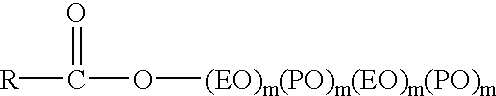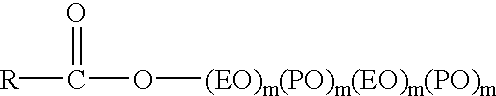Warewashing system containing nonionic surfactant that performs both a cleaning and sheeting function and a method of warewashing
a non-ionic surfactant and warewashing technology, applied in the field of warewashing detergent, can solve the problems of adding additional expense and complexity to the institution's warewashing machine, and not suitable for non-ionic materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Into a stirred and heated mixing tank is added 50 grams of a PO-EO-PO block copolymer having an average of about 18 moles PO, 14 moles EO and 18 moles PO, and 50 grams of a benzyl ether of a C.sub.10-14 linear alcohol (12.4) mole ethoxylate. The tank agitator was energized and warmed to 195.degree. F. About 20 parts by weight of water were added and the surfactant mixture was warmed until the tank reached 195.degree. F. Into the stirred tank was added about 60 grams of a nonionic comprising a benzyl capped C.sub.10-14 linear alcohol 12 mole ethoxylate. Into the stirred surfactant blend was added 175 grams of sodium carbonate (anhydrous). The organic inorganic mixture was agitated until uniform and heated to a portable viscosity (approximately 142.degree. F. After uniformity was achieved, about 165 grams of sodium tripolyphosphate were added to the stirred blend. The viscosity was monitored and held between 6,000 and 20,000 cP at about 150.degree. F. The stirred blend was cast into 8...
example 2
In a second test sequence, a "typical" set of conditions were run in a low temperature dishmachine to compare a standard detergent and rinse aid (Ecolab Solid Ultra Klene Plus and Solid Ultra Dry) versus the test detergent / rinse aid combination formula.
In test 1, a standard detergent and rinse aid 1100 ppm of Slid Ultra Klene Plus and 6 grams of Solid Rinse Additive were run through a 10 cycle spot and film test. In test 2, 1160 ppm of the test detergent shown below run with no rinse additive and the results after 10 cycles were at least as good as those observed with test 1. Furthermore, a third test was run where Solid Ultra Klene Plus was run with the rinse additive reduced to 0.7 grams per rack. This test was stopped after 8 cycles, due to the glassware being severely spotted and filmed.
In conclusion, a "standard" detergent needs to be run with a rinse additive in order to get acceptable results, while the test detergent formula gave very good results without the addition of a s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com