Patents
Literature
2345 results about "Centre of rotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
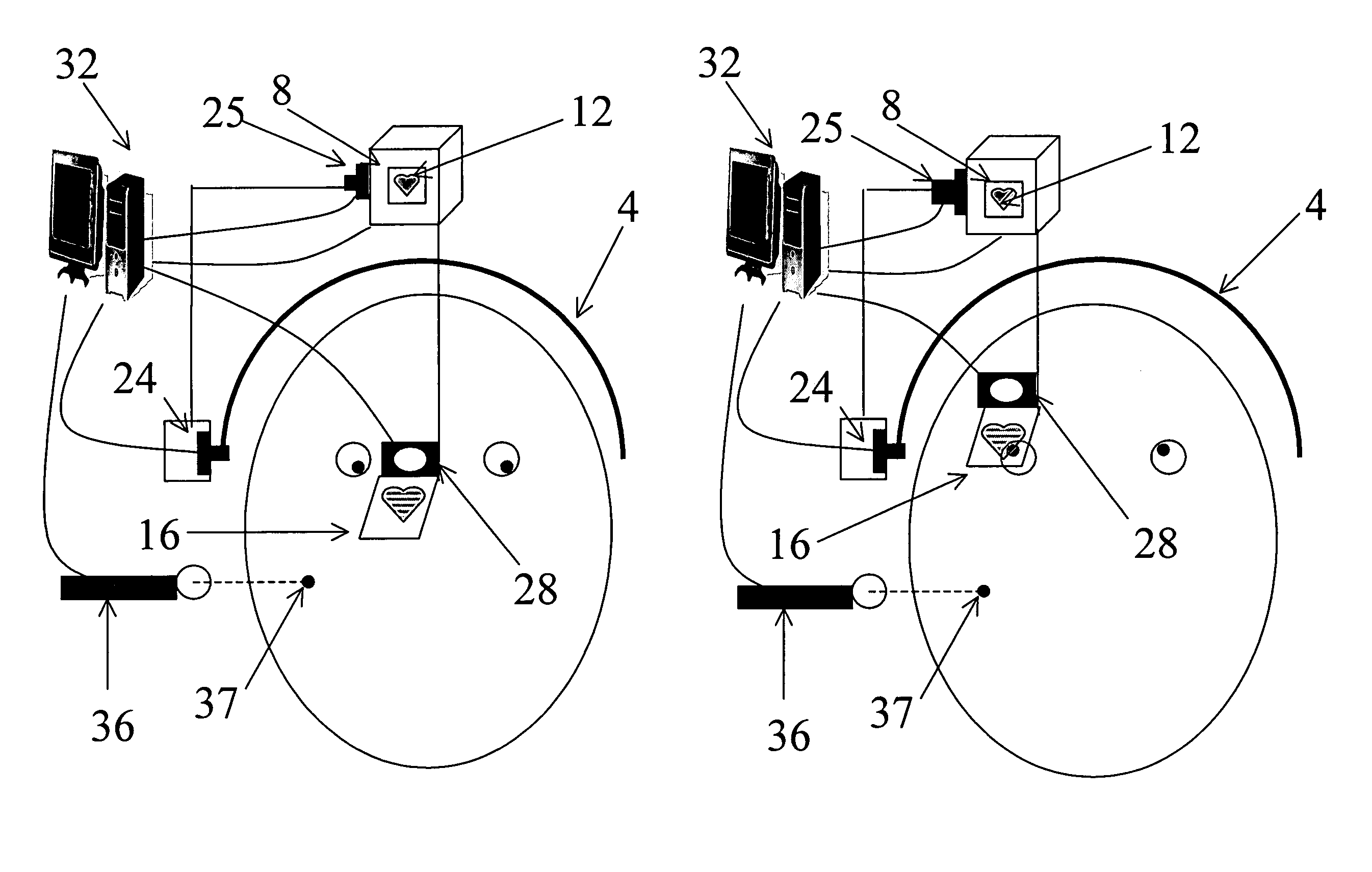
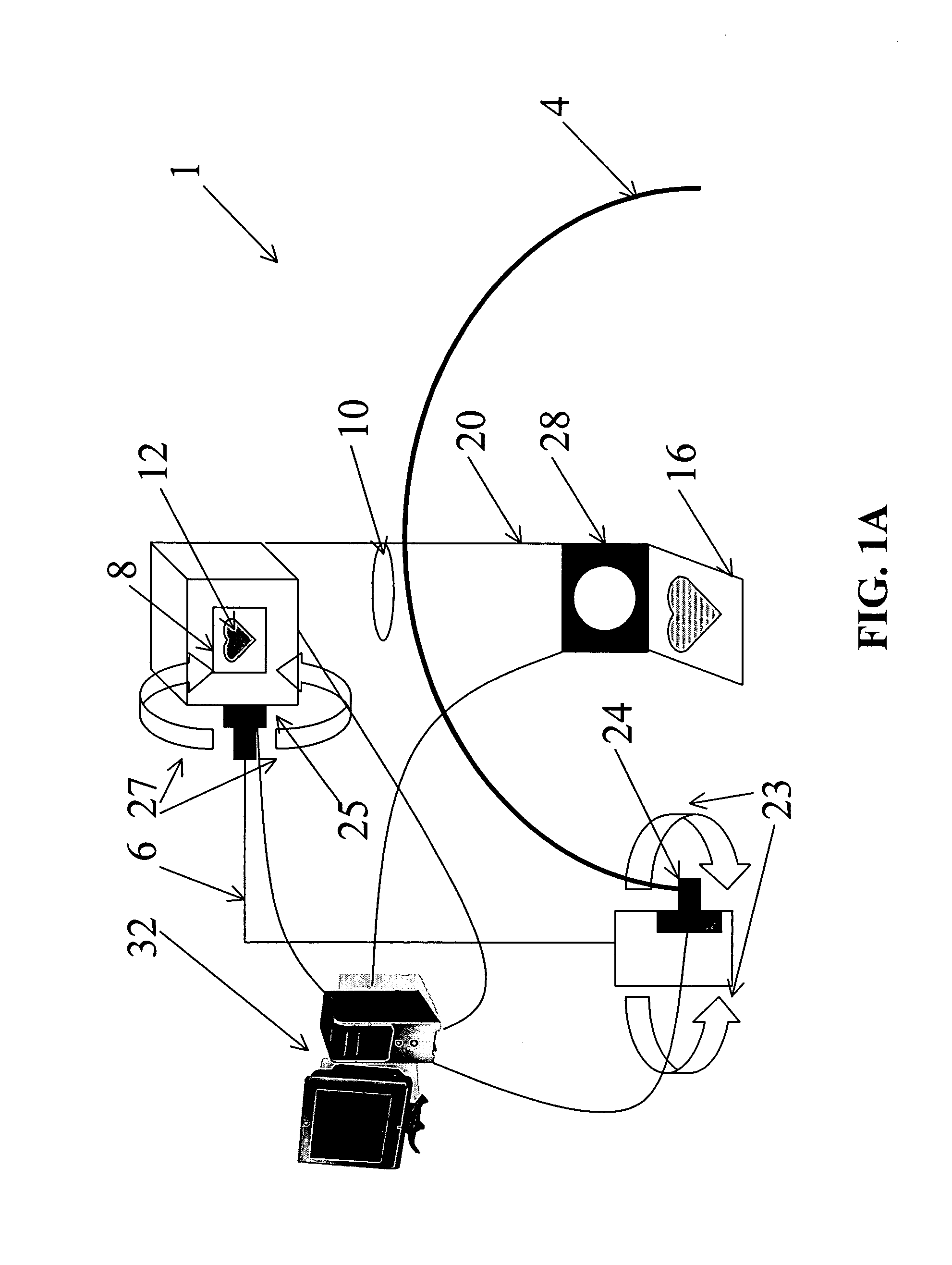
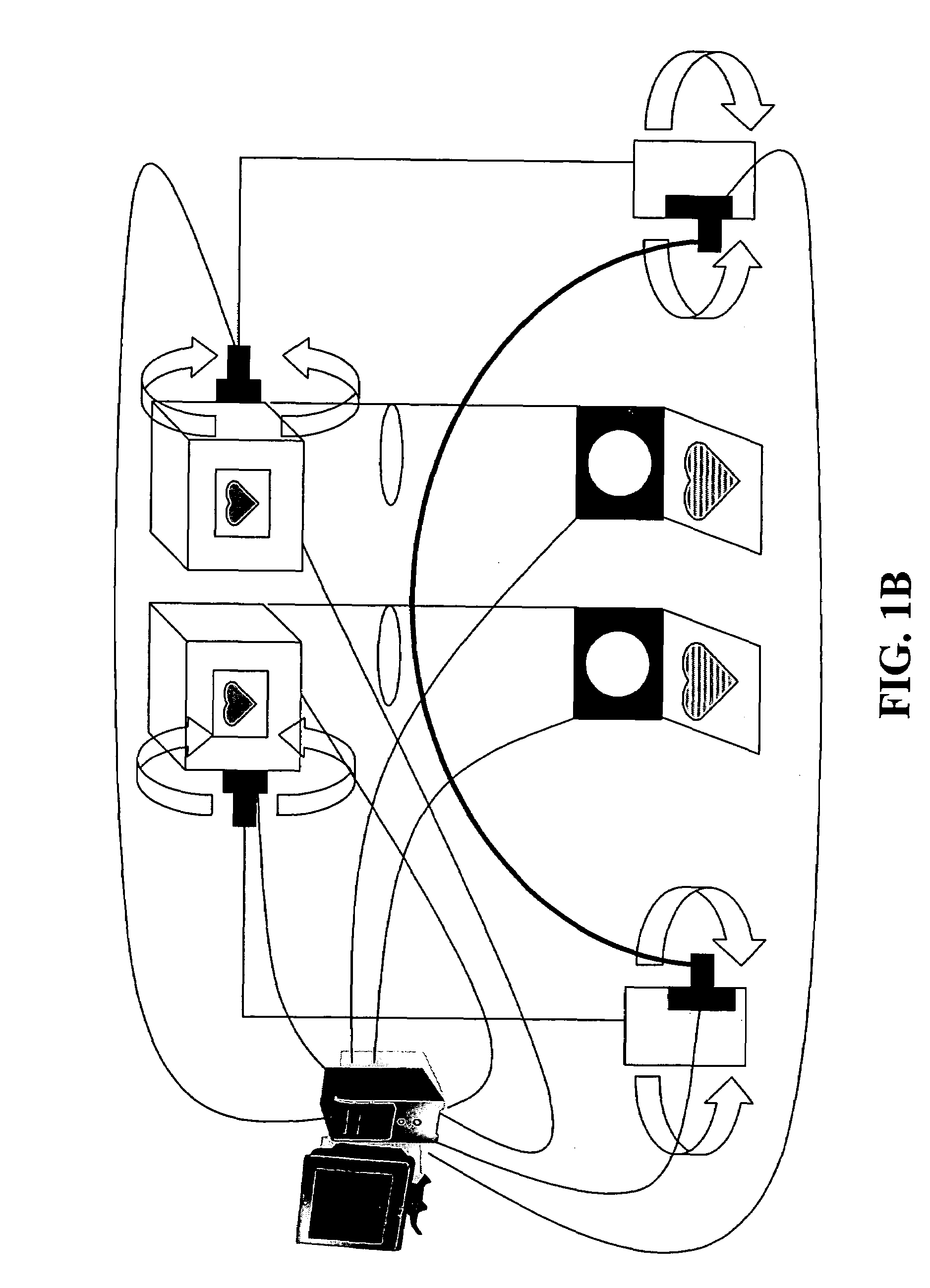
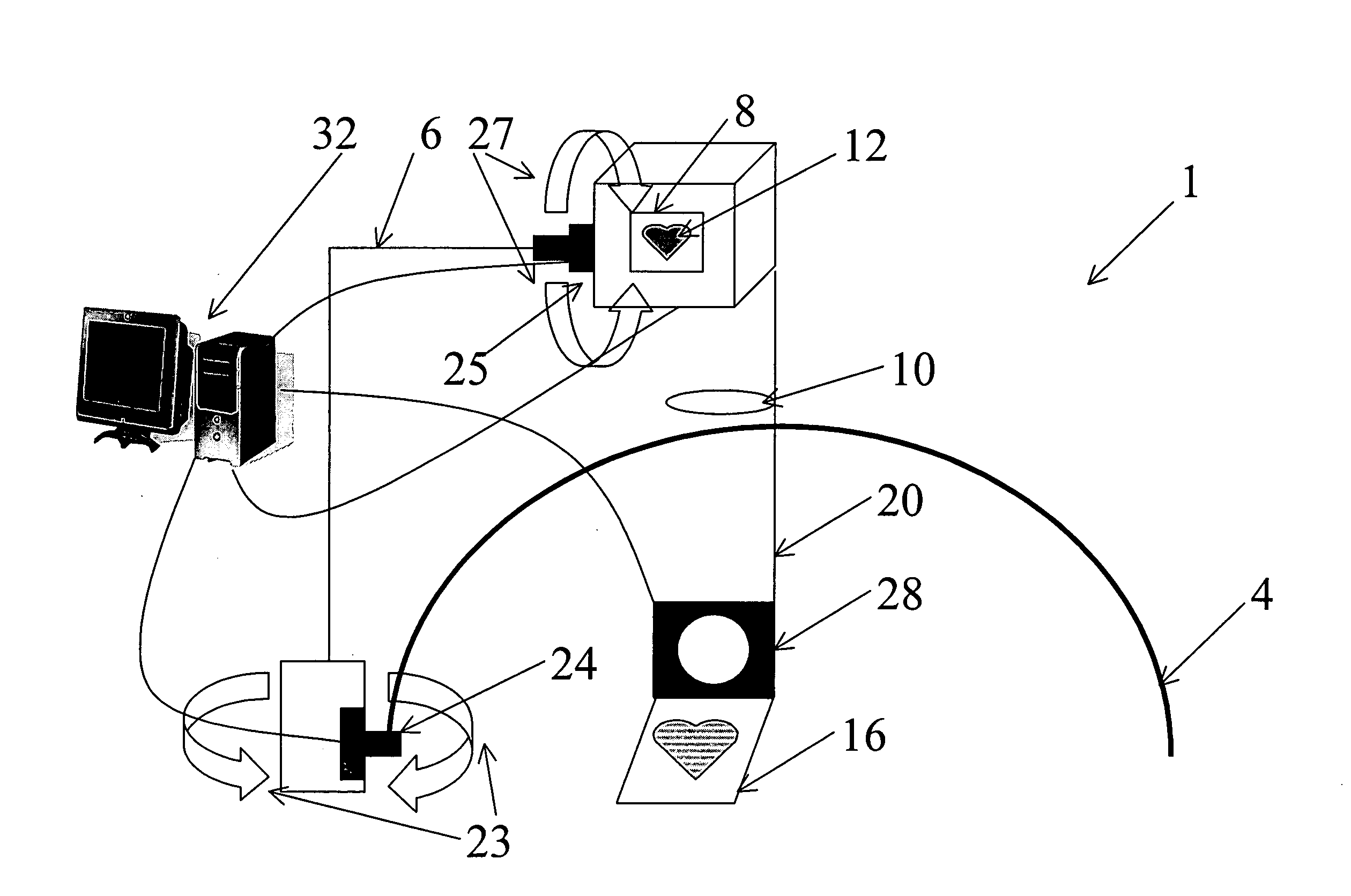
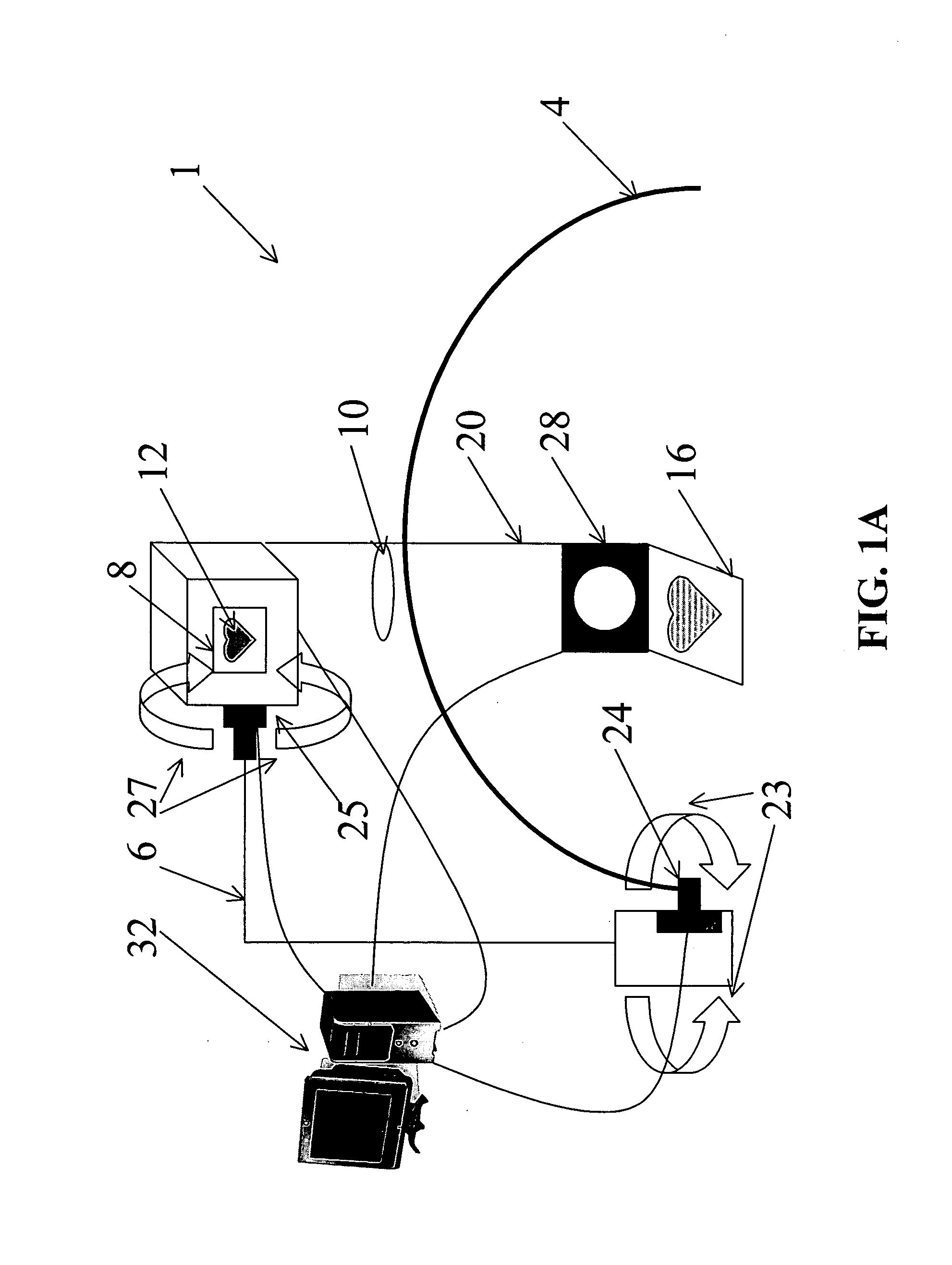
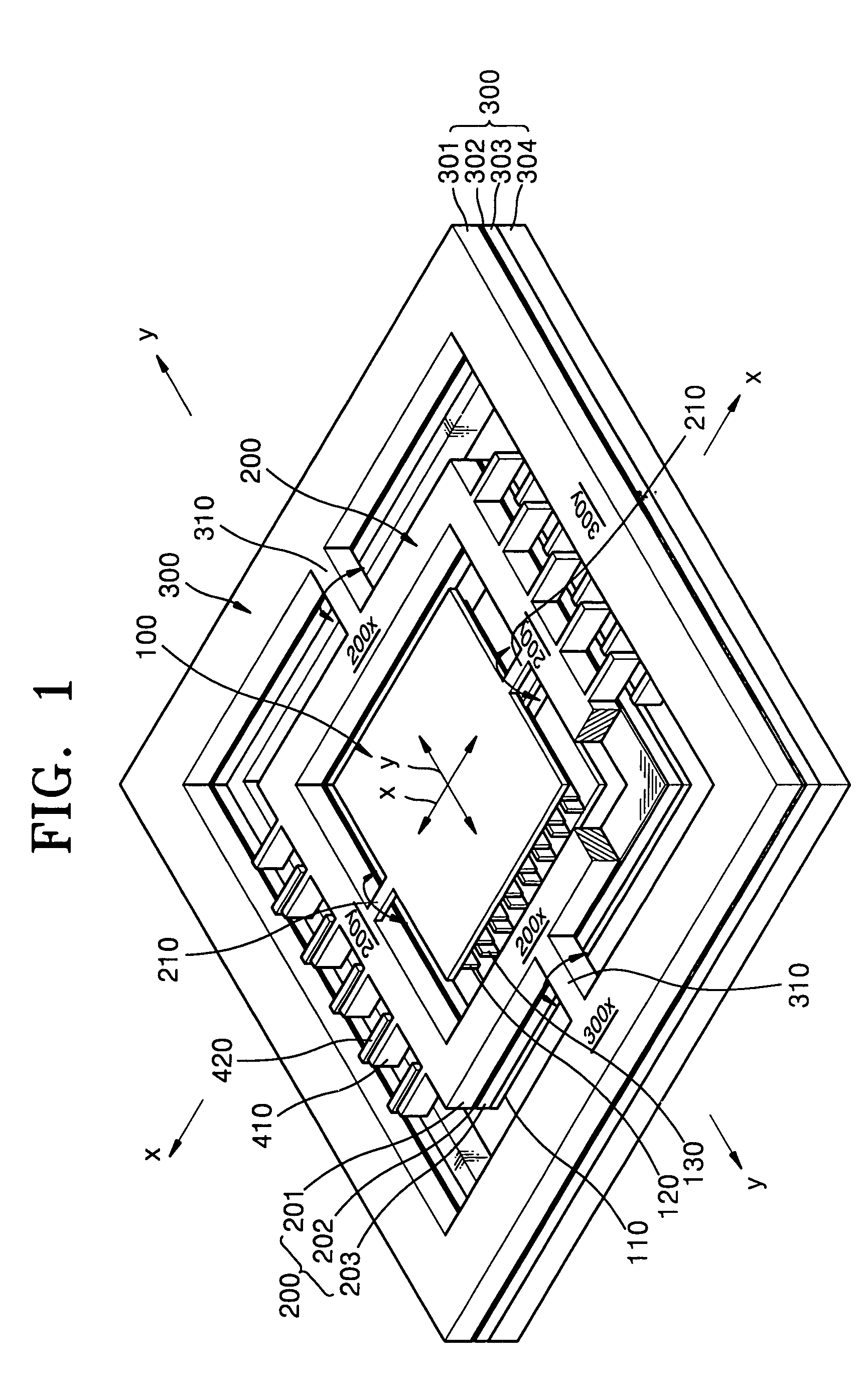
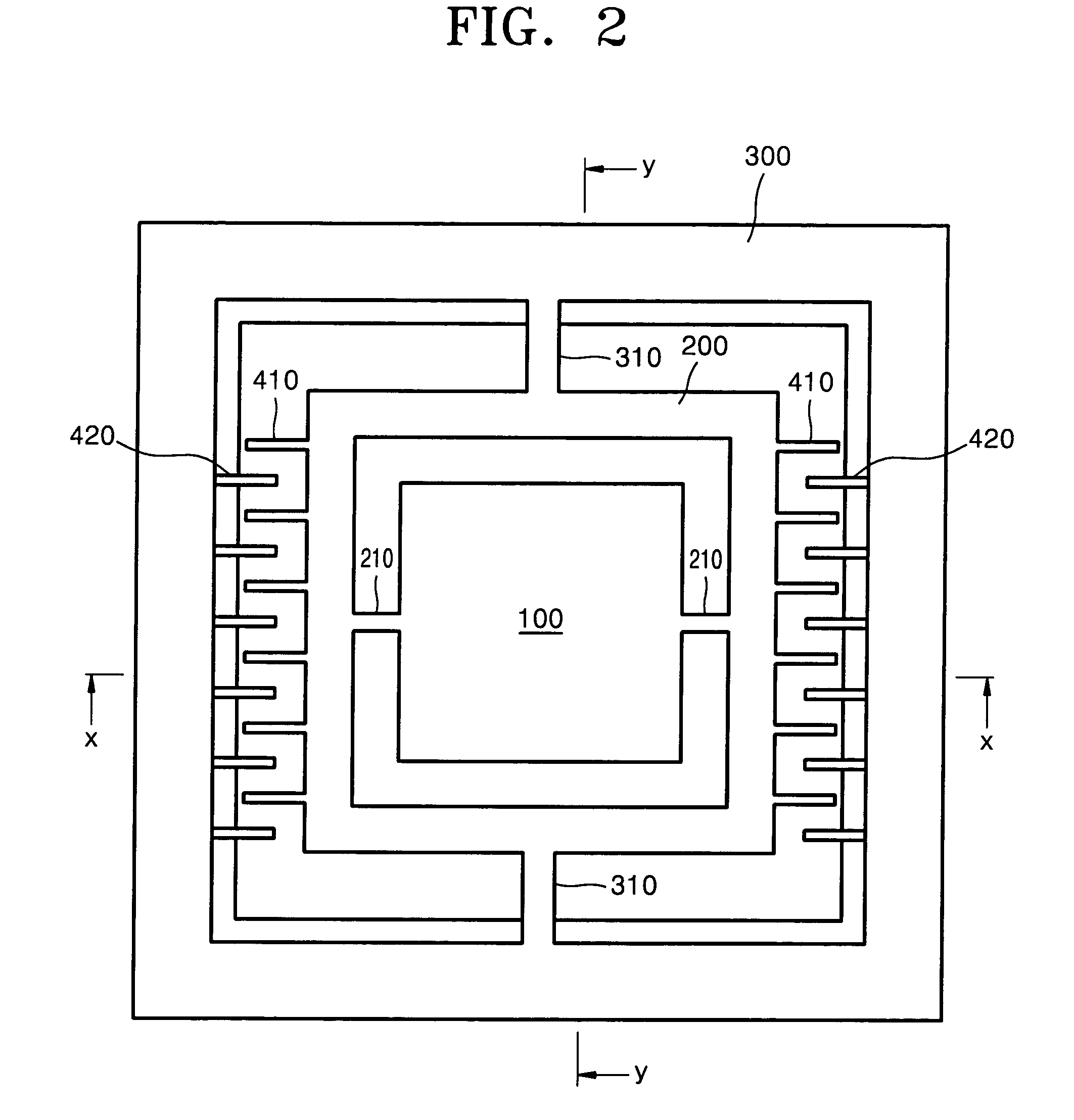
Eye tracking head mounted display
InactiveUS7542210B2Not salientImprove matching characteristicsCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsBeam splitterCentre of rotation
A head mounted display device has a mount which attaches the device to a user's head, a beam-splitter attached to the mount with movement devices, an image projector which projects images onto the beam-splitter, an eye-tracker which tracks a user's eye's gaze, and one or more processors. The device uses the eye tracker and movement devices, along with an optional head-tracker, to move the beam-splitter about the center of the eye's rotation, keeping the beam-splitter in the eye's direct line-of-sight. The user simultaneously views the image and the environment behind the image. A second beam-splitter, eye-tracker, and projector can be used on the user's other eye to create a stereoptic, virtual environment. The display can correspond to the resolving power of the human eye. The invention presets a high-resolution image wherever the user looks.
Owner:TEDDER DONALD RAY
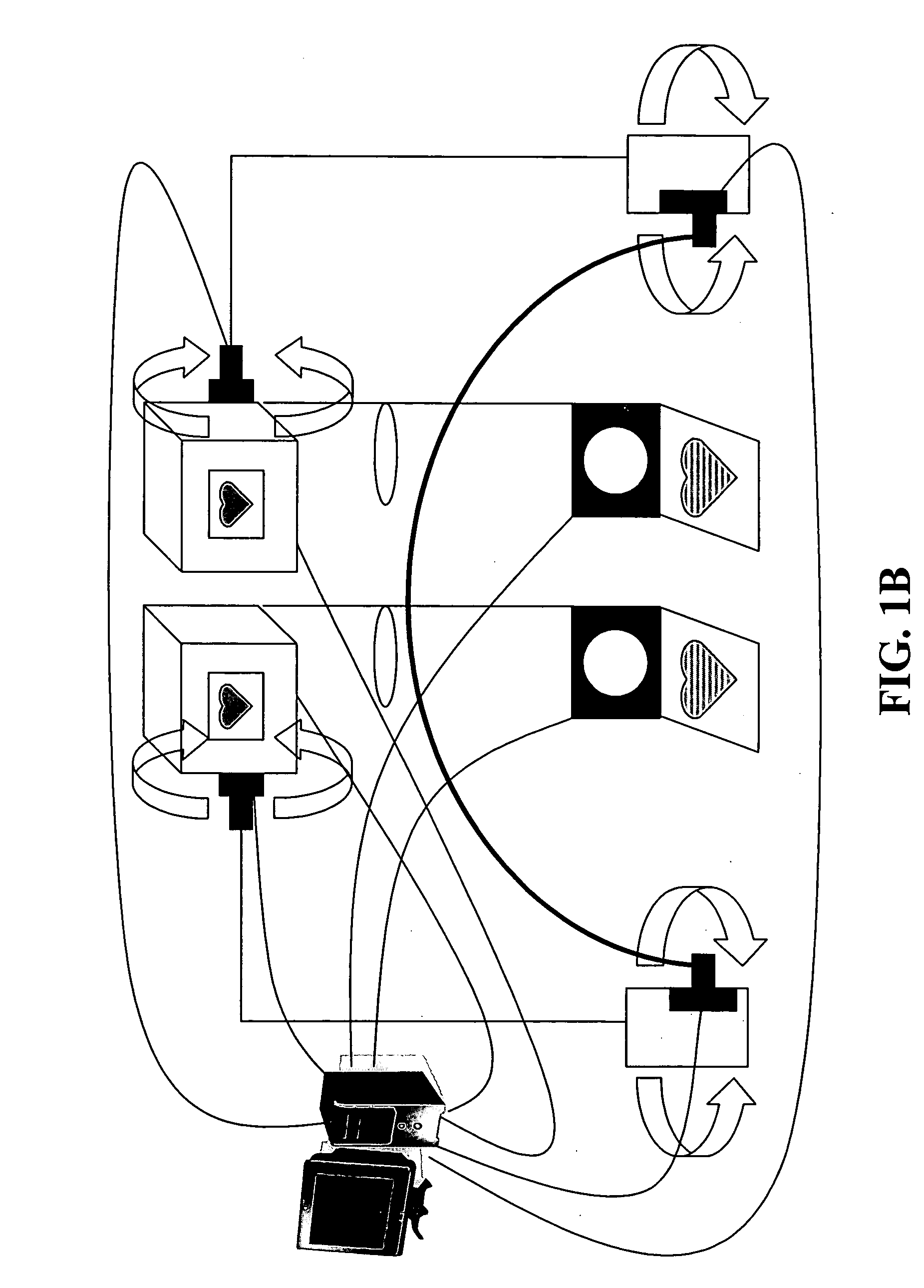
Eye tracking head mounted display
InactiveUS20080002262A1Not salientImprove matching characteristicsCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsBeam splitterDisplay device
A head mounted display device has a mount which attaches the device to a user's head, a beam-splitter attached to the mount with movement devices, an image projector which projects images onto the beam-splitter, an eye-tracker which tracks a user's eye's gaze, and one or more processors. The device uses the eye tracker and movement devices, along with an optional head-tracker, to move the beam-splitter about the center of the eye's rotation, keeping the beam-splitter in the eye's direct line-of-sight. The user simultaneously views the image and the environment behind the image. A second beam-splitter, eye-tracker, and projector can be used on the user's other eye to create a stereoptic, virtual environment. The display can correspond to the resolving power of the human eye. The invention presets a high-resolution image wherever the user looks.
Owner:TEDDER DONALD RAY
Self-balancing adjustable flat panel mounting system
A self-balanced adjustable mounting system for a flat panel display. A display interface having a hollow, semi-spherical shell portion is attached to the flat panel display. The semi-spherical shell is formed with a generally constant radius of curvature. The center of the radius of curvature is disposed proximate the center of gravity of the flat panel display with the display interface attached. The display interface is received in a guide structure that has a bearing portion engaging the outer surface of the semi-spherical shell, and a second bearing portion engaging the inner surface of the semi-spherical shell through an aperture formed in the semi-spherical shell. The semi-spherical shell is guided between the first and second bearing portions so that the flat panel display and device interface are generally rotatable about the center of the radius of curvature of the semi-spherical shell. The display is self balancing in virtually any position in the range of travel of the device due to the location of the center of rotation proximate the center of gravity.
Owner:LEGRAND AV INC
Intervertebral prosthetic disc with metallic core
ActiveUS20060025862A1Inhibit wearAvoid tearingSpinal implantsCoatingsIntervertebral discCentre of rotation
A prosthetic disc for insertion between adjacent vertebrae includes a core having upper and lower curved surfaces and upper and lower plates. At least one of the curved surfaces of the core is metallic, and in some embodiments the entire core is metallic. Each plate has an outer surface which engages a vertebra and a metallic inner curved surface which is shaped to slide over one of the curved surfaces of the core. In some embodiments, the center of rotation of the core is free to move relative to the upper and lower metallic plates. In some embodiments, one or more channels extend across one or both of the curved surfaces of the core for allowing passage of bodily fluid to promote lubrication between the core and at least one of the plates.
Owner:SIMPLIFY MEDICAL PTY LTD
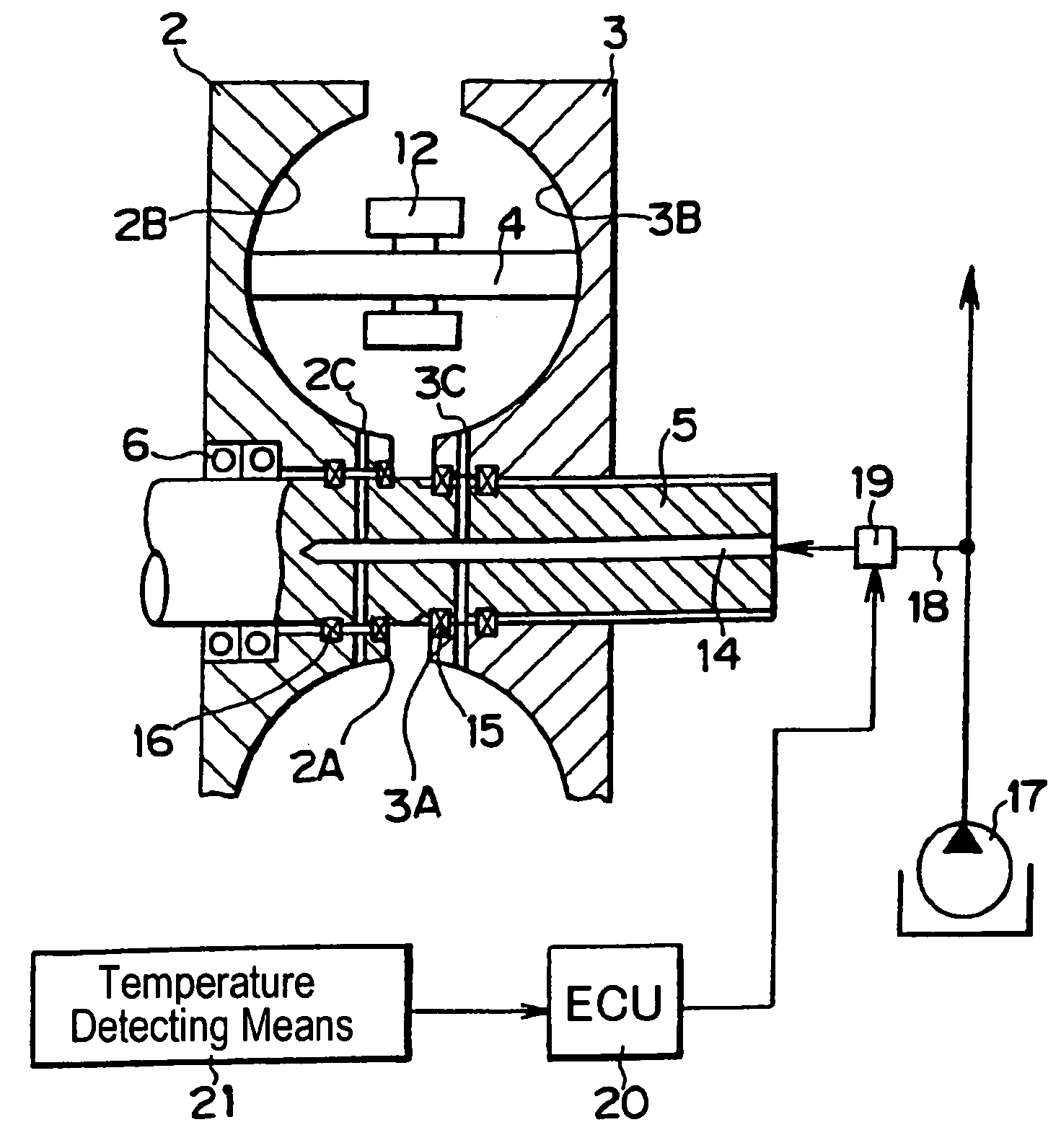
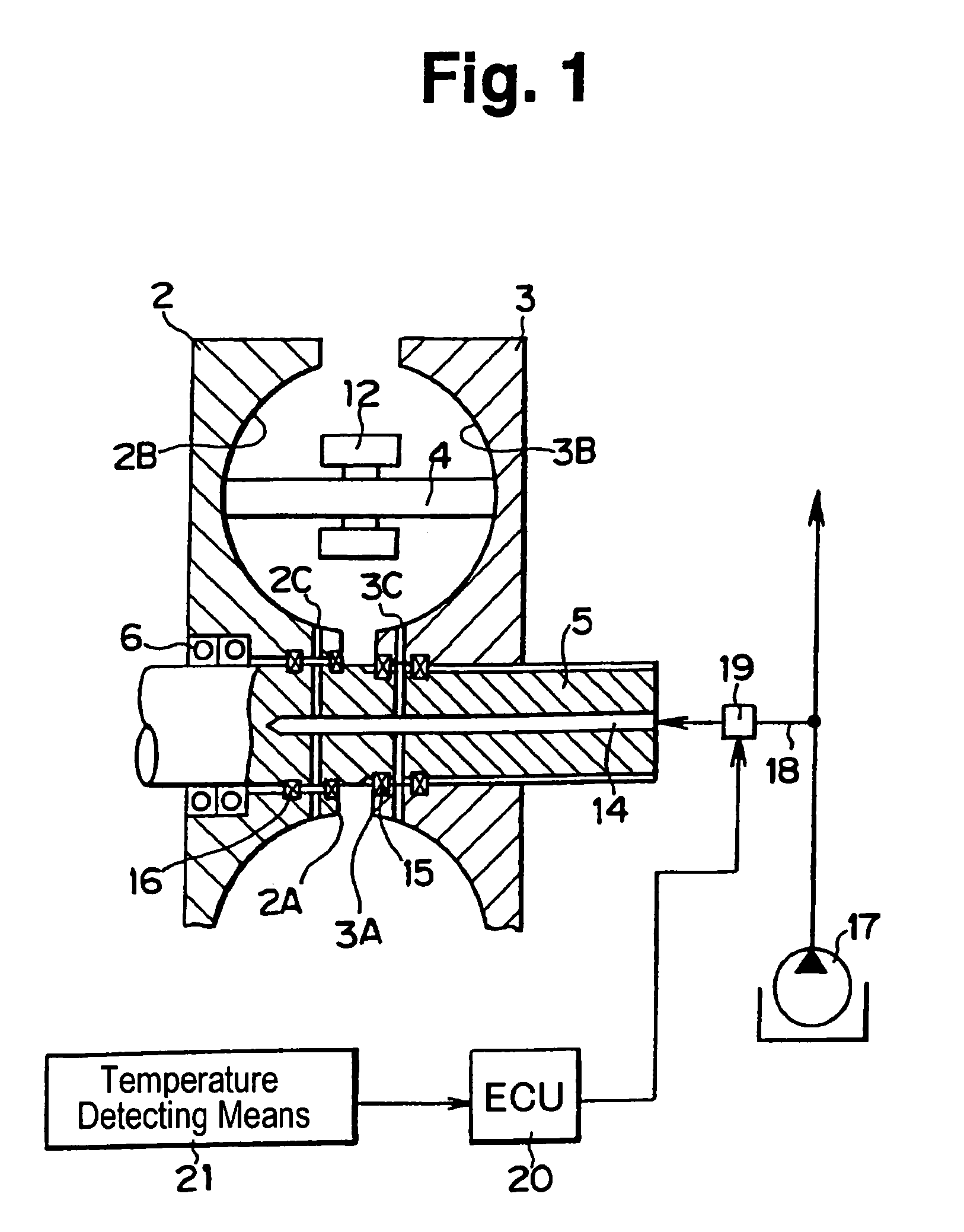
Toroidal type continuoulsy variable transmission
InactiveUS7029418B2Deterioration of hardnessAvoid unnecessary wasteGear lubrication/coolingDynamo-electric brake controlCentre of rotationVariator
A toroidai type continuously variable transmission wherein a rolling member is clamped between rotary members; and wherein a rolling face of rotary members being opposed to each other has a curved face, in which its sectional face along the plane including a center axis of rotation is shaped into an arc, in order to allow said rolling face of said rolling member inclining against the center axis of the rotation of said rotary member, characterized by: an oiling hole formed on the portion on the center side of the rotation in said rolling face of the rotary members being opposed to each other, or on the portion on the center side of the rotation leading to said rolling face; and the oil passage for feeding the lubricating oil to the oiling hole, formed on the center side of the rotation in said rotary member, with being communicated with the oiling hole.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Smart tow
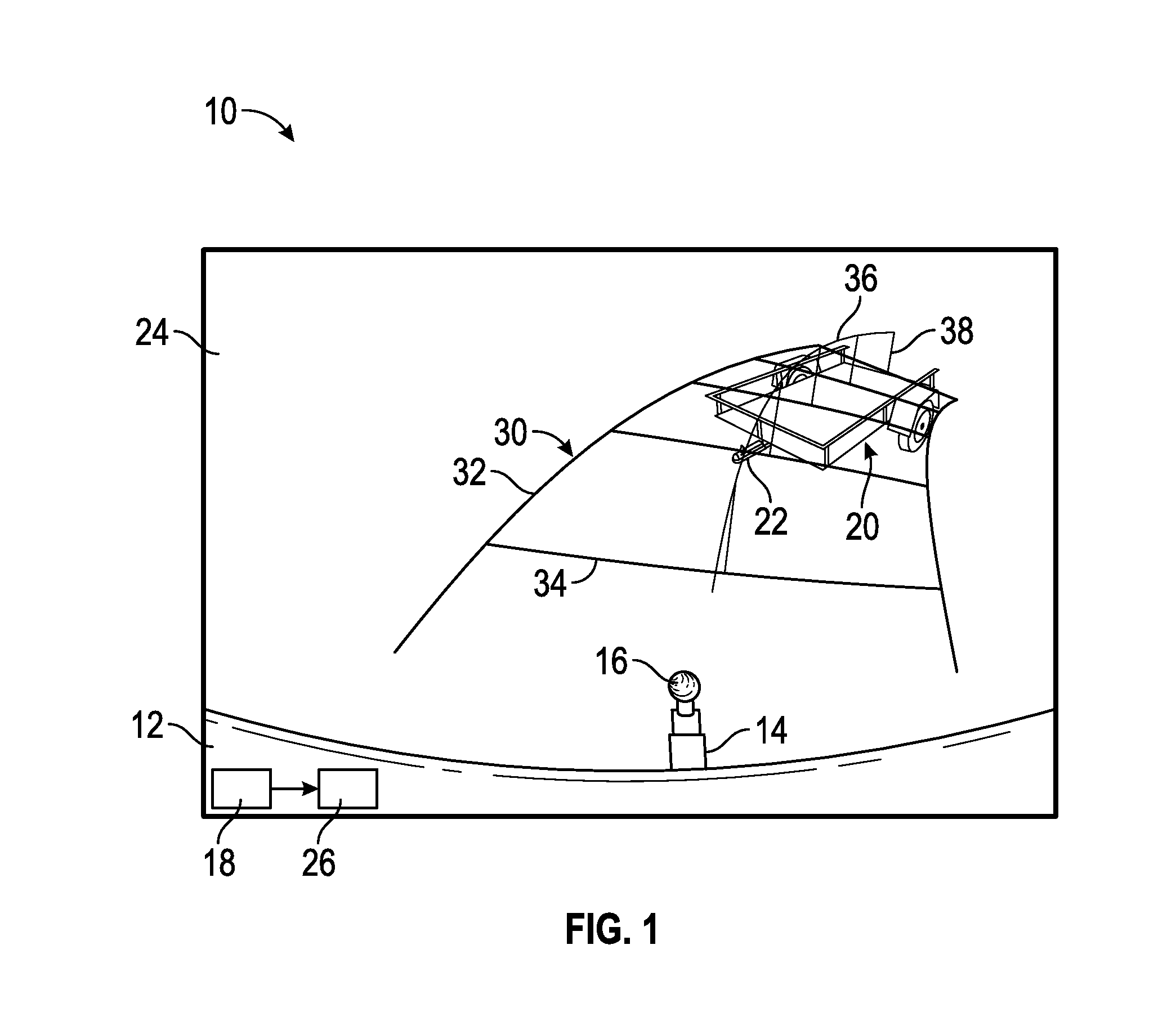
InactiveUS20150115571A1Character and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsVehicle dynamicsCamera image
A system and method for providing visual assistance through a graphic overlay super-imposed on a back-up camera image for assisting a vehicle operator when backing up a vehicle to align a tow ball with a trailer tongue. The method includes providing camera modeling to correlate the camera image in vehicle coordinates to world coordinates, where the camera modeling provides the graphic overlay to include a tow line having a height in the camera image that is determined by an estimated height of the trailer tongue. The method also includes providing vehicle dynamic modeling for identifying the motion of the vehicle as it moves around a center of rotation. The method then predicts the path of the vehicle as it is being steered including calculating the center of rotation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Continuously variable transmission mechanism and transmission using the same
InactiveUS20110319222A1Increase rotation speedRotational radiusFriction gearingsRotation velocityControl theory
A continuously variable transmission adapted to set a speed change ratio in accordance with a tilt angle of a rolling member mediating a torque being transmitted, and to transmit a torque among three elements. The transmission mechanism is provided with a rolling member having a smooth outer face and capable of tilting a rotational center axis thereof, and a rotary member arranged to be contacted with a predetermined portion of the outer face of the rolling member in a torque transmittable manner. Specifically, the continuously variable transmission mechanism is configured to vary a rotational speed of the rotary member by changing a rotation radius of a contact point between the rolling member and the rotary member by tilting the rotational center axis of the rolling member.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Angle-tunable transmissive grating
InactiveUS20070160325A1High spectral purityHigh Power Handling CapabilitySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsOptical resonator shape and constructionRotational axisGrating
A tunable transmissive grating comprises a transmissive dispersive element, a reflective element, and an angle θ formed between the two elements. A first optical path is formed according to the angle θ, wherein light dispersing from the dispersive element is directed onto the reflective element and reflects therefrom. At least one element is rotatable about a rotational center to cause a second optical path and thereby tune the wavelength of the light reflecting from the reflective element. Both elements can be rotatable together around a common rotational center point according to certain embodiments, and / or each element can be independently rotated around a rotational axis associated only with that element. According to some embodiments, the relative angle θ formed between the elements is held constant; however, in other embodiments θ can vary.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
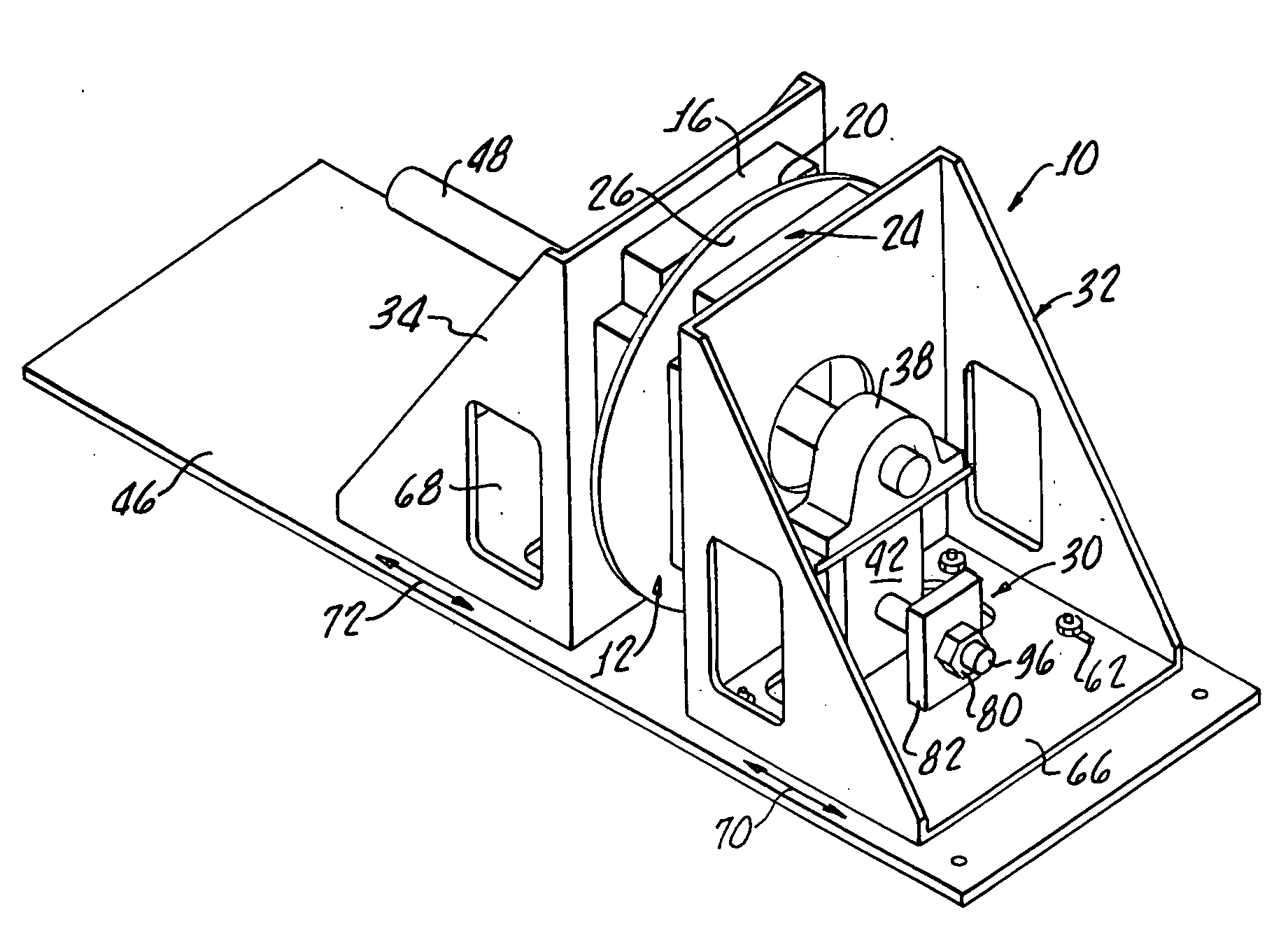
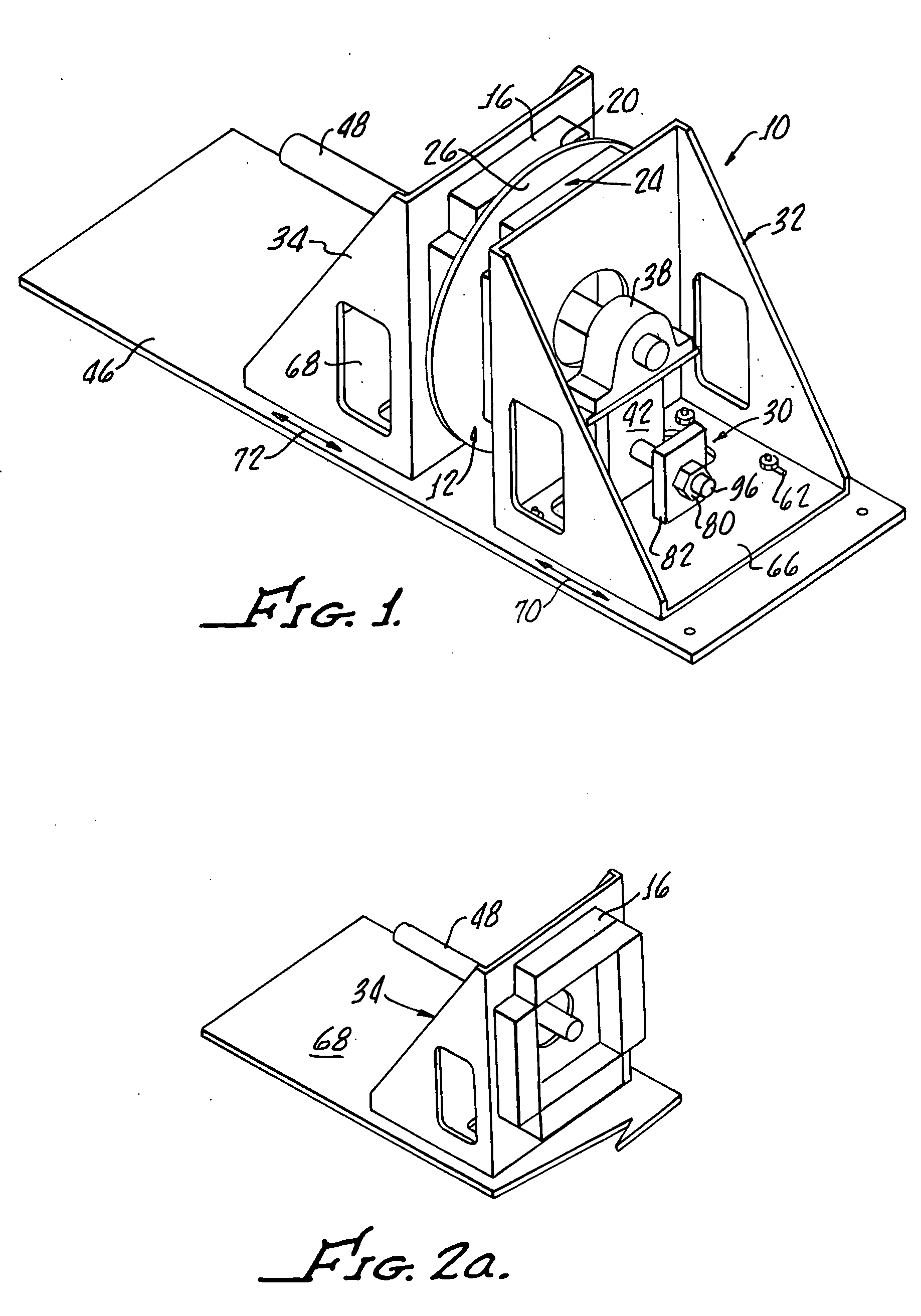
Method and apparatus for operational low-stress optical fiber storage
A reel for storing optical fiber is disclosed that significantly reduces the torsional force applied to optical fiber as the fiber is being wound onto the reel for storage. The optical fiber reel comprises two spindles that are offset with respect to the rotational center of the reel. Such an arrangement causes the fiber to be wound onto the reel in a substantially linear fashion, thus preventing the torsional force and resulting twisting that cause micro-cracks to develop. The spindles are of a sufficiently large diameter to facilitate operational use of the fiber while stored on the spindle without increasing the attenuation of signals that could result from the use of a smaller diameter spindle.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Substrate processing apparatus and method for adjusting a substrate transfer position
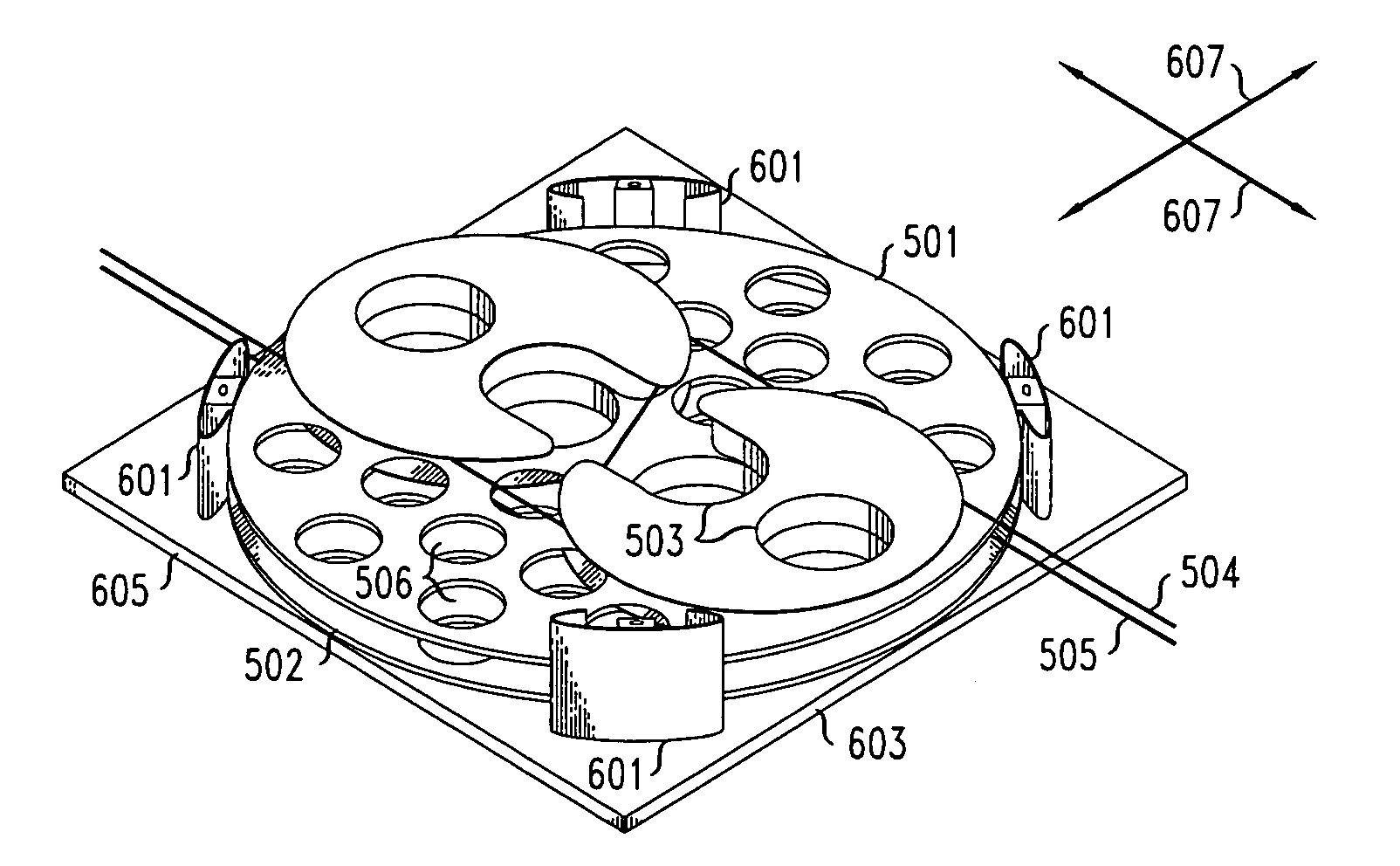
ActiveUS20050016818A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedConveyorsDigital data processing detailsCentre of rotationEngineering
A substrate processing apparatus can align a substrate with a high precision and a high speed by monitoring a mark formed on a surface of the substrate; operating an amount of misalignment between the center of the substrate and a rotation center of a substrate support member; determining a presence of the misalignment and adjusting the substrate such that the center of the substrate coincides with the rotation center of the substrate support member.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Hollow turbine
InactiveUS20050005592A1General water supply conservationSeawater treatmentFree rotationCentre of rotation
A versatile turbine suitable for both hydraulic and pneumatic applications. The turbine's blades are affixed to the inner surface of a cylindrical shell which is free to rotate about an outside supporting structure. Rotational energy is transferred from the outer surface of the rotating cylindrical shell, usually by means of a gear; however, there may be applications better suited for a pulley means of transfer. The vacant central axis of rotation can be closed, by incorporating taller blades to achieve a larger surface area, resulting in greater efficiency, or open, by means of shorter blades forming a hole with the distal edges of the blades, to allow for passing fish and or debris to safely exit. The preferred embodiment further includes a means for electricity generation, water purification, and hydrogen production.
Owner:FIELDER WILLIAM SHERIDAN
Dome Type Camera
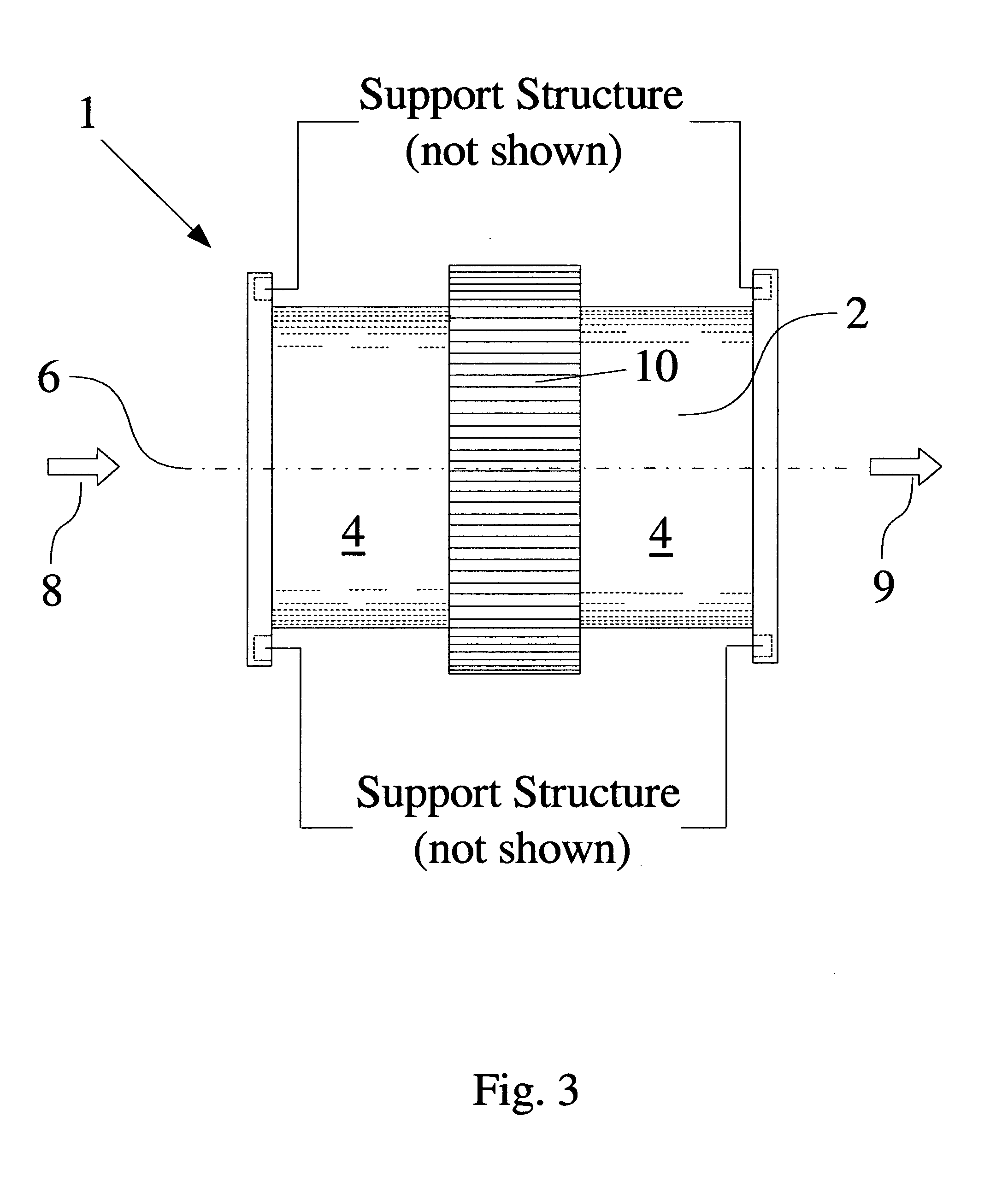
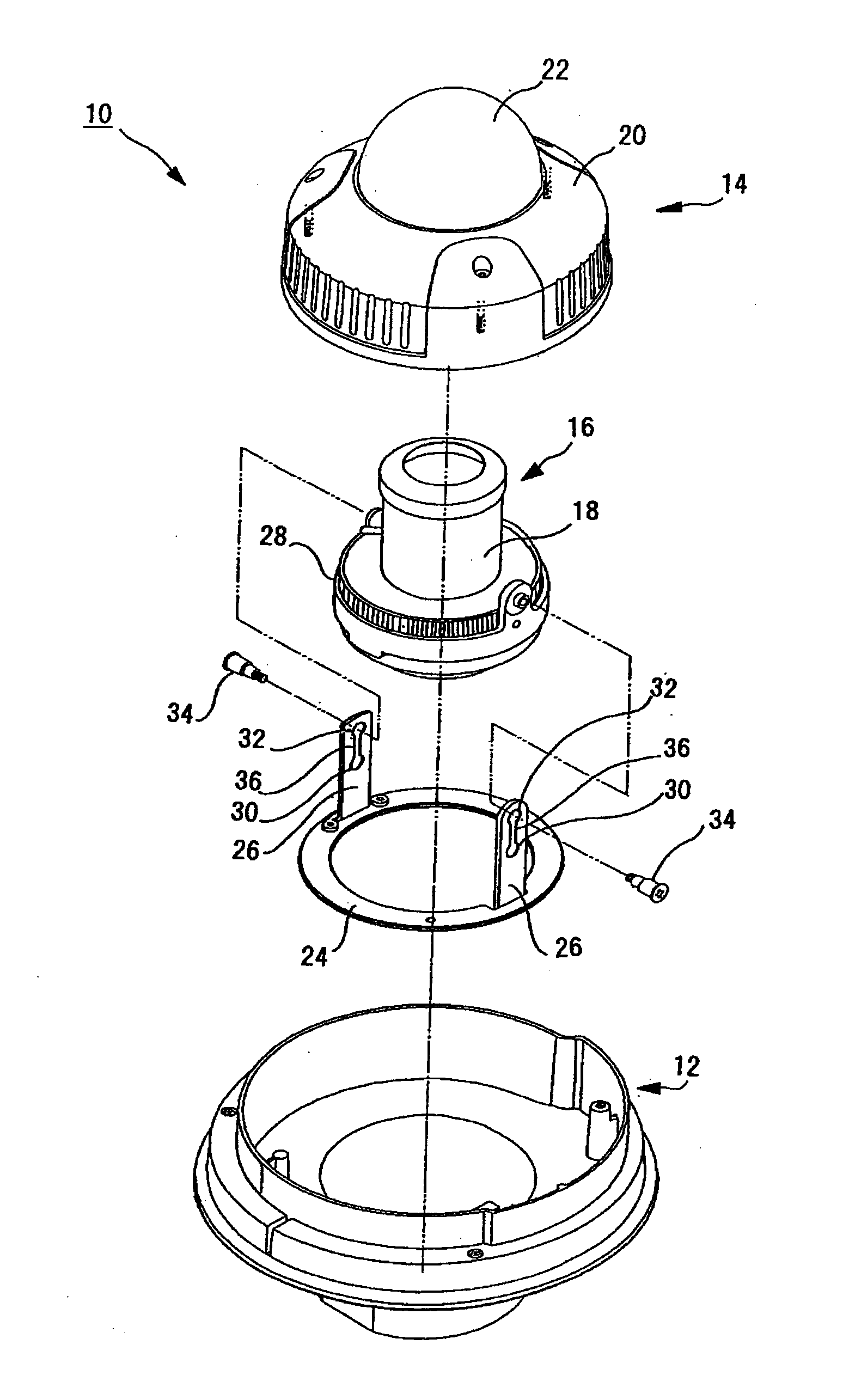
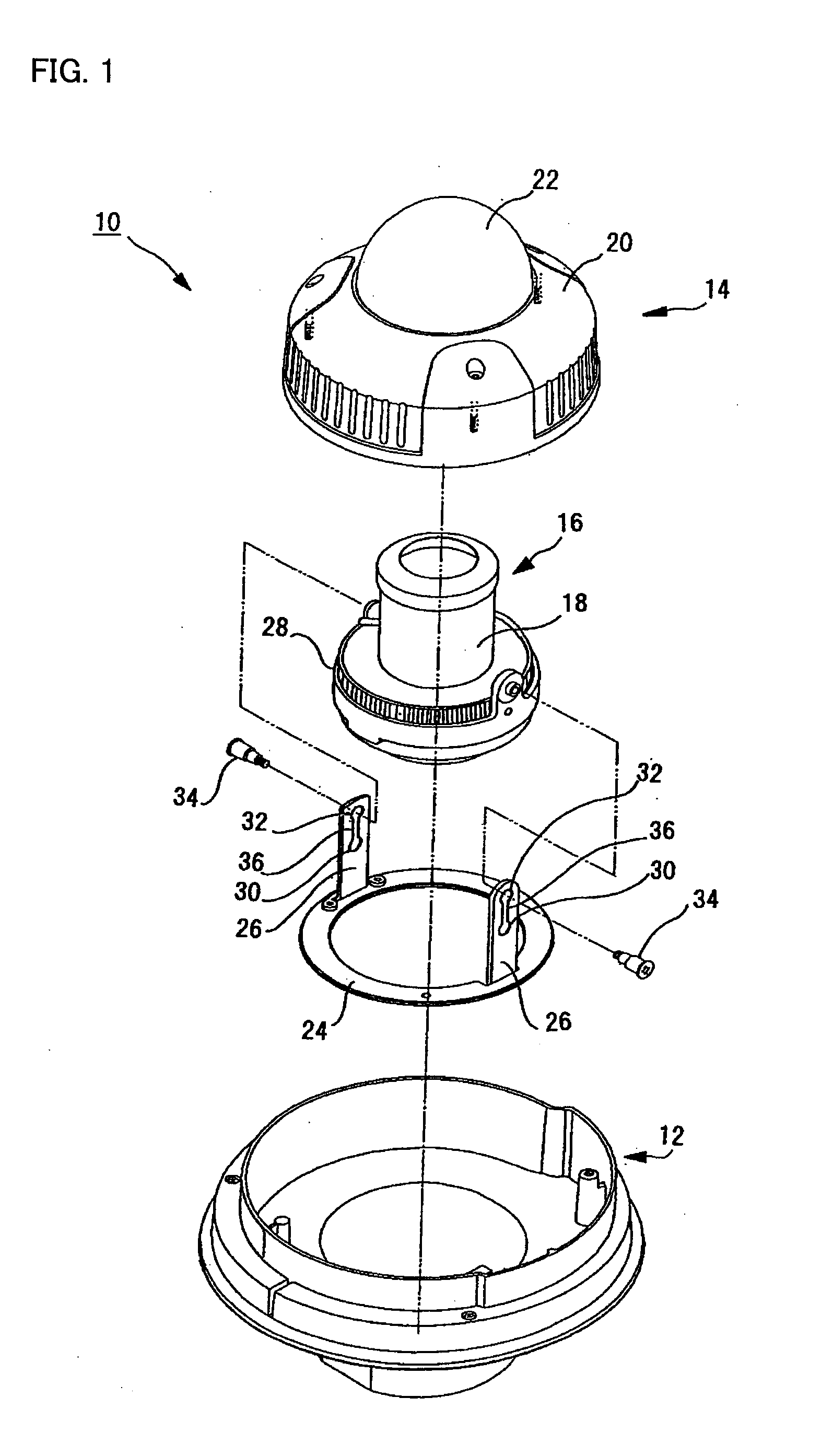
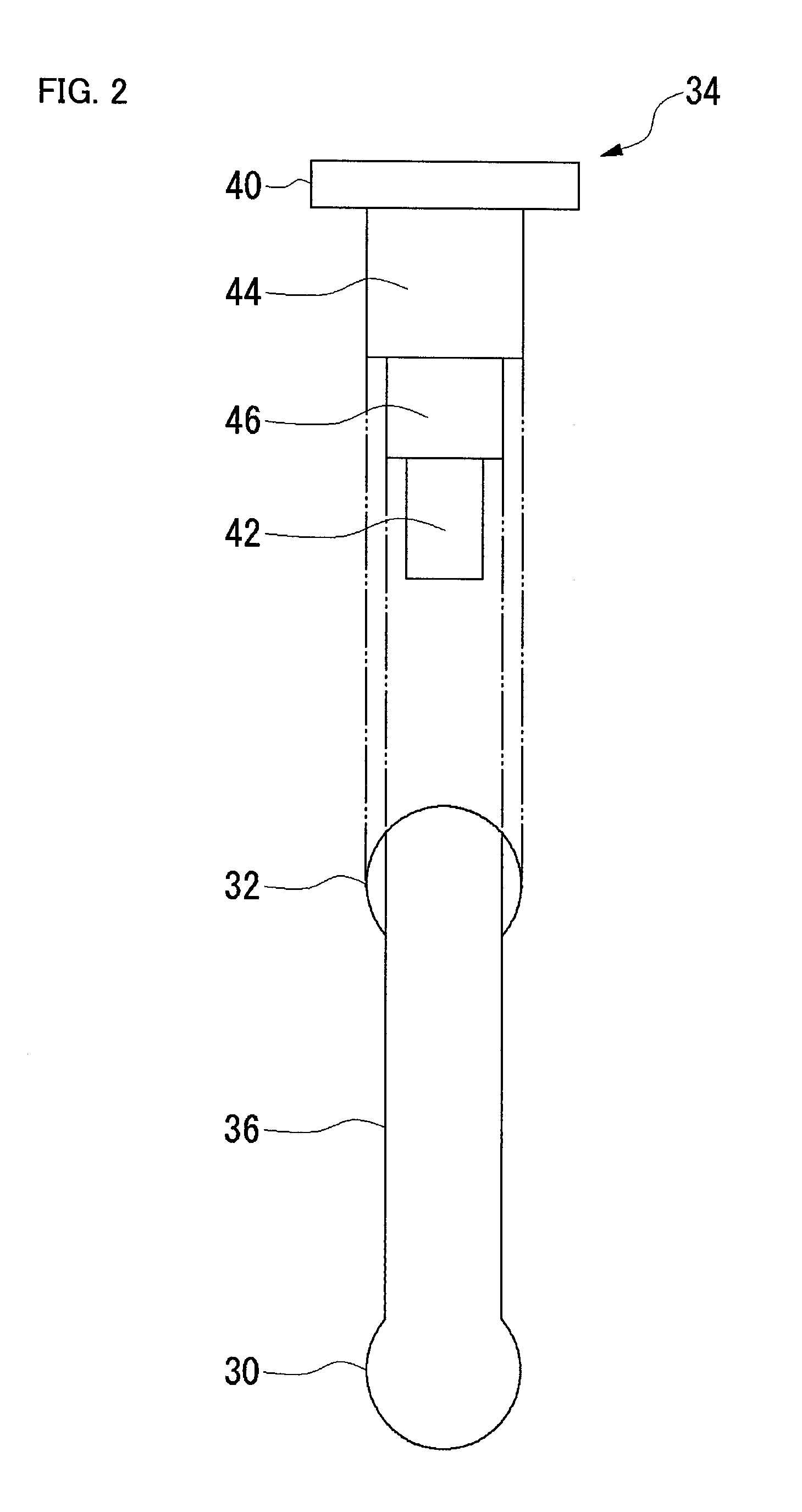
InactiveUS20080231699A1Enhance the imageTelevision system detailsPrintersElevation angleCentre of rotation
A lens (16) is rotatably provided inside a dome cover (22). The lens (16) is supported so that the center of rotation can be moved from the center of a dome to a position apart therefrom in the zenith direction. A lens moving mechanism for moving the lens (16) according to a rotation in the tilt direction of the lens (16) may be provided. The lens moving mechanism may be a cam structure. The cam structure is set so that the rotation axis of the lens (16) is held at the center of the dome in a predetermined center hold angle range corresponding to the direction of an elevation angle, and that the rotation axis of the lens (16) is moved from the center of the dome in the zenith direction at angles lower than the center hold angle range. Good images can be obtained even when shooting in the direction of a depression angle.
Owner:PANASONIC I PRO SENSING SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Balance ring
InactiveUS7099112B1Record information storageRecord carrier accessoriesCentre of rotationEngineering
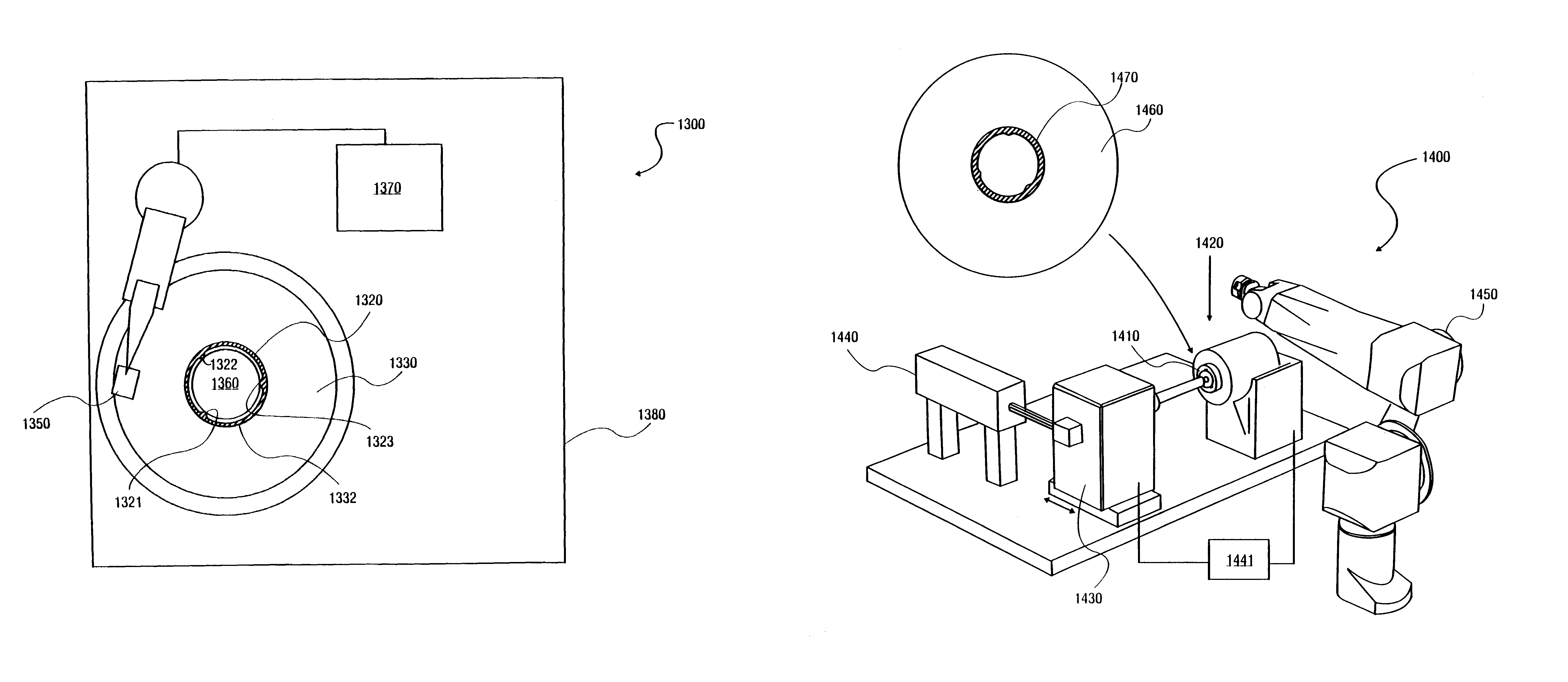
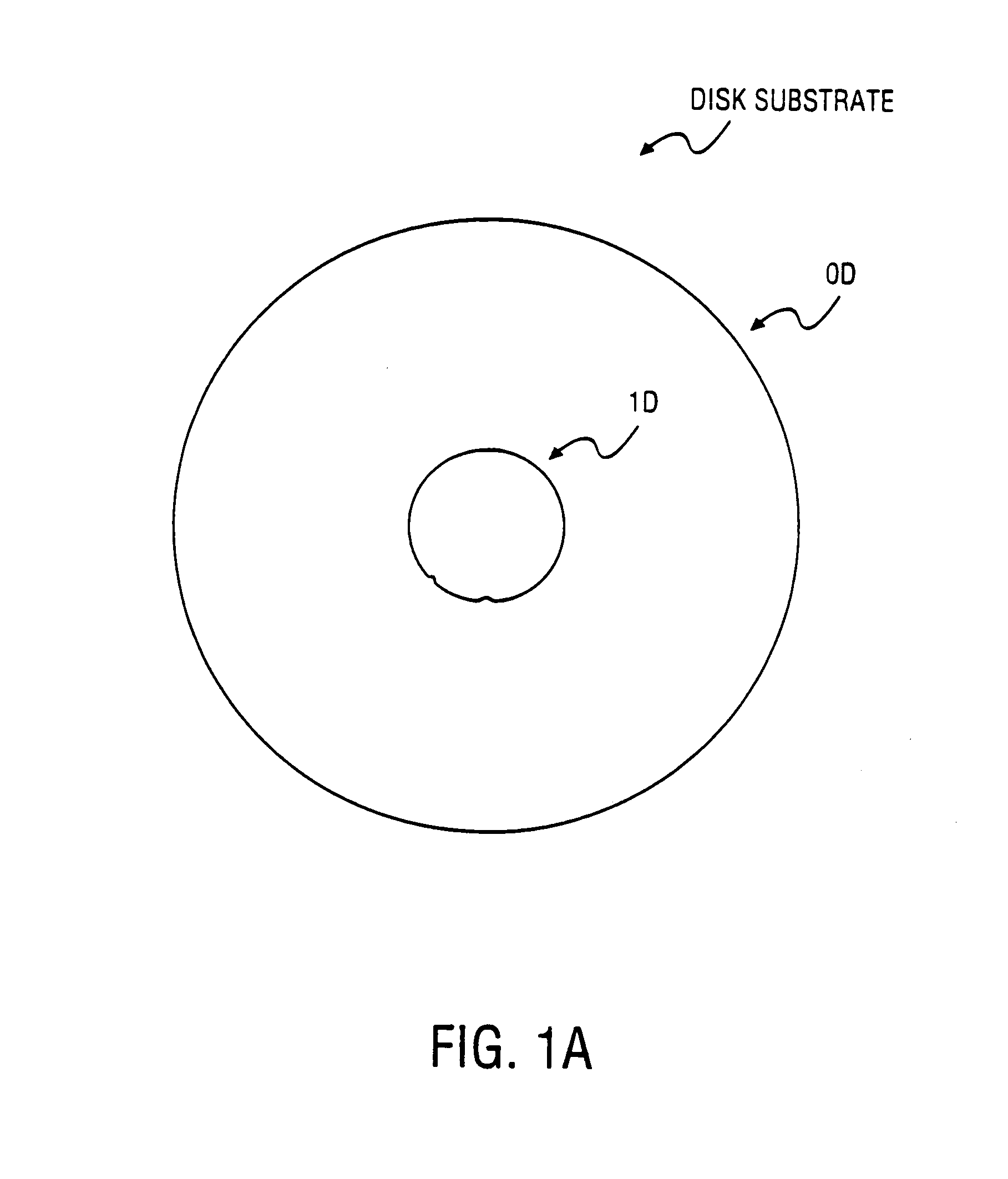
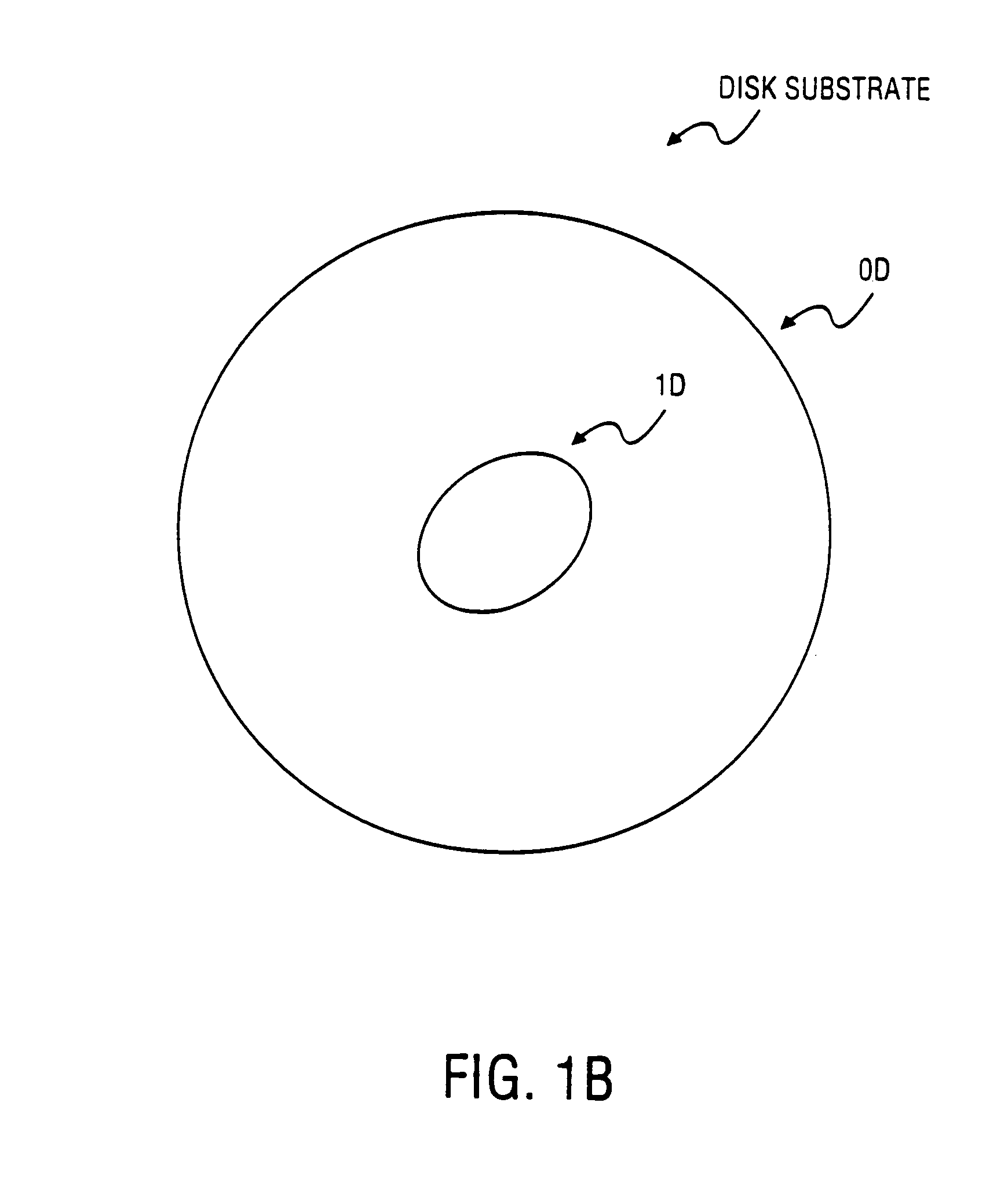
An apparatus and method for balancing a disk are described. A balance ring may be a circular band for placement along the inner diameter of a disk. On the outer diameter of the balance ring, one or more clamp structures may extend outward to attach the balance ring to the inner diameter of a disk. The inner diameter of the balance ring may have a number of protuberances that, when trimmed, establish a new rotational center of the disk / balance ring coincident with the mass center. The disk and balancing ring may be mounted on a disk balancing system to determine a mass center and trim the protuberances, accordingly, to establish adjust the rotational center of the disk / balance ring to be coincident with the mass center. The protuberances may be trimmed using, for example, laser energy.
Owner:WD MEDIA
Self-position estimating device for leg type movable robots
ActiveUS20050126833A1Improve accuracyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLeg typeTemporal change
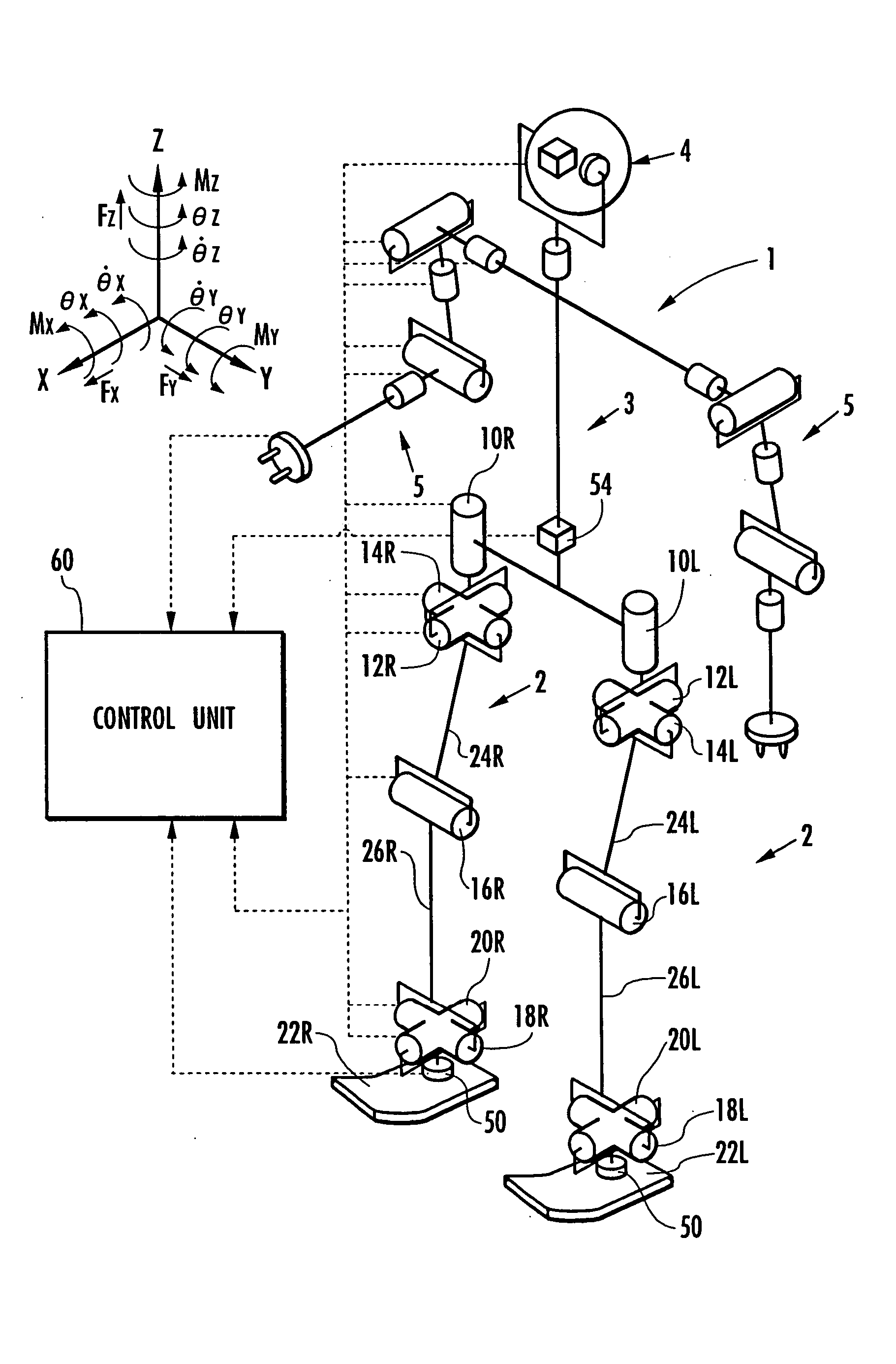
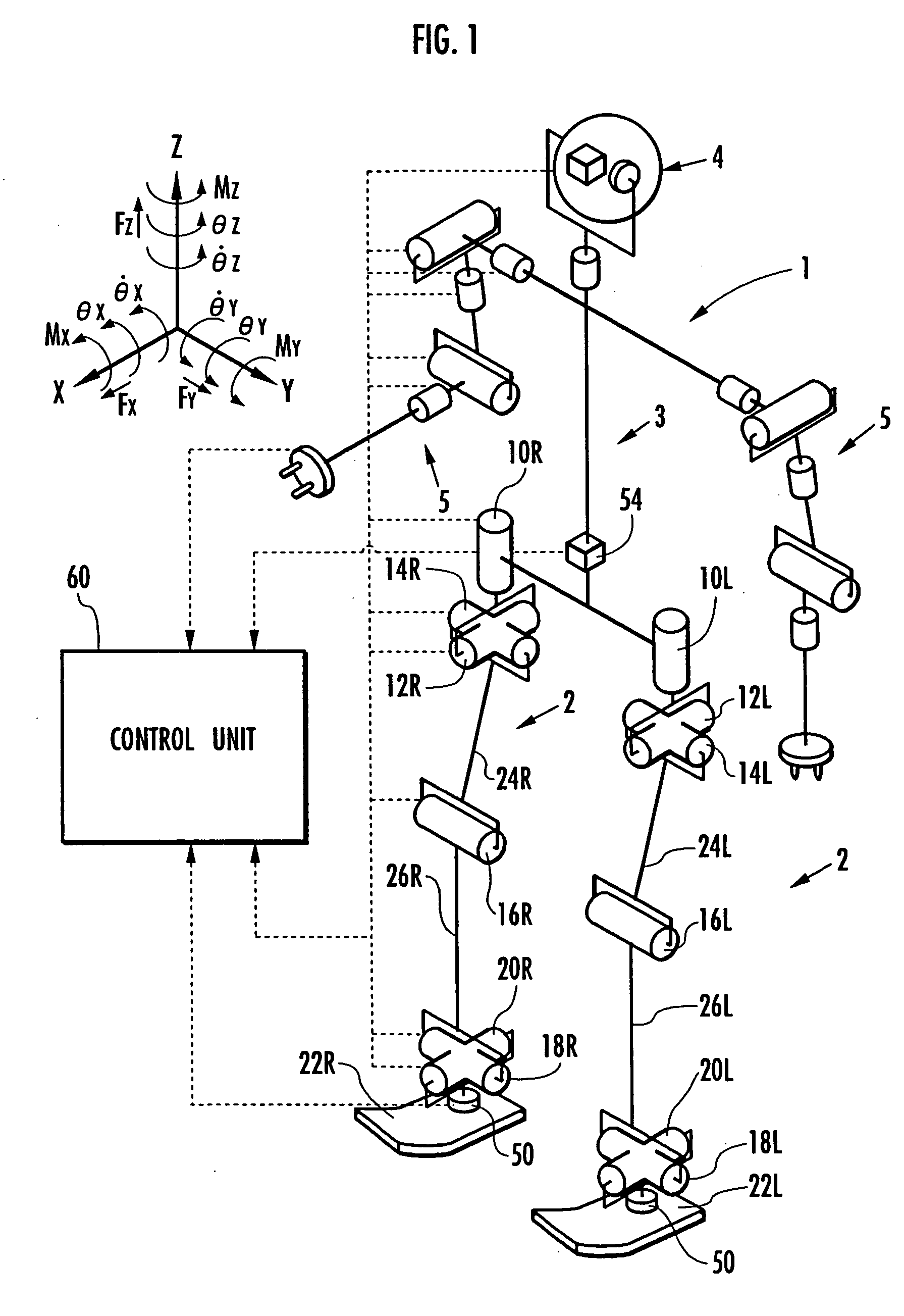
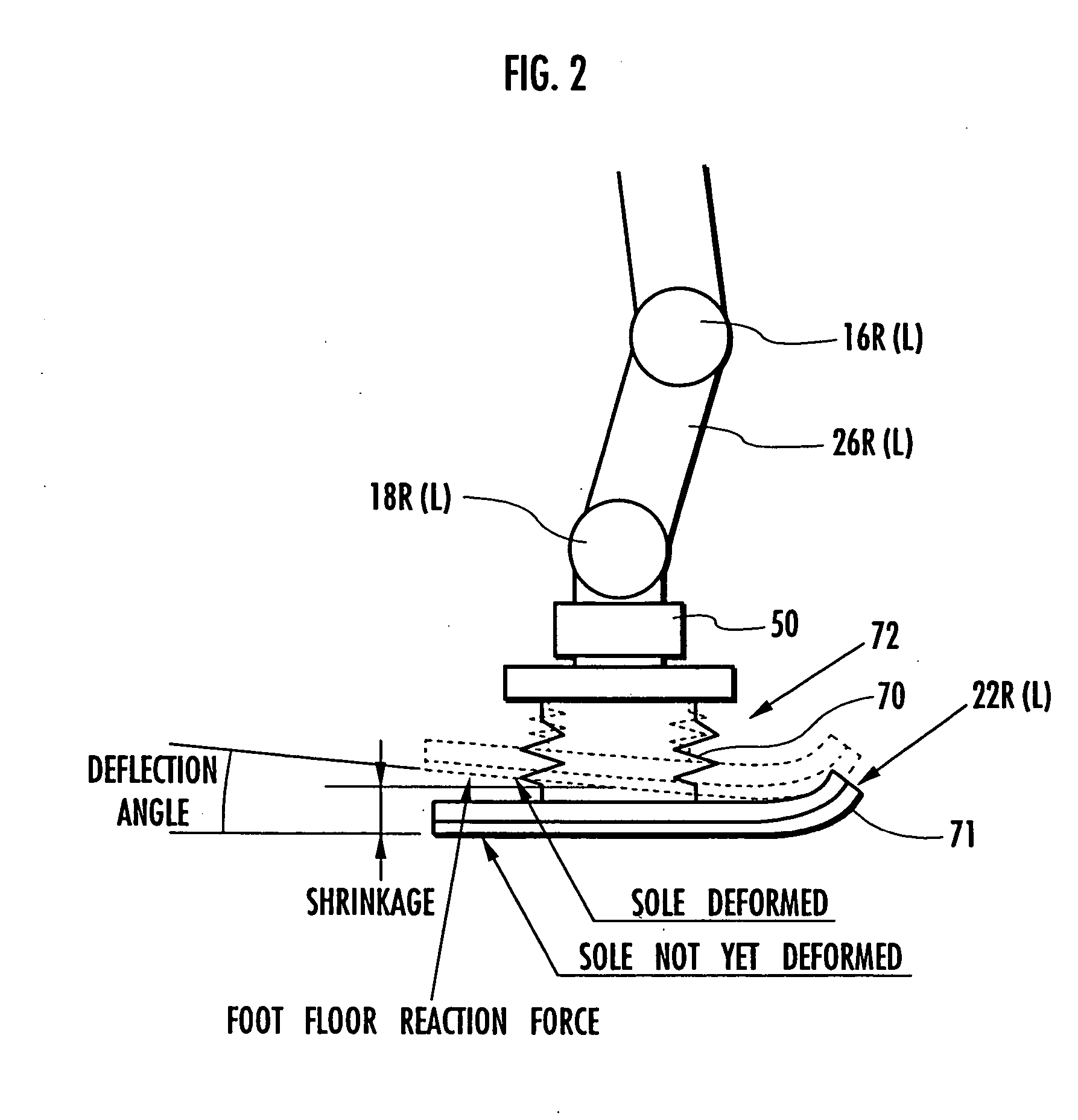
Based on a detected or estimated value of an actual posture of a predetermined part, such as a body 3, of a robot 1 and a deviation the actual posture from a posture of a desired gait, a posture rotational deviation's variation is determined as the temporal variation of the deviation, and the position of the robot 1 (for example, the position where the robot comes into contact with a floor) is estimated on the assumption that the robot 1 rotates about a rotation center by the rotational deviation's variation. In addition, in accordance with the difference between the estimated position and the estimated position of the robot 1 determined by an inertial navigation method using an accelerometer or the like, the estimated position of the robot 1 determined by the inertial navigation method is corrected, thereby improving the precision of the estimated position.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Head position control for a disk drive which performs recording about the rotational center even if the recorded servo information is eccentric
InactiveUS6128153AAverage power consumptionReduce power consumptionTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageCentre of rotationPosition control
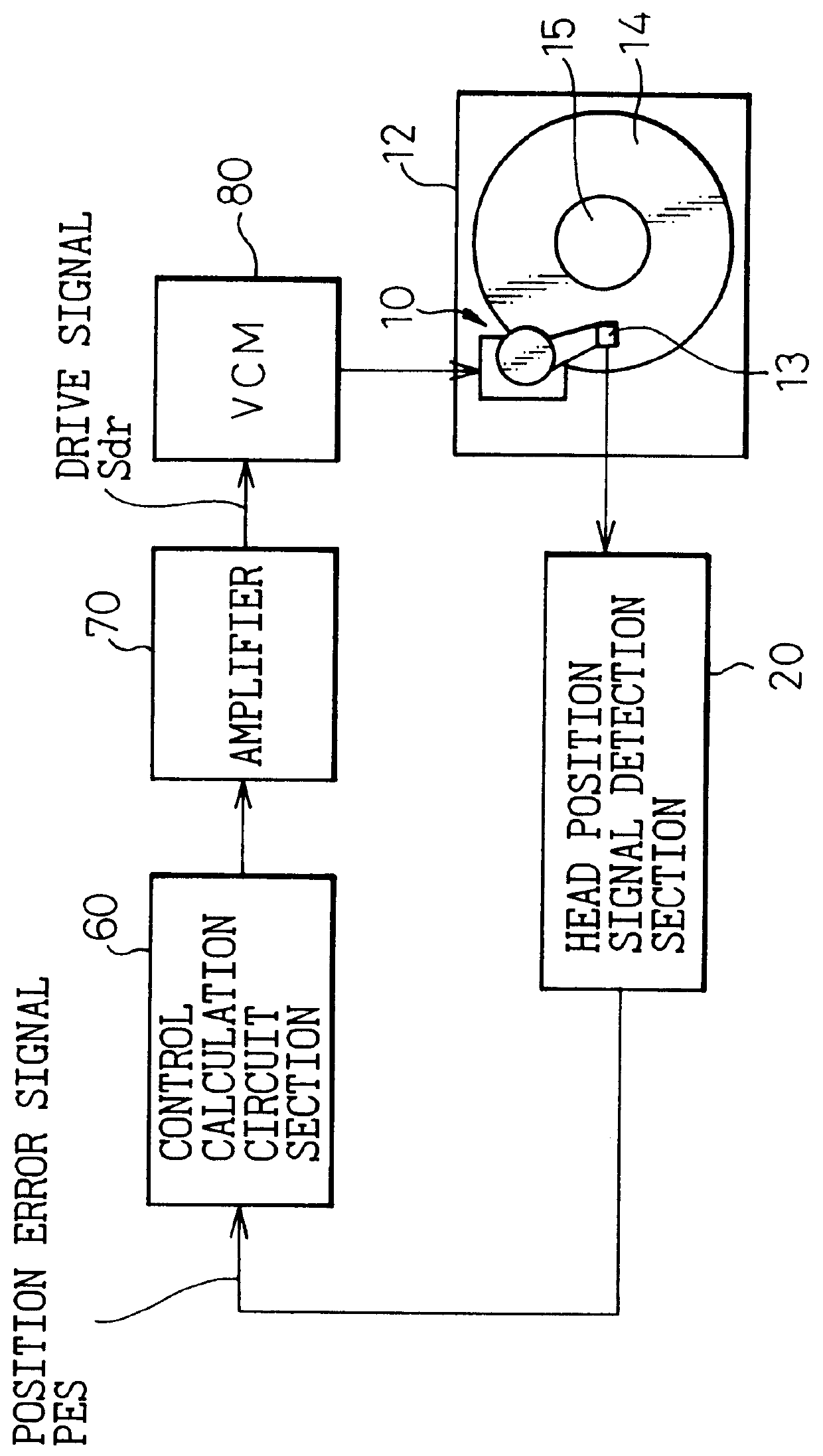
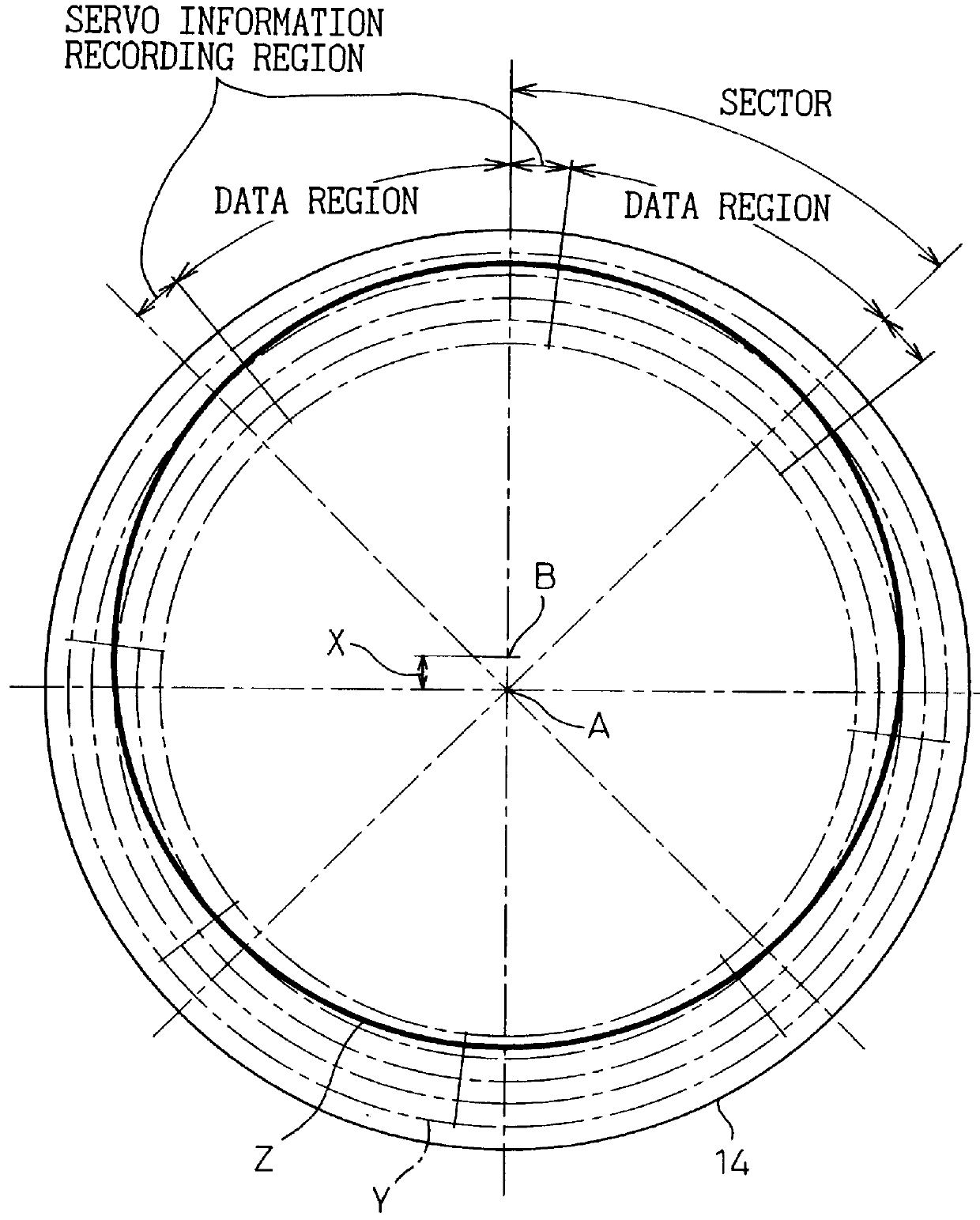
Head position control is implemented in a disk drive for the case in which a disk is assembled into the disk drive after a precise track is recorded onto it using an external apparatus, which is capable of high-speed access even if there is eccentricity between a track defined by servo information and the center of rotation of the track. Two phase servo bursts consisting of servo information are recorded onto each of the servo information regions of a disk surface, in mutual alternation, the strength ratio between signals detected from these two phase servo bursts being used to determine to which side the head is displaced. By performing control so that this strength ratio is a prescribed value at each angular position, control is achieved so that the head moves along a circular path of rotation, even if there is eccentricity in the servo circular path defined by the recorded servo information with respect to the center of rotation.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
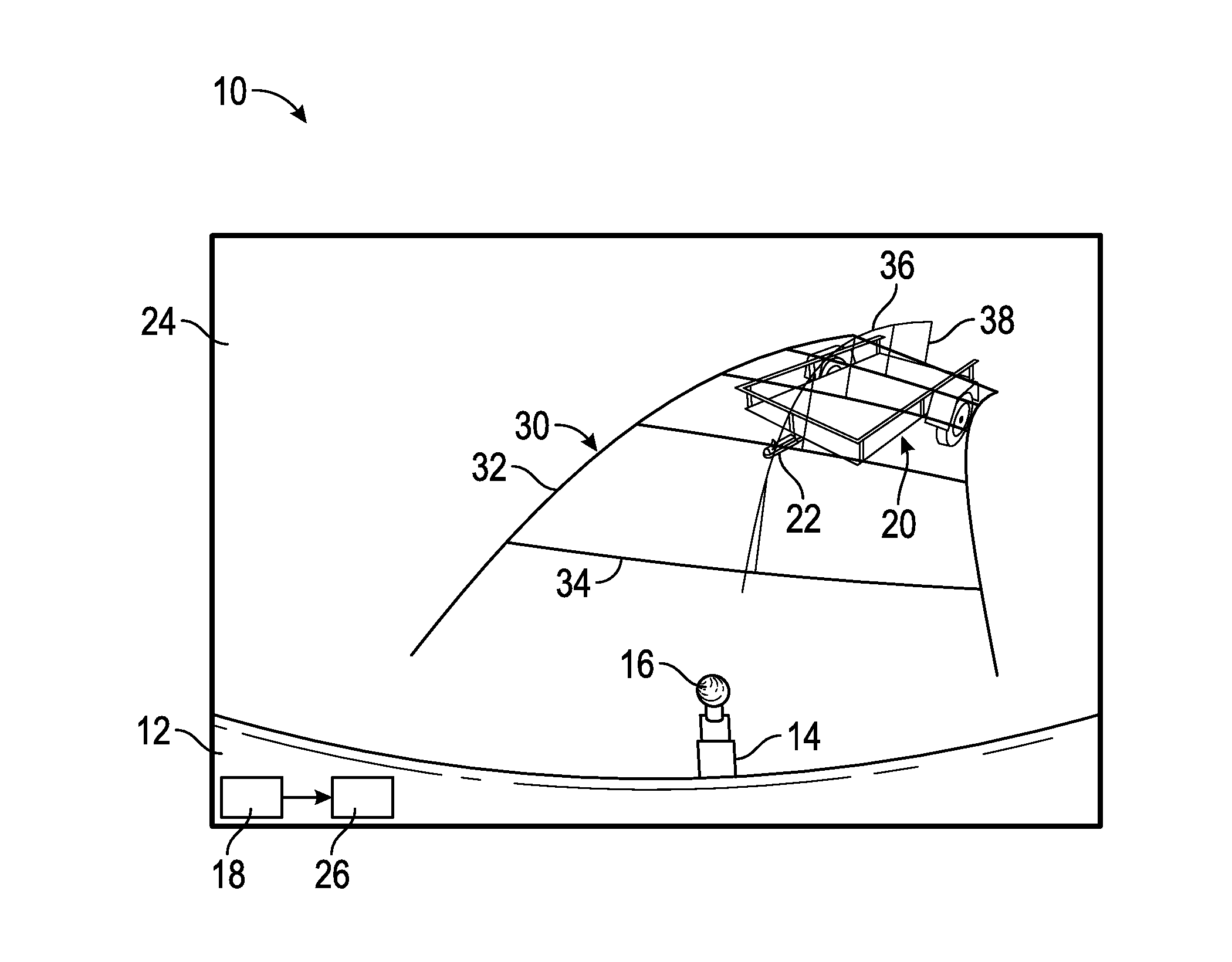
Bicycle rear suspension system
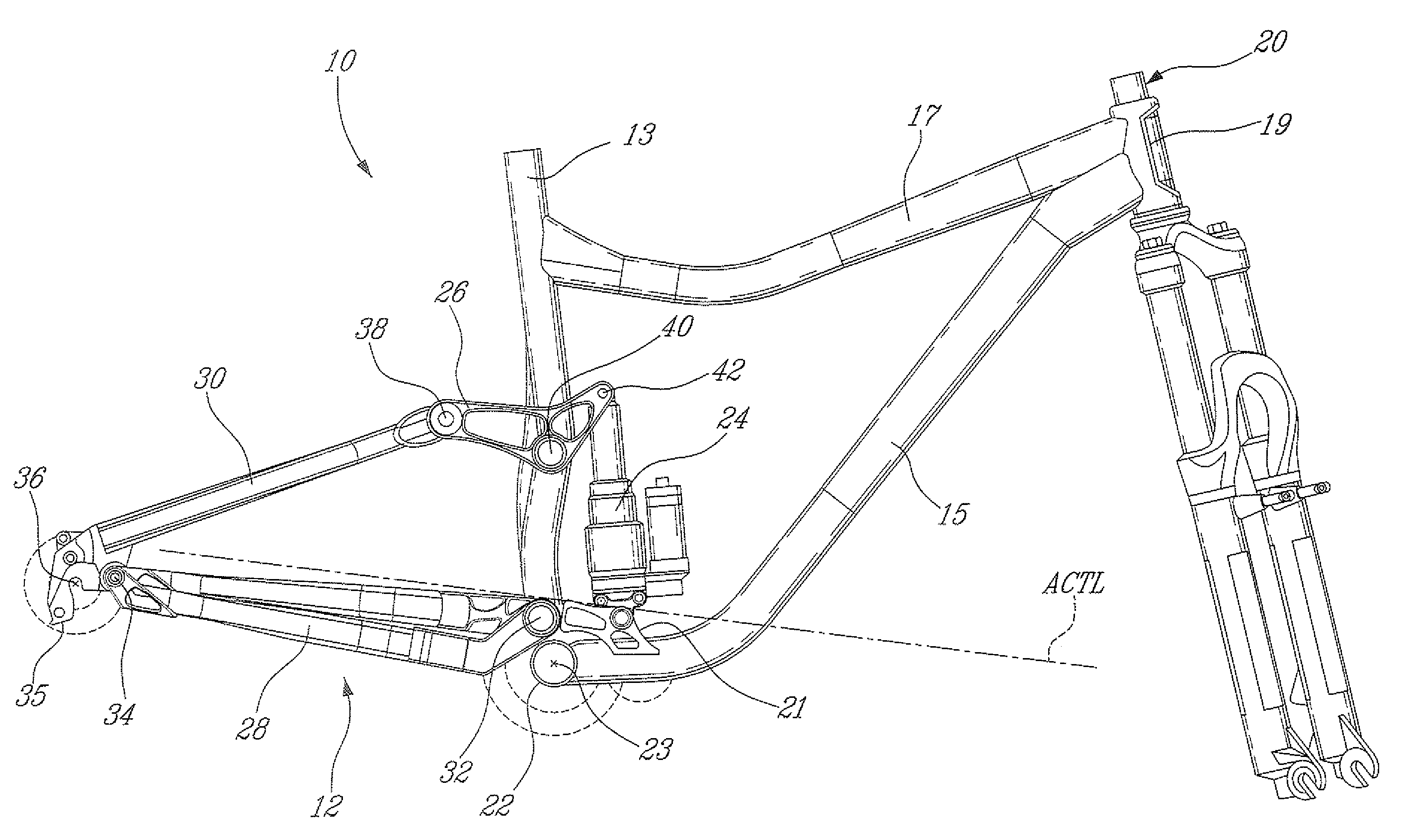
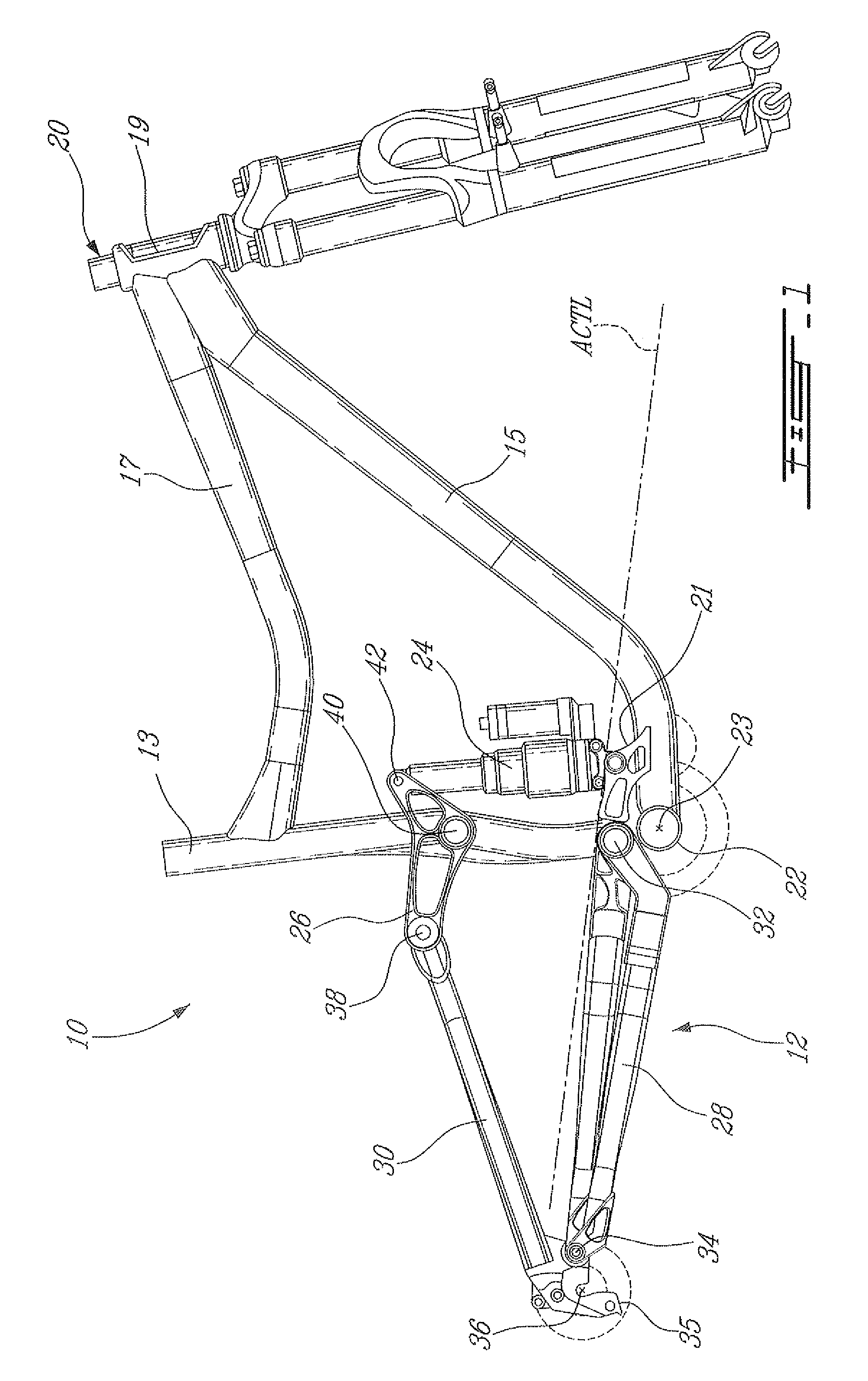
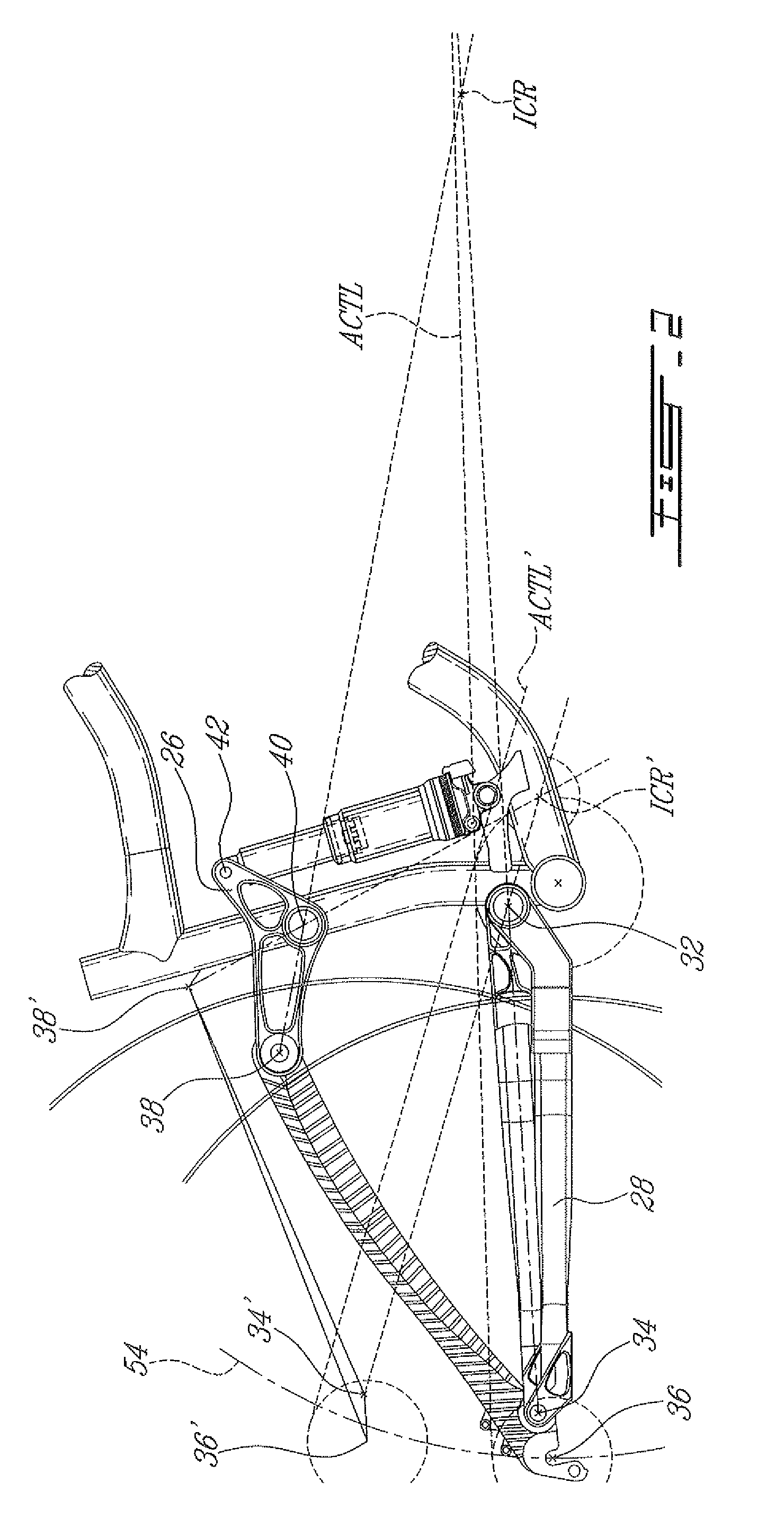
ActiveUS20080303242A1Improve riding performancePassenger cyclesChildren cyclesVehicle frameCentre of rotation
A bicycle rear wheel suspension system includes an upper link and a lower link both pivotally attached to the frame and to a rear stay member. An instantaneous center of rotation of the rear stay member is defined at an intersection between an upper axis extending through first and second pivots of the upper link and a lower axis extending through third and fourth pivots of the lower link. Throughout a travel distance of a shock absorber of the suspension system, the instantaneous center of rotation remains below an average chain torque line of the bicycle, the lower axis remains above an axle axis extending through the rear wheel axle, and a portion of the lower axis defined between the third and fourth pivots extends below the average chain torque line.
Owner:IND RAD
Reduced-size apparatus for non-intrusively inspecting an object
InactiveUS7027554B2Radiation/particle handlingX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentClosest pointReduced size
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
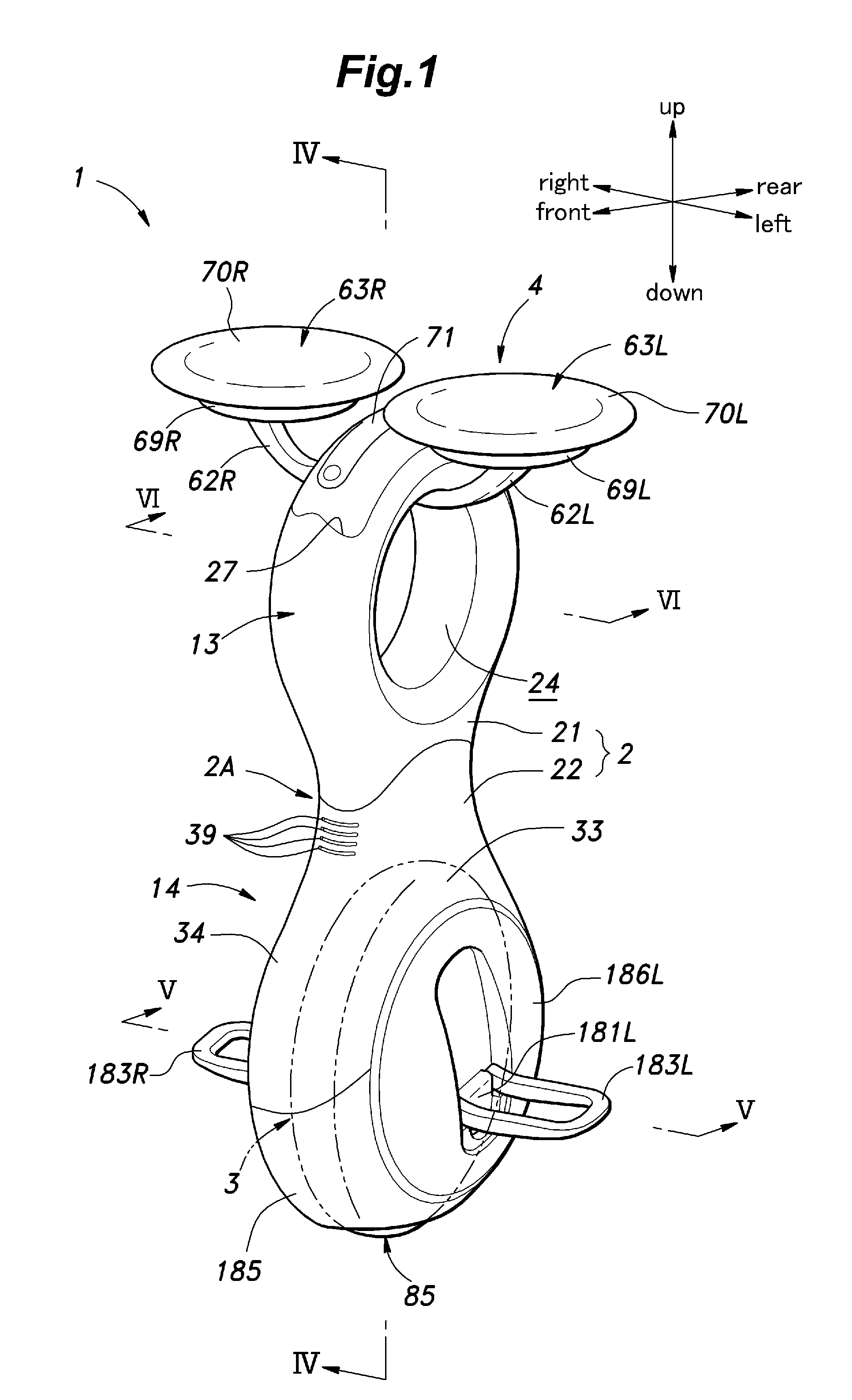
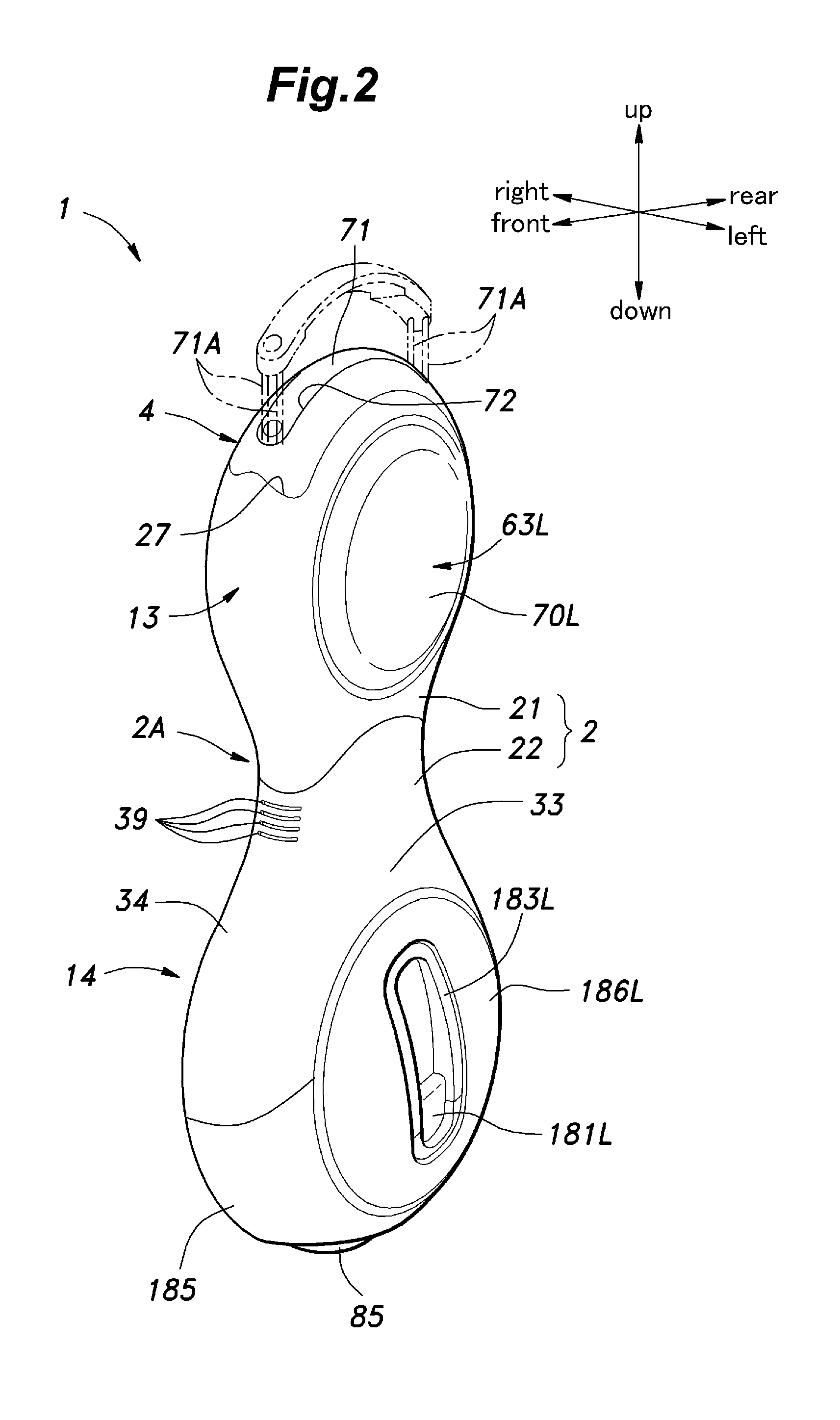
Inverted pendulum type vehicle
ActiveUS8522902B2Get aboard the vehicle with easeSit on the saddle with easeUnicyclesRussian swingsMarine engineeringCentre of rotation
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Axial rotary eddy current brake with adjustable braking force
InactiveUS20070000741A1Dynamo-electric brakes/clutchesNon-rotating vibration suppressionCentre of rotationEngineering
The present invention relates to an axial adjustable, rotary brake device using eddy current resistance, having an annular rotating conductive reaction member fastened on a central axle, having a frame, and fitted with permanent magnets disposed on either one side or both sides of said member, wherein the magnets produce a magnetic field between the magnet arrays, and through the member. Relative motion of the member and magnets produces eddy current resistance opposing the movement of the member. The magnets are mounted such that their respective positions relative to each other and thus to the intermediate conductive member can be changed by an adjusting Structure to increase or decrease the space between magnets and member, (air gap), distance from the rotational center or their relationship to each other. Various other configurations for changing the spatial relationship of magnets and members are presented which can be employed to produce many embodiments and variations of the present invention.
Owner:MAGNETAR TECH
Small container fluid dynamics to produce optimized inspection conditions
ActiveUS20050248765A1Improve imaging characteristicReduce radiant energyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationIndividual particle analysisMeniscusEngineering
The generation of a desired non-linear resonance in the toroidal flow of liquid in a cylindrical injectable product is described. The resulting liquid flow pattern generated with an approximately smooth meniscus is down at the walls, across to the center of rotation, up on the center of rotation, across the meniscus to complete the pattern. The controlled flow pattern results in a predictable location for particle of varying mass and hydraulic shape. This predictability of location transforms the problem of particle detection from a chance occurrence to a deterministic task. The deterministic location of particle position is a contributor to the demonstrated capability to measure the size of visible particle range in a range from 33 μm to 1,000 μm with a median deviation of 1% and a maximum deviation from NIST dimensional accuracy of 3%.
Owner:BUDD GERALD WALTER +1
Force balanced asymmetric drilling reamer and methods for force balancing
A force balanced asymmetric drilling reamer comprising a plurality of blades, each blade having at least one cutter section and a gage section. The cutter section is designed to have a plurality of cutting devices for cutting through swelling formations and cutting free sloughing formations. The gage section has a full bore diameter with gage elements flushly coupled to gage section's outer surface. The blades may be curve / concave shaped or boomerang / chevron shaped, which thereby agitate the cutting beds. At least a portion of the drilling reamer's diameter is incrementally force balanced, starting from the outermost diameter, so that the net radial force is less than 10% of weight on bit with respect to the center of rotation. This balancing allows a greater cutter longevity and provides for a better wellbore condition. Optionally, at least a portion of the drilling reamer's surface may be treated by nitriding for repelling the cuttings.
Owner:VAREL INT IND
2-D actuator and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20040081391A1Increase speedPrecision positioning equipmentSoldering apparatusCentre of rotationEngineering
An actuator includes a stage having a first direction and a second direction perpendicular to the first direction and seesawing around a third direction perpendicular to the first direction and the second direction with respect to a rotation center axis placed along the first direction. A first support portion supports a seesaw motion of the stage. A base facing the stage under the stage at a predetermined interval is supported by the first support portion. A stage driving portion has a plurality of first driving comb electrodes and a plurality of first stationary comb electrodes corresponding to the first driving comb electrodes which are respectively formed on a lower surface of each of the stages and an upper surface of the base facing the stages. A second support portion supports the first support portion so that the first support portion seesaws with respect to a rotation center axis placed along the second direction. A first support portion driving portion has a second driving comb electrode provided at the first support portion and a second stationary comb electrode fixedly positioned to correspond to the second driving comb electrode to generate a seesaw motion of the first support portion.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
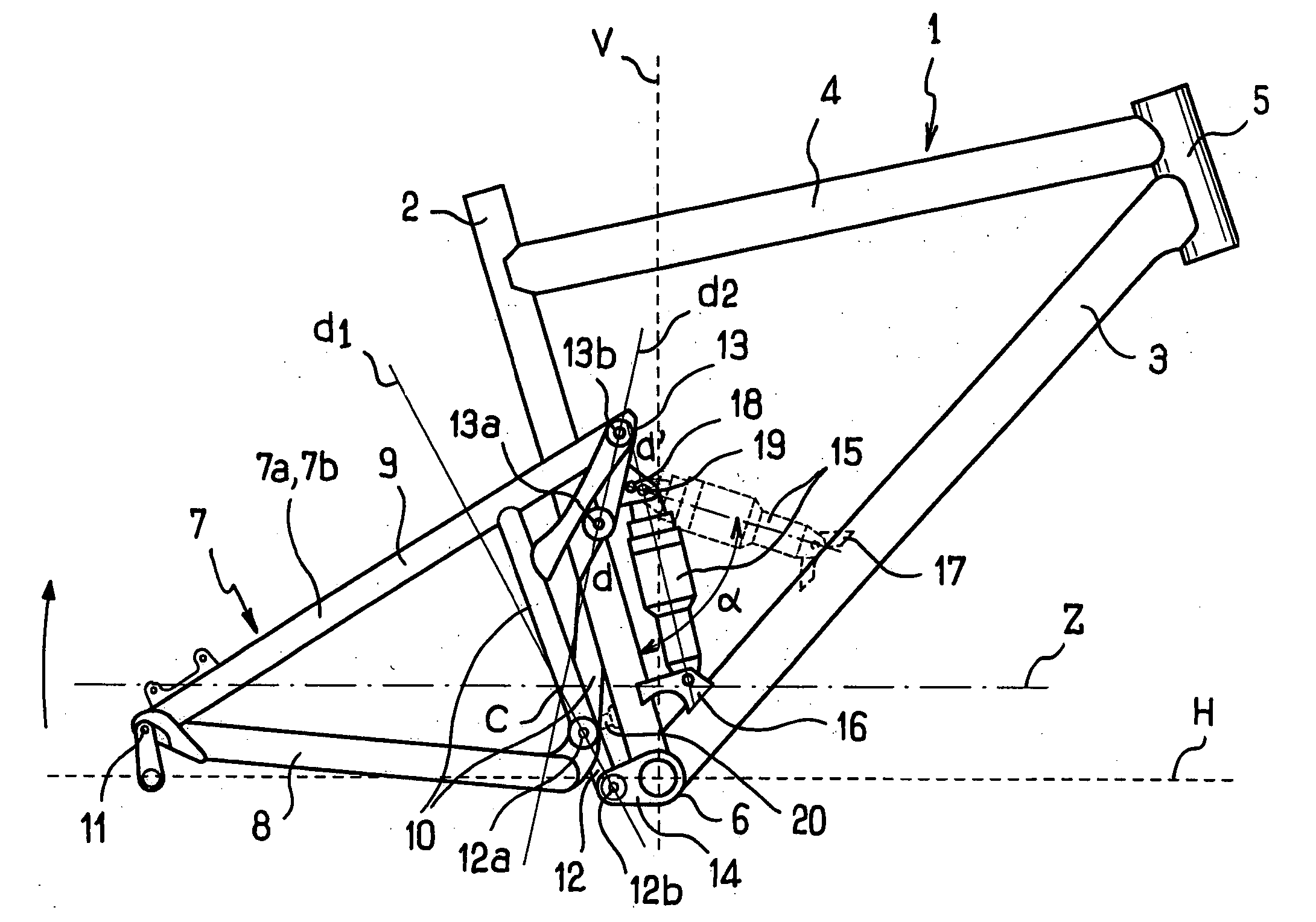
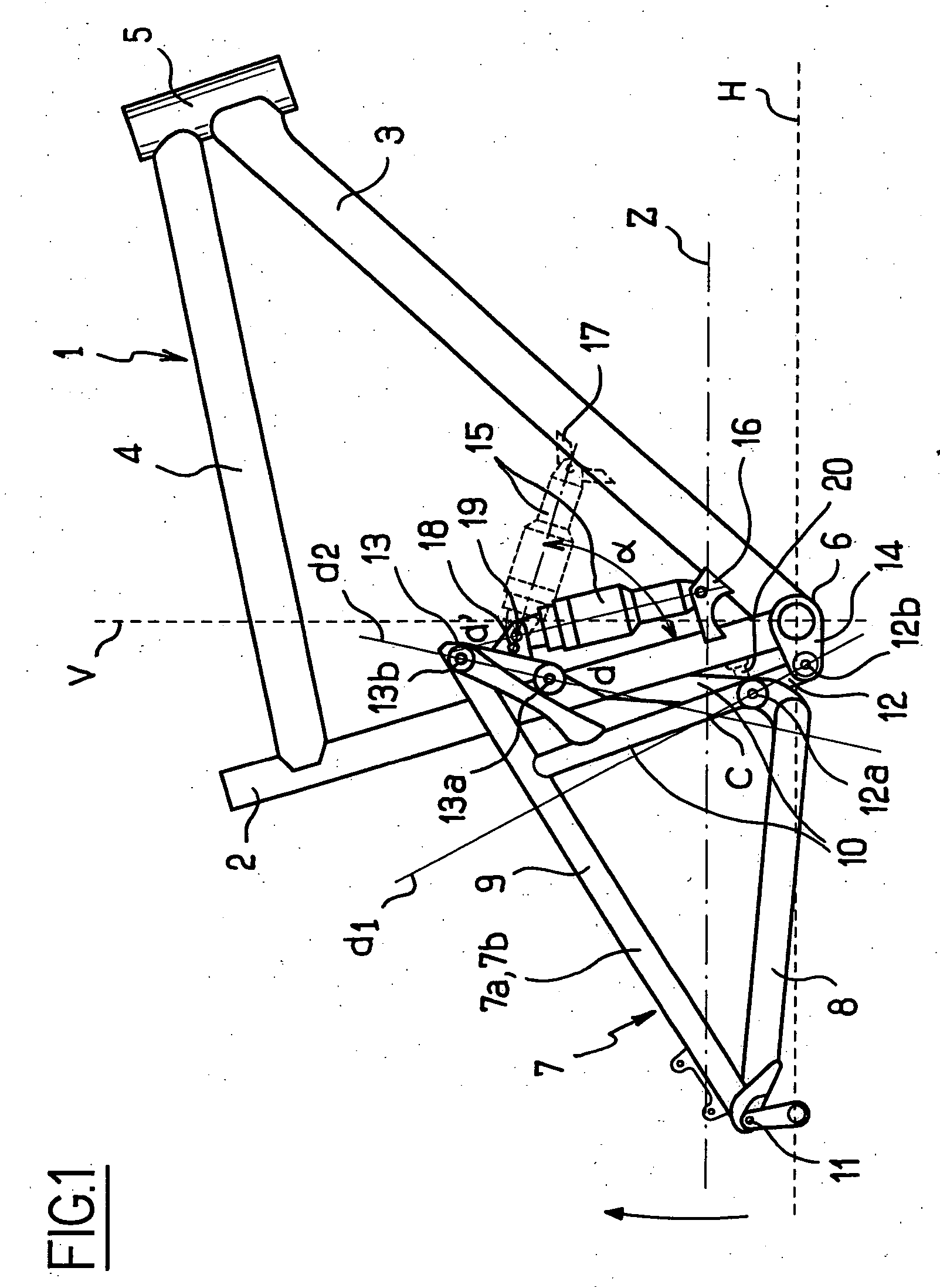
Rear suspension of a two-wheel vehicle or the like
InactiveUS20060061059A1Eliminates kick-back effectSimple designPassenger cyclesChildren cyclesDrive wheelVehicle frame
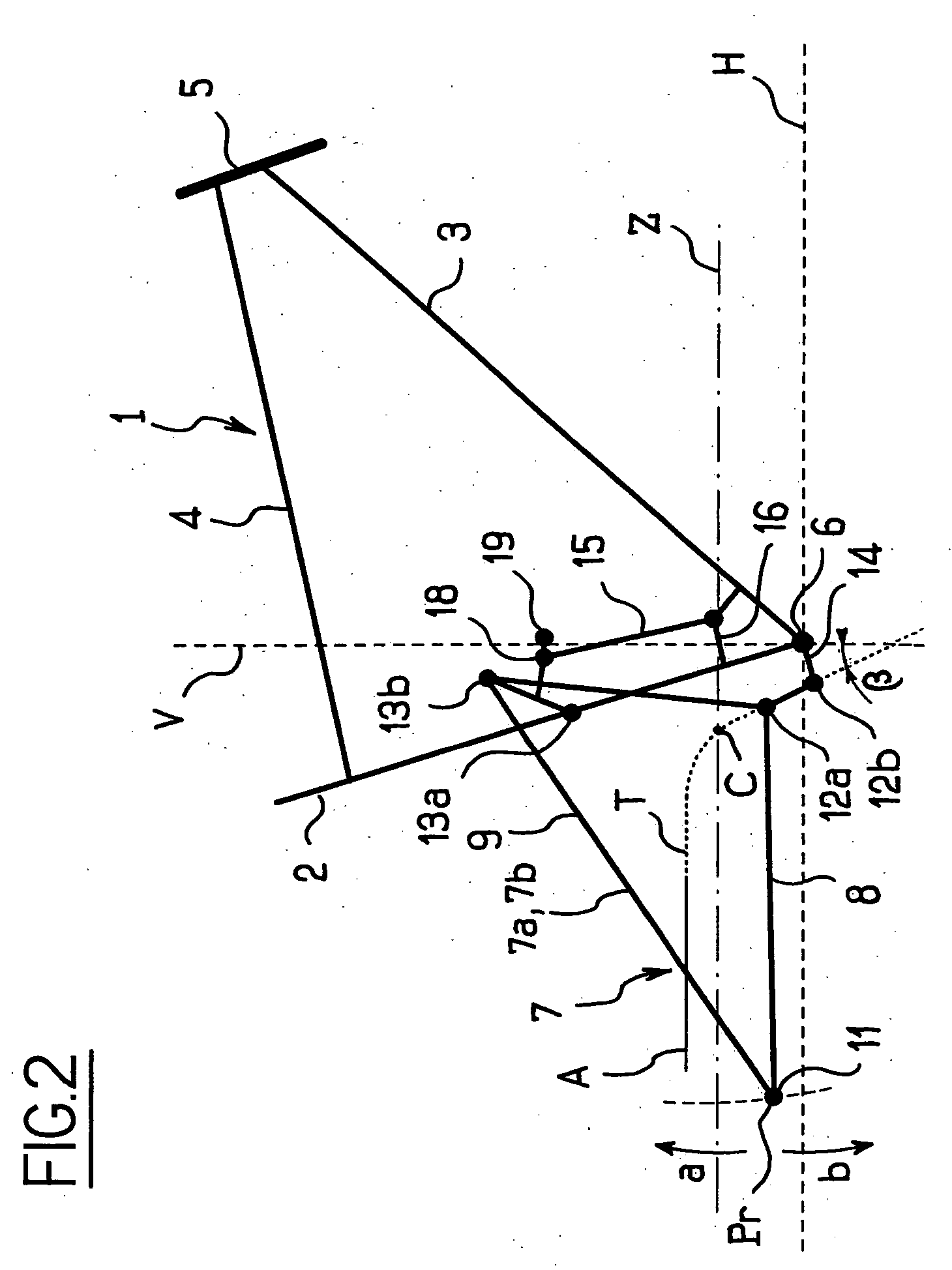
The present invention relates to a rear suspension for a vehicle such as a bicycle, a motorcycle or the like, of the type that includes a frame (1), a swinging arm (7) integral with the frame (1) carrying the axle (11) of the hub of a drive wheel and a shock absorber (15) whose ends are secured, respectively, to the frame (1) and to the swinging arm (7), the drive torque being transmitted to the drive wheel by a chain (Z) extending between a drive sprocket secured to the frame (1) and a driven sprocket secured to the axle (11) of the hub of the drive wheel, said chain (Z) between the drive and driven sprockets forming two strands; the stretched, upper one, which transmits the drive torque to the rear drive wheel, and the other, “return” lower one, the swinging arm (7) being secured to said frame (1) by at least two articulation means (12, 13) so that the swinging arm (7) pivots about an “instantaneous centre of rotation” point C that is movable when the hub of the drive wheel is displaced on either side of its reference position Pr corresponding to the position of the axle (11) of the hub of the drive wheel when the vehicle is in a static equilibrium position, characterized in that the instantaneous centre of rotation C is displaced upwards along a parabolic path T, the asymptote A of which is oriented towards the rear free end of the swinging arm (7) carrying the axle (11) of the hub of the drive wheel when said hub of the drive wheel is displaced above its reference position Pr.
Owner:CYCLES LAPIERRE
Motor for rotating a disk-shaped information recording medium in a disk drive apparatus
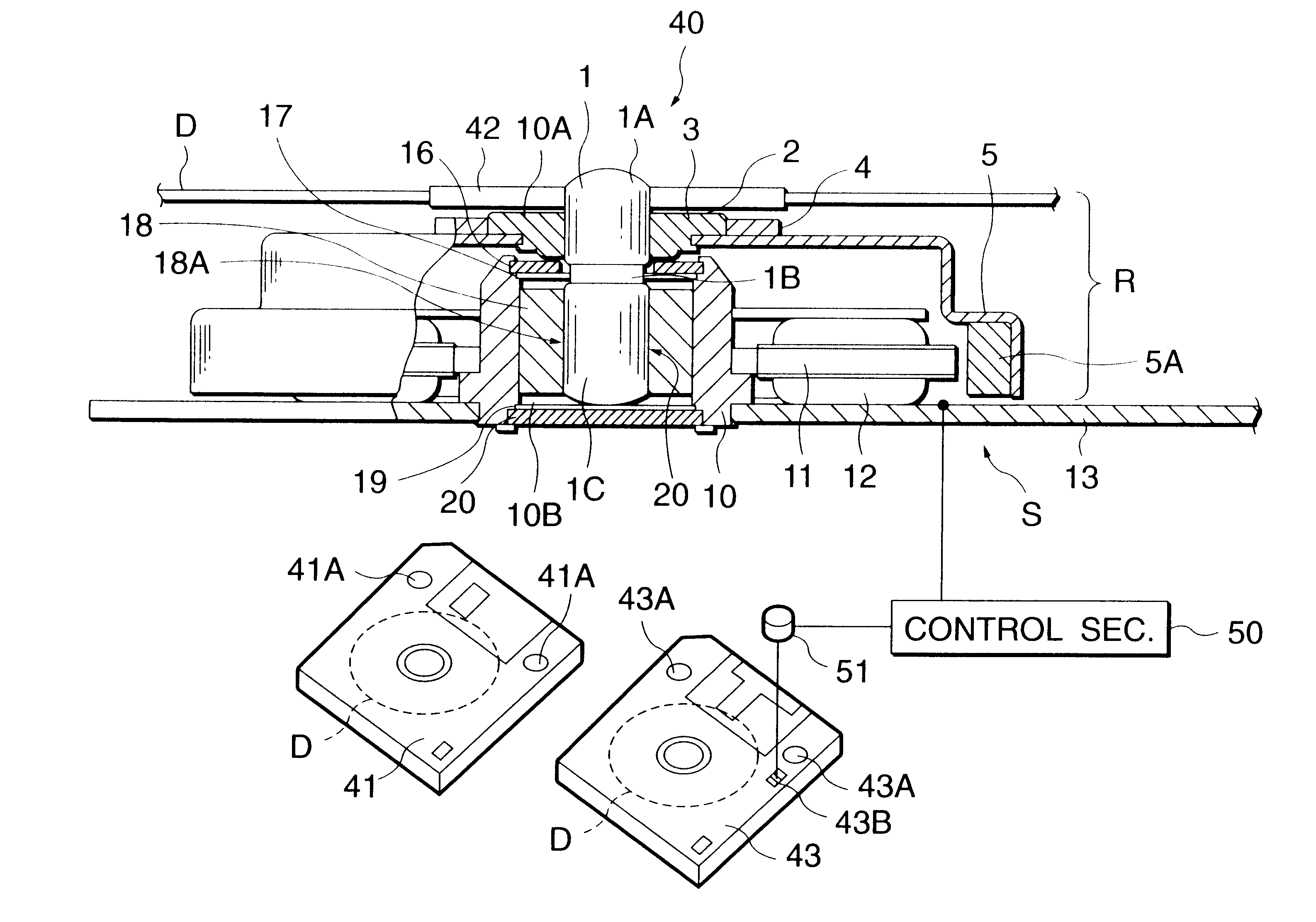
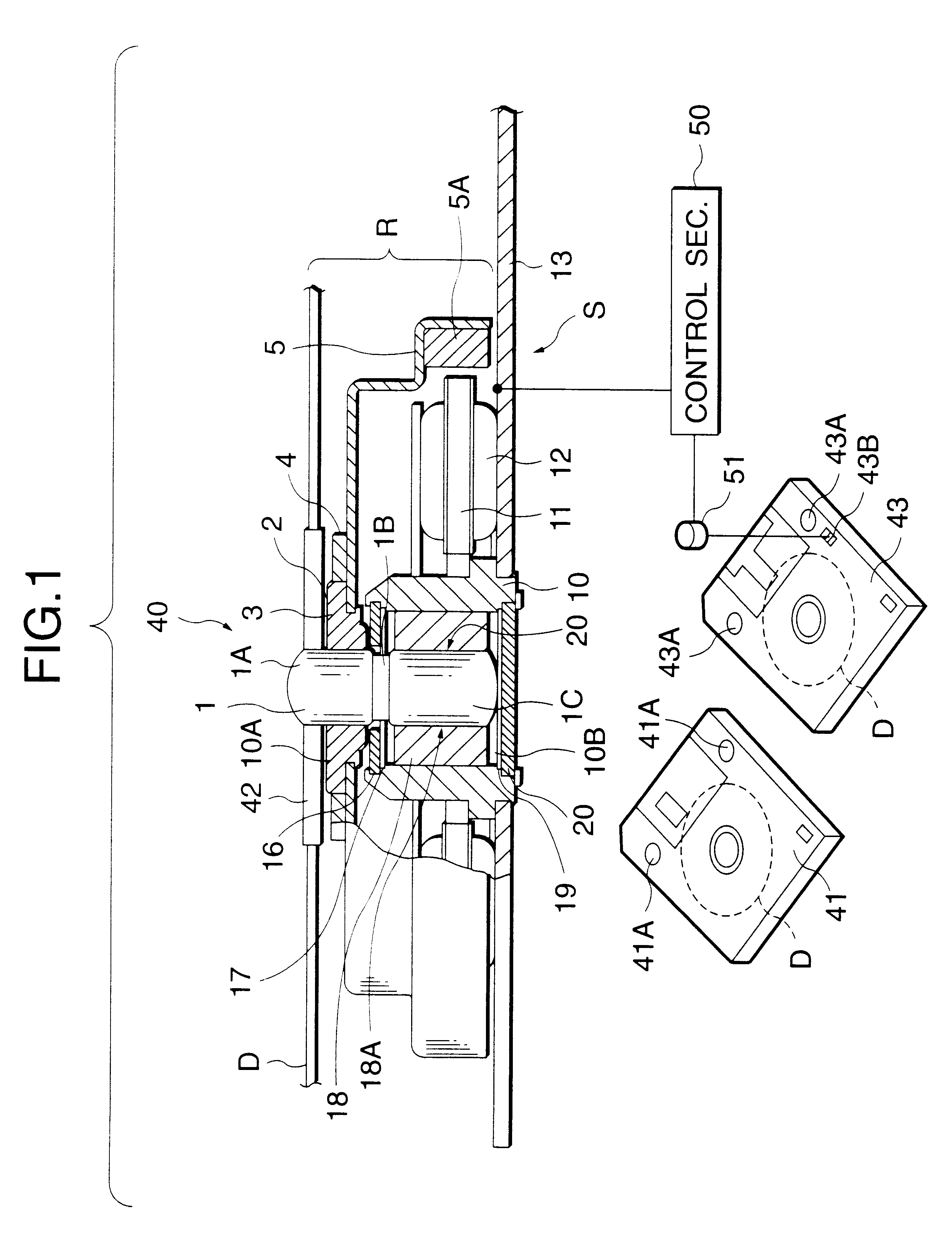
A motor for rotating a disk-shaped information recording medium for a disk drive apparatus which is capable of rotating a higher-capacity information recording medium and a relatively lower-capacity recording medium at different speeds. This motor includes a stator; a rotor that rotates with respect to the stator with a shaft as the center of rotation when a drive winding is energized; a bearing that is provided on the side of the stator and rotatably supports the shaft of the rotor; a dynamic pressure generation section for generating dynamic pressure by filling a fluid between the bearing and the shaft when the shaft is rotated above a predetermined speed; a judging member for judging whether the disk-shaped information recording medium that is attached to the rotor is a relatively lower-capacity medium or a higher-capacity medium; and a control section for supplying the drive winding of the stator with a drive signal for a first rotation speed when a judgment signal produced by the judging member indicates the relatively lower-capacity medium, and with a drive signal for a second rotation speed that is higher than the first rotation speed when the judgment signal indicates the higher-capacity medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
Fixing device
ActiveUS20070014599A1Avoid temperature riseElectrographic process apparatusInduction heating apparatusCouplingCentre of rotation
A fixing apparatus can prevent an excessive rise in temperature of a paper non-passage area due to diverted flow of magnetic flux from a paper passage area of a heat-producing element to a paper non-passage area thereof has a small configuration, A center core is rotated by a rotation section, bringing cutaway parts to a magnetic path masking position, and the degree of magnetic coupling between the center core and a heat-producing roller is weakened, suppressing an excessive rise in temperature of paper non-passage areas of the heat-producing roller. With this fixing apparatus, switching of the intensity of magnetic coupling between the center core and heat-producing roller can be performed simply by rotating the center core. Also, with this fixing apparatus, it is not necessary for magnetism suppressing elements to be provided as separate members, enabling the configuration to be made simpler and less expensive.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
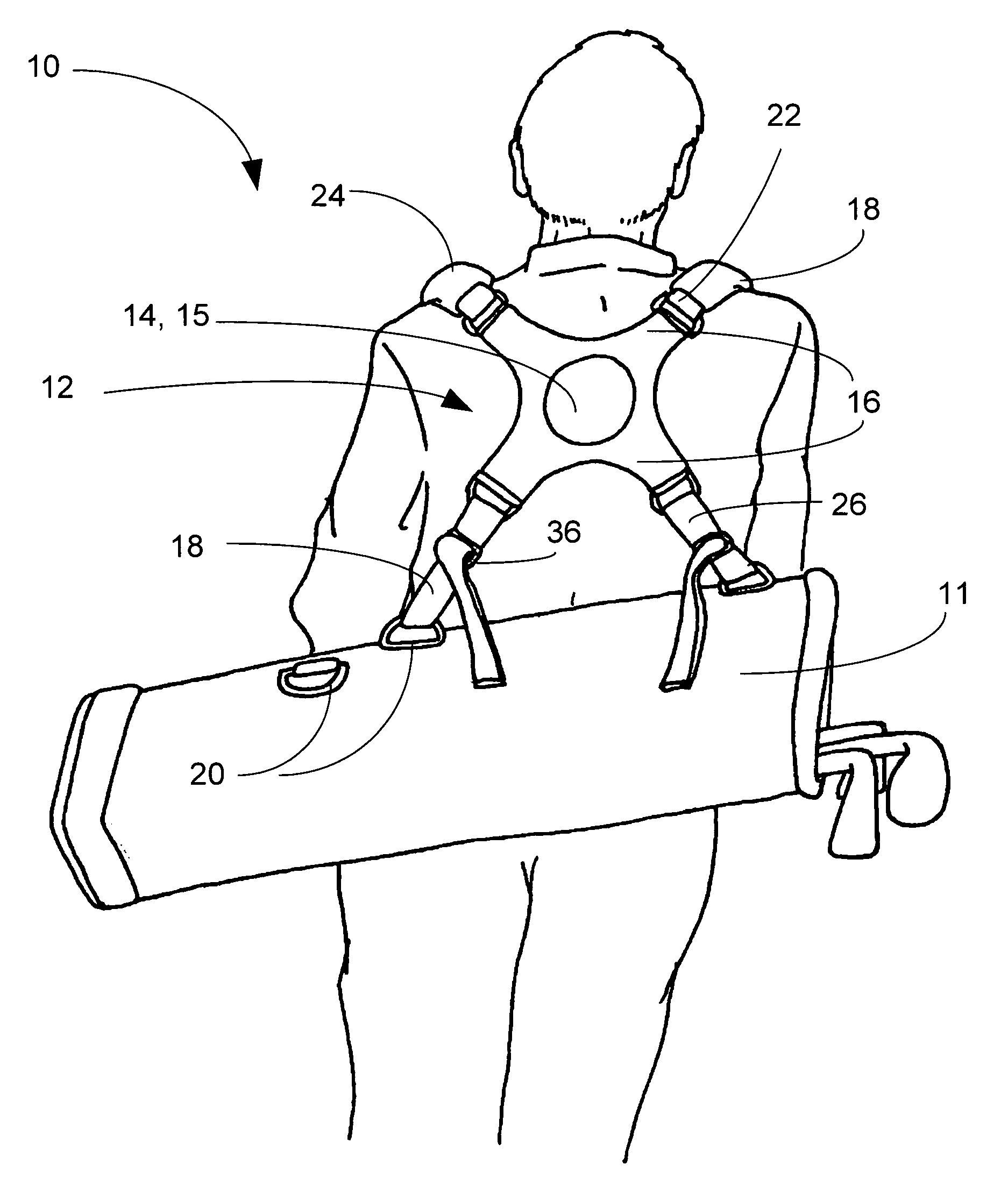
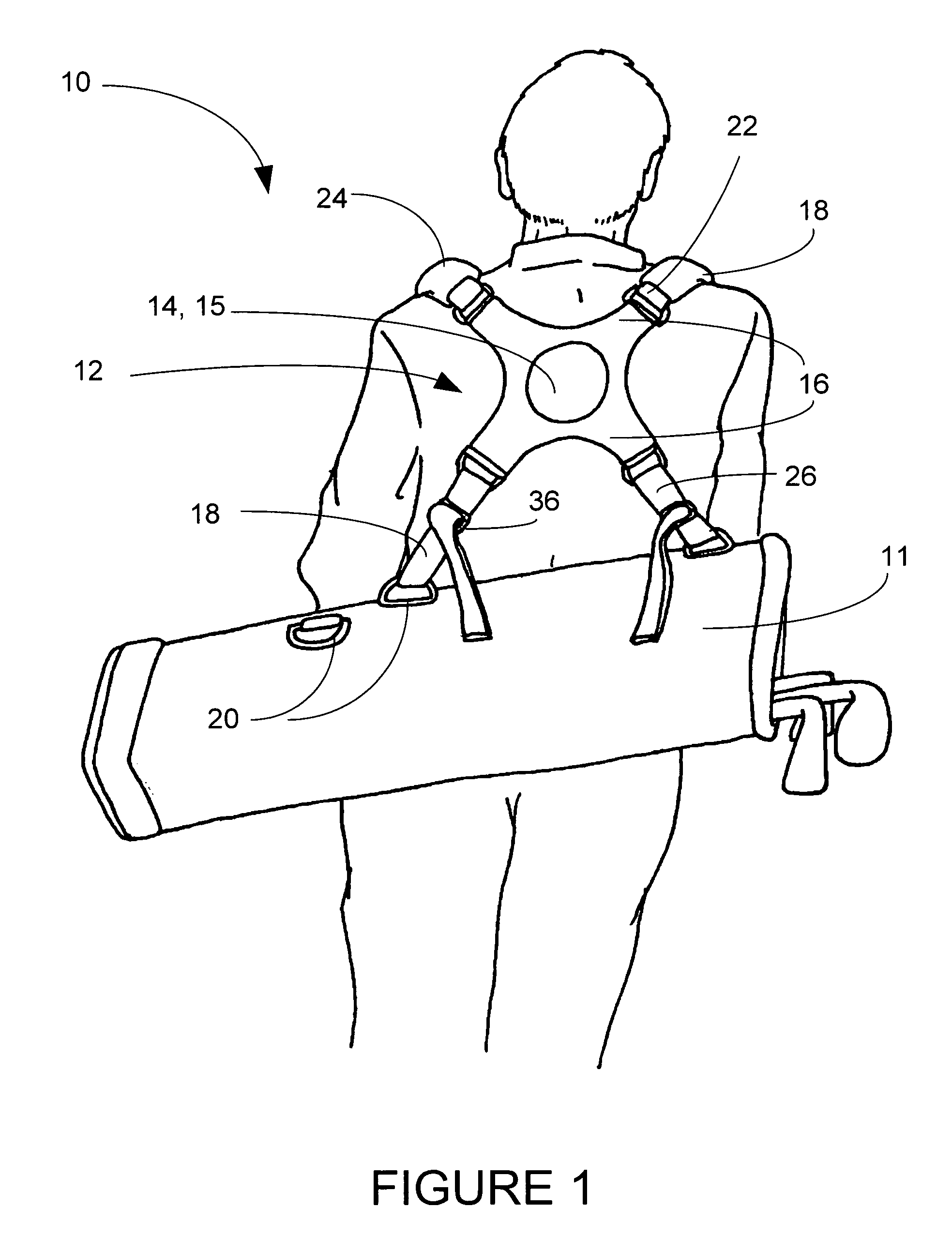
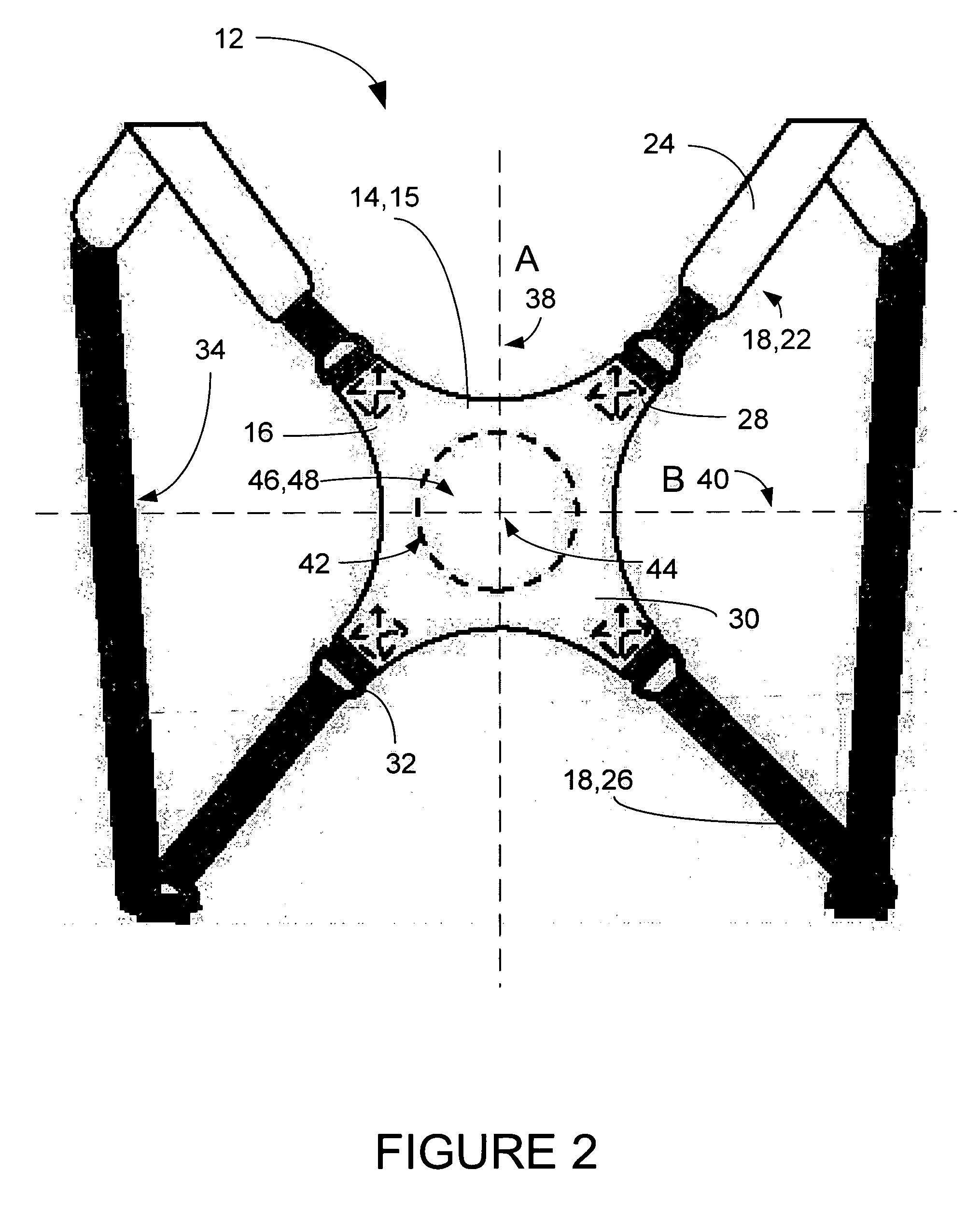
Golf bag and strap system
InactiveUS7131534B2Vibration minimizationImprove balanceTravelling sacksOther accessoriesCentre of rotationEngineering
A golf bag and strap system for supporting a golf bag, having a central hub including a number of arms. Each arm has at least one attachment point to which straps are connected. The arms include upper arms and lower arms, and upper straps are attached to the upper arms, and lower straps are attached to the lower arms. Each attachment point preferably includes a D-ring. The central hub also preferably includes a padded portion having a raised portion which acts as a center of rotation for movement of the central hub.
Owner:SUN MOUNTAIN SPORTS INC
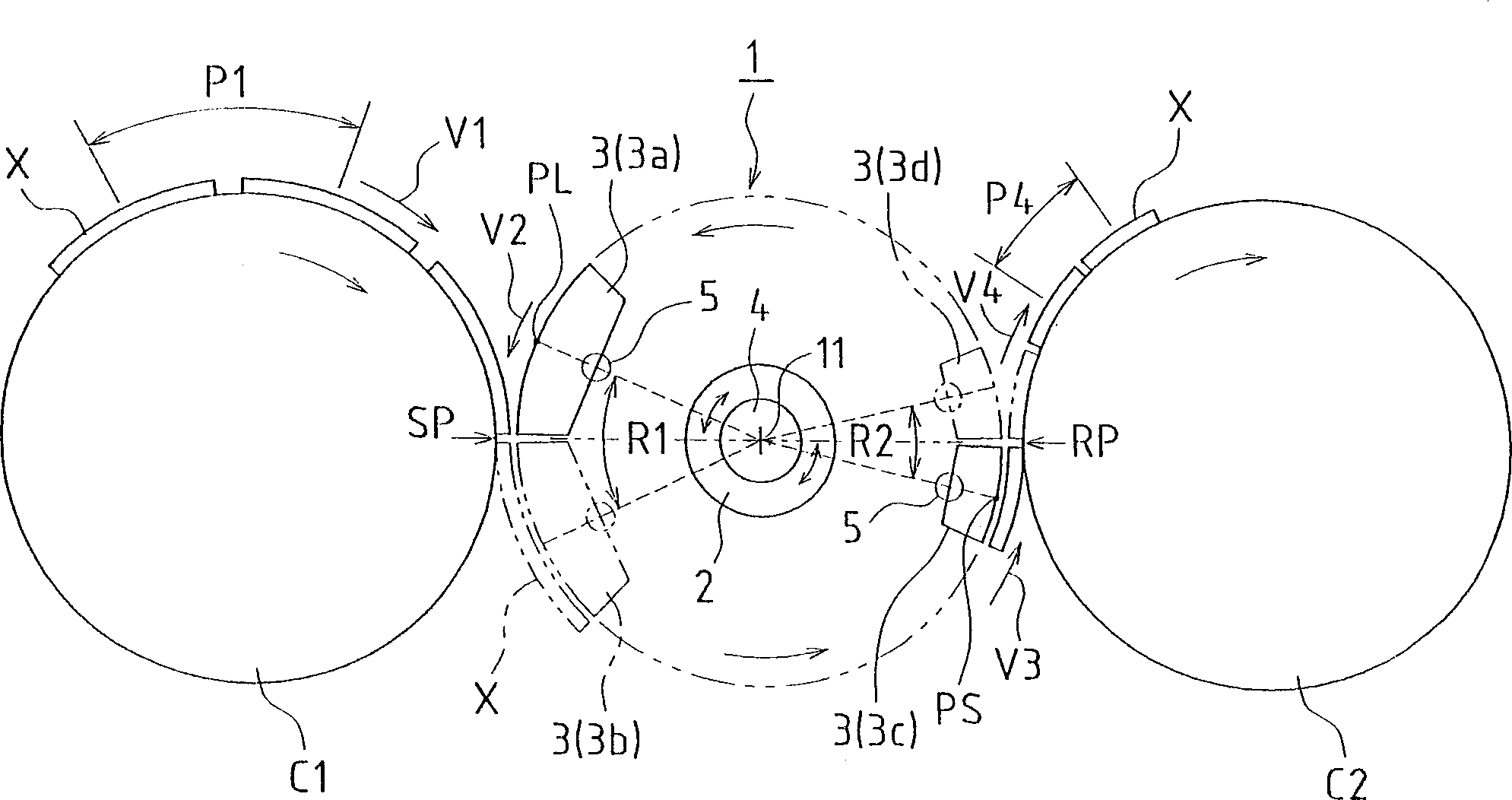
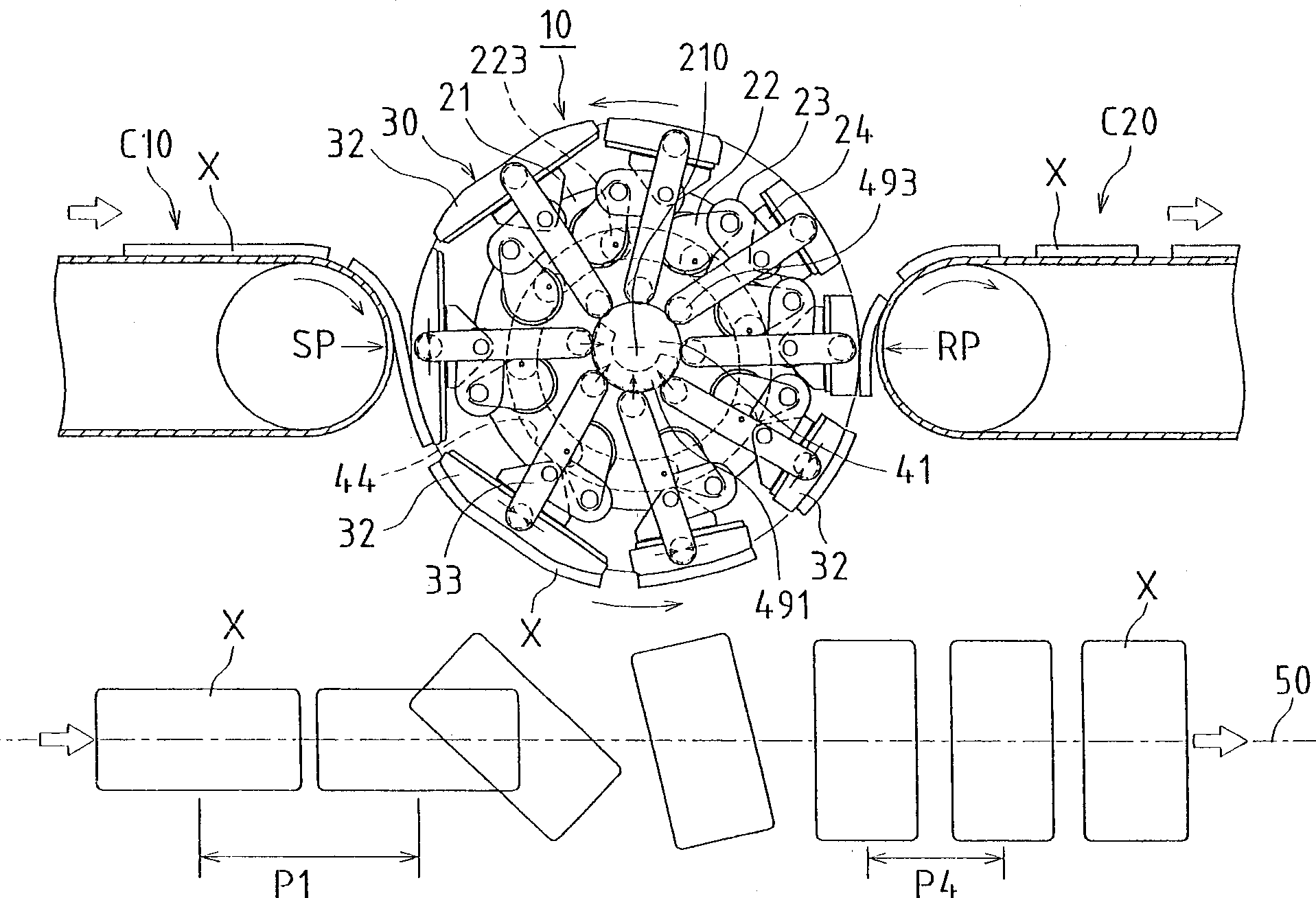
Method and device for transportation
A transportation device (10) comprising crank arms (22) installed rotatably on a drive wheel (21), link levers (23) each having one end pin-connected to the tip of each of the crank arms (22), and swing parts (30) each having the other end pin-connected to each of the link levers (23) and held at a specified distance from a rotating shaft (210) of the drive wheel (21), wherein a speed changing cam roller (223) is installed on the crank arm (22) projectedly at a position apart from the rotating center thereof, and the transmission cam roller (223) is engaged for guiding with a transmission cam groove (44) formed eccentrically with respect to the rotating shaft (210) of the drive wheel (21), whereby the tips of the crank arms (22) are swung with in one rotation frequency of the drive wheel (21), and the angular velocities of the link levers and the swing part (30) connected thereto are increased or decreased periodically relative to the angular velocity of the drive wheel (21).
Owner:ZUIKO CORP
Air blower apparatus having blades with outer peripheral bends
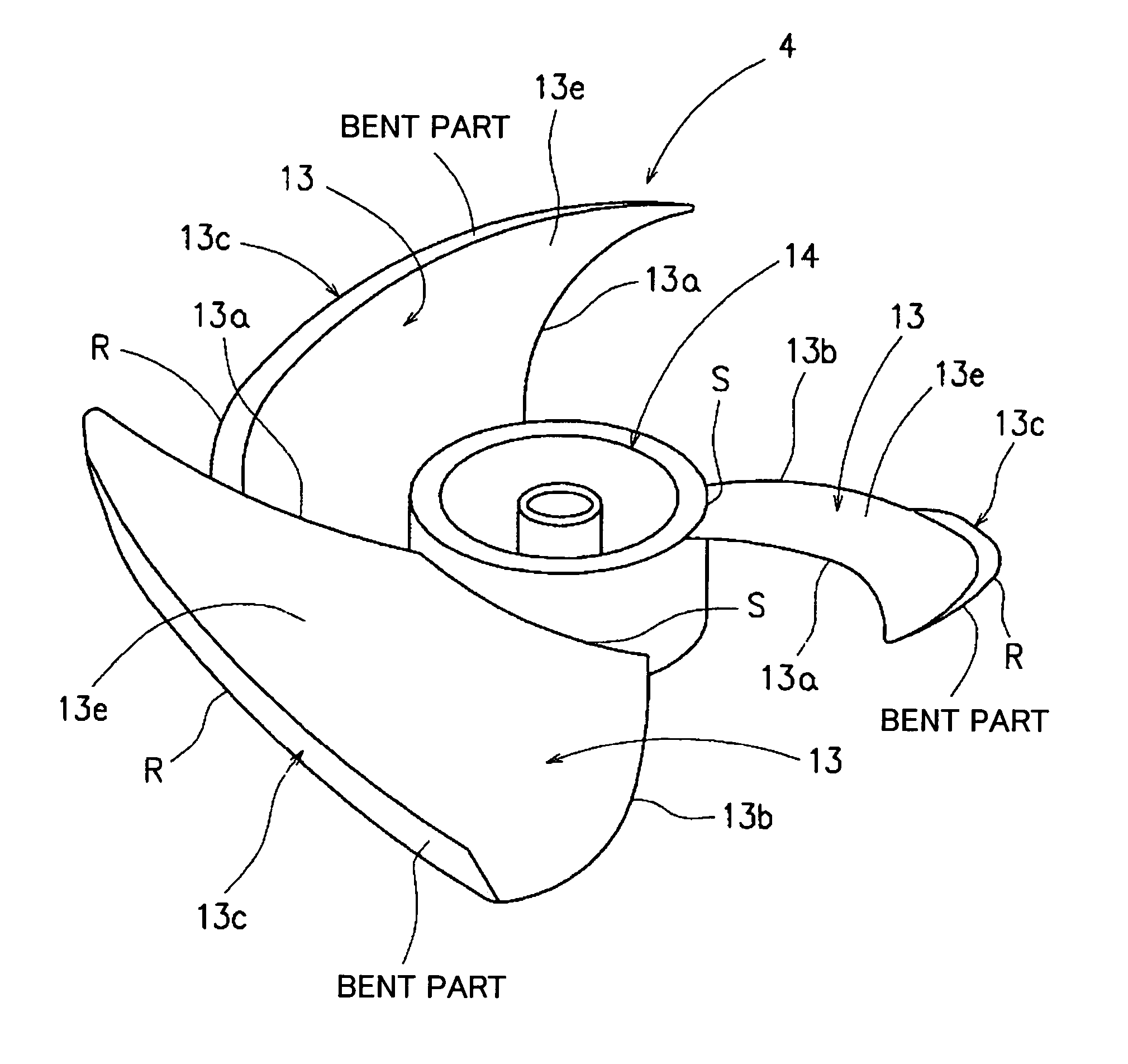
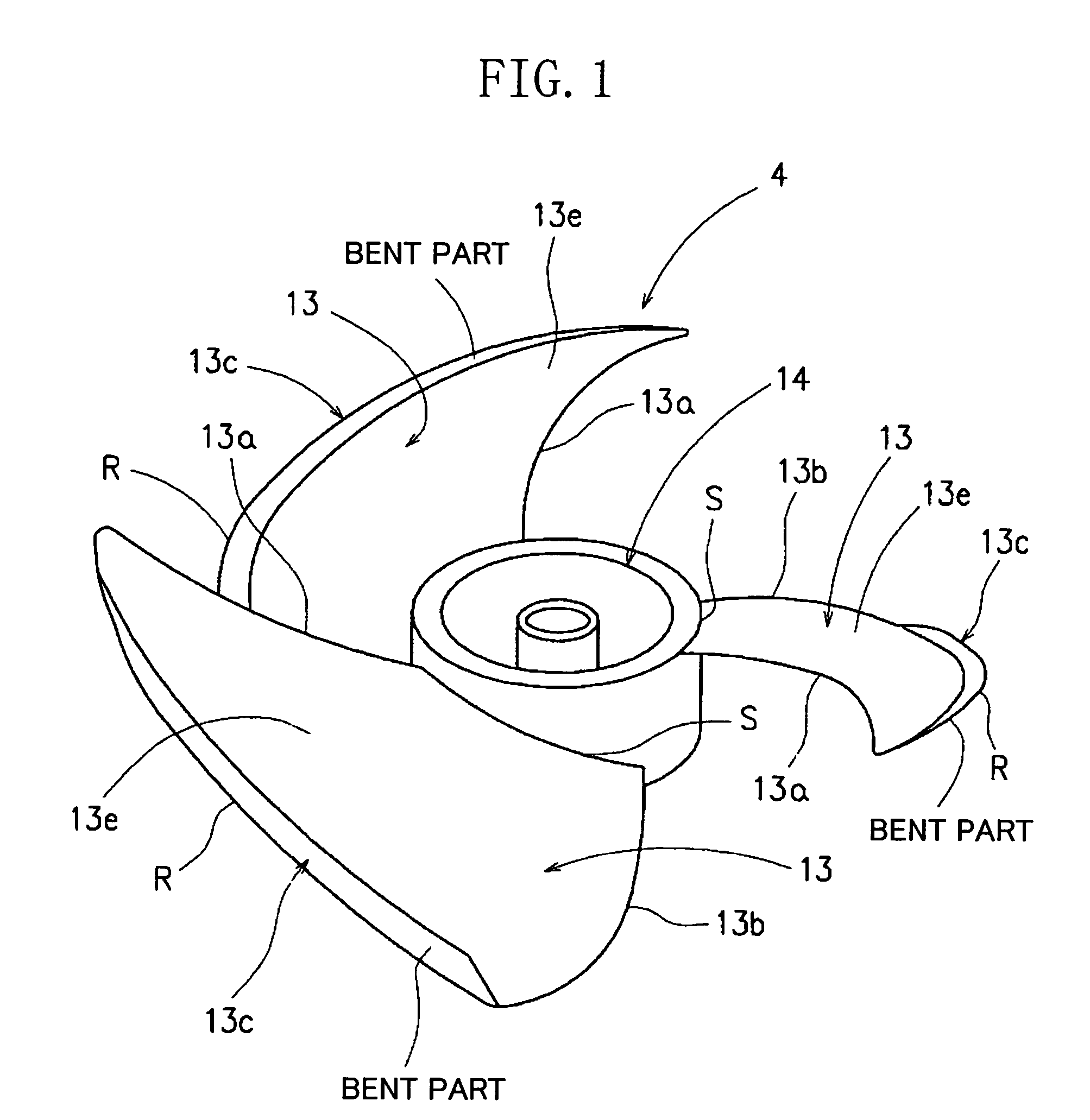
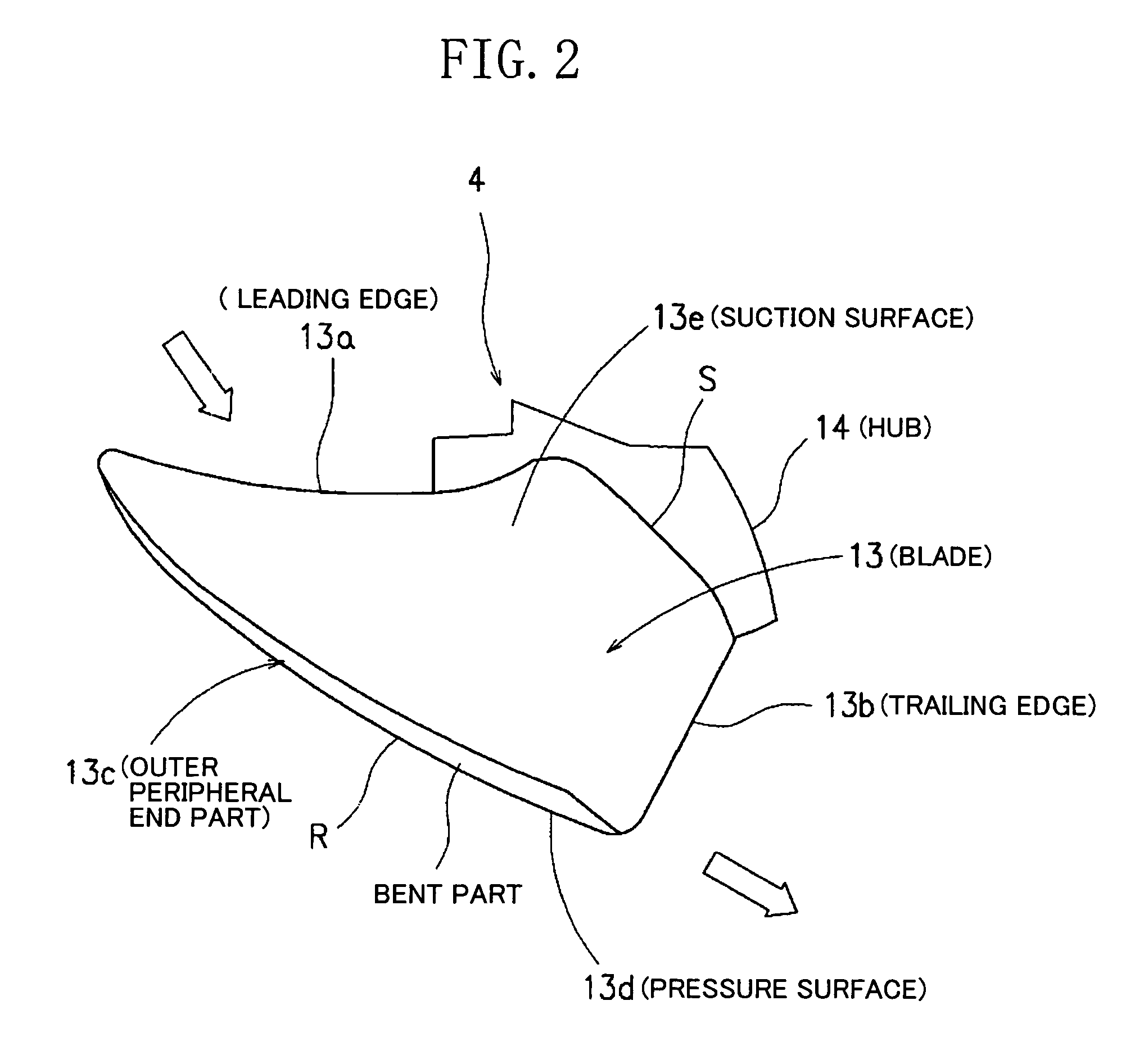
InactiveUS6994523B2Outdoor unit is reduced effectively.Improve noise reductionPropellersPump componentsLeading edgeSuction force
An air blower apparatus is provided including a hub which is a center of rotation, and a plurality of blades disposed along an outer peripheral surface of the hub and having leading and trailing edges and where both an outer peripheral end of the leading edge and an outer peripheral end of the trailing edge lie ahead relative to the rotative direction. An outer peripheral part of the blade may be bent toward the suction side in such a way as to form a starting point at which an airflow starts leaking, and the radial-direction width, W, of the bent part gradually increases from the vicinity of the leading edge to the vicinity of the trailing edge. A blade tip vortex (β) generated from a blade positioned ahead relative to the rotational direction F and a separation vortex from a pressure surface of a blade positioned behind relative to the rotational direction F offset each other, so that discharge vortexes are suppressed.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
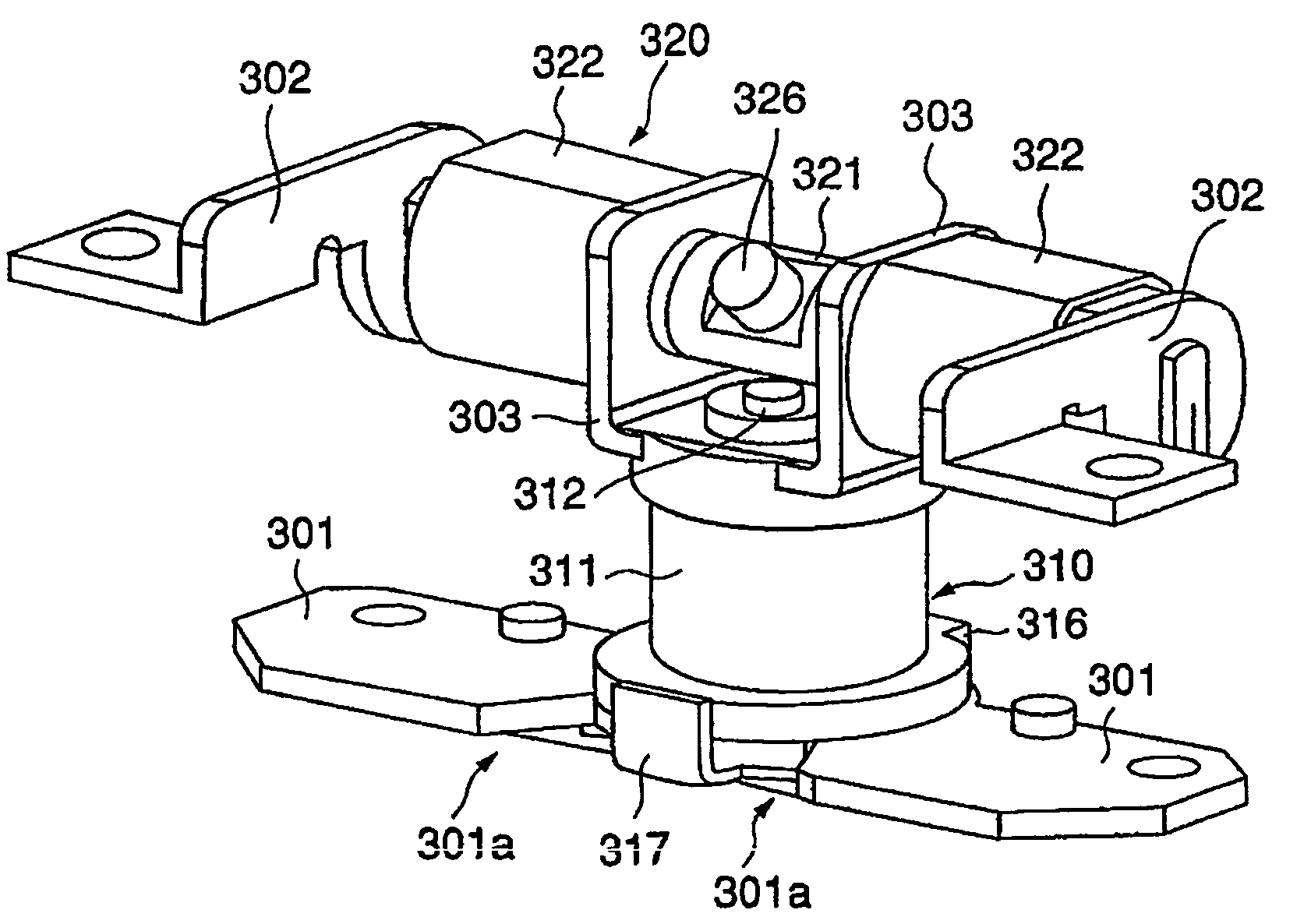
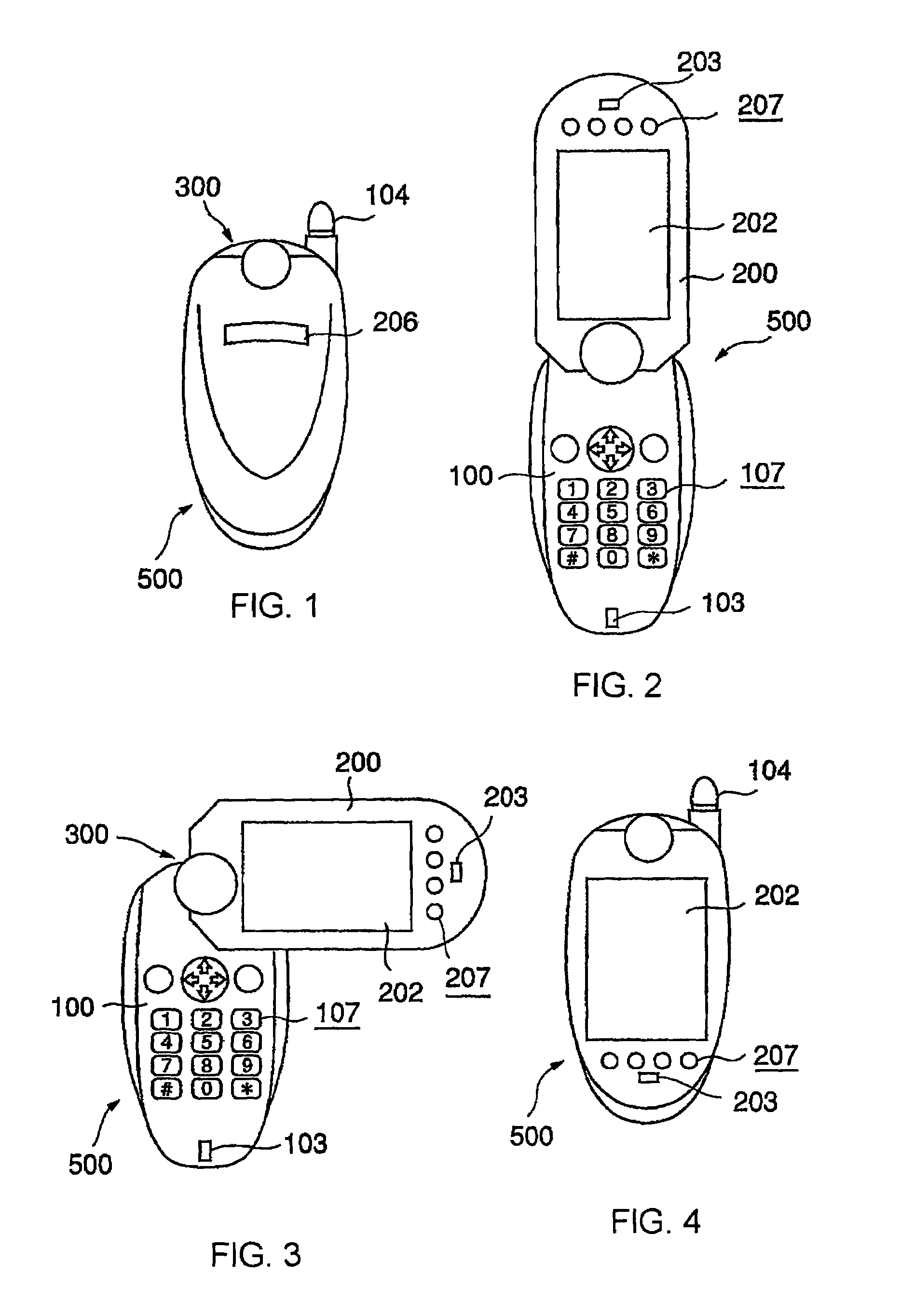
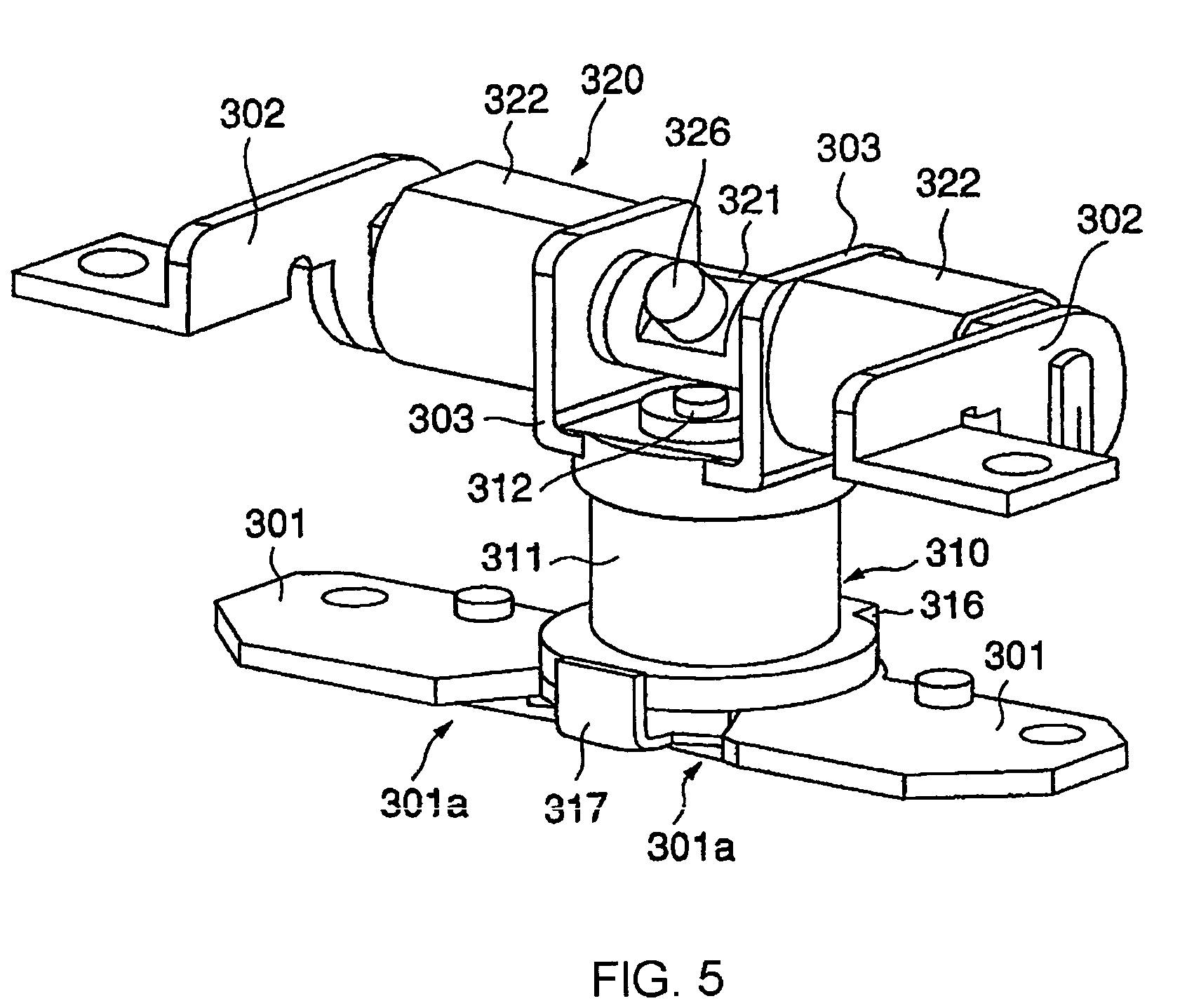
Foldable and portable mobile communication terminal
InactiveUS7158816B1Facilitates talkingEasy to operateInterconnection arrangementsWing accessoriesCentre of rotationComputer terminal
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Developer supply container, and coupling-driving member for developer supply container
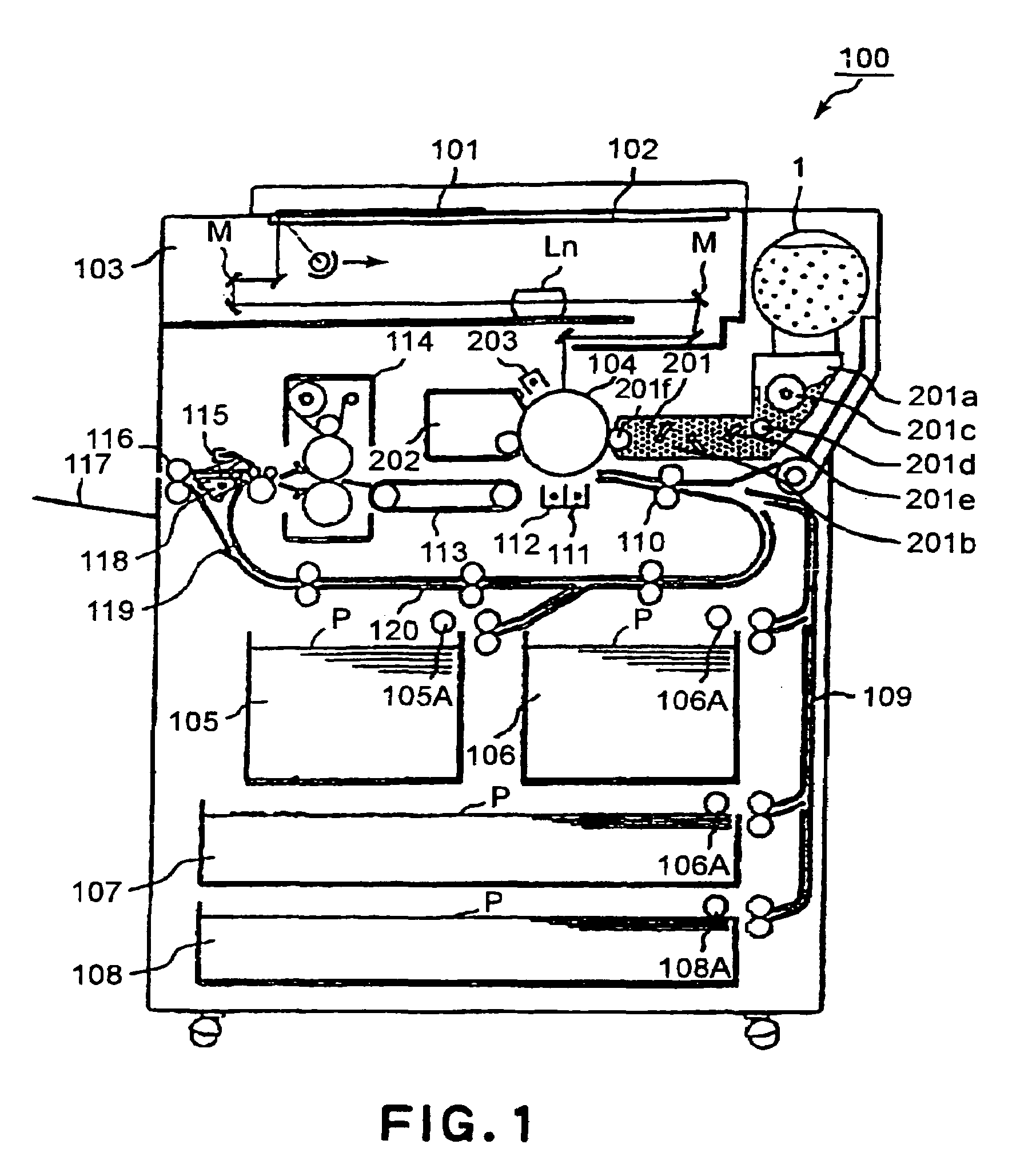
ActiveUS6993273B2Accurate transmissionPowdered material dispensingElectrographic process apparatusSufficient timeCentre of rotation
A developer supply container detachably mountable to an image forming apparatus, the container includes a container body for accommodating the developer; drive connection member, provided substantially at a rotation center of the developer supply container, for driving engagement with a driving member provided in the image forming apparatus, wherein the drive connection member has a drive transmitting portion for transmitting a rotational force received from the driving member to the container body, wherein the drive transmitting portion is disposed so as to be idly rotatable for a sufficient time after start of rotation of the drive transmitting portion and before engagement with the container body.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com