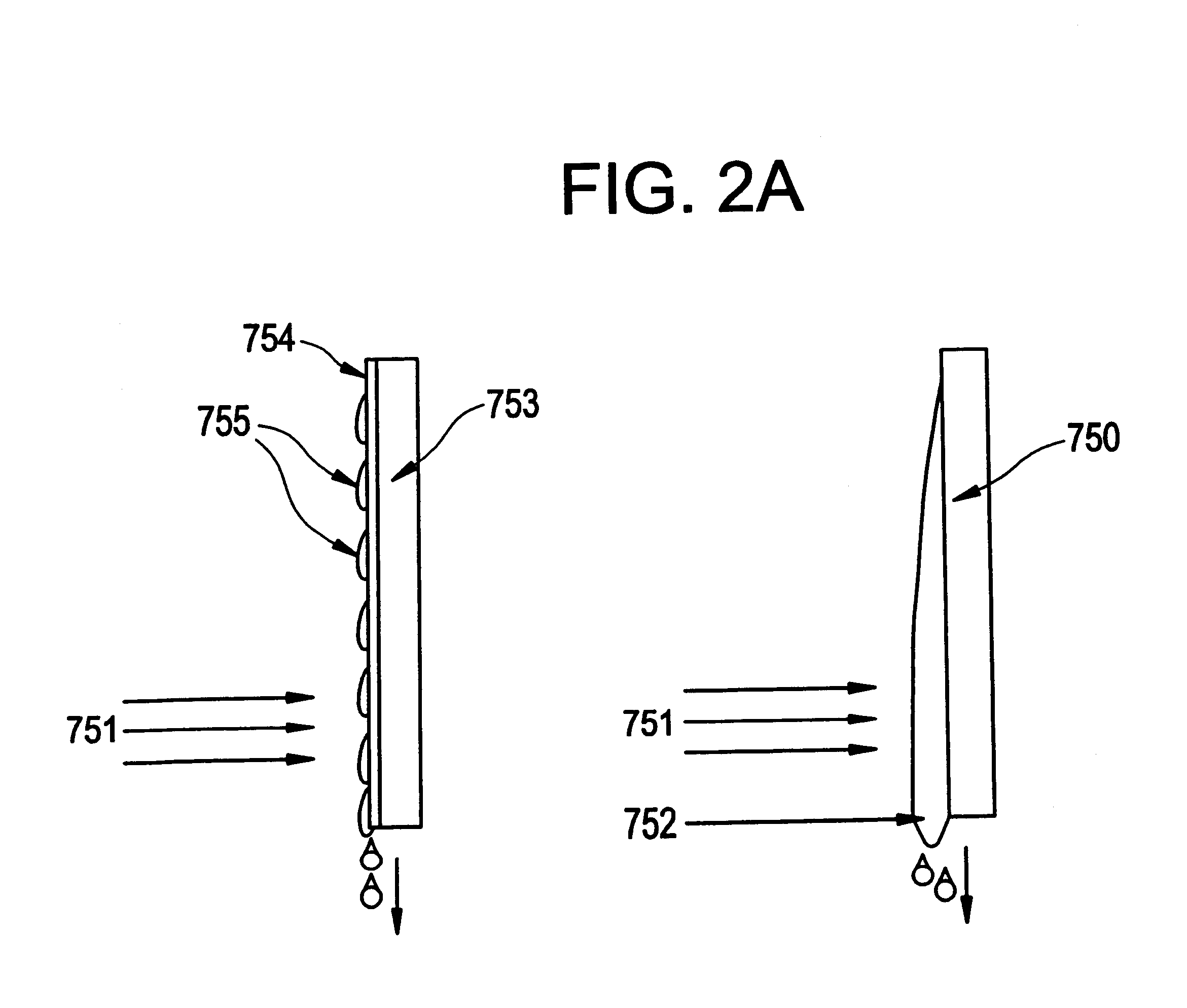
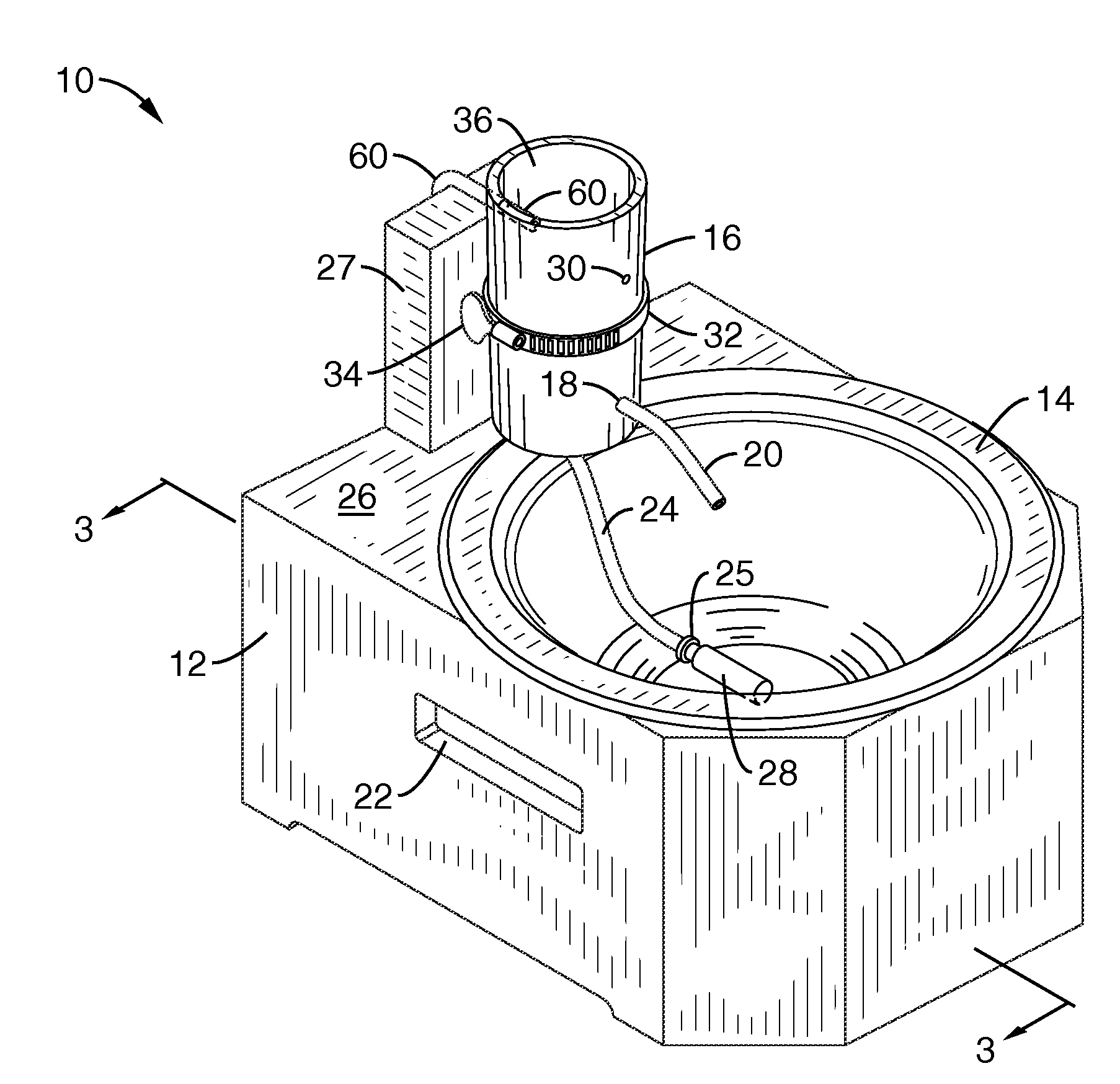
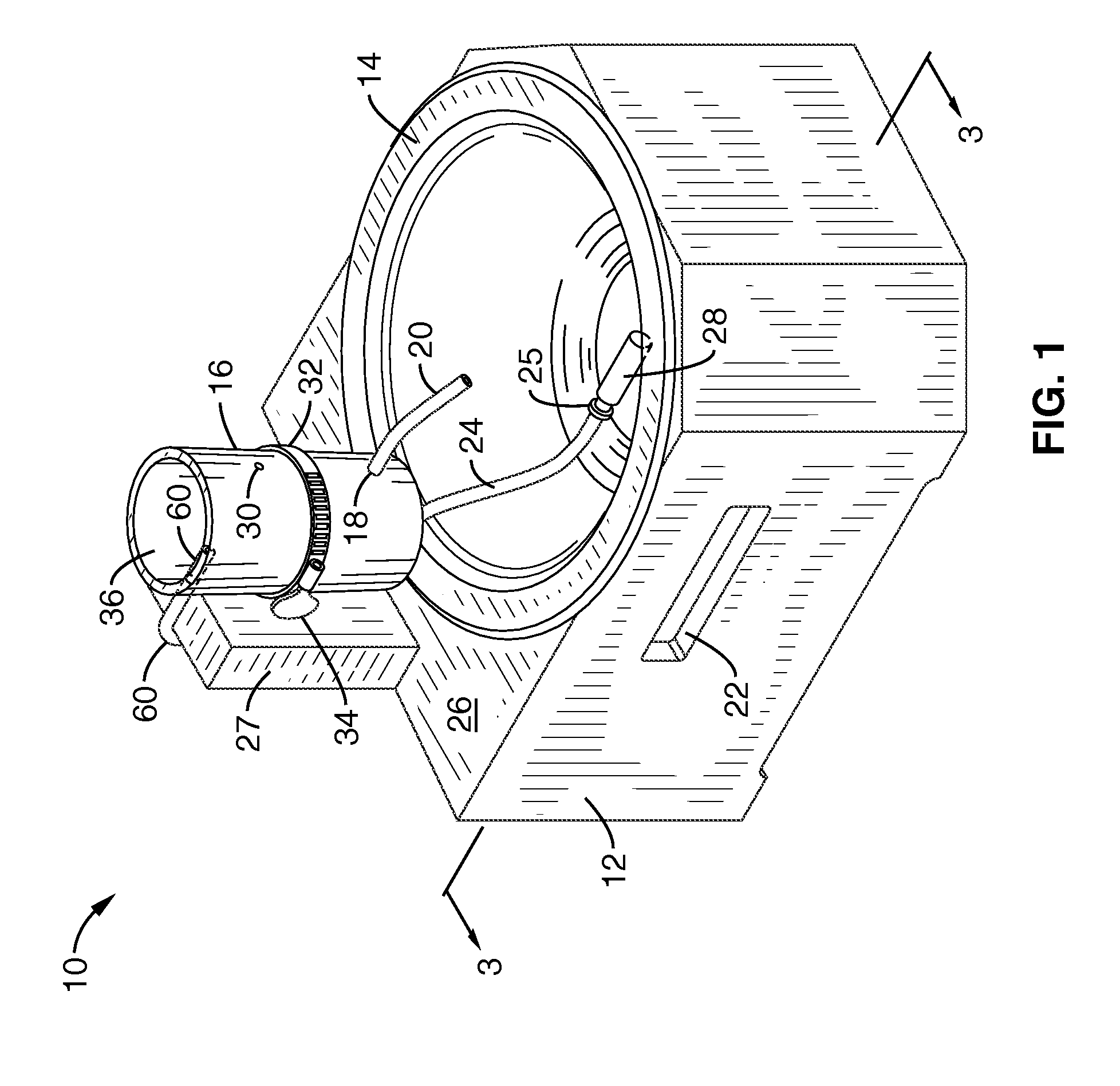
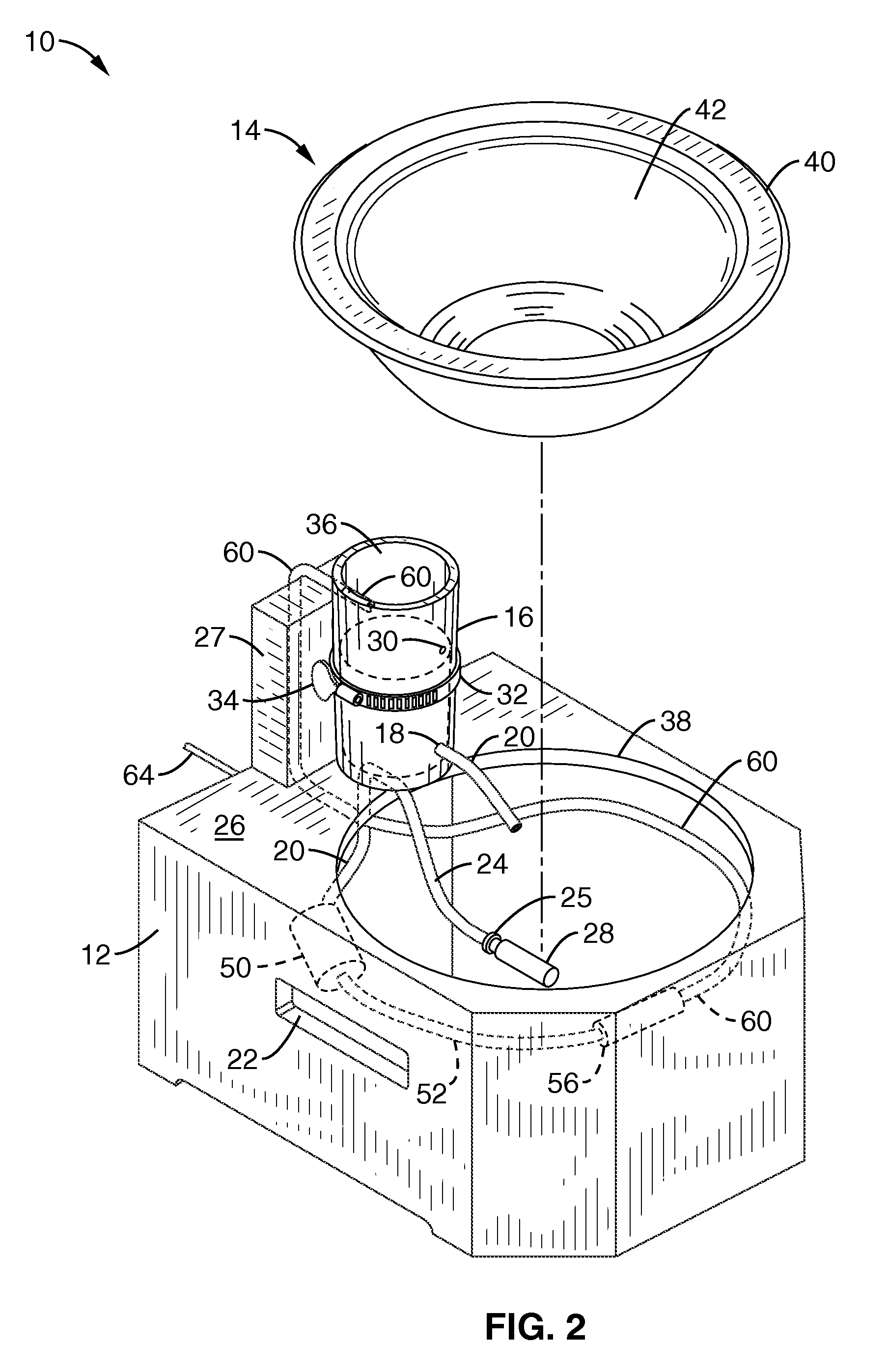
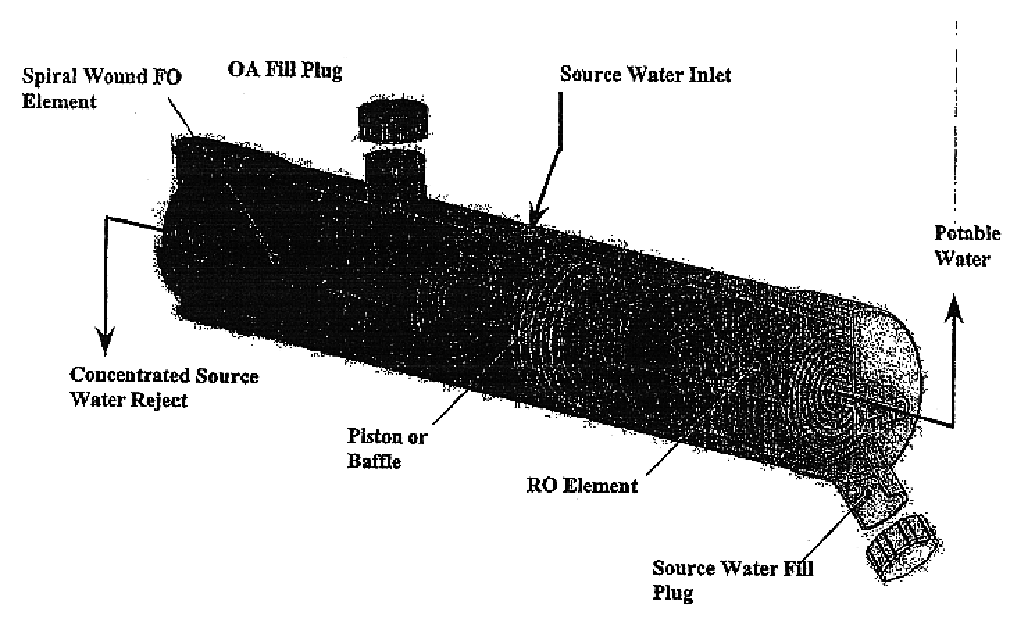
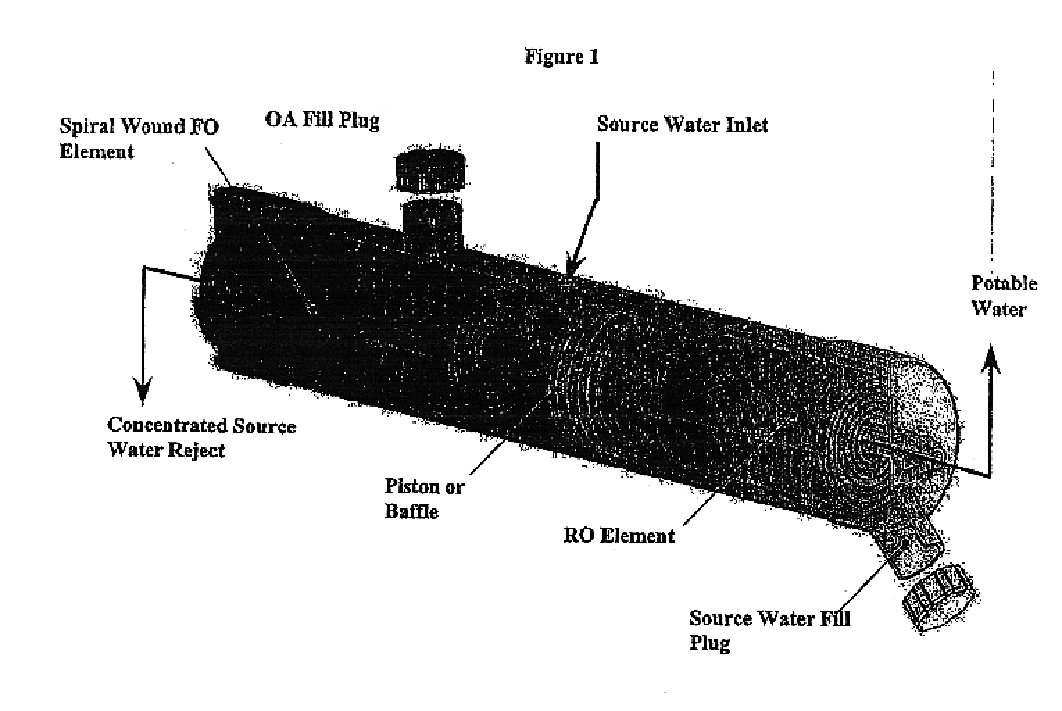
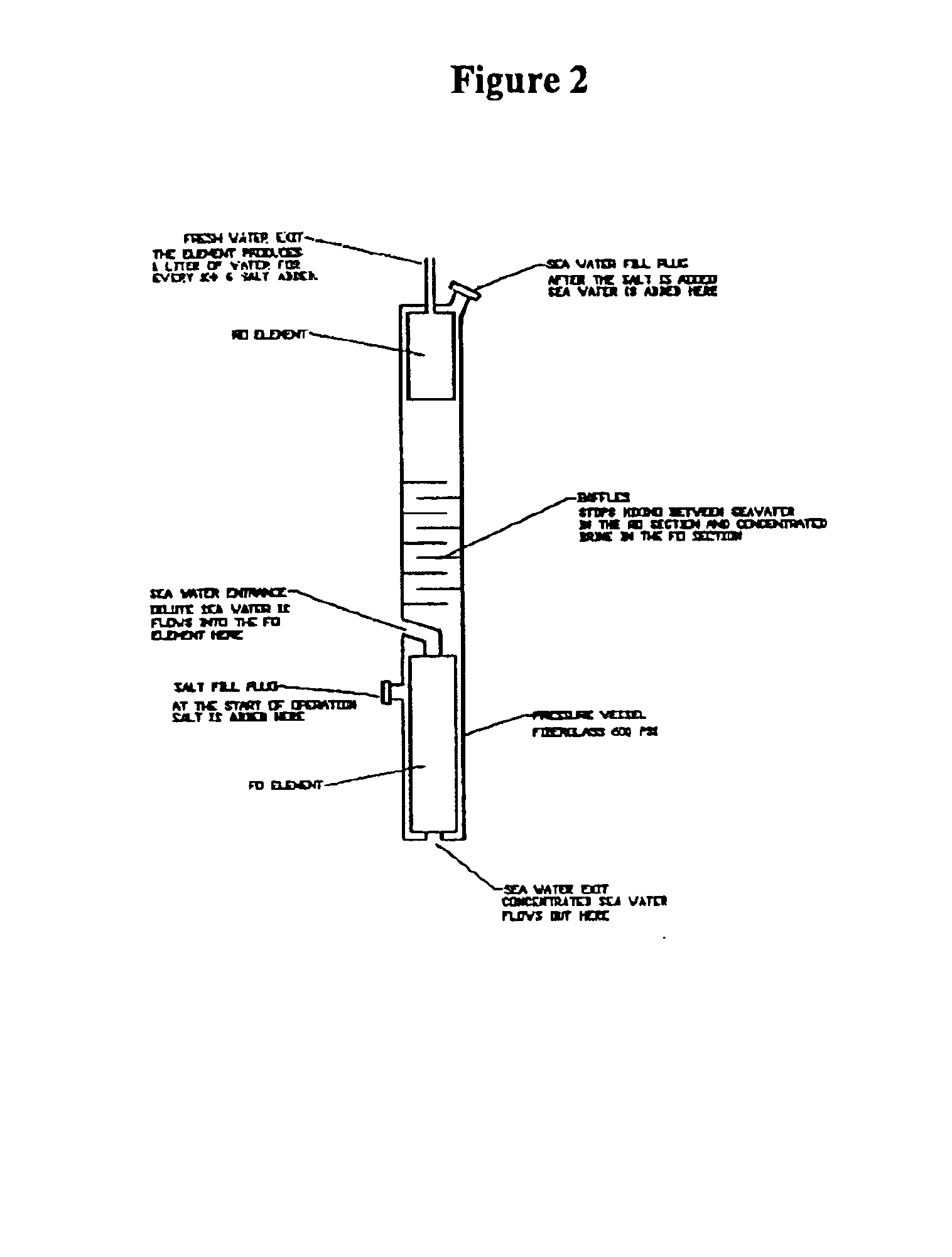
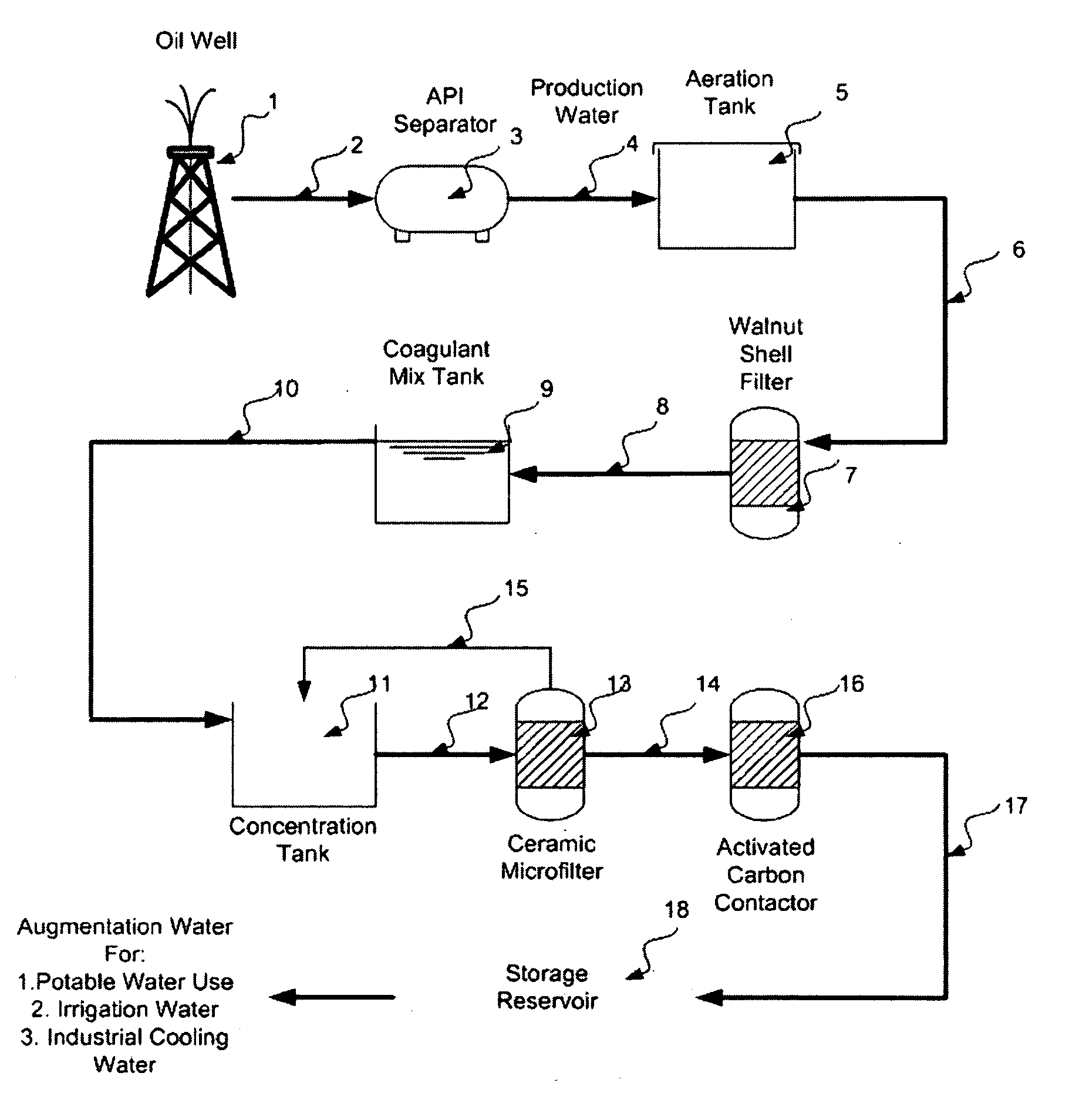
Patents
Literature
3492 results about "Potable water" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Potable water is water that is considered safe to drink. Tap water has usually been treated by the local municipality to make it potable, but there are times when the supply has been contaminated and you must treat water before using it. Non-potable water is untreated water from lakes, rivers,...
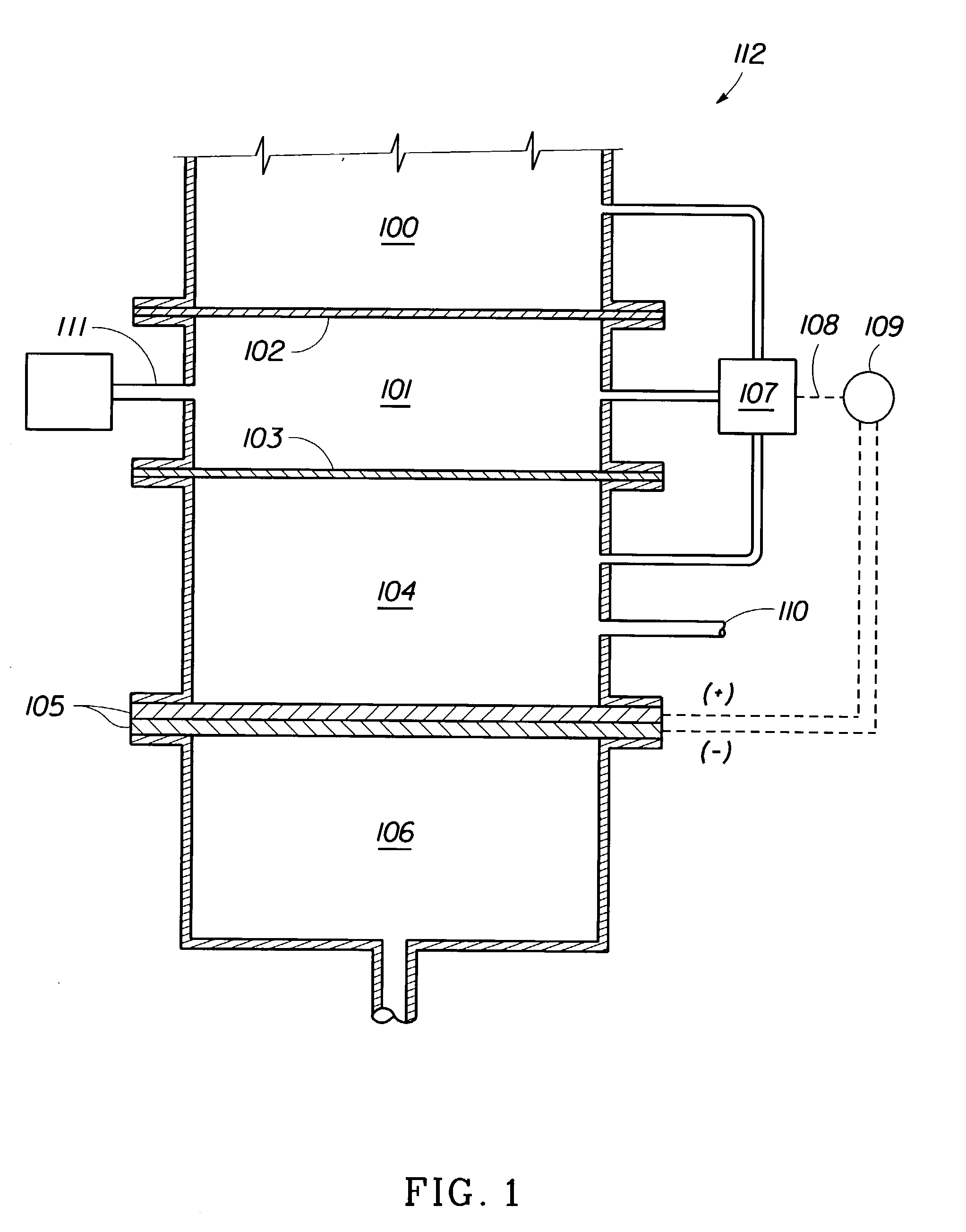
Water treatment process for membranes
InactiveUS6416668B1Effective and safe and reliable to produceCapital and operating costMembranesUltrafiltrationZeta potentialFiltration
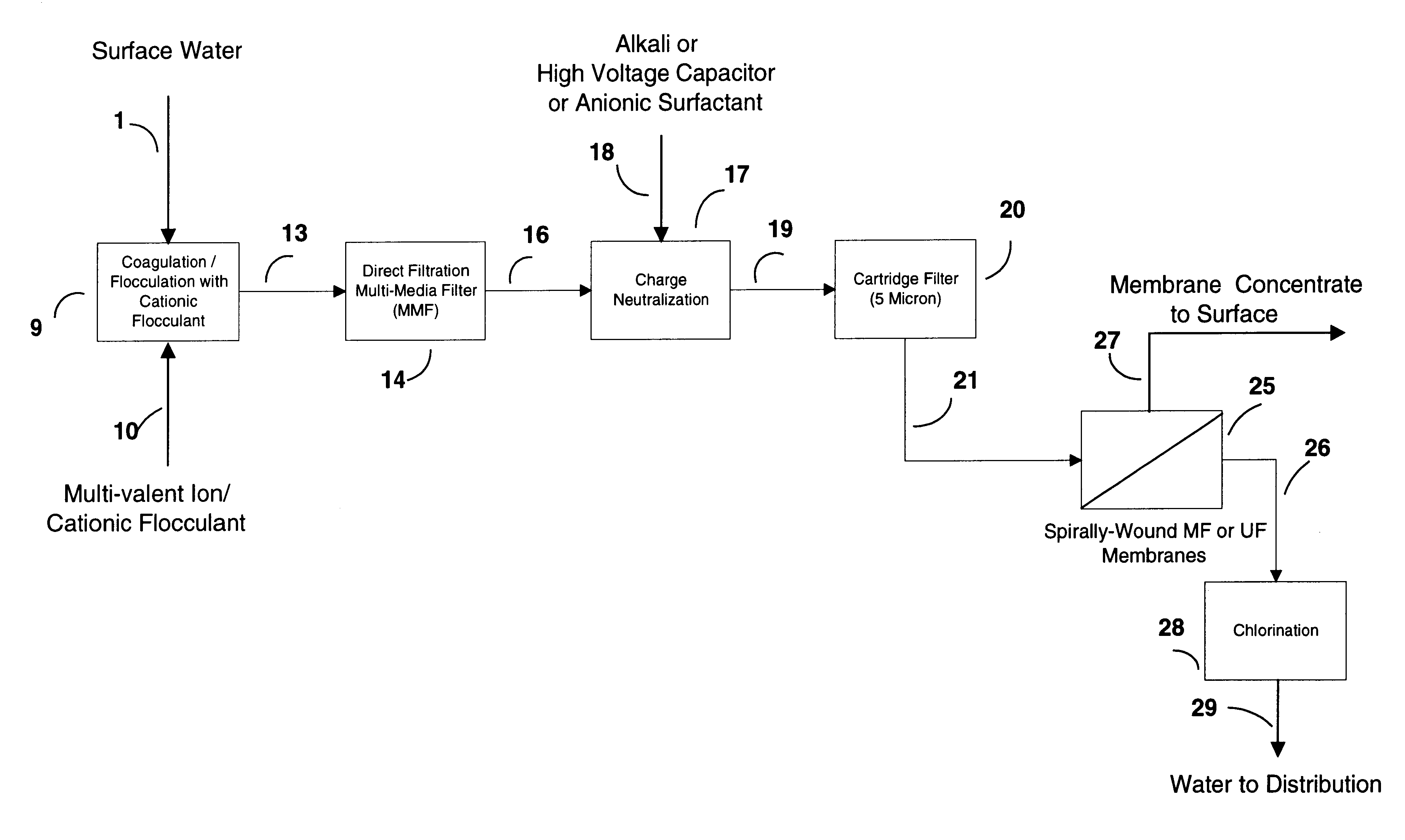
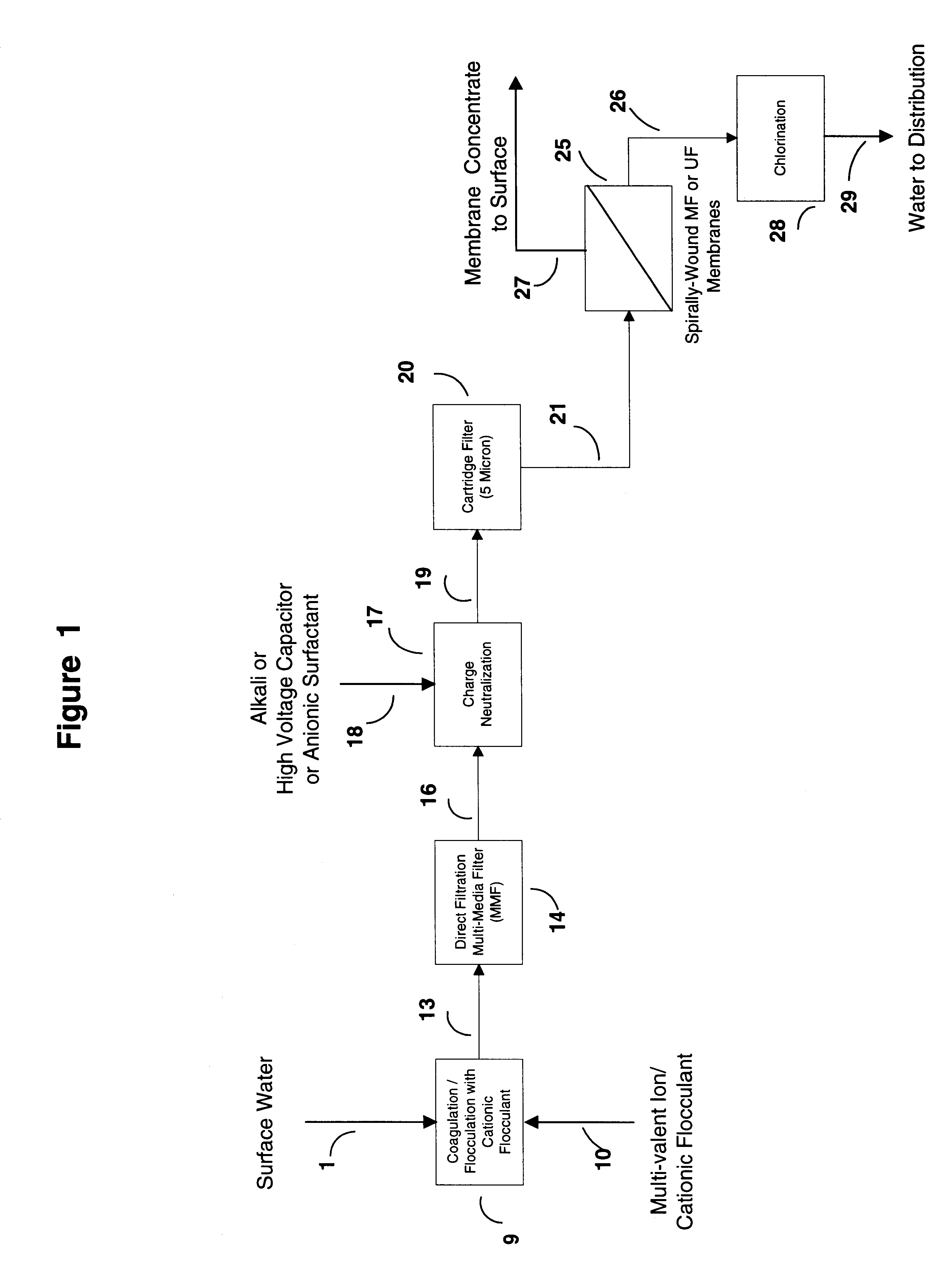
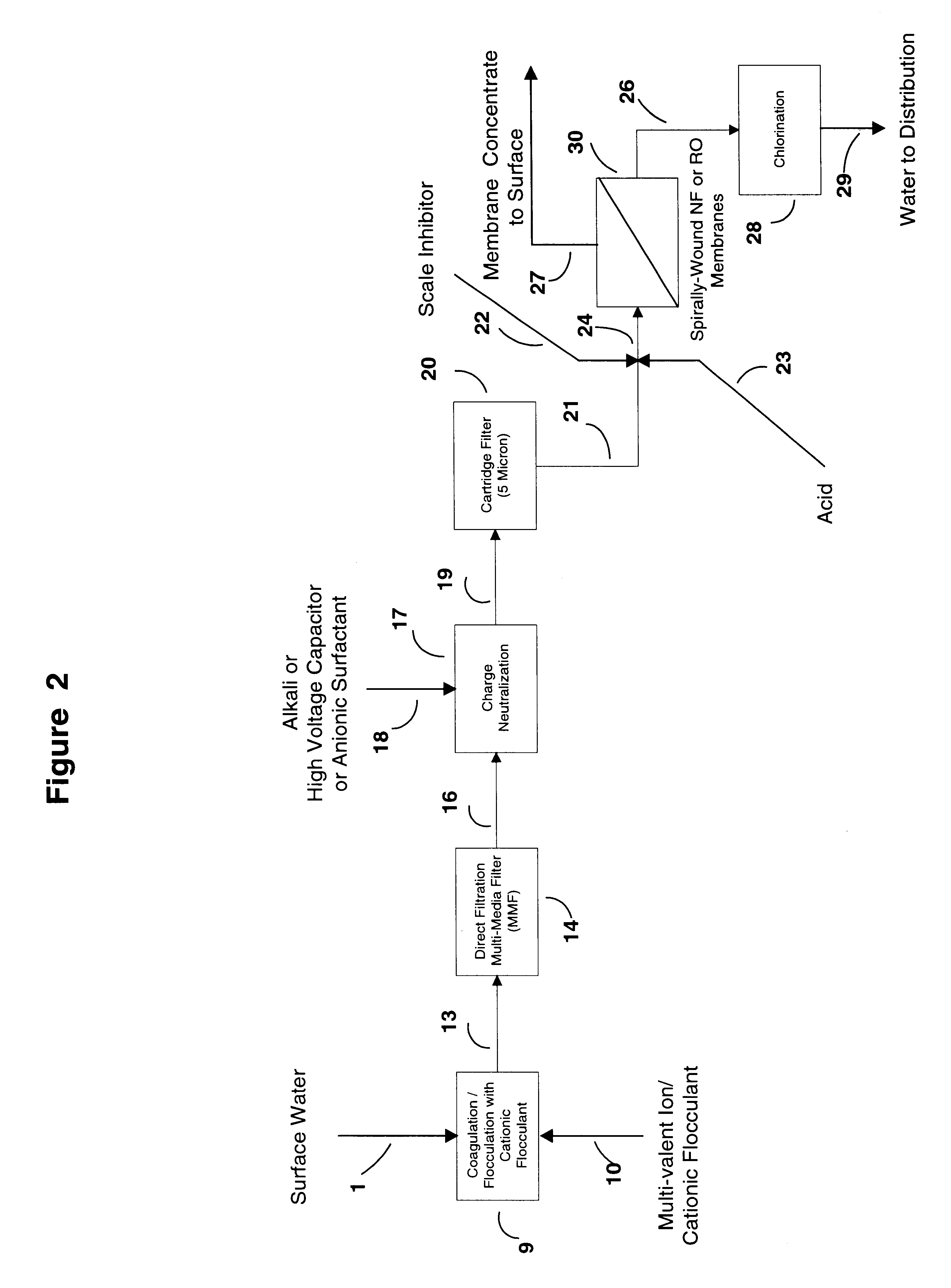
This invention discloses a cost-effective process for separating contaminants and a wide-range of fouling material from surface water, ground water and from industrial effluents. Having undergone effective pre-treatment, the water can be purified further by using high-surface area spirally wound micro-filtration (MF), ultra-filtration (UF), nano-filtration (NF) or reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. High-quality potable water free from pathogen and other contaminants is thus produced at low-cost from the pre-treated surface water and ground-water. Conversely, pre-treated industrial effluents are further purified at a relatively low-cost using NF or RO membranes, thus producing water suitable for recycle or surface discharge. The process of this invention uses cationic inorganic and / or polymeric flocculants to coagulate and flocculate the water-borne colloidal matter (e.g. clays, iron hydroxides, naturally occurring matter (NOM's), etc.), followed by filtration using a multi-media filter, charge neutralization and reversal and final filtration using a 5-micron cartridge filter. These pre-treatment steps provides a good quality water having a low Silt Density Index and a significant negative zeta potential, thereby ensuring against irreversible chemical fouling of the spirally-wound membranes.
Owner:AL SAMADI RIAD A
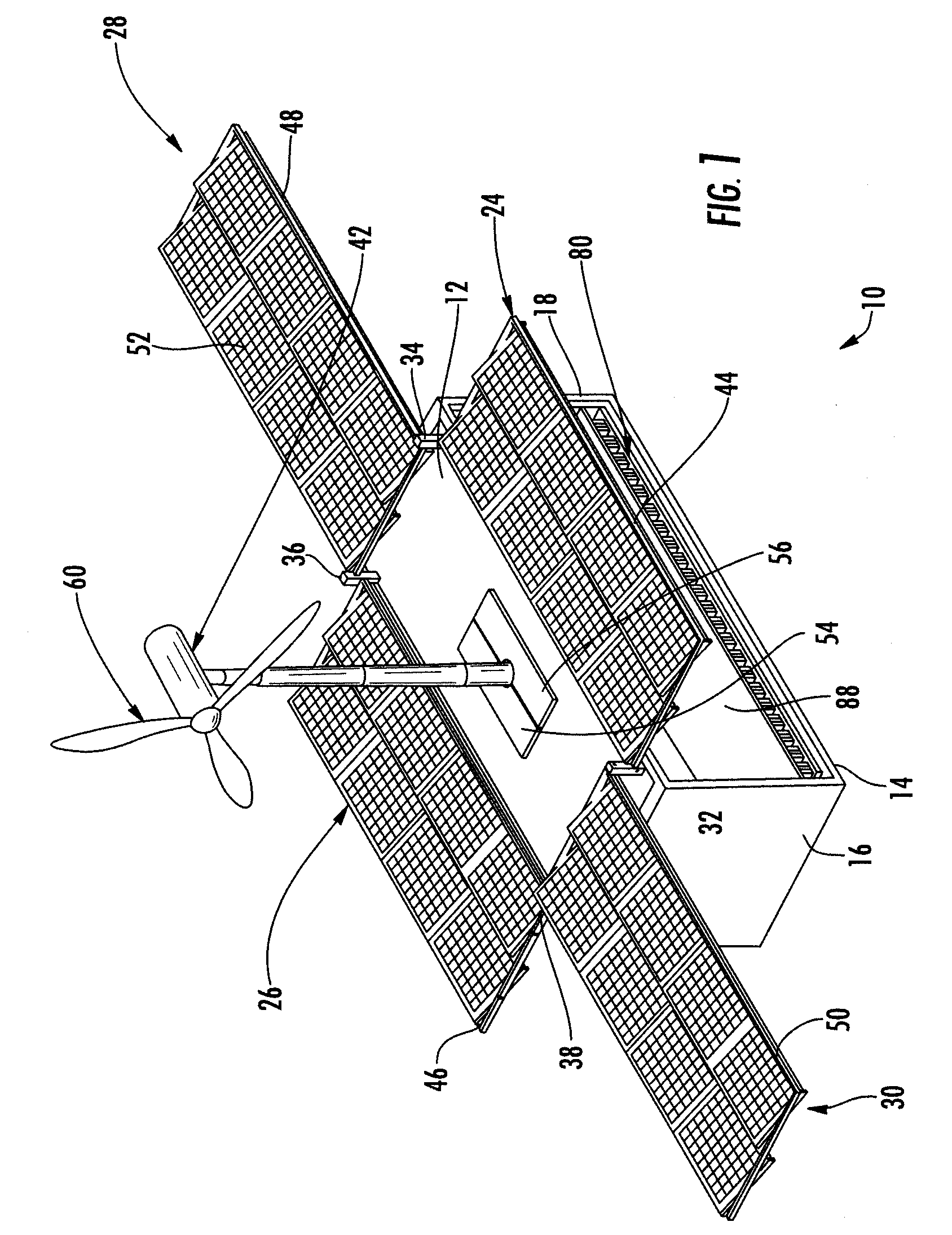
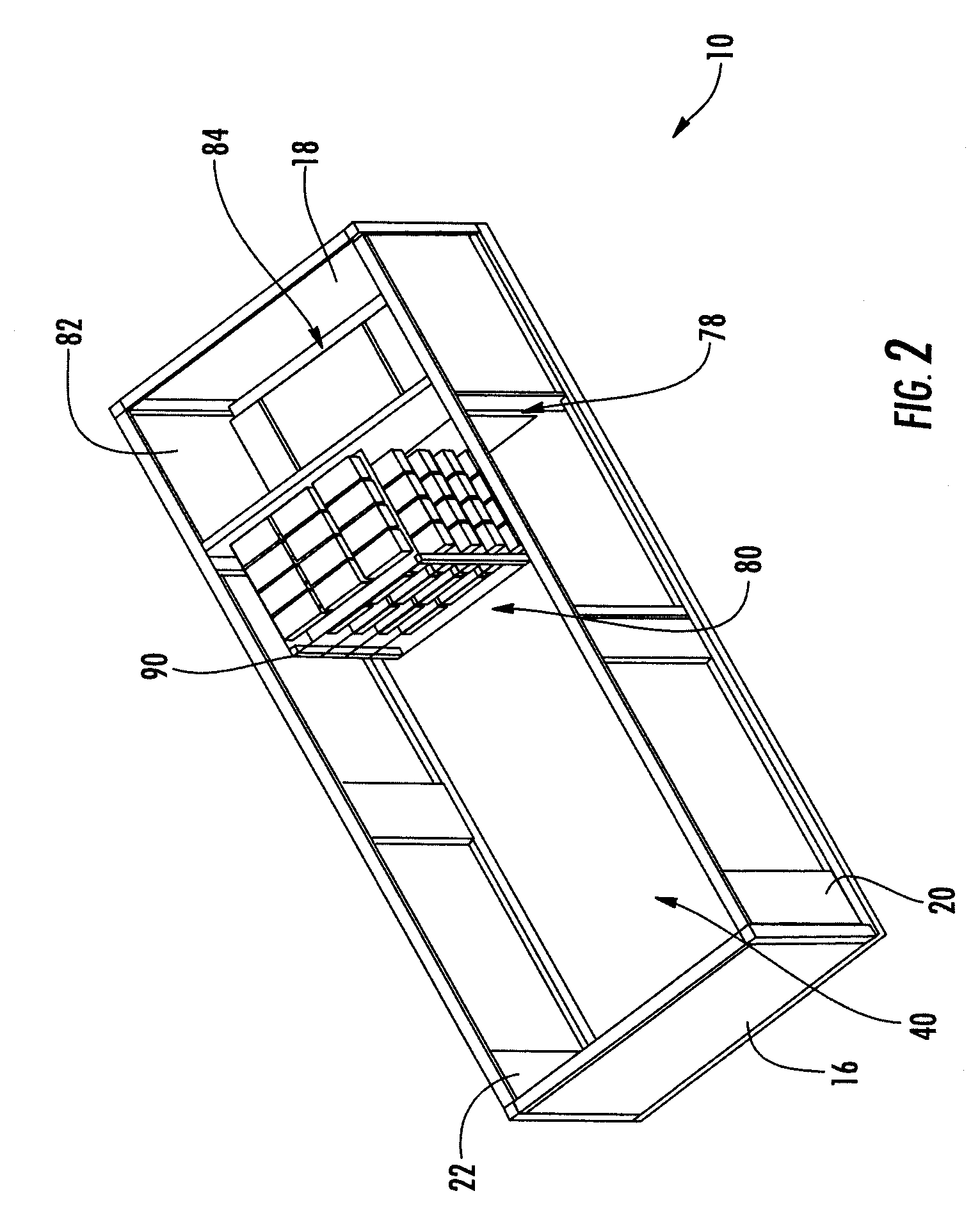
Portable, self-sustaining power station
InactiveUS20080196758A1Improve stabilityQuickly and easily deployed by a single personPhotovoltaic supportsPropellersElectricityPower station
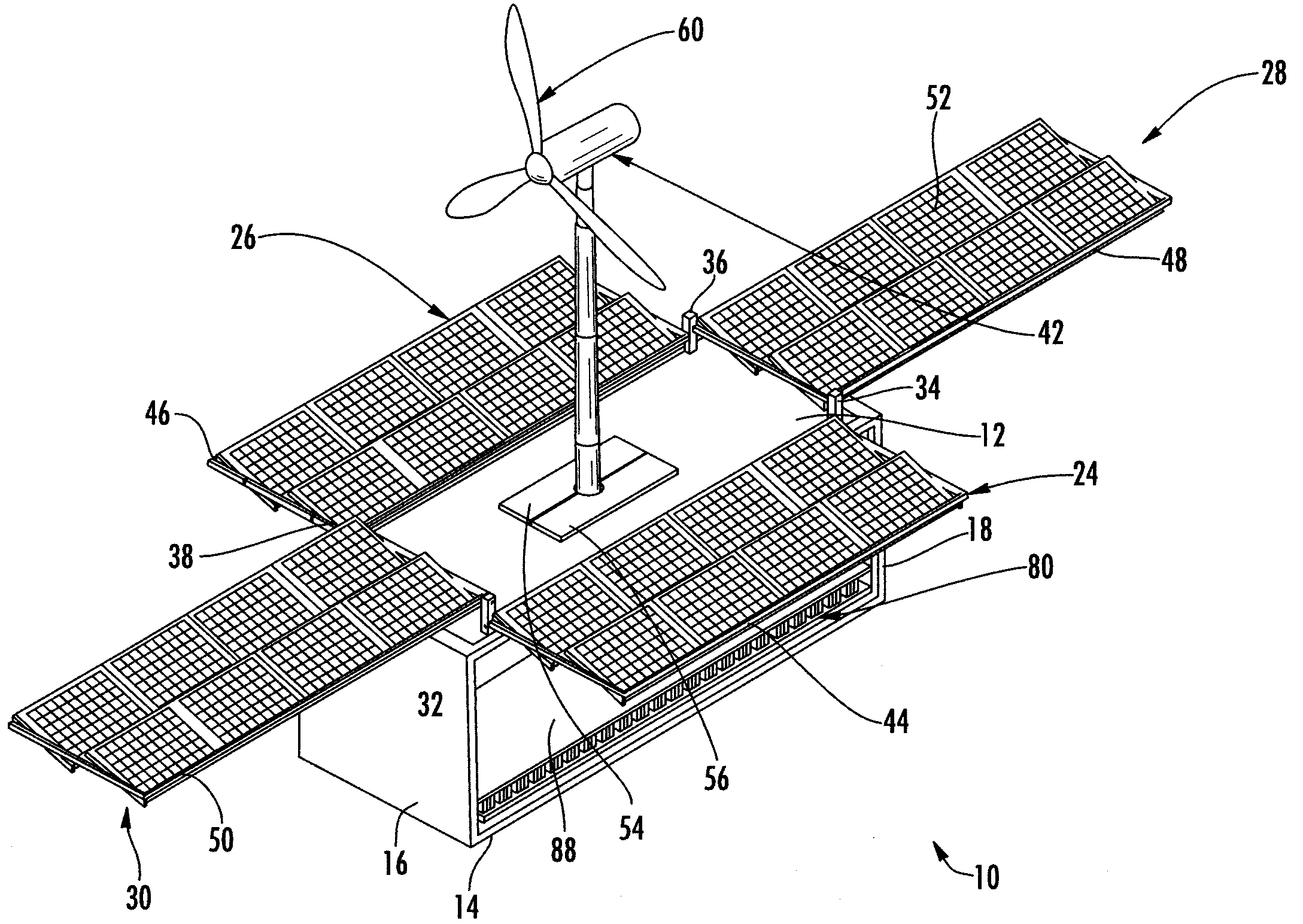
A self-sustaining, portable, power station that may be moved by land, air, or sea to an area that has no utilities. The station is provided with at least one wind turbine and / or solar panel arrays in communication with at least one electrical distribution and storage means. The derived electricity is used to power various systems including, albeit not limited to, a communications system, a water filtration system, a water distribution system to allow the public to draw potable water and provide basic hygiene. The electricity derived may also be used to run outside systems, such as schools, hospitals, or the like.
Owner:ECOSPHERE TECH
Process for desalination of saline water, especially water, having increased product yield and quality
InactiveUS6508936B1General water supply conservationSeawater treatmentTotal dissolved solidsDistillation
A desalination process is disclosed which combining two or more substantially different water treatment processes in a unique manner to desalinate saline water, especially sea water, to produce a high yield of high quality fresh water, including potable water, at an energy consumption equivalent to or less than much less efficient prior art desalination processes. In this process a nanofiltration step is synergistically combined with at least one of sea water reverse osmosis, multistage flash distillation. multieffect distillation of vapor compression distillation to provide an integrated desalination system by which sea water can be efficiently and economically converted to high quality potable water in yields which are at least 70%-80% greater than the yields available from the prior art processes. Typically a process of this invention using the nanofiltration initial step will produce, with respect to sea water feed properties, calcium, magnesium, sulfate and bicarbonate ion content reductions of 63%-94%, pH decreases of about 0.4-0.5 units and total dissolved solids content reductions of 35%-50%.
Owner:SALINE WATER CONVERSION CORP
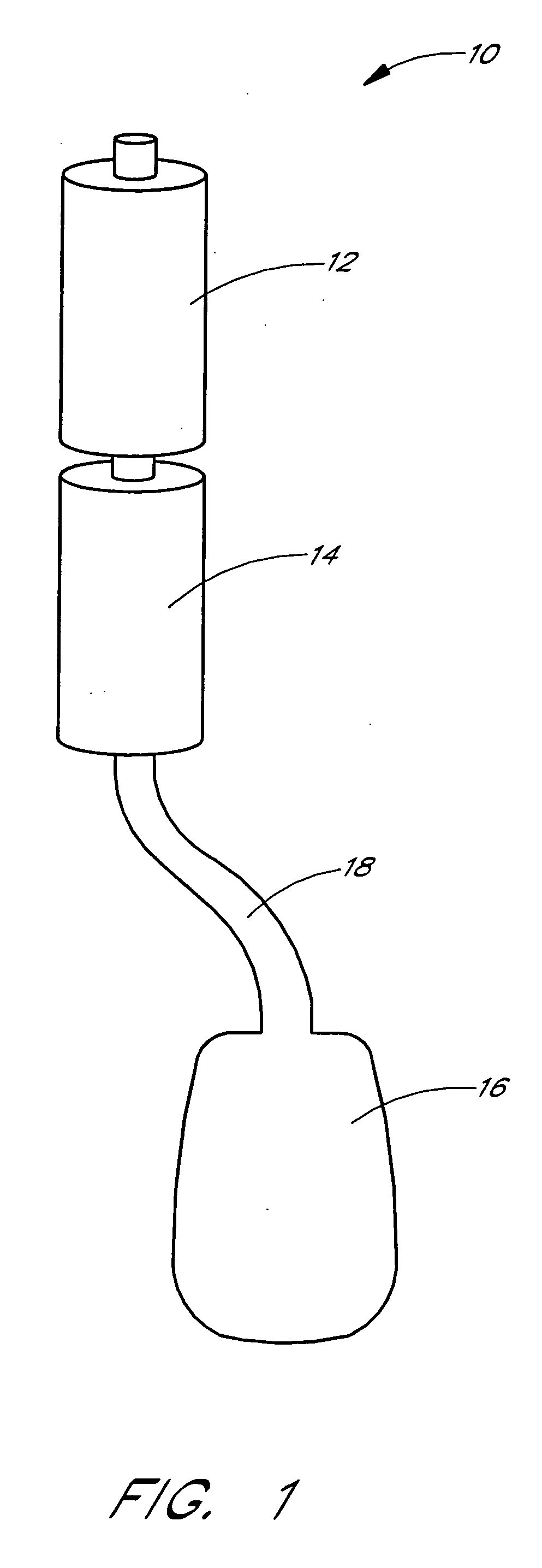
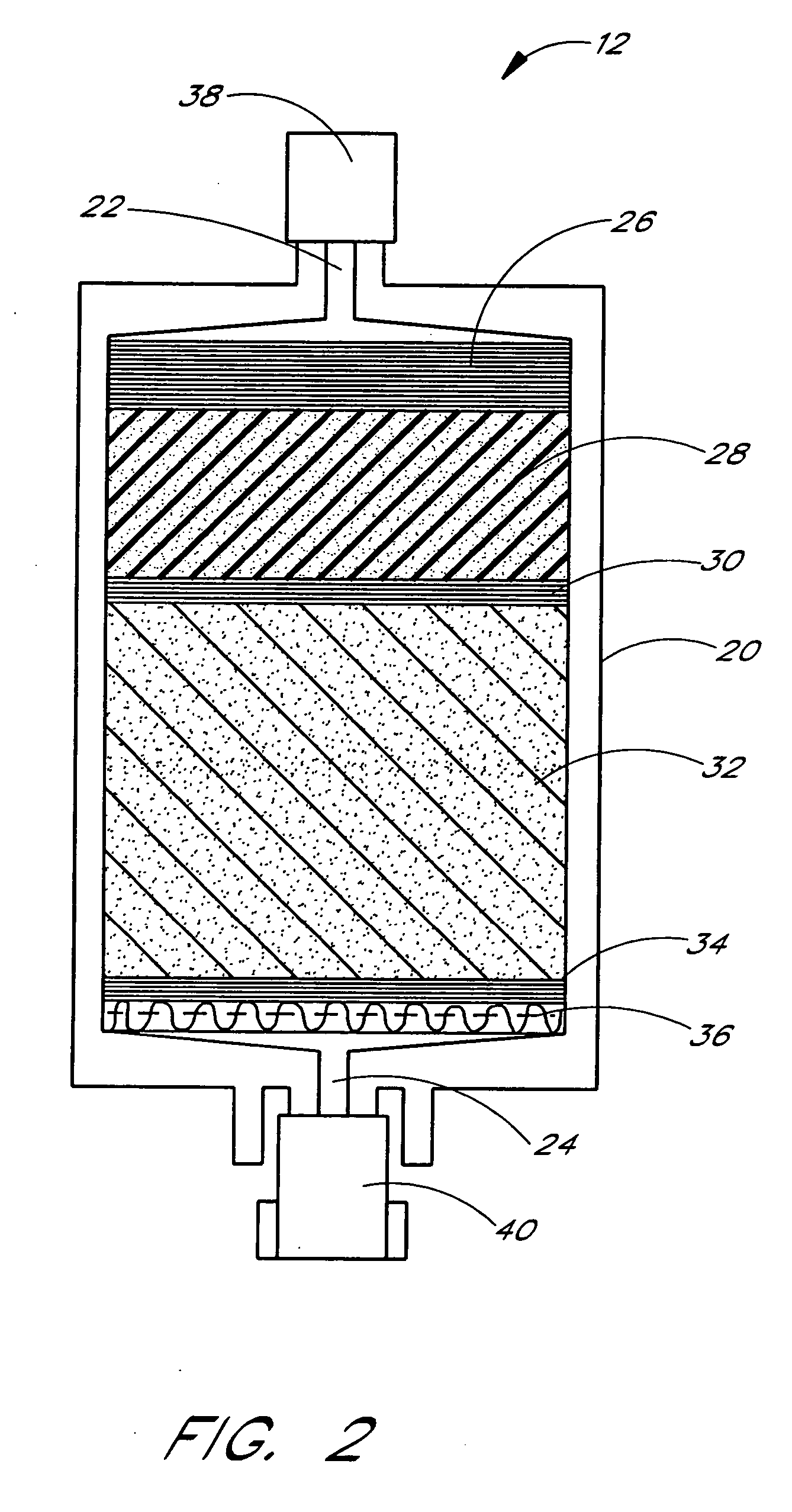
Method and apparatus for producing potable water from air including severely arid and hot climates
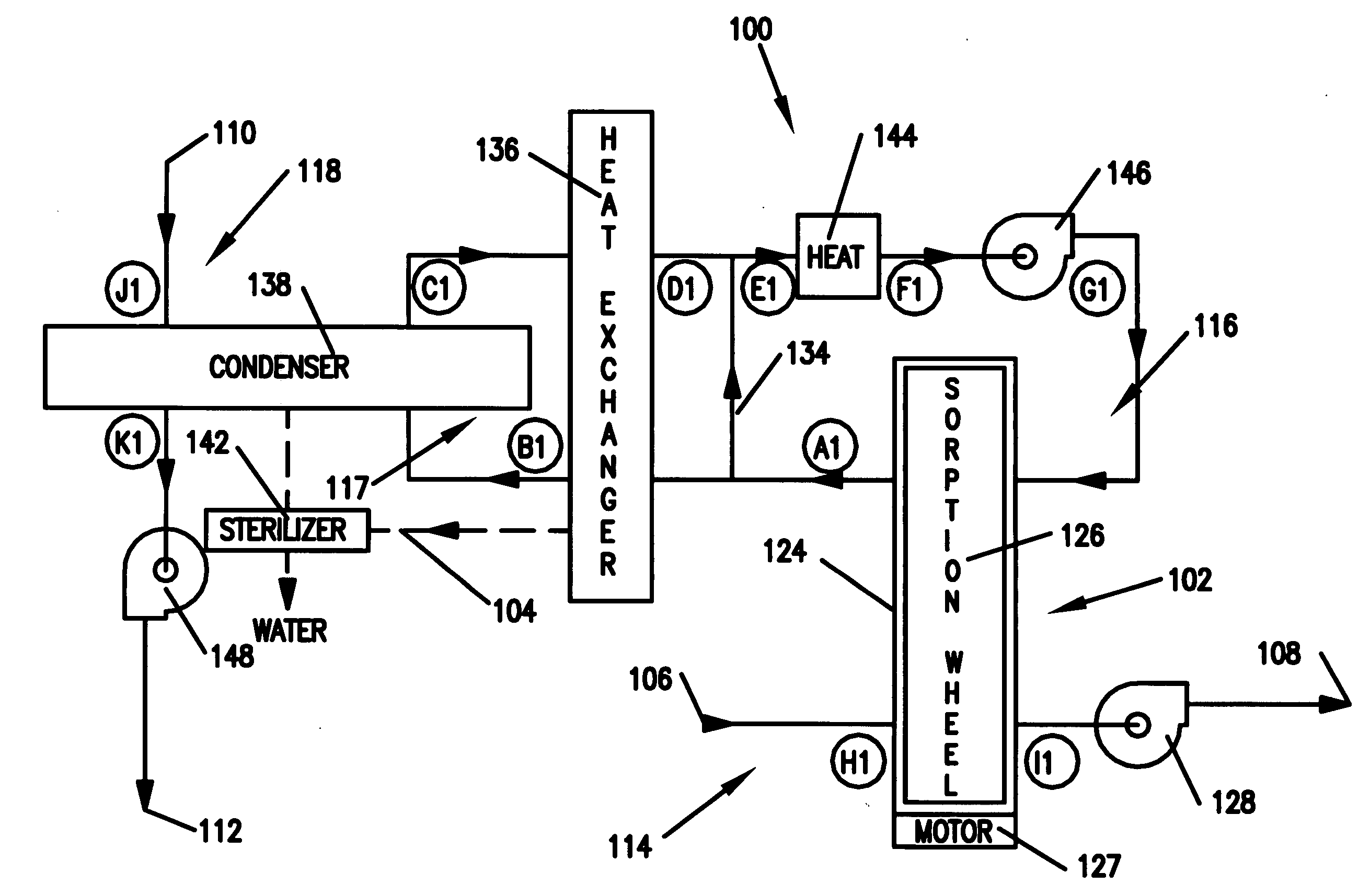
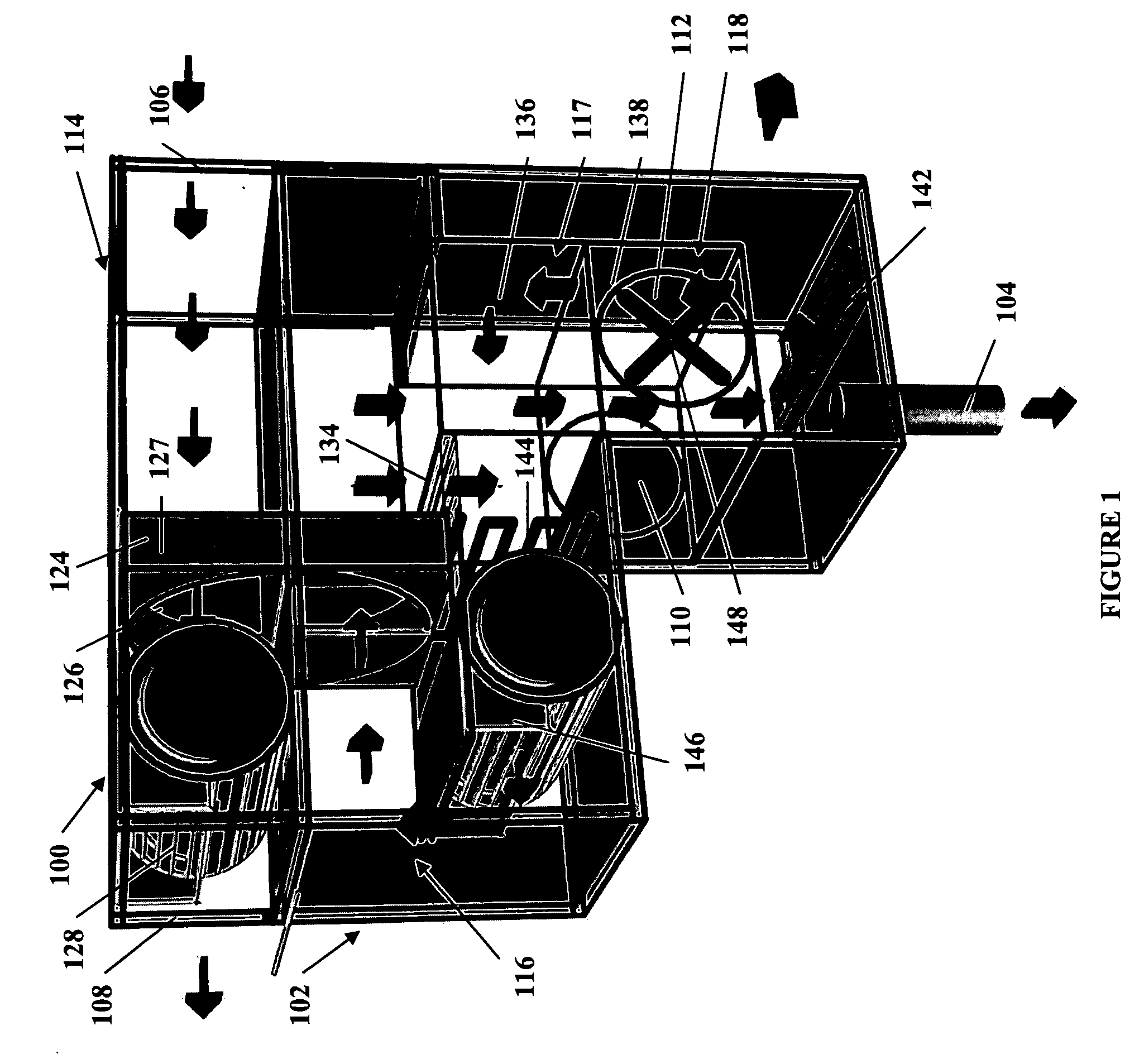
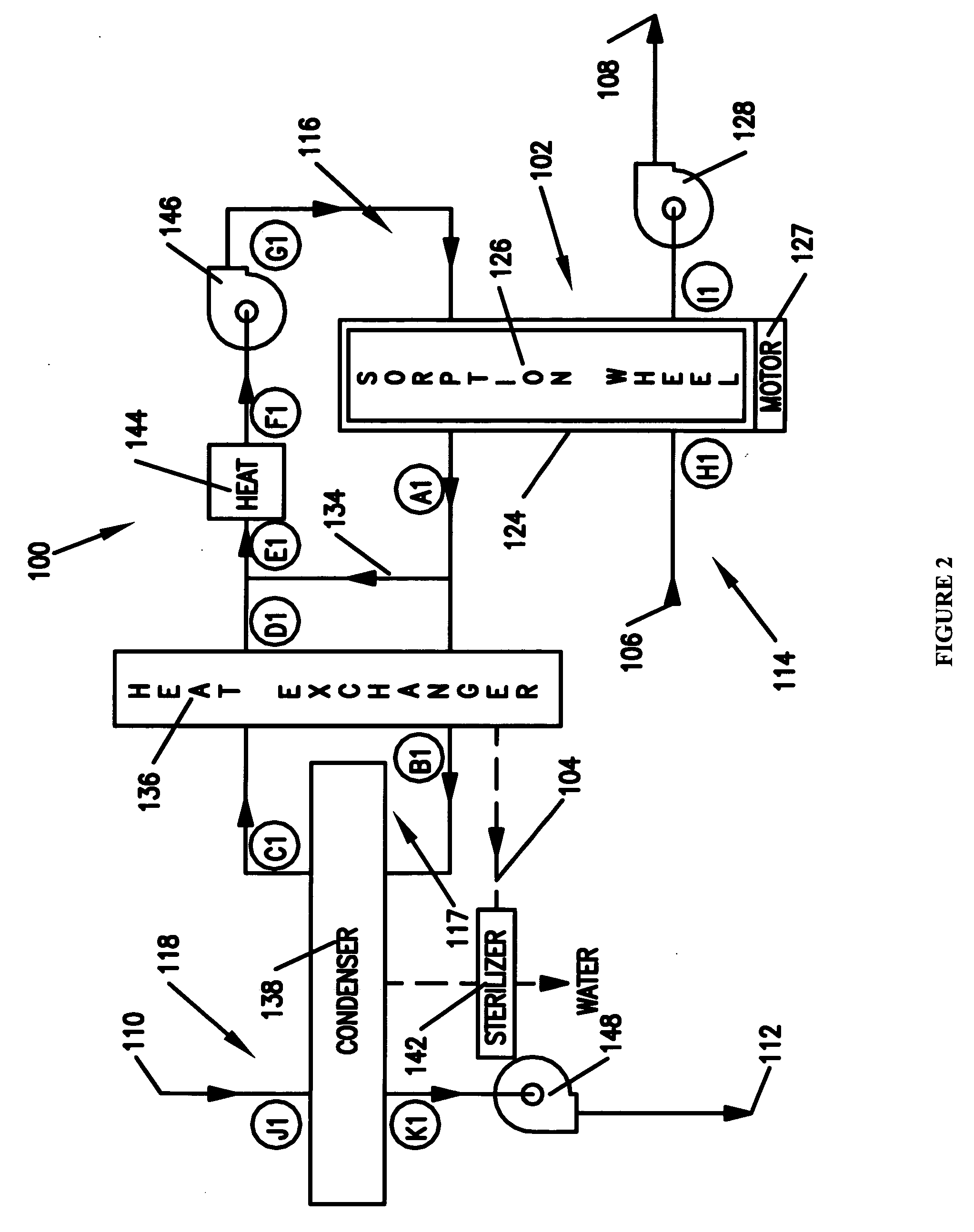
Methods and apparatus for extracting liquid water from ambient air, including ambient air in severely arid and hot climates, are described. An example apparatus uses a sorption-desorption-condensation cycle using a sorption wheel to extract moisture from ambient air and concentrate the water vapor driven off from the sorption material in a circulating gas, with condensation of liquid water from the circulating gas.
Owner:EPLEE DUSTIN M +1
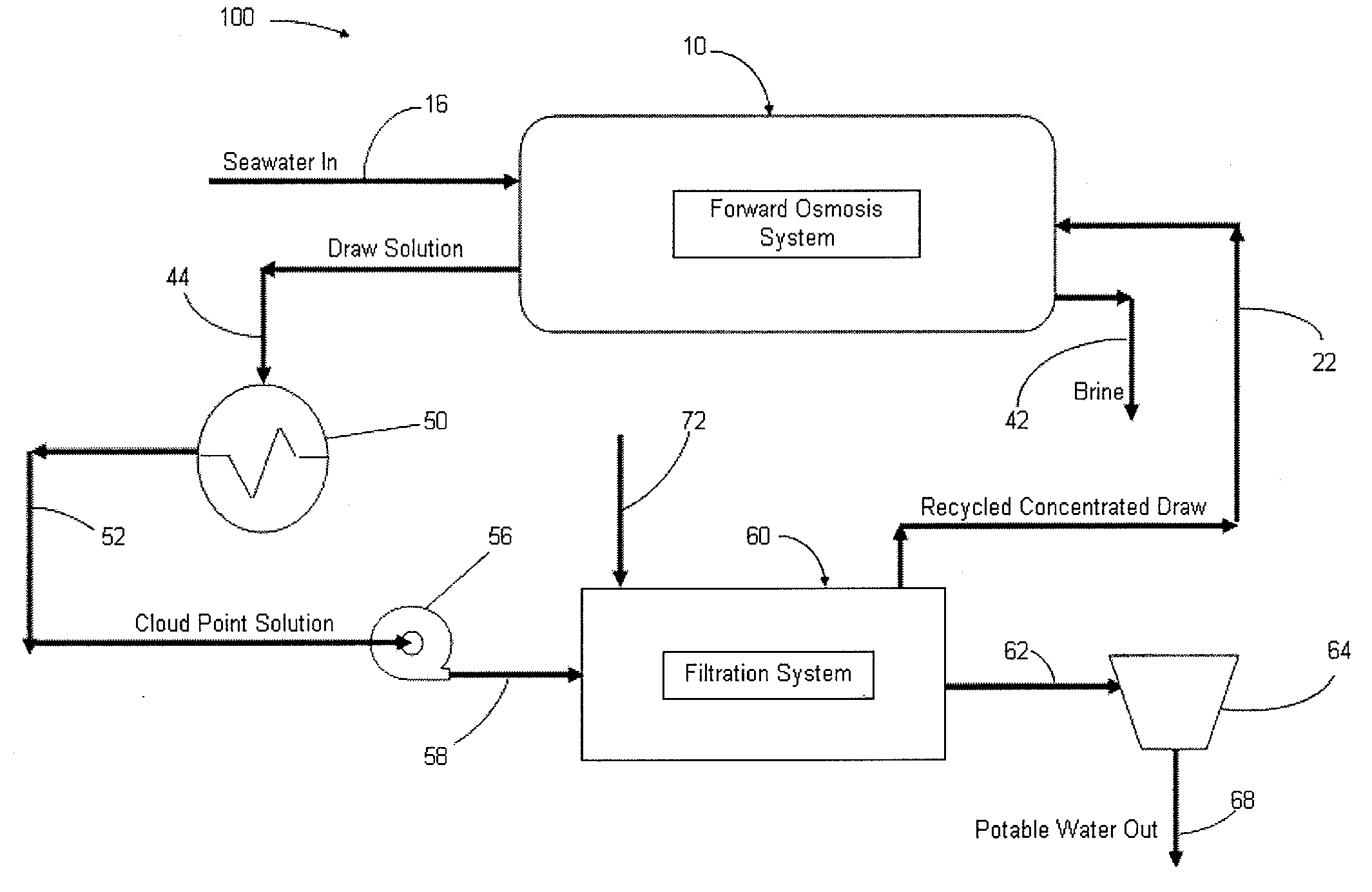
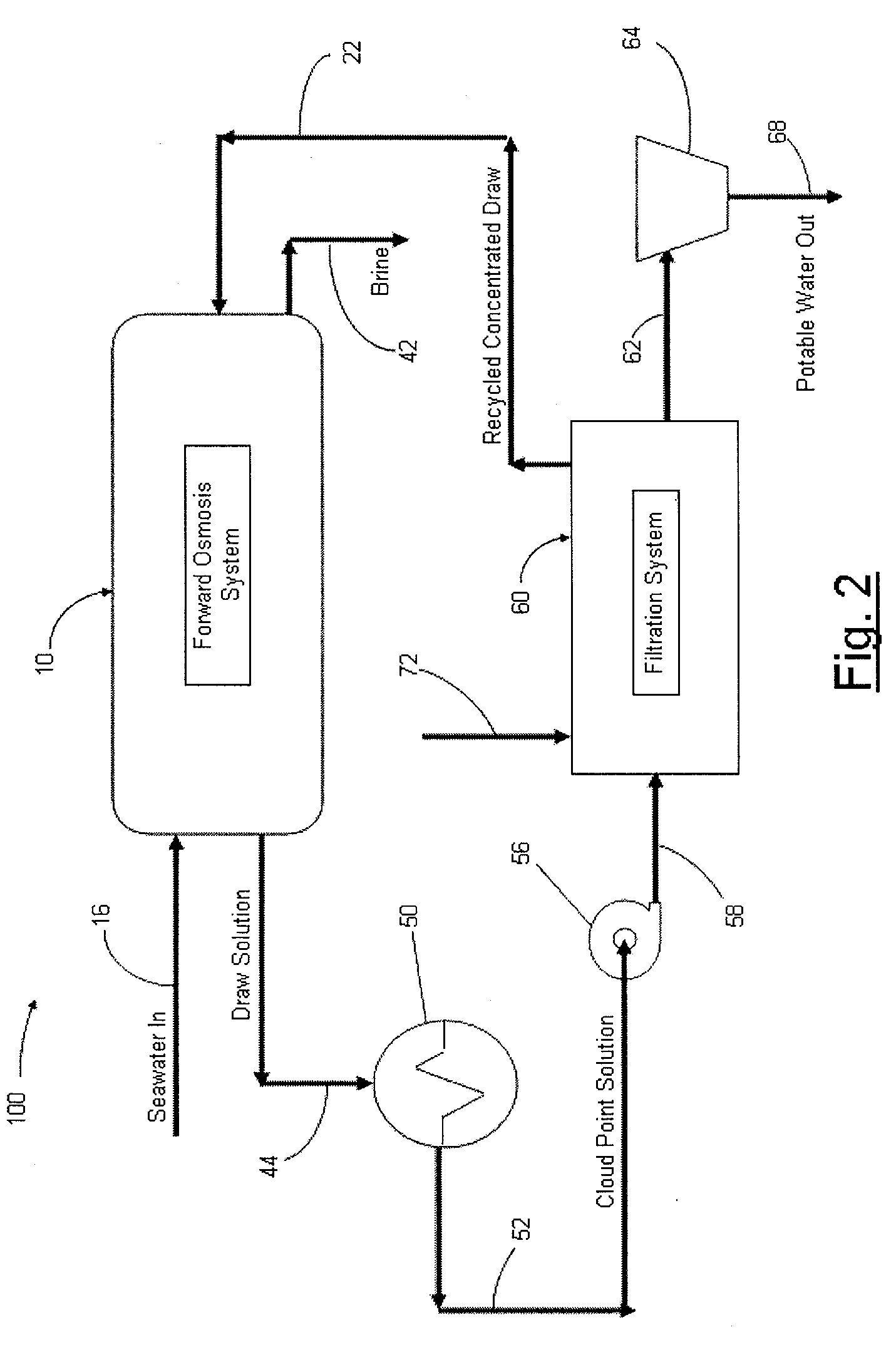
Systems and methods for forward osmosis fluid purification
ActiveUS20100155329A1Improve efficiencyFunction increaseGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentSaline waterDesalination
A process for purification of fluids, for example, desalination of seawater or brackish water, using organic solutes in a concentrated water solution for use in a forward osmosis process, to extract fresh water out of salt water through the forward osmosis membrane, and subsequently separating the organic solutes out of the diluted forward osmosis permeate by cloud point extraction, thereby regenerating a concentrated organic solution for recycling to the forward osmosis process, and fresh water for potable water use.
Owner:JFEENG CORP
Microorganism control of point of use potable water sources
InactiveUS20030080467A1Keep it cleanPrevent freezingCellsSpecific water treatment objectivesMedical equipmentWater source
The present invention provides for the electrochemical generation of ozone for use in "point-of-use" applications. The electrochemical ozone generators or systems of the present invention may be used to provide disinfected water, ozone-containing water, and / or ozone gas. Disinfected water may be produced by introducing ozone gas into a potable or purified water source for the purpose of disinfecting or controlling the microorganisms in the water source. Ozonated water or ozone gas may be produced and provided for various anti-microbial and cleansing applications of the consumer, such as washing food, clothing, dishes, countertops, toys, sinks, bathroom surfaces, and the like. Furthermore, the ozone generator may be used to deliver a stream of ozone-containing water for the purpose of commercial or residential point-of-use washing, disinfecting, and sterilizing medical instruments and medical equipment. For example, the ozone-containing water may be used directly or used as a concentrated sterilant for the washing, disinfecting, and sterilizing of medical instruments or equipment. Ozone gas may also be used in many of the foregoing examples, as well as in the deodorization of air or various other applications. The invention allows the electrochemical ozone generator to operate in a nearly or entirely passive manner with simplicity of design.
Owner:LYNNTECH INT
Apparatuses and Methods for Managing Liquid Volume in a Container
ActiveUS20120097567A1Beneficial to healthGood for healthTable equipmentsOther accessoriesEngineeringVolume change
The present invention proposes an apparatus (100) and method for managing the liquid volume in a container. The apparatus (100) comprises a detector (101) for detecting liquid volume changes in said container during a first preset period, a first determiner (102) for determining whether said changes are lower than said first preset threshold value and a presenter (103) for presenting the first prompt information in the case of said changes being lower than said preset threshold value. The apparatus and method provided in the present invention can prompt people to drink drinkable liquids such as water in time, enable people to control their drinking intake and are beneficial to their health.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
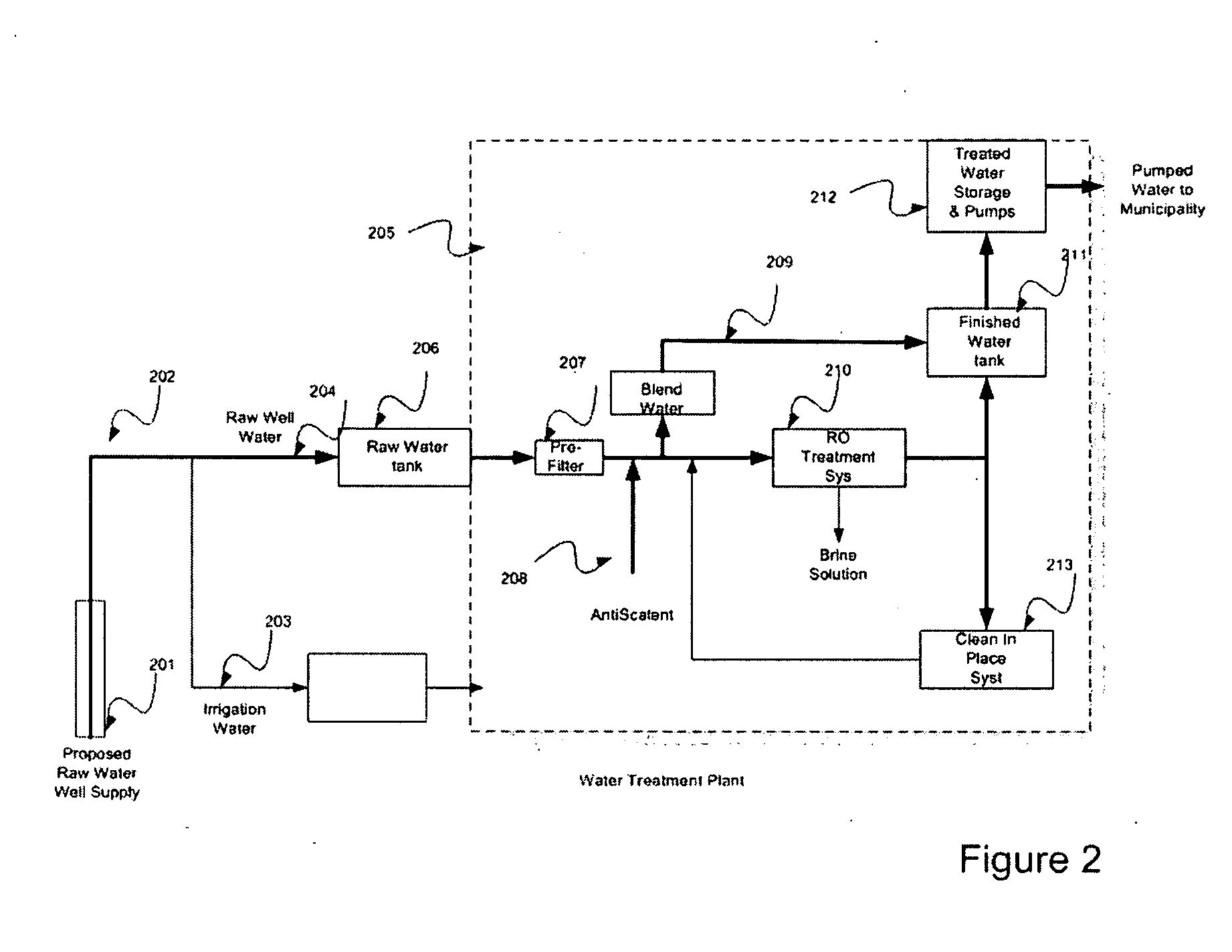
Enhanced water treatment for reclamation of waste fluids and increased efficiency treatment of potable waters
ActiveUS20090050572A1Low costCurrent expensiveWaste water treatment from quariesTreatment involving filtrationLiquid wastePotable water
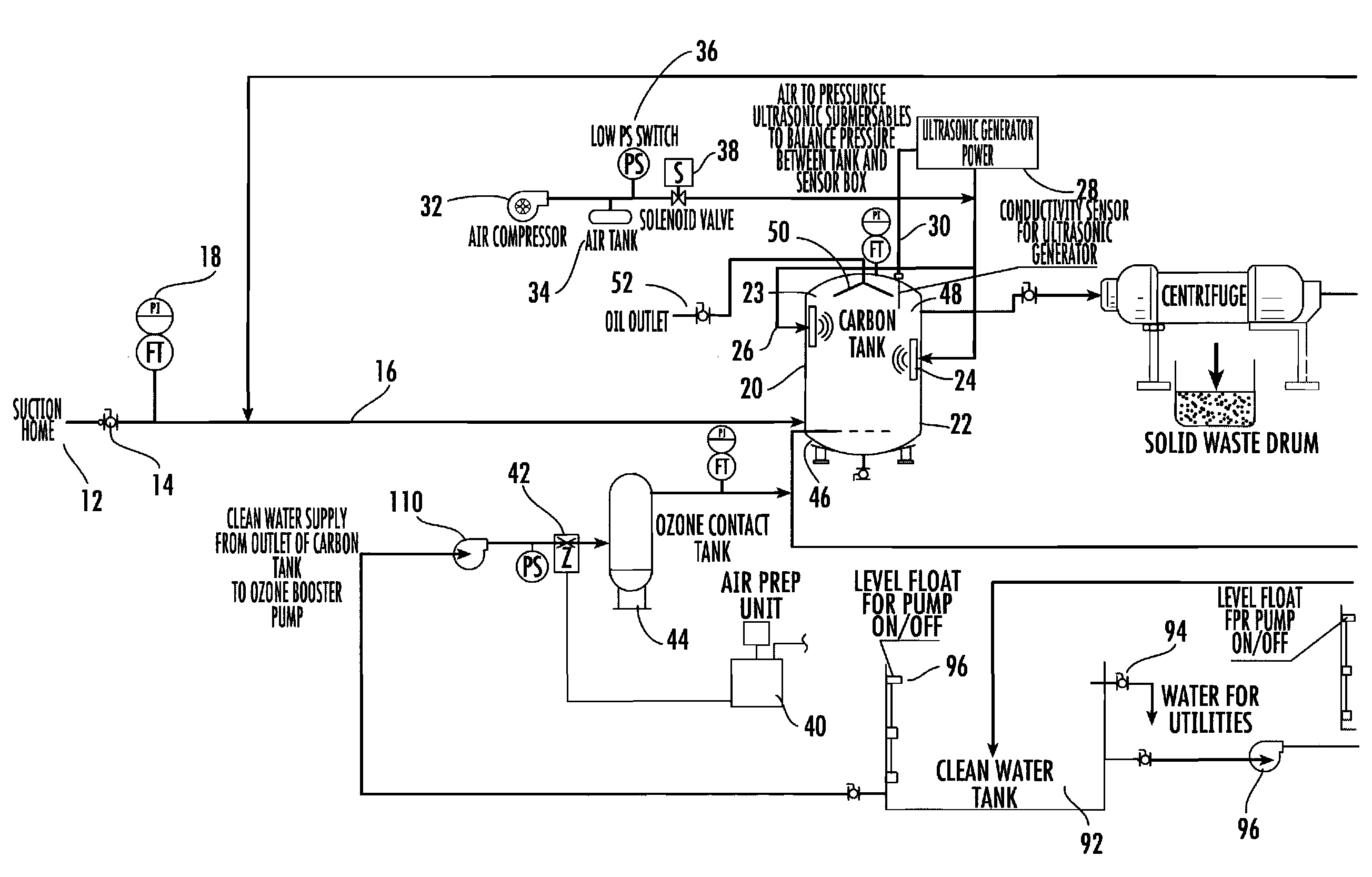
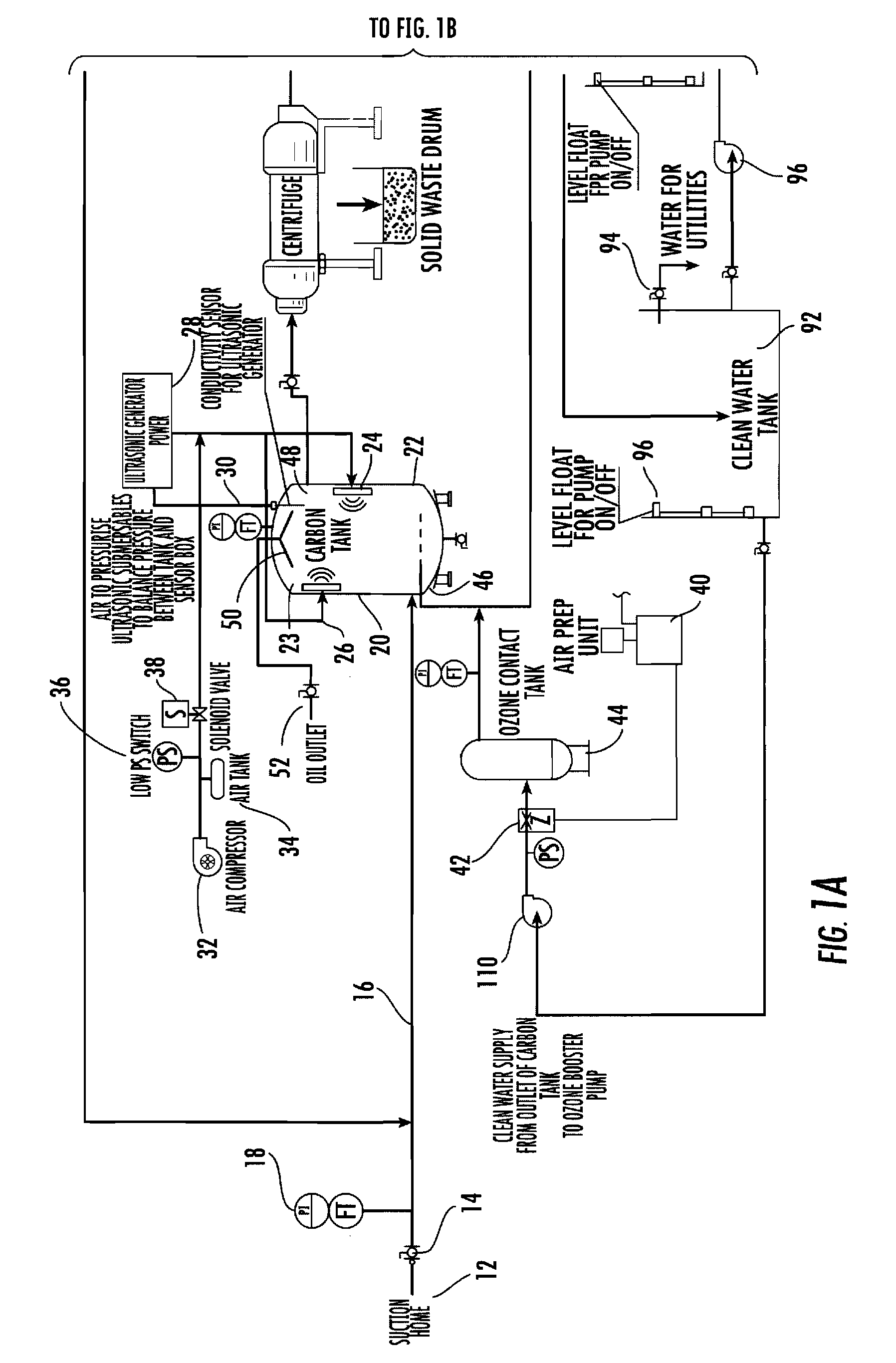
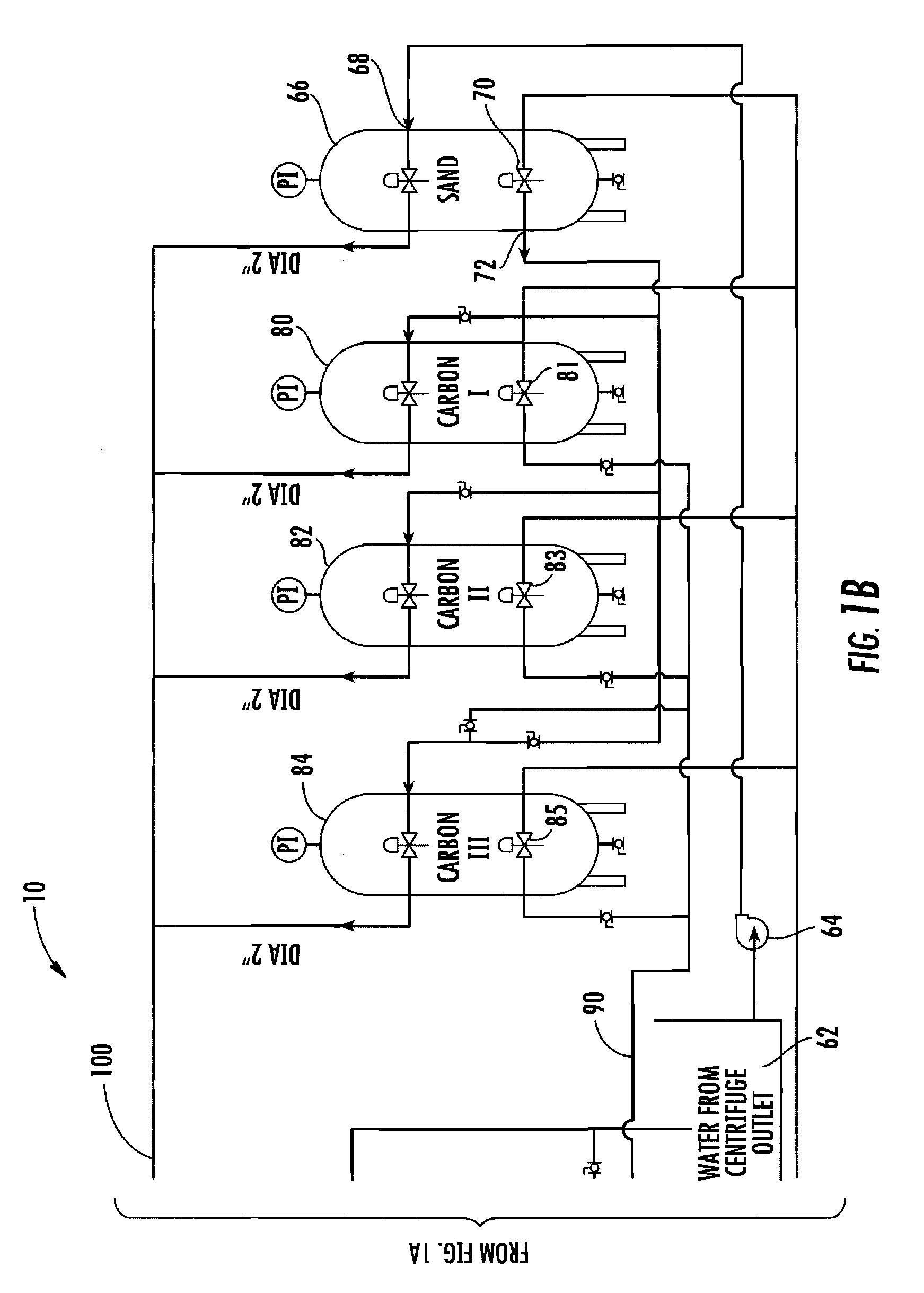
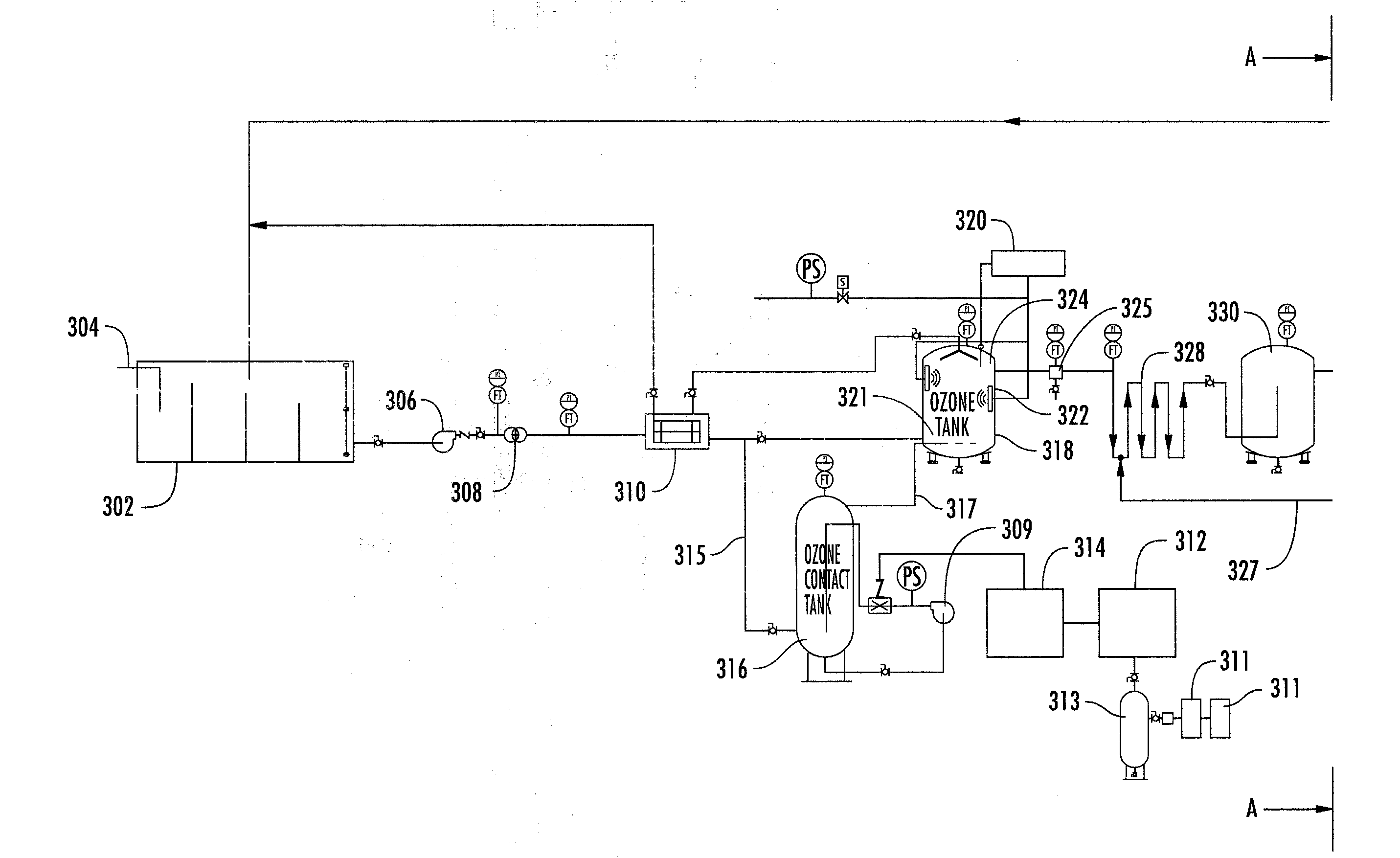
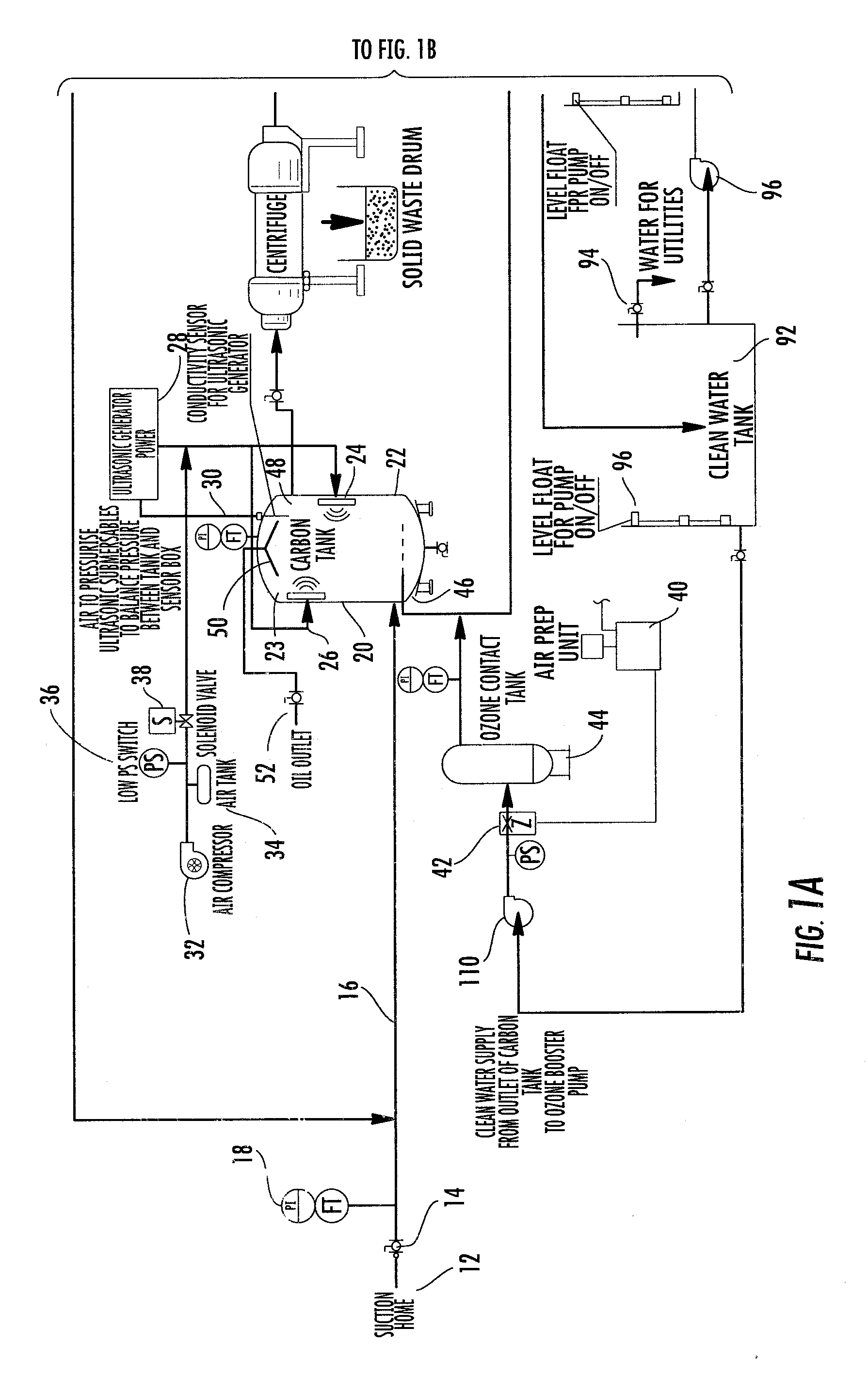
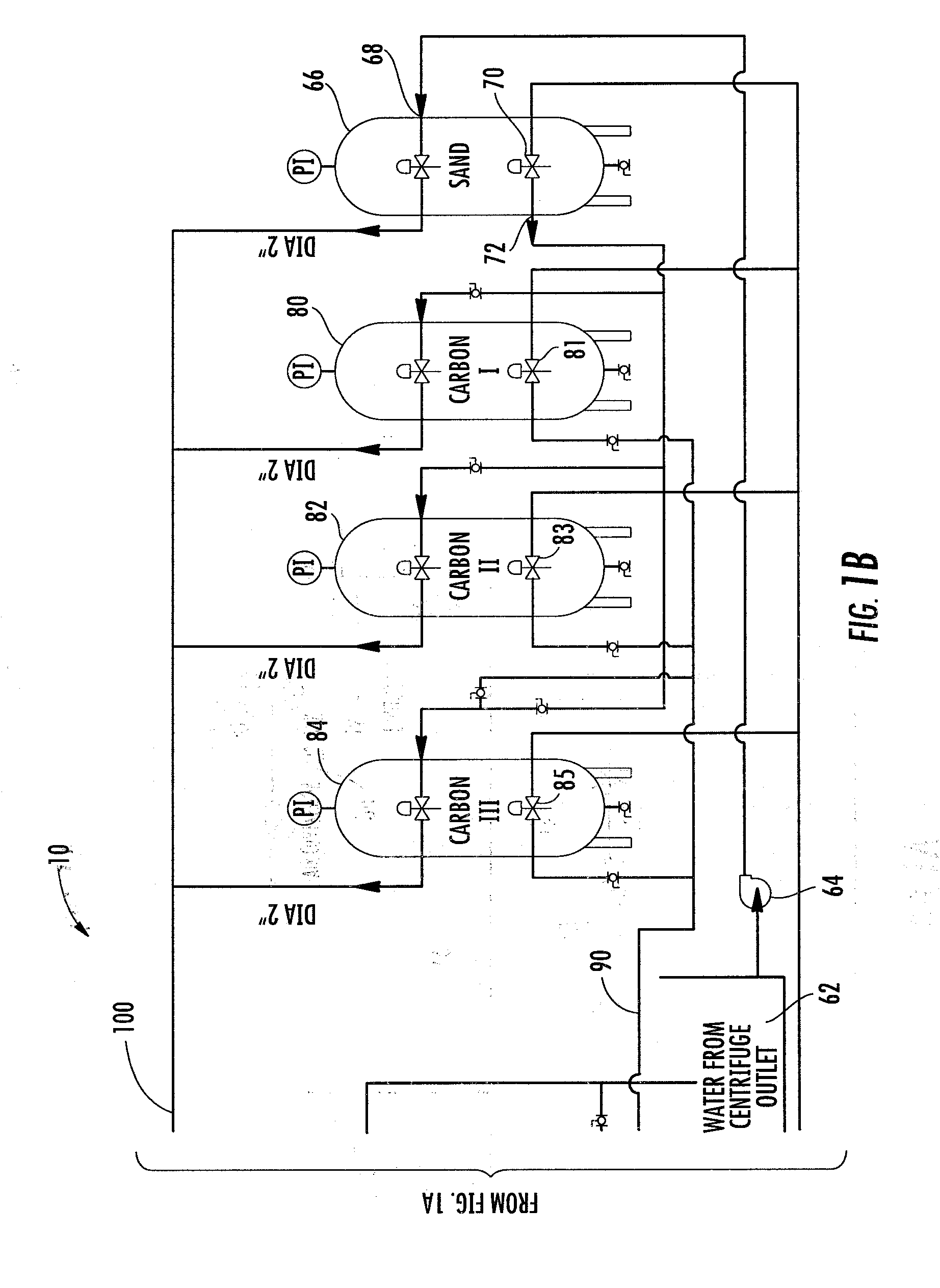
Disclosed is a process for reclamation of waste fluids. A conditioning container is employed for receipt of waste material on a continuous flow for treatment within the container by immersible transducers producing ultrasonic acoustic waves in combination with a high level of injected ozone. The treated material exhibits superior separation properties for delivery into a centrifuge for enhanced solid waste removal. The invention discloses a cost efficient and environmentally friendly process and apparatus for cleaning and recycling of flowback, or frac water, which has been used to stimulate gas production from shale formations. The apparatus is mobile and containerized and suitable for installation at the well site.
Owner:BRISBEN WATER SOLUTIONS
Water filter materials and water filters containing a mixture of microporous and mesoporous carbon particles
InactiveUS20050279696A1Reduce bacteriaReduce virusMembrane filtersLoose filtering material filtersWater filterActivated carbon filtration
A filter and filter material for providing or treating potable water is provided. The filter includes a housing having an inlet and an outlet, a filter material disposed within the housing, the filter material formed at least in part from a mixture of a plurality of mesoporous and microporous activated carbon particles. Preferably, at least some of the mesoporous activated carbon filter particles are coated with a cationic polymer, and even more preferably, at least some of the particles are coated with a cationic polymer and silver or a silver containing material. Kits comprising filters and information relating to the reduction, killing or removal of bacteria, viruses, microbials, and TTHM are also provided.
Owner:PUR WATER PURIFICATION PRODUCTS INC +2
Process and apparatus for purifying impure water using microfiltration or ultrafiltration in combination with reverse osmosis
InactiveUS20070181496A1Avoid Particulate ContaminationReduces and eliminates amountGeneral water supply conservationUltrafiltrationWater usePotable water
A method of purifying impure water contaminated with a filterable impurity and a dissolved impurity, such as sea-water, comprising the steps of: providing impure water to a primary microfiltration or ultrafiltration unit to remove the filterable impurity and produce impure filtered water contaminated with a dissolved impurity; providing the impure filtered water contaminated with a dissolved impurity to a reverse osmosis unit to produce a potable water stream and a residual reverse osmosis stream; and treating the residual reverse osmosis stream prior to reuse. The treatment may be in the form of passing through a secondary filter (such as another microfiltration or ultrafiltration membrane or a cartridge filter, and the subsequently treated reverse osmosis reject may be used to backwash the microfiltration or ultrafiltration unit.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
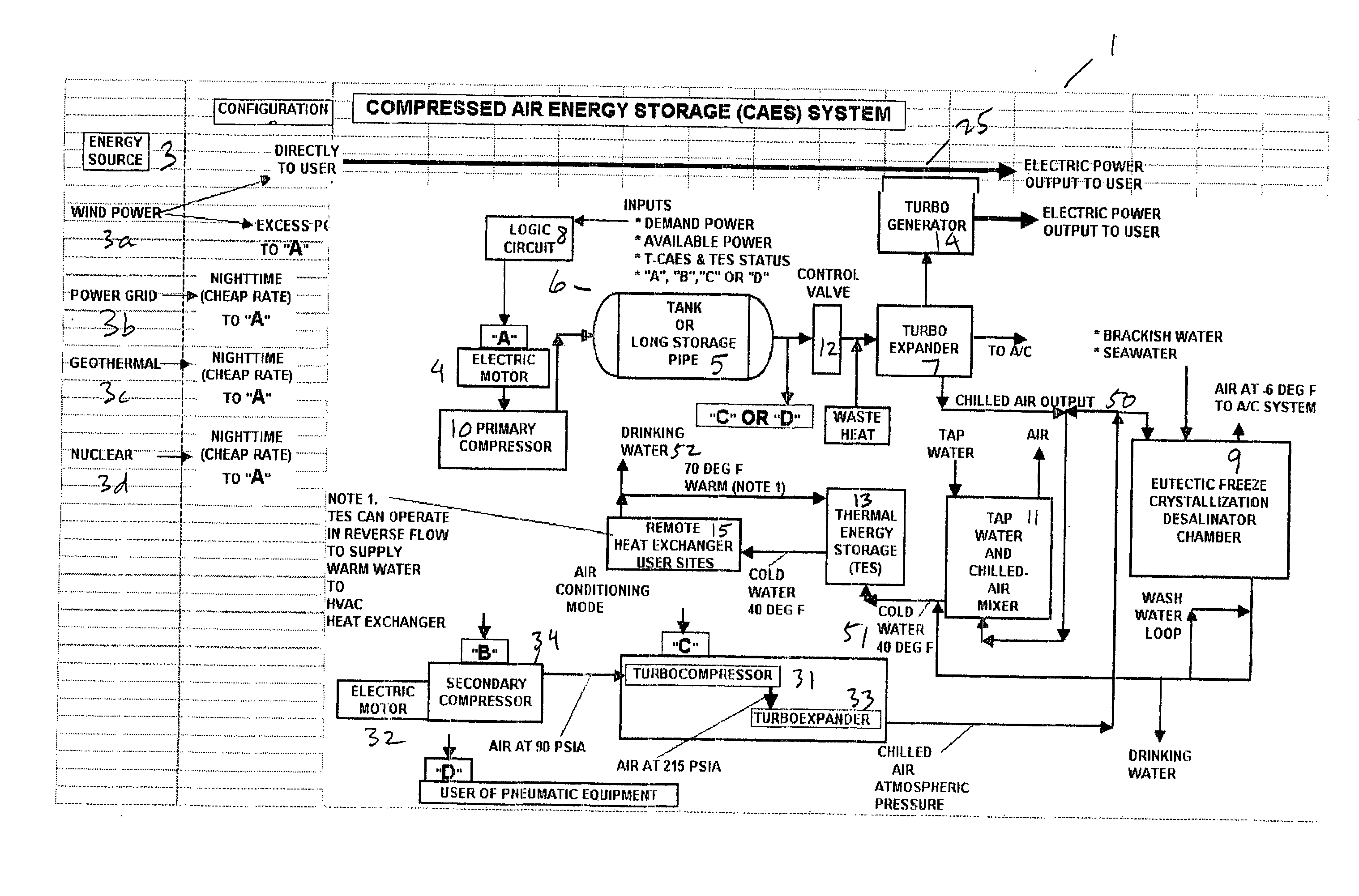
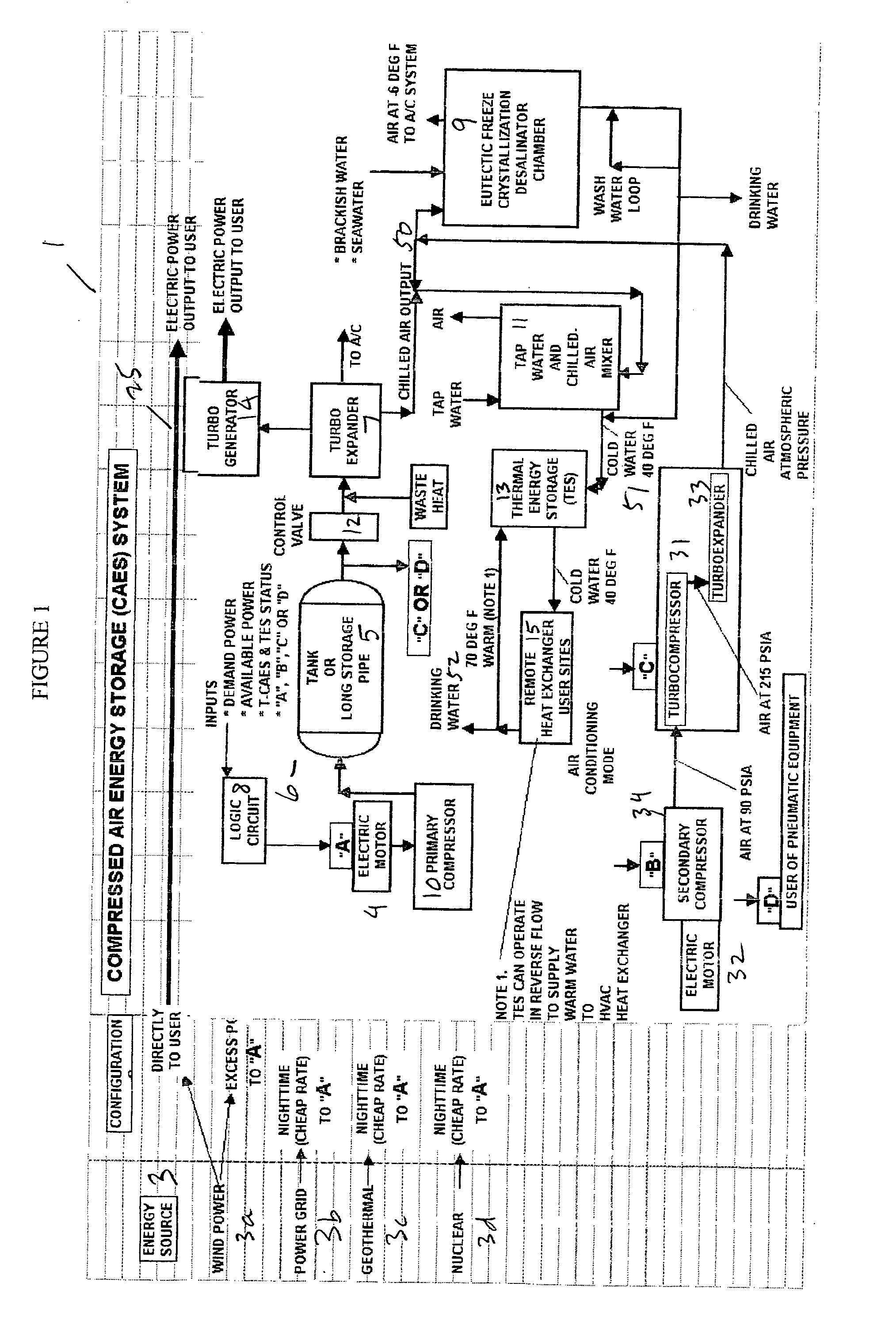
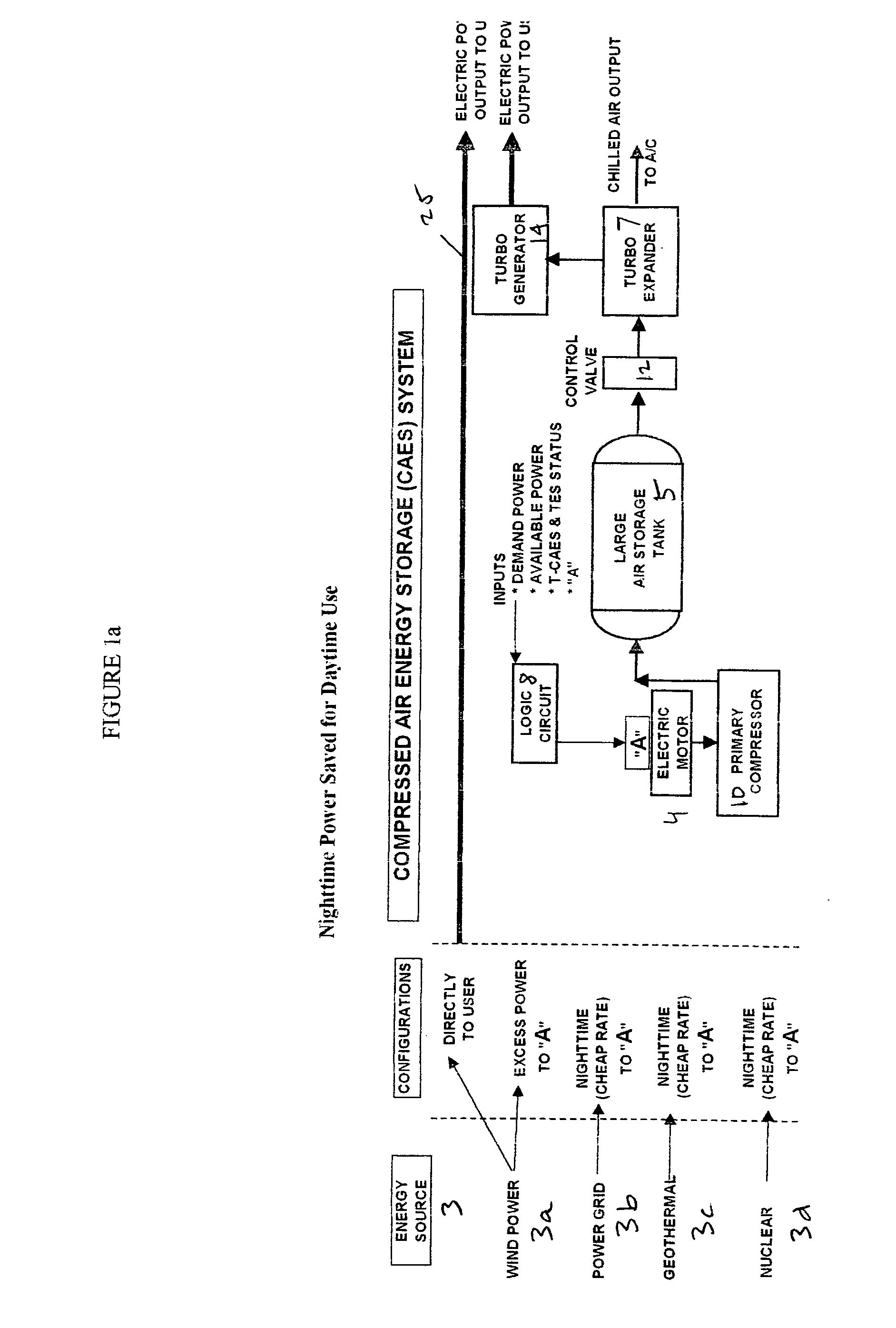
Thermal energy storage system using compressed air energy and/or chilled water from desalination processes
InactiveUS20070234749A1Reducing end-user cost of energyEnergy efficiencyWater treatment parameter controlGeneral water supply conservationThermal energyThermal energy storage system
The invention relates to a universal system for producing cost effective energy particularly for cooling purposes. In one embodiment, wind turbines are used to generate electricity and compressed air energy, wherein the compressed air energy is used to co-generate electricity and chilled air. The chilled air is then used to chill water in either a mixing chamber, or a desalination system, wherein the chilled water is stored in a separation tank, wherein it can later be used to provide cooling for an air conditioning system for a facility. When desalination is used, the system produces chilled fresh drinking water which can be used for air conditioning, and then used as fresh drinking water. Any exhaust chilled air can be used directly for air conditioning.
Owner:ENIS BEN M +1
Water purification pack
InactiveUS20050113796A1General water supply conservationTransportation and packagingHuman bodyQuality level
An apparatus and methods are disclosed for purifying fluid, such as potable water, to quality levels suitable for medical application, particularly to applications involving injection of the fluid into a human body. The apparatus comprises a portable purification pack constructed for a single use. The pack houses depth filtration, activated carbon, mixed bed ion exchange resins and terminal filtration stages in series. The terminal filter comprises a fine (microfiltration or ultrafiltration), permeable membrane, treated with an endotoxin-binding chemistry. In contrast with semi-permeable osmotic membranes, the permeable membrane produces high flow rates at relatively low pressures, while still safely purifying fluid to injection quality.
Owner:TAYLOR MICHAEL A
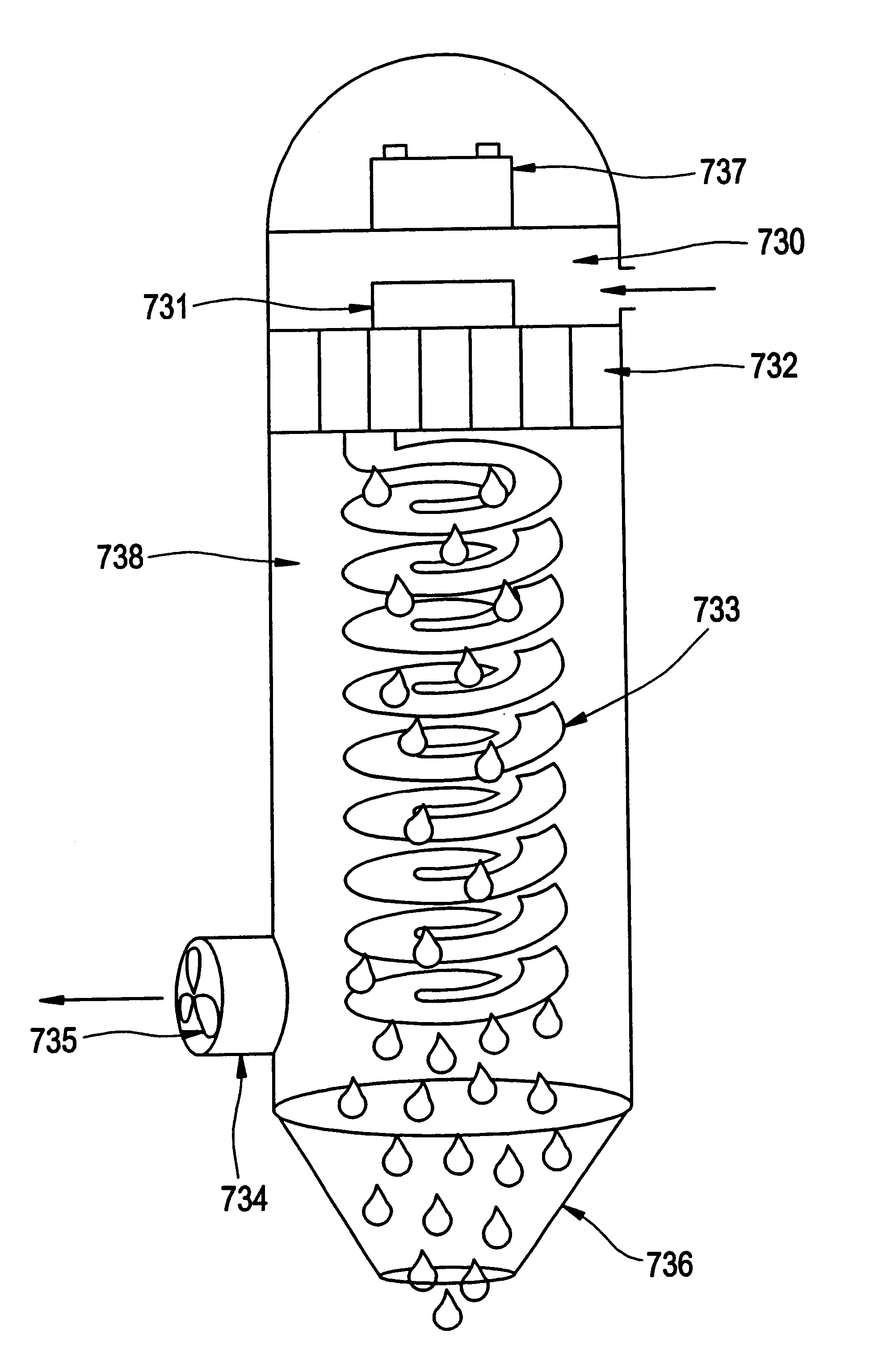
Production of potable water and freshwater needs for human, animal and plants from hot and humid air
InactiveUS6868690B2Reduces cargo spaceMinimize any benefitGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentParticulatesFresh water organism
Systems and methods are disclosed for extracting freshwater from atmospheric humidity in extremely hot and humid climates and supplying freshwater to a small group of people, a building, a farm, or forestation area. The freshwater is treated to provide drinking water by disinfecting to eliminate microorganisms and filtration to remove suspended particulates from air, erosion or corrosion products, and disinfected waste. Compact units provide drinking water for individuals, passengers in cars, vans, trucks, or recreational boats, or crewmembers on a seagoing cargo ship whether from atmospheric humidity or from moisture-laden gases. Furthermore, systems are disclosed for the ample supply of freshwater with minimal treatment for small- to large-sized buildings in a manner that alleviates the heat load on buildings. Collection of freshwater from hot humid ambient air is also provided for other uses, such as irrigation and farm animal drinking. Various methods are used for condensation of water vapor suspended in the air as alternative to conventional refrigeration cycles using CFC refrigerants. Devices are disclosed using naturally occurring brackish cold water, circulation of cooling water cooled by thermoelectric cooling or thermoacoustic refrigeration as well as evaporative cooling and transpiration cooling. Water produced by the systems may flow under gravitational forces entirely or with the assistance of boasting pumps.
Owner:FAKIEH RES & DEV CENT
Water dispenser for pets
InactiveUS20080190374A1Encourage adequate hydrationEasy to cleanAnimal watering devicesDiseaseMetabolic waste
An aseptic watering system for pets is that has a unique filtration and sterilization system for providing a source of drinking water substantially free of toxins, pathogens, resultant metabolic wastes, or other contaminants that may cause bothersome and life threatening diseases. The system also includes means for cooling the drinking water to make it more desirable to a pet.
Owner:FARRIS BARRY LEE
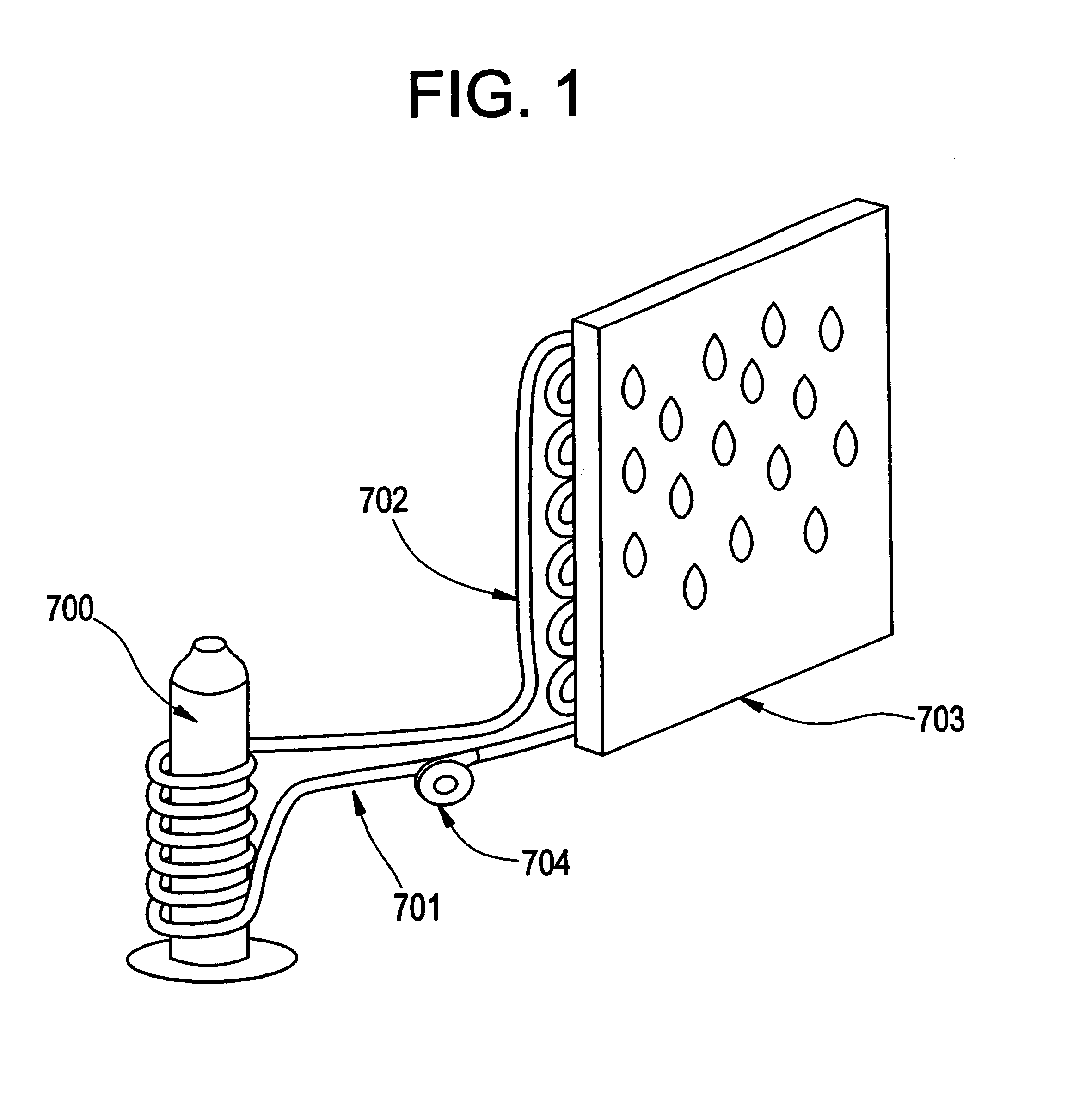
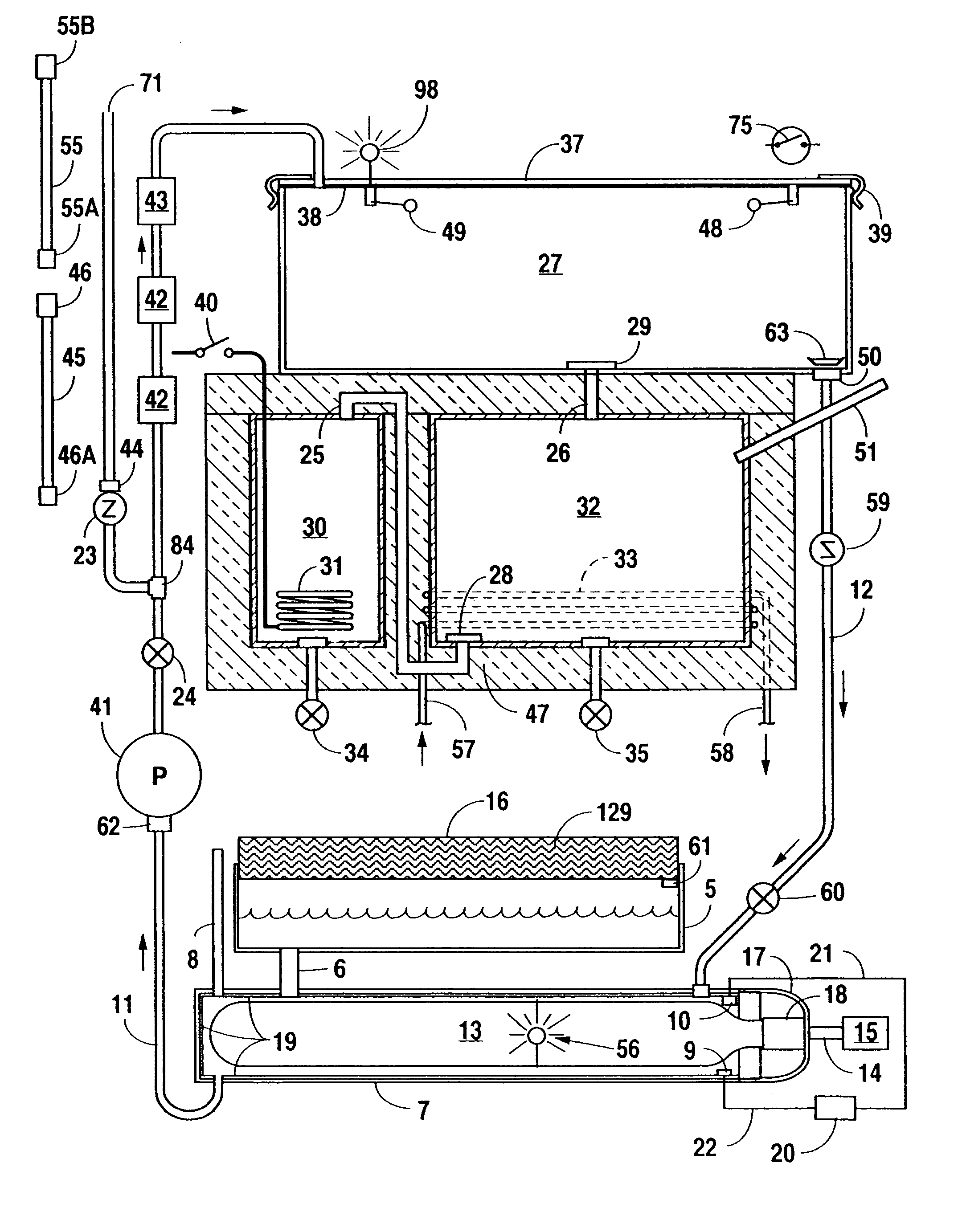
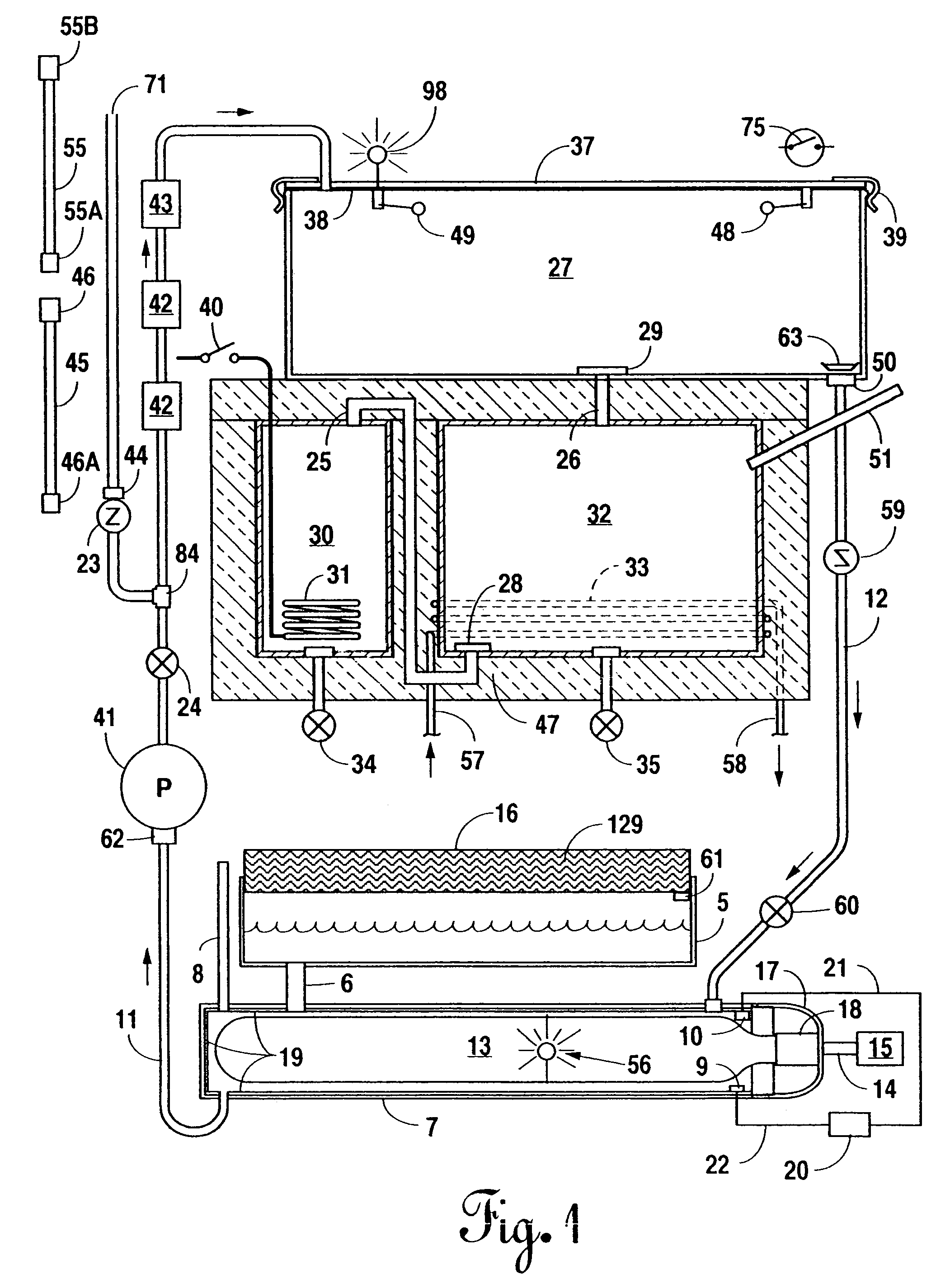
Portable, potable water recovery and dispensing apparatus
InactiveUS7089763B2Maximum efficiencyMaximum productionLiquefactionSpace heating and ventilationParticulatesBiological body
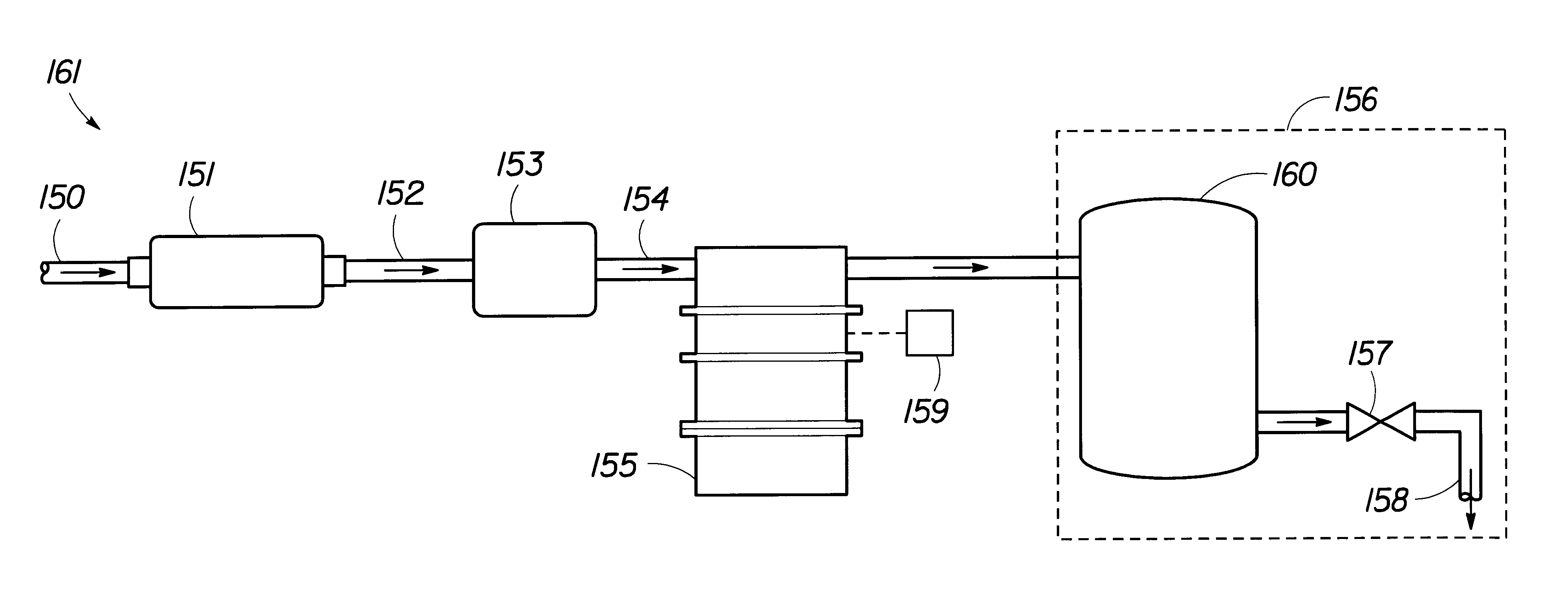
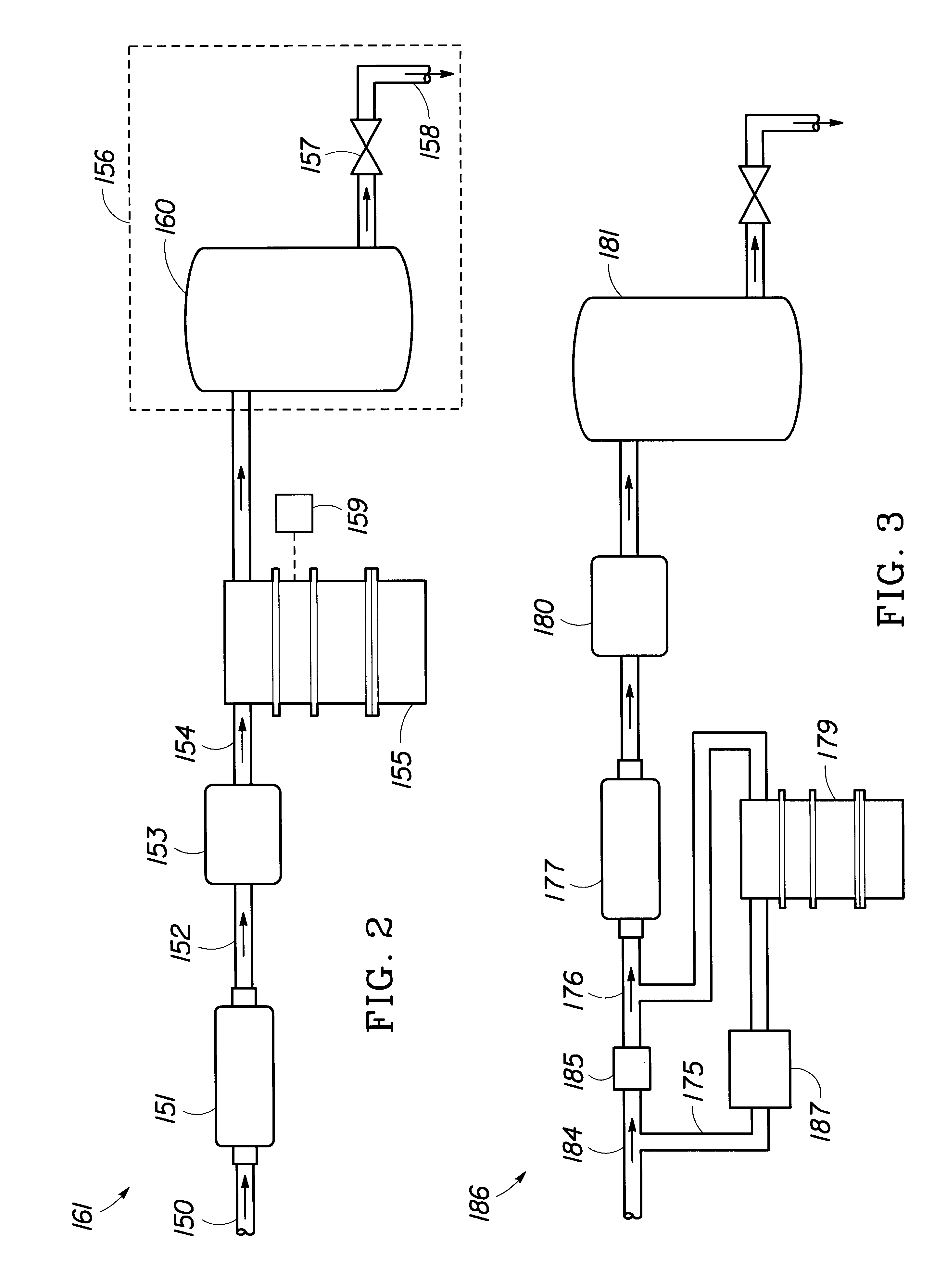
A portable, potable-water generator for producing high-purity liquid water by condensation of water vapor from ambient air. The generator (125) employs an air filter (119) to remove particulates and aerosols from the incoming air. An enclosed heat absorber cools the filtered air to its dew point and collects droplets of condensate into a condensate collector (5). Before discharge, the collected dew is treated in a bacteriostat loop to destroy adventitious living organisms and to filter out undesirable and dangerous contaminants. A recirculation loop provides the ability to recirculate stored condensate, including during periods of inactivity. Further, quick disconnect fittings (55b) and variable length flexible tubing allows use of the invention to serve remote dispensers and / or appliances and allow use of municipal water treated through the apparatus in low condensate situations.
Owner:WORLDWIDE WATER INC
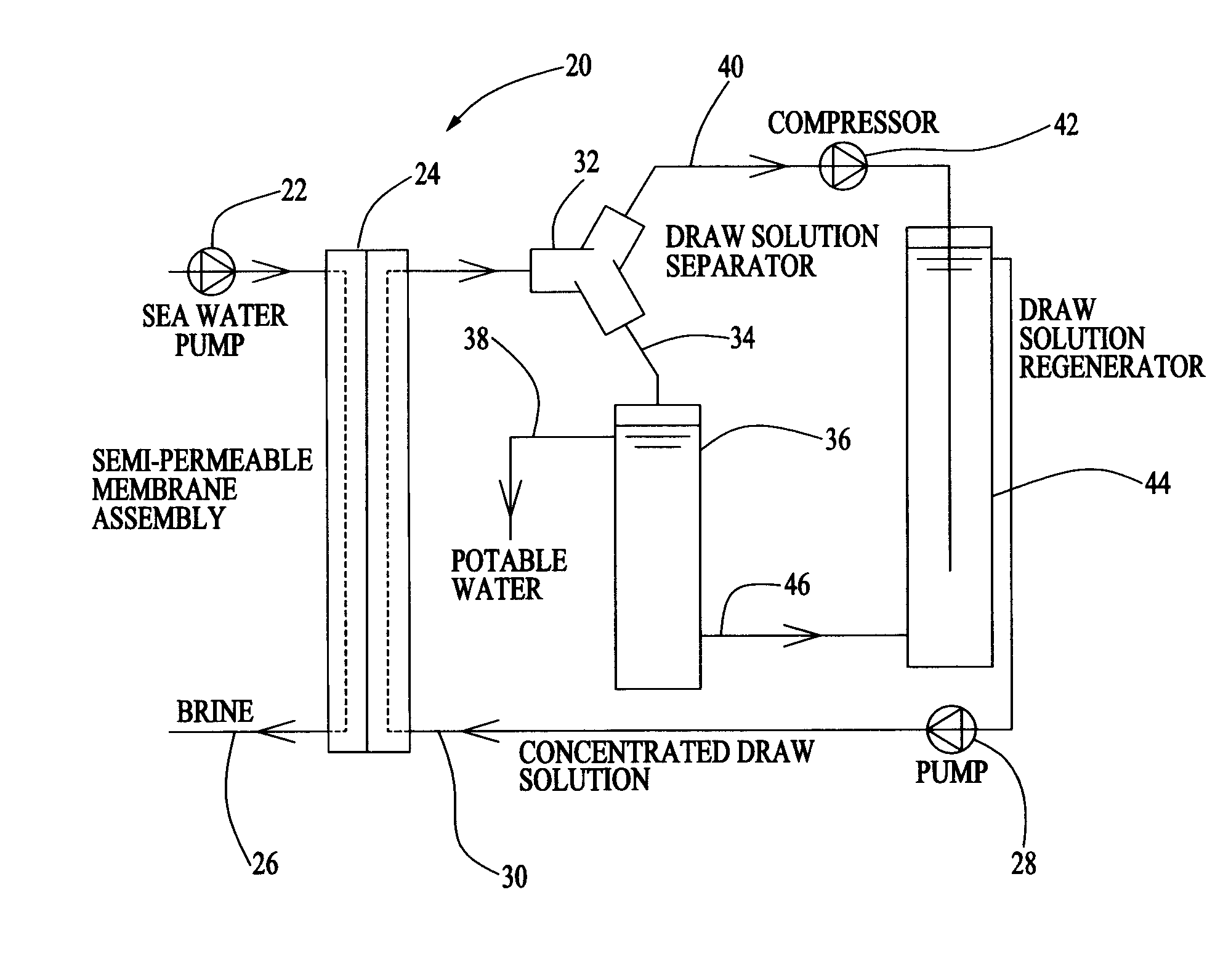
Method and Apparatus for Producing Potable Water from Seawater Using Forward Osmosis
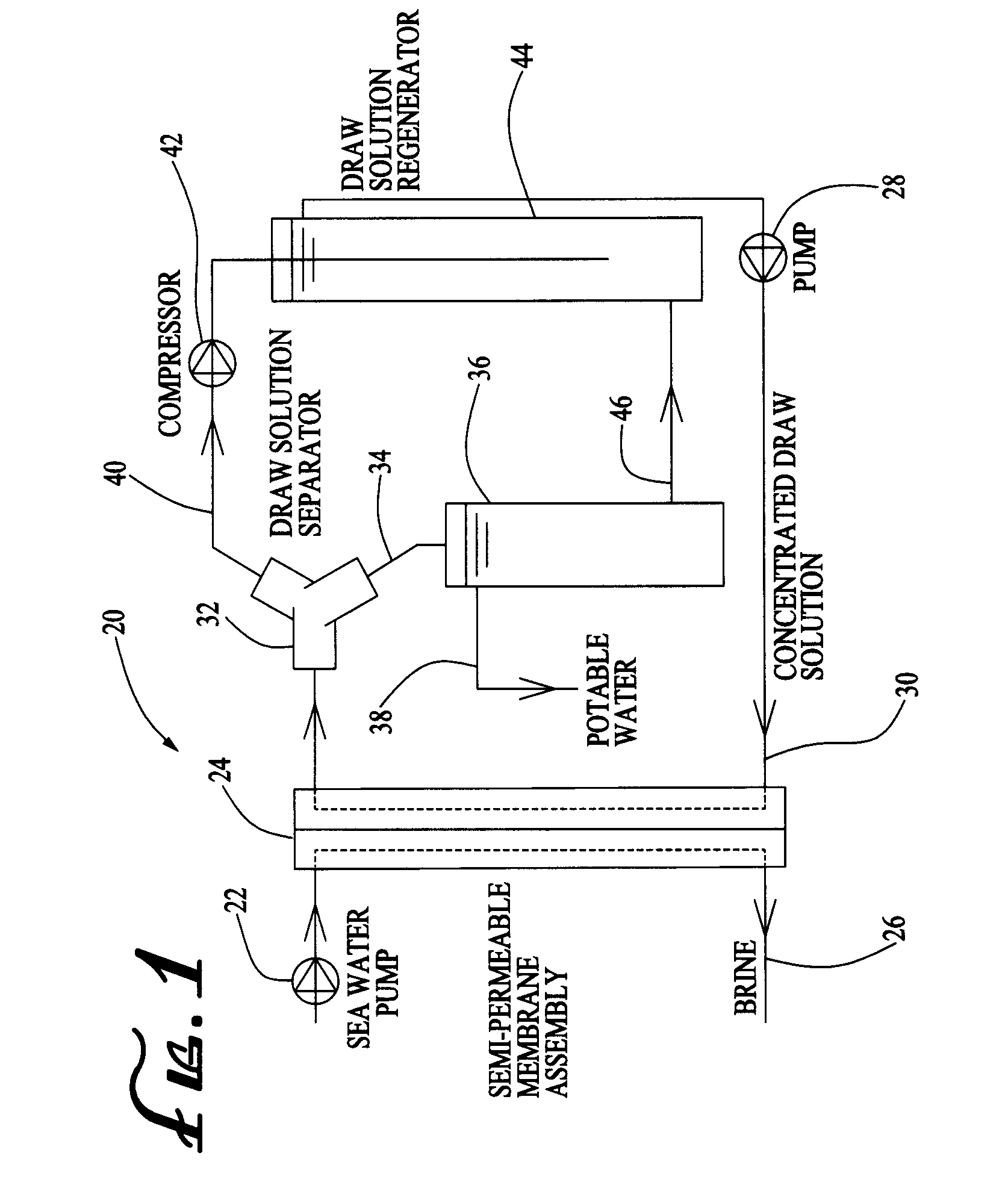
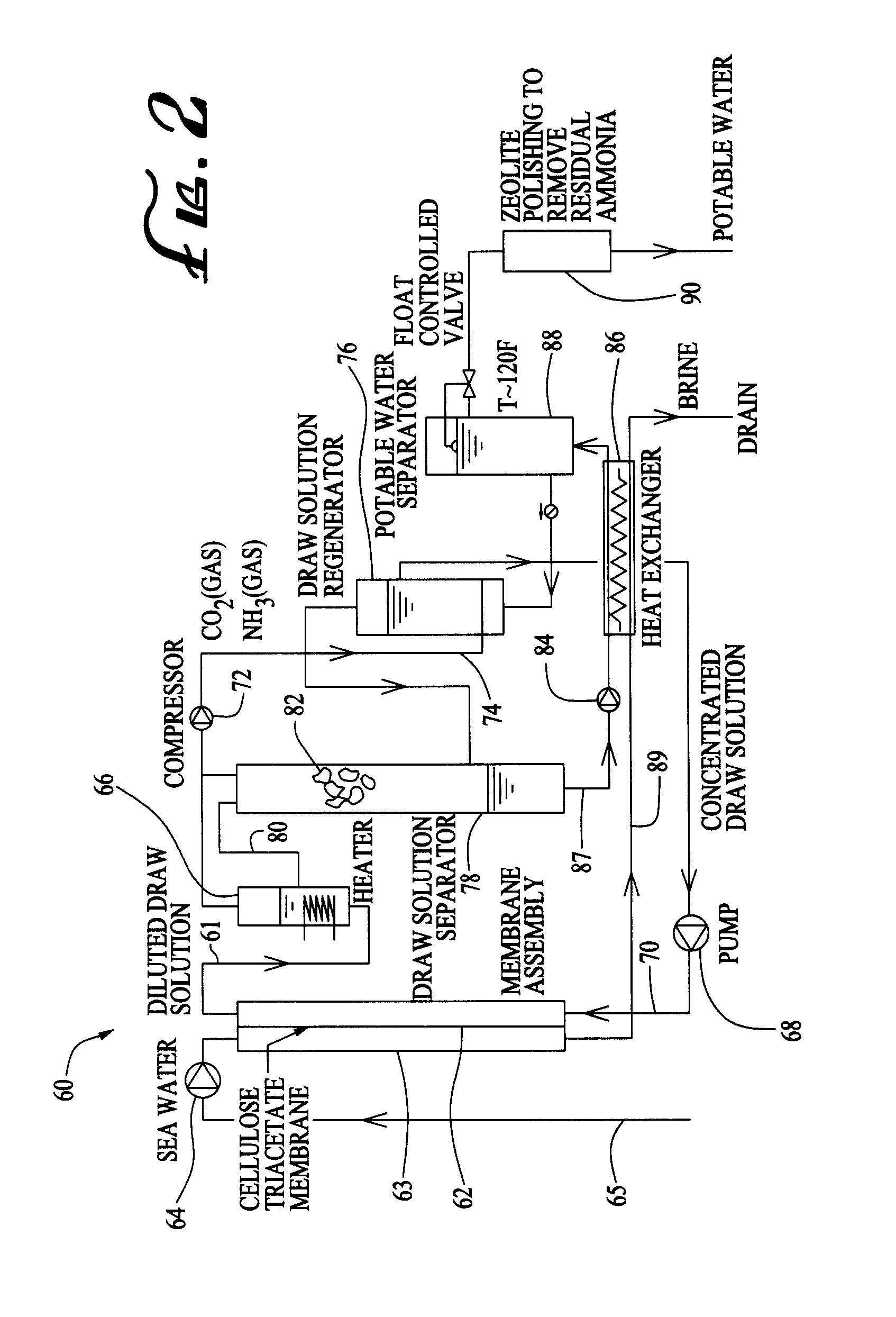
ActiveUS20090308727A1Efficient and effectiveAuxillariesGeneral water supply conservationDesalinationPotable water
A method and apparatus for desalinating seawater which uses an ammonia bicarbonate forward osmosis desalination process. Seawater is pumped through one side of a membrane assembly. A draw solution is pumped through the other side of the membrane assembly. The draw solution withdraws water molecules from the seawater through the membrane into the draw solution. A draw solution separator receives a heated draw solution which then decomposes into ammonia, carbon dioxide and water. Potable water is separated from ammonia has and carbon dioxide gas. The ammonia gas and carbon dioxide gas are recombined with a portion of the potable water stream to reform the ammonium bicarbonate draw solution.
Owner:USA REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY
Water treatment compositions
InactiveUS20040217326A1Improve filter characteristicsImprove performanceWater softeningSedimentation separationDisinfectantWater soluble
Compositions, methods and kits for purifying and clarifying and / or nutrifying contaminated drinking water and which comprise a primary coagulant material, a microbiocidal disinfectant and an oxidant system. Highly preferred compositions also contain one or more of a bridging flocculent material, the levels and ratios of coagulant to flocculent preferably falling within certain ranges, a cationic coagulant aid, especially chitosan, a water-soluble alkali, a water-insoluble silicate, and a food additive or nutrient source. The purified water remains free of discoloration for extended periods of storage.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBNE CO
Inland aquaculture of marine life using water from a saline aquifer
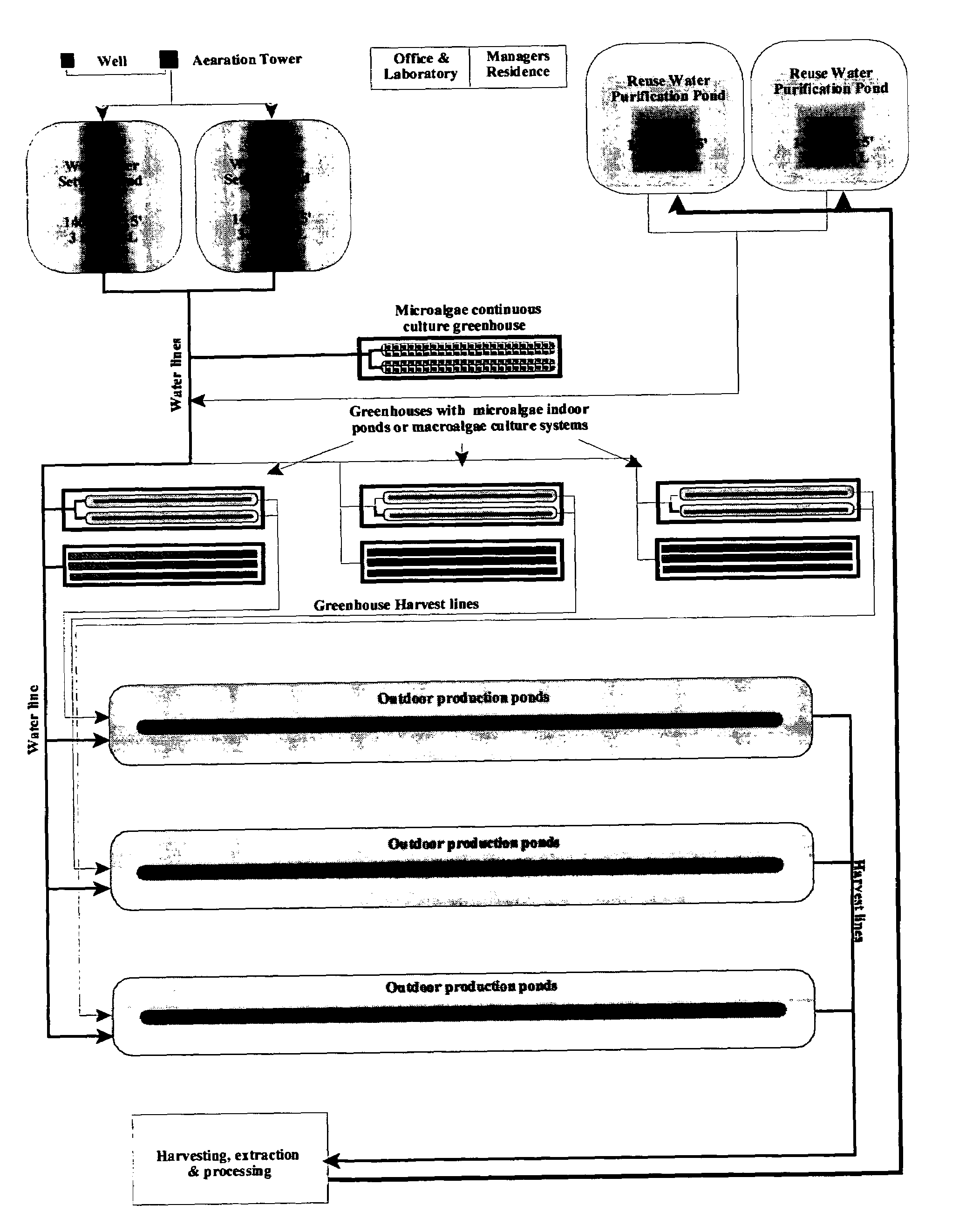
InactiveUS6986323B2Overcome disadvantagesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaInland saline aquacultureWater layer
A method and system for the inland aquaculture of marine species using water from a saline aquifer having a heavy metals content within the acceptable limits of the EPA guidelines for drinking water. The aquifer is preferably the Coconino aquifer located in Arizona and New Mexico. The system can be used to culture microalgae, macroalgae, fish, shrimp and many other marine species. Nutrients and fertilizers can be added to the water to optimize culture conditions for particular species. Useful products can be isolated from the marine species or the cultured marine species can be harvested as useful products themselves.
Owner:ALGAE BIOSCI
Microorganism control of point-of-use potable water sources
InactiveUS6458257B1Keep it cleanPrevent freezingCellsSpecific water treatment objectivesOzone generatorMedical equipment
The present invention provides for the electrochemical generation of ozone for use in "point-of-use" applications. The electrochemical ozone generators or systems of the present invention may be used to provide disinfected water, ozone-containing water, and / or ozone gas. Disinfected water may be produced by introducing ozone gas into a potable or purified water source for the purpose of disinfecting or controlling the microorganisms in the water source. Ozonated water or ozone gas may be produced and provided for various anti-microbial and cleansing applications of the consumer, such as washing food, clothing, dishes, countertops, toys, sinks, bathroom surfaces, and the like. Furthermore, the ozone generator may be used to deliver a stream of ozone-containing water for the purpose of commercial or residential point-of-use washing, disinfecting, and sterilizing medical instruments and medical equipment. For example, the ozone-containing water may be used directly or used as a concentrated sterilant for the washing, disinfecting, and sterilizing of medical instruments or equipment. Ozone gas may also be used in many of the foregoing examples, as well as in the deodorization of air or various other applications. The invention allows the electrochemical ozone generator to operate in a nearly or entirely passive manner with simplicity of design.
Owner:LYNNTECH INT
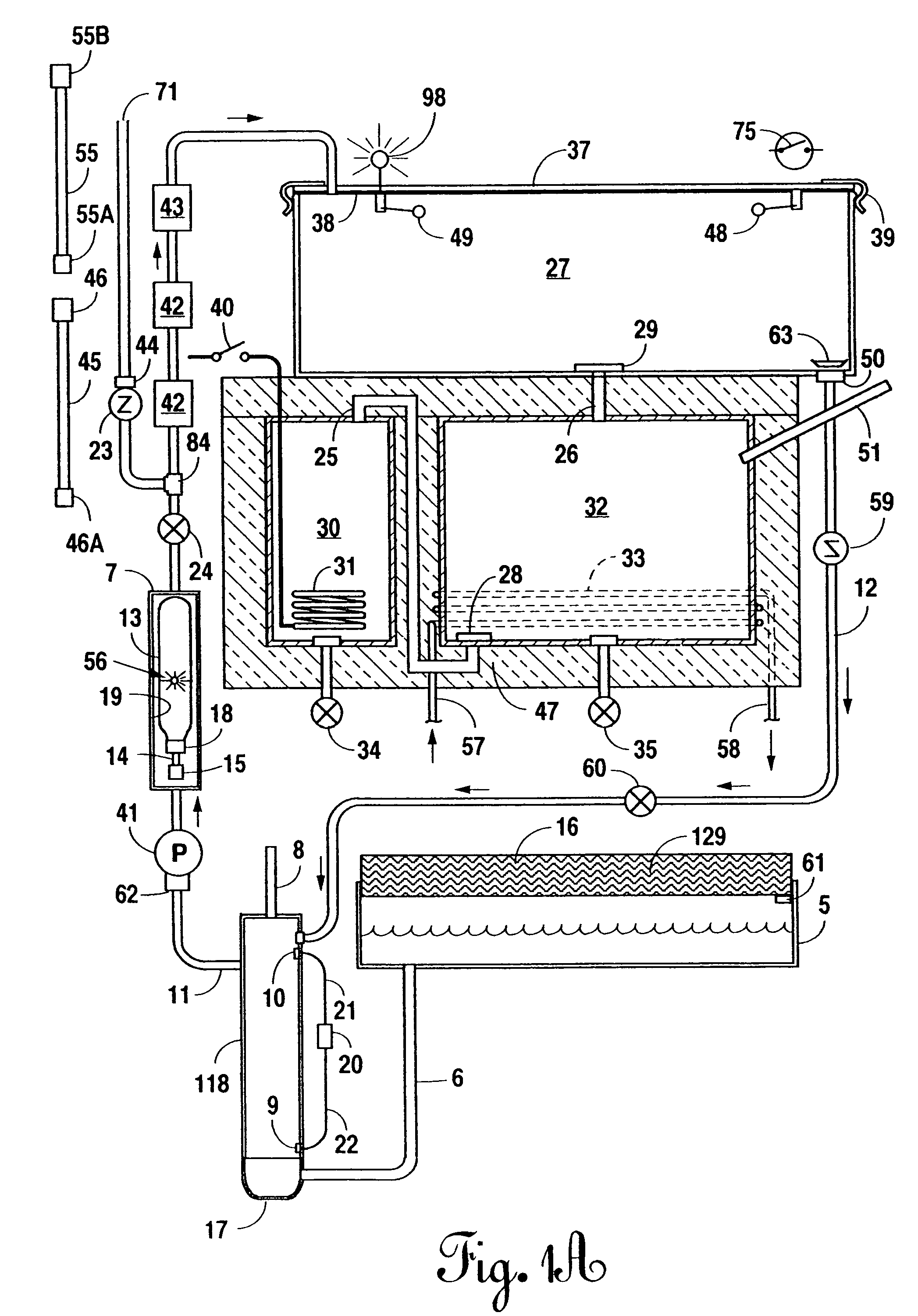
Portable, potable water recovery and dispensing apparatus
InactiveUS20050139552A1Maximum productionMaximum efficiencyLiquefactionSpace heating and ventilationParticulatesBiological body
A portable, potable-water generator for producing high-purity liquid water by condensation of water vapor from ambient air. The generator (125) employs an air filter (119) to remove particulates and aerosols from the incoming air. An enclosed heat absorber cools the filtered air to its dew point and collects droplets of condensate into a condensate collector (5). Before discharge, the collected dew is treated in a bacteriostat loop to destroy adventitious living organisms and to filter out undesirable and dangerous contaminants. A recirculation loop provides the ability to recirculate stored condensate, including during periods of inactivity. Further, quick disconnect fittings (55b) and variable length flexible tubing allows use of the invention to serve remote dispensers and / or appliances and allow use of municipal water treated through the apparatus in low condensate situations.
Owner:WORLDWIDE WATER INC
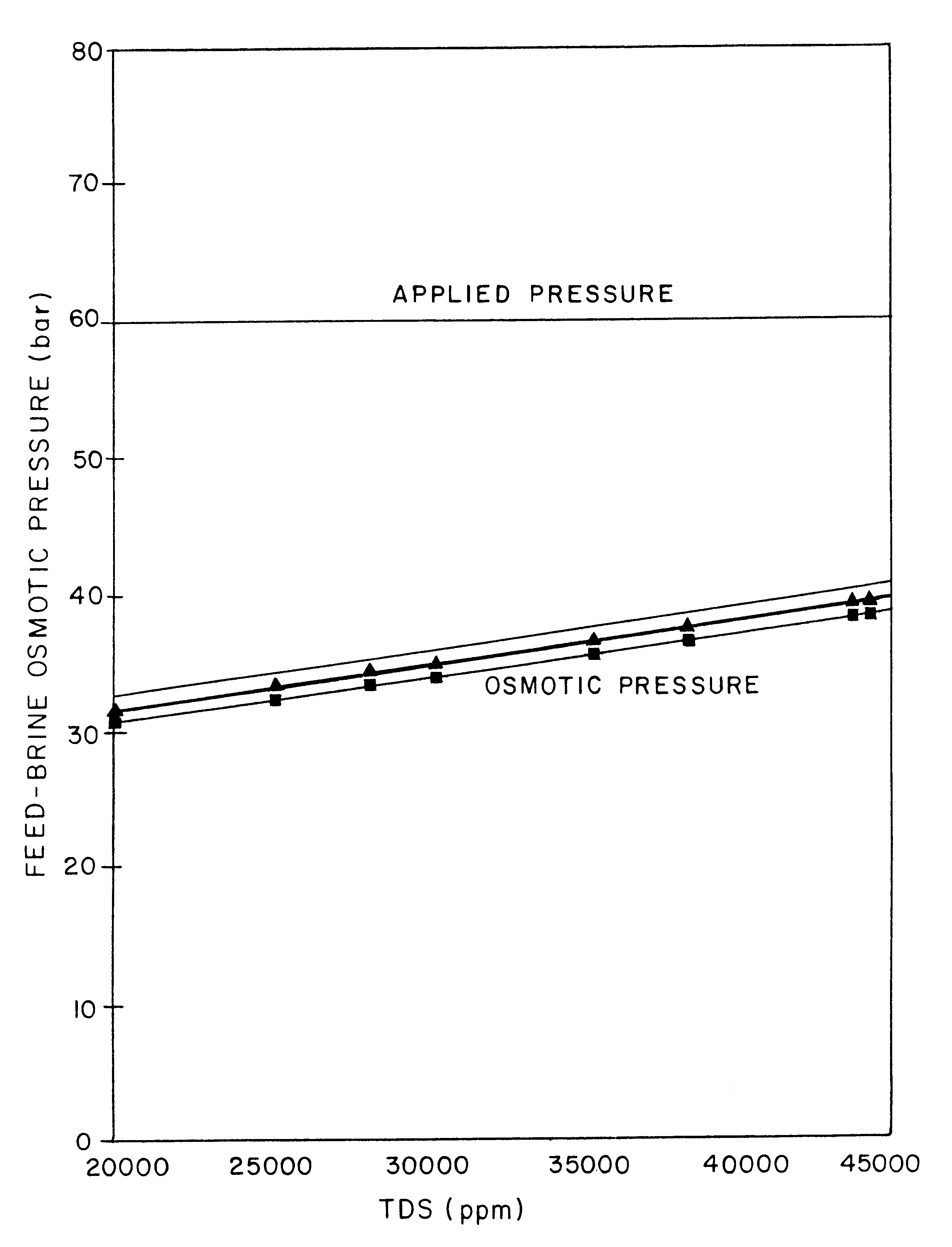
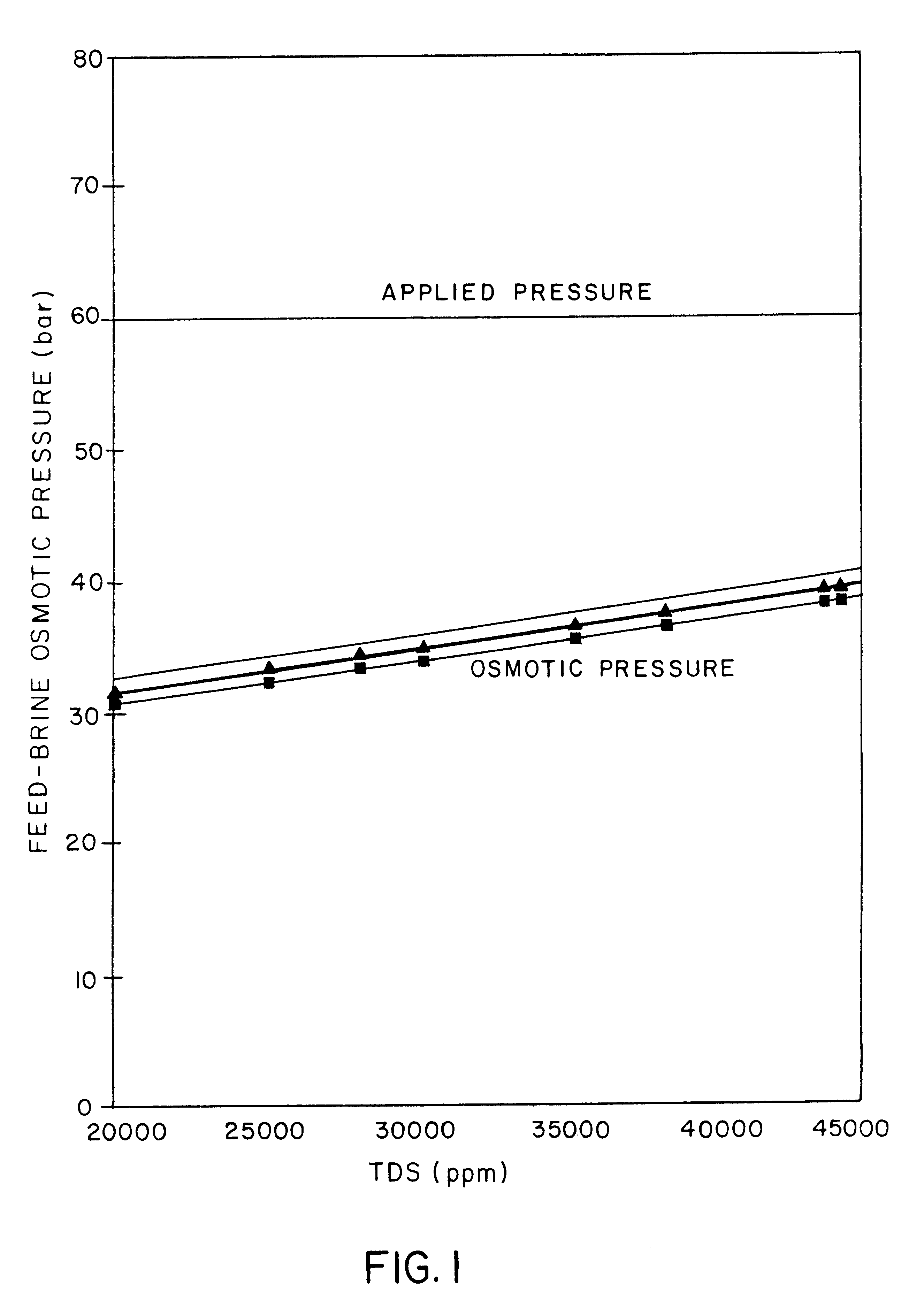
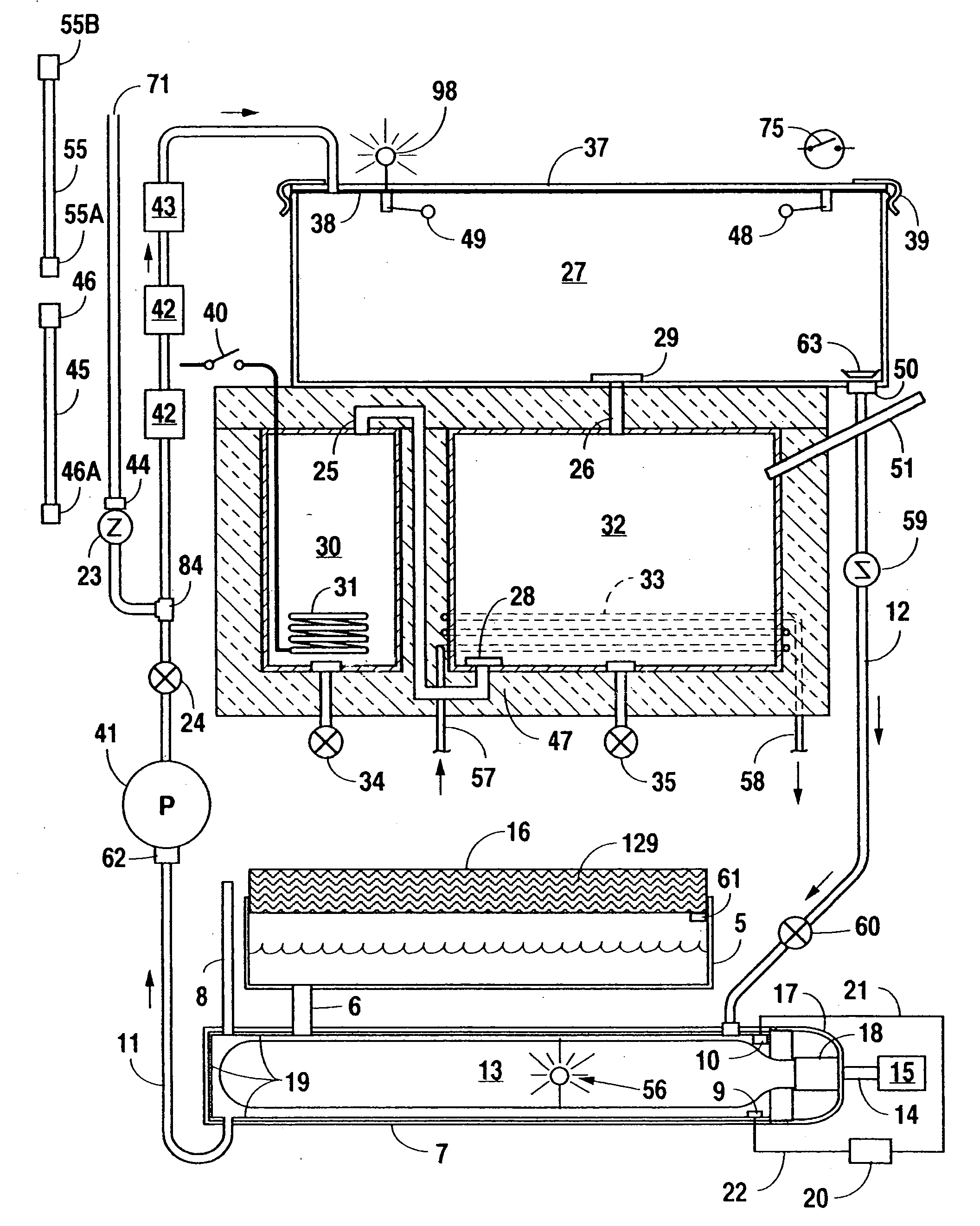
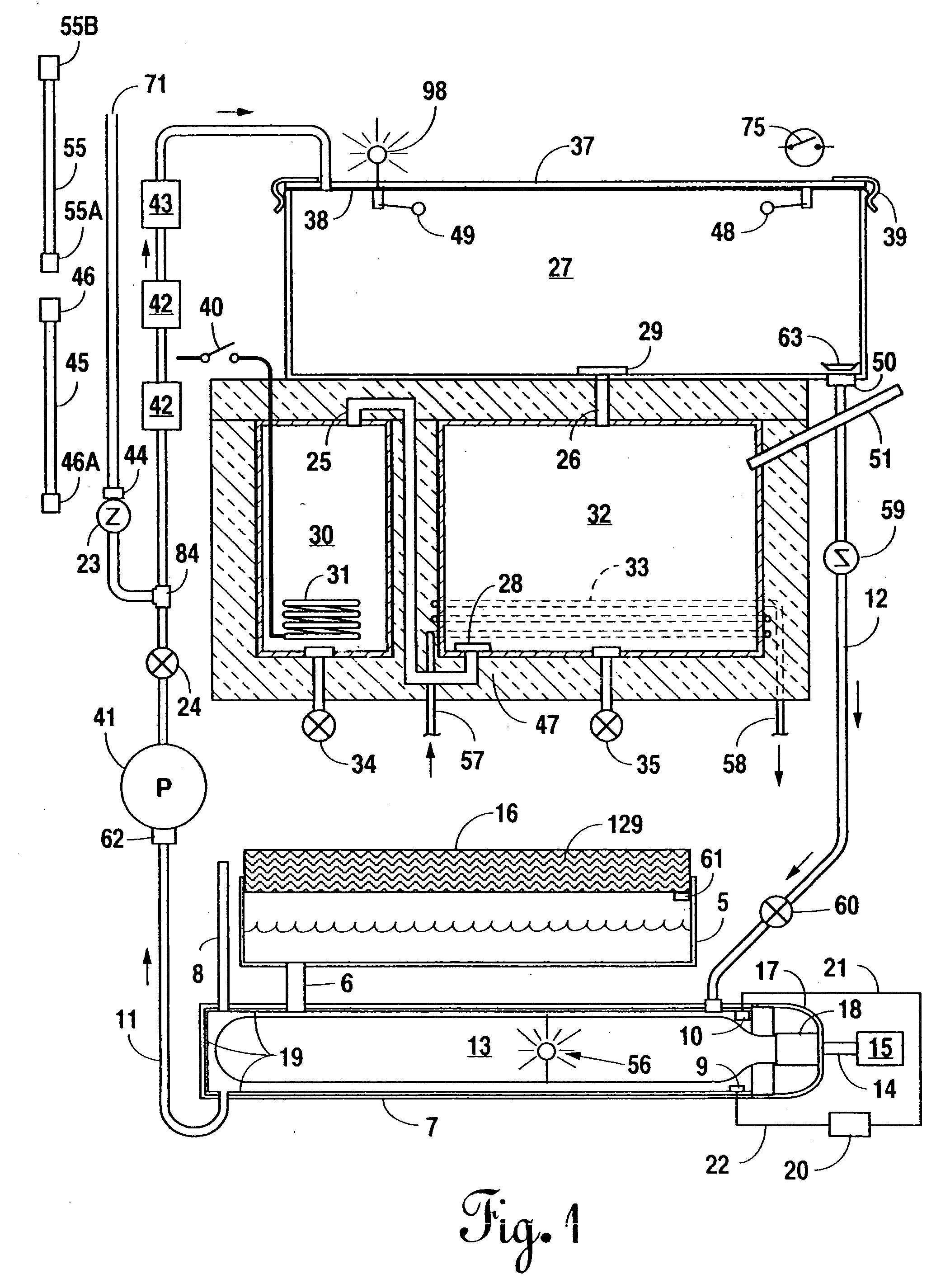
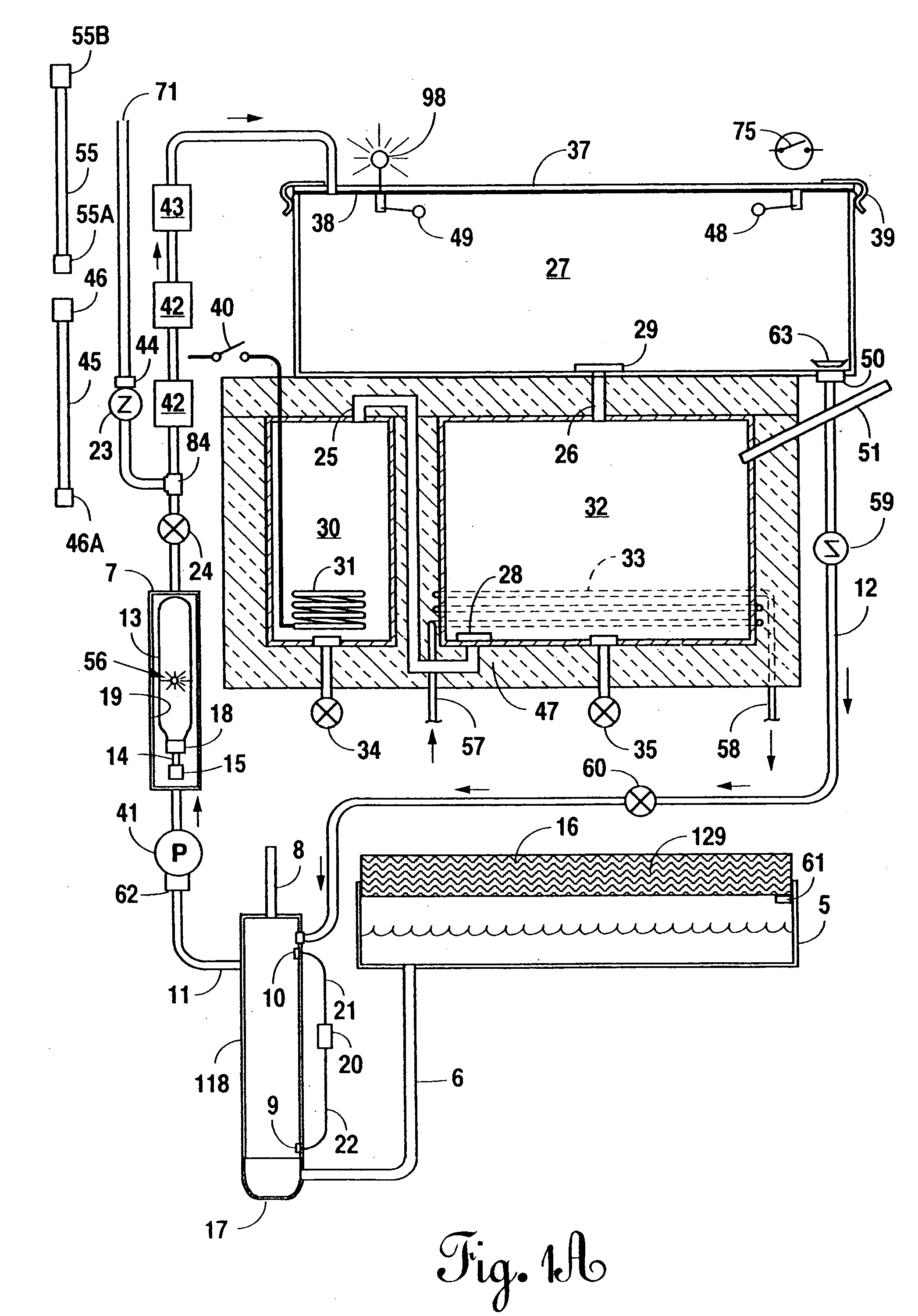
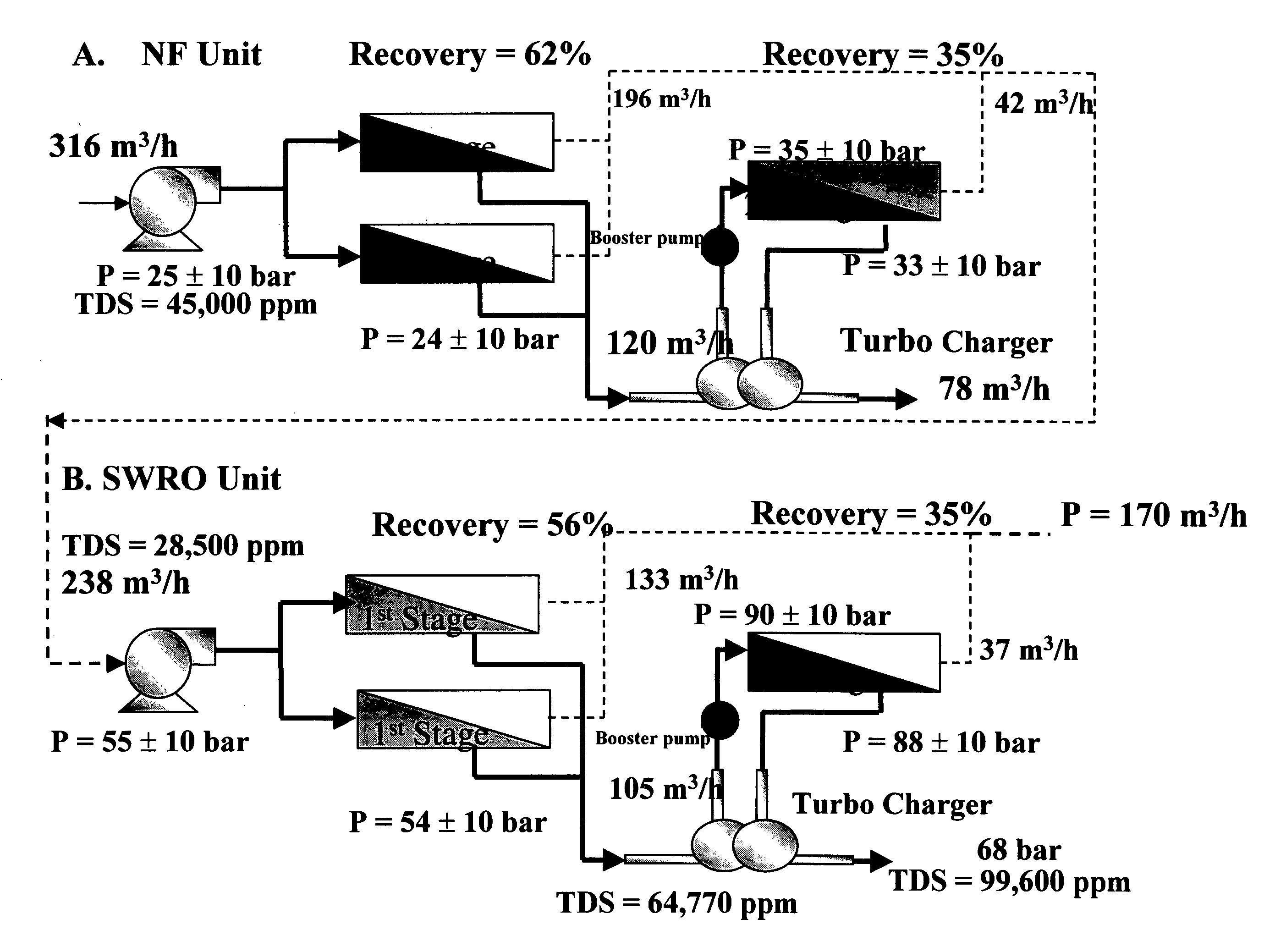
Fully integrated NF-thermal seawater desalination process and equipment
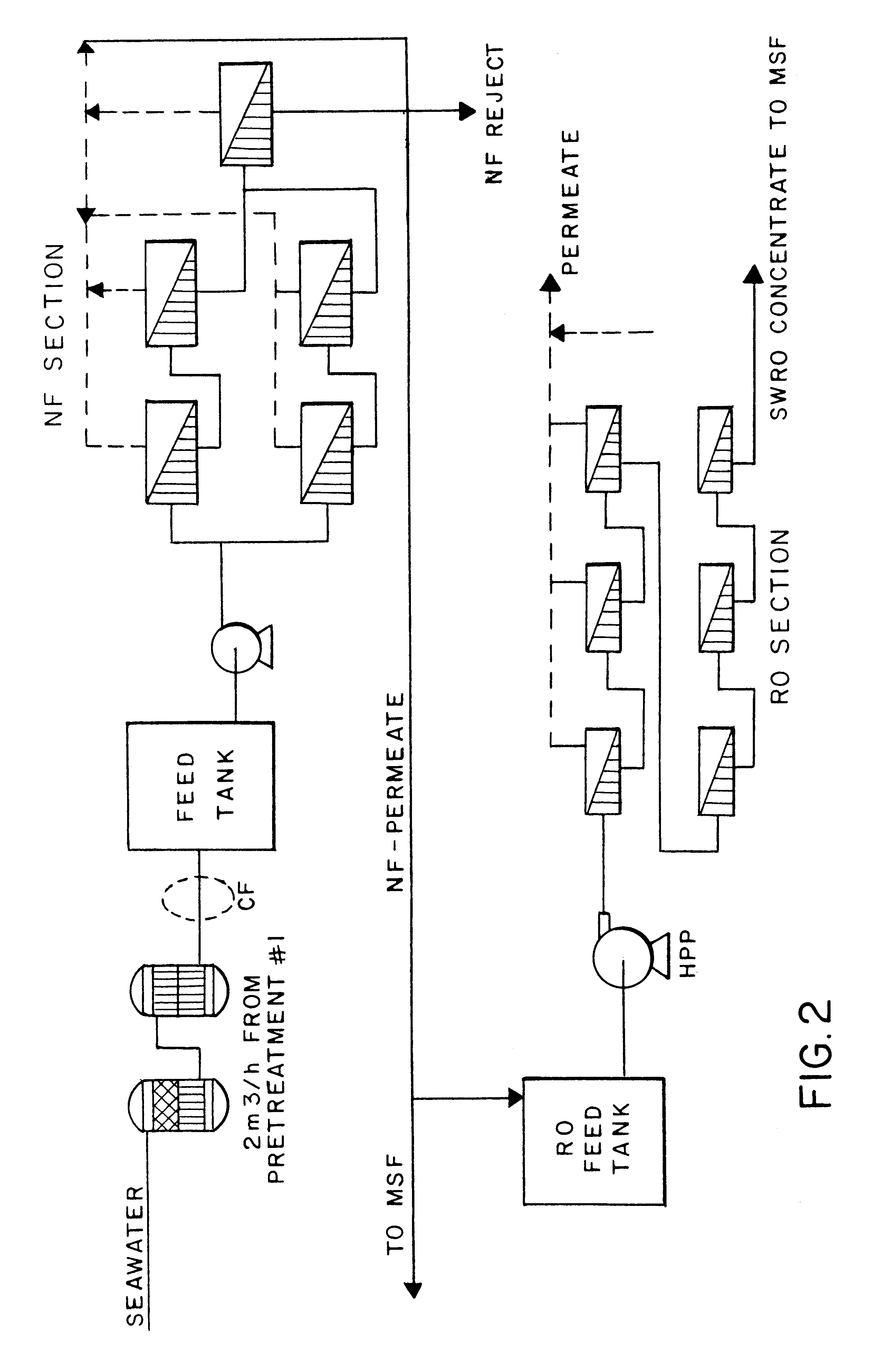
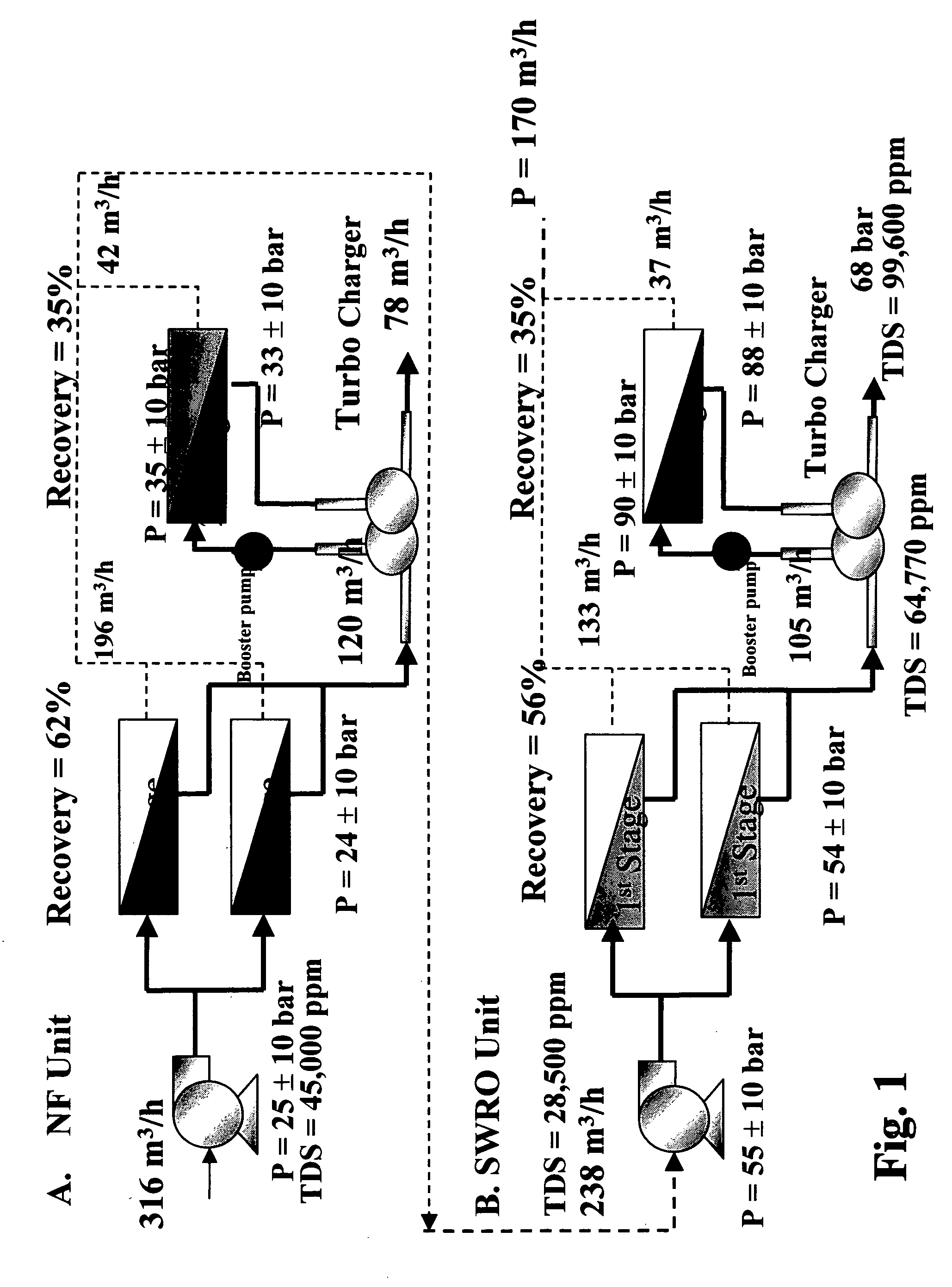
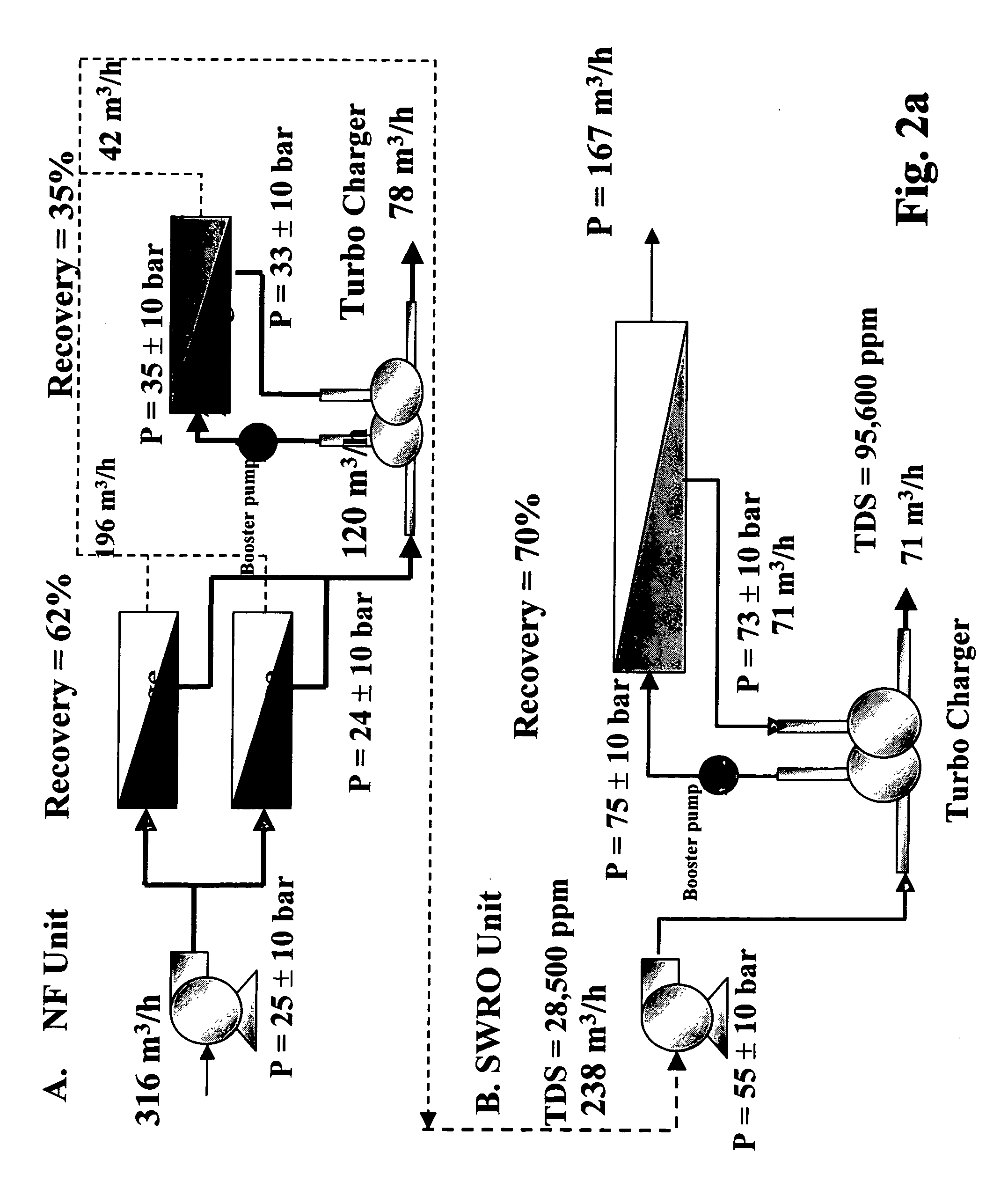
InactiveUS20060157410A1High yieldEffectively and efficiently dealGeneral water supply conservationReverse osmosisDistillationEngineering
An optimal thermal seawater desalination process is disclosed, which combines two or more substantially different water pretreatment processes in a unique manner and in a special configuration, hereto unknown to prior desalination arts, to produce a high yield of high quality fresh water, including potable water. In this process a two stage NF membrane pretreatment unit (NF2) with an energy recovery turbo charger (TC) device in between the stages or equipped with an energy recovery pressure exchanger (PX) is synergistically combined with at least one thermal desalination unit to form a dual hybrid of NF2-Thermal (FIG. 4 ), or alternatively the two stage NF2 unit is synergistically combined with a two stage SWRO unit (SWRO2) with an energy recovery TC in between the stages or combined with one stage SWRO (SWRO1) equipped with an energy recovery TC or PX system and the reject from the SWRO2 or SWRO1 unit is made make-up to a thermal unit to form a tri-hybrid of NF2-SWRO2 reject-Thermal (FIG. 5 ). In both the cases of di- or trihybrids the thermal unit is equivalent to a multistage flash distillation (MSFD) or multieffect distillation (MED) or vapor compression distillation (VCD) or thermal reheat (RH) evaporator. Typically a process of this invention using the two stage NF2 initial pretreatment step will perform a semi-desalination step by reducing feed TDS by about 35 to 50%, but most important, especially to the thermal seawater desalination process, it removes the water recovery limiting, scale forming hardness ions of Ca++ and Mg++ by better than 80% and their covalent anions of sulfate to better than 95% and bicarbonate to about 65%. The removal of scale forming hardness ions, especially SO4=, and bicarbonates allowed for the operation of thermal unit in the above hybrids at top brine temperature (TBT) much greater than its present TBT limit by the singular conventional process of 120° C. for MSFD and operation of MED or VCD or RH unit at TBT much higher than their present TBT limit of 65-70° C., with many advantages gained by this process over prior art sweater desalination processes. The process of this invention exceeds all prior thermal seawater desalination arts in efficiency, including water yield, product water recovery ratio and unit water cost as well as in energy consumption per unit product which is equivalent or less than other efficient prior art seawater thermal desalination processes. By this process, an NF product recovery ratio of 75 and 80% or better is achieved from the high salinity Gulf sea (TDS≈45,000 ppm) and about an equal product recovery ratio is also obtained from the SWRO or thermal unit when it is operated on NF product for a total water recovery ratio in excess of 52% for seawater
Owner:SALINE WATER CONVERSION CORP SWCC
Transportable, modular, self contained shipping container building
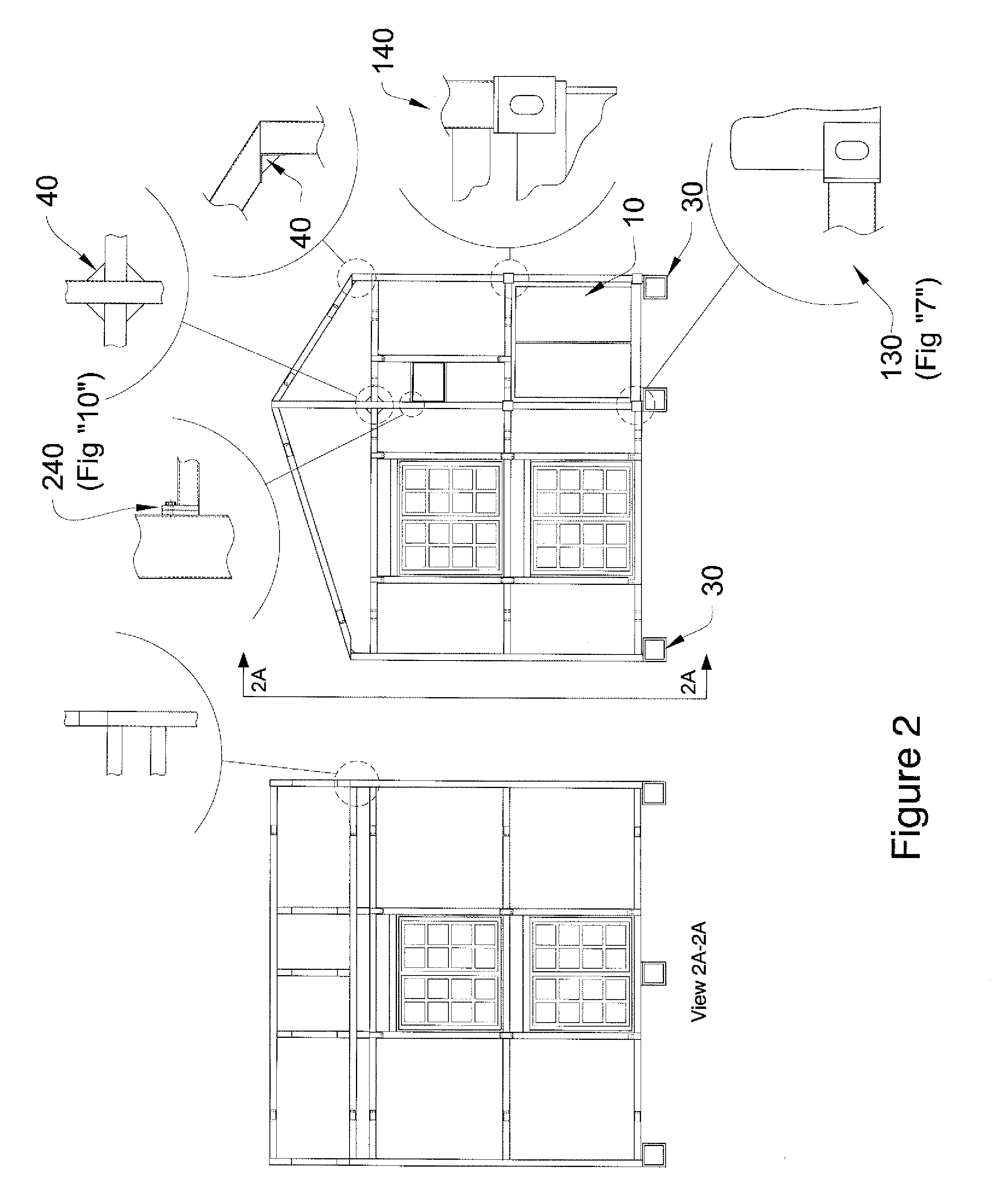
ActiveUS20100018131A1Reduce un-supported beam lengthSolar heating energySolar heat devicesNatural resourcePotable water
A transportable, modular, self-contained shipping container building which has an optional means to collect, store, and distribute power from natural resources and a means to collect store, distribute and / or purify potable and / or non-potable water.
Owner:GREEN JAMES E
Enhanced water treatment for reclamation of waste fluids and increased efficiency treatment of potable waters
ActiveUS20090230059A1Low costCurrent expensiveSolid sorbent liquid separationSedimentation separationLiquid wastePotable water
Disclosed is a process for reclamation of waste fluids. A conditioning container is employed for receipt of waste material on a continuous flow for treatment within the container by immersible transducers producing ultrasonic acoustic waves in combination with a high level of injected ozone. The treated material exhibits superior separation properties for delivery into a centrifuge for enhanced solid waste removal. The invention discloses a cost efficient and environmentally friendly process and apparatus for cleaning and recycling of flowback, or frac water, which has been used to stimulate gas production from shale formations. The apparatus is mobile and containerized and suitable for installation at the well site.
Owner:BRISBEN WATER SOLUTIONS
Forward osmosis pressurized device and process for generating potable water
There is disclosed a process and device for Forward Osmosis (FO) Pressurized Device (FOPD) in general and one hydraulically coupled to a reverse osmosis (RO device for a FOPRO (Forward Osmosis Pressurized Reverse Osmosis). Specifically, there is disclosed a passive device (that is, not needed energy input) for using forward osmosis to generate significant hydraulic pressure that can be used to drive a reverse osmosis process, wherein the reverse osmosis process (not needed external energy to run pumps) can separate salt from salt water to generate potable water from water with high salt content (such as sea water, urine, sweat, brackish water and the like).
Owner:HYDRATION SYST
Water treatment
InactiveUS20060000784A1Good removal effectReduce needWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsSludgePotable water
This is a method of water and wastewater treatment for removal of pollutants in at least two-step process comprising (a) treatment of water producing at least partially treated intermediate effluent, (b) treatment of the intermediate effluent with a sacrificial metal and producing ions of said sacrificial metal, and providing very thoroughly treated effluent, (c) recuperating sacrificial metal ions generated in the step (b) and recycling the recuperated ions in the step (a), the recuperated and recycled ions from the step (c) improve treatment efficiency of step (a) by additionally removing pollutants from the intermediate effluent using recuperated ions, resulting in cleaner intermediate effluent, and, therefore, the pollutant loading rate in step (b) is reduced, intermediate effluent is further treated more thoroughly, and the demand for the sacrificial metal in step (b) is reduced. Step (a) can preferably be a biological, biological-abiotic, physical chemical, or combination of these steps. Step (b) is preferably a spontaneous cementation-driven electrochemical process. The combination of said steps (a), (b) and (c) produces a synergistic effect resulting in improved removal of said pollutants and in reduced need in said sacrificial metal. For example, a drinking quality water can be very economically and reliably obtained from wastewater. In addition to the superb treatment efficiency and reduced reagent requirements, the waste sludge from the system is beneficially disposed in-sewers, in sanitary landfills or on land.
Owner:KHUDENKO BORIS
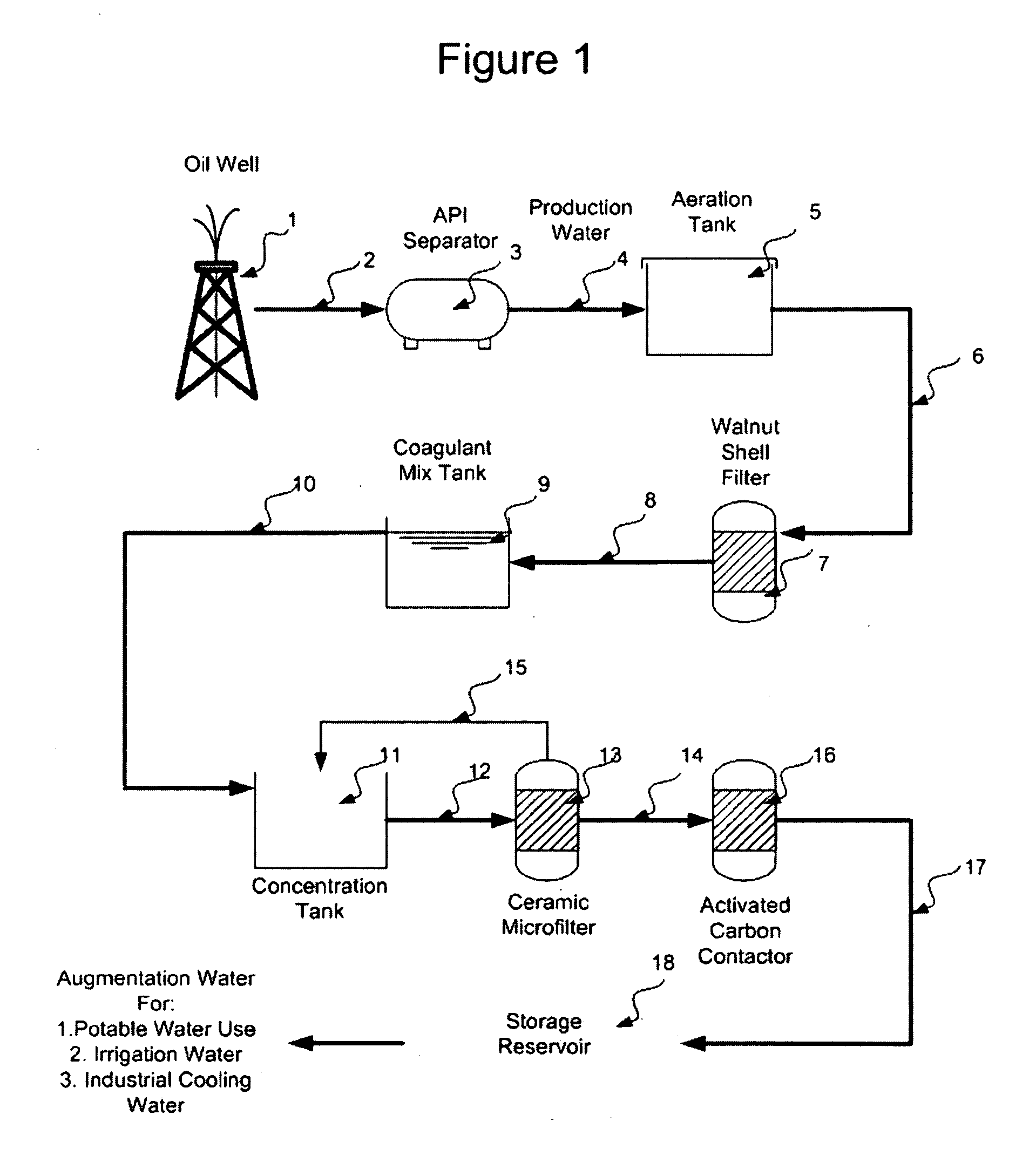
Purification of Oil Field Production Water for Beneficial Use
A method for generating new water with attached water rights comprising identifying a source of production water and treating the water in appropriate ways to provide water appropriate for beneficial use such as agriculture, irrigation, industrial or municipal or potable applications. Appropriate permits are obtained to create the new water with attached water rights.
Owner:PRODD WATER DEV
Water treatment compositions
Compositions, methods and kits for purifying and clarifying and / or nutrifying contaminated drinking water and which comprise a primary coagulant material and a bridging flocculent material, the levels and ratios of coagulant to flocculent preferably falling within certain ranges. Highly preferred compositions also contain one or more of a cationic coagulant aid, especially chitosan, a microbiocidal disinfectant, a water-soluble alkali, a water-insoluble silicate, and a food additive or nutrient source.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
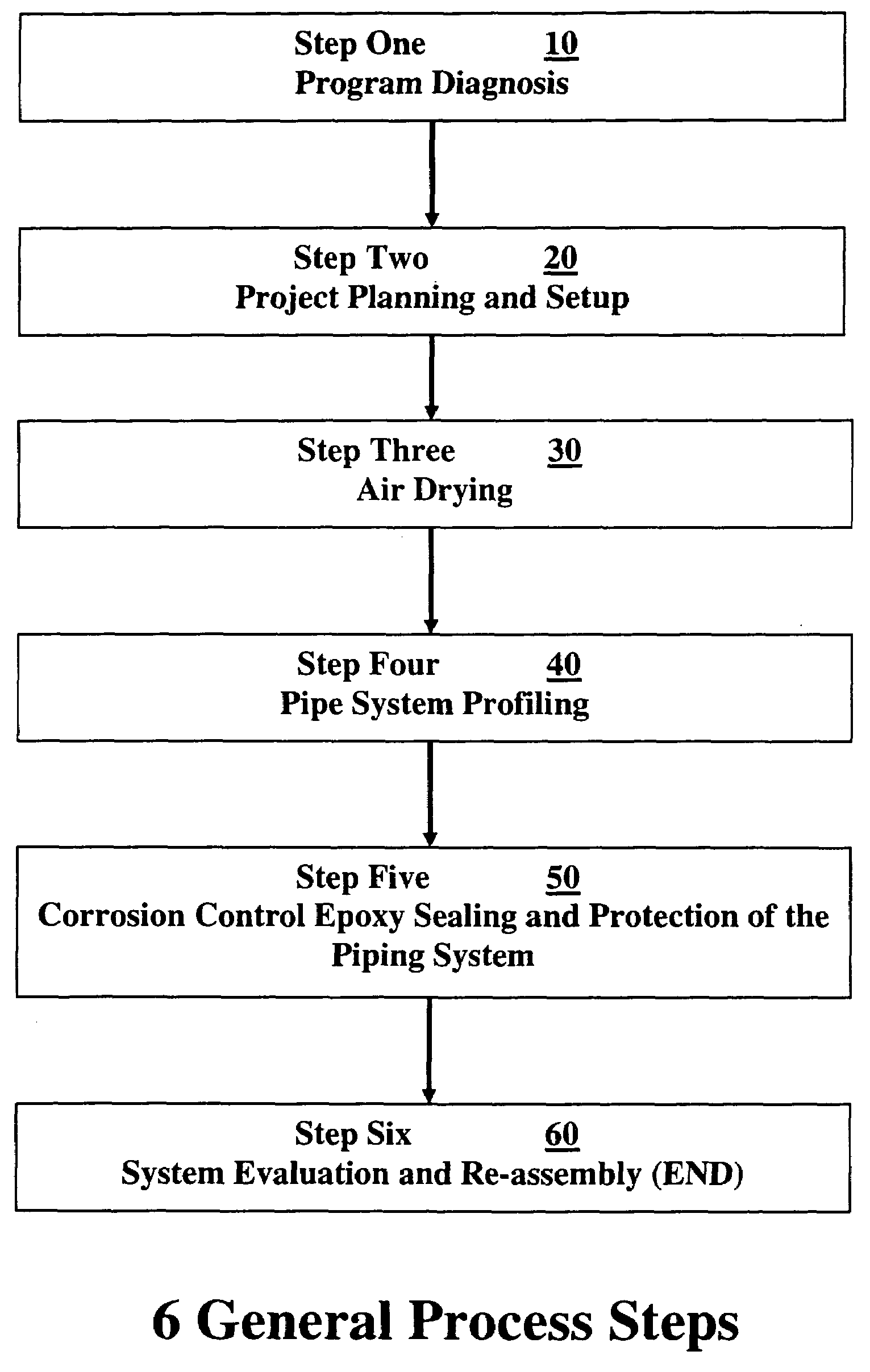
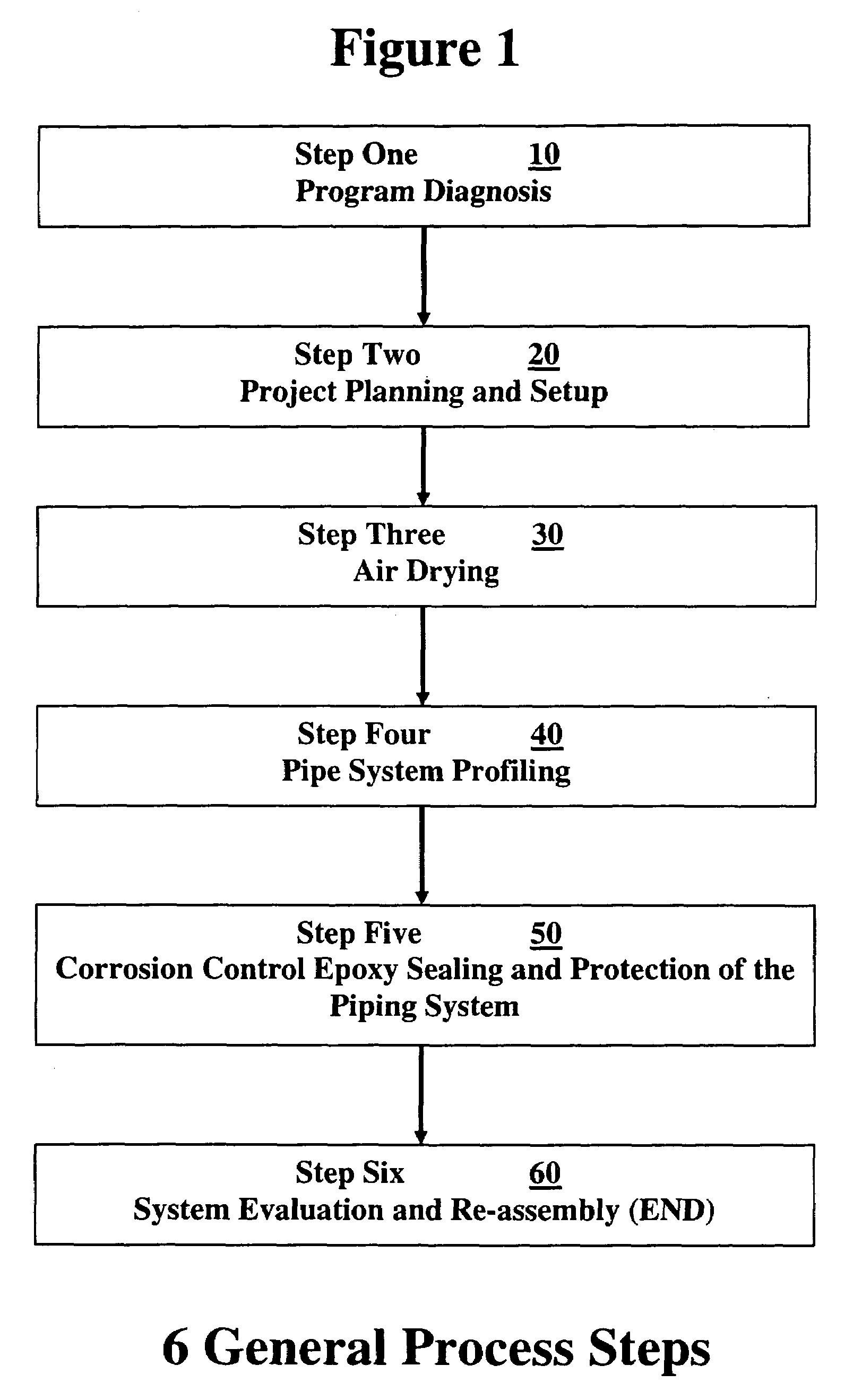
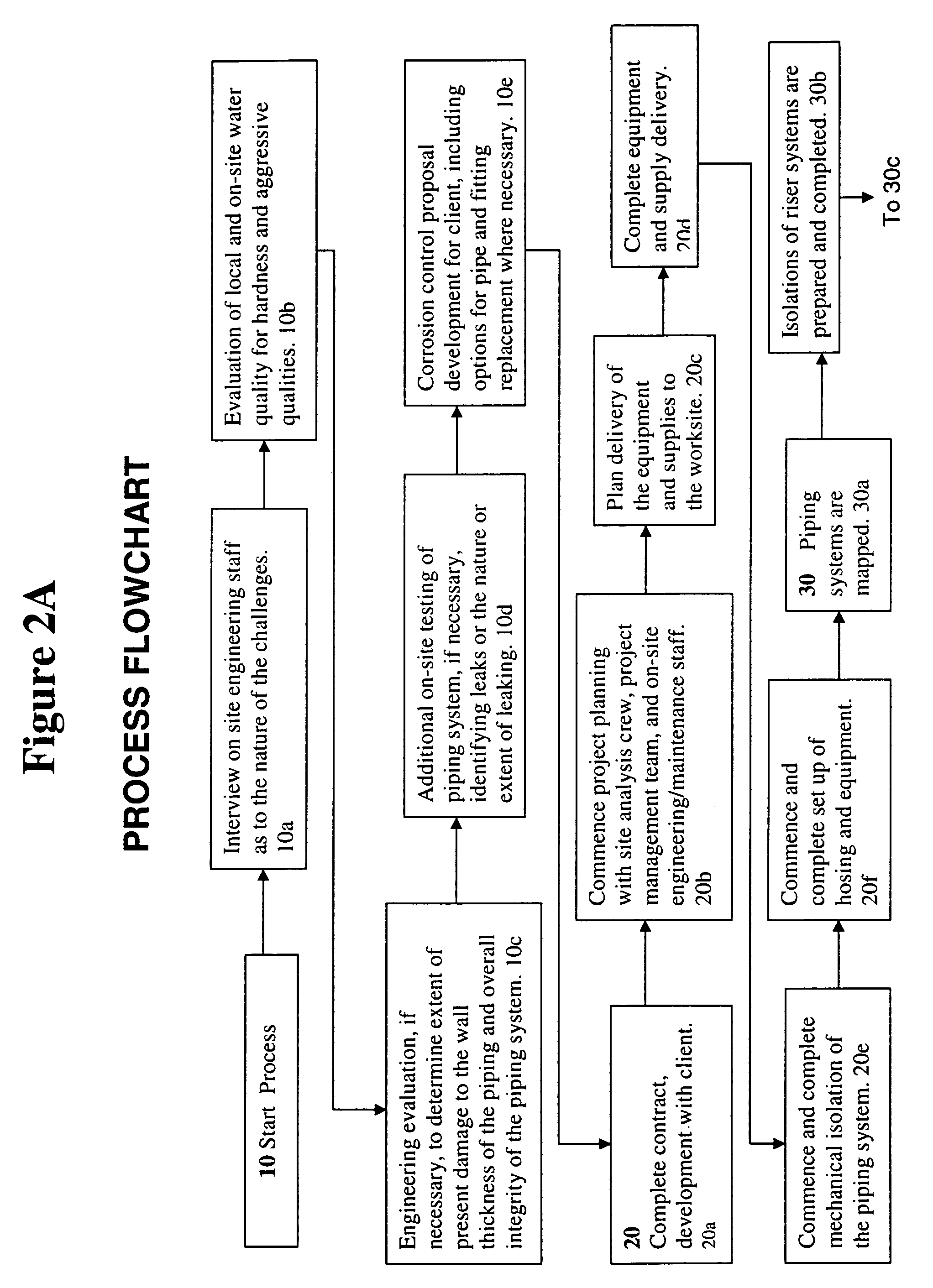
Barrier coating corrosion control methods and systems for interior piping systems
Methods and systems for cleaning and providing barrier coatings to interior walls of piping systems. An entire piping system can be cleaned in one single pass by dry particulates forced by air and the piping system coated in one single pass. Pipes can be protected from water corrosion, erosion and electrolysis. Pipes having diameters of approximately ⅜″ up to approximately 6″ are treatable. Piping systems such as potable water lines, natural gas lines, HVAC, drains, and fire sprinkler systems in homes, apartments, high-rise hotel / resorts, office towers, high-rise apartment and condominiums and schools, can be treated. The coating forms an approximately 4 mils or greater covering inside the pipes. Buildings can return to service within approximately 24 to approximately 96 hours.
Owner:PIPE RESTORATION TECH
Warewashing system containing nonionic surfactant that performs both a cleaning and sheeting function and a method of warewashing
InactiveUSRE38262E1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsActive agentPotable water
We have found an alkaline warewashing detergent composition that can contain a critical amount of a nonionic rinse agent that when used in automatic warewashing machines permits the use of a potable water rinse without the addition of a separate rinse agent. Sufficient residual nonionic surfactant from the alkaline detergent remains on the surface ware and internal machine and rack surfaces after washing to promote adequate sheeting in the rinse cycle. The residual nonionic surfactant on internal surfaces dissolves in the rinse water to create an effective aqueous rinse agent. The nonionic rinse agents can be a single nonionic for both foam reduction cleaning and sheeting or can be a blend of nonionic materials providing these functions. The detergent can be in the form of a particulate, pelletized or block solid. The detergent can be used in a variety of high temperature and low temperature automatic warewashing machines including large multizone conveyor machines, or relatively small institutional machines that have a single washing chamber.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Treatment method of high-concentration wastewater
InactiveCN103663860AReduce wasteReduce dosageMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationChemical oxygen demand
The invention relates to a treatment method of high-concentration wastewater. The treatment method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment; (2) flocculent sedimentation treatment; (3) biochemical treatment; (4) membrane biological reaction treatment; (5) adsorption treatment; (6) oxidation treatment; (7) filtration treatment; (8) membrane treatment; (9) disinfection treatment; and (10) evaporative crystallization treatment. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the wastewater with the COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) concentration up to 96000mg / L can be treated and the COD removing rate is up to 99.98% to ensure that the treated wastewater meets the standards of drinking water and an unexpected technical effect is brought; compared with a dozen or dozens of hours in the prior art, the aerobic reaction time and the anaerobic reaction time are greatly shortened and the treatment efficiency is obviously increased; and the concentrated solution finally generated in the method only accounts for below 2% of water inflow, which is greatly reduced compared with the prior art, so that the waste of water is obviously reduced and the treatment cost is saved.
Owner:曹寅亮
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com