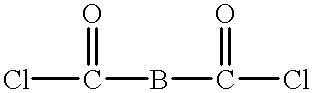Patents
Literature
10863results about "Wood working apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
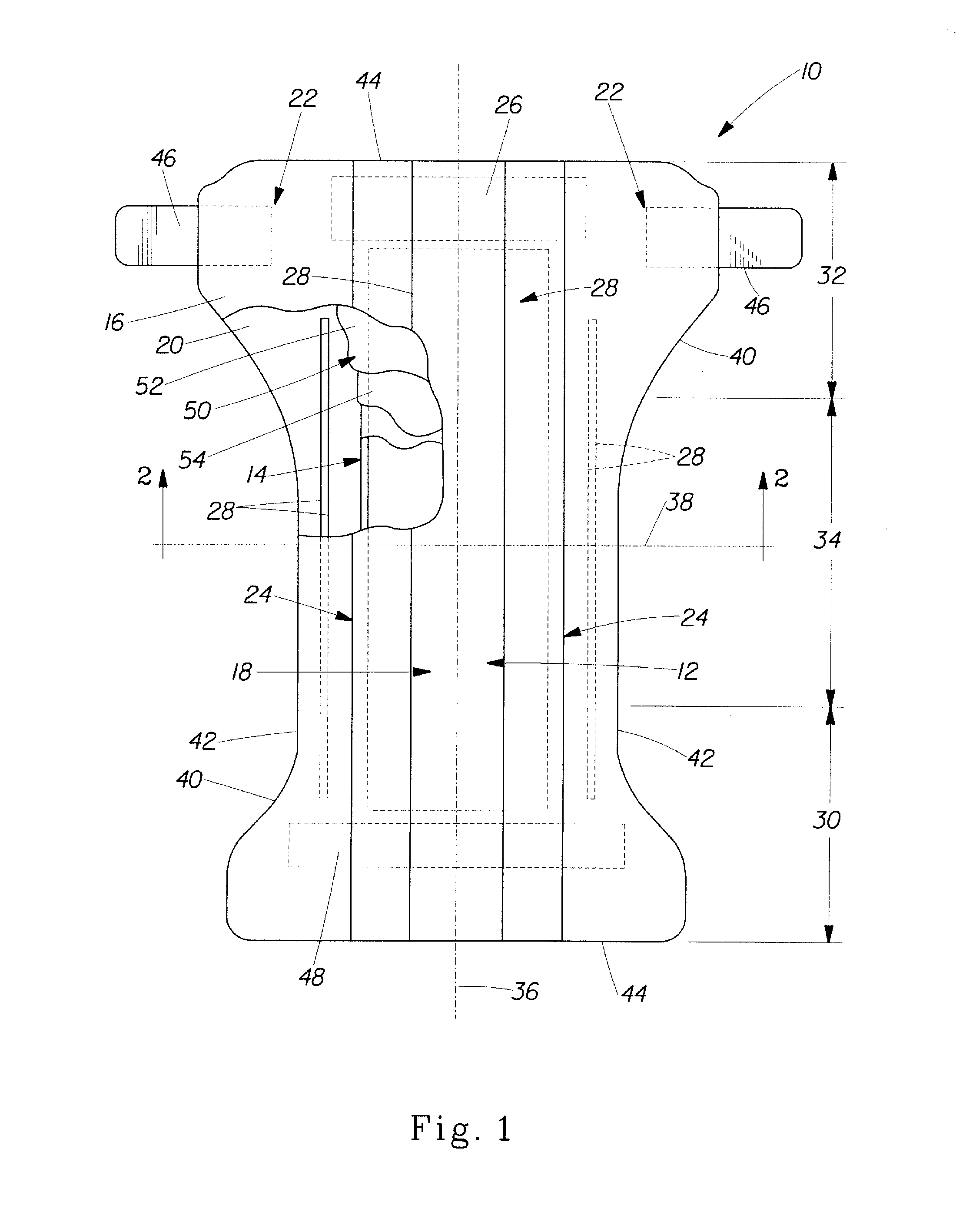
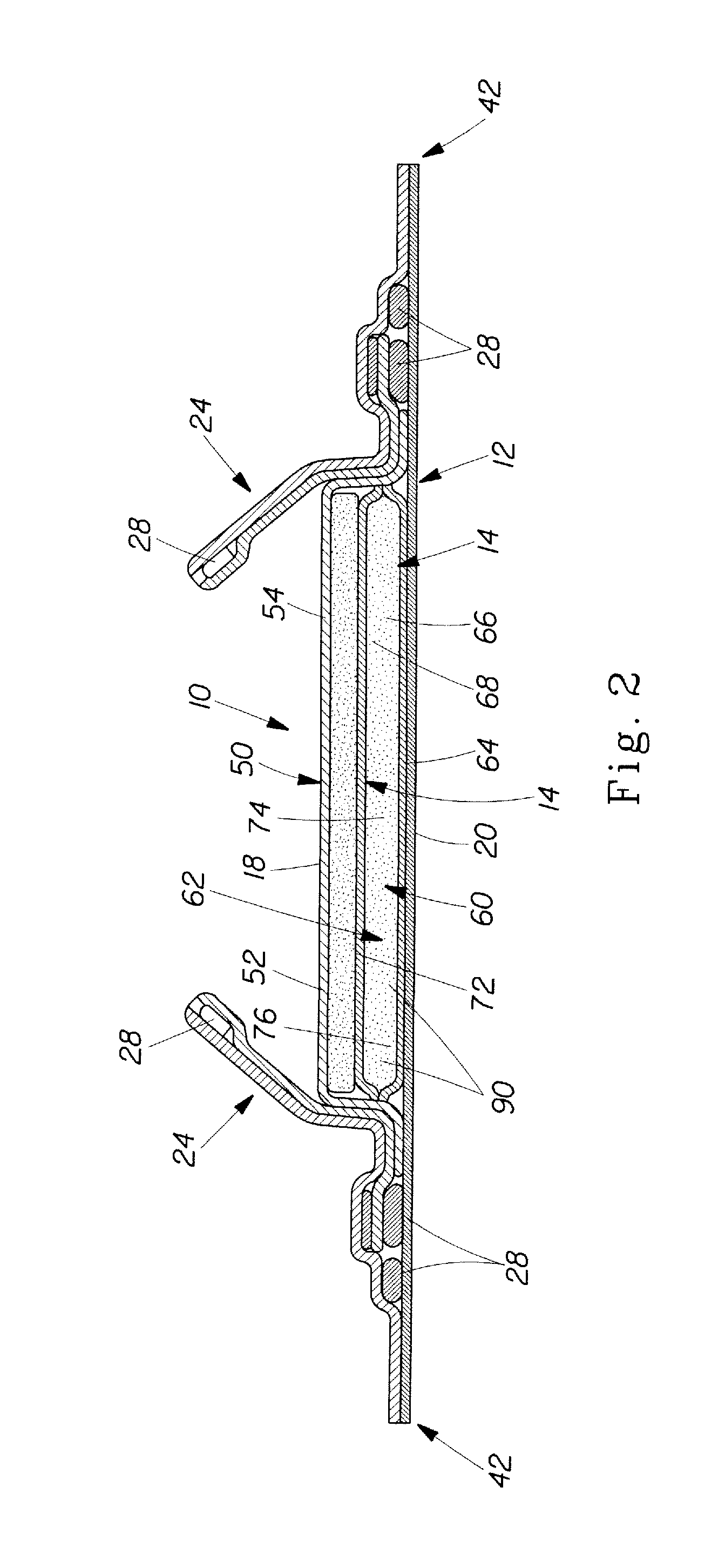
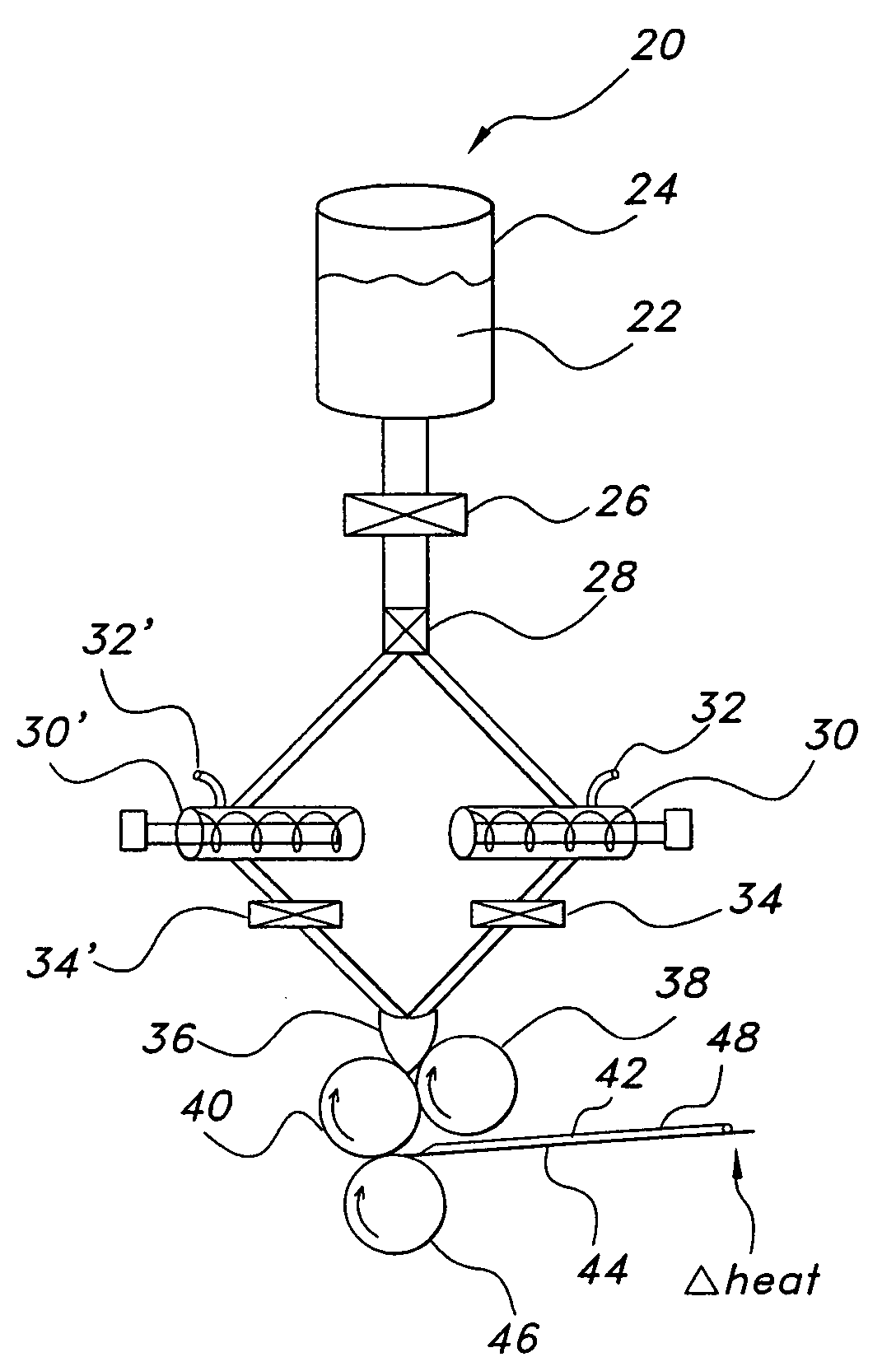
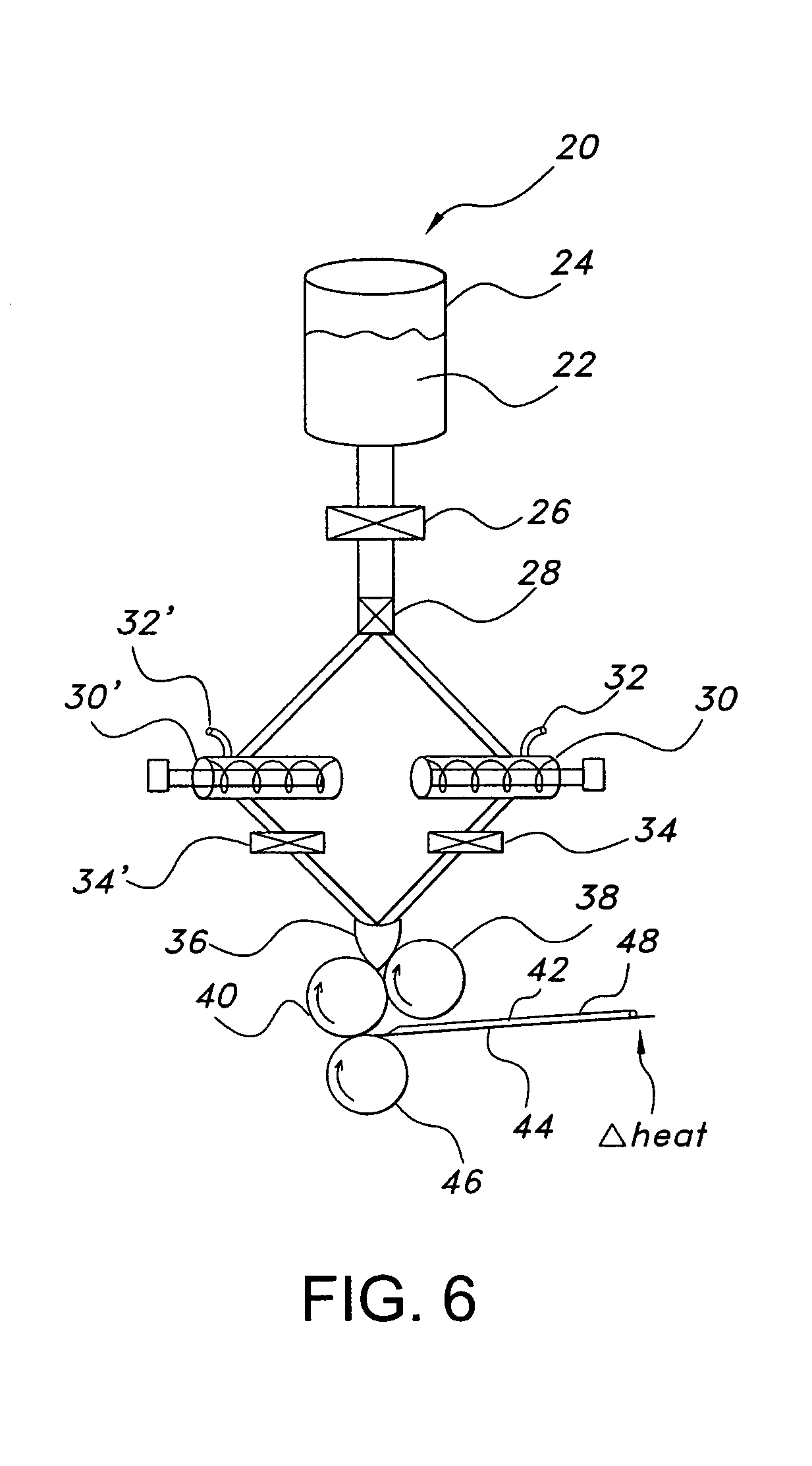
Wound closure material
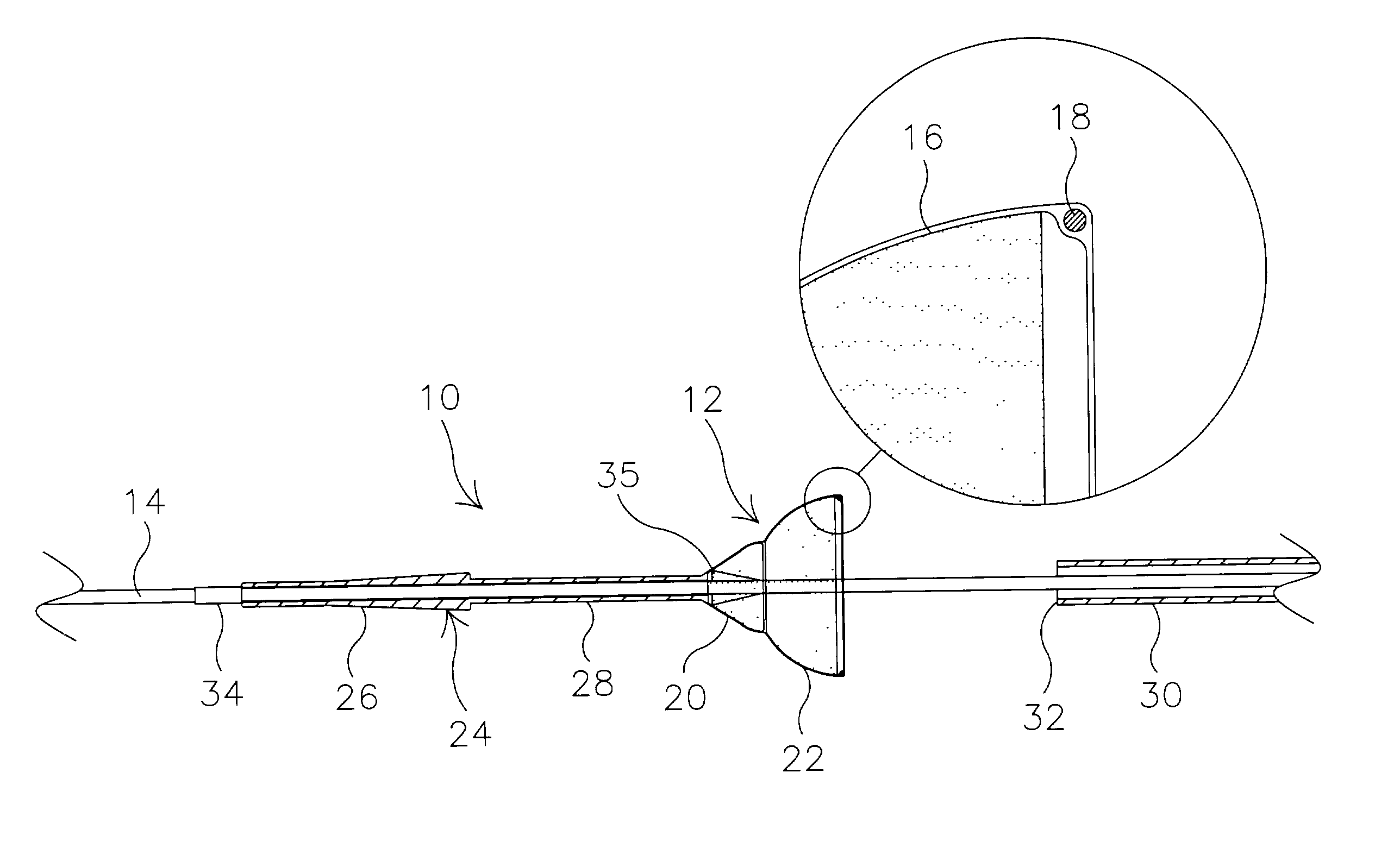
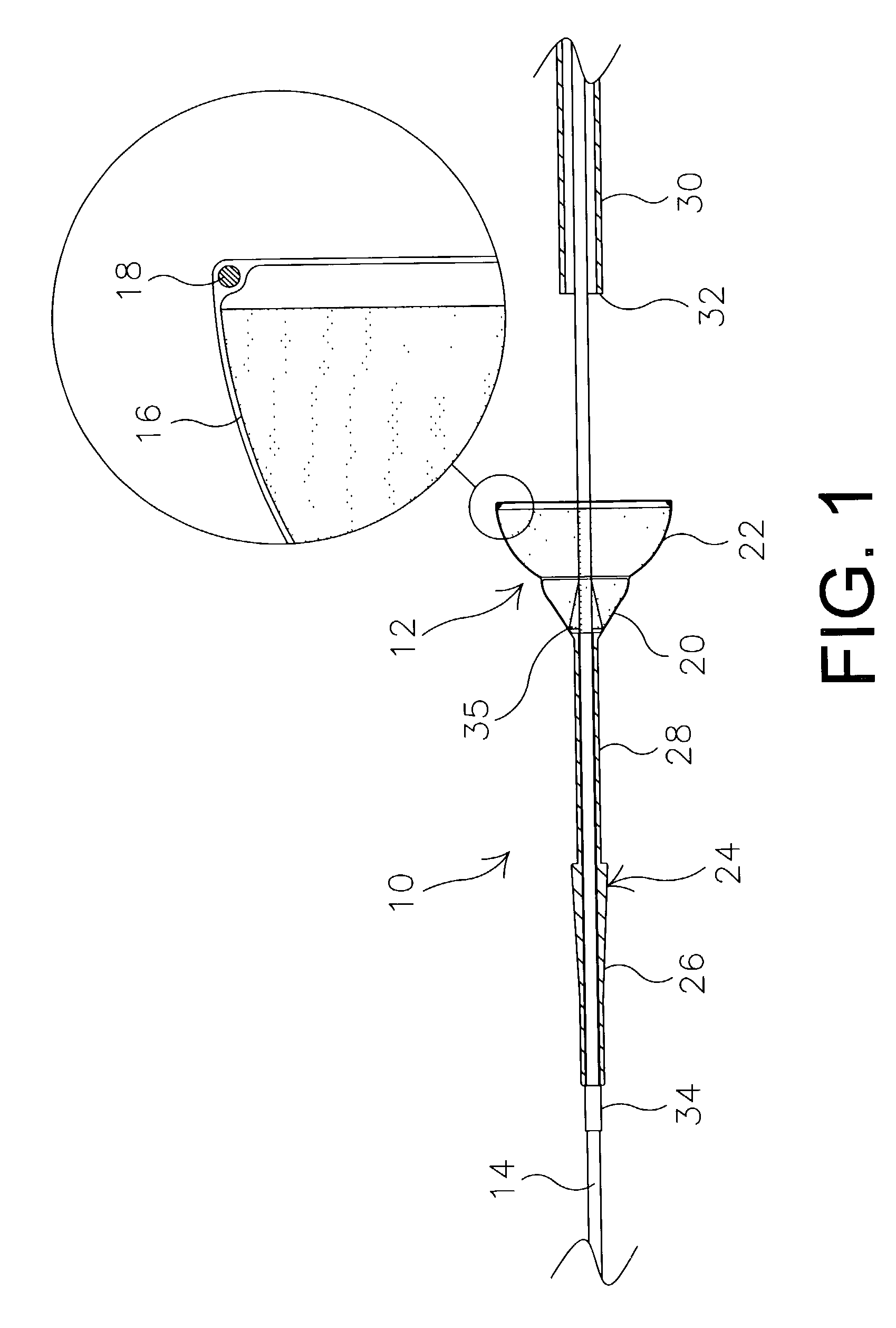
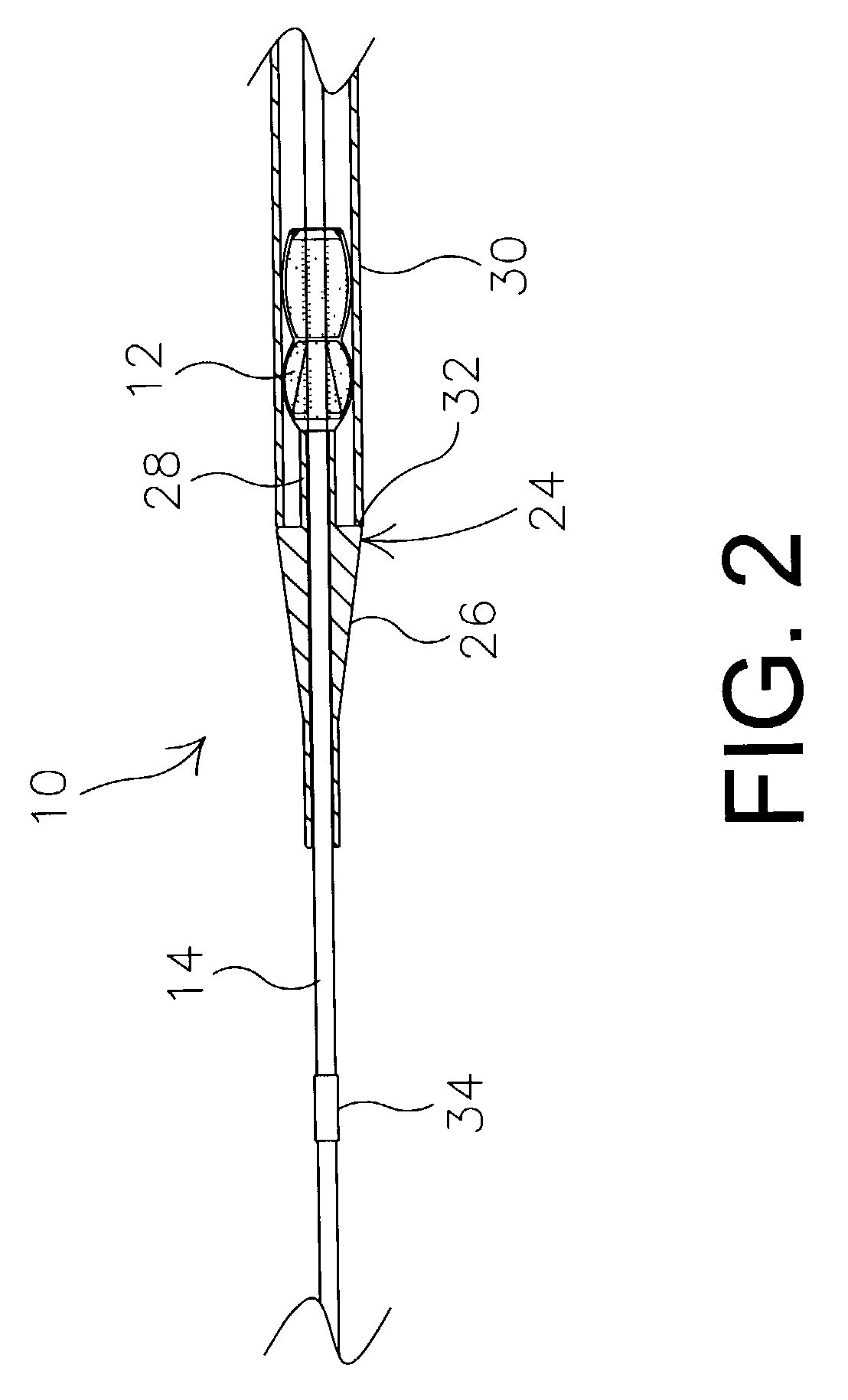
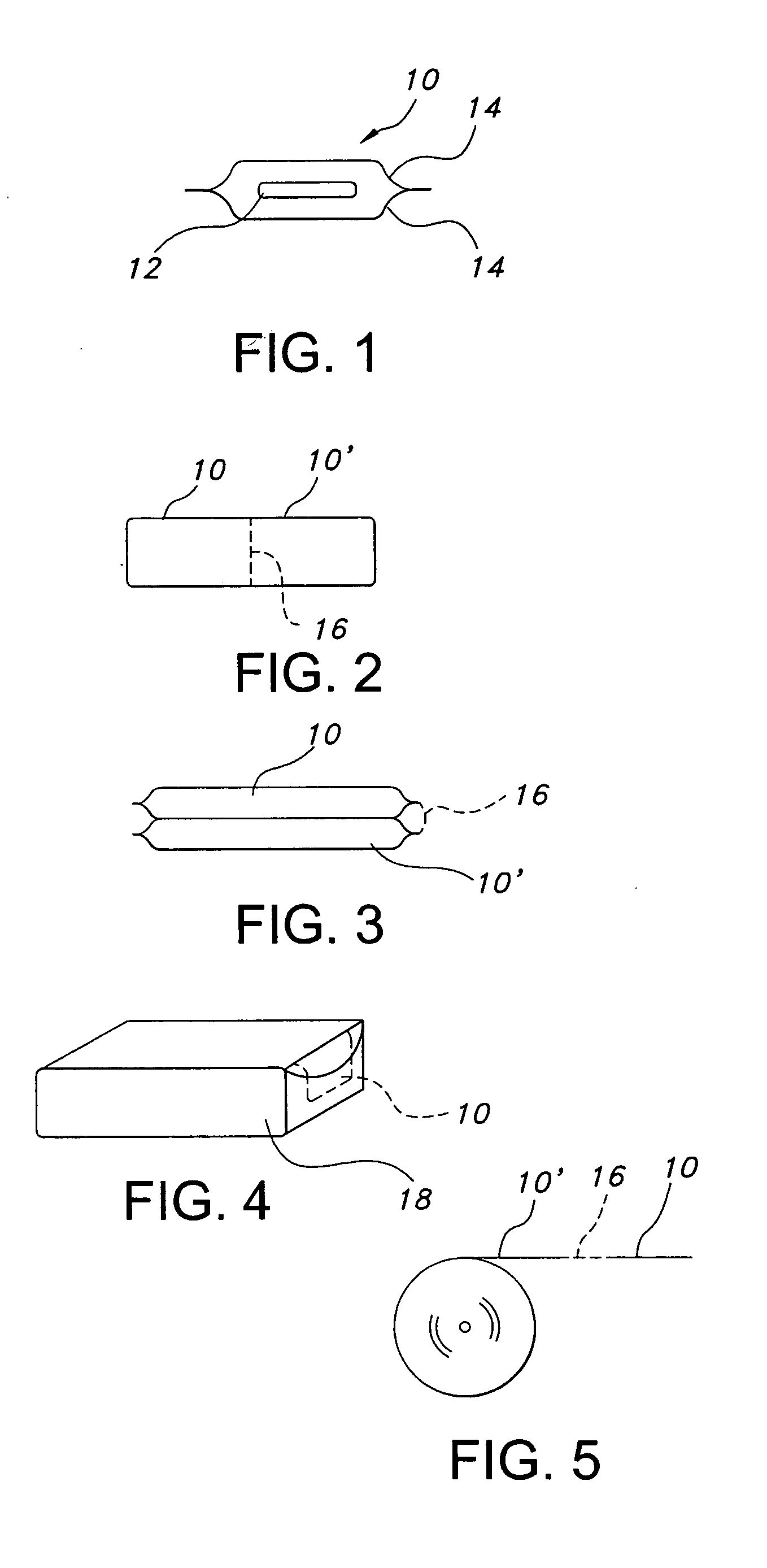
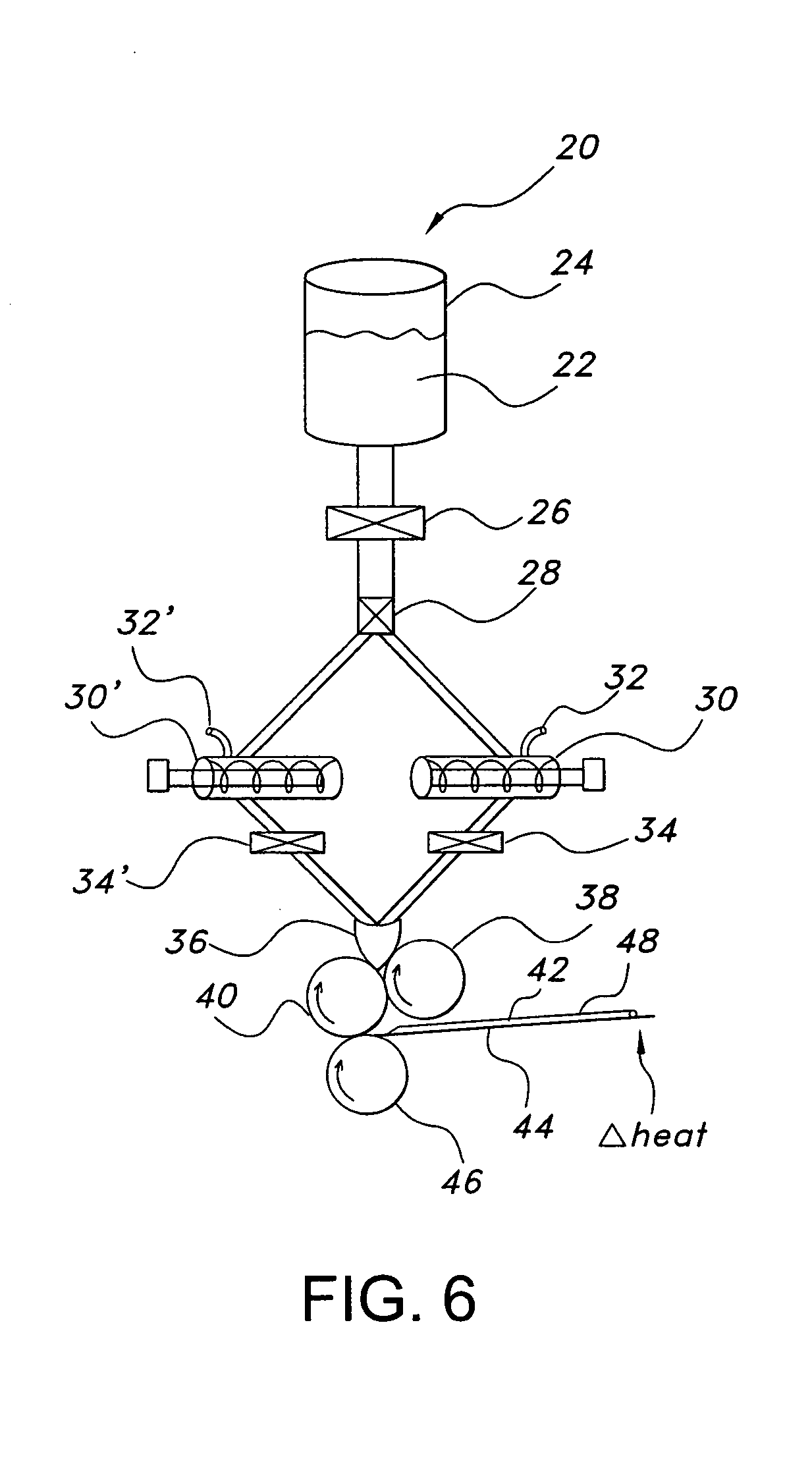
Articles are provided having no orientation or a multi-directional orientation. Such articles may be in the form of films, ribbons, sheets, and / or tapes and may be utilized as buttresses with a surgical stapling apparatus or as reinforcing means for suture lines.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Method of making an embolic filter
Embolic protection filters and methods of making and using such devices are disclosed. An illustrative method of making a device for filtering embolic debris from a body may include the steps of molding a filter assembly that includes a distal tip and a filter portion, forming a plurality of apertures within the filter portion, and coupling a support member to the filter assembly that is adapted to shift the filter portion between a collapsed configuration and an expanded configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method And Apparatus For Making Disposable Absorbent Article With Absorbent Particulate Polymer Material And Article Made Therewith
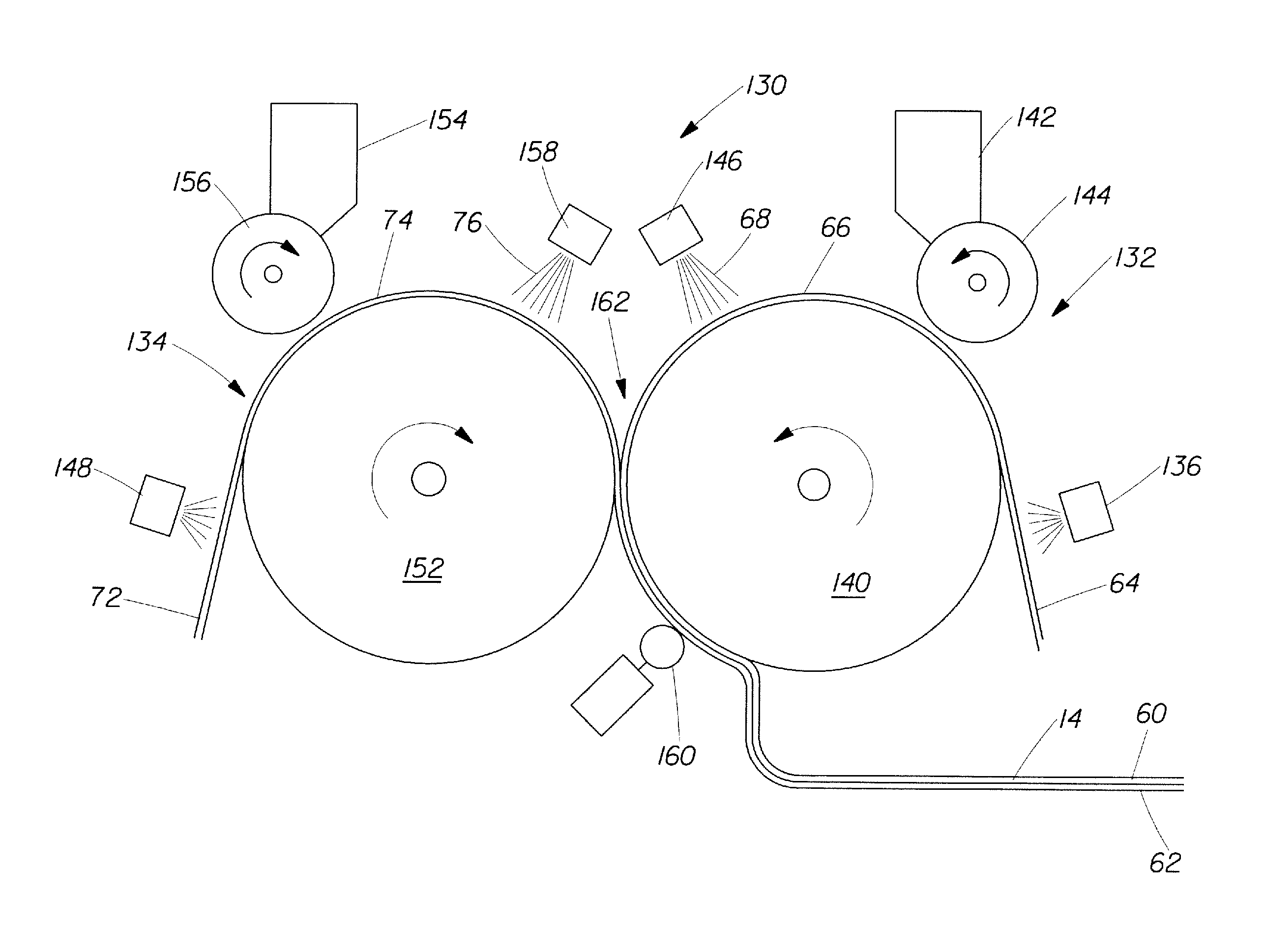
A method for making a disposable absorbent core comprises depositing absorbent particulate polymer material from a plurality of reservoirs in a printing roll onto a substrate disposed on a grid of a support which includes a plurality of cross bars extending substantially parallel to and spaced from one another so as to form channels extending between the plurality of cross bars. The plurality of reservoirs in the first peripheral surface are arranged in an array comprising rows extending substantially parallel to and spaced from one another. The support and printing roll are arranged such that the plurality of cross bars are substantially parallel to the rows of the plurality of reservoirs and the absorbent particulate polymer material is deposited on the substrate in a pattern such that the absorbent particulate polymer material collects in rows on the first substrate formed between the first plurality of cross bars. A thermoplastic adhesive material is deposited on the absorbent particulate polymer material and the substrate to cover the absorbent particulate polymer material on the substrate and form an absorbent layer. A disposable absorbent article and apparatus for making an absorbent article are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
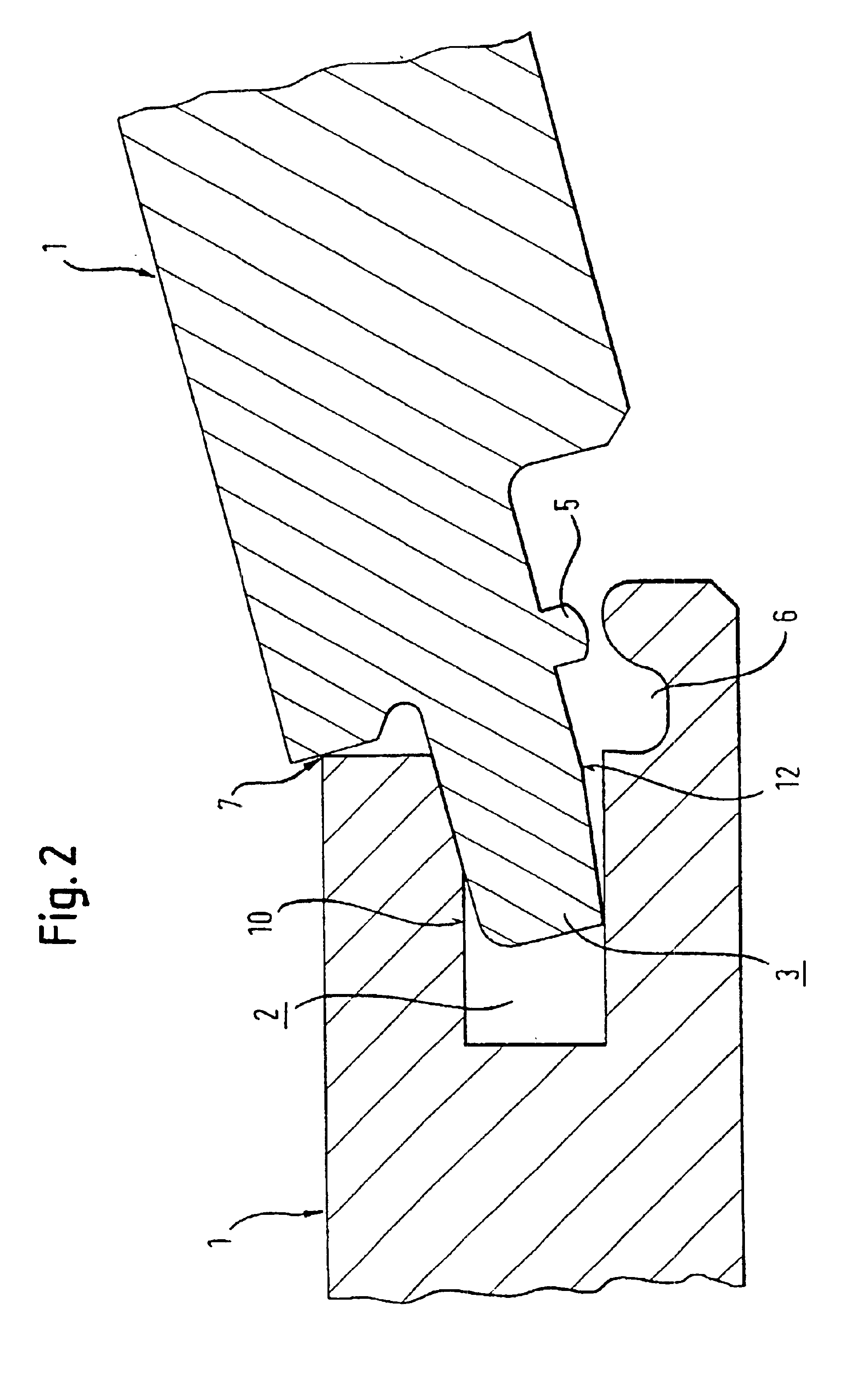
Panel element
InactiveUS6880307B2Simple glueless layingKeep in touchStrutsCovering/liningsEngineeringFloor covering
The invention relates to a panel element for forming a floor covering, consisting of several identical interconnectable panel elements and having the following features: two first sides of each panel element, called the “longitudinal sides”, these sides having a groove and a tongue; the tongue of a panel element which is positioned at an angle with an installation level of a first, identical panel element can be introduced into the groove of the first panel element; the tongue interacts with the groove of the adjacent, identical panel element in such a way that two interconnected panel elements are protected against separating forces which are exerted along both of the axes extending perpendicularly to the longitudinal side of the panel elements; two second sides of the panel element, called the end sides, are provided with fixing means and a groove and tongue, these forming an end-side connection between two adjacent panel elements; the end-side grooves and tongue can be interconnected by means of the panel element being lowered onto an identical panel element that has already been installed, essentially crosswise to the installation level, so that the panel element is protected from lifting forces, i.e. forces which are exerted considerably perpendicularly to the installation level.
Owner:FLOORING IND LTD
Three-Dimensional Adhesive Device Having a Microelectronic System Embedded Therein
InactiveUS20080275327A1Simple and inexpensive wayModerate viscosityWave amplification devicesLayered productsCapacitanceElectronic systems
Accordingly, the present invention relates to a three-dimensional adhesive device to be attached to the body surface of a mammal comprising a microelectronic sensing system characterized by(a) a three-dimensional adhesive body made of a pressure sensitive adhesive having an upper surface and a bottom surface;(b) a microelectronic system embedded in the body of the pressure sensitive adhesive;(c) one or more cover layer(s) attached to the upper surface; and(d) optionally a release liner releasable attached to the bottom surface of the adhesive device.Suitably the microelectronic system is a microelectronic sensing system capable of sensing physical input such as pressure, vibration, sound, electrical activity (e.g. from muscle activity), tension, blood-flow, moisture, temperature, enzyme activity, bacteria, pH, blood sugar, conductivity, resistance, capacitance, inductance or other chemical, biochemical, biological, mechanical or electrical properties.
Owner:BRAEMAR MFG +2
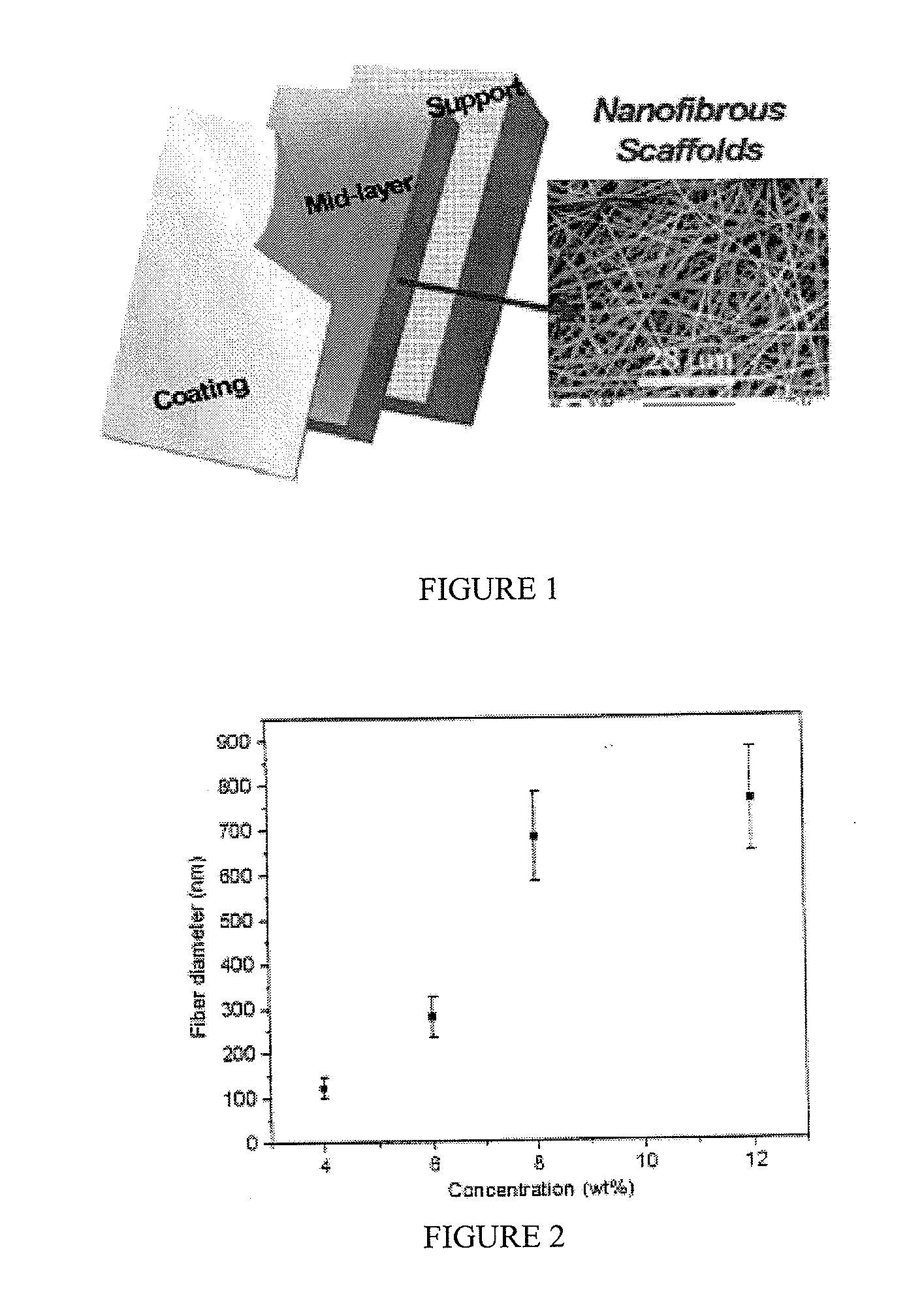
Articles Comprising a Fibrous Support
Articles comprising a fibrous support of nanofibers and an interfacially polymerized polymer layer disposed on a surface of the fibrous support are useful, e.g., as fluid separation membranes.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for manufacturing susceptor
ActiveUS20100163524A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorMetallurgy
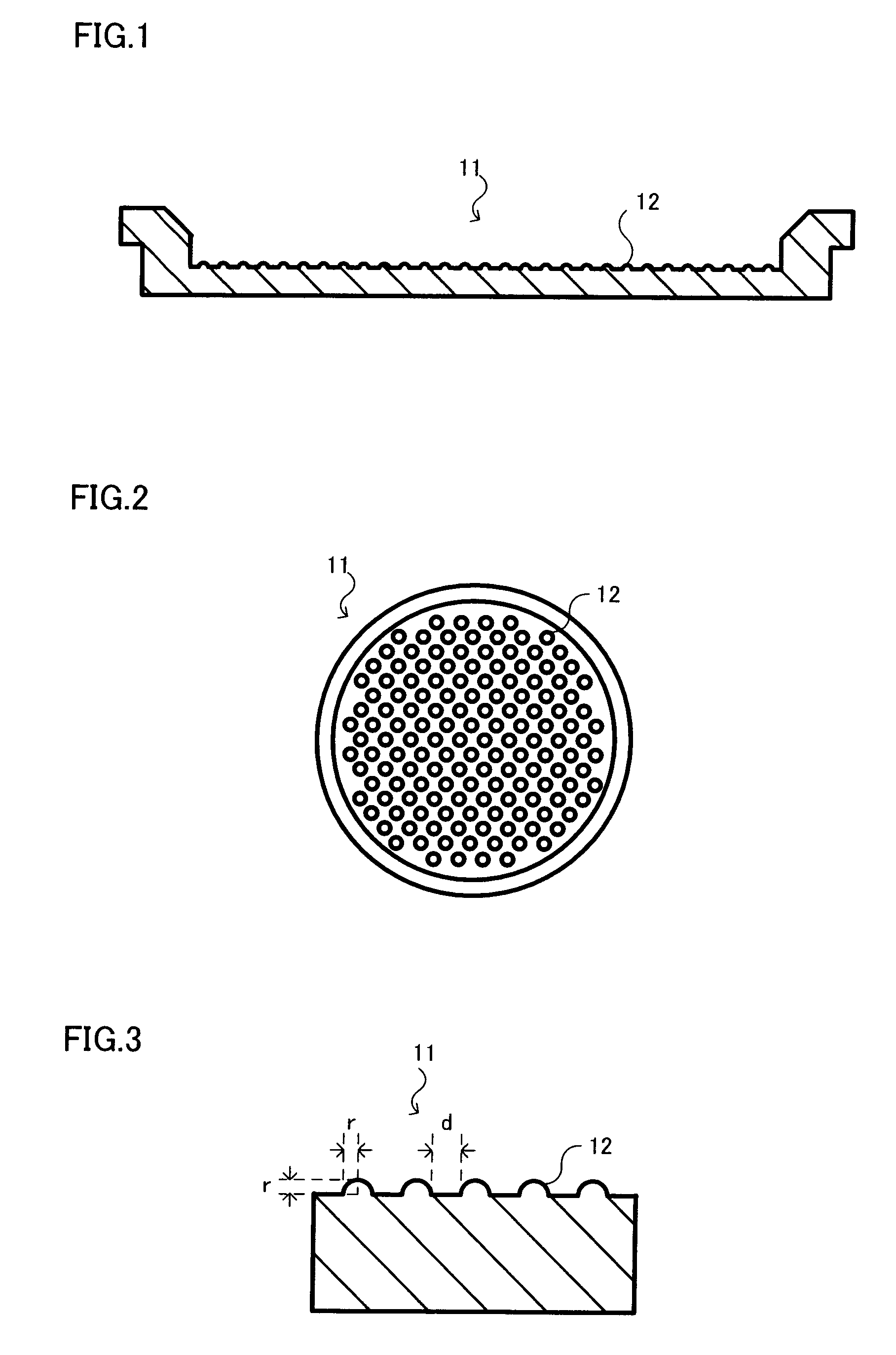
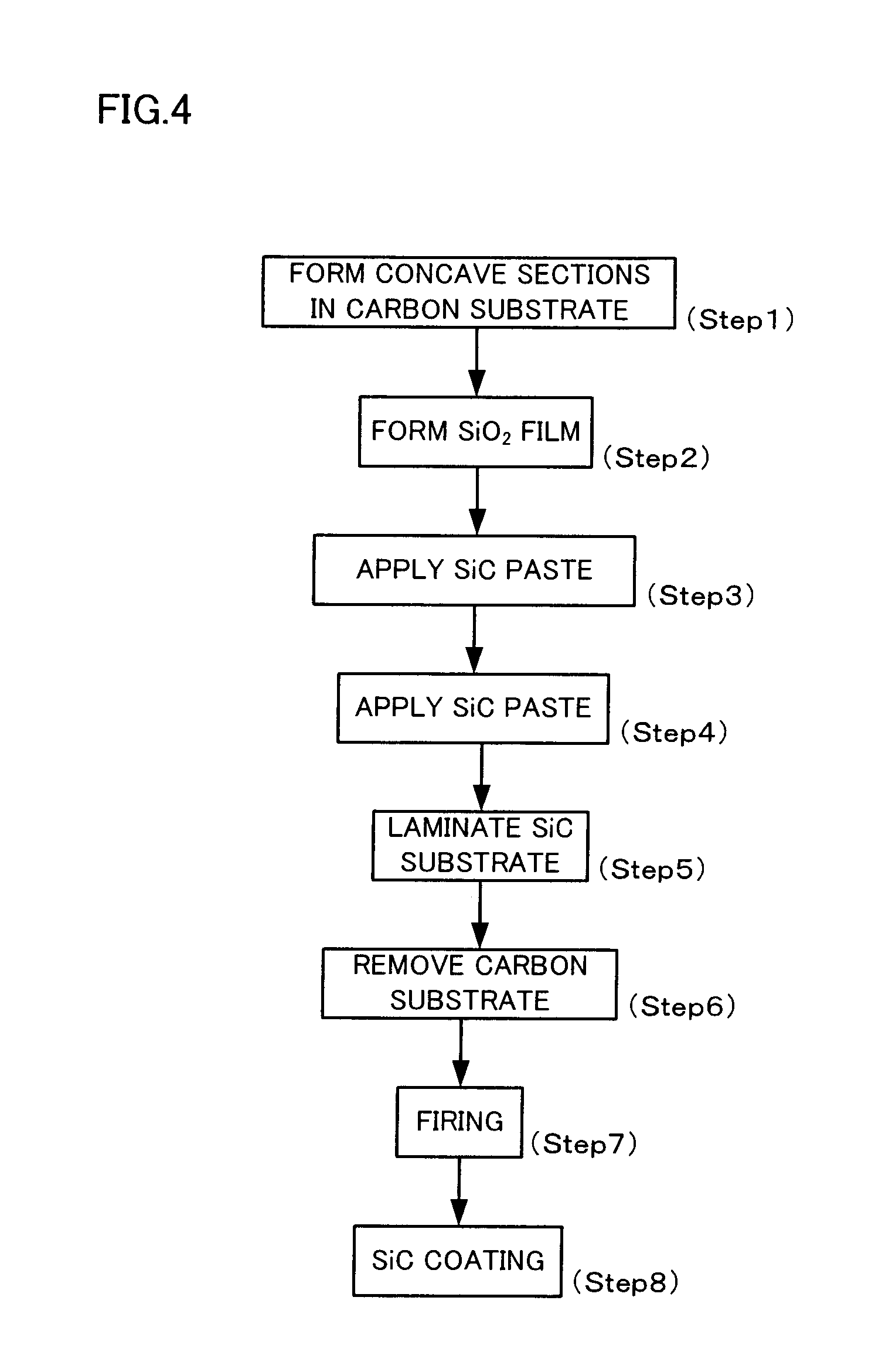
A method for manufacturing a susceptor includes: forming a concave pattern in a surface of a substrate to be processed; applying a SiC paste containing a SiC powder and a sintering agent to the surface of the substrate to be processed to fill the concave pattern to form a SiC coating layer; laminating a SiC substrate on the SiC coating layer; and firing the SiC coating layer to form a SiC layer having at least one convex section on the surface of the SiC substrate.
Owner:NUFLARE TECH INC
Reinforced composite stamp for dry transfer printing of semiconductor elements
ActiveUS7927976B2Easy to controlPrecise and repeatable vertical motionTurning machine accessoriesMouldsSemiconductor structureContact force
Provided are reinforced composite stamps, devices and methods of making the reinforced composite stamps disclosed herein. Reinforced composite stamps of certain aspects of the present invention have a composition and architecture optimized for use in printing systems for dry transfer printing of semiconductor structures, and impart excellent control over relative spatial placement accuracy of the semiconductor structures being transferred. In some embodiments, for example, reinforced composite stamps of the present invention allow for precise and repeatable vertical motion of the patterned surface of the printing apparatus with self-leveling of the stamp to the surface of a contacted substrate. Reinforced composite stamps of certain aspect of the present invention achieve a uniform distribution of contact forces between the printing apparatus patterned surface and the top surface of a substrate being contacted by the reinforced composite stamp of the printing apparatus.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for manufacturing composite structures
Composite structures having a single continuous skin may be formed using automated fiber placement methods. These composite structures include frameless aircraft fuselage components offering an increased interior cabin width over conventional fuselage components. The composite structures may be constructed of multiple layers of fibers and other materials placed on a fiber placement tool that includes a mandrel body surrounded by a bladder or an integral bladder / caul sheet having expansion spaces created within the caul sheet section. Uncured composite structures may be created by placing fibers around the fiber placement tool in a plurality of discontinuous segments that are capable of moving or sliding in relation to each other so that the uncured composite structure is expandable from within. Fluid openings may be provided in the outer surface of the mandrel body for the application of vacuum and / or fluid pressure to secure the bladder to the mandrel body and to assist in the removal of the bladder from the mandrel body, respectively. Uncured composite structures may be sealed between the bladder and is clam shell molds. The uncured structures may be expanded against the inner surface of the molds by creating a vacuum between the bladder and molds.
Owner:BEECHCRAFT
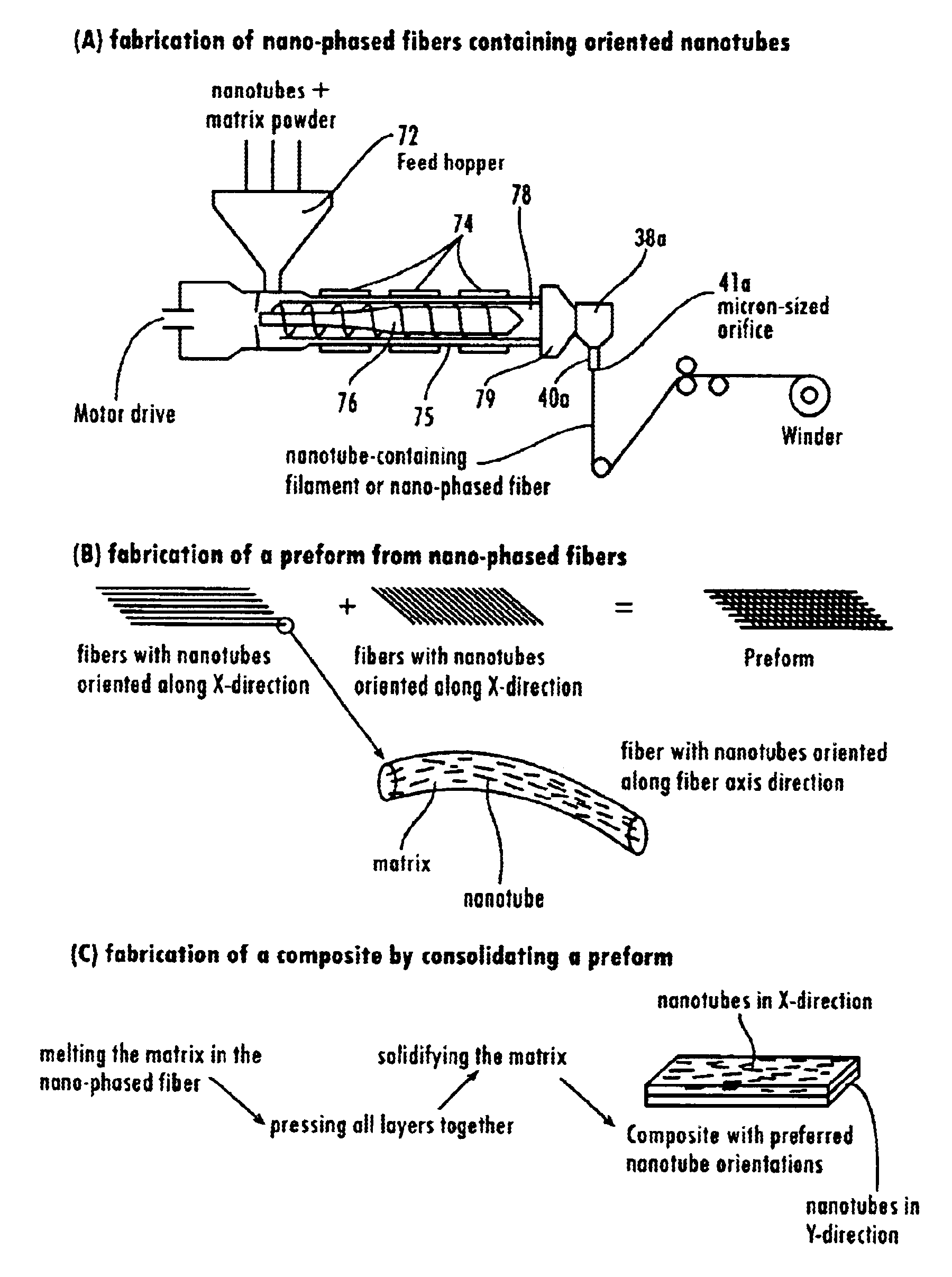
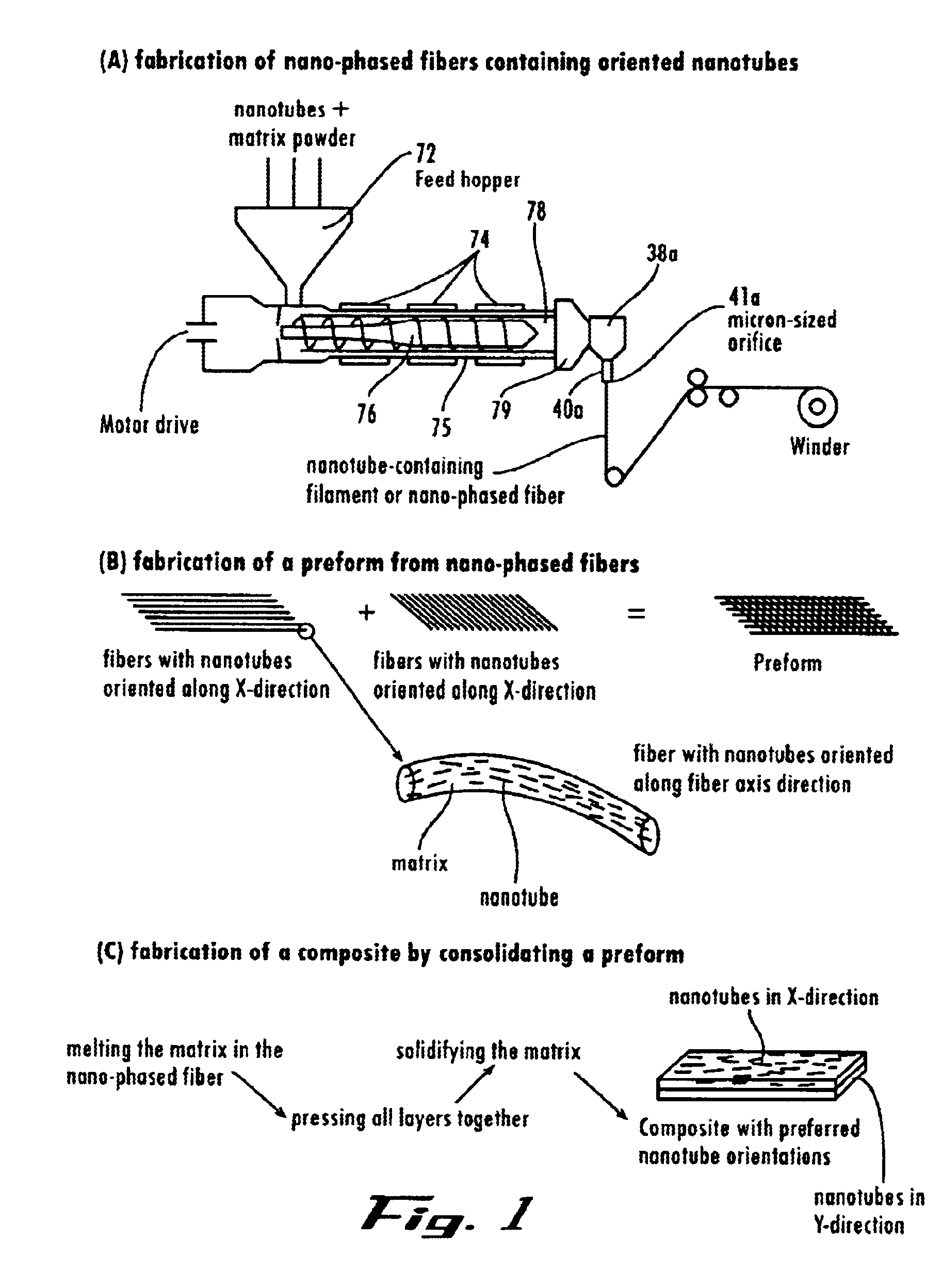
Nanotube fiber reinforced composite materials and method of producing fiber reinforced composites
InactiveUS6934600B2Requires minimizationGenerate efficientlyMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusFiber-reinforced compositeMotion controller
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
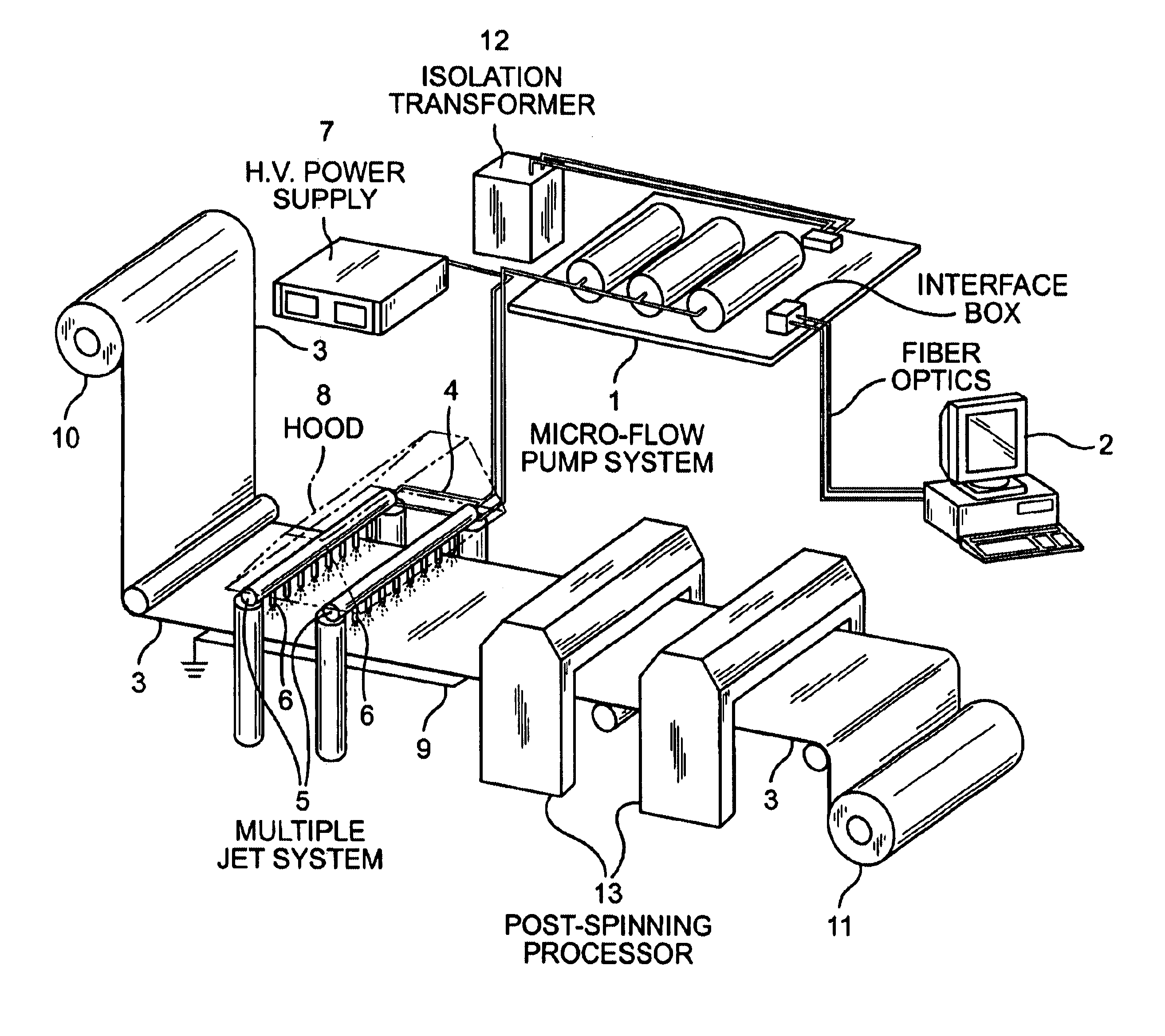
Apparatus and methods for electrospinning polymeric fibers and membranes
InactiveUS6713011B2Easy to controlLarge specific surface areaElectric discharge heatingConfectioneryFiberElectrospinning
An apparatus and method for electrospinning polymer fibers and membranes. The method includes electrospinning a polymer fiber from a conducting fluid in the presence of a first electric field established between a conducting fluid introduction device and a ground source and modifying the first electric field with a second electric field to form a jet stream of the conducting fluid. The method also includes electrically controlling the flow characteristics of the jet stream, forming a plurality of electrospinning jet streams and independently controlling the flow characteristics of at least one of the jet streams. The apparatus for electrospinning includes a conducting fluid introduction device containing a plurality of electrospinning spinnerets, a ground member positioned adjacent to the spinnerets, a support member disposed between the spinnerets and the ground member and movable to receive fibers formed from the conducting fluid, and a component for controlling the flow characteristics of conducting fluid from at least one spinneret independently from another spinneret.
Owner:RES FOUND THE
Dimensionally stable, breathable, stretch-thinned, elastic films
A method for producing a stretch-thinned elastic article having dimensional stability over time and at elevated temperatures in which a thermoplastic block copolymer is melt-processed into a stretchable article such as a film or fiber. The article is then conditioned at an elevated temperature greater than or equal to a glass transition temperature (Tg) of a hard phase of the thermoplastic block copolymer. The article is stretch-thinned at the elevated temperature to a desired percentage stretch, forming a stretch-thinned article, after which it is cooled to a temperature below the glass transition temperature of the hard phase of the thermoplastic block copolymer. Films produced by this method are suitable for use in durable and disposable articles including personal care articles such as diapers, incontinence wear, training pants, and feminine care articles, as well as wound dressings, wipes, towels, napkins, and protective apparel.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Panel element
InactiveUS20030037504A1Simple yet reliable layingPrecise arrangementCovering/liningsWallsEngineeringFloor covering
The invention relates to a panel element for forming a floor covering, consisting of several identical interconnectable panel elements and having the following features: two first sides of each panel element, called the "longitudinal sides", these sides having a groove and a tongue; the tongue of a panel element which is positioned at an angle with an installation level of a first, identical panel element can be introduced into the groove of the first panel element; the tongue interacts with the groove of the adjacent, identical panel element in such a way that two interconnected panel elements are protected against separating forces which are exerted along both of the axes extending perpendicularly to the longitudinal side of the panel elements; two second sides of the panel element, called the end sides, are provided with fixing means and a groove and tongue, these forming an end-side connection between two adjacent panel elements; the end-side grooves and tongue can be interconnected by means of the panel element being lowered onto an identical panel element that has already been installed, essentially crosswise to the installation level, so that the panel element is protected from lifting forces, i.e. forces which are exerted considerably perpendicularly to the installation level.
Owner:FLOORING IND LTD
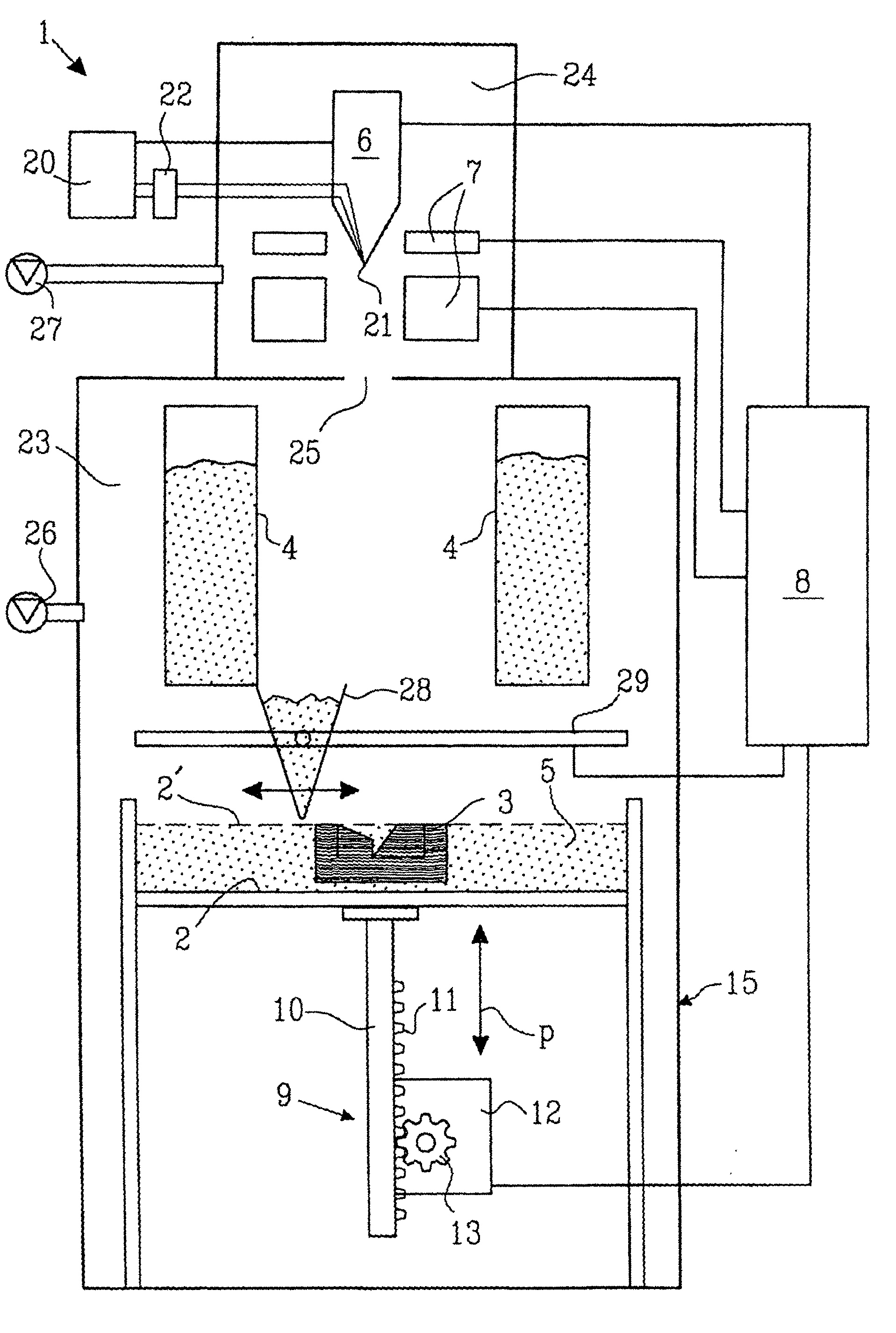
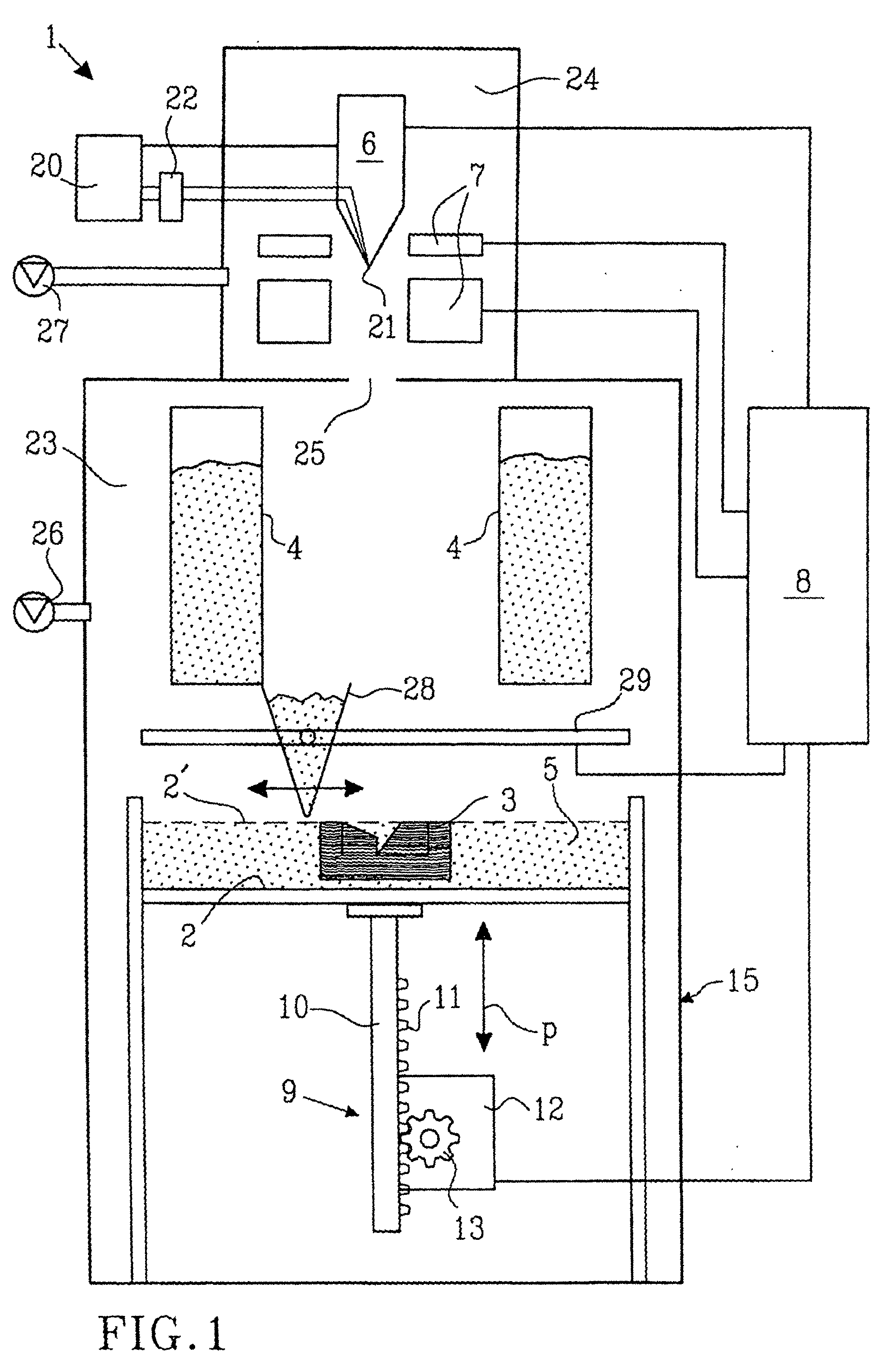
Method and device for manufacturing three-dimensional bodies
A method for producing three-dimensional bodies of a large number of mutually connected layers of a particle-shaped material such as a powder, and where the information of the appearance of each layer is achieved from a computer's CAD-unit or similar. An essentially even particle layer (7) of building material is applied on a support base (6) and on a masking device (9) is arranged a masking pattern in accordance with the information from the CAD-unit, which masking device is led over said particle layer and close to it. A radiation producer (8) is arranged or is led over the masking device (9), whereby the particles which are not covered by the masking pattern are exposed for radiation and thereby are attached to each other. The masking pattern is removed from the masking device and new sequences in accordance with the above are carried through until the three-dimensional body (19) is produced.
Owner:SPEED PART RP
Pattern forming method and pattern forming apparatus
Owner:CANON KK
Graphite-based heat sink
InactiveUS6503626B1Improve cooling effectIncreased anisotropyLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNuclear engineeringGraphite
The present invention relates to a system for managing the heat from a heat source like an electronic component. More particularly, the present invention relates to a system effective for dissipating the heat generated by an electronic component using a heat sink formed from a compressed, comminuted particles of resin-impregnated flexible graphite mat or sheet.
Owner:GRAFTECH INT HLDG INC
Polyethylene oxide-based films and drug delivery systems made therefrom
The invention relates to the film products and methods of their preparation that demonstrate a non-self-aggregating uniform heterogeneity. Desirably, the films disintegrate in water and may be formed by a controlled drying process, or other process that maintains the required uniformity of the film. The films contain a polymer component, which includes polyethylene oxide optionally blended with hydrophilic cellulosic polymers. Desirably, the films also contain a pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent with no more than a 10% variance of the active agent pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent per unit area of the film.
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
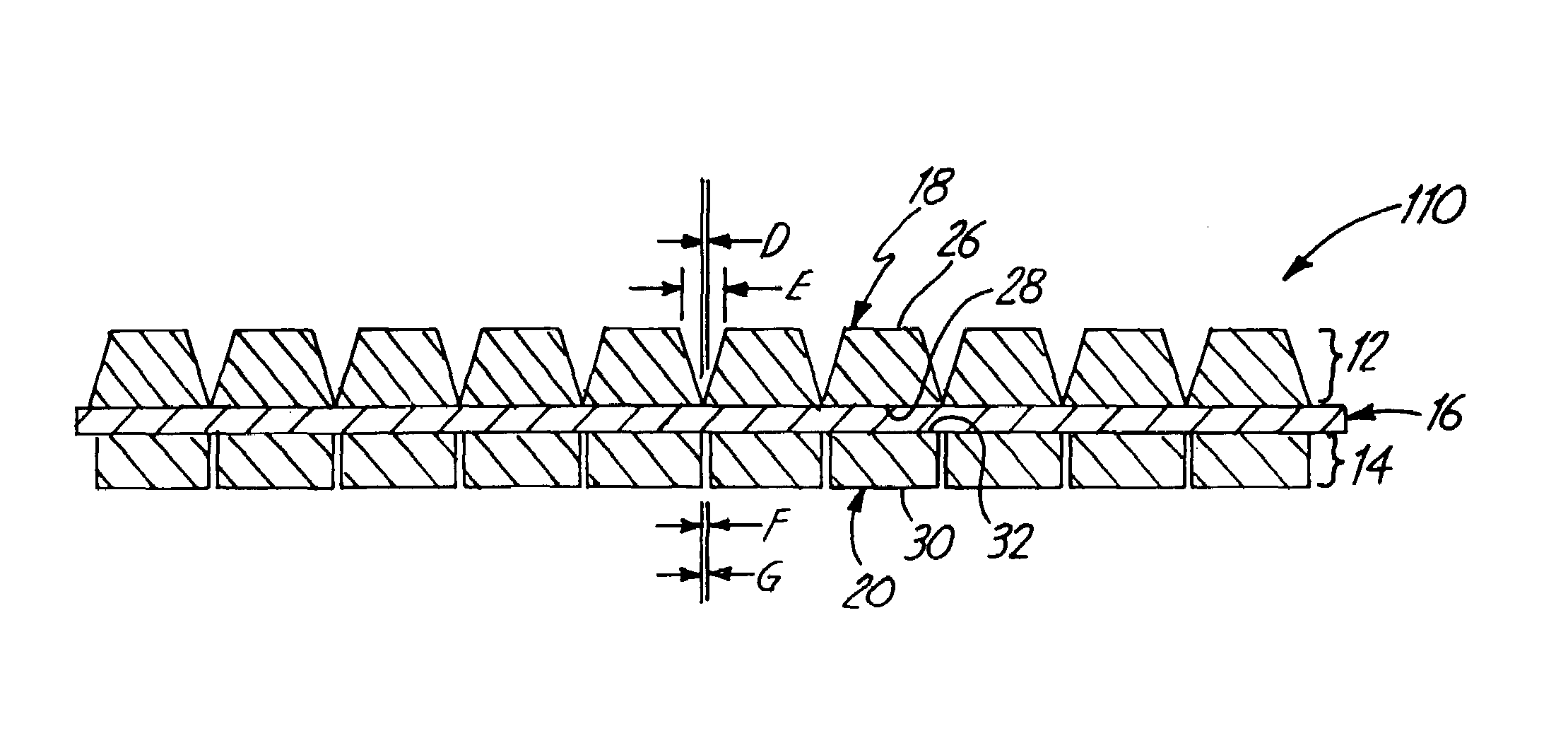
Impact absorbing composite
An impact absorbing composite structure (10), the impact absorbing composite structure including a plurality of impact absorbing members (18) and a flexible layer (16), each impact absorbing member (18) integral with the flexible layer (16).
Owner:GOLDFINE ANDREW A
Process for the manufacturing of surface elements with a structured upper surface
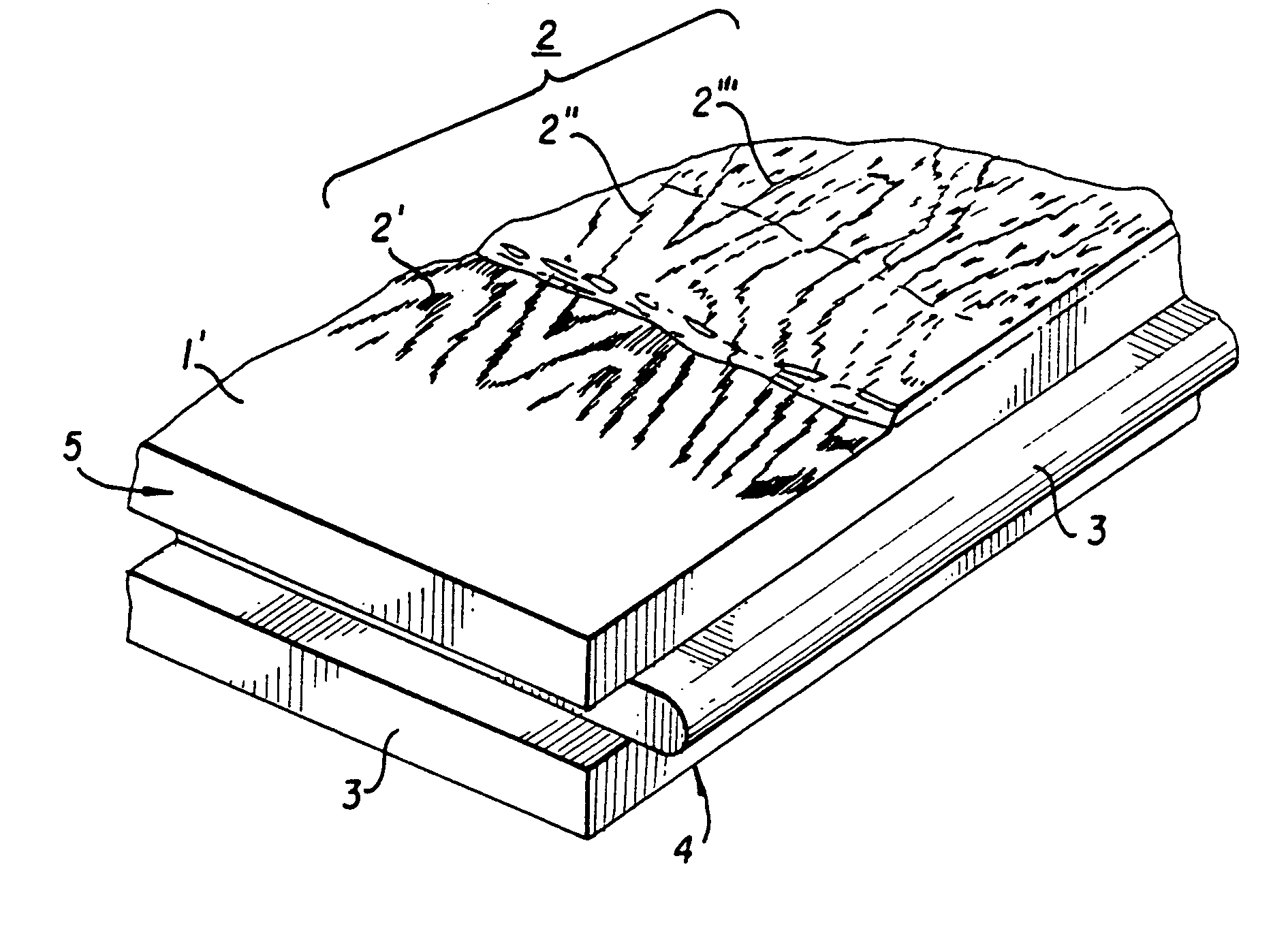
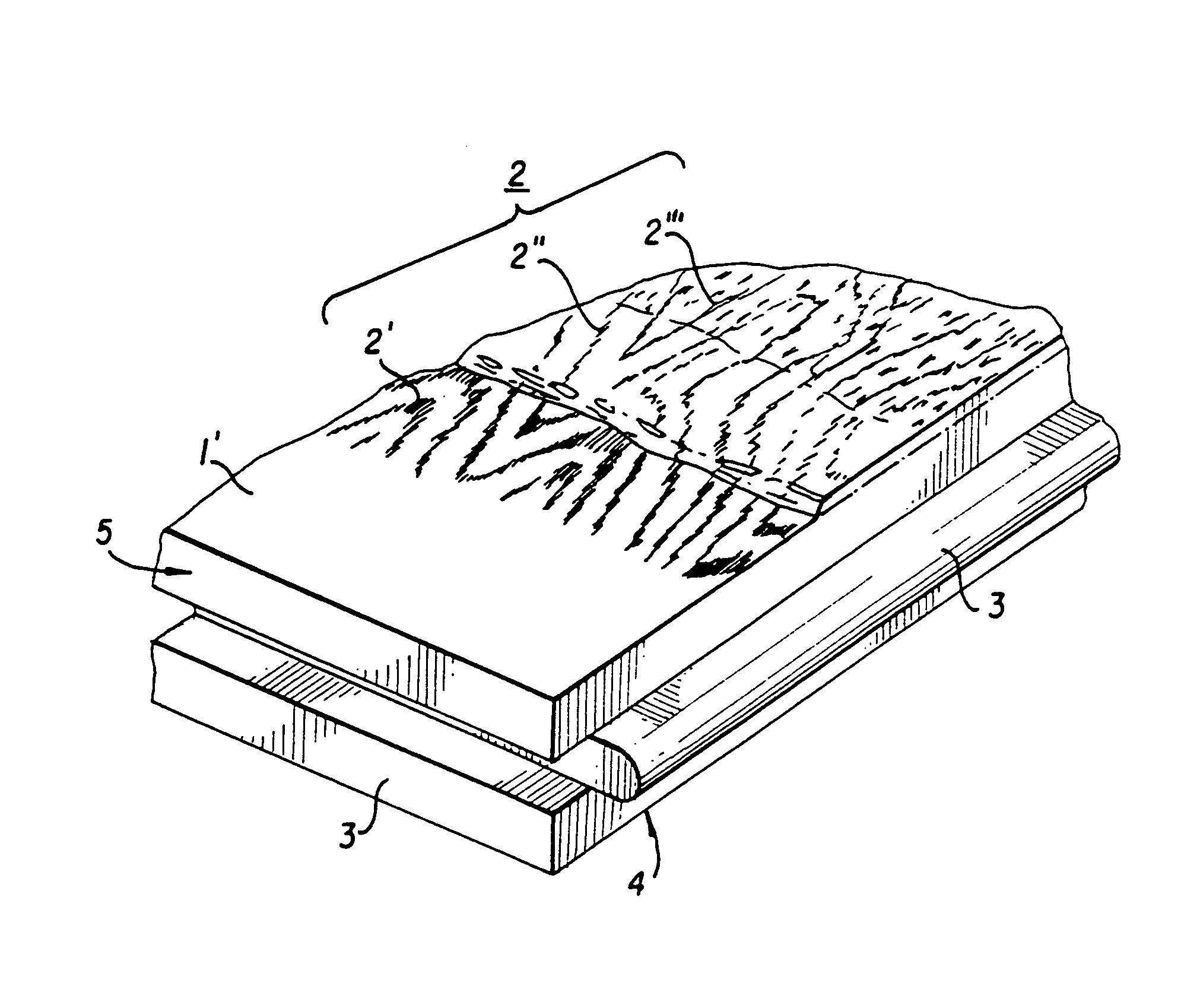
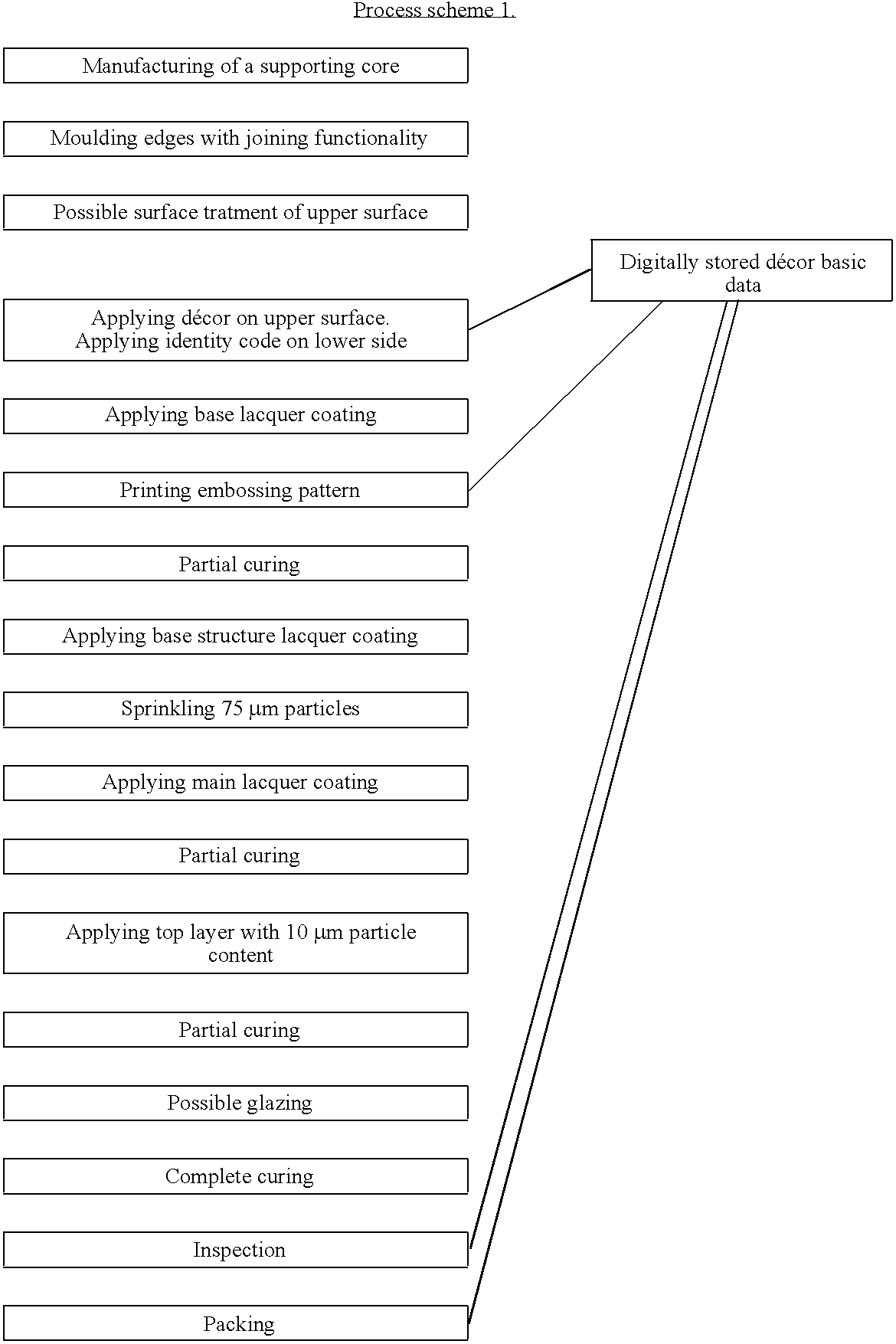
InactiveUS6991830B1High resolutionRearrange décorCovering/liningsOrnamental structuresLacquerEngineering
A process for the manufacturing of a decorative surface element, which element comprises a base layer and a decorative upper surface. A wetting repellent lacquer is printed in a predetermined pattern on the decorative upper surface. The wetting repellent lacquer covers only parts of the decorative upper surface. A wear layer of a UV or electron beam curing lacquer is then applied on top of the decorative upper surface which UV or electron beam curing lacquer is repelled from the parts of the surface being covered by the wetting repellent lacquer whereby a surface structure is achieved.
Owner:UNILIN NORDIC AB
Building panel with compressed edges and method of making same
ActiveUS20080034701A1Efficient productionImproved abrasionWallsSpecial ornamental structuresSurface layerEngineering
Floorboards comprising a core and a surface layer with curved edge portions, which are formed by a compression of the core.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Device and arrangement for producing a three-dimensional object
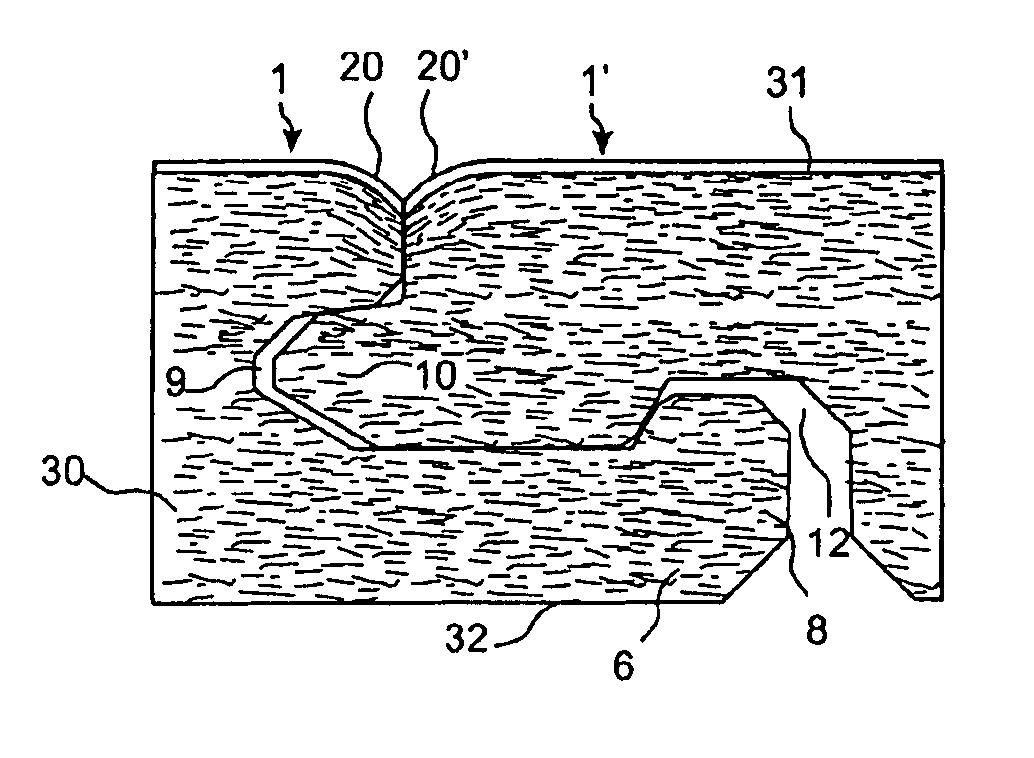
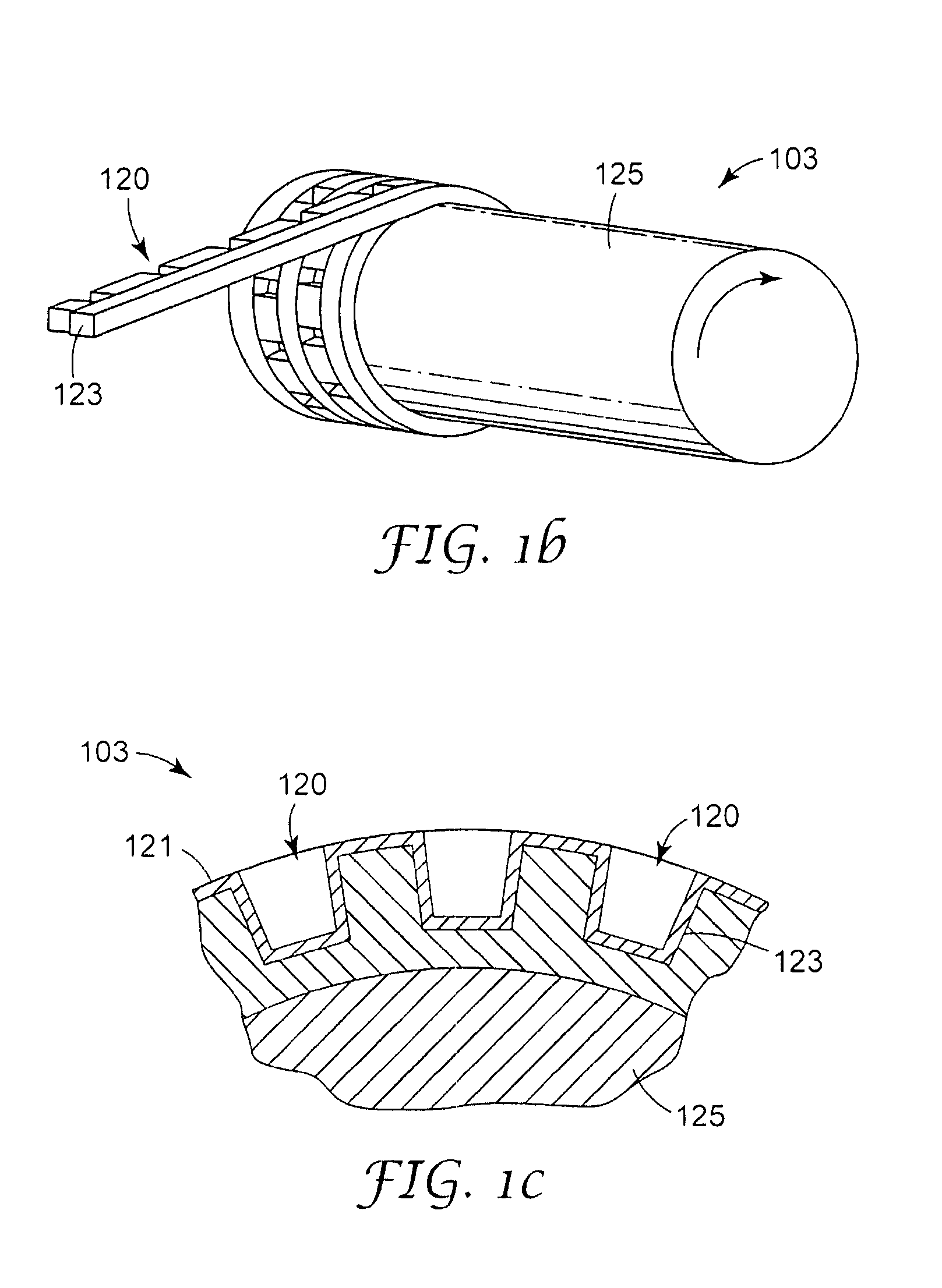
InactiveUS20040026807A1Reduced form requirementsSmall sizeConfectioneryWood working apparatusThin layerRunning time
A device for manufacturing a three-dimensional product, which device comprises a work table on which said three-dimensional product is to be built, a powder dispenser which is arranged to lay down a thin layer of powder on the work table for the formation of a powder bed, a ray gun for giving off energy to the powder whereby fusion of the powder takes place, members for controlling of the beam released by the ray gun across said powder bed for the formation of a cross section of said three-dimensional product through fusion of parts of said powder bed, and a controlling computer in which information about successive cross sections of the three-dimensional product is stored, which cross sections build the three-dimensional product, the controlling computer intended to control said members for guiding the ray gun across the powder bed according to a running schedule forming a cross section of said three-dimensional body, whereby said three-dimensional product is formed by successive fusion of successively formed cross sections from powder layers successively laid down by the powder dispenser.
Owner:ARCAM AB
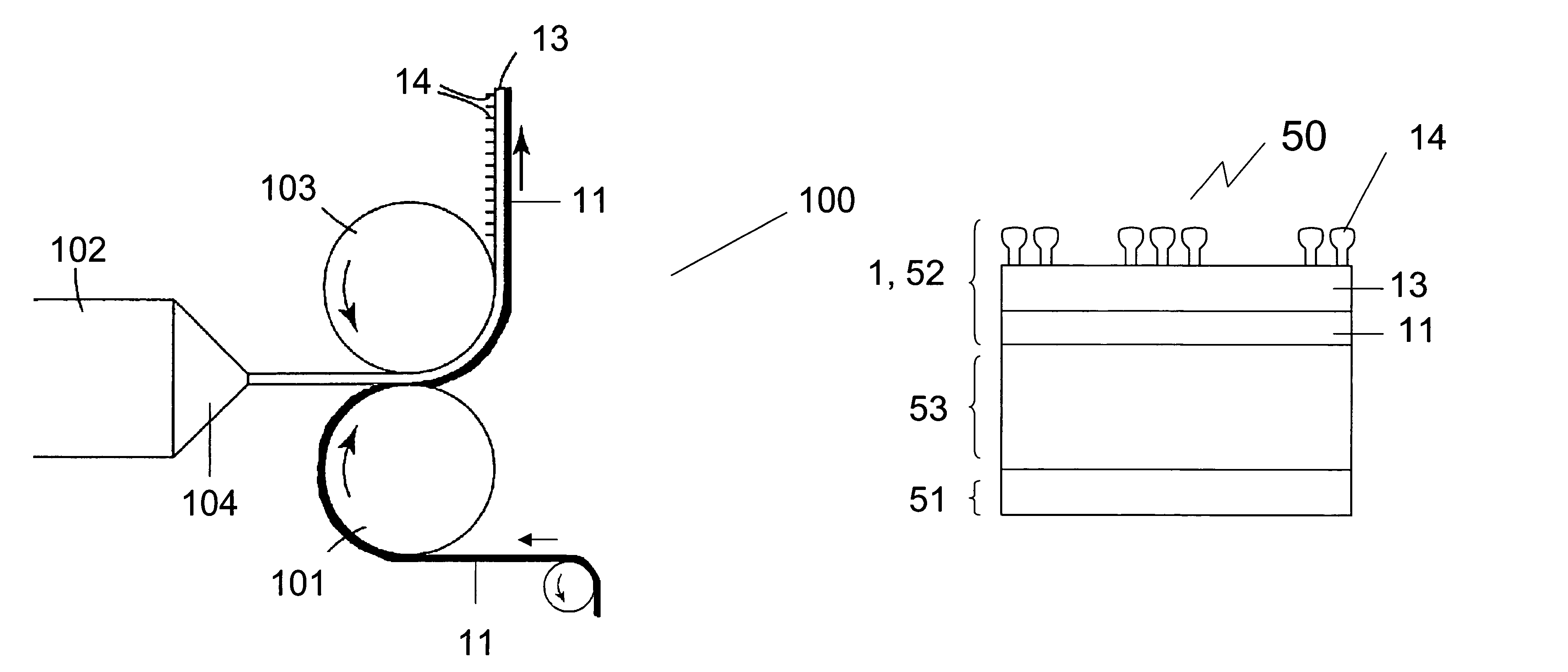
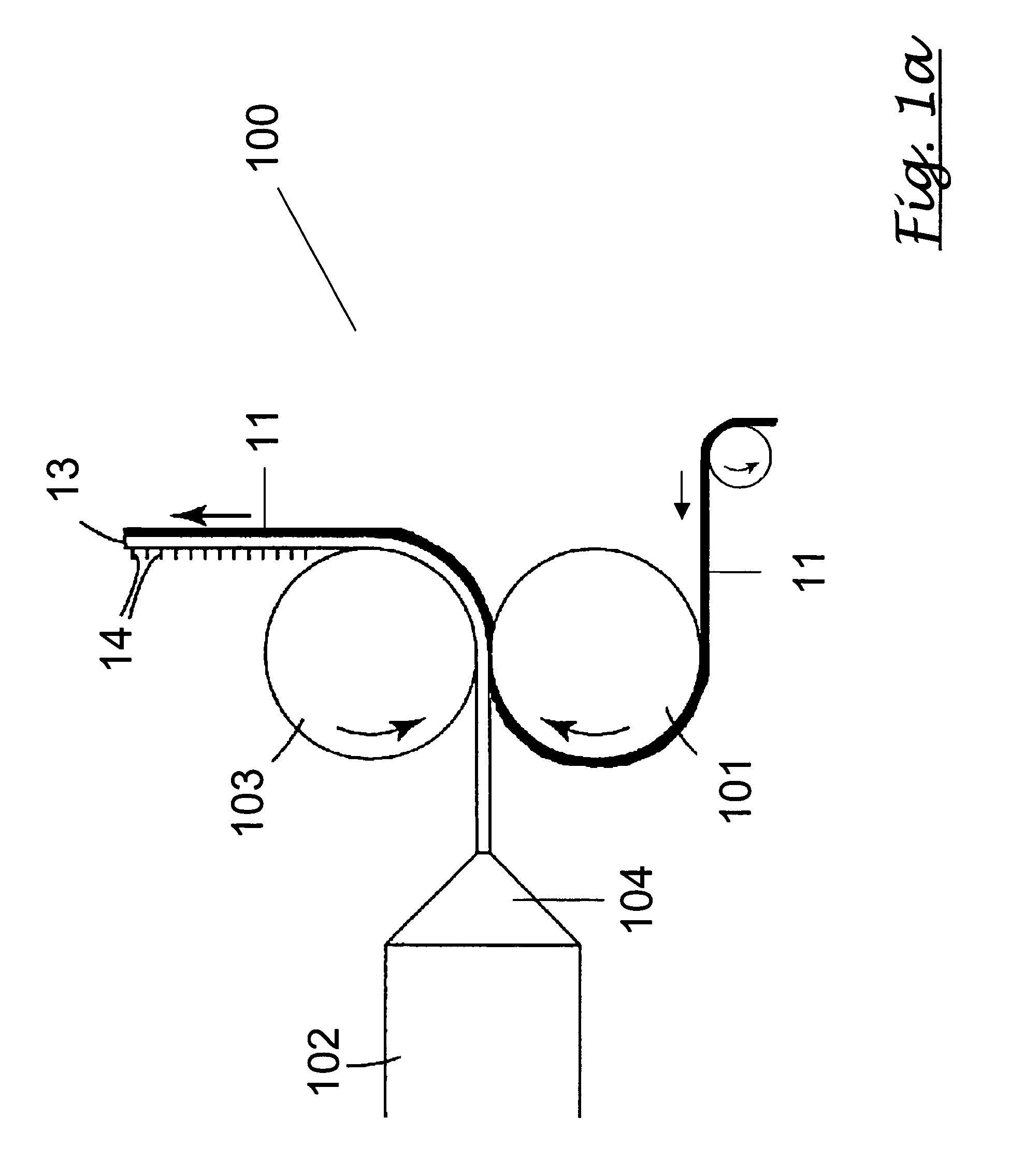
Methods of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate
InactiveUS7897078B2Reduce basis weightSnap fastenersWood working apparatusFiberVolumetric Mass Density
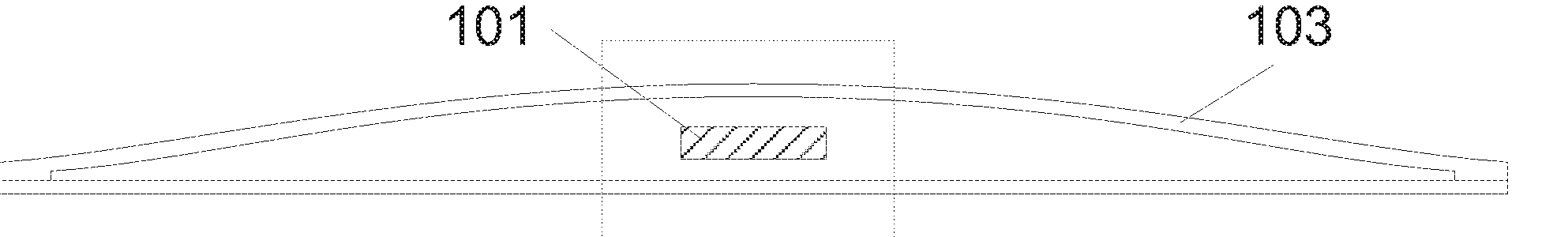
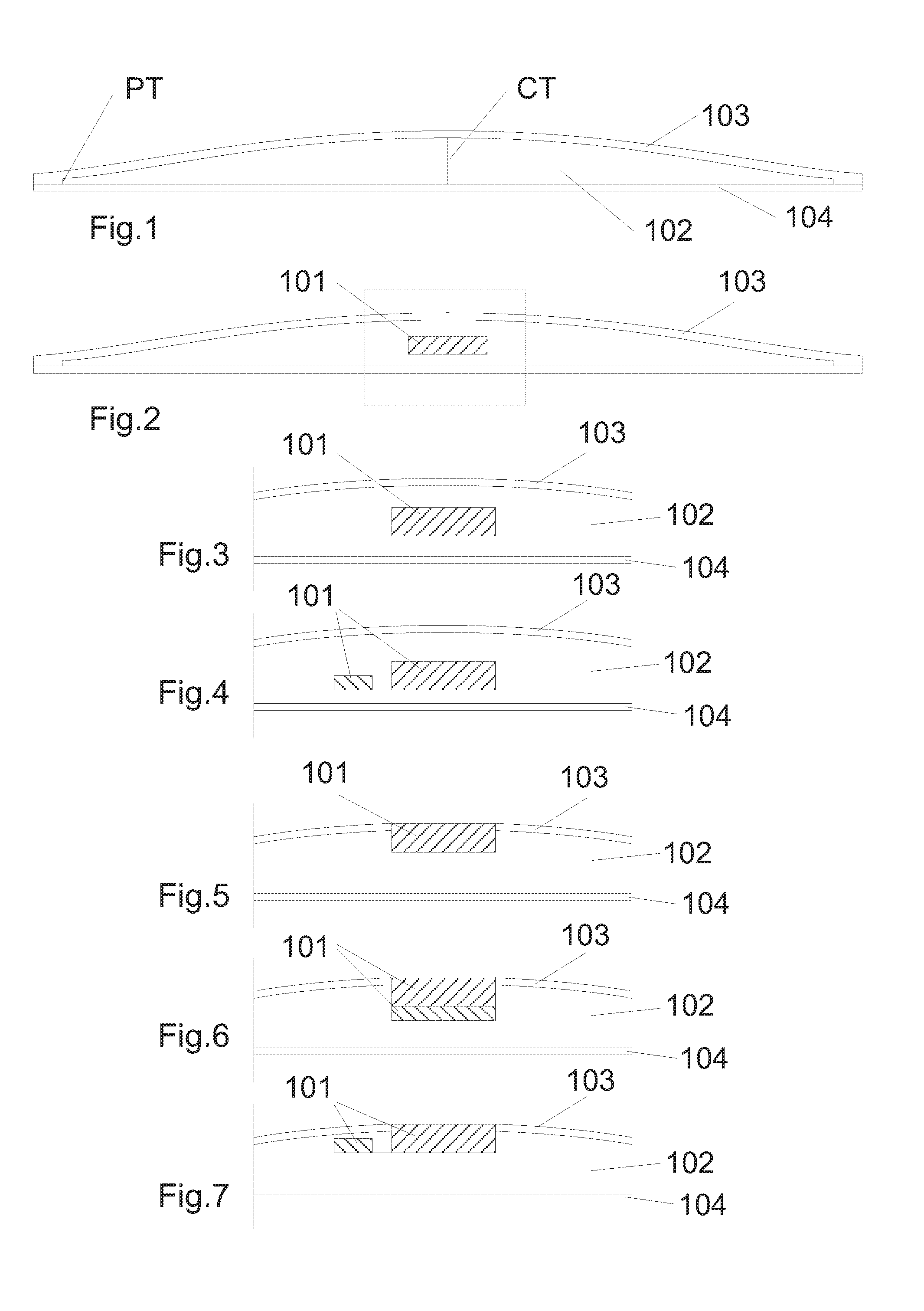
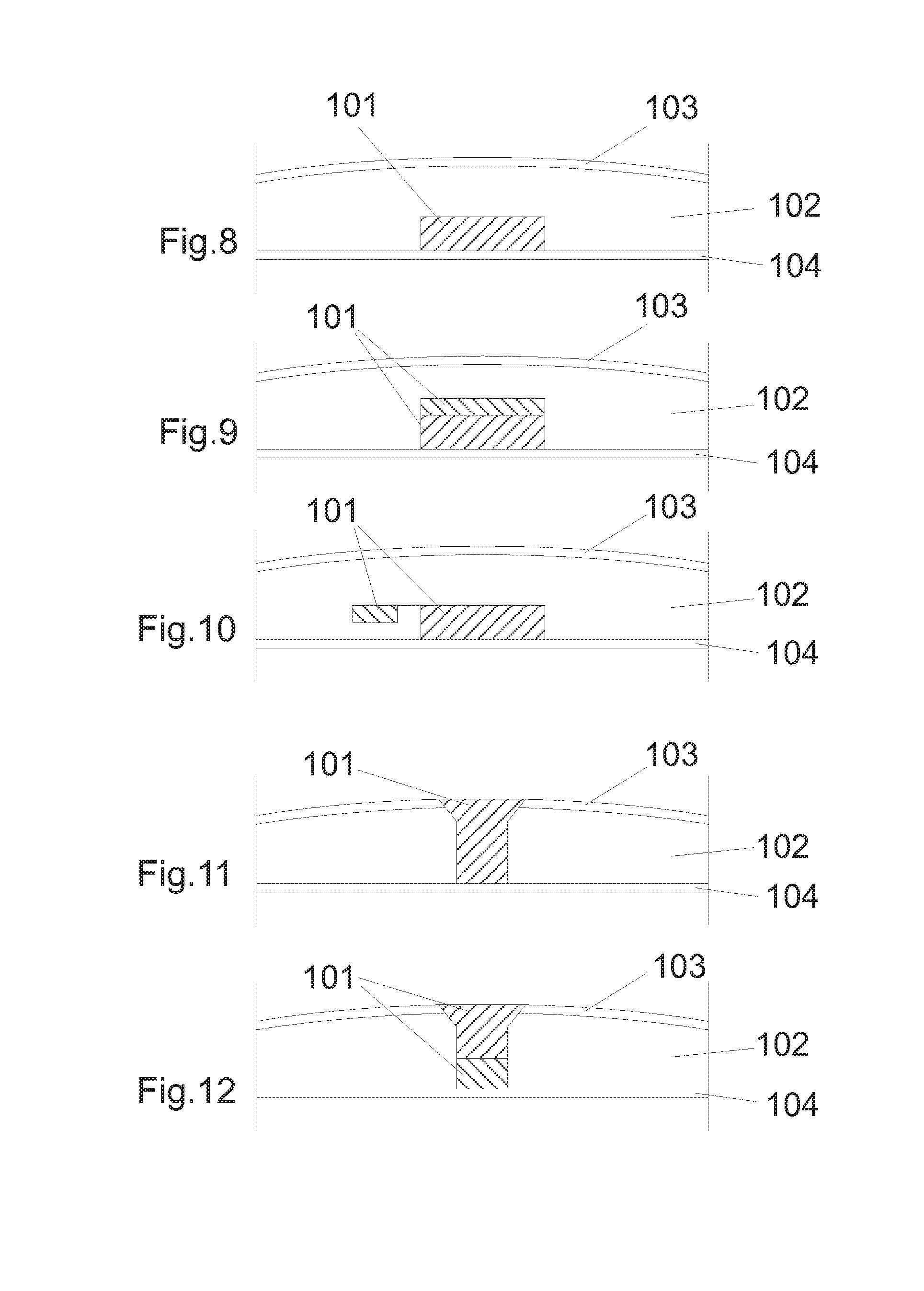
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate (1) comprising a thermoplastic web layer (13) having two major surfaces, one of the major surfaces bearing a multitude of male fastening elements (14) suitable for engagement with a corresponding female fastening material, and on its other major surface a fibrous web layer (11), said method comprising the steps of(i) providing the fibrous web layer (11) having an initial basis weight,(ii) passing the fibrous web layer (11) through a nip formed by two rolls (101), (103), one of them having cavities (120) that are the negatives of a plurality of male fastening elements (14), introducing a molten thermoplastic resin into the cavities (120) in excess of an amount that would fill the cavities (120) which excess forms the thermoplastic web layer (13), allowing the resin to at least partially solidify and stripping of a precursor web laminate (10) thus formed comprising the fibrous web layer (11) and the thermoplastic web layer (13) bearing a plurality of male fastening elements (14), from the cylindrical roll (103) having cavities (120) whereby the thermoplastic web layer (13) has an initial thickness and an initial hook density, and(iii) stretching the precursor web laminate (10) monoaxially or biaxially thereby decreasing the basis weight of the fibrous web layer (11) and the thickness of the thermoplastic web layer (13) from their respective initial values to provide a stretched mechanical fastening laminate (1) having a basis weight of less than 100 g·m−2.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Wood fibre based panels with a thin surface layer
ActiveUS20100092731A1Large market shareImprove impact resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsCovering/liningsSurface layerWood fibre
Building panels with a thin and embossed surface layer and a sub layer between a surface layer and a core.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Particle filter system incorporating nanofibers
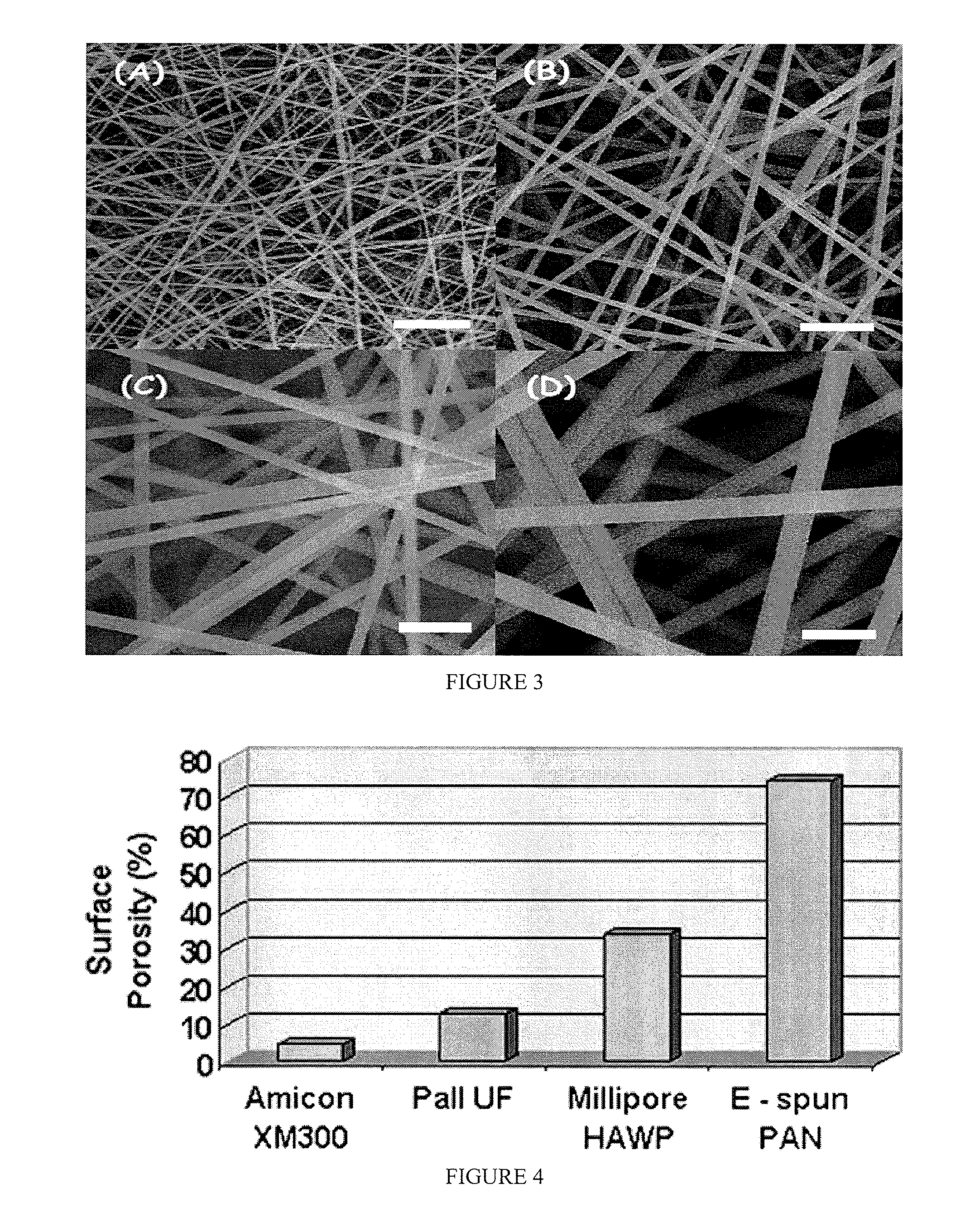
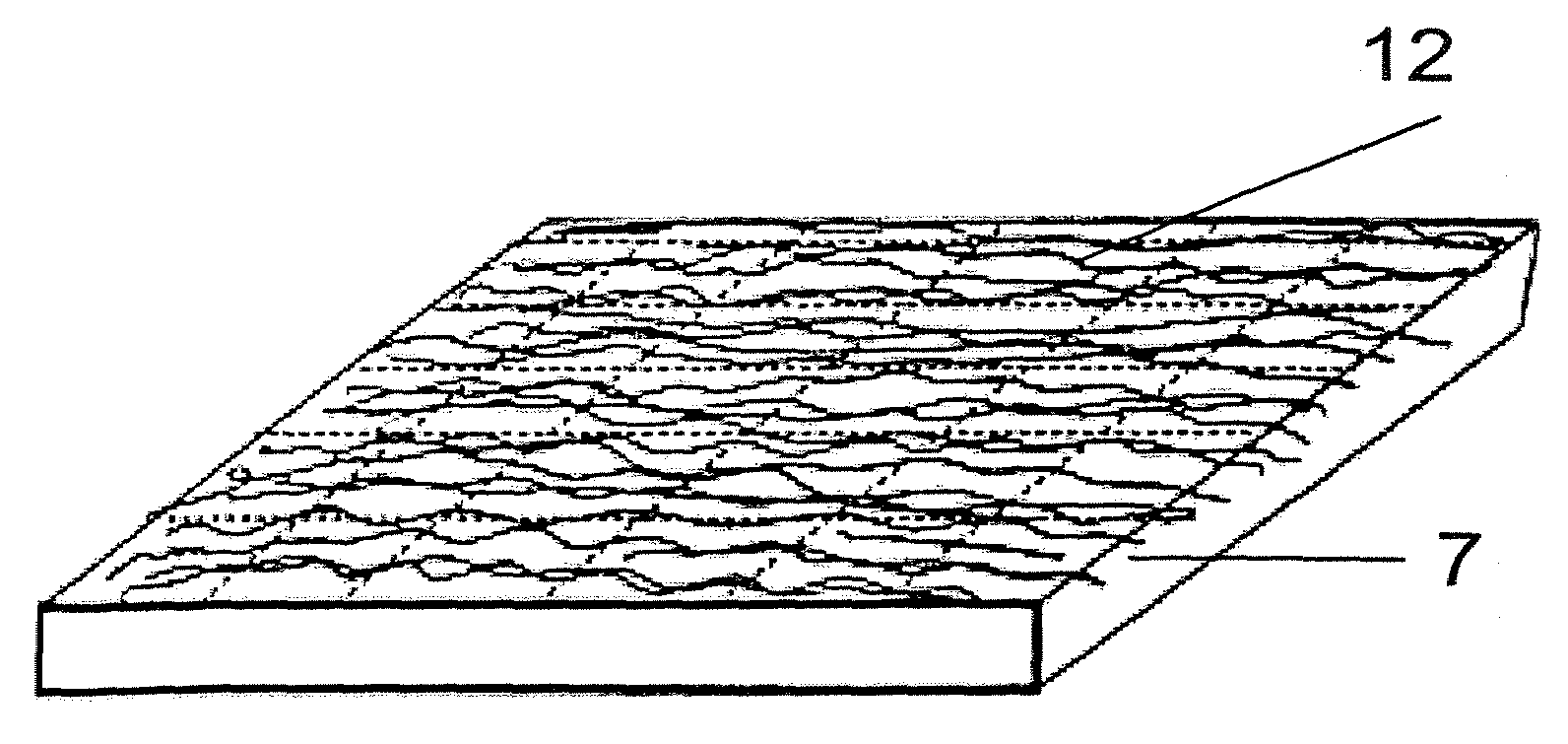
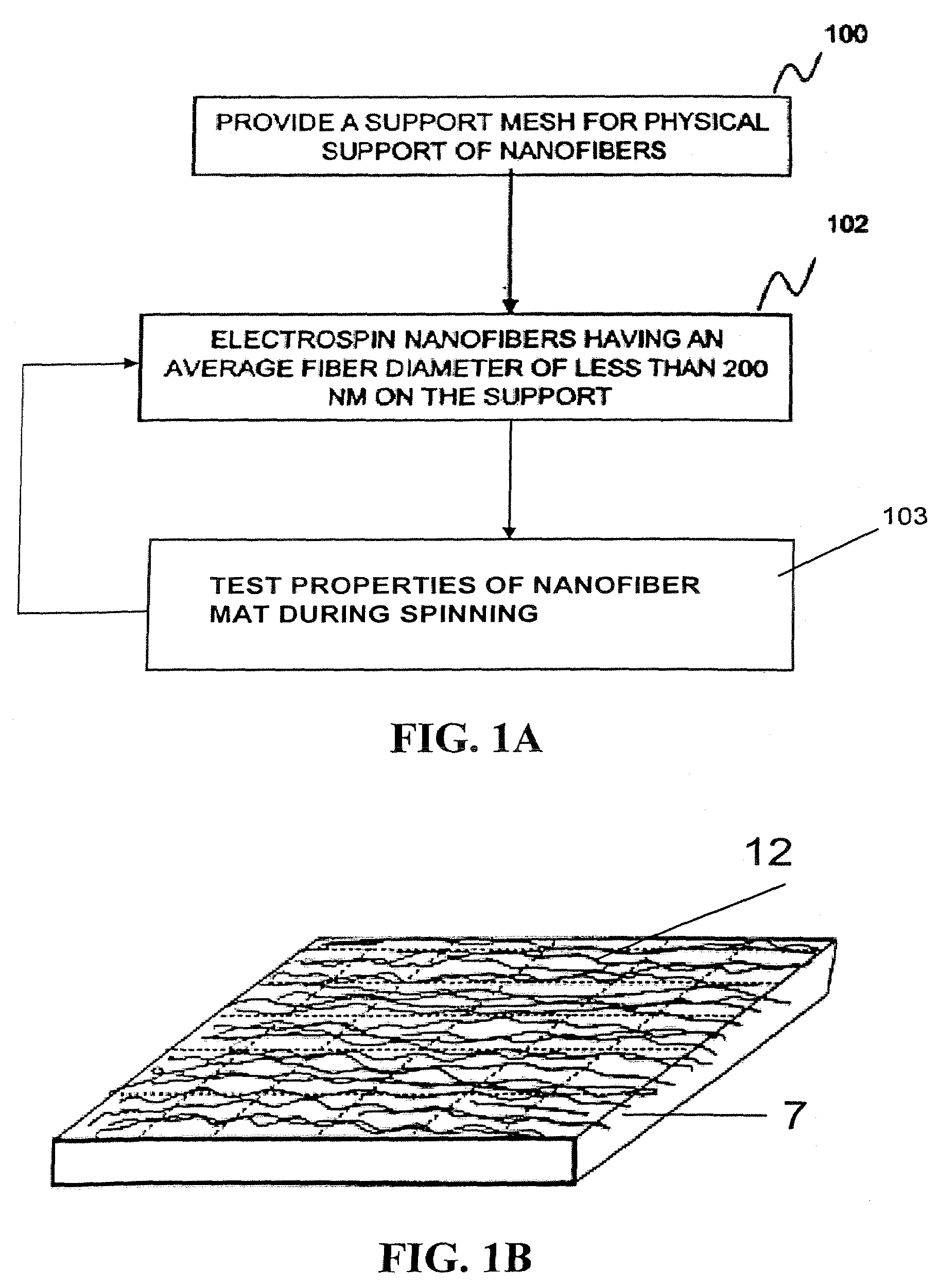
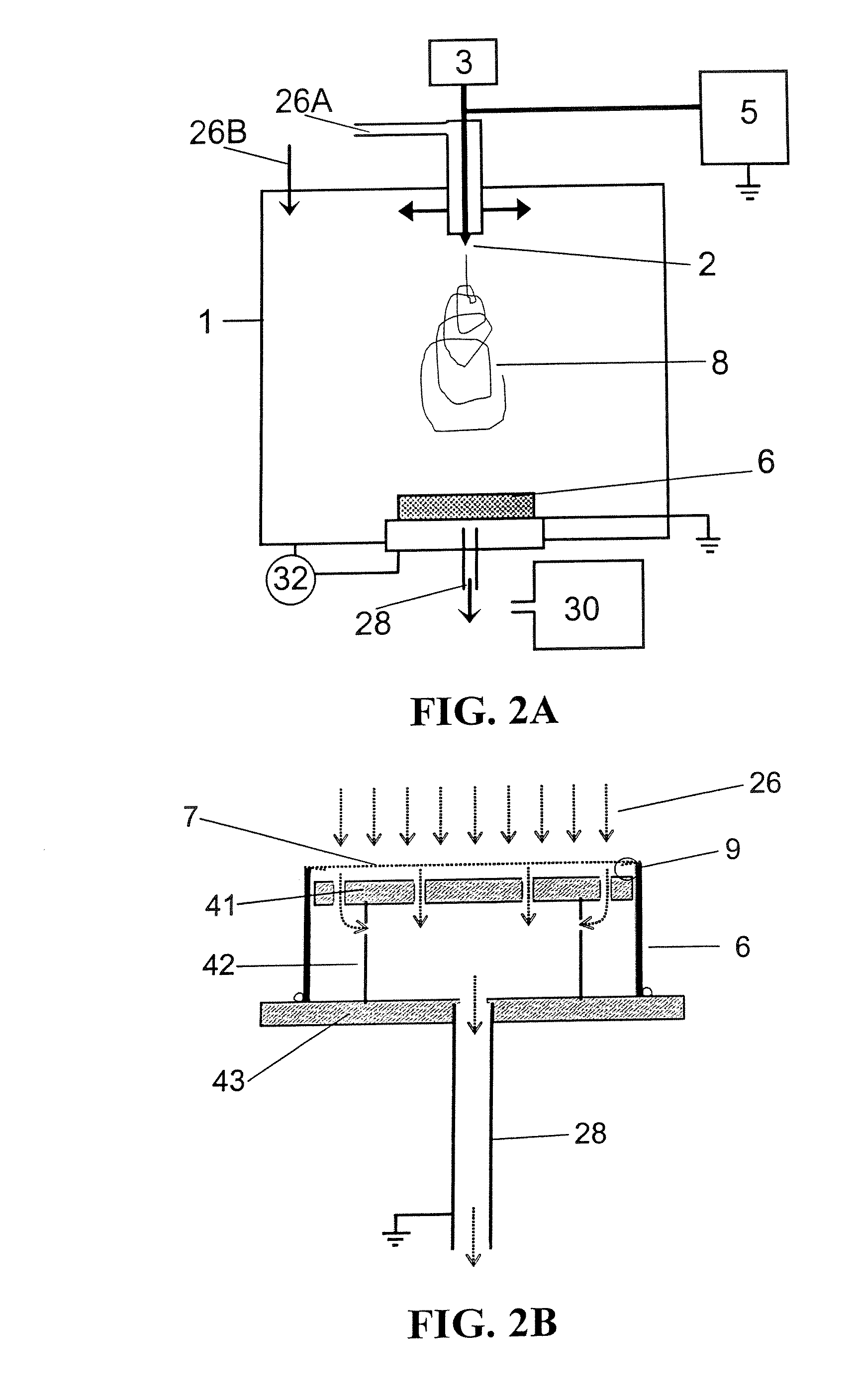
ActiveUS20080110342A1Electric discharge heatingFilament/thread formingElectric field modulationFiber
A filtration device including a filtration medium having a plurality of nanofibers of diameters less than 1 micron formed into a fiber mat in the presence of an abruptly varying electric field. The filtration device includes a support attached to the filtration medium and having openings for fluid flow therethrough. A device for making a filter material. The device includes an electrospinning element configured to electrospin a plurality of fibers from a tip of the electrospinning element, a collector opposed to the electrospinning element configured to collect electrospun fibers on a surface of the collector, and an electric field modulation device configured to abruptly vary an electric field at the collector at least once during electrospinning of the fibers. A method for making a filter material. The method provides a support having openings for fluid flow therethrough, electrospins nanofibers across an entirety of the openings, and abruptly varies an electric field at the collector at least once during electrospinning of the fibers.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Reinforced polymers
InactiveUS6331265B1Less tangleImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyWood working apparatusPolymer scienceNanotube
Provided is a method for the production of a reinforced polymer, which method comprises:(a) introducing carbon nanotubes into a polymer to provide a mixture of the polymer and the nanotubes;(b) stretching the mixture at or above the melting temperature (Tm) of the polymer to orient the carbon nanotubes; and(c) stretching the mixture in the solid state to further orient the carbon nanotubes.
Owner:FINA RES SA
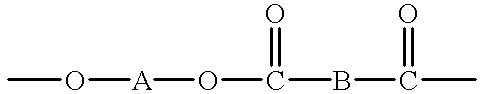
Blend material including macrocyclic polyester oligomers and processes for polymerizing the same
A blend of a macrocyclic polyester oligomer and a polymerization catalyst as a one component ready-to-use material with a long shelf life enables production of parts from macrocyclic polyester oligomers without the modification of existing equipment, thereby reducing time and cost of manufacture while expanding the application of macrocyclic polyester oligomers. In this blend material, the macrocyclic polyester oligomer remains intact in solid state at ambient conditions. Upon melting, the blend material initially forms low viscosity fluid, and then rapidly polymerizes to form high molecular weight polyesters which subsequently solidify to form crystalline polymers. In the case of certain macrocyclic polyester oligomers, for example, poly(1,4-butylene terephthalate), demolding can take place at the polymerization temperature, e.g., at about 180° C. to 200° C., because the resulting polyester polymer solidifies fairly rapidly at that temperature without cooling. In one aspect, the invention generally features a blend material that includes a macrocyclic polyester oligomer, a polymerization catalyst, and optionally, a filler. In another aspect, the invention generally features a process for preparing a blend material. In yet another aspect, the invention features processes such as rotational molding, resin film infusion, pultrusion, resin transfer molding, filament winding, making and using powder-coated or hot melt prepreg, compression molding, and roll wrapping, which use the blend material.
Owner:CYCLICS CORP
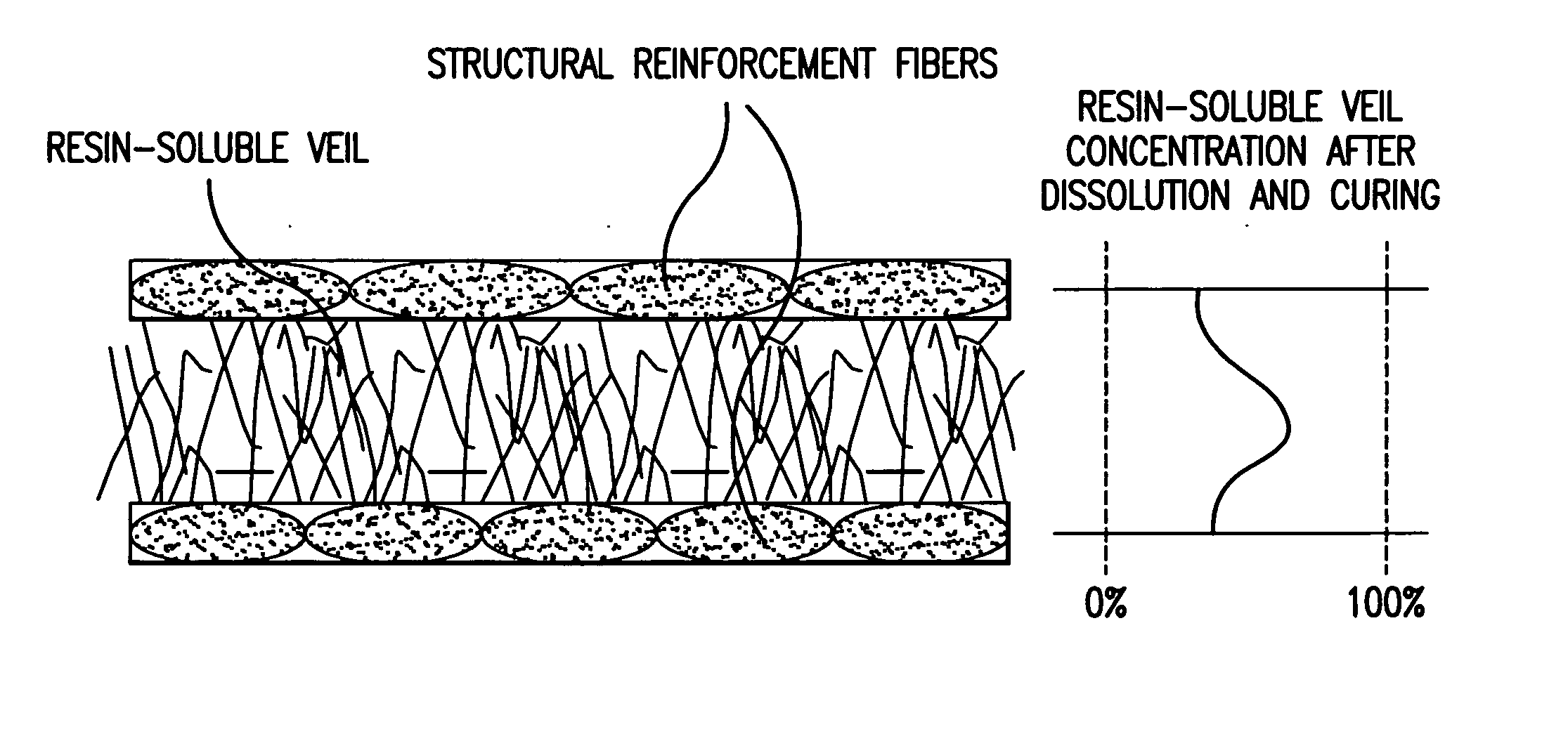
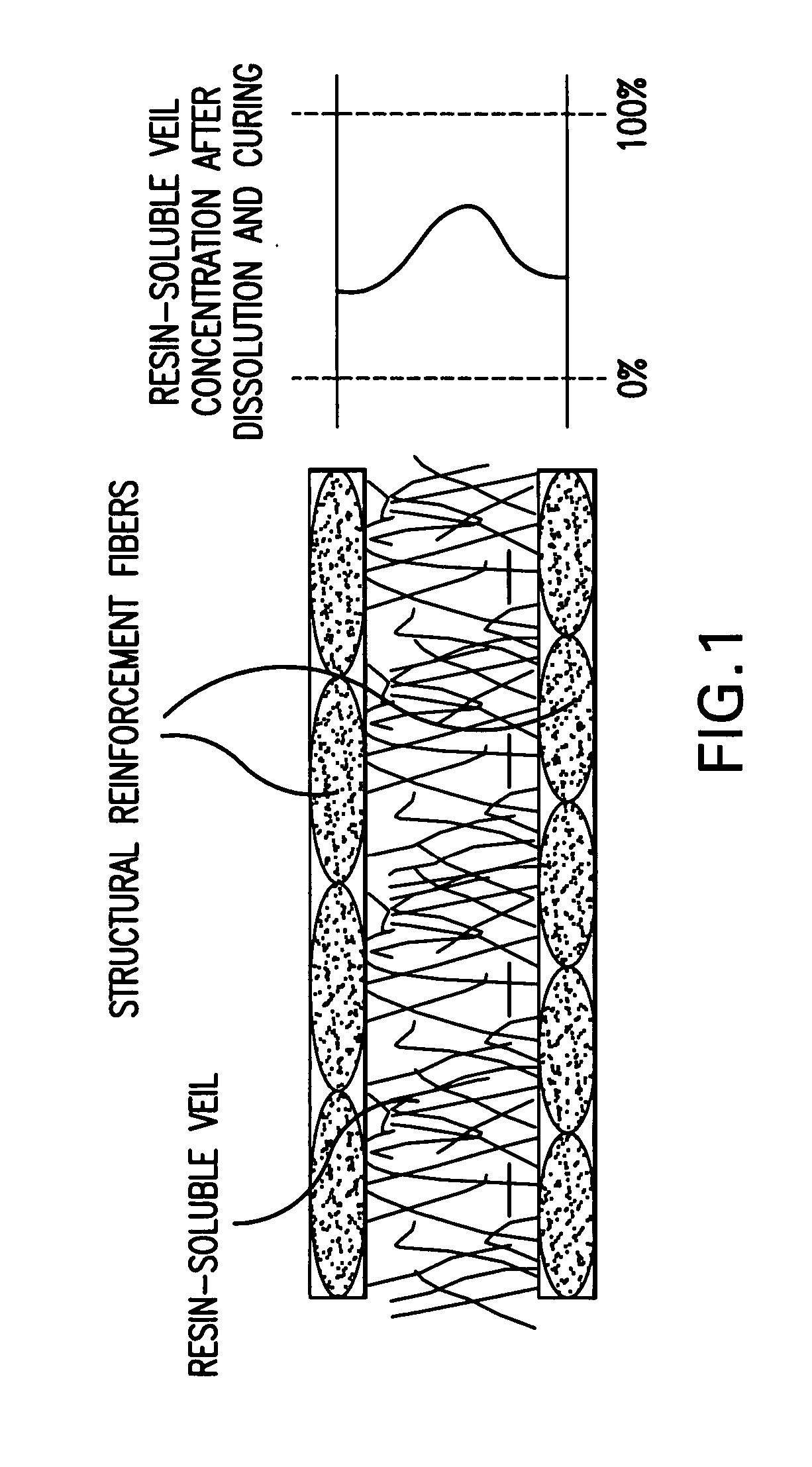
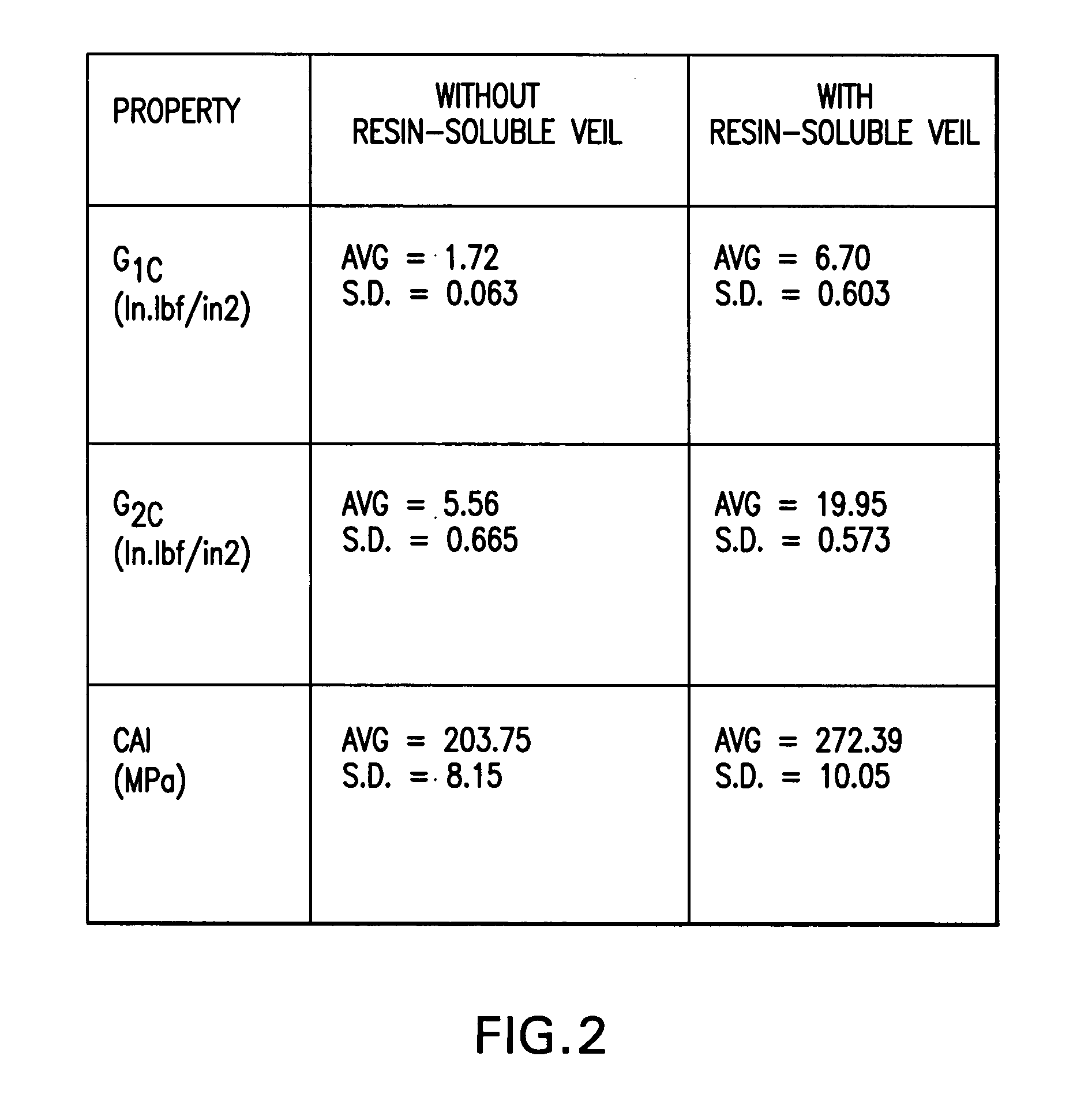
Resin-soluble thermoplastic veil for composite materials
ActiveUS20060252334A1Improve the level ofImprove toughnessWood working apparatusVehicle componentsFiberResin matrix
A resin-soluble thermoplastic polymer veil toughening element for a curable composition wherein the polymer element is a non-woven veil in solid phase adapted to undergo at least partial phase transition to fluid phase on contact with a component of the curable resin matrix composition in which it is soluble at a temperature which is less than the temperature for substantial onset of gelling and / or curing of the curable composition and which temperature is less than the polymer elements melt temperature; a method for the preparation thereof, a preform support structure for a curable composition comprising the at least one thermoplastic veil element together with structural reinforcement fibers, methods for preparation thereof, a curable composition comprising the at least one thermoplastic veil element or the support structure and a curable resin matrix composition, a method for preparation and curing thereof, and a cured composite or resin body obtained thereby, and known and novel uses thereof.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Structured material substrates for flexible, stretchable electronics
ActiveUS20100330338A1Reduce strainCircuit bendability/stretchabilityLayered productsStretchable electronicsPatterned substrate
A flexible and stretchable patterned substrate is provided having a strain-permitting material comprising a patterned conformation that allows the flexible patterned substrate to experience local strain or local strain domains lower than the macroscopic strain of the flexible and stretchable patterned substrate.
Owner:INFINITE CORRIDOR TECH
Polyethylene oxide-based films and drug delivery systems made therefrom
The invention relates to the film products and methods of their preparation that demonstrate a non-self-aggregating uniform heterogeneity. Desirably, the films disintegrate in water and may be formed by a controlled drying process, or other process that maintains the required uniformity of the film. The films contain a polymer component, which includes polyethylene oxide optionally blended with hydrophilic cellulosic polymers. Desirably, the films also contain a pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent with no more than a 10% variance of the active agent pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent per unit area of the film.
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com