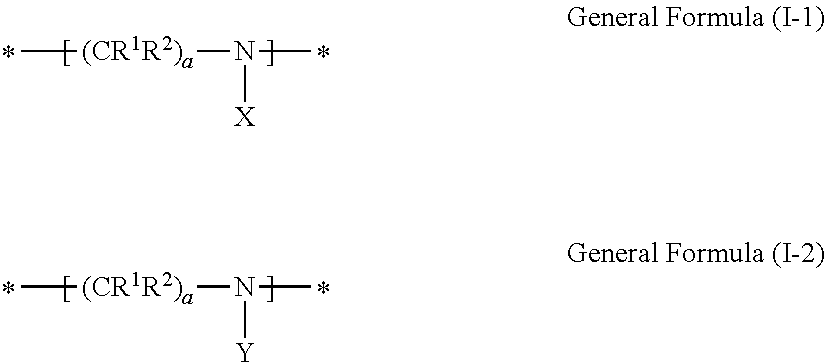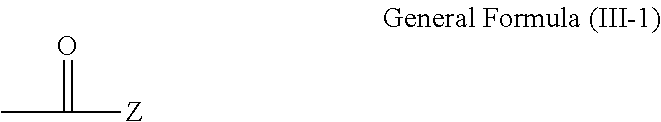Patents
Literature
31076results about How to "Evenly dispersed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
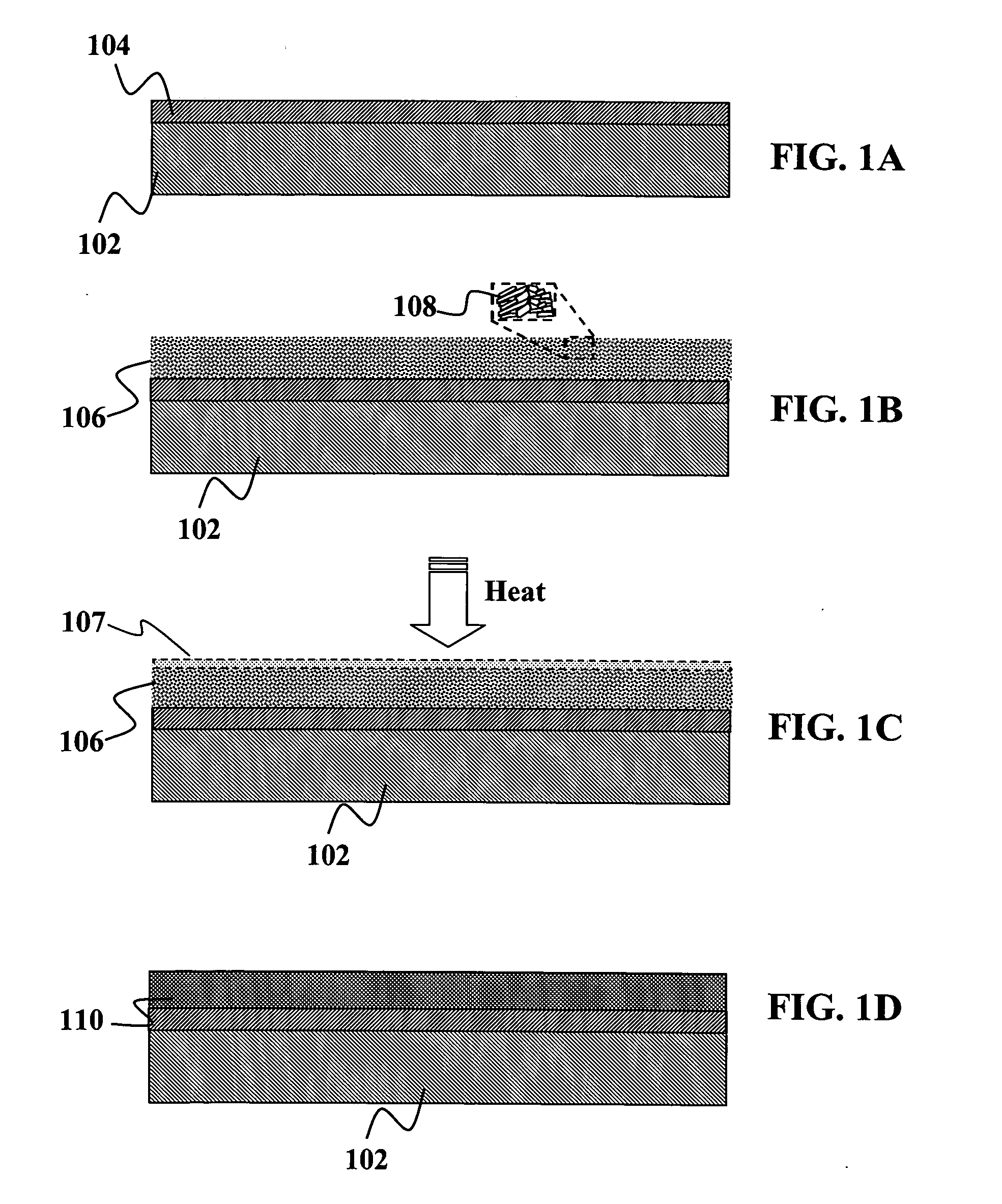
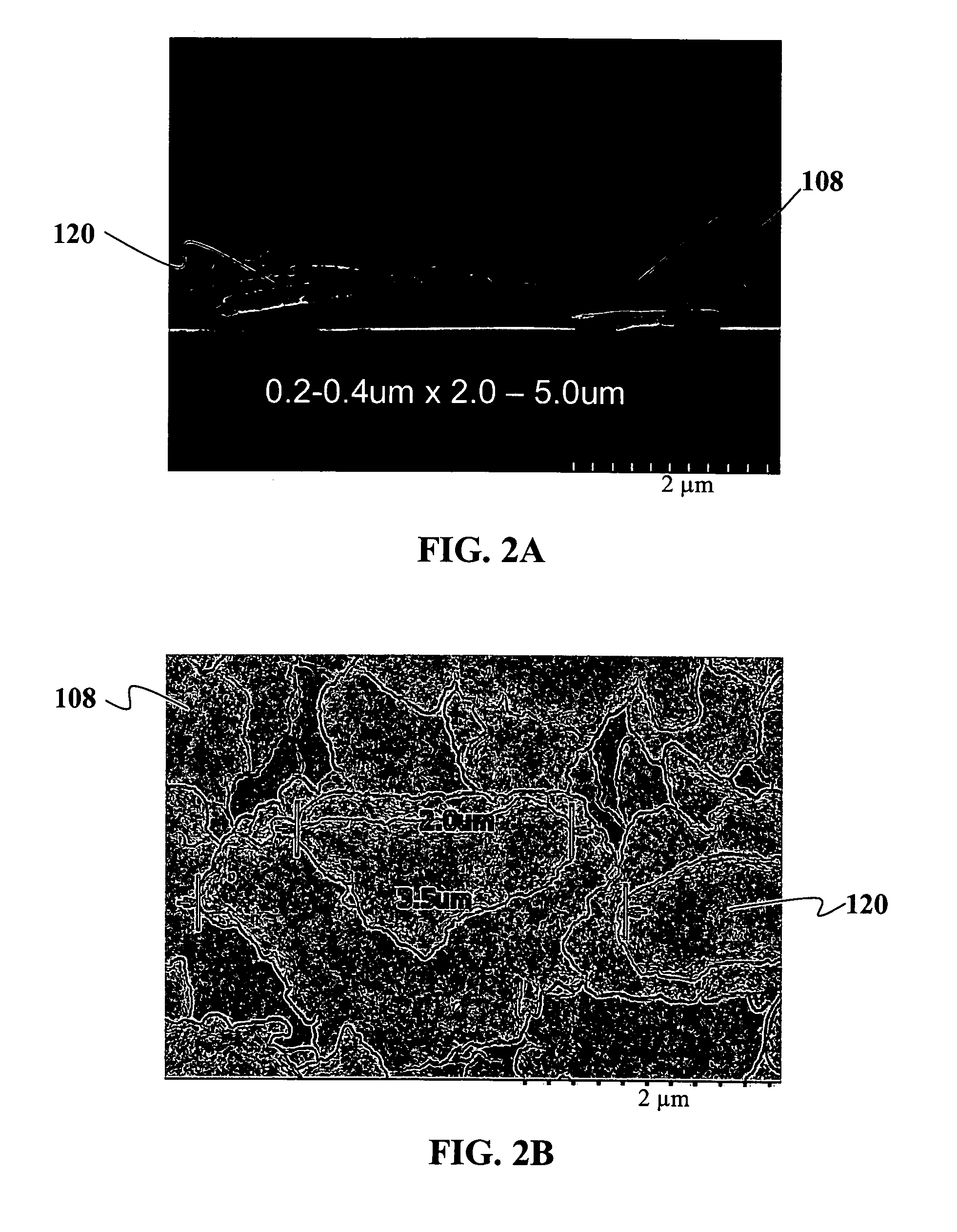
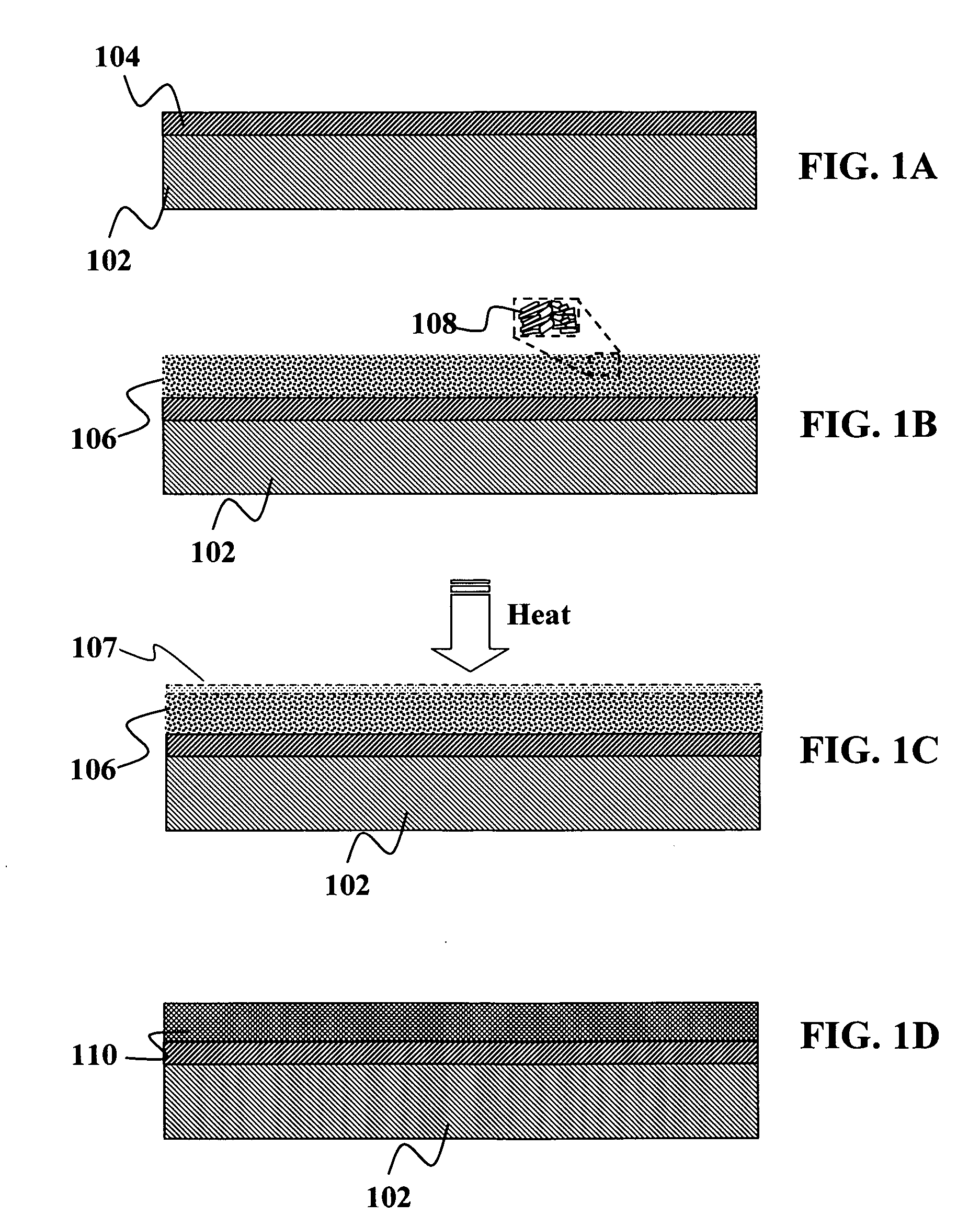
Method for preparing graphene compounds and graphene oxide compounds with high efficiency
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene compounds and graphene oxide compounds with high efficiency, relating to the method for preparing the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds. The invention solves the problems of easy composition of graphene or graphene oxide per se and many process steps, higher cost and difficult dispersedness for preparing the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds by the traditional method at the same time. The invention adopts a mechanical stripping method to obtain the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds. In the invention, an automatic machine is utilized, solid particles are used for assisting stripping, the contact area and the stripping number of the stripping process are greatly increased, and carbon material powder experiences a lot of stripping processes through the action of shear and impact, thereby obviously improving the stripping efficiency and achieving the purpose of uniform dispersedness to the composites. The method is suitable for industrial mass production of the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Milled particles
InactiveUS6634576B2Increase incorporationOptimal for incorporationPowder deliveryInorganic non-active ingredientsParticulatesPolymer science
A process for milling a solid substrate in the milling chamber of a dispersion or media mill in the presence of a two or more compositions of milling media bodies is disclosed wherein all milling media bodies contribute to the grinding of the solid substrate and wherein at least one composition of media bodies provides fragments of milling media bodies that are retained with the milled solid substrate particles in the form of a synergetic commixture produced in the milling process. More specifically, a process is disclosed for preparing a synergetic commixture comprising small particles of a solid substrate and small particulates of a first material of a desired size comprising the steps of (a) providing to the milling chamber of a media mill a contents comprising a pre-mix of a solid substrate, a fluid carrier, a plurality of milling bodies of a first material having a fracture toughness Kc1, and a plurality of milling bodies of a second material having a fracture toughness Kc2; (b) operating the media mill to grind the solid substrate and degrade at least a portion of the milling bodies of first material to produce a dispersion in the fluid carrier comprising a synergetic commixture of small particulates of the first material and small particles of the solid substrate having a desired size equal to or less than a size Sp; (c) separating the dispersion from any milling bodies and solid substrate particles having a size larger than Sp; and (d) optionally removing the fluid carrier from the dispersion to form a synergetic commixture free of fluid and comprising the particles and the small particulates, wherein KC2 is greater than KC1.
Owner:RTP PHARMA +1
Preparation method of polymer/graphene composite material through in situ reduction
ActiveCN101864098AEvenly dispersedQuality improvementSpecial tyresNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialElectrical conductorVulcanization
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polymer / graphene composite material through in situ reduction, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: adopting ultrasonic wave or grinding to evenly disperse the graphite oxide prepared by a Hummers method into polymer dispersion; introducing reducing agent into the polymer dispersion for in situ reduction, enabling the graphite oxide to be reduced into the grapheme so as to obtain stable polymer / graphene composite emulsion; carrying out demulsification, agglomeration and drying to obtain the composite polymer / grapheme composite master batch; adding the dried polymer / grapheme composite master batch and various assistants into the polymeric matrix according to a certain ratio; and carrying out double-roller mixing, vulcanization, melt extrusion or injection molding to obtain the polymer / graphene composite material with excellent physical and mechanical properties.
Owner:成都创威新材料有限公司
Fabric coating containing energy absorbing phase change material and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS6514362B1Evenly dispersedEqually distributedDecorative surface effectsHeat storage plantsMicrosphereEnergy absorption
A coating composition for fabrics includes wetted microspheres containing a phase change material dispersed throughout a polymer binder, a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a thickener. Preferred phase change materials include paraffinic hydrocarbons. The microspheres may be microencapsulated. To prepare the coating composition, microspheres containing phase change material are wetted and dispersed in a dispersion in a water solution containing a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a polymer mixture. The coating is then applied to a fabric. In an alternative embodiment, an extensible fabric is coated with an extensible binder containing microencapsulated phase change material to form an extensible, coated fabric. The coated fabric is optionally flocked. The coated fabrics are manufactured using transfer techniques.
Owner:OUTLAST TECH LLC
Ceramic slurry preparation and 3D (three dimensional) printing light curing molding method
ActiveCN106810215ALow viscosityHigh solid contentAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusFlexural strengthVolumetric Mass Density
The invention provides a ceramic slurry preparation and 3D (three dimensional) printing light curing molding method. 25-85vol% of ceramic powder and 15-75vol% of an optical resin premix solution are mainly involved, and the method includes: A), preparation of the optical resin premix : namely stirring a low polymer, a reactive diluent, a photoinitiator, a dispersing agent, a photosensitizer and a sensitizer according to a certain proportion under intermediate speed for 0.5-3 hours to enable the components to be mixed evenly; B), placing the premix solution and the ceramic powder in a ball mill according to certain volume for ball-milling for 5-15 hours to prepare the ceramic slurry high in solid content and low in viscosity; subjecting the ceramic slurry to curing molding layer by layer gradually on a 3D light curing molding machine to obtain a ceramic green body prior to aftertreatment of drying, degreasing, sintering and the like to obtain ceramic part. The method is high in preparation molding precision and free of molds to prepare complex structure parts, the ceramic product can reach more than 92% in density, 320-1750MPa in flexural strength and 1800-4500MPa in compression strength.
Owner:重庆摩方科技有限公司
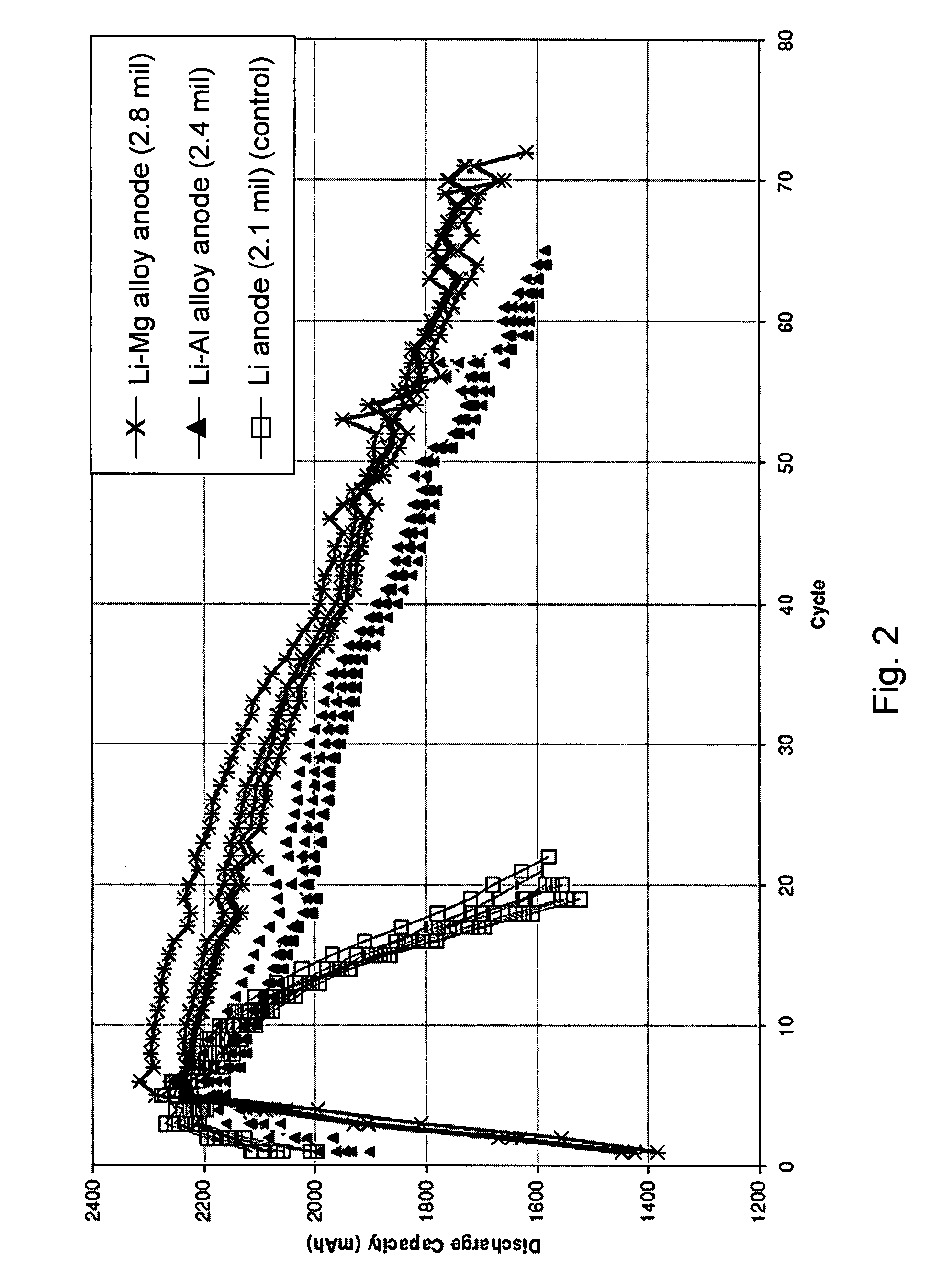
Lithium alloy/sulfur batteries
Electrochemical cells including anode compositions that may enhance charge-discharge cycling efficiency and uniformity are presented. In some embodiments, alloys are incorporated into one or more components of an electrochemical cell, which may enhance the performance of the cell. For example, an alloy may be incorporated into an electroactive component of the cell (e.g., electrodes) and may advantageously increase the efficiency of cell performance. Some electrochemical cells (e.g., rechargeable batteries) may undergo a charge / discharge cycle involving deposition of metal (e.g., lithium metal) on the surface of the anode upon charging and reaction of the metal on the anode surface, wherein the metal diffuses from the anode surface, upon discharging. In some cases, the efficiency and uniformity of such processes may affect cell performance. The use of materials such as alloys in an electroactive component of the cell have been found to increase the efficiency of such processes and to increase the cycling lifetime of the cell. For example, the use of alloys may reduce the formation of dendrites on the anode surface and / or limit surface development.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Exhaust aftertreatment system using urea water
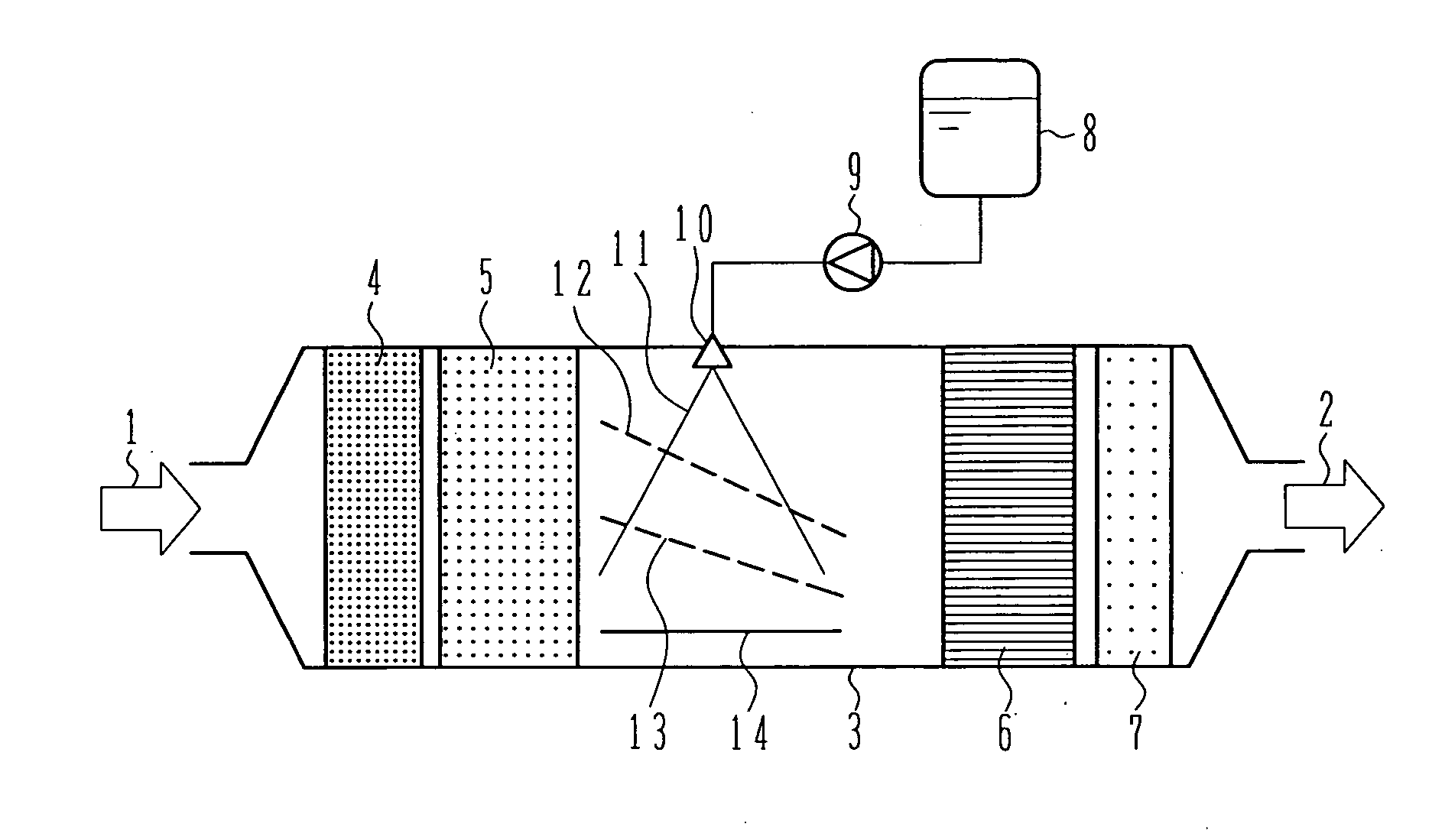
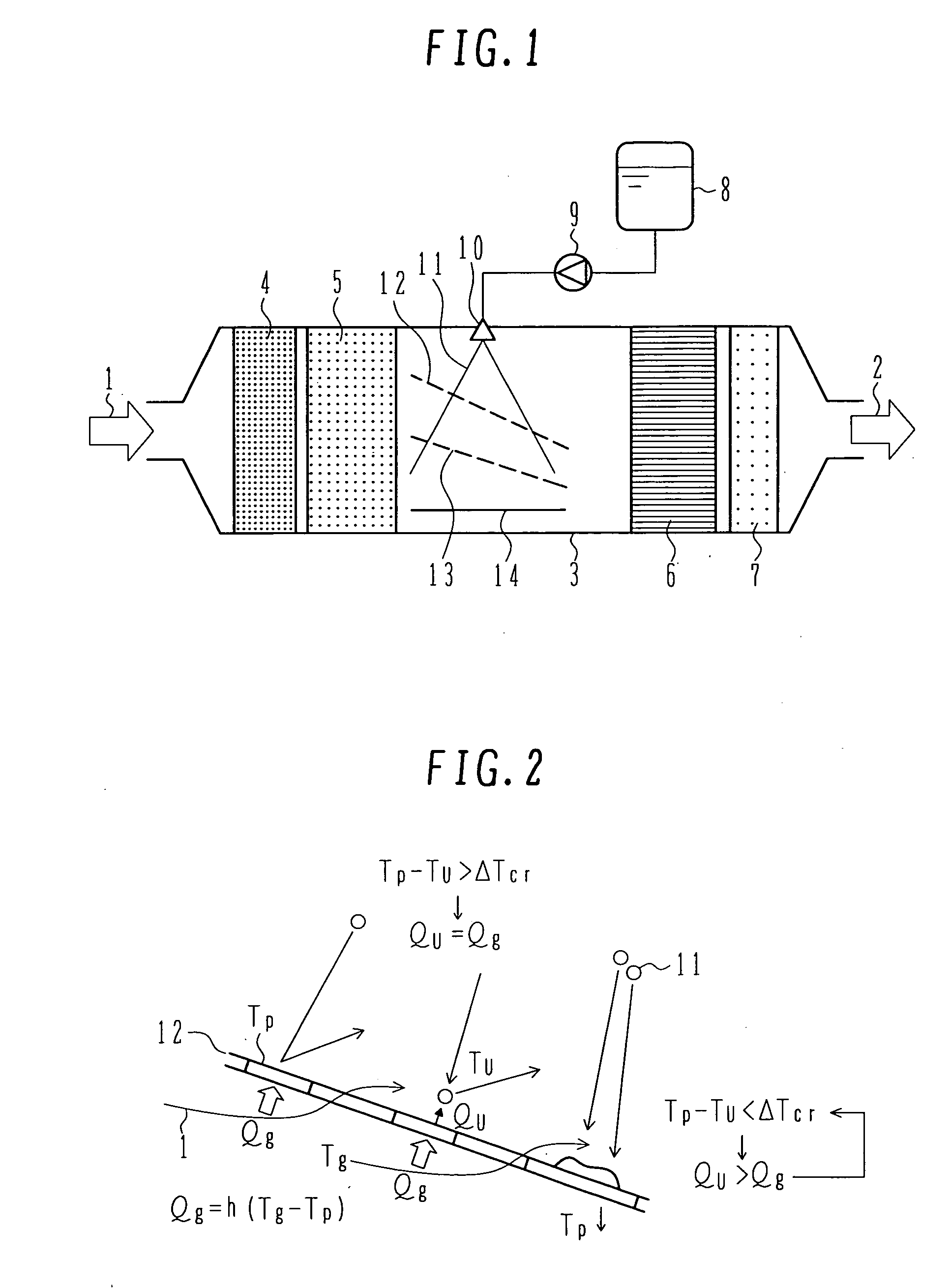
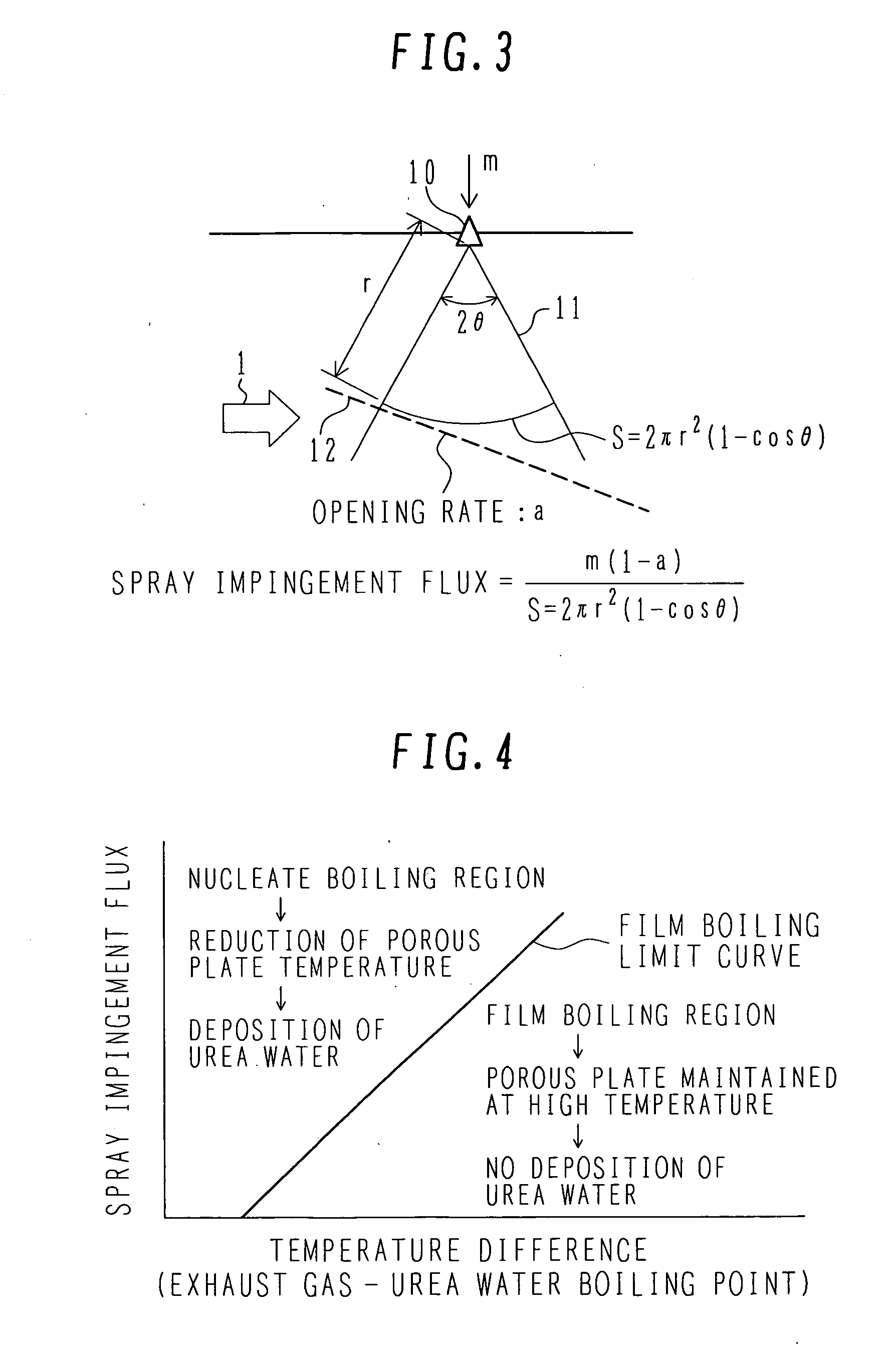
InactiveUS20070036694A1Avoid depositionReduced responseCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesHandling systemMultiple stages
An exhaust aftertreatment system comprises an injector for injecting urea water into an exhaust duct, and a denitration catalyst disposed downstream of the injector with respect to a flow of exhaust gas. The exhaust aftertreatment system reduces nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gas by the denitration catalyst while using ammonia produced from the urea water injected from the injector. The urea water is injected along a direction of the flow of the exhaust gas within the exhaust duct, and a porous plate is disposed in multiple stages in a space of the exhaust duct such that droplets of the injected urea water impinge against the porous plate before reaching a wall surface of the exhaust duct. A surface of the porous plate subjected to the impingement of the droplets is arranged to face downstream with respect to the flow of the exhaust gas. Deposition of the urea water is prevented by causing film boiling when the droplets impinge against the porous plate, and the urea water reflected by the porous plate is uniformly dispersed into the exhaust gas. Thus, the urea water is uniformly dispersed into the exhaust gas without increasing a pressure loss of the exhaust gas. The urea water is prevented from depositing on the wall surface and producing a precipitate in the form of a solid.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP +2
Polymer wood composite
InactiveUS6015612AHigh modulusHigh compressive strengthWood working apparatusRecord information storageFiberThermoplastic
The invention relates to a composition comprising a polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer and wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
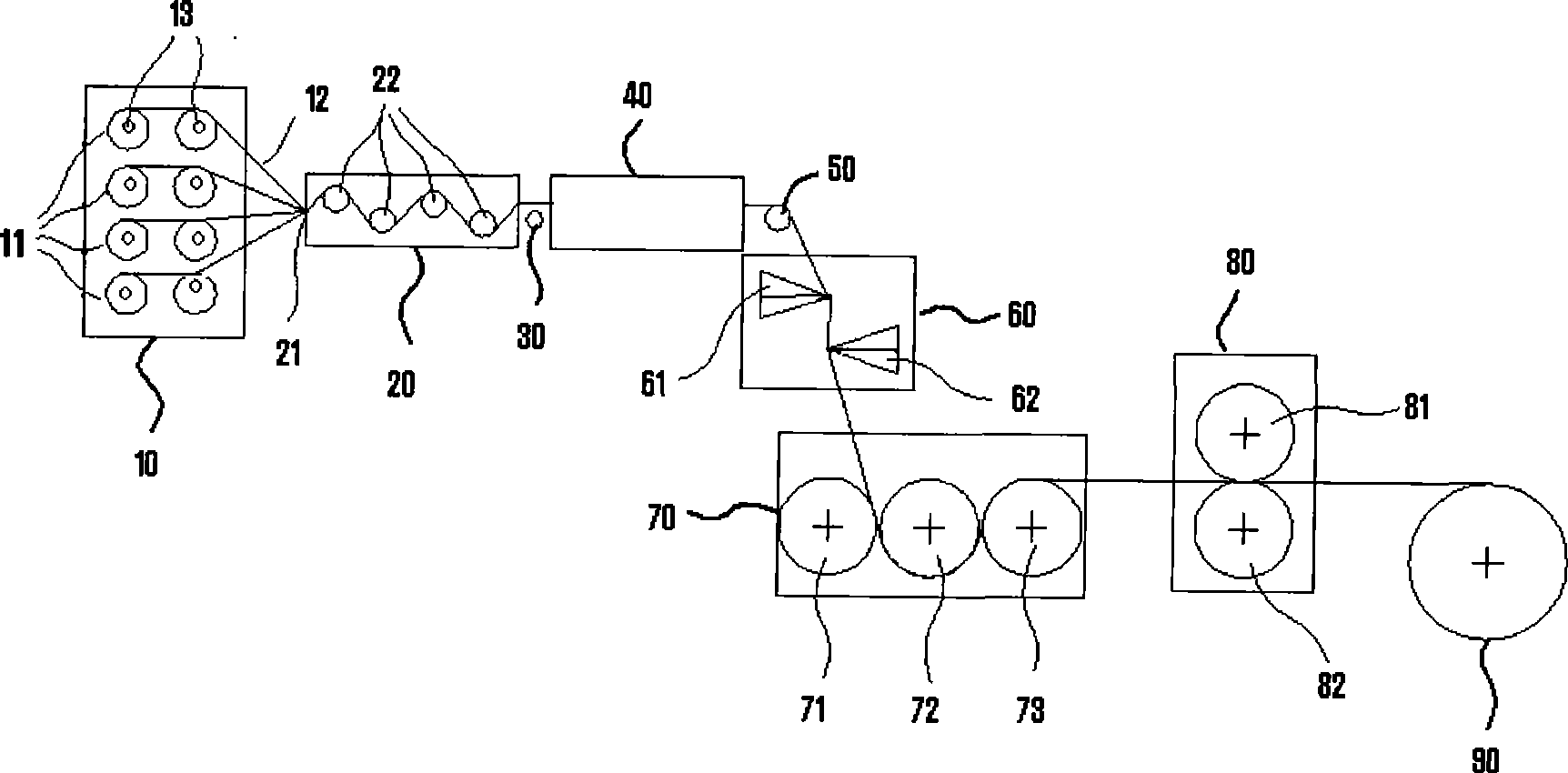
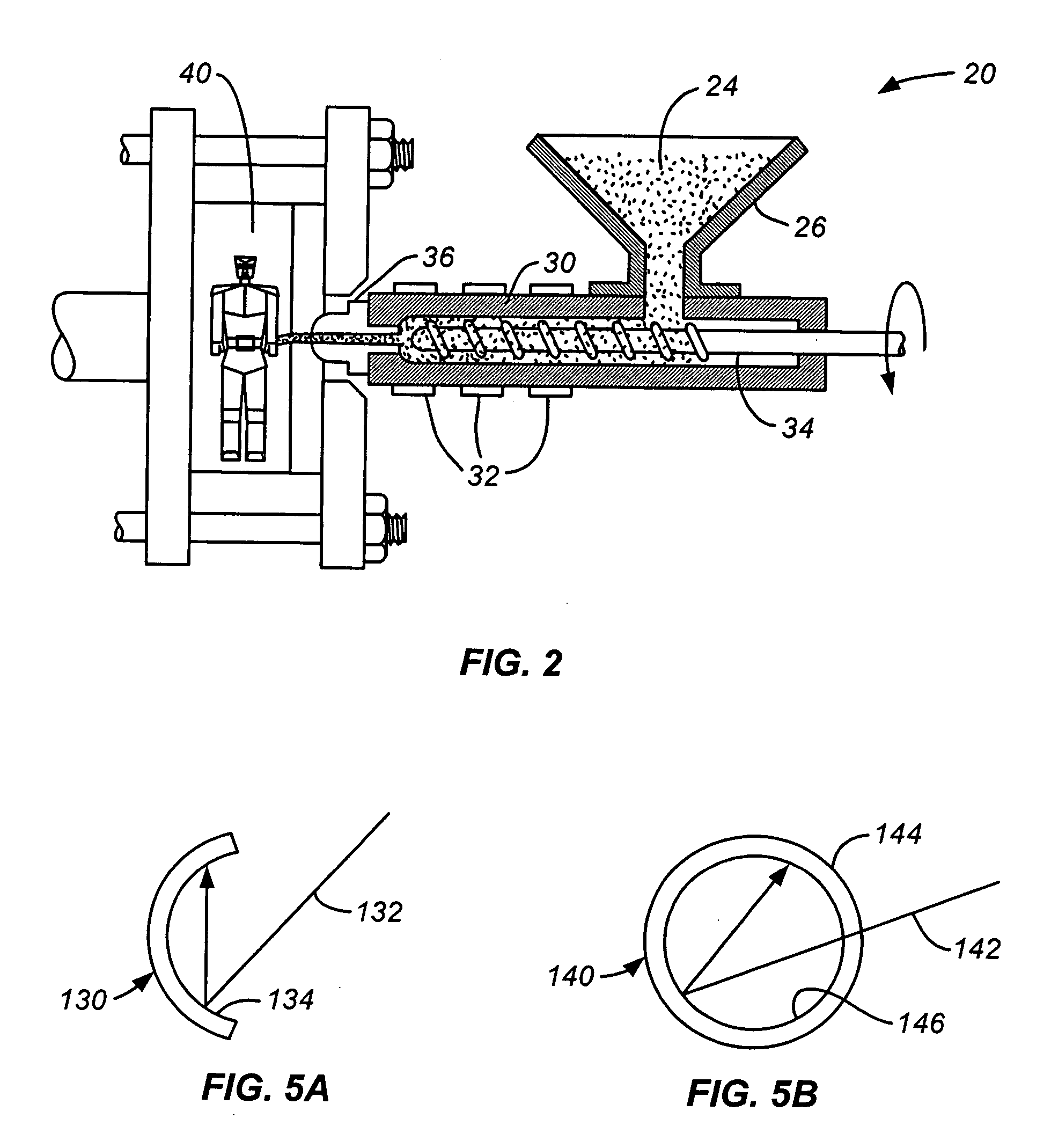
Equipment for preparing continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material presoaked belt and use thereof
The invention relates to an apparatus for preparing a continuous filament reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material prepreg tape, which comprises a yarn stand (10), a tension adjusting device (20), an electrostatic eliminating device (30), a preheating oven (40), a tension adjusting device (50), a dual-extruding die head (60), a three-roller dipping device (70), a cooling roll-in device (80) and a traction and winding device (90). The apparatus adopts the staggered dual-extruding die head (60) to pre-dip the continuous filament tape. Compared with the prior art, the apparatus has the advantages that the apparatus is simple, the continuous filament reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material prepreg tape prepared by the apparatus has low cost, the filament is dipped completely and the void ratio is kept to be not higher than 0.2 percent.
Owner:LIAONING LIAOJIE SCI & TECH
Resin, pigment dispersion, colored curable composition, color filter produced using the same, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20110003241A1High color purityIncrease contrastPhotosensitive materialsOptical filtersOligomerBackbone chain
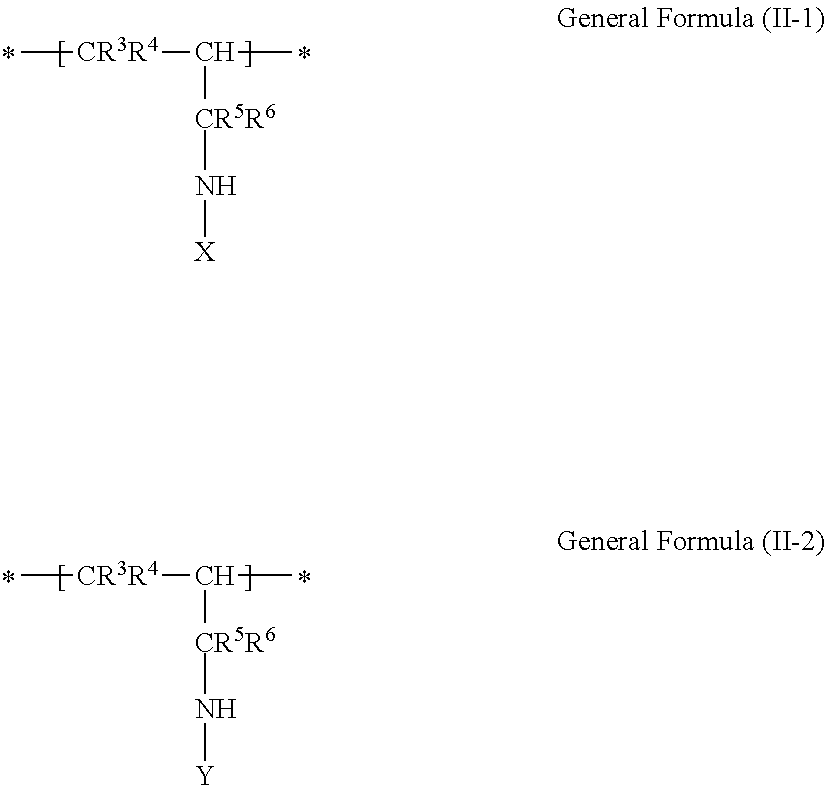
A resin including (i) a main chain portion containing a nitrogen atom, (ii) a group X that has a functional group having a pKa of 14 or less and is bonded to a nitrogen atom present in the main chain portion, and (iii) an oligomer chain or polymer chain Y having a number average molecular weight of from 500 to 1,000,000 in a side chain.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Light-emitting apparatus
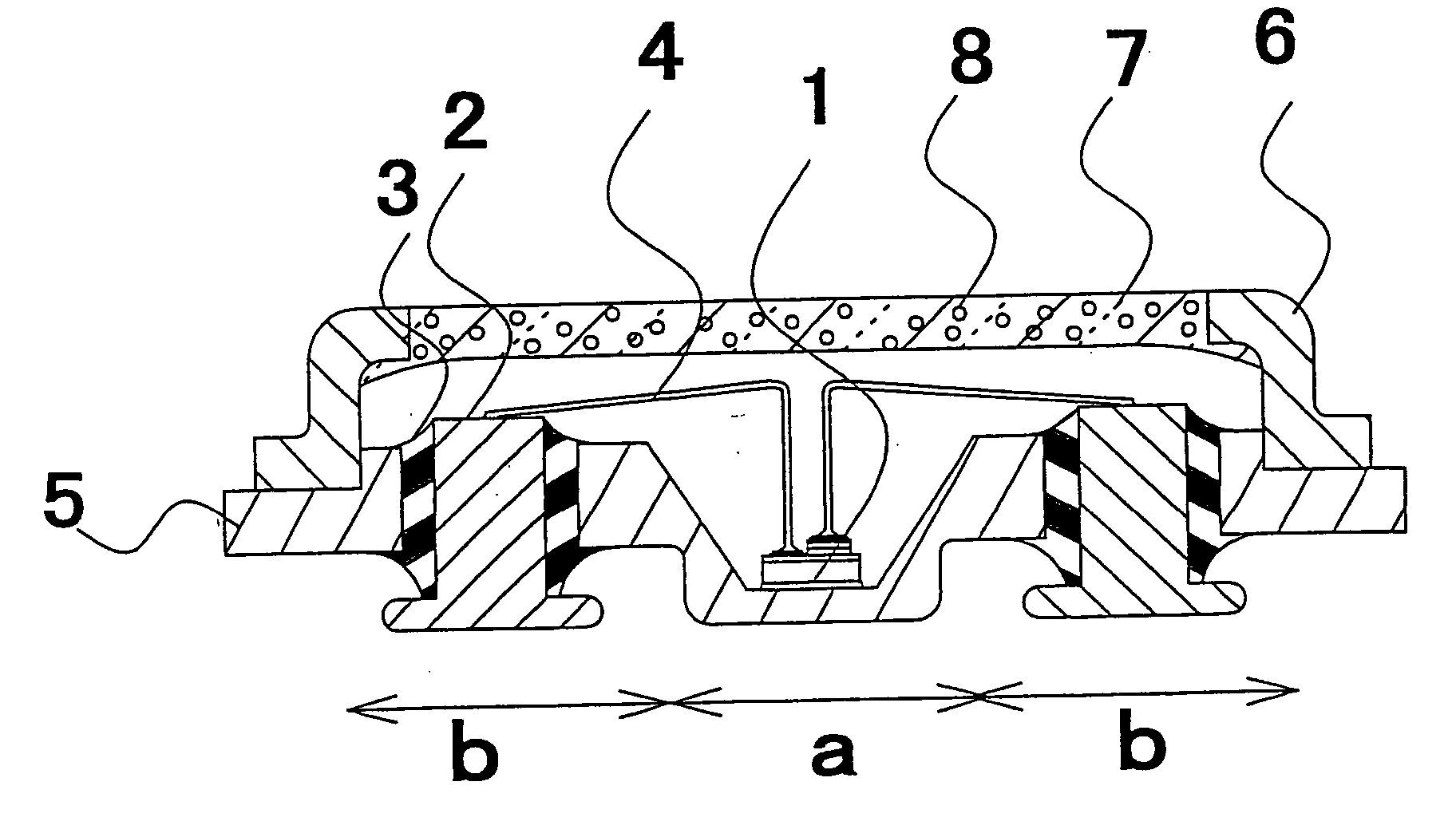
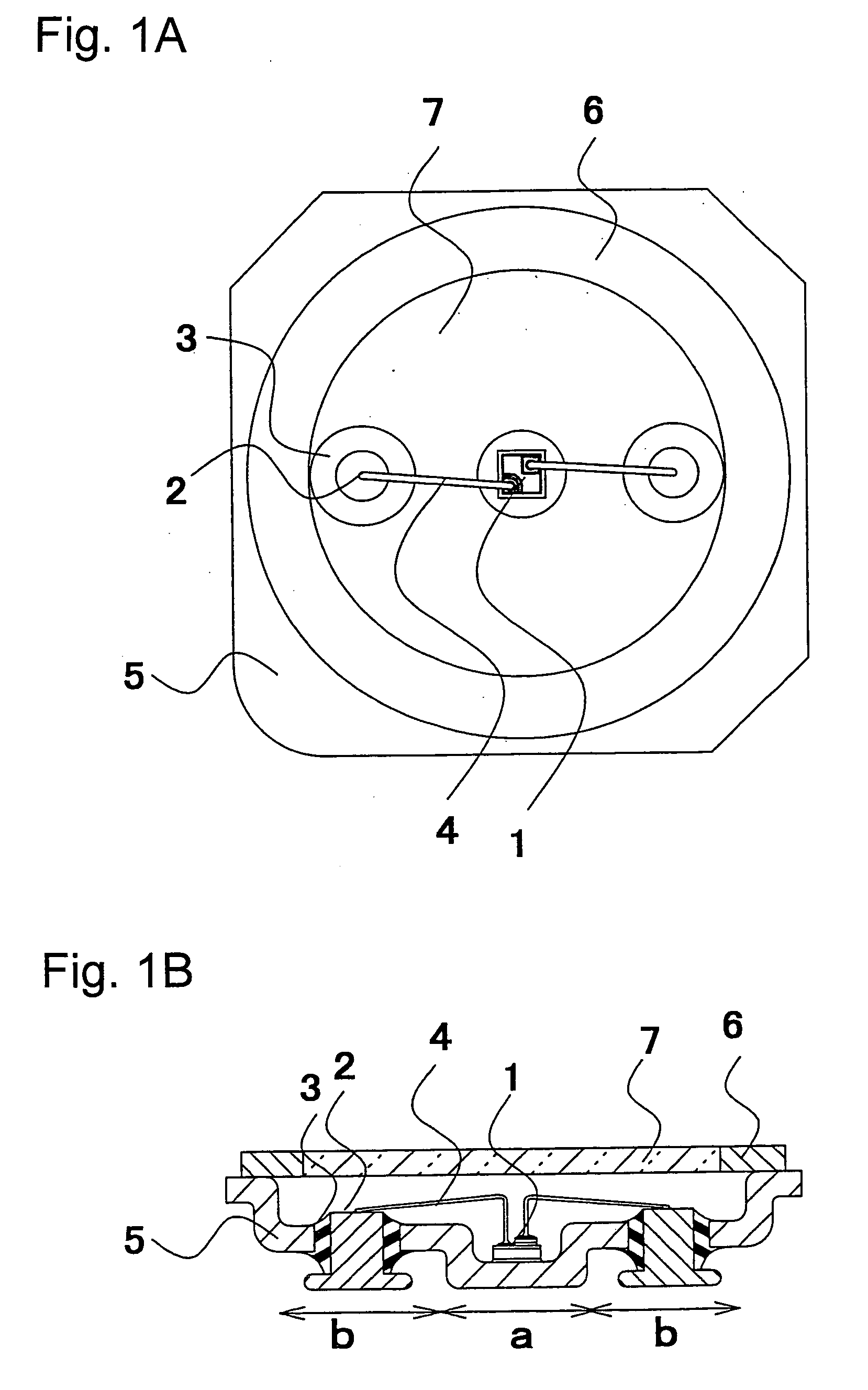
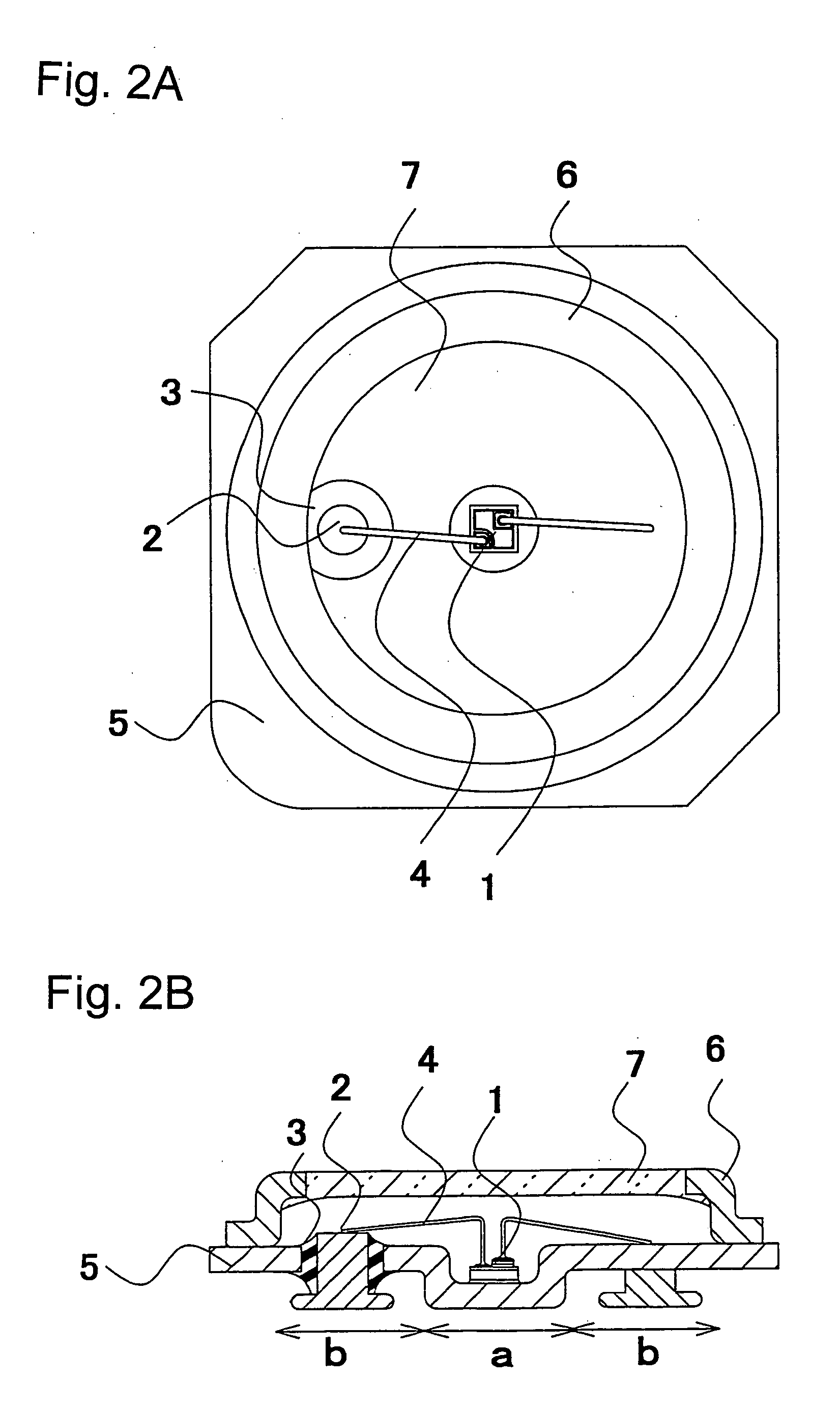
InactiveUS20040120155A1Improve reliabilityImprove productivityMeasurement apparatus componentsVehicle interior lightingEngineeringLight emitting device
A light emitting device comprises a light emitting element, a metal package having a recess part for housing the light emitting element and a base part which has one or more through holes, one or more lead electrode pins which penetrate the through holes and are separated from the through holes by a insulating member respectively, wherein the bottom faces of the lead electrode pins project out from the bottom face of the base part and positioned on a same plane including a outer bottom face of the recess part. With this configuration, the light emitting device which has a good heat radiating characteristic and high mechanical strength.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Reusable Plastic Ammunition Casing
InactiveUS20160265886A1Evenly dispersedCartridge ammunitionPlastic injection moldingStructural failure
A reloadable plastic ammunition casing is provided for firearm use. The plastic casing is preferably constructed from currently available polymeric materials using plastic injection molding techniques. In the preferred embodiment the casing includes a cylindrical body having a top portion and a bottom portion. The top portion having an open end for receiving a propellant and a top lip for retaining a projectile. The bottom portion has an internal casing floor that includes at least one concentric step down towards a centrally located primer pocket such that an installed primer is located in blast communication with the concentric steps on the casing floor. The concentric steps uniformly disburse, distribute, and deflect the heat and gas pressures within the casing when fired, thereby avoiding structural failure, allowing for multiple reloads of a casing constructed entirely out of plastic.
Owner:ALDRICH LONNIE +2
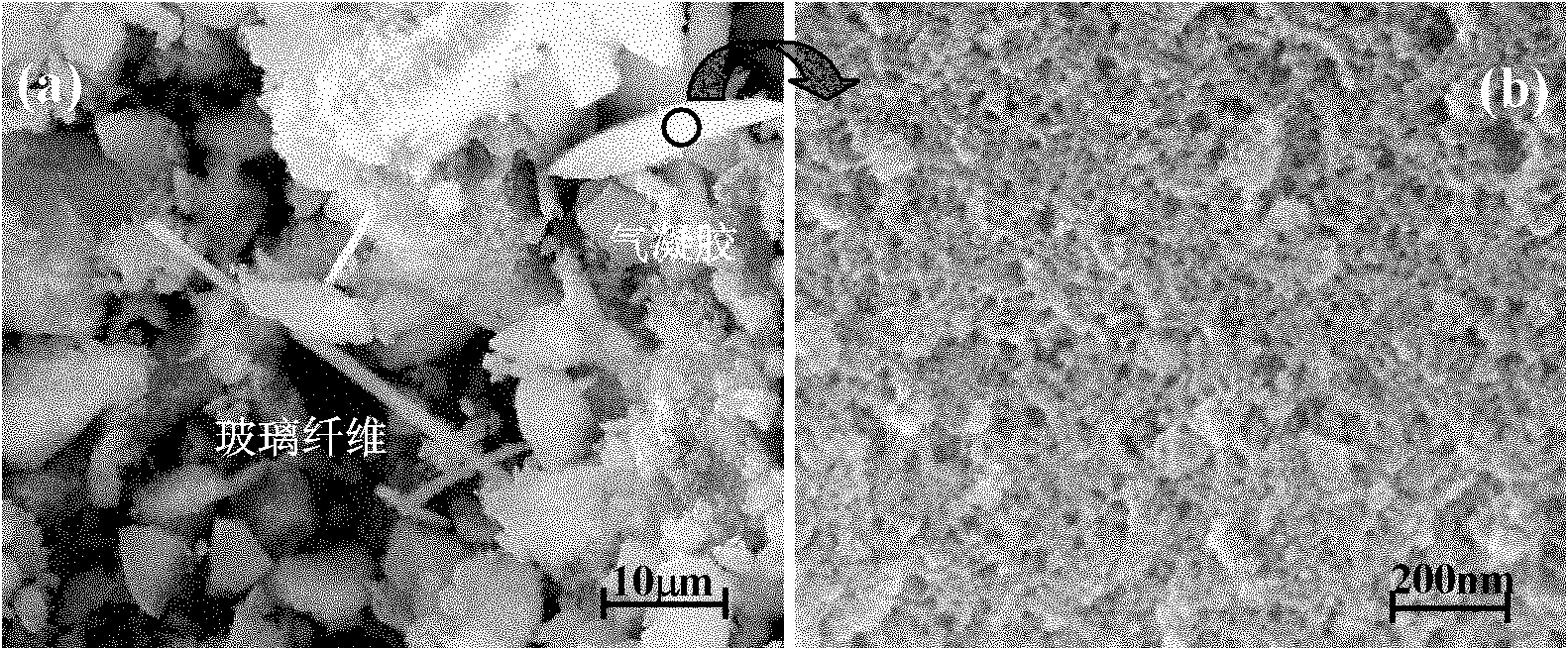
Glass fiber reinforced silicon dioxide aerogel composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an aerogel composite material, in particular to a glass fiber reinforced silicon dioxide aerogel composite material and a preparation method thereof. The excellent properties of aerogel are maintained, the mechanical properties of the aerogel are reinforced, and the glass fiber reinforced silicon dioxide aerogel composite material has good integrity and certain strength. The glass fiber reinforced silicon dioxide aerogel composite material is prepared by compounding glass fiber and silicon dioxide aerogel, wherein the glass fiber is a reinforcement, and the content ofthe glass fiber accounts for 1-15% total mass of a sample; the silicon dioxide aerogel is a matrix, tetraethoxysilane is a silicon source material, and methyltrimethoxysilane or methyltriethoxysilaneis used as a silicon source co-precursor. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, pretreating the glass fiber; then, preparing glass fiber reinforced silicon dioxide composite wet gel; and finally, aging, secondarily modifying and drying the silicon dioxide composite wet gel.
Owner:ZHONGKE RUNZI (CHONGQING) ENERGY SAVING TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor light emitting device
A semiconductor light emitting device with improved efficiency in extracting light is provided. The semiconductor light emitting device comprises a first conductive type semiconductor layer, a light emitting layer, and a second conductive semiconductor layer stacked in this order, electrodes respectively connected to the first and second conductive semiconductor layers, the electrode connected to the second conductive type semiconductor layer comprising a lower conductive oxide film and an upper conductive oxide film disposed on the lower conductive oxide film, and a metal film disposed only on the upper conductive oxide film. The upper and lower conductive oxide films comprise an oxide including at least one element selected from the group consisting of zinc (Zn), indium (In), tin (Sn), and magnesium (Mg).
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Radiation detectable and protective articles
InactiveUS20050211930A1Attribute be easilyPresence be easilyNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsEmulsionCompound (substance)
Compositions and processes for forming radiopaque polymeric articles are disclosed. In one embodiment, radiation inspection apparatuses and methods are then used to determine the presence and attributes of such radiopaque polymeric articles. A radiopaque polymeric article of the present invention can be created by mixing a radiopaque material, such as barium, bismuth, tungsten or their compounds, with a powdered polymer, pelletized polymer or liquid solution, emulsion or suspension of a polymer in solvent or water. In addition to creating radiation detectable objects, the radiopaque polymeric materials of the present invention can be used to create radiation protective articles, such as radiation protective garments and bomb containment vessels. Enhanced radiation protection can also be achieved through the use of nano-materials. The principals of the present invention can be used to provide protection against other types of hazards, including fire, chemical, biological and projectile hazards.
Owner:MERIDIAN RES & DEV
Advanced compatible polymer wood fiber composite
InactiveUS6210792B1Improve compatibilityGood material compatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsThermoplasticFiber
The invention relates to a composition comprising a thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer, the fiber or both can be modified to increase compatibility. The wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Injectable hyaluronic acid derivative with pharmaceuticals/cells
InactiveUS6699471B2Improve bioavailabilityPrevent further deteriorationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkMicrosphere
Owner:ANIKA THERAPEUTICS SRL
High-throughput printing of semiconductor precursor layer from chalcogenide microflake particles
InactiveUS20080121277A1Efficient and simplified creationIncrease contactMolten spray coatingTransportation and packagingNanoparticleParticle method
Methods and devices are provided for high-throughput printing of semiconductor precursor layer from microflake particles. In one embodiment, the method comprises of transforming non-planar or planar precursor materials in an appropriate vehicle under the appropriate conditions to create dispersions of planar particles with stoichiometric ratios of elements equal to that of the feedstock or precursor materials, even after settling. In particular, planar particles disperse more easily, form much denser coatings (or form coatings with more interparticle contact area), and anneal into fused, dense films at a lower temperature and / or time than their counterparts made from spherical nanoparticles. These planar particles may be microflakes that have a high aspect ratio. The resulting dense film formed from microflakes is particularly useful in forming photovoltaic devices. In one embodiment, at least one set of the particles in the ink may be inter-metallic flake particles (microflake or nanoflake) containing at least one group IB-IIIA inter-metallic alloy phase.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Hydrotreating catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102049265AImprove pore structureReduce manufacturing costMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsReactive siteNitrogen
The invention discloses a bulk hydrotreating catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst comprises three active metal components, namely Mo, W and Ni, and the sum of active metal oxides is 30 to 70 weight percent. In the method, a proper amount of water-soluble nitrogen-containing compound is added in the bulk catalyst gelatinating process, the pore structure of the catalyst is improved, more metal active sites are exposed on the surface of the catalyst, the utilization rate of active metals is improved, the catalyst has obviously high activity compared with the common bulk catalyst under the condition of the same metal content, and the consumption of the active metals for the common bulk catalyst can be reduced and the preparation cost of the catalyst can be reduced under thecondition of the equivalent activity. In addition, the bulk catalyst has increased pore diameter and pore volume, the Ni-W high active center is fully utilized, complicated macromolecules are easier to contact the active center, and the effect is particularly more obvious when the catalyst treats distillates with high macromolecule content.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Active material for positive electrode used in lithium secondary battery and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS6372385B1Easy to implementEvenly dispersedElectrode thermal treatmentActive material electrodesLithium-ion batteryMetal
Disclosed is active material for a positive electrode used in lithium secondary batteries of Formula 1 below and a method manufacturing the same, a surface of the active material being coated with metal oxide. The method includes the steps of producing a crystalline powder or a semi-crystalline powder of Formula 1; coating the crystalline powder or the semi-crystalline powder with metal alkoxide sol; and heat-treating the powder coated with the metal alkoxide sol.where 0<x<=0.3, 0<=y<=0.01, andA is an element selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co and Mn; B is an element selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Mn, B, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ti, V, Cr, Fe, Cu and Al; and C is an element selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Mn, B, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ti, V, Cr, Fe, Cu and Al.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS DEVICES CO LTD
Advanced polymer wood composite
InactiveUS6015611AHigh modulusHigh compressive strengthSynthetic resin layered productsPlastic recyclingWater basedThermoplastic
A composition in the form of pellets comprising a thermoplastic and wood fiber composite material suitable for forming structural members as a replacement for wood in the manufacture of doors and windows. The composite has less than about 10 wt % water based on pellet weight and a Young's modulus of at least about 500,000. Structural members are typically formed from the composite in an extrusion or an injection molding process.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Composite clay material and method for producing the same, blend material and composite clay rubber using the same and production method thereof
InactiveUS6103817ASufficiently disperseImprove dynamic propertyPigmenting treatmentSpecial tyresMolecular levelSide chain
A composite clay material with the interlayer distance sufficiently expanded by dispersing clay mineral in a low polar polymer on a molecular level and the method for producing the same, blend material and composite clay rubber material using the same and the production method thereof. The composite clay material is formed of a clay mineral rendered compatible with an organic material through ionic bonding to an organic onium ion having 6 or more carbon number and a main guest molecule having a polar group in its main chain and side chain and molecular length equal to or larger than that of said organic onium ion. The main guest molecule is incorporated at least partially into an interlayer section of the clay mineral which has a hydrogen bonding with the polar group of the main guest molecule. The main guest molecule preferably has a molecular weight ranging from about 100 to 100000. Alternatively a first guest molecule having a polar group and molecular length equal to or smaller than that of the organic onium ion and a second guest molecule having no polar group therein and molecular length larger than that of the organic onium ion are incorporated into the interlayer section of the clay mineral instead of the main guest molecule. The above obtained clay composite material may be mixed with the rubber material.
Owner:DENSO CORP
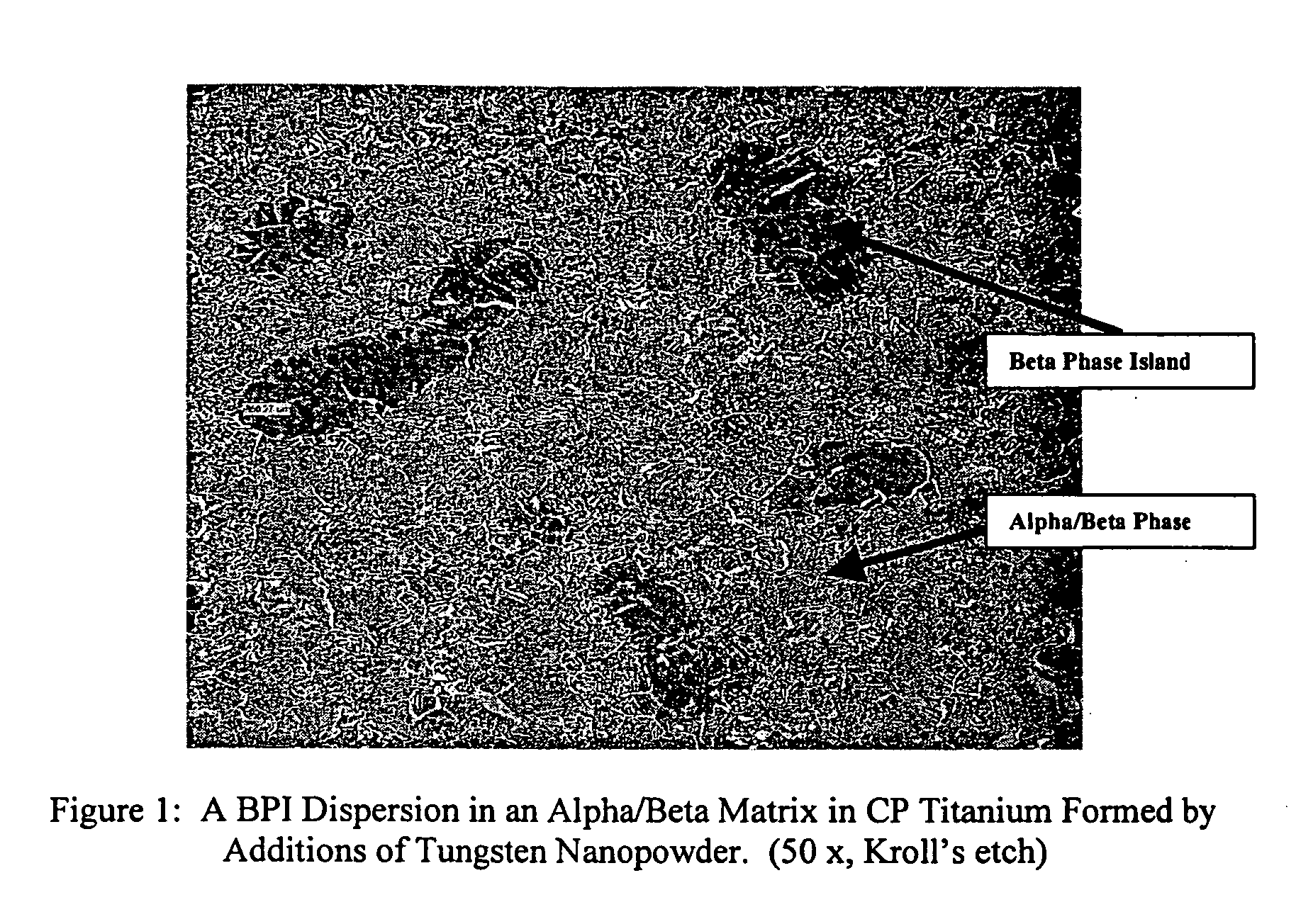
Titanium tungsten alloys produced by additions of tungsten nanopowder
Disclosed herein are titanium-tungsten alloys and composites wherein the tungsten comprises 0.5% to 40% by weight of the alloy. Also disclosed is a method of making such alloys and composites using powders of tungsten less then 3 μm in size, such as 1 μm or less. Also disclosed is a method of making the titanium alloy by powder metallurgy, and products made from such alloys or billets that may be cast, forged, or extruded. These methods of production can be used to make titanium alloys comprising other slow-diffusing beta stabilizers, such as but not limited to V, Nb, Mo, and Ta.
Owner:DYNAMET TECH
Preparation method of polyurethane-nano kaolin composite material
InactiveCN102002141AGood for uniform dispersionGood for product performancePigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsDimethyl formamideEthyl acetate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polyurethane-nano kaolin composite material. The composite material mainly comprises polyurethane and nano kaolin. The preparation method is as follows: firstly, carrying out organic intercalation modification on the nano kaolin to obtain organically modified nano kaolin with larger interlamellar spacing; and then using a body-(in-situ) intercalative polymerization method to prepare the polyurethane-nano kaolin composite material. The preparation method is characterized in that the nano kaolin with lower price and better performance is utilized, the composite material is a novel efficient halogen-free retardant agent, and no benzene, toluene, N,N'-dimethyl formamide, ethyl acetate and other harmful solvents are used, therefore environmental requirements are met. By adding a small amount of kaolin, the mechanical property, heat insulation performance and heat resistance of the polyurethane elastomer can be significantly improved. In addition, the material has simple preparation process, low cost and excellent integrated performance, and can be widely applied to mining equipment, sports equipment, area pavement materials and other industries, thereby having wide market prospects.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Photovoltaic devices printed from nanostructured particles
InactiveUS20070163638A1Efficient and simplified creationIncrease contactMolten spray coatingTransportation and packagingParticle methodSolar cell
Methods and devices are provided for high-throughput printing of semiconductor precursor layer from microflake particles. In one embodiment, a solar cell is provided that comprises of a substrate, a back electrode formed over the substrate, a p-type semiconductor thin film formed over the back electrode, an n-type semiconductor thin film formed so as to constitute a pn junction with the p-type semiconductor thin film, and a transparent electrode formed over the n-type semiconductor thin film. The p-type semiconductor thin film results by processing a dense film formed from a plurality of microflakes having a material composition containing at least one element from Groups IB, IIIA, and / or VIA, wherein the dense film has a void volume of about 26% or less. The dense film may be a substantially void free film.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Dry powder inhaler devices, multi-dose dry powder drug packages, control systems, and associated methods
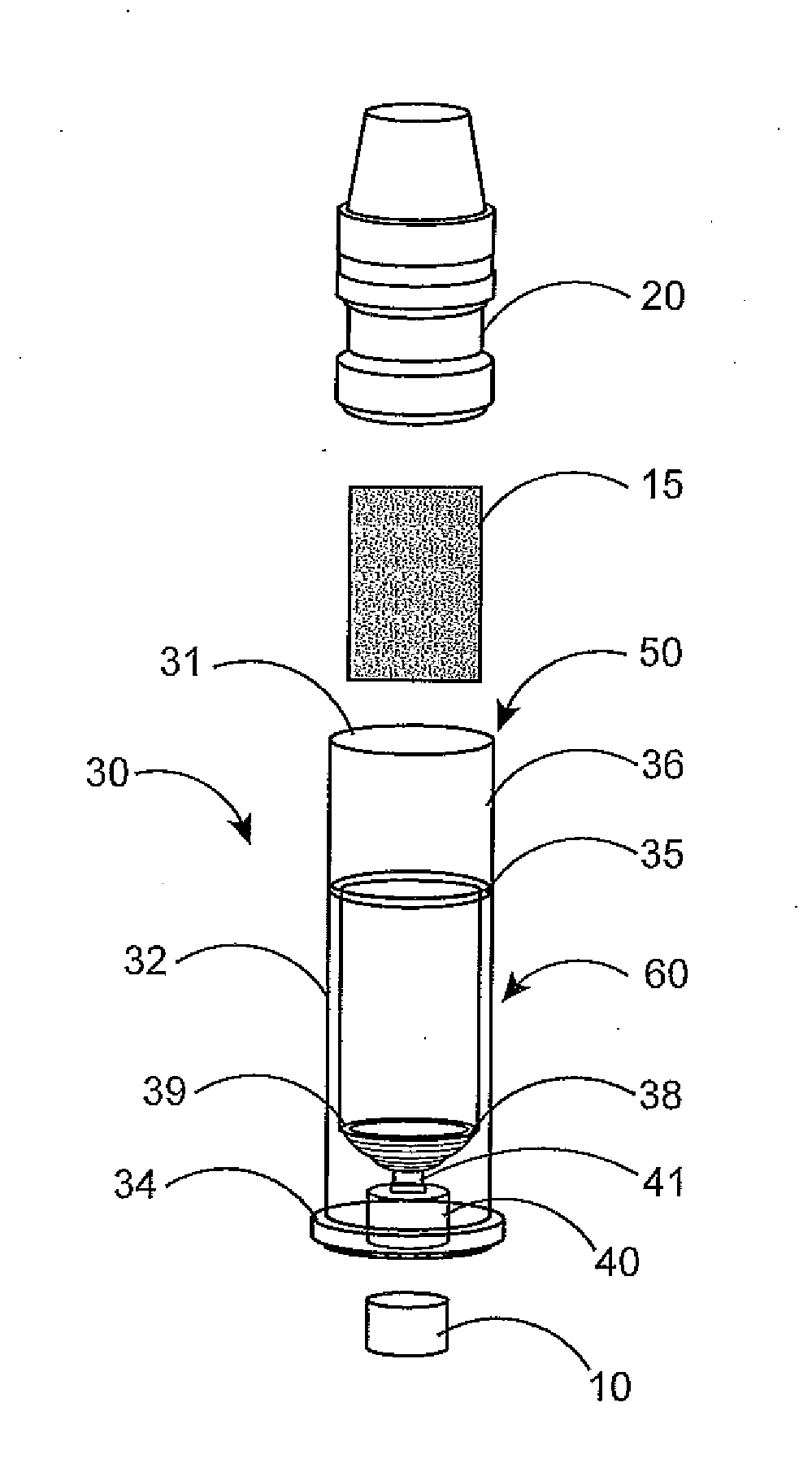
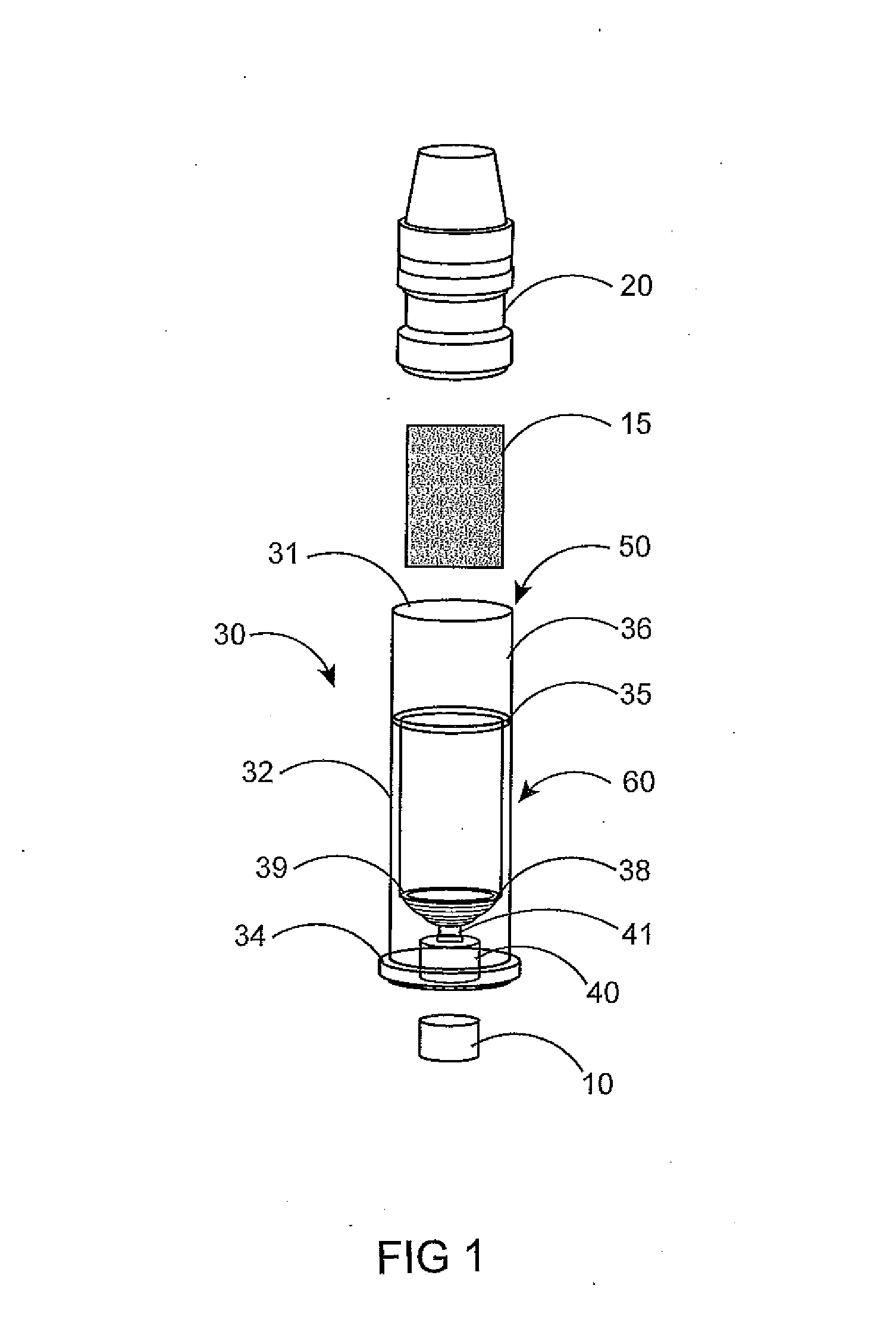
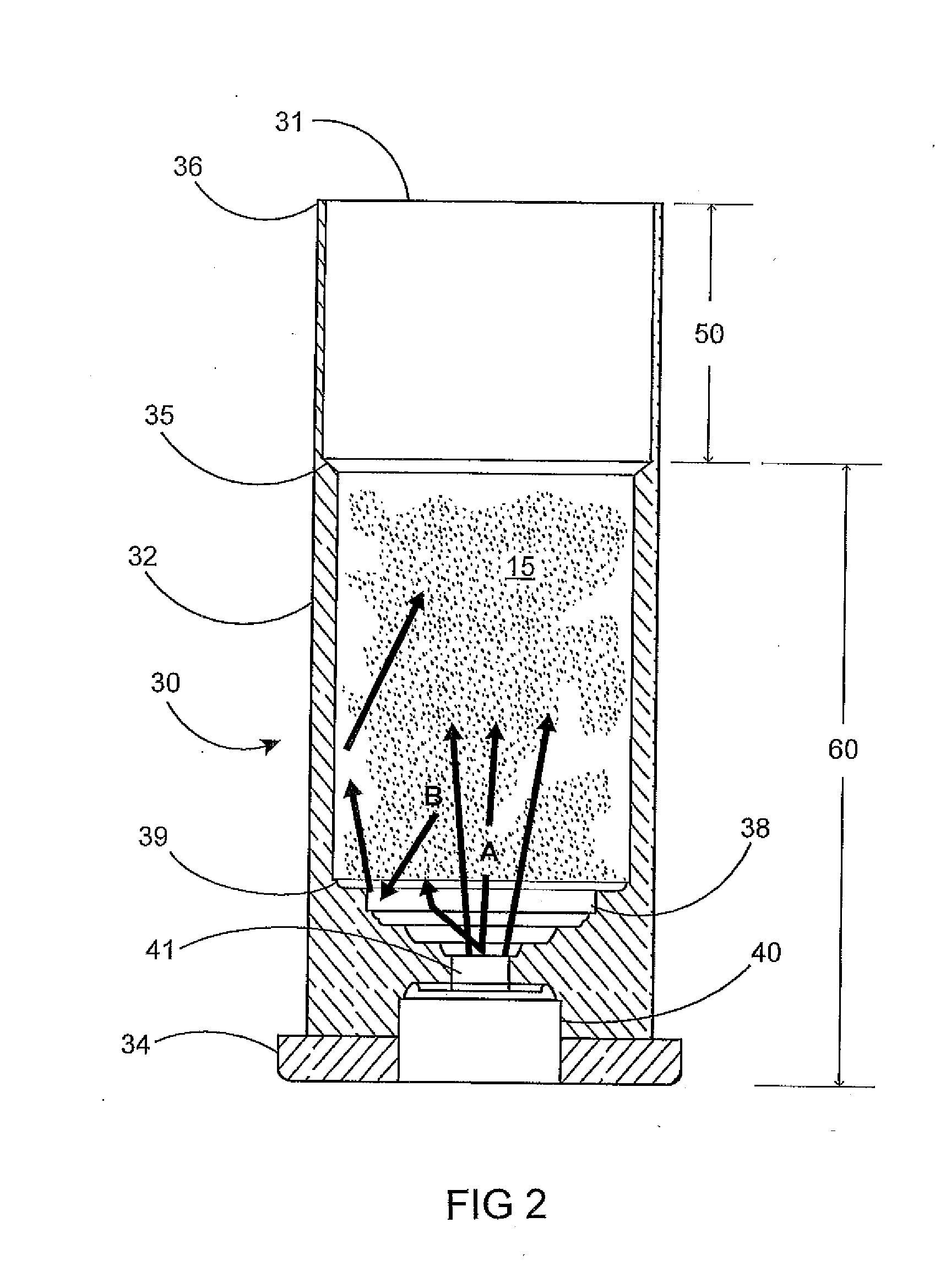
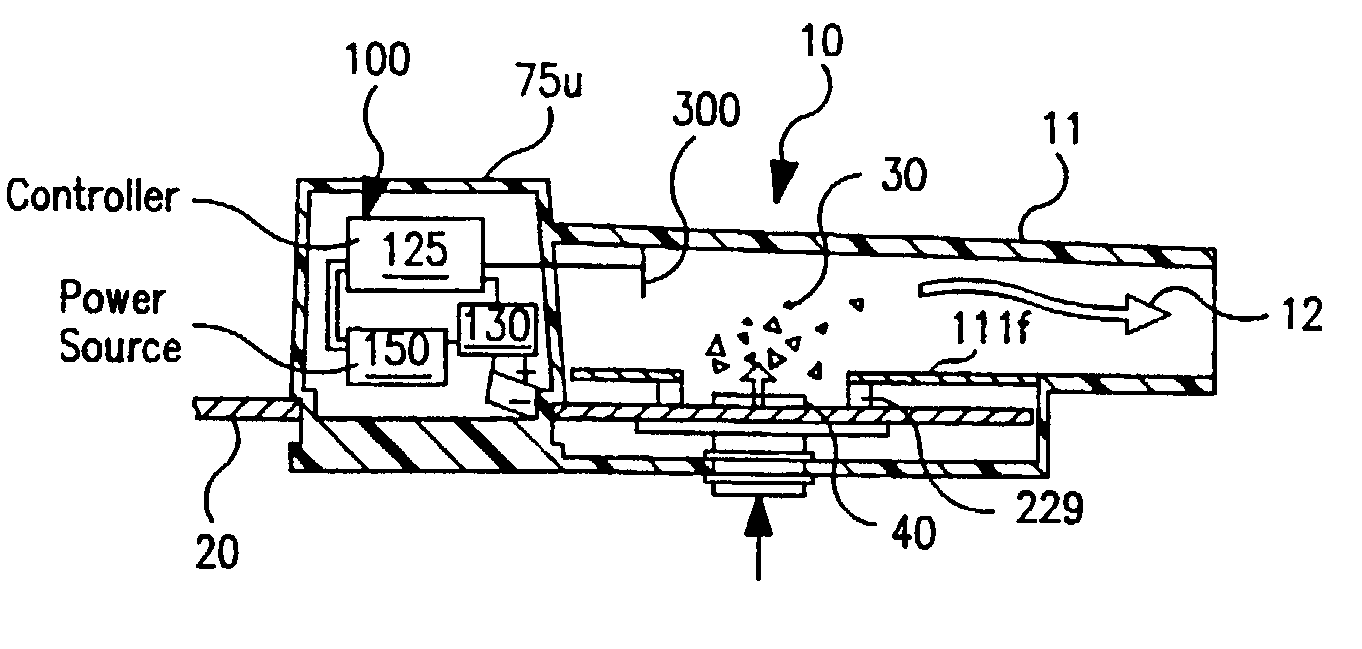
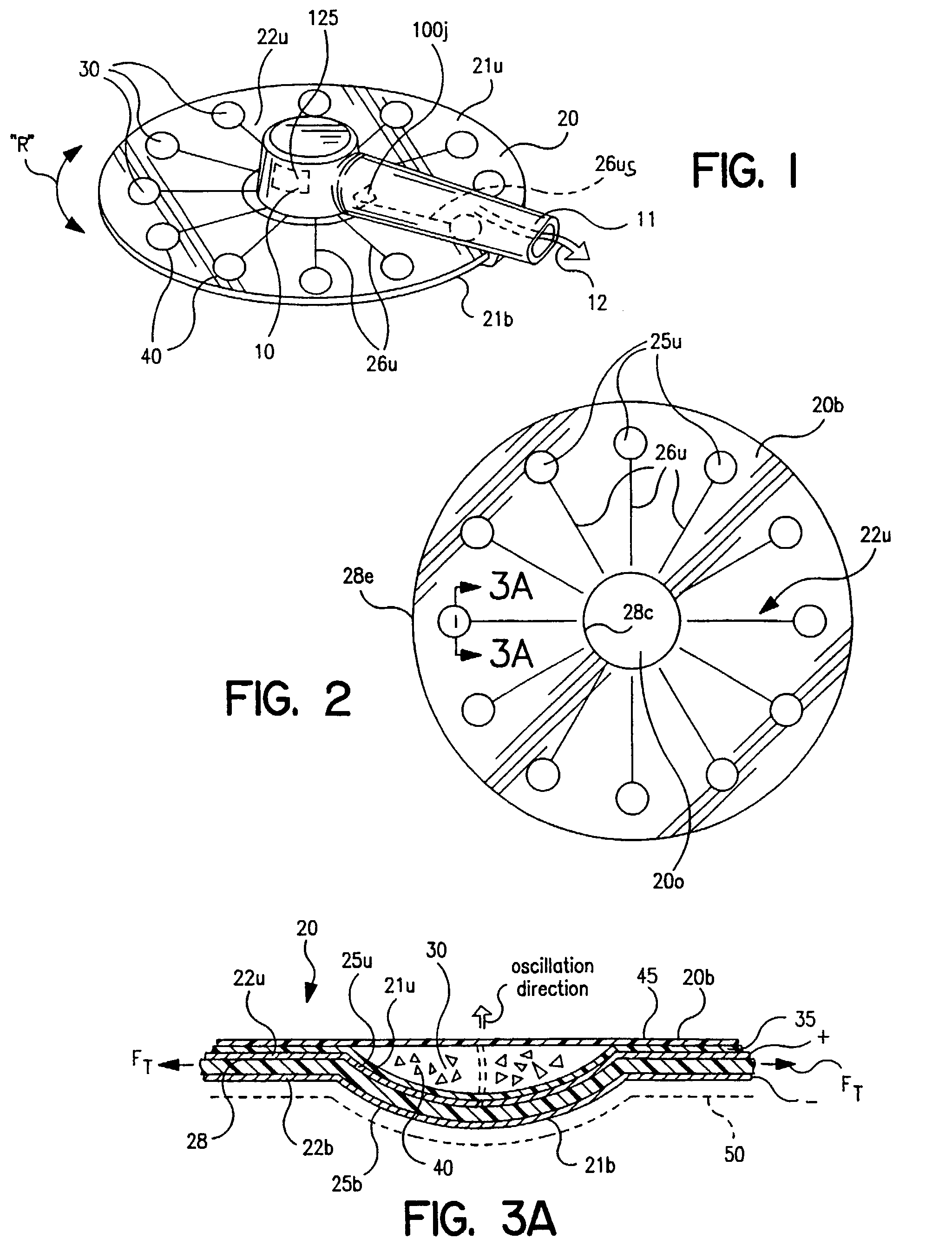
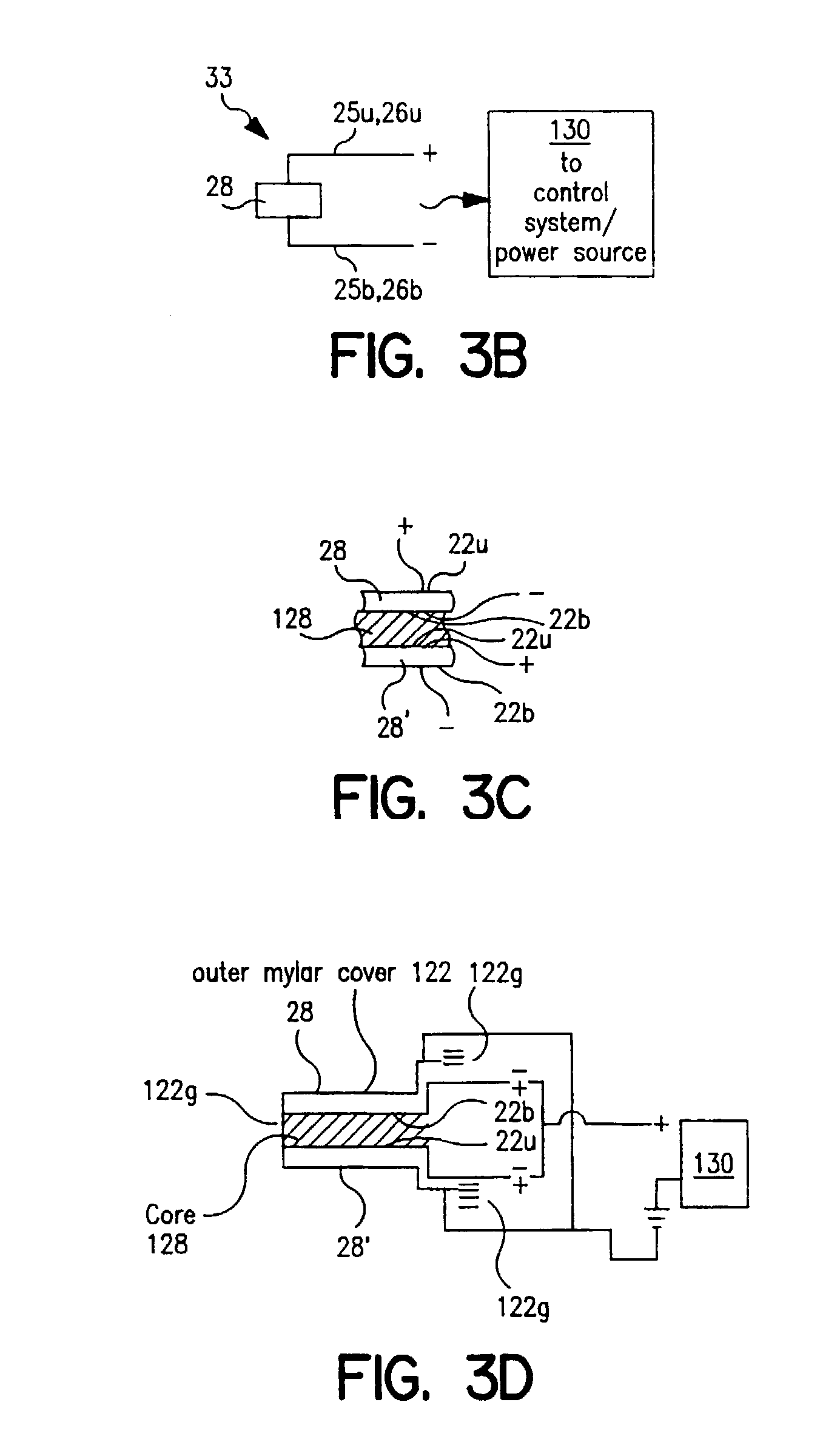
InactiveUS6971383B2Evenly dispersedFacilitate dispersion and releaseRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsPowder InhalerPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Dry powder inhalers (FIG. 1) with integrated active energy patient assist dispersal systems are configured with control systems which provide adjustable energy output responsive to the user's inspiratory capabilities and / or the flowability of the dry powder being administered. The multi-dose dry drug package (FIG. 2) a piezoelectric polymer substrate which flexes to deform and provide mechanical oscillation in a selected region of the package corresponding to the dry powder drug which is dispersed during inhalation by a user. Control system (FIG. 12) employs fuzzy logic to relate in response to a user's inspiratory effort.
Owner:ORIEL THERAPEUTICS INC
High-throughput printing of semiconductor precursor layer from inter-metallic microflake articles
InactiveUS20070163642A1Efficient and simplified creationIncrease contactFinal product manufactureLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingNanometreAspect ratio
Methods and devices are provided for high-throughput printing of semiconductor precursor layer from microflake particles. In one embodiment, the method comprises of transforming non-planar or planar precursor materials in an appropriate vehicle under the appropriate conditions to create dispersions of planar particles with stoichiometric ratios of elements equal to that of the feedstock or precursor materials, even after settling. In particular, planar particles disperse more easily, form much denser coatings (or form coatings with more interparticle contact area), and anneal into fused, dense films at a lower temperature and / or time than their counterparts made from spherical nanoparticles. These planar particles may be microflakes that have a high aspect ratio. The resulting dense film formed from microflakes are particularly useful in forming photovoltaic devices. In one embodiment, at least one set of the particles in the ink may be inter-metallic flake particles (microflake or nanoflake) containing at least one group IB-IIIA inter-metallic alloy phase.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
High-throughput printing of semiconductor precursor layer from nanoflake particles
InactiveUS20070163637A1Efficient and simplified creationIncrease contactFinal product manufactureTransportation and packagingNanoparticleParticle method
Methods and devices are provided for transforming non-planar or planar precursor materials in an appropriate vehicle under the appropriate conditions to create dispersions of planar particles with stoichiometric ratios of elements equal to that of the feedstock or precursor materials, even after selective forces settling. In particular, planar particles disperse more easily, form much denser coatings (or form coatings with more interparticle contact area), and anneal into fused, dense films at a lower temperature and / or time than their counterparts made from spherical nanoparticles. These planar particles may be nanoflakes that have a high aspect ratio. The resulting dense films formed from nanoflakes are particularly useful in forming photovoltaic devices.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Graphene composite material and preparation method thereof
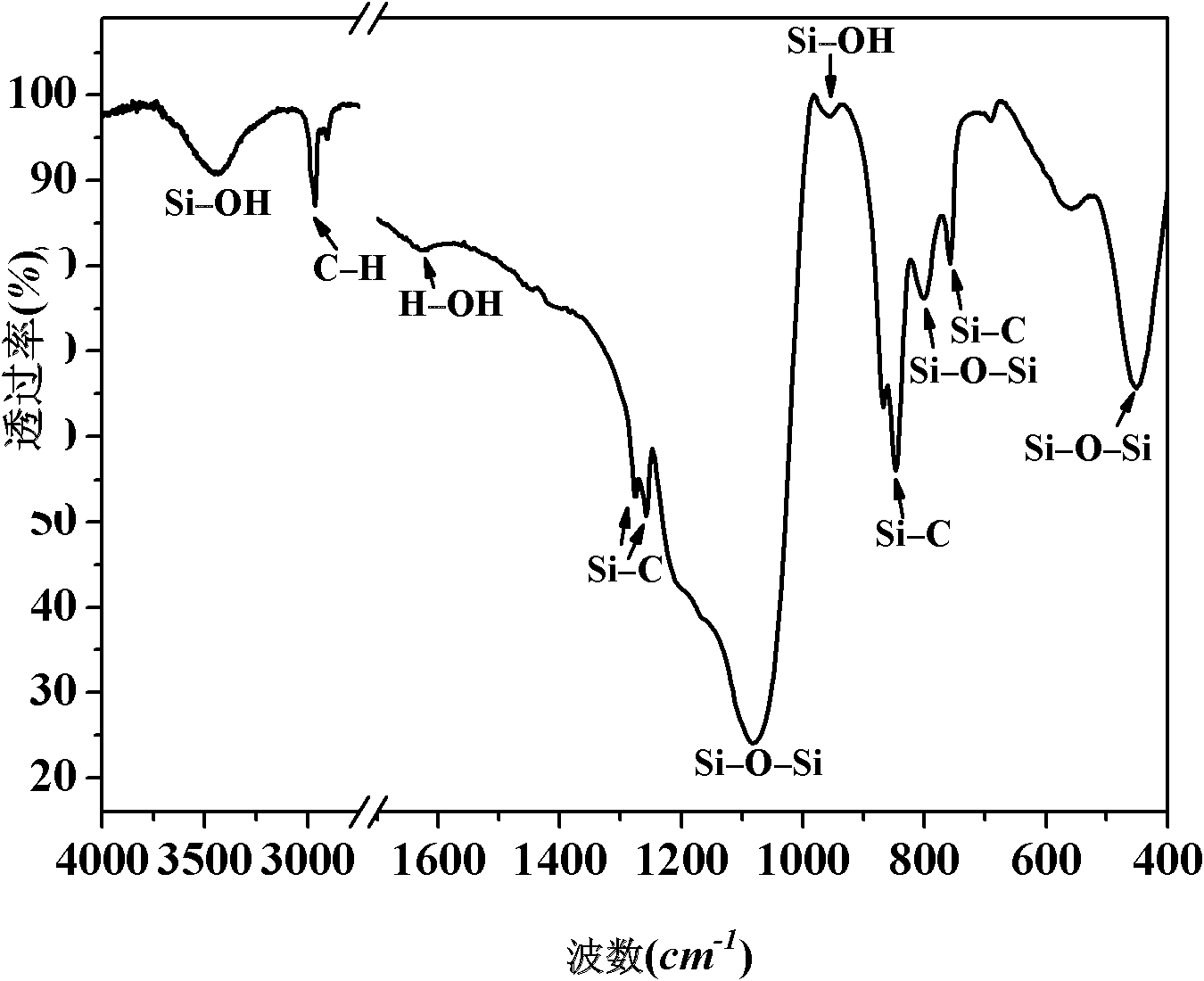
The embodiment of the invention discloses a graphene composite material and a preparation method thereof. In the method, graphene and organosilane are taken as reactants; the organosilane undergoes a hydrolysis reaction, and then undergoes a dehydration condensation reaction with hydroxyl on the graphene so as to obtain organosilane-modified graphene. Compared with the prior art, the organosilane-modified graphene expands the interlayer spacing of graphene, so that the organosilane-modified graphene is difficultly agglomerated when the organosilane-modified graphene is mixed with a polymer, the organosilane-modified graphene is uniformly dispersed in a polymer substrate, and a prepared graphene composite material has an enhanced effect. Moreover, the organosilane-modified graphene undergoes chemical bonding or intermolecular force with the polymer, so that the prepared graphene composite material has excellent interface compatibility. Proved by experiment results, the graphene composite material prepared in the invention has high mechanical property.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System for identifying defects in a composite structure
InactiveUS6871684B2Accurate identificationShorten the timeRadiation pyrometryInvestigating composite materialsComputer scienceStructural integrity
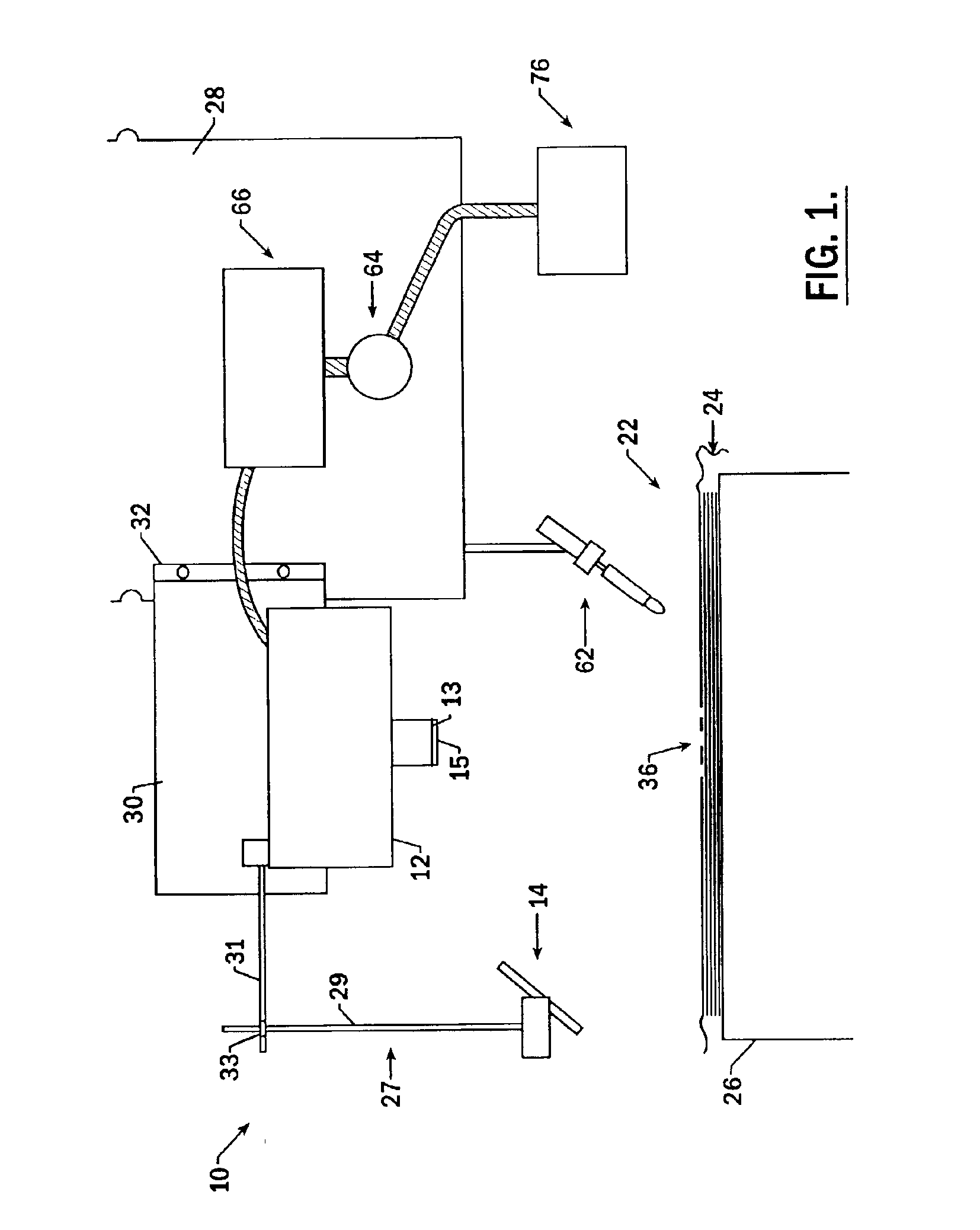
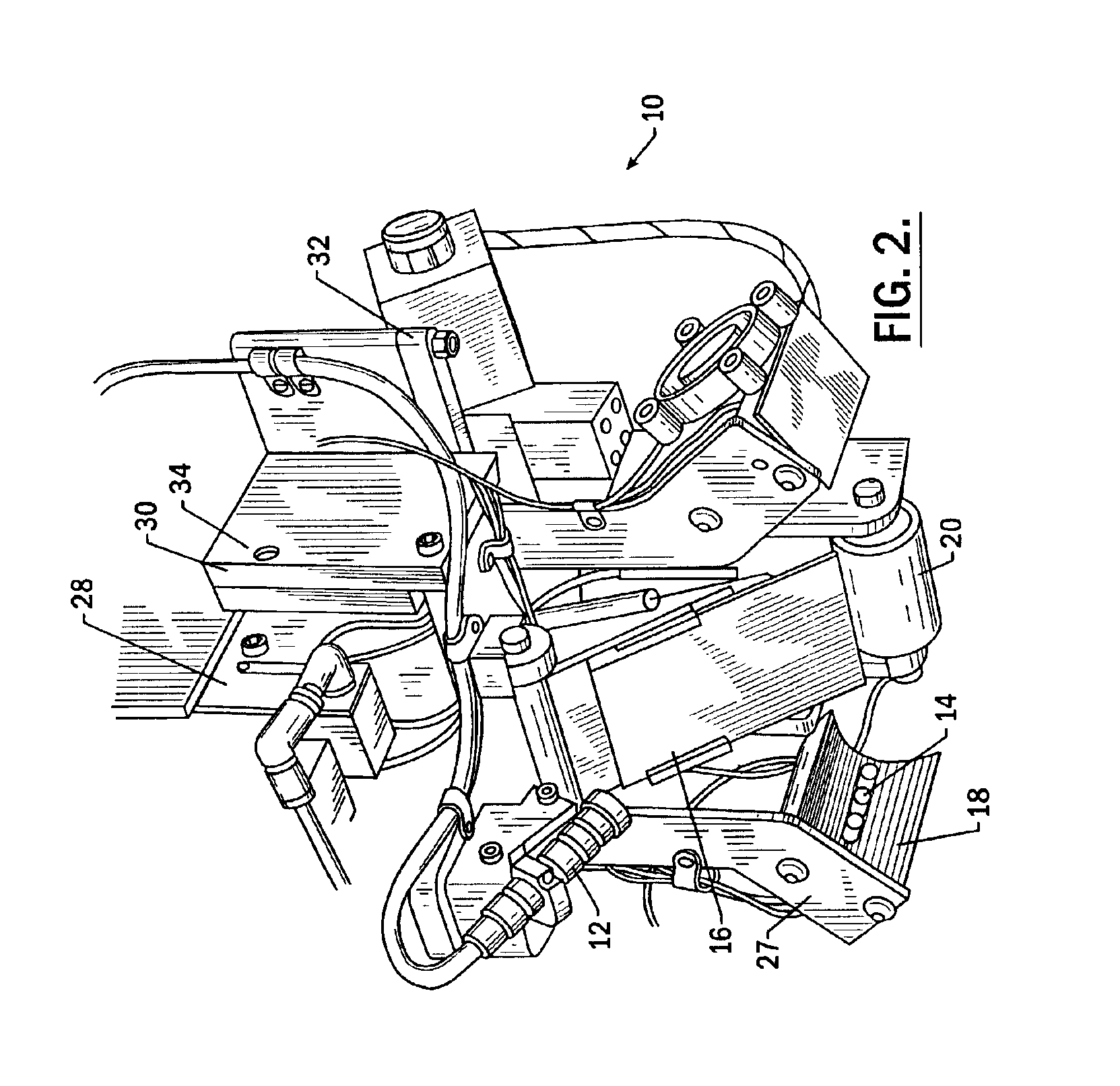
The present invention provides an improved system for identifying defects in a composite structure by providing a light source such that defects, and in particular dark defects on a dark background and / or light defects on a light background, can be identified by capturing images of the illuminated composite structure. In particular, the improved system for identifying defects in a composite structure may provide a reflective surface, dispersion elements, and multiple and / or moveable light source(s) and / or camera(s) in order to ensure that the most accurate images of any area of the composite structure, even curved or contoured areas, are captured and processed. As a result, the system of the present invention permits the operator to quickly identify and correct defects which would otherwise create structural flaws or inconsistencies that may affect the integrity of the composite structure.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com