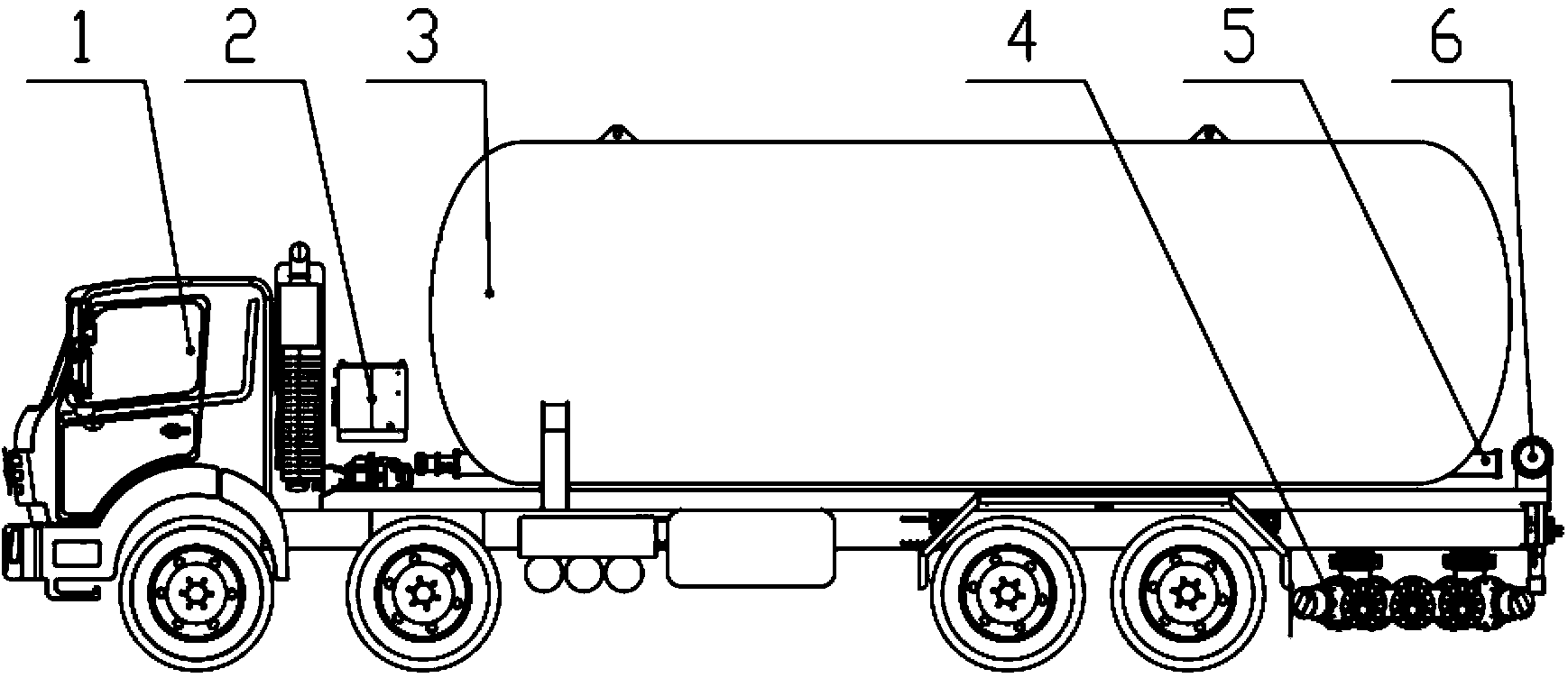
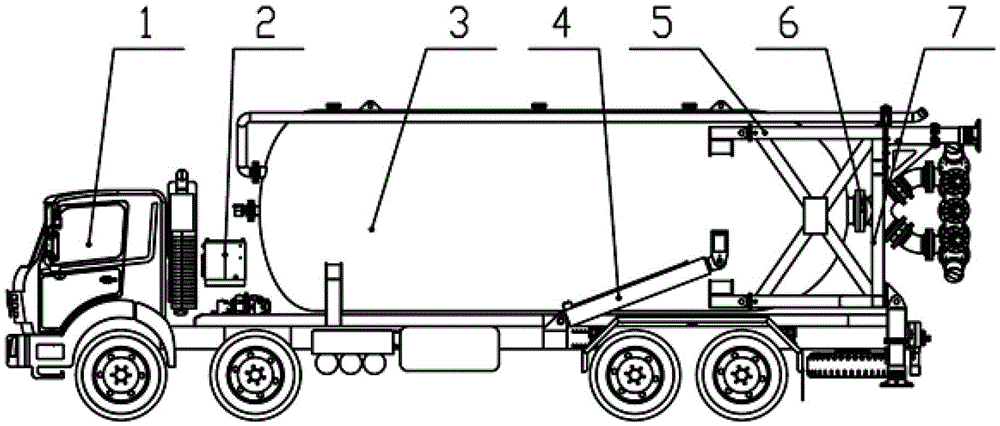
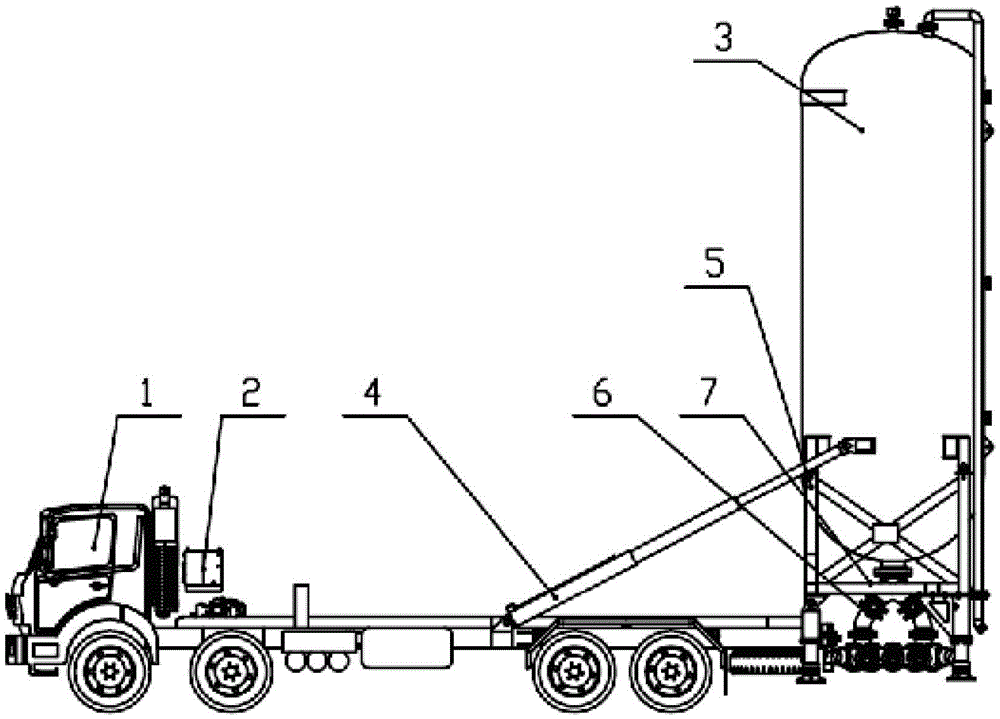
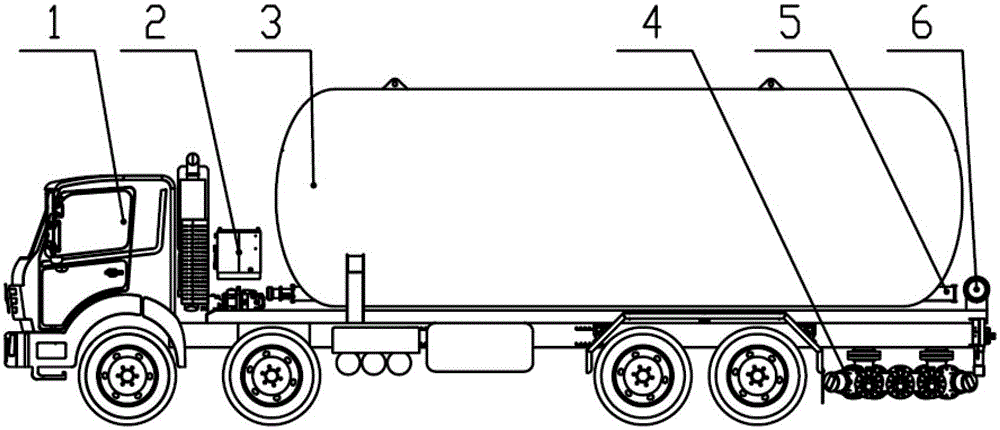
Patents
Literature
9812 results about "Solid particle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
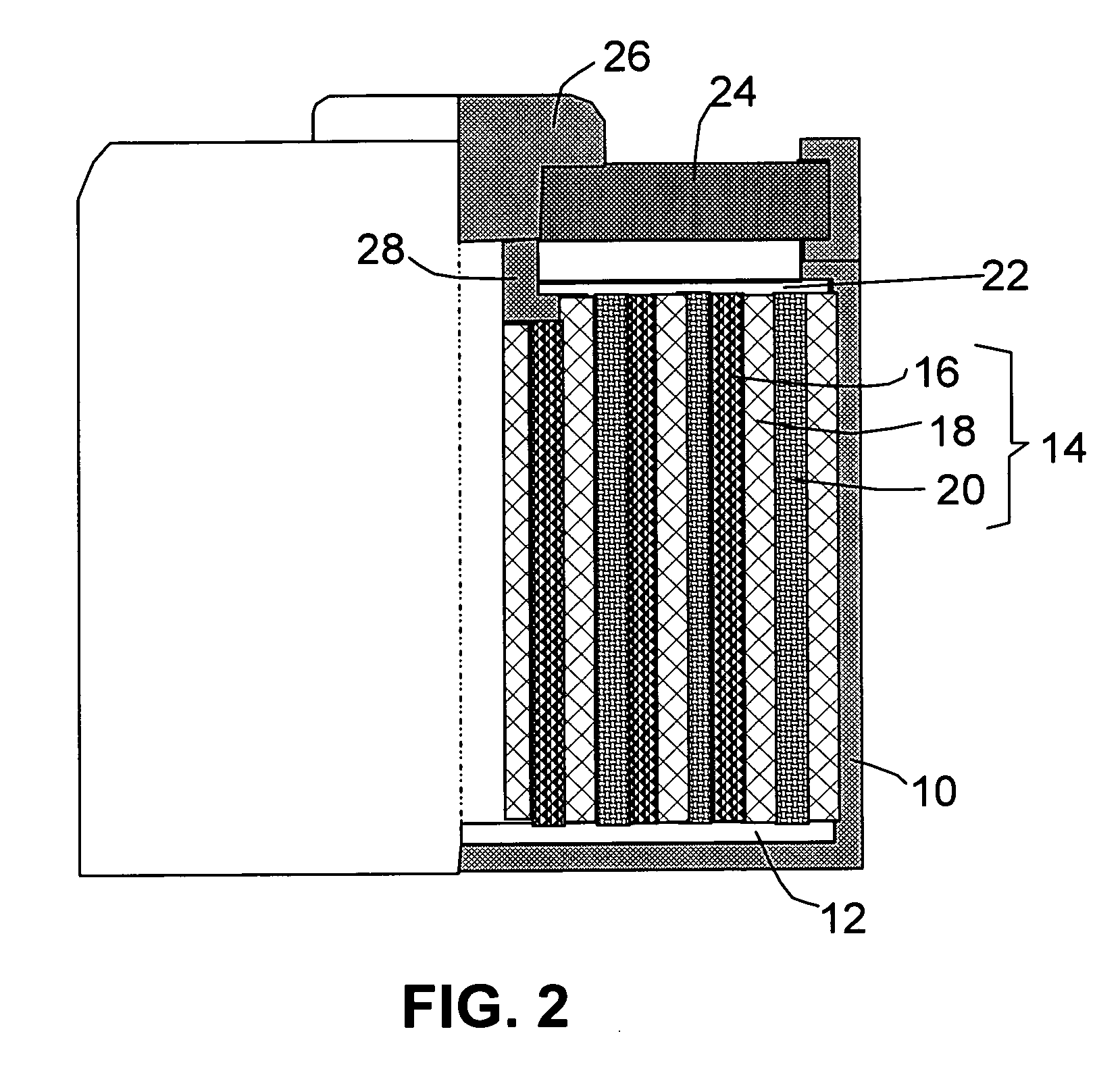
Solid particles. Solid particles multiply continuously in hydraulic systems. These particles flow through the hydraulic system under high pressure and at high speed and sandblast its components (pumps, valves, seals and cylinders). Particularly the tiniest particles which are either equal in size or smaller than the critical dynamic clearances...
Method for preparing graphene compounds and graphene oxide compounds with high efficiency
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene compounds and graphene oxide compounds with high efficiency, relating to the method for preparing the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds. The invention solves the problems of easy composition of graphene or graphene oxide per se and many process steps, higher cost and difficult dispersedness for preparing the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds by the traditional method at the same time. The invention adopts a mechanical stripping method to obtain the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds. In the invention, an automatic machine is utilized, solid particles are used for assisting stripping, the contact area and the stripping number of the stripping process are greatly increased, and carbon material powder experiences a lot of stripping processes through the action of shear and impact, thereby obviously improving the stripping efficiency and achieving the purpose of uniform dispersedness to the composites. The method is suitable for industrial mass production of the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
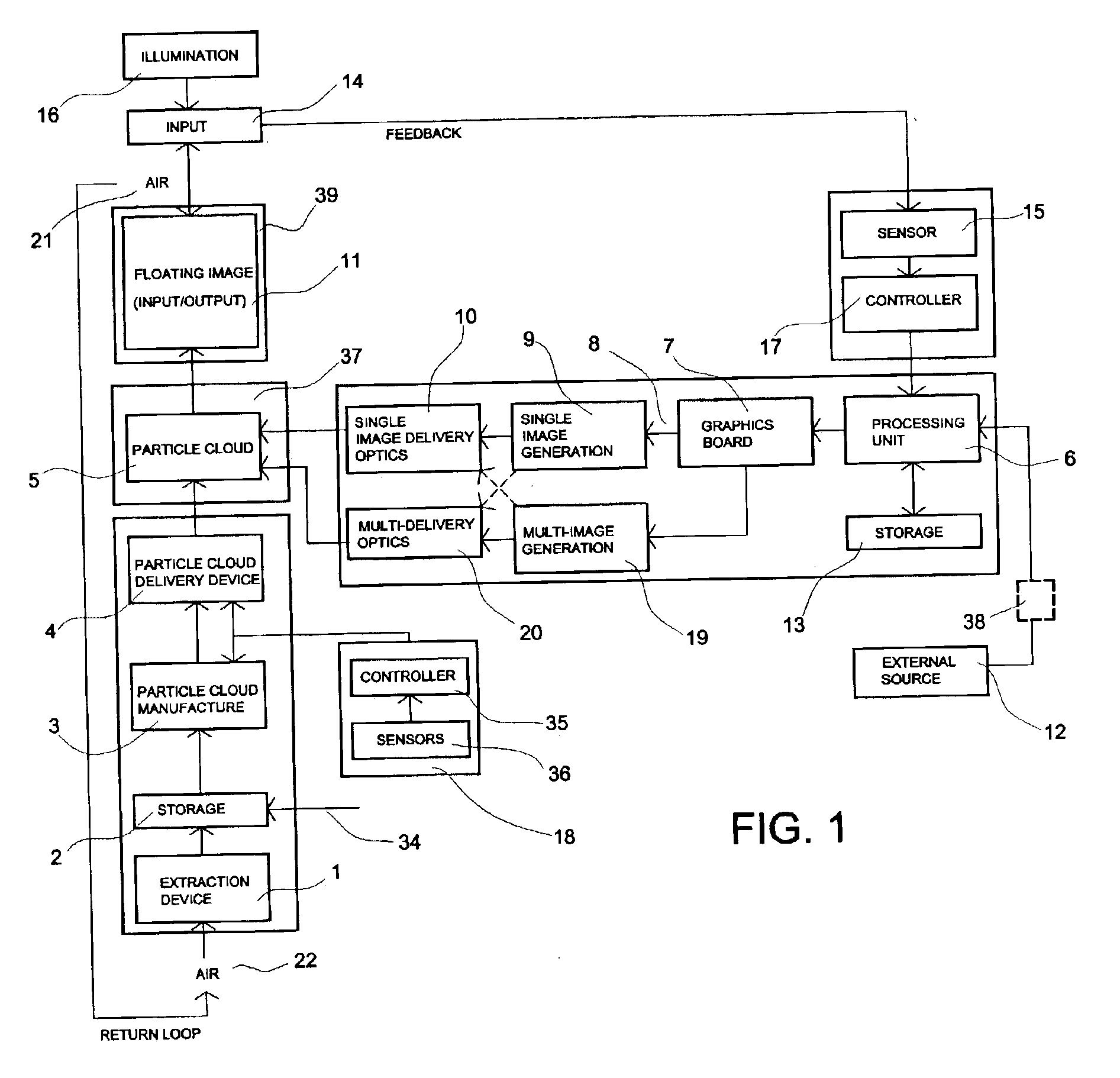
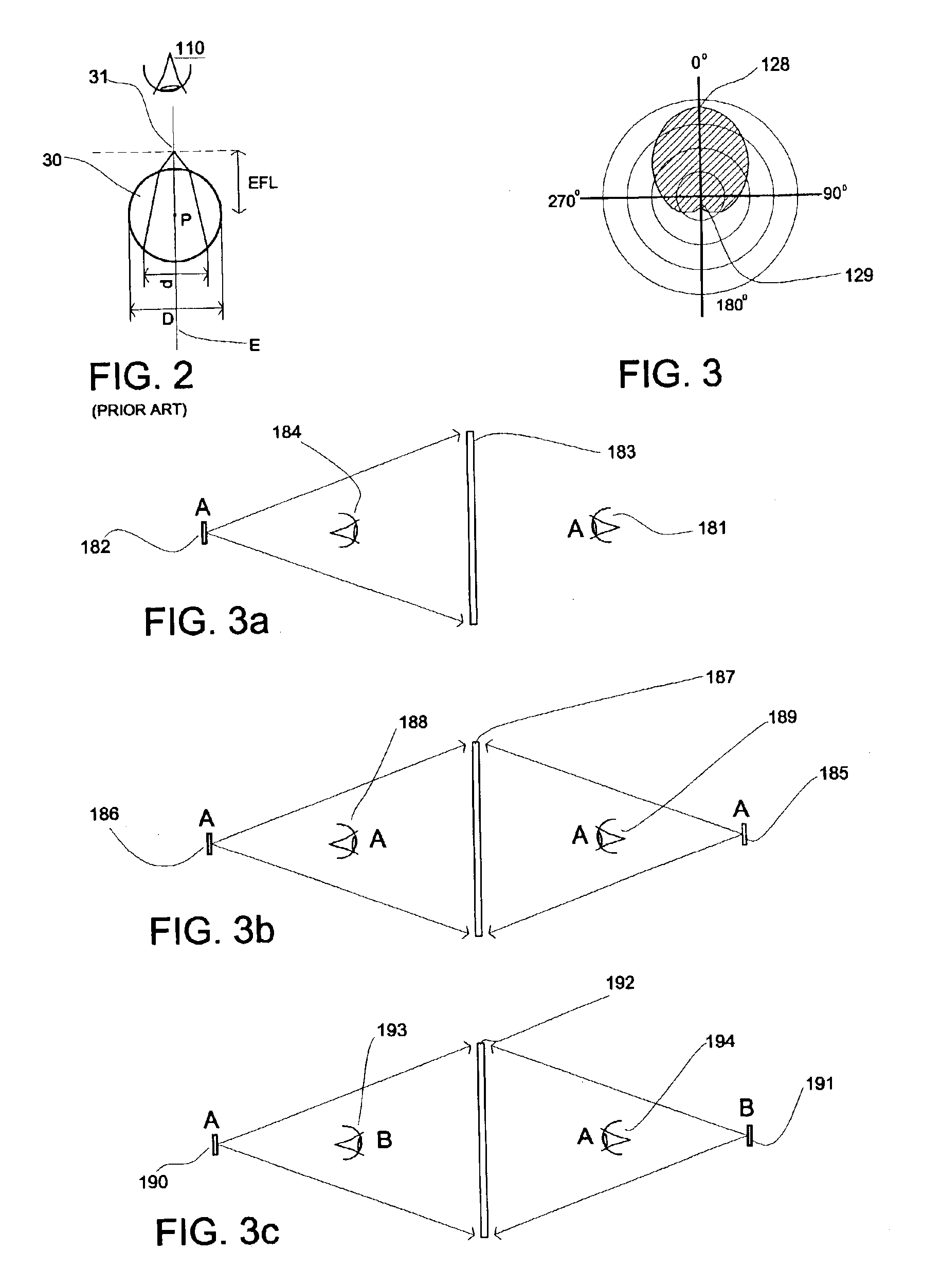
Method and system for free-space imaging display and interface
InactiveUS6857746B2Reduce the pressure gradientReducing boundary layer frictionProjector film strip handlingCamera film strip handlingProjection opticsImage resolution
This invention comprises a method and system for displaying free-space, full color, high-resolution video or still images while simultaneously enabling the user to have real-time direct interaction with the visual images. The system comprises a self-generating means for creating a dynamic, non-solid particle cloud by ejecting atomized condensate present in the surrounding air, in a controlled fashion, into an invisible particle cloud. A projection system consisting of an image generating means and projection optics, projects an image onto the particle cloud. Any physical intrusion, occurring spatially within the image region, is captured by a detection system and the intrusion information is used to enable real-time user interaction in updating the image. This input / output (I / O) interface provides a display and computer link, permitting the user to select, translate and manipulate free-space floating visual information beyond the physical constraints of the device creating the image.
Owner:IO2 TECH
Method for preparing graphene or graphene oxide by using high-efficiency and low-cost mechanical stripping
InactiveCN101817516AImprove stripping efficiencyLight in massHigh volume manufacturingSolid particle
The invention provides a method for preparing graphene or graphene oxide by using high-efficiency and low-cost mechanical stripping and relates to a preparation method of the graphene or the graphene oxide, solving the problems that the traditional micro-mechanical stripping method has low efficiency and can not be used for large-batch production. The method comprises the following step of separating carbon materials by utilizing solid particles and a liquid working medium (or gas working medium) and adopting mechanical stripping to obtain the graphene or the graphene oxide, wherein the carbon materials comprise graphite powder, expanded graphite, expandable graphite or graphite powder oxide. By using automatic machinery and using a great deal of solid particles for assisting stripping processes, the invention greatly increases the contact areas and the stripping times of the stripping processes, the carbon materials are subject to a great amount of stripping processes in a short time through the shearing and impacting functions of the solid particles on the carbon materials, and thereby the method obviously improves the stripping efficiency, has low cost and is suitable for the industrial and large-batch production of the graphene or the graphene oxide.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
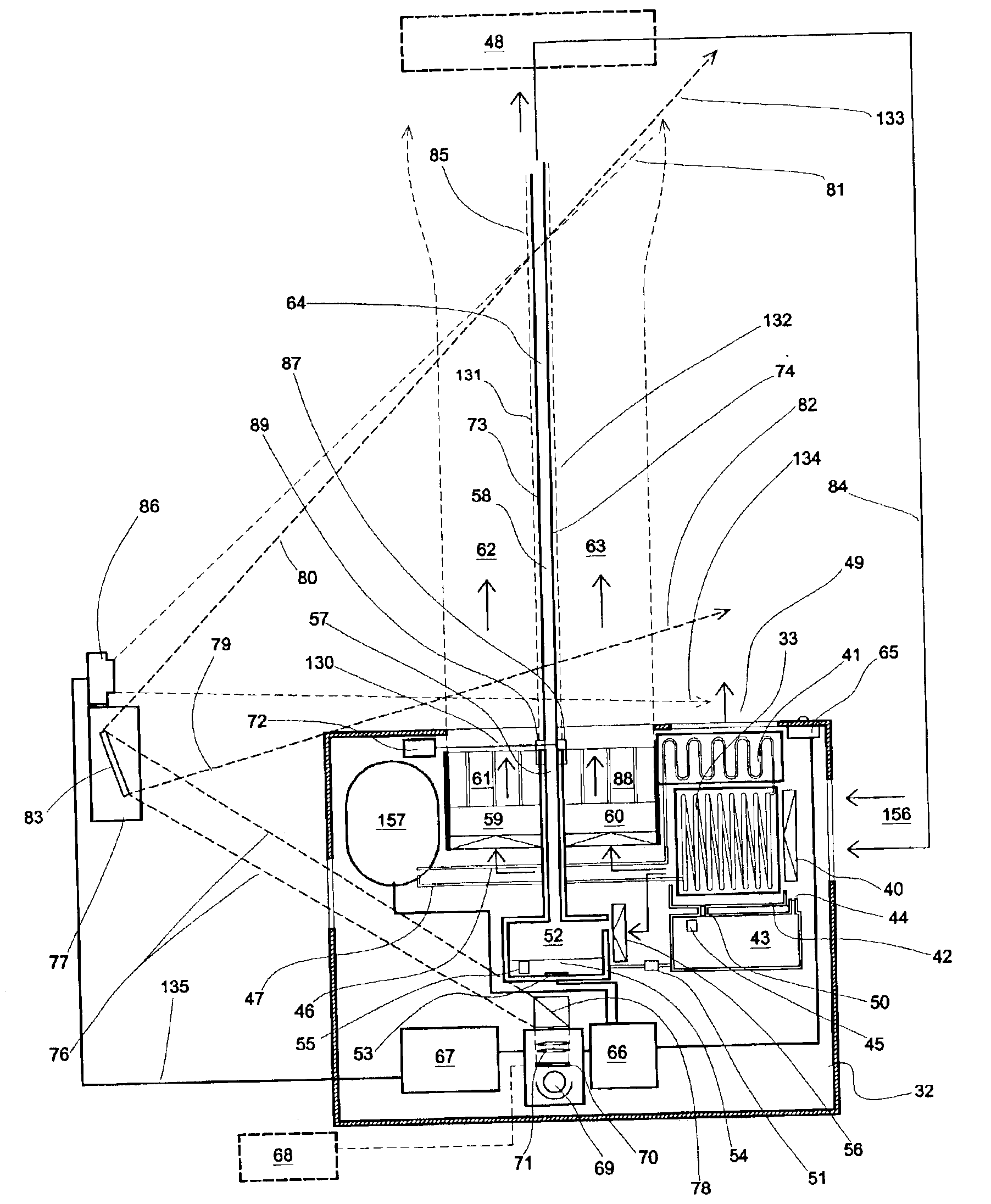
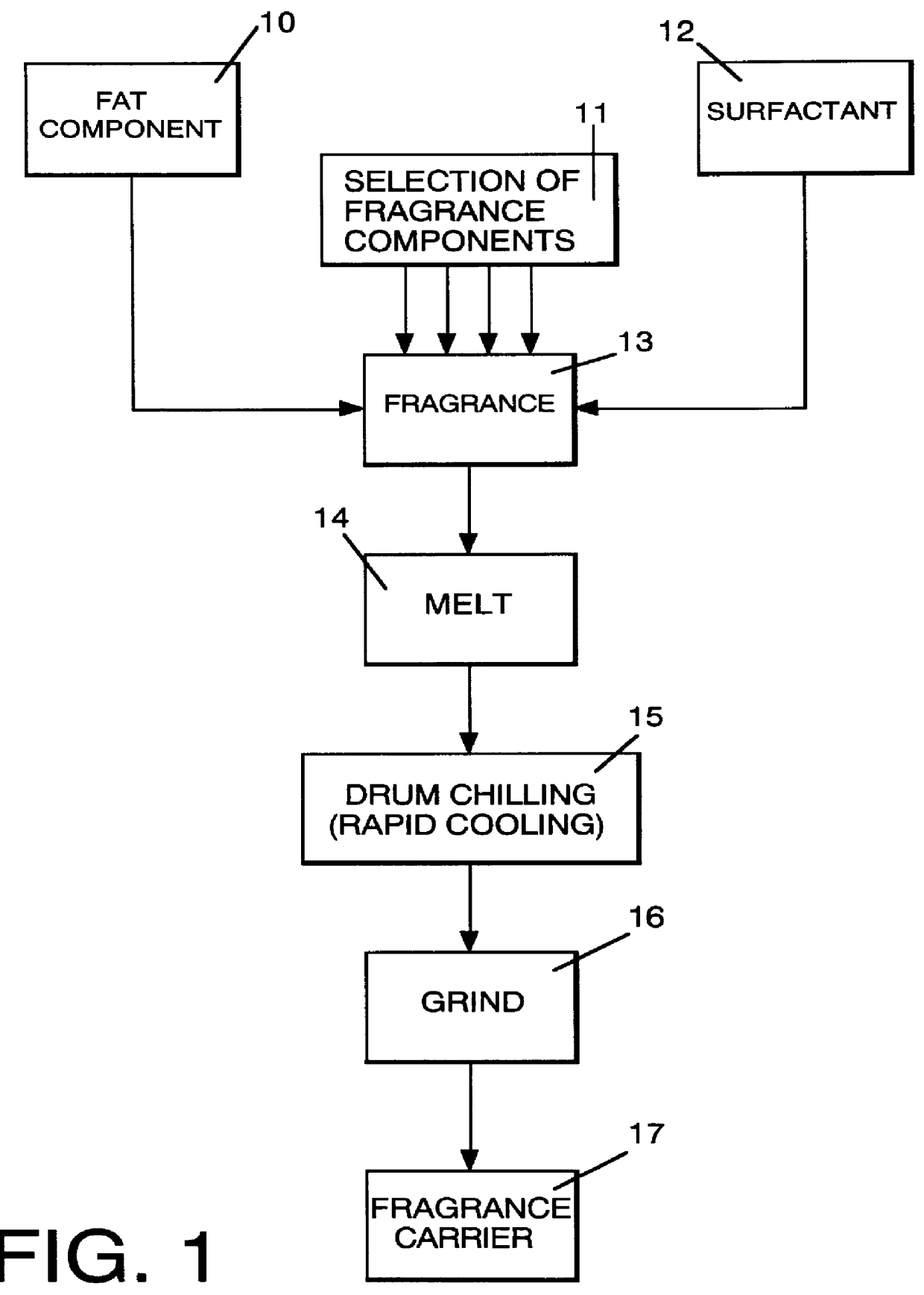
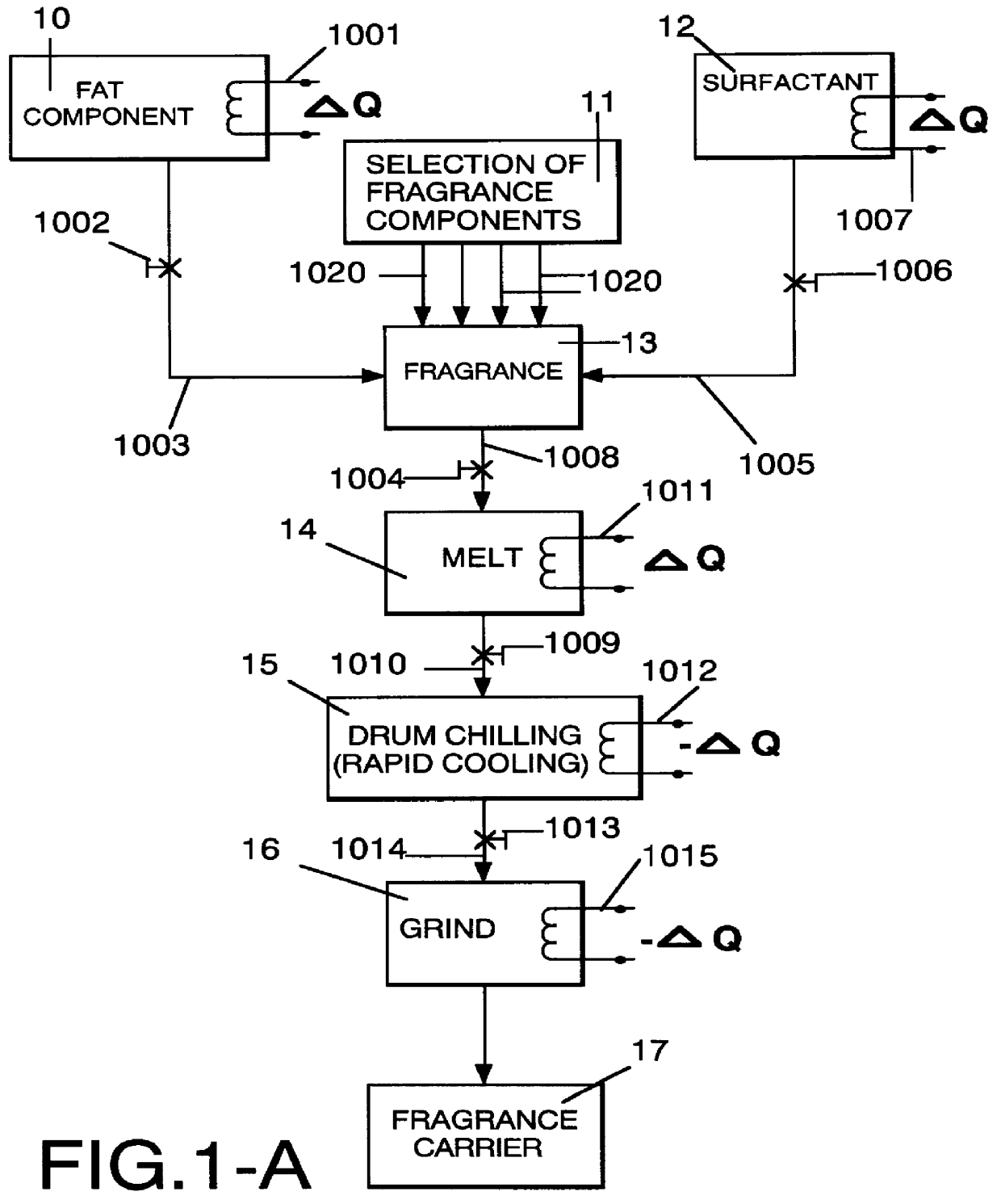
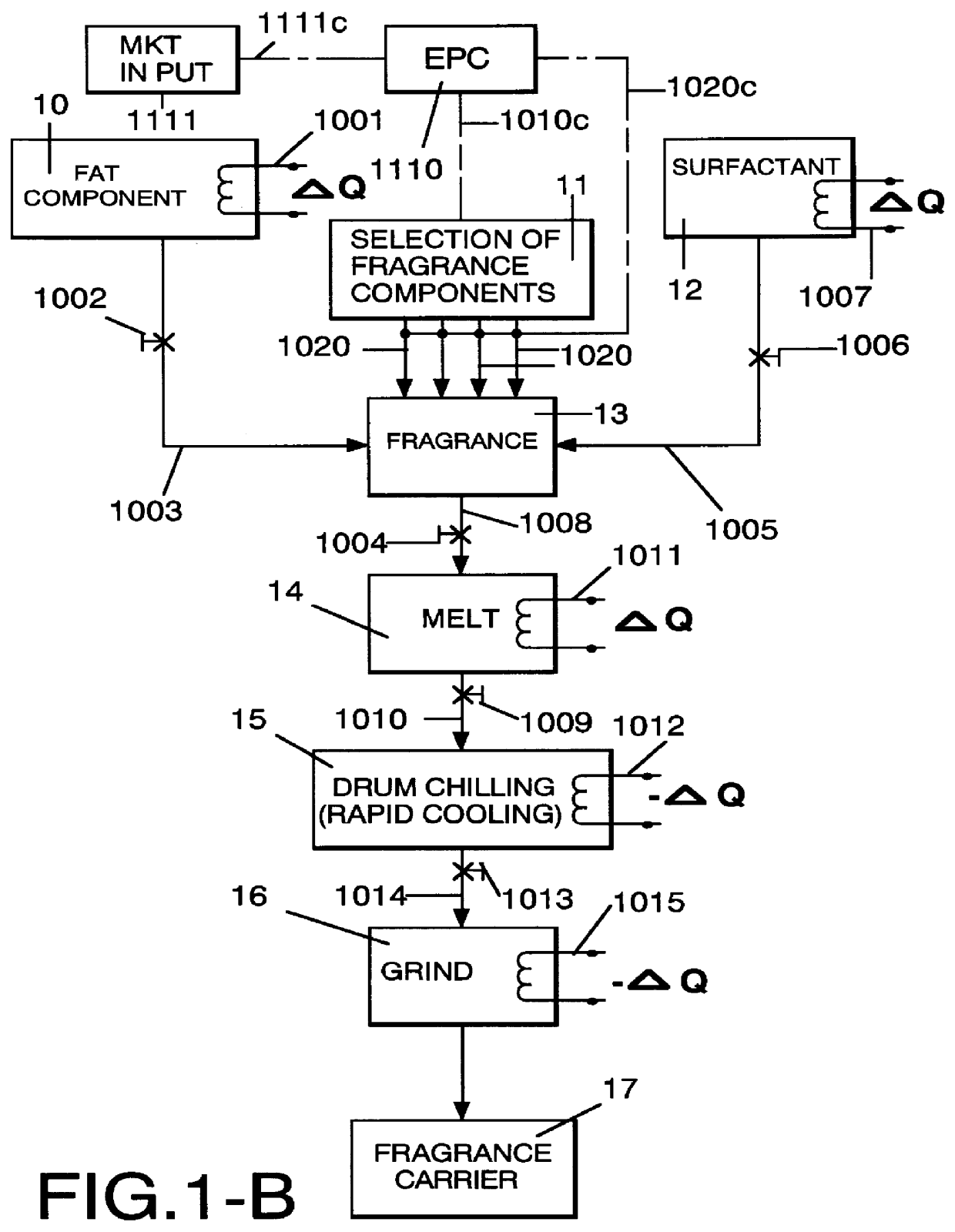
Method employing drum chilling and apparatus therefor for producing fragrance-containing long lasting solid particle
InactiveUS6051540AImproved substantivityMaximum flexibilityNon-ionic surface-active compoundsGaseous substancesDesiccantSolid particle
A method and apparatus is disclosed for producing a fragrance-containing solid particle, capable of controllably releasing the fragrance to the environment in which the particle is contained for incorporation into laundry detergents, fabric softener compositions and drier-added fabric softener articles.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
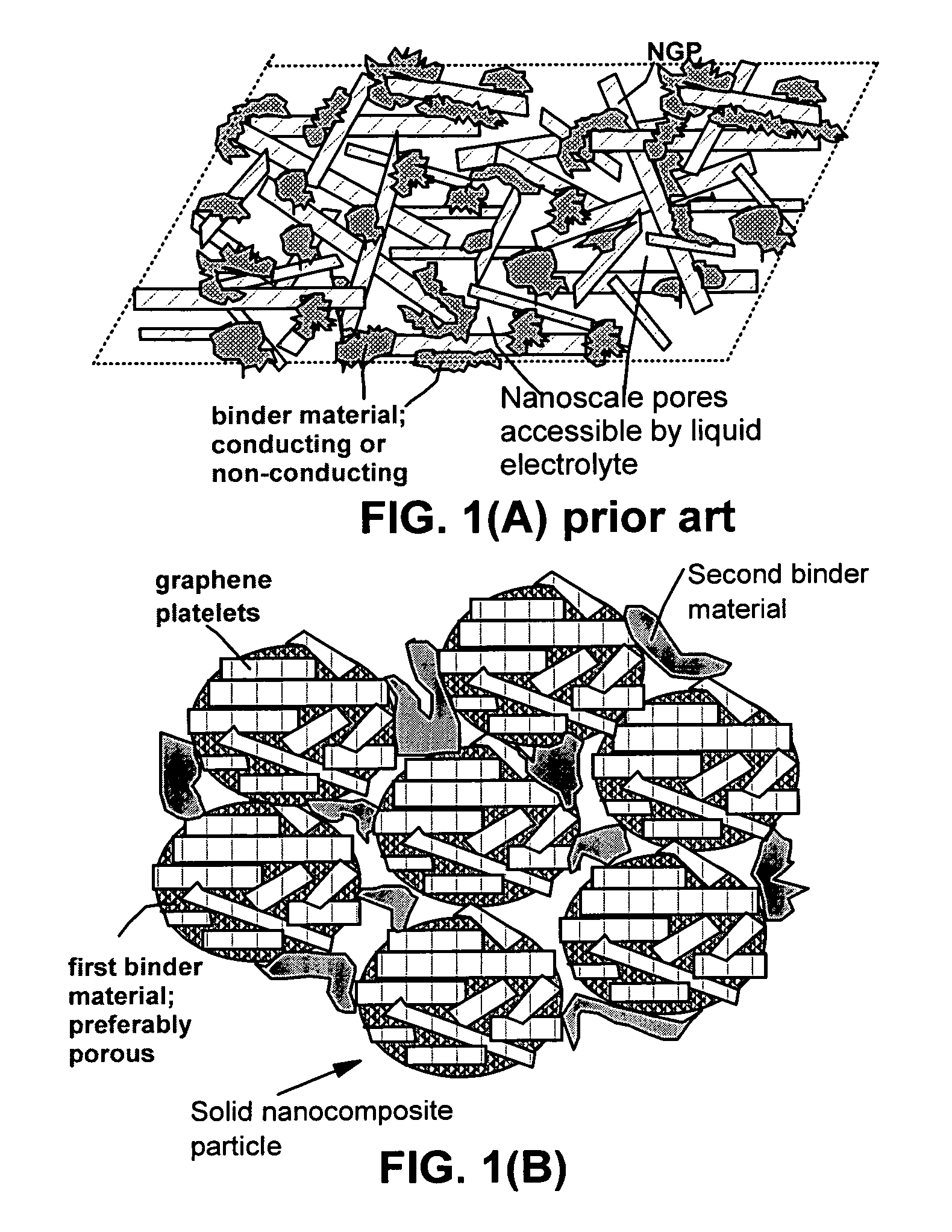
Graphene nanocomposites for electrochemical cell electrodes
ActiveUS20100021819A1High and reversible anode capacityTedious and energy-intensiveMicroscopic fiber electrodesHybrid capacitor electrodesGraphene nanocompositesSolid particle
A composite composition for electrochemical cell electrode applications, the composition comprising multiple solid particles, wherein (a) a solid particle is composed of graphene platelets dispersed in or bonded by a first matrix or binder material, wherein the graphene platelets are not obtained from graphitization of the first binder or matrix material; (b) the graphene platelets have a length or width in the range of 10 nm to 10 μm; (c) the multiple solid particles are bonded by a second binder material; and (d) the first or second binder material is selected from a polymer, polymeric carbon, amorphous carbon, metal, glass, ceramic, oxide, organic material, or a combination thereof. For a lithium ion battery anode application, the first binder or matrix material is preferably amorphous carbon or polymeric carbon. Such a composite composition provides a high anode capacity and good cycling response. For a supercapacitor electrode application, the solid particles preferably have meso-scale pores therein to accommodate electrolyte.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
Viscosity reduction of viscoelastic surfactant based fluids
InactiveUS6881709B2Improve efficiencyImproves and optimizes conditionOther chemical processesFluid removalAlcoholSolid particle
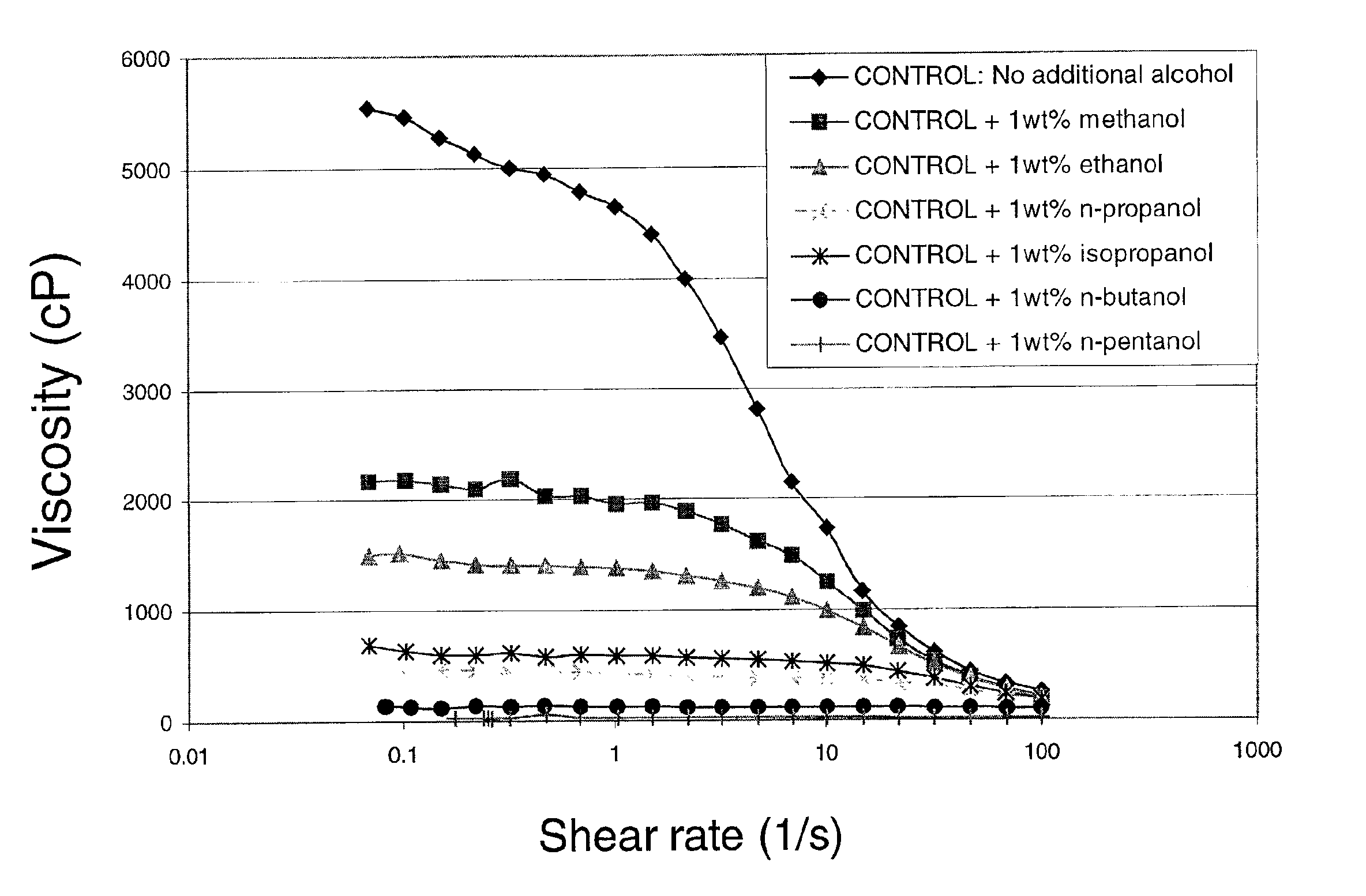
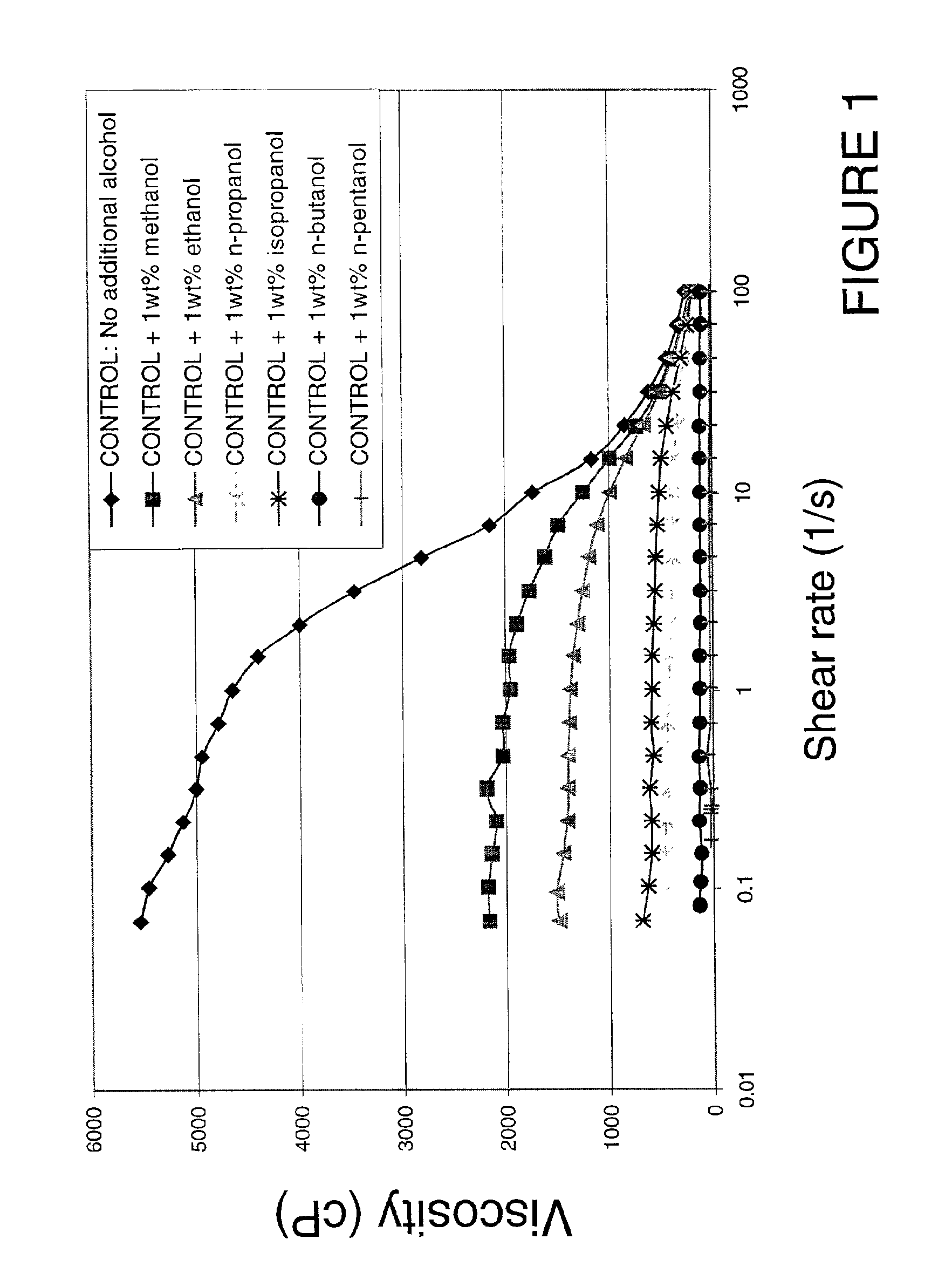
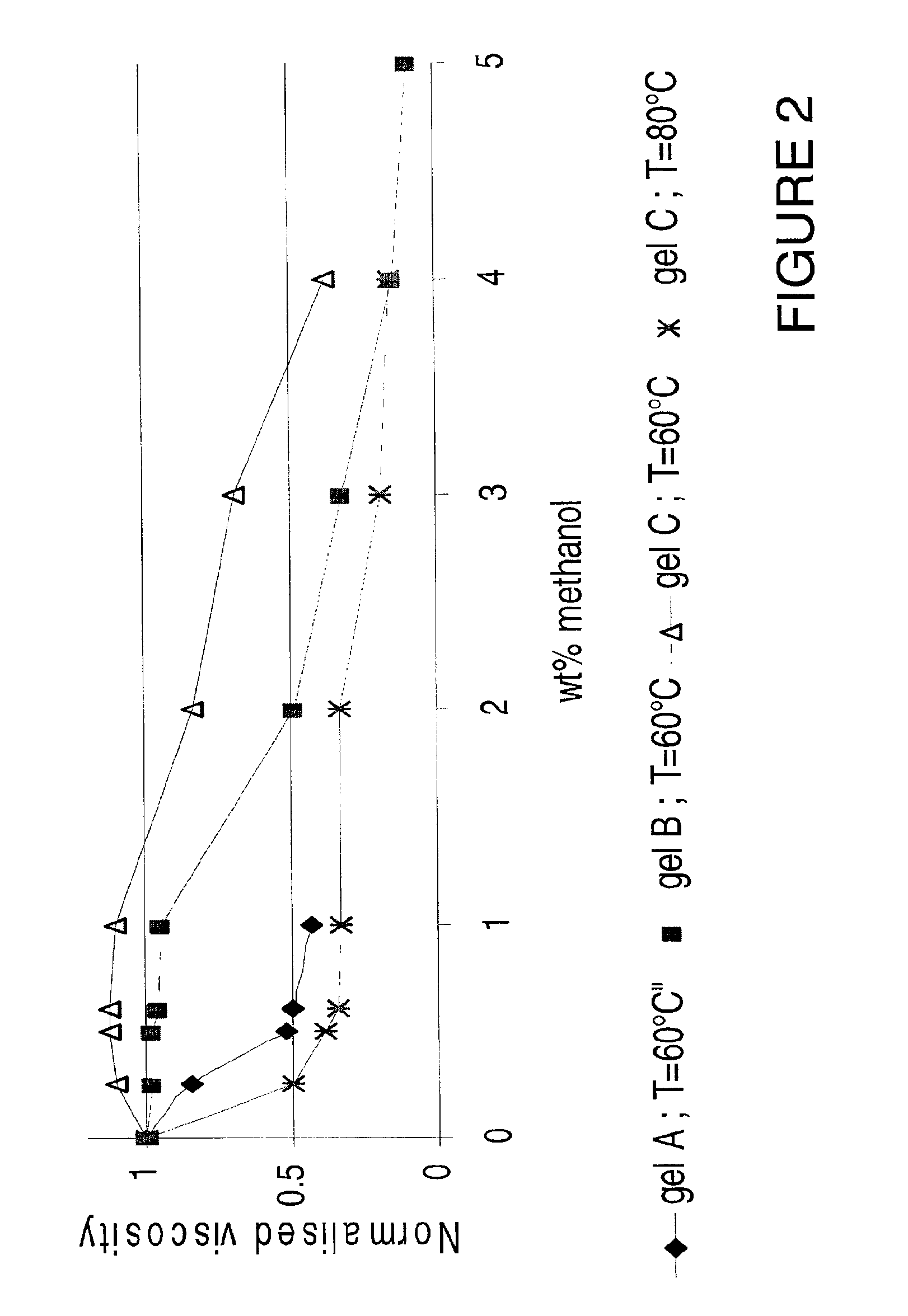
Methods and compositions are disclosed for controlled addition of components that decrease the viscosity of the viscoelastic surfactant fluids or for controlled changes in the electrolyte concentration or composition of the viscoelastic surfactant fluids. One aspect of the invention relates to the use of internal breakers with a delayed activation. Another aspect of the invention relates to the use of precursors that release a breaking system such as alcohol by a process such as melting, slow dissolution, reaction with a compound present in the fluid or added to the fluid during or after the step of injecting, rupture of an encapsulating coating and de-adsorption of a breaking agent absorbed into solid particles. In another aspect of the invention, alcohols are included in a pad to reduce the low-shear viscosity and reduce the resistance to flow of the treatment fluids during a desired phase of the treatment.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
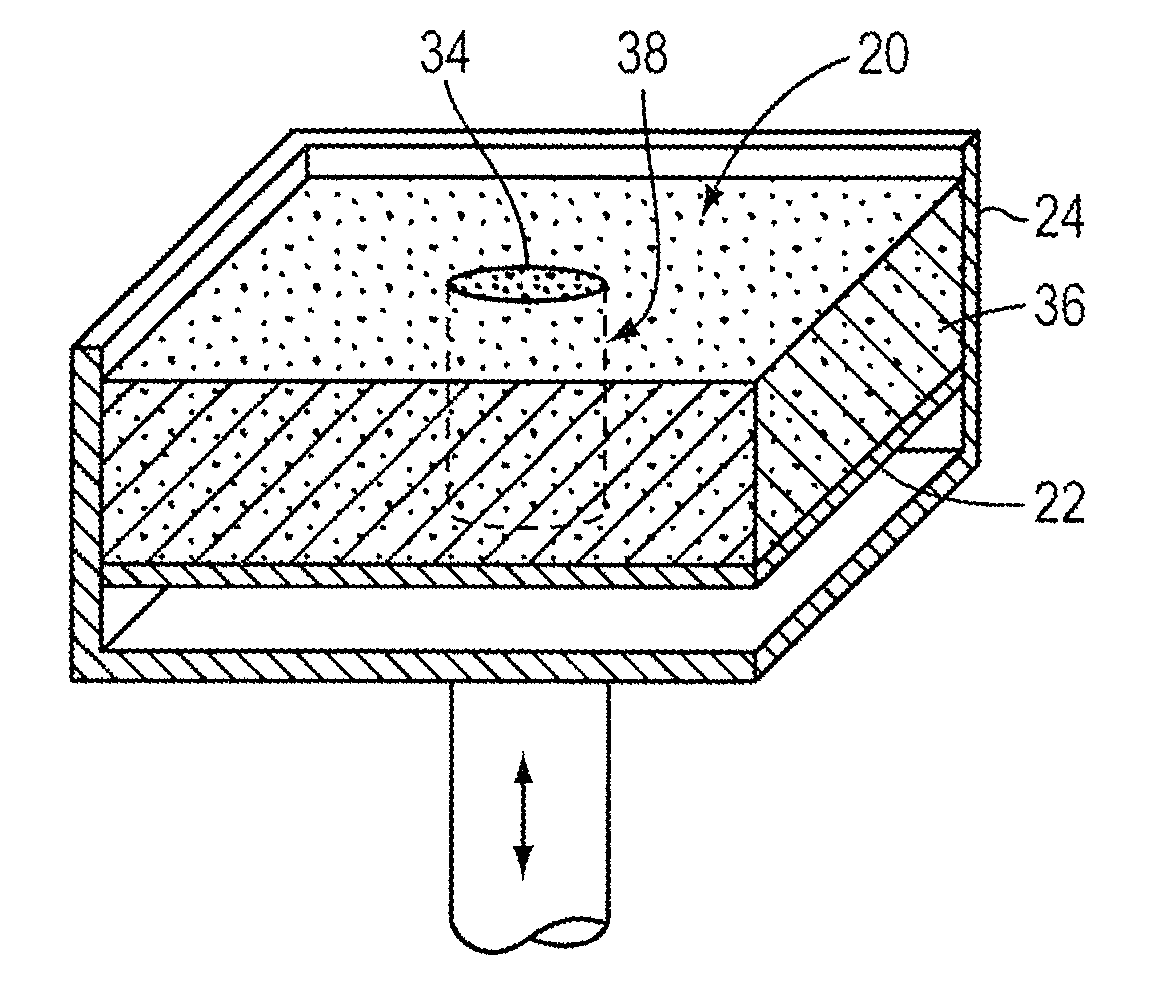
Torus-shaped mechanical gripper
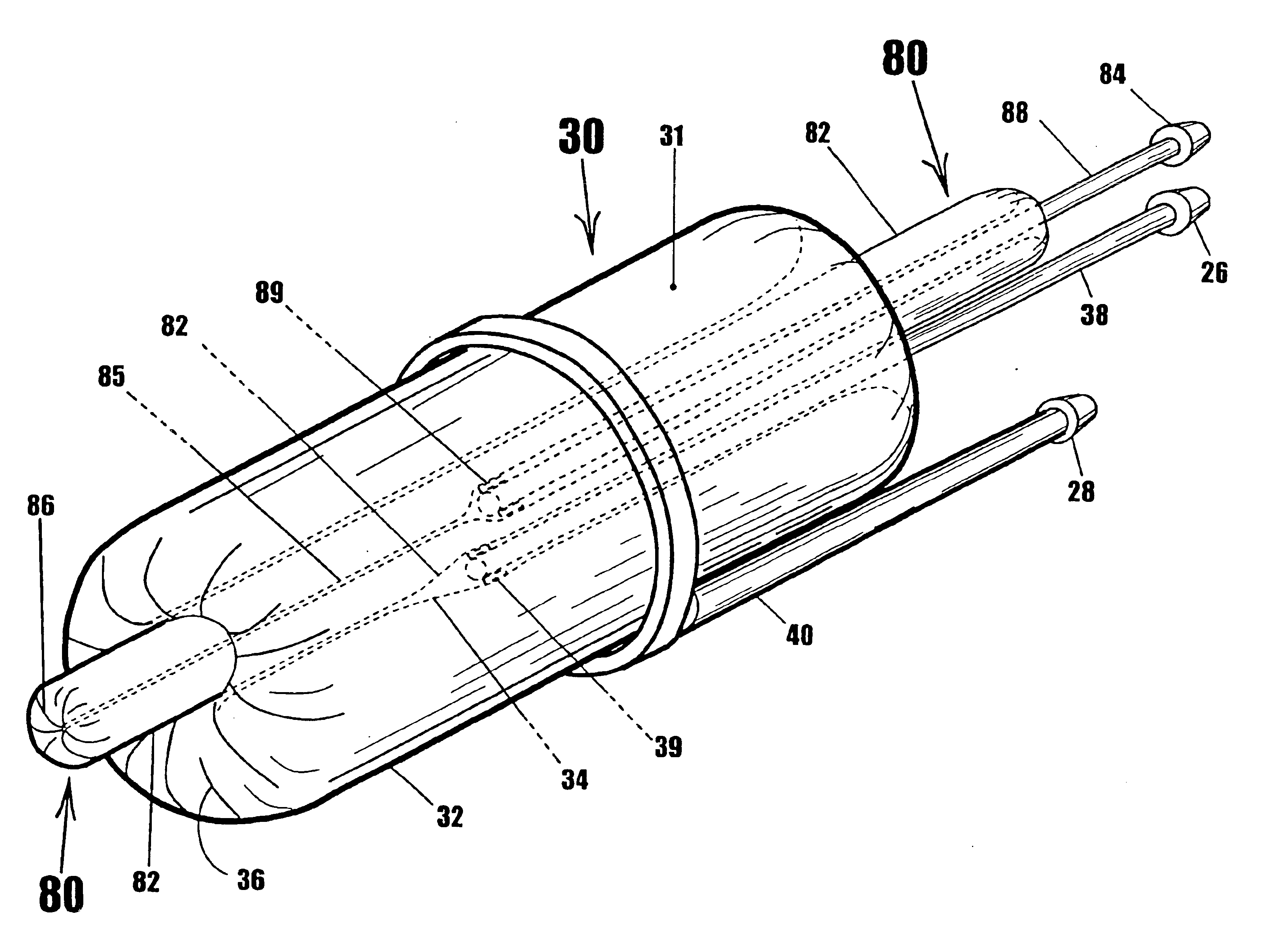
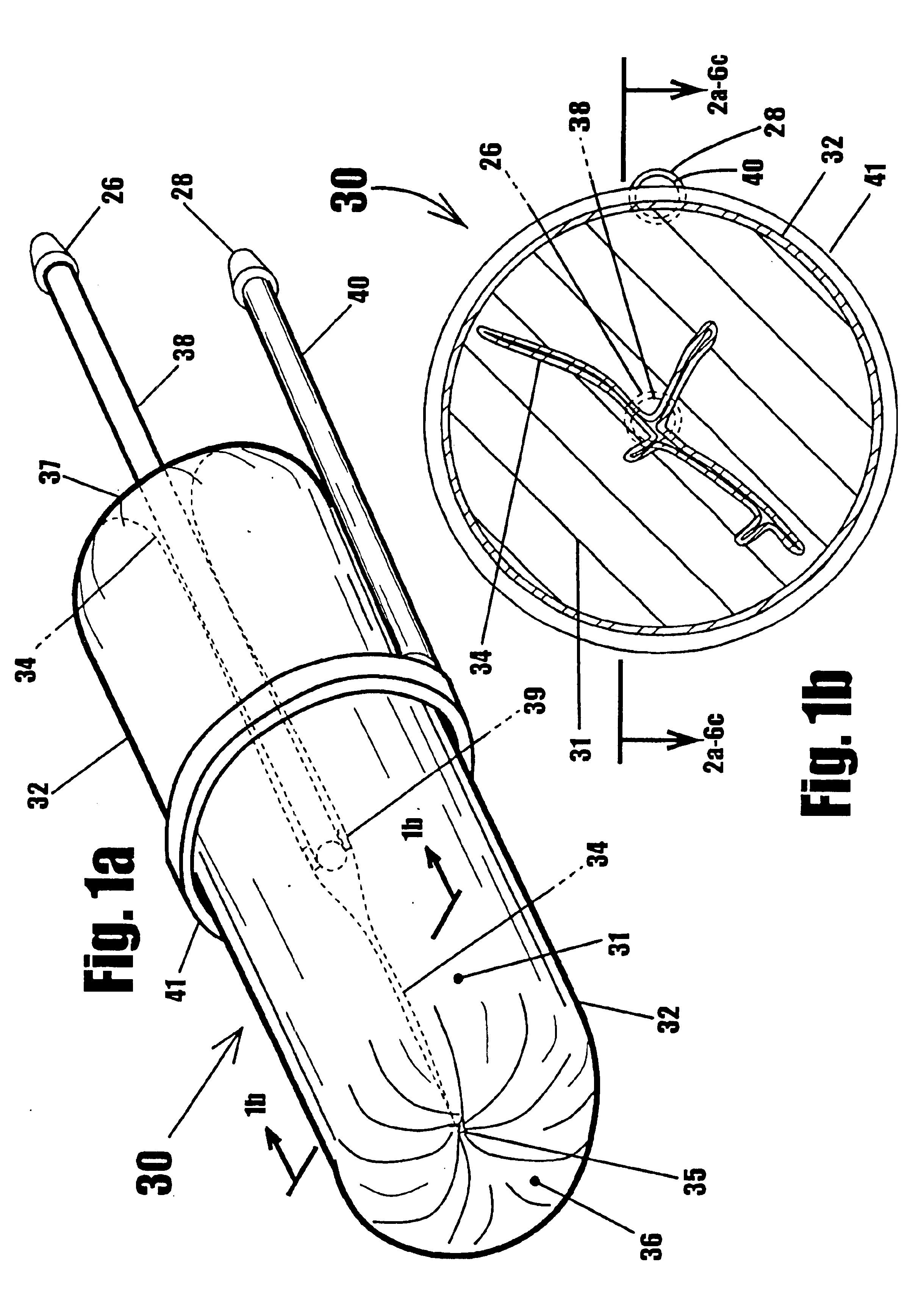
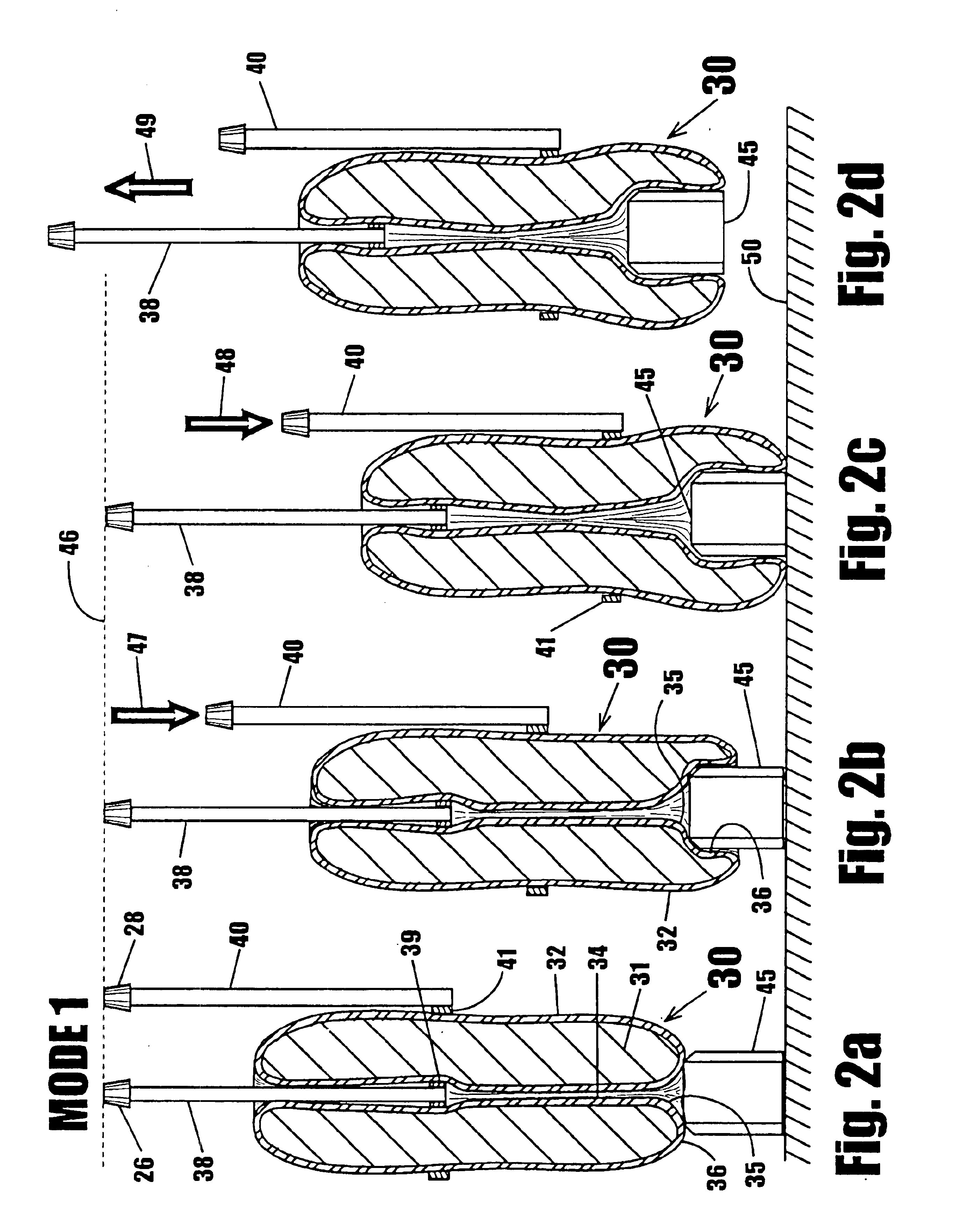
A device for gripping, holding, and releasing objects of varying sizes and shapes, which comprises an elongated torus (30) enclosing a fluid material (31), an external control rod (40), and an internal control rod (38). Torus (30) may be made of a flexible membrane and able to seal in fluid material (31). Fluid material (31) can be a gas, liquid, solid particles, semisolid particles, or mixtures of these. Central channel (34) of torus (30) is collapsed due to pressure of fluid material (31) within torus (30). Both control rods are securely attached to torus (30), with rod (38) attached to the interior portion of the torus along collapsed central channel (34), and rod (40) attached to the exterior portion of the torus on outer surface (32). Gripping action is achieved by differential linear motion of control rods (38) and (40) along the longitudinal (elongated) axis of torus (30). This causes front portion (36) of the torus to slide radially inward or outward to grip objects. Further movement of the control rods can cause the object to be pulled completely inside the collapsed channel for secure gripping by completely surrounding the object. The soft flexible nature of torus (30) allows grasping even the most delicate objects without damaging them. Even over-ripe strawberries can be rapidly grasped without bruising.
Owner:RAGNER GARY DEAN +1
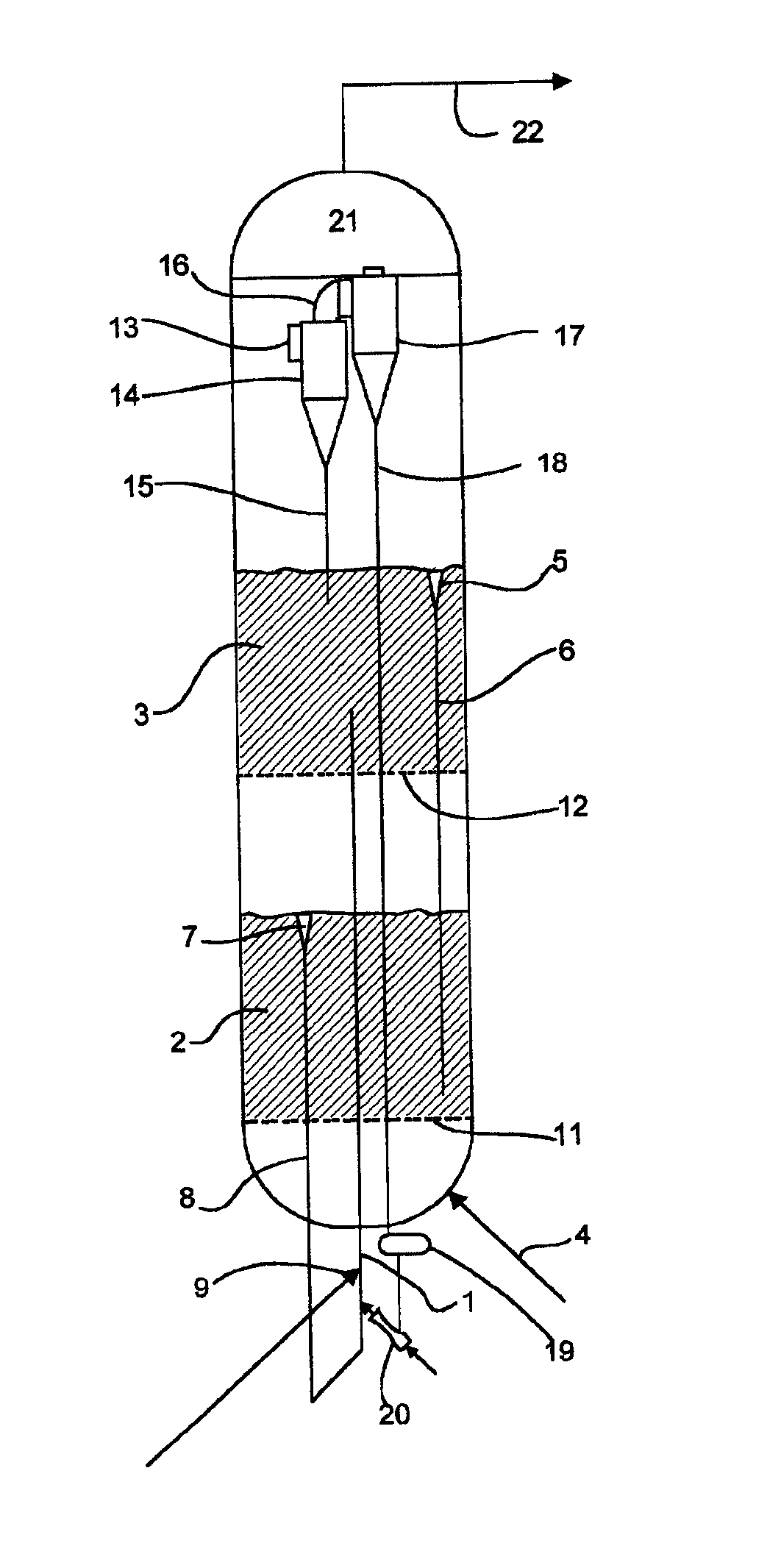
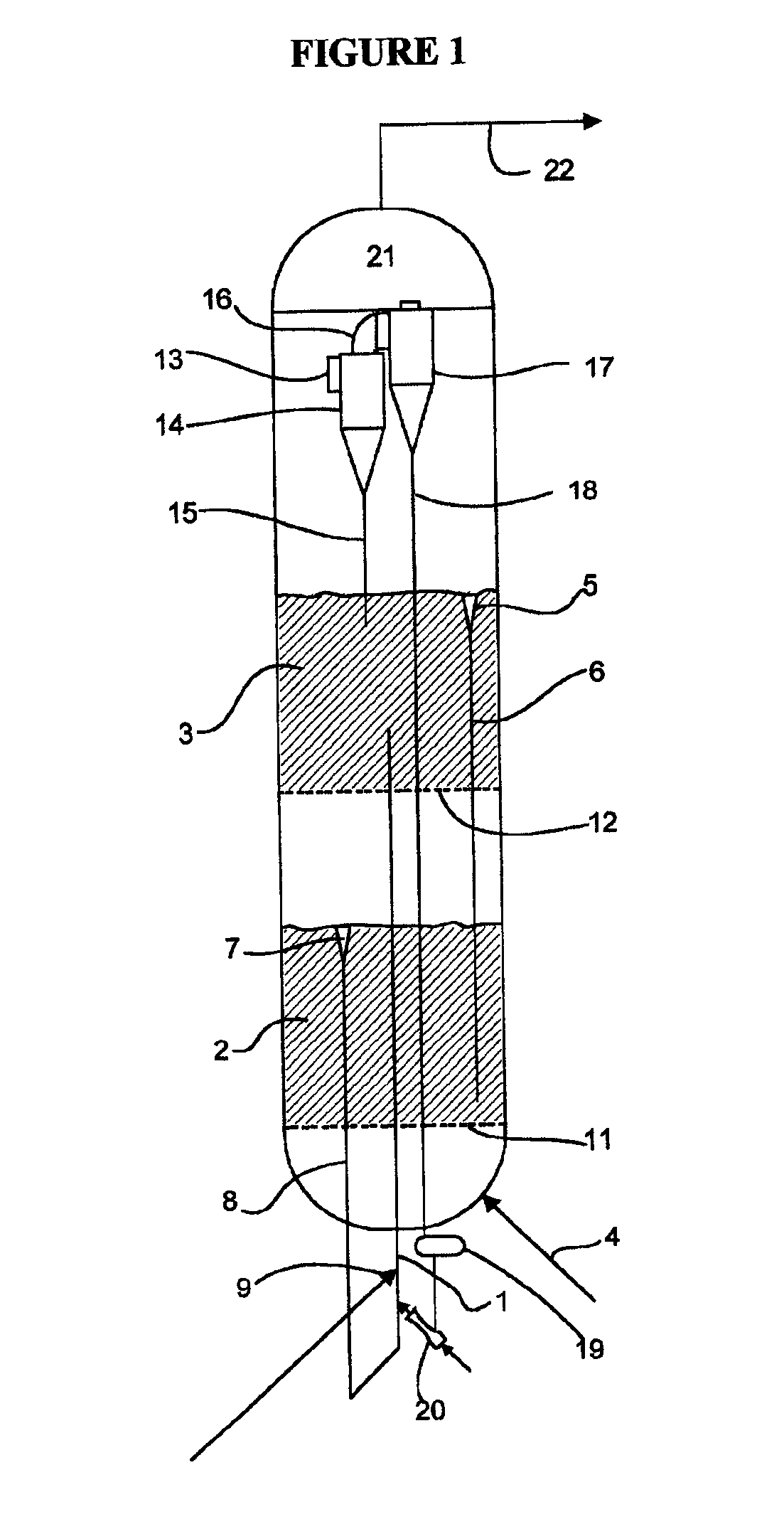
Method for gas-solid contacting in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor
InactiveUS6894183B2Eliminate and drastically reduce bypassEffective contactThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingForming gasSolid particle
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Conversion of petroleum residua to methane
InactiveUS6955695B2Eliminate needReduce usageThermal non-catalytic crackingElectrolysis componentsParticulatesGas phase
This invention discloses improvements on previous inventions for catalytic conversion of coal and steam to methane. The disclosed improvements permit conversion of petroleum residua or heavy crude petroleum to methane and carbon dioxide such that nearly all of the heating value of the converted hydrocarbons is recovered as heating value of the product methane. The liquid feed is distributed over a fluidized solid particulate catalyst containing alkali metal and carbon as petroleum coke at elevated temperature and pressure from the lower stage and transported to the upper stage of a two-stage reactor. Particulate solids containing carbon and alkali metal are circulated between the two stages. Superheated steam and recycled hydrogen and carbon monoxide are fed to the lower stage, fluidizing the particulate solids and gasifying some of the carbon. The gas phase from the lower stage passes through the upper stage, completing the reaction of the gas phase.
Owner:PETRO2020
Bandgap grading in thin-film devices via solid group IIIA particles
InactiveUS20080057616A1Efficient and simplified creationPrevent leaching and phase separationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationHigh concentrationBandgap grading
Methods and devices are provided for forming thin-films from solid group IIIA-based particles. In one embodiment, a method is provided for bandgap grading in a thin-film device using such particles. The method may be comprised of providing a bandgap grading material comprising of an alloy having: a) a IIIA material and b) a group IA-based material, wherein the alloy has a higher melting temperature than a melting temperature of the IIIA material in elemental form. A precursor material may be deposited on a substrate to form a precursor layer. The precursor material comprising group IB, IIIA, and / or VIA based particles. The bandgap grading material of the alloy may be deposited after depositing the precursor material. The alloy in the grading material may react after the precursor layer has begun to sinter and thus maintains a higher concentration of IIIA material in a portion of the compound film that forms above a portion that sinters first.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Solid lipid particles, particles of bioactive agents and methods for the manufacture and use thereof
InactiveUS6207178B1Suppresses decrease in specific surface areaImprove bioavailabilityBiocideCosmetic preparationsLipid formationLipid particle
The present invention is in the area of administration forms and delivery systems for drugs, vaccines and other biologically active agents. More specifically the invention is related to the preparation of suspensions of colloidal solid lipid particles (SLPs) of predominantly anisometrical shape with the lipid matrix being in a stable polymorphic modification and of suspensions of micron and submicron particles of bioactive agents (PBAs); as well as to the use of such suspensions or the lyophilizates thereof as delivery systems primarily for the parenteral administration of preferably poorly water-soluble bioactive substances, particularly drugs, and to their use in cosmetic, food and agricultural products. SLPs and PBAs are prepared by the following emulsification process: (1) A solid lipid or bioactive agent or a mixture of solid lipids or bioactive agents is melted. (2) Stabilizers are added either to the lipid or bioactive agent and to the aqueous phase or to the aqueous phase only depending on their physicochemical characteristics. Stabilizers may also be added or exchanged after homogenization. (3) Drugs or other bioactive substances to be incorporated into the SLPs may be melted together with the lipids if the physicochemical characteristics of the substance permit or may be dissolved, solubilized or dispersed in the lipid melt before homogenization. (4) The aqueous phase is heated to the temperature of the melt before mixing and may contain for example stabilizers, isotonicity agents, buffering substances, cryoprotectants and / or preservatives. (5) The molten lipid compounds and the bioactive agents are emulsified in an aqueous phase preferably by high-pressure homogenization.
Owner:PHARMACIA AB
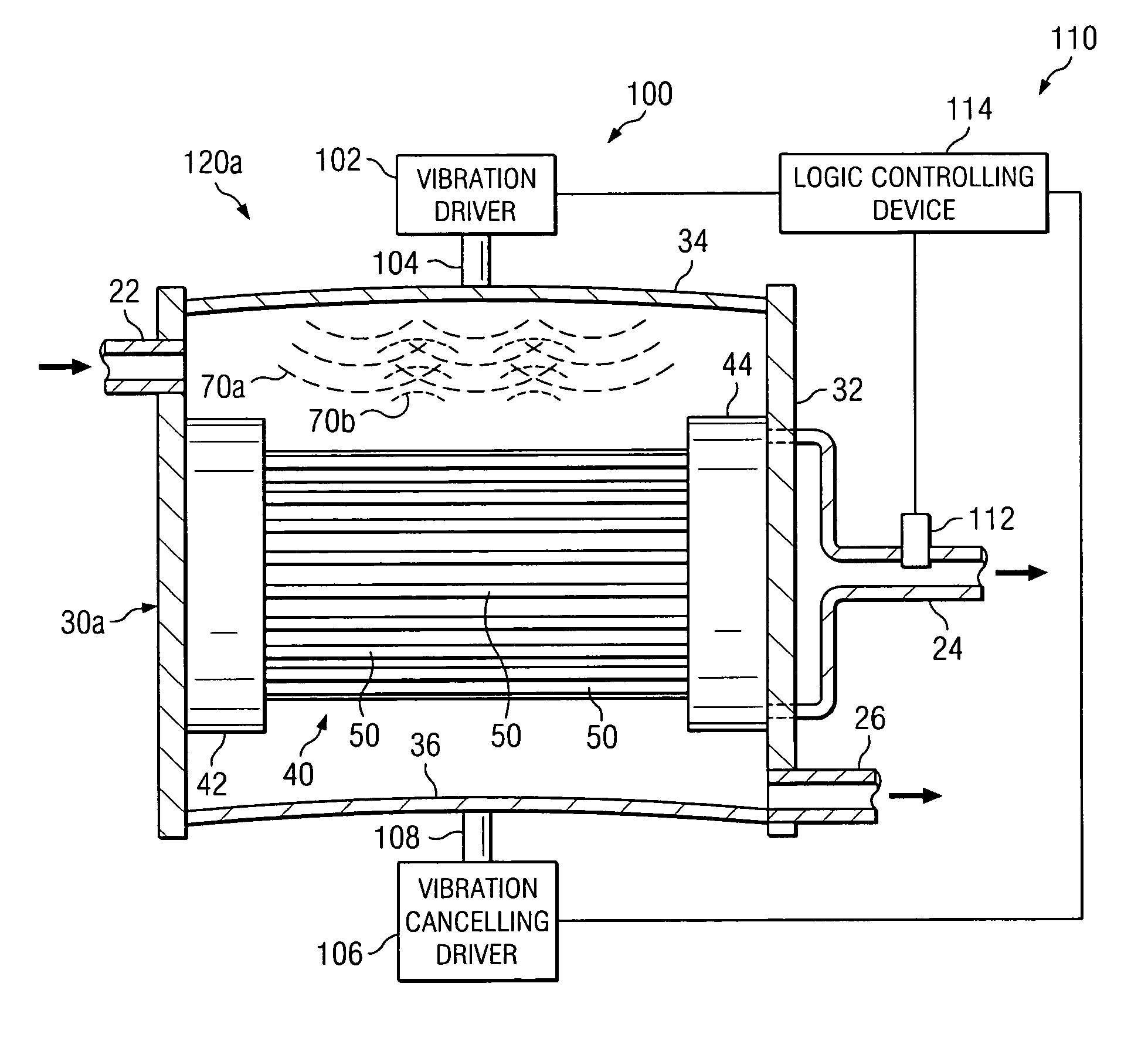
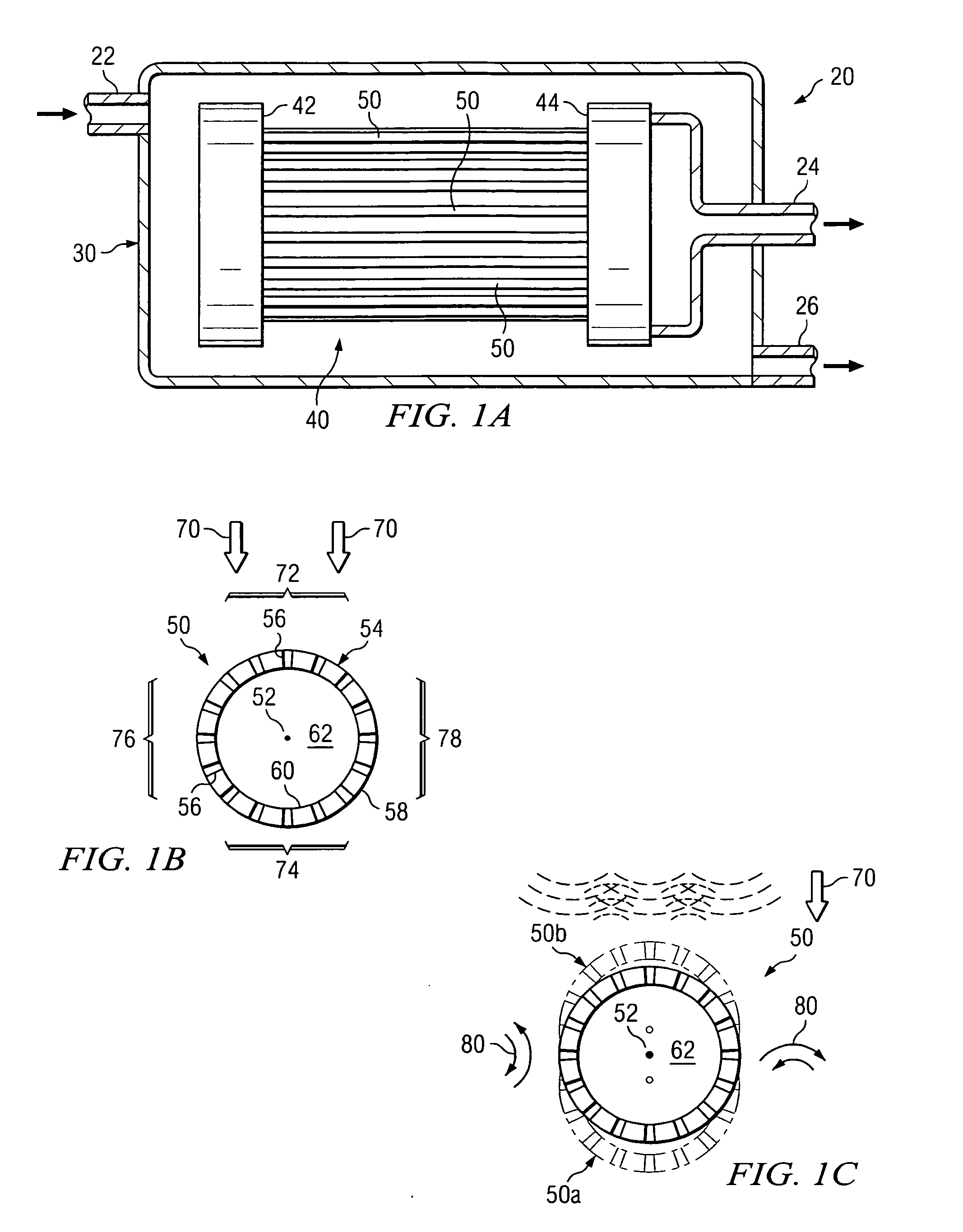
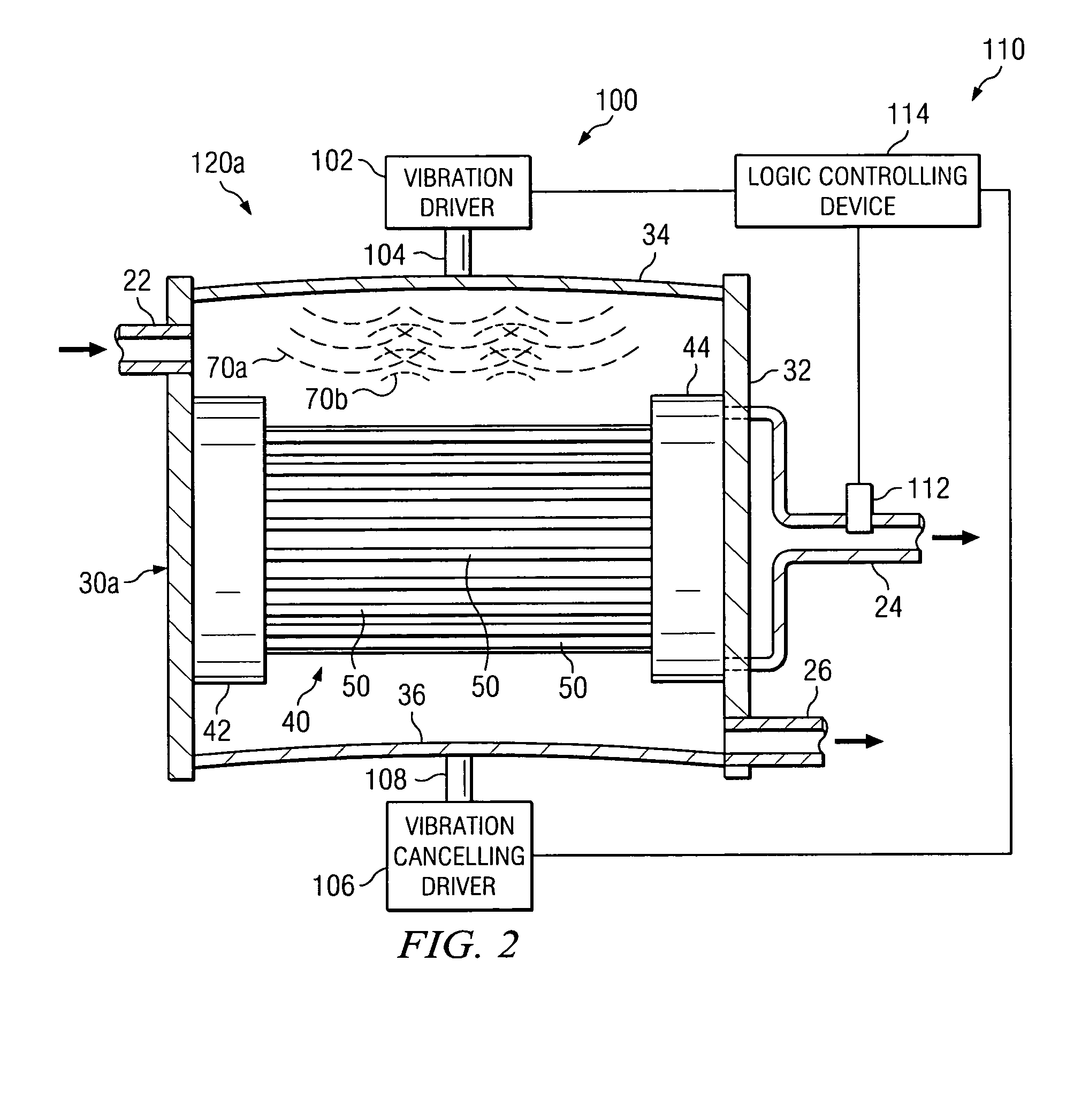
Cleaning hollow core membrane fibers using vibration
InactiveUS20050077227A1Minimize returnMinimize bounce backMembranesSpecific water treatment objectivesParticulatesFiber
A filtration system is provided with hollow membrane filter elements operable to remove solids, particulate and colloidal matter from a process fluid. Acoustic, vibration and ultrasonic energy may be used to clean exterior portions of the hollow membrane filter elements to allow substantially continuous filtration of process fluids. The filtration system may be satisfactorily used with process fluids having a relatively high concentrations of solids, particulate and colloidal matter.
Owner:PHASE
Process for preparing composite enzyme and product thereof
A compound ferment production process and a product thereof are applicable to the technical field of foods. The formulation of the product comprises fruit vegetable ferment raw juice, plant ferment raw juice, corn ferment, peas ferment and multielement alditol. The production process comprises the following: a step of preparing fruit vegetable ferment liquid, during which, selecting and cutting fresh fruits and vegetables into slices or pieces, blending the slices or pieces, adding apple vinegar on the slices or the pieces, and storing the fruits and vegetables hermetically at room temperature to prepare the fruit vegetable ferment raw juice through natural fermentation; a step of preparing the plant ferment liquid, during which, selecting, chipping and blending herbal plants, adding common salt into the sliced herbal plants, and storing the sliced herbal plants hermetically at room temperature to prepare the plant ferment raw juice through natural fermentation; and a step of fermentation and product processing, during which, taking the fruit vegetable ferment raw juice, the plant ferment raw juice, the corn ferment and the peas ferment, carrying out the second fermentation at room temperature, adding the multielement alditol during the second fermentation, using a sealed jar during the fermentation, preparing the compound ferment product after a postmaturation process, and preparing the liquid, powdery and solid particle ferment through mechanical processing and forming. The process and the product thereof which have a novel and scientific design and long-term maturation through the natural fermentation can increase the vitality of the ferment, facilitate the demand of a human body and improve the health of the human body through frequent edibility.
Owner:沈阳麦金利食品制造有限公司
Three-Dimensional Printing Material System With Improved Color, Article Performance, and Ease of Use
ActiveUS20080187711A1Strong and durable prototypeHigh green part strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusOther chemical processesParticulatesWhitening Agents
A materials system and methods are provided to enable the formation of articles by three dimensional printing. The materials system includes particulate mixtures having a whitening agent and a solid particulate additive comprising an acid, the latter adapted for modifying a cure rate of an infiltrant. The materials system also includes aqueous fluids including optical brightening agents.
Owner:3D SYST INC
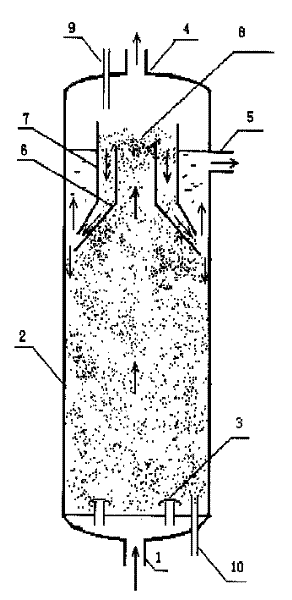
Boiling bed reactor
InactiveCN1448212AEasy to storeGood fluidizationChemical/physical processesChemical reactionNuclear engineering
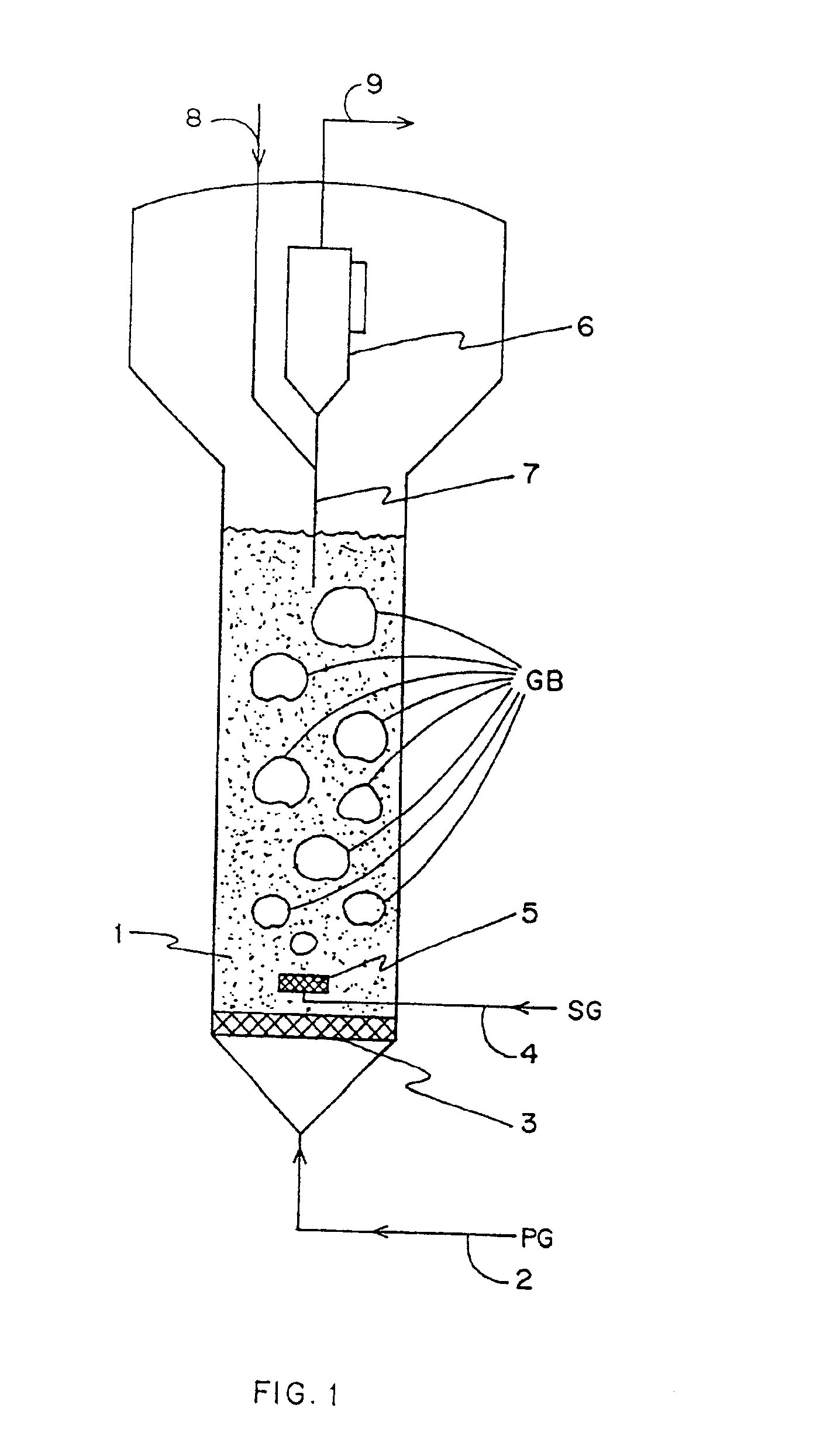
The improved fluidized bed reactor includes cylindrical reactor casing perpendicular to ground and phase separator in the upper part of the casing. The casing has material inlet in the bottom and product outlet on the upper side, and the phase separator consists of two, one inner and one outer, concentric cylinders of different inner diameters as well as the inner wall of the casing, with the inner cylinder having a lower top-less conic opening. The reactor is suitable mainly for the chemical reaction between different liquid and gas matters under the contact with solid particles, and has the advantages of great catalyst holding amount, high reactor utilization, simple structure, easy operation, etc.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Fracturing sand mixing device
The invention provides a fracturing sand mixing device used for mixing fracturing fluid. The fracturing sand mixing device comprises a solid-liquid mixing device, and the solid-liquid mixing device is a pressure container. The solid-liquid mixing device comprises a solid lead-in port capable of leading in solid particles of the fracturing fluid, a base fluid lead-in port for leading in base fluid of the fracturing fluid, a mixing inner cavity for accommodating the solid particles and the base fluid and a solid-liquid lead-out port for leading out the fracturing fluid formed by mixing. Substances such as carbon dioxide or petroleum gas which are in a gas state under normal temperature can be kept in a liquid state by high pressure through the fracturing sand mixing device and are mixed with the solid particles to form the fracturing fluid, and the goal of preparing the fracturing fluid with liquid carbon dioxide or liquefied petroleum gas (propane) serving as the base fluid is achieved.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH OILFIELD SERVICES GROUP
Exhaust system for a vehicular positive ignition internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20110158871A1Reduce frequencyImprove filtering effectCombination devicesCation exchanger materialsParticulatesPorous substrate
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Method of introducing leak detection dye into an air conditioning or refrigeration system including solid or semi-solid fluorescent dyes
InactiveUSRE36951E1Reduce riskDetection of fluid at leakage pointOther chemical processesFluorescenceSemi solid
PCT No. PCT / US95 / 04262 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 21, 1995 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 21, 1995 PCT Filed Apr. 6, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 07088 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 7, 1996A method of introducing a leak detection dye into a closed refrigeration system through circulation of the refrigerant. A predetermined amount of the leak detection dye, which is soluble in the refrigerant and the system lubricant, is installed in a component of the refrigeration system, such as in a desiccant bag placed in a dehydrator. The leak detection dye may come in various forms including as a leak detection additive having the leak detection dye implanted on and absorbed into a host swatch of a substrate material, as a powder, as a solid pellet of powdered dye concentrate and inert ingredients, or as a slurry. The refrigeration system is assembled, charged and operated, by which the refrigerant and system lubricant flowing through the component, such as a desiccant bag in the dehydrator, and mixes the dye with the refrigerant and system lubricant.
Owner:SPECTRONICS
Polymeric drug delivery system for hydrophobic drugs
InactiveUS20050249799A1Low oral bioavailabilityStable against aggregationAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryHydrophobic polymerImmediate release
An oral delivery system for Class II drugs that have low oral bioavailability due to their insolubility in water and slow dissolution kinetics and method for making such a drug delivery system are disclosed herein. The formulation may be a controlled release or immediate release formulation. The immediate release formulation contains a Class II drug, together with a hydrophobic polymer, preferably a bioadhesive polymer. In one embodiment, the drug and polymer are co-dissolved in a common solvent. The solution is formed into small solid particles by any convenient method, particularly by spray drying. The resulting particles contain drug dispersed as small particles in a polymeric matrix. The particles are stable against aggregation, and can be put into capsules or tableted for administration. The controlled release formulations contain a BCS Class II drug and a bioadhesive polymer. The controlled release formulations may be in the form of a tablet, capsules, mini-tab, microparticulate, or osmotic pump. Enhancement of oral uptake of the drug from use of bioadhesive polymers occurs through (1) increased dissolution kinetics due to stable micronization of the drug, (2) rapid release of the drug from the polymer in the GI tract; and (3) prolonged GI transit due to bioadhesive properties of the polymers. The combination of these effects allows the preparation of a compact, stable dosage form suitable for oral administration of many class II drugs.
Owner:SPHERICS
Solid-liquid mixing device
The invention provides a solid-liquid mixing device which is used for mixing a fracturing fluid. The solid-liquid mixing device contains a low-temperature and pressure resistant enclosed mixing container, a solid introducing port which is arranged on the mixing container and used for introducing solid particles of the fracturing fluid into an inner chamber of the mixing container, a liquid introducing port which is disposed on the mixing container and used for introducing a base solution of the fracturing fluid into the inner chamber, and a solid-liquid outlet which is arranged on the mixing container and used for exporting the fracturing fluid out of the inner chamber. According to the solid-liquid mixing device provided by the invention, by the adoption of the low-temperature and pressure resistant enclosed mixing container, the solid-liquid mixing device can meet mixing requirements for low temperature under pressure; and as the mixing container is respectively provided with the solid introducing port, the liquid introducing port and the solid-liquid outlet, the process of putting the solid particles and the base solution into the mixing container and the process of exporting the fracturing fluid out of the mixing container will not interfere with each other, and mixing of the fracturing fluid can be continuously carried out.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH OILFIELD SERVICES GROUP
Fracturing sand mixing device
The invention provides a fracturing sand mixing device used for mixing fracturing fluid. The fracturing sand mixing device comprises a solid conveying device and a solid-liquid mixing device communicated with the solid conveying device, wherein the solid-liquid mixing device is a pressure container. The solid-liquid mixing device comprises a solid lead-in port capable of leading in solid particles of the fracturing fluid output by the solid conveying device, a base fluid lead-in port for leading in base fluid of the fracturing fluid, a mixing inner cavity for accommodating the solid particles and the base fluid and a solid-liquid lead-out port for leading out the fracturing fluid formed by mixing. Substances such as carbon dioxide or petroleum gas which are in a gas state under normal temperature can be kept in a liquid state by high pressure through the fracturing sand mixing device and are mixed with the solid particles to form the fracturing fluid, and the goal of preparing the fracturing fluid with liquid carbon dioxide or liquefied petroleum gas (propane) serving as the base fluid is achieved.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH OILFIELD SERVICES GROUP
A fracturing sand mixing device
The invention provides a fracturing sand mixing device used for mixing fracturing fluid. The fracturing sand mixing device comprises a solid-liquid mixing device, and the solid-liquid mixing device is a pressure container. The solid-liquid mixing device comprises a solid lead-in port capable of leading in solid particles of the fracturing fluid, a base fluid lead-in port for leading in base fluid of the fracturing fluid, a mixing inner cavity for accommodating the solid particles and the base fluid and a solid-liquid lead-out port for leading out the fracturing fluid formed by mixing. Substances such as carbon dioxide or petroleum gas which are in a gas state under normal temperature can be kept in a liquid state by high pressure through the fracturing sand mixing device and are mixed with the solid particles to form the fracturing fluid, and the goal of preparing the fracturing fluid with liquid carbon dioxide or liquefied petroleum gas (propane) serving as the base fluid is achieved.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH OILFIELD SERVICES GROUP
A fracturing sand mixing device
The invention provides a fracturing sand mixing device used for mixing fracturing fluid. The fracturing sand mixing device comprises a solid conveying device and a solid-liquid mixing device communicated with the solid conveying device, wherein the solid-liquid mixing device is a pressure container. The solid-liquid mixing device comprises a solid lead-in port capable of leading in solid particles of the fracturing fluid output by the solid conveying device, a base fluid lead-in port for leading in base fluid of the fracturing fluid, a mixing inner cavity for accommodating the solid particles and the base fluid and a solid-liquid lead-out port for leading out the fracturing fluid formed by mixing. Substances such as carbon dioxide or petroleum gas which are in a gas state under normal temperature can be kept in a liquid state by high pressure through the fracturing sand mixing device and are mixed with the solid particles to form the fracturing fluid, and the goal of preparing the fracturing fluid with liquid carbon dioxide or liquefied petroleum gas (propane) serving as the base fluid is achieved.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH OILFIELD SERVICES GROUP
Oily cosmetic composition in aerosol form
InactiveUS20080031908A1Process stabilityHappy to useCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsParaffin waxSolid particle
Aerosol product containing an oily composition containing at least one oil, and at least one hydrocarbon compound having a melting point greater than or equal to 30° C., the compound being in the form of solid particles and one or more propellants. The hydrocarbon compound can notably be a paraffin or a fatty acid amide. Used for cleaning and / or make-up removal of the skin and / or of the hair, care of the skin and / or of the hair, for protecting the skin against the sun, and for make-up of the skin.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Linearly retractable pressure hose
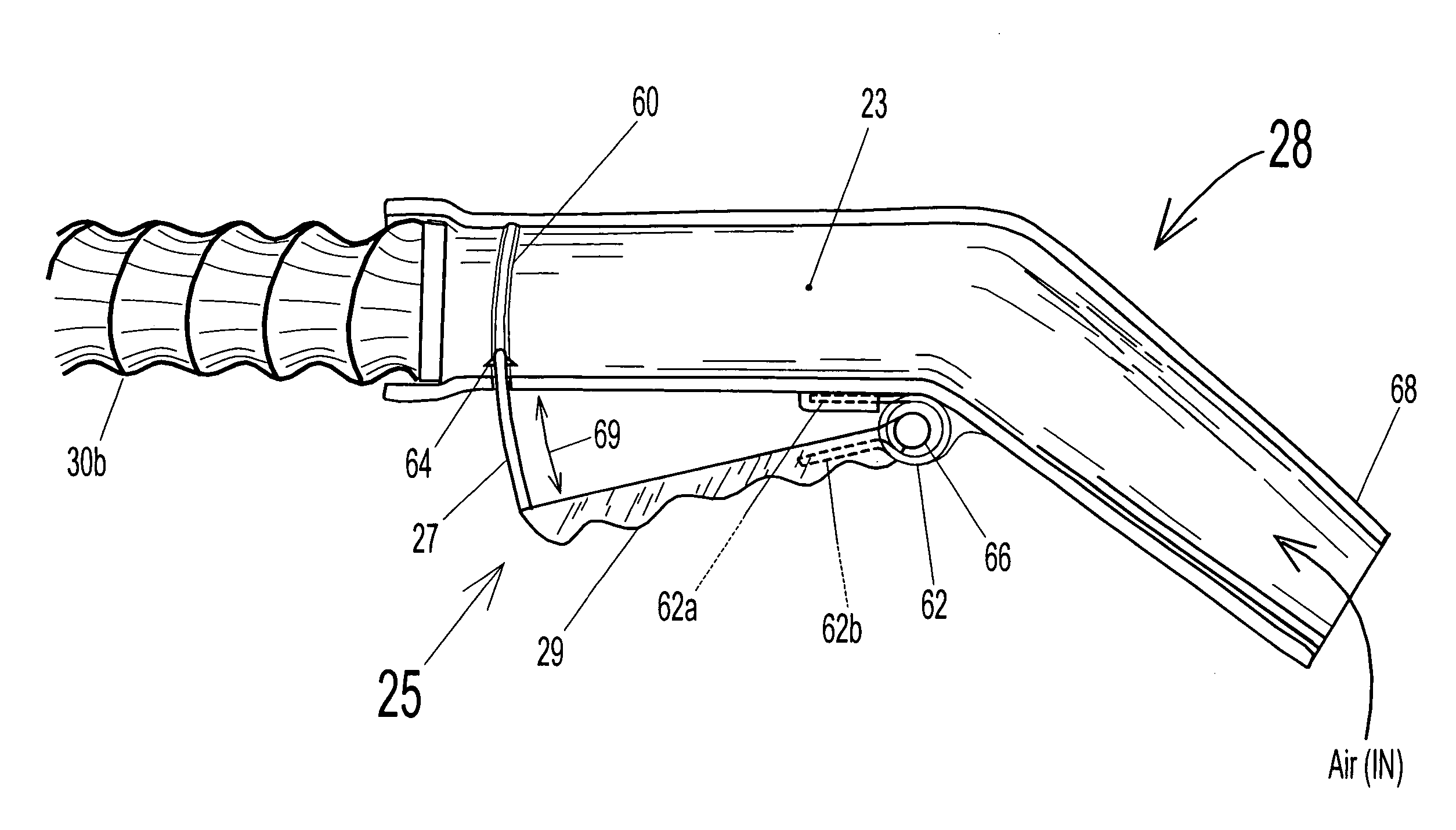
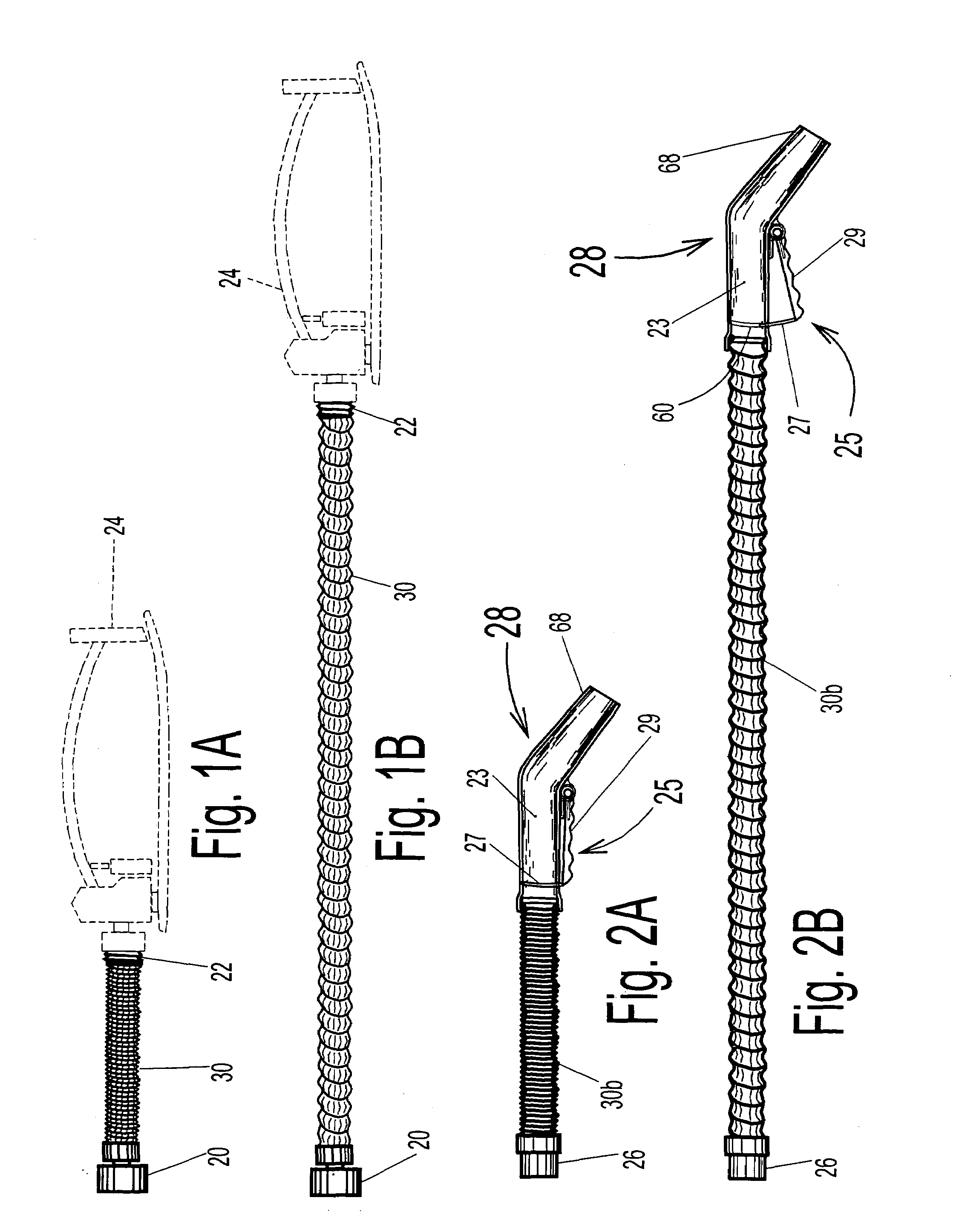
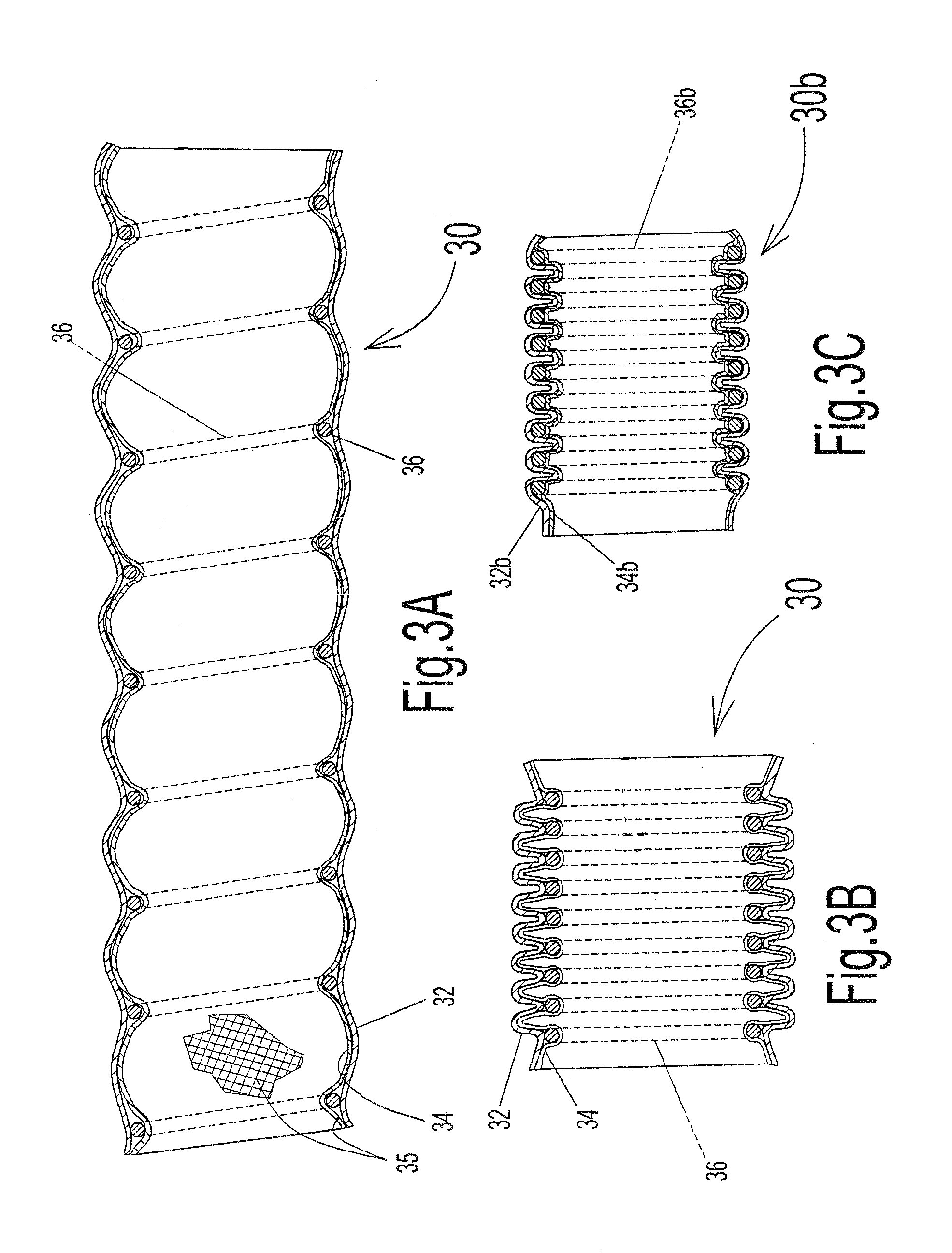
A linearly self-actuated hose for use in transporting fluids (liquids, gases, solid particles, and combinations of these three). Hose (30) has a biasing spring (36) that extends along its full length, and can comprise single or multiple springs and / or multiple diameter spring coils. Spring (36) is covered with hose cover material (32) on the outside and hose cover material (34) on the inside to form a sealed hose and are bowed inward or outward radially between the individual spring coils depending on the intended use of hose (30) to give the cover materials room to move out of the way when the hose retracts and the coils of spring (36) are forced close together. The Linearly Retractable Hose is operated by changing internal pressure within the hose relative to the ambient pressure on the exterior of the hose. Control of fluid pressure within hose (30) is what allows the hose to operate as an automatically extendable and retractable hose. The biasing of spring (36) depends on the type of use for the hose. For hose (30b), which will be used as a vacuum hose then the biasing spring (30b) must exert an extending force on the cover material (opposite that for a pressure hose). If the hose is to be used as a pressure hose (garden hose, etc.), spring (36) will need to have a bias that exerts a retracting force on cover materials (32) and (34).
Owner:TELEBRANDS CORP
Fine-grained metallic coatings having the coefficient of thermal expansion matched to the one of the substrate
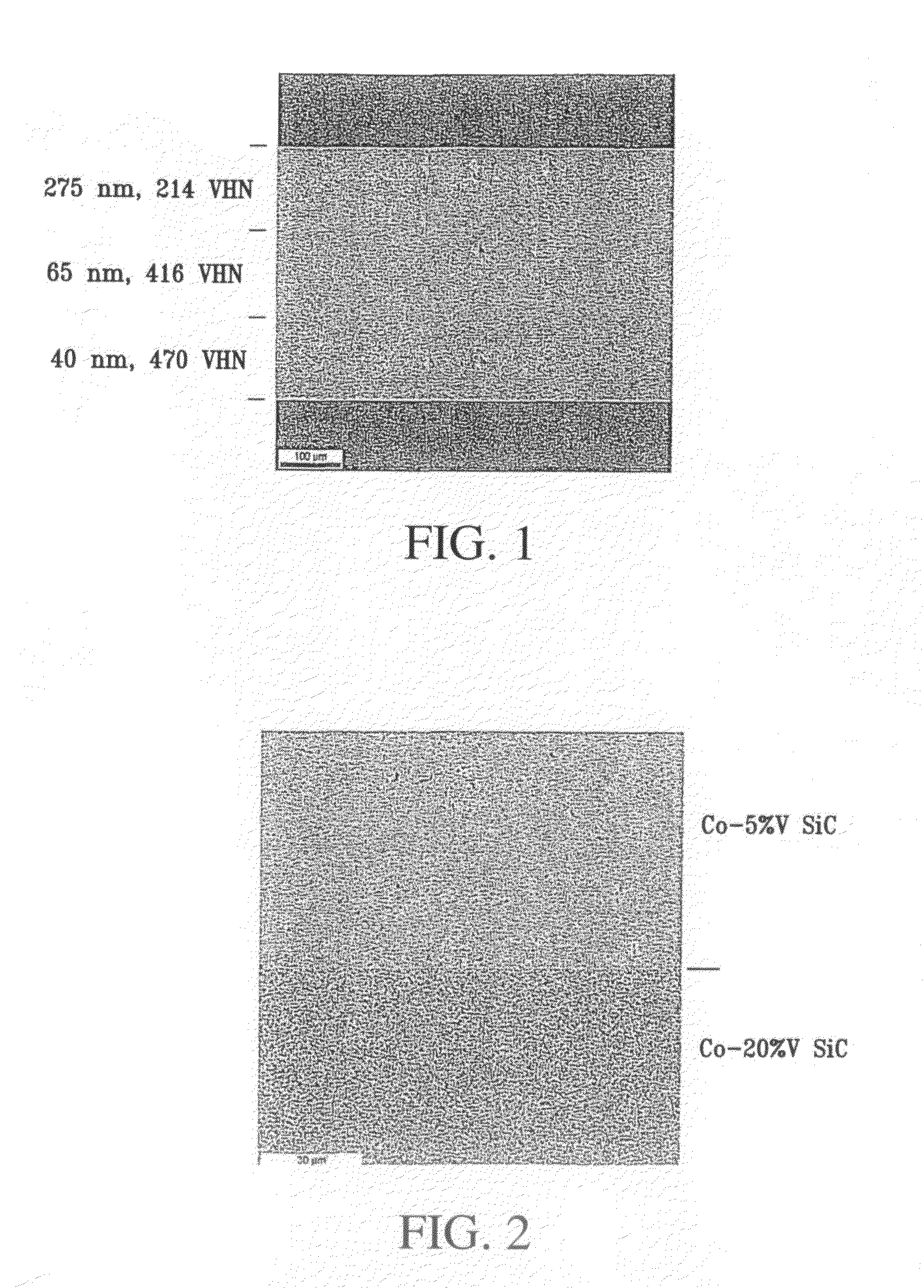
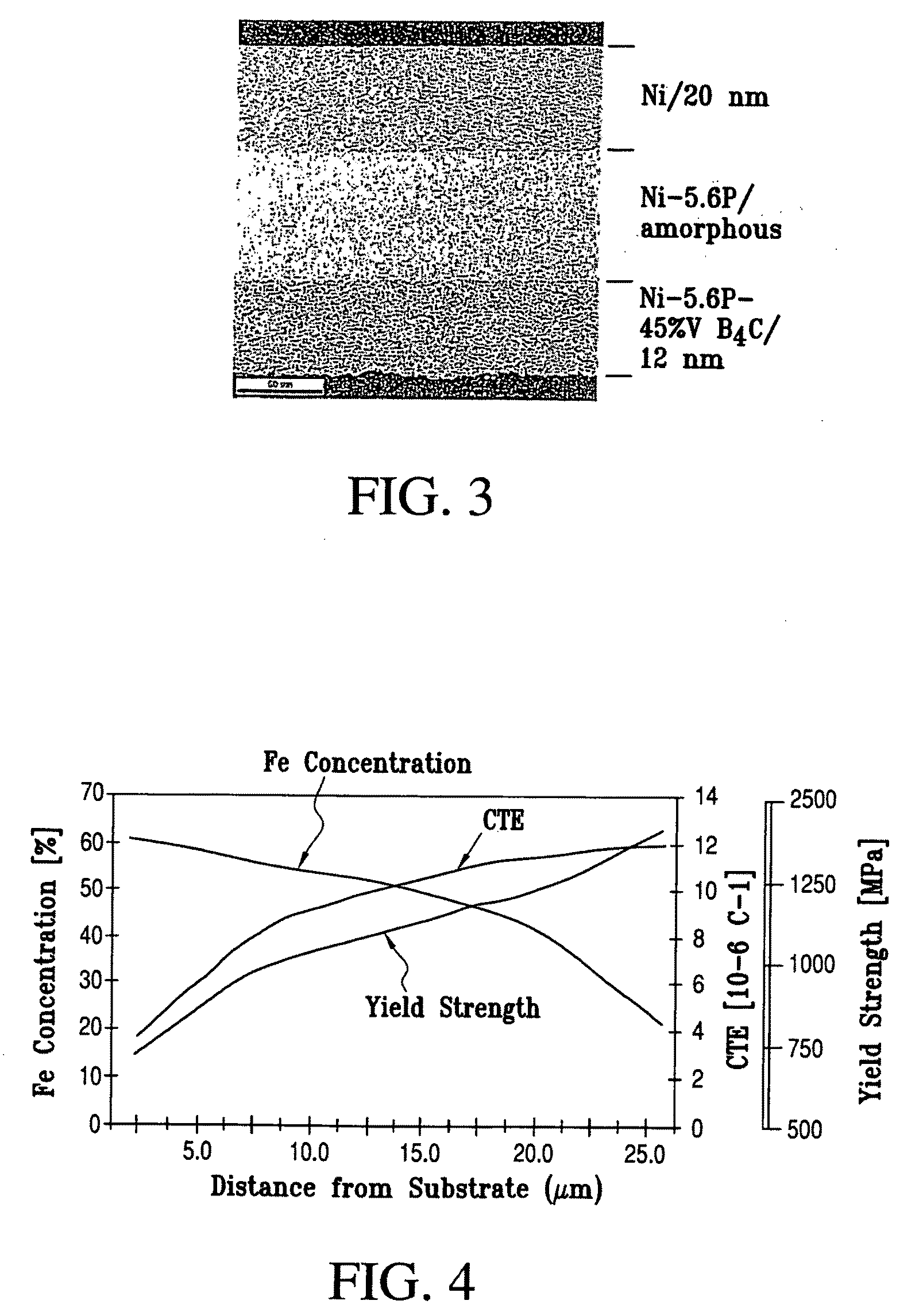
ActiveUS7320832B2Good thermal cycle performanceHigh strengthMaterial nanotechnologyRodsParticulatesChemical composition
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Solid group IIIA particles formed via quenching
InactiveUS20080057203A1Efficient and simplified creationPrevent leaching and phase separationPretreated surfacesCoatingsSolid particleAlloy
Methods and devices are provided for forming thin-films from solid group IIIA-based particles. In one embodiment, a process for forming solid particles is provided. The method includes providing a first suspension of solid and / or liquid particles containing at least one group IIIA element. A material may be added to substantially increase the melting point of at least one set of group IIIA-containing particles in the suspension into higher-melting solid particles comprising an alloy of the group IIIA element and at least a part of the added material. The suspension may be deposited onto a substrate to form a precursor layer on the substrate and the precursor layer is reacted in a suitable atmosphere to form a film.
Owner:NANOSOLAR
Hollow fiber microfiltration membranes and a method of making these membranes
InactiveUS6890435B2Narrow pore size distributionHigh mechanical strengthSemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiberHollow fibre membrane
A hollow fiber microfiltration (MF) membrane is provided. The casting solution used to make this membrane includes a fiber-forming polymer having a degree of polymerization greater than about 1000, a water-soluble polymer, an anhydride with about 2 to 12 carbon atoms, and a solvent. The membrane is formed by mixing and heating these components to form a viscous dope and then extruding the dope through an annular orifice to form a hollow fiber MF membrane. The hollow fiber membrane is then fed through a coagulation bath and two leaching baths. The membrane is especially useful for filtering liquids, such as wine and juice, so as to remove bacteria, gel, and solid particles from the liquids.
Owner:KOCH MEMBRANE SYST
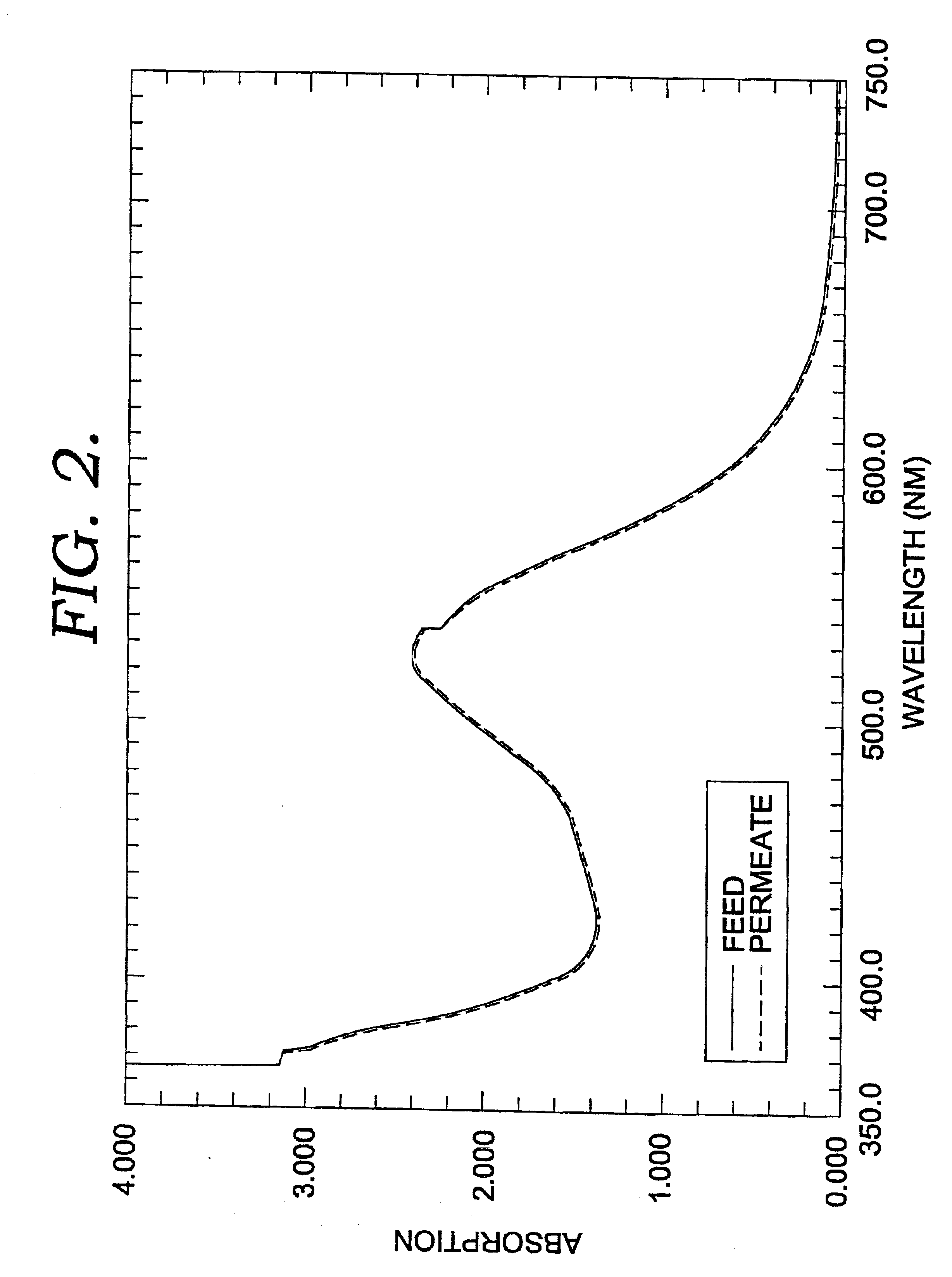
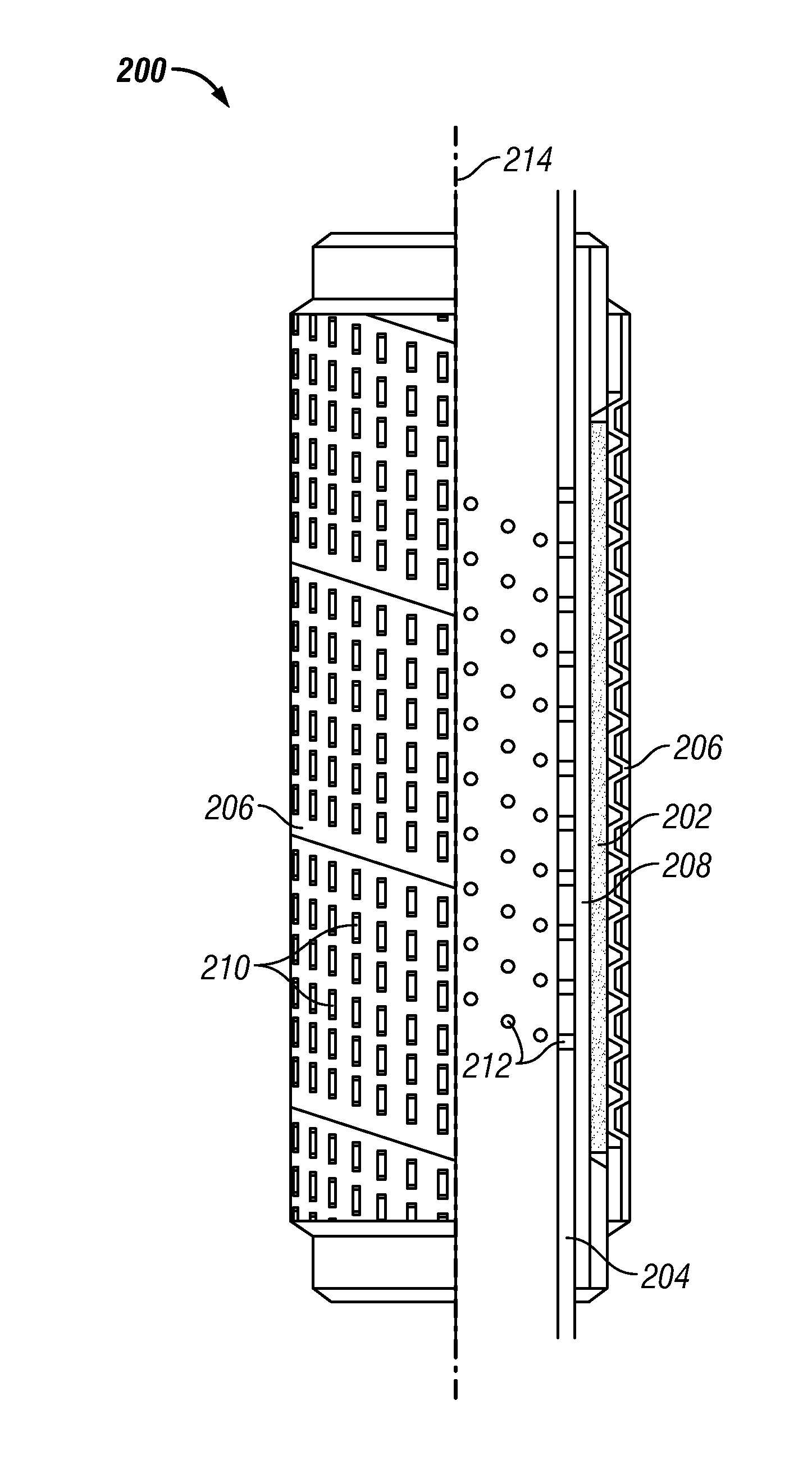
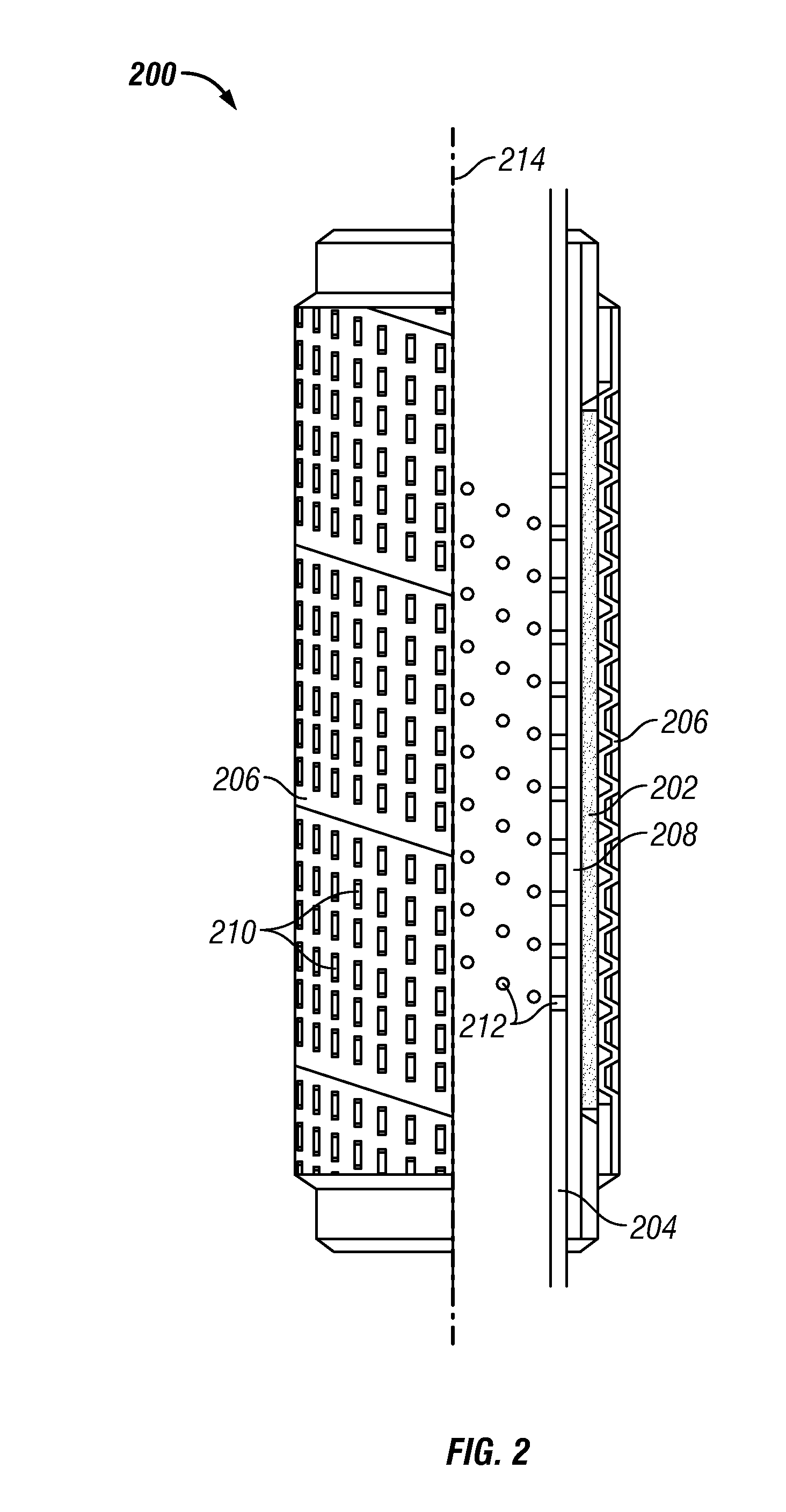
Wellbore Flow Control Devices Using Filter Media Containing Particulate Additives in a Foam Material
In one aspect a apparatus is provided that in one embodiment may include a permeable member made by combining a particulate additive to one or more materials, which materials when processed without the particulate additive form a substantially impermeable mass, wherein the permeable member inhibits flow of solid particles above a particular size through the permeable member.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Variable property electrodepositing of metallic structures
ActiveUS20090159451A1Increase floor spaceAdd equipmentCellsElectrolytic coatingsParticulatesMetallic materials
Variable property deposit, at least partially of fine-grained metallic material, optionally containing solid particulates dispersed therein, is disclosed. The electrodeposition conditions in a single plating cell are suitably adjusted to once or repeatedly vary at least one property in the deposit direction. In one embodiment denoted multidimension grading, property variation along the length and / or width of the deposit is also provided. Variable property metallic material deposits containing at least in part a fine-grained microstructure and variable property in the deposit direction and optionally multidimensionally, provide superior overall mechanical properties compared to monolithic fine-grained (average grain size: 2 nm-5 micron), entirely coarse-grained (average grain size: >20 micron) or entirely amorphous metallic material deposits.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com