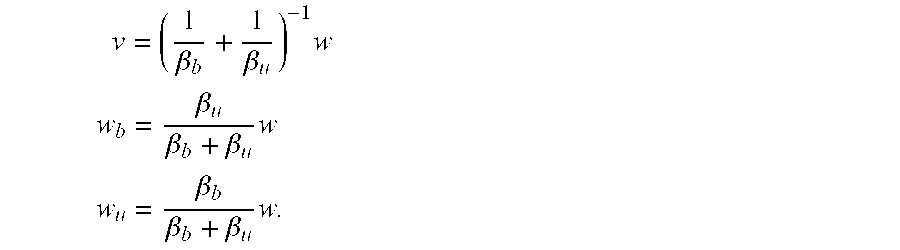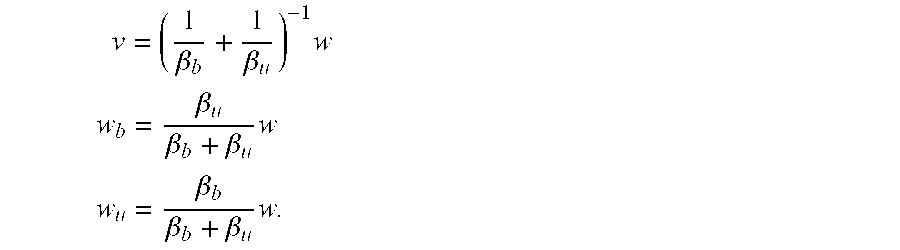Patents
Literature
219 results about "Weight on bit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
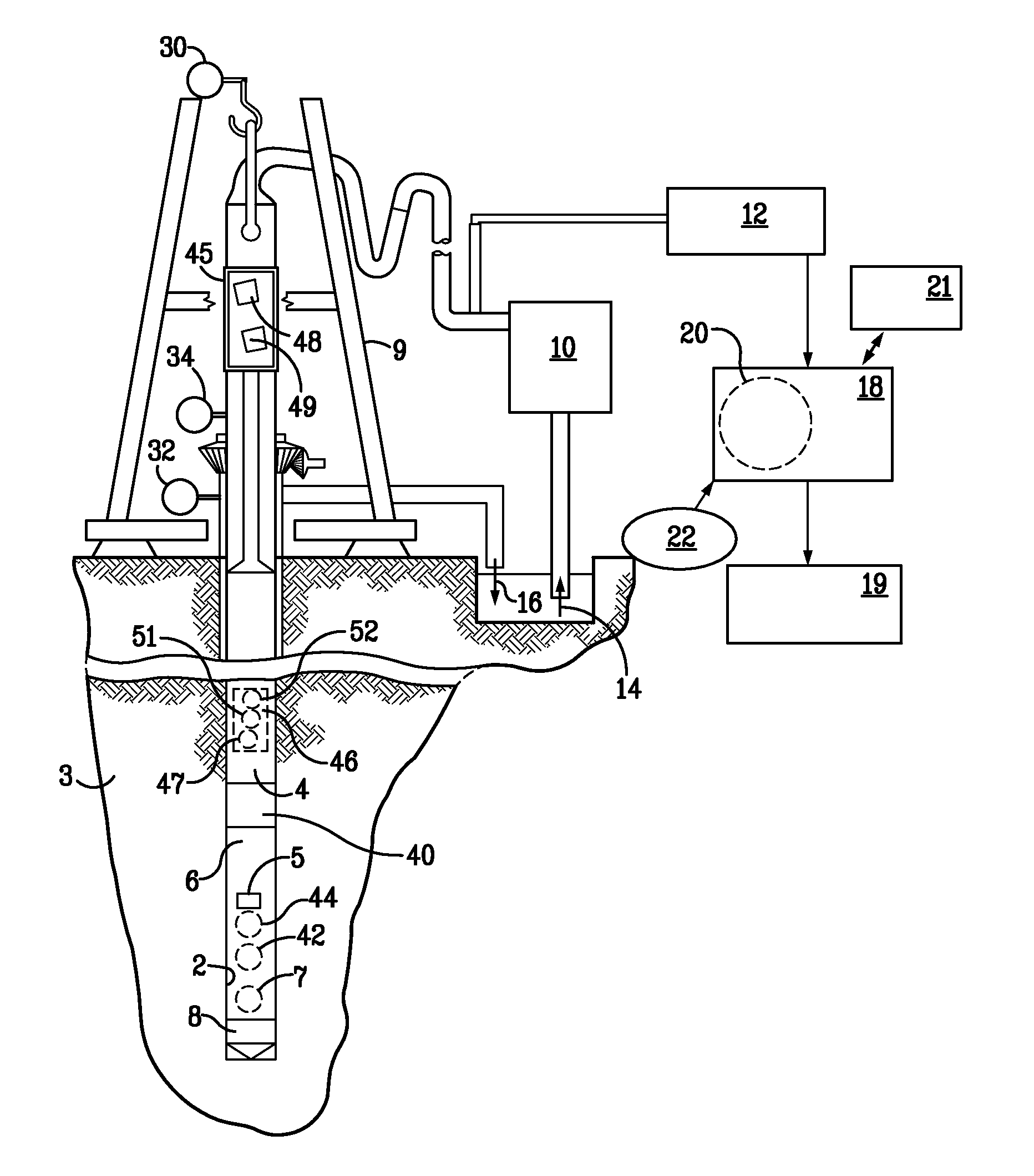
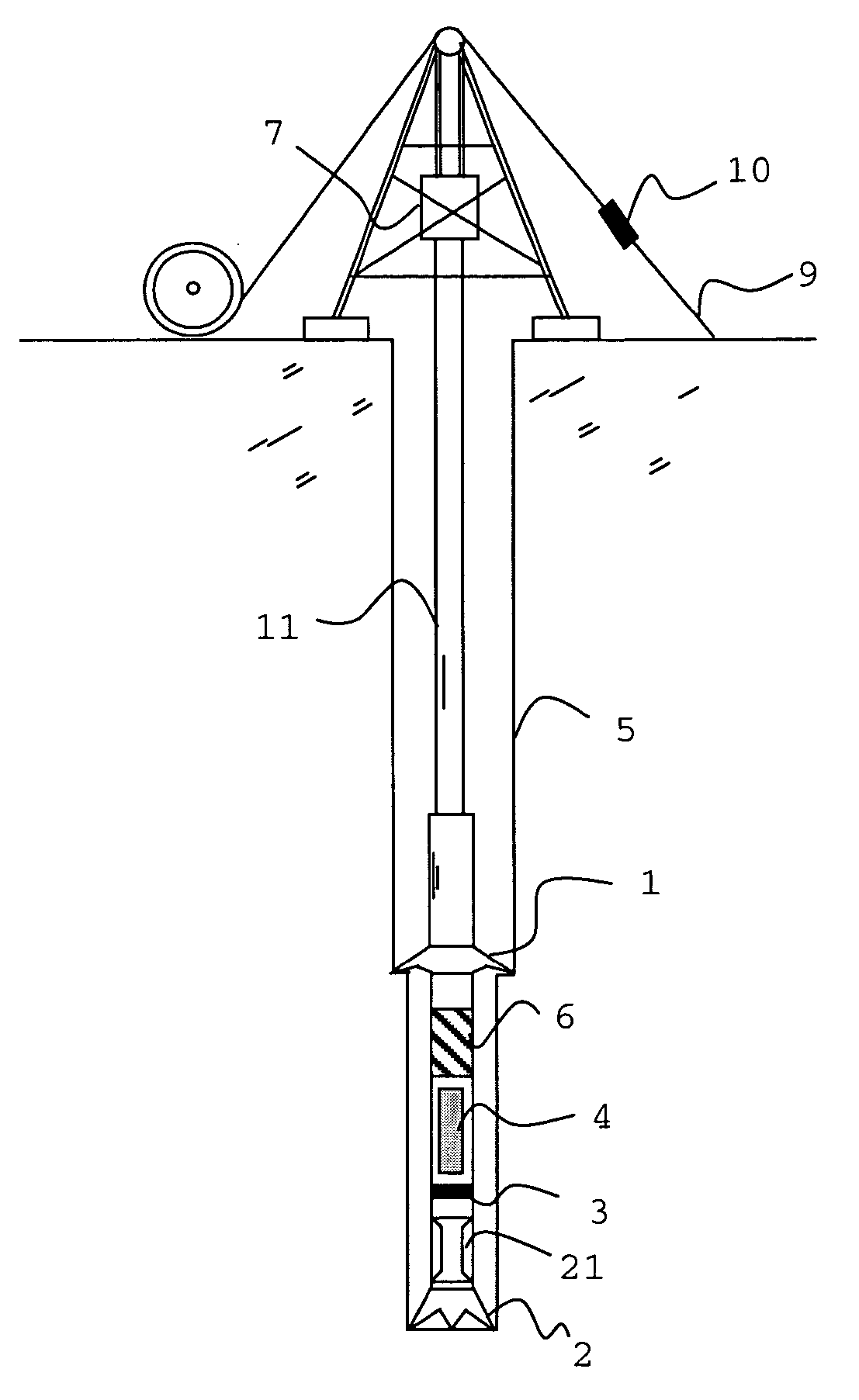
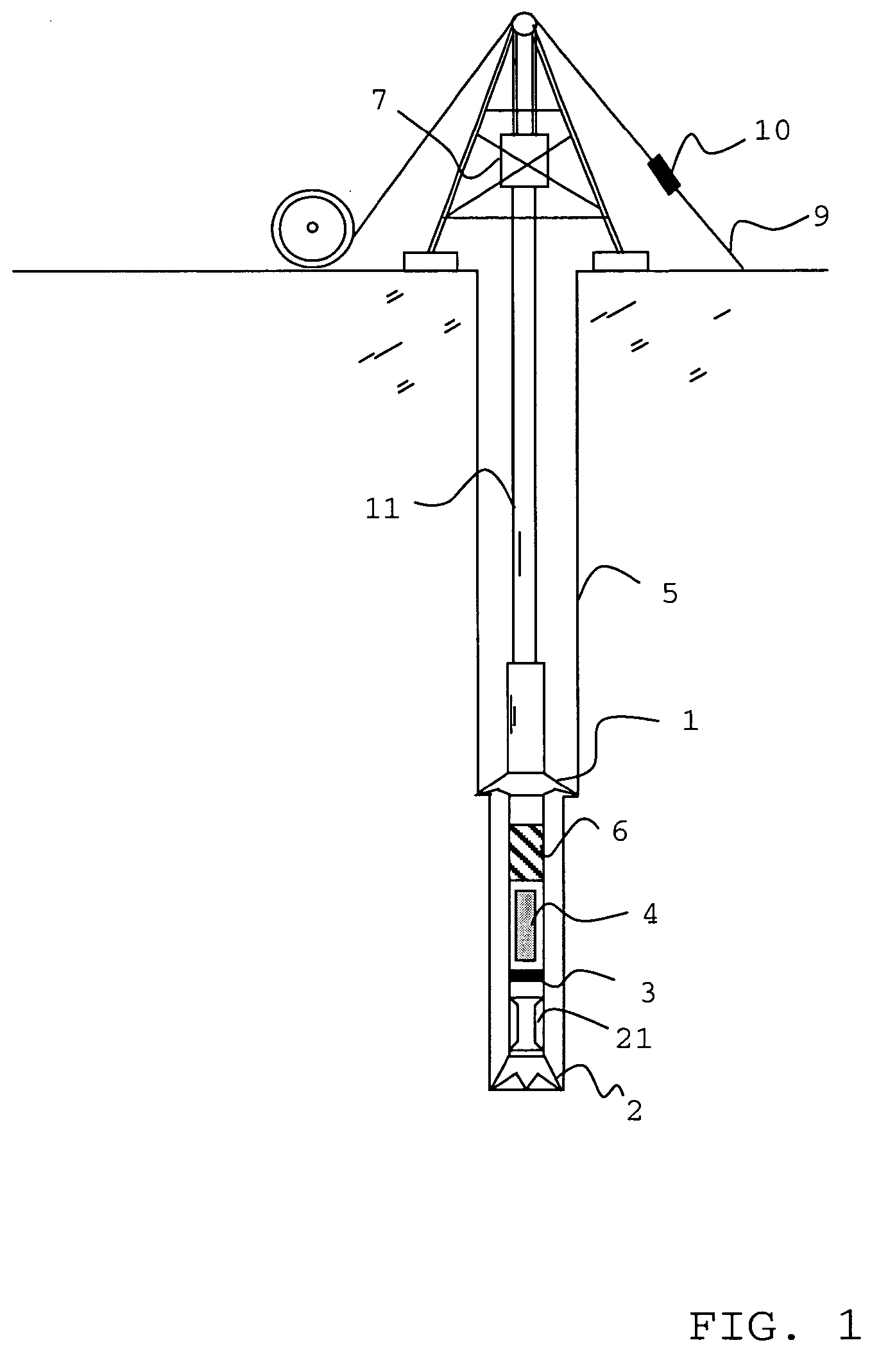
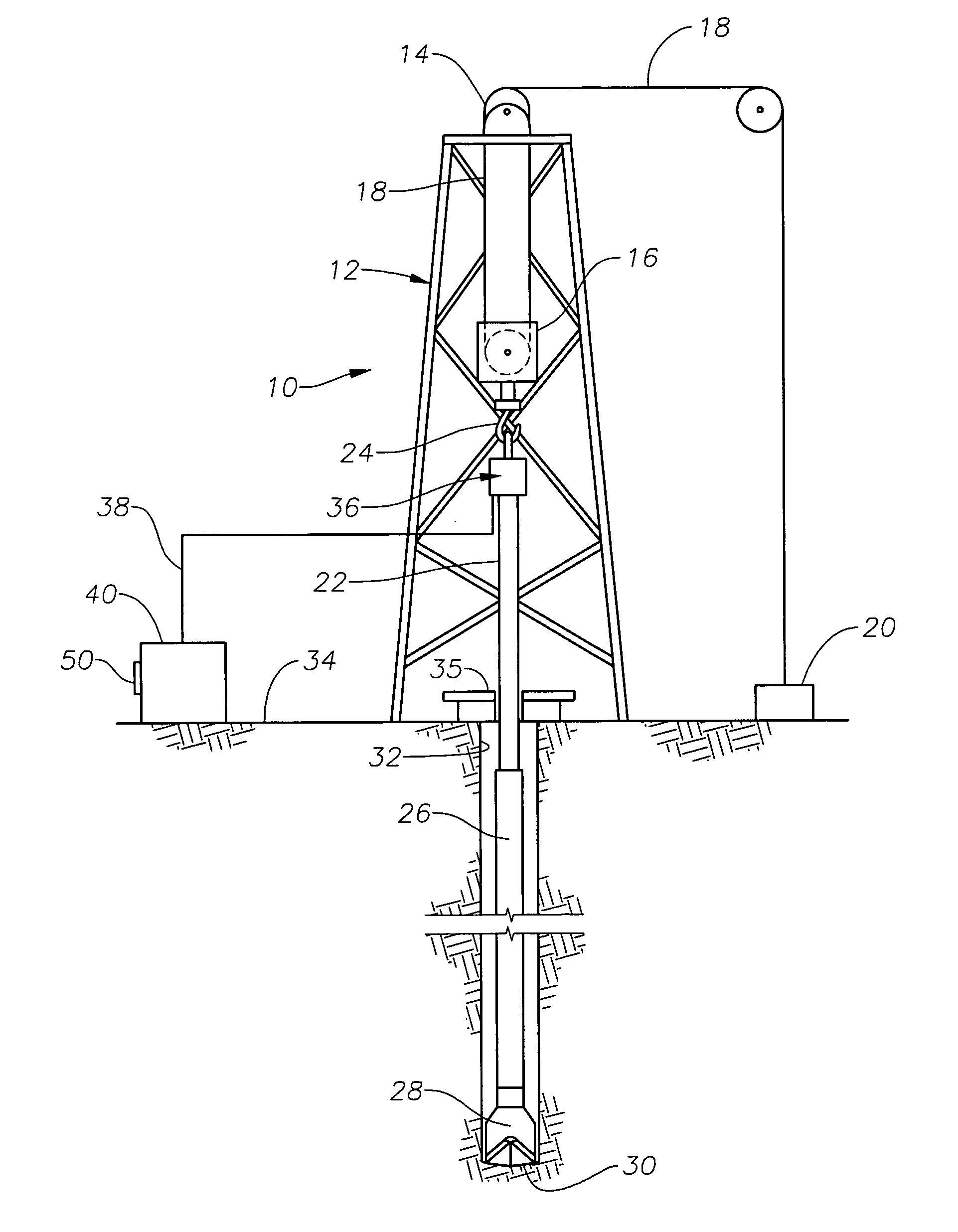
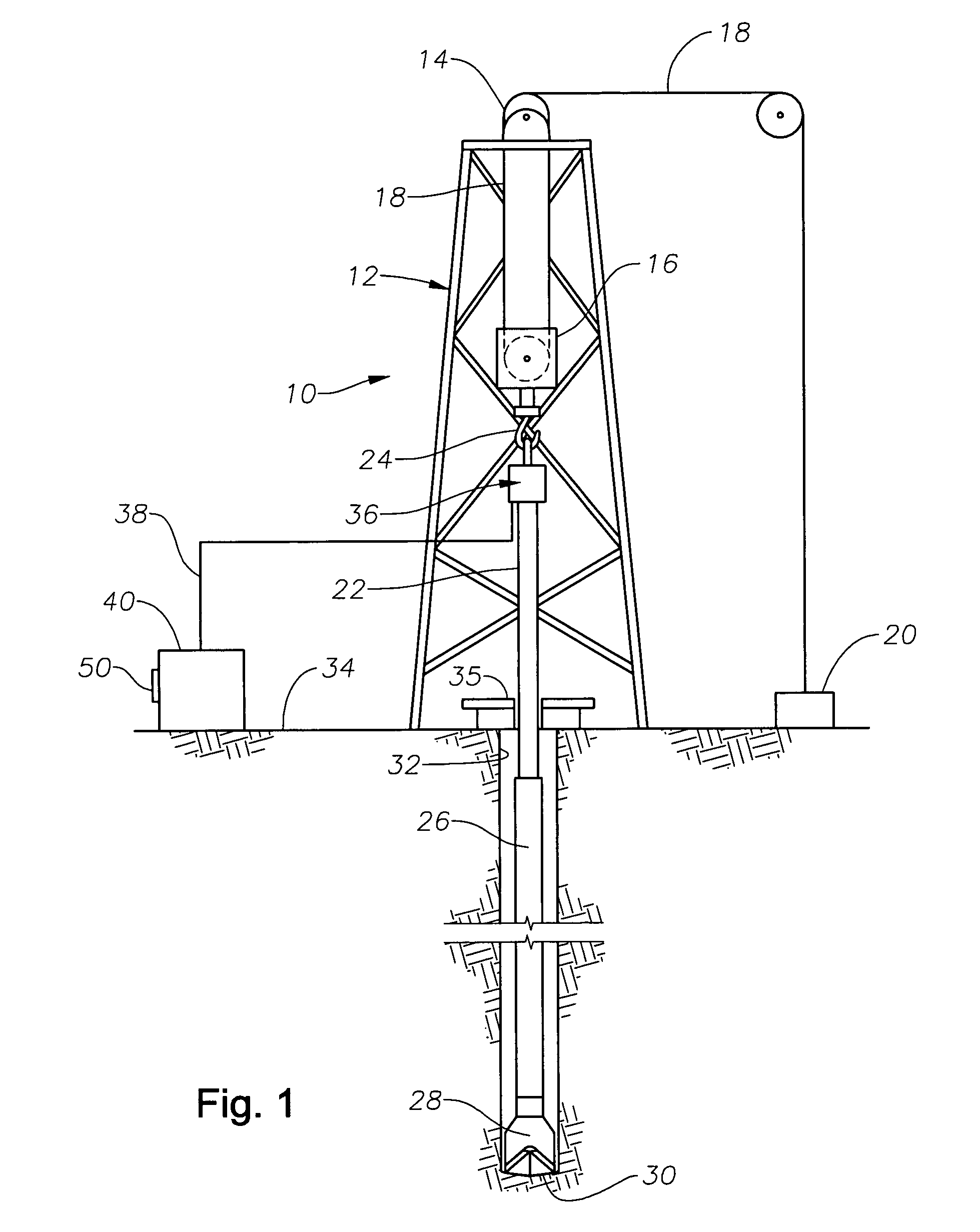
Weight on bit (WOB), as expressed in the oil industry, is the amount of downward force exerted on the drill bit and is normally measured in thousands of pounds. Weight on bit is provided by drill collars, which are thick-walled tubular pieces machined from solid bars of steel, usually plain carbon steel but sometimes of nonmagnetic nickel-copper alloy or other nonmagnetic premium alloys. Gravity acts on the large mass of the collars to provide the downward force needed for the bits to efficiently break rock. To accurately control the amount of force applied to the bit, the driller carefully monitors the surface weight measured while the bit is just off the bottom of the wellbore. Next, the drillstring (and the drill bit), is slowly and carefully lowered until it touches bottom. After that point, as the driller continues to lower the top of the drillstring, more and more weight is applied to the bit, and correspondingly less weight is measured as hanging at the surface. If the surface measurement shows 20,000 pounds [9080 kg] less weight than with the bit off bottom, then there should be 20,000 pounds force on the bit (in a vertical hole). Some downhole Measurement While Drilling (MWD) sensors can measure weight-on-bit more accurately and transmit the data to the surface.
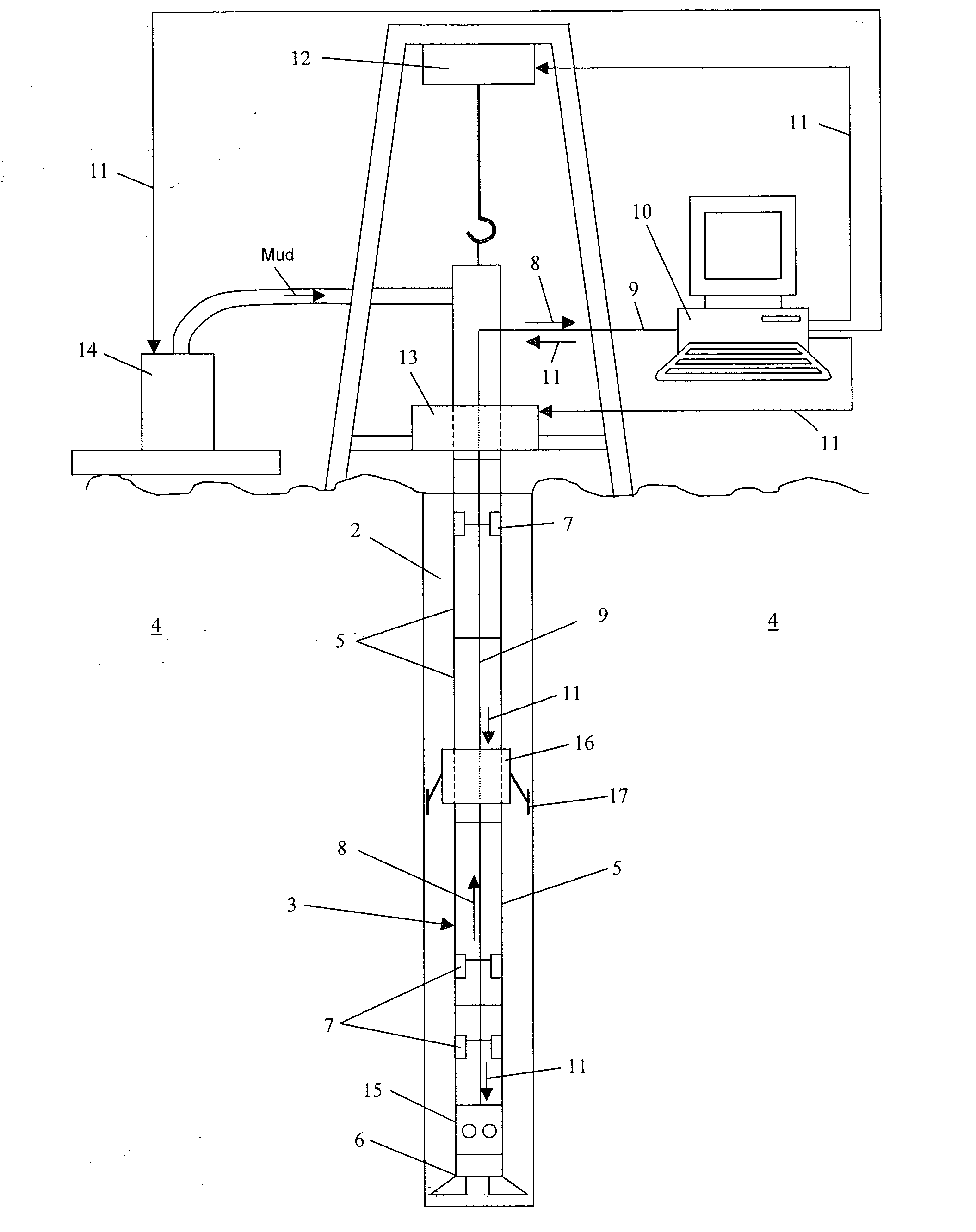
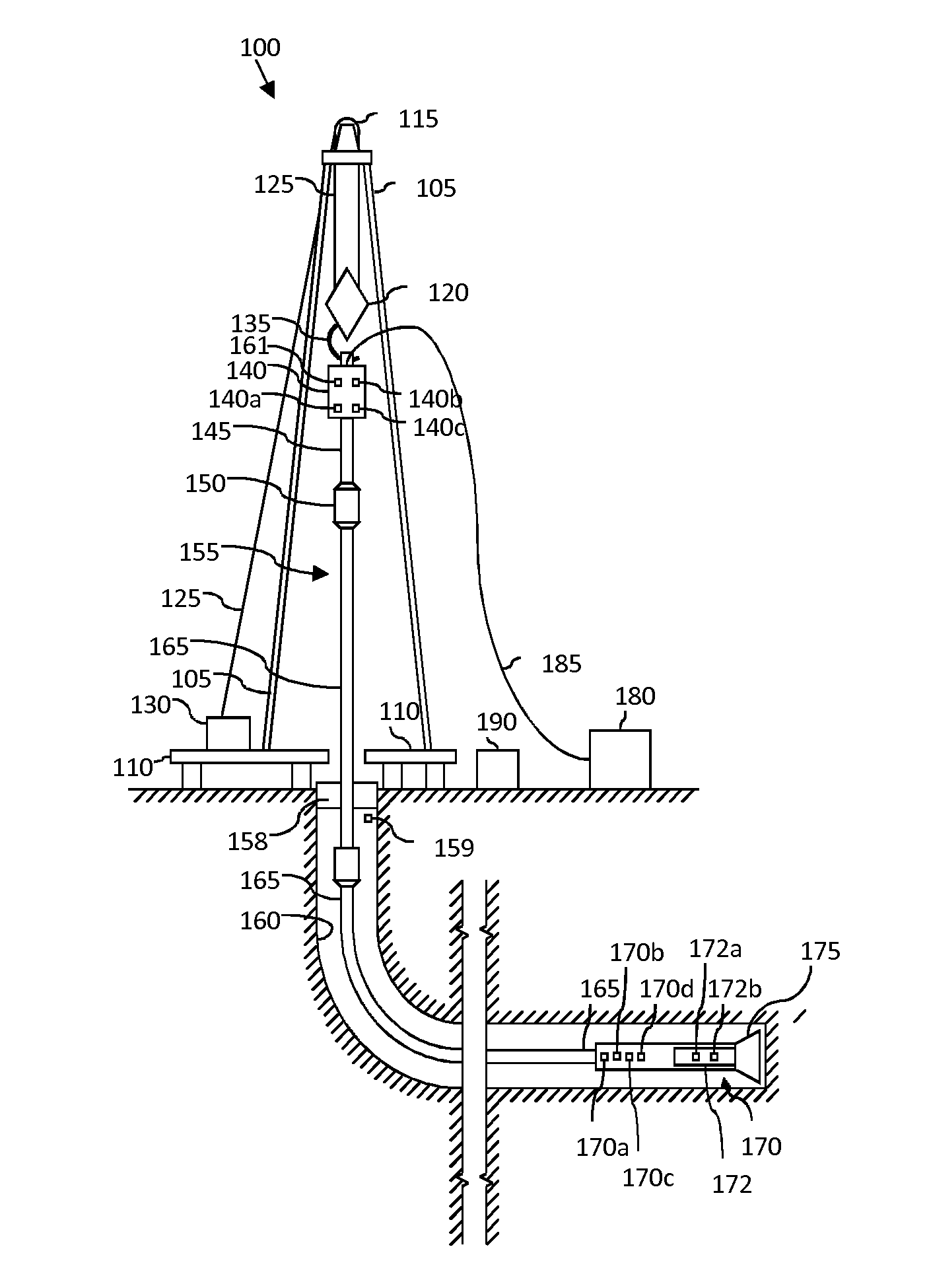
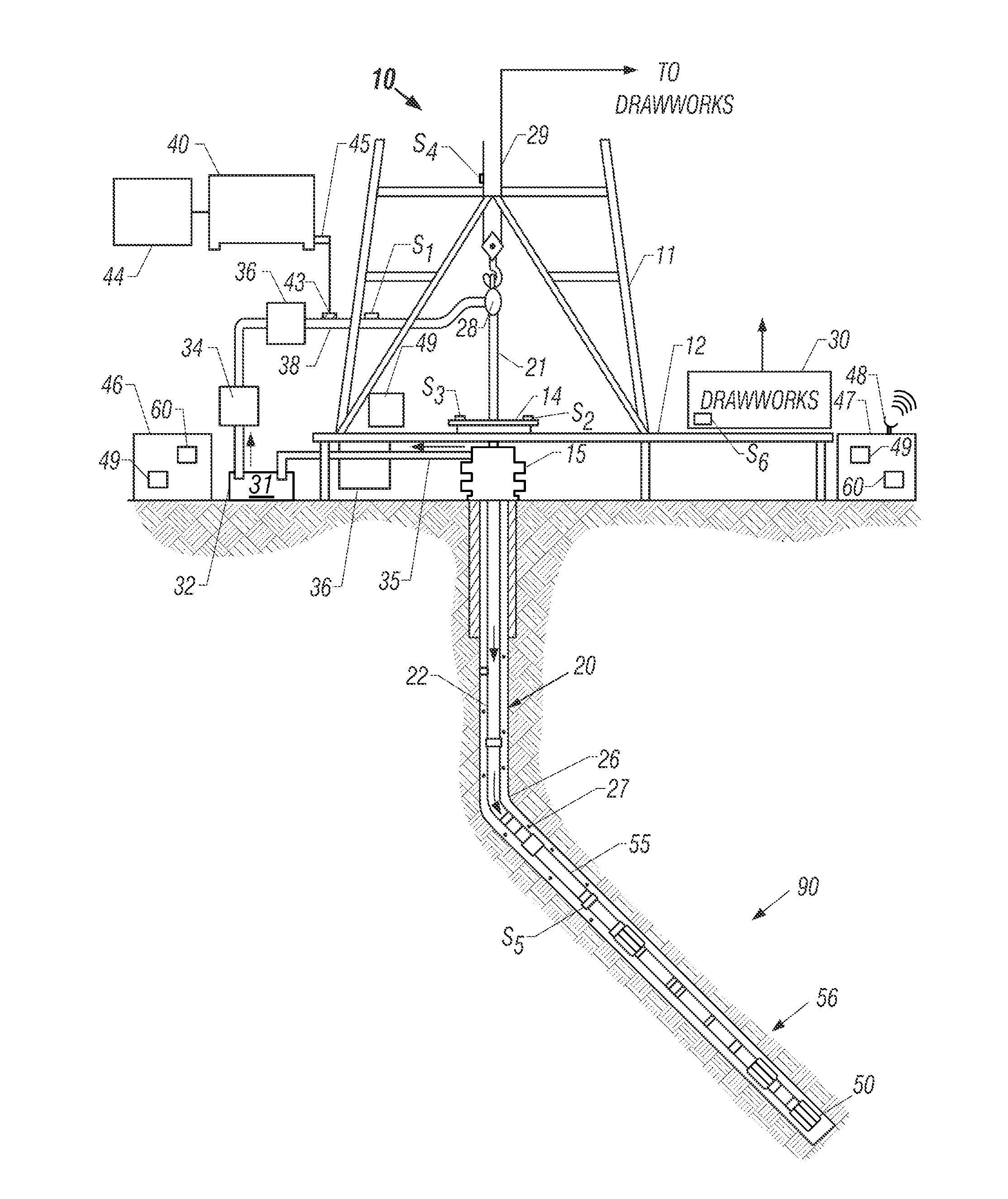
System and Method for Monitoring and Controlling Underground Drilling
ActiveUS20110186353A1Reduce the differenceVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingFinite element techniqueResonance
A system and method for monitoring underground drilling in which vibration is monitored by creating a model of the drill string using finite element techniques or finite difference techniques and (i) predicting vibration by inputting real time values of operating parameters into the model, and then adjusting the model to agree with measured vibration data, (ii) predicting the weight on bit and drill string and mud motor speeds at which resonance will occur, as well as when stick-slip will occur, so that the operator can avoid operating regimes that will result in high vibration, (iii) determining vibration and torque levels along the length of the drill string based on the measured vibration and torque at one or more locations, (iv) determining the remaining life of critical components of the drill string based on the history of the vibration to which the components have been subjected, and (v) determining the optimum drilling parameters that will avoid excessive vibration of the drill string.
Owner:APS TECH
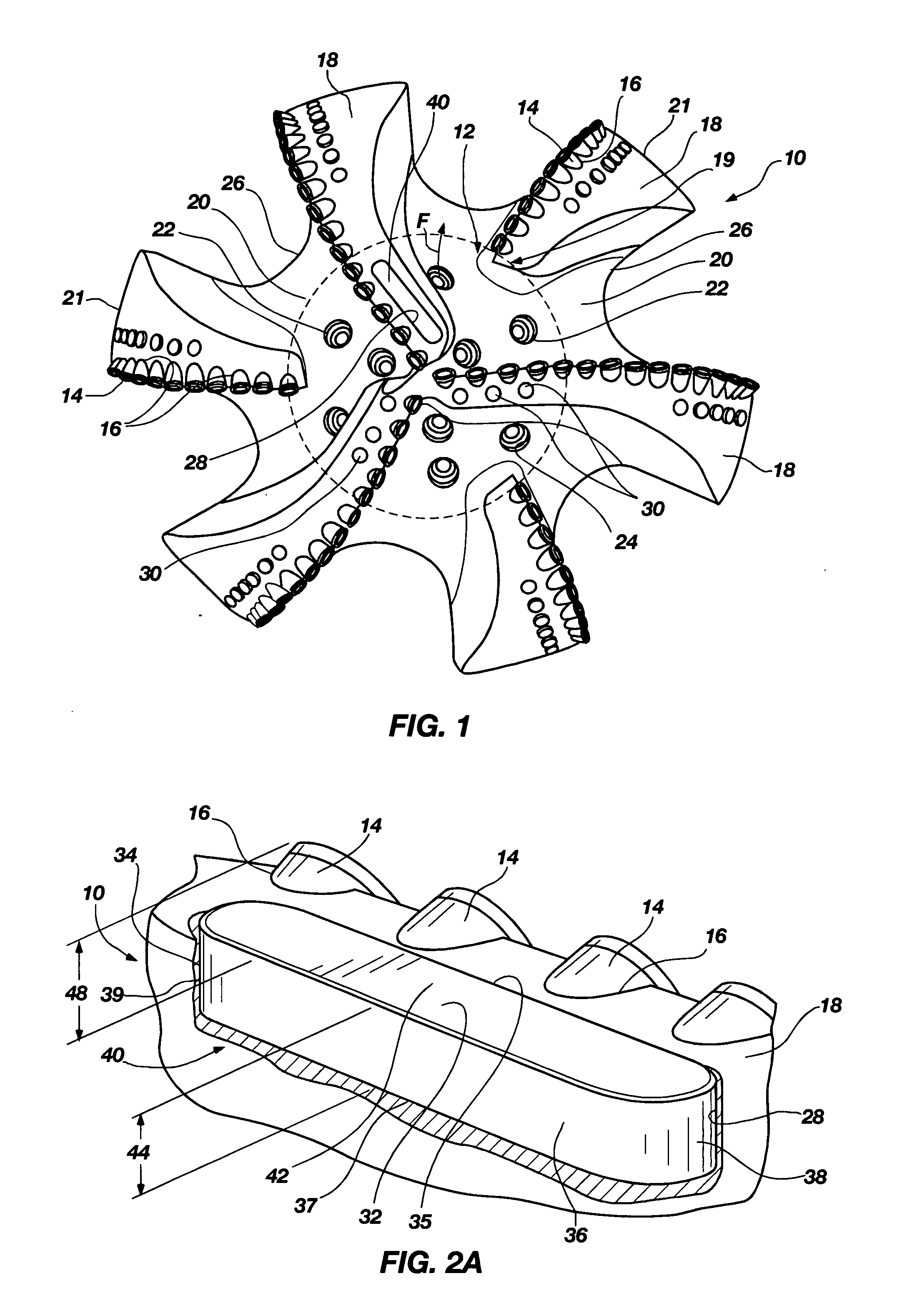
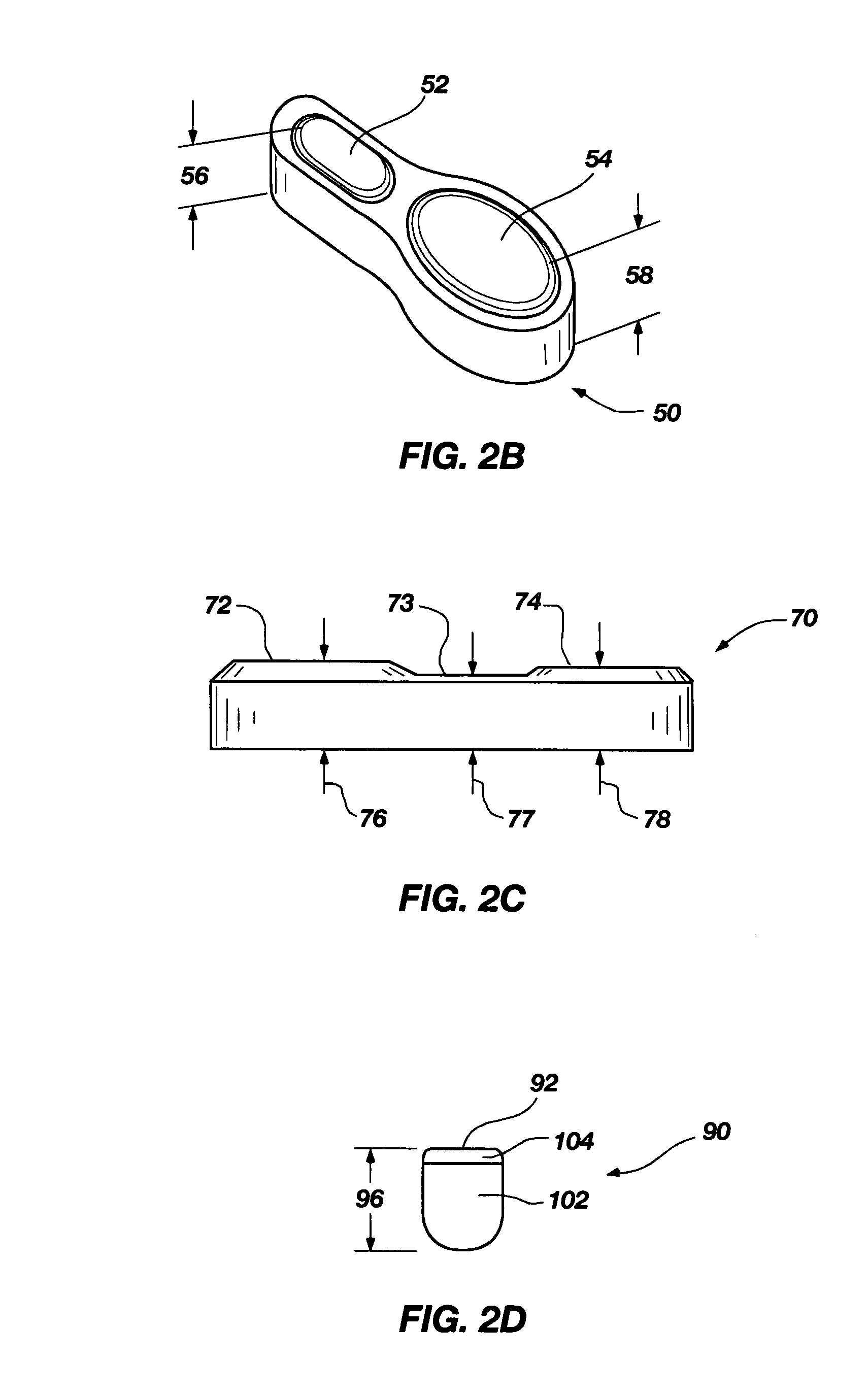
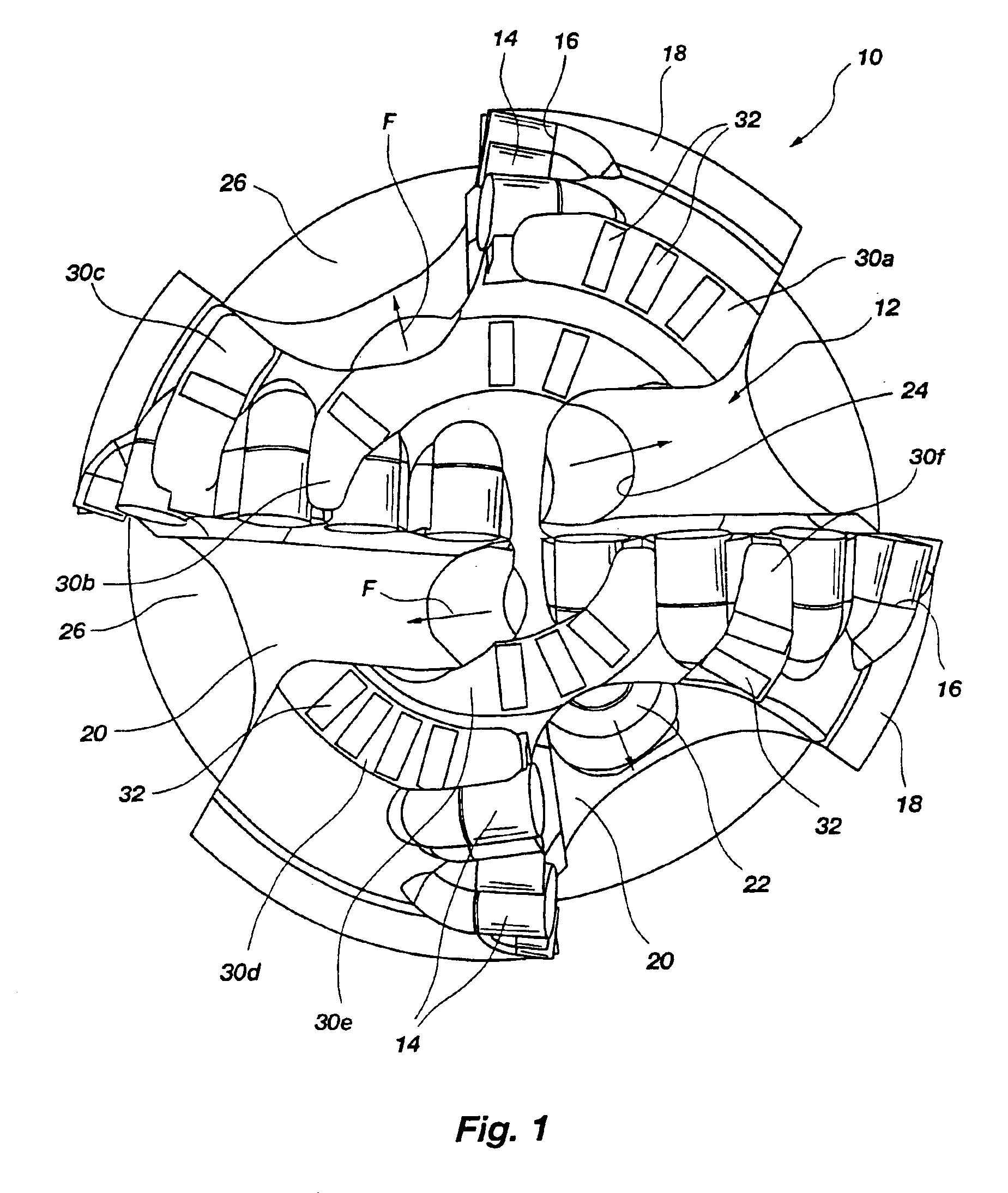
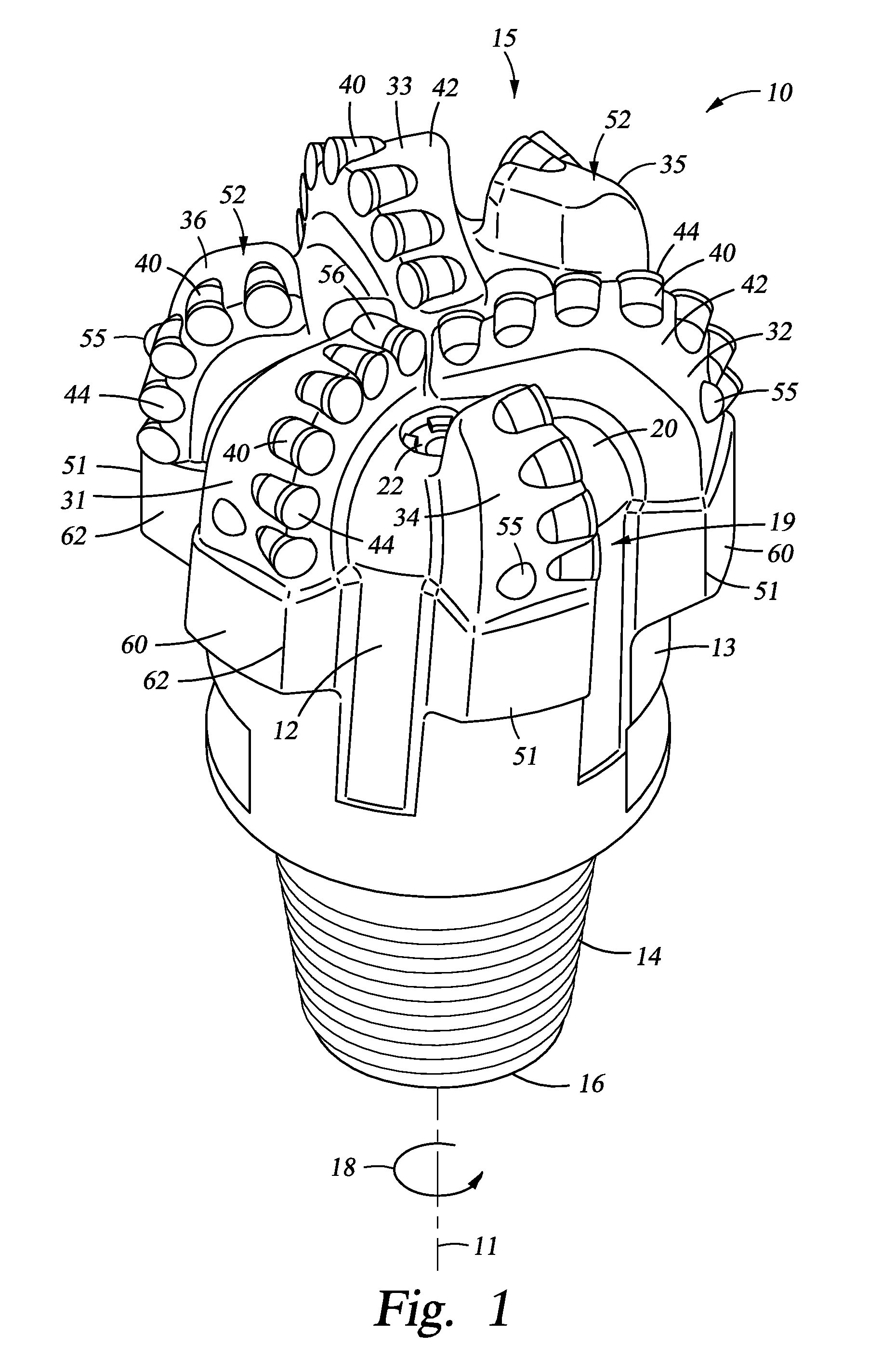
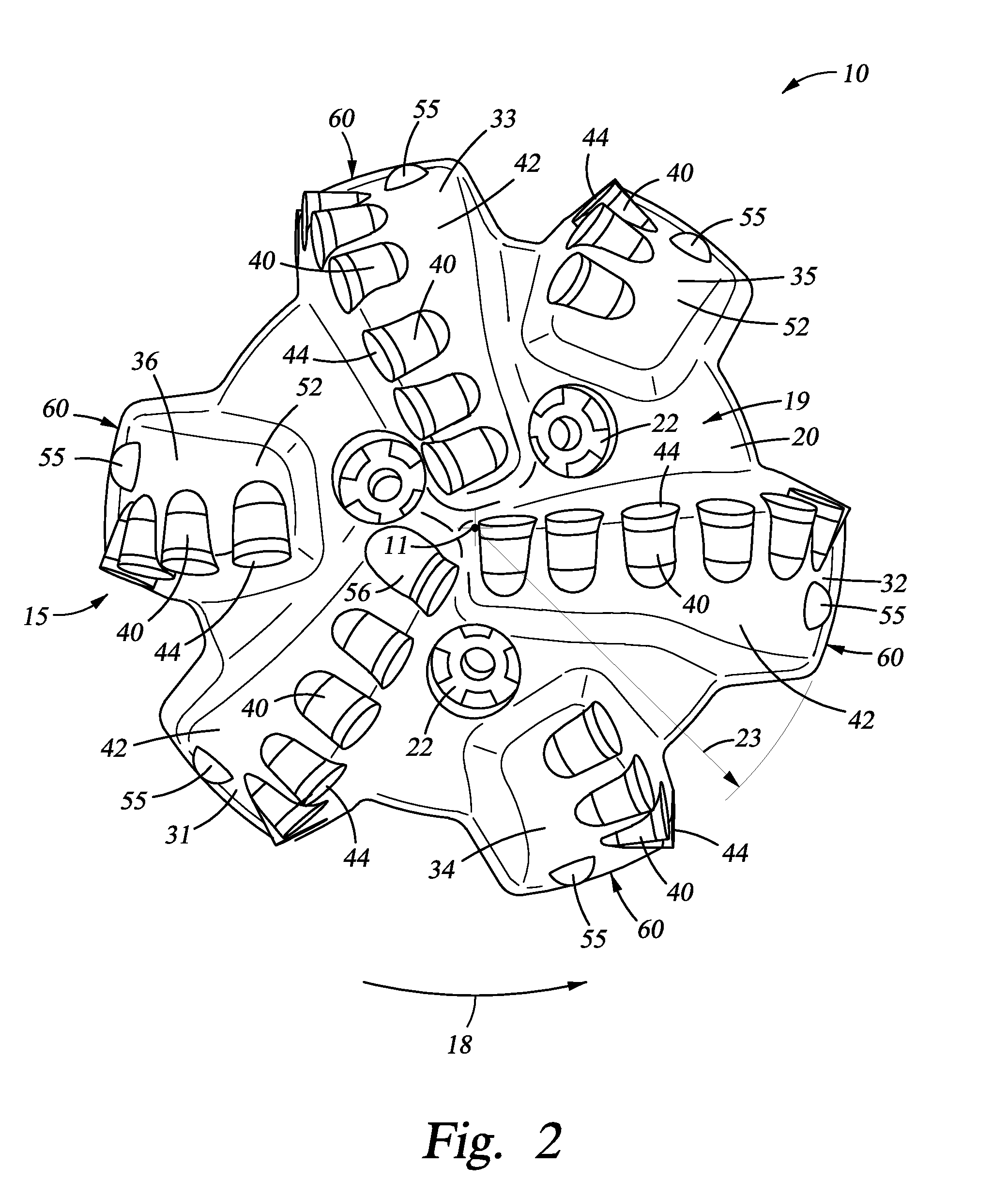
Interchangeable bearing blocks for drill bits, and drill bits including same
ActiveUS20080308321A1Minimize manufacturing tolerance uncertaintyReduce complexityEarth drilling toolsDrill bitsEngineeringRubbing
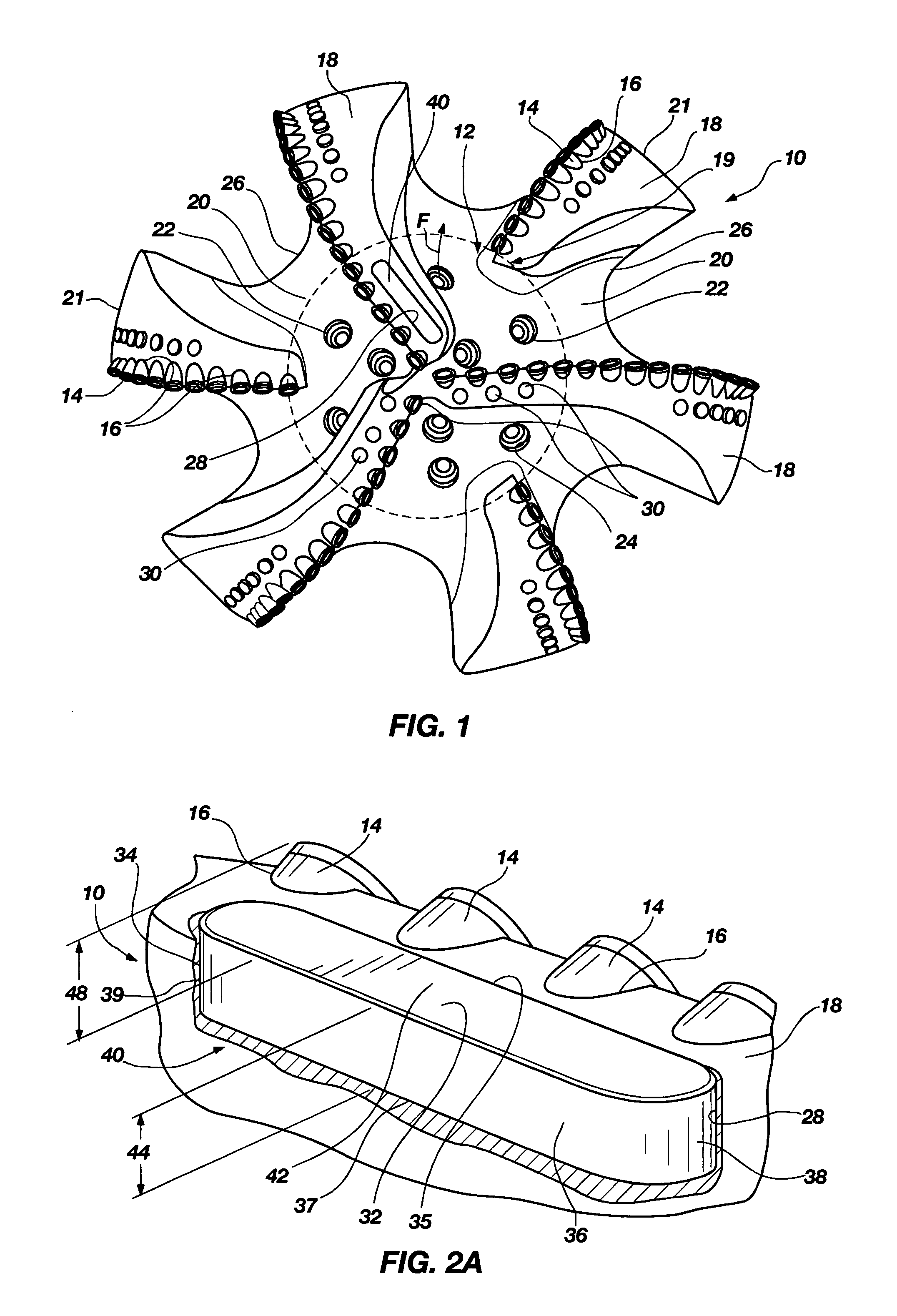
A bearing block is provided that may be used with a drag bit body or frame to limit depth of cut of cutters on a bit. The bearing block is designed so that it may be interchangeably replaced or repaired without necessitating alteration to a standardized bit frame. The interchangeable bearing block may be used to provide a target depth of cut (TDOC) and / or a selected contact or rubbing area to support weight on bit and limit depth of cut (DOC) for improving drilling performance of a bit. The interchangeable bearing block brings manufacturing selectability by providing a customizable product in terms of depth of cut selection and cutter penetration control for different formations, which is suitable for use with a common bit frame. A rotary drill bit assembly, a unitary cone insert bearing block for a drill bit, and a bit frame are also provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Drill bits with reduced exposure of cutters
InactiveUS6935441B2Easy to implementTorque is limitedEarth drilling toolsDrill bitsEngineeringCompressive strength
A rotary drag bit and method for drilling subterranean formations, including a bit body being provided with at least one cutter thereon exhibiting reduced, or limited, exposure to the formation, so as to control the depth-of-cut of the at least one cutter, so as to control the volume of formation material cut per bit rotation, as well as to control the amount of torque experienced by the bit and an optionally associated bottomhole assembly regardless of the effective weight-on-bit are all disclosed. The exterior of the bit preferably includes a plurality of blade structures carrying at least one such cutter thereon and including a sufficient amount of bearing surface area to contact the formation so as to generally distribute an additional weight applied to the bit against the bottom of the borehole without exceeding the compressive strength of the formation rock.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Acoustical telemetry
Method, apparatus and article of manufacture for monitoring and characterizing the operation of a transducer (i.e., motor or pump) downhole. In particular, transducer RPMs are determined by analysis of acoustic information. An acoustical source (signal generator) located on a downhole tool (e.g., a drill string) creates acoustic energy which is received and processed by a receiving unit, which may be located at the surface of a wellbore. The acoustical source is operably connected to the transducer, so that the frequency of the signal produced by the acoustical source corresponds to the speed of the transducer. The acoustic signal of the acoustical source may then be isolated from other acoustical energy produce by downhole equipment, such as a drill bit. Having determined transducer speed by isolation of the acoustic signal, other operating parameters may be determined. Illustrative operating parameters include torque, flow, pressure, horsepower, and weight-on-bit.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Latchable reaming bit
A drilling assembly supports a liner for making a wellbore. The BHA comprises a pilot bit and a reamer above it that is larger in diameter than the suspended liner. If the BHA needs to be pulled out, the reamer is brought into contact with the liner and a latch mechanism between the two engages as another latch that had held the reamer bit to the BHA is released. The reamer bit stays with the liner as the BHA is pulled and later reinserted. On the way in the BHA latches to the reamer bit which then unlatches from the liner bottom. Preferably, splines and a shoulder on the BHA are used to drive the reamer bit as opposed to any power being transmitted through the latch between the BHA and the reamer bit. However, the latch mechanism between the BHA and the reamer bit could also provide torque and weight on bit for drilling operations. The process may be repeated.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Bottom hole assembly
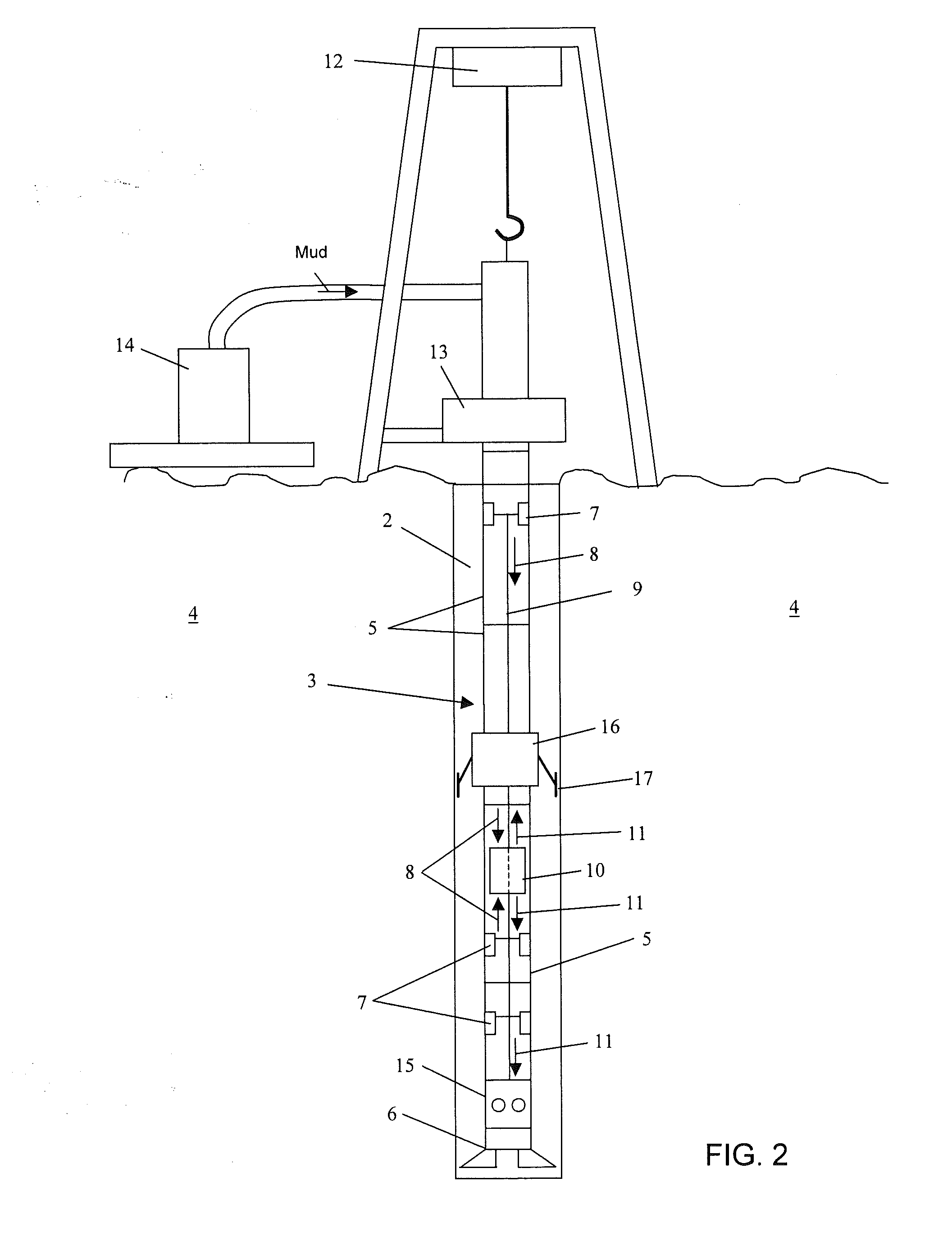
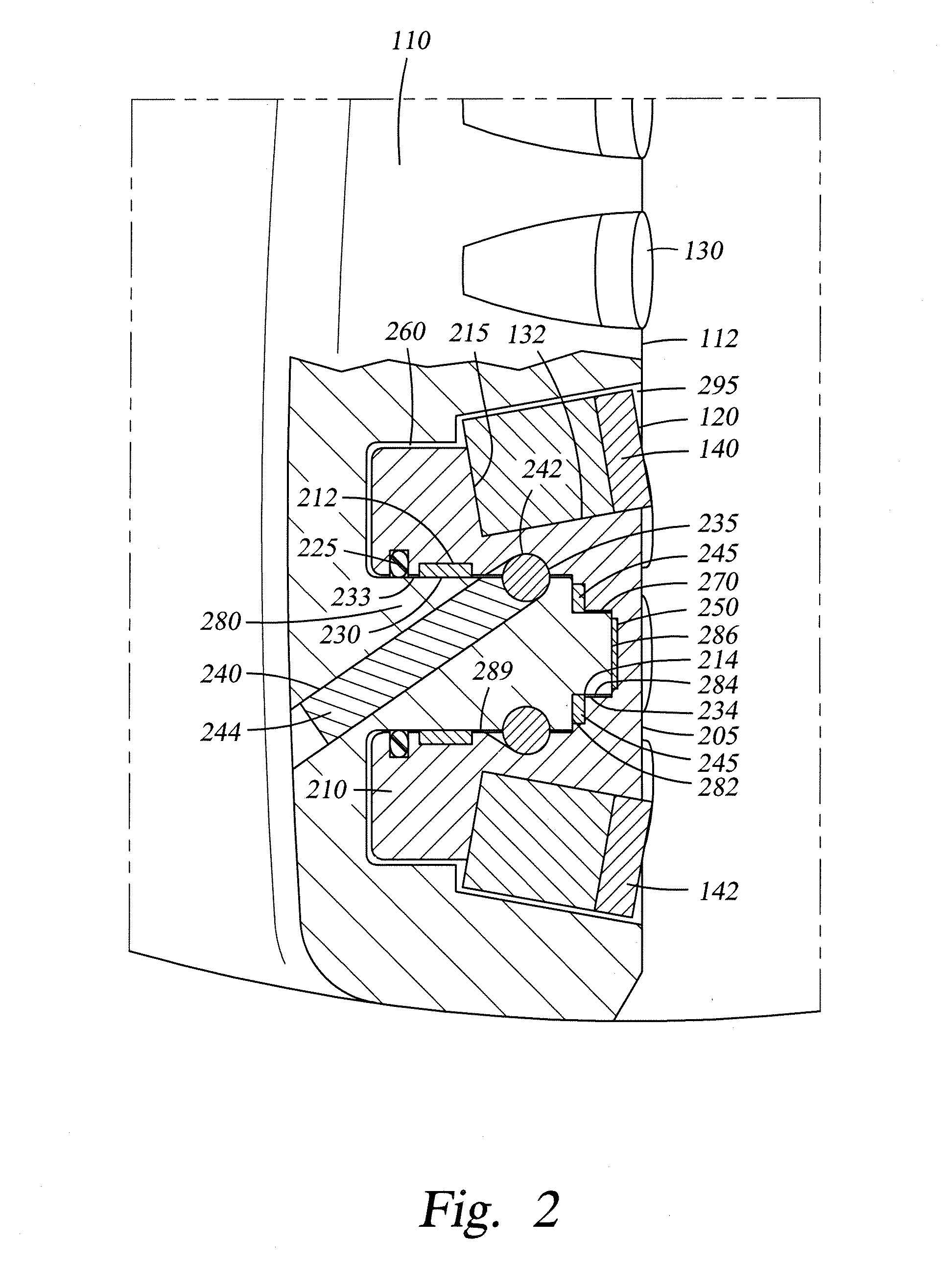
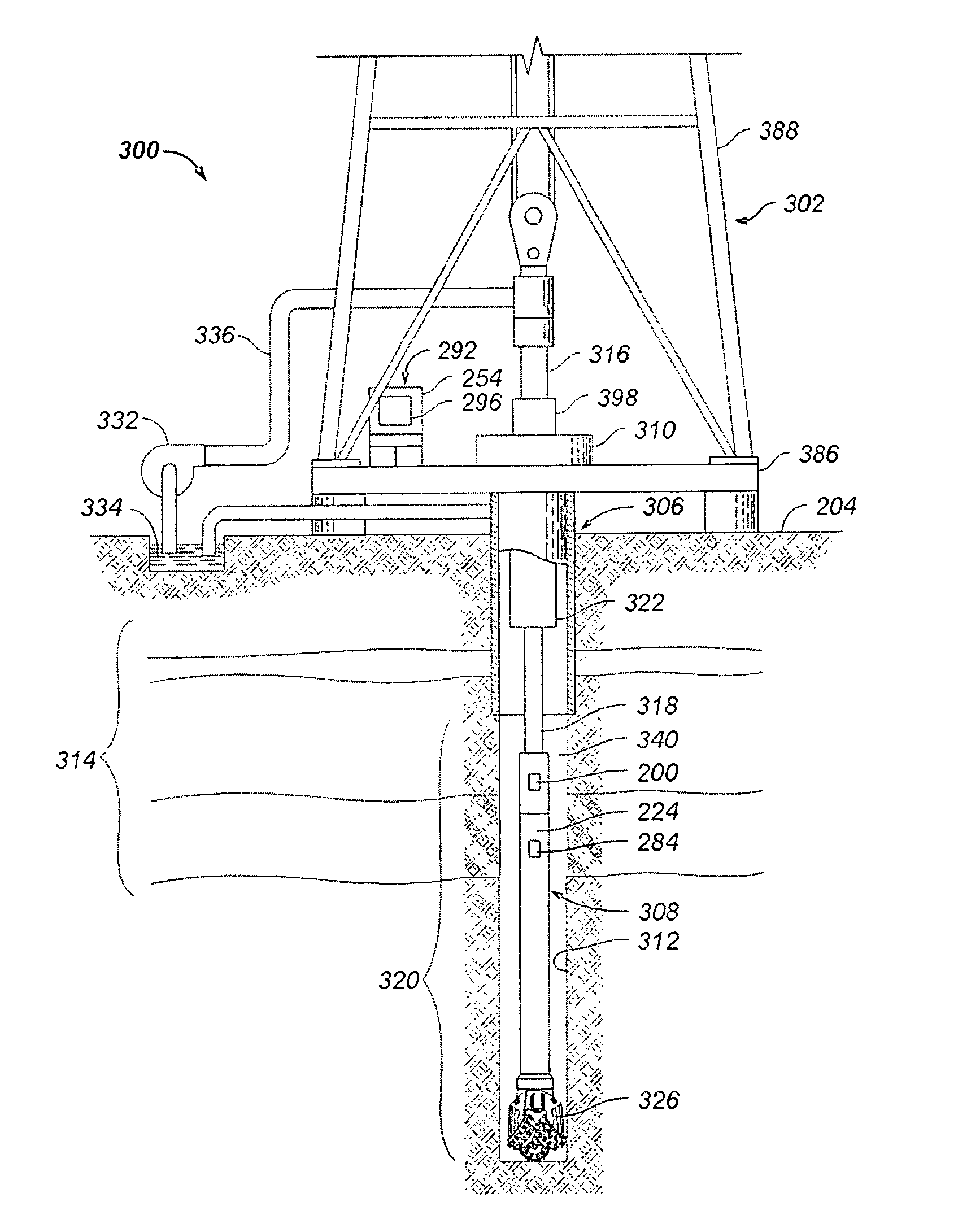
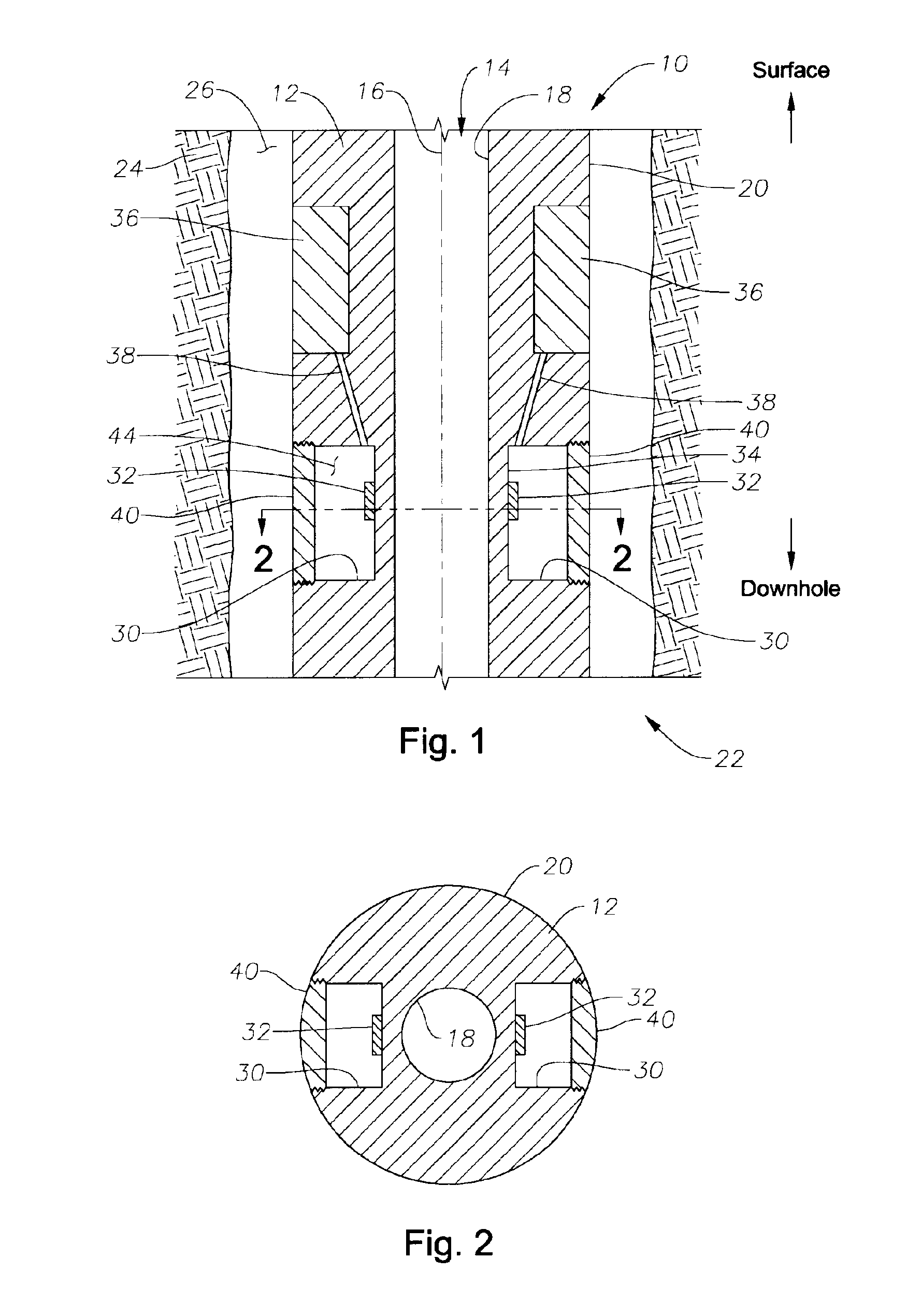
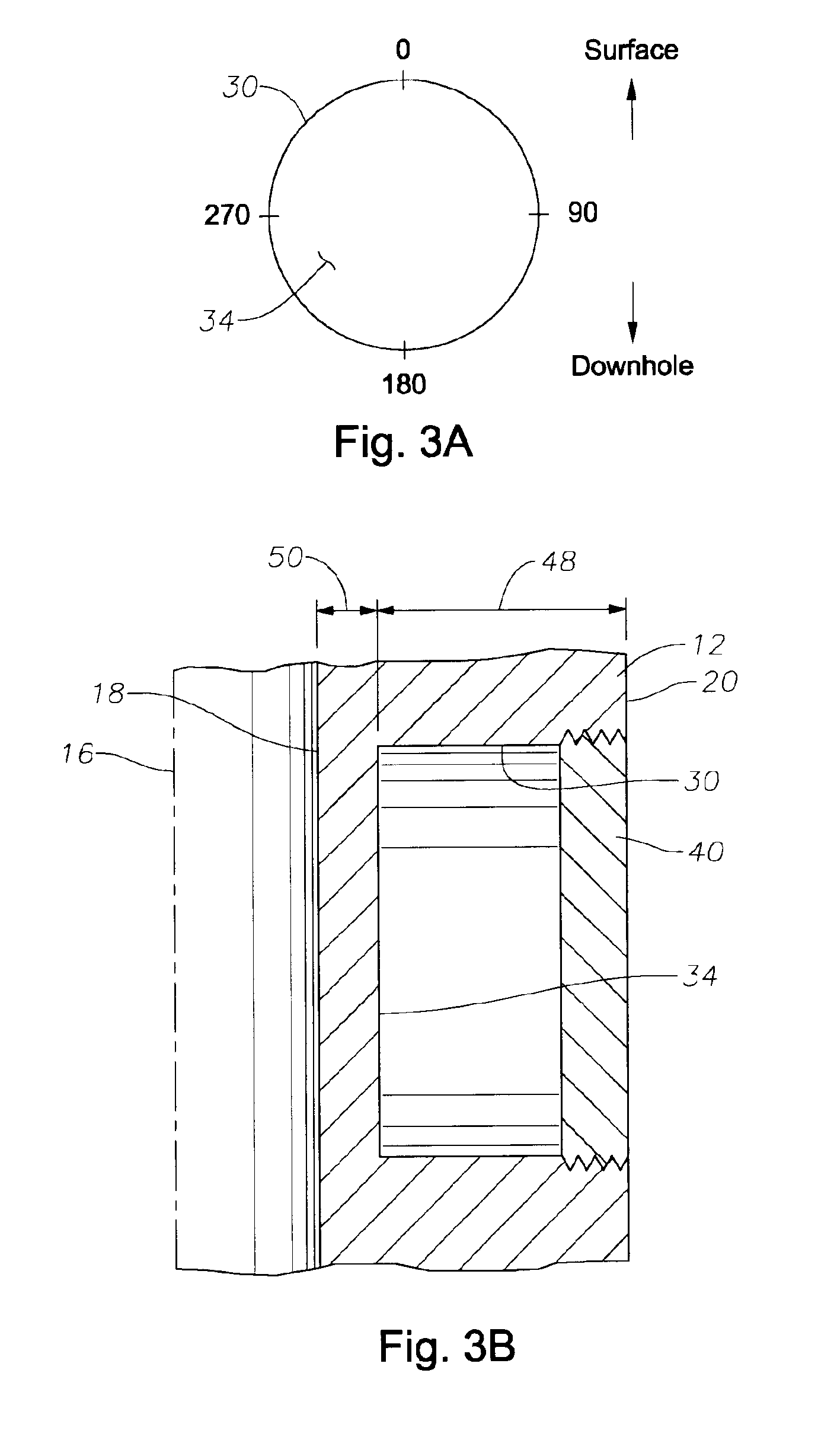
A bottom hole assembly has a drill bit and an under-reamer on the up-hole side of the drill bit. In one aspect, the assembly further has a compliant element linking the drill bit to the under-reamer, the compliant element allowing displacement of the drill bit relative to the under-reamer in the axial direction of the assembly. In another aspect, the assembly further has a sensor element which is arranged to measure the weight-on-bit and / or the applied torque of the drill bit, and a transmitter for transmitting the weight-on-bit and / or applied torque measurements to the surface.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for wellbore operations using calculated wellbore parameters in real time
InactiveUS6443242B1Simple processSimple toElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyMathematical modelCoiled tubing
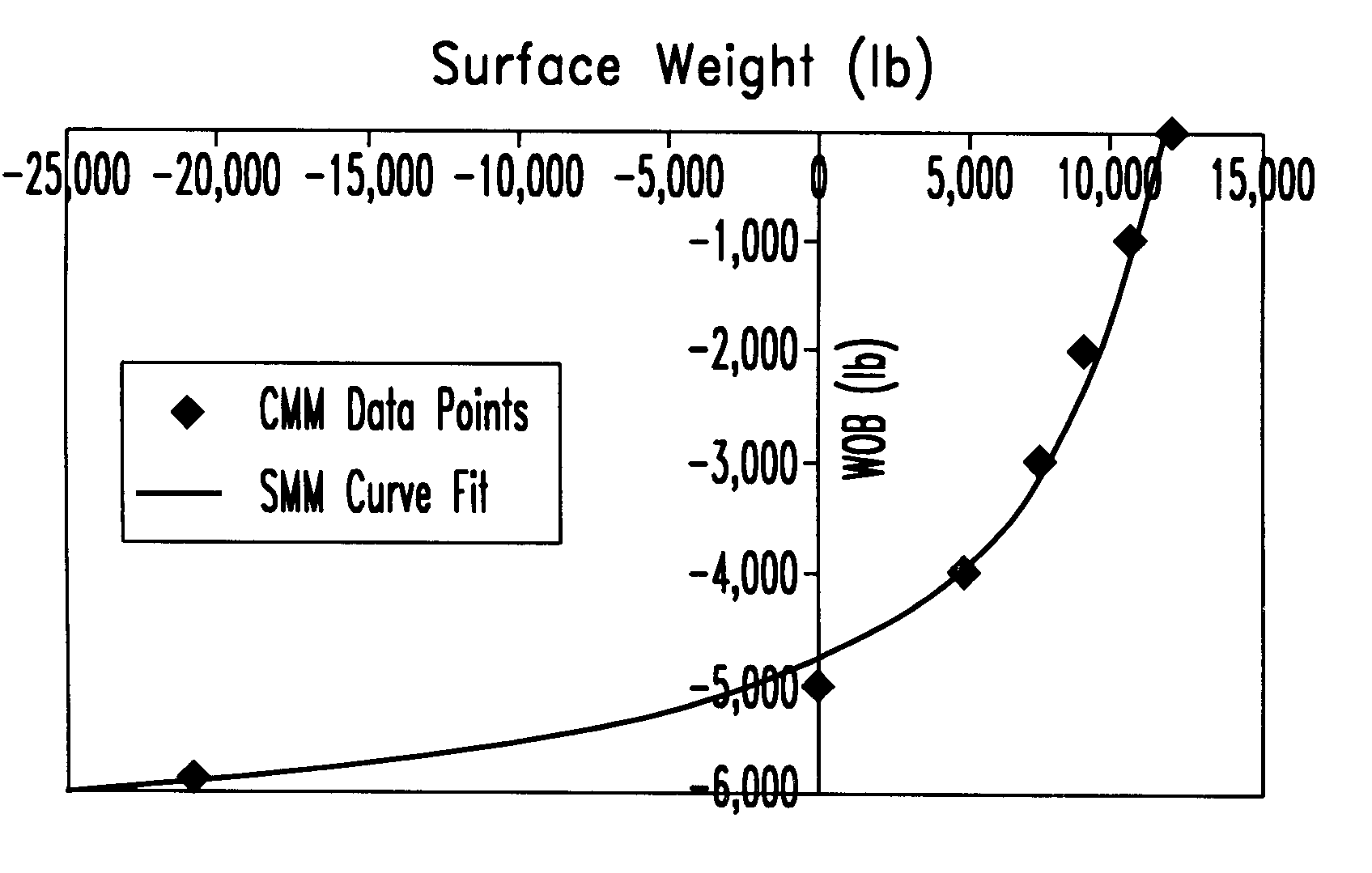
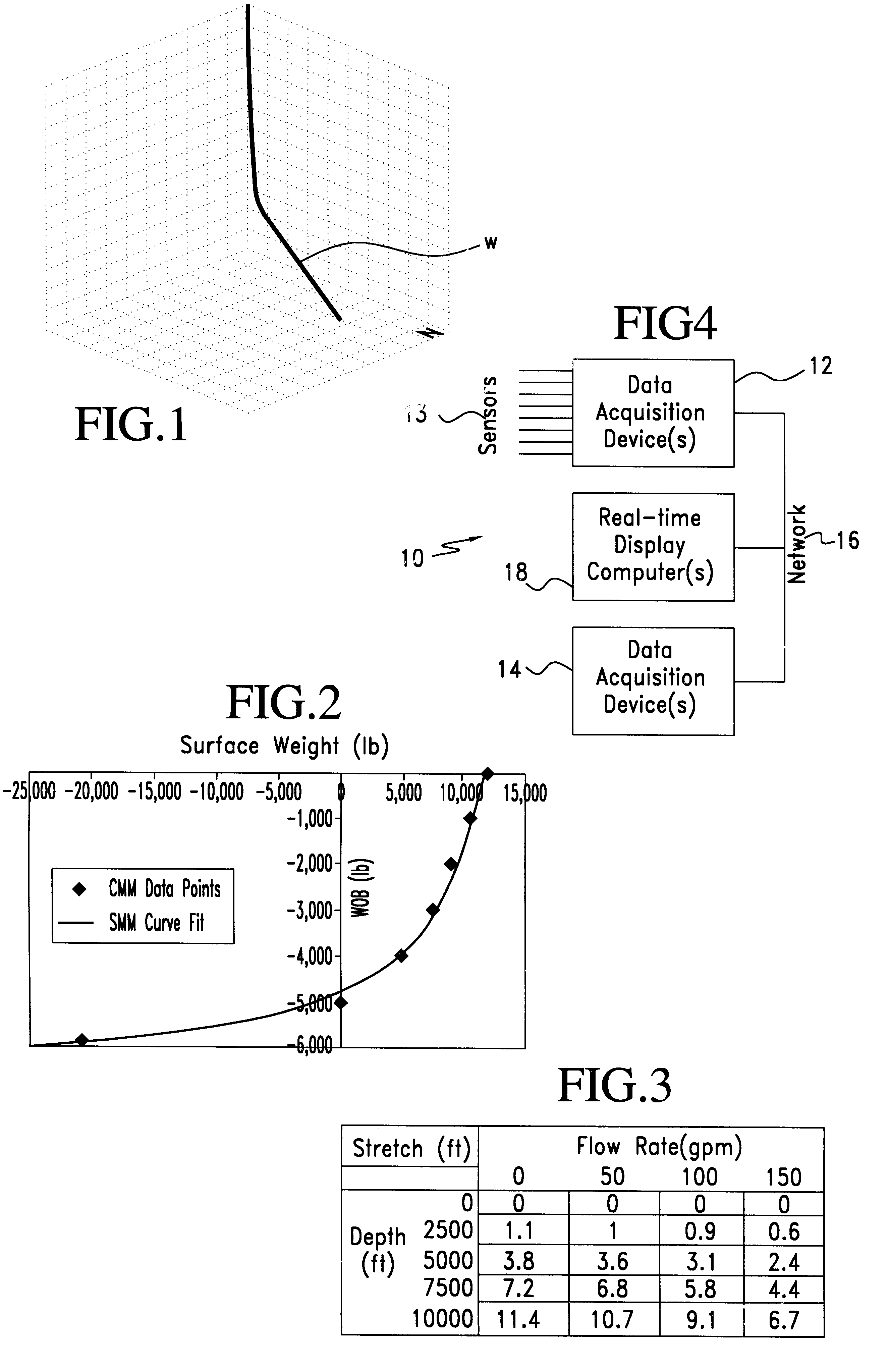
A method for taking into account the effects of complex conveyance method model technique results in real time in a wellbore operation, the method including, in certain aspects, calculating with a conveyance method model technique a series of data points based on wellbore data (actual and / or predicted), modeling the relationship between the series of data points and the wellbore data using a simple mathematical model technique to develop a model for predicting a wellbore operations parameter, and using the model to predict a wellbore operations parameter; and, in one aspect, a procedure for drilling a wellbore in the earth using such a method to predict, among other things, weight on bit, torque on bit and stretch of a conveyance system (coiled tubing, wireline, drill pipe string) used to move the bit in a wellbore.
Owner:COILED TUBING ENG SERVICES
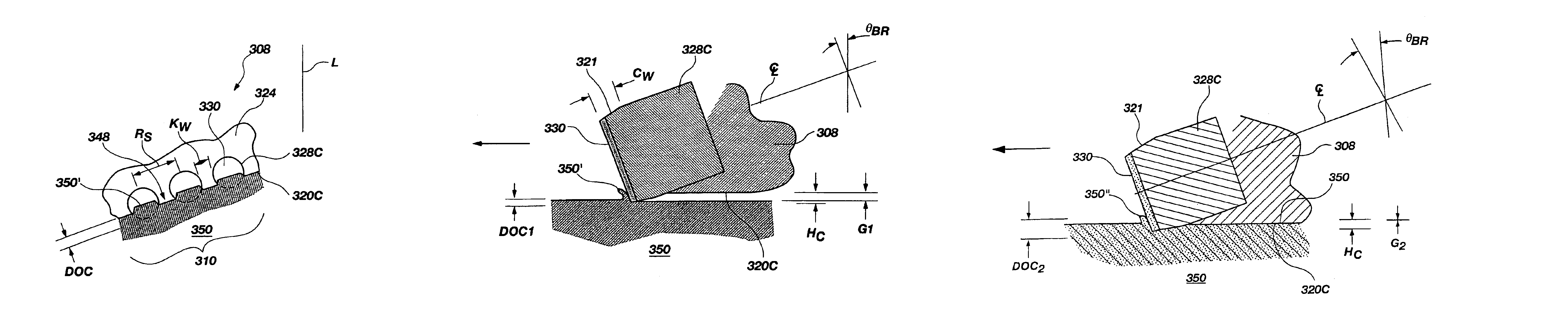
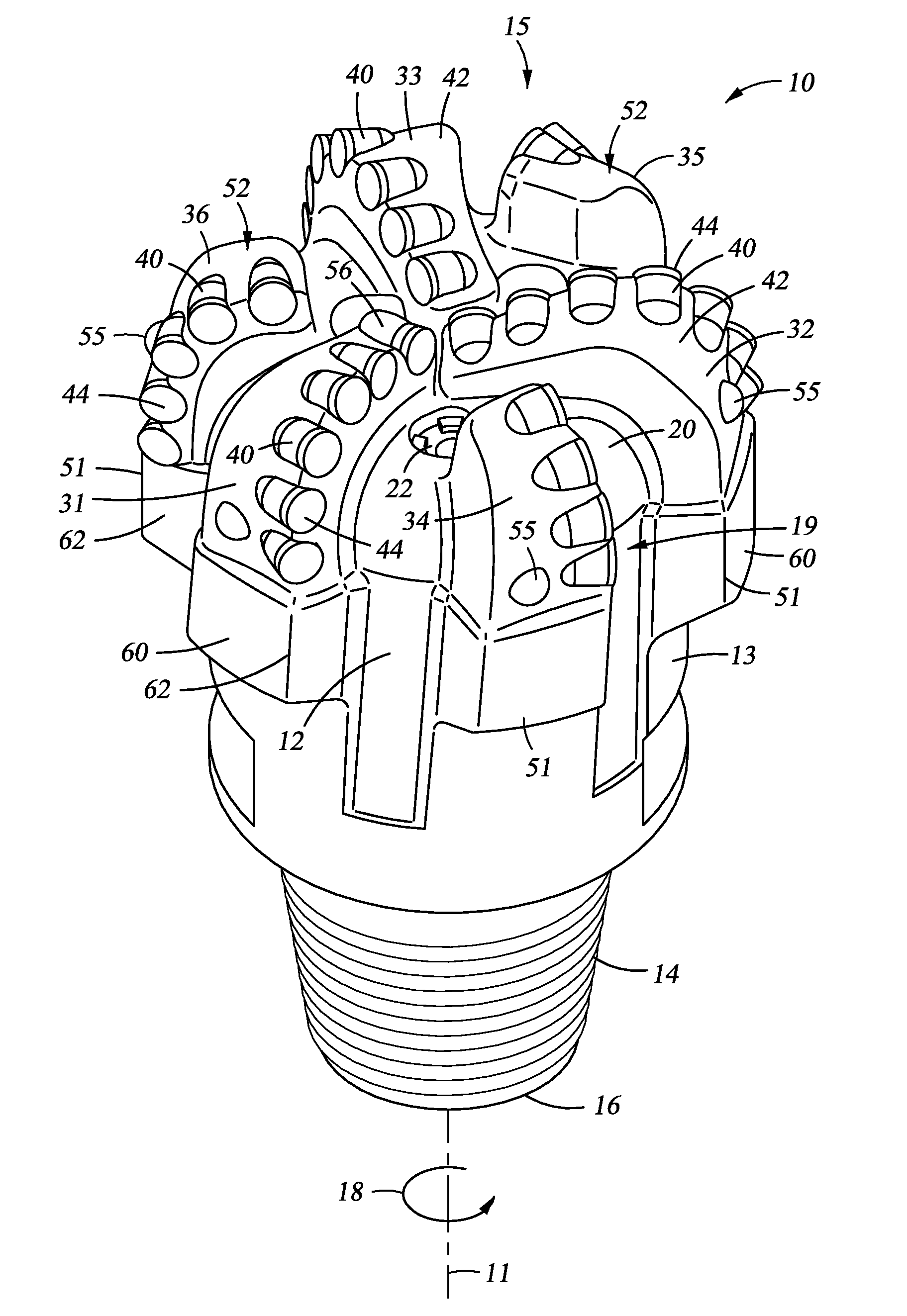
Drill Bit Cutting Structure and Methods to Maximize Depth-0f-Cut For Weight on Bit Applied
A drill bit for drilling a borehole in earthen formations comprises a bit body including a cone region, a shoulder region, and a gage region. In addition the bit comprises a first primary blade and a second primary blade. Further, the bit comprises a plurality of primary cutter elements mounted to the first primary blade in different radial positions. Still further, the bit comprises a plurality of primary cutter elements mounted to the second primary blade in different radial positions. Moreover, a first primary cutter element of the plurality of primary cutter elements on the first primary blade and a first primary cutter element of the plurality of primary cutter elements on the second primary blade are each positioned in the cone region and are redundant. The shoulder region has a total cutter redundancy percentage that is less than a total cutter redundancy percentage in the cone region.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
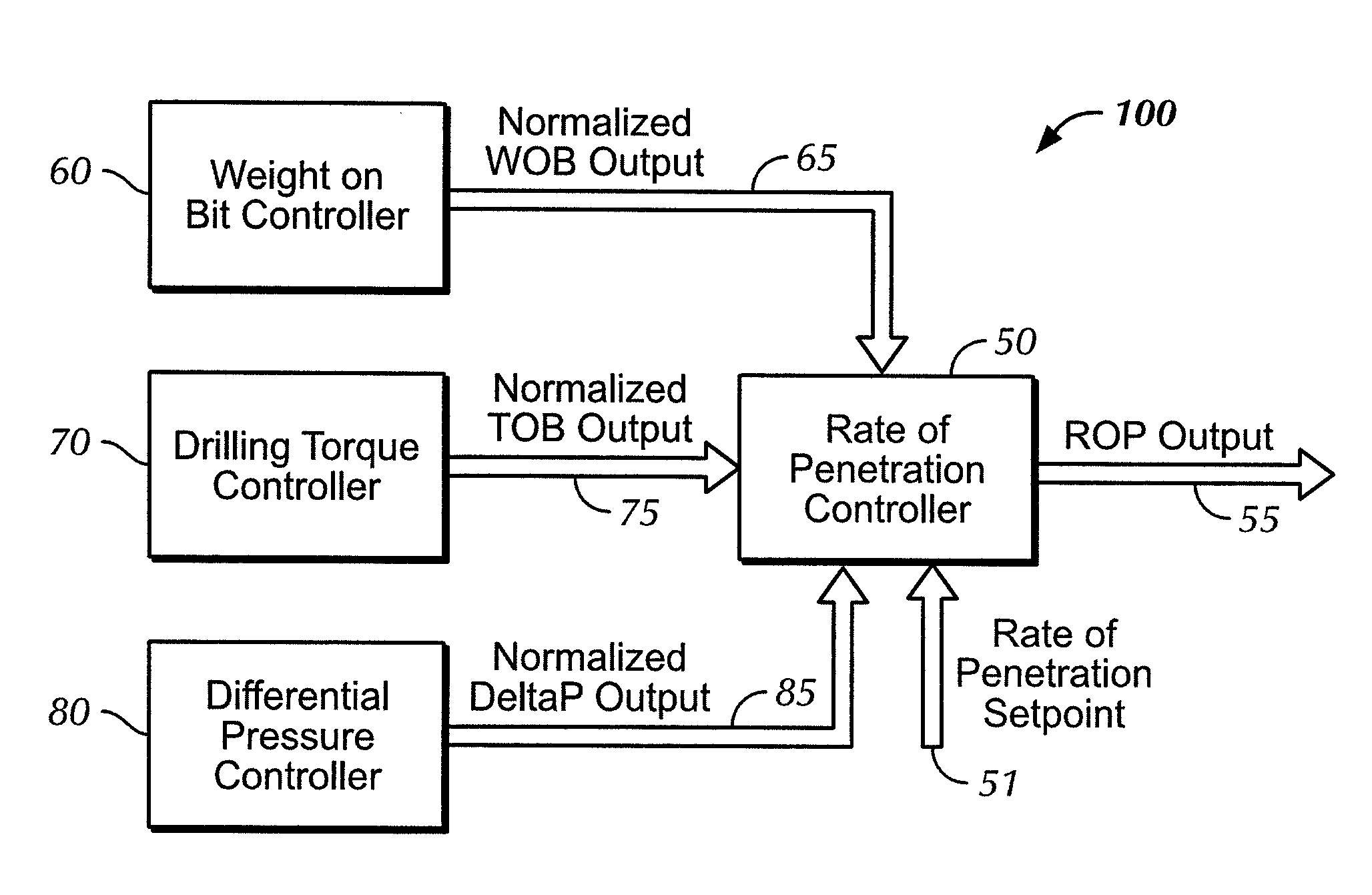
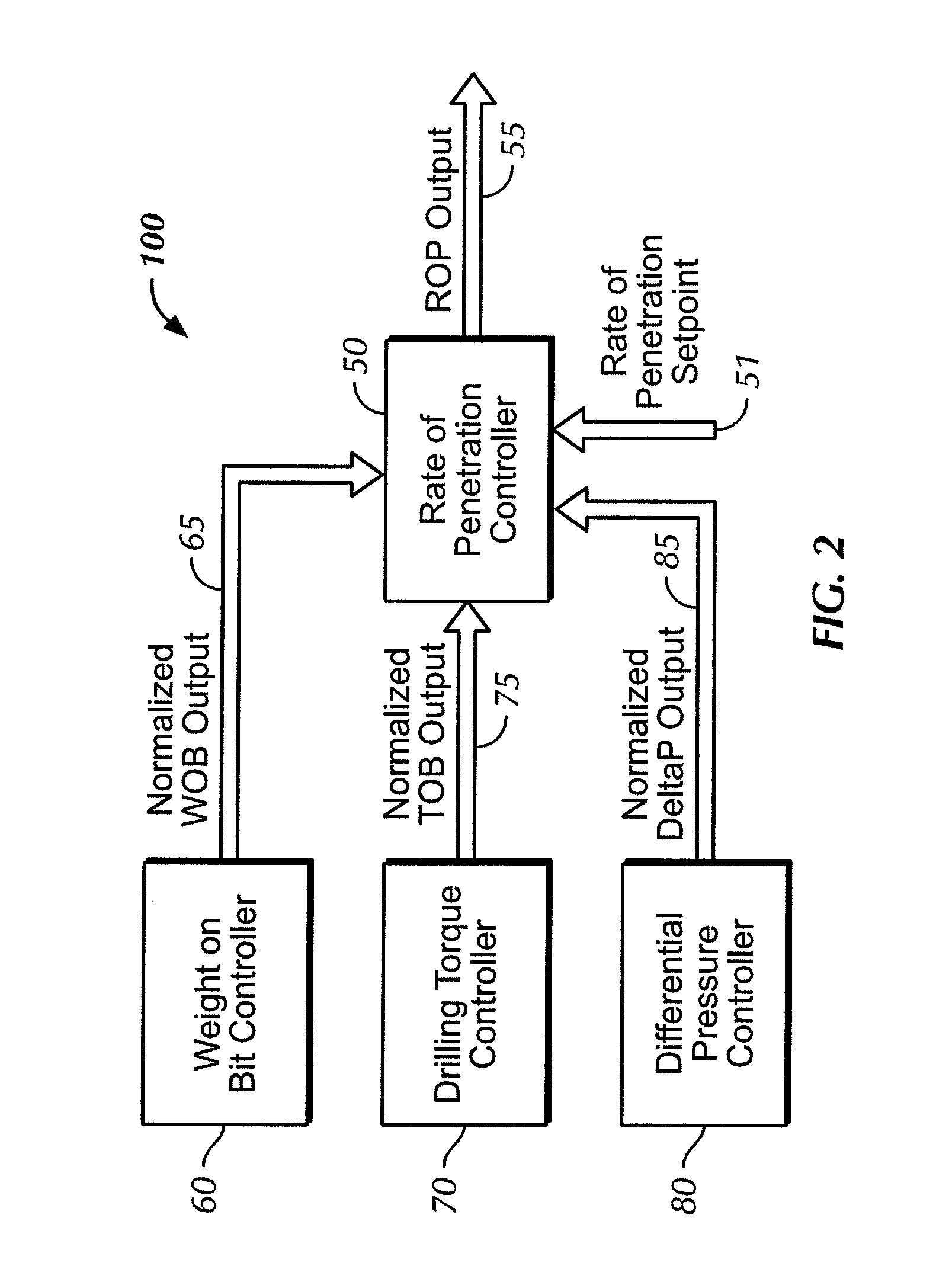
Adaptive drilling control system
A system for optimizing a rate-of-penetration of a drill string, the system including: a plurality of sensors in operable communication with the drill string; and a controller in operable communication with the plurality of sensors, the controller connectable to a drill string motivator and capable of outputting a signal to the drill string motivator for optimizing the rate-of-penetration of the drill string, the signal configured to provide at least one of weight on bit, an amount of speed to rotate the drill string, an amount of torque to be applied to the drill string, and an amount of mudflow to the drill string.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Systems and methods for automatic weight on bit sensor calibration and regulating buckling of a drillstring
ActiveUS20140231141A1Easy constructionEasy to adaptElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyEngineeringBottom hole assembly
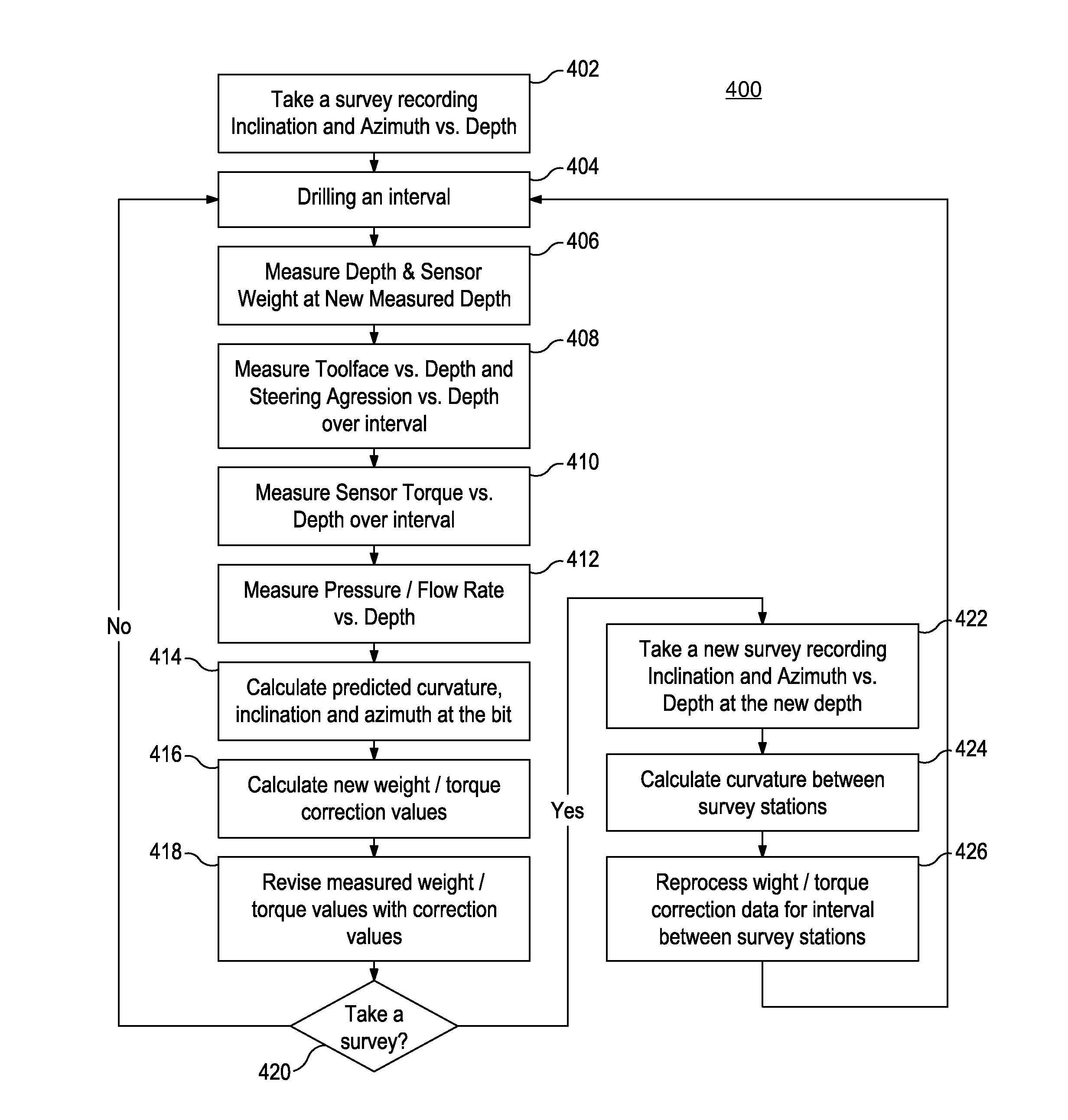
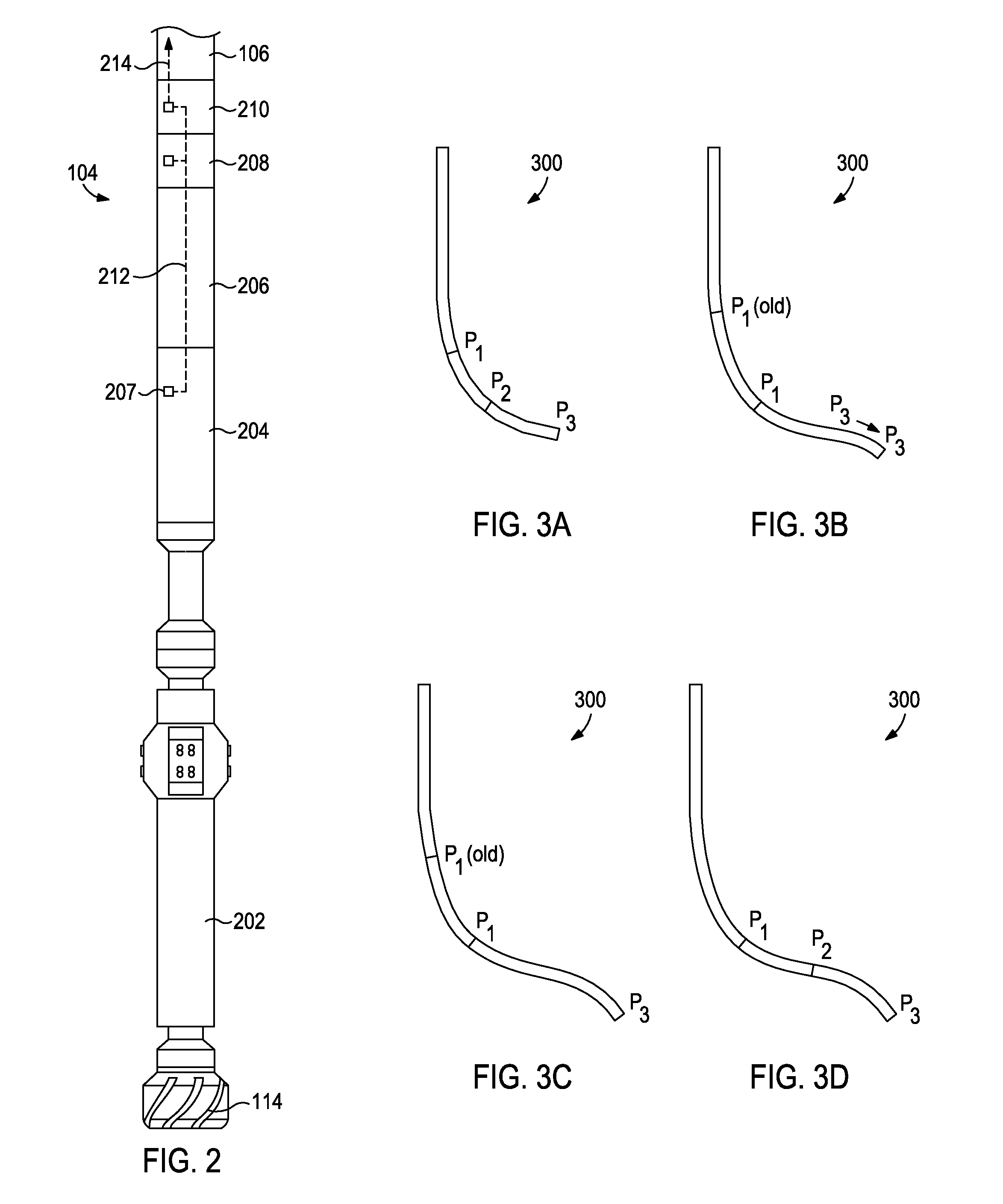
Disclosed are systems and methods for automatic weight on bit sensor calibration and regulating buckling of a drillstring. One method includes taking a first survey recording at a first depth within a borehole, the first survey recording providing inclination and azimuth of a drillstring at the first depth, measuring a weight on a drill bit at the first depth with a sensor sub arranged on a bottom hole assembly, the bottom hole assembly forming part of the drillstring and the drill bit being disposed at an end of the drillstring, calculating a predicted borehole curvature at a second depth within the borehole, the predicted curvature including a predicted inclination and a predicted azimuth of the drillstring at the second depth, calculating a weight correction value based on the predicted hole curvature, and calibrating the sensor sub with the weight correction value.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method and system for detecting the longitudinal displacement of a drill bit
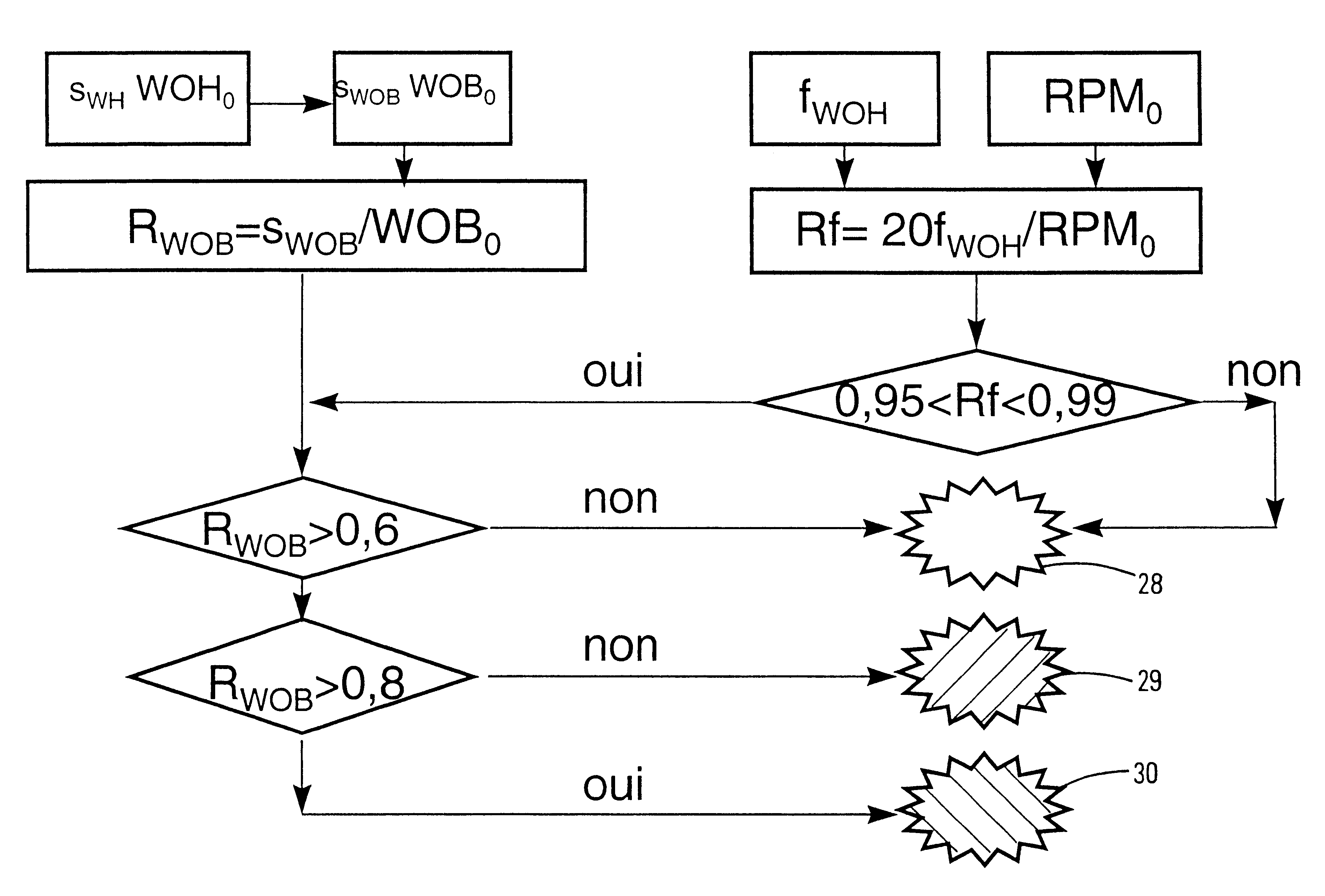
The present invention is a system and method for generating an alarm relative to effective longitudinal behavior of a drill bit fastened to the end of a drill string driven in rotation in a well by a driving device situated at the surface, using a physical model of the drilling process based on general mechanics equations. The following steps are carried out: the model is reduced so to retain only pertinent modes, at least two values Rf and Rwob are calculated, Rf being a function of the principal oscillation frequency of weight on hook WOH divided by the average instantaneous rotating speed at the surface, Rwob being a function of the standard deviation of the signal of the weight on bit WOB estimated by the reduced longitudinal model from measurement of the signal of the weight on hook WOH, divided by the average weight on bit WOB0, defined from the weight of the string and the average weight on hook. Any danger from the longitudinal behavior of the drill bit is determined from the values of Rf and Rwob.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Force balanced asymmetric drilling reamer and methods for force balancing
A force balanced asymmetric drilling reamer comprising a plurality of blades, each blade having at least one cutter section and a gage section. The cutter section is designed to have a plurality of cutting devices for cutting through swelling formations and cutting free sloughing formations. The gage section has a full bore diameter with gage elements flushly coupled to gage section's outer surface. The blades may be curve / concave shaped or boomerang / chevron shaped, which thereby agitate the cutting beds. At least a portion of the drilling reamer's diameter is incrementally force balanced, starting from the outermost diameter, so that the net radial force is less than 10% of weight on bit with respect to the center of rotation. This balancing allows a greater cutter longevity and provides for a better wellbore condition. Optionally, at least a portion of the drilling reamer's surface may be treated by nitriding for repelling the cuttings.
Owner:VAREL INT IND
Fixed cutter drill bit with rotating cutter disc
A fixed cutter drill bit that includes one or more integrally-mounted rotating disc with cutters around the circumference of the disc. Each disc is mounted to bearings to handle the torque generated and the weight on bit required to cut the formation. The mounting angle of the disc generates a torque causing the disc to rotate. As the disc rotates, new cutters are presented to the formation. The discs may vary in size, mounting location and number so as to cover entire bladed or just a certain portions of blades. The exposure of the disc could also be set to enable it to rotate while under load, e.g., the cutters on the outside of the bit may contact the formation while the inner half of the disc is protected by a fixed blade.
Owner:ULTERRA DRILLING TECH LP
Interchangeable bearing blocks for drill bits, and drill bits including same
ActiveUS7814997B2Reduce complexityReduce inventory quantityDrill bitsDrilling rodsEngineeringRubbing
A bearing block is provided that may be used with a drag bit body or frame to limit depth of cut of cutters on a bit. The bearing block is designed so that it may be interchangeably replaced or repaired without necessitating alteration to a standardized bit frame. The interchangeable bearing block may be used to provide a target depth of cut (TDOC) and / or a selected contact or rubbing area to support weight on bit and limit depth of cut (DOC) for improving drilling performance of a bit. The interchangeable bearing block brings manufacturing selectability by providing a customizable product in terms of depth of cut selection and cutter penetration control for different formations, which is suitable for use with a common bit frame. A rotary drill bit assembly, a unitary cone insert bearing block for a drill bit, and a bit frame are also provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Drillstring motion analysis and control
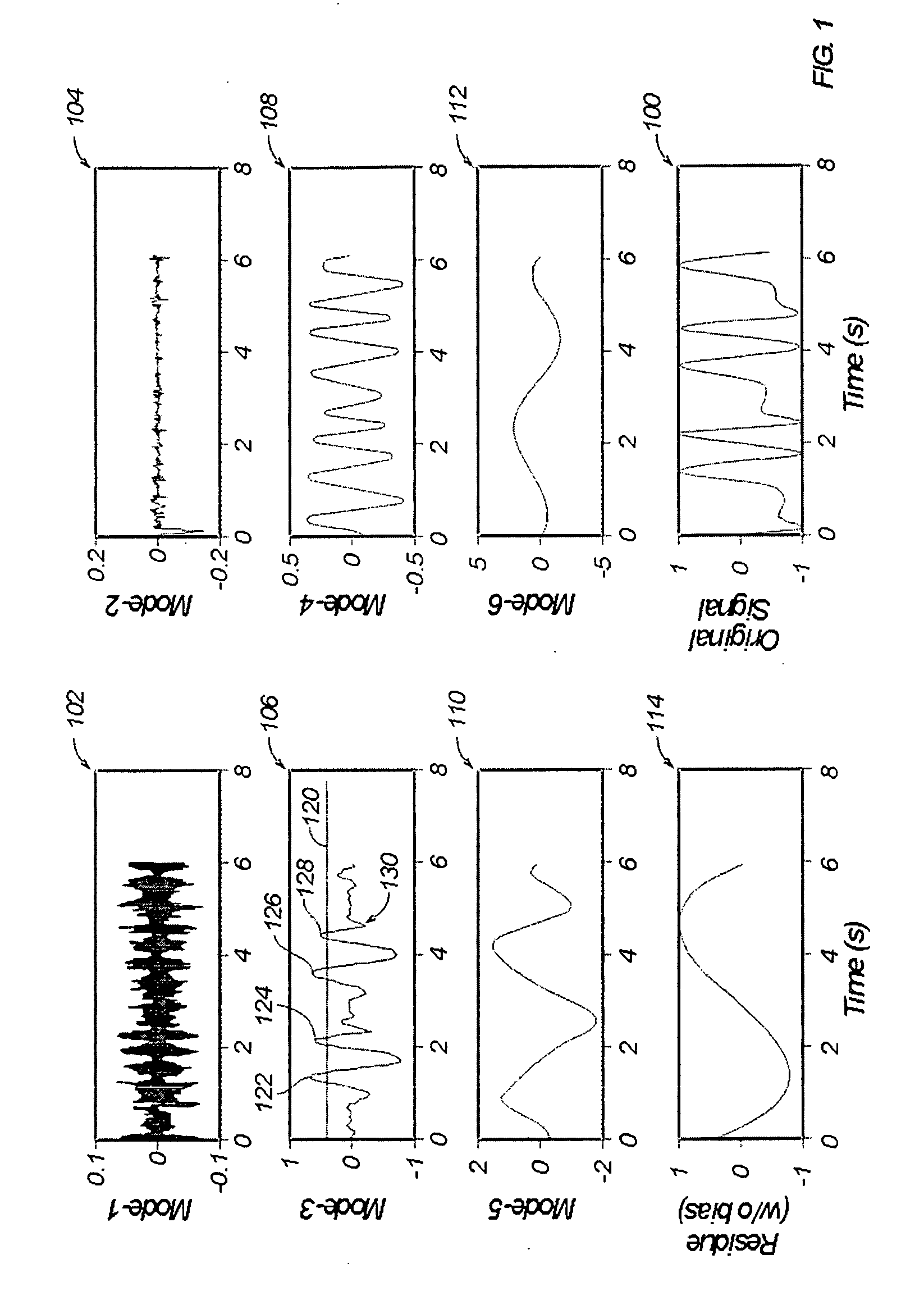
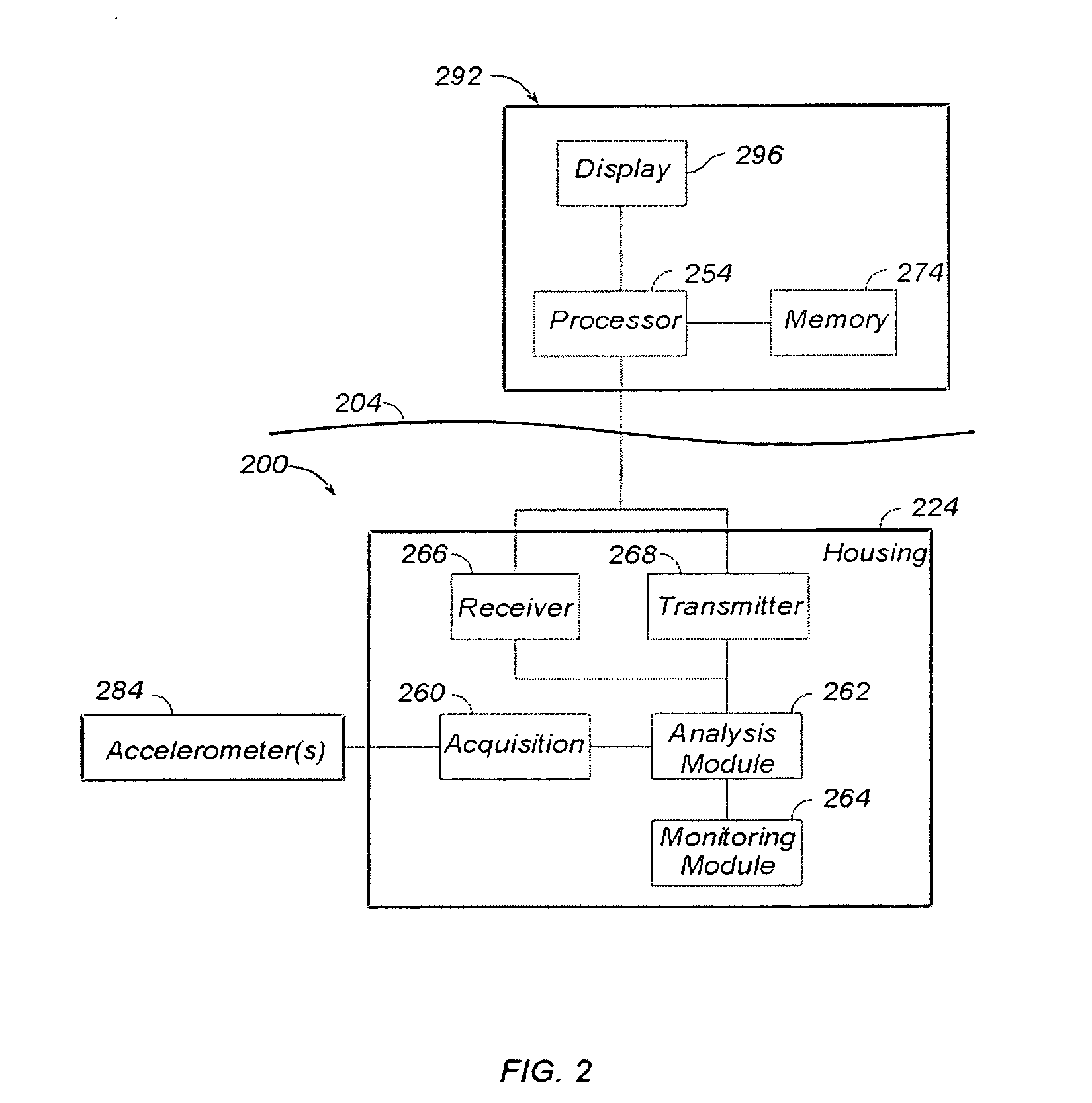
Apparatus, systems, and methods may operate to obtain acceleration data from an operational drillstring, decompose the acceleration data into one or more empirical modes, monitor the amplitude of at least one of the empirical modes to detect indications exceeding a preselected threshold, and modify drillstring operational parameters comprising at least one of rotational speed, weight on bit, or mud flow, based on the indications. Additional apparatus, systems, and methods are disclosed.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
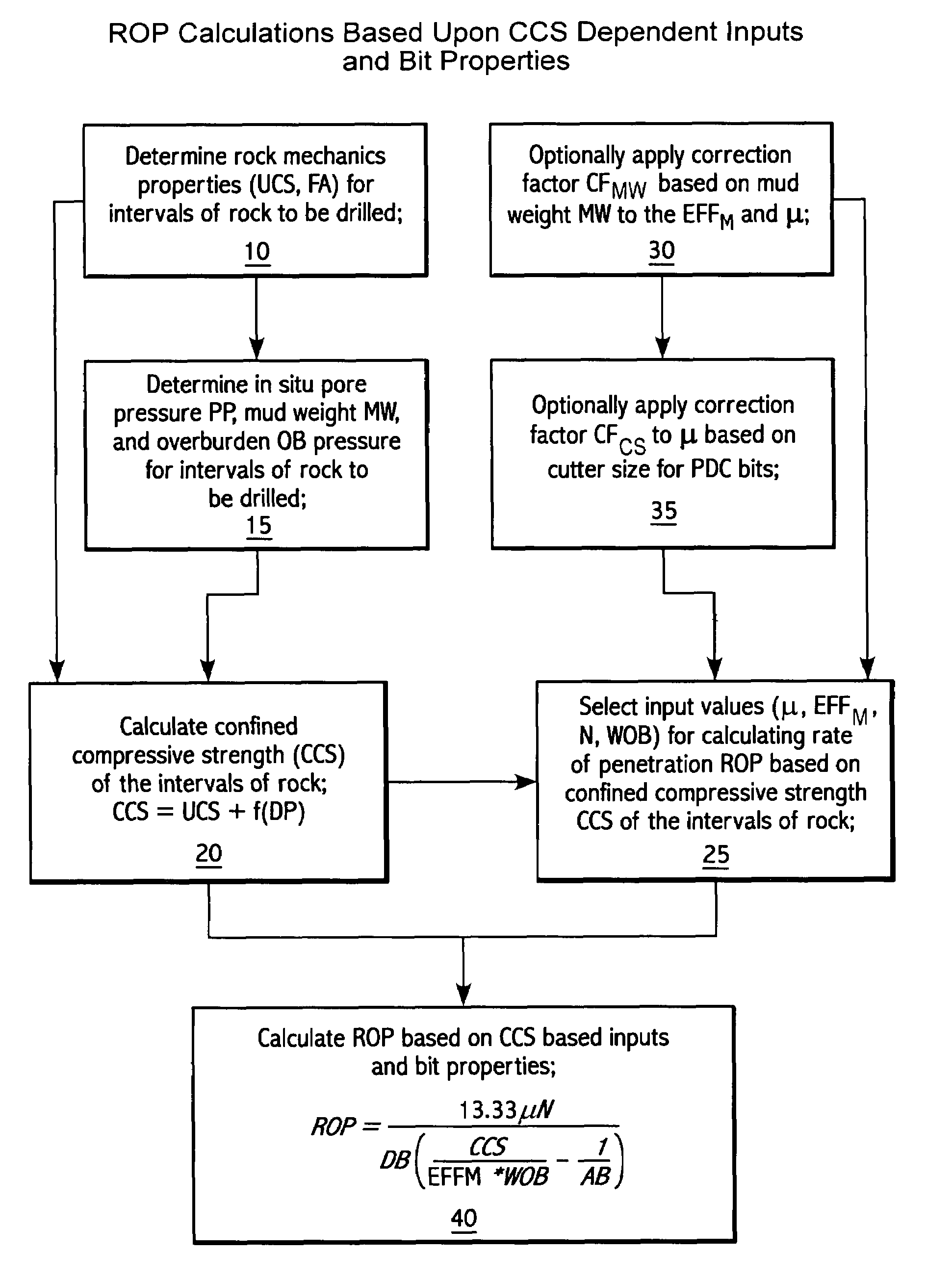
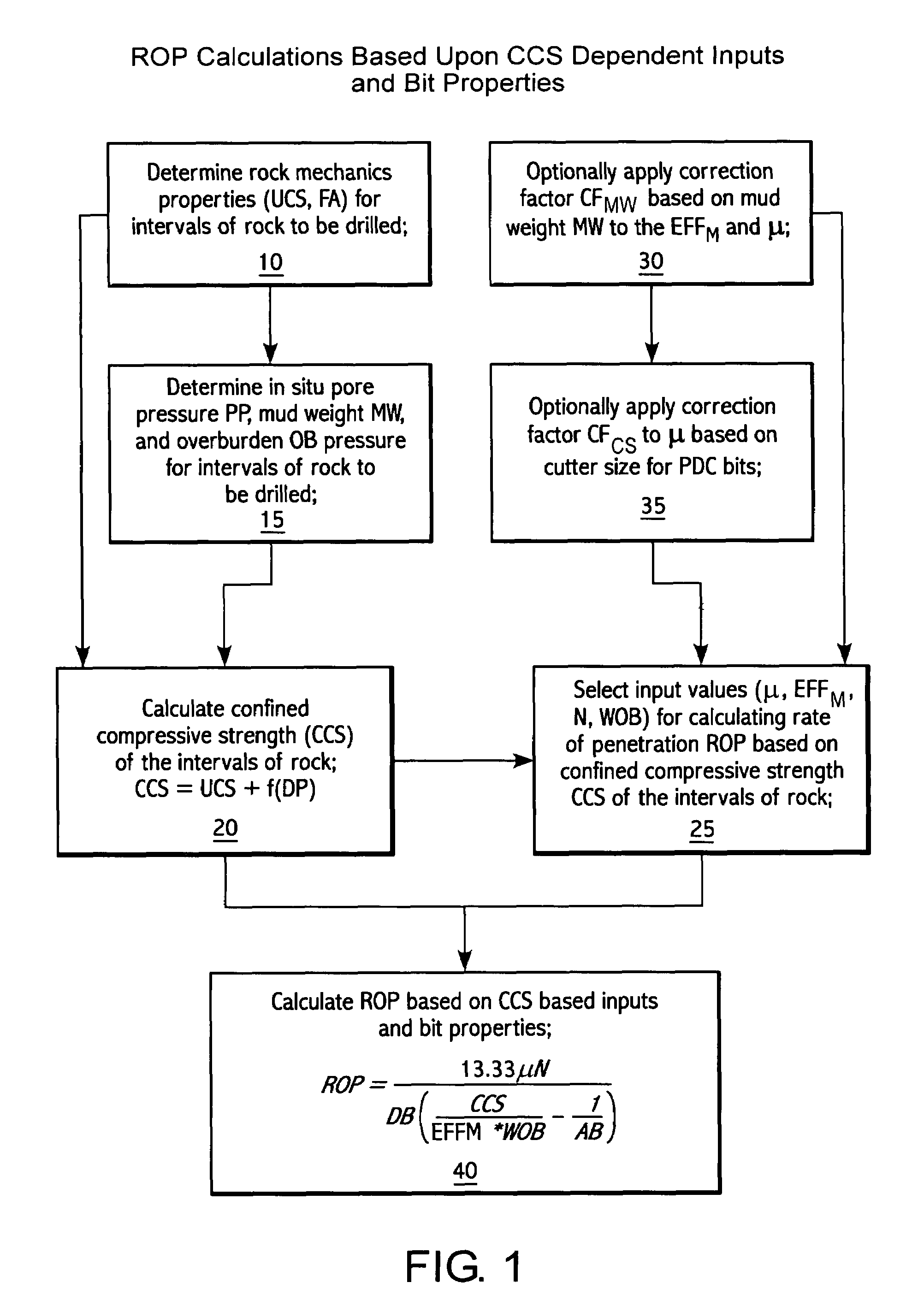
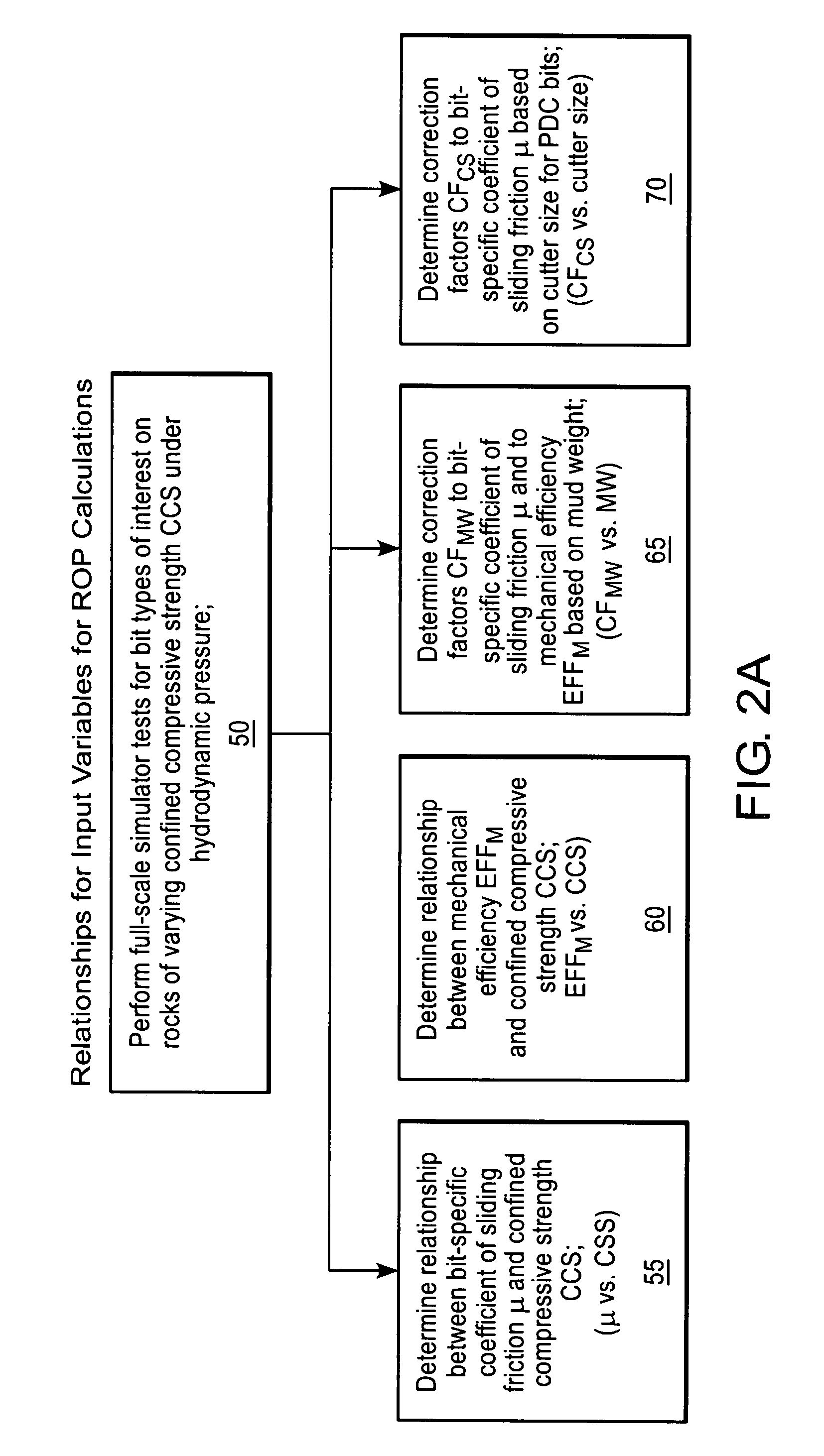
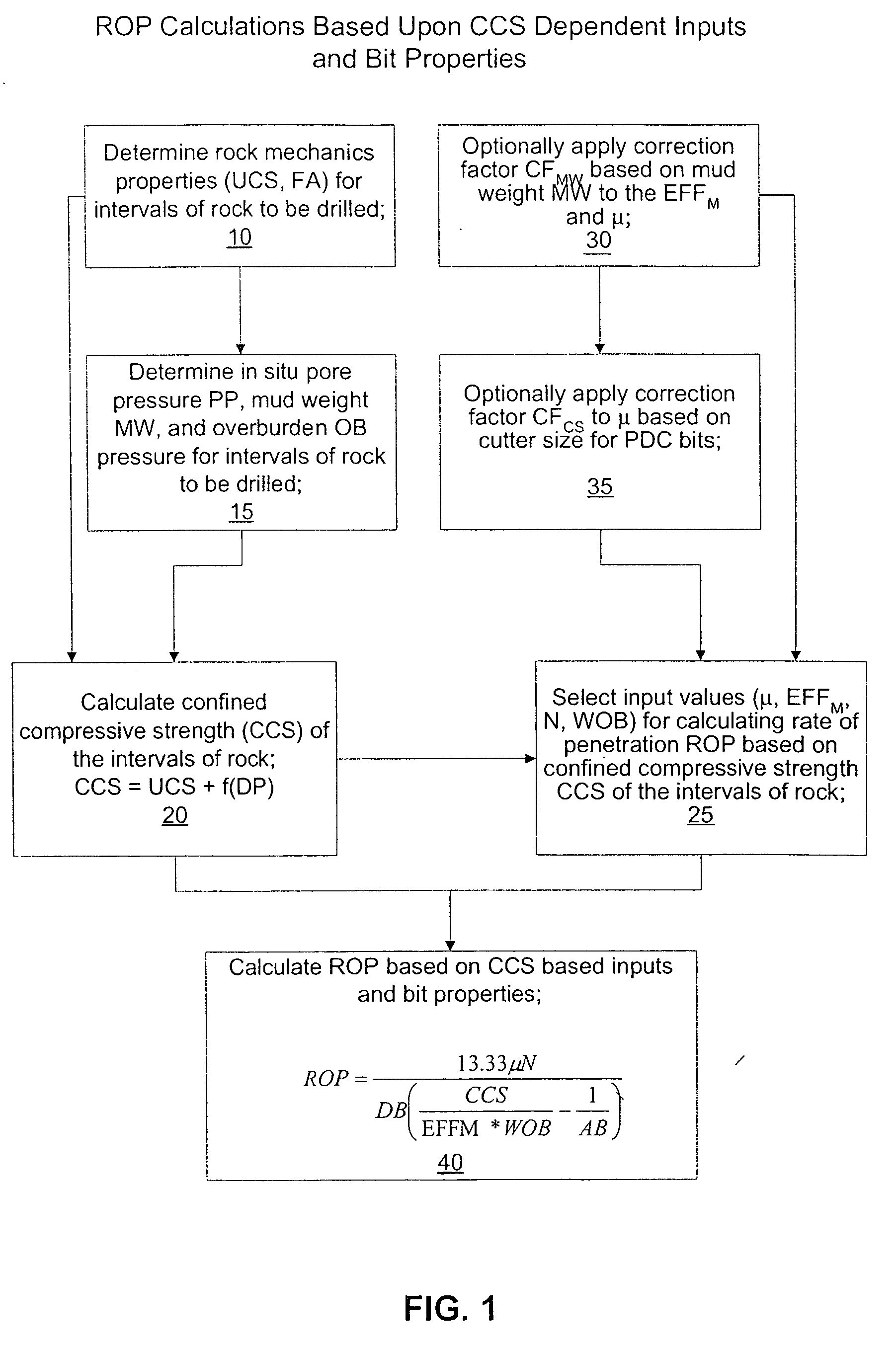
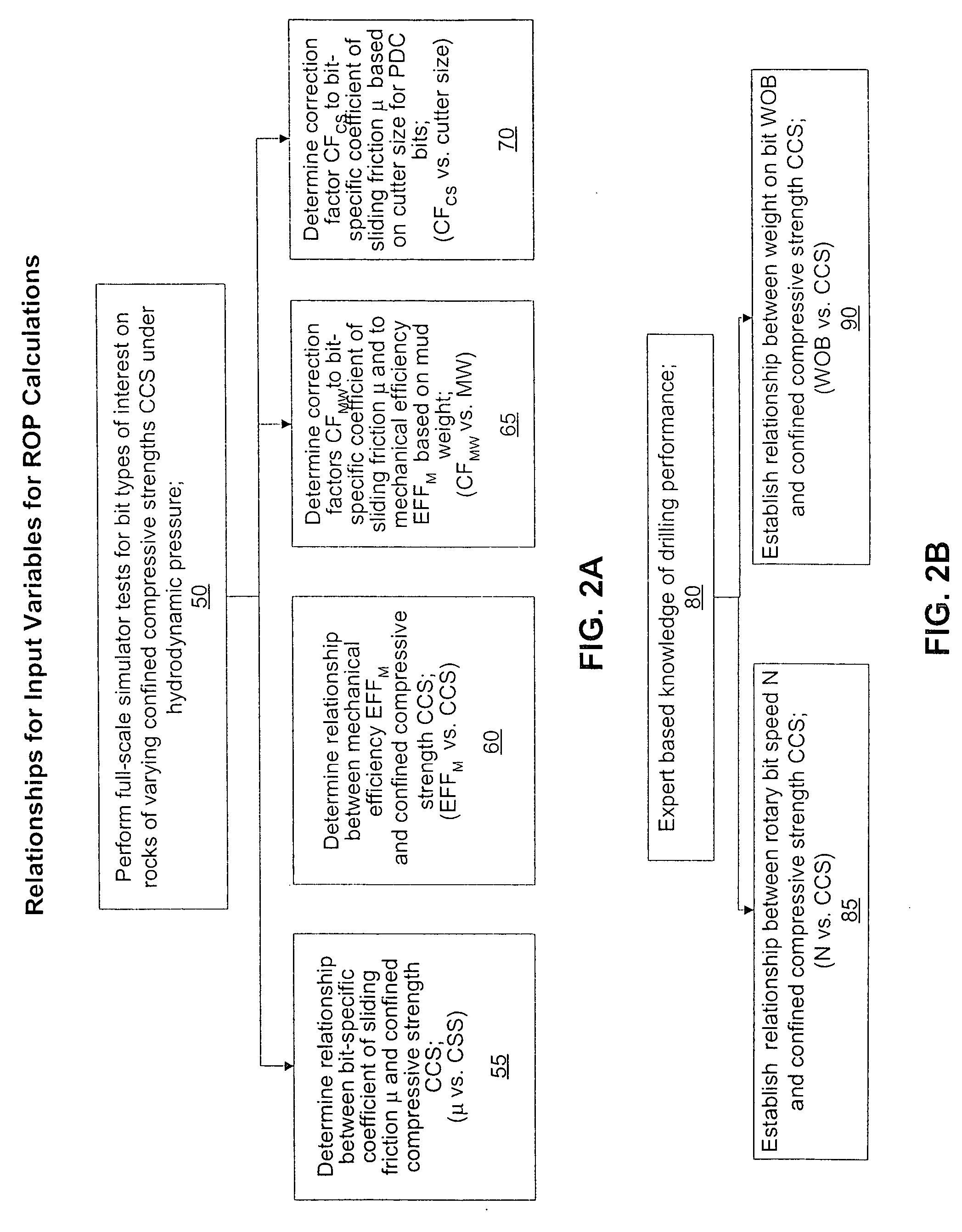
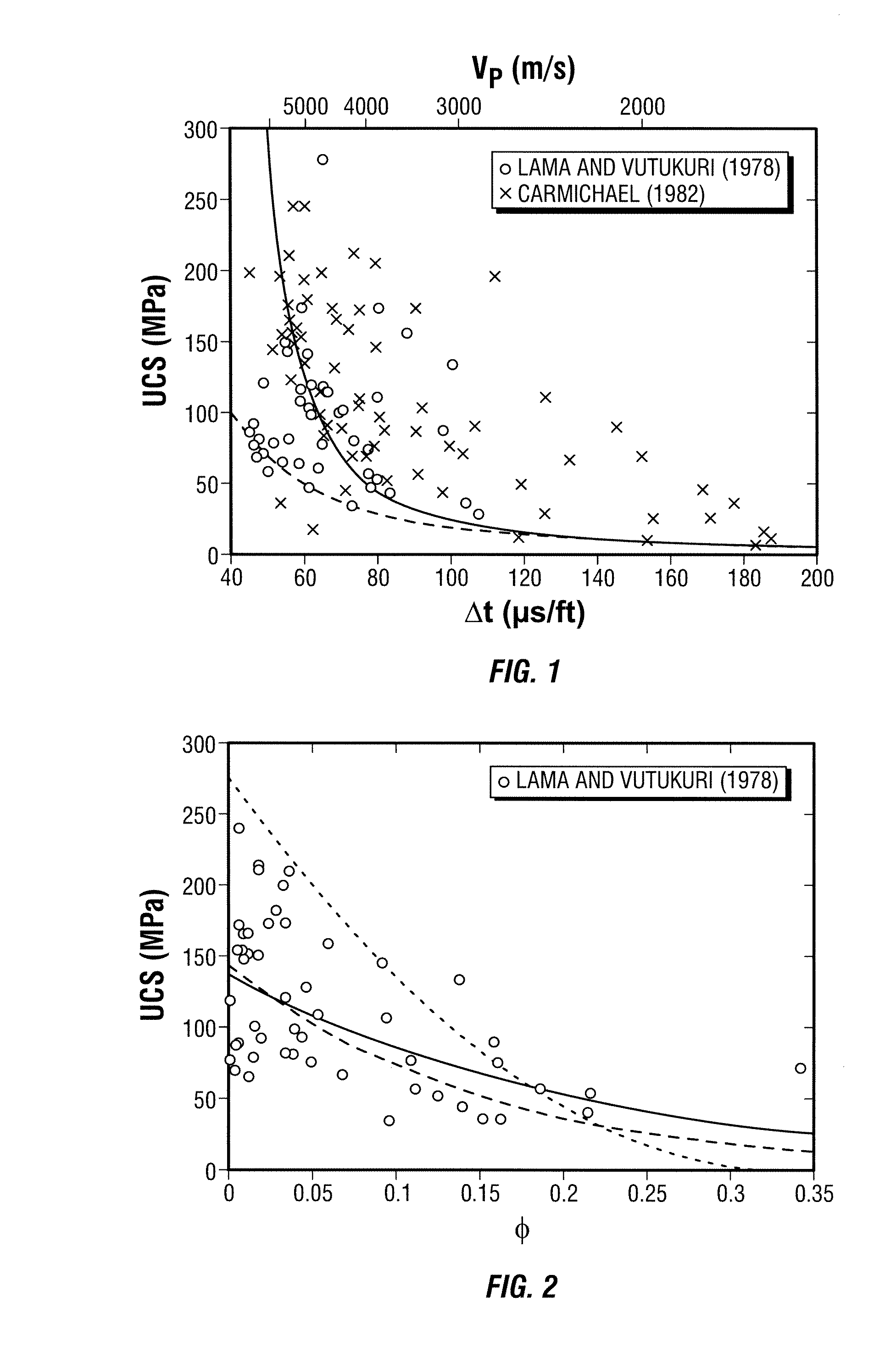
Method for predicting rate of penetration using bit-specific coefficient of sliding friction and mechanical efficiency as a function of confined compressive strength
InactiveUS7412331B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingRate of penetrationCompressive strength
A method for predicting the rate of penetration (ROP) of a drill bit drilling a well bore through intervals of rock of a subterranean formation is provided. The method uses an equation based upon specific energy principles. A relationship is determined between a bit-specific coefficient of sliding friction μ and confined compressive strength CCS over a range of confined compressive strengths CCS. Similarly, another relationship for the drill bit is determined between mechanical efficiency EFFM and confined compressive strength CCS over a range of confined compressive strengths CCS. Confined compressive strength CCS is estimated for intervals of rock through which the drill bit is to be used to drill a well bore. The rate of penetration ROP is then calculated utilizing the estimates of confined compressive strength CCS of the intervals of rock to be drilled and those determined relationships between the bit-specific coefficient of sliding friction μ and the mechanical efficiency EFFM and the confined compressive strengths CCS, as well as using estimated drill bit speeds N (RPM) and weights on bit (WOB).
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Bottom hole assembly
A bottom hole assembly has a drill bit and an under-reamer on the up-hole side of the drill bit. In one aspect, the assembly further has a compliant element linking the drill bit to the under-reamer, the compliant element allowing displacement of the drill bit relative to the under-reamer in the axial direction of the assembly. In another aspect, the assembly further has a sensor element which is arranged to measure the weight-on-bit and / or the applied torque of the drill bit, and a transmitter for transmitting the weight-on-bit and / or applied torque measurements to the surface.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Processes and systems for drilling a borehole
InactiveUS20130146358A1Reduce the amount requiredWithout sacrificing rate of penetrationSurveyDrilling rodsReal-time dataEnergy reduction
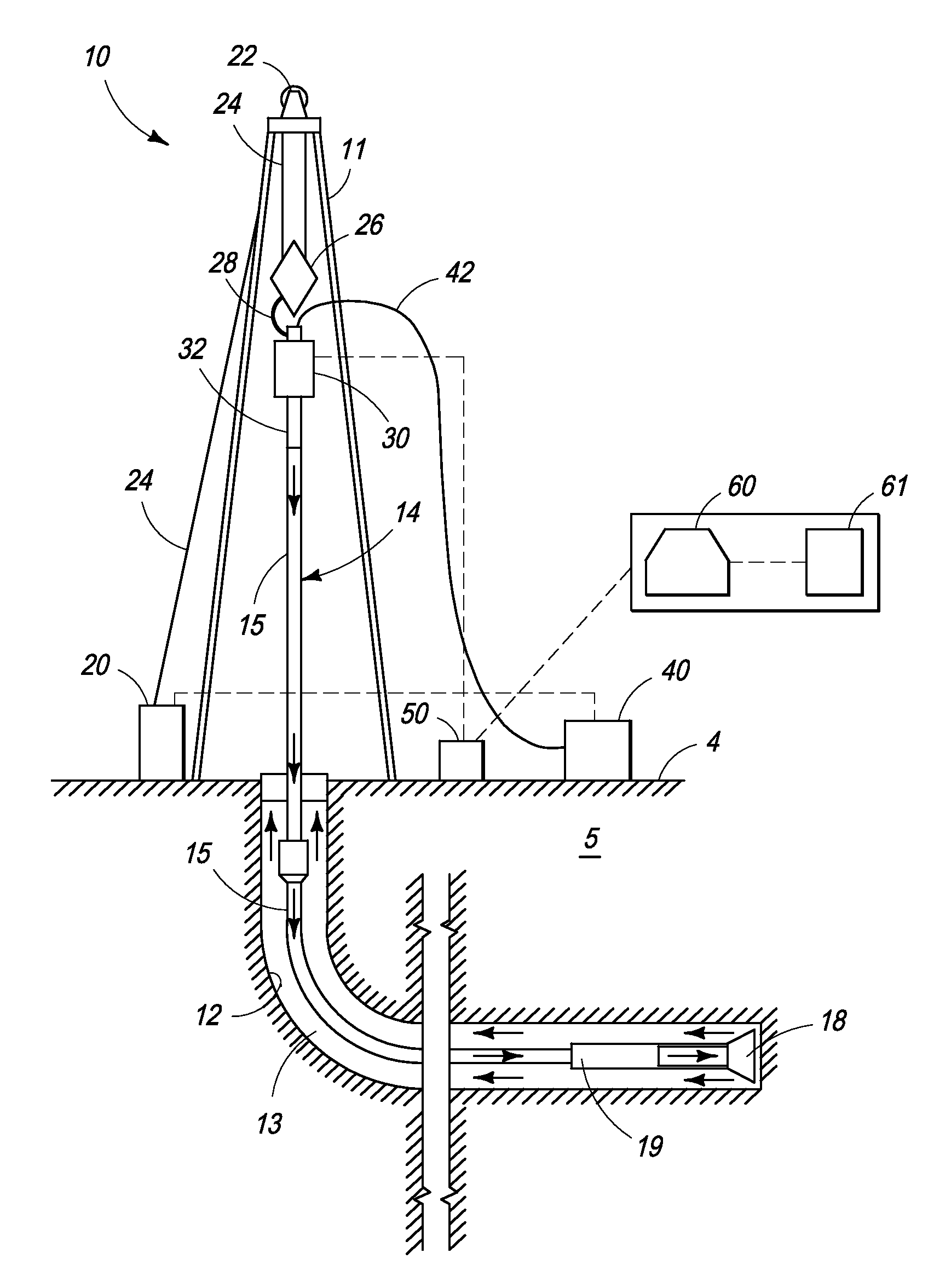
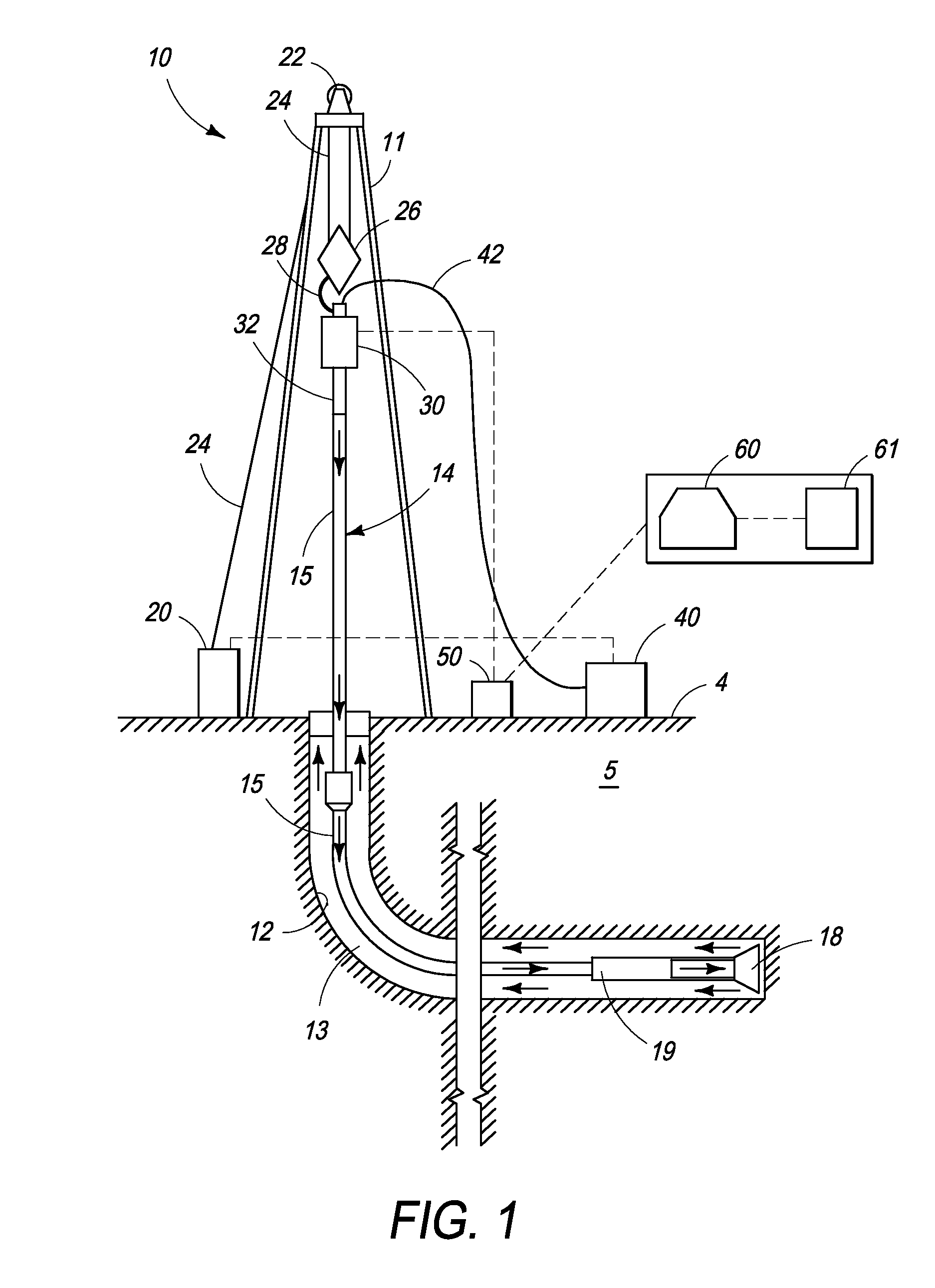
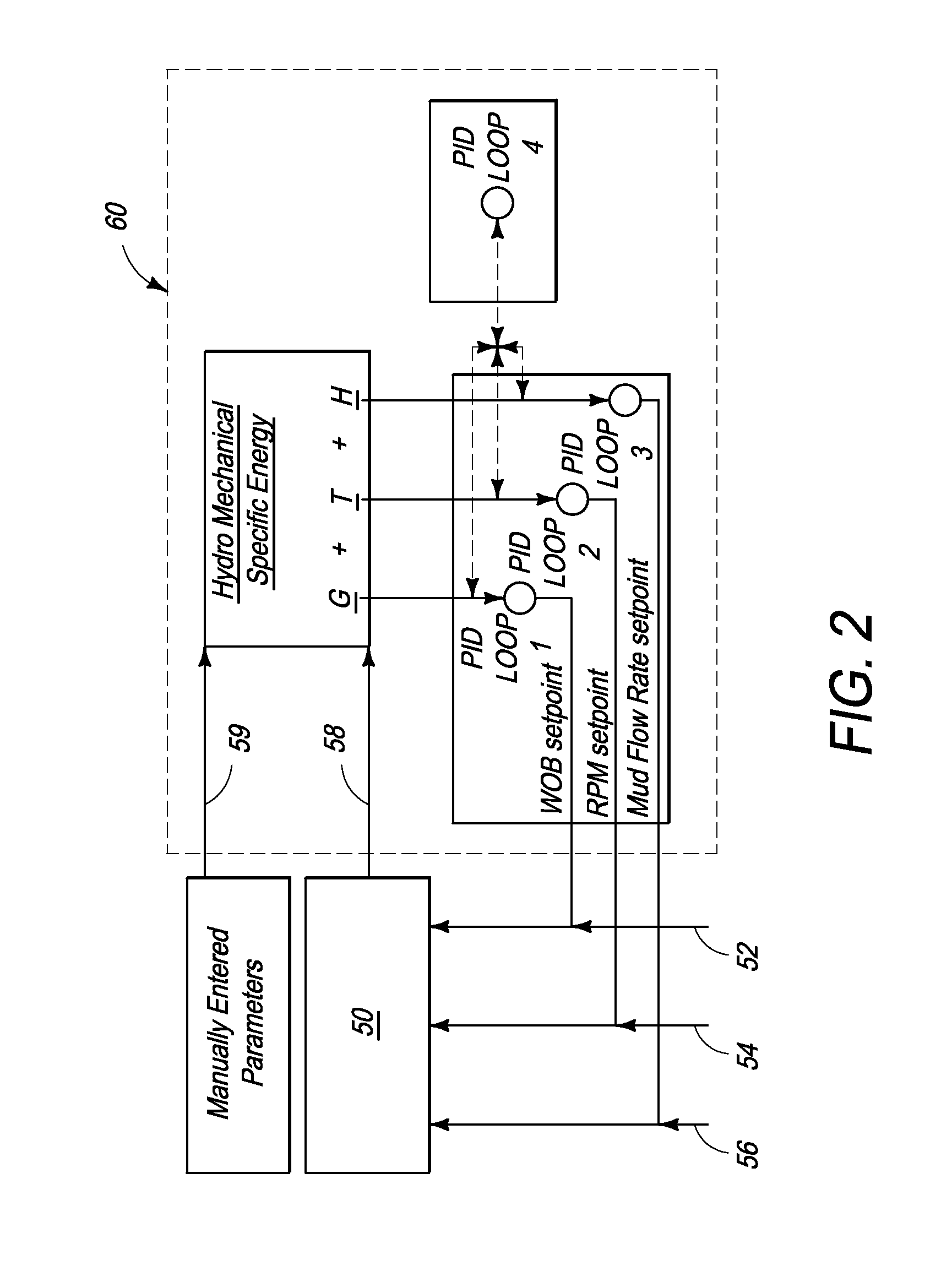
Processes and systems for drilling a borehole wherein a gravitational energy term, a torsional energy term, a hydraulic energy term and a hydromechanical specific energy which is the sum thereof may be determined using real-time data and compared against corresponding setpoints. The hydraulic energy term may include a hydraulic energy reduction factor so as to account for the distance between the fluid nozzle of the drill bit and the rock and may include the kinematic viscosity of drilling fluid. One or more drilling parameters, such as weight on bit, revolutions per minute, drilling fluid flow rate, or combinations thereof, may be adjusted based upon such comparison to approximate the least amount of energy required to destroy and remove a given unit volume of rock. The setpoints may be changed manually or automatically at the direction of the user.
Owner:DISANTIS JOSEPH R
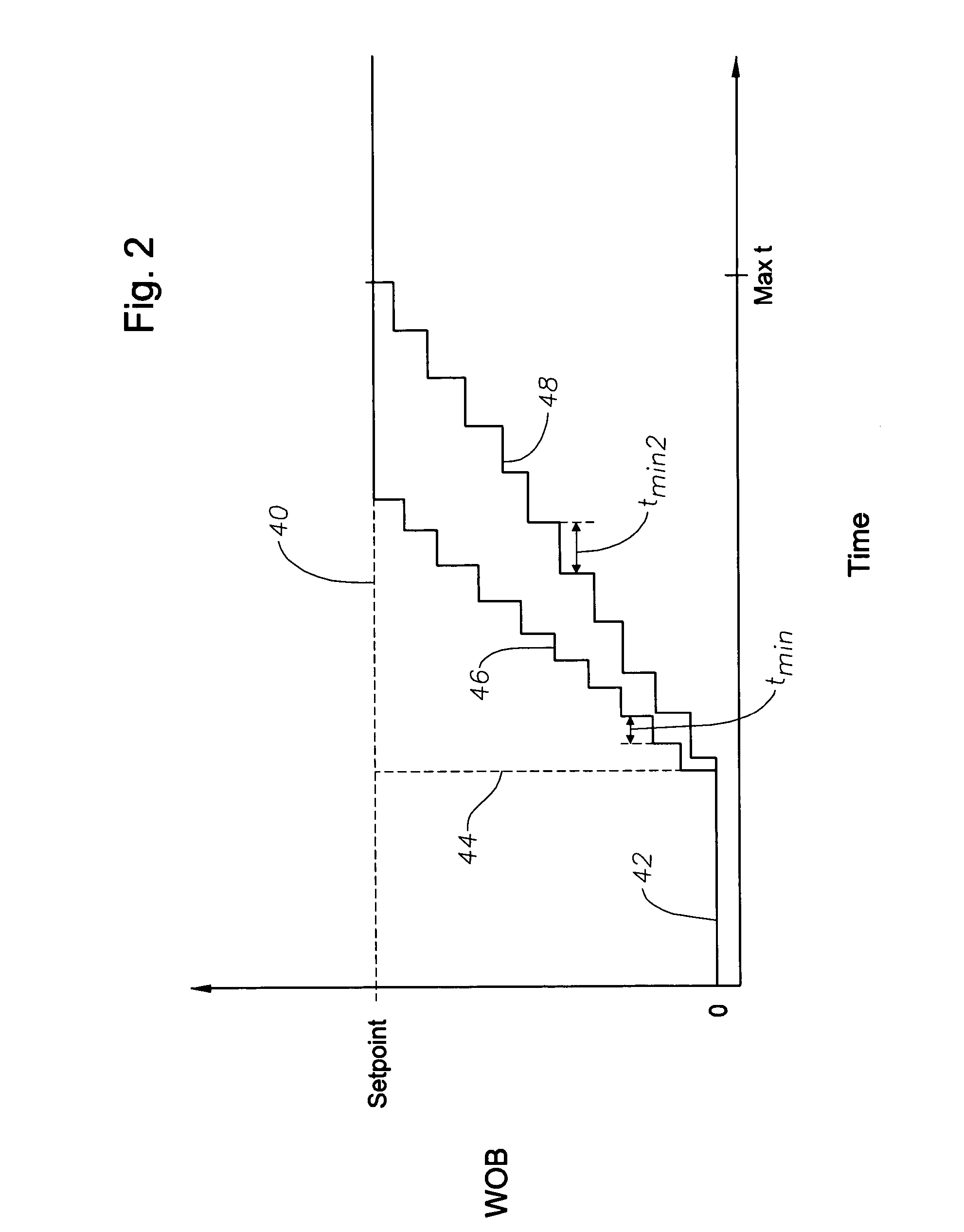
Autodriller bit protection system and method
A controller provides an automatic bit protection sequence for an autodriller that can be initiated during the initial stage of set down of the bit within the formation. The automatic protection sequence establishes a setpoint for a parameter of interest (such as weight on bit, ROP, torque) associated with operation of the drilling system and then initiates a gradual increase in that parameter in order to achieve the setpoint. The bit protection sequence may be adjustable so that varying degrees of gradualness may be selected. The controller of the autodriller may also be provided with measured data for torque, rate of penetration (ROP) and / or the differential pressure of the mud motor of the drilling system. Each of these parameters is provided with a predetermined setpoint, and each may be selected as the controlling parameter for operation of the autodriller.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Automated control of toolface while slide drilling
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for controlling slide drilling on a drilling rig are described. The methods include detecting current differential pressure of a mud motor and / or weight on bit (WOB) at a surface of a borehole, predicting current reactive torque of the mud motor based on the current differential pressure and / or WOB, and automatically adjusting surface torque and / or angular offset of a tubular adjacent the surface to counteract the current reactive torque and to keep the mud motor at a desired toolface orientation in the borehole.
Owner:NABORS DRILLING TECH USA INC
Method for predicting rate of penetration using bit-specific coefficient of sliding friction and mechanical efficiency as a function of confined compressive strength
InactiveUS20060149478A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingRate of penetrationCompressive strength
A method for predicting the rate of penetration (ROP) of a drill bit drilling a well bore through intervals of rock of a subterranean formation is provided. The method uses an equation based upon specific energy principles. A relationship is determined between a bit-specific coefficient of sliding friction μ and confined compressive strength CCS over a range of confined compressive strengths CCS. Similarly, another relationship for the drill bit is determined between mechanical efficiency EFFM and confined compressive strength CCS over a range of confined compressive strengths CCS. Confined compressive strength CCS is estimated for intervals of rock through which the drill bit is to be used to drill a well bore. The rate of penetration ROP is then calculated utilizing the estimates of confined compressive strength CCS of the intervals of rock to be drilled and those determined relationships between the bit-specific coefficient of sliding friction μ and the mechanical efficiency EFFM and the confined compressive strengths CCS, as well as using estimated drill bit speeds N (RPM) and weights on bit (WOB).
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
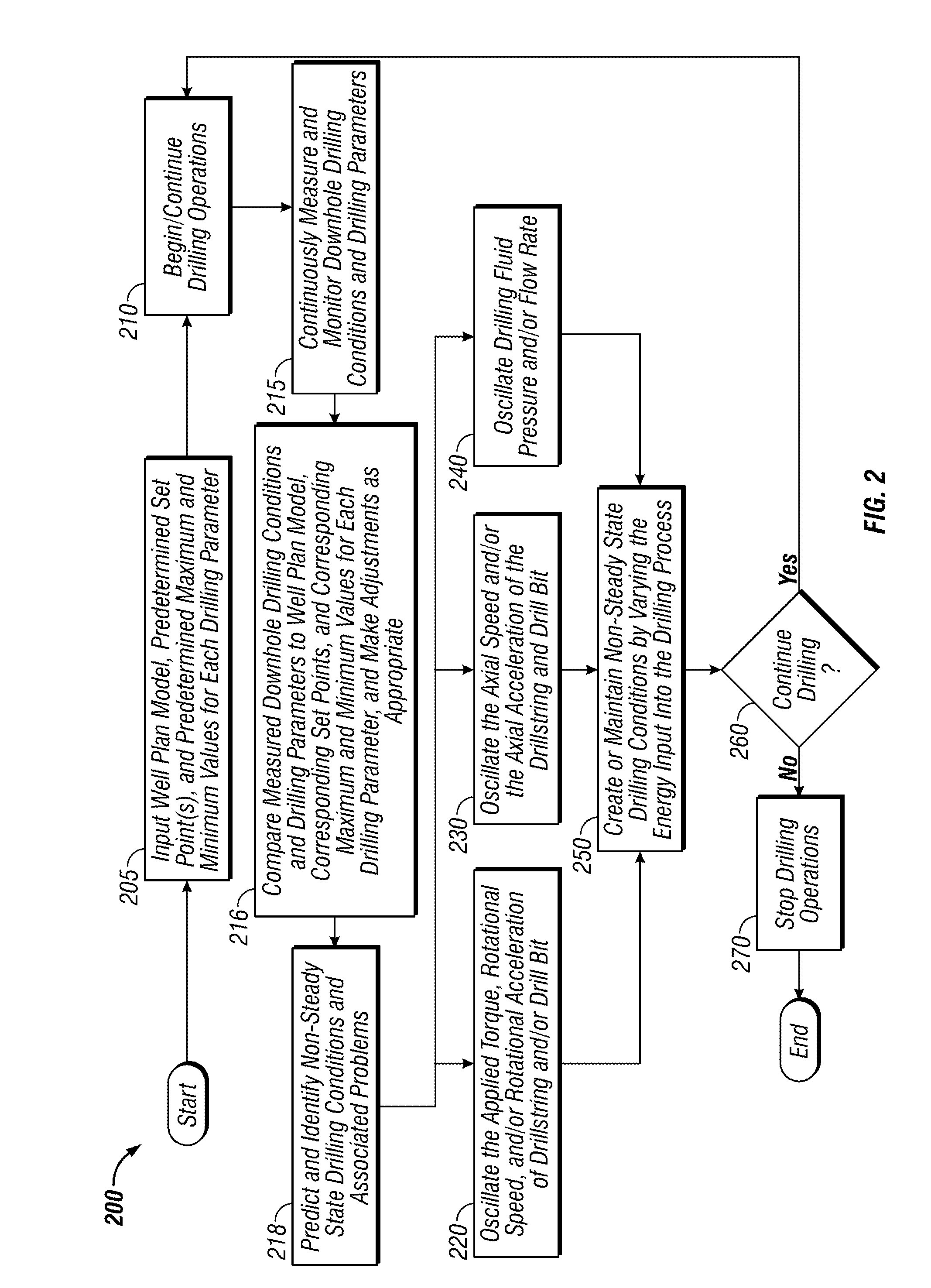
Systems and methods for improving drilling efficiency
ActiveUS20120217067A1Readily apparentDrilling machines and methodsAutomatic control for drillingWell drillingDrilling system
A method for drilling a borehole in an earthen formation comprises (a) providing a drilling system including a drillstring having a longitudinal axis, a bottom-hole assembly coupled to a lower end of the drillstring, and a drill bit coupled to a lower end of the bottom-hole assembly. In addition, the method comprises (b) rotating the drill bit at a rotational speed. Further, the method comprises (c) applying weight-on-bit to the drill bit and advancing the drill bit through the formation to form the borehole. Still further, the method comprises (d) pumping a drilling fluid down the drillstring to the drill bit. The drilling fluid has a flow rate down the drillstring. Moreover, the method comprises (e) oscillating the rotational speed of the drill bit during (c). The method also comprises (f) generating non-steady state conditions in the borehole during (e).
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
Method And System For Controlling Force In A Down-Hole Drilling Operation
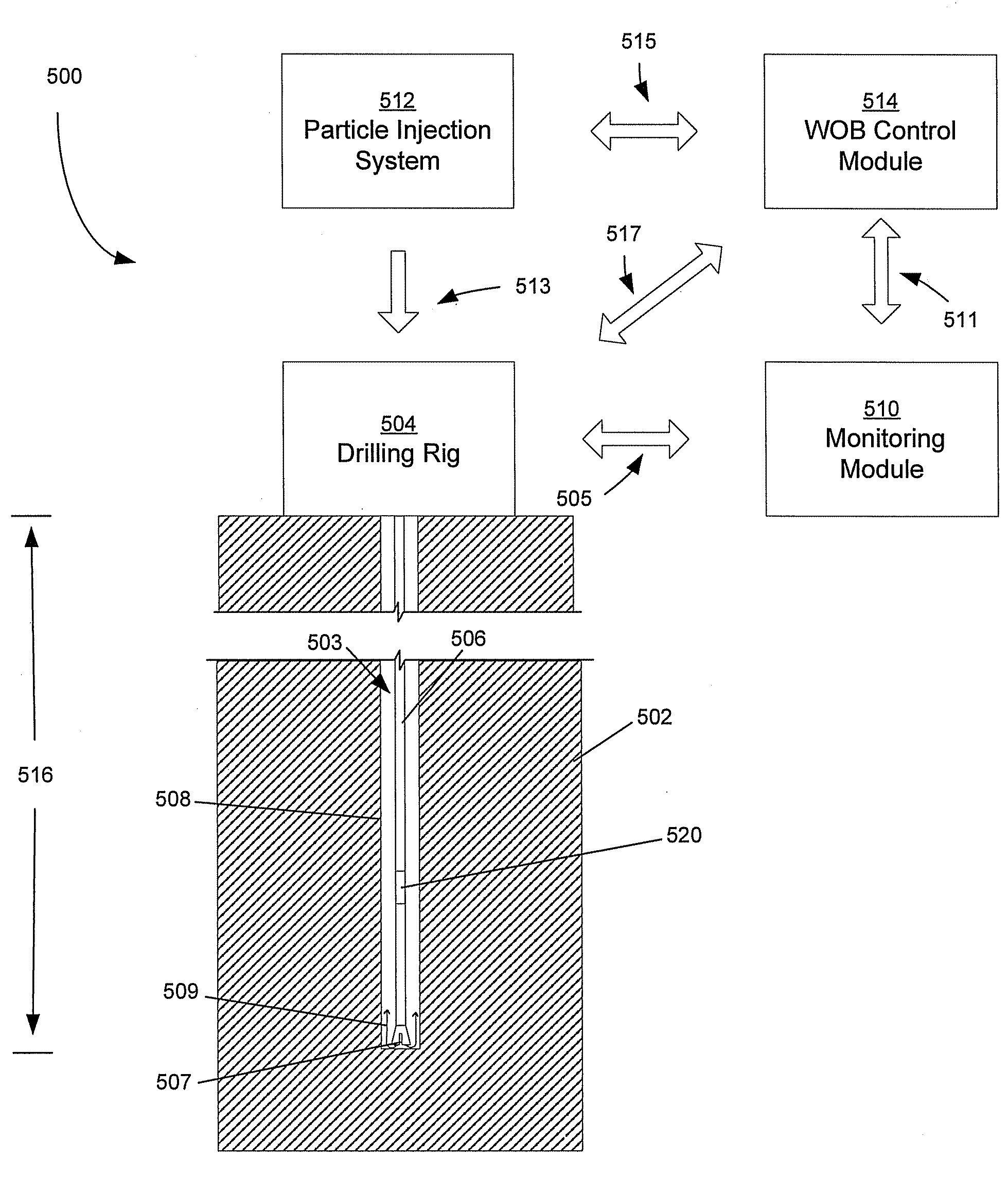
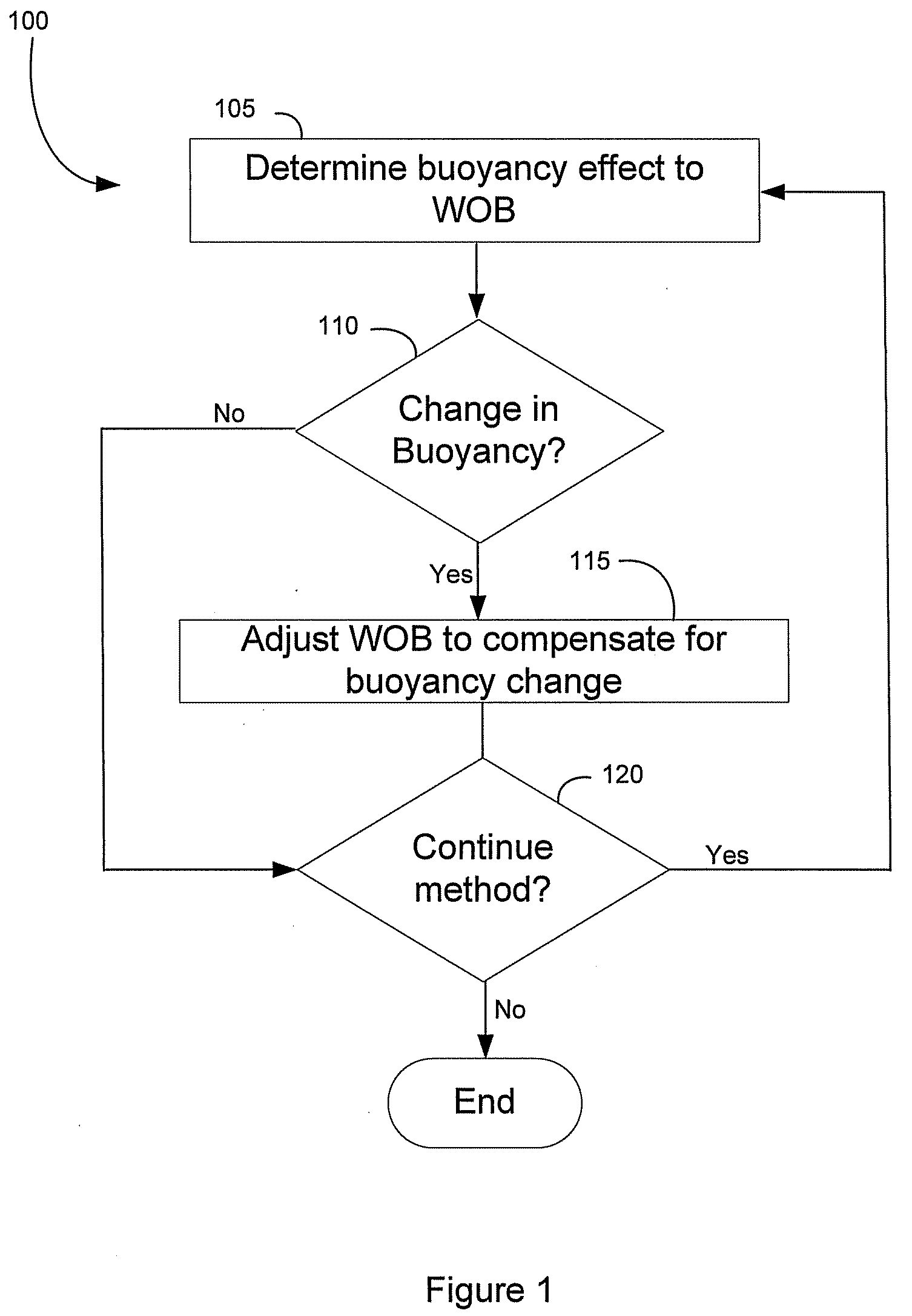
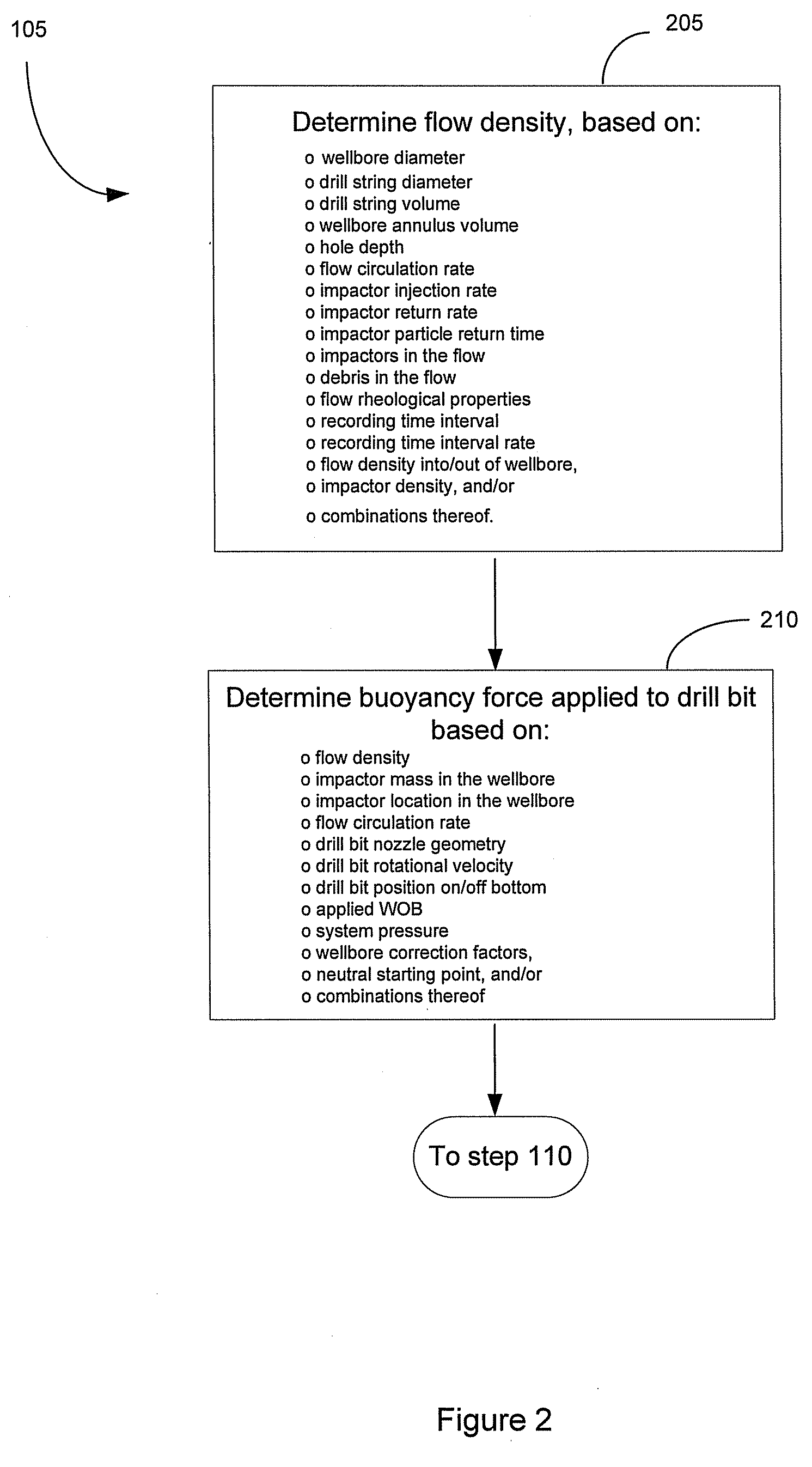
ActiveUS20090126994A1Compensation changesIncrease in estimated realized WOBDrilling rodsConstructionsEngineeringControl force
A method and system of subterranean excavating that estimates a buoyancy force applied to a downhole excavating system from drilling fluid. The estimated buoyancy force is used to derive a true weight on bit (WOB) at the borehole bottom. The derived realized WOB is compared to a target WOB to obtain a change in WOB. Based on the change in WOB, the excavating system is adjusted so the realized WOB approximates the target WOB. The excavating system adjustment includes applying a compensating force to the string. Compensating forces can be produced by manipulating a block assembly or deploying a thruster device in the string.
Owner:PDTI HLDG
Well drilling control system
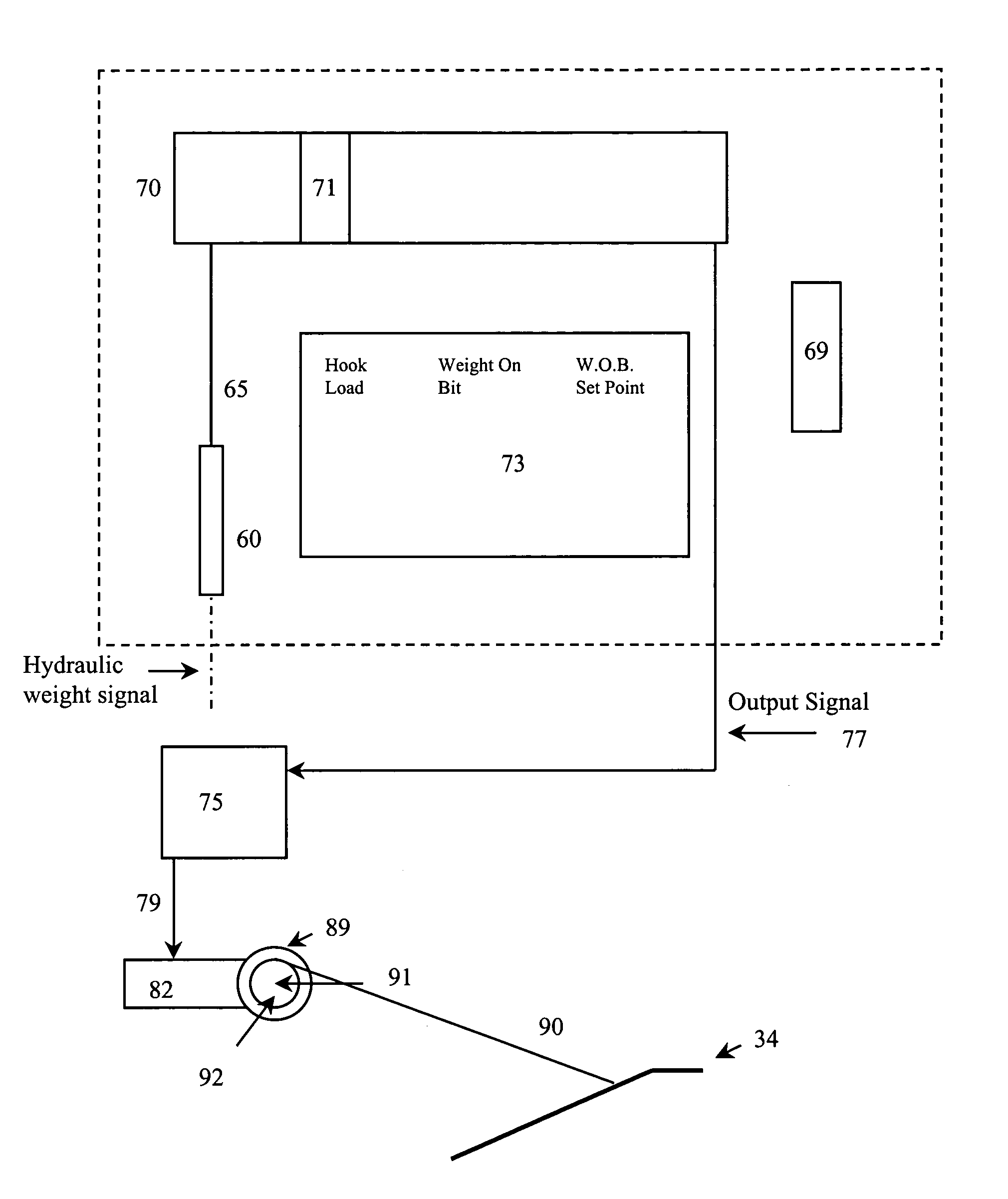
InactiveUS6994172B2Automate processingAccurate startDrilling rodsConstructionsRate of penetrationControl system
An improved oil and gas drilling control system which utilizes improved braking and feedback technology which, in turn, permits more precise weight-on-bit control and more smooth transitions of weight-on-bit than any existing technology. In addition, the system also permits more accurate feedback and control with respect to drilling depth, pipe transitions, and rate of penetration than prior systems.
Owner:AUTO DRILL INC
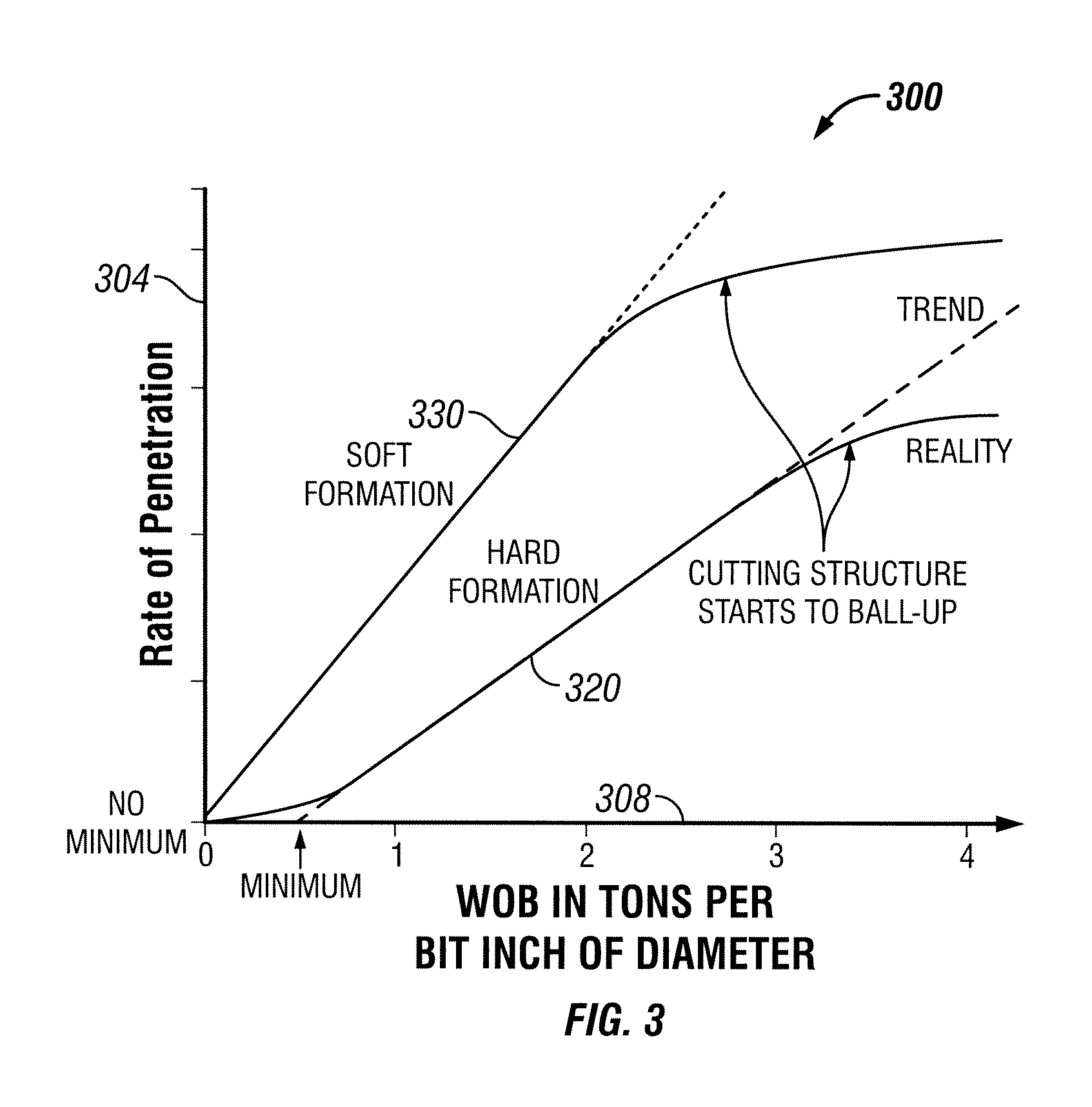
Methods, systems, and tool assemblies for distributing weight between an earth-boring rotary drill bit and a reamer device
Methods, systems, and tool assemblies for distributing weight between a bit and a reamer device are disclosed. For example, at least one of the drill bit and the reamer may be configured to selectively distribute a weight-on-bit between the drill bit and the reamer, such as within a predetermined range. Additionally, methods of drilling wellbores may include selectively distributing a weight-on-bit applied to a bottom hole assembly between a drill bit and a reamer of the bottom hole assembly. Also, a reamer may be configured to exhibit a first maximum rate-of-penetration into a relatively hard formation, and a drill bit may be configured to exhibit a second maximum rate-of-penetration into a relatively soft formation that is less than the first maximum rate-of-penetration.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Multiple input scaling autodriller
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method to determine rock properties from drilling logs
ActiveUS20100191471A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingPorosityRate of penetration
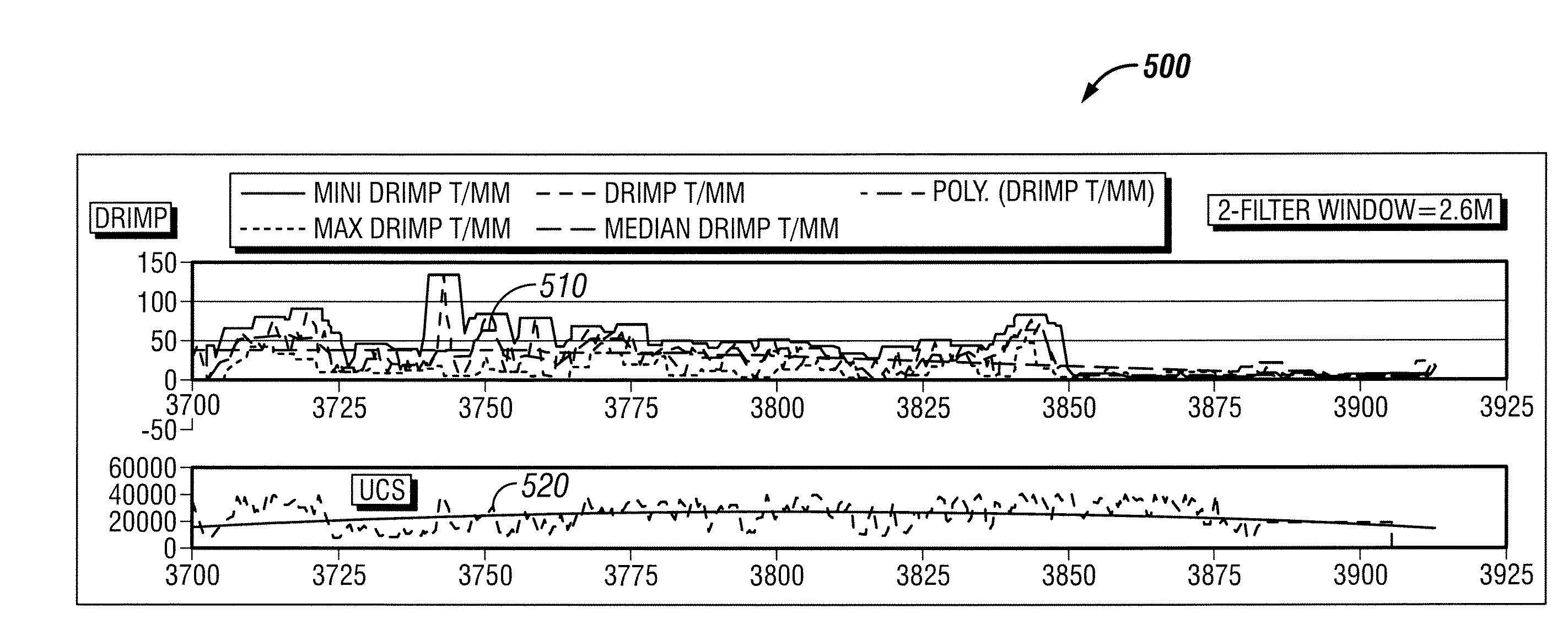
A method of identifying one or more rock properties and / or one or more abnormalities occurring within a subterranean formation. The method includes obtaining a plurality of drilling parameters, which include at least the rate of penetration, the weight on bit, and the bit revolutions per minute, and then normalizing these plurality of drilling parameters by calculating a depth of cut and an intrinsic drilling impedance. Typically, the intrinsic drilling impedance is specific to the type of bit used to drill the wellbore and includes using a plurality of drill bit constants. From this intrinsic drilling impedance, the porosity and / or the rock strength may be determined which is then compared to the actual values to identify the specific type of the one or more abnormalities occurring. Additionally, the intrinsic drilling impedance may be compared to other logging parameters to also identify the specific type of the one or more abnormalities occurring.
Owner:VAREL INT IND
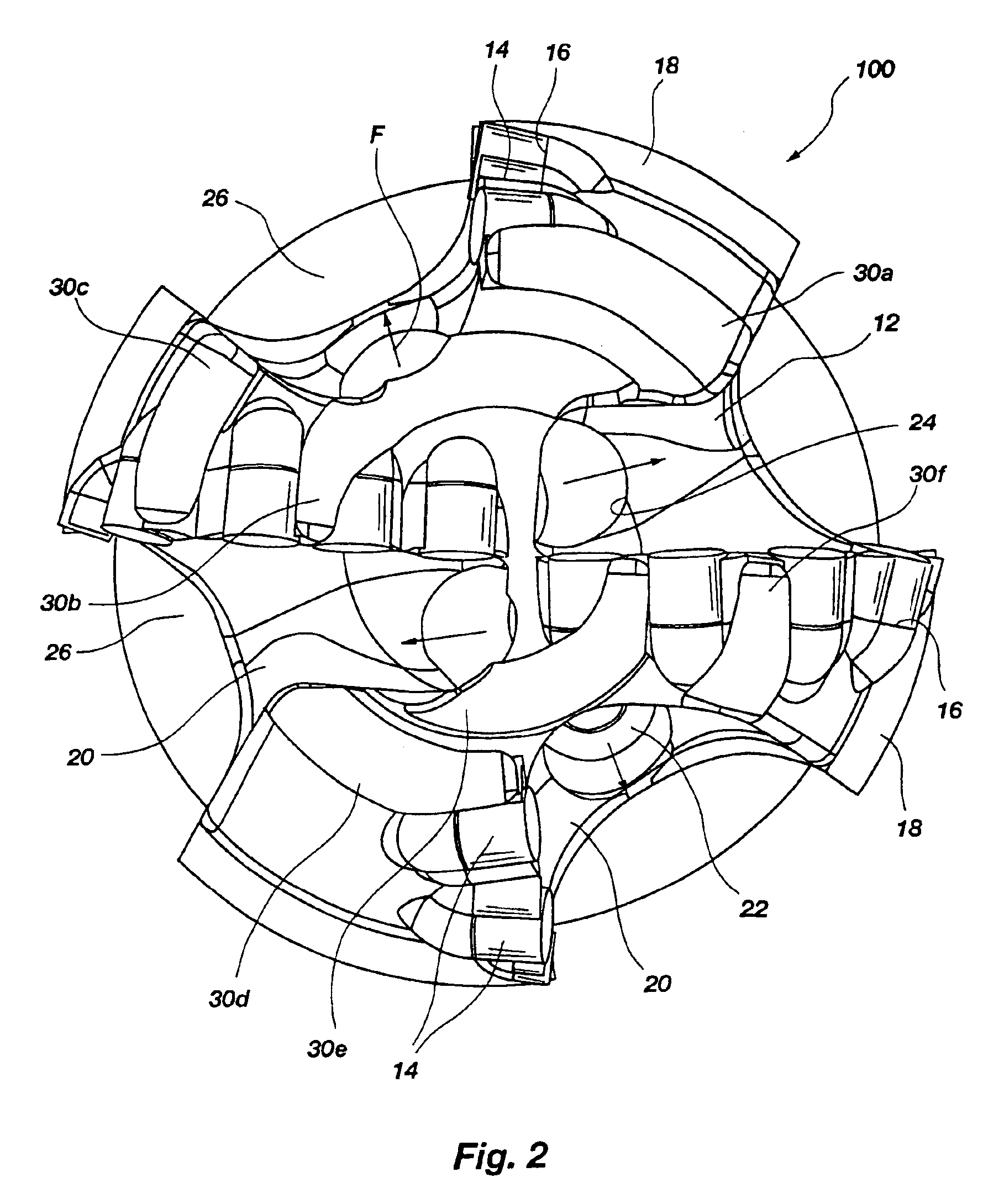
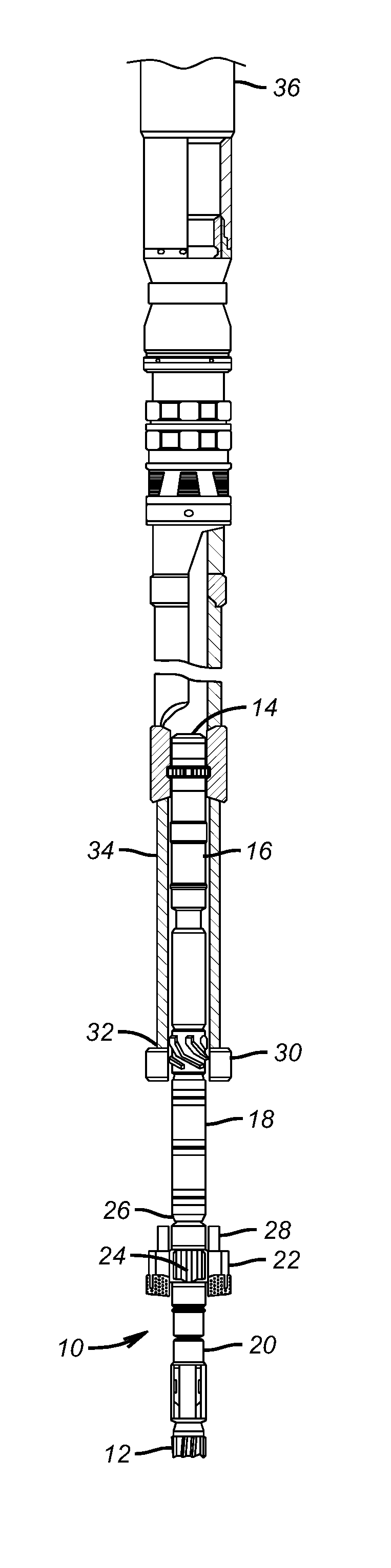
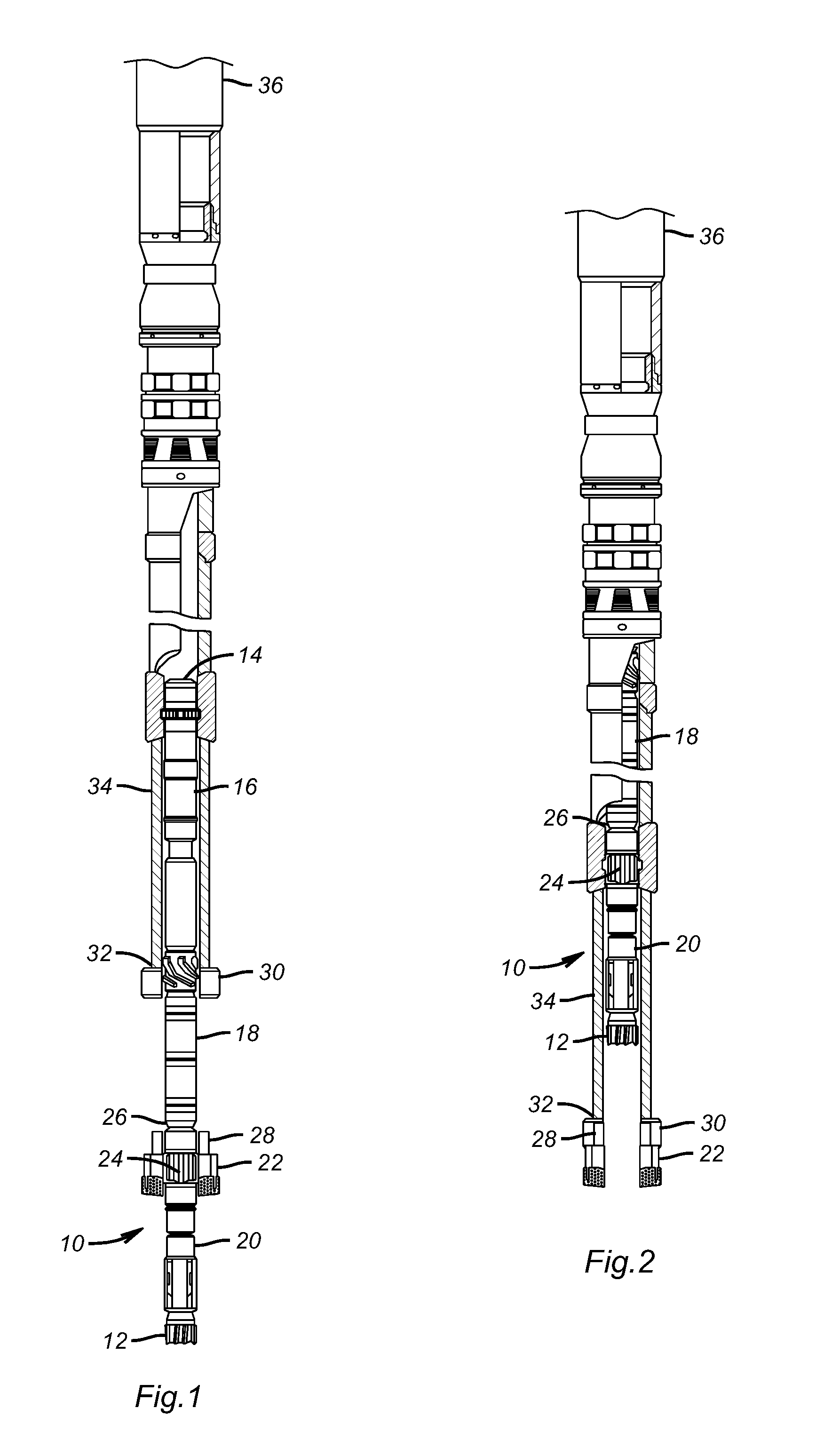
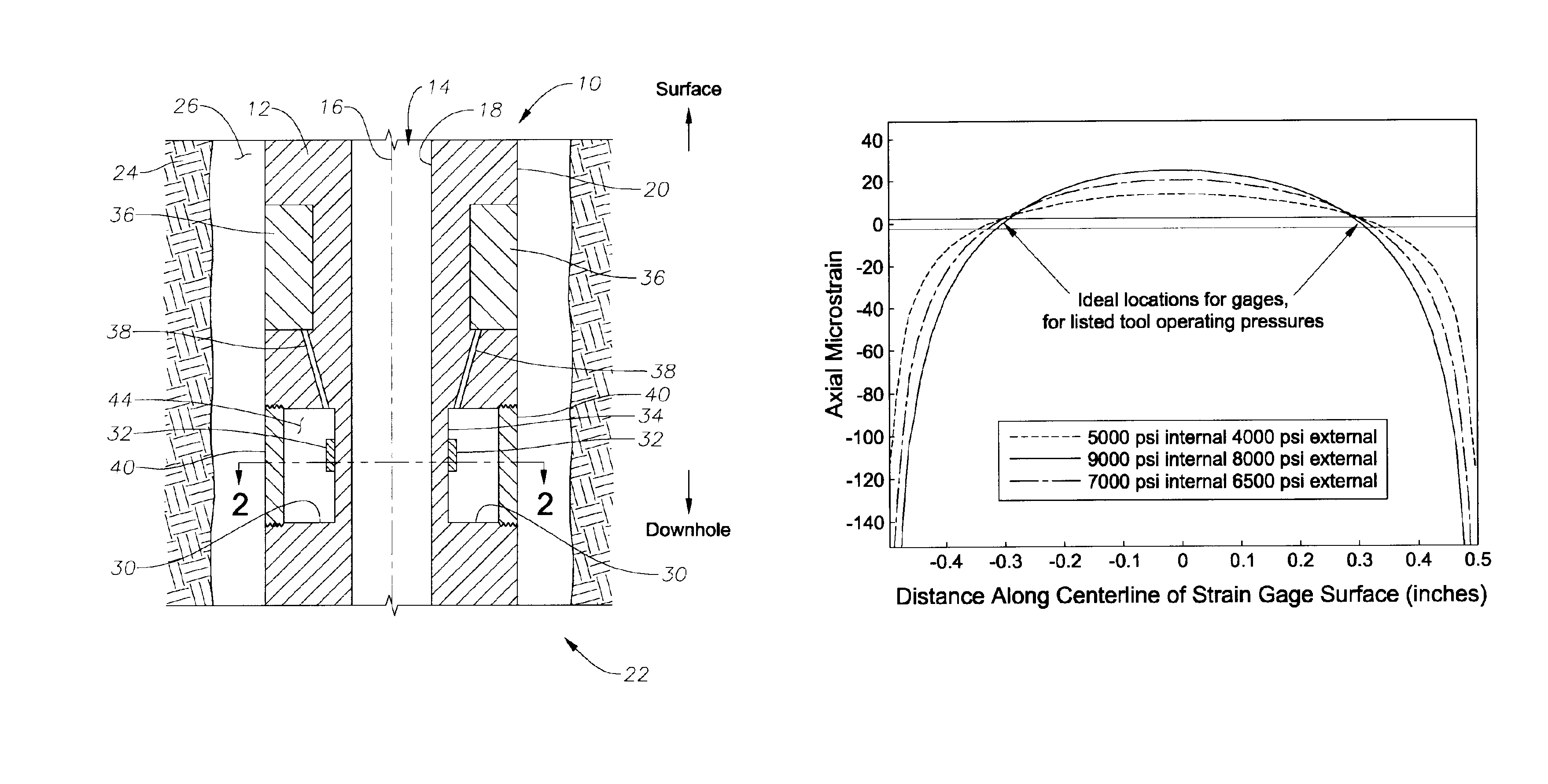
Apparatus for weight on bit measurements, and methods of using same
The present invention is generally directed to a tool for obtaining downhole measurements and methods of using such a tool. In one illustrative embodiment the tool comprises a body, at least one strain gauge cavity in the body, the strain gauge cavity having a strain gauge mounting surface that is located at a position such that a region of approximately zero strain due to at least one downhole operating condition exists on the mounting surface when the tool is subjected to downhole operating conditions, and a strain gauge operatively coupled to the mounting face above the region of approximately zero strain. In another illustrative embodiment, the method comprises providing a measurement tool comprised of a body, at least one strain gauge cavity in the body, the strain gauge cavity having a strain gauge mounting surface that is located at a position such that a region of approximately zero strain due to at least one downhole operating condition exists on the mounting surface when the tool is subjected to downhole operating conditions, and a strain gauge coupled to the mounting face above the region of approximately zero strain. The method further comprises positioning the tool in a subterranean well bore and obtaining measurement data using the strain gauge in the tool.
Owner:GP USA HLDG LLC
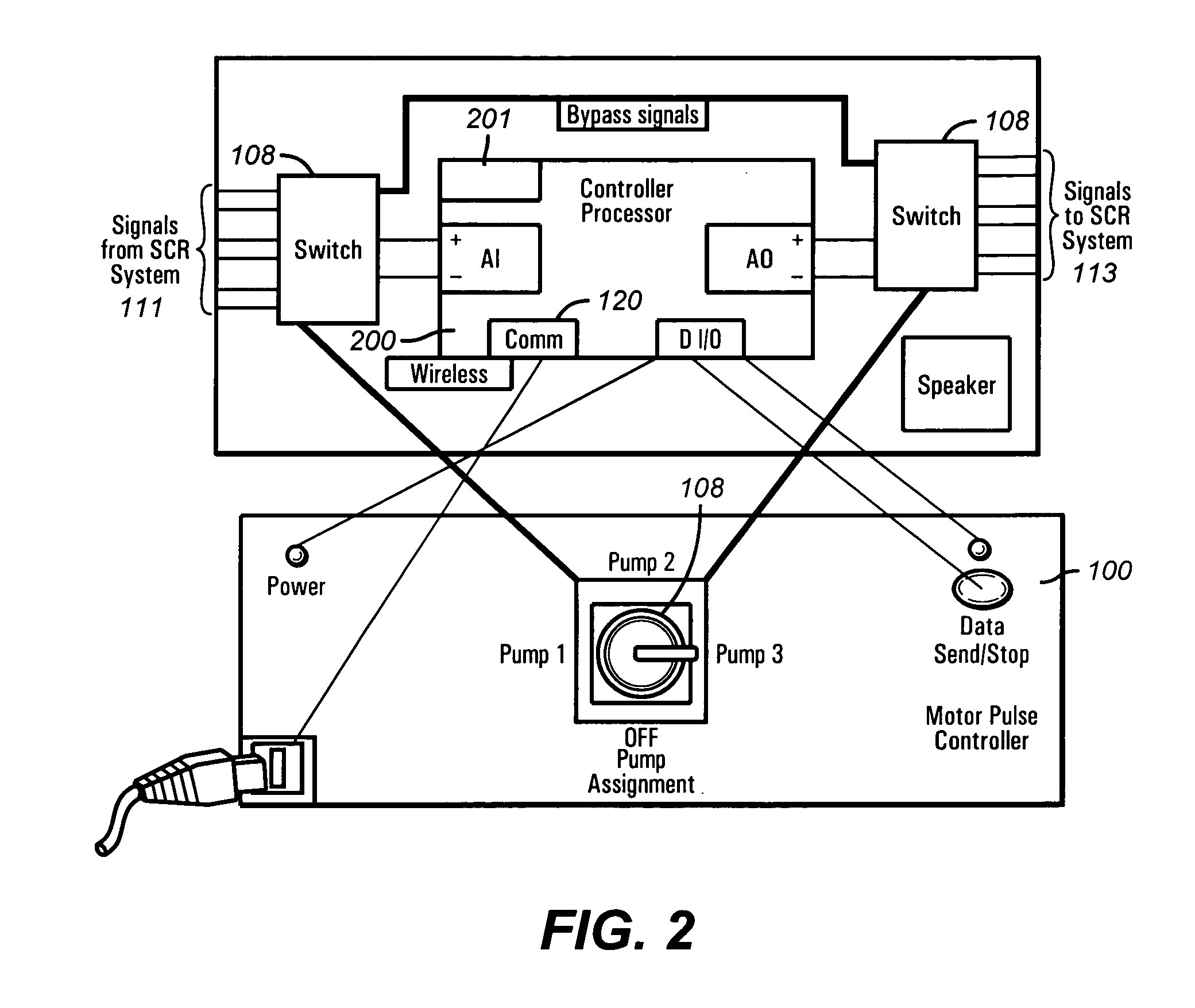
Motor pulse controller
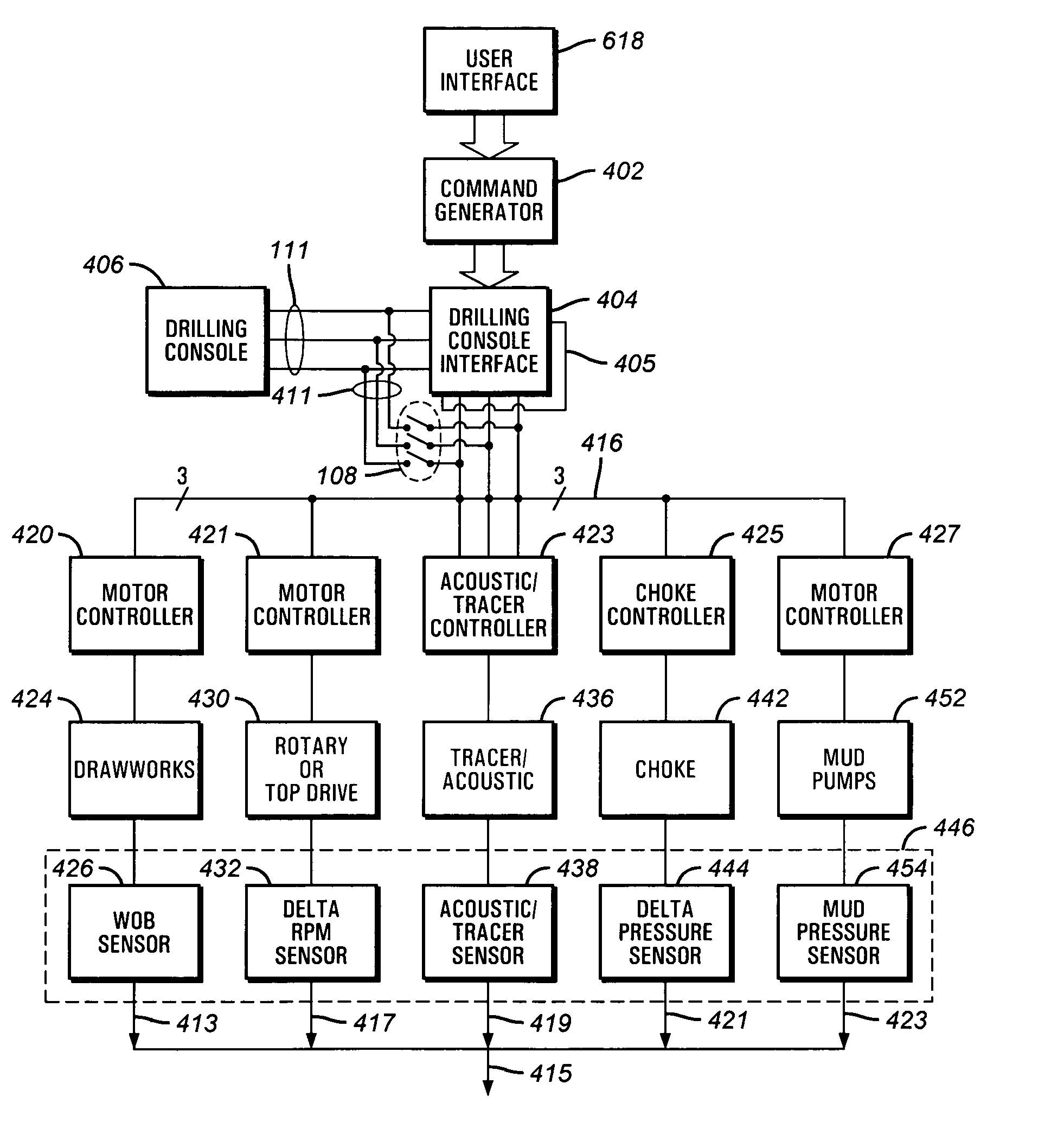
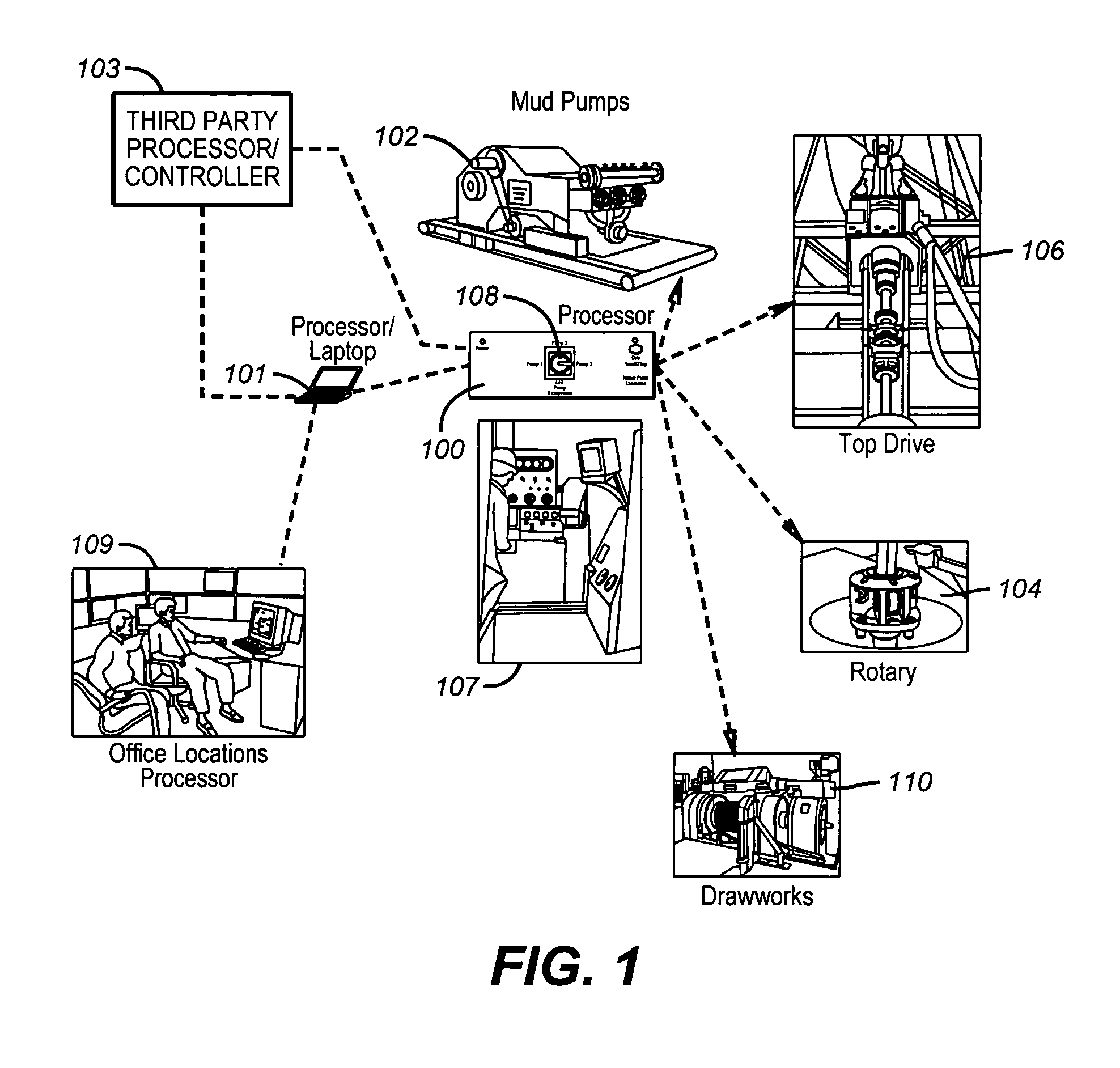
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for generating one or more than one physically detectable physical influence changes to control or manipulate a down hole device. The present invention intercepts existing control signals to various controllers on the rig and superimposes an encoded command on these existing control signals. The controllers comprise of motor drives, choke controllers, acoustic pulse generators, tracer injectors and other controllers that are used to generate a physically detectable changes in the rig environment. The encoded command acting on existing or new controllers generates a perceptible change in a physical parameter such as a variation in drilling mud pressure, a variation in drill string rotation speed, a variation is weight on bit, generation of acoustic pulse, or a variation in tracer injection properties. The physical change is sensed by a down hole device and interpreted as information indicating to the down hole device that it is to execute a command or adjust an operating parameter.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Spring-operated Anti-stall tool
ActiveUS20090173539A1Maintaining WOBIncreasing WOBDrilling rodsConstructionsReciprocating motionWorking pressure
An anti-stall tool in an oil well drilling assembly that controls reciprocation of the drill bit by controller that alters weight-on-bit (WOB) depending upon measured downhole pressure or torque. The downhole controller keeps the drill bit rotating by maintaining WOB during normal drilling operations, increasing WOB if sensed working pressure indicates that drill bit loading or torque is undesirably low, and reversing WOB by applying a spring force for retracting the drill bit if excessive working pressure or torque is sensed.
Owner:WWT NORTH AMERICA HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com