Patents
Literature
1098 results about "Oil shale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced, called shale oil (not to be confused with tight oil—crude oil occurring naturally in shales). Shale oil is a substitute for conventional crude oil; however, extracting shale oil from oil shale is more costly than the production of conventional crude oil both financially and in terms of its environmental impact. Deposits of oil shale occur around the world, including major deposits in the United States. A 2016 estimate of global deposits set the total world resources of oil shale equivalent of 6.05 trillion barrels (962 billion cubic metres) of oil in place.
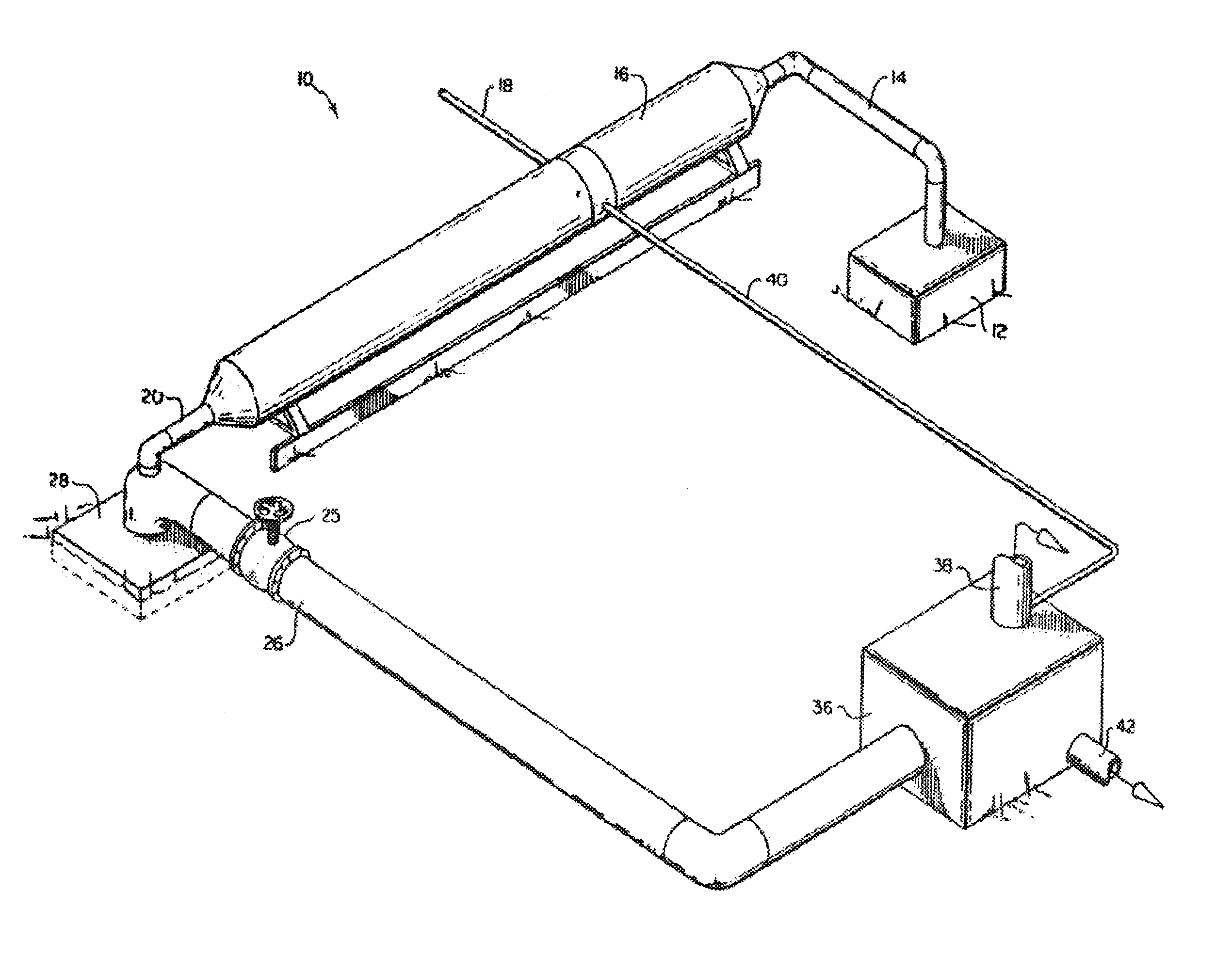
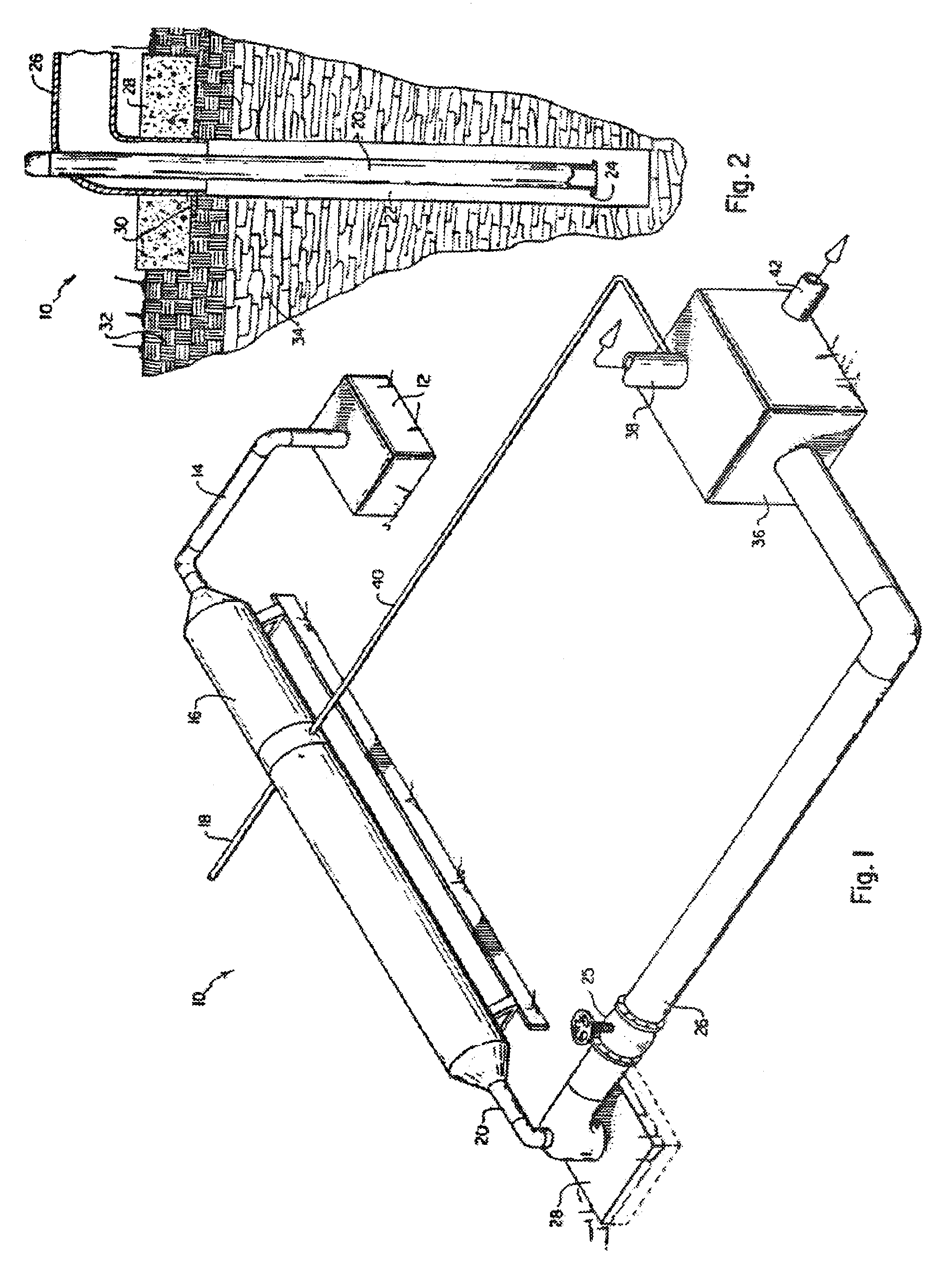
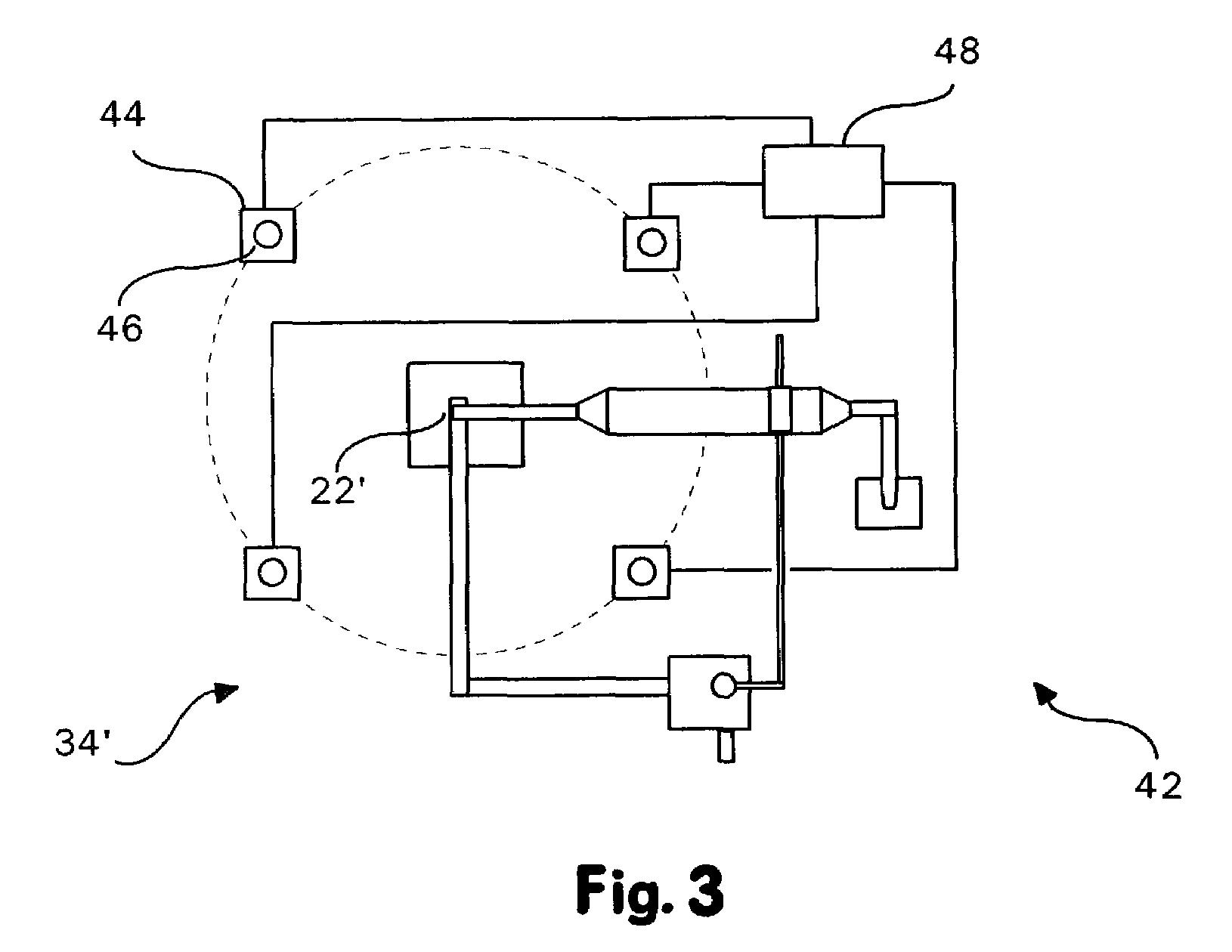
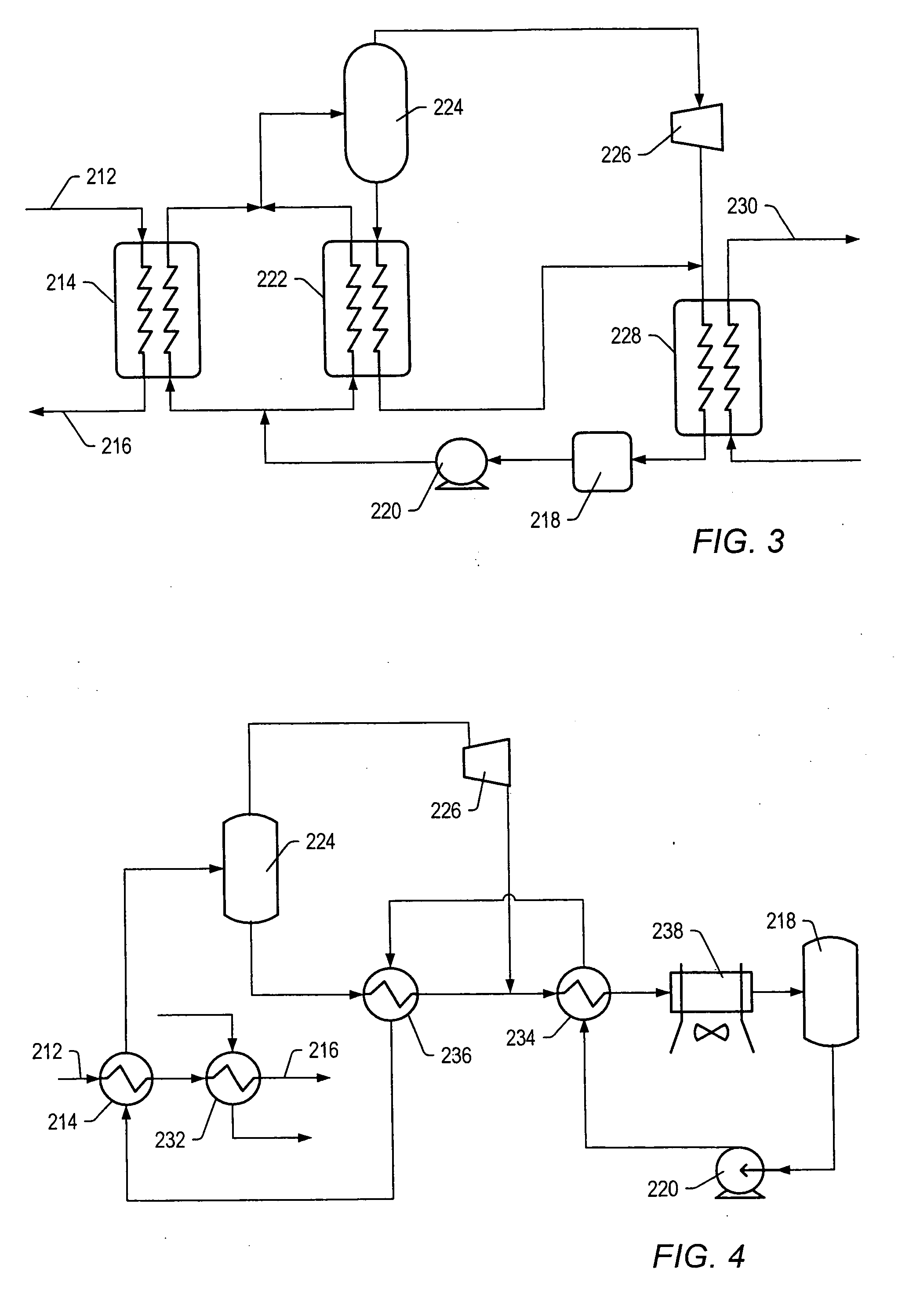
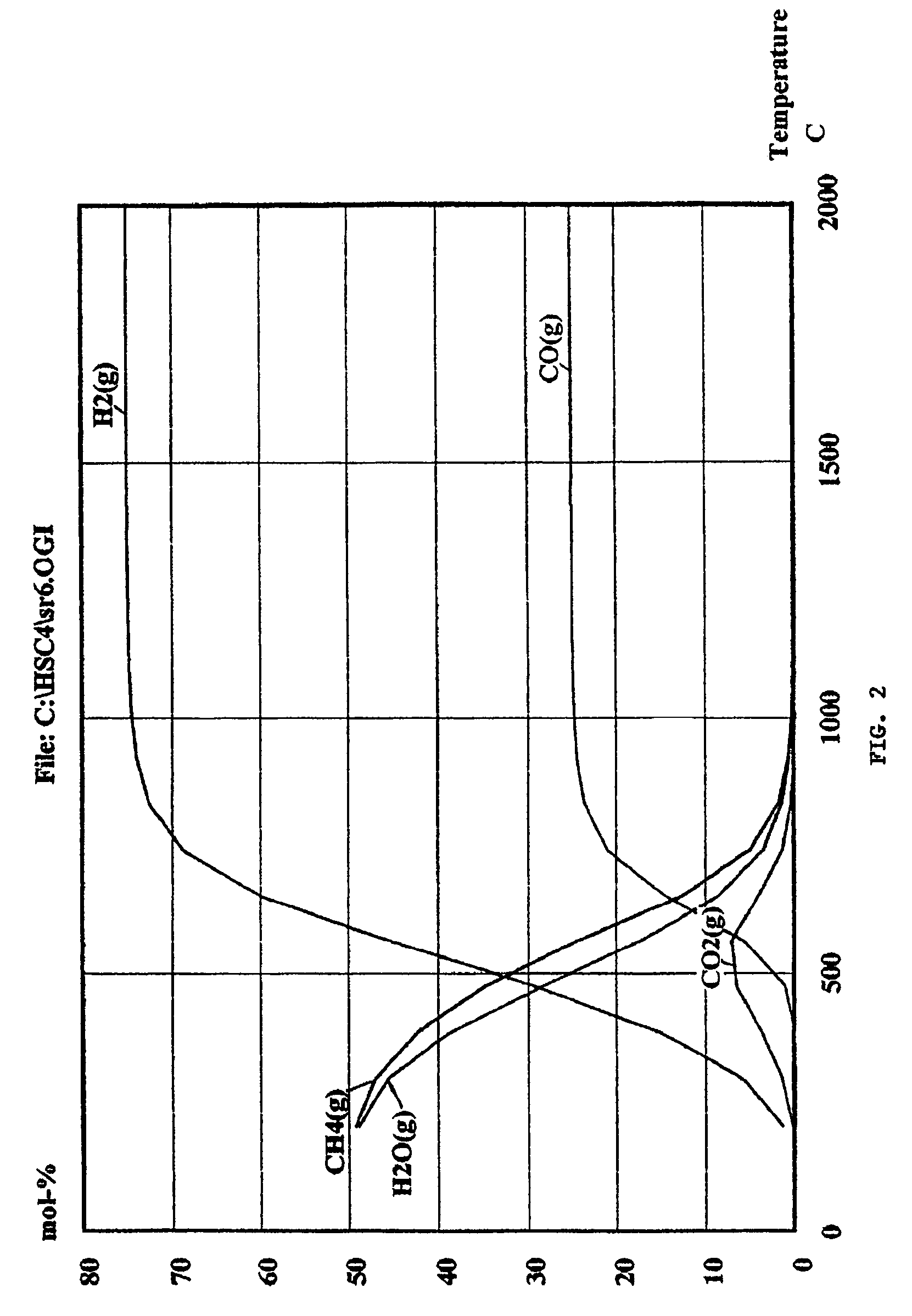
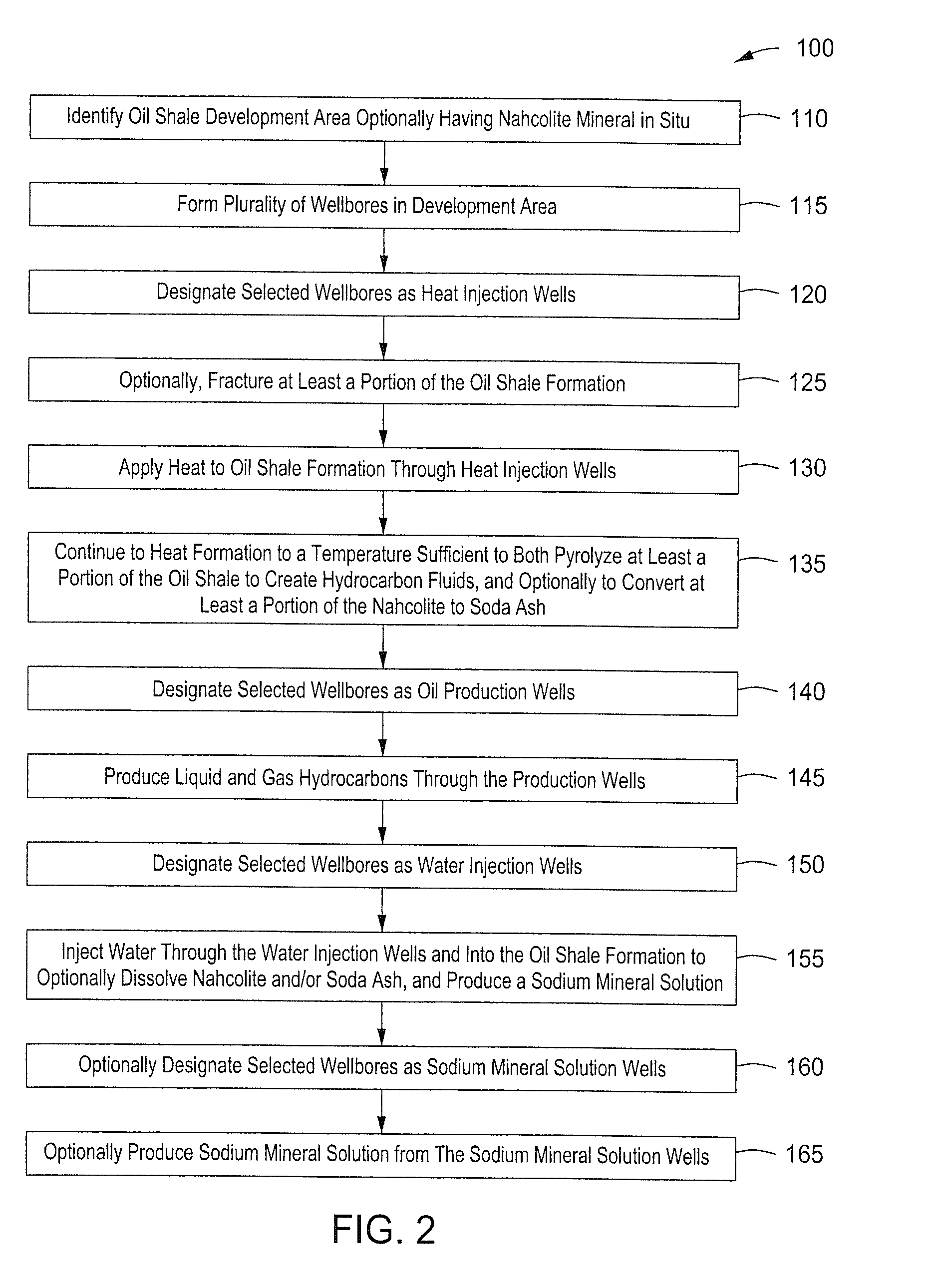
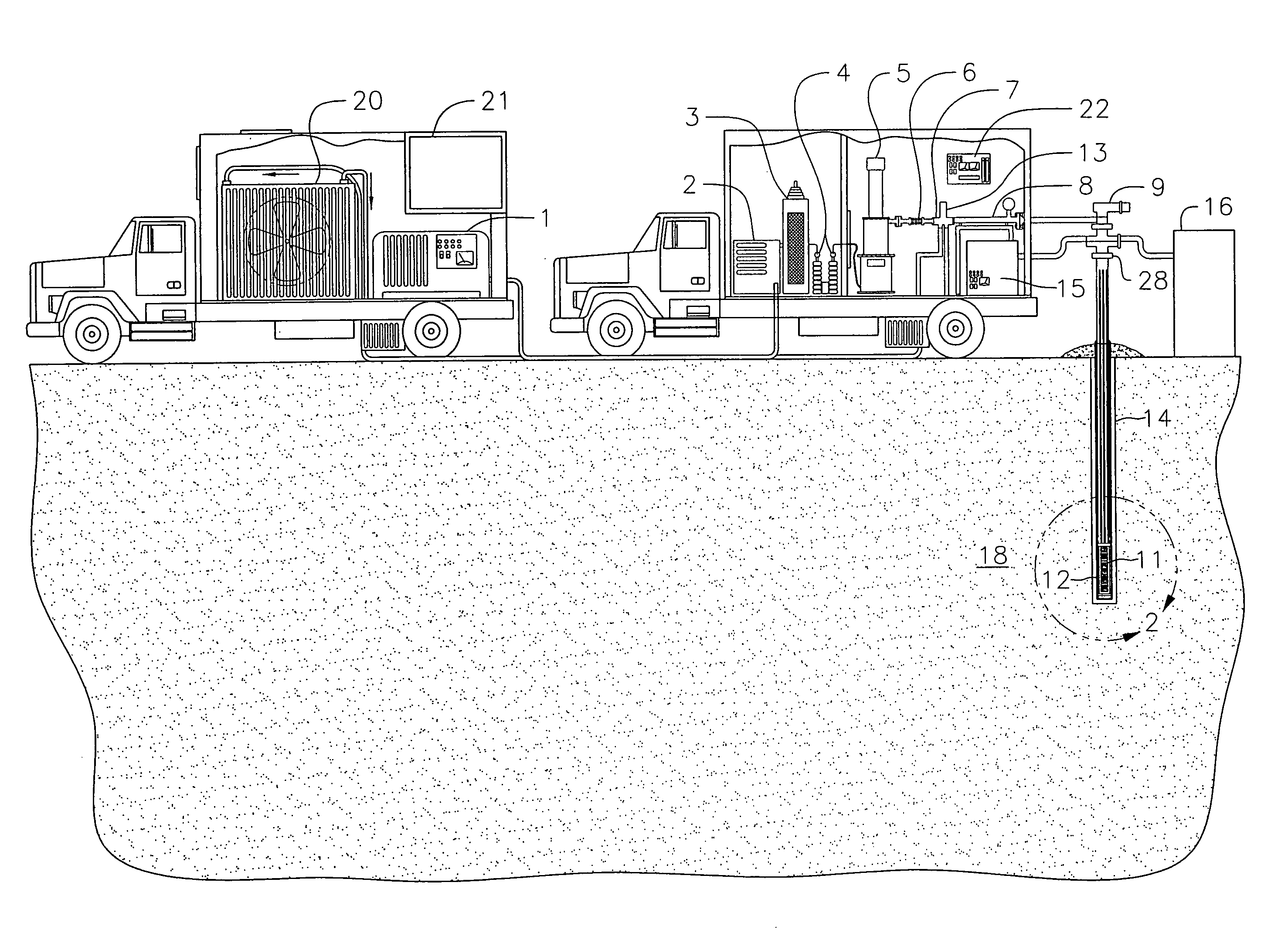
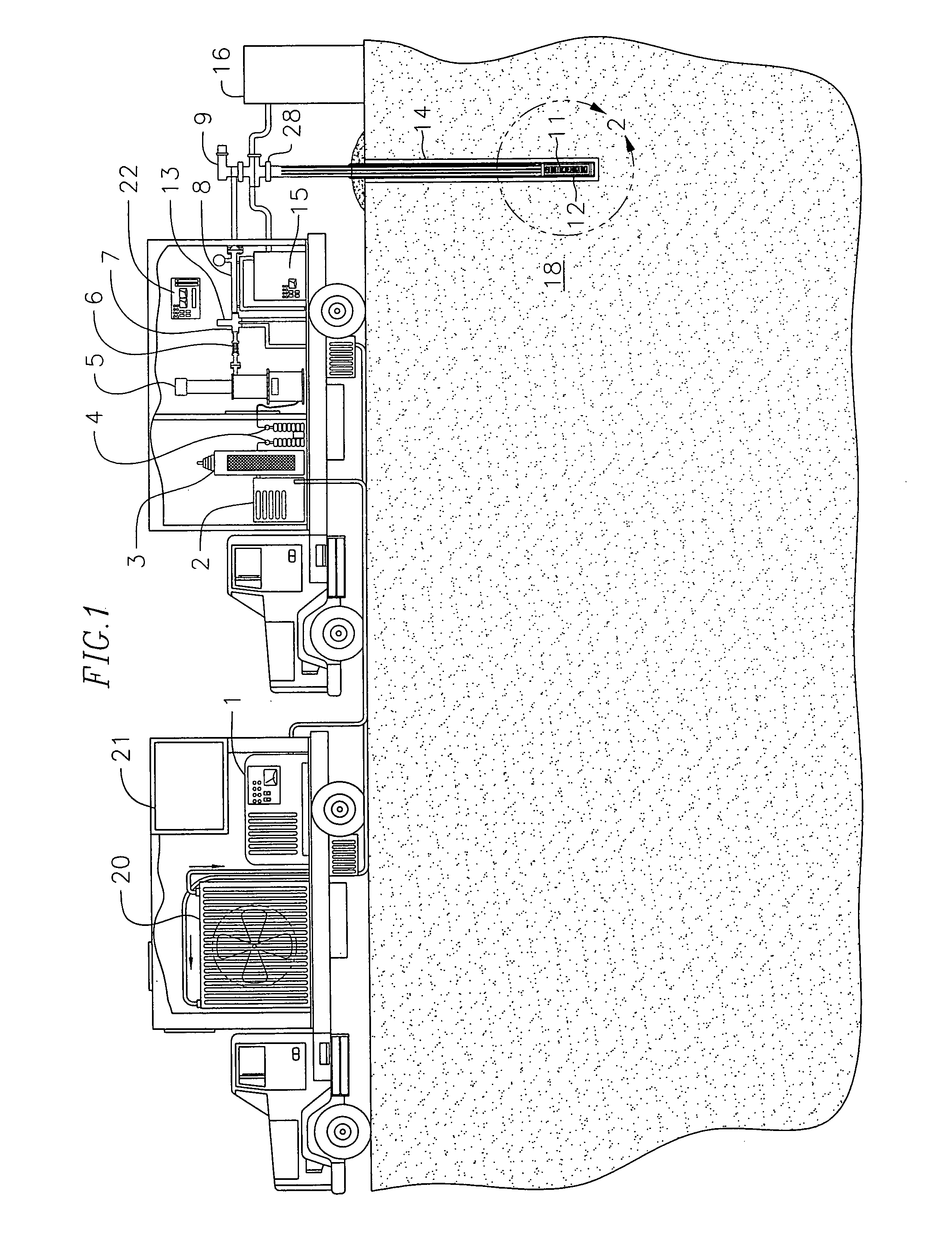
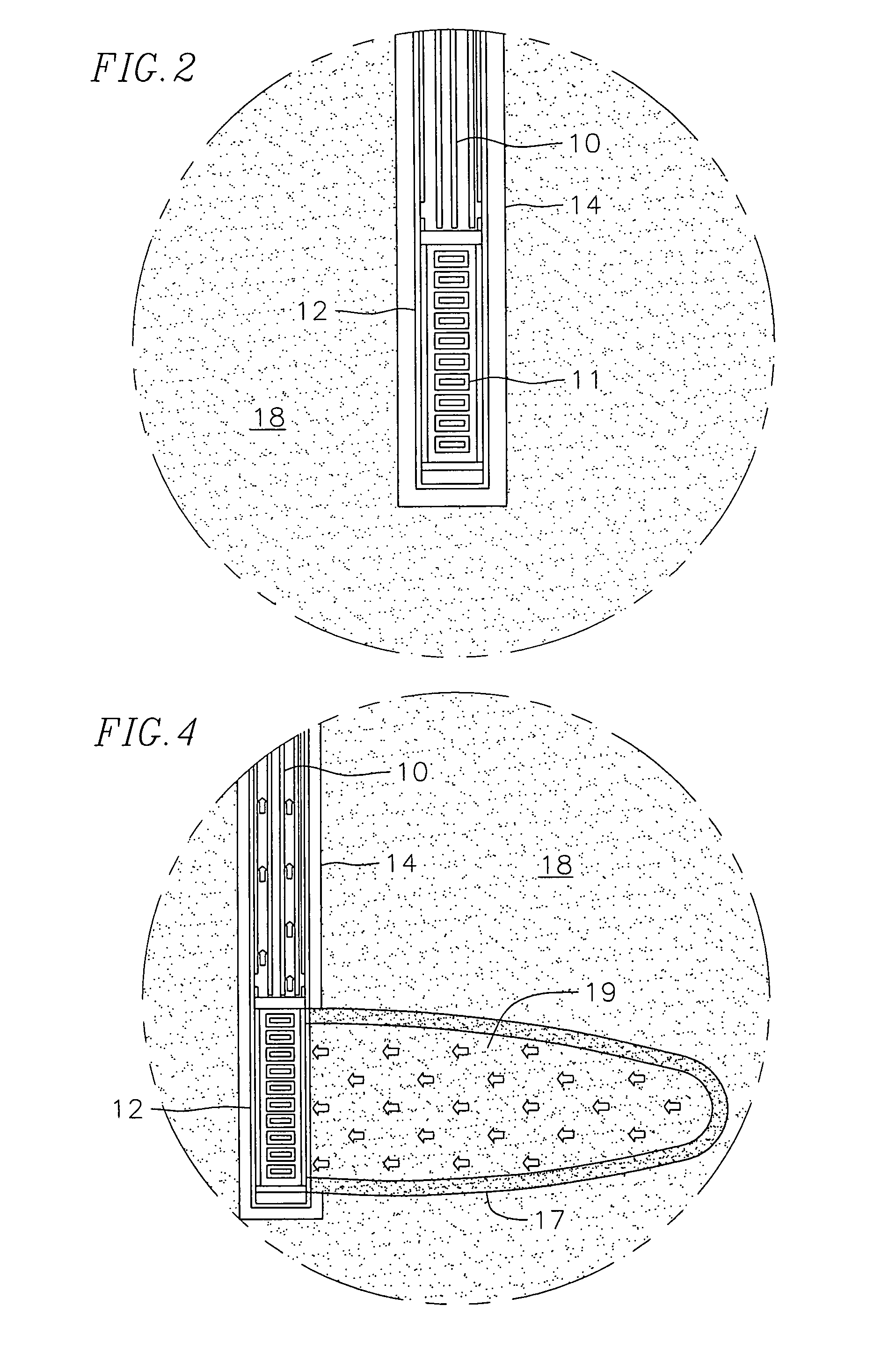
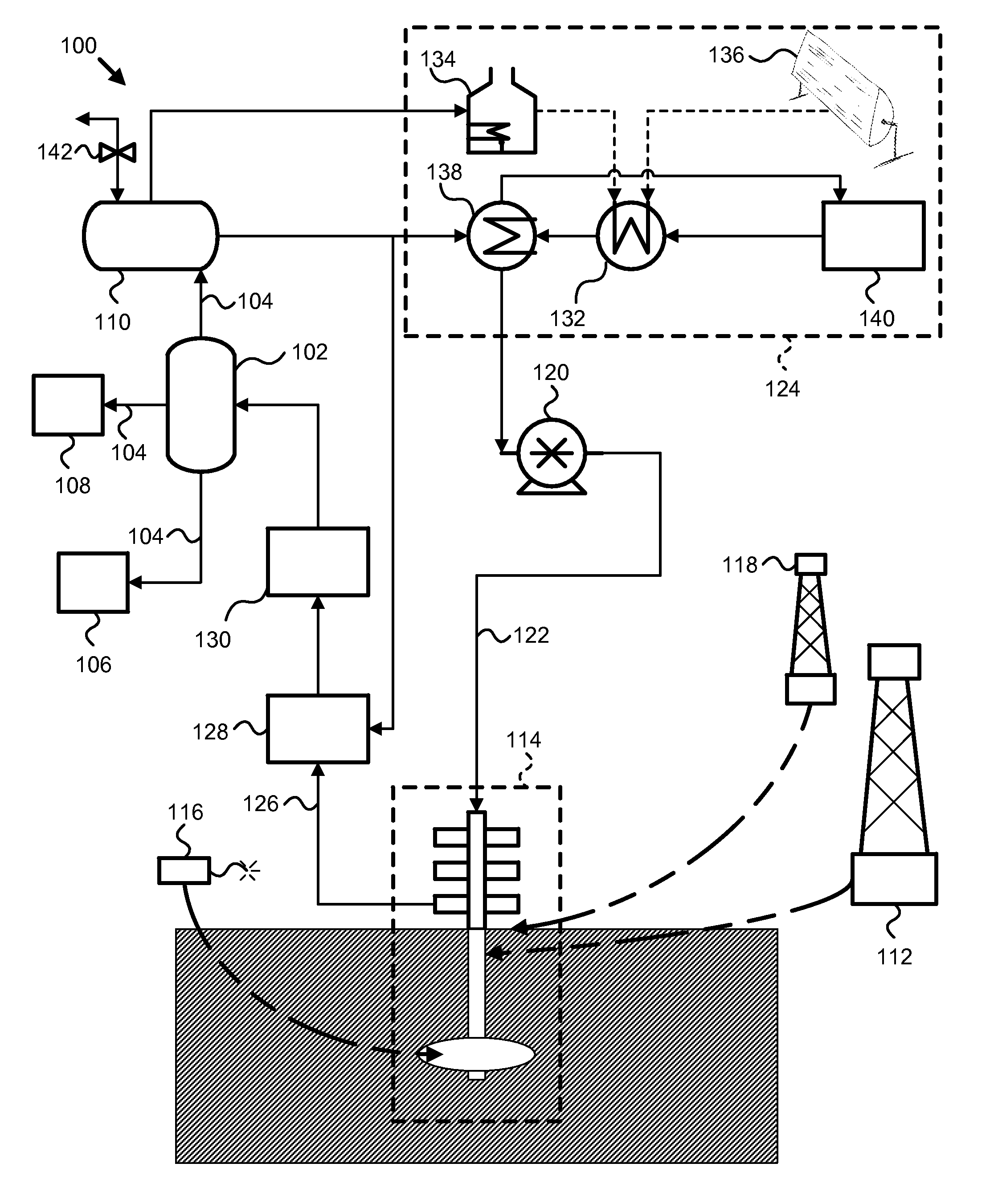
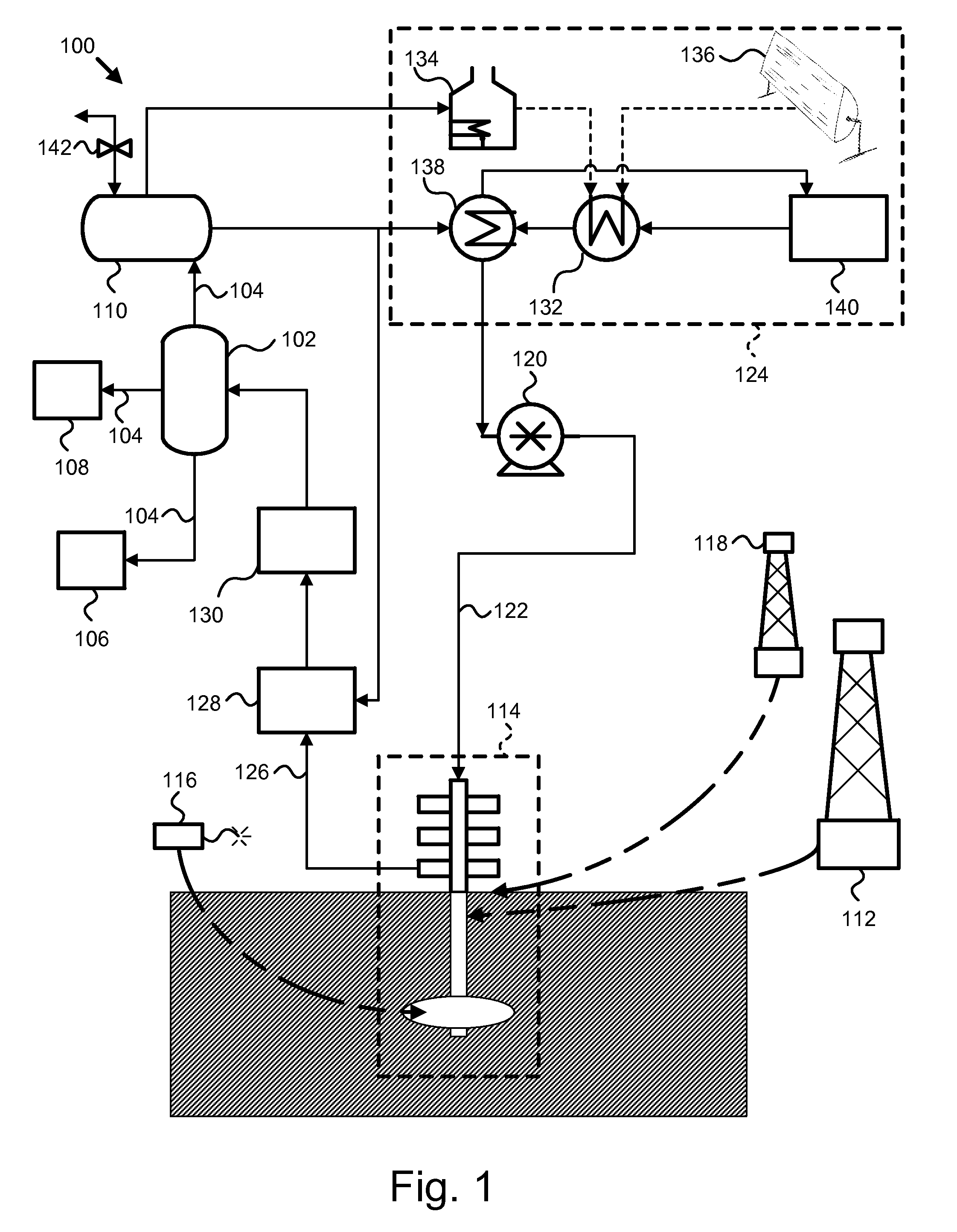
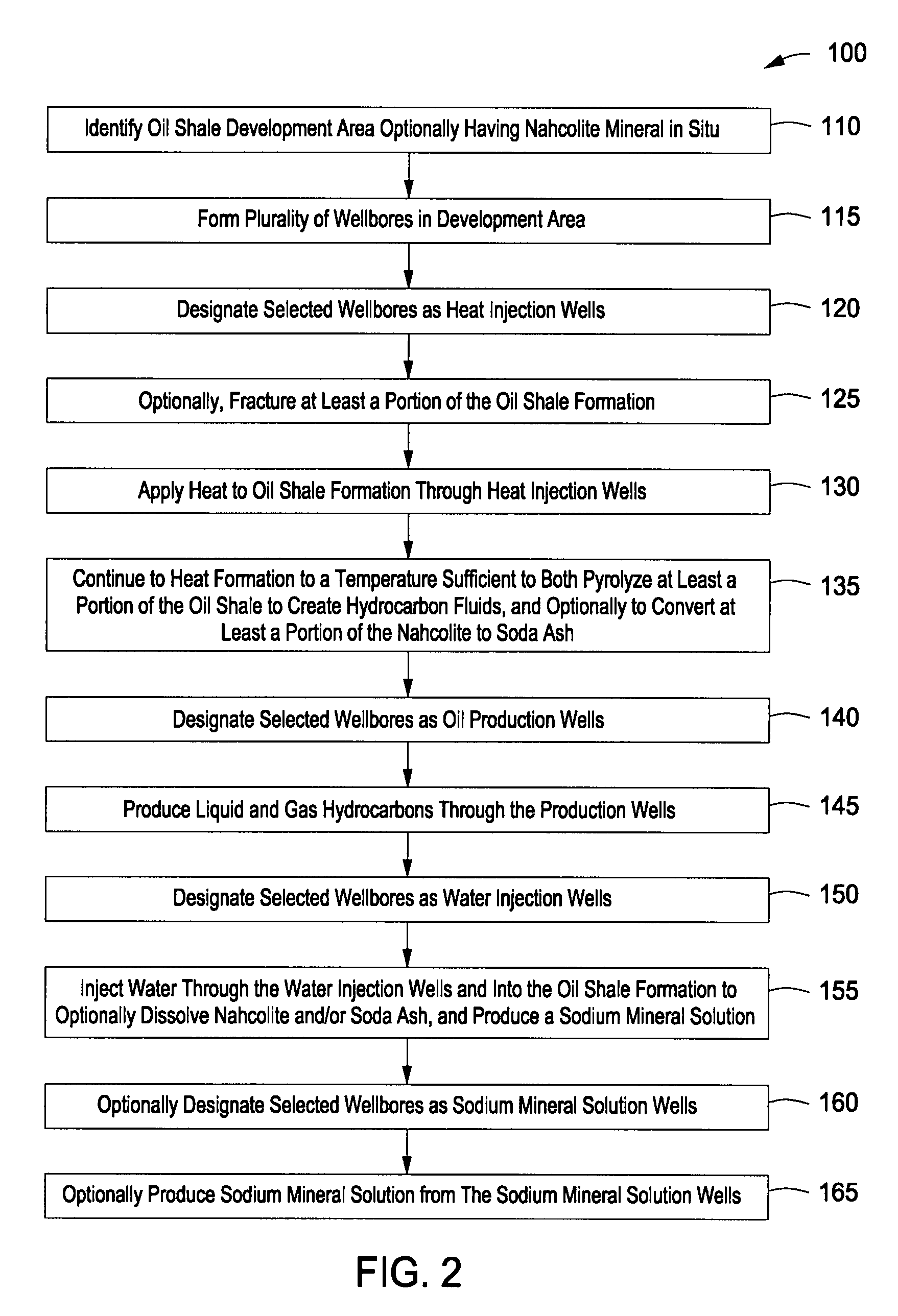
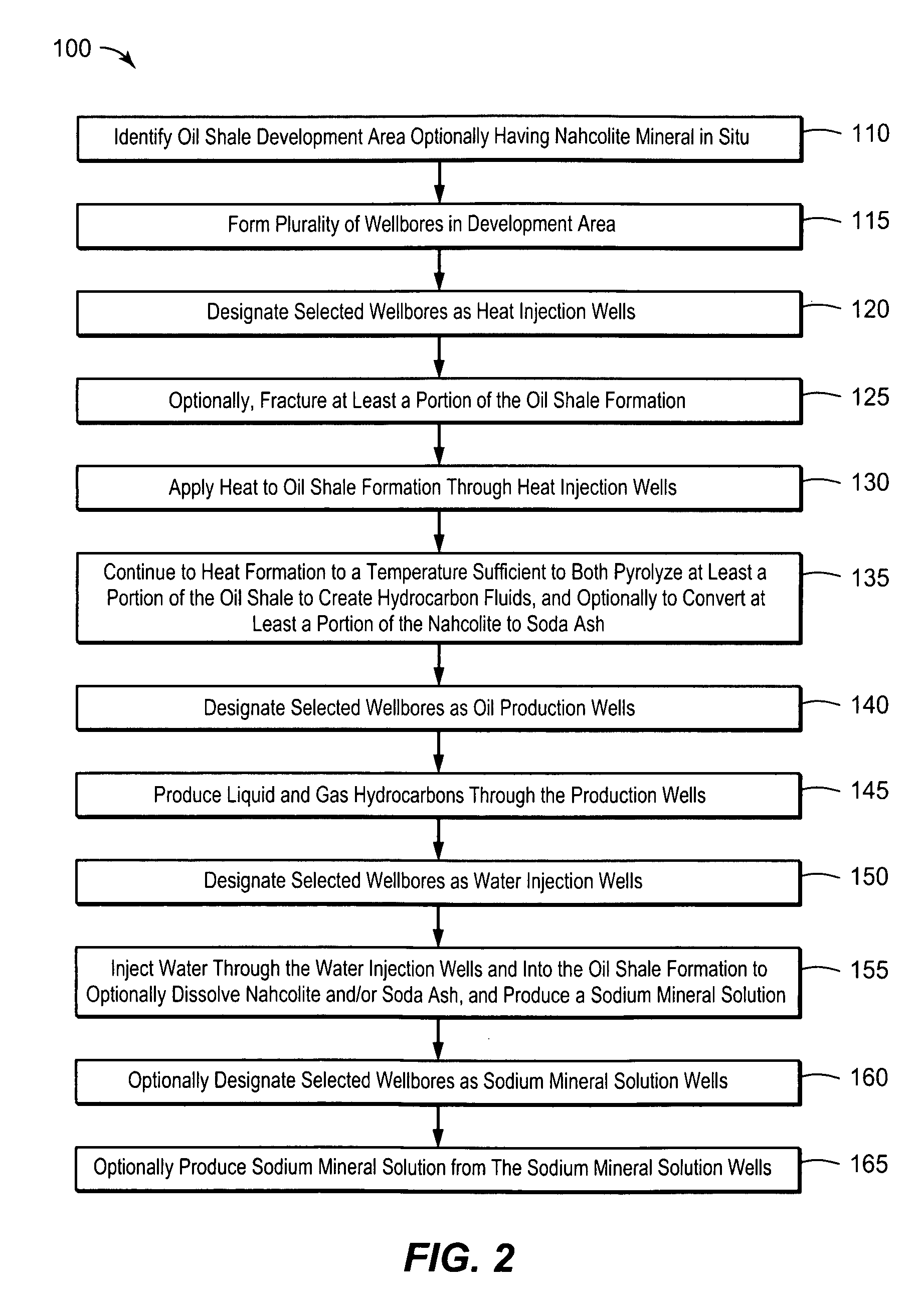
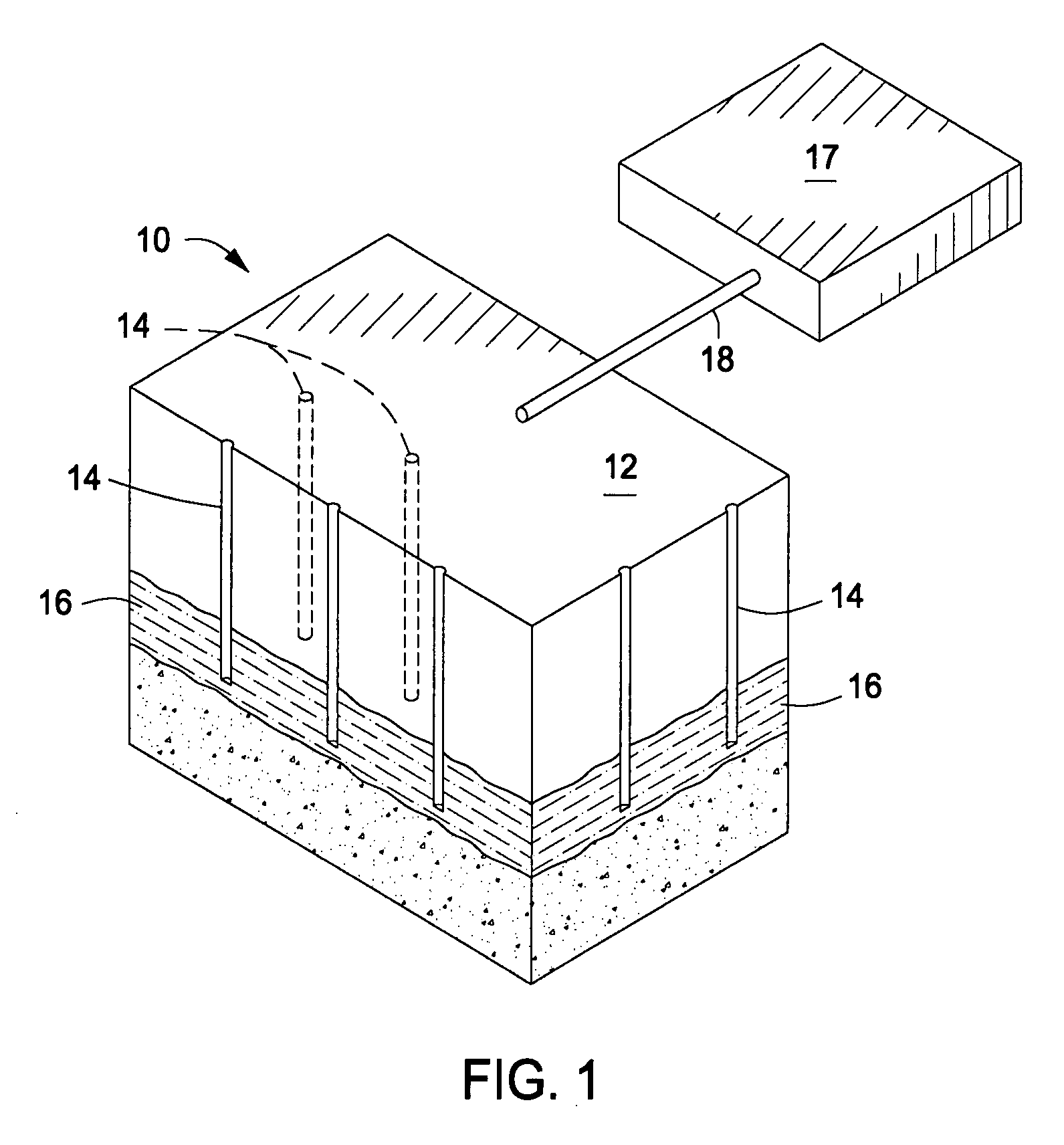
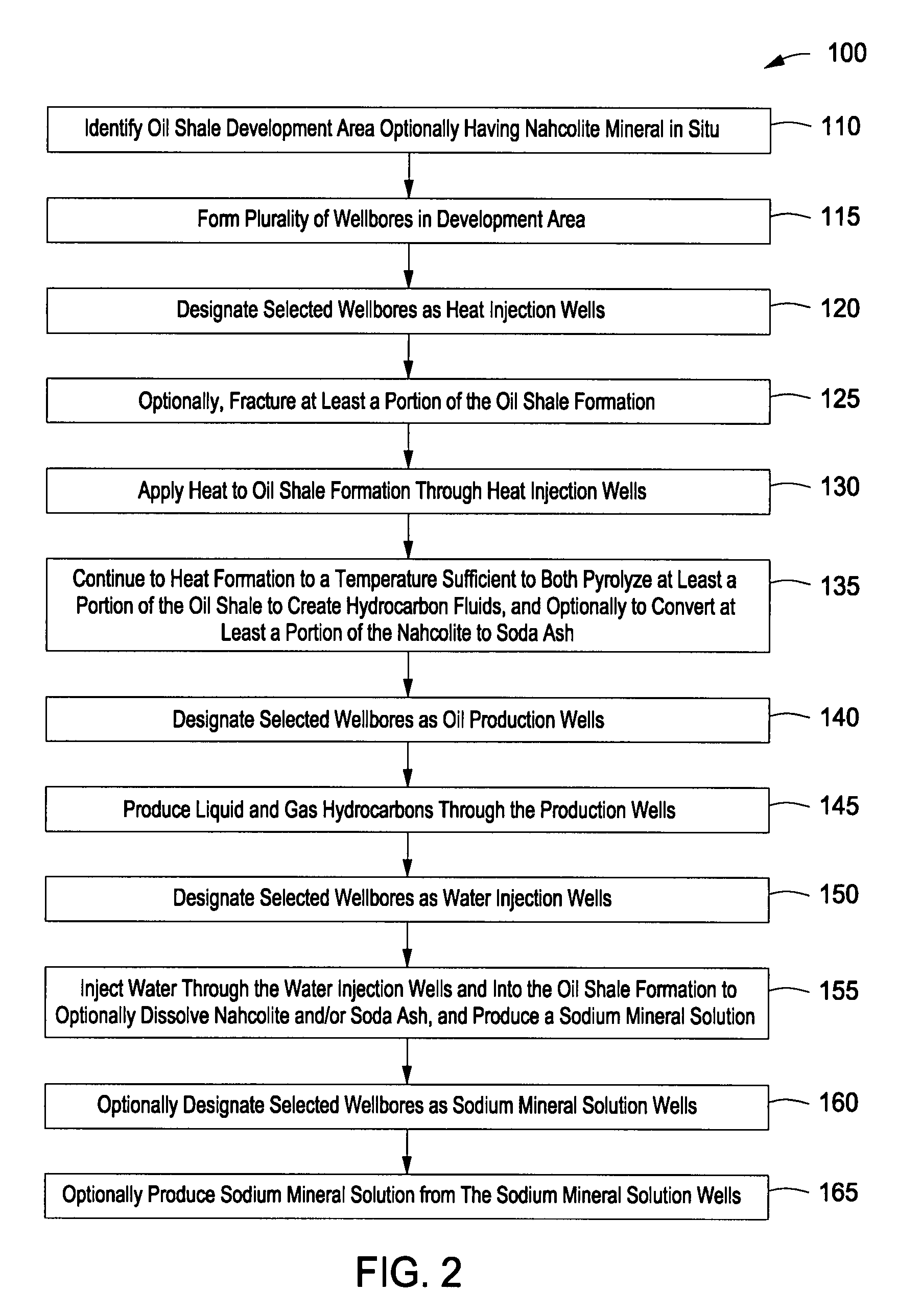
Recovery of products from oil shale
InactiveUS7048051B2Maximize recoveryProcedure is time-consume and expensiveFluid removalKerogenThermal energy
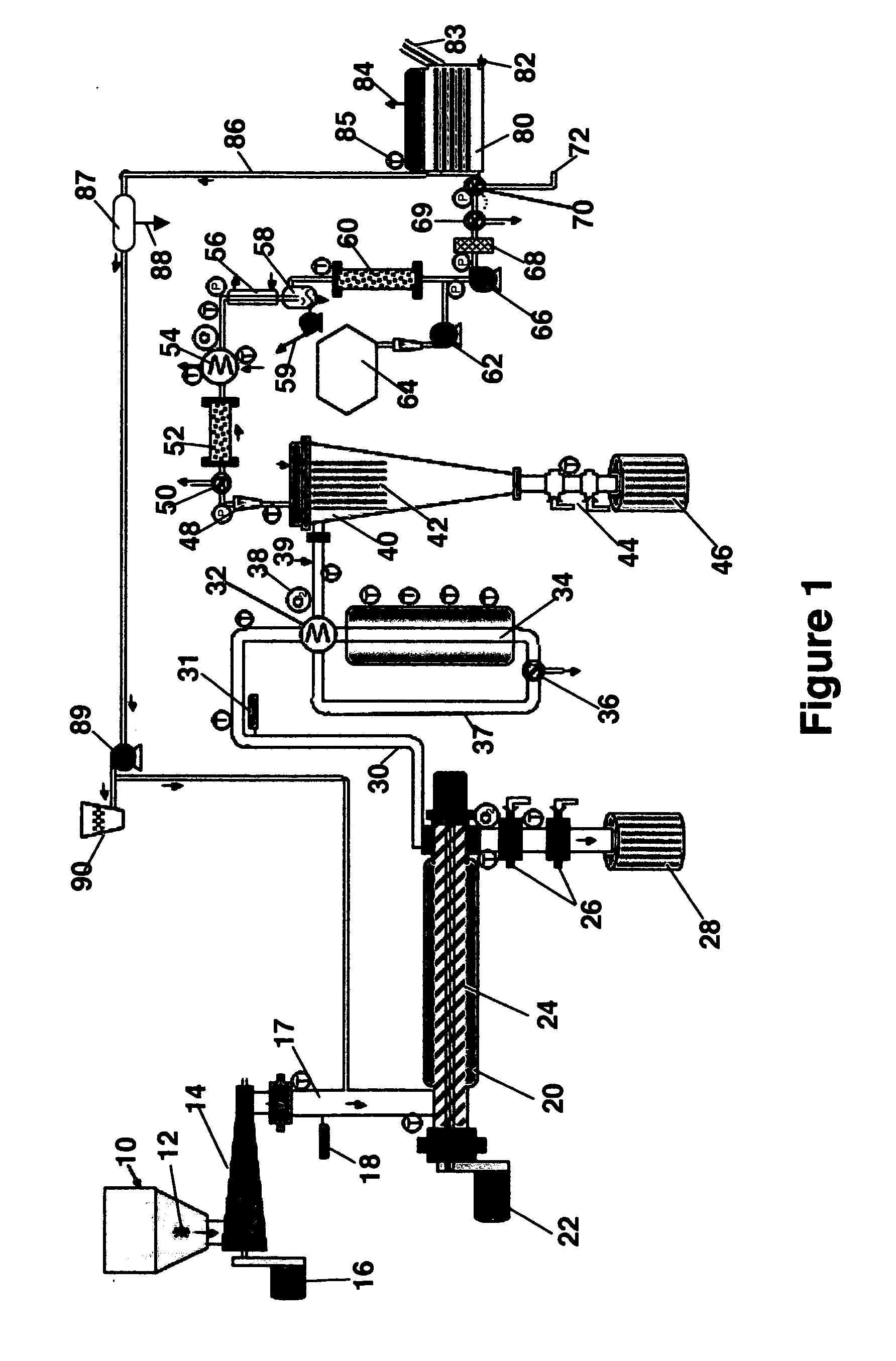
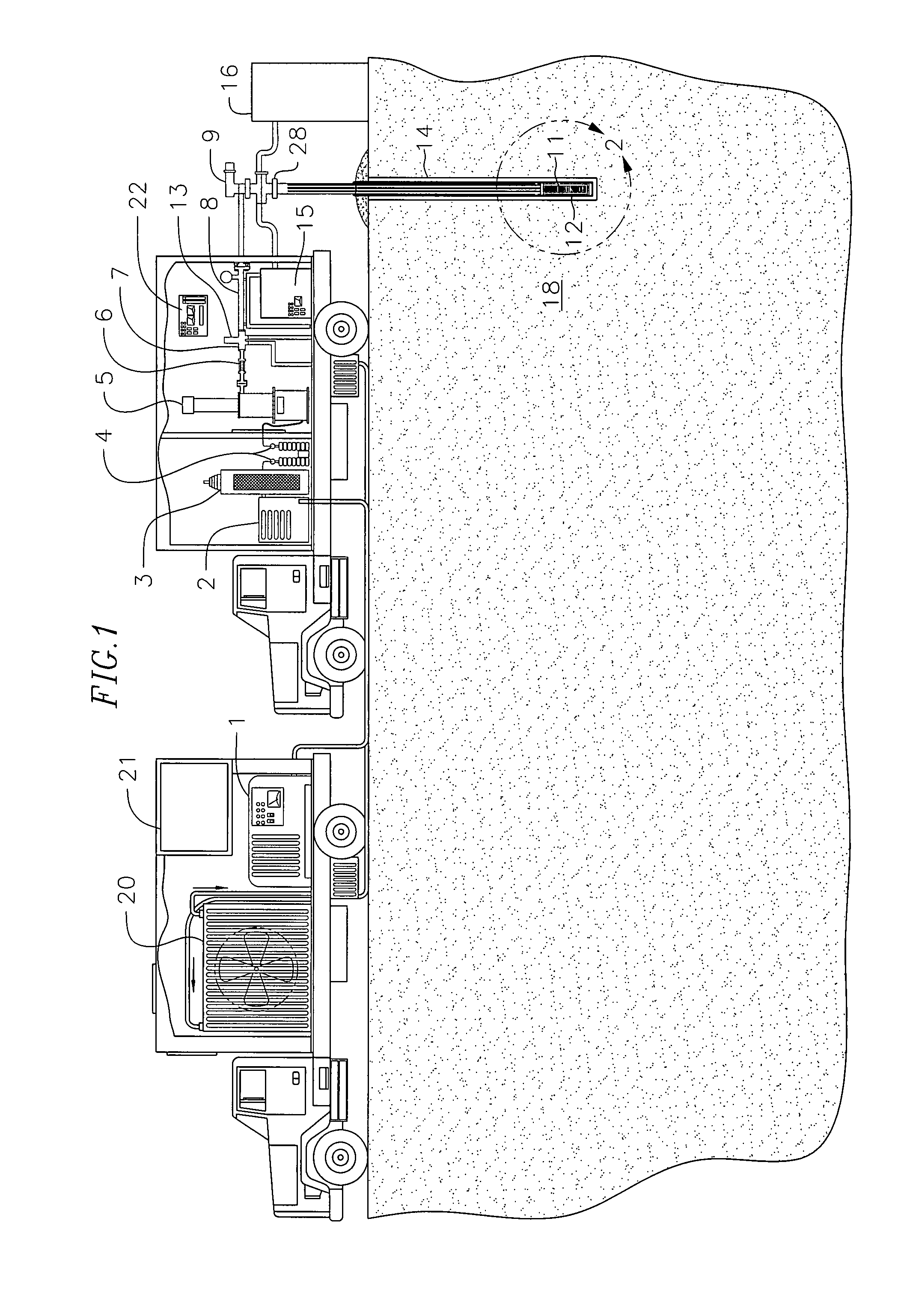
A process and system for recovering hydrocarbonaceous products from in situ oil shale formations. A hole is drilled in the oil shale formation and a processing gas inlet conduit is positioned within the hole. A processing gas is pressurized, heated, and introduced through the processing gas inlet conduit and into the hole. The processing gas creates a nonburning thermal energy front within the oil shale formation so as to convert kerogen in the oil shale to hydrocarbonaceous products. The products are withdrawn with the processing gas through an effluent gas conduit positioned around the opening of the hole, and are then transferred to a condenser wherein a liquid fraction of the products is formed and separated from a gaseous fraction.
Owner:GENERAL SYNFUELS INT
Process and system for converting carbonaceous feedstocks into energy without greenhouse gas emissions
ActiveUS20070099038A1High hydrogen contentFuel cells groupingHydrogen separation using solid contactPetroleum cokePetroleum
The process of the invention converts carbonaceous feedstock such as coal, hydrocarbon oil, natural gas, petroleum coke, oil shale, carbonaceous-containing waste oil, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing military waste, carbonaceous-containing industrial waste, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing sewage sludge and municipal solid waste, carbonaceous-containing agricultural waste, carbonaceous-containing biomass, biological and biochemical waste, and mixtures thereof into electrical energy without the production of unwanted greenhouse emissions. The process uses a steam / CO2 reformer operating in the exit range of at least 700° to about 1600° C. (1300-2900°0 F.) to convert the carbonaceous feedstock and a greenhouse gas stream into a synthesis gas comprising mostly carbon monoxide and hydrogen that contains poisons and the compounds that poison fuel cells. The syngas is sent to an interface zone to remove these poisons and other fouling compounds that are electrochemically oxidized in an electricity-producing fuel cell into an exit gas comprising carbon dioxide and water.
Owner:RAVEN SR INC
Solution mining dawsonite from hydrocarbon containing formations with a chelating agent
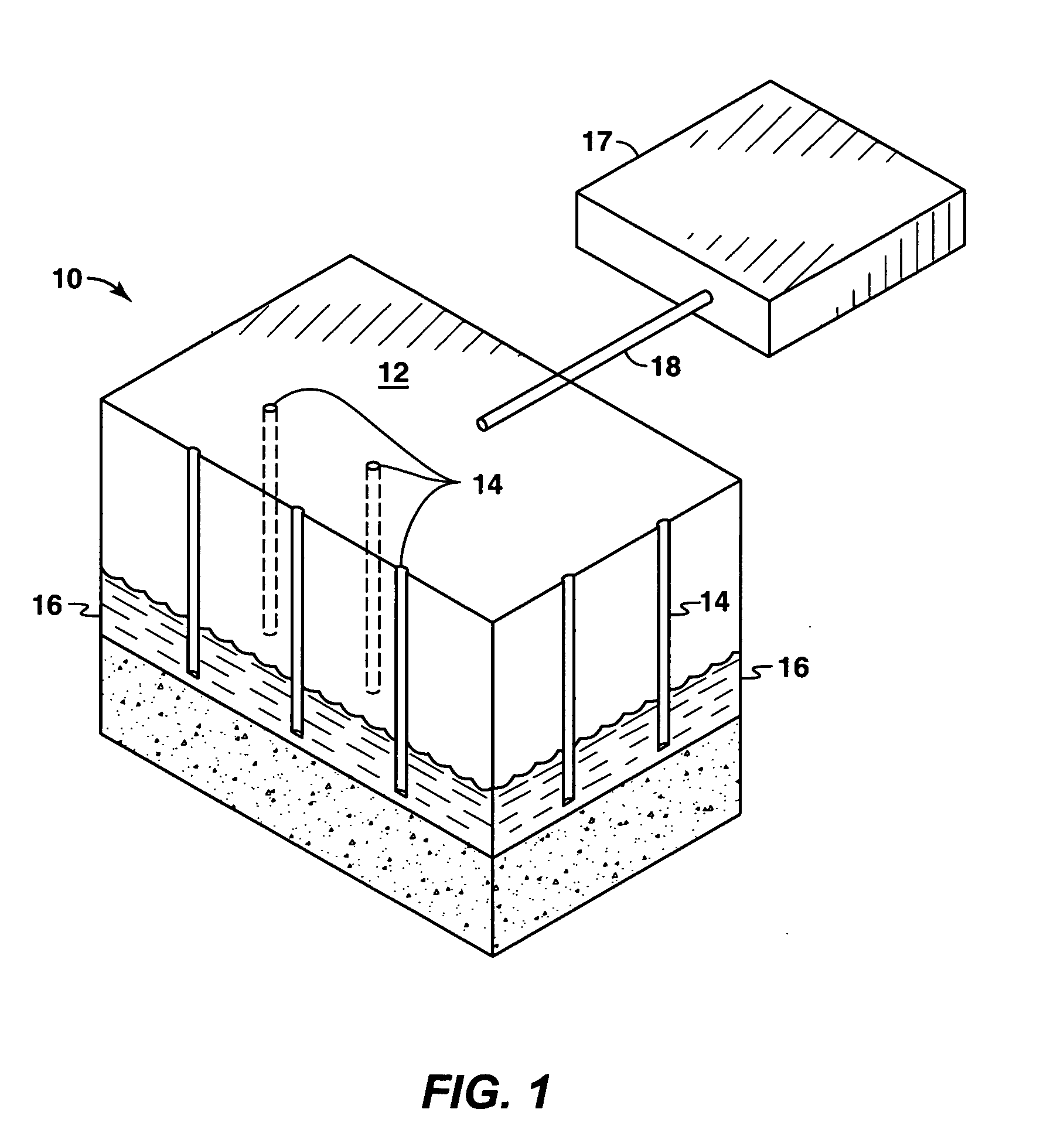
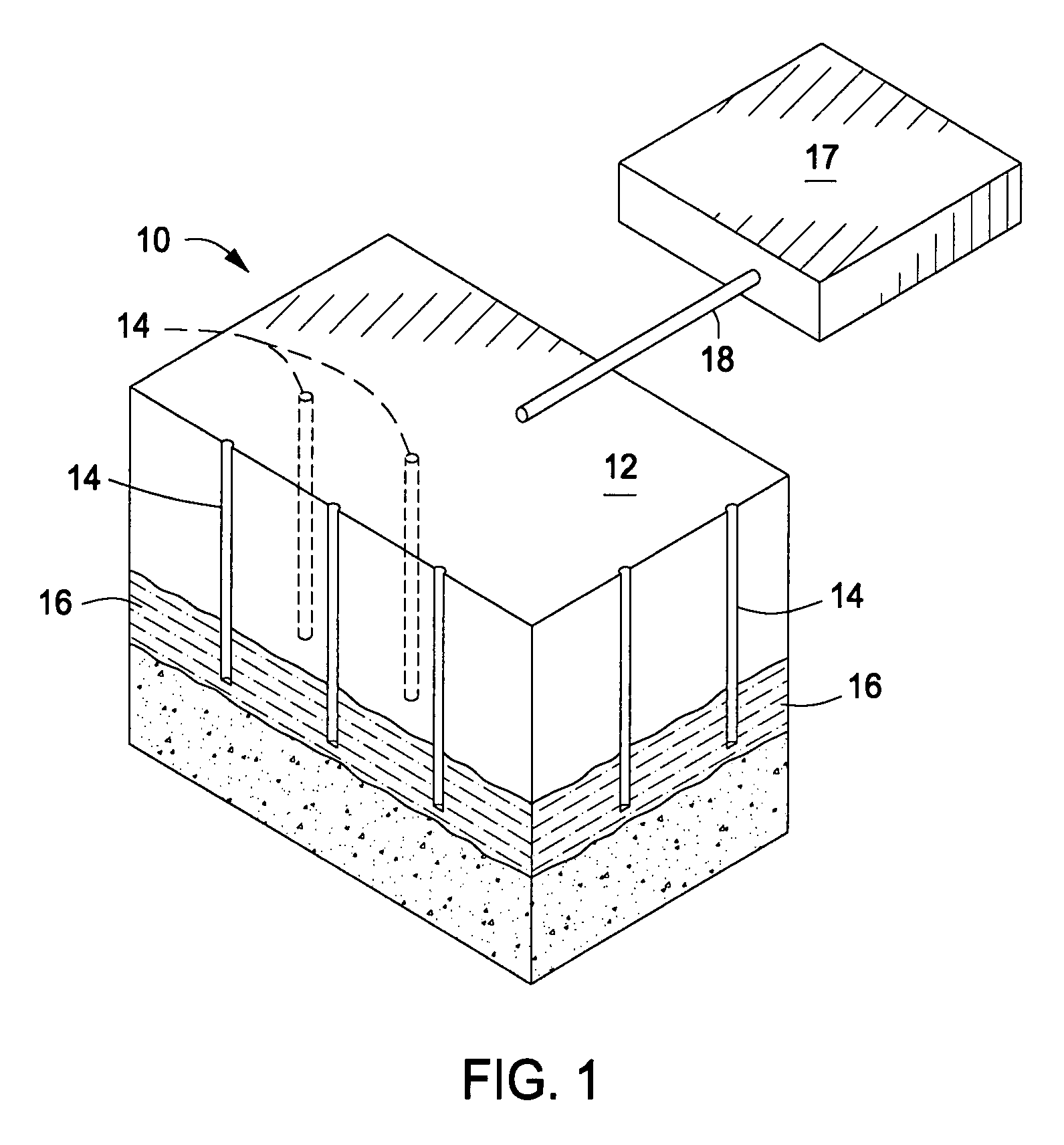
A method for treating an oil shale formation comprising dawsonite includes providing heat from one or more heaters to the formation to heat the formation. Hydrocarbon fluids are produced from the formation. At least some dawsonite in the formation is decomposed with the provided heat. A chelating agent is provided to the formation to dissolve at least some dawsonite decomposition products. The dissolved dawsonite decomposition products are produced from the formation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Process for producing Hydrocarbon fluids combining in situ heating, a power plant and a gas plant
An in situ method of producing hydrocarbon fluids from an organic-rich rock formation is provided. The method may include heating an organic-rich rock formation, for example an oil shale formation, in situ to pyrolyze formation hydrocarbons, for example kerogen, to form a production fluid containing hydrocarbon fluids. The method may include separating the production fluid into at least a gas stream and a liquid stream, where the gas stream is a low BTU gas stream. The low BTU gas stream is then fed to a gas turbine where it is combusted and is used to generate electricity.
Owner:KAMINSKY ROBERT D +4
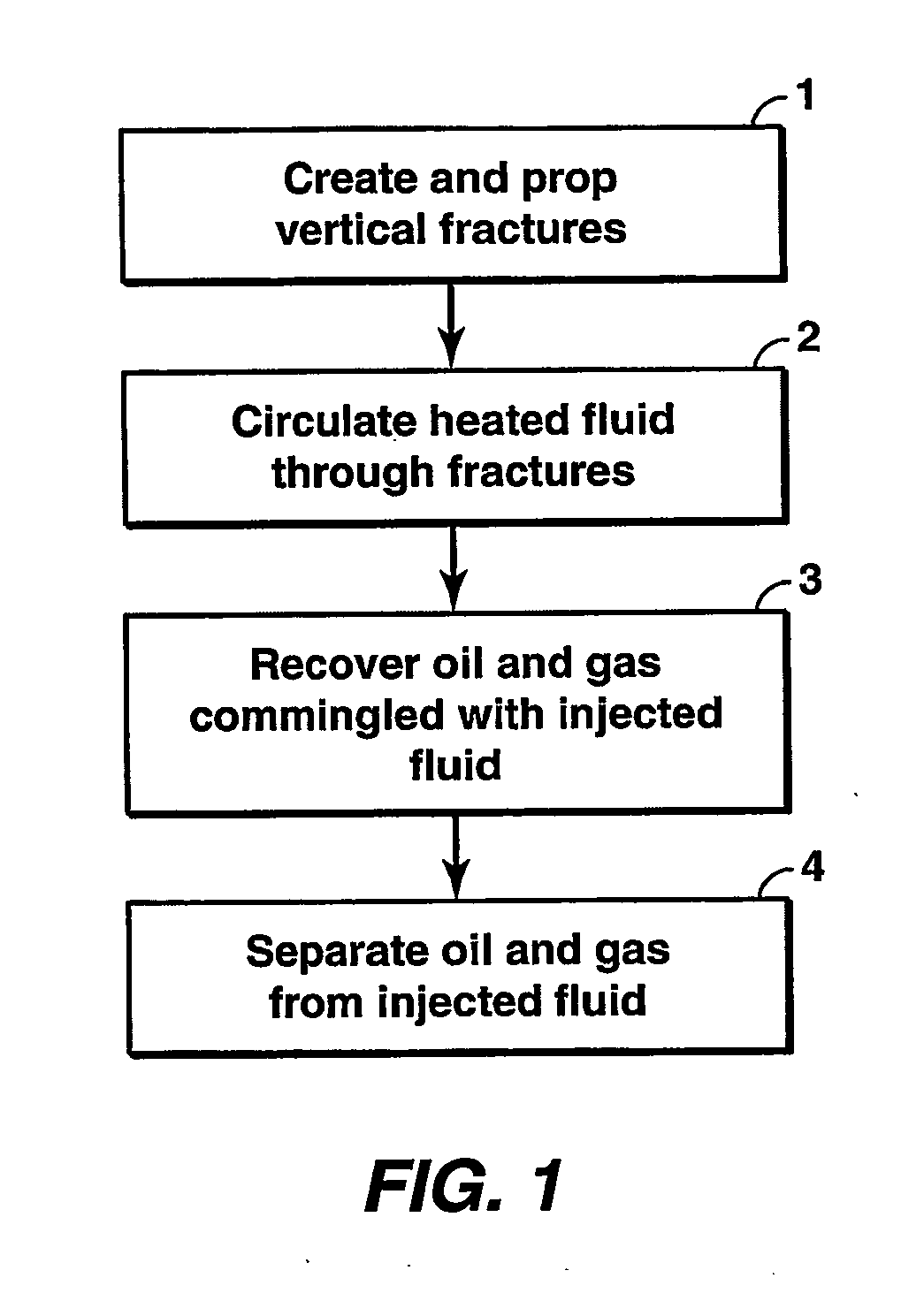
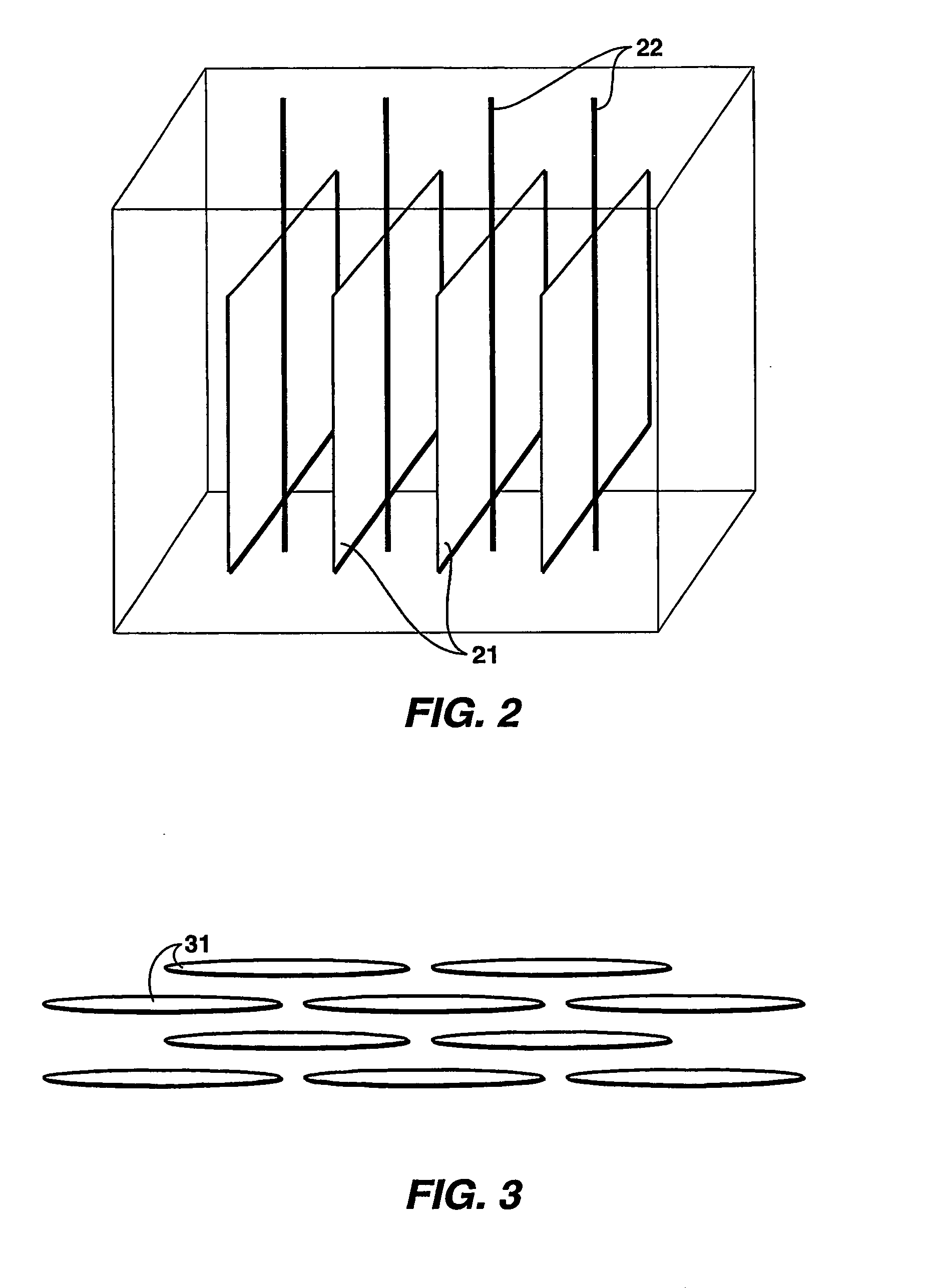
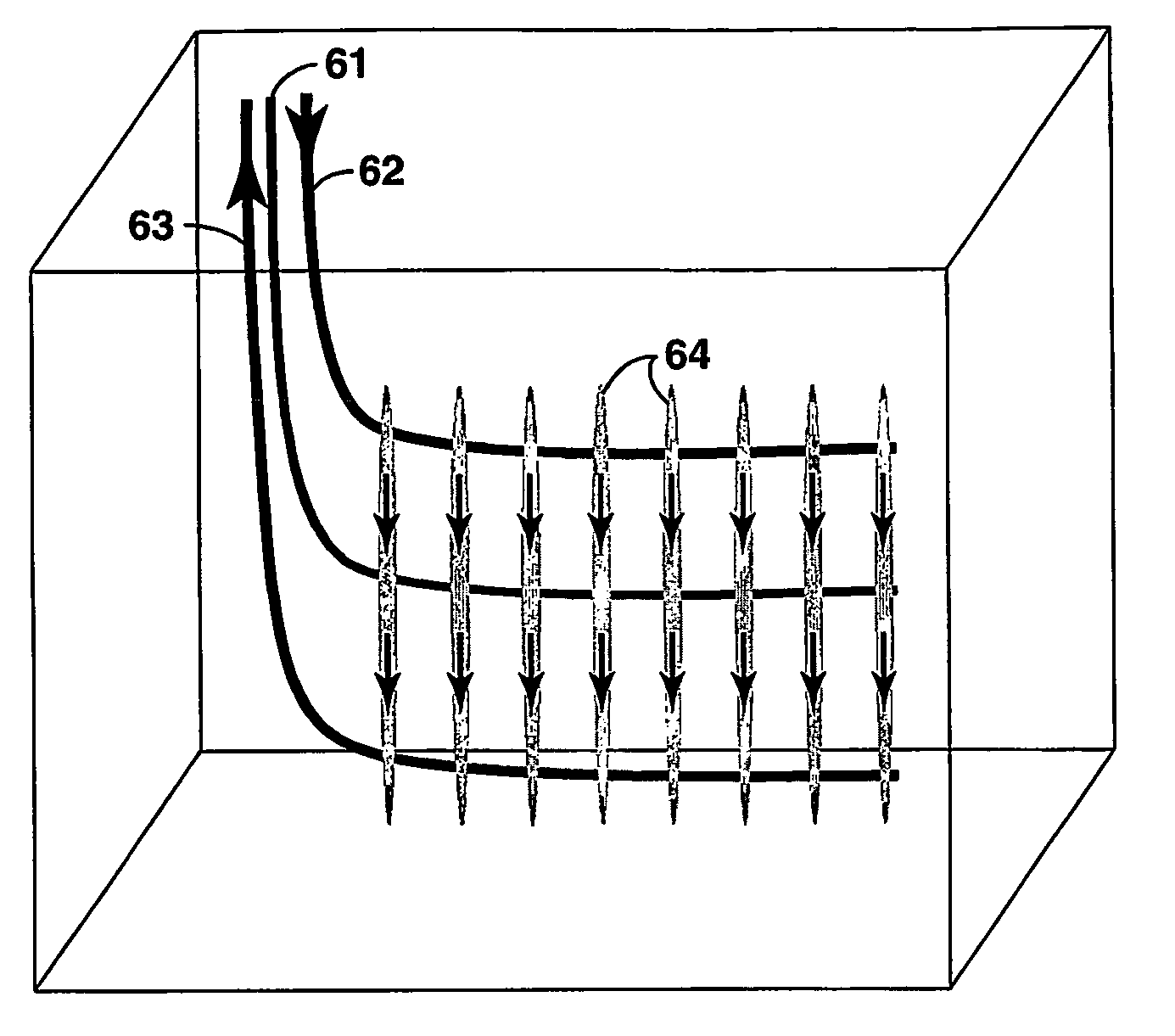
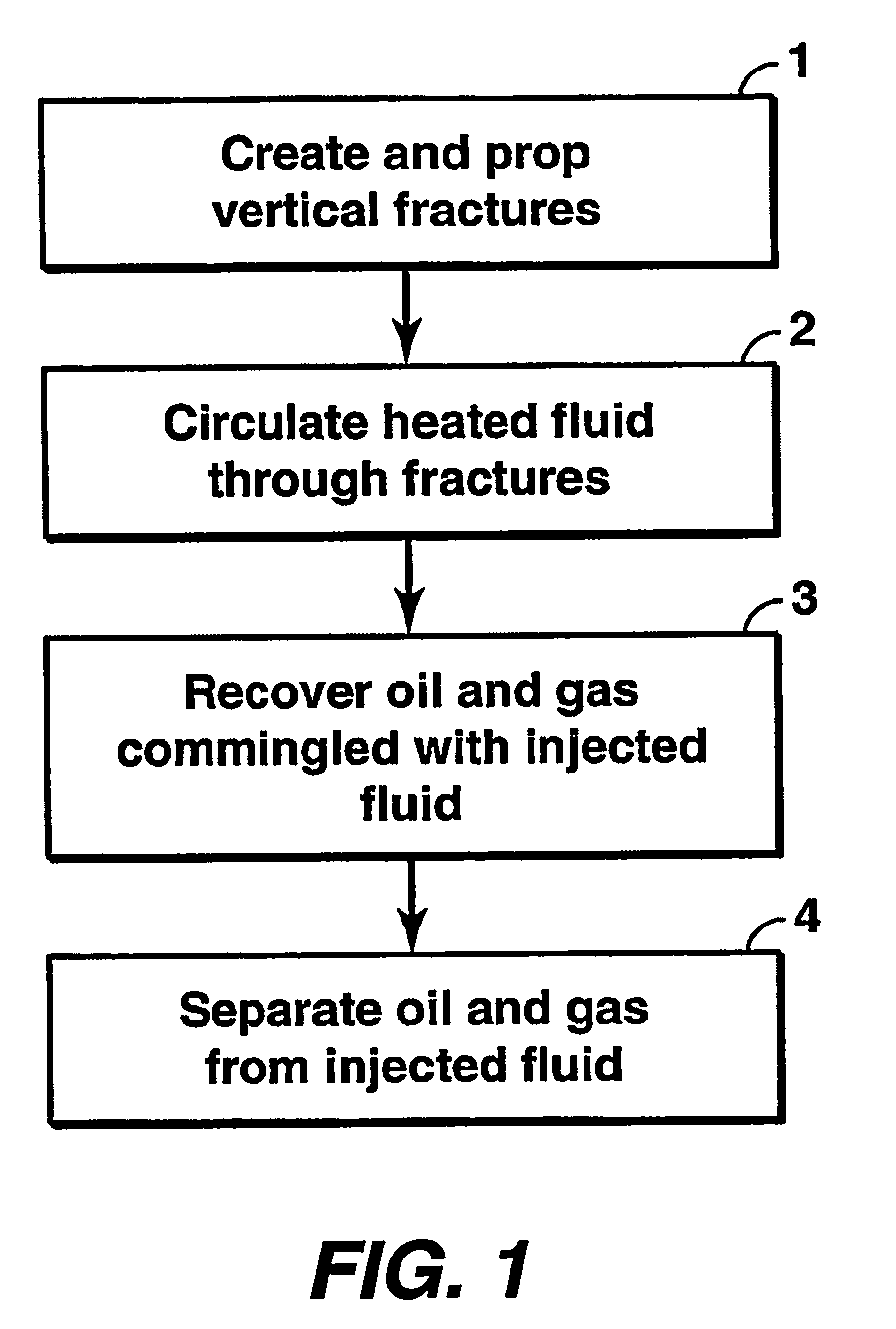
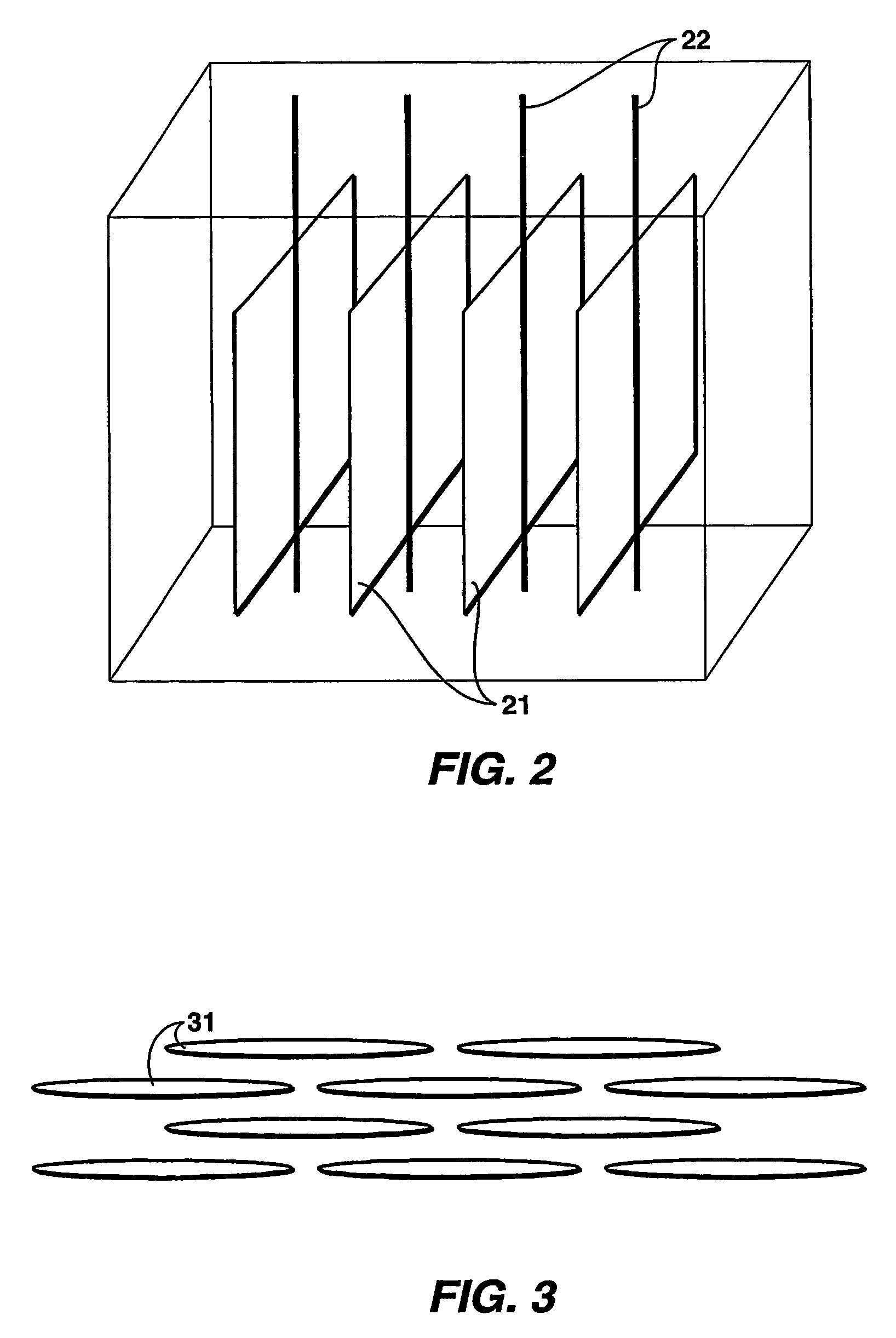
Hydrocarbon recovery from impermeable oil shales
InactiveUS20070023186A1Reduce penetrationAvoid insufficient heatingInsulationFluid removalKerogenCooling fluid
An economic method for in situ maturing and production of oil shale or other deep-lying, impermeable resources containing immobile hydrocarbons. Vertical fractures are created using horizontal or vertical wells. The same or other wells are used to inject pressurized fluids heated to less than approximately 370° C., and to return the cooled fluid for reheating and recycling. The heat transferred to the oil shale gradually matures the kerogen to oil and gas as the temperature in the shale is brought up, and also promotes permeability within the shale in the form of small fractures sufficient to allow the shale to flow into the well fractures where the product is collected commingled with the heating fluid and separated out before the heating fluid is recycled.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
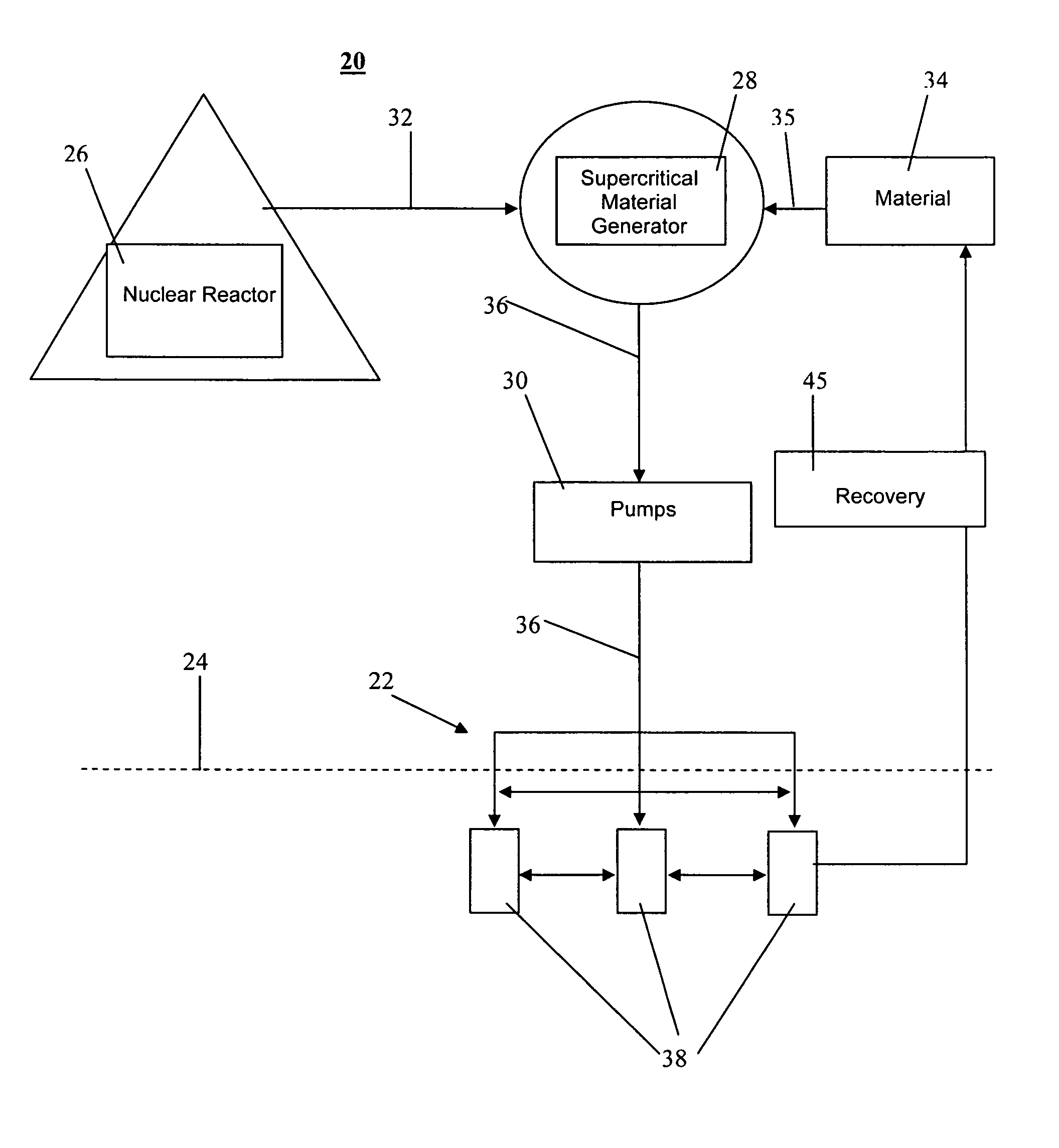
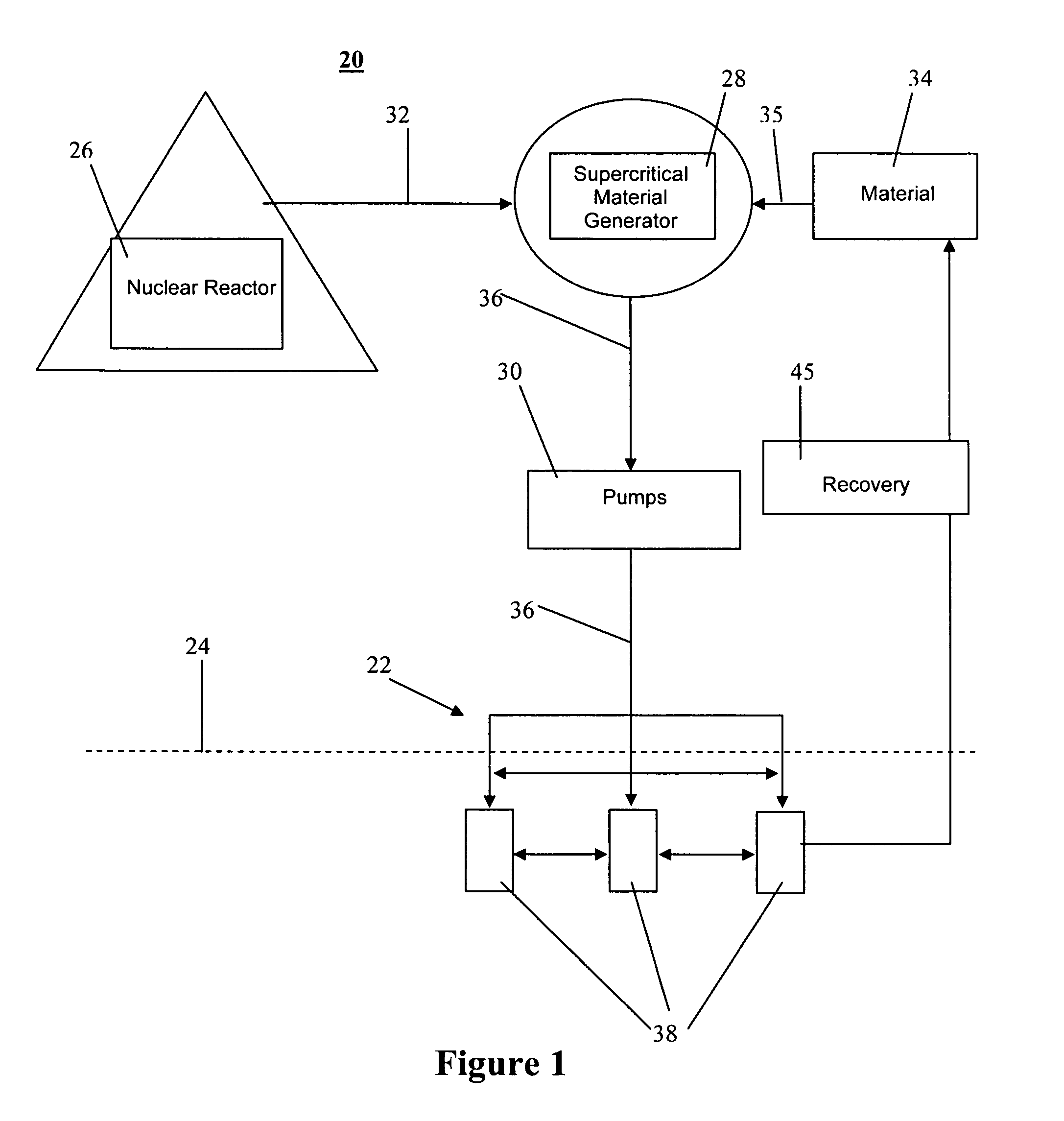
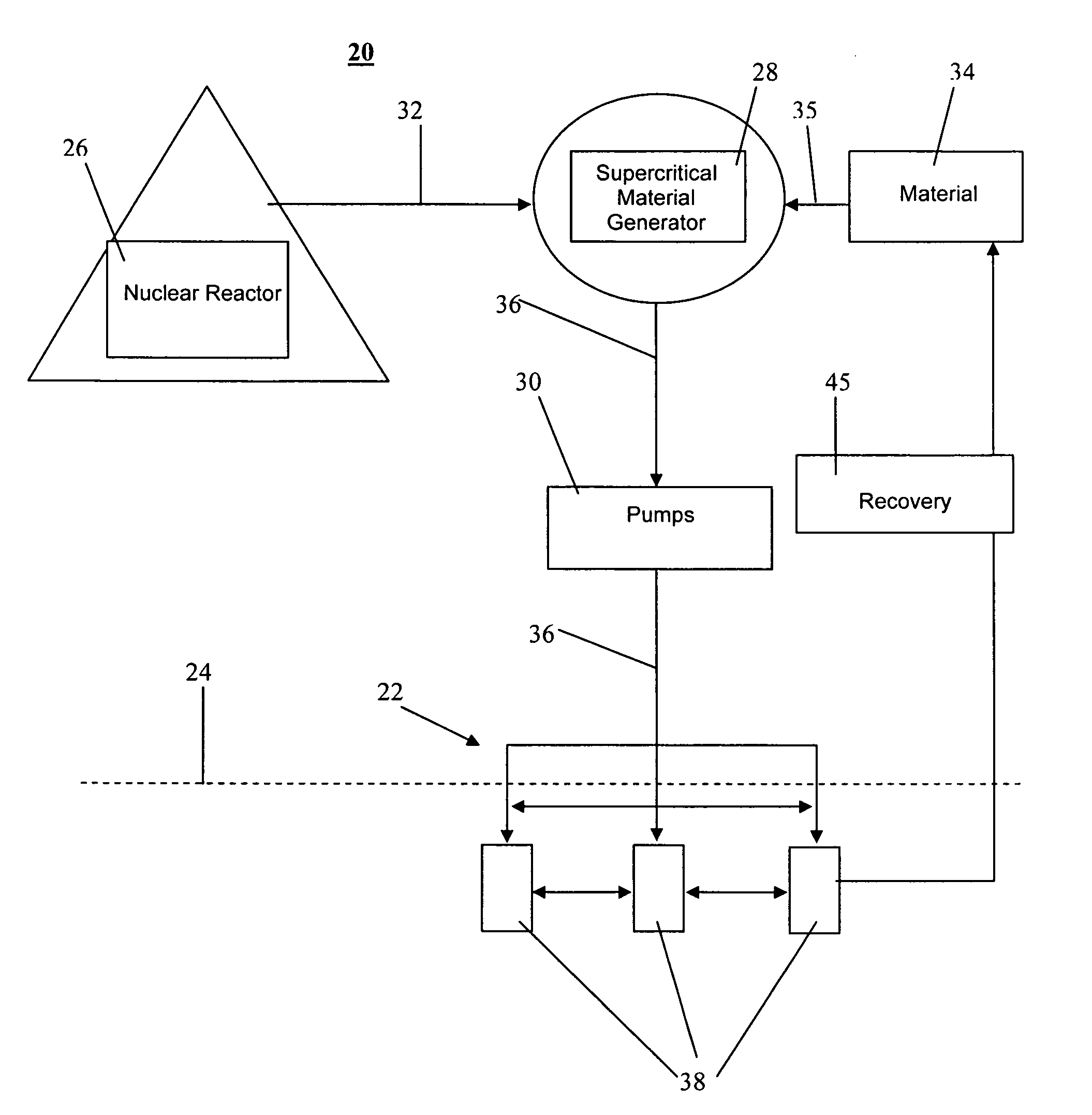
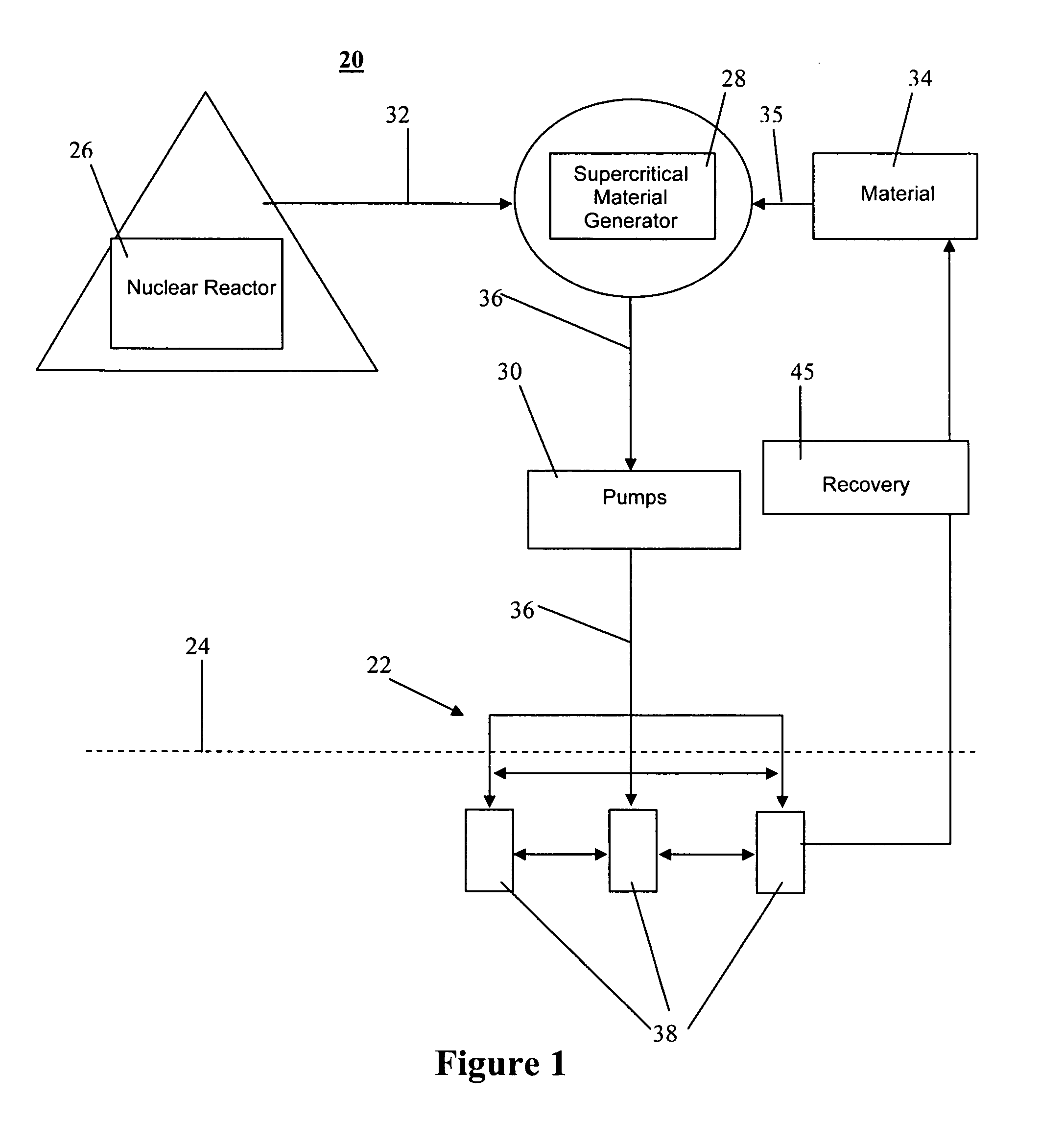
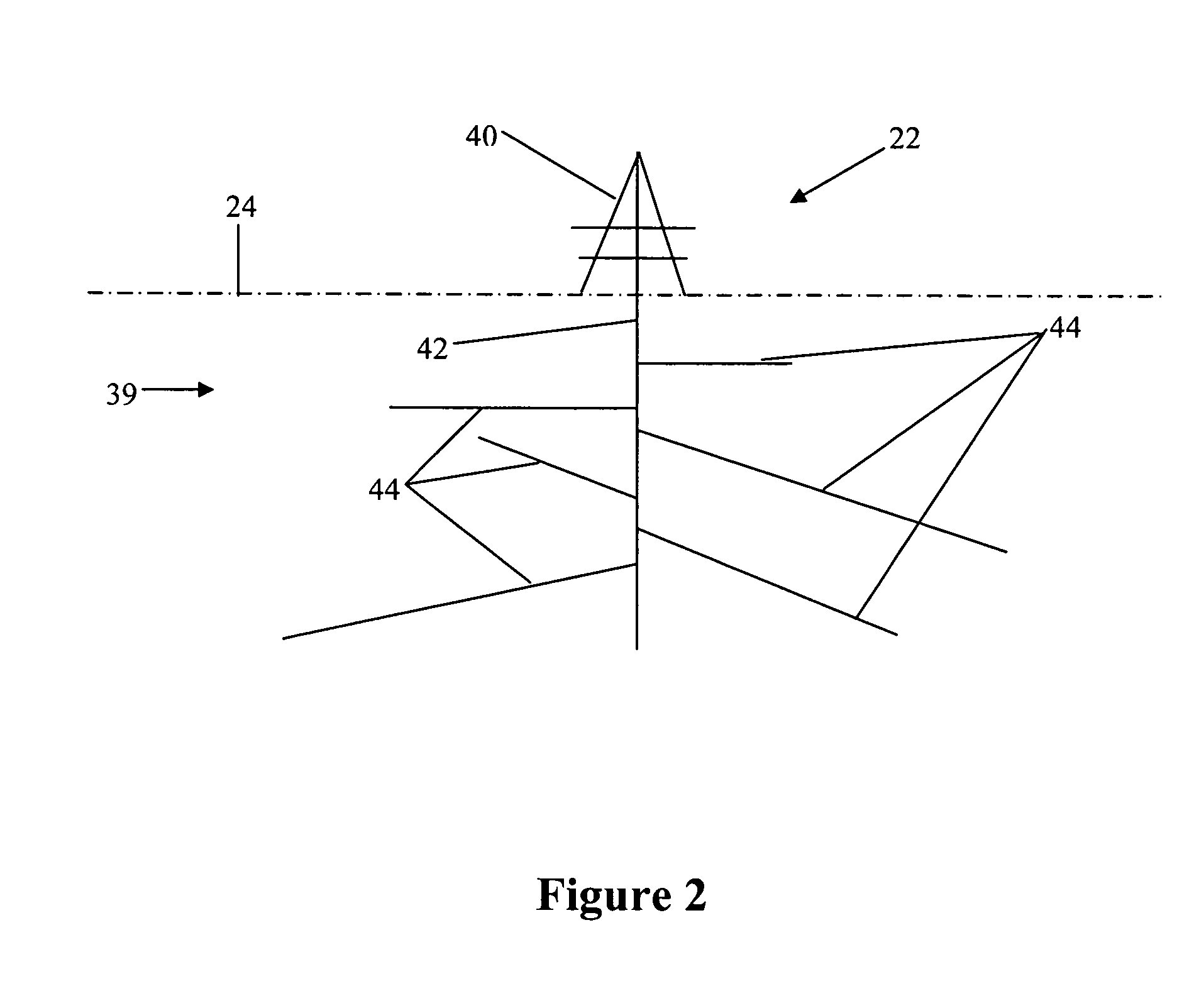
Method and system for extraction of hydrocarbons from oil shale
Owner:ULTRA SAFE NUCLEAR CORP
Process and system for converting carbonaceous feedstocks into energy without greenhouse gas emissions
InactiveUS7220502B2Improve efficiencyHigh hydrogen contentFuel cell auxillariesWaste based fuelPetroleum cokeToxic industrial waste
The process and system of the invention converts carbonaceous feedstock such as coal, hydrocarbon oil, natural gas, petroleum coke, oil shale, carbonaceous-containing waste oil, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing military waste, carbonaceous-containing industrial waste, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing sewage sludge and municipal solid waste, carbonaceous-containing agricultural waste, carbonaceous-containing biomass, biological and biochemical waste, and mixtures thereof into electrical energy without the production of unwanted greenhouse emissions. The process and system uses a combination of a gasifier, e.g., a kiln, operating in the exit range of at least 700° to about 1600° C. (1300-2900° F.) to convert the carbonaceous feedstock and a greenhouse gas stream into a synthesis gas comprising mostly carbon monoxide and hydrogen without the need for expensive catalysts and or high pressure operations. One portion of the synthesis gas from the gasifier becomes electrochemically oxidized in an electricity-producing fuel cell into an exit gas comprising carbon dioxide and water. The latter is recycled back to the gasifier after a portion of water is condensed out. The second portion of the synthesis gas from the gasifier is converted into useful hydrocarbon products.
Owner:RAVEN SR INC
Method for extracting oil and gas by convection heating of oil shale
A kind of mining oil gas method of the convection heating up oil-shale, involves the underground solid state energy and the mineral mining method improvement. The existing technical mining method efficiency is low, the cost is high, the scale is small, the big area implements and lacks the market competition ability with difficulty. This invention through in the ground arrangement group well, and selects the compression fracture method causes the group well to be interlinked, then the gap takes turns to choose the note hot-well and work-well, hot-well pours into 400 deg.C - 700 deg.C steam along the note oil-shale the ore level, heats up the ore level causes cheese root thermal decomposition to form the oil gas, and carries after the low temperature steam or the water along the production separates to the ground, finally forms the oil gas product. In the separation process may simultaneously the pre- hot water, and uses the water-injection well withdraws with work-well the convection way dries up oil-shale and the ore level around shale region afterheat, thus realized the goal of this invention is fast, big scale, low cost from oil-shale ore level mining oil gas.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
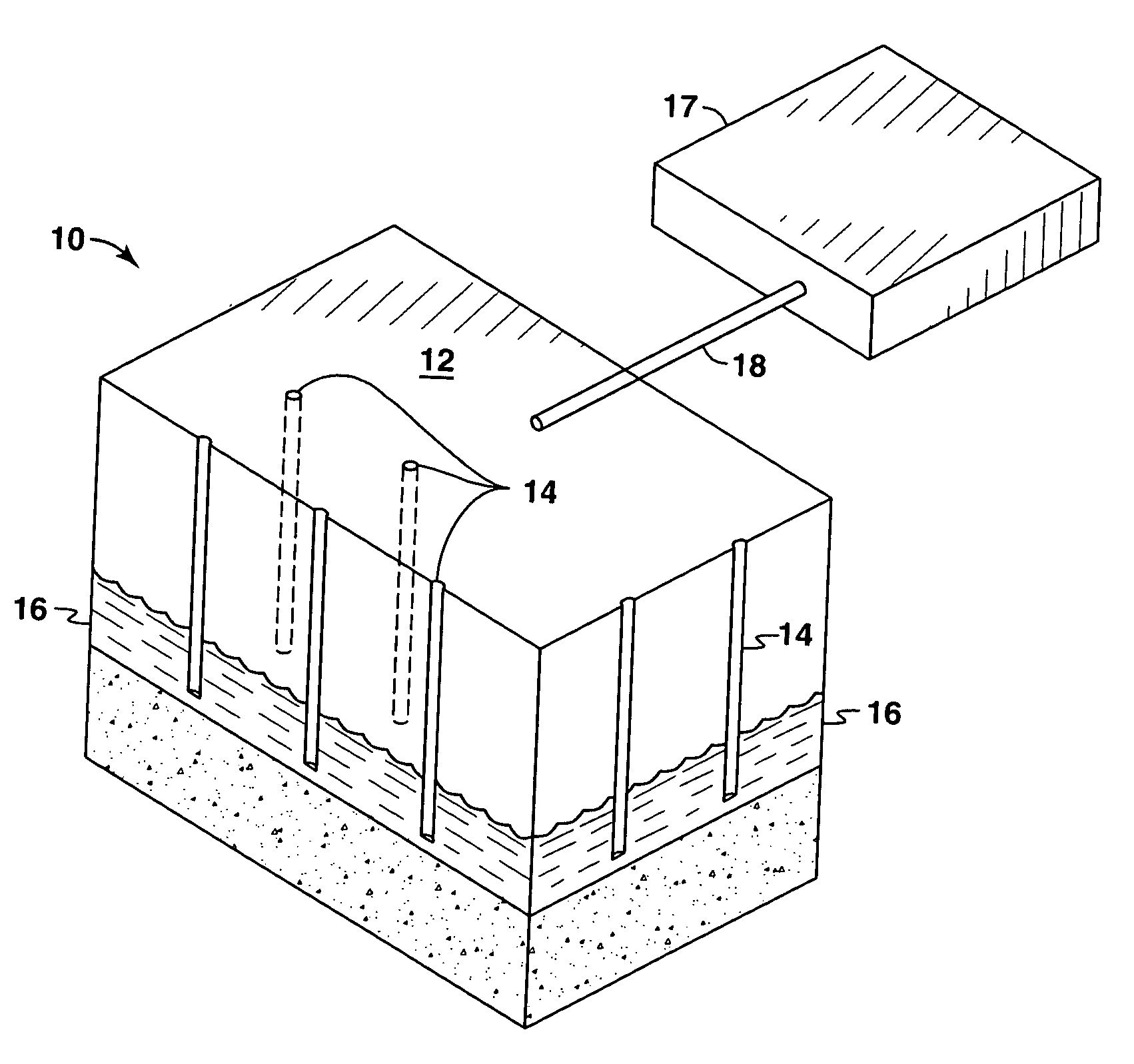
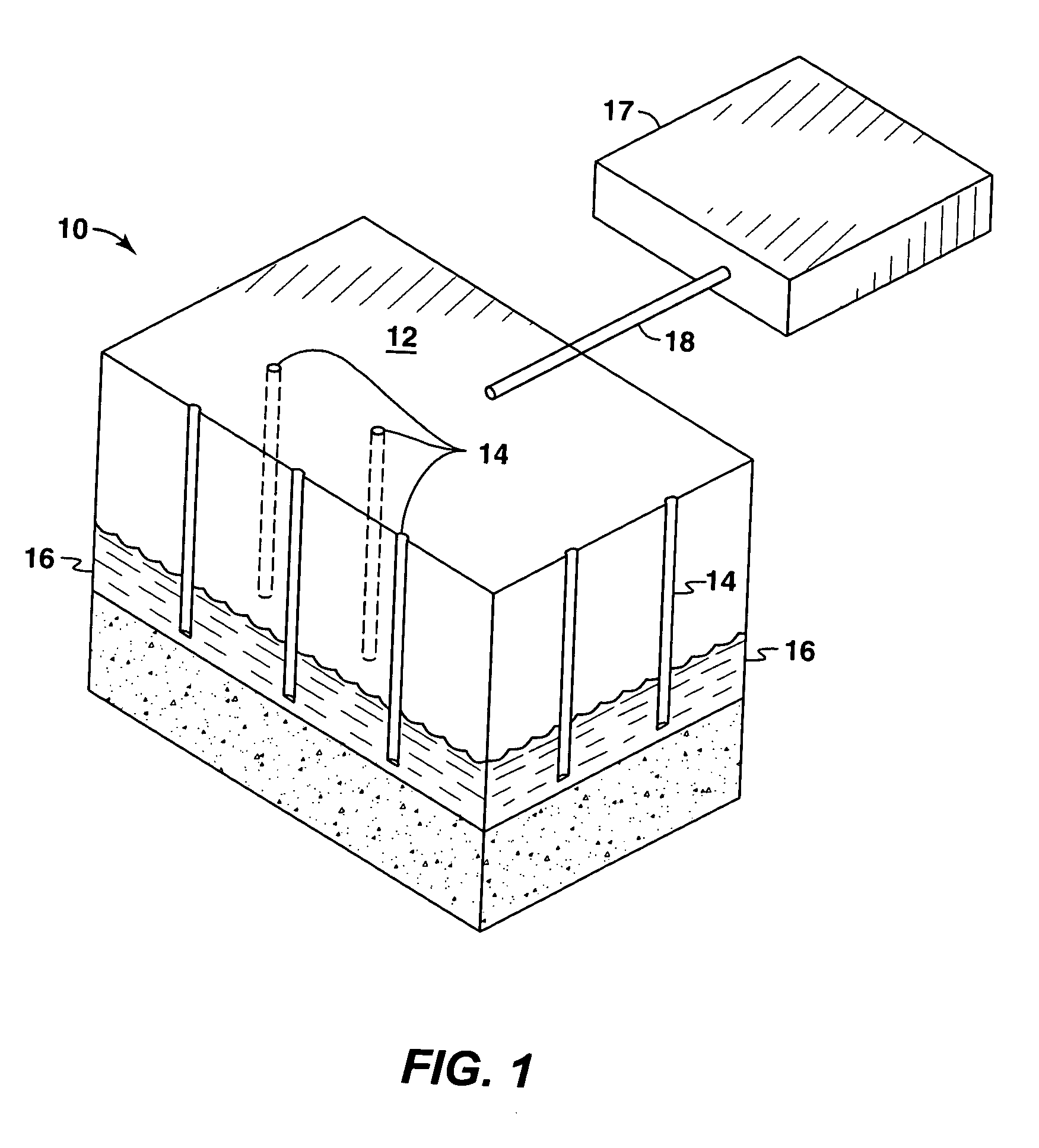
In-situ method of producing oil shale and gas (methane) hydrates, on-shore and off-shore
A method is provided for in-situ production of oil shale and gas (methane) hydrates wherein a network of fractures is formed by injecting liquified gases into at least one substantially horizontally disposed fracturing borehole. Heat is thereafter applied to liquify the kerogen or to dissociate the gas (methane) hydrates so that oil shale oil and / or gases can be recovered from the fractured formations.
Owner:MAGUIRE JAMES Q
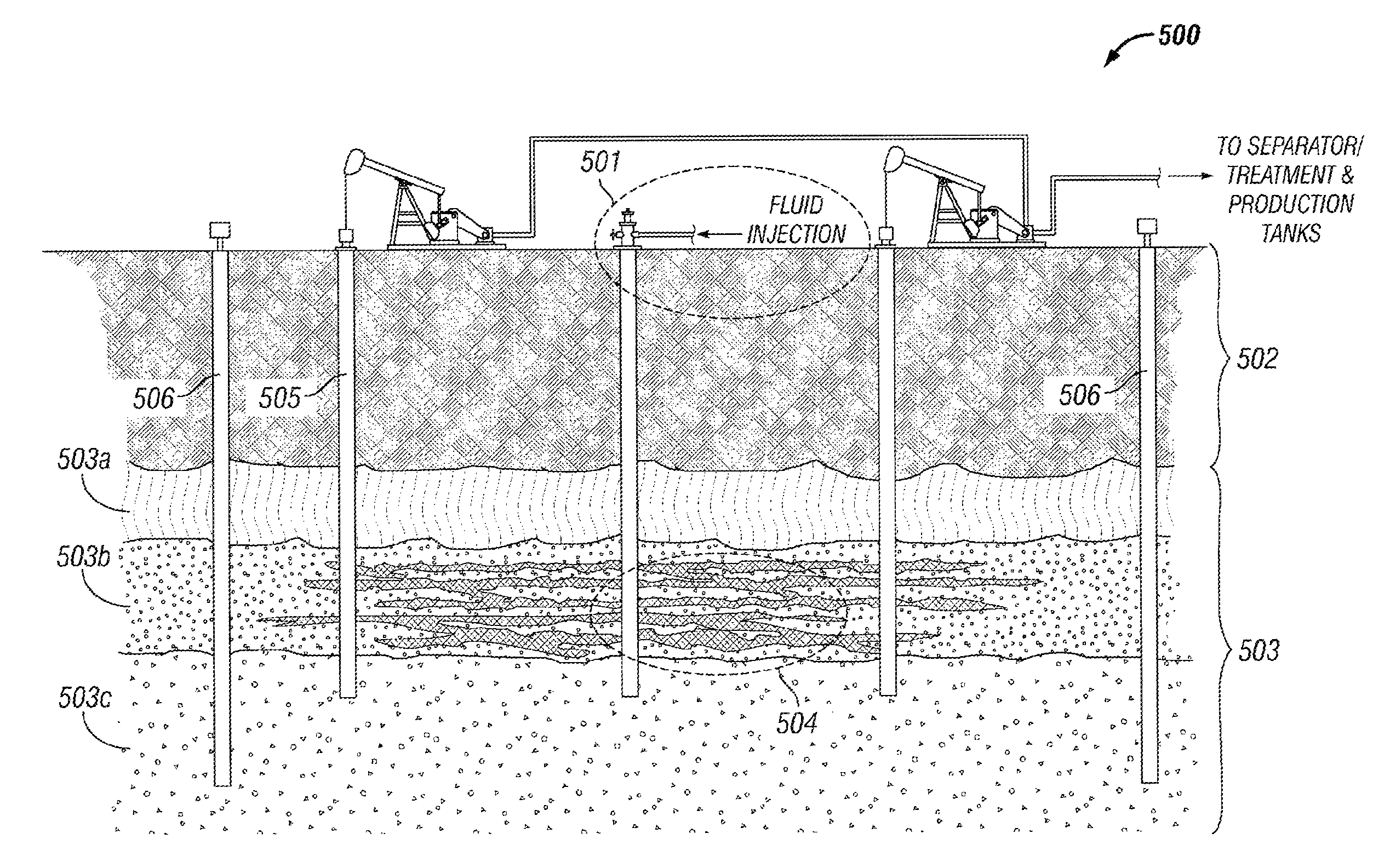
Heavy Oil Recovery and Apparatus
A thermal in-situ method and apparatus are provided for recovering hydrocarbons from subterranean hydrocarbon-containing formations such as oil sands, oil shale and other heavy oil systems. Recovery of viscous hydrocarbon by hot fluid injection into subterranean formations is assisted by using a specially designed wellbore with an active hydraulic seal, with a axial communication zone with multiple injection perforations separated from the production perforations by a moveable packer. In addition, a novel downhole thermal sensing apparatus is used to monitor and control oil production. A producing mechanism including pumping equipment lifts the produced oil from the central cavity to the surface.
Owner:CRICHLOW HENRY B
Burning-free block brick prepared from bulky industrial waste residues
The invention relates to a burning-free block brick prepared from bulky industrial waste residues. The burning-free block brick is characterized in that the block brick comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight or volume: 10-80 parts of at least one of tailing, magnesium slag, basic slag, mountain flour, cinder, fly ash, coal gangue, oil shale waste and sulfuric acid slag, 0-80 parts of at least one of gravel, waste sand, construction waste, garbage to be burnt, steel slag, mineral slag, copper slag, iron slag with gold, ardealite, phosphorous slag and carbide slag, 0-50 parts of active cementing material, 0-30 parts of cement clinker, 2-15 parts of cement and a defined amount of water. The preparation method of all types of burning-free and steaming-free standard bricks, perforated bricks, hollow blocks, paving tiles, road edge bricks and fence railings which have low cost and high strength, is as follows: proportioning, stirring for 1-6 minutes, adding a defined amount of water to stir, placing in moulds to form in a machine and performing natural curing for 7-28 days. The burning-free block brick has high raw material selectability, simple technology and wide development and application prospects, and is environmental-friendly.
Owner:司密花 +2
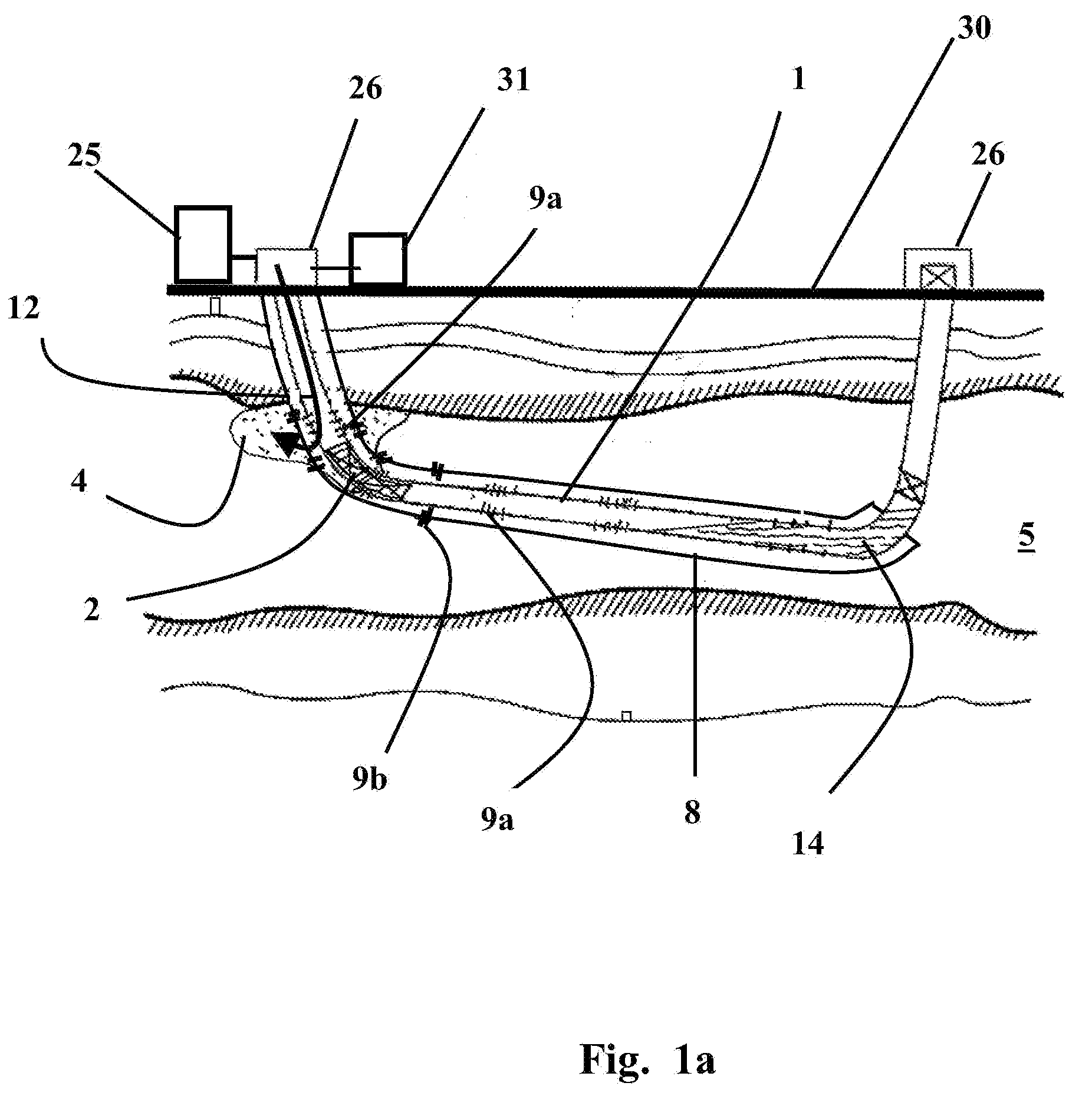
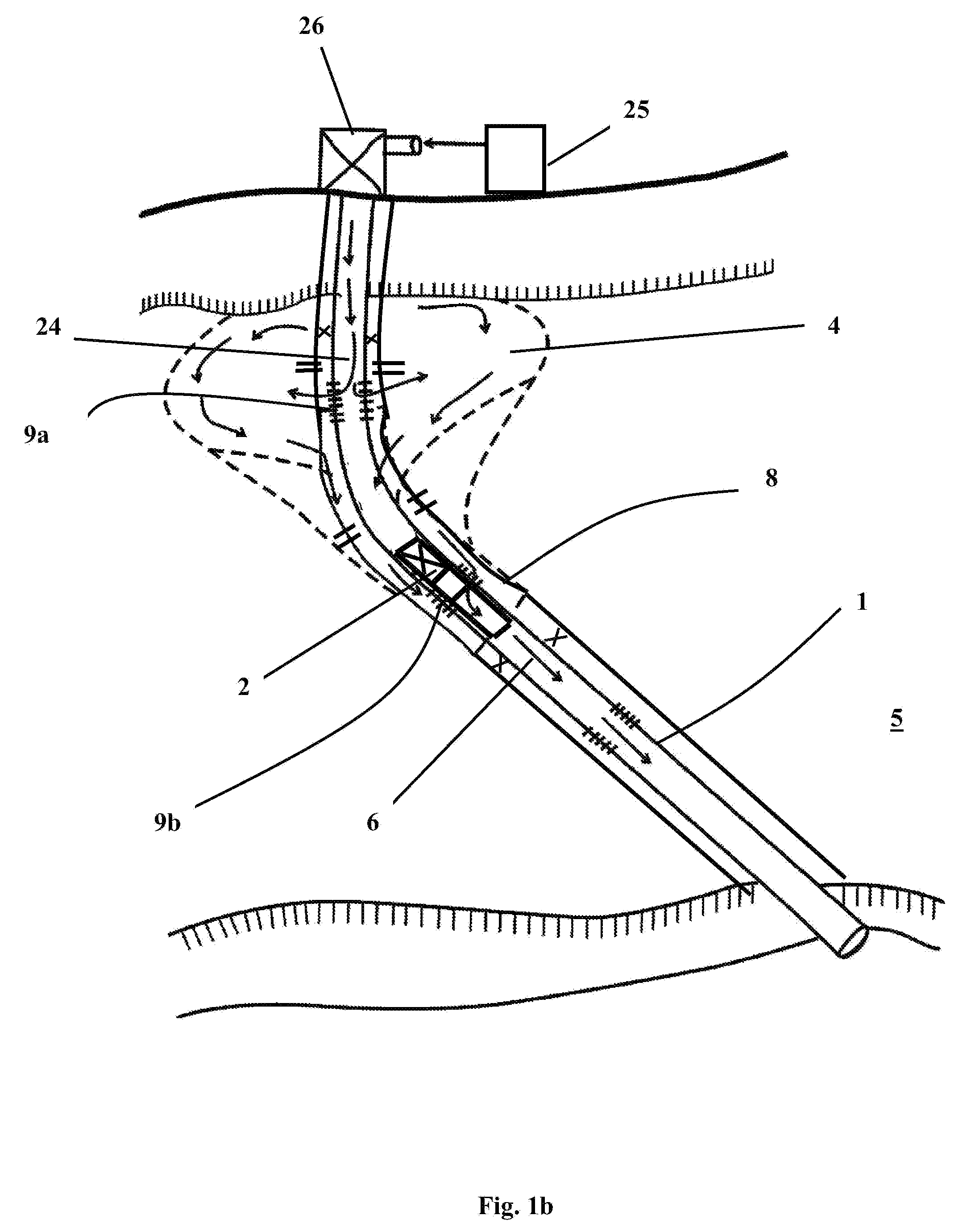
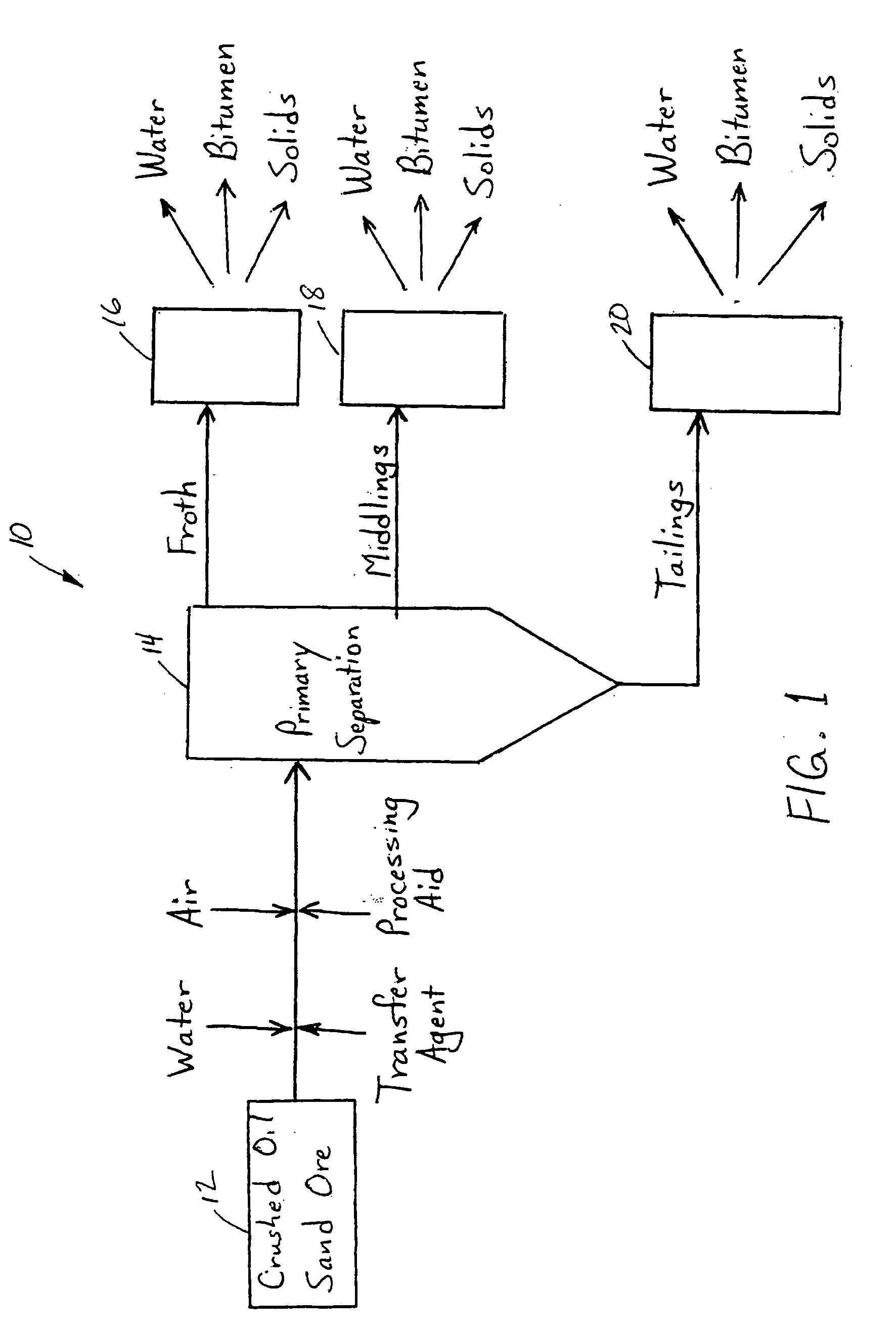
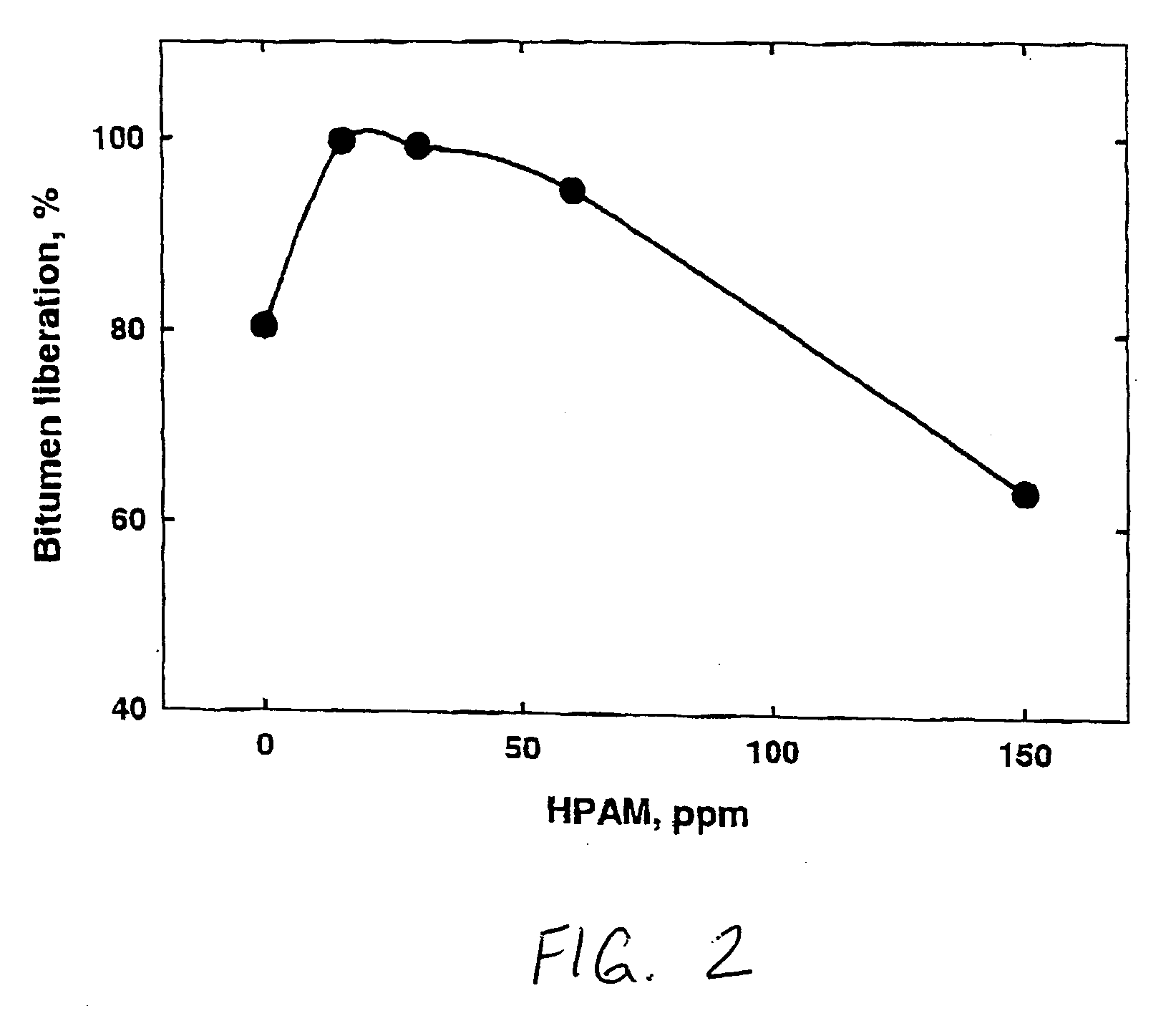
Processing aids for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery from oil sands, oil shale and other petroleum residues
InactiveUS20050194292A1Liberation of additionalPromote recoveryDewatering/demulsification with chemical meansLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSlurry
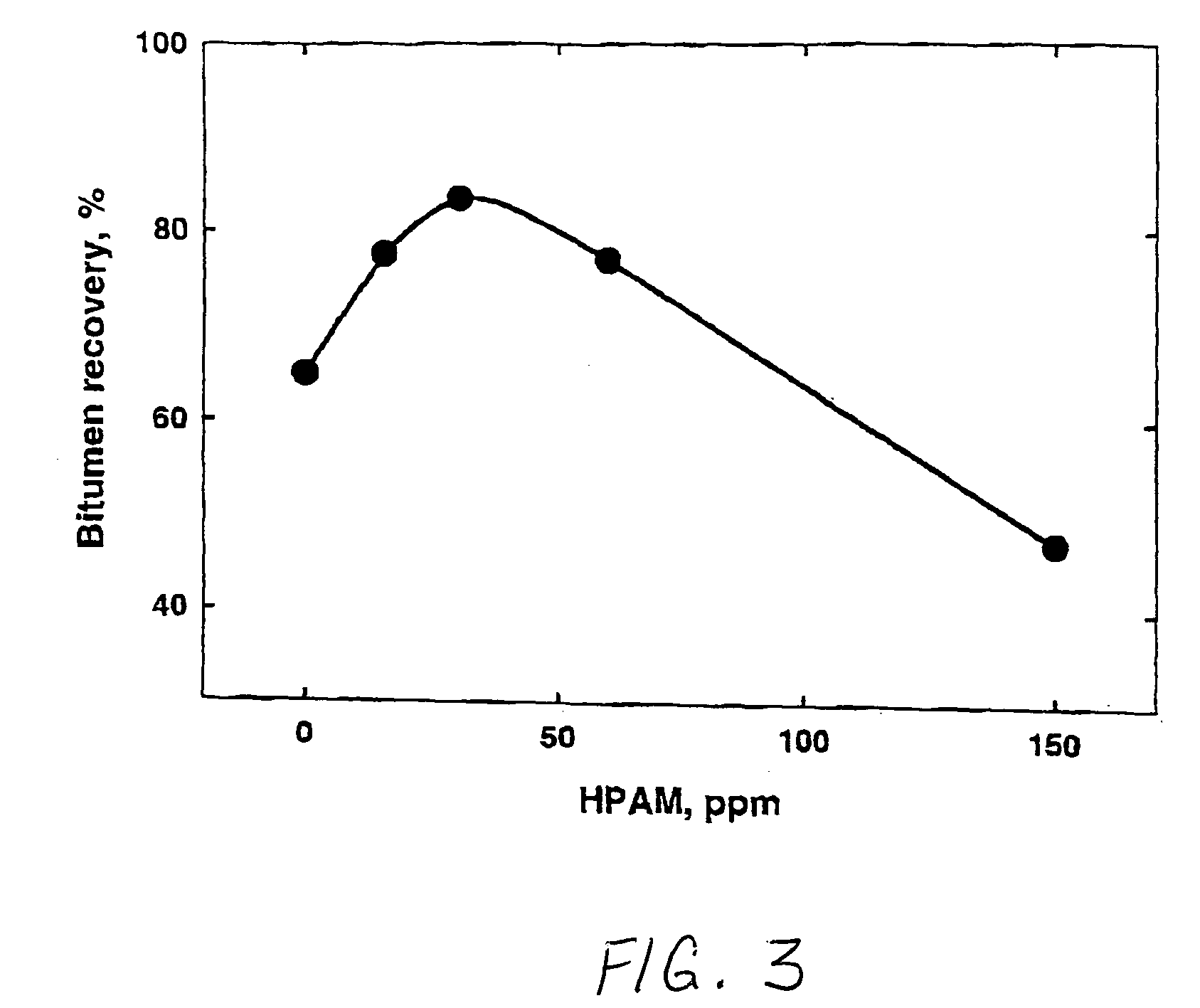
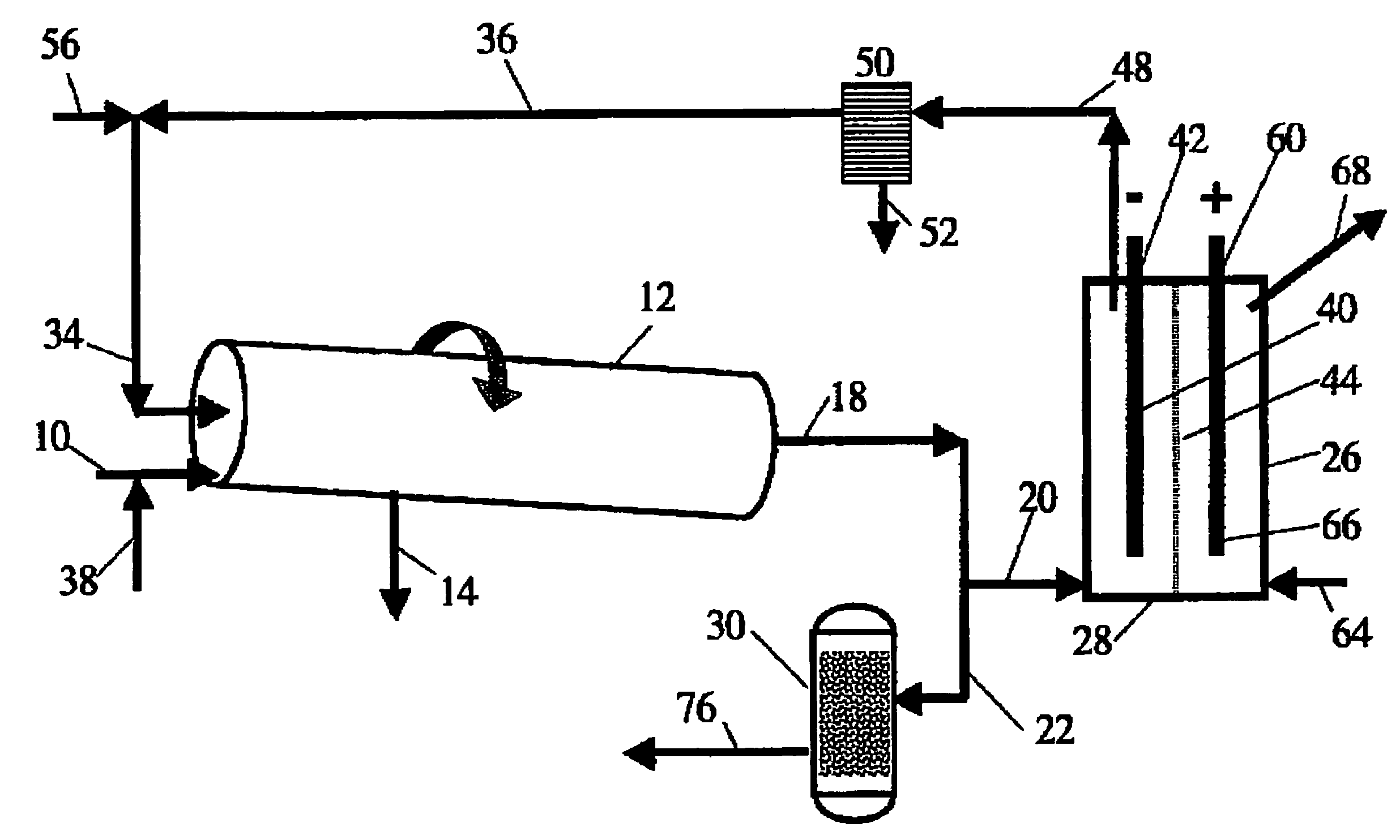
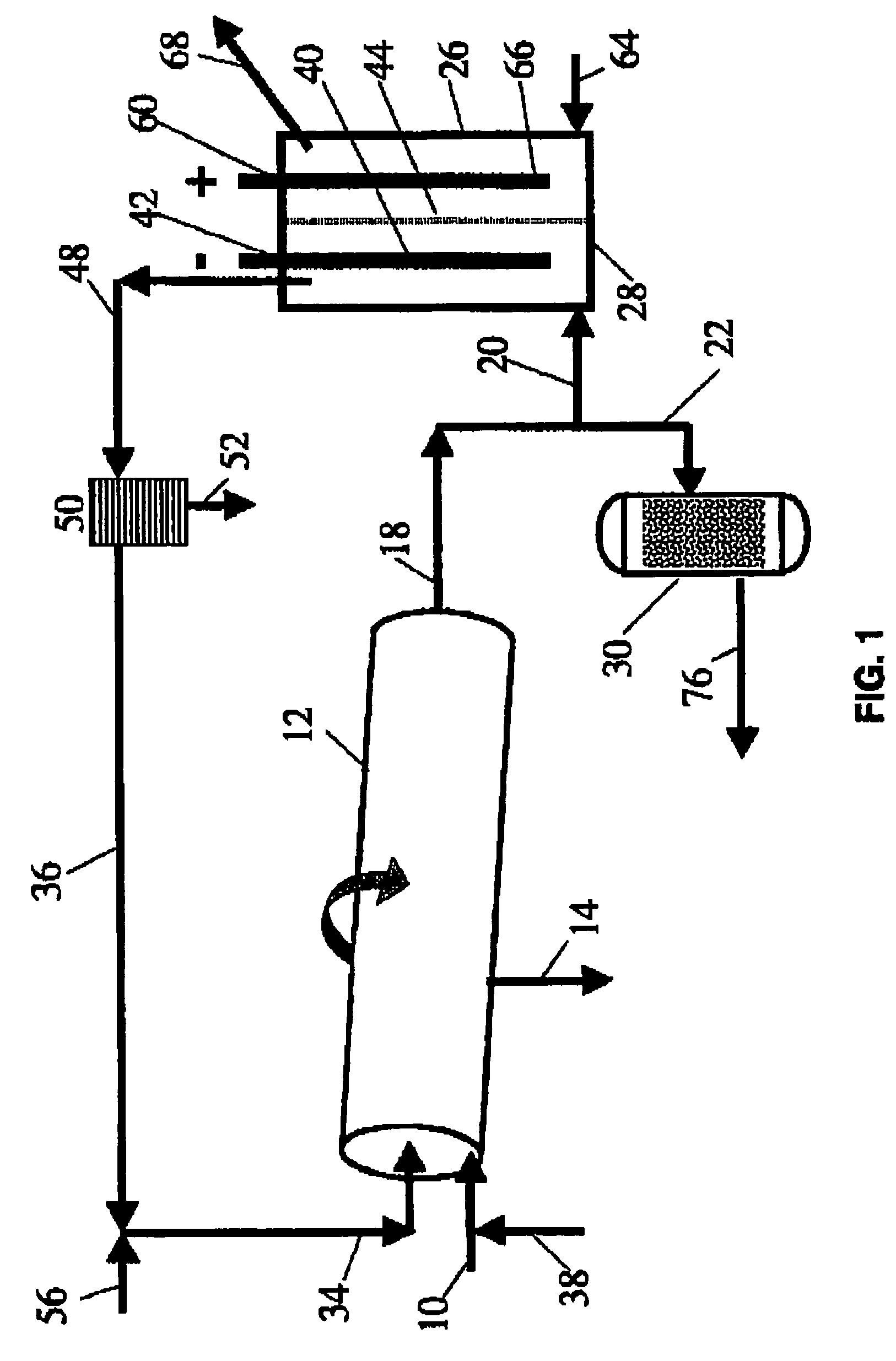
A method of improving hydrocarbon recovery from oil sands, oil shale, and petroleum residues includes adding a polymeric or nonpolymeric processing aid capable of sequestering cations, such as the multivalent calcium, magnesium and iron cations. The hydrocarbons are preferably contacted with the processing aid before a primary separation of the hydrocarbons in order to increase bitumen recovery. A processing aid is provided in an effective amount to increase the liberation of the hydrocarbons from inorganic solids, particularly when the source is a poor processing ore. Preferred processing aids include citric acid or a polymeric acid selected from polyacrylic acid, polymethacrylic acid, salts of these acids, partial salts of these acids, and combinations thereof. The processing aids significantly increase the hydrocarbon recovery typically with concentrations less than 50 ppm and the polymeric processing aids can also provide beneficial flocculation of solids in tailings slurry.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Process and system for converting carbonaceous feedstocks into energy without greenhouse gas emissions
ActiveUS7132183B2Improve efficiencyHigh hydrogen contentFuel cell auxillariesGasification processes detailsWaste oilHigh pressure
The process and system of the invention converts carbonaceous feedstock such as coal, hydrocarbon oil, natural gas, petroleum coke, oil shale, carbonaceous-containing waste oil, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing hazardous waste, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, and mixtures thereof into electrical energy without the production of unwanted greenhouse emissions. The process and system uses a combination of a gasifier, e.g., a kiln, operating in the exit range of at least 700° to about 1600° C. (1300–2900° F.) to convert the carbonaceous feedstock and a greenhouse gas stream into a synthesis gas comprising mostly carbon monoxide and hydrogen without the need for expensive catalysts and or high pressure operations. One portion of the synthesis gas from the gasifier becomes electrochemically oxidized in an electricity-producing fuel cell into an exit gas comprising carbon dioxide and water. The latter is recycled back to the gasifier after a portion of water is condensed out. The second portion of the synthesis gas from the gasifier is converted into useful hydrocarbon products.
Owner:RAVEN SR INC
Hydrocarbon recovery from impermeable oil shales
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Microwave process for intrinsic permeability enhancement and hydrocarbon extraction from subsurface deposits
Hydrocarbons are extracted from a target formation, such as oil shale, tar sands, heavy oil and petroleum reservoirs, by apparatus and methods which cause fracturing of the containment rock and liquification or volatization of the hydrocarbons by microwave energy directed by a radiating antenna in the target formation.
Owner:GEOSCI SERVICES +1
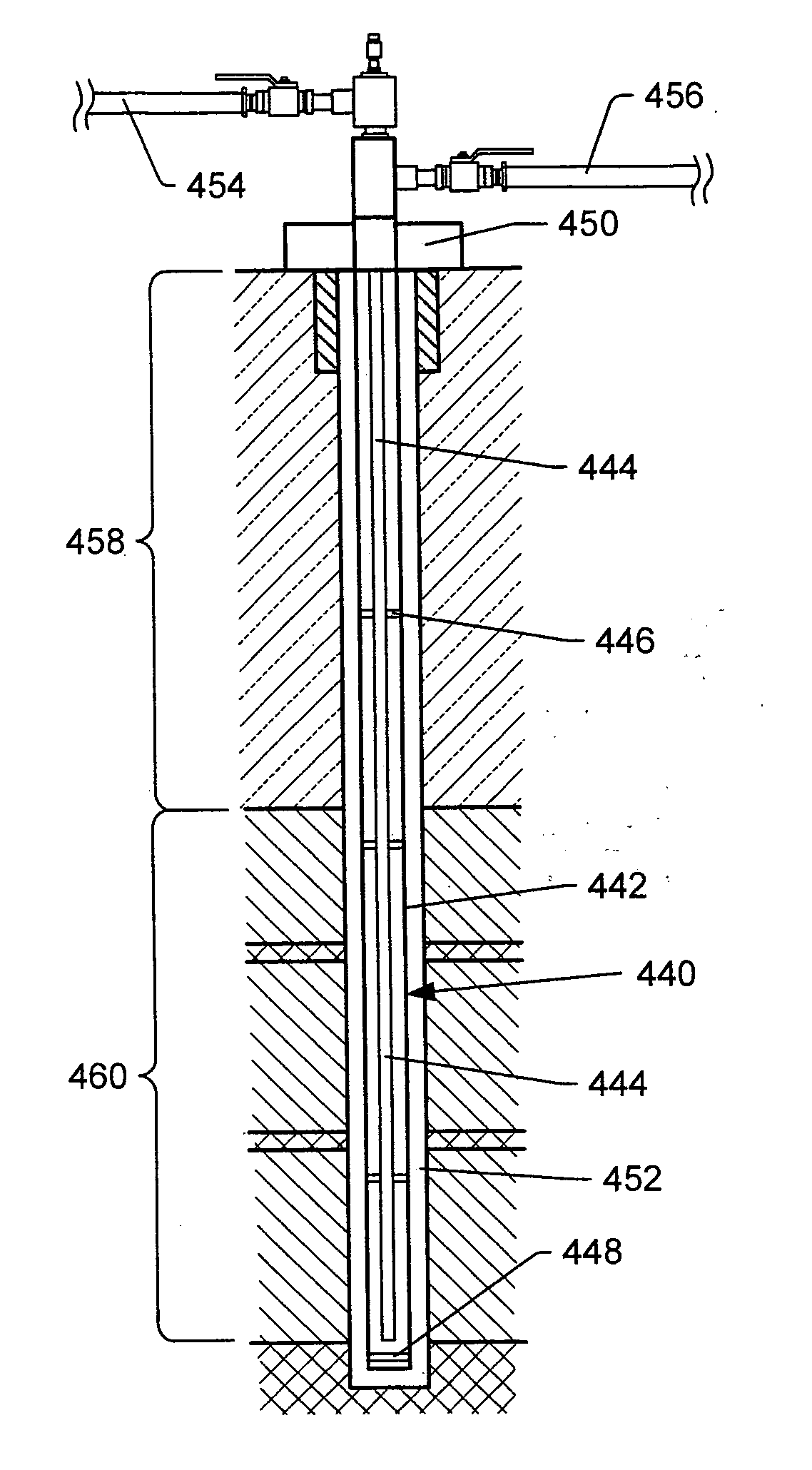
Downhole burners for in situ conversion of organic-rich rock formations
InactiveUS20090050319A1Reduction factorDecrease in heat transfer coefficientInsulationFluid removalCombustorChemical measurement
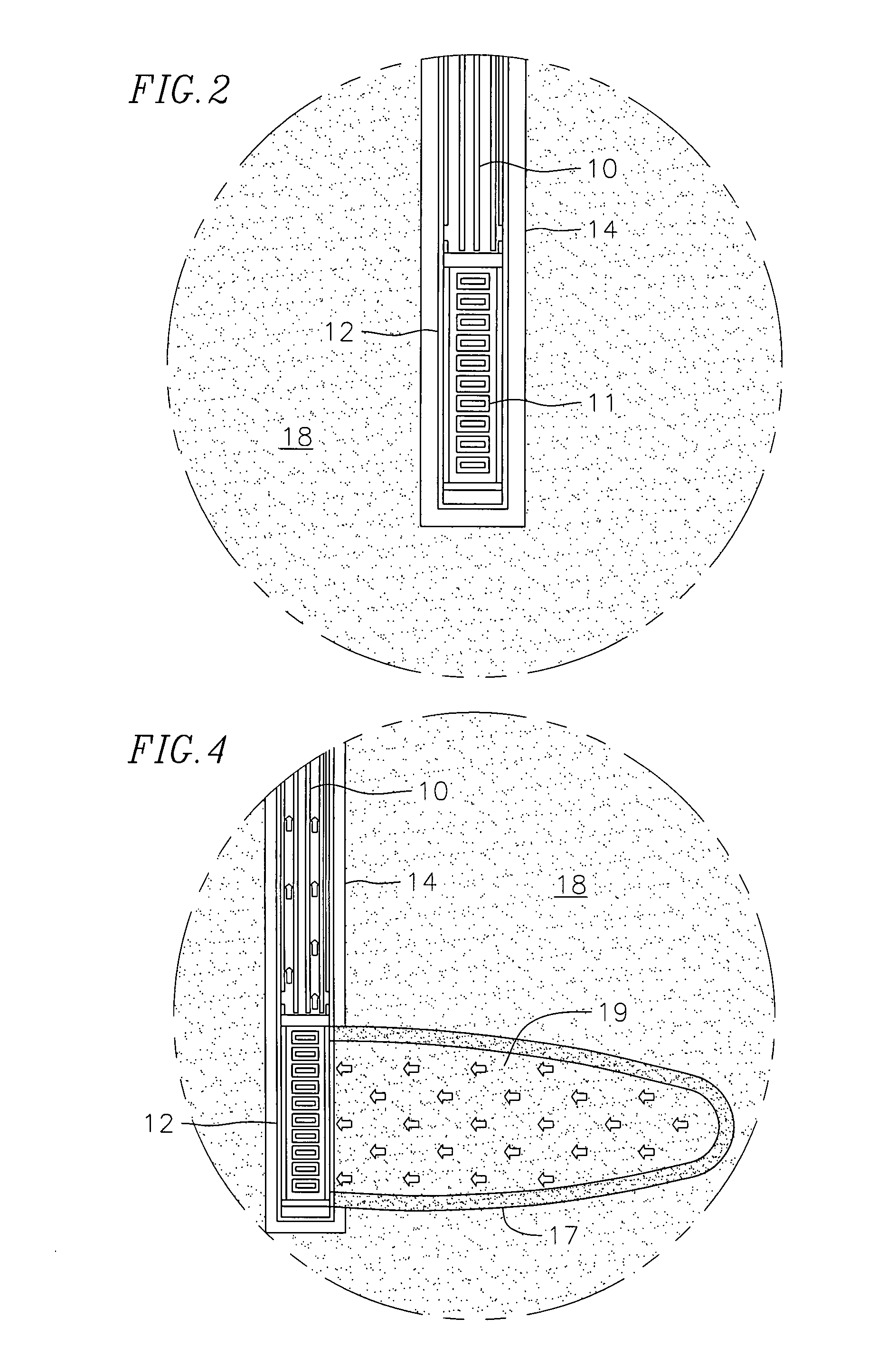
A method for in situ heating of a selected portion of a targeted organic-rich rock formation such as an oil shale formation is provided. The method includes the steps of providing casing in a wellbore extending to a depth within or below the selected portion of the organic-rich rock formation, and also providing a tubing within the casing. An annular region is formed between the tubing and the surrounding casing. Air or other oxidant and a combustible fuel are injected into the wellbore. Either the air or the combustible fuel is in stoichiometric combustion excess. The method also includes providing hardware in the wellbore so as to cause the air and the combustible fuel to mix and to combust at substantially the depth of the organic-rich rock formation. The hardware may include more than one burner. Insulation may be placed along the tubing adjacent the first burner in order to reduce the heat transfer coefficient within the tubing and to provide a more uniform temperature within the annulus.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Microwave process for intrinsic permeability enhancement and hydrocarbon extraction from subsurface deposits
Hydrocarbons are extracted from a target formation, such as oil shale, tar sands, heavy oil and petroleum reservoirs, by apparatus and methods which cause fracturing of the containment rock and liquification or volatization of the hydrocarbons by microwave energy directed by a radiating antenna in the target formation.
Owner:GEOSCI SERVICES +1
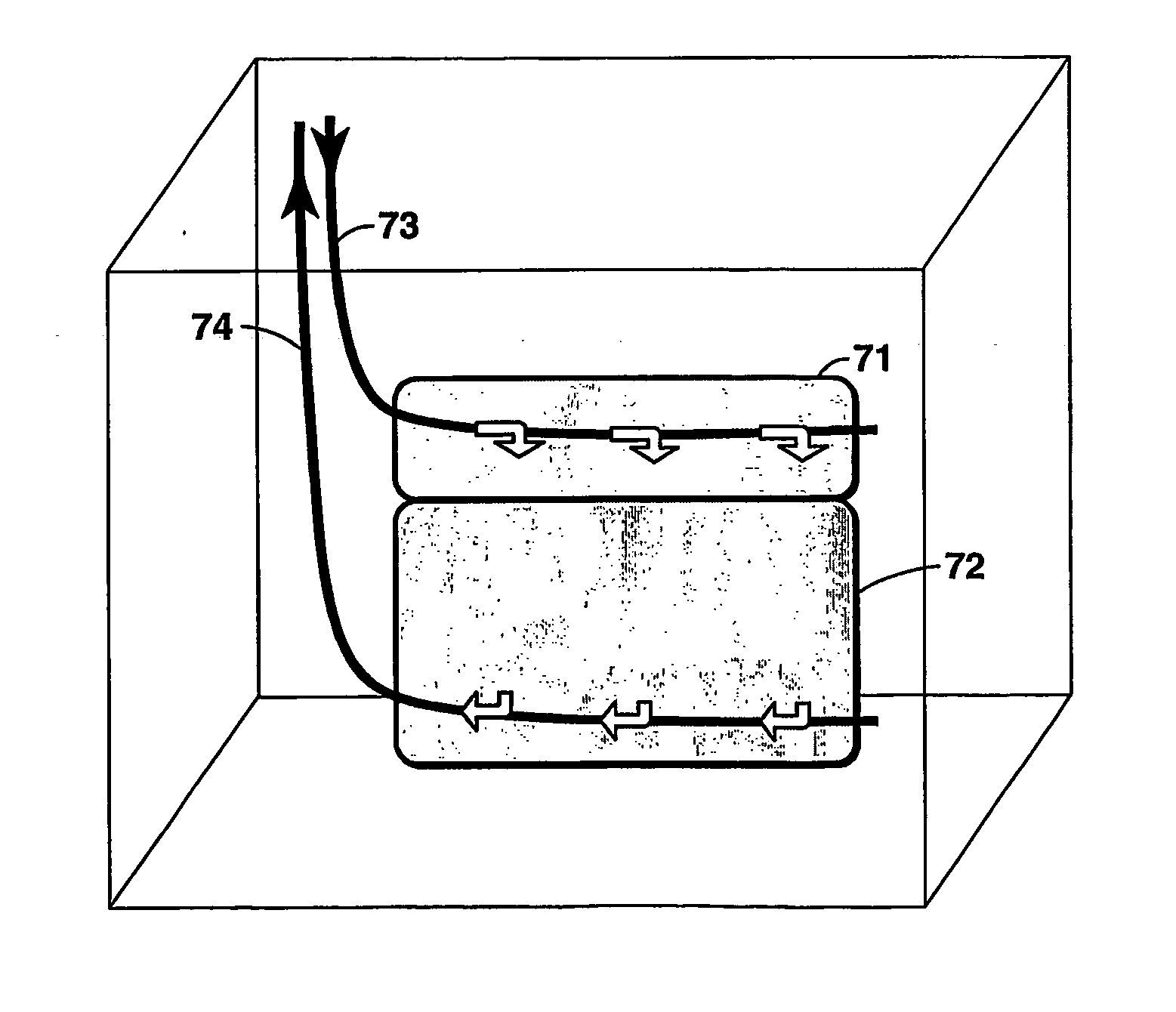
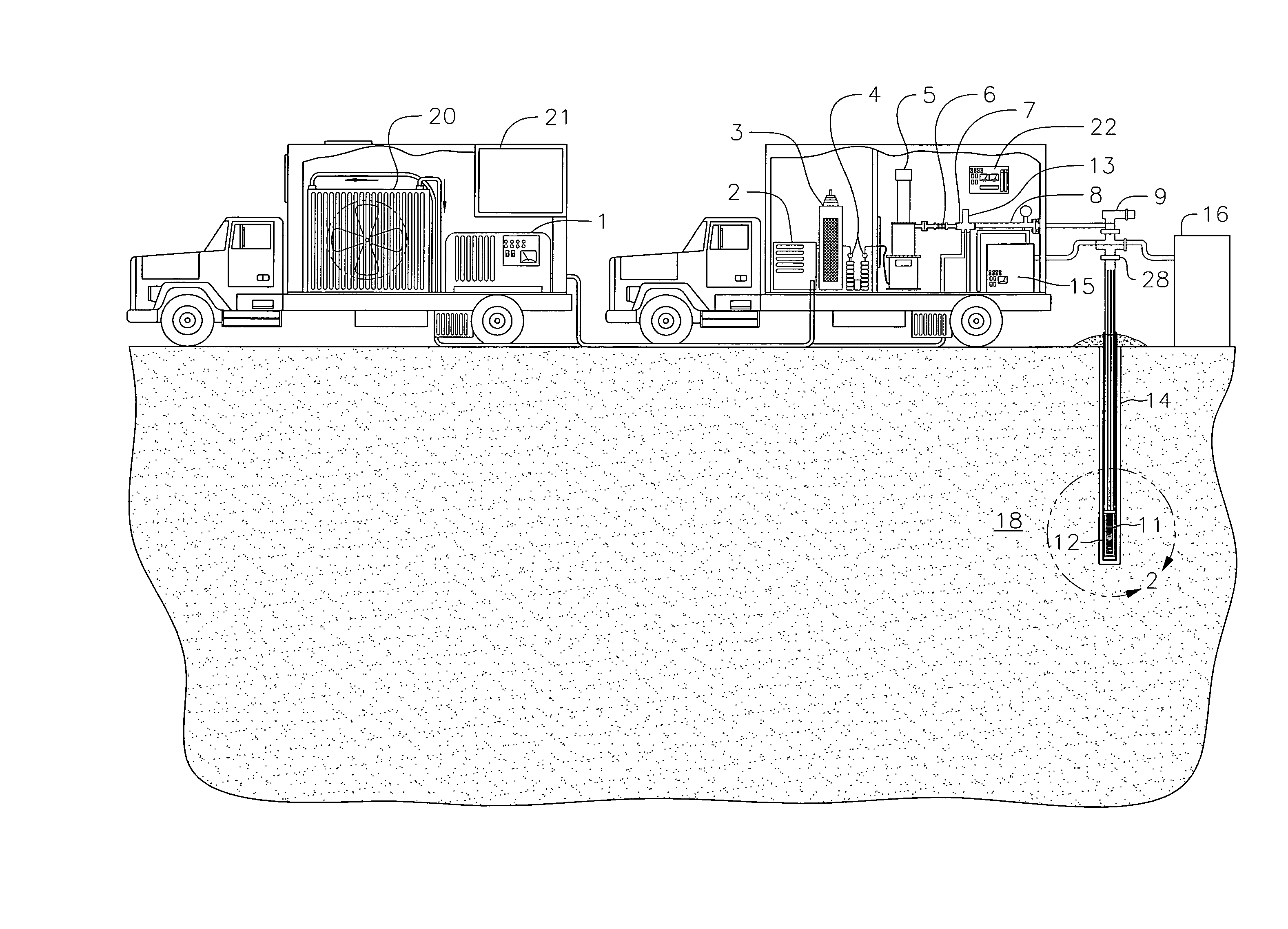
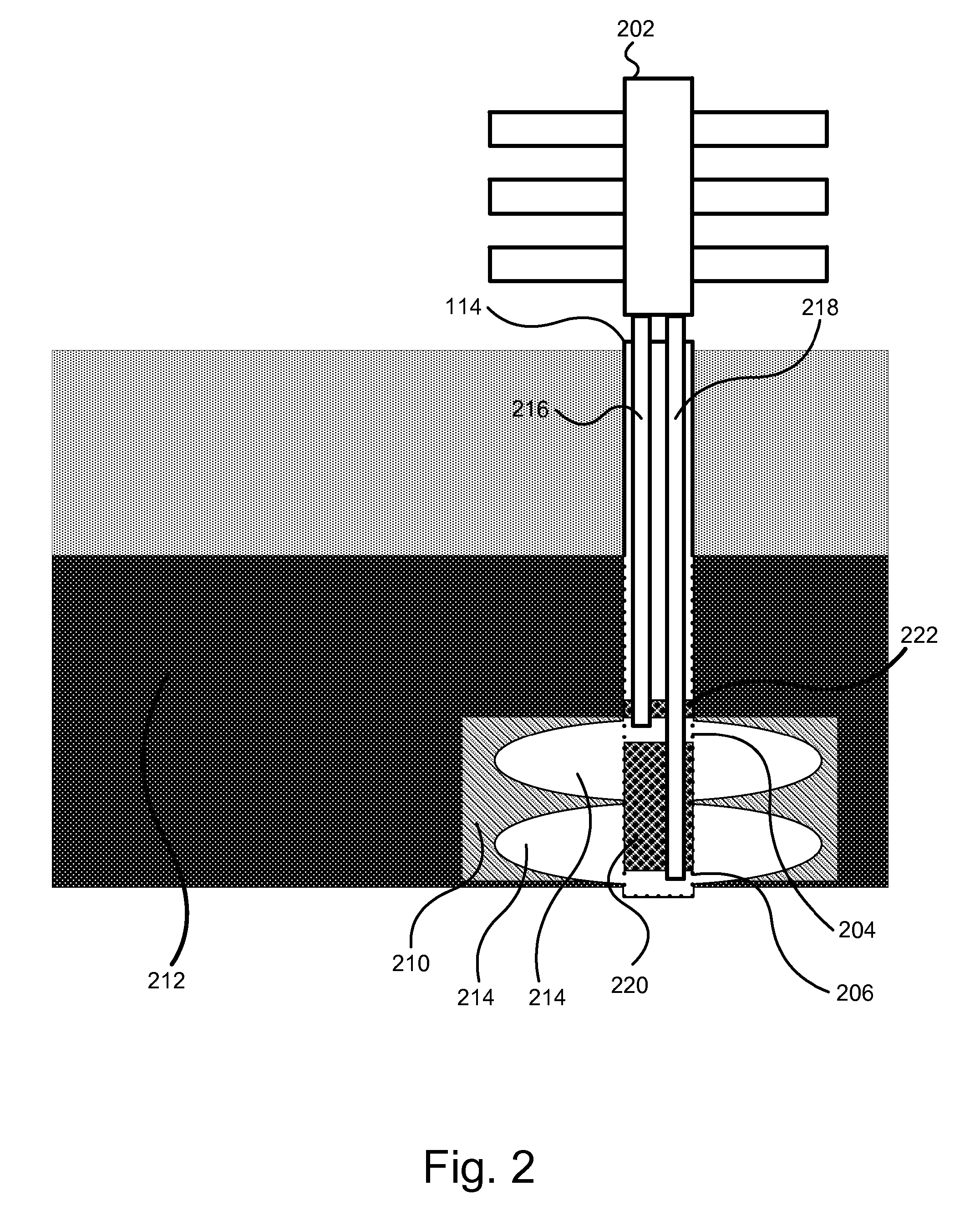
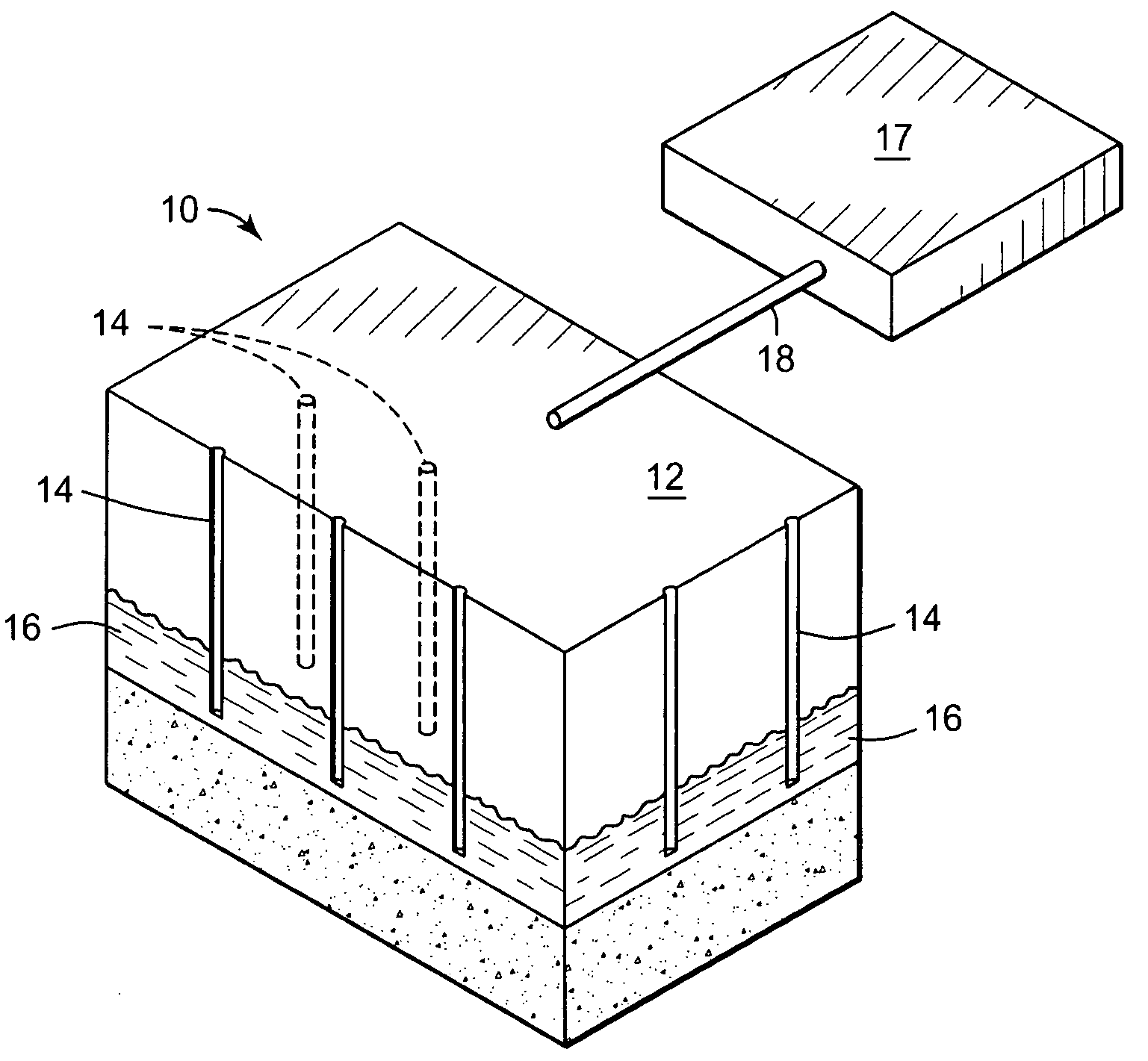
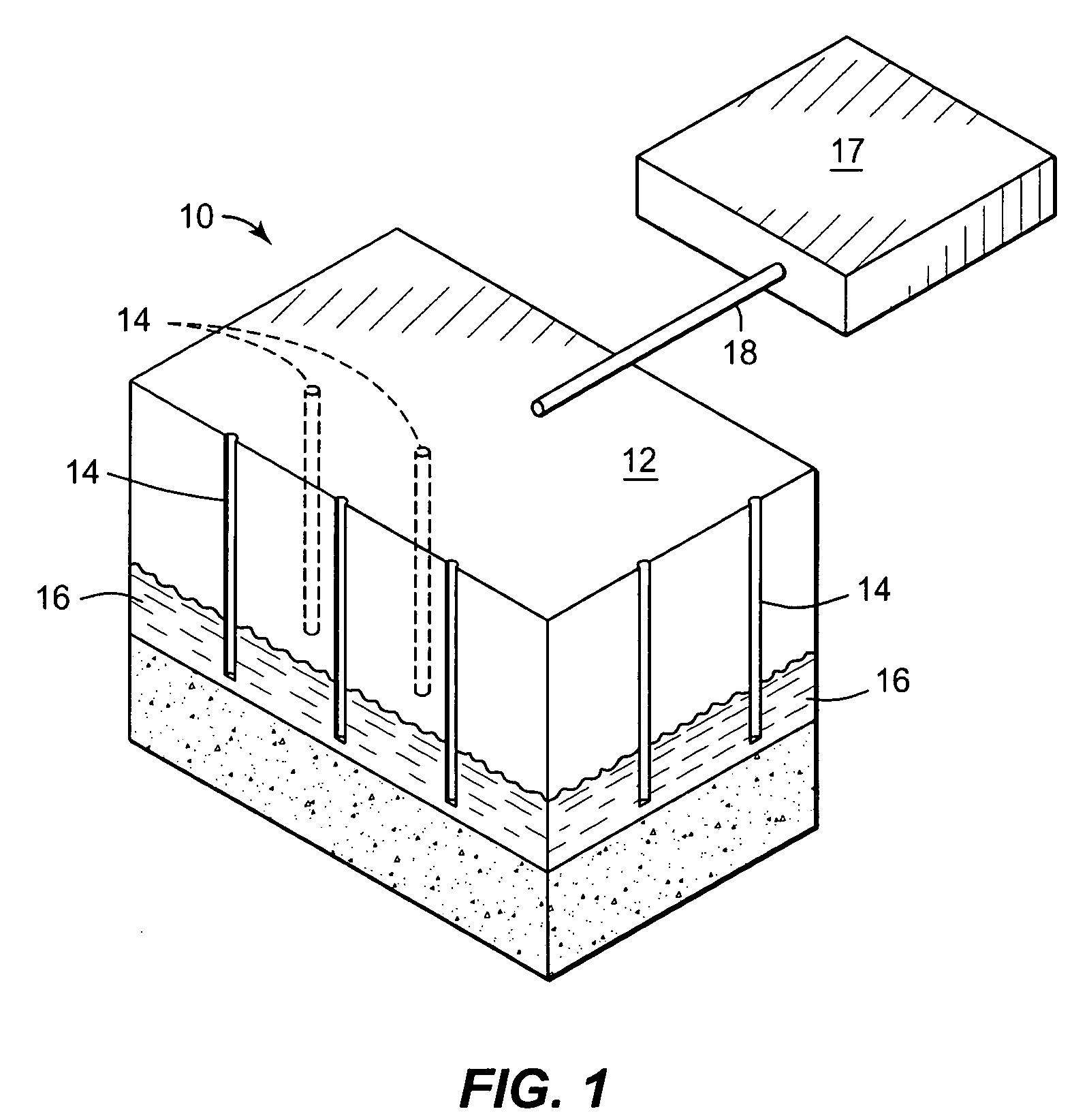
Apparatus, system, and method for in-situ extraction of oil from oil shale
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for in-situ extraction of oil from oil shale. The method comprises drilling a fluid conduit in fluid communication with a top and a bottom of a target zone within an oil shale formation. The method includes stimulating the target zone. The method further includes injecting a heated fluid into the bottom of the target zone such that the heated fluid entrains the kerogen within the target zone into the injected fluid to generate a production fluid. The method concludes with producing the production fluid, containing the in-situ kerogen, from the top of the target zone to the surface.
Owner:MOUNTAIN WEST ENERGY
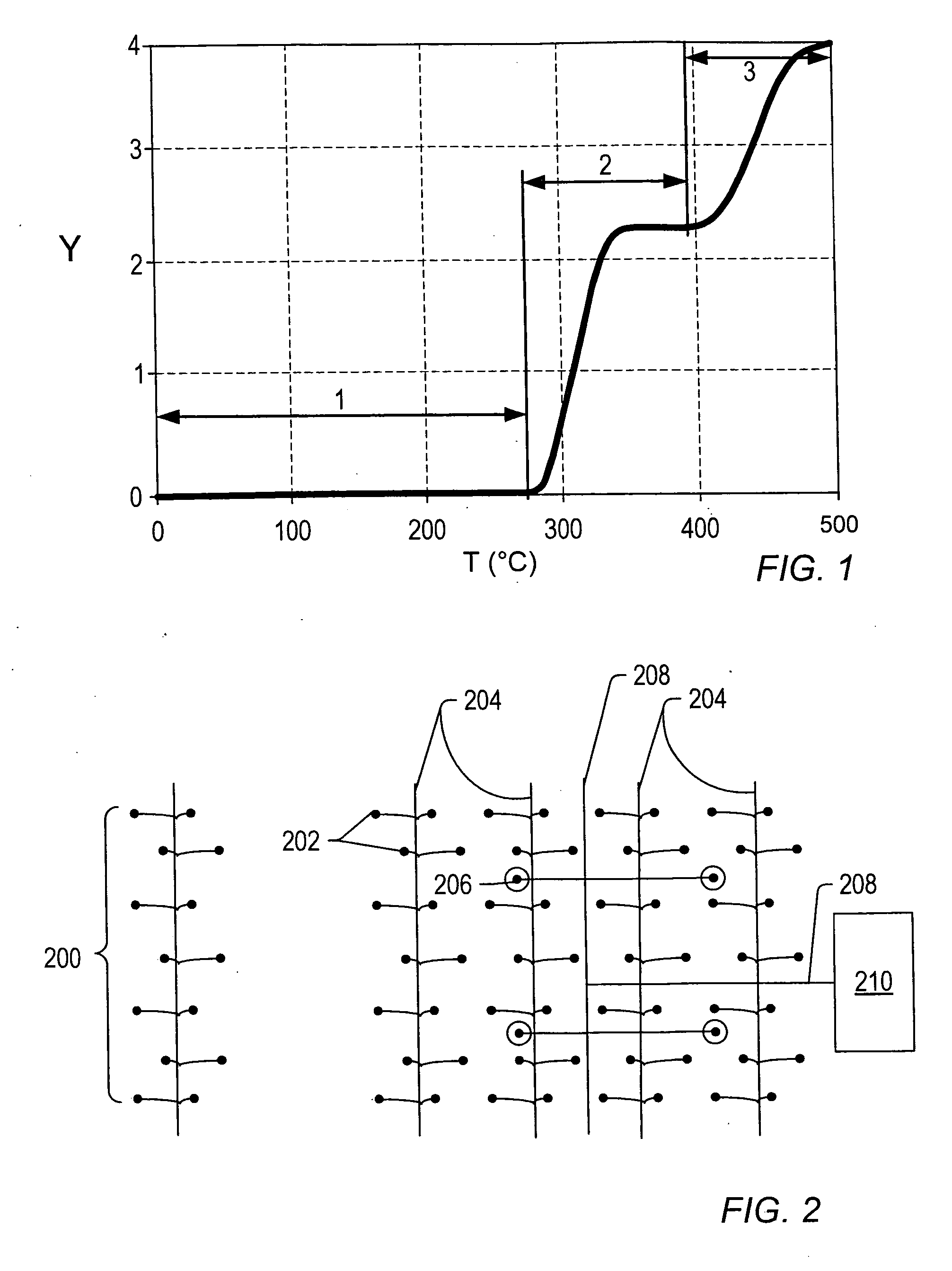
Testing Apparatus For Applying A Stress To A Test Sample
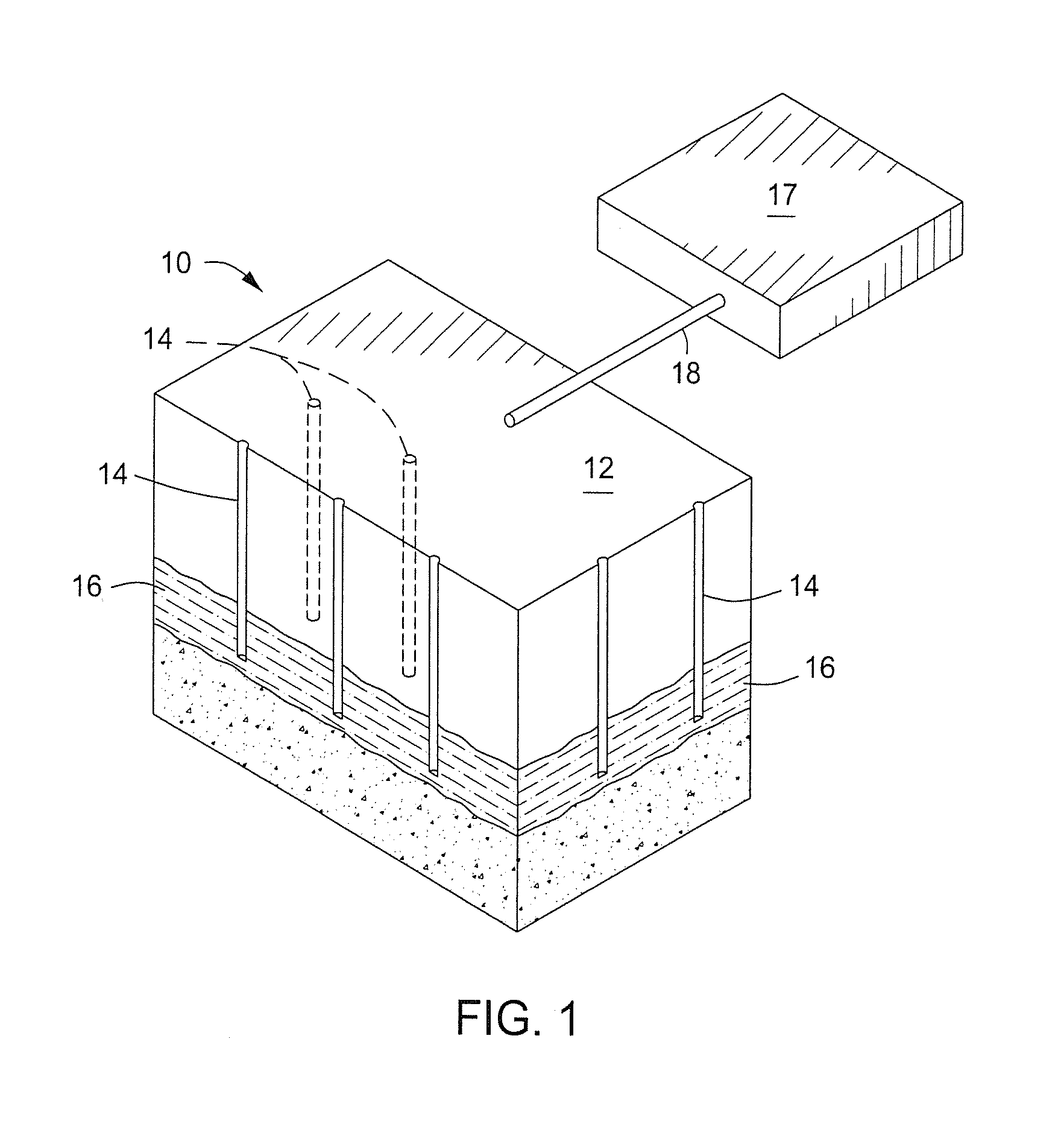
A testing apparatus which is suitable for applying a stress load to a test specimen is provided. The testing apparatus may be used to simulate lithostatic stress on a test specimen, which may be, for example, a portion of a geologic formation. The testing apparatus may also be used in a method of evaluating the expected production of fluids obtainable from in situ pyrolysis of oil shale.
Owner:SYMINGTON WILLIAM A +2
In-situ method of producing oil shale and gas (methane) hydrates, on-shore and off-shore
A method is provided for in-situ production of oil shale and gas (methane) hydrates wherein a network of fractures is formed by injecting liquified gases into at least one substantially horizontally disposed fracturing borehole. Heat is thereafter applied to liquify the kerogen or to dissociate the gas (methane) hydrates so that oil shale oil and / or gases can be recovered from the fractured formations.
Owner:MAGUIRE JAMES Q
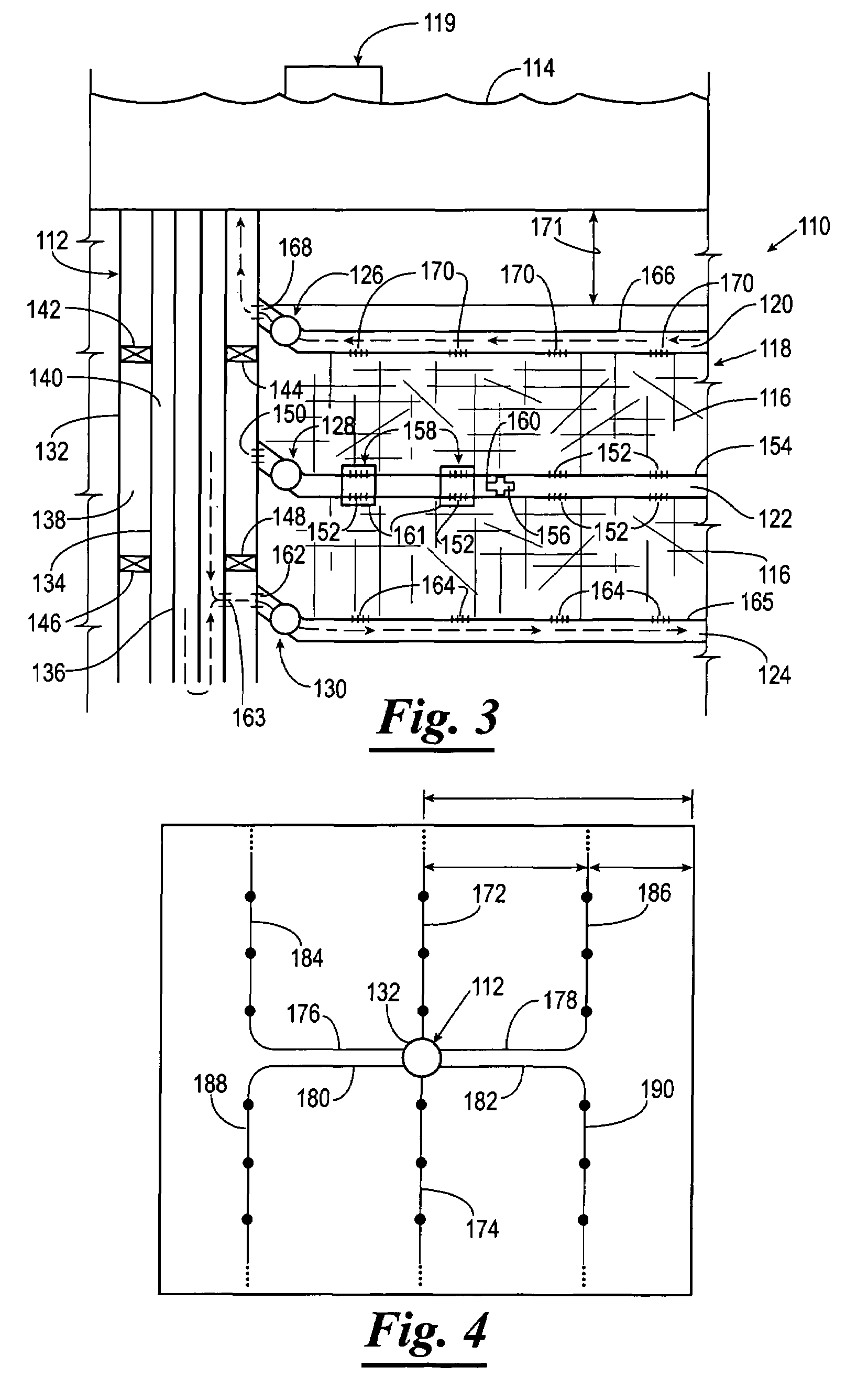
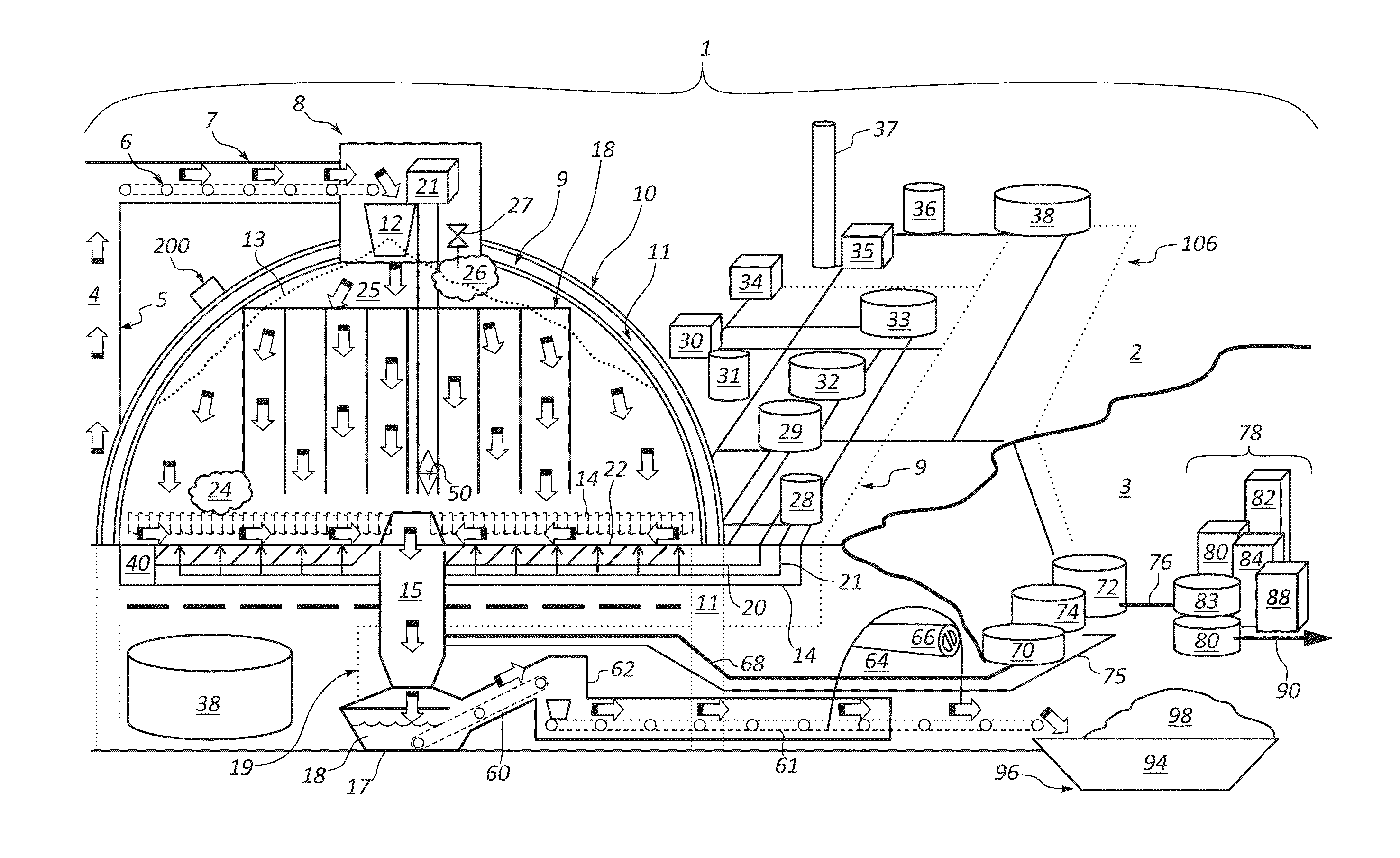
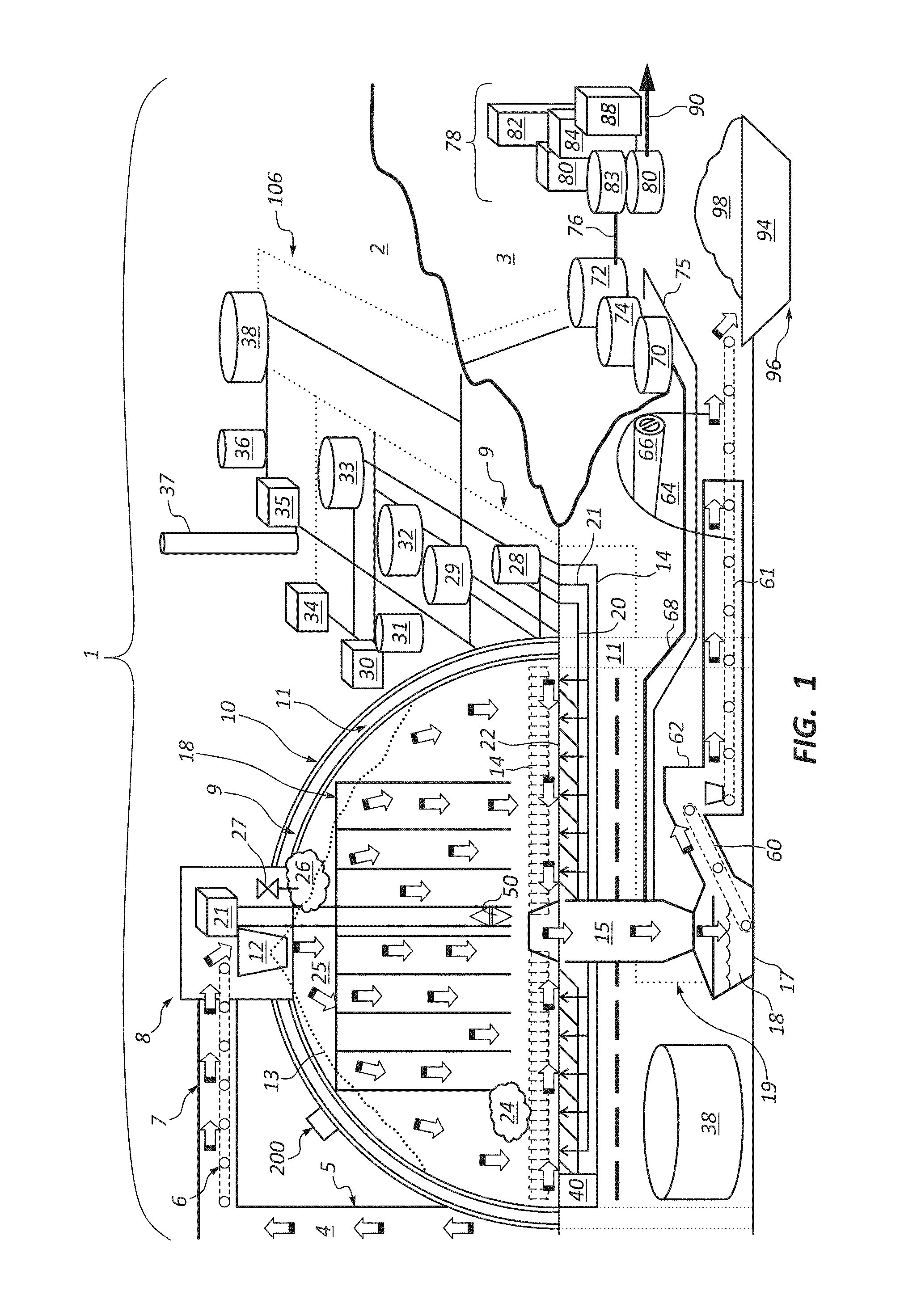
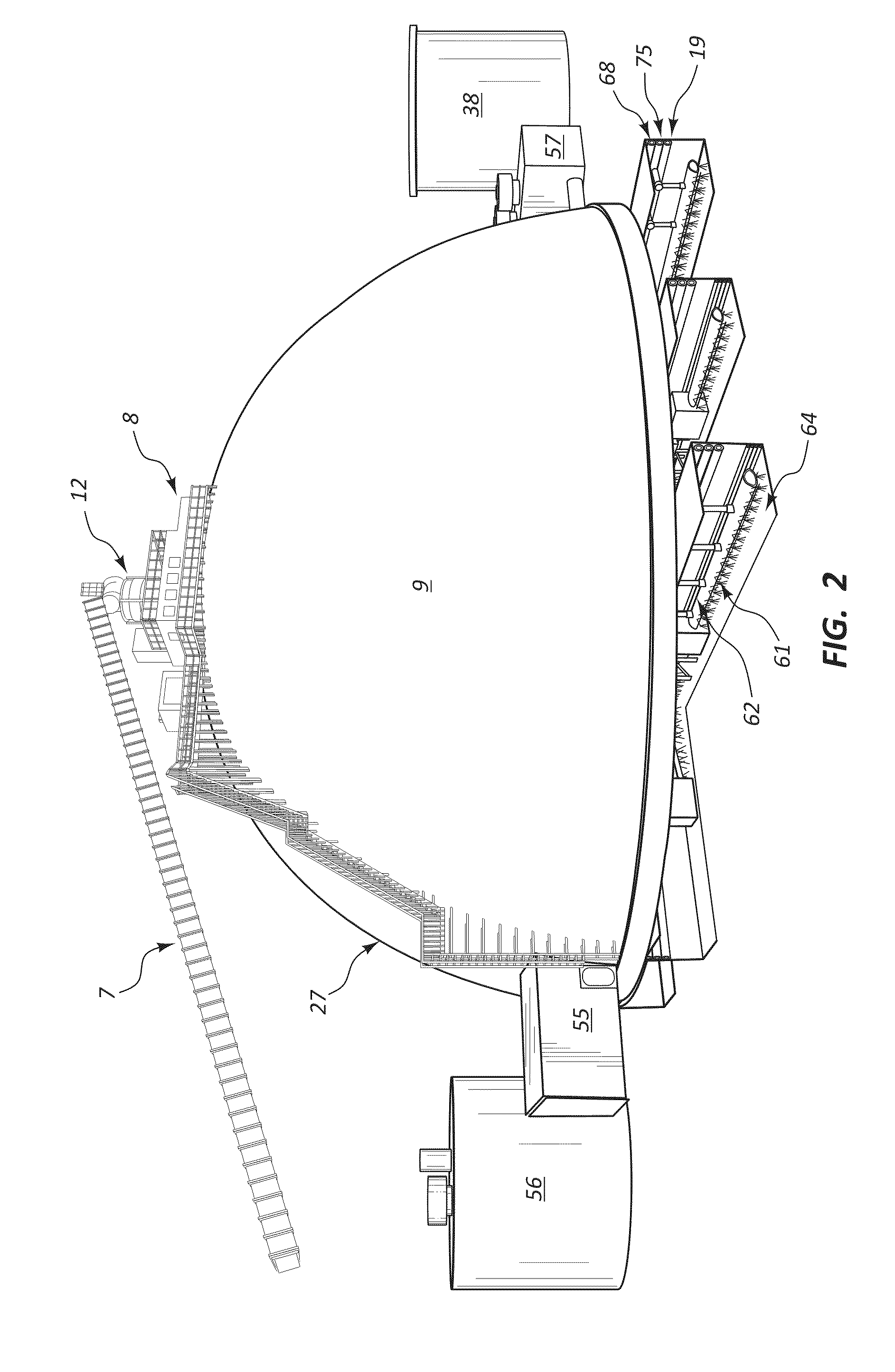
Systems, Apparatus and Methods of a Dome Retort
InactiveUS20110313218A1Increased material throughputLower cost of capitalPressurized chemical processDirect heating destructive distillationBasementControl system
A system, apparatus and method for hydrocarbon extraction from feedstock material that is or includes organic material, such as oil shale, coal, lignite, tar sands, animal waste and biomass. A retort system including at least one retort vessel may include a monolithic dome structure surrounded by a process isolation barrier, the dome structure being sealingly engaged with the process isolation barrier. The dome structure and the process isolation barrier define a retort chamber, at least a portion of which may comprise a subterranean chamber. A lower end of the dome retort structure provides an exit for collected hydrocarbons and spent feedstock material. Systems may include a plurality of such dome retort structures. A control system may be used for controlling one or more operating parameters of a retorting process performed within such a dome retort structure for extraction and collection of hydrocarbons.
Owner:DANA TODD C
Generation of Hydrogen from Hydrocarbon Bearing Materials
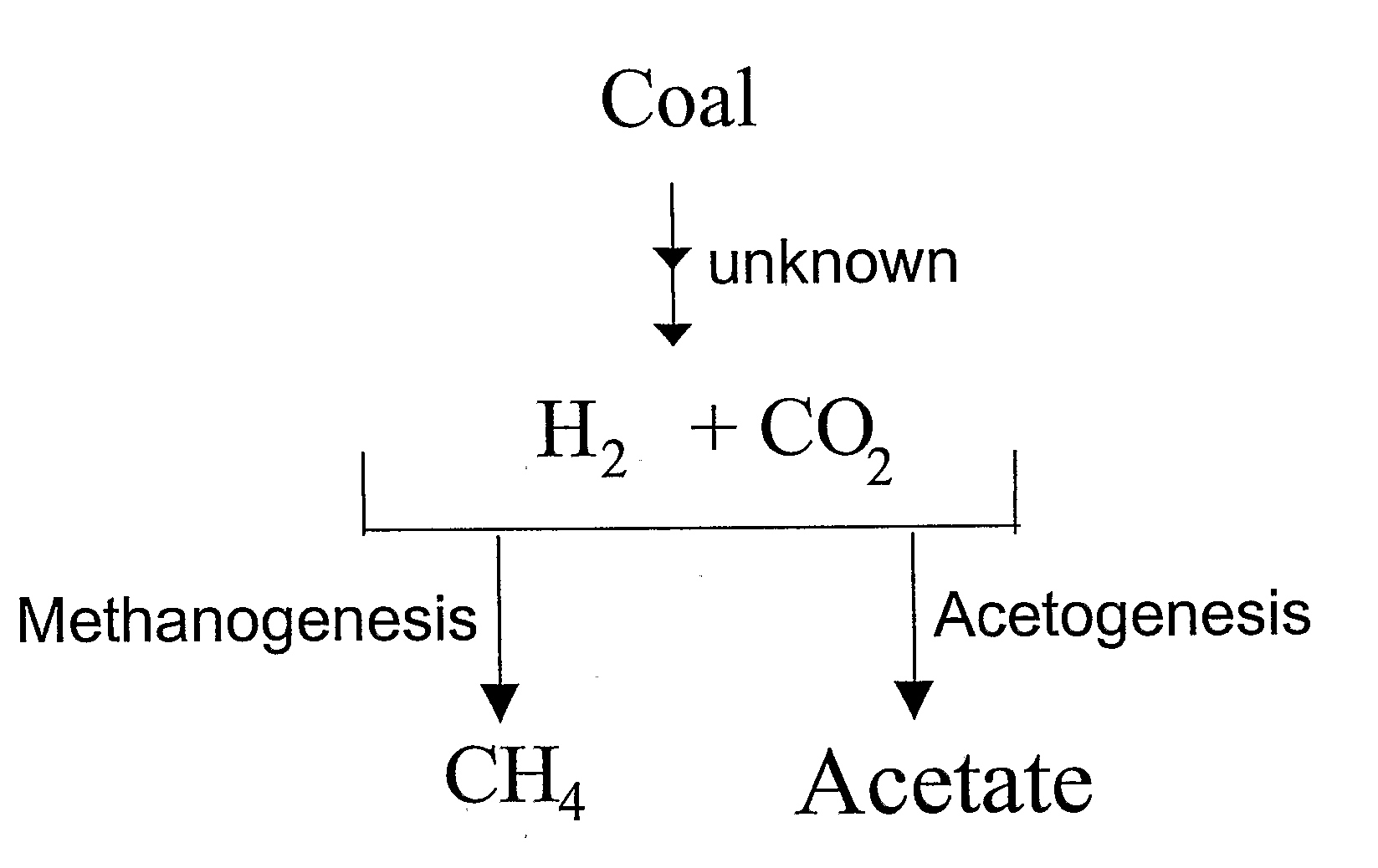
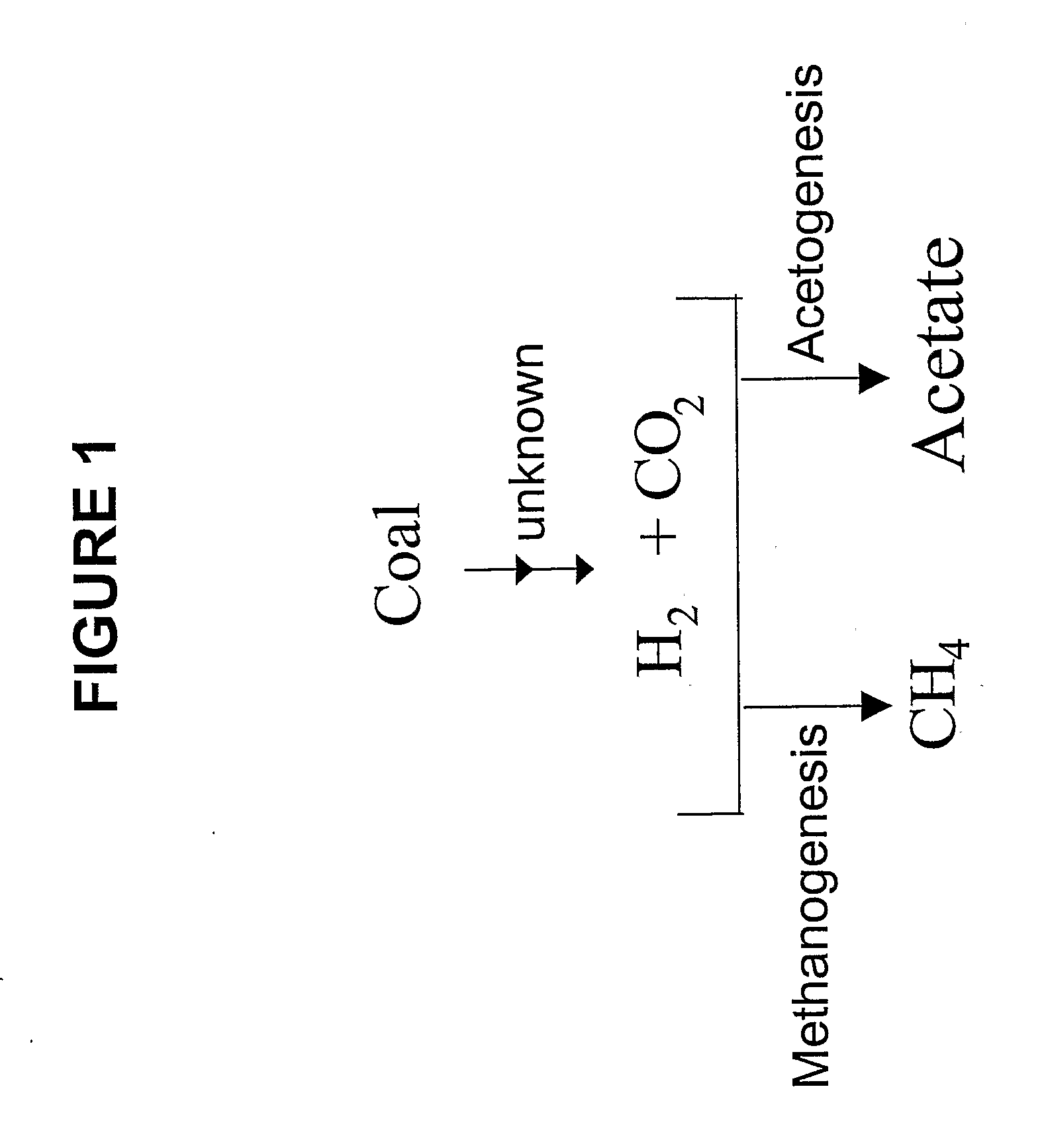
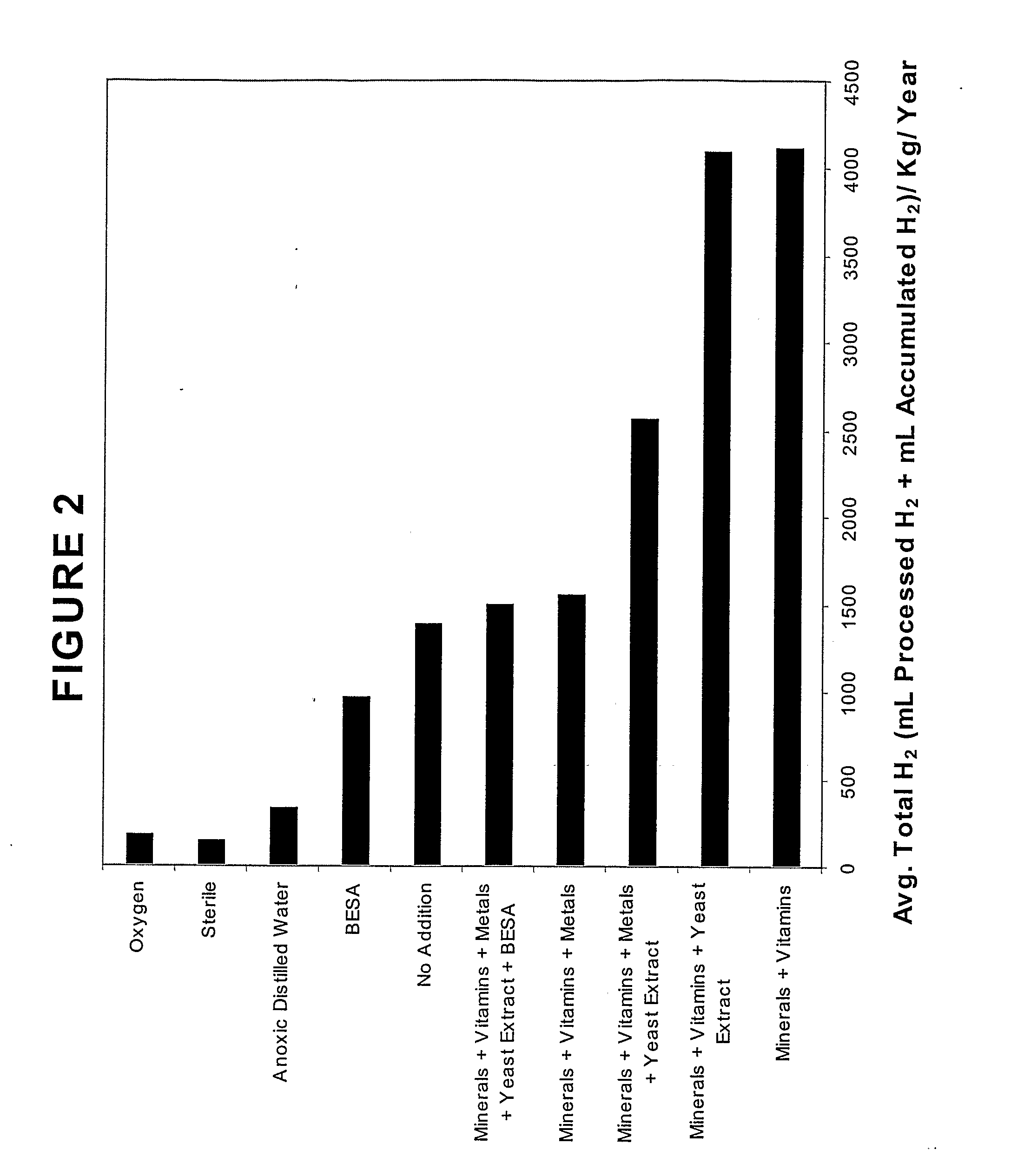
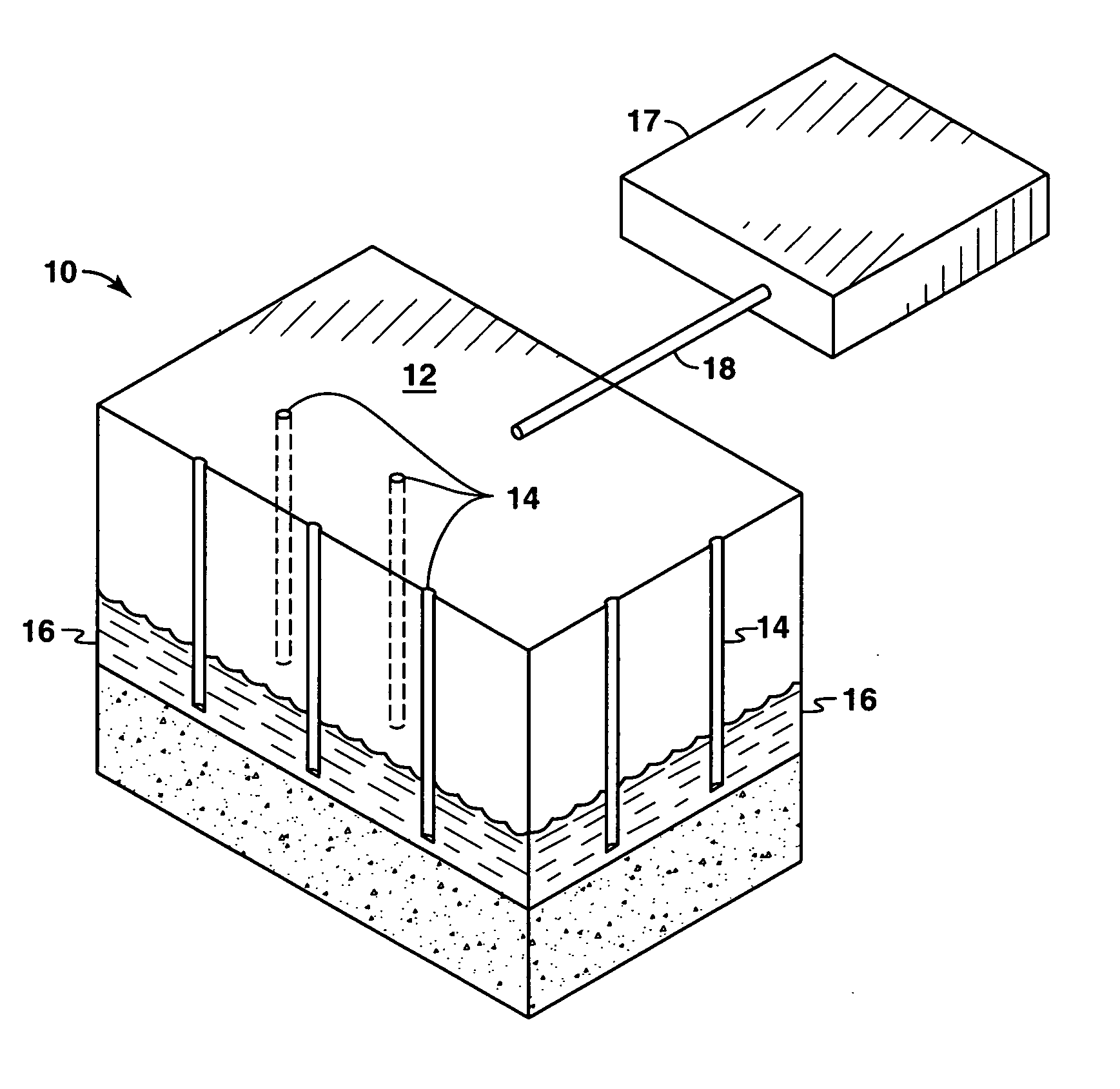
ActiveUS20070248531A1Enhanced methanogenesisIncreased hydrogen productionHydrogenWaste based fuelHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSand granules
Disclosed are strategies for the economical microbial generation of hydrogen, useful as an alternative energy source, from hydrocarbon-rich deposits such as coal, oil and / or gas formations, oil shale, bitumen, tar sands, carbonaceous shale, peat deposits and sediments rich in organic matter through the management of the metabolism of microbial consortia.
Owner:TRANSWORLD TECH
Utilization of low BTU gas generated during in situ heating of organic-rich rock
A method for utilizing gas produced from an in situ conversion process is provided. The method may include heating an organic-rich rock formation, for example an oil shale formation, in situ. The method may further include producing a production fluid from the organic-rich rock formation where the production fluid having been at least partially generated as a result of pyrolysis of formation hydrocarbons, for example oil shale, located in the organic-rich rock formation. The method may include obtaining a gas stream from the production fluid, where the gas stream comprises combustible hydrocarbon fluids. The method may include separating the gas stream into a first composition gas stream and a second composition gas stream, where the composition of the first composition gas stream is a low BTU gas stream maintained in a substantially constant condition and passing the first composition gas stream through a first gas turbine to form a first gas turbine exhaust stream, where the first gas turbine being configured to provide energy to a first electrical generator.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method of developing a subsurface freeze zone using formation fractures
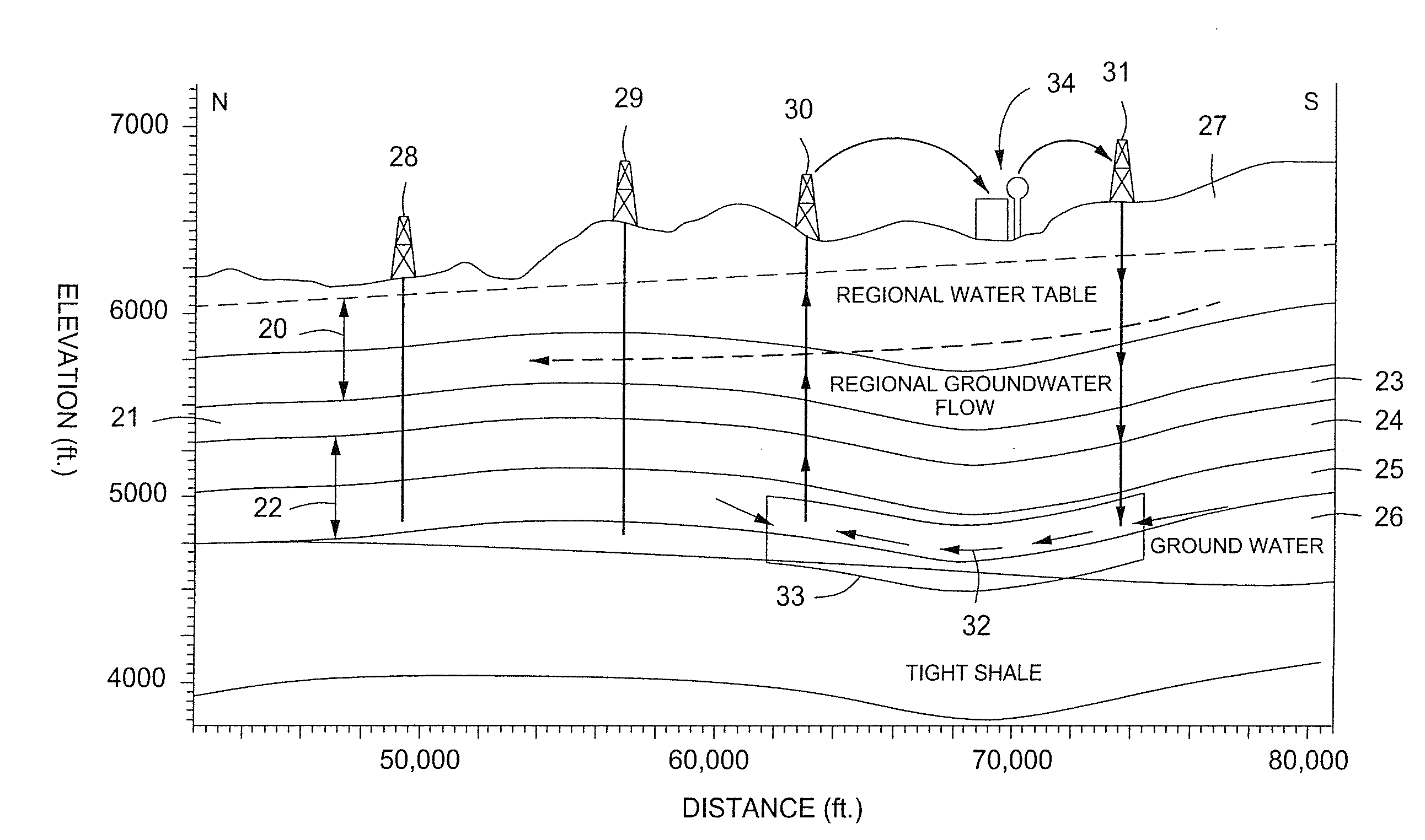
InactiveUS7516787B2Improve cooling efficiencyReduce the amount requiredSurveyInsulationCooling fluidWellbore
A method for lowering the temperature of a portion of a subsurface formation is provided. Preferably, the formation is an oil shale formation. The method includes the step of injecting a cooling fluid under pressure into a wellbore, with the wellbore having been completed at or below a depth of the subsurface formation. The wellbore has an elongated tubular member for receiving the cooling fluid and for conveying it downhole to the subsurface formation. The wellbore also has an expansion valve in fluid communication with the tubular member through which the cooling fluid flows. The method then includes the steps of injecting a cooling fluid under pressure into the wellbore, and expanding the cooling fluid across the first expansion valve. In this way, the temperature of the cooling fluid is reduced. The temperature of the surrounding formation is likewise reduced through thermal conduction and convection.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
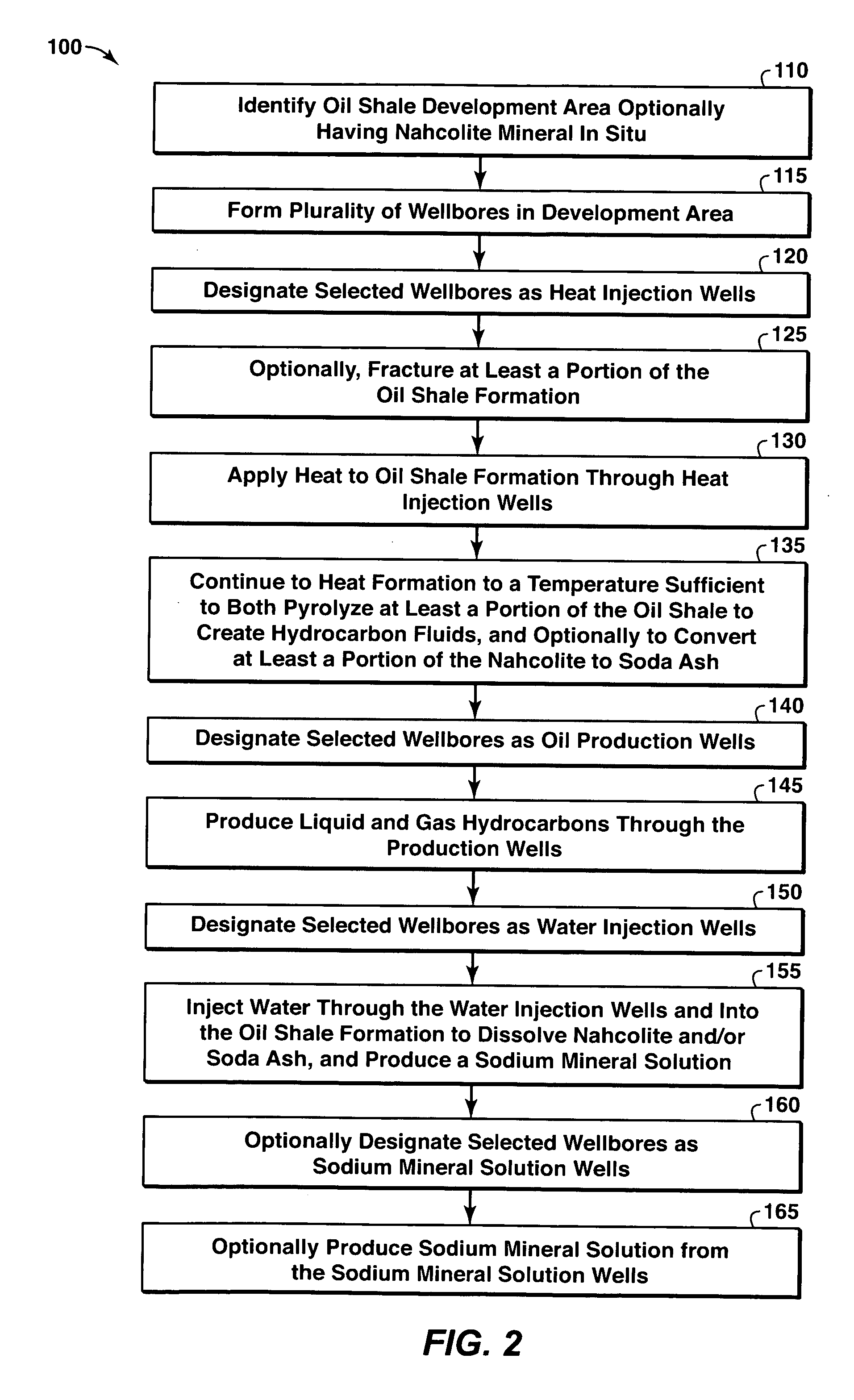
Heating an organic-rich rock formation in situ to produce products with improved properties
InactiveUS20080207970A1Carbon-dioxide storageLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionKerogenHydrocarbon
A method of producing hydrocarbon fluids with improved hydrocarbon compound properties from a subsurface organic-rich rock formation, such as an oil shale formation, is provided. The method may include the step of heating the organic-rich rock formation in situ. In accordance with the method, the heating of the organic-rich rock formation may pyrolyze at least a portion of the formation hydrocarbons, for example kerogen, to create hydrocarbon fluids. Thereafter, the hydrocarbon fluids may be produced from the formation. Hydrocarbon fluids with improved hydrocarbon compound properties are also provided.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
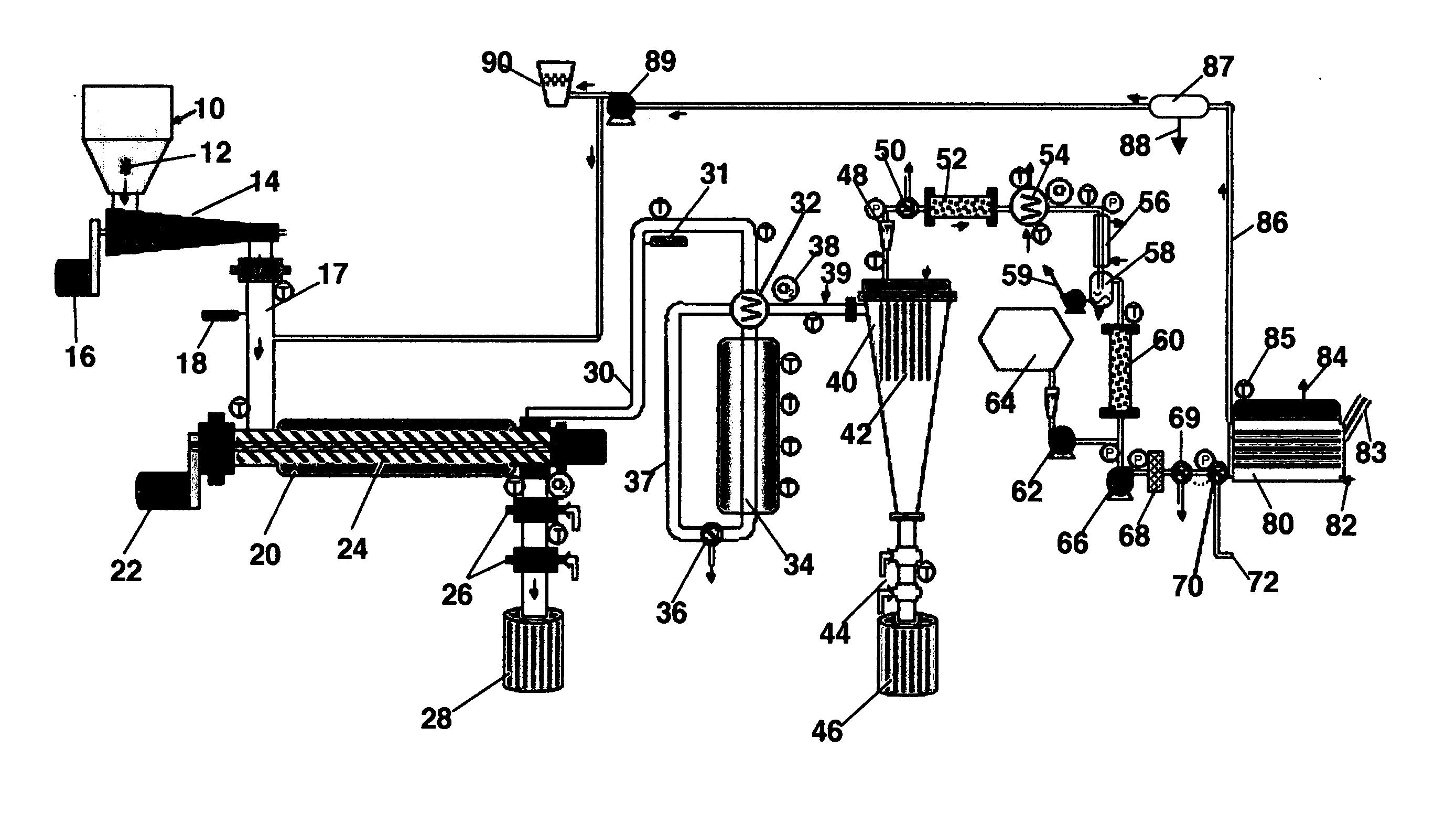
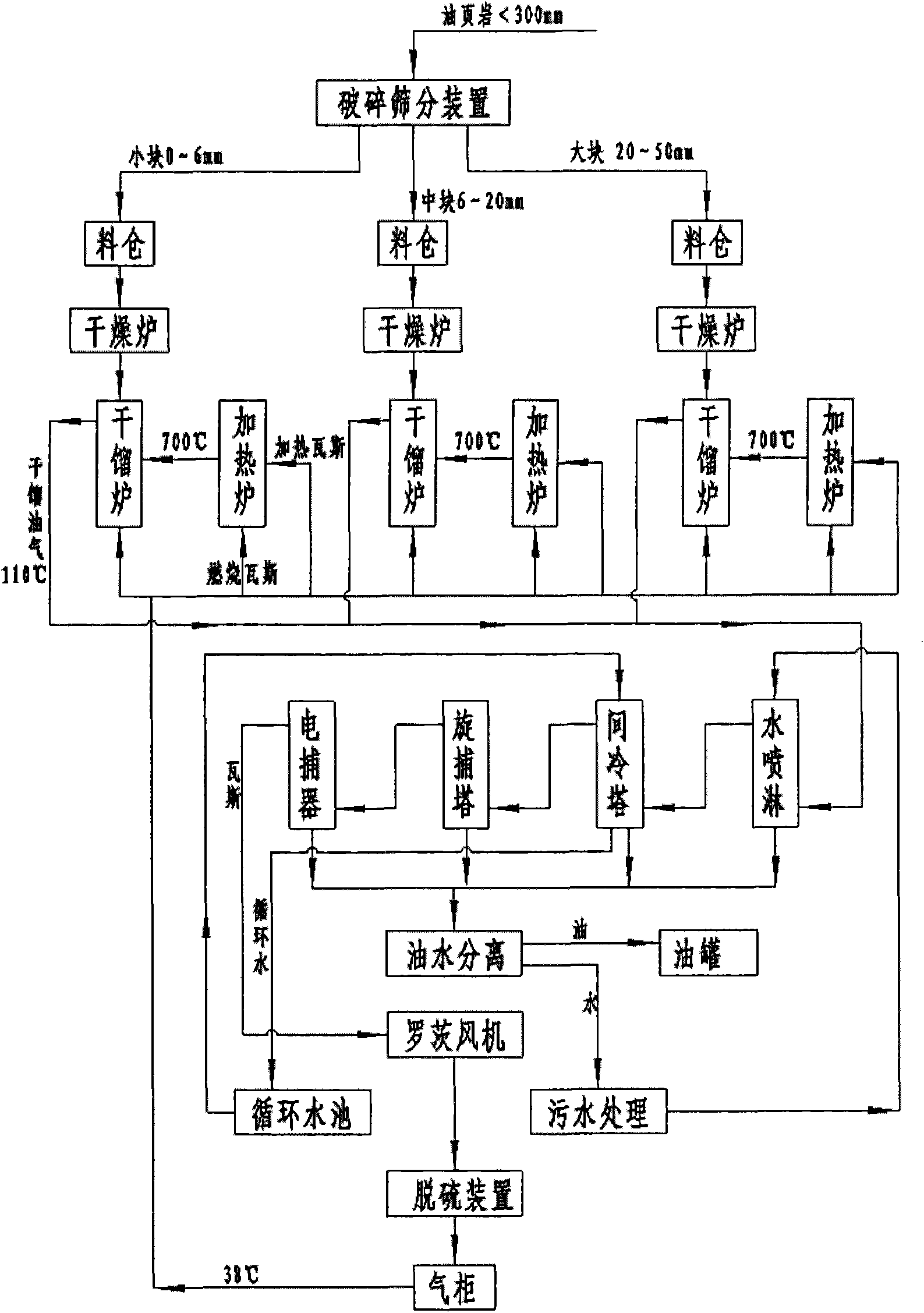
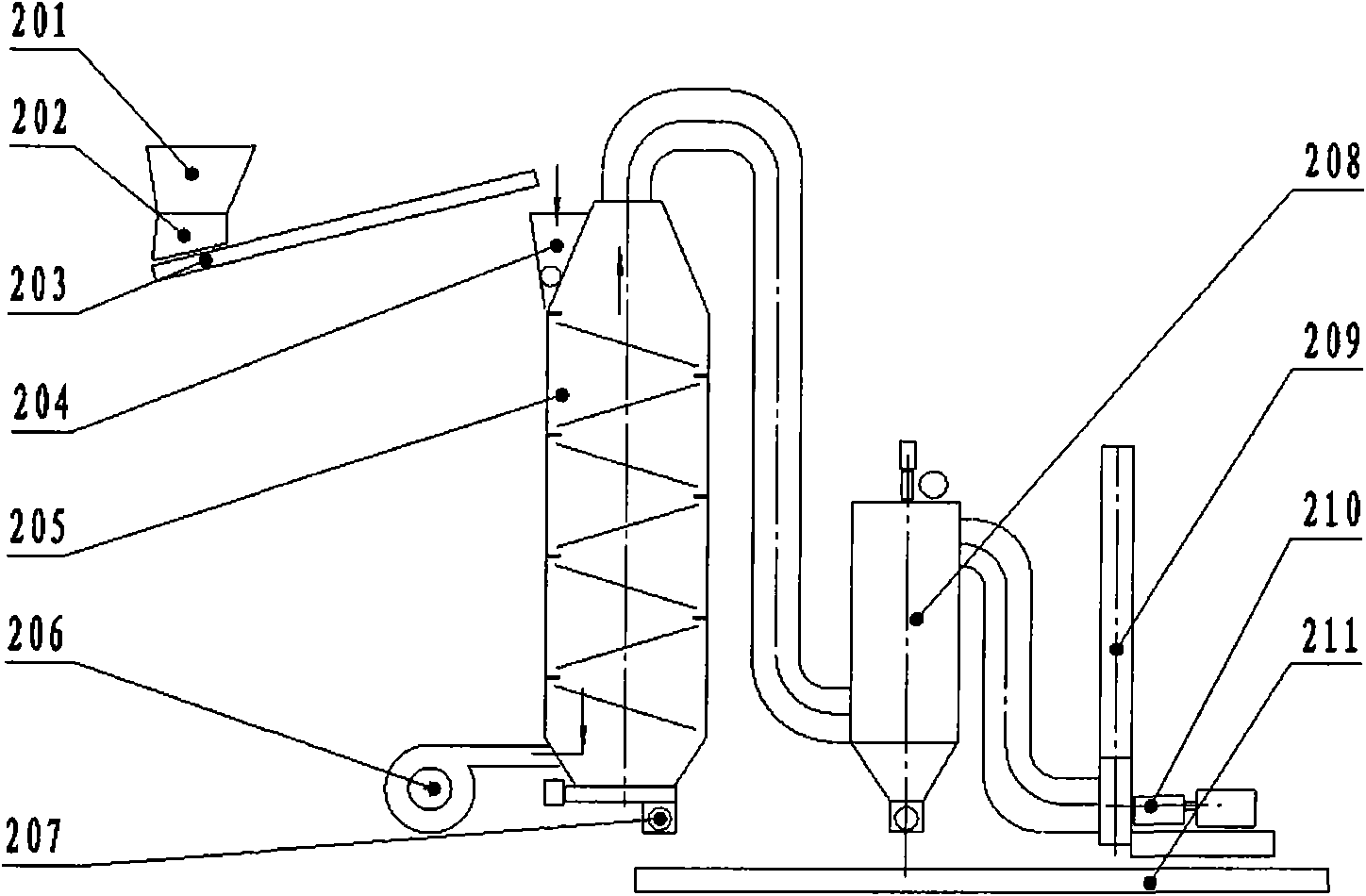
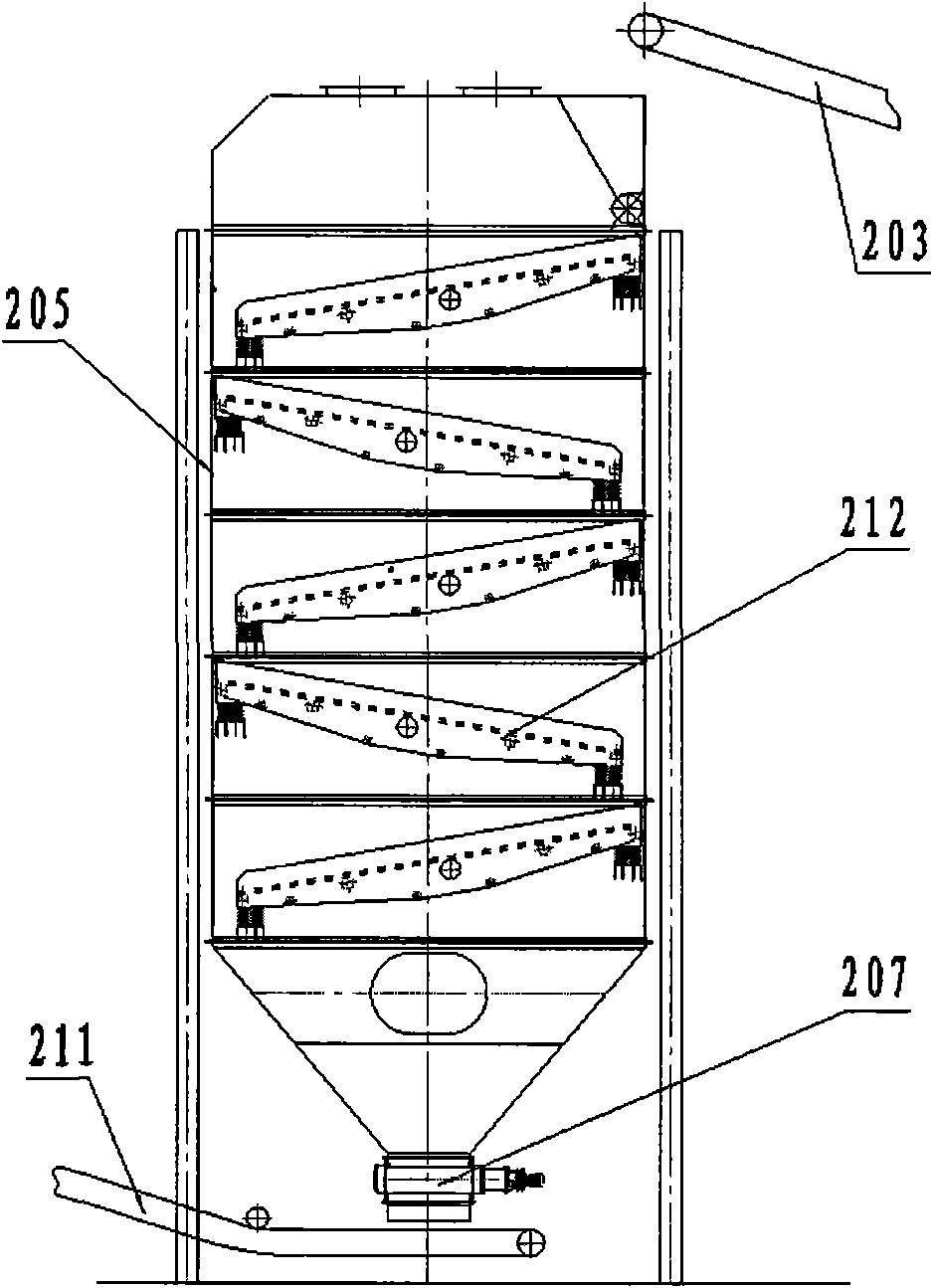
Huadian type process and device for dry distillation of oil shale
ActiveCN101942313AGuaranteed to be heatedGuaranteed temperature requirementsDirect heating destructive distillationCombustible gas purificationHeat carrierCooling tower
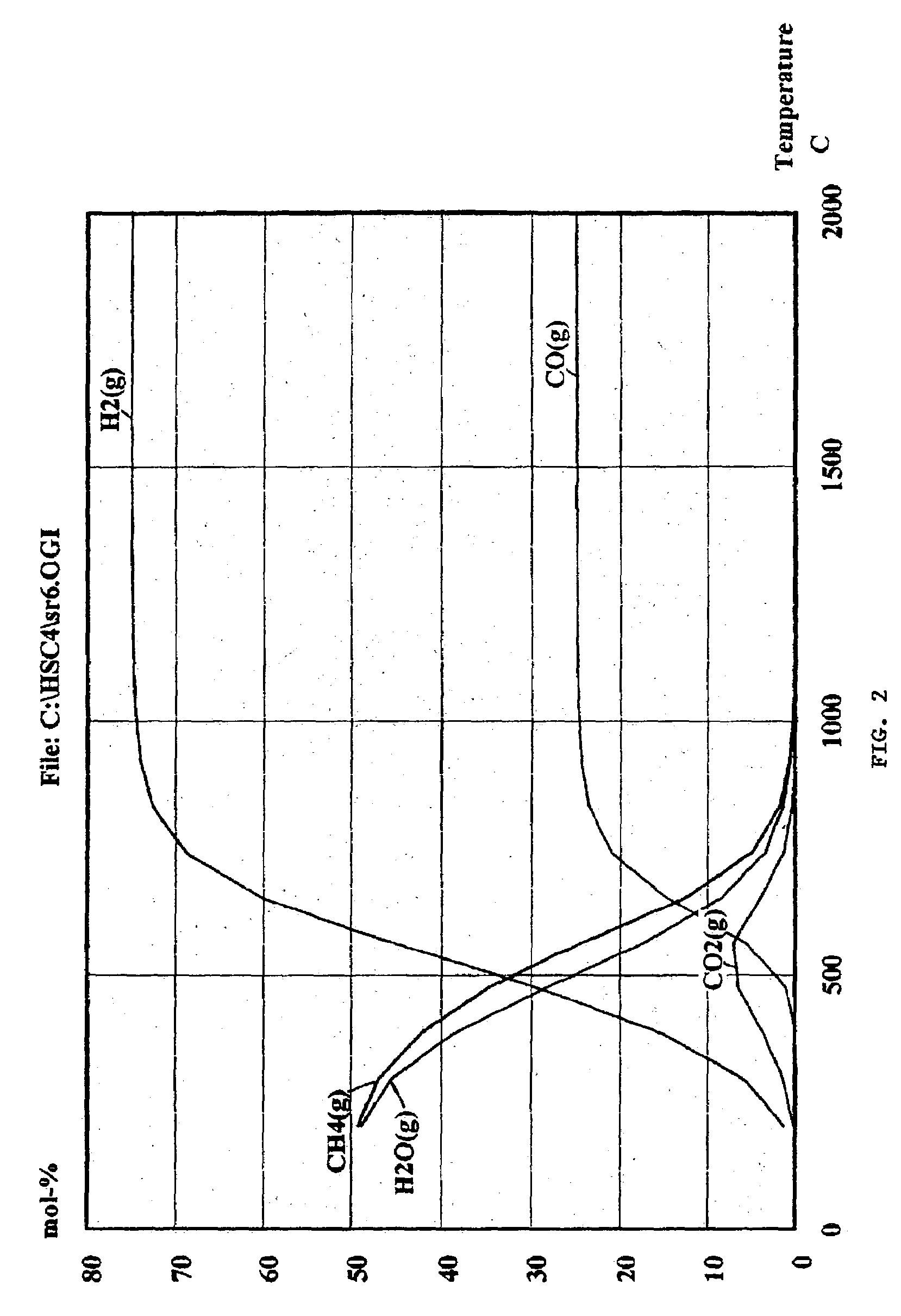
The invention provides a process and device for carrying out stage dry distillation on oil shale under the state of full recycle, with the gas as the heat carrier. The oil shale is divided into three different sizes (such as 0-6mm, 6-20mm and 20-50mm) through crushing and screening, and the oil shale is firstly dried and heated to the temperature between 50 DEG C and 150 DEG C by the waste smoke exhausted from gas heating furnaces and then enters into the different sizes of furnaces for dry distillation to undergo dry distillation. After being treated by water spraying and an indirect cooling tower, a rotary trapper and an electric trapper for oil collection, the dry distillation oil and gas undergo oil-gas-water separation, and after separation, the oil enters into a storage tank, the water enters into a circulating water tank and the first part of gases serves as the heat carrier and is recycled, the second part of gases is used as the fuels for the heating furnaces and the third part of gases is used as the fuel gases for power generation.
Owner:辽宁成大能源科技有限公司
Method of developing a subsurface freeze zone using formation fractures
InactiveUS20080087426A1Improve cooling efficiencyReduction of cooling lossSurveyInsulationCooling fluidConvection
A method for lowering the temperature of a portion of a subsurface formation is provided. Preferably, the formation is an oil shale formation. The method includes the step of injecting a cooling fluid under pressure into a wellbore, with the wellbore having been completed at or below a depth of the subsurface formation. The wellbore has an elongated tubular member for receiving the cooling fluid and for conveying it downhole to the subsurface formation. The wellbore also has an expansion valve in fluid communication with the tubular member through which the cooling fluid flows. The method then includes the steps of injecting a cooling fluid under pressure into the wellbore, and expanding the cooling fluid across the first expansion valve. In this way, the temperature of the cooling fluid is reduced. The temperature of the surrounding formation is likewise reduced through thermal conduction and convection.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
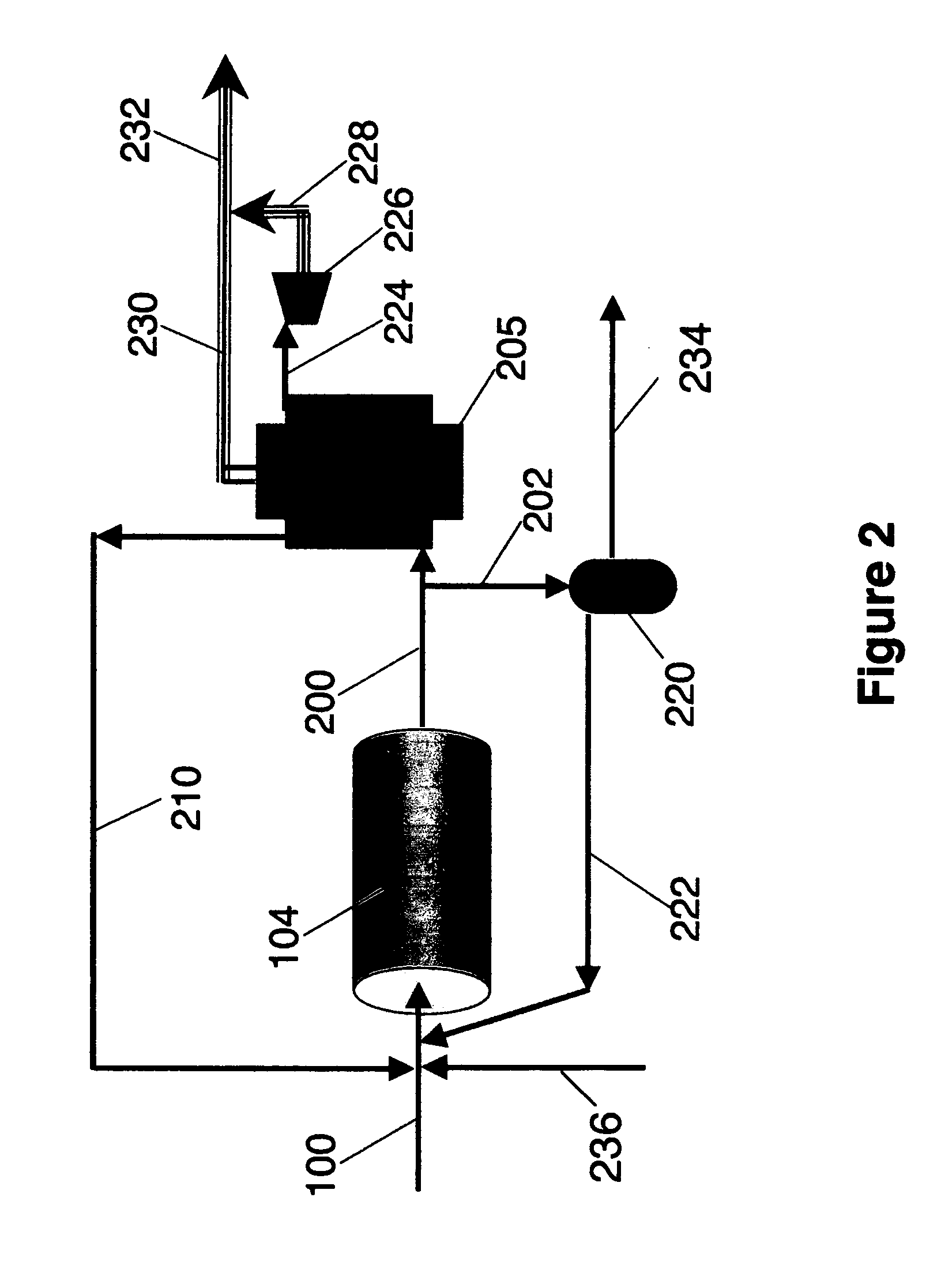
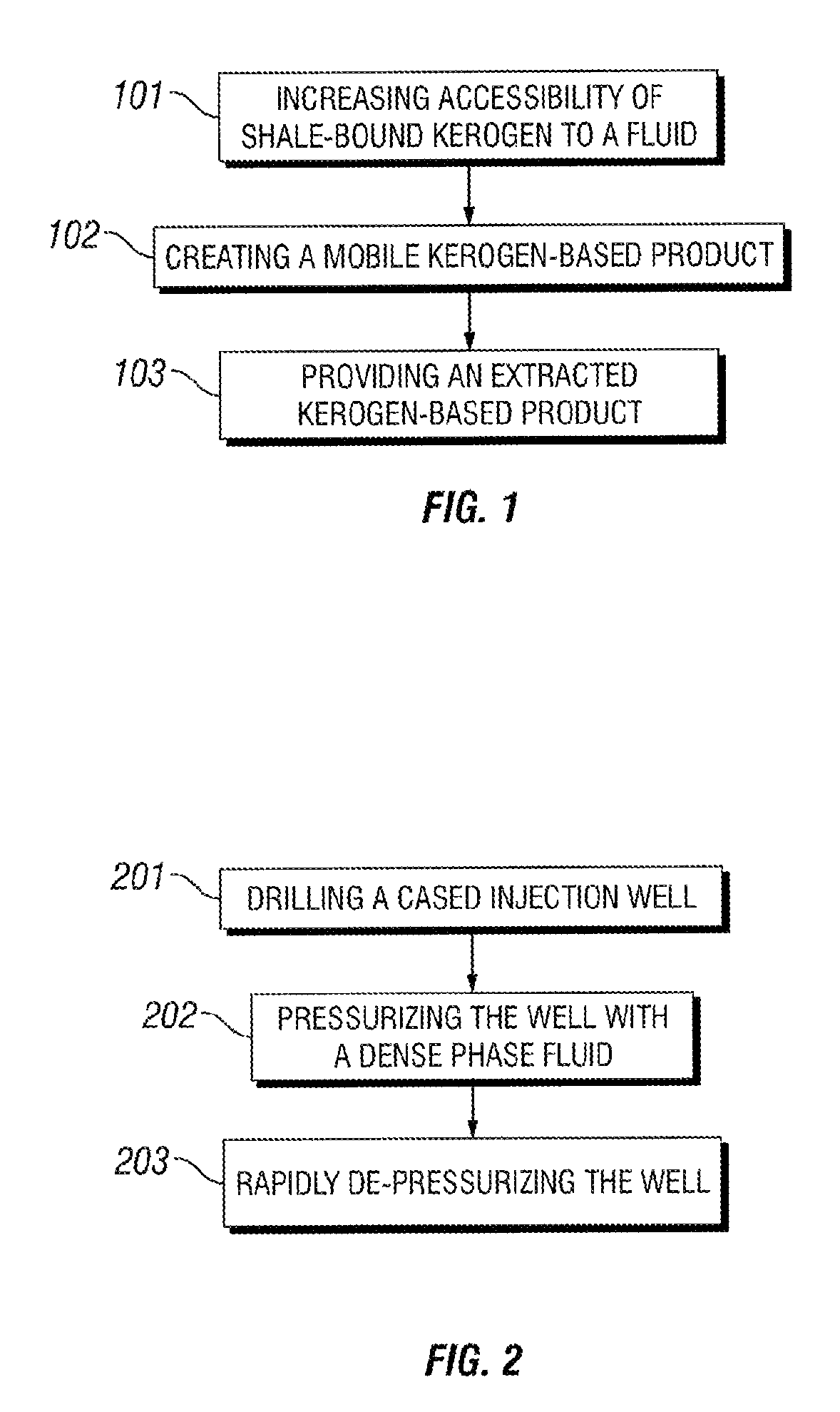
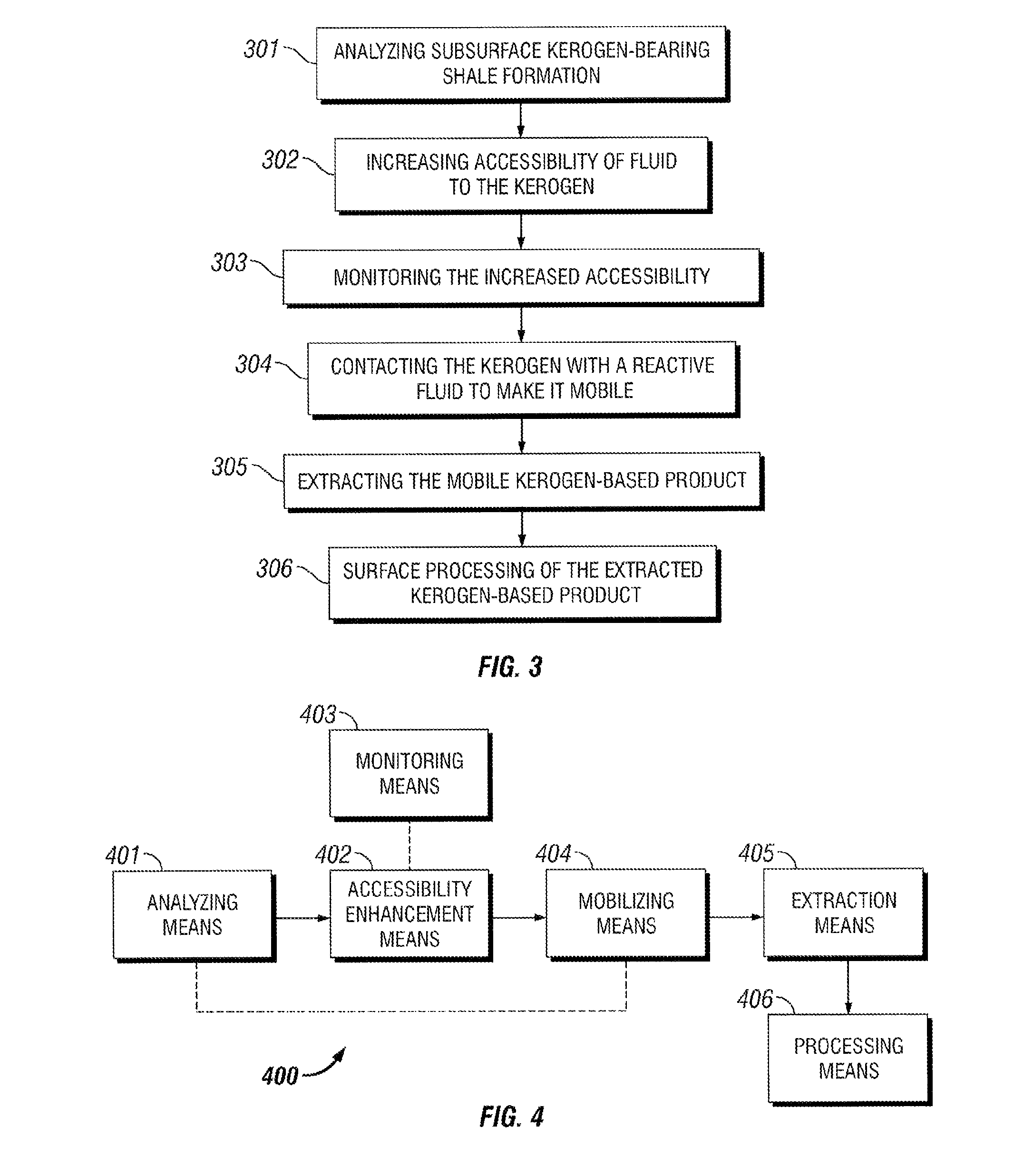
Kerogen extraction from subterranean oil shale resources
The present invention is directed to methods for extracting a kerogen-based product from subsurface (oil) shale formations, wherein such methods rely on fracturing and / or rubblizing portions of said formations so as to enhance their fluid permeability, and wherein such methods further rely on chemically modifying the shale-bound kerogen so as to render it mobile. The present invention is also directed at systems for implementing at least some of the foregoing methods. Additionally, the present invention is also directed to methods of fracturing and / or rubblizing subsurface shale formations and to methods of chemically modifying kerogen in situ so as to render it mobile.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC +1
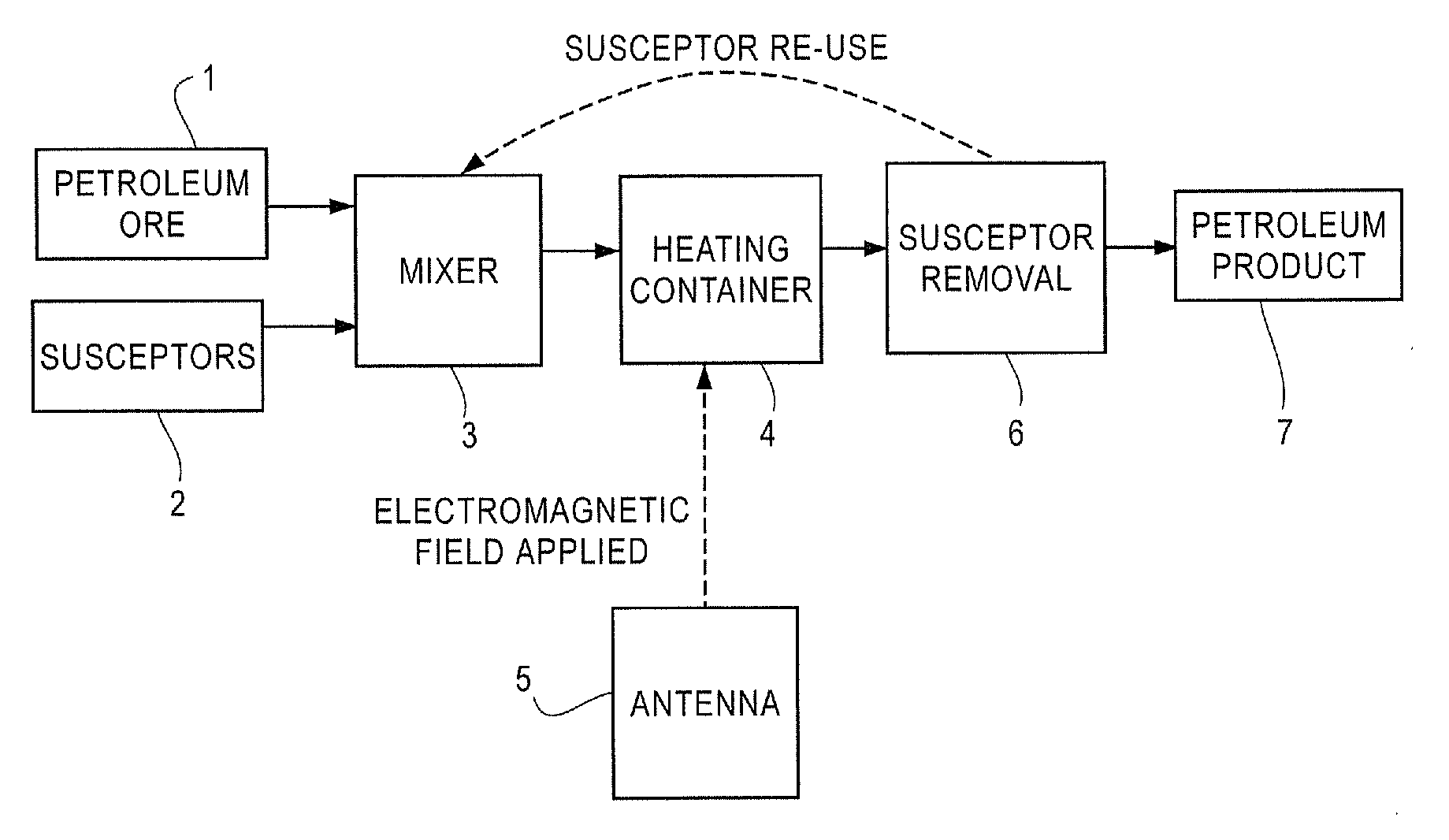
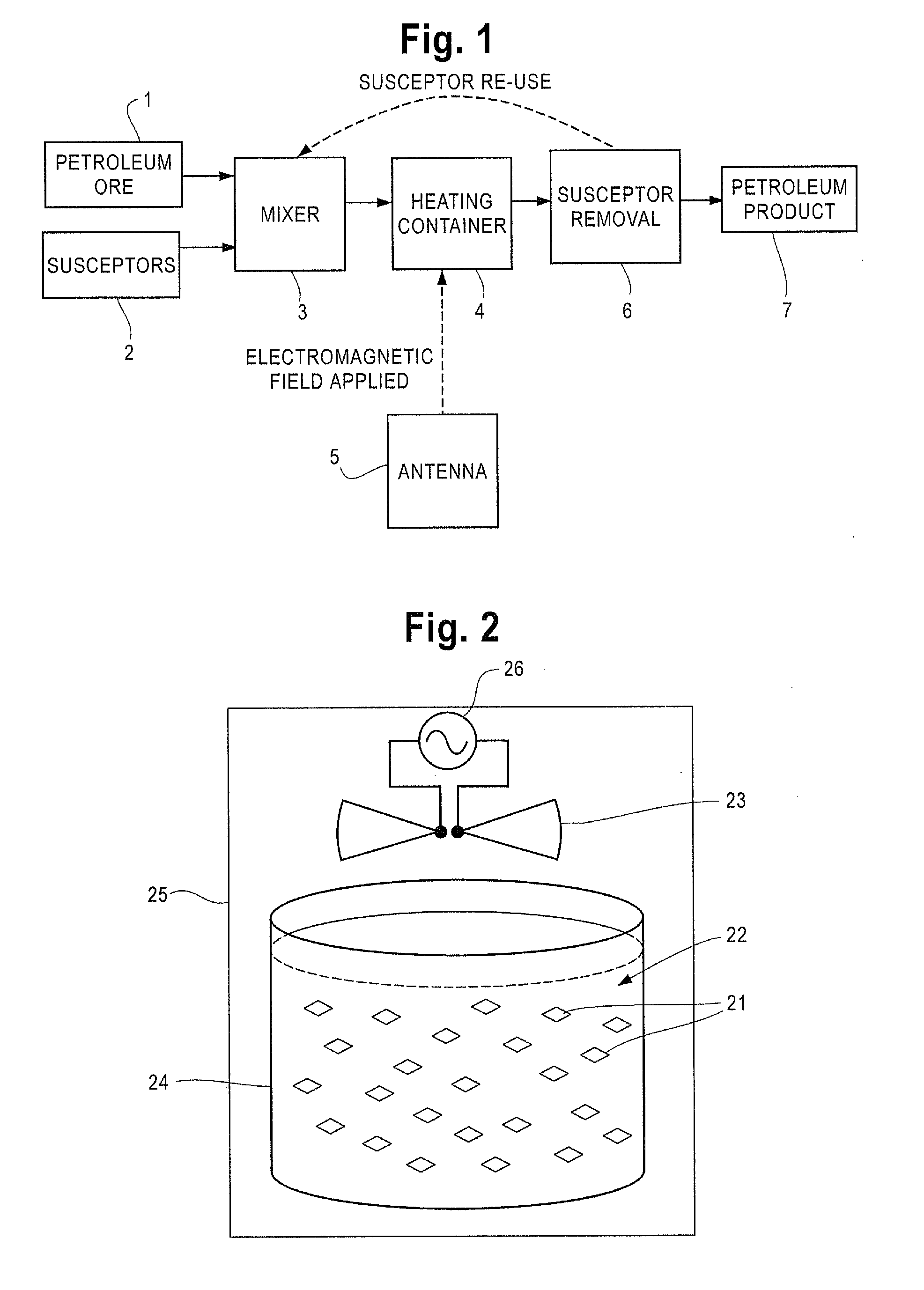
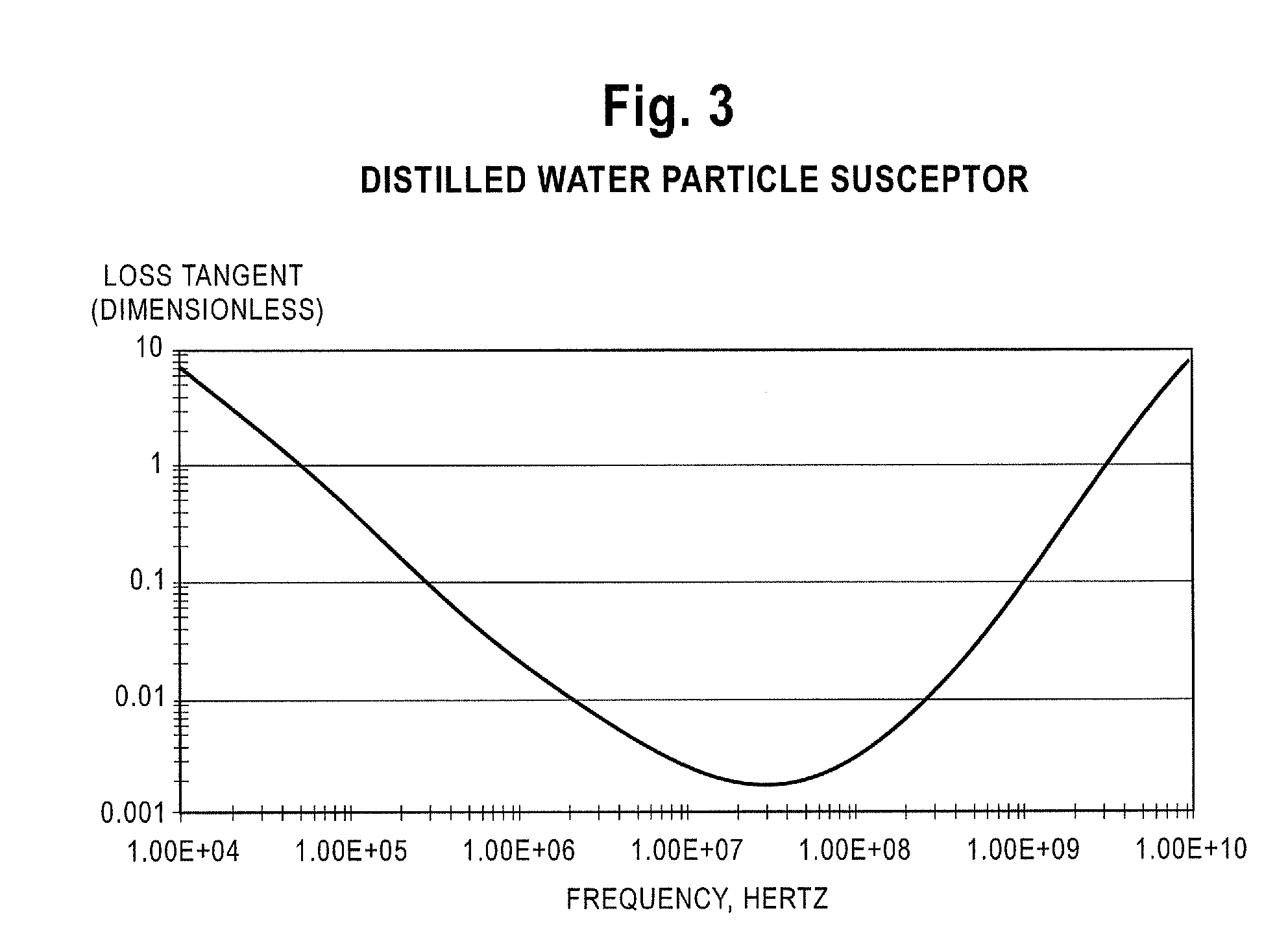
Radio frequency heating of petroleum ore by particle susceptors
ActiveUS20100219107A1Increase temperatureThermal non-catalytic crackingMagnetic paintsSusceptorDistillation
A method for heating materials by application of radio frequency (“RF”) energy is disclosed. For example, the disclosure concerns a method for RF heating of petroleum ore, such as bitumen, oil sands, oil shale, tar sands, or heavy oil. Petroleum ore is mixed with a substance comprising susceptor particles that absorb RF energy. A source is provided which applies RF energy to the mixture of a power and frequency sufficient to heat the susceptor particles. The RF energy is applied for a sufficient time to allow the susceptor particles to heat the mixture to an average temperature greater than about 212° F. (100° C.). Optionally, the susceptor particles can be removed from the mixture after the desired average temperature has been achieved. The susceptor particles may provide for anhydrous processing, and temperatures sufficient for cracking, distillation, or pyrolysis.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Method and system for extraction of hydrocarbons from oil shale
InactiveUS20070181301A1Improve permeabilityHigh porosityInsulationFluid removalOil shale gasEnergy source
A system and method for extracting hydrocarbon products from oil shale using nuclear energy sources for energy to fracture the oil shale formations and provide sufficient heat and pressure to produce liquid and gaseous hydrocarbon products. Embodiments of the present invention also disclose steps for extracting the hydrocarbon products from the oil shale formations.
Owner:ULTRA SAFE NUCLEAR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com