Patents
Literature
5643results about "Catalytic cracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for performing a function in a plant using process performance monitoring with process equipment monitoring and control
InactiveUS7206646B2Easy to operateBetter stateSafety arrangmentsCatalytic crackingProcess equipmentOptimal control
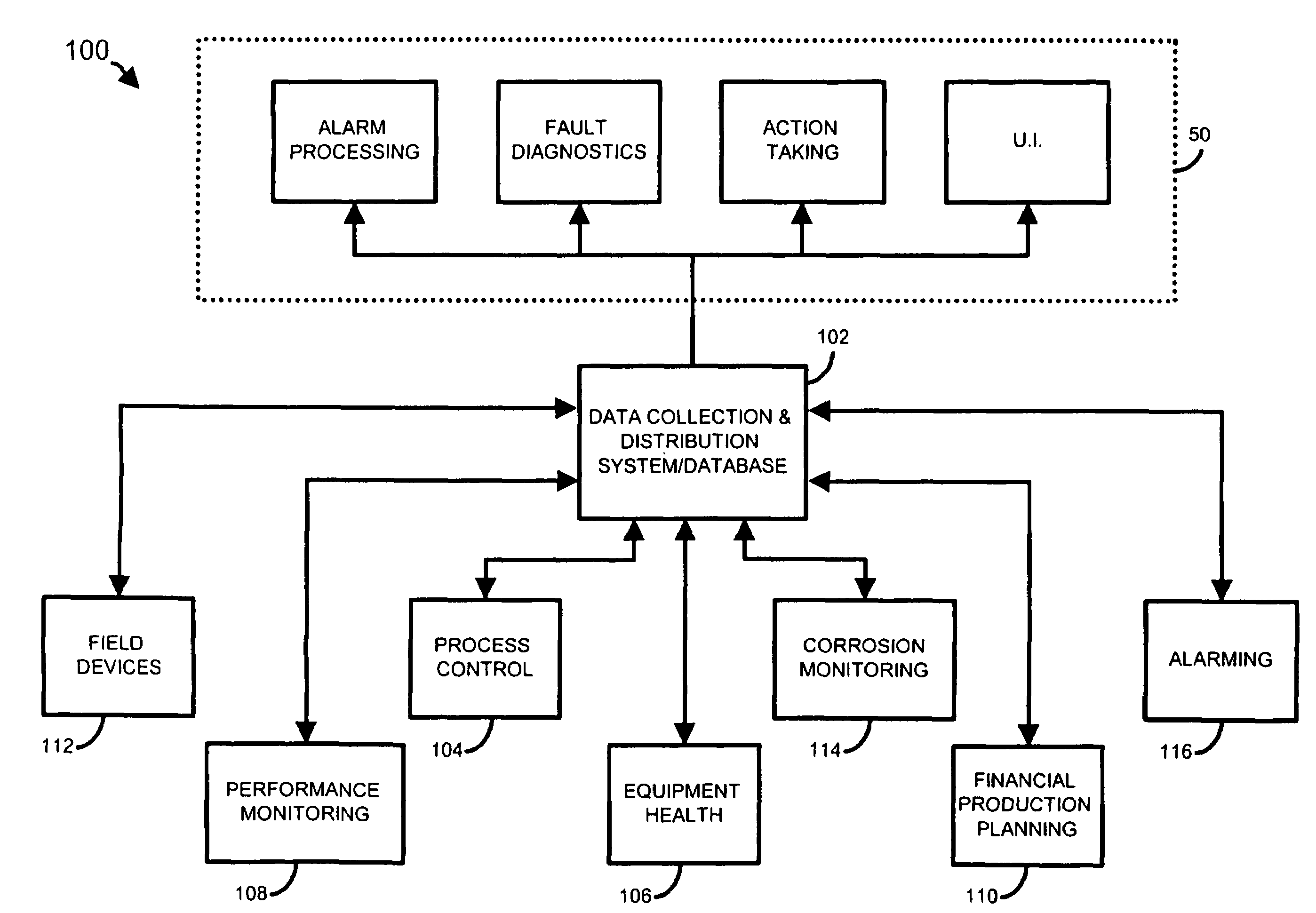
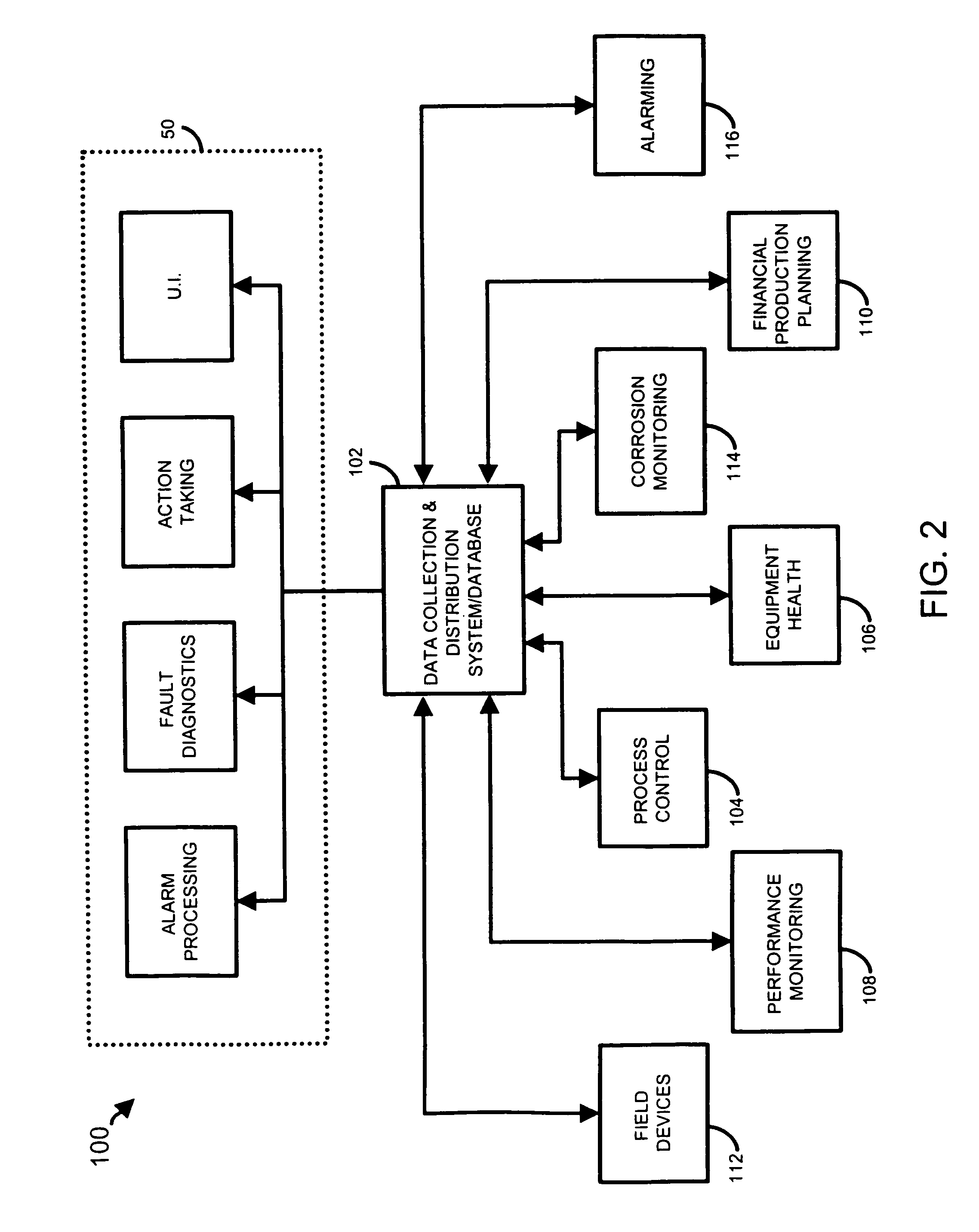
A process control system uses a data collection and distribution system and an asset utilization suite to collect data or information pertaining to the assets of a process plant from various sources or functional areas of the plant including, for example, the process control functional areas, the maintenance functional areas and the process performance monitoring functional areas. This data and information is manipulated in a coordinated manner by the data collection and distribution system and is redistributed to other applications where this it is used to perform overall better or more optimal control, maintenance and business activities. Information or data may be collected by maintenance functions pertaining to the health, variability, performance or utilization of a device, loop, unit, area, etc. and this information may then be sent to and displayed to a process operator or maintenance person to inform that person of a current or future problem. A user interface is provided that enables users to access and manipulate the expert engine to optimize plant operation or cause optimization of plant operation, to get information about the operation of the plant, etc. Furthermore, applications, such as work order generation applications may automatically generate work orders, parts or supplies orders, etc. based on events occurring within the plant.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Method for producing a crude product with reduced tan
InactiveUS20070000810A1Catalytic crackingRefining with metal saltsOrganic chemistryContact condition
Contacting a crude feed with one or more catalysts to produce a total product that includes the crude product is described. The crude feed has a TAN of at least 1. At least one of the catalysts includes one or more metals from Columns 6-10 of the Periodic Table and / or one or more compounds of one or more metals from Columns 6-10 of the Periodic Table. Contacting conditions are controlled contacting such that the crude product has a TAN from about 0.001 to about 0.5.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Subsurface heaters with low sulfidation rates
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Cogeneration systems and processes for treating hydrocarbon containing formations
InactiveUS20070095536A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingElectricityNuclear engineering
A system for treating a hydrocarbon containing formation includes a steam and electricity cogeneration facility. At least one injection well is located in a first portion of the formation. The injection well provides steam from the steam and electricity cogeneration facility to the first portion of the formation. At least one production well is located in the first portion of the formation. The production well in the first portion produces first hydrocarbons. At least one electrical heater is located in a second portion of the formation. At least one of the electrical heaters is powered by electricity from the steam and electricity cogeneration facility. At least one production well is located in the second portion of the formation. The production well in the second portion produces second hydrocarbons. The steam and electricity cogeneration facility uses the first hydrocarbons and / or the second hydrocarbons to generate electricity.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method for gas-solid contacting in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor
InactiveUS6894183B2Eliminate and drastically reduce bypassEffective contactThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingForming gasSolid particle
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Multiple riser reactor
InactiveUS7102050B1Reduce the overall diameterReduce widthCatalytic crackingOrganic chemistry methodsHydrocarbonChemistry
The present invention is directed to a hydrocarbon conversion apparatus. The apparatus comprises the following: a plurality of riser reactors, each of the riser reactors having a first end into which a catalyst can be fed and a second end through which the catalyst can exit the riser reactor; a separation zone into which the second ends of the riser reactors extend, the separation zone being provided to separate the catalyst from products of a reaction conducted in the hydrocarbon conversion apparatus; and at least one catalyst return in fluid communication with the separation zone and the first ends of the riser reactors, the catalyst return being provided to transfer the catalyst from the separation zone to the first ends of the riser reactors.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
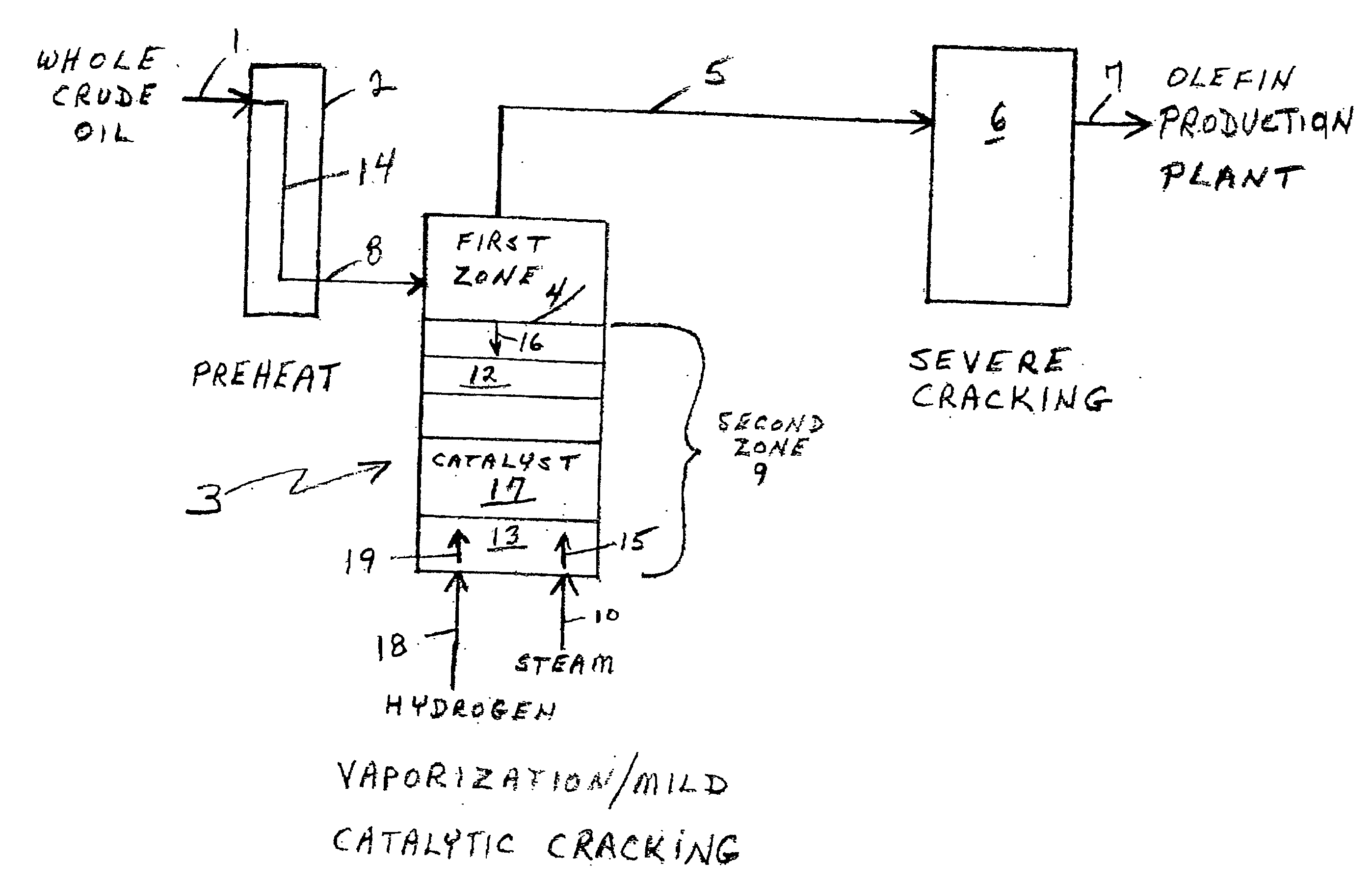
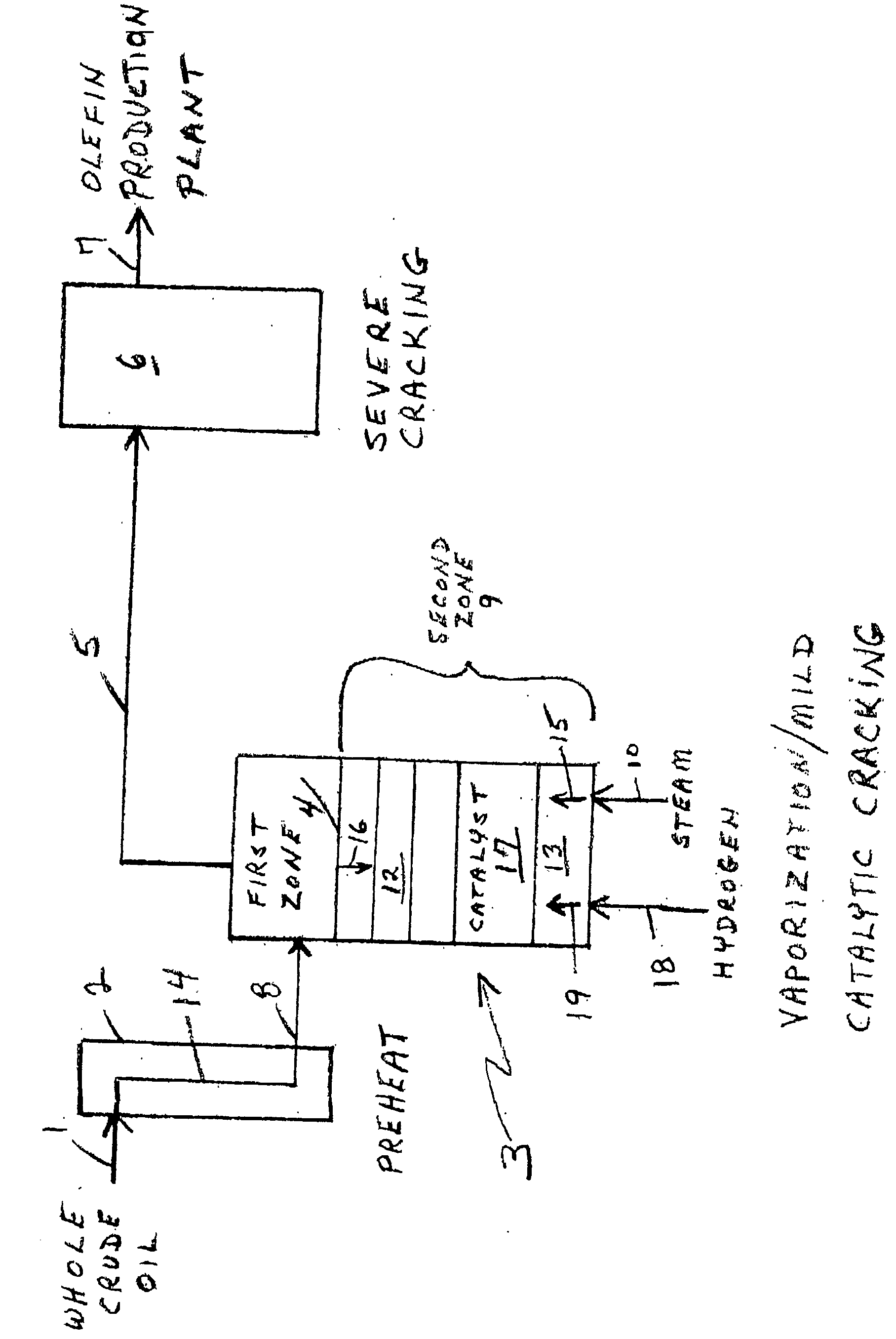
Olefin production utilizing whole crude oil and mild catalytic cracking
InactiveUS20040054247A1Lower temperature rangeImproved vaporizationThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingChemistryPyrolysis
A method for utilizing whole crude oil as a feedstock for the pyrolysis furnace of an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock after preheating is subjected to mild catalytic cracking conditions until substantially vaporized, the vapors from the mild catalytic cracking being subjected to severe cracking in the radiant section of the furnace.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Process for upgrading naphtha
A method for upgrading a naphtha feed to a naphtha product containing less than about 10 wppm of nitrogen and less than about 15 wppm sulfur, the method comprising contacting said naphtha feed with hydrogen in the presence of a bulk multimetallic catalyst under effective reactor conditions to hydrodesulfurize and hydrodenitrogenize said naphtha feed to produce said naphtha product, wherein said bulk multimetallic catalyst comprises at least one Group VIII non-noble metal and at least two Group VIB metals.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Solution mining dawsonite from hydrocarbon containing formations with a chelating agent
A method for treating an oil shale formation comprising dawsonite includes providing heat from one or more heaters to the formation to heat the formation. Hydrocarbon fluids are produced from the formation. At least some dawsonite in the formation is decomposed with the provided heat. A chelating agent is provided to the formation to dissolve at least some dawsonite decomposition products. The dissolved dawsonite decomposition products are produced from the formation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Systems, methods, and catalysts for producing a crude product
InactiveUS20050133414A1Reduce contentCatalytic crackingRefining with metal saltsOxygen contentChemistry
Contact of a crude feed with one or more catalysts produces a total product that includes a crude product. The crude feed may include Micro-Carbon Residue (MCR), oxygen, sulfur, or mixtures thereof. The crude product is a liquid mixture at 25° C. and 0.101 MPa. The crude product may have a MCR residue and / or oxygen content of at most 90% of the MCR residue content and / or oxygen content of the crude feed. In some instances, the crude product may have a sulfur content of about 30% to about 70% of the sulfur content of the crude feed. One or more other properties of the crude product may be changed by at least 10% relative to the respective properties of the crude feed.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Non-ferromagnetic overburden casing
Systems, methods, and heaters for treating a subsurface formation are described herein. At least one system for electrically insulating an overburden portion of a heater wellbore is described. The system may include a heater wellbore located in a subsurface formation and an electrically insulating casing located in the overburden portion of the heater wellbore. The casing may include at least one non-ferromagnetic material such that ferromagnetic effects are inhibited in the casing.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Cracking catalyst for petroleum hydrocarbon, and preparation method
A cracking catalyst for petroleum hydrocarbon is proportionally prepared from clay, aluminum oxide prepared from alpha-AlO(OH), Y-type molecular sieve containing RE and P and silicon oxide. Its advantages are strong power to convert heavy oil and high output rate of diesel oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Systems, methods, and catalysts for producing a crude product
InactiveUS20050133417A1Reduce contentCatalytic crackingRefining with metal saltsAcid valueTotal acid
Contact of a crude feed with one or more catalysts produces a total product that include a crude product. The crude feed may a total acid number of at least 0.3. The crude product is a liquid mixture at 25° C. and 0.101 MPa. The crude product may have a total acid number of at most 90% of the total acid number of the crude feed. At least one of the catalysts may include one or more Column 6 metals of the Periodic Table and one or more Column 10 metals of the Periodic Table. One or more other properties of the crude product may be changed by at least 10% relative to the respective properties of the crude feed.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
FCC process with improved yield of light olefins
InactiveUS7312370B2Increase productionImprove olefin selectivityCatalytic crackingHydrocarbonsHydrocarbonZeolite
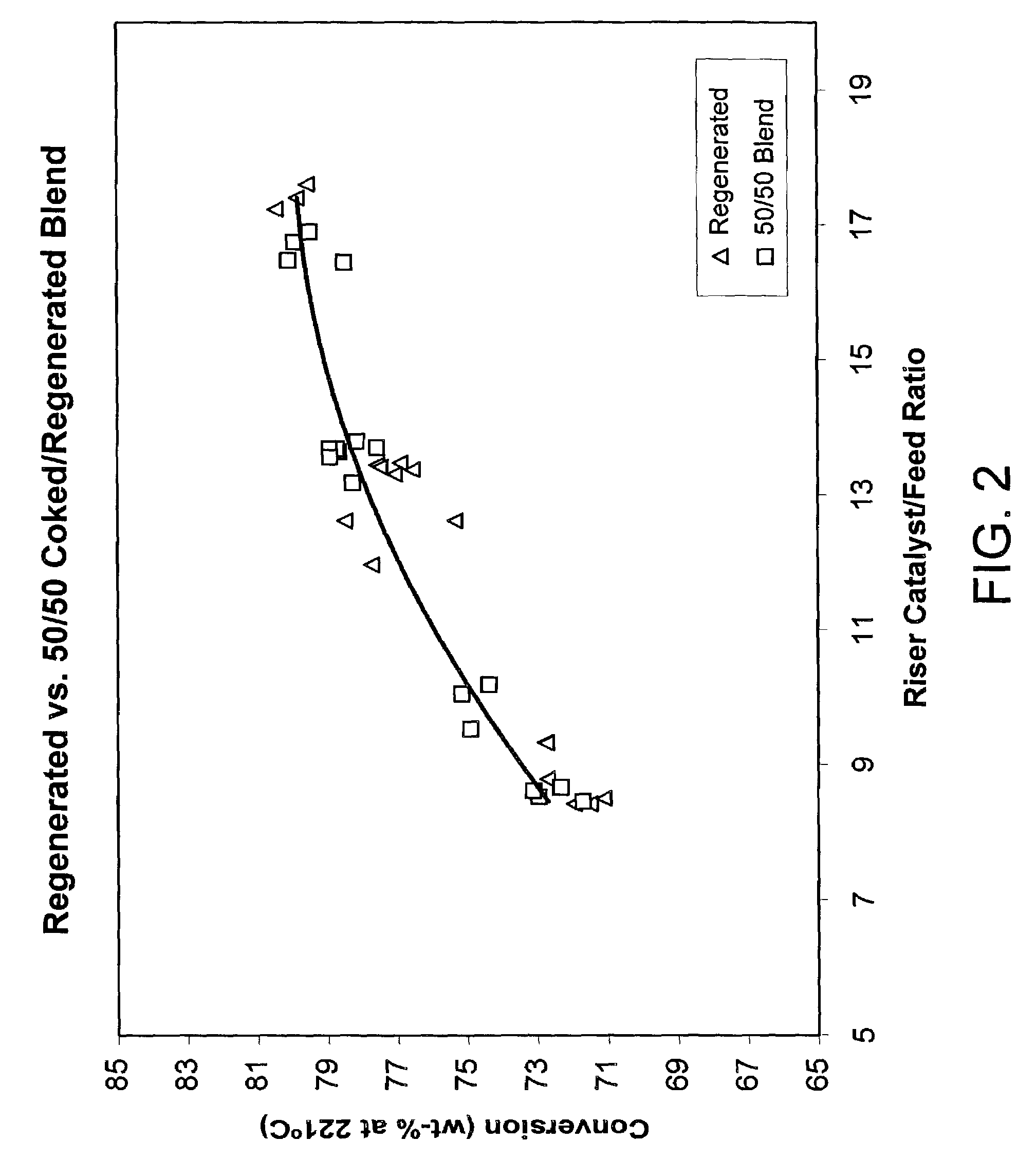
An FCC process for obtaining light olefins comprises contacting a hydrocarbon feed stream with blended catalyst comprising regenerated catalyst and coked catalyst. The catalyst has a composition including a first component and a second component. The second component comprises a zeolite with no greater than medium pore size wherein the zeolite comprises at least 1 wt-% of the catalyst composition. The contacting occurs in a riser to crack hydrocarbons in the feed stream and obtain a cracked stream containing hydrocarbon products including light olefins and coked catalyst. The cracked stream is passed out of an end of the riser such that the hydrocarbon feed stream is in contact with the blended catalyst in the riser for less than or equal to 2 seconds on average. The hydrocarbon products including light olefins are separated from the coked catalyst. The first portion of the coked catalyst is passed to a regeneration zone in which coke is combusted from the catalyst to produce a regenerated catalyst. A second portion of the coked catalyst is blended with the regenerated catalyst and introduced to the riser. The regenerated catalyst has substantially the same relative proportions of the first component and the second component as the blended catalyst that contact the hydrocarbon feed stream.
Owner:UOP LLC
Compositions produced using an in situ heat treatment process
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
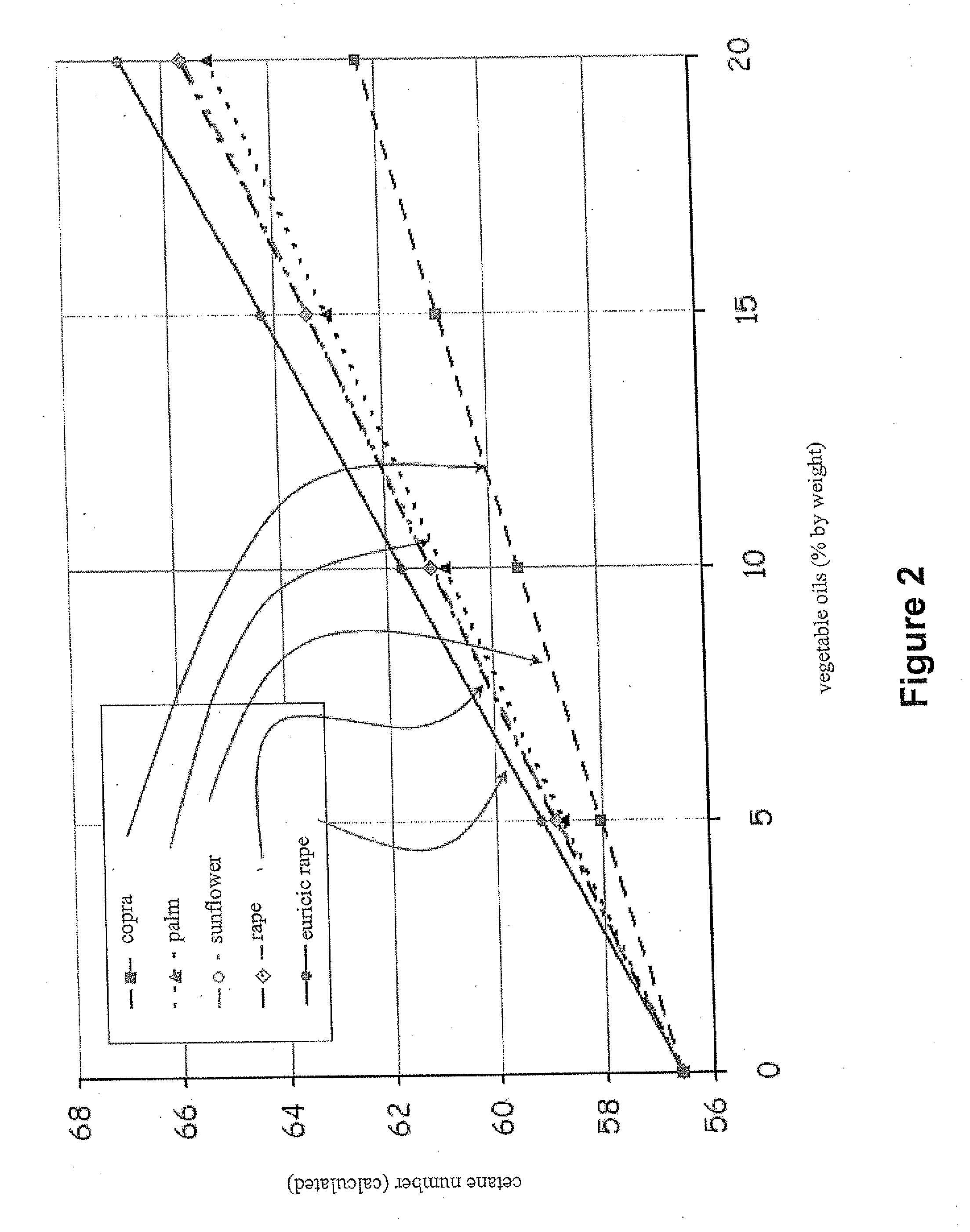
Methods of hydrotreating a mixture made up of oils of animal or vegetable origin and of petroleum cuts with intermediate stripping
ActiveUS20080161614A1Low costLimit consumption of hydrogenThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingVegetable oilVolumetric Mass Density
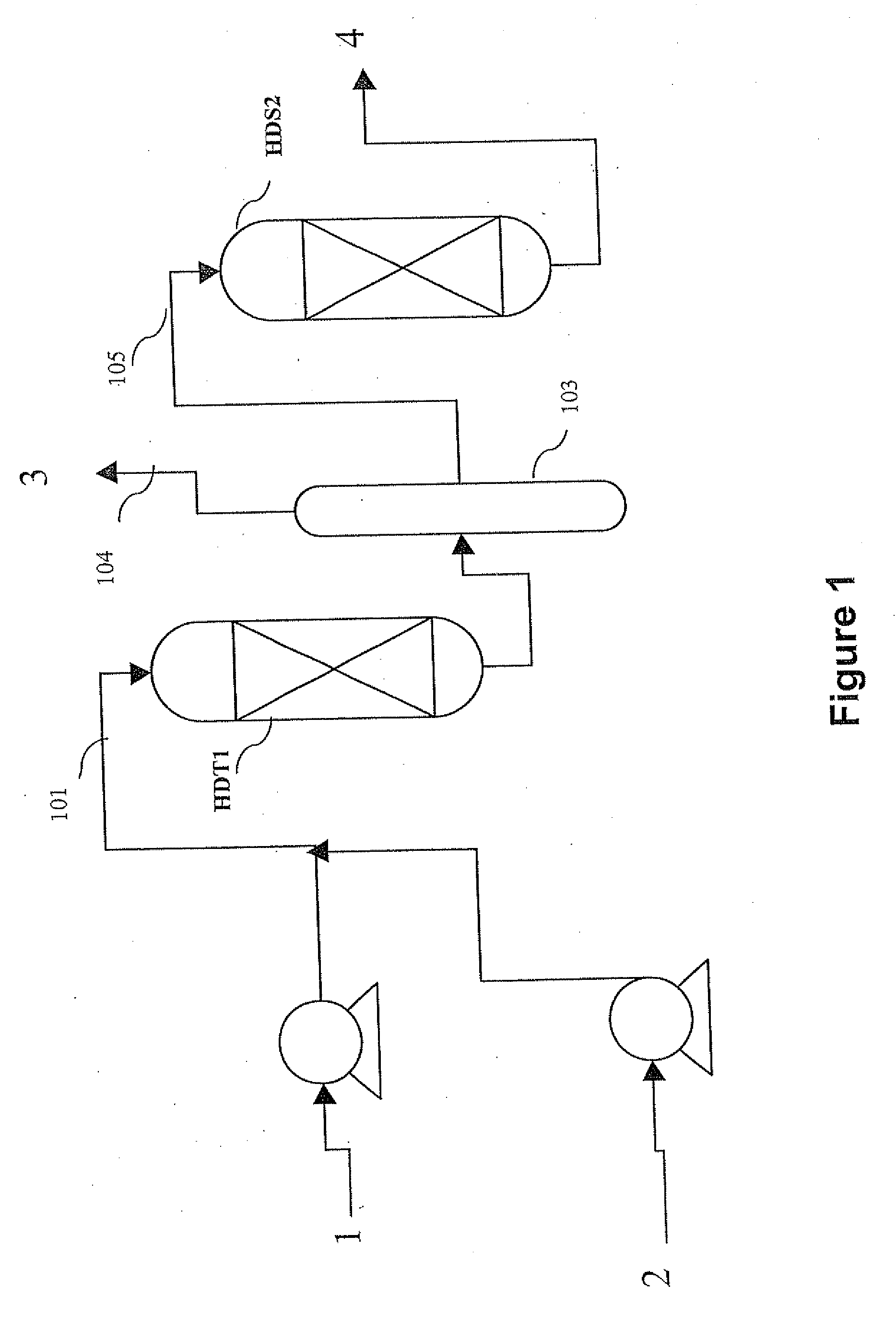
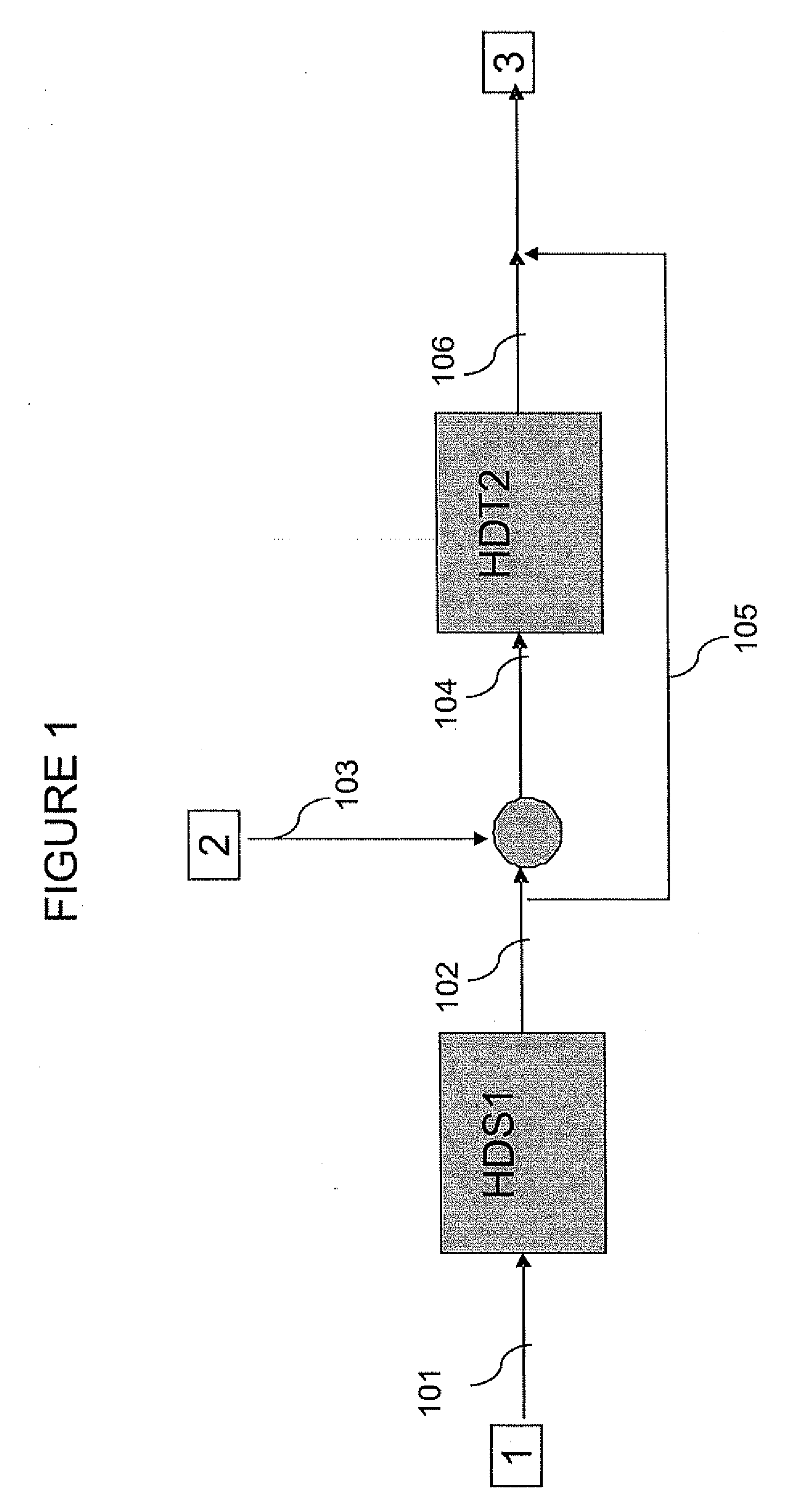
The invention relates to a hydrotreating method (HDT) using two plants working under different operating conditions with an intermediate stripping for co-treating a mixture made up of oils of vegetable or animal origin and petroleum cuts (gas oil cuts (GO) and middle distillates) in order to produce gas oil fuel bases meeting specifications. The first plant (HDT1) is more particularly dedicated to the reactions concerning oils of vegetable or animal origin in comixture while pretreating the hydrocarbon feed, whereas the second plant (HDS2) works under more severe conditions to obtain diesel fuel according to standards, in particular in terms of effluent sulfur content, density and cold properties. The process economy, the activity and the stability of the catalyst of the second plant are greatly improved by the intermediate stripping.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for converting carbon-based energy carrier material
InactiveUS20090308787A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
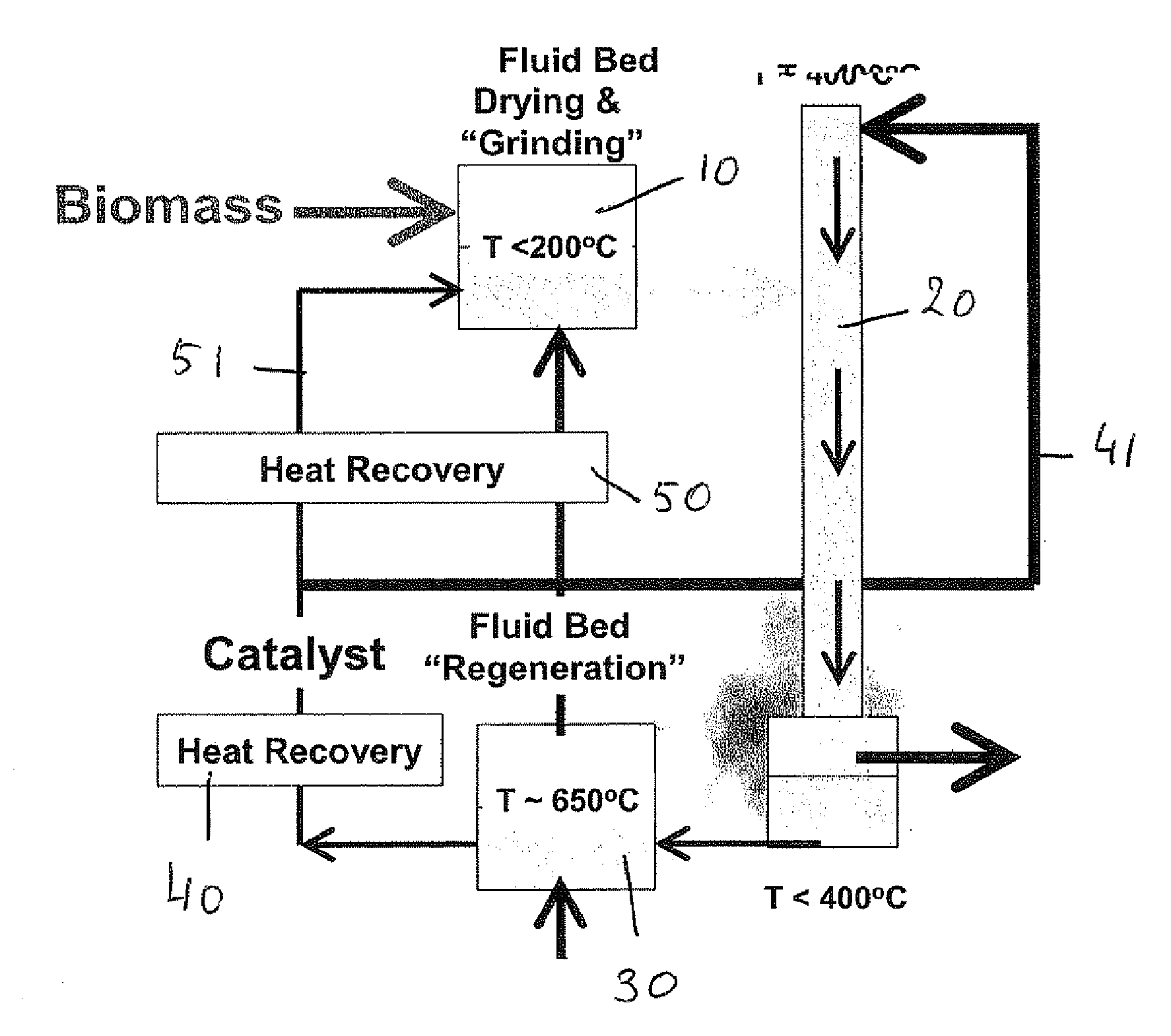
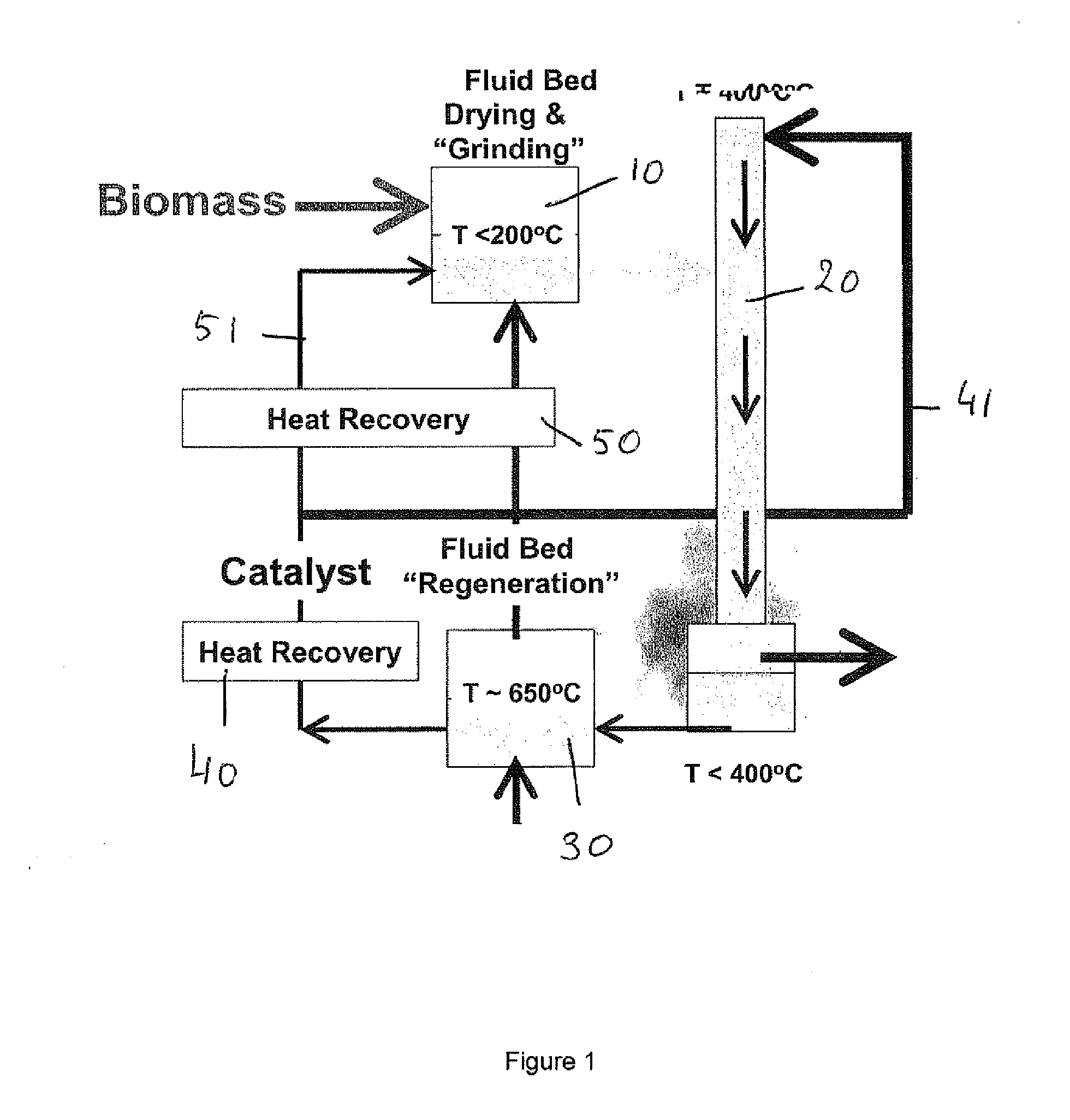
A process is disclosed process for converting a solid or highly viscous carbon-based energy carrier material to liquid and gaseous reaction products, said process comprising the steps of: a) contacting the carbon-based energy carrier material with a particulate catalyst material b) converting the carbon-based energy carrier material at a reaction temperature between 200° C. and 450° C., preferably between 250° C. and 350° C., thereby forming reaction products in the vapor phase. In a preferred embodiment the process comprises the additional step of: c) separating the vapor phase reaction products from the particulate catalyst material within 10 seconds after said reaction products are formed; In a further preferred embodiment step c) is followed by: d) quenching the reaction products to a temperature below 200° C.
Owner:MARD INC
Process of paraffin hydrocarbon isomerisation catalysed by an ionic liquid in the presence of a cyclic hydrocarbon additive
InactiveUS6797853B2High selectivityHigh degree of branchingHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneIonic liquid
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
Doped spherically-shaped supported catalyst and process for hydrotreating and hydroconverting metal-containing oil fractions
ActiveUS20050211603A1Catalytic crackingCatalyst activation/preparationCatalytic metalSilicon dioxide
The present invention concerns a catalyst for hydrotreating and / or hydroconverting heavy metal-containing hydrocarbon feeds, said catalyst comprising a support in the form of beads based on alumina, at least one catalytic metal or a compound of a catalytic metal from group VIB (column 6 in the new periodic table notation), optionally at least one catalytic metal or compound of a catalytic metal from group VIII (columns 8, 9 and 10 of the new periodic table notation), with a pore structure composed of a plurality of juxtaposed agglomerates, each formed by a plurality of acicular platelets, the platelets of each agglomerate being generally radially orientated with respect to each other and with respect to the center of the agglomerate. The catalyst also comprises at least one doping element selected from the group constituted by phosphorus, boron, silicon (or silica which does not belong to that which could be contained in the selected support) and halogens. The invention also concerns the use of said catalyst in converting metal-containing feeds.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method and apparatus for making a middle distillate product and lower olefins from a hydrocarbon feedstock
ActiveUS20060178546A1Yield maximizationCatalytic crackingCatalytic naphtha reformingPetroleum productGasoline
Disclosed is a process for making middle distillate and lower olefins. The process includes catalytically cracking a gas oil feedstock within a riser reactor zone by contacting under suitable catalytic cracking conditions within the riser reactor zone the gas oil feedstock with a middle distillate selective cracking catalyst that comprises amorphous silica alumina and a zeolite to yield a cracked gas oil product and a spent cracking catalyst. The spent cracking catalyst is regenerated to yield a regenerated cracking catalyst. Within an intermediate cracking reactor such as a dense bed reactor zone and under suitable high severity cracking conditions a gasoline feedstock is contacted with the regenerated cracking catalyst to yield a cracked gasoline product and a used regenerated cracking catalyst. The used regenerated cracking catalyst is utilized as the middle distillate selective catalyst.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Wide-cut synthetic isoparaffinic lubricating oils
A wide-cut lubricant base stock is made by hydroisomerizing and then catalytically dewaxing a waxy Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon fraction feed and comprises the entire dewaxate having an initial boiling point in the 650-75O° F.+ range. Formulated lubricating oils made by admixing the base stock with a commercial automotive additive package meet all specifications, including low temperature properties, for multigrade internal combustion engine crankcase oils. The waxy feed has an initial boiling point in the 650-750° F. range and continuously boils to an end point of at least 1050° F.+. Lower boiling hydrocarbons produced by the process are separated from the base stock by simple flash distillation. The base stock comprises the entire dewaxate having an initial boiling point in the 650-750° F. range.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for upgrading naphtha
A method for upgrading a naphtha feed to a naphtha product containing less than about 10 wppm of nitrogen and less than about 15 wppm sulfur, the method comprising contacting said naphtha feed with hydrogen in the presence of a bulk multimetallic catalyst under effective reactor conditions to hydrodesulfurize and hydrodenitrogenize said naphtha feed to produce said naphtha product, wherein said bulk multimetallic catalyst comprises at least one Group VIII non-noble metal and at least two Group VIB metals.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
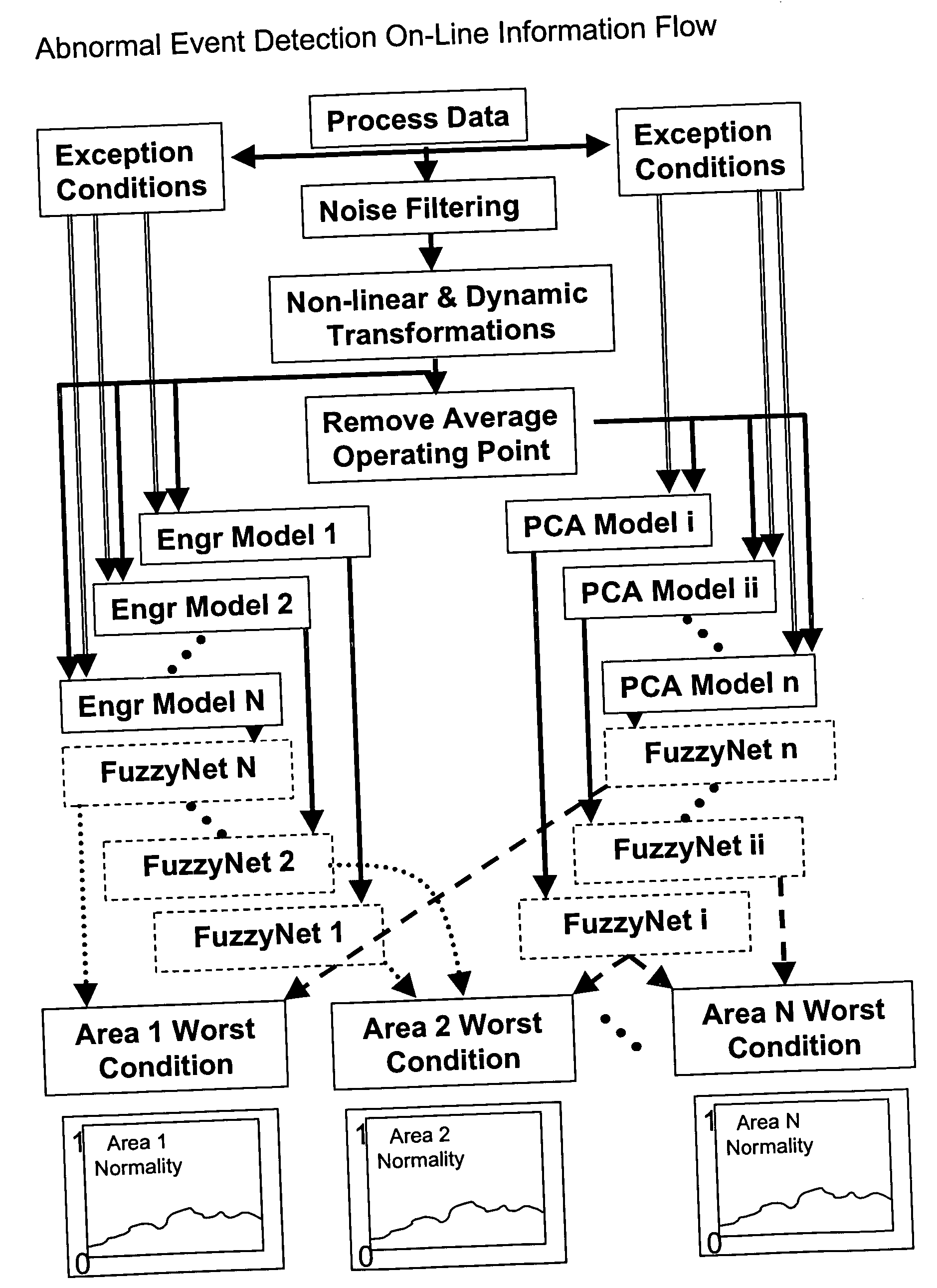
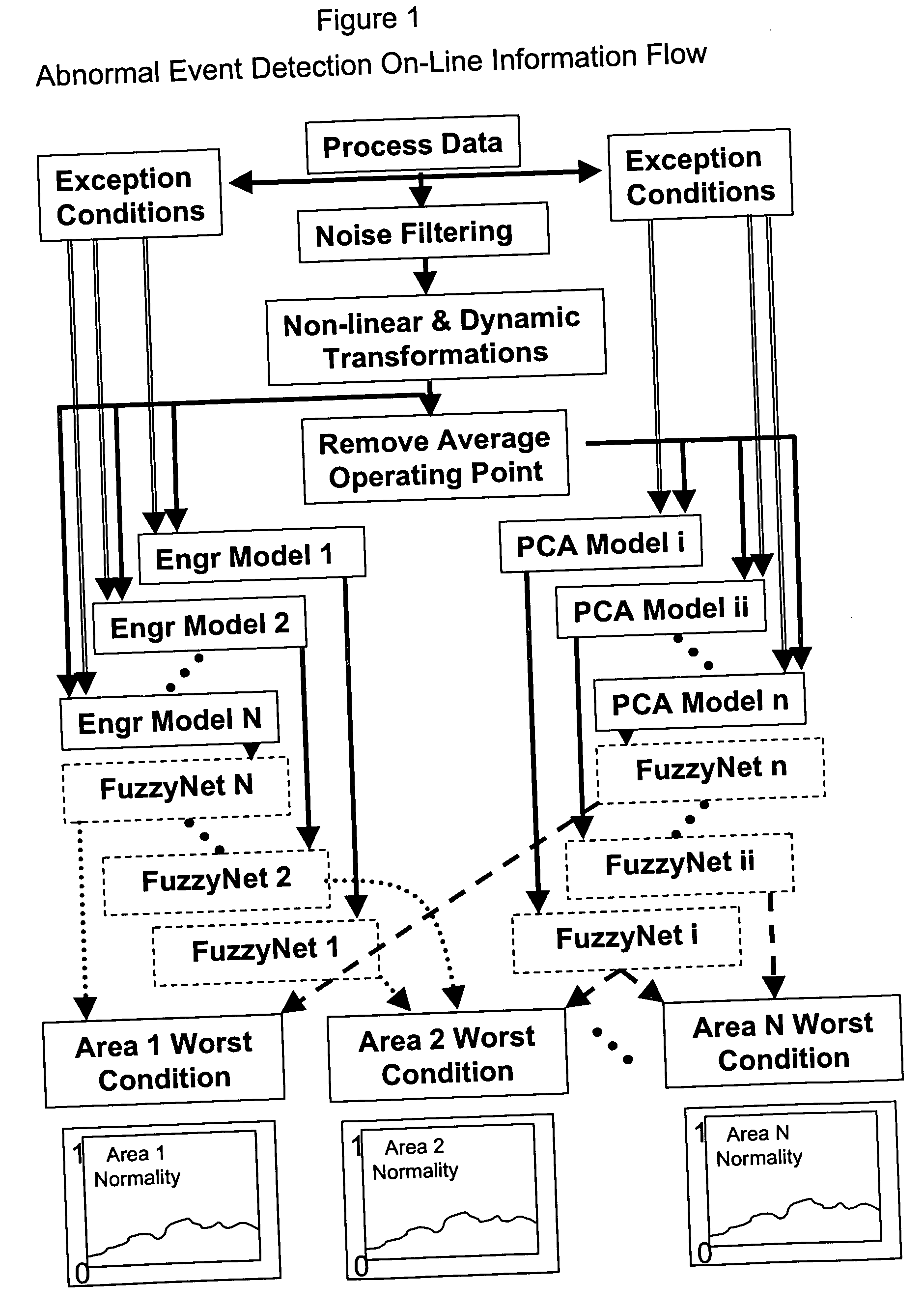
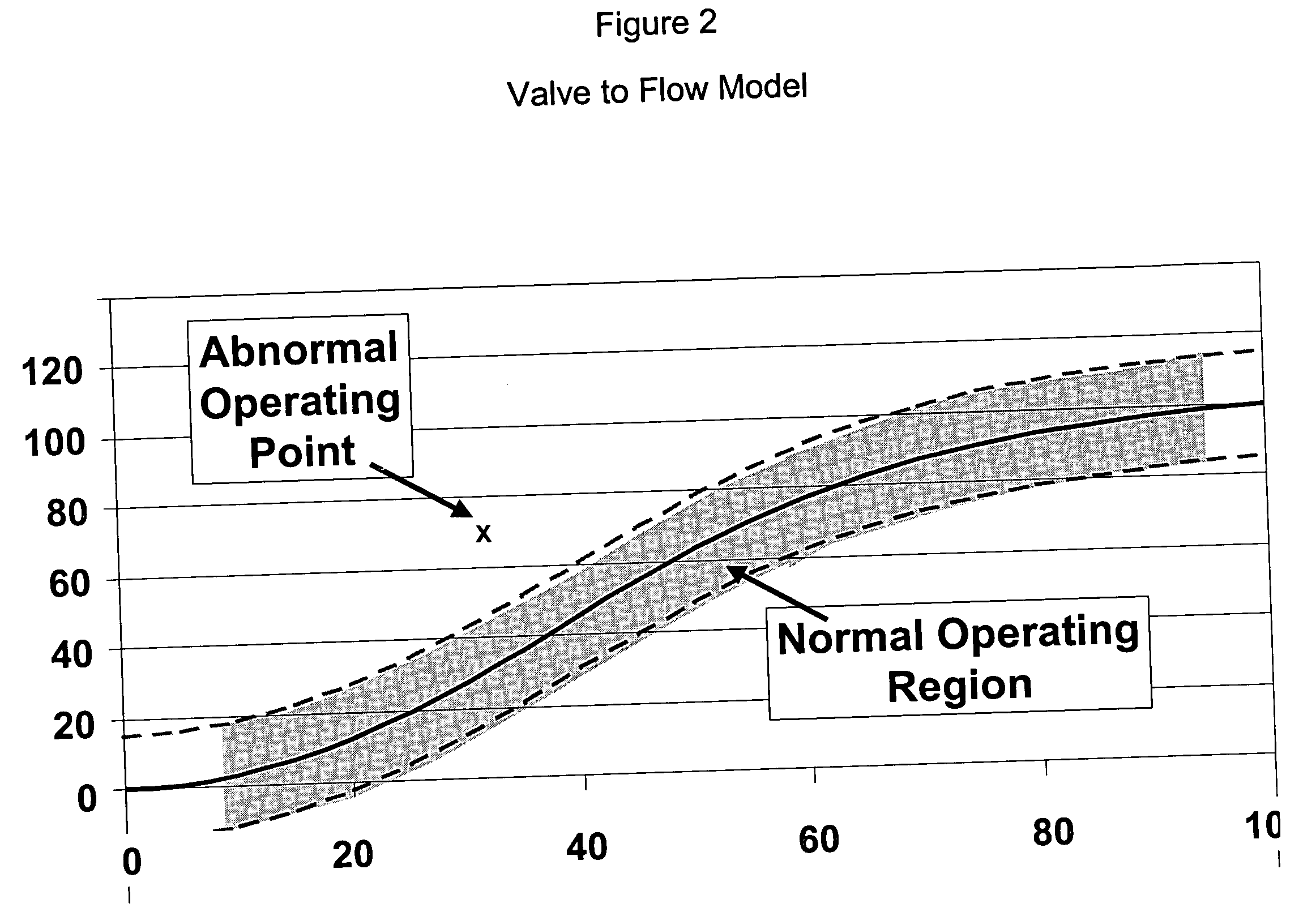
System and method for abnormal event detection in the operation of continuous industrial processes
ActiveUS20060058898A1Eliminate the effects ofEasy to monitorCatalytic crackingTesting/monitoring control systemsMultivariate statisticsPrincipal component analysis
Thousands of process and equipment measurements are gathered by the modern digital process control systems that are deployed in refineries and chemical plants. Several years of these data are historized in databases for analysis and reporting. These databases can be mined for the data patterns that occur during normal operation and those patterns used to determine when the process is behaving abnormally. These normal operating patterns are represented by sets of models. These models include simple engineering equations, which express known relationships that should be true during normal operations and multivariate statistical models based on a variation of principle component analysis. Equipment and process problems can be detected by comparing the data gathered on a minute by minute basis to predictions from these models of normal operation. The deviation between the expected pattern in the process operating data and the actual data pattern are interpreted by fuzzy Petri nets to determine the normality of the process operations. This is then used to help the operator localize and diagnose the root cause of the problem.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Fluid cat cracking with high olefins prouduction
InactiveUS20020003103A1Increase productionMaximize lightThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyNaphthaOrganic chemistry
The propylene production of a fluid catalytic cracking unit employing a large pore zeolite cracking catalyst, produces more propylene by adding a naphtha cracking riser and a medium pore zeolite catalytic component to the unit, and recycling at least a portion of the naphtha crackate to the naphtha riser. The large pore size zeolite preferably comprises a USY zeolite and the medium pore size is preferably ZSM-5. Propylene production per unit of naphtha feed to the naphtha riser is maximized, by using the 60-300.degree. F. naphtha crackate as the feed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Methods of hydrotreating a liquid stream to remove clogging compounds
A method includes producing formation fluid from a subsurface in situ heat treatment process. The formation fluid is separated to produce a liquid stream and a gas stream. At least a portion of the liquid stream is provided to a hydrotreating unit. At least a portion of selected in situ heat treatment clogging compositions in the liquid stream are removed to produce a hydrotreated liquid stream by hydrotreating at least a portion of the liquid stream at conditions sufficient to remove the selected in situ heat treatment clogging compositions.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
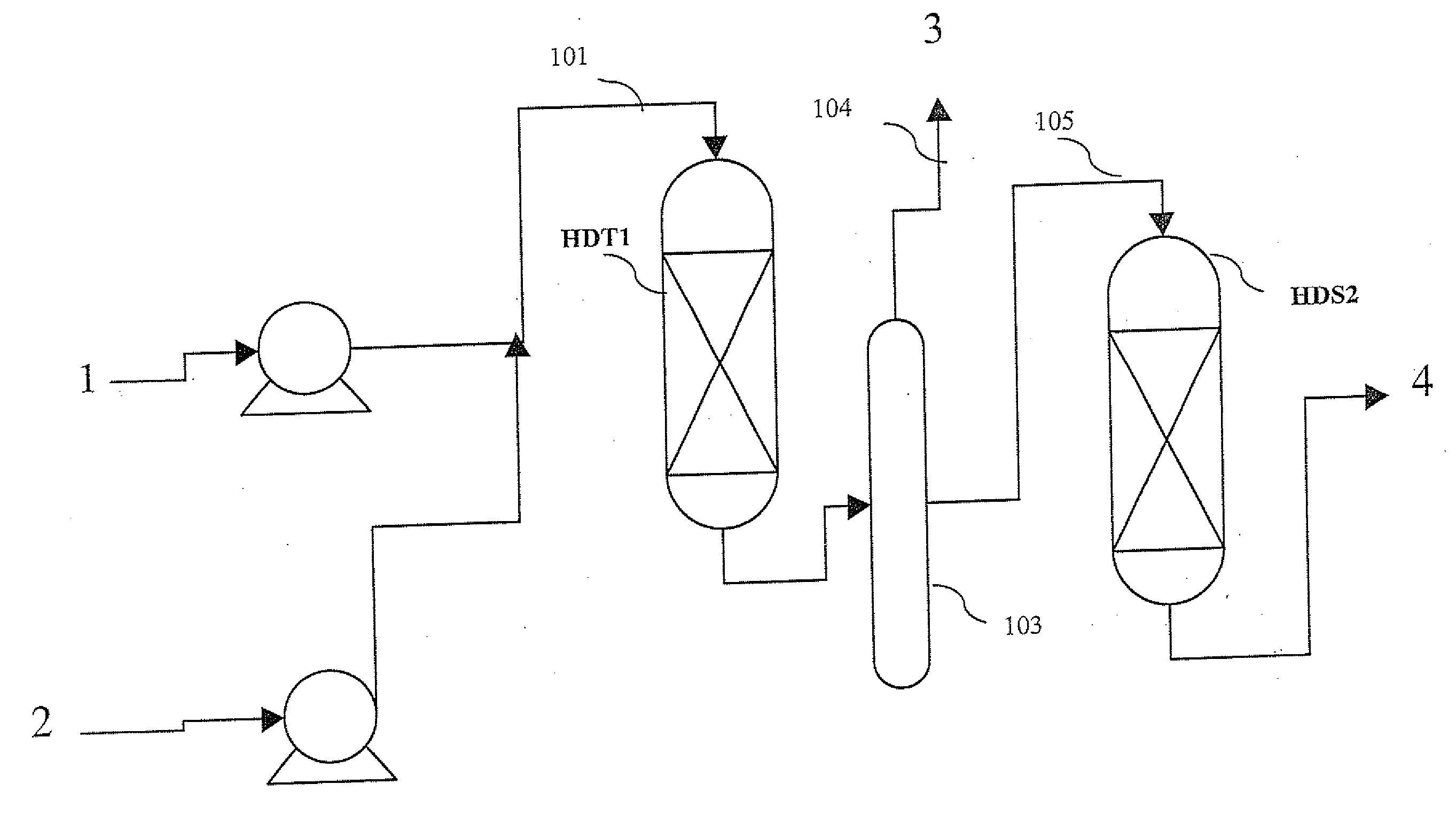
Methods of hydrotreating a mixture made up of oils of animal or vegetable origin and of petroleum cuts with quench injection of the oils on the last catalyst bed
ActiveUS20080173570A1Low costReduce use costCatalytic crackingHydrocarbon oil crackingDistillates petroleumVegetable oil
A hydrotreating method uses two catalyst beds with the introduction, on the last catalyst bed, of oils of animal or vegetable origin for co-treating a mixture made up of oils of vegetable or animal origin and of petroleum cuts (gas oil cuts (GO) and middle distillates) in order to produce gas oil effluents meeting specifications with an improved cetane number. The first catalyst bed is dedicated to only the deep desulfurization reactions (HDS1) of a petroleum type feed. The effluents of the first catalyst bed having an effluent sulfur content below or equal to 50 mg / kg are separated into two streams. The first stream, which is predominant, is sent to the gas oil pool. The second stream is mixed with oils of vegetable or animal origin. The resultant oil-petroleum cut mixture is then subjected to a milder hydrotreatment (HDT2). The effluents obtained at the outlet of the second catalyst bed can optionally be mixed with the predominant stream from the first bed. The process economy, the tolerance to the specifications relative to oils of animal or vegetable origin and the quality of the products obtained are thus greatly improved.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for removal of nitrogen and poly-nuclear aromatics from hydrocracker feedstocks
A feedstream to a hydrocracking unit is treated to remove or reduce the content of polynuclear aromatics and nitrogen-containing compounds by contacting the feedstream with an adsorbent compound selected from attapulgus clay, alumina, silica gel and activated carbon in a fixed bed or slurry column and separating the treated feedstream that is lower in the undesired compounds from the adsorbent material. The adsorbent can be mixed with a solvent for the undesired compounds and stripped for re-use.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Fcc dual elevation riser feed distributors for gasoline and light olefin modes of operation
InactiveUS20070205139A1Increase flexibilityWiden the optionsCatalytic crackingFeed devicesHigh elevationPolymer science
A fluid catalytic cracking process includes feeding hydrocarbon into a riser in the presence of a catalyst, cracking the hydrocarbon in the riser in the presence of the catalyst to form a cracked stream, and separating the catalyst from the cracked stream. When in a gasoline mode, the hydrocarbon is fed through a first distributor into the riser, and when in a light olefin mode, the hydrocarbon is fed through a second distributor into the riser. The second distributor is positioned at a higher elevation than the first distributor.
Owner:UOP LLC
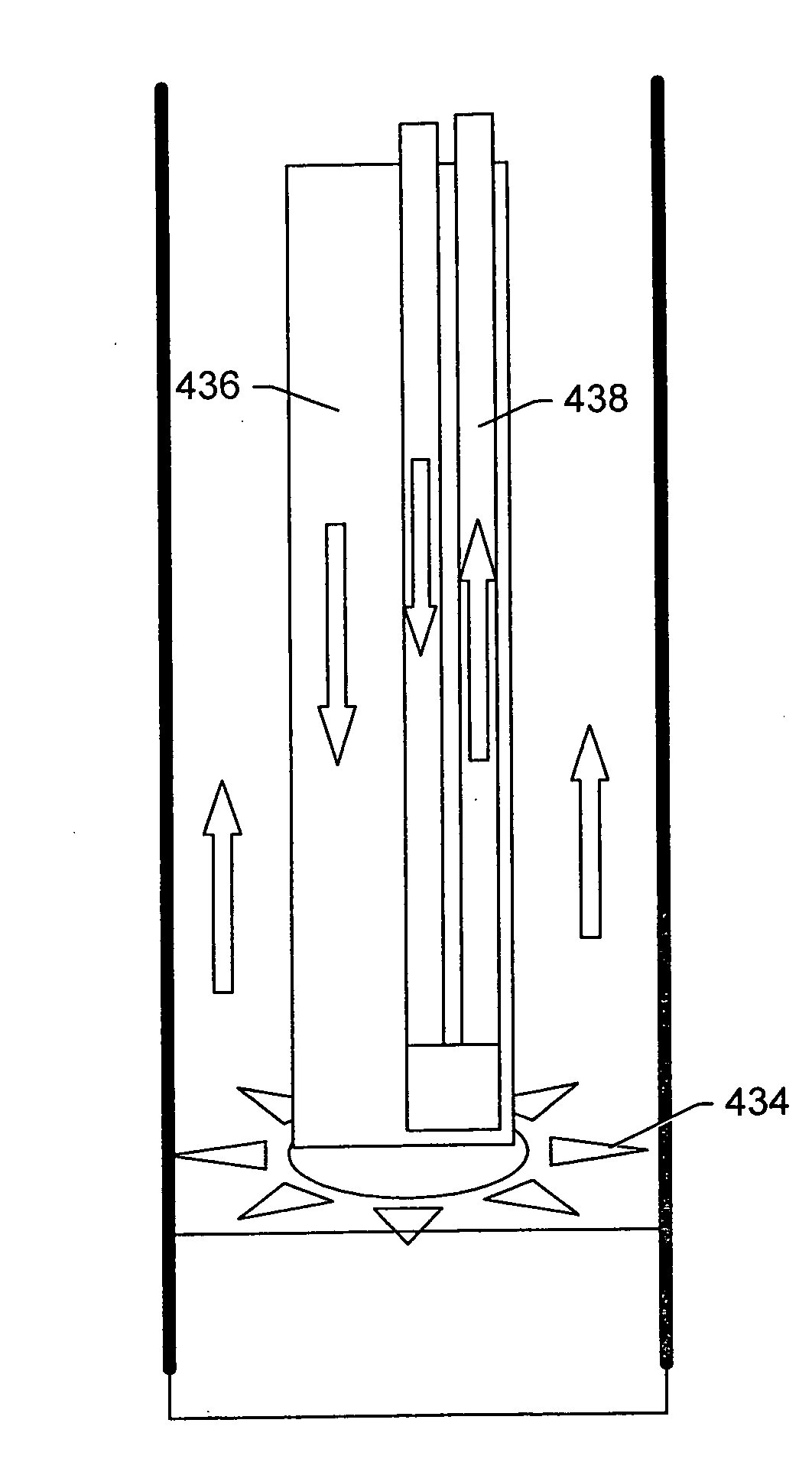
FCC feed injection using subcooled water sparging for enhanced feed atomization
Atomization of a high boiling point, hot liquid, such as a hydrocarbon feed oil for a fluid cat cracker, is enhanced by injecting subcooled water into the hot liquid, to form a two-phase fluid of the liquid and steam, upstream of the atomization. The hot liquid is at conditions of temperature and pressure effective for the injected, subcooled water to vaporize into steam, when the water contacts it. Typically this means that the hot liquid is hotter and at a lower pressure than the water. In an FCC process, the subcooled water is sparged into the flowing hot oil in a conduit in a riser feed injector. This produces a spray of hot oil in the riser reaction zone in which the oil drops are smaller and more uniformly distributed in the spray.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com