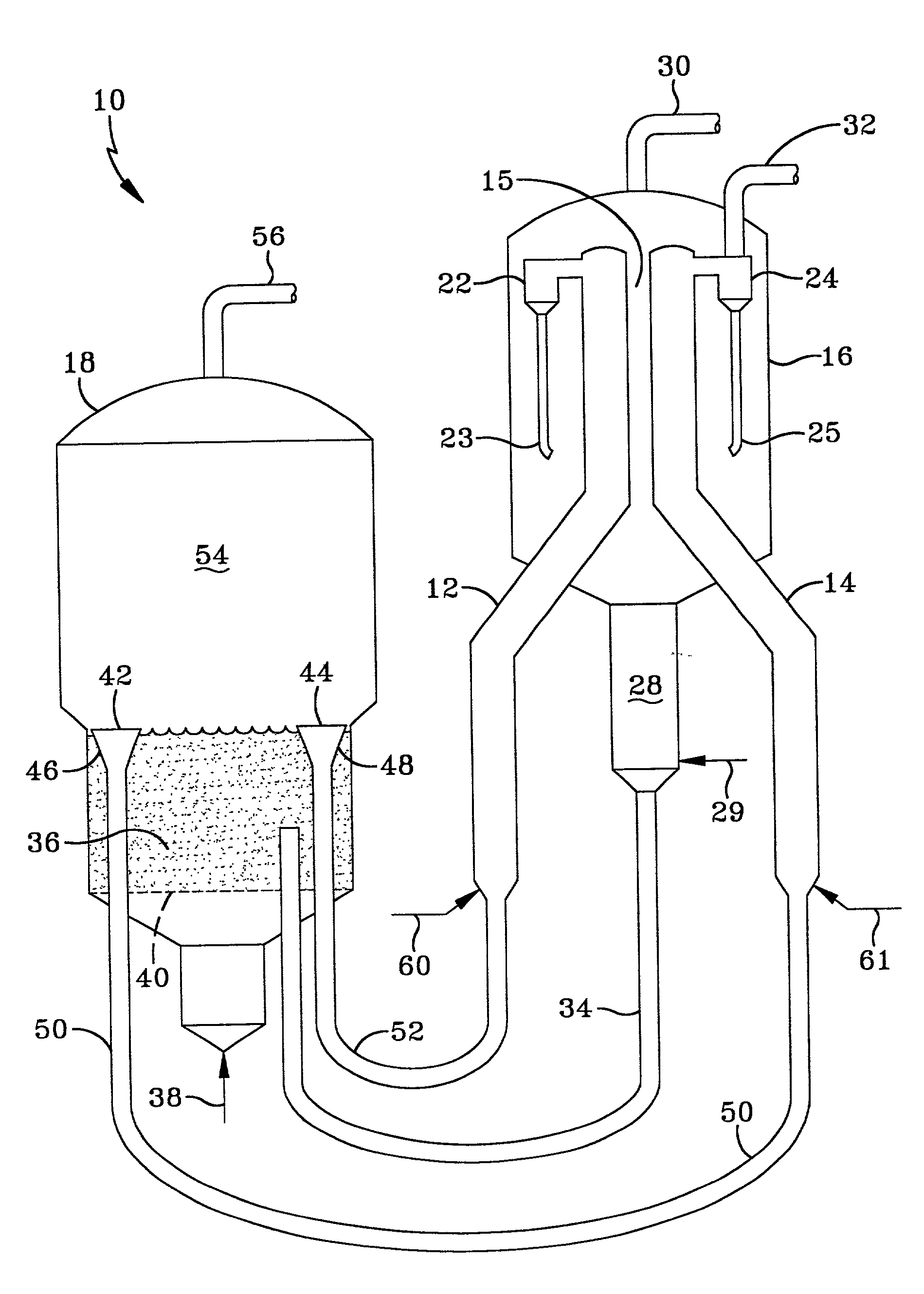
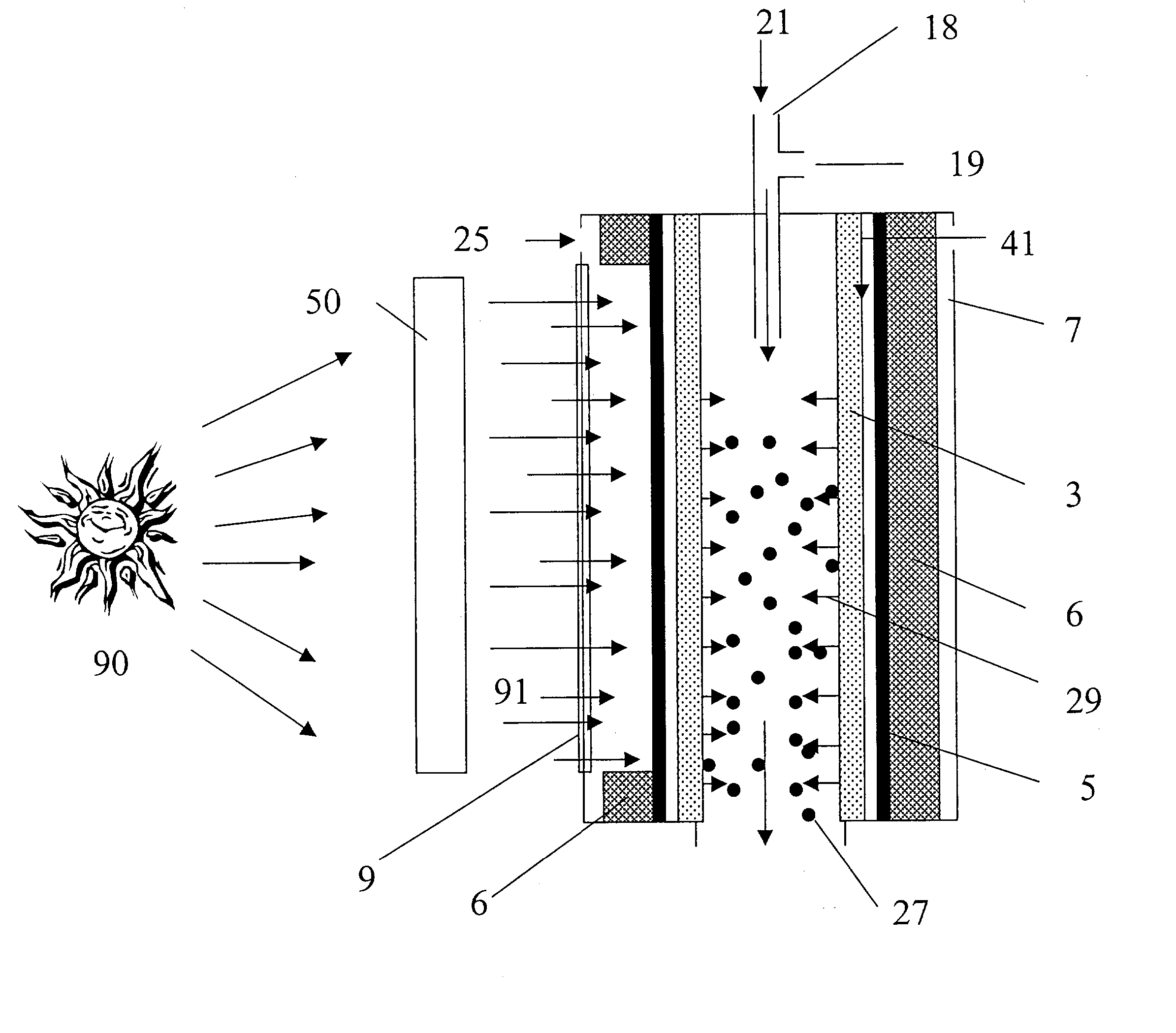
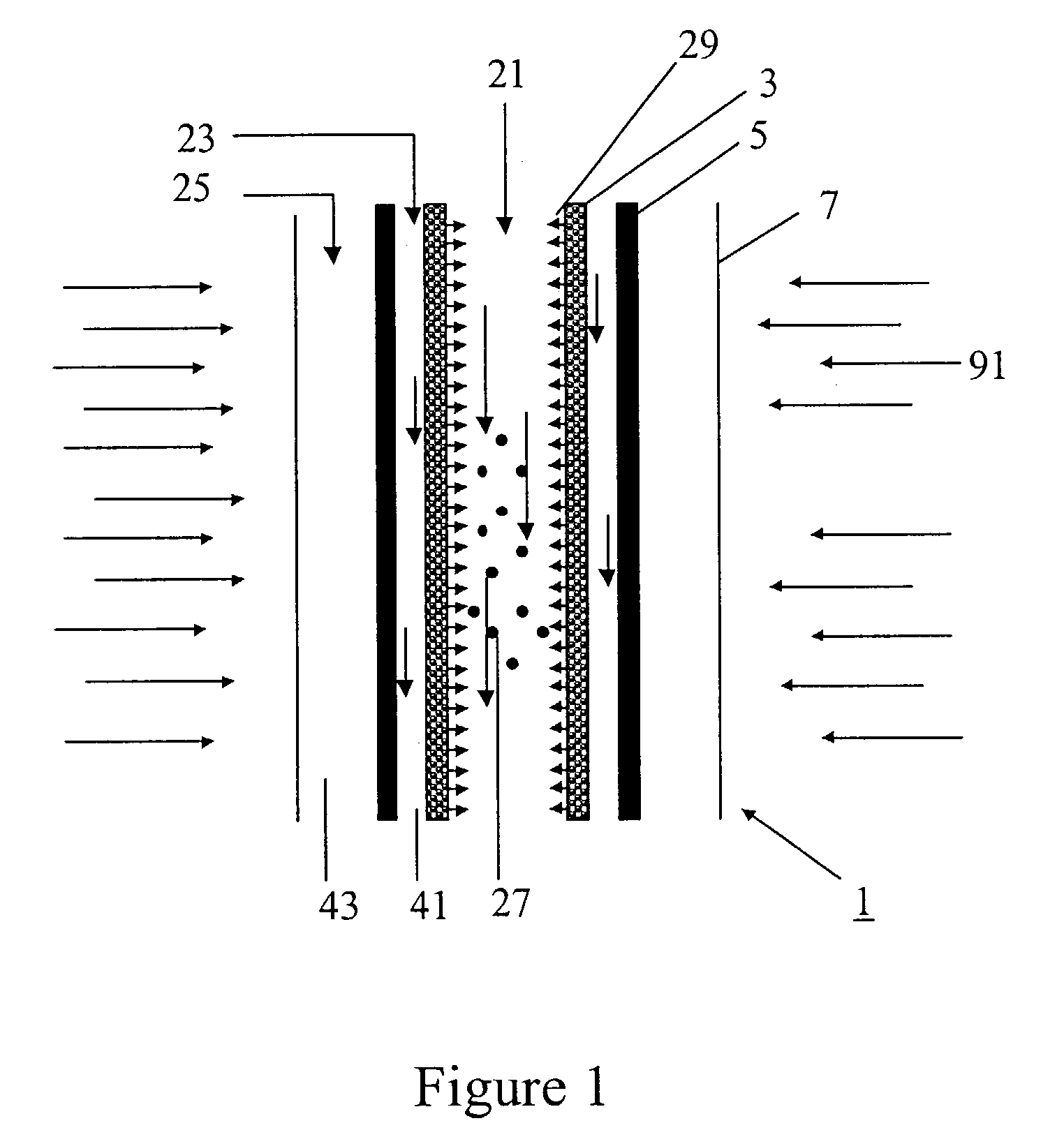
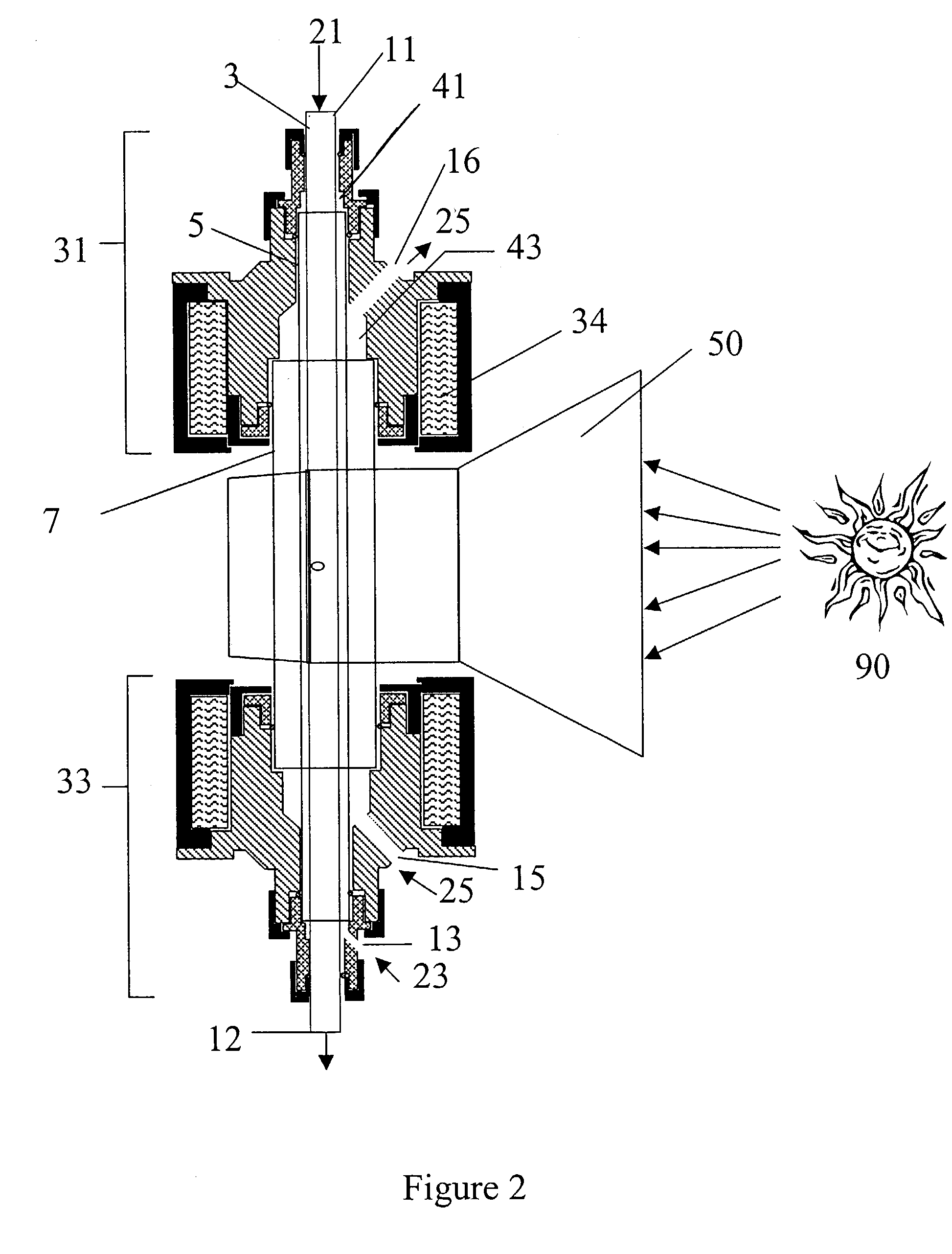
Patents
Literature
3163results about "Thermal non-catalytic cracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Production of synthetic lubricant and lubricant base stock without dewaxing
InactiveUS6103099AThermal non-catalytic crackingRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAutomatic transmissionBoiling point
A lubricating base stock useful for forming lubricants such as a multigrade automotive oils, automatic transmission oils, greases and the like is prepared by hydroisomerizing a waxy hydrocarbon feed fraction having an initial boiling point in the 650-750 DEG F. range and an end point of at least 1050 DEG F., synthesized by a slurry Fischer-Tropsch hydrocarbon synthesis process. The hydroisomerization forms a hydroisomerate containing the desired base stock which is recovered, without dewaxing the hydroisomerate. The hydroisomerization is conducted at conditions effective to convert at least 67 wt. % of the 650-750 DEG F.+ waxy feed hydrocarbons to lower boiling hydrocarbons. When combined with a standard lubricant additive package, these base stocks have been formed into multigrade automotive crankcase oils, transmission oils and hydraulic oils meeting the specifications for these oils.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Thermal cracking of crude oil and crude oil fractions containing pitch in an ethylene furnace
InactiveUS6632351B1Cheap sourceMinimizing coke formationThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbonsEthyleneChemistry
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Pre-passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus, and passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus during the initial reacation
ActiveUS20100282645A1Reduce operational riskReduce contentThermal non-catalytic crackingPhysical/chemical process catalystsLiquid productReaction temperature
The present invention relates to a pre-passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus prior to the reaction, or a passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus during the initial reaction, comprising loading a reforming catalyst into the continuous reforming apparatus, starting the gas circulation and raising the temperature of a reactor, injecting sulfide into the gas at a reactor temperature ranging from 100-650° C., controlling the sulfur amount in the recycle gas within a range of 0.5-100×10−6 L / L so as to passivate the apparatus.The process of the present invention may also comprise the following steps:(1) loading a reforming catalyst into the continuous reforming apparatus, starting the gas circulation and raising the temperature of a reactor, feeding the reforming feedstock into the reaction system when the temperature of the reactor is increased to 300-460° C., introducing sulfide into the reaction system while or after the reforming feedstock is fed, controlling the ratio of the total sulfur amount introduced into the system to the reforming feedstock within the range of 0.5 μg / g-50 μg / g, reducing the content of sulfide introduced into the system when hydrogen sulfide concentration in the recycle gas reaches to 2.0 μL / L˜30 μL / L; and(2) maintaining the reforming reactor at a temperature of 460-490° C., controlling the ratio of the total sulfur amount introduced into the system to the reforming feedstock within the range of 0.2 μg / g-0.5 μg / g, adjusting the amount of the reforming feedstock to the design value of the apparatus, increasing the reforming reaction temperature to 490-545° C. according to the requirements on the octane number of the liquid product, and letting the reforming apparatus run under normal operating conditions.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
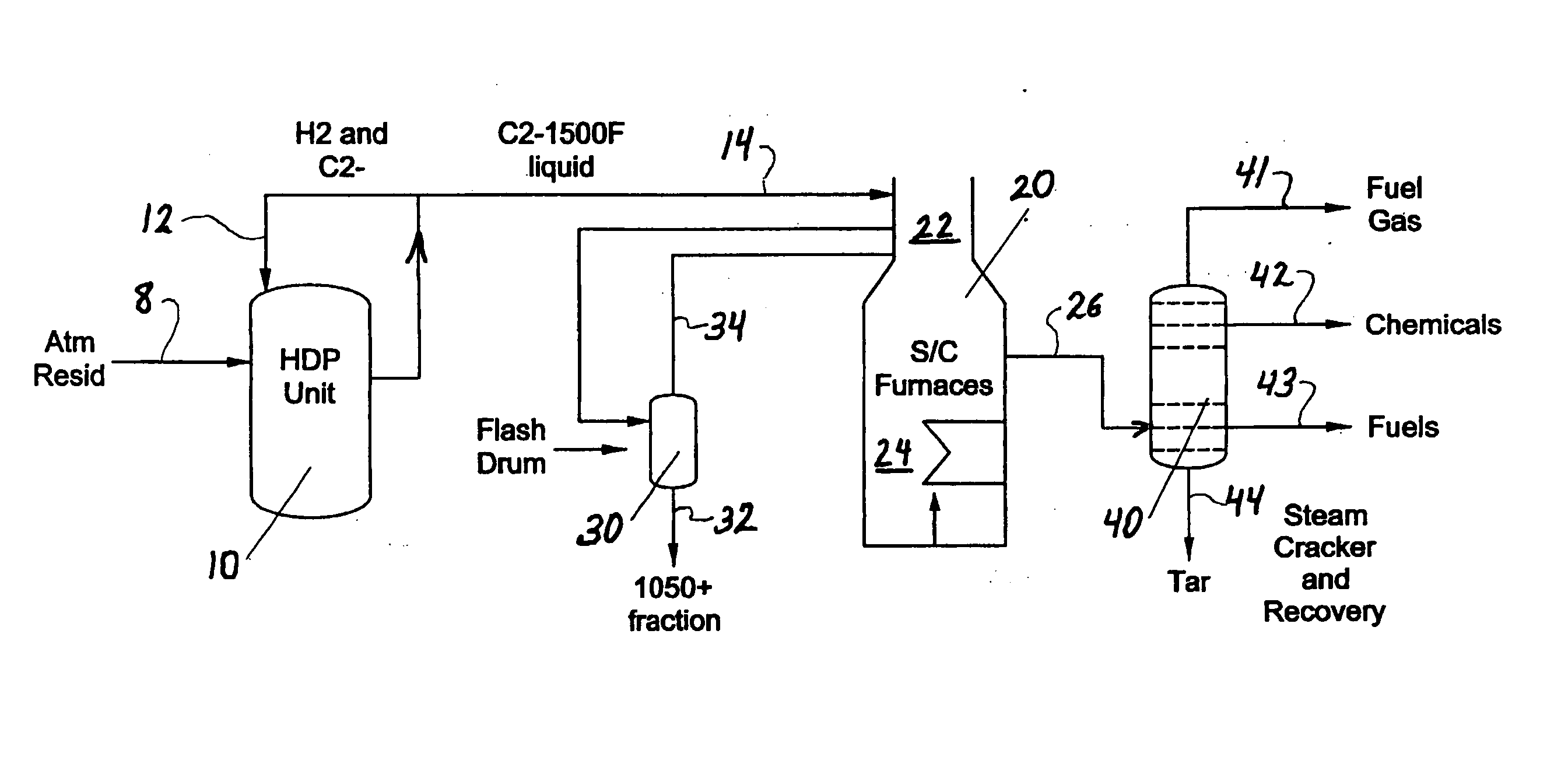
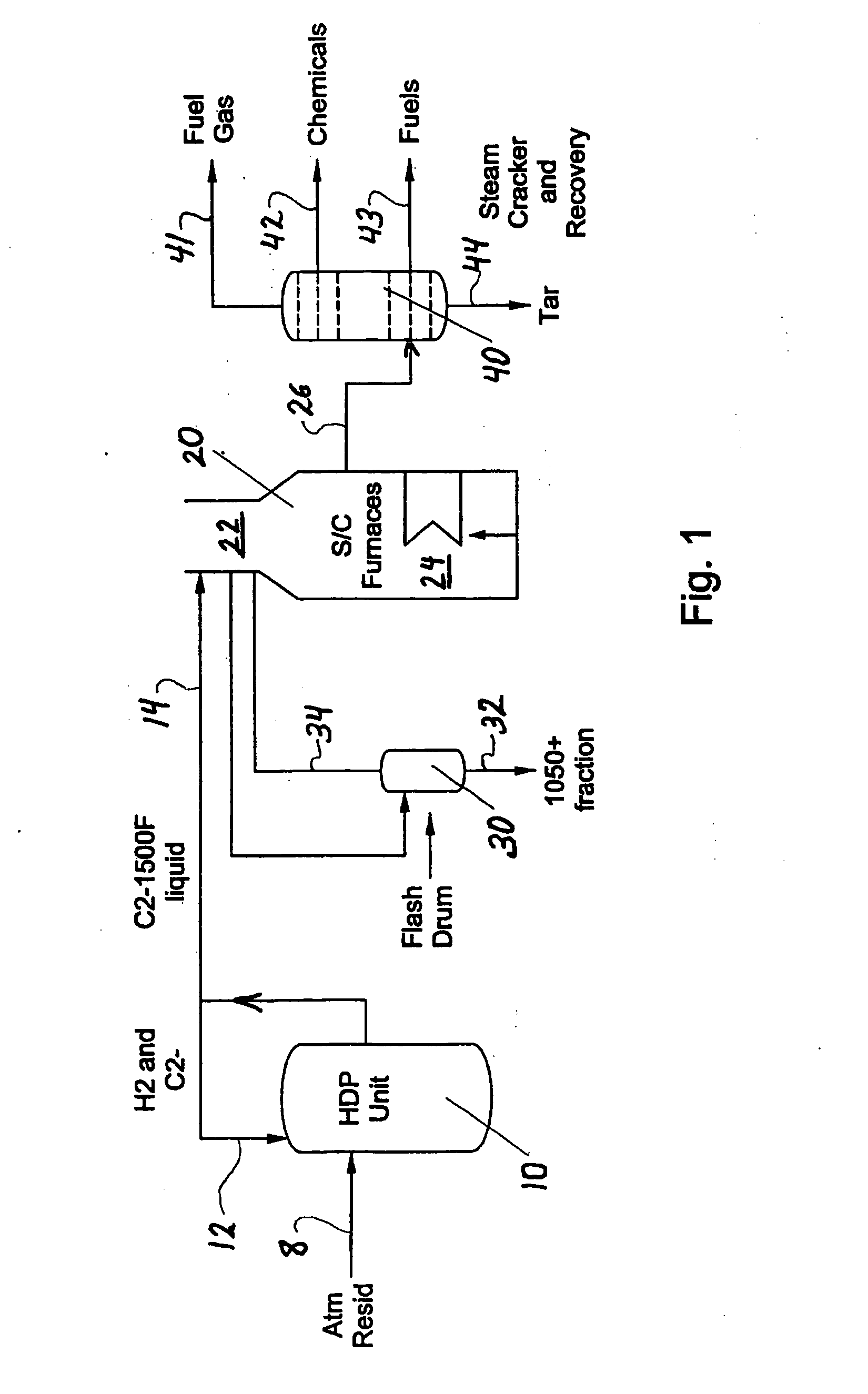
Hydrocarbon resid processing
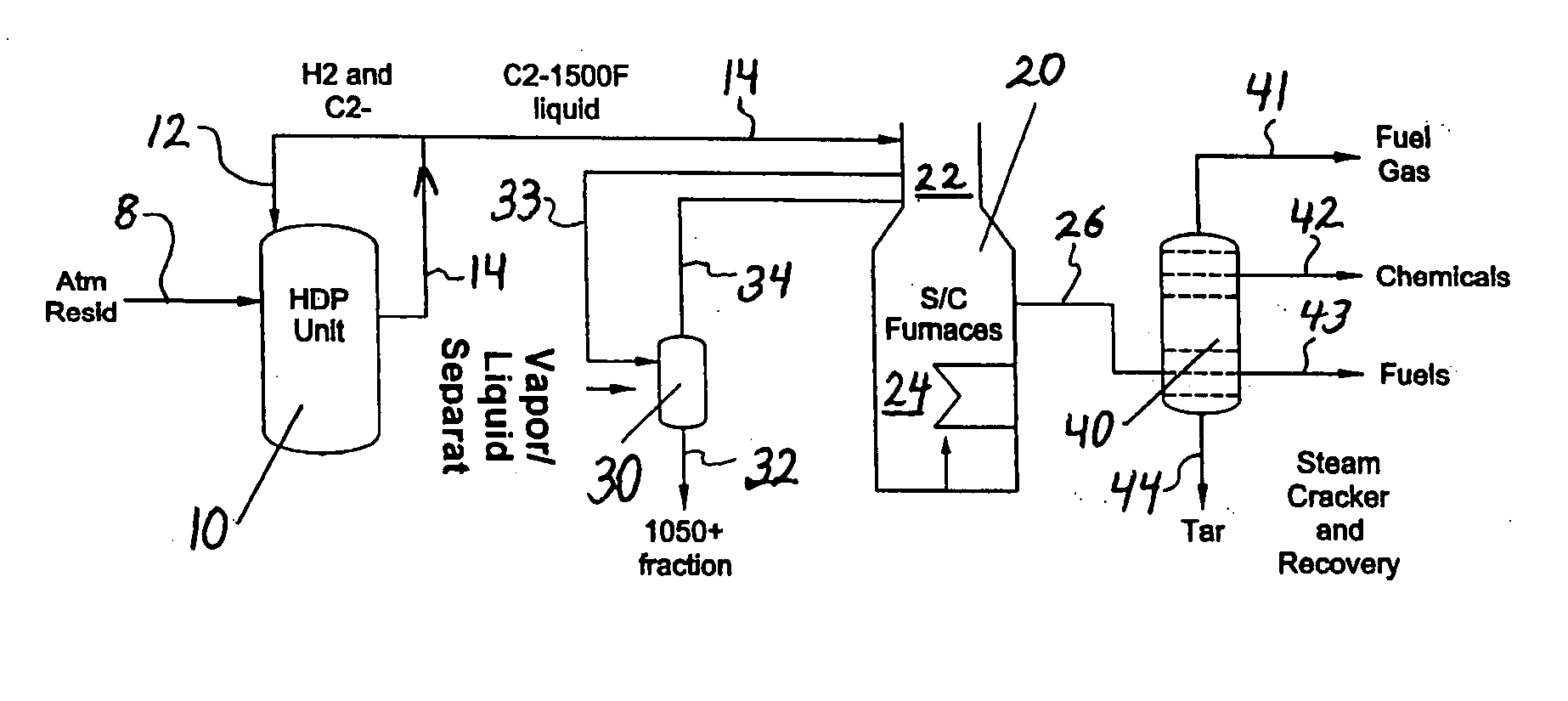
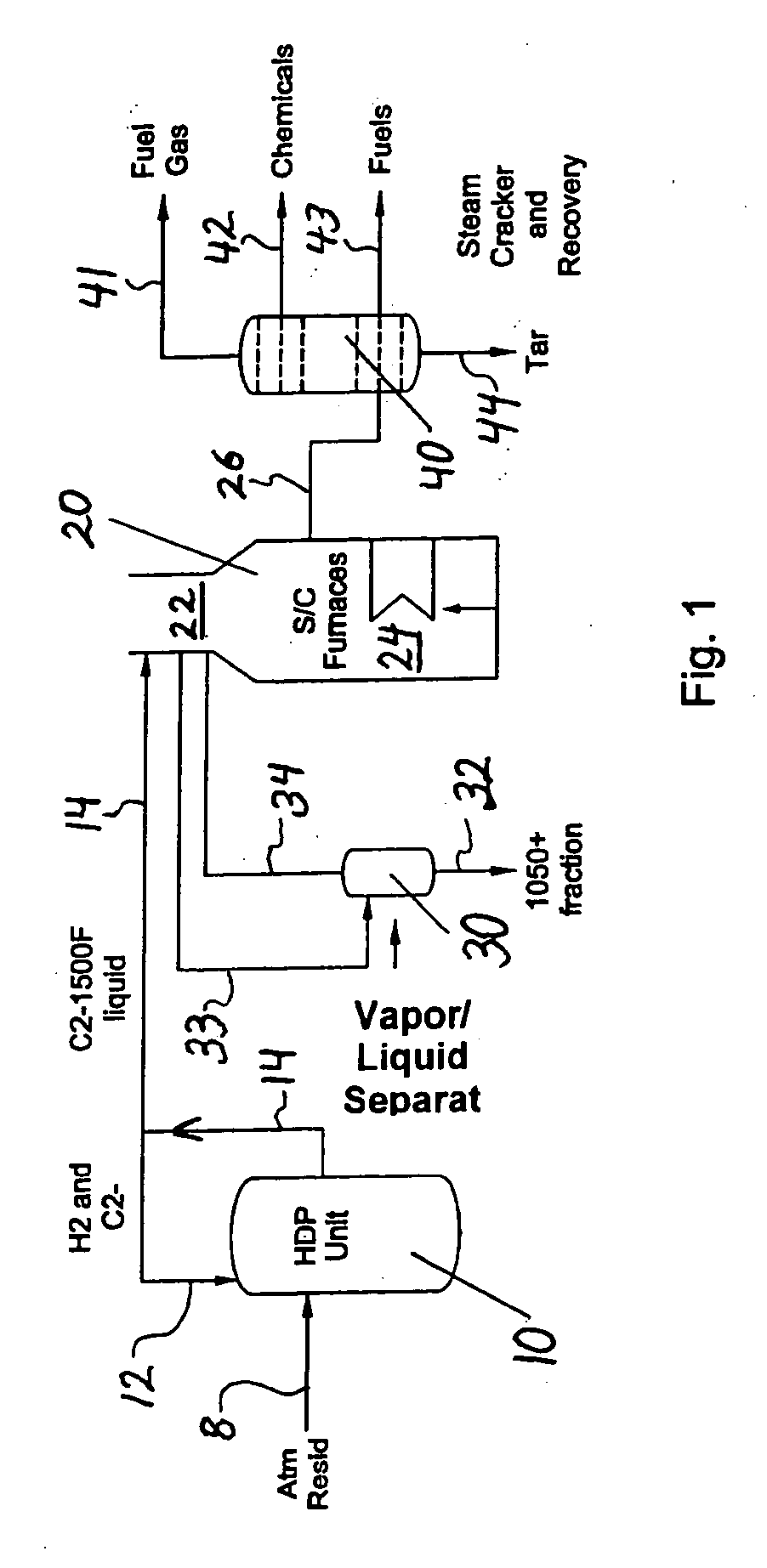
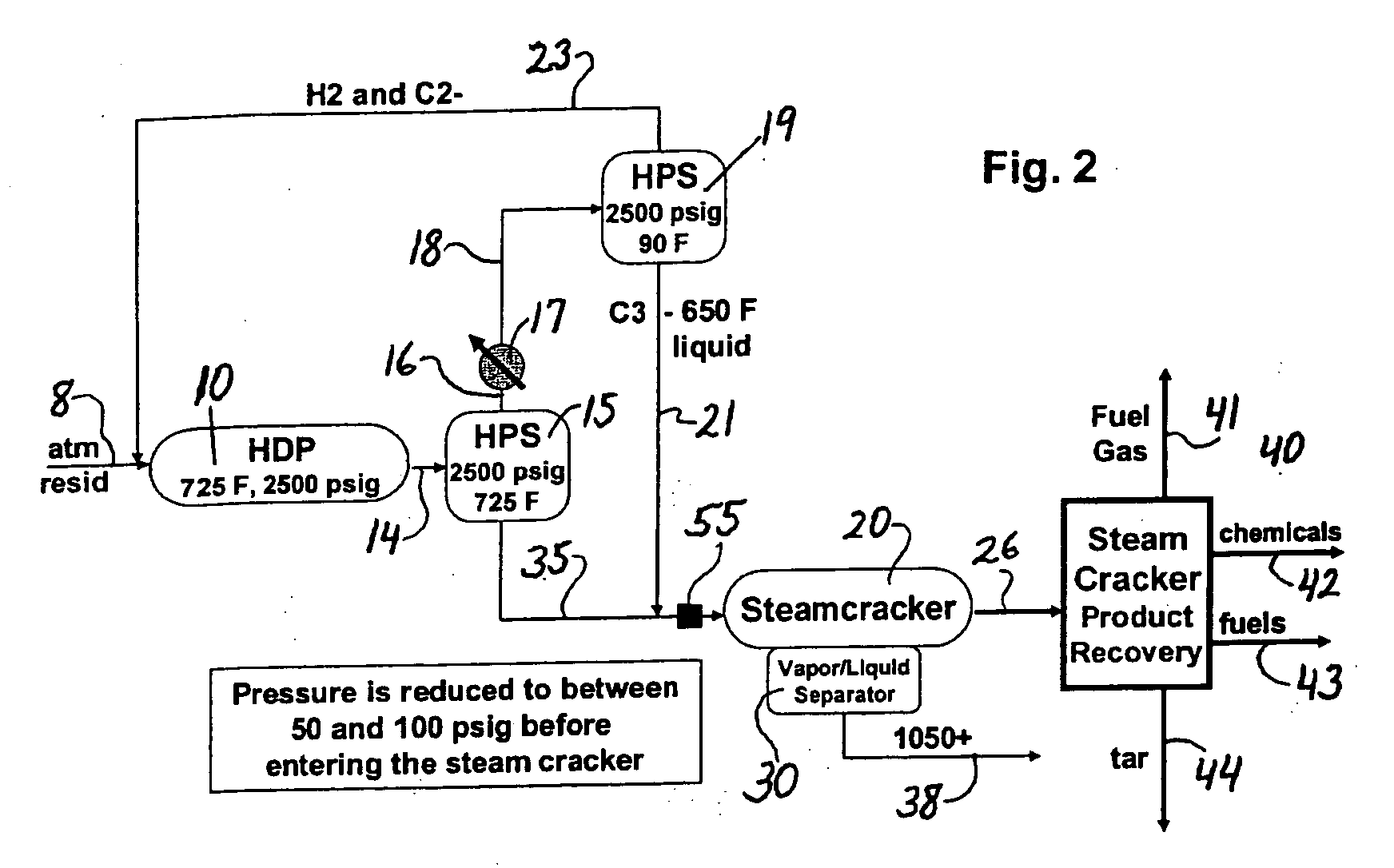
ActiveUS20070090018A1Increase in severityReduce pressureThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon oil cracking processHydrocarbonChemistry
The invention concerns integration of hydroprocessing and steam cracking. A feed comprising crude or resid-containing fraction thereof is severely hydrotreated and passed to a steam cracker to obtain an olefins product.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
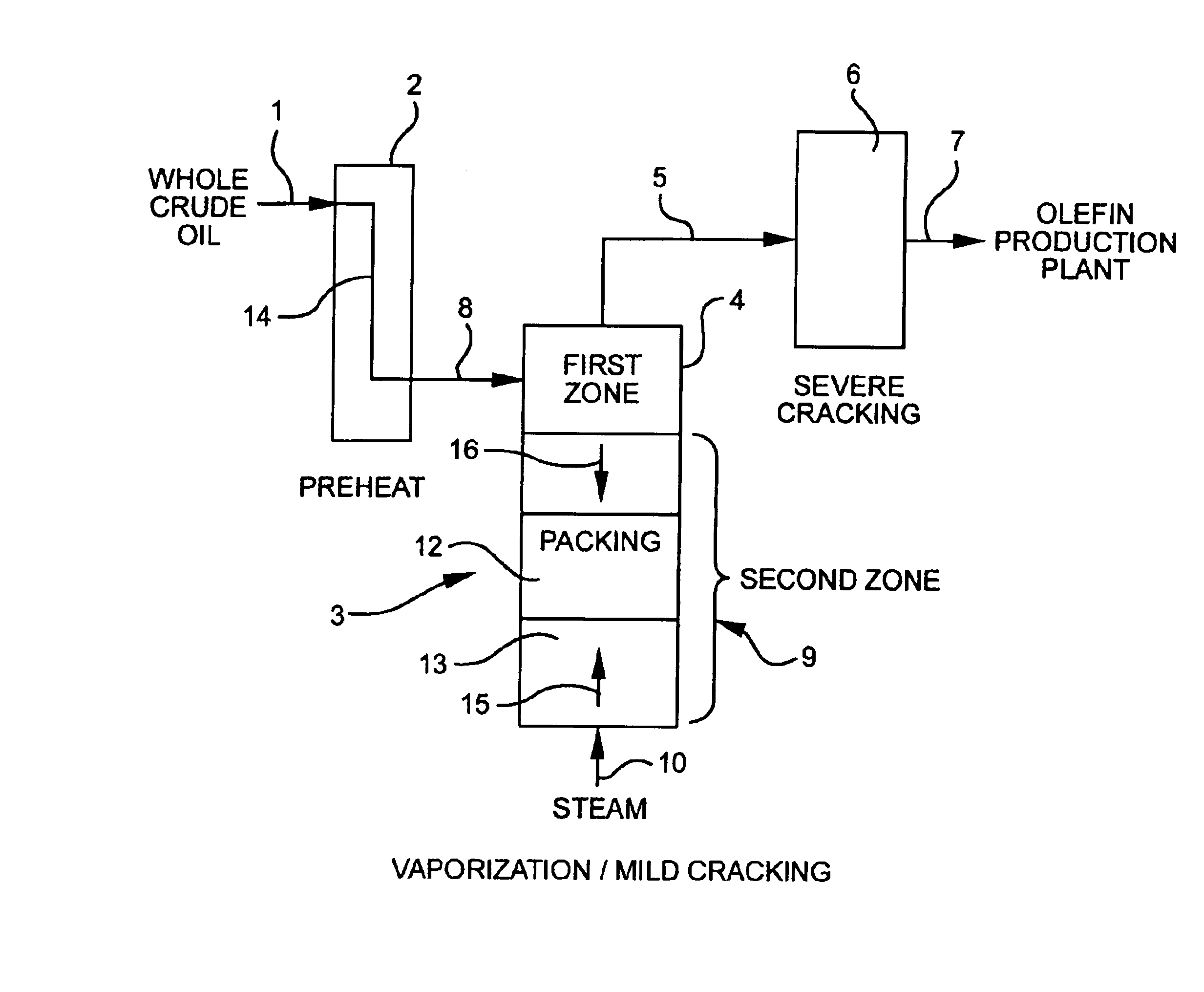
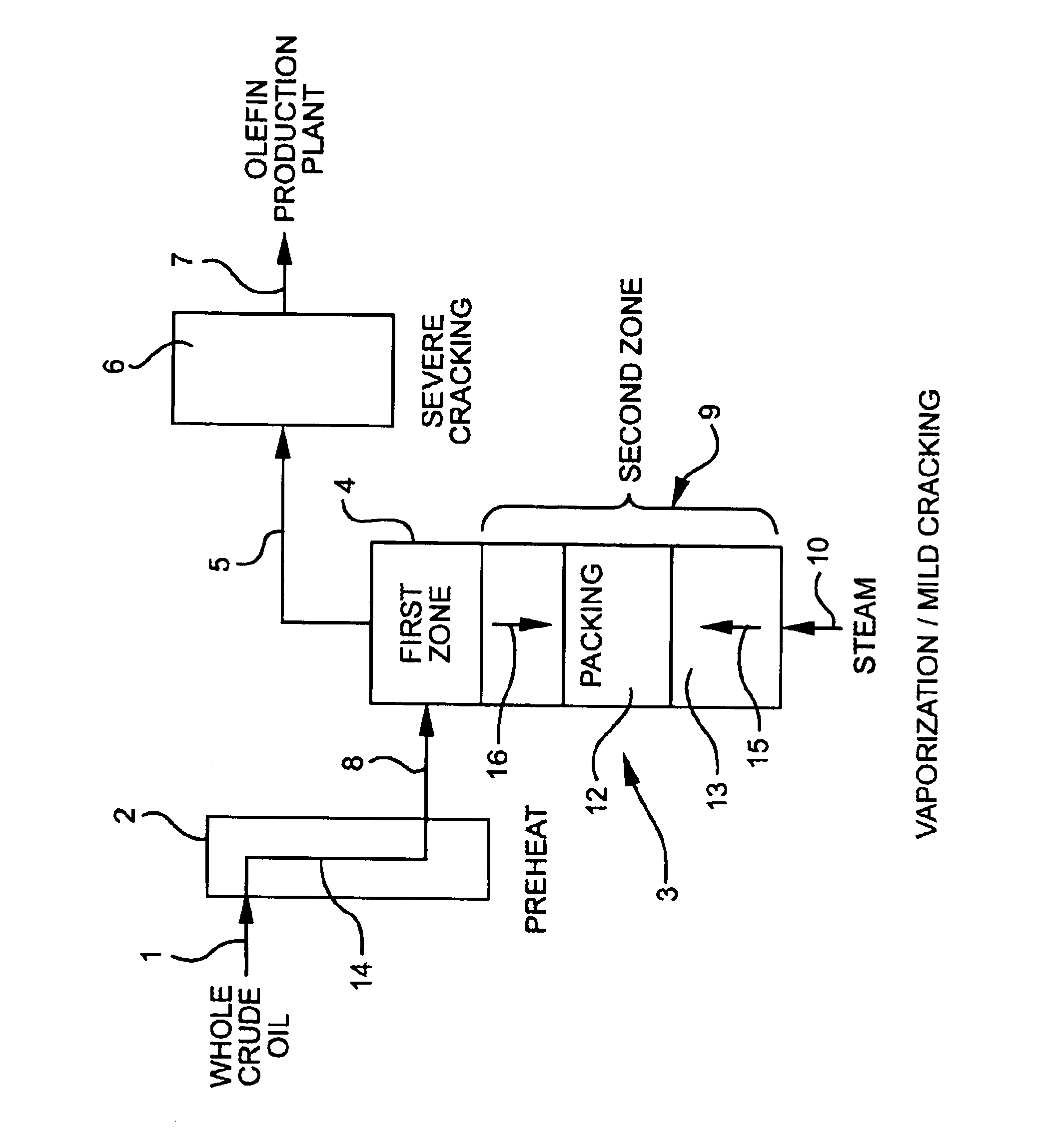
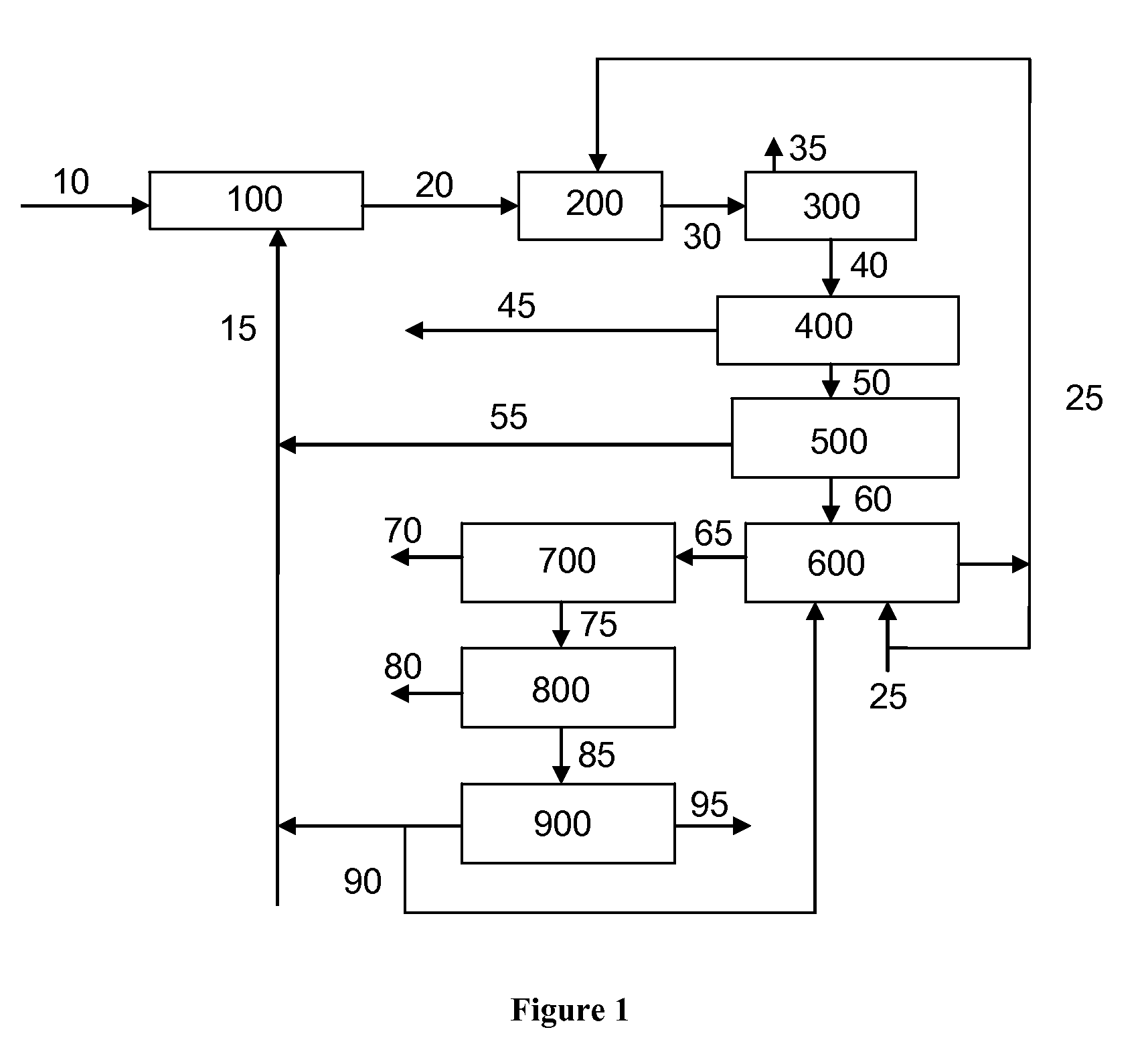
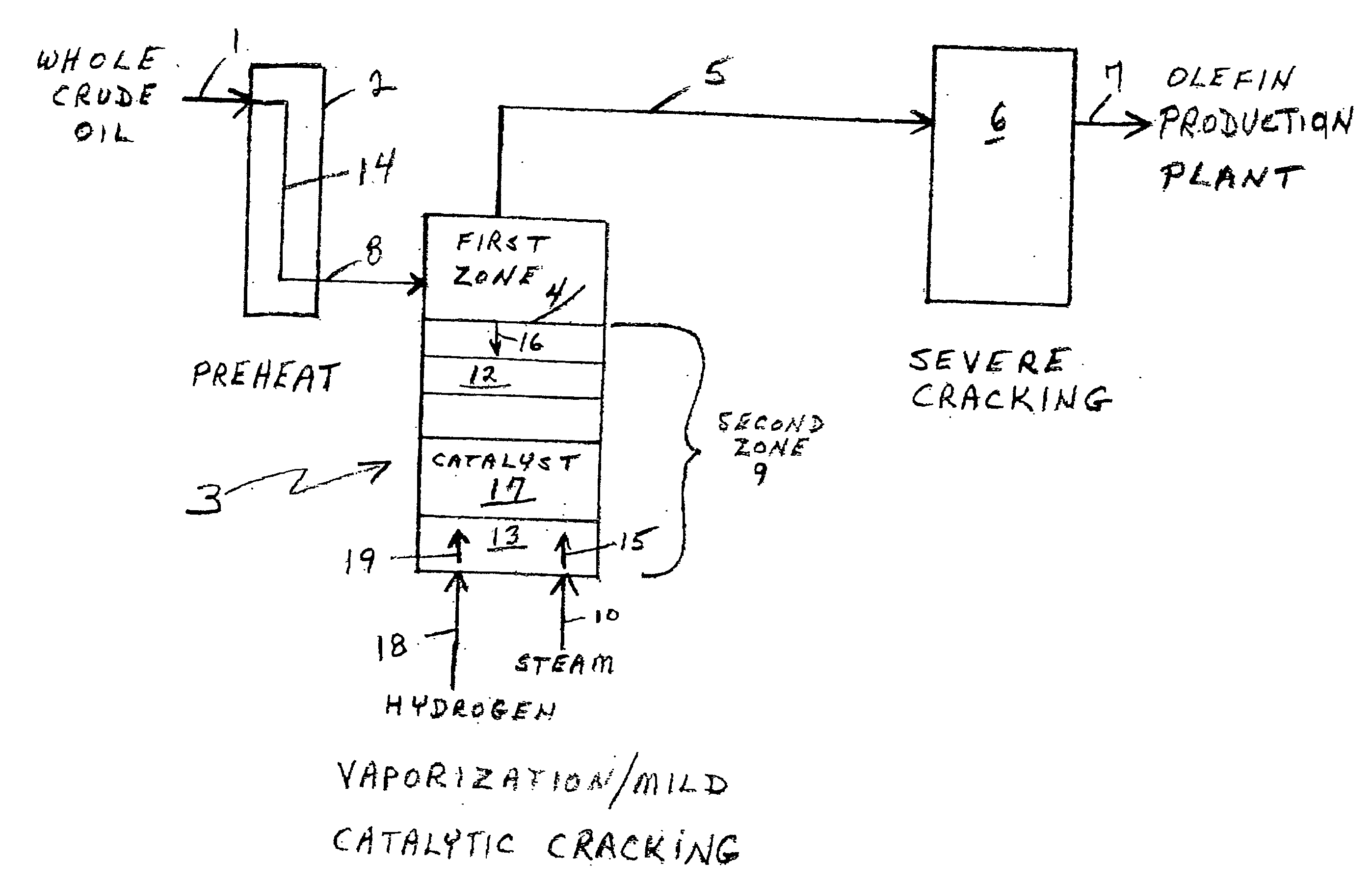
Olefin production utilizing whole crude oil
InactiveUS6743961B2Lower temperature rangeReduce molecular weightThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbonsOil productionAlkene
A method for utilizing whole crude oil as a feedstock for the pyrolysis furnace of an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock after preheating is subjected to mild cracking conditions until substantially vaporized, the vapors from mild cracking being subjected to severe cracking in the radiant section of the furnace.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
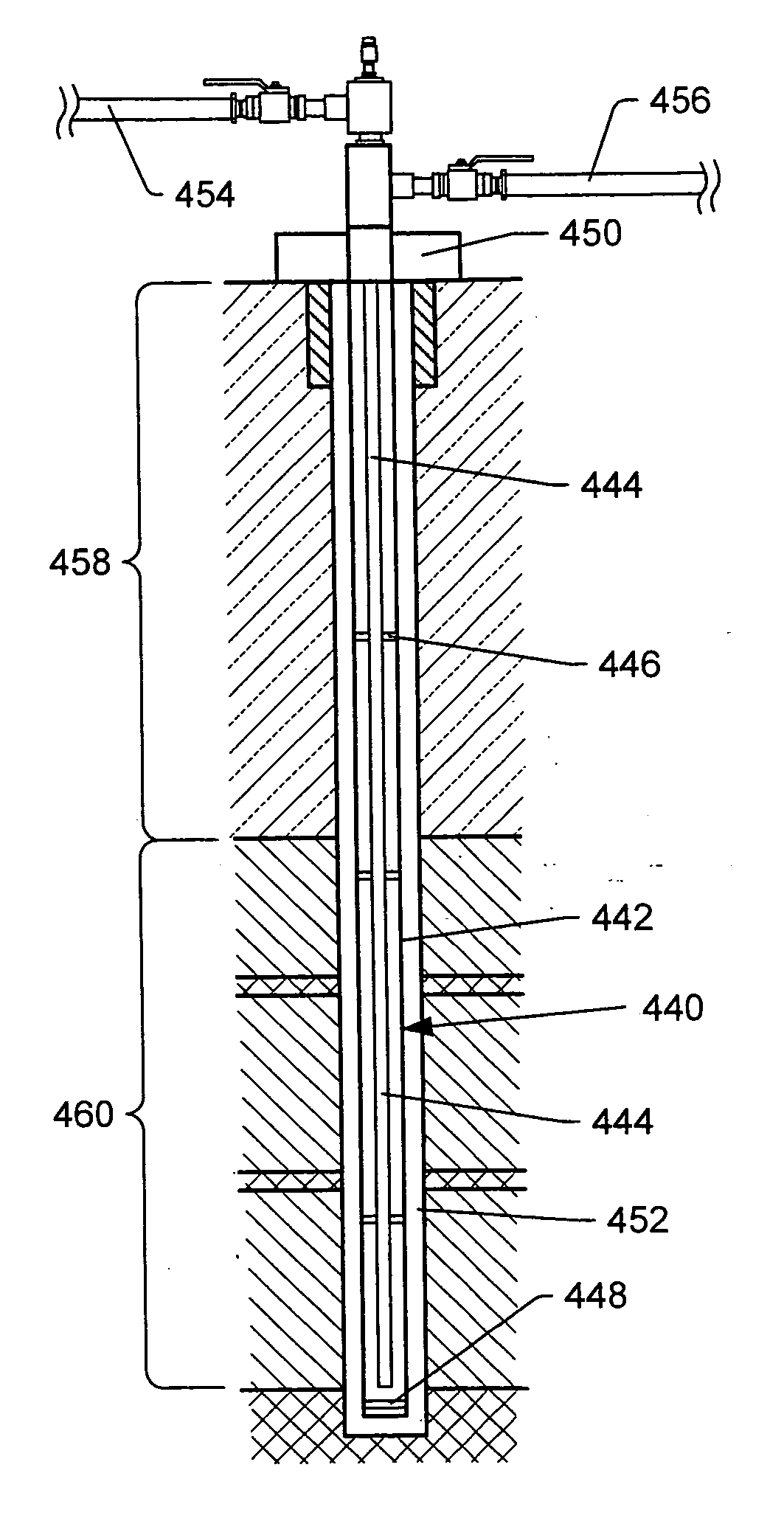
Subsurface heaters with low sulfidation rates
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Cogeneration systems and processes for treating hydrocarbon containing formations
InactiveUS20070095536A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingElectricityNuclear engineering
A system for treating a hydrocarbon containing formation includes a steam and electricity cogeneration facility. At least one injection well is located in a first portion of the formation. The injection well provides steam from the steam and electricity cogeneration facility to the first portion of the formation. At least one production well is located in the first portion of the formation. The production well in the first portion produces first hydrocarbons. At least one electrical heater is located in a second portion of the formation. At least one of the electrical heaters is powered by electricity from the steam and electricity cogeneration facility. At least one production well is located in the second portion of the formation. The production well in the second portion produces second hydrocarbons. The steam and electricity cogeneration facility uses the first hydrocarbons and / or the second hydrocarbons to generate electricity.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
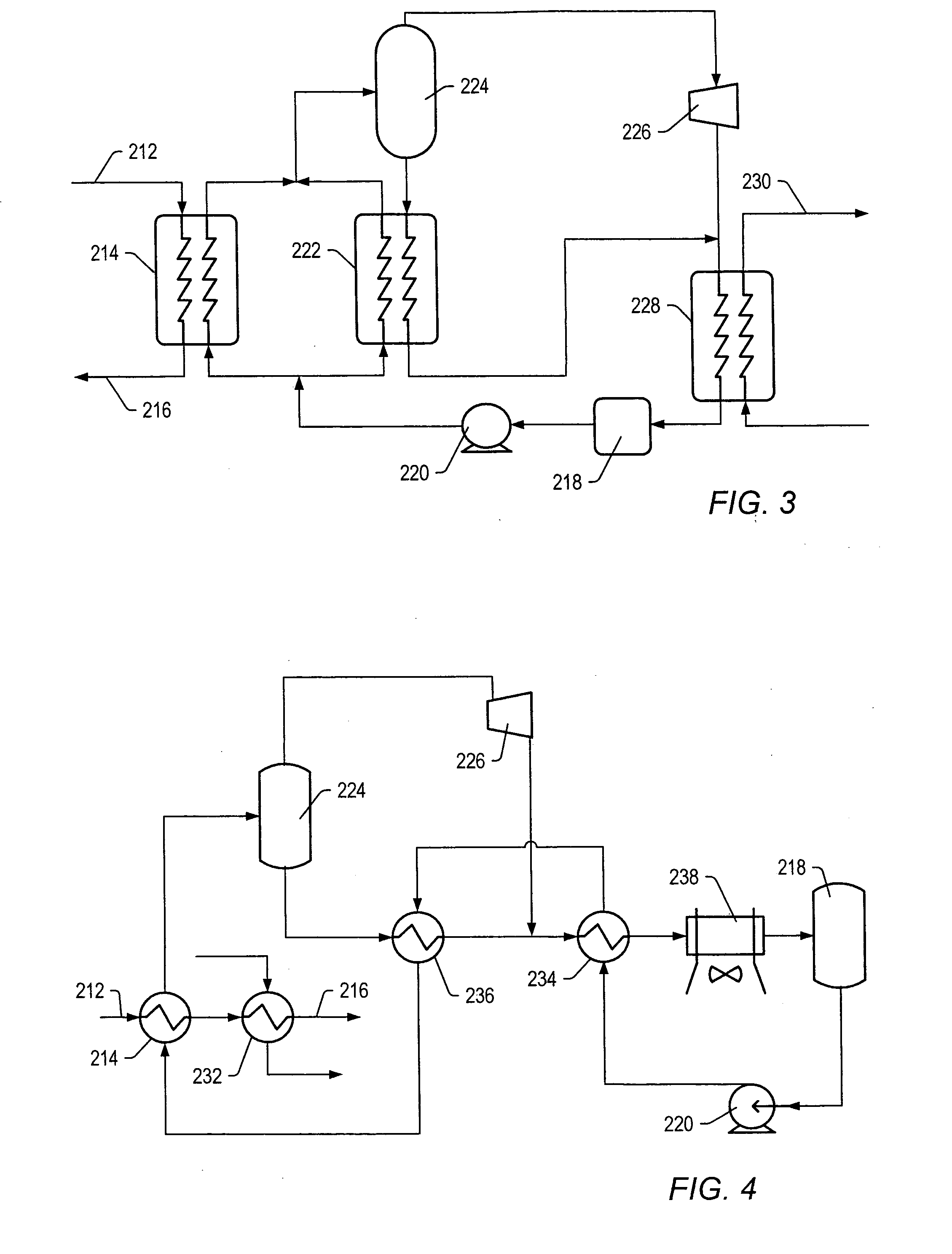
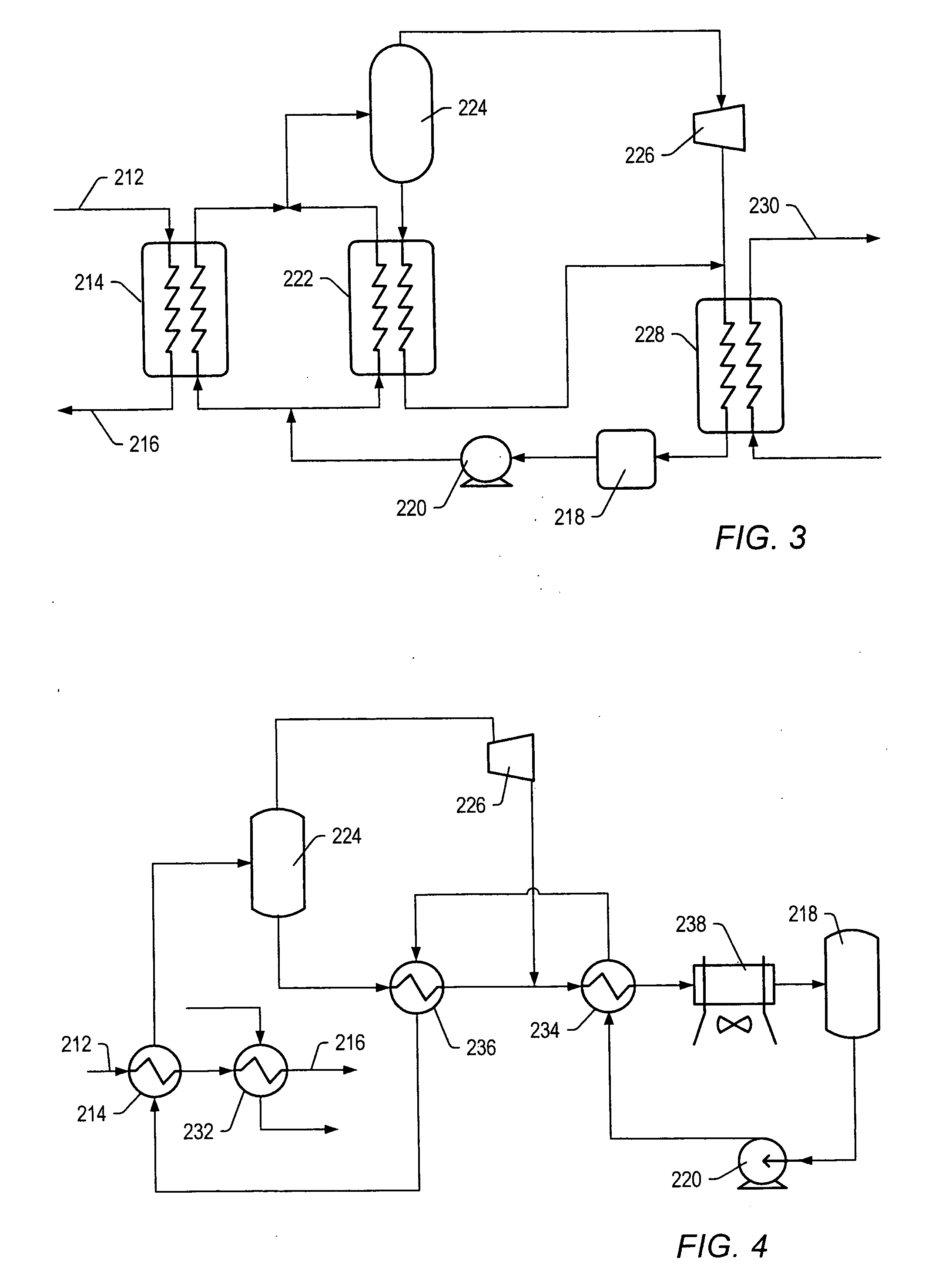
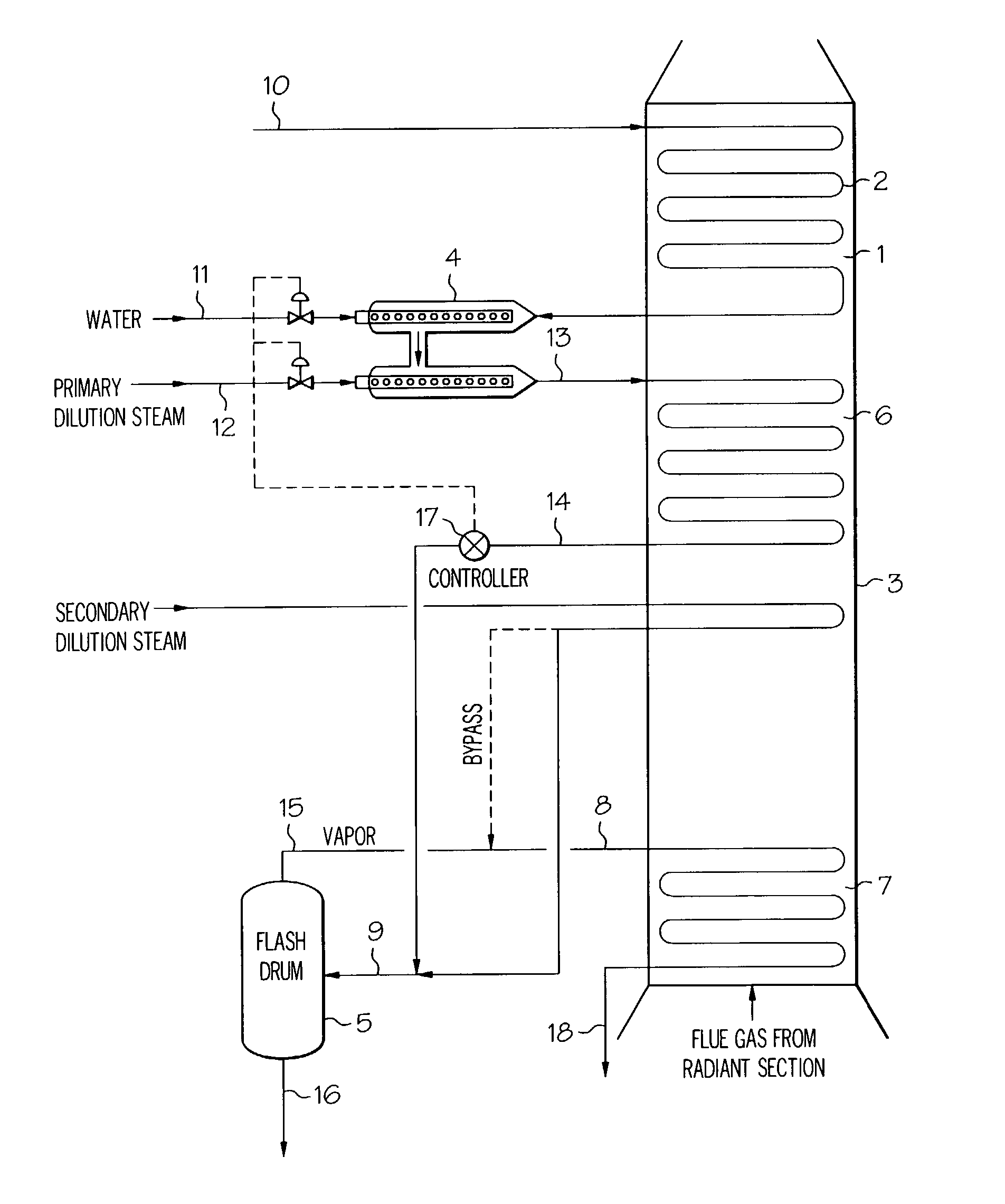
Process for steam cracking heavy hydrocarbon feedstocks
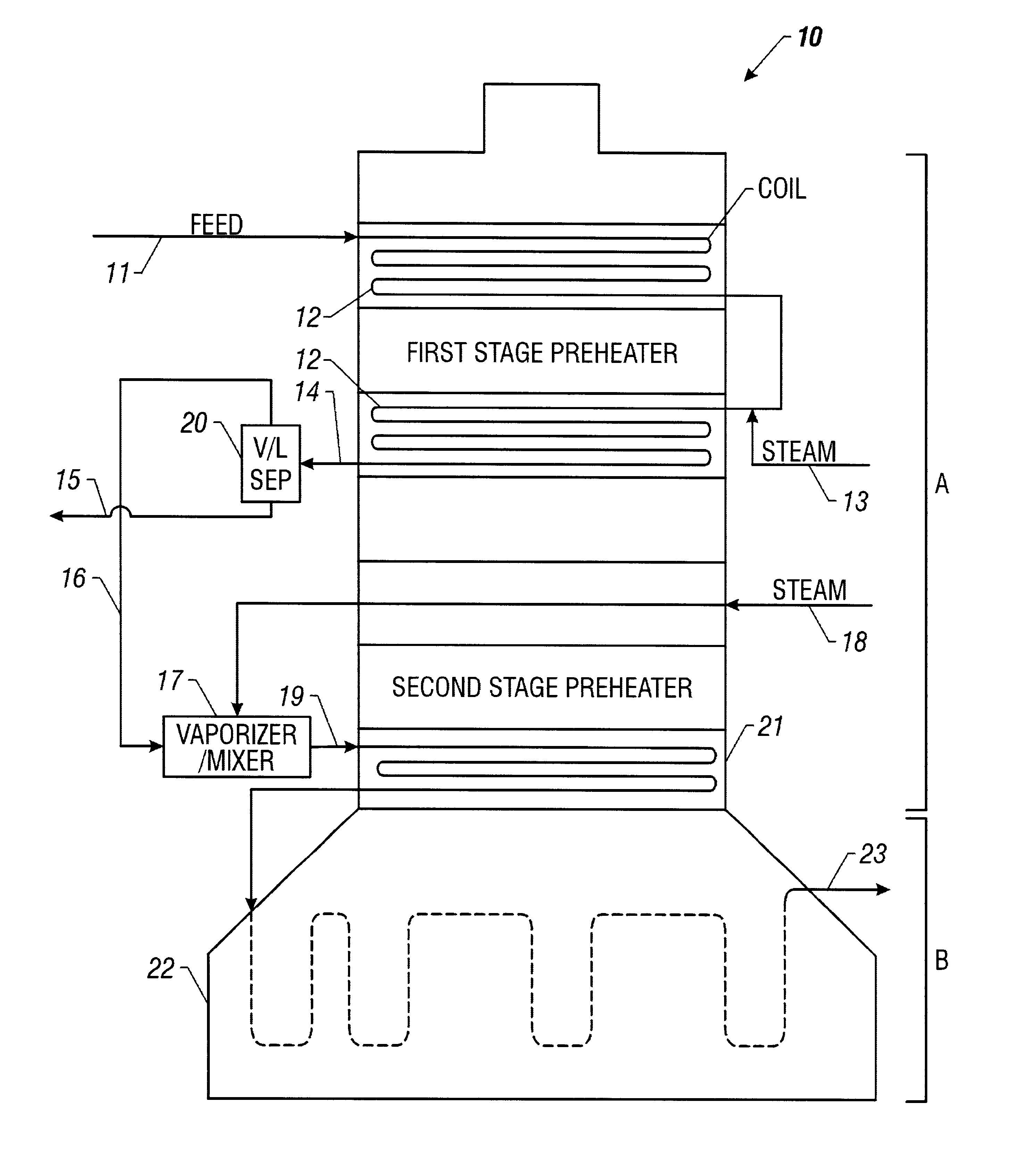
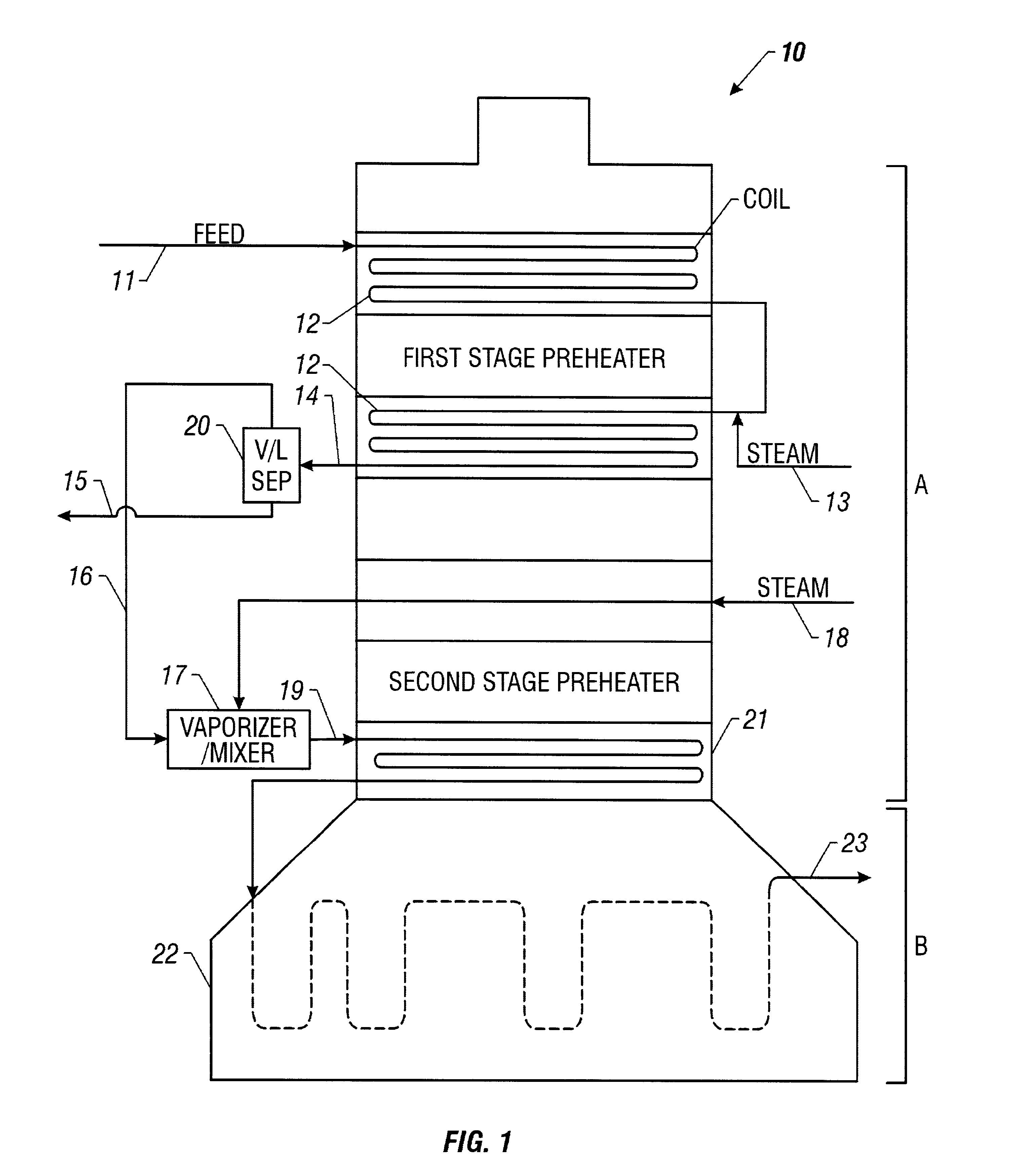
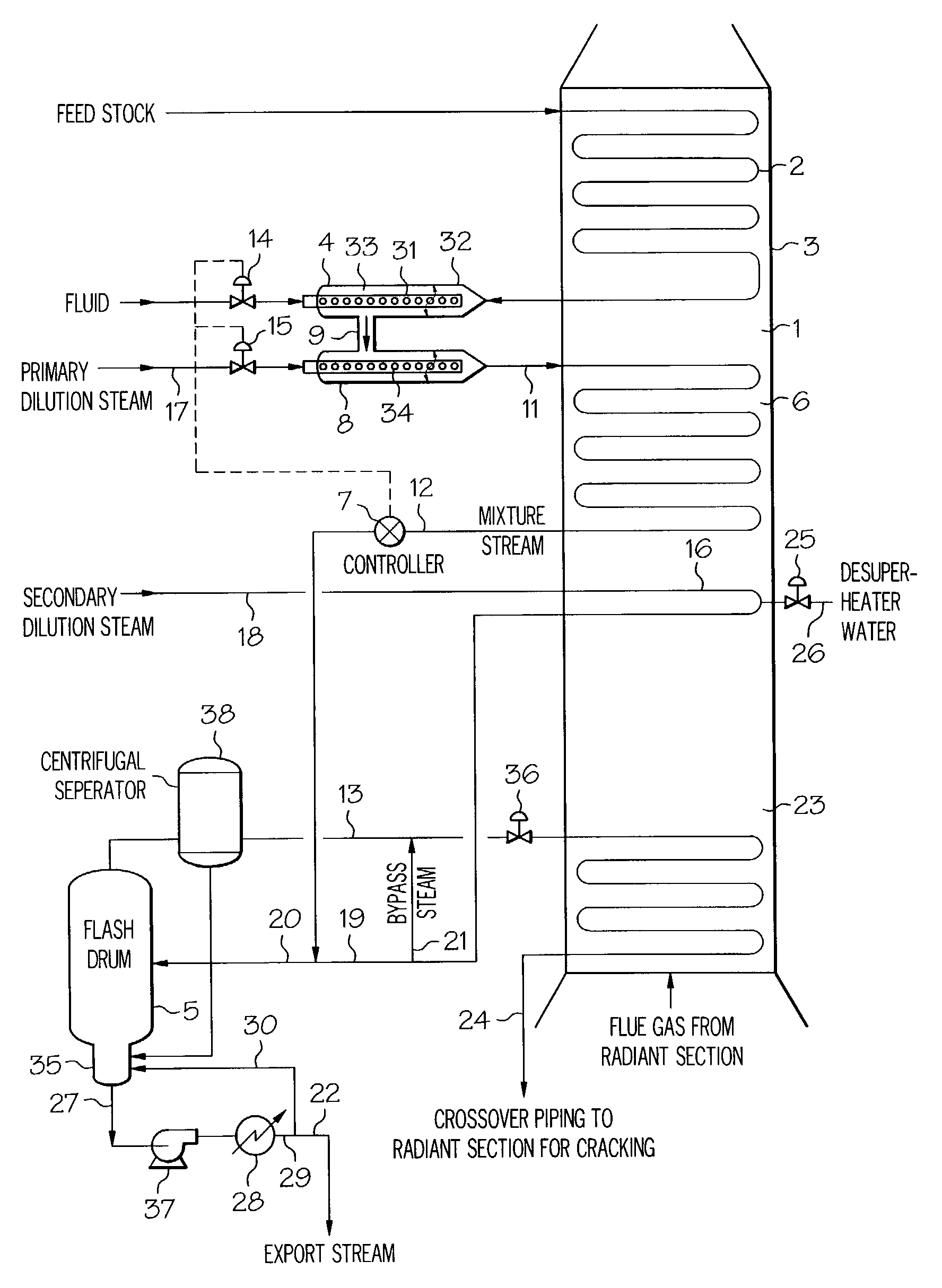
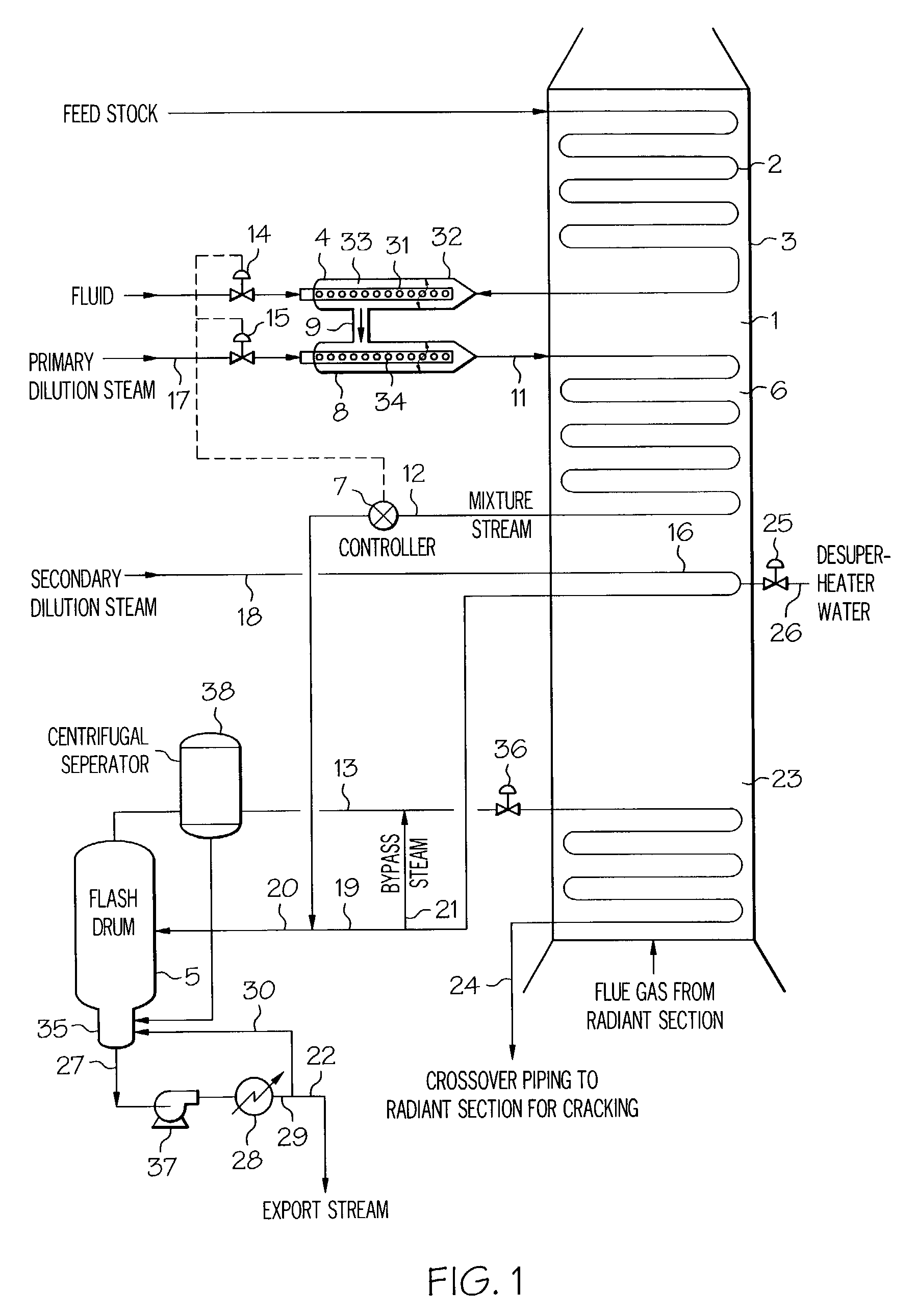
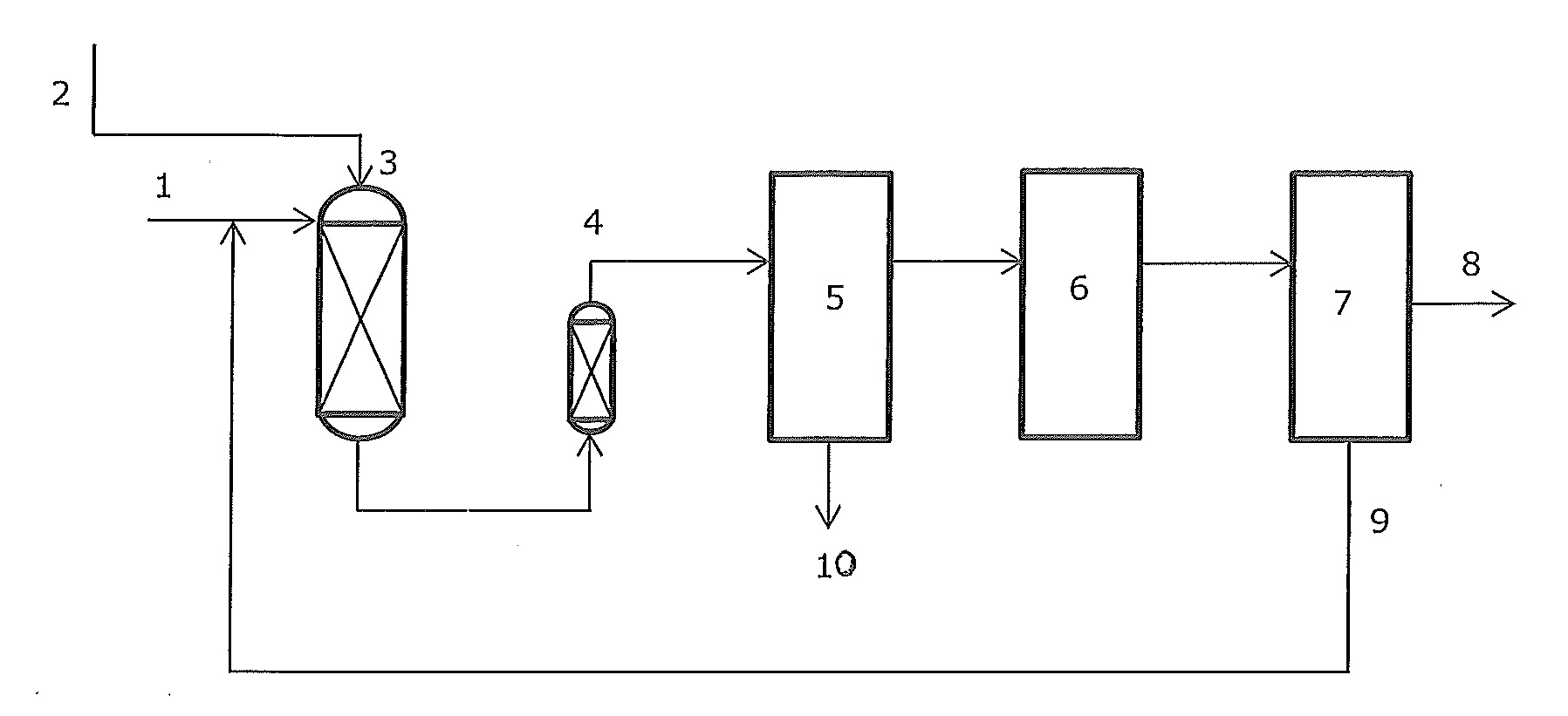
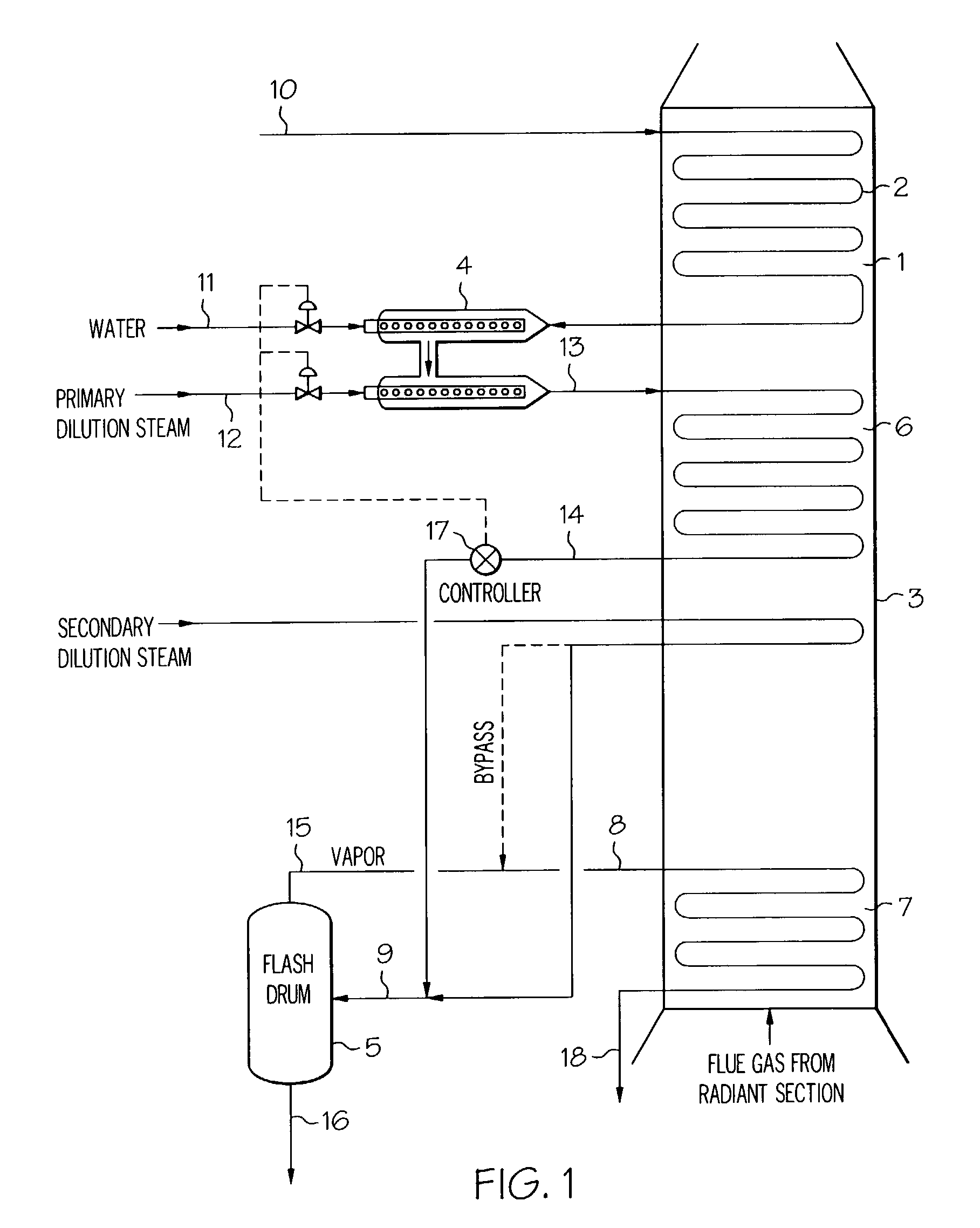
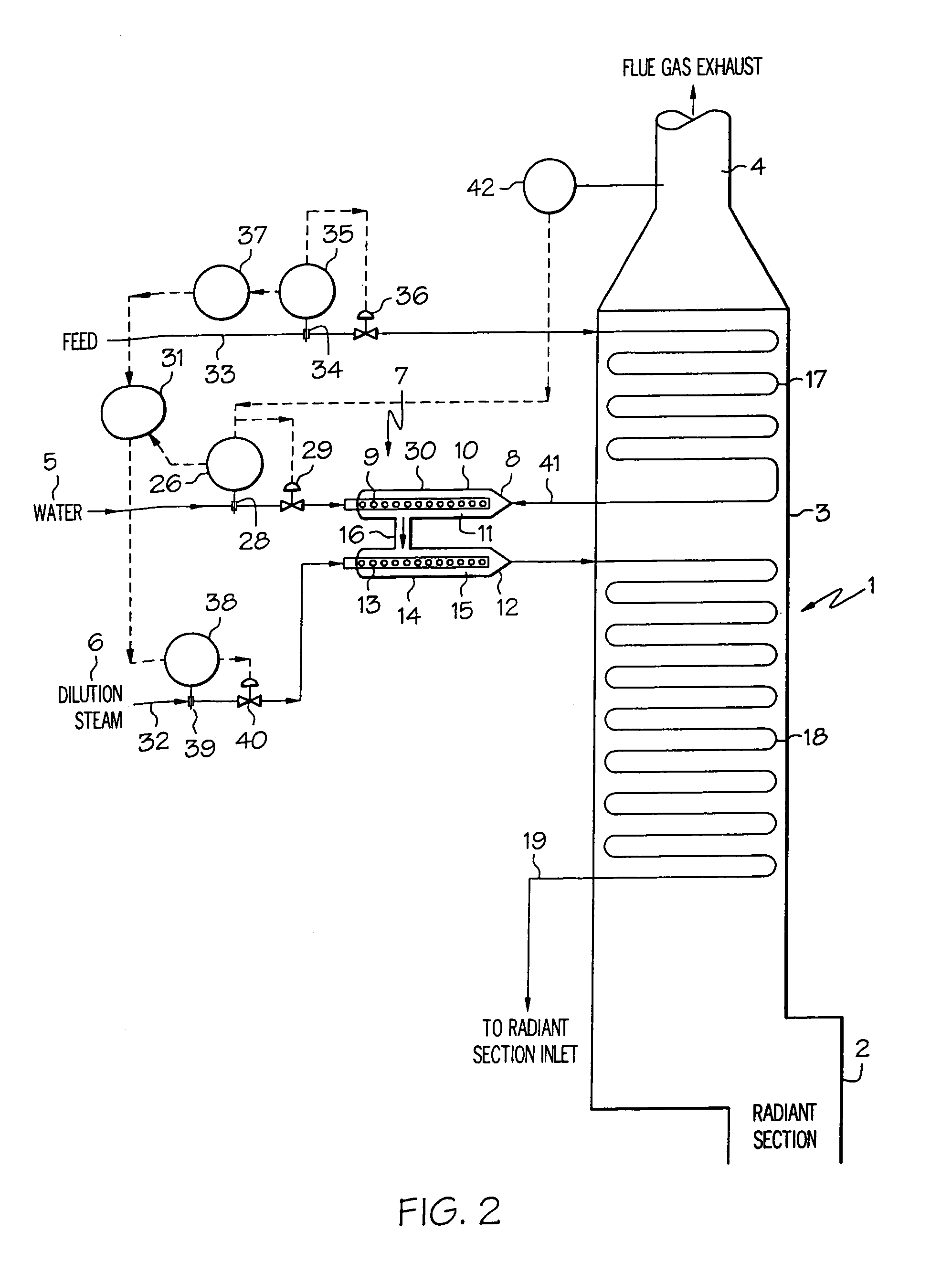
A process for feeding or cracking heavy hydrocarbon feedstock containing non-volatile hydrocarbons comprising: heating the heavy hydrocarbon feedstock, mixing the heavy hydrocarbon feedstock with a fluid and / or a primary dilution steam stream to form a mixture, flashing the mixture to form a vapor phase and a liquid phase, and varying the amount of the fluid and / or the primary dilution steam stream mixed with the heavy hydrocarbon feedstock in accordance with at least one selected operating parameter of the process, such as the temperature of the flash stream before entering the flash drum.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
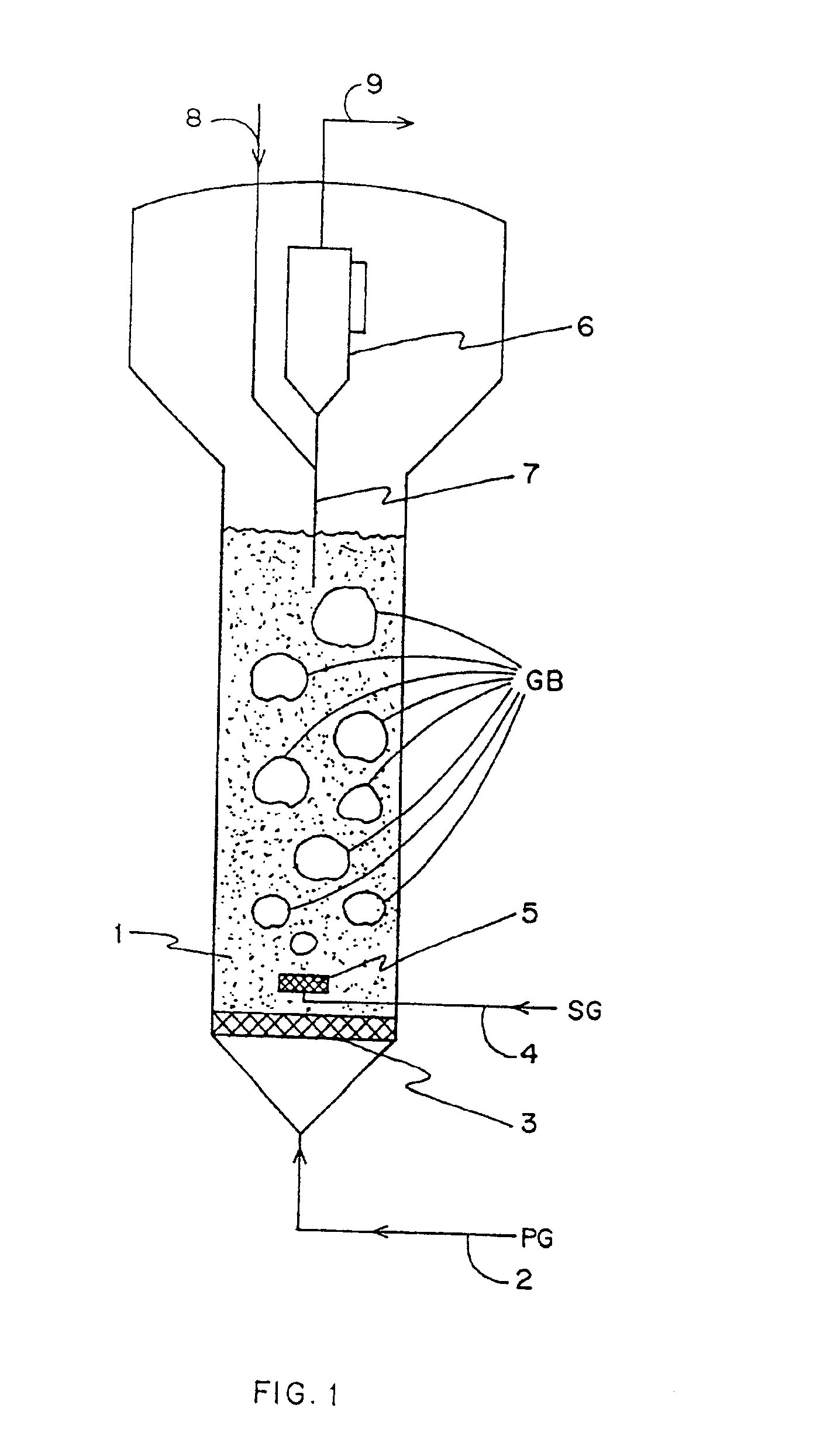
Method for gas-solid contacting in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor
InactiveUS6894183B2Eliminate and drastically reduce bypassEffective contactThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingForming gasSolid particle
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Conversion of petroleum residua to methane
InactiveUS6955695B2Eliminate needReduce usageThermal non-catalytic crackingElectrolysis componentsParticulatesGas phase
This invention discloses improvements on previous inventions for catalytic conversion of coal and steam to methane. The disclosed improvements permit conversion of petroleum residua or heavy crude petroleum to methane and carbon dioxide such that nearly all of the heating value of the converted hydrocarbons is recovered as heating value of the product methane. The liquid feed is distributed over a fluidized solid particulate catalyst containing alkali metal and carbon as petroleum coke at elevated temperature and pressure from the lower stage and transported to the upper stage of a two-stage reactor. Particulate solids containing carbon and alkali metal are circulated between the two stages. Superheated steam and recycled hydrogen and carbon monoxide are fed to the lower stage, fluidizing the particulate solids and gasifying some of the carbon. The gas phase from the lower stage passes through the upper stage, completing the reaction of the gas phase.
Owner:PETRO2020
Catalytic Gasification Process with Recovery of Alkali Metal from Char
ActiveUS20090169448A1Quantity minimizationThermal non-catalytic crackingMuffle furnacesPhysical chemistryAlkali metal
Processes are described for the extraction and recovery of alkali metal from the char that results from catalytic gasification of a carbonaceous material. Among other steps, the processes of the invention include a hydrothermal leaching step in which a slurry of insoluble particulate comprising insoluble alkali metal compounds is treated with carbon dioxide and steam at elevated temperatures and pressures to effect the conversion of insoluble alkali metal compounds to soluble alkali metal compounds. Further, processes are described for the catalytic gasification of a carbonaceous material where a substantial portion of alkali metal is extracted and recovered from the char that results from the catalytic gasification process.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Catalytic Gasification Process with Recovery of Alkali Metal from Char
ActiveUS20090169449A1Quantity minimizationThermal non-catalytic crackingMuffle furnacesParticulatesSlurry
Processes are described for the extraction and recovery of alkali metal from the char that results from catalytic gasification of a carbonaceous material. Among other steps, the processes of the invention include a hydrothermal leaching step in which a slurry of insoluble particulate comprising insoluble alkali metal compounds is treated with carbon dioxide and steam at elevated temperatures and pressures to effect the conversion of insoluble alkali metal compounds to soluble alkali metal compounds. Further, processes are described for the catalytic gasification of a carbonaceous material where a substantial portion of alkali metal is extracted and recovered from the char that results from the catalytic gasification process.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
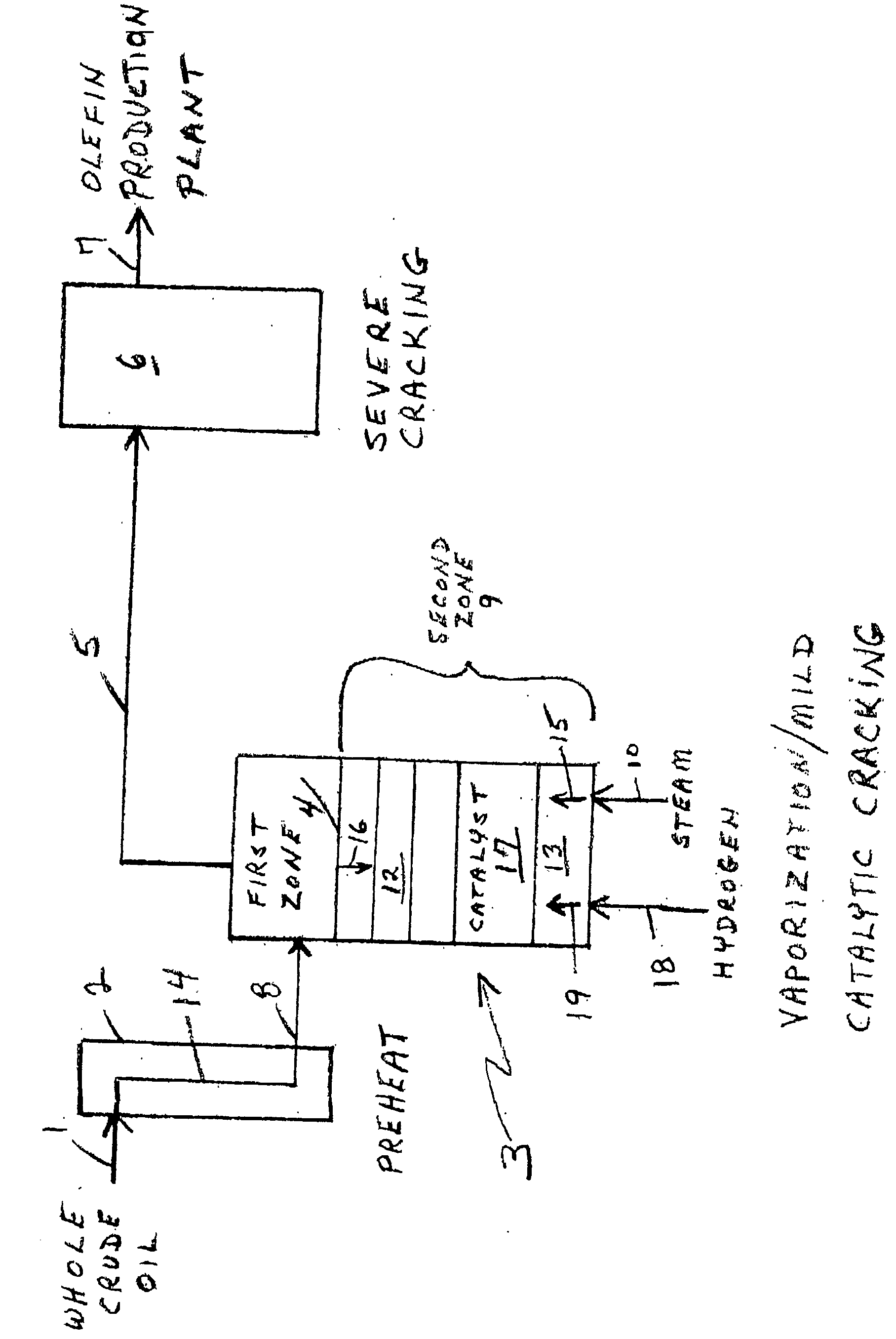
Olefin production utilizing whole crude oil and mild catalytic cracking
InactiveUS20040054247A1Lower temperature rangeImproved vaporizationThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingChemistryPyrolysis
A method for utilizing whole crude oil as a feedstock for the pyrolysis furnace of an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock after preheating is subjected to mild catalytic cracking conditions until substantially vaporized, the vapors from the mild catalytic cracking being subjected to severe cracking in the radiant section of the furnace.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Grafted polymers as gas hydrate inhibitors
InactiveUS6867262B1Low ground water pollution classificationReduce security risksThermal non-catalytic crackingUsing liquid separation agentPolymerHydrate
Owner:BASF AG
Solution mining dawsonite from hydrocarbon containing formations with a chelating agent
A method for treating an oil shale formation comprising dawsonite includes providing heat from one or more heaters to the formation to heat the formation. Hydrocarbon fluids are produced from the formation. At least some dawsonite in the formation is decomposed with the provided heat. A chelating agent is provided to the formation to dissolve at least some dawsonite decomposition products. The dissolved dawsonite decomposition products are produced from the formation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
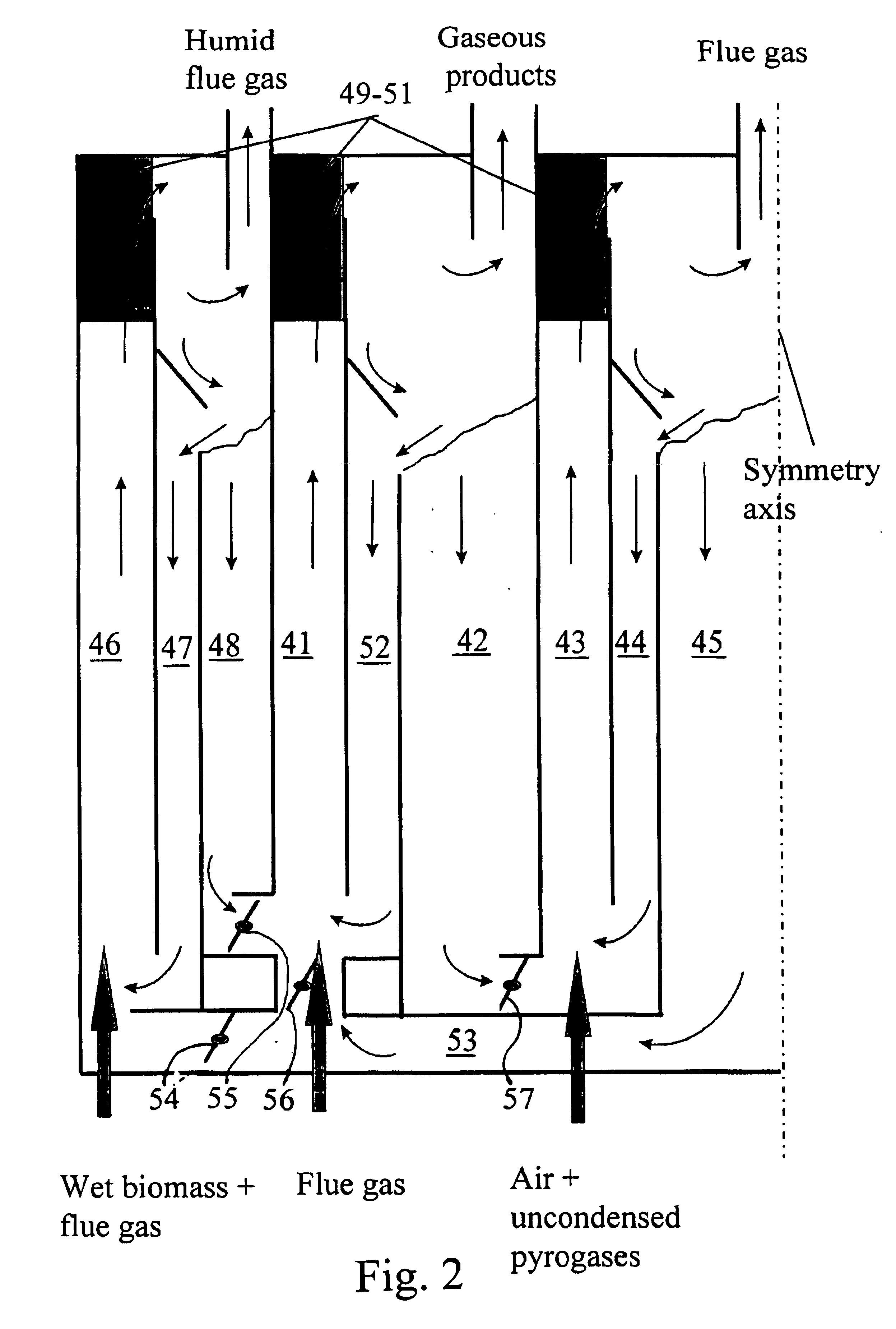
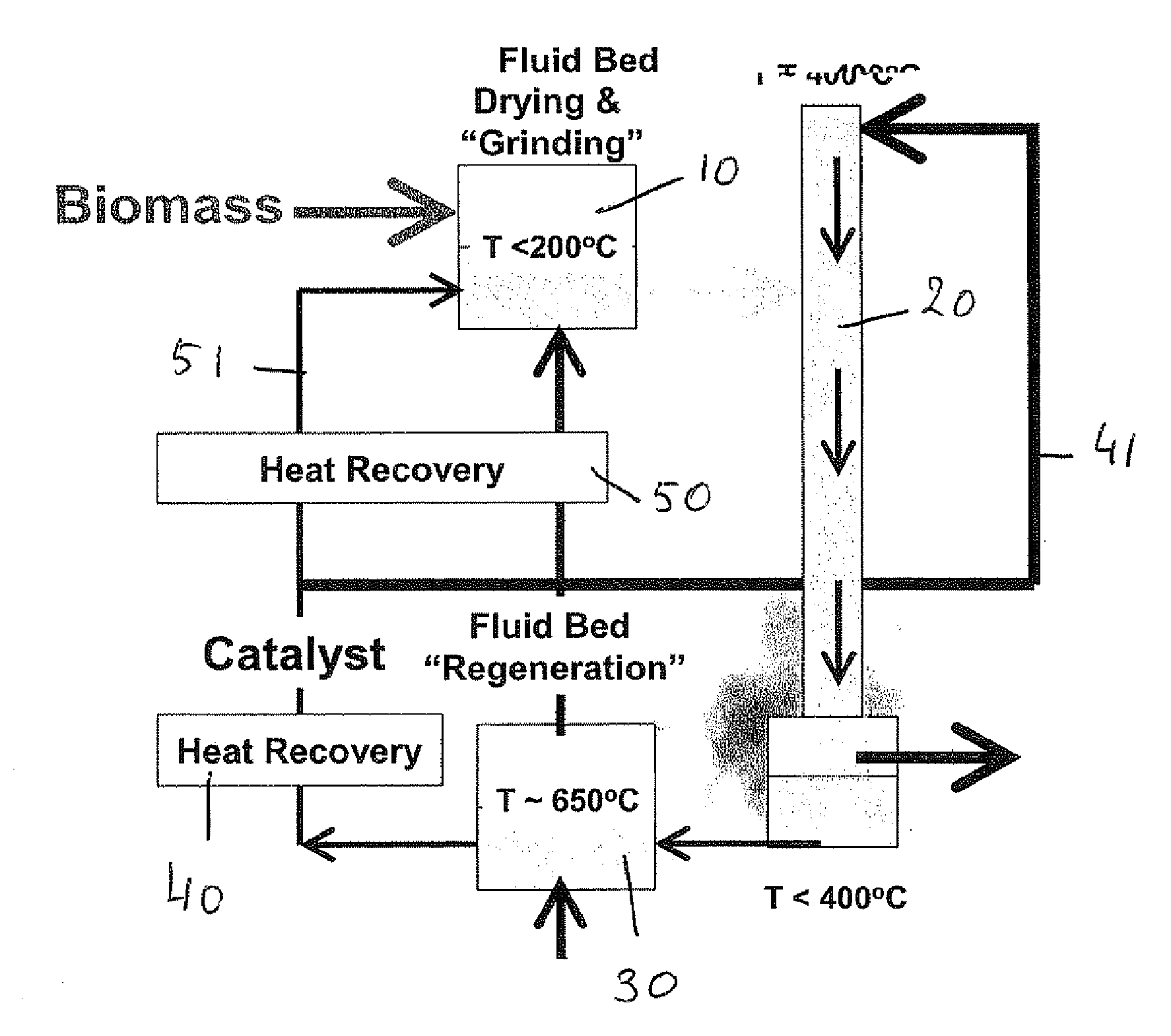
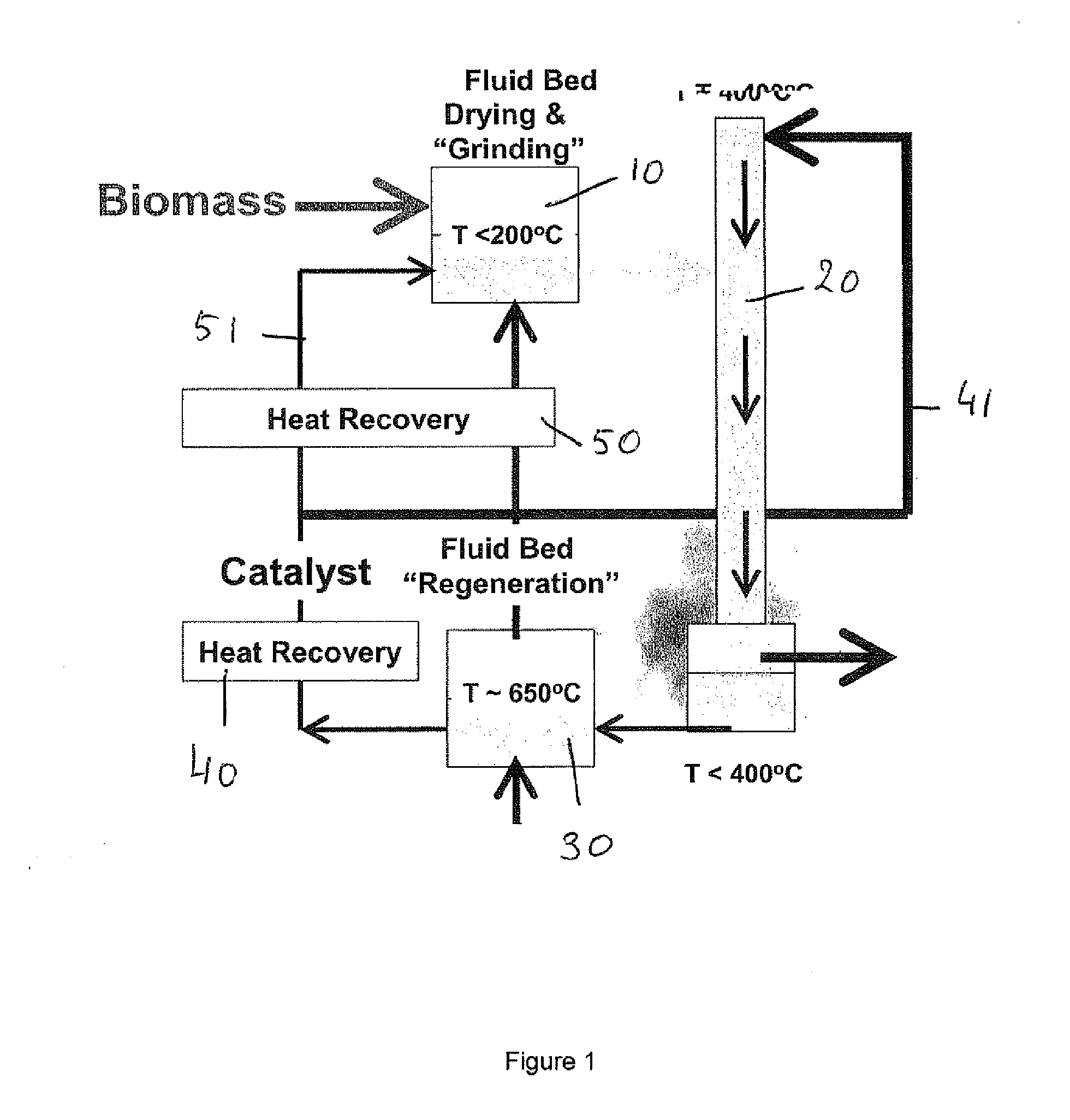
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
ActiveUS7905990B2Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingSolid waste disposalLiquid productHeat carrier
A rapid thermal conversion process for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. Biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. The liquid product may itself be used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
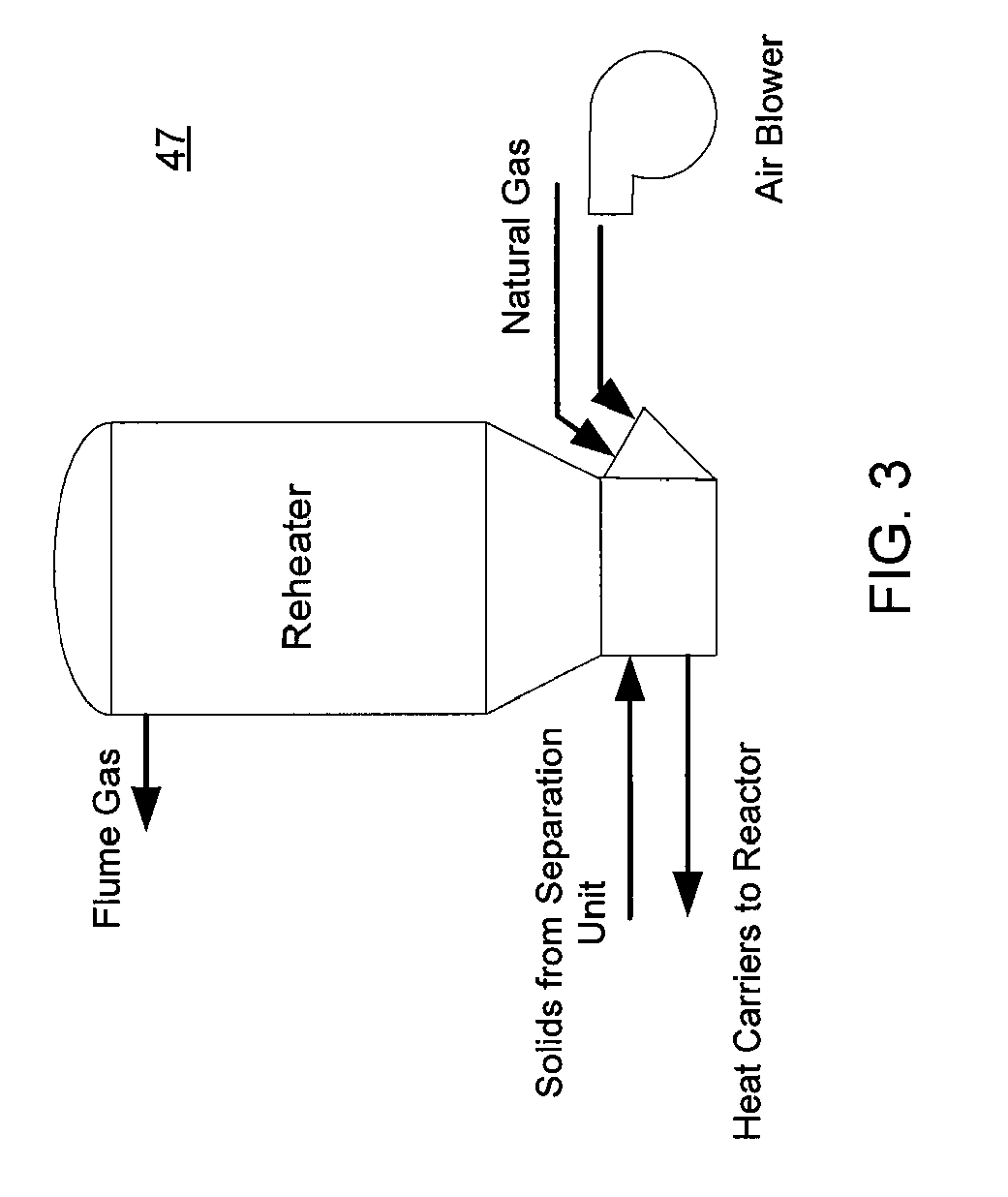
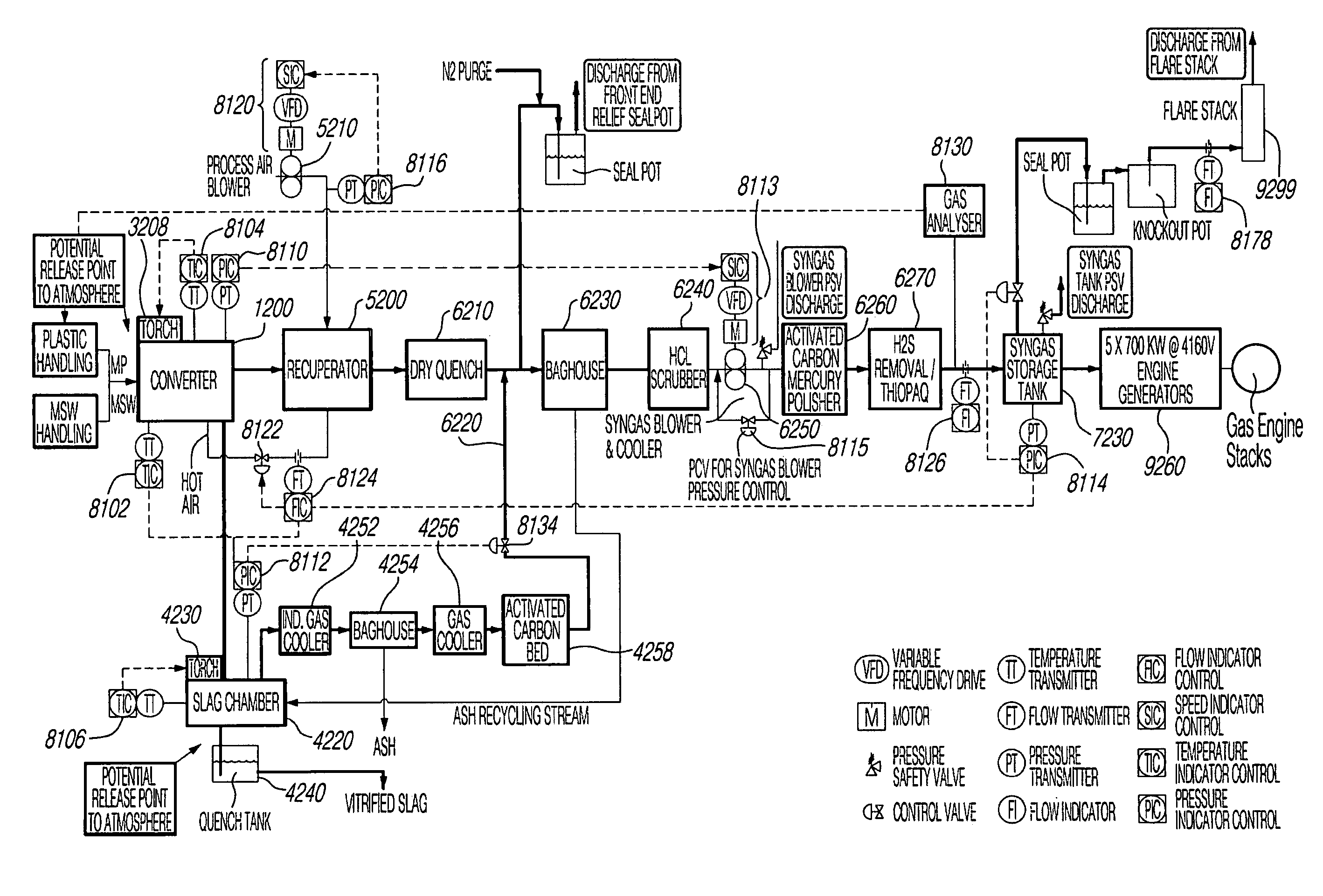
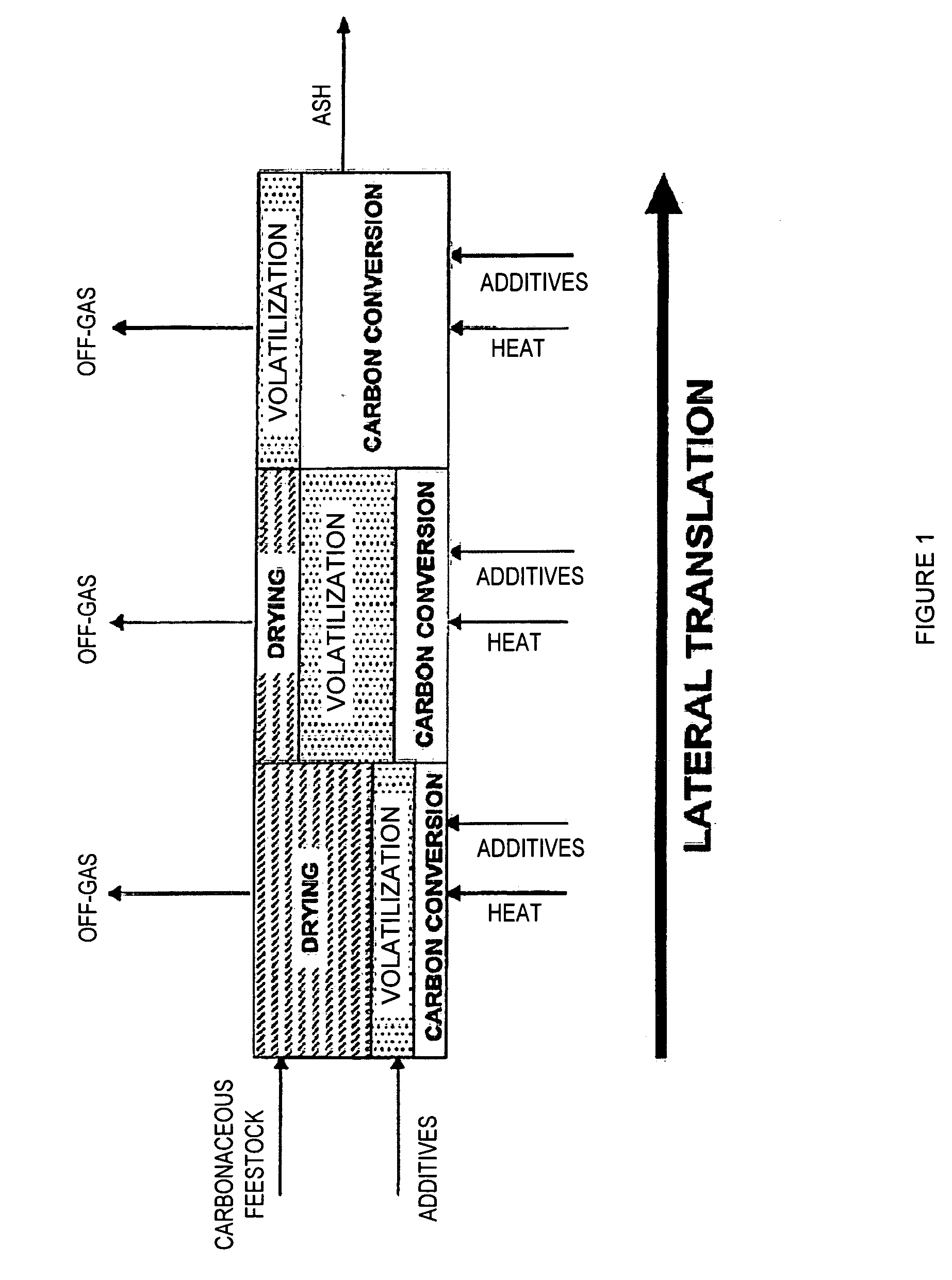
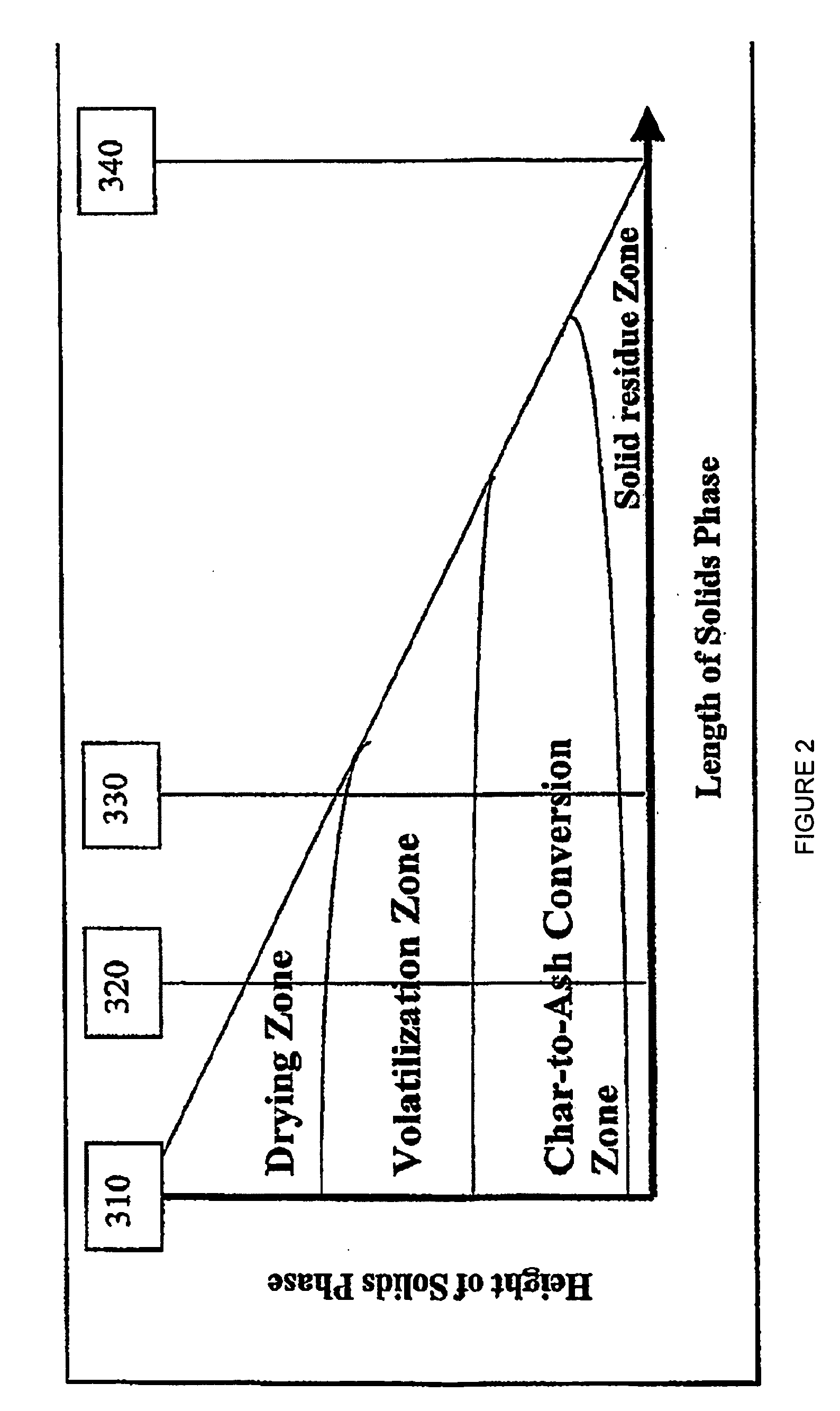
Low Temperature Gasification Facility with a Horizontally Oriented Gasifier
A low-temperature gasification system comprising a horizontally oriented gasifier is provided that optimizes the extraction of gaseous molecules from carbonaceous feedstock while minimizing waste heat. The system comprises a plurality of integrated subsystems that work together to convert municipal solid waste (MSW) into electricity. The subsystems comprised by the low-temperature gasification system are: a Municipal Solid Waste Handling System; a Plastics Handling System; a Horizontally Oriented Gasifier with Lateral Transfer Units System; a Gas Reformulating System; a Heat Recycling System; a Gas Conditioning System; a Residue Conditioning System; a Gas Homogenization System and a Control System.
Owner:PLASCO CONVERSION TECH INC
Steam Cracking with Naphtha Dearomatization
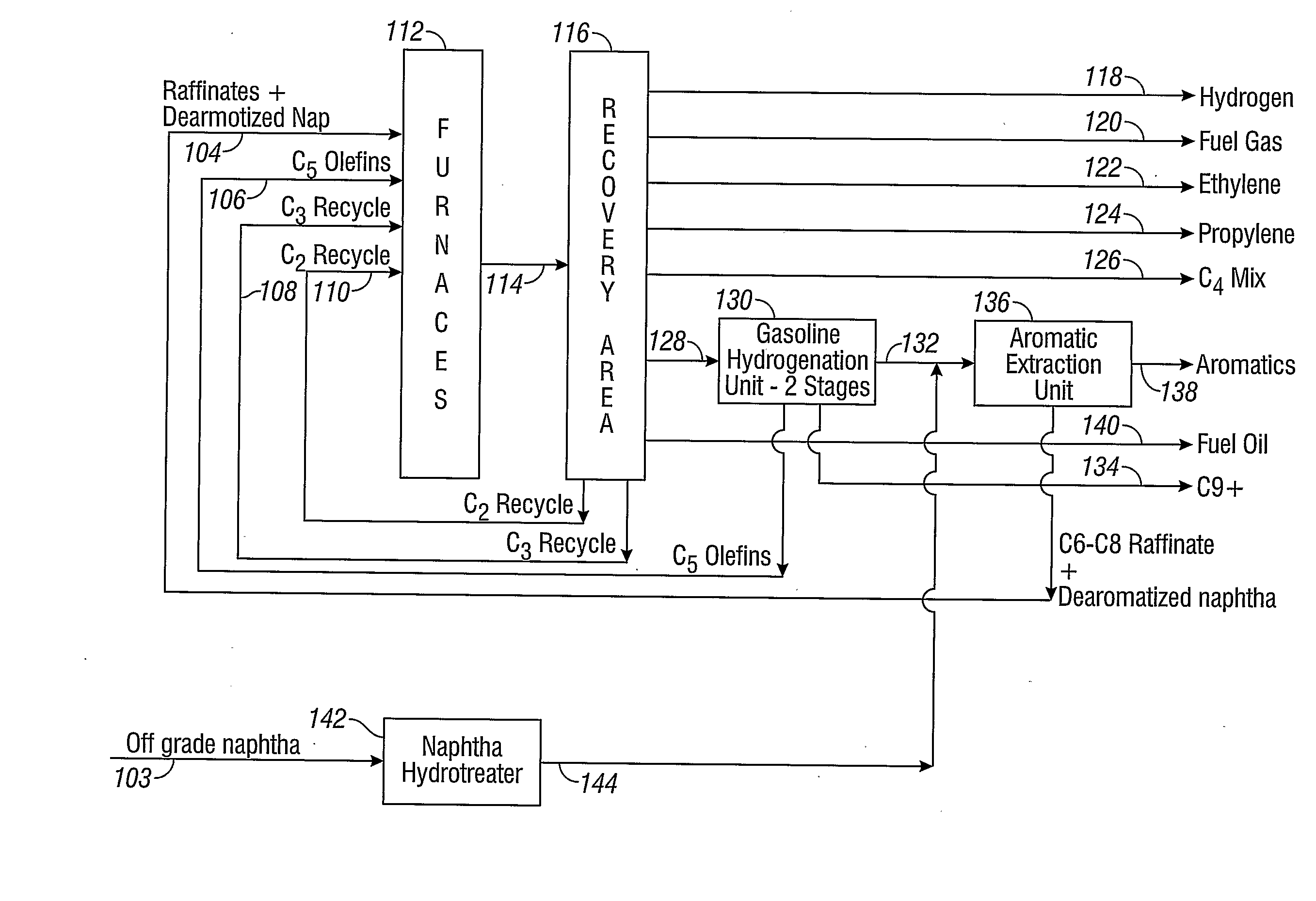
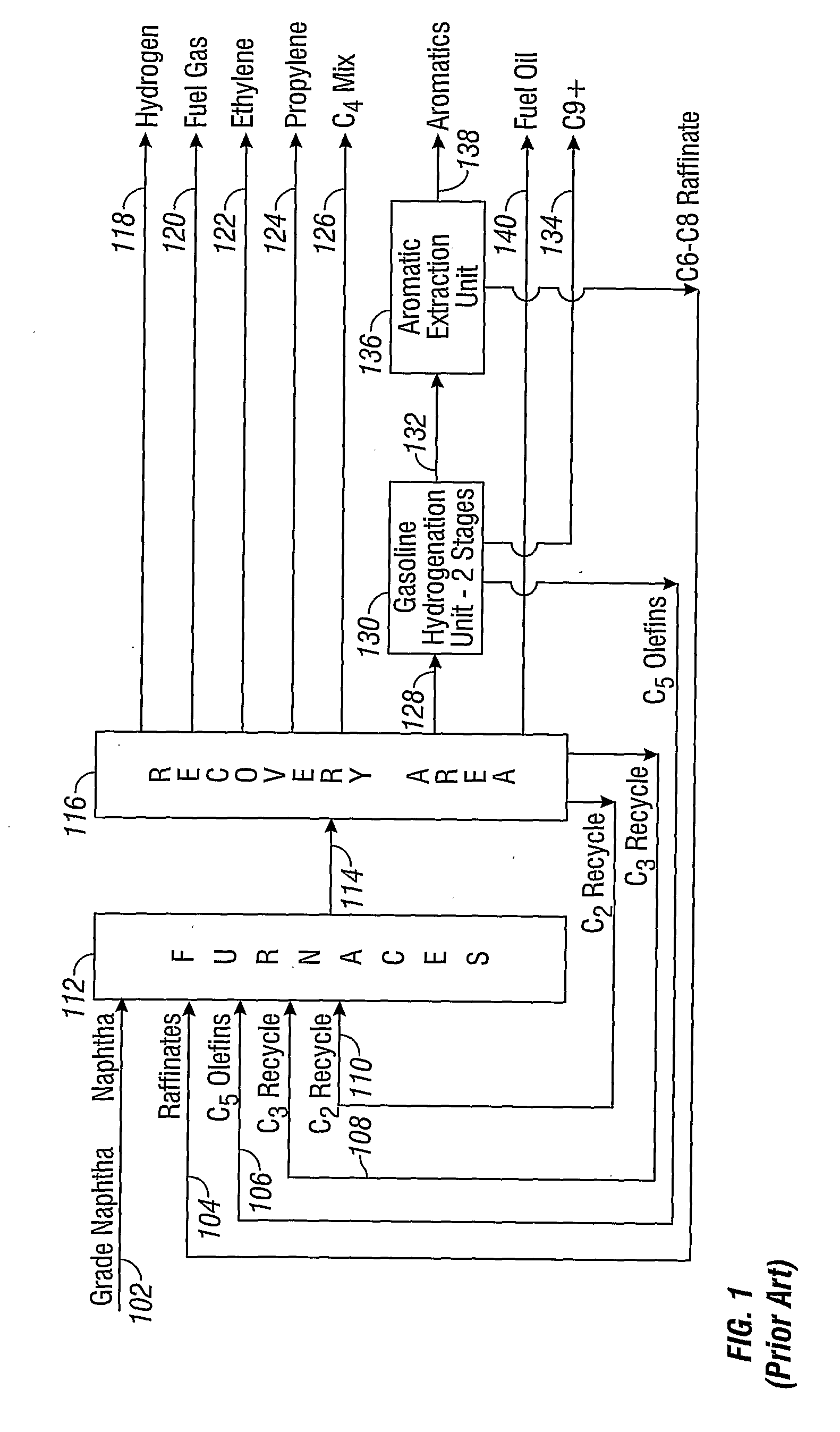
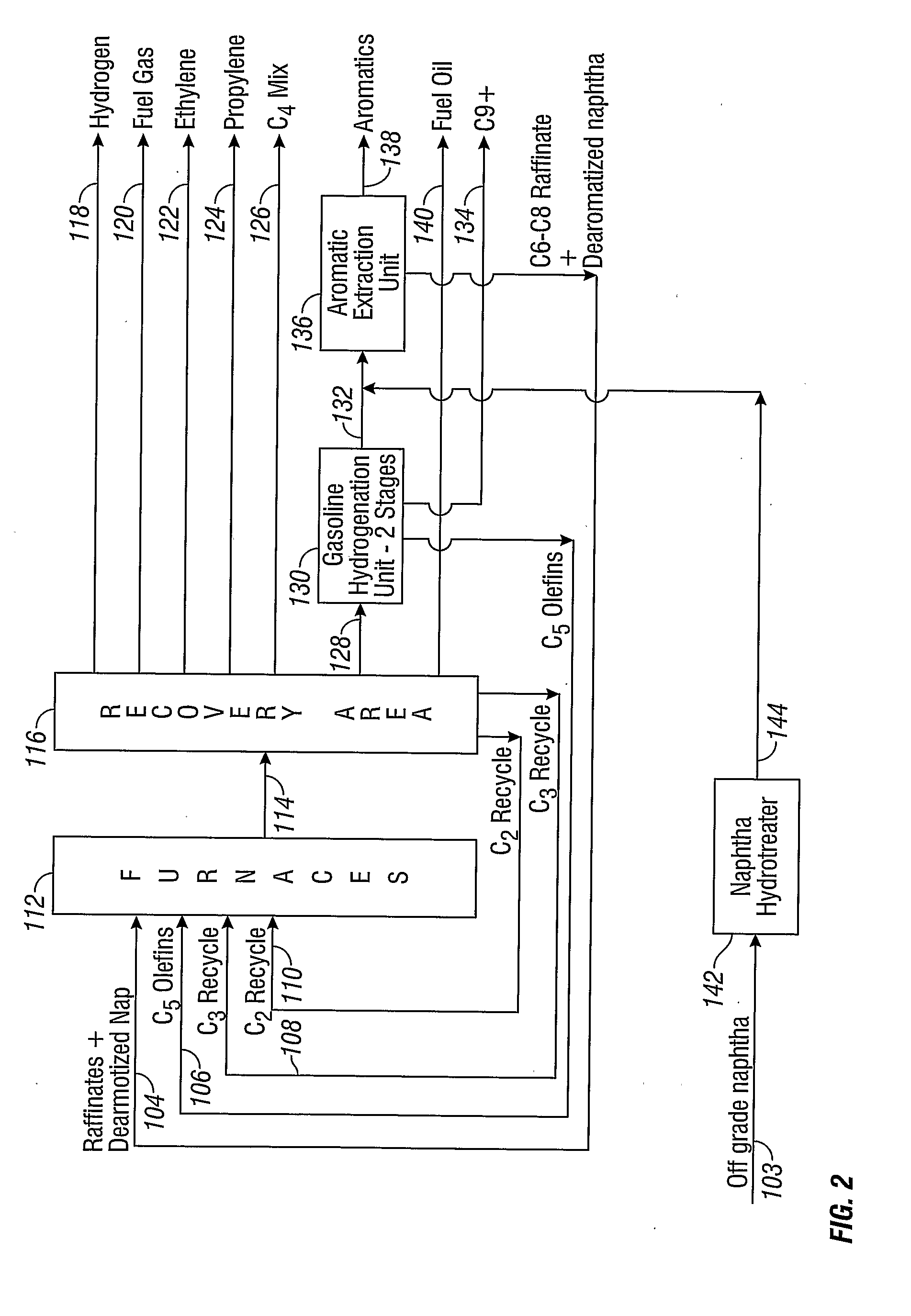
Disclosed is a process for upgrading a naphtha feed stream comprising light naphtha, heavy naphtha, or a combination thereof, for supplying to a cracking process. A naphtha feed stream can be supplied to a hydrotreater 142 to remove impurities, followed by dearomatization in an aromatics extraction unit 136. A dearomatized naphtha stream 104 can be supplied to a cracking process 112 and a recovery process 116 to produce various streams including ethylene 122 and propylene 124 for collection, ethane 110 and propane 108 for recycle to the cracking process 112, and a pyrolysis gas stream 128 which can be further treated to produce a C5 olefins stream 106, a C6-C8 stream 104, a C9+ stream 134, and a fuel oil stream 140.
Owner:BHIRUD VASANT L
Methods of hydrotreating a mixture made up of oils of animal or vegetable origin and of petroleum cuts with intermediate stripping
ActiveUS20080161614A1Low costLimit consumption of hydrogenThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingVegetable oilVolumetric Mass Density
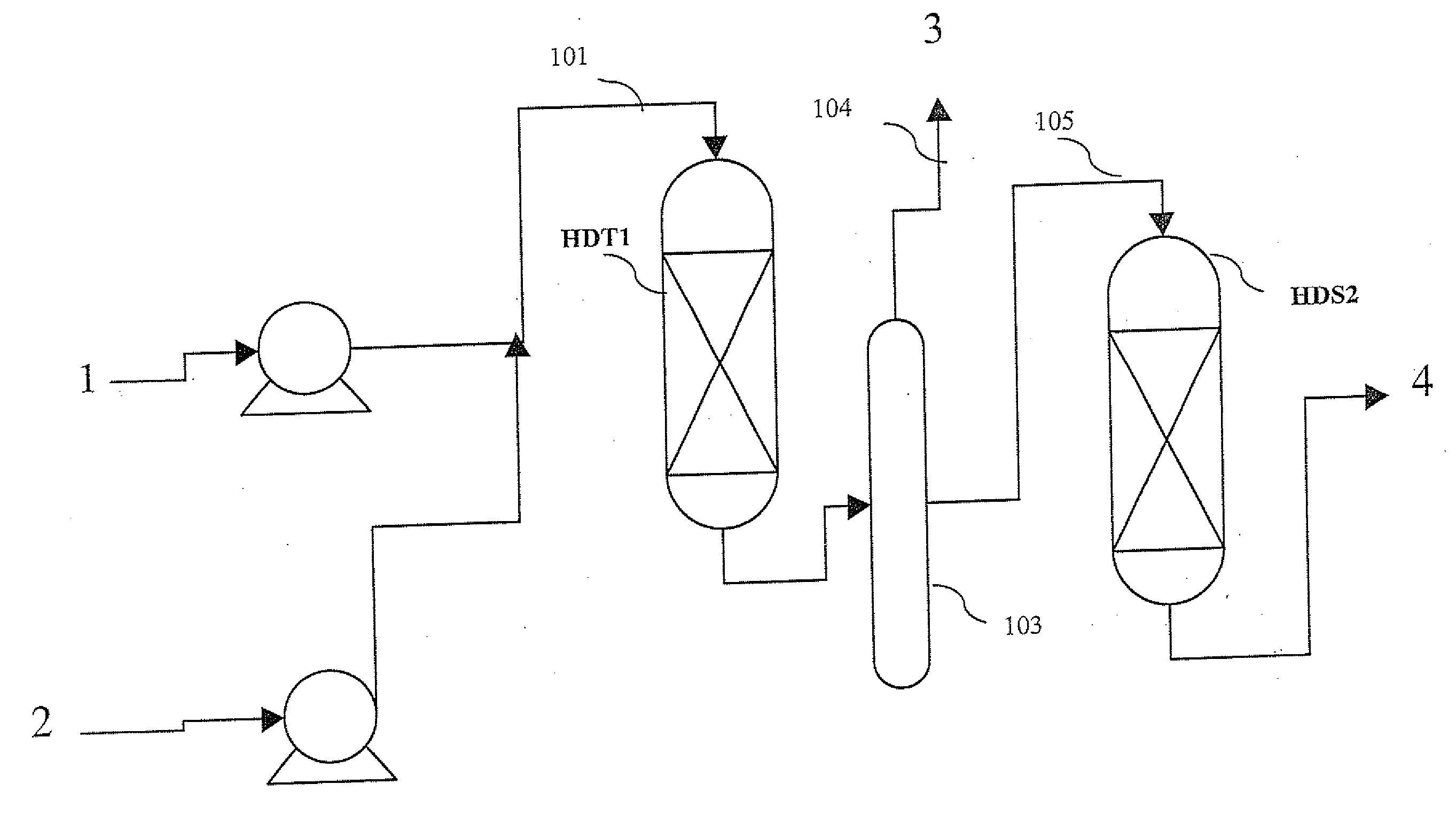
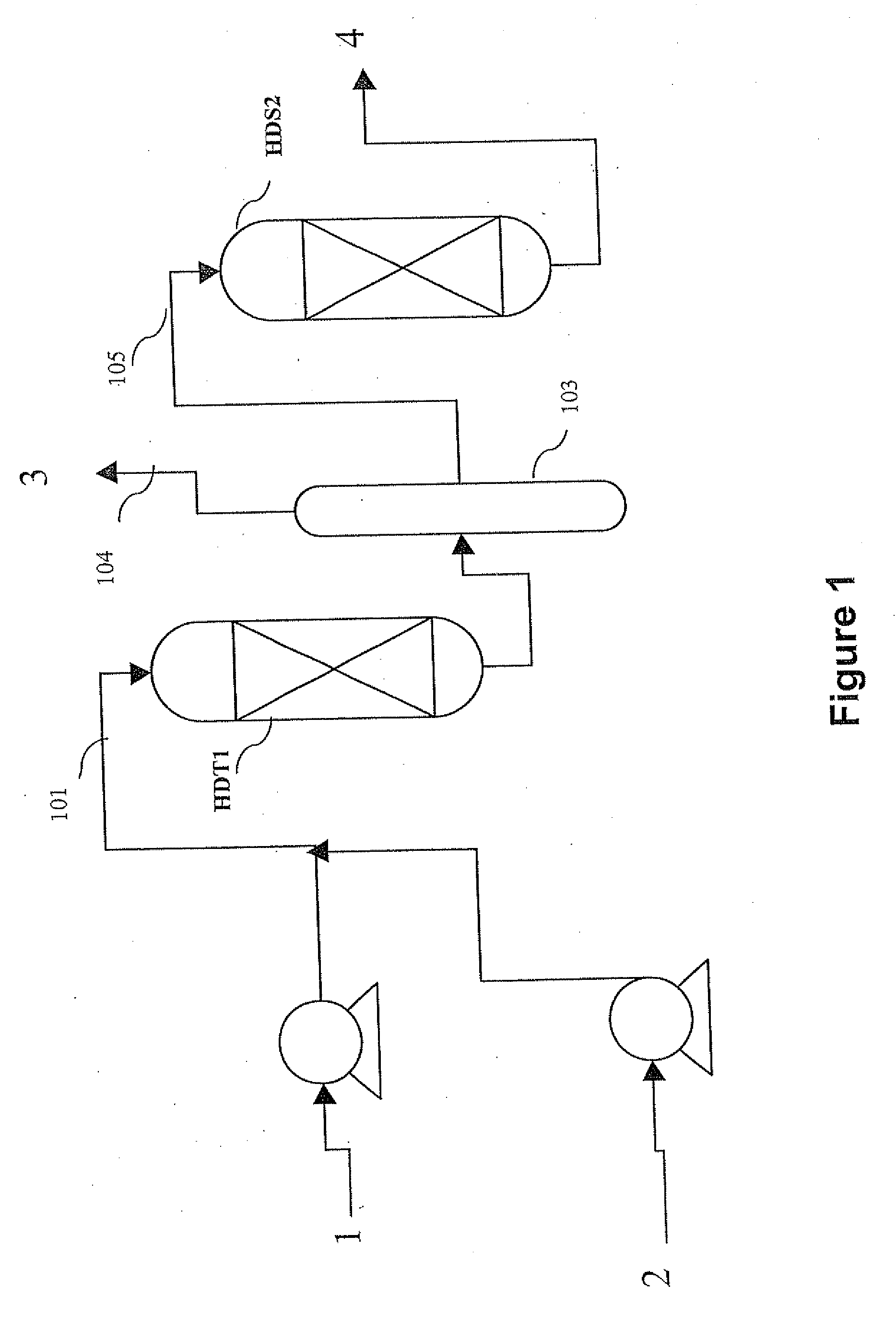
The invention relates to a hydrotreating method (HDT) using two plants working under different operating conditions with an intermediate stripping for co-treating a mixture made up of oils of vegetable or animal origin and petroleum cuts (gas oil cuts (GO) and middle distillates) in order to produce gas oil fuel bases meeting specifications. The first plant (HDT1) is more particularly dedicated to the reactions concerning oils of vegetable or animal origin in comixture while pretreating the hydrocarbon feed, whereas the second plant (HDS2) works under more severe conditions to obtain diesel fuel according to standards, in particular in terms of effluent sulfur content, density and cold properties. The process economy, the activity and the stability of the catalyst of the second plant are greatly improved by the intermediate stripping.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
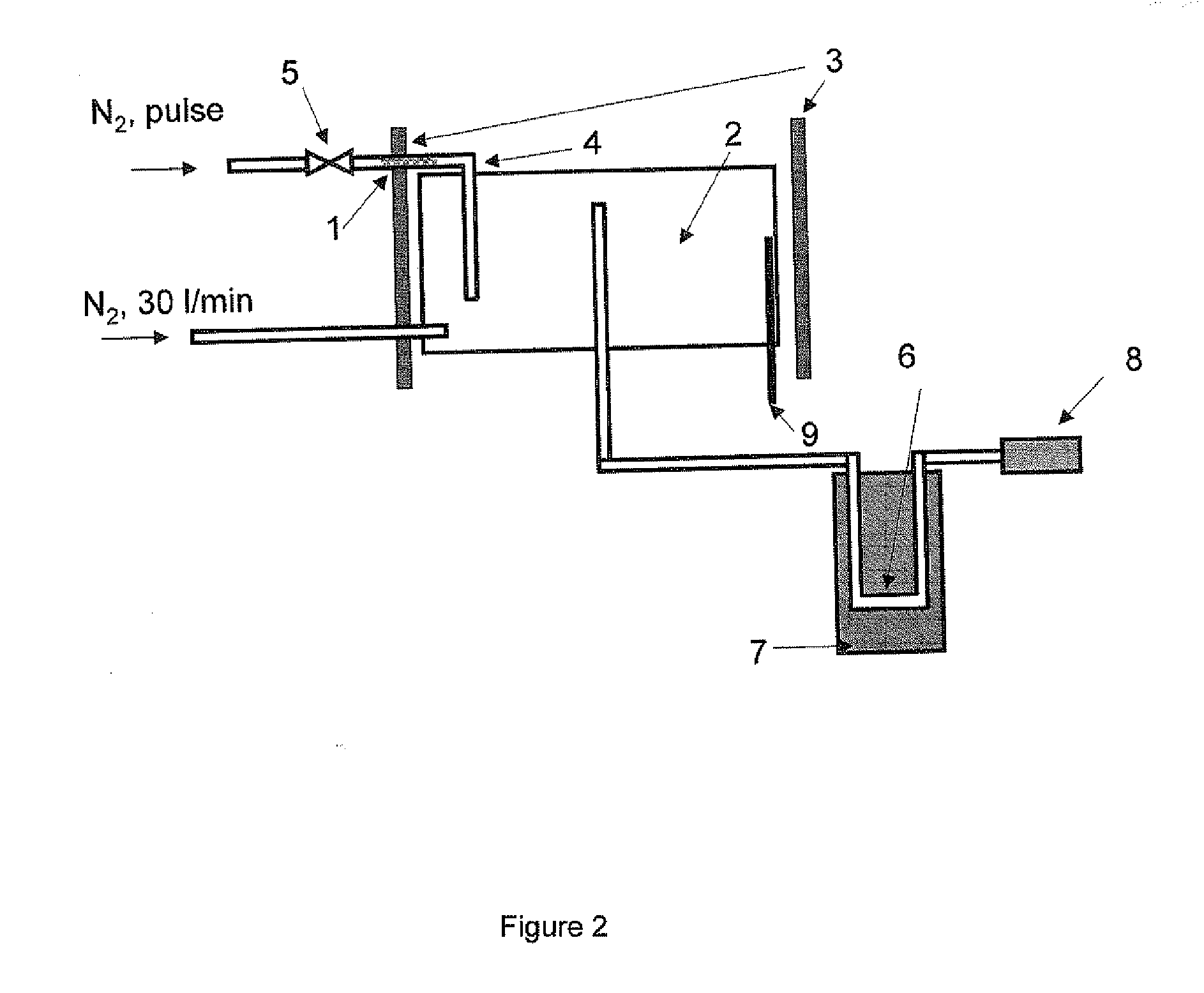
Process for pyrolyzing carbonaceous feedstocks
InactiveUS6814940B1Reduce gas velocityReduce dwell timeThermal non-catalytic crackingMuffle furnacesProcess engineeringProduct gas
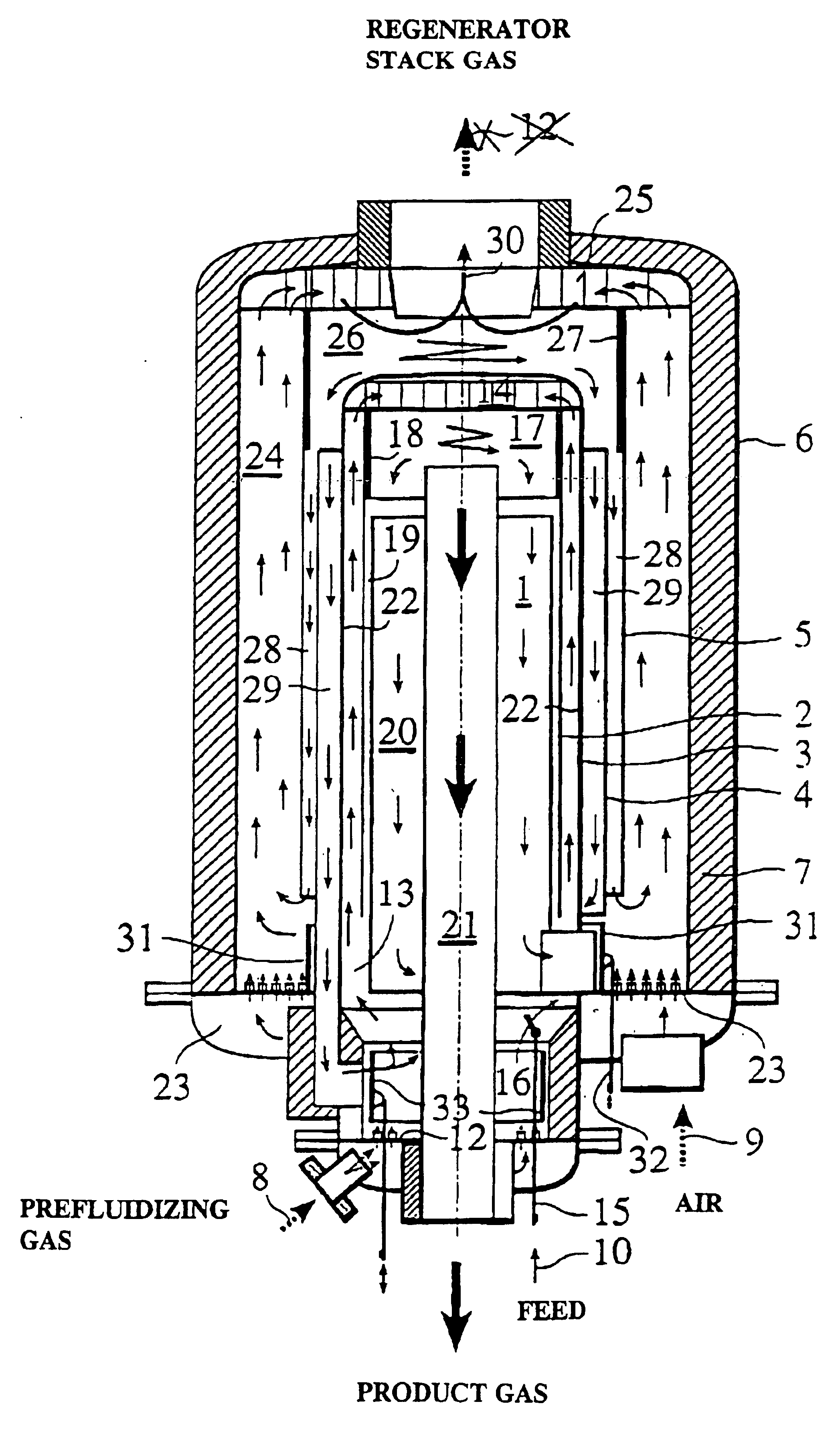
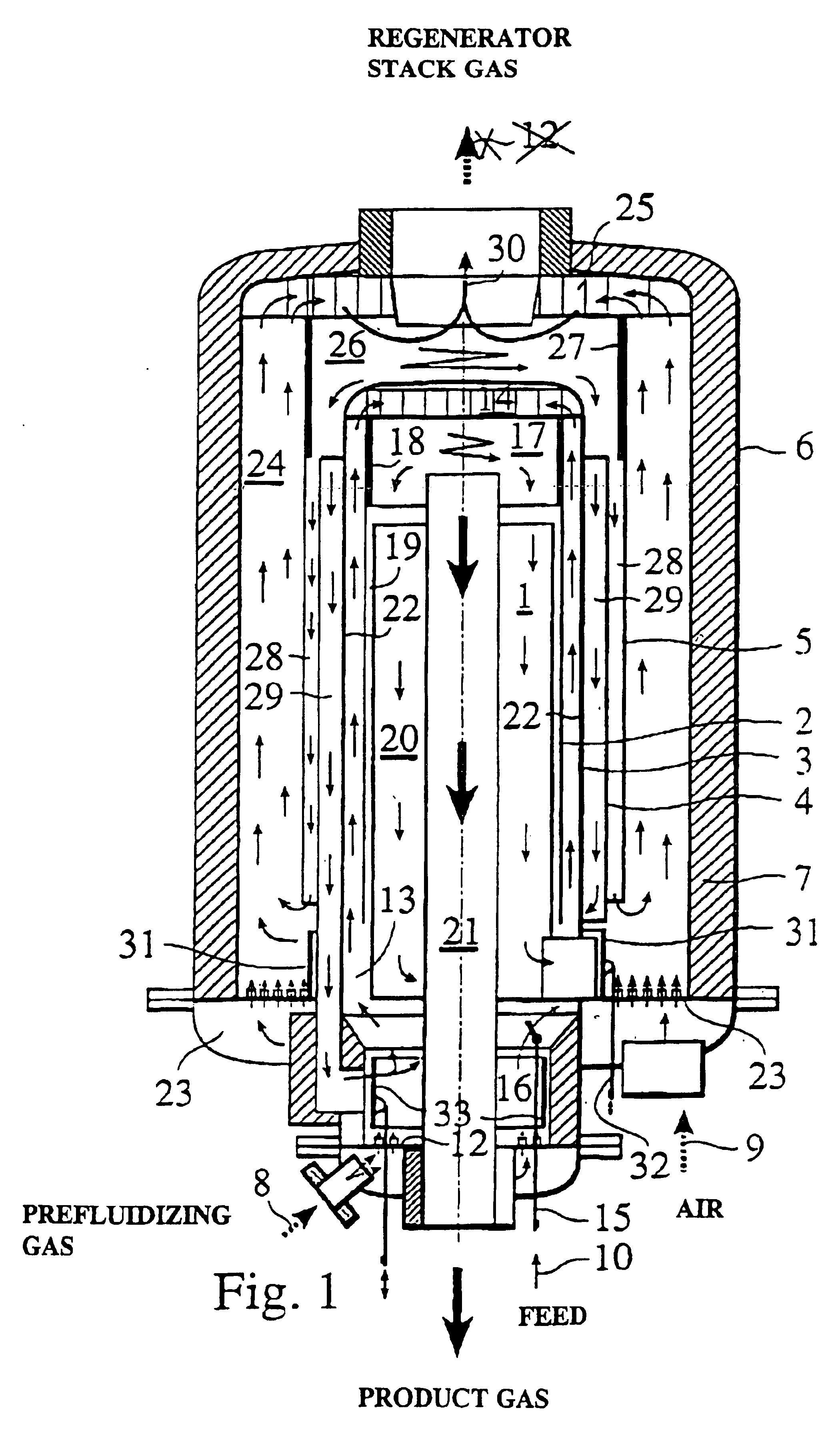
The present invention concerns a process and an apparatus for thermal conversion of biomass and organic wastes. According to the invention, the feedstock is fed into a fluidized-bed reactor, wherein the feed is converted at an elevated temperature under the influence of particulate matter kept in a fluidized state by a fluidizing gas, the particulate matter is transferred from the reactor to a regenerator for regeneration and then recirculated to the reactor after the regeneration, and the converted hydrocarbon products are recovered from the reactor. Both the reactor and the regenerator comprise risers having an axially annular cross section and being equipped with multi-inlet cyclones for the separation of particulate matter. By means of the invention, it is possible to producer pyrolysis oil, the quality of which is higher than that of oil produced with the processes of the prior art. The incorporation of multi-inlet cyclones into the reactor configuration reduces gas velocities, reduces the physical size of the cyclone and shortens the residence time of gases in the cyclone.
Owner:FORTUM OY
Process for converting carbon-based energy carrier material
InactiveUS20090308787A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
A process is disclosed process for converting a solid or highly viscous carbon-based energy carrier material to liquid and gaseous reaction products, said process comprising the steps of: a) contacting the carbon-based energy carrier material with a particulate catalyst material b) converting the carbon-based energy carrier material at a reaction temperature between 200° C. and 450° C., preferably between 250° C. and 350° C., thereby forming reaction products in the vapor phase. In a preferred embodiment the process comprises the additional step of: c) separating the vapor phase reaction products from the particulate catalyst material within 10 seconds after said reaction products are formed; In a further preferred embodiment step c) is followed by: d) quenching the reaction products to a temperature below 200° C.
Owner:MARD INC
Complex comprising oxidative dehydrogenation unit
ActiveUS20140249339A1Consumes lotThermal non-catalytic crackingSequential/parallel process reactionsAlkaneDehydrogenation
Oxidative dehydrogenation of paraffins to olefins provides a lower energy route to produce olefins. Oxidative dehydrogenation processes may be integrated with a number of processes in a chemical plant such as polymerization processes, manufacture of glycols, and carboxylic acids and esters. Additionally, oxidative dehydrogenation processes can be integrated with the back end separation process of a conventional steam cracker to increase capacity at reduced cost.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
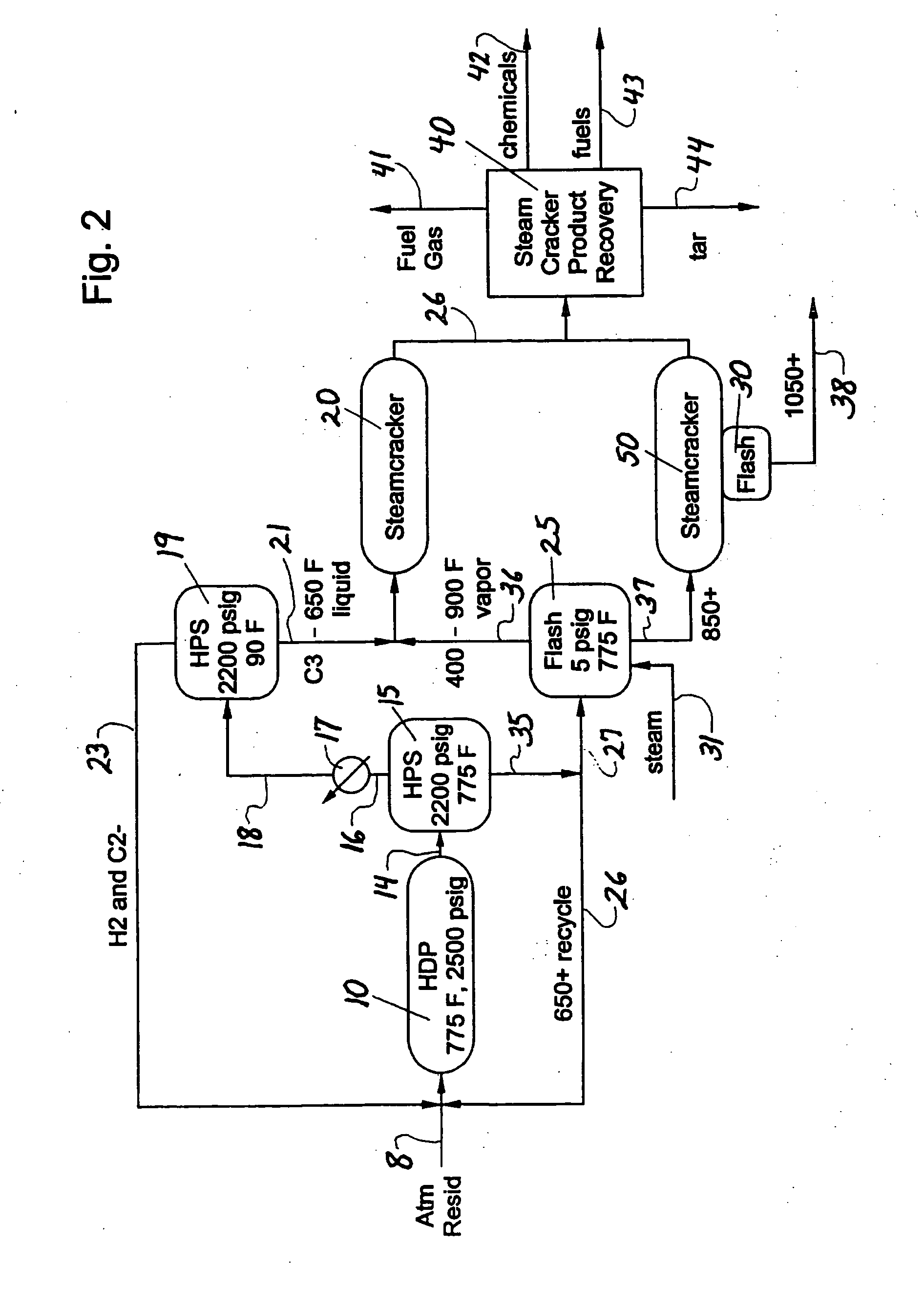
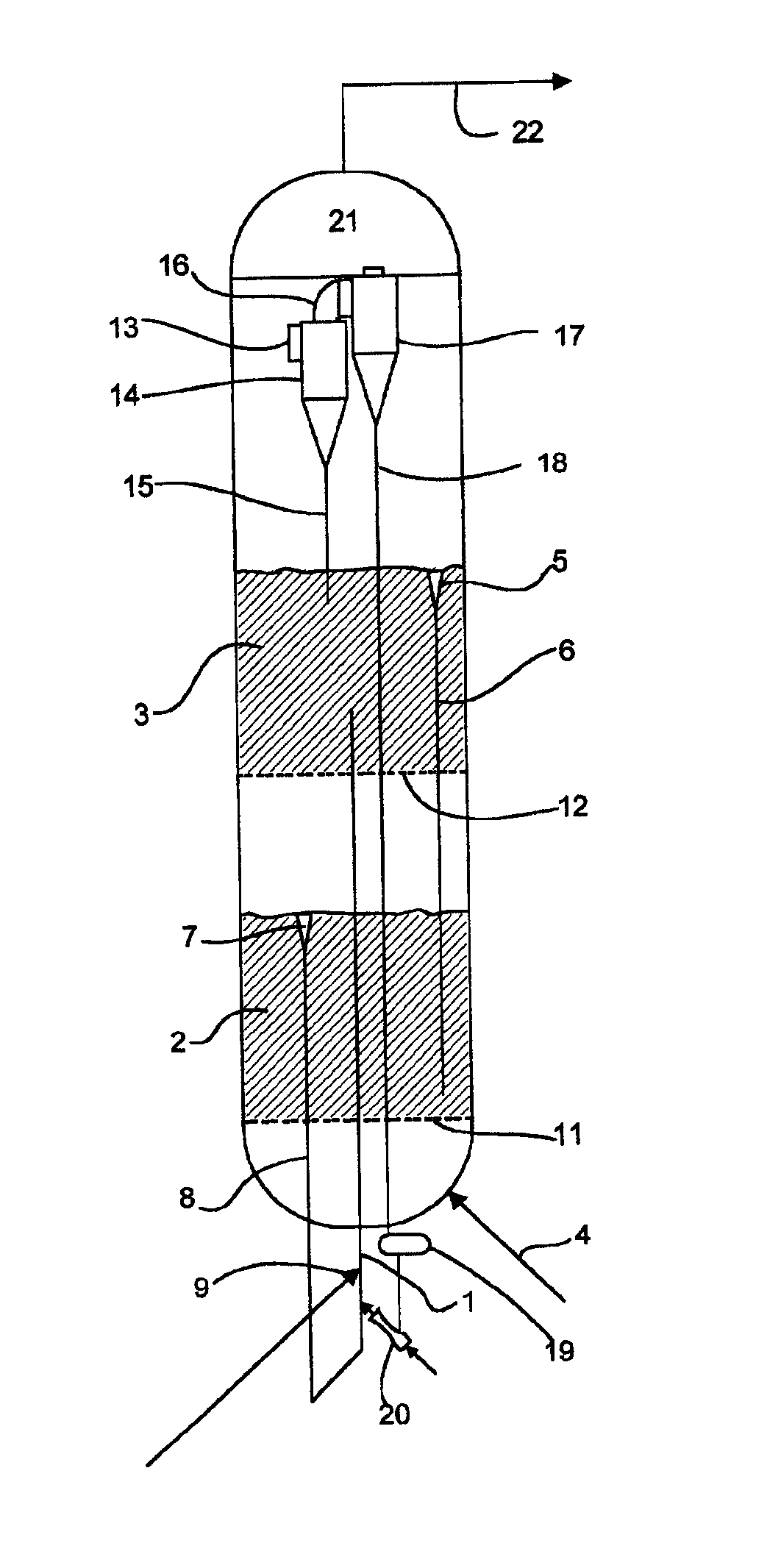
Converting mist flow to annular flow in thermal cracking application
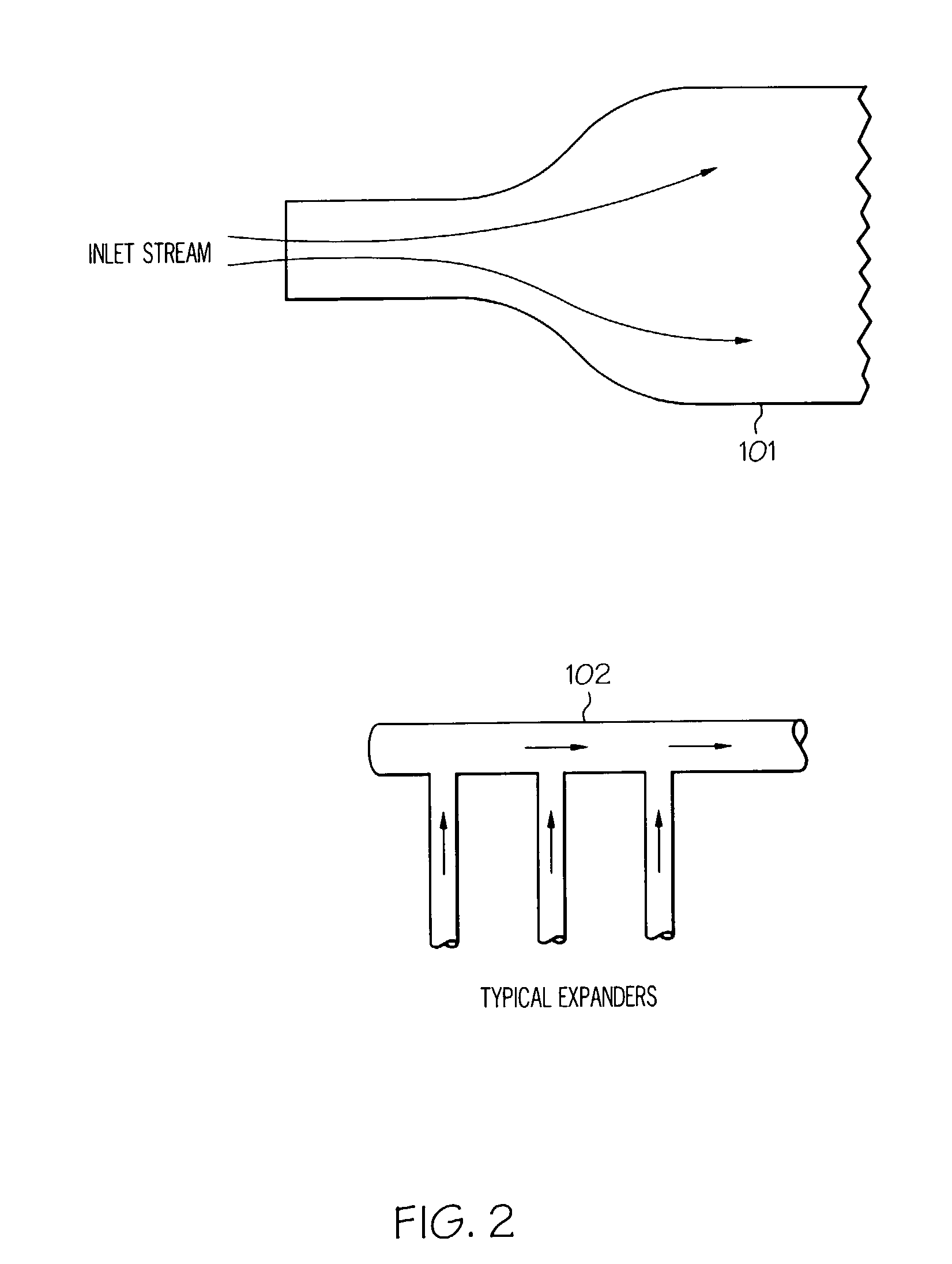
ActiveUS7097758B2Reduce flow rateShorten speedThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon oil cracking processGas phaseEngineering
A process to increase the non-volatile removal efficiency in a flash drum in the steam cracking system. The gas flow from the convection section is converted from mist flow to annular flow before entering the flash drum to increase the removal efficiency. The conversion of gas flow from mist flow to annular flow is accomplished by subjecting the gas flow first to at least one expander and then to bends of various degrees and force the flow to change directions at least once. The change of gas flow from mist to annular helps coalesce fine liquid droplets and thus being removed from the vapor phase.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for cracking hydrocarbon feed with water substitution
InactiveUS7090765B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon oil cracking processHydrocarbonHydrocotyle bowlesioides
A process for treating hydrocarbon feed in a furnace, the process comprising: (a) heating hydrocarbon feed, (b) adding water to the heated feed, (c) adding dilution steam to the heated feed to form a mixture, (d) heating the resulting mixture and feeding the resulting heated mixture to the furnace, wherein the water in (b) is added in an amount of from at least about 1% to 100% based on water and dilution steam by weight.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Resid processing for steam cracker feed and catalytic cracking
ActiveUS20070090020A1High hydrogen contentEliminate needThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon oil cracking processProcess engineeringAlkene
The invention concerns integration of hydroprocessing and steam cracking. A feed comprising crude or resid-containing fraction thereof is treated by hydroprocessing and visbreaking and then passed to a steam cracker to obtain a product comprising olefins.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Fluid cat cracking with high olefins prouduction
InactiveUS20020003103A1Increase productionMaximize lightThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyNaphthaOrganic chemistry
The propylene production of a fluid catalytic cracking unit employing a large pore zeolite cracking catalyst, produces more propylene by adding a naphtha cracking riser and a medium pore zeolite catalytic component to the unit, and recycling at least a portion of the naphtha crackate to the naphtha riser. The large pore size zeolite preferably comprises a USY zeolite and the medium pore size is preferably ZSM-5. Propylene production per unit of naphtha feed to the naphtha riser is maximized, by using the 60-300.degree. F. naphtha crackate as the feed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Solar-thermal fluid-wall reaction processing
InactiveUS7033570B2Reduce and preventShort stayThermal non-catalytic crackingSolar heating energyHydrogenReactor system
The present invention provides a method for carrying out high temperature thermal dissociation reactions requiring rapid-heating and short residence times using solar energy. In particular, the present invention provides a method for carrying out high temperature thermal reactions such as dissociation of hydrocarbon containing gases and hydrogen sulfide to produce hydrogen and dry reforming of hydrocarbon containing gases with carbon dioxide. In the methods of the invention where hydrocarbon containing gases are dissociated, fine carbon black particles are also produced. The present invention also provides solar-thermal reactors and solar-thermal reactor systems.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Methods of hydrotreating a liquid stream to remove clogging compounds
A method includes producing formation fluid from a subsurface in situ heat treatment process. The formation fluid is separated to produce a liquid stream and a gas stream. At least a portion of the liquid stream is provided to a hydrotreating unit. At least a portion of selected in situ heat treatment clogging compositions in the liquid stream are removed to produce a hydrotreated liquid stream by hydrotreating at least a portion of the liquid stream at conditions sufficient to remove the selected in situ heat treatment clogging compositions.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Electrophoretic displays using nanoparticles
InactiveUS20030096113A1Increase volumeThermal non-catalytic crackingMechanical clocksElectrophoresisNanoparticle
An electrophoretic display comprises a fluid and a plurality of nanoparticles having diameters substantially less the wavelengths of visible light such that, when the nanoparticles are in a dispersed state and uniformly dispersed throughout the fluid, the fluid presents a first optical characteristic, but when the nanoparticles are in an aggregated state in which they are gathered into aggregates substantially larger than the individual nanoparticles, the fluid presents a second optical characteristic different from the first optical characteristic. The electrophoretic display further comprises at least one electrode arranged to apply an electric field to the nanoparticle-containing fluid and thereby move the nanoparticles between their dispersed and aggregated states. Various compound particles comprising multiple nanoparticles, alone or in combination with larger objects, and processes for the preparation of such compound particles, are also described.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
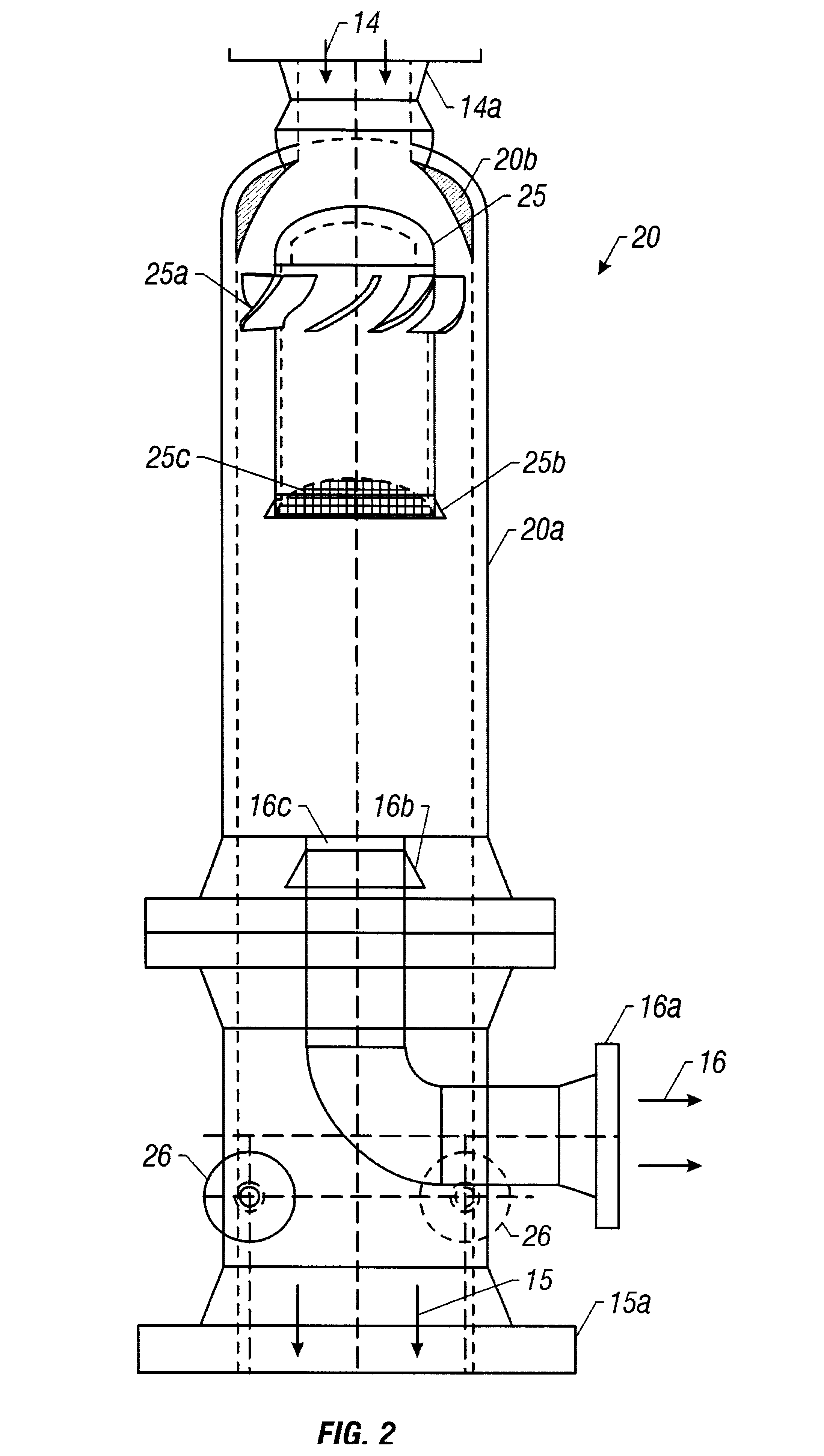
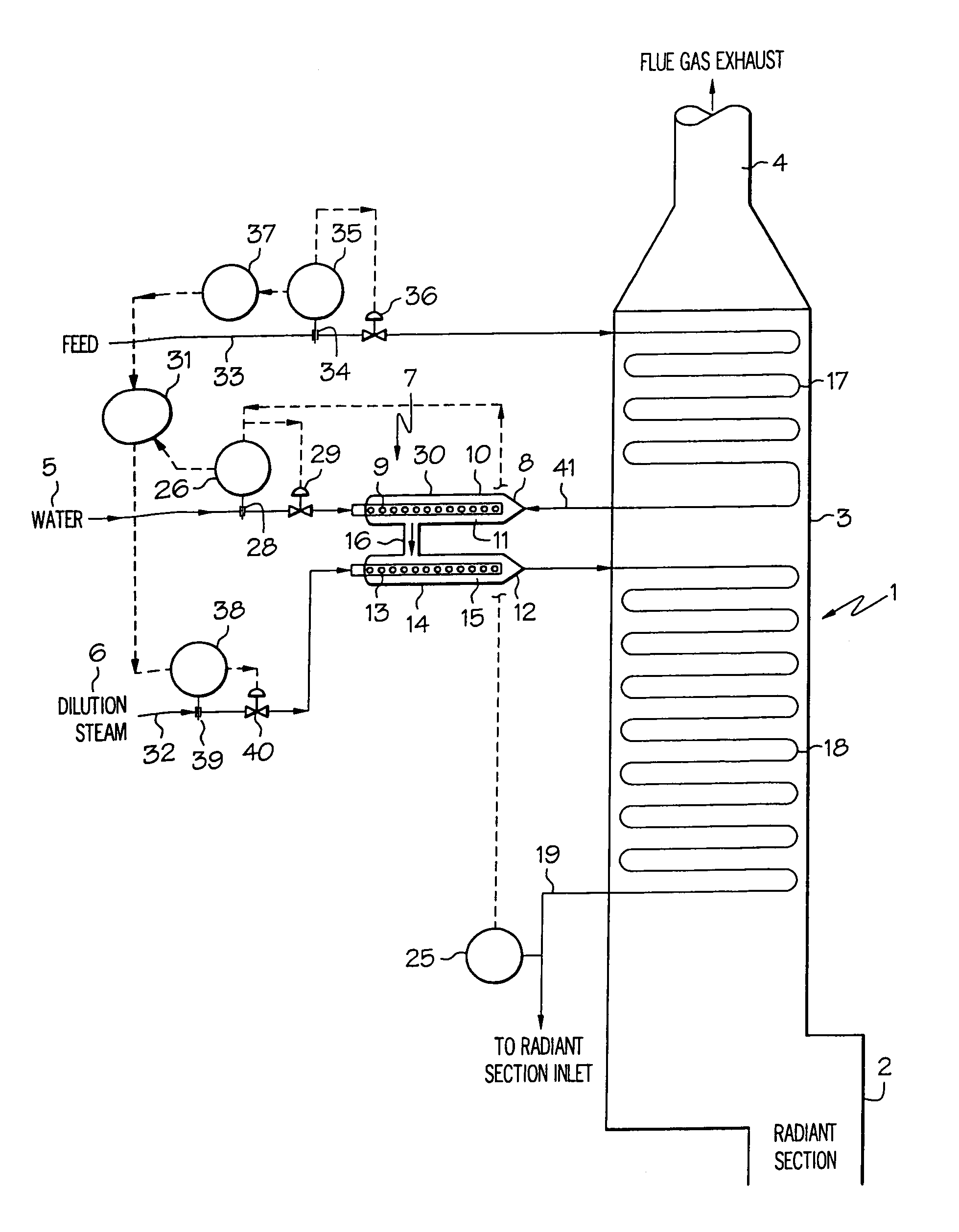
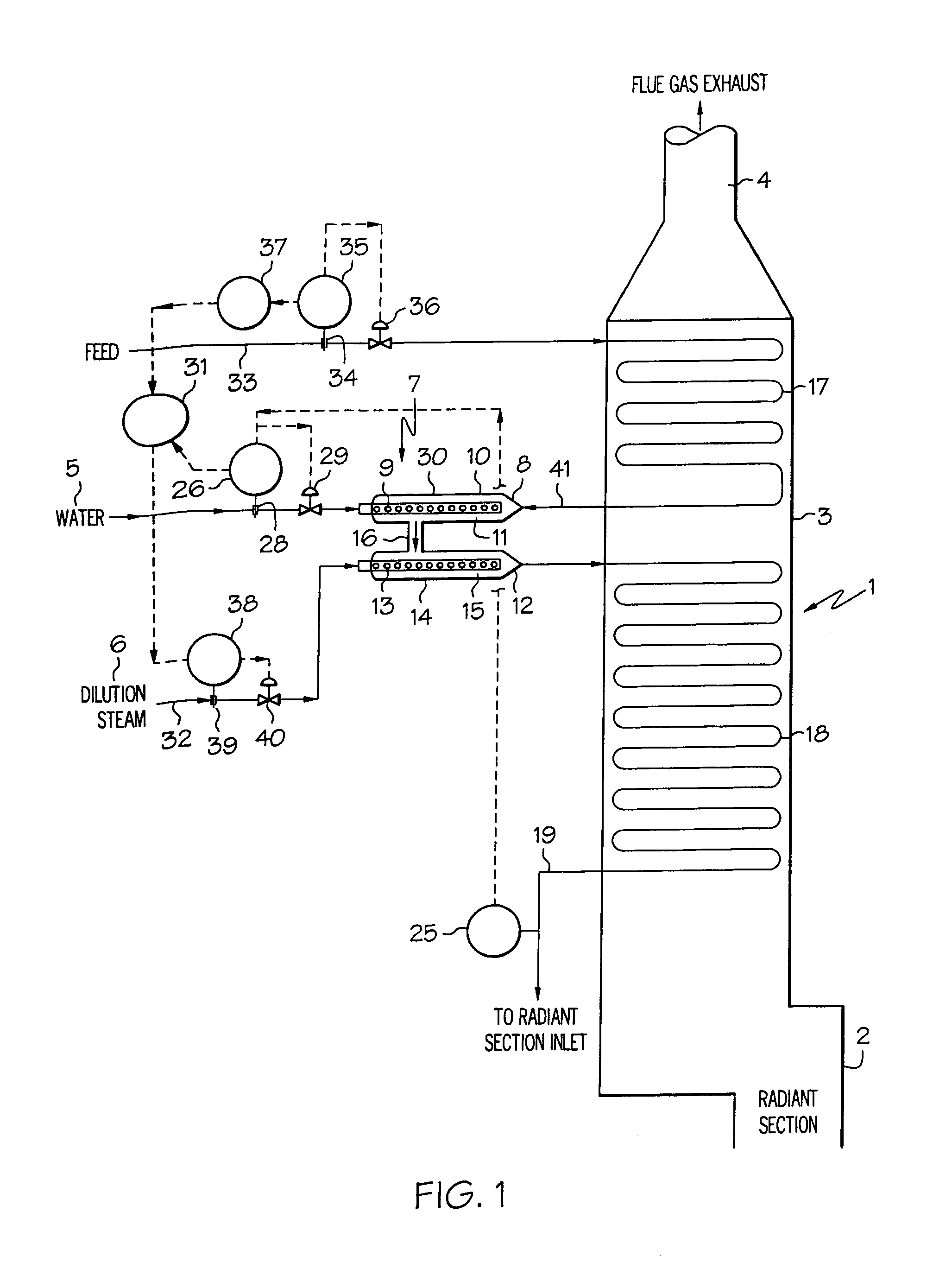
Cracking hydrocarbon feedstock containing resid utilizing partial condensation of vapor phase from vapor/liquid separation to mitigate fouling in a flash/separation vessel
A process is provided for cracking hydrocarbon feedstock containing resid comprising: heating the feedstock, mixing the heated feedstock with a fluid and / or a primary dilution steam stream to form a mixture, optionally further heating the mixture, flashing the mixture within a flash / separation vessel to form a vapor phase and a liquid phase, partially condensing the vapor phase by contacting with a condenser within the vessel, to condense at least some coke precursors within the vapor while providing condensates which add to the liquid phase, removing the vapor phase of reduced coke precursors content as overhead and the liquid phase as bottoms, heating the vapor phase, cracking the vapor phase in a radiant section of a pyrolysis furnace to produce an effluent comprising olefins, and quenching the effluent and recovering cracked product therefrom. An apparatus for carrying out the process is also provided.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Popular searches
Hydrocarbon by hydrogenation Liquid hydrocarbon mixture production Treatment with hydrotreatment processes Base-materials Petroleum wax recovery Petroleum chemical modification Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Organic compound preparation Oxygen compounds preparation by reduction Hydrocarbon oil cracking
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com