Patents
Literature
12051 results about "Boiling point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
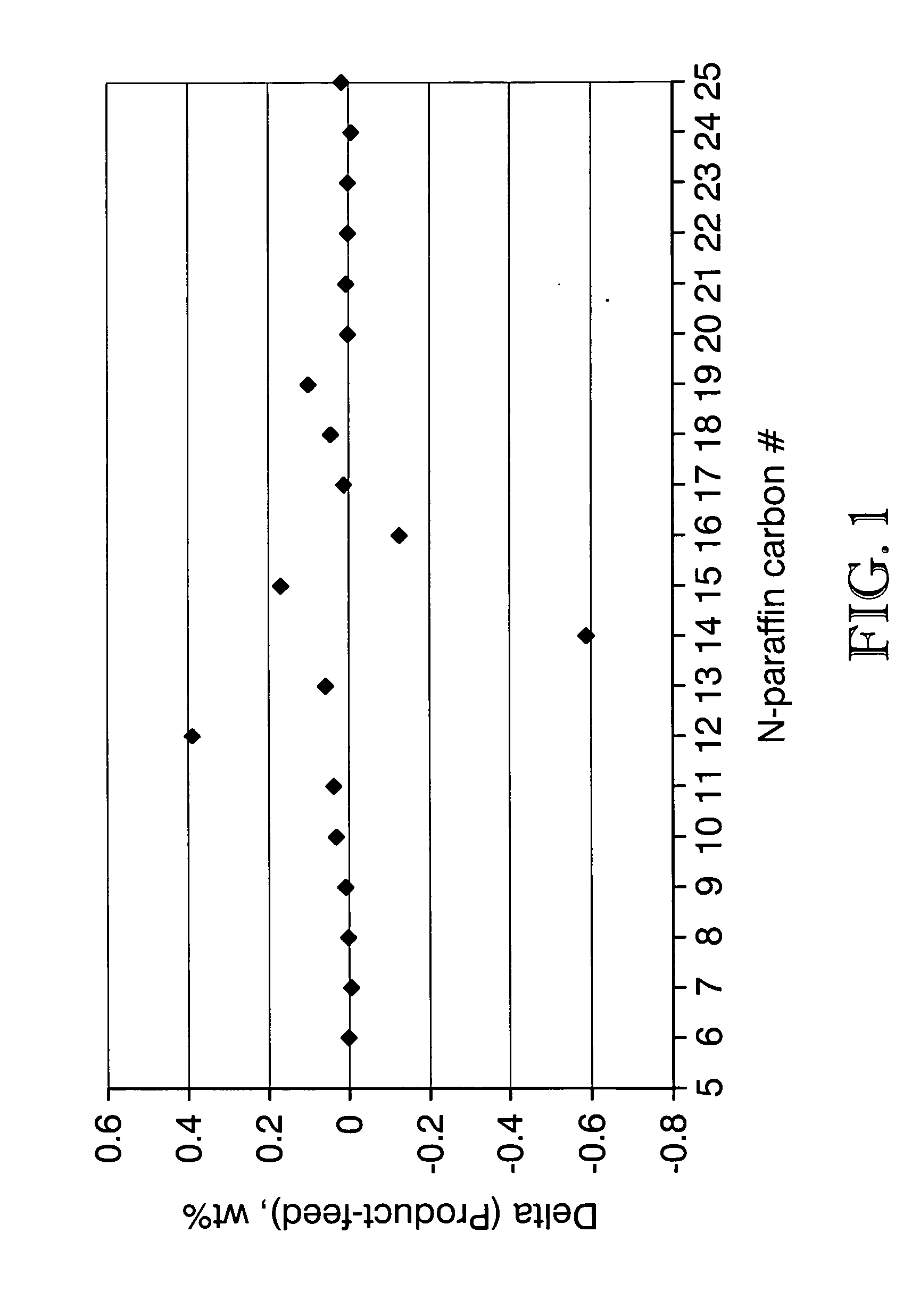
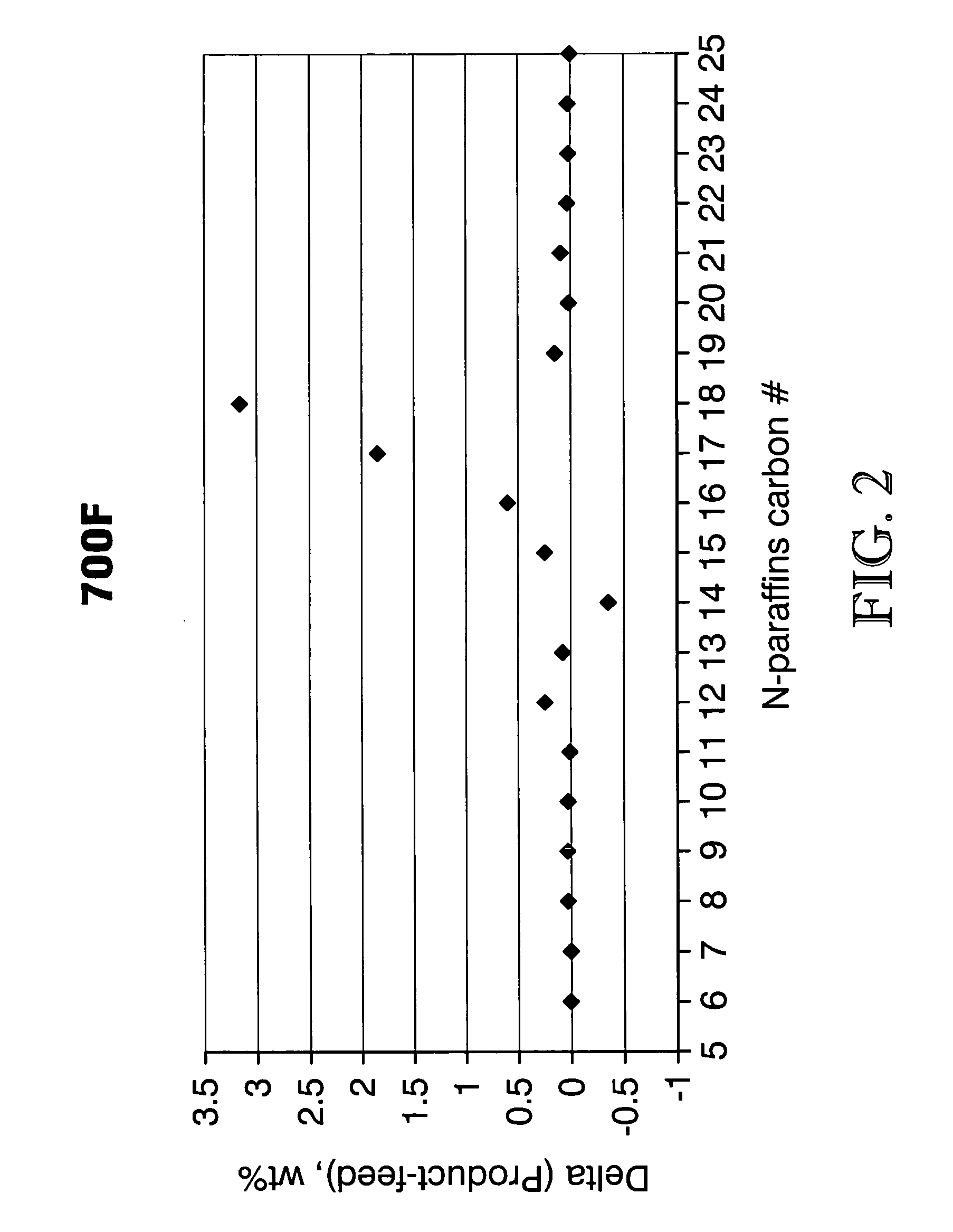
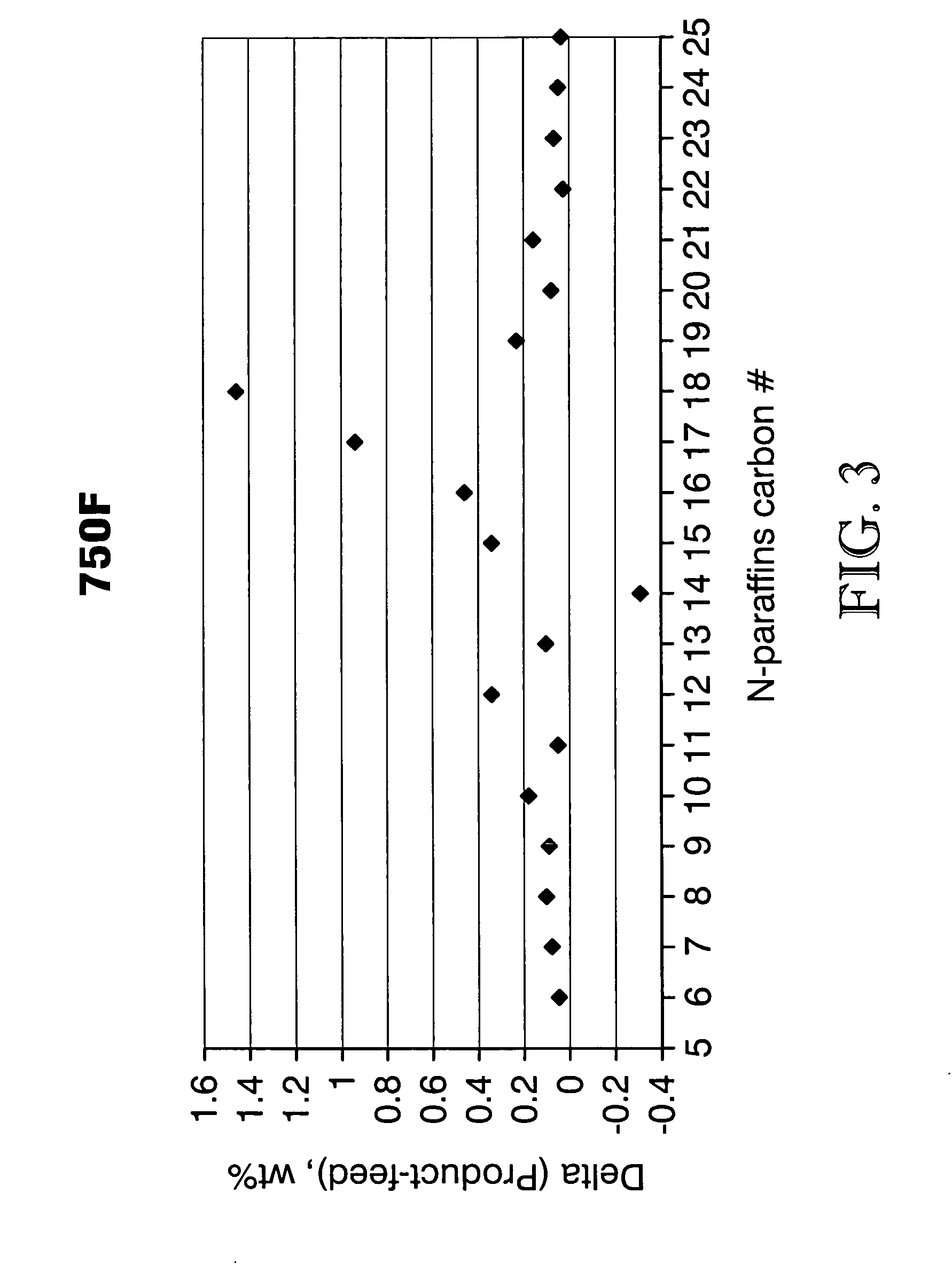
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A liquid in a partial vacuum has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. A liquid at high pressure has a higher boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. For example, water boils at 100 °C (212 °F) at sea level, but at 93.4 °C (200.1 °F) at 1,905 metres (6,250 ft) altitude. For a given pressure, different liquids will boil at different temperatures.
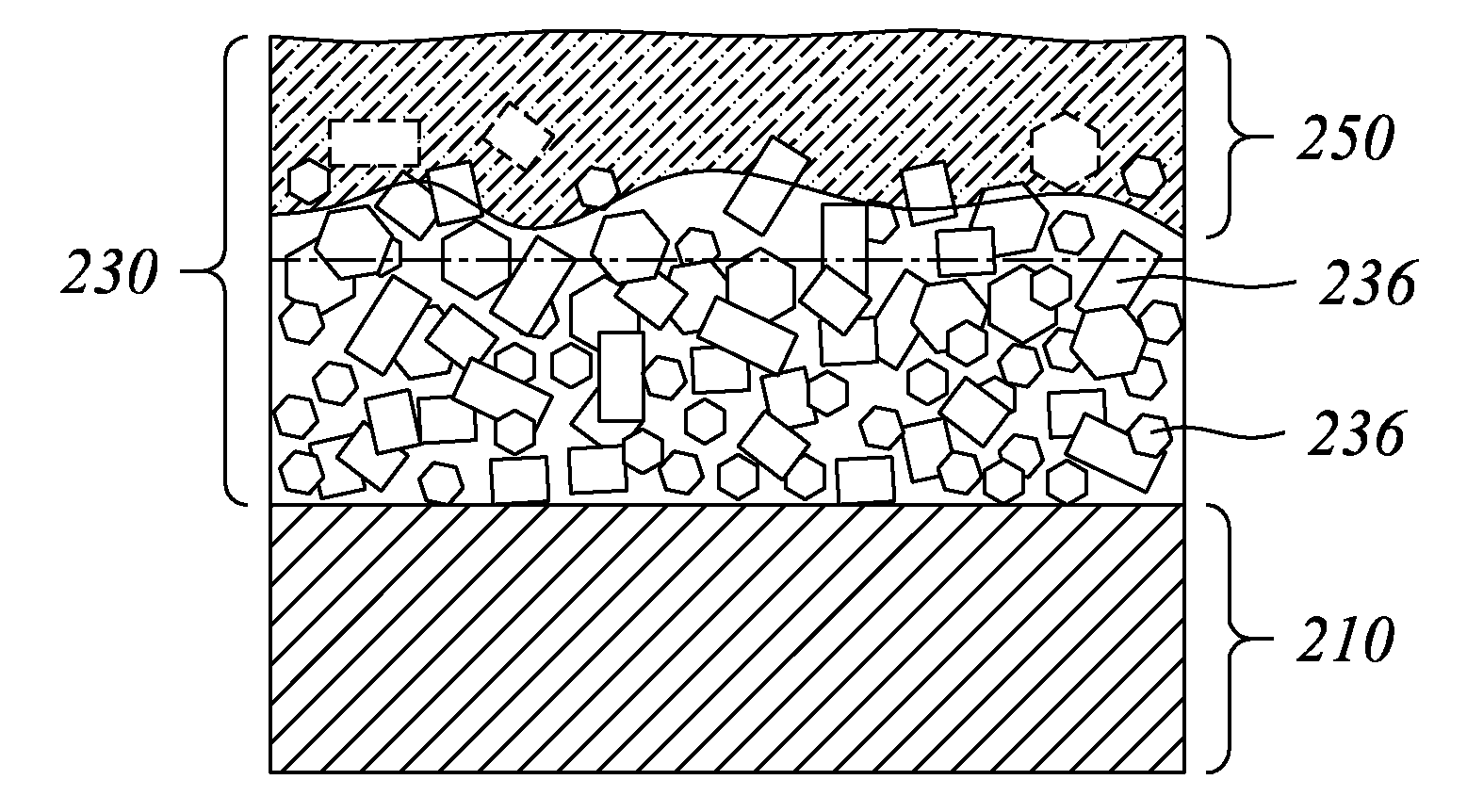
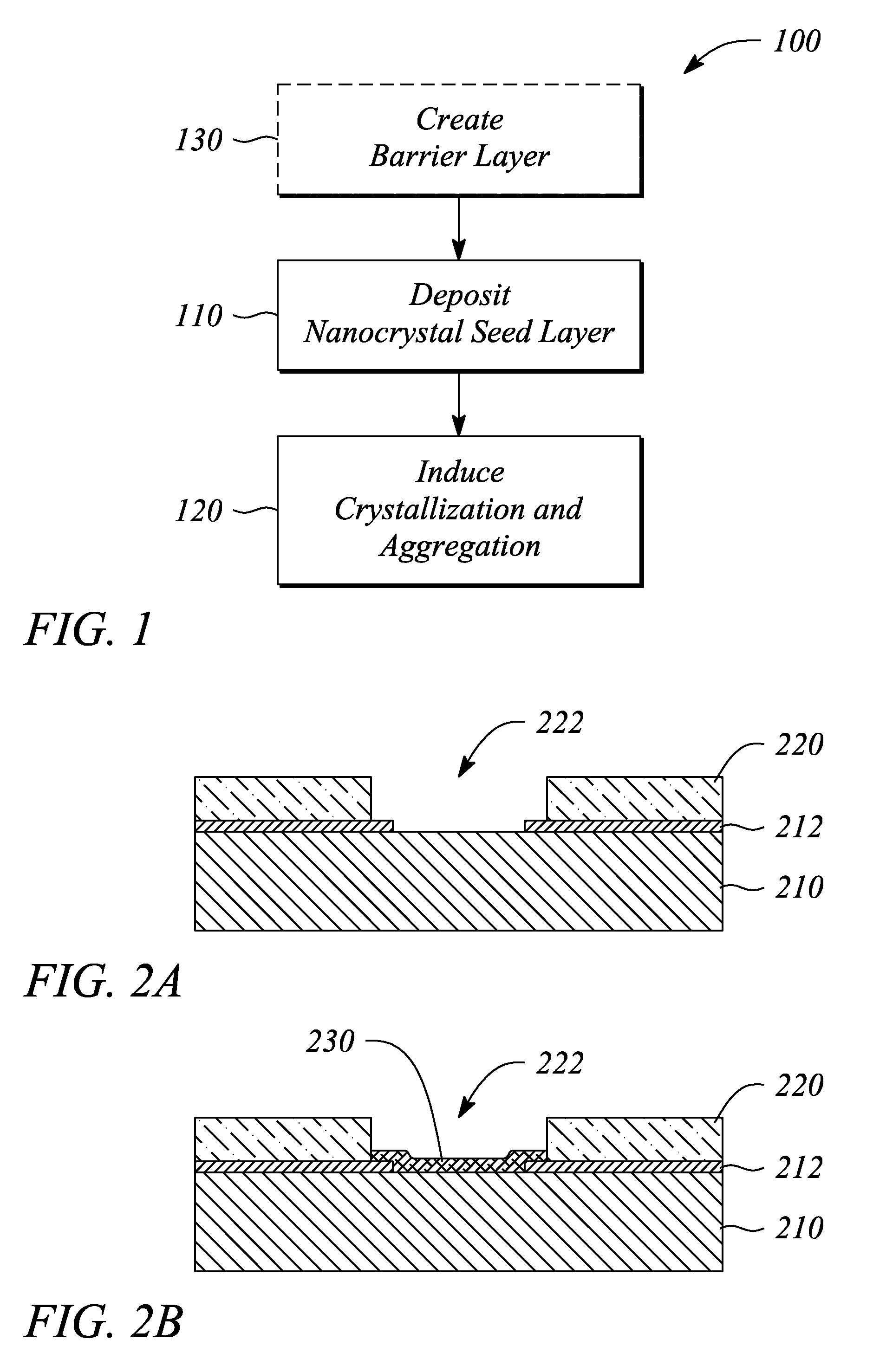
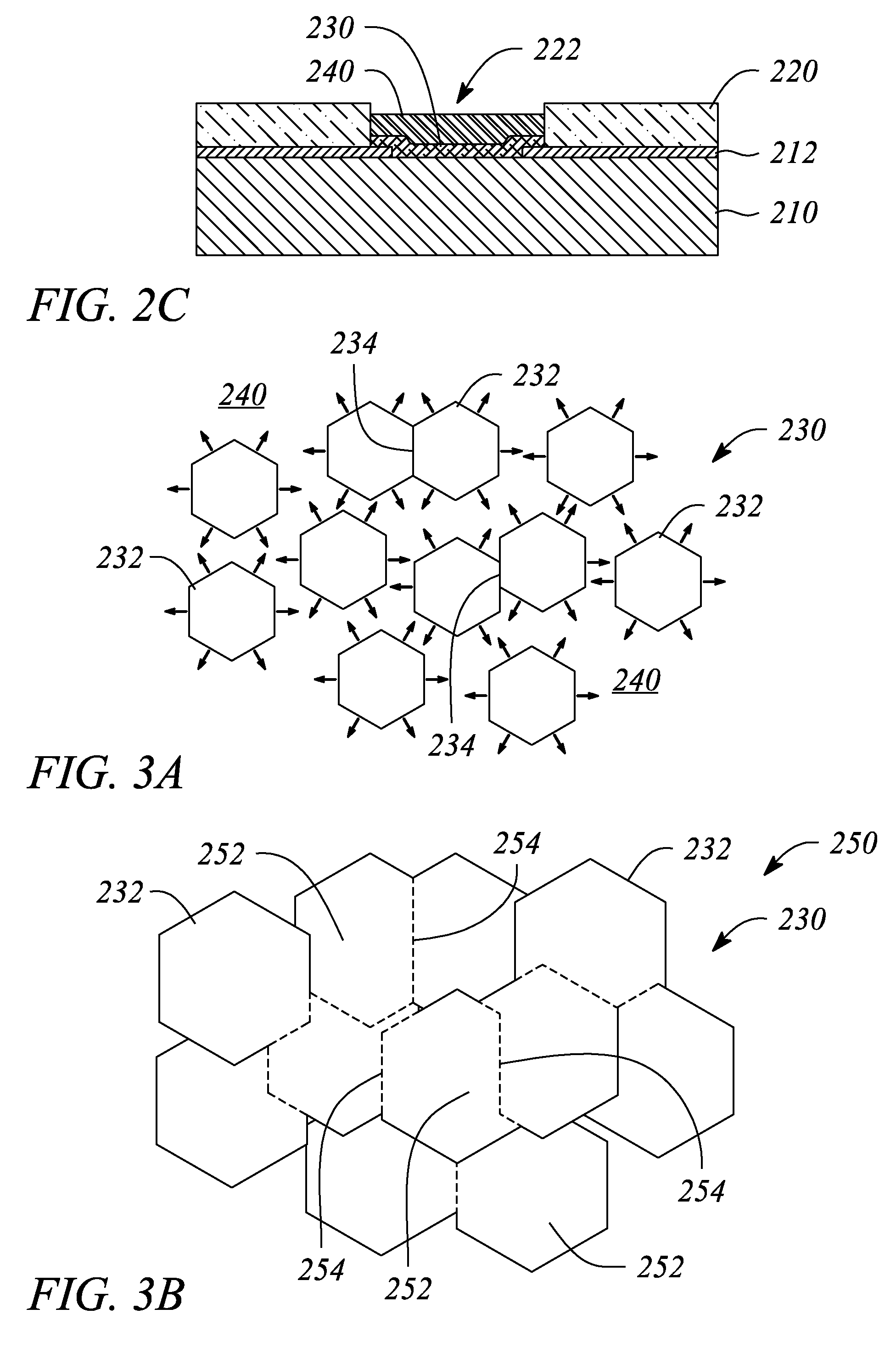
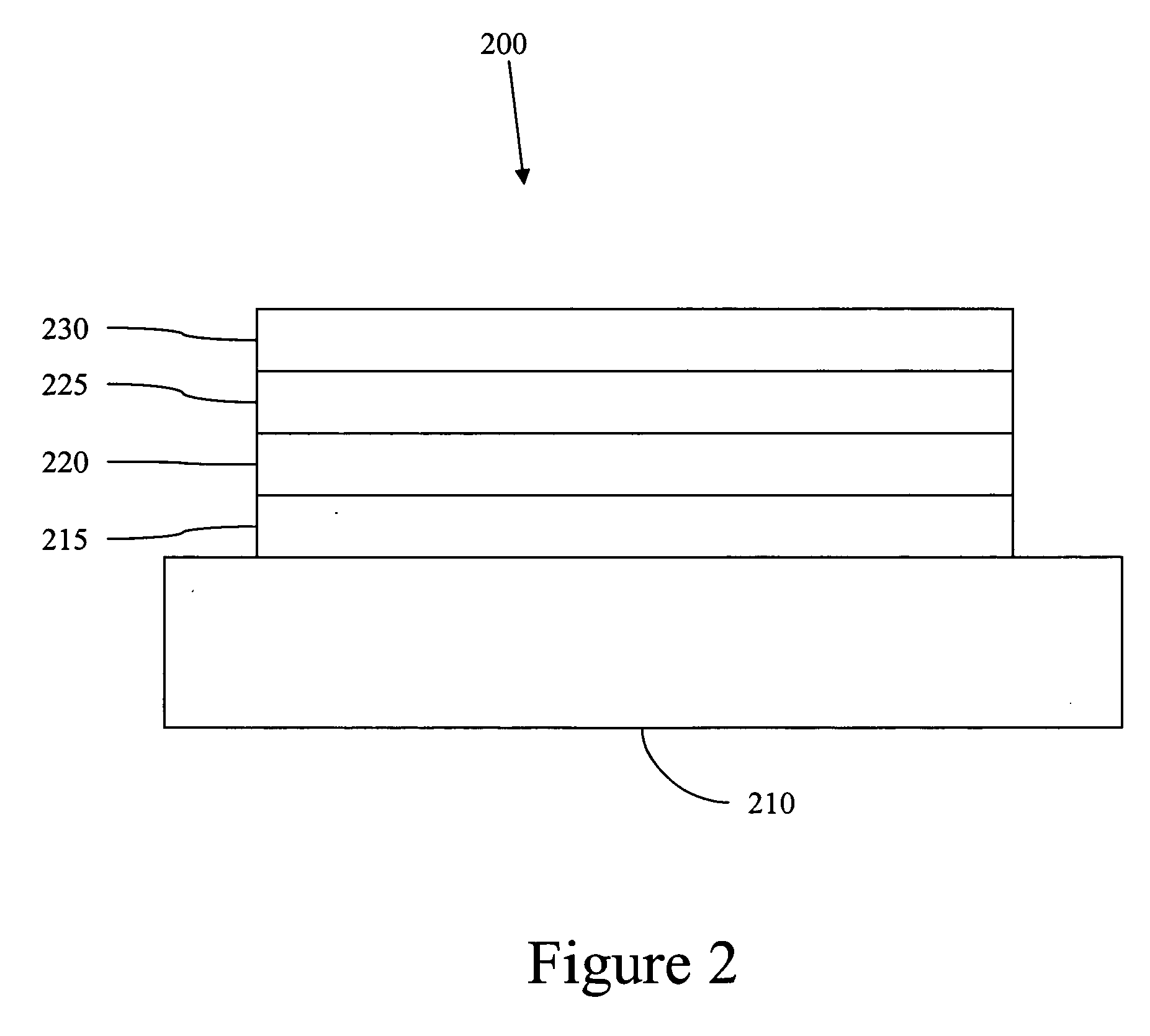
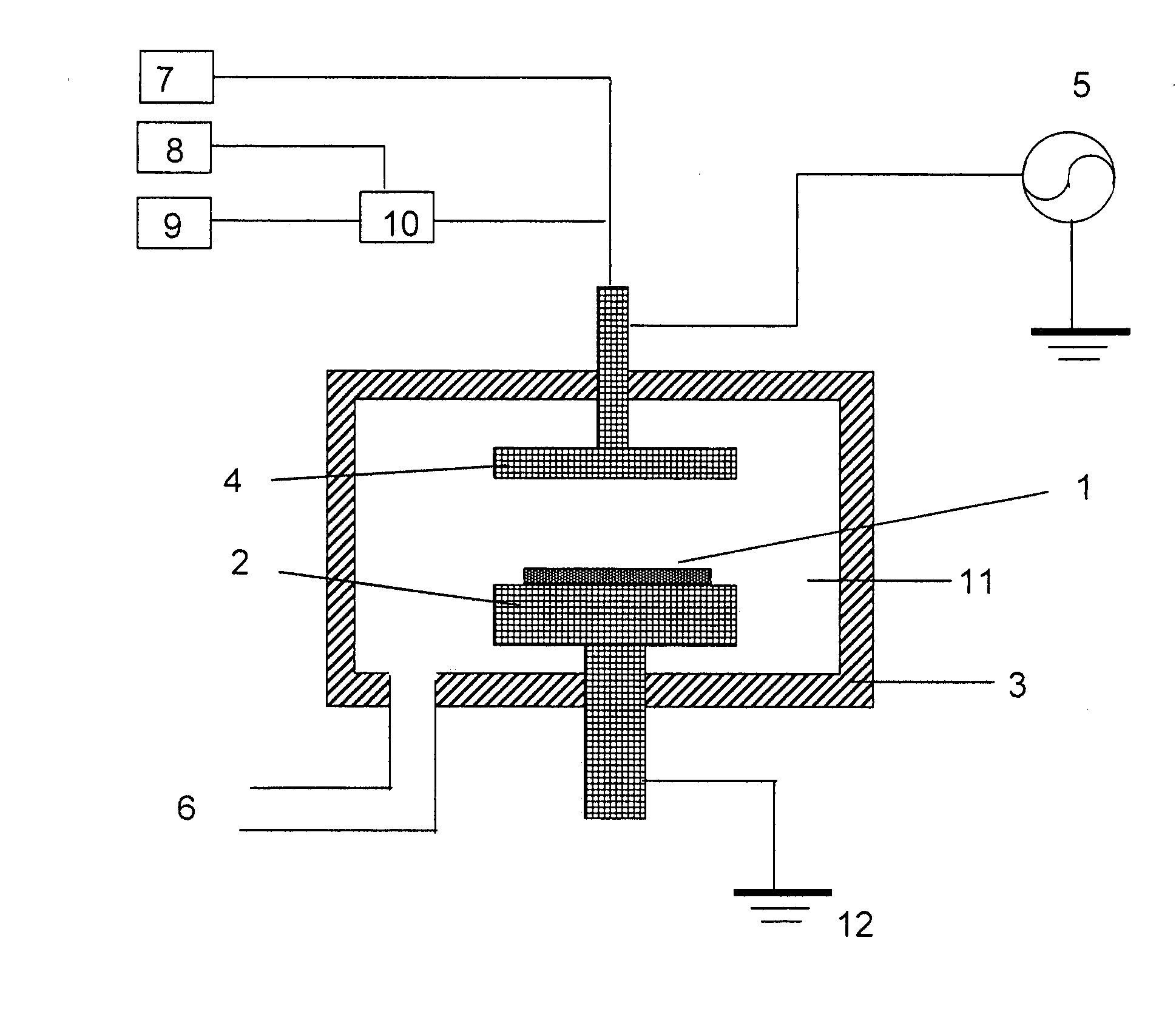
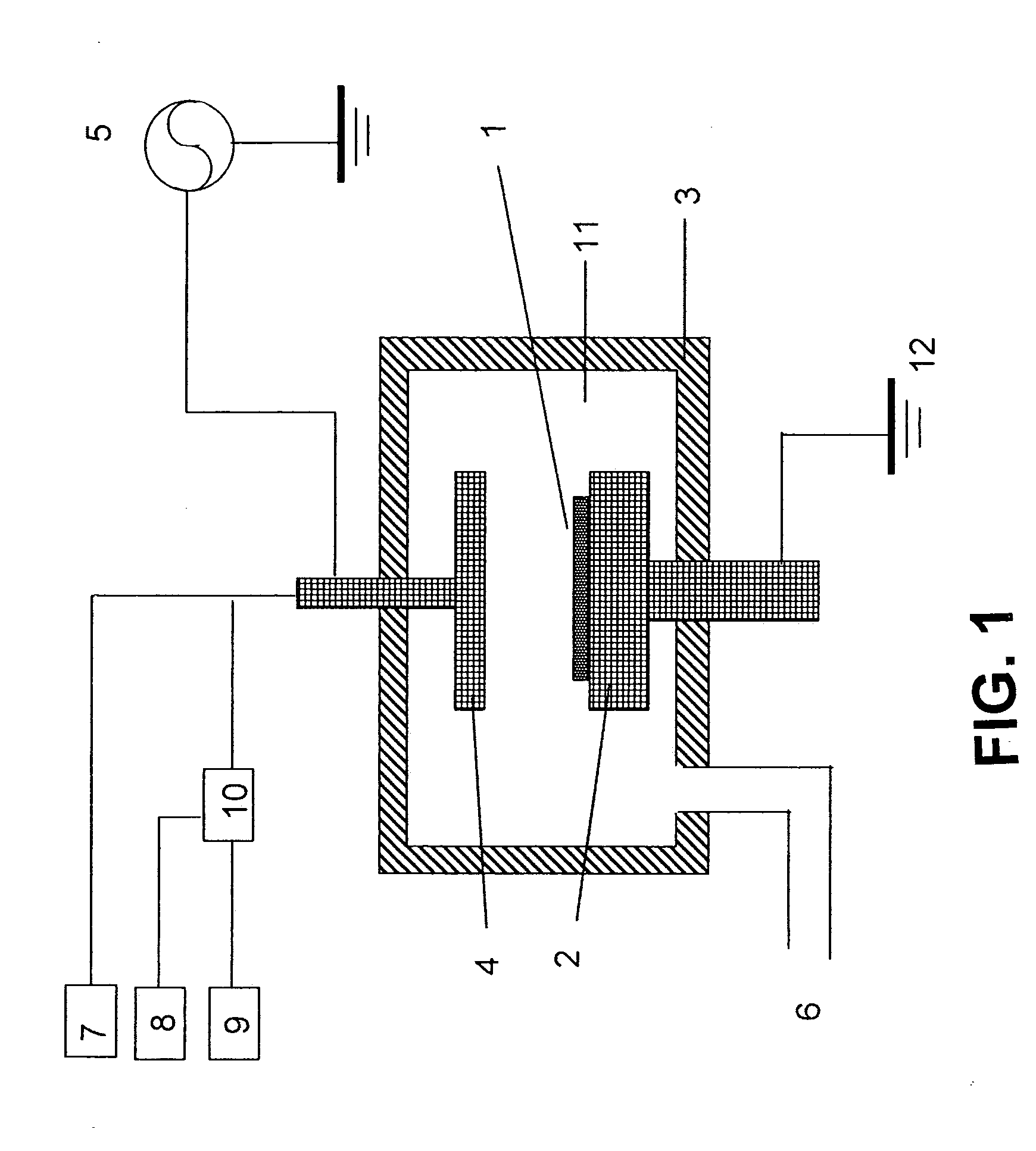
Fused nanocrystal thin film semiconductor and method
A thin film semiconductor and a method of its fabrication use induced crystallization and aggregation of a nanocrystal seed layer to form a merged-domain layer. The nanocrystal seed layer is deposited onto a substrate surface within a defined boundary. A reaction temperature below a boiling point of a reaction solution is employed. A thin film metal-oxide transistor and a method of its production employ the thin film semiconductor as a channel of the transistor. The merged-domain layer exhibits high carrier mobility.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
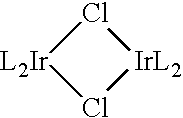
Carbene containing metal complexes as OLEDs
ActiveUS20050258742A1Indium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic solventAlcohol
A process for preparing a compound having the formula L2IrL′ is provided. The process comprises: combining and L′ in the presence of an organic solvent to form a mixture, wherein L is a suitable carbene ligand precursor coordinated to Ir; and L′ is a bidentate ligand or two monodentate ligands, and L is different from L′; Also provided is a process for preparing a compound having the formula The process comprises: (a) combining L, a carbene ligand precursor, with an organic solvent; (b) maintaining the mixture of step (a) at a temperature from about 175° C. to less than the boiling point of the organic solvent in (a). A process for preparing a compound with the formula L3Ir is also provided. This process comprises combining and L in the presence of alcohol and a base to form a mixture, wherein L is a bidentate ligand that may form a five-membered chelate ring.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY +1
Premium wear resistant lubricant
A premium synthetic lubricant having antiwear properties comprises a synthetic isoparaffinic hydrocarbon base stock and an effective amount of at least one antiwear additive. The antiwear additive is preferably at least one of a metal phosphate, a metal dialkyldithiophosphate, a metal dithiophosphate a metal thiocarbamate, a metal dithiocarbamate, an ethoxylated amine dialkyldithiophosphate and an ethoxylated amine dithiobenzoate. Metal dialkyldithiophosphates are preferred, particularly zincdialkyldithiophosphate (ZDDP). The base stock is derived from a waxy, Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon feed fraction comprising hydrocarbons having an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750 DEG F., by a process which comprises hydroisomerizing the feed and dewaxing the isomerate. The lubricant may also contain hydrocarbonaceous and synthetic base stock material in admxture with the Fischer-Tropsch derived base stock.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
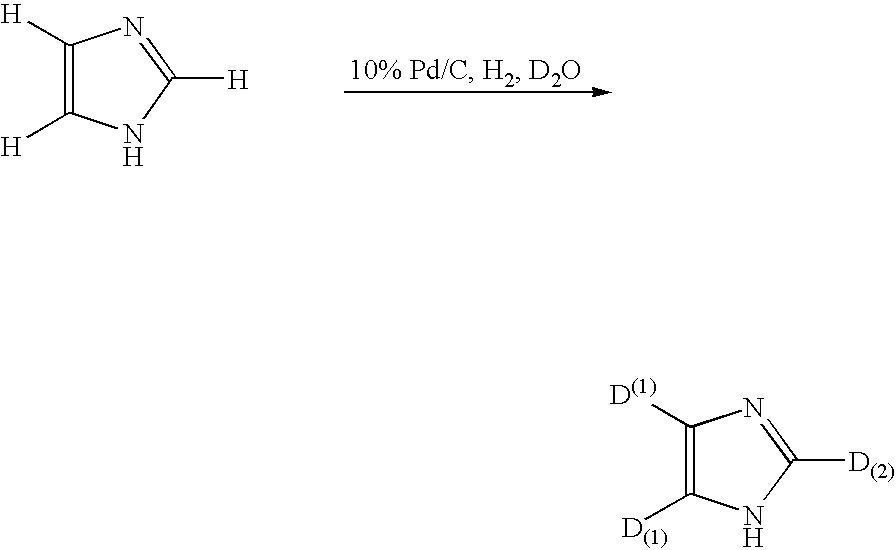
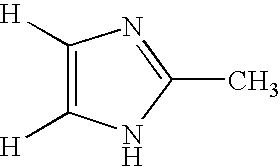
Method for deuteration of a heterocyclic ring
ActiveUS7517990B2Isotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsSugar derivativesNickel catalystHydrogen atom
The present invention relates to a method for deuteration of a heterocyclic ring, which comprises subjecting a compound having a heterocyclic ring to sealed refluxing state in a deuterated solvent in the presence of an activated catalyst selected form a palladium catalyst, a platinum catalyst, a rhodium catalyst, a ruthenium catalyst, a nickel catalyst and a cobalt catalyst. In accordance with a method of the present invention, a hydrogen atom belonging to a heterocyclic ring of a compound having a heterocyclic ring can be very efficiently deuterated because temperature of deuteration reaction can be maintained at higher than boiling point of the solvent.Further, a method for deuteration of the present invention can be applied widely to deuteration of various compounds having a heterocyclic ring which are liable to decomposition under supercritical conditions or acidic conditions, leading to industrial and efficient deuteration of a compound having a heterocyclic ring.
Owner:FUJIFILM WAKO PURE CHEM CORP
Production of synthetic lubricant and lubricant base stock without dewaxing
InactiveUS6103099AThermal non-catalytic crackingRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAutomatic transmissionBoiling point
A lubricating base stock useful for forming lubricants such as a multigrade automotive oils, automatic transmission oils, greases and the like is prepared by hydroisomerizing a waxy hydrocarbon feed fraction having an initial boiling point in the 650-750 DEG F. range and an end point of at least 1050 DEG F., synthesized by a slurry Fischer-Tropsch hydrocarbon synthesis process. The hydroisomerization forms a hydroisomerate containing the desired base stock which is recovered, without dewaxing the hydroisomerate. The hydroisomerization is conducted at conditions effective to convert at least 67 wt. % of the 650-750 DEG F.+ waxy feed hydrocarbons to lower boiling hydrocarbons. When combined with a standard lubricant additive package, these base stocks have been formed into multigrade automotive crankcase oils, transmission oils and hydraulic oils meeting the specifications for these oils.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
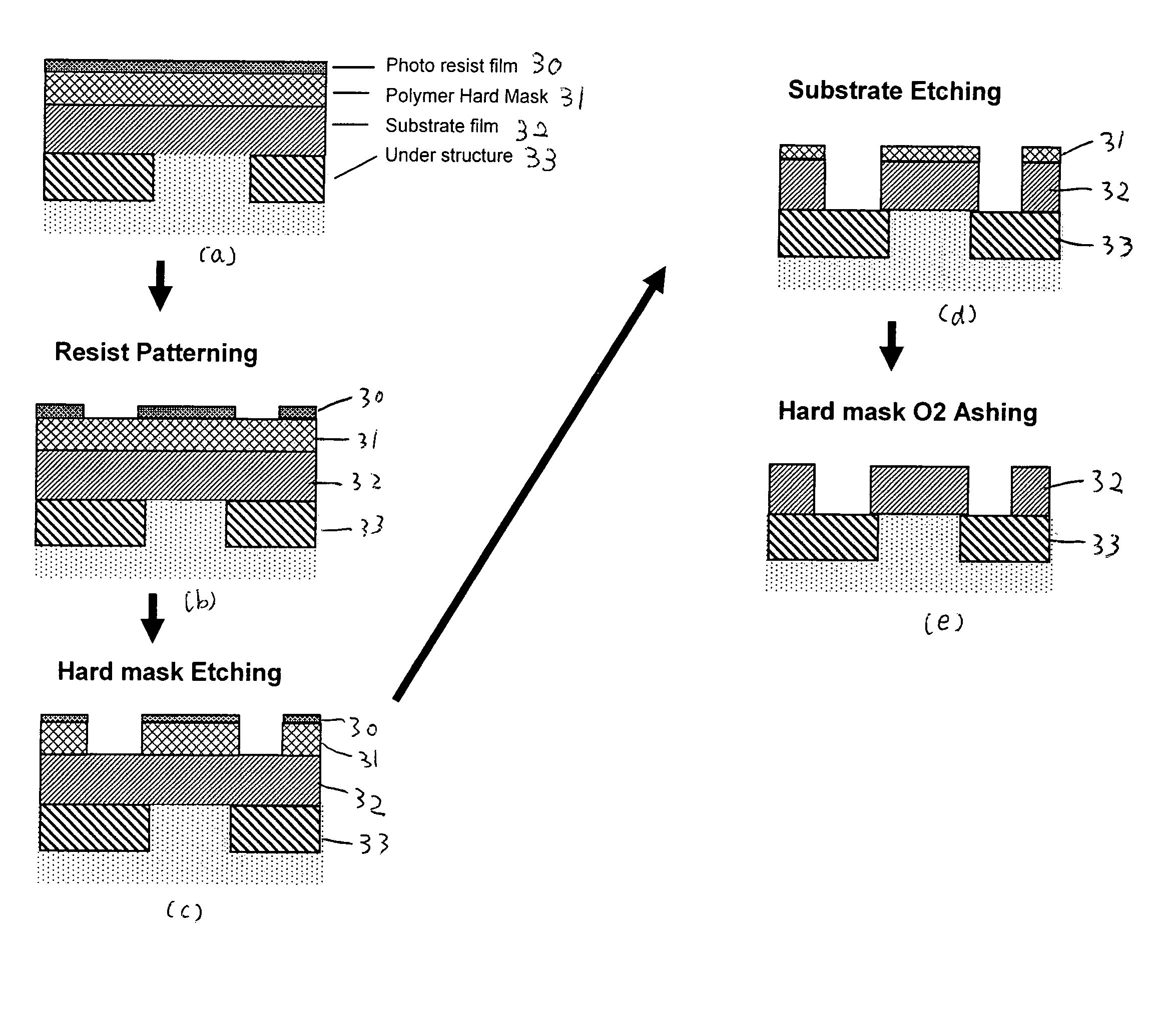
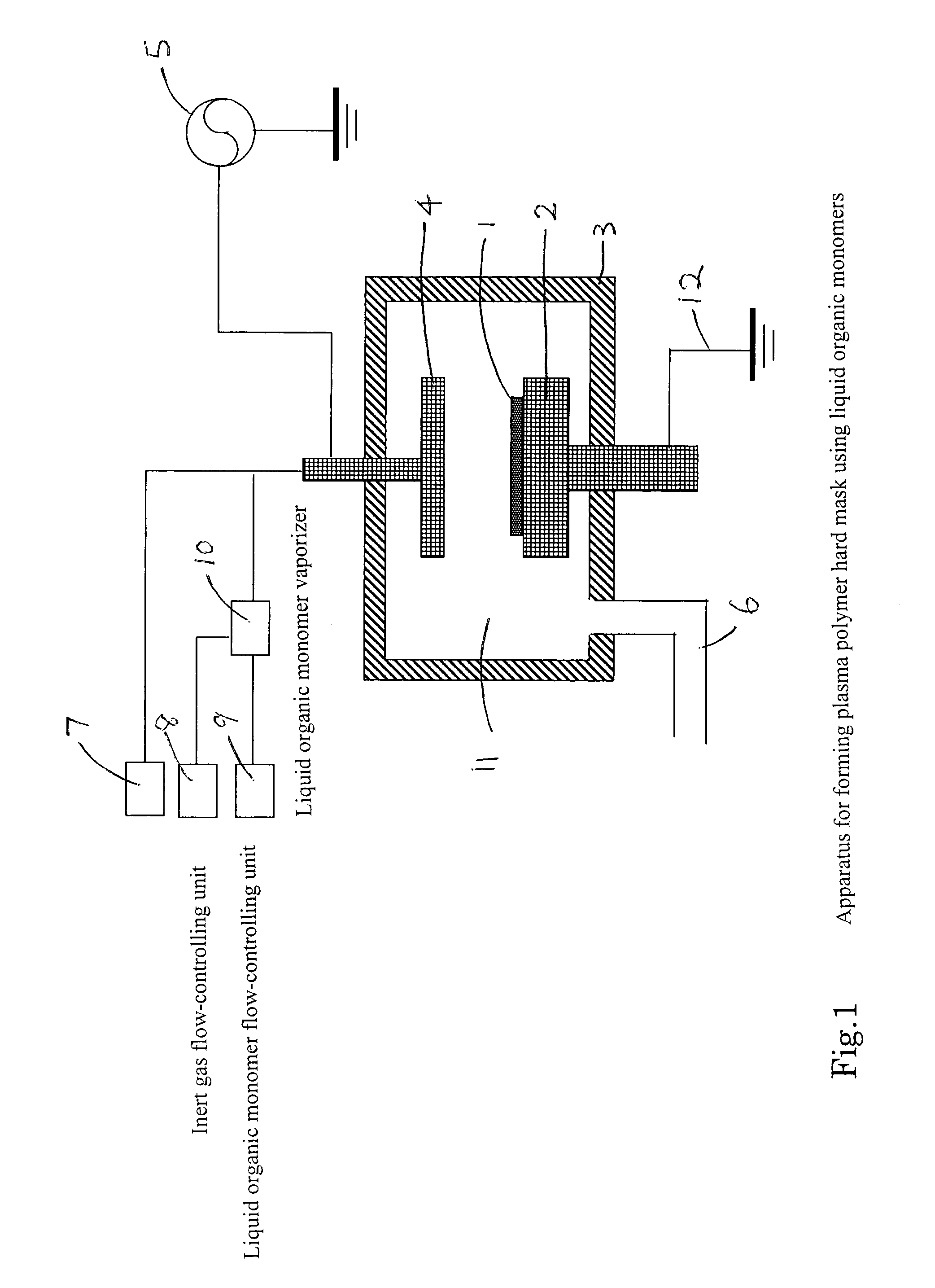
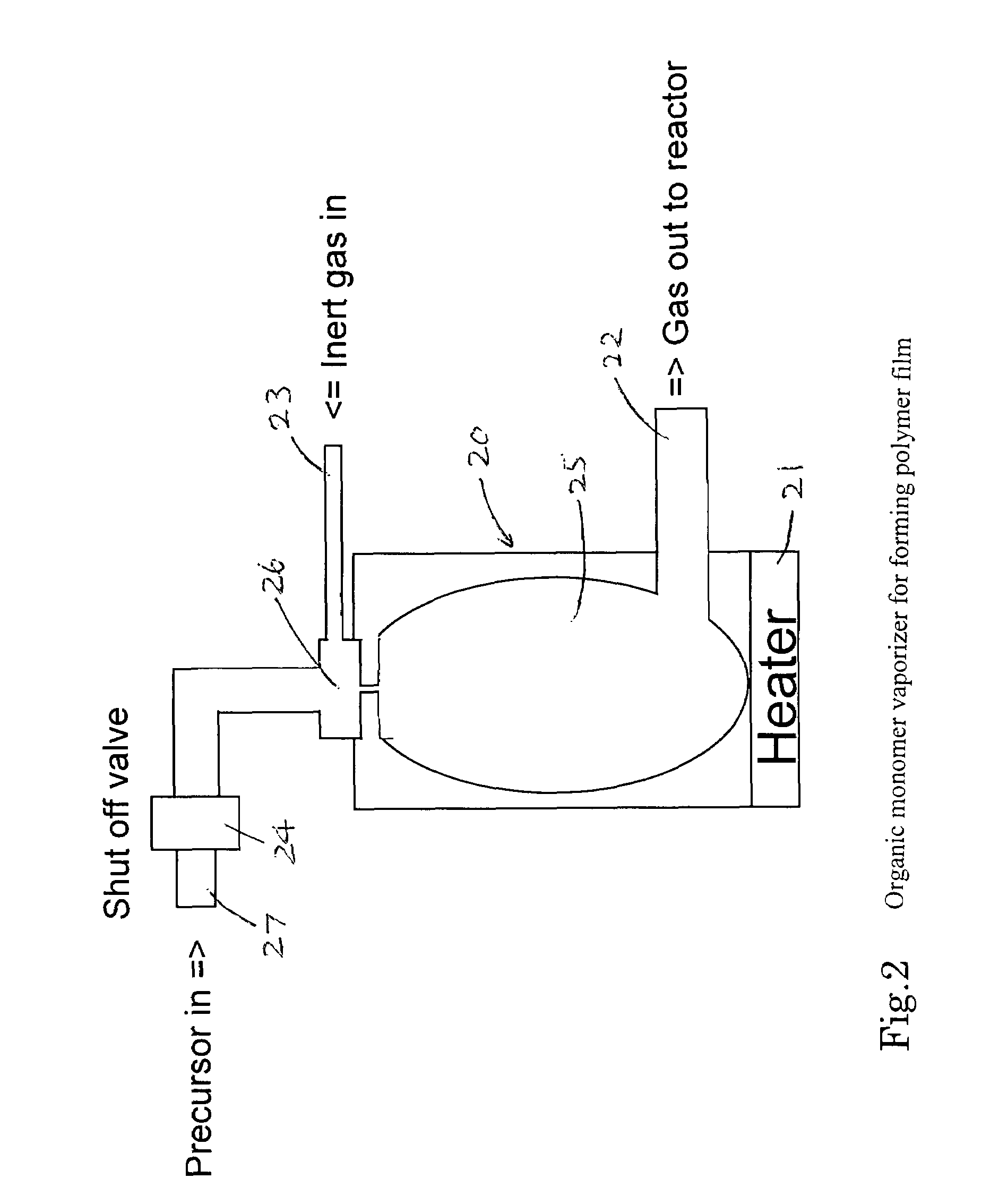
Method of forming a carbon polymer film using plasma CVD
ActiveUS20070218705A1Improve featuresFunction increaseLiquid surface applicatorsPhotomechanical apparatusCapacitanceBoiling point
A method forms a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on a semiconductor substrate by a capacitively-coupled plasma CVD apparatus. The method includes the steps of: vaporizing a hydrocarbon-containing liquid monomer (CαHβXγ, wherein α and β are natural numbers of 5 or more; γ is an integer including zero; X is O, N or F) having a boiling point of about 20° C. to about 350° C.; introducing the vaporized gas into a CVD reaction chamber inside which a substrate is placed; and forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on the substrate by plasma polymerization of the gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method for forming low-carbon CVD film for filling trenches
ActiveUS20100143609A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid state diffusion coatingBoiling pointSilicon membrane
A method of forming a low-carbon silicon-containing film by CVD on a substrate having trenches includes: introducing a silicon-containing compound having three or less hydrocarbon units in its molecule and having a boiling temperature of 35° C. to 220° C.; applying RF power to the gas; and depositing a film on a substrate having trenches wherein the substrate is controlled at a temperature such that components of the silicon-containing compound are at least partially liquidified on the substrate, thereby filling the trenches with the film.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
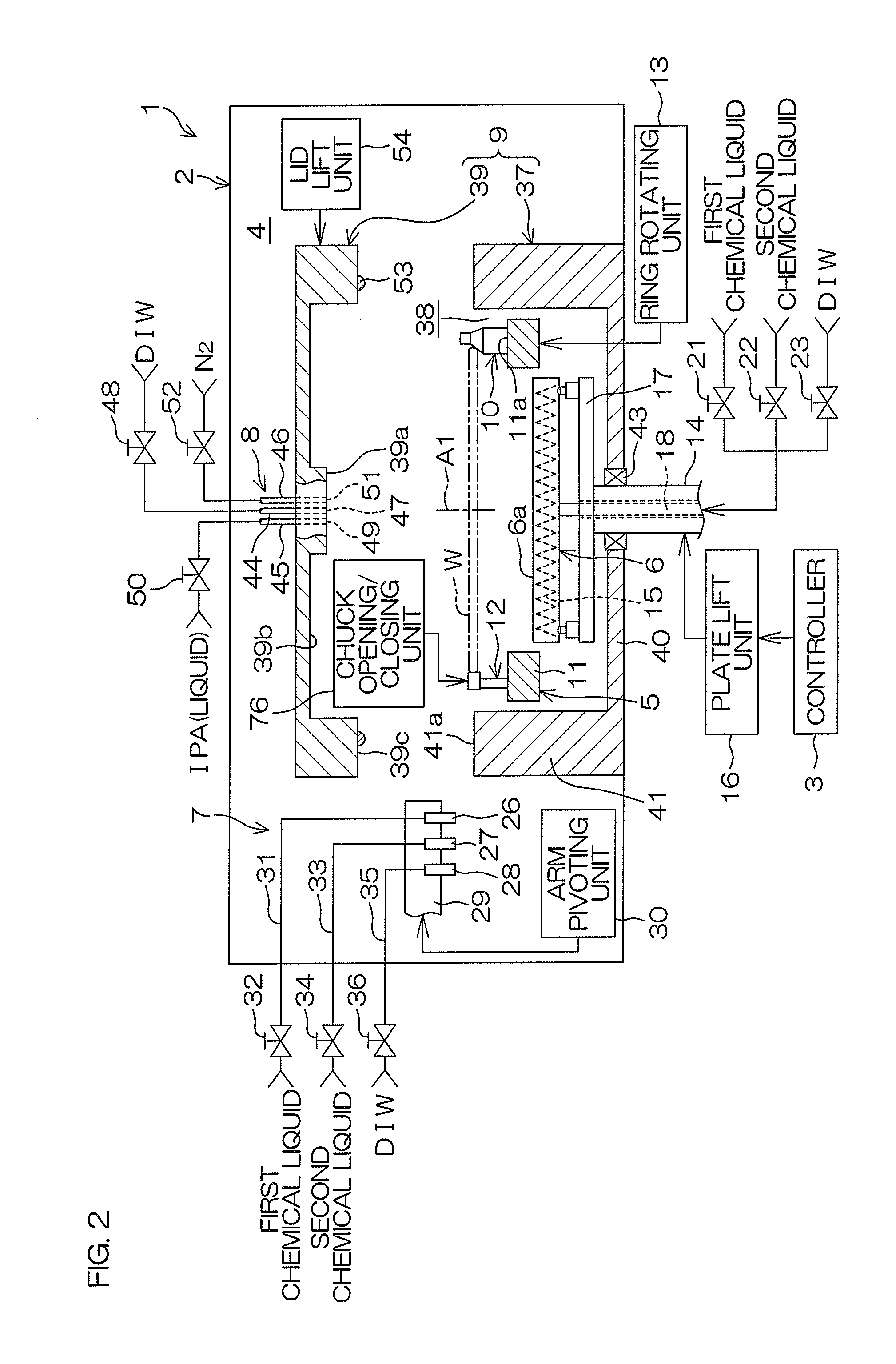
Substrate treatment method and substrate treatment apparatus
ActiveUS20150279708A1Reduce surface tensionLess attractiveSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsOrganic solventBoiling point
A substrate treatment method is provided, which includes: an organic solvent replacing step of supplying an organic solvent, whereby a liquid film of the organic solvent is formed on the substrate as covering the upper surface of the substrate to replace a rinse liquid with the organic solvent; a substrate temperature increasing step of allowing the temperature of the upper surface of the substrate to reach a first temperature level higher than the boiling point of the organic solvent after the formation of the organic solvent liquid film, whereby a vapor film of the organic solvent is formed below the entire organic solvent liquid film between the organic solvent liquid film and the substrate to levitate the organic solvent liquid film above the organic solvent vapor film; and an organic solvent removing step of removing the levitated organic solvent liquid film from above the upper surface of the substrate.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Method of forming carbon polymer film using plasma CVD
ActiveUS20070224833A1High film strengthReduction factorLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsBoiling pointCapacitance
A method of forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on a semiconductor substrate by a capacitively-coupled plasma CVD apparatus. The method includes the steps of: vaporizing a hydrocarbon-containing liquid monomer (CαHβXγ, wherein α and β are natural numbers of 5 or more; γ is an integer including zero; X is O, N or F) having a boiling point of about 20° C. to about 350° C. which is not substituted by a vinyl group or an acetylene group; introducing the vaporized gas and CO2 gas or H2 gas into a CVD reaction chamber inside which a substrate is placed; and forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on the substrate by plasma polymerization of the gas, thereby reducing extinction coefficient (k) at 193 nm and increasing mechanical hardness.
Owner:ASM JAPAN +1
Method of forming a carbon polymer film using plasma CVD
ActiveUS7504344B2Improve featuresFunction increaseLiquid surface applicatorsPhotomechanical apparatusCapacitanceBoiling point
A method of forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on a semiconductor substrate by a capacitively-coupled plasma CVD apparatus. The method includes the steps of: vaporizing a hydrocarbon-containing liquid monomer (CαHβXγ, wherein α and β are natural numbers of 5 or more; γ is an integer including zero; X is O, N or F) having a boiling point of about 20° C. to about 350° C. which is not substituted by a vinyl group or an acetylene group; introducing the vaporized gas into a CVD reaction chamber inside which a substrate is placed; and forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on the substrate by plasma polymerization of the gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
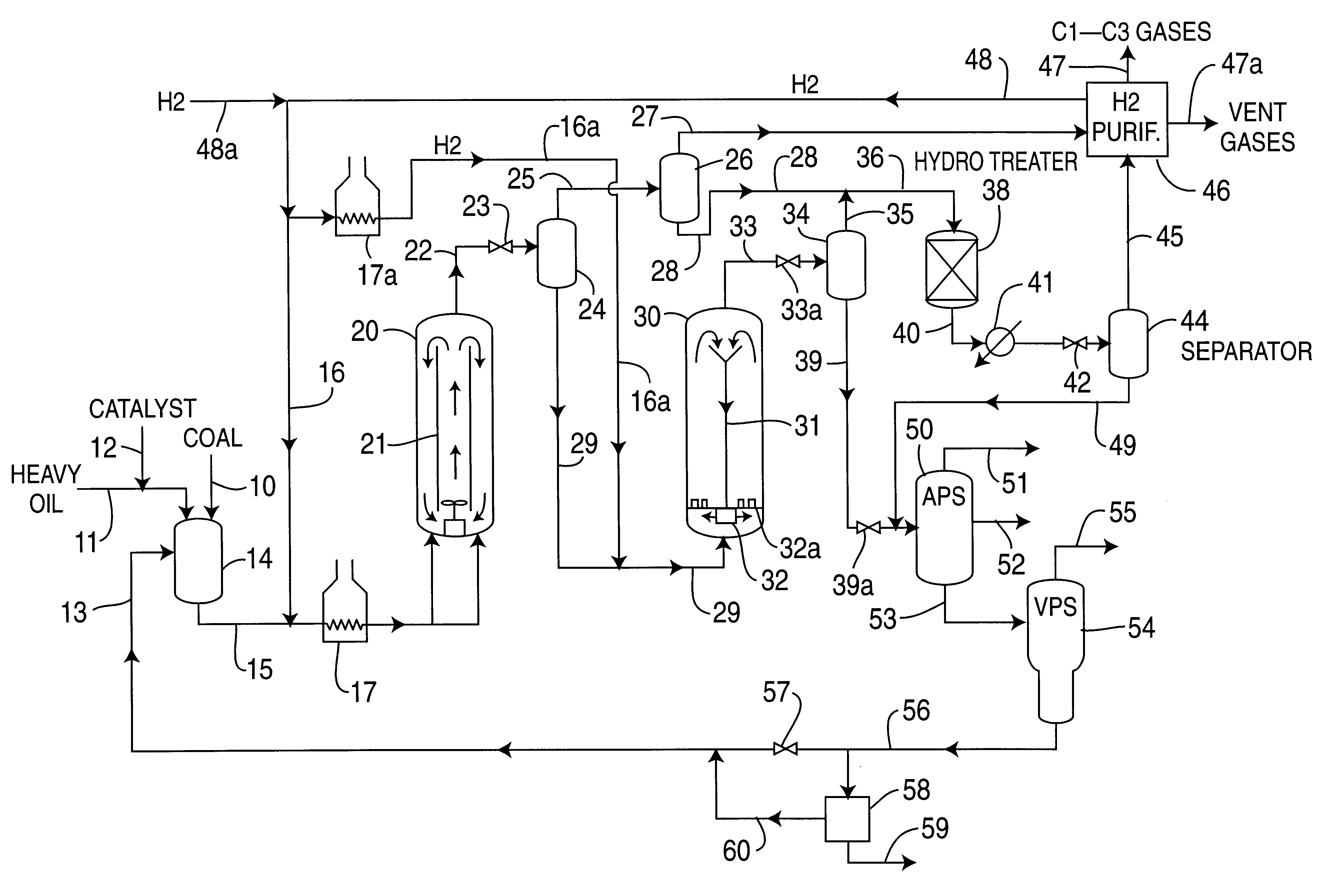
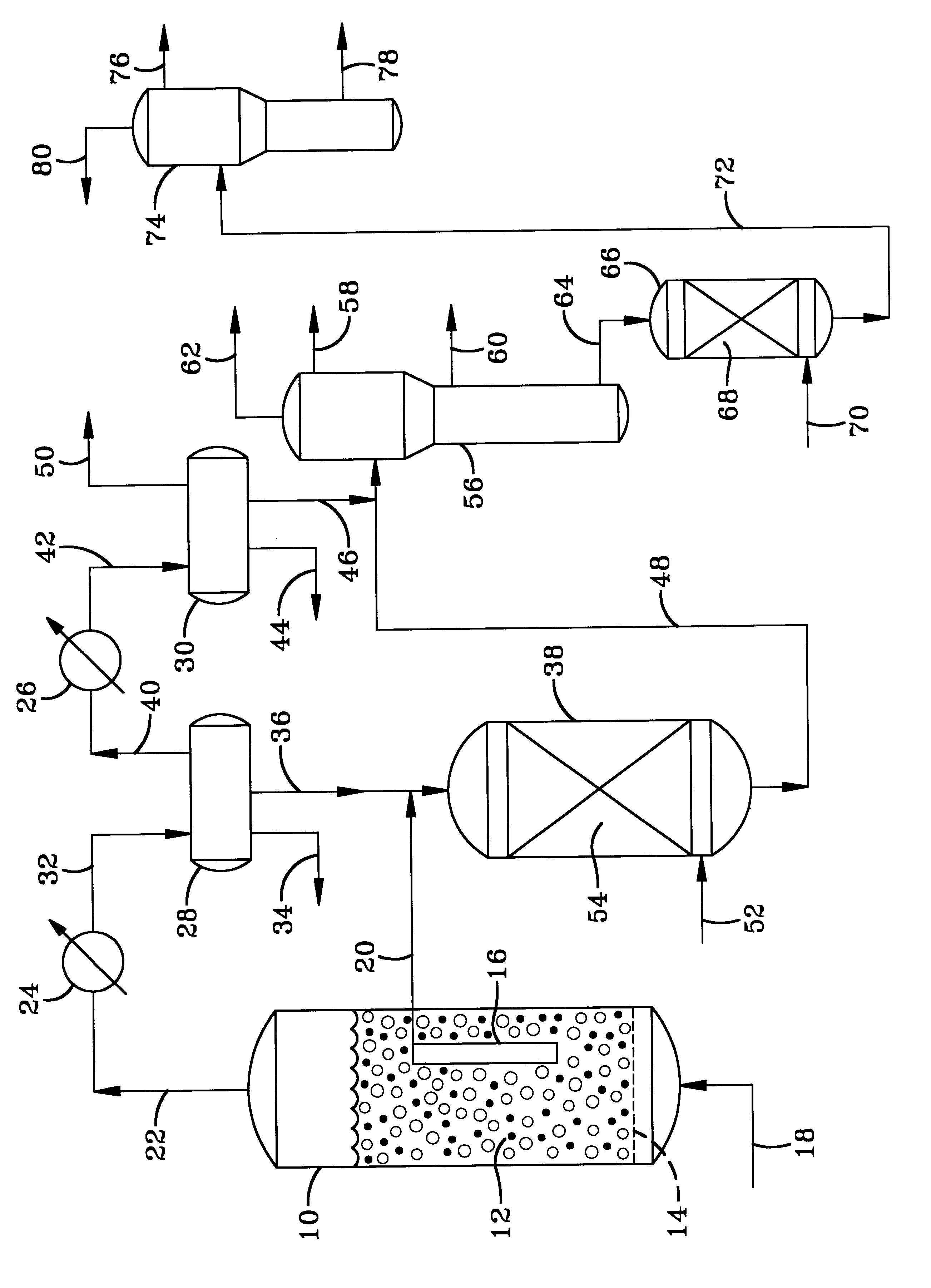
Catalytic multi-stage process for hydroconversion and refining hydrocarbon feeds
InactiveUS6190542B1Improve distillation yieldQuality improvementCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionLiquid productDistillates petroleum
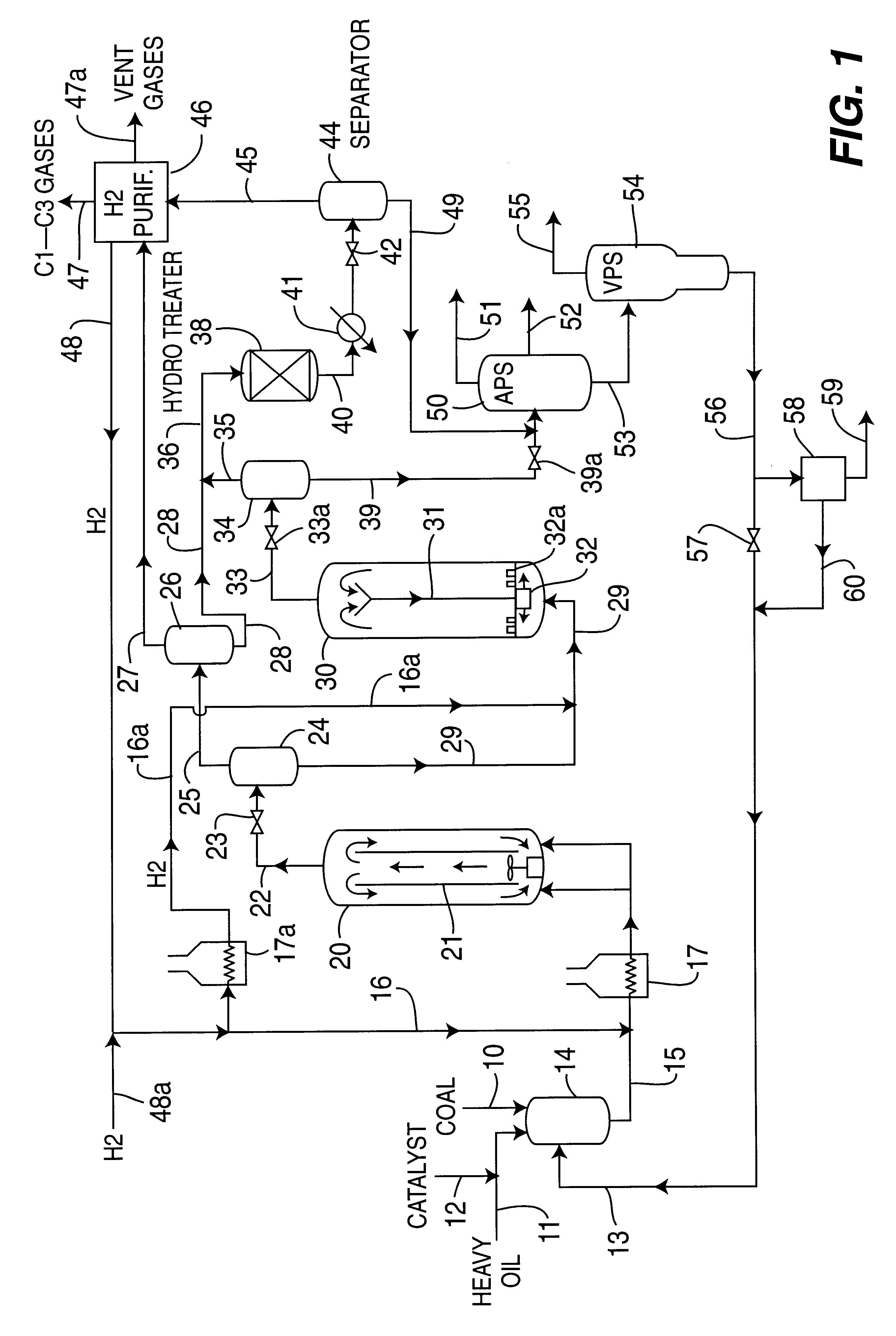
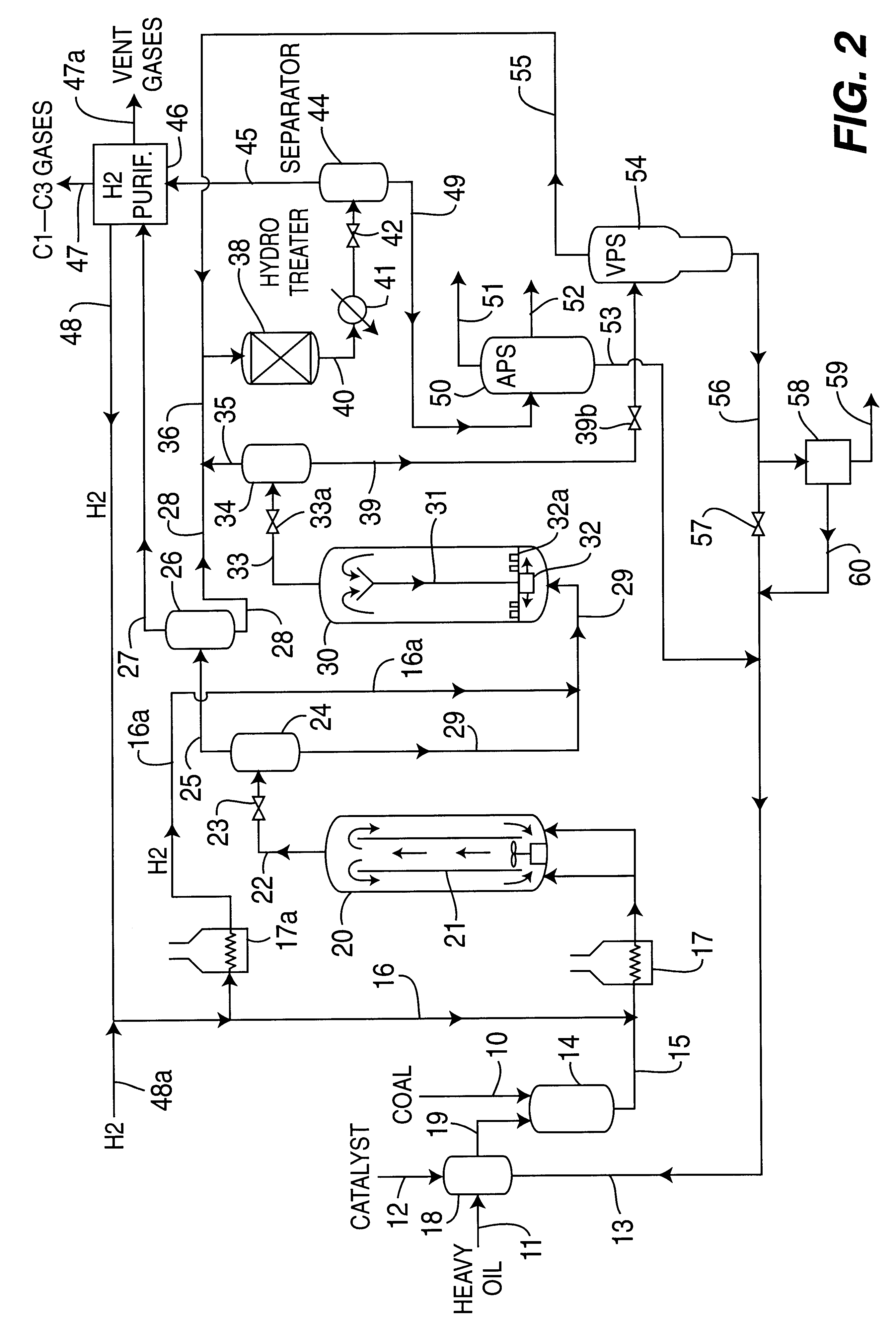
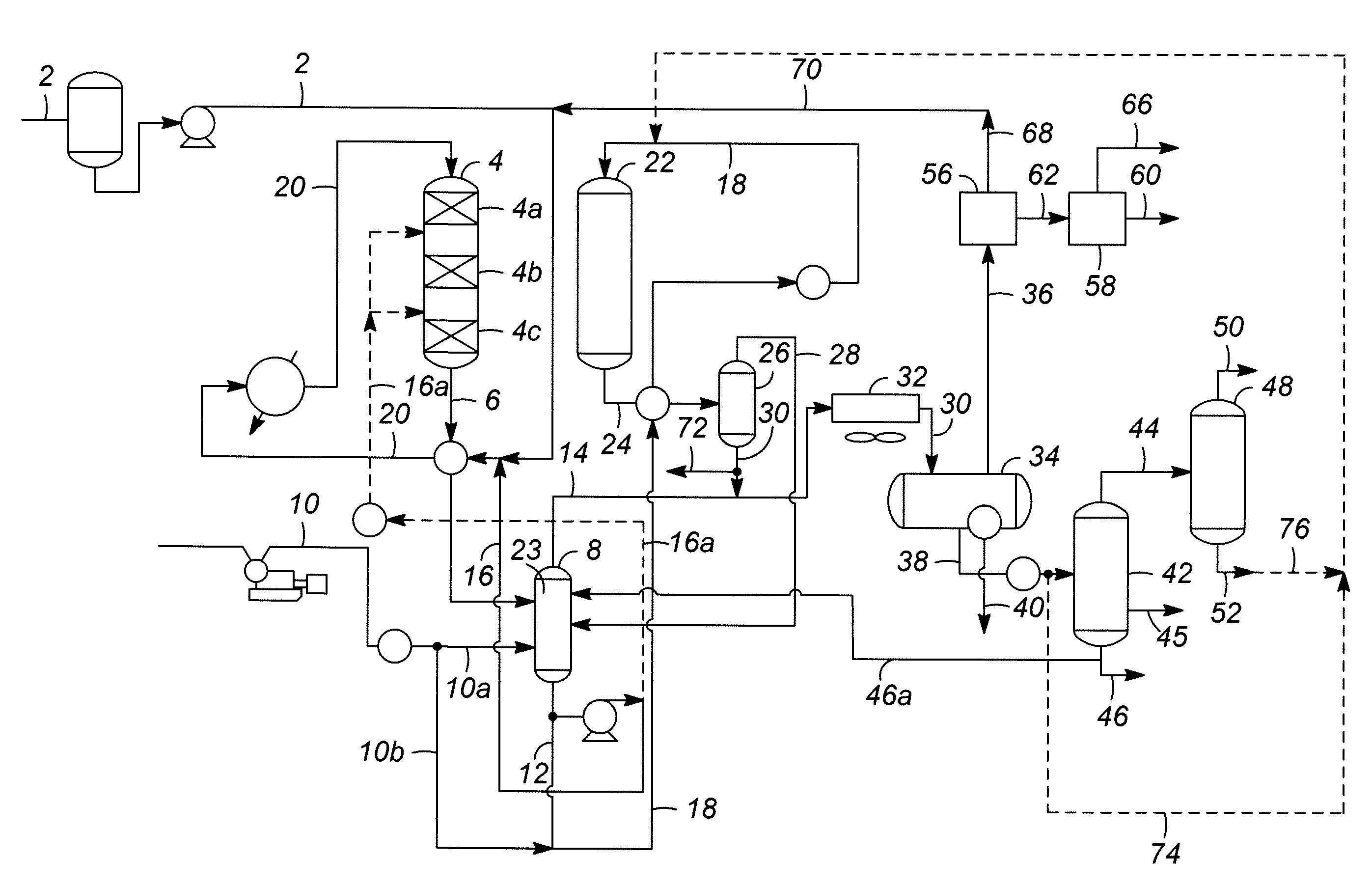
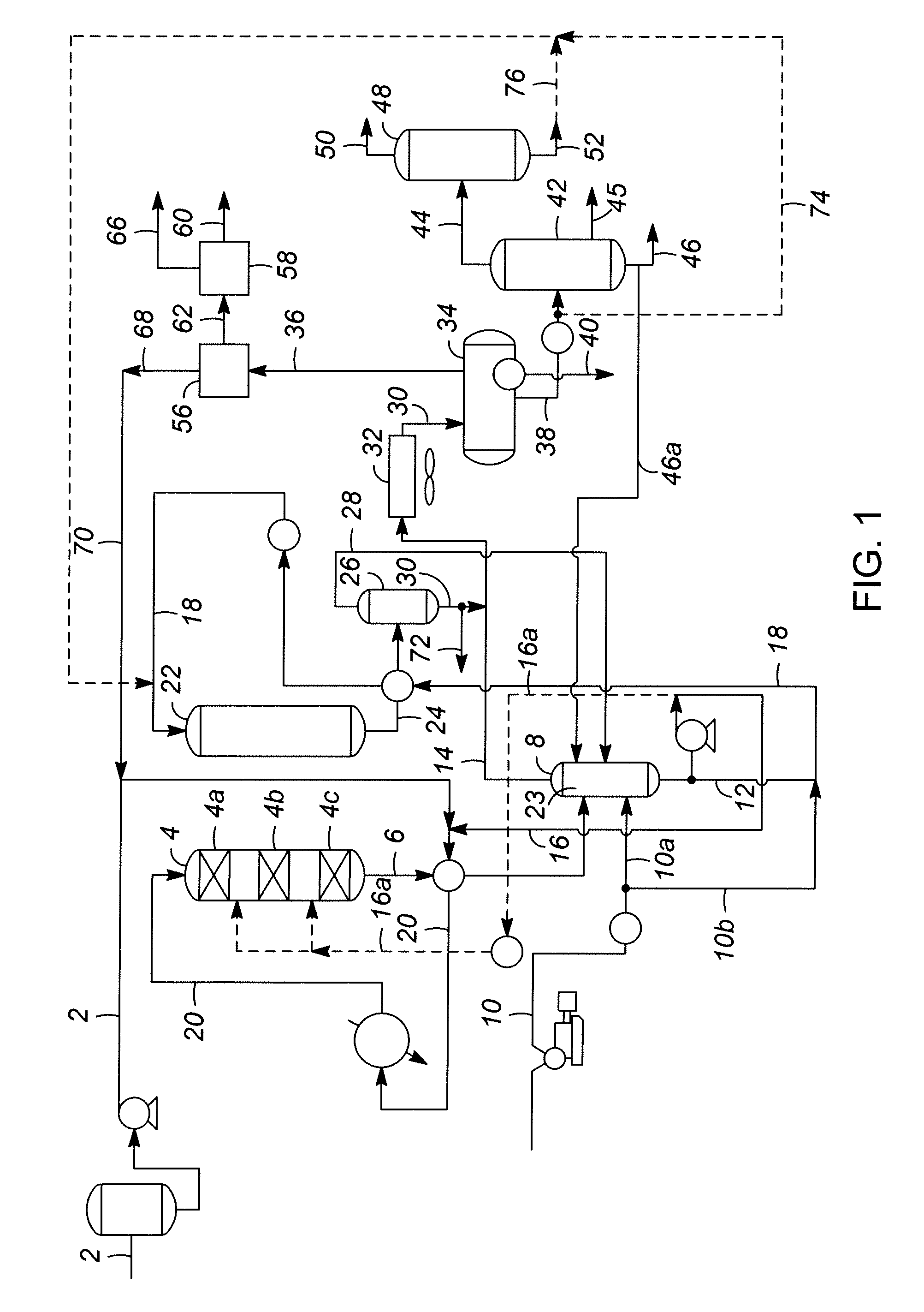
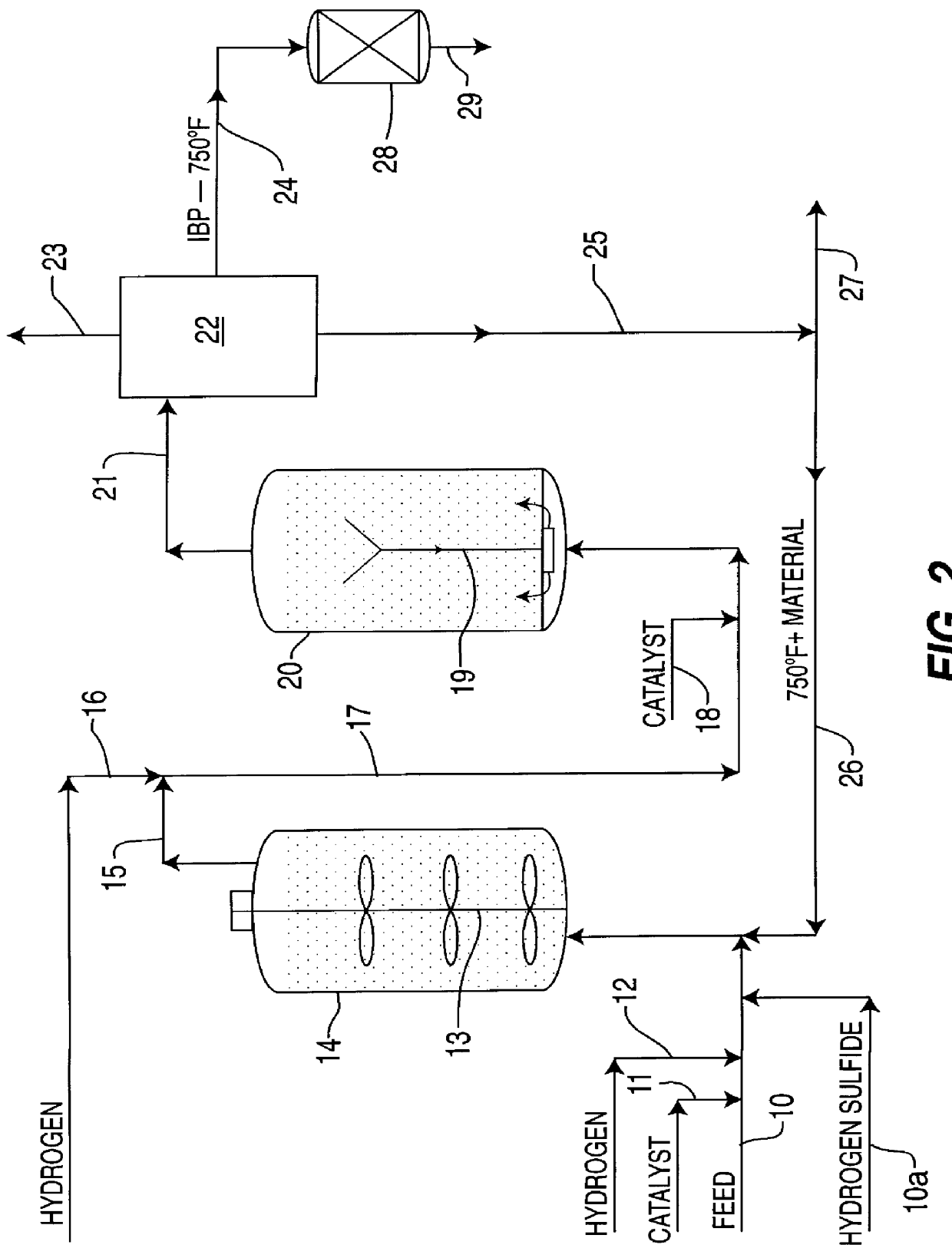
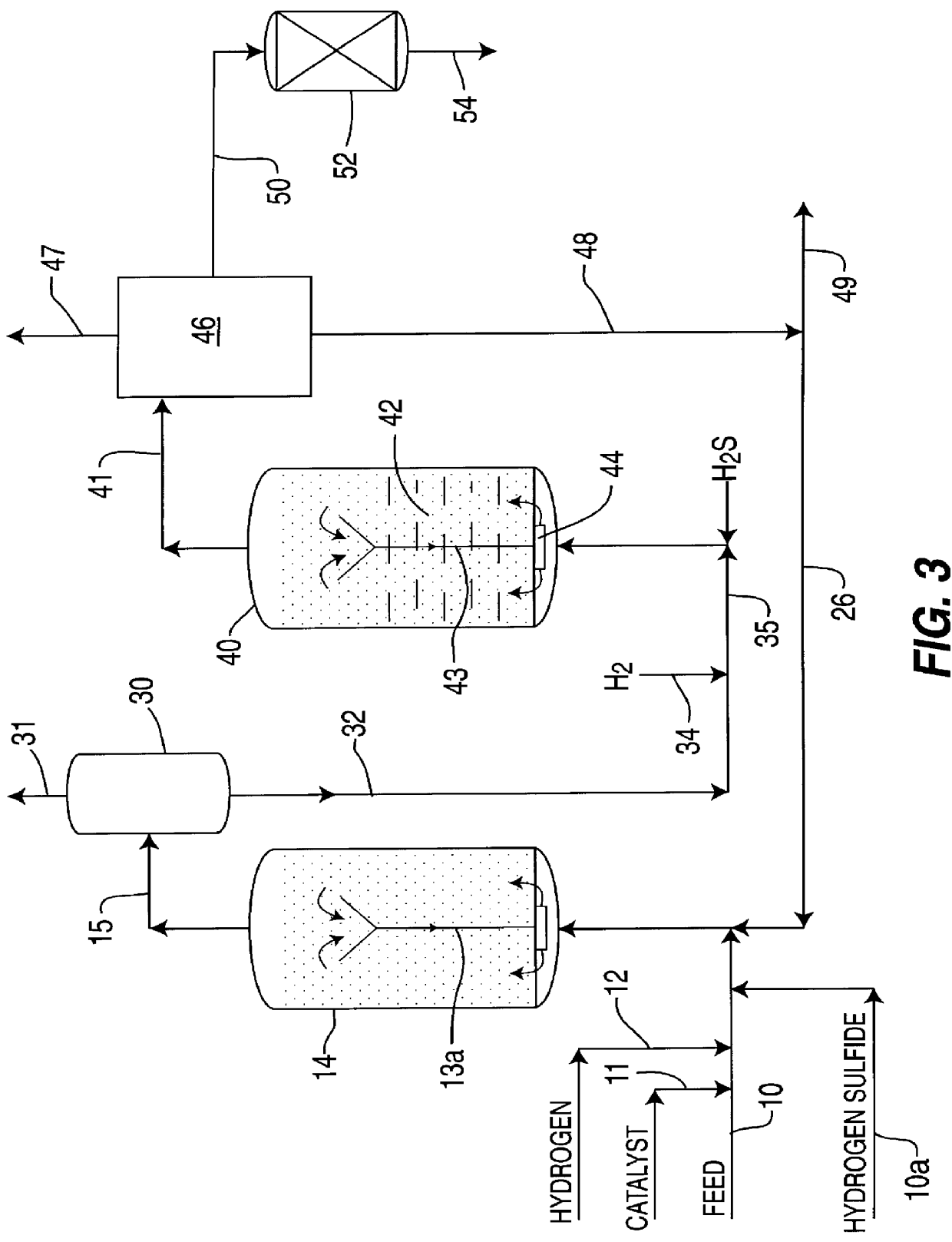
A multi-stage catalytic hydrogenation and hydroconversion process for heavy hydrocarbon feed materials such as coal, heavy petroleum fractions, and plastic waste materials. In the process, the feedstock is reacted in a first-stage, back-mixed catalytic reactor with a highly dispersed iron-based catalyst having a powder, gel or liquid form. The reactor effluent is pressure-reduced, vapors and light distillate fractions are removed overhead, and the heavier liquid fraction is fed to a second stage back-mixed catalytic reactor. The first and second stage catalytic reactors are operated at 700-850.degree. F. temperature, 1000-3500 psig hydrogen partial pressure and 20-80 lb. / hr per ft.sup.3 reactor space velocity. The vapor and light distillates liquid fractions removed from both the first and second stage reactor effluent streams are combined and passed to an in-line, fixed-bed catalytic hydrotreater for heteroatom removal and for producing high quality naphtha and mid-distillate or a full-range distillate product. The remaining separator bottoms liquid fractions are distilled at successive atmospheric and vacuum pressures, low and intermediate-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products are withdrawn, and heavier distillate fractions are recycled and further upgraded to provide additional low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products. This catalytic multistage hydrogenation process provides improved flexibility for hydroprocessing the various carbonaceous feedstocks and adjusting to desired product structures and for improved economy of operations.
Owner:HEADWATERS CTL
Acid generator, sulfonic acid, sulfonic acid derivatives and radiation-sensitive resin composition
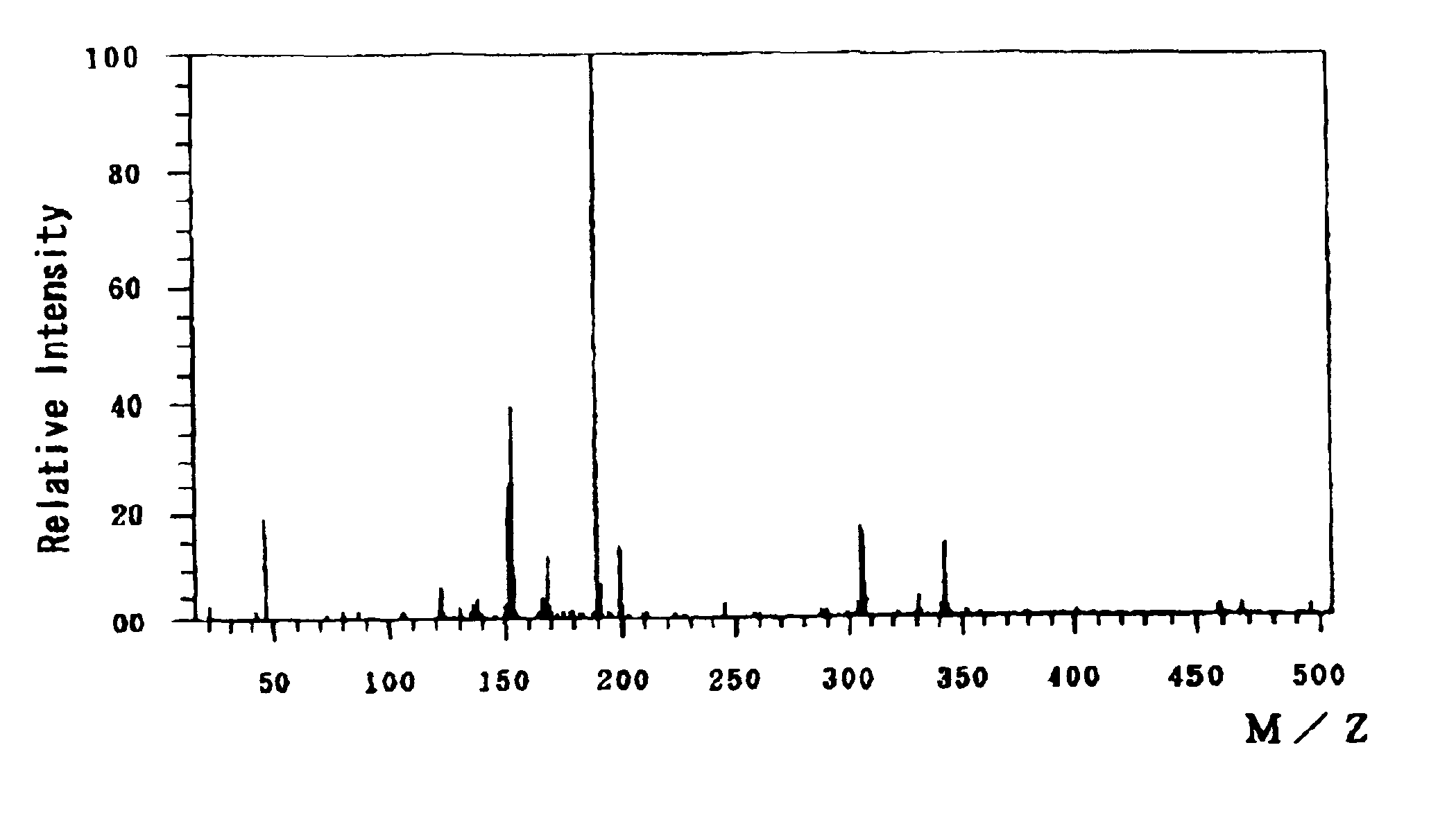
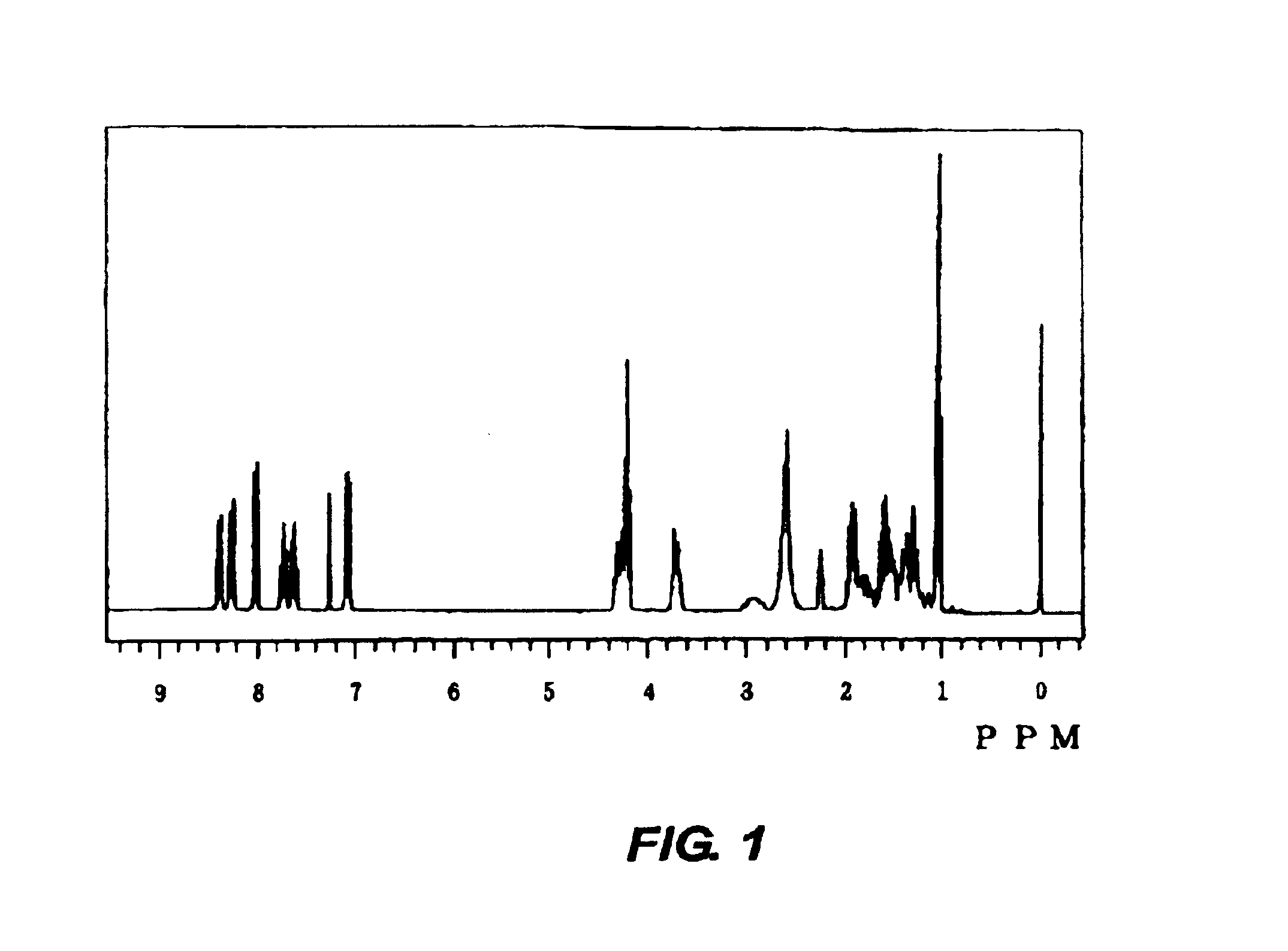
A novel photoacid generator containing a structure of the following formula (I), wherein R is a monovalent organic group with a fluorine content of 50 wt % or less, a nitro group, a cyano group, or a hydrogen atom, and Z1 and Z2 are individually a fluorine atom or a linear or branched perfluoroalkyl group having 1-10 carbon atoms, is provided. When used in a chemically amplified radiation-sensitive resin composition, the photoacid generator exhibits high transparency, comparatively high combustibility, and no bioaccumulation, and produces an acid exhibiting high acidity, high boiling point, moderately short diffusion length in the resist coating, and low dependency to mask pattern density.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
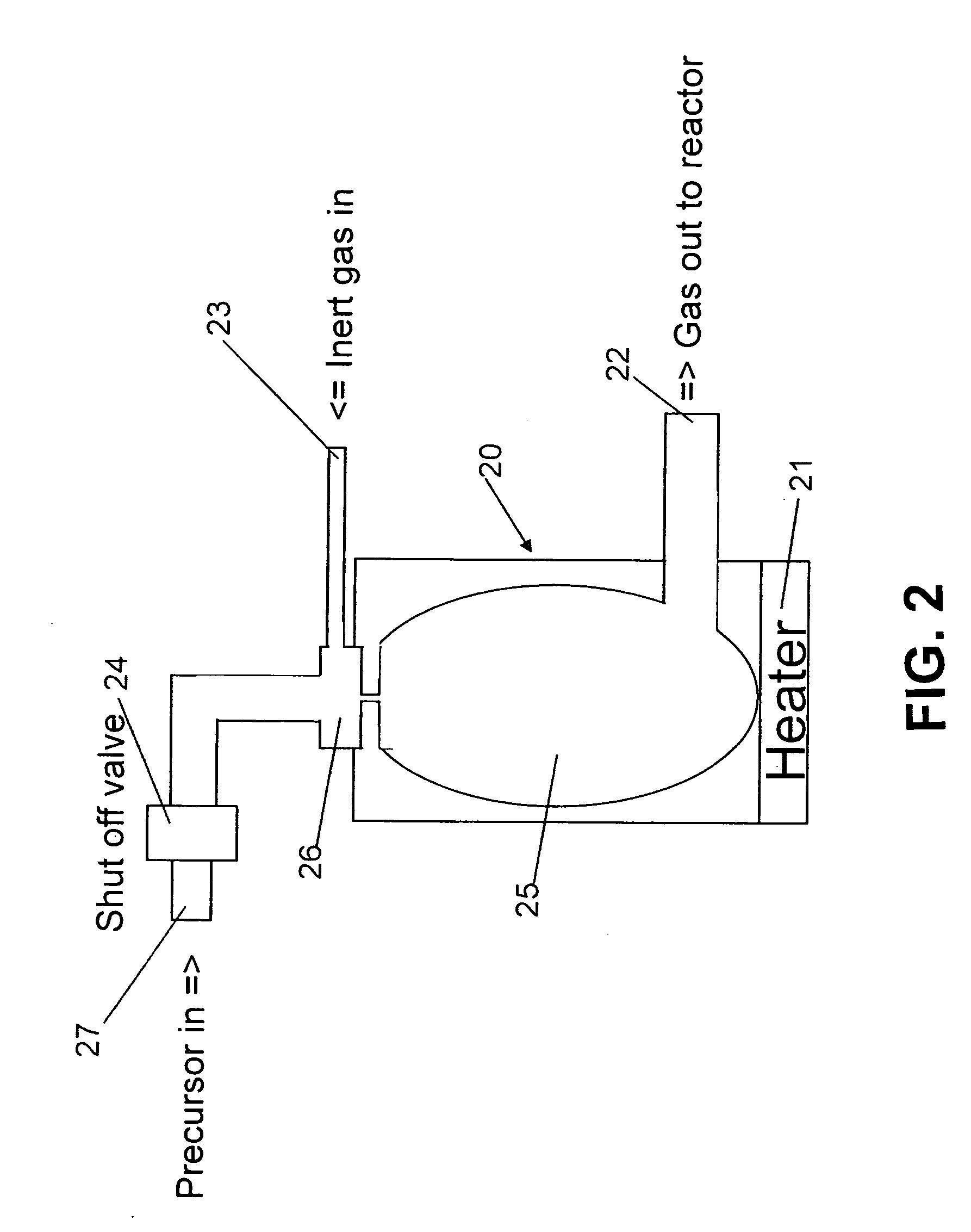
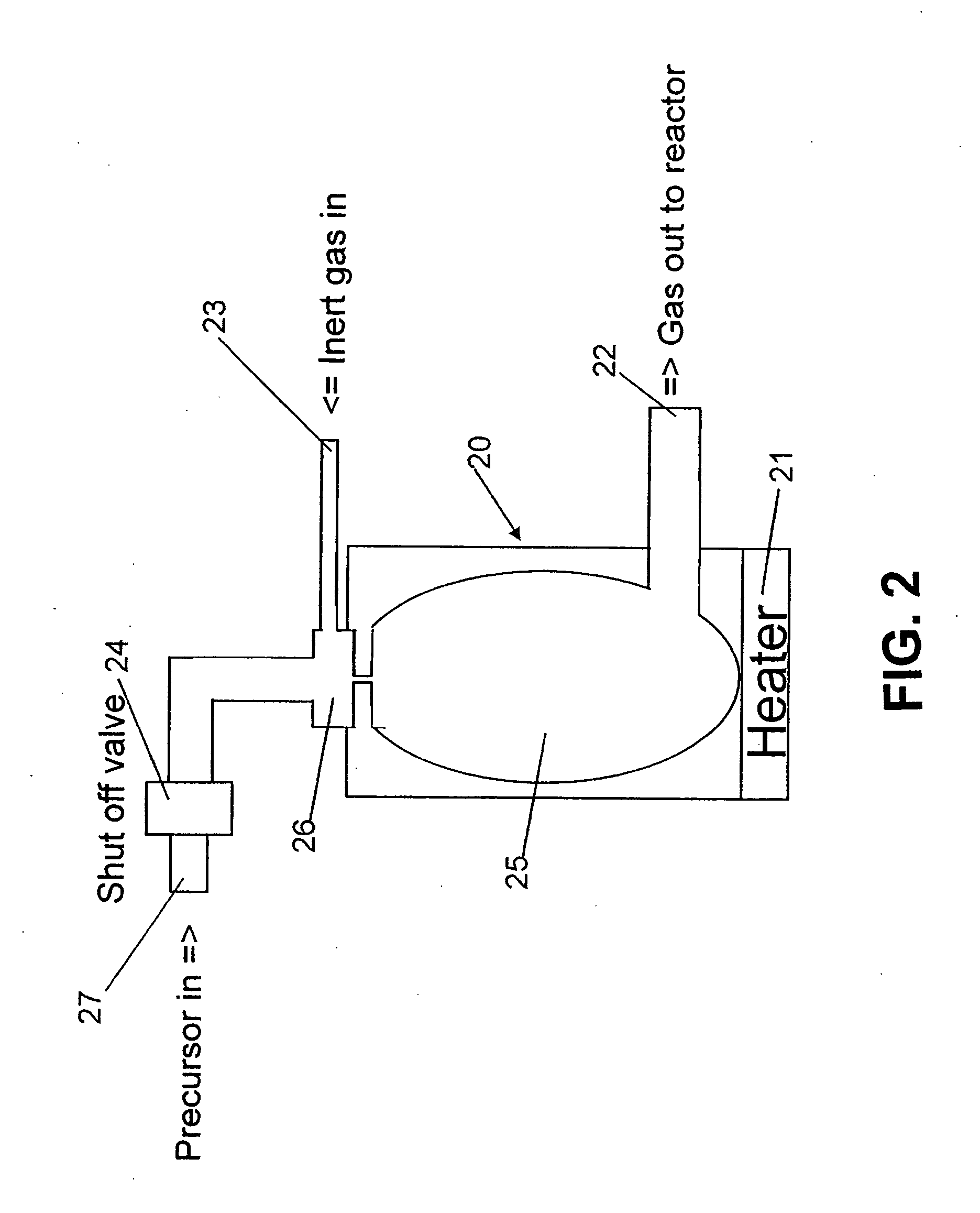
Method and apparatus for feeding a gas for epitaxial growth
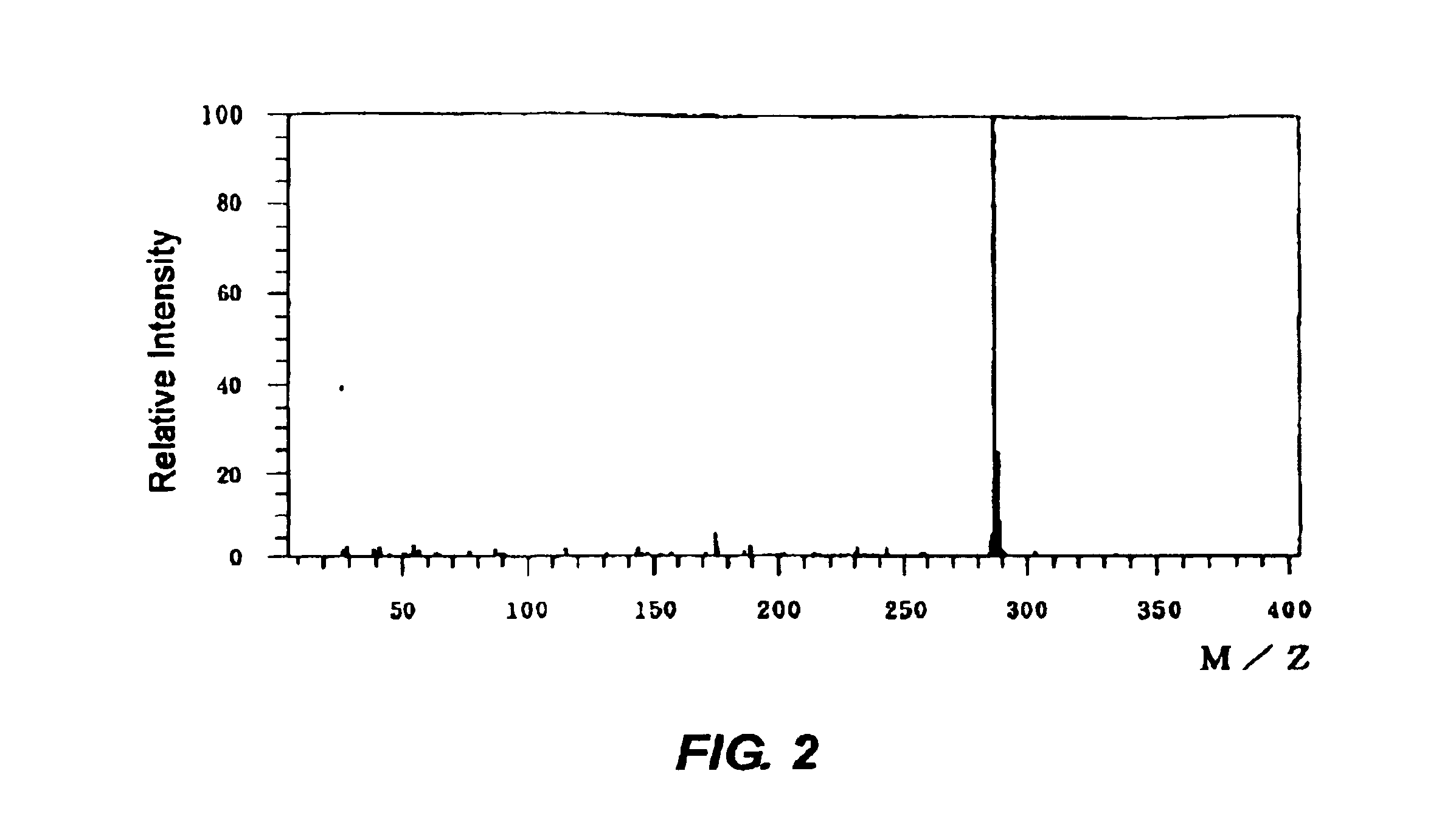
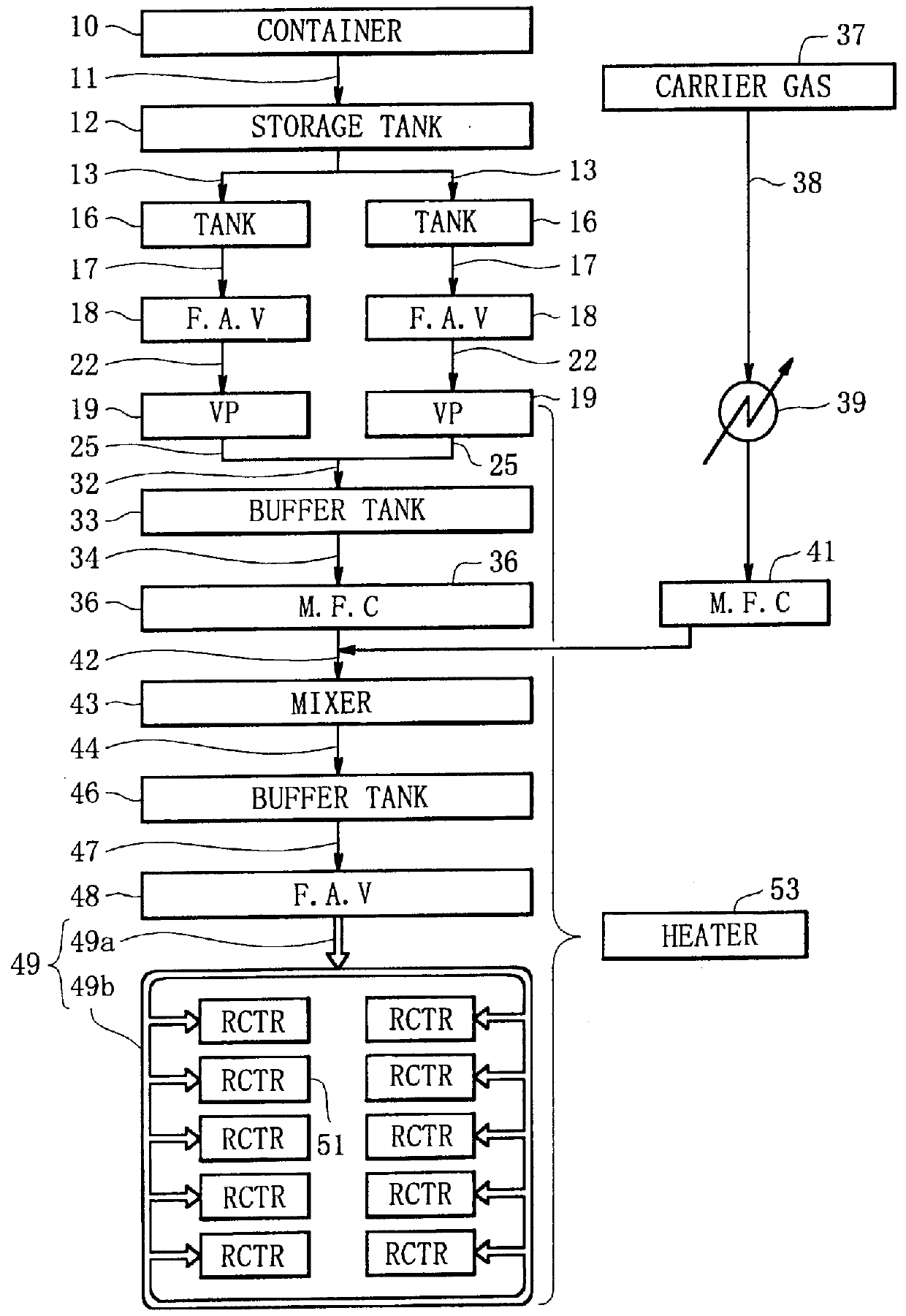
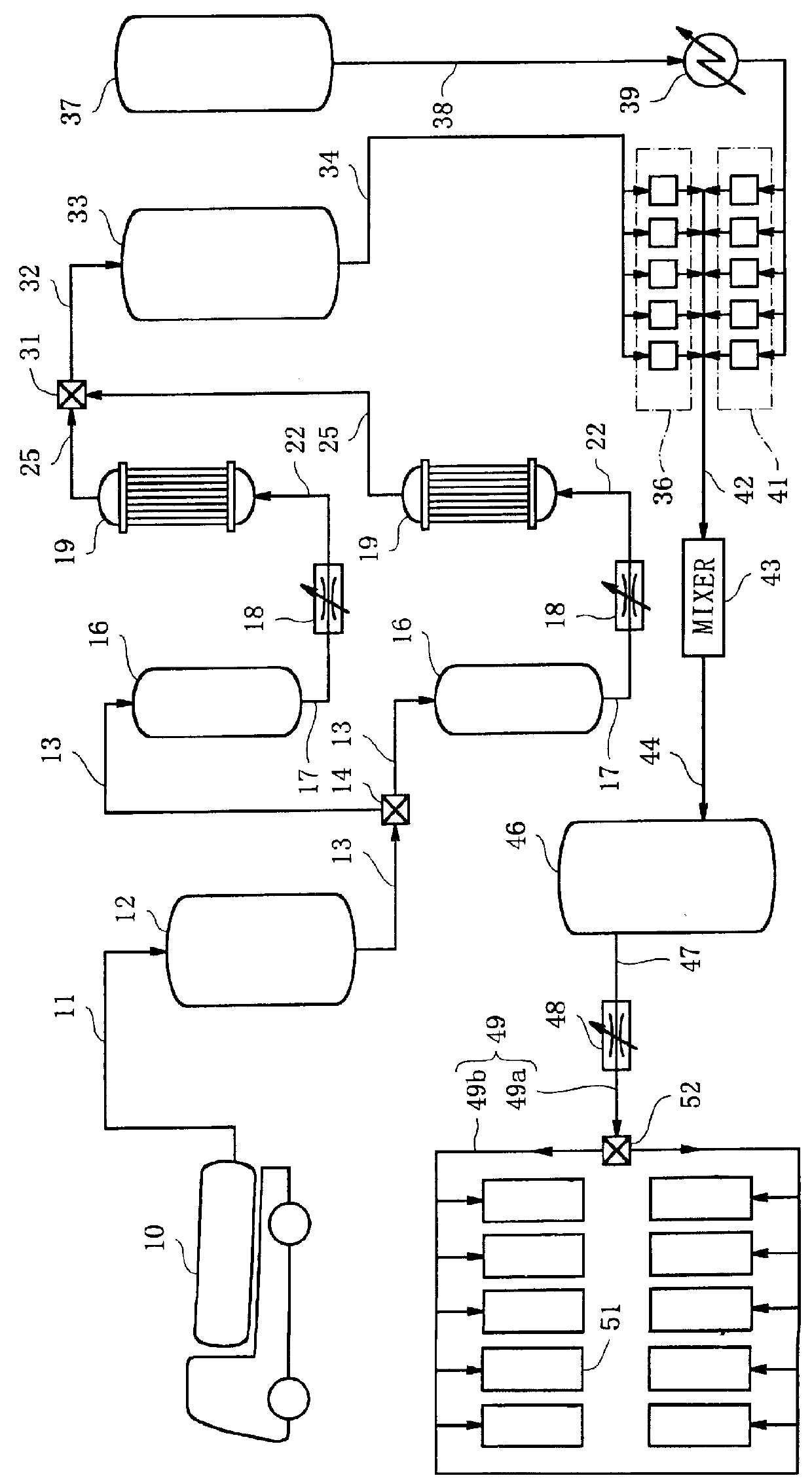
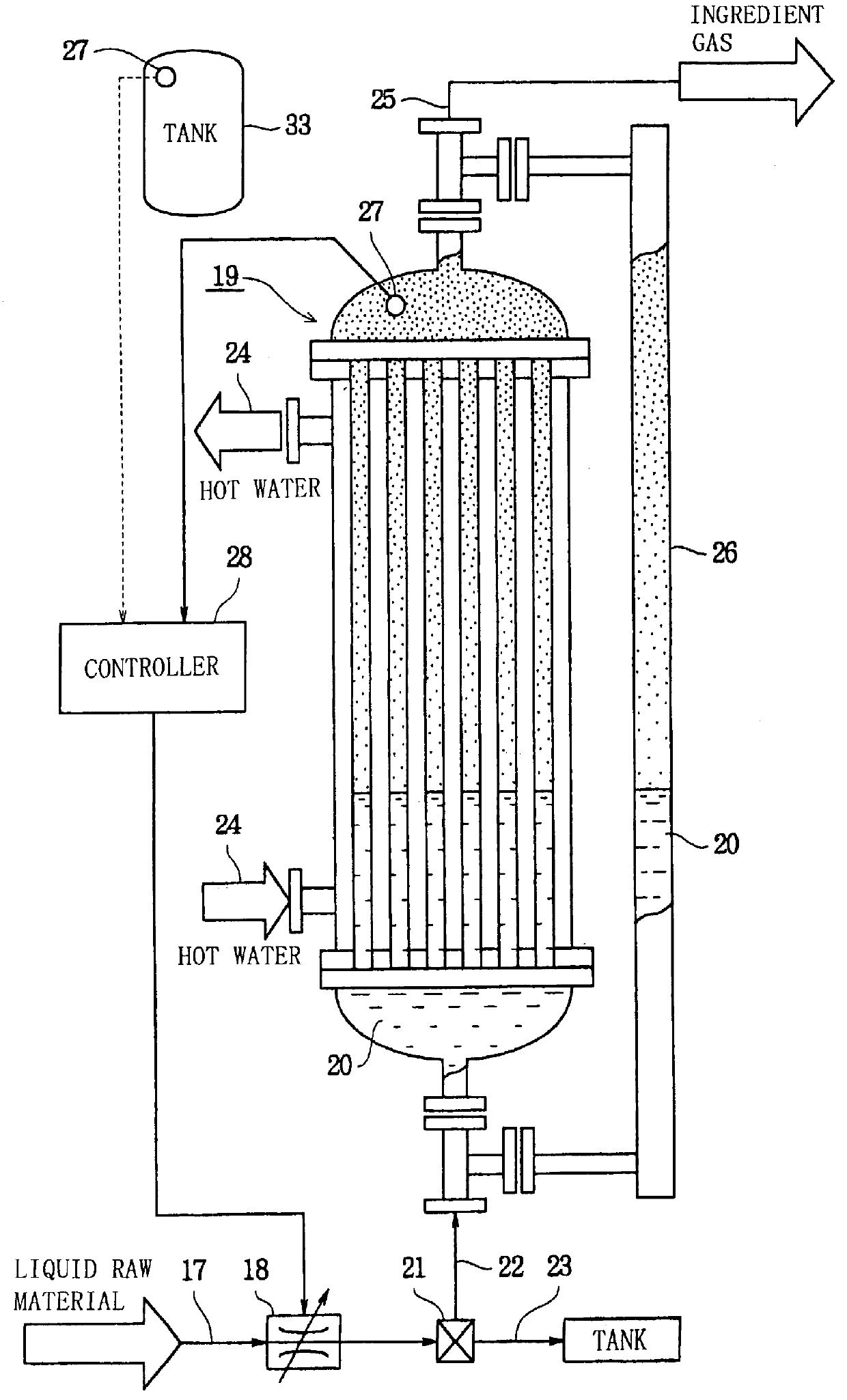
InactiveUS6039809APolycrystalline material growthTransportation and packagingBoiling pointProduct gas
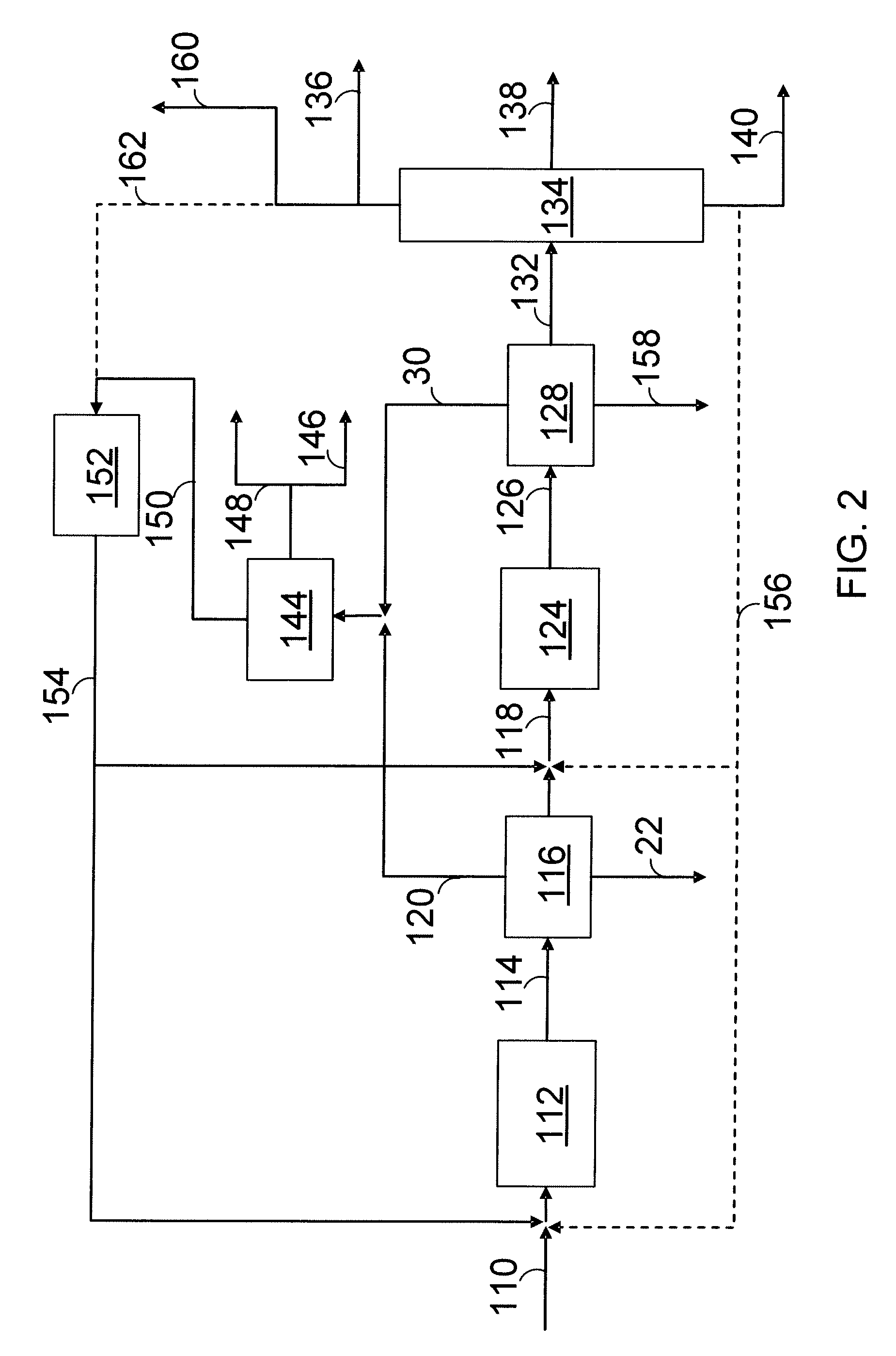
A liquid raw material is heated to its boiling point or higher at a vaporizer to mix the vaporized ingredient gas and a carrier gas at a mixer at predetermined concentrations. The flow of the mixed gas is adjusted while the mixed gas is heated to over its condensing point and the temperature thereof is kept. Subsequently, the mixed gas is fed to a reactor for epitaxial growth while the mixed gas is heated to over its condensing point and the temperature thereof is kept. When the temperature of a heating medium is kept constant at the vaporizer to vaporize the liquid raw material and the feeding amount of the liquid into the vaporizer is adjusted by the pressure of the gas inside the vaporizer, the liquid surface level can be controlled to be constant.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Production of Blended Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
A process for producing a blended fuel from a paraffin rich component and a cyclic rich component, where each of the components are generated from a renewable feedstock, is presented. The paraffin rich component is generated from a first renewable feedstock comprising at least one component selected from the group consisting of glycerides, free fatty acids, biomass, lignocellulose, free sugars, and combinations thereof. The cyclic rich component is generated from a second renewable feedstock comprising at least one component selected from the group consisting of glycerides, free fatty acids, free fatty alkyl esters, biomass, lignocellulose, free sugars, and combinations thereof. The blended fuel may a gasoline boiling point range blended fuel, a diesel boiling point range blended fuel, an aviation boiling point range blended fuel, any combination thereof, or any mixture thereof.
Owner:UOP LLC
Heat-expandable microcapsules, process for producing the same, and method of utilizing the same
InactiveUS6235394B1High TgHigh heat-resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolymer scienceHeat resistance
A heat-expandable microcapsule comprising a polymer shell formed by polymerizing (I) acrylonitrile, a main monomer component, (II) a monomer having carboxyl and (III) a monomer having groups reactive with the carboxyl of the monomer (II) and of a liquid having a boiling point lower than the softening point of the polymer and being encapsulated in the polymer shell. The heat-expandable microcapsules expand within high temperature range, 240° C. or above, and have heat-resistance.
Owner:MATSUMOTO YUSHI SEIYAKU
Silicone hydrogels comprising desirable water content and oxygen permeability
The present invention relates to a process comprising the steps of reacting a reactive mixture comprising at least one silicone-containing component, at least one hydrophilic component, and at least one diluent to form an ophthalmic device having an advancing contact angle of less than about 80°; and contacting the ophthalmic device with an aqueous extraction solution at an elevated extraction temperature, wherein said at least one diluent has a boiling point at least about 10° higher than said extraction temperature.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Silicone hydrogels comprising n-vinyl amides and hydroxyalkyl (meth)acrylates or (meth)acrylamides
The present invention relates to a process comprising the steps of reacting a reactive mixture comprising at least one silicone-containing component, at least one hydrophilic component, and at least one diluent to form an ophthalmic device having an advancing contact angle of less than about 80°; and contacting the ophthalmic device with an aqueous extraction solution at an elevated extraction temperature, wherein said at least one diluent has a boiling point at least about 10° higher than said extraction temperature.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Process for producing 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoro-propane and/or 1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene
InactiveUS6403847B1Point becomes highManufactured continuously and efficientlyPreparation by dehalogenationPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offBoiling pointPropane
One or more materials selected from 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane, 1,1,3,3-tetrachloropropene and 1,3,3,3-tetrachloropropene are used as the specific materials described above. Before submitting the materials and HF to a fluorination reaction, almost all water is removed from them.To continuously manufacture useful intended products efficiently as well as to prevent deactivation of the catalyst and the accumulation of organic substances with high boiling points when manufacturing said useful 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane and / or 1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene, by fluorinating the specific materials with HF in the presence of a catalyst.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Premium synthetic lubricants
InactiveUS6475960B1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationAntioxidantBoiling point
Premium synthetic lubricants comprise a synthetic isoparaffinic hydrocarbon base stock and an effective amount of at least one, and typically a plurality of lubricant additives such as a detergent, dispersant, antioxidant, antiwear additive, pout point depresant, VI improver and the like. The base stock is derived from a waxy, paraffinic, Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon feed fraction having an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750° F. and continuously boiling up to at least 1050° F., by a process which comprises hydroisomerizing the feed and dewaxing the isomerate. The waxy feed has a T90-T10 temperature difference of at least 350° F. and is preferably hydroisomerized without any pretreatment, other than optional fractionation. The lubricant may also contain hydrocarbonaceous and synthetic base stock material. Lubricants, such as fully formulated multigrade automotive crankcase and transmission oils formed by adding a suitable additive package to the isoparaffinic base stock have exhibited performance superior to similar fully formulated oils based on both PAO and conventional, petroleum derived base stocks.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Iron-based ionic liquid catalysts for hydroprocessing carbonaceous feeds
InactiveUS6139723AIncrease hydrocracking ability of catalystIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid productIron salts
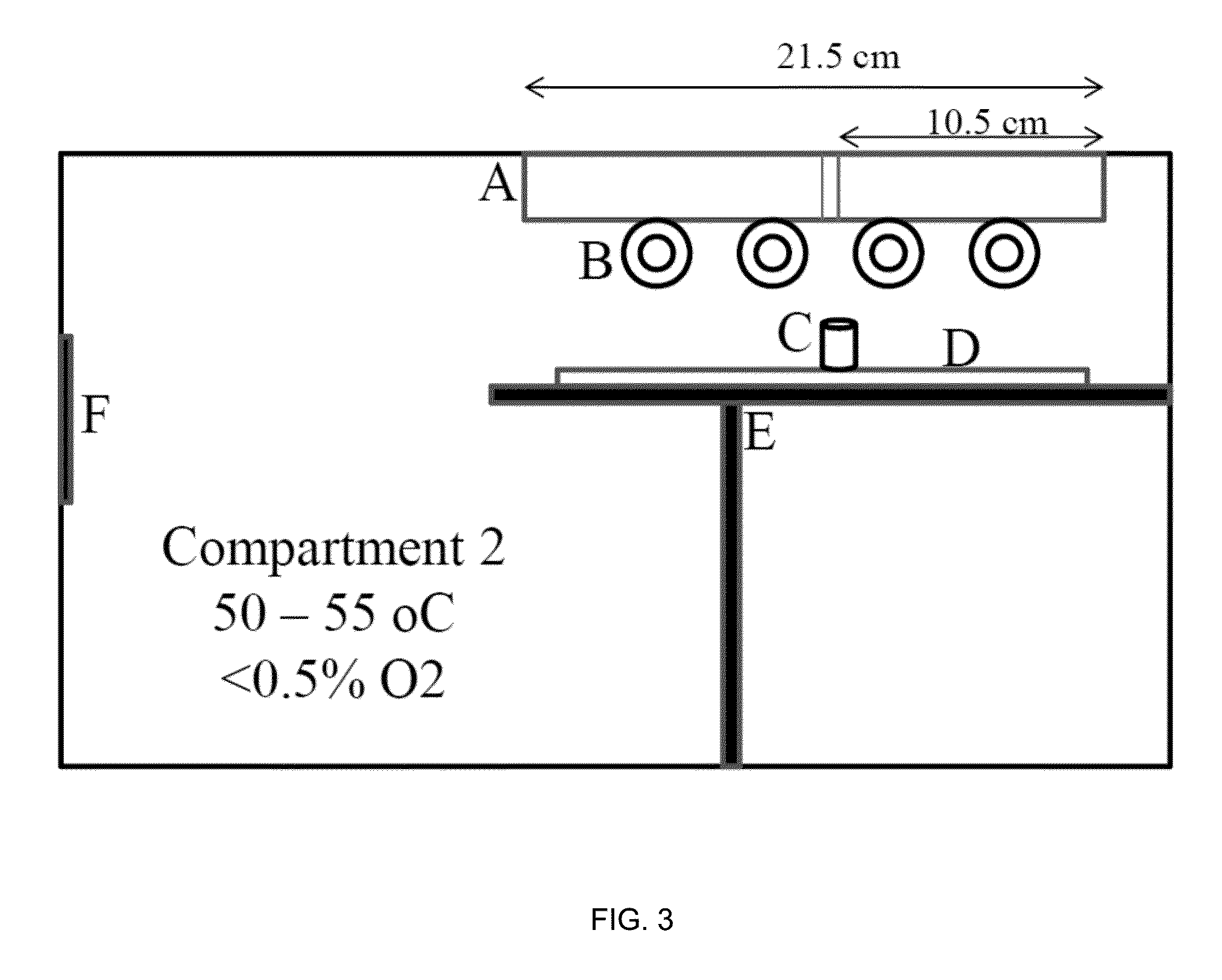
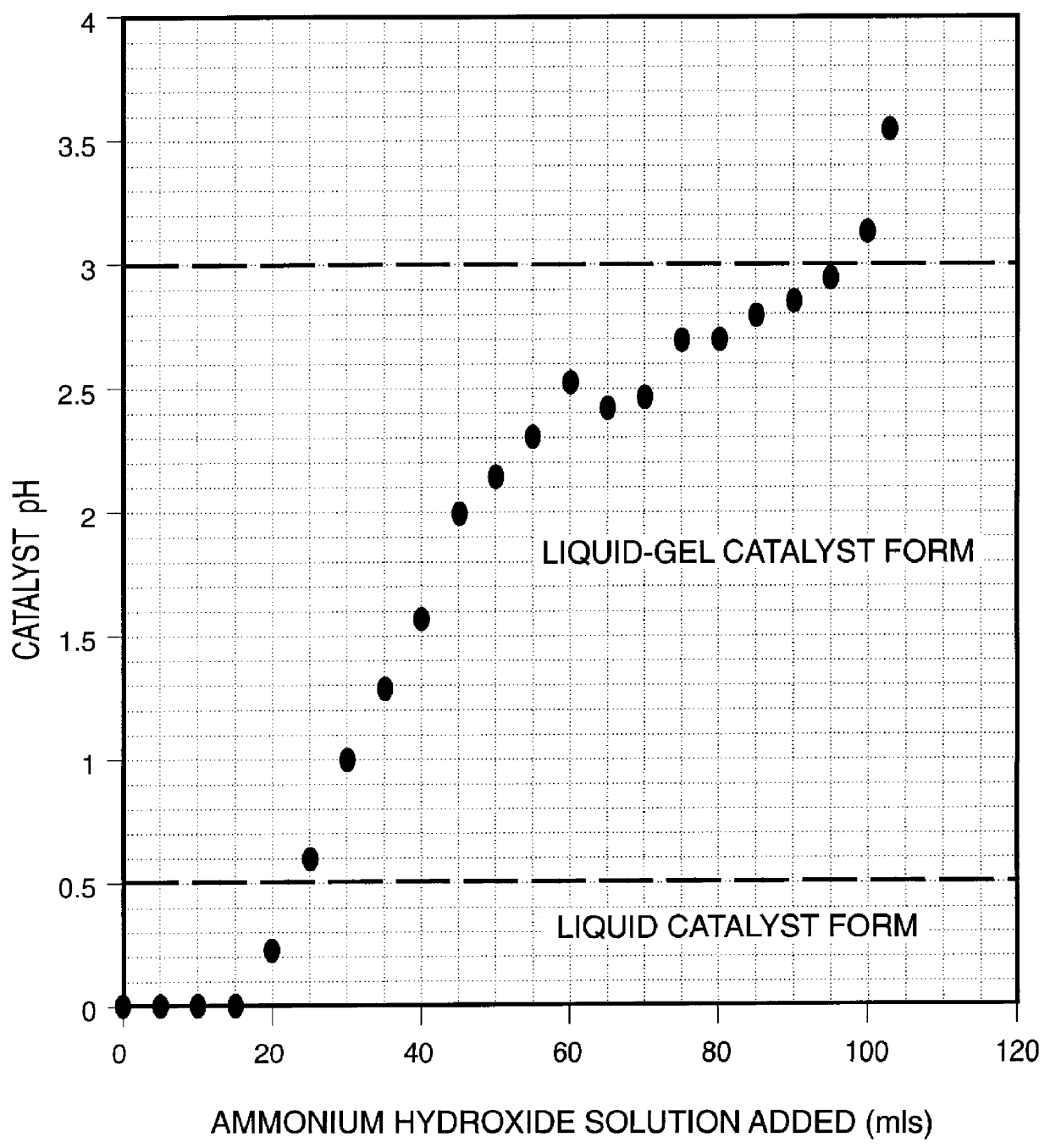
A highly dispersed iron-based ionic liquid or liquid-gel catalyst which may be anion-modified and metals-promoted has high catalytic activity, and is useful for hydrocracking / hydrogenation reactions for carbonaceous feed materials. The catalyst is produced by aqueous precipitation from saturated iron salt solutions such as ferric sulfate and ferric alum, and may be modified during preparation with anionic sulfate (SO42-) and promoted with small percentages of at least one active metal such as cobalt, molybdenum, palladium, platinum, nickel, or tungsten or mixtures thereof. The resulting catalyst may be used in a preferred ionic liquid form or in a liquid-gel form, and either fluidic form can be easily mixed and reacted with carbonaceous feed materials such as coal, heavy petroleum fractions, mixed plastic waste, or mixtures thereof. The invention includes methods for making the ionic liquid or liquid-gel catalyst, and processes for using the fluidic catalysts for hydroprocessing the carbonaceous feed materials to produce desirable low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products.
Owner:HEADWATERS CTL
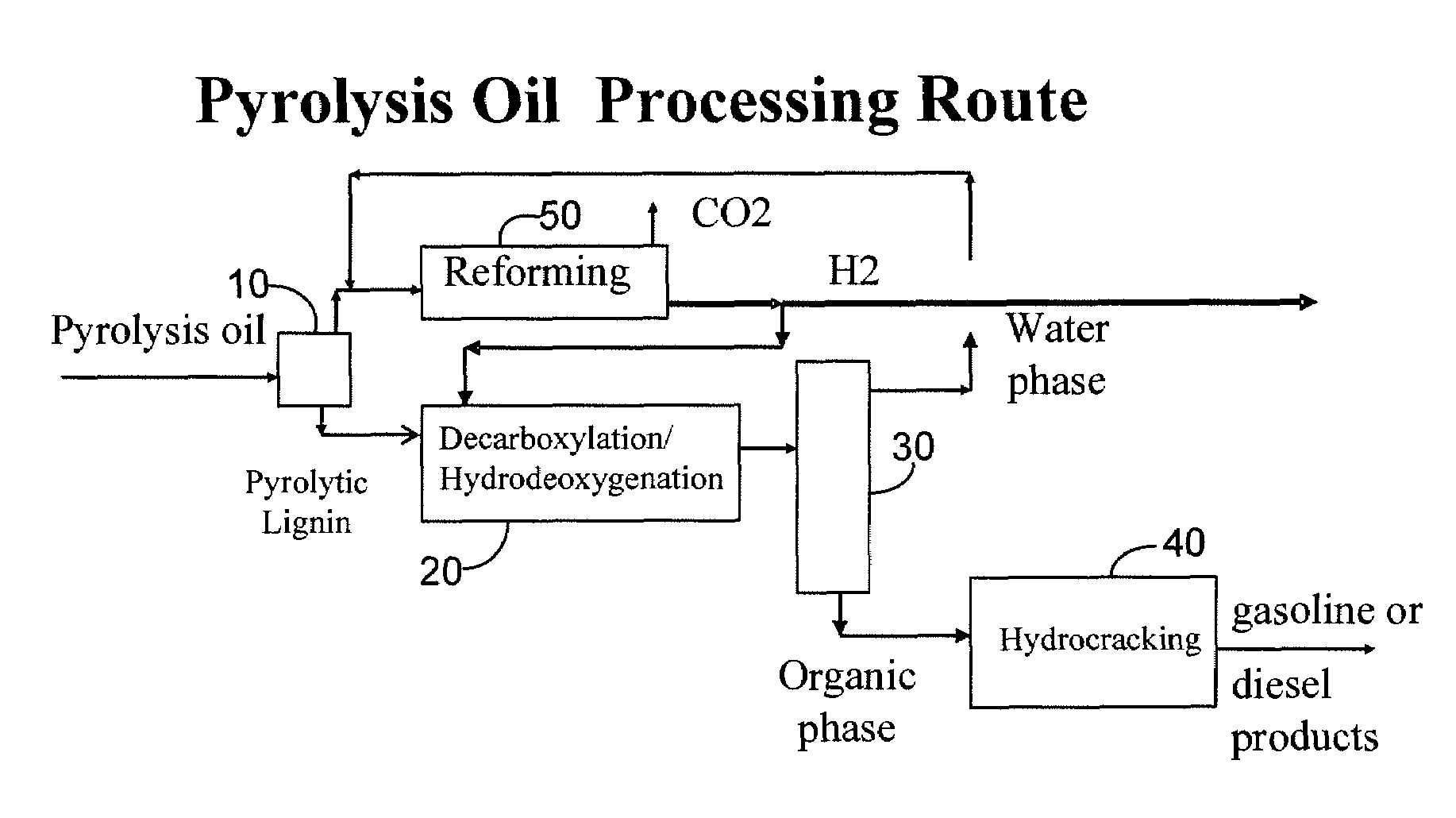
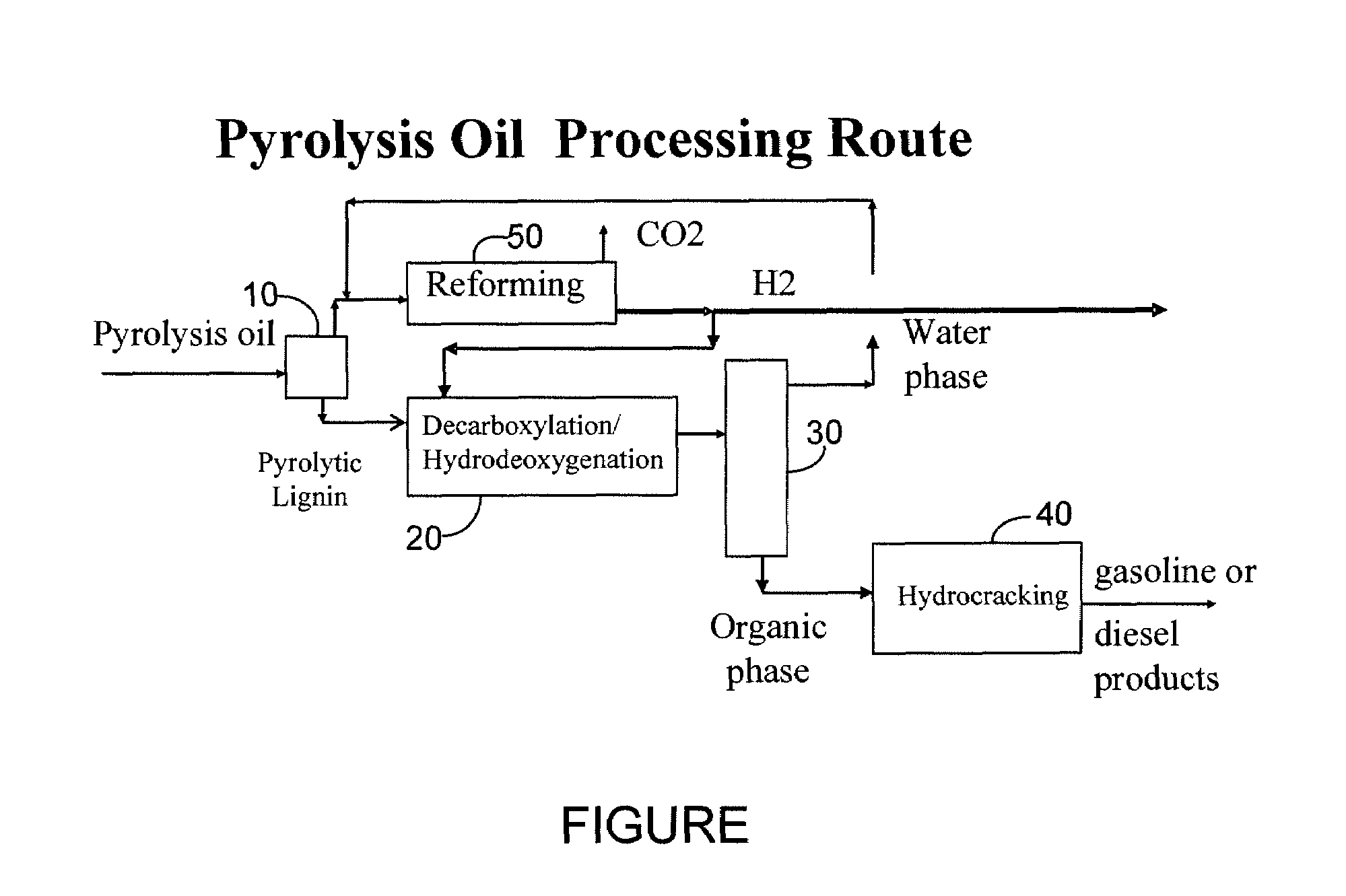
Gasoline and diesel production from pyrolytic lignin produced from pyrolysis of cellulosic waste
InactiveUS7578927B2Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural serial stages onlyCelluloseNaphtha
A process for the conversion of biomass to a liquid fuel is presented. The process includes the production of diesel and naphtha boiling point range fuels by hydrocracking of pyrolysis lignin extracted from biomass.
Owner:UOP LLC
Cryosurgical devices and methods for endometrial ablation
A cryoablation system including a cannula having a proximal end, a distal end, and a longitudinal axis, an expandable balloon extending from the distal end of the cannula and fluidly connected to a source of heat transfer fluid by at least one fluid path, a pump for circulating the heat transfer fluid into and out of the balloon, a probe handle coupled to the proximal end of the cannula and in fluidic communication with the balloon through the cannula, and a heat exchanger for varying the temperature of the heat transfer fluid, wherein the heat exchanger is fluidly connected to a secondary refrigerant source. The heat exchanger may be positioned within the probe handle, within the cannula, or at least partially within the balloon. The heat transfer fluid of this cryoablation system preferably has a freezing point lower than about −110° C. and a boiling point greater than about 50° C.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
Method for manufacturing cleaner fuels
InactiveUS6248230B1Long catalyst lifeReduce hydrogen consumptionLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionTreatment with hydrotreatment processesBoiling pointGasoline
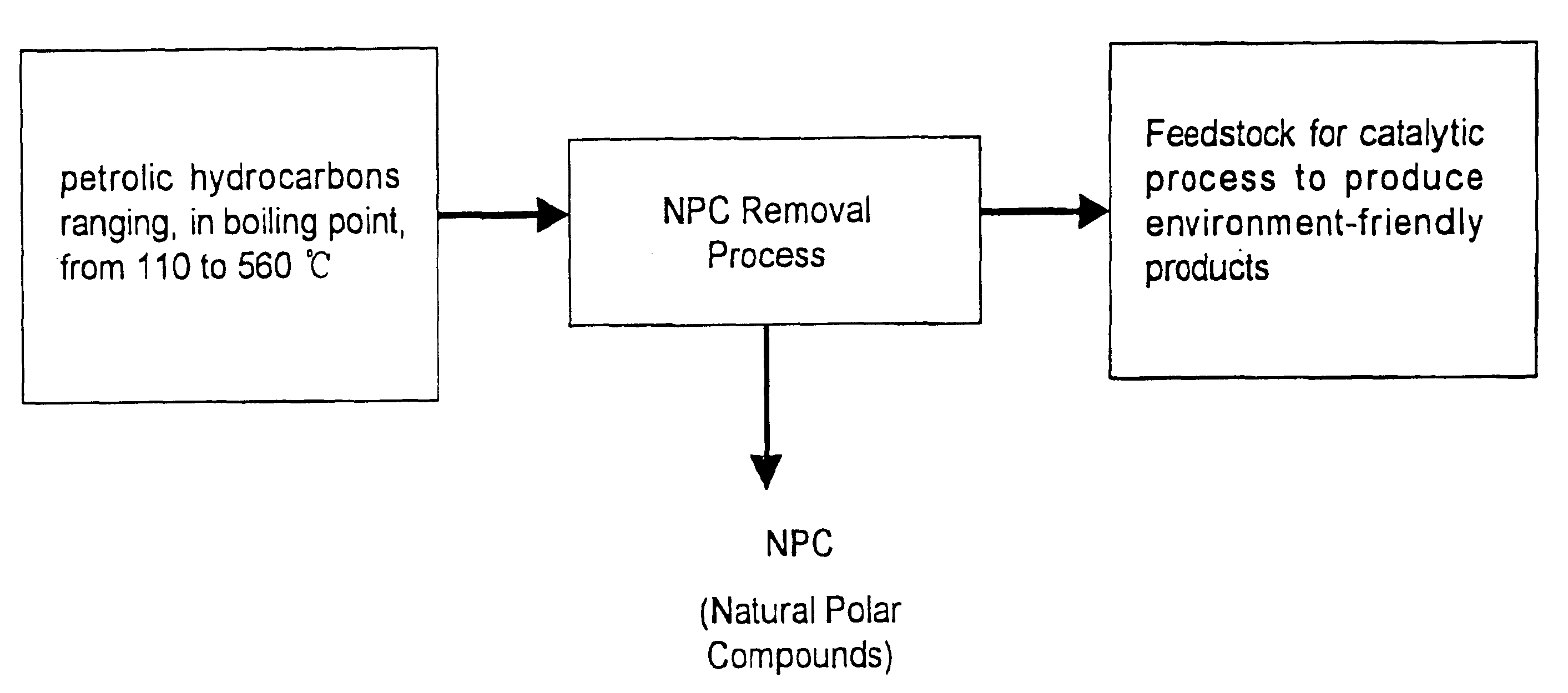
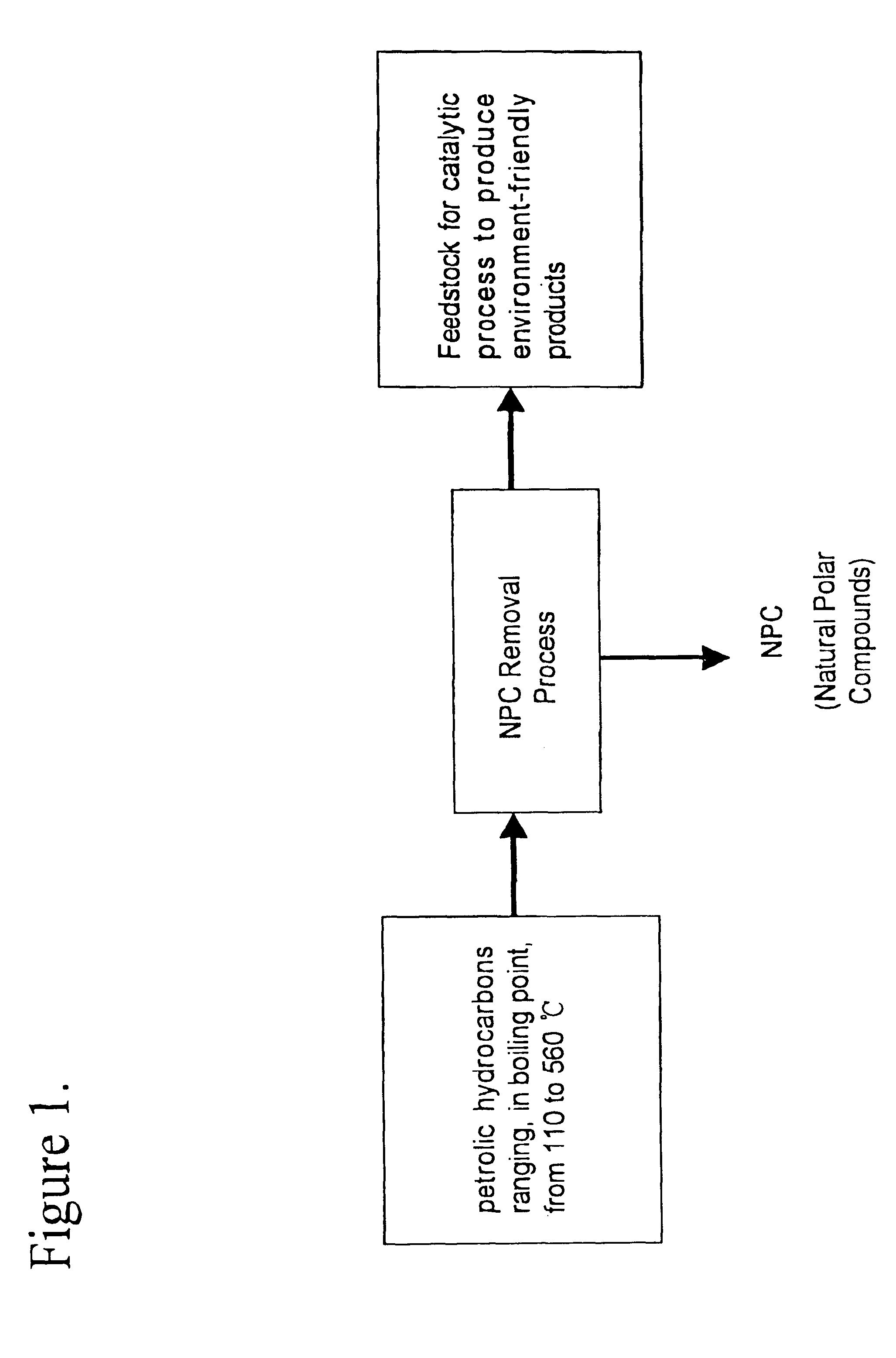
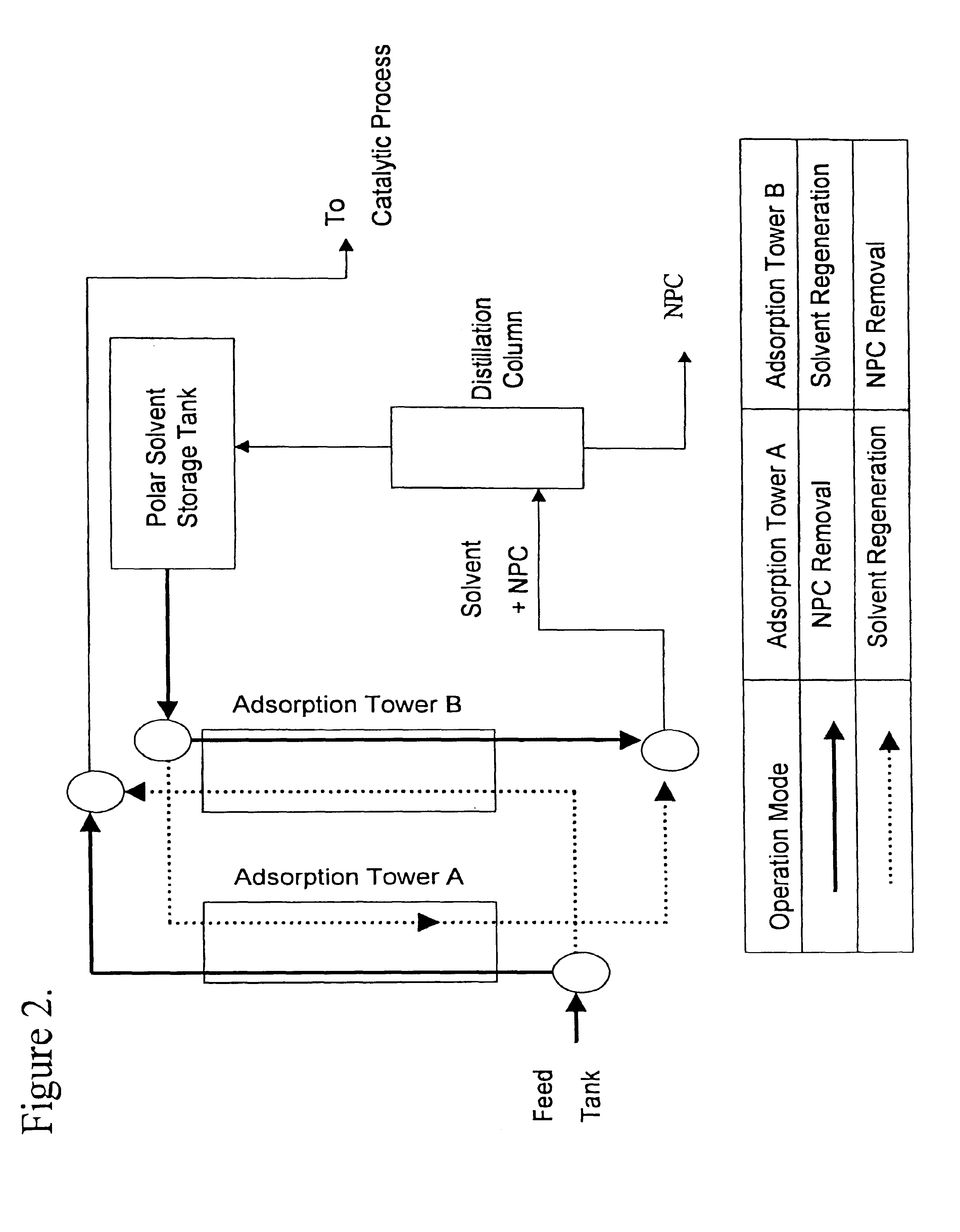
A method is provided for manufacturing cleaner fuels, in which NPC (Natural Polar Compounds), naturally existing in small quantities within various petrolic hydrocarbon fractions, are removed from the petrolic hydrocarbon fractions ranging, in boiling point, from 110 to 560° C. and preferably from 200 to 400° C., in advance of catalytic hydroprocessing. The removal of NPC improves the efficiency of the catalytic process and produces environment-friendly products, such as diesel fuel with a sulfur content of 50 ppm (wt) or lower. Also, the NPC can be used to improve fuel lubricity.
Owner:SK ENERGY CO LTD (KR)
Isoparaffinic base stocks by dewaxing fischer-tropsch wax hydroisomerate over Pt/H-mordenite
A high VI and low pour point lubricant base stock is made by hydroisomerizing a high purity, waxy, paraffinic Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon fraction having an initial boiling point in the range of 650-750° F., followed by catalytically dewaxing the hydroisomerate using a dewaxing catalyst comprising a catalytic platinum component and an H-mordenite component. The hydrocarbon fraction is preferably synthesized by a slurry Fischer-Tropsch using a catalyst containing a catalytic cobalt component. This combination of the process, high purity, waxy paraffinic feed and the Pt / H-mordenite dewaxing catalyst, produce a relatively high yield of premium lubricant base stock.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for converting triglycerides to hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20070175795A1High reaction yieldIncrease cetane numberBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsBoiling pointHydrocotyle bowlesioides
Processes for the conversion of hydrocarbons boiling in the temperature range of from about 80° F. to about 1000° F. to diesel boiling range hydrocarbons, and processes for increasing the cetane number and amount of n-C17 hydrocarbon products in such processes. Diesel boiling range hydrocarbons may be produced by contacting a hydrocarbon boiling in the above-mentioned boiling range with a triglyceride-containing compound to form a mixture, and then contacting the mixture with a hydrotreating catalyst under suitable reaction conditions.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Recording ink as well as ink media set, ink cartridge, ink recorded matter, inkjet recording apparatus and inkjet recording method
InactiveUS20070197685A1High image densityLow backside densityLayered productsInksSolid componentBoiling point
A recording ink containing at least a solid component which contains a colorant and a resin and is a solid at 25° C., a liquid component which has a higher boiling point than that of water and is a liquid at 25° C. and water, wherein the total content of the liquid component in the recording ink is 20% by mass or less, the total content of the solid component in the recording ink is 20% by mass or more, and the total content of a resin component in the solid component is 40% by mass to 95% by mass relative to a total amount of the solid component is provided.
Owner:RICOH KK
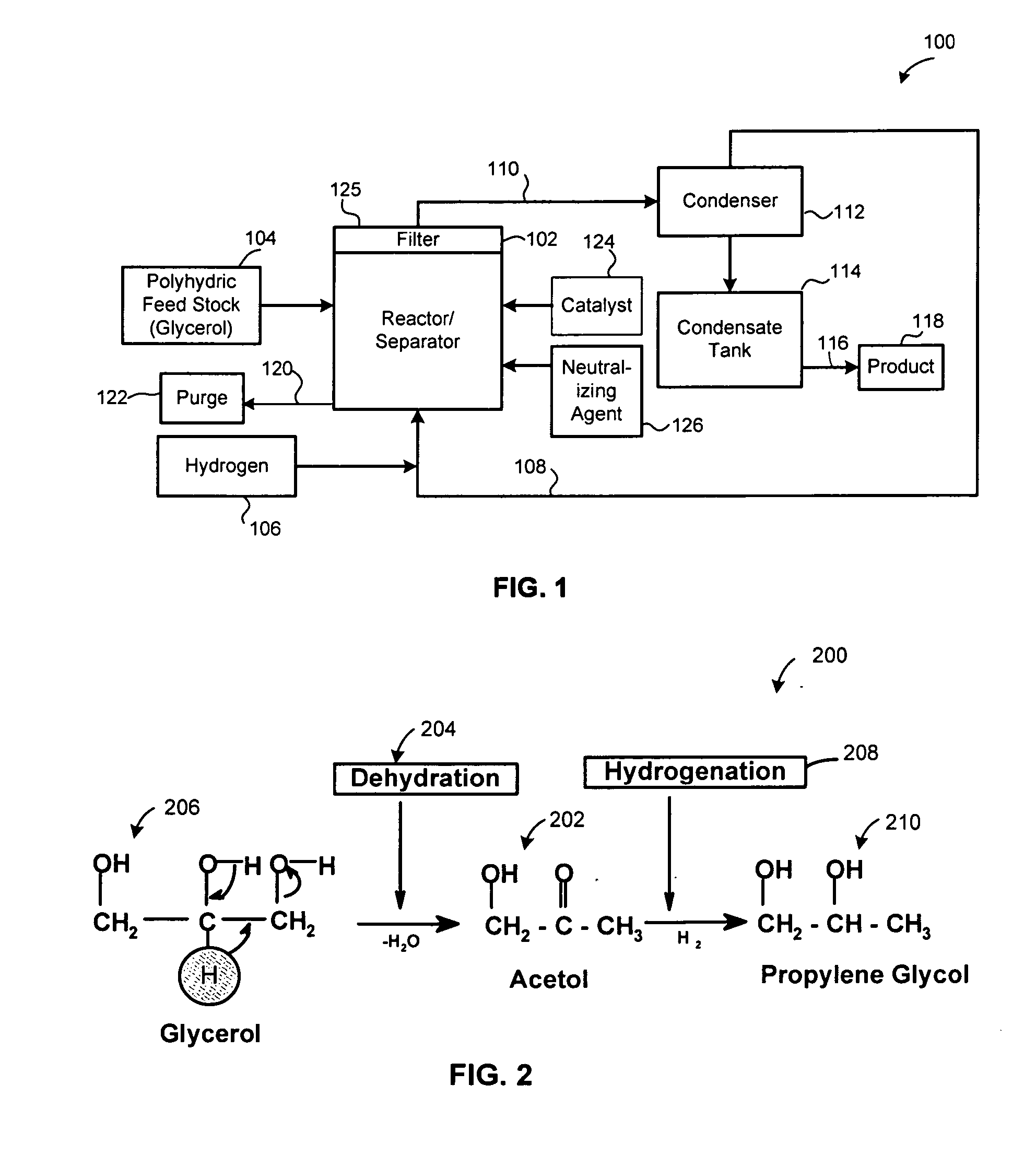
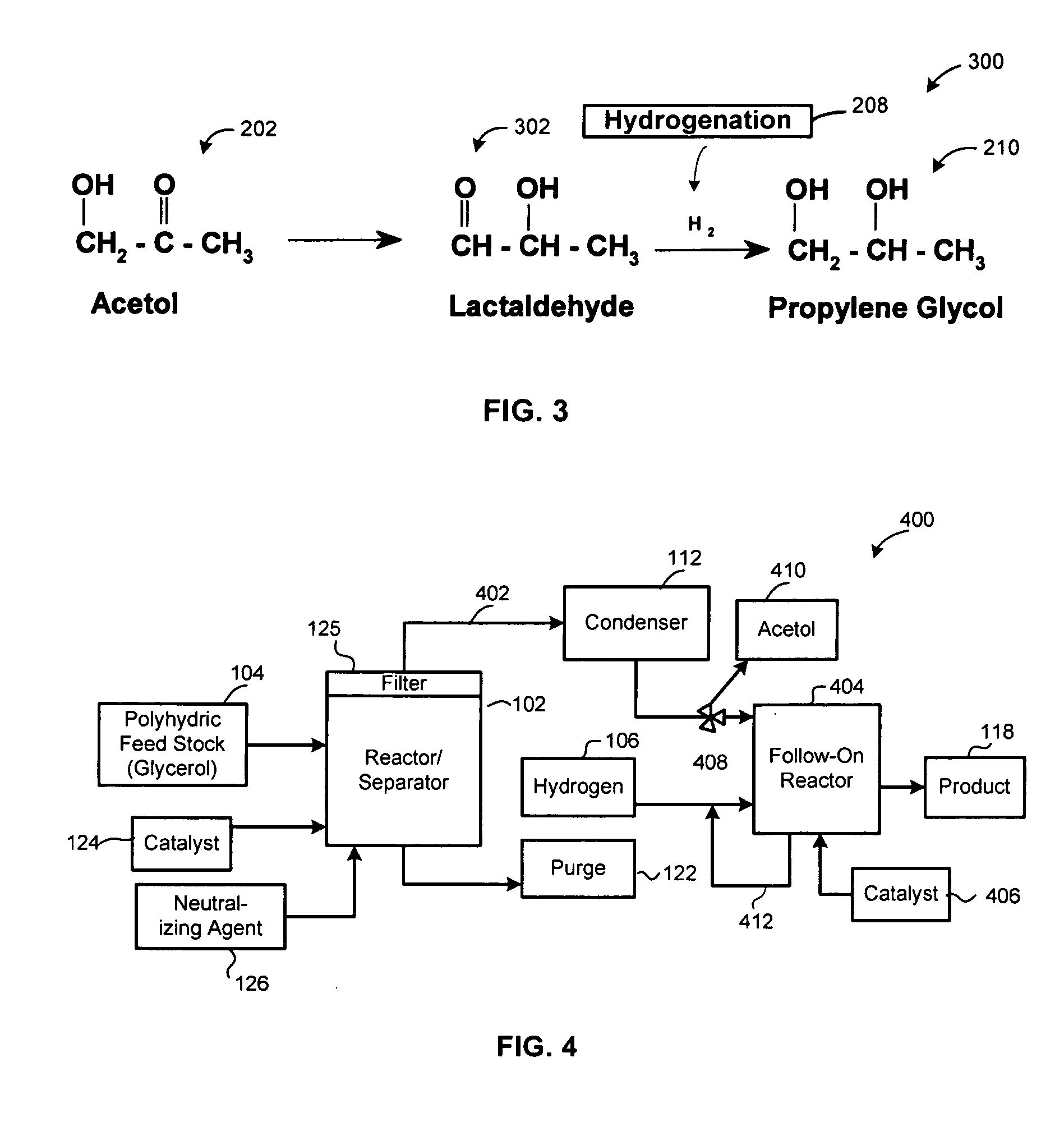
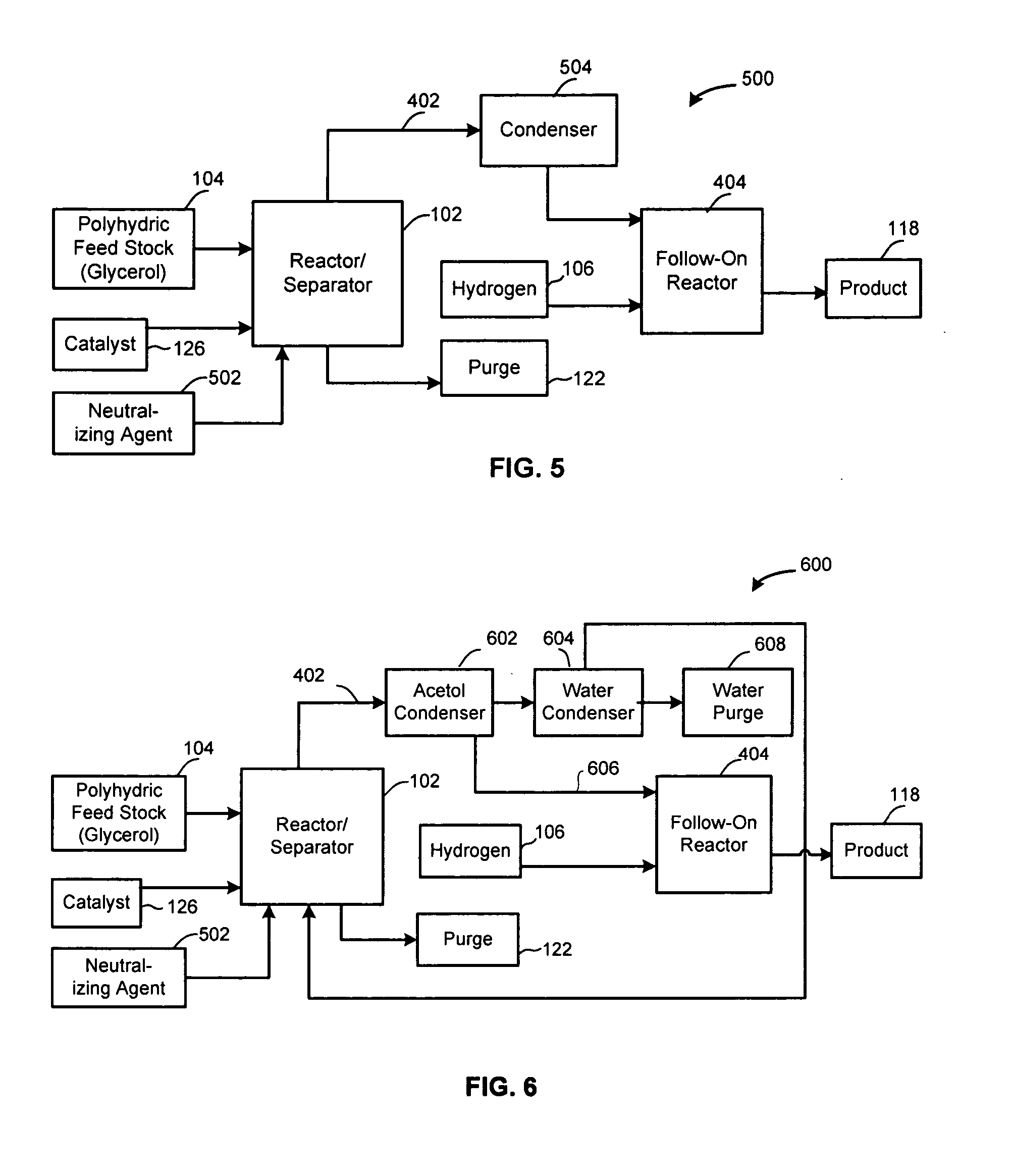
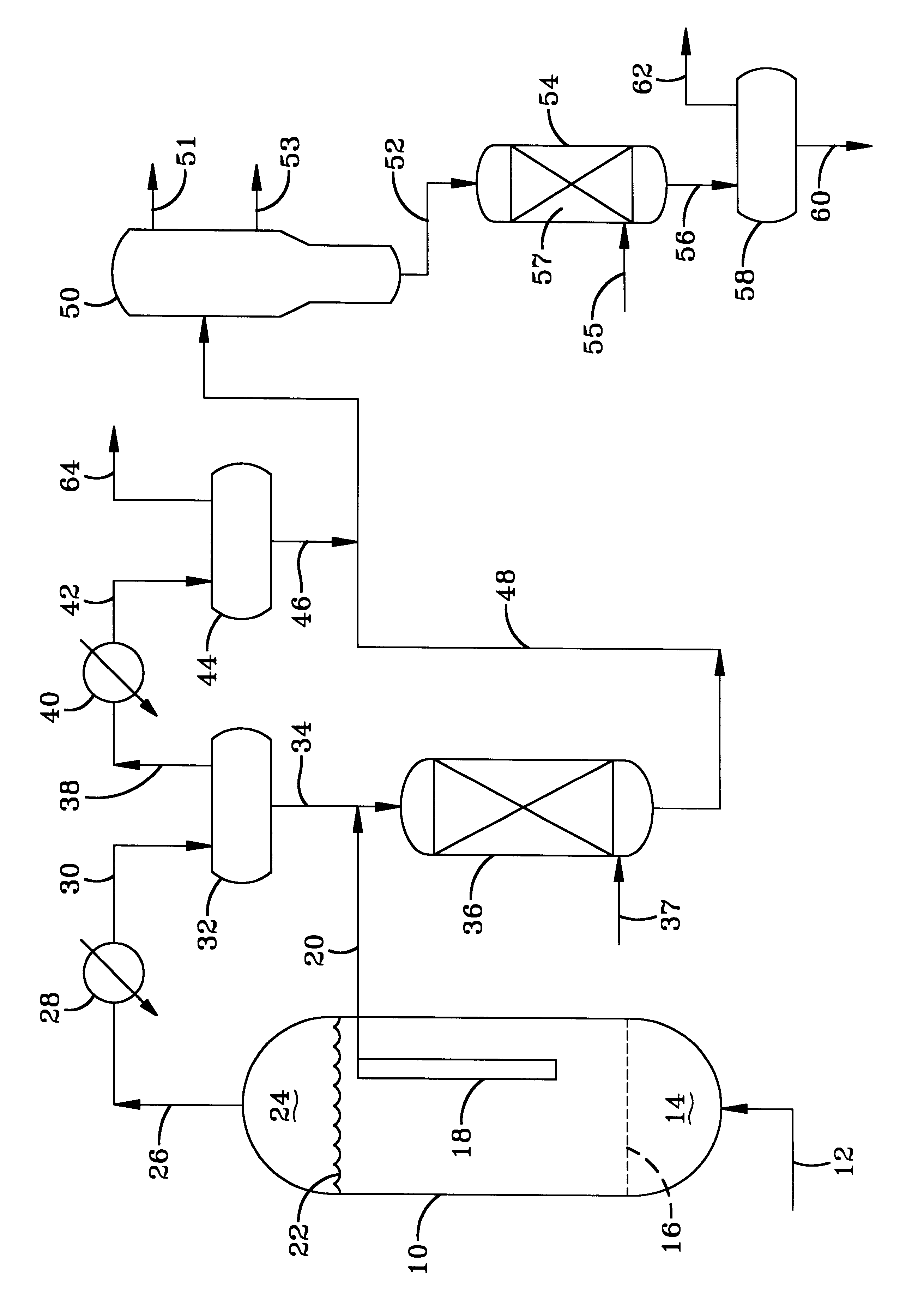
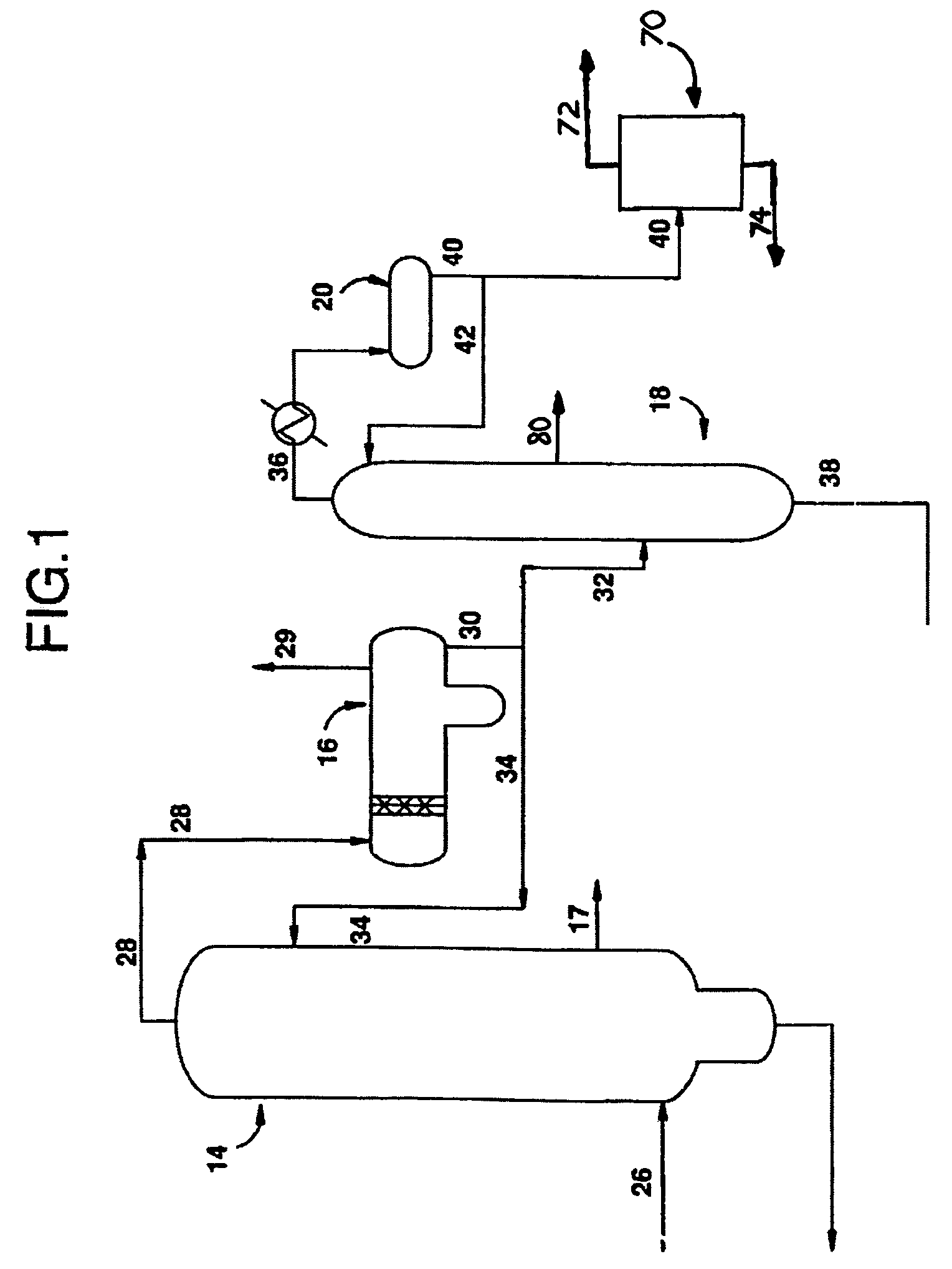
Method of producing lower alcohols from glycerol
ActiveUS20050244312A1High selectivityOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAlcoholBoiling point
A reactive-separation process converts glycerin into lower alcohols, having boiling points less than 200° C., at high yields. Conversion of natural glycerin to propylene glycol through an acetol intermediate is achieved at temperatures from 150° to 250° C. at a pressure ranging from 1 and 25 bar. The preferred applications of the propylene glycol are as an antifreeze, deicing compound, or anti-icing compound. The preferred catalyst for this process in a copper-chromium powder.
Owner:RENEWABLE ALTERNATIVES LLC +1
Wide-cut synthetic isoparaffinic lubricating oils
A wide-cut lubricant base stock is made by hydroisomerizing and then catalytically dewaxing a waxy Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon fraction feed and comprises the entire dewaxate having an initial boiling point in the 650-75O° F.+ range. Formulated lubricating oils made by admixing the base stock with a commercial automotive additive package meet all specifications, including low temperature properties, for multigrade internal combustion engine crankcase oils. The waxy feed has an initial boiling point in the 650-750° F. range and continuously boils to an end point of at least 1050° F.+. Lower boiling hydrocarbons produced by the process are separated from the base stock by simple flash distillation. The base stock comprises the entire dewaxate having an initial boiling point in the 650-750° F. range.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for the production of acetic acid
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
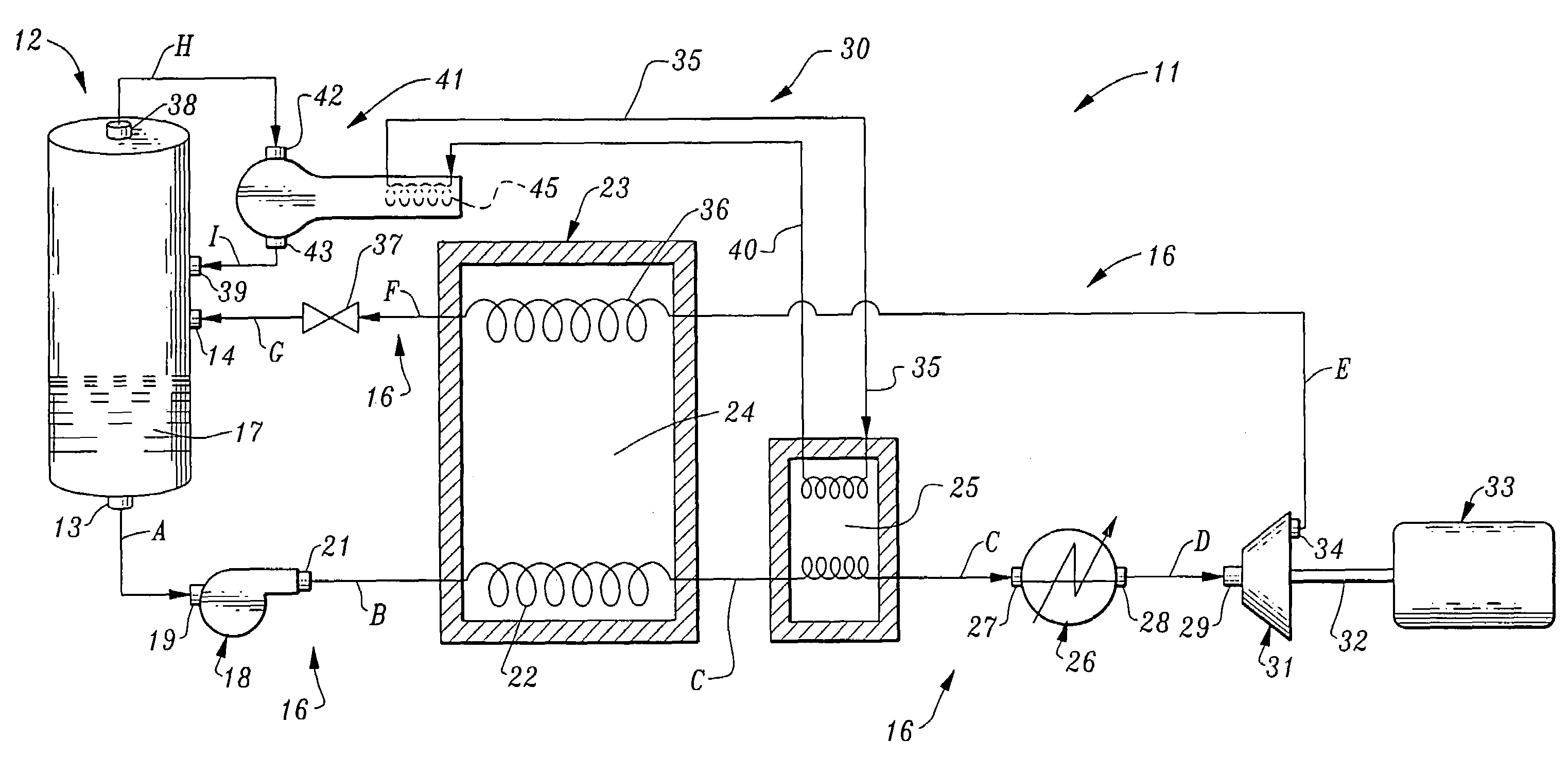
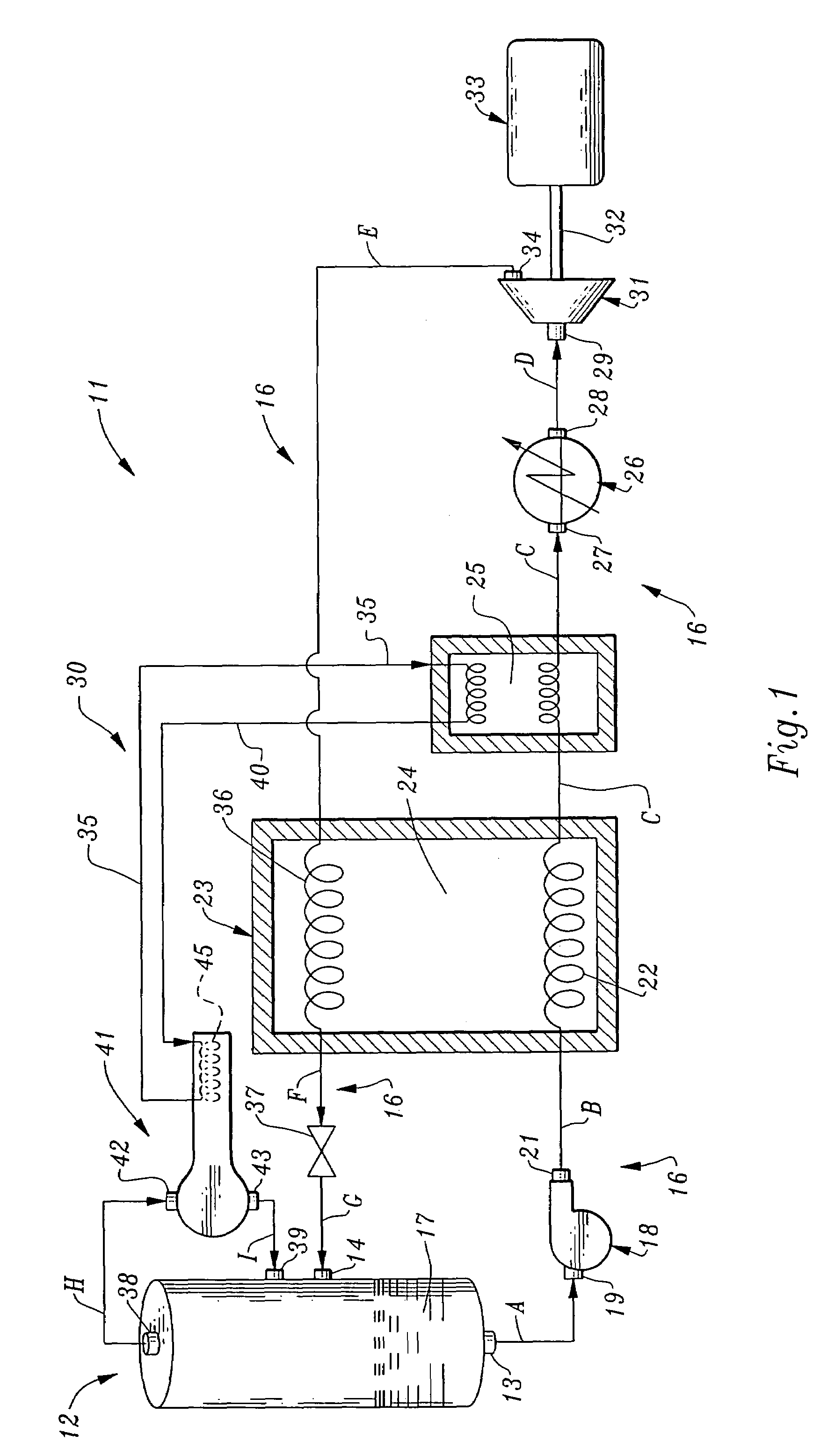
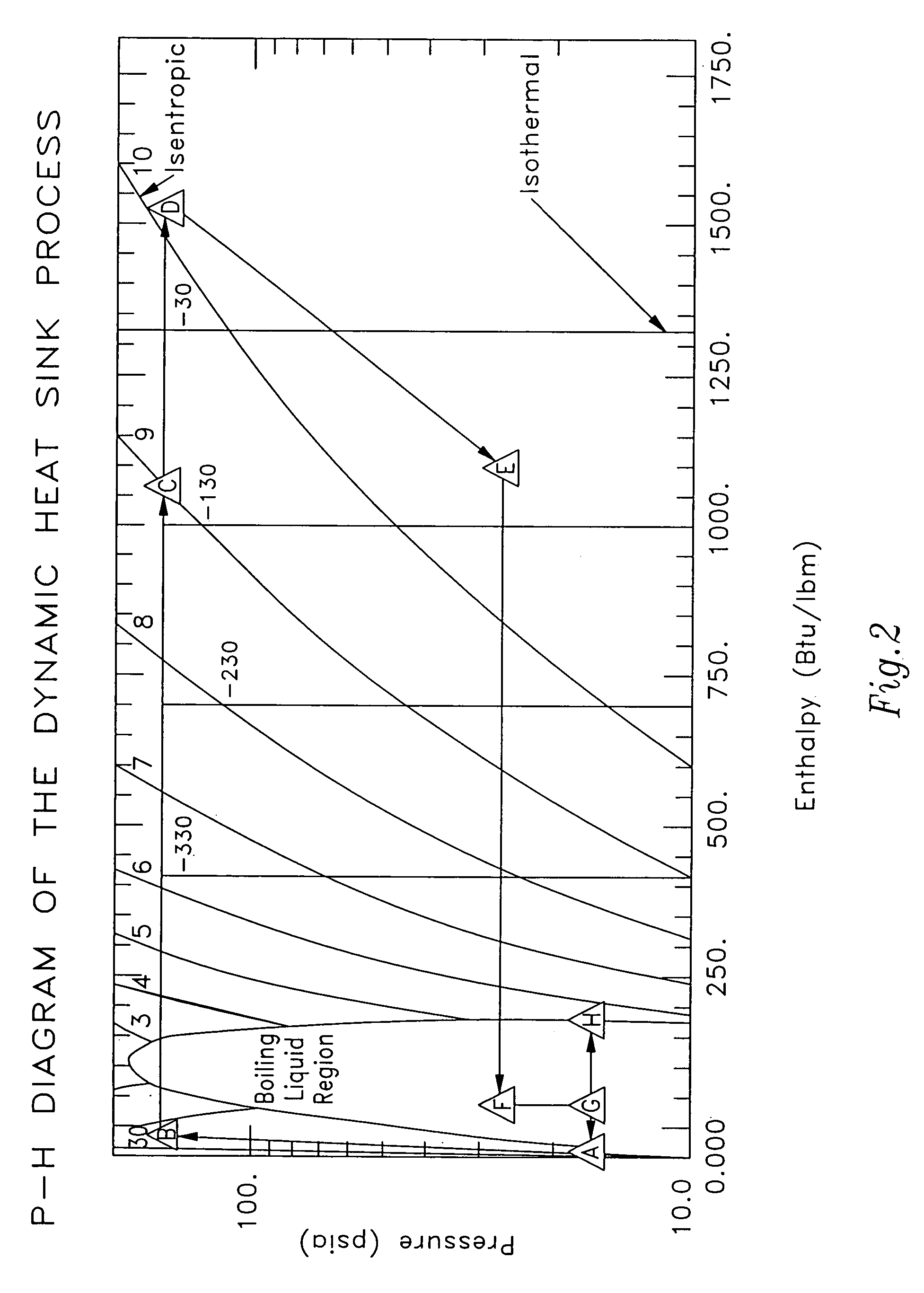
Dynamic heat sink engine
InactiveUS7047744B1Decrease in overall heat dutyImprove the coefficient of performanceFrom solar energySteam accumulatorsLiquid lineWorking fluid
A dynamic heat sink engine including a storage vessel having a working fluid outlet and a working fluid inlet. The lower portion of the storage vessel contains a cryogenic working fluid, such as liquid hydrogen, at a temperature at near its boiling point. The engine further includes a working fluid circuit extending between the working fluid outlet and the working fluid inlet of the storage vessel. The working fluid circuit includes the serial connection of the following components from the working fluid outlet to the working fluid inlet: a fluid pump; a vaporizer having a liquid line passing therethrough; a heater; an expansion engine having a rotary output shaft; an electrical generator connected to the rotary output shaft of the expansion engine; a vapor line passing through the vaporizer, the vaporizer including a heat exchanger providing thermal communication between the liquid line and the vapor line.
Owner:ROBERTSON STUART J +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com