Patents
Literature
5021 results about "Liquid injection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
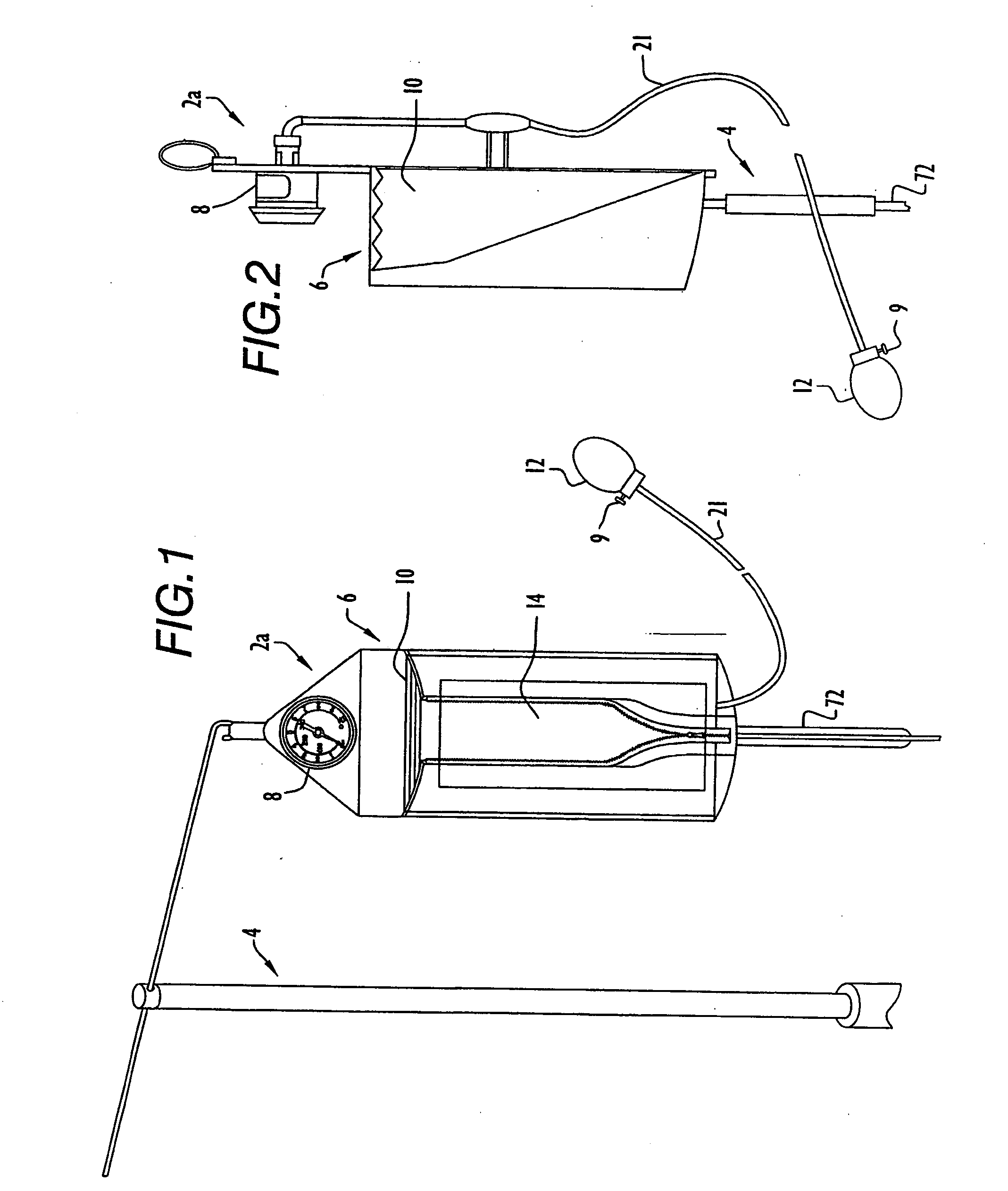
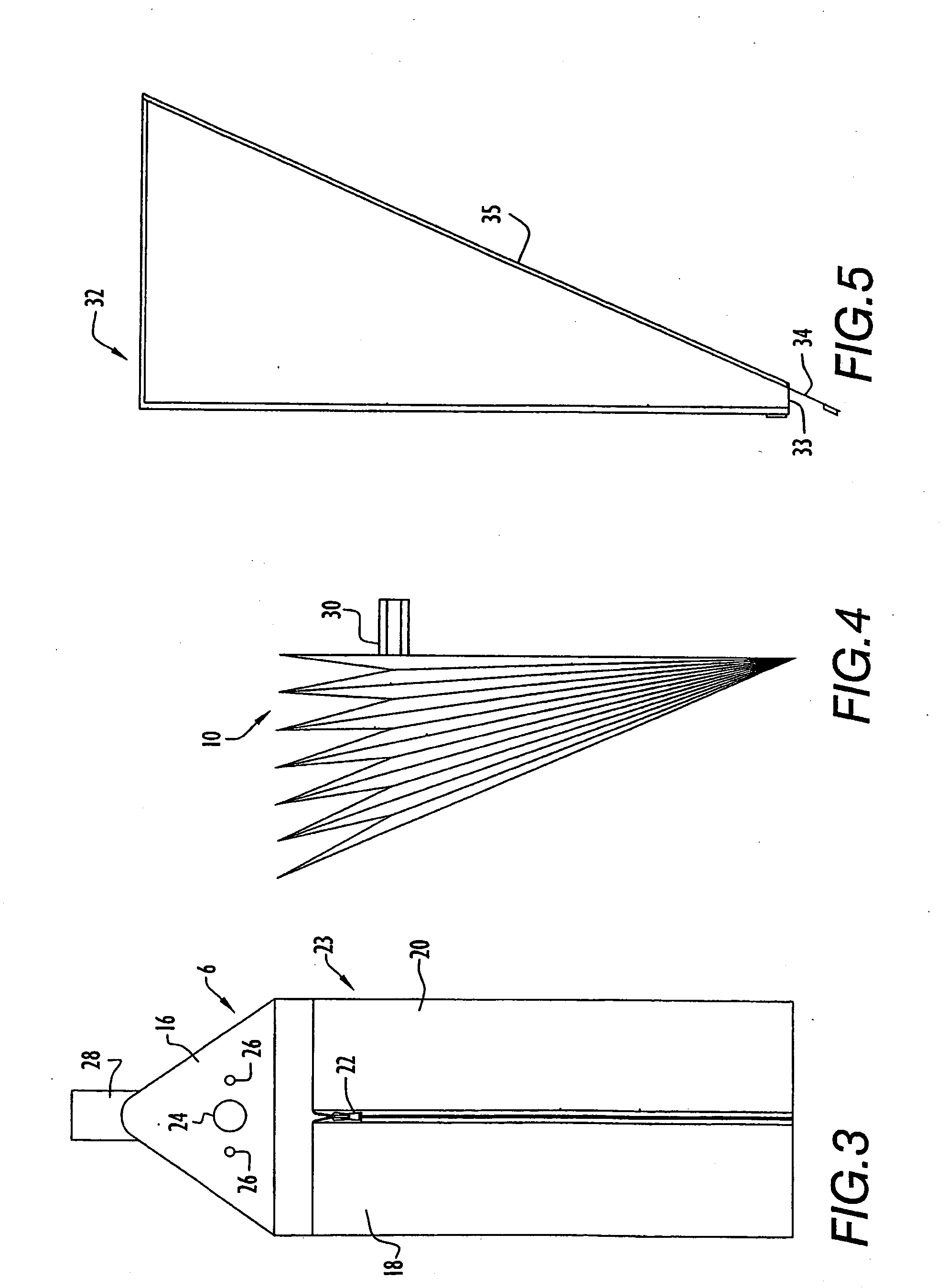
The Liquid Injection System utilizes a true liquid inject valve to inject a liquid sample into a flowing gas stream. This injection, in effect, lowers the dewpoint of the sample to where it can now be measured by the NGC. Once the sample has been delivered to the NGC it can be measured by a variety of methods.
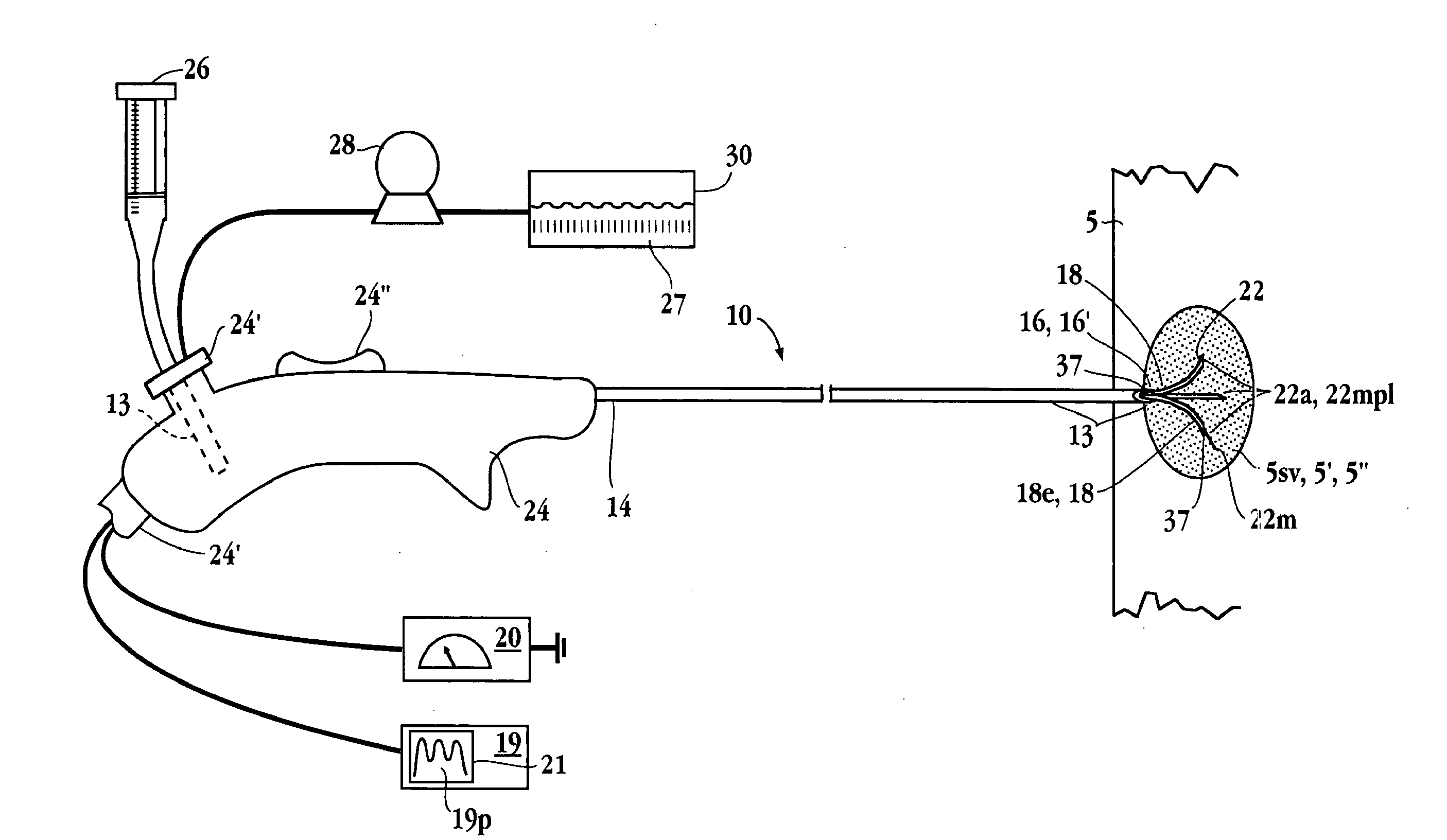
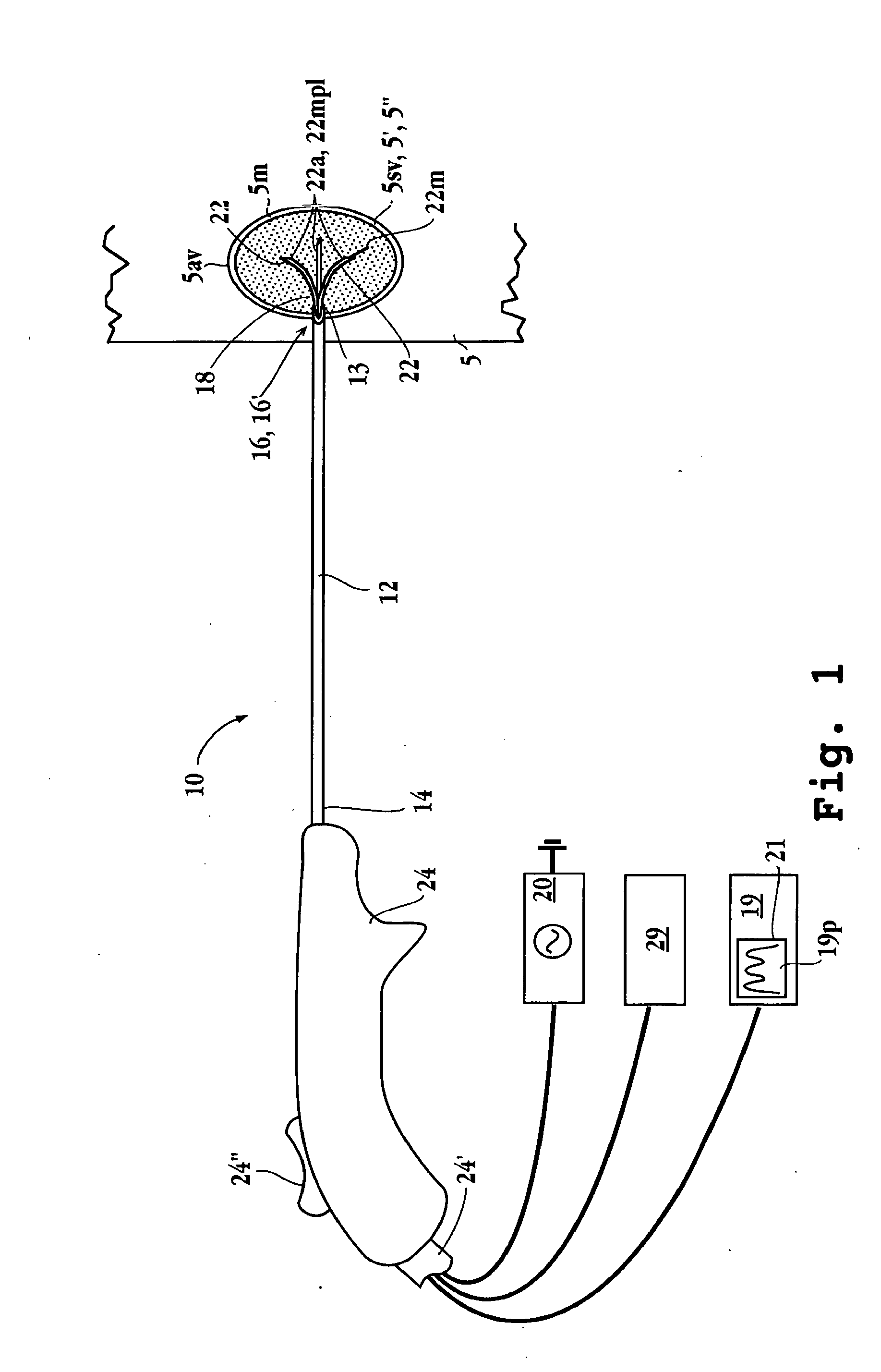
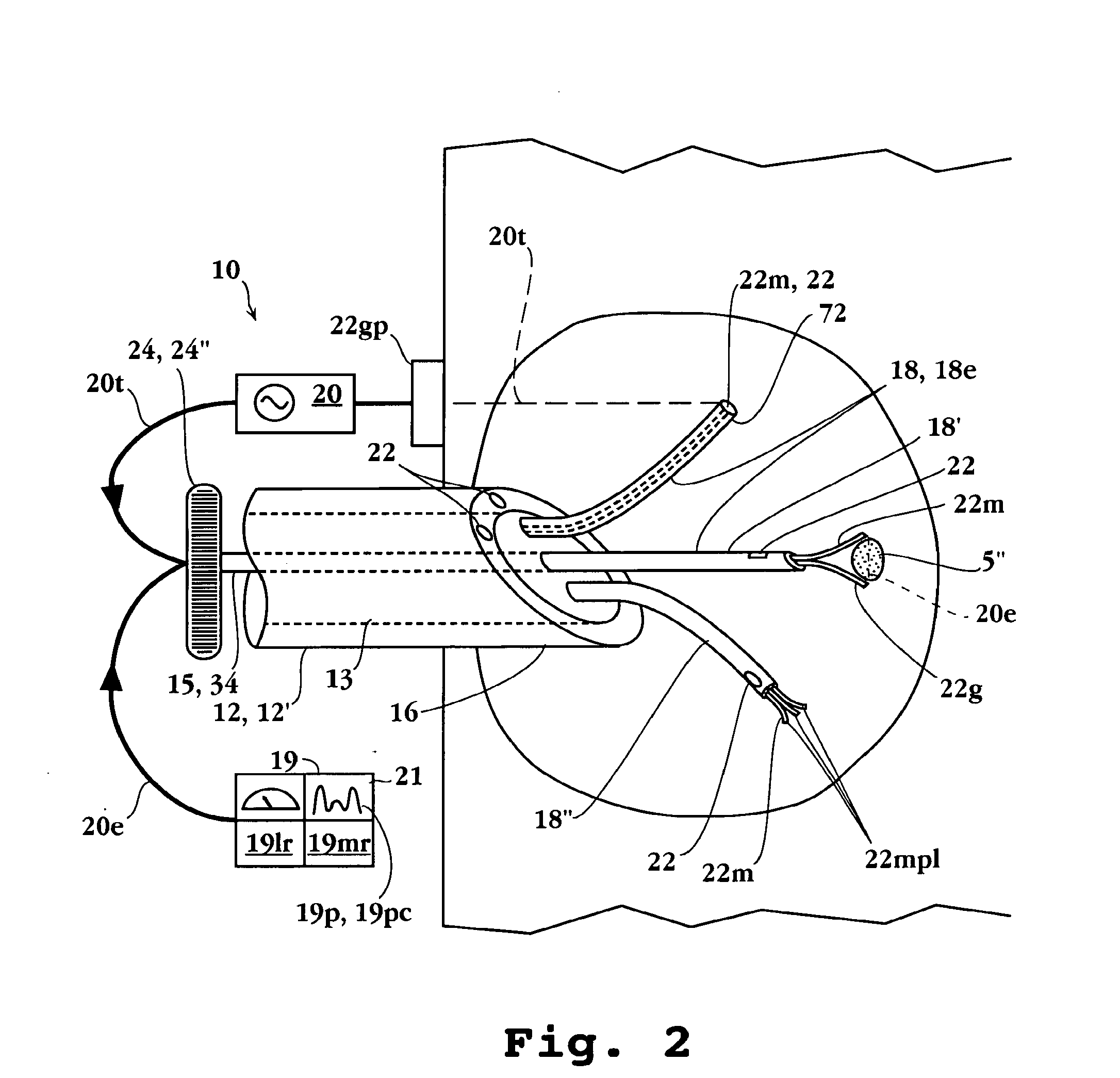
Tissue ablation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080287944A1Improve the level ofIncrease in sizeSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringRf ablationTarget tissue
A method and apparatus for carrying our thermal ablation of target tissue is disclosed. The apparatus includes an RF ablation device having a multi-electrode electrode assembly designed to be deployed in target tissue, defining a selected-volume tissue region to be ablated, and having infusion channels for infusing a liquid into the target tissue during the ablation process. A control unit in the apparatus is operably connected to an RF energy source, for controlling the RF power level supplied to the electrodes, and to an infusion device, for controlling the rate of infusion of a liquid through the device into the tissue. During both electrode deployment and tissue ablation, impedance and or temperature measurements made within the tissue are used to control the RF source and infusion device, for optimizing the time and extent of tissue ablation.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
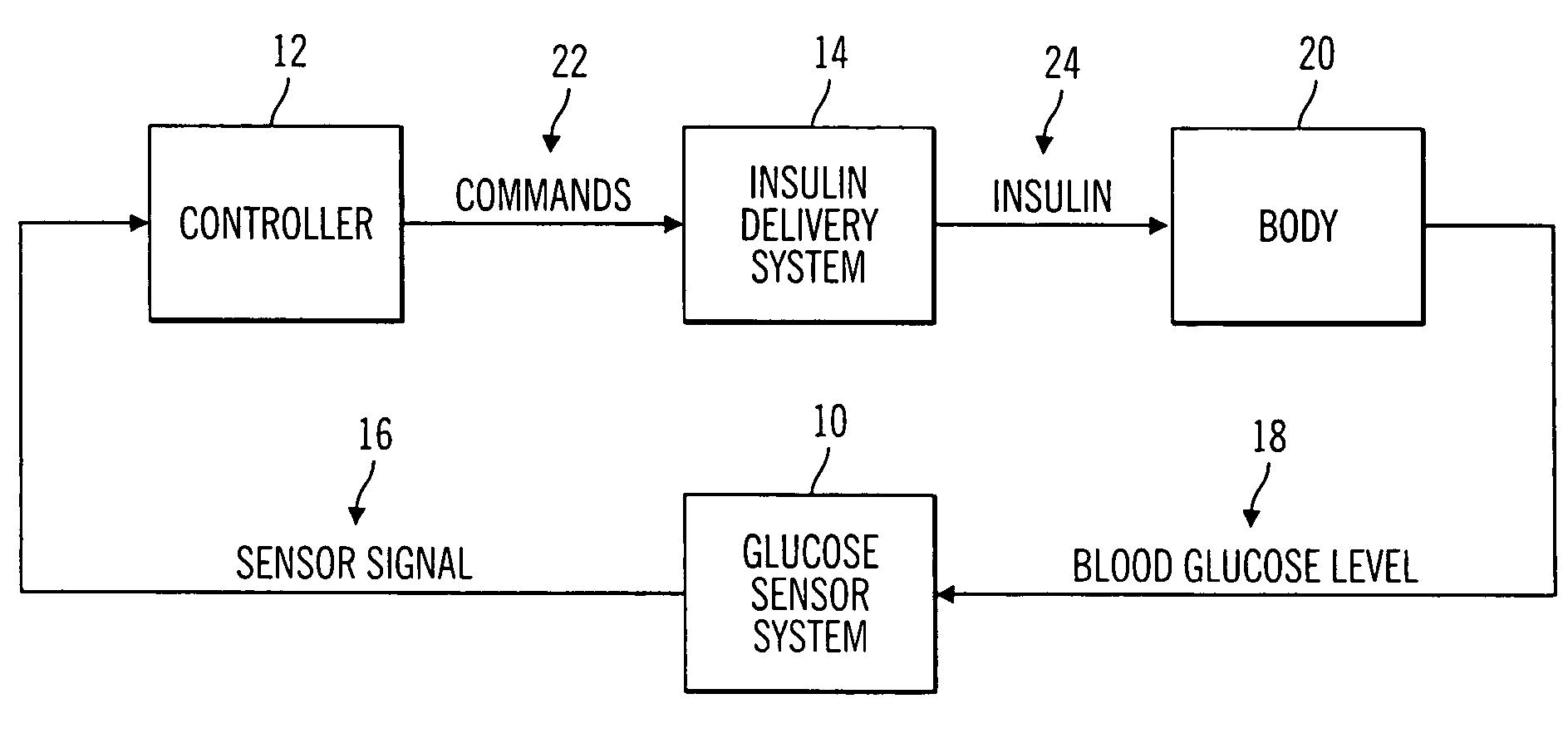
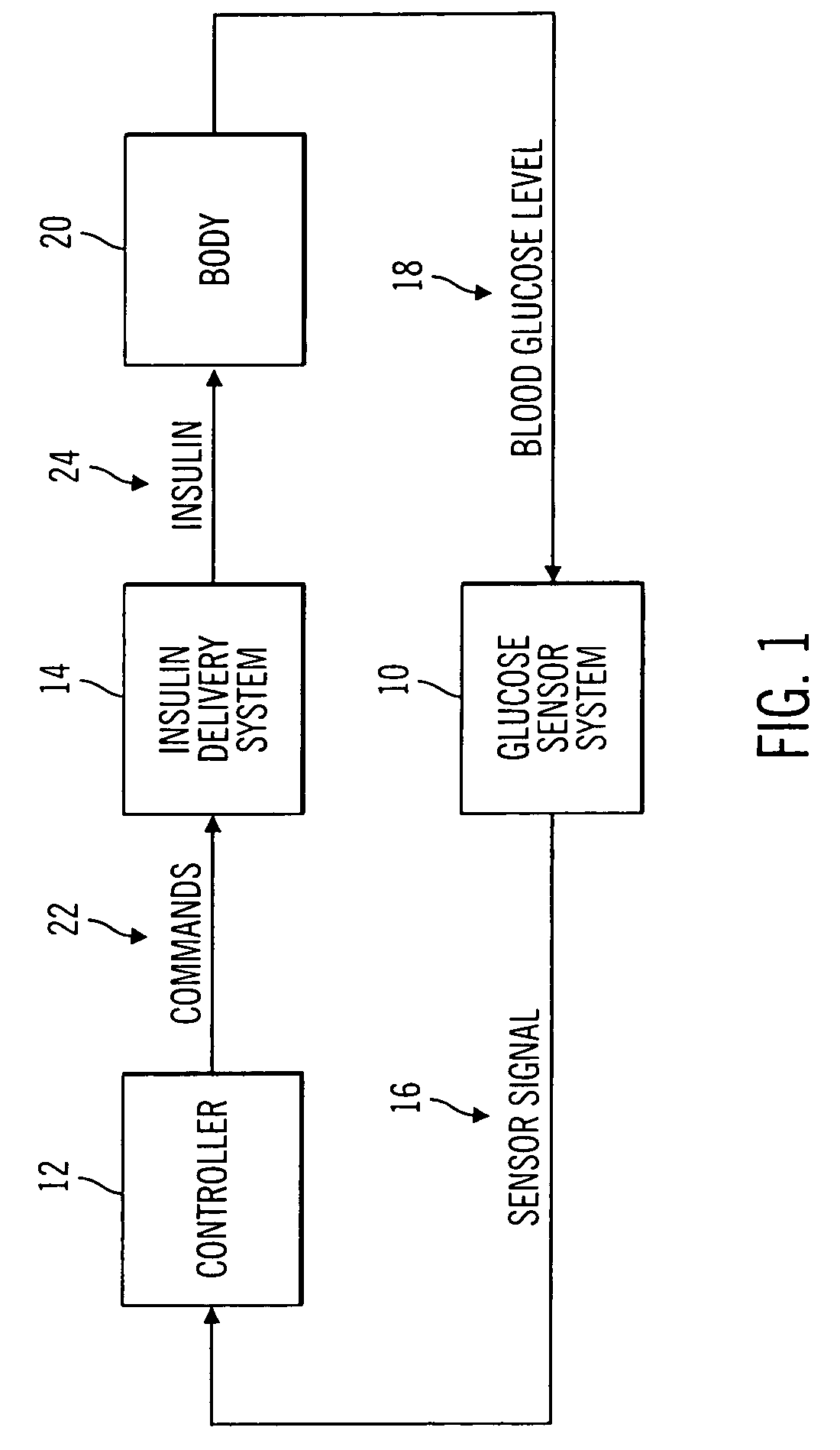
Closed-loop method for controlling insulin infusion
A closed loop infusion system controls the rate that fluid is infused into the body of a user. The closed loop infusion system includes a sensor system, a controller, and a delivery system. The sensor system includes a sensor for monitoring a condition of the user. The sensor produces a sensor signal, which is representative of the condition of the user. The sensor signal is used to generate a controller input. The controller uses the controller input to generate commands to operate the delivery system. The delivery system infuses a liquid into the user at a rate dictated by the commands from the controller. Preferably, the sensor system monitors the glucose concentration in the body of the user, and the liquid infused by the delivery system into the body of the user includes insulin.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
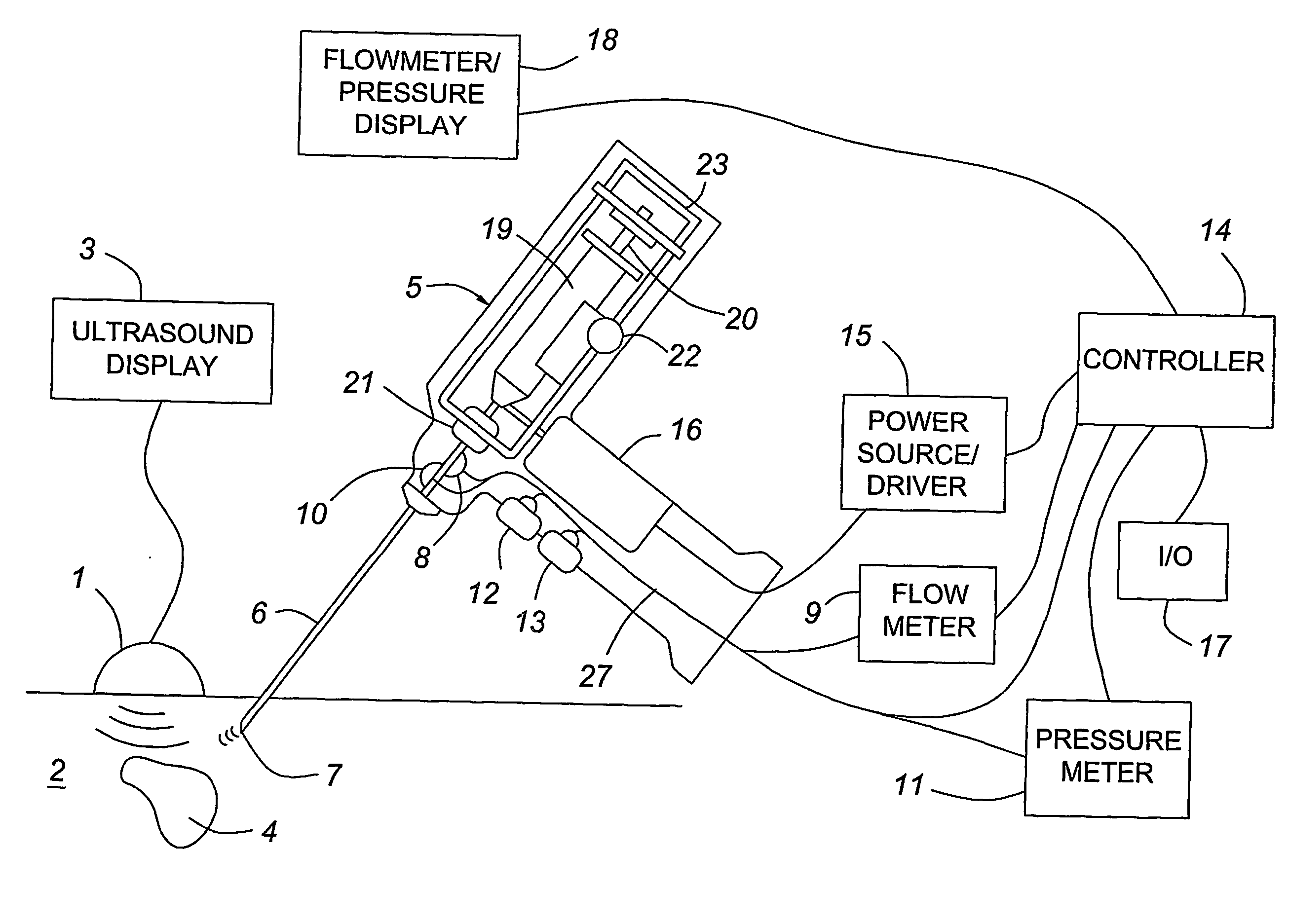
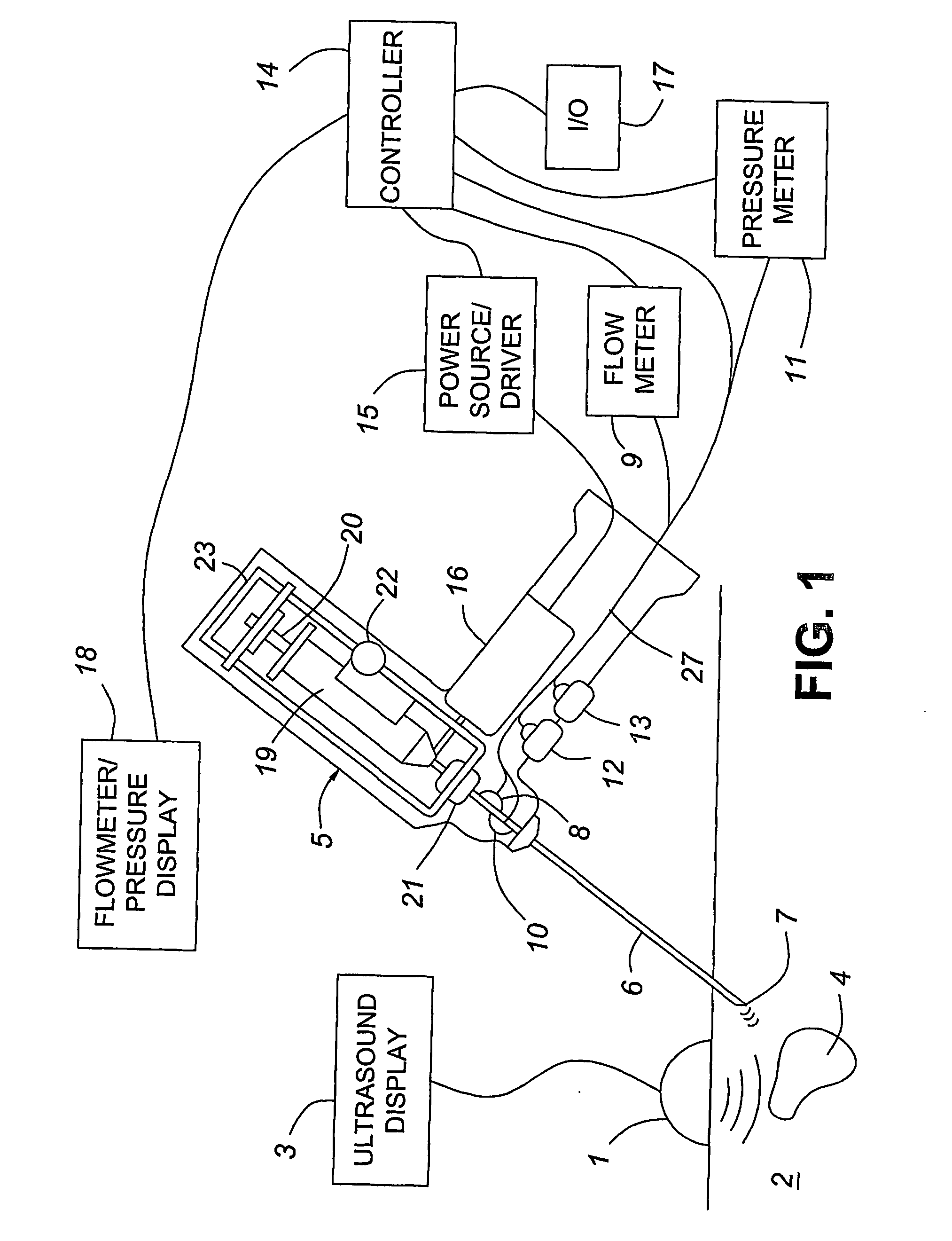
Medical devices with enhanced ultrasonic visibilty
InactiveUS20070197954A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyTip positionSolid tissue
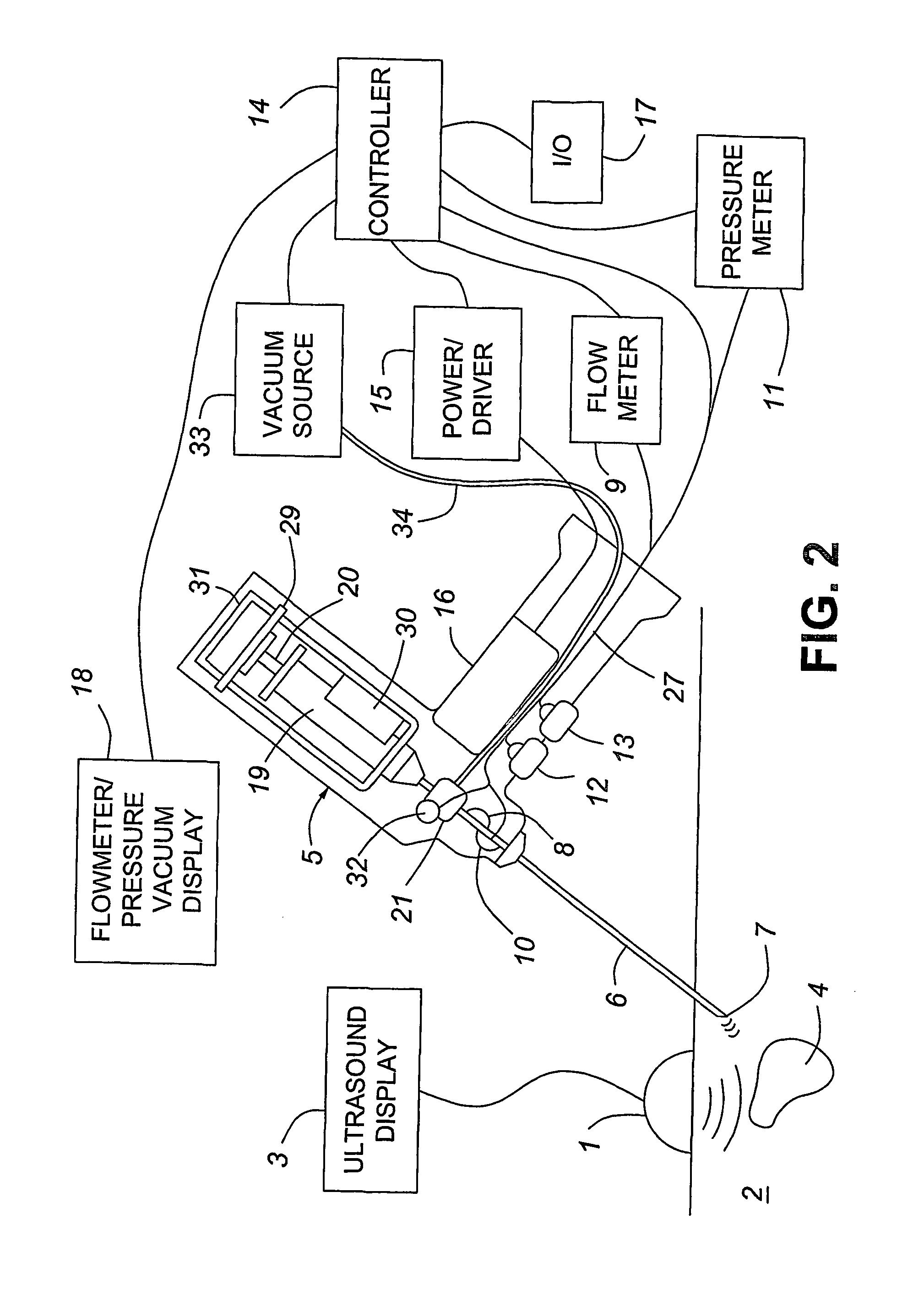
A medical device having enhanced ultrasonic visibility is provided. The device permits localized drug delivery, probe positioning, fluid drainage, biopsy, or ultrasound pulse delivery, through the real-time ultrasound monitoring of the needle tip position within a patient. The device permits controlled dispersion of a drug into solid tissue, the lodging of particles into solid tissue, and drug delivery into specific blood vessels. As a needle is inserted, a fluid that contrasts echogenically with the organ environment is injected into the patient. The fluid travels a brief distance before being slowed and stopped by the patient's tissue and this fluid flow will be detectable by ultrasound. The needle position during insertion will be monitored using ultrasound until it is at the desired point of action. A therapeutic drug is then delivered or a probe inserted
Owner:ARTENGA
Direct liquid injection system and method for forming multi-component dielectric films
InactiveUS20060110930A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom chemically reactive gasesDielectricVaporization
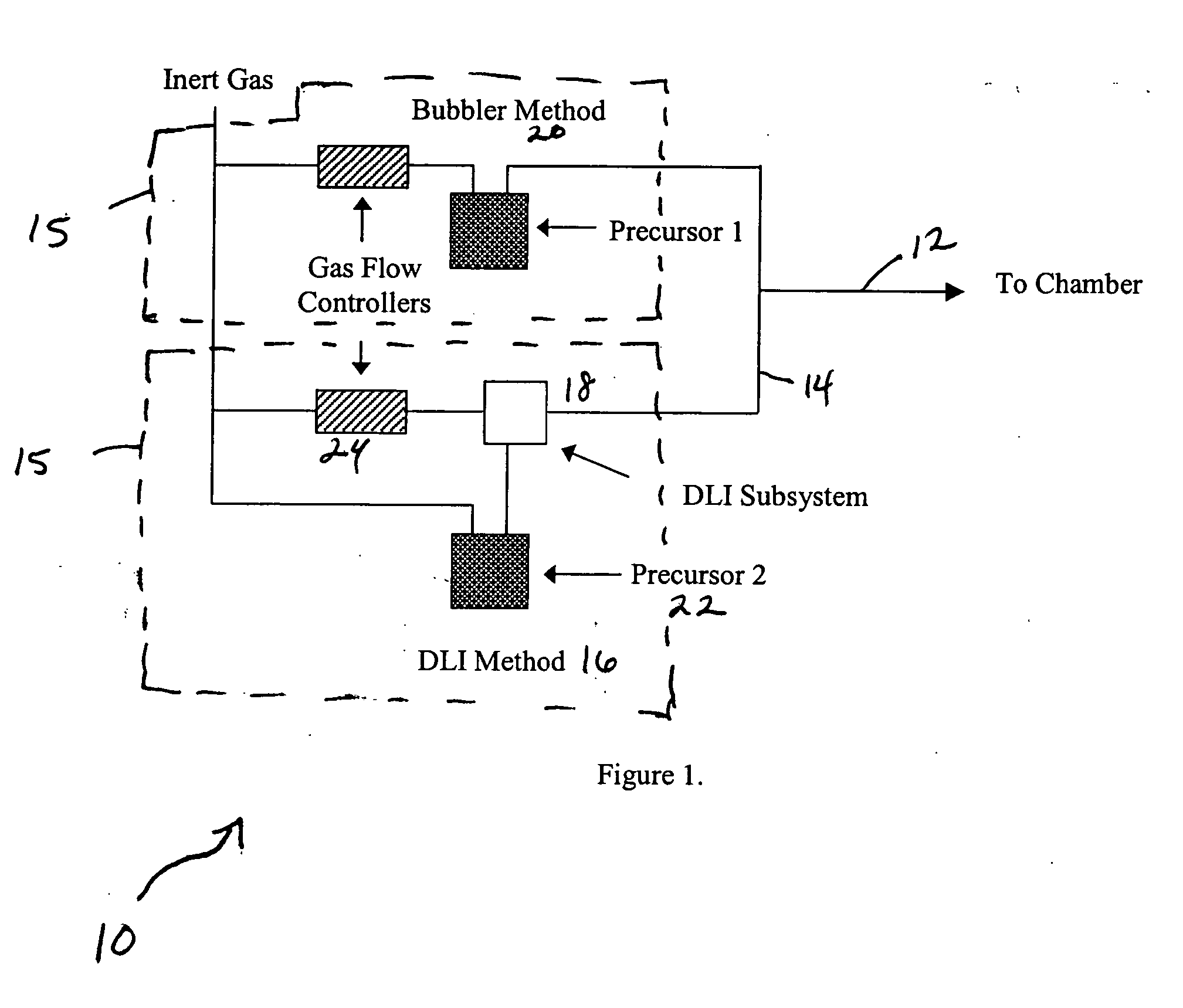
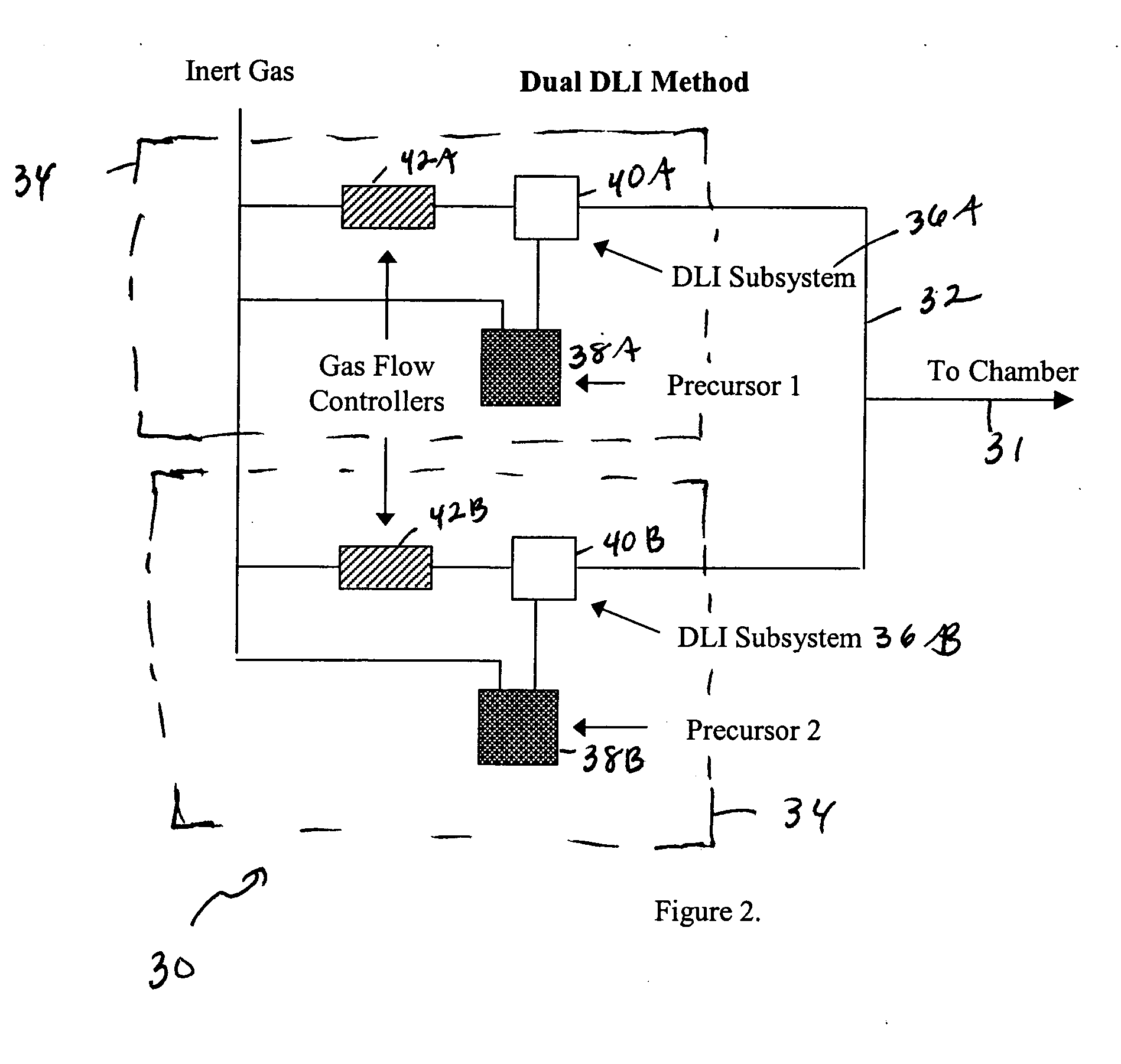
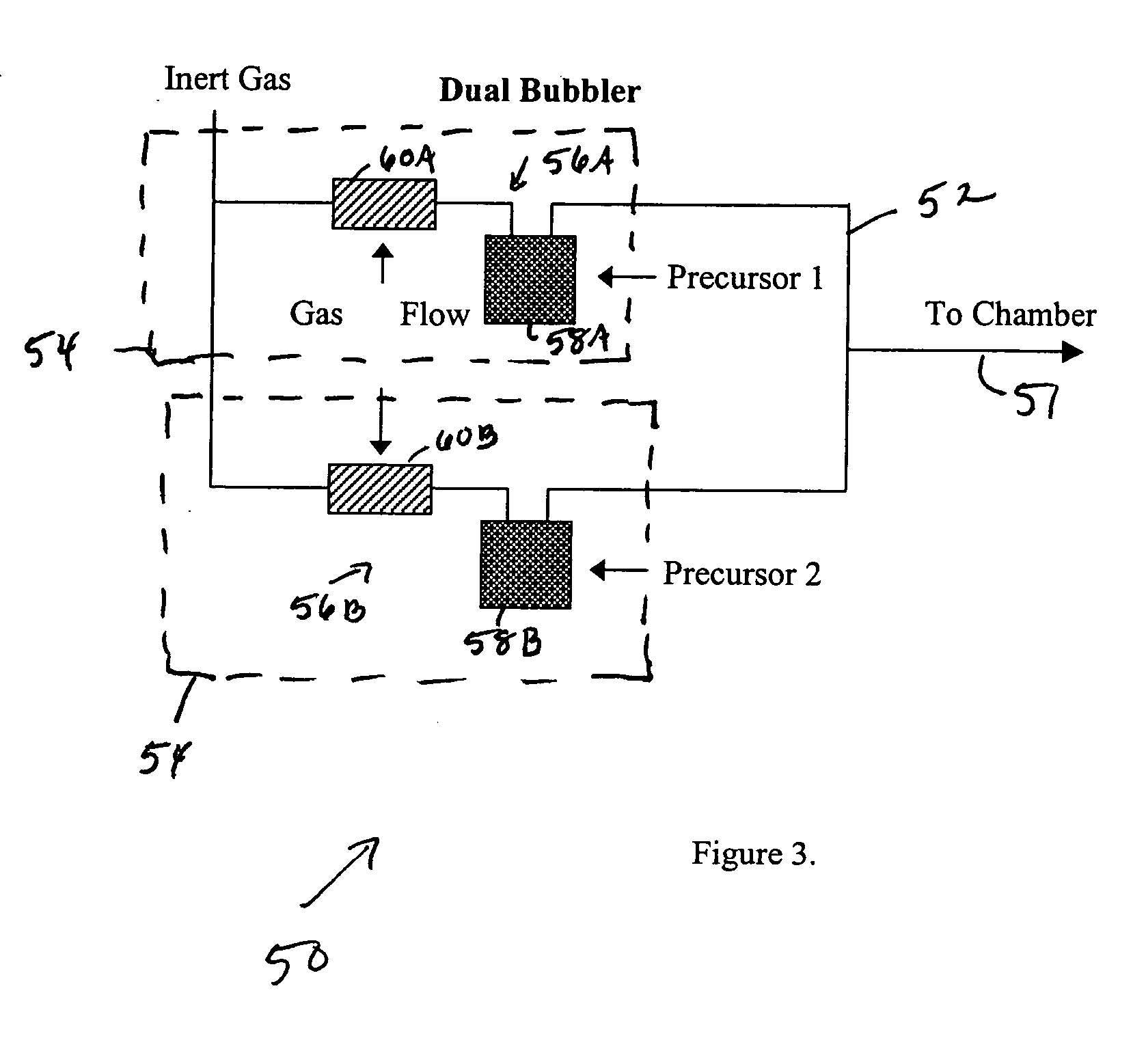
The present invention provides methods and systems for atomic layer deposition (ALD). In some embodiments a system is provided comprising: at least one direct liquid injection system configured to inject one or more deposition precursors into one or more vaporization chambers, at least one bubble system configured to vaporize one or more deposition precursors; and a process chamber coupled to said direct liquid injection system and said bubblers system, said process chamber being configured to receive the deposition precursors from said direct liquid injection and bubbler systems and being adapted to carry out an ALD process. In an alternative embodiment, the system is comprised of two separate bubbler systems. In another alternative embodiment, the system is comprised of two separate direct liquid injection systems.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC
Volatile dihydropyrazinly and dihydropyrazine metal complexes
ActiveUS20150030782A1Improve responseHighly effectiveGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsVacuum evaporation coatingProtonationRuthenium
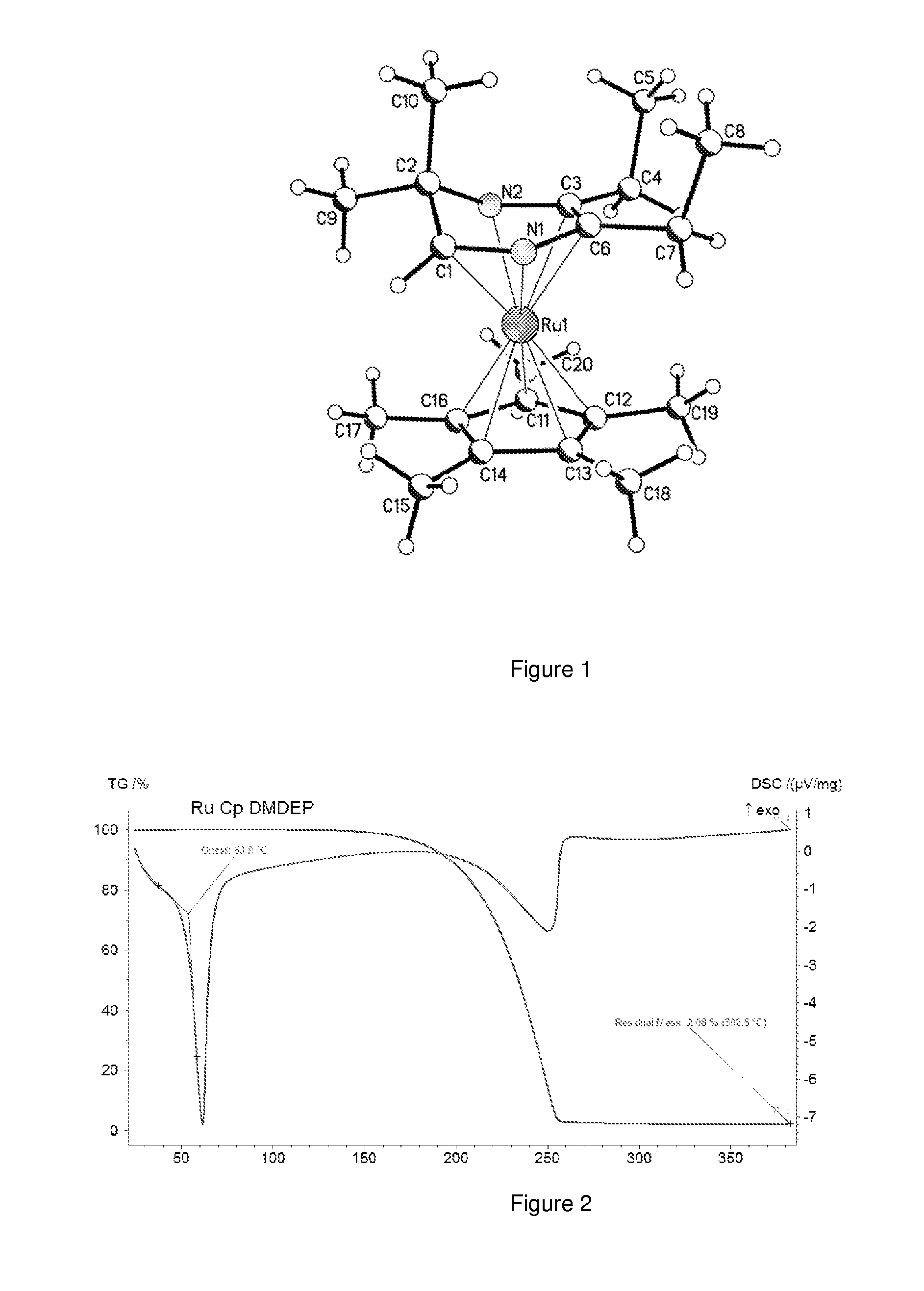
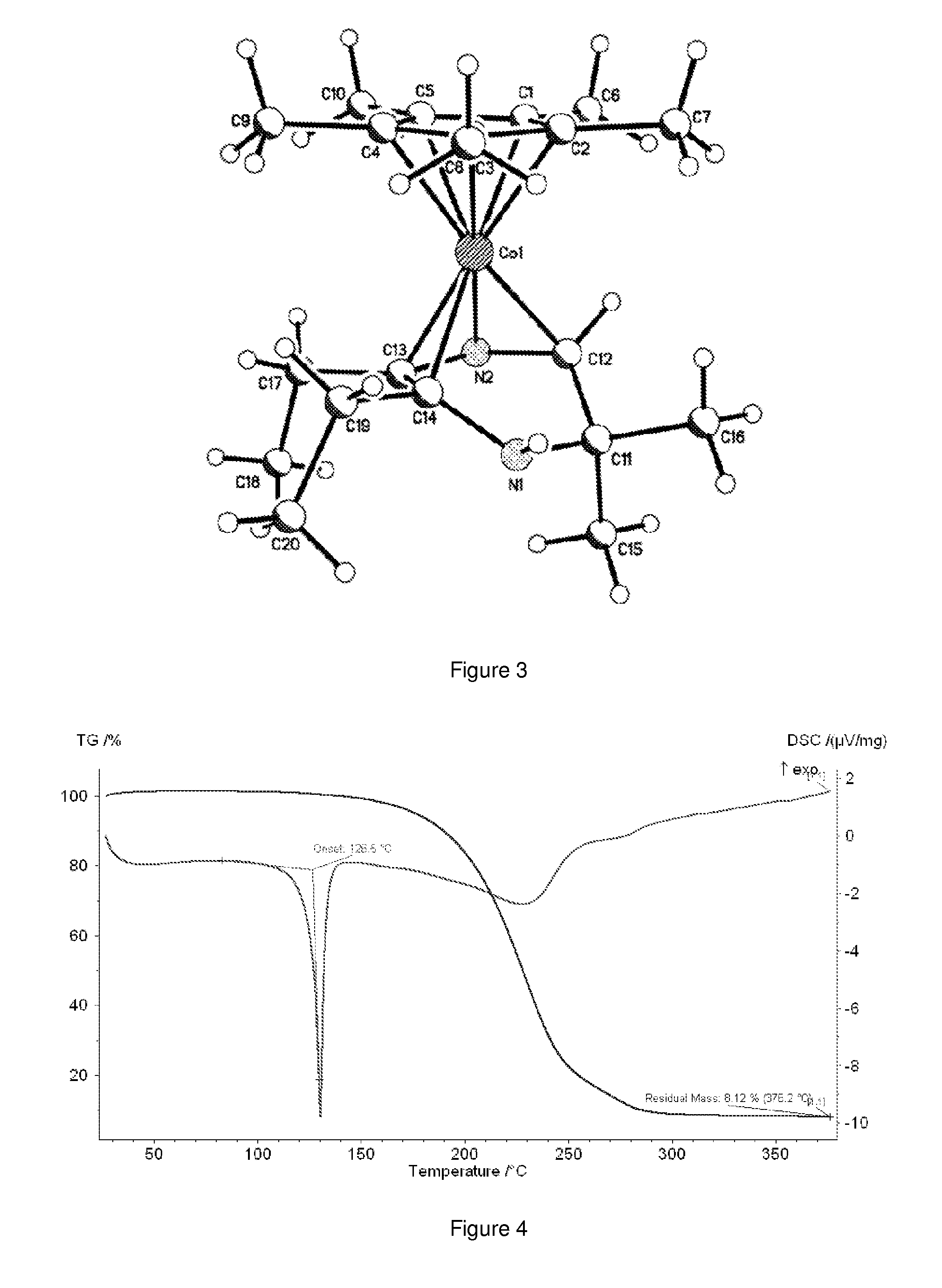
A composition comprising dihydropyrazinyl anions that can be coordinated as 6 electron ligands to a broad range of different metals to yield volatile metal complexes for ALD and CVD depositions are described herein. Also described herein are undeprotonated dihydropyrazines that can coordinate to metals as stabilizing neutral ligands. In one embodiment, the composition is used for the direct liquid injection delivery of the metal dihydropyrazinyl complex precursor to the chamber of an ALD or CVD chamber for the deposition of metal-containing thin films such as, for example, ruthenium or cobalt metal films.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
System and method for augmenting power output from a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20070059159A1Wide rangeSimple hardwareHollow article cleaningGas turbine plantsMultiple modesTurbine
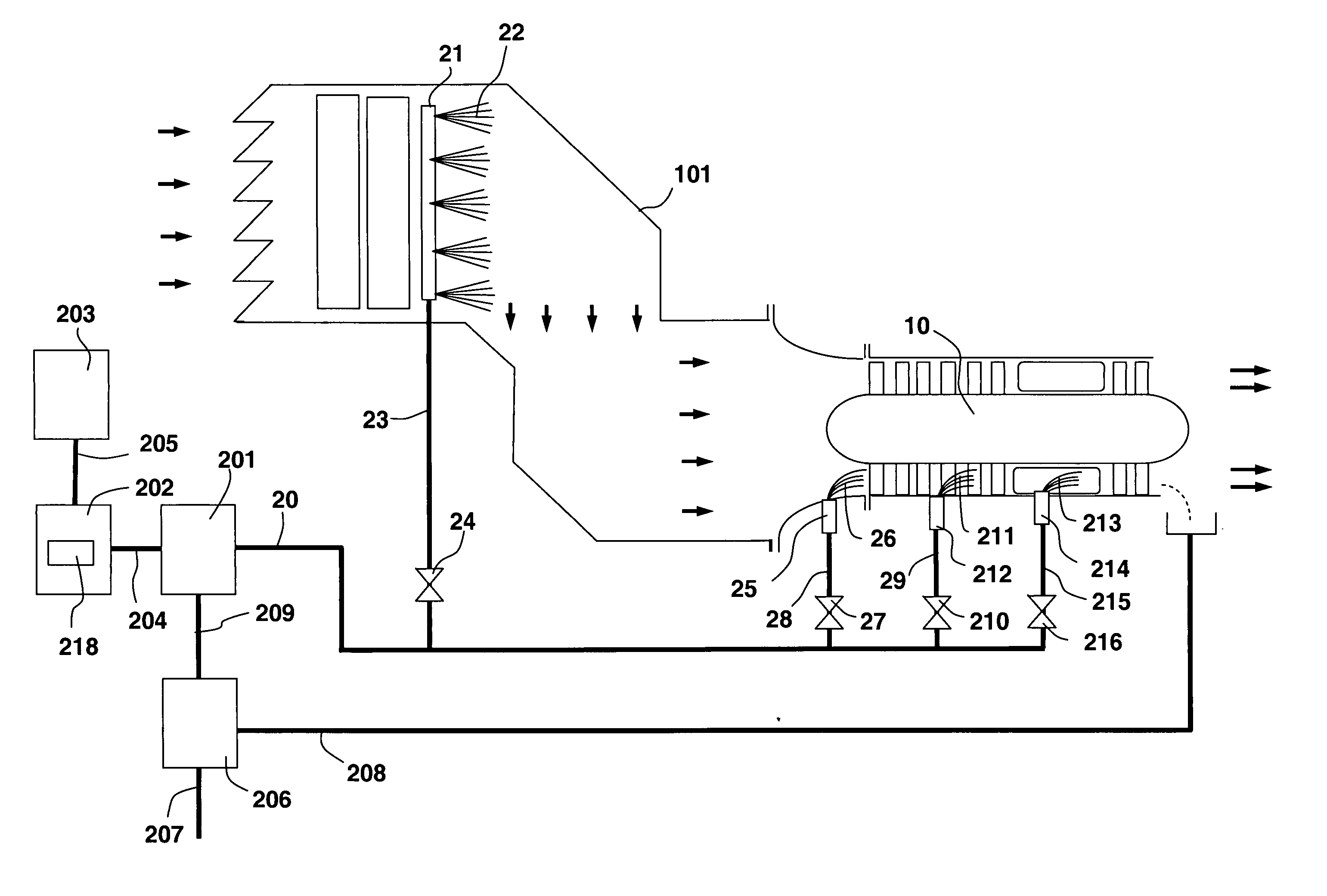
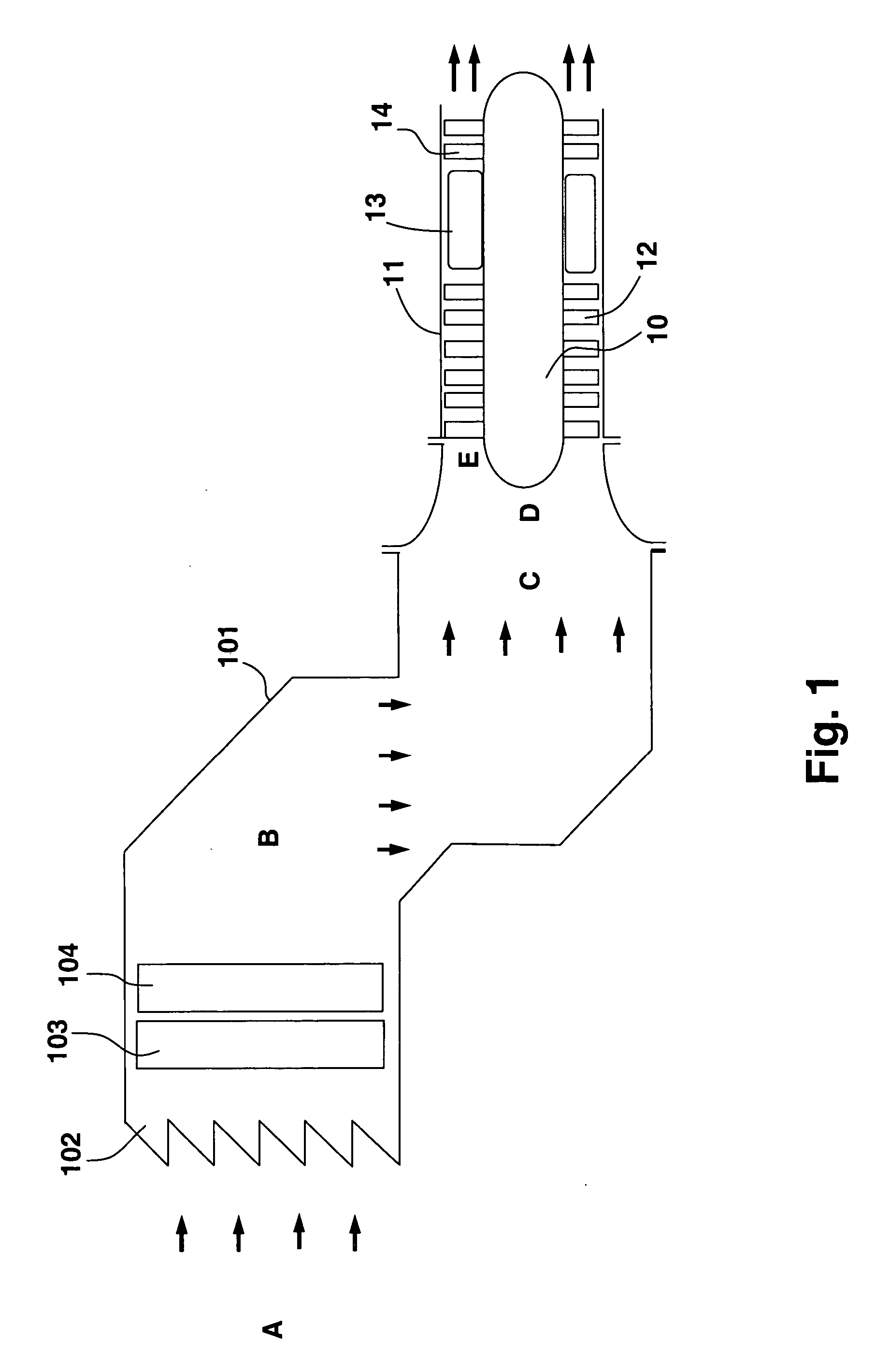
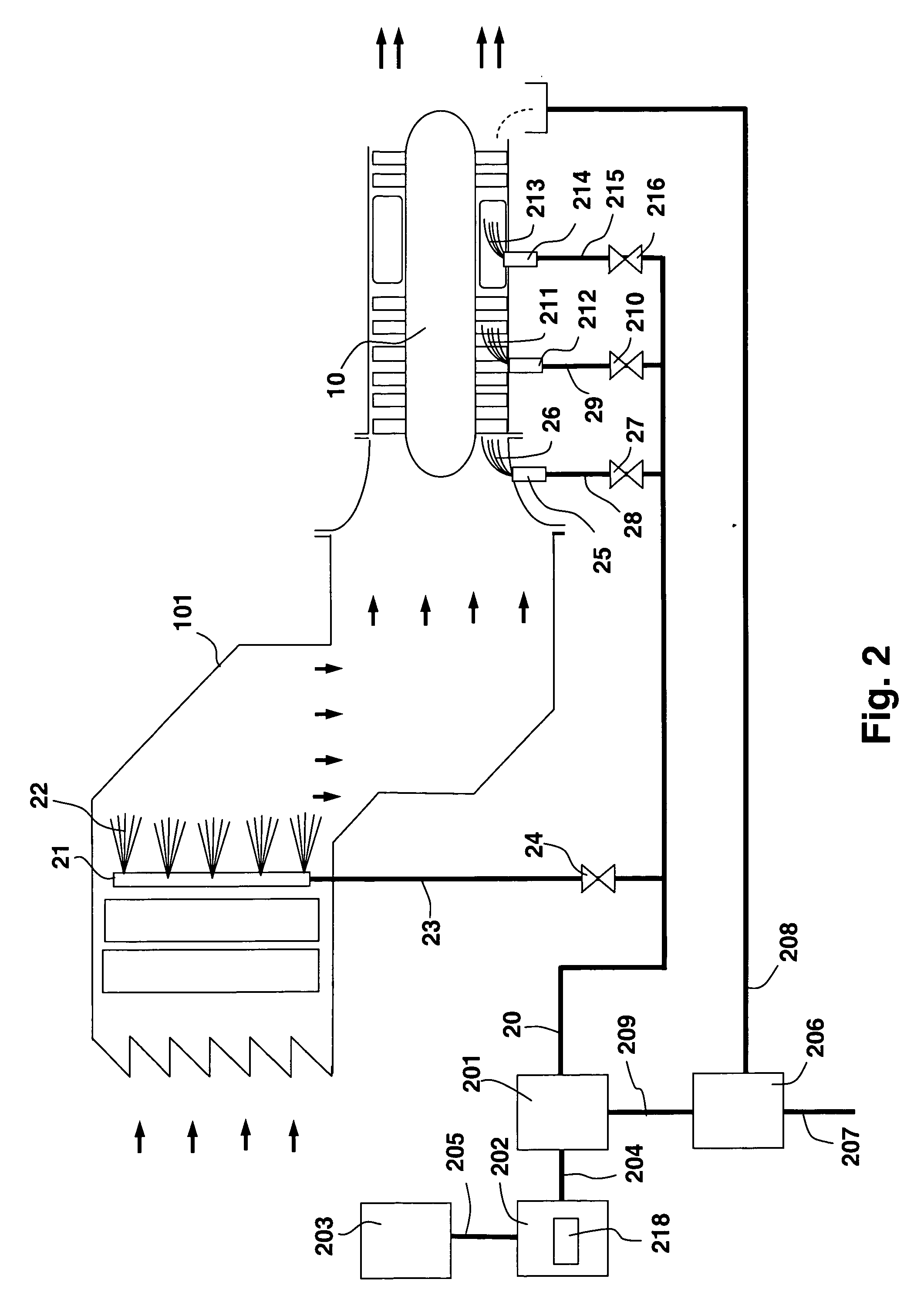
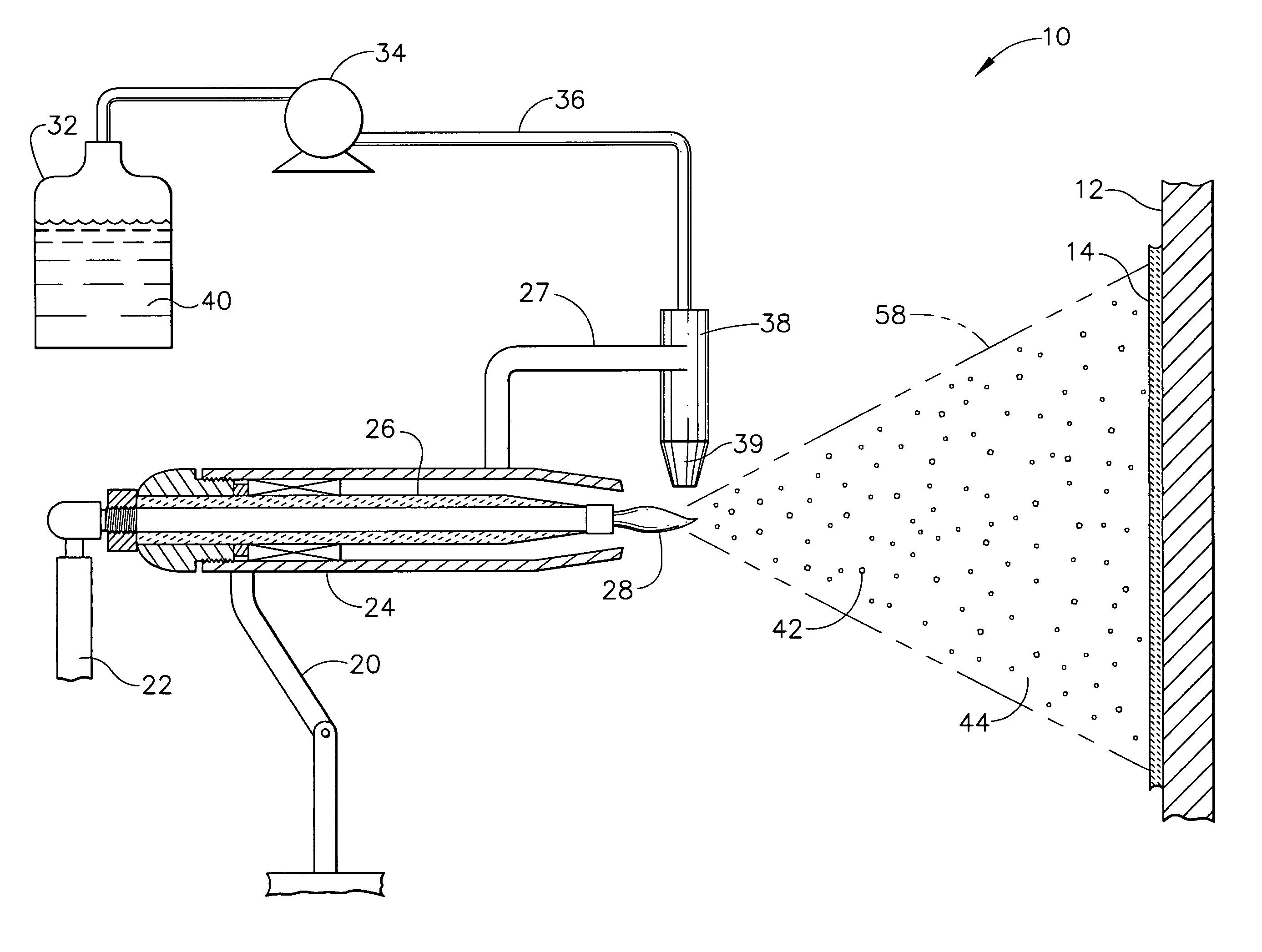
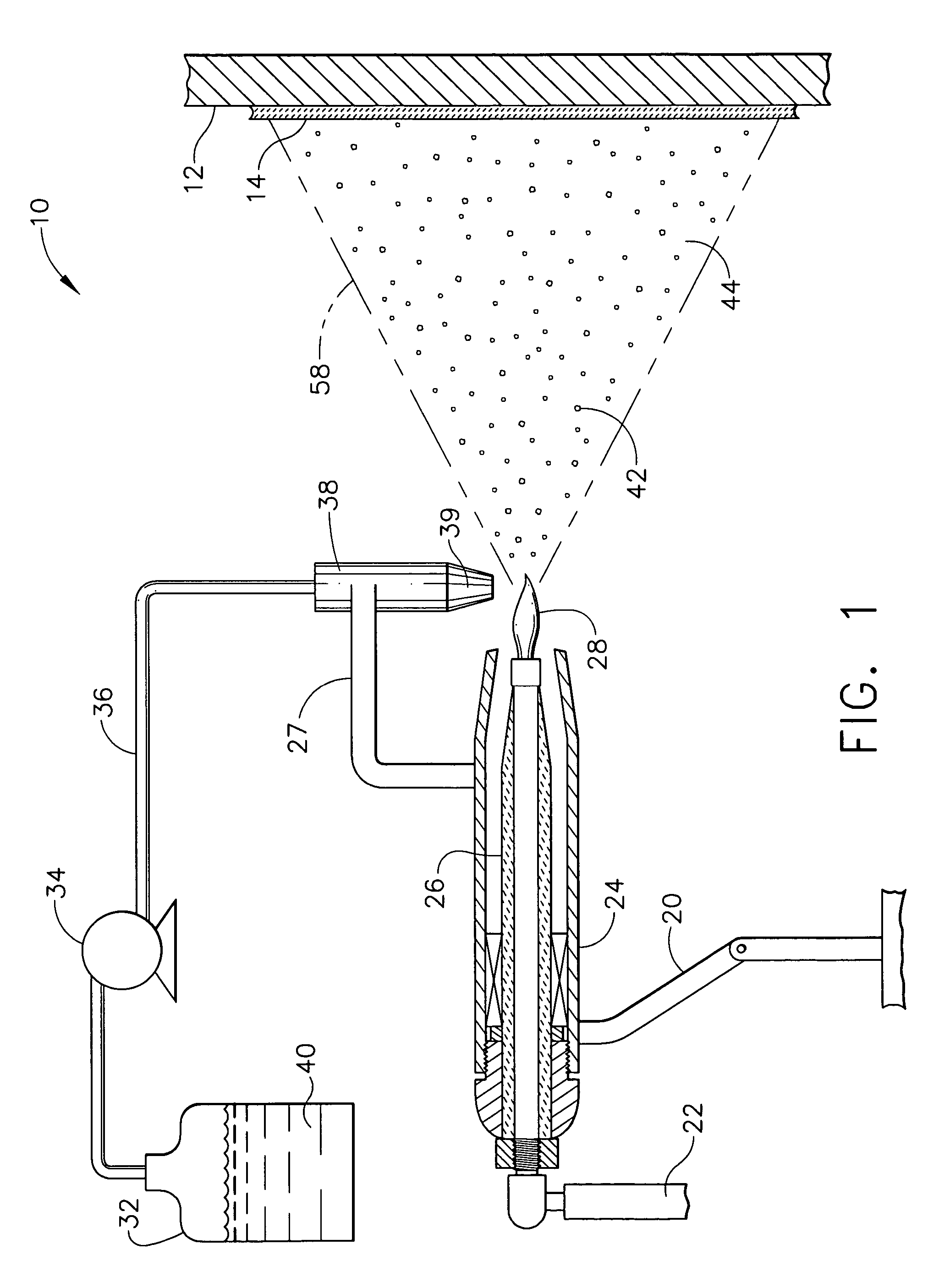
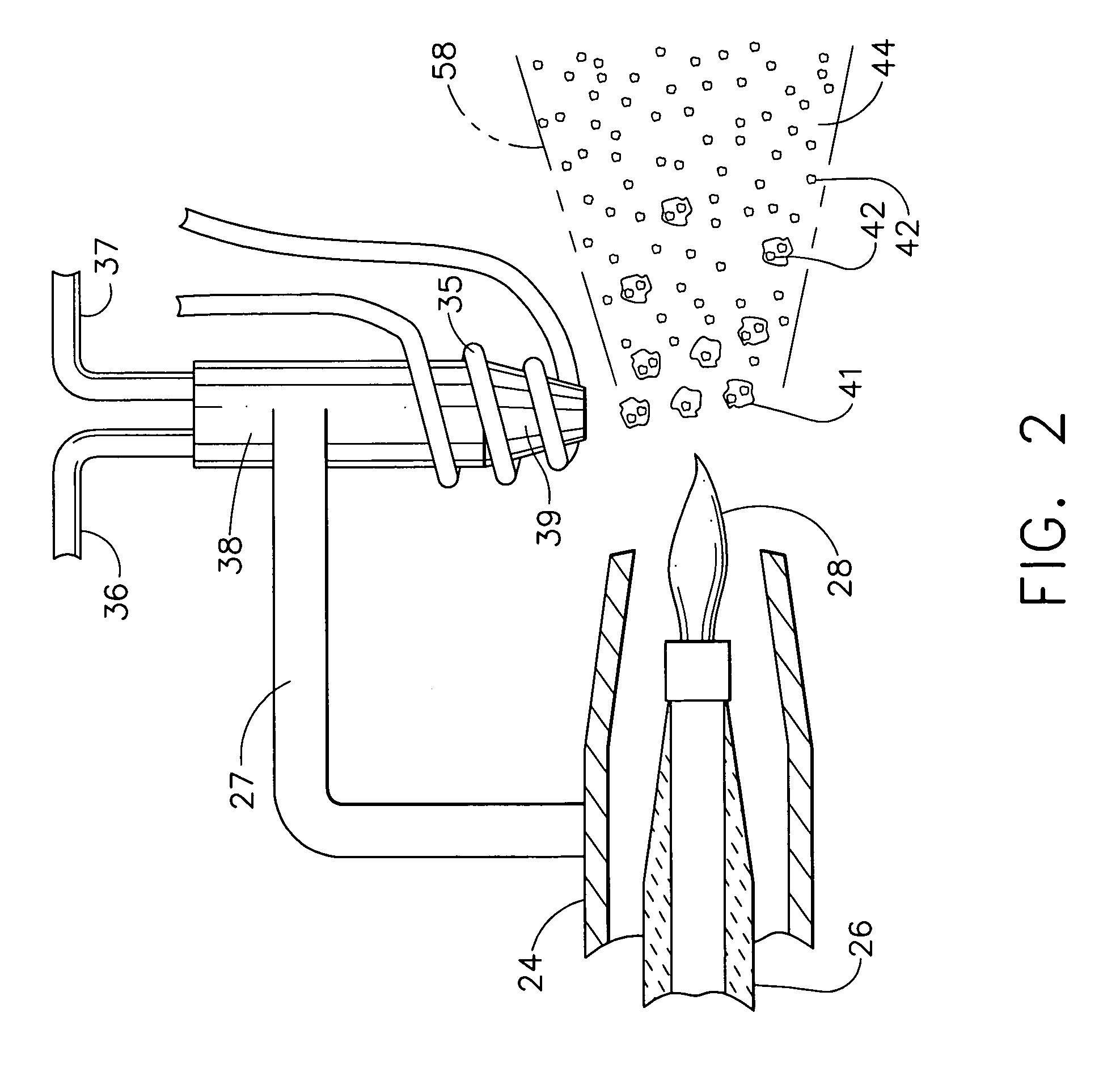
The present invention discloses a method and system for augmenting shaft output of stationary gas turbines that can be used in multiple modes of operation. The system comprises a washing unit (25, 27, 28) adapted to inject a spray (26) of atomized liquid so as to impinge on the compressor blades (12) in order to wet said blades (12), thereby obtaining a release of fouling material from said blades (12); and at least one liquid injection unit (21, 23, 24, 29, 210, 212, 214, 215, 216) adapted to inject a spray (22, 211, 213) of atomized liquid into an air stream of said turbine duct (101) or at the gas turbine (10) in order to increase a mass flow of said air flow, wherein the power output from said gas turbine engine can be augmented. With the invention follows also benefits such as fuel savings and improved environmental performance by reduction of emissions.
Owner:GTE TURBINE EFFICIENCY SWEDEN AB
Mist Generator and Mist Emission Rendering Apparatus
InactiveUS20080223953A1Improve atomization efficiencyImprove overall utilizationLighting and heating apparatusUltrasonic humidifiersHeat flowMaintainability
[OBJECTS AND PROBLEMS] Relating to a mist generator capable of emitting any of chemical substances used in life, such as perfumes, pharmaceuticals and pesticides, in the form of fog or vapor. An object of the invention is to attain means for efficiently atomizing liquid, means for easily and rapidly switching the type of chemical substance emitted and a compact apparatus of good maintainability. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] An apparatus comprises an ultrasonic transducer; an ultrasonic propagation medium disposed so as to fill a plane of vibration of the transducer; liquid retaining means disposed so as to be in contact with an end face of the medium; and an ultrasonic focusing reflecting mechanism (concave reflection mirror) disposed in an ultrasonic propagation path, thereby the apparatus attains discharging into air and atomization of the liquid by means of ultrasonic waves. Atomization efficiency is enhanced by the use of an ultrasonic reflection tube, and mist emission is carried out. Use is made of a compact liquid container equipped at its bottom with an ultrasonic transmission membrane. Various types of liquids can be atomized by changing the direction of ultrasonic course. Mist can be emitted by means of a thermal current as heating means. IC tag is attached to the liquid retaining means or liquid injection means.
Owner:TOMONO AKIRA
Wet/dry automatic injector assembly
InactiveUS6953445B2Extended shelf lifeObstruct passageAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesBiological activationBiomedical engineering
Owner:MERIDIAN MEDICAL TECH
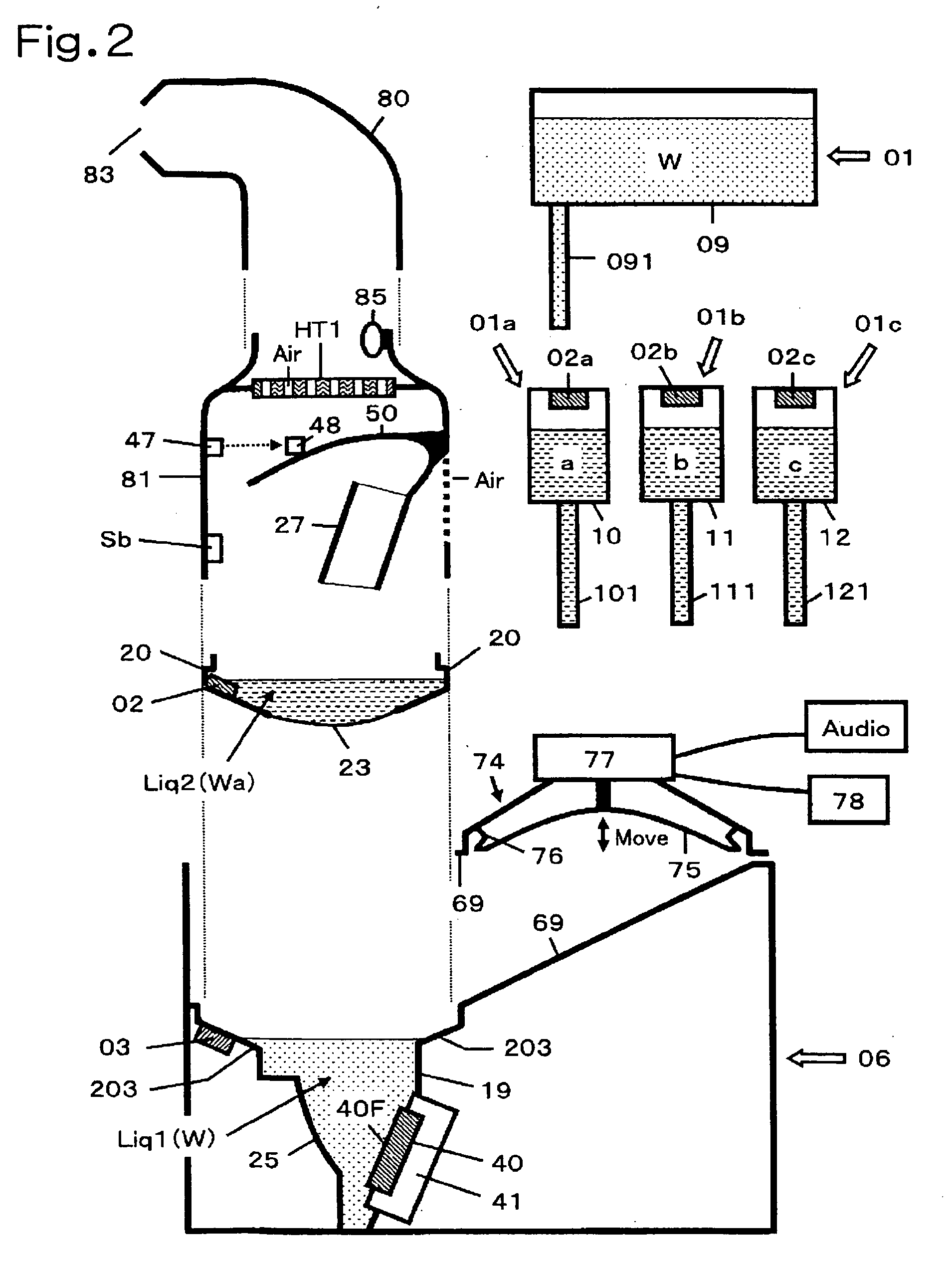
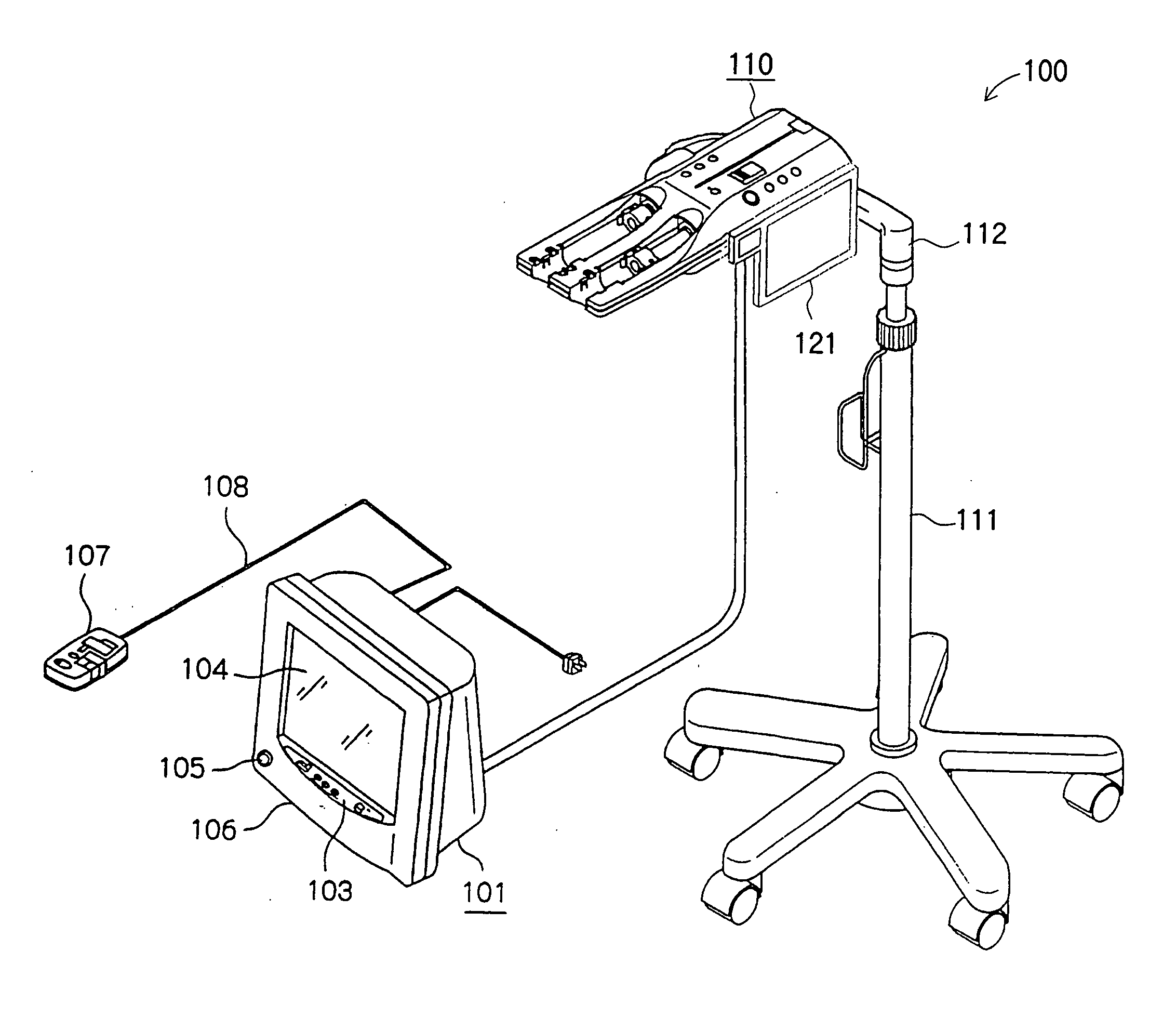
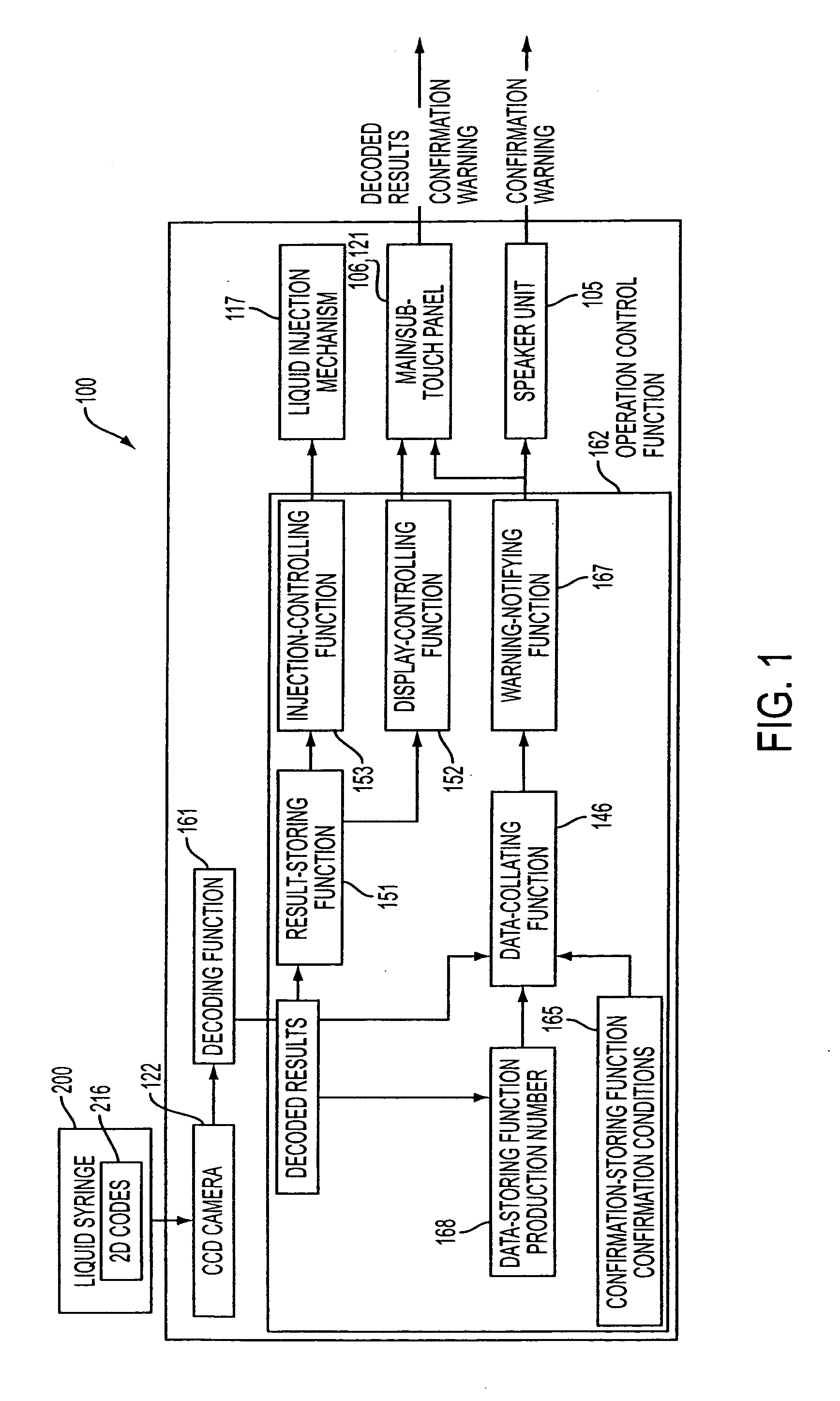
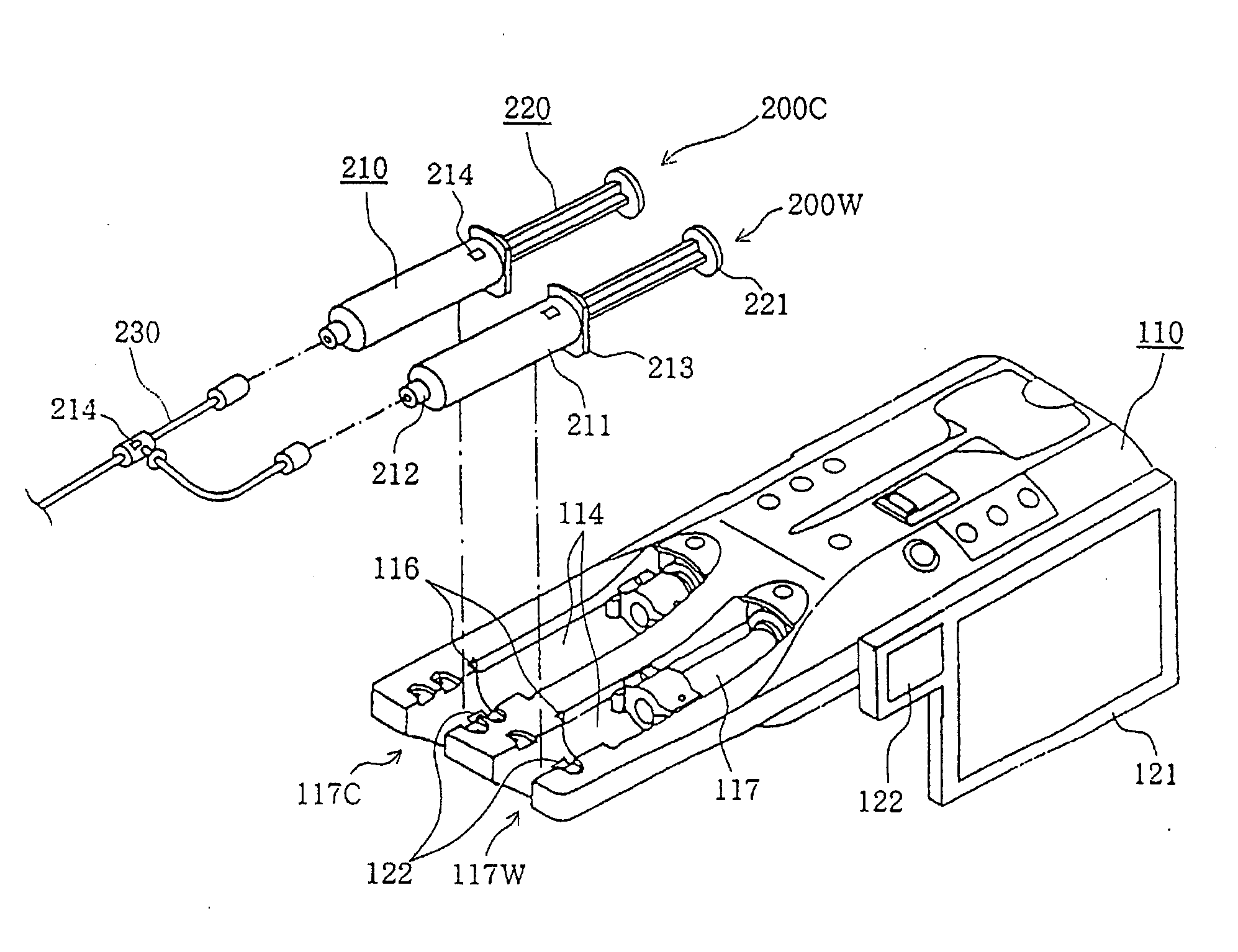
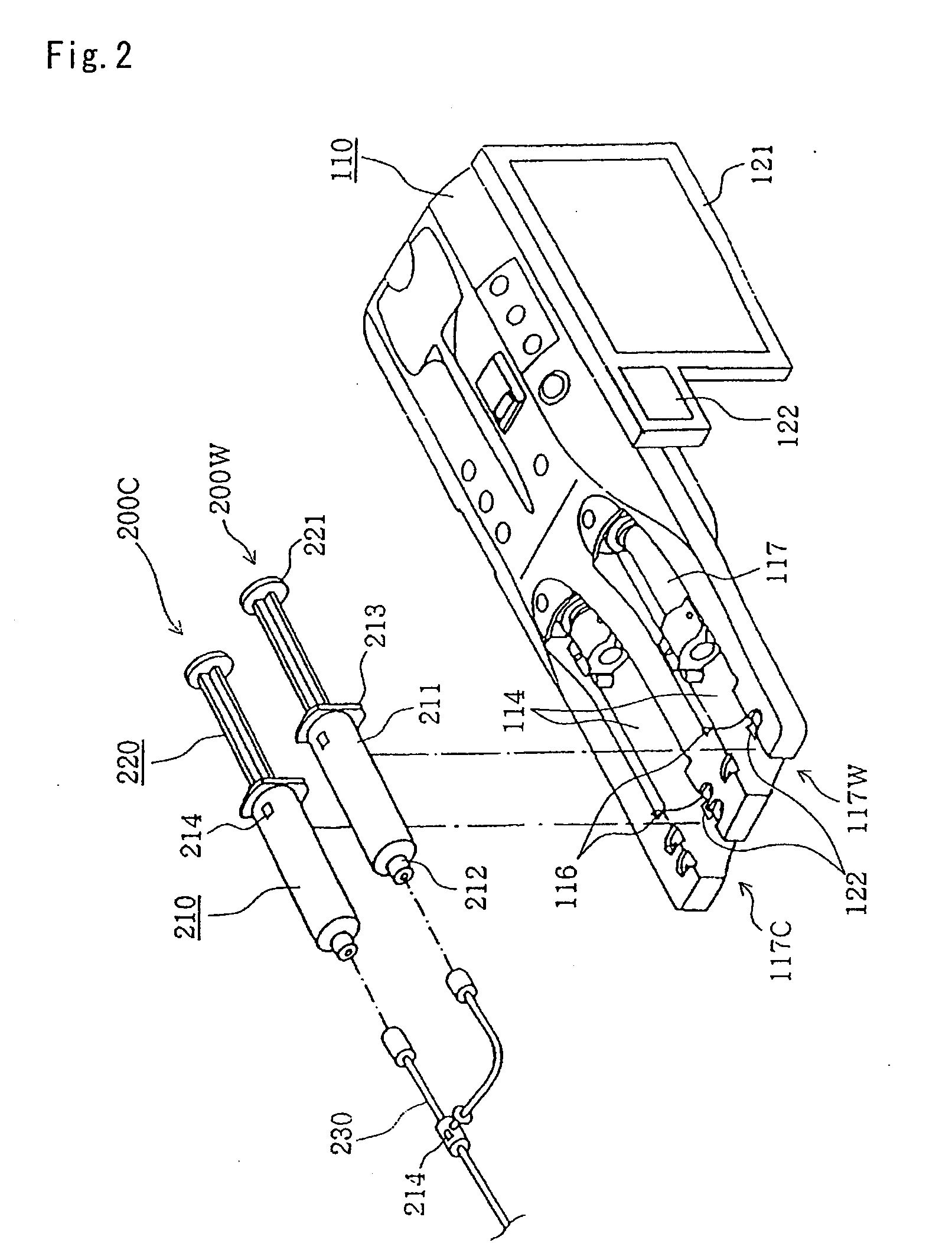
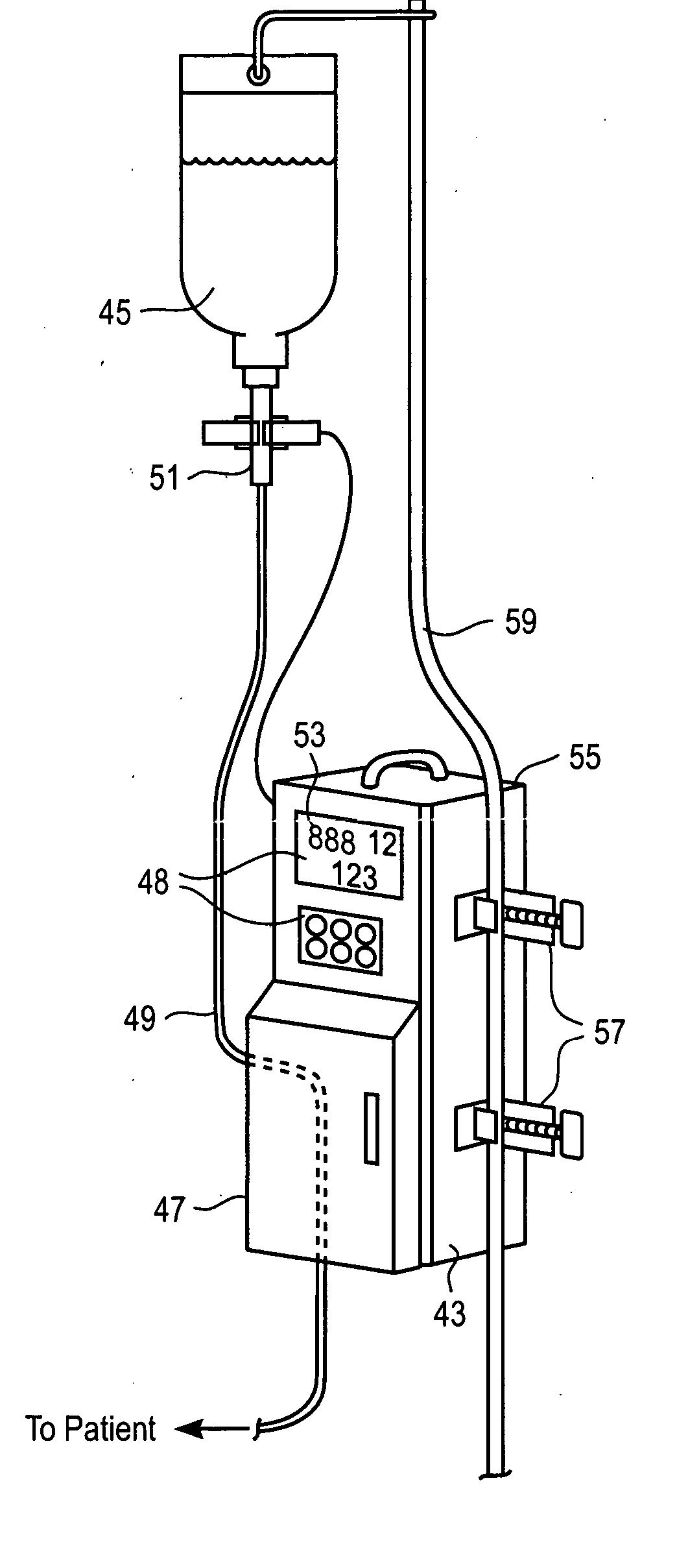
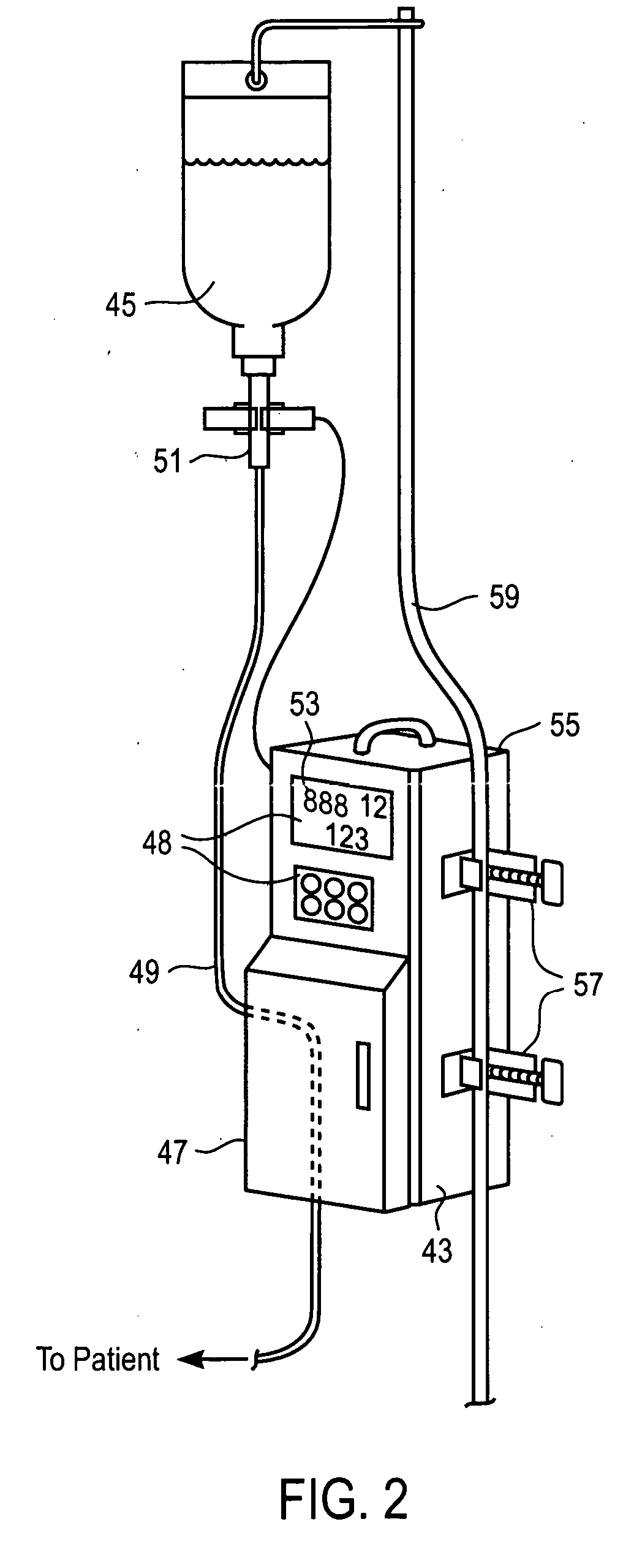
Liquid injection system having liquid injector capable of optically reading two-dimensional code assigned to liquid syringe
The liquid syringe has various kinds of data items recorded in the two-dimensional code format. The liquid injector optically reads the two-dimensional codes, decodes them, and executes a predetermined operations corresponding to the decoded results. Recording, for example, a variable pattern for the liquid of interest in the two-dimensional code format on the liquid syringe makes it possible for the liquid injector to inject the liquid in accordance with the predetermined variable pattern.
Owner:NEMOTO KYORINDO KK
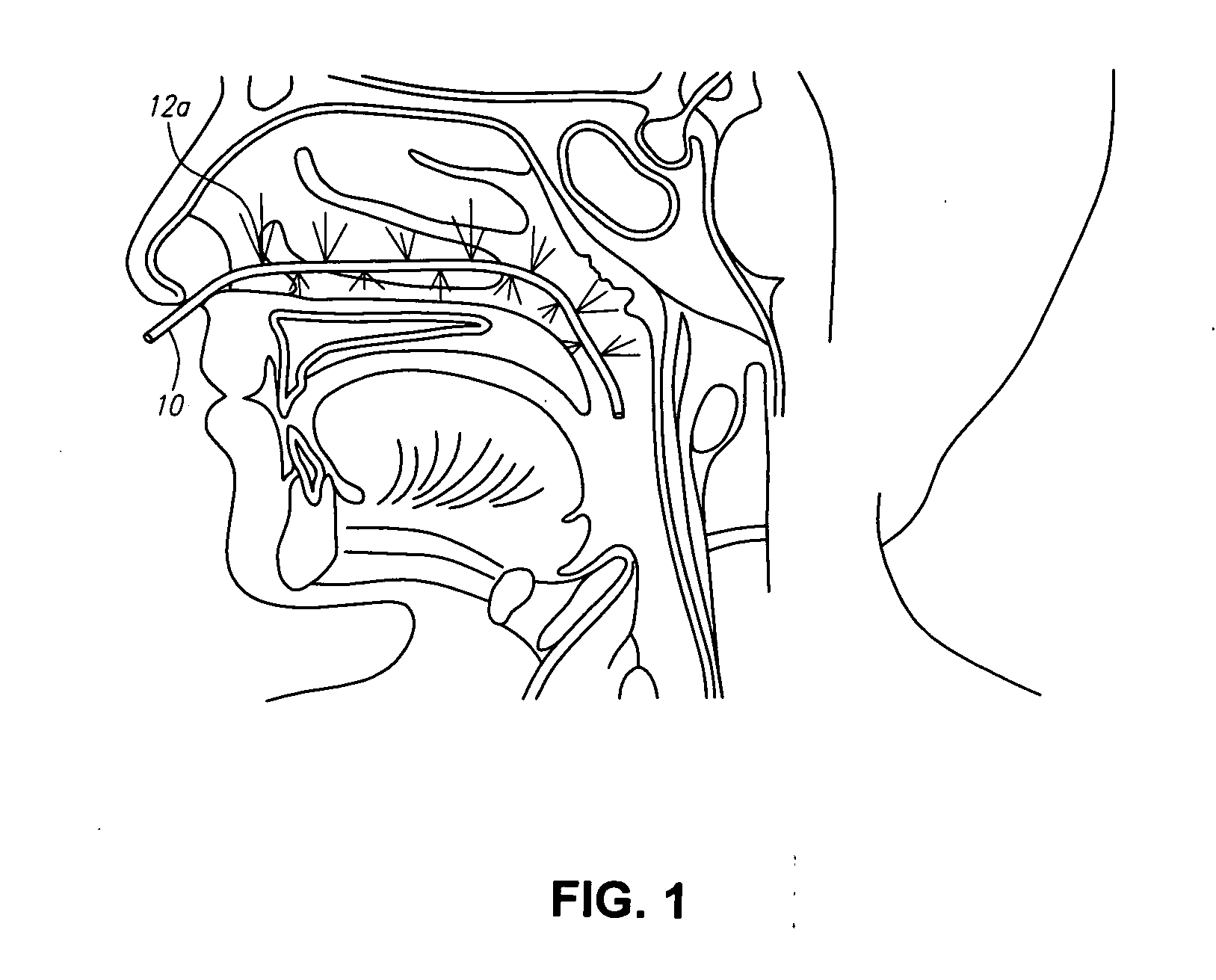
Methods and devices for non-invasive cerebral and systemic cooling
ActiveUS20060276552A1Minimize neurologic deficitMaximize coolingBiocideHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsWhole bodyNon invasive
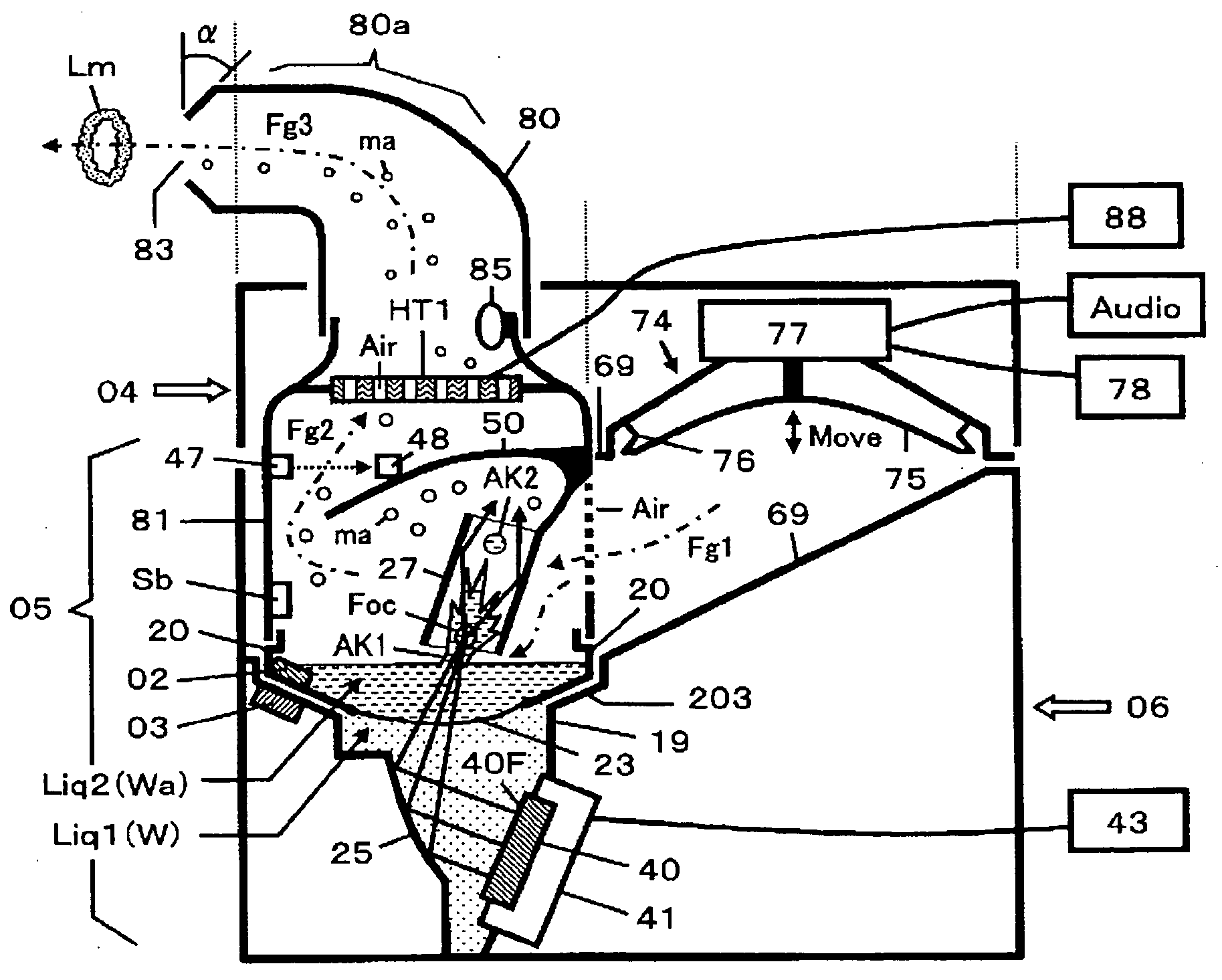
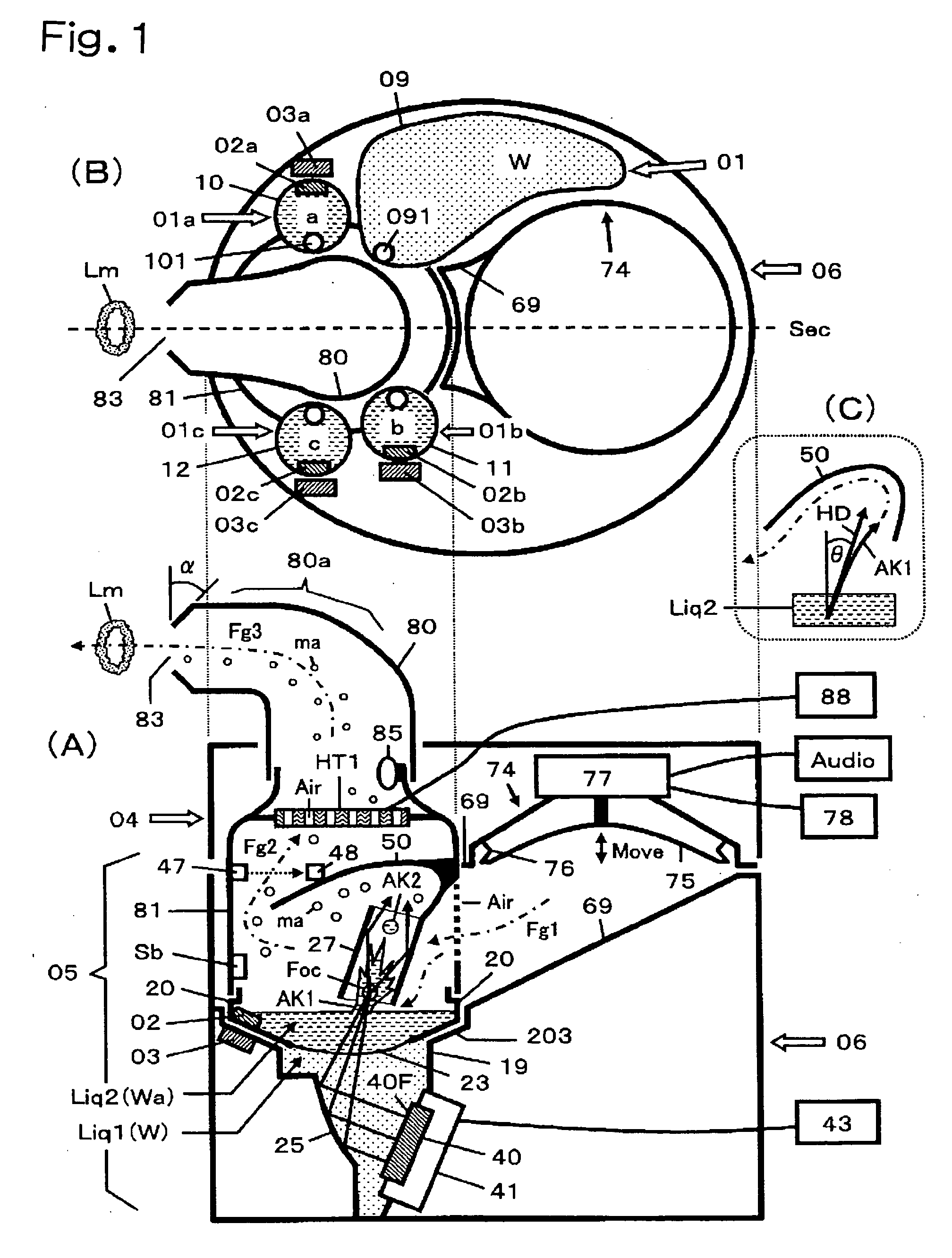
A method for cerebral and systemic cooling by providing a nebulized liquid having a boiling point of 38-300° C. The nebulized liquid is delivered as a mist or a spray via the nasal and / or oral cavities of a patient. The mist causes cooling by direct heat transfer through the nasopharynx and hematogenous cooling through the carotids and the Circle of Willis. Compositions and medical devices for cerebral and systemic cooling are also provided. Cooling assemblies, and methods of use, are also provided that include flexible balloon assemblies that are inserted to various locations in a patient's body. The flexible balloons are then infused with a liquid having a temperature between about −20° C. and about 37° C. The flexible balloon assemblies can be inserted into the nasal cavity, oral cavity, throat, stomach, and other locations to effect cerebral cooling.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY +1
Method for applying a plasma sprayed coating using liquid injection
InactiveUS20060222777A1Improve processing efficiencyReduce the amount requiredLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPlasma jetPlasma sprayed coating
A method for applying a plasma prayed coating using liquid injection is disclosed. The method includes providing a mixture of a liquid and solid particles. The solid particles are constituents of a thermal barrier coating. The mixture is injected into a plasma jet of a plasma spray device and the plasma jet is directed toward a substrate to deposit a gradient film formed from the constituents onto the substrate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
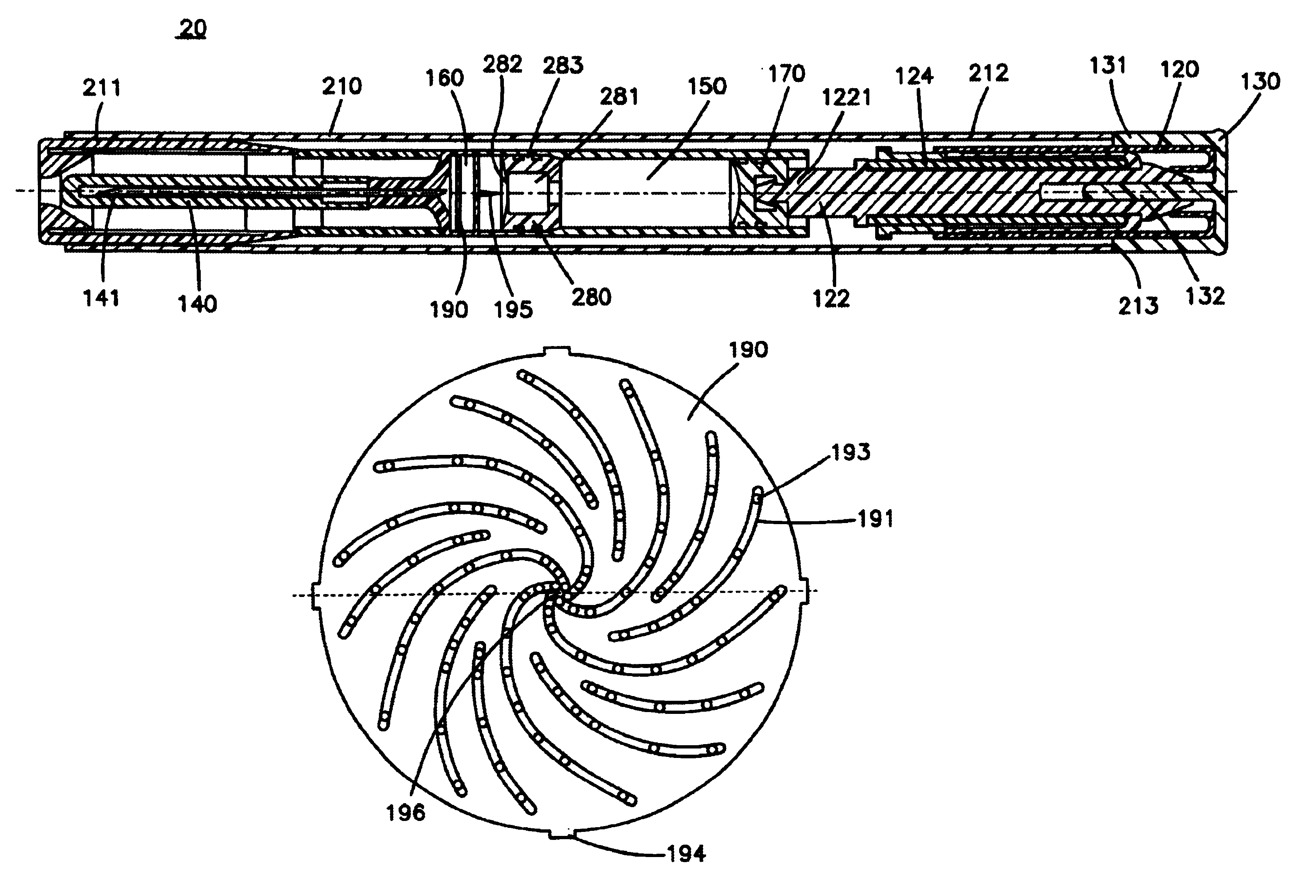
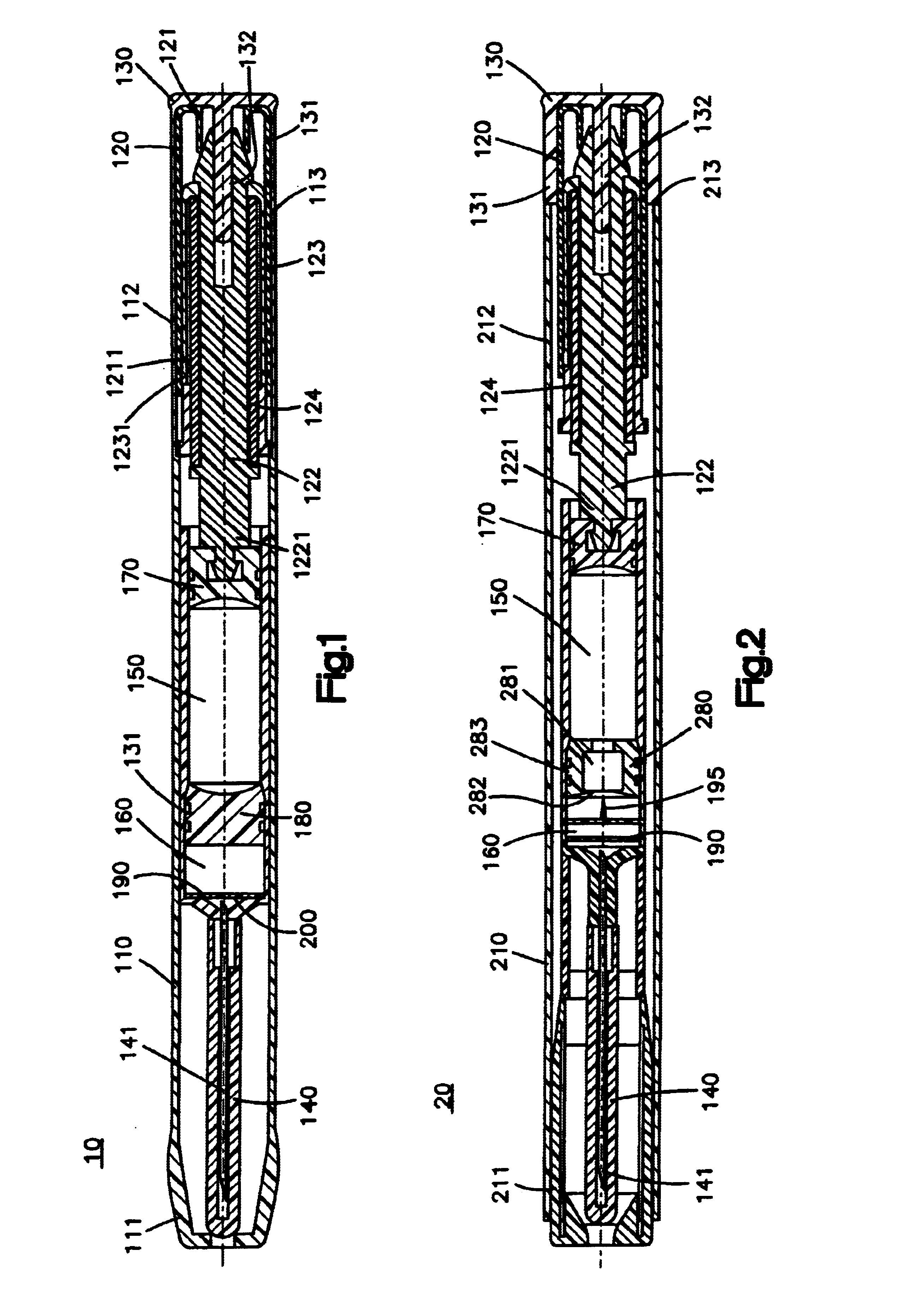
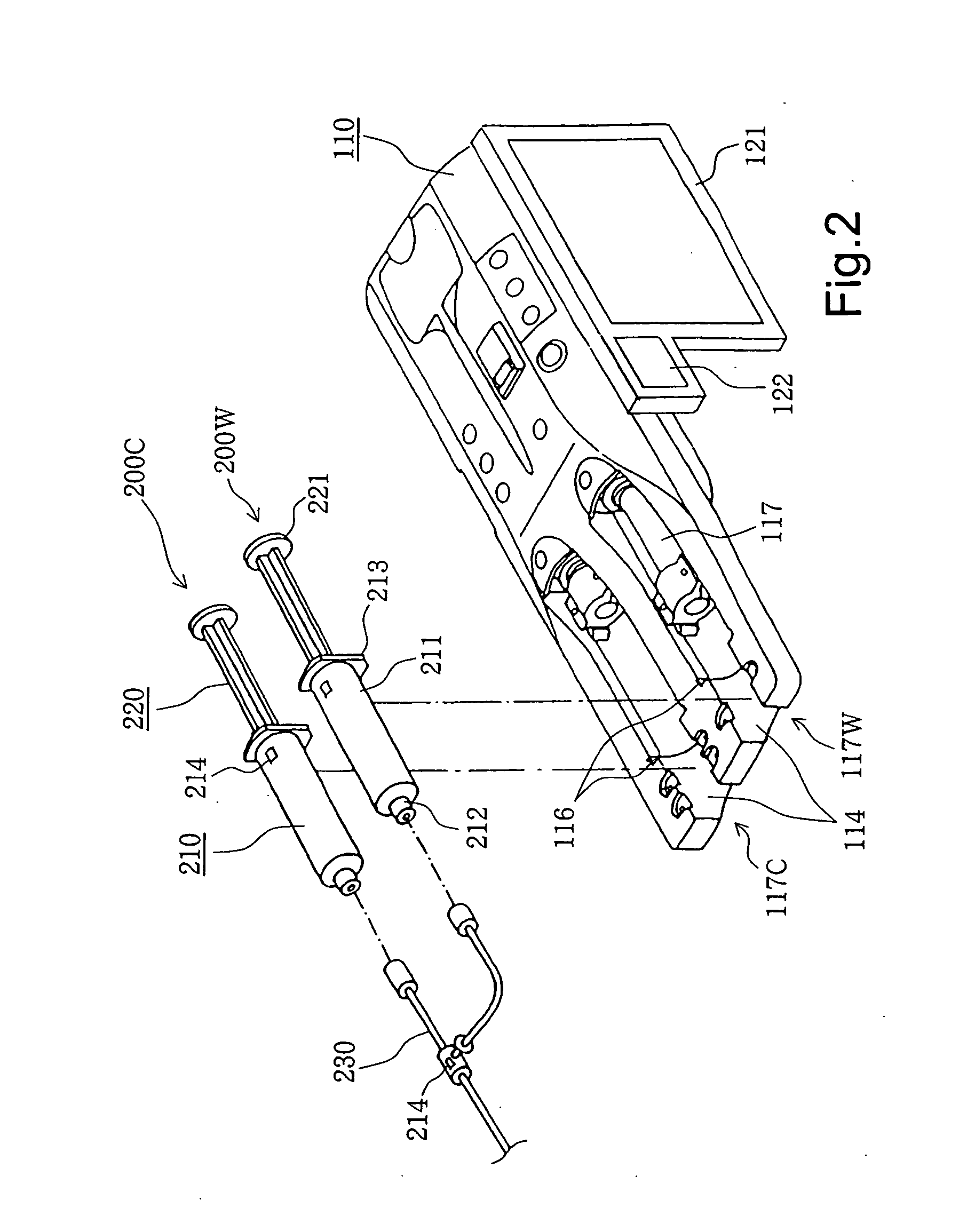
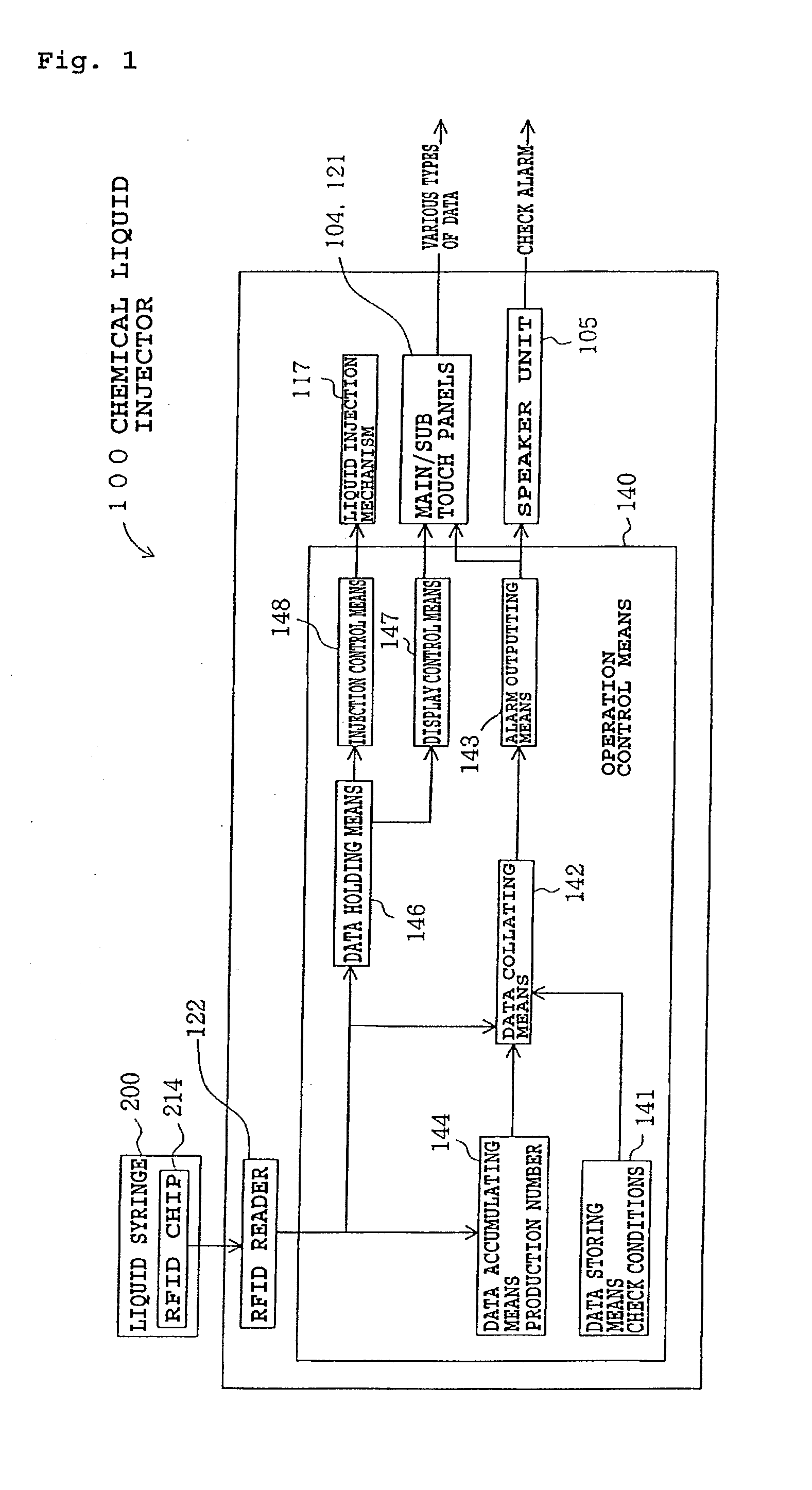
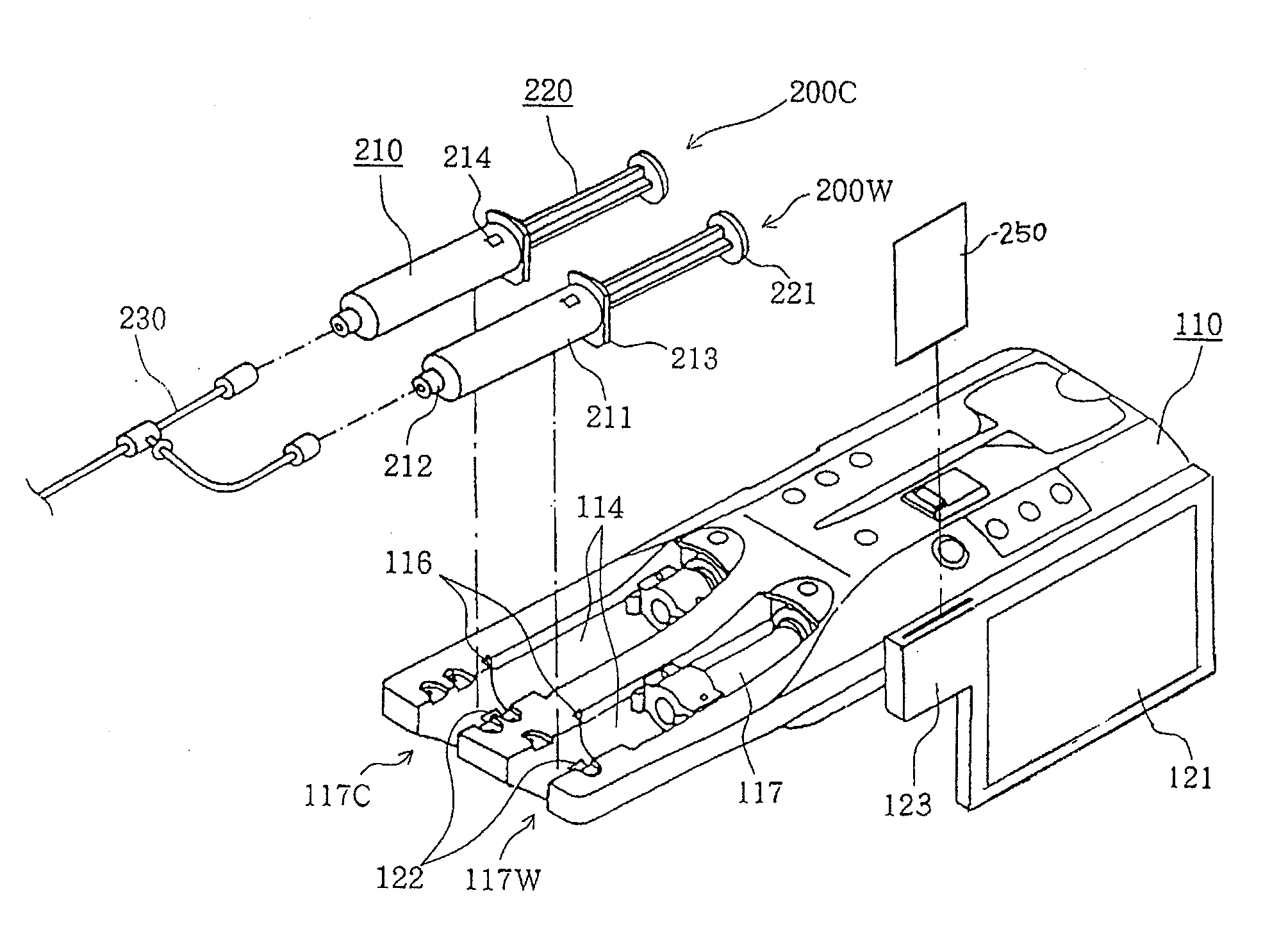
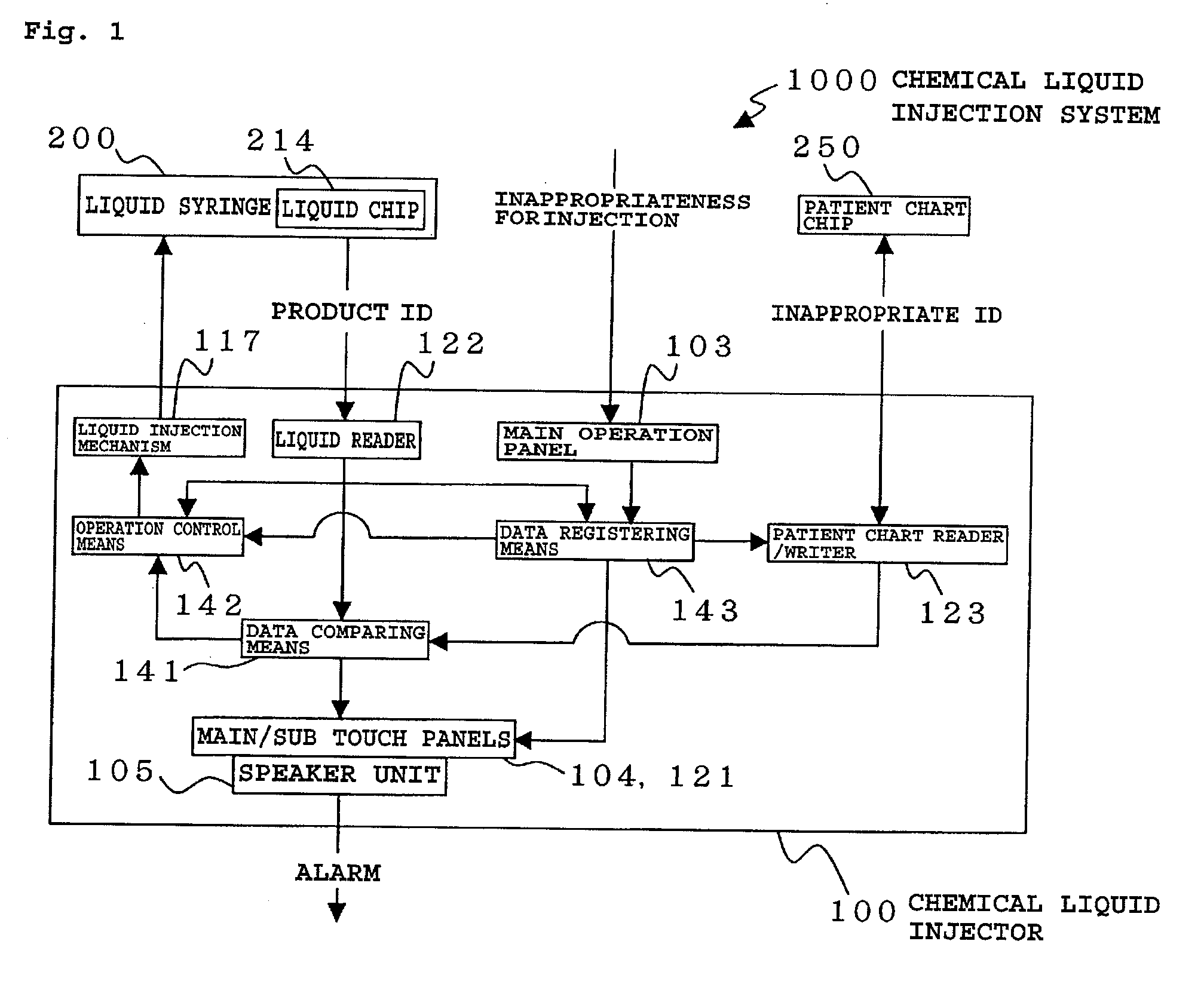
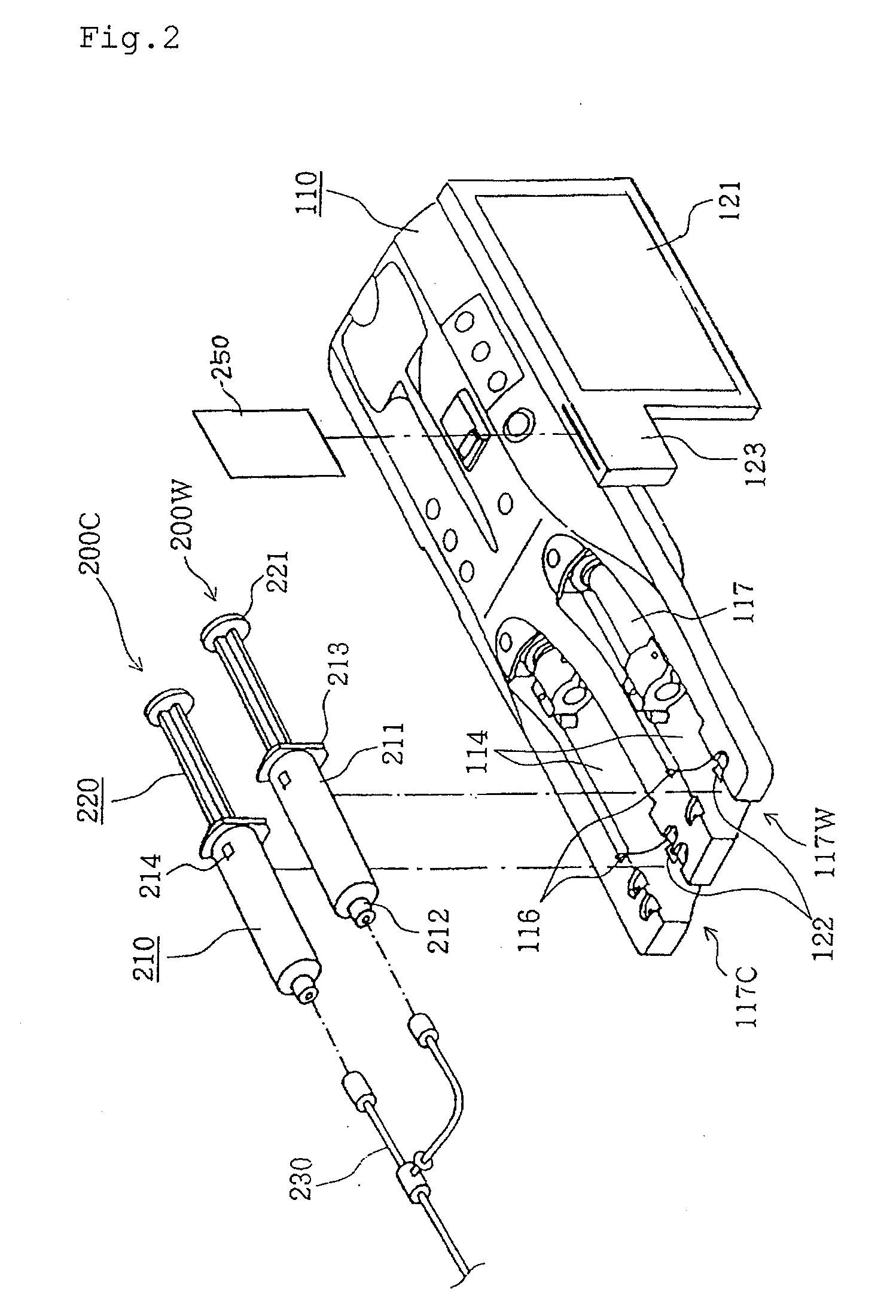
Chemical liquid injection system
RFID chip (214) having various types of data is mounted on liquid syringe (200). Chemical liquid injector (100) obtains the various types of data from RFID chip (214) to perform a predetermined operation in accordance with at least some of the various types of data. For, example, a variable pattern for liquid can be recorded on RFID chip (214) of liquid syringe (200) to allow chemical liquid injector (100) to inject the liquid in accordance with the predetermined variable pattern. Thus, a large amount of data can be easily input to the chemical liquid injector to perform the various operations.
Owner:NEMOTO KYORINDO KK
Dual microcontroller-based liquid infusion system
Owner:AMRITA VISHWA VIDYAPEETHAM
Method and Apparatus for Pressure Infusion and Temperature Control of Infused Liquids
A method and apparatus for pressure infusion and temperature control of infused liquids includes a receptacle for receiving a liquid-filled bag containing intravenous solution or other liquid and an inflatable pressure device. The inflatable pressure device is disposed within a pressure device bag and is positioned proximate the liquid-filled bag in the receptacle. The inflatable pressure device expands within the pressure device bag upon inflation and exerts pressure on the liquid-filled bag. A heating element may be disposed on the inflatable pressure device bag to heat the liquid-filled bag to a desired temperature. The liquid may alternatively be maintained at a desired temperature, while flowing to a patient via a heating assembly disposed along a tube. The heating assembly includes a sleeve having a slot for receiving the tube and a plurality of individually controlled heaters. An infrared sensing device is mounted proximate a drip chamber to ascertain a drip count, while a temperature sensor is disposed within a holder that is positioned toward the entry site on a patient. A heat controller controls the heaters based on a drip count, while a safety controller disables heater operation in response to liquid temperature exceeding the desired temperature. Thus, the safety controller and heat controller, in combination, control the heating assembly heaters based on liquid temperature and flow rate, respectively. Alternatively, the liquid-filled bag may be heated to a desired temperature whereby the heating assembly includes a single heater controlled by a controller to maintain the liquid at the desired temperature during infusion of the liquid into a patient.
Owner:MEDICAL SOLUTIONS INC
Apparatus, system, and method for generating electricity from a chemical hydride
InactiveUS20080026269A1Satisfies electric loadSatisfy loadingFuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlElectricityFuel cells
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed to generate electric power from a chemical hydride. A fuel cartridge produces hydrogen by reacting a liquid with a chemical hydride. A fuel cell stack generates electric power using an oxygen source and the produced hydrogen. An electric power storage device is coupled with the fuel cell stack. The electric power storage device stores and supplies electric power. One or more liquid sources inject the liquid into the fuel cartridge at a variable rate. A controller calculates a liquid injection rate for the one or more liquid sources based on power demands of an electric load.
Owner:TRULITE INC
Method and apparatus to apply surface release coating for imprint mold
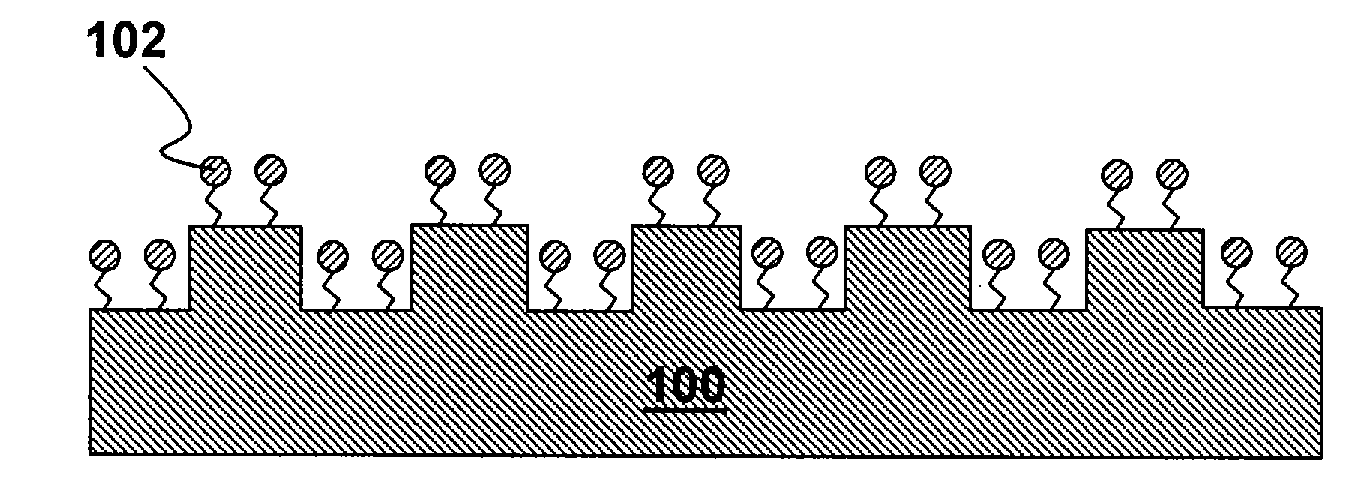
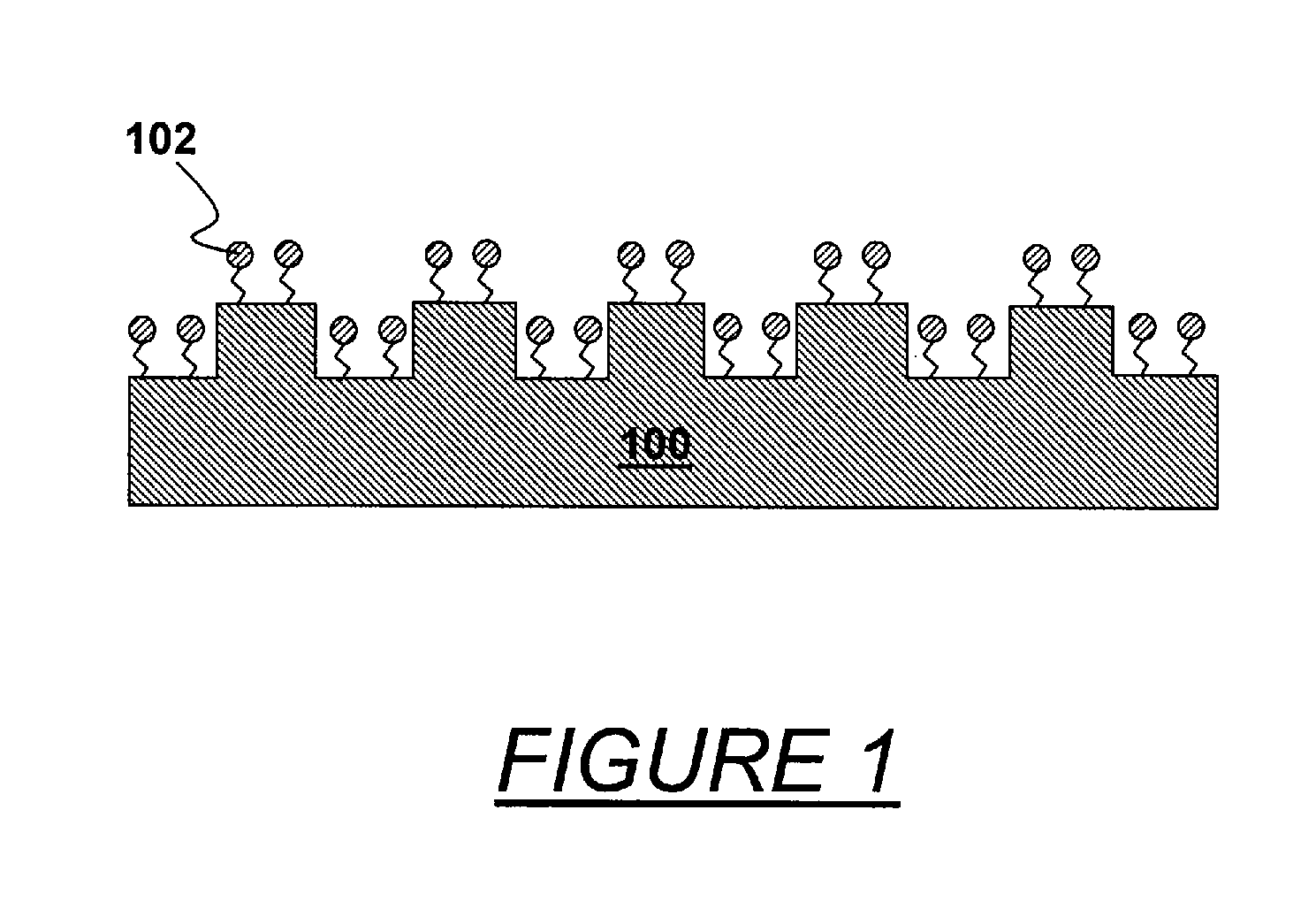
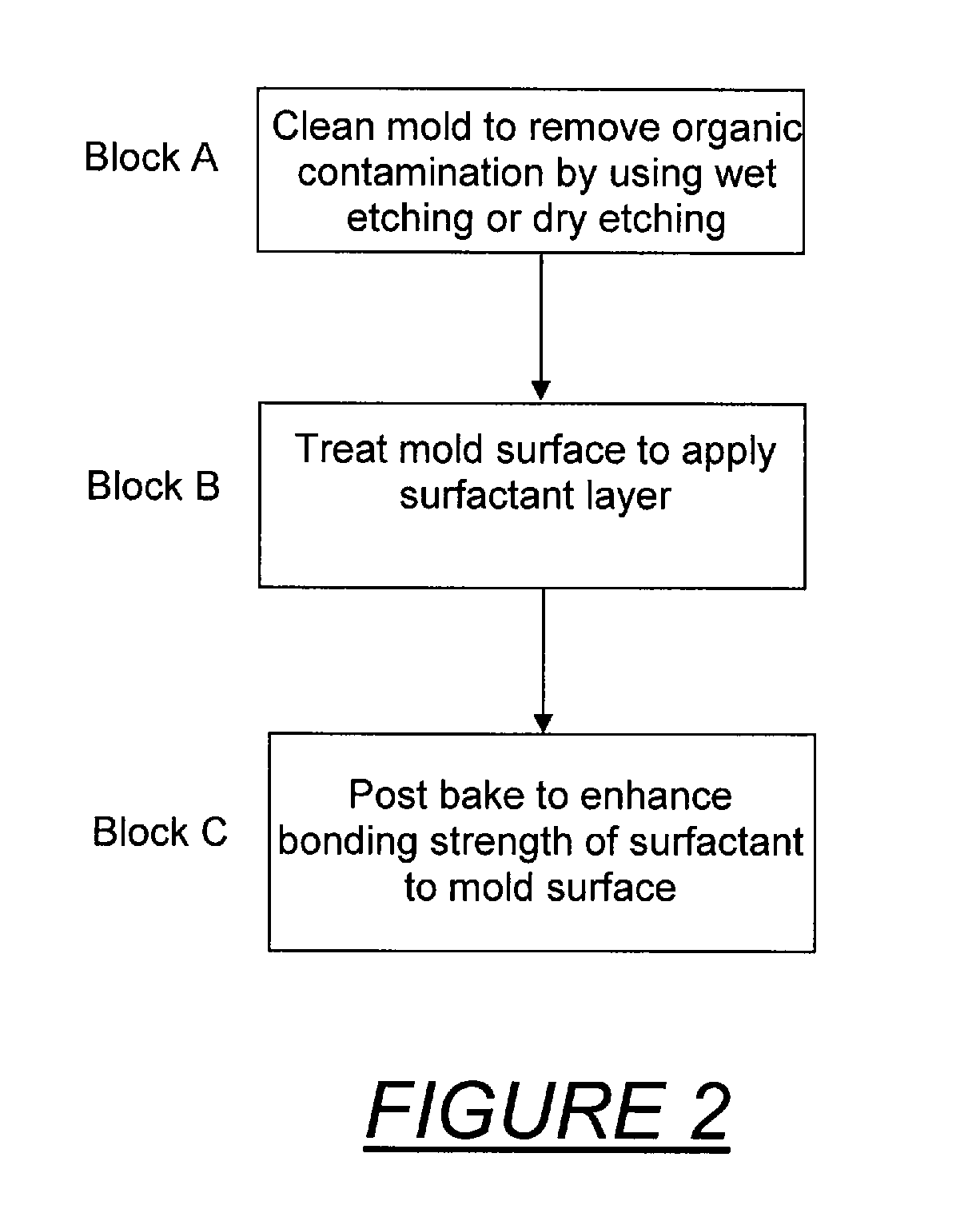
In imprint lithography, the mold is coated with a surface release layer for a non-sticking separation. Bonding strength of the release layer to the mold depends on the cleanness of the surface and the process of release layer deposition. In accordance with the invention, the mold is disposed in an evacuable chamber, cleaned to remove surface organic contamination and coated with the surface release layer in a chamber, all without relocation or undesired time delay. The chamber encloses a support chuck for the mold or substrate, a surface cleaner unit adjacent the support, a heating source adjacent the support, and advantageously, sensors of measuring chamber pressure, vapor partial pressure and moisture concentration. A vapor source connected to the chamber supplies release surfactant vapor. The mold is cleaned, and the cleaning is followed by vapor phase deposition of the surfactant. The mold is advantageously heated. Typical ways of cleaning include exposure to ozone or plasma ion etch. Surfactant vapor may be generated by liquid surface vaporization, liquid injection or spray vaporization. A surface adhesion promoter can be coated on the substrate by a similar method with the same apparatus.
Owner:NANONEX
Liquid infusion apparatus
InactiveUS20060173412A1Reduction of magnetic materialEliminate the problemDC motor speed/torque controlFlexible member pumpsPeristaltic pumpEngineering
Liquid infusion apparatus includes non-magnetic materials in a pumping structure and ultrasonic drive motor therefor, and in a controller that supplies drive signals to the motor to facilitate convenient operation in intense magnetic fields without distorting the magnetic fields and without radiating objectionable radio-frequency interference. A non-MRI-compatible liquid infusion apparatus is temporarily replaced with MRI-compatible, non-magnetic liquid infusion apparatus without disconnecting a patient from an installed intravenous infusion set to continue infusing liquid within the MRI environment. The pumping apparatus operates on a segment of a liquid conduit that is mounted in tension between a linear peristaltic pump and platen, with associated safety interlocks to assure proper operation of infusing liquid into a patient compatibly with conditions in an MRI environment. Drive circuitry generates low-harmonic signals for operating the ultrasonic motor at variable speeds to compensate for flow rate discontinuities through the peristaltic pumping cycles.
Owner:IRADIMED CORP
Atomizer and electronic cigarette having same
The present disclosure relates to an atomizer for an electronic cigarette. The atomizer includes a housing, a liquid chamber, an atomizing unit, and a deformable valve. The liquid chamber is in the housing and configured for storing tobacco liquid. The liquid chamber has a liquid injecting opening The atomizing unit is configured for absorbing and atomizing the tobacco liquid. The deformable valve is arranged in the liquid injecting opening The valve is capable of being pushed open by an external injector, so that the tobacco liquid can be injected into the liquid chamber. The valve is capable of restoring to its original shape to seal the liquid injecting opening when the injector is removed.
Owner:SHENZHEN FIRST UNION TECH CO LTD
Methods of atomic layer deposition using hafnium and zirconium-based precursors
Methods of forming a metal-containing film by atomic layer deposition is provided. The methods comprise delivering at least one precursor to a substrate, wherein the at least one precursor corresponds in structure to Formula II:wherein: M is Hf or Zr; R is C1-C6-alkyl; n is zero, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5; L is C1-C6-alkoxy. Further methods are provided of forming a metal-containing film by liquid injection atomic layer deposition. The methods comprise delivering at least one precursor to a substrate, wherein the at least one precursor corresponds in structure to Formula III:wherein: M is Hf or Zr; R is C1-C6-alkyl; n is zero, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5; L is amino, wherein the amino is optionally independently substituted 1 or 2 times with C1-C6-alkyl.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Filling capping device
ActiveCN102701127ALow costImprove space utilizationThreaded caps applicationLiquid fillingElectric machineryBottle cap
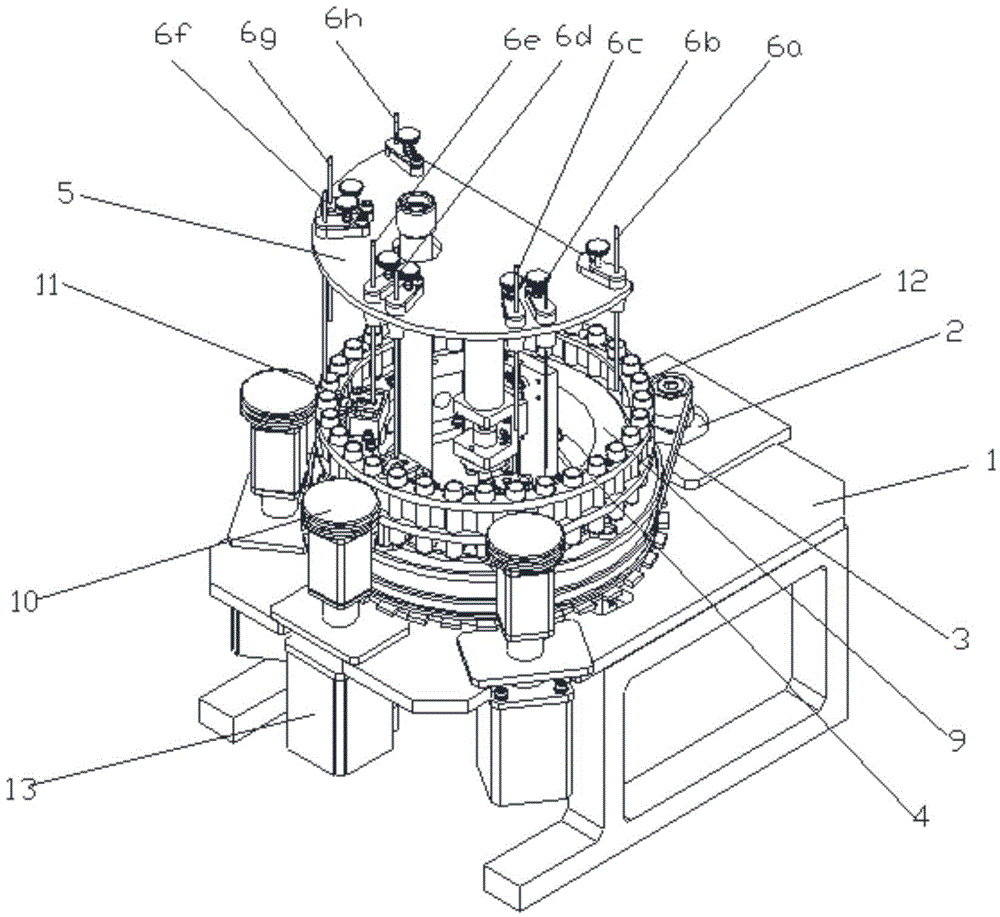
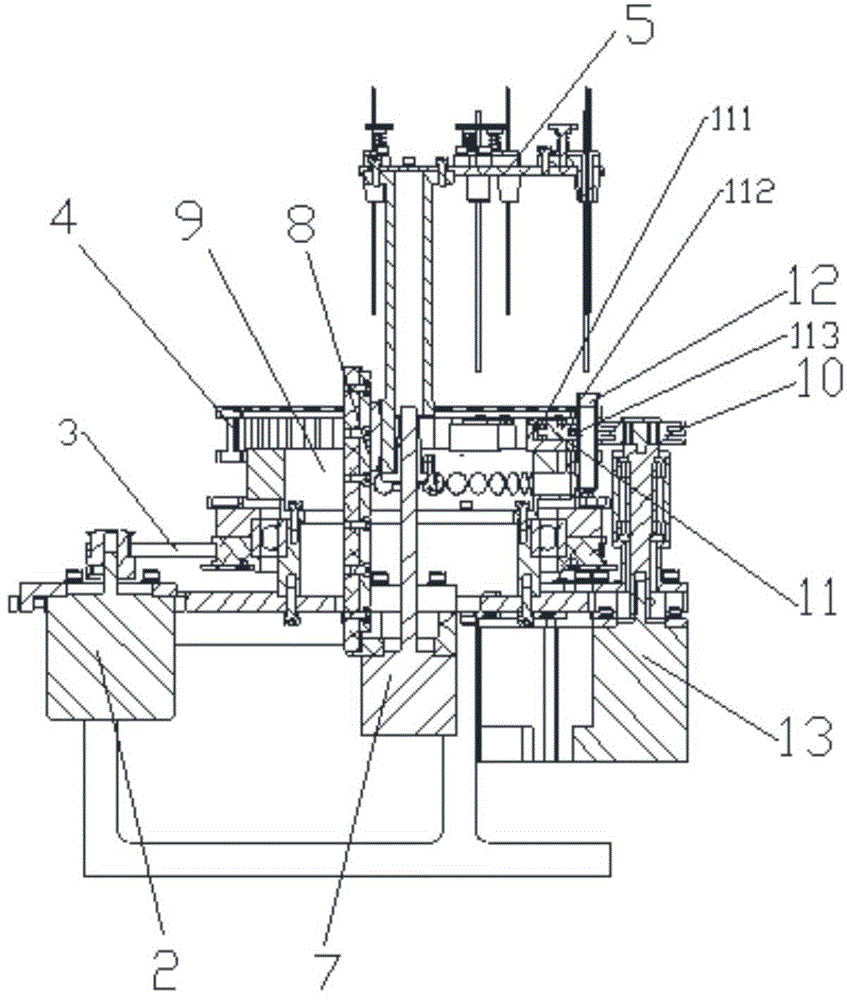
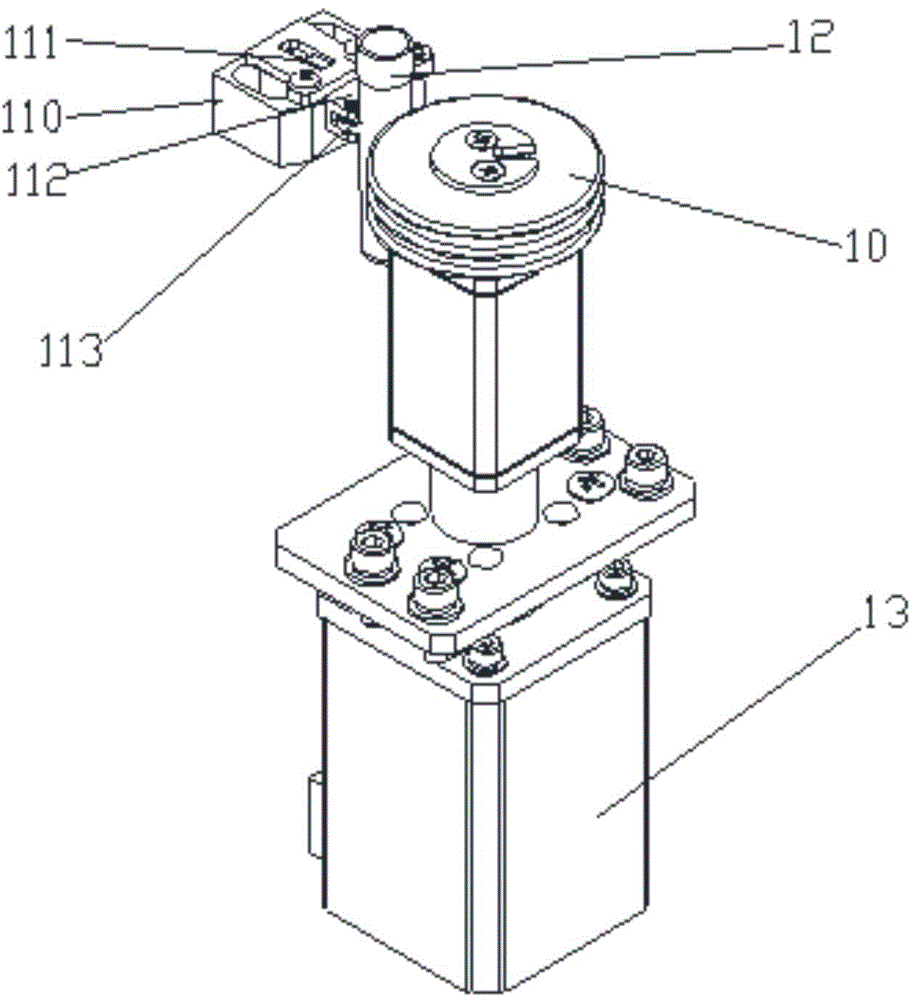
The invention discloses a filling capping device comprising a rotary disk component, a filling component, a cap pressing component and a screw capping component. The rotary disk component comprises a rotary disk and a pneumatic division plate which is used for driving the rotary disk to intermittently rotate; the filling component comprises a liquid injection needle, a liquid feeding pipe and a liquid injection lifting cylinder for driving the liquid injection needle to move up and down; the cap pressing component comprises a storage barrel, a transverse push cylinder and a cap pressing cylinder for pushing downwards a bottle cap to be added pushed by the transverse push cylinder; and the screw capping component comprises a screw capping motor, a screw capping lifting cylinder for driving the screw capping motor to move up and down and a rotating sleeve arranged at the free end of the screw capping motor, and a screw capping core arranged in the rotating sleeve. The filling capping device has a simple structure and is low in equipment cost; as the rotary disk is adopted to convey bottles, the volume of the entire device is reduced and subsequently the occupied area of the device is reduced; the filling capping device can be used for teaching demonstration; and furthermore, the space utilization rate of a workshop is improved.
Owner:广东三向智能科技股份有限公司
Chemical liquid injection system
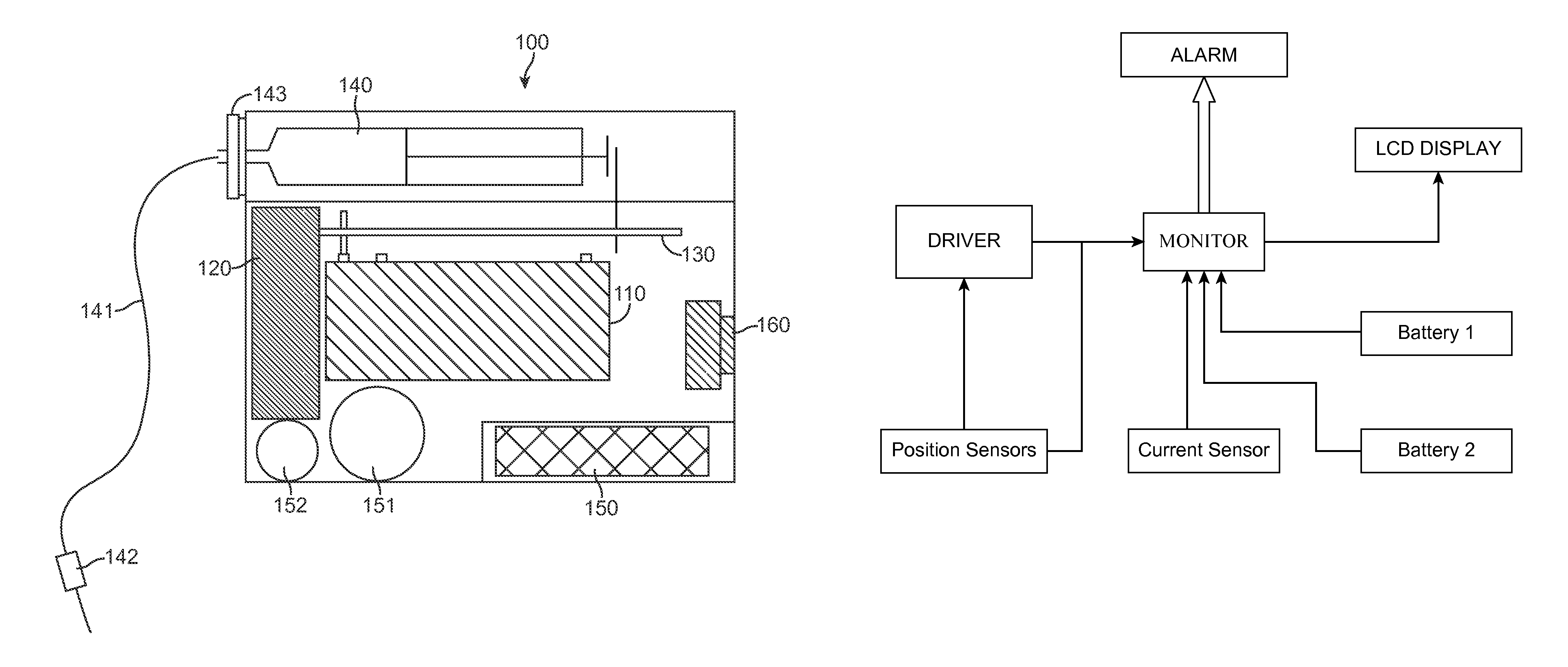
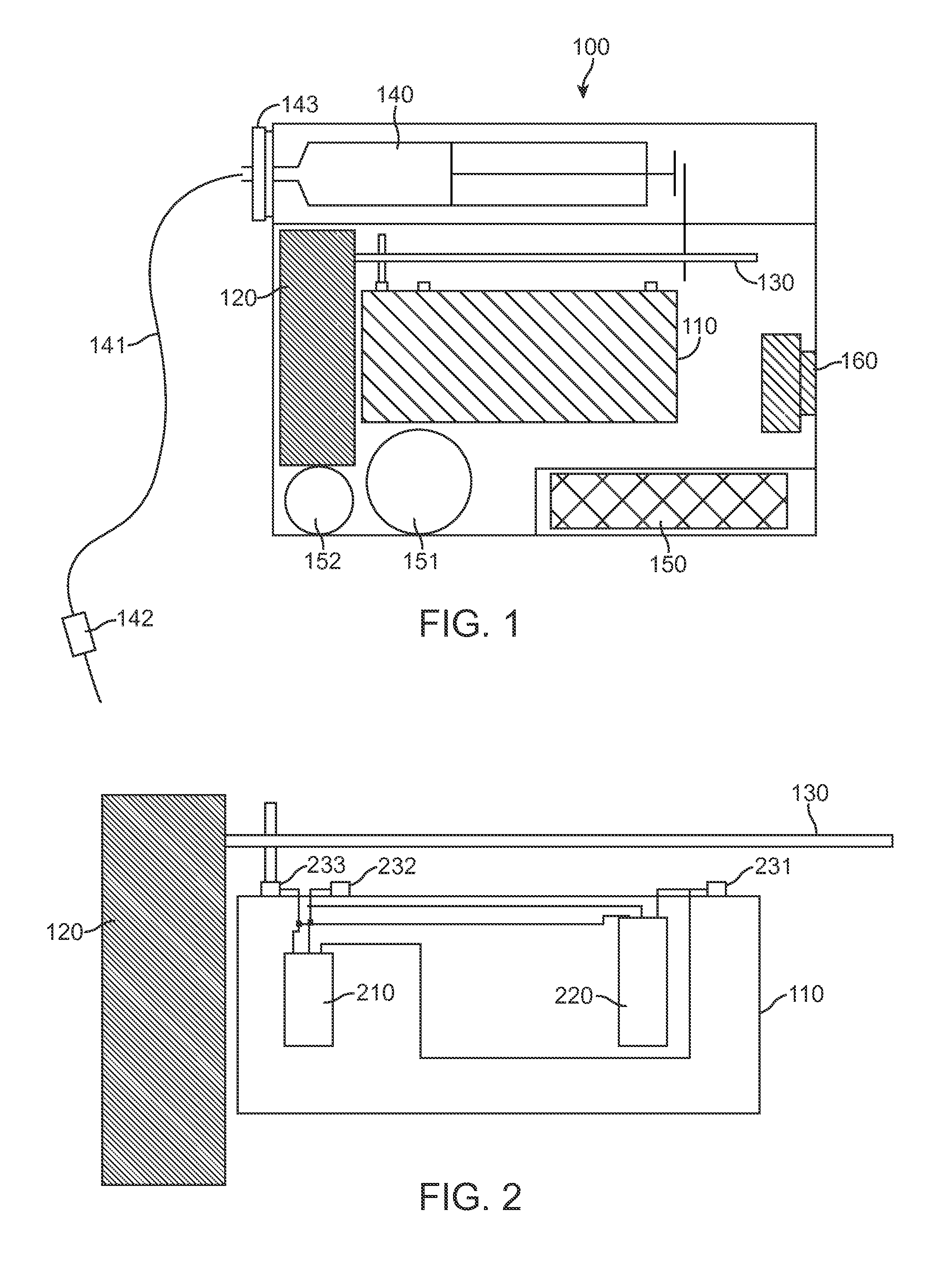
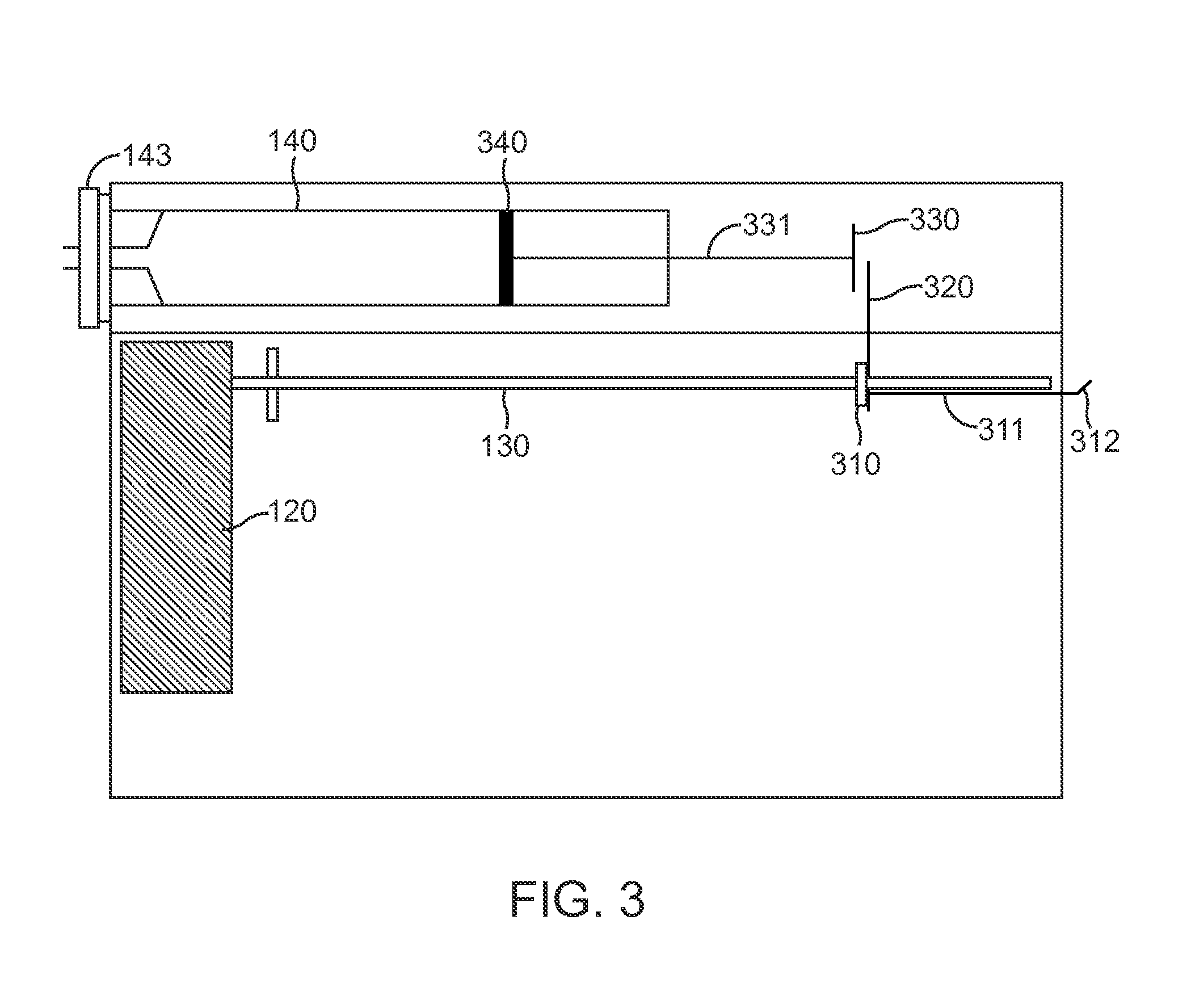
The present invention provides a chemical liquid injection system in which a chemical liquid injector can detect whether or not the injection of a liquid from a liquid syringe into a patient is inappropriate for a personal reason such as the development of a side effect although the liquid is of an appropriate type for the injection system, and the chemical liquid injector can issue an alarm to notify the inappropriate injection. Chemical liquid injector 100 acquires a product ID of the liquid recorded on liquid chip 214 of liquid syringe 200 and an inappropriate ID recorded in a electric chart to output a notification when the product ID matches the inappropriate ID.
Owner:NEMOTO KYORINDO KK
Methods and devices for non-invasive cerebral and systemic cooling
ActiveUS20070123813A1Minimize neurologic deficitsReduce perfusionHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsElectrotherapyWhole bodyNon invasive
A method for cerebral and systemic cooling by providing a nebulized liquid having a boiling point of 38-300° C. The nebulized liquid is delivered as a mist or a spray via the nasal and / or oral cavities of a patient. The mist causes cooling by direct heat transfer through the nasopharynx and hematogenous cooling through the carotids and the Circle of Willis. Compositions and medical devices for cerebral and systemic cooling are also provided. Cooling assemblies, and methods of use, are also provided that include flexible balloon assemblies that are inserted to various locations in a patient's body. The flexible balloons are then infused with a liquid having a temperature between about −20° C. and about 37° C. The flexible balloon assemblies can be inserted into the nasal cavity, oral cavity, throat, stomach, and other locations to effect cerebral cooling.
Owner:BRAINCOOL +1
Method of preparing rheological materials for bone and cartilage repair
InactiveUS20070026030A1Volume maximizationEliminate exposureBiocideInternal osteosythesisCartilage repairAnimal body
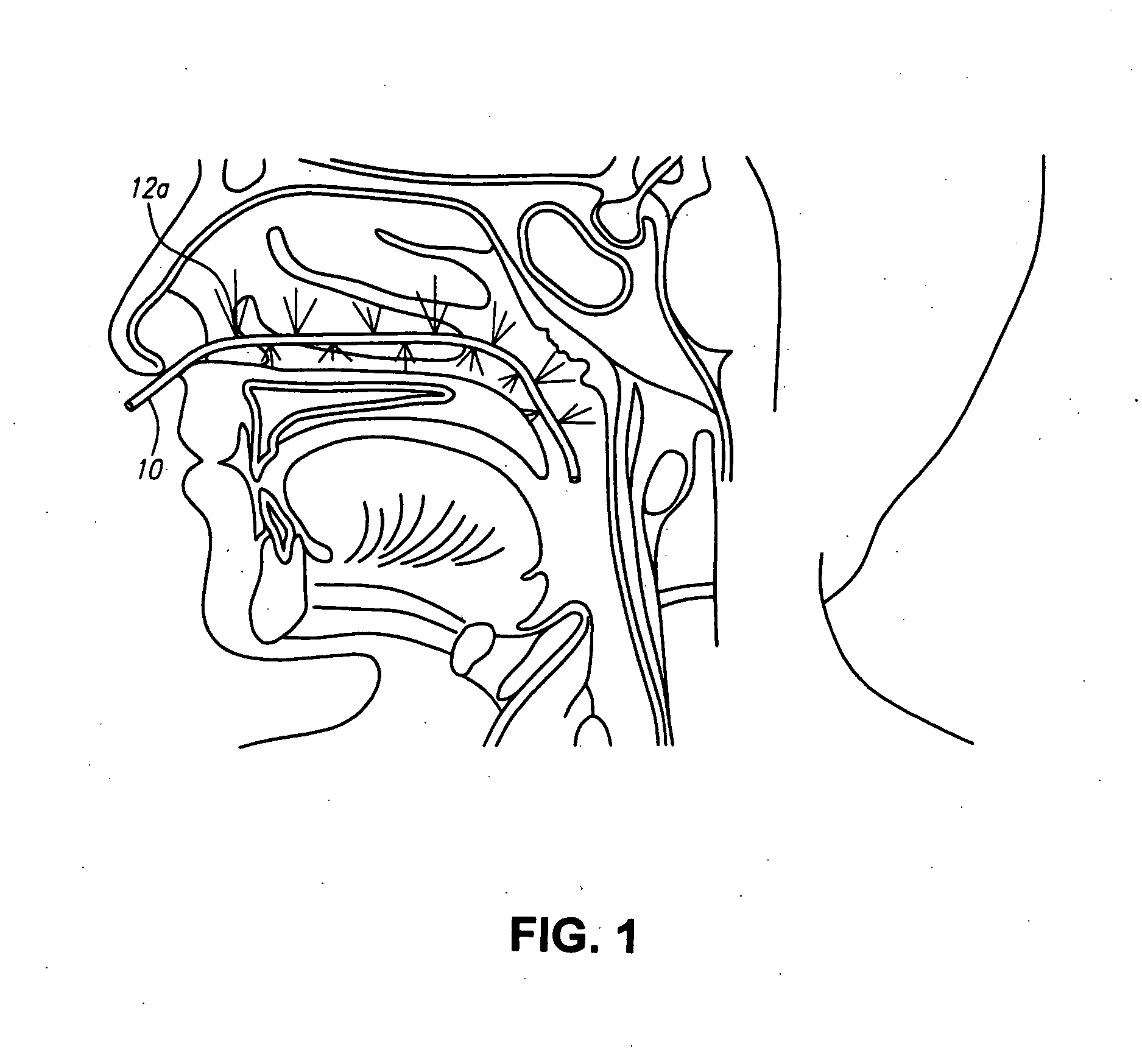
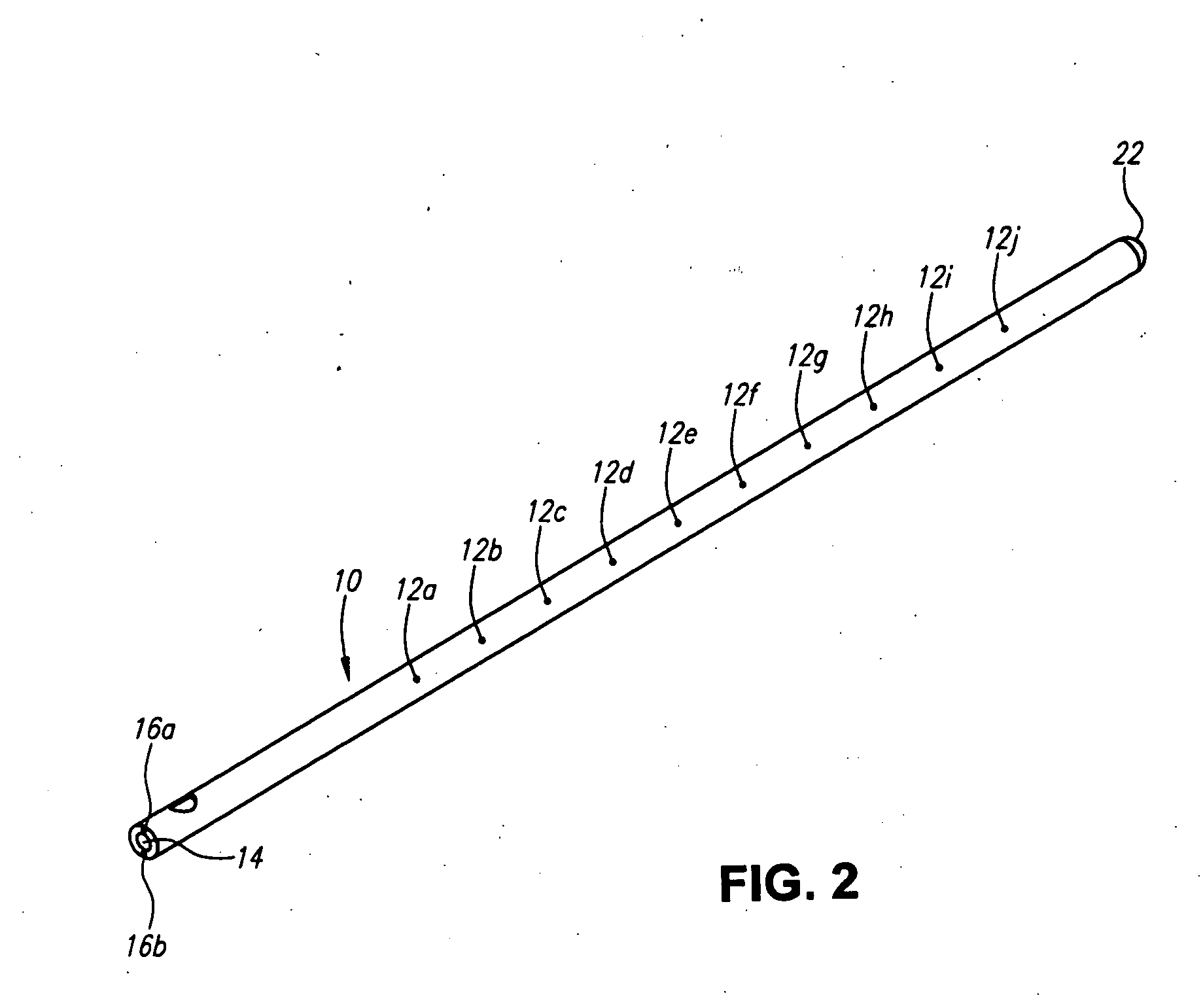
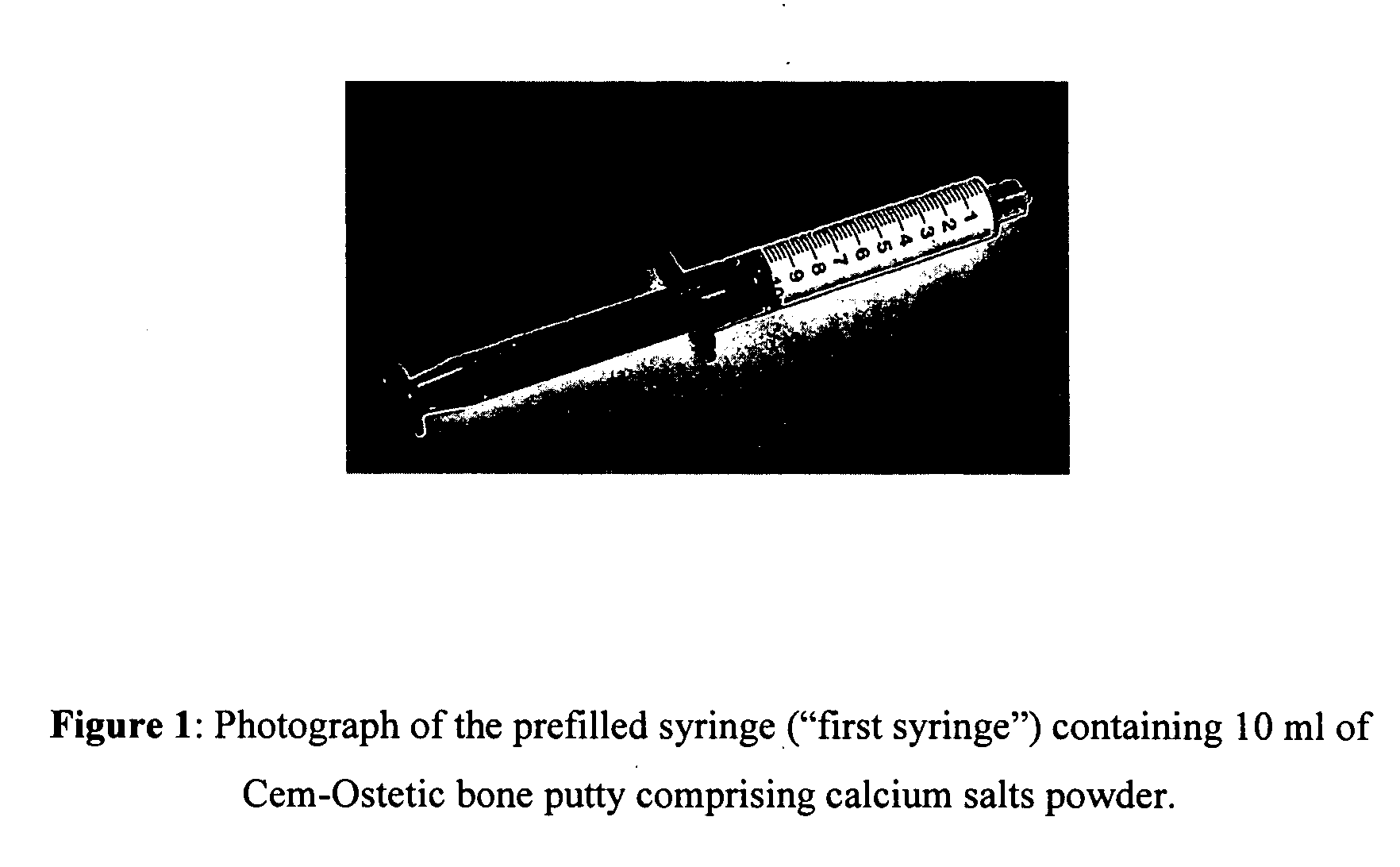
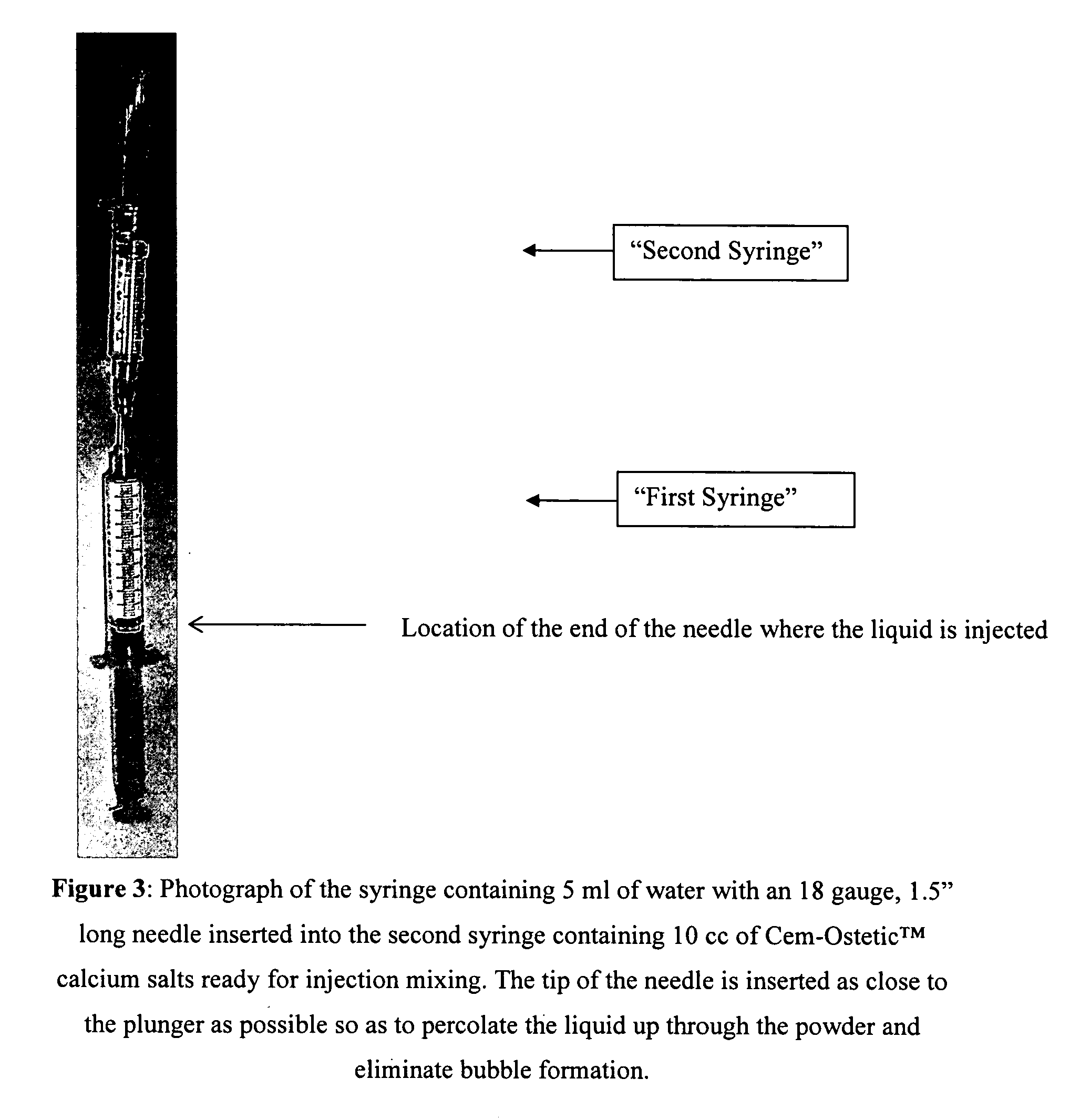
Methods of mixing delivering biocompatible cement, paste, putty, or gel for bone and cartilage repair are described in this invention. Powder-like solid materials are loaded into a first syringe. Liquids are loaded into one or multiple syringes. The liquids are injected into the first syringe containing the solid materials. To force the liquids through the solid, prevent bubble formation and provide intimate intermixing, the liquids are injected in the very proximity of the plunger end of the syringe containing the solid materials. The first syringe is preferably held vertical with the tip facing up so as to avoid bubble formation that in turn could cause back-pressure build-up and plug the first syringe during injection. The described methods of mixing the liquids with the solids allows to form a rheological paste, cement, putty, or gel in the first syringe. As injection into the human or animal body proceeds, the paste then flows without complications often caused by entrapped bubbles or improper / heterogeneous mixing. The preparation and injection processes can be conducted at temperatures that do not damage live tissue or denature proteins. The paste, cement, putty, or gel can be injected into bone through the cannula by hand or with a pressurizing system. The method reduces the amount of time needed to prepare the paste and load it into the syringe and provides a device that is easily prepared for injection.
Owner:BERKELEY ADVANCED BIOMATERIALS
Full-automatic chemiluminescence immune analyzer magnetic bead washing device
ActiveCN103599898ARealize pipeline cleaningReduce lossesCleaning using liquidsLiquid wasteIndependent function
A full-automatic chemiluminescence immune analyzer magnetic bead washing device comprises a reaction cup rotation disc, a lifting needle support, a magnetic bead absorbing device and mixing devices. The lifting needle support is driven by a lead screw motor to move vertically along a linear sliding track. An eight-washing-needle assembly is arranged on the lifting needle support, four needles are liquid injecting needles and used for injecting washing liquid into a reaction cup, and other four needles are liquid sucking needles and used for sucking waste liquid in the reaction cup. The eight washing needles conduct washing liquid injection movement and waste liquid sucking movement on the reaction cup sequentially, and once diluting and three-time washing are conducted on magnetic beads in the reaction cup. An annular magnetic bead absorbing device is arranged below the inner side of the reaction cup rotation disc, and the plurality of mixing devices are arranged above two sides of the reaction cup rotation disc respectively. By means of the device, assembly line type washing of the magnetic beads is achieved, washing is thorough, magnetic bead loss is smaller, structure is optimized, control is simple, relatively independent functions are achieved, and the device is suitable for a whole automatic system.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
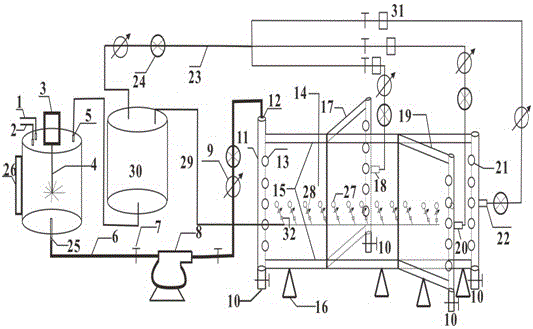
Device and method for simulating shale complex crack sand pavement
The invention relates to a testing device and method for simulating pavement of propping agents in a complex manual crack. The testing device is composed of a fracturing fluid preparing tank, a fluid injection pump, a simulation shaft, a plurality of adjustment valves, a flow meter, a pressure meter and the complex manual crack. The manual crack is composed of a primary crack body and a plurality of secondary crack bodies on the periphery of the primary crack body. Different crack states can be simulated. The manual crack is made of transparent organic glass, and the width and the complex degree can be manually arranged. By means of the testing device and method, the flow conditions of sand carrying fluid in the complex manual crack and the pavement conditions of the popping agents under the conditions of different crack widths, different sand carrying fluid sand proportions, different fracturing fluid leak-off rates, different crack complex degrees and the like can be simulated, and the visualization of migration and sedimentation of the propping agents in the complex manual crack can be achieved in the test process.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GEOLOGY & MINERAL RESOURCES
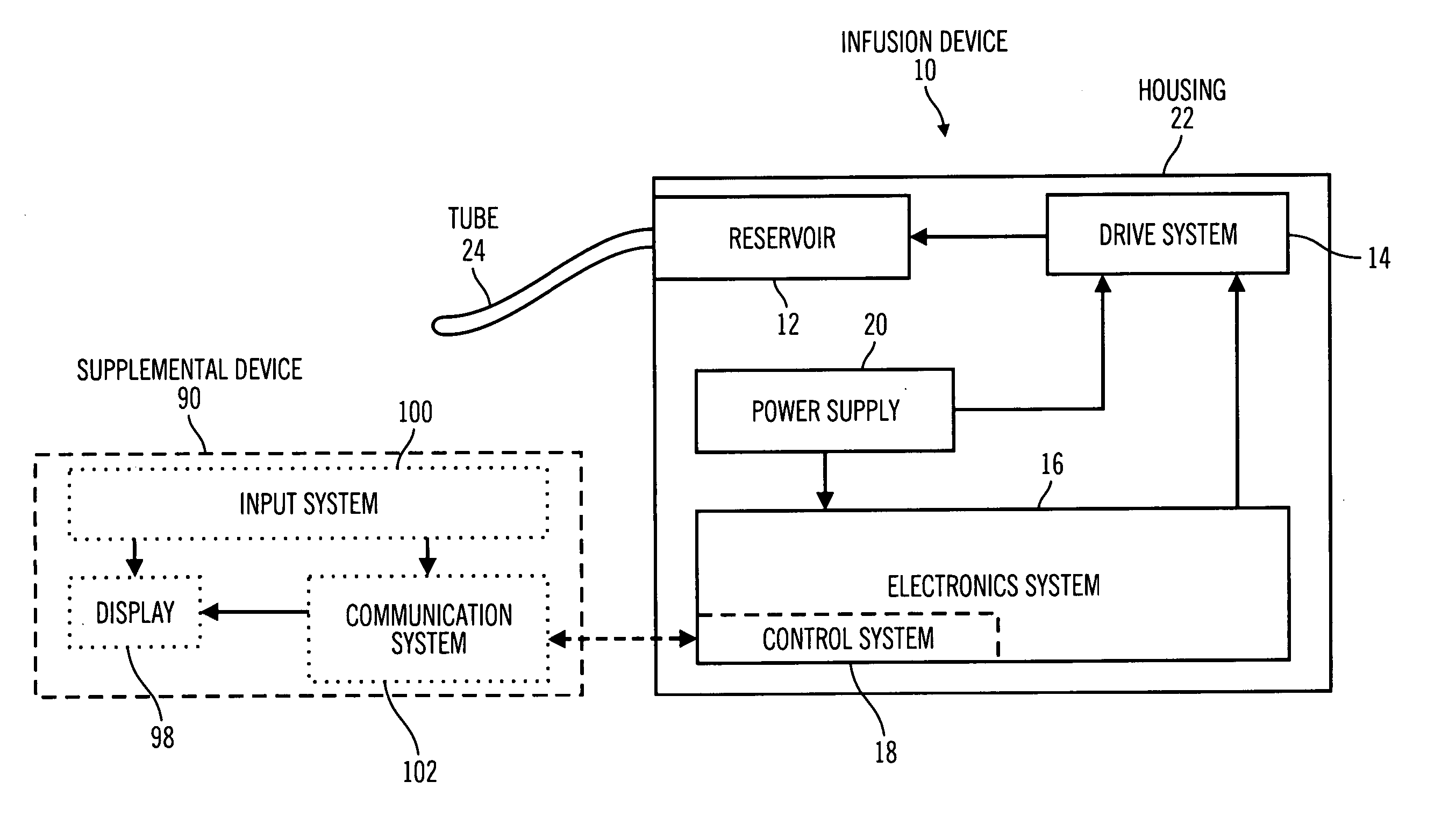
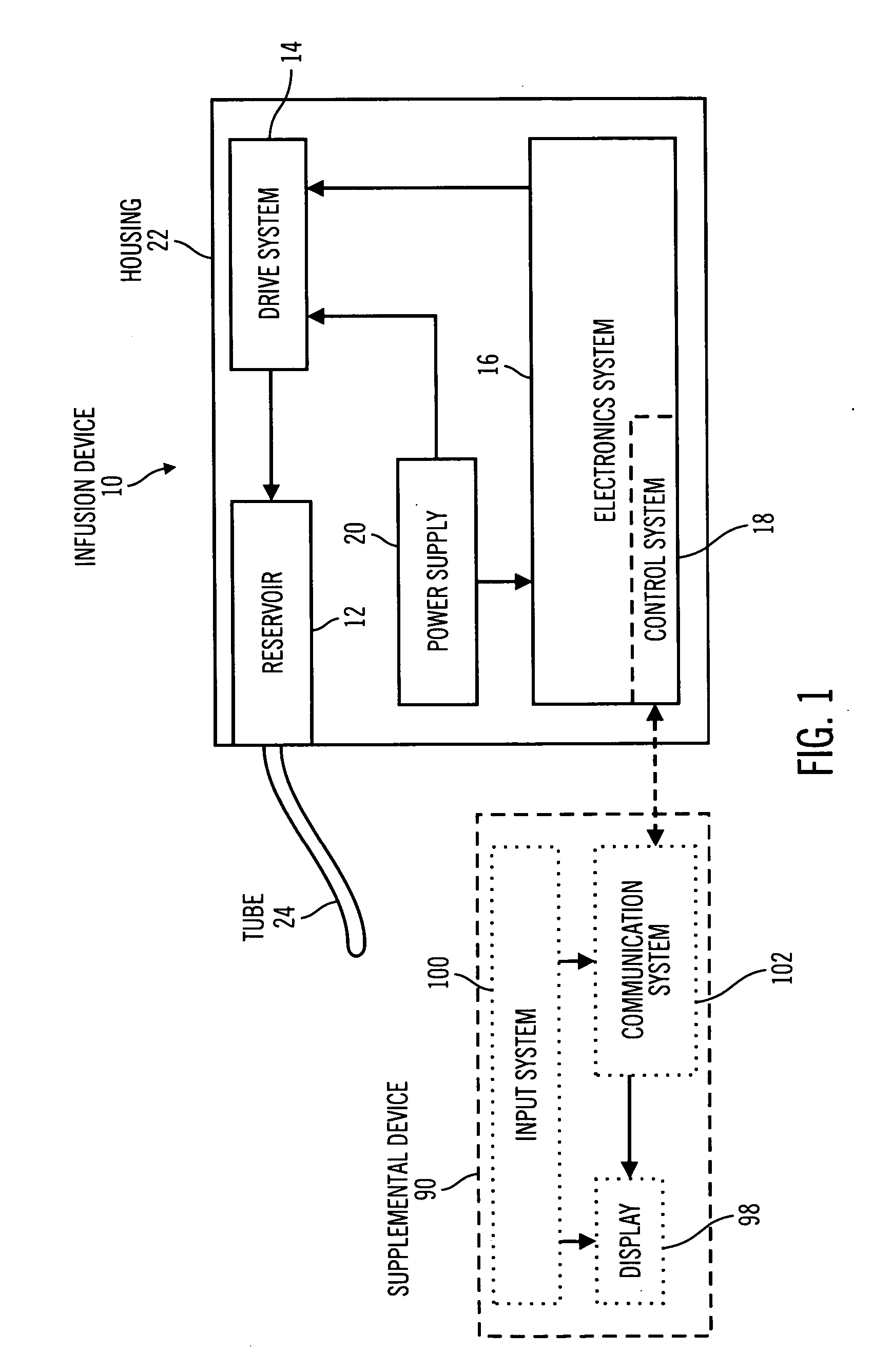
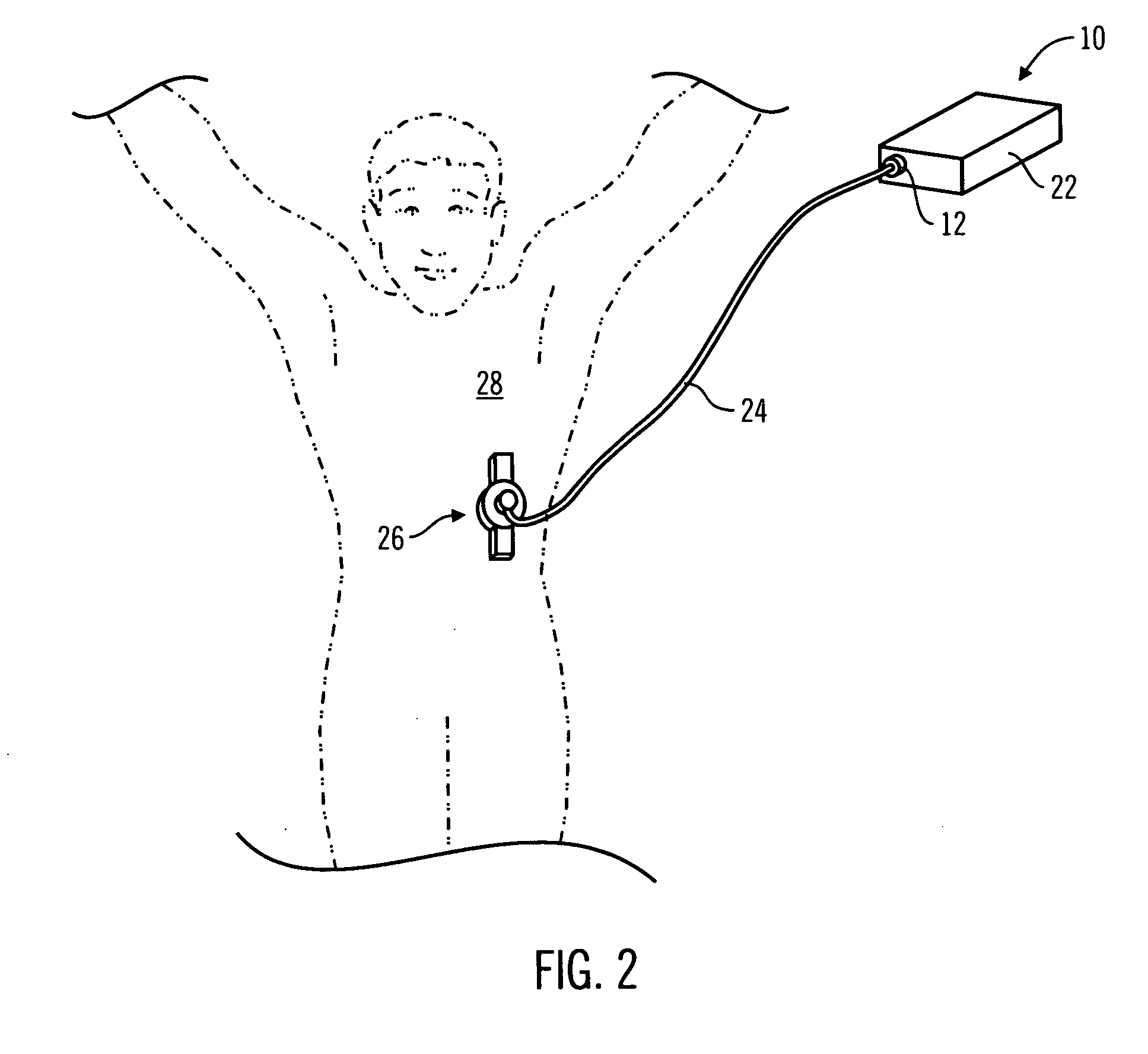
Control tabs for infusion devices and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20070100283A1Improve water resistanceImprove the immunityOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesFuel tankElectrical element
An external infusion device that infuses a fluid into an individual's body includes a housing, a reservoir, a drive system, a power supply, electrical elements, and a tab. The reservoir contains the fluid, and the drive system forces the fluid from the reservoir. The electrical elements control the power to the drive system to regulate the rate that fluid is forced from the reservoir. The tab mates with the housing, and contains at least one electrical element. The tab is removable, and may be replaced with a different tab. The different tab may change the rate fluid is forced from the reservoir. A tab may be removed from one external infusion device and installed in a different external infusion device. The tab may be limited to use in a predetermined number of external infusion devices and may include a power supply.
Owner:MINIMED
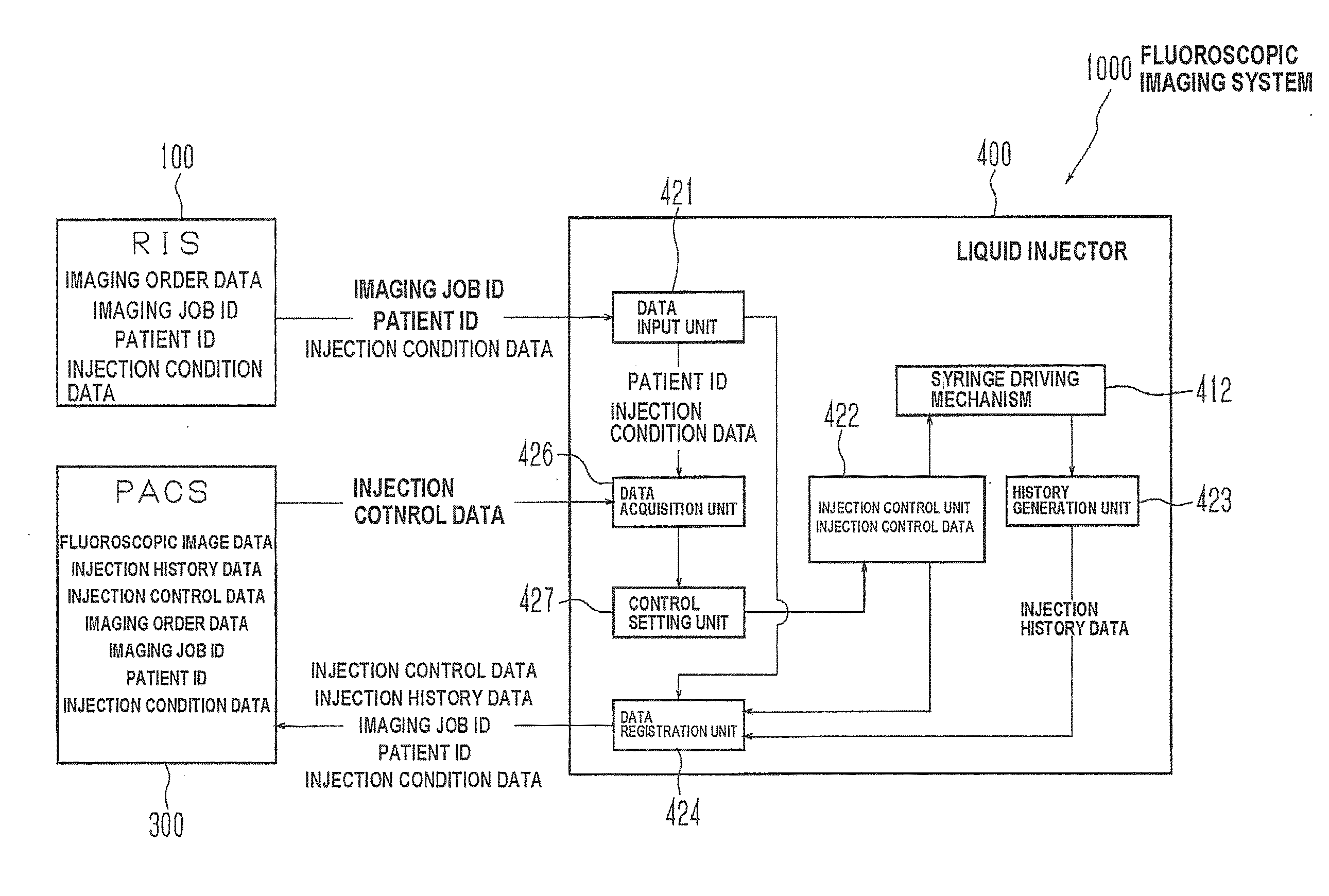
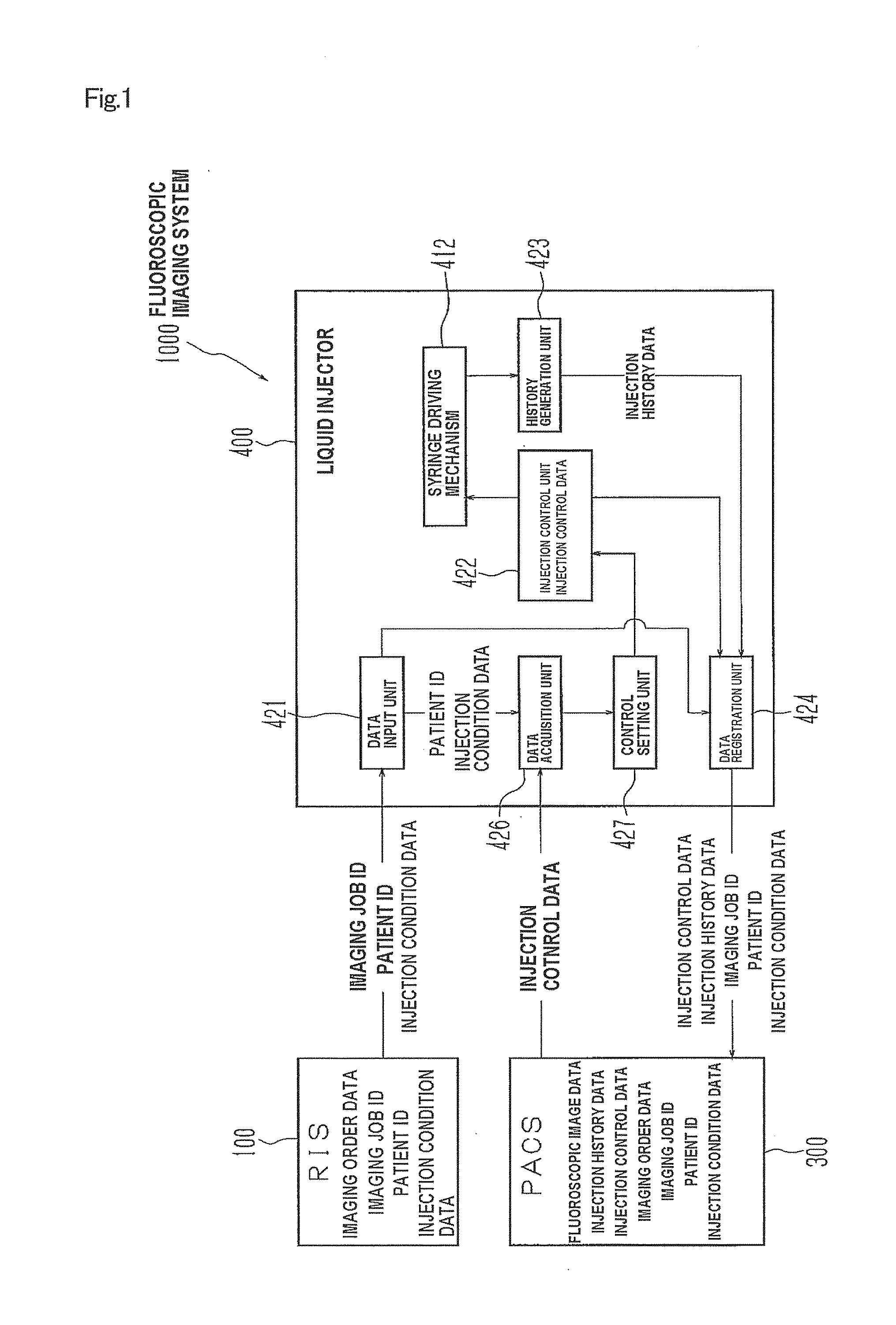
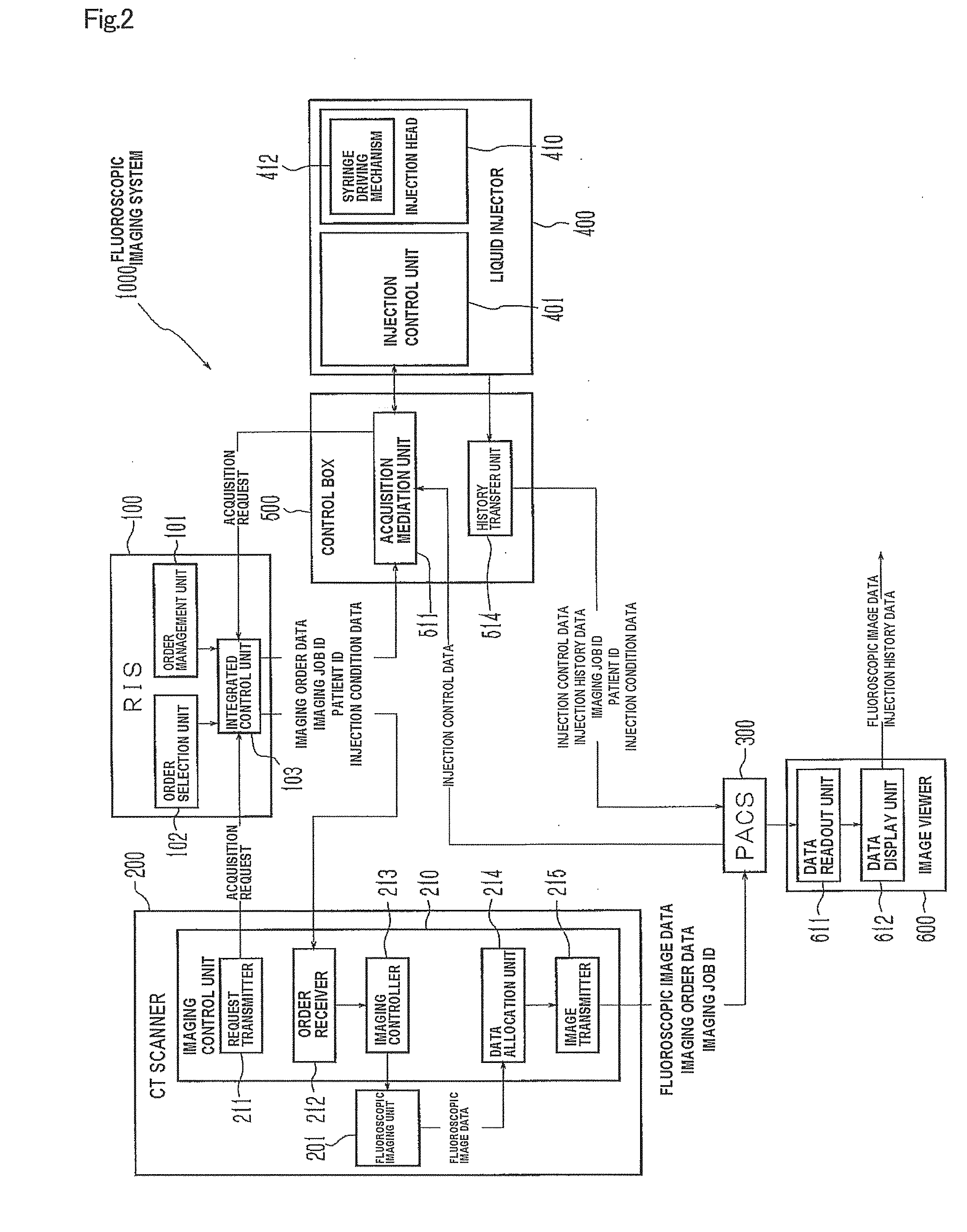
Liquid injector, fluoroscopic imaging system, and computer program
InactiveUS20100174181A1Easy to set upEliminate needData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsFluoroscopic imagingControl data
Once a patient ID and injection control data are input to a liquid injector and liquid injection is executed, the injection control data and injection history data are registered with the patient ID in a PACS. When the same patient is to undergo the second or subsequent liquid injection, the previous injection control data and injection history data are acquired by inputting the patient ID, and set as renewed injection control data. Such arrangement eliminates the need to input the same injection control data for the patient. Further, since the injection control data of each patient is registered and acquired utilizing the patient ID as index, erroneous setting of inappropriate injection control data can be automatically prevented, when the patient undergoes the injection. The liquid injector allows, therefore, easily setting the injection control data, and yet prevents liquid injection based on inappropriate injection control data.
Owner:NEMOTO KYORINDO KK
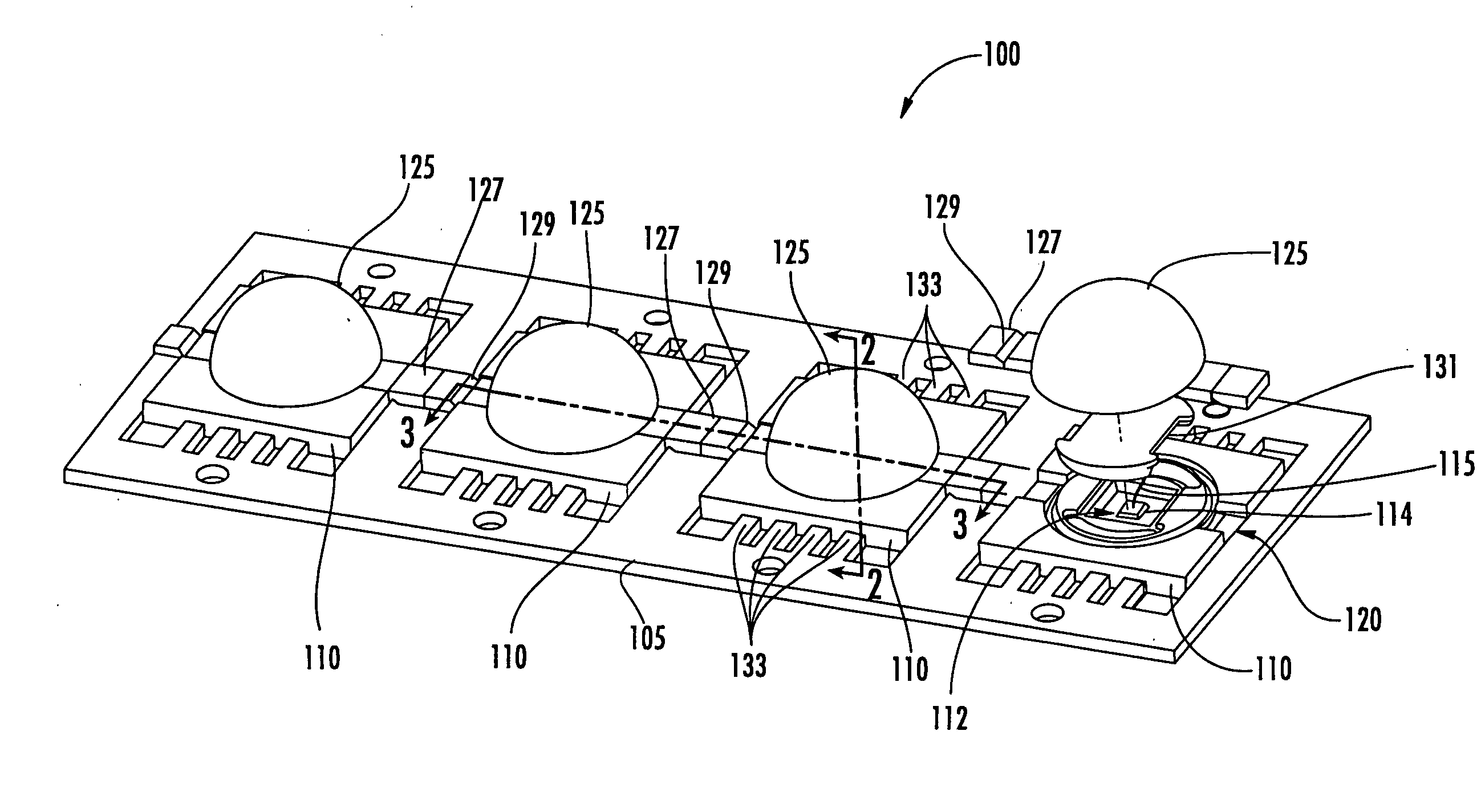
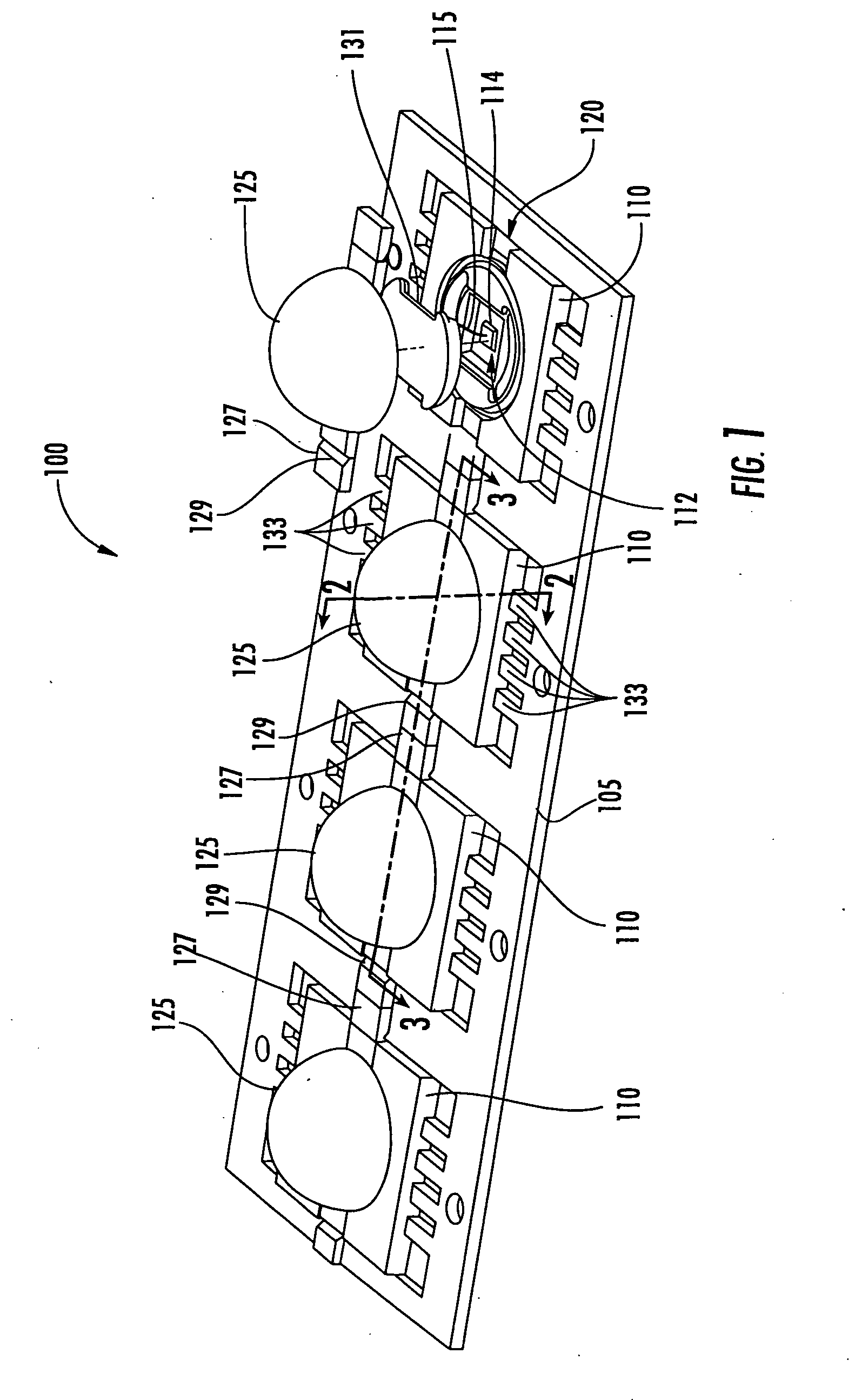
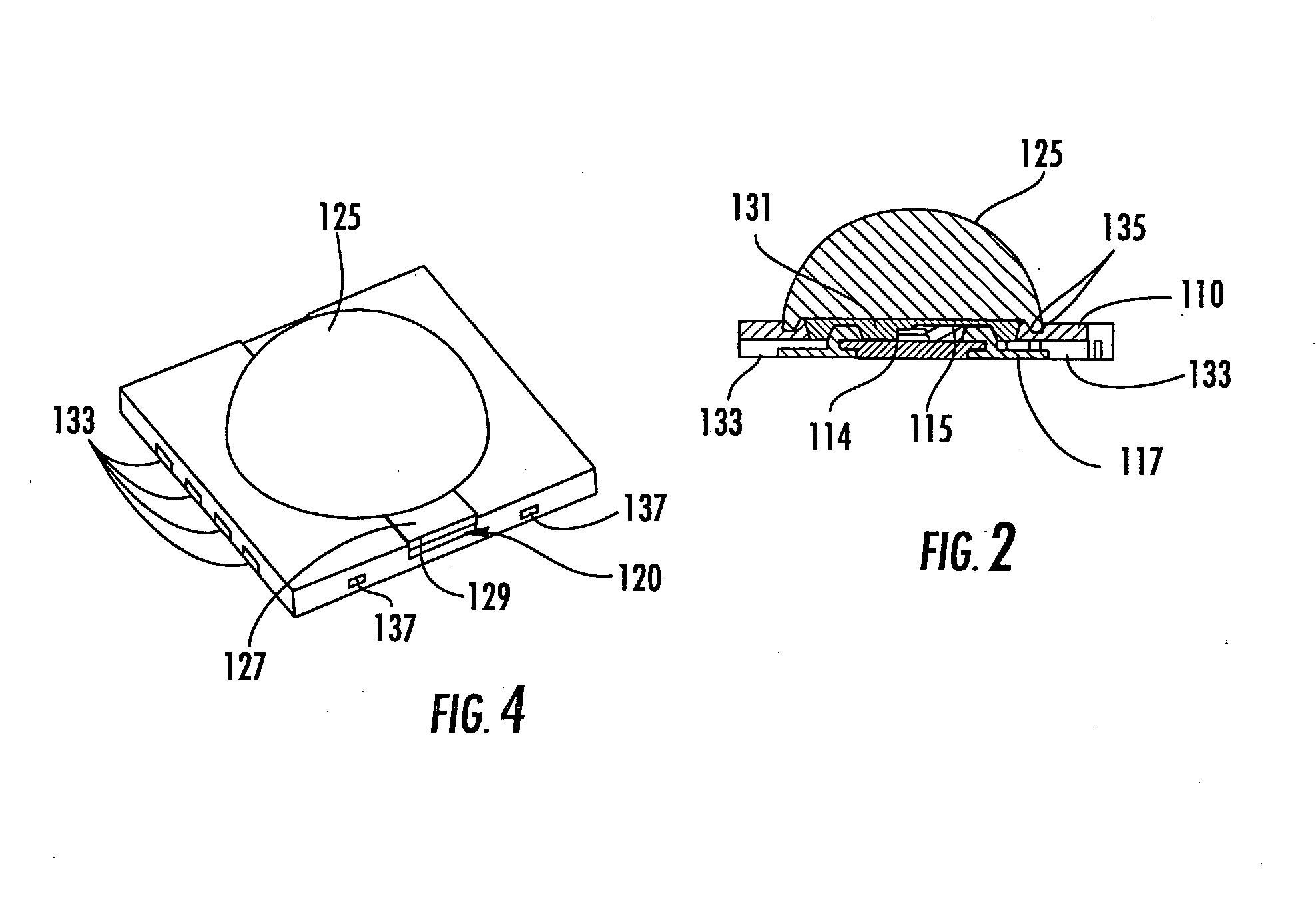
Methods of forming semiconductor light emitting device packages by liquid injection molding and molded semiconductor light emitting device strips
ActiveUS20080044934A1Limit formation of air pocketSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emitting deviceSemiconductor
Semiconductor light emitting device packaging methods include fabricating a substrate configured to mount a semiconductor light emitting device thereon. The substrate may include a cavity configured to mount the semiconductor light emitting device therein. The semiconductor light emitting device is mounted on the substrate and electrically connected to a contact portion of the substrate. The substrate is liquid injection molded to form an optical element bonded to the substrate over the semiconductor light emitting device. Liquid injection molding may be preceded by applying a soft resin on the electrically connected semiconductor light emitting device in the cavity. Semiconductor light emitting device substrate strips are also provided.
Owner:CREELED INC
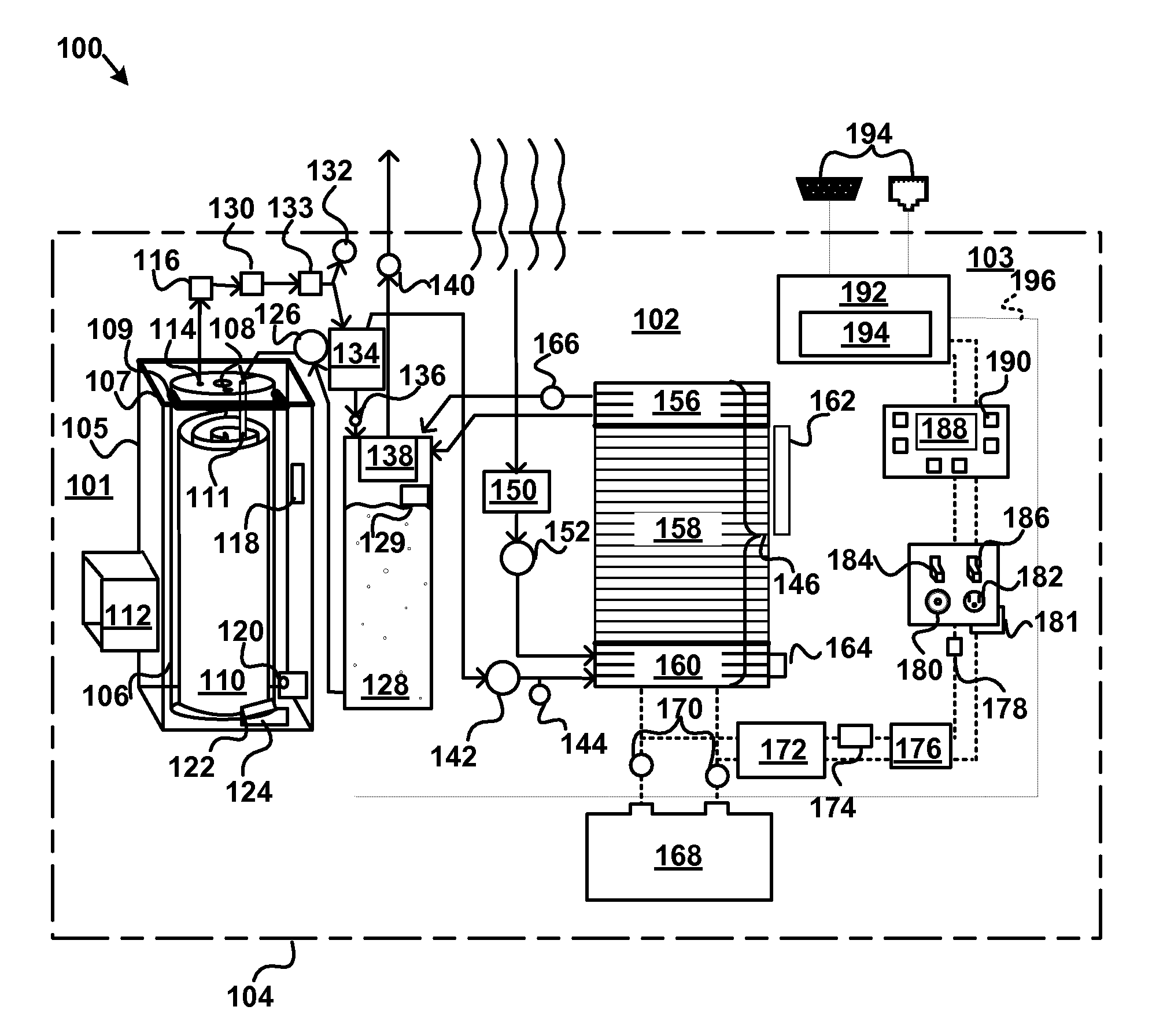
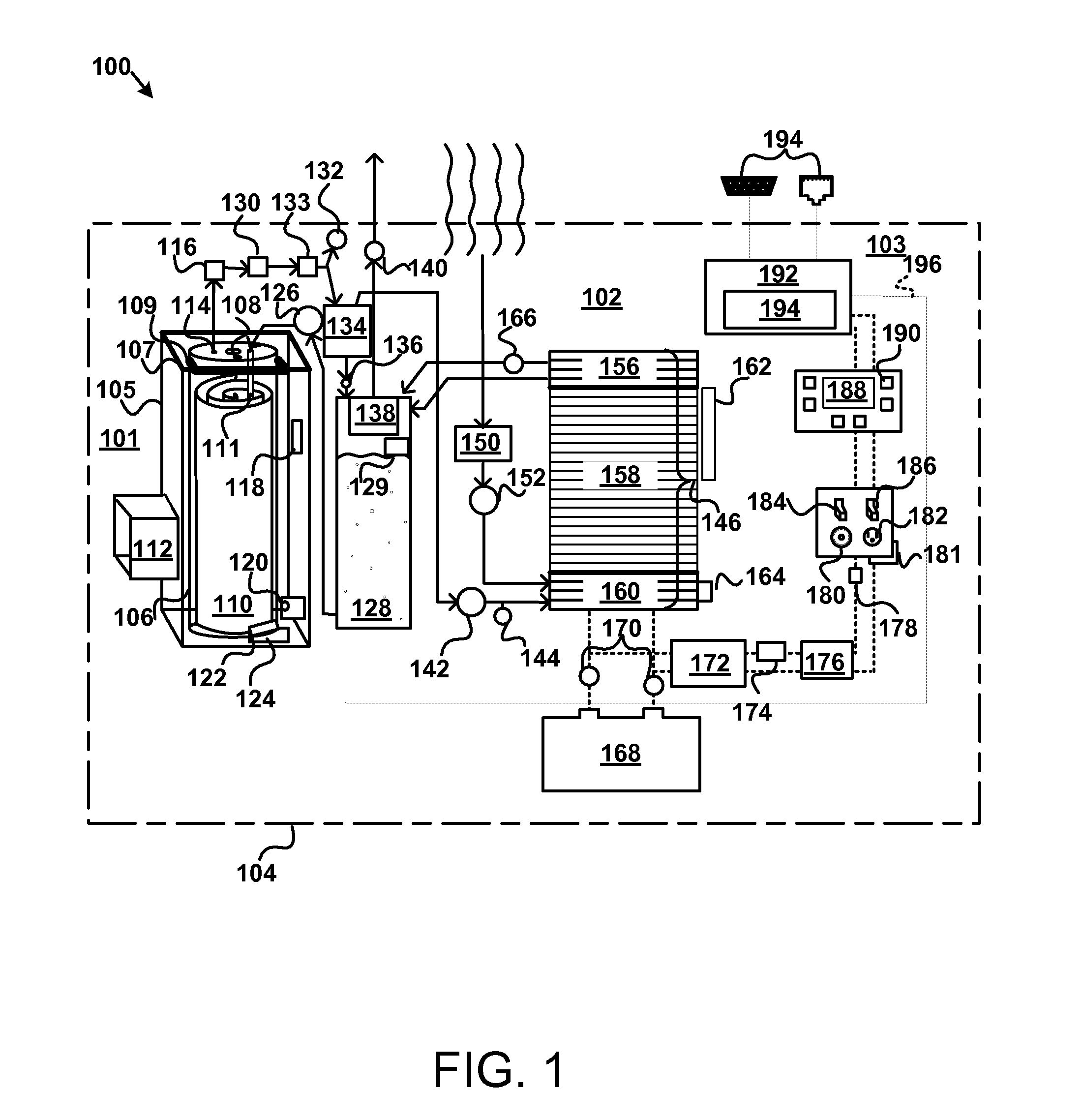
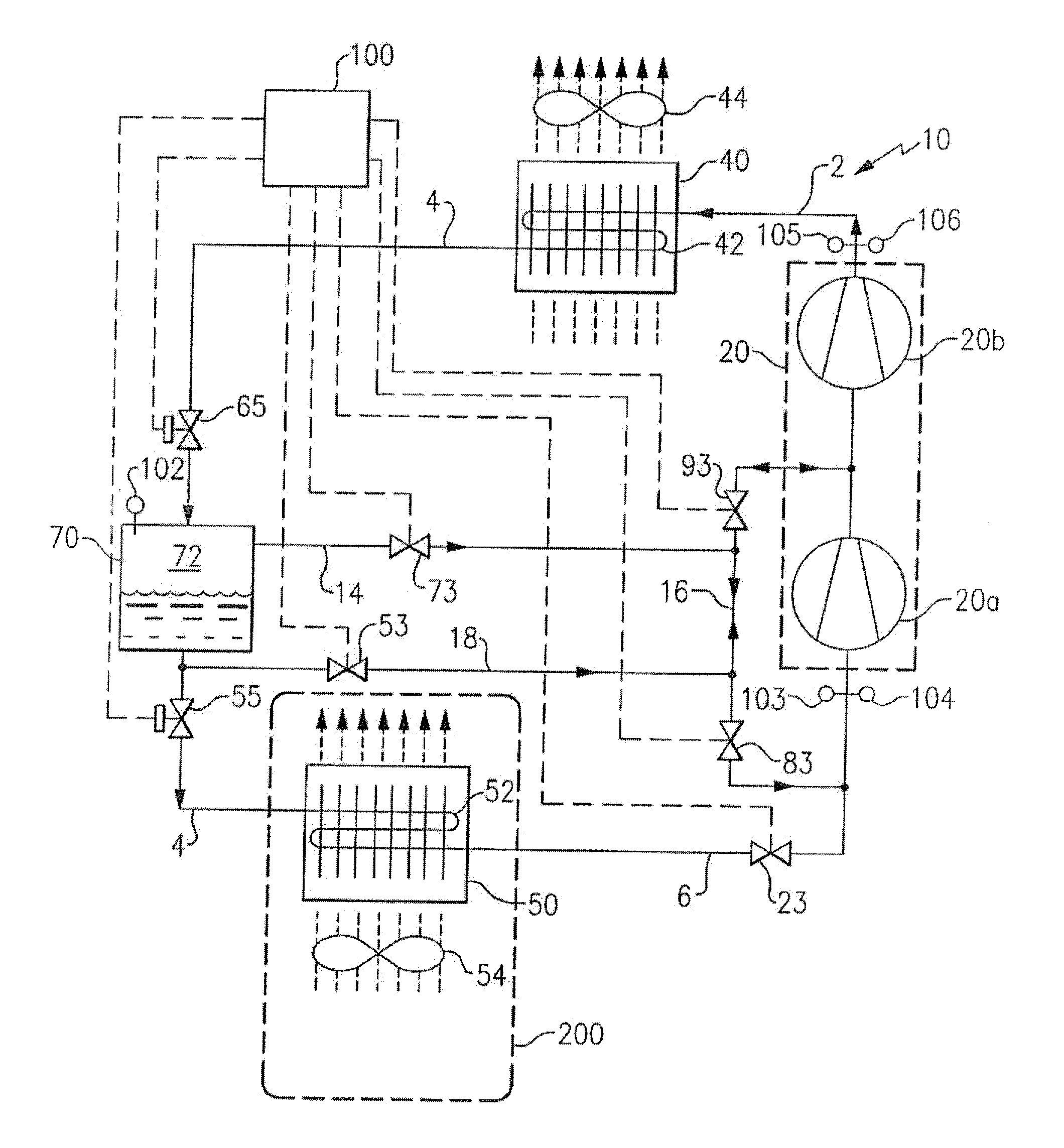
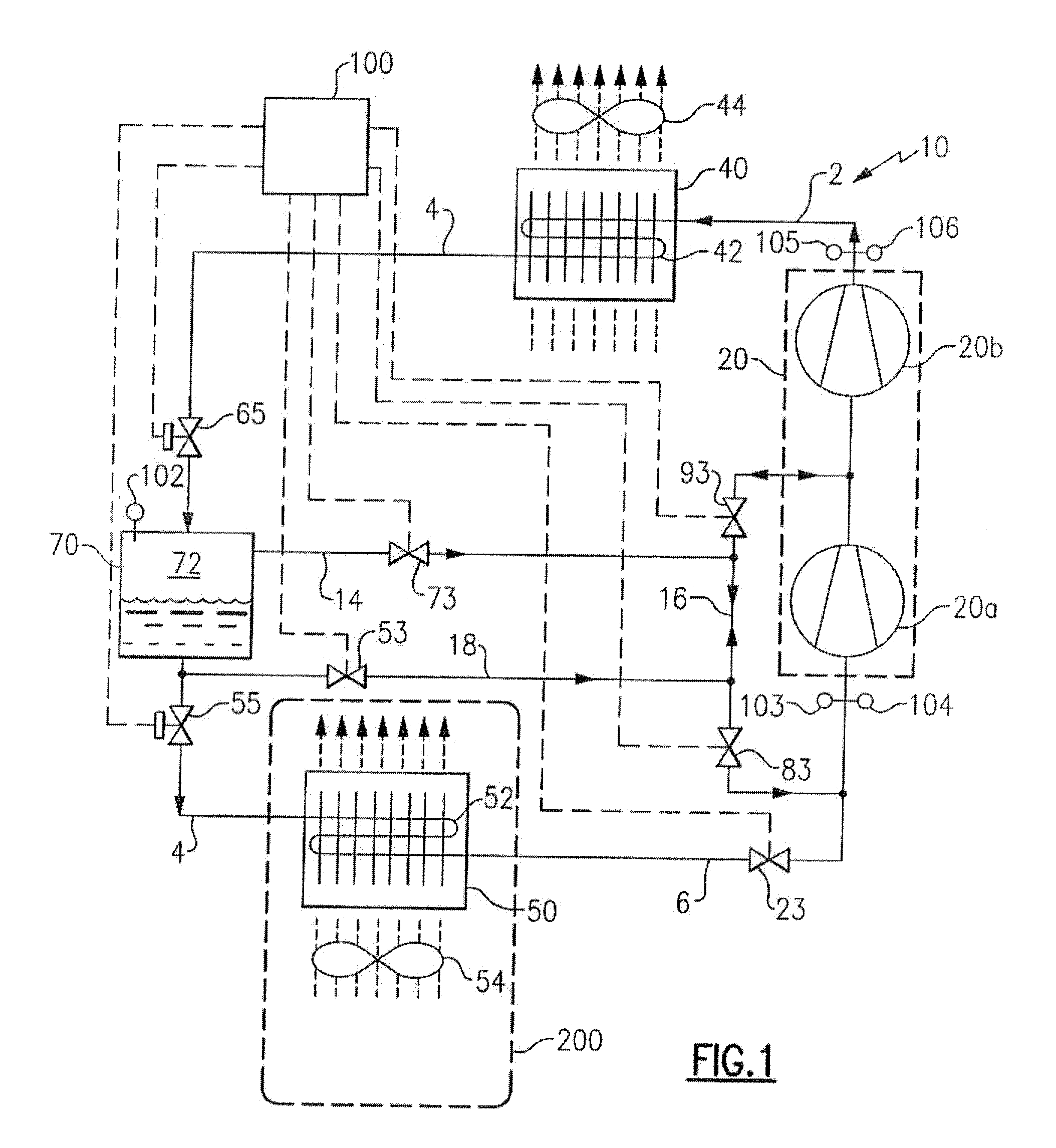
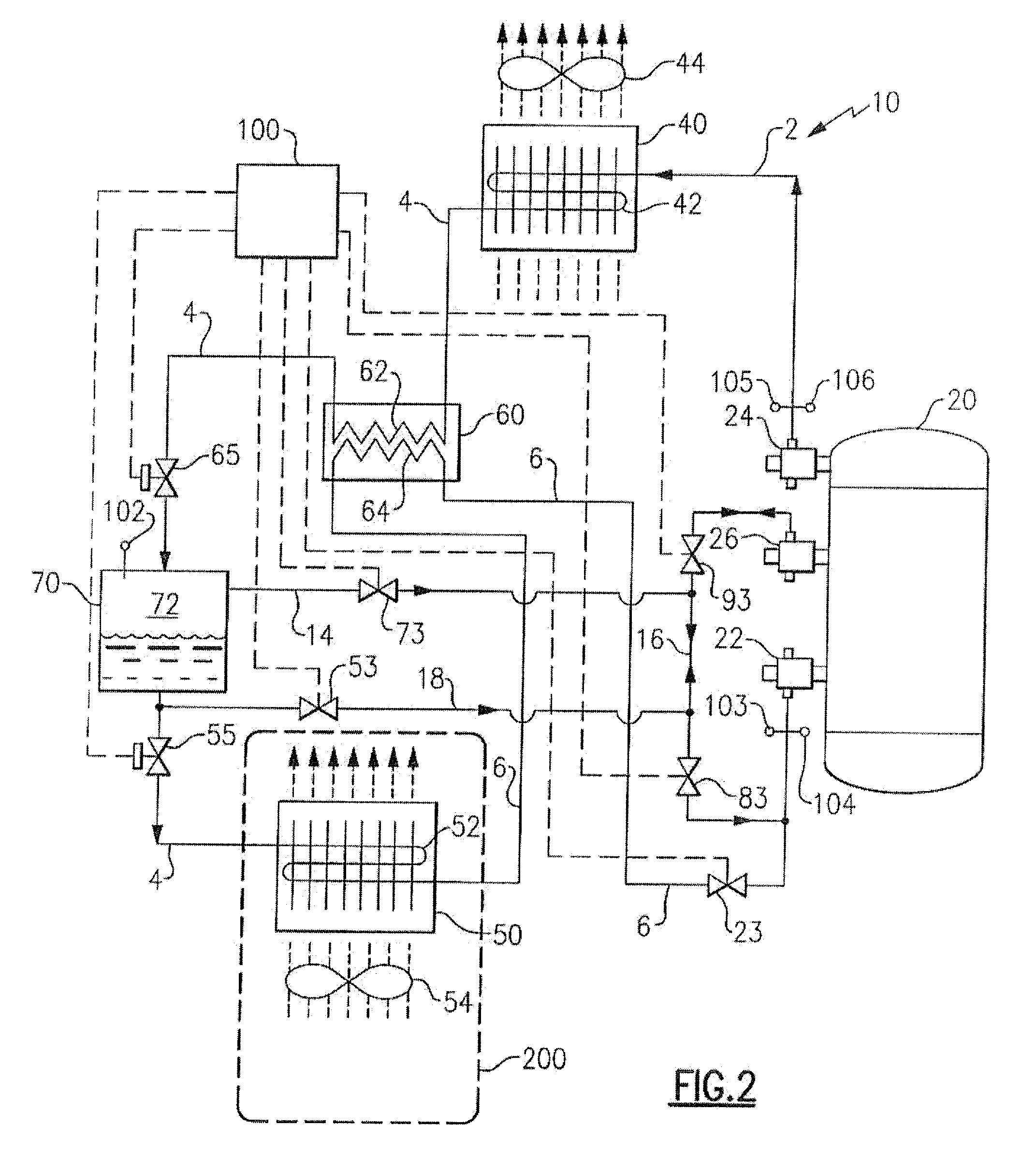
Refrigerant vapor compression system and method of transcritical operation
A refrigerant vapor compression system includes a flash tank economizer defining a separation chamber is disposed in the refrigerant circuit intermediate a refrigerant heat rejection heat exchanger and a refrigerant heat absorption heat exchanger. A primary expansion valve is interdisposed in the refrigerant circuit in operative association with and upstream of the refrigerant heat absorption heat exchanger and a secondary expansion valve is interdisposed in the refrigerant circuit in operative association and upstream of the flash tank economizer. A refrigerant vapor injection line establishes refrigerant flow communication between an upper portion of the separation chamber and an intermediate pressure stage of the system's compression device and a suction pressure portion of the refrigerant circuit. A refrigerant liquid injection line establishes refrigerant flow communication between a lower portion of said separation chamber and an intermediate pressure stage of the compression device and a suction pressure portion of the refrigerant circuit.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Apparatus for infusing liquid to a body
ActiveUS20100331826A1Improve mobilityLow long-term costPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElastomerEngineering
An infusion device having a housing with a reusable control portion and an expendable reservoir portion includes a precise drive for an infusion pump. The drive includes a piezoelectric bender assembly, a limiter and at least one contact stop. The piezoelectric bender assembly includes a cantilevered piezoelectric bender having an member of predetermined thickness fixed to move with the second end. A limiter of dimensionally stable material including a gap and at least a first mounting hole extending to the gap. The member of predetermined thickness extends into the gap. A first contact stop is positioned in the gap to define a critical gap distance limiting movement of the member of predetermined thickness in the gap. A base has a mounting surface, a port through the base and extending to the mounting surface. The port includes a first length having a smaller diameter at the mounting surface and a second length displaced from the mounting surface and having a larger diameter. A rigid cannula extends from the base through the port. The rigid cannula has a diameter smaller than the smaller diameter of the port, and the first length of the port has an annular open gap for lateral or pivotal movement of the rigid cannula. A mount of elastomeric material in the length having the larger diameter mounts the rigid cannula. The cannula includes hydrogel material in a desiccated state coating the surface of the cannula, including the beveled end, which rehydrates upon placement in the patient.
Owner:MEDSOLVE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com