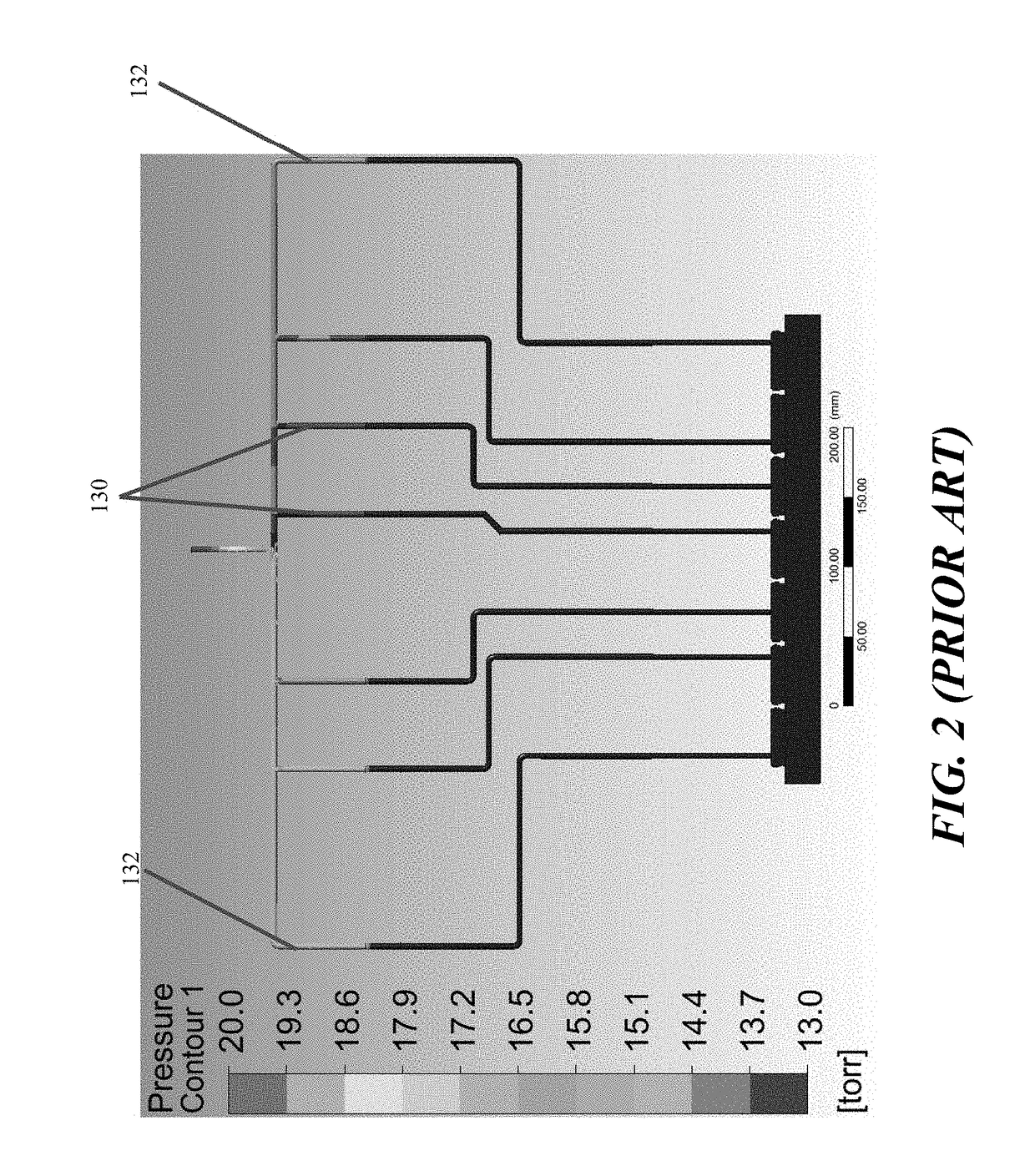
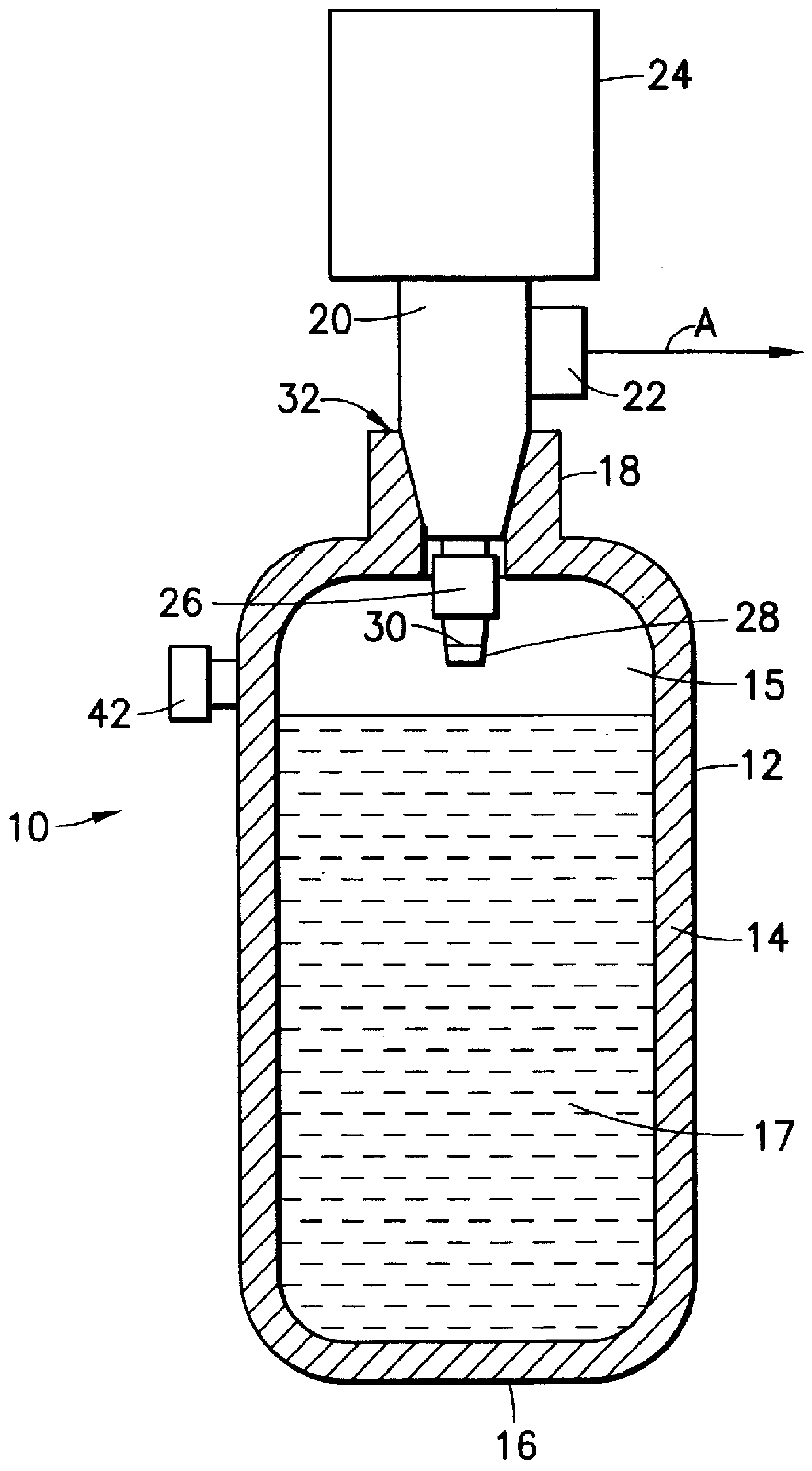
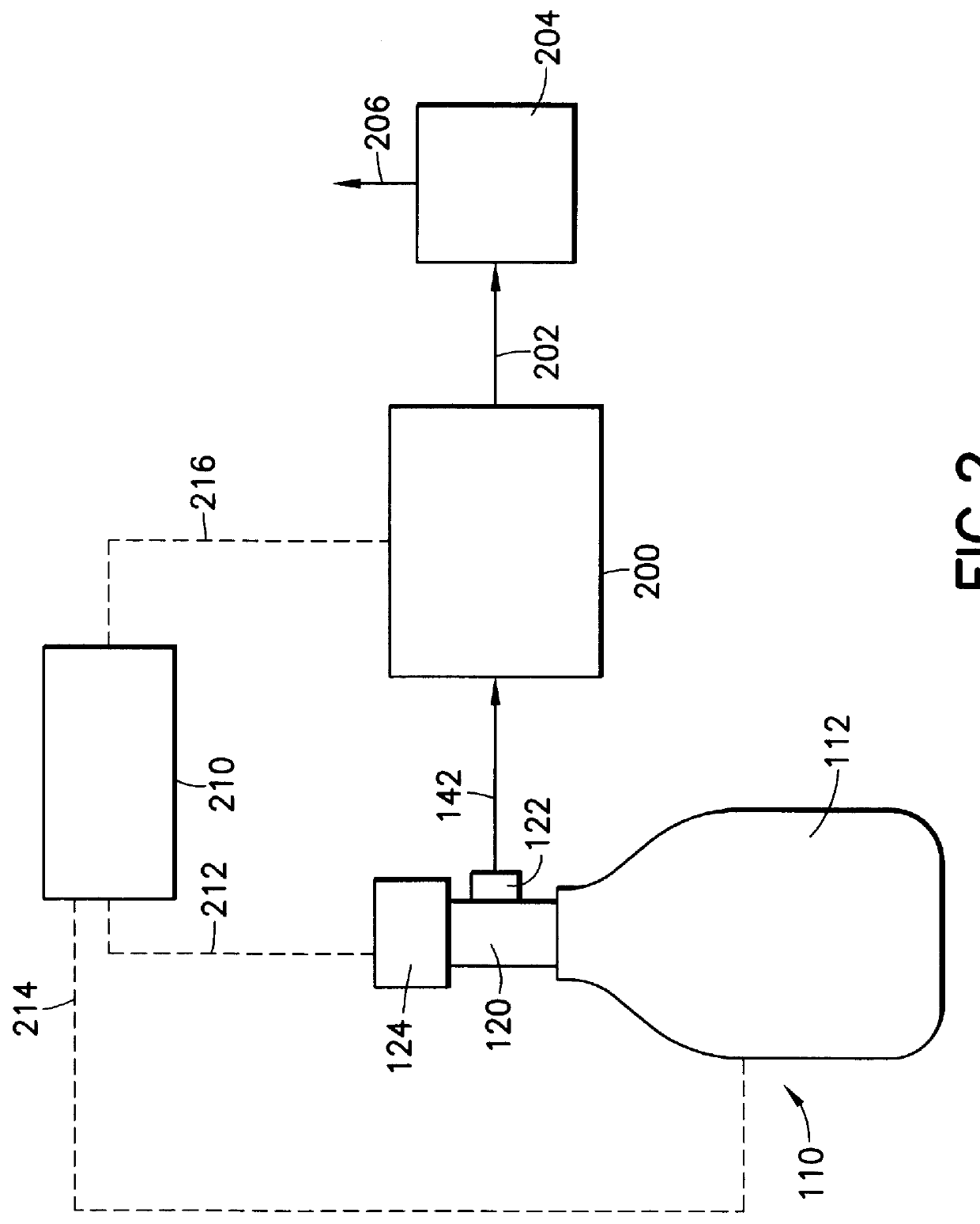
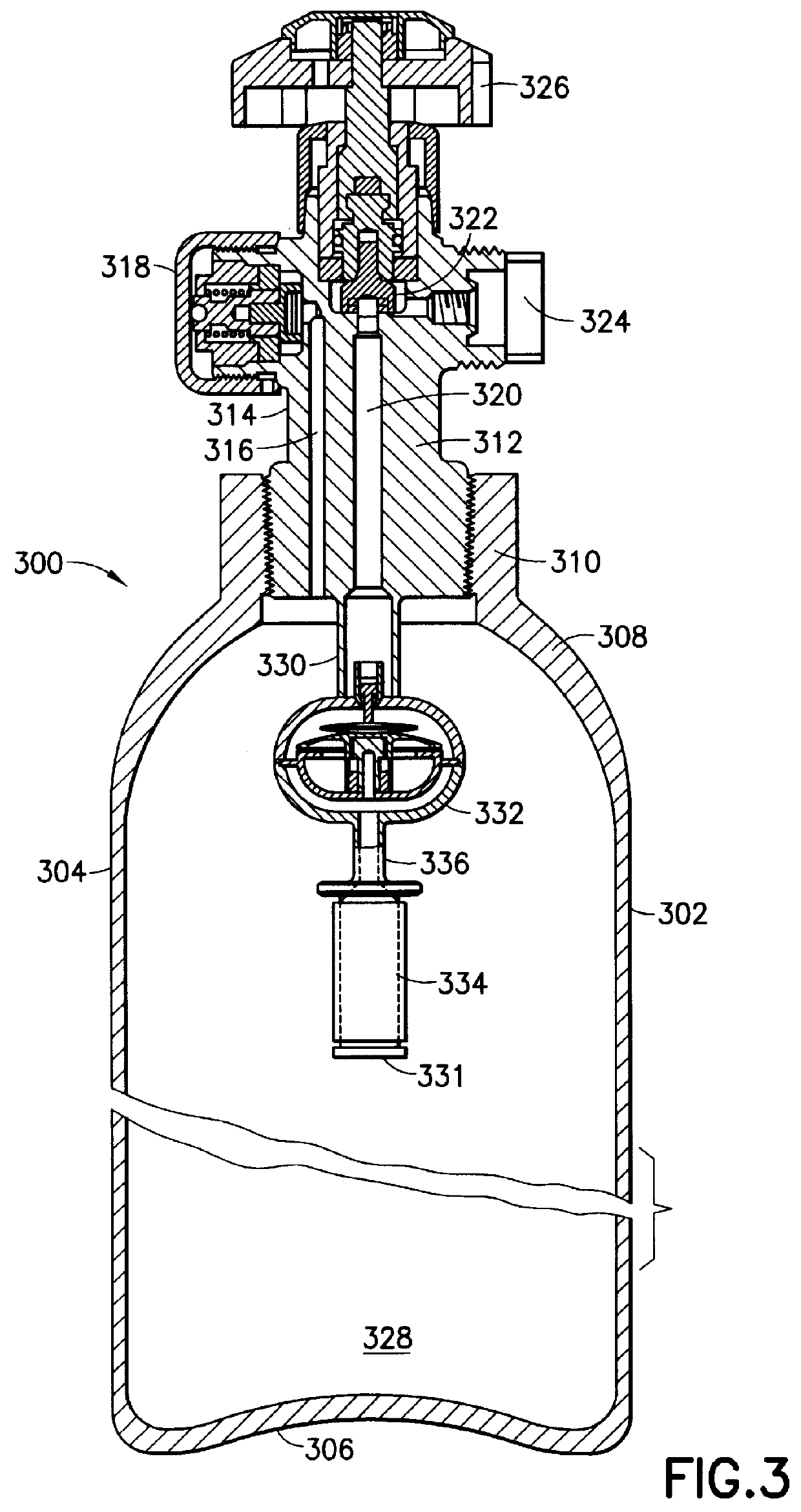
Patents
Literature
31137 results about "Streamflow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Streamflow, or channel runoff, is the flow of water in streams, rivers, and other channels, and is a major element of the water cycle. It is one component of the runoff of water from the land to waterbodies, the other component being surface runoff. Water flowing in channels comes from surface runoff from adjacent hillslopes, from groundwater flow out of the ground, and from water discharged from pipes. The discharge of water flowing in a channel is measured using stream gauges or can be estimated by the Manning equation. The record of flow over time is called a hydrograph. Flooding occurs when the volume of water exceeds the capacity of the channel.
Immersible thermal mass flow meter
ActiveUS6971274B2Quality improvementImprove measurement qualityVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsThin film sensorEngineering
Owner:SIERRA INSTR
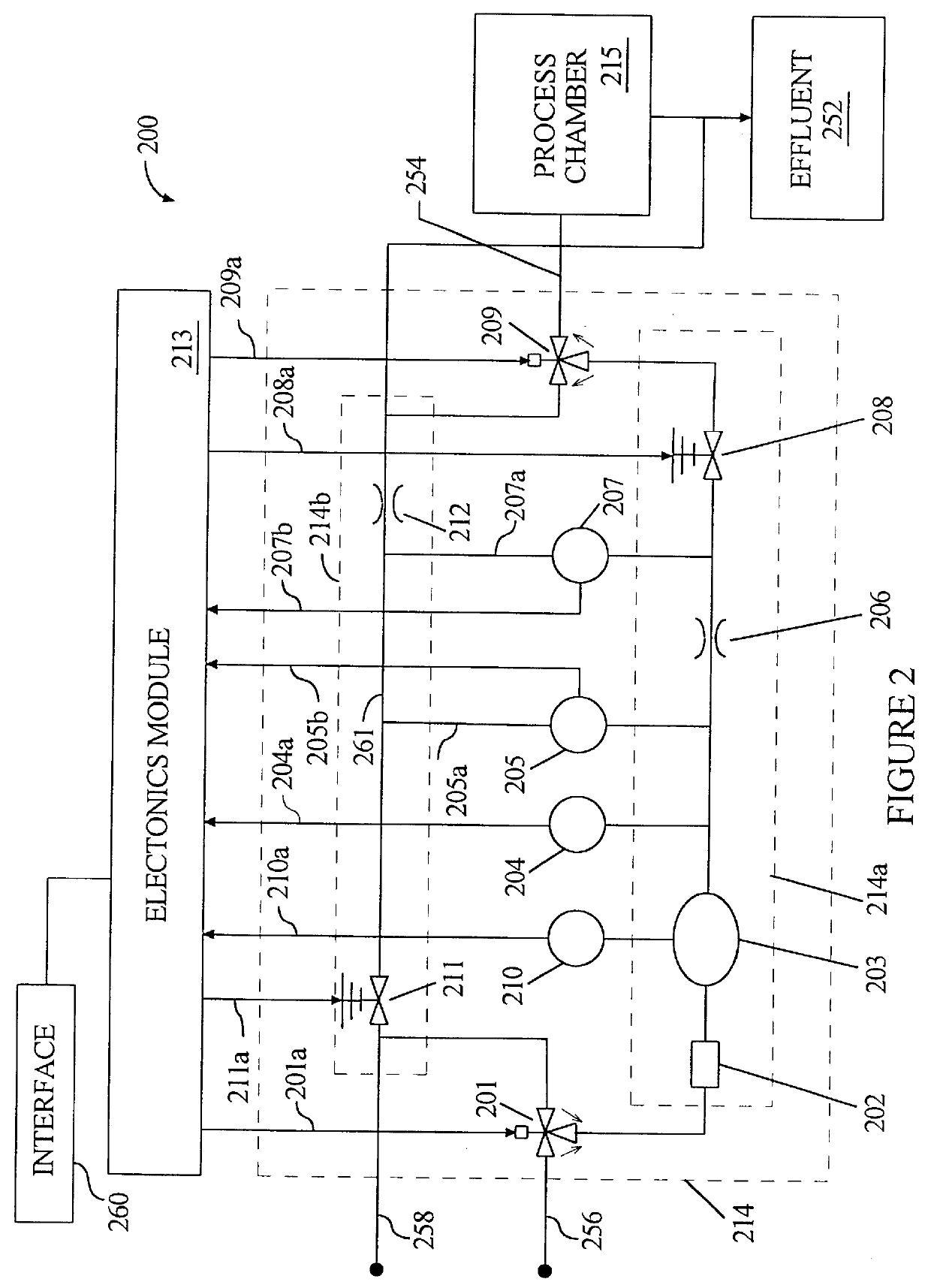
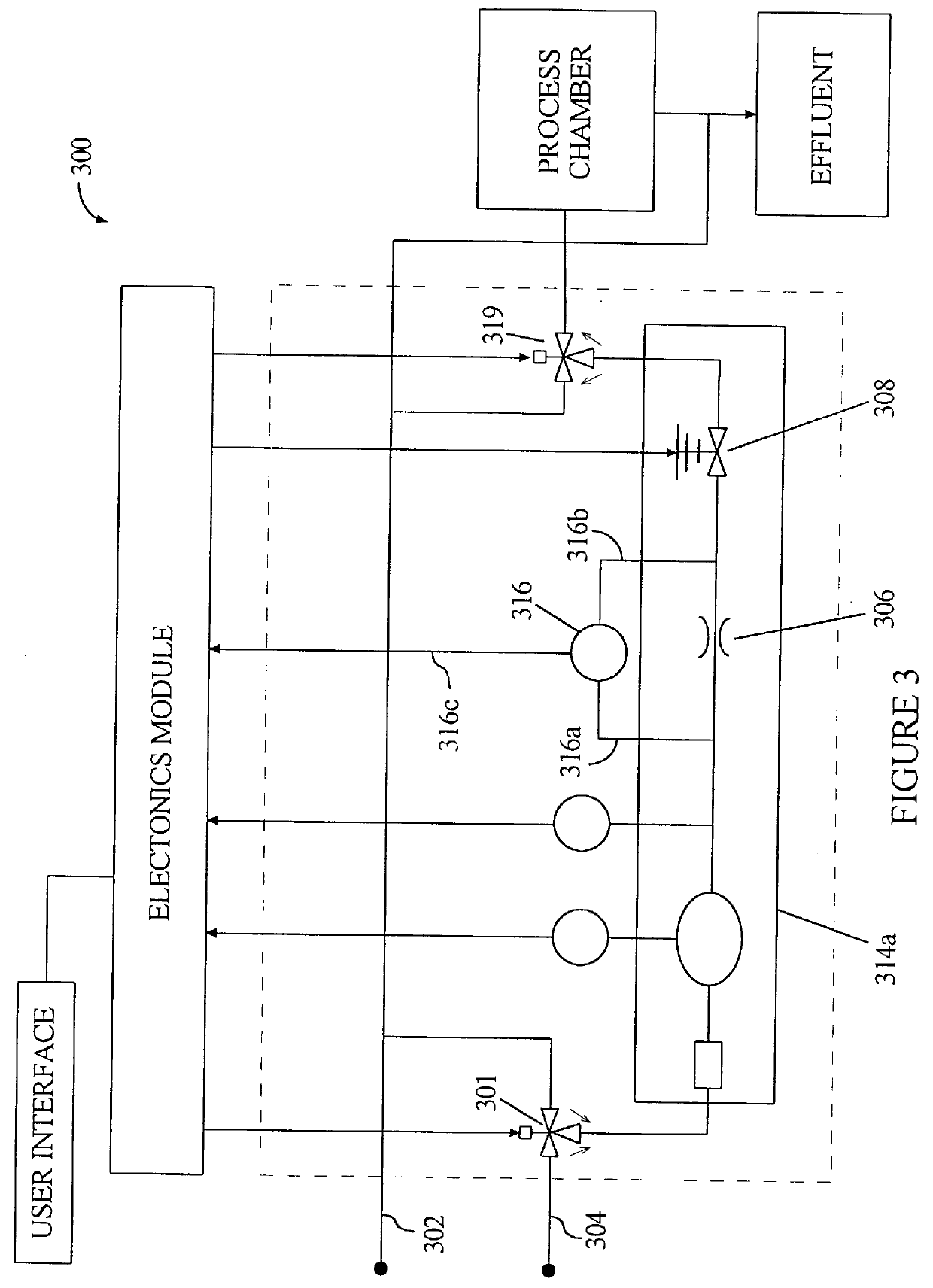
Method for wide range gas flow system with real time flow measurement and correction
InactiveUS6119710AAccurate measurementAccurate flowOperating means/releasing devices for valvesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsDifferential pressureInlet valve
A gas delivery system accurately measures and optionally regulates mass flow rate in real time. A fluid conduit connects an inlet valve, calibration volume, flow restrictor, and outlet valve in series. Pressure and temperature sensors are coupled to the calibration volume. One or more pressure sensors may be attached across the flow restrictor. Alternatively, an absolute pressure sensor may be attached upstream of the flow restrictor. One embodiment of differential pressure sensors comprises a floating reference differential pressure sensor, including a first transducer attached to the fluid conduit upstream of the flow restrictor and a second transducer attached to the conduit downstream of the flow restrictor. In this embodiment, each transducer receives a reference pressure from a reference source, and optionally, after the calibration volume is charged, the floating reference differential pressure transducers are calibrated. When gas flow is initiated, differential and / or absolute pressure measurements are repeatedly taken, and a measured mass flow rate calculated thereon. Gas flow is adjusted until the measured mass flow rate reaches a target mass flow. Using the temperature / pressure sensors at the calibration volume, repeated calculations of actual flow rate are made to uncover any discrepancy between actual and measured mass flow rates. Whenever a discrepancy is found, the manner of calculating measured mass flow is conditioned to account for the discrepancy; thus, the measured mass flow rate more accurately represents the actual mass flow rate thereby providing an actual mass flow rate more accurately achieving the target mass flow rate.
Owner:CYBER INSTR TECH LLC AN ARIZONA LIMITED LIABILITY +1
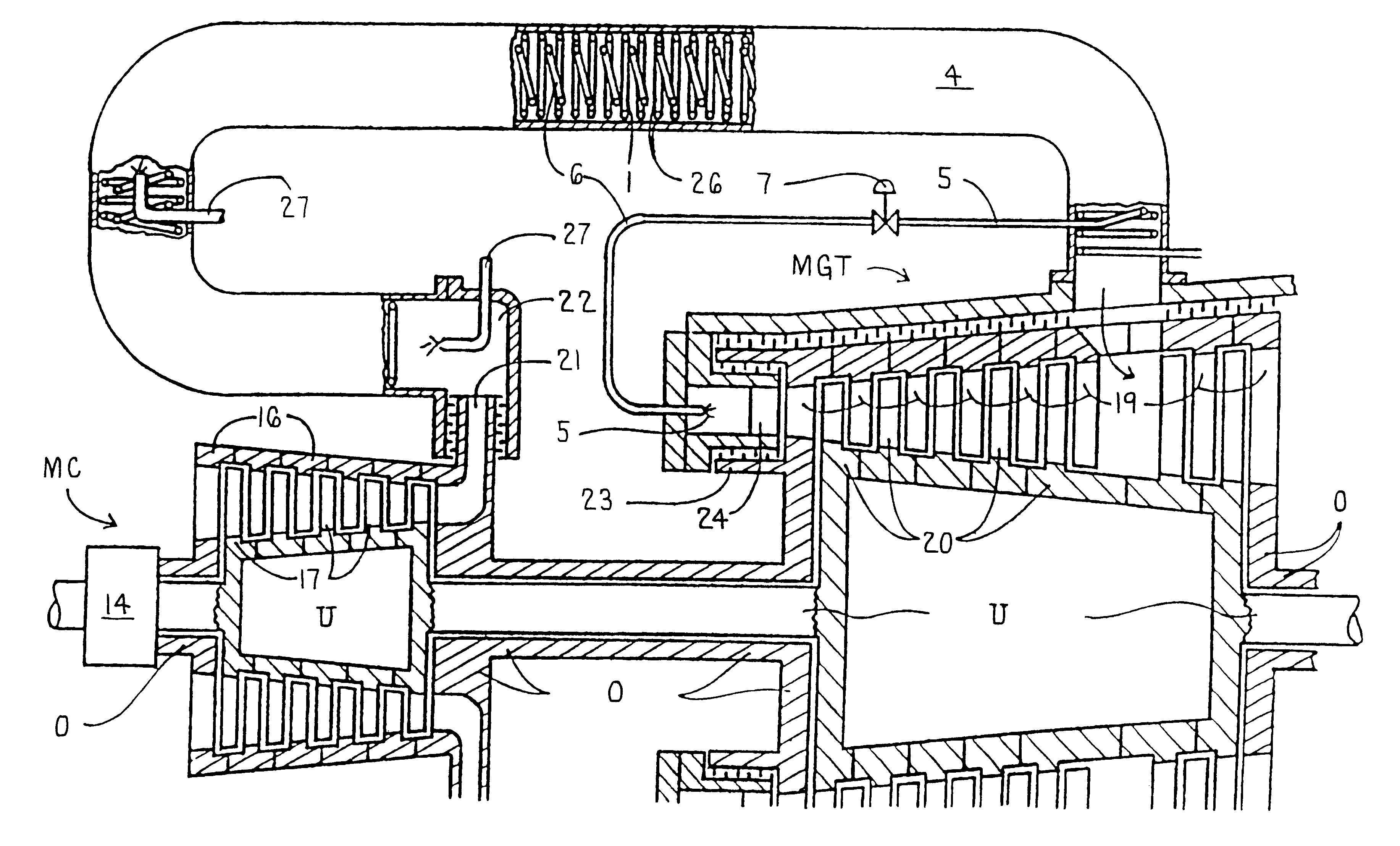
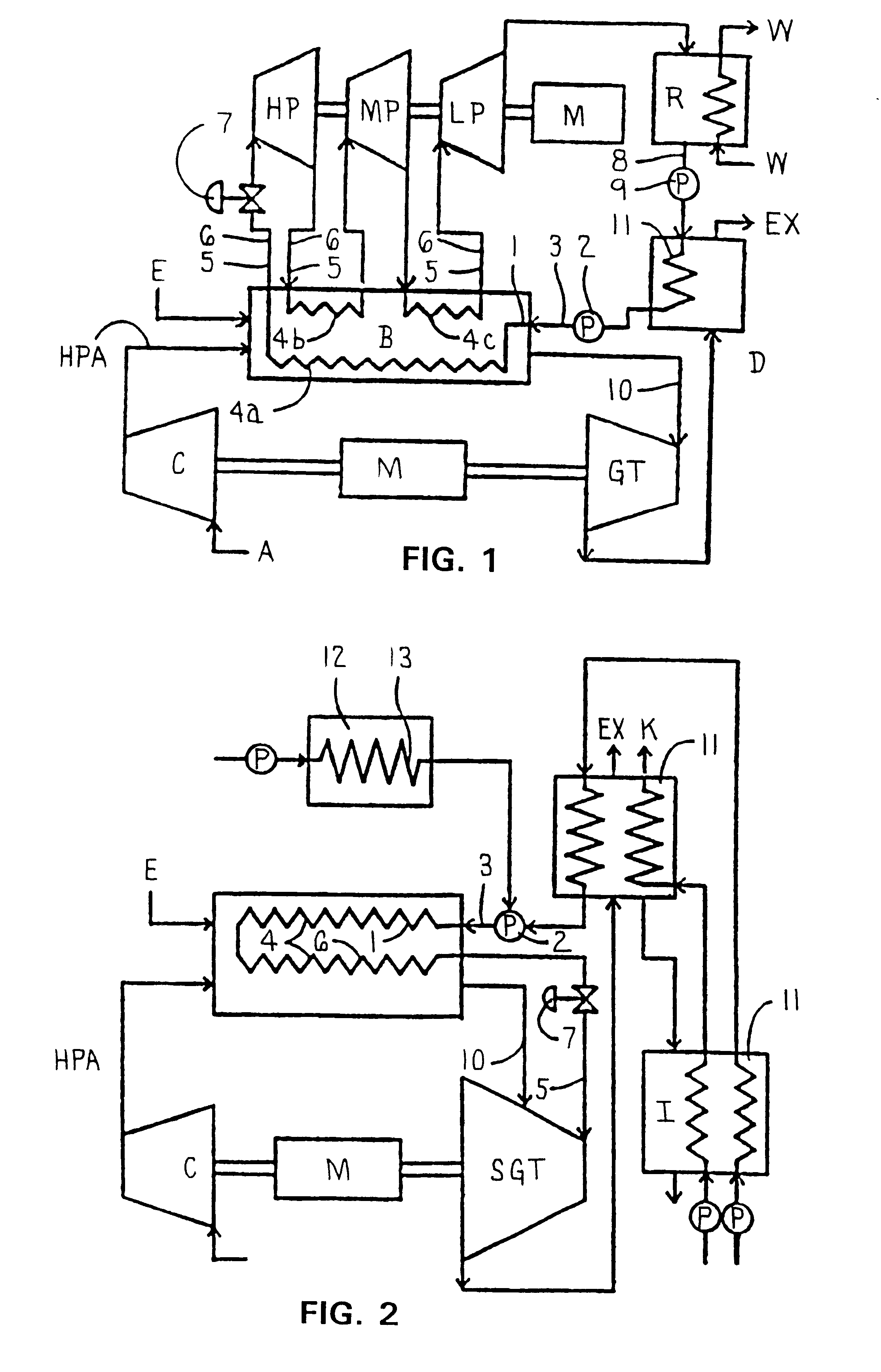
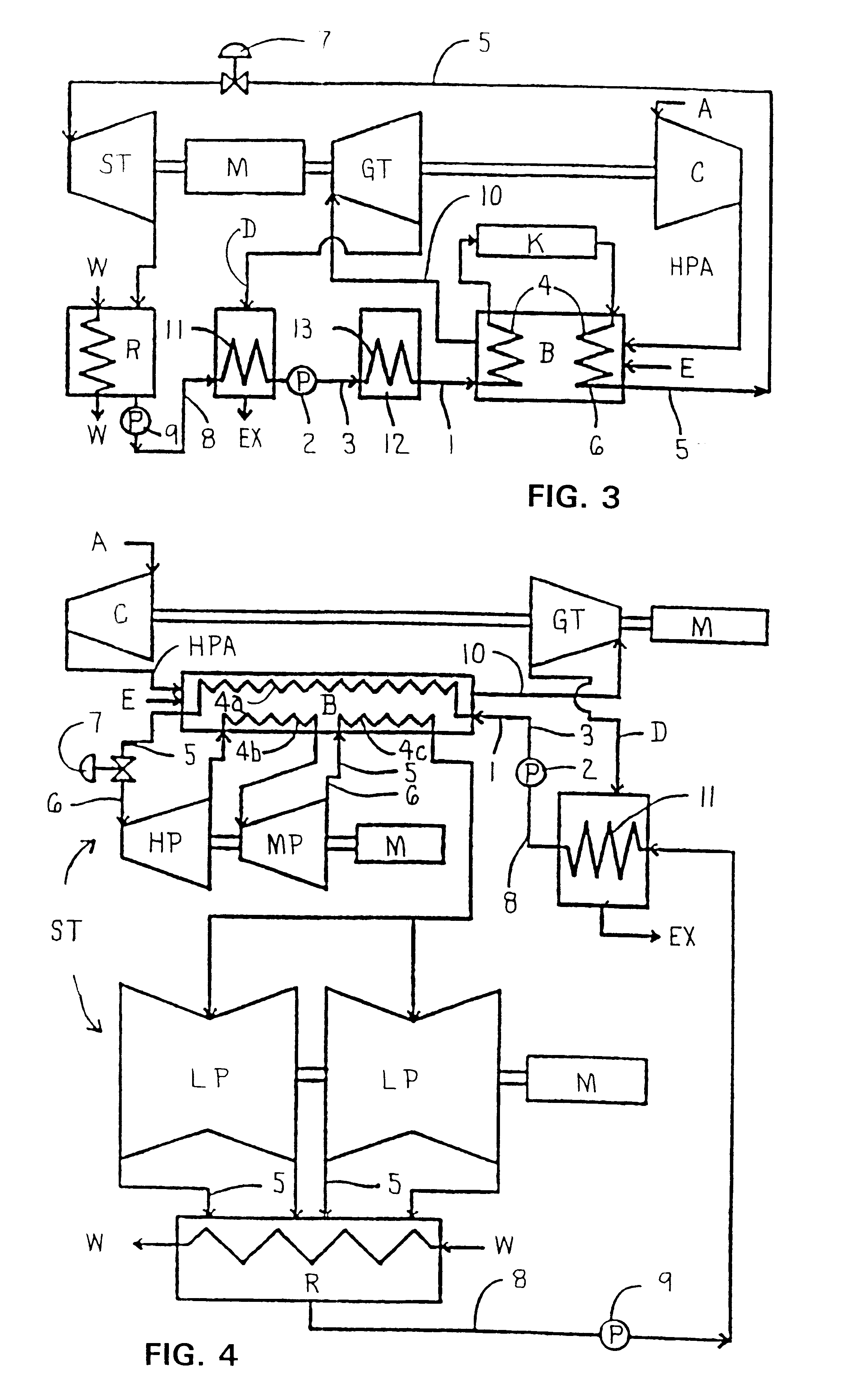
Combined steam and gas turbine engine with magnetic transmission
InactiveUS6263664B1Wide areaImprove system efficiencyContinuous combustion chamberGearingThermal energyCombustion chamber
In a combined steam and gas turbine engine cycle, a combustion chamber is made durable against high pressure and enlarged in length to increase the operation pressure ratio, without exceeding the heat durability temperature of the system while increasing the fuel combustion gas mass flow four times as much as the conventional turbine system and simultaneously for greatly raising the thermal efficiency of the system and specific power of the combined steam and gas turbine engine.Water pipes and steam pipes are arranged inside the combustion chamber so that the combustion chamber can function as a heat exchanger and thereby convert most of the combustion thermal energy into super-critical steam energy for driving a steam turbine and subsequently raising the operation pressure ratio and the thermal efficiencies of the steam turbine cycle and gas turbine cycle. The combustion gas mass flow can be also increased by four times as much as the conventional turbine system (up to the theoretical air to fuel ratio) and the thermal efficiency and the specific power of the gas turbine cycle are considerably increased.Further, the thermal efficiency of the combined system is improved by installing a magnetic friction power transmission system to transmit the power of the system to outer loads.
Owner:TANIGAWA HIROYASU +1
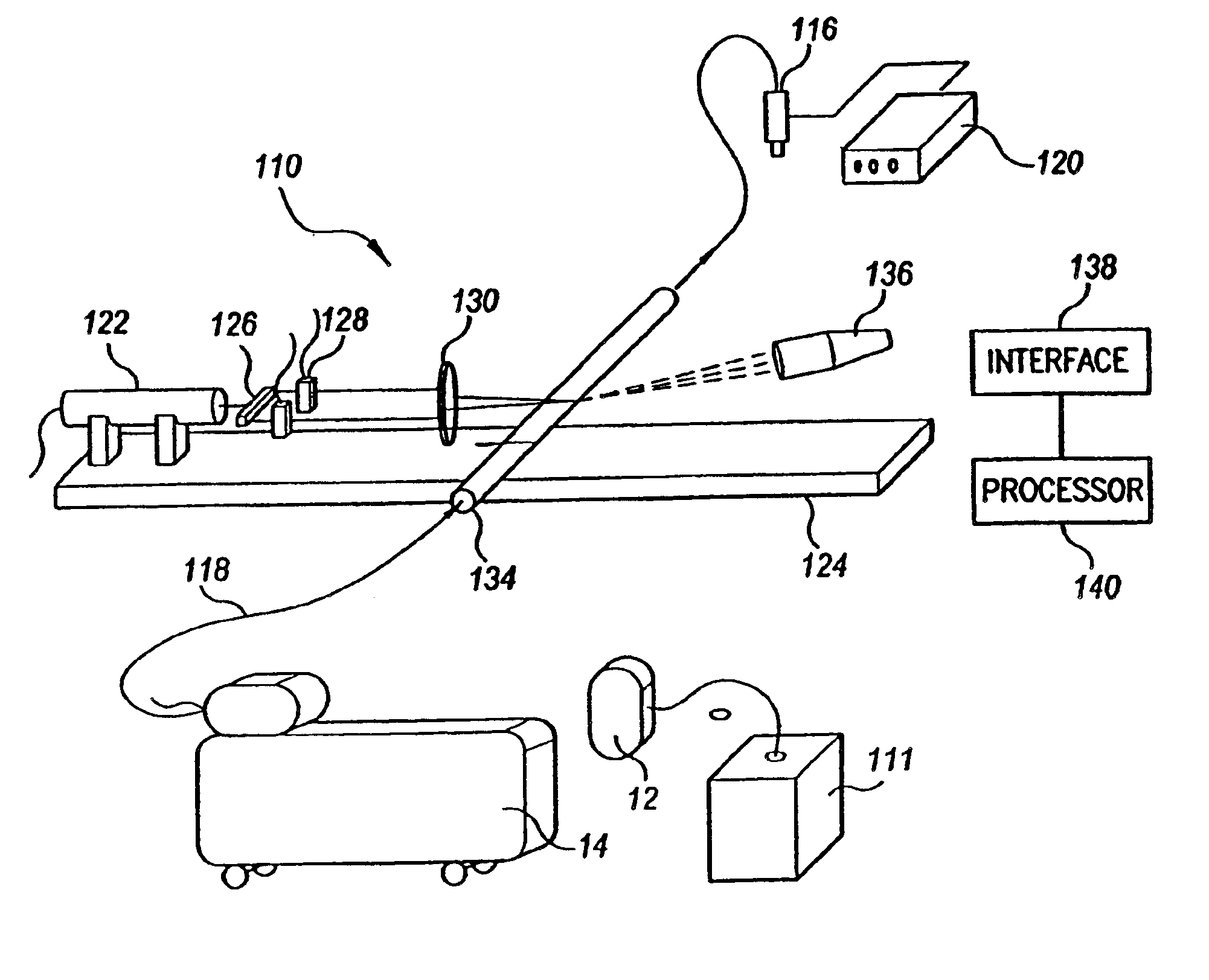
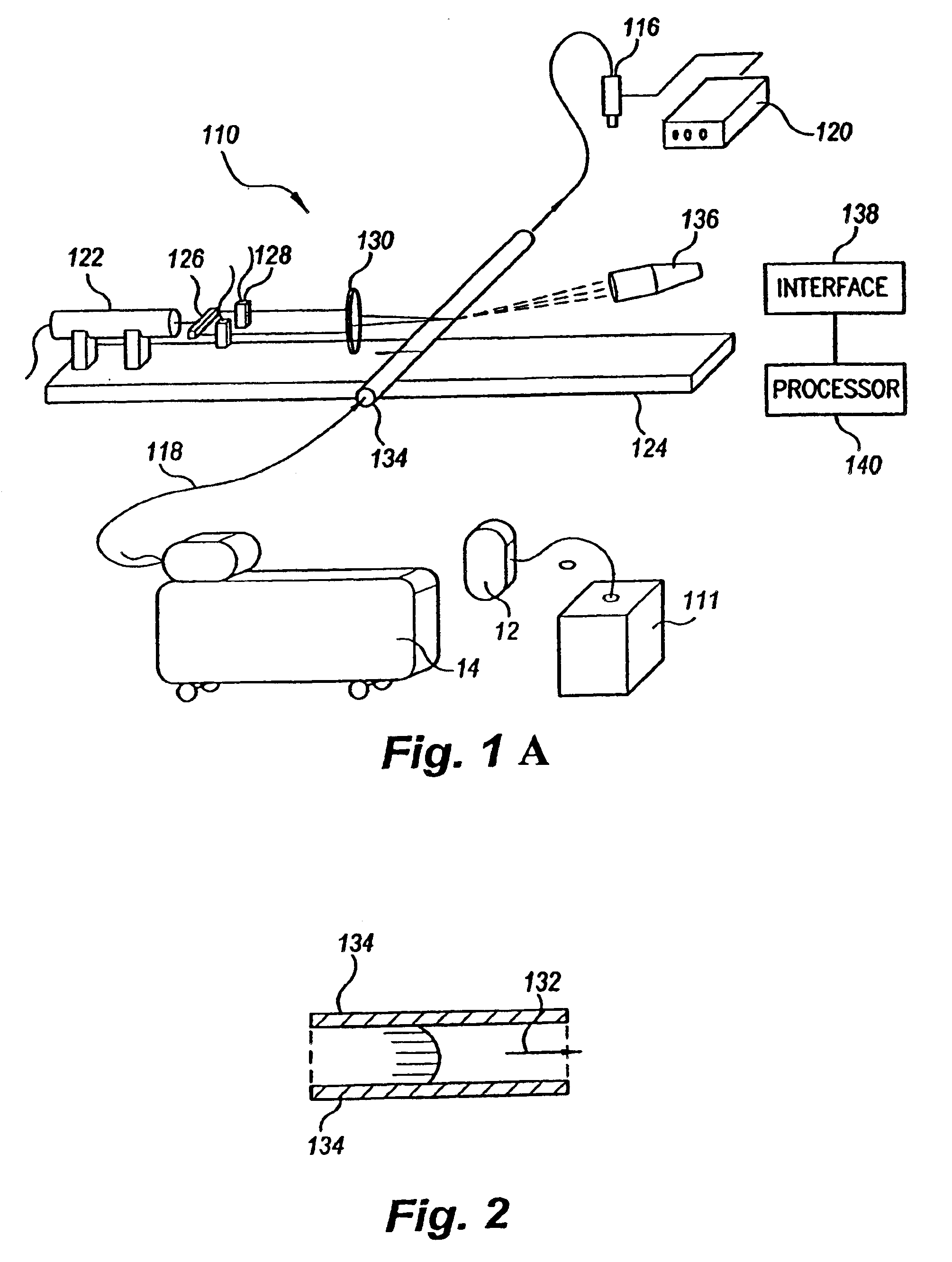
Flow meter
Various embodiments of the present invention provide a flow meter device having a laser Doppler anemometer (LDA) which measures the instantaneous center line velocity of fluid flow in a pipe. The flow meter may process the instantaneous velocity so obtained to compute the volumetric flow rate, mass rate, and / or other flow characteristics (e.g., as instantaneous quantities and / or integrated over a time interval) The flow meter may use an electronic processing method. The electronic processing method may provide essentially an exact solution to the Navier-Stokes equations for any periodically oscillating flow.
Owner:COMBUSTION DYNAMICS
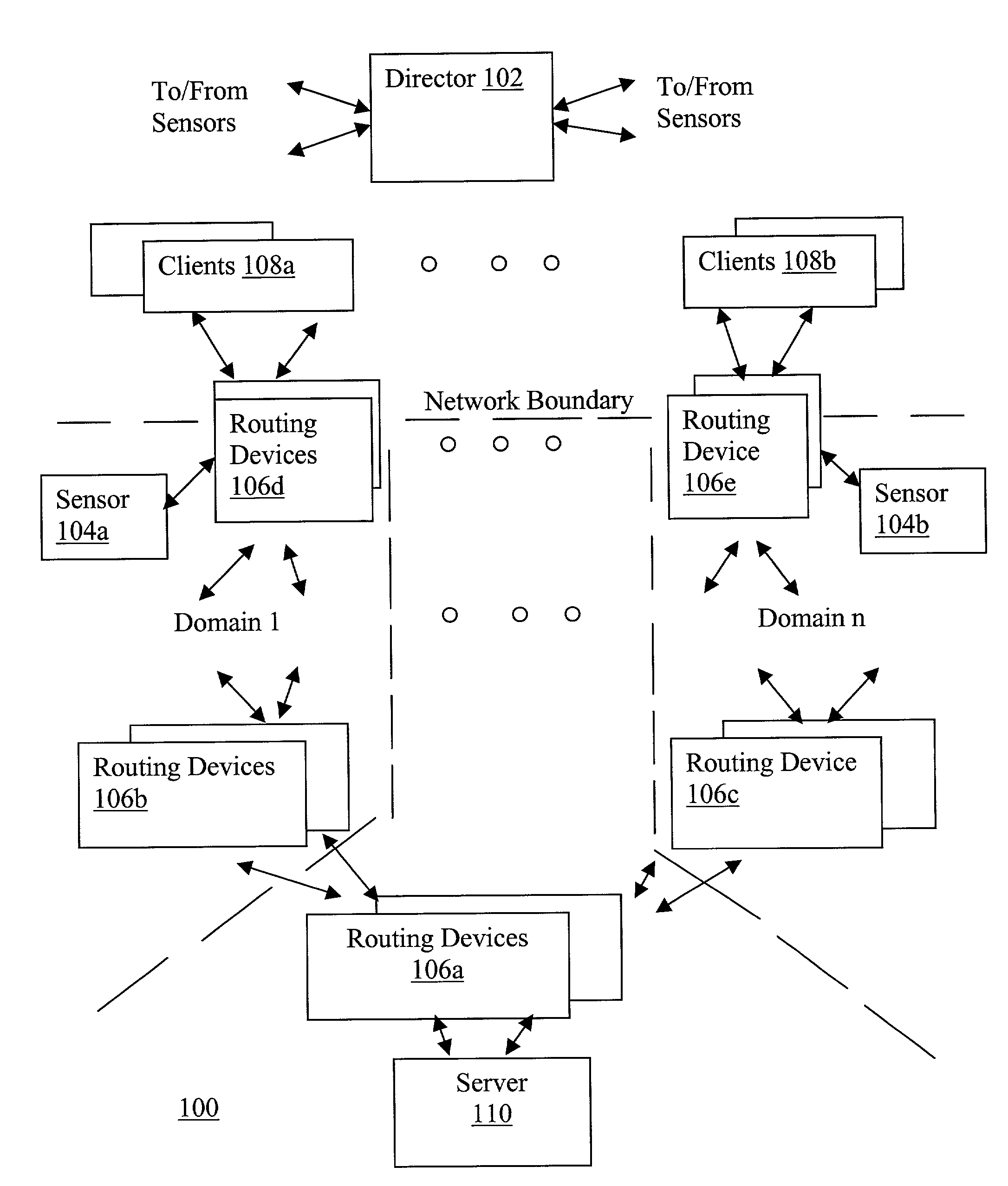
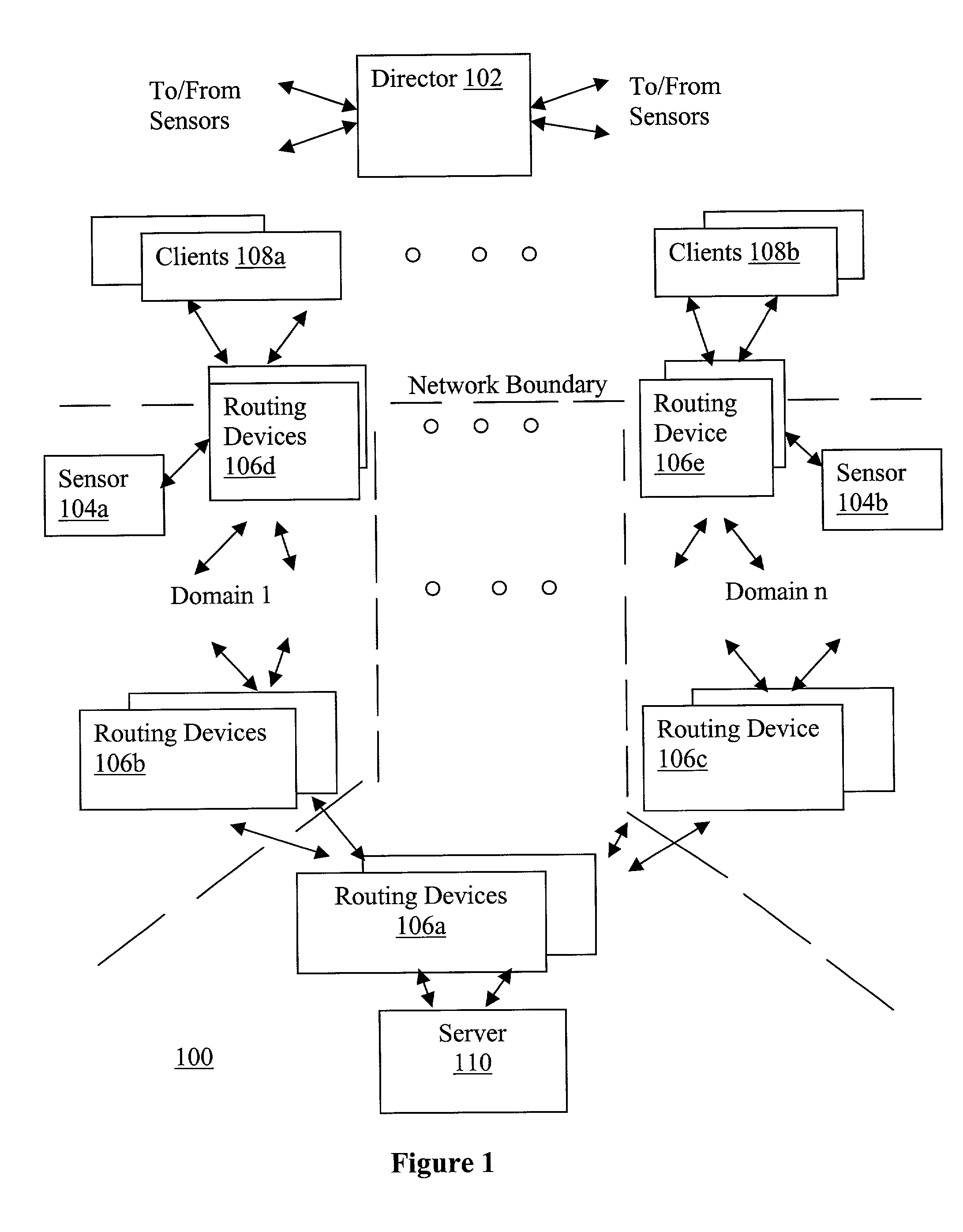
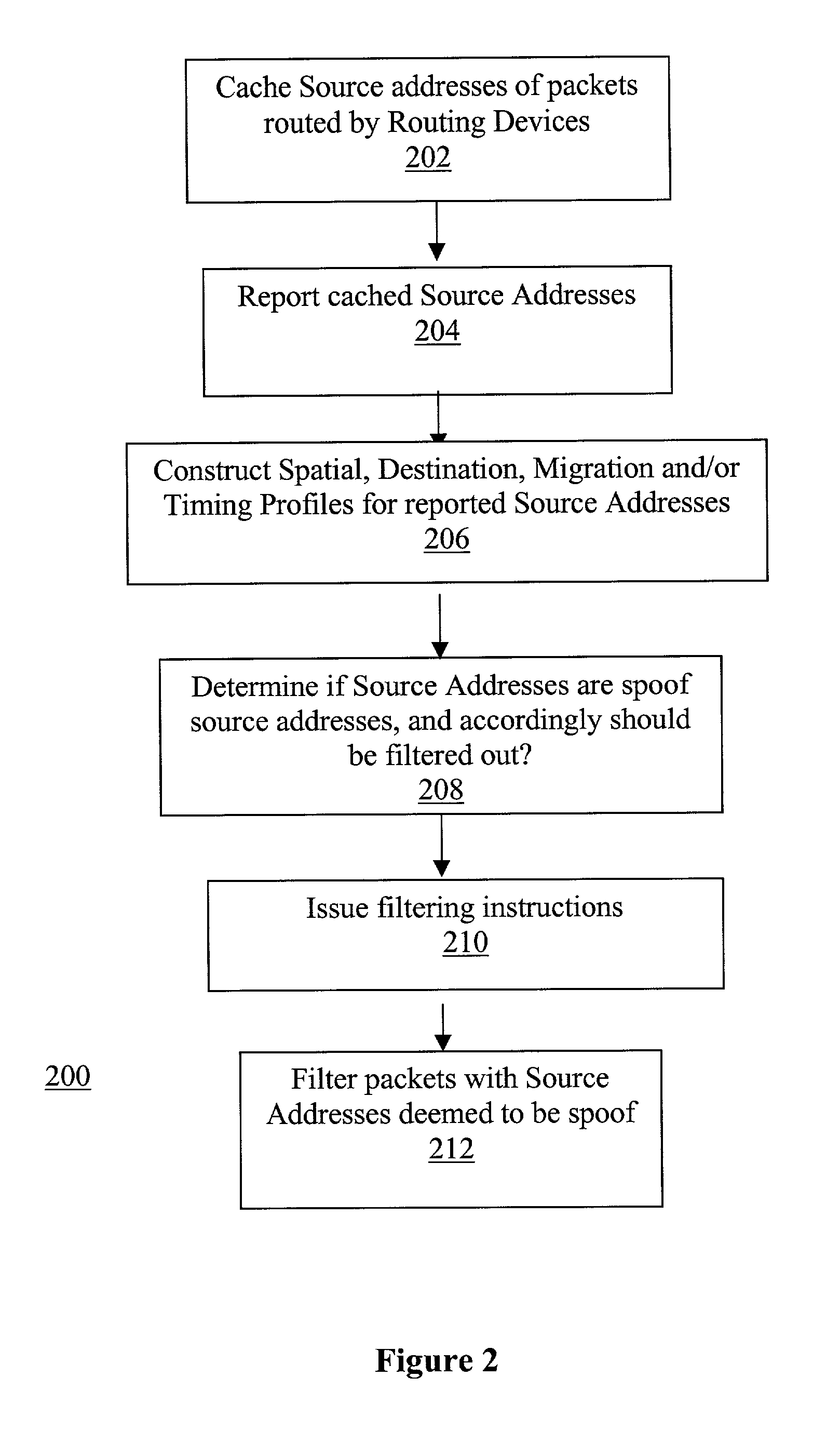
Network traffic regulation including consistency based detection and filtering of packets with spoof source addresses
InactiveUS7444404B2Ensuring quality of serviceEnsure qualityRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationTraffic capacityReporting source
A director is provided to receive source address instances of packets routed through routing devices of a network. The director determines whether any of the reported source address instances are to be deemed as spoof source address instances. The director further determines where filtering actions are to be deployed to filter out packets having certain source addresses deemed to be spoof instances. The director makes its determinations based at least in part on a selected one of a number of consistency measures. The consistency measures may include but are not limited to spatial consistency, destination consistency, migration consistency, and temporary consistency. The consistency measures are evaluated using spatial, destination source address range, migration and timing S / D / M / T distribution profiles of the reported source addresses. In some embodiments, the determinations are based further in view of reference S / D / M / T distribution profiles, which may be an exemplary S / D / M / T distribution profile of a typical non-spoof source address or a historical S / D / M / T distribution profile of the source address.
Owner:ARBOR NETWORKS
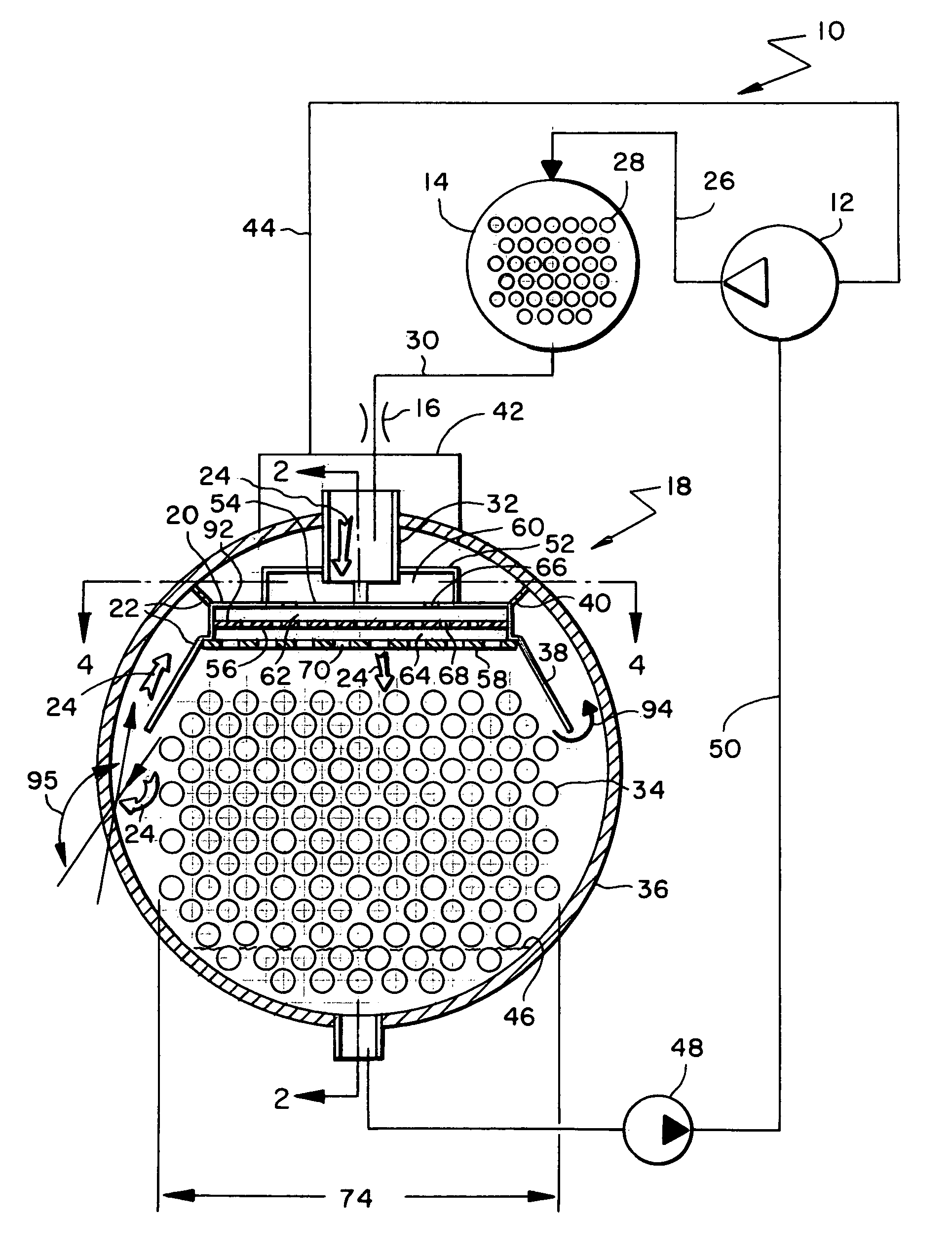
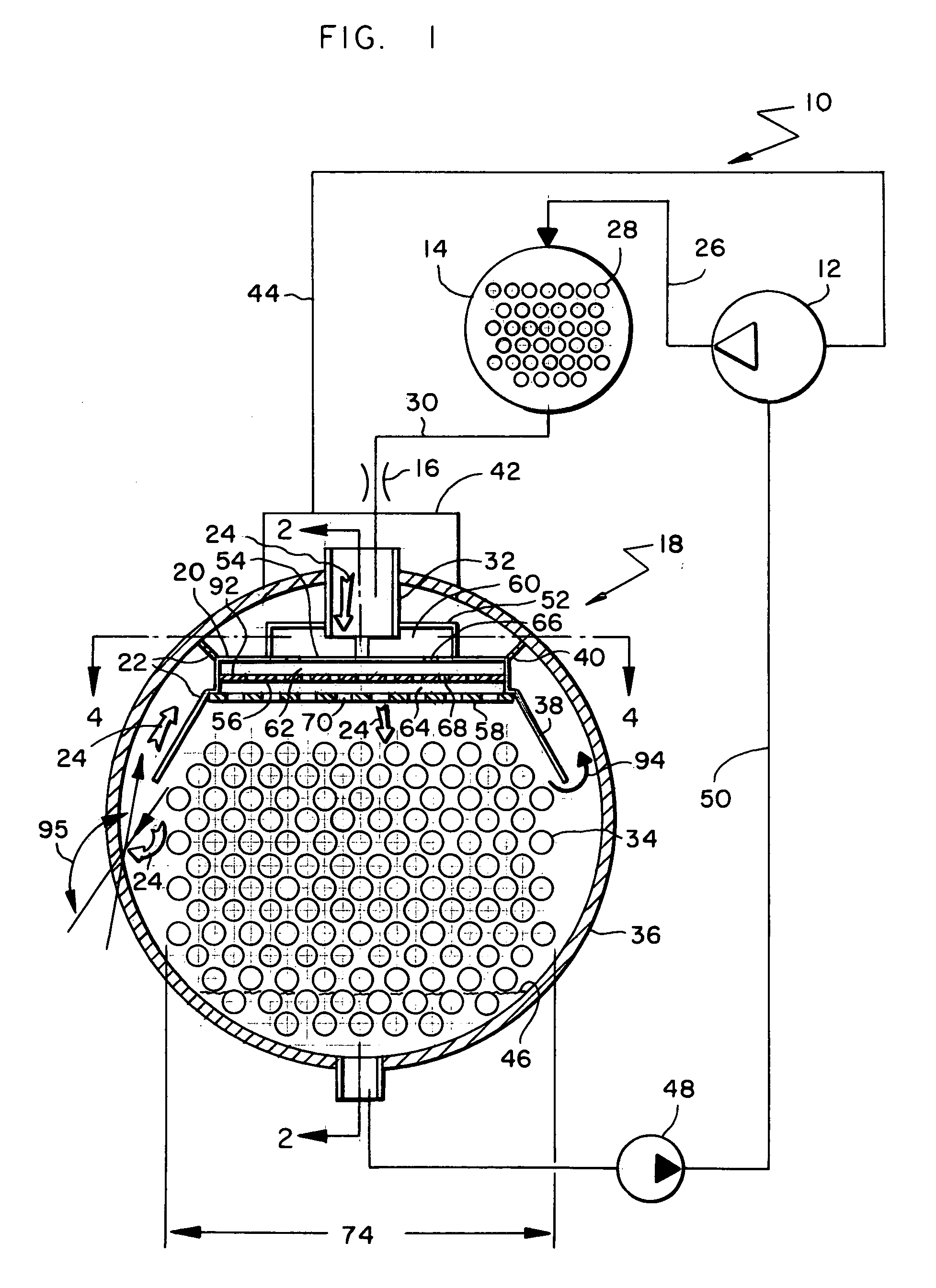
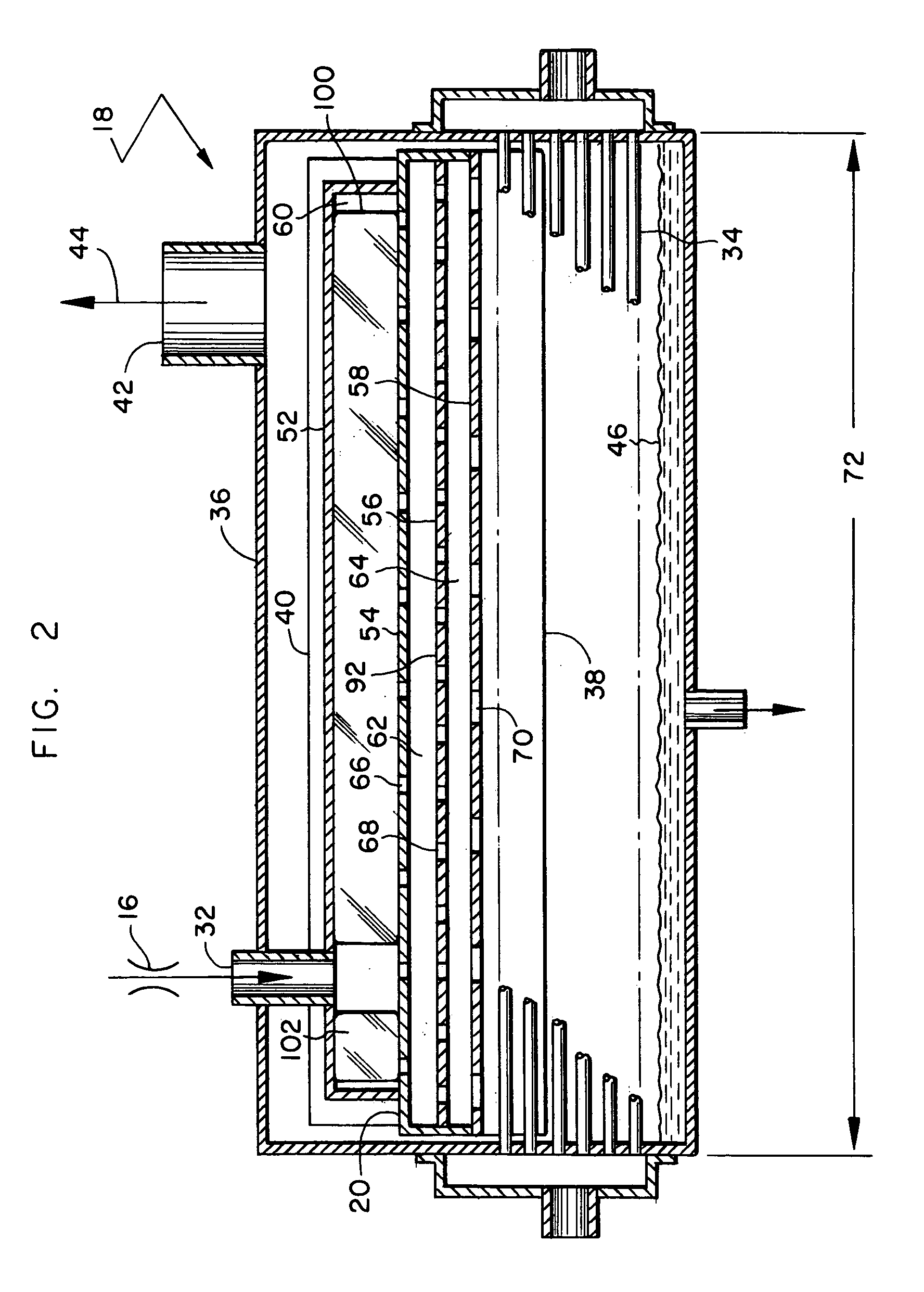
System and method for monitoring pressure, flow and constriction parameters of plumbing and blood vessels
InactiveUS6237398B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringPulsatile flow
The present invention provides a system and method of quantifying flow, detecting a location of an obstruction and quantifying a degree of the obstruction in a pipe characterized in pulsatile flow. The method includes the steps of (a) attaching at least two spaced pressure sensors onto inner walls of the pipe; (b) using the at least two spaced pressure sensors for recording pressure records associated with each of the at least two pressure sensors within the pipe; and (c) using the pressure records for quantifying the pulsatile flow in the pipe, for detecting the location of the obstruction in the pipe and for quantifying the degree of the obstruction in the pipe.
Owner:TELESENSE
Gas distribution apparatus for improved film uniformity in an epitaxial system
ActiveUS20170260649A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom chemically reactive gasesDistribution systemEngineering
A gas distribution system is disclosed in order to obtain better film uniformity on a wafer. The better film uniformity may be achieved by utilizing an expansion plenum and a plurality of, for example, proportioning valves to ensure an equalized pressure or flow along each gas line disposed above the wafer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Fluid storage and dispensing system
InactiveUS6089027ACostPerformanceContainer filling methodsVacuum evaporation coatingSingle stageSorbent
A fluid storage and dispensing system comprising a vessel for holding a fluid at a desired pressure. The vessel has a pressure regulator, e.g., a single-stage or multi-stage regulator, associated with a port of the vessel, and set at a predetermined pressure. A dispensing assembly, e.g., including a flow control means such as a valve, is arranged in gas / vapor flow communication with the regulator, whereby the opening of the valve effects dispensing of gas / vapor from the vessel. The fluid in the vessel may be constituted by a liquid that is confined in the vessel at a pressure in excess of its liquefaction pressure at prevailing temperature conditions, e.g., ambient (room) temperature. In another aspect, the vessel contains a solid-phase sorbent material having sorbable gas adsorbed thereon, at a pressure in excess of 50 psig. The vessel may have a >1 inch NGT threaded neck opening, to accommodate the installation of an interior regulator.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
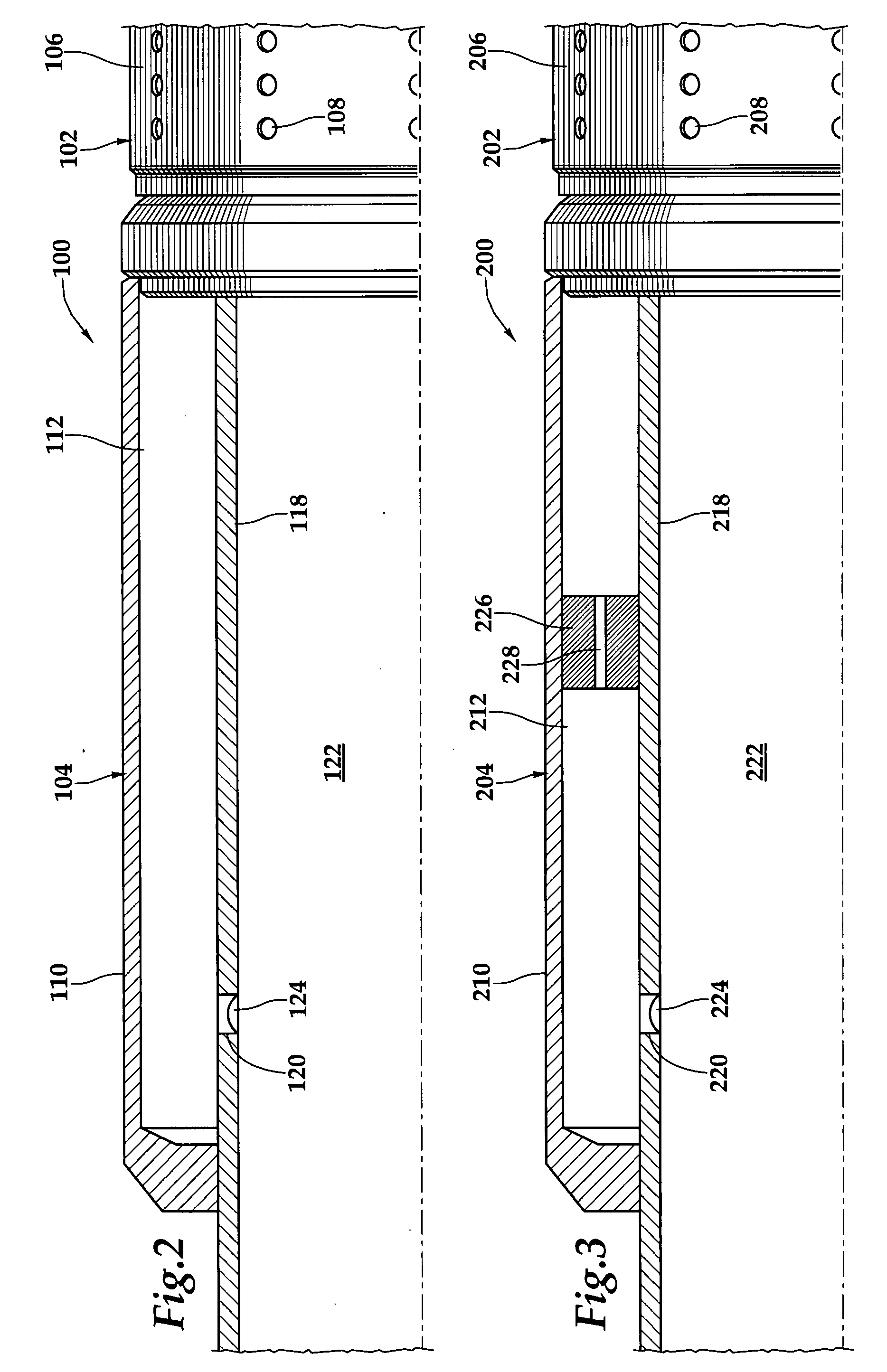
Apparatus for autonomously controlling the inflow of production fluids from a subterranean well
InactiveUS20080283238A1Reduce trafficReduce the cross-sectional areaFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringActuator
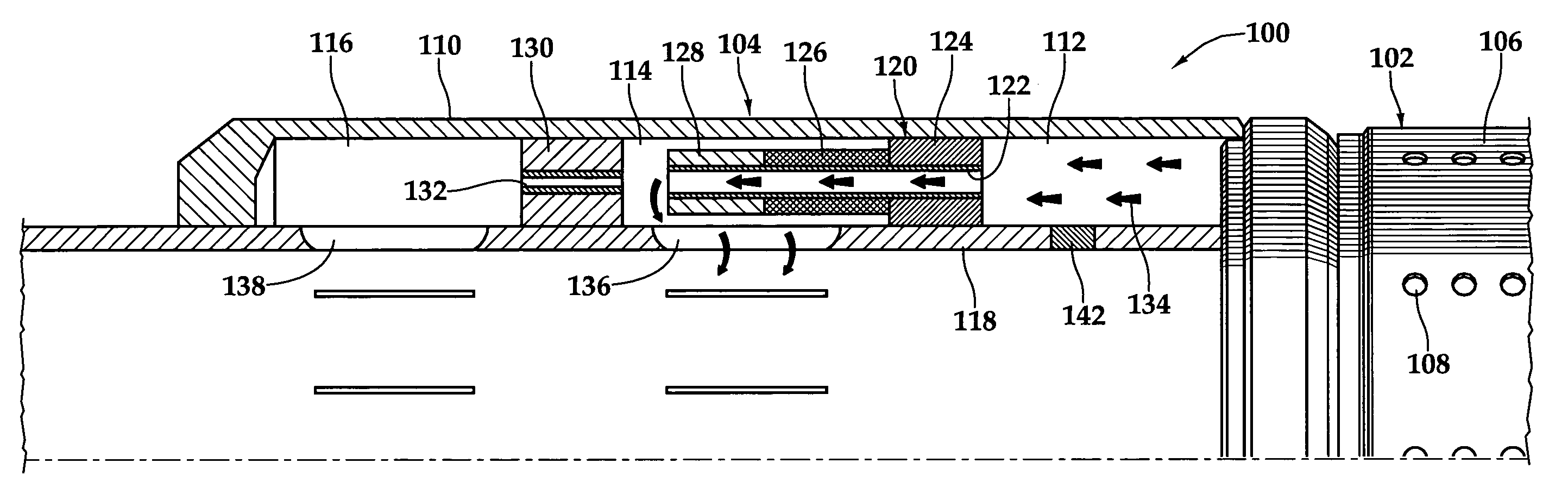
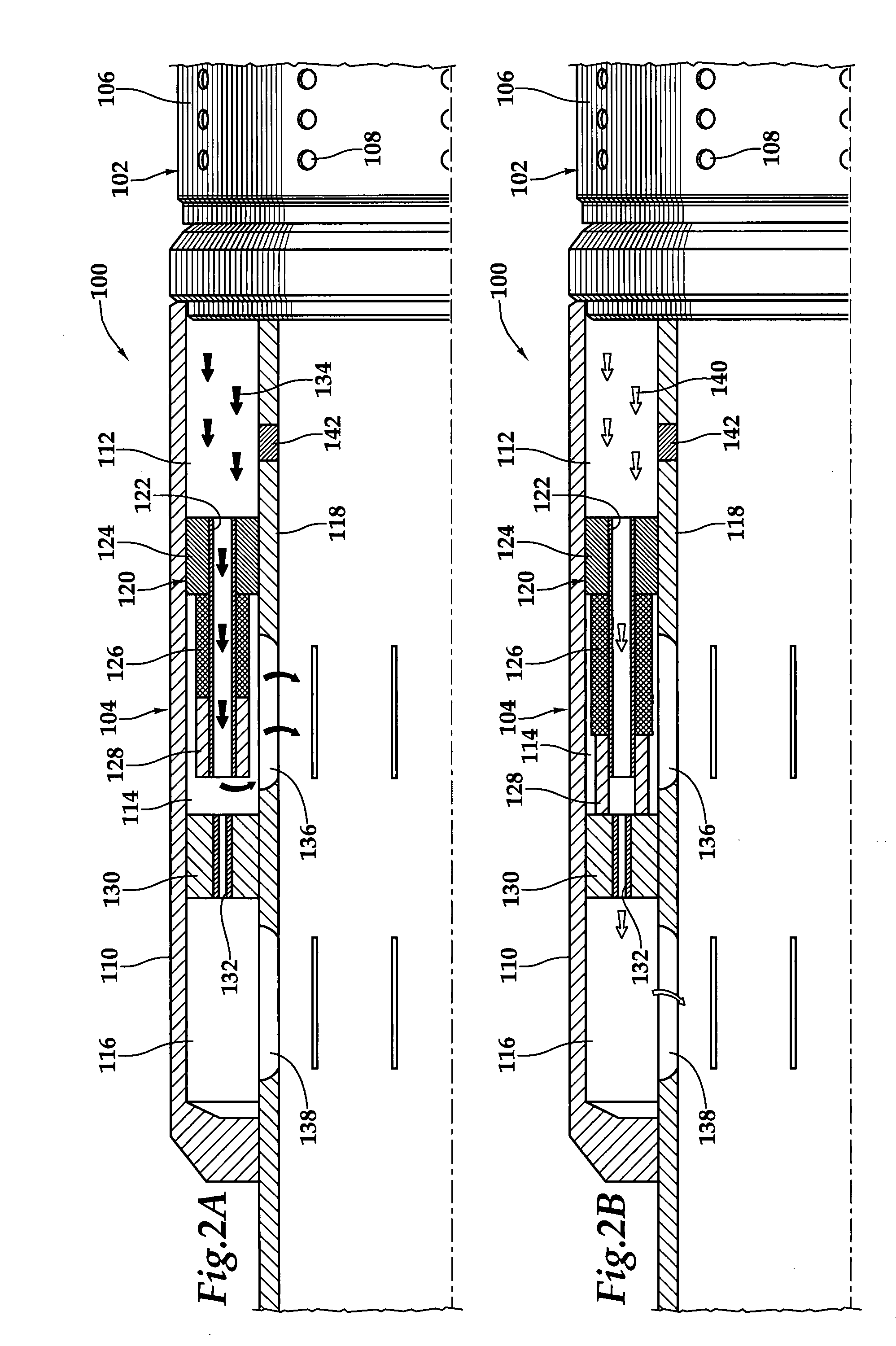
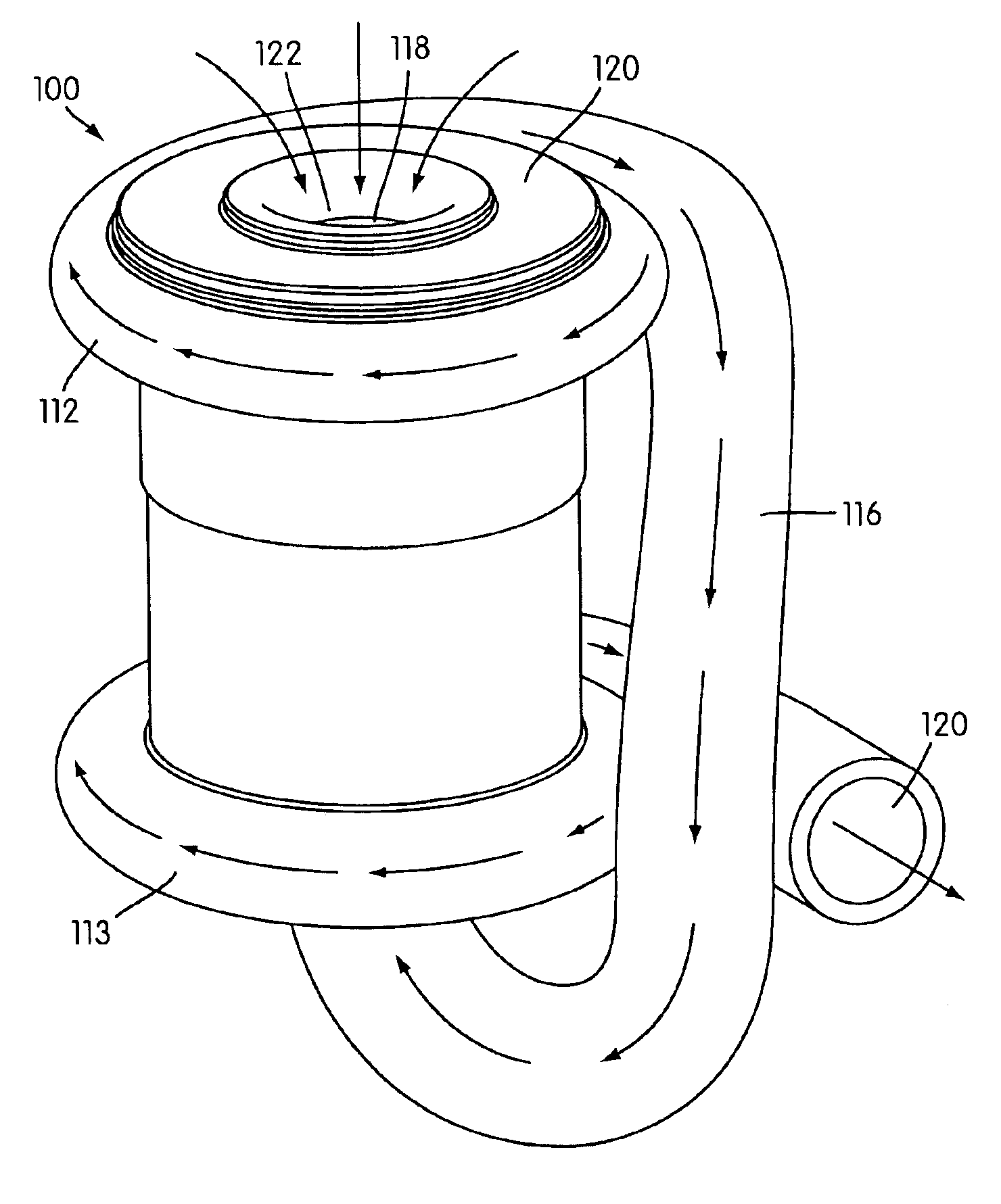
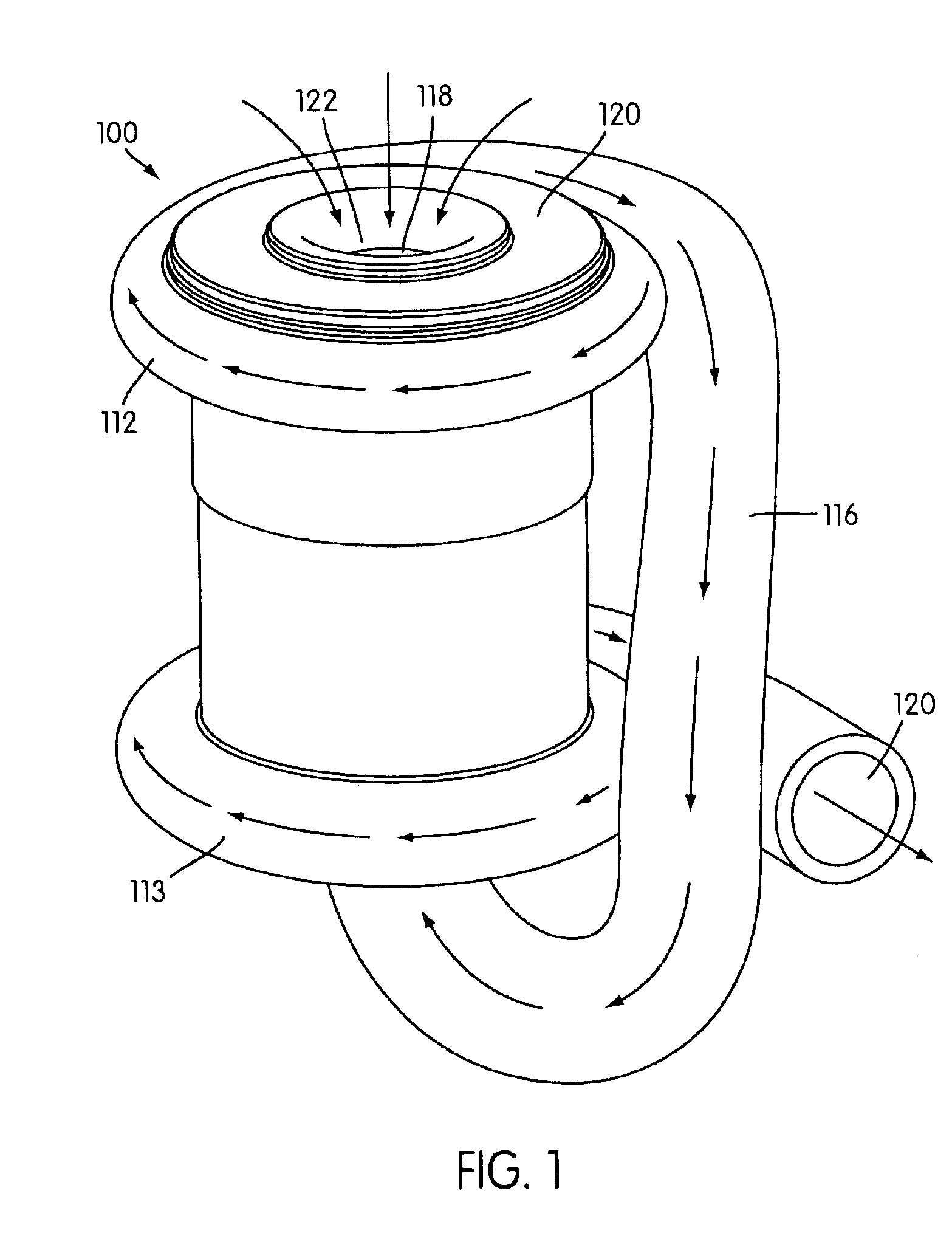
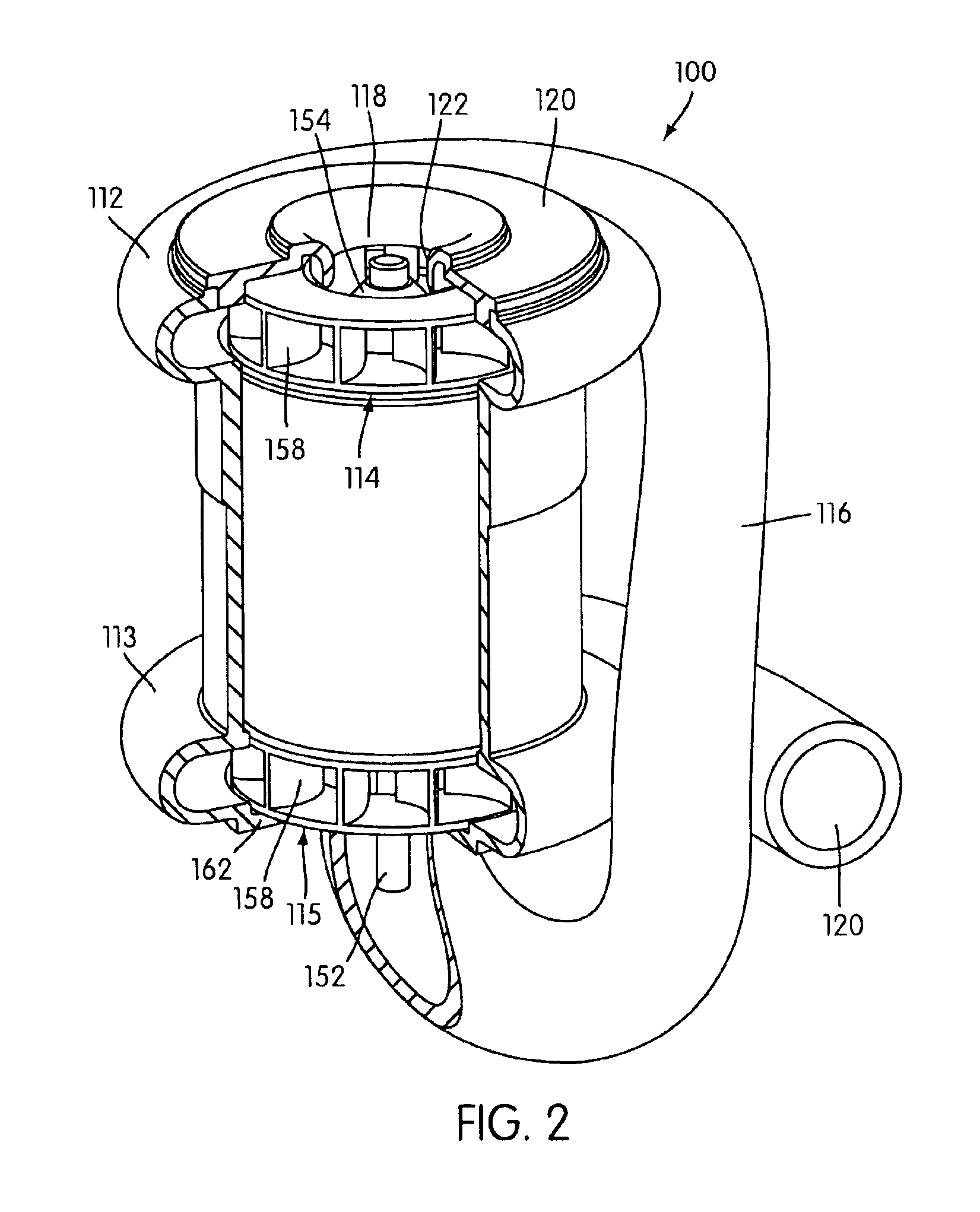
A flow control apparatus (100) for controlling the inflow of production fluids (134, 140) from a subterranean well includes a tubular member (118) having at least one opening (138) that allows fluid flow between an exterior of the tubular member (118) and an interior flow path of the tubular member (118) and a flow restricting device (120) operably positioned in a fluid flow path between a fluid source and the at least one opening (138). The flow restricting device (120) includes a valve (128, 130) and an actuator (126). The actuator (126) includes a material that swells in response to contact with an undesired fluid (140), such as water or gas. The flow restricting device (120) is operable to autonomously reduce the fluid flow through the flow control apparatus (100) in response to contact between the material and the undesired fluid (140).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method of providing hydraulic/fiber conduits adjacent bottom hole assemblies for multi-step completions
A technique for providing auxiliary conduits in multi-trip completions is disclosed. The technique has particular applicability to liner mounted screens which are to be gravel packed. In the preferred embodiment, a protective shroud is run with the gravel pack screens with the auxiliary conduits disposed in between. The auxiliary conduits terminate in a quick connection at a liner top packer. The gravel packing equipment can optionally be secured in a flow relationship to the auxiliary conduits so as to control the gravel packing operation. Subsequent to the removal of the specialized equipment, the production tubing can be run with an auxiliary conduit or conduits for connection down hole to the auxiliary conduits coming from the liner top packer for a sealing connection. Thereafter, during production various data on the well can be obtained in real time despite the multiple trips necessary to accomplish completion. The various completion and / or production activities can also be accomplished using the auxiliary conduits such as actuation of down hole flow control devices, chemical injection, pressure measurement, distributed temperature sensing through fiber optics, as well as other down hole parameters.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Multi-reservoir pressure control system
InactiveUS6915679B2Sufficient oscillationAccurate and stable and reliable assayAnalysis by electrical excitationLaboratory glasswaresFluid transportFlow resistivity
Improved microfluidic devices, systems, and methods allow selective transportation of fluids within microfluidic channels of a microfluidic network by applying, controlling, and varying pressures at a plurality of reservoirs. Modeling the microfluidic network as a series of nodes connected together by channel segments and determining the flow resistance characteristics of the channel segments may allow calculation of fluid flows through the channel segments resulting from a given pressure configuration at the reservoirs. To effect a desired flow within a particular channel or series of channels, reservoir pressures may be identified using the network model. Viscometers or other flow sensors may measure flow characteristics within the channels, and the measured flow characteristics can be used to calculate pressures to generate a desired flow. Multi-reservoir pressure modulator and pressure controller systems can optionally be used in conjunction with electrokinetic or other fluid transport mechanisms.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Thermal management algorithm for phacoemulsification system
A control system for managing power supplied to a phacoemulsification hand piece includes a power source that provides power to the hand piece and a controller that controls the power source. The controller calculates a thermal value based on irrigation fluid flow and a power level and decreases the power level in proportion to the calculated thermal value when the calculated thermal value exceeds a threshold thermal value. Irrigation fluid flow can be calculated from irrigation fluid pressure.
Owner:ALCON INC
Cryotherapy system
ActiveUS7083612B2Reduce pressureDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringCryotherapy
A cryotherapy system is provided with multiple cryoprobes, each of which has a shaft with a closed distal end adapted for insertion into a body and conduits for flowing a cryogenic fluid through the shaft to reduce a temperature of the distal end. A source is provided for the cryogenic fluid, and flow-control metering valves are provided in fluid communication with the conduits and source of the cryogenic fluid. A compressor is provided in fluid communication with the conduits of the cryoprobes to define a self-contained fluid system. The flow-control metering valves and the compressor are controlled by a computer processor to provide the desired flows of the cryogenic fluid through the conduits of the self-contained fluid system.
Owner:ADAGIO MEDICAL
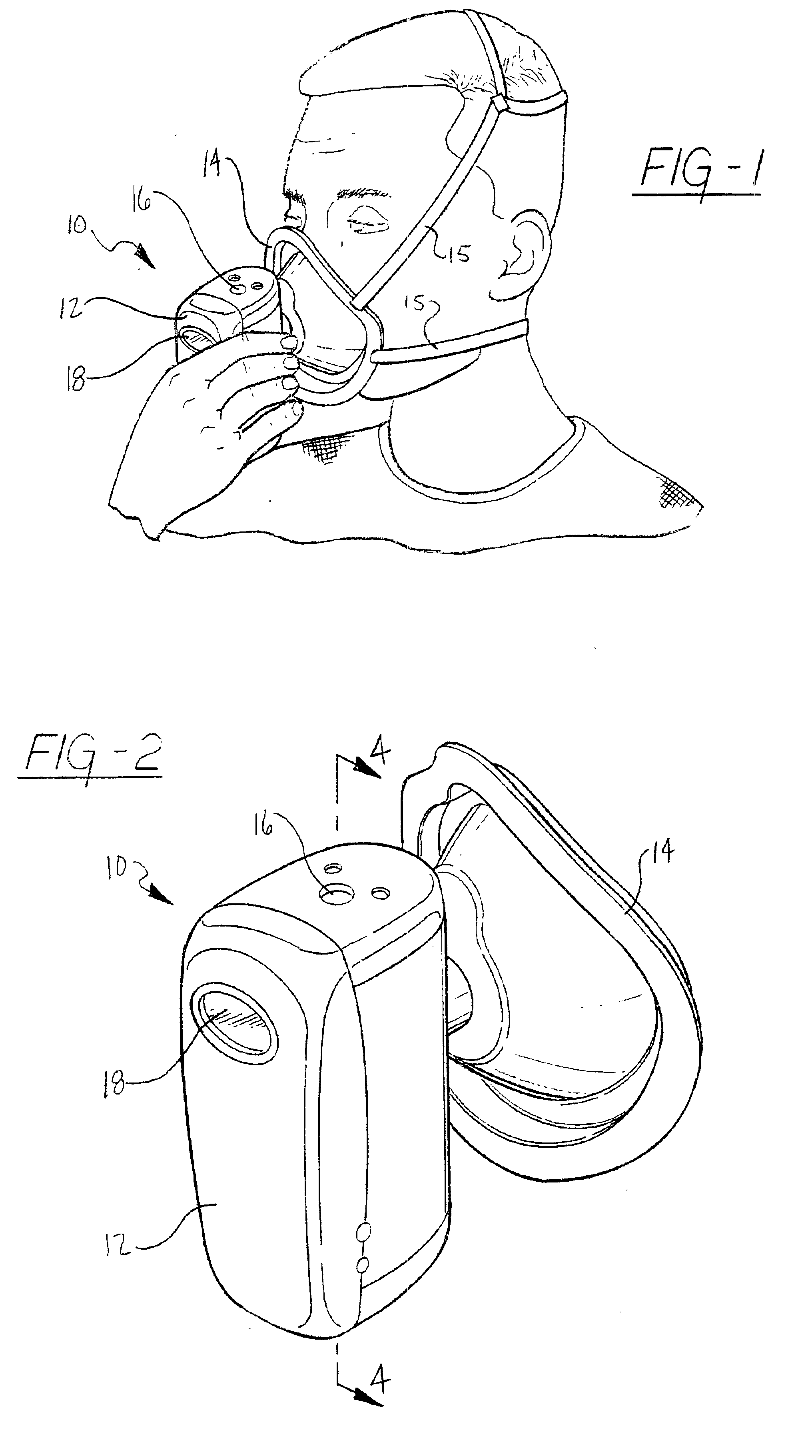
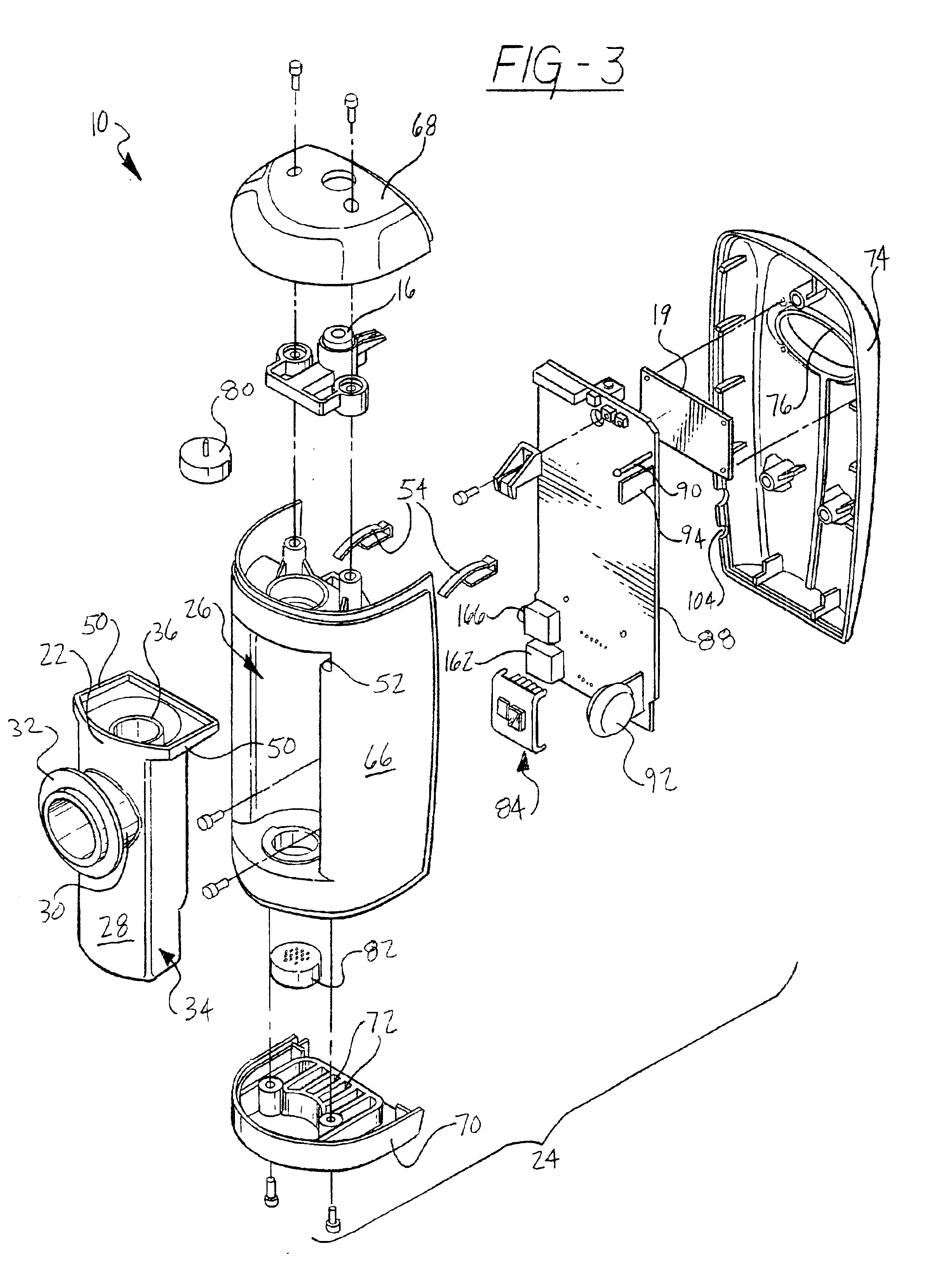
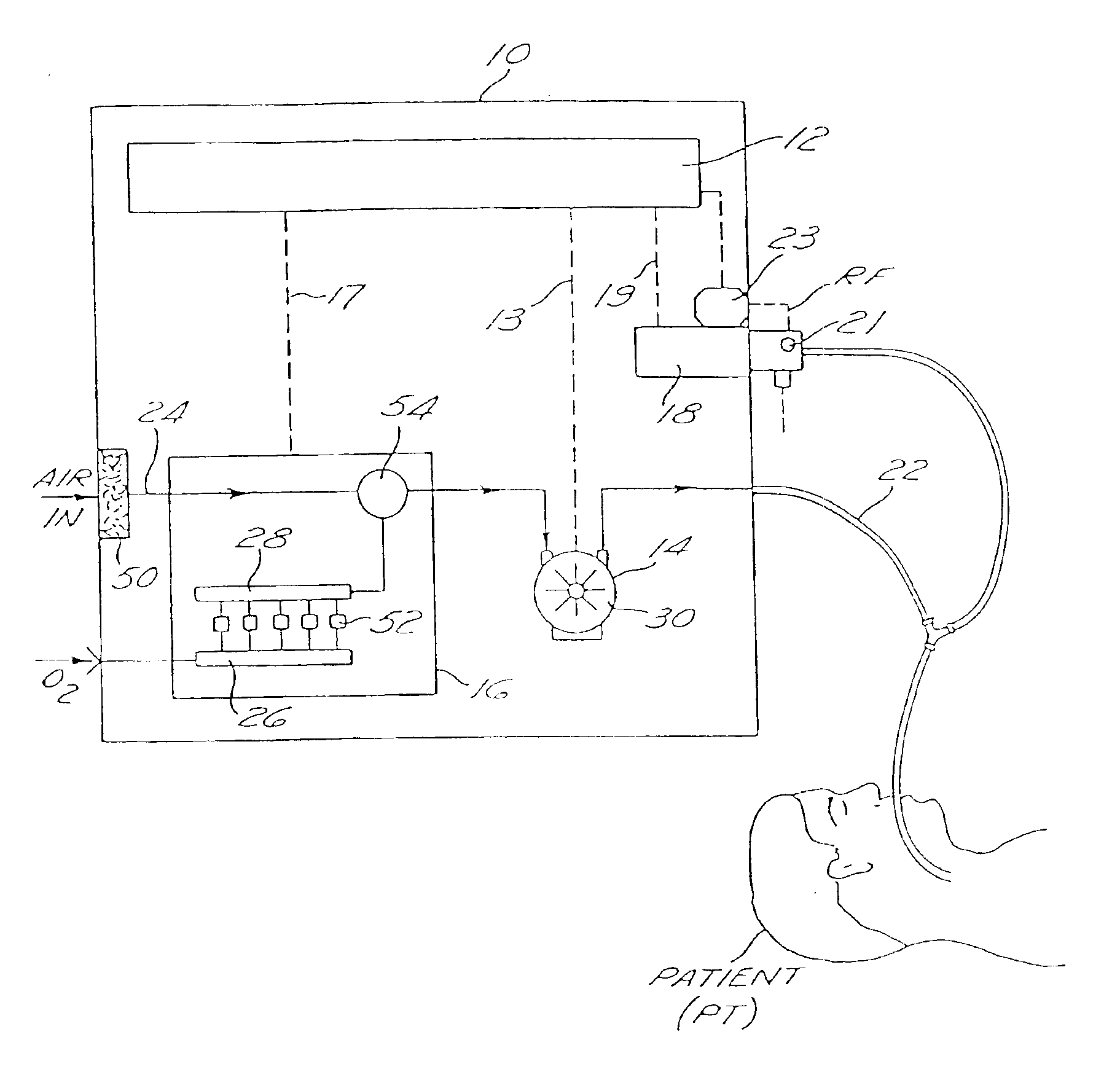
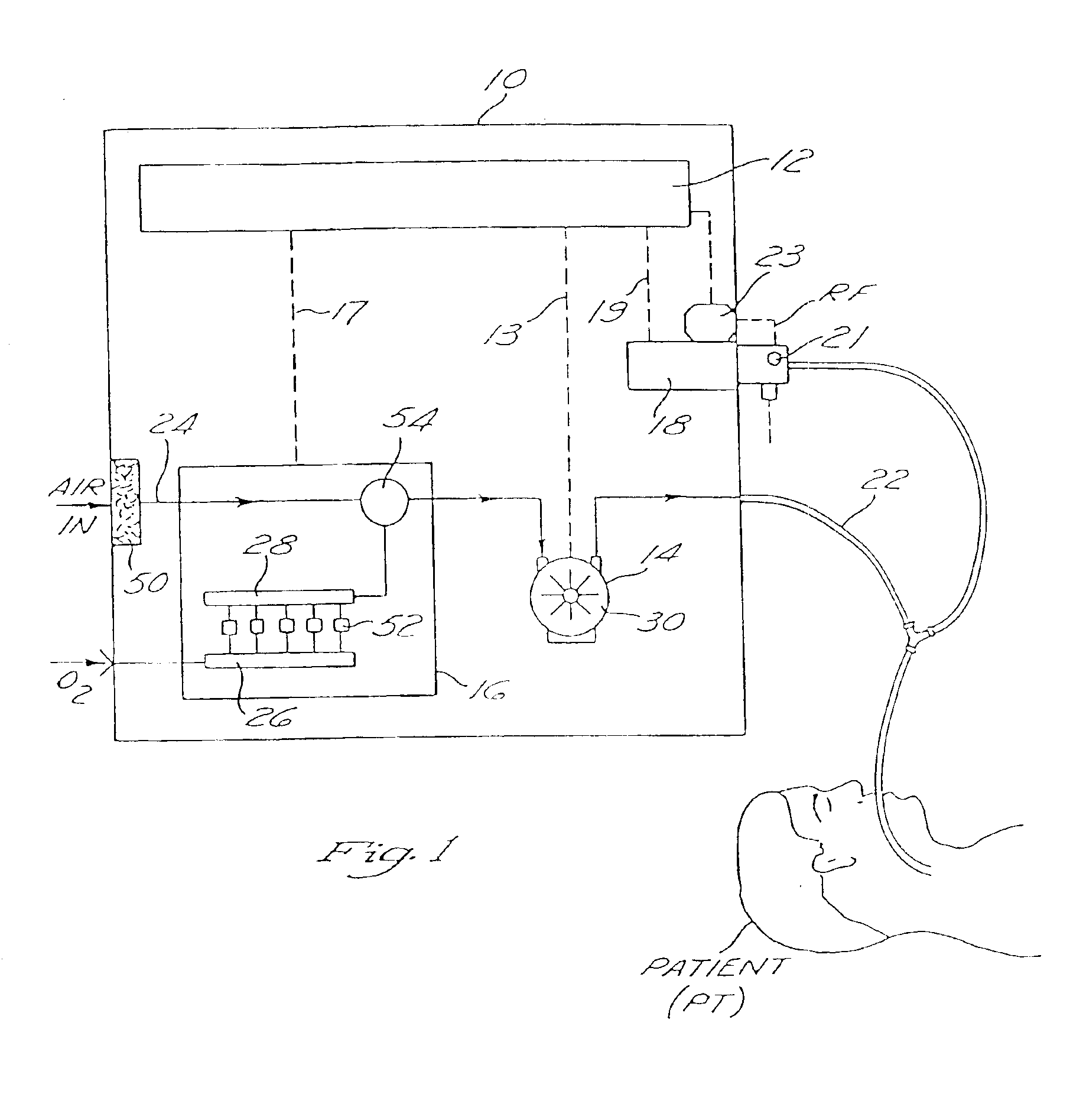
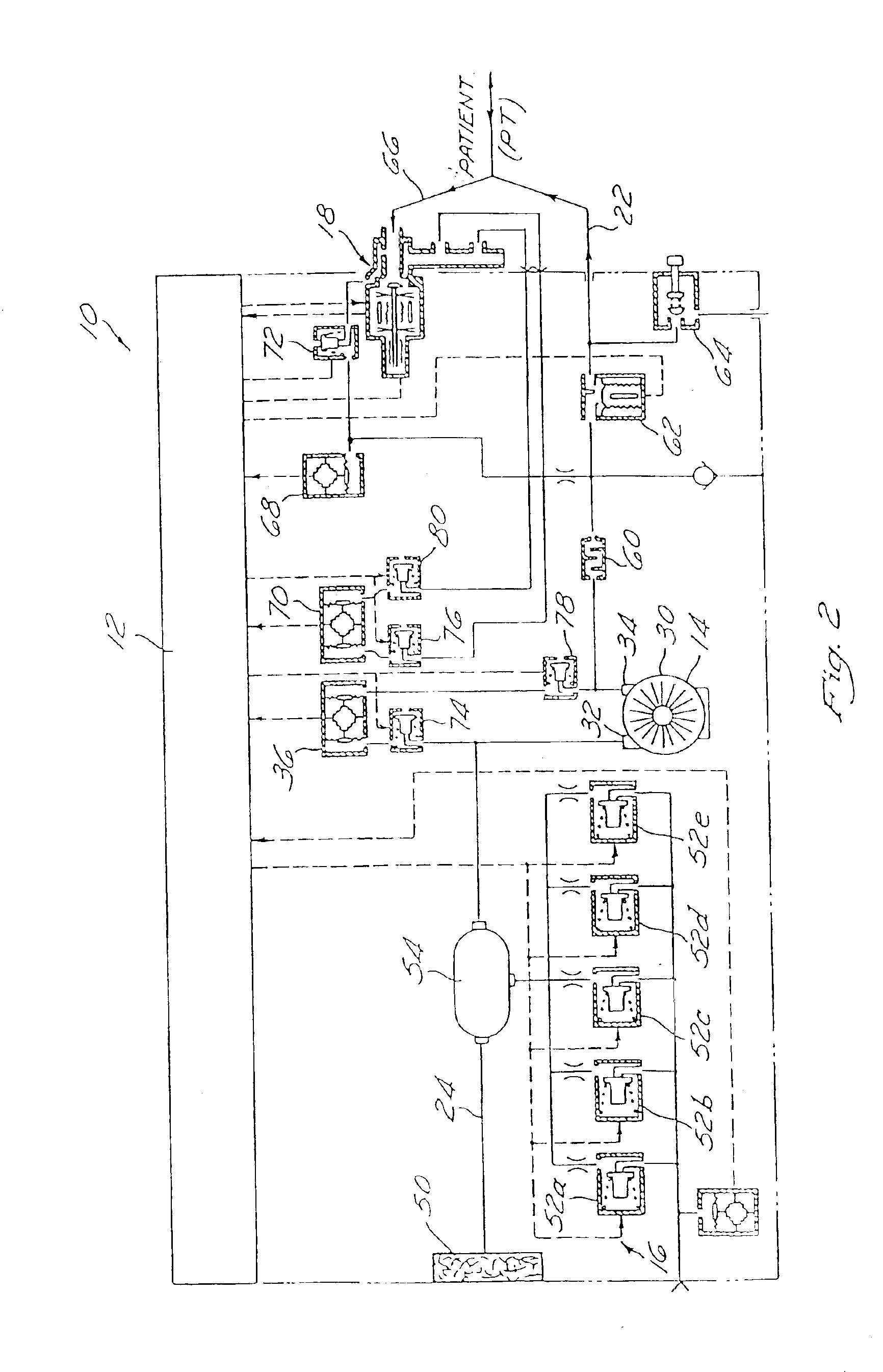
Metabolic calorimeter employing respiratory gas analysis
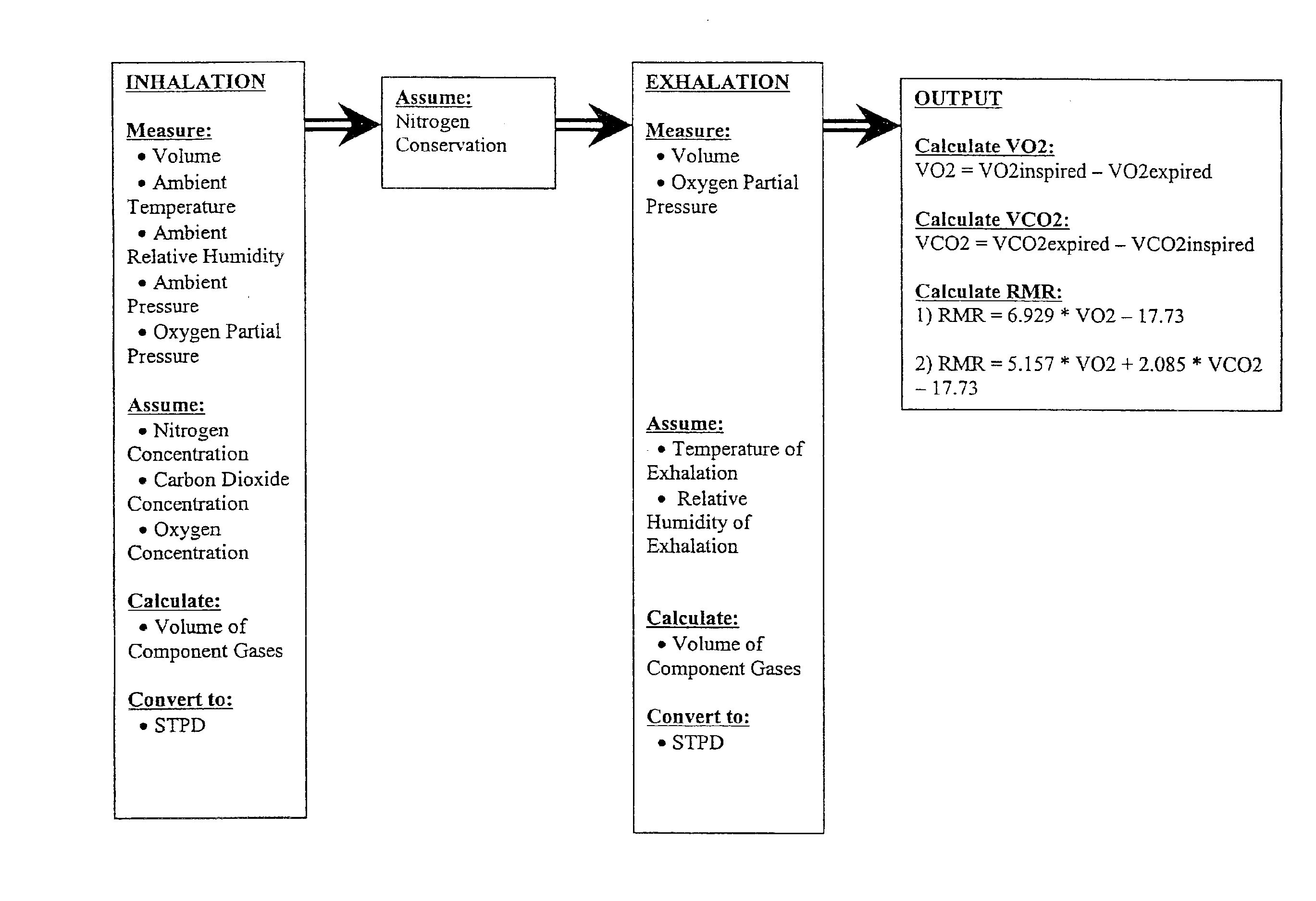
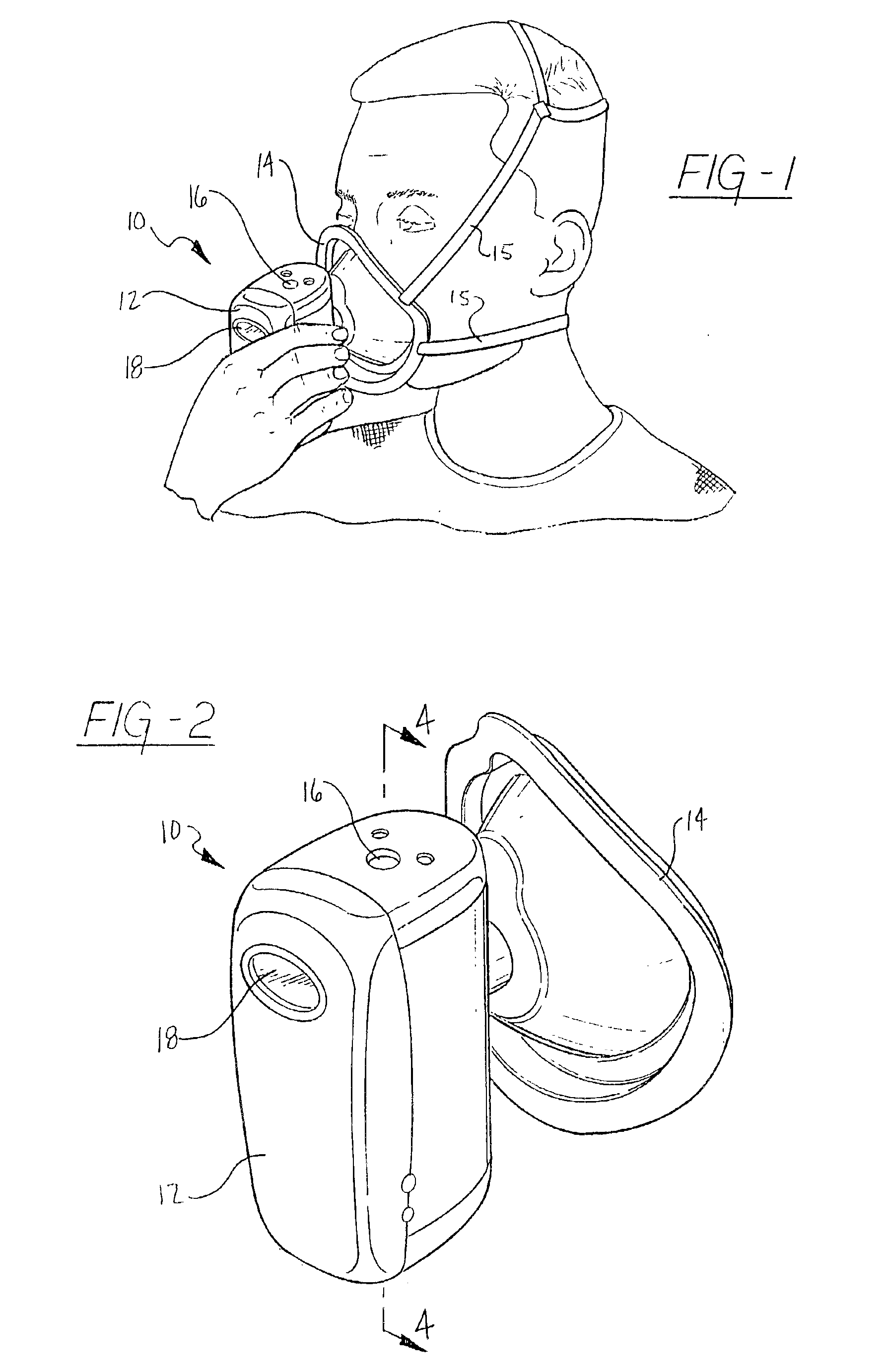
An indirect calorimeter for measuring the metabolic rate of a subject includes a disposable portion and a reusable portion. The disposable portion includes a respiratory connector configured to be supported in contact with the subject so as to pass inhaled and exhaled gases as the subject breathes. The disposable portion also includes a flow pathway operable to receive and pass inhaled and exhaled gases, having a first end in fluid communication with the respiratory connector and a second end in fluid communication with a source and sink for respiratory gases. The disposable portion is disposed within the reusable portion, which includes a flow meter, a component gas concentration sensor, and a computation unit. The flow meter generates a signal as a function of the instantaneous flow volume of respiratory gases passing through the flow pathway and the component gas concentration sensor generates a signal as a function of the instantaneous fraction of a predetermined component gas in the exhaled gases. The computation unit receives the electrical signals from the flow meter and the concentration sensor and calculates at least one respiratory parameter for the subject as the subject breathes through the calorimeter.
Owner:MICROLIFE MEDICAL HOME SOLUTIONS
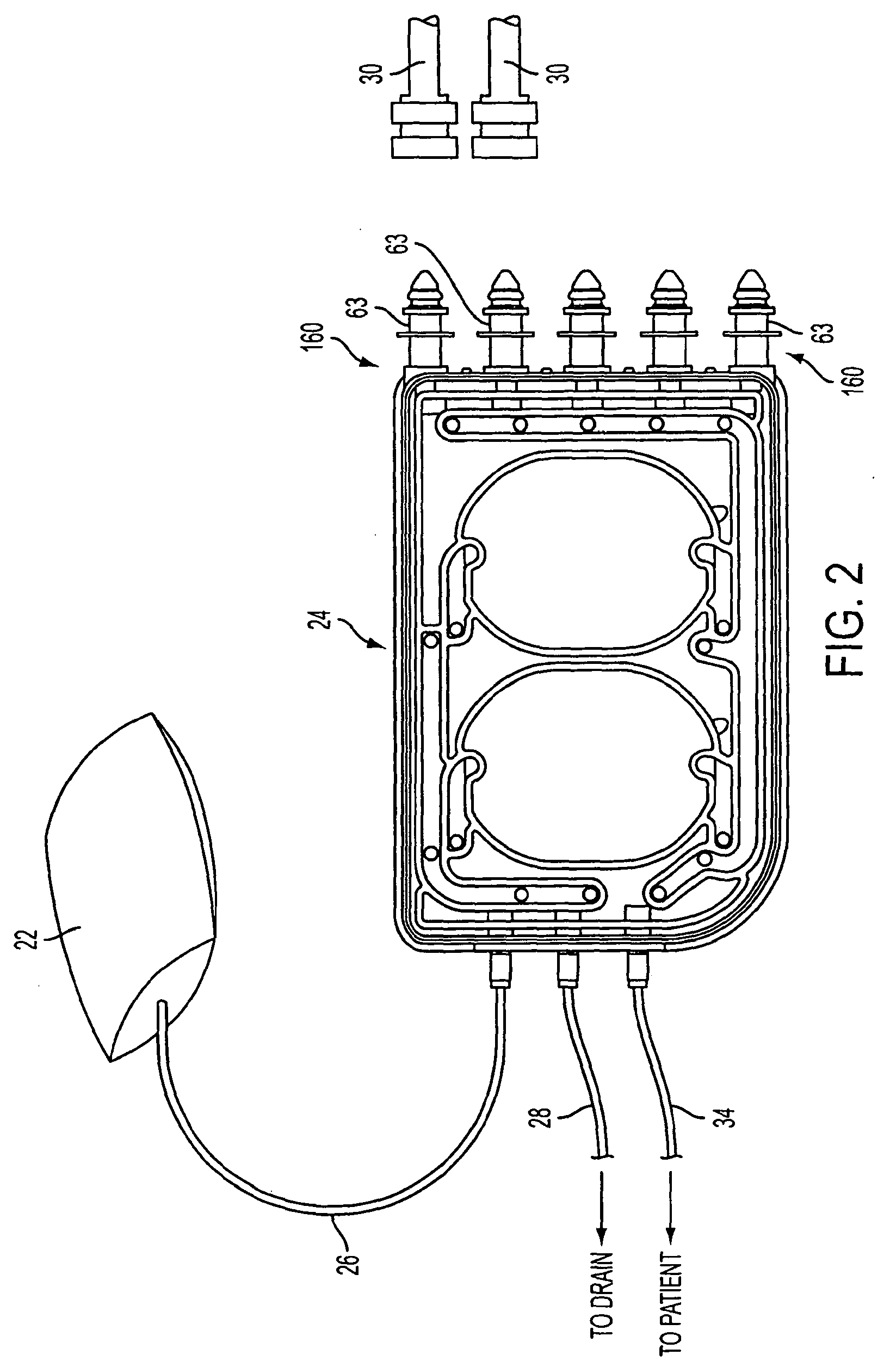
Fluid volume determination for medical treatment system
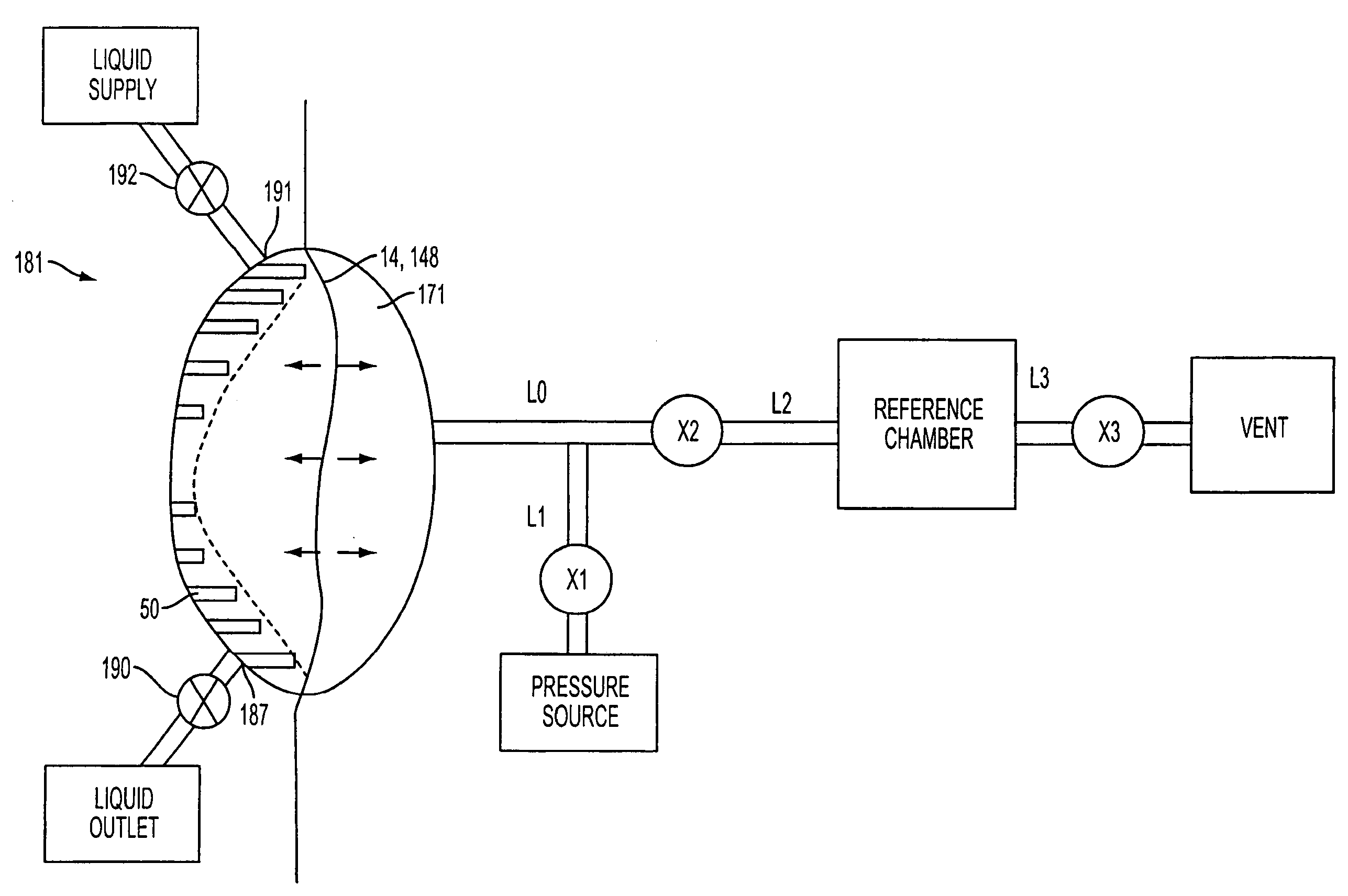
ActiveUS20110071465A1Deformation MinimizationPreventing sticking of the membraneMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesFlexible member pumpsPump chamberMathematical model
A volume of fluid moved by a pump, such as a pump in an APD system, may be determined without direct measurement of the fluid, such as by flow meter, weight, etc. For example, a volume of a pump chamber (181) (having a movable element that varies the volume of the pump chamber) may be determined by measuring pressure in the pump chamber and a reference chamber, both while the two chambers are isolated from each other, and after the two chambers are fluidly connected so that pressures in the chambers may equalize. Equalization of the pressures may be assumed to occur in an adiabatic way, e.g., a mathematical model of the system that is based on an adiabatic pressure equalization process may be used to determine the pump chamber volume. In one embodiment, pressures measured after the chambers are fluidly connected may be measured at a time before complete pressure equalization has occurred, and thus the pressures for the pump and reference chambers measured after the chambers are fluidly connected may be unequal, yet still be used to determine the pump chamber volume.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Metabolic calorimeter employing respiratory gas analysis
An indirect calorimeter for measuring the metabolic rate of a subject includes a respiratory connector configured to be supported in contact with the subject so as to pass inhaled and exhaled gases as the subject breathes, a flow pathway, and a hygiene barrier positioned to block a predetermined pathogen from the exhaled gases. The indirect calorimeter also includes a flow pathway having a first end in fluid communication with the respiratory connector and a second end in fluid communication with a source and sink for respiratory gases. The flow pathway includes a flow tube through which the inhaled and exhaled gases pass, an outer housing surrounding the flow tube, and a chamber disposed between the flow tube and the first end. The indirect calorimeter also includes a flow meter configured to generate electrical signals as a function of the instantaneous flow volume of inhaled and exhaled gases passing through the flow pathway, and a component gas concentration sensor operable to generate electrical signals as a function of the instantaneous fraction of a predetermined component gas in the exhaled gases as the gases pass through the flow pathway. The indirect calorimeter further includes a computation unit operable to receive the electrical signals from the flow meter and the concentration sensor and operative to calculate at least one respiratory parameter for the subject as the subject breathes through the calorimeter.
Owner:MICROLIFE MEDICAL HOME SOLUTIONS
Flow distributor and baffle system for a falling film evaporator
ActiveUS6868695B1Even flow distributionEasy to separateMilk preservationEvaporators/condensersEngineeringRefrigerant
A falling film evaporator includes a flow distributor for uniformly distributing a two-phase refrigerant mixture across a tube bundle. The flow distributor includes a stack of at least three perforated plates each of which are separated by nearly full-width, full-length gaps or chambers. The flow distributor may also include a suction baffle and / or a distributor baffle. The distributor baffle extends downward to provide a hairpin turn past which refrigerant travels before exiting the evaporator. This directional change helps separate liquid from a primarily gaseous refrigerant stream. The suction baffle has various size openings to ensure that the flow rate of refrigerant through the hairpin turn is generally uniform and is maintained low enough to ensure liquid disentrainment over and along the length of the tube bundle within the evaporator.
Owner:TRANE INT INC
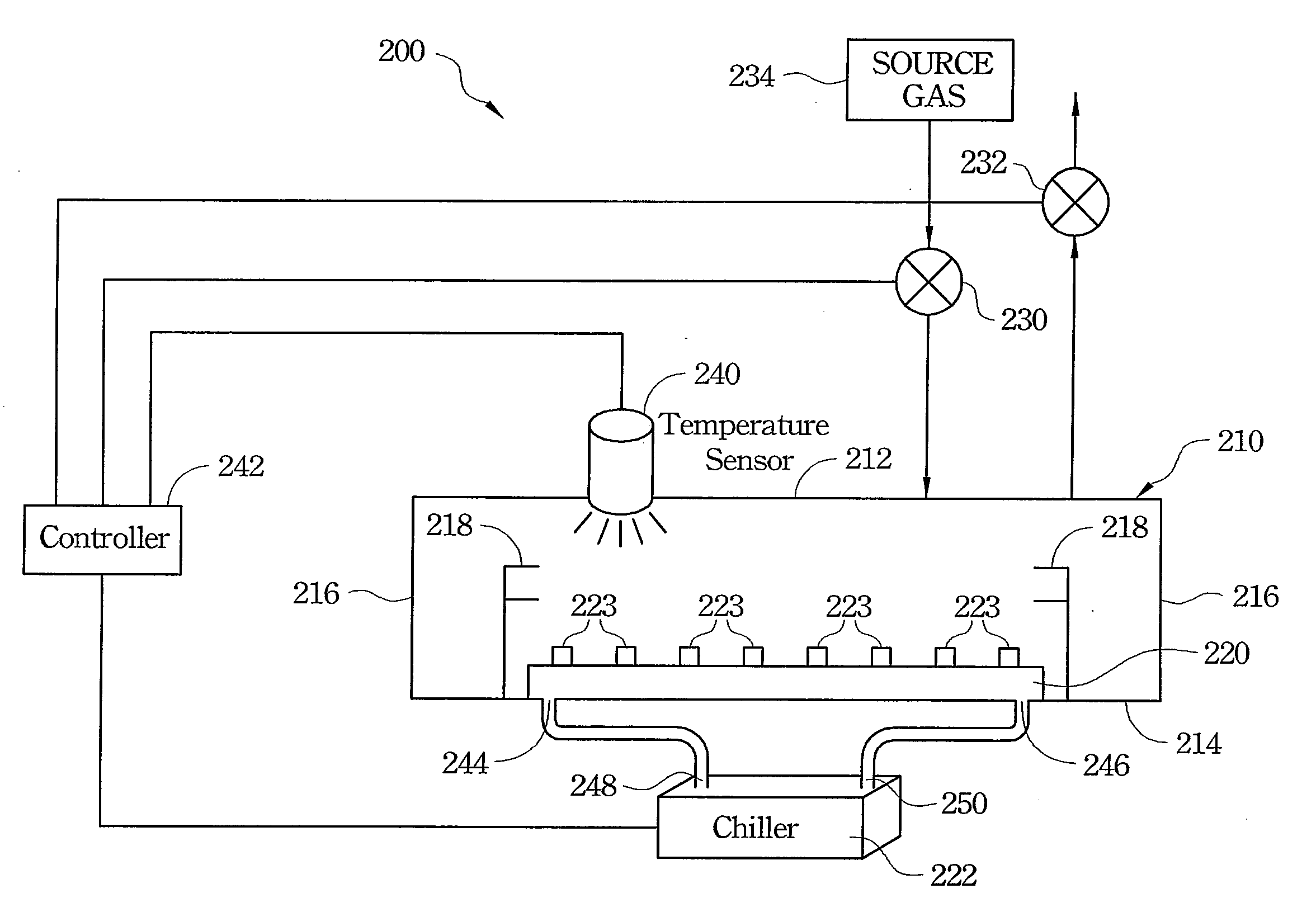
Temperature Controlled Loadlock Chamber
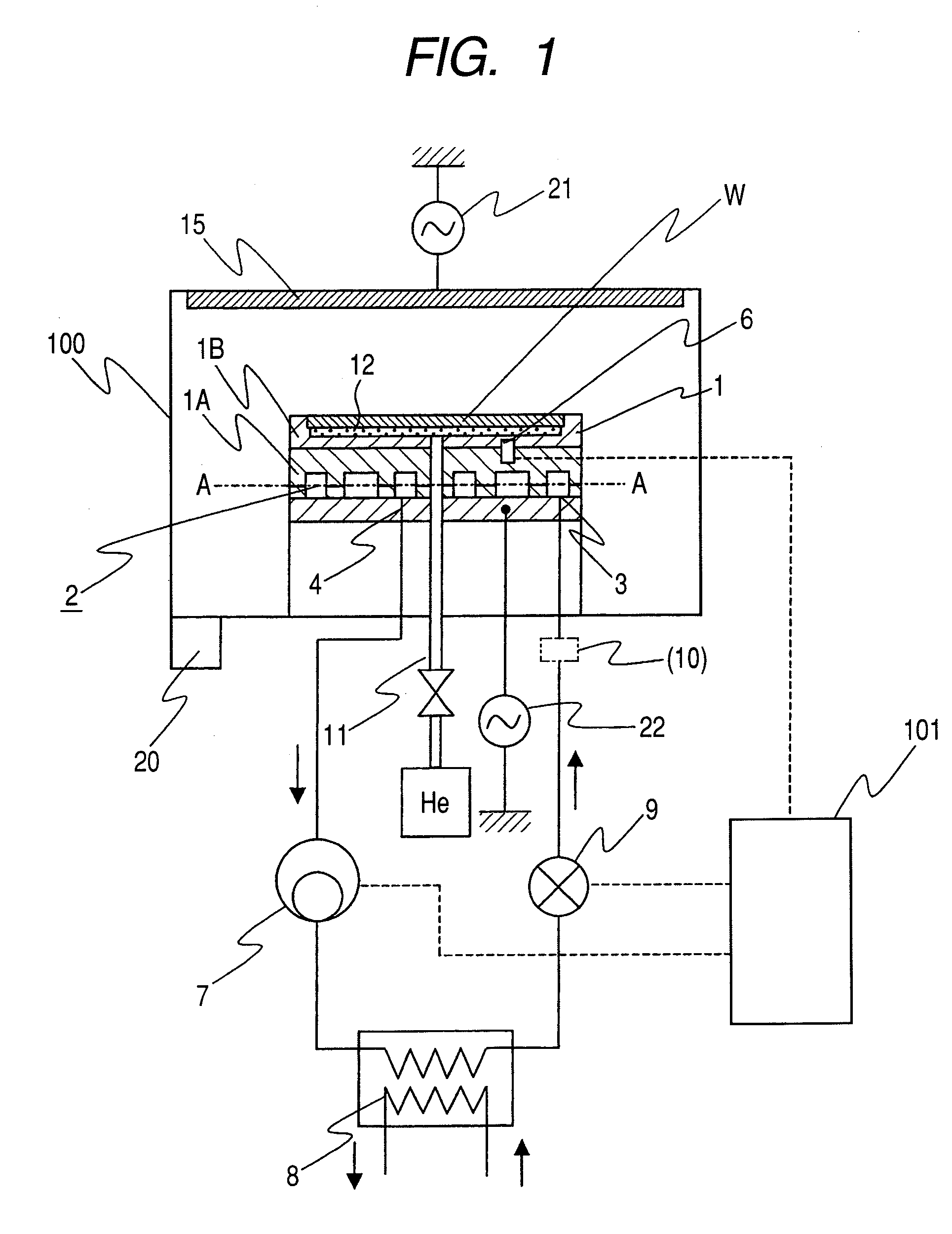
ActiveUS20090000769A1Uniform temperatureUniform processingTemperatue controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringStreamflow
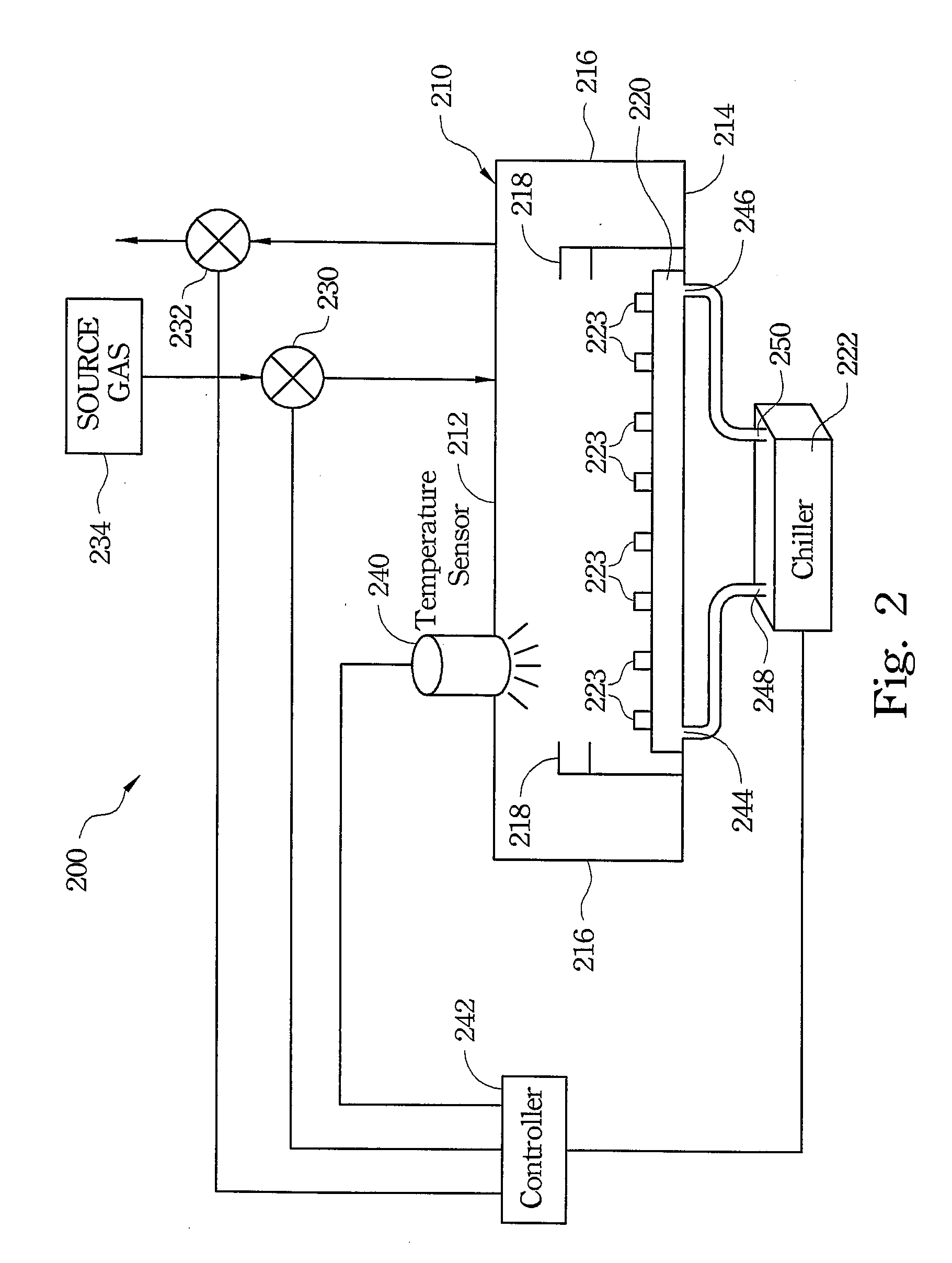
A temperature controlled loadlock chamber for use in semiconductor processing is provided. The temperature controlled loadlock chamber may include one or more of an adjustable fluid pump, mass flow controller, one or more temperature sensors, and a controller. The adjustable fluid pump provides fluid having a predetermined temperature to a temperature-controlled plate. The mass flow controller provides gas flow into the chamber that may also aid in maintaining a desired temperature. Additionally, one or more temperature sensors may be combined with the adjustable fluid pump and / or the mass flow controller to provide feedback and to provide a greater control over the temperature. A controller may be added to control the adjustable fluid pump and the mass flow controller based upon temperature readings from the one or more temperature sensors.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method of respiratory gas analysis using a metabolic calorimeter
A method of determining a respiratory parameter for a subject using an indirect calorimeter is provided. The indirect calorimeter includes a respiratory connector for passing inhaled and exhaled gases, a flow pathway operable to receive and pass inhaled and exhaled gases having a flow tube within the flow pathway through which the inhaled and exhaled gases pass, a flow meter for determining an instantaneous flow volume of the inhaled and exhaled gases, a component gas concentration sensor for determining an instantaneous fraction of a predetermined component gas and a computation unit having a processor and a memory. The method includes the steps of initializing the indirect calorimeter and the subject breathing into the respiratory connector if the indirect calorimeter is initialized, sensing the flow volume of the inhaled and exhaled gases passing through the flow pathway using the flow meter and transmitting a signal representing the sensed flow volume to the computation unit. The method also includes the steps of sensing a concentration of a predetermined component gas as the inhaled and exhaled gases pass through the flow pathway using the component gas sensor, and transmitting a signal representing the sensed concentration of the predetermined component gas to the computation unit. The method further includes the steps of calculating at least one respiratory parameter for the subject as the subject breathes through the calorimeter using the sensed flow volume and the sensed concentration of the predetermined component gas, and providing the subject with the at least one respiratory parameter.
Owner:MICROLIFE MEDICAL HOME SOLUTIONS
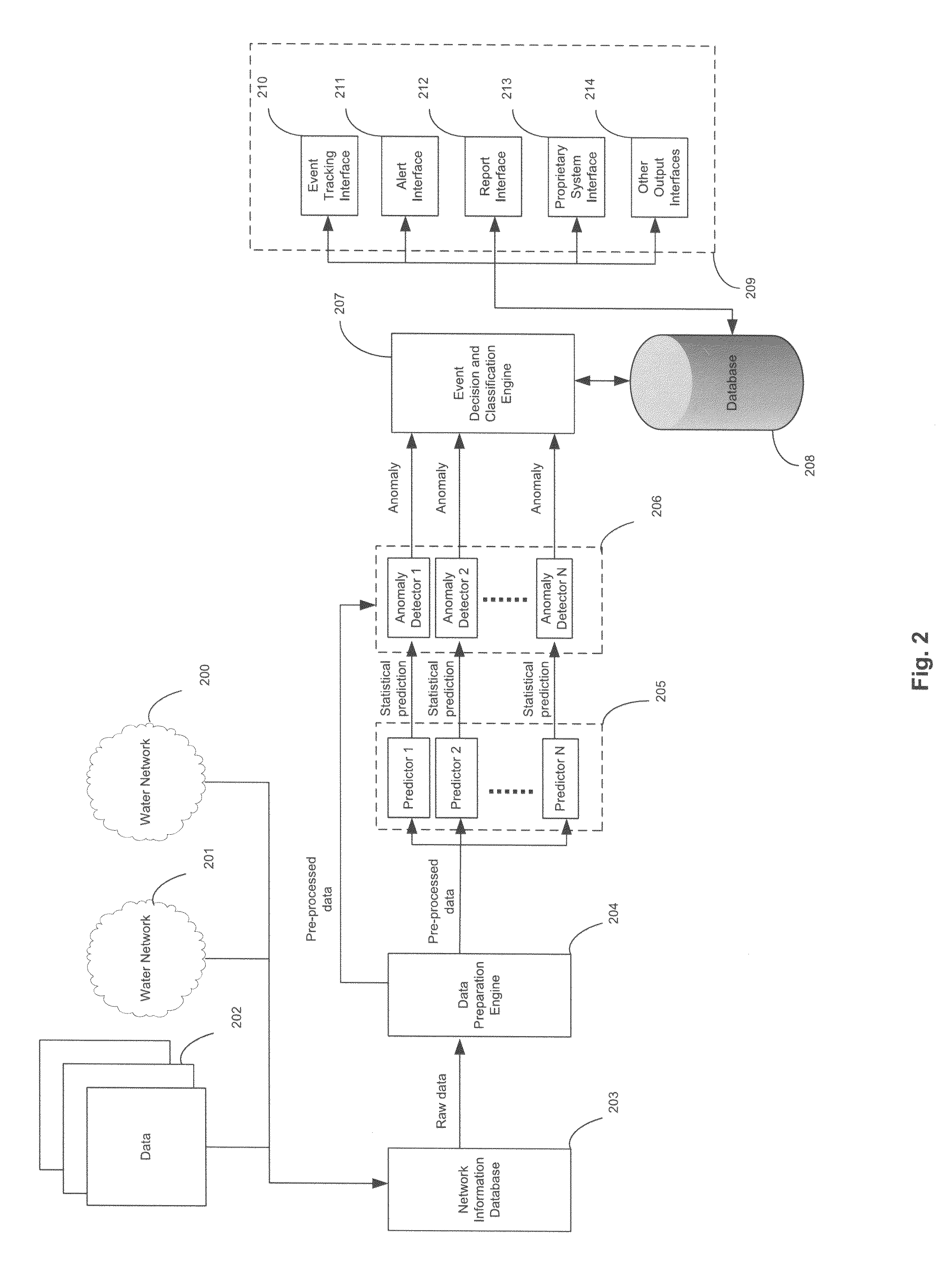
Flows based visualization of packet networks with network performance analysis, troubleshooting, optimization and network history backlog
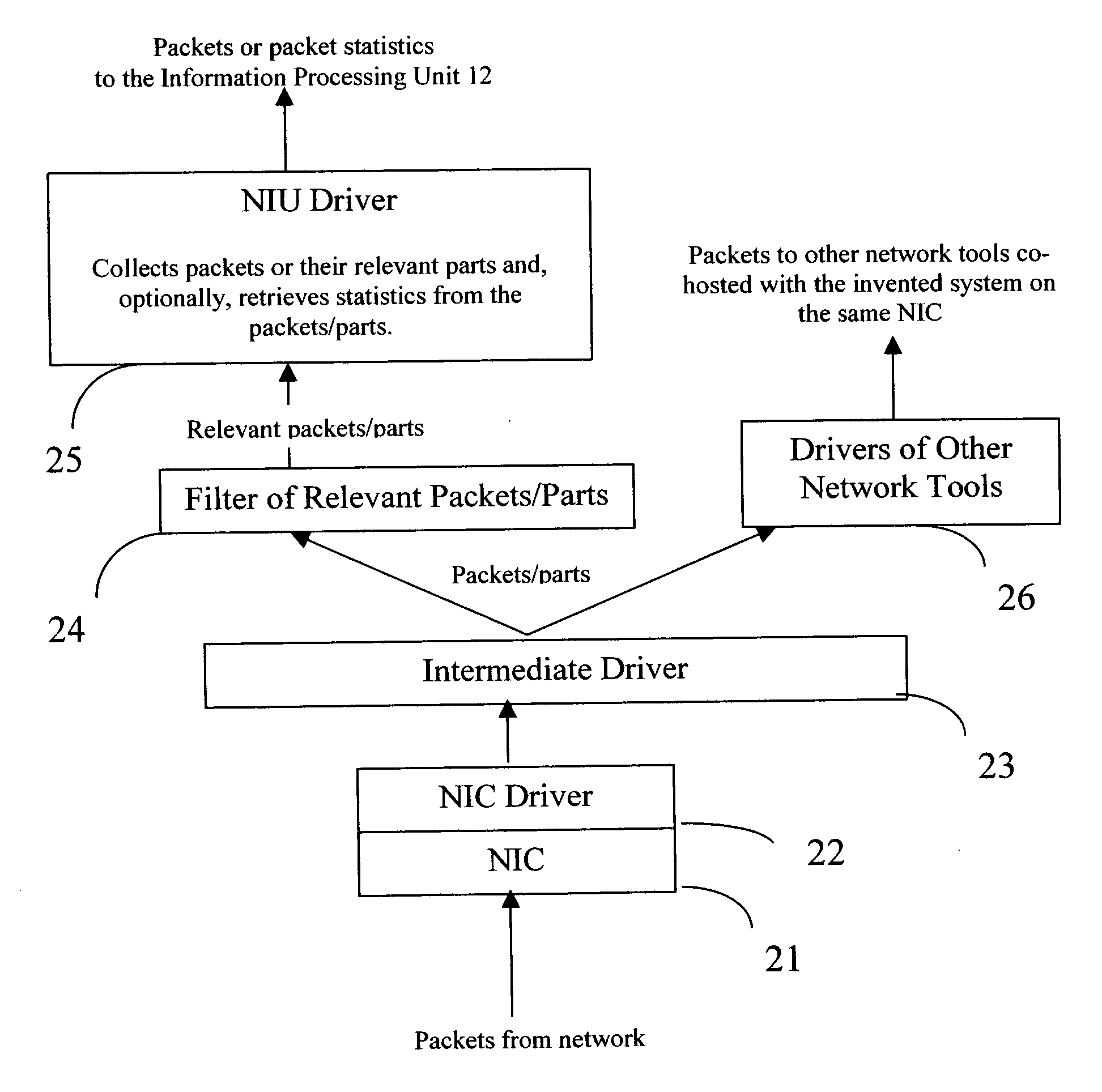
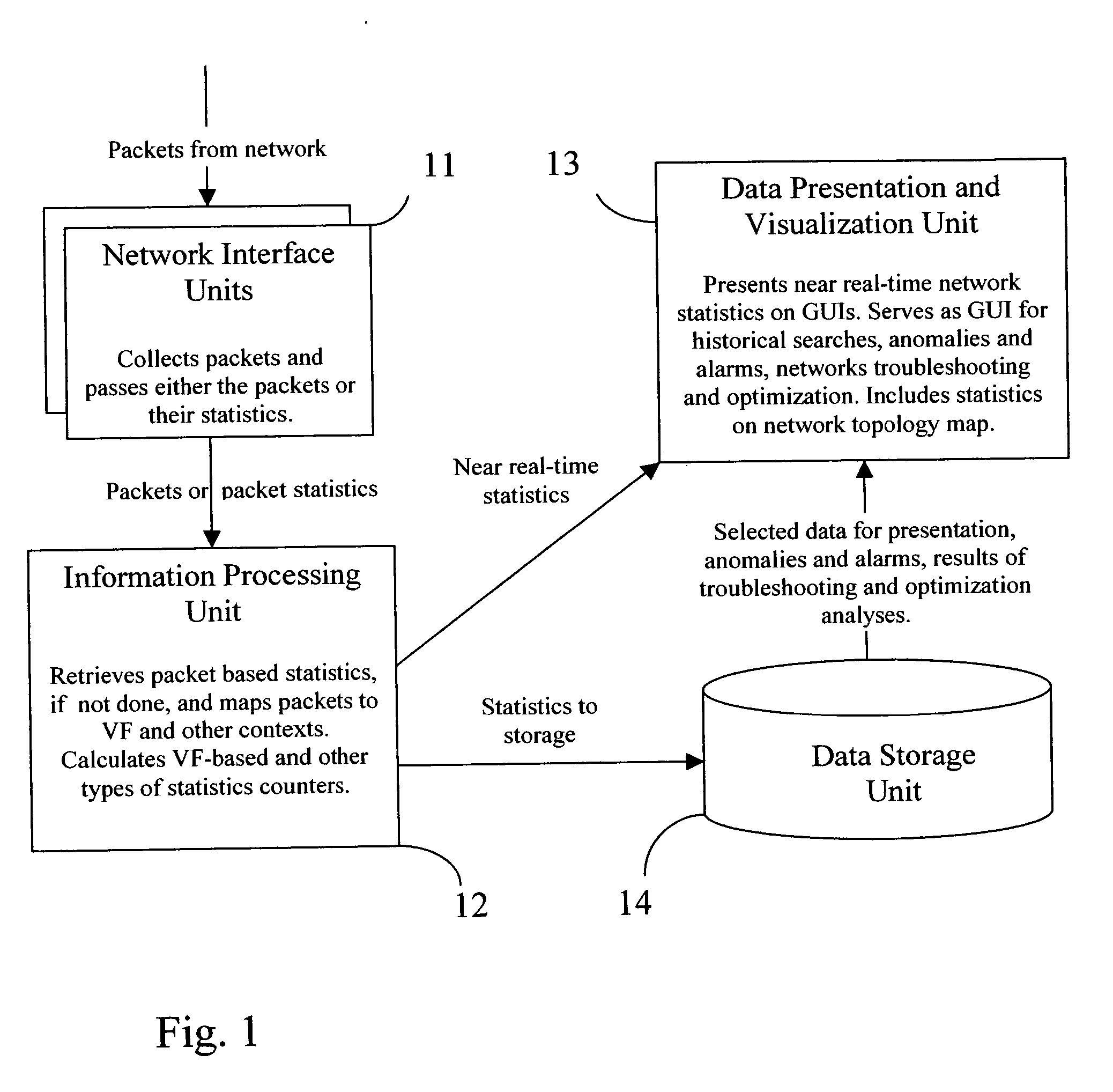
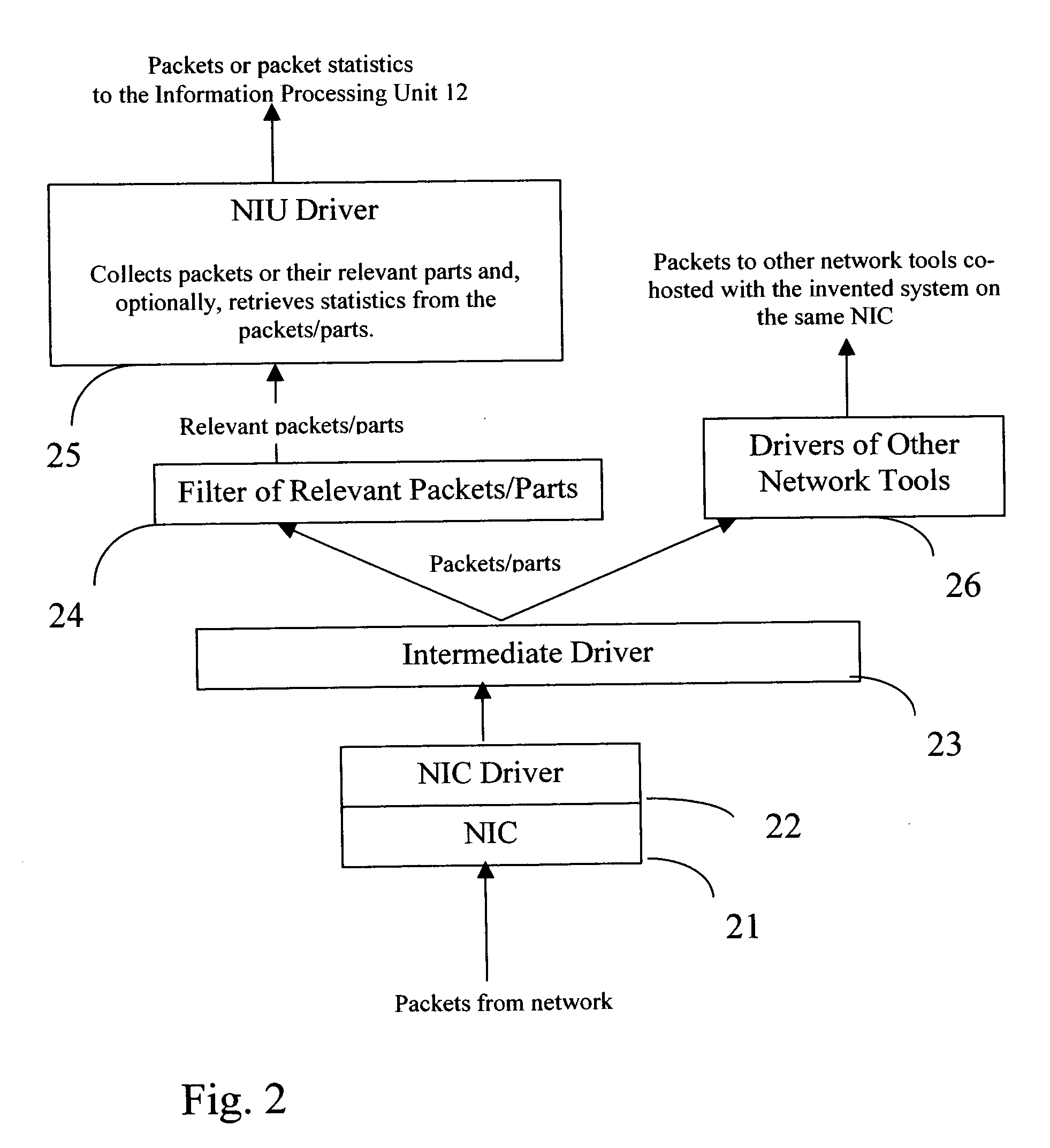
InactiveUS20060028999A1Improve network securityEasy to highlightError preventionTransmission systemsProcess informationStreamflow
The present invention is a computer system and a method for gathering, processing and analysis of network information resulting in presentation and visualization of packet networks in the form of individual virtual flows, sometimes also called connections or sessions, containing their statistical characteristics in a time-sampled dynamics. The system, deployed as a separate device or co-hosted with other network devices, collects and processes information from all valid packets in network, classifies and maps gathered statistics to the statistics of relevant virtual flows. The statistical information is further processed by the system to provide near-real presentation, as well as stored in a searchable database for future analyses. The invention to be used by network engineers and administrators as a tool for a near real-time control of network traffic, as an analytical tool for solving network bottlenecks, network performance optimization and troubleshooting analyses, cutting costs by optimizing network layout, appropriate organization of traffic and intelligent configuration of QoS, routers and other network devices.
Owner:IAKOBASHVILI ROBERT +1
Double-ended blower and volutes therefor
InactiveUS6910483B2Faster pressure rise timeImprove reliabilityPropellersElement comparisonMotor speedImpeller
A double-ended variable speed blower for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) ventilation of patients includes two impellers in the gas flow path that cooperatively pressurize gas to desired pressure and flow characteristics. Thus, the double-ended blower can provide faster pressure response and desired flow characteristics over a narrower range of motor speeds, resulting in greater reliability and less acoustic noise.
Owner:RESMED LTD
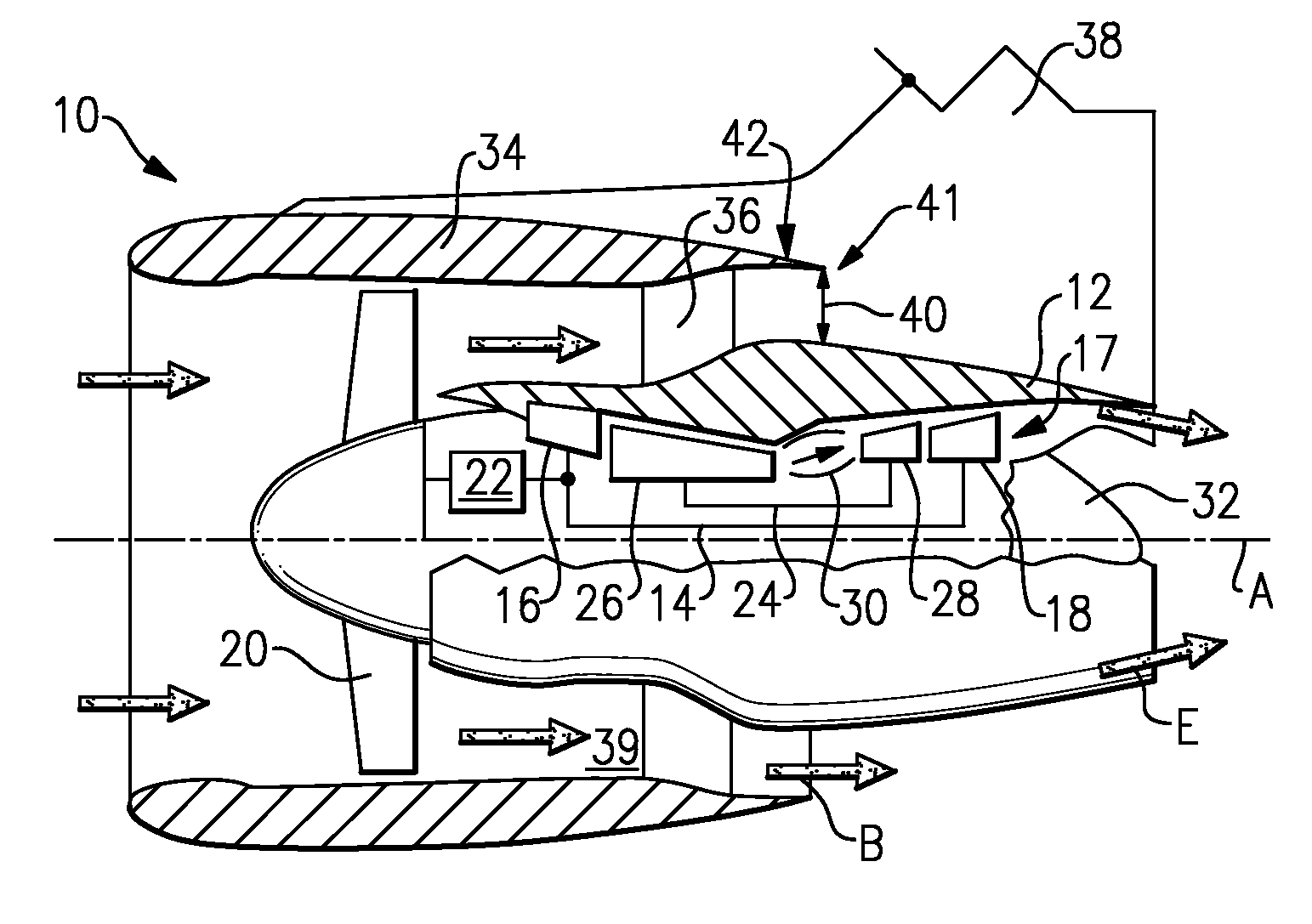
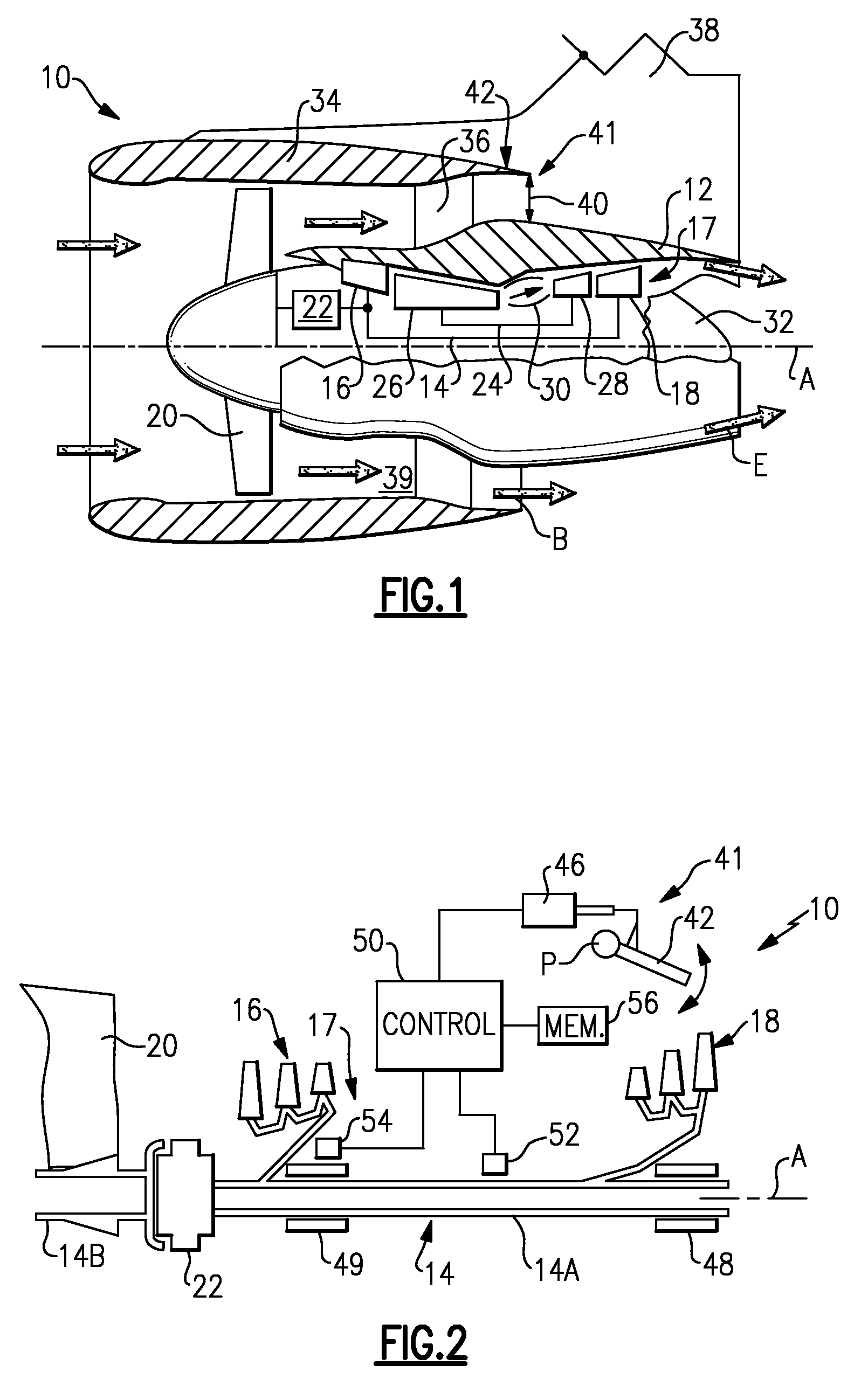
Managing spool bearing load using variable area flow nozzle
A turbine engine provides a spool supporting a turbine. The spool is arranged in a core nacelle and includes a thrust bearing. A fan is arranged upstream from the core nacelle and is coupled to the spool. A fan nacelle surrounds the fan and core nacelle and provides a bypass flow path that includes a fan nozzle exit area. A flow control device is adapted to effectively change the fan nozzle exit area. A controller is programmed to monitor the thrust bearing and command the flow control device in response to an undesired load on the thrust bearing. Effectively changing the fan nozzle exit area with the flow control device actively manages the bearing thrust load to desired levels.
Owner:RTX CORP
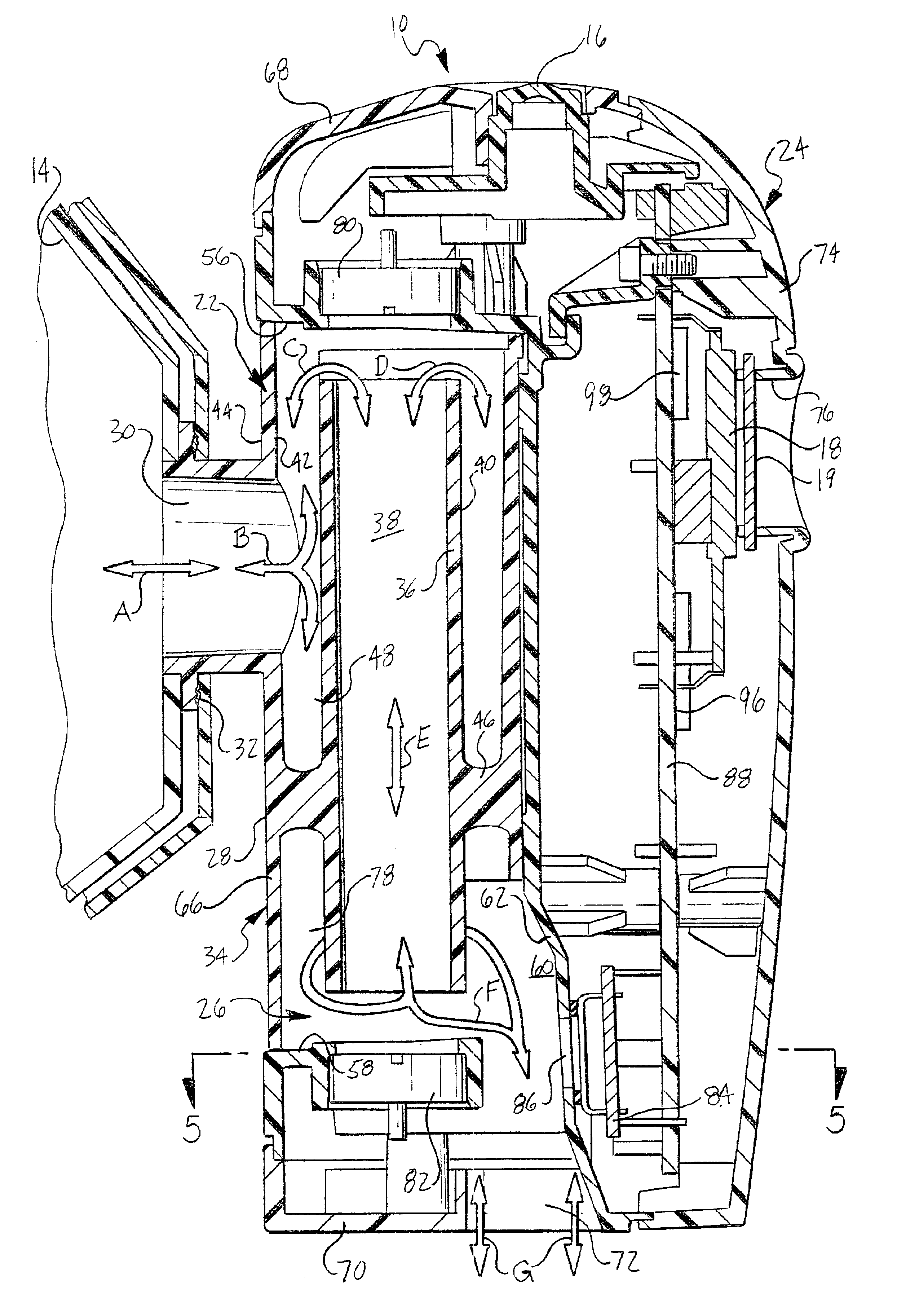
Portable drag compressor powered mechanical ventilator
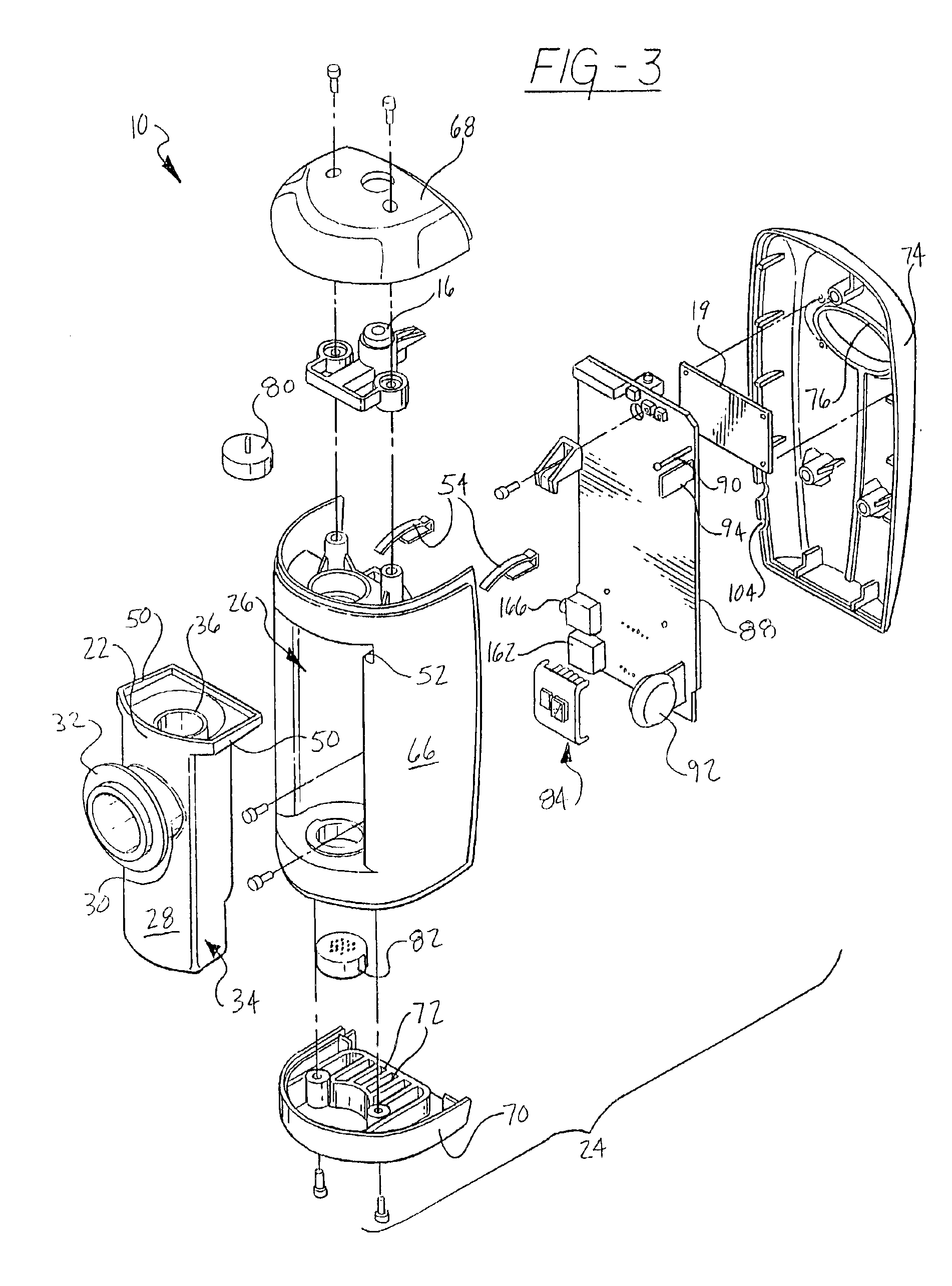
InactiveUS6877511B2Accurate measurementMinimize fabrication inaccuracyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSolenoid valveEngineering
A ventilator device and system comprising a rotating compressor, preferably a drag compressor, which, at the beginning of each inspiratory ventilation phase, is accelerated to a sufficient speed to deliver the desired inspiratory gas flow, and is subsequently stopped or decelerated to a basal flow level to permit the expiratory ventilation phase to occur. The ventilator device is small and light weight enough to be utilized in portable applications. The ventilator device is power efficient enough to operate for extended periods of time on internal or external batteries. Also provided is an oxygen blending apparatus which utilizes solenoid valves having specific orifice sizes for blending desired amounts of oxygen into the inspiratory gas flow. Also provided is an exhalation valve having an exhalation flow transducer which incorporates a radio frequency data base to provide an attendant controller with specific calibration information for the exhalation flow transducer.
Owner:BIRD PRODS
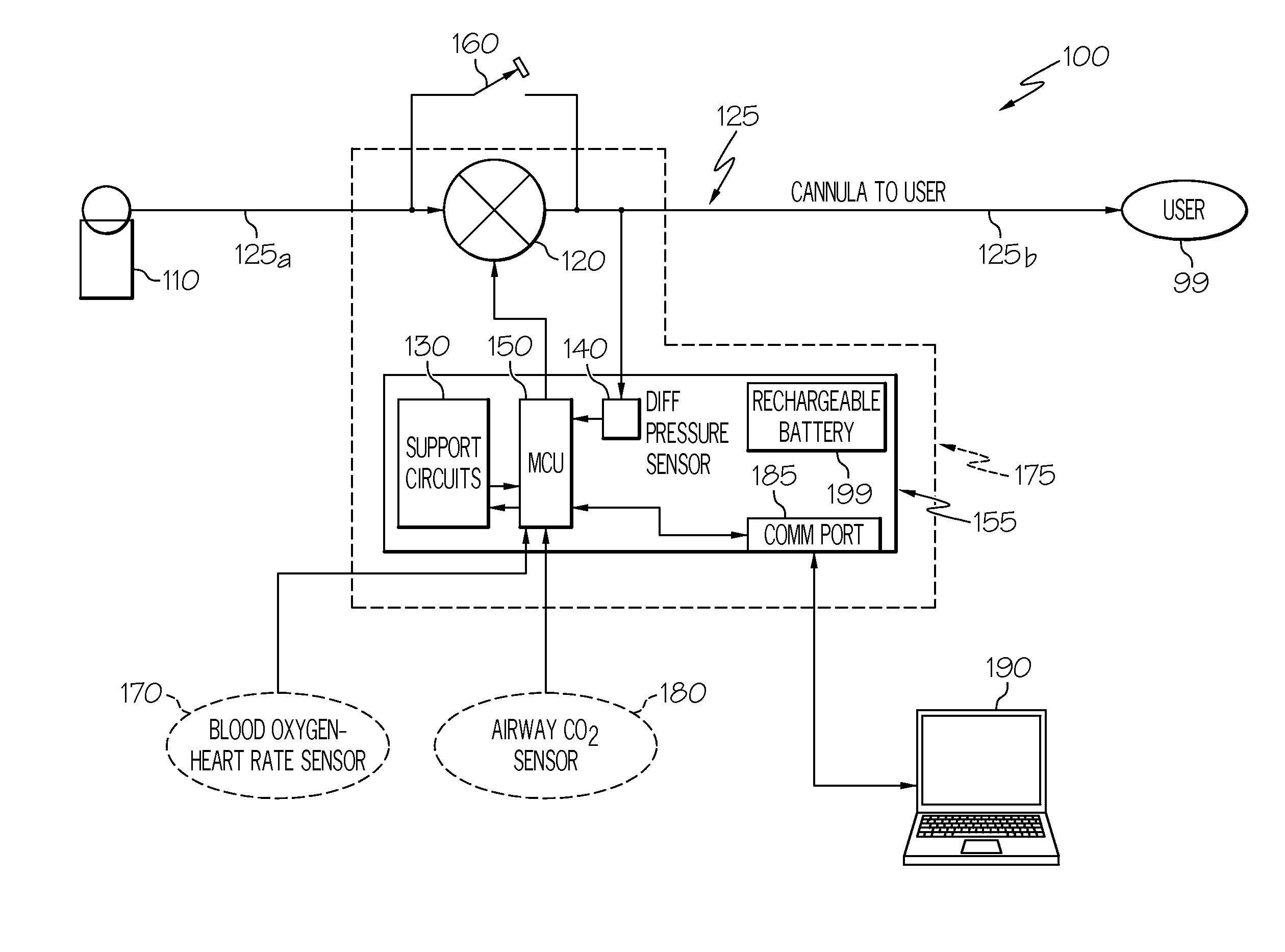
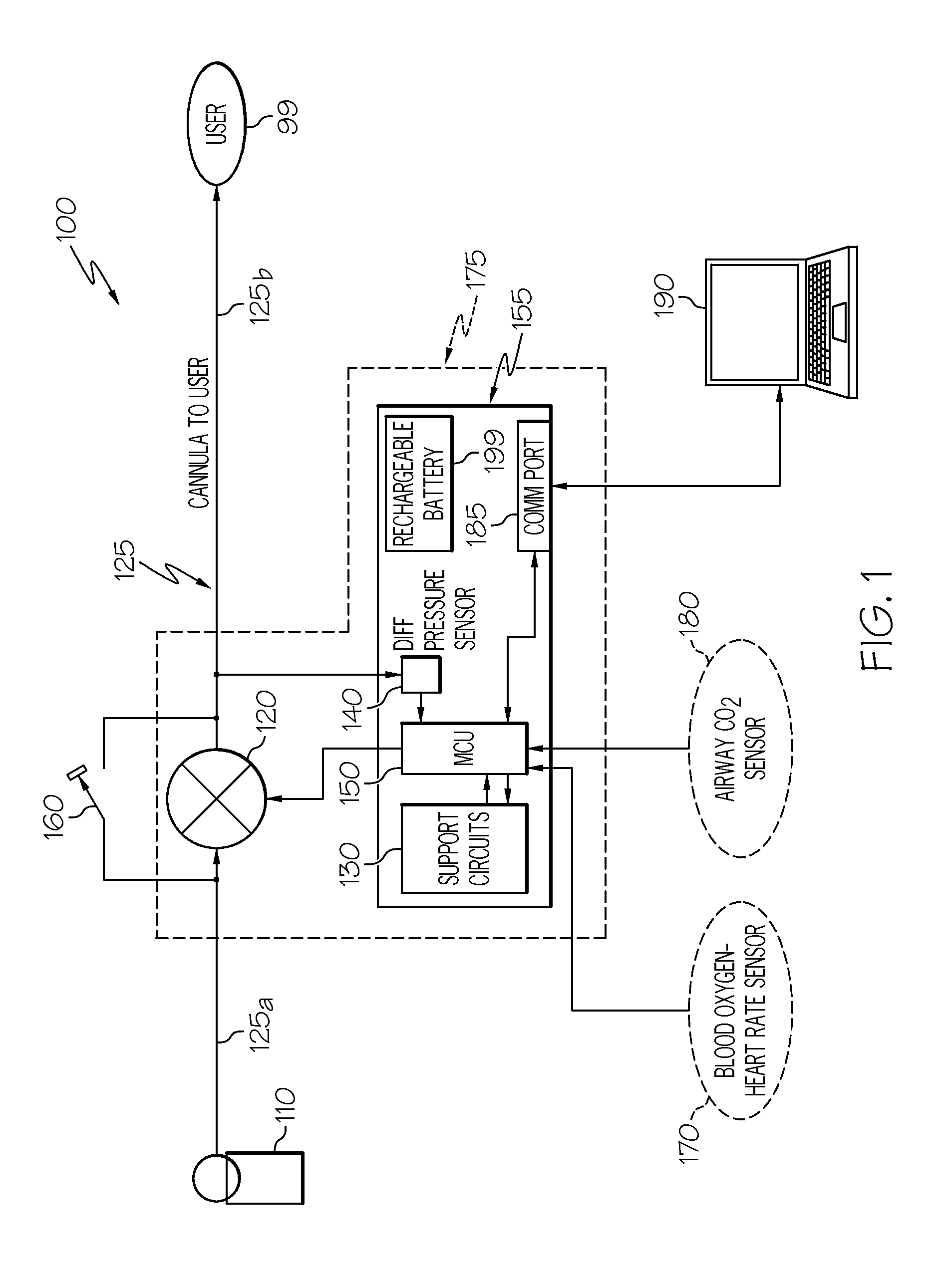
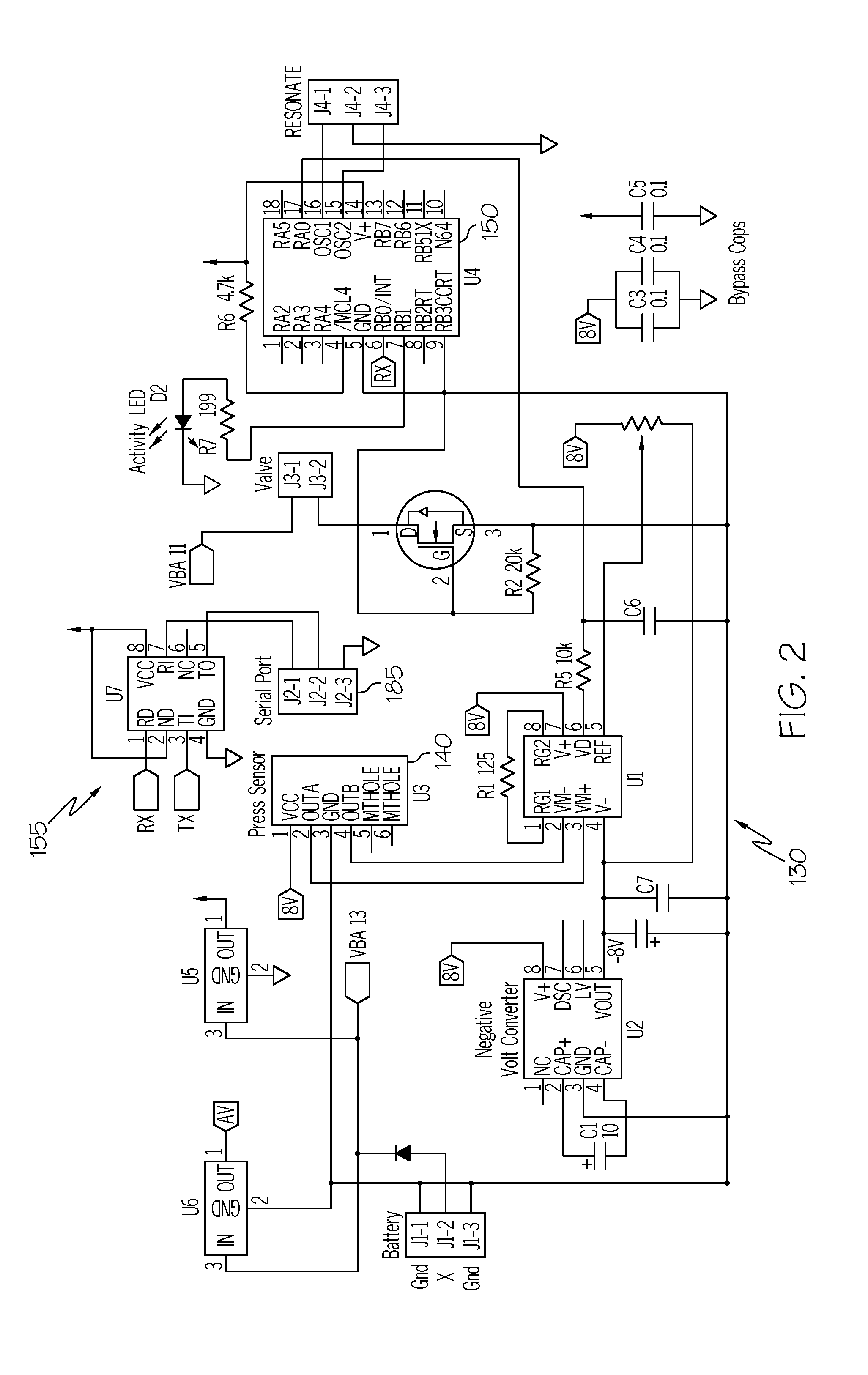
Automated fluid delivery system and method
InactiveUS20130152933A1Convenient amountRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDifferential pressureEngineering
An automated fluid delivery system and method are disclosed. The system includes distensible tubing, a flow controller, and a fluid flow adjustment module. The fluid flow adjustment module may be configured to detect differential pressure in the tubing and adjust the flow controller to provide an amount of fluid through the tubing during inhalation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
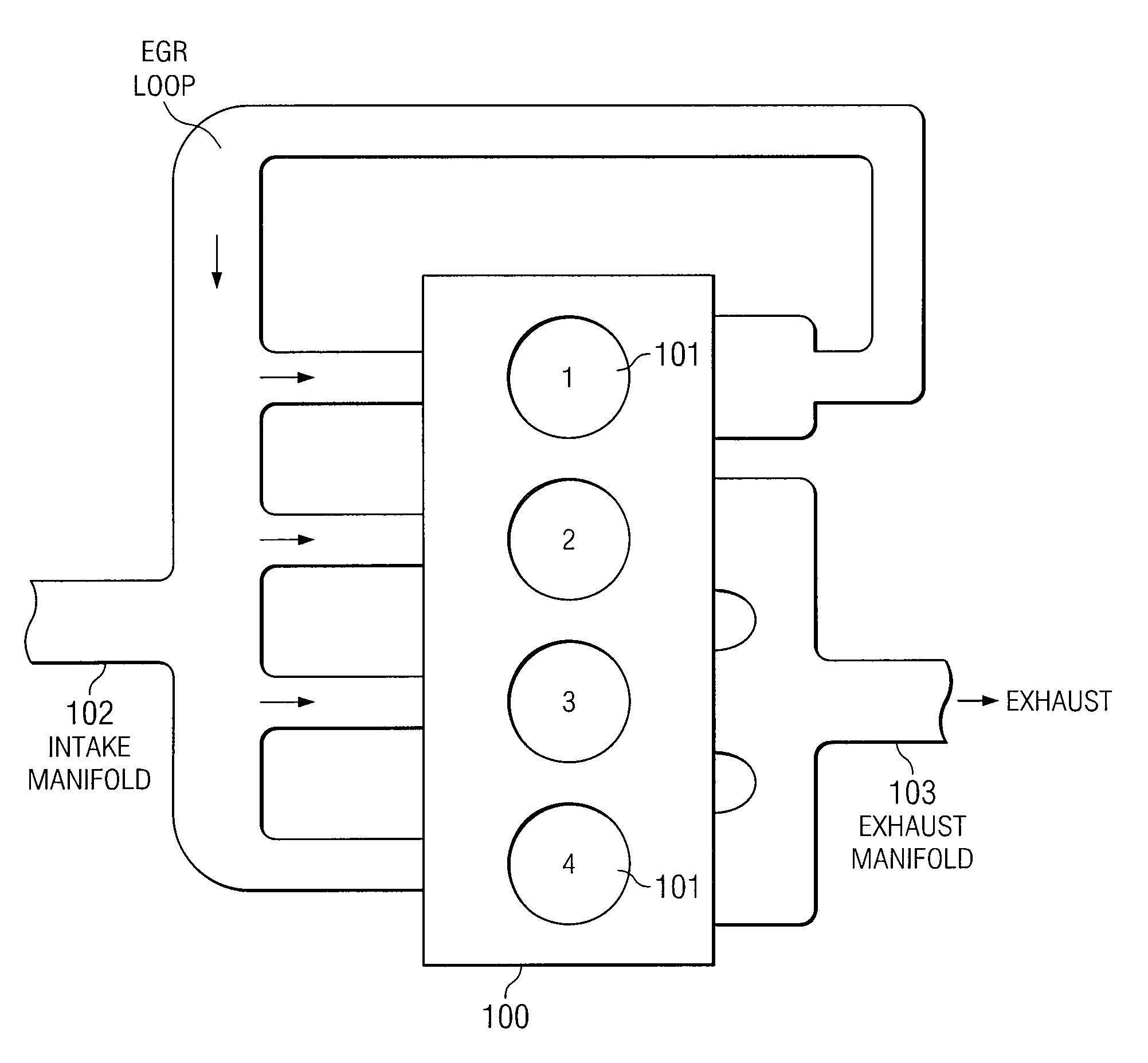
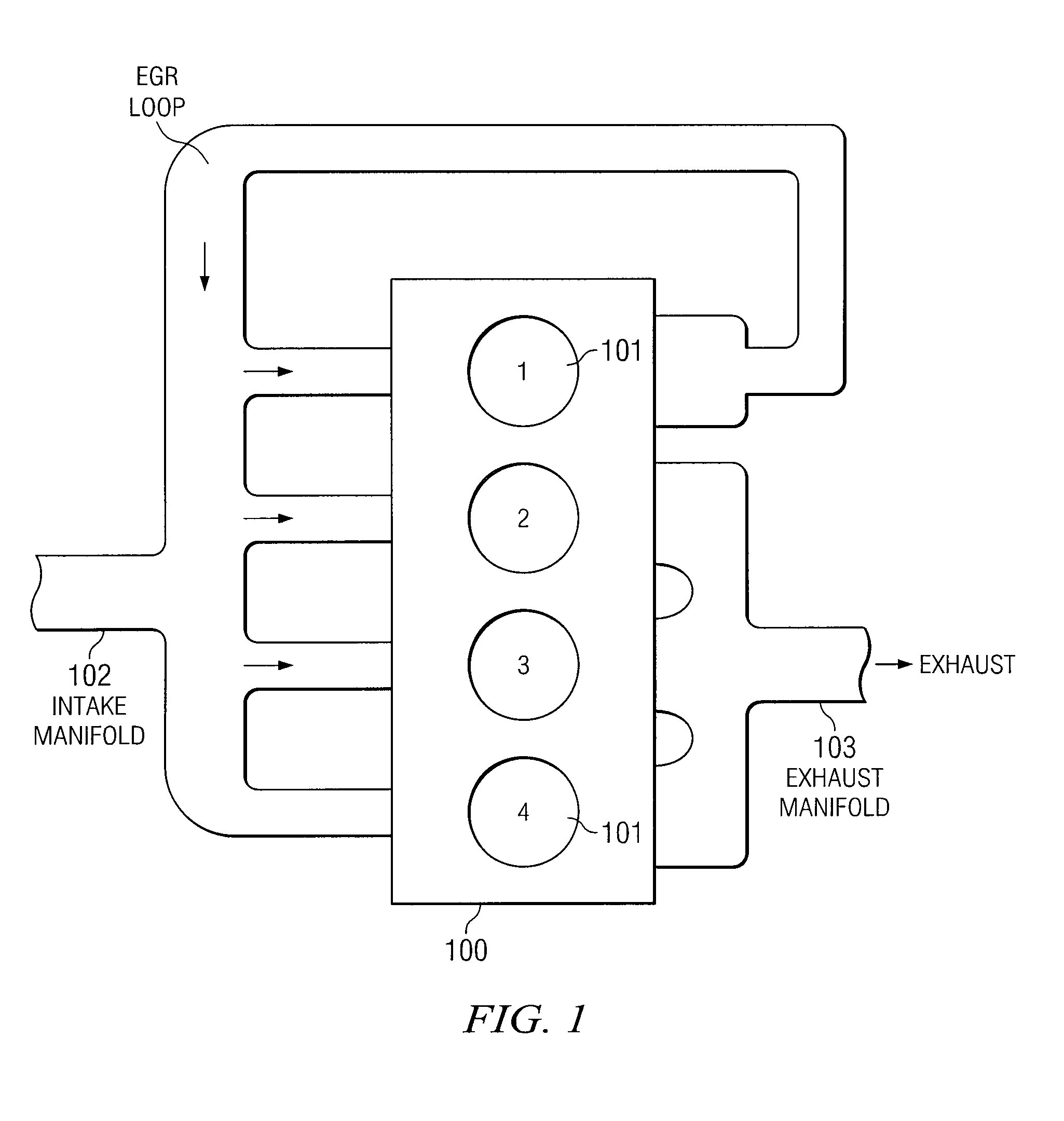
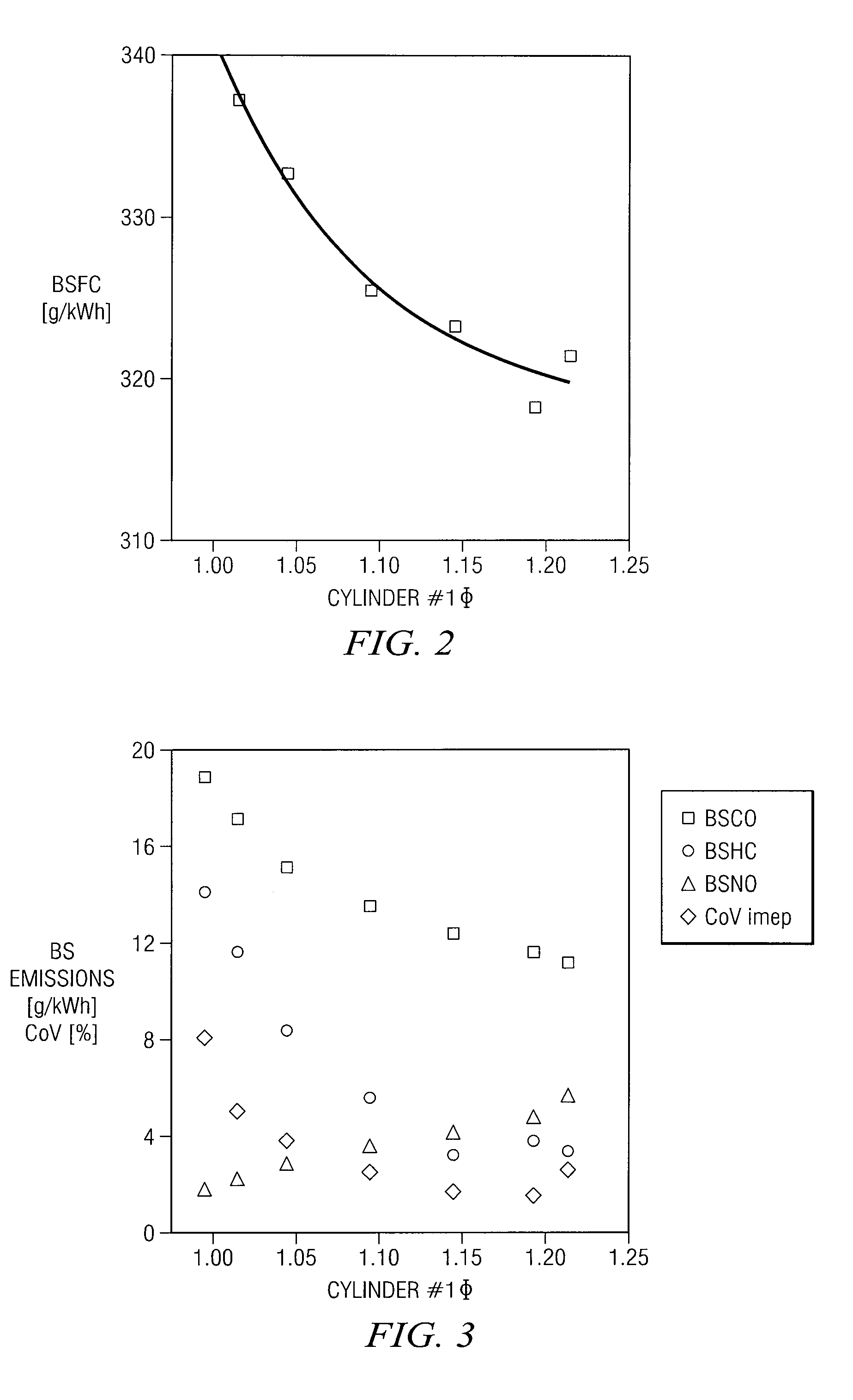
Egr system with dedicated egr cylinders
Improved exhaust gas recirculation system and methods that use one or more of the engine's cylinders as dedicated EGR cylinders. All of the exhaust from the dedicated EGR cylinders is recirculated back to the engine intake. Thus, the EGR rate is constant, but the EGR mass flow may be controlled by adjusting the air-fuel ratio of the dedicated EGR cylinders or by using various variable valve timing techniques.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
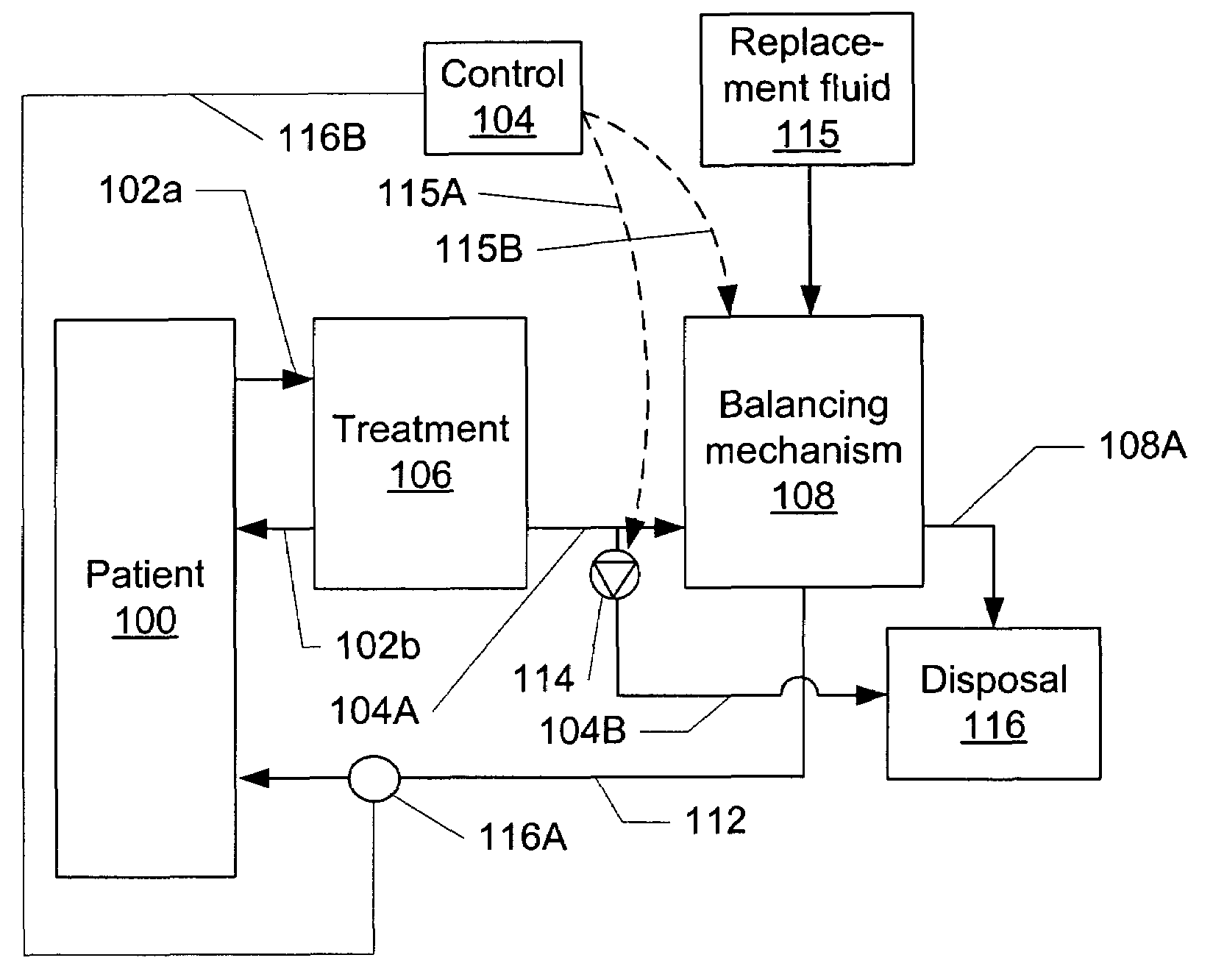
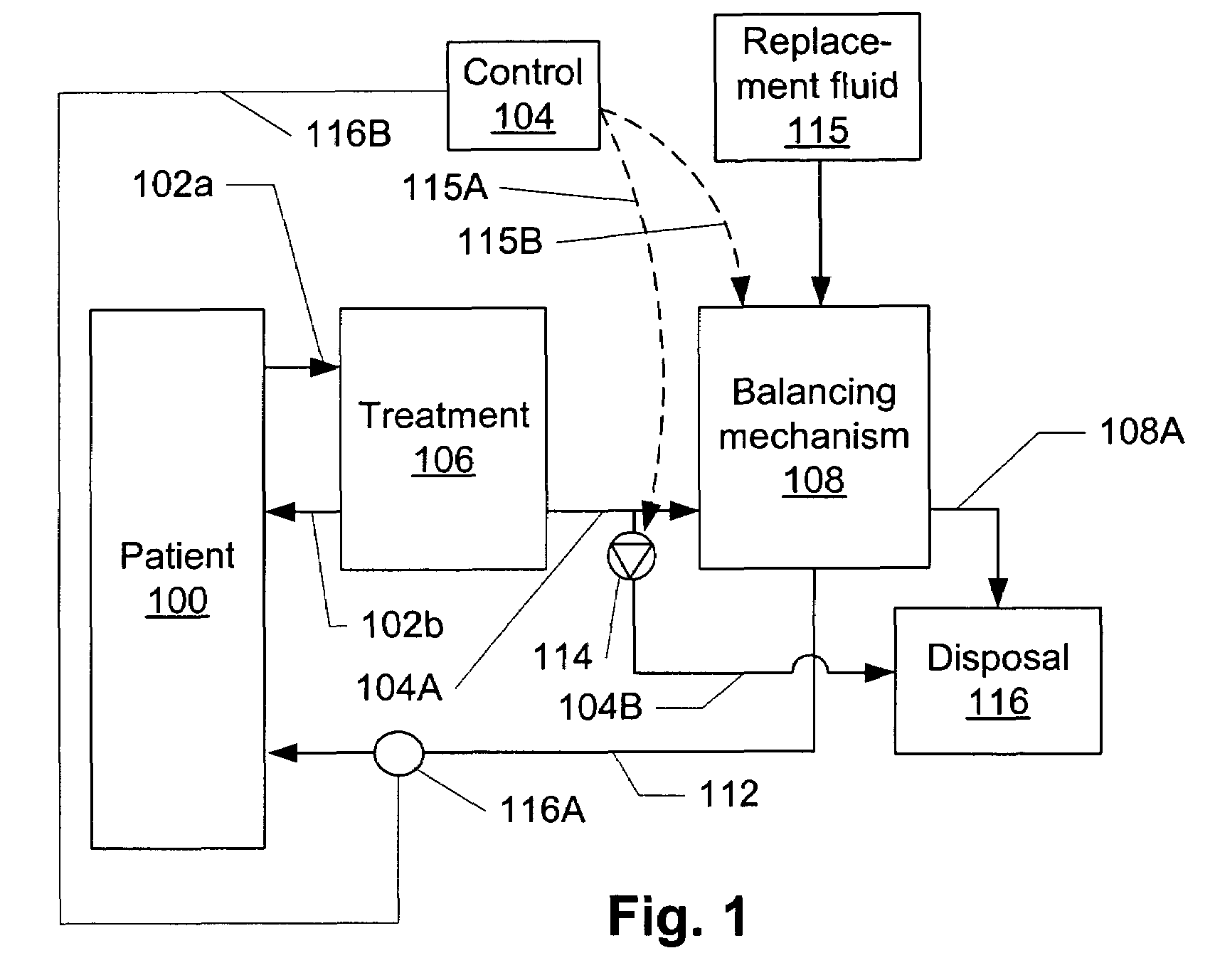
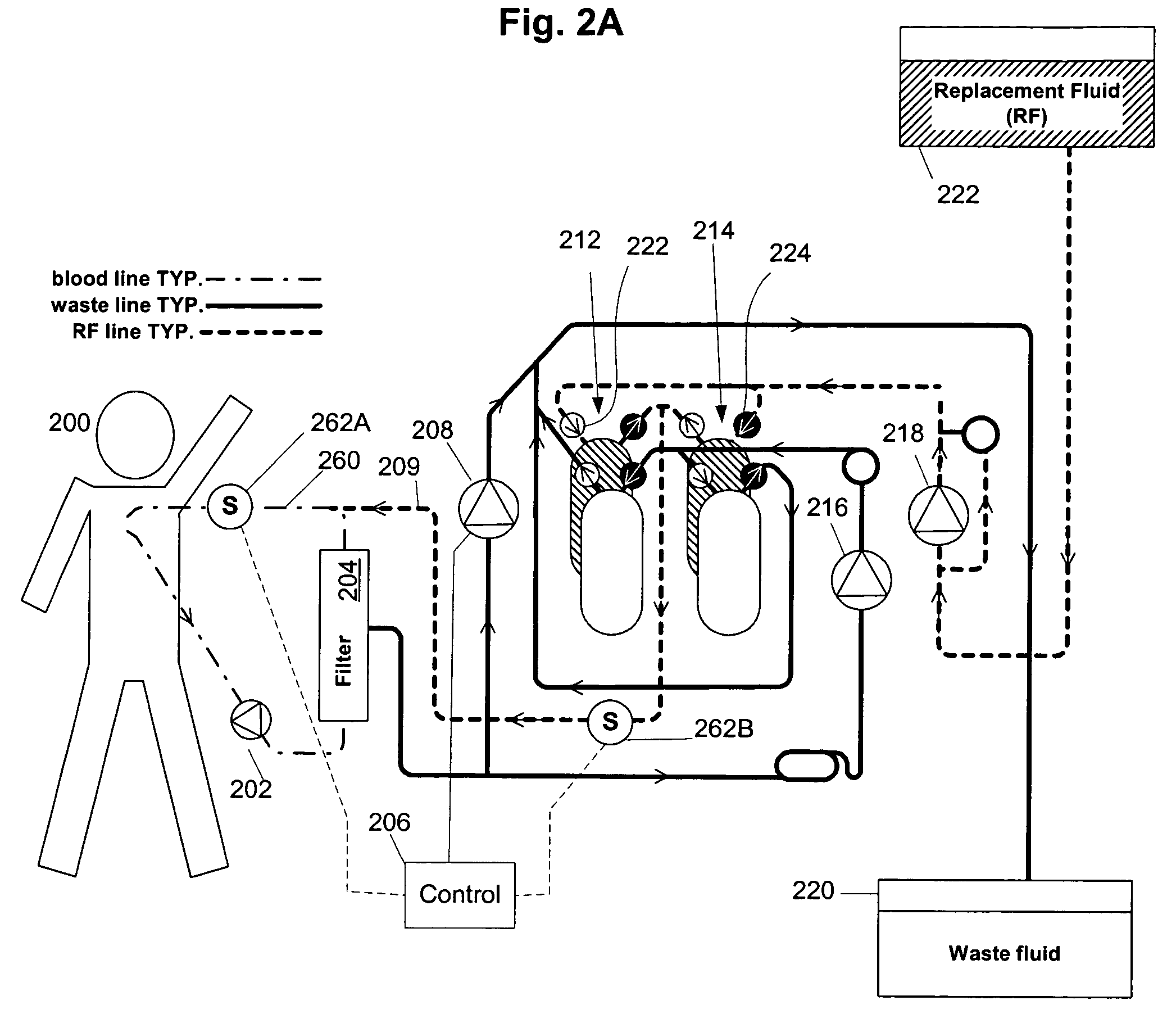
Volumetric fluid balance control for extracorporeal blood treatment
ActiveUS7112273B2Effective compensationDetectability of a fluid volume imbalanceHaemofiltrationSettling tanks feed/dischargeBlood treatmentsFluid balance
A method and device for adjusting a volumetric flow balancing system for an extracorporeal blood treatment system receives a pressure signal and calculates a compensation factor that is used to adjust the relative flow rates of the volumetrically balanced fluids. For example, in a hemofiltration system, the flow of waste and and replacement fluid may be balanced volumetrically. Ultrafiltrate may be pumped in a bypass circuit in such a system. The rate of ultrafiltrate flow may be adjusted by the compensation signal. The compensation signal may be empirically derived.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL INC
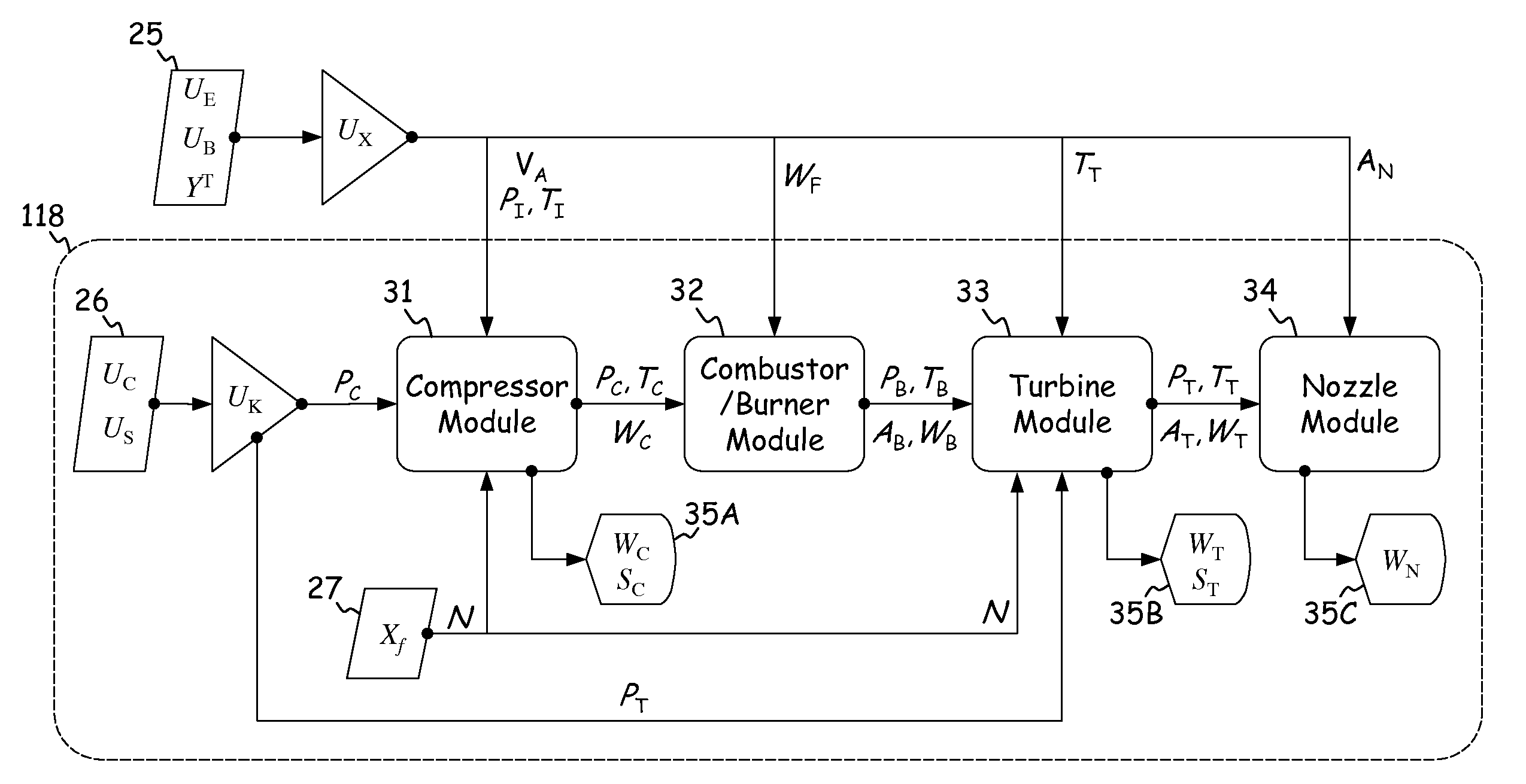
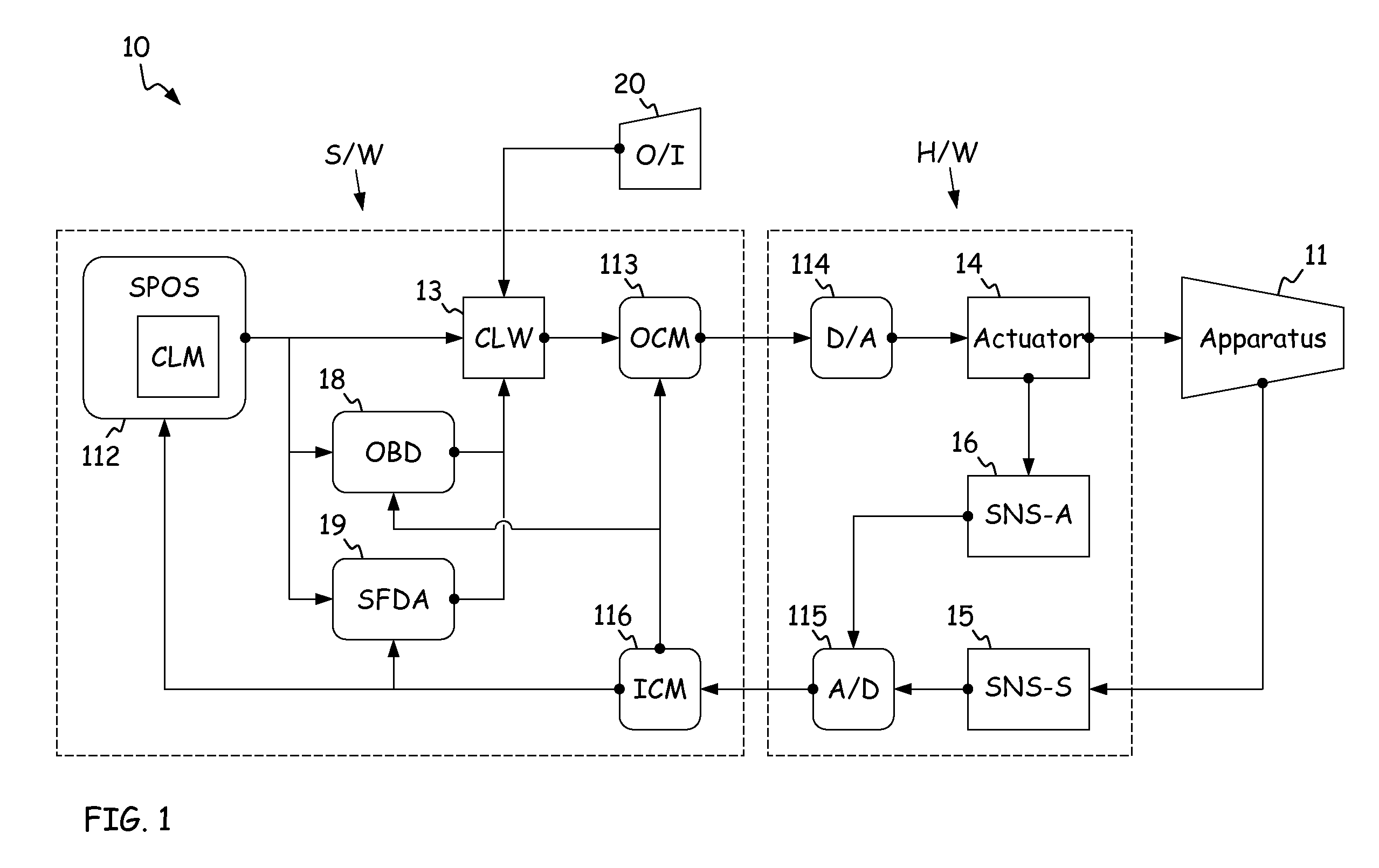
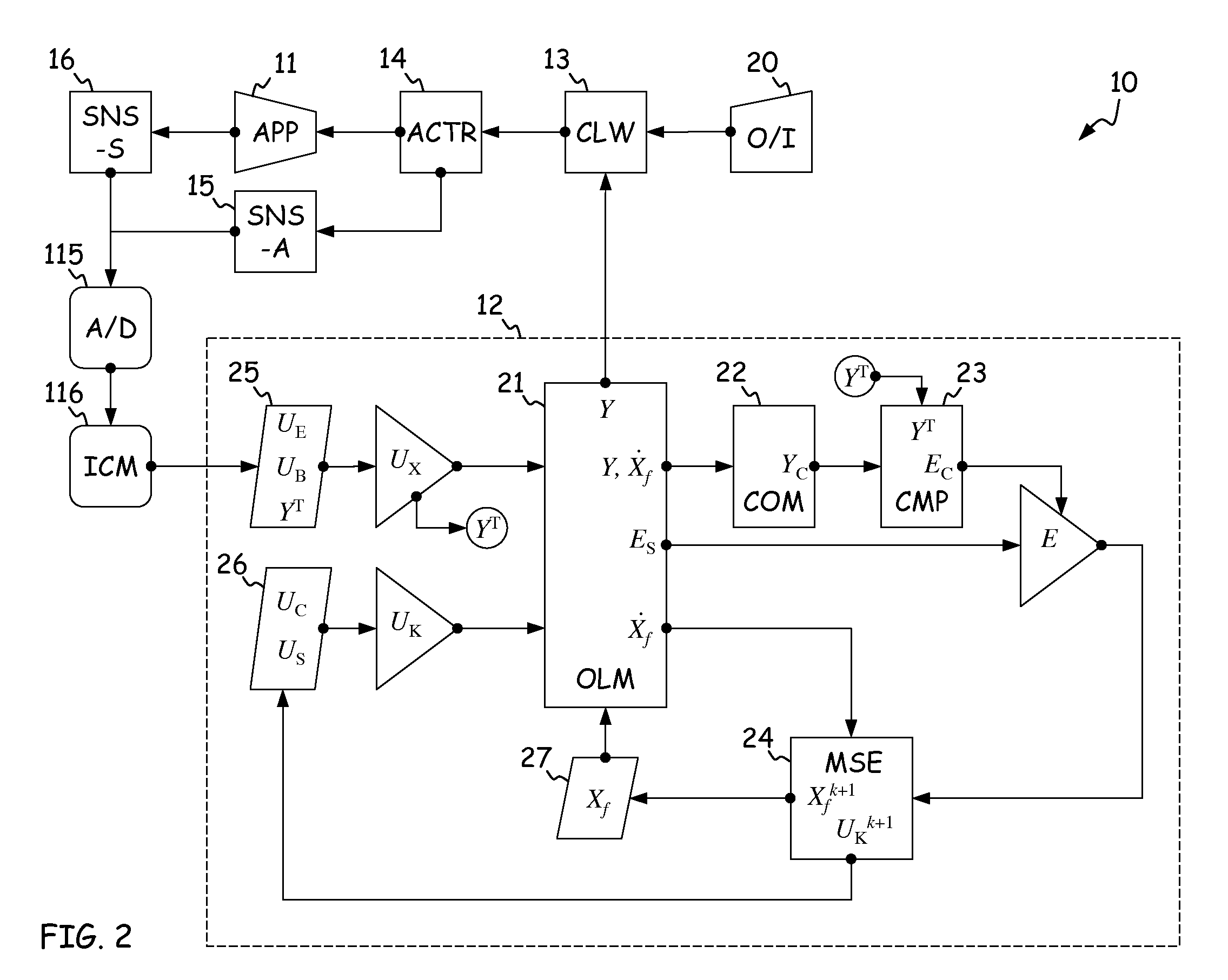
High fidelity integrated heat transfer and clearance in component-level dynamic turbine system control
ActiveUS20110054704A1Turbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTemperatue controlControl flowEngineering
A system comprises a rotary apparatus, a control law and a processor. The rotary apparatus comprises a rotor and a housing forming a gas path therebetween, and the control law controls flow along the gas path. The processor comprises an output module, a plurality of temperature modules, a thermodynamic module, a comparator and an estimator. The output module generates an output signal as a function of a plurality of rotor and housing temperatures defined along the gas path, and the temperature modules determine time derivatives of the rotor and housing temperatures. The thermodynamic module models boundary conditions for the gas path, and the comparator determines errors in the boundary conditions. The estimator estimates the rotor and housing temperatures based on the time derivatives, such that the errors are minimized and the flow is controlled.
Owner:RTX CORP
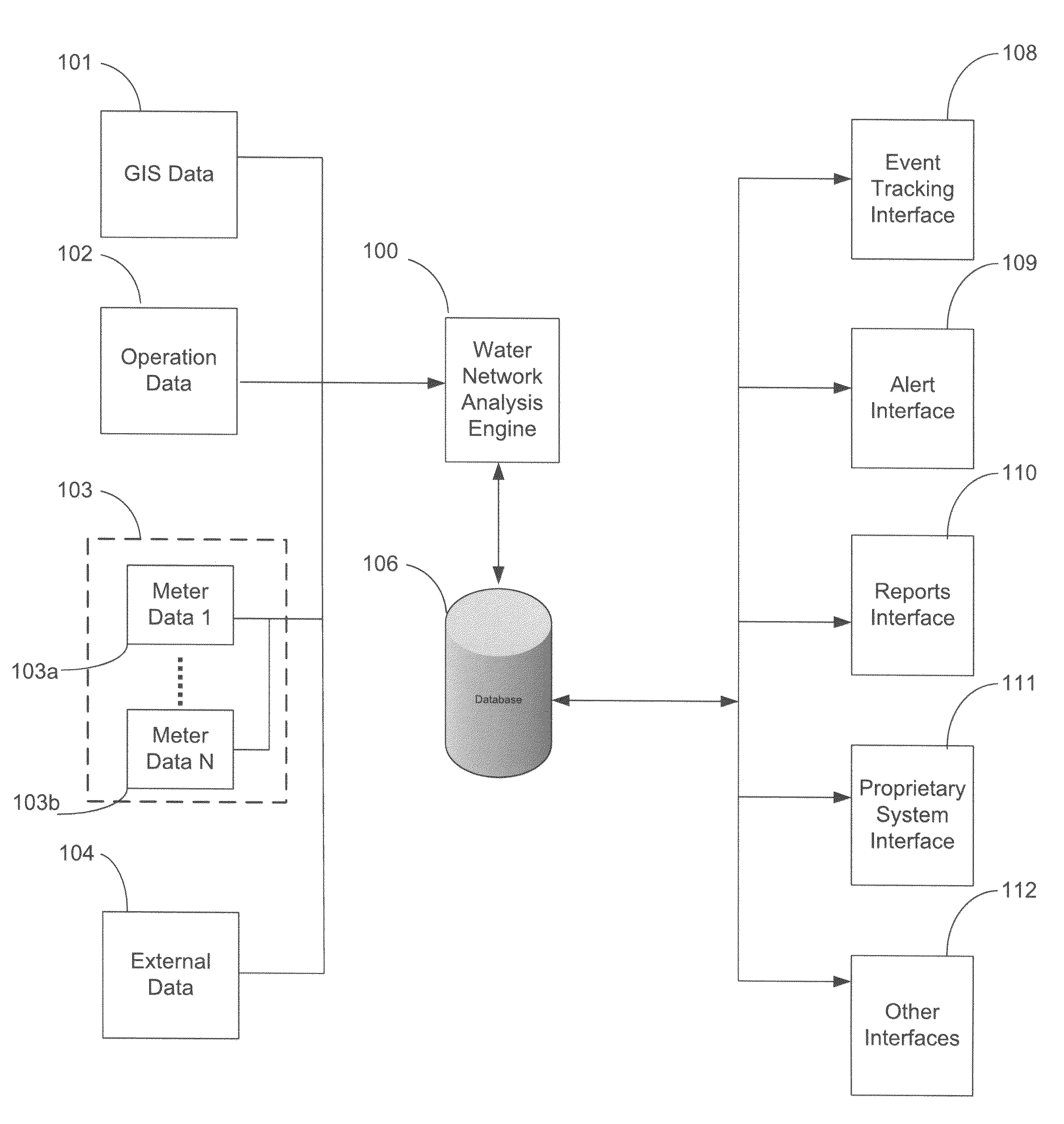
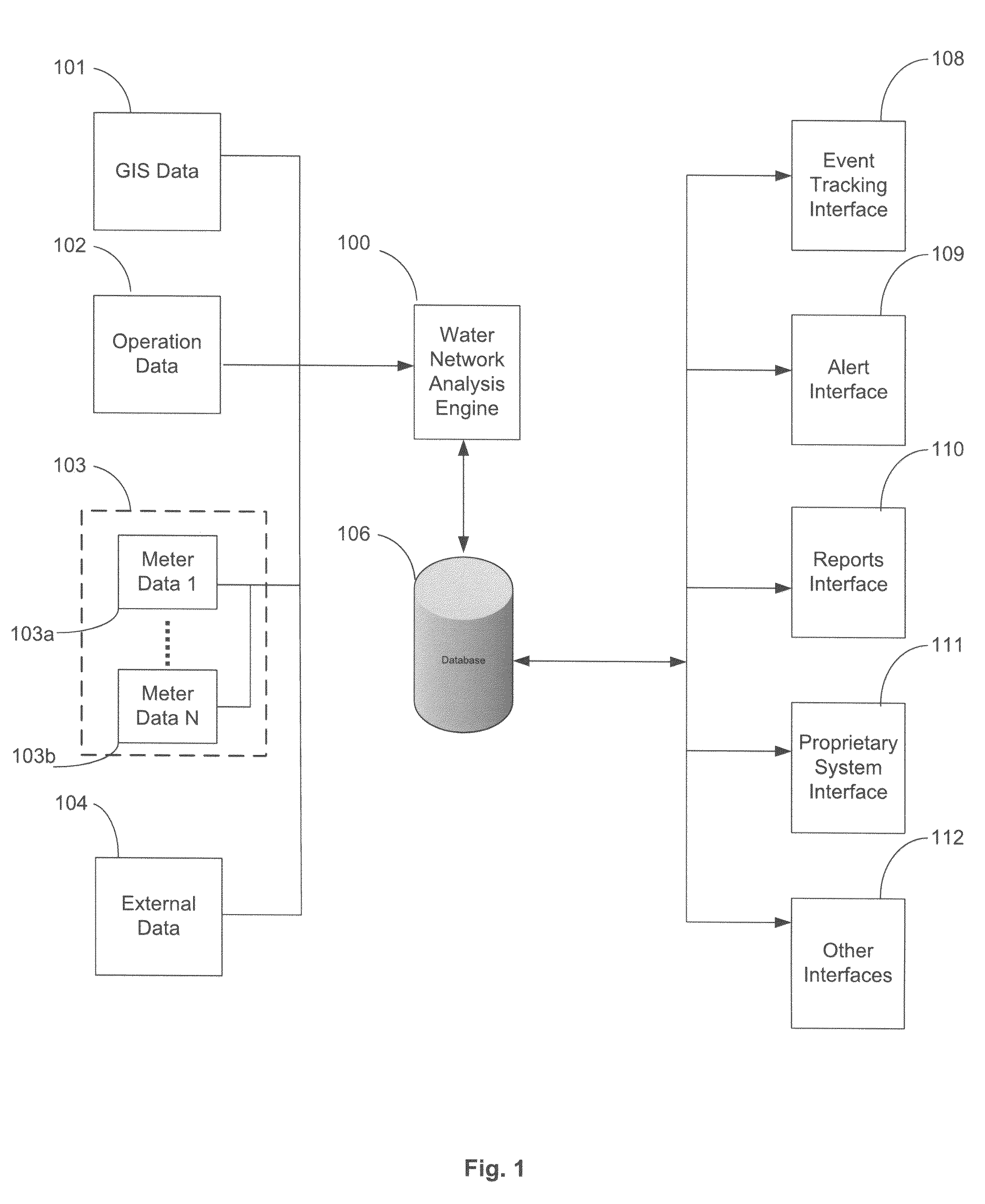
System and method for monitoring resources in a water utility network
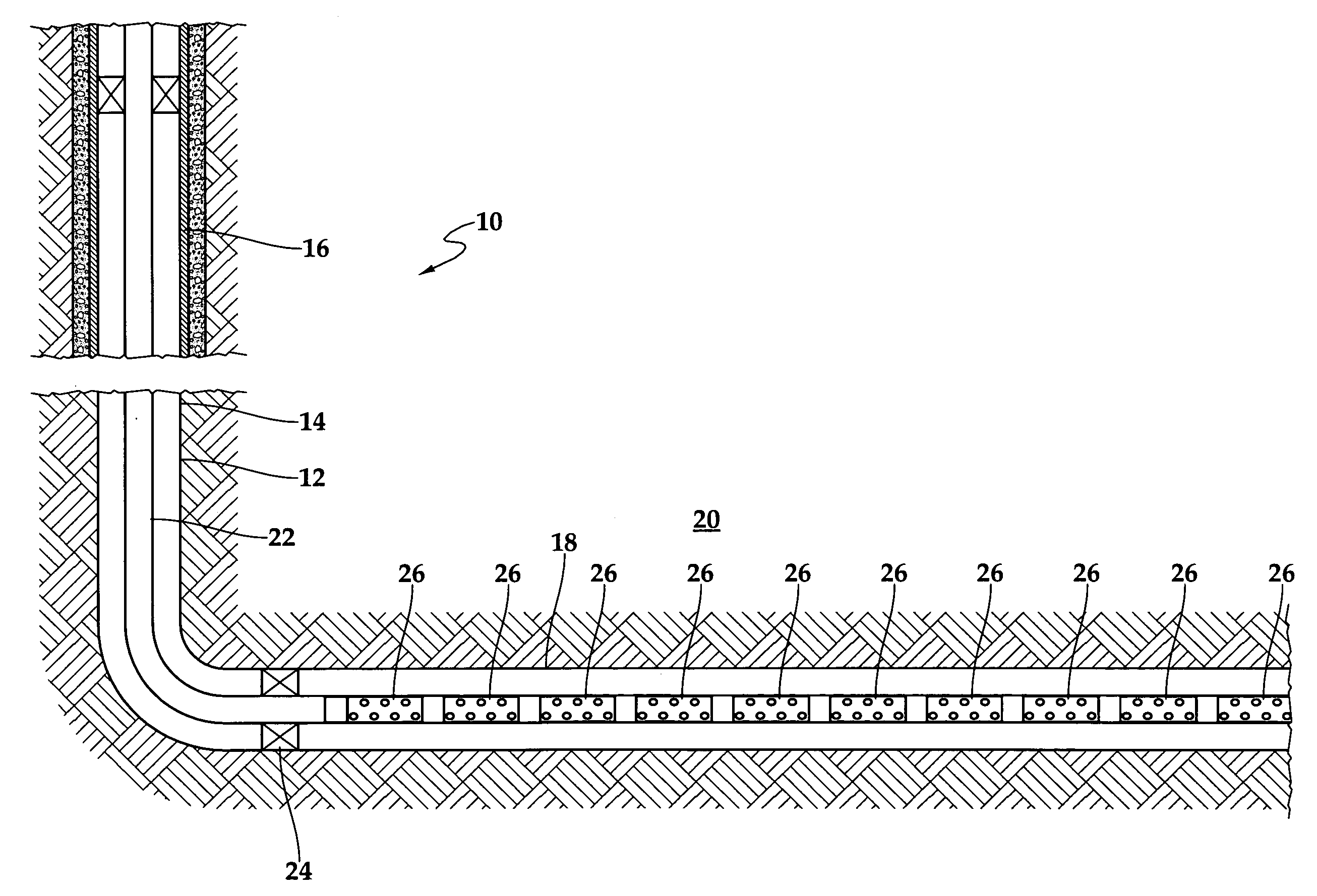
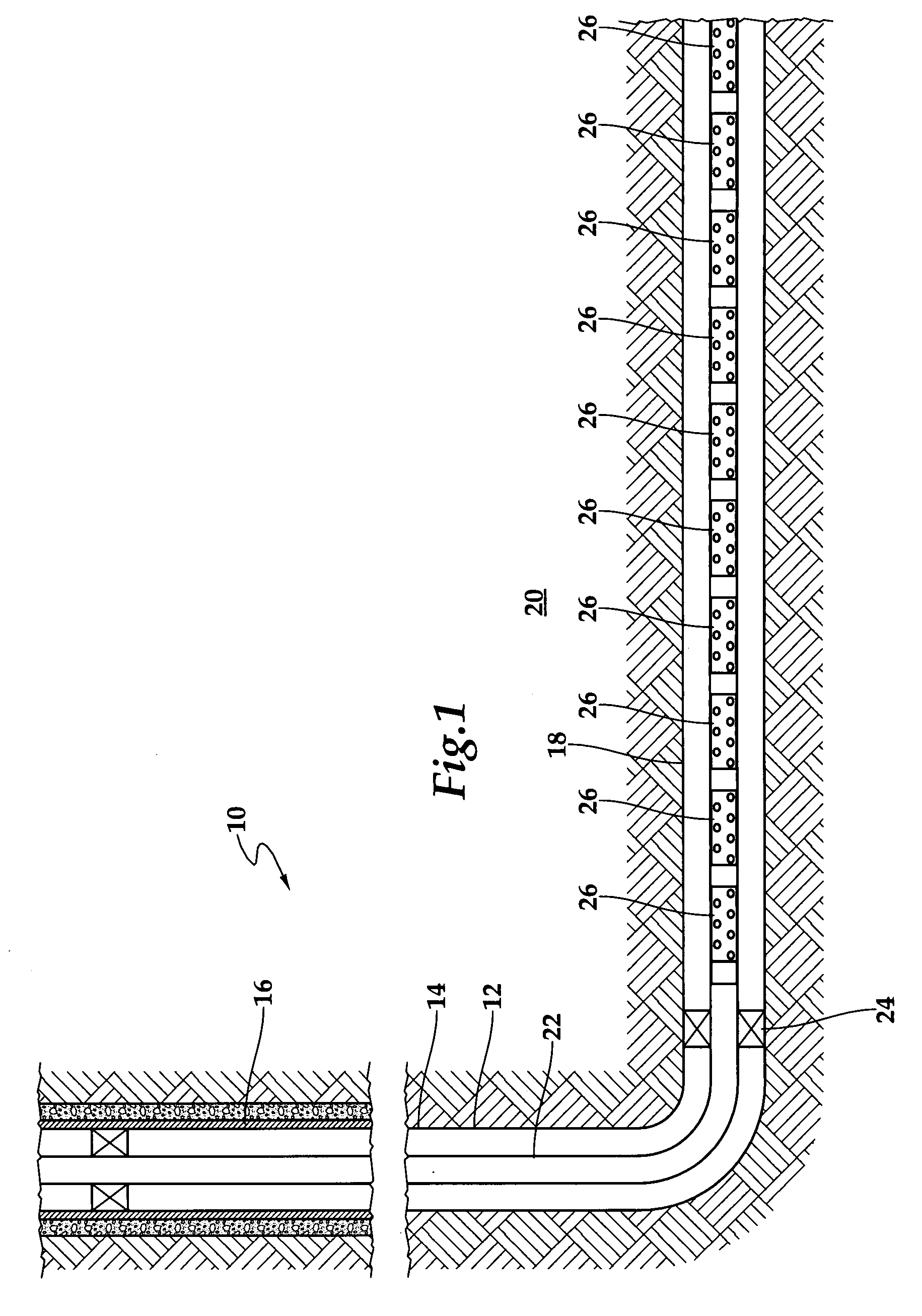
ActiveUS7920983B1Easy to detectIncrease consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsTesting/calibration apparatusWater utilityUtility industry
A computerized method for monitoring a water utility network, the water utility network comprising a network of pipes for delivering water to consumers and a plurality of meters positioned within the pipes across the water distribution network. The method includes receiving meter data representing parameters measured by the meters, such as flow, pressure, chlorine level, pH and turbidity of the water being distributed through the pipes. The method also includes receiving secondary data from sources external to the meters and representing conditions affecting consumption of water in a region serviced by the water utility network such as weather and holidays. The meter and secondary data is analyzed using statistical techniques to identify water network events including leakage events and other events regarding quantity and quality of water flowing through the pipes and operation of the water network. The events are reported to users via a user interface.
Owner:TAKADU
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
InactiveUS20080178608A1Reduce unevennessUniform maintenanceElectric discharge tubesHeat exhanger conduitsIn planeEngineering
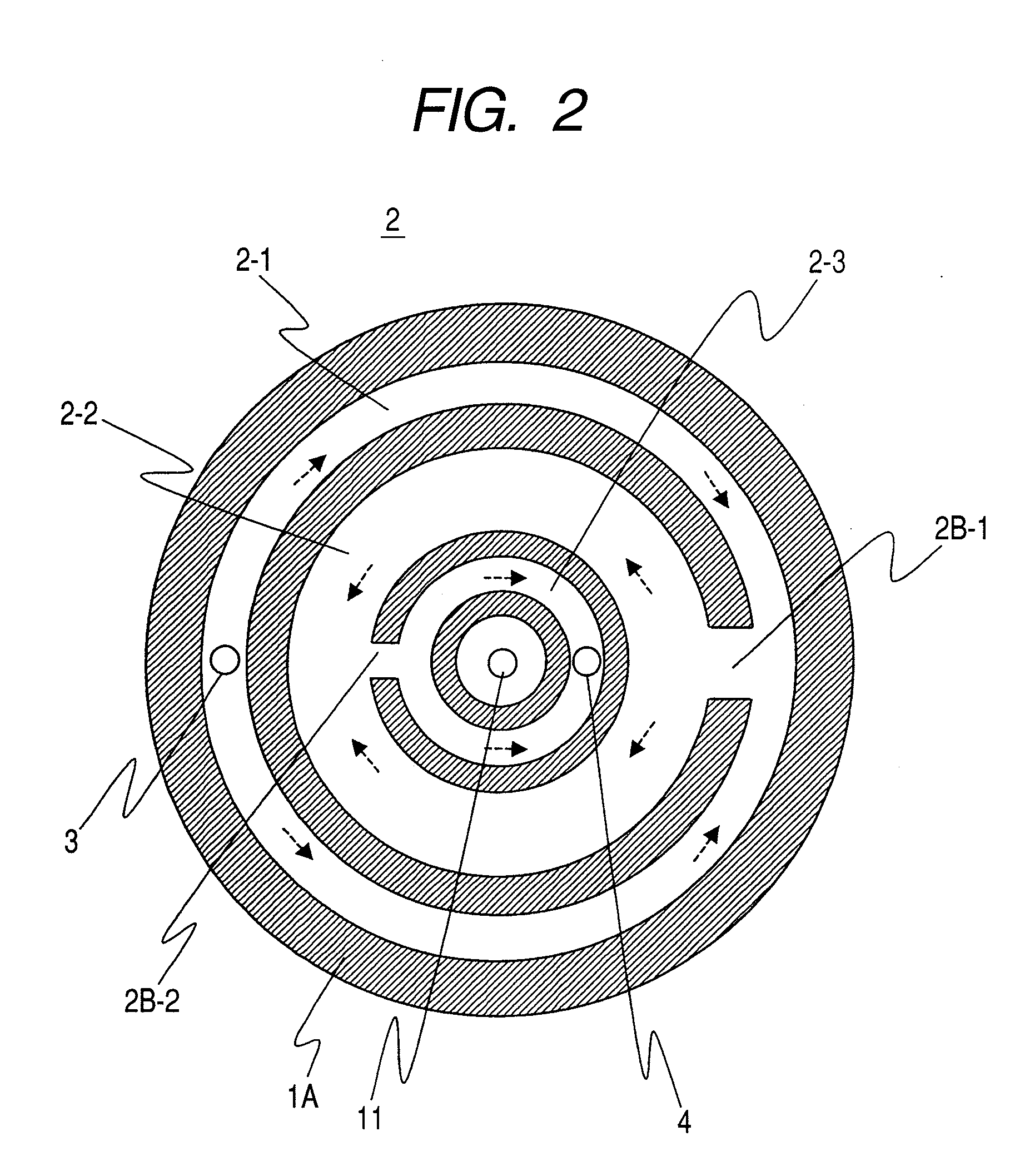
There is provided a means for uniformly controlling the in-plane temperature of a semiconductor wafer at high speed in a high heat input etching process. A refrigerant channel structure in a circular shape is formed in a sample stage. Due to a fact that a heat transfer coefficient of a refrigerant is largely changed from a refrigerant supply port to a refrigerant outlet port, the cross sections of the channel structure is structured so as to be increased from a first channel areas towards a second channel areas in order to make the heat transfer coefficient of the refrigerant constant in the refrigerant channel structure. Thereby, the heat transfer coefficient of the refrigerant is prevented from increasing by reducing the flow rate of the refrigerant at a dry degree area where the heat transfer coefficient of the refrigerant is increased. Further, the cross section of the channel structure is structured so as to be reduced from the second channel areas towards a third channel areas, and thereby the heat transfer coefficient of the refrigerant is prevented from decreasing. Accordingly, the heat transfer coefficient of the refrigerant can be uniformed in the channel structure.
Owner:TANDOU TAKUMI +2
Apparatus for adjustably controlling the inflow of production fluids from a subterranean well
InactiveUS20090084556A1Fluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com