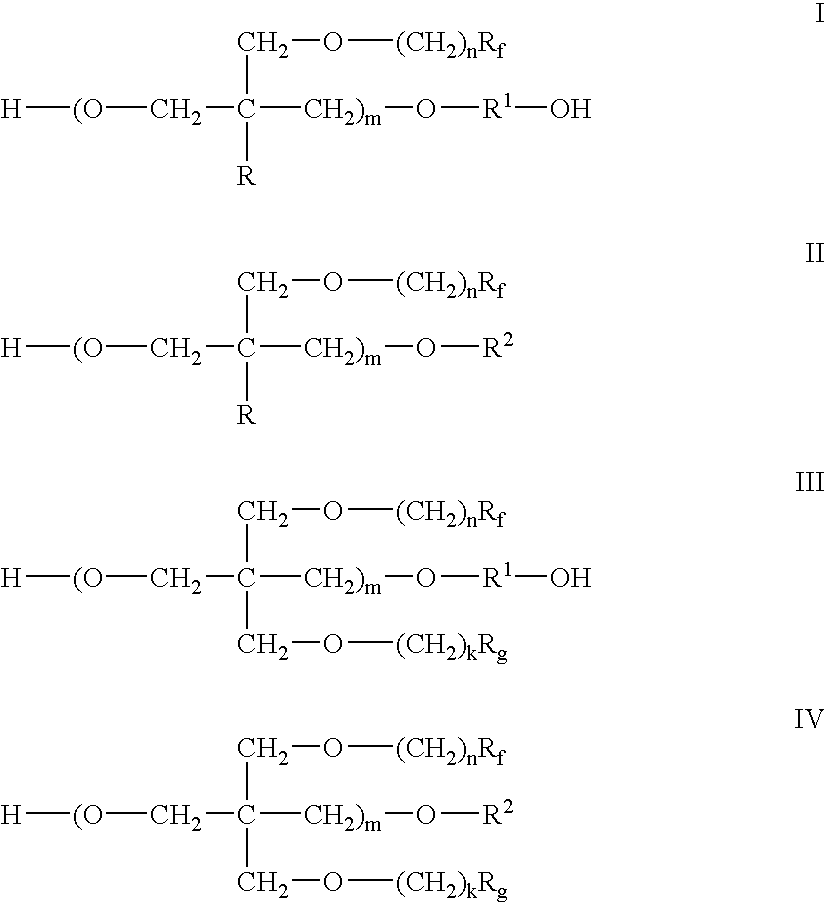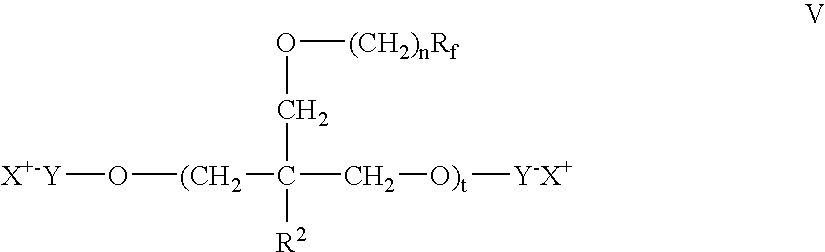Patents
Literature
3137 results about "Fouling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fouling is the accumulation of unwanted material on solid surfaces to the detriment of function. The fouling materials can consist of either living organisms (biofouling) or a non-living substance (inorganic and/or organic). Fouling is usually distinguished from other surface-growth phenomena, in that it occurs on a surface of a component, system or plant performing a defined and useful function, and that the fouling process impedes or interferes with this function.
Hybrid catalyst system for exhaust emissions reduction
InactiveUS20060010857A1Improve efficiencySpeed up the conversion processHydrogenGas treatmentExhaust fumesEngineering
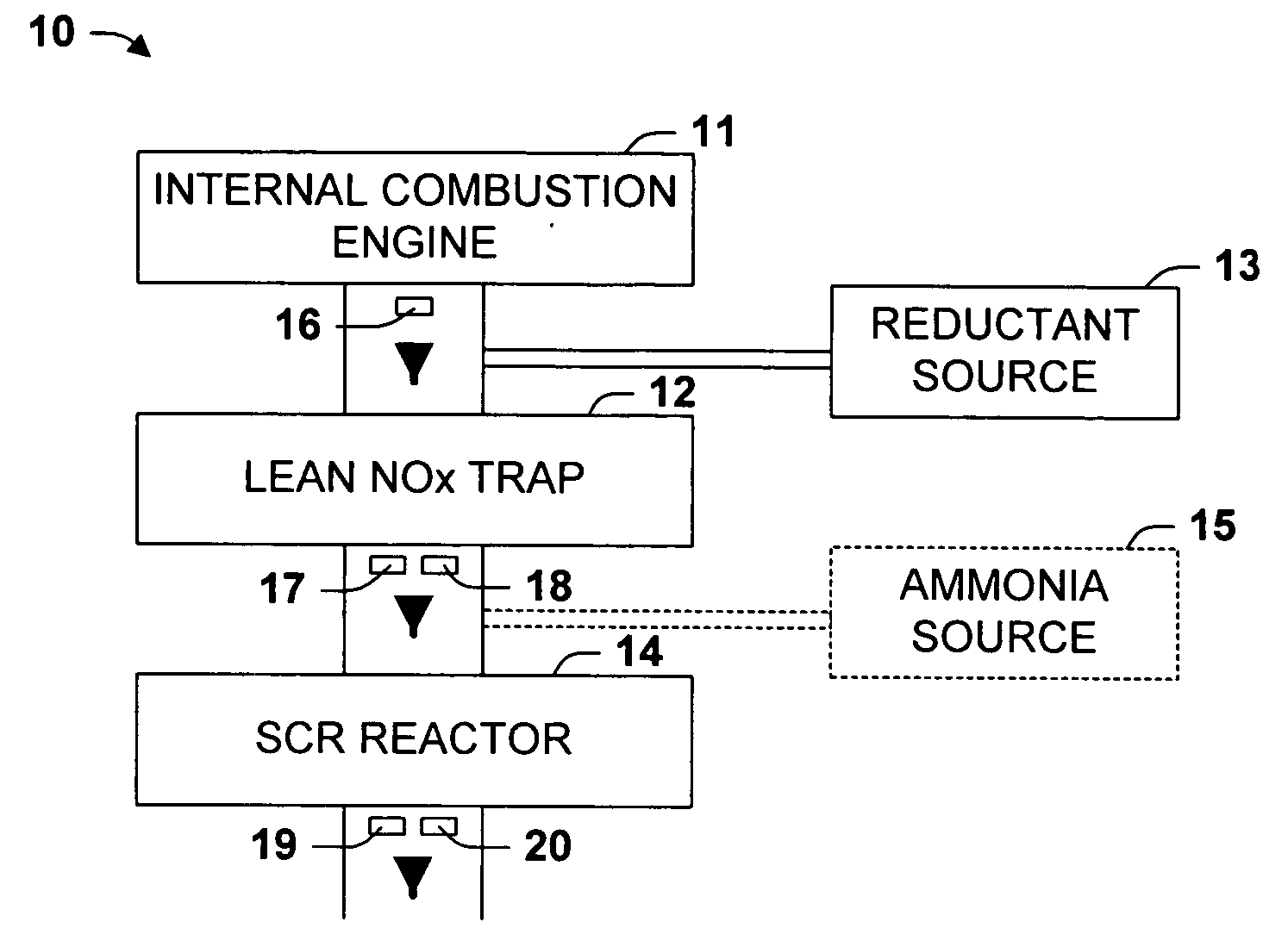
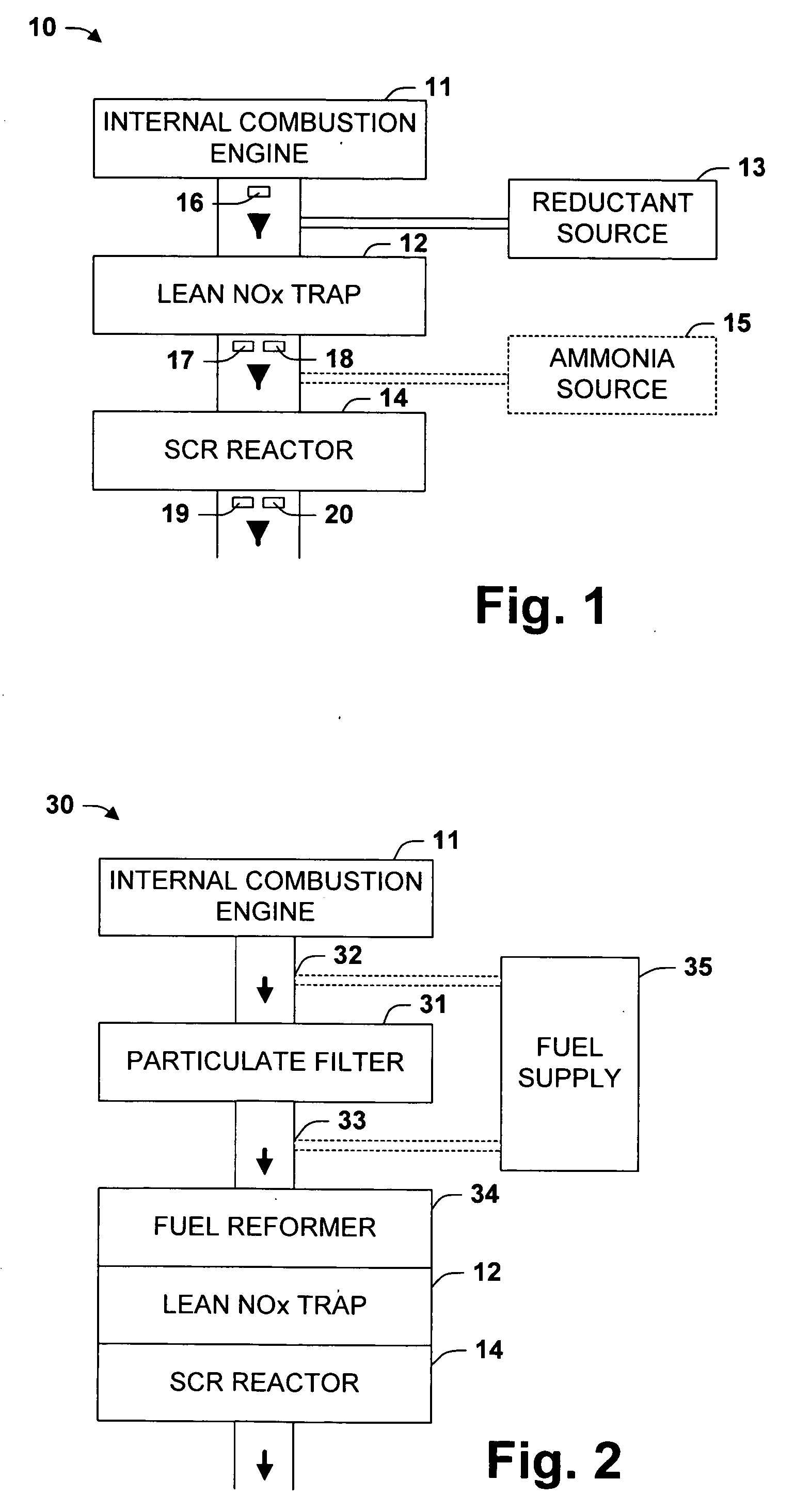
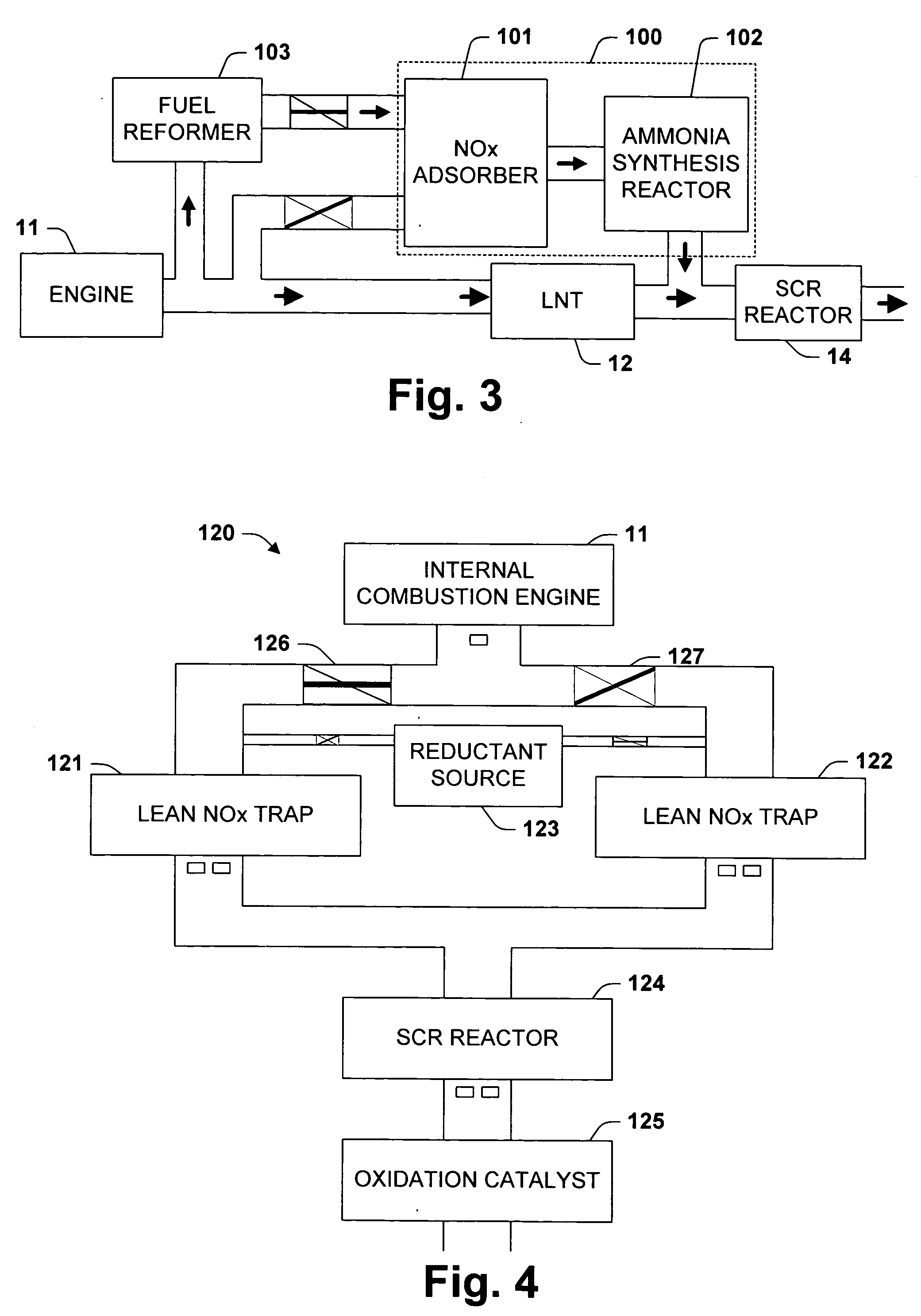
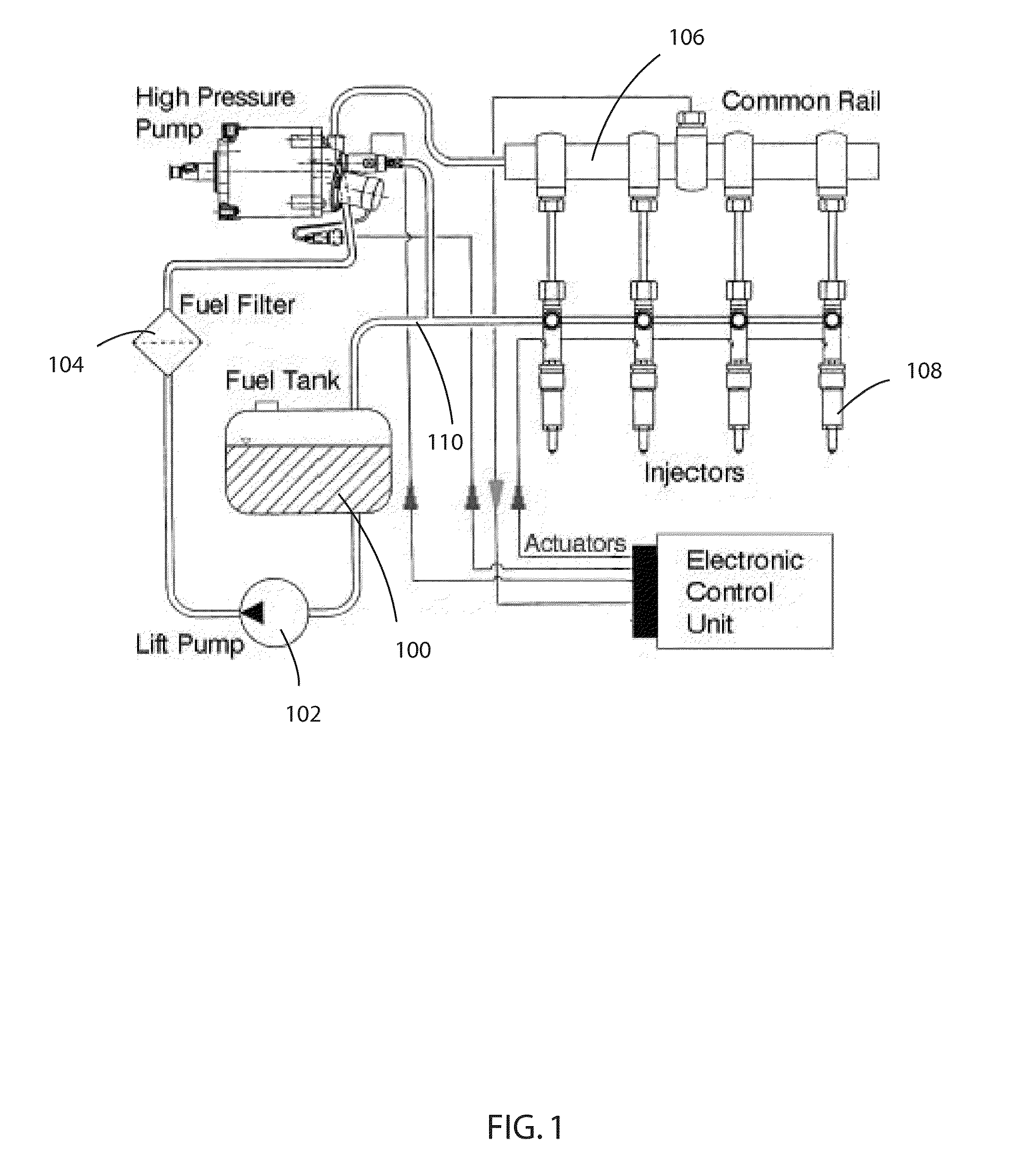
One aspect of the invention relates an exhaust treatment system having an SCR reactor following a NOx adsorber. Syn gas is used to regenerate the NOx adsorber. Another aspect relates to an LNT / SCR provided with an ammonia source separate from the LNT. A further aspect relates to a system comprising first and second LNTs and one or more SCRs downstream of the LNTs. A still further aspect relates to a device comprising first and second NOx adsorbers contained in a single housing. Another aspect relates to coating a surface of a moving part in an exhaust system with an oxidation catalyst to mitigate fouling. Additional aspects of the invention relate to strategies for controlling one or more of the time to initiate a regeneration cycle, the time to terminate a regeneration cycle, and the reductant injection rate during regeneration of LNT / SCR exhaust treatment systems.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Raindrop fouling-resistant paint film, coating composition, film-forming method, and coated article
InactiveUS6013724ASatisfactory fouling resistanceHigh acid resistanceAntifouling/underwater paintsOther chemical processesCrack resistancePolymer chemistry
Owner:NIPPON PAINT CO LTD
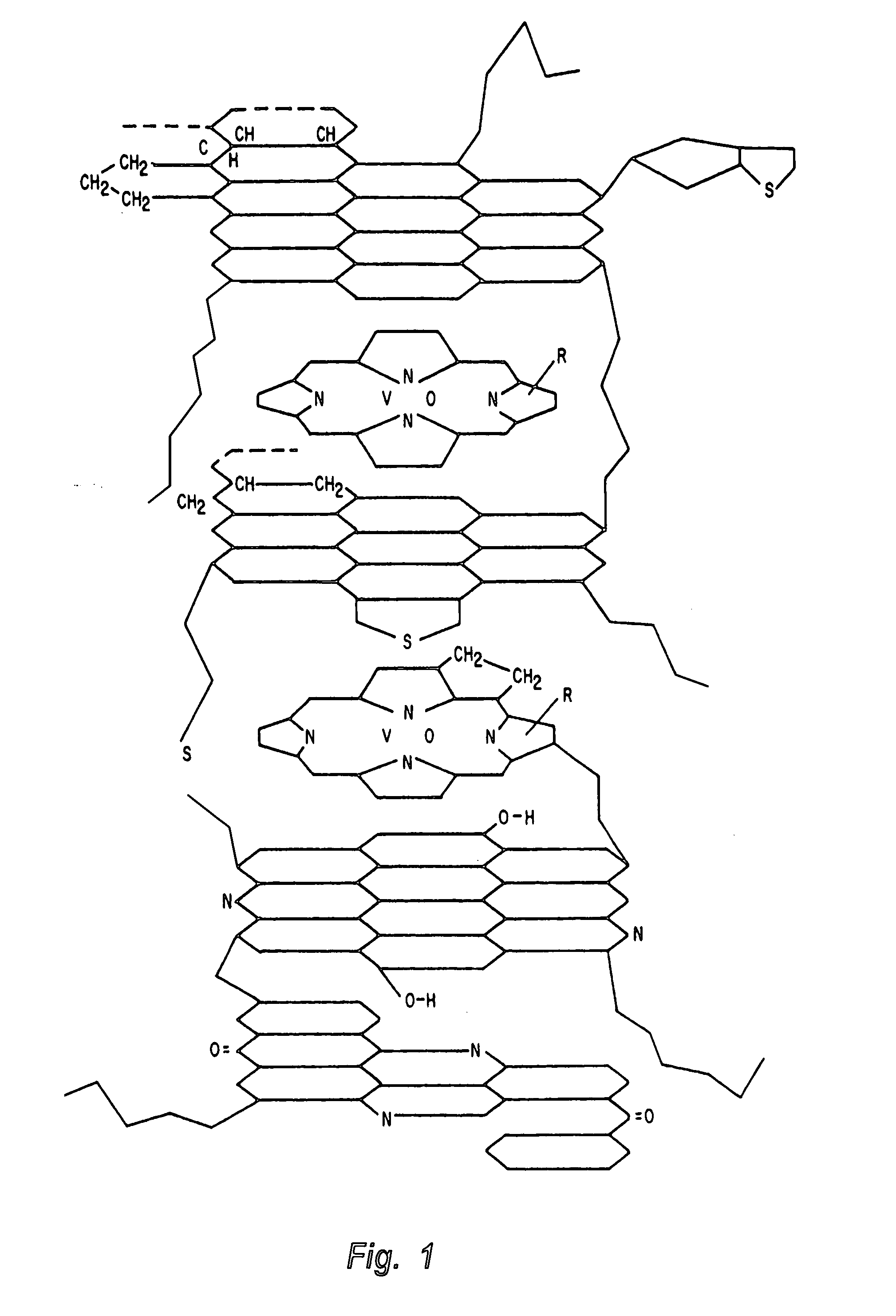
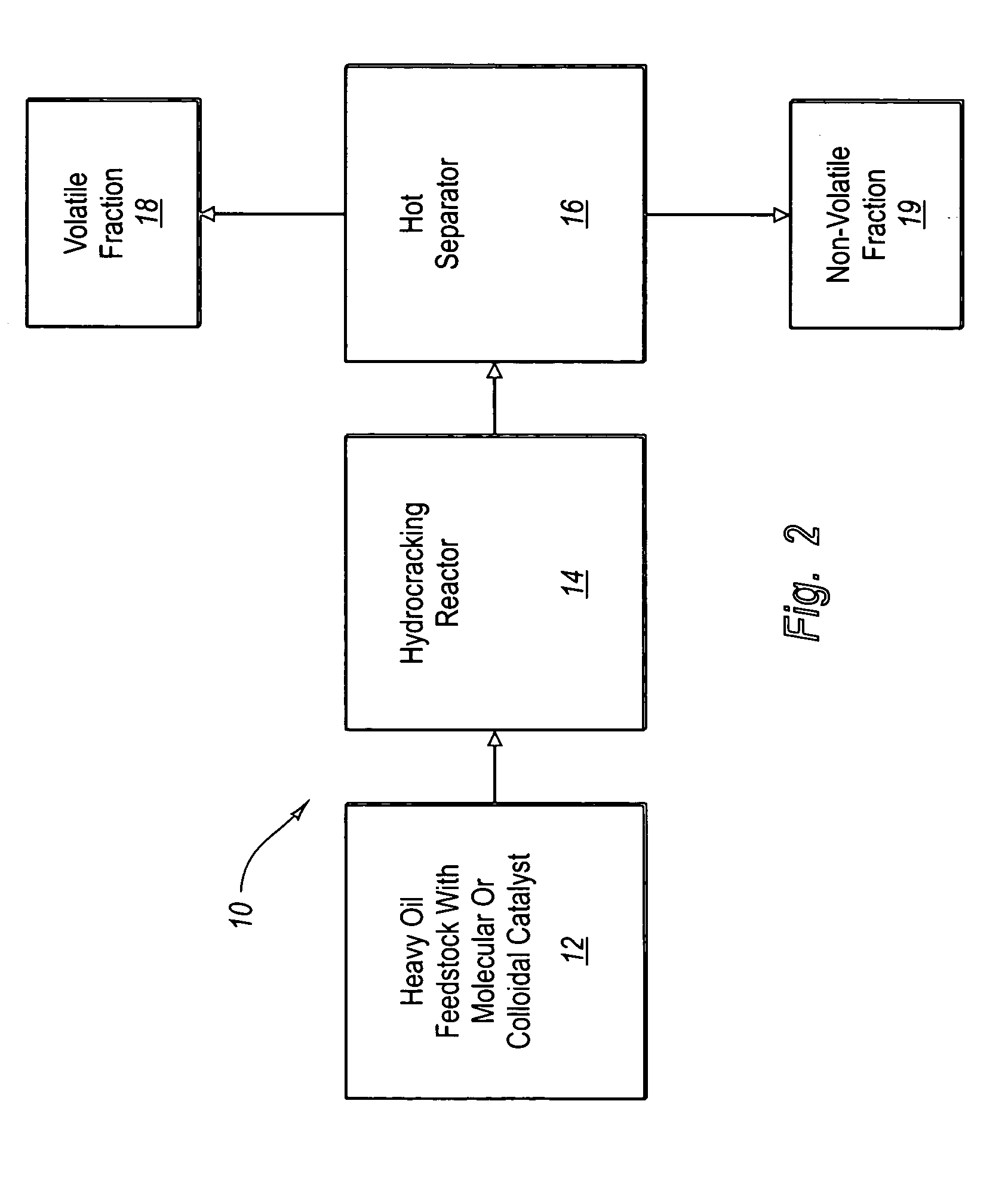
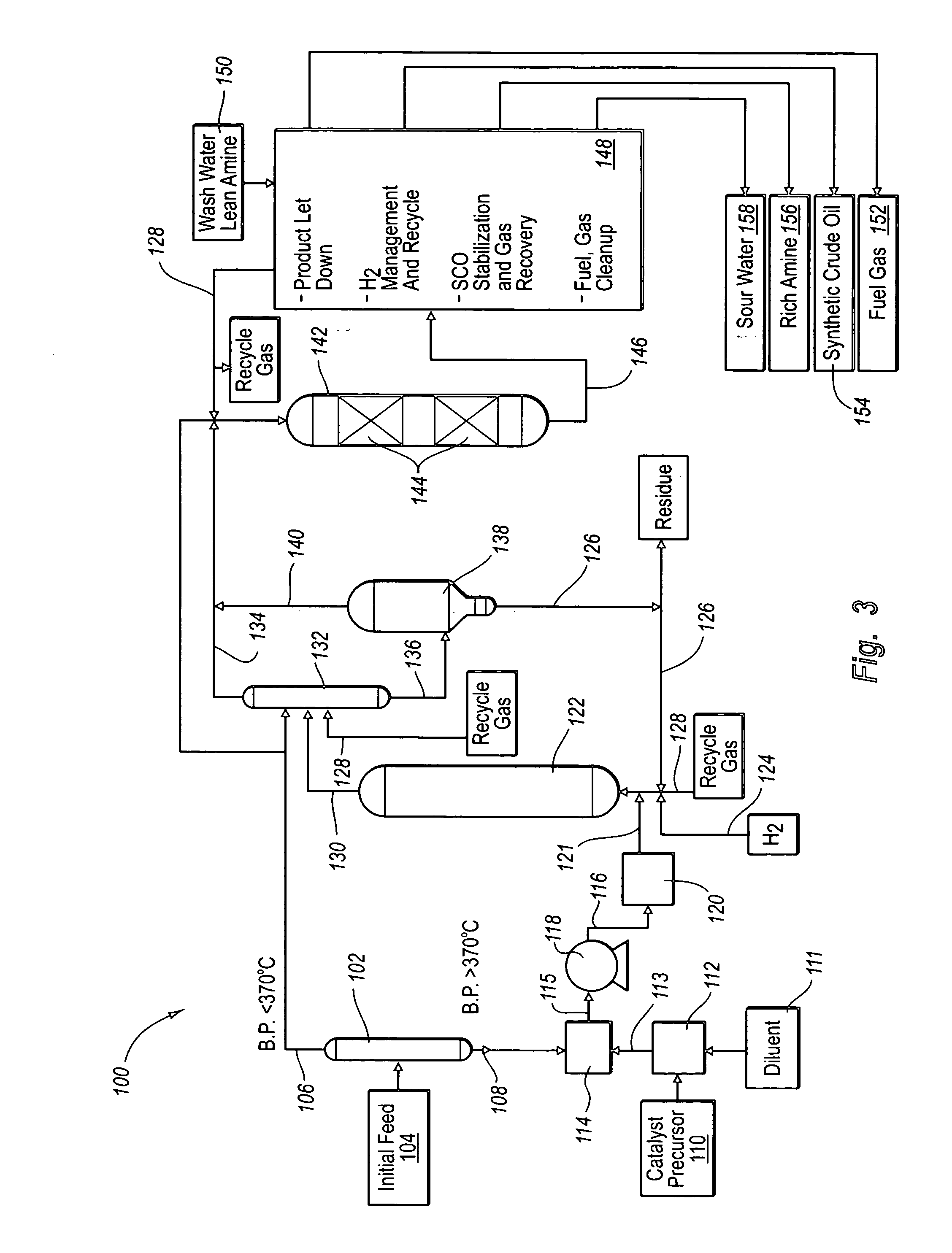
Hydroprocessing method and system for upgrading heavy oil using a colloidal or molecular catalyst
ActiveUS20050241993A1Inhibits eliminates formationEasy to useCatalyst regeneration/reactivationCatalyst activation/preparationColloidFuel oil
Methods and systems for hydroprocessing heavy oil feedstocks to form an upgraded material involve the use of a colloidal or molecular catalyst dispersed within a heavy oil feedstock, a hydrocracking reactor, and a hot separator. The colloidal or molecular catalyst promotes hydrocracking and other hydroprocessing reactions within the hydrocracking reactor. The catalyst is preferentially associated with asphaltenes within the heavy oil feedstock, which promotes upgrading reactions involving the asphaltenes rather than formation of coke precursors and sediment. The colloidal or molecular catalyst overcomes problems associated with porous supported catalysts in upgrading heavy oil feedstocks, particularly the inability of such catalysts to effectively process asphaltene molecules. The result is one or more of reduced equipment fouling, increased conversion level, and more efficient use of the supported catalyst if used in combination with the colloidal or molecular catalyst.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION LLC
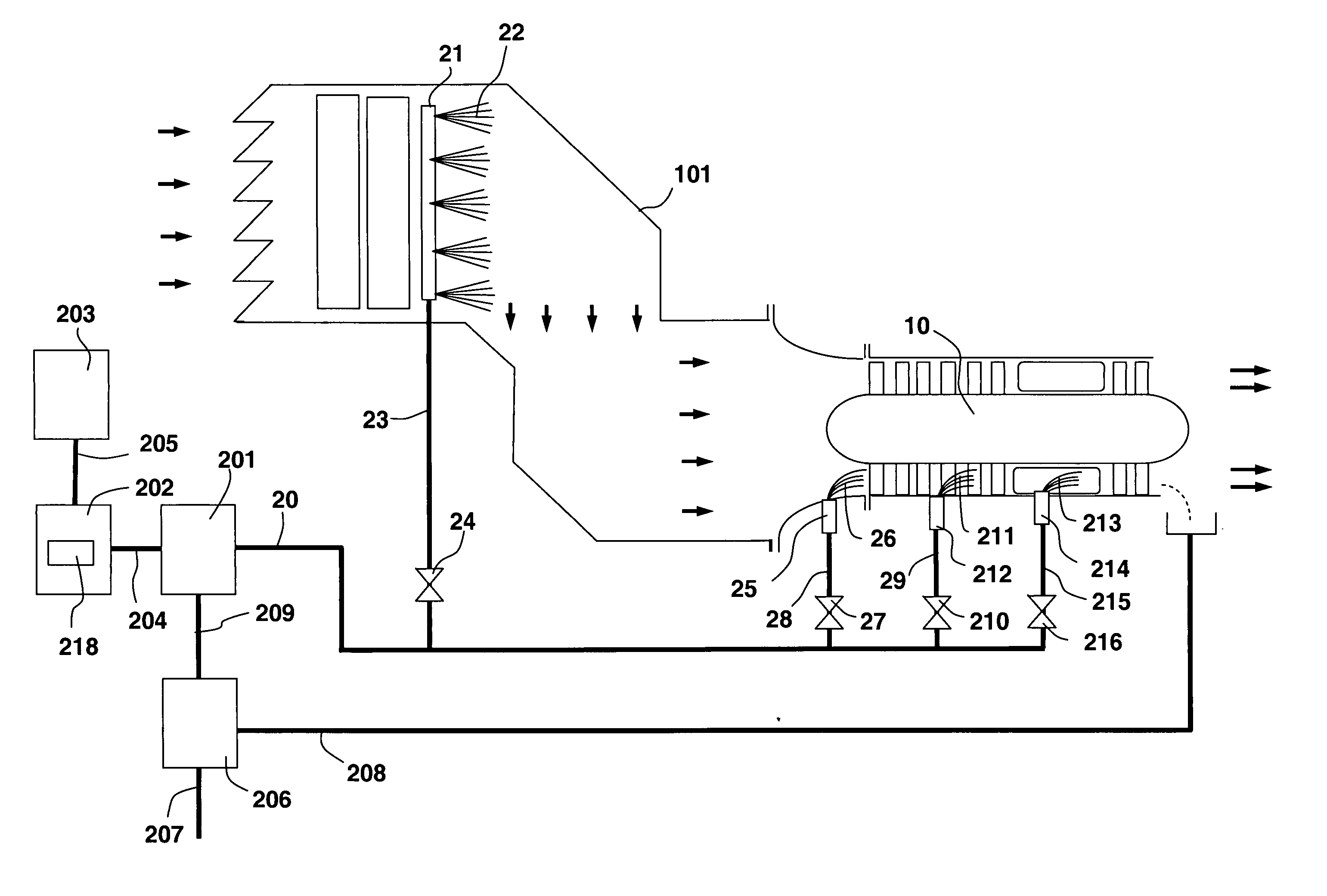
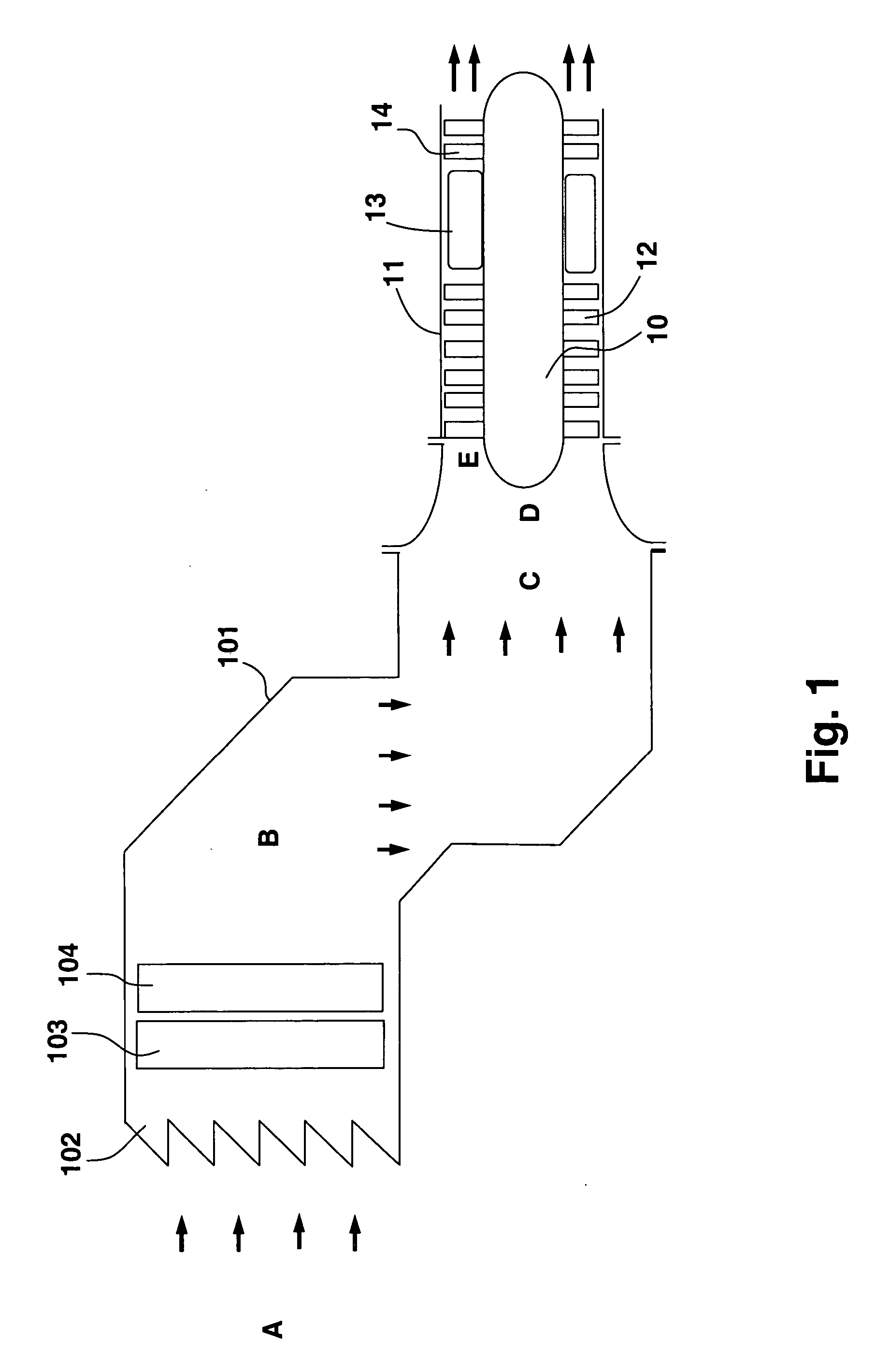
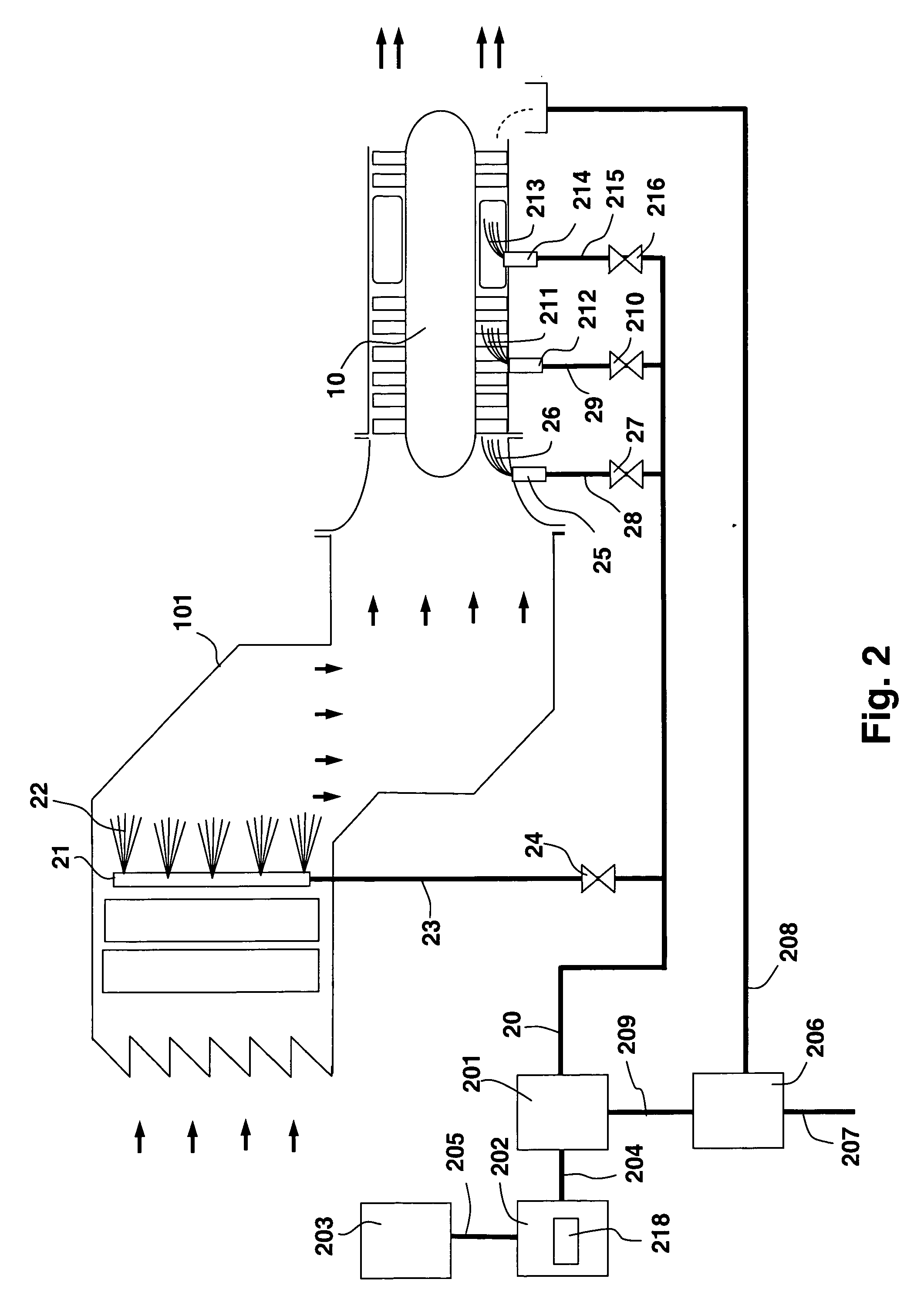
System and method for augmenting power output from a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20070059159A1Wide rangeSimple hardwareHollow article cleaningGas turbine plantsMultiple modesTurbine
The present invention discloses a method and system for augmenting shaft output of stationary gas turbines that can be used in multiple modes of operation. The system comprises a washing unit (25, 27, 28) adapted to inject a spray (26) of atomized liquid so as to impinge on the compressor blades (12) in order to wet said blades (12), thereby obtaining a release of fouling material from said blades (12); and at least one liquid injection unit (21, 23, 24, 29, 210, 212, 214, 215, 216) adapted to inject a spray (22, 211, 213) of atomized liquid into an air stream of said turbine duct (101) or at the gas turbine (10) in order to increase a mass flow of said air flow, wherein the power output from said gas turbine engine can be augmented. With the invention follows also benefits such as fuel savings and improved environmental performance by reduction of emissions.
Owner:GTE TURBINE EFFICIENCY SWEDEN AB
Non-fouling, Anti-microbial, Anti-thrombogenic graft-from compositions
InactiveUS20100152708A1Reduce penetrationRadiation applicationsSurgeryMicroorganismPolymer substrate
Substrates, optionally coated with an undercoating layer, having grafted there from one or more non-fouling materials are described herein. The non-fouling, polymeric material can be grafted from a variety of substrate materials, particularly polymeric substrates and / or polymeric undercoating layers. The graft-from techniques described herein can result in higher surface densities of the non-fouling material relative to graft-to formulations. Graft-from methods can be used to produce covalently tethered polymers. The compositions described herein are highly resistant protein absorption, particularly in complex media and retain a high degree of non-fouling activity over long periods of time. The compositions described herein may also demonstrate antimicrobial and / or anti-thrombogenic activity. The non-fouling material can be grafted from the substrate, or optionally from an undercoating layer on the substrate, preferably without significantly affecting the mechanical and / or physical properties of the substrate material.
Owner:ARROW INT INC
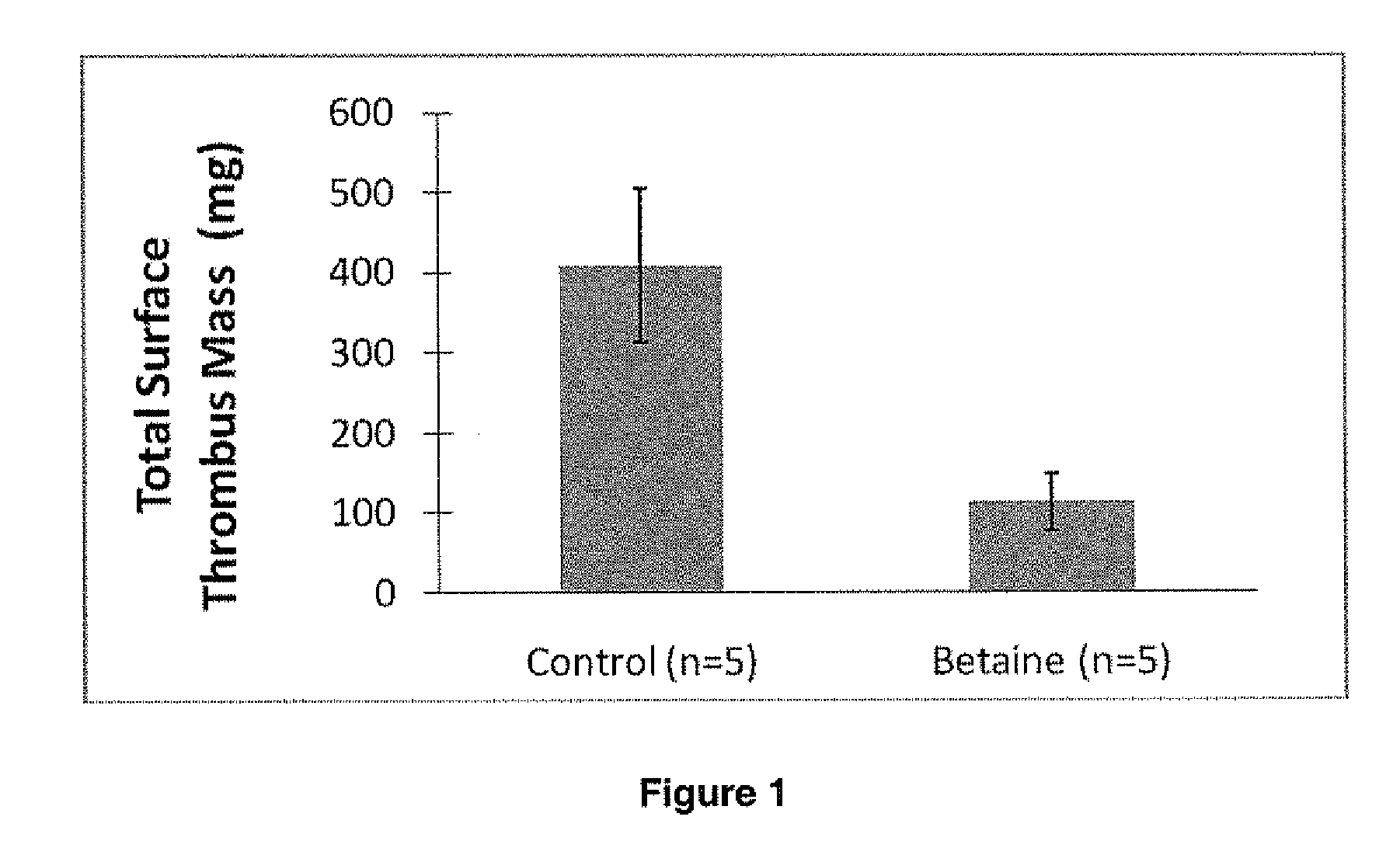
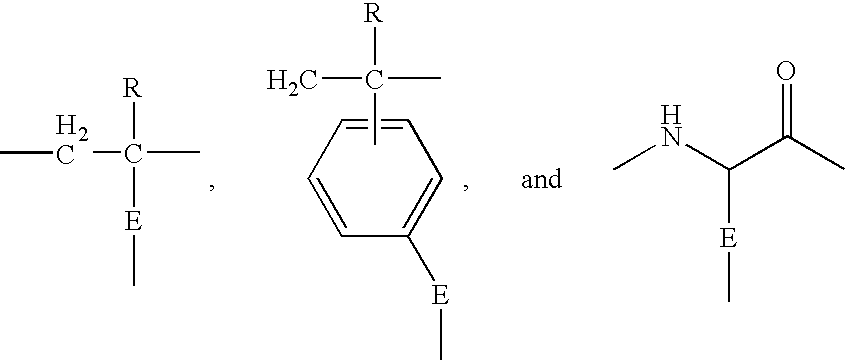
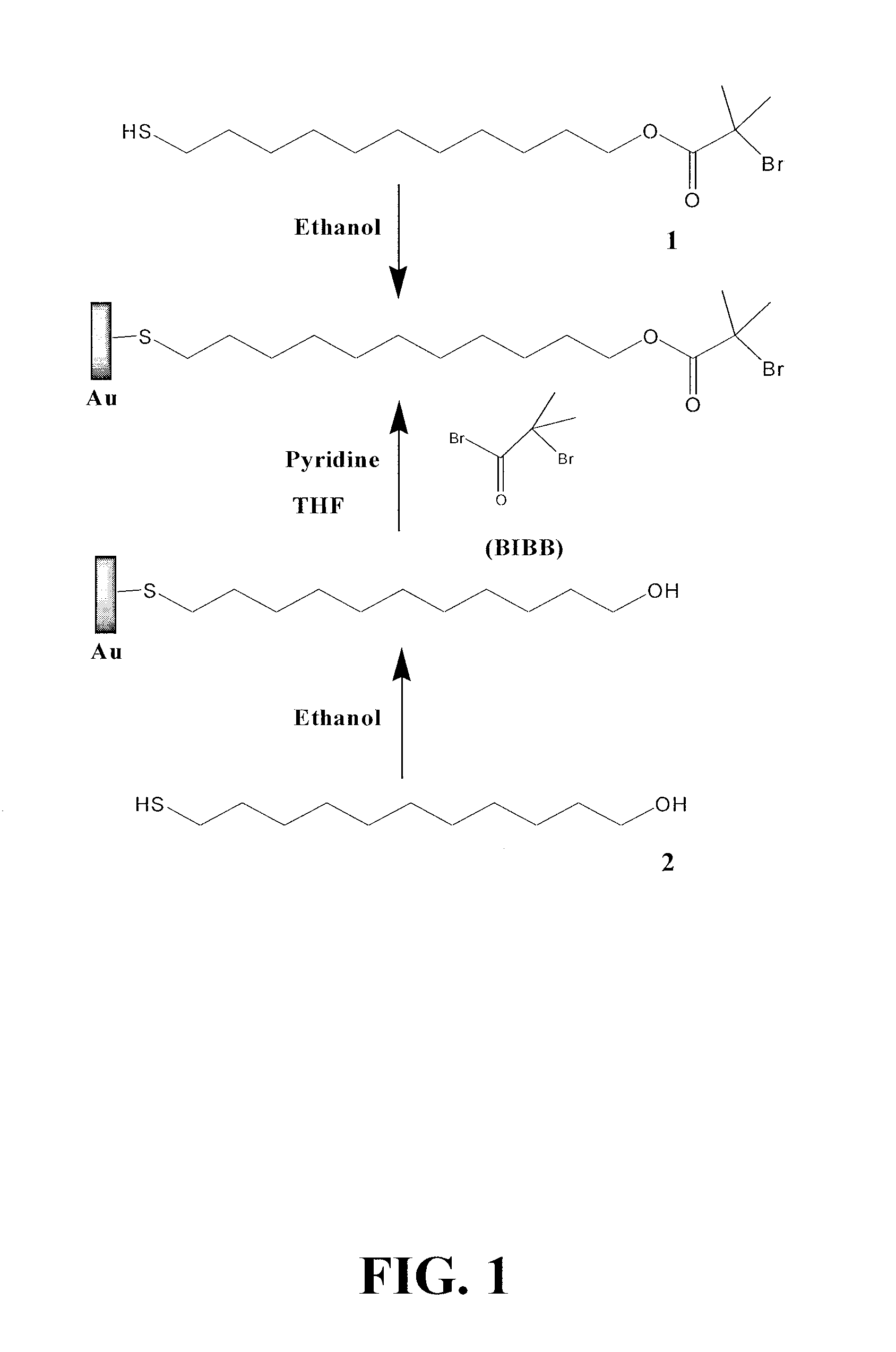
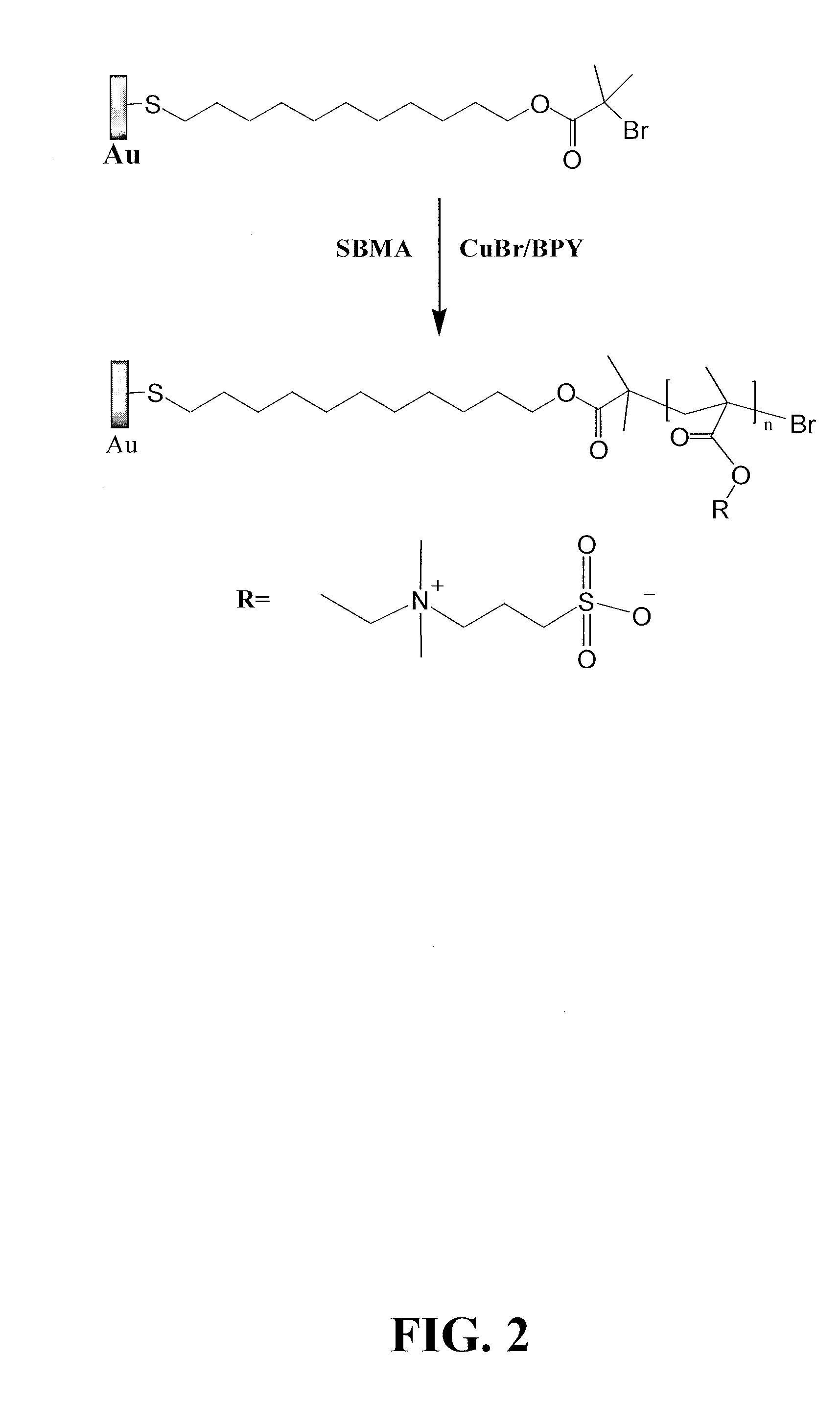
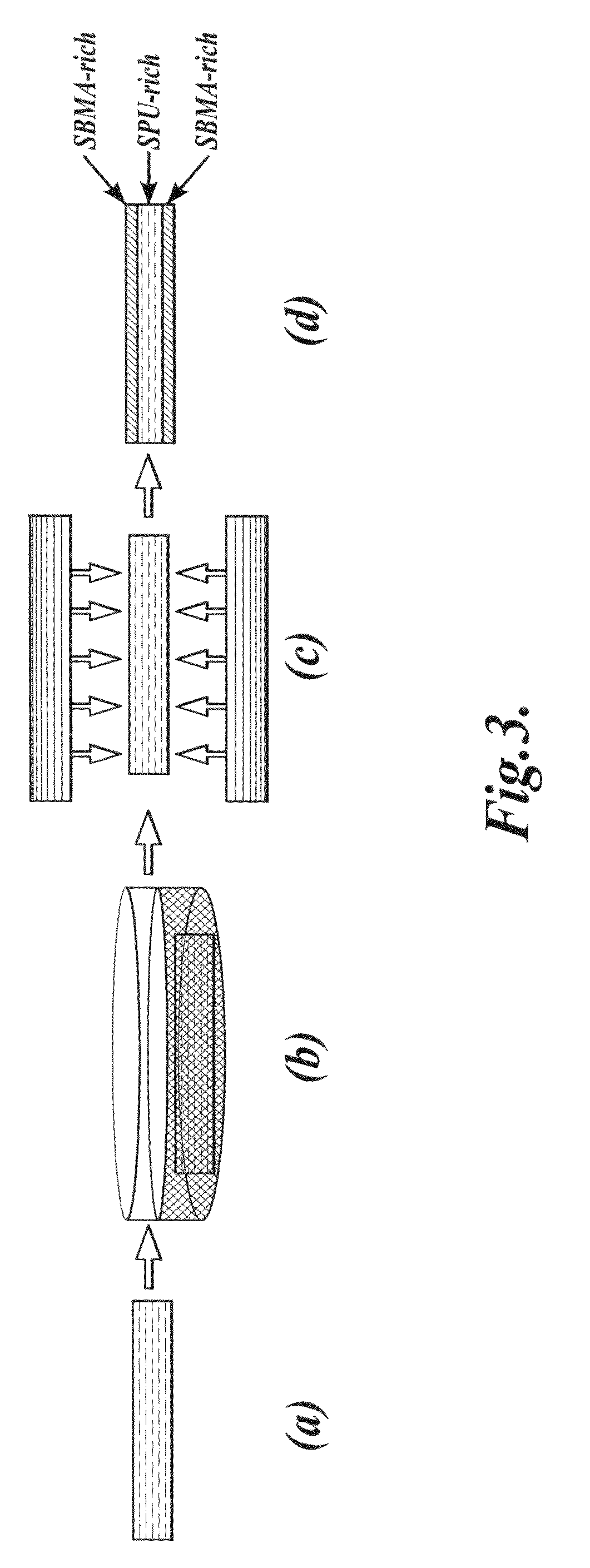
Super-low fouling sulfobetaine and carboxybetaine materials and related methods
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Process of reducing fouling during heat processing of foods and beverages
InactiveUS20060240159A1Reduce dirtFood preservationPackaging protectionMethyl cellulosePasteurization
A pasteurization or sterilization process reduces fouling of a food or beverage composition containing protein during the heat treatment. An antifouling agent is added to the food or beverage composition that is selected from hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) with a hydroxypropyl molar substitution of greater than 3.0 and a weight average molecular weight (Mw) as measured by SEC of greater than 350,000 Dalton, methylhydroxypropylcellulose (MHPC) with a methoxyl content of greater than 17% and a hydroxypropyl content of greater than 3%, methylcellulose (MC) with a methoxyl content greater than 17% and a viscosity in water at ambient temperatures and a concentration of 2% of greater than 1,000 cps, or mixtures thereof, This food or beverage composition is then heated in a first heat exchanger at a temperature between 50 and 100° C. for a time of from about 2 seconds to 30 minutes for pasteurization or it is further heated to sterilization temperatures before being packaged out or further processed. The improvements of this process is that the heat exchangers are fouled at least 10% by weight less or run-time increased at least 10% as compared to when heat-treating a similar food or beverage composition without the antifouling agent.
Owner:HERCULES INC
Layered non-fouling, antimicrobial antithrombogenic coatings
ActiveUS20100145286A1Improve antifouling performanceImprove bindingSuture equipmentsSugar derivativesPhysical propertyPolymer
Substrates, optionally coated with an undercoating, having grafted thereto one or more non-fouling materials are described herein. The non-fouling, polymeric material can be grafted to a variety of functionalized substrate materials, particularly polymeric substrates and / or polymeric undercoatings immobilized on a substrate. The compositions described herein are highly resistant protein absorption, particularly in complex media and retain a high degree of non-fouling activity over long periods of time. The compositions described herein may also demonstrate antimicrobial and / or anti-thrombogenic activity. The non-fouling material can be grafted to a functionalized substrate, or optionally from an undercoating on the substrate, preferably without significantly affecting the mechanical and / or physical properties of the substrate material
Owner:ARROW INT INC
Non-fouling, Anti-microbial, Anti-thrombogenic graft-from compositons
ActiveUS20110305872A1Reduce microbial colonizationShorten the counting processLayered productsPretreated surfacesFibrinogenBlood plasma
A method for preparing and resulting articles of manufacture comprising a substrate having a surface, a bulk beneath the surface, and a grafted polymer layer on the substrate surface, the substrate surface and the grafted polymer layer, in combination, constituting a modified surface having a fibrinogen adsorption of less than about 125 ng / cm2 in a fibrinogen binding assay in which the modified surface is incubated for 60 minutes at 37° C. in 70 μg / mL fibrinogen derived from human plasma containing 1.4 μg / mL I-125 radiolabeled fibrinogen.
Owner:ARROW INT INC
Selective membrane having a high fouling resistance
InactiveUS6913694B2Improve antifouling performanceImprove the immunitySemi-permeable membranesSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxyCross-link
Owner:SAEHAN INDS CO LTD
Direct drive fan system with variable process control
ActiveUS20140244051A1System smoothReduce vibrationTransportation and packagingEngine fuctionsCooling towerHigh torque
The present invention is directed to a direct-drive fan system and a variable process control system for efficiently managing the operation of fans in a cooling system such a as wet-cooling tower or air-cooled heat exchanger (ACHE), HVAC systems, mechanical towers or chiller systems. The present invention is based on the integration of key features and characteristics such as tower thermal performance, fan speed and airflow, motor torque, fan pitch, fan speed, fan aerodynamic properties, and pump flow. The variable process control system processes feedback signals from multiple locations in order control a high torque, variable speed, permanent magnet motor to drive the fan. Such feedback signals represent certain operating conditions including motor temperature, basin temperature, vibrations, and pump flow rates. Other data processed by the variable process control system in order to control the motor include turbine back pressure set-point, condenser temperature set-point and plant part-load setting. The variable process control system processes this data and the aforesaid feedback signals to optimize the operation of the cooling system in order to prevent disruption of the industrial process and prevent equipment (turbine) failure or trip. The variable process control system alerts the operators for the need to conduct maintenance actions to remedy deficient operating conditions such as condenser fouling. The variable process control system increases cooling for cracking crude and also adjusts the motor RPM, and hence the fan RPM, accordingly during plant part-load conditions in order to save energy.
Owner:PRIME DATUM
Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces and biological applications thereof
ActiveUS20140187666A1Inhibit inflammationPrevents wound healingAntifouling/underwater paintsSurgical adhesivesSelf-healingHigh density
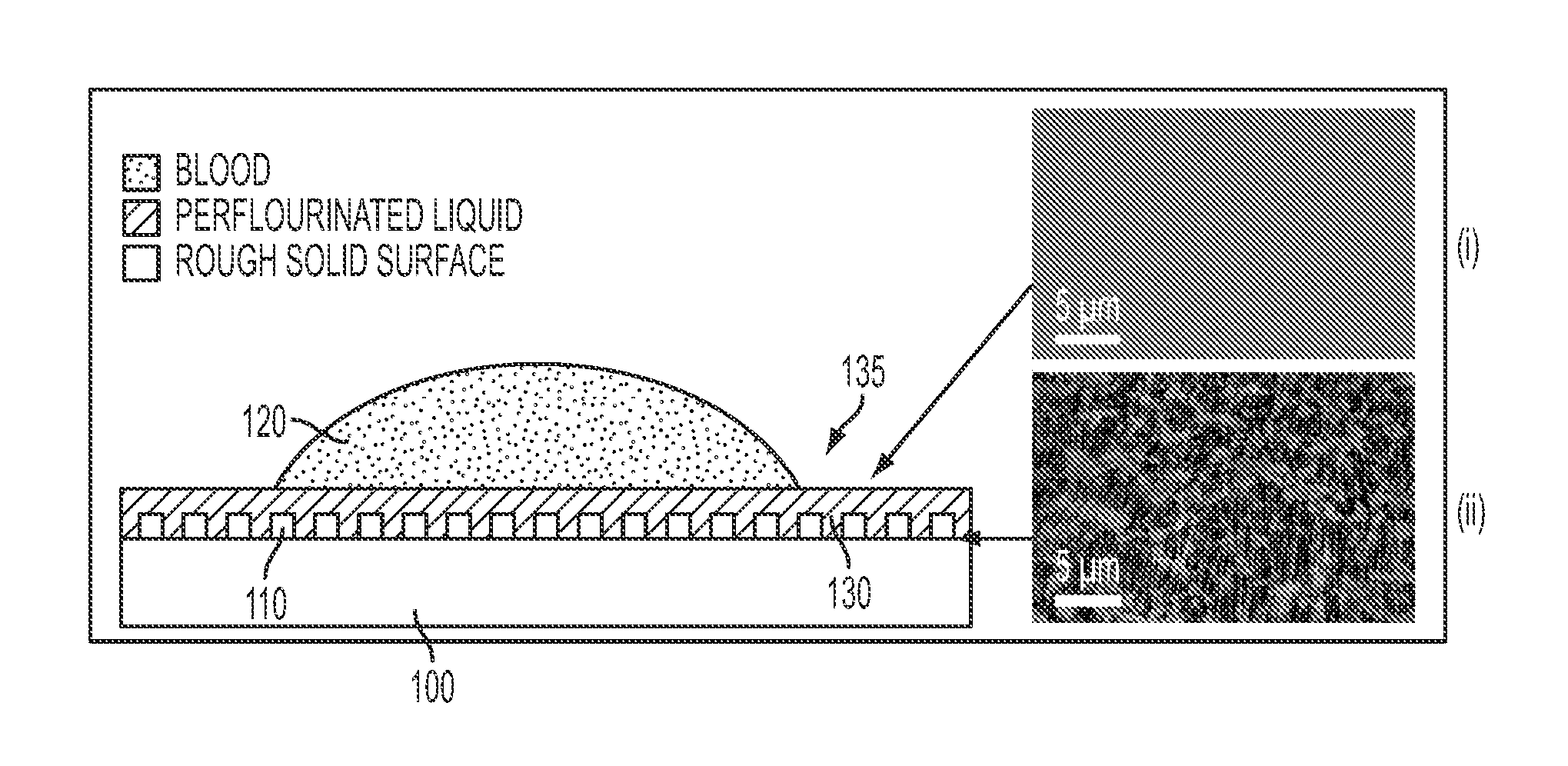
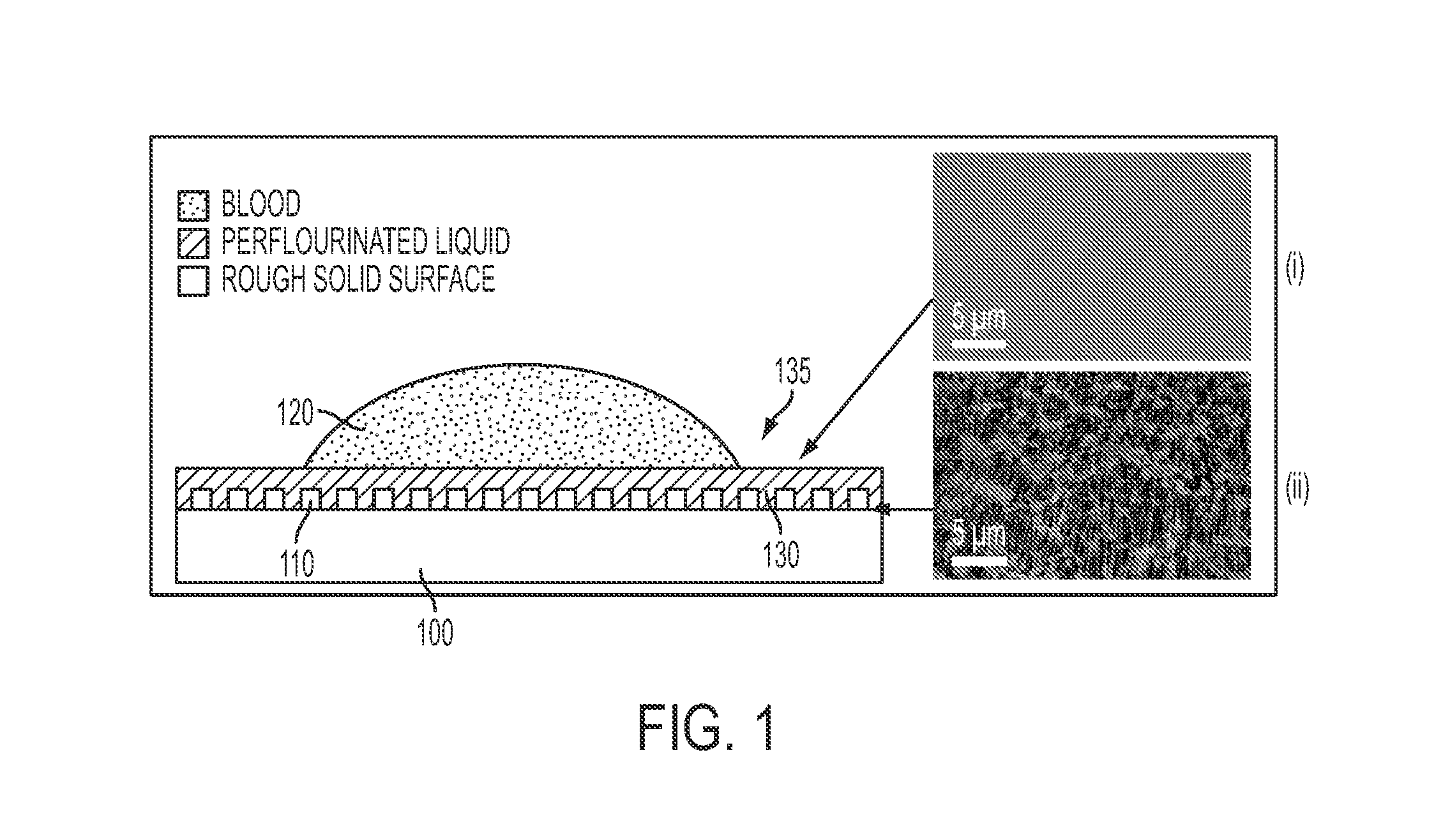
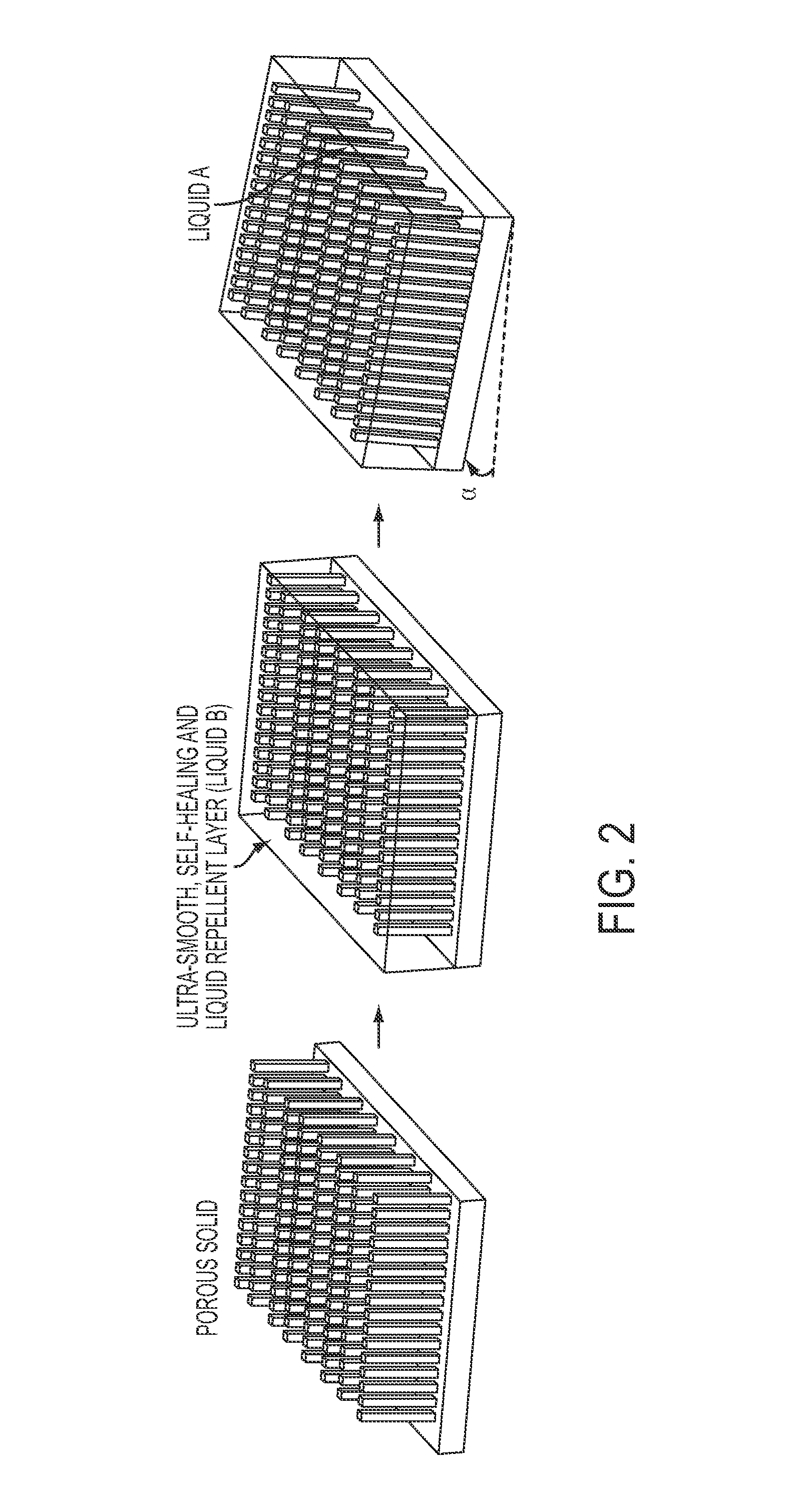
A self-healing, scratch resistant slippery surface that is manufactured by wicking a chemically-inert, high-density liquid coating over a roughened solid surface featuring micro and nanoscale topographies is described. Such a slippery surface shows anti-wetting properties, as well as exhibits significant reduction of adhesion of a broad range of biological materials, including particles in suspension or solution. Specifically, the slippery surfaces can be applied to medical devices and equipment to effectively repel biological materials such as blood, and prevent, reduce, or delay coagulation and surface-mediated clot formation. Moreover, the slippery surfaces can be used to prevent fouling by microorganisms such as bacteria.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Dielectrophoresis devices and methods therefor
InactiveUS20120085649A1Easy maintenanceAvoid contactDielectrophoresisSludge treatmentSample integrityElectrophoresis
Devices and methods for performing dielectrophoresis are described. The devices contain a sample channel which is separated by physical barriers from electrode channels which receive electrodes. The devices and methods may be used for the separation and analysis of particles in solution, including the separation and isolation of cells of a specific type. As the electrodes do not make contact with the sample, electrode fouling is avoided and sample integrity is better maintained.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Mitigation of Biomolecular Adsorption with Hydrophilic Polymer Additives
ActiveUS20090280251A1Reduce surface tensionInhibit bindingSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementHydrophilic polymersPhenyl Ethers
Molecular adsorption to the microfluidic device surfaces can be passively and actively mitigated by mixing certain hydrophilic polymers (organic polymers with repeating hydrophilic groups—the preferred polymers being amphipathic surfactants—with the sample liquid during or prior to relevant microfluidic operations. Nonionic surfactants such as polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate and polyoxyethylene octyl phenyl ether are especially effective. High molecular weight polyethylene polymers are also effective. The hydrophilic polymers appear to prevent binding of the fouling molecules to the microfluidic by occupying the surface sites in place of the fouling molecules or by interacting with the fouling molecules to prevent binding of the fouling molecules the surface. When surface adsorption is thus mitigated, microfluidic devices can readily handle samples containing biomolecules to enable active sample concentration, filtering, washing, transport, mixing and other sample handling operations.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Methods and kits for locking and disinfecting implanted catheters
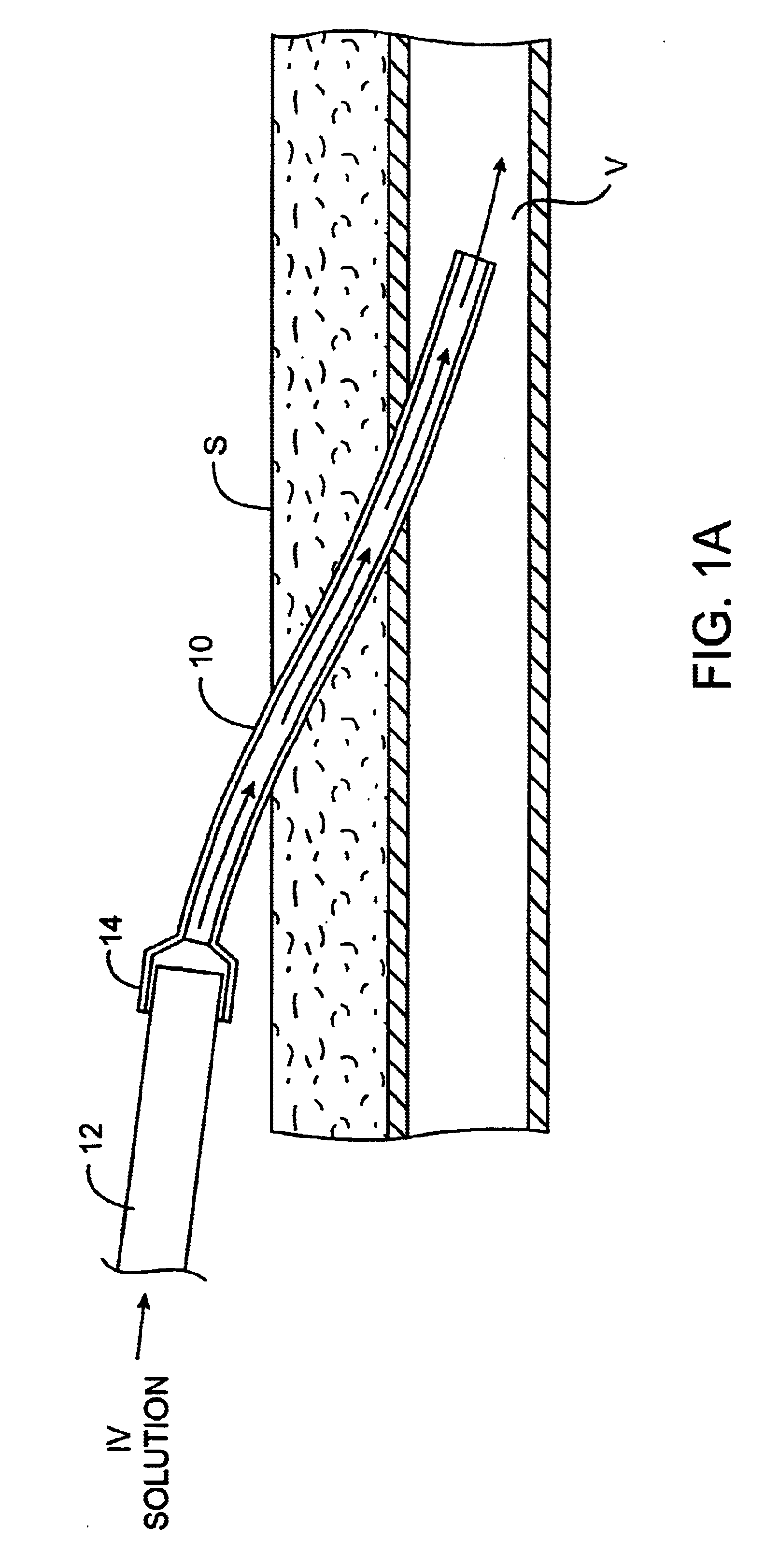
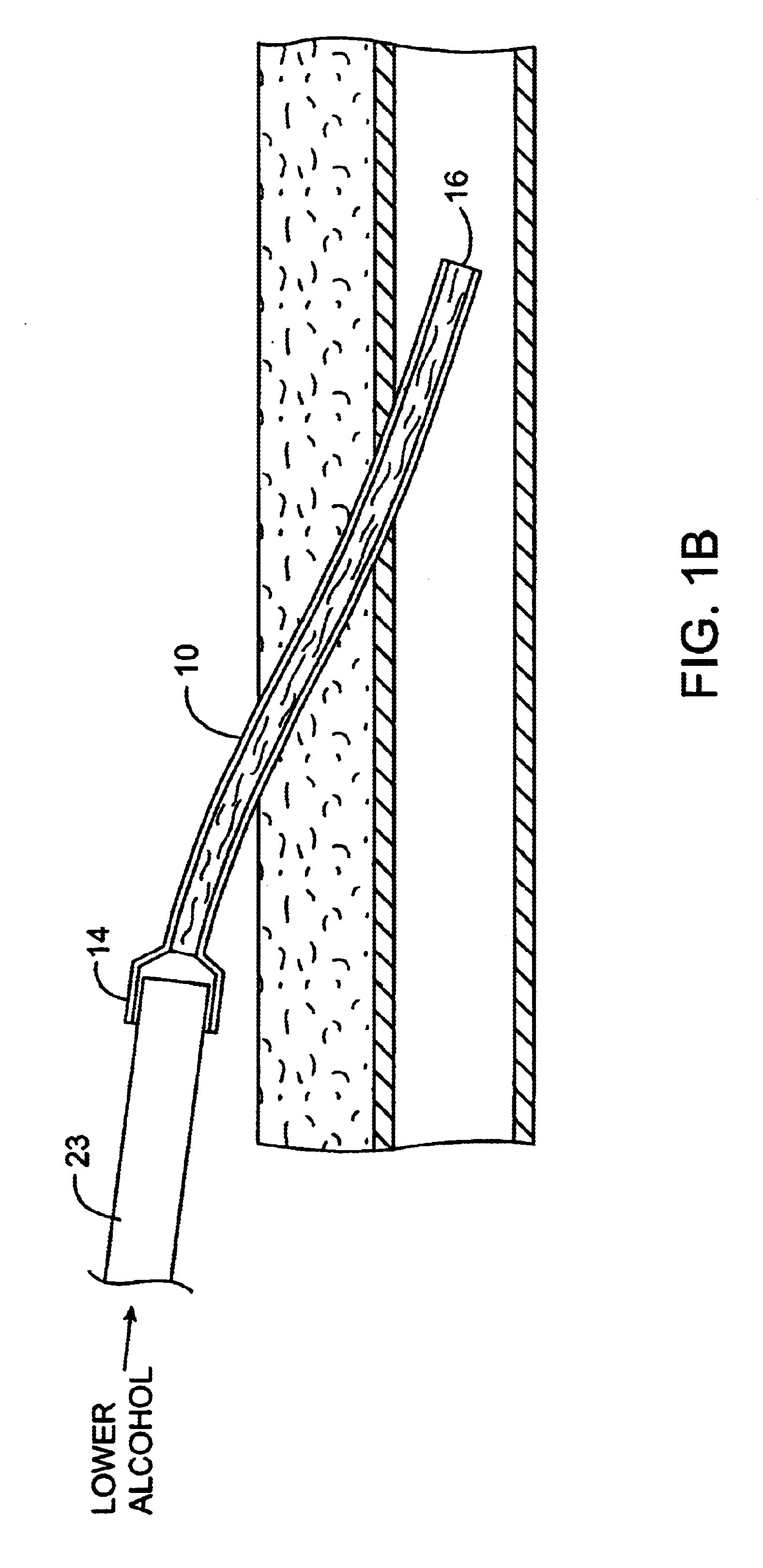
InactiveUS6685694B2Reduce riskInhibiting fouling and plugging of the lumenDialysis systemsMedical devicesTriclosanThrombus
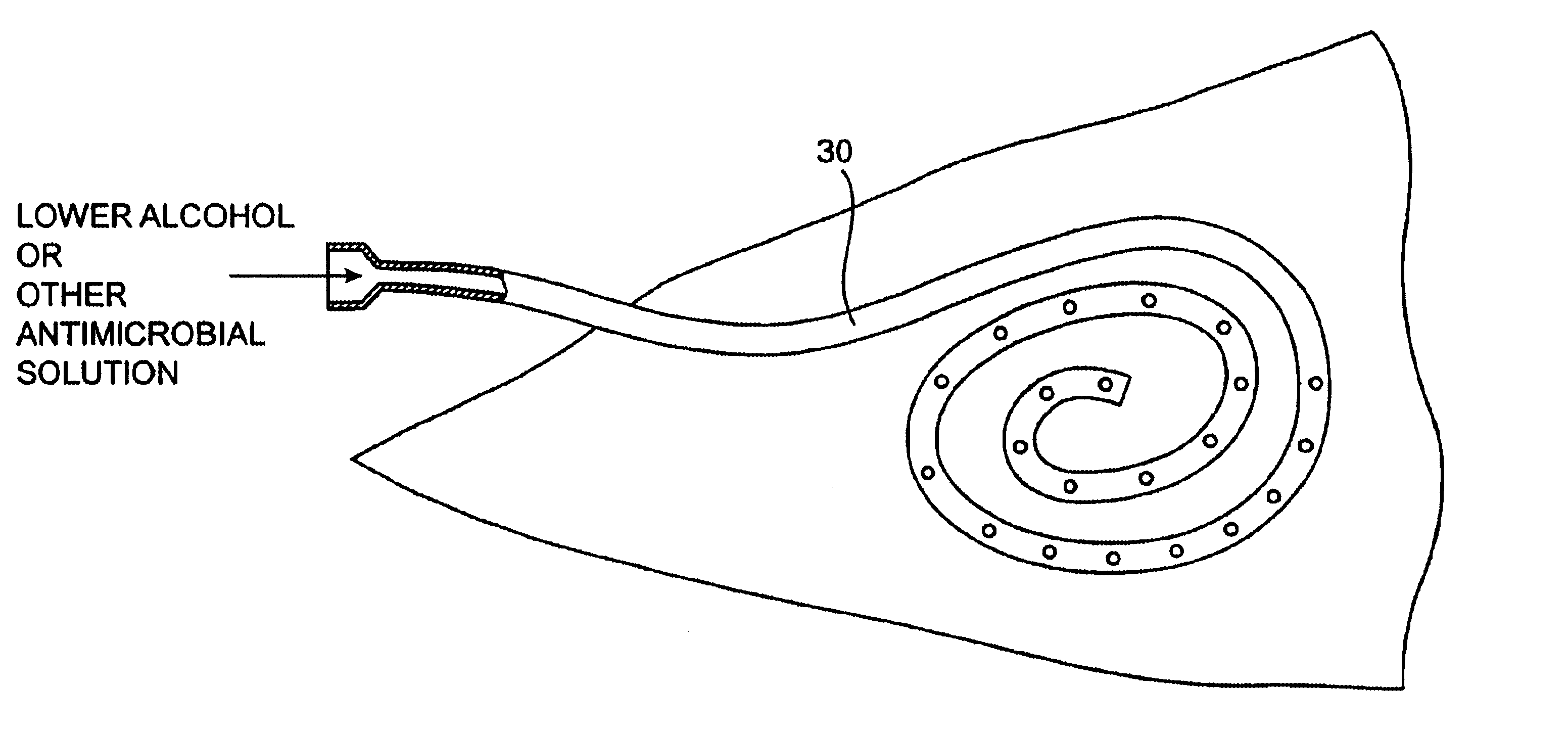
Implanted catheters are locked with a solution comprising a lower alcohol, typically ethanol, propanol, or butanol, in a range from 1% to 99% by volume, and an additive in a range from 1% to 99% by volume, the additive comprising an anti-microbial, typically taurolidine or triclosan, or an anti-coagulant, typically riboflavin, sodium citrate, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, or citric acid. The use of an alcohol and additive solution can effectively reduce fouling of the catheter, particularly clotting and thrombus in intravascular catheters, as well as eradicate existing infections and / or reduce the risk of potential infections. Existing infections and / or potential infections can be further reduced by employing a catheter body which permits an anti-microbial solution to penetrate into the catheter body and preferably through the catheter into tissue surrounding the implanted catheter.
Owner:EXCELSIOR MEDICAL
Human Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Antibody
ActiveUS20070264253A1Neutralize EGFRInhibit bindingSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFiberEngineering
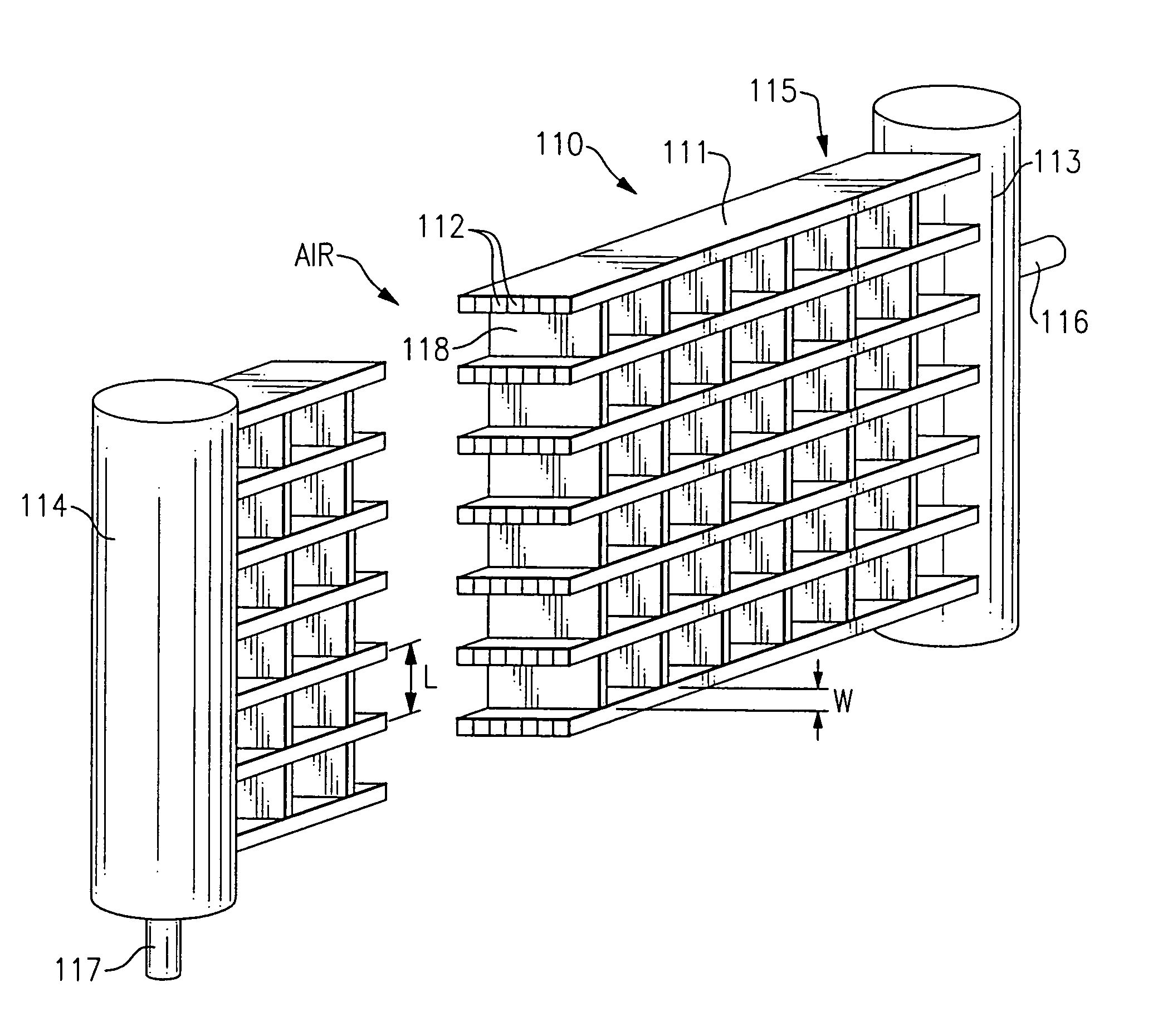
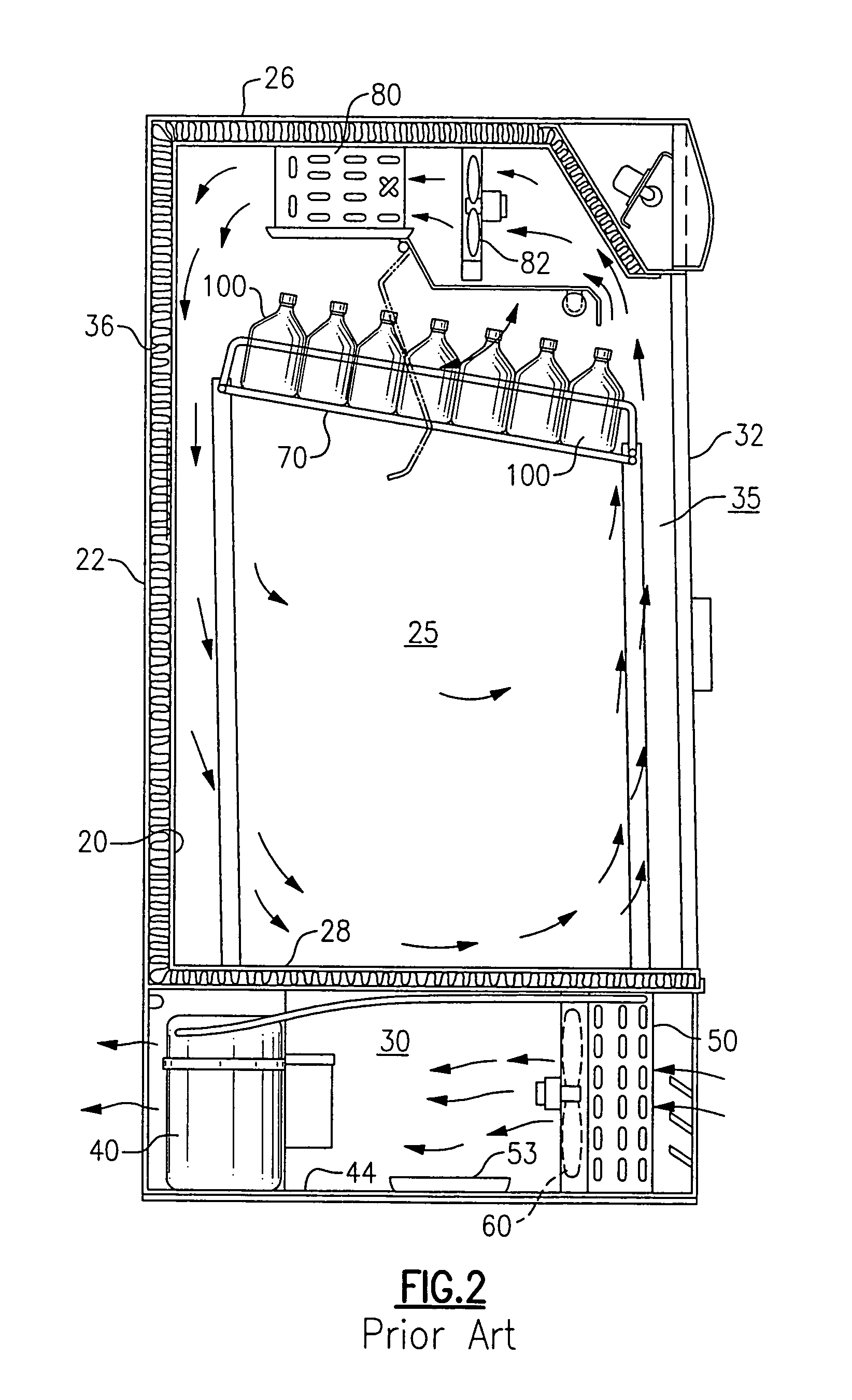
A condenser coil for a refrigerated beverage and food service merchandiser includes a plurality of parallel fins be-tween adjacent tubes. In order to reduce the likelihood of fouling by the bridging of fibers therebetween, the spacing of the fins is maintained at a distance of 0.4 to 0.8 inches apart. In one embodiment, the tubes comprise microchannel tubes, with no fins there-between, and the spacing between the microchannel tubes is maintained in the range of 0.75 inches to optimize the heat transfer performance while minimizing the occurrence of fouling. A supporting structure is provided between microchannel tubes when no fins are included. Also, plural rows of microchannel tubes are provided with separate inlet headings and with the rows being stag-gered in transverse relationship to enhance the heat transfer characteristic while minimizing the likelihood of fouling.
Owner:IMCLONE SYSTEMS
Polymers for implantable devices exhibiting shape-memory effects
InactiveUS20090035350A1Promote tissue regenerationMaintaining vascular patencyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBiodegradable copolymersDevice form
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Polyalkyl succinic anhydride derivatives as additives for fouling mitigation in petroleum refinery processes
InactiveUS20100170829A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingOrganic chemistryParticulatesFouling mitigation
The present invention provides a method for reducing fouling, including particulate-induced fouling, in a hydrocarbon refining process including the steps of providing a crude hydrocarbon for a refining process; adding at least one polyalkyl succinic anhydride derivative additive disclosed herein. The additive can be complexed with a boronating agent, such as boric acid, to yield a boron-containing polyalkyl succinic anhydride derivative.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
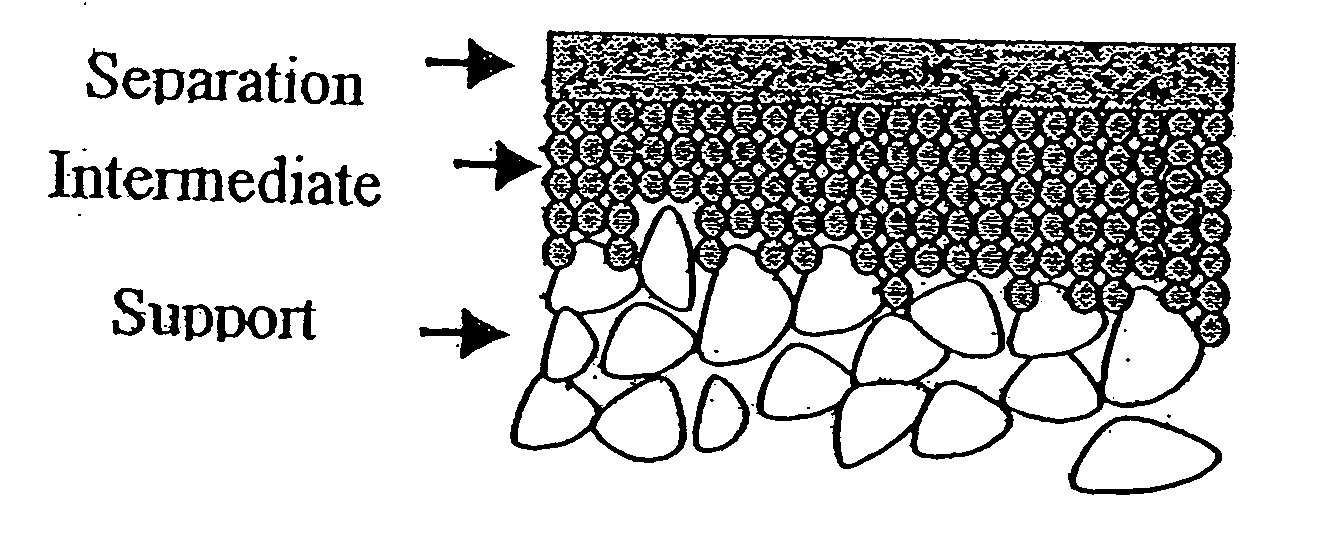
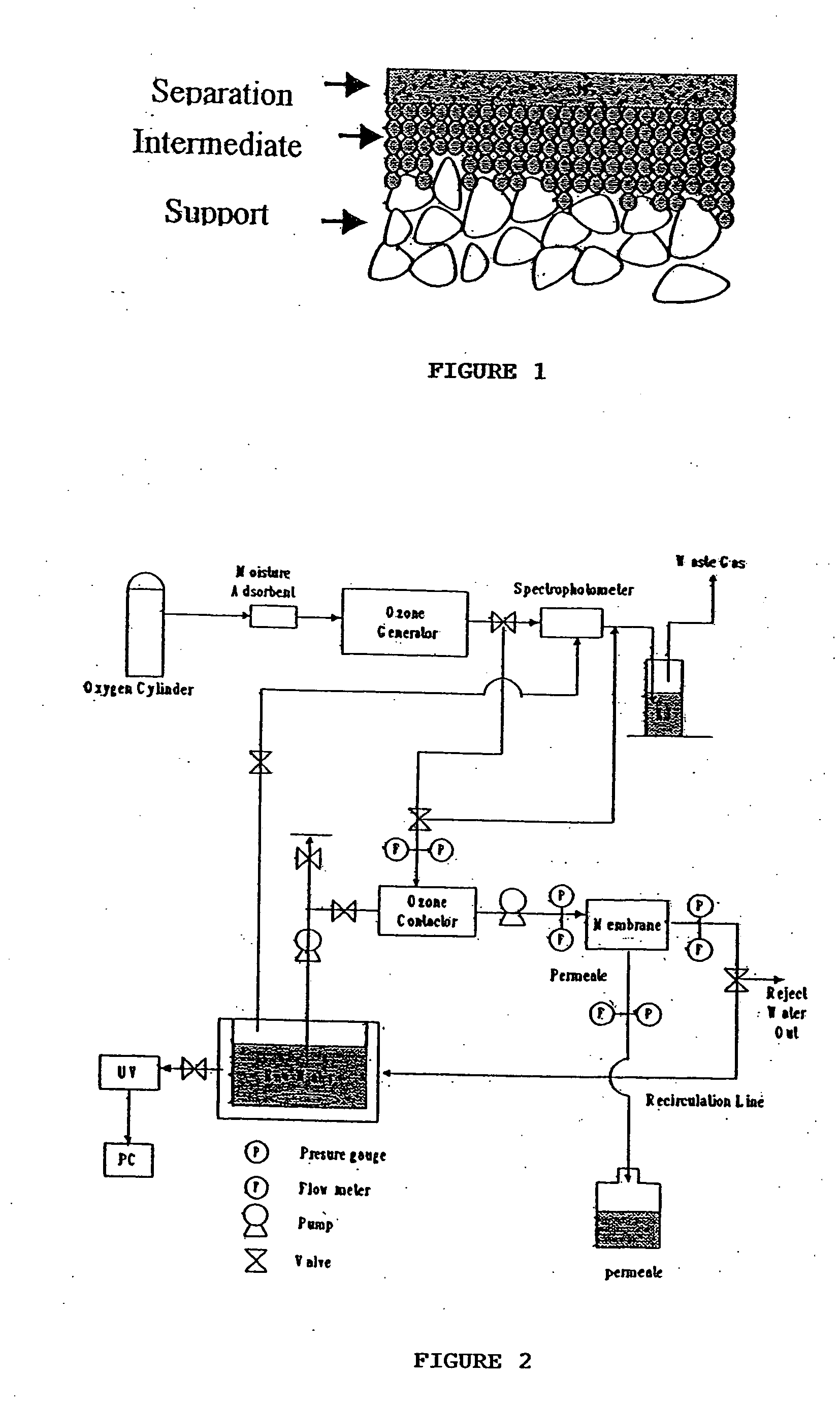
Ceramic membrane water filtration
A process for combined ozone degradation and filtration using a multi-layered, nanocrystalline, sintered ceramic, metal oxide catalyst and ceramic membrane filter is described. The process reduces fouling of the membrane and degrades ozone remaining in the water from ozonation of water to kill microorganisms.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Liquid filtration media, filter elements and methods
ActiveUS20110198280A1Permeability efficiencyPore size efficiencyLiquid carbonaceous fuelsMembrane filtersFiberFilter media
A filter and filter media configured and arranged for placement in a fuel stream is disclosed. The filter and filter media allow for filtering of liquid fuels, such as diesel fuel. In certain embodiments the filter media includes a media fiber (such as glass) and a binder fiber (such as bicomponent) that combine to create a media structure having low solidity and relatively low compressibility, and which contain a pore structure that avoids premature fouling of the filter by fuel degradation products.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Gas propelled munitions Anti-fouling system
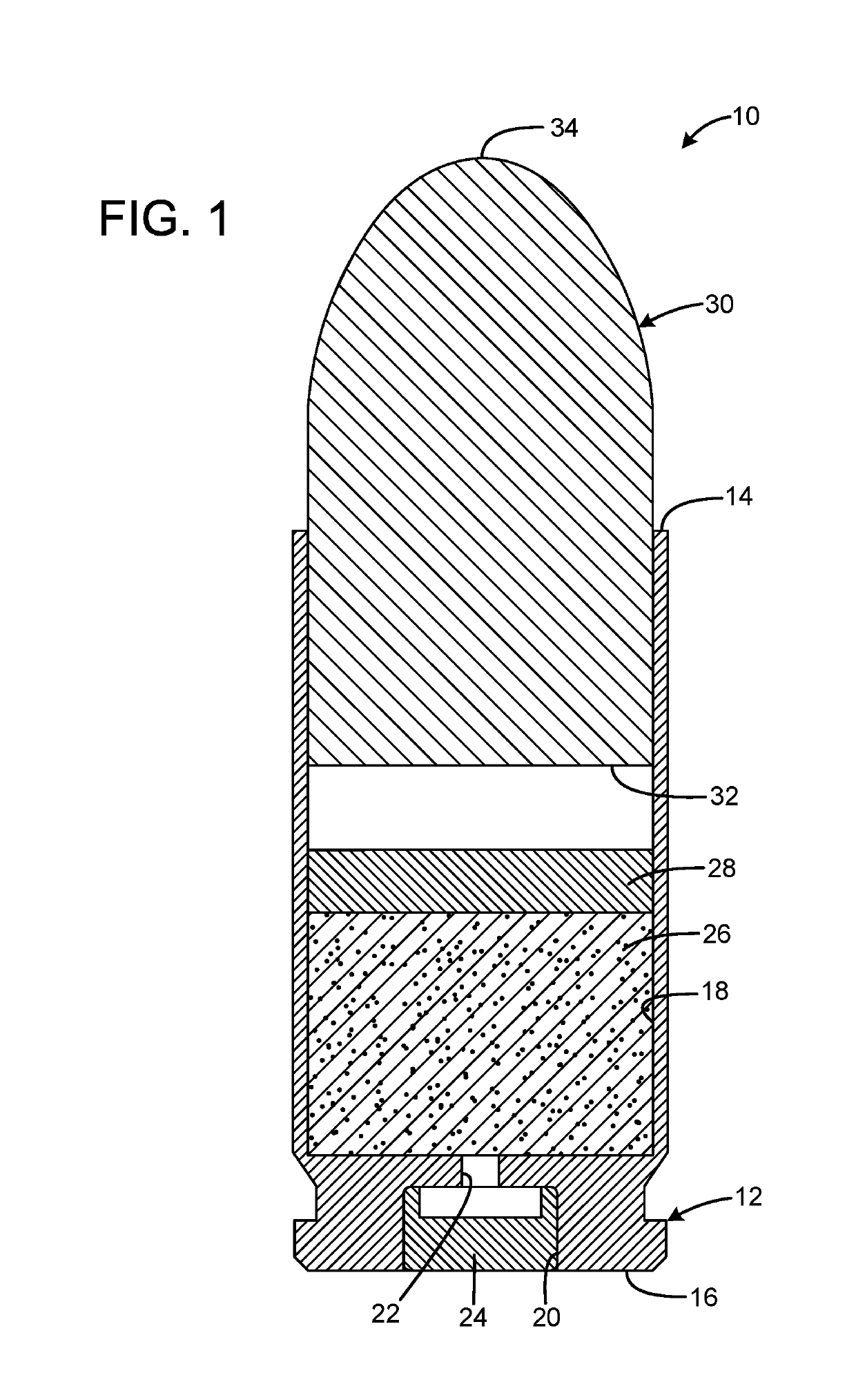
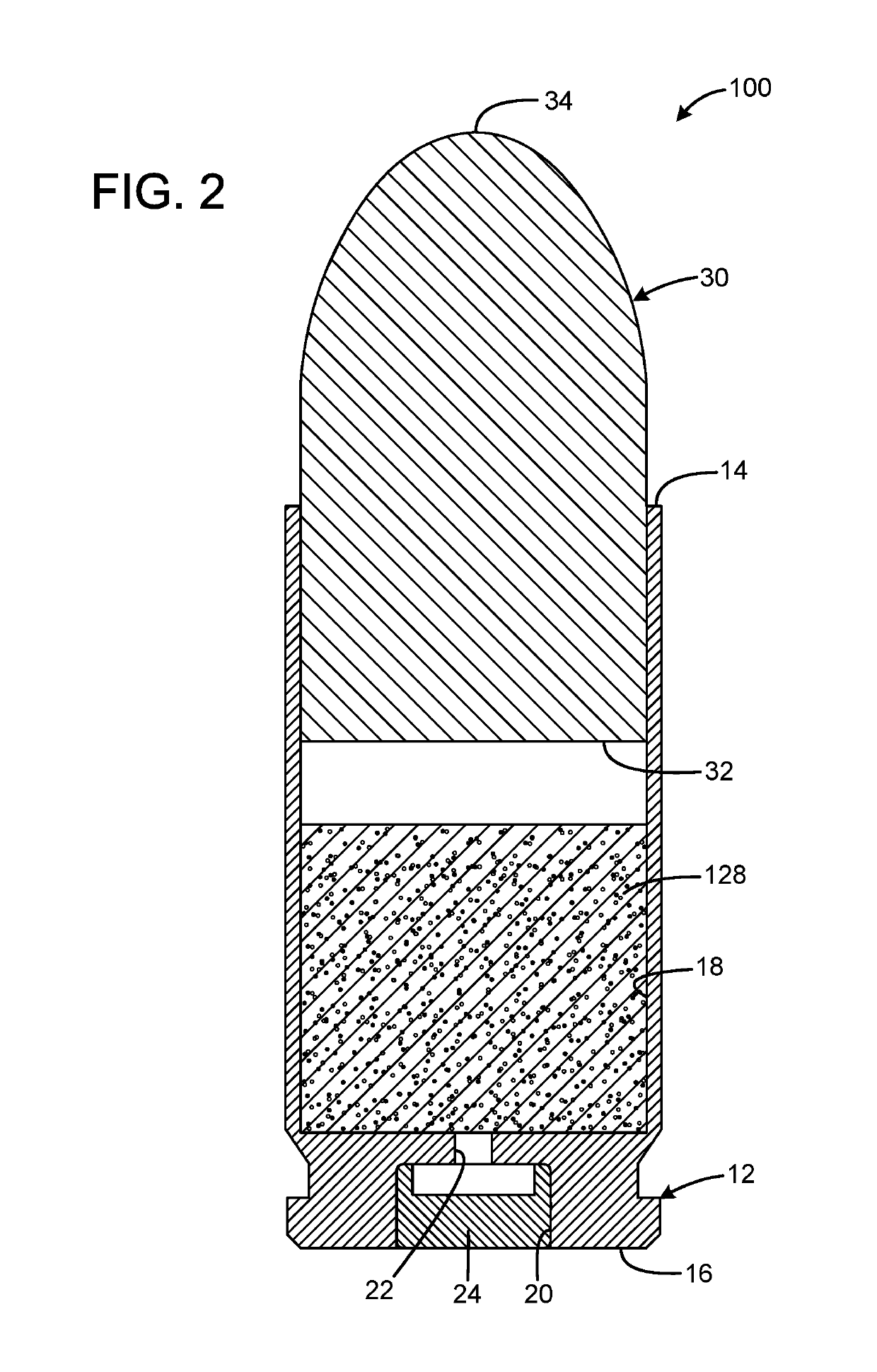
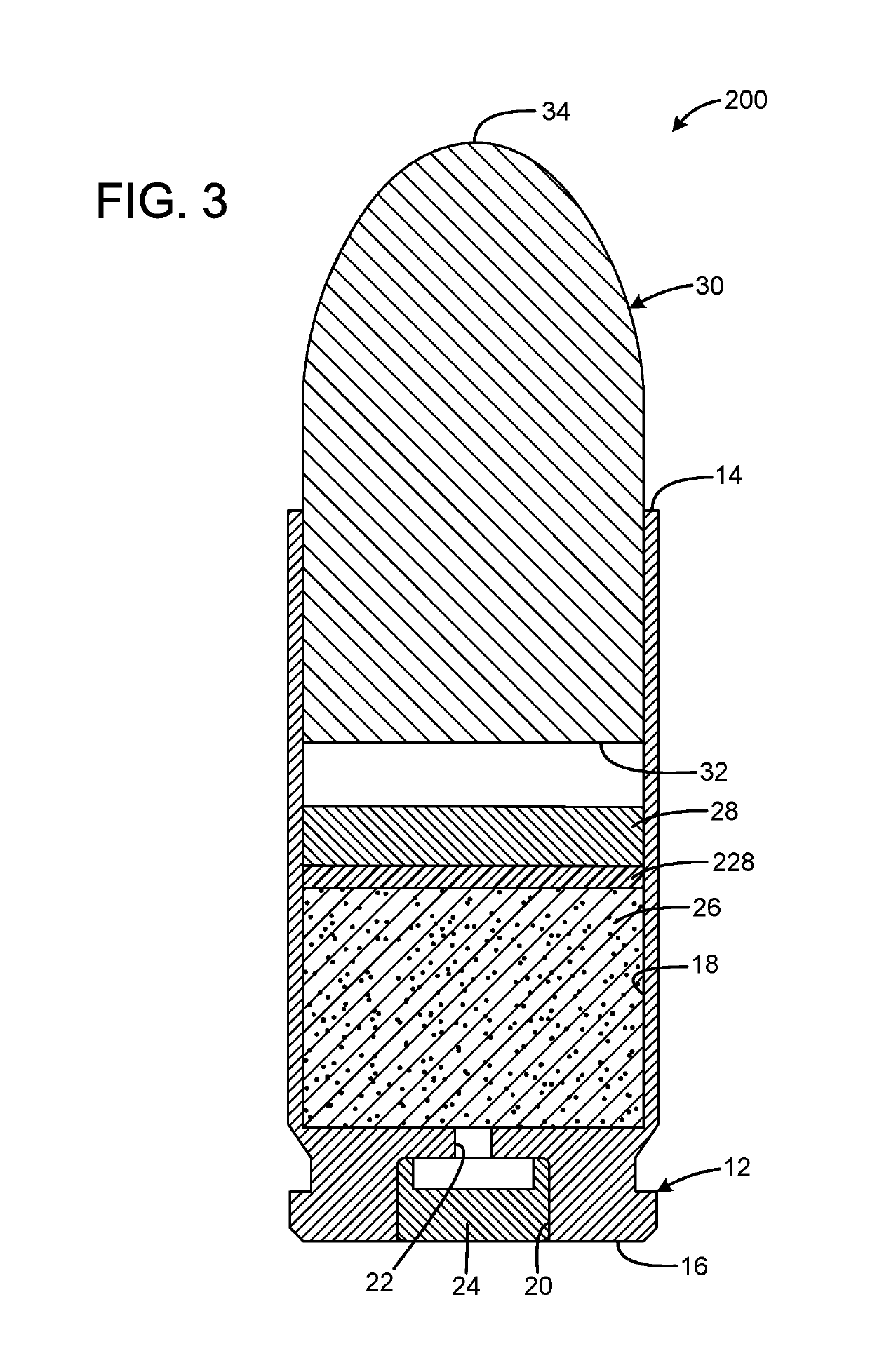
InactiveUS20190106364A1Great contributionShotgun ammunitionNon-explosive/non-thermic compositionsEngineeringCitric acid
A gas propelled munitions anti-fouling system has a case having an open forward mouth end, a rear end, and an interior, the rear end defining a pocket that receives a primer and a passage communicating between the pocket and the interior of the case, a quantity of propellant received within the interior of the case, a quantity of anti-fouling composition received within the interior of the case, and a bullet having a rear portion inserted into the open forward mouth end of the case. The anti-fouling composition may have at least one salt and at least one acid. The acid may be anhydrous. The salt may be sodium chloride or sodium nitrate. The acid may be anhydrous citric acid. The anti-fouling composition may have at least one abrasive. The abrasive may be stannic acid. The anti-fouling composition may be 50% salt by weight and 50% acid by weight.
Owner:ADLER CAPITAL LLC
Polymer-fluorosurfactant associative complexes
ActiveUS20060234901A1Increase resistanceImprove protectionOrganic detergent compounding agentsOther chemical processesWater dispersibleWater soluble
The present invention relates to associative complexes of water soluble and / or water dispersible polymers and polymeric fluorosurfactants, compositions and methods for modifying substrates to provide treated articles with surface protective properties including easier cleaning, increased stain and / or soil repellency, and increased resistance to bio-fouling and environmental contamination.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Polymerization process using a metallocene catalyst system
InactiveUS6894131B2Improved reactor performanceReducing and eliminating needOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationLeaving groupFluoride
Provided is a process for polymerizing olefins in the presence of a metallocene catalyst compound having at least one fluoride or fluorine containing leaving group. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a process and catalyst composition having improved reactor performance, reducing or eliminating the need for anti-fouling additives to the catalyst composition and / or the reactor. In one embodiment, the invention is a process of polymerizing olefins comprising contacting ethylene and at least one comonomer with a supported catalyst system comprising a metallocene catalyst compound, the metallocene catalyst compound comprising at least one fluoride ion or fluorine containing leaving group; and wherein the supported catalyst system comprises an inorganic oxide support having an average particle size of from 35 μm or less and a pore volume of from 1 to 2 cm3 / g. The polymer product resulting therefrom is, in one embodiment, a copolymer having a density in the range of from 0.910 g / cm3 to 0.940 g / cm3; a molecular weight distribution of from 1.8 to 4; and an I2 of from 0.1 dg / min to 10 dg / min and is suitable for such articles as films.
Owner:UNIVATION TECH LLC
Foul-resistant condenser using microchannel tubing
ActiveUS7000415B2Reducing and eliminating occurrenceShow cabinetsEvaporators/condensersFiberEngineering
A condenser coil for a refrigerated beverage and food service merchandiser includes a plurality of parallel fins between adjacent tubes. In order to reduce the likelihood of fouling by the bridging of fibers therebetween, the spacing of the fins is maintained at a distance of 0.4 to 0.8 inches apart. In one embodiment, the tubes comprise microchannel tubes, with no fins therebetween, and the spacing between the microchannel tubes is maintained in the range of 0.75 inches to optimize the heat transfer performance while minimizing the occurrence of fouling. A supporting structure is provided between microchannel tubes when no fins are included. Also, plural rows of microchannel tubes are provided with separate inlet headings and with the rows being staggered in transverse relationship to enhance the heat transfer characteristic while minimizing the likelihood of fouling.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Automatic judging method, device and system for service life of filter screen
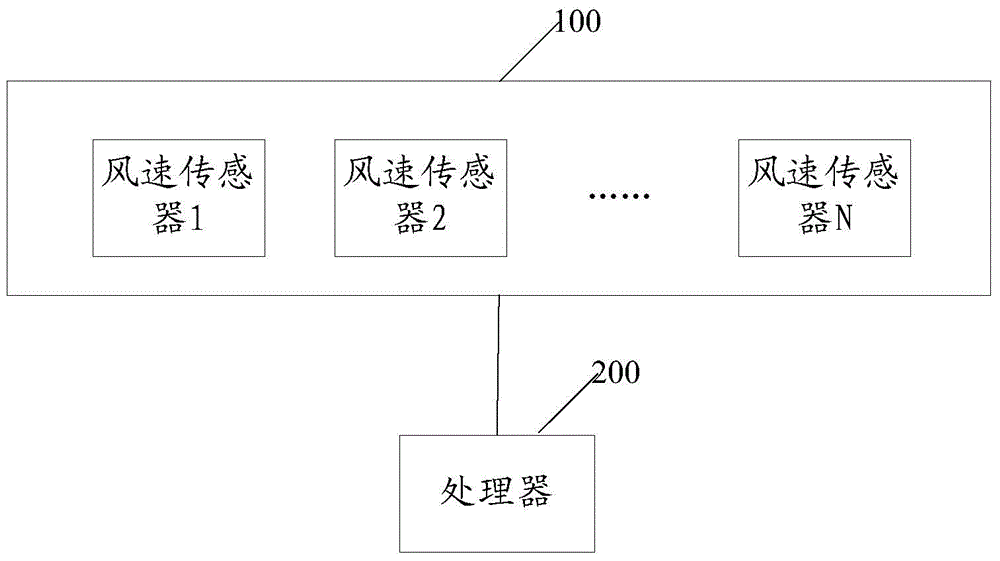
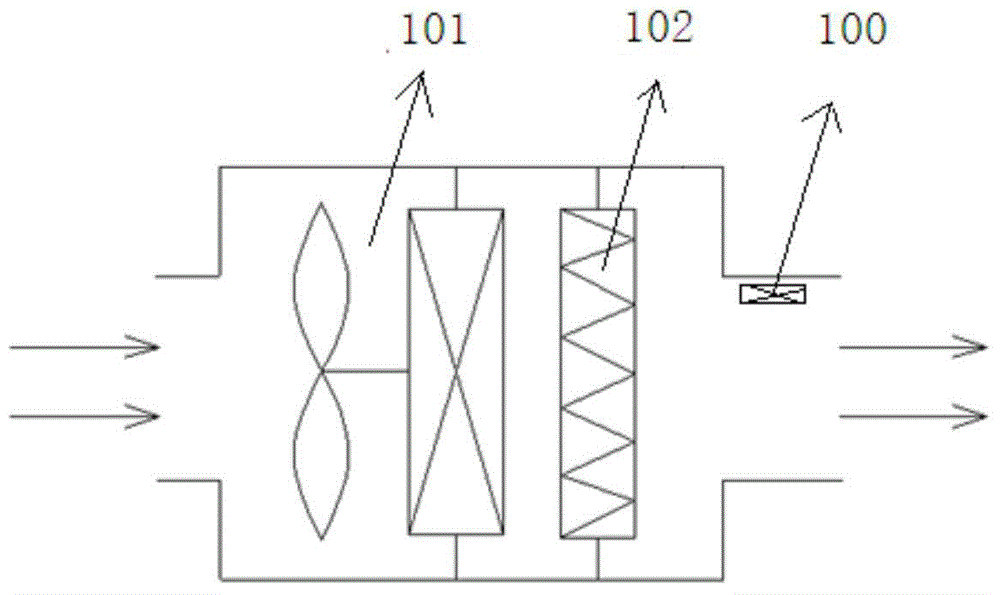
ActiveCN104390322AAvoid dependenceEasy to useMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsUltrasound attenuationQuality level
The invention discloses an automatic judging method, device and system for the service life of a filter screen. According to the automatic judging method, device and system, a wind speed sensor is used for detecting the wind speed change, the fouling and blockage situations of the filter screen are judged according to the attenuation rate of the wind speed, because an air conditioner fan has a fixed wind speed under each of different wind gears, the wind speed would be gradually reduced along with the dirtying and blockage of the filter screen, after the wind speed is reduced to a certain degree, different degrees of warnings are given to the user. Compared with the prior art, the automatic judging method, device and system for the service life of the filter screen solve the dependency on air quality level, do not need air quality detection cost and do not need the user to set manually according to the local air quality level, and therefore, the problem of imprecision due to judging according to the air quality level is solved, and moreover, the user does not need to manually set the air quality level and manually clear the accumulated time; the automatic judging method, device and system for the service life of the filter screen are more intelligent and more friendly to human and very convenient for the user.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Antimicrobial semi-permeable membranes
Cast semi-permeable membranes made from synthetic polymer used in reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration and microfiltration are treated with a non-leaching antimicrobial agent to prevent its bio-fouling and bacterial breakthrough. The semi-permeable membranes include a polymeric material and a non-leaching antimicrobial agent that is incorporated into and homogeneously distributed throughout the polymeric material. The polymeric material, in the case of one membrane, may be cellulose acetate. In the case of thin film composite polyamide membranes, the antimicrobial agent is incorporated in a microporous polysulfone layer that is sandwiched between a reinforcing fabric and an ultrathin polyamide material. The invention also includes a treatment of flat and hollow fiber semipermeable membranes made with polysulfones and polyvinylidene fluoride.
Owner:MICROBAN PROD CO INC
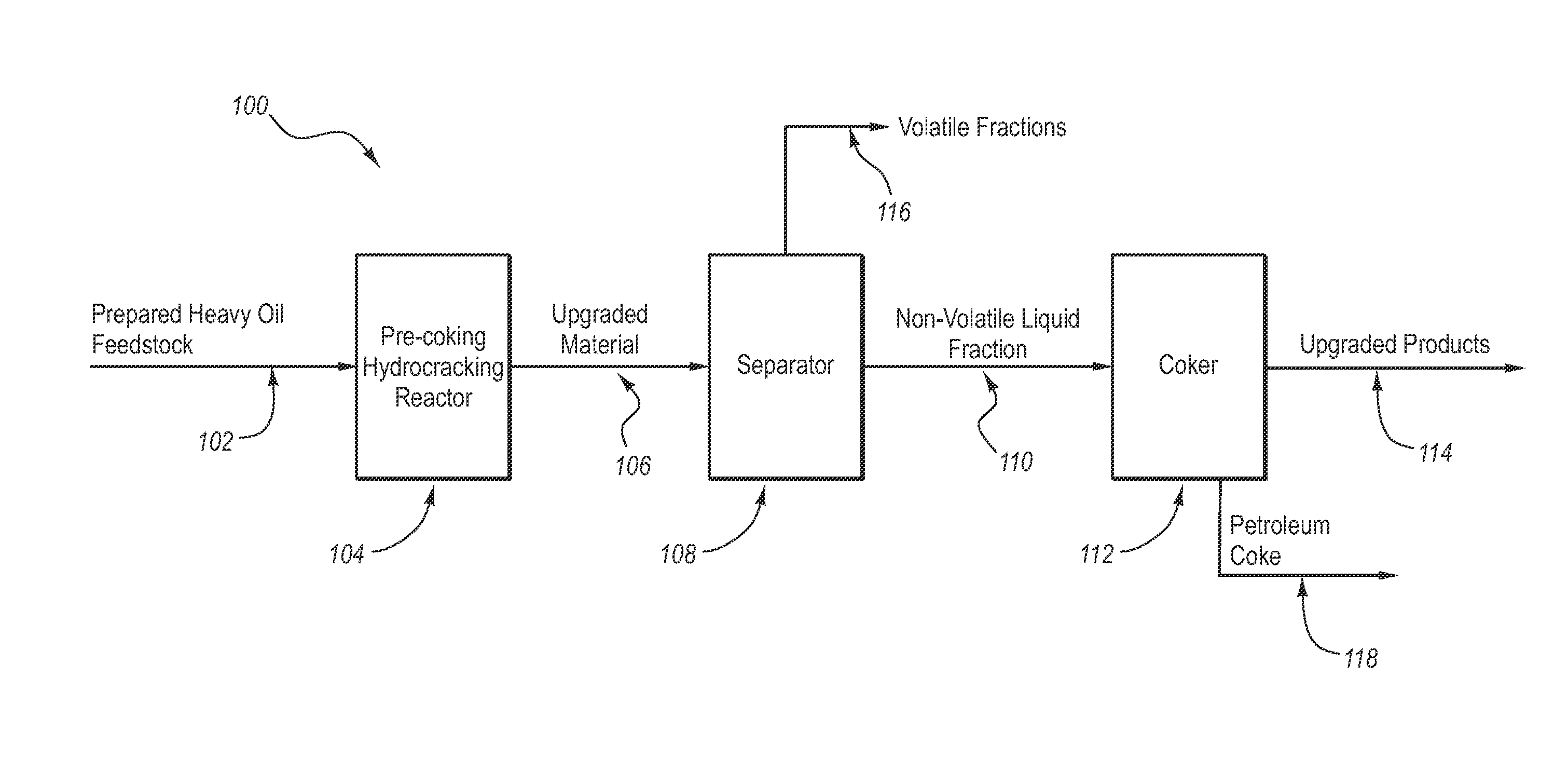
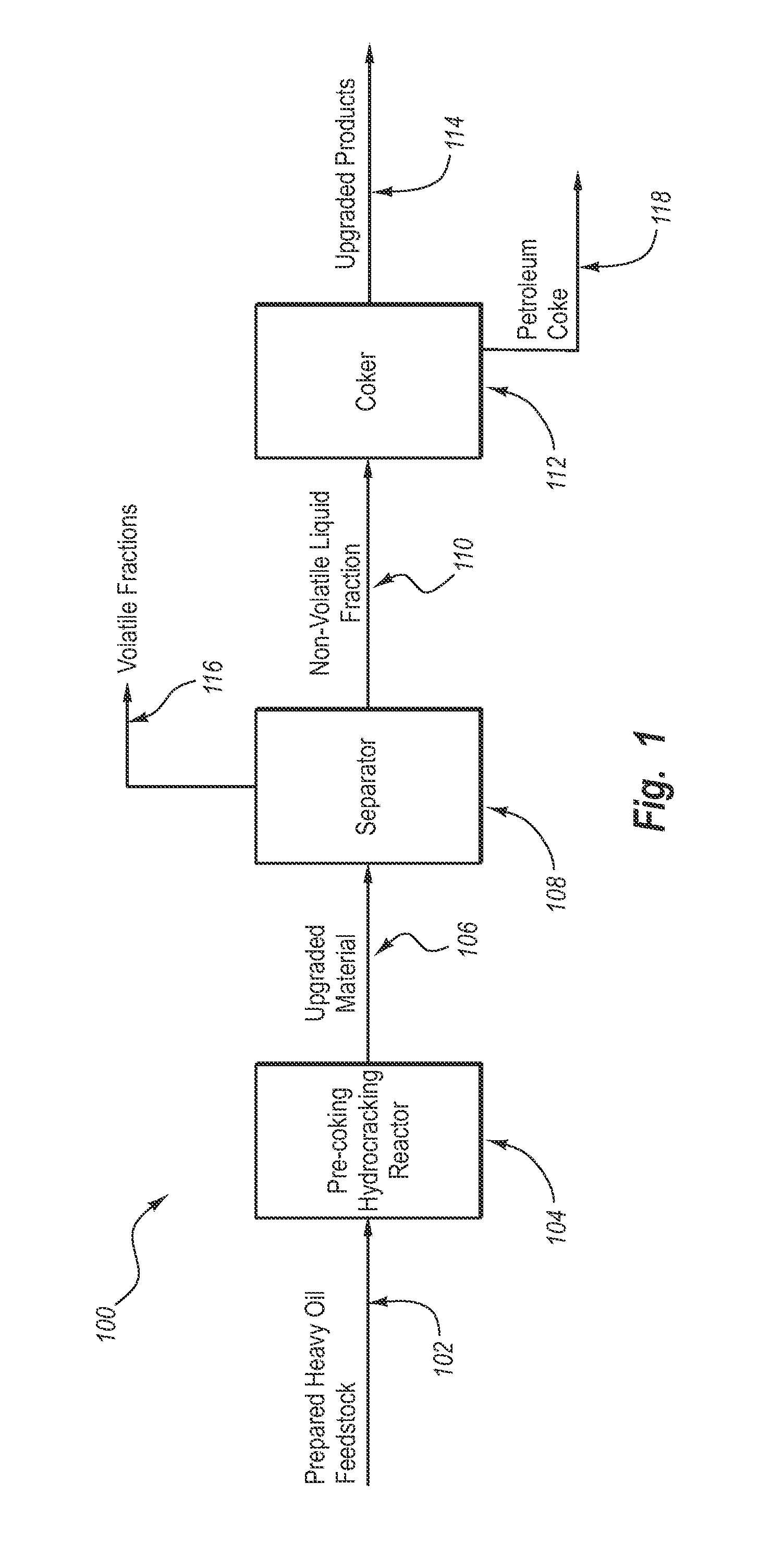
Methods and systems for upgrading heavy oil using catalytic hydrocracking and thermal coking
ActiveUS20140027344A1Speed up the conversion processImprove distillation yieldThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogenBoiling point
Methods and systems for hydroprocessing heavy oil feedstocks to form upgraded material use a colloidal or molecular catalyst dispersed within heavy oil feedstock, pre-coking hydrocracking reactor, separator, and coking reactor. The colloidal or molecular catalyst promotes upgrading reactions that reduce the quantity of asphaltenes or other coke forming precursors in the feedstock, increase hydrogen to carbon ratio in the upgraded material, and decrease boiling points of hydrocarbons in the upgraded material. The methods and systems can be used to upgrade vacuum tower bottoms and other low grade heavy oil feedstocks. The result is one or more of increased conversion level and yield, improved quality of upgraded hydrocarbons, reduced coke formation, reduced equipment fouling, processing of a wider range of lower quality feedstocks, and more efficient use of supported catalyst if used with the colloidal or molecular catalyst, as compared to a conventional hydrocracking process or a conventional thermal coking process.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION LLC
Water purification membranes with improved fouling resistance
ActiveUS20100051538A1Increase membrane hydrophilicityMitigation of membrane foulingMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCoated membraneAir purification
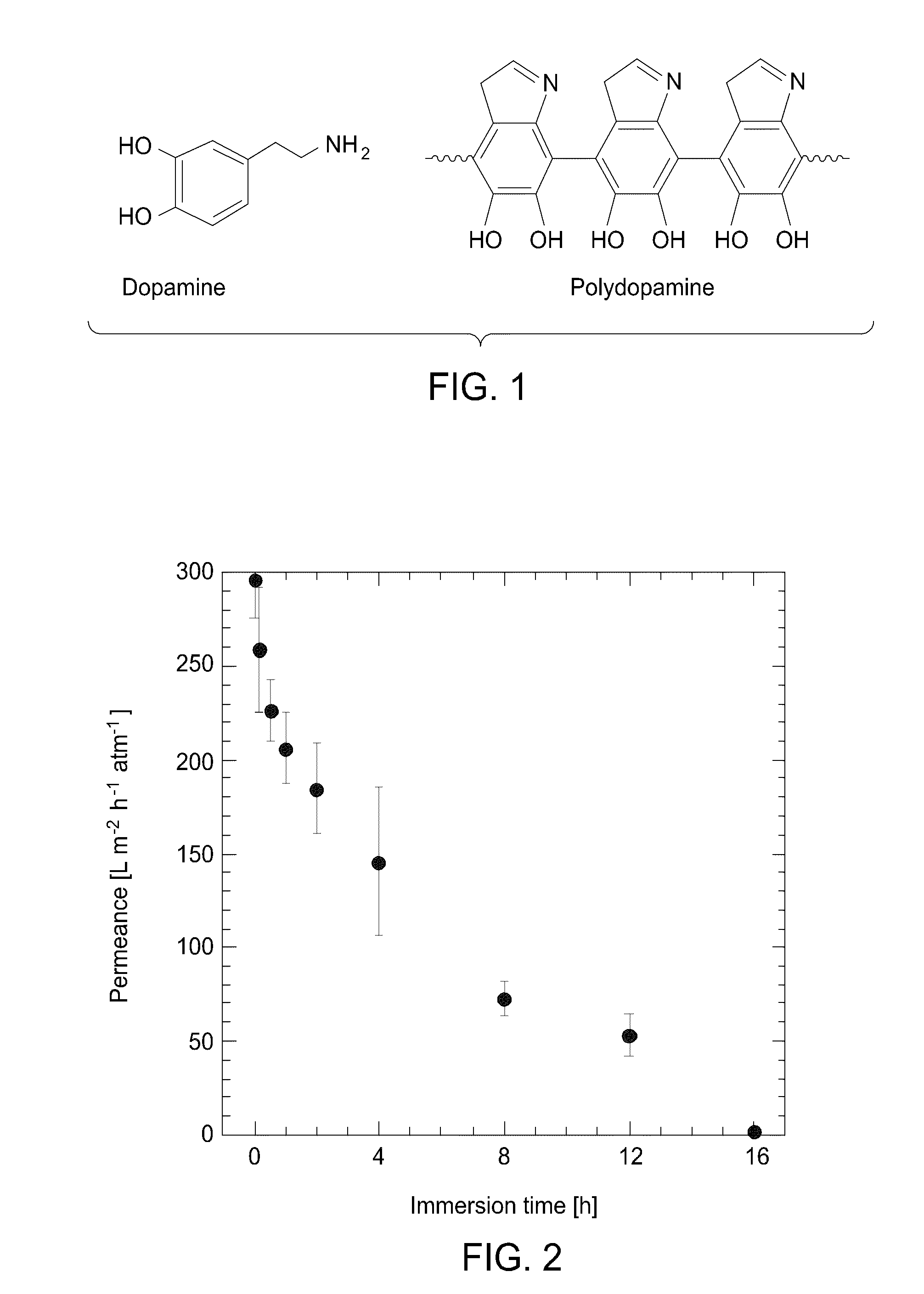
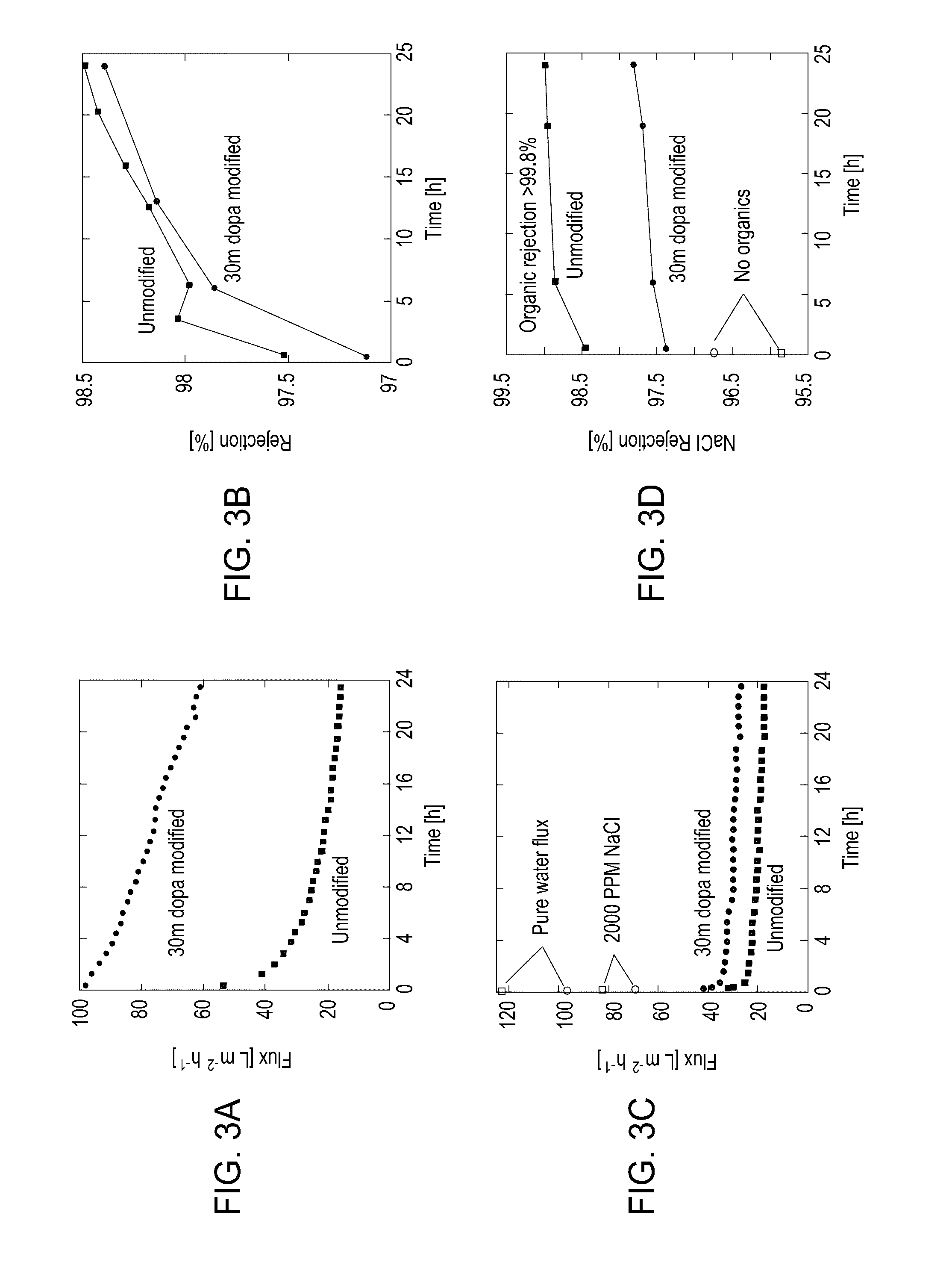
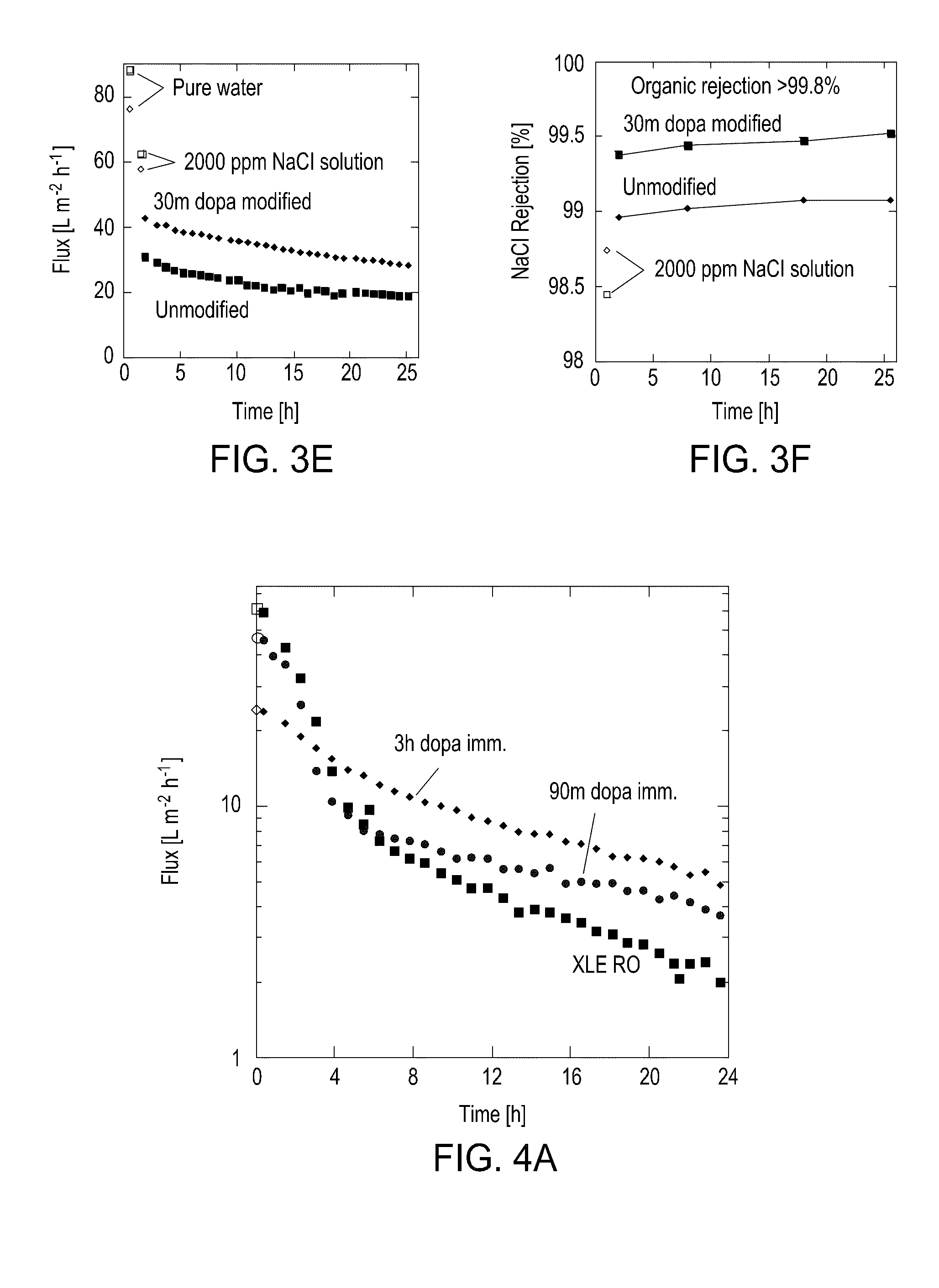
The present invention includes methods and compositions for liquid separation and water purification. The present invention includes a purification membrane having a polymer matrix purification membrane that has been treated with dopamine to form a polydopamine coated membrane with a high water flux and a high hydrophilicity.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Anti-Fouling Coating Compositions and Methods For Preventing the Fouling of Surfaces
ActiveUS20120312192A1Prevent surface foulingPrevent scalingSilicaAntifouling/underwater paintsBiological membraneLong chain
A xerogel film exhibiting antifouling properties. The films are made using long-chain alkyltrialkoxysilanes, short-chain alkyltrialkoxysilanes, aminoalkyltrialkoxysilanes, alkylaminoalkyltrialkoxysilanes, dialkylaminoalkyltrialkoxysilanes, and perfluororalkyltrialkoxysilanes as sol-gel precursors. The films can be used as coatings on surfaces to reduce or eliminate fouling resulting from attachment and / or growth of biofoulants such as algae, diatoms, bacteria, barnacles, and biofilms.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Membrane cleaning with pulsed arilift pump
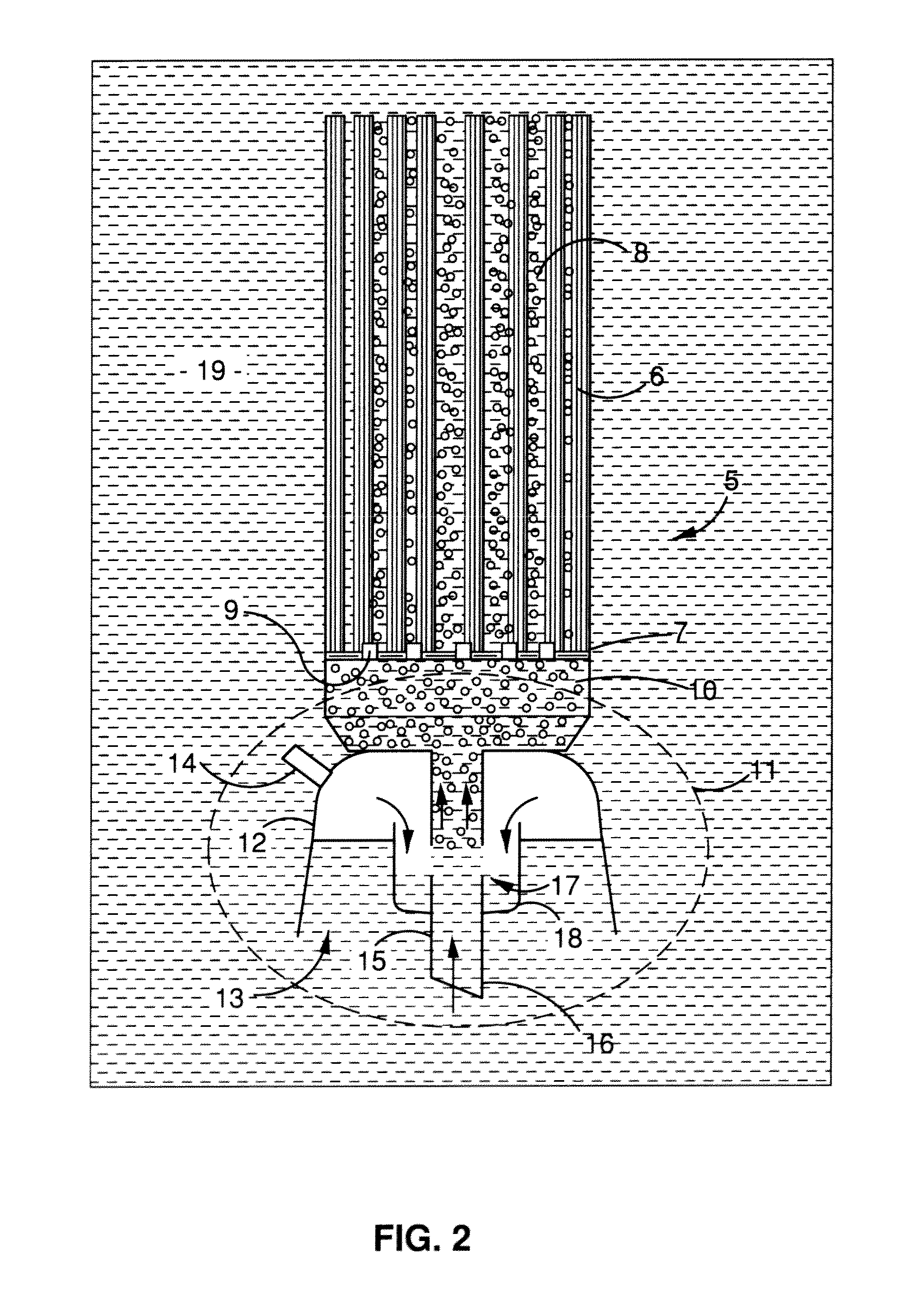
ActiveUS20110100907A1Easy to cleanReduces solid concentration polarisationMembranesTreatment using aerobic processesLiquid mediumPorous membrane
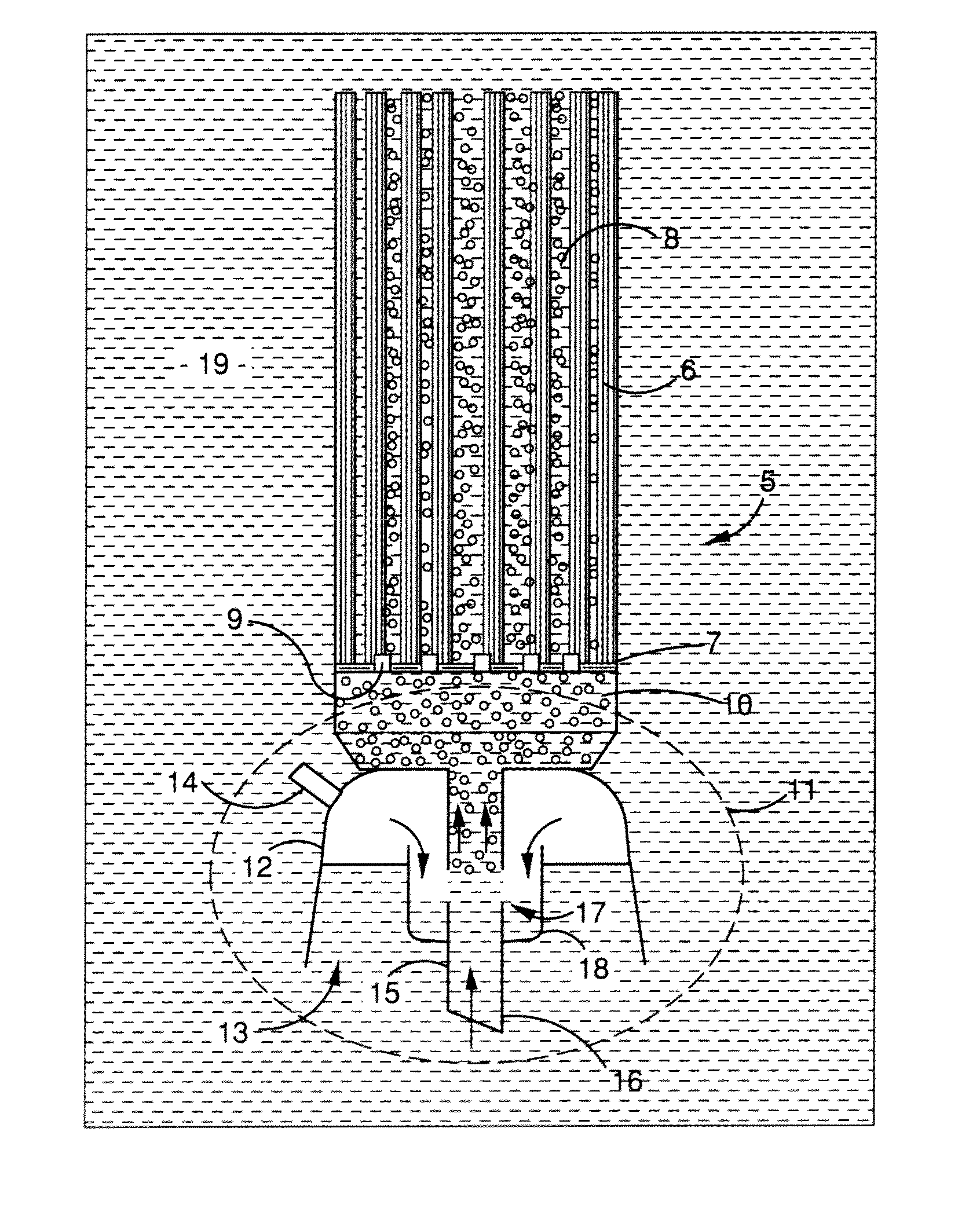
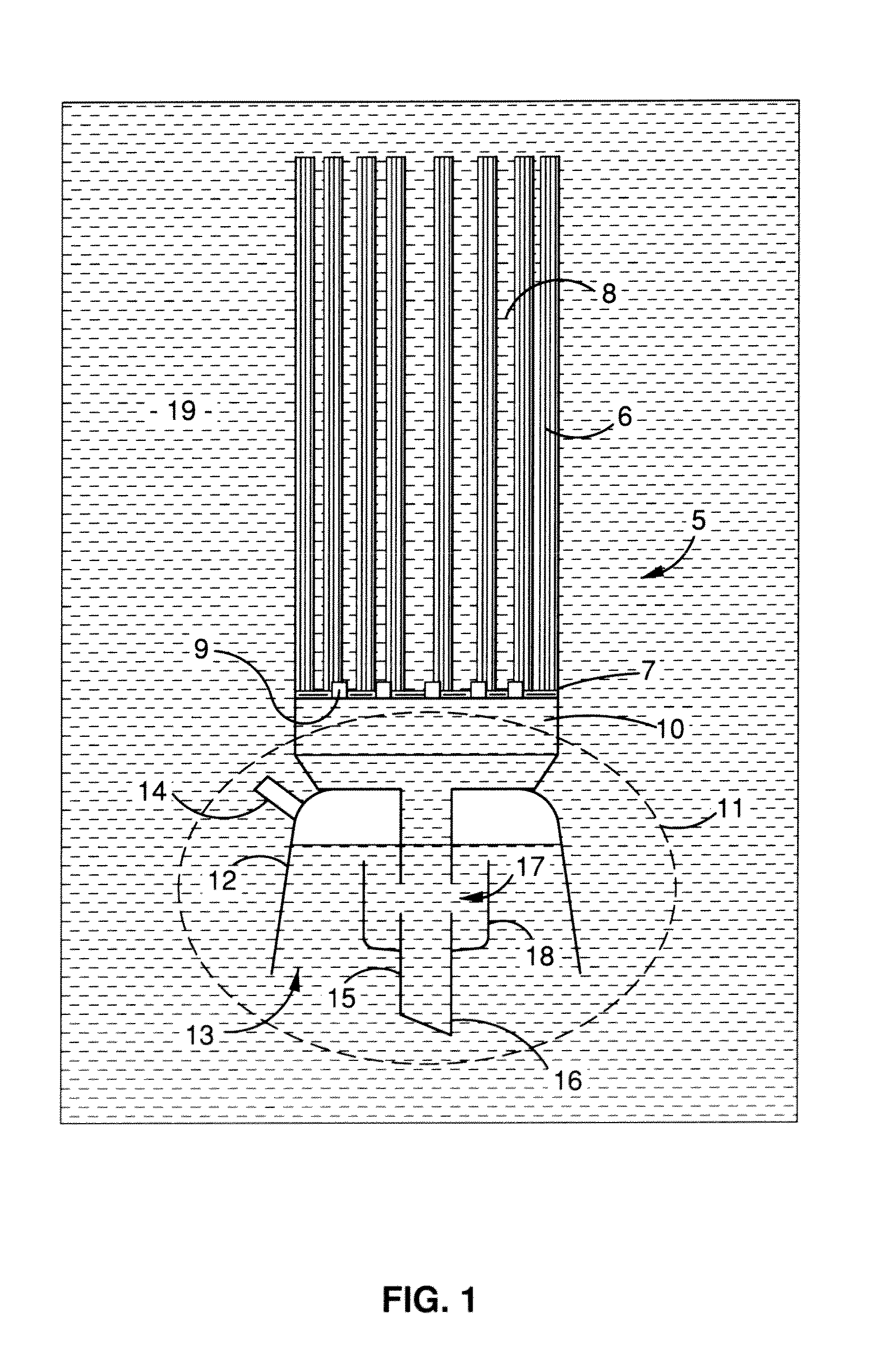
A method of cleaning a membrane surface immersed in a liquid medium with a fluid flow, including the steps of providing a randomly generated intermittent or pulsed fluid flow along the membrane surface to dislodge fouling materials therefrom. A membrane module is also disclosed comprising a plurality of porous membranes (6) or set of membrane modules (5) and a device (11) for providing a generally randomly generated, pulsed fluid flow such that, in use, said fluid flow moves past the surfaces of said membranes (6) to dislodge fouling materials therefrom.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com