Patents
Literature
55508 results about "Turbine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
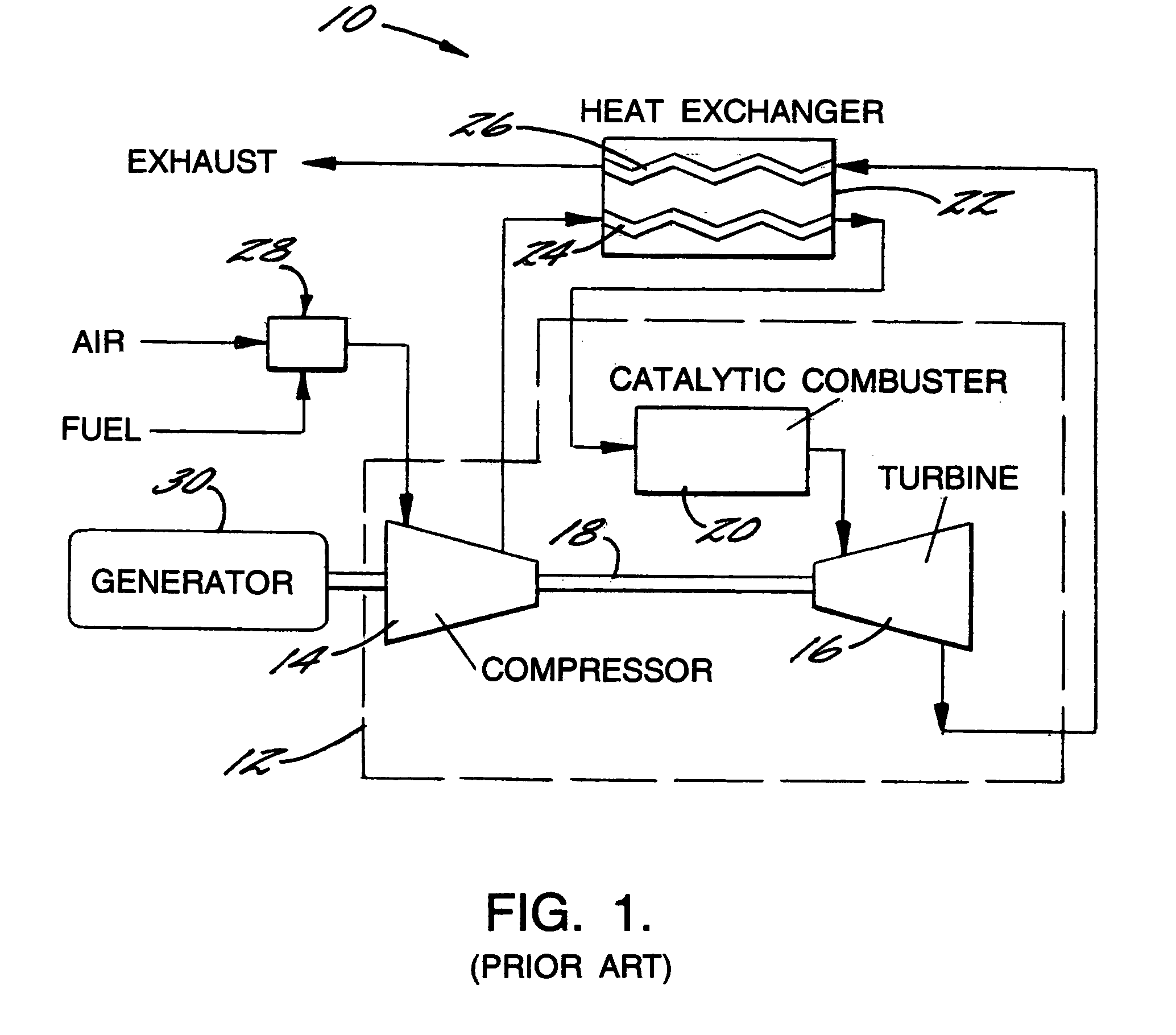
A turbine (from the Latin turbo, a vortex, related to the Greek τύρβη, tyrbē, meaning "turbulence") is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels.
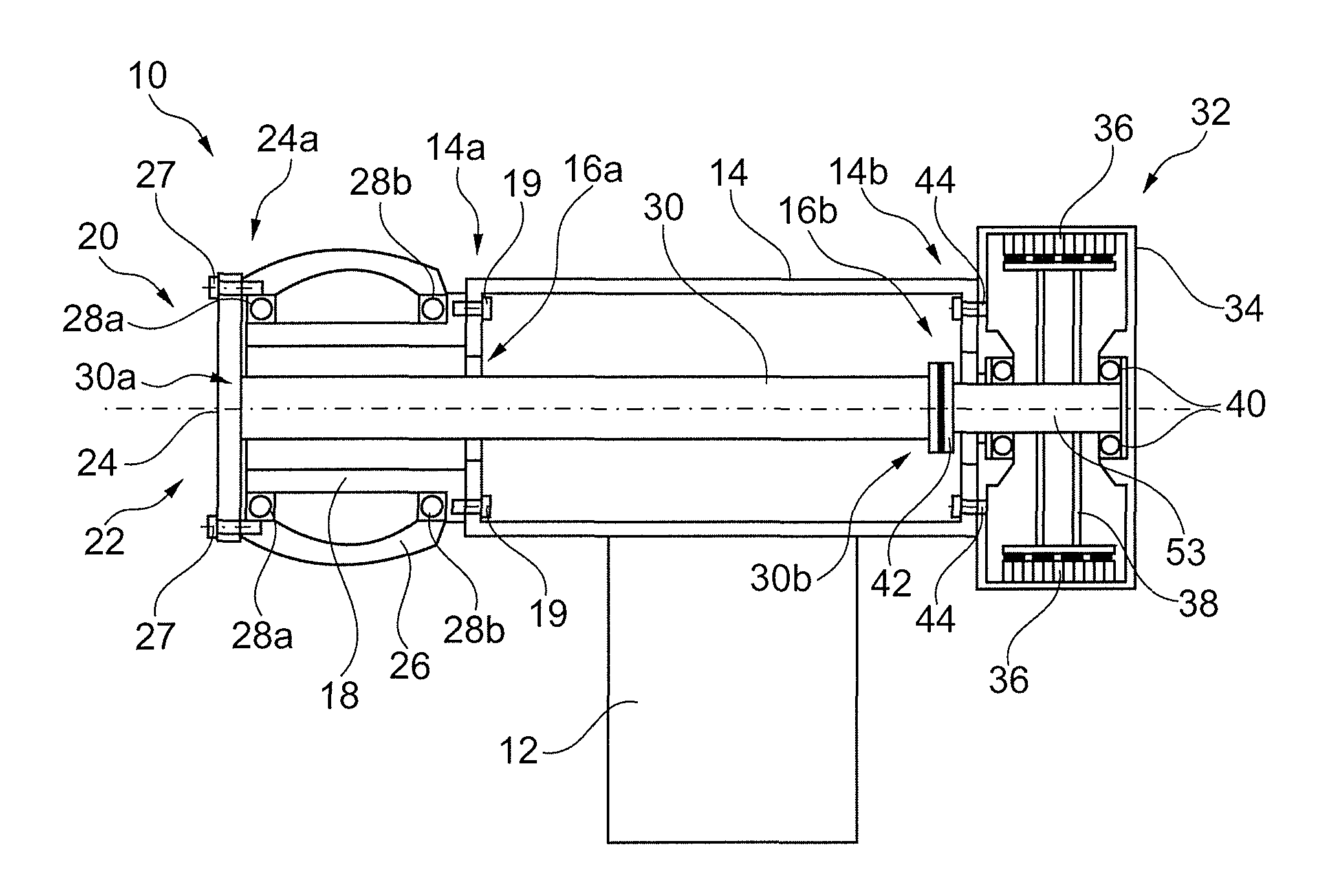
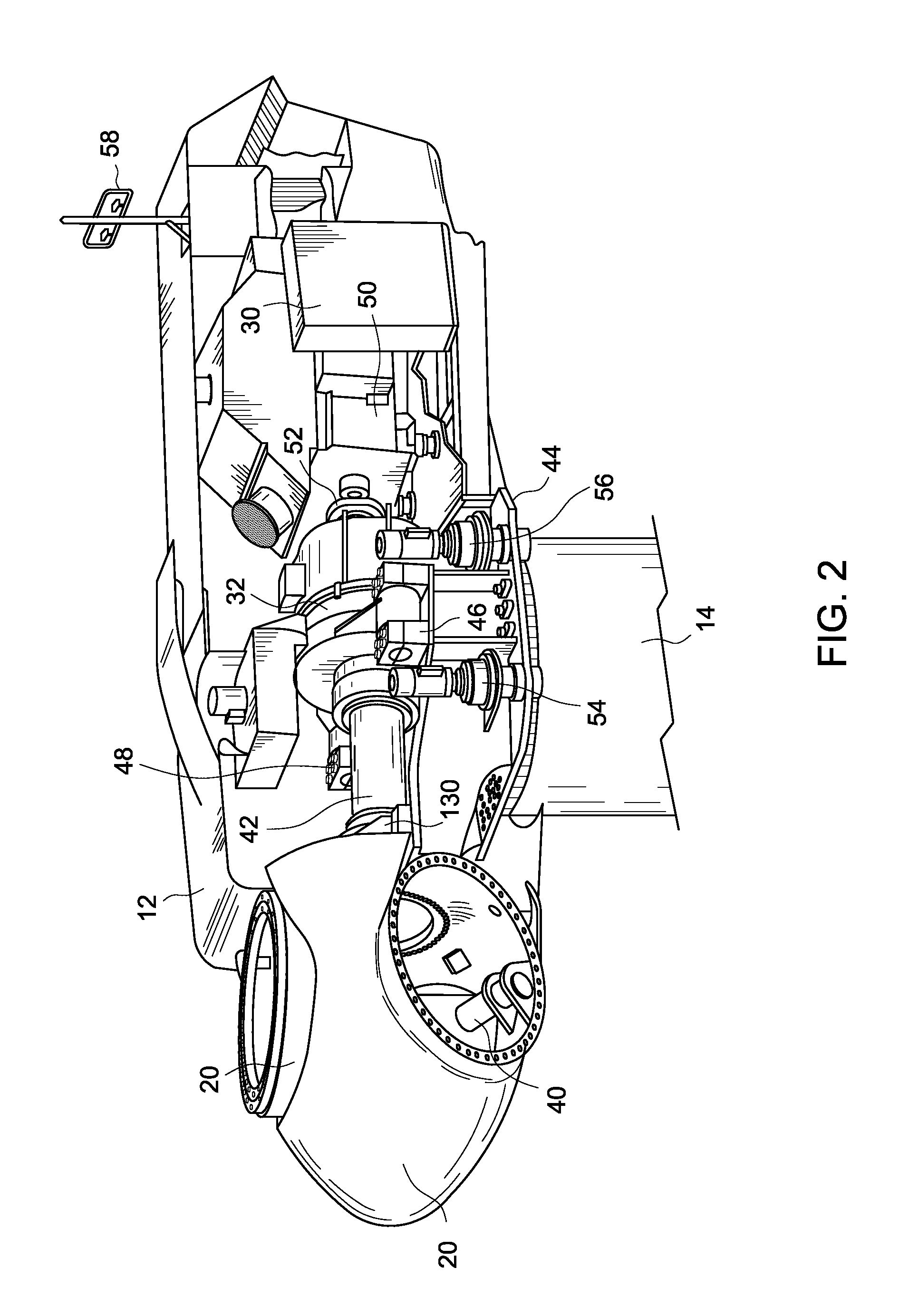
Wind turbine and a shaft for a wind turbine
InactiveUS8664792B2Little strengthImproves buckling stabilityEngine fuctionsFinal product manufactureDrive shaftTurbine
A drive shaft for a wind turbine is shaped so as to allow for increased bending of the shaft, while being suitable for transferring torque in a wind turbine system. An example of such a shaping is a drive shaft having a helical rib defined on the surface of the shaft. A wind turbine incorporating such a shaft, and a method of manufacture of such a shaft are also described.
Owner:ENVISION ENERGY DENMARK
Actively controlled rotary steerable system and method for drilling wells
InactiveUS6092610AEfficient rotary speedPromote productionDrilling rodsConstructionsAccelerometerDirectional drilling
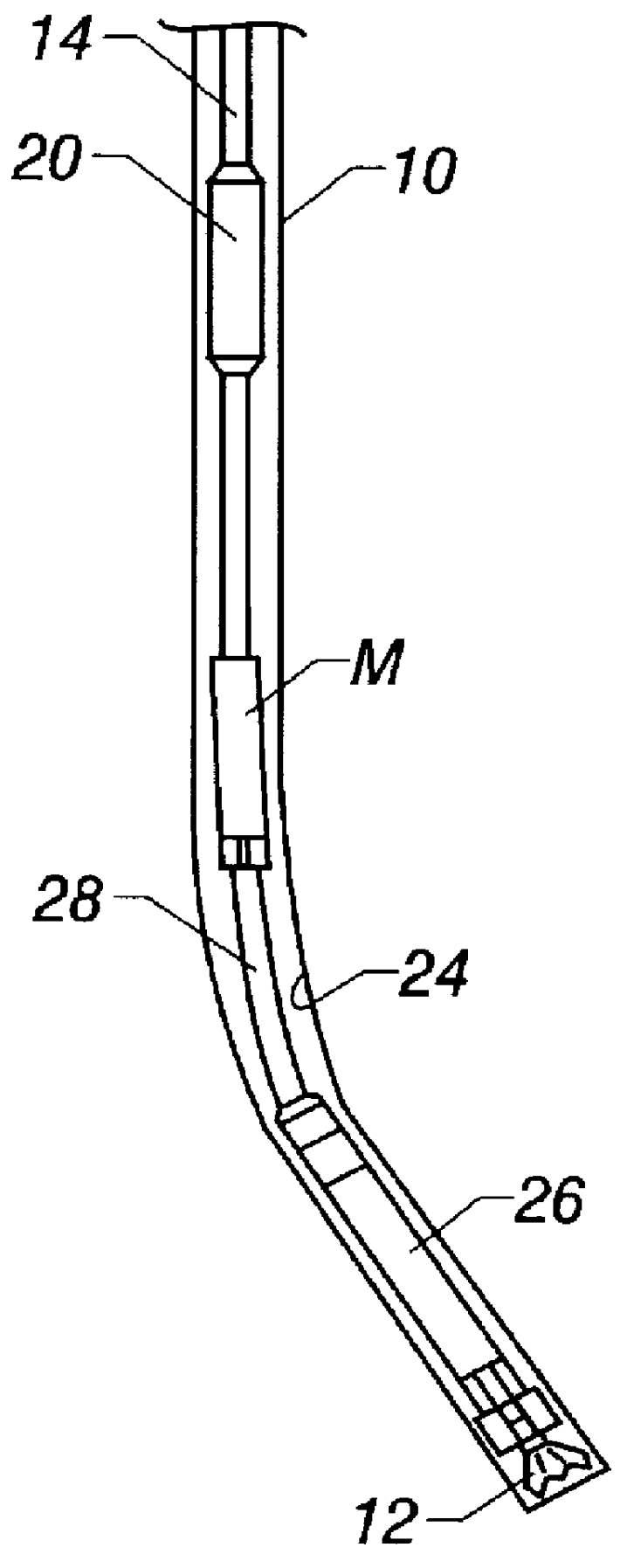
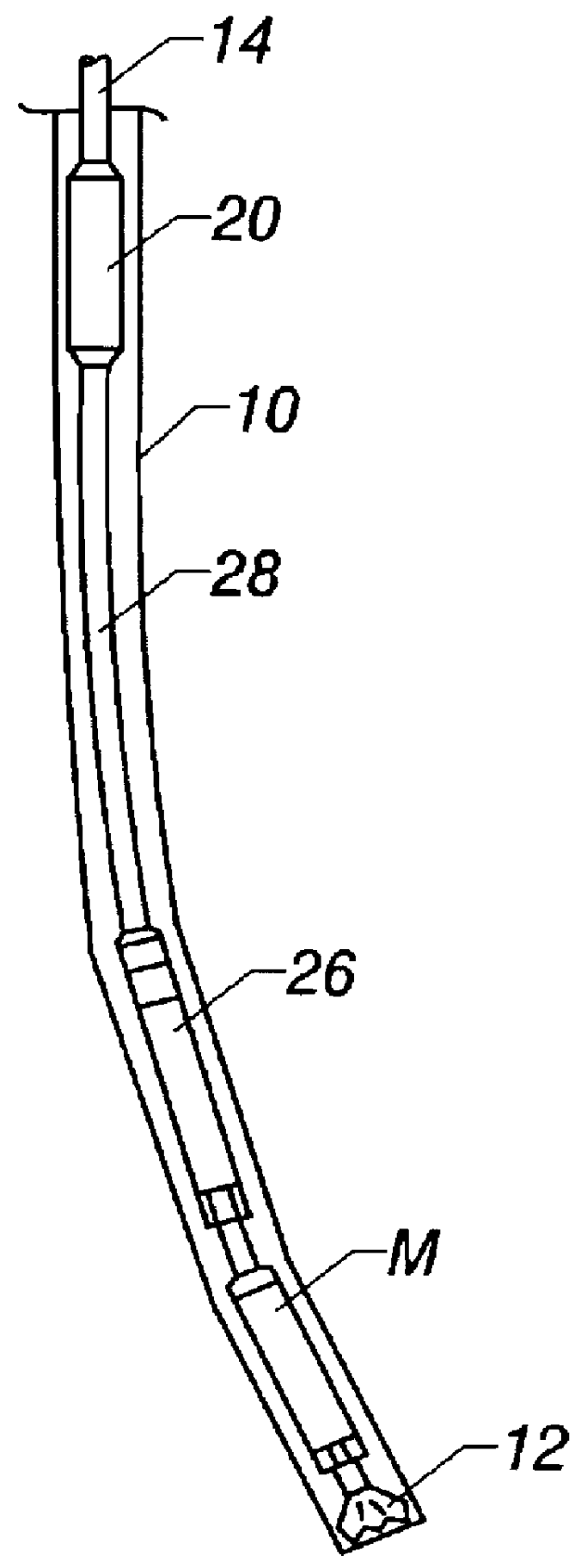
An actively controlled rotary steerable drilling system for directional drilling of wells having a tool collar rotated by a drill string during well drilling. A bit shaft has an upper portion within the tool collar and a lower end extending from the collar and supporting a drill bit. The bit shaft is omni-directionally pivotally supported intermediate its upper and lower ends by a universal joint within the collar and is rotatably driven by the collar. To achieve controlled steering of the rotating drill bit, orientation of the bit shaft relative to the tool collar is sensed and the bit shaft is maintained geostationary and selectively axially inclined relative to the tool collar during drill string rotation by rotating it about the universal joint by an offsetting mandrel that is rotated counter to collar rotation and at the same frequency of rotation. An electric motor provides rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and is servo-controlled by signal input from position sensing elements such as magnetometers, gyroscopic sensors, and accelerometers which provide real time position signals to the motor control. In addition, when necessary, a brake is used to maintain the offsetting mandrel and the bit shaft axis geostationary. Alternatively, a turbine is connected to the offsetting mandrel to provide rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and a brake is used to servo-control the turbine by signal input from position sensors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Combined steam and gas turbine engine with magnetic transmission
InactiveUS6263664B1Wide areaImprove system efficiencyContinuous combustion chamberGearingThermal energyCombustion chamber
In a combined steam and gas turbine engine cycle, a combustion chamber is made durable against high pressure and enlarged in length to increase the operation pressure ratio, without exceeding the heat durability temperature of the system while increasing the fuel combustion gas mass flow four times as much as the conventional turbine system and simultaneously for greatly raising the thermal efficiency of the system and specific power of the combined steam and gas turbine engine.Water pipes and steam pipes are arranged inside the combustion chamber so that the combustion chamber can function as a heat exchanger and thereby convert most of the combustion thermal energy into super-critical steam energy for driving a steam turbine and subsequently raising the operation pressure ratio and the thermal efficiencies of the steam turbine cycle and gas turbine cycle. The combustion gas mass flow can be also increased by four times as much as the conventional turbine system (up to the theoretical air to fuel ratio) and the thermal efficiency and the specific power of the gas turbine cycle are considerably increased.Further, the thermal efficiency of the combined system is improved by installing a magnetic friction power transmission system to transmit the power of the system to outer loads.
Owner:TANIGAWA HIROYASU +1
Systems and methods for additive manufacturing and repair of metal components
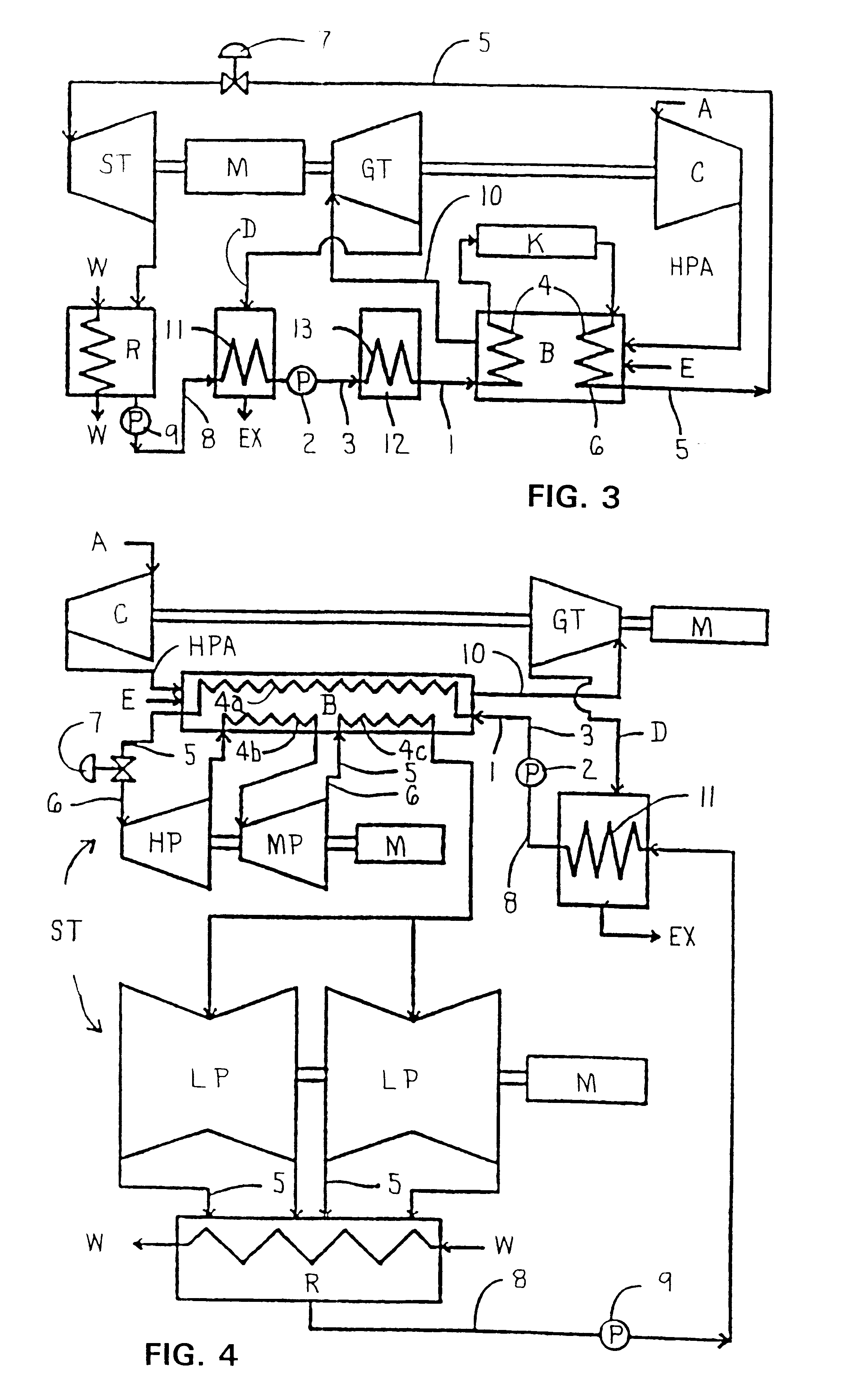
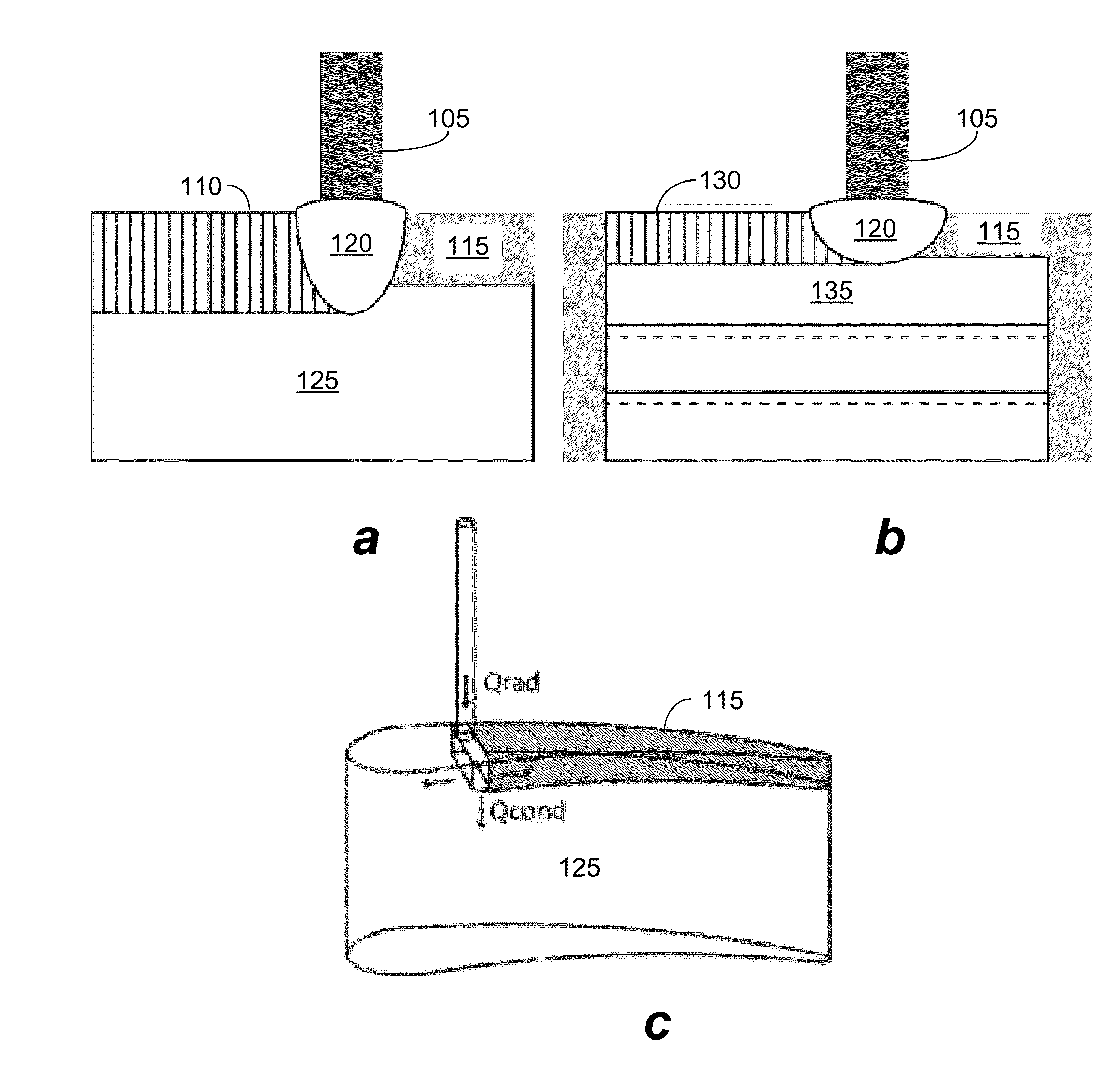
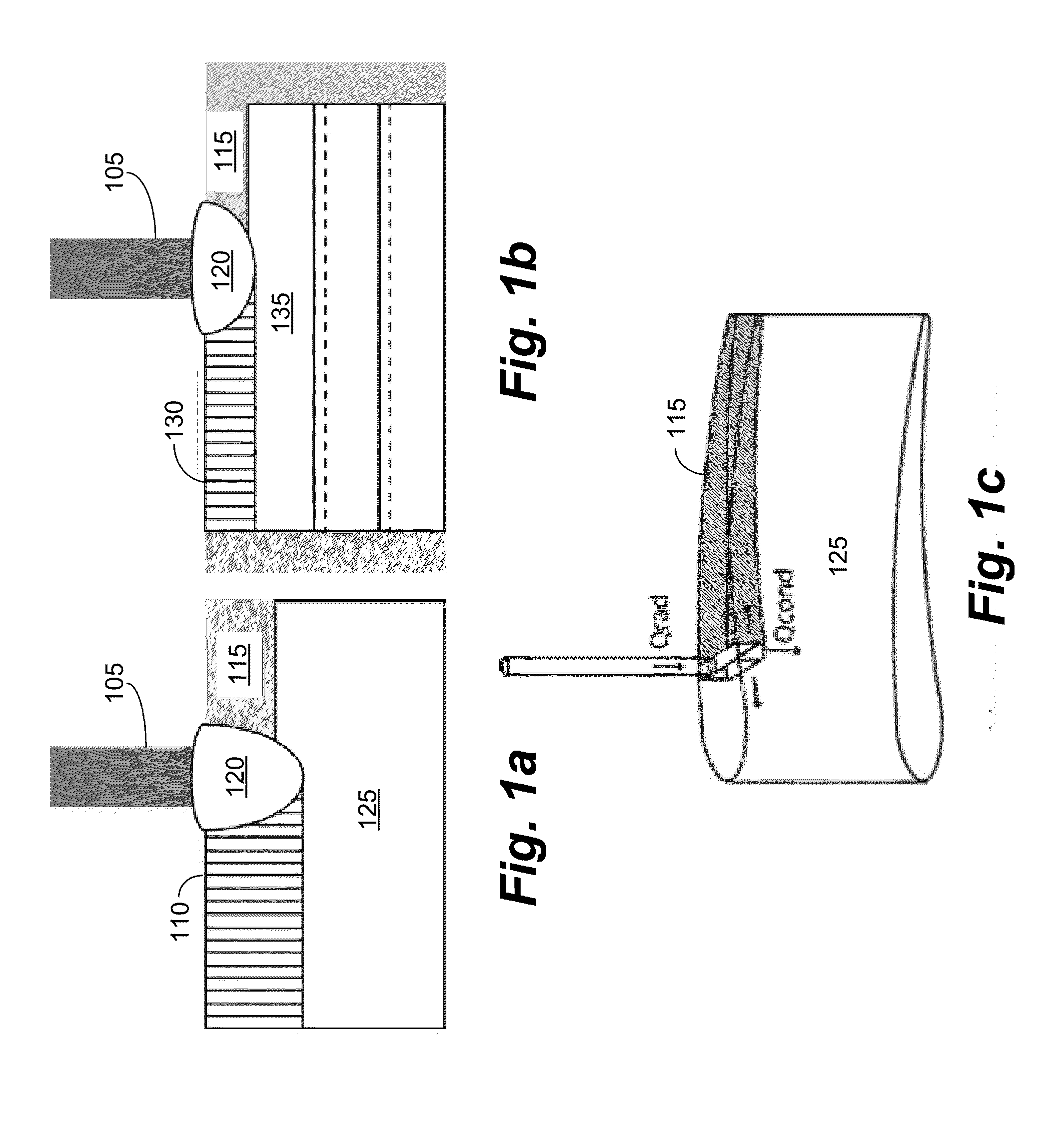
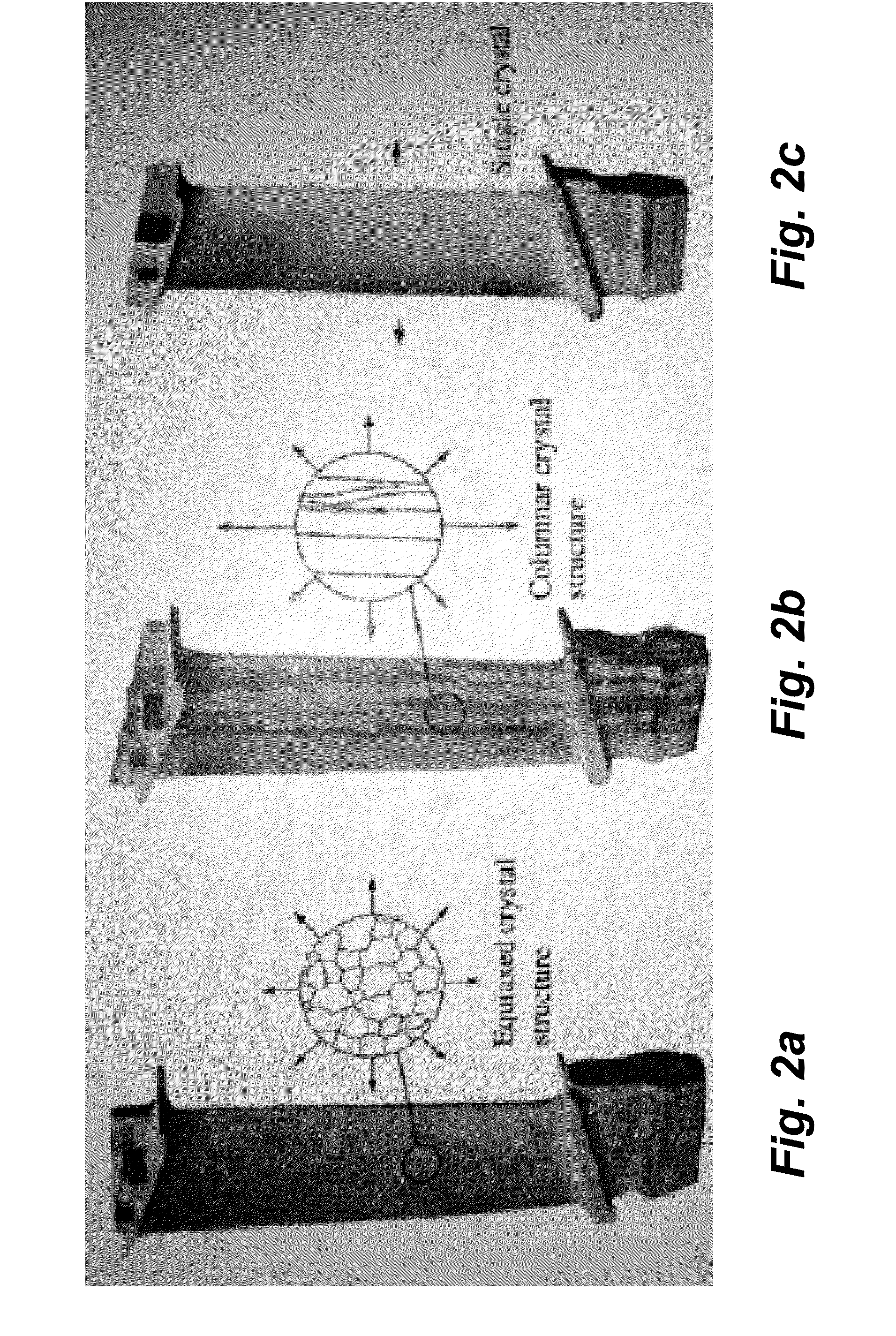
Scanning Laser Epitaxy (SLE) is a layer-by-layer additive manufacturing process that allows for the fabrication of three-dimensional objects with specified microstructure through the controlled melting and re-solidification of a metal powders placed atop a base substrate. SLE can be used to repair single crystal (SX) turbine airfoils, for example, as well as the manufacture functionally graded turbine components. The SLE process is capable of creating equiaxed, directionally solidified, and SX structures. Real-time feedback control schemes based upon an offline model can be used both to create specified defect free microstructures and to improve the repeatability of the process. Control schemes can be used based upon temperature data feedback provided at high frame rate by a thermal imaging camera as well as a melt-pool viewing video microscope. A real-time control scheme can deliver the capability of creating engine ready net shape turbine components from raw powder material.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Aircraft with disengageable engine and auxiliary power unit components
InactiveUS20060260323A1Avoid damageSufficient torqueEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsFlight vehicleGround testing
Several improvements to an aircraft turbine engine and Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) are disclosed, as well as methods of using these improvements in routine and emergency aircraft operations. The improvements comprise the addition of cockpit-controllable clutches that can be used to independently disconnect the engine's integrated drive generator (IDG), engine driven pump (EDP), fuel pump, and oil pump from the engine gearbox. These engine components may then be connected to air turbines by the use of additional clutches and then powered by the turbines. Similar arrangements are provided for the APU components. Cranking pads, attached to various engine and APU components, are disclosed to provide a means for externally powering the components for testing purposes and to assist with engine and APU start. Detailed methods are disclosed to use the new components for routine ground-testing and maintenance and for the enhancement of flight safety, minimization of engine component damage, and extension of engine-out flying range in the case of an emergency in-flight engine shutdown.
Owner:MOULEBHAR DJAMAL
Film cooling hole for turbine airfoil
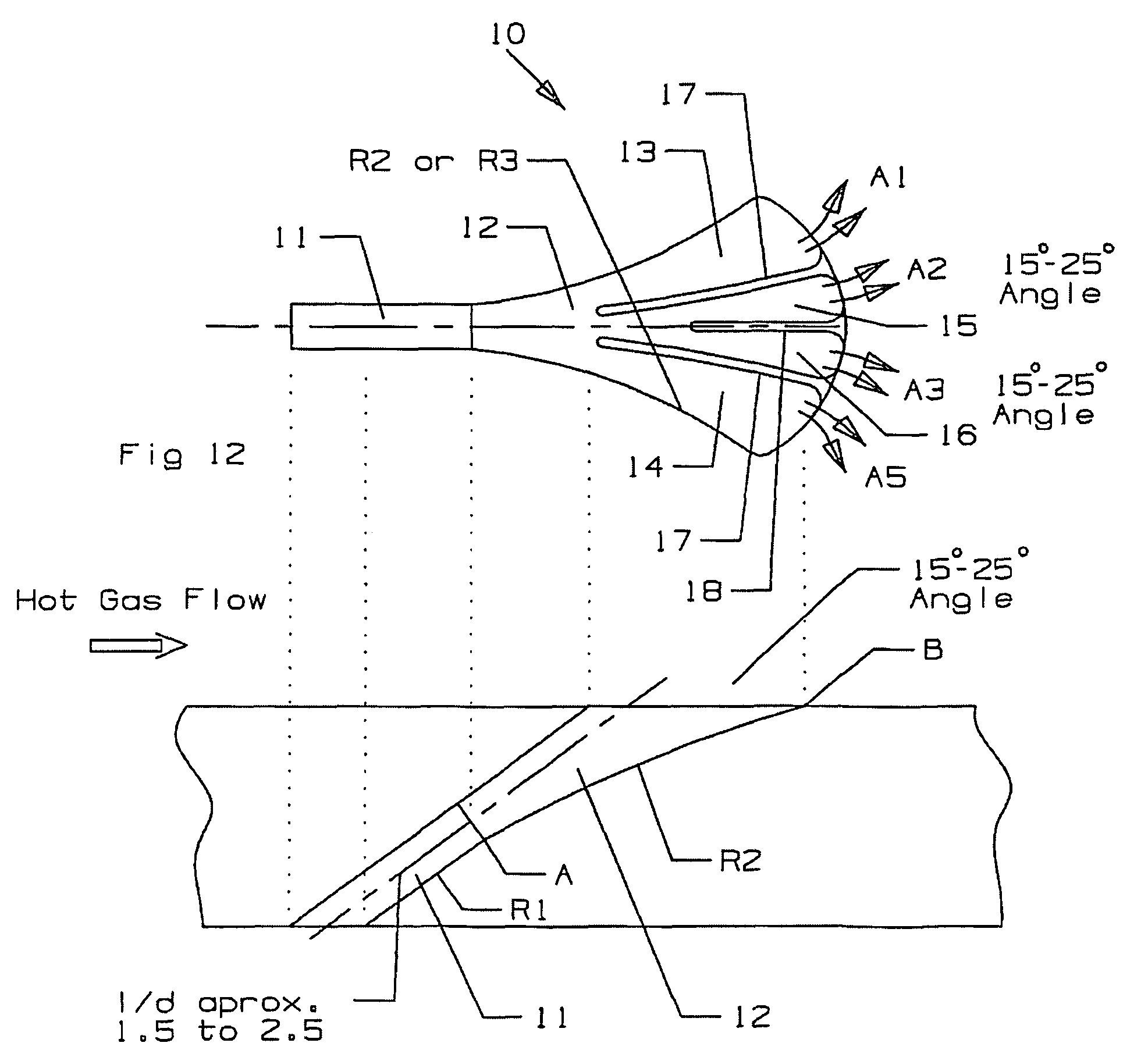
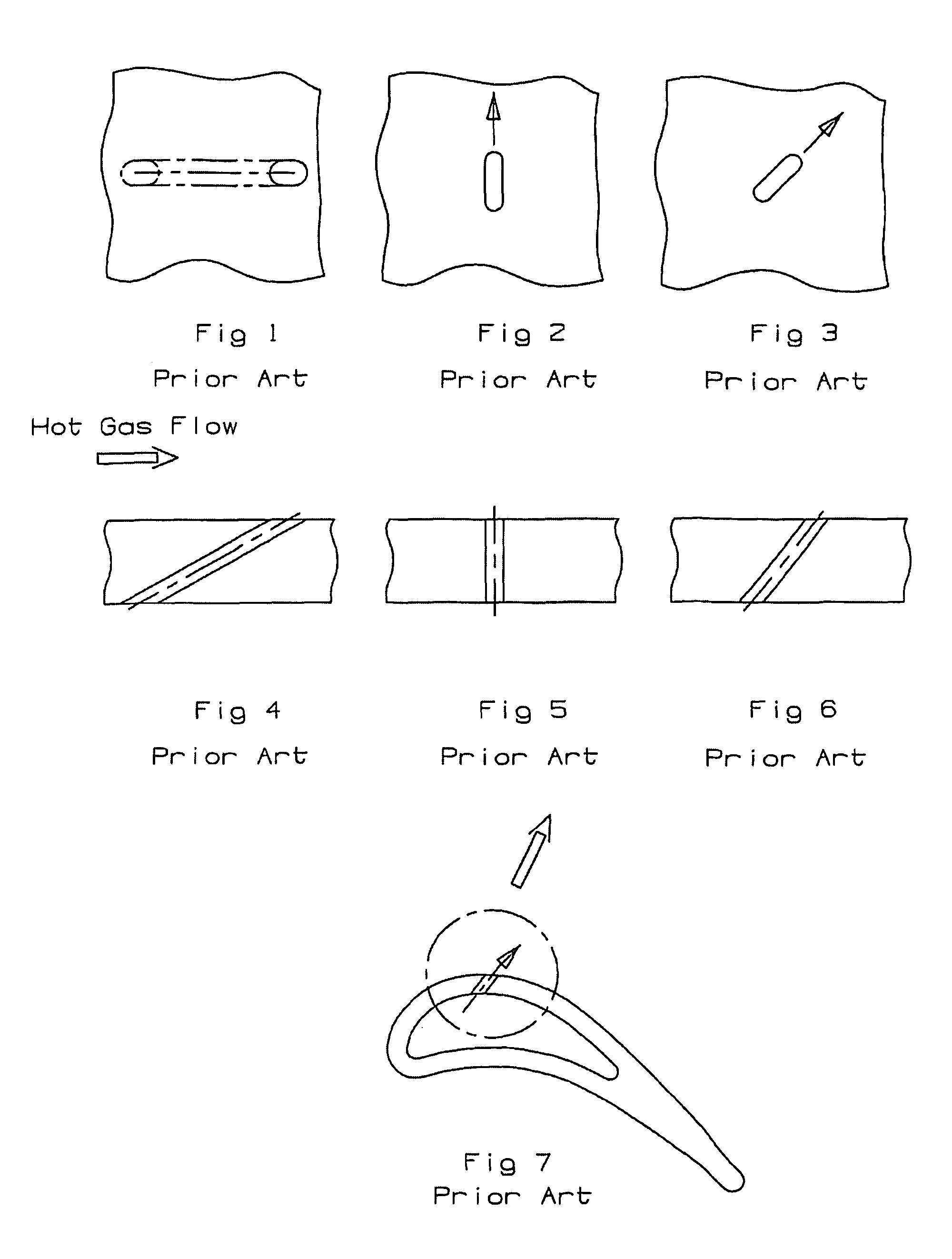
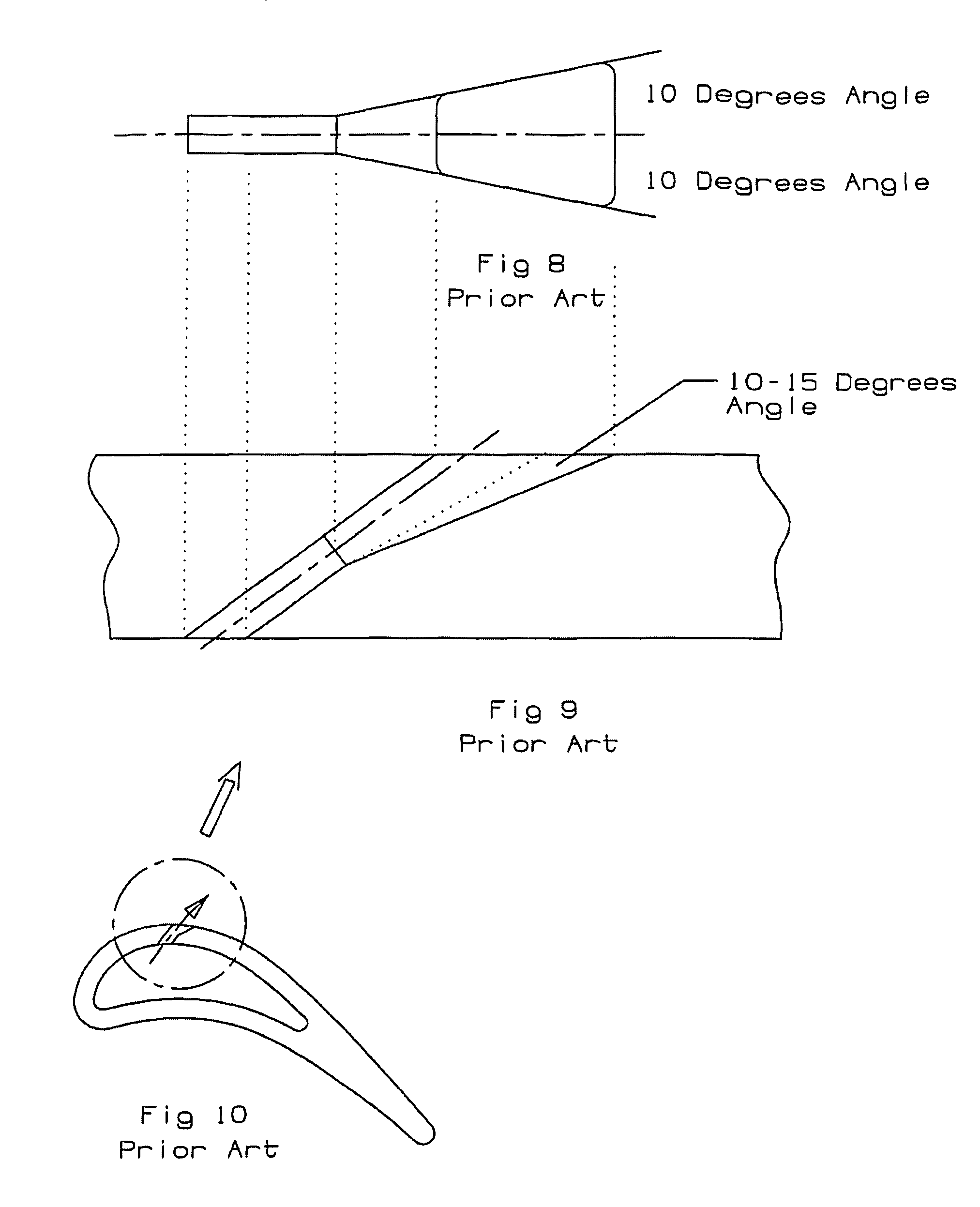
InactiveUS7997868B1Less turbulenceMinimize shear mixingEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsStructural engineeringTurbine
A turbine airfoil with a film cooling hole having a bell mouth shaped opening that has expansion in both the side walls and the downstream wall of from 15 to 25 degrees. The film cooling hole includes an expansion section formed with two long ribs and one short rib to form three inlets of equal cross sectional areas so that the flows into the three passages are the same. The short rib forms two middle passages to combine with two outer passages to form four exit passages for the film hole. The two side walls are curved outward in the stream-wise oriented film hole and have an expansion of from 0 to 5 degrees in the compound angled film hole.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
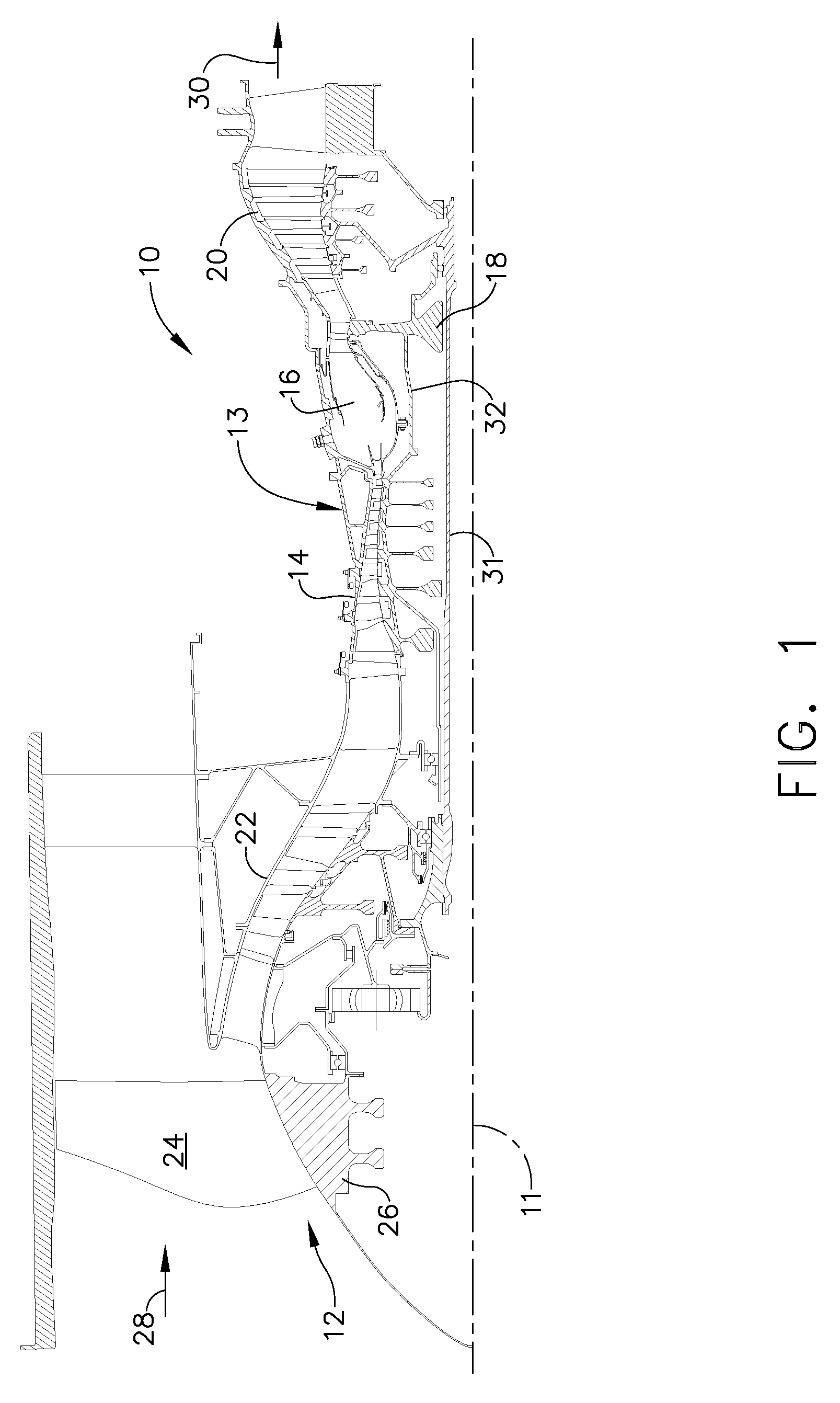
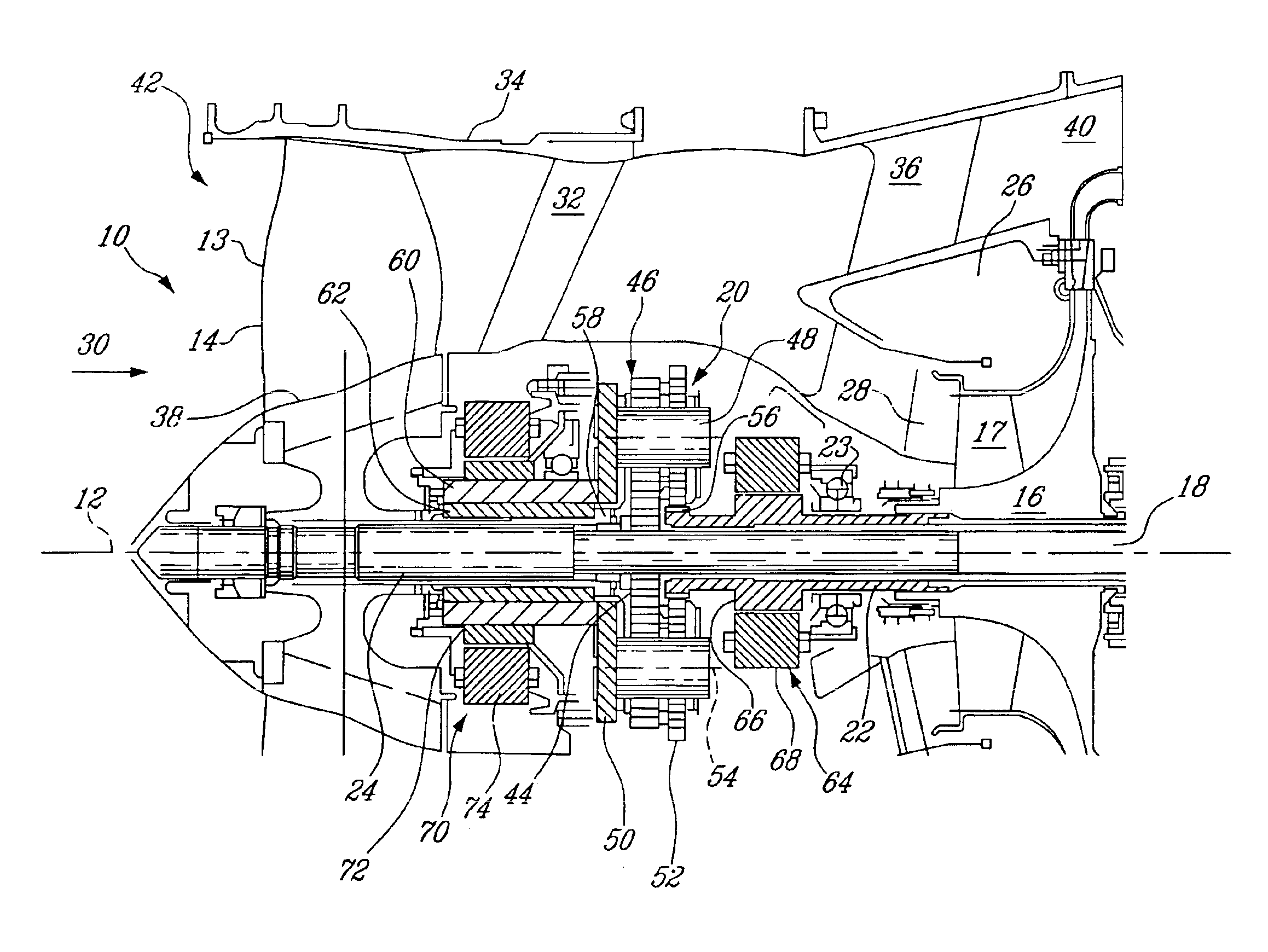
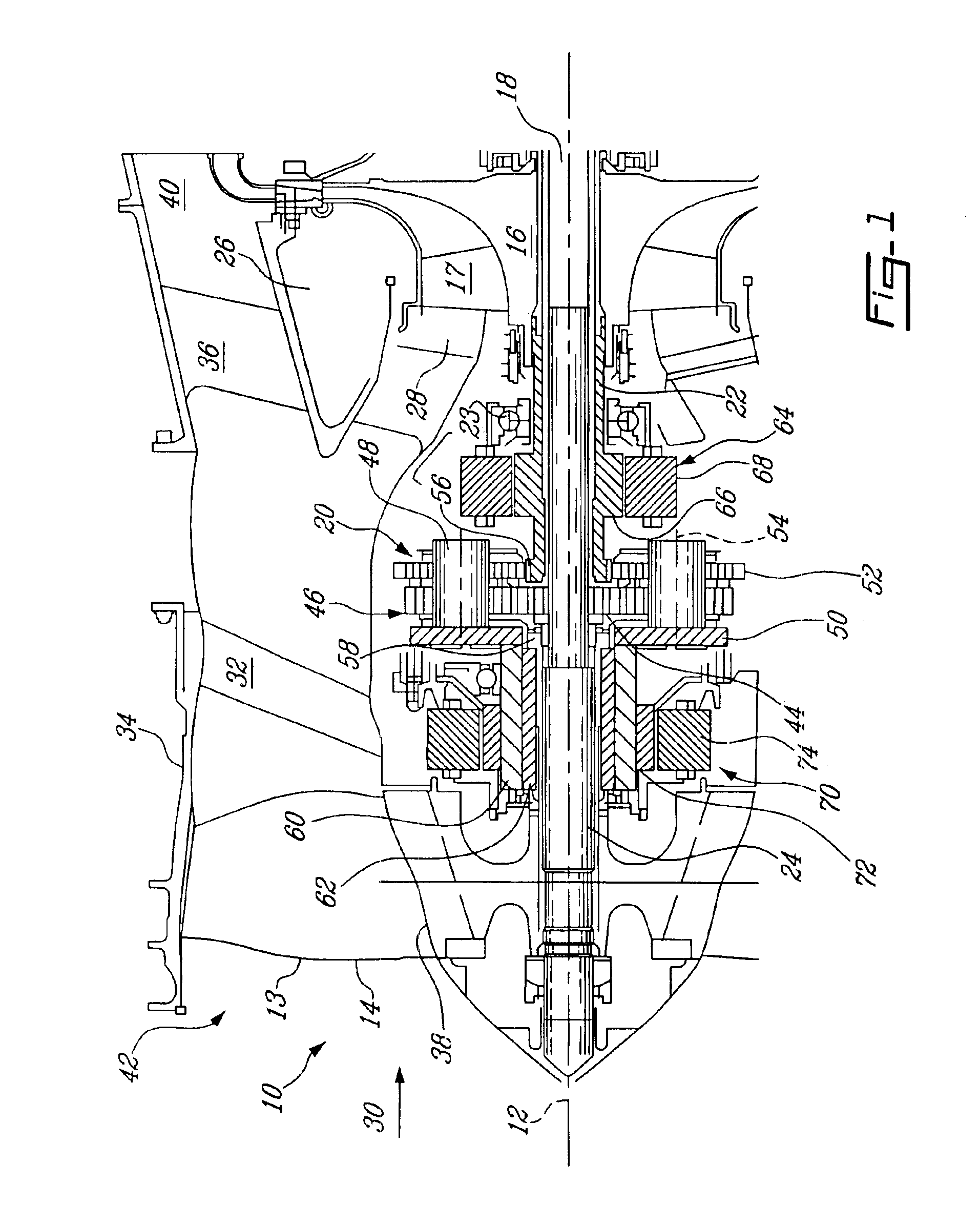
Aircraft engine with inter-turbine engine frame
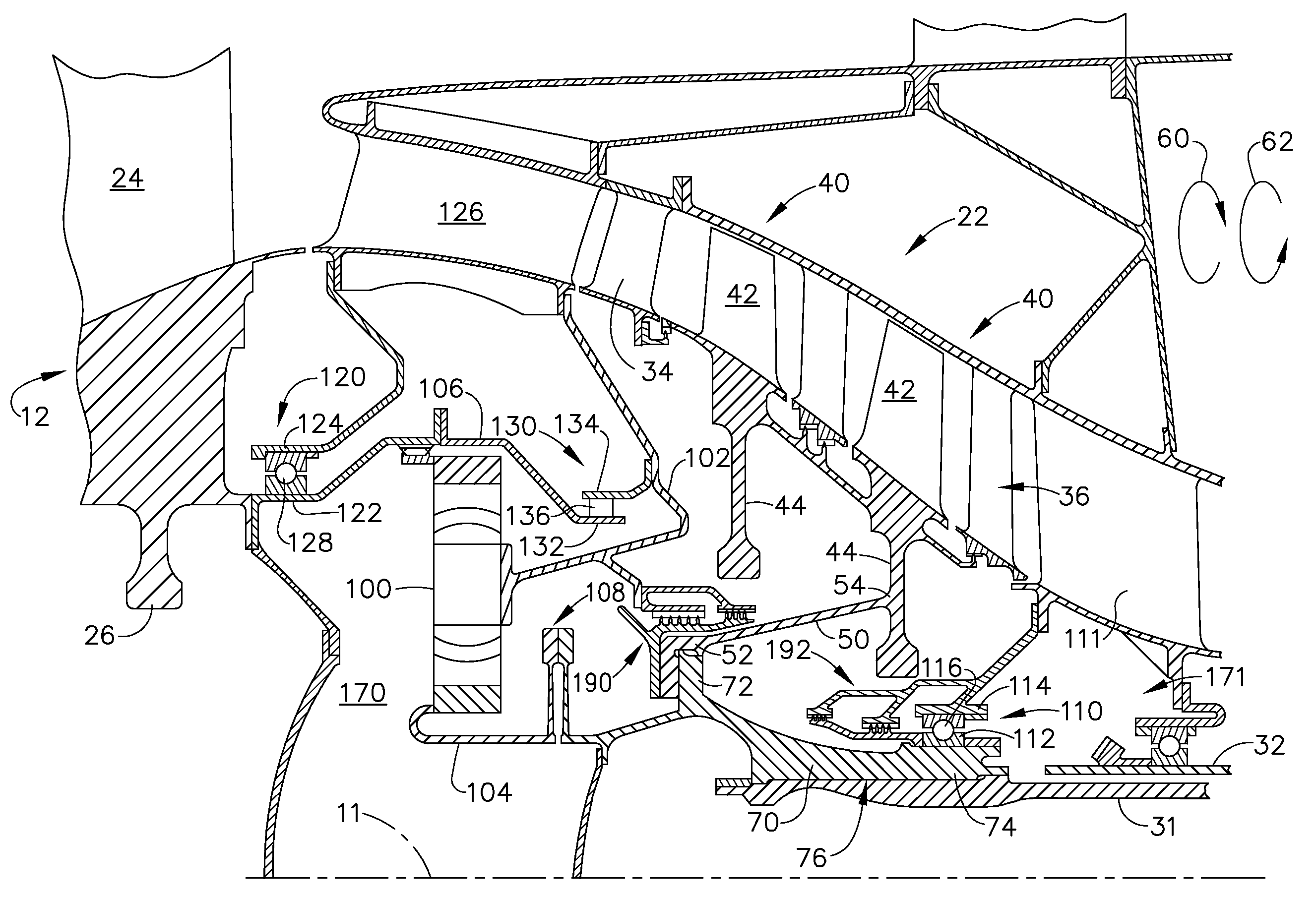
An aircraft engine turbine frame includes a first structural ring, a second structural ring disposed co-axially with and radially spaced inwardly of the first structural ring about a centerline axis. A plurality of circumferentially spaced apart struts extend between the first and second structural rings. Forward and aft sump members having forward and aft central bores are fixedly joined to forward and aft portions of the turbine frame respectively. A frame connecting means for connecting the engine to an aircraft is disposed on the first structural ring. The frame connecting means may include a U-shaped clevis. The frame may be an inter-turbine frame axially located between first and second turbines of first and second rotors of a gas turbine engine assembly. An axial center of gravity of the second turbine passes though or very near a second turbine frame bearing supported by the aft sump member.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
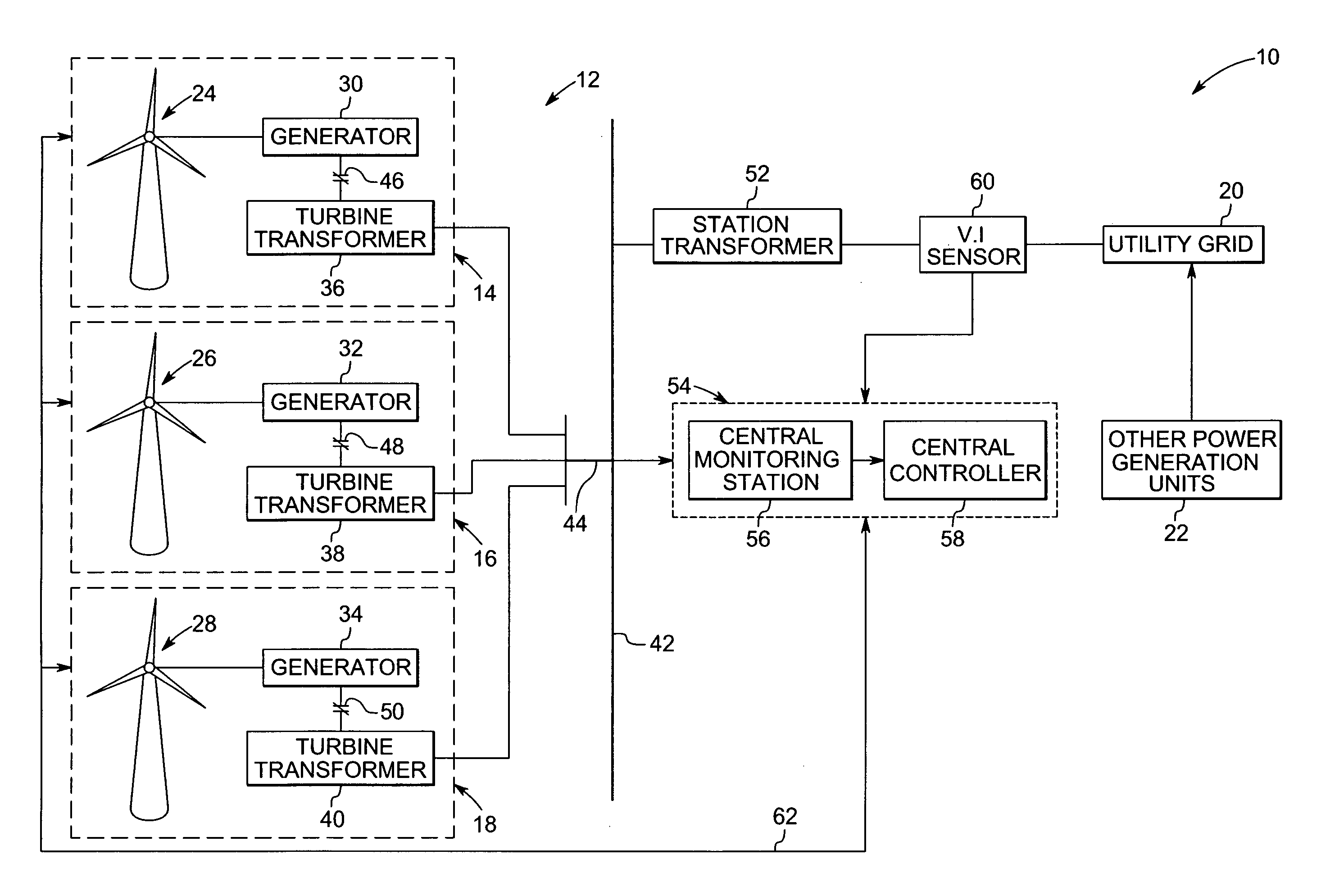
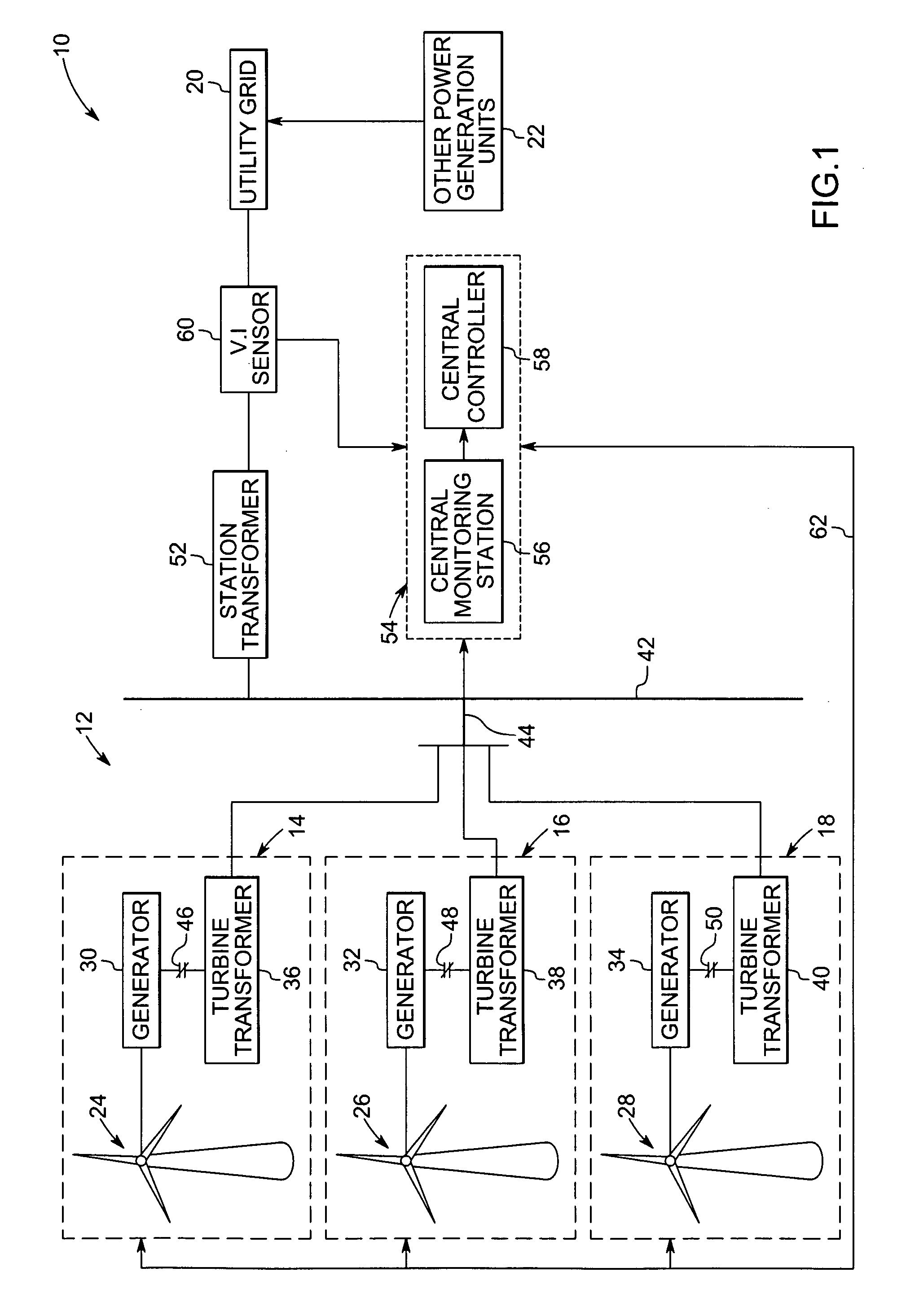
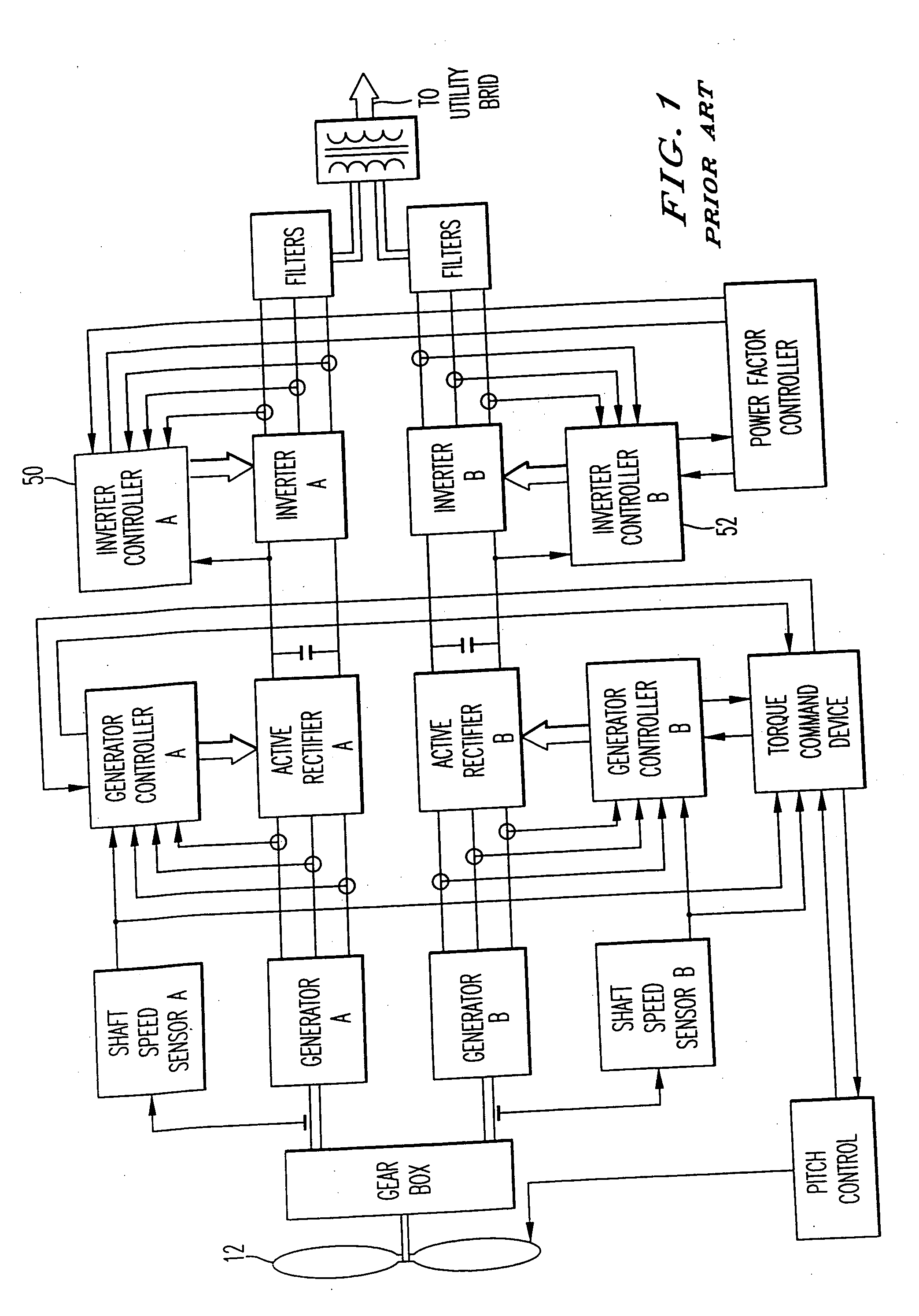
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS20050012339A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesElectric power transmissionPermanent magnet rotor
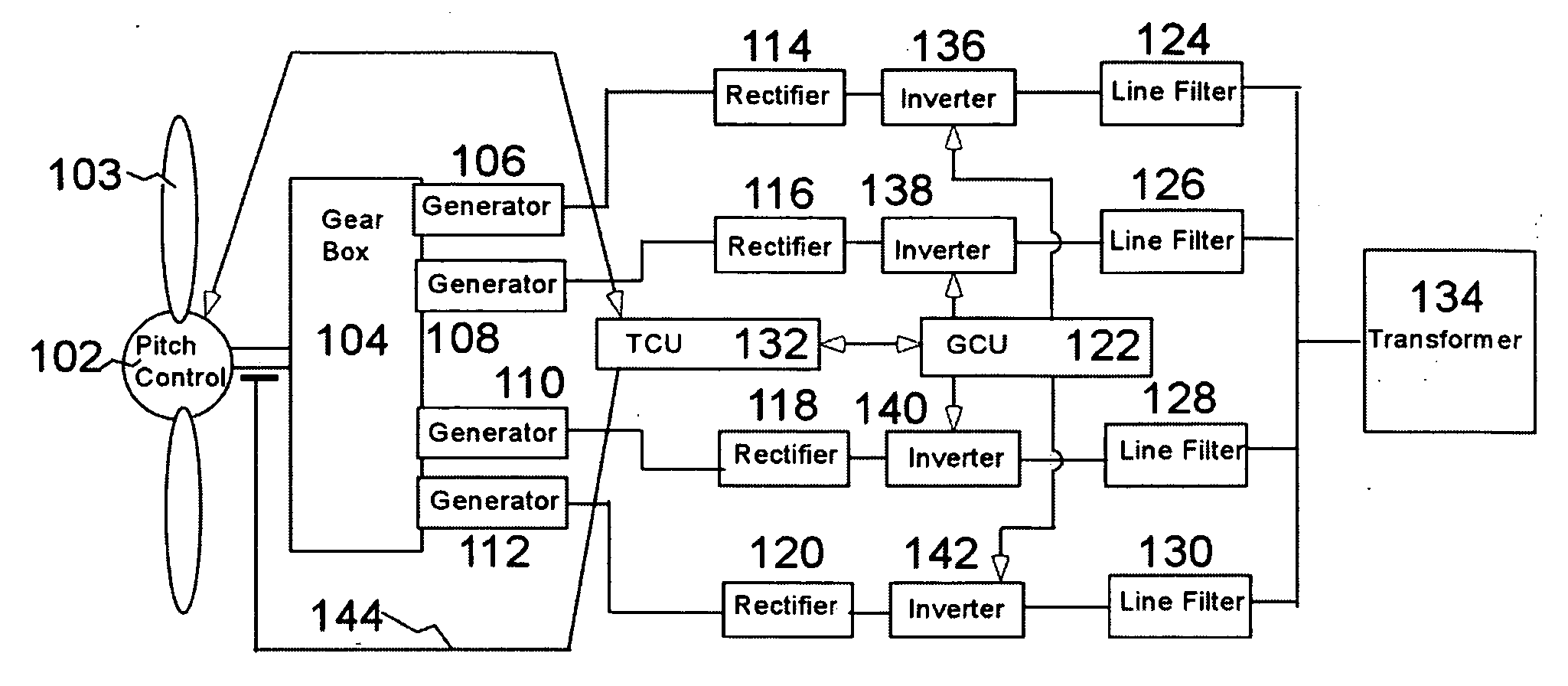
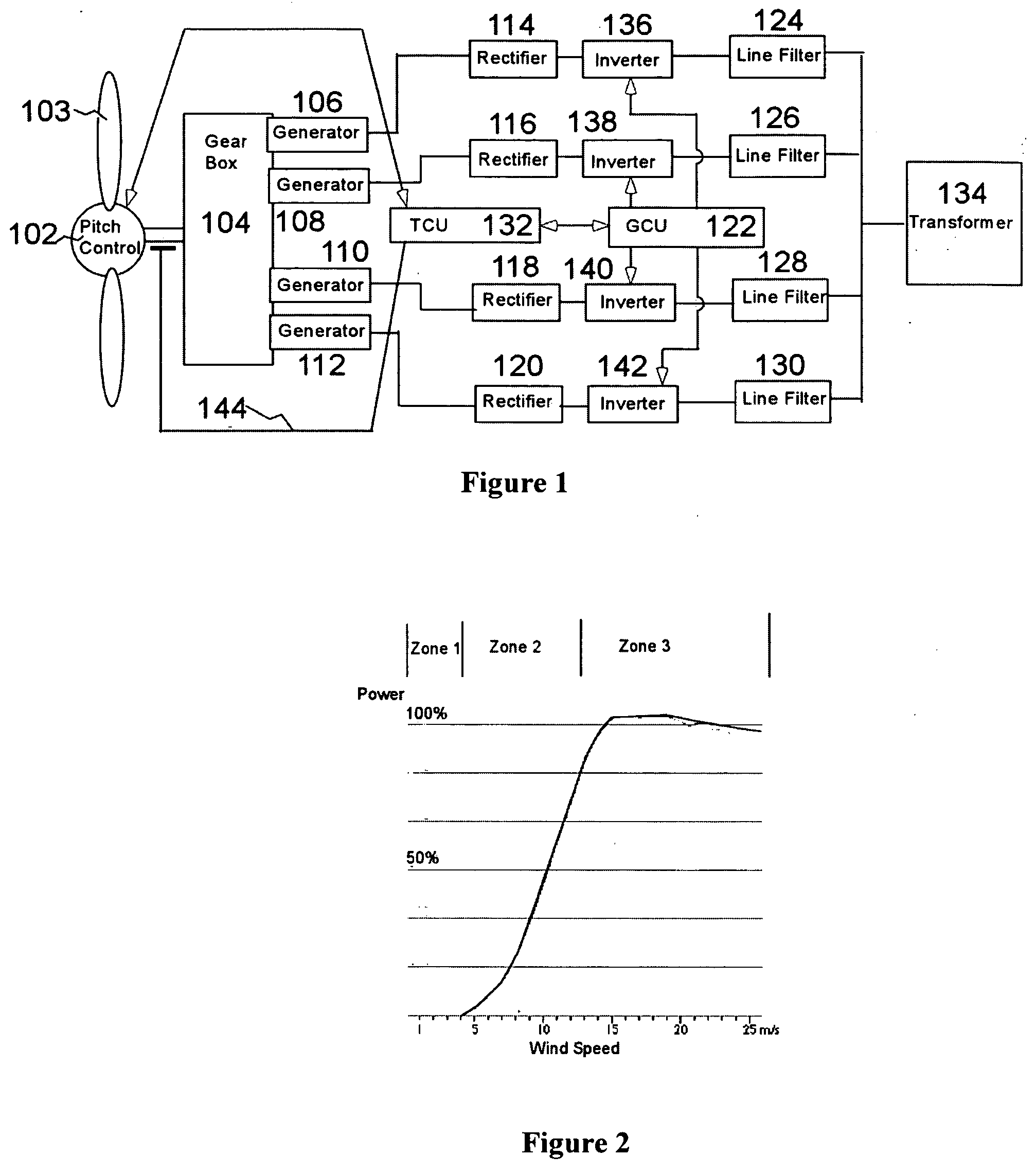
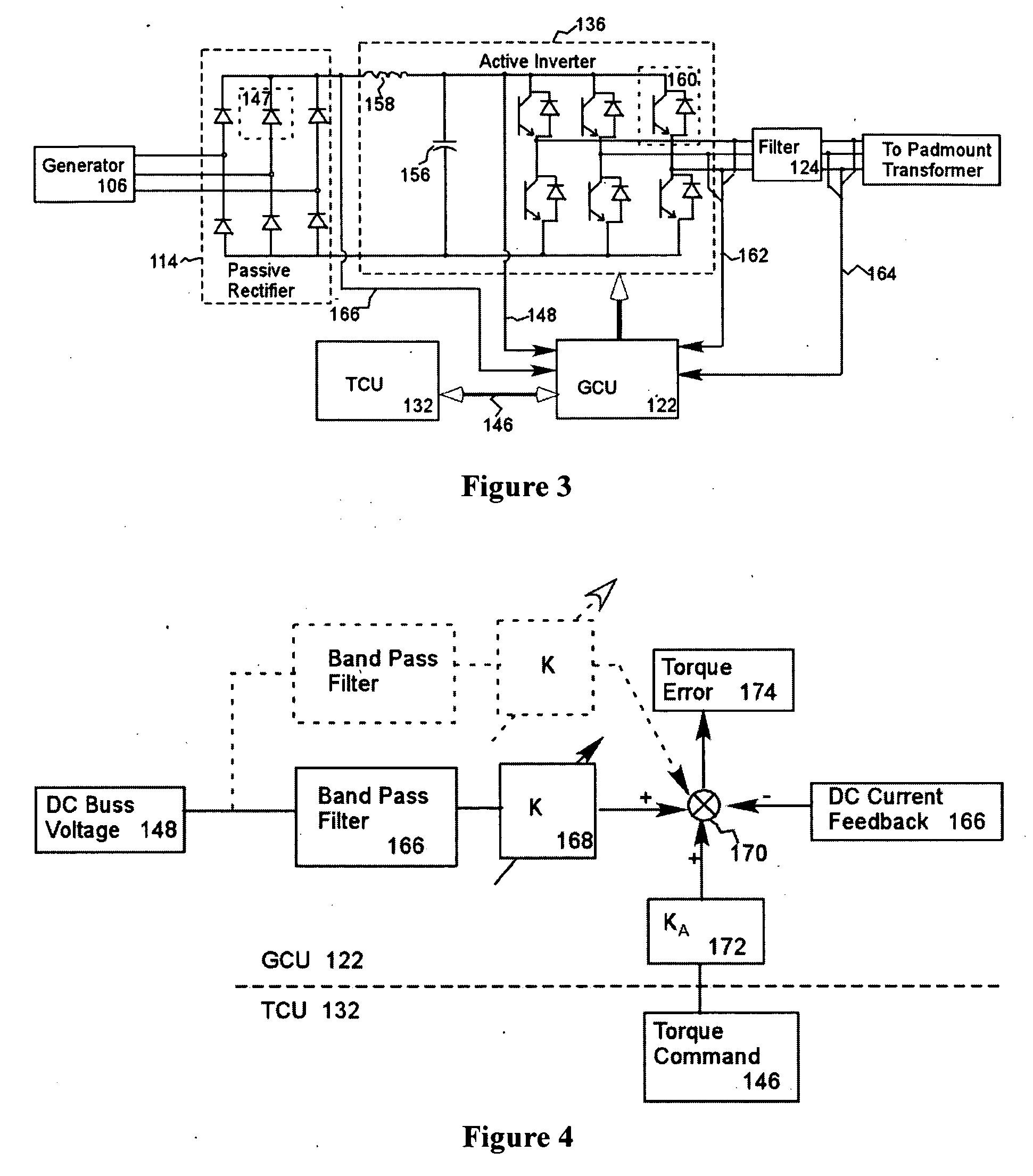
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Method for Generating Energy in an Energy Generating Installation Having a Gas Turbine, and Energy Generating Installation Useful for Carrying Out the Method
InactiveUS20080010967A1Efficient removalImprove efficiencyDispersed particle separationGas turbine plantsCyclic processCombustion chamber
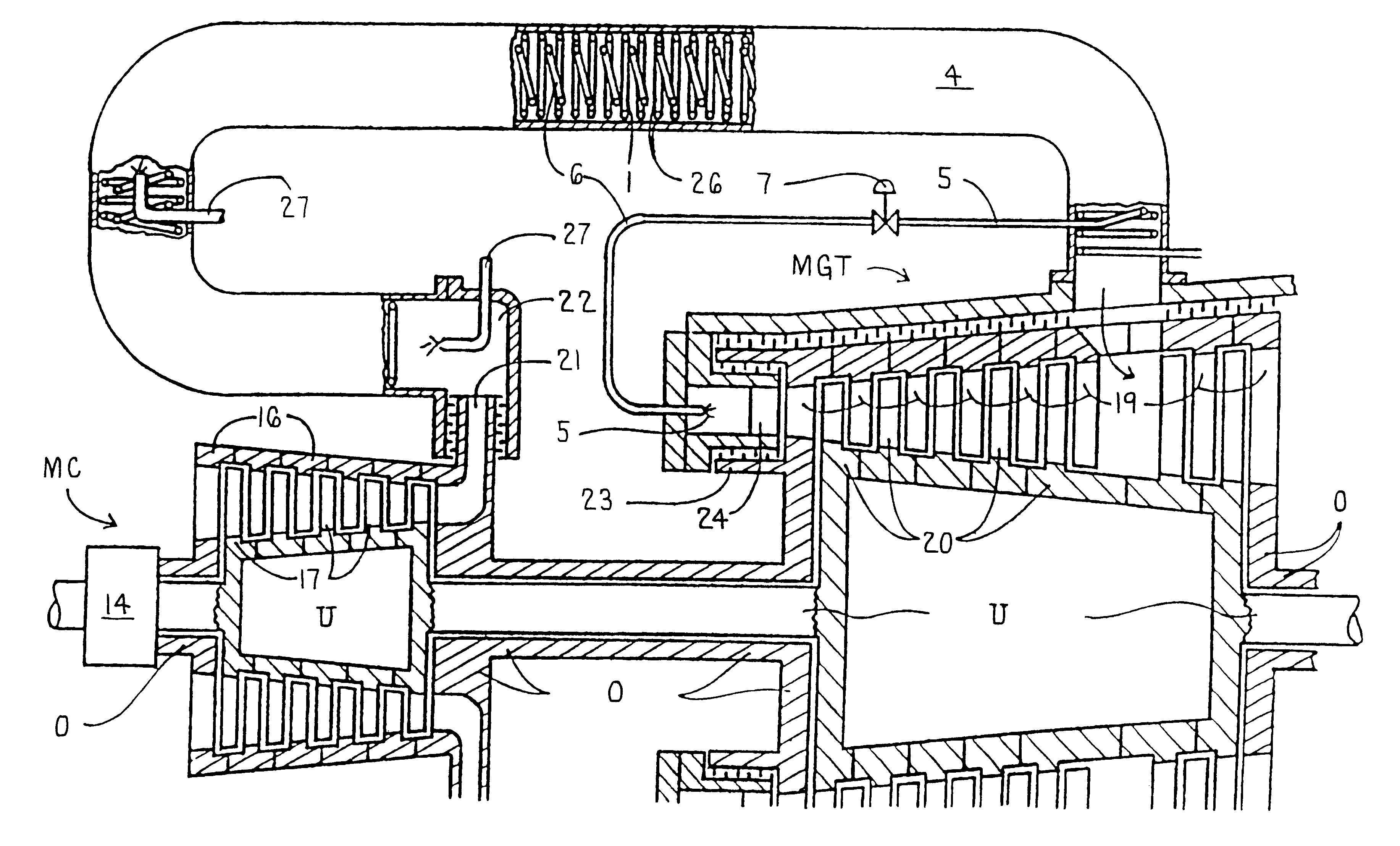
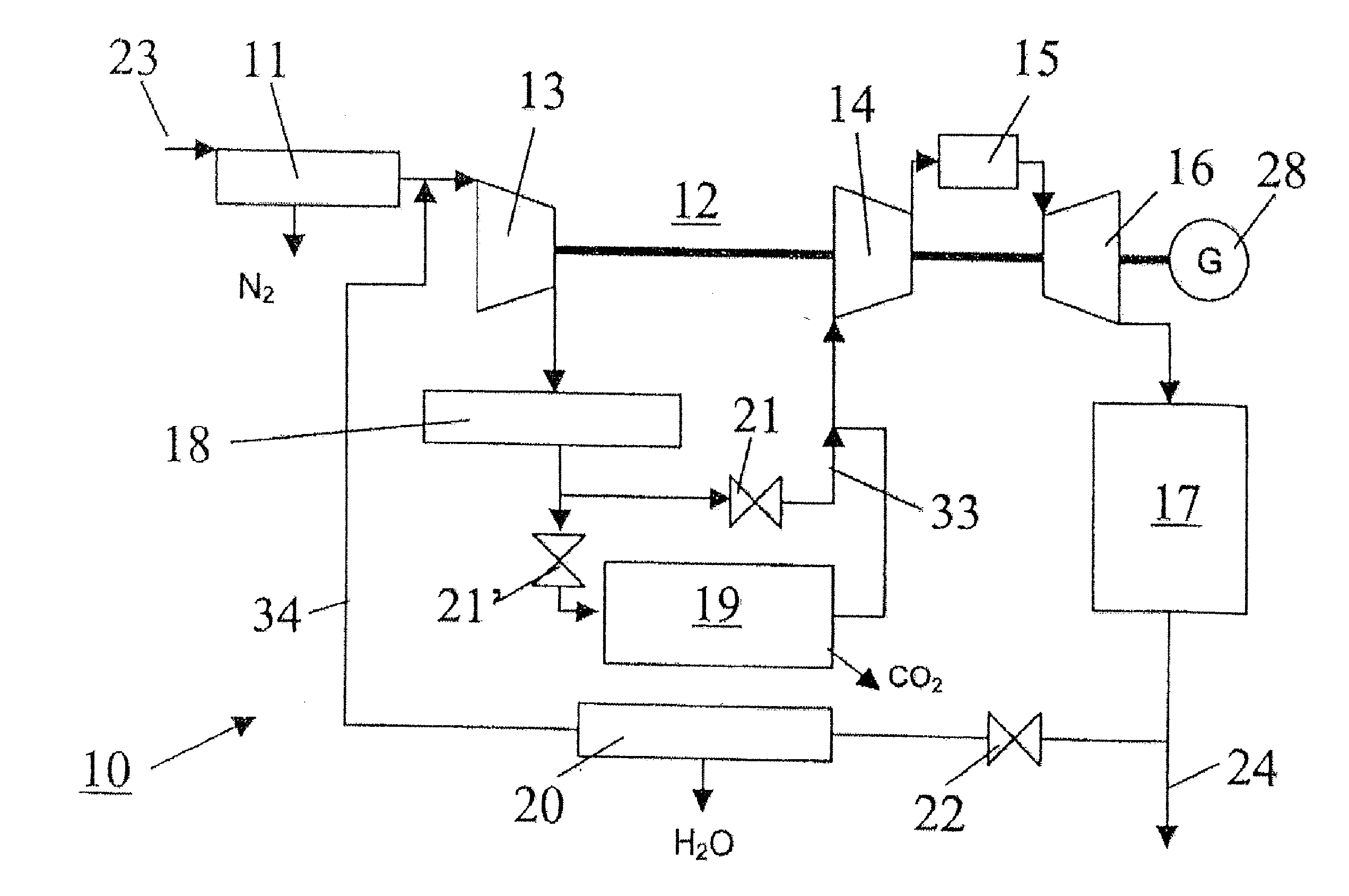
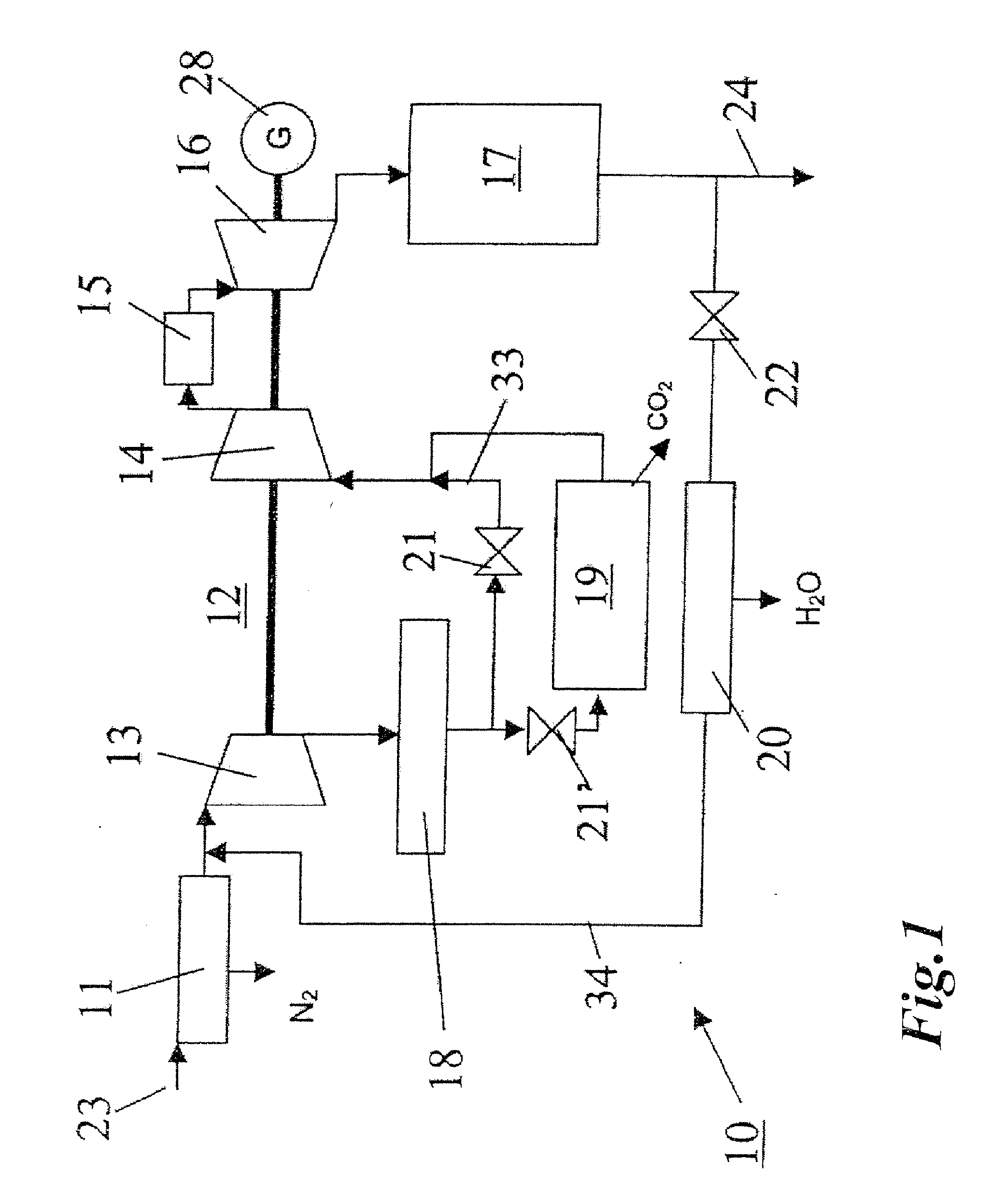
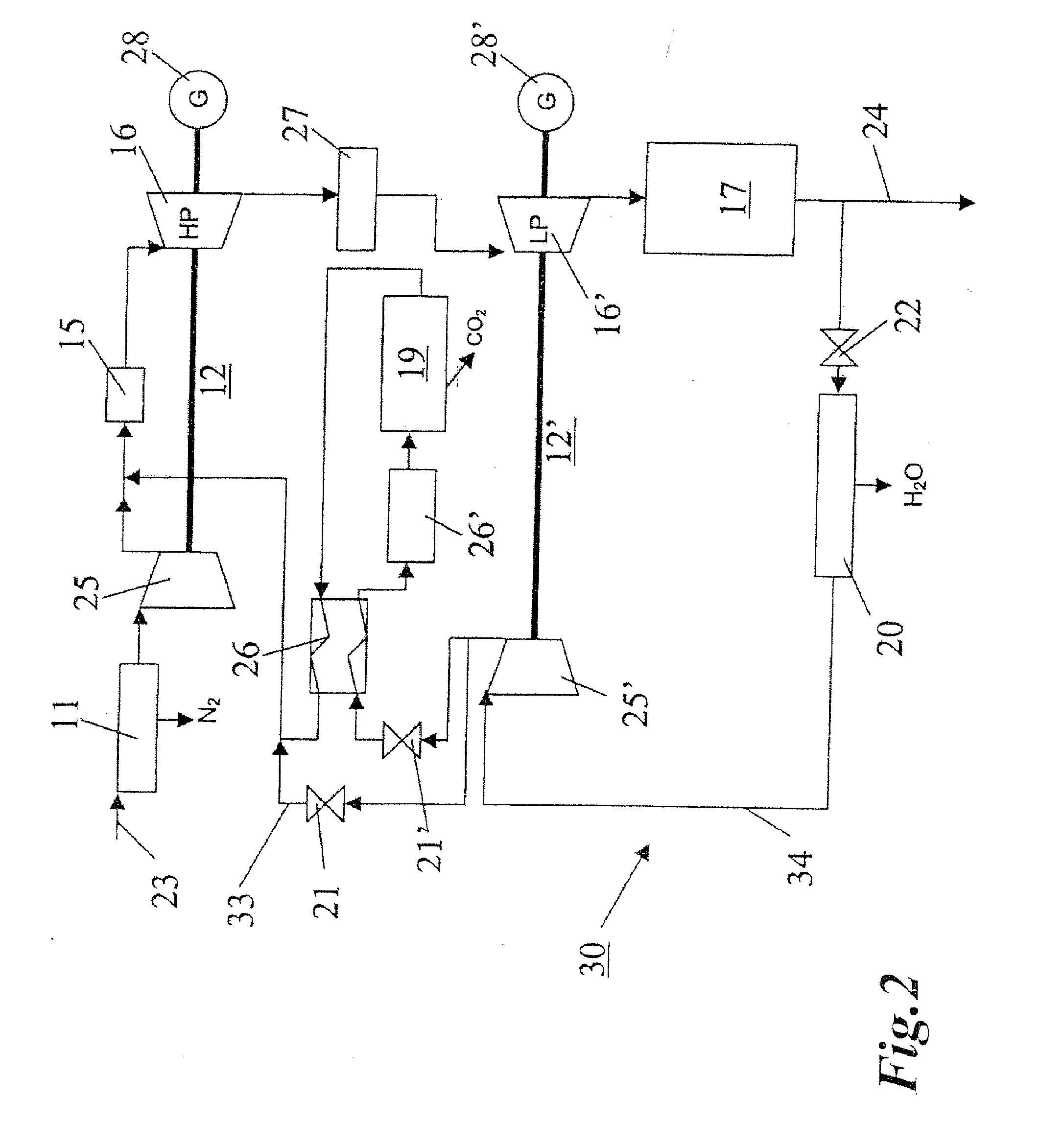
In a method for generating energy in an energy generating installation (10) having a gas turbine (12), in a first step, an oxygen-containing gas is compressed in a compressor (13, 14) of the gas turbine (12), in a second step the compressed gas is supplied, with the addition of fuel, for combustion in a combustion chamber (15), in a third step the hot flue gas from the combustion chamber (15) is expanded in a turbine (16) of the gas turbine (12) so as to perform work, and, in a fourth step, a branched-off part stream of the expanded flue gas is recirculated into a part of the gas turbine (12) lying upstream of the combustion chamber (15) and is compressed. A reduction in the CO2 emission, along with minimal losses of efficiency, is achieved in that carbon dioxide (CO2) is separated from the circulating gas in a CO2 separator (19), and in that measures are taken to compensate for the efficiency losses in the gas turbine cyclic process which are associated with the CO2 separation.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
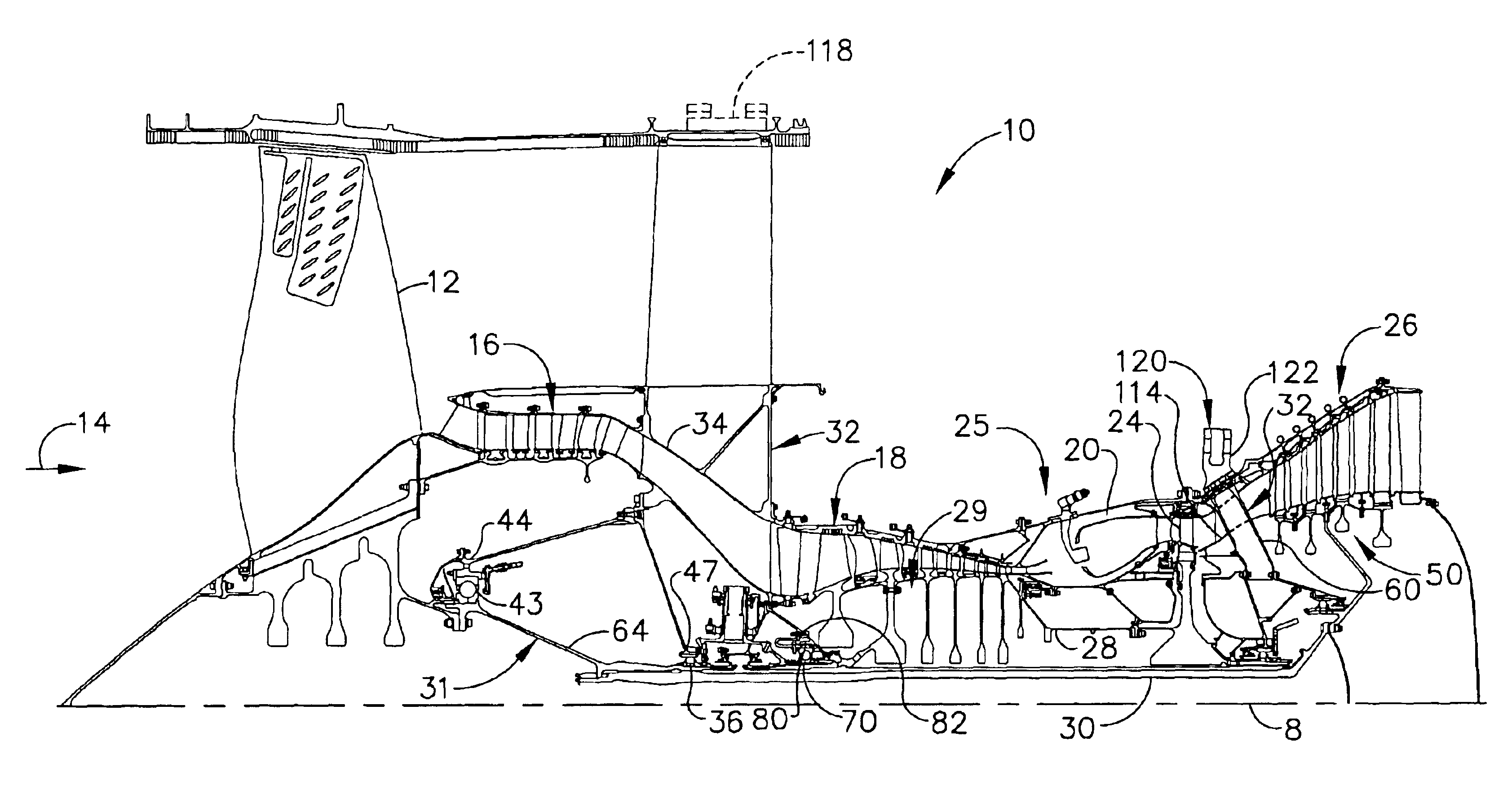
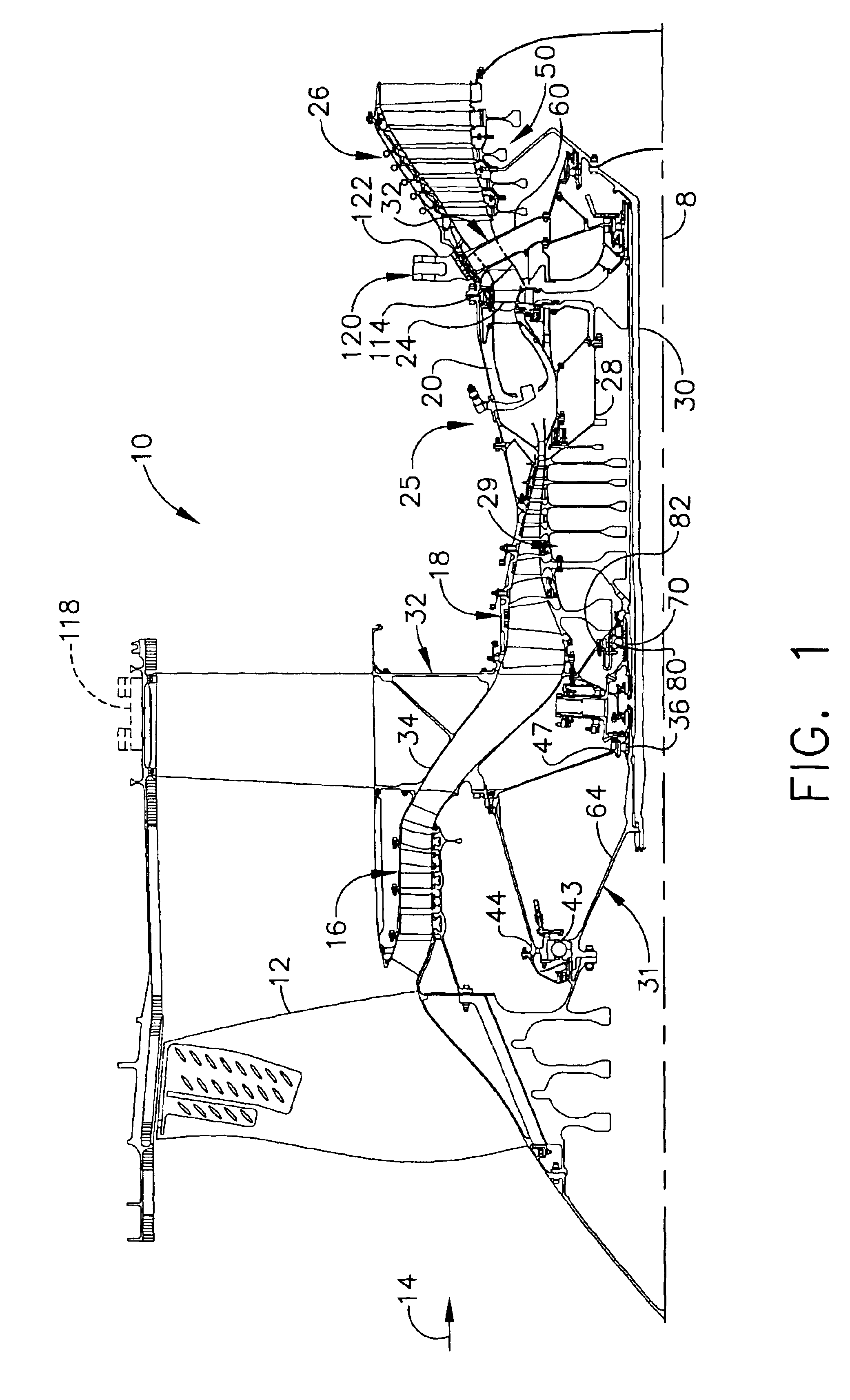
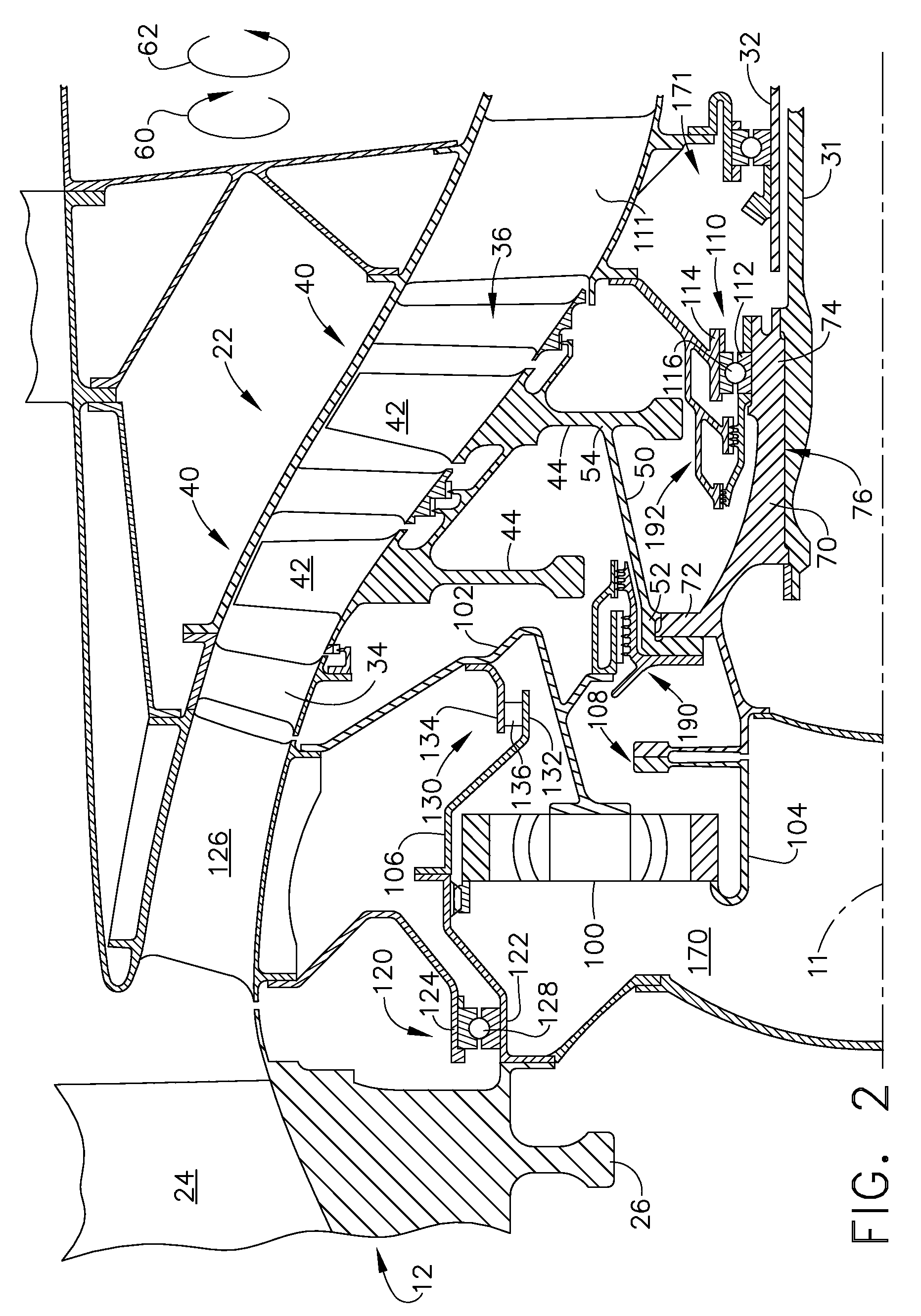
Gas turbine engine assembly and method of assembling same
A method of assembling a gas turbine assembly includes providing a core gas turbine engine including a high-pressure compressor, a combustor, and a turbine, coupling a low-pressure turbine axially aft from the core gas turbine engine, coupling a fan assembly axially forward from the core gas turbine engine, and coupling a booster compressor to the low-pressure turbine such that the booster compressor and the low-pressure turbine rotate at a first rotational speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for rotor blade ice detection
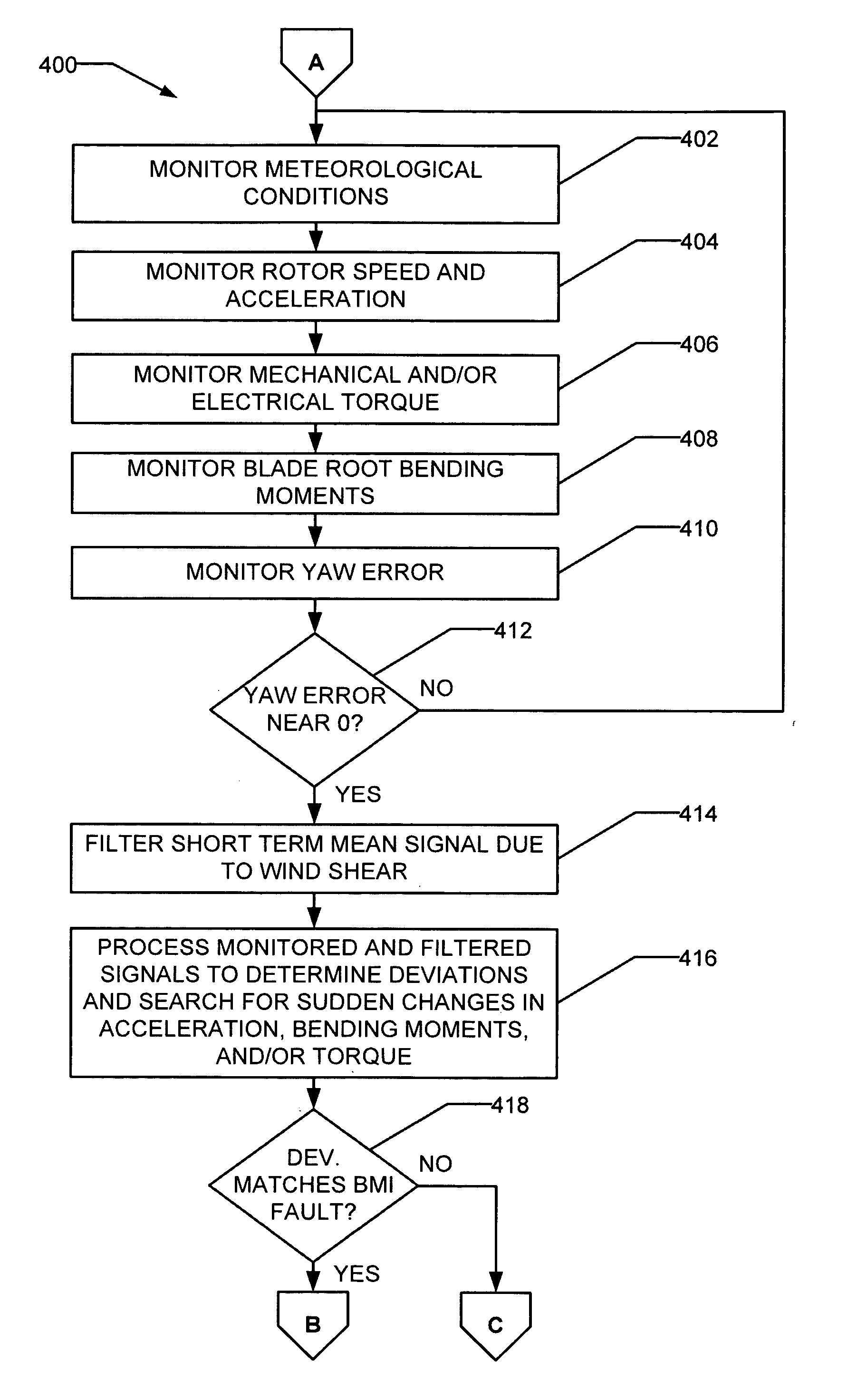
ActiveUS20050276696A1Reduced lifting capabilityDiminished aerodynamic rotor blade performancePropellersWind motor controlIcing conditionsEngineering
A method for detecting ice on a wind turbine having a rotor and one or more rotor blades each having blade roots includes monitoring meteorological conditions relating to icing conditions and monitoring one or more physical characteristics of the wind turbine in operation that vary in accordance with at least one of the mass of the one or more rotor blades or a mass imbalance between the rotor blades. The method also includes using the one or more monitored physical characteristics to determine whether a blade mass anomaly exists, determining whether the monitored meteorological conditions are consistent with blade icing; and signaling an icing-related blade mass anomaly when a blade mass anomaly is determined to exist and the monitored meteorological conditions are determined to be consistent with icing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for operating a wind farm under high wind speed conditions
ActiveUS20060273595A1Efficiently and cost-effectively harnessSimple designWind motor controlMachines/enginesTurbineWind force
A technique is provided for operating a wind farm at increased rated power output. The technique includes sensing a plurality of operating parameters of the wind turbine generator, assessing the plurality of operating parameters with respect to respective design ratings for the operating parameters, and intermittently increasing a rated power output of the wind turbine generator based upon the assessment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Organic Rankine Cycle Mechanically and Thermally Coupled to an Engine Driving a Common Load
InactiveUS20090211253A1Maximize efficiencyEngine componentsSteam engine plantsPtru catalystOrganic Rankine cycle
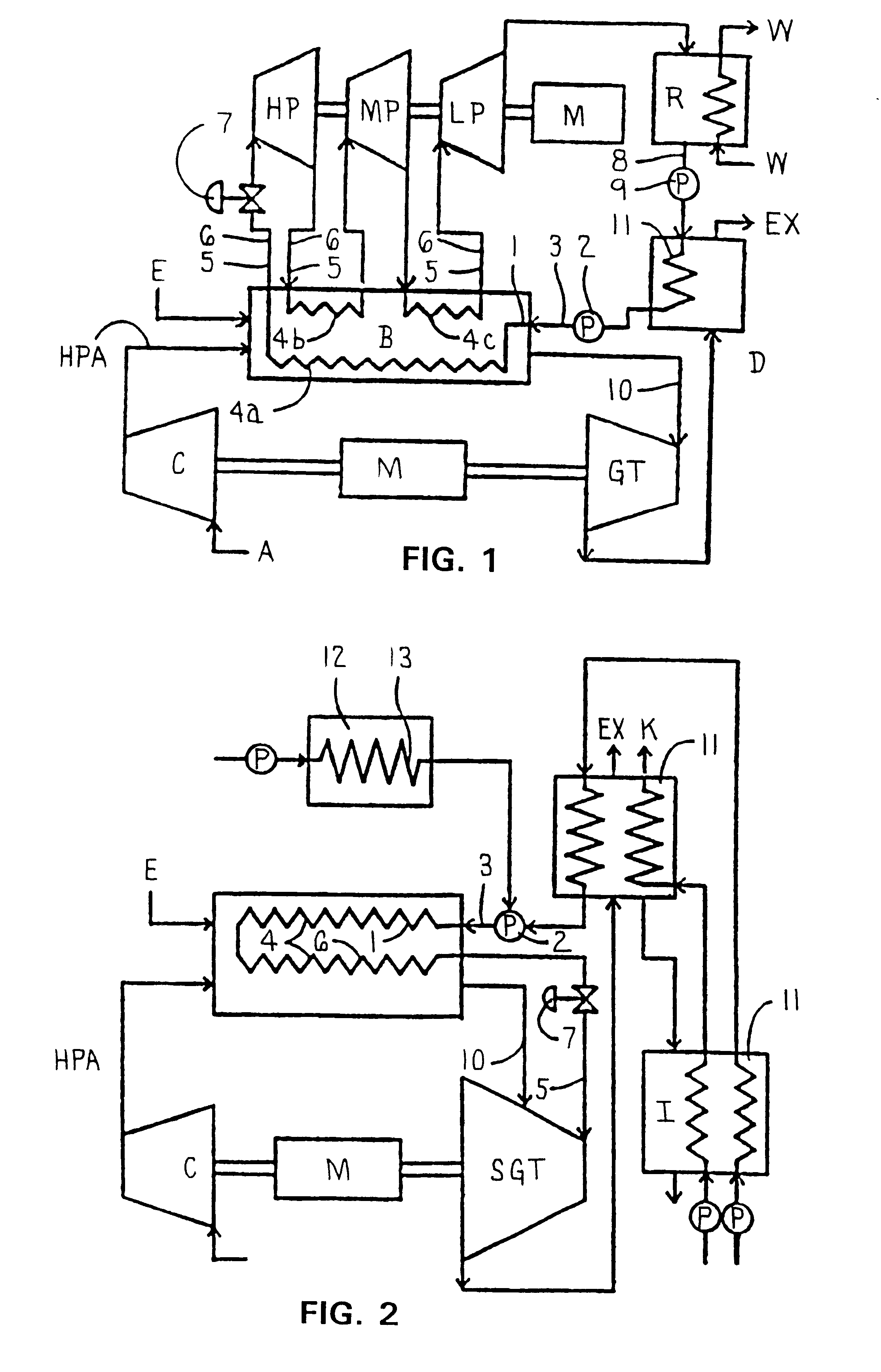
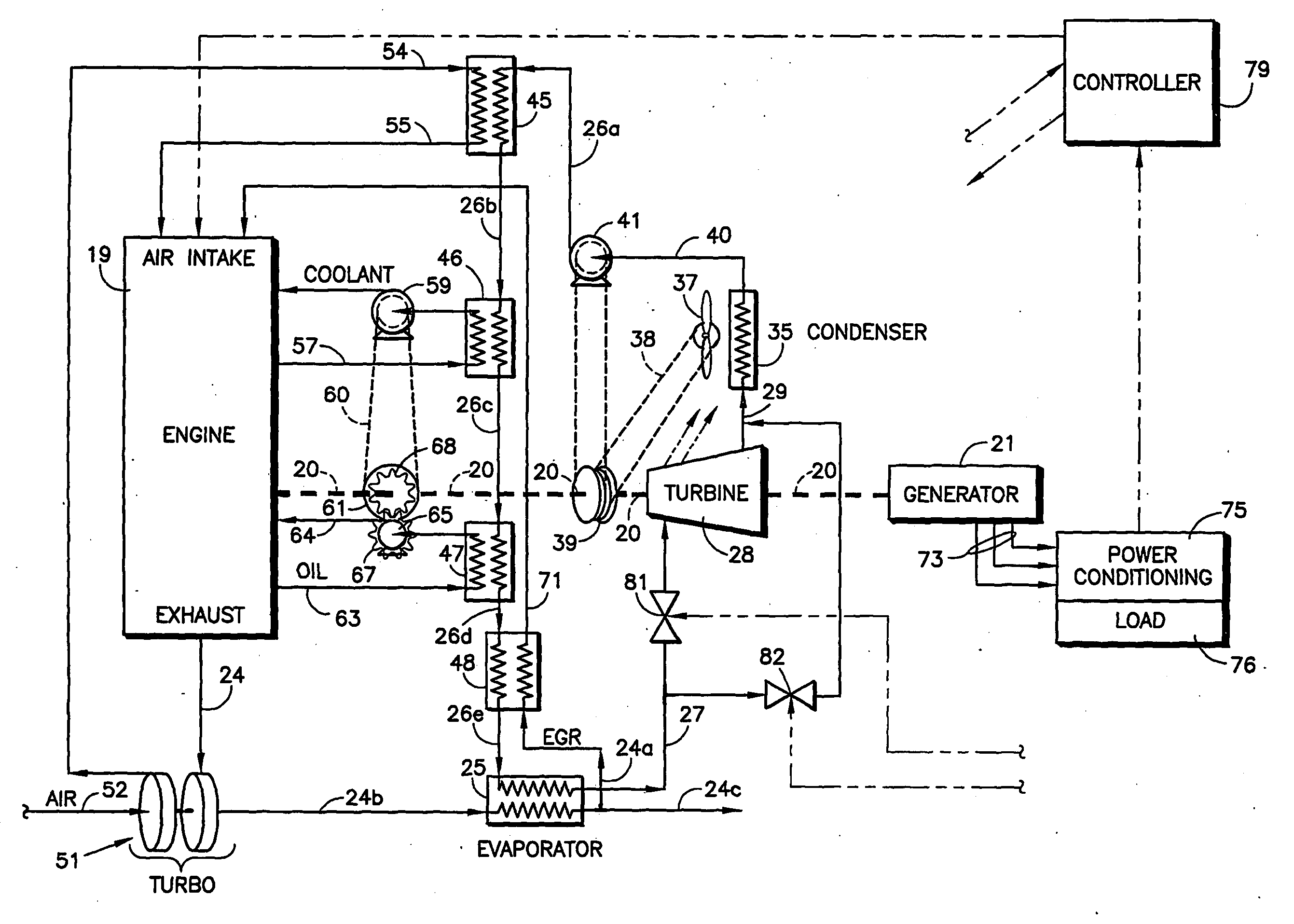
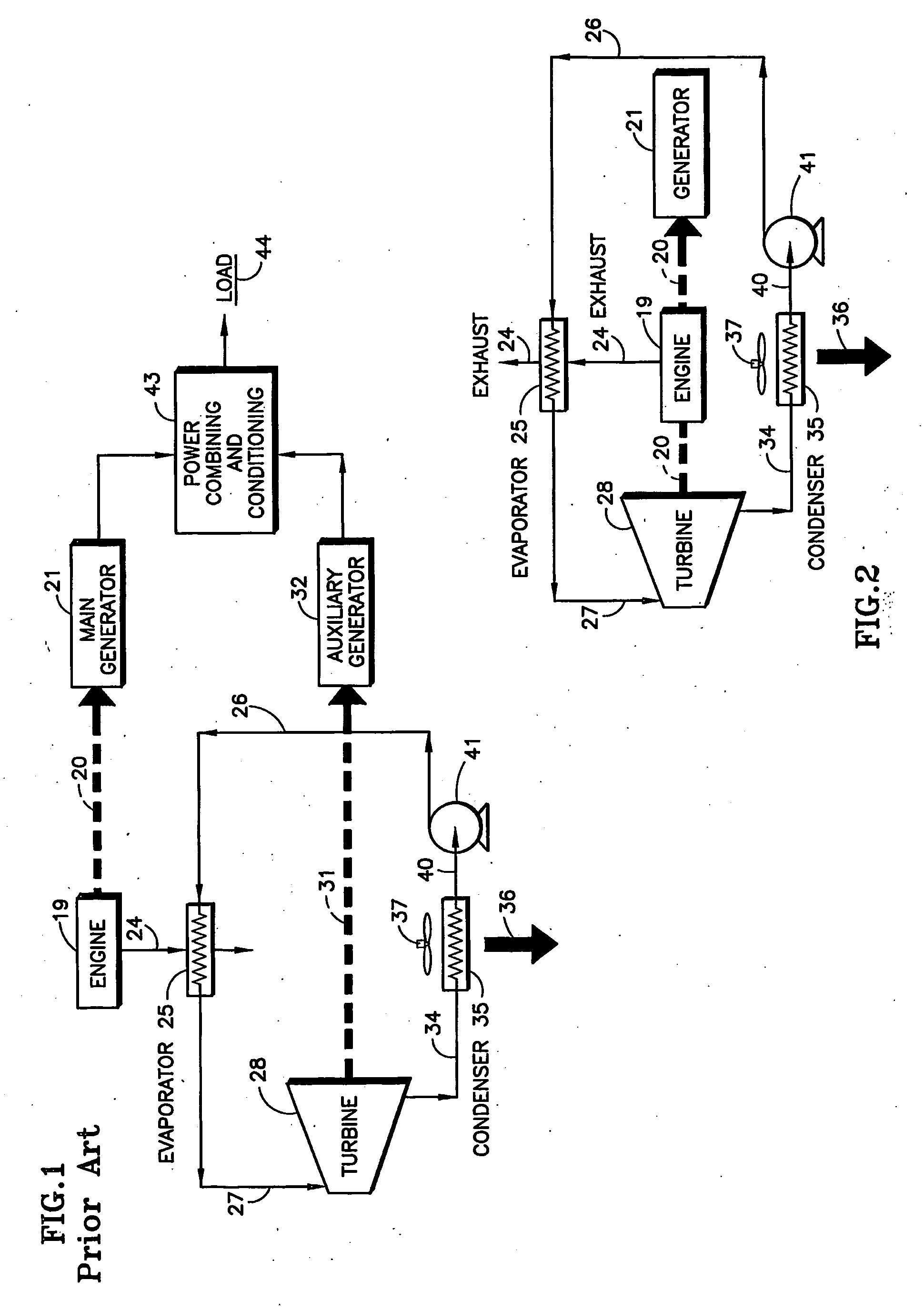
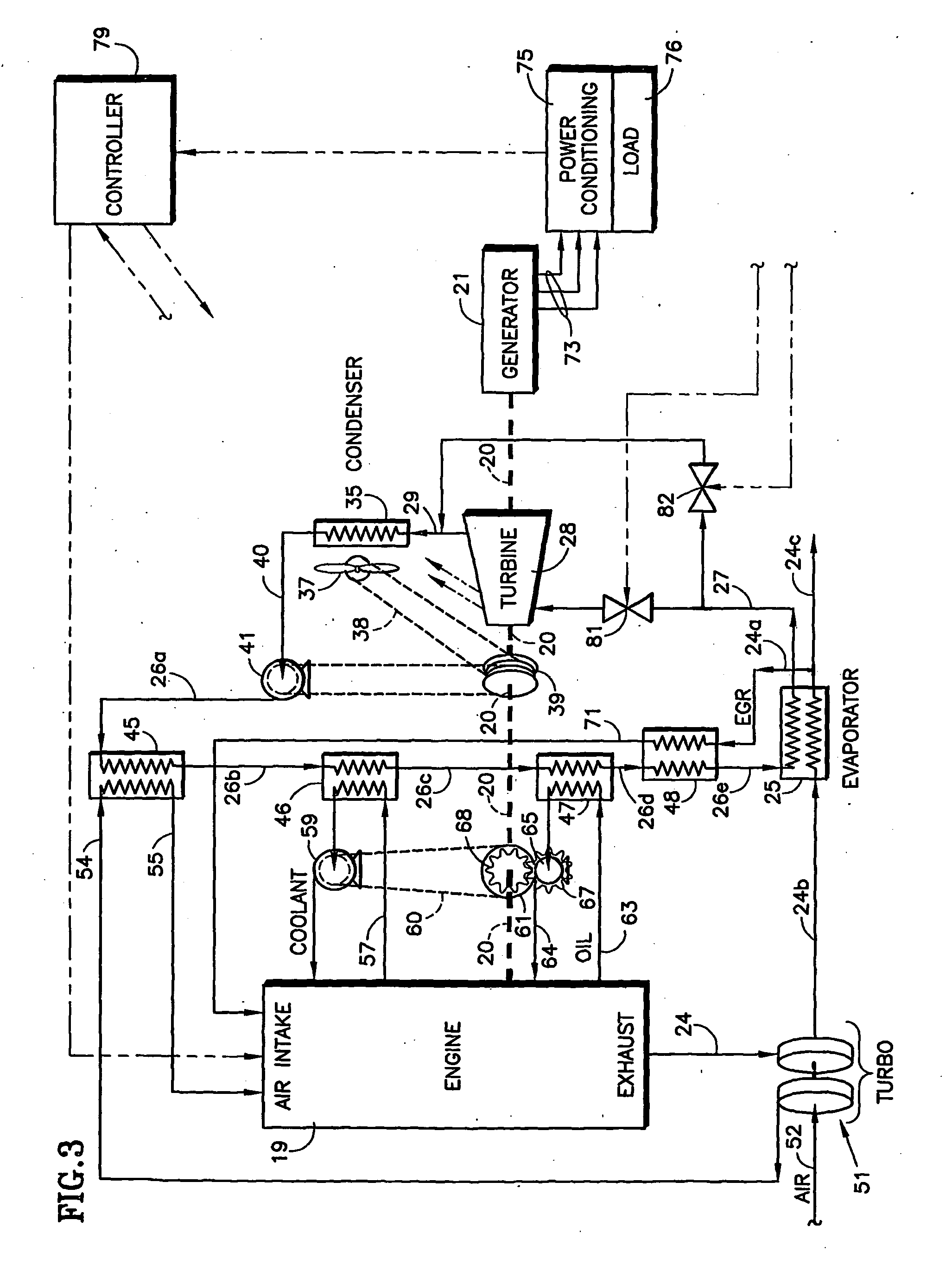
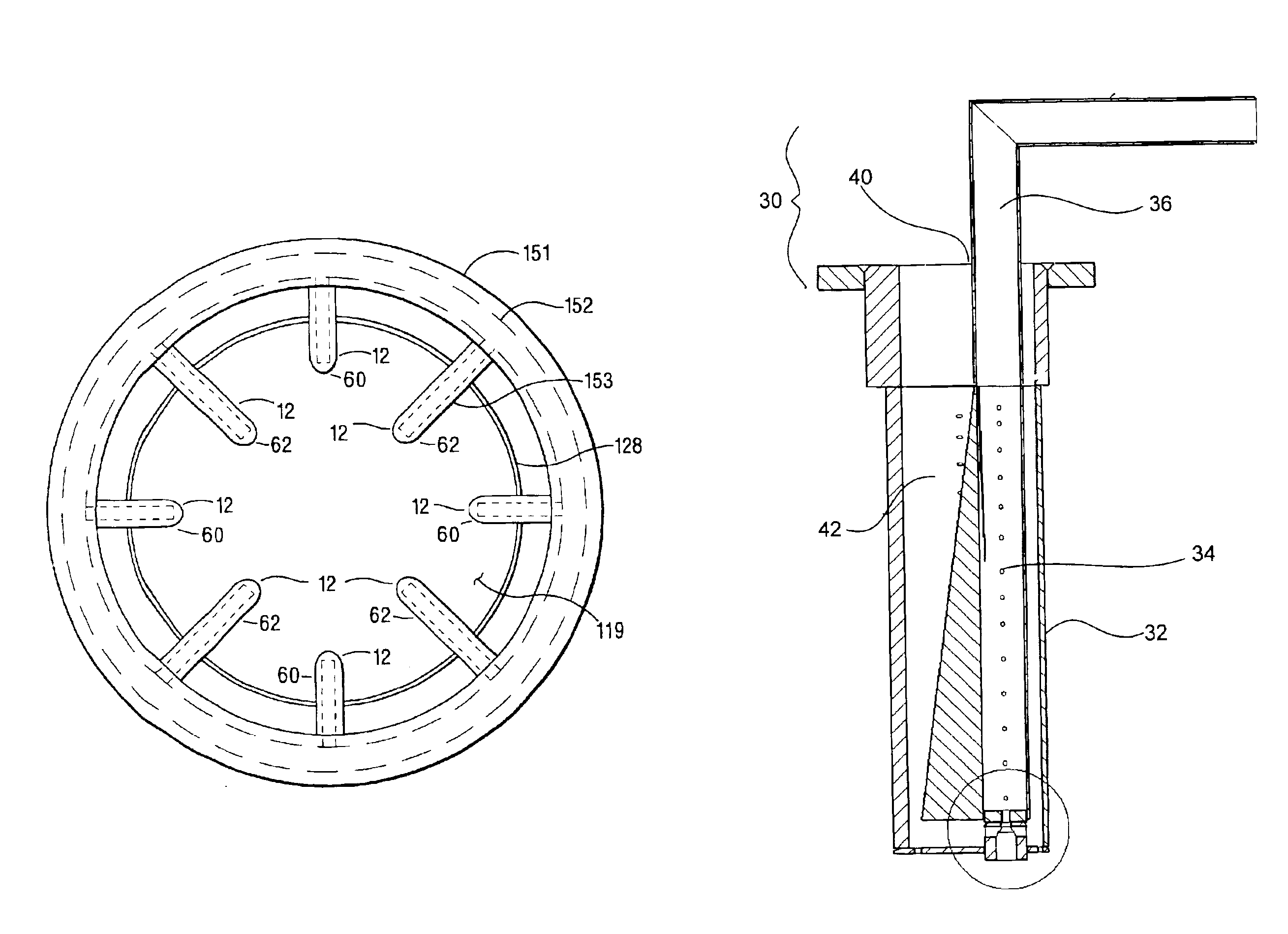
The shaft (20) of an engine (19) is coupled to a turbine (28) of an organic Rankine cycle subsystem which extracts heat (45-48, 25) from engine intake air, coolant, oil, EGR and exhaust. Bypass valves (92,94, 96, 99) control engine temperatures. Turbine pressure drop is controlled via a bypass valve (82) or a mass flow control valve (113). A refrigeration subsystem having a compressor (107) coupled to the engine shaft uses its evaporator (45a) to cool engine intake air. The ORC evaporator (25a) may comprise a muffler including pressure pulse reducing fins (121, 122), some of which have NOx and / or particulate reducing catalysts thereon.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Turbine containing system and an injector therefor
A turbine containing system is disclosed. The system includes an intake section, a compressor section downstream from the intake section, a combustor section having a primary combustion system downstream from the intake section, a secondary combustion system downstream from the primary combustion system, a turbine section, an exhaust section and a load. The secondary combustion system includes an injector for transversely injecting a secondary fuel into a stream of combustion products of the primary combustion system. The injector including a coupling, a wall defining an airfoil shape circumscribing a fuel mixture passage, and at least one exit for communication between said fuel mixture passage and said stream of primary combustion products.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Supercharging system for gas turbines
InactiveUS7065953B1Increase turbine capacityReduce installation costsEfficient propulsion technologiesGas turbine plantsCombustorPower station
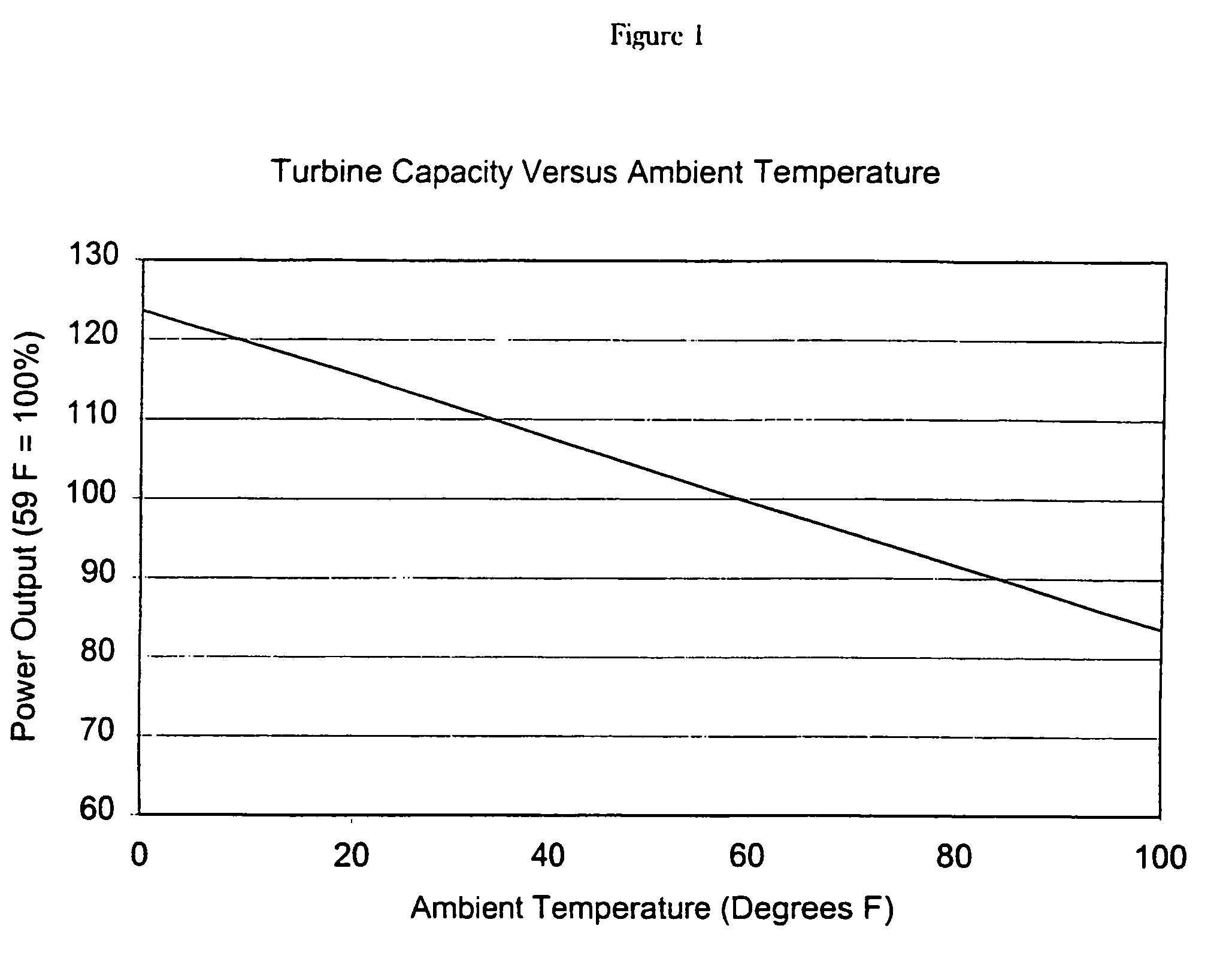
A supercharging system for gas turbine power plants (11). The system includes a supercharging fan (30, 32) and controller (50) for limiting turbine power output to prevent overload of the generator (28) at lower ambient temperatures. The controller can limit power output by burner control, inlet temperature control, control of supercharging fan pressure and other options. The system can be retrofit on an existing turbine without replacing the generator and associated parts.
Owner:ENHANCED TURBINE OUTPUT HLDG
Hydrocarbon combustion power generation system with CO2 sequestration
InactiveUS7043920B2Eliminate needReduce electricity demandReciprocating combination enginesSolidificationAtmospheric airOxygen
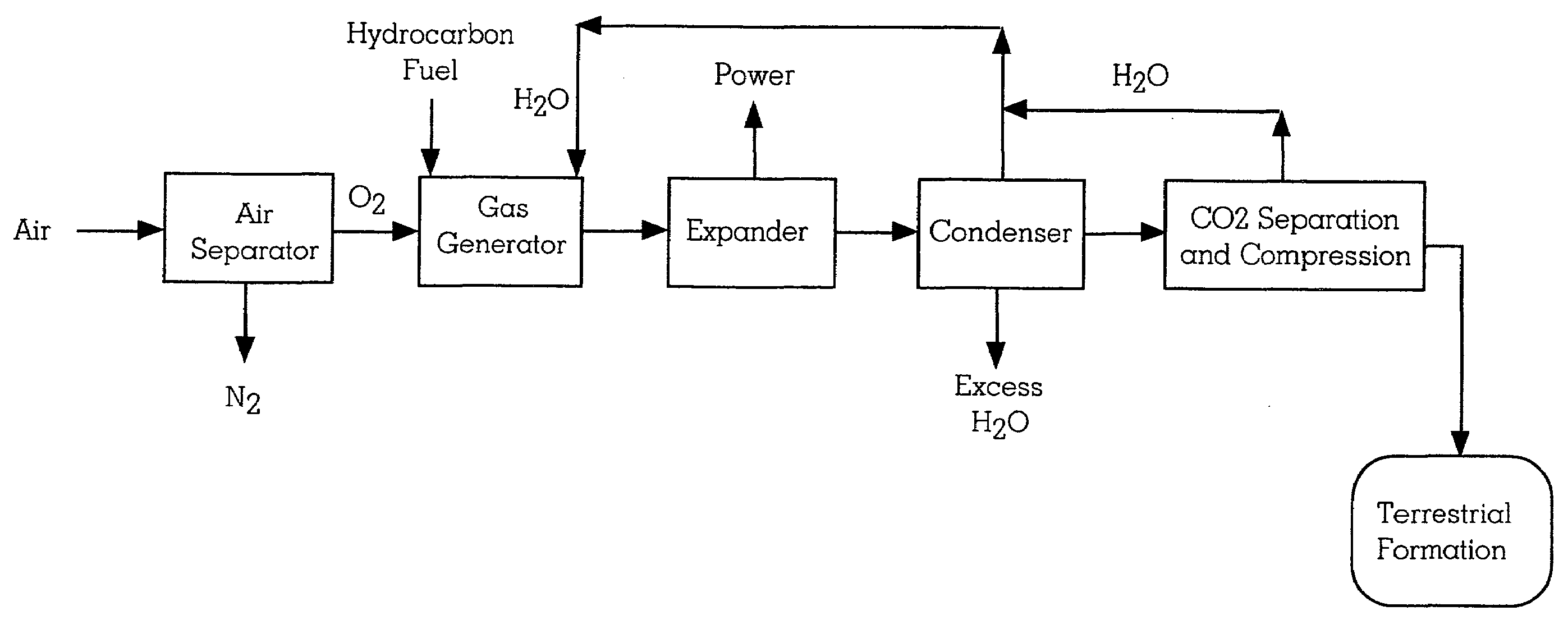
A low or no pollution engine is provided for delivering power for vehicles or other power applications. The engine has an air inlet which collects air from a surrounding environment. At least a portion of the nitrogen in the air is removed. The remaining gas is primarily oxygen, which is then routed to a gas generator. The gas generator has inputs for the oxygen and a hydrocarbon fuel. The fuel and oxygen are combusted within the gas generator, forming water and carbon dioxide. The combustion products are then expanded through a power generating device, such as a turbine or piston expander to deliver output power for operation of a vehicle or other power uses. The combustion products are then passed through a condenser where the steam is condensed and the carbon dioxide is collected or discharged. A portion of the water is routed back to the gas generator. The carbon dioxide is compressed and delivered to a terrestrial formation from which return of the CO2 into the atmosphere is inhibited.
Owner:CLEAN ENERGY SYST
Portable, self-sustaining power station
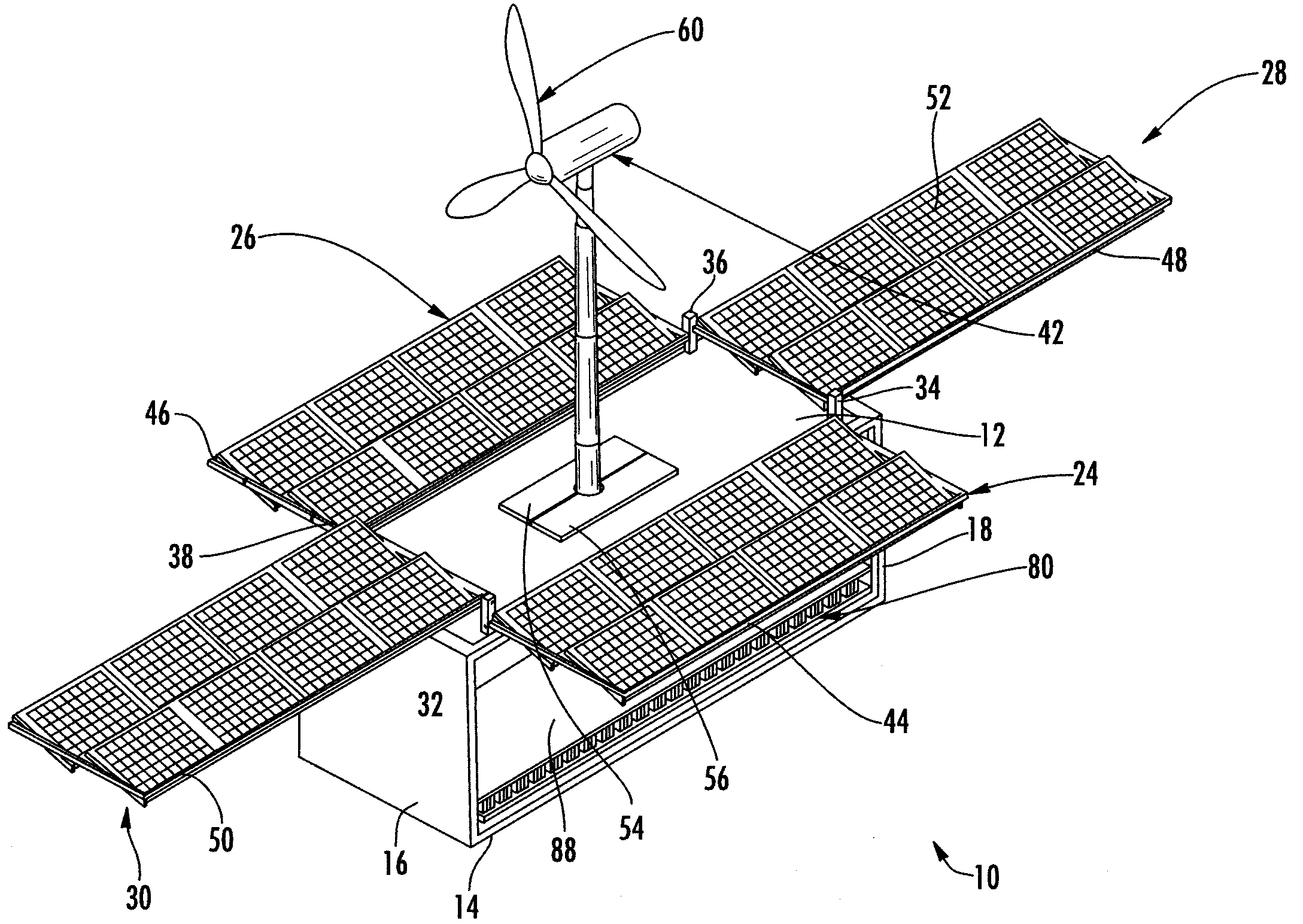
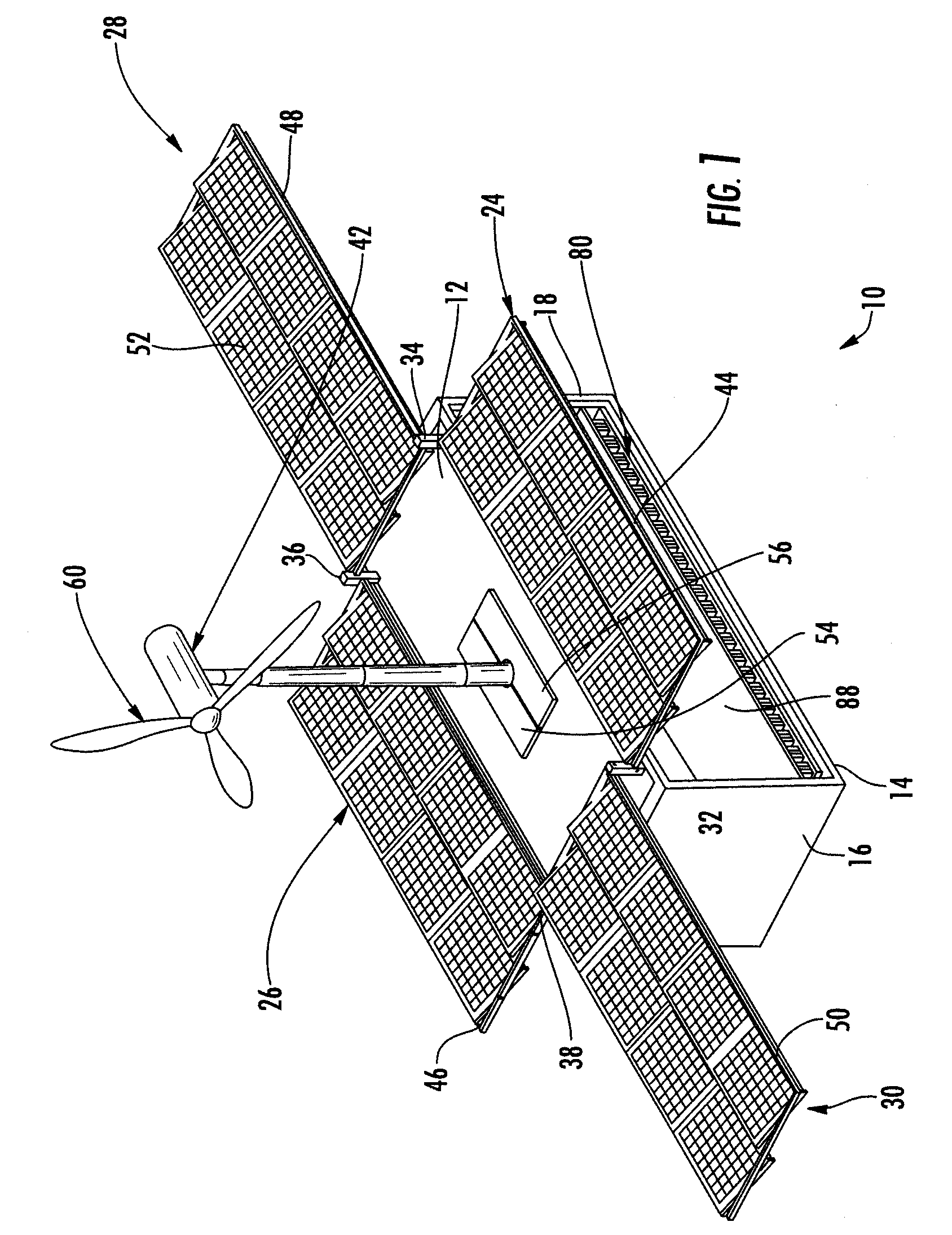
InactiveUS20080196758A1Improve stabilityQuickly and easily deployed by a single personPhotovoltaic supportsPropellersElectricityPower station
A self-sustaining, portable, power station that may be moved by land, air, or sea to an area that has no utilities. The station is provided with at least one wind turbine and / or solar panel arrays in communication with at least one electrical distribution and storage means. The derived electricity is used to power various systems including, albeit not limited to, a communications system, a water filtration system, a water distribution system to allow the public to draw potable water and provide basic hygiene. The electricity derived may also be used to run outside systems, such as schools, hospitals, or the like.
Owner:ECOSPHERE TECH
Method and apparatus for cooling combustor liner and transition piece of a gas turbine
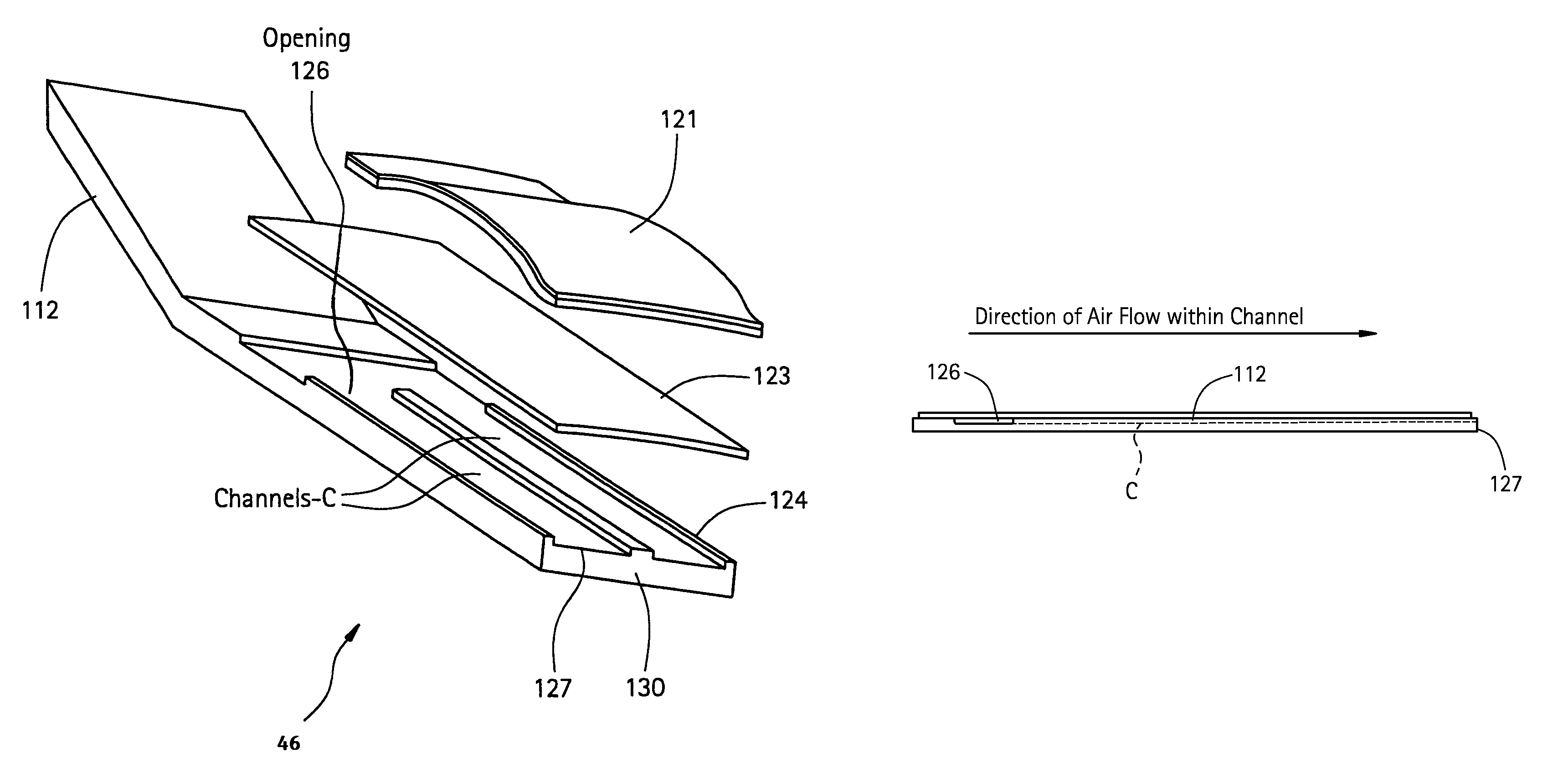
ActiveUS7010921B2Easy to installContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine coolingCombustorTurbine
A method and apparatus for cooling a combustor liner and transitions piece of a gas turbine include a combustor liner with a plurality of circular ring turbulators arranged in an array axially along a length defining a length of the combustor liner and located on an outer surface thereof; a first flow sleeve surrounding the combustor liner with a first flow annulus therebetween including a plurality of axial channels (C) extending over a portion of an aft end portion of the liner parallel to each other, the cross-sectional area of each channel either constant or varying along the length of the channel, the first flow sleeve having a plurality of rows of cooling holes formed about a circumference of the first flow sleeve for directing cooling air from the compressor discharge into the first flow annulus; a transition piece connected to the combustor liner and adapted to carry hot combustion gases to a stage of the turbine; a second flow sleeve surrounding the transition piece a second plurality of rows of cooling apertures for directing cooling air into a second flow annulus between the second flow sleeve and the transition piece; wherein the first plurality of cooling holes and second plurality of cooling apertures are each configured with an effective area to distribute less than 50% of compressor discharge air to the first flow sleeve and mix with cooling air from the second flow annulus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
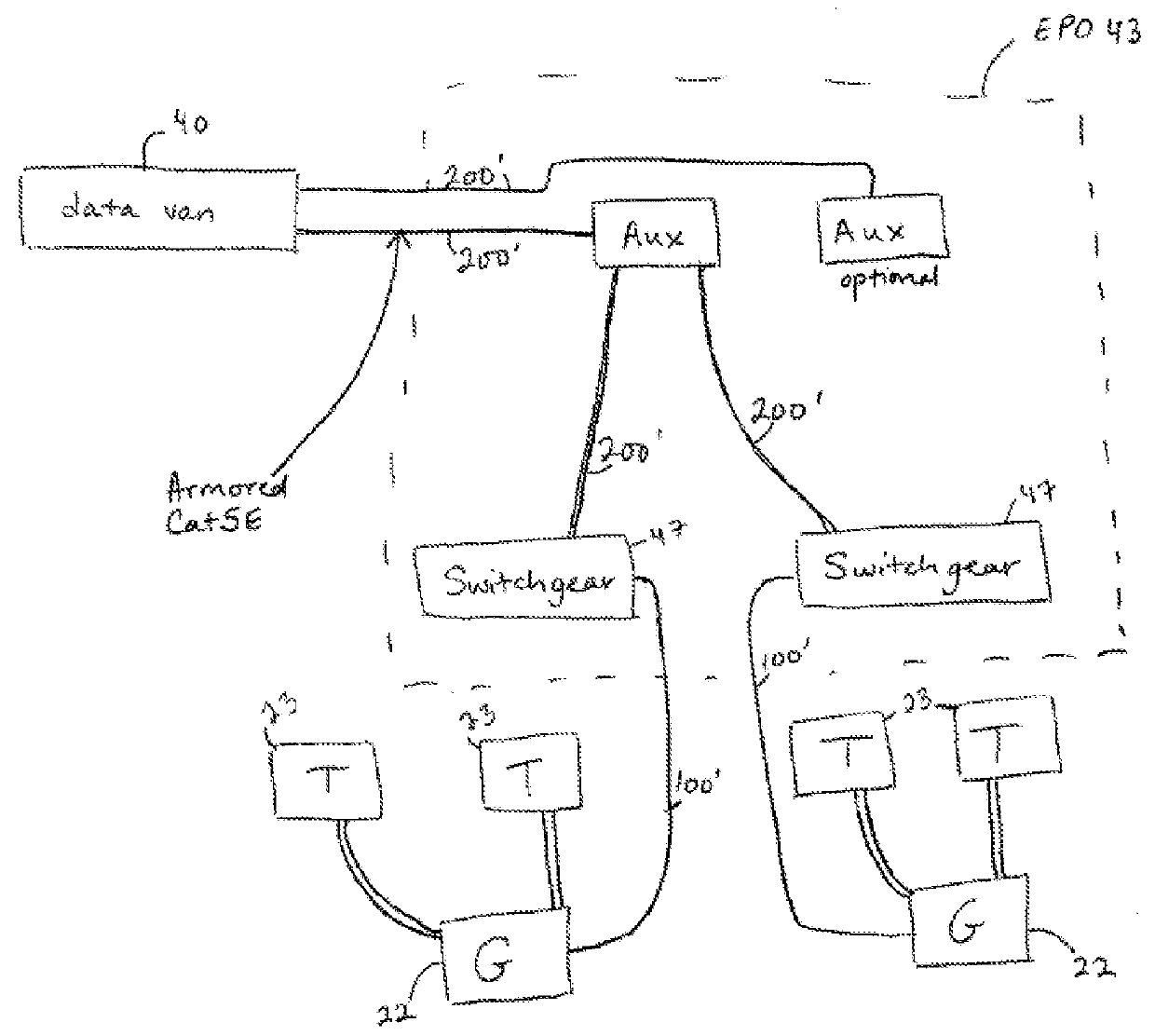
System for centralized monitoring and control of electric powered hydraulic fracturing fleet
A system and method are disclosed for centralized monitoring and control of a hydraulic fracturing operation. The system includes an electric powered fracturing fleet and a centralized control unit coupled to the electric powered fracturing fleet. The electric powered fracturing fleet can include a combination of one or more of: electric powered pumps, turbine generators, blenders, sand silos, chemical storage units, conveyor belts, manifold trailers, hydration units, variable frequency drives, switchgear, transformers, and compressors. The centralized control unit can be configured to monitor and / or control one or more operating characteristics of the electric powered fracturing fleet.
Owner:US WELL SERVICS LLC
Differential geared turbine engine with torque modulation capability
InactiveUS6895741B2Improve efficiencyMinimal numberEngine fuctionsEfficient propulsion technologiesTorque regulationTurbine
A method and apparatus for controllable distribution of power from a turbine of a gas turbine engine between two rotatable loads of the gas turbine engine, comprises transferring a shaft power of the turbine to the respective rotatable loads using differential gearing operatively coupled with the turbine and the rotatable loads, respectively; and controlling the power transfer using machines operatively coupled with the respective rotatable loads, operable as a generator or a motor for selectively taking power from one of the rotatable loads to drive the other of the rotatable loads, or the reverse.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Recuperated gas turbine engine system and method employing catalytic combustion
InactiveUS7007487B2Maximize efficiencyReduce air pollutionTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorCold weather
A recuperated gas turbine engine system and associated method employing catalytic combustion, wherein the combustor inlet temperature can be controlled to remain above the minimum required catalyst operating temperature at a wide range of operating conditions from full-load to part-load and from hot-day to cold-day conditions. The fuel is passed through the compressor along with the air and a portion of the exhaust gases from the turbine. The recirculated exhaust gas flow rate is controlled to control combustor inlet temperature.
Owner:MES INT INC
Method of generating energy in a power plant comprising a gas turbine, and power plant for carrying out the method
InactiveUS20050028529A1Small sizeLow costContinuous combustion chamberDispersed particle separationPower stationCombustor
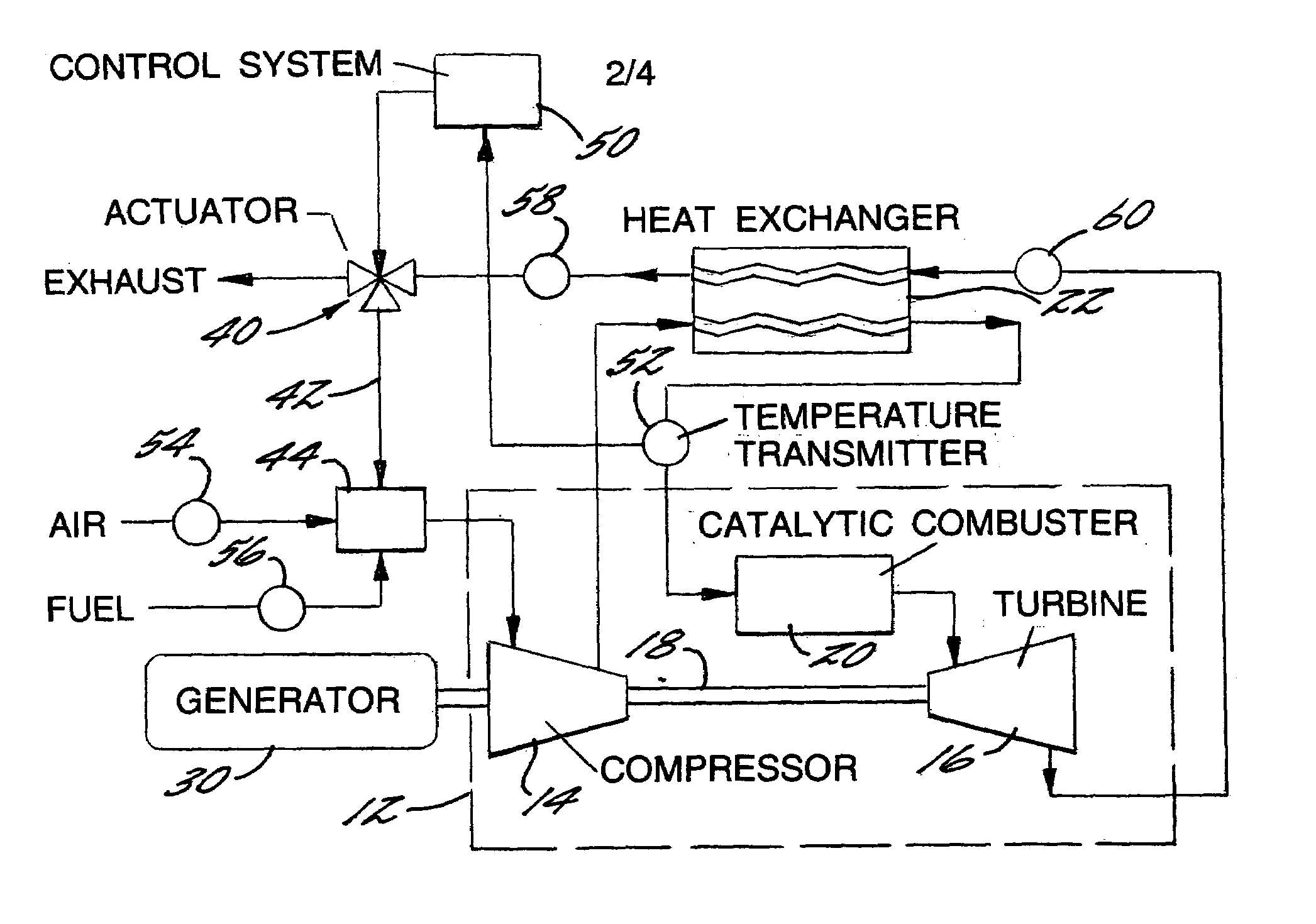
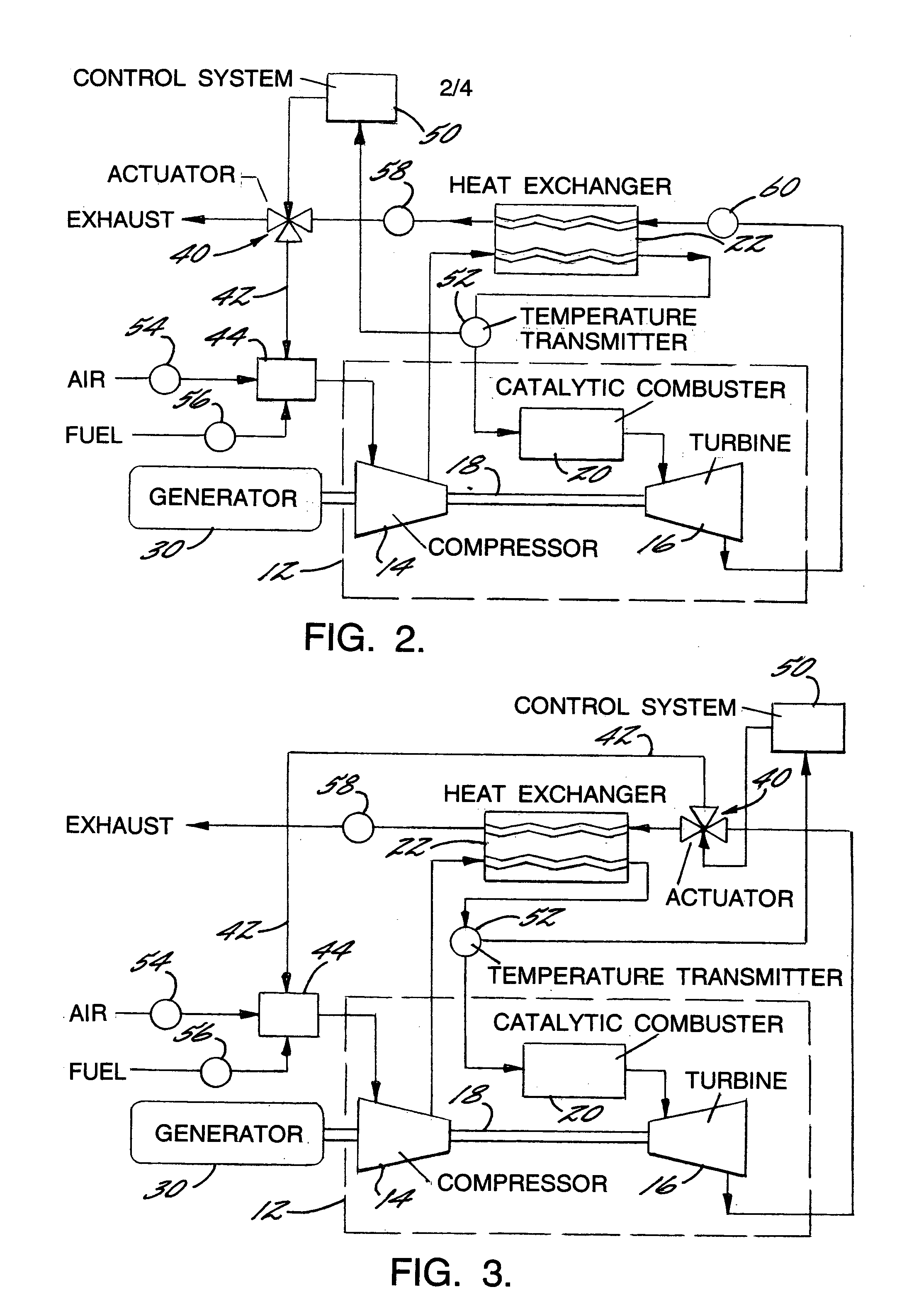
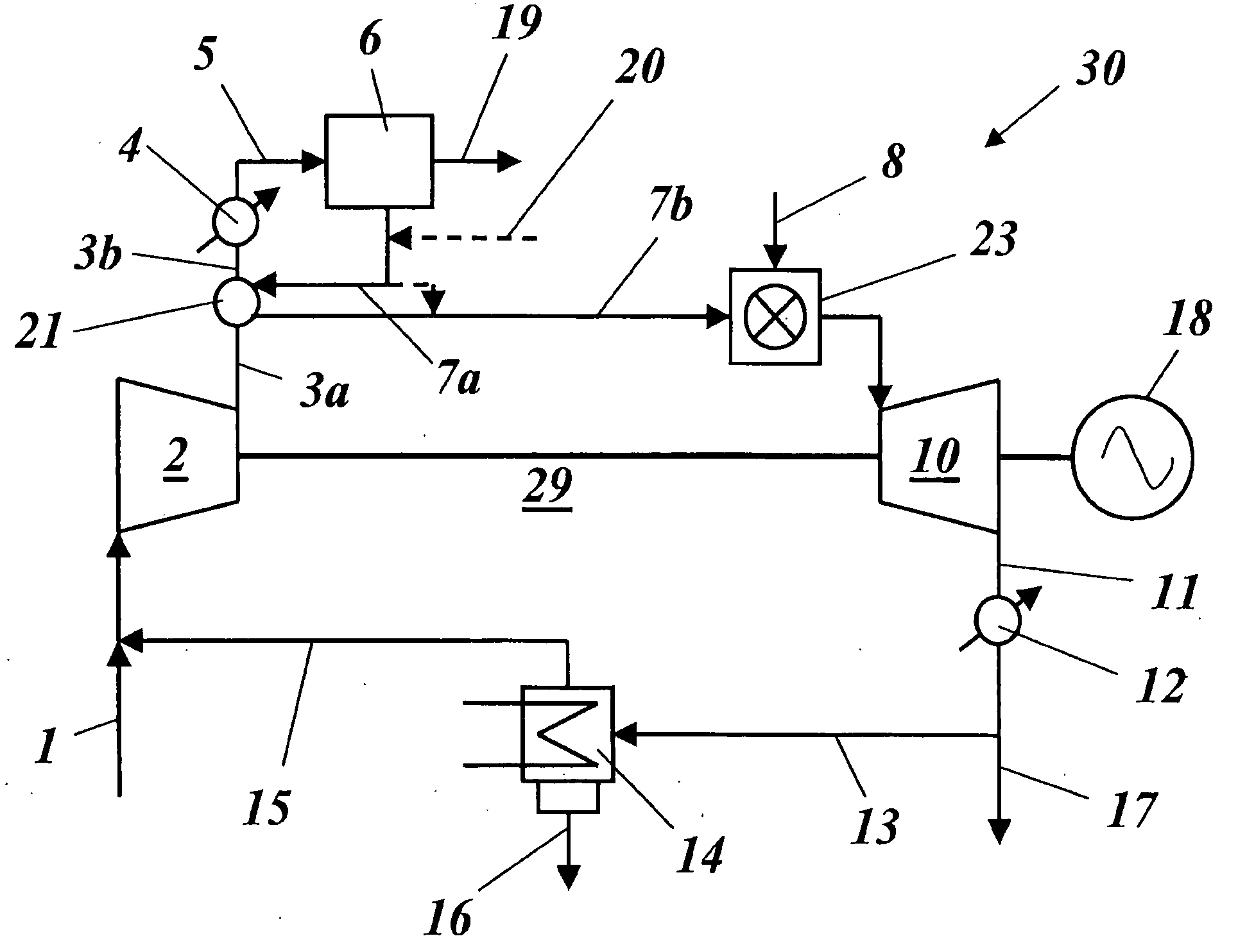
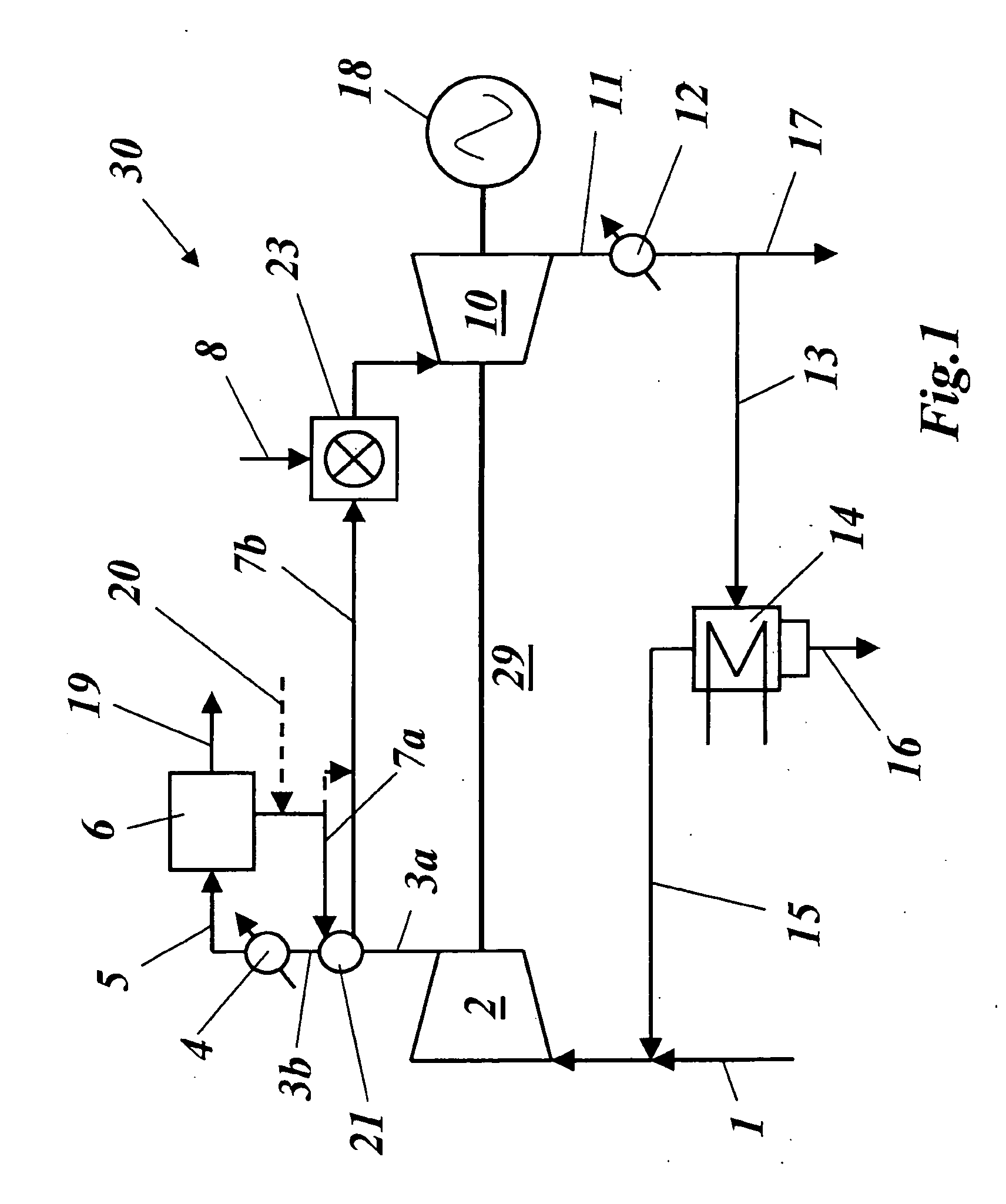
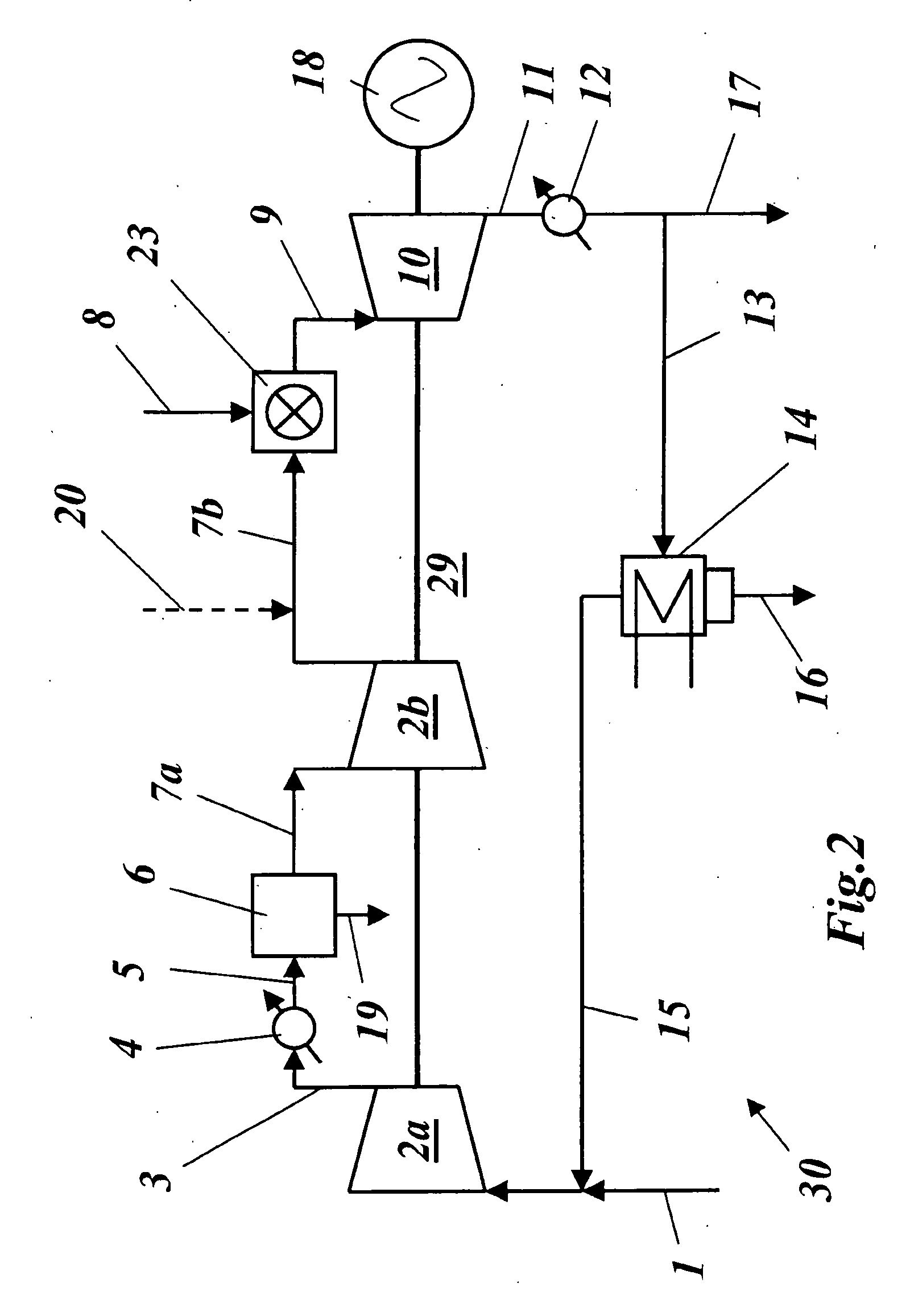
A method of generating energy in a power plant (30) having a gas turbine (29), includes a first step a gas containing air (1) is compressed in a first compressor (2) of the gas turbine (29), a second step the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5; 7a, 7b) is fed to a combustion process with the addition of fuel (8) in a combustor (23), a third step the hot flue gas (9) from the combustor (23) is expanded in an expander or a turbine (10), driving a generator (18), of the gas turbine (29) while performing work, and a fourth step a partial flow of the expanded flue gas (11) is recirculated to the inlet of the first compressor (2) and admixed with the gas containing air (1). Carbon dioxide (CO2) is separated from the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5; 7a, 7b) in a CO2 separator (6) before the third step. In such a method, the overall size and energy costs are reduced by virtue of the fact that, to permit increased CO2 concentrations in the CO2 separator (6), not more than about 70% of the carbon dioxide contained in the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5, 5a, 5b; 7a, 7b) is removed from the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5, 5a, 5b; 7a, 7b).
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
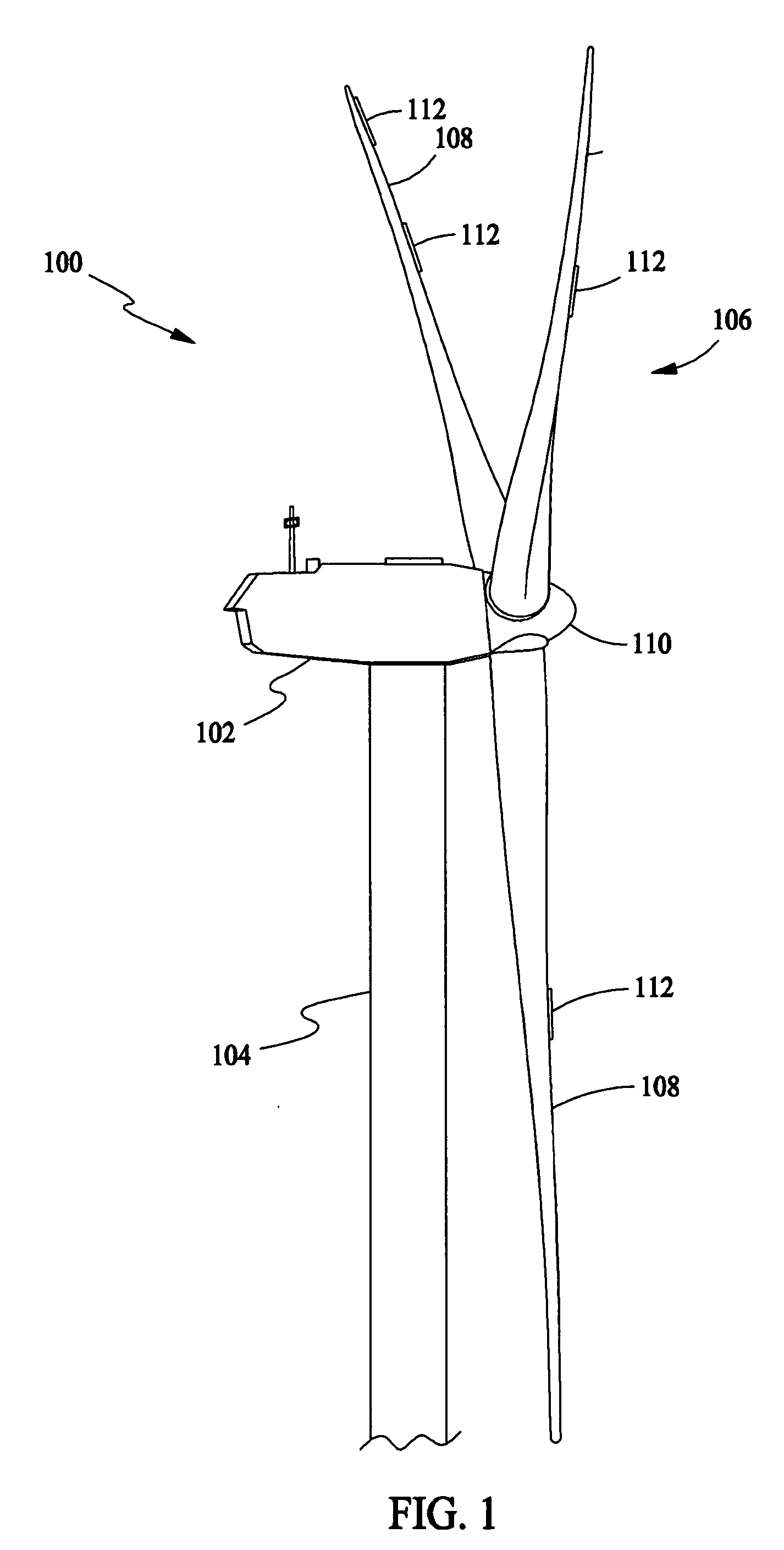
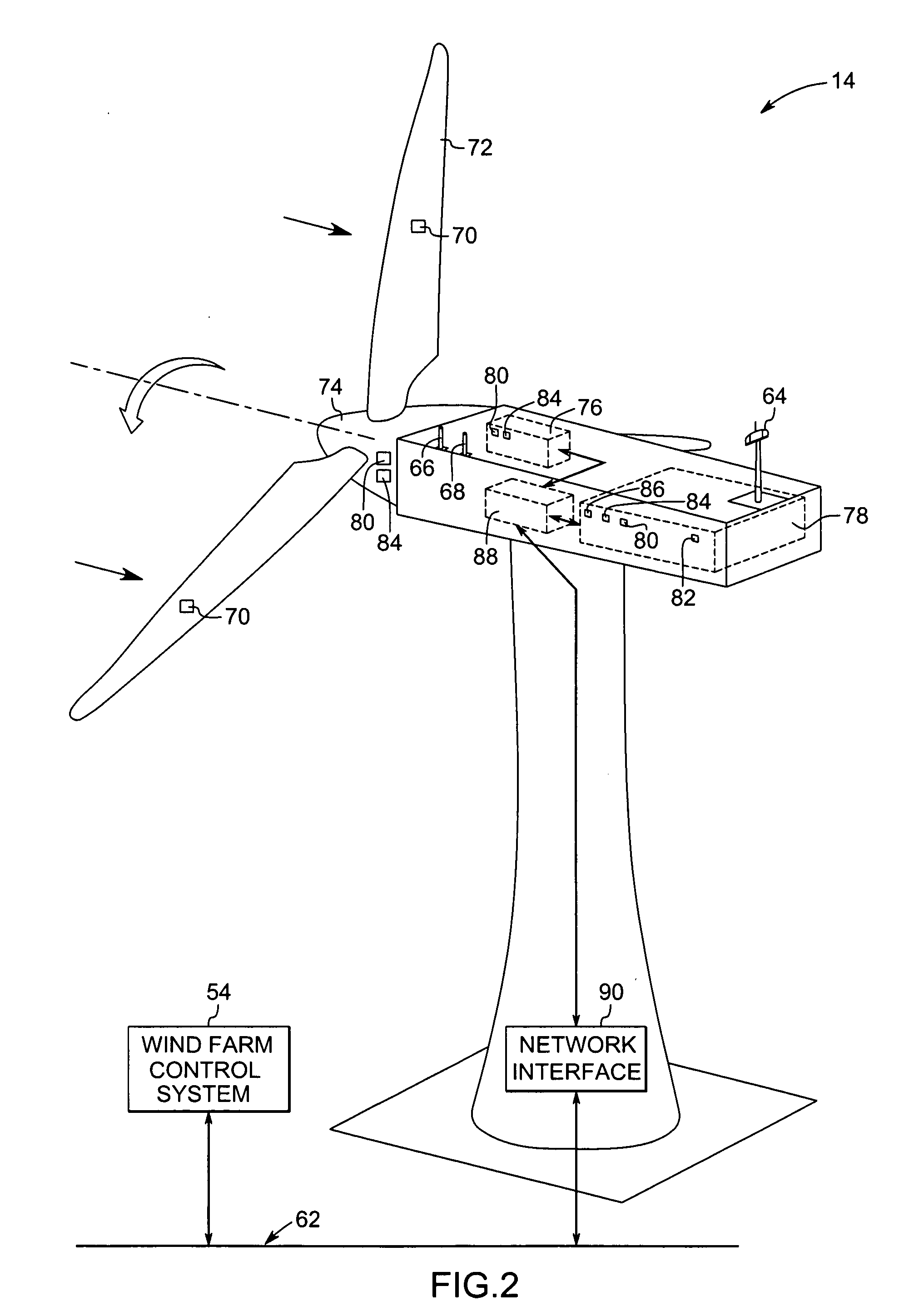
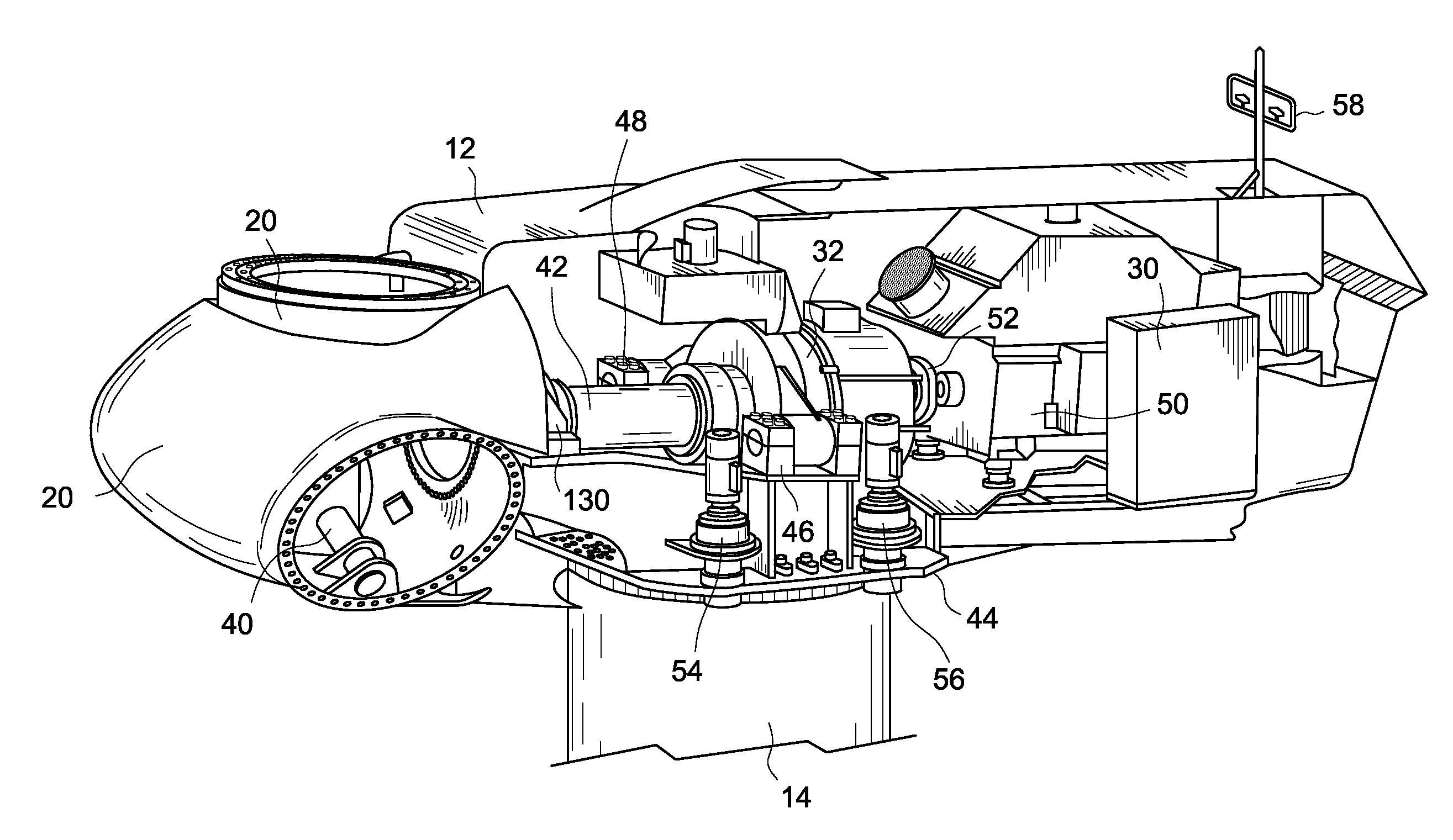
System and method for monitoring wind turbine gearbox health and performance
A system and method are provided to monitor the health and performance of a wind turbine gearbox. A plurality of sensors coupled to the wind turbine gearbox provide input to a controller. The controller generates output information that includes performance and health information of the wind turbine gearbox based on the input received from each of the sensors.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
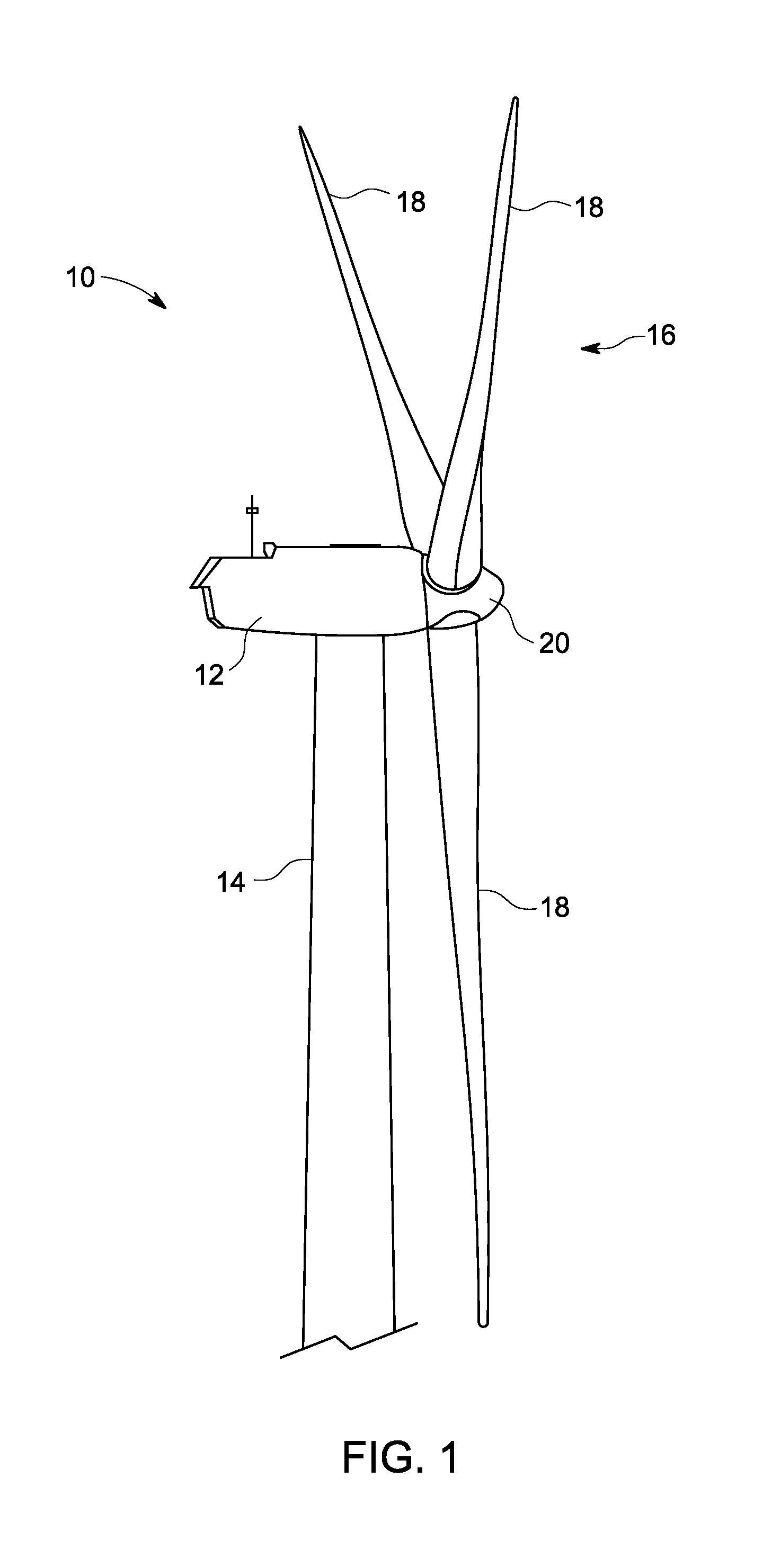
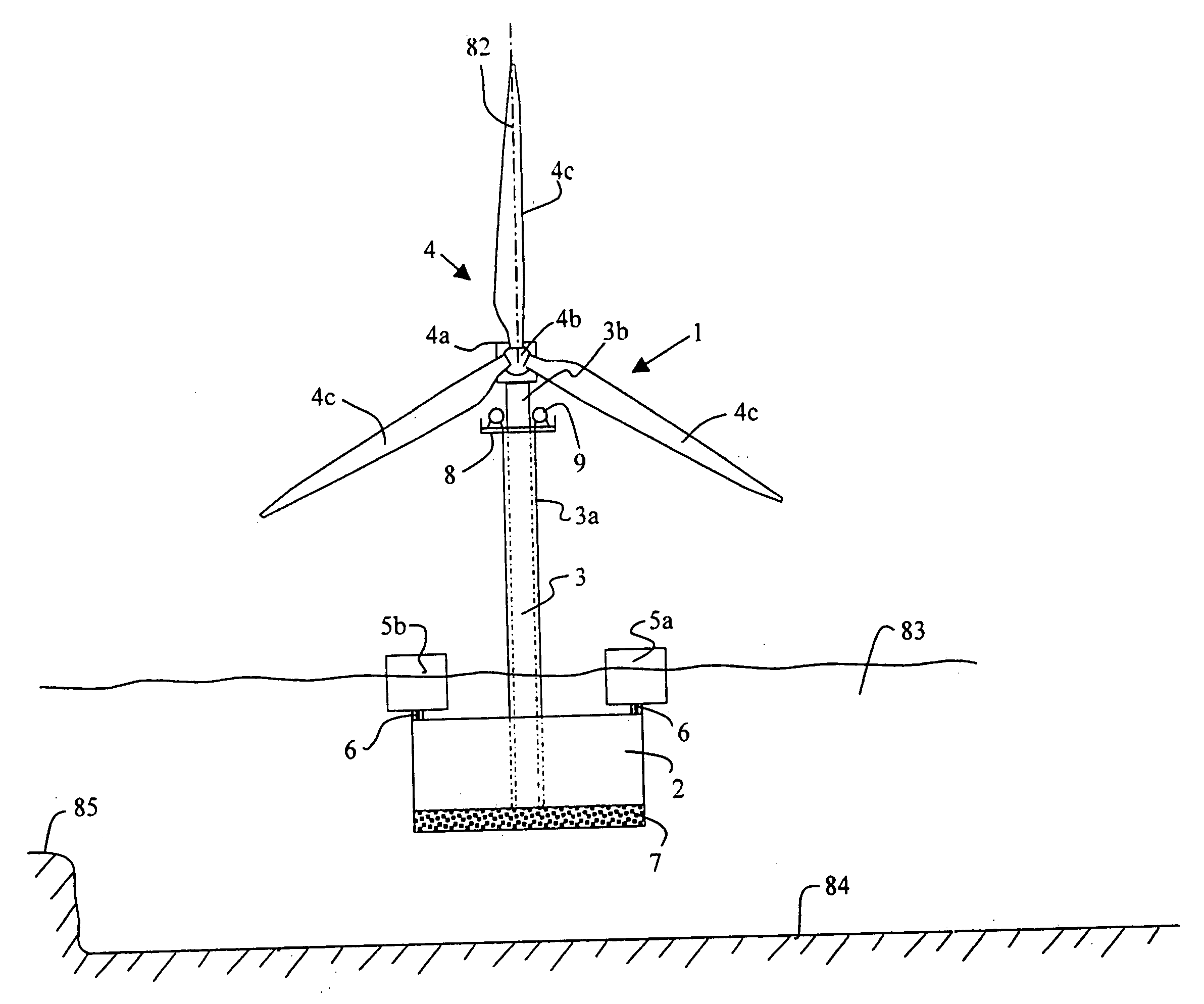
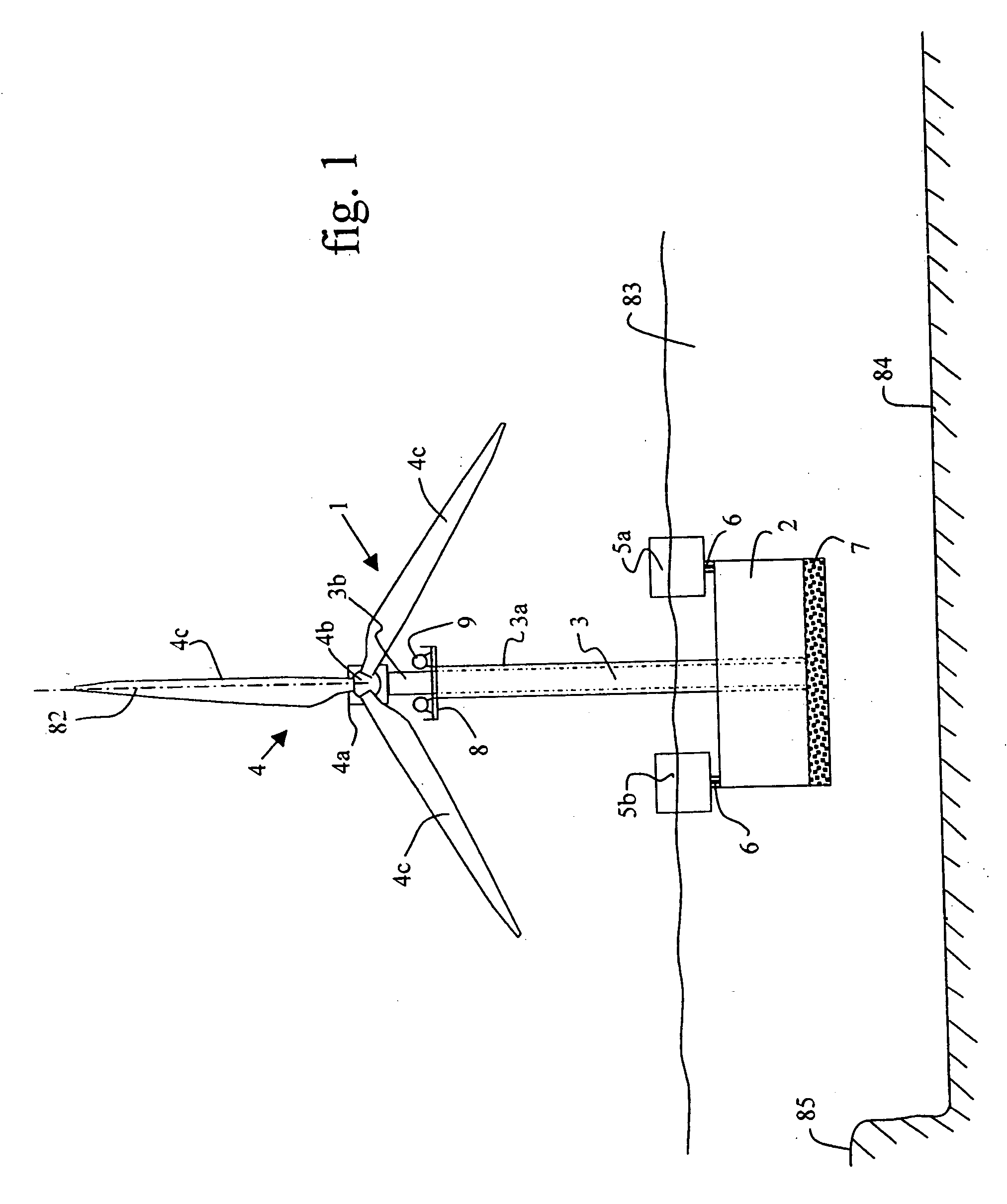
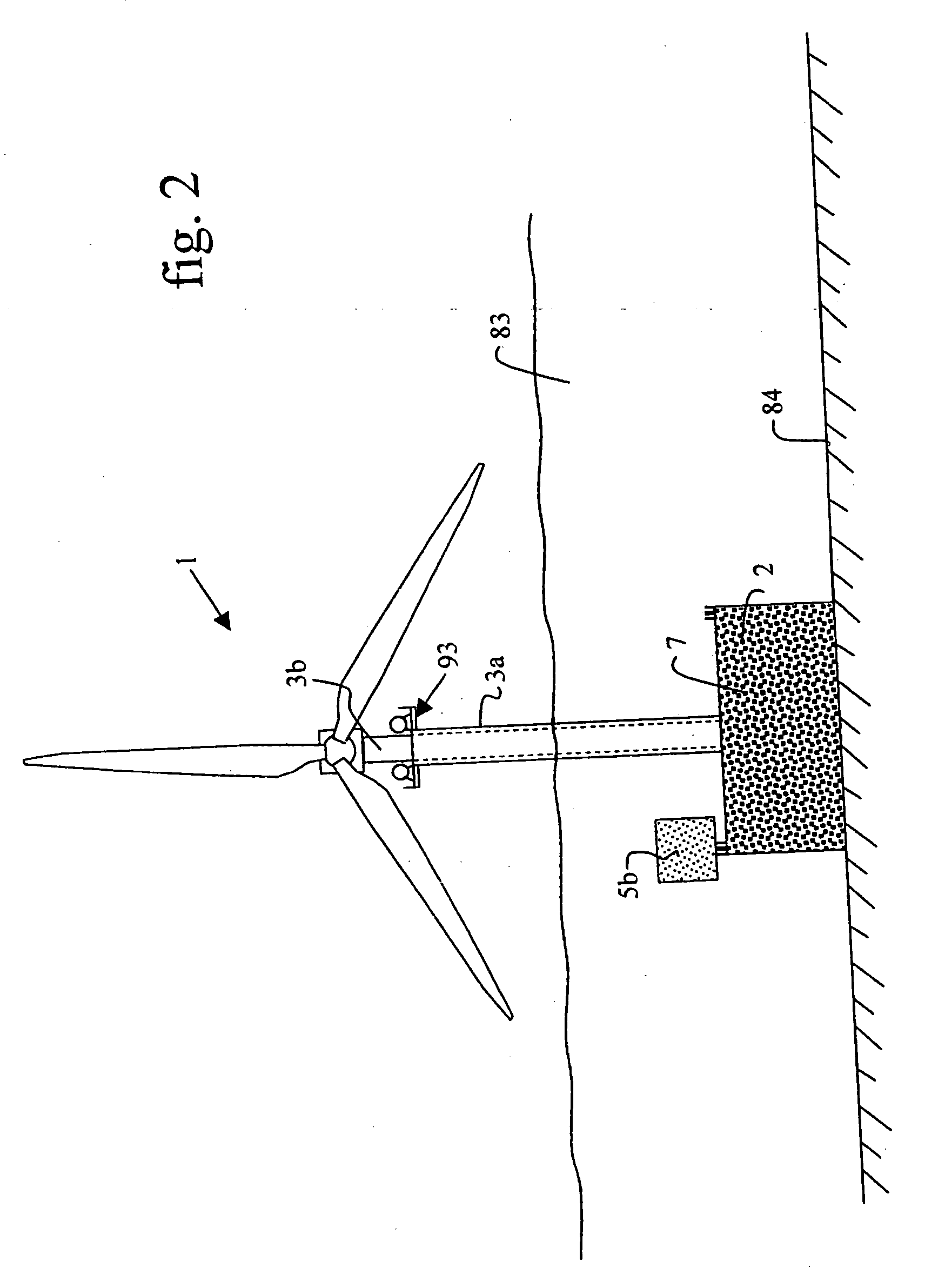
Offshore wind turbine and method for making same
InactiveUS20040169376A1Reduce usageEasy to transportEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureElectricityEngineering
The present invention relates to wind generators installed off-shore, in particular at sea, to support structures forming a part of such wind generators, and to methods of making and installing such wind generators. The technical field of the invention is that of making, transporting, and installing wind generators for producing electricity, more particularly off-shore, and in large numbers, so as to form wind "farms". The wind generator of the invention comprises a wind turbine and a deployable telescopic pylon or support supporting the turbine, and a gravity base supporting the pylon or support.
Owner:SAIPEM SA
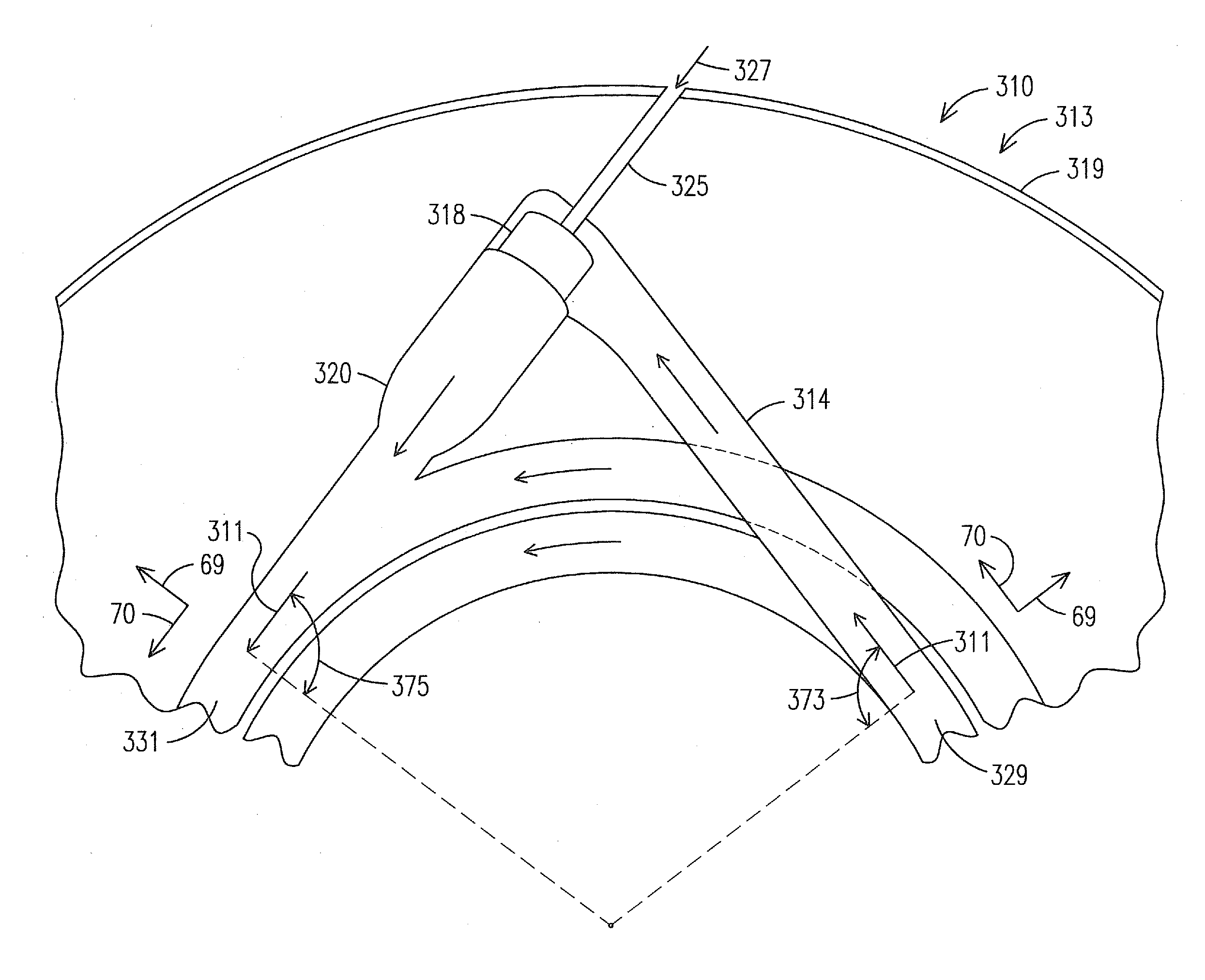
Mid-section of a can-annular gas turbine engine with an improved rotation of air flow from the compressor to the turbine
InactiveUS20130219853A1Easy to operateReduce lossesContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustorTurbine
A midframe portion (313) of a gas turbine engine (310) is presented and includes a compressor section with a last stage blade to orient an air flow (311) at a first angle (372). The midframe portion (313) further includes a turbine section with a first stage blade to receive the air flow (311) oriented at a second angle (374). The midframe portion (313) further includes a manifold (314) to directly couple the air flow (311) from the compressor section to a combustor head (318) upstream of the turbine section. The combustor head (318) introduces an offset angle in the air flow (311) from the first angle (372) to the second angle (374) to discharge the air flow (311) from the combustor head (318) at the second angle (374). While introducing the offset angle, the combustor head (318) at least maintains or augments the first angle (372).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
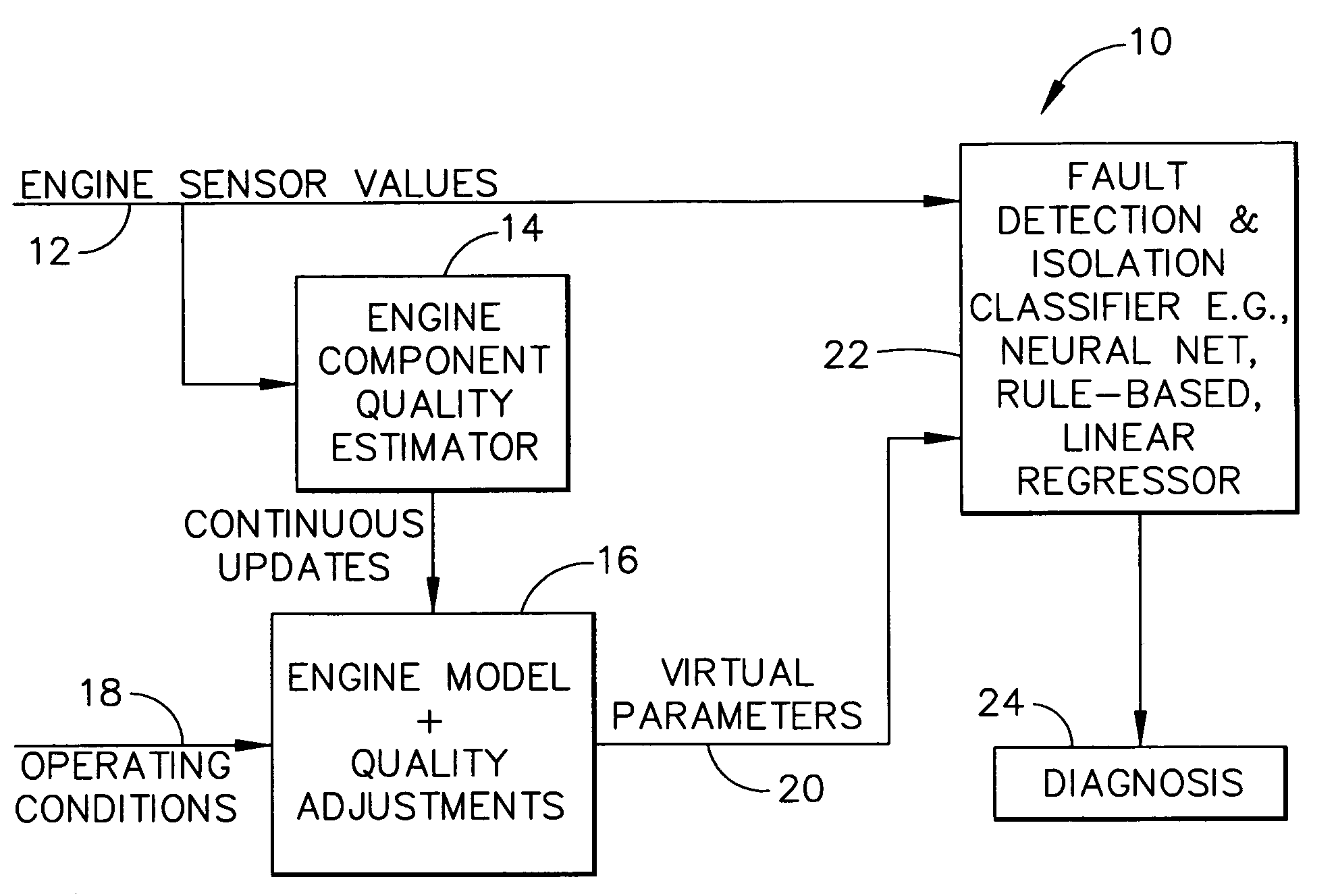
Methods and apparatus for model based diagnostics
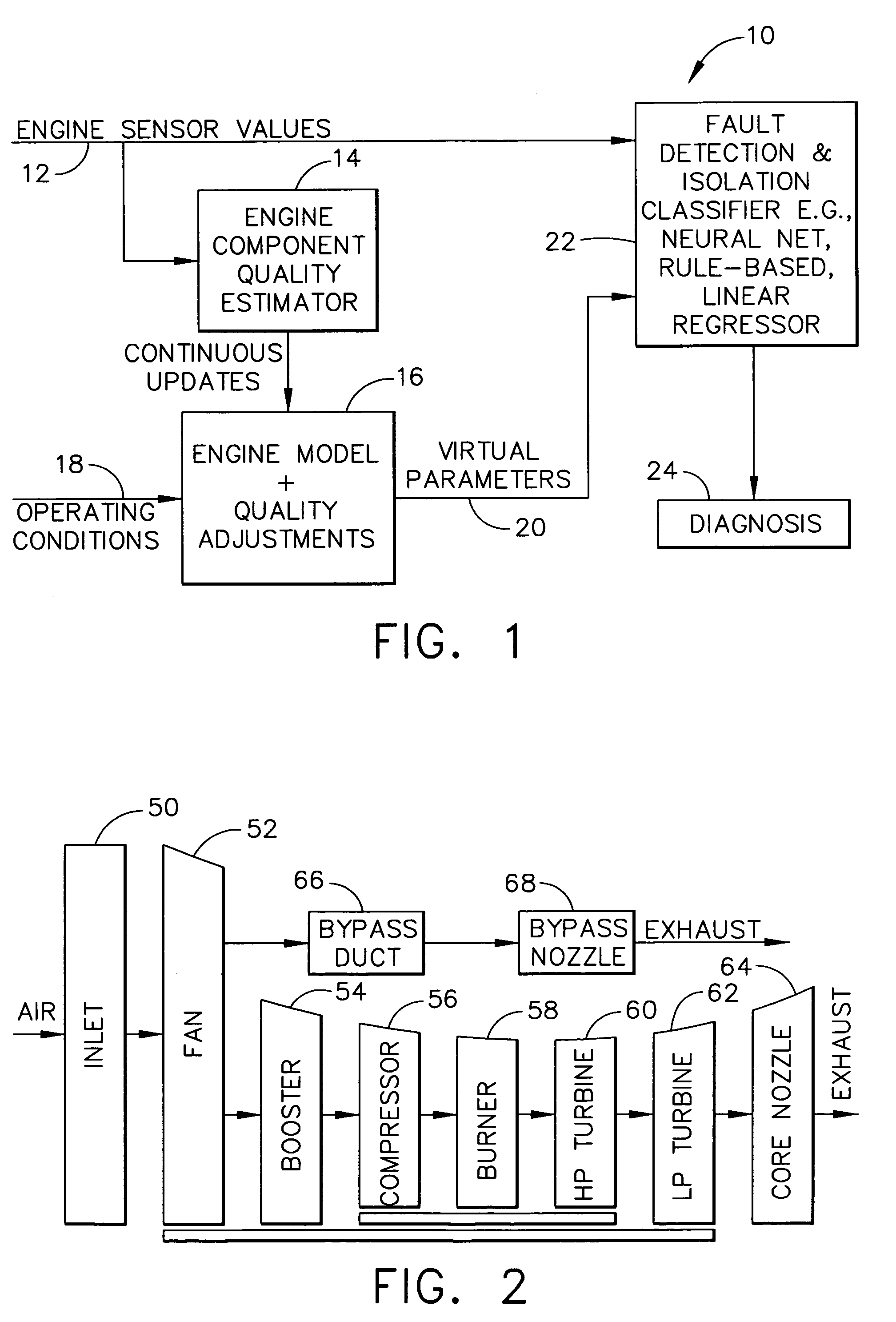
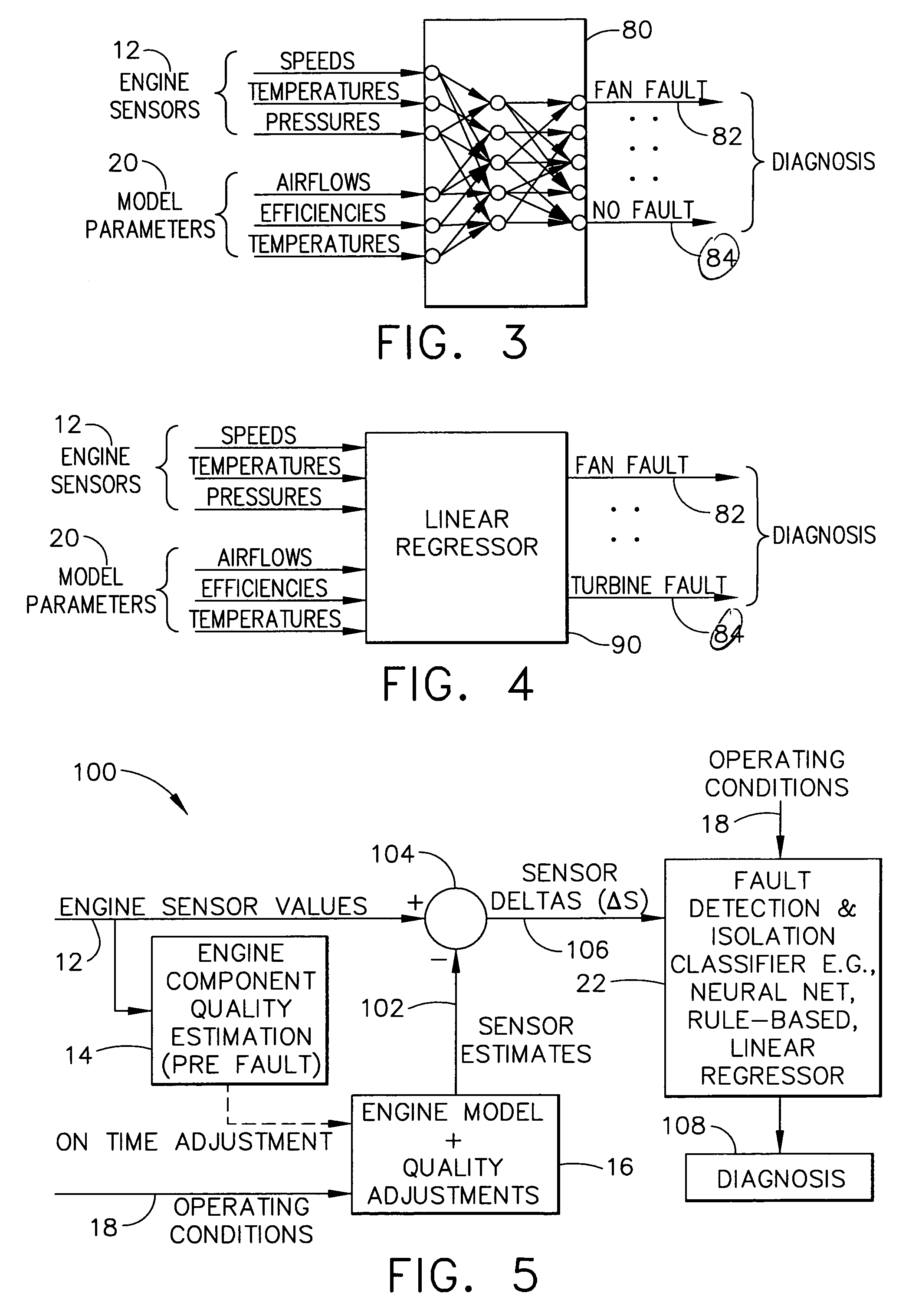
Systems and methods for performing module-based diagnostics are described. In an exemplary embodiment, sensor values from an actual engine plant are input to an engine component quality estimator which generates performance estimates of major rotating components. Estimated performance differences are generating by comparing the generated performance estimates to a nominal quality engine. The estimated performance differences, which are indicative of component quality, are continuously updated and input to a real-time model of the engine. The model receives operating conditional data and the quality estimates are used to adjust the nominal values in the model to more closely match the model values to the actual plant. Outputs from the engine model are virtual parameters, such as stall margins, specific fuel consumption, and fan / compressor / turbine efficiencies. The virtual parameters are combined with the sensor values from the actual engine plant in a fault detection and isolation classifier to identify abnormal conditions and / or specific fault classes, and output a diagnosis.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System for centralized monitoring and control of electric powered hydraulic fracturing fleet
A system and method are disclosed for centralized monitoring and control of a hydraulic fracturing operation. The system includes an electric powered fracturing fleet and a centralized control unit coupled to the electric powered fracturing fleet. The electric powered fracturing fleet can include a combination of one or more of: electric powered pumps, turbine generators, blenders, sand silos, chemical storage units, conveyor belts, manifold trailers, hydration units, variable frequency drives, switchgear, transformers, and compressors. The centralized control unit can be configured to monitor and / or control one or more operating characteristics of the electric powered fracturing fleet.
Owner:US WELL SERVICS LLC
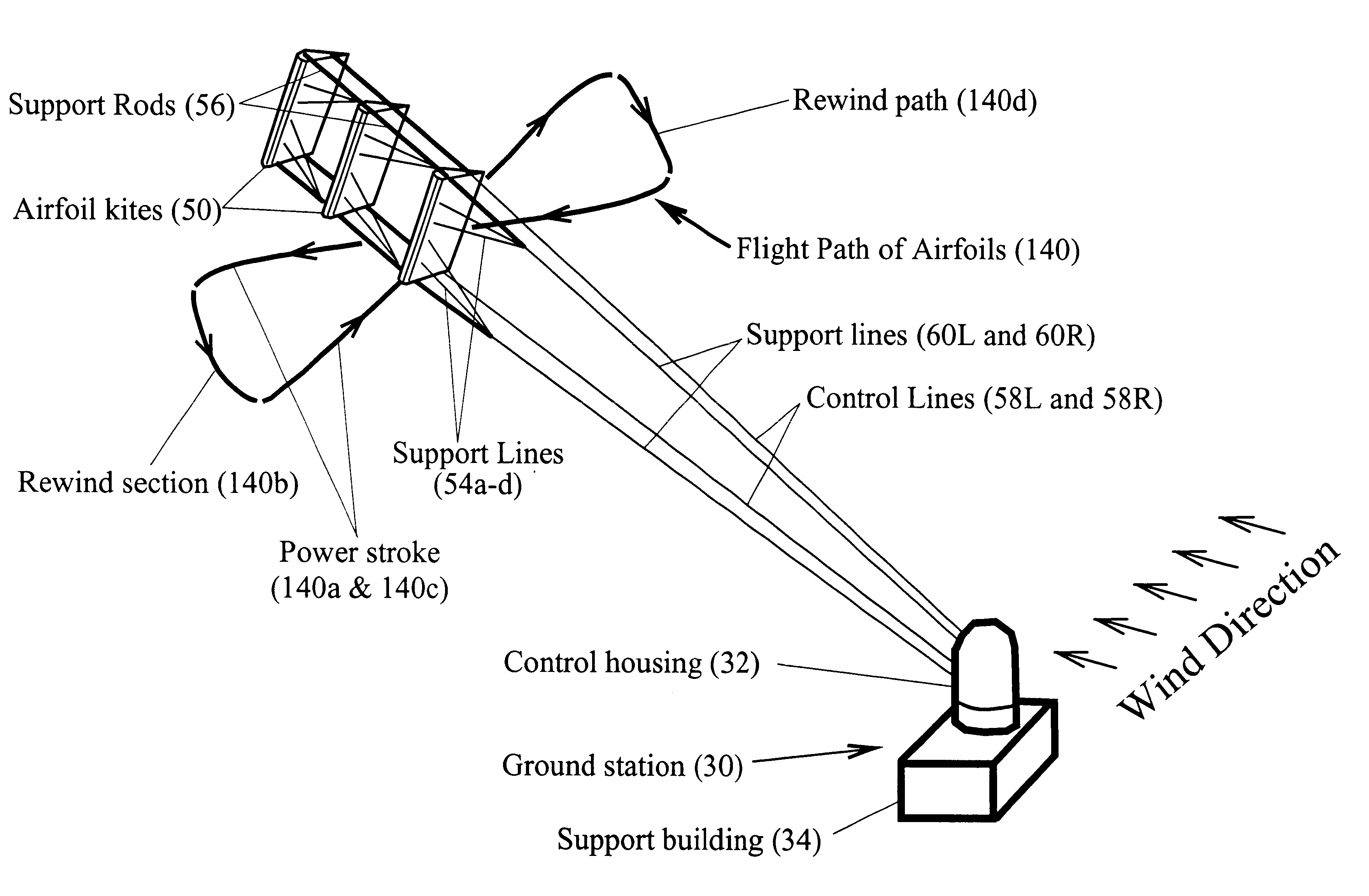
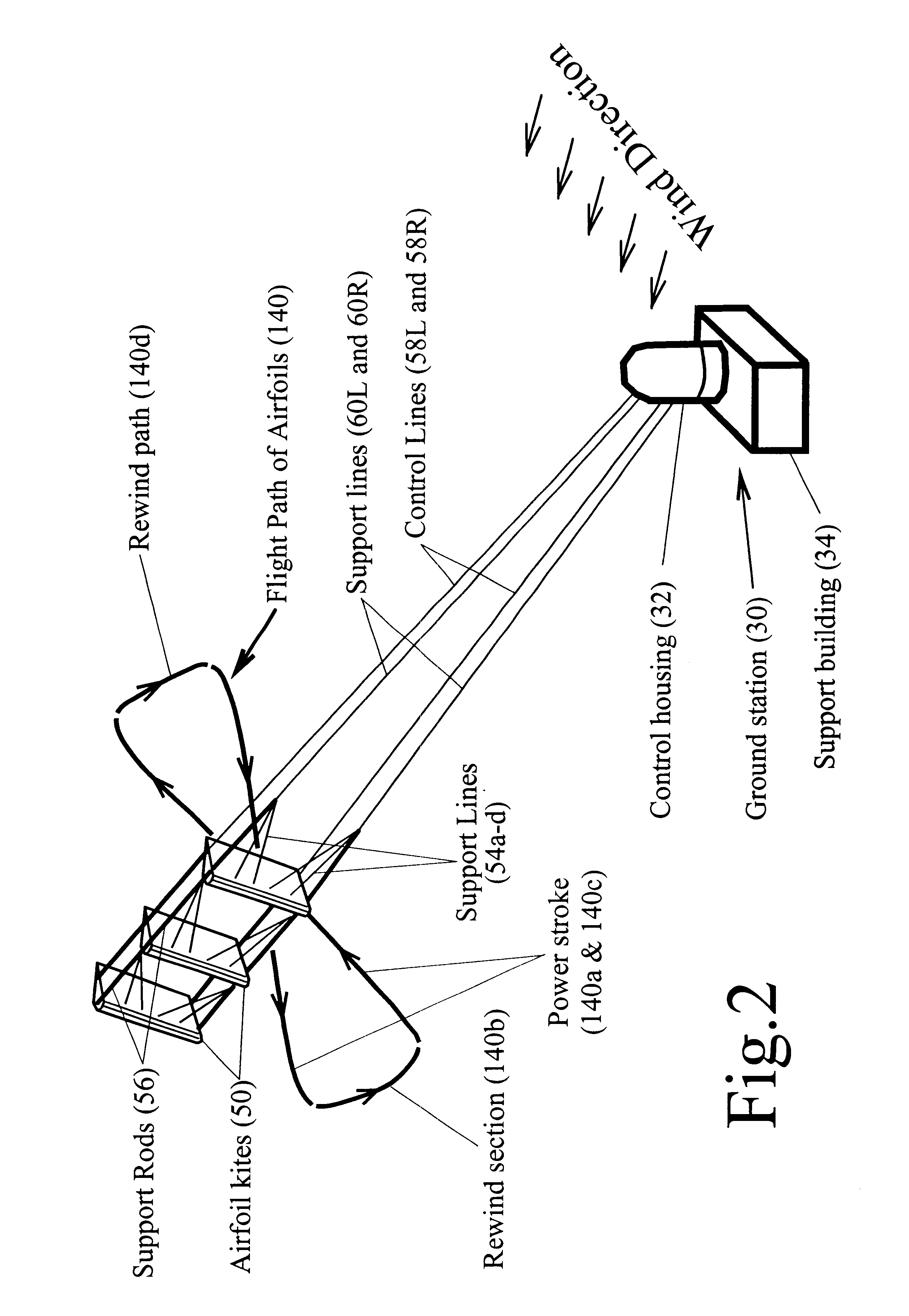
Axial-mode linear wind-turbine
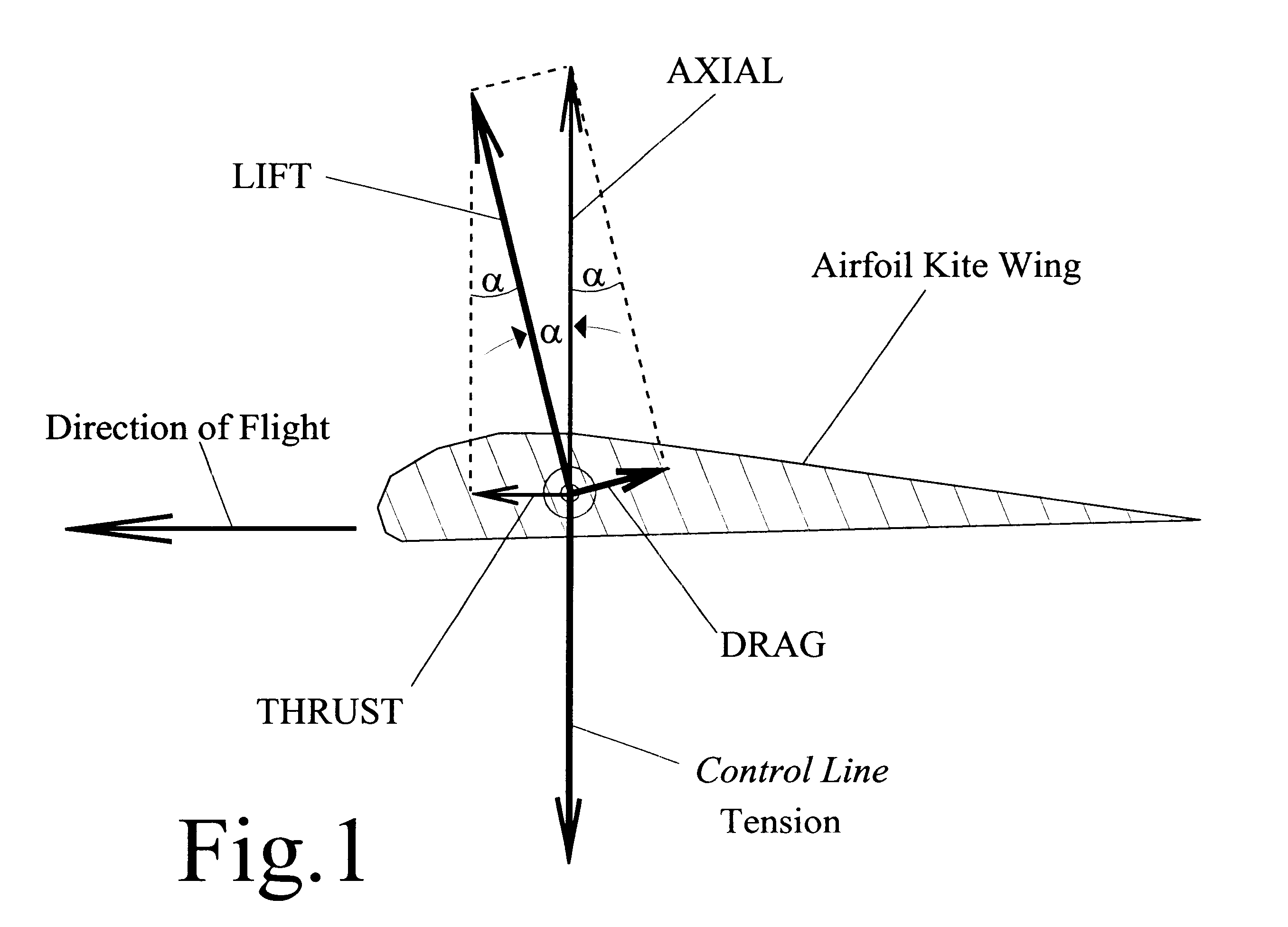
A wind harnessing system using a plurality of self supporting airfoil kites 50 for production of useful power. The system comprising multiple airfoil kites 50 in tandem attached to a pivotal control housing 32 by control lines 58L and 58R and support lines 60L and 60R. Control lines 58L and 58R can change length with respect to the length of support lines 60L and 60R to control the airfoil kites' 50 angle-of-attack, pitch angle, direction of flight, and flight speed. The length of control lines 58L and 58R are controlled from ground station 30 by a movable pulley system in control housing 32 to adjust the airfoils' direction to follow a specific flight path 140. Control lines 58R and 58L and support lines 60R and 60L are also wound on a power shaft and pulley system in control housing 32. As the airfoil kites are propelled by the wind at very-high speed, the airfoils generate a powerful AXIAL force. The control lines 58L and 58R and support lines 60L and 60R are then reeled-out under this AXIAL tension causing the power shaft and pulley system in control housing 32 to turn a generator to generate electricity. After airfoil kites 50 have finished their reel-out power stroke 140a, the airfoil's pitch angle is made negative so they can be reeled-in by their control and support lines using a minimum of force along path 140b. Once the airfoils have been rewound to the proper distance, the airfoils are again angled for high-speed operation to generate powerful AXIAL force and reeled-out along 140c to provide another power stroke. The airfoil kites are then reeled-in again along path 140d and the entire process repeats starting with power stroke 140a. Since the force to rewind the airfoils is much less than the force generated during reel-out, there is net power generated.
Owner:RAGNER GARY DEAN
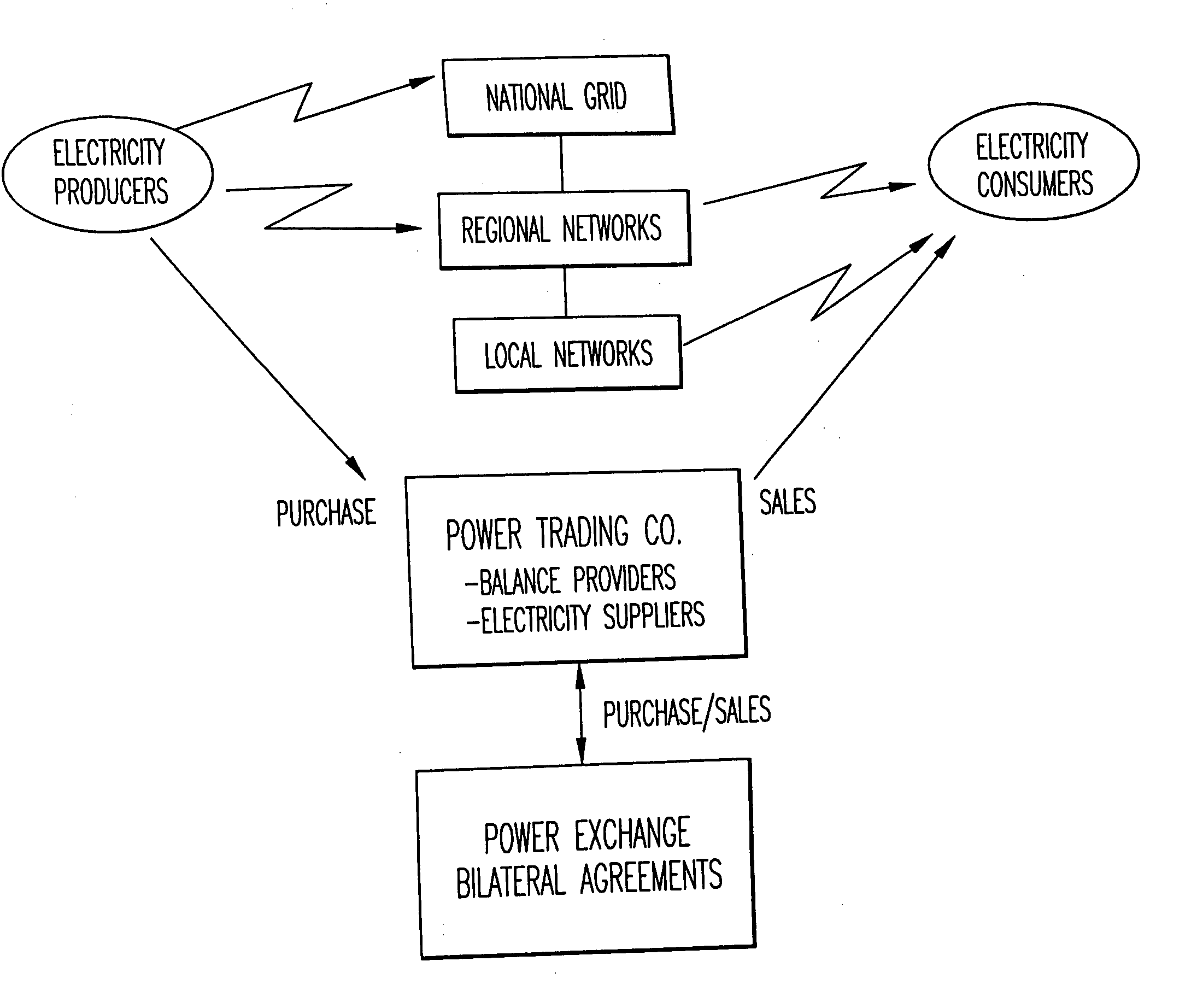
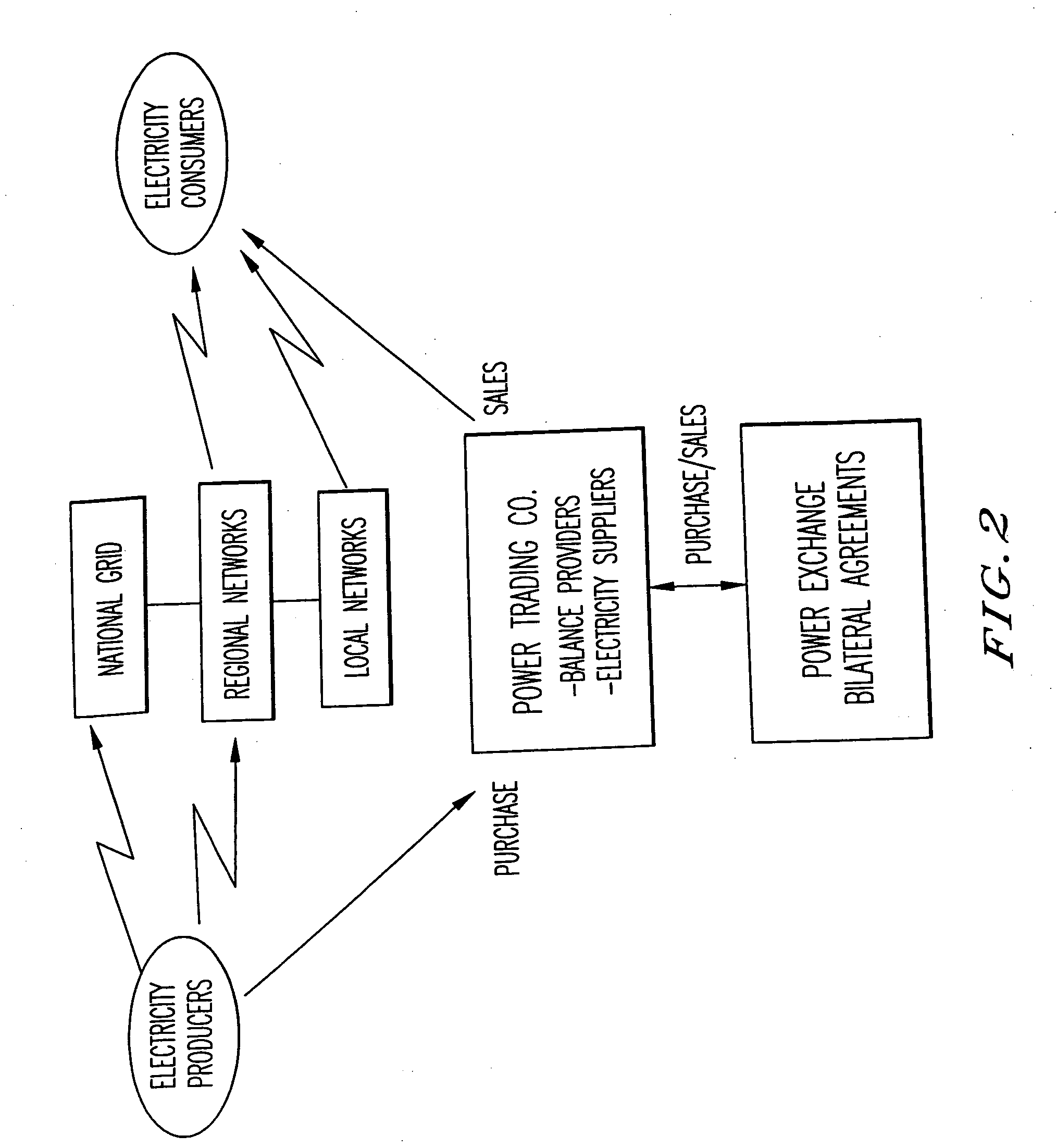
System, method and computer program product for enhancing commercial value of electrical power produced from a renewable energy power production facility
InactiveUS20050127680A1Increase power valueInherent market valueWind motor controlEngine fuctionsPower exchangeRenewable power generation
A method, system and computer program product enhance the commercial value of electrical power produced from a wind turbine production facility. Features include the use of a premier power conversion device that provides an alternative source of power for supplementing an output power of the wind turbine generation facility when lull periods for wind speed appear. The invention includes a communications infrastructure and coordination mechanism for establishing a relationship with another power production facility such that when excess electrical power is produced by the wind turbine facility, the excess may be provided to the power grid while the other energy production facility cuts back on its output production by a corresponding amount. A tracking mechanism keeps track of the amount of potential energy that was not expended at the other facility and places this amount in a virtual energy storage account, for the benefit of the wind turbine facility. When, the wind turbine power production facility experiences a shortfall in its power production output it may make a request to the other source of electric power, and request that an increase its power output on behalf of the wind turbine facility. This substitution of one power production facility for another is referred to herein as a virtual energy storage mechanism. Furthermore, another feature of the present invention is the use of a renewal power exchange mechanism that creates a market for trading renewable units of power, which have been converted into “premier power” and / or “guaranteed” by secondary sources of power source to provide a reliable source of power to the power grid as required by contract.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method for analysis of the operation of a gas turbine
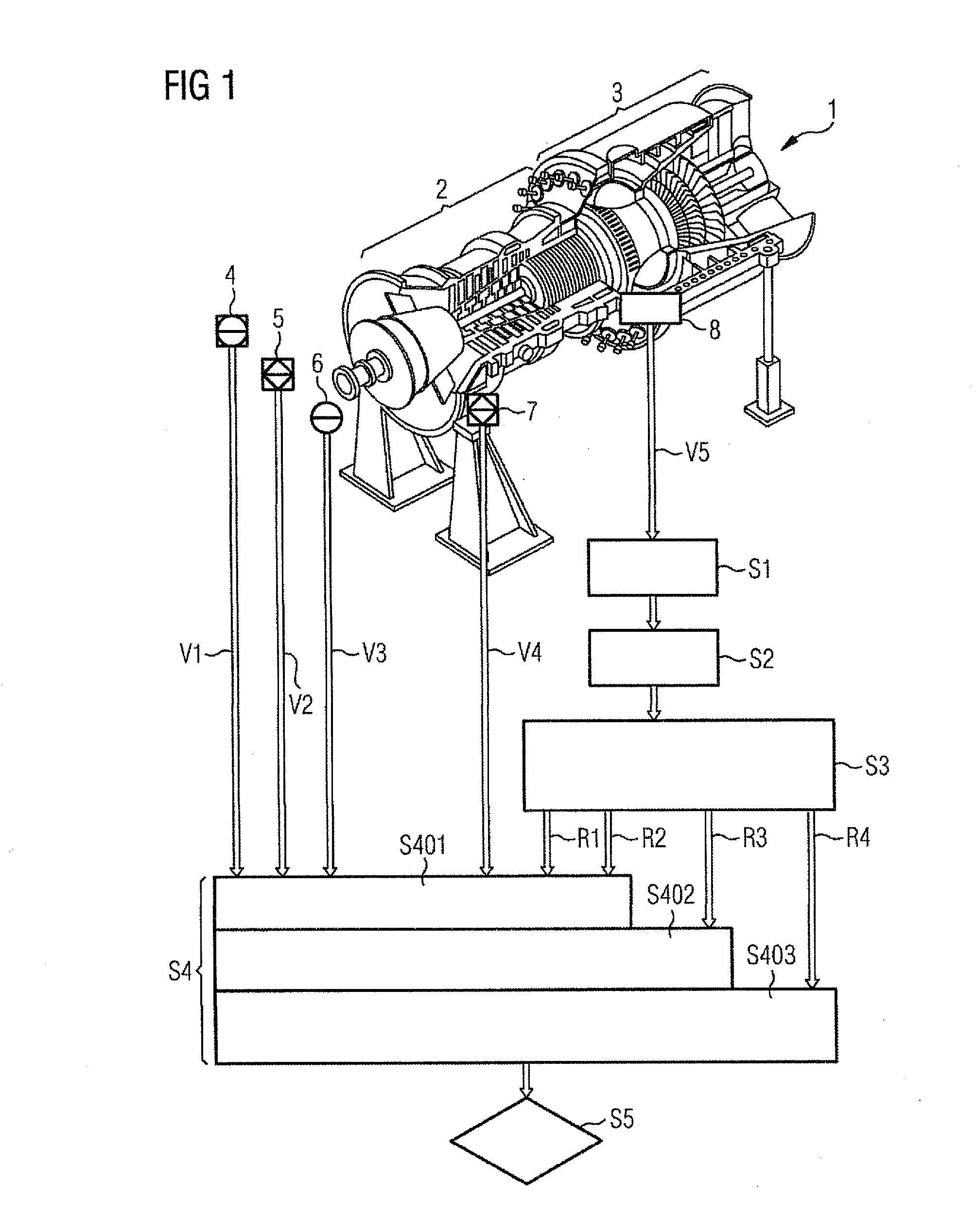
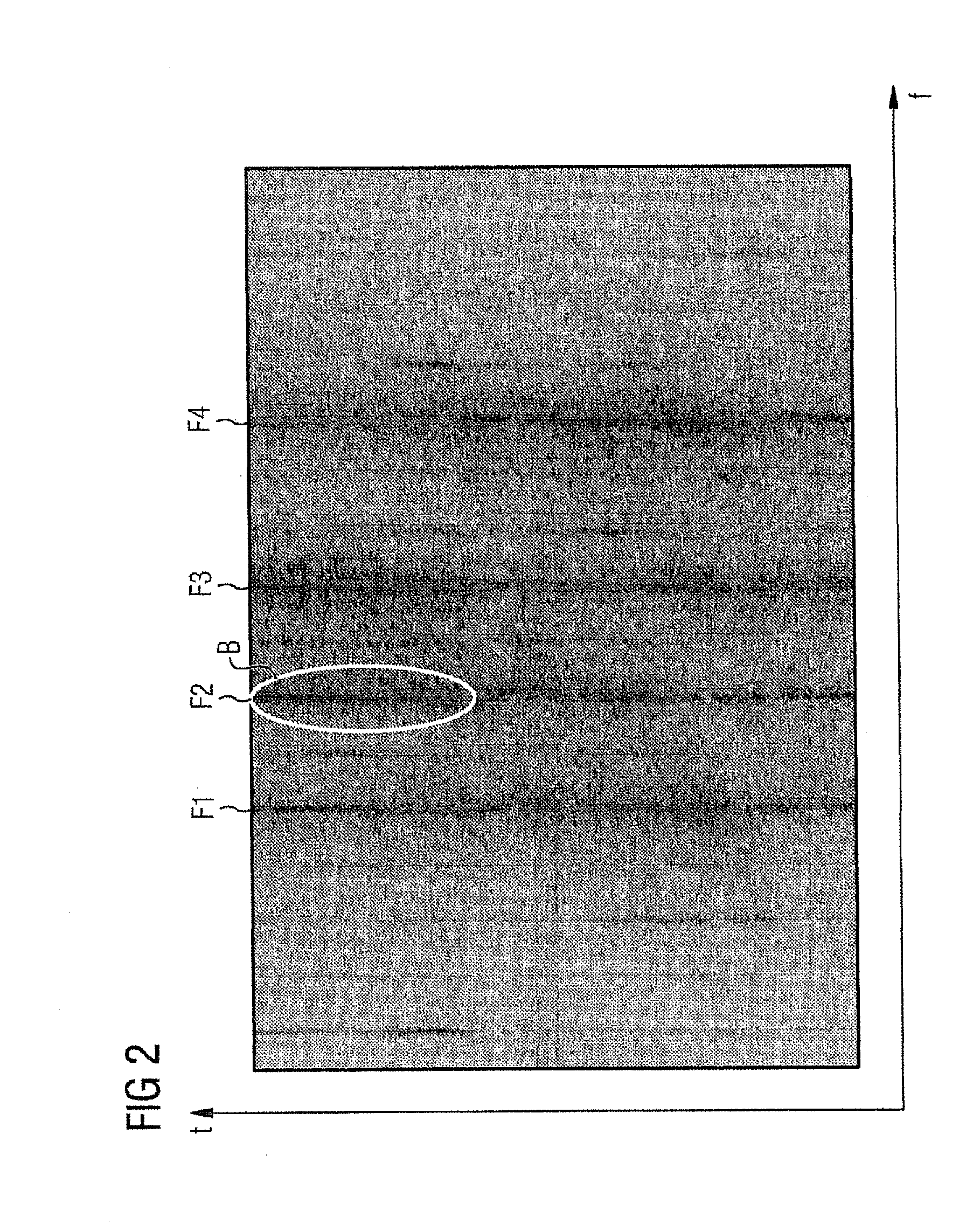
ActiveUS20100262401A1Accurate diagnosisLess sensorsGas-turbine engine testingEngine fuctionsFrequency spectrumEngineering
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com