Patents
Literature
1128 results about "Wood fibre" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wood fibres (also spelled wood fibers, see spelling differences) are usually cellulosic elements that are extracted from trees and used to make materials including paper. The end paper product (paper, paperboard, tissue, cardboard, etc.) dictates the species, or species blend, that is best suited to provide the desirable sheet characteristics, and also dictates the required fibre processing (chemical treatment, heat treatment, mechanical "brushing" or refining, etc.).
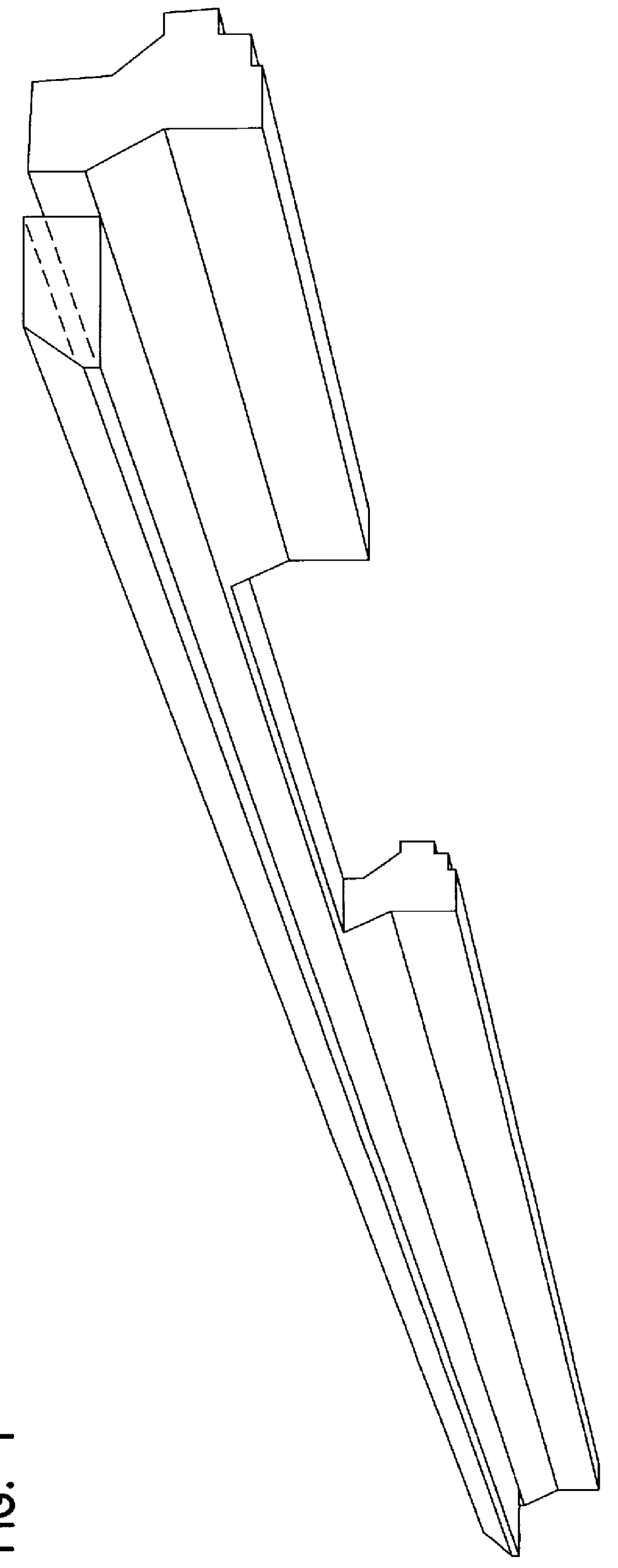
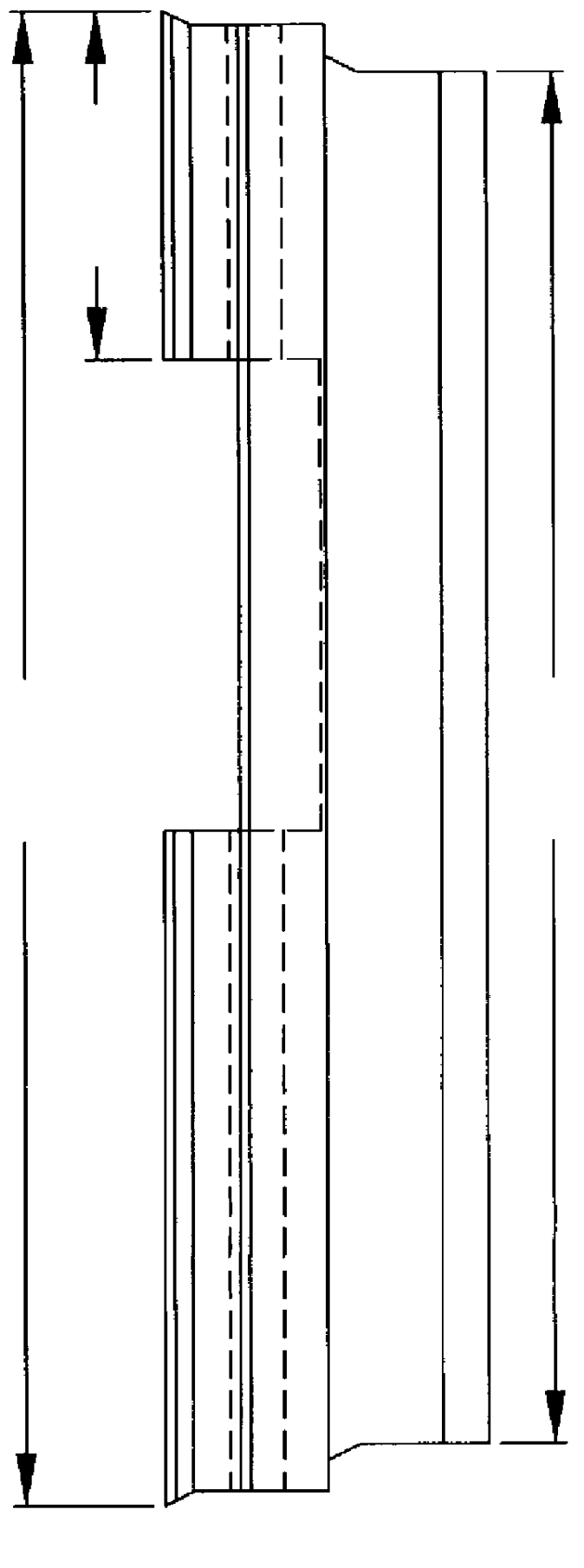
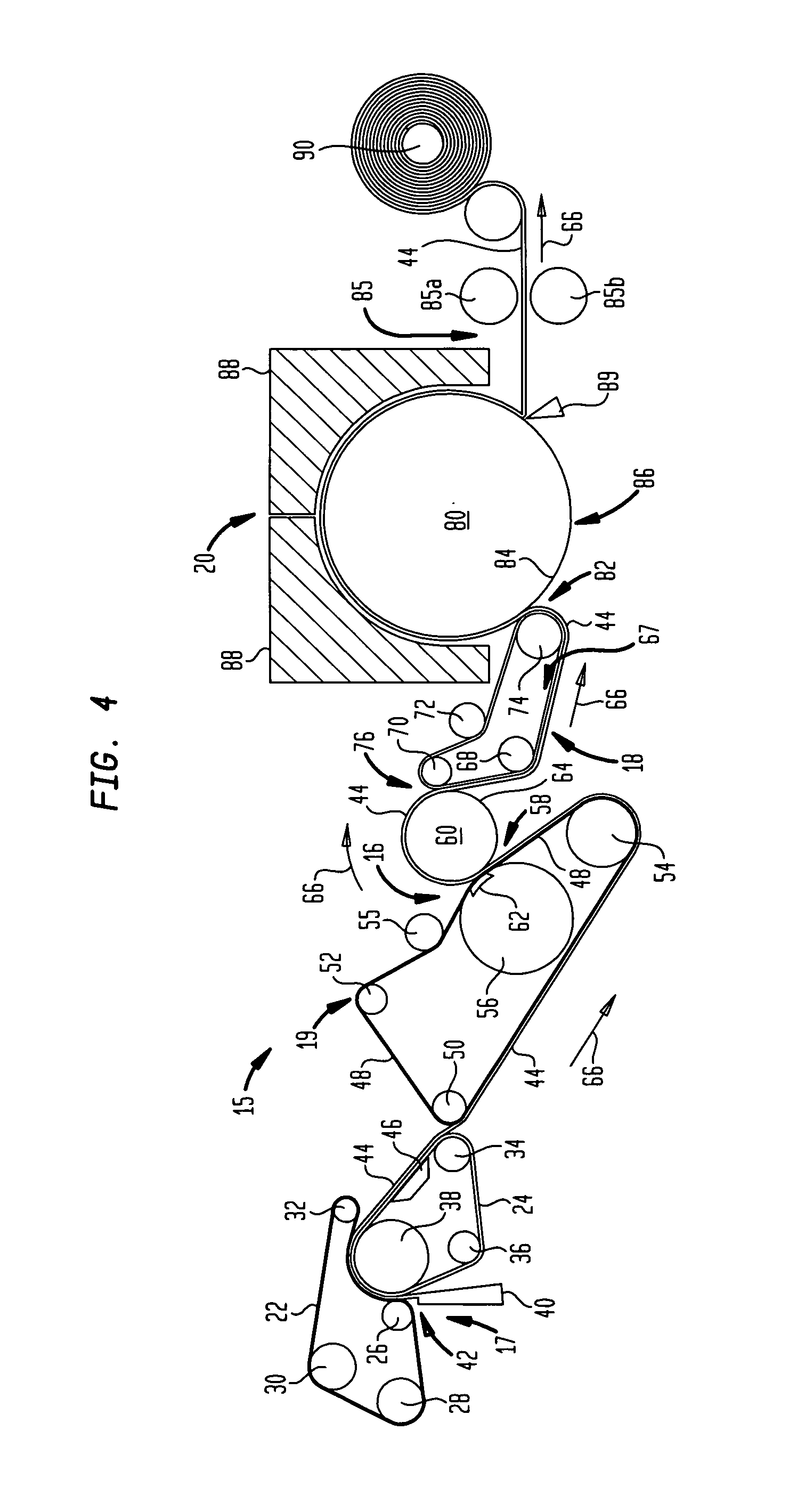
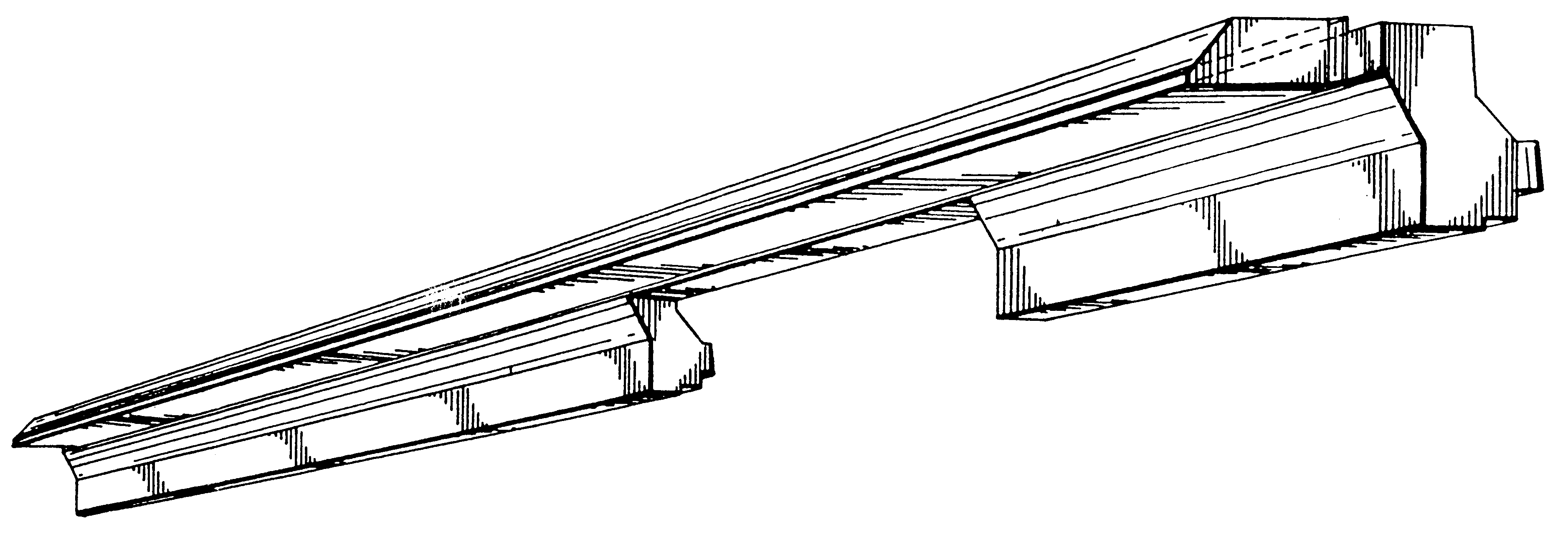
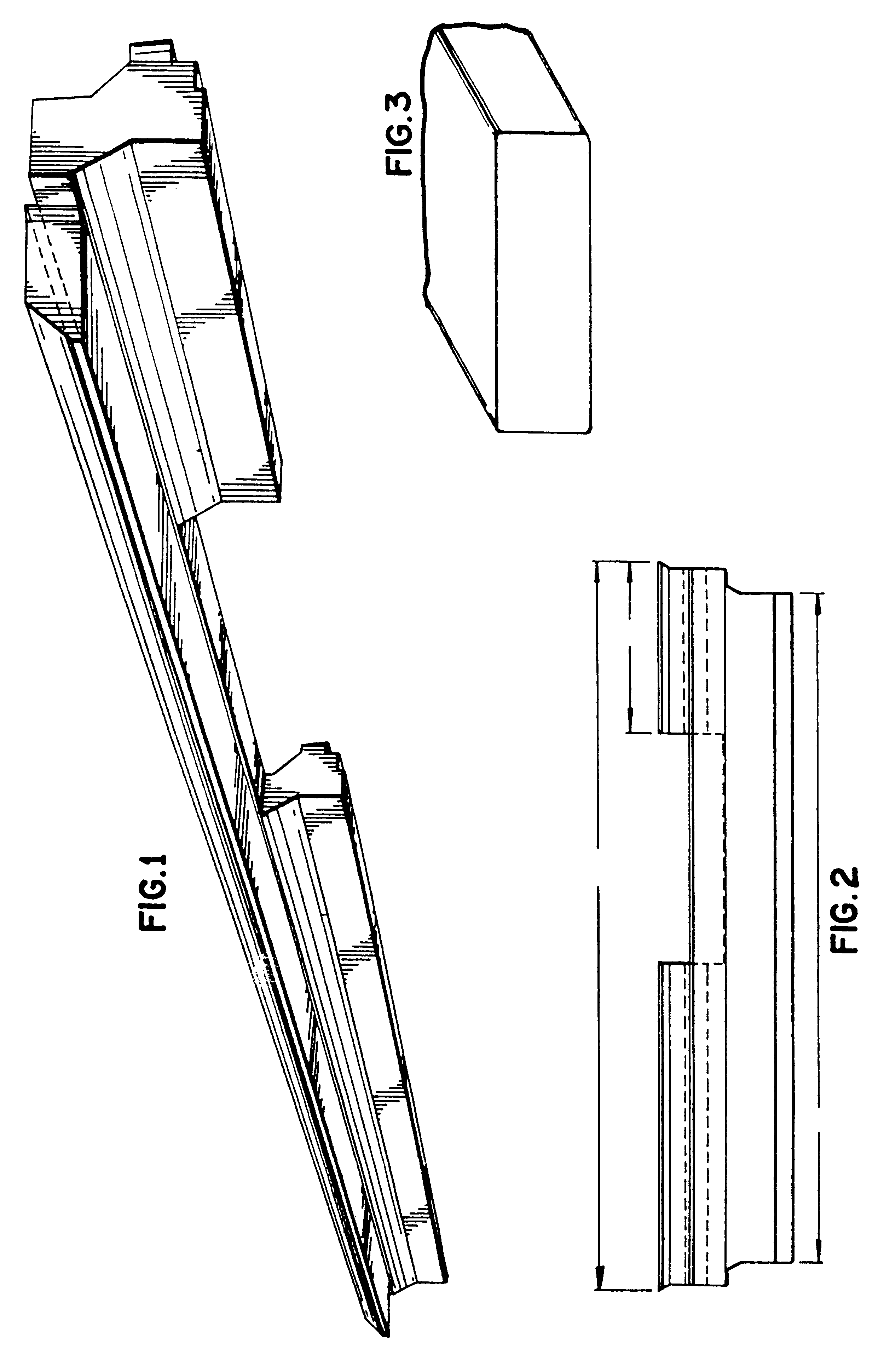
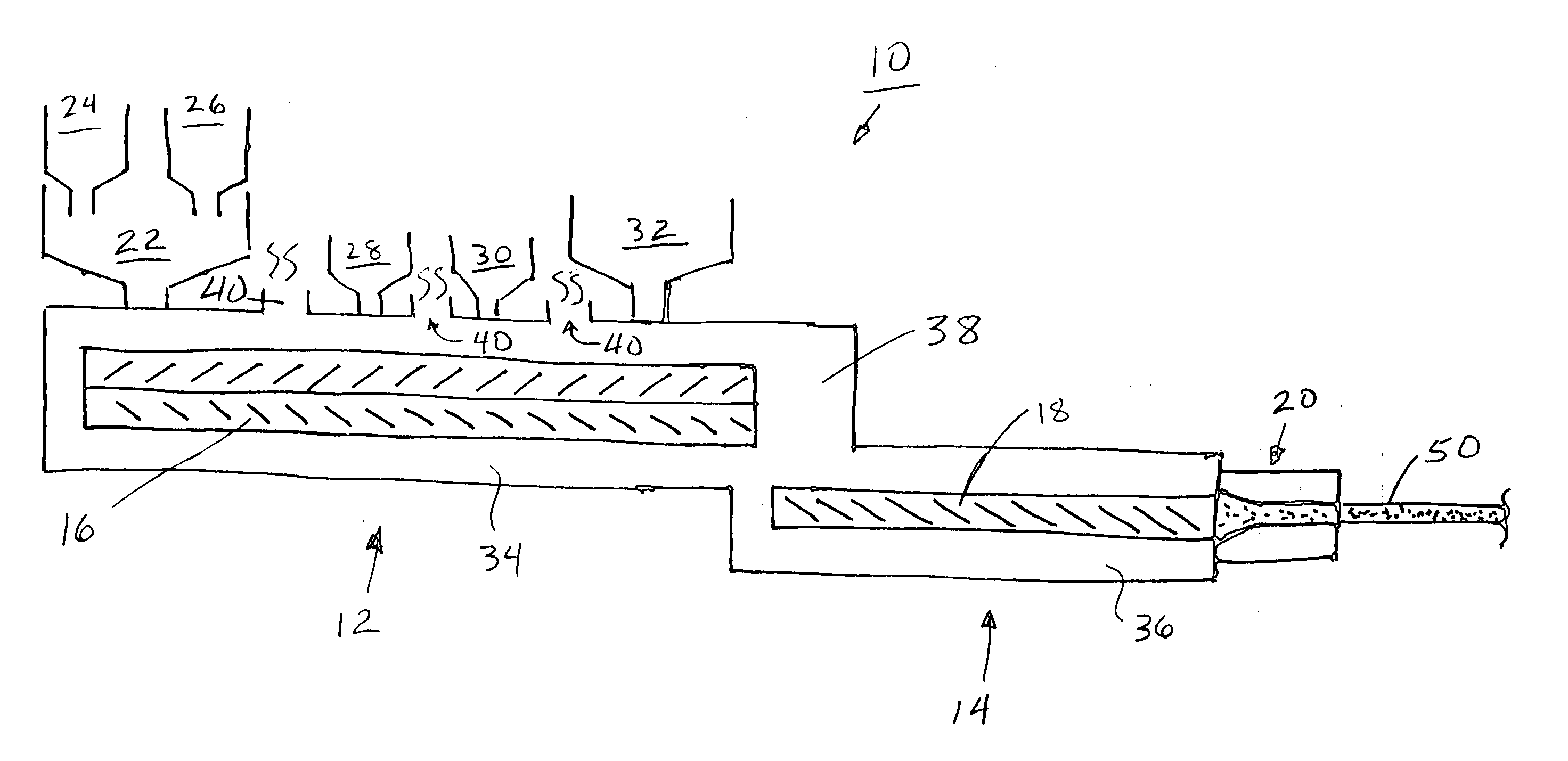
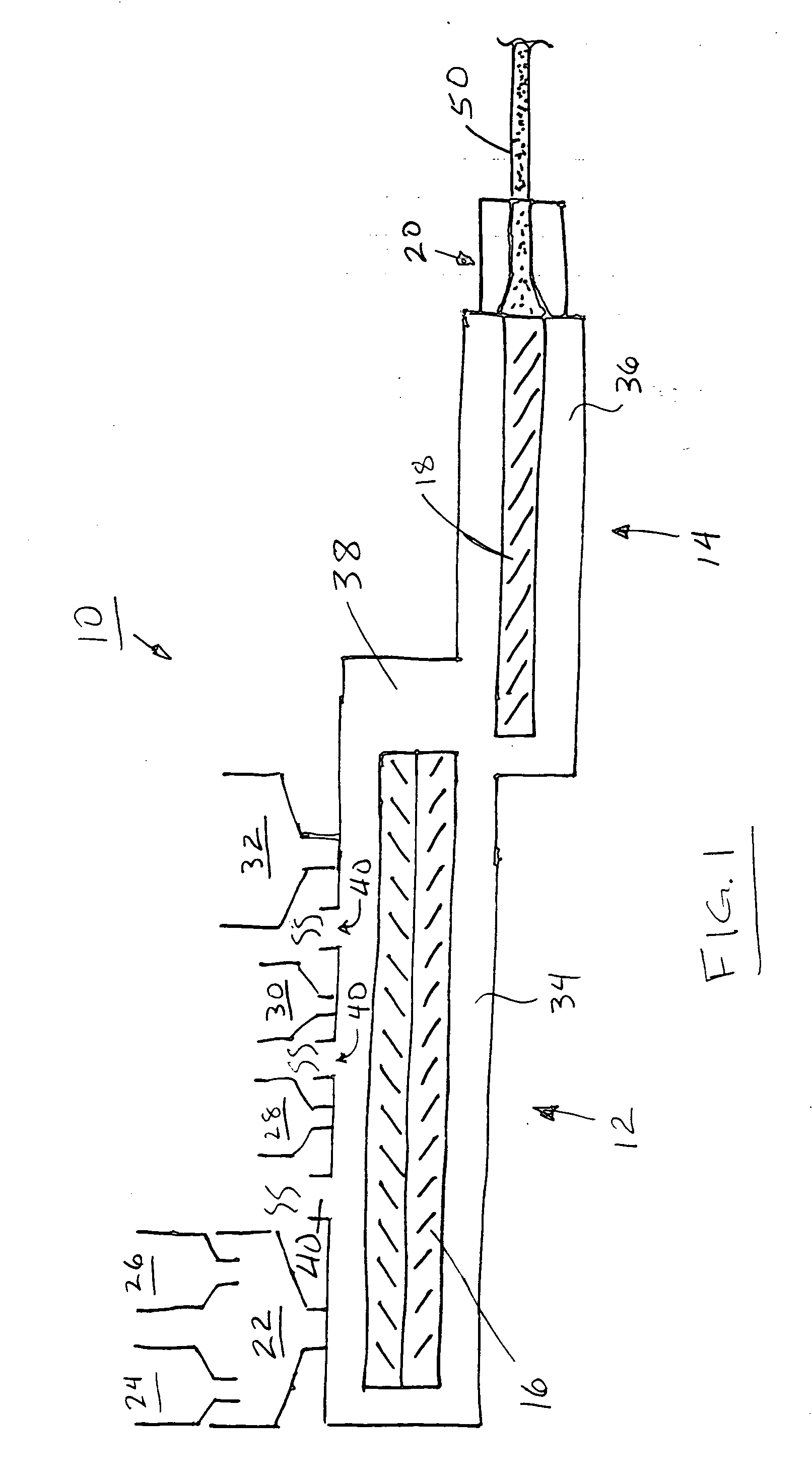
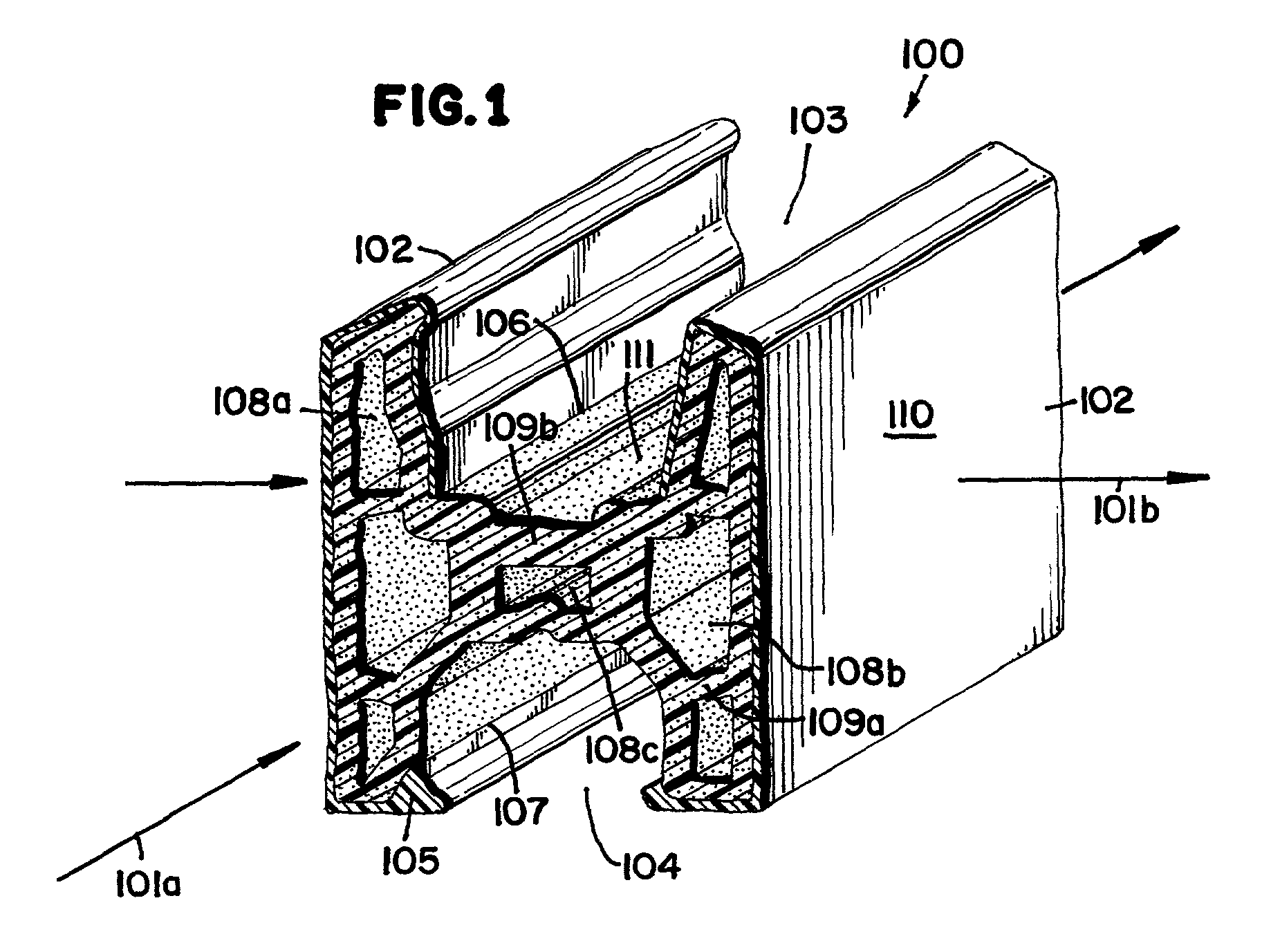
Foamed thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber profile and member
InactiveUS6054207AHigh compressive strengthImproved fastener retentionConstruction materialLoad-supporting elementsComposite constructionThermoplastic
Advanced structural components comprising a foamed thermoplastic that can be used in virtually any application where wooden components have a use. Such structural components can comprise sized lumber, shaped trim, posts, beams or shaped structural members. An advanced profile composite structural component comprising an exterior capping layer with an interior comprising a foamed thermoplastic can be used in the assembly of fenestration units adapted to residential and commercial structures. Preferably the profile structural component can be used in a window or door assembly. The profile member is adapted for ease of construction of the fenestration units, can be easily installed in a rough opening to framing members, and can be trimmed and adjusted on site. The profile is structurally strong, thermally stable, shrink resistant and will accept and retain the insertion of fasteners such as staples, nails and screws permanently with substantial retention and little or no damage to the units. The profile structural components possess strength that permits the manufacture of a structurally sound fenestration unit from two or more foamed profile members or other conventional members.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
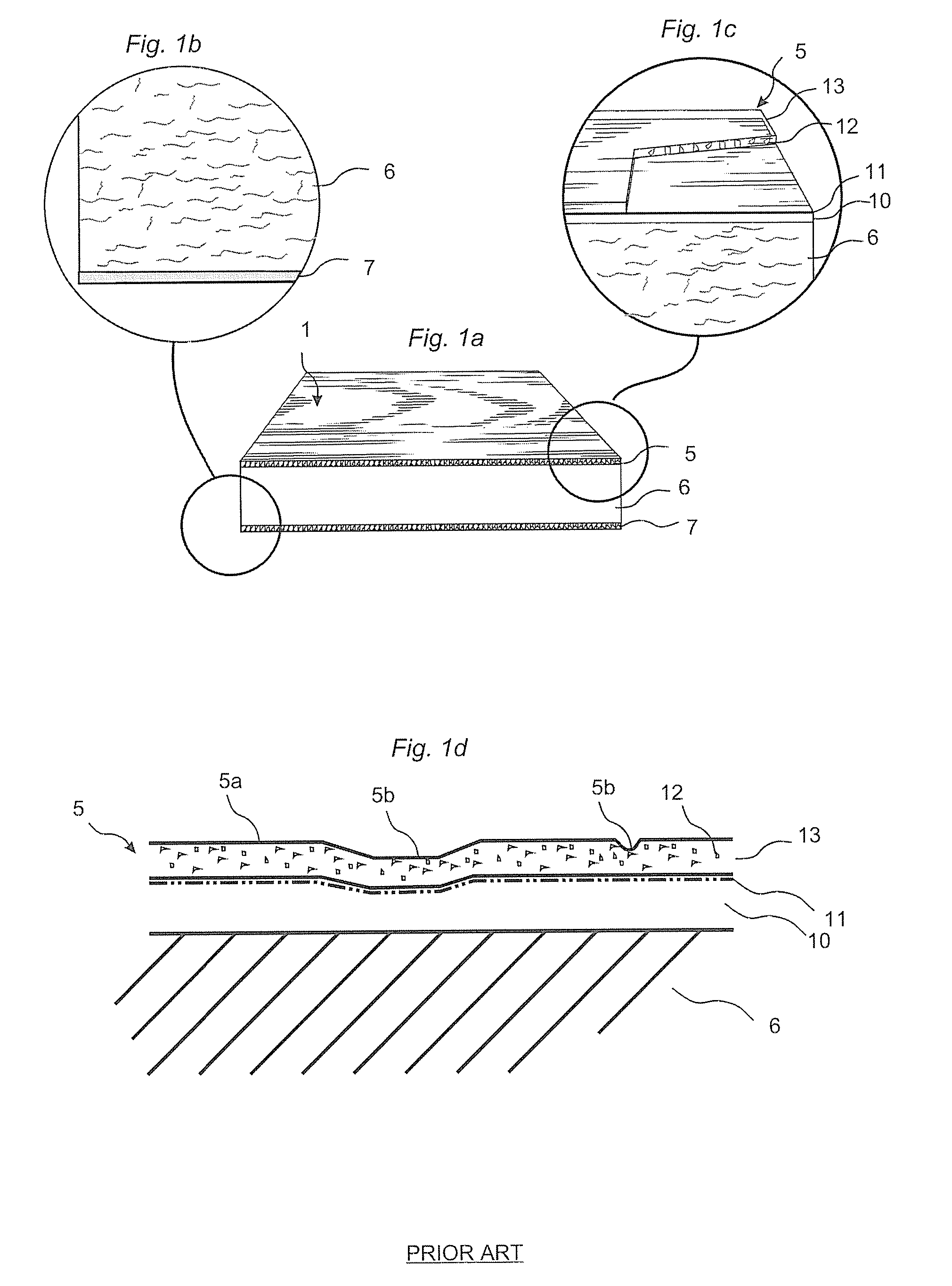
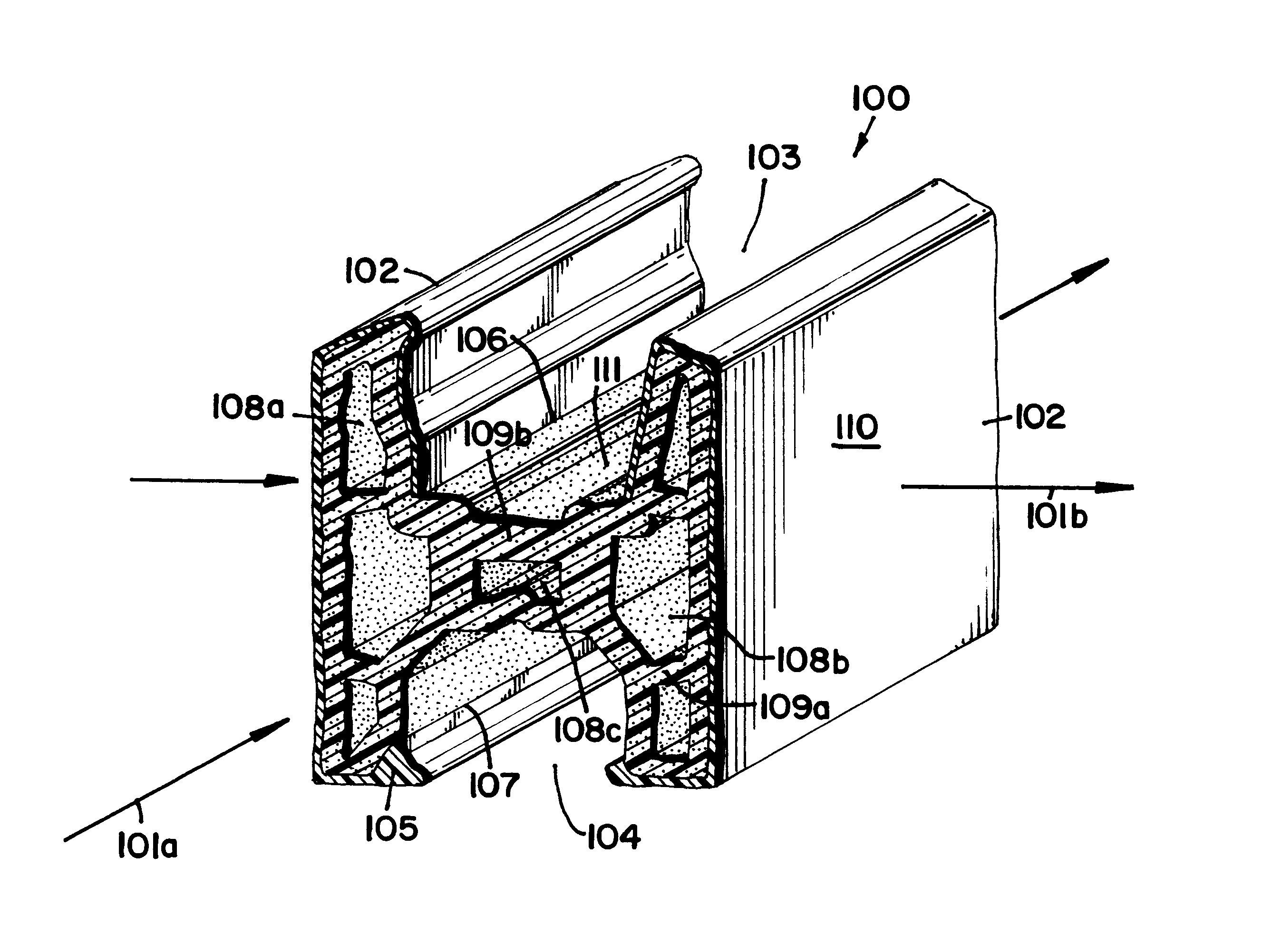
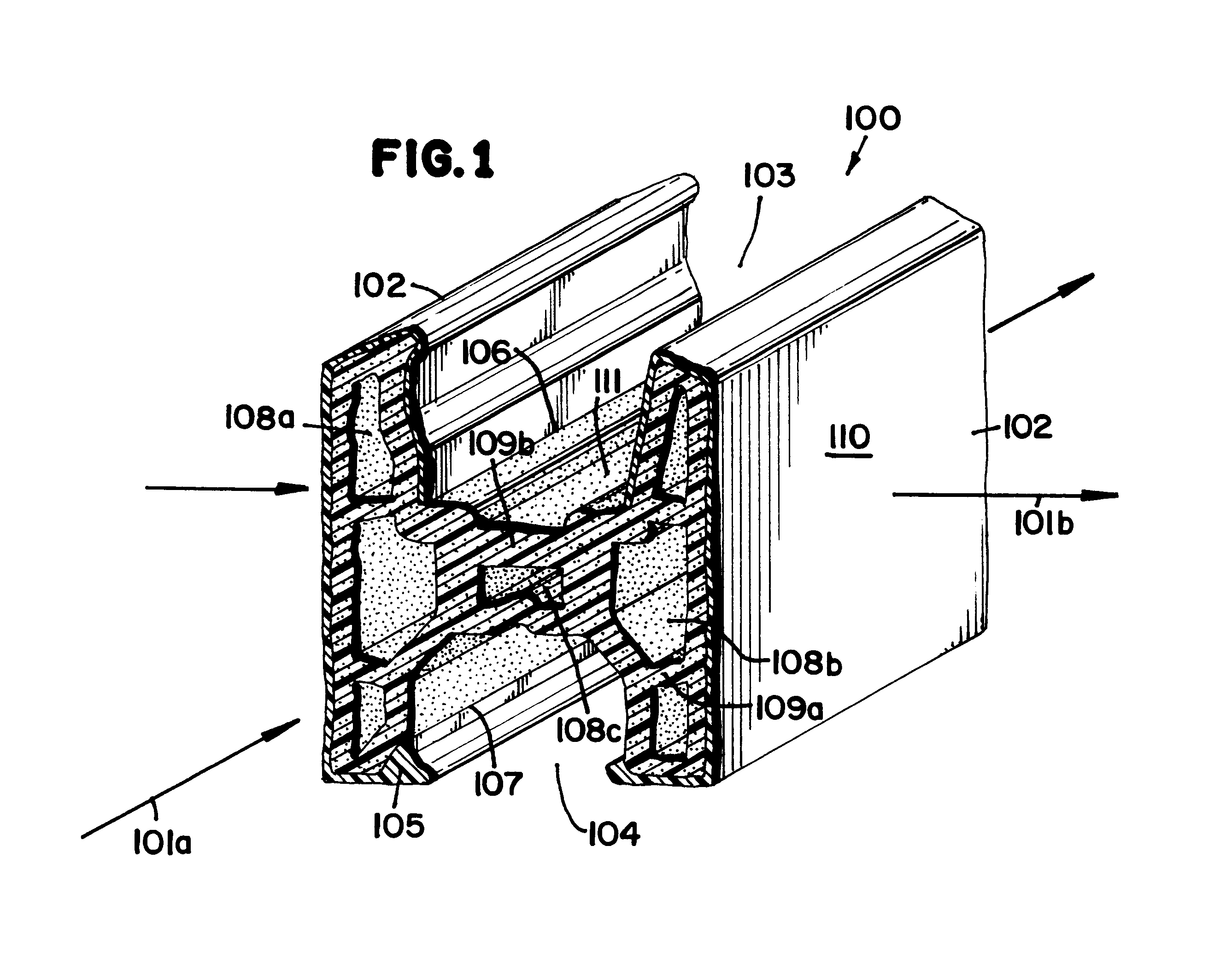
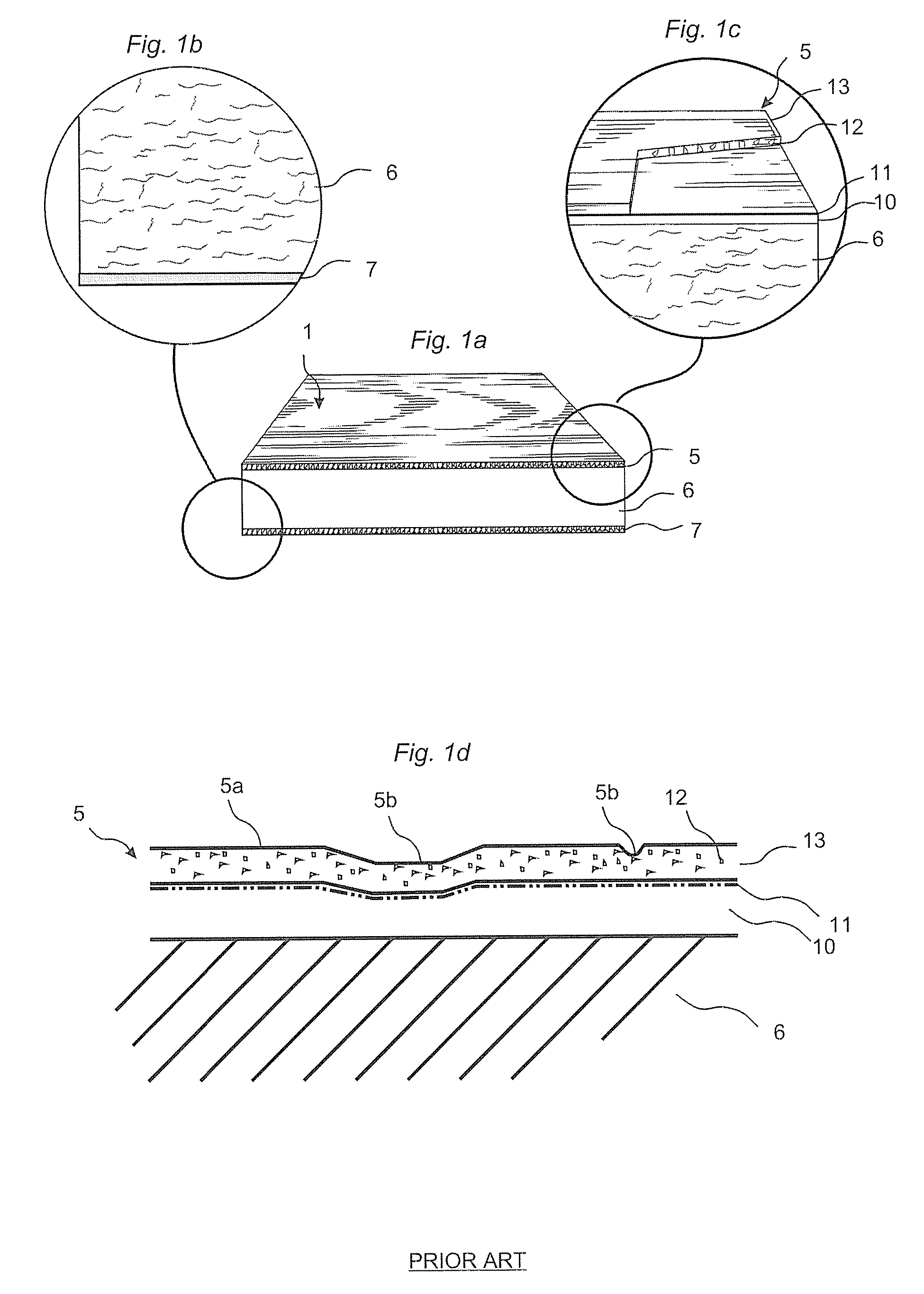
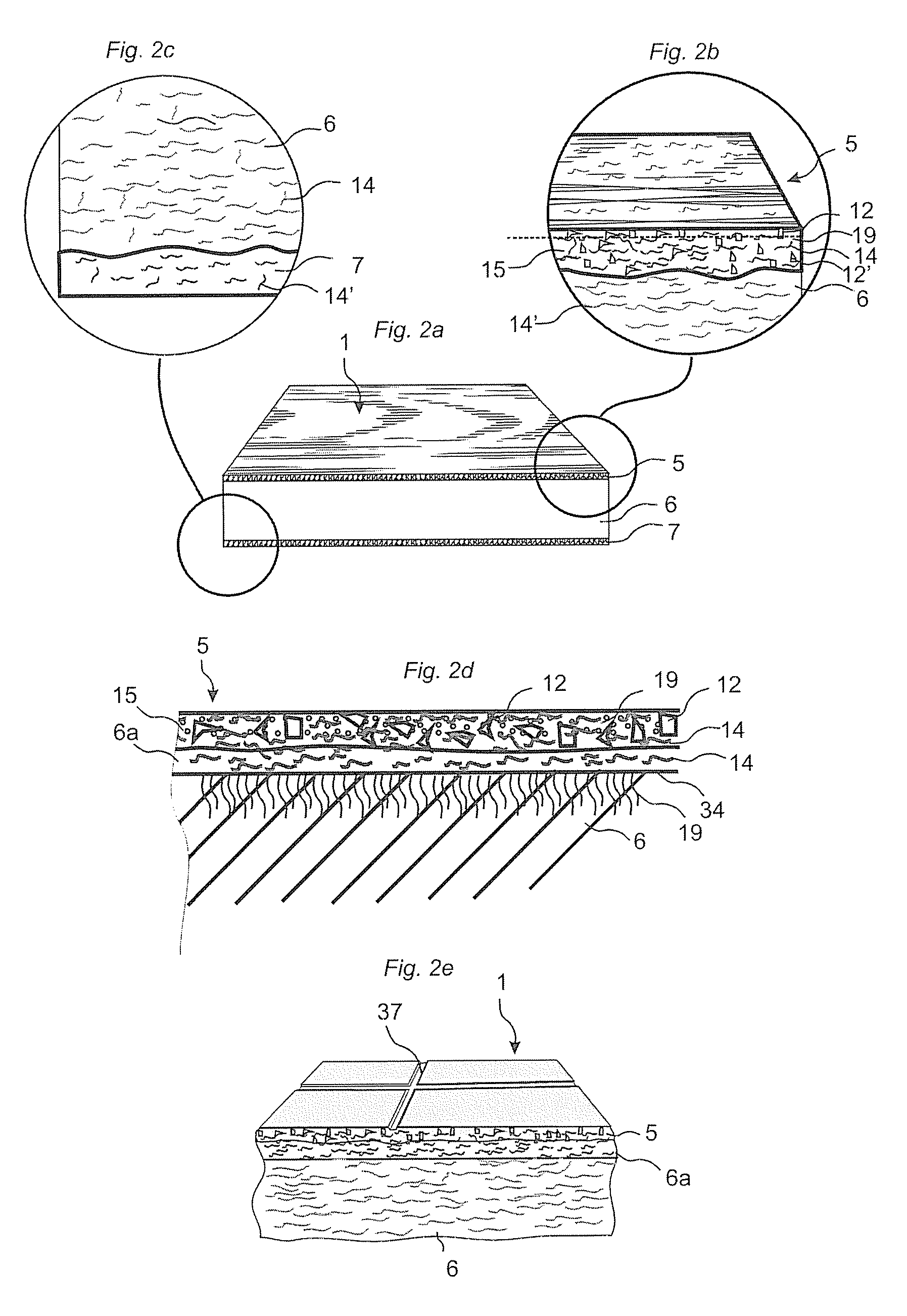
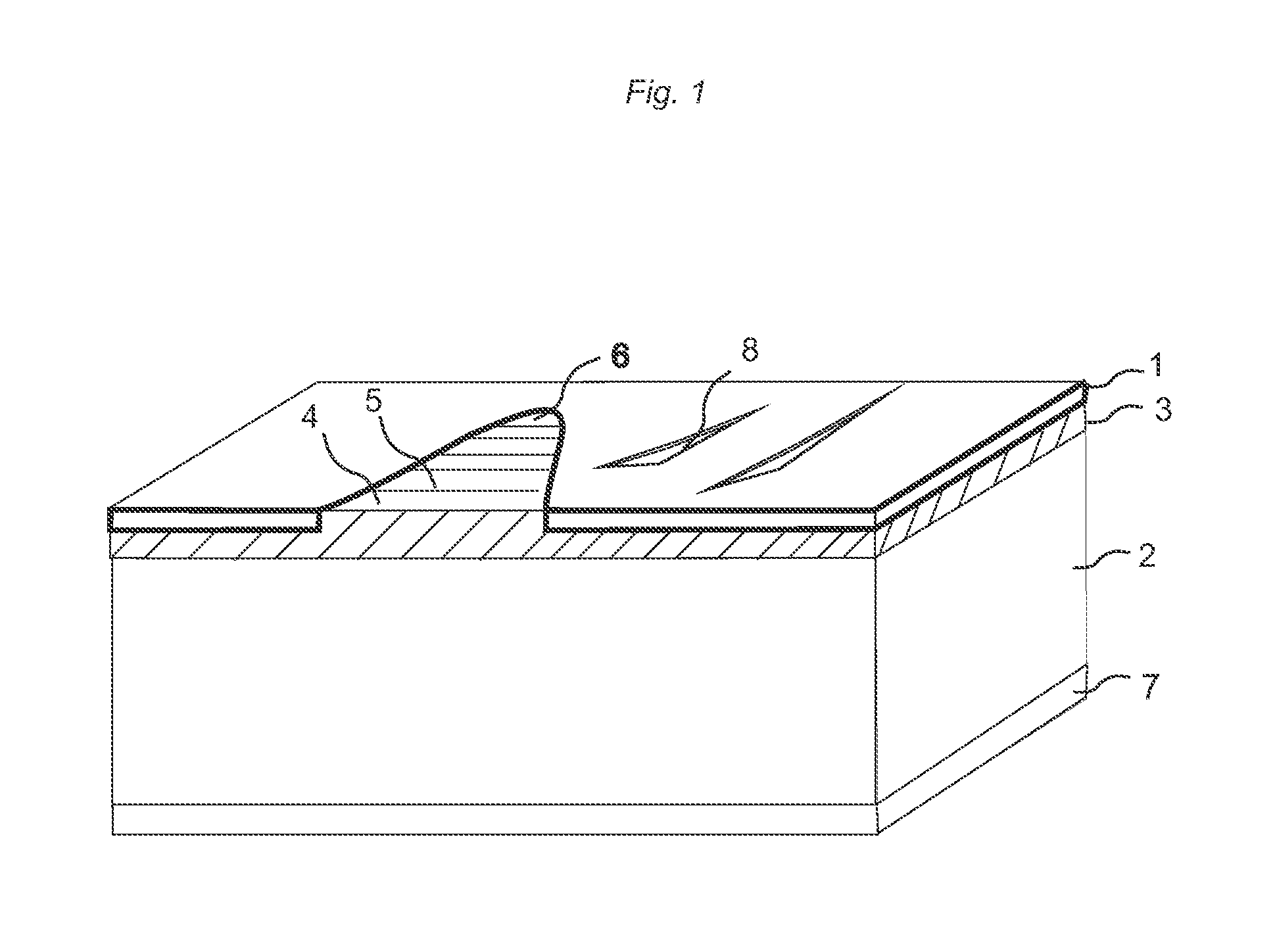
Wood fibre based panels with a thin surface layer
ActiveUS20100092731A1Large market shareImprove impact resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsCovering/liningsSurface layerWood fibre
Building panels with a thin and embossed surface layer and a sub layer between a surface layer and a core.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Polymer wood composite
InactiveUS6015612AHigh modulusHigh compressive strengthWood working apparatusRecord information storageFiberThermoplastic
The invention relates to a composition comprising a polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer and wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
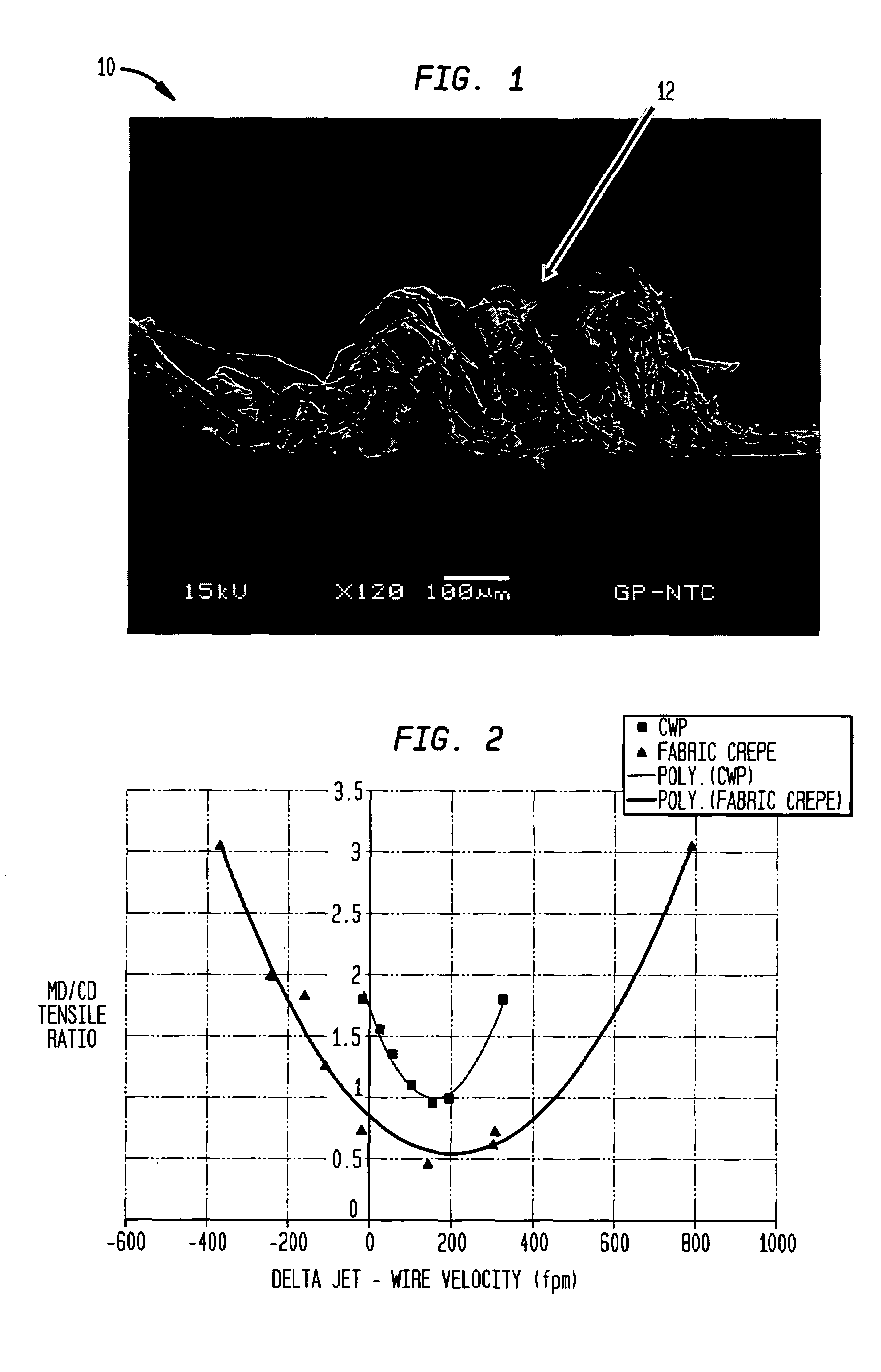
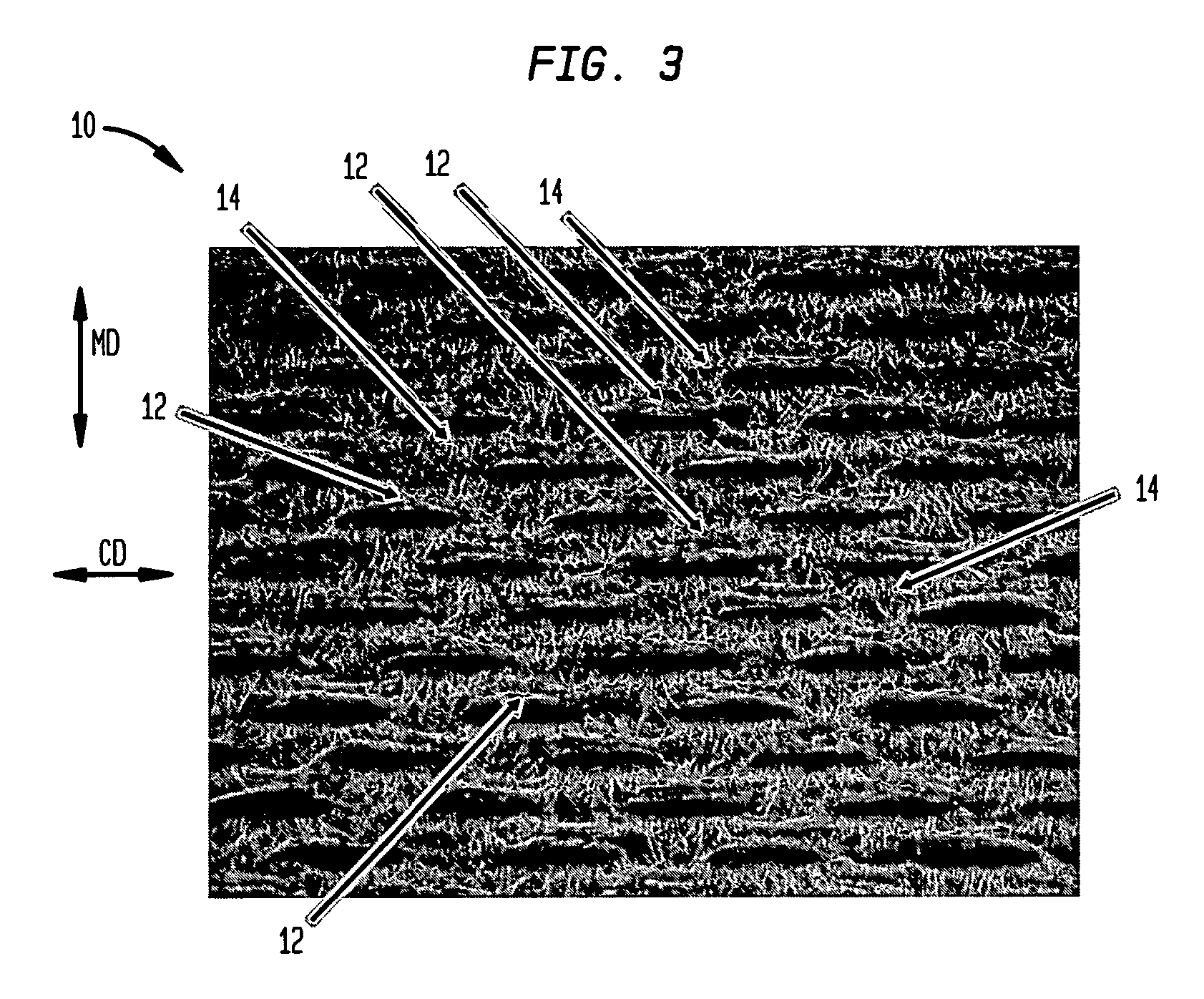
Wet-pressed tissue and towel products with elevated CD stretch and low tensile ratios made with a high solids fabric crepe process
An absorbent sheet of cellulosic fibers includes a mixture of hardwood fibers and softwood fibers arranged in a reticulum having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking regions whose fiber orientation is biased along the machine direction between pileated regions interconnected thereby, wherein the sheet exhibits a % CD stretch which is at least about 2.75 times the dry tensile ratio of the sheet. Tensile ratios of from about 0.4 to about 4 are readily achieved.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Advanced compatible polymer wood fiber composite
InactiveUS6210792B1Improve compatibilityGood material compatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsThermoplasticFiber
The invention relates to a composition comprising a thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer, the fiber or both can be modified to increase compatibility. The wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Polyolefin wood fiber composite
InactiveUS6265037B1Improve mechanical propertiesImproved chemicalConstruction materialCovering/liningsPolyolefinEngineering
An improved composite structural member comprising a complex profile structural member, made of a composite comprising a polypropylene polymer and a wood fiber. The material is useful in conventional construction applications. The complex profile, in the form of an extruded thermoplastic composite member can be used in residential and commercial structures as described. Preferably, the structural member is used in the manufacture of the fenestration components such as windows and doors. Such linear members are designed with specifically configured cross-sectional shapes to form structural elements in the fenestration units. Structural elements must possess sufficient strength, thermal stability and weatherability to permit the manufacture of a structurally sound window unit that can be easily installed into a rough opening but can maintain its attractive appearance and structural integrity over the life of the window unit often twenty years or more. The structural member comprises a hollow complex cross-section with at least one structural web or one fastener web formed within the component. The exterior of the extruded component has a visible capstock layer and is shaped and adapted for installation in rough openings. The exterior also contains shape and components capable of supporting the elements of the fenestration unit such as a window, sash or movable door unit. The improved polypropylene structural members have unique advantages and can be assembled in thermoplastic weld processes.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Advanced polymer wood composite
InactiveUS6015611AHigh modulusHigh compressive strengthSynthetic resin layered productsPlastic recyclingWater basedThermoplastic
A composition in the form of pellets comprising a thermoplastic and wood fiber composite material suitable for forming structural members as a replacement for wood in the manufacture of doors and windows. The composite has less than about 10 wt % water based on pellet weight and a Young's modulus of at least about 500,000. Structural members are typically formed from the composite in an extrusion or an injection molding process.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
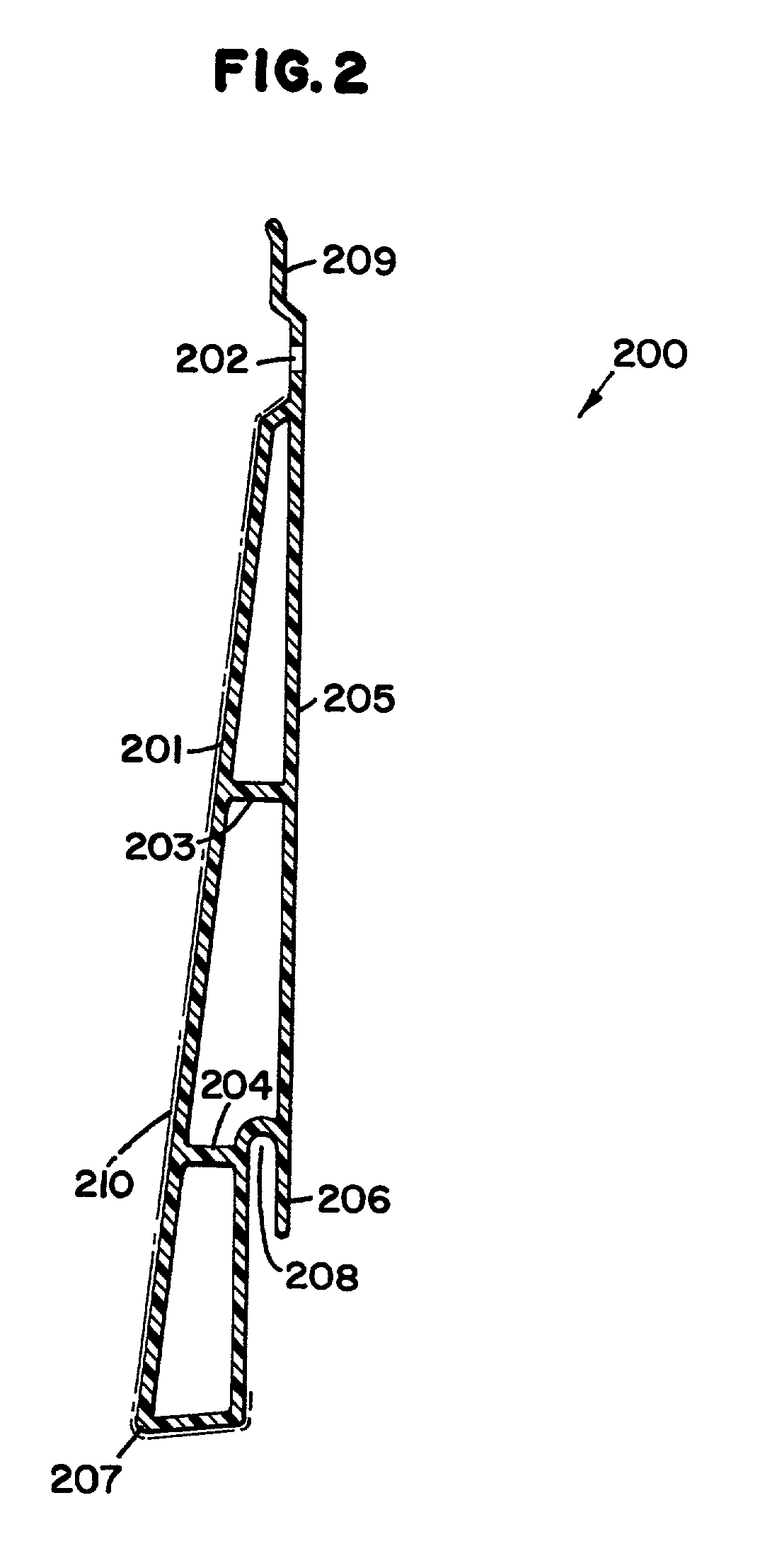
Method of forming a foamed thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber profile and member
InactiveUS6342172B1Improved thermal and physical propertyImprove performanceSemi-permeable membranesLaminationComposite constructionThermoplastic
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Wood fibre based panels with a thin surface layer
ActiveUS8419877B2Larger market shareImprove impact resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsCovering/liningsSurface layerWood fibre
Building panels with a thin and embossed surface layer and a sub layer between a surface layer and a core.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Wooden flooring strip with enhanced flexibility and straightness
Owner:AFI LICENSING +1
Method of selecting and/or processing wood according to fibre characteristics
InactiveUS6773552B1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDigestersSolid woodWood fibre
The invention provides a method for predictively assessing one or more characteristics of wood pulp produced from solid wood. The method comprises the steps of determining the velocity of sound through the solid wood, and assessing characteristic(s) of wood fiber or wood pulp produced from the wood by reference to the velocity of sound through the solid wood. The method may also comprise the steps of causing a sound wave to be transmitted through the wood, determining the velocity of the sound wave through the wood, and comparing the result to stored information on fiber characteristic(s) versus sound velocity through the wood-type to determine the fiber characteristic(s) for the wood.
Owner:FIBER GEN INSTR
Method and installation for producing a wood-fiber board
ActiveUS20100223881A1Simple methodImprove pattern qualitySpecial ornamental structuresWood working apparatusWood fibreMaterials science
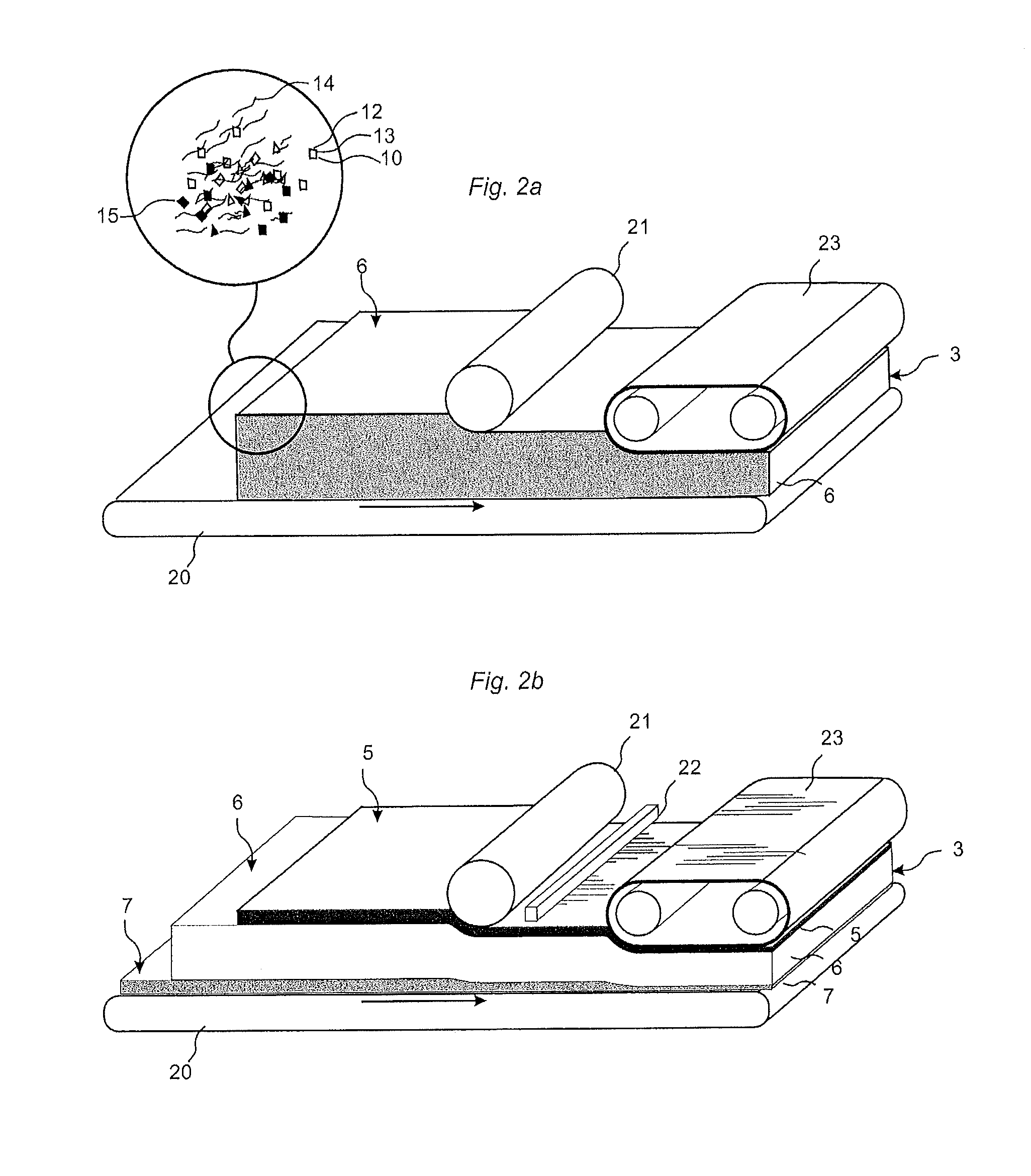
A method for producing a wood-fiber board, which has a pattern on the top, in that glued wood fibers are scattered at least one layer to form a fiber cake, and the fiber cake is subsequently compressed under pressure and temperature to form a board of the desired thickness, is characterized in that the pattern is applied to the fiber cake before compression. An installation for producing a wood-fiber board with a scattering device, by means of which a fiber cake comprising at least one layer of wood fibers glued with resin is scattered, and a conveyor device, which conveys the fiber cake in a process direction to a pressing device in which the fiber cake is pressed to form a board of the desired thickness, is characterized in that a printing device is arranged above the conveyor device between the scattering device and the pressing device.
Owner:FLOORING TECH
Heat and pressure generated design
InactiveUS20110177319A1Increased chemicalImprove mechanical propertiesLiquid surface applicatorsConstruction materialSurface layerWood fibre
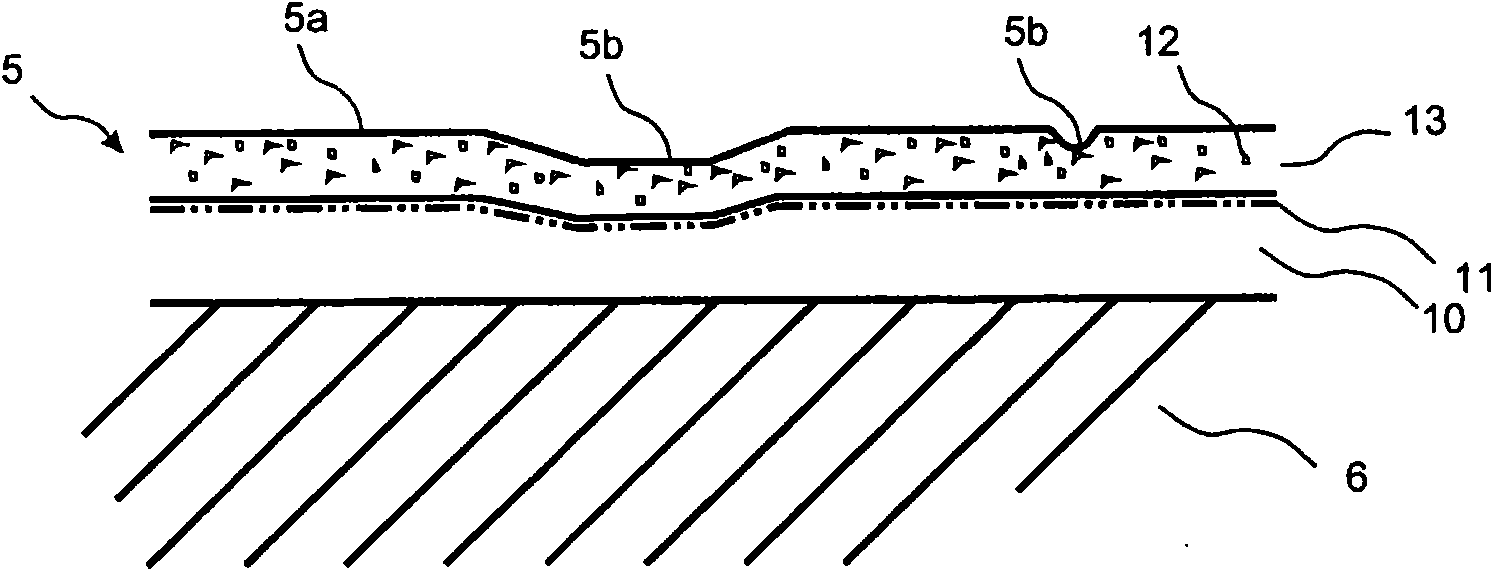
A wood fibre based panel with surfaces layer with lower parts which has less binders than the upper parts. Also, a method of manufacturing a building panel having a structured surface with a design that has colour variation in register with the structure obtained by a varying pressure distribution applied on the surface.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
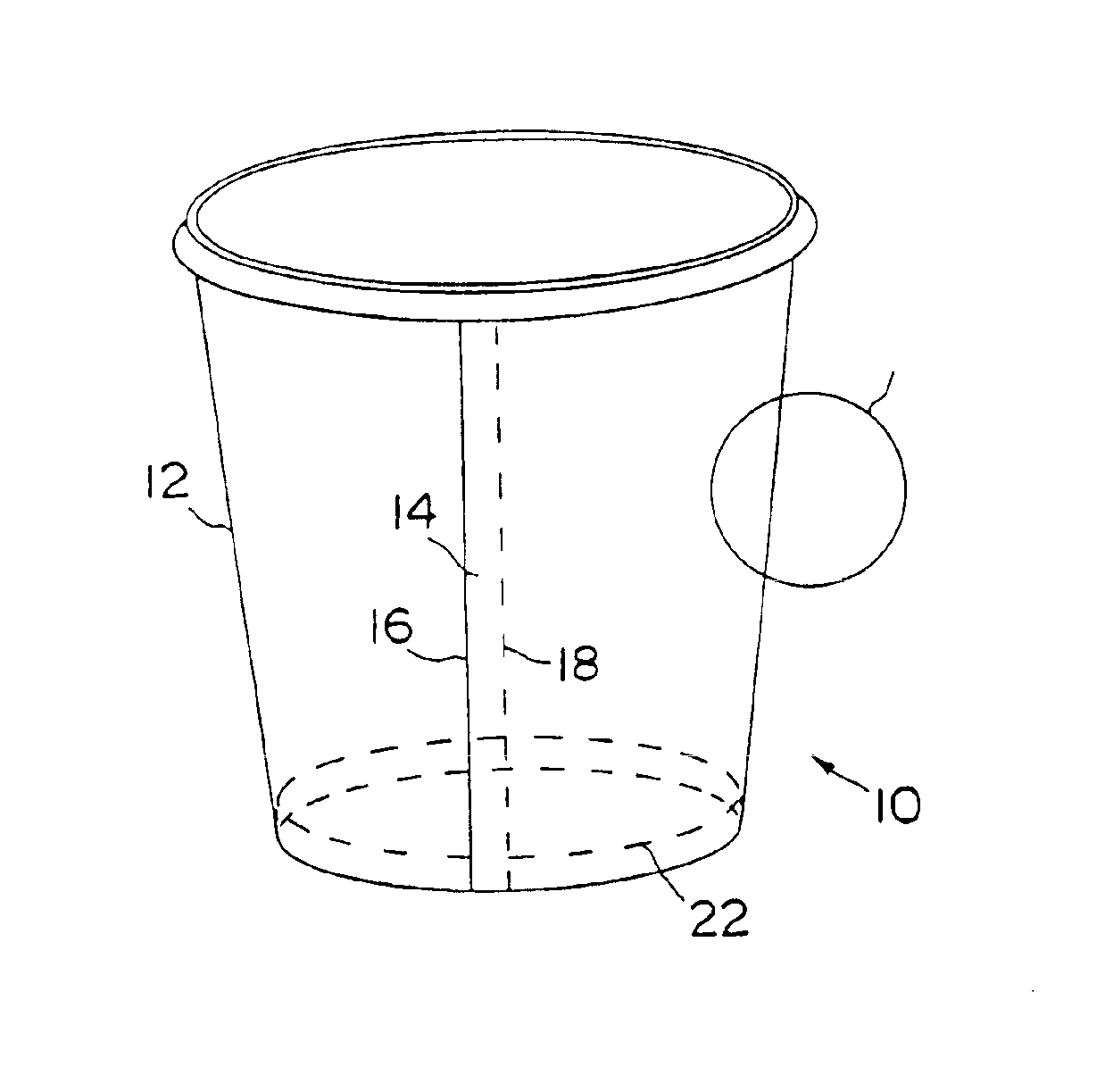
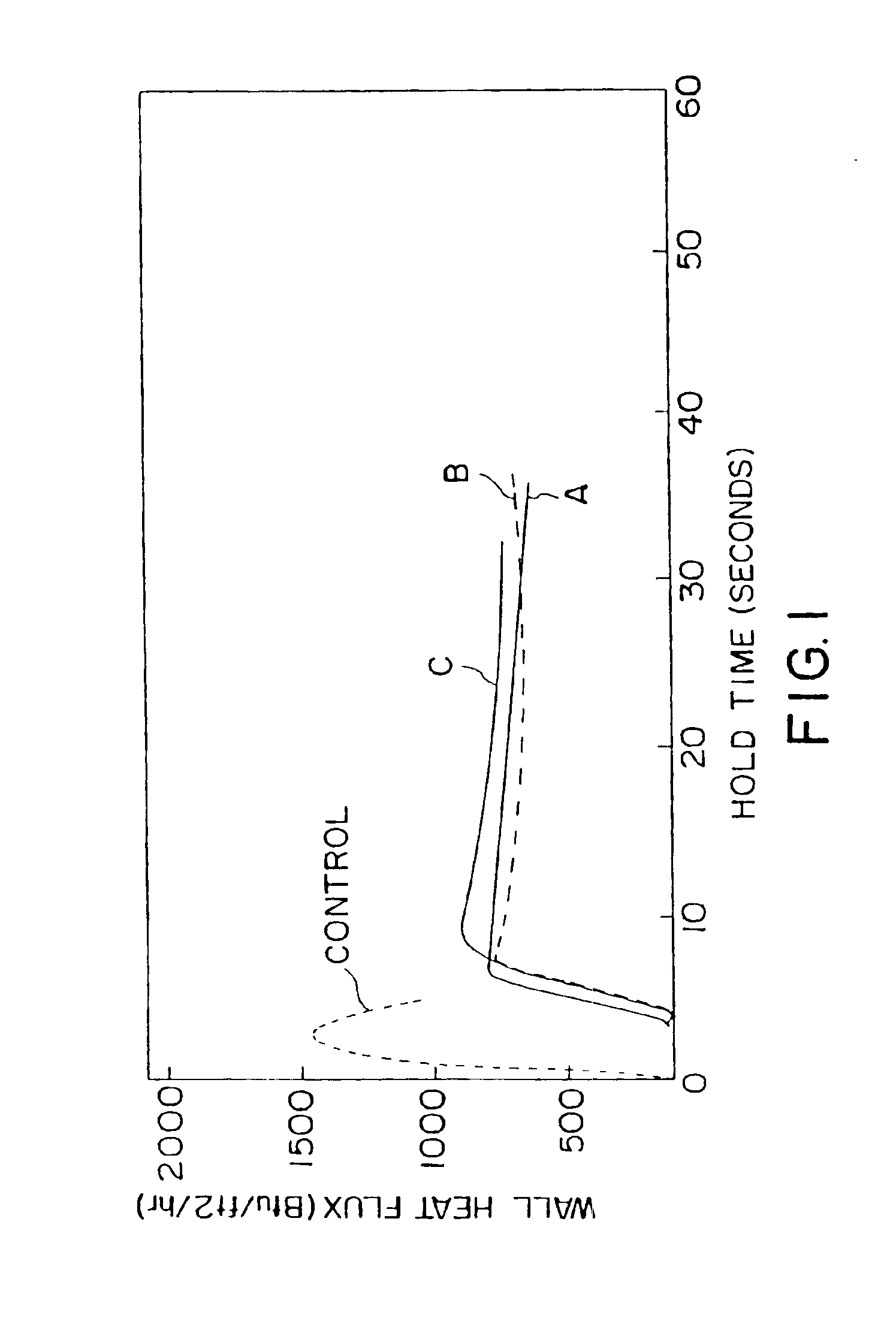
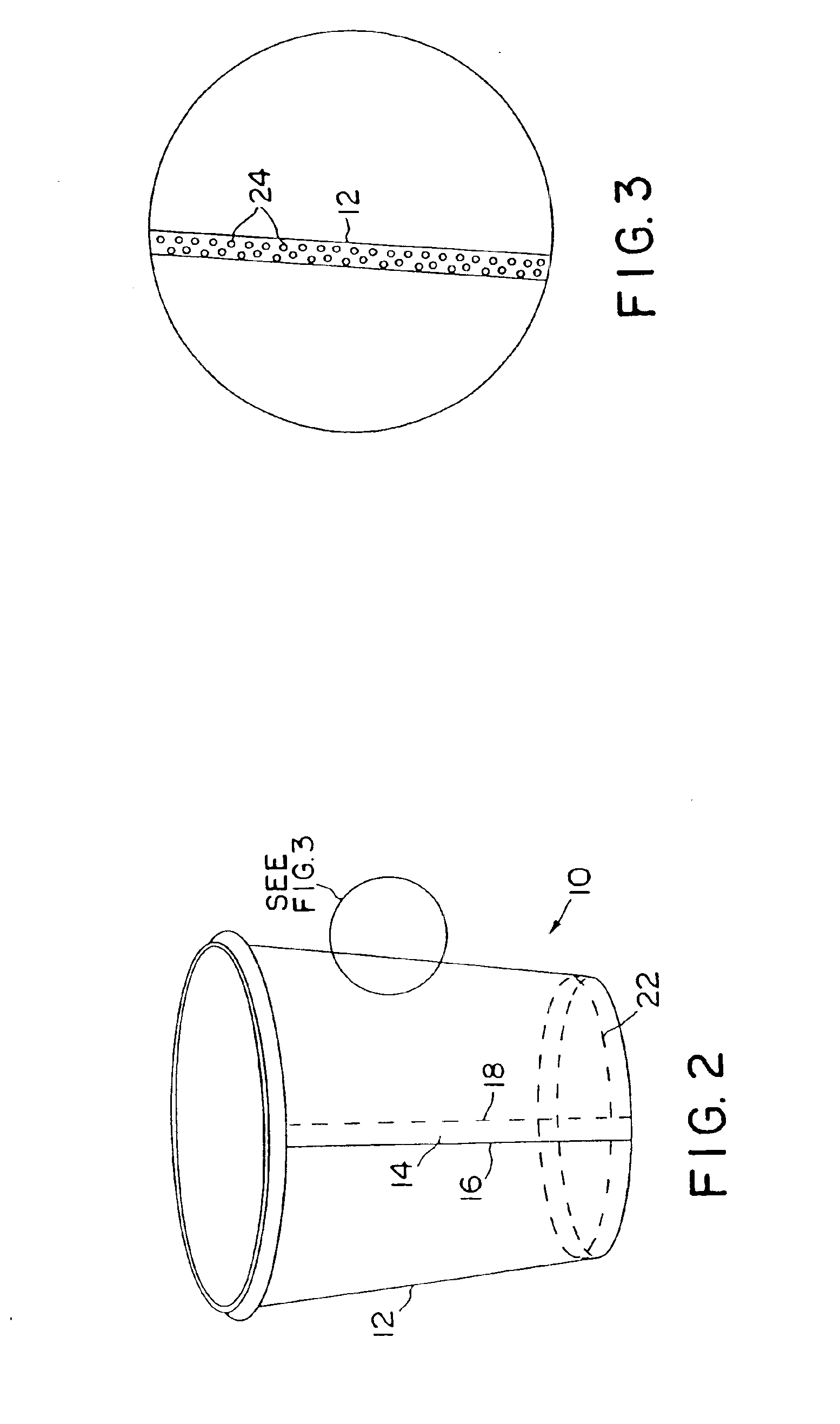
Low density paperboard articles
InactiveUS6846529B2Improve insulation performanceLess-expensive to produceNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The invention provides a low density paperboard material for use in producing an insulated container, and is especially well-suited for making cups. The paperboard material comprises a paperboard web including wood fibers and expanded microspheres, and has a relatively low density ranging from about 6 to about 10 lb / 3MSF / mil, a relatively high caliper ranging from about 24 to about 35 mil, and an internal bond strength of at least about 80×10−3 ft-lbf preferably at least 100×10−3 ft-lbf. For applications such as cups the material is also coated on one or both sides with a barrier coating, preferably low density polyethylene, to limit liquid penetration into the web. The low density paperboard material of the invention is convertible for manufacture of containers, particularly cups, and the surface of the low density board may have a Sheffield smoothness of 300 SU or greater.
Owner:GRAPHIC PACKAGING INT
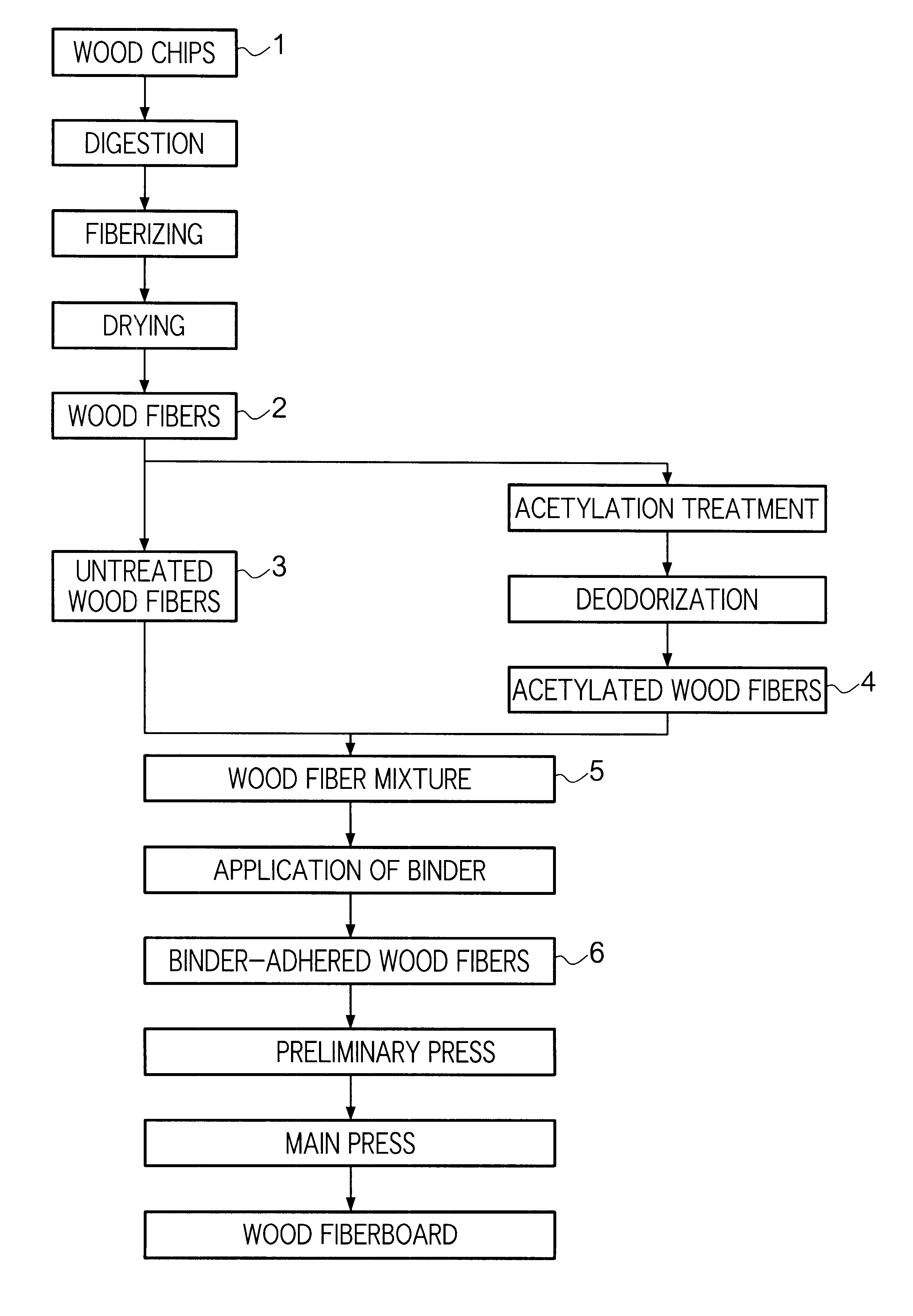
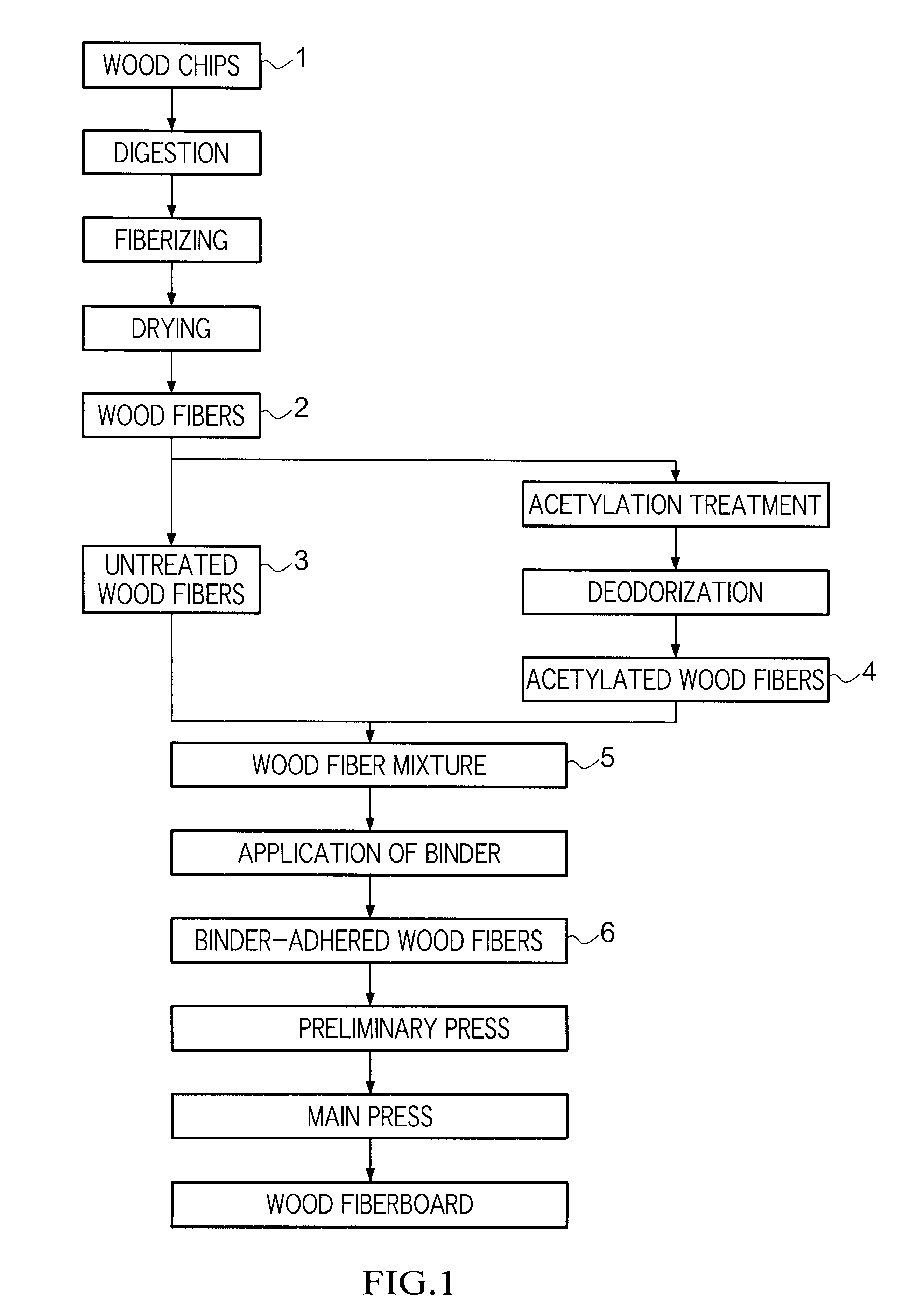
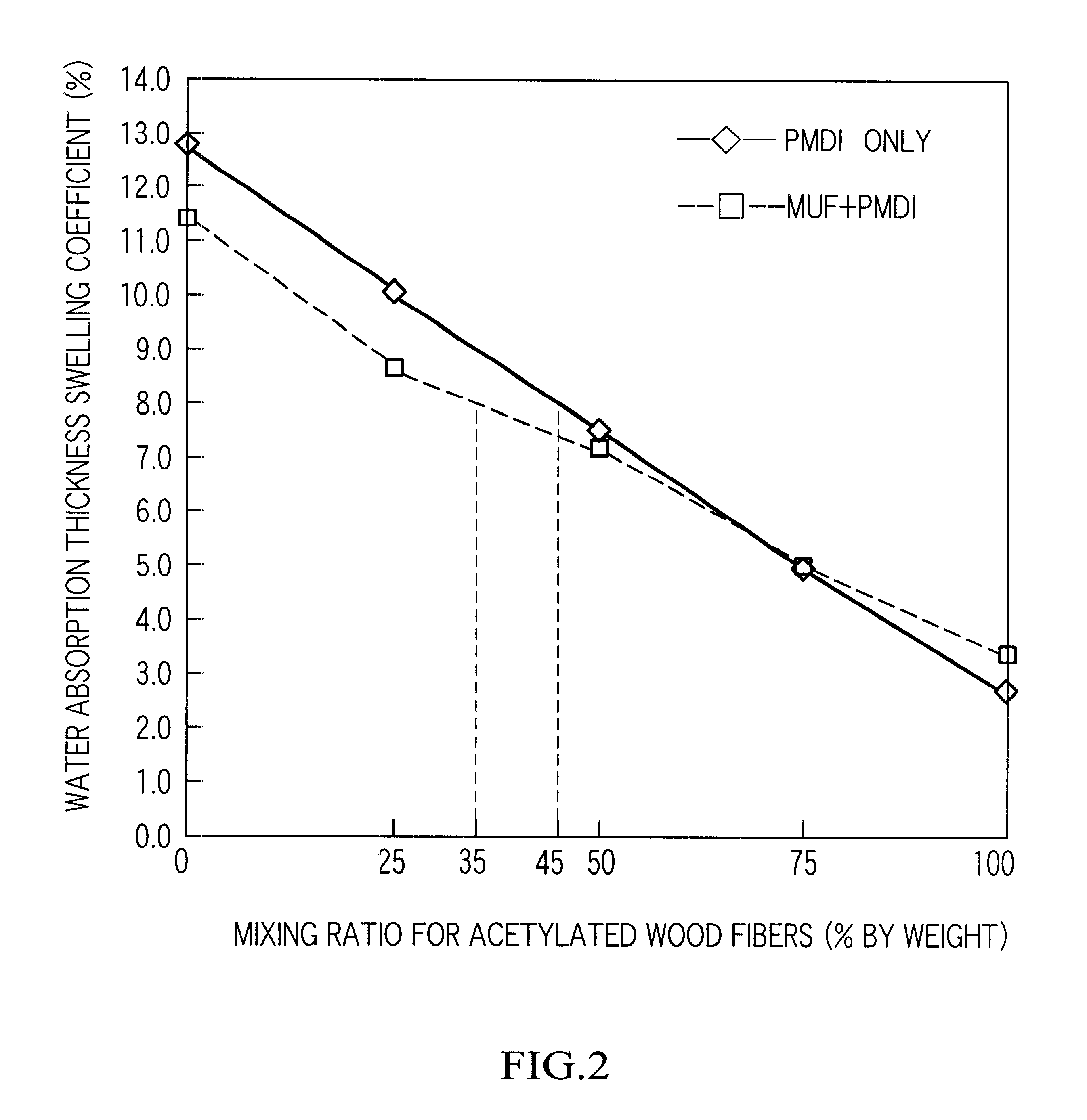
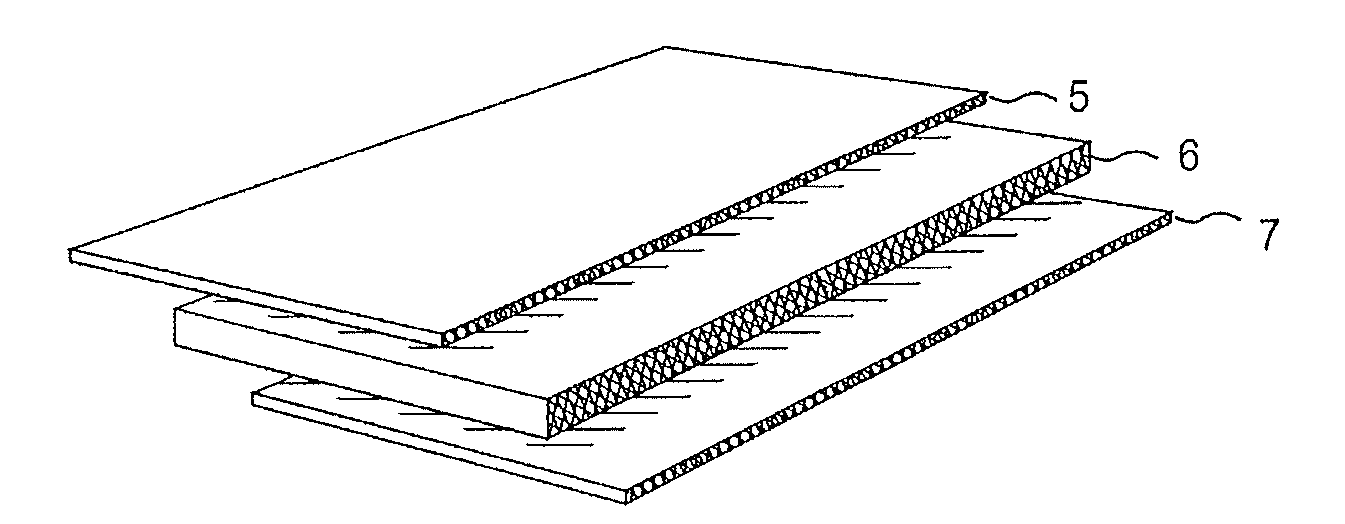
Wood fiberboard and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS6376582B1Improve balanceGood dimensional stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesPolymer scienceWood fibre
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Advanced polymer wood composite
InactiveUS20020106498A1High modulusHigh modulus of elasticityFibreboardWood working apparatusThermoplasticPolymer science
The invention relates to a composition comprising a polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer and wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprise, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of an elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Recycling of laminate floorings
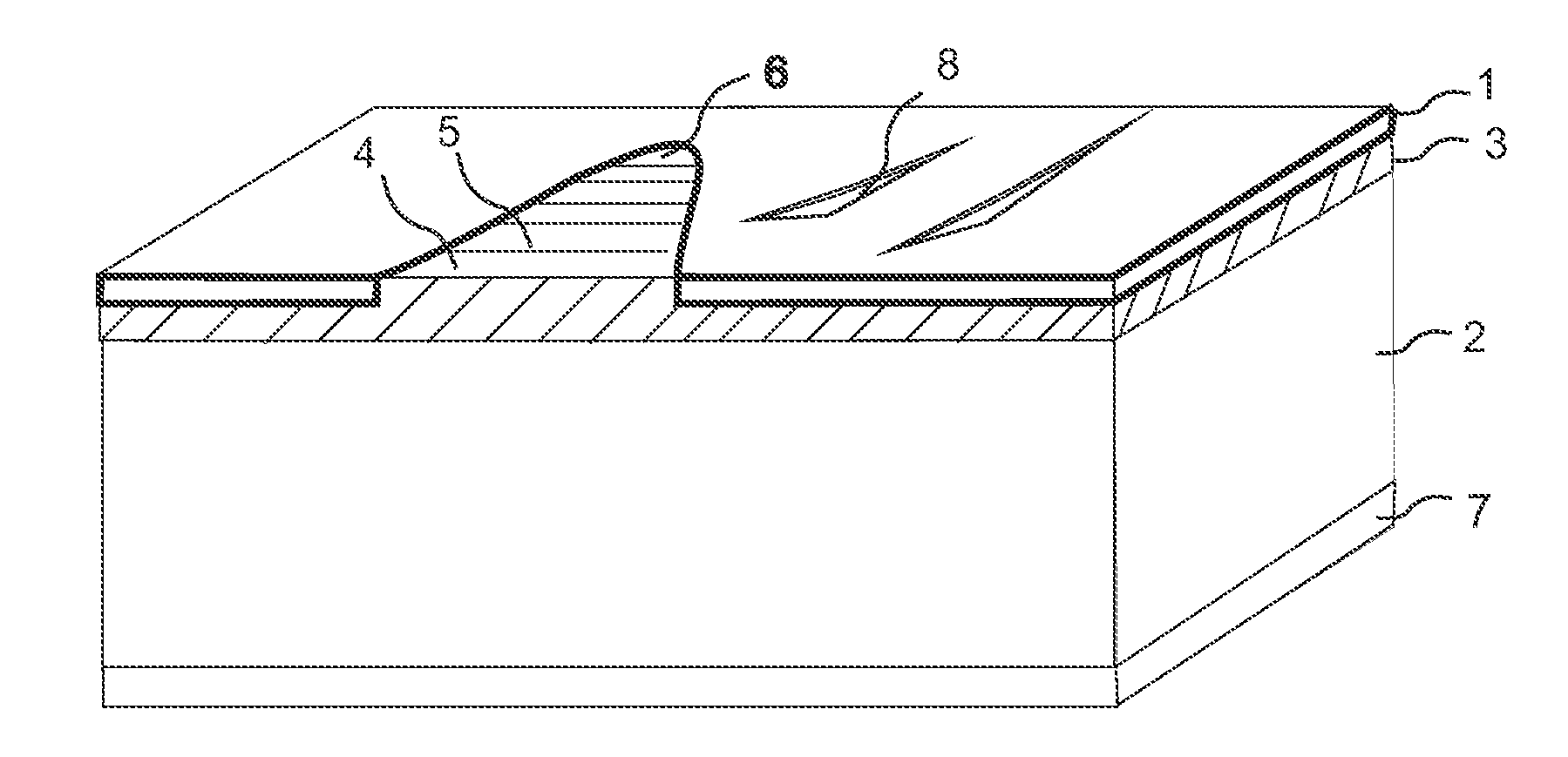
ActiveUS20130095315A1Solve the real problemFloorsSpecial ornamental structuresSurface layerWood fibre
Recycling of laminate flooring based on a separation of the panels (1) into particles which are connected with a binder and formed to a new sheet shaped material. A building panel includes a surface layer and a wood fiber based core, and the wood fiber based core includes aluminium oxide particles.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
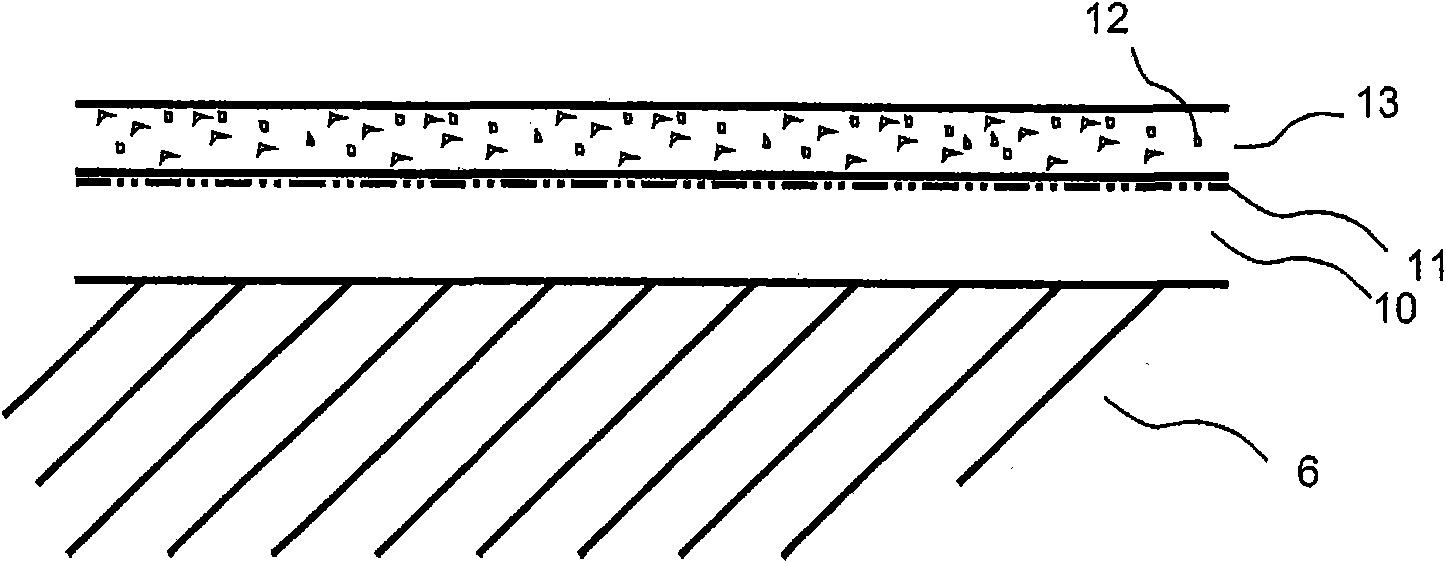
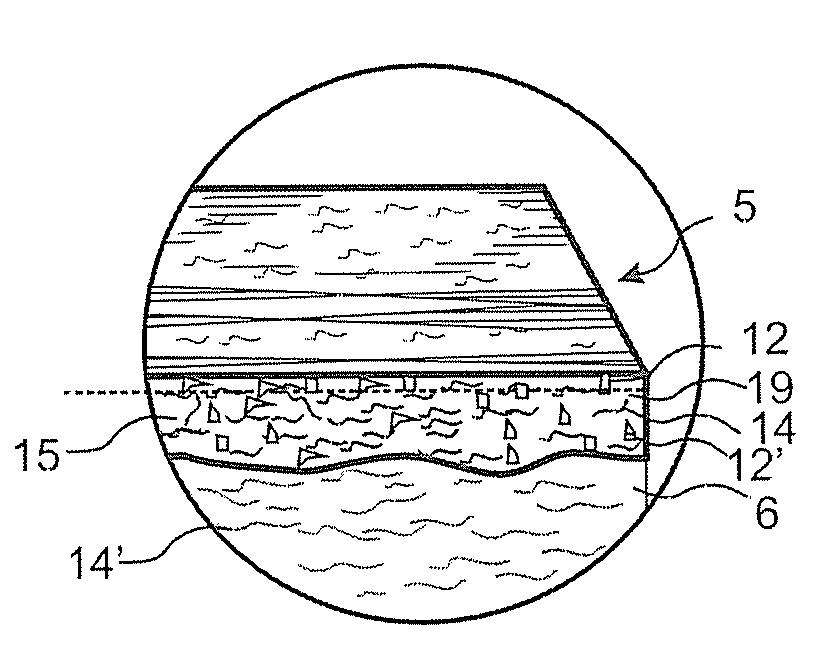
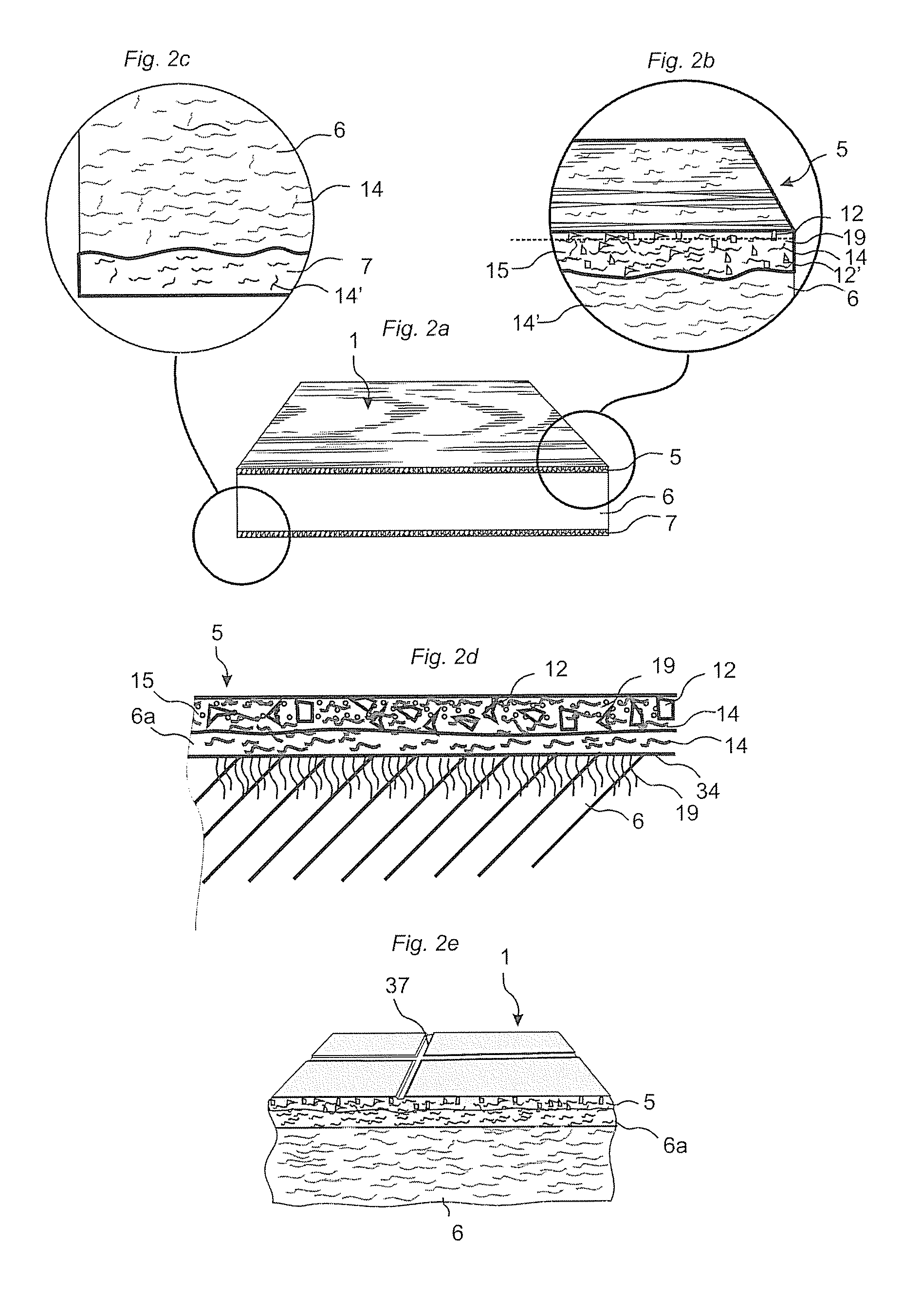
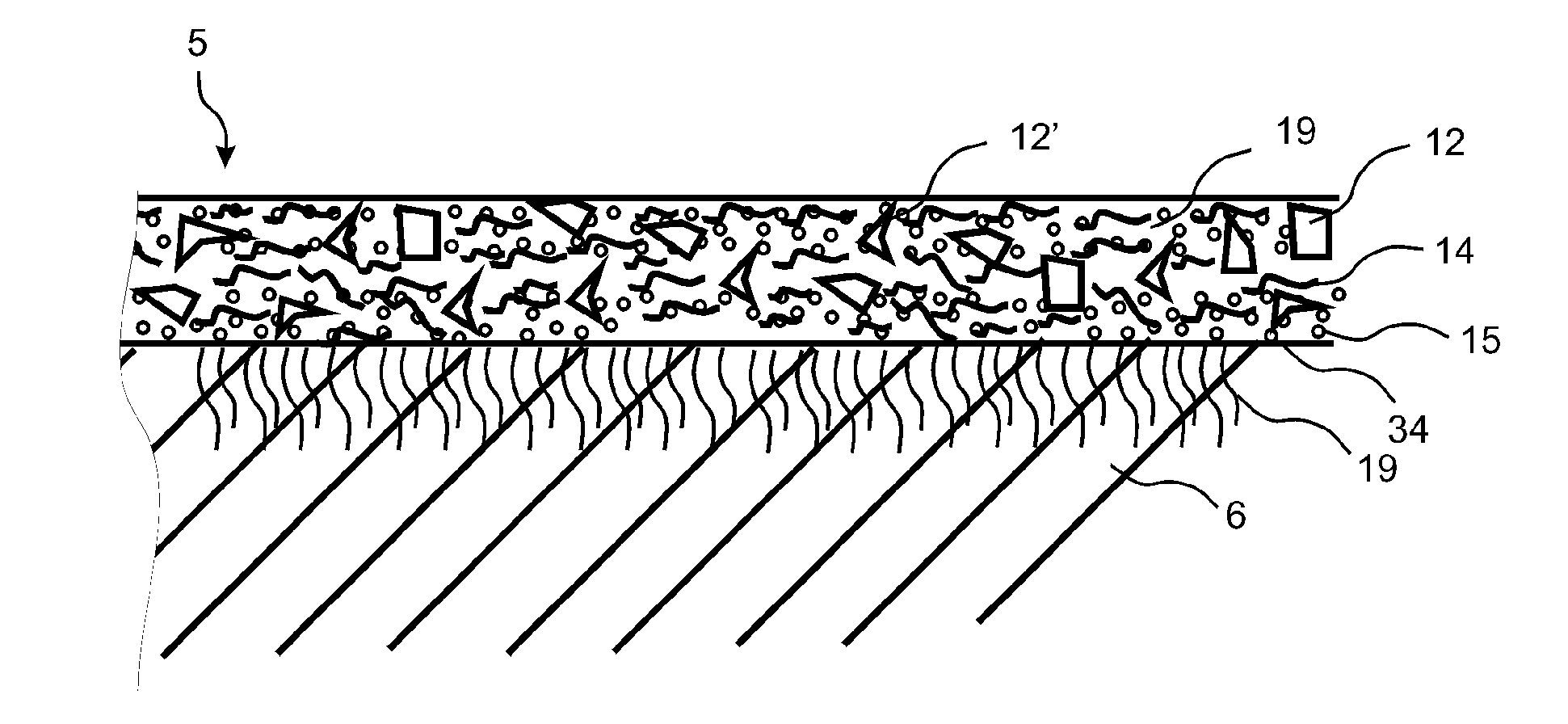
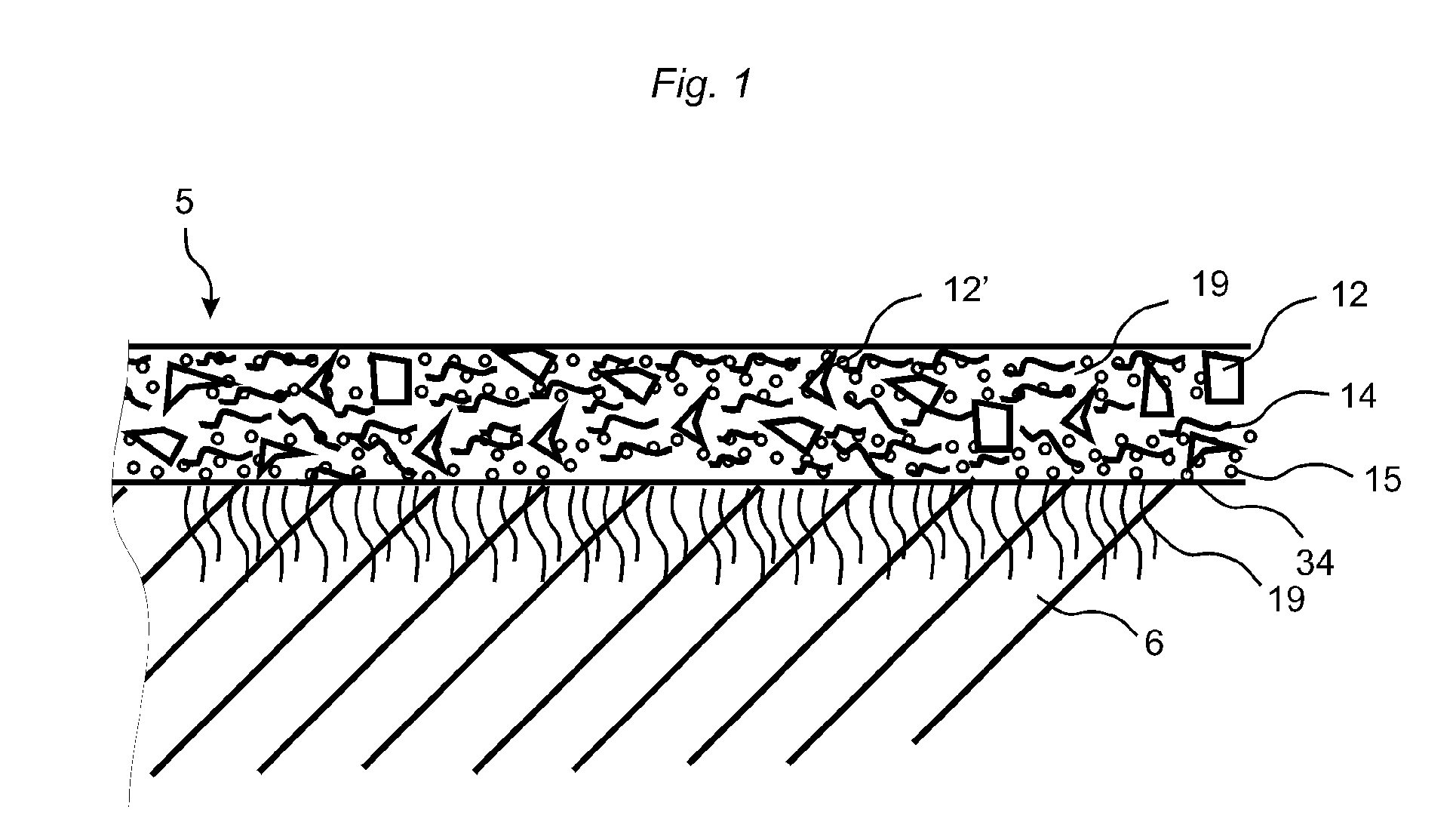
Fibre based panels with a wear resistance surface
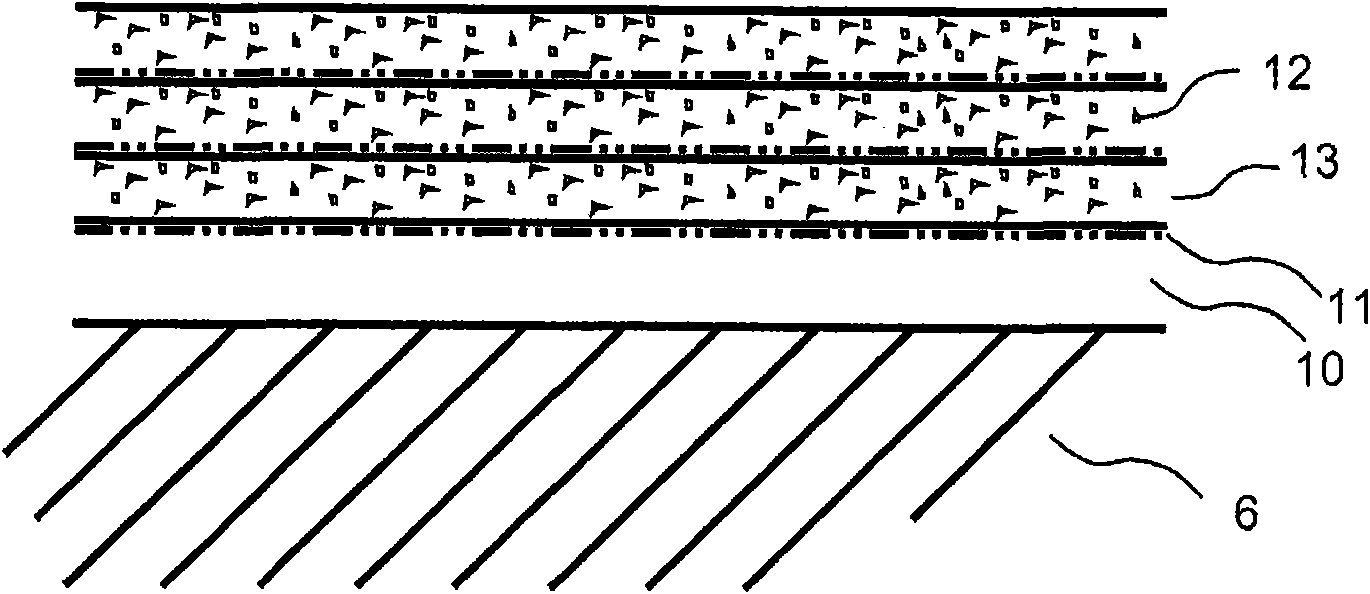
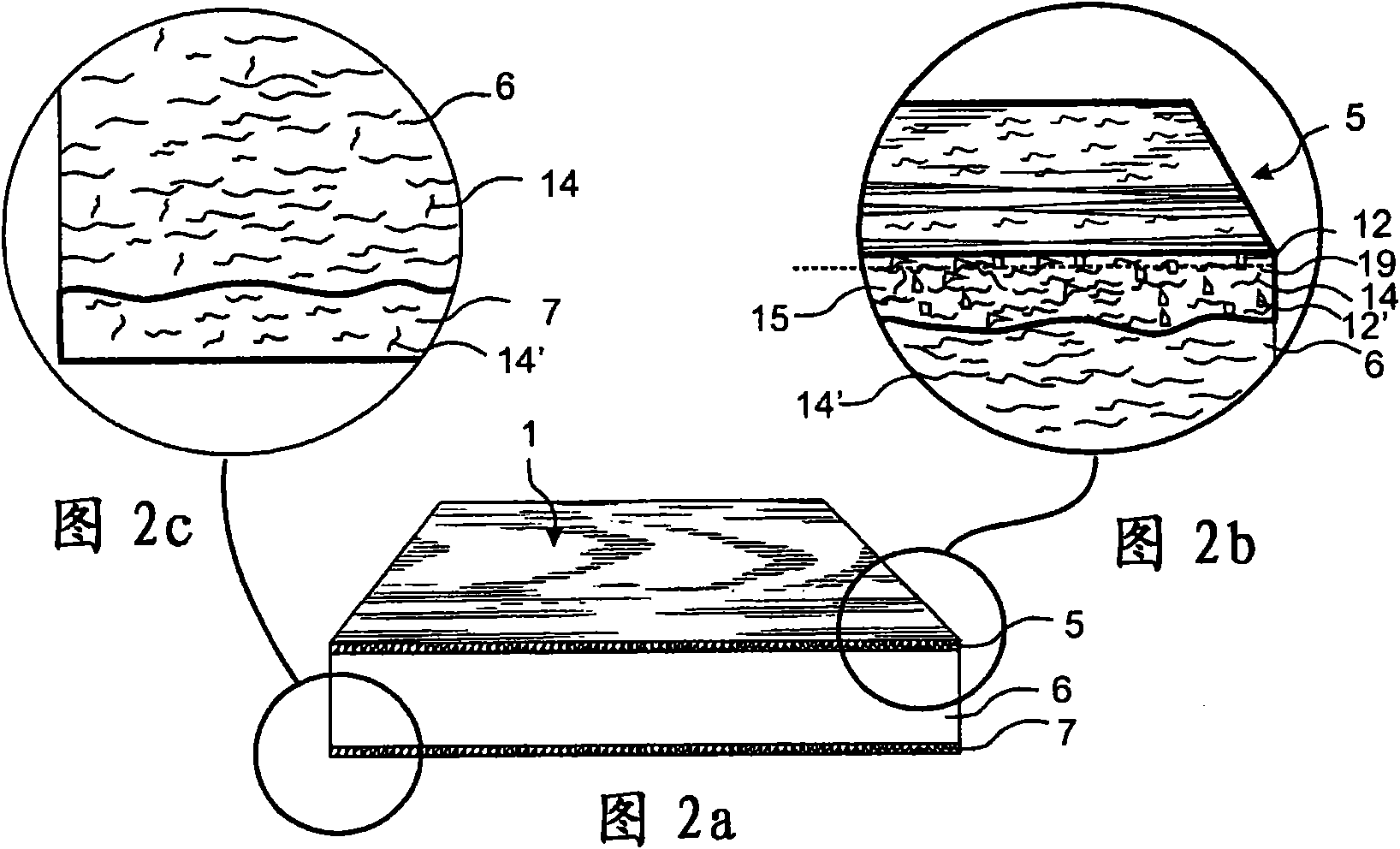
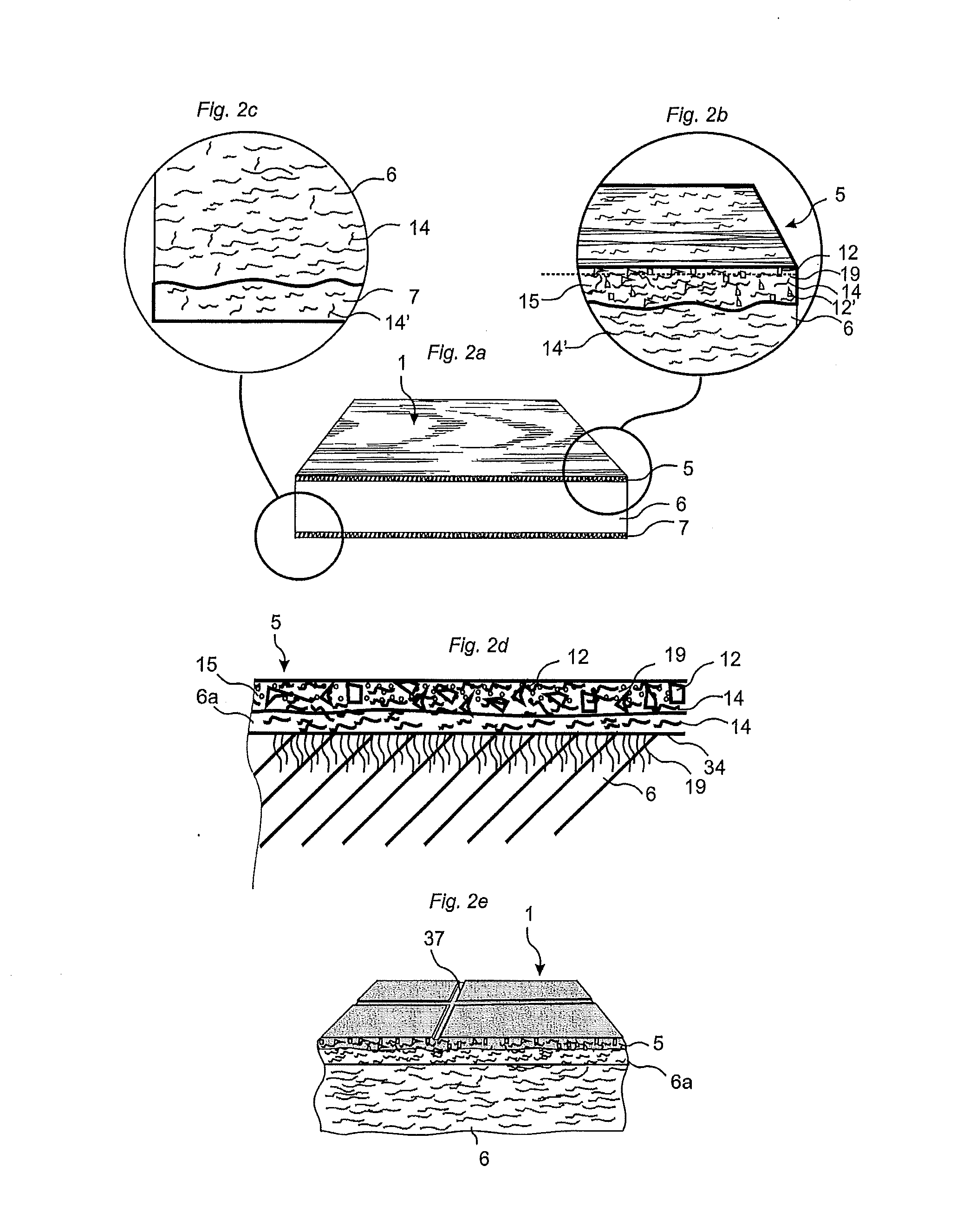
ActiveCN101909836AImprove wear resistanceImprove impact resistanceCovering/liningsSpecial ornamental structuresSurface layerWear resistant
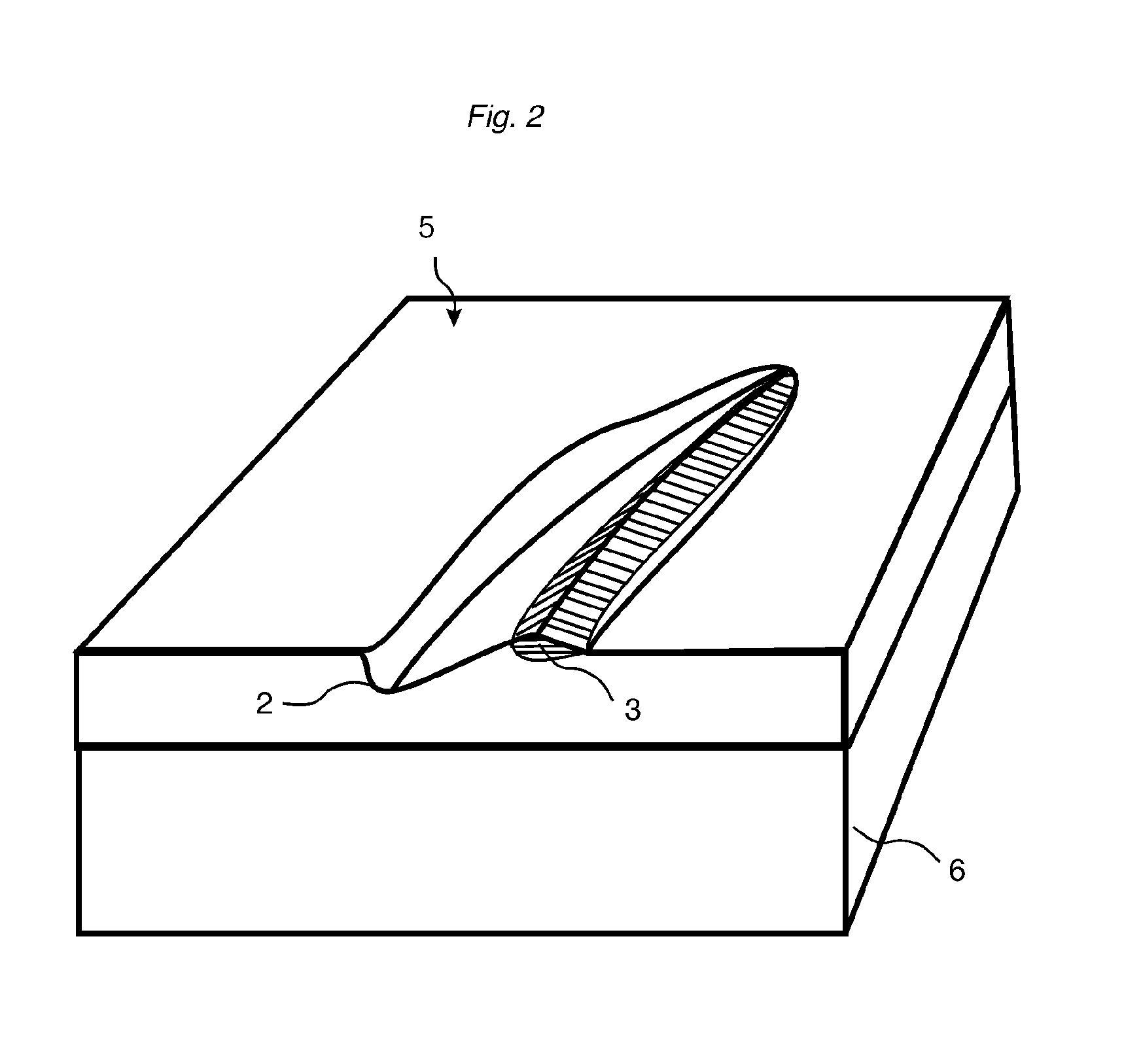
A flooring panel (1) comprising a core (6) and a surface layer (5), the surface layer (5) comprising cork particles (14) or wood fibres (14) comprising lignin resin, melamine resin as binder (19), colour pigments (15), and aluminium oxide as wear resistant particles (12), all components being homogenously mixed, and the core (6) comprising fibres and binder and being provided with a mechanical locking system (4) at its edges and a rear balancing layer (7). Also disclosed is a method of manufacturing said flooring panel by - homogenously mixing the dry particles of the surface layer; - scattering them on an embossed pressure matrix; - applying the core layer as scattered or prefabricated layer on the surface layer; - applying a balancing layer as scattered or prefabricated layer on the core layer; - pre-pressing the panel; - printing and brusching the surface layer; - forming the panel by a further pressing and heating step; - machining the mechanical locking system.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
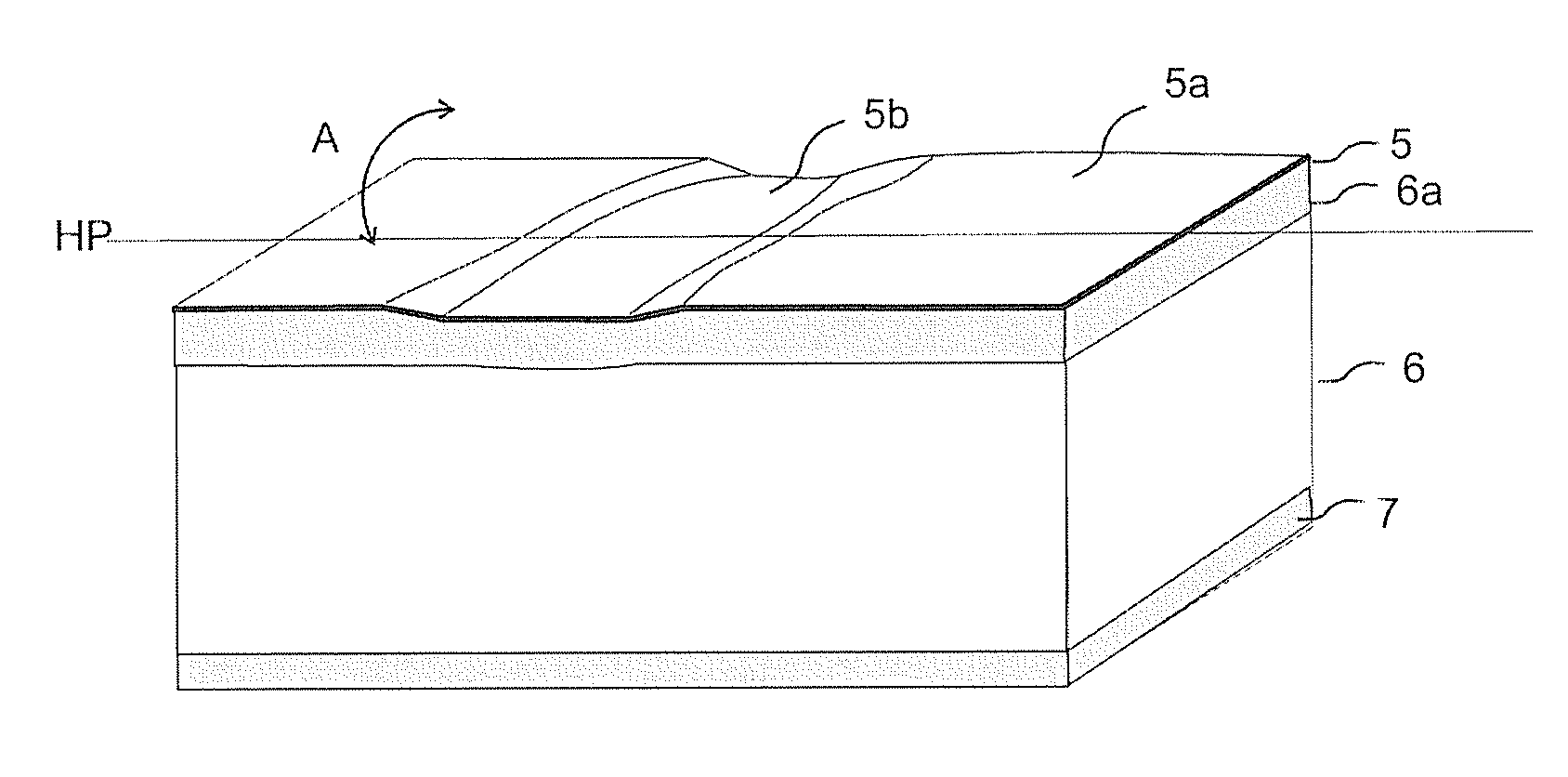
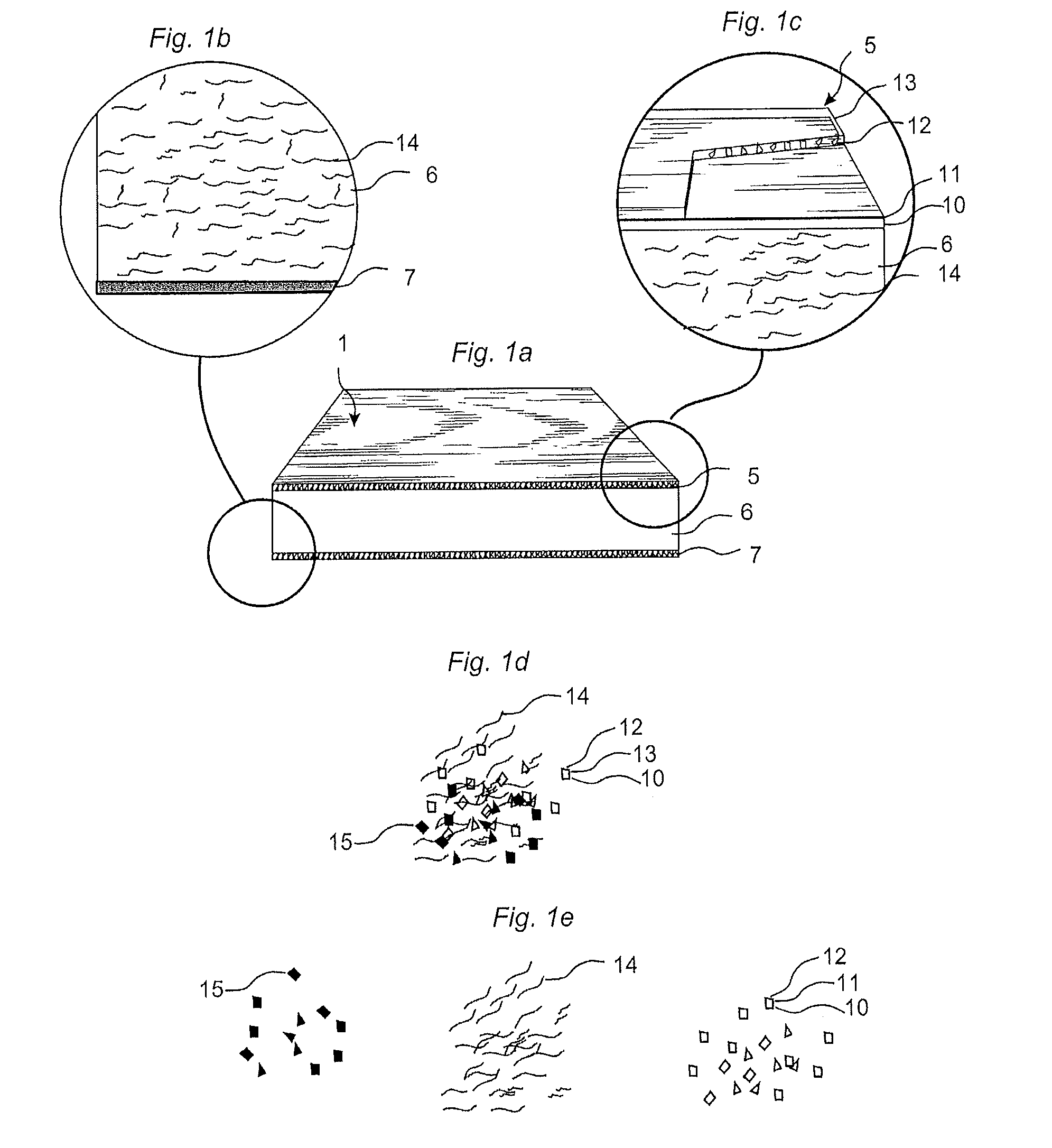
Wood fibre based panel with a surface layer
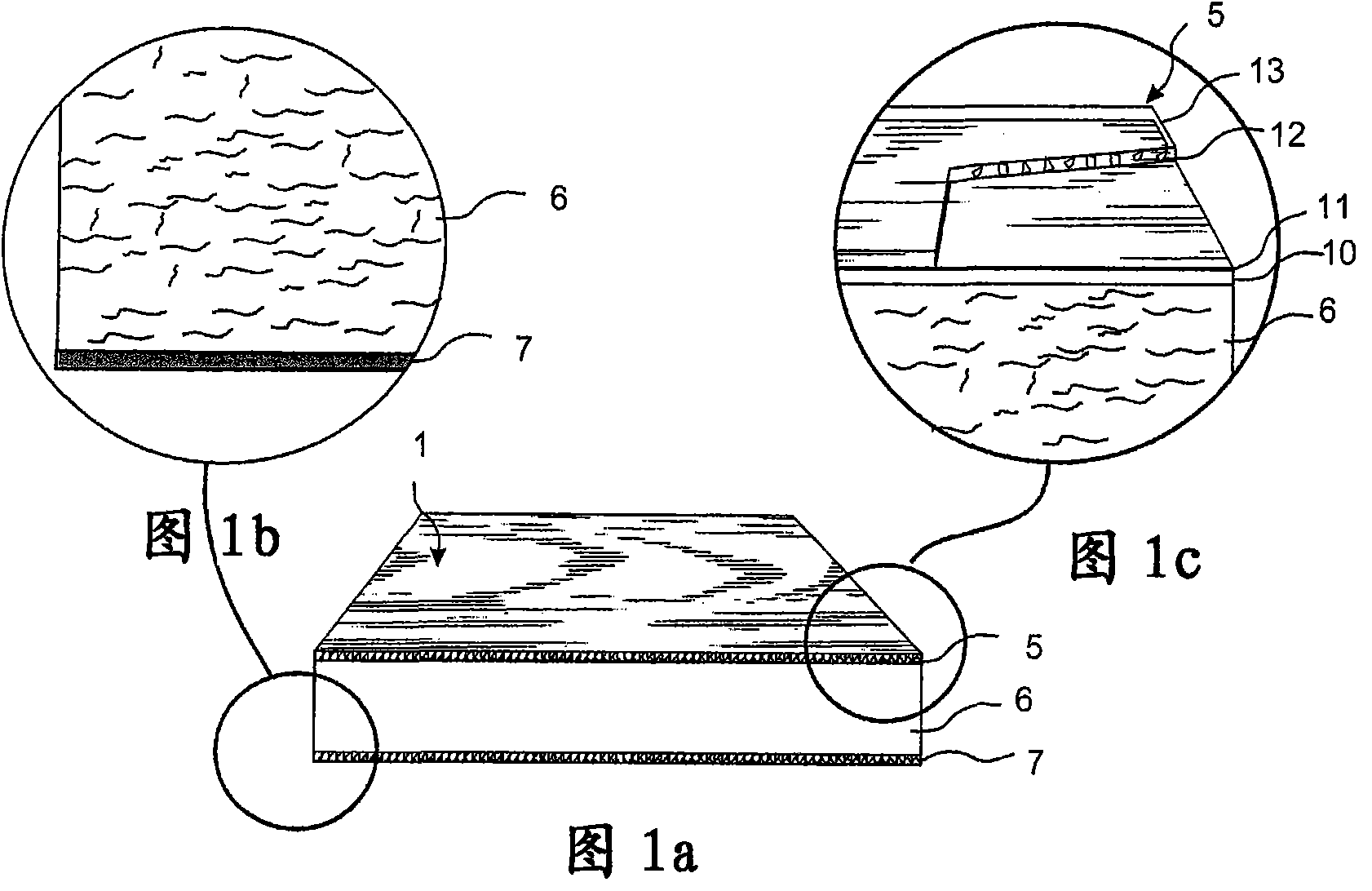
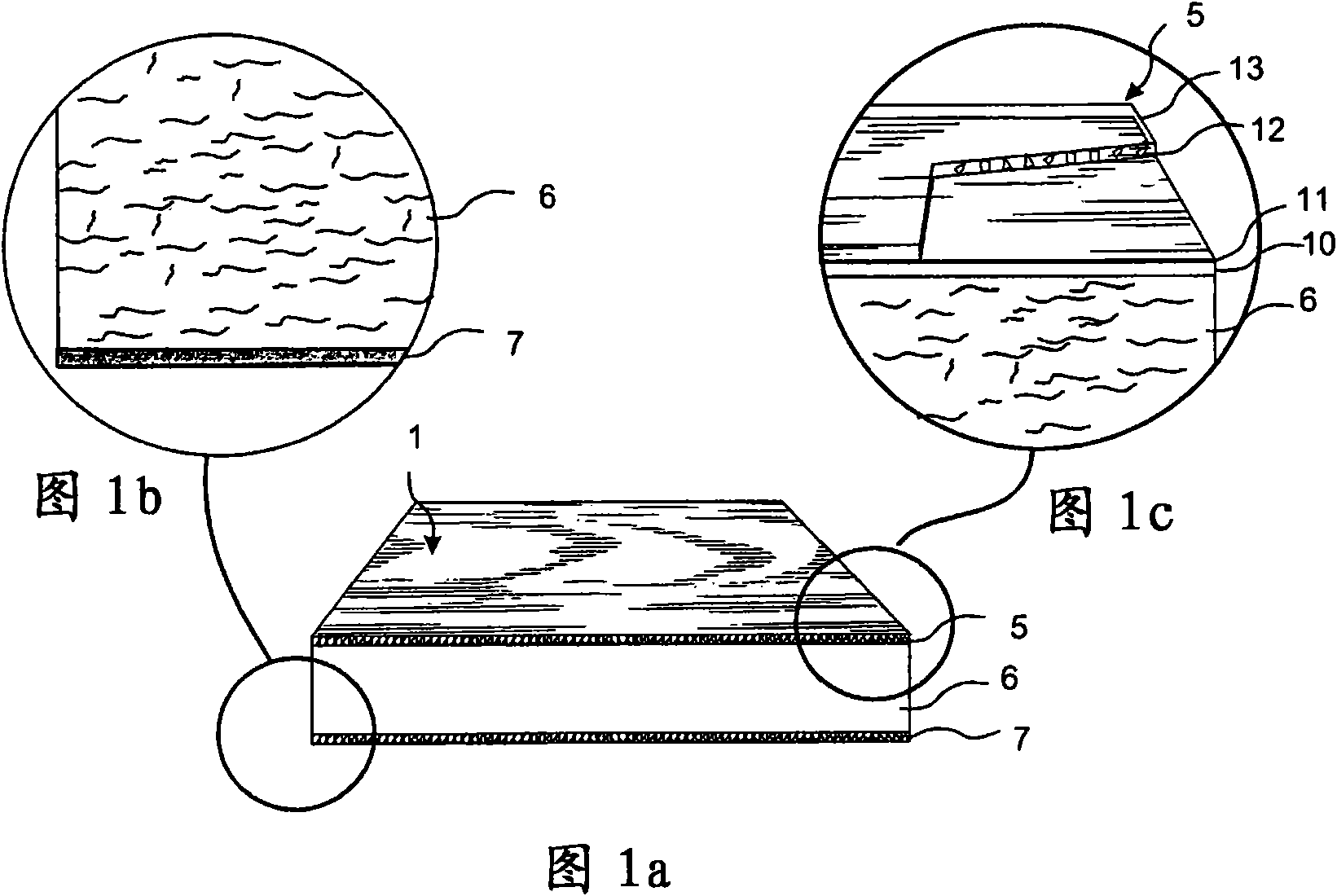
ActiveUS20150197942A1Attractive surface designSurface property and cost structureDecorative surface effectsSpecial ornamental structuresWood veneerSurface layer
A building panel with a surface layer (1) including a wood veneer, a wood fibre based core (2) and a sub-layer (3) between the surface layer (1) and the core (2). The sub-layer (3) includes wood fibres (4) and a binder (5). The surface layer (1) has surface portions (6) including material from the sub-layer (3). The surface portions (6) including material from the sub-layer (3) extend into the wood veneer.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Method of producing a powder layer or a granular layer
InactiveUS20120308774A1Optimize allocationEqually distributedLayered productsSpecial ornamental structuresWood fibreMaterials science
A method for producing a panel including scattering of a wood fibre powder on a carrier is disclosed and a device for the scattering step.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Method for producing wood fibre composite products
A process for producing a thermoformable fibre-plastics composite product comprising lignolcellulosic or natural fibres, particularly but not exclusively useful as an intermediate product in subsequent manufacture, comprises conveying the fibres in a dry or wet air stream and applying to the fibres a thermoplastic binding agent, and forming the fibres into a solid or semi-solid product such as a panel, which is thermoformable. In at least a preferred embodiment the process may be carried out in known plant for manufacture of medium density fibre board.
Owner:NEW ZEALAND FOREST RES INST
Fibre based panels with a wear resistance surface
ActiveCN101998896AImprove impact resistanceEasy to moveLiquid surface applicatorsLamination ancillary operationsWood veneerSurface layer
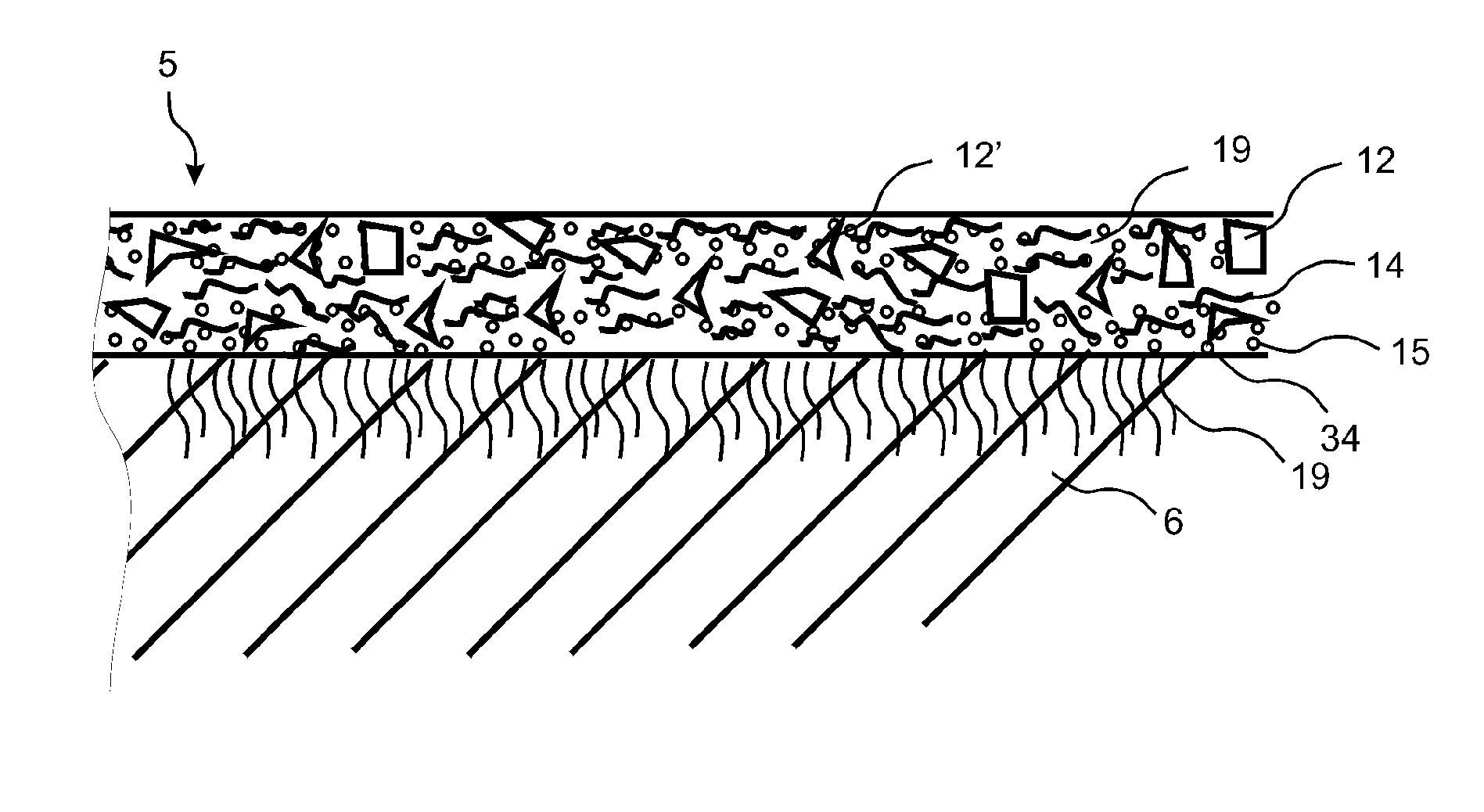
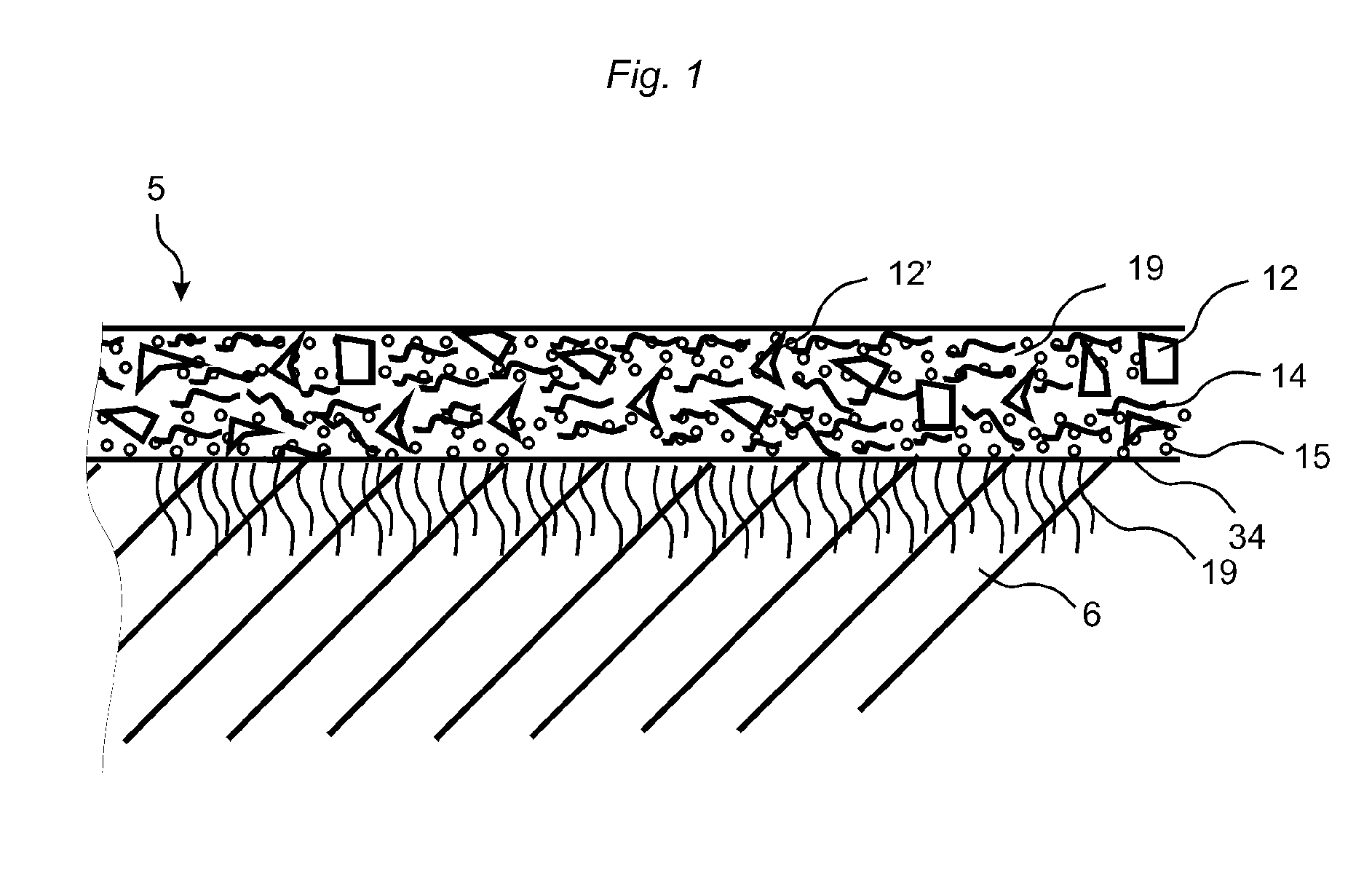
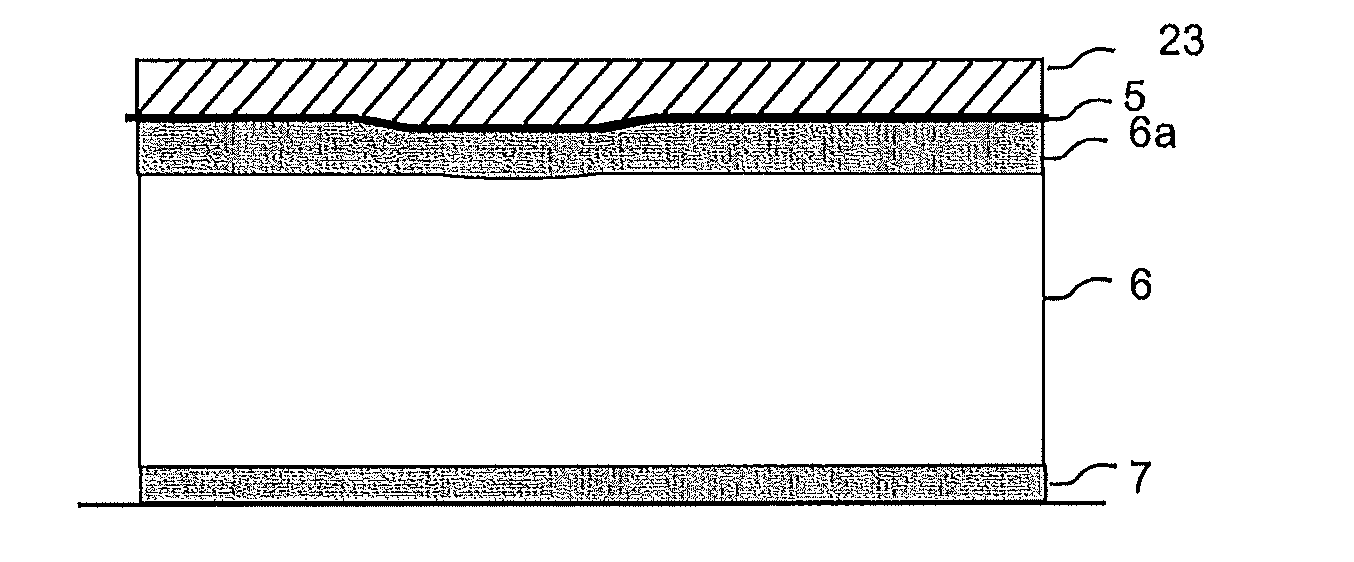
Floor board (1) comprising a wood fibre based core (6) such as HDF, a thin surface layer (5) such as wood veneer, and a sub layer (6a) between the surface layer (5) and the core (6). The sub layer (6a) comprises wood fibres (14) and an uncured binder (19) and is applied on the core (6) as a powder. The layers (5, 6a) are connected to the core (6) and embossed in register by heating and pressing, the uncured sub layer (6a) behaving similar to a paste or a liquid substance and creating a uniform counter pressure under the thin surface layer (5), thus providing an easier forming of deep and sharp embossing without damaging the surface layer (5).
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Manufacture of extruded synthetic wood structural materials
InactiveUS20050087904A1Drive water vaporWood working apparatusDomestic articlesPolymer scienceWater vapor
Extruded synthetic wood structural material comprises at wood fiber, plastic, and a coloring agent. In its manufacture, finely divided wood fiber having an initial moisture content of 0.5% to 20%, and a coloring agent, are placed together and fed to a heated mixer. Water vapor is driven off. The plastic resin is added to the mixture, which is then forced through an extrusion die, cooled, and cut to length. The resulting extruded material is homogeneously colored, and has zero or very low water content. The extruded synthetic wood structural material comprises from 20% to 60% by weight of wood fiber content, from 20% to 60% by weight of plastic resin content, and from 0.5% to 5.0% by weight of coloring agent.
Owner:BRYAN HLDG
Heat and pressure generated design
A wood fibre based panel with surfaces layer with lower parts which has less binders than the upper parts. Also, a method of manufacturing a building panel having a structured surface with a design that has colour variation in register with the structure obtained by a varying pressure distribution applied on the surface.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Soil conditioner, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107118018APromote absorptionEfficient use ofCalcareous fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersFiberSoil conditioner
The invention relates to the field of environmental protection and discloses a soil conditioner, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The soil conditioner comprises raw materials in parts by weight: 50 to 60 parts of wood fibers, 14 to 18 parts of biochar, 25 to 30 parts of humus, 3 to 6 parts of polysaccharide, 1 to 3 parts of seaweed essence, 0.001 to 0.005 part of Trichoderma and 0.001 to 0.005 part of nitrogen fixation bacteria. The invention also discloses a preparation method, the application and a using method of the soil conditioner, the soil conditioner has the advantages of improving soil physical and chemical properties and promoting the turf forming performance of plants, and the preparation and application methods are simple and convenient, so that the popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:JOFO GREEN CO LTD
Polyolefin wood fiber composite
An improved composite structural member comprising a complex profile made of a composite comprising a polyolefin polymer and a wood fiber. The material is useful in conventional structural applications. The complex profile, in the form of an extruded thermoplastic composite member can be used in residential and commercial structures as described. Preferably, the profile is used in the manufacture of the fenestration components such as windows and doors. Such linear members are designed with specifically configured cross-sectional shapes to form structural elements in the fenestration units. Structural elements must possess sufficient strength, thermal stability and weatherability to permit the manufacture of a structurally sound window unit that can be easily installed into a rough opening but can maintain its attractive appearance and structural integrity over the life of the window unit often twenty years or more. The structural member comprises a hollow complex cross-section with at least one structural web or one fastener web formed within the component. The exterior of the extruded component has a visible capstock layer and is shaped and adapted for installation in rough openings. The exterior also contains shape and components capable of supporting the elements of the fenestration unit such as a window, sash or movable door unit. The improved polypropylene structural members have unique advantages and can be assembled using thermoplastic weld processes.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
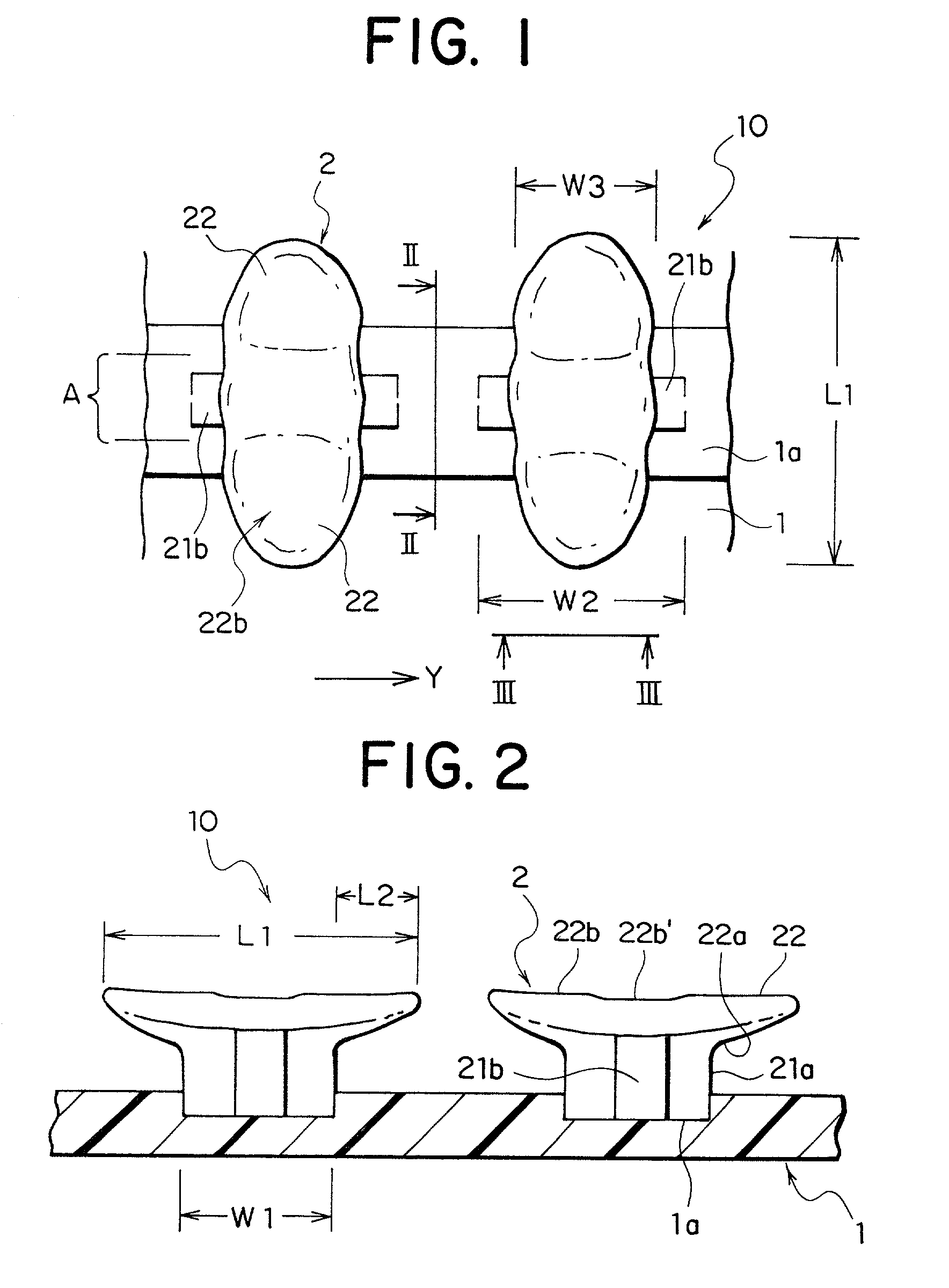
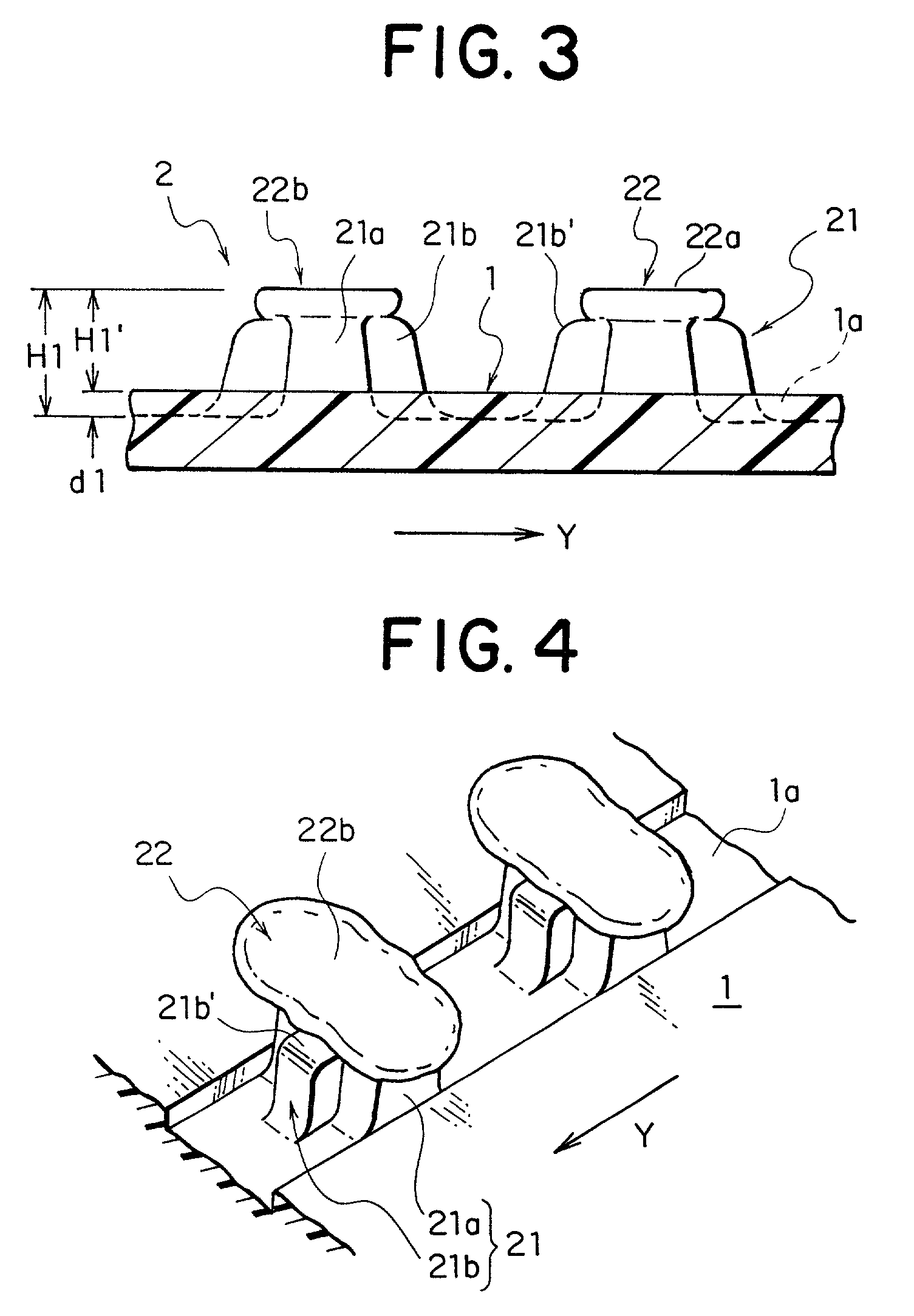
Integral molded surface fastener, and continuous manufacturing method and continuous manufacturing apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20020124359A1Increase participation rateSatisfactory durabilitySnap fastenersLayered productsFiberEngineering
An integral molded surface fastener having minute and peculiar engaging elements, which engage with minute, thickly wooded fiber piles securely while each engaging element secures appropriate engagement strength, shearing strength and separation strength is provided. Further, texture of a surface of the surface fastener is improved and a height of the engaging elements protruded from a surface of a substrate is lower than a conventional type, thereby preventing the engaging elements from being fallen down by a pressing strength. At the same time, a high engaging ratio with a mating pile piece is secured and a durability required for this kind of fastener is satisfied. Preferably, a desired plasticity and tearing strength of the flat substrate are secured. More specifically, a molded surface fastener having minute engaging elements of thermoplastic resin formed together with a substrate by continuous molding is provided, the engaging elements being hook-type engaging elements each comprised of a single column portion having a substantially cross-shaped section provided by intersection of a first column portion and a second column portion and rectangular thin plate-like engaging heads extended in the shape of wings in opposite directions along the width direction of the first column portion intersecting the second column portion around a top end of the column portion, and having substantially the same width dimension as the width dimension of a top end of the second column portion.
Owner:YKK CORP
Process for cutting out panels or the like
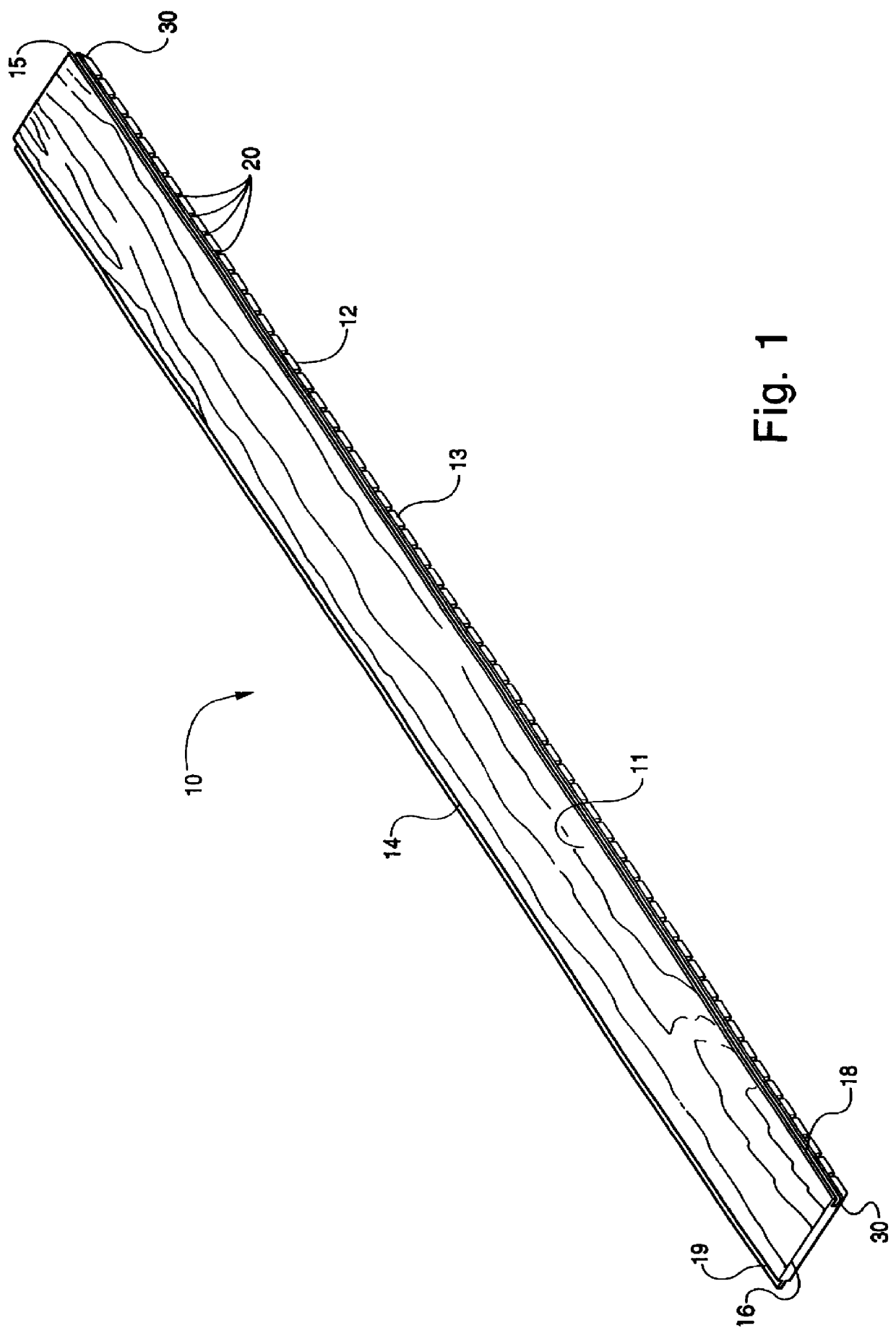
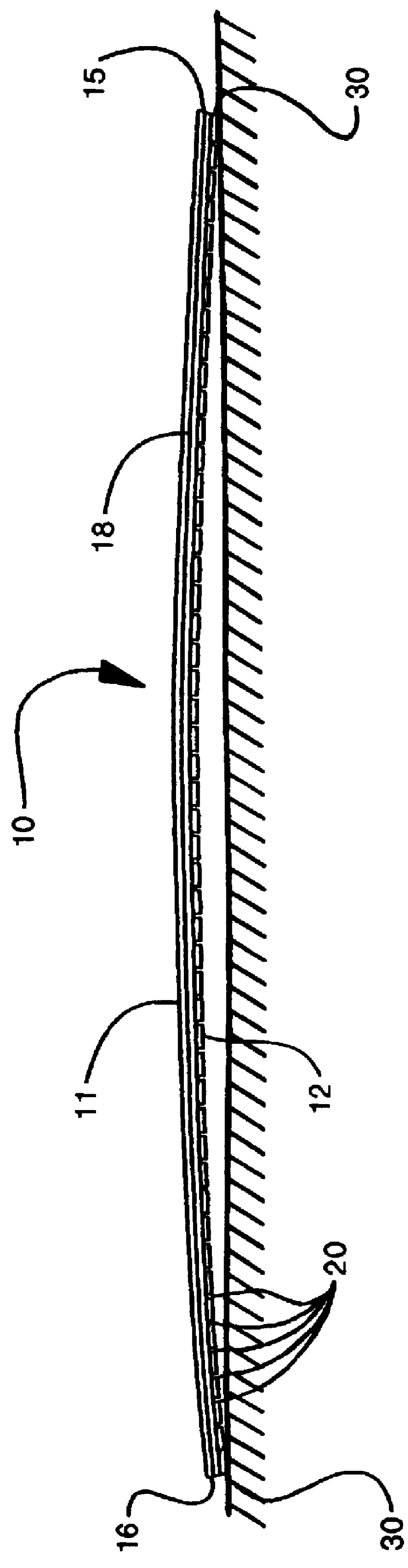
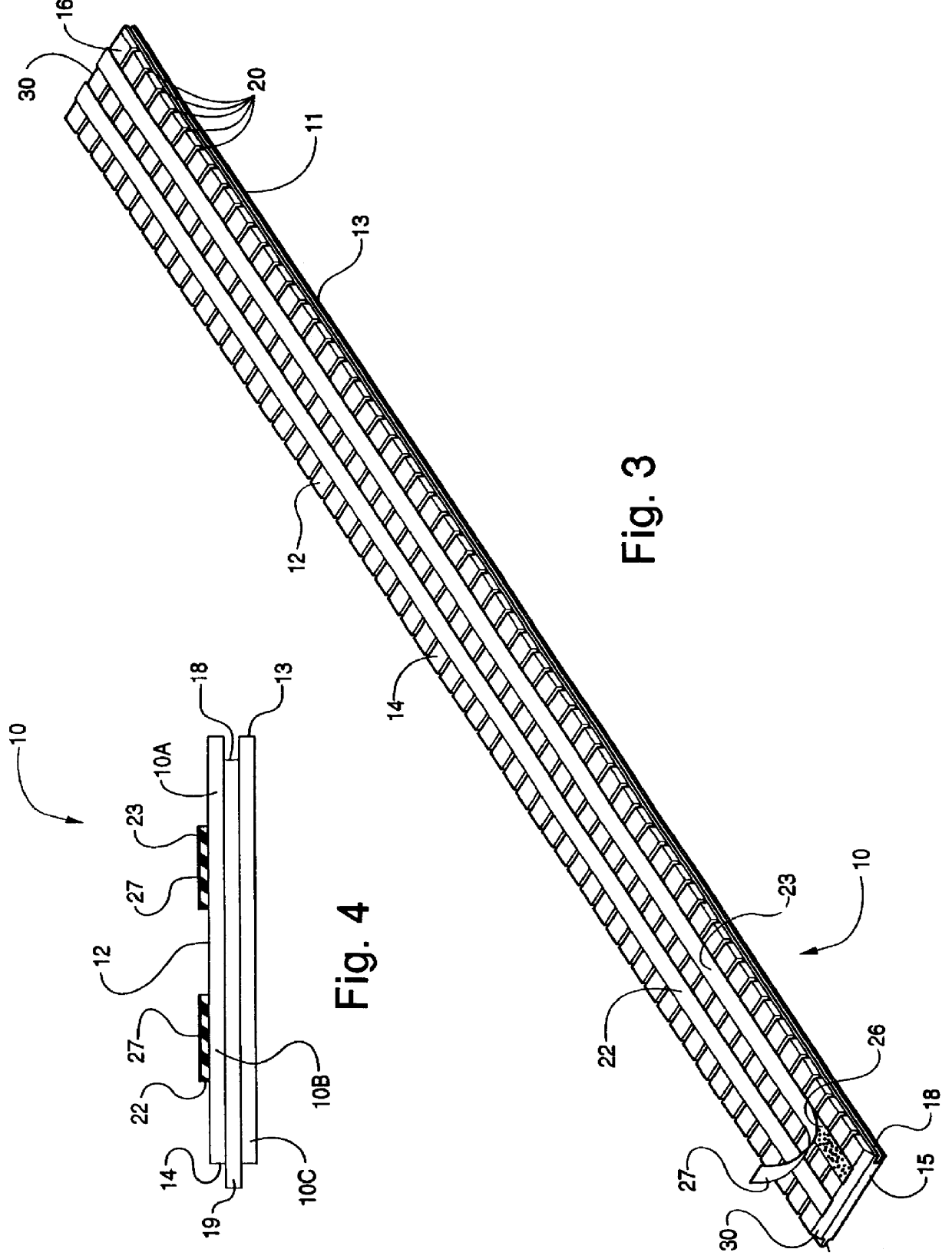
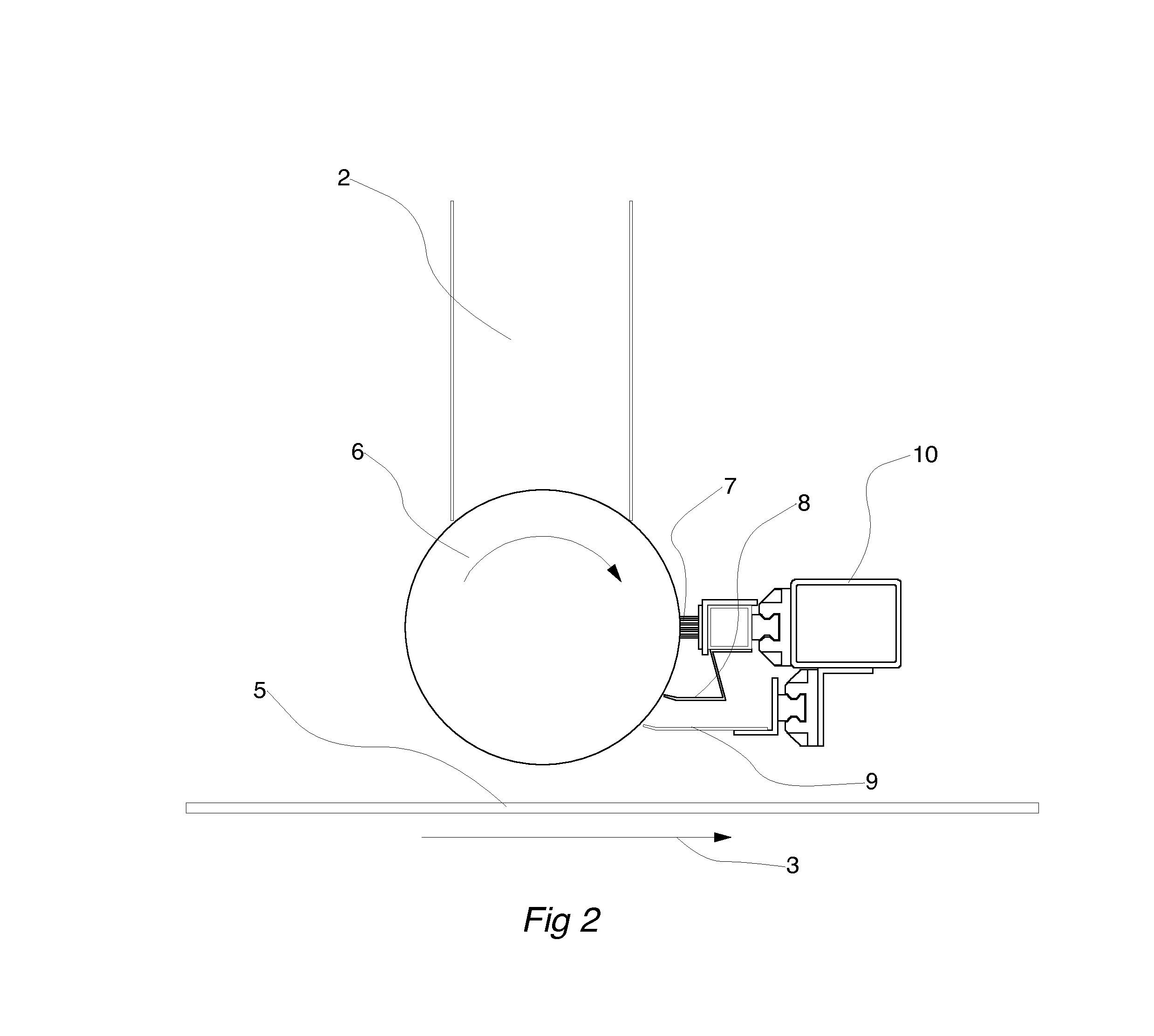
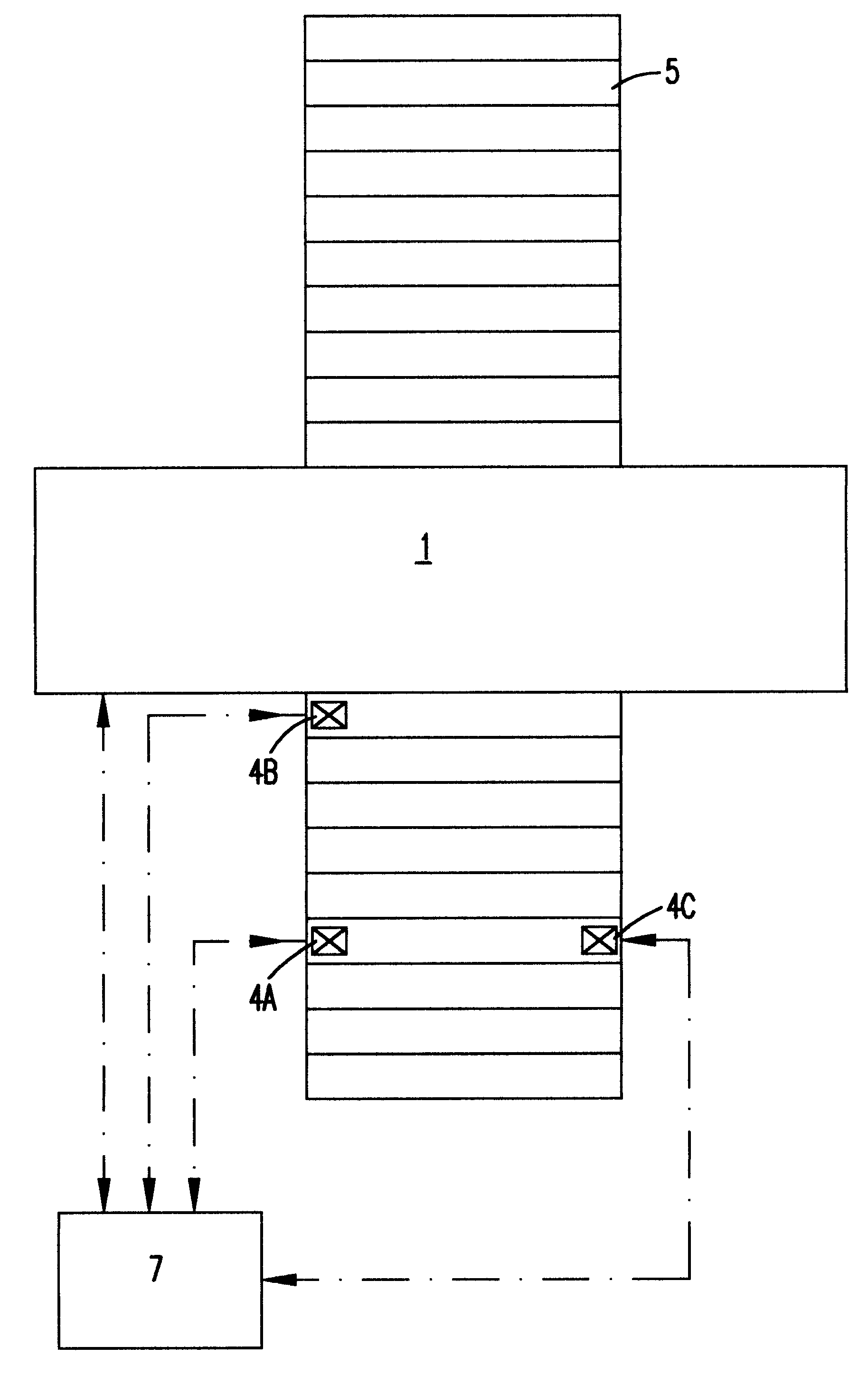
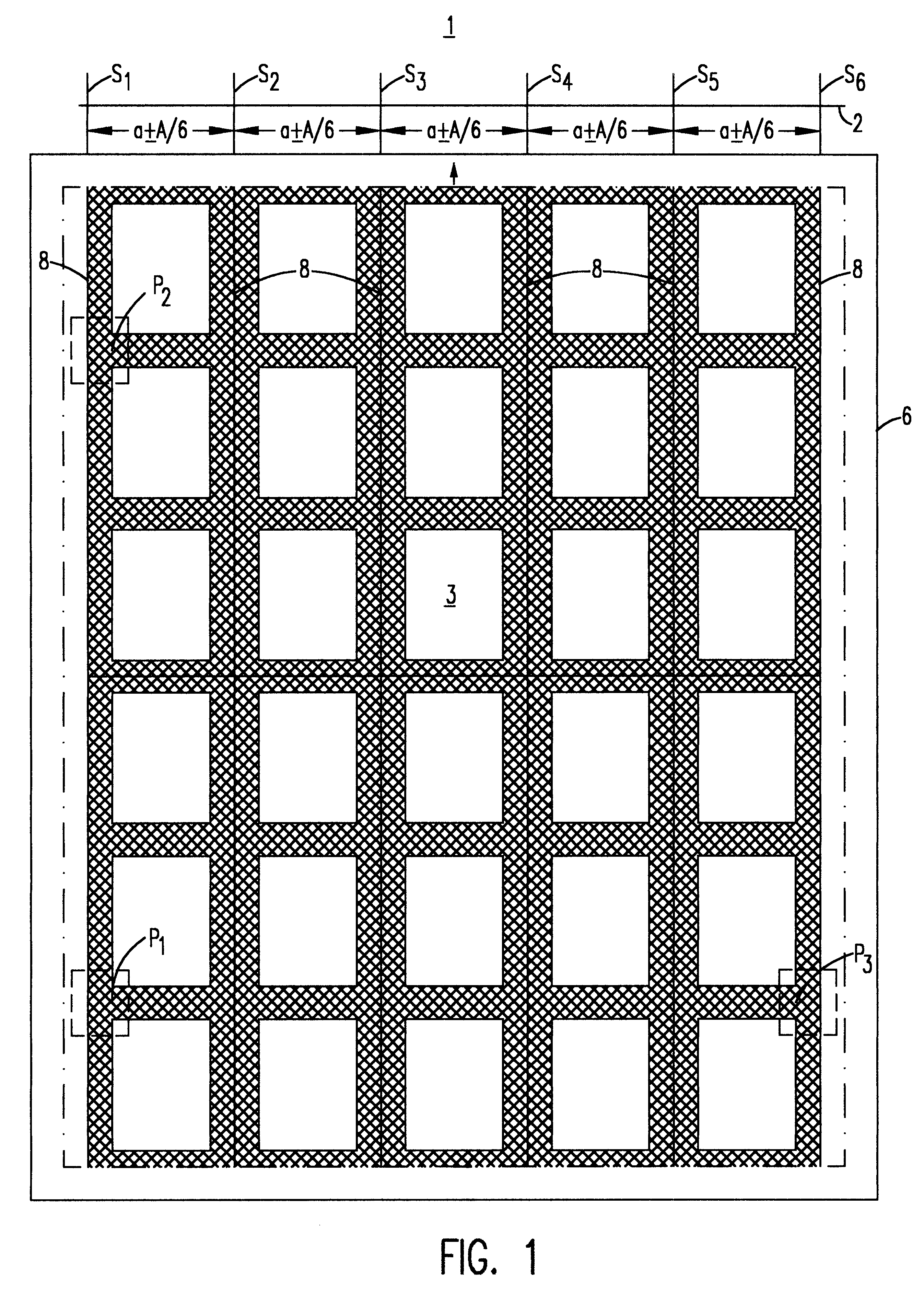
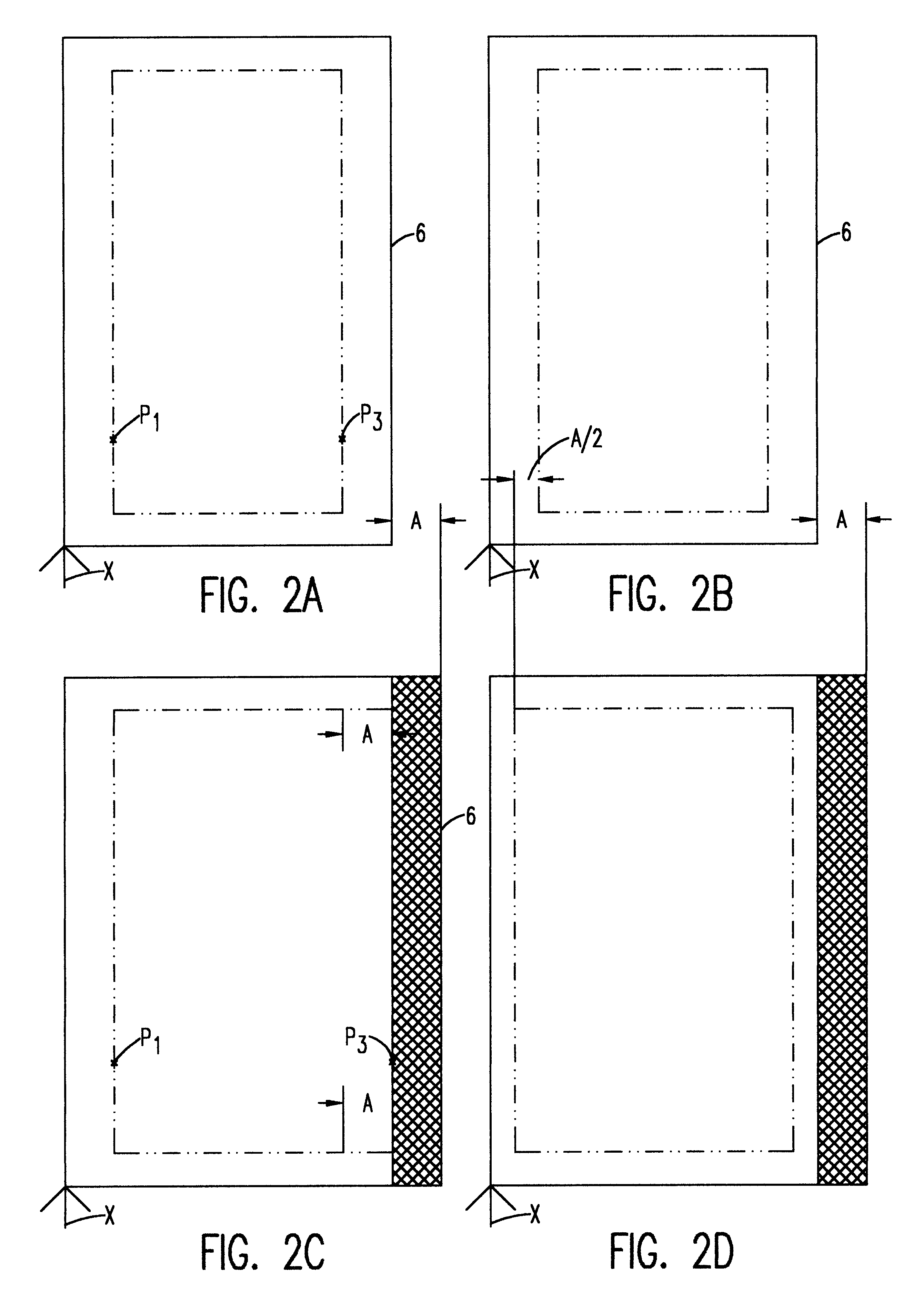
InactiveUS6569272B2Quality improvementAutomatic control devicesLamination ancillary operationsWood fibreEngineering
A wood fiber board (6) which is provided with a decorative layer (3) of paper or similar material, and where the length or width value of the decorative layer (3) deviates from its original value after it is applied to the wood fiber board (6), is cut into uniform panels using a board-dividing apparatus that compensates for these deviations. The board-dividing apparatus has a saw (1) that preferably has a plurality of saw blades (S1, S2, . . . Sn) which are adjustably spaced in parallel fashion. The board-dividing apparatus is equipped with a number of cameras and with controller which utilizes deviation measurement information to adjust the spacing of the saw blades. The wood fiber board (6) is first aligned with at least one initial camera (4a) at a point P1. Then, predetermined points (P1 and P2) in the decorative layer (3) are recorded by the first camera (4a) and a second camera (4b). A distance (L) between the points (P1 and P2) is determined, and thee discrepancy in the width or length value is determined by comparison of the actual position and the desired position of the points (P1 and P2). Then, the value of the determined discrepancy (A) is placed in relation to the number (n) of the saw blades (Sn), and the parallel spacing (a) of the saw blades (Sn) is modified by the value of the ratio of the discrepancy to the number of saw blades (A / n). The orientation of the wood fiber board (6) to the saw (1) is displaced to one side in the amount of one half the determined discrepancy (A), and then the wood fiber board (6) is transported toward the saw (1) for cutting out the panels.
Owner:KRONOTEC
Internal wall putty and production process thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of building materials, and particularly relates to an internal wall putty which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 150-300 parts of white cement, 500-900 parts of calcium carbonate powder, 10-50 parts of grey desert soil, 1-8 parts of cellulose ether, 7-30 parts of polymer latex powder, 1-10 parts of water repellent, 0.05-3 parts of starch ether and 0.5-7 parts of wood fiber. Compared with the prior art, the internal wall putty has the advantages that 107 glue water or 801 glue water is not used, thus formaldehyde is not contained, the environment is protected; and pregelatinized starch is not used, and the water repellent is added, thus the internal wall putty has the function of preventing water and moisture. In addition, with the white cement and the calcium carbonate powder as the strength basis and the grey desert soil as an auxiliary strength material, the strength of the internal wall putty is ensured; due to the synergistic effect of the cellulose ether and the starch ether, the water-retaining property and the application property of the internal wall putty are ensured; and because the polymer latex powder is added, the flexibility of the internal wall putty and the adhesion of the polymer latex powder and the wall are improved.
Owner:黄明杰
Wood fibre based panels with a thin surface layer
ActiveUS20160114495A1Large market shareImprove impact resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsCovering/liningsSurface layerWood fibre
A method of manufacturing a building panel, including mixing wood fibre particles and a binder to form a first mix, applying the first mix, while the first mix is in powder form, on a core for forming a sub layer on the core, applying a surface layer on the sub layer, wherein the surface layer comprises a second mix of wood fibre particles and a binder, pressing the core, the surface layer, and the sub layer, under increased pressure and temperature, and forming them into a building panel. A building panel formed by the method.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com