Patents
Literature
511results about How to "Efficient change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
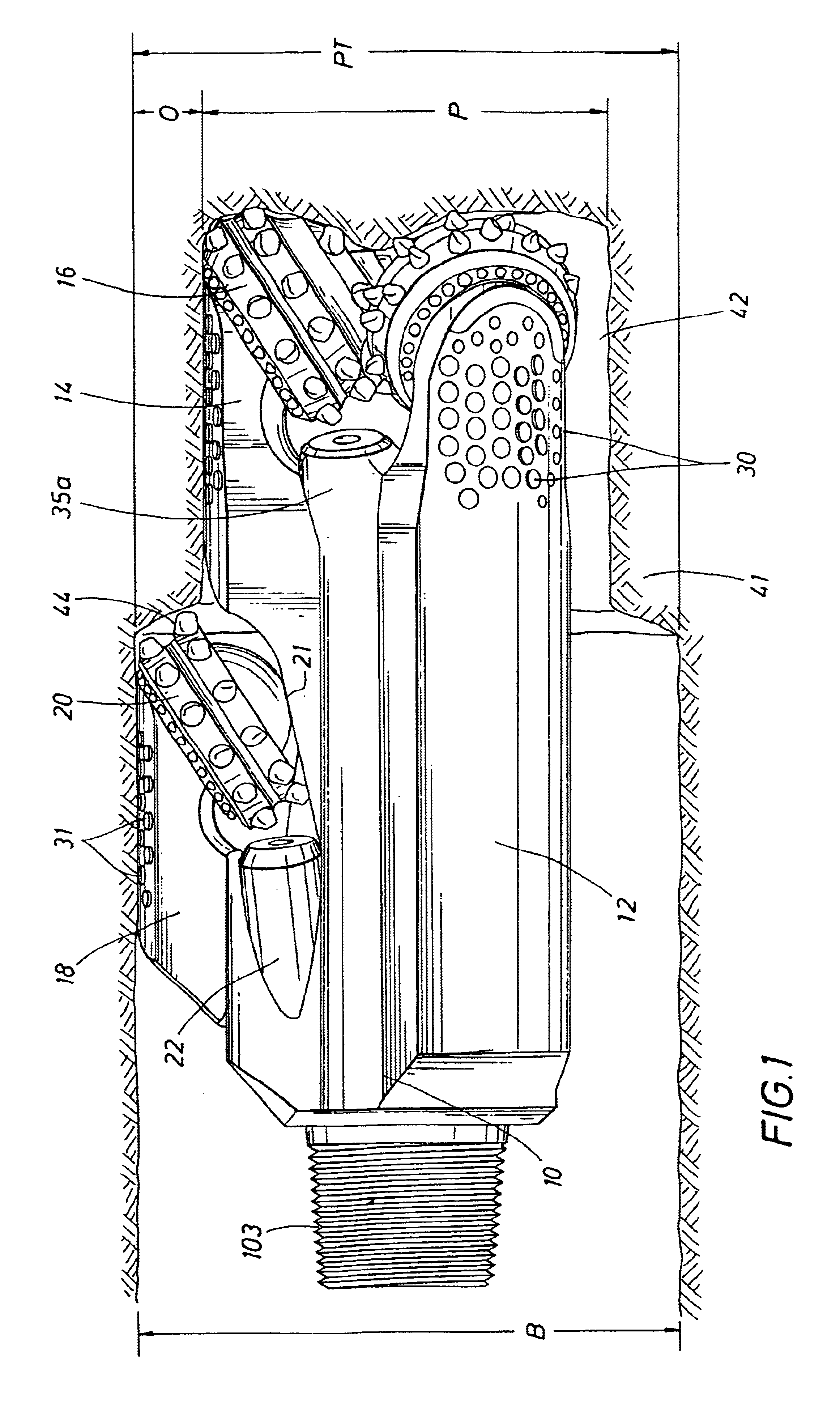
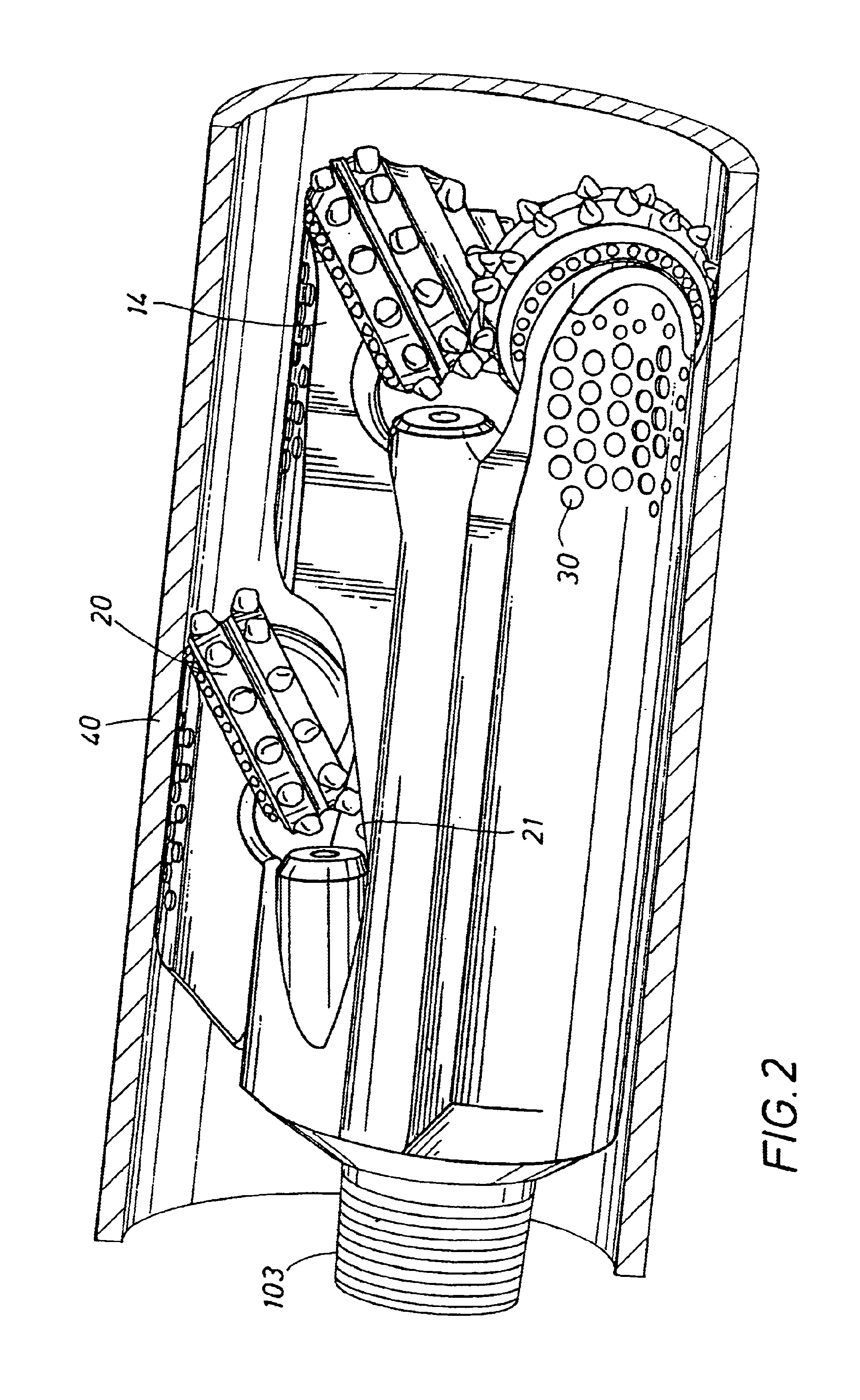
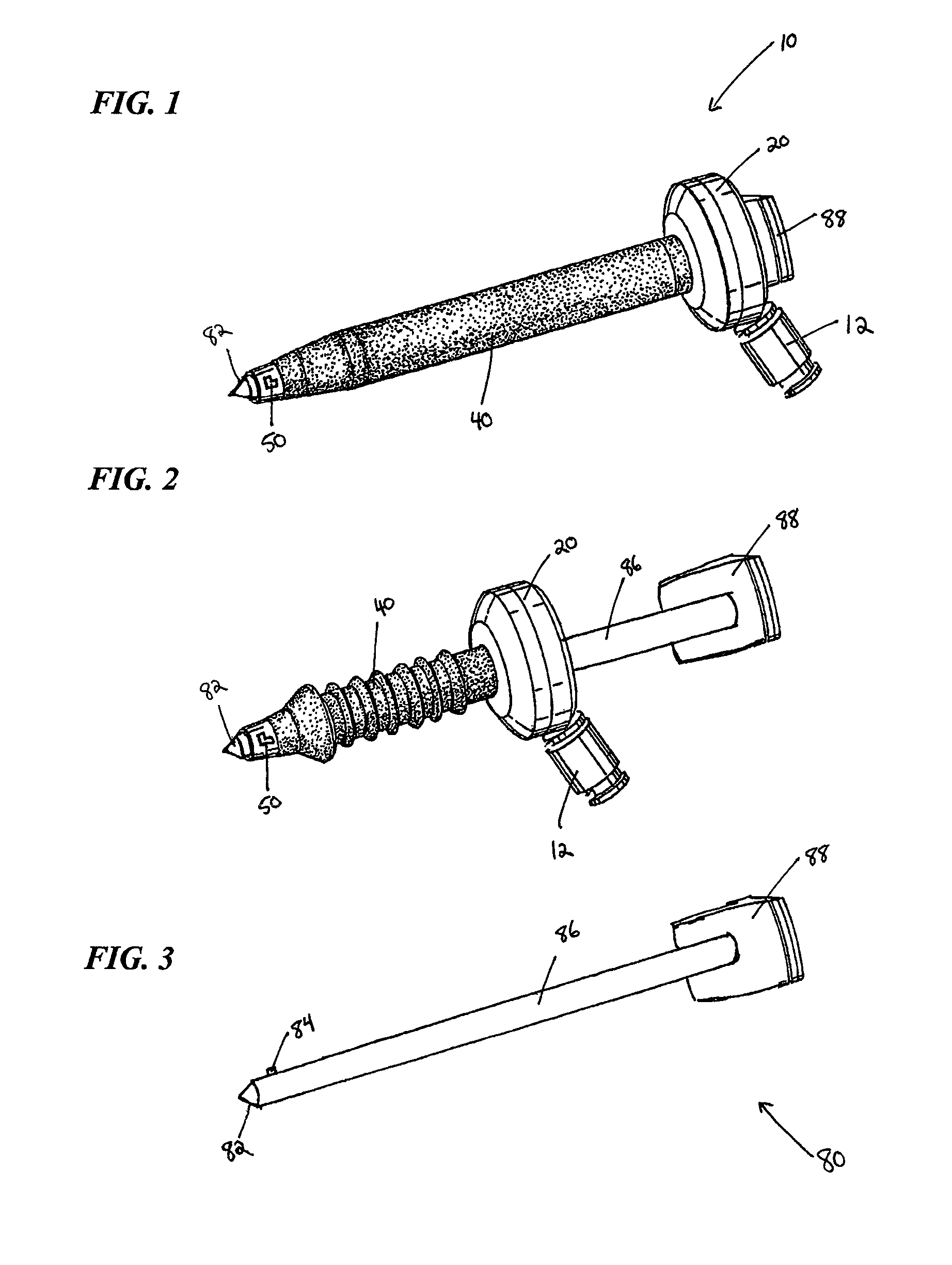
Intraocular lens
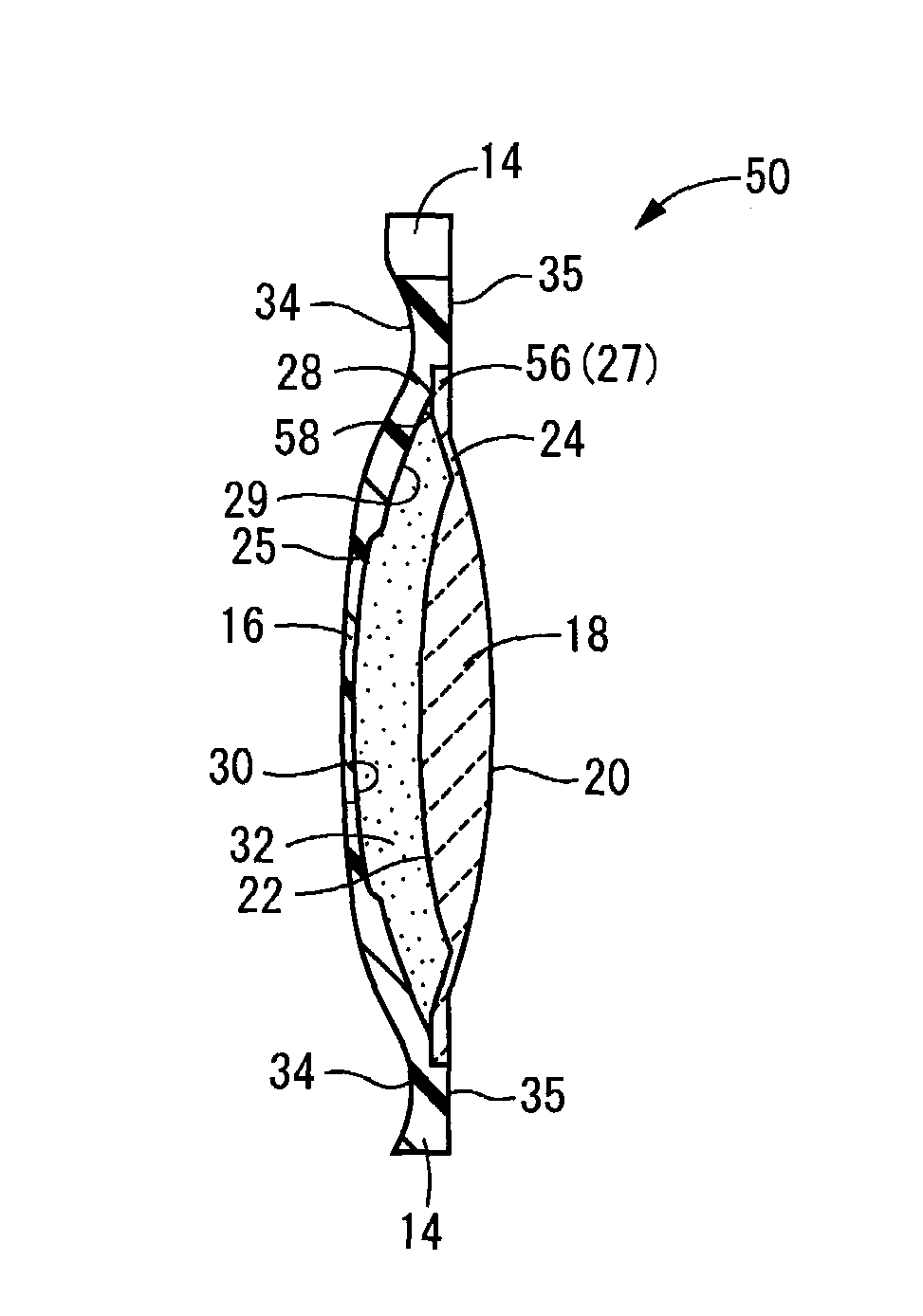
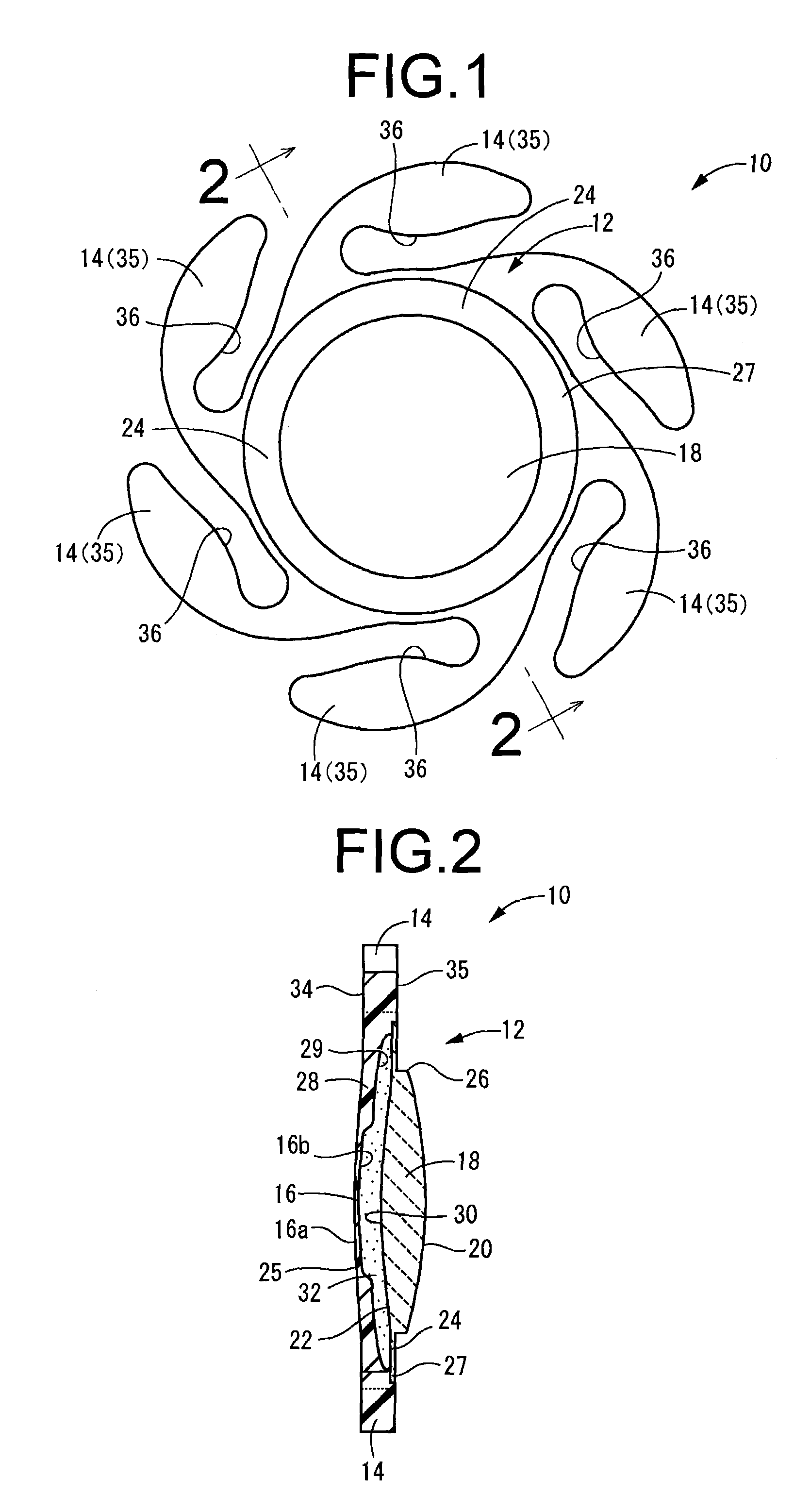
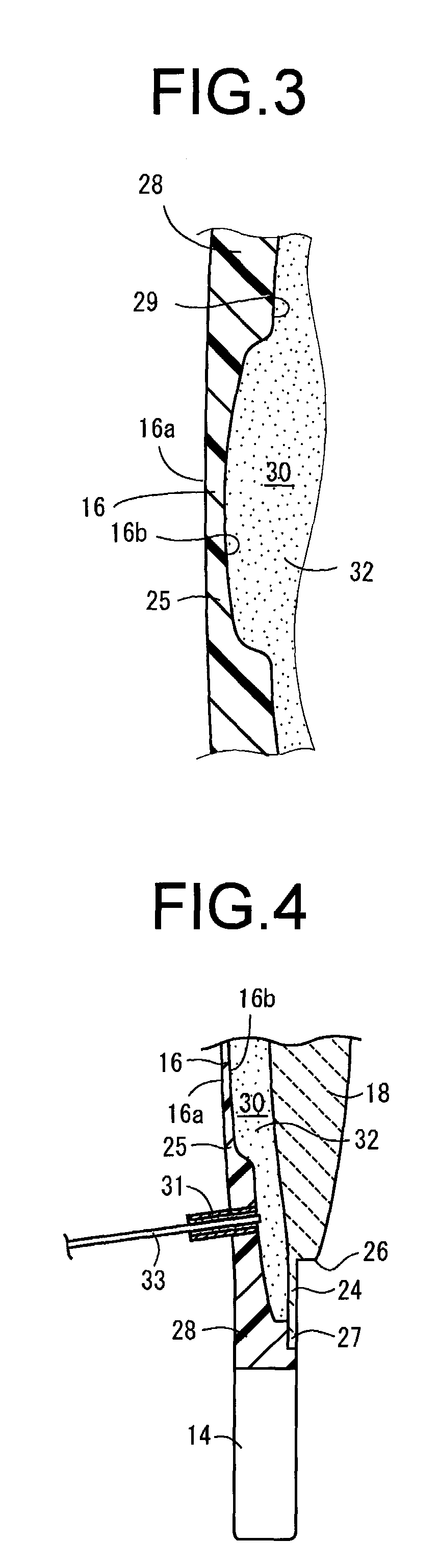
An intraocular lens of novel structure exhibiting an excellent focus adjusting power. A hollow capsule structure is filled with a transparent liquid-like or gel-like filler (32). A front wall of the capsule structure is composed of a flexible lens front film (16), and a rear wall of the capsule structure is composed of an optical lens (18) having a diameter larger than that of the flexible lens front film (16). Under a state inserted into and attached to a capsula lentis, pressure variation of a corpus vitreum acts on the optical lens (18) to enable focal refraction power to be adjusted by utilizing swelling deformation of the lens front film (16).
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
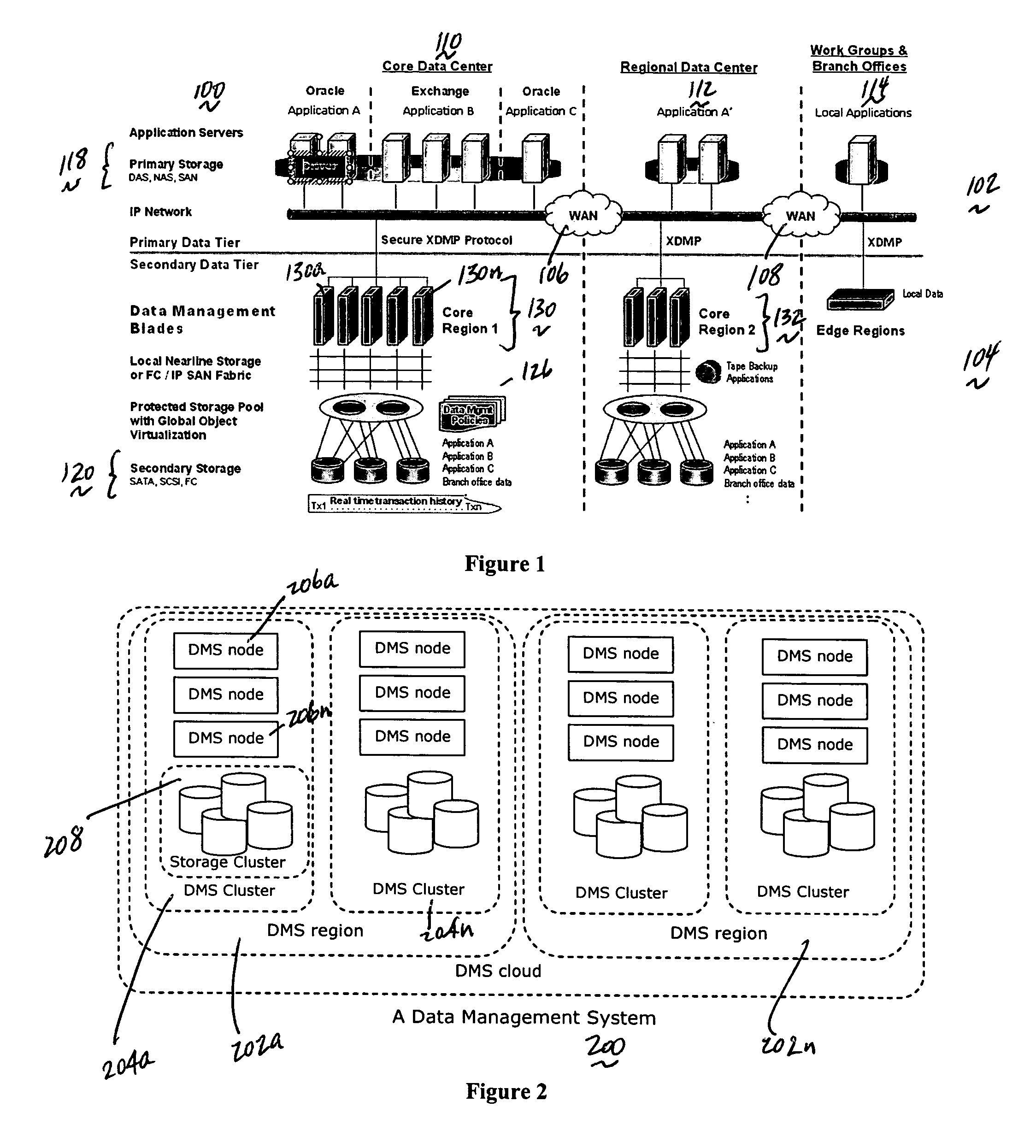
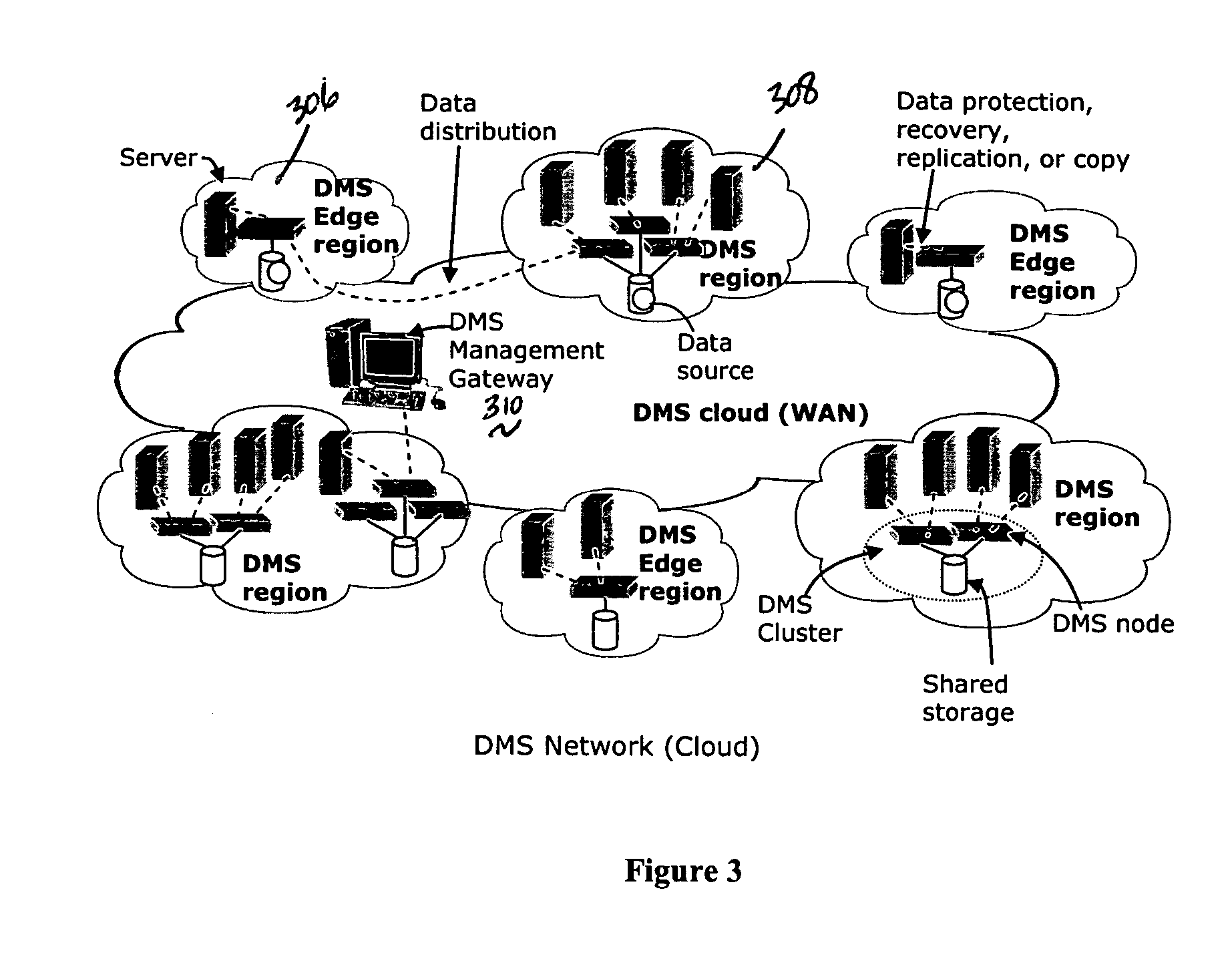
System for moving real-time data events across a plurality of devices in a network for simultaneous data protection, replication, and access services
ActiveUS20050262097A1Efficiently parallel processEfficiently route application-aware data changeDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData connectionData stream
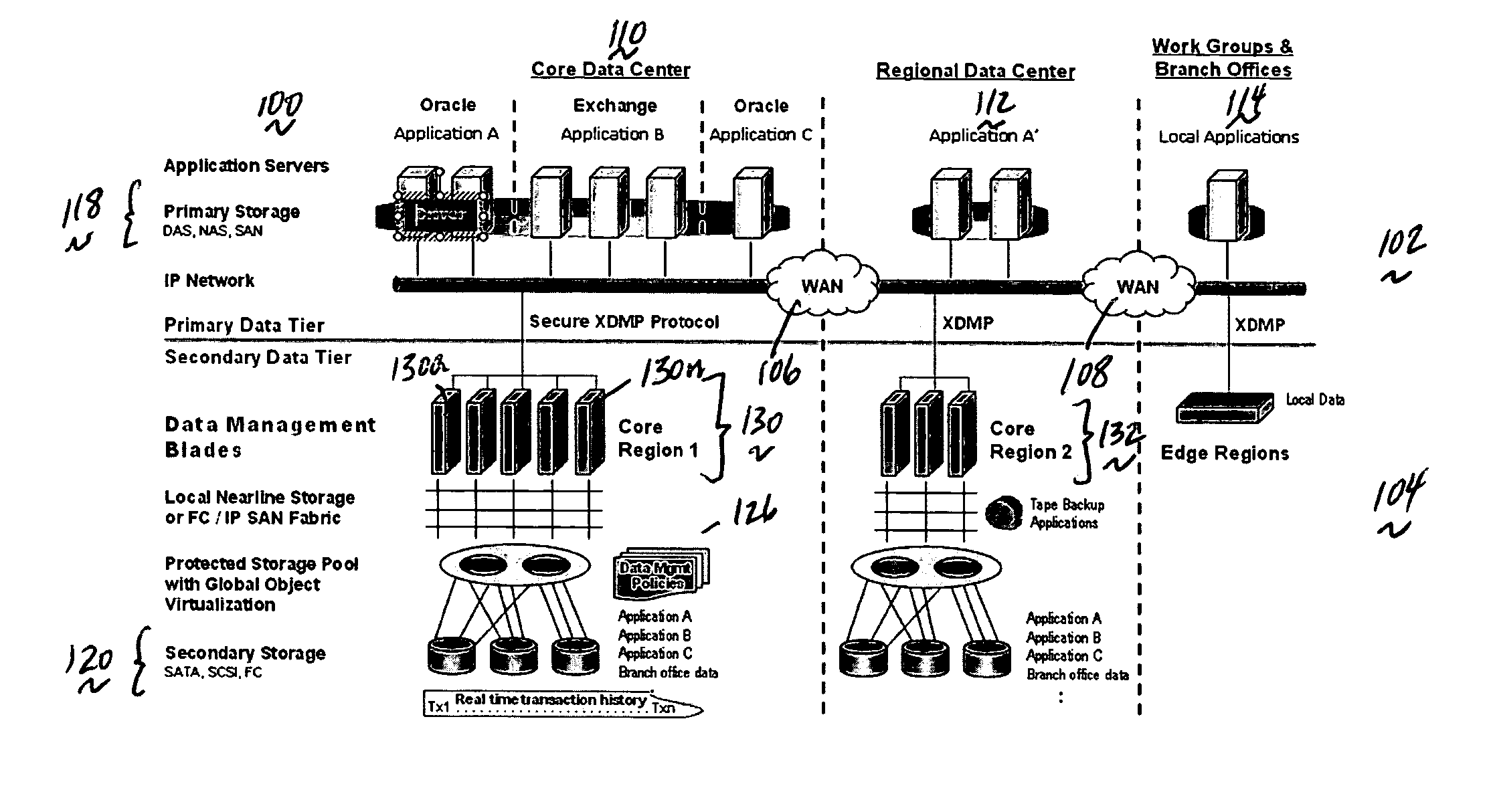
A data management system or “DMS” provides a wide range of data services to data sources associated with a set of application host servers. The data management system typically comprises one or more regions, with each region having one or more clusters. A given cluster has one or more nodes that share storage. To facilitate the data service, a host driver embedded in an application server connects an application and its data to a cluster. The host driver provides a method and apparatus for capturing real-time data transactions in the form of an event journal that is provided to the data management system. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. Using the streams generated in this manner, the DMS offers a wide range of data services that include, by way of example only: data protection (and recovery), disaster recovery (data distribution and data replication), data copy, and data query and access.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
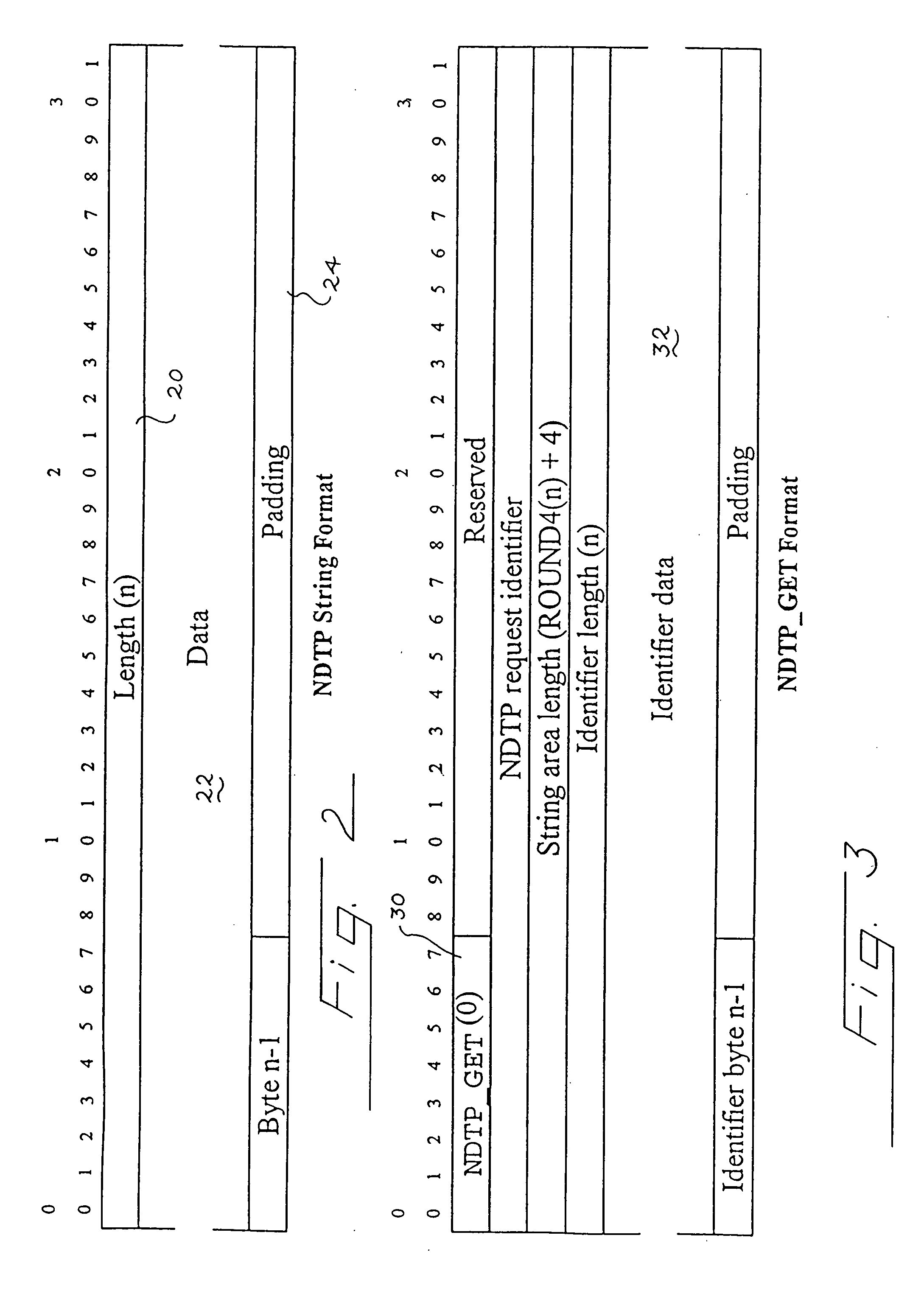
Network distributed tracking wire transfer protocol
InactiveUS20070011267A1Efficient changeEfficient managementDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsData acquisitionWire transfer
A network distributed tracking wire transfer protocol for storing and retrieving data across a distributed data collection. The protocol includes a location string for specifying the network location of data associated with an entity in the distributed data collection, and an identification string for specifying the identity of an entity in the distributed data collection. According to the protocol, the length of the location string and the length of the identification string are variable, and an association between an identification string and a location string can be spontaneously and dynamically changed. The network distributed tracking wire transfer protocol is application independent, organizationally independent, and geographically independent. A method for using the protocol in a distributed data collection environment and a system for implementing the protocol are also provided.
Owner:KOVE IO INC
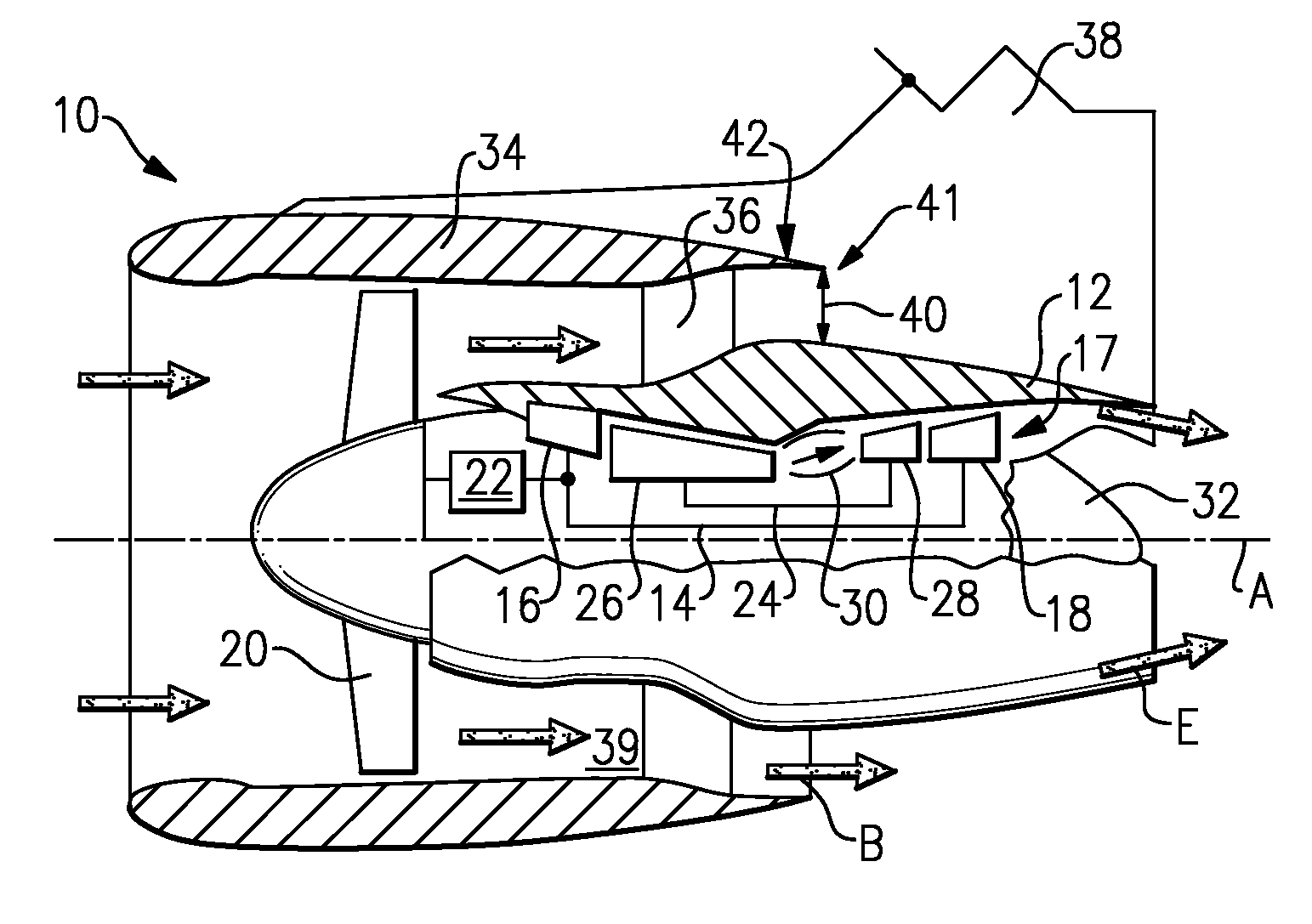
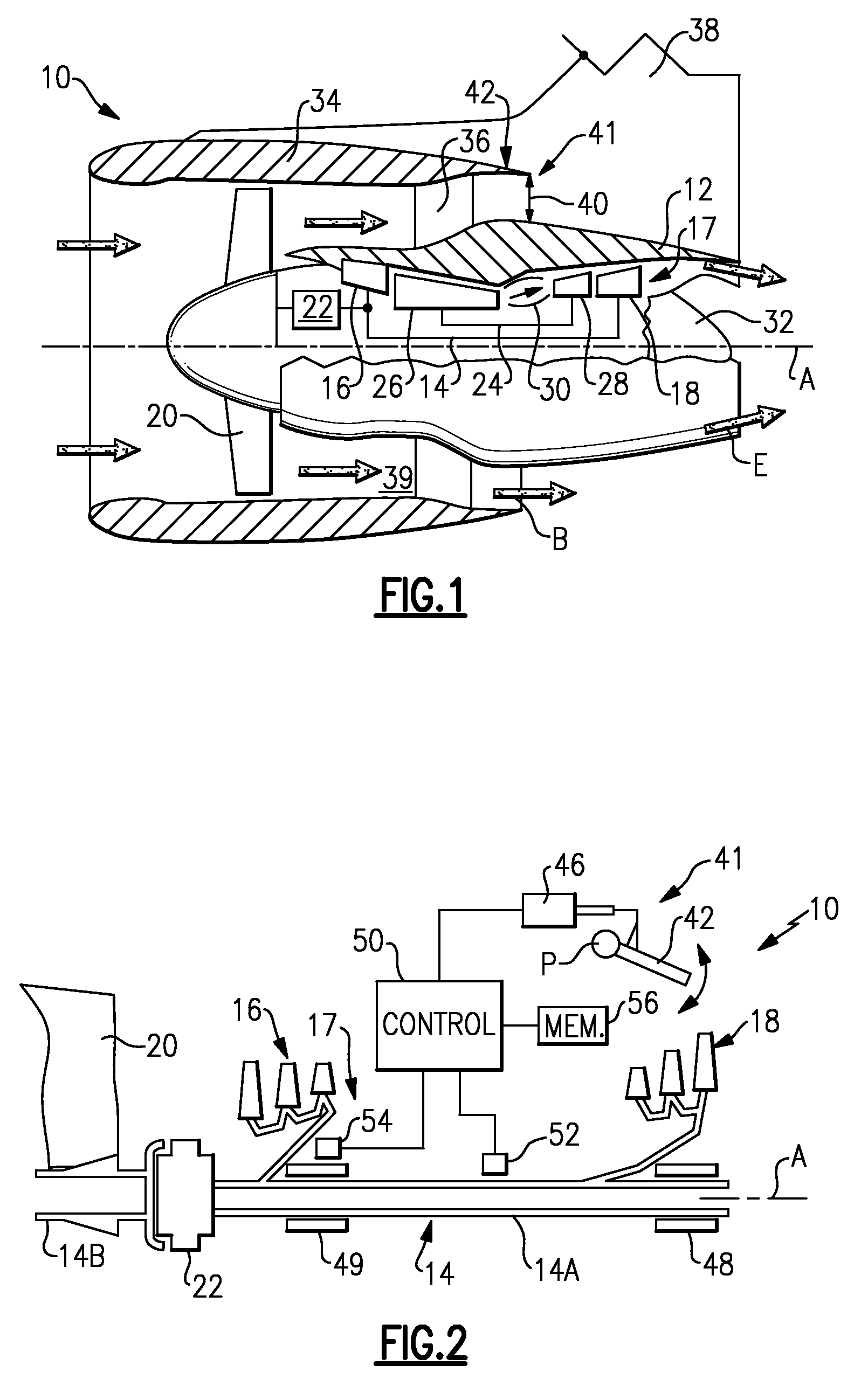
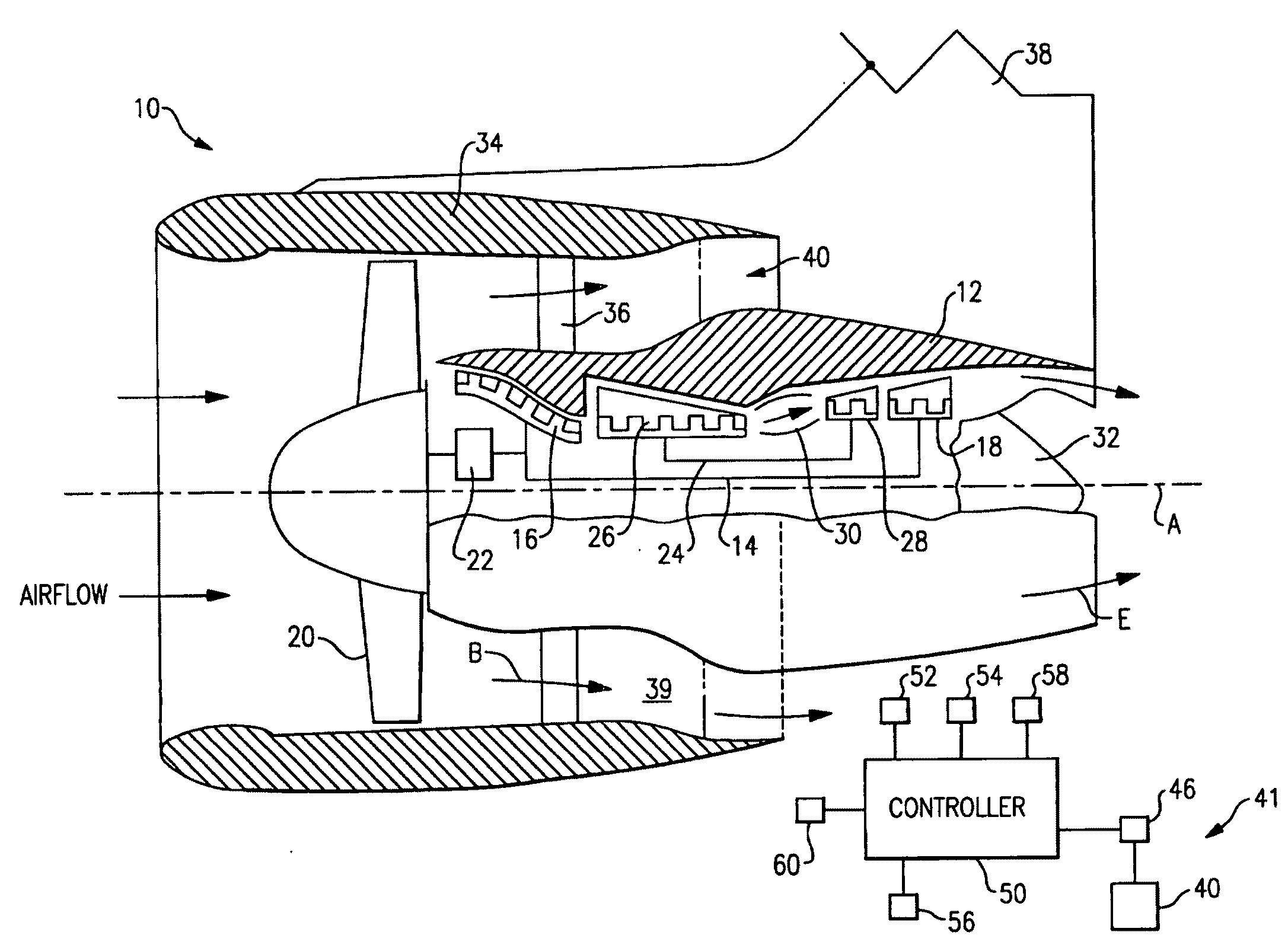
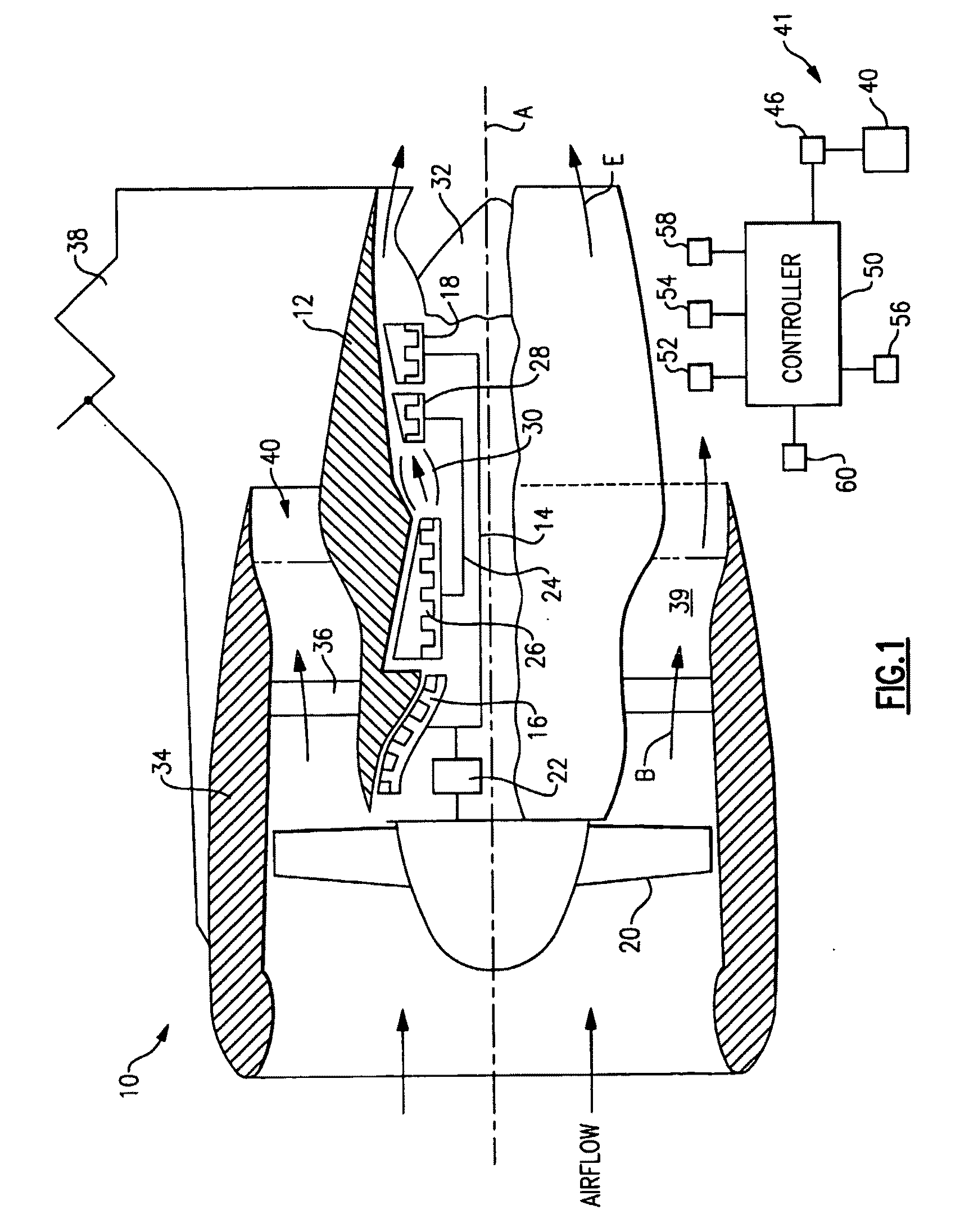
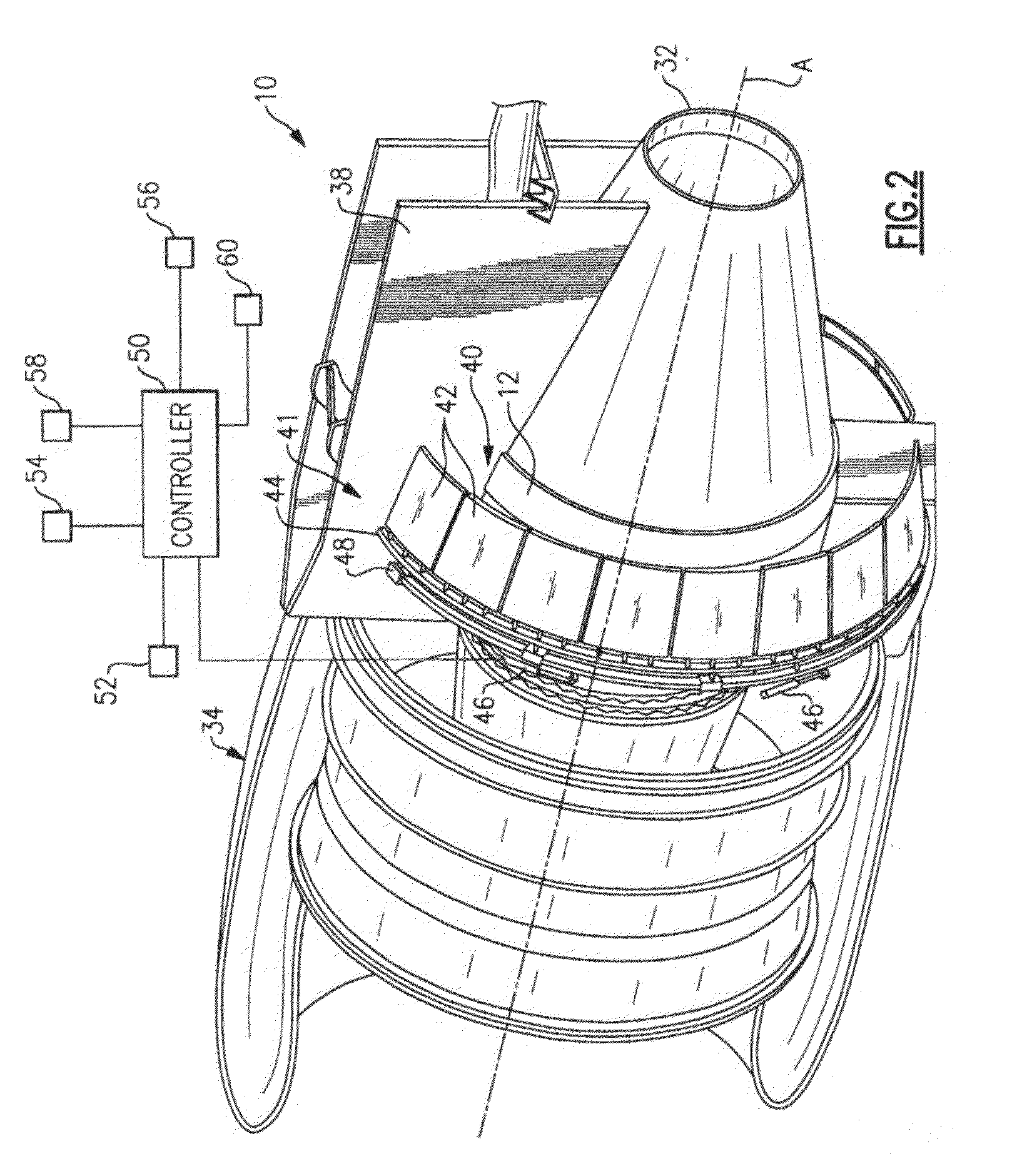
Managing spool bearing load using variable area flow nozzle
A turbine engine provides a spool supporting a turbine. The spool is arranged in a core nacelle and includes a thrust bearing. A fan is arranged upstream from the core nacelle and is coupled to the spool. A fan nacelle surrounds the fan and core nacelle and provides a bypass flow path that includes a fan nozzle exit area. A flow control device is adapted to effectively change the fan nozzle exit area. A controller is programmed to monitor the thrust bearing and command the flow control device in response to an undesired load on the thrust bearing. Effectively changing the fan nozzle exit area with the flow control device actively manages the bearing thrust load to desired levels.
Owner:RTX CORP
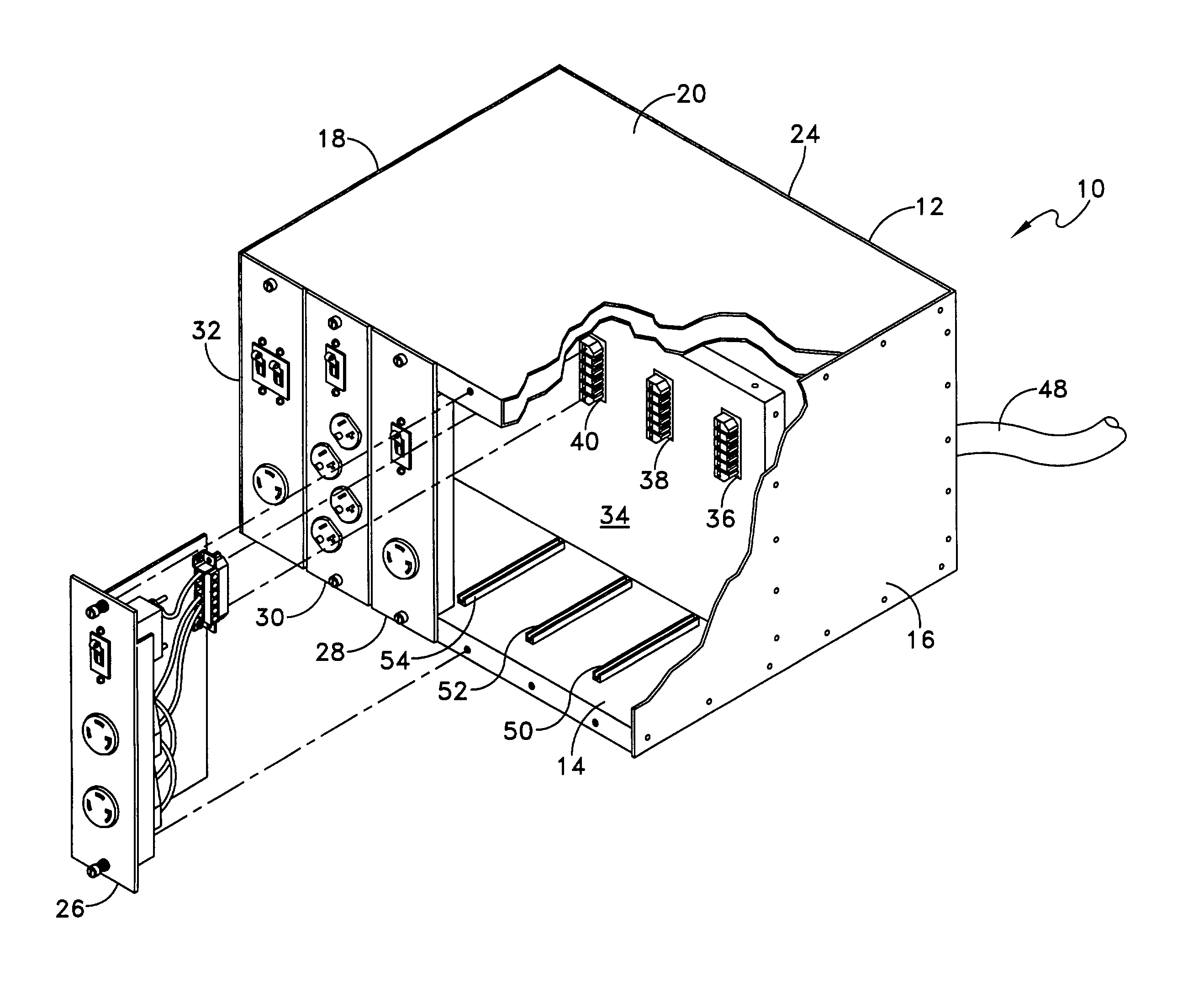
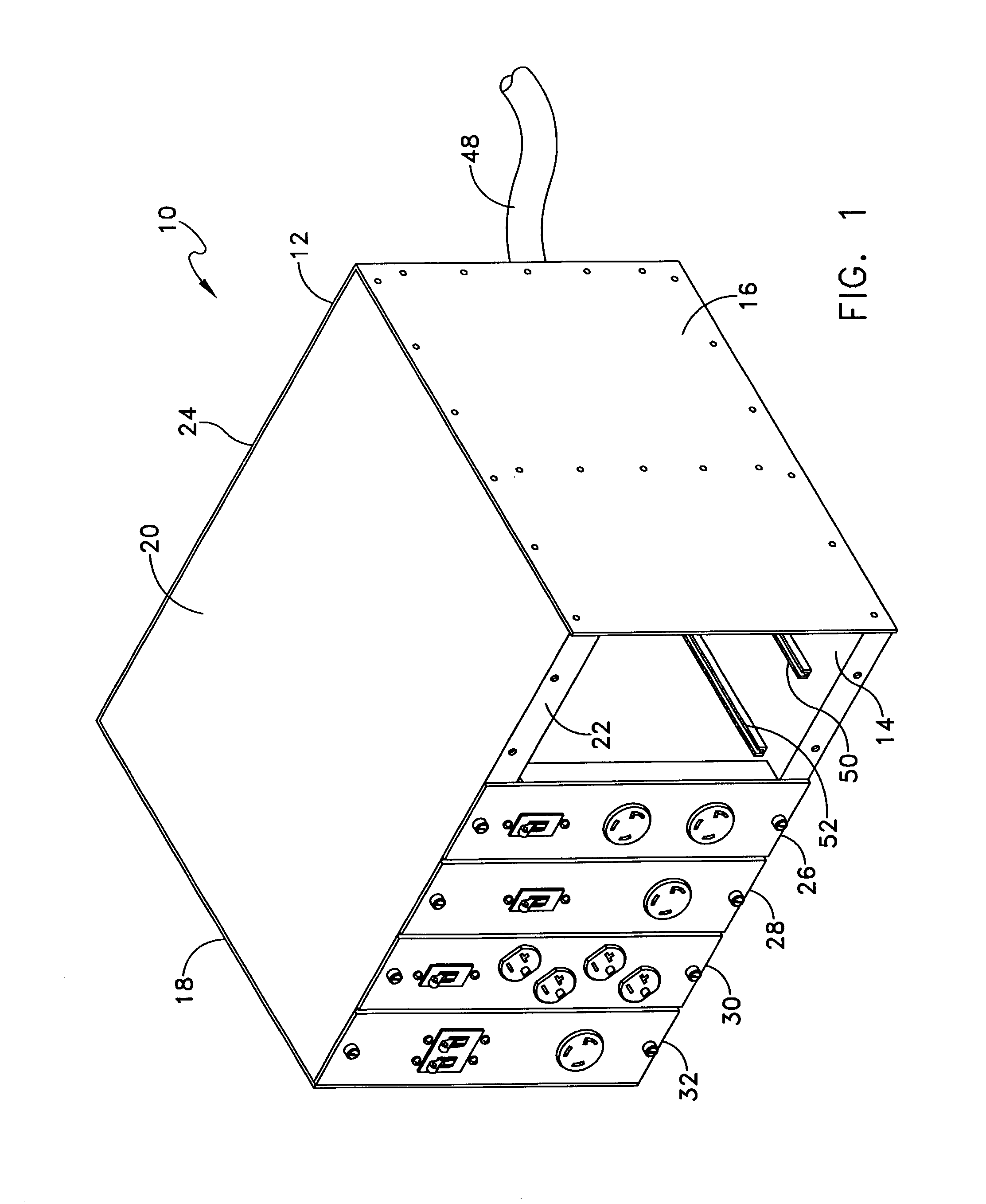
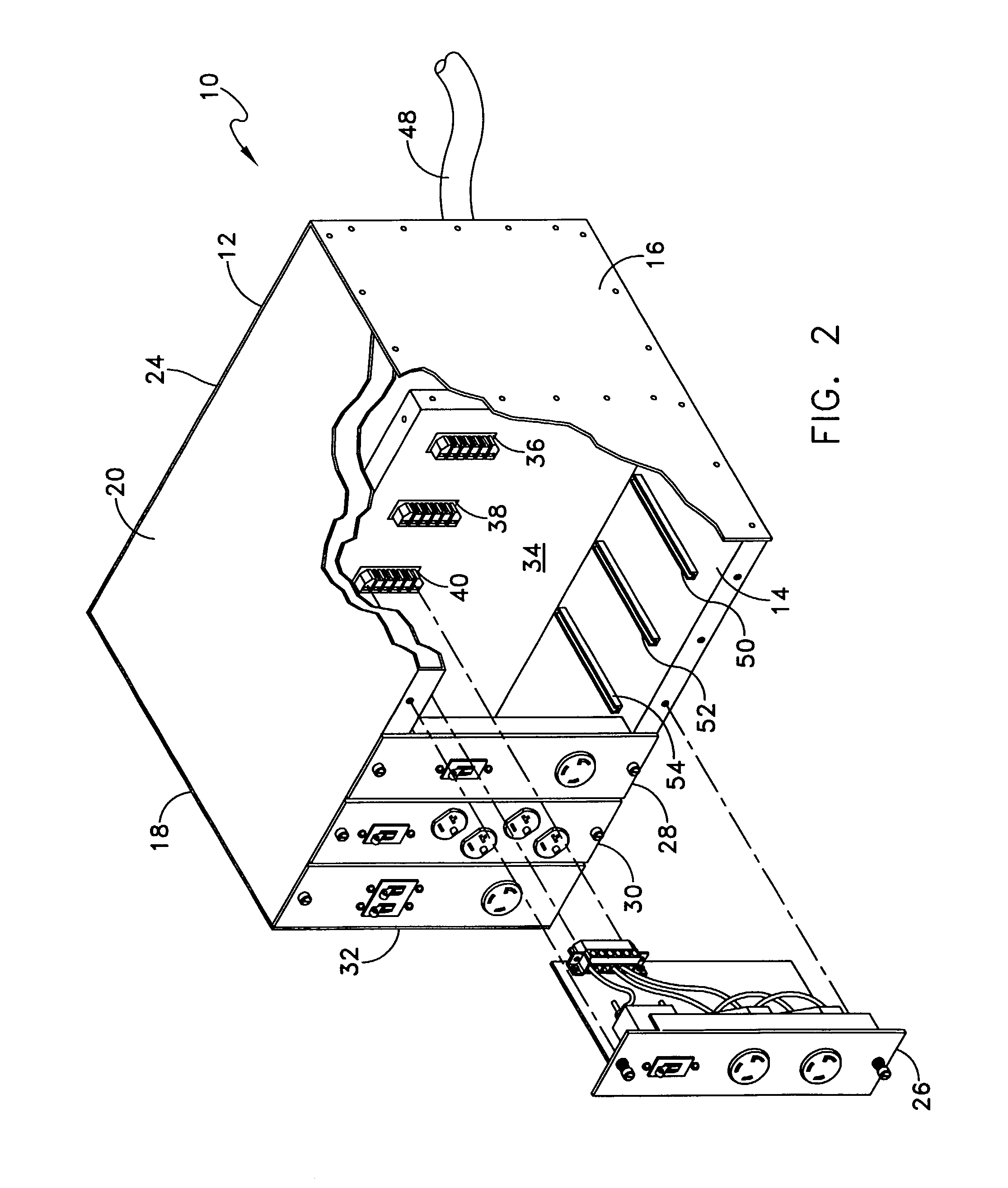
Modular power distribution unit, module for the power distribution unit, and method of using the same
A modular power distribution unit (PDU) for supplying electric power to attached equipment in environments such as data centers, computer rooms, and communication centers, where power requirements for attached equipment may vary. The power distribution unit includes a frame and one or more user-replaceable power modules, which fit into slots in the frame. Each power module provides one of more plug receptacles for attaching equipment to provide power thereto. The power modules are available in a variety of receptacle types, receptacle numbers, and power rating configurations to accommodate various equipment in a particular environment, as needed. The frame includes an internal connector panel for distributing power from a power source to the power modules when they are inserted in the frame. The power modules may be removed, installed, and interchanged in the frame without interrupting power to other power modules or to the power distribution unit.
Owner:DONAHUE IV WILLIAM F
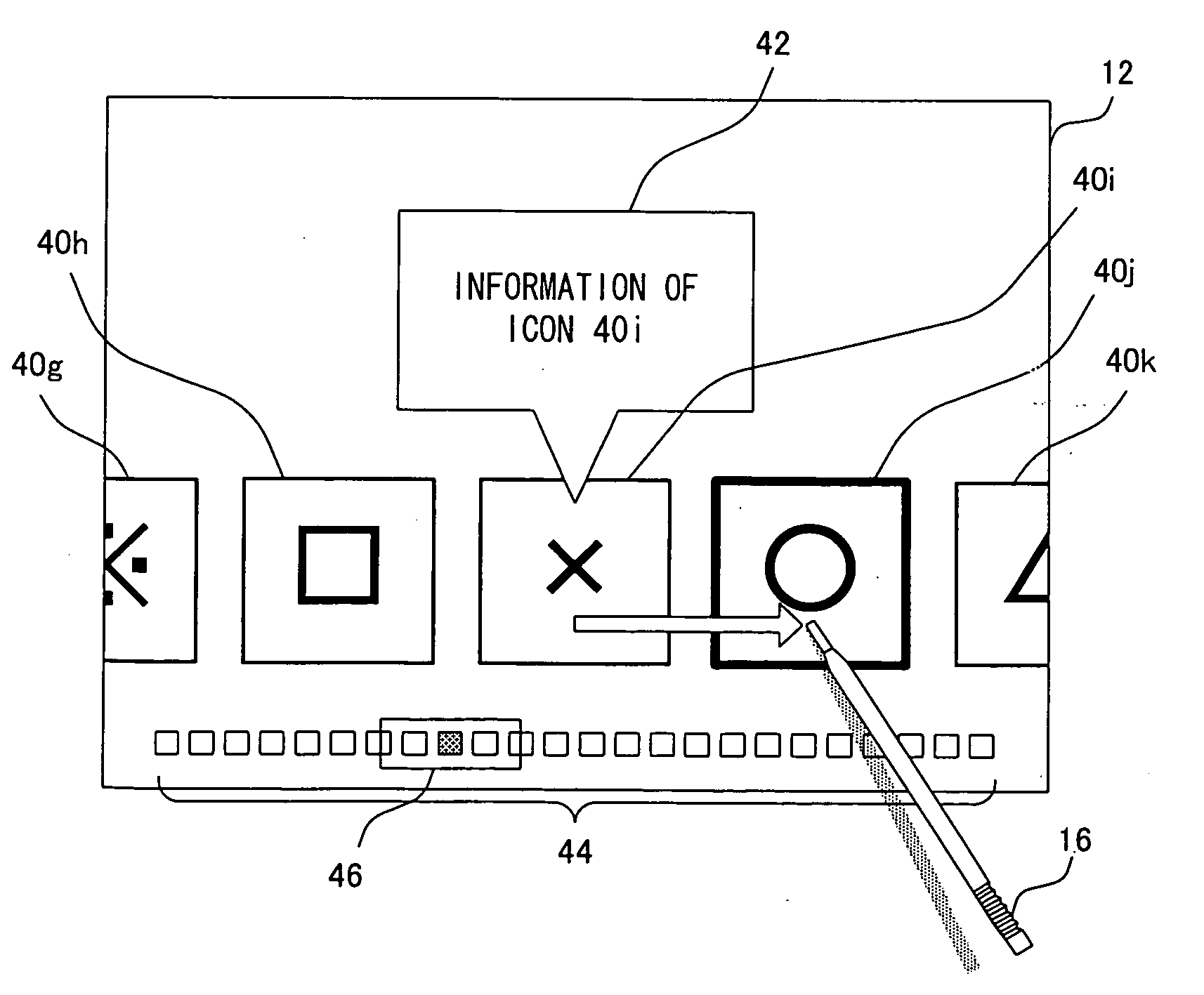
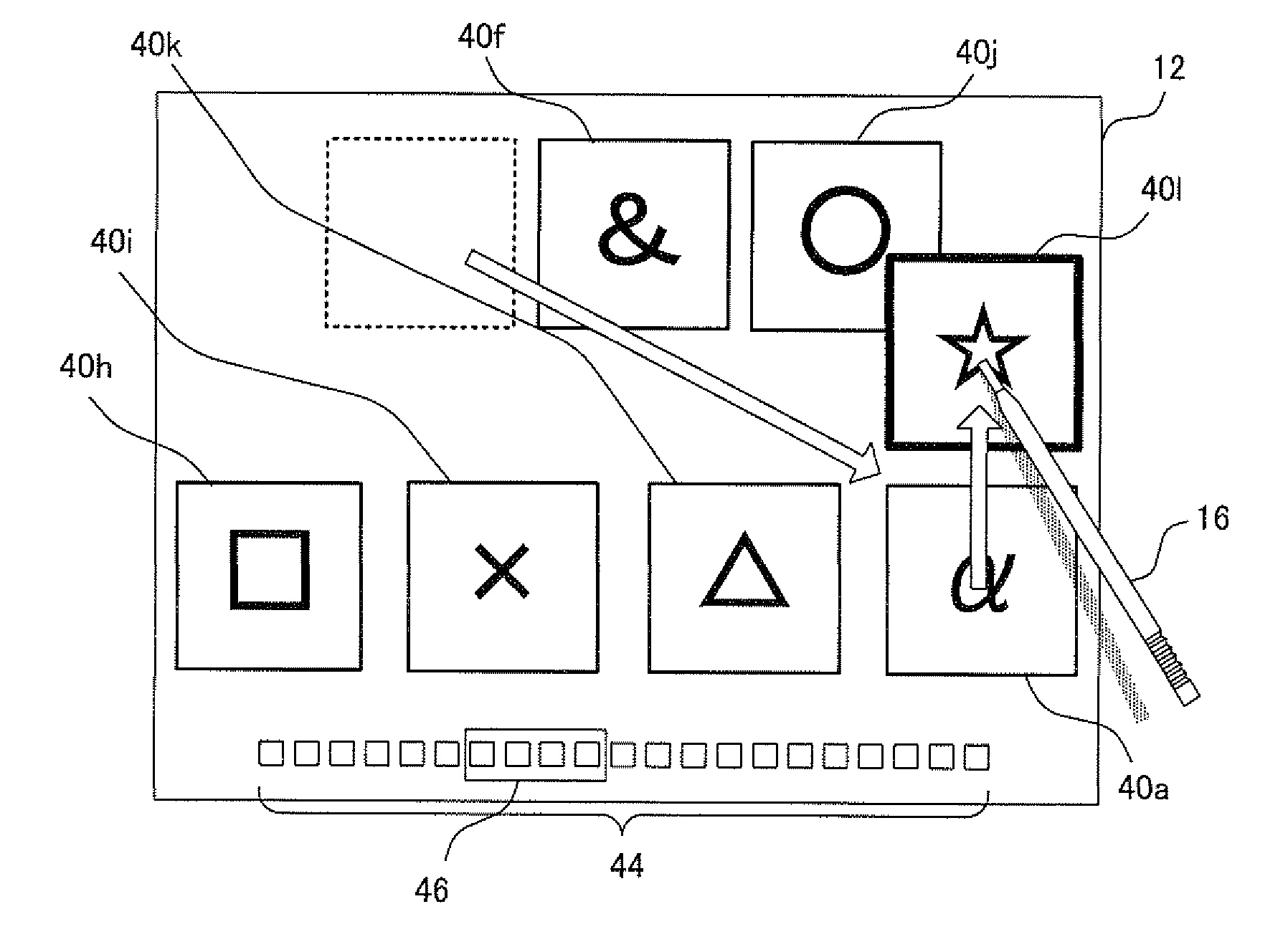
Object display order changing program and apparatus
ActiveUS20090271723A1Easy to changeAvoid difficult choicesExecution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingDisplay OrderHuman–computer interaction
An icon line is displayed on a screen so as to align icons laterally. When a user slides a stick laterally based on an originating point corresponding to a point on an icon of the icon line, it is possible to scroll the icon line laterally in accordance with the stick being moved, and when a user slides a stick vertically based on an originating point corresponding to a point on an icon of the icon line, it is possible to move only the icon of the icon line in accordance with the stick being moved. Therefore, a user is allowed to easily change the display order in which a plurality of objects are displayed on the screen.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Etching solution and method for removing low-k dielectric layer
InactiveUS20060097220A1Easy to prepareReagents is relatively inexpensiveDecorative surface effectsDetergent mixture composition preparationSingle stageOxidizing agent
Etching solutions are disclosed for etching low-k dielectric layers on substrates, said solutions including effective proportions of an oxidant for oxidizing a low-k dielectric layer and effective proportions of an oxide etchant for removing oxides. It is possible to easily remove a low-k dielectric layer using such etching solutions by a single-stage treatment process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
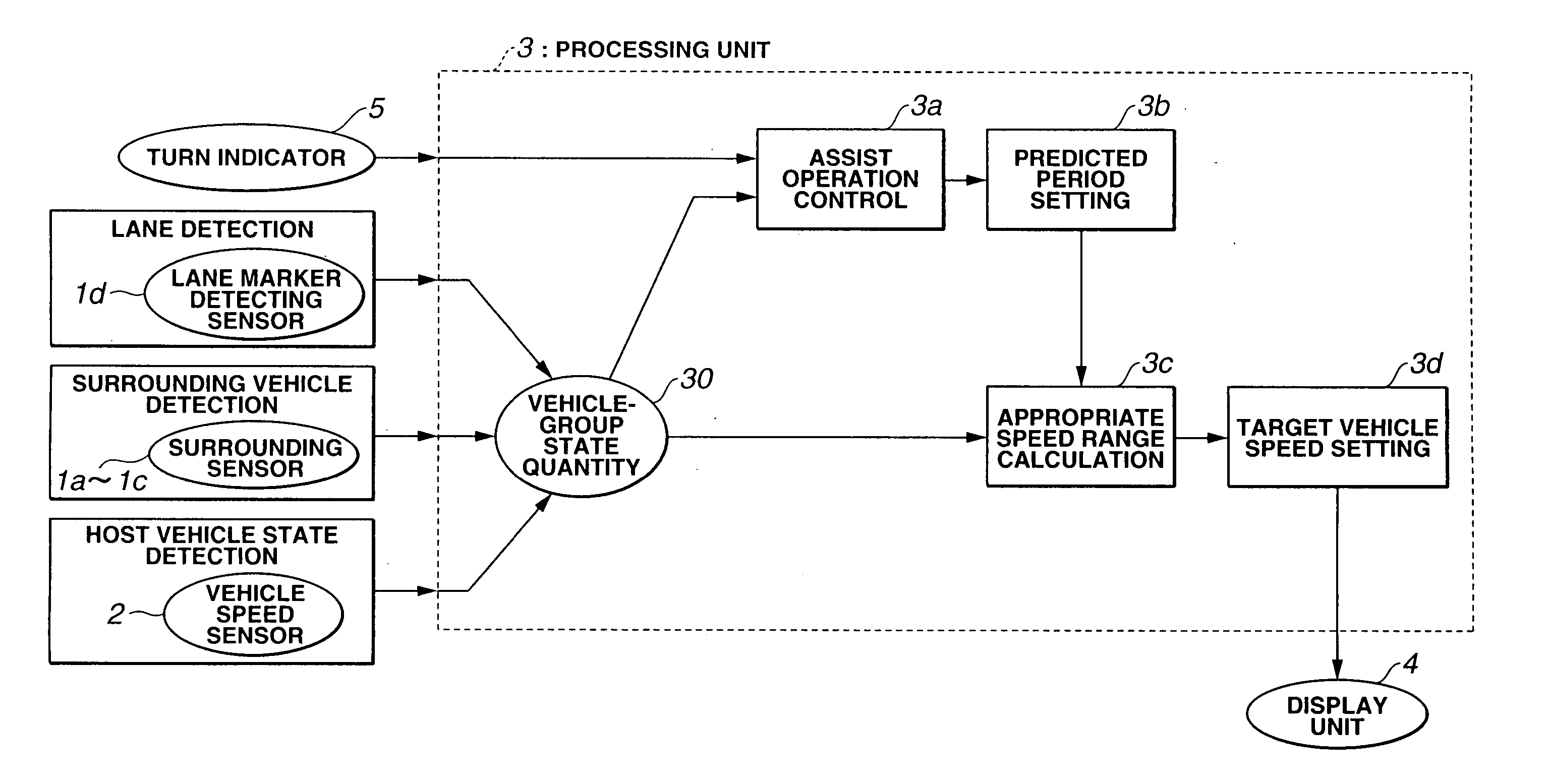
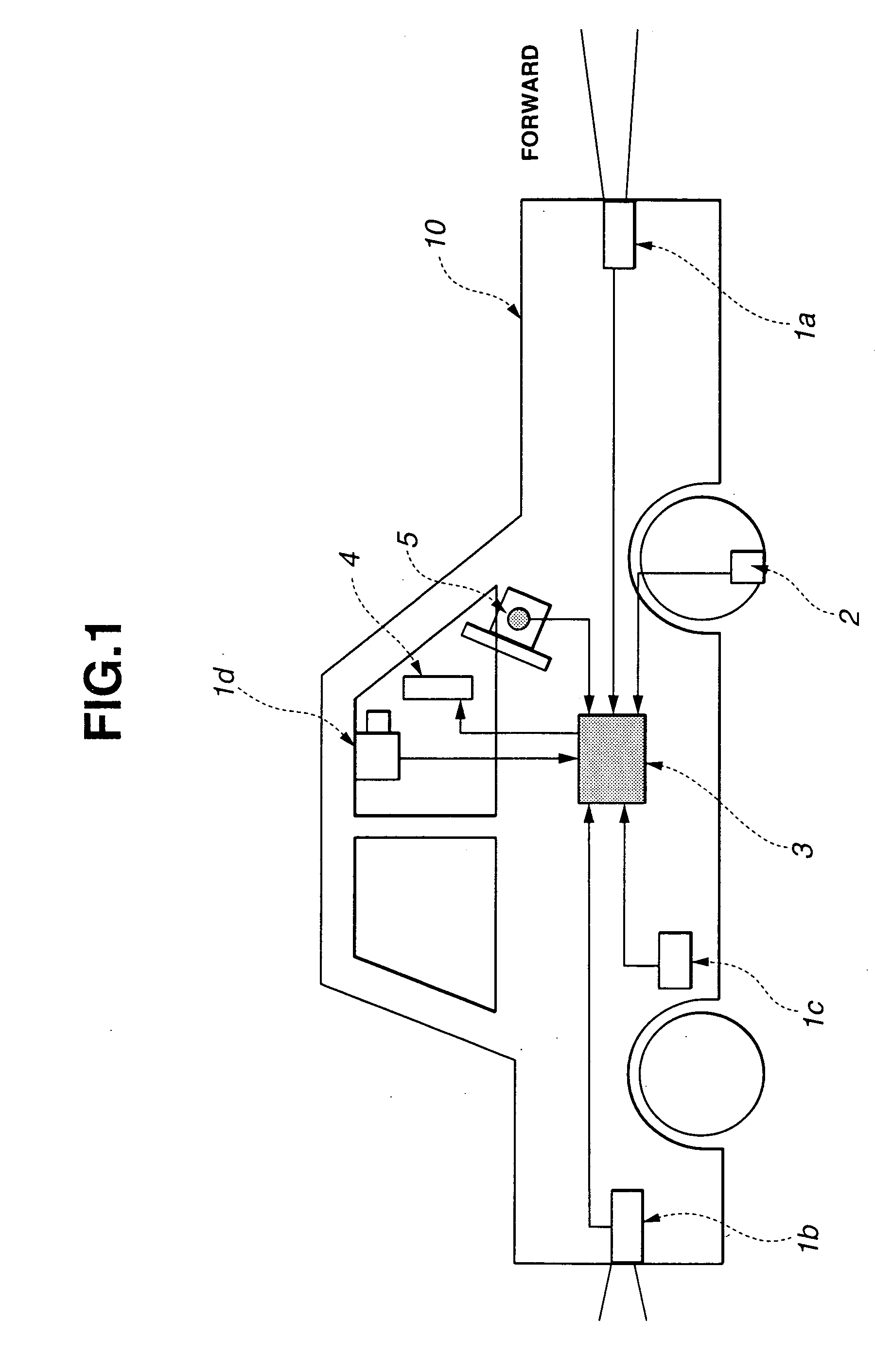
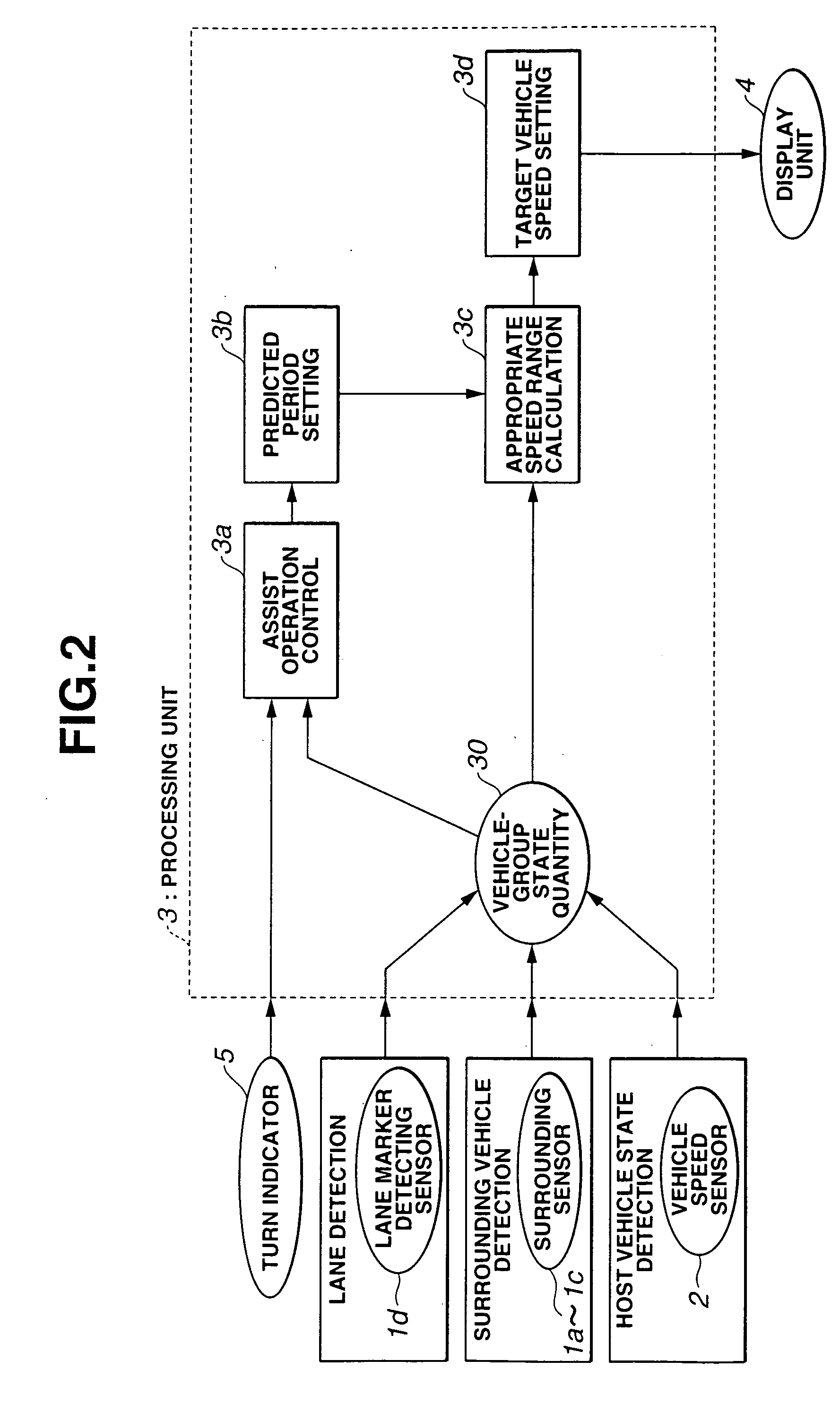
Lane change assist system
InactiveUS20050256630A1Effective lane change assistEfficient changeVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringLane detection
A lane change assist system is comprised of a host vehicle state detecting device that detects a host vehicle traveling condition, a surrounding vehicle detecting device that detects other vehicle located around the host vehicle, a lane detecting device that detects a lane around the host vehicle, and a processing unit. The processing unit is arranged to set a target lane, to determine a period of a lane change assist, to set a predicted period for an evaluation of a lane change to the target lane based on a prediction, to obtain an appropriate speed range during the predicted period for each gap, and to select a target vehicle speed from the appropriate speed range.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
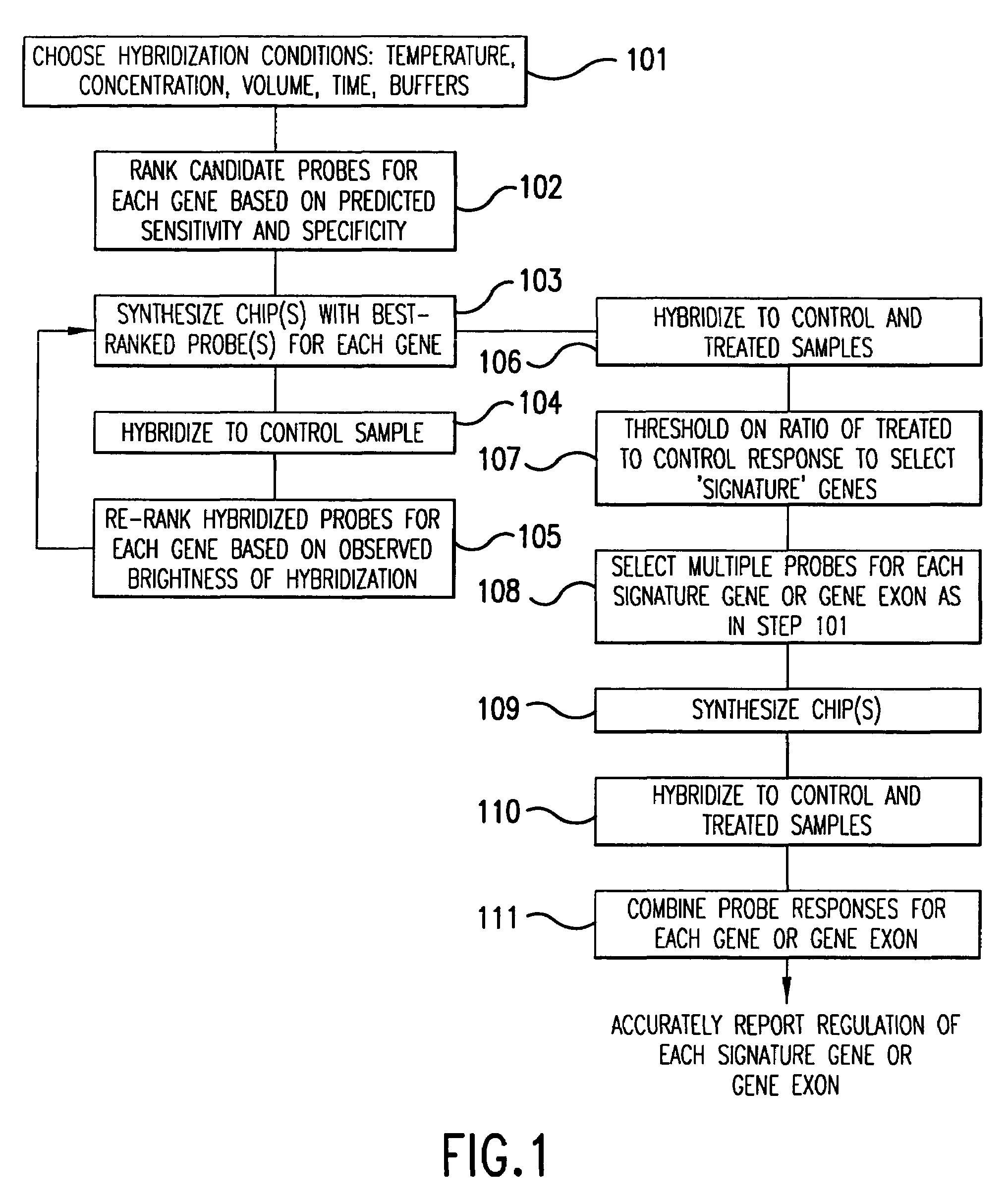
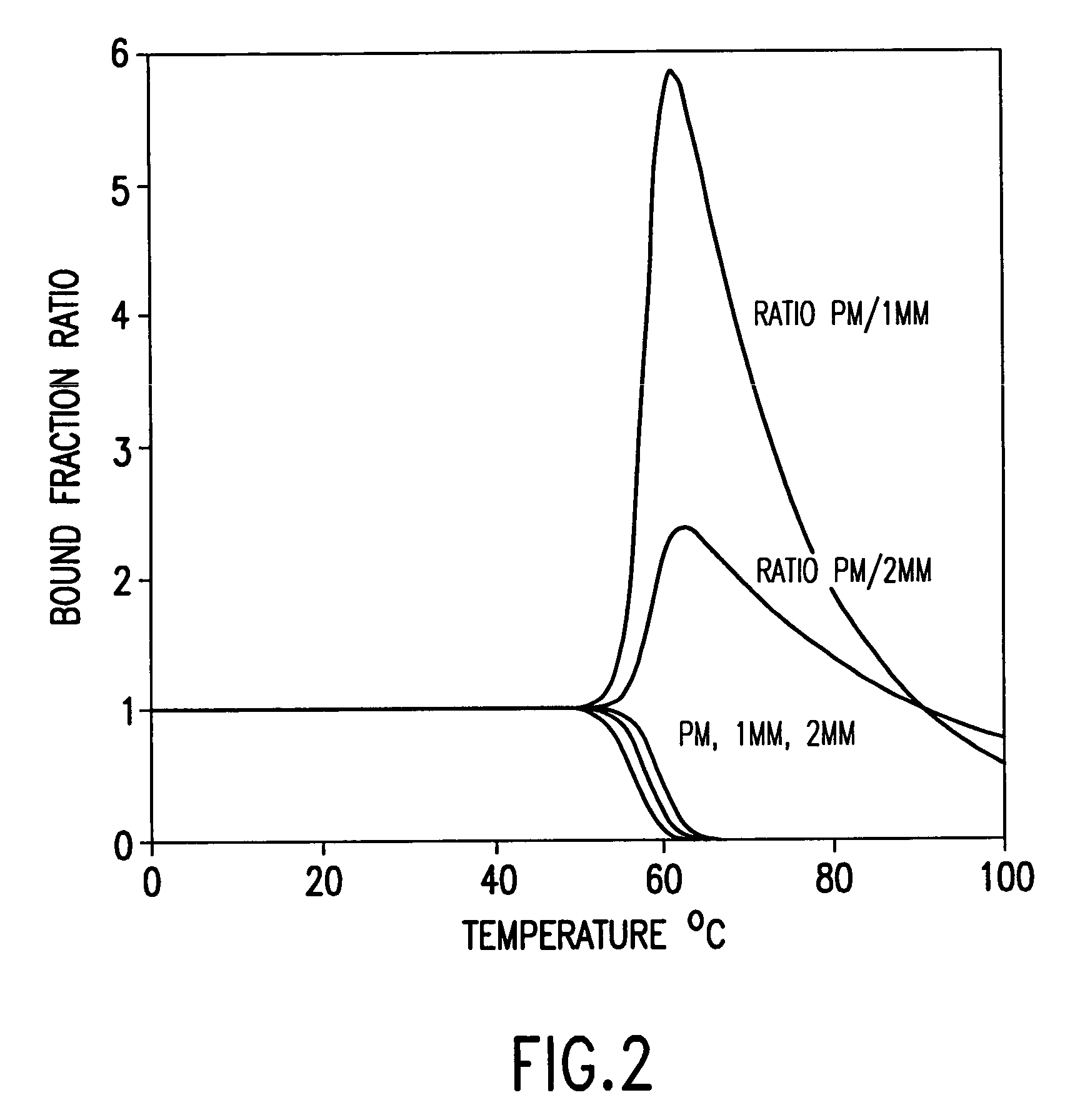
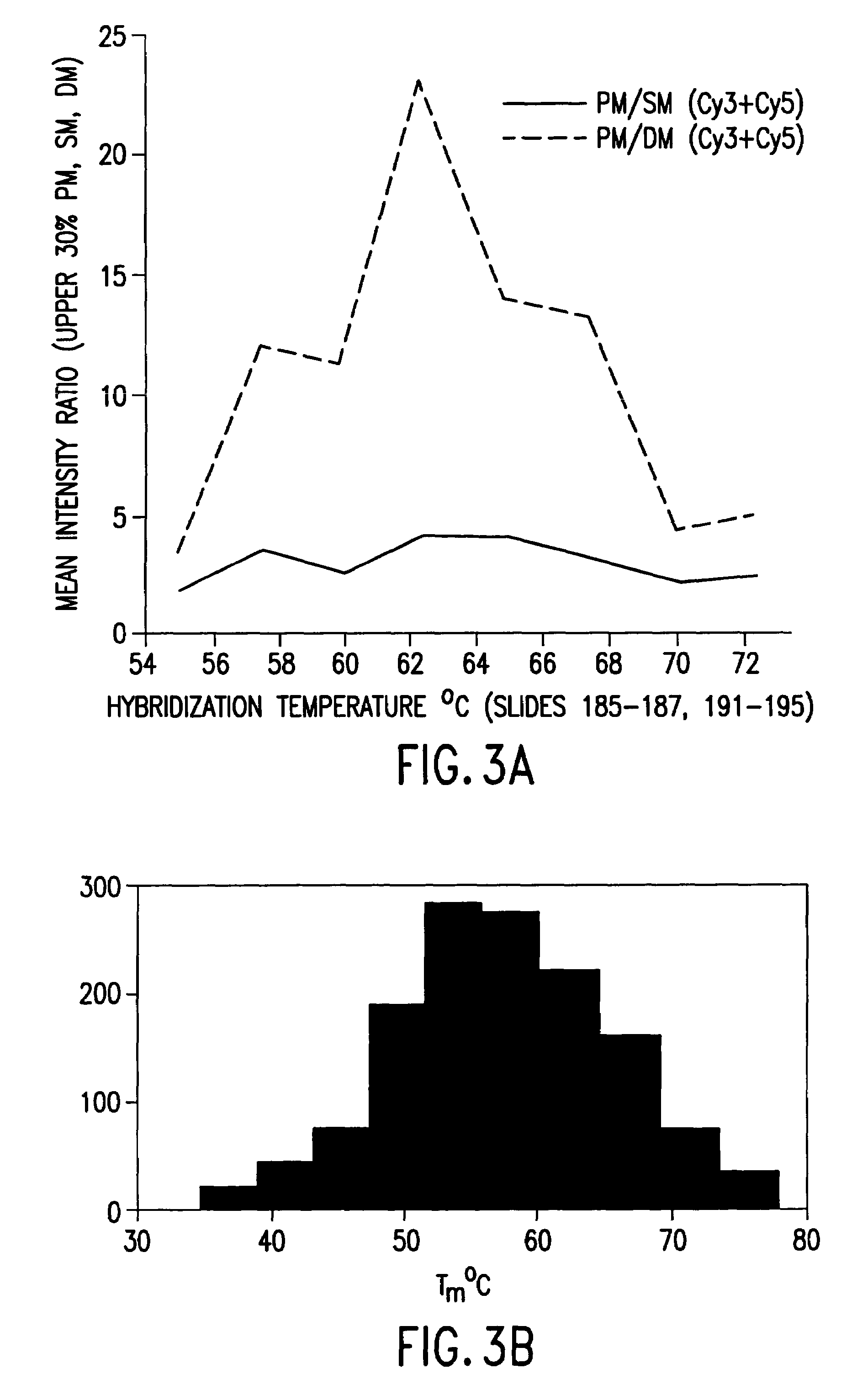
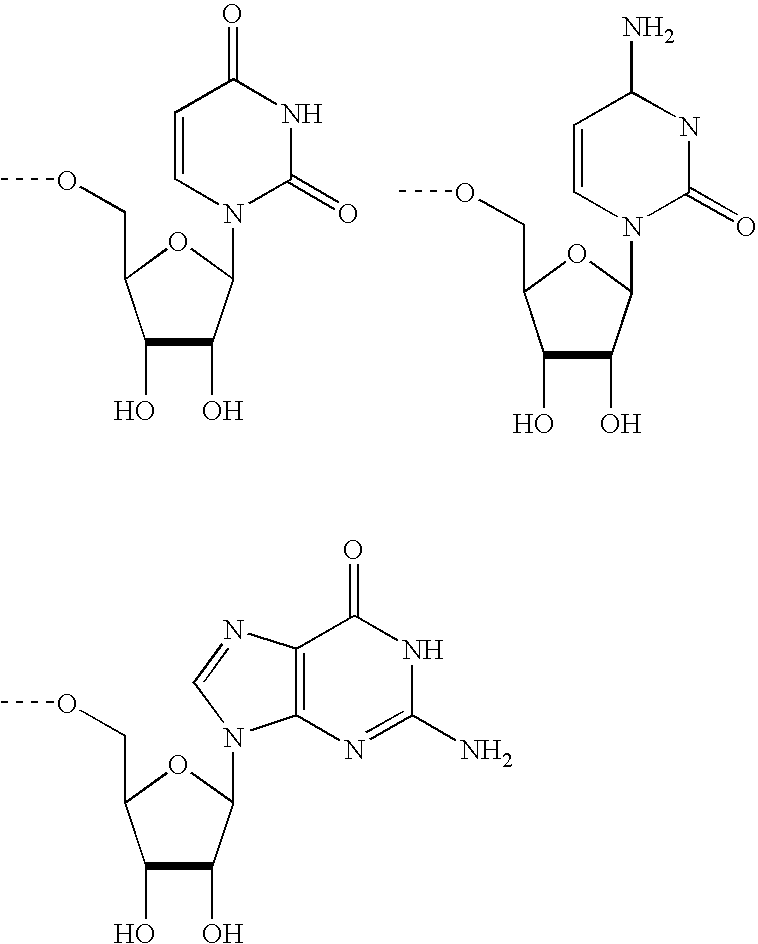
Iterative probe design and detailed expression profiling with flexible in-situ synthesis arrays
InactiveUS7013221B1Efficient changeEfficient detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyNucleotide
Methods and compositions are provided that are useful for detecting and reporting a plurality of different target polynucleotide sequences in a sample, such as polynucleotides corresponding to a plurality of different genes expressed by a cell or cells. In particular, the invention provides methods for screening a plurality of candidate polynucleotide probes to evaluate both the sensitivity and the specificity with which each candidate probe hybridizes to a target polynucleoide sequence. Candidate polynucleotide probes can then be ranked according to both their sensitivity and specificity, and probes that have optimal sensitivity and specificity for a target polynucleotide sequence can be selected. In one embodiment, polynucleotide probes can be selected according to the methods described herein to prepare “screening chips” wherein a large number of target polynucleotide sequences are detected using a single microarray have a few (e.g., 1–5) probes for each target polynucleotide sequence. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the invention provides a screening chip that can detect genetic transcripts from the entire genome of an organism. In an alternative embodiment, polynucleotide probes can be selected according to the methods described herein to prepare “signature chips” to more accurately detect certain selected “signature genes” using several polynucleotide probes (e.g., 10–20) for each signature gene. The invention additionally provides microarrays containing polynucleotide probes for a large number of genes expressed by a cell or organism. Further, methods for detecting a plurality of polynucleotide molecules, including a large number of genes expressed by a cell or organism, are also provided.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
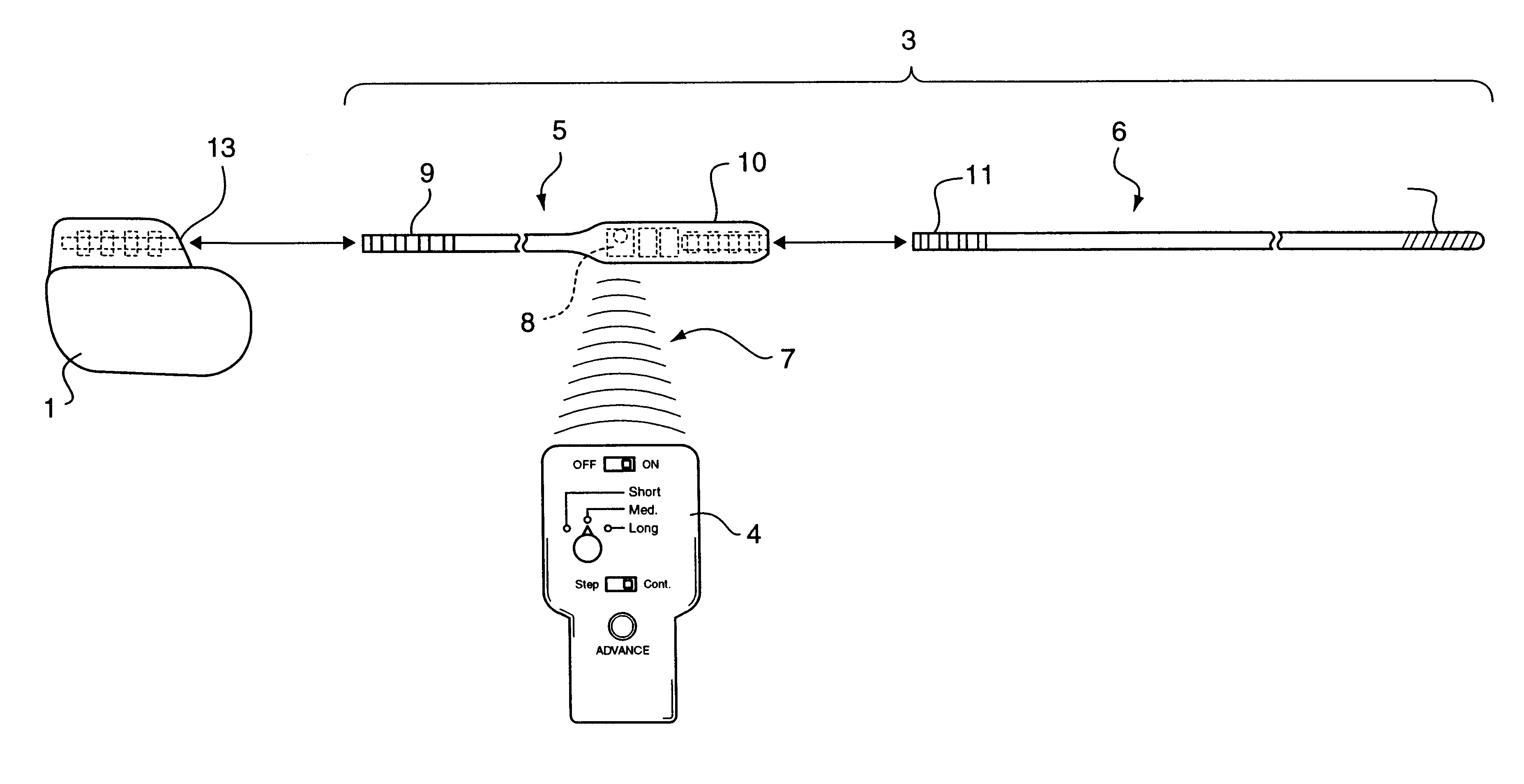
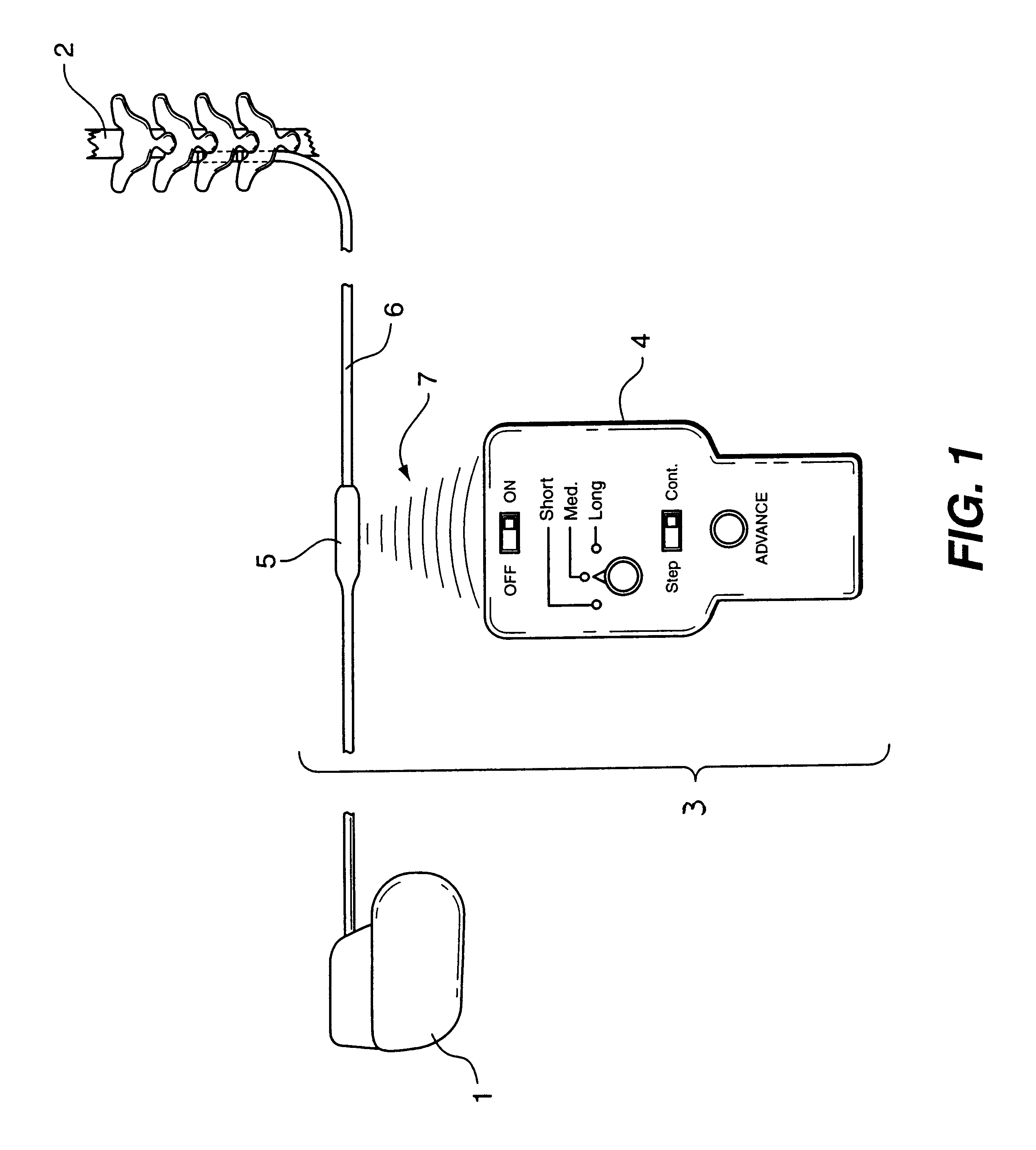
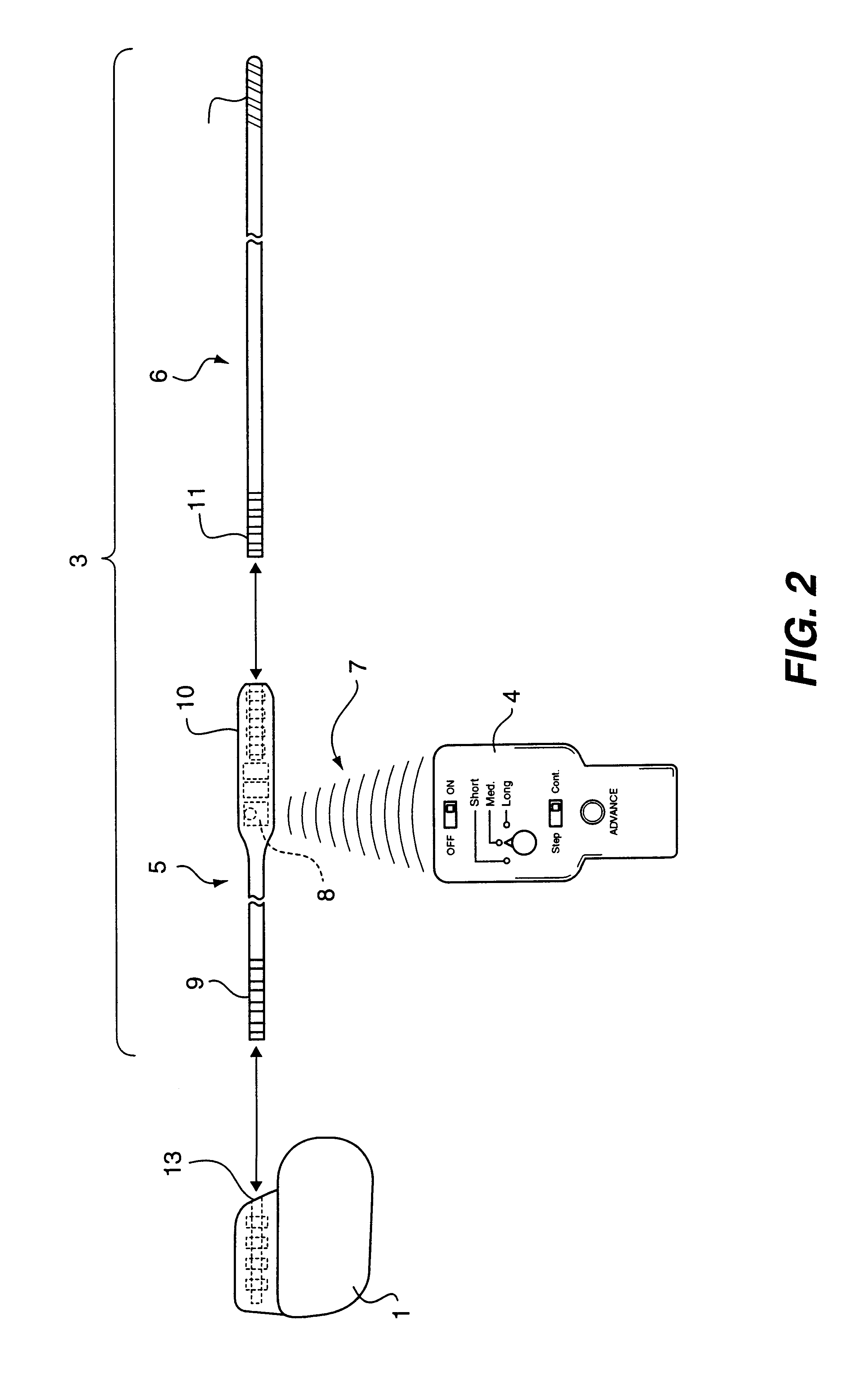
Non-invasively maneuverable lead system
The method and system for non-invasively repositioning at least one stimulating electrode on a lead relative to tissue, such as nerve tissue, in a body includes elements for carrying out the method and the steps of: providing a lead having at least one stimulating electrode thereon which is located skew to an elongate axis of the lead; implanting the lead in a body; implanting in the body a drive mechanism having structure for engaging and rotating the lead; and, providing an exterior signal generating and transmitting mechanism for transmitting electromagnetic signals from outside the body to the drive mechanism implanted in the body for causing the drive mechanism to rotate the lead thereby to adjust the position of the at least one stimulating electrode on the lead relative to tissue in the body.
Owner:PLEXUS
Methods and devices for accessing a body cavity
InactiveUS20110144440A1Efficiently rotatedEfficient changeCannulasSurgical needlesSurgical siteGeneral surgery
Methods and devices are provided for accessing a surgical site. In one embodiment, an access device is provided having a housing and a cannula extending distally therefrom. The cannula and the housing can define a working channel extending longitudinally therethrough. The cannula can be movable between an insertion configuration and a deployed configuration. The access device can also include an obturator insertable through the working channel. In one embodiment, the obturator can be configured to selectively mate with the cannula such that rotation of the obturator is effective to cause corresponding rotation of the cannula. In another embodiment, the obturator can be configured to move the cannula from the insertion configuration to the deployed configuration when the obturator is fully disposed within the cannula.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL
Methods using non-genic sequences for the detection, modification and treatment of any disease or improvement of functions of a cell
InactiveUS20050164252A1Promote recoveryDiagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBiological bodyRNA Sequence
This invention provides the use of conserved non-genic sequences so commonly found in most species of plants and animals for the detection of a disease and condition. The intimate and ultimately important link of the corresponding DNA sequences and expressed RNA sequences with their conserved non-genic sequence makes the detection possible. Apart from the diagnostic use, the combination of the conserved non-genic sequences with the corrected or designed DNA or RNA sequences makes treatment or improvement possible for living organisms.
Owner:YEUNG WAH HIN
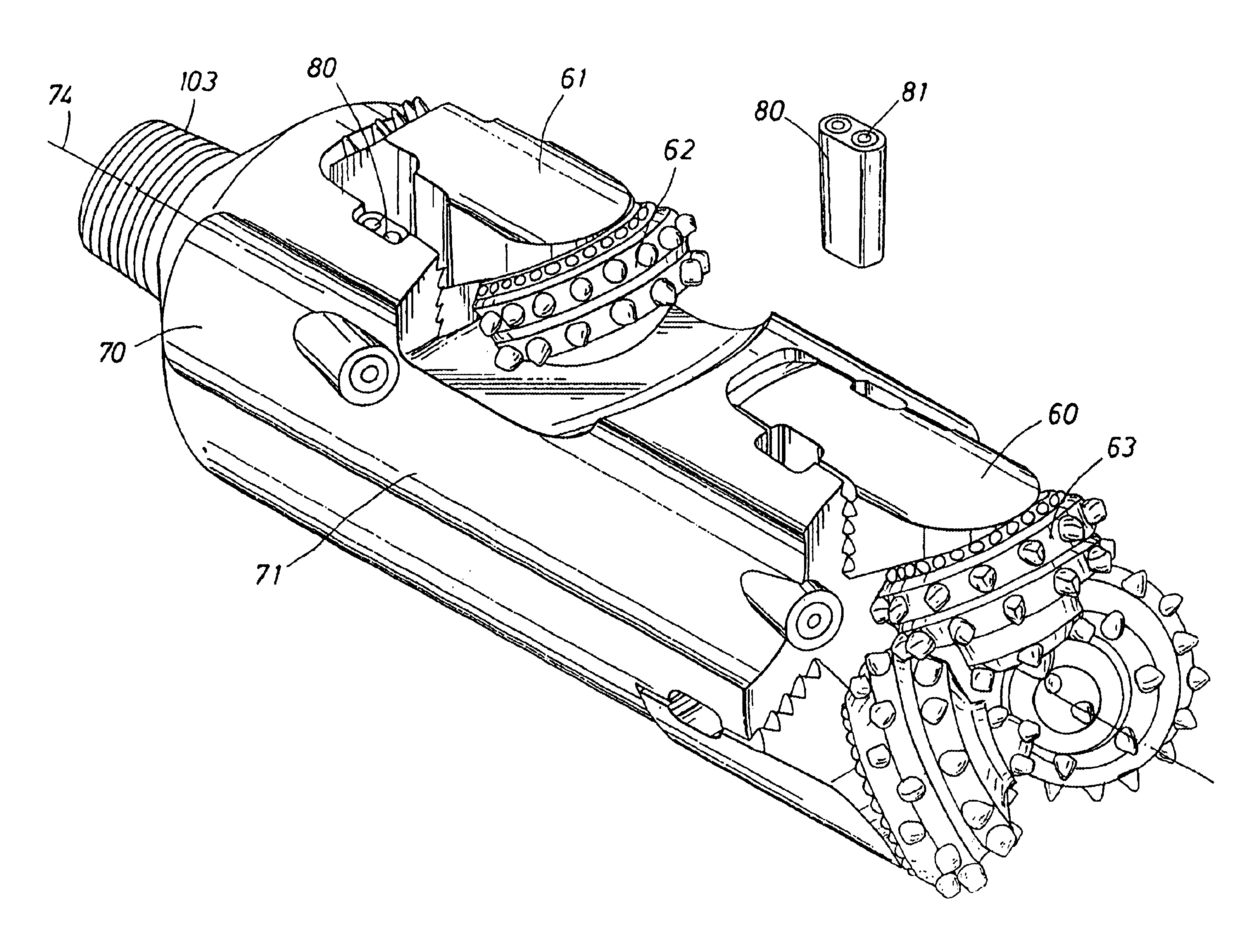
Roller cone bi-center bit
InactiveUS6902014B1Enhance drilling outEasy to disassemble and replaceDrill bitsCutting machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A roller cone bi-center bit for economically drilling an enlarged borehole below casing in earth formation is provided. The bi-center bit includes a rolling cone cutter or other appropriate cutter to enlarge a pilot bore also made by rolling cone or other type of cutters. The bit comprises a single-diameter body with a recess to accommodate the trailing cutter which enlarges the pilot bore. The bi-center bit may also provide the ability to change out the cutters efficiently in the field. The cutters are oriented to enhance drilling out the cement plug at the bottom of the casing. The cone cutter may be also be mounted on segments which are designed to be easily removed for replacement or adjustment in position in the field.
Owner:ROCK BIT INT +2
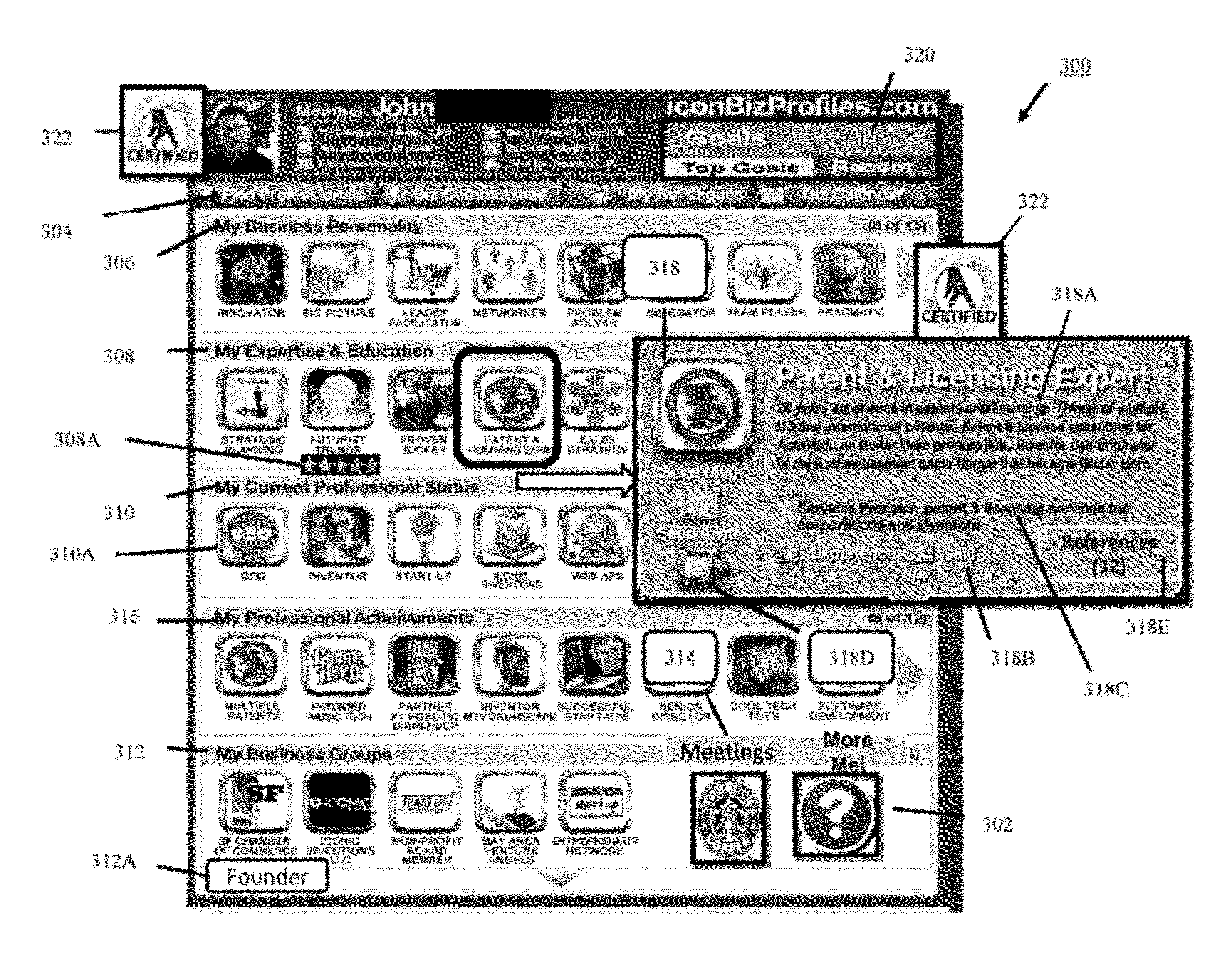
System and method for an interactive mobile-optimized icon-based professional profile display and associated search, matching and social network
InactiveUS20120311462A1Improve accuracyImprove preferenceInput/output for user-computer interactionAdvertisementsPersonalizationFile system
An icon-based interactive professional profile, search and matching system configured within professional network platforms and technologies enabling a user to generate a personalized interactive icon-based business or resume profile representing icon profile elements optimized for display and functionality on mobile devices. The icon profile system utilizes and integrates selected personalized icon profile elements and associated data for searching, compatibility matching, invitations, communities, and calendar functions. In professional network environments, icon elements are unitized to aggregate users based on a selected icon profile element and in further environments automatically compare and report compatibility between unknown users, which vastly improves professional network functionality.
Owner:DEVECKA JOHN
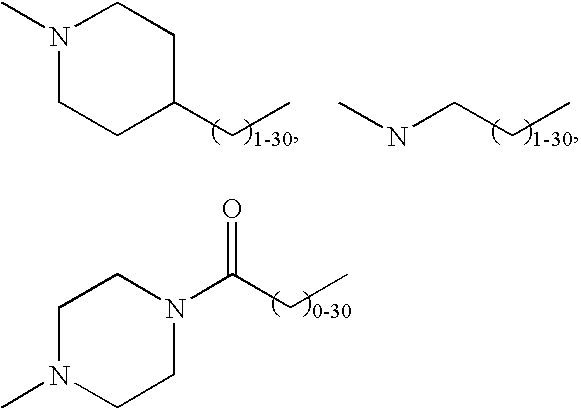
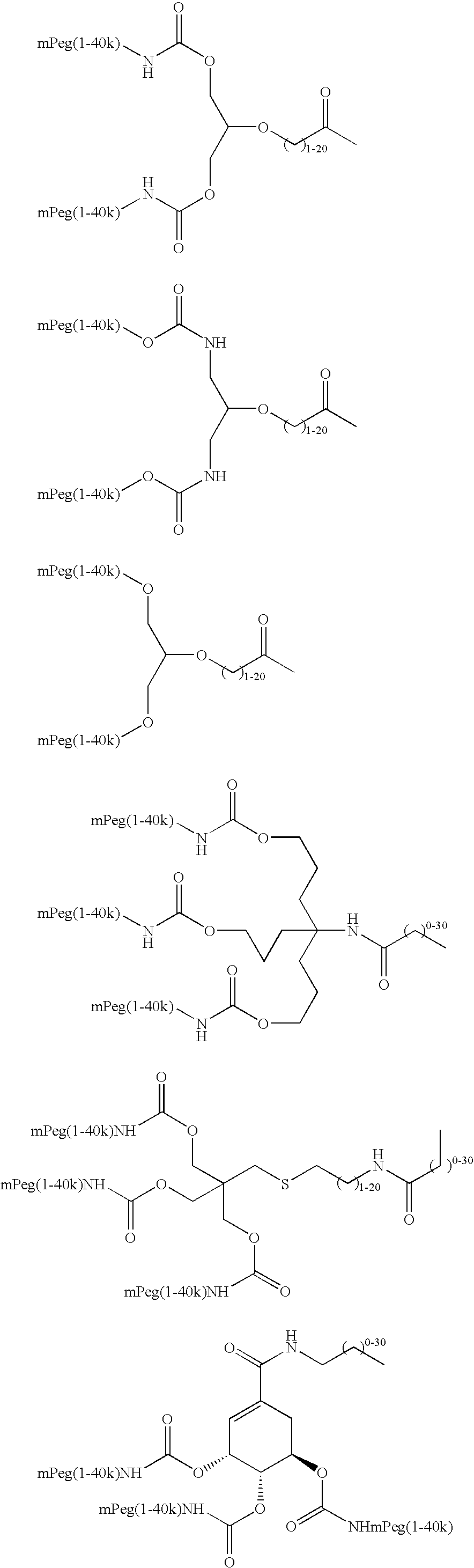
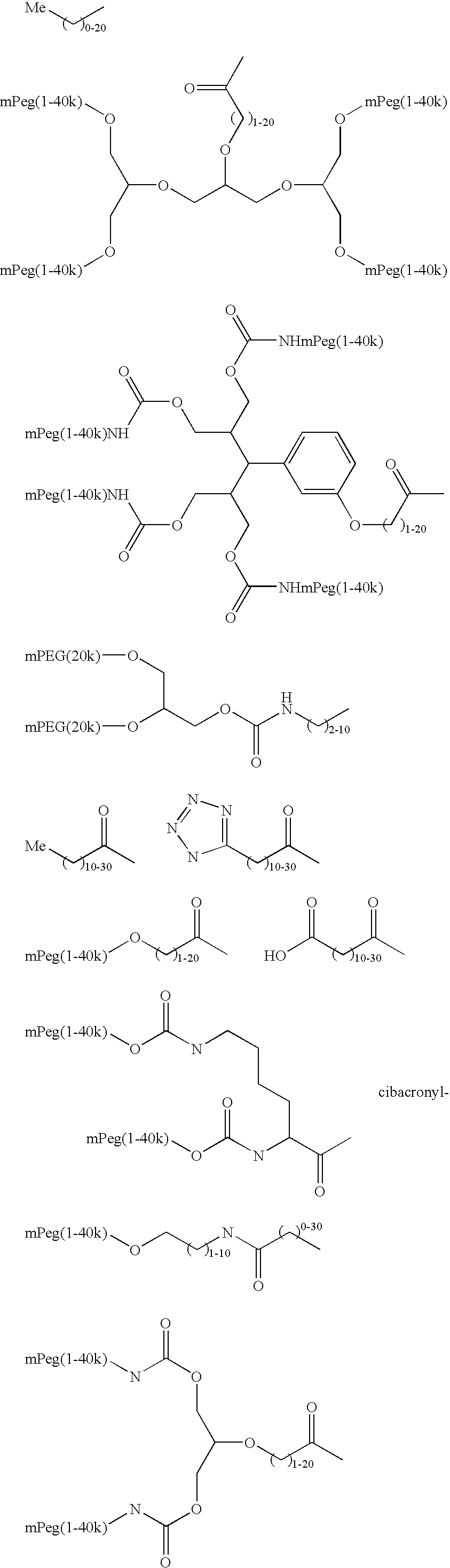
Modified Proteins
InactiveUS20080108557A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeReduce in quantityPeptide/protein ingredientsAlbumin peptidesGlycosyltransferasePeptide
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
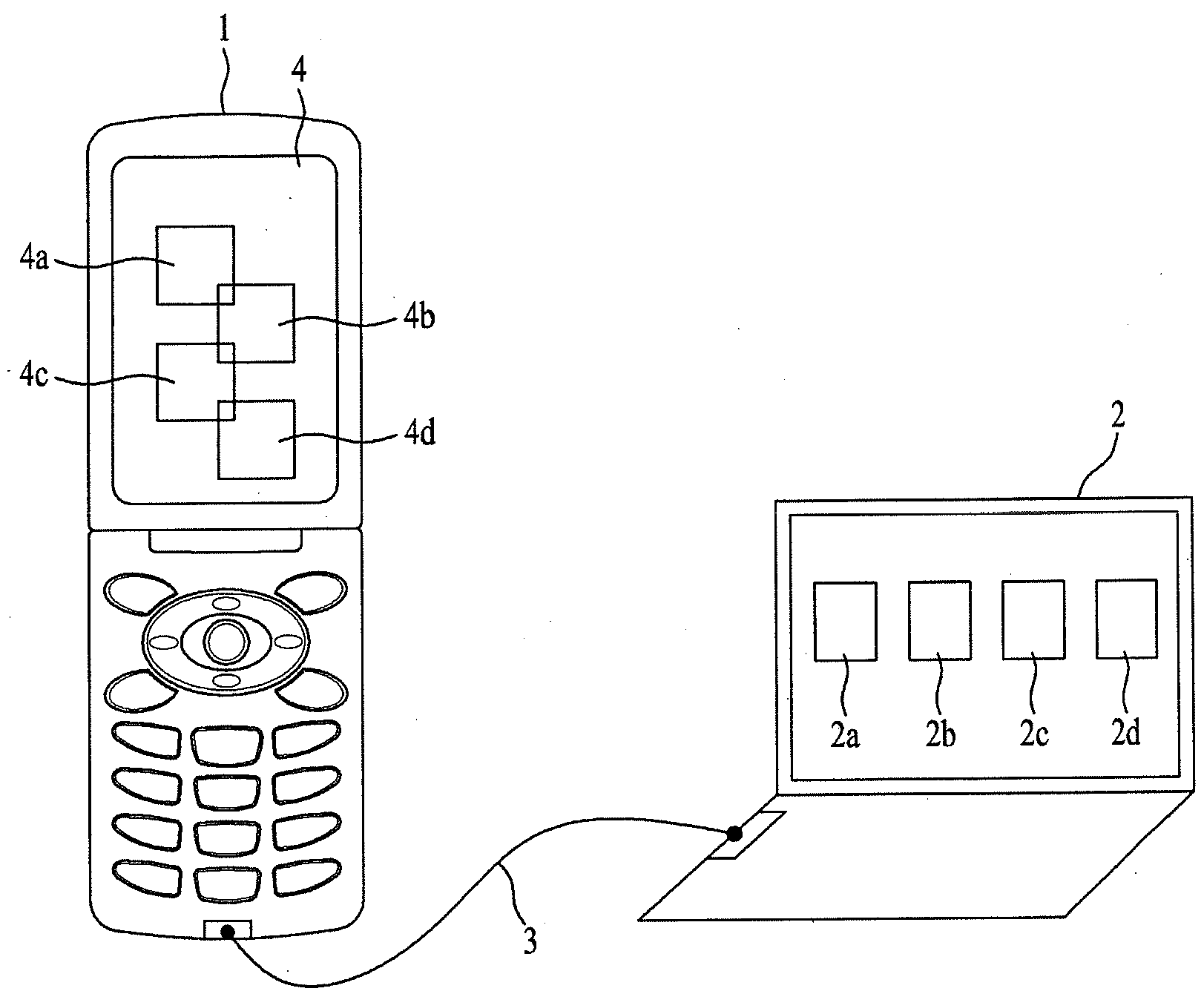
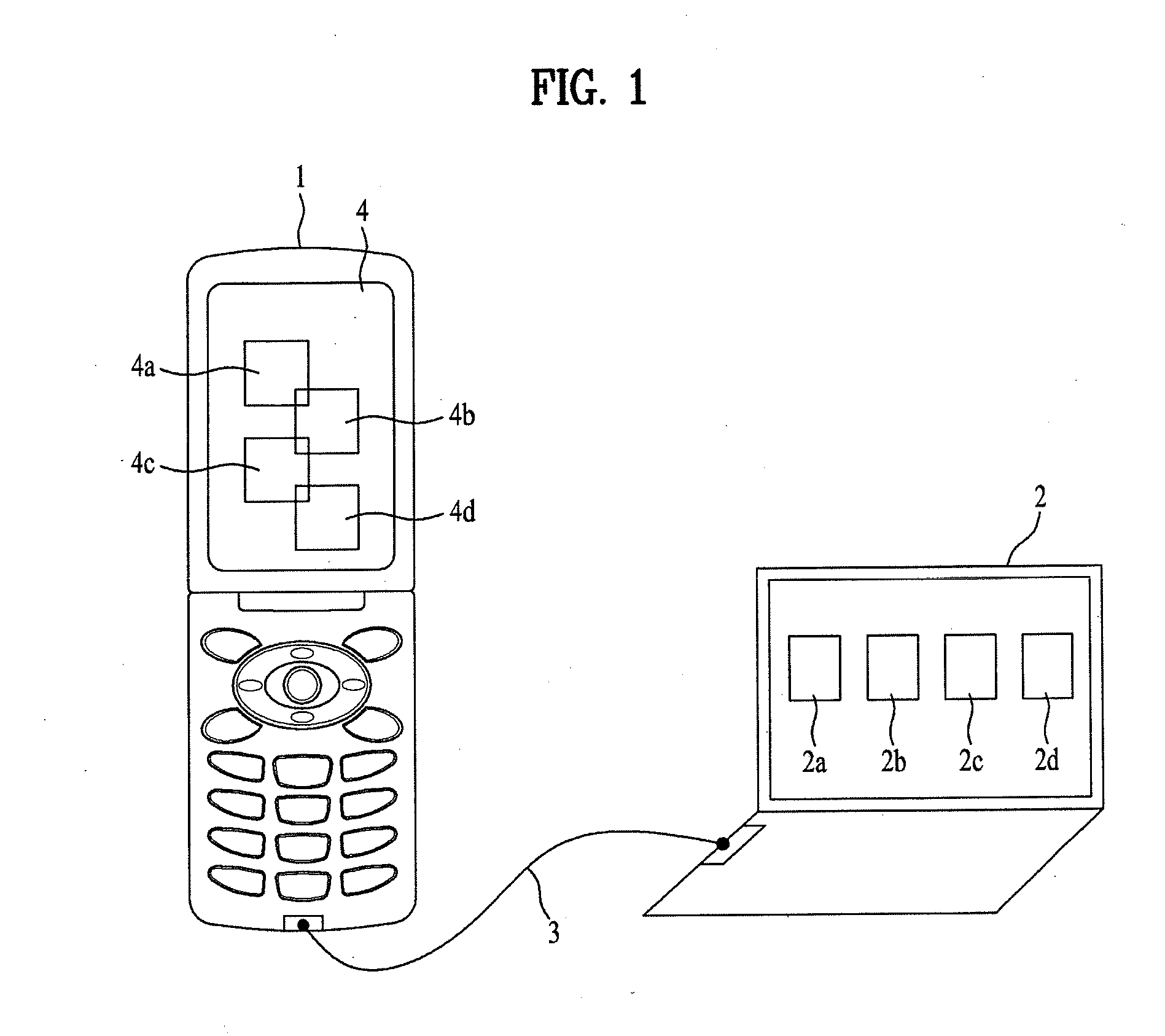
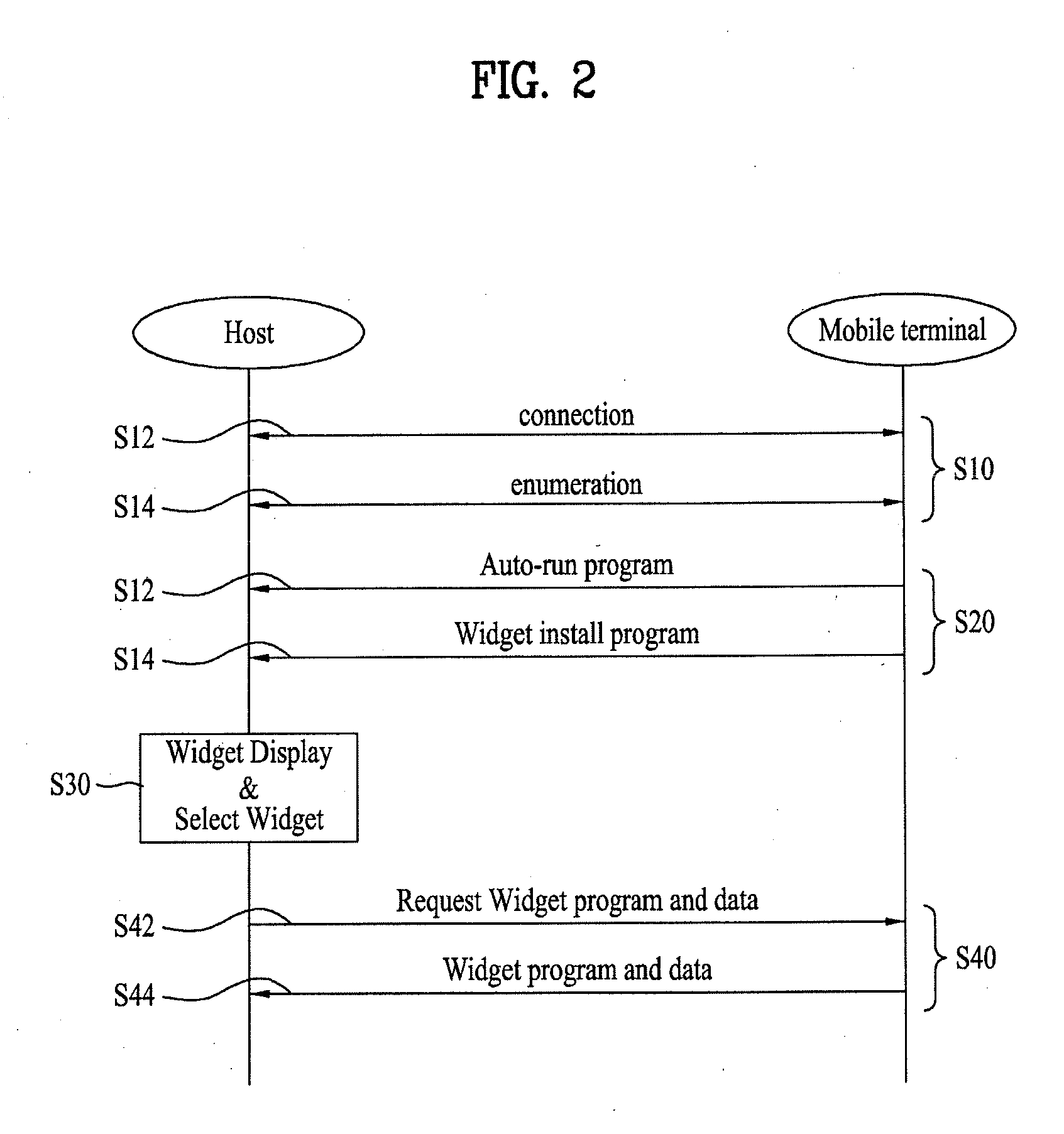
Communication device and a host device, a method of processing signal in the communication device and the host device, and a system having the communication device and the host device
InactiveUS20090307679A1Efficient managementEfficient changeSoftware engineeringSubstation equipmentComputer hardwareControl signal
A method of communicating between a mobile terminal and a personal computer. The method includes communicating between the personal computer and the mobile terminal using a first communication mode, transmitting an executable program from the mobile terminal to the personal computer, the executable program configured to be executed on the personal computer and to display on the personal computer at least one copy widget program respectively corresponding to at least one original widget program executing on the mobile terminal, receiving on the mobile terminal from the personal computer a modification control signal corresponding to a modification of the at least one copy widget program displayed on the personal computer, and modifying the at least one original widget program on the mobile terminal with modifications made to the at least one copy widget program displayed on the personal computer.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Modified proteins
InactiveUS20100056428A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeReduce in quantityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycoprotein iOrganic chemistry
Method of conjugating glycoproteins by means of chemical modification is provided as well as new modified glycoproteins.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Methods and devices for accessing a body cavity
InactiveUS8435174B2Efficient changeEffective movementCannulasSurgical needlesSurgical siteBody cavity
Methods and devices are provided for accessing a surgical site. In one embodiment, an access device is provided having a housing and a cannula extending distally therefrom. The cannula and the housing can define a working channel extending longitudinally therethrough. The cannula can be movable between an insertion configuration and a deployed configuration. The access device can also include an obturator insertable through the working channel. In one embodiment, the obturator can be configured to selectively mate with the cannula such that rotation of the obturator is effective to cause corresponding rotation of the cannula. In another embodiment, the obturator can be configured to move the cannula from the insertion configuration to the deployed configuration when the obturator is fully disposed within the cannula.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
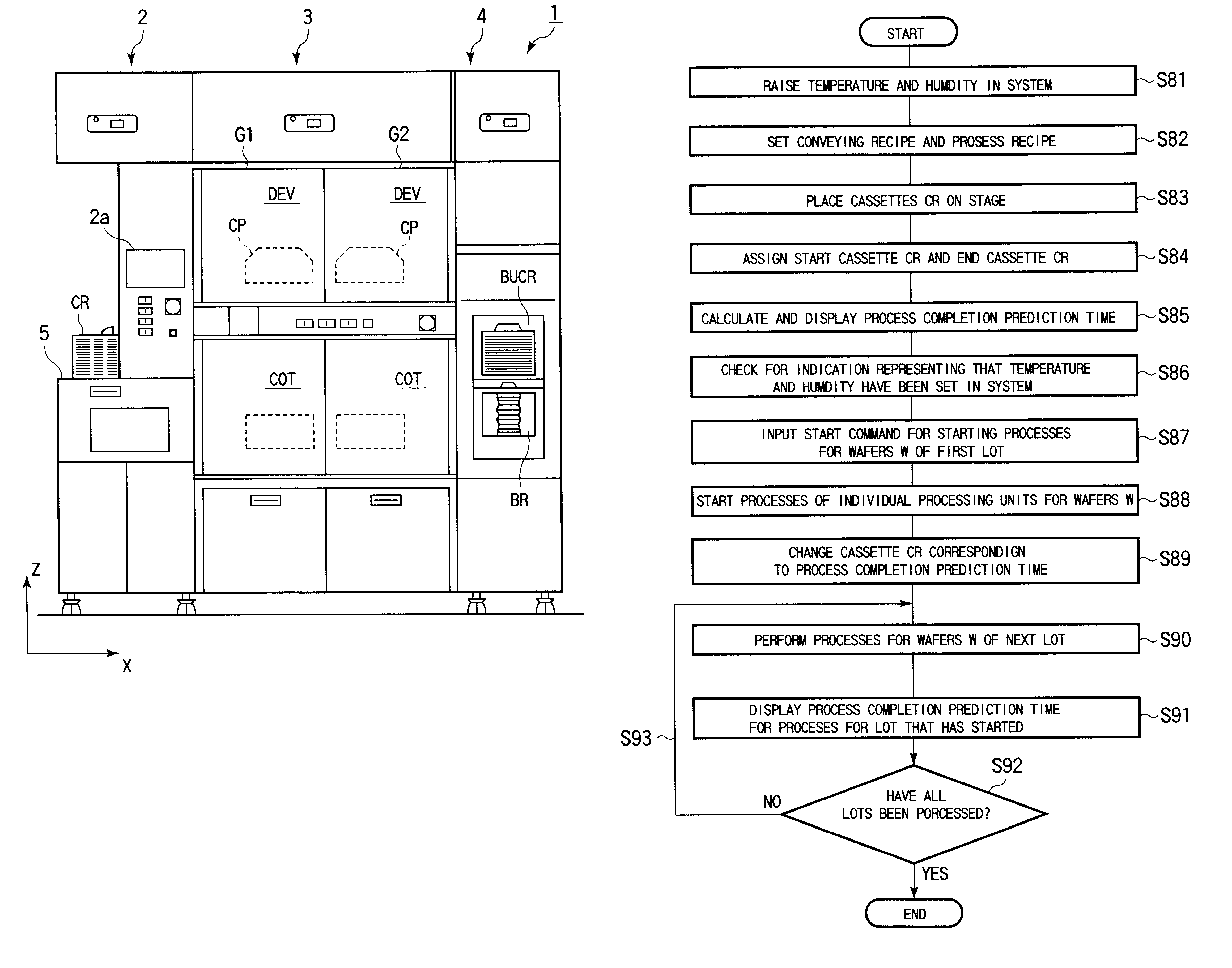
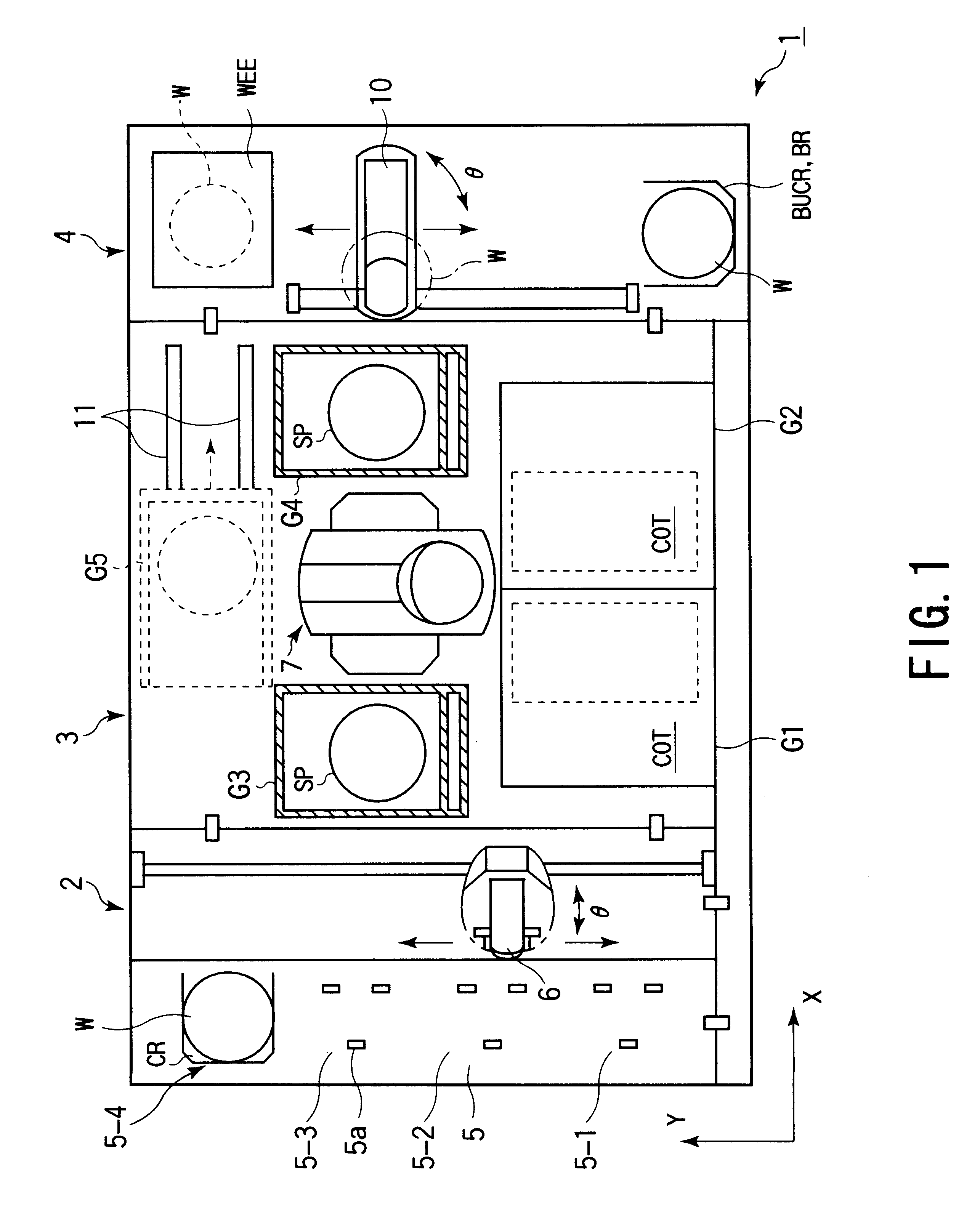
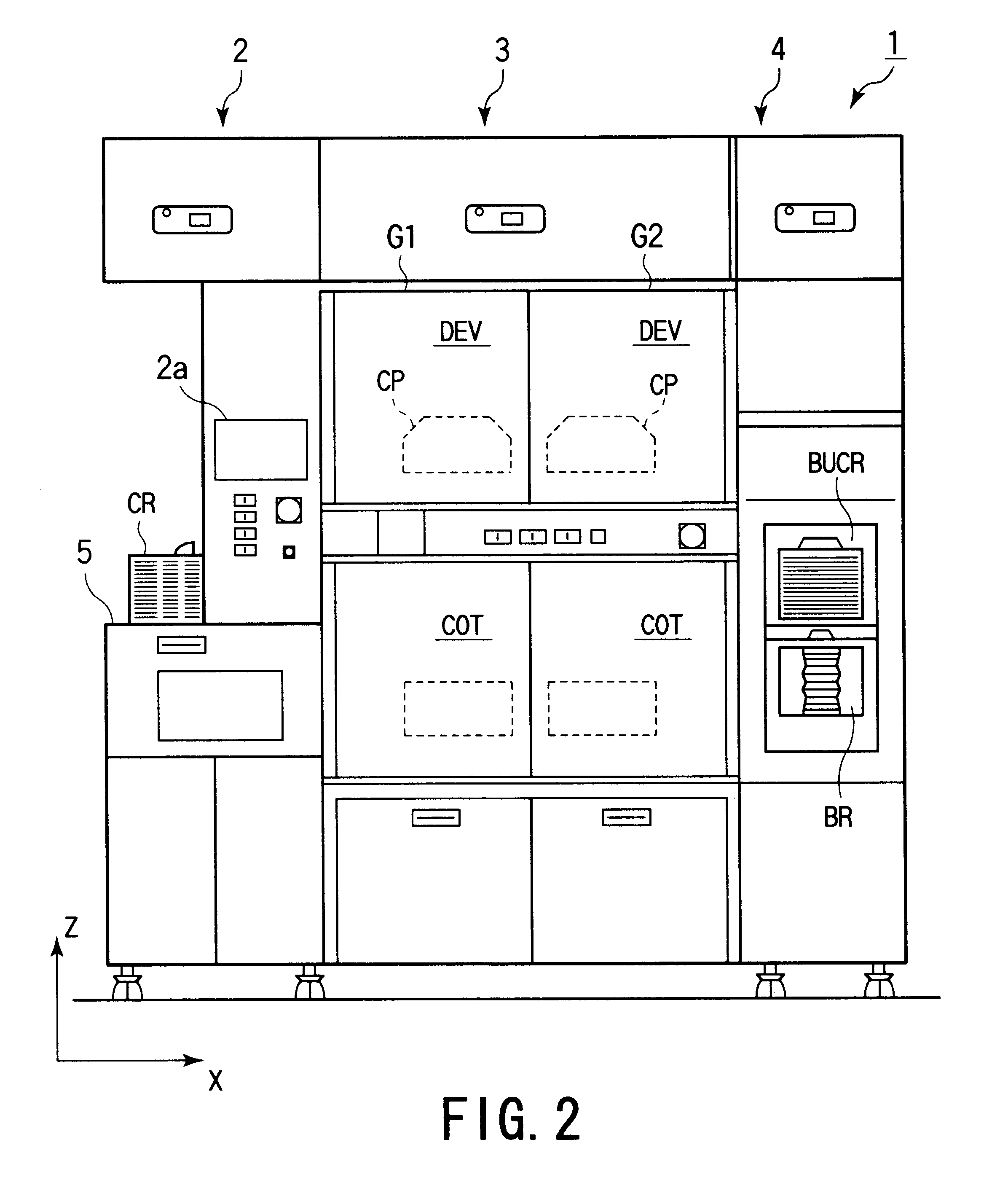
Substrate processing system and substrate processing method
InactiveUS6526329B2Efficient changeDigital data processing detailsGripping headsComputational scienceMagnetic tape
The present invention is a substrate processing method comprising the steps of successively extracting unprocessed wafers from a cassette, successively conveying the extracted wafers to a plurality of processing units, causing the processing units to process the wafers in parallel, and returning the processed wafers to a cassette. A process completion prediction time at which processes for one lot are completed is calculated and displayed corresponding to a process recipe that has been set to a plurality of wafers for at least one lot. Corresponding to the process completion prediction time, a cassette that contains a plurality of unprocessed wafers for one lot is accepted. A cassette that contains a plurality of processed wafers for one lot is returned.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
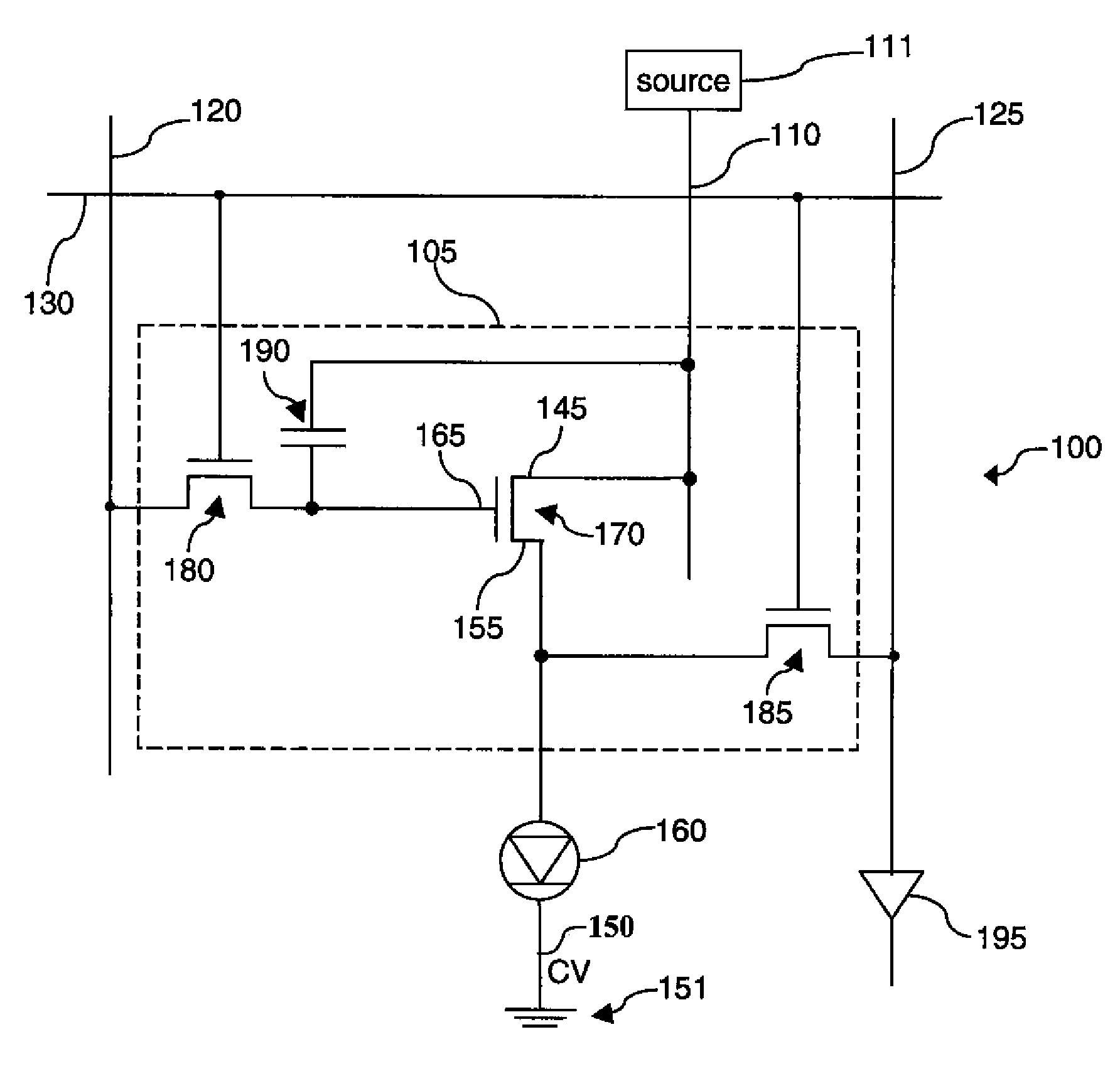
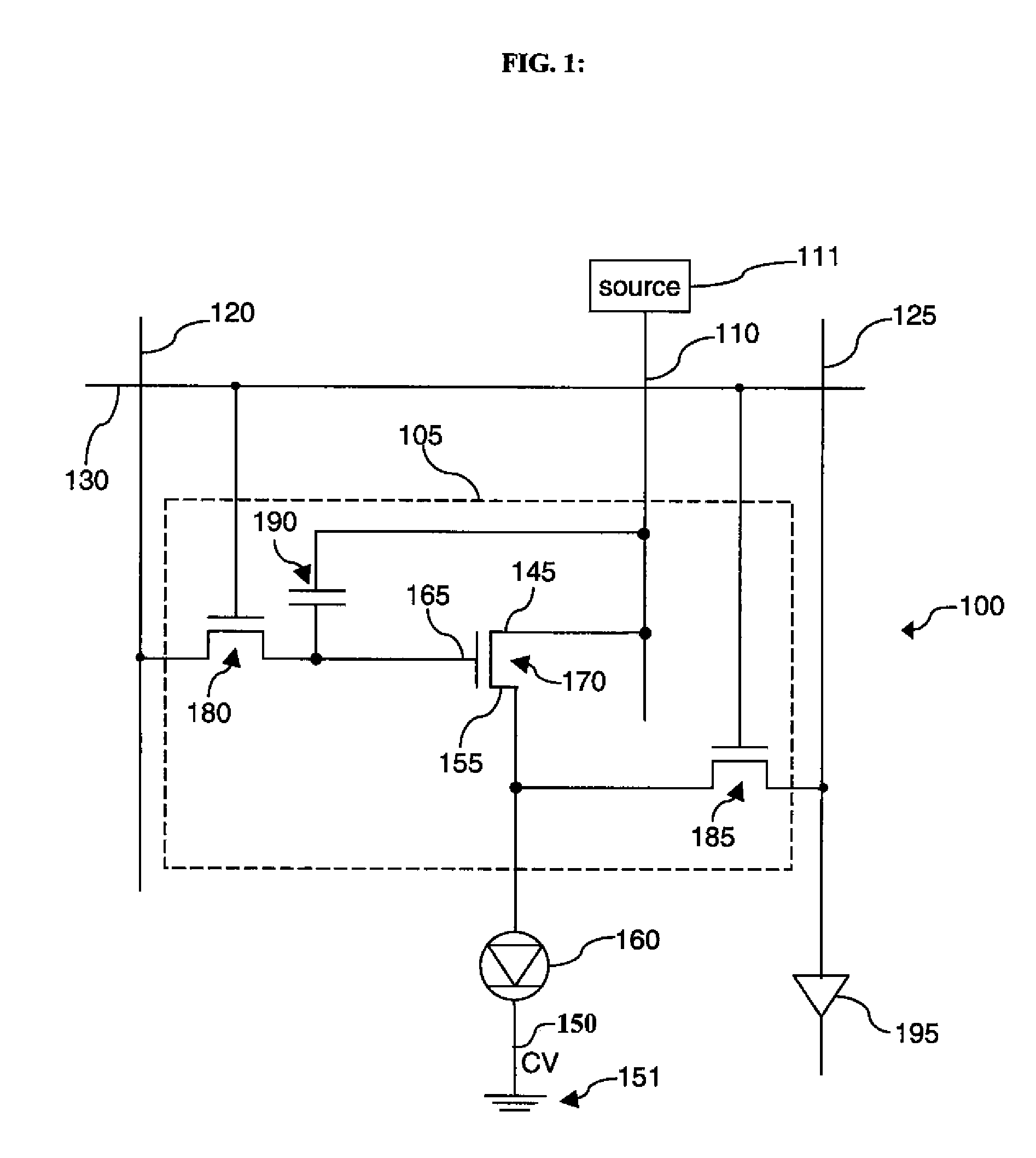
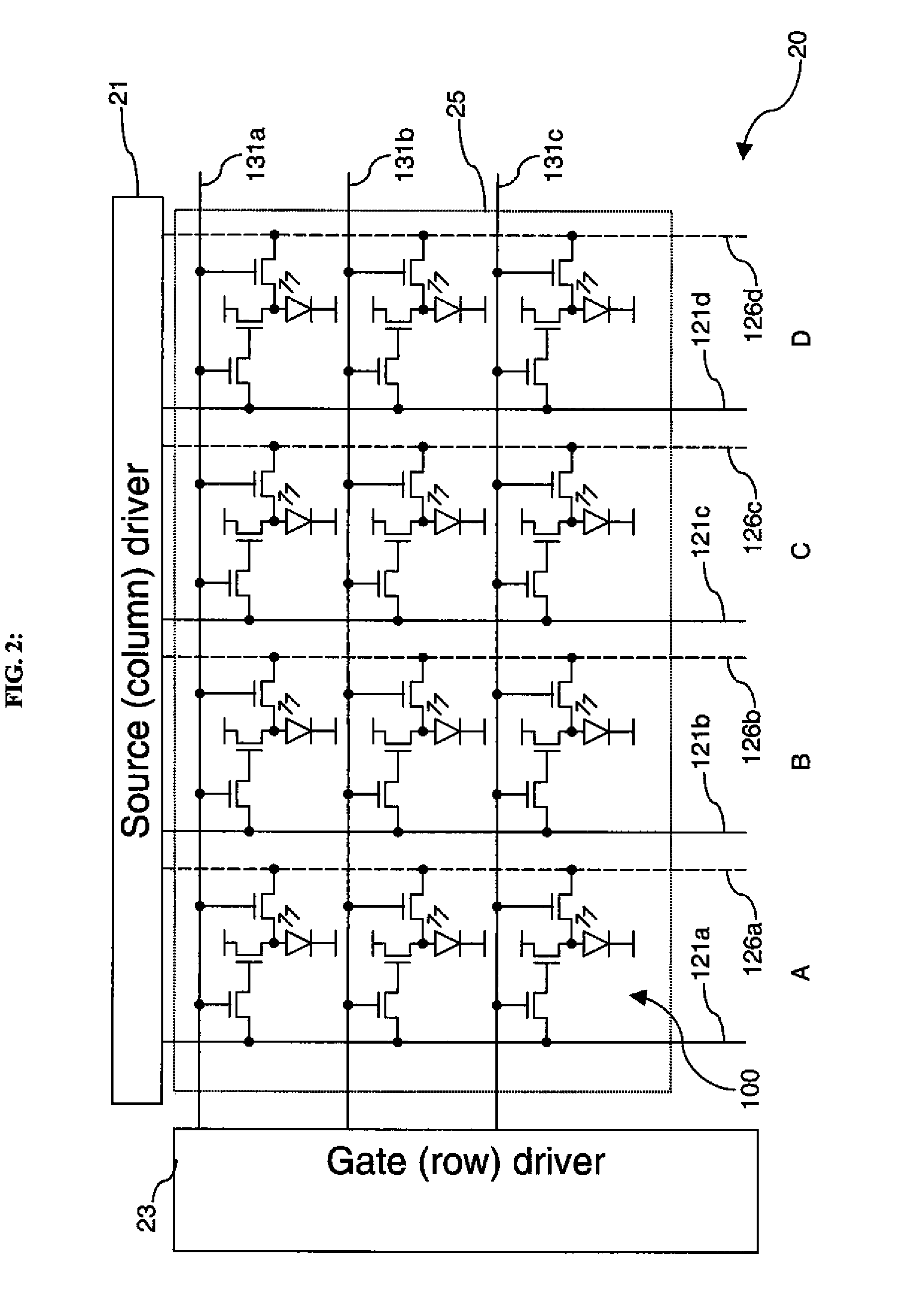
Compensation scheme for multi-color electroluminescent display
ActiveUS20090295423A1Efficient changeEasy to measureStatic indicating devicesIndividual semiconductor device testingElectricityVoltage source
A method of determining characteristics of transistors and electroluminescent devices, includes: providing an electroluminescent display; providing for pairs of electroluminescent devices drive circuits and a single readout line, each drive circuit including a readout transistor electrically connected to the readout line; providing a first voltage source; providing a second voltage source; providing a current source; providing a current sink; providing a test voltage source; providing a voltage measurement circuit; sequentially testing the drive transistors to provide a first signal representative of characteristics of the drive transistor of the first drive circuit and a second signal representative of characteristics of the drive transistor of the second drive circuit, whereby the characteristics of each drive transistor are determined; and simultaneously testing the first and second electroluminescent devices to provide a third signal representative of characteristics of the pair of electroluminescent devices, whereby the characteristics of both electroluminescent devices are determined.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
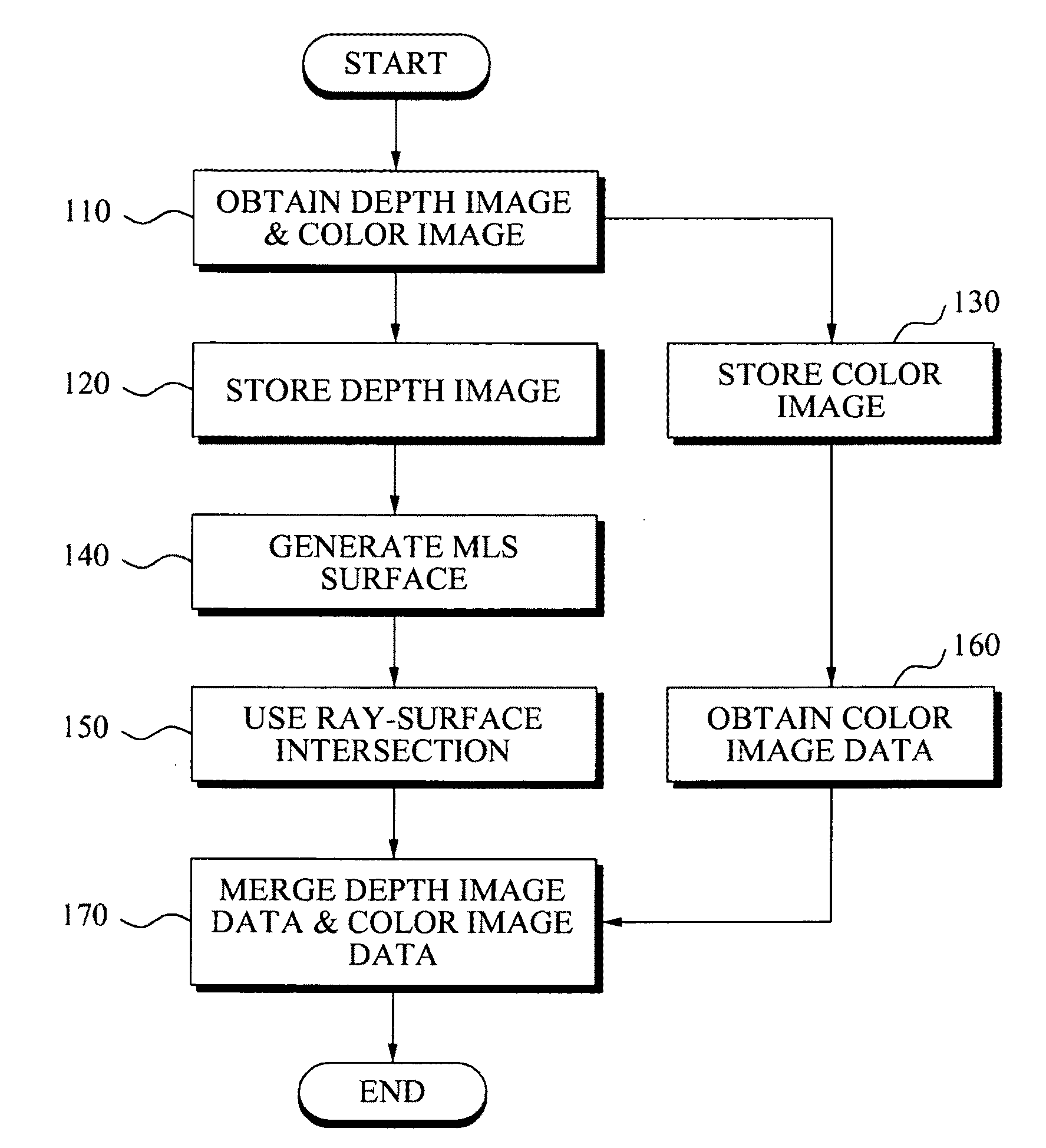
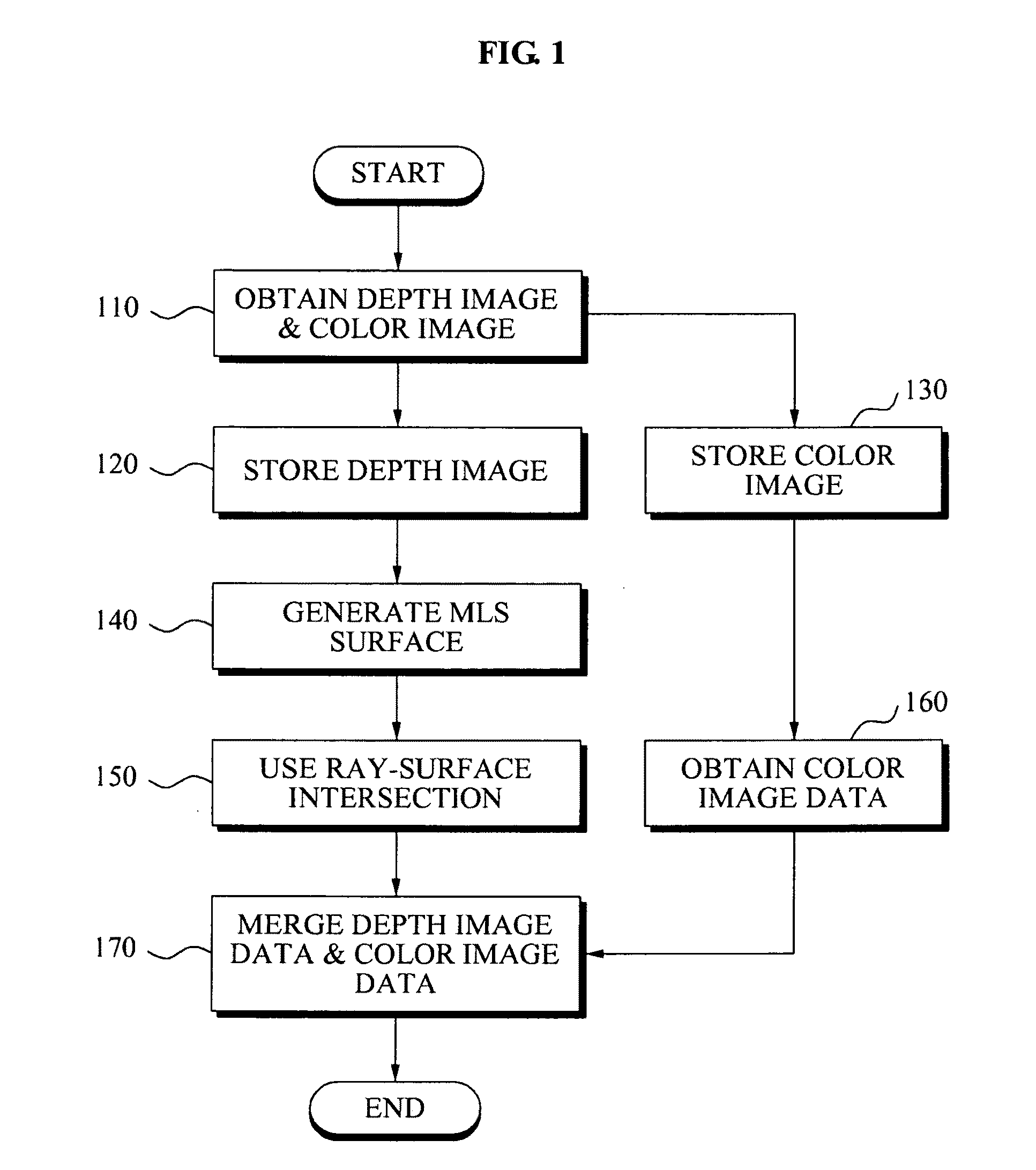
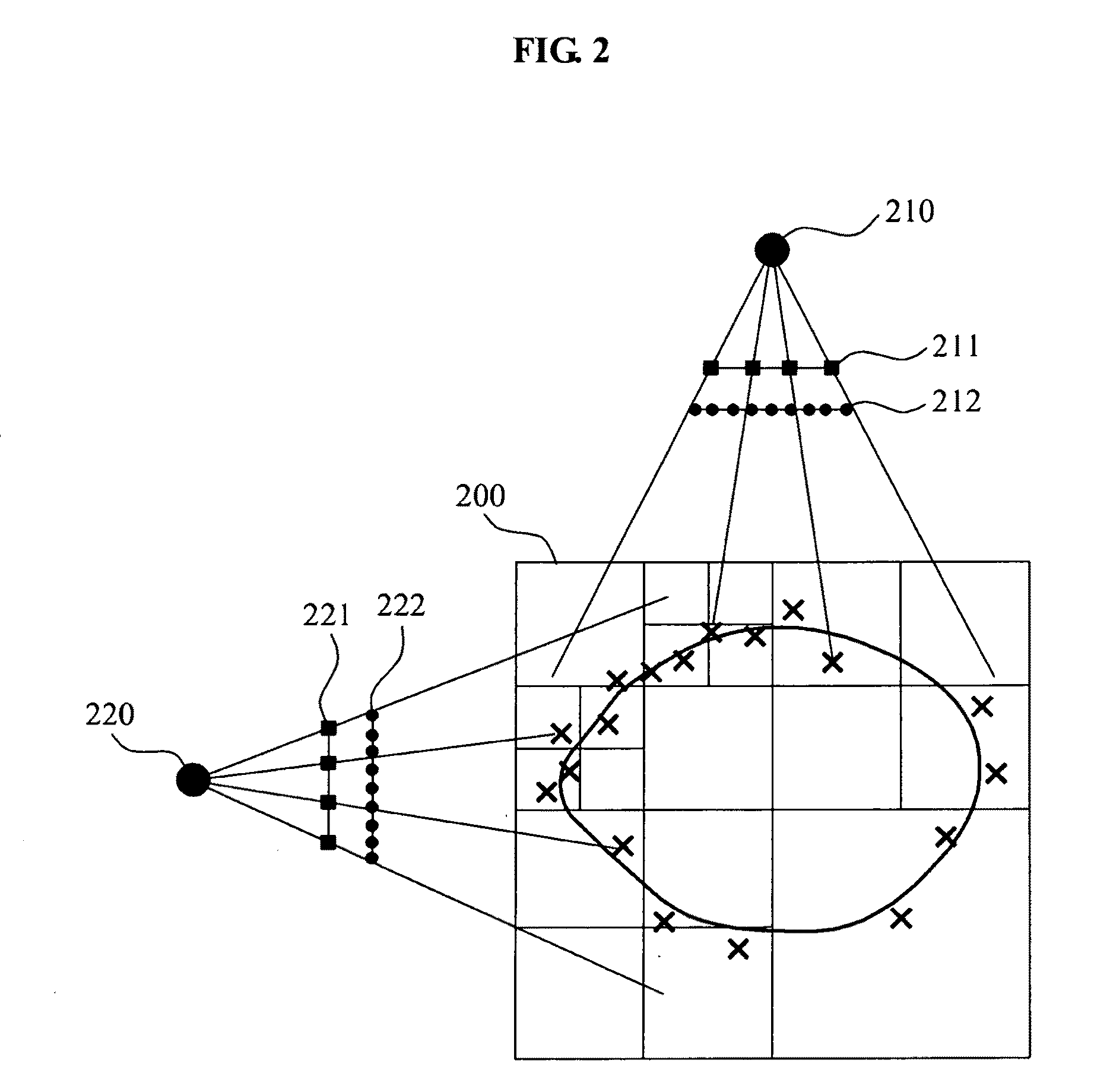
Method and apparatus for processing three-dimensional (3D) images
ActiveUS20090213240A1Efficient changeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsColor imageCMOS
Provided is point-based efficient three-dimensional (3D) information representation from a color image that is obtained from a general Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) / Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) camera, and a depth image that is obtained from a depth camera. A 3D image processing method includes storing a depth image associated with an object as first data of a 3D data format, and storing a color image associated with the object as color image data of a 2D image format, independent of the first data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Turbofan engine
A turbofan engine is provided that includes a fan nacelle surrounding a core nacelle. The core nacelle houses a spool. The fan and core nacelles provide a bypass flow path having a nozzle exit area. A turbofan is arranged within the fan nacelle upstream from the core nacelle. A flow control device is adapted to effectively change the nozzle exit area to obtain a desired operating condition for the turbofan engine. A gear train couples the spool and turbofan for reducing a turbofan rotational speed relative to a spool rotational speed. A controller is programmed to respond to at least one sensor. The controller is programmed to effectively control the nozzle area.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
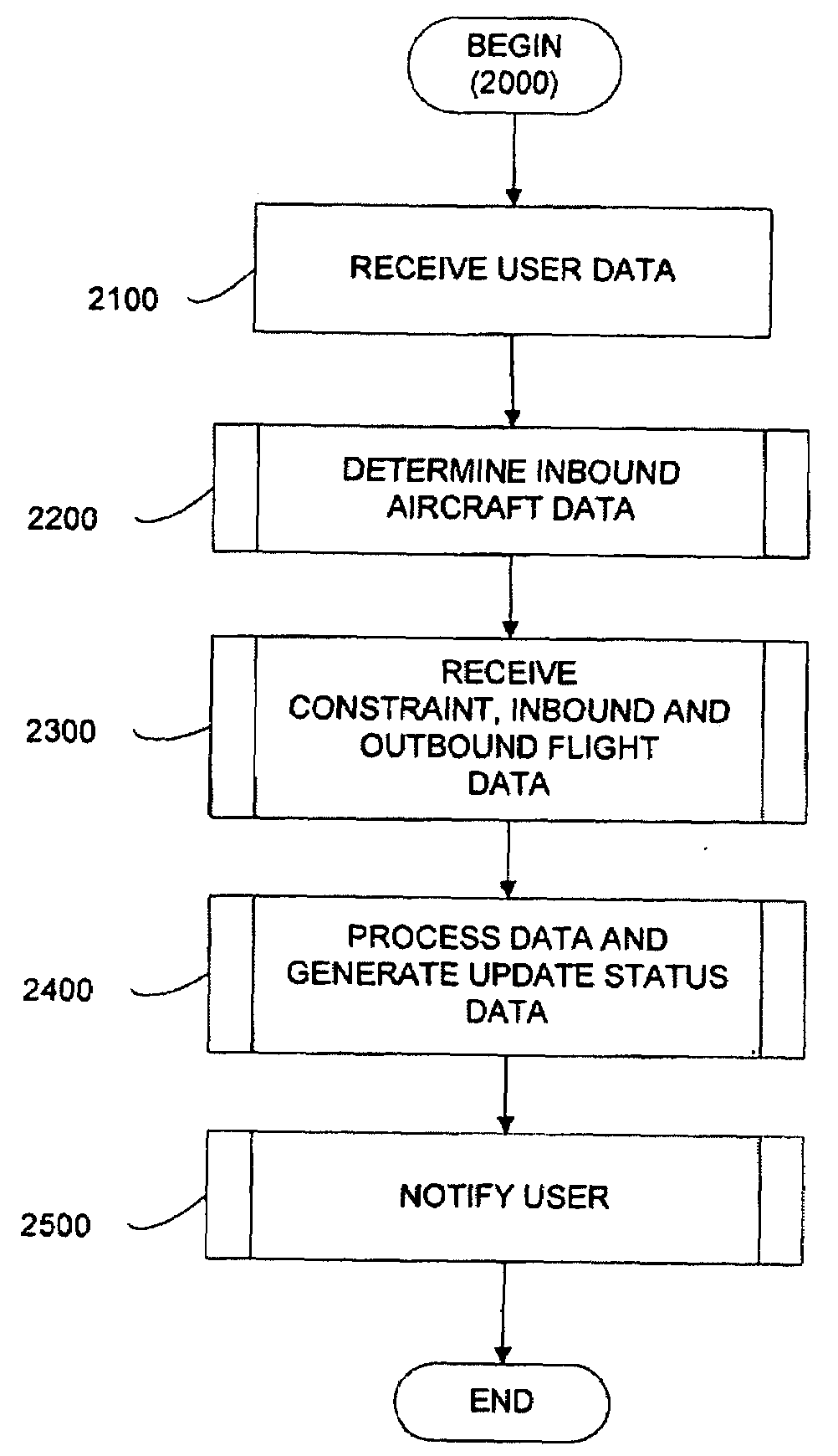
Process and system to determine commercial airline arrivals
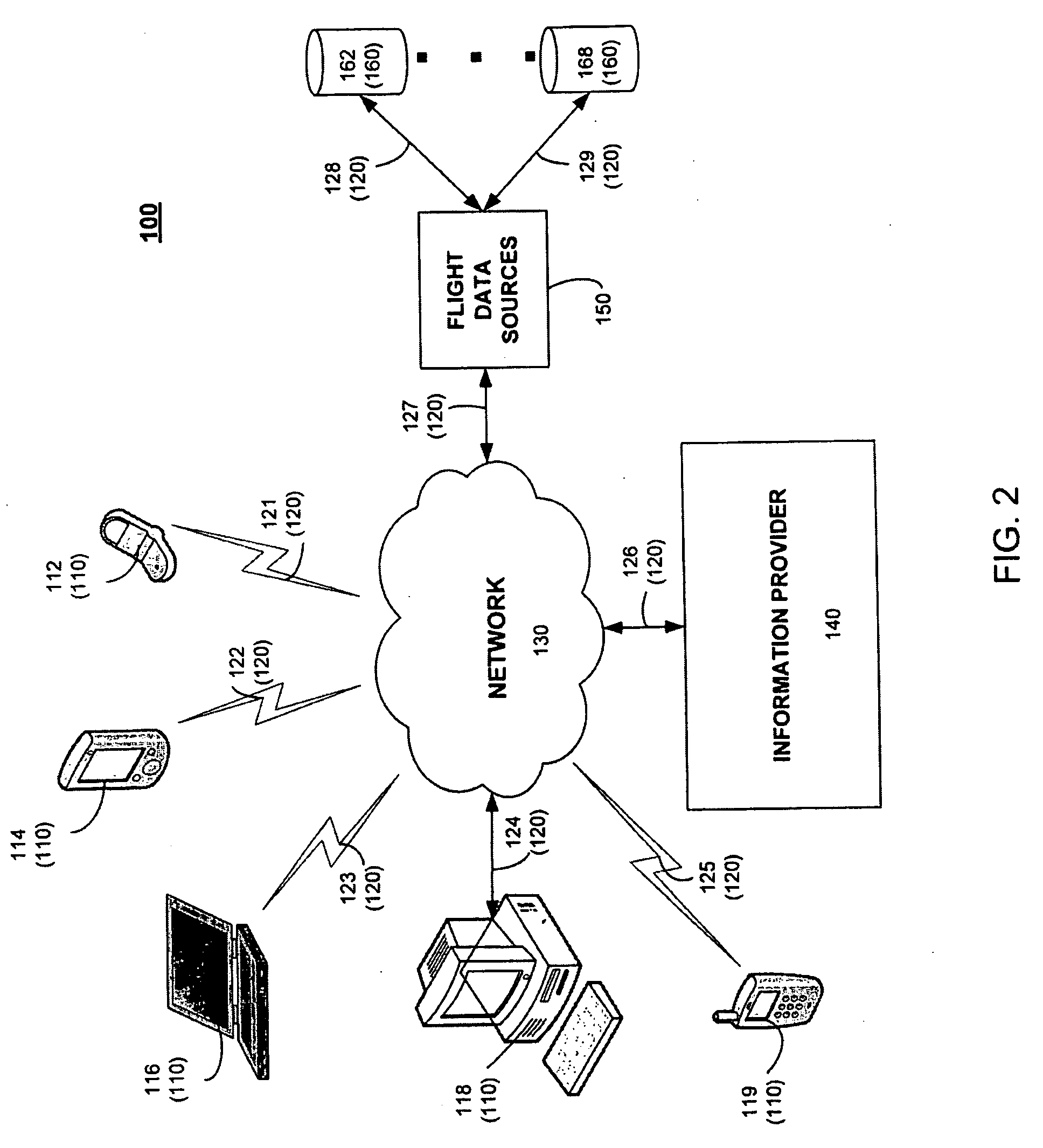
InactiveUS20090276250A1Accurately informedIncrease valueReservationsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer scienceAirplane
An apparatus, a method, a system and a computer program for providing users with early and accurate information relating to a status of a particular flight. Early and accurate information relating to a status of a particular flight is provided to the user. The method includes receiving user data that includes aircraft departure information, determining inbound aircraft data based on the user data, receiving constraint status information, generating update status data based on the inbound aircraft data, outbound aircraft data and constraint status information, and sending an update status message to the user.
Owner:TRAVEL TECH SYST
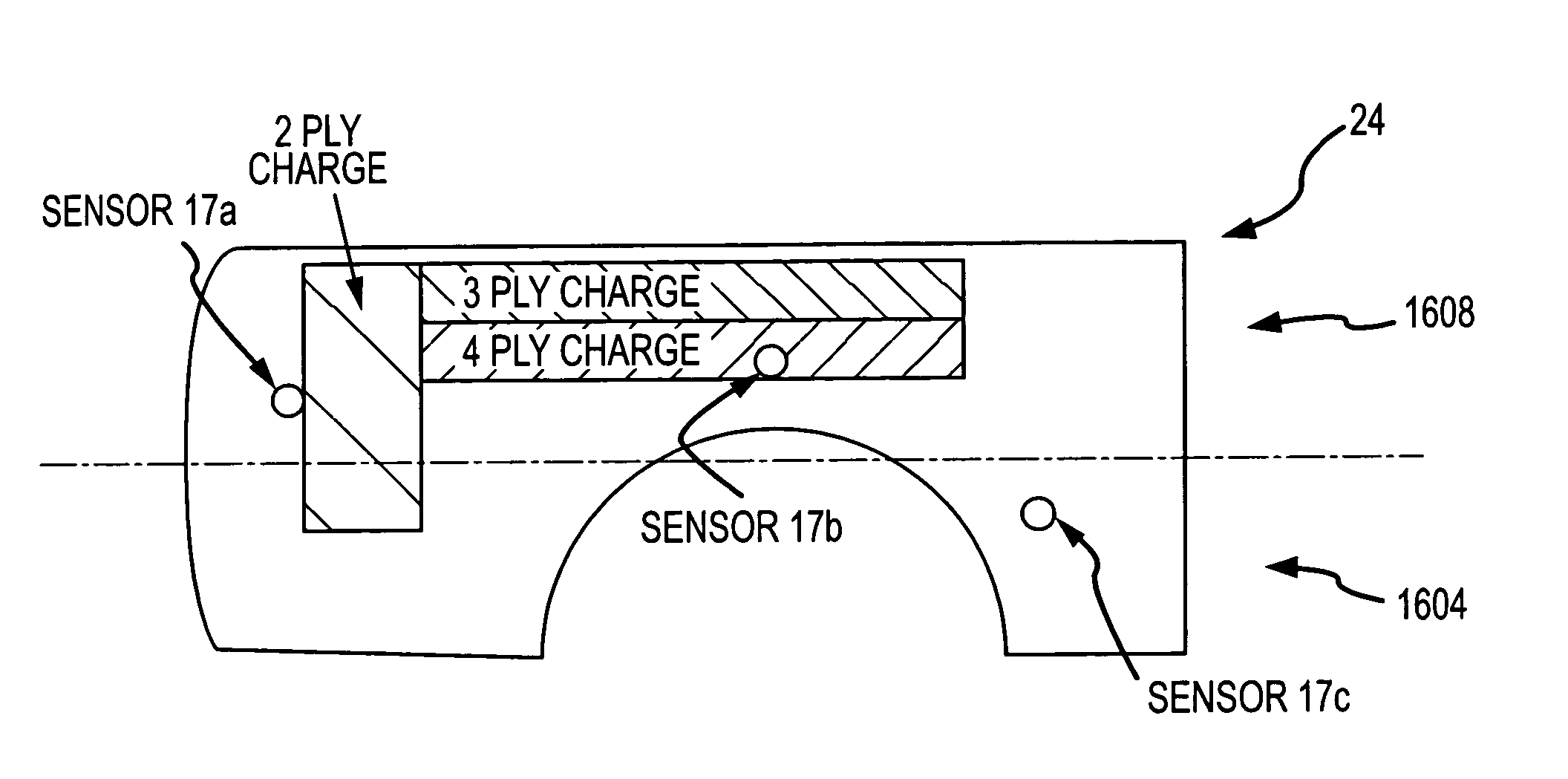
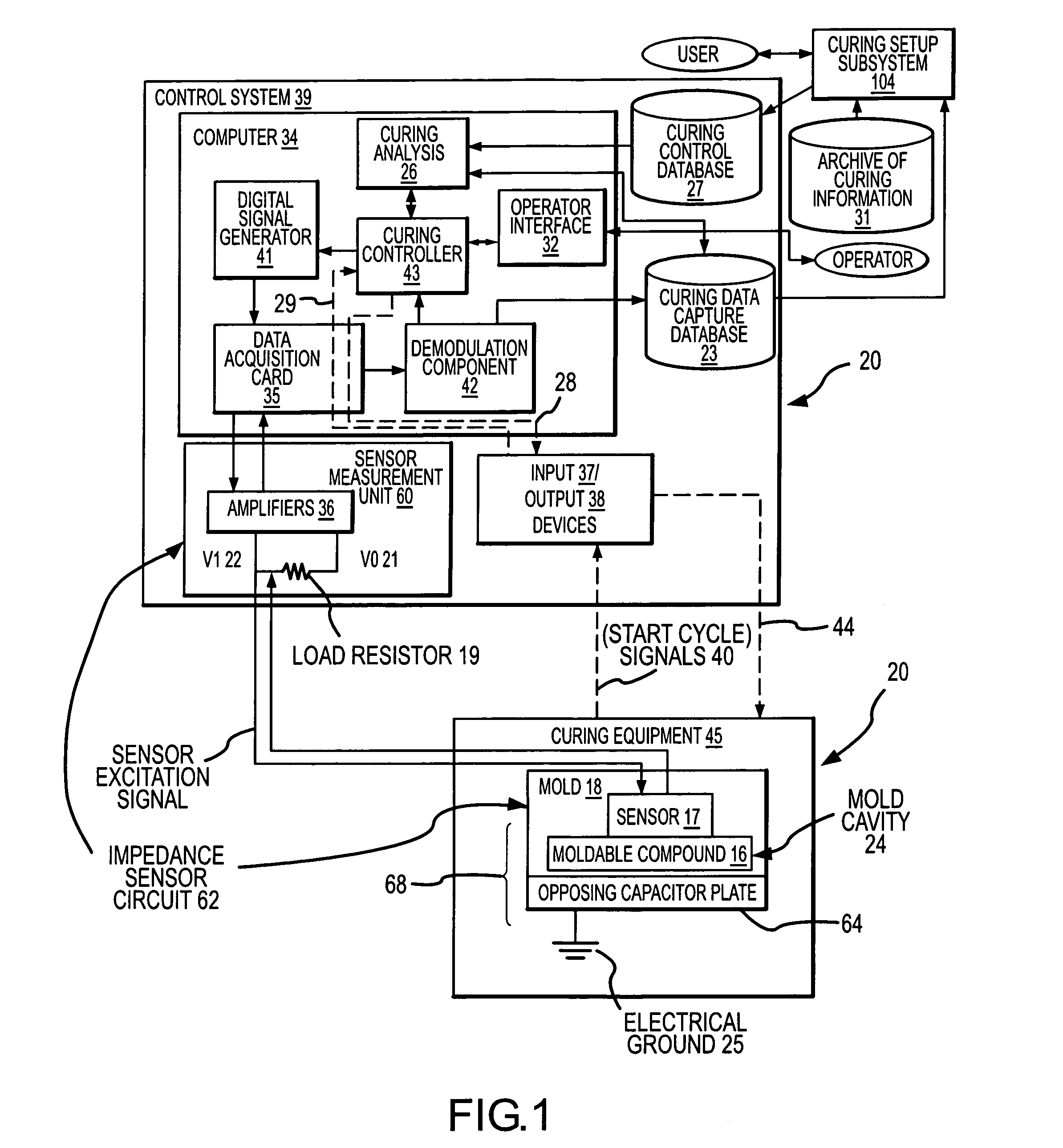
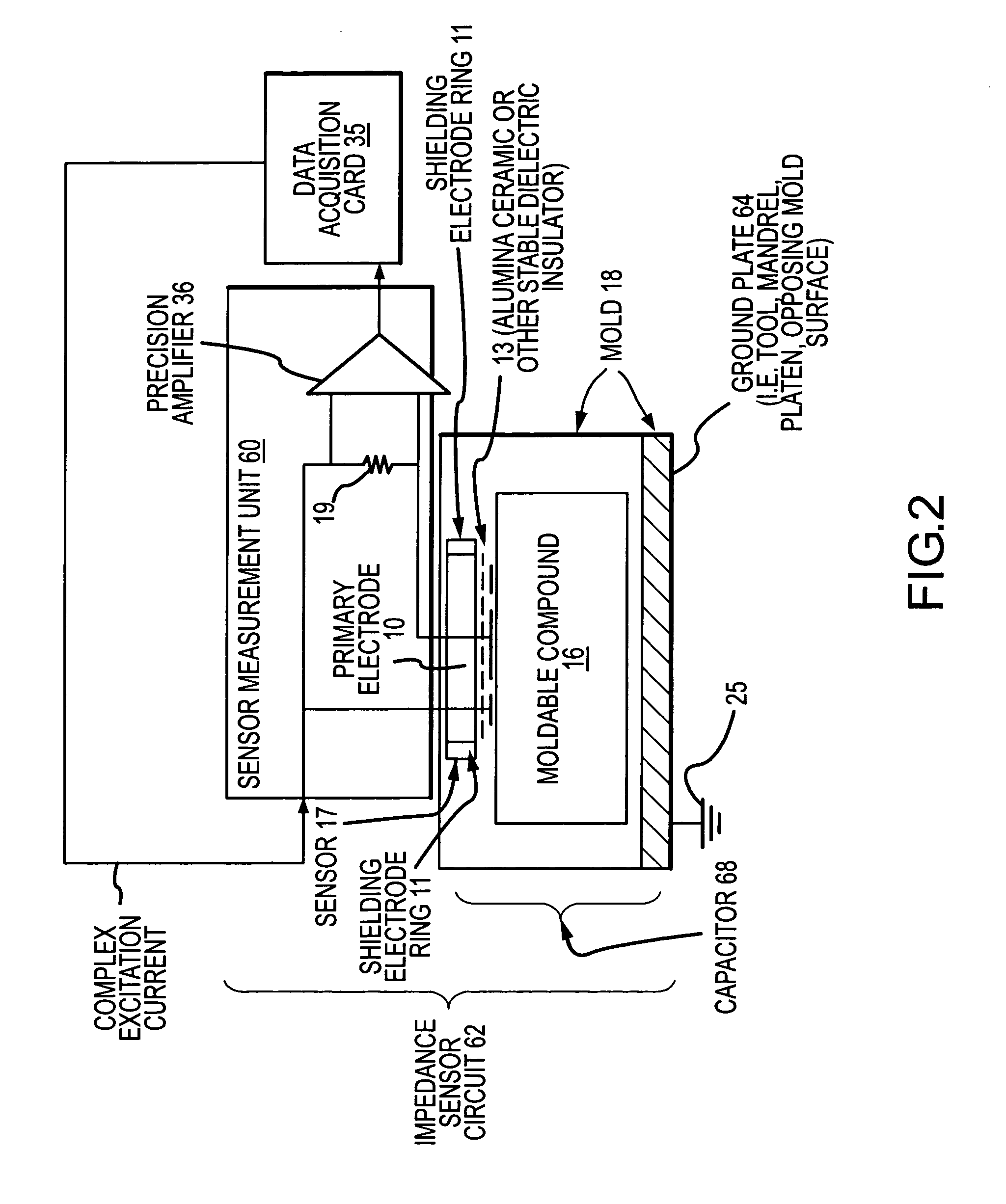
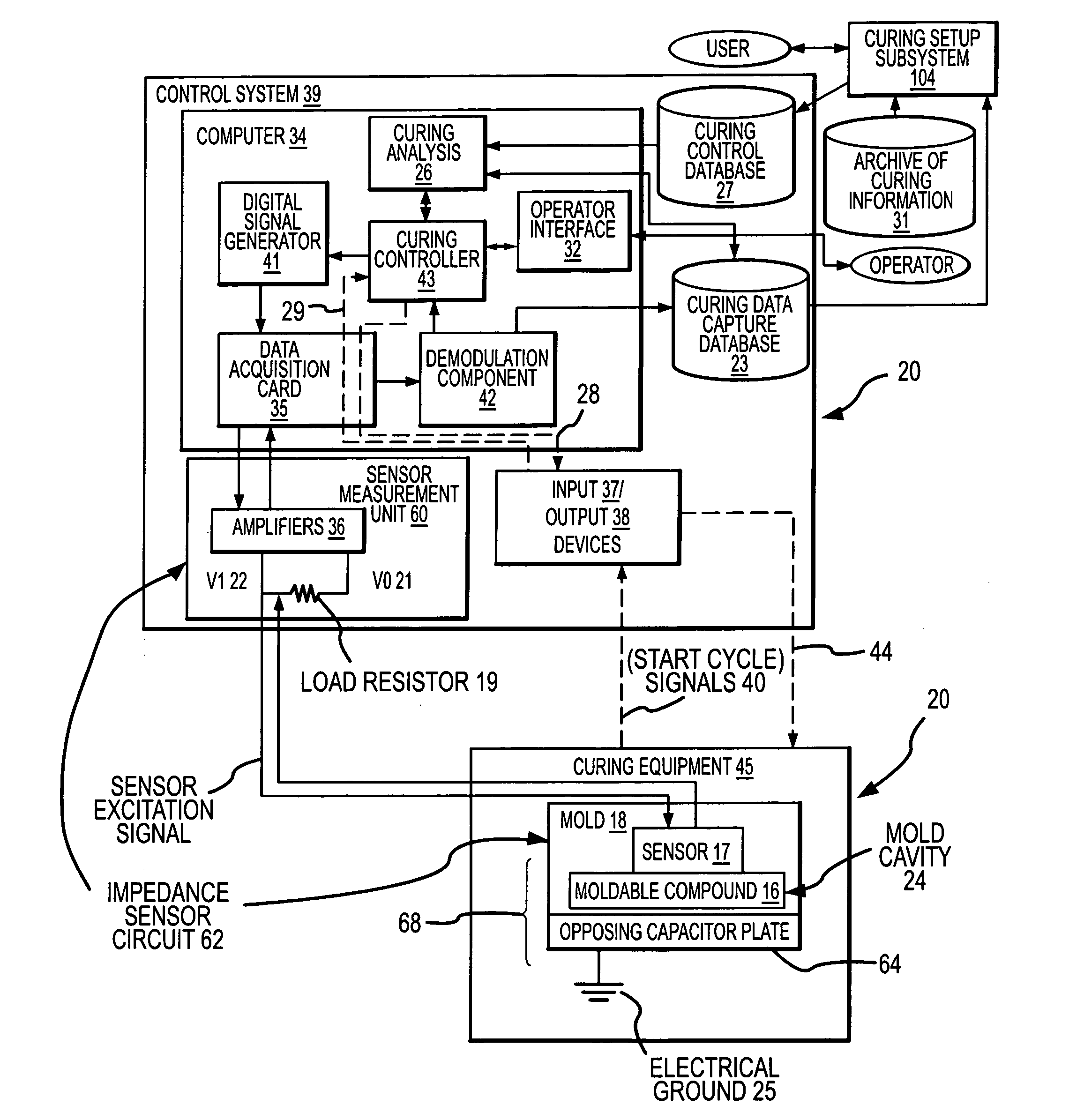
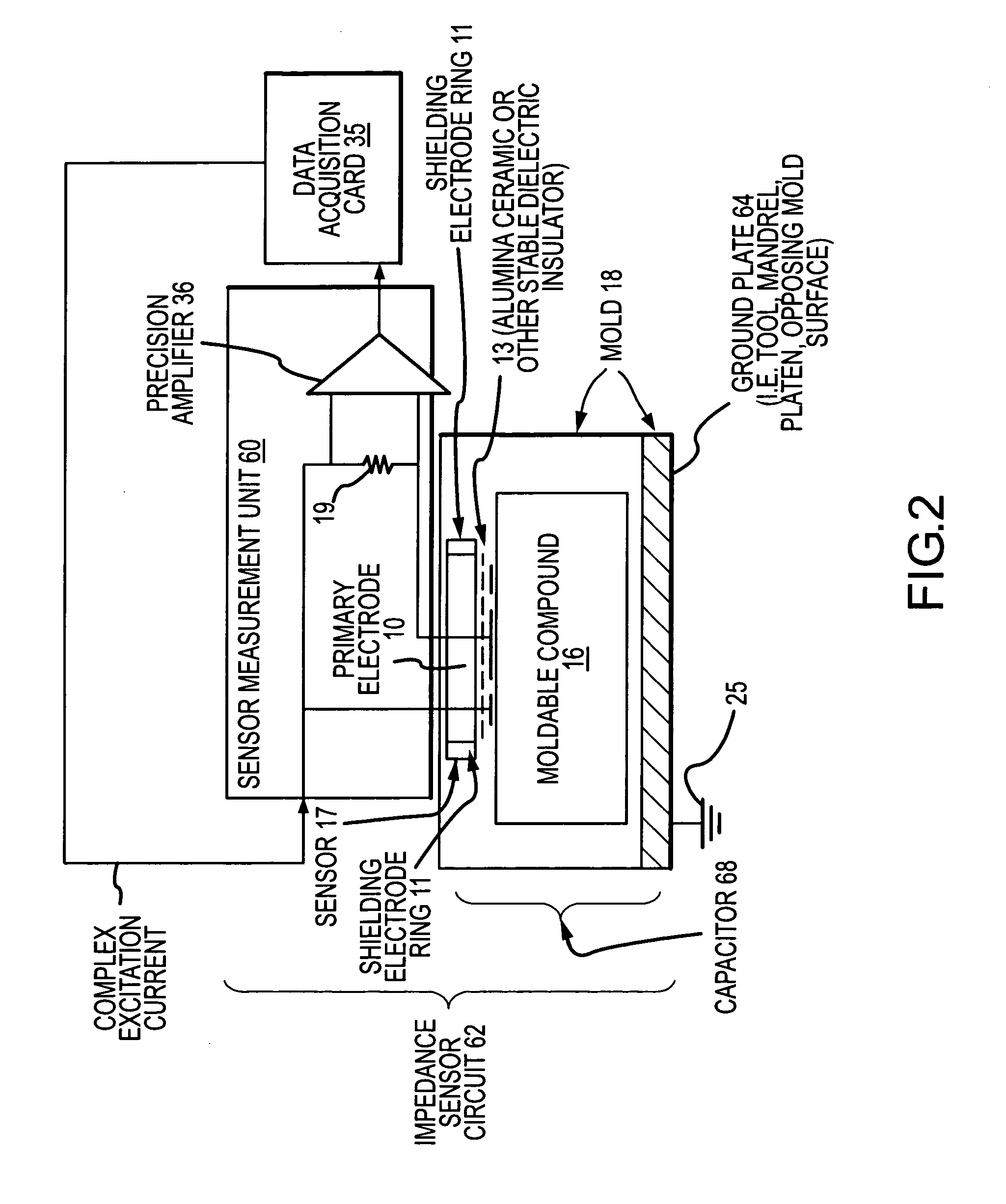
Process and apparatus for improving and controlling the curing of natural and synthetic moldable compounds
InactiveUS7167773B2Efficient changeAdd partsFlow propertiesVolume/mass flow measurementCompound aData stream
A process for curing a moldable compound under a plurality of curing conditions by: (1) obtaining time dependent data streams of dielectric or impedance values from a plurality of sensors distributed within a curing mold, wherein the moldable compound is a dialectric for each of the sensors; (2) determining impedance related measurements from the data streams for the plurality of sensors; (3) determining predictive and / or corrective curing actions for enhancing the curing process using the impedance related measurements for the plurality of sensors; and (4) controlling the mass production curing of parts to obtain cured parts having one or more desired properties.
Owner:SIGNATURE CONTROL ENG LLC
Computer-readable storage medium having object display order changing program stored therein and apparatus
ActiveUS20100017732A1Easily changeEasy to changeExecution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingDisplay Order
An icon line is displayed on a screen. A display order for the icon line can be changed by using switch input means enabling a direction input. When an input in a first direction is made, objects are scrolled so as to sequentially display each object at a specific position or the objects are scrolled across the specific position. When an input in the second direction is made, an object positioned at the specific position is saved at a saving position or an object positioned at the saving position is positioned at the specific position. Thus, a user is allowed to easily change the display order in which a plurality of objects are displayed on a screen.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Method and apparatus for dynamically selecting timer durations
ActiveUS7411901B1Increases transmission frequencyIncreases packet sizeError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemTimer
A data communication system dynamically selects timer durations to ensure delivery of data at a desired bit rate. A source or proxy source transmits data, such as streaming media, to a destination according to a dynamic bit rate timer, where the timer regulates the transmission frequency and / or the packet size of the data being transmitted. The timer dynamically adapts the transmission frequency or packet size according to the relative positioning of data pointers in a buffer and effectively changes the rate of data delivery. In this way, data may be delivered at the desired average bit rate to the destination despite network capacity fluctuations.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
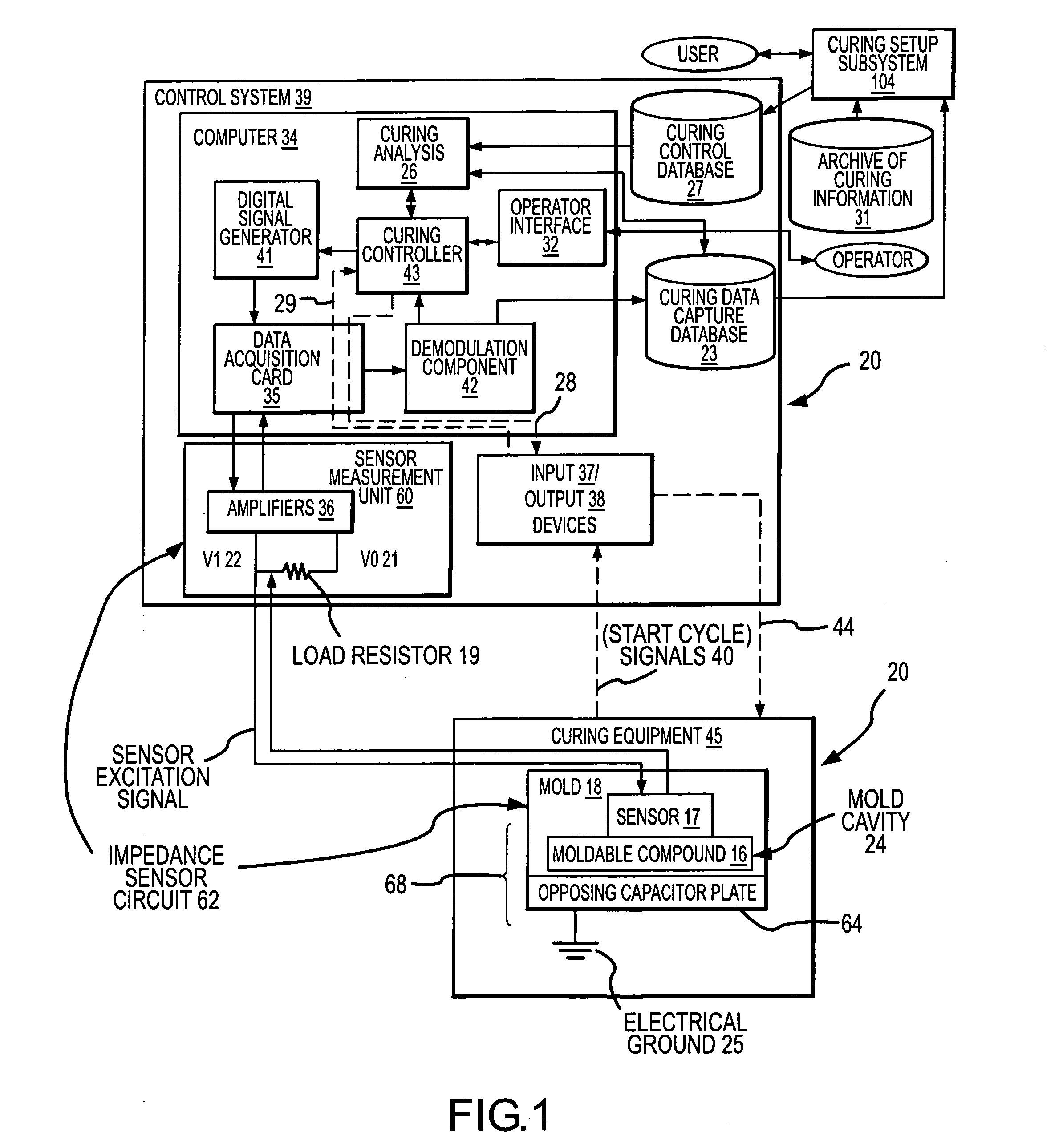
Process and apparatus for improving and controlling the curing of natural and synthetic moldable compounds
InactiveUS20050173820A1Robust and repeatableEfficient changeFlow propertiesVolume/mass flow measurementCompound aMedicine
A process for curing a moldable compound under a plurality of curing conditions by: (1) obtaining time dependent data streams of dielectric or impedance values from a plurality of sensors distributed within a curing mold, wherein the moldable compound is a dialectric for each of the sensors; (2) determining impedance related measurements from the data streams for the plurality of sensors; (3) determining predictive and / or corrective curing actions for enhancing the curing process using the impedance related measurements for the plurality of sensors; and (4) controlling the mass production curing of parts to obtain cured parts having one or more desired properties.
Owner:SIGNATURE CONTROL ENG LLC
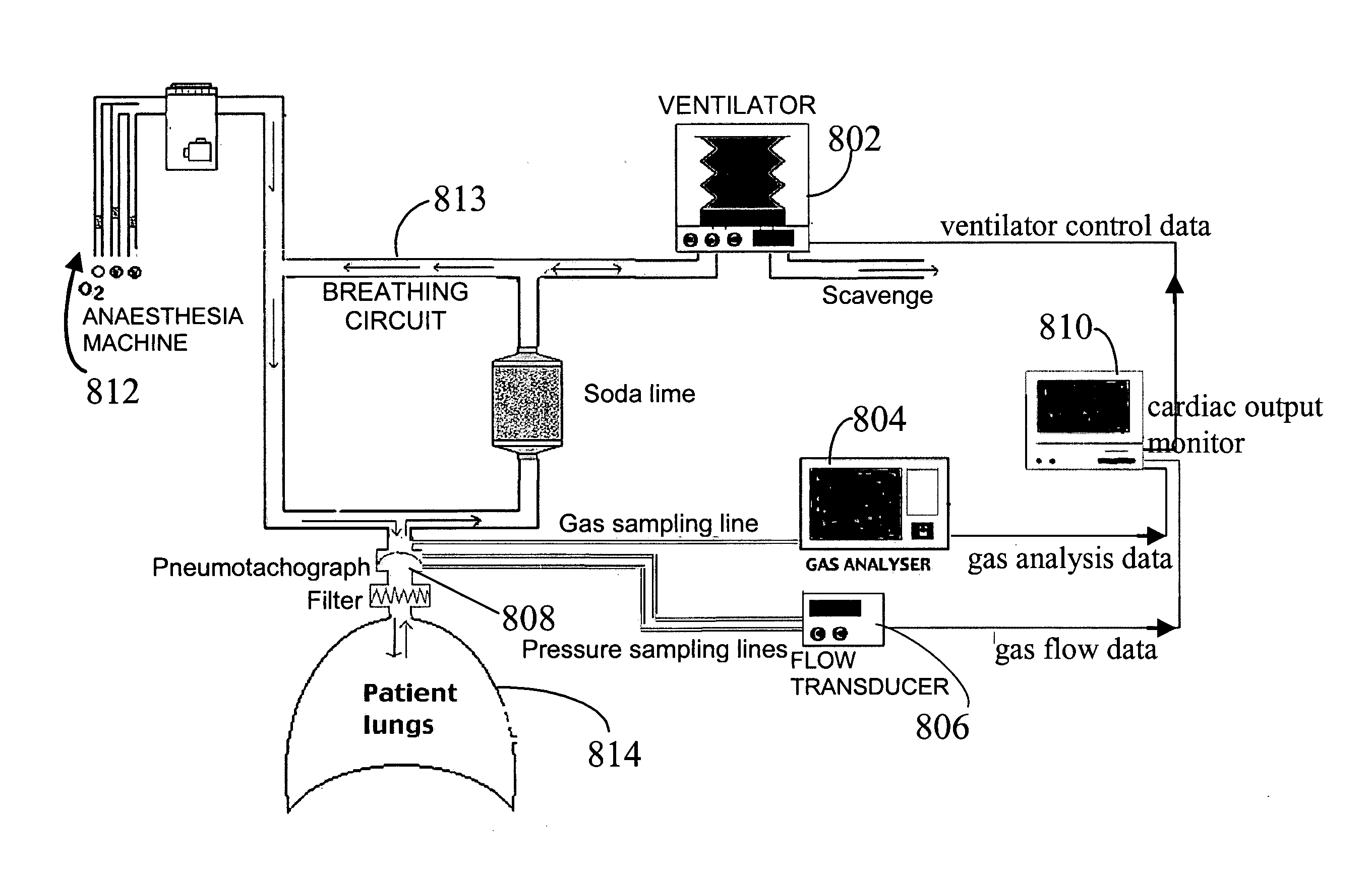
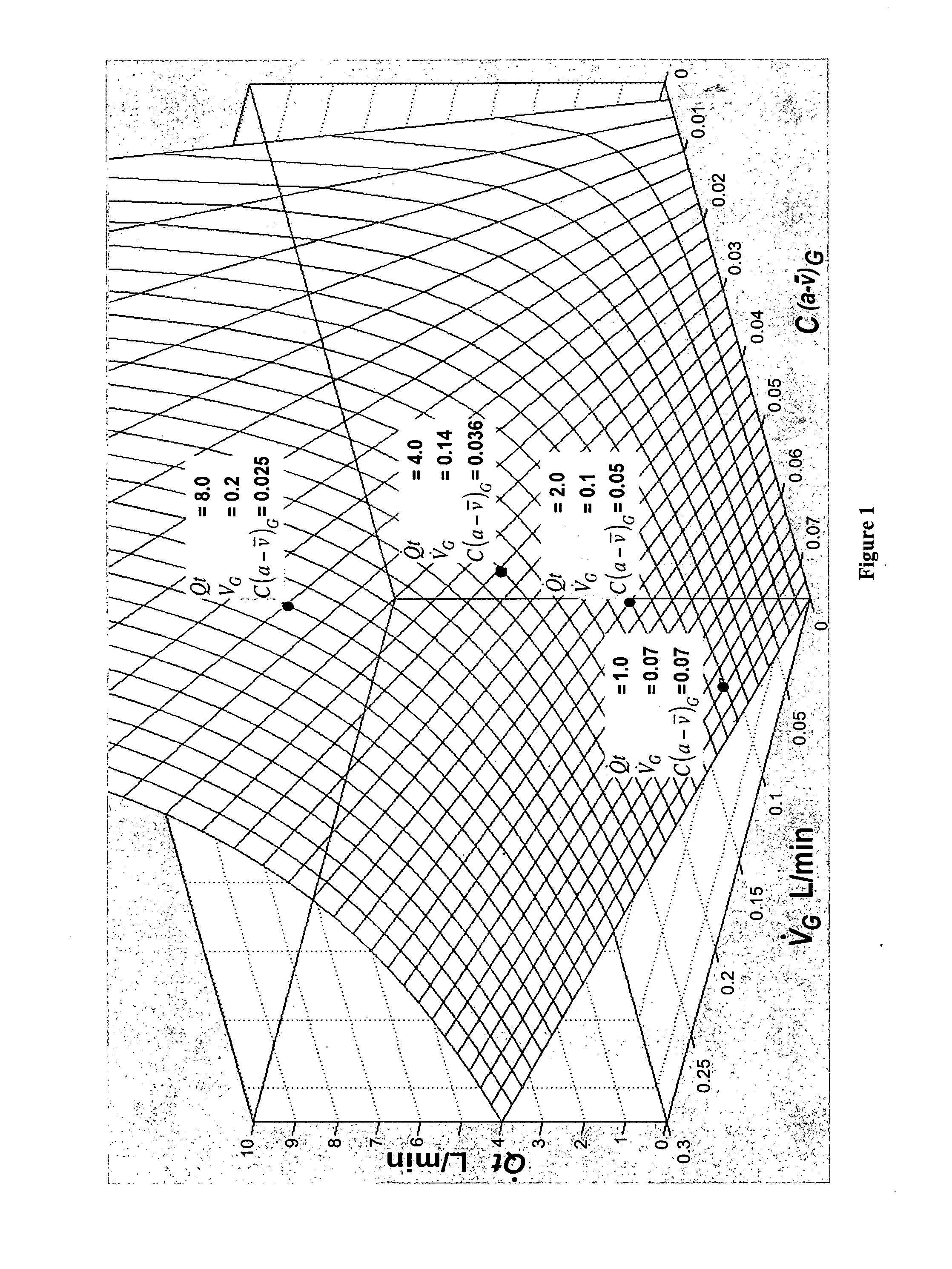
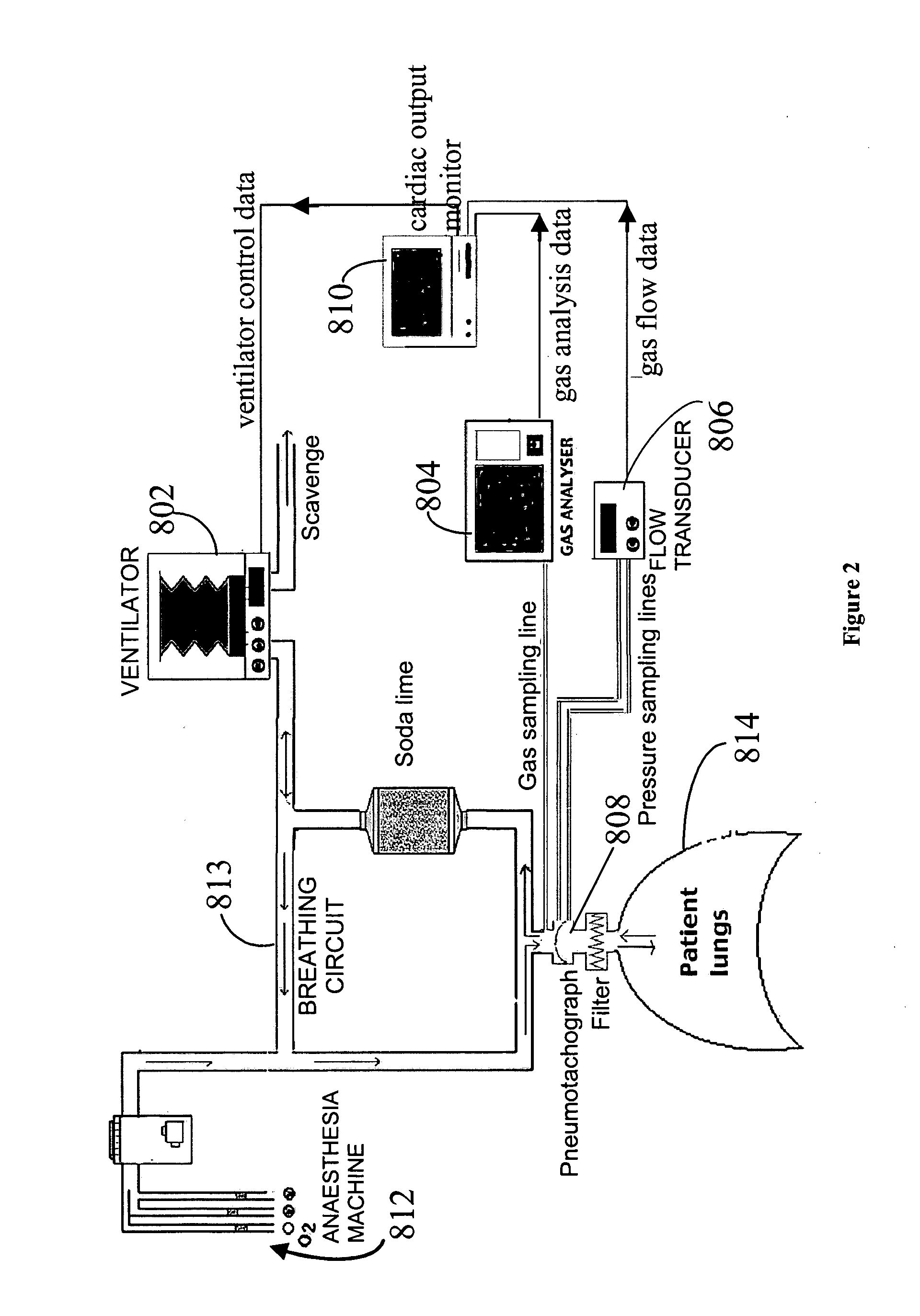
System and method for monitoring cardiac output
ActiveUS20110004108A1Accurately determineEfficient changeRespiratorsMedical devicesIntensive care medicinePulmonary blood flow
A method for monitoring cardiac output (pulmonary blood flow) of a subject, the method including: measuring a first net pulmonary uptake or elimination of a breathed gas species by the subject and a first partial pressure of the gas species at a first time, and at a second time later than the first time, determining a first pulmonary blood flow of the patient at the first time, and determining a pulmonary blood flow of the subject at the second time on the basis of the first pulmonary blood flow, the first net pulmonary uptake or elimination, the second net pulmonary uptake or elimination, the first partial pressure, and the second partial pressure.
Owner:AUSTIN HEALTH
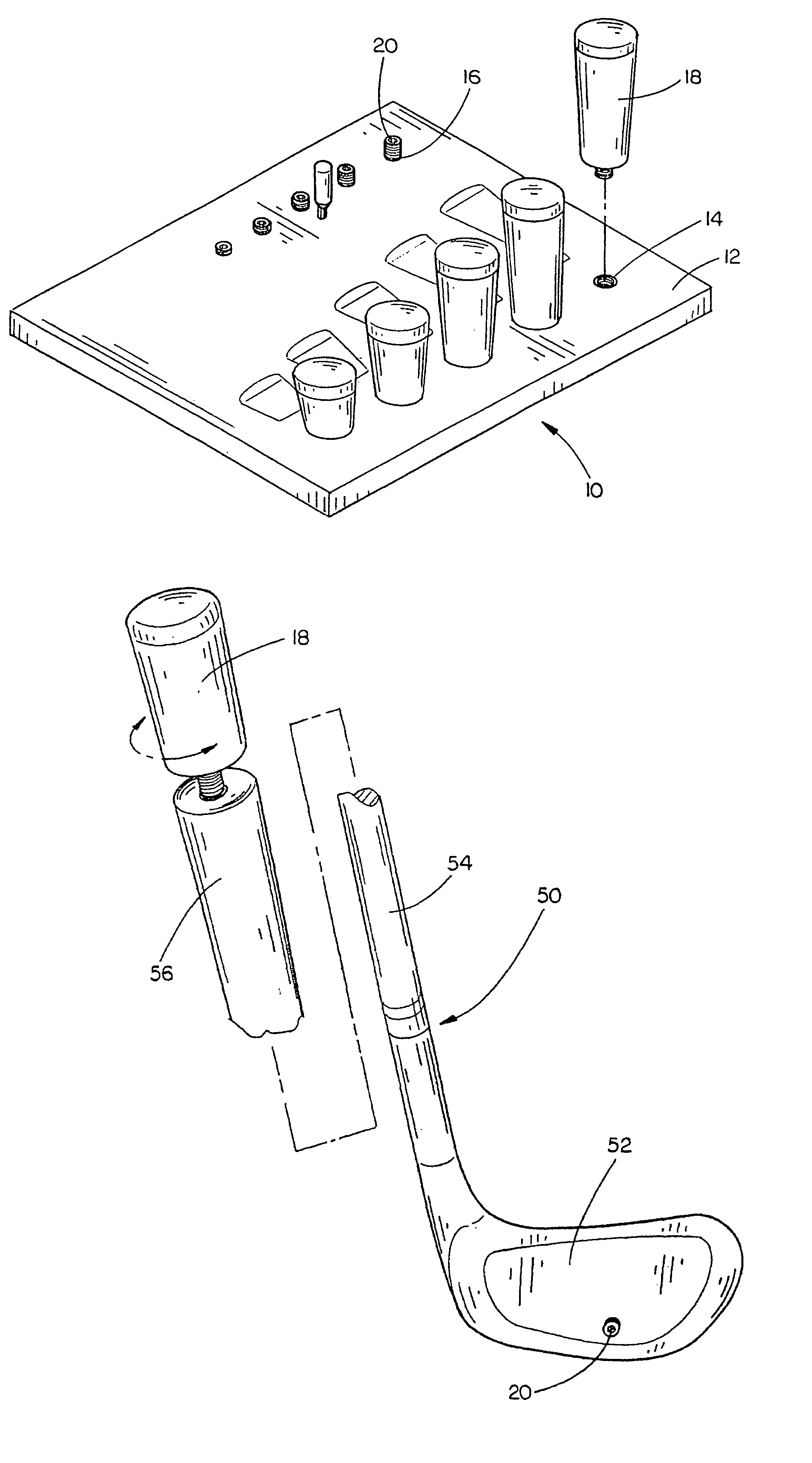
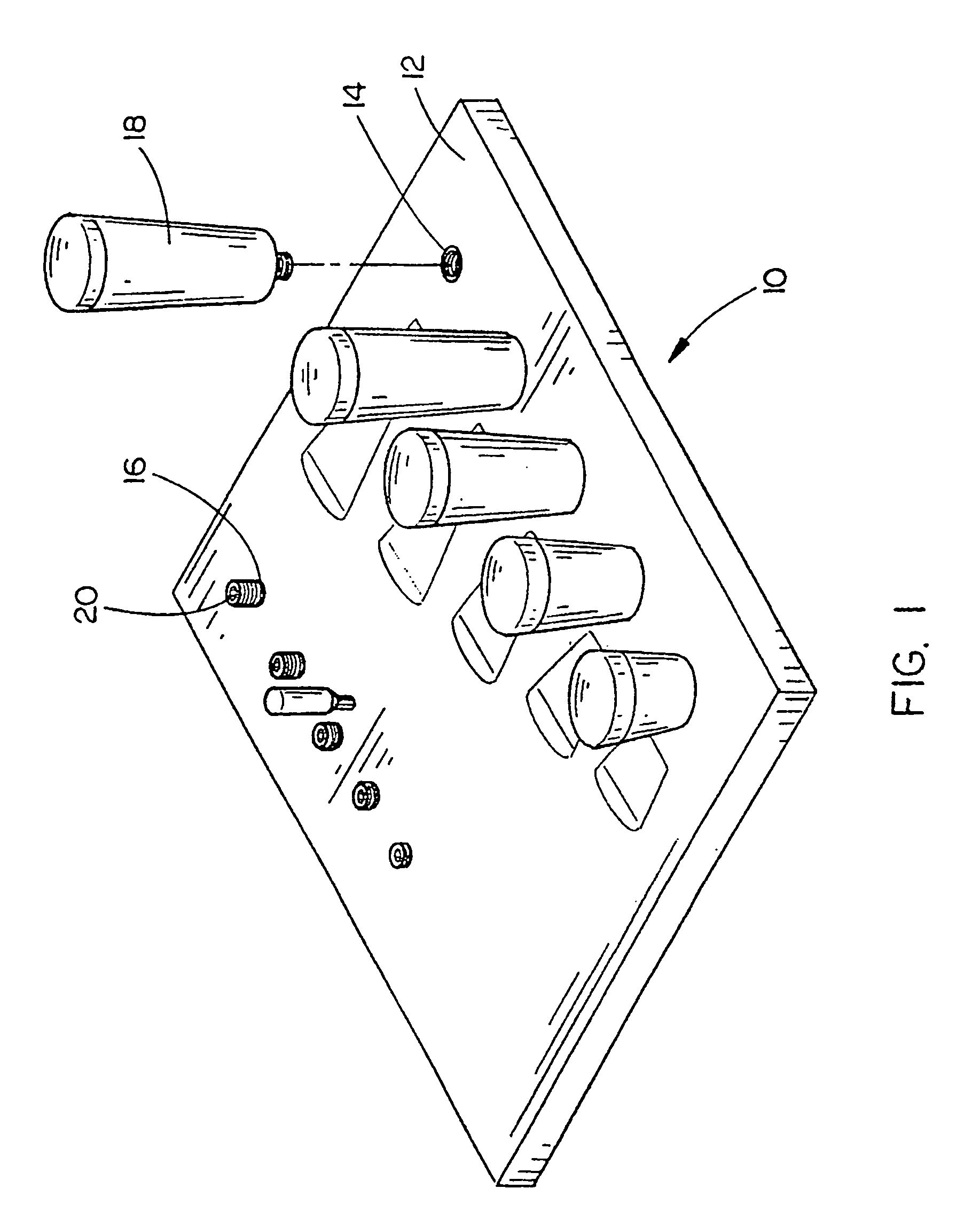
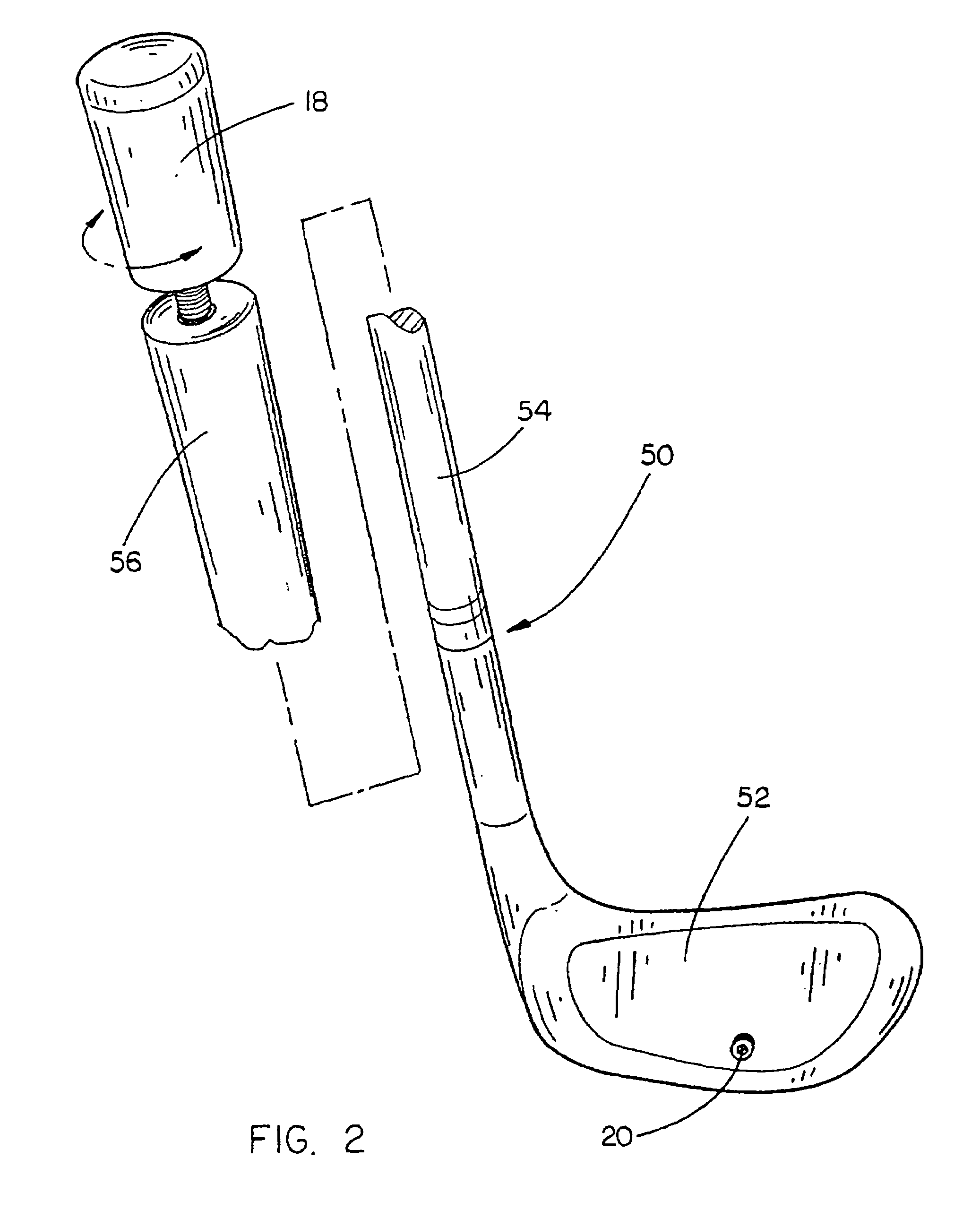
Golf club fitting system
An improved golf club fitting system for fitting a set of golf clubs to a player includes the steps of measuring a player's hand grip strength and selecting a representative golf club having a dead weight directly proportional to the player's grip strength. The club length and the swing weight of the representative golf club are then determined by standard testing procedures commonly used in the golf club industry. A balance index (BI) for the representative golf club is then computed by dividing the dead weight (DW) by the swing weight (SW) (DW / SW=BI) and the balance index (BI) is compared to the dead weight to determine generally corresponding values for the remaining other golf clubs in the set such that the system user can match different irons and woods to the representative golf club thereby creating an ideal matched set of golf clubs for the player.
Owner:PRO FIT PERFORMANCE CLUB FITTING L L C
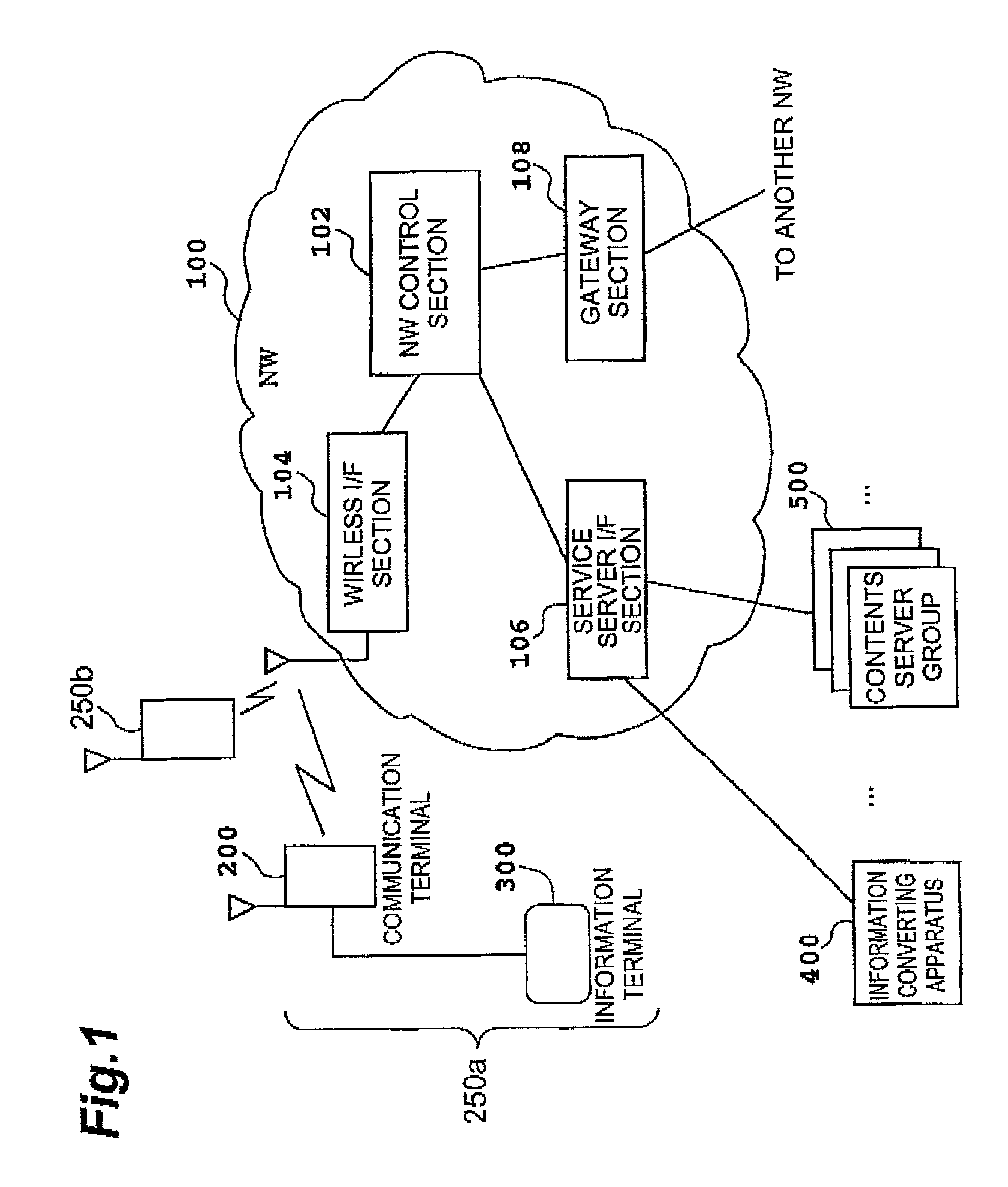
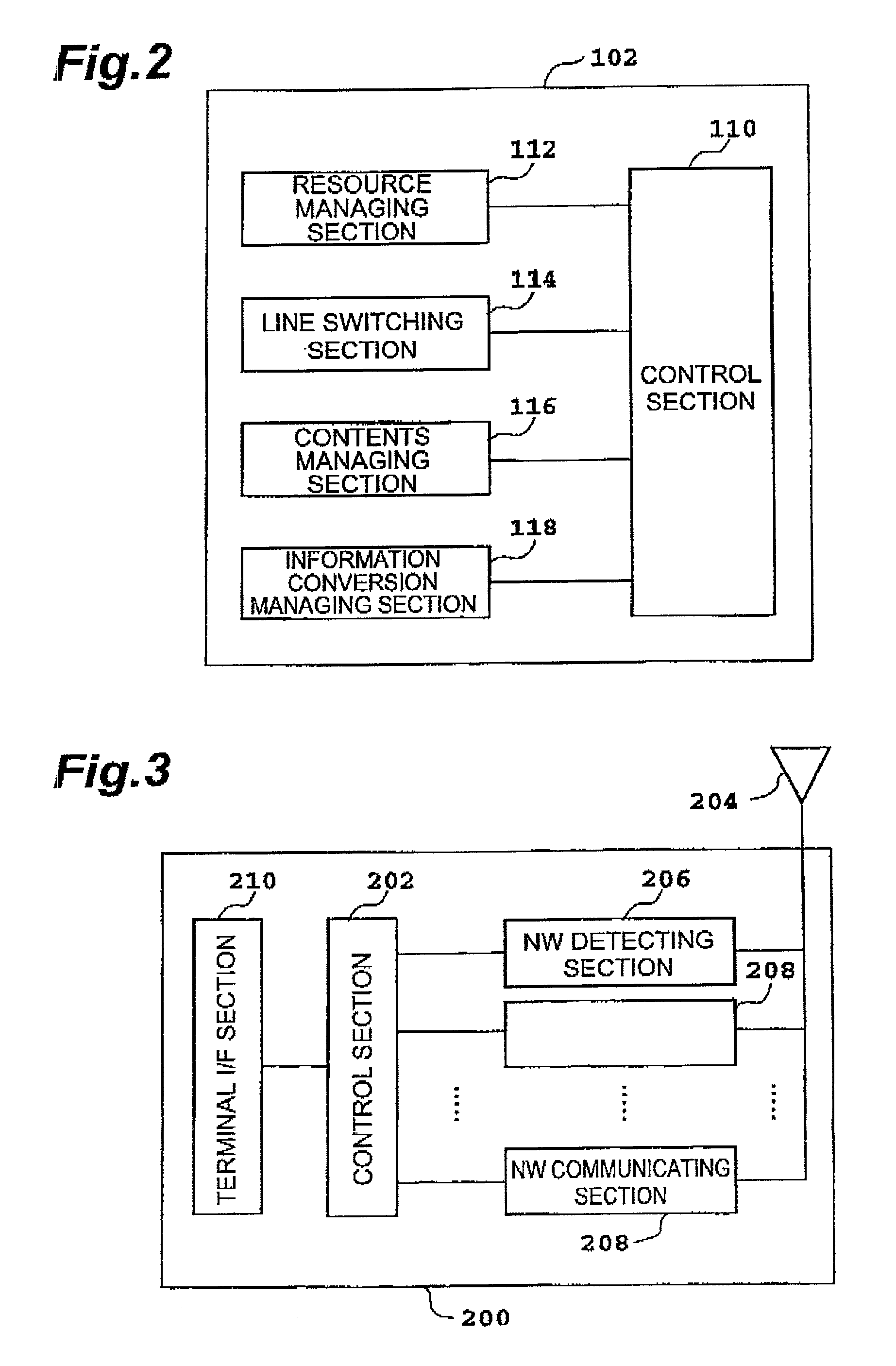
Mobile communication system, resource switching method thereof, network control apparatus included therein, same and network control method
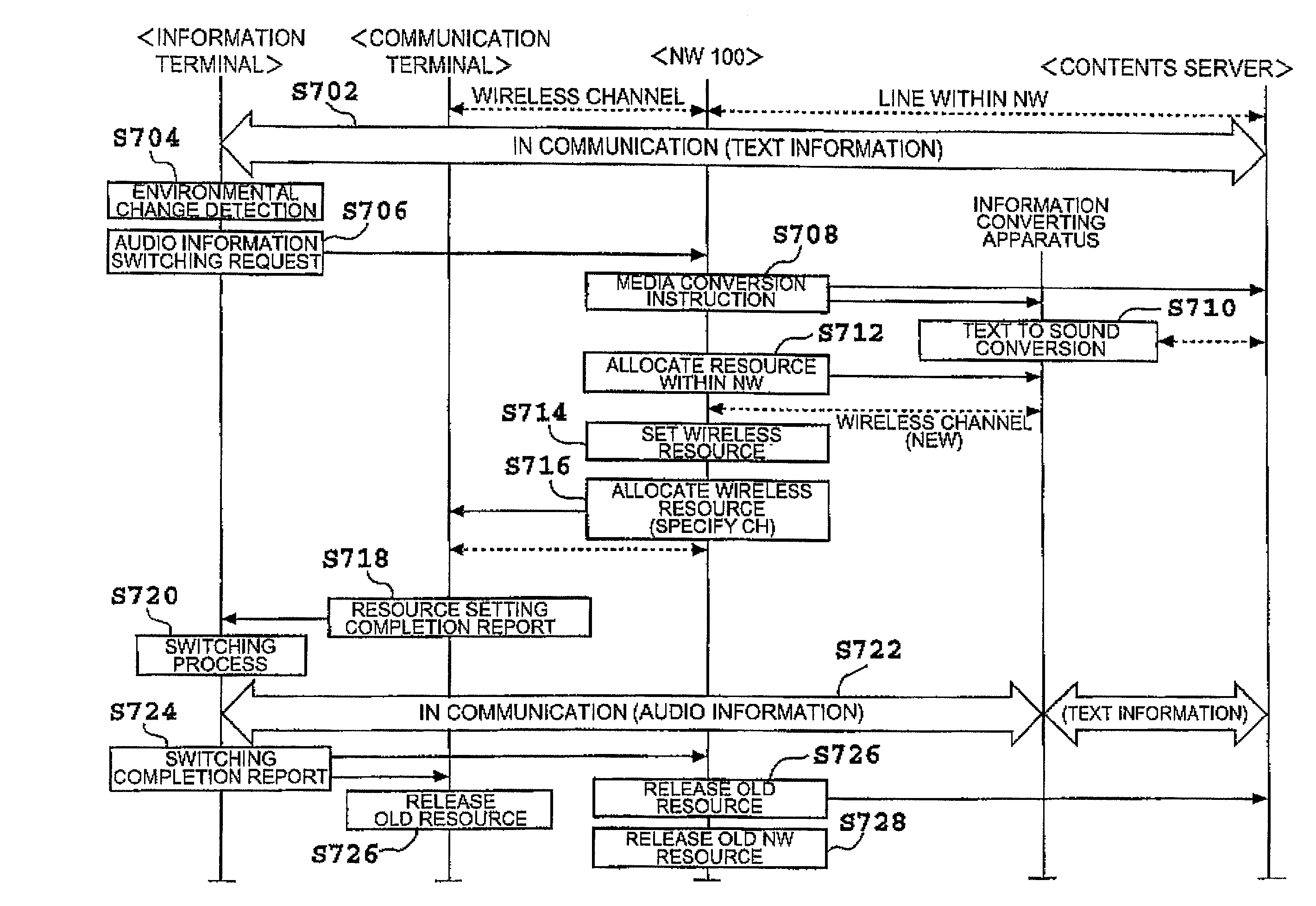
InactiveUS7142847B2Efficiently detects changeEliminate seamsInformation formatSpecial service for subscribersNetwork controlMobile communication systems
The present invention relates to a mobile communication system comprising a structure for realizing “network seamless” for roaming between different kinds of networks, “contents seamless” for converting different kinds of encoding or media therebetween, and “device seamless” for making it possible to utilize optimum I / O devices in conformity to surrounding environments. This mobile communication system detects a change in an environment in use concerning an object such as a mobile terminal, for example, notifies at least one apparatus relating to the change of the result of detection, sets various resources constituting a network in conformity to a new environment, and switches them. This makes it possible to construct a seamless network which automatically eliminates seams (restrictions) concerning changes in the environment and the like.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com