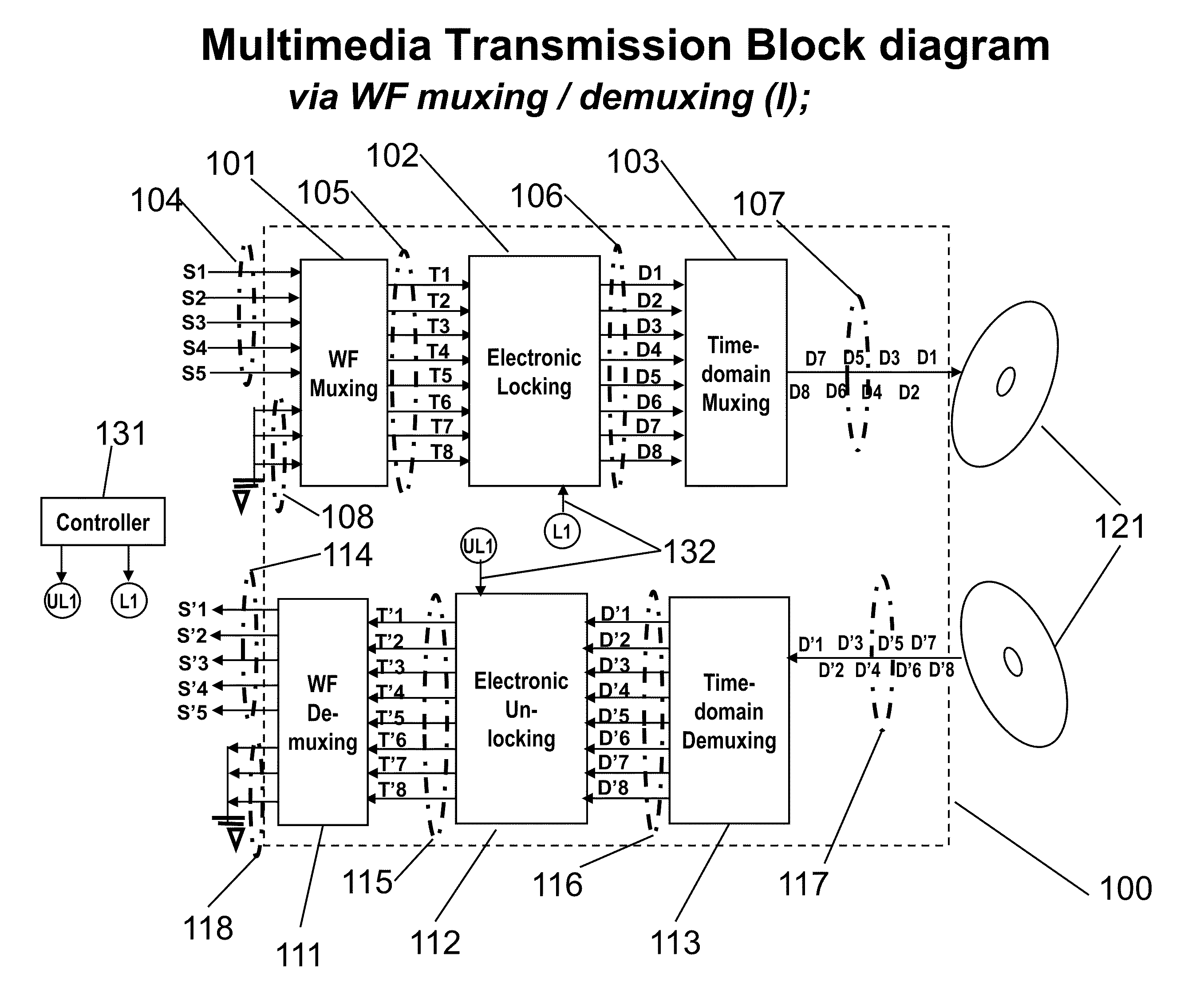
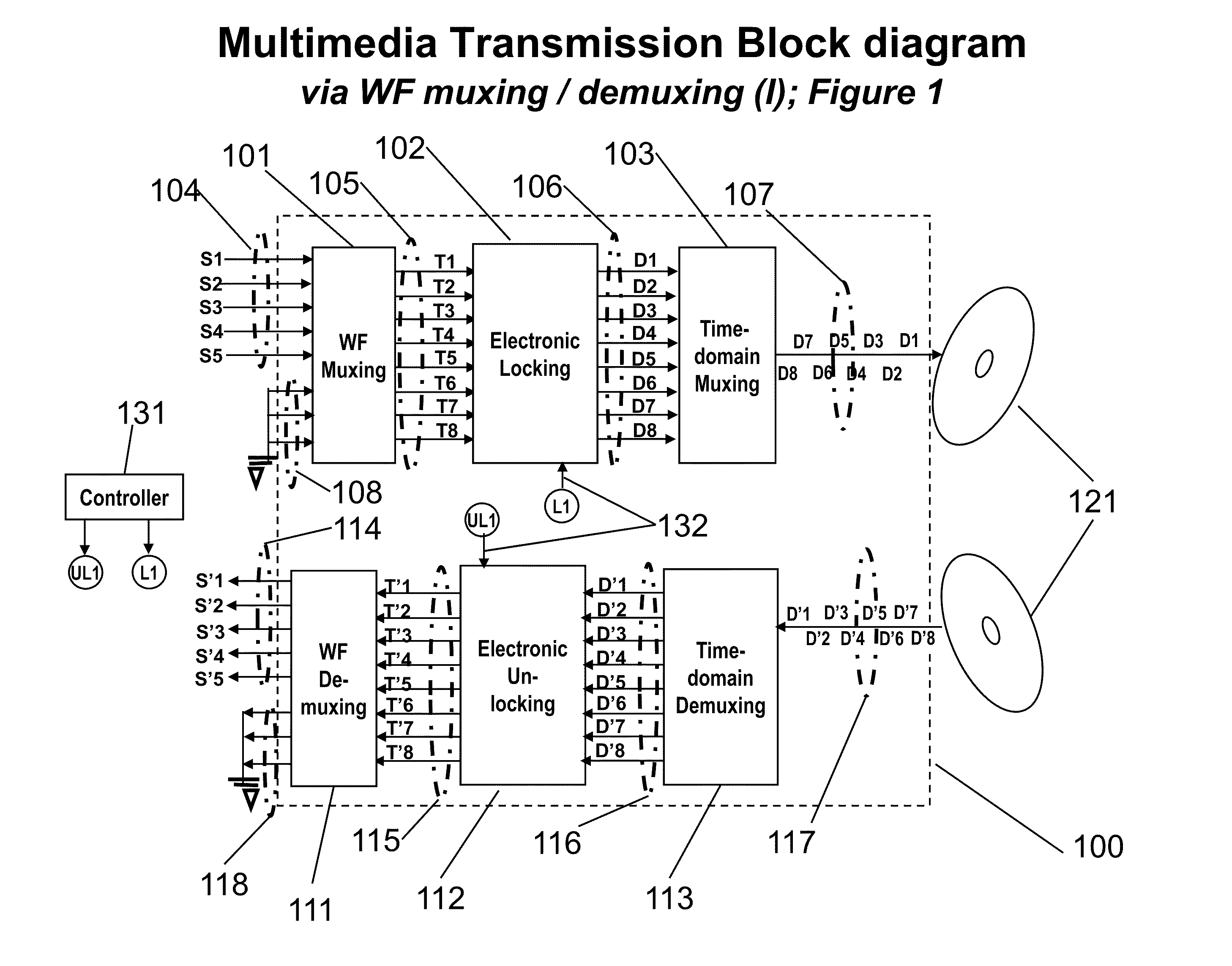
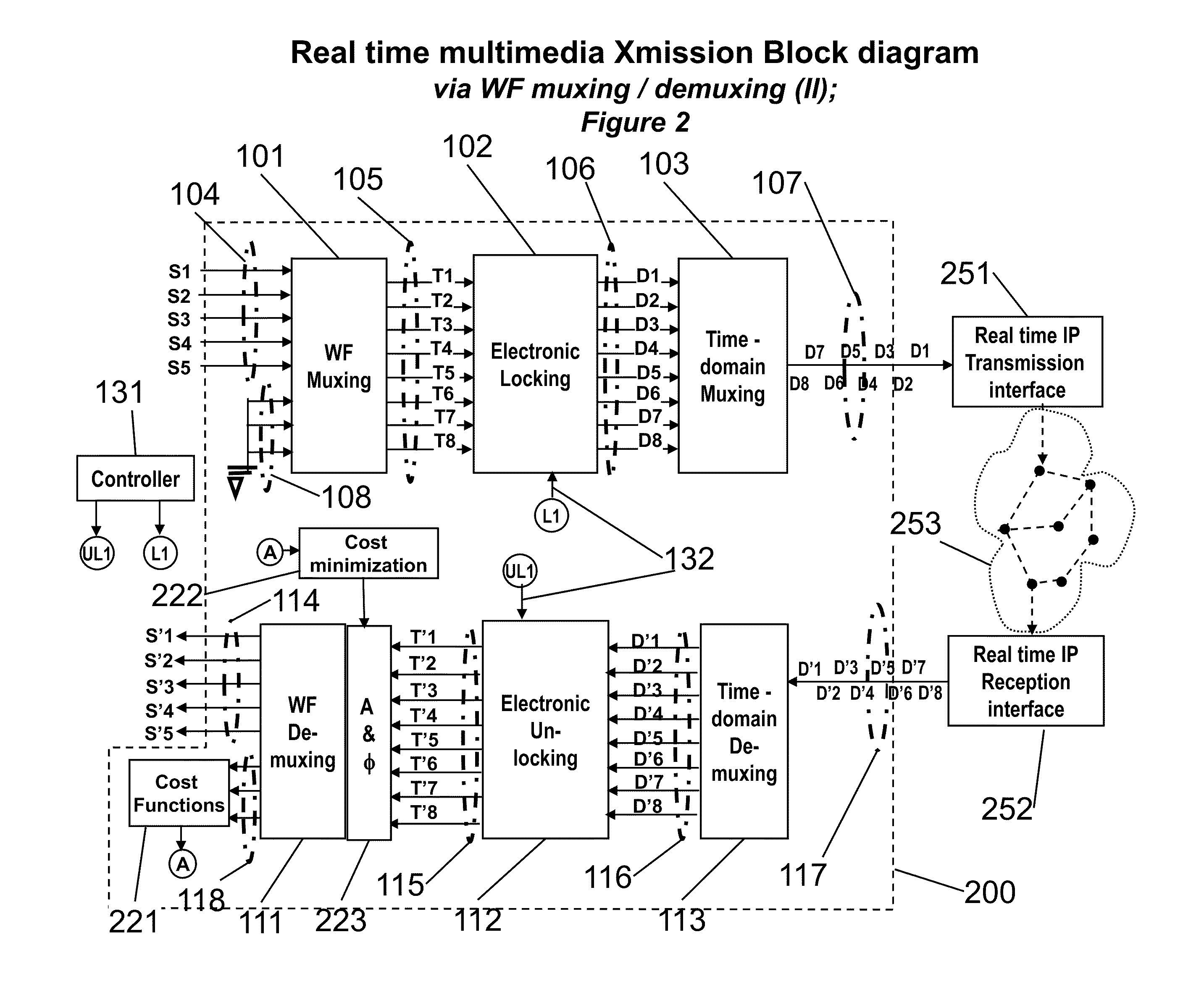
An advanced channel storage and retrieving system is achieved that is capable of simultaneously transporting multiple-stream data concurrently, with encryptions and error detection and limited correction capability using wavefront (WF) multiplexing (muxing) at the pre-processing and WF demultiplexing (de-muxing) in the post-processing. The WF muxing and demuxing processing can be applied for multiple signal streams with similar contents and format such as cable TV delivery systems or multiple signal streams with very distinct contents and format such as Karaoke multimedia systems. The stored or transported data are preprocessed by a WF muxing processor and are in the formats of multiple sub-channels. Signals in each sub-channel are results of unique linear combination of all the input signals streams. Conversely, an input signal stream is replicated and appears on all the sub-channels. Furthermore the replicated streams in various sub-channels are “linked” together by a unique phase weighting vector, which is called “wavefront” or WF. Various input signal streams will feature different WFs among their replicated signal streams in the sub-channels. The WF muxing processing is capable to generating a set of orthogonal WFs, and the WF demuxing processing is capable of reconstituting the input signal streams based on the retrieved sub-channel data only if the orthogonal characteristics of a set of WFs are preserved. Without the orthogonality among the WF, the signals in sub-channels are mixed and become effectively pseudo random noise. Therefore, an electronic locking mechanism in the preprocessing is implemented to make the WFs un-orthogonal among one another. Similarly, an electronic un-locking mechanism in the post-processing is implemented to restore the orthogonal characteristics among various WFs embedded in the sub-channel signals. Some of the phenomena due to the selected locking mechanisms are reproducible in nature, such as wave propagating effects, and other are distinctively man-made; such as switching sub-channel sequences. There are other conventional encryption techniques using public and private keys which can be applied in conjunction with the WF muxing and de-muxing processor, converting plain data streams into ciphered data streams which can be decoded back into the original plain data streams. An encryption algorithm along with a key is used in the encryption and decryption of data. As to the optional parallel to serial and serial to parallel conversions in the pre and post processing, respectively, we assume that transmissions with single carrier are more efficient than those with multiple carriers. We also assume single channel recording is more cost effective than multiple channel recording. However, there are occasions that continuous spectrum is hard to come-by. We may use fragmented spectrum for transmissions. There are techniques to convert wideband waveforms using continuous spectra into multiple fragmented sub-channels distributed on non-continuous frequency slots. Under these conditions we may replace the parallel to serial conversion processing by a frequency mapping processor.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
Light emitting device and lighting apparatus using the same
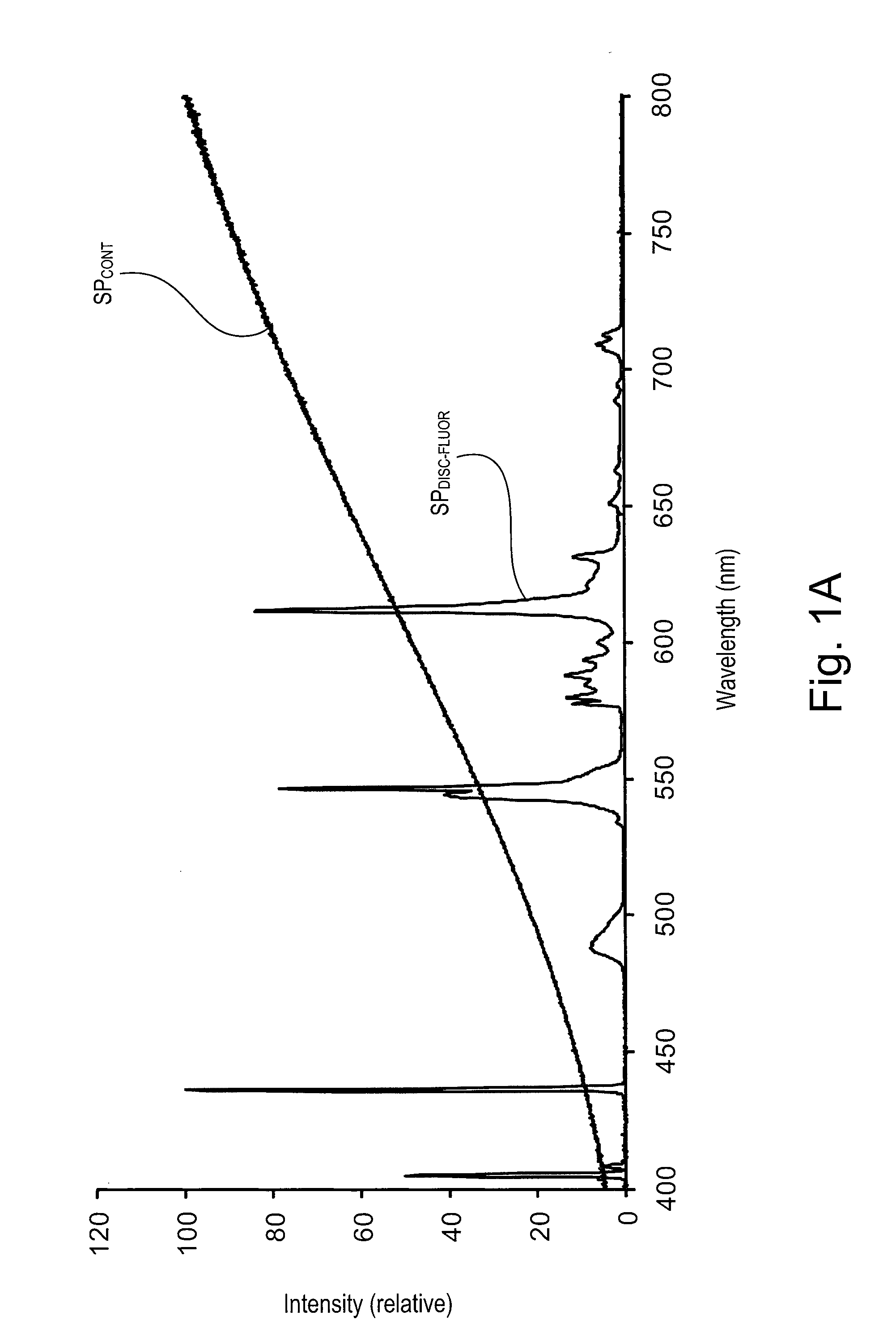
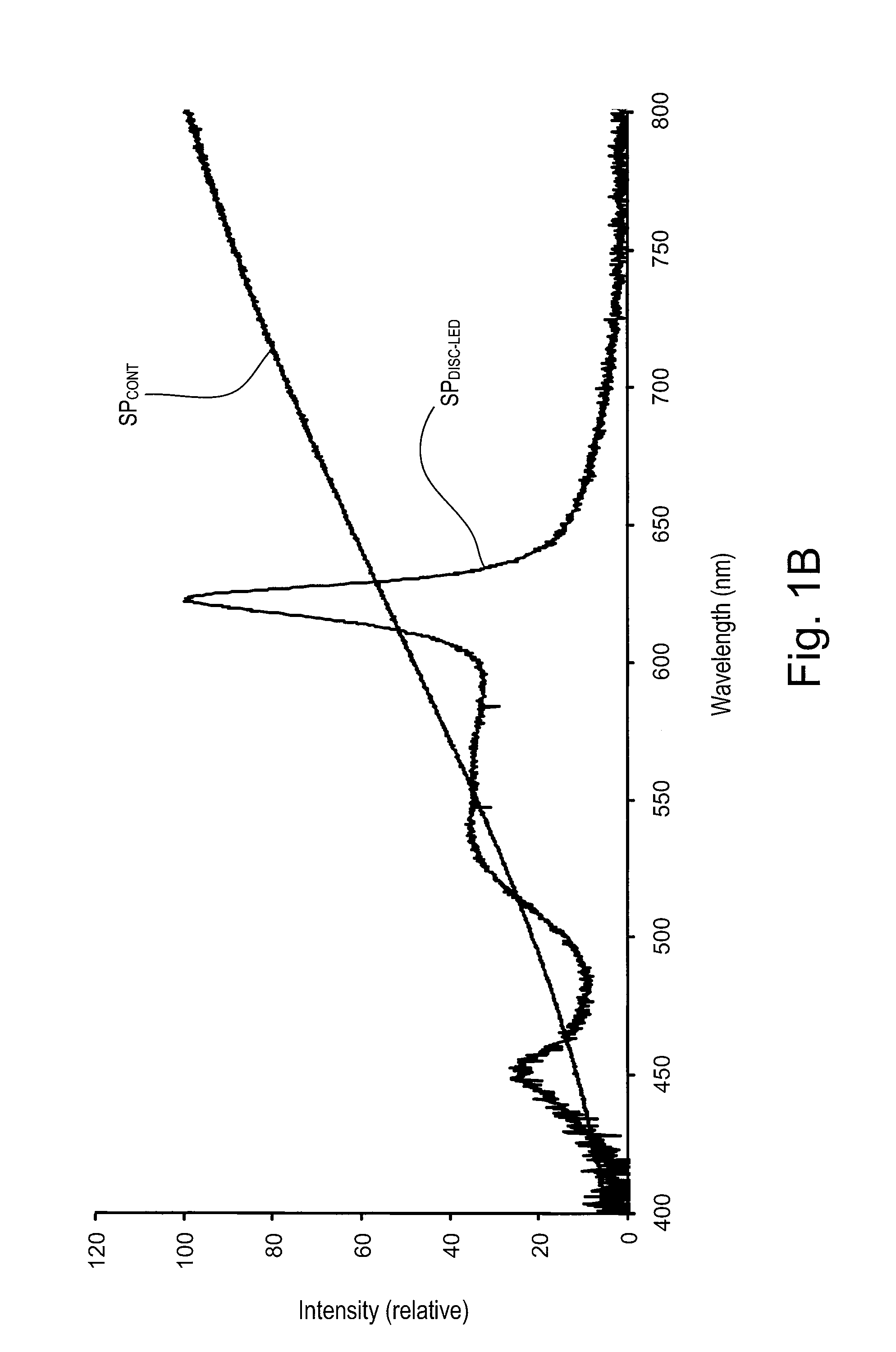
A light emitting device capable of readily produce a pseudo-continuous spectrum covering a wide wavelength regions at low costs, and of totally solving various problems which have resided in the conventional light sources, and a lighting apparatus using this device is provided. The light emitting device 10 is configured so that an active layer in a double hetero light emitting layer portion composed of compound semiconductors comprises a plurality of emission unit layers differing from each other in band gap energy, and so as to emit a simulatively synthesized light having a pseudo-continuous spectrum ensuring an emission intensity of 5% or more of a peak intensity over a wavelength region of 50 nm or more.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
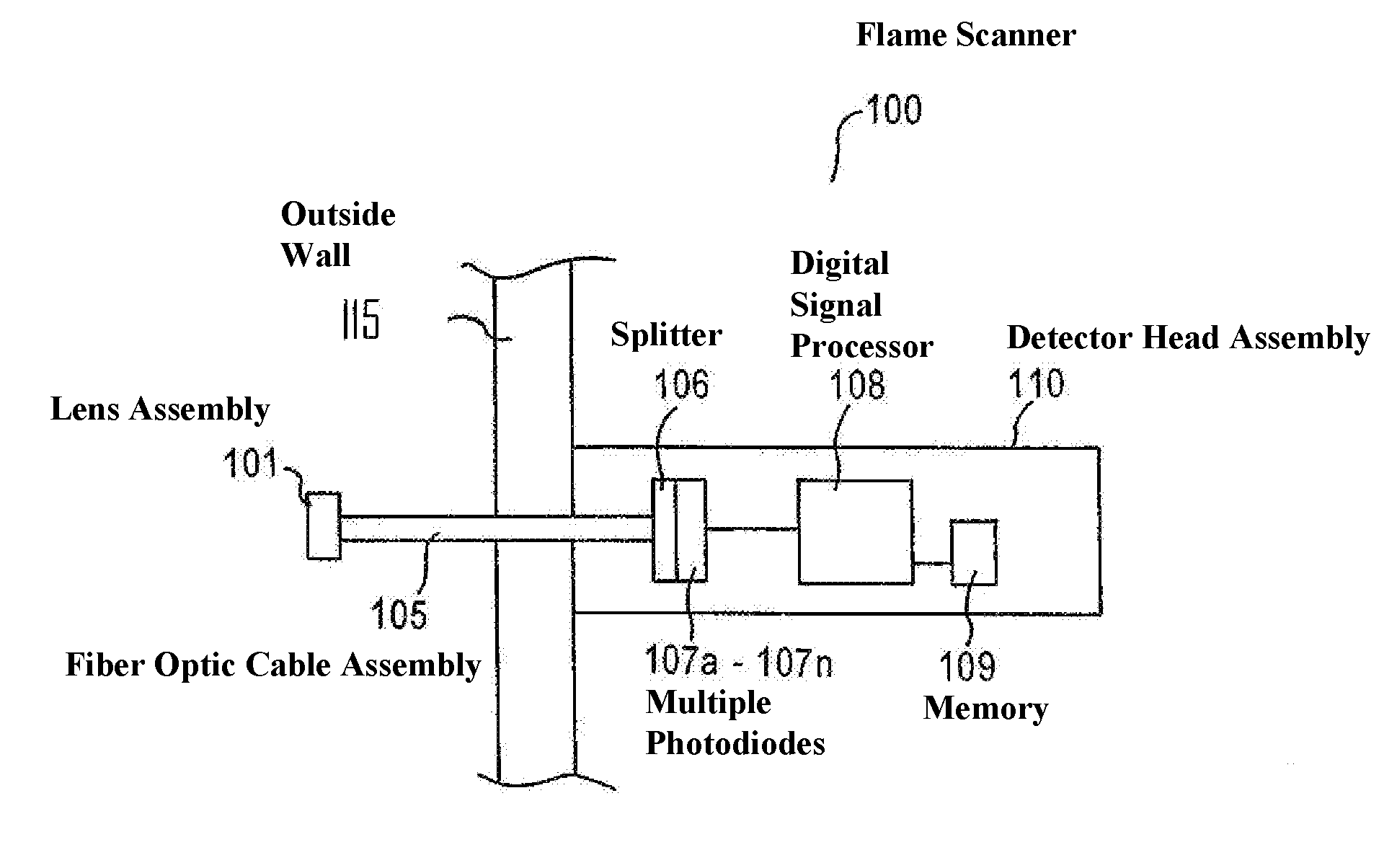
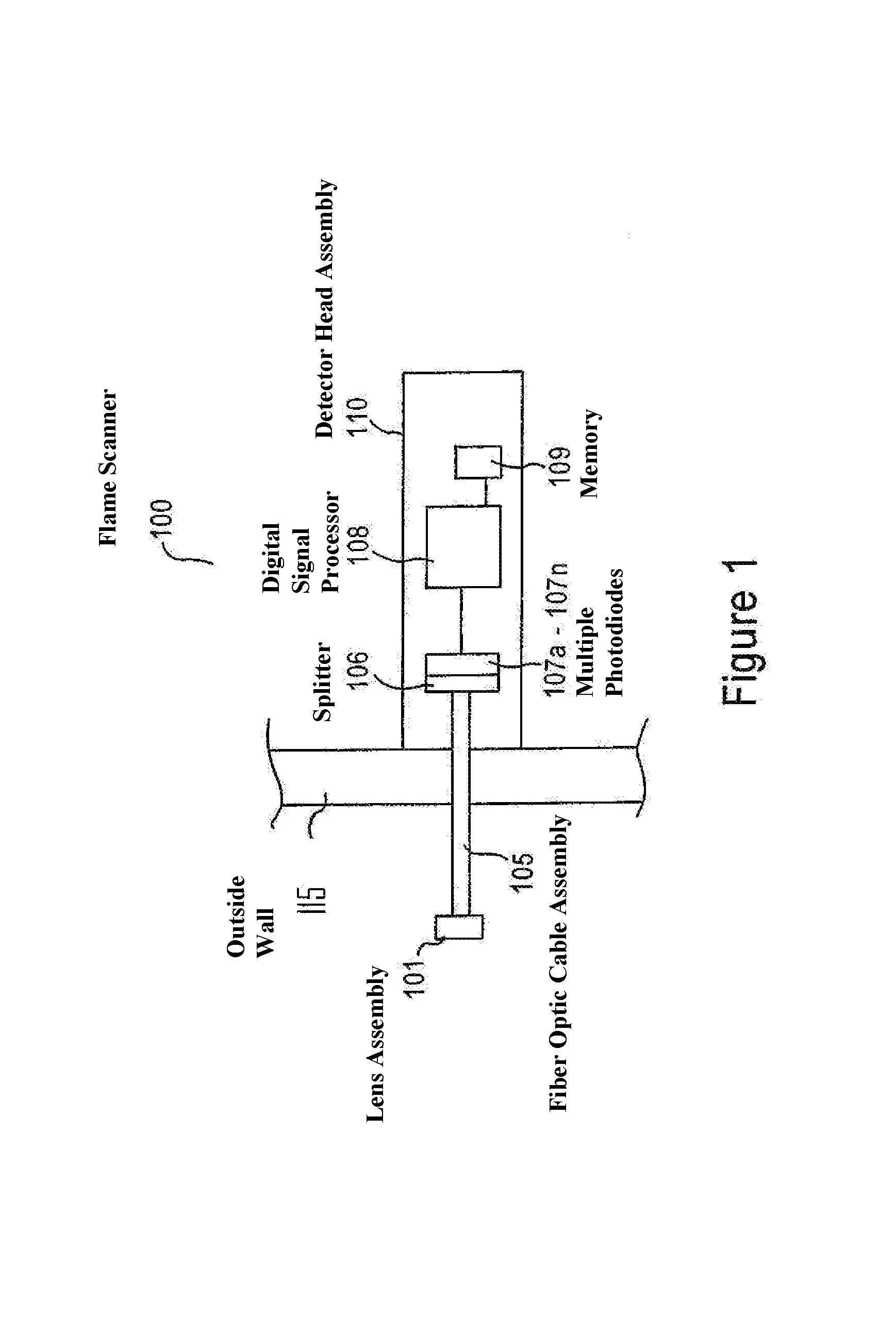
Intelligent flame scanner
InactiveUS7289032B2Reduced wiring requirementsSuitable redundancyCharacter and pattern recognitionAnalysis by thermal excitationMechanical engineeringOptics
Techniques for determining a characteristic of a flame are provided by the present invention. Provided are methods as well as devices. A flame is monitored across a contiguous spectral range to detect light emitted by the monitored flame. The contiguous spectral range is segmented into a plurality of discrete ranges, and detected light across each of the one or more of the plurality of discrete ranges is respectively processed to determine at least one characteristic of the flame.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
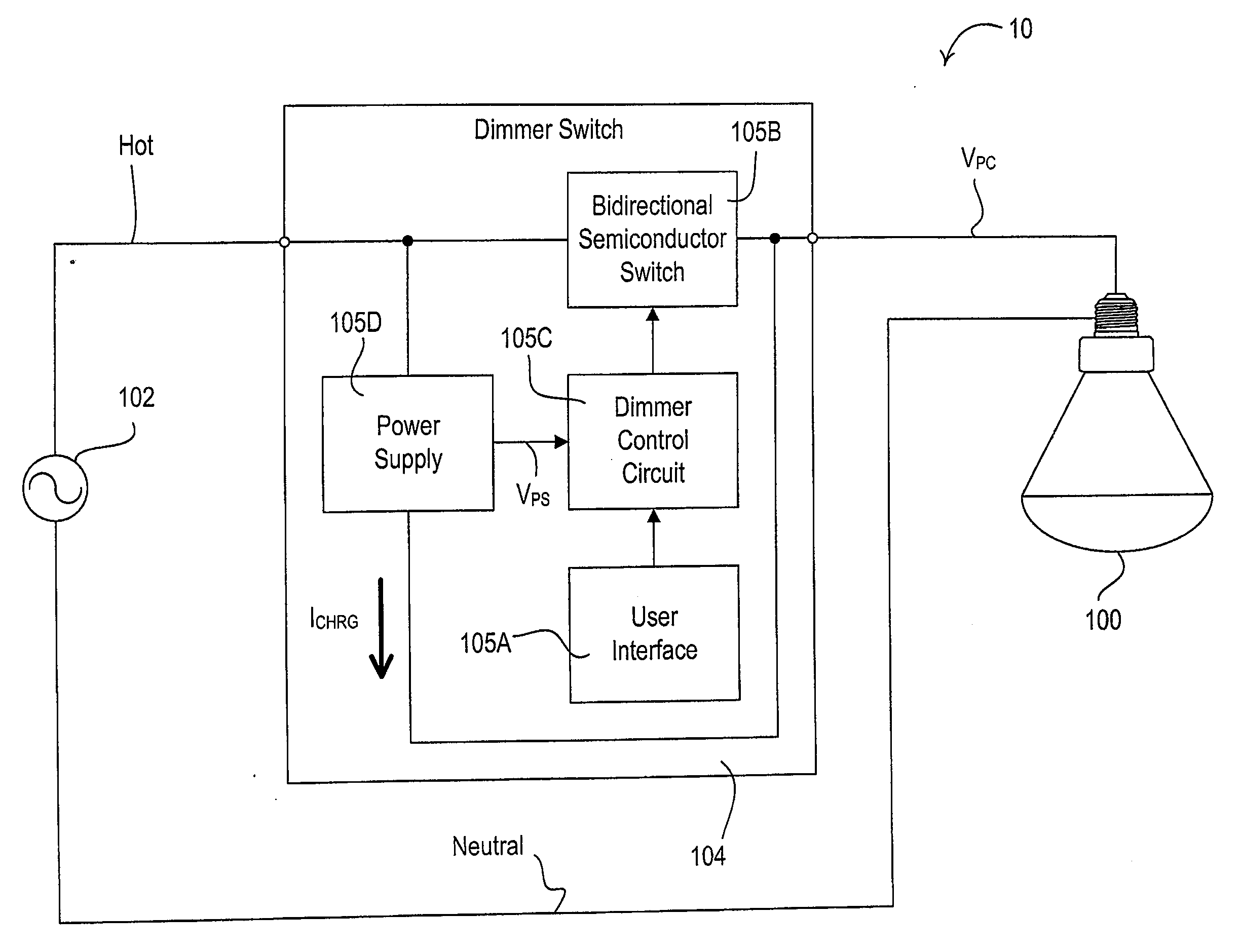
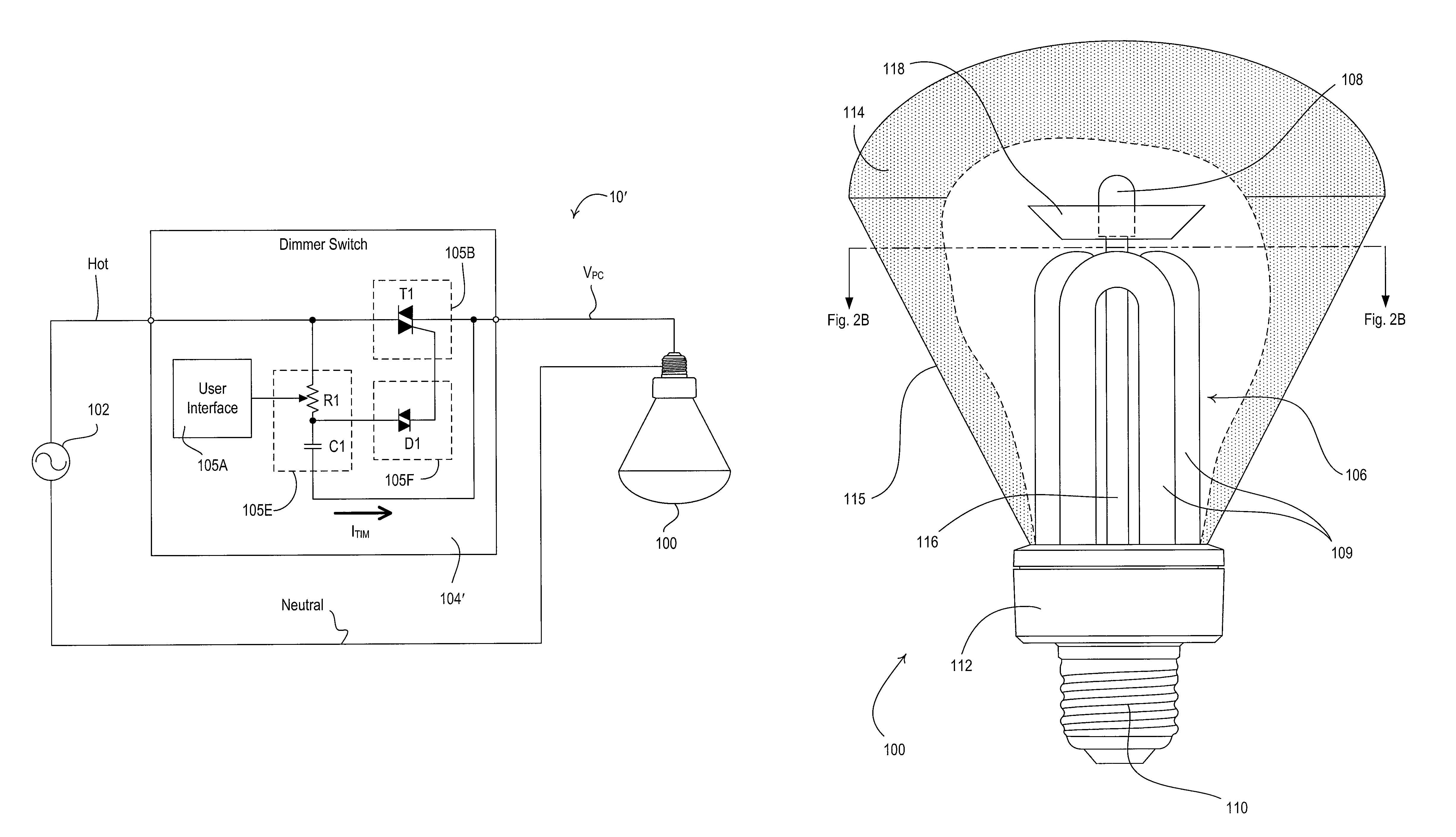
Hybrid light source
InactiveUS20100141158A1Low color temperatureReduce light outputElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringFluorescent lamp
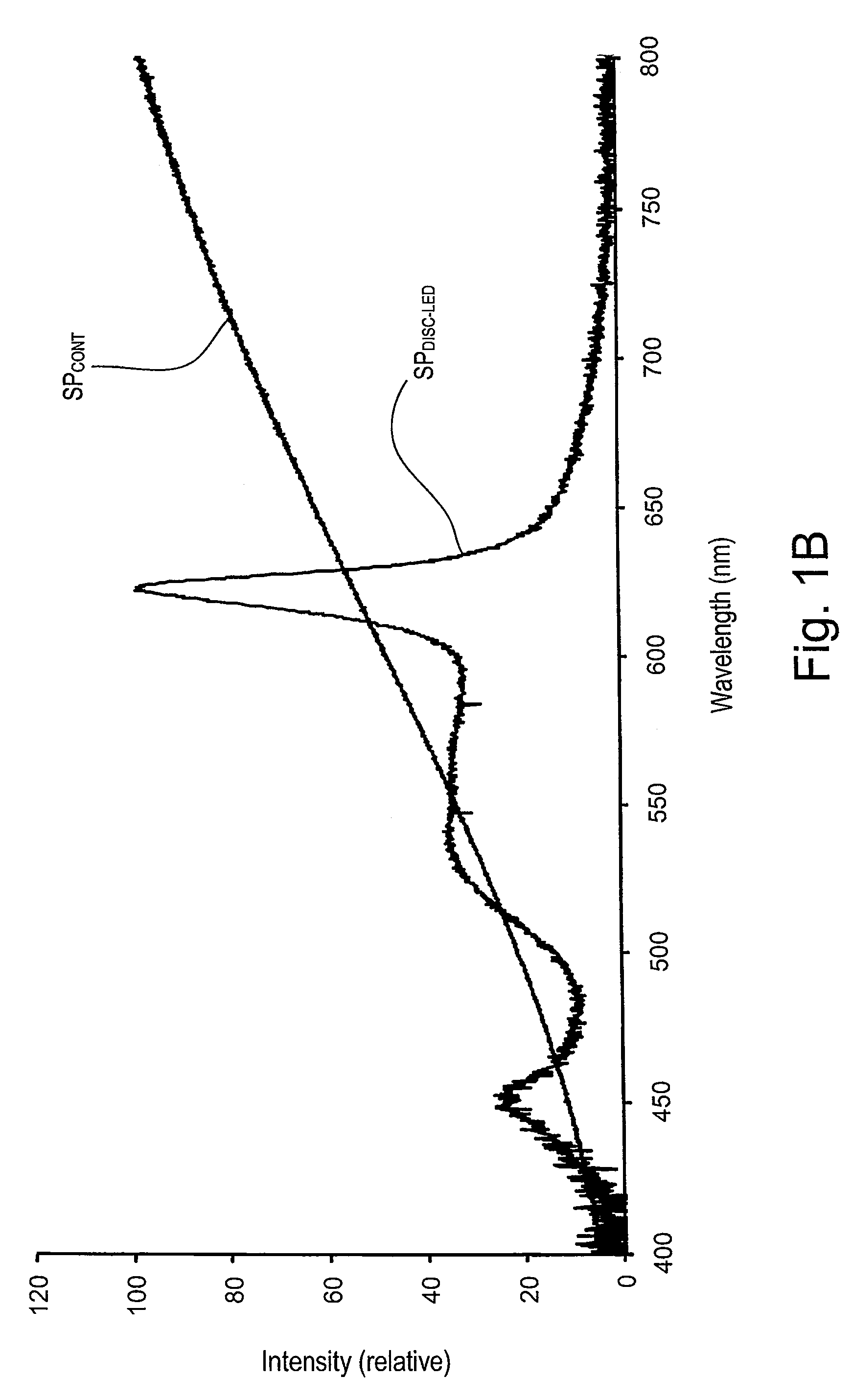
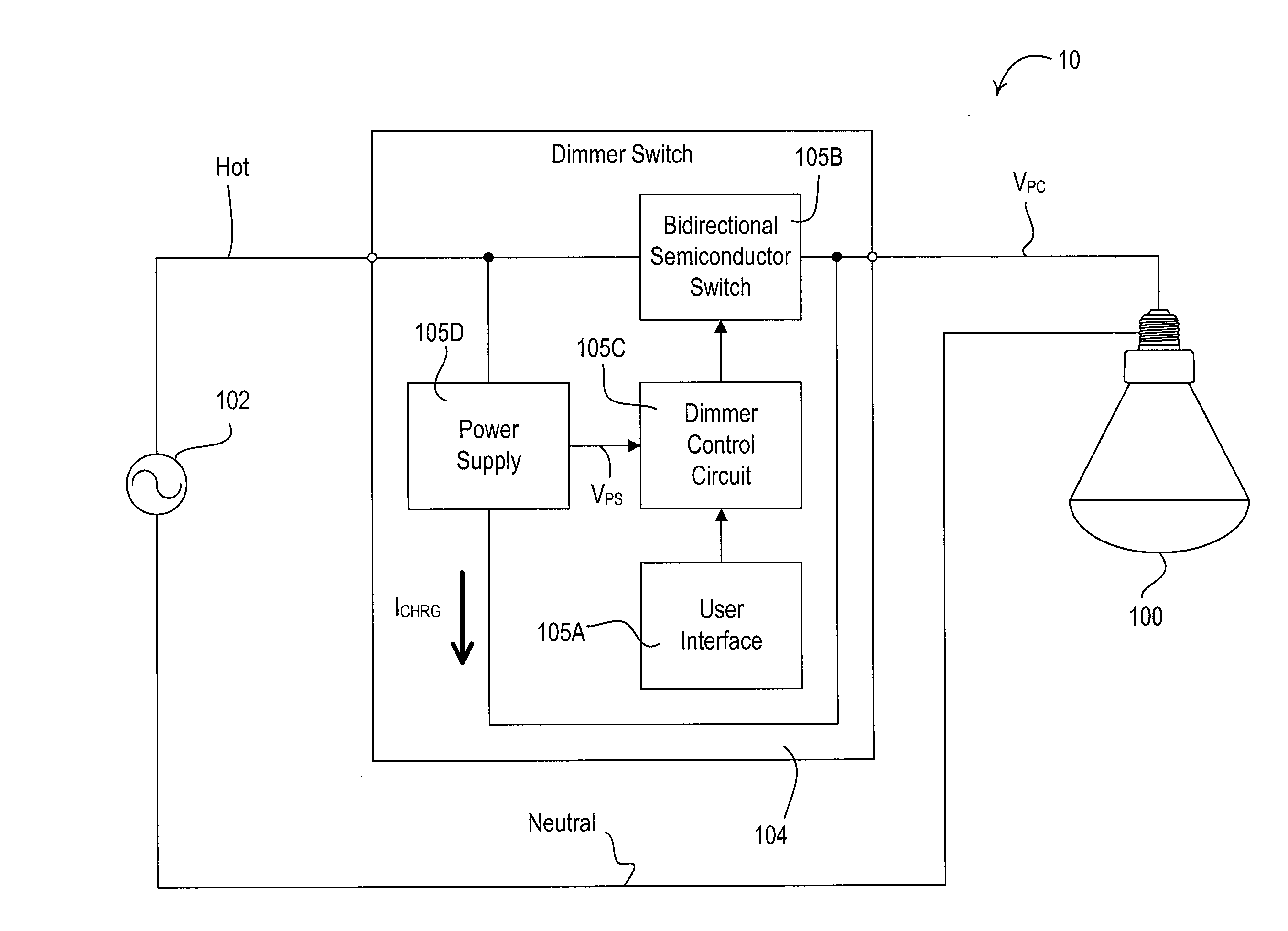
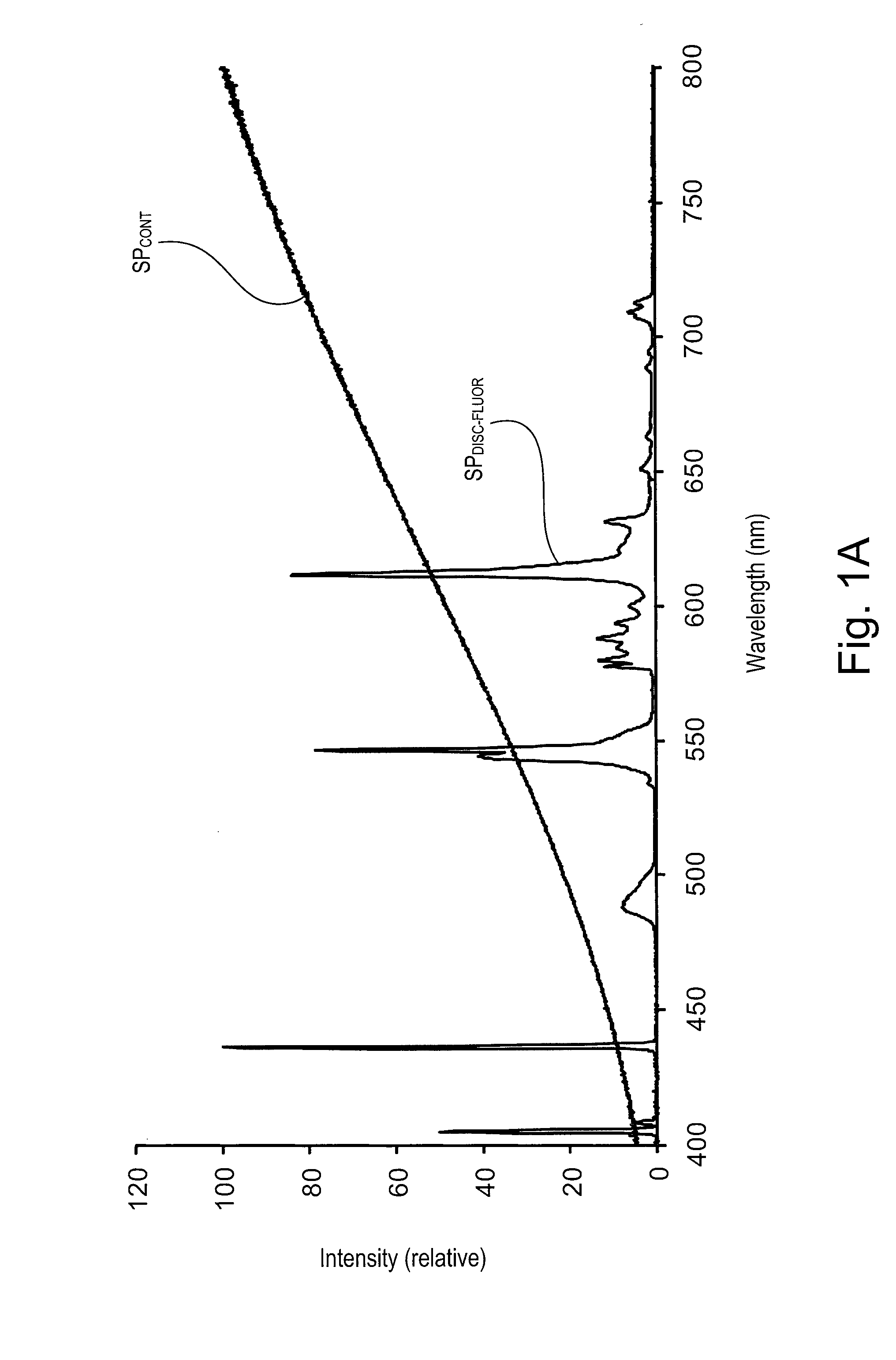
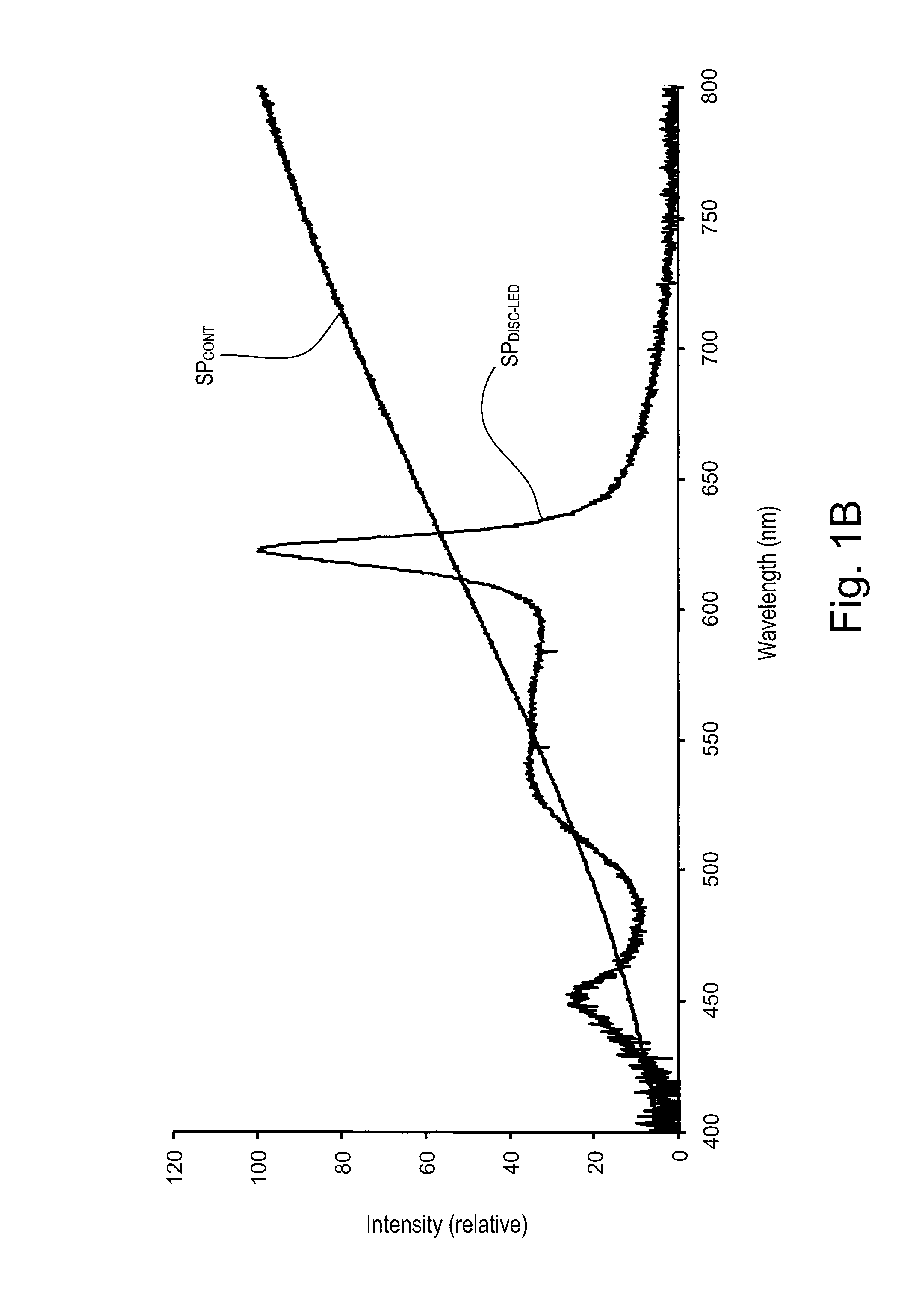
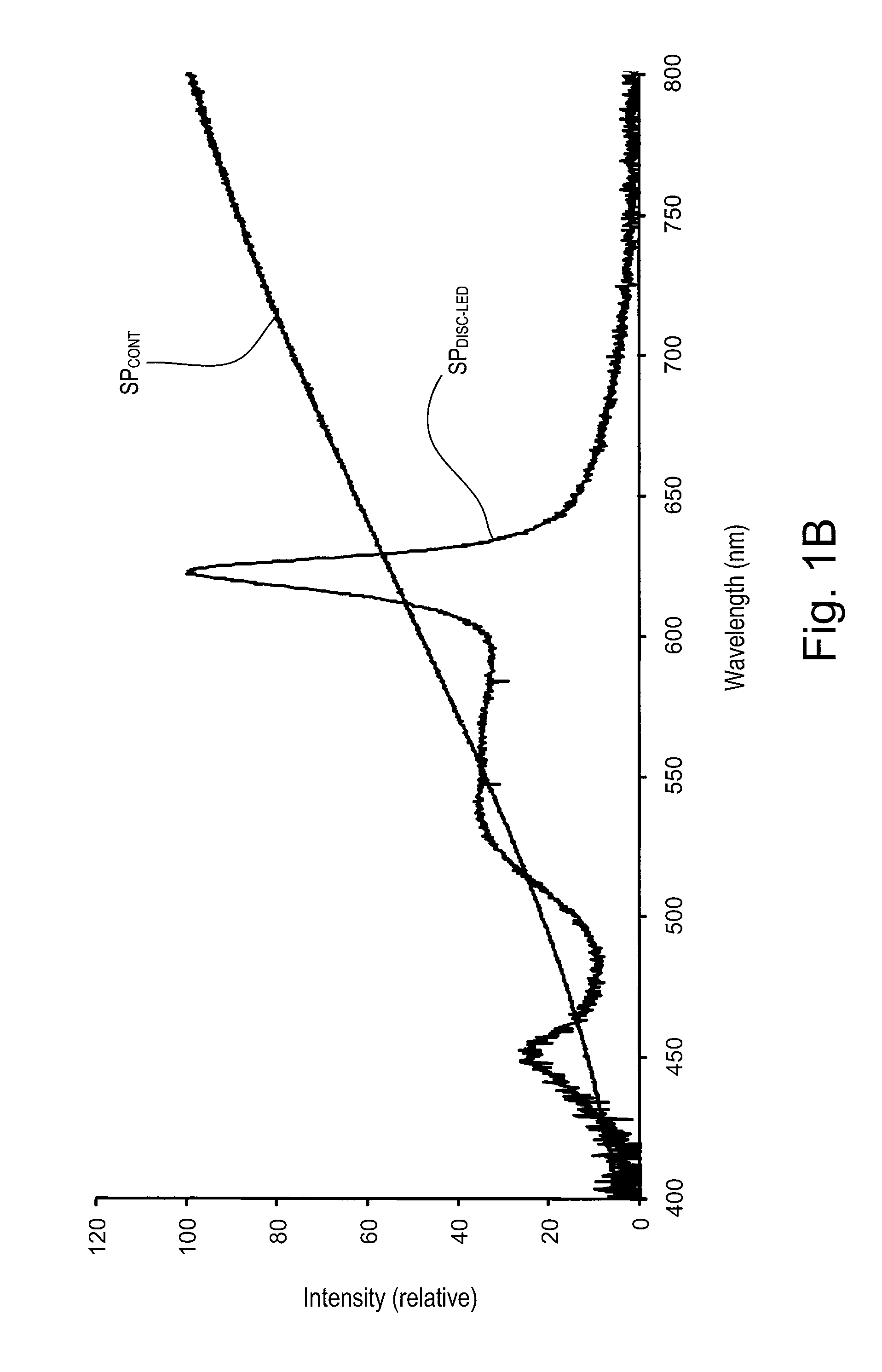
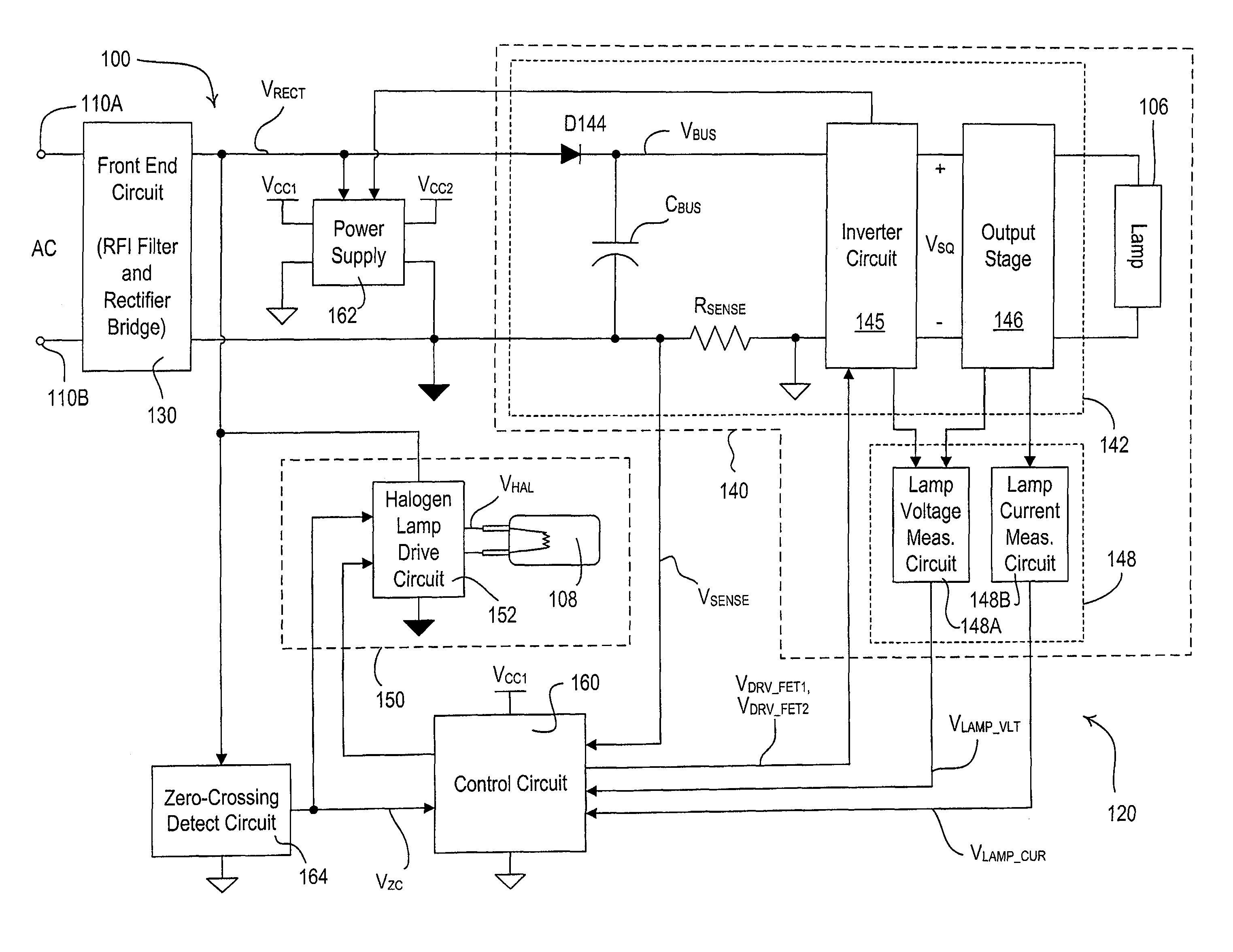
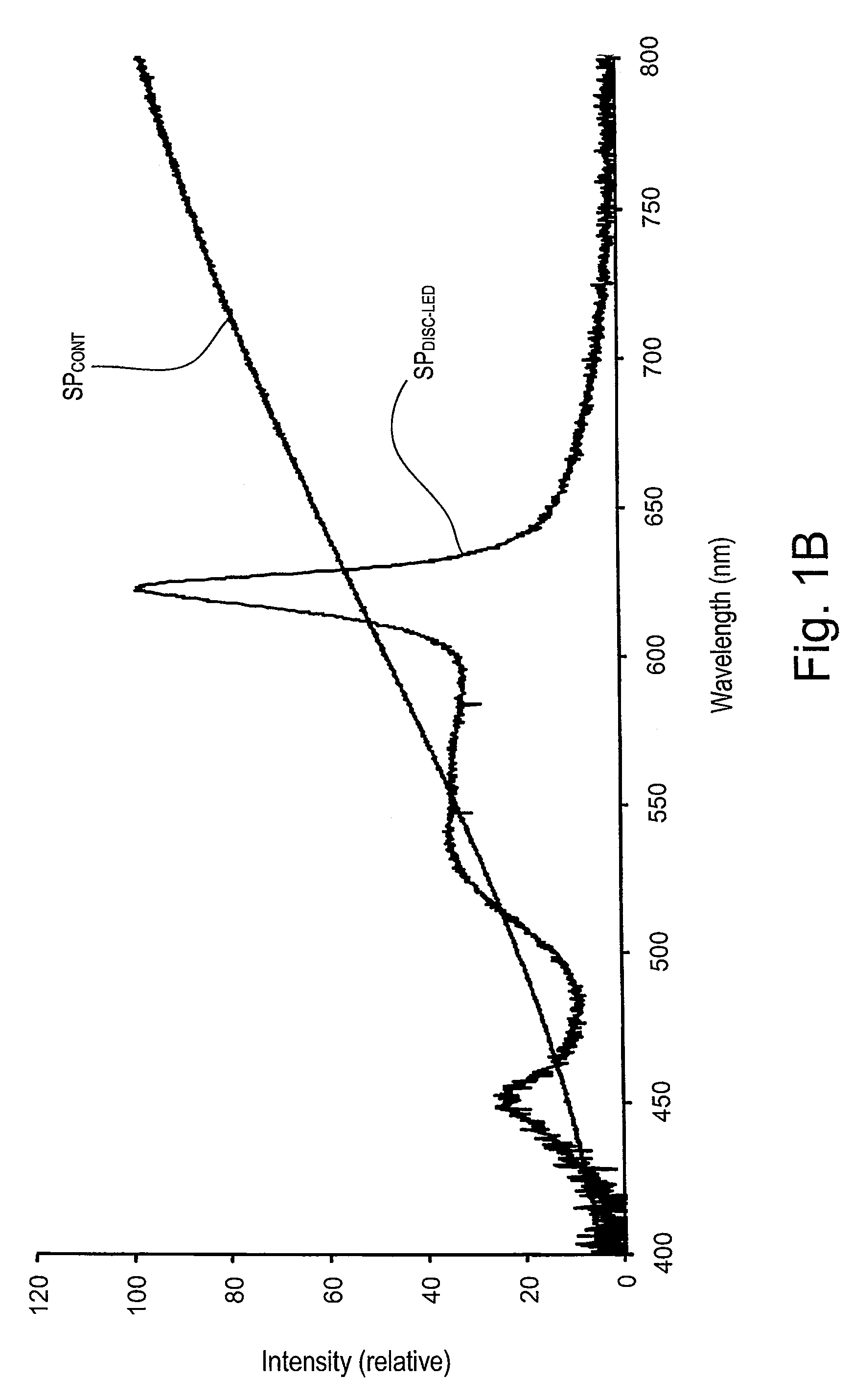
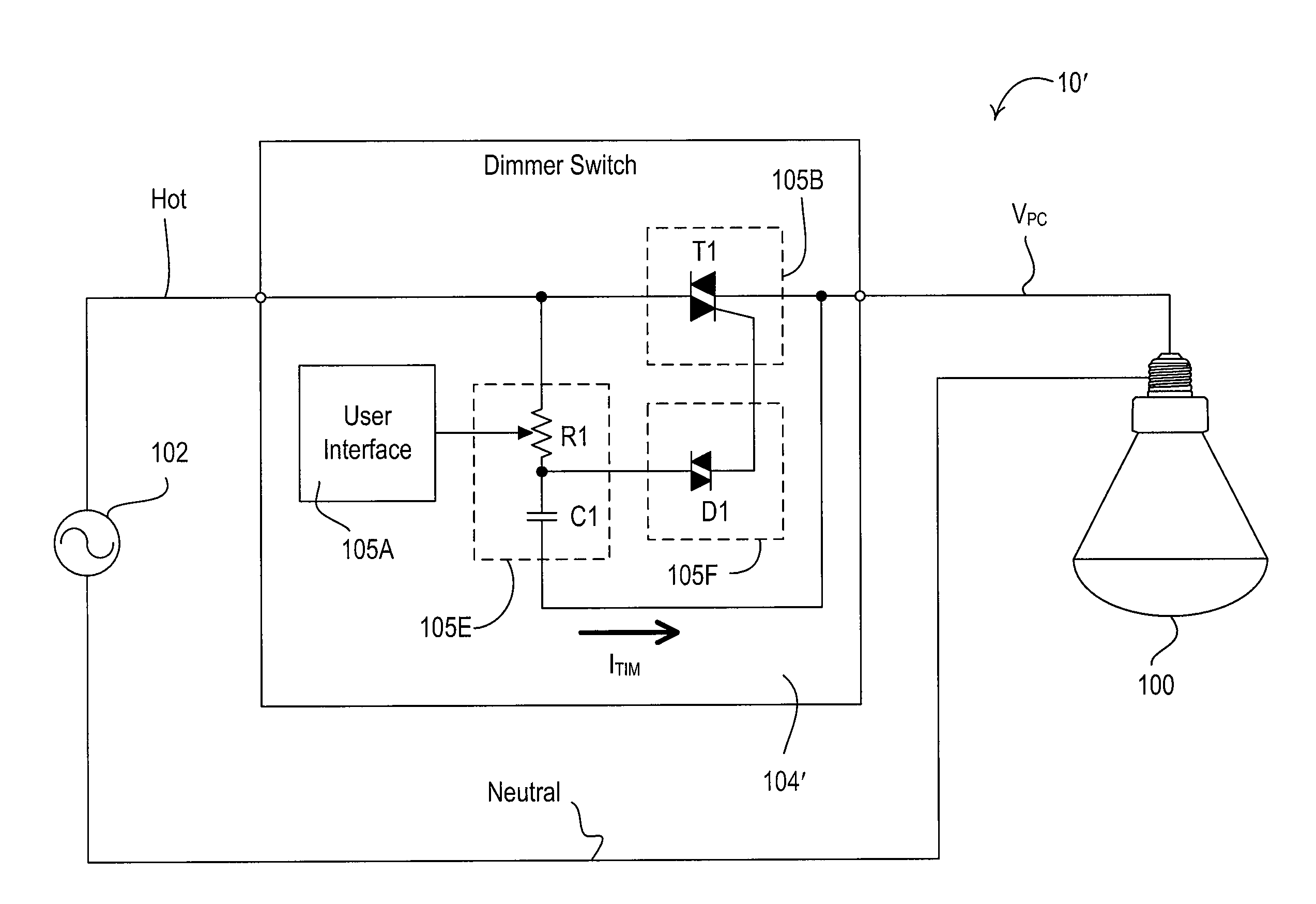
A hybrid light source comprises a discrete-spectrum lamp (for example, a fluorescent lamp) and a continuous-spectrum lamp (for example, a halogen lamp). A control circuit individually controls the amount of power delivered to the discrete-spectrum lamp and the continuous-spectrum lamp in response to a phase-controlled voltage generated by a connected dimmer switch, such that a total light output of the hybrid light source ranges throughout a dimming range. The discrete-spectrum lamp is turned off and the continuous-spectrum lamp produces all of the total light intensity of the hybrid light source when the total light intensity is below a transition intensity. The continuous-spectrum lamp is driven by a continuous-spectrum lamp drive circuit, which is operable to conduct a charging current of a power supply of the dimmer switch and to provide a path for enough current to flow through the hybrid light source, such that the magnitude of the current exceeds rated latching and holding currents of a thyristor of the dimmer.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Hybrid light source
InactiveUS20100066260A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringFluorescent lamp
A hybrid light source comprises a discrete-spectrum lamp (for example, a fluorescent lamp) and a continuous-spectrum lamp (for example, a halogen lamp). A control circuit individually controls the amount of power delivered to the discrete-spectrum lamp and the continuous-spectrum lamp in response to a phase-controlled voltage generated by a connected dimmer switch, such that a total light output of the hybrid light source ranges throughout a dimming range. The discrete-spectrum lamp is turned off and the continuous-spectrum lamp produces all of the total light intensity of the hybrid light source when the total light intensity is below a transition intensity. The continuous-spectrum lamp is driven by a continuous-spectrum lamp drive circuit, which is operable to conduct a charging current of a power supply of the dimmer switch and to provide a path for enough current to flow through the hybrid light source, such that the magnitude of the current exceeds rated latching and holding currents of a thyristor of the dimmer.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
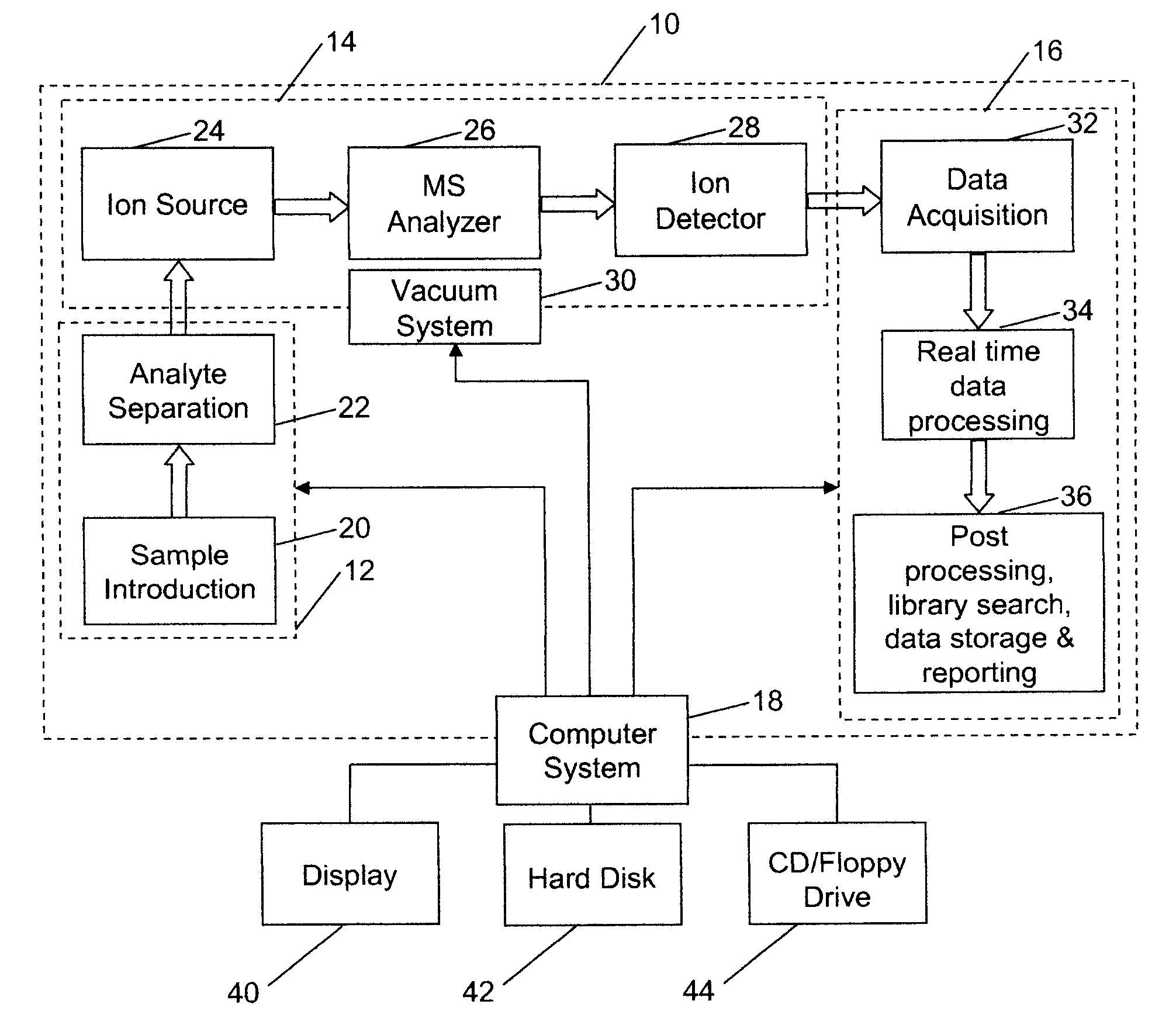
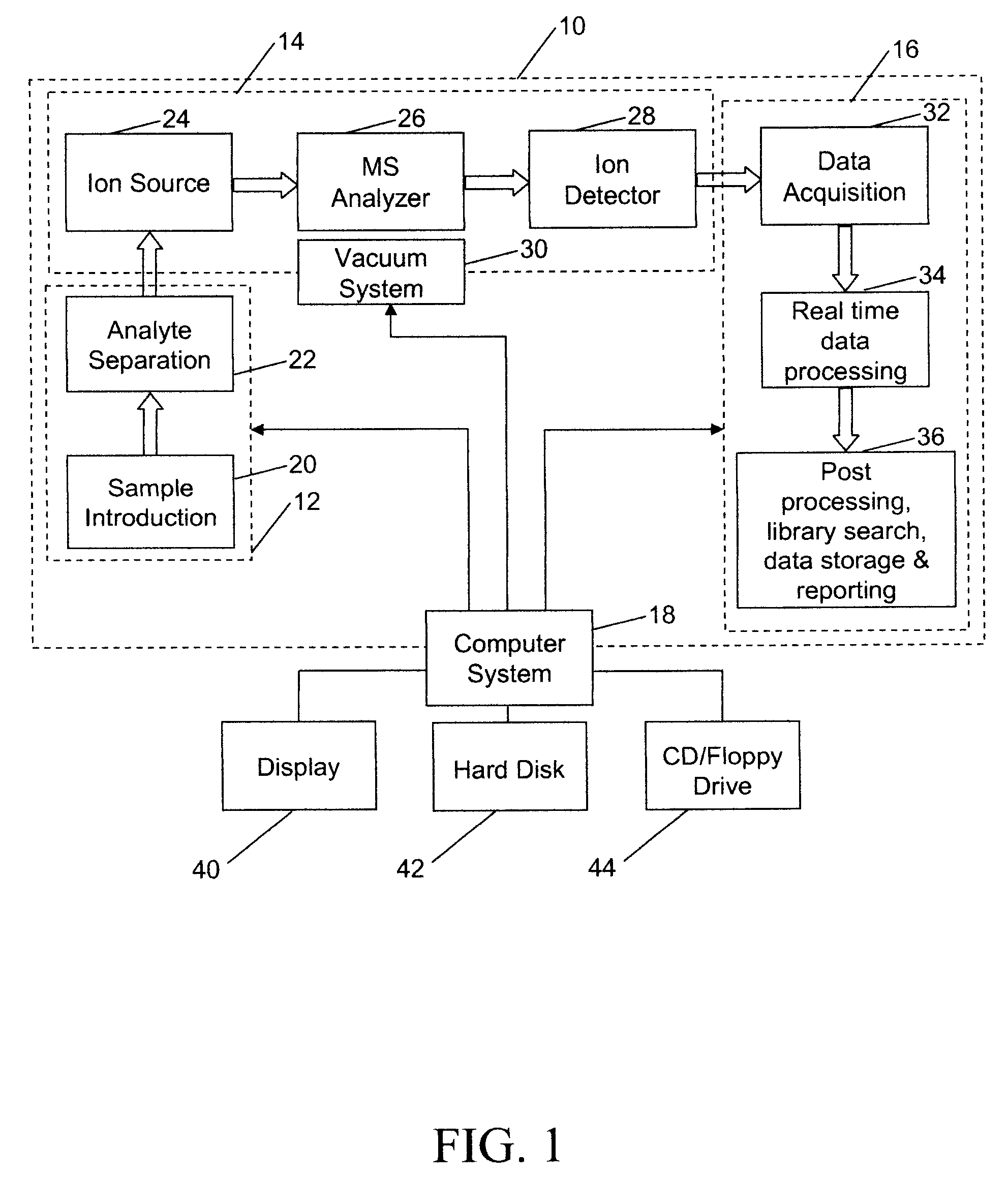
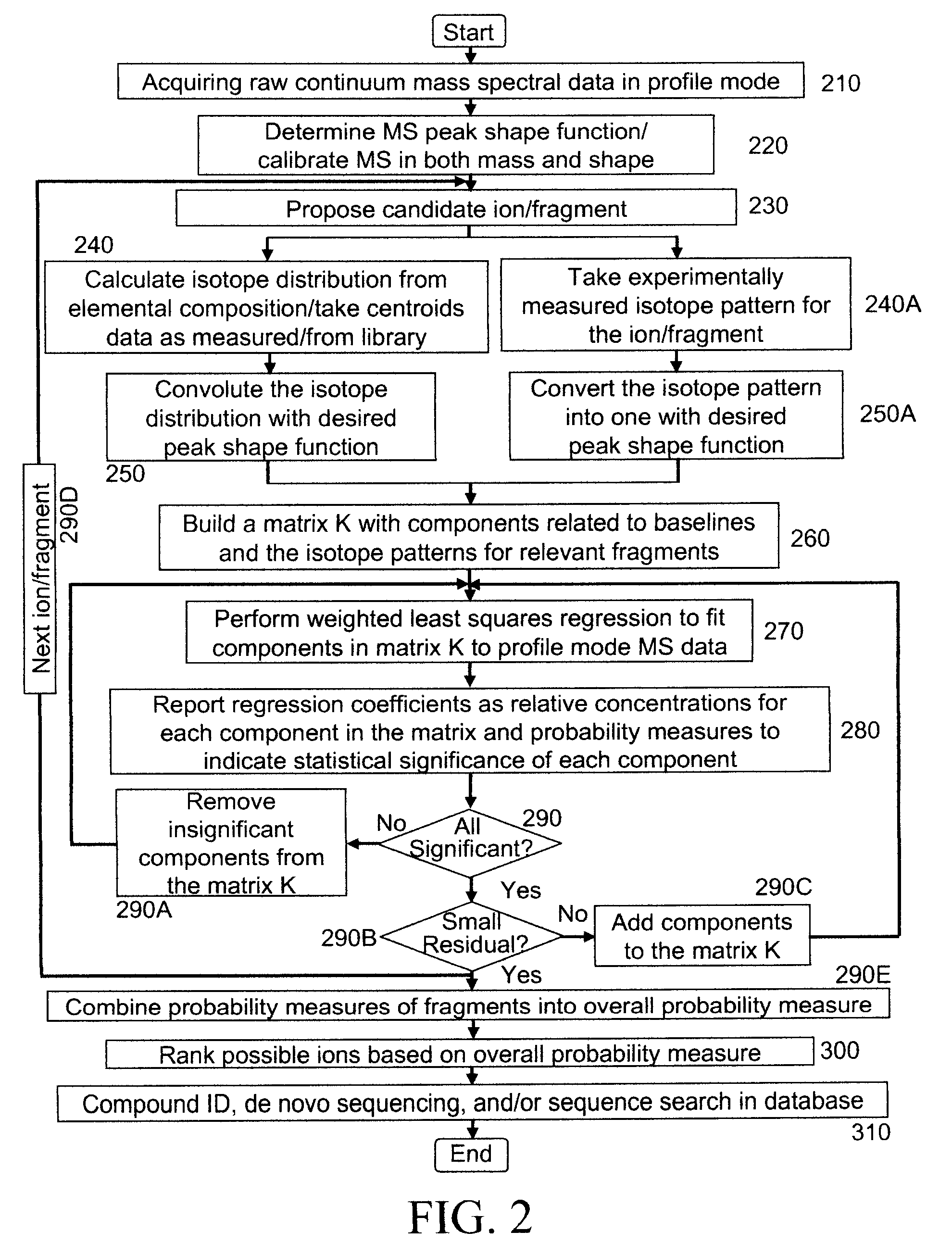
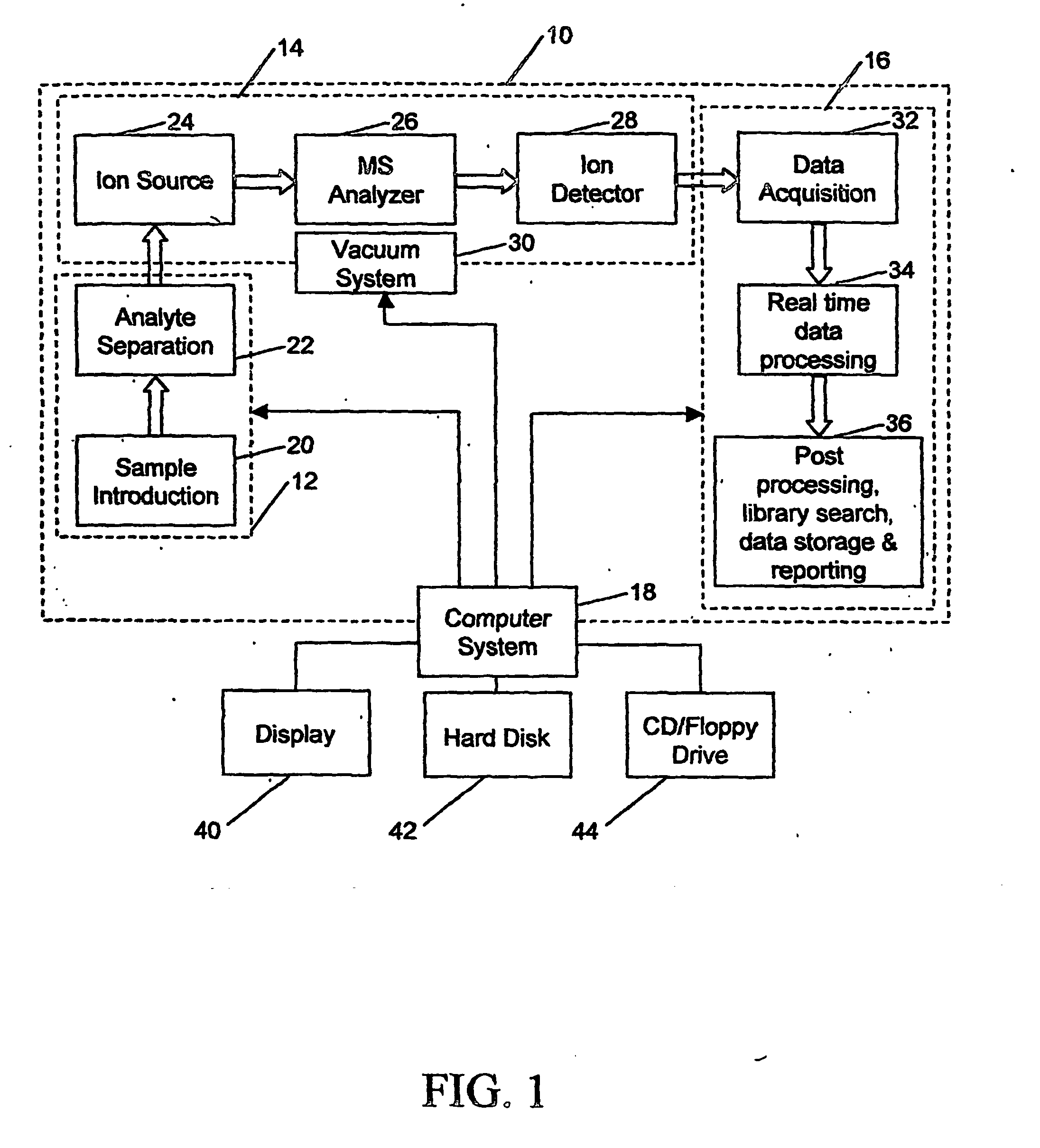
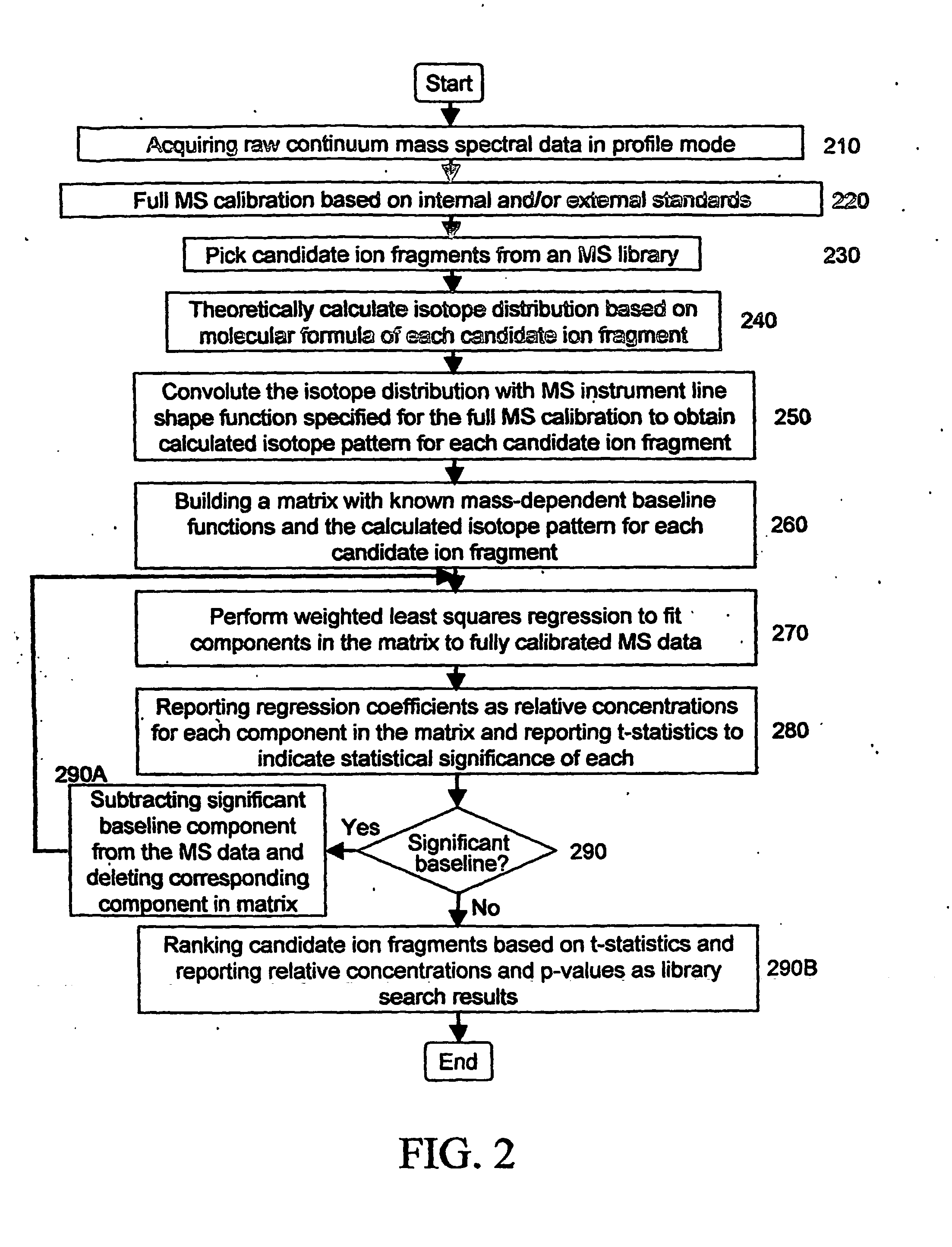
Analyzing mass spectral data
InactiveUS20080001079A1Rich relevant informationSpectral/fourier analysisMolecular entity identificationComputer scienceLeast squares
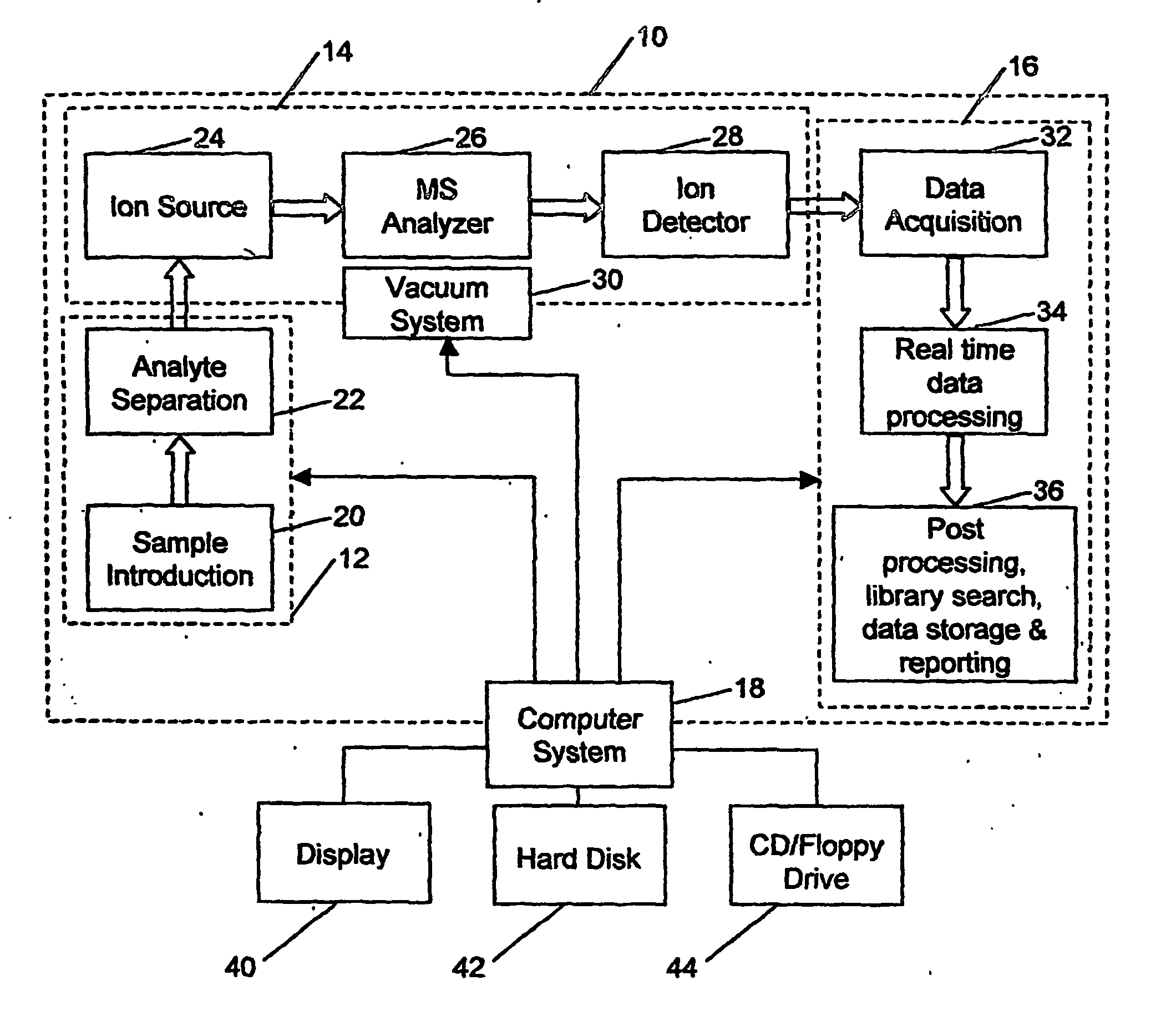
A method for analyzing data from a mass spectrometer comprising obtaining calibrated continuum spectral data by processing raw spectral data; obtaining library spectral data which has been processed to form calibrated library data; and performing a least squares fit, preferably using matrix operations (equation 1), between the calibrated continuum spectral data and the calibrated library data to determine concentrations of components in a sample which generated the raw spectral data. A mass spectrometer system (FIG. 1) that operates in accordance with the method, a data library of transformed mass spectra, and a method for producing the data library.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
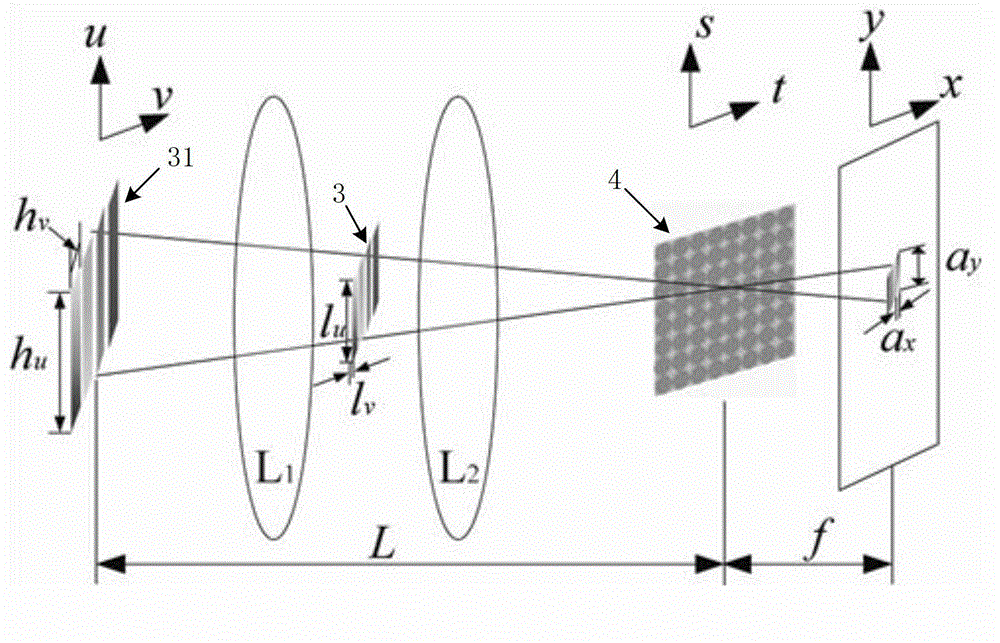
Spectral imaging method and spectrum imaging instrument of snapshot-type high throughput
ActiveCN102944305AImprove throughputPixel Count ReductionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicro lens arrayPrimary mirror
The invention relates to a spectral imaging method and a spectrum imaging instrument of a snapshot-type high throughput, which aim at realizing a picture-type photograph. The spectrum instrument comprises a linear gradient filter array and an optical-field imaging mechanism, and the optical-field imaging mechanism comprises a primary mirror, a micro lens array and a detector. The filter array is arranged on an aperture diaphragm between lenses of the primary mirror, the filter array consists of a plurality of filters which have identical width and are arranged at intervals, and the filter is a linear gradient filter band with continuous spectrum. The micro lens array is arranged on an imaging surface of a front-mounted optical imaging system, and the detector is arranged on a focus plane of the micro lens array. The spectrum imaging method is characterized in that light in different directions transmitted or reflected by a target is imaged on one micro lens after being modulated by the primary mirror and the filter array, the light is dispersed by the micro lens onto a picture element of the detector to form a subimage, and finally three-dimensional spectrum image data is obtained. The complete spectrum image information of the target can be obtained through the photograph in one step, and the spectral imaging method and the spectrum imaging instrument can be used for monitoring and tracking a rapid variable or movable target.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Hybrid light source
A hybrid light source comprises a discrete-spectrum lamp (for example, a fluorescent lamp) and a continuous-spectrum lamp (for example, a halogen lamp). A control circuit individually controls the amount of power delivered to the discrete-spectrum lamp and the continuous-spectrum lamp in response to a phase-controlled voltage generated by a connected dimmer switch, such that a total light output of the hybrid light source ranges throughout a dimming range. The discrete-spectrum lamp is turned off and the continuous-spectrum lamp produces all of the total light intensity of the hybrid light source when the total light intensity is below a transition intensity. The continuous-spectrum lamp is driven by a continuous-spectrum lamp drive circuit, which is operable to conduct a charging current of a power supply of the dimmer switch and to provide a path for enough current to flow through the hybrid light source, such that the magnitude of the current exceeds rated latching and holding currents of a thyristor of the dimmer.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Hybrid light source
A hybrid light source comprises a discrete-spectrum lamp (for example, a fluorescent lamp) and a continuous-spectrum lamp (for example, a halogen lamp). A control circuit individually controls the amount of power delivered to the discrete-spectrum lamp and the continuous-spectrum lamp in response to a phase-controlled voltage generated by a connected dimmer switch, such that a total light output of the hybrid light source ranges throughout a dimming range. The discrete-spectrum lamp is turned off and the continuous-spectrum lamp produces all of the total light intensity of the hybrid light source when the total light intensity is below a transition intensity. The continuous-spectrum lamp is driven by a continuous-spectrum lamp drive circuit, which is operable to conduct a charging current of a power supply of the dimmer switch and to provide a path for enough current to flow through the hybrid light source, such that the magnitude of the current exceeds rated latching and holding currents of a thyristor of the dimmer.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Apparatus and method of optical compensation for submarine optical cable
InactiveUS20080310858A1Avoid adjustmentEasy to controlOptical multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionEngineeringEqualization
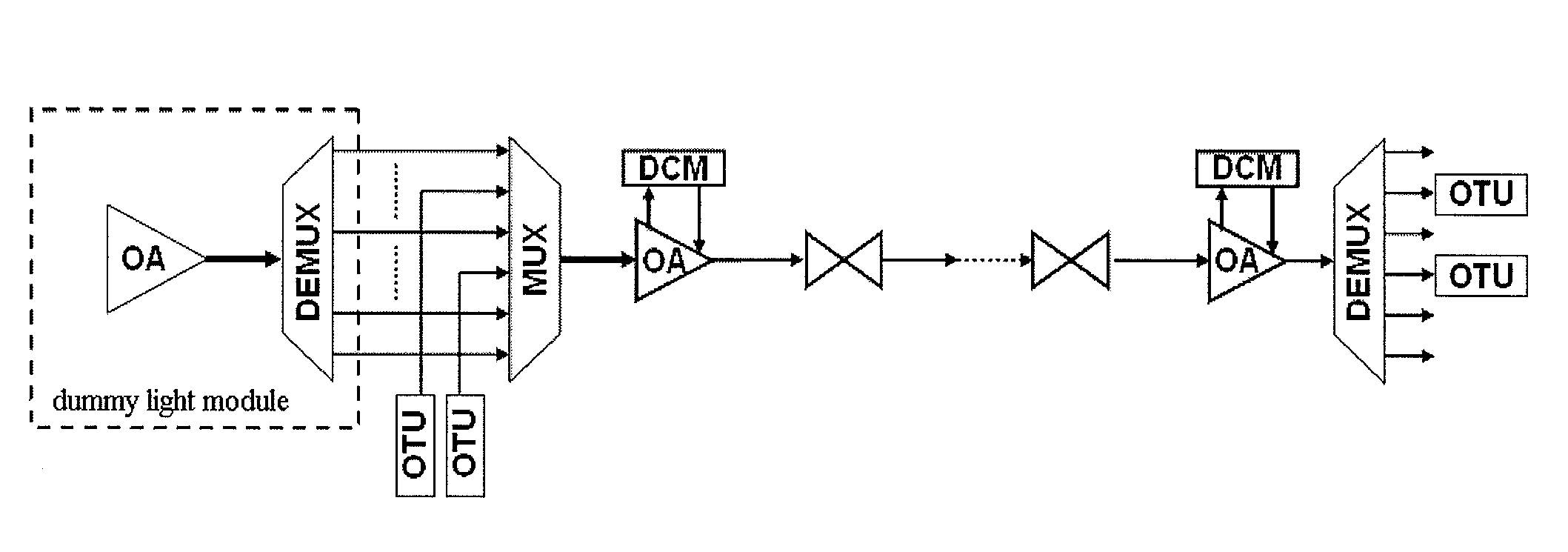
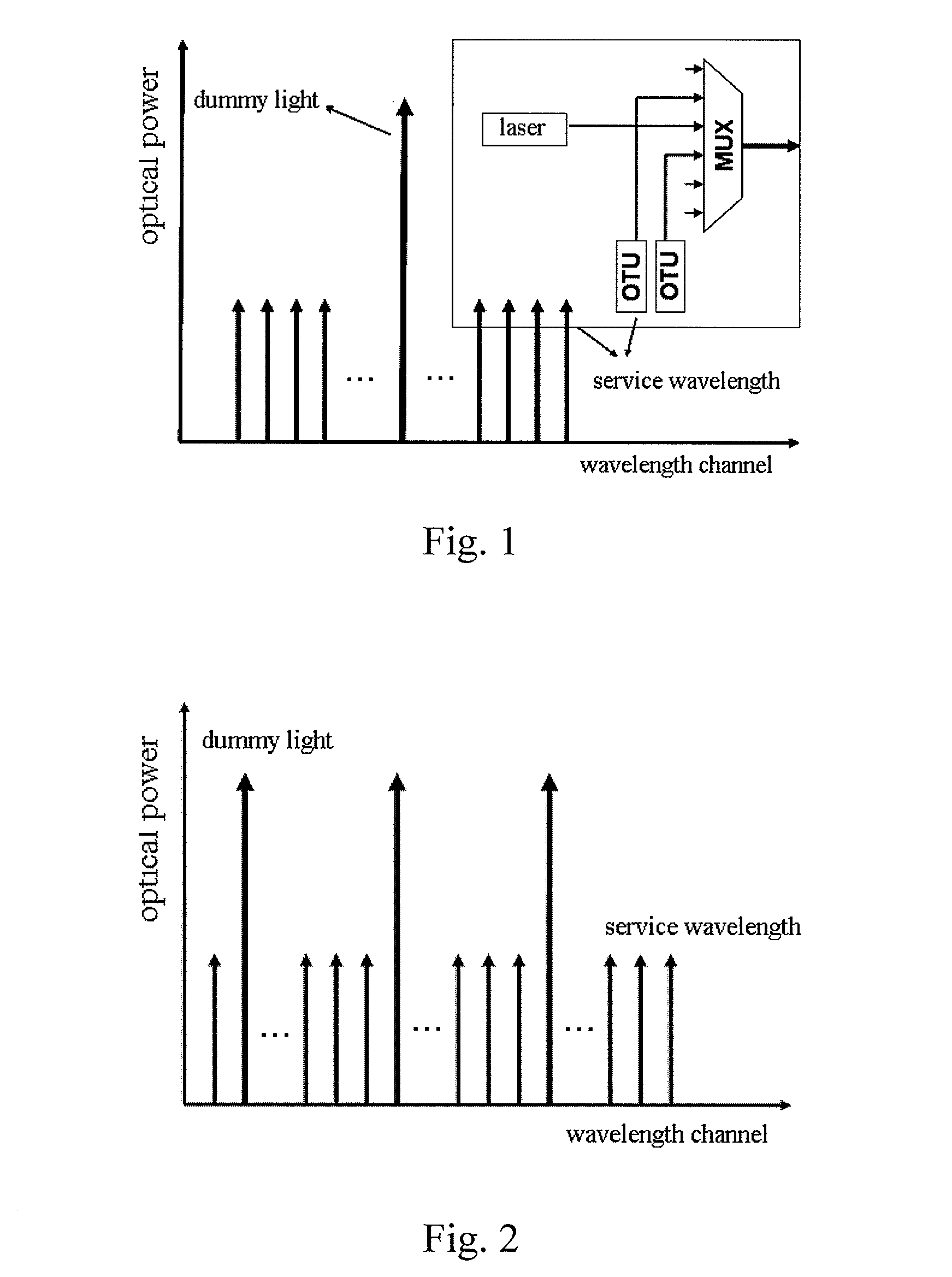
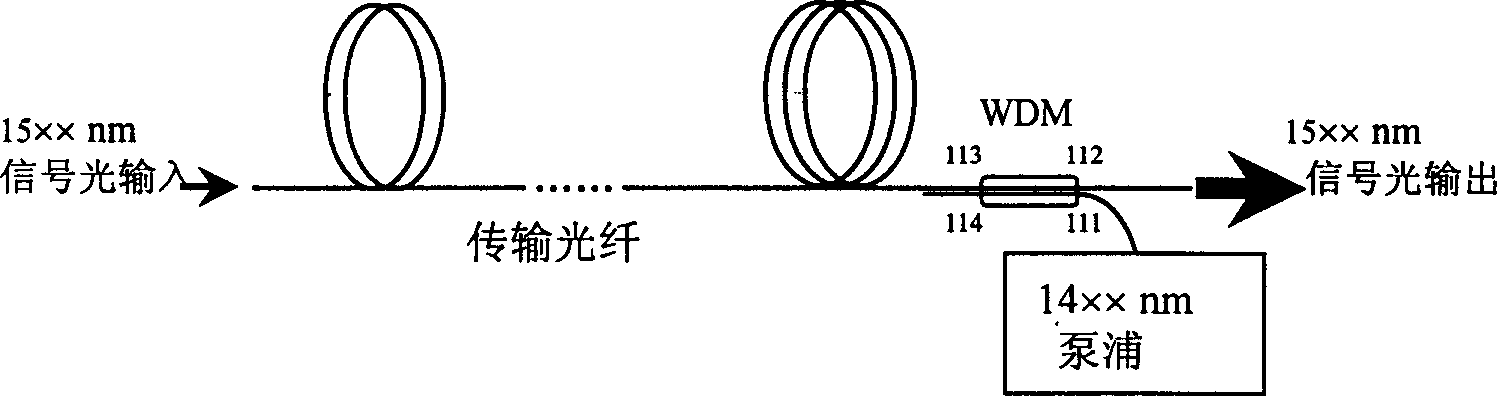
The present invention provides optical compensation for a submarine optical cable optical. A dummy light module generates a dummy light signal according to a continuous spectrum in a predetermined range and a combining module combines a service signal with the dummy light signal. When the dummy light is used for the compensation, conventional problems are solved, including complicated control, difficult realization of the pre-equalization function and inflexible configuration. When service signals are increased, the adjustment for the power of the dummy light signal is avoided; therefore, the control for the dummy light is simplified. In the pre-equalization operation, power control is only performed on the dummy light signal in the single channel or the continuous dummy light signal; therefore, the realization of the pre-equalization function is easy.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Computational method and system for mass spectral analysis
InactiveUS20060217911A1Reduce throughputIncreased reagent costTime-of-flight spectrometersMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometrySpectral analysis
A method for analyzing data from a mass spectrometer comprising obtaining calibrated continuum spectral data by processing raw spectral data; obtaining library spectral data which has been processed to form calibrated library data; and performing a least squares fit, preferably using matrix operations (equation 1), between the calibrated continuum spectral data and the calibrated library data to determine concentrations of components in a sample which generated the raw spectral data. A mass spectrometer system (FIG. 1) that operates in accordance with the method, a data library of transformed mass spectra, and a method for producing the data library.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
Blower volute structure of top-sucking kitchen ventilator
InactiveCN1348065AOutflow smoothlyImprove the efficiency of oil extractionDomestic stoves or rangesPump componentsEngineeringCasting
The blower volute structure of top-sucking kitchen ventilator includes upper casting, lower casing and the middle annular casing connecting the aforesaid casing through continuous and smooth transition, and features that the upper casing the lower casing has asymmetrical structure with the curvature radius of the lower casing edge at volute tongue being smaller than that of upper casing. The asymmetrical structure makes the airflow form one new noise source at volute tongue with continuous spectrum and the new noise can counteract partial original noise of the kitchen ventilator to reduce total noise and make it possible to install great power motor with great noise in kitchen ventilator.
Owner:NINGBO FOTILE KITCHEN WARE CO LTD
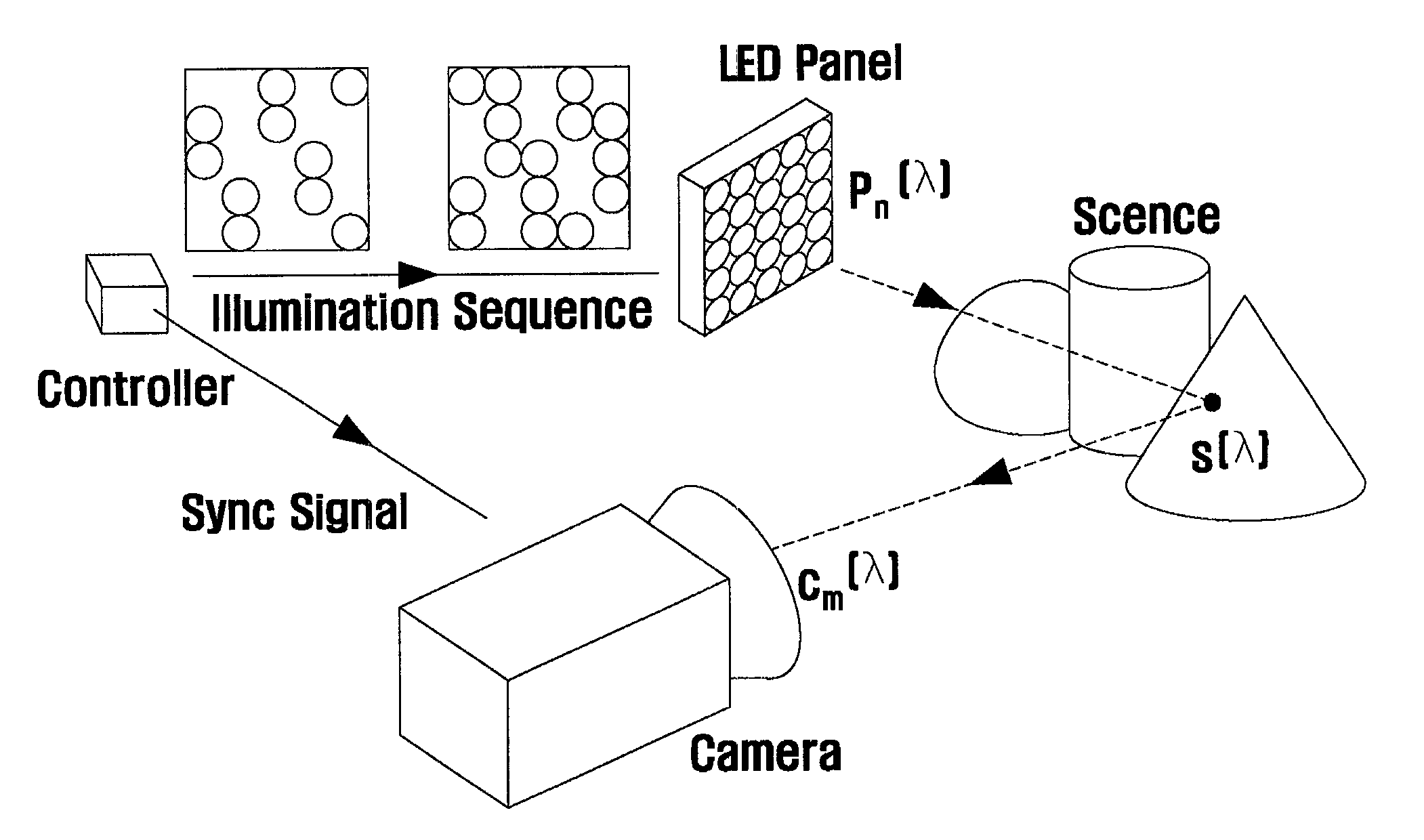
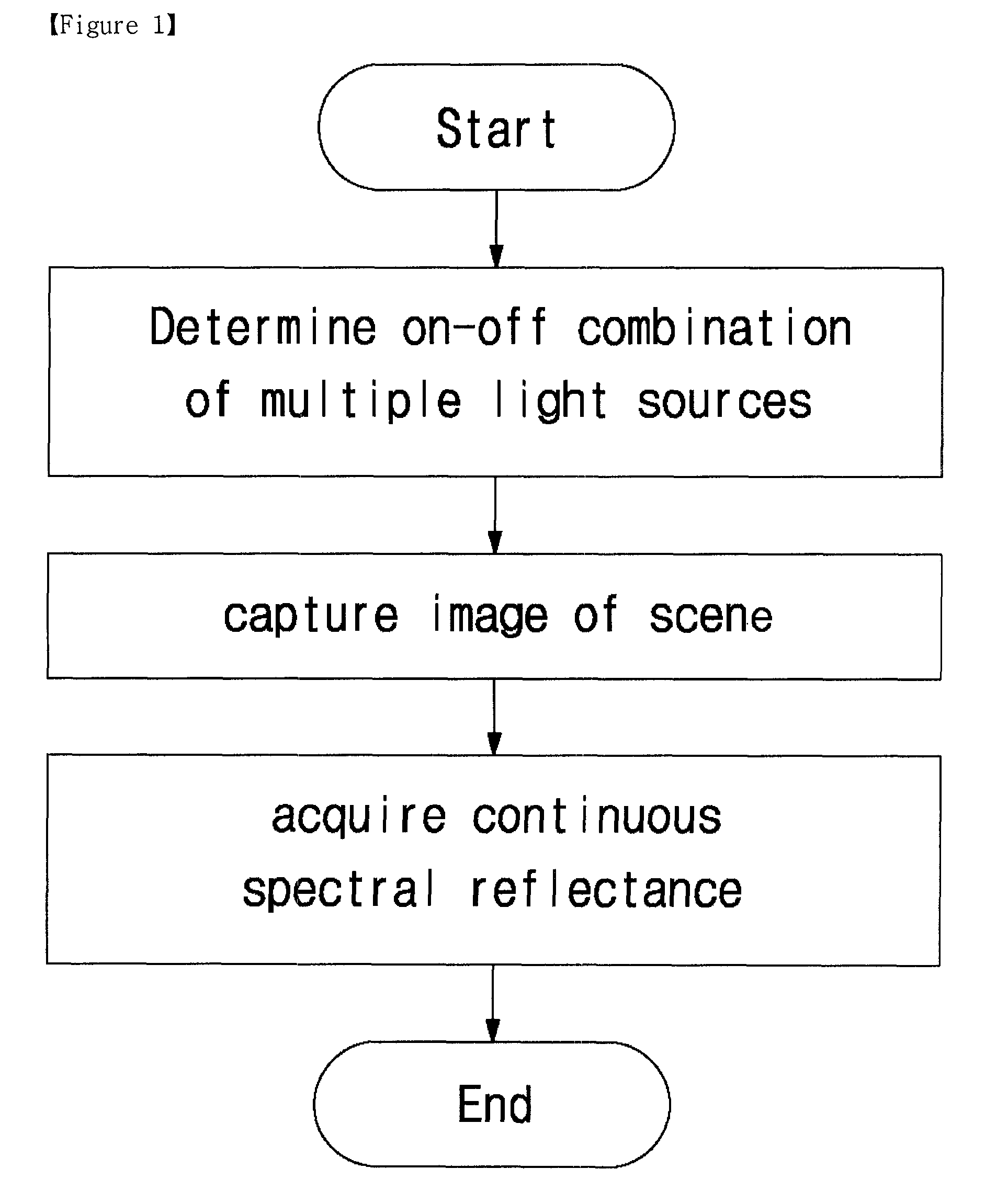
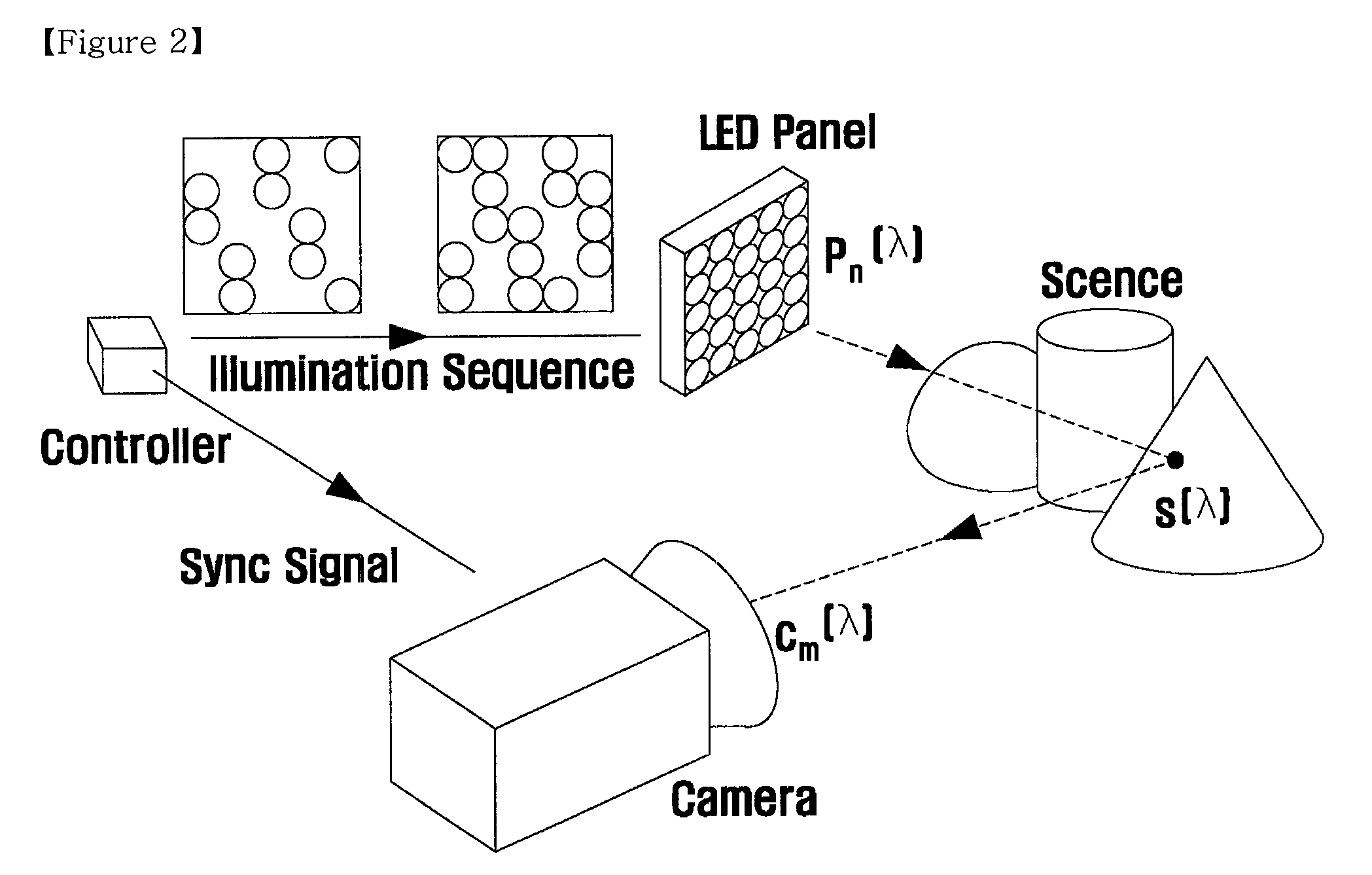
Method of multispectral imaging and an apparatus thereof
InactiveUS8284279B2Minimize the numberControl performanceTelevision system detailsImage analysisMicrocontrollerControl signal
A multispectral imaging method and system is provided. A multispectral imaging method of the present invention includes determining an on-off combination of a plurality of light sources illuminating a scene; illuminating the scene with the light sources according to the on-off combination selected on the basis of a first control signal generated by a microcontroller; capturing an image of the scene by operating a camera on the basis of a second control signal synchronized with the first control signal; determining a plurality of spectral basis functions and weights of the spectral basis functions; and acquiring a continuous spectral reflectance by summing values obtained by multiplying the spectral basis functions and respective weights. The multispectral imaging method of the present invention is practical and efficient in that a continuous spectral reflectance image can be acquired with a minimized number of measurements required for obtaining spectral reflectance. Accordingly, the multispectral imaging method of the present invention can be applied to various fields, such as image reproduction and medical imaging, while overcoming performance limits of the conventional RGB imaging techniques.
Owner:PARK JONG IL +3
Single crystal tunable broad band noncolinear femtosecond light parameter magnification method and apparatus
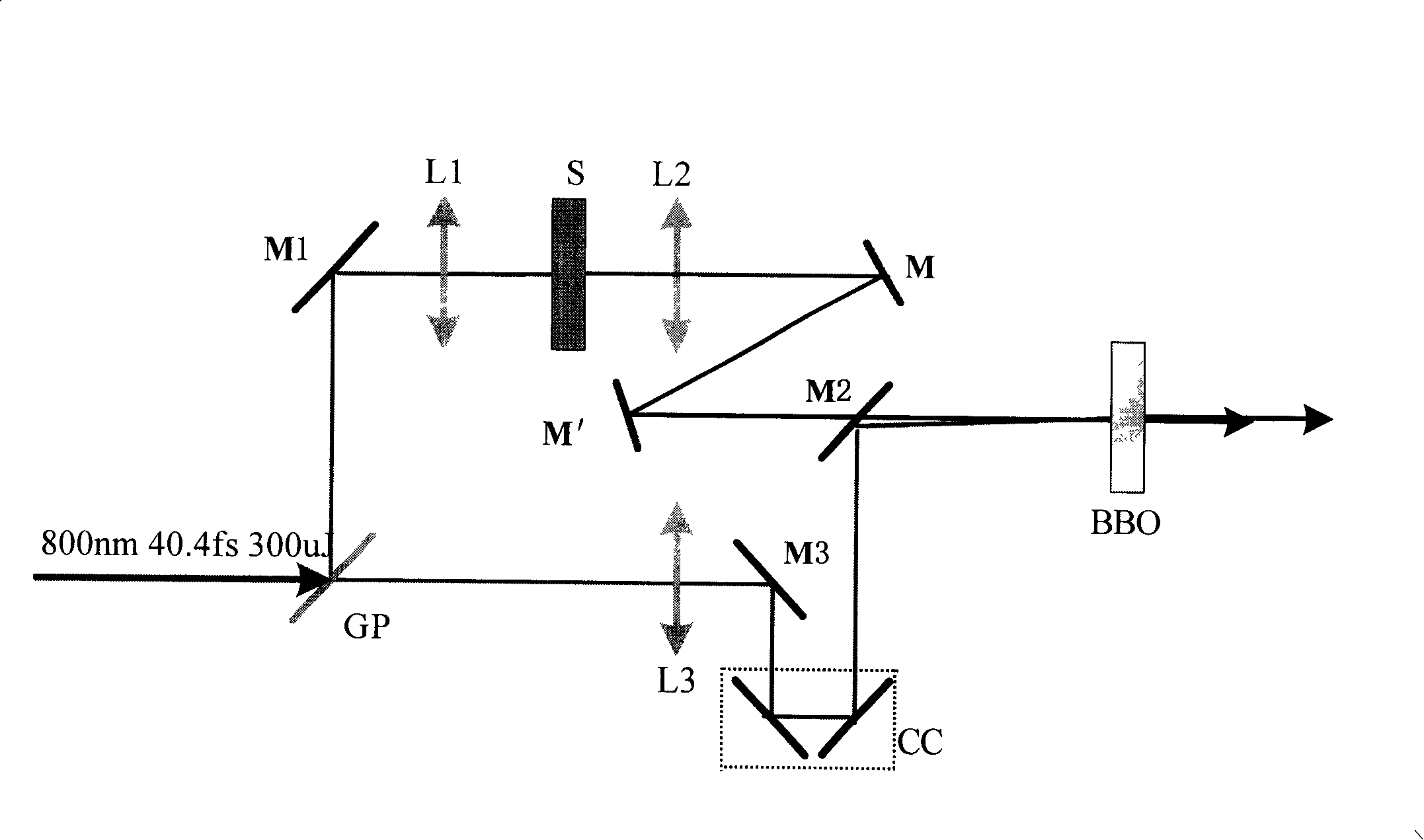
The invention relates to a method and a device for amplifying a single crystal tunable broadband non-collinear femtosecond optical parameter. Light output from a pump source is divided into two beams by passing a glass piece GP: one beam of reflection light is focused after passing through a lens L1 onto a crystal S which generates a super-continuous spectrum, then is collimated by a collimating lens L2 and is incident to a non-linear crystal BBO by an all reflection mirror M2, so as to form a signal light which has an amplified optical parameter and is horizontally polarized; the other beam of transmission light passes through a lens L3, and is delayed to synchronize with the signal light by a delay device CC, and is incident to the non-linear crystal BBO, and then is converted to a pump light which is vertically polarized. The pump light and the signal light generate a type I phase matching non-collinear optical parametric amplification by the non-linear crystal BBO; at the same time, the signal light which satisfies the frequency multiplication phase matching angle and the non-collinear optical parametric amplification phase matching angle is amplified. The invention solves the technical problems such as complicated structure of the background art and the higher cost. The invention has simple assembly, small size and good stability.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for soil content prediction based on a limited number of mid-infrared absorbances
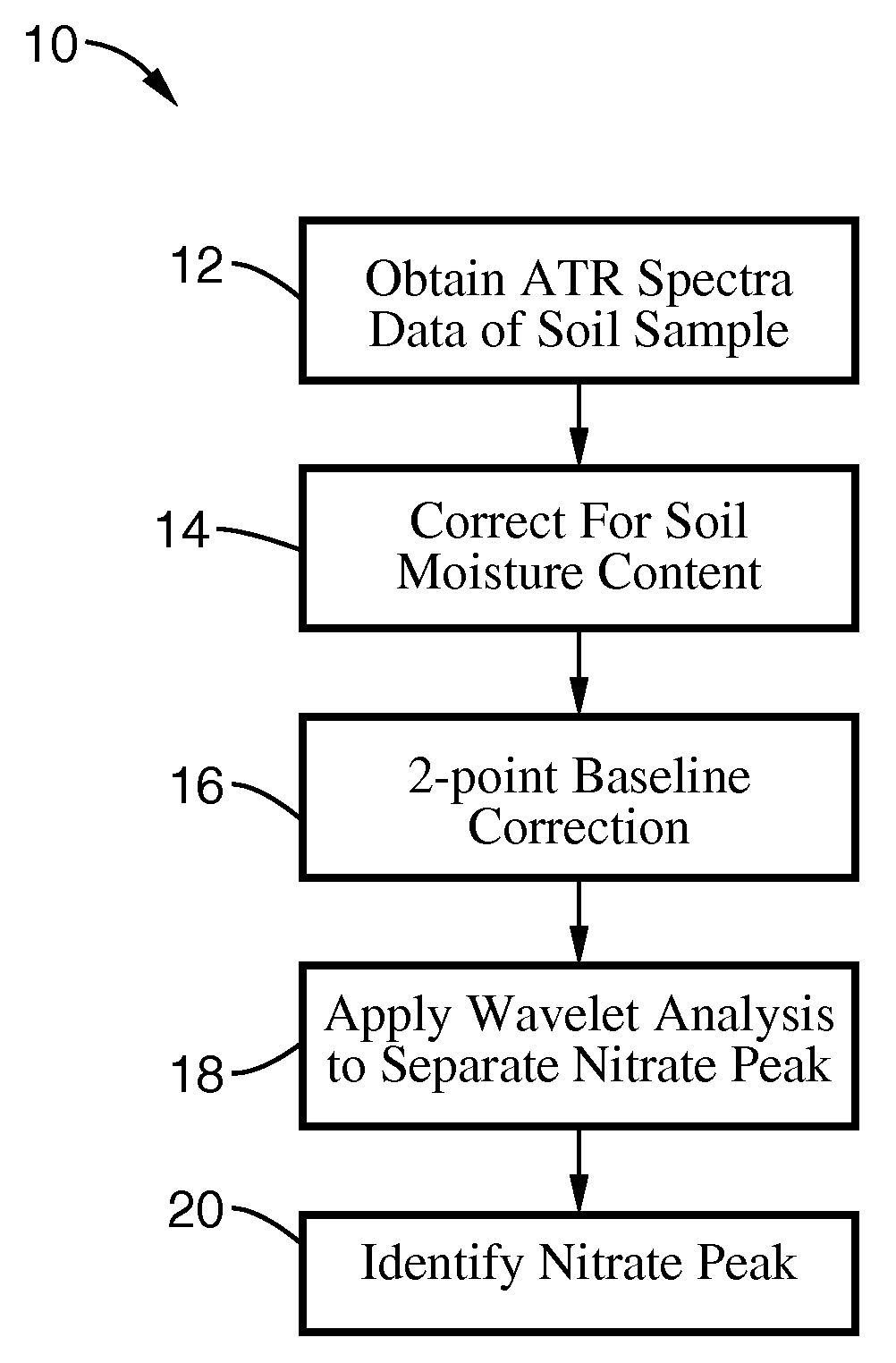
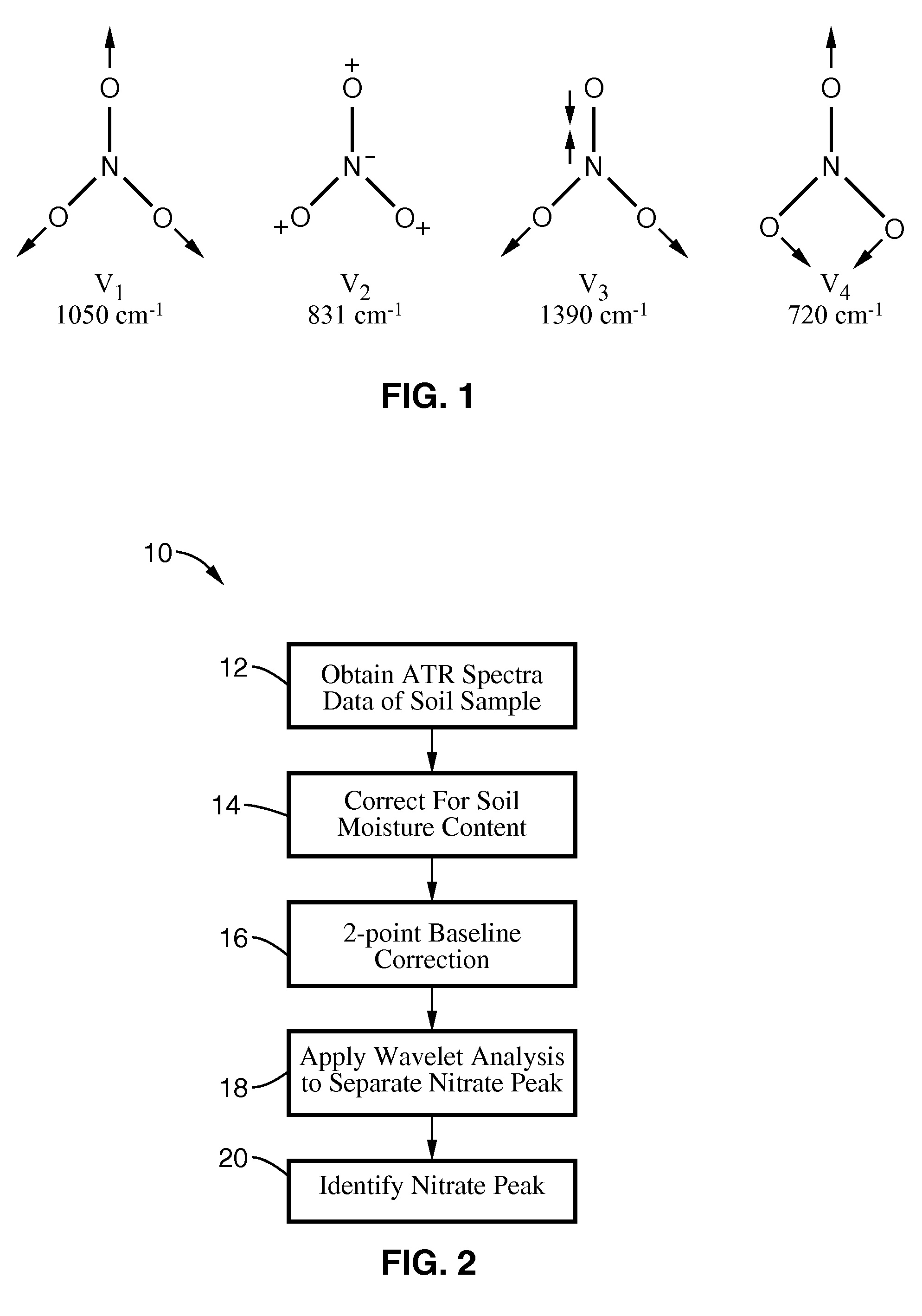
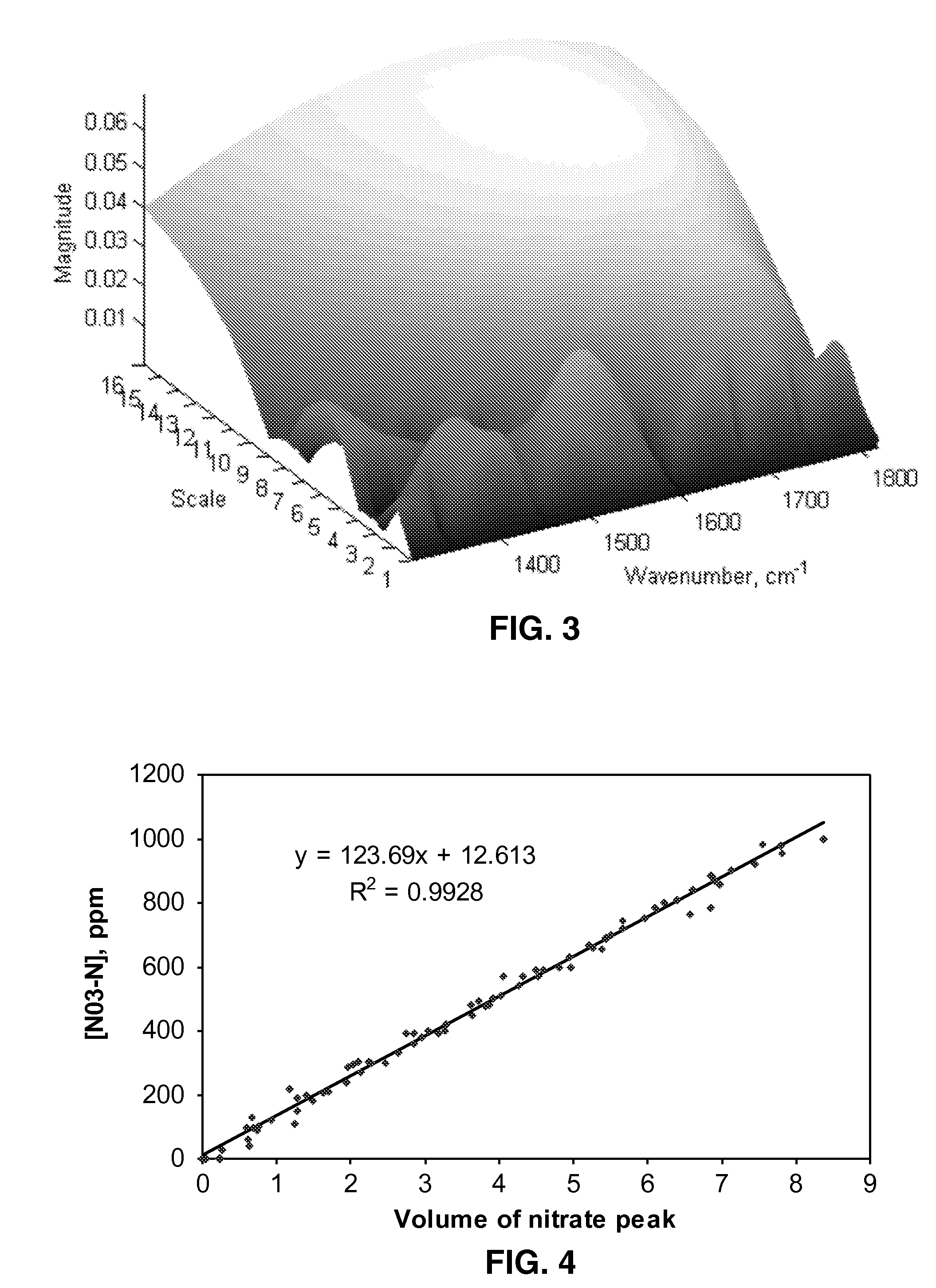
A single absorbance value was found in the mid infrared (mid-IR) region that correlated directly to soil nitrate content while not being influenced by other components in the soil, such as carbonate and organic matter. Using one or two absorbance values, at which interference from other ions is a minimum, to predict a component's concentration as opposed to the conventional method of using a continuous spectrum allows for an in-situ real-time soil nitrate content sensor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Hybrid light source
InactiveUS20120268020A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringCharged current
A hybrid light source comprises a discrete-spectrum lamp (for example, a fluorescent lamp) and a continuous-spectrum lamp (for example, a halogen lamp). A control circuit individually controls the amount of power delivered to the discrete-spectrum lamp and the continuous-spectrum lamp in response to a phase-controlled voltage generated by a connected dimmer switch, such that a total light output of the hybrid light source ranges throughout a dimming range. The continuous-spectrum lamp is driven by a continuous-spectrum lamp drive circuit, which is operable to conduct a charging current of a power supply of the dimmer switch and to provide a path for enough current to flow through the hybrid light source, such that the magnitude of the current exceeds rated latching and holding currents of a thyristor of the dimmer.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Near-infrared spectrometer
InactiveCN101201319ASimple structureLow costColor/spectral properties measurementsAdditive ingredientPhotodetector
The invention provides a near-infrared spectrograph, which belongs to the technical field of photoelectric test. The invention is characterized in that a near infrared light source and a collimating lens are matched up to constitute an illuminant system. The back position of the collimating lens is suitably provided with a light intensity modulation disc and an optical filter, and then is suitably provided with a dual-light path changer consisting of a dual-light path episcotister and a reflector. The dual-light path changer is connected with an integrating sphere light path arranged on the front part. A rotary sample cell and a photodetector connected with a signal processor are suitably arranged on an integrating sphere. The invention has simple structure, and the cost is low. Like a continuous wavelength type spectrograph when used, the invention makes use of a scaling method based on continuous spectrum to analyze a special ingredient, and the characteristic wavelength of the instrument does not need determining at the phase of research and development of the instrument. The invention makes use of the characteristics of large band width of the optical filter-type one, and the structures of the integrating sphere, the dual light paths, the rotary sample cell and so on to achieve the technical effects of a quasicontinuous wavelength type spectrograph, thus significantly improving the signal to noise ratio, the stability and the versatility.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Color temperature adjustable, LED based, white light source
ActiveUS9560714B1Easy constructionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesColor rendering indexPlanckian locus
Assemblies of temperature monitored, semiconductor light emitting diodes (LEDs) are disclosed that produce color temperature adjustable white light sources. Warm-white LEDs are combined with green and blue LEDs to produce light have continuous spectrum spanning the wavelength range of 400 to 700 nm with a white light point located at a selectable Planckian locus location and a color rendering index greater than 80. The circuitry includes LED temperature monitoring used to adjust LEDs spectral and luminosity output. Alternate arrangements combine warm-white LEDs with green, blue and red LEDs; warm-white and cool-white LEDs with green, blue and red LEDs; warm-white and cool-white LEDs with green LEDs; and a warm-white and cool-white LEDs with green-white LEDs.
Owner:HJERDE MORTEN
Solar simulator light source and realizing method thereof
InactiveCN103022328ASimulation is accurateAchieve extensivePoint-like light sourceSolid-state devicesElectricityPhotoluminescence
The invention provides a solar simulator light source and a realizing method thereof. The solar simulator light source at least comprises a substrate, a first lighting component and a light filter, wherein the first lighting component comprises a first kind of LED chips, a first kind of package bodies and fluorescent powder filled in the first kind of package bodies and corresponding to the first kind of LED chips. By combining electroluminescence of the LED chips with photoluminescence of the fluorescent powder and selecting the proper type of the LED chips to reasonably match with the broadband-spectrum fluorescent powder, light emitted by the LED chips can trigger the fluorescent powder while being combined with the same to form continuous broadband-spectrum light sources, and the light filter performs spectrum screening to obtain the continuous solar simulator light source good in matching with required application, so that the solar simulator light source can be widely applied to accurate simulation of solar continuous spectrum and realization of a broadband-spectrum near-infrared light source and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
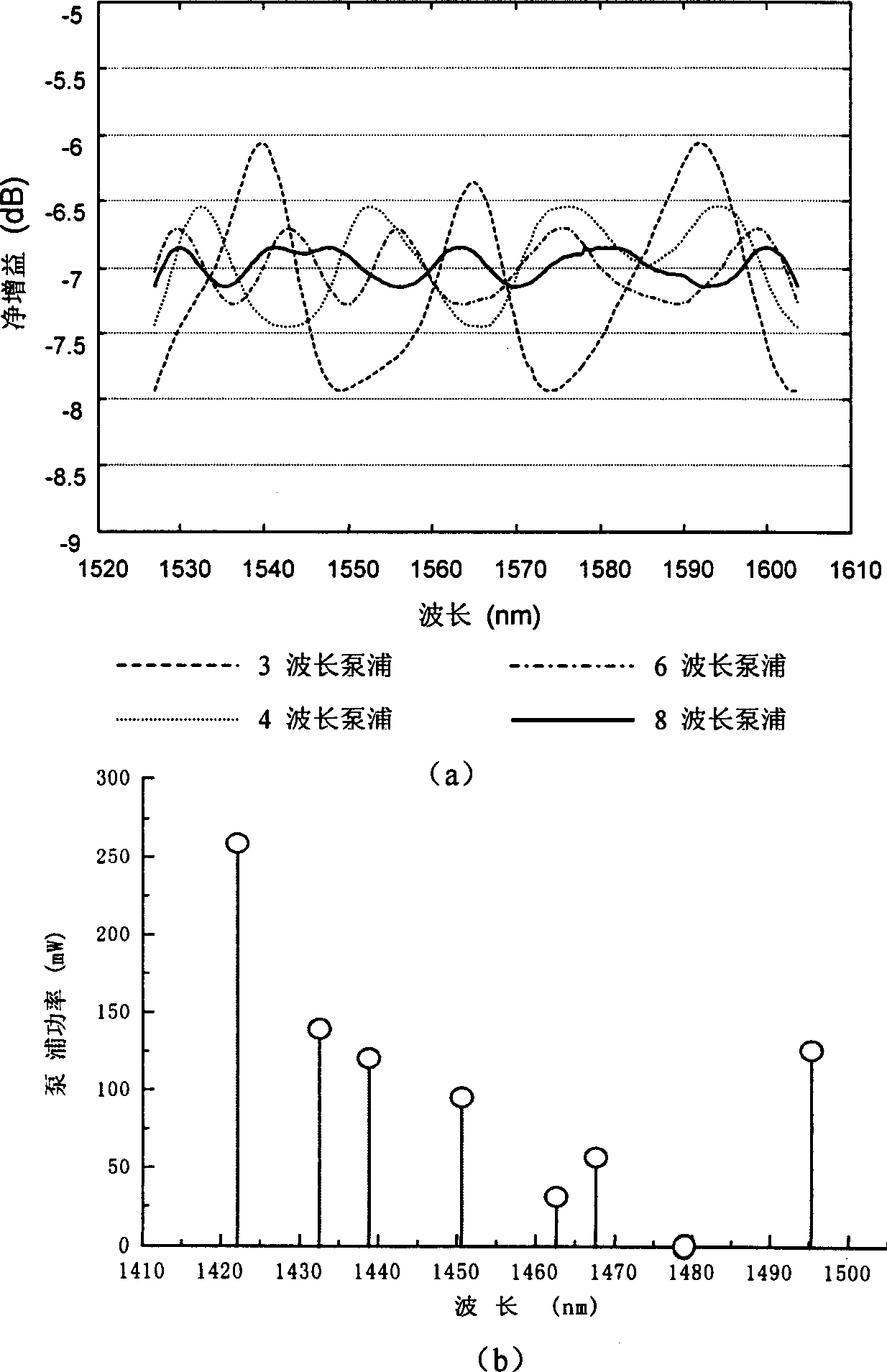
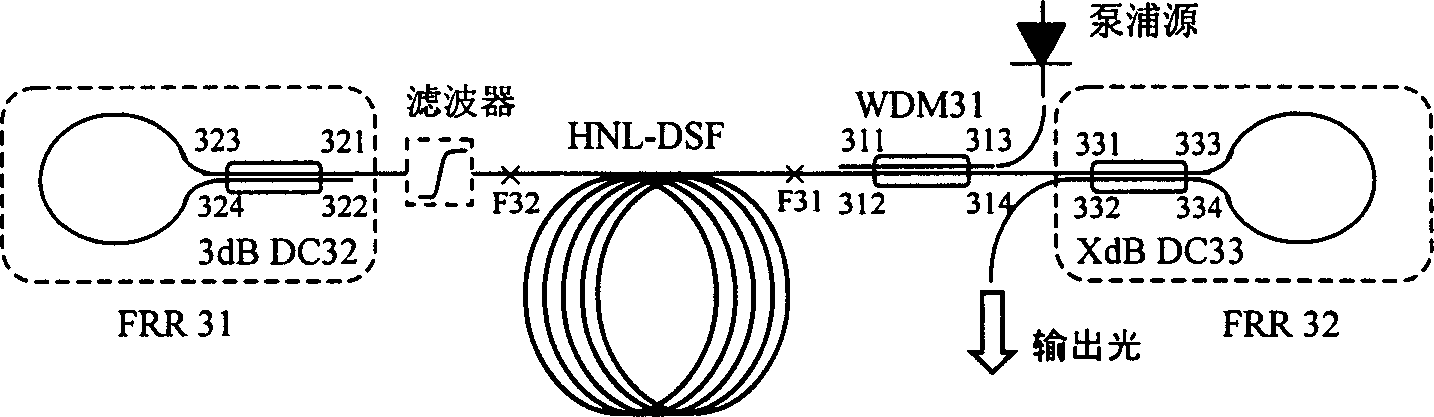
All optical fibre adjustable width continuous spectrum laser pump source for superflat wide-band Raman amplification
InactiveCN1477739AFlexible adjustmentAchieving Broadband Ultra-PlanarizationLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCircular cavityRaman laser
The present invention relates to an all-optical-fibre adjustable bandwidth continuous spectrum laser pump source (FBCSL) for ultraflat wideband Raman amplification, belonging to the field of high-speed wideband optical fibre communication technology. It adopts a high optical non-linear optical fibre (HNL-DSF) with approaching flat zero dispersion characteristics at Raman laser wavelength place as gain medium, and on the two ends of the above-mentioned HNL-DSF) a wideband reflector can be connected to form all the optical fibre Fabry-Perot (F-P) adjustable bandwidth continuous spectrum Raman laser or a wideband wavelength division multiplexing optical fibre coupler is connected to form all-optical-fibre circular cavity adjustable bandwidth continuous spectrum Raman laser.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
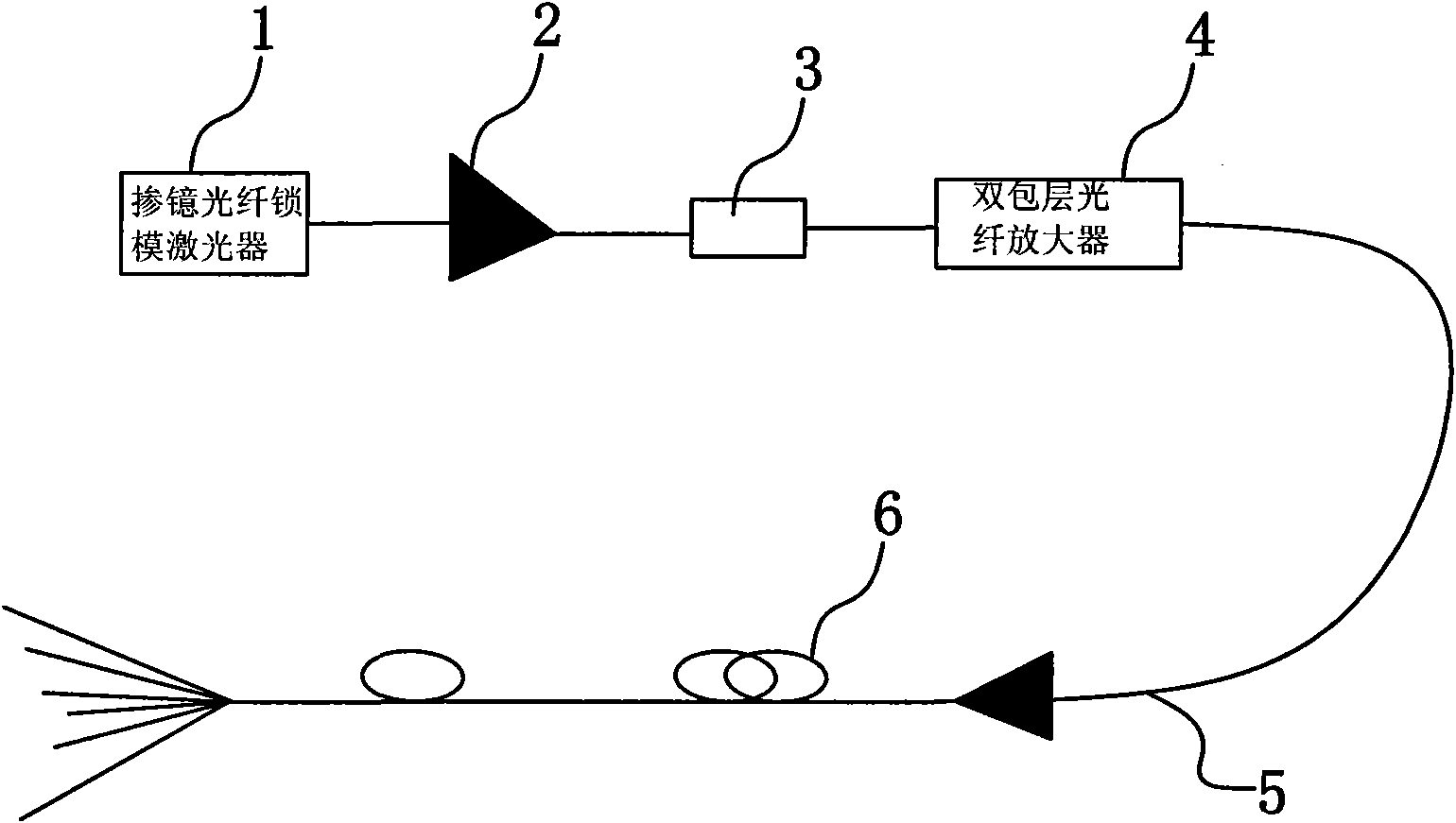
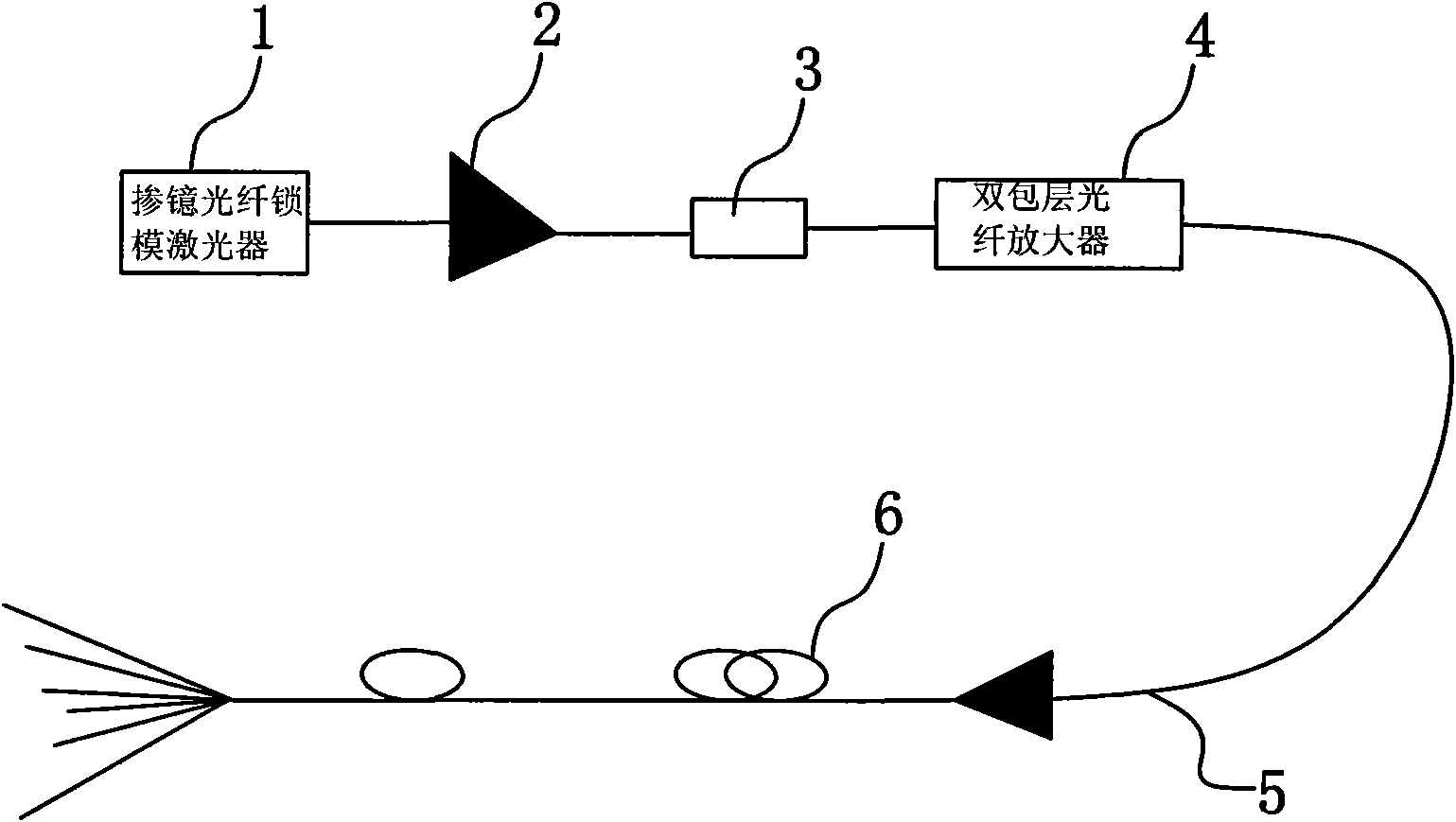
Visible light strengthened super continuous spectrum laser system with all-optical-fiber structure
InactiveCN101770132ASimple structureReduce volumeCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesDouble-clad fiberHigh power lasers
A visible light strengthened super continuous spectrum laser system with an all-optical-fiber structure comprises an optical fiber mode-locked laser, a single mode fiber amplifier, an opto-isolator, a double cladding fiber amplifier, a nonlinear photonic crystal fiber. The single mode fiber amplifier is connected with the output of the optical fiber mode-locked laser through an optical fiber; the opto-isolator is connected with the output of the single mode fiber amplifier through the optical fiber; the double cladding fiber amplifier is connected with the output of the opto-isolator through the optical fiber; and an output end of the double cladding fiber amplifier is connected with an input end of the nonlinear photonic crystal fiber through a pulling optical fiber. The system of the invention solves the technical problems that the high-power laser coupling device of the background art has huge volume, low coupling efficiency and limited spectral region. The system has the advantages of simple structure, small volume, high coupling efficiency, reliable engineering, capability of covering the visible light wave band and the like.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
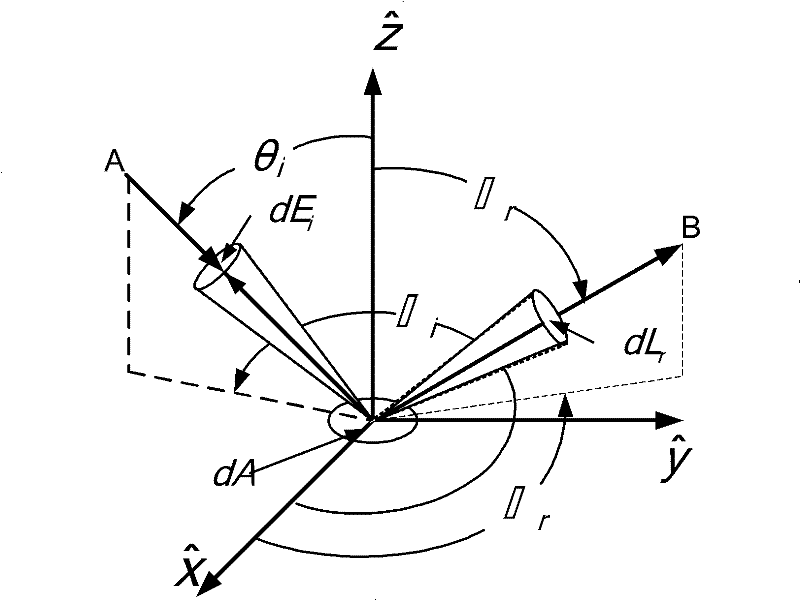
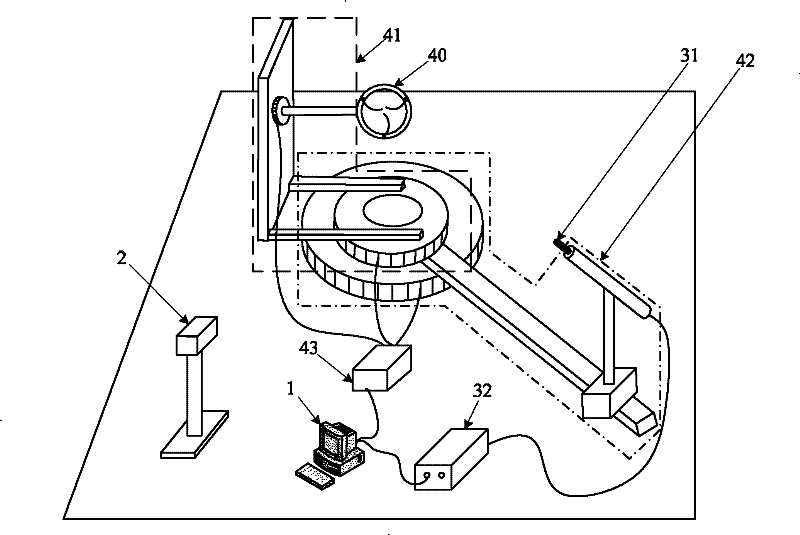
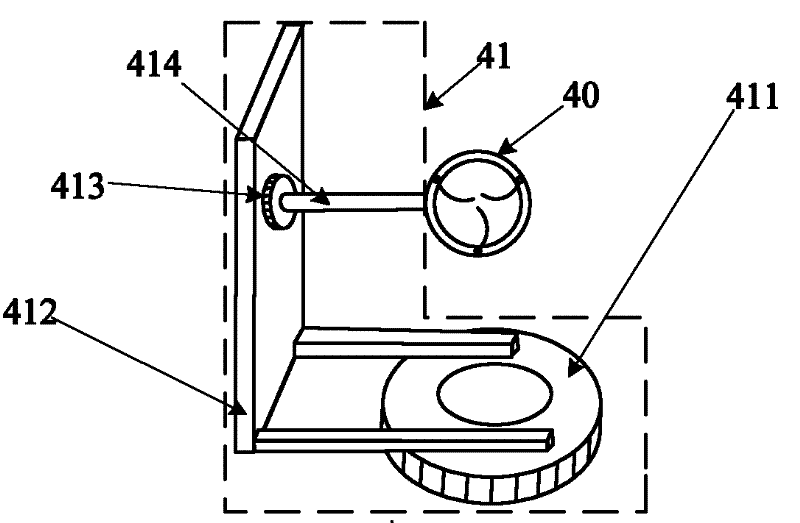
Measuring device of continuous spectrum bidirectional reflectance distribution function
InactiveCN102175650AImprove reflectivityContinuous Spectral BRDF DataScattering properties measurementsStands/trestlesMeasurement deviceCentre of rotation
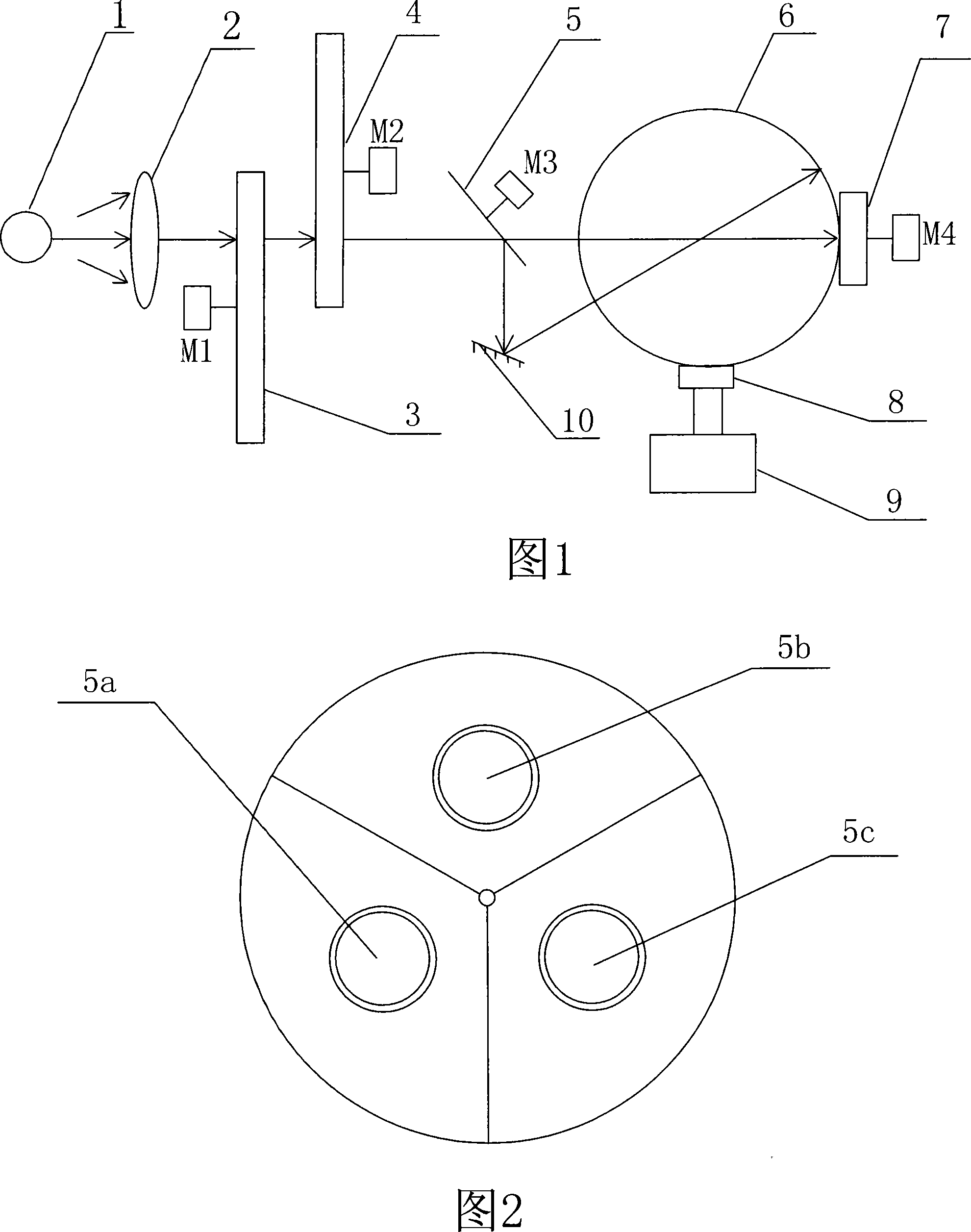
The invention relates to a measuring device of a continuous spectrum bidirectional reflectance distribution function, belonging to the fields of spectroscopy, computer graphics and machine vision and solving the problem that the traditional device can not measure the continuous spectrum BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) within a visible light wave band. A center point of a sample ring is a rotation center, and the sample ring is arranged on a sample horizontal and vertical direction rotating bracket; the sample horizontal and vertical direction rotating bracket is used for driving the sample ring to rotate on a horizontal surface and a vertical surface perpendicular to the horizontal surface by taking the rotation center as the center point; an optical fiber probe is arranged on a detector position regulation bracket, and a light path points at the rotation center; the detector position regulation bracket is used for driving the optical fiber probe to rotate on the horizontal surface by taking the rotation center as the center point and driving the optical fiber probe to make a one-dimensional linear motion with a motion trail penetrating through the rotation center; the signal output end of the optical fiber probe is connected with the input end of a spectrograph; a rotation controller is used for controlling the rotation of the sample horizontal and vertical direction rotating bracket and the detector position regulation bracket; a PC (Personal Computer) is connected with the spectrograph and the rotation controller; and light beams of a light source assembly are irradiated on the sample ring. The measuring device is used for measuring the continuous spectrum BRDF within the visible light wave band.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
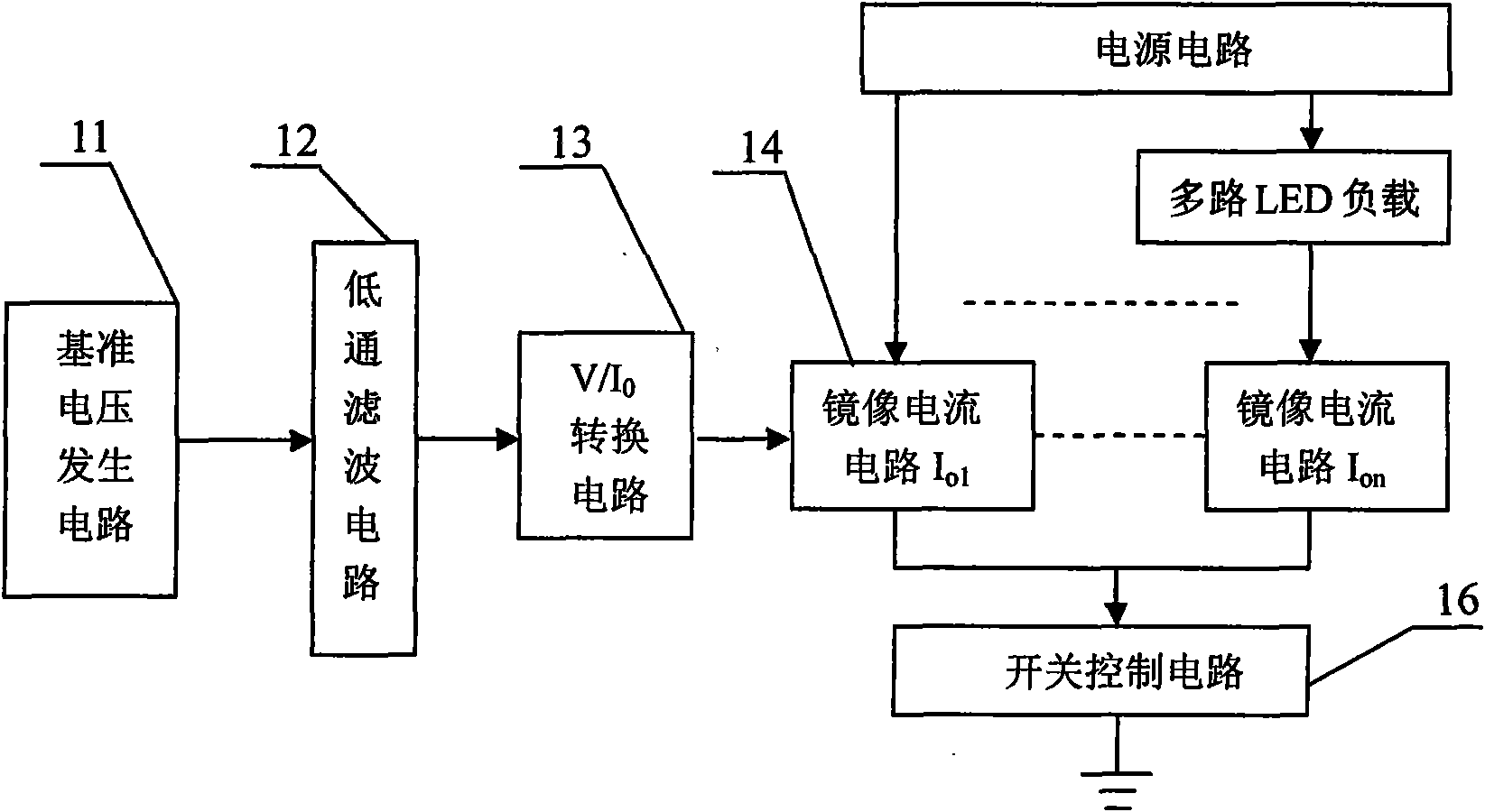
Image ratio constant flow source circuit driving multipath light emitting diode
InactiveCN101572984AHigh luminous intensityEasy to usePoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsLow-pass filterEngineering
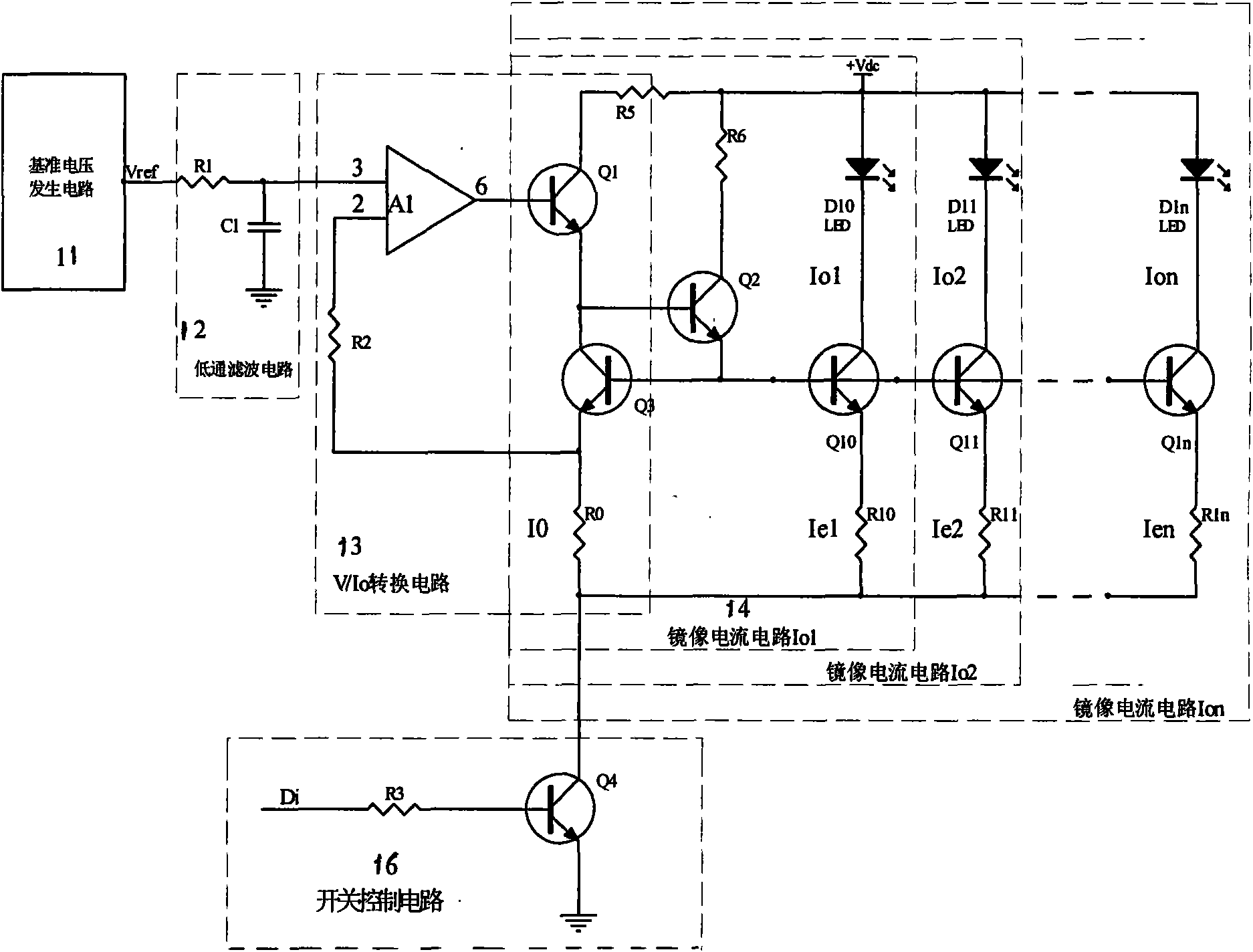
The invention provides an image ratio constant flow source circuit driving a multipath light emitting diode, belonging to the electronic technical field. The circuit structure comprises a pedestal generation circuit (11), a low-pass filter circuit (12), a V / I0 conversion circuit (13), a multipath image ratio constant flow source circuit (14) and a switch control circuit (16), wherein the image ratio constant flow source circuit (14) comprises transistors (Q10, Q11, ... Q1n), Light Emitting Diode loads (D10, D11, ... D1n), ratio resistors (R10, R11, ... R1n) and a sampling resistor (R0); the switch control circuit (16) comprises a third resistor (R3) and a fourth transistor (Q4), and completes control action by a digital signal (Di). The circuit of the invention leads illumination intensity of the multipath light emitting diode to be stable, can obtain continuous spectrum or modulated spectrum, has convenient use, low cost and electricity conservation, and is convenient for portable instrument use.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Super-continuous spectrum light source based on multicore photonic crystal fiber
InactiveCN102967981ARaise power capSimple structureCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guidePigtailLength wave
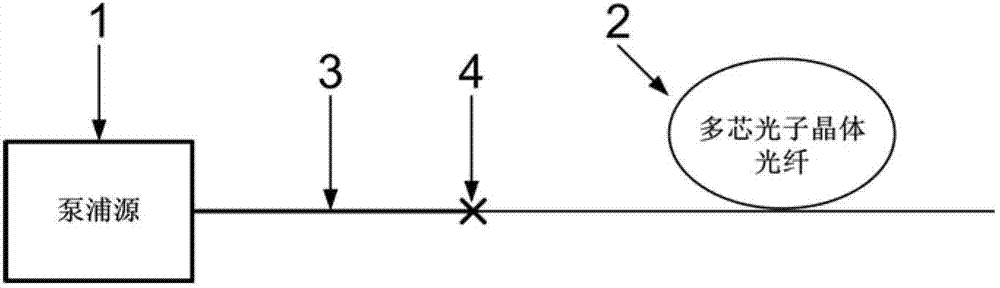
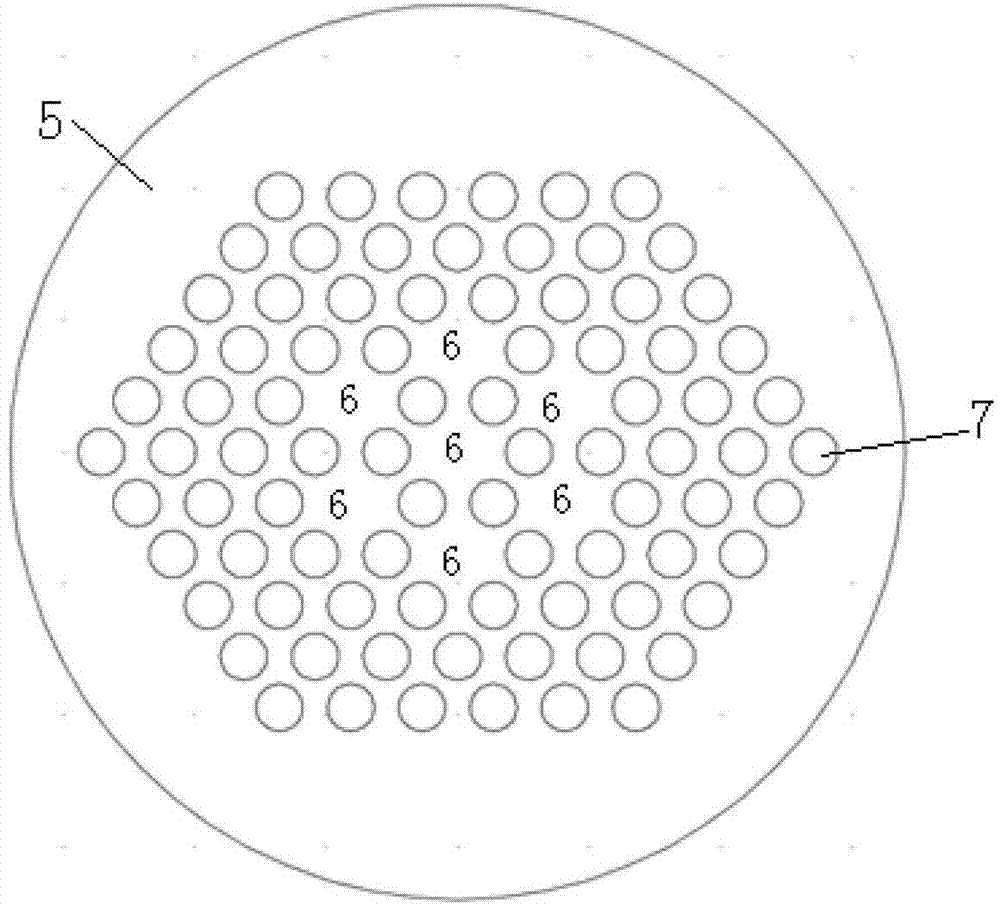
The invention provides a super-continuous spectrum light source based on a multicore photonic crystal fiber, which comprises a pump laser with an output pigtail, and a multicore photonic crystal fiber. The output pigtail of the selected pump laser is welded with an input end of the multicore photonic crystal fiber with matched mode field and a dispersion characteristic to form a whole-fiber super-continuous spectrum light source. The multicore photonic crystal fiber with larger mode field area and adjustable dispersion characteristic can be taken as a generating medium of the super-continuous spectrum, which effectively solves the problems that the normal single-core photonic crystal fiber as the generating medium of the super-continuous spectrum is difficult to weld with the pump laser, and the dispersion characteristic of the photonic crystal fiber is not matched with the operating wavelength of the pump laser, when generating the high-average power whole-fiber super-continuous spectrum, can effectively realize output of the high-average power whole-fiber super-continuous spectrum, and at the same time, greatly improve the power upper limit of the system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
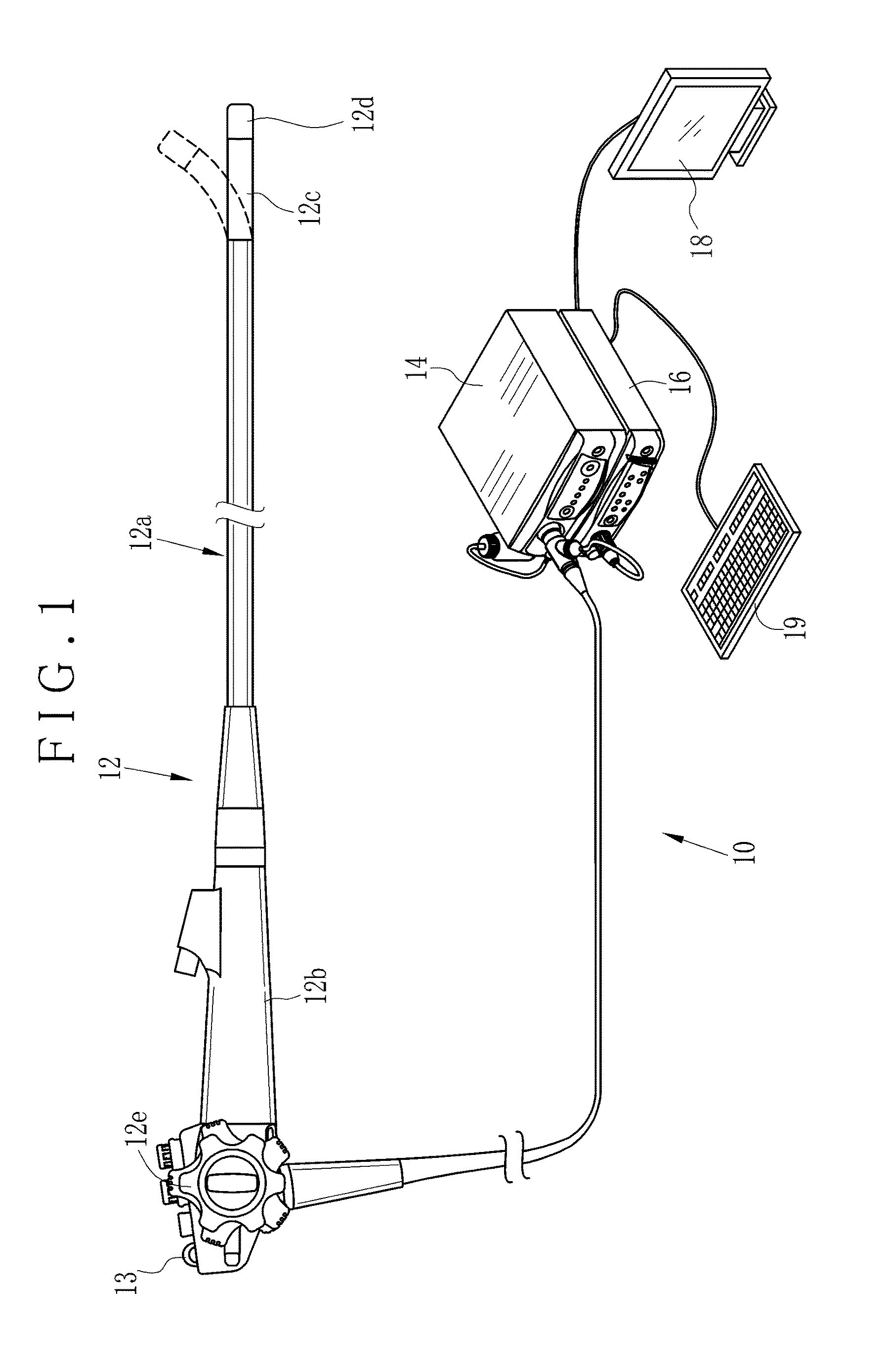
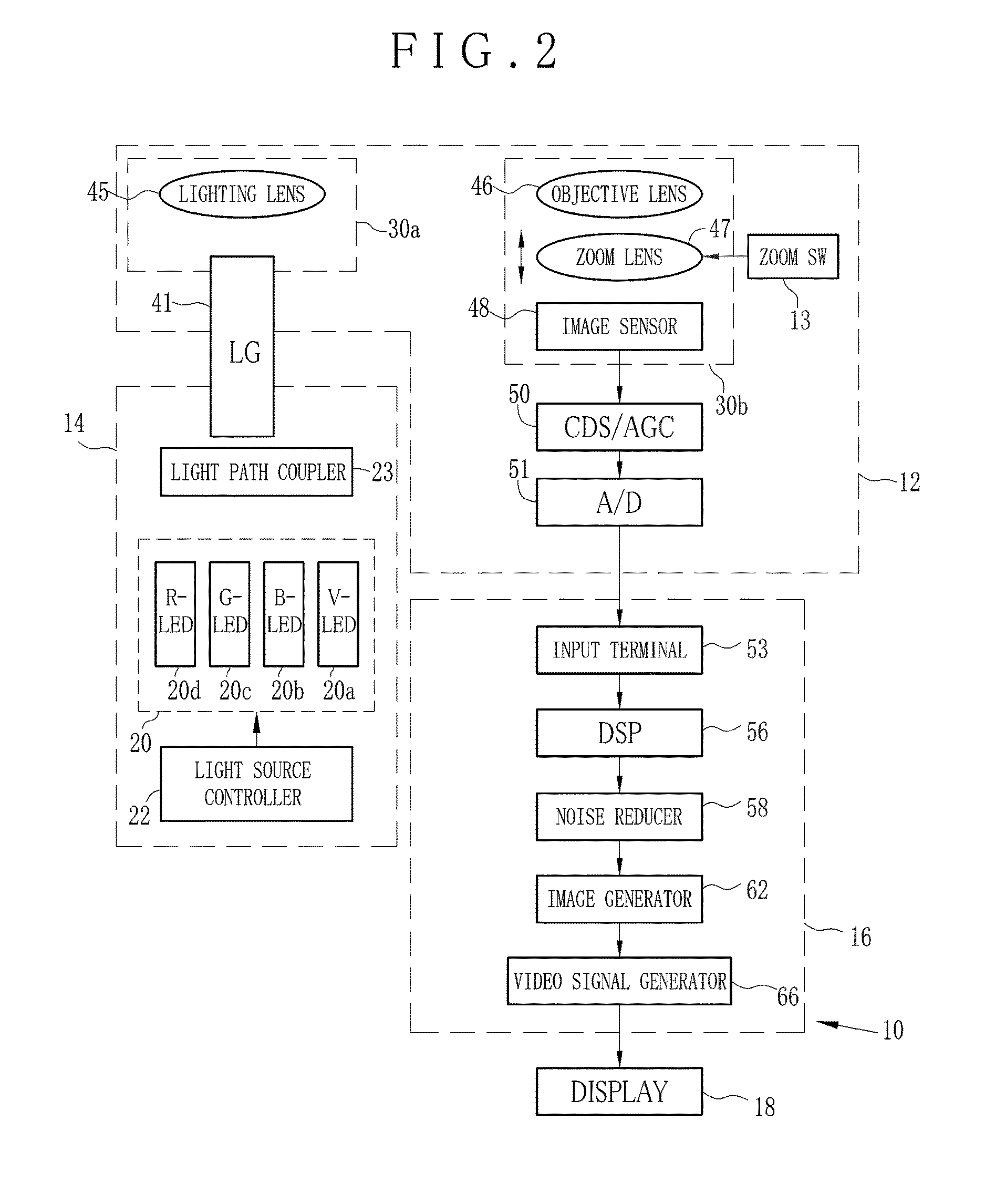
Endoscope system and method of operating endoscope system
ActiveUS20170006202A1High whitenessAcceptable imageTelevision system detailsElectric lighting sourcesColor imageEndoscope
An endoscope system includes a color image sensor, having pixels sensitive to plural colors different from one another, for imaging an object. Plural LEDs discretely generate light of colors different from one another, to apply polychromatic light constituted by spectrally combining the light of the colors to the object. A light source controller controls the plural LEDs, to correct an intensity ratio of an integrated emission intensity between the plural colors according to receiving the first polychromatic light with respectively the pixels of the plural colors, so that the intensity ratio becomes equal to a target ratio of an integrated emission intensity between the plural colors according to receiving continuous spectrum light with respectively the pixels of the plural colors, the continuous spectrum light having an at least partial wavelength range of light emitted by a white light source.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Super-resolution microscopic imaging method and device based on micro waveguide
InactiveCN102928384AHigh resolution finenessSimple structureScattering properties measurementsMicroscopesMicroscopic imageFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a super-resolution microscopic imaging method based on micro waveguide. The super-resolution microscopic imaging method comprises following steps of: (1) leading continuous spectrum laser coupling into the micro waveguide, placing the micro waveguide on the surface of a sample with a sub-wavelength detail, wherein the surface detail has an effect of modulating light transmitted in the micro waveguide to form scattered light; (2) collecting scattered light signals, and imaging to acquire corresponding images; (3) performing spectral analysis on images in the step (2) to acquire a spectrum distribution diagram; and (4) performing frequency shift reconstruction on the spectrum distribution diagram, and inverting to acquire a sample surface image capable of resolving subwavelength. The invention also discloses a super-resolution microscopic imaging device based on the micro waveguide. The super-resolution microscopic imaging method and device have the advantages of high fineness of resolution and high functional expansibility and can be effectively applied to the super-resolution microscopic imaging of the sub-wavelength detail on the surface of the sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device to enhance image quality in digital video processing systems using dithering
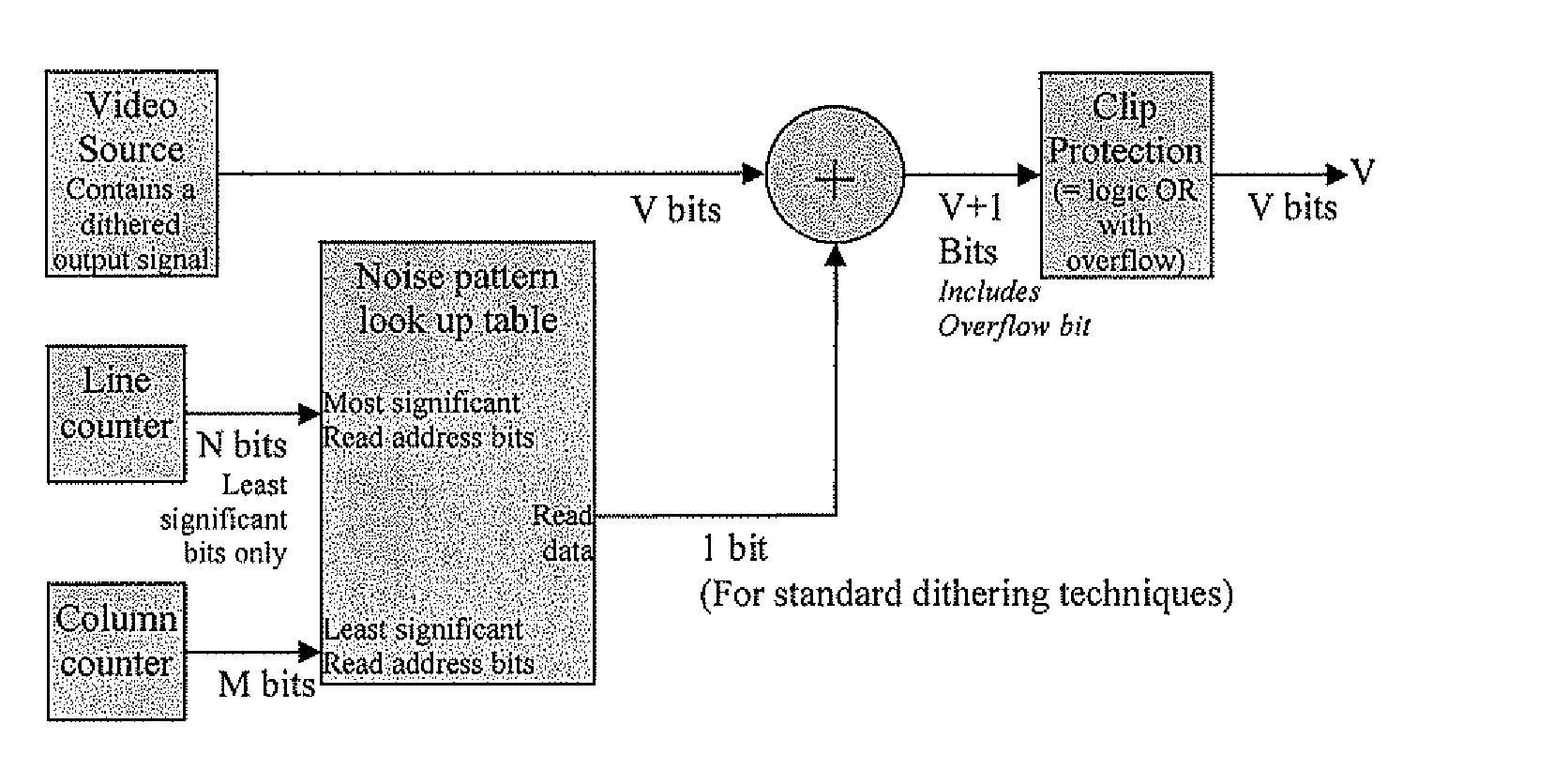
ActiveUS20100259553A9Speed up the processSuitable for processingTelevision system detailsTexturing/coloringPattern recognitionDigital video
A processing chain for a digital image signal (12) applies a dither pattern (14), having a first spectrum, to the image signal at a point in the processing chain. A further noise pattern (10) is applied to the image signal during the processing chain. The noise pattern (10) has a second spectrum which is configured such that the combination of the first spectrum and second spectrum results in a more continuous spectrum. Another aspect describes a noise pattern (10) which can be used as an offset dither pattern for digital images, especially before colour bit depth reduction. The noise pattern comprises an array of values which are linearly distributed across a range, with each value in the range occurring an equal number of times. Similar values at extreme ends of the range of values are dispersed within the array. The pattern has a Poisson-disk two-dimensional spectral energy distribution. Values are positioned in the array based on distance to similar values in neighbouring repetitions of the array. The array has “magic square” properties.
Owner:BARCO NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com