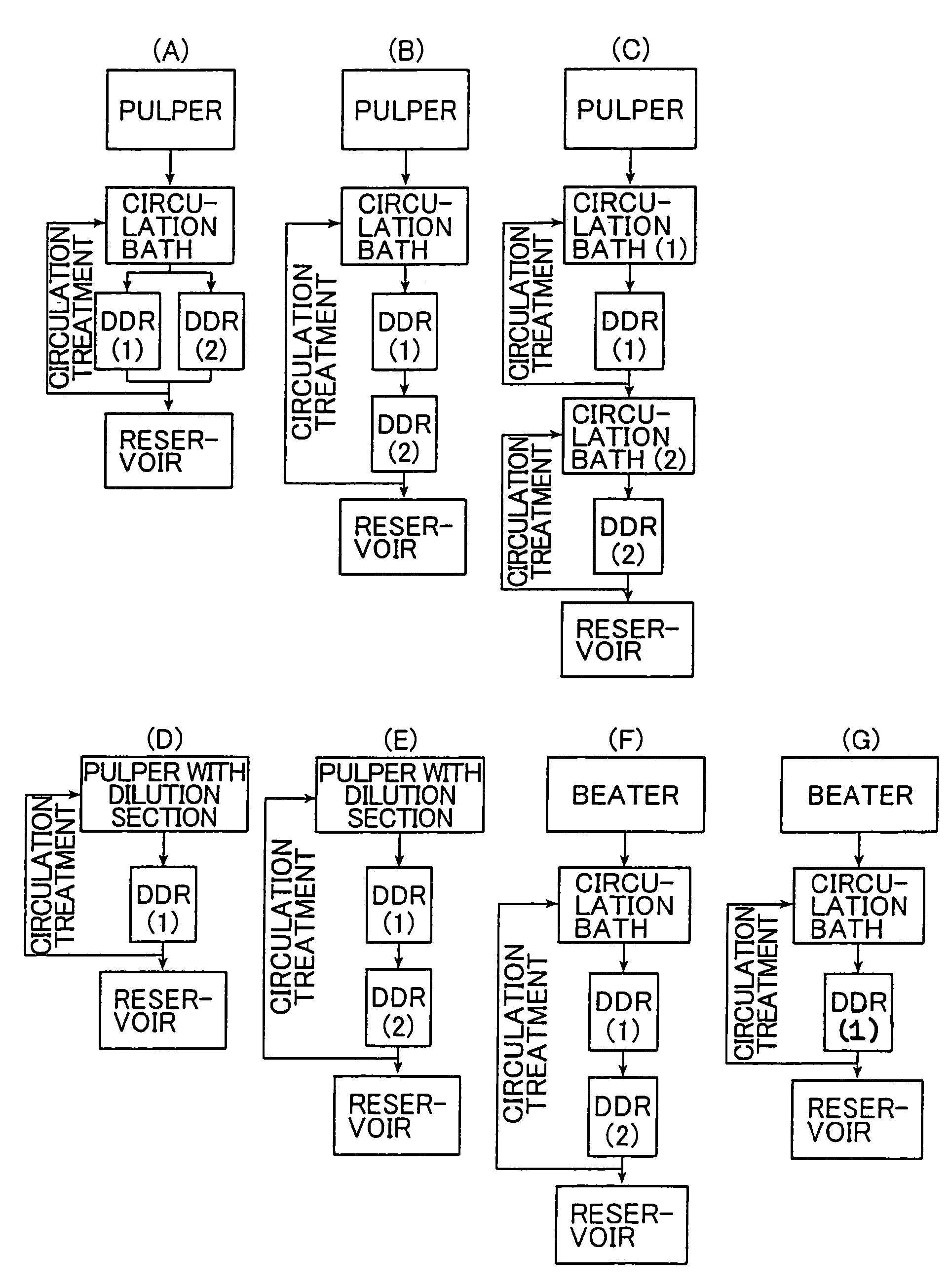
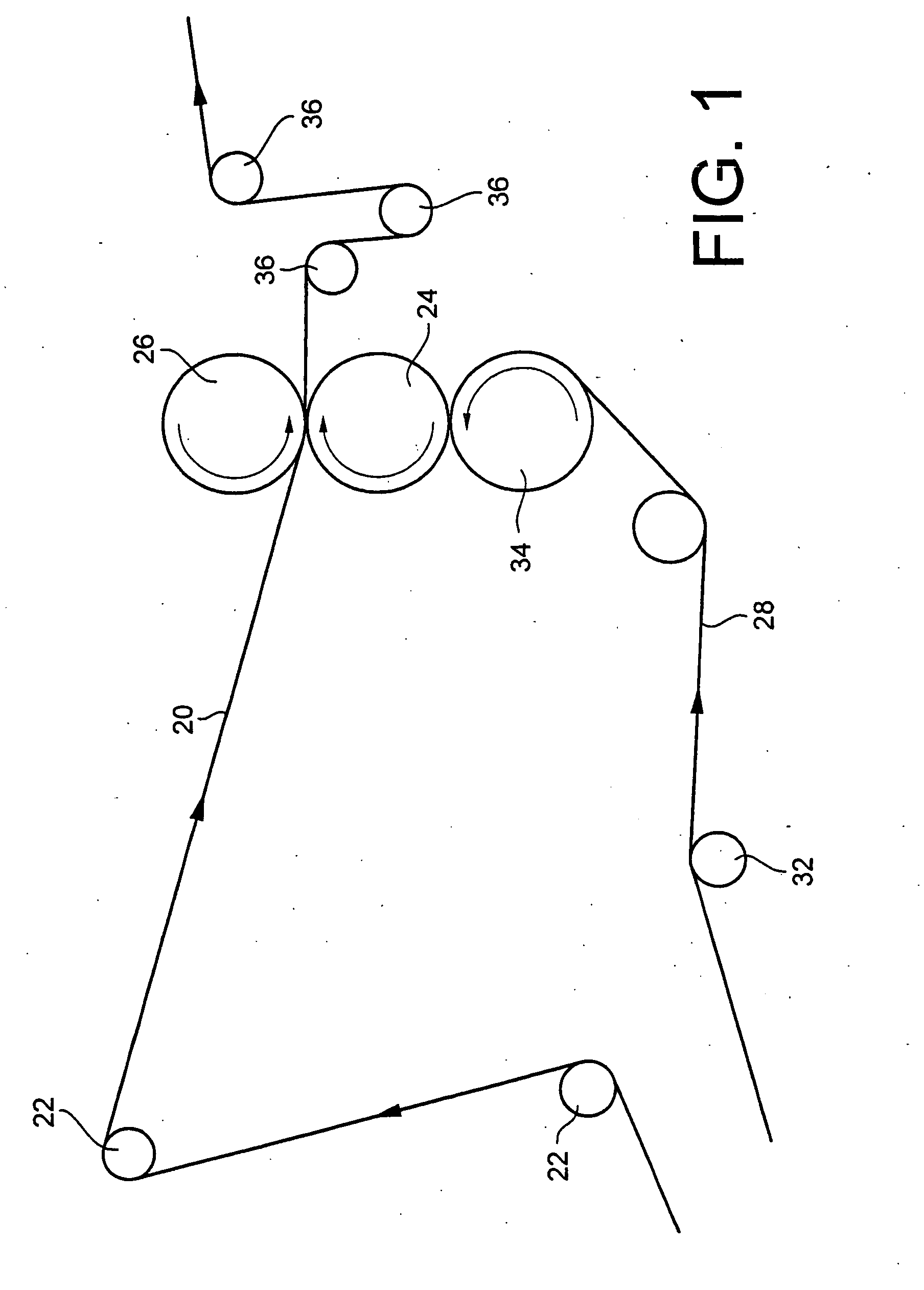
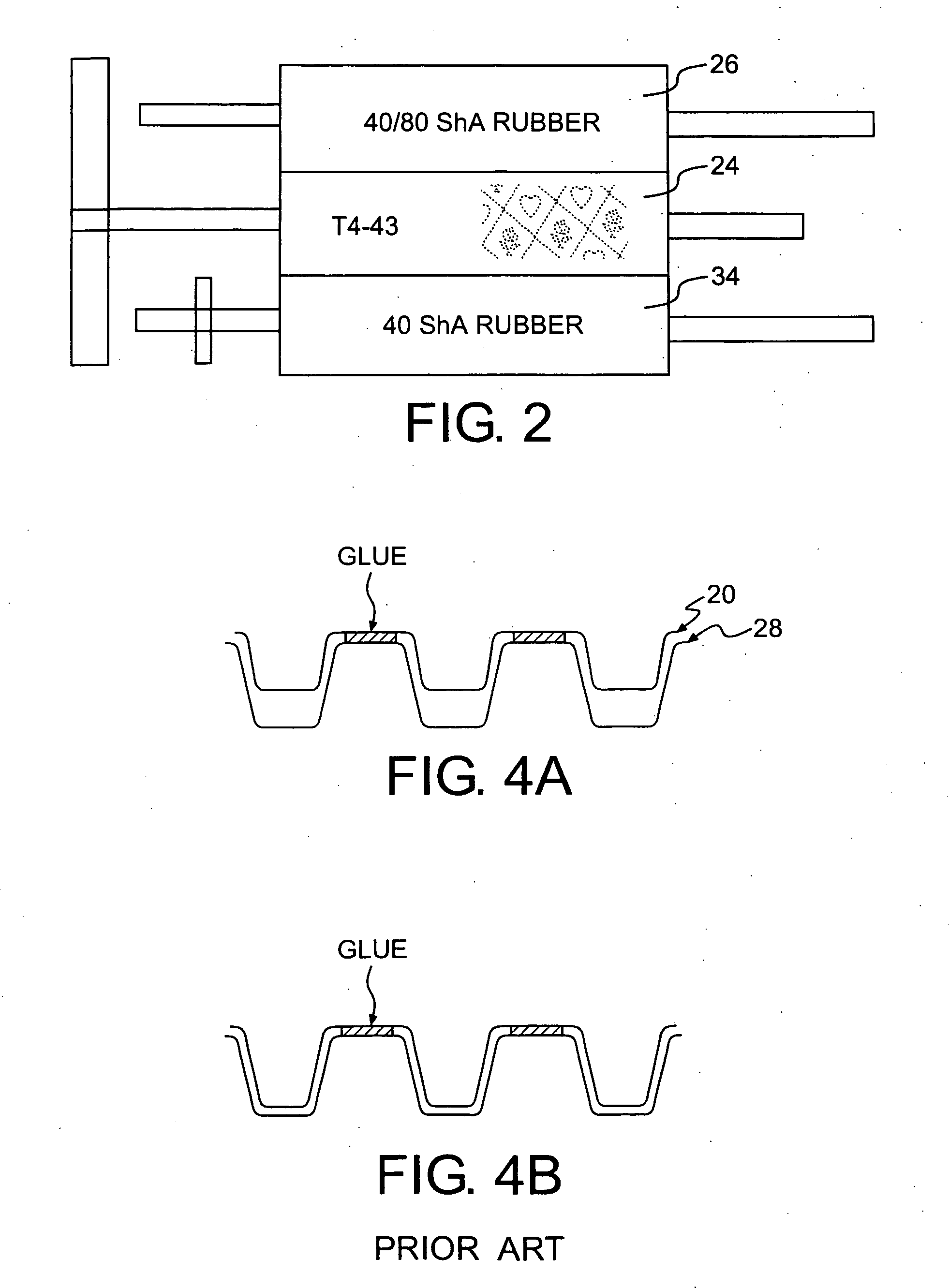
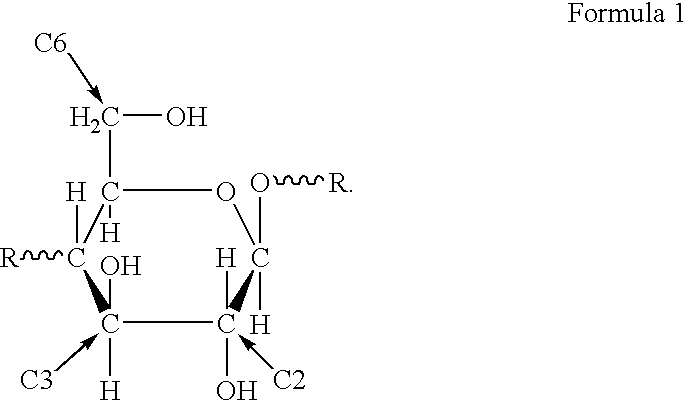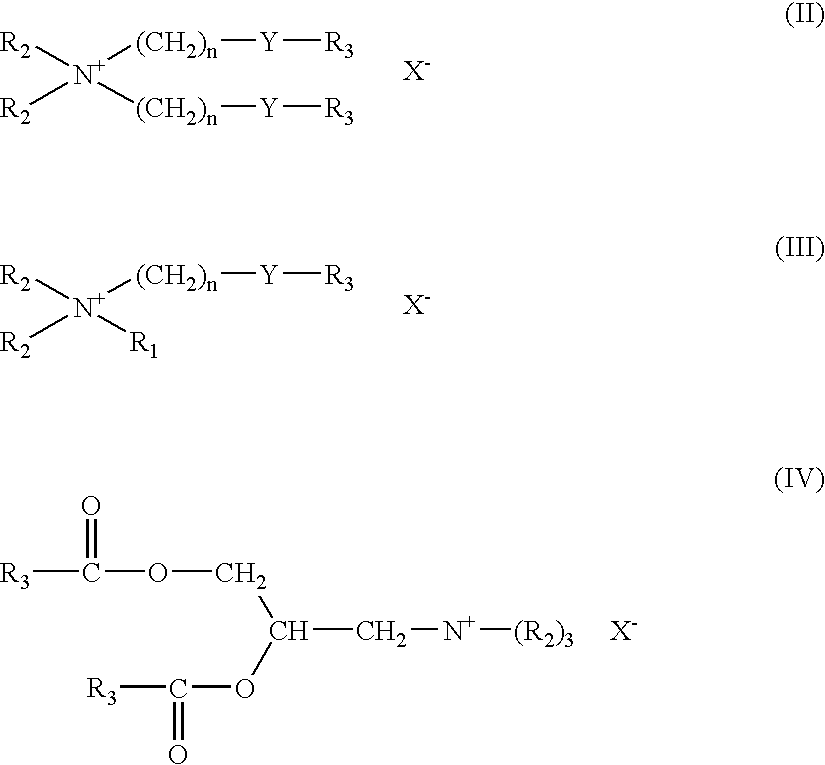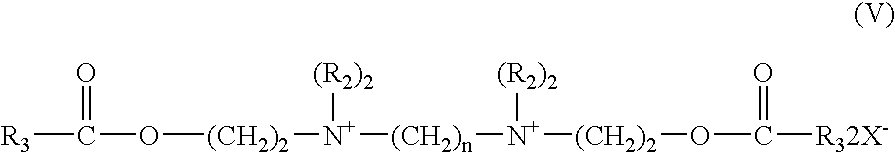Patents
Literature
4920 results about "Cellulose fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
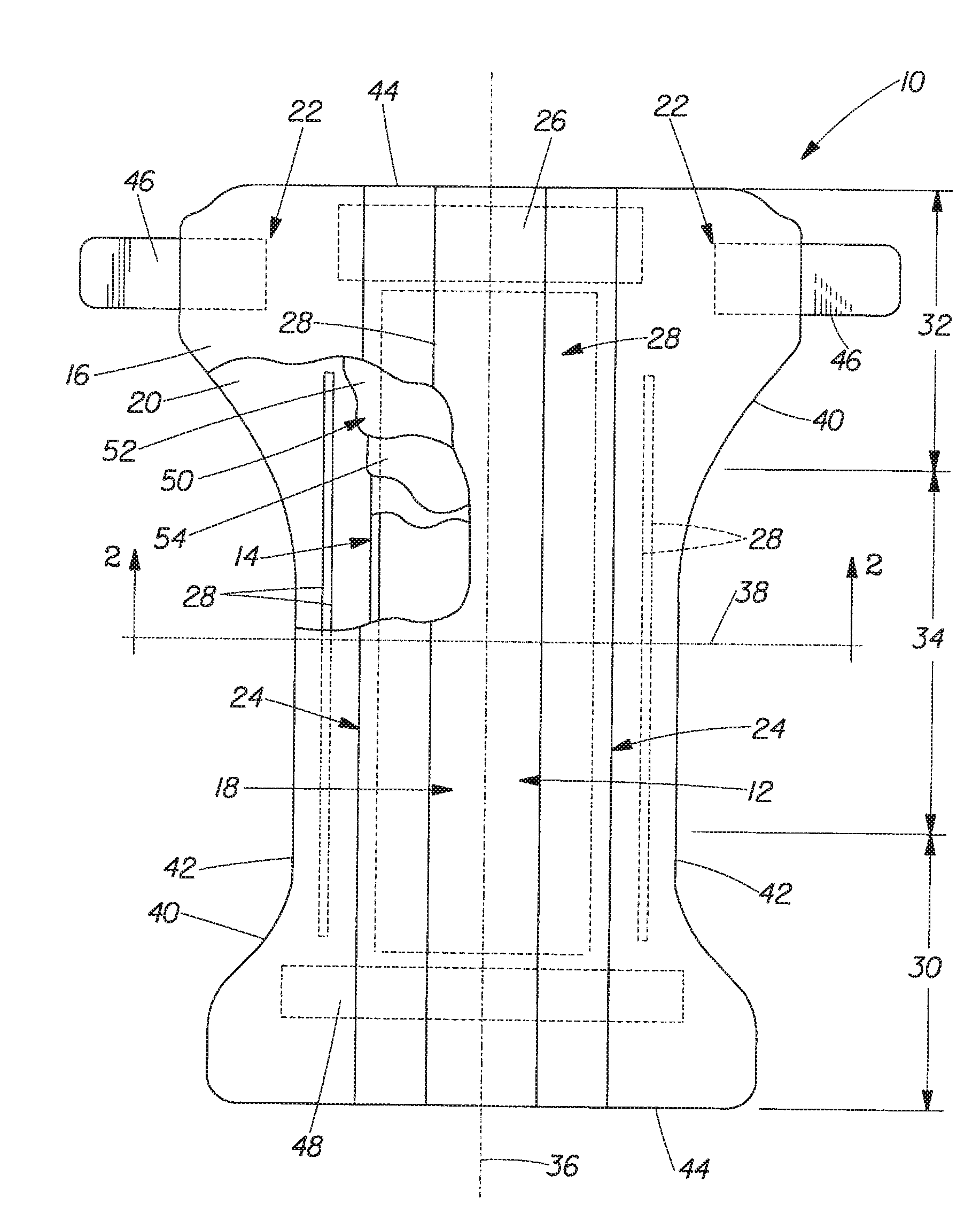
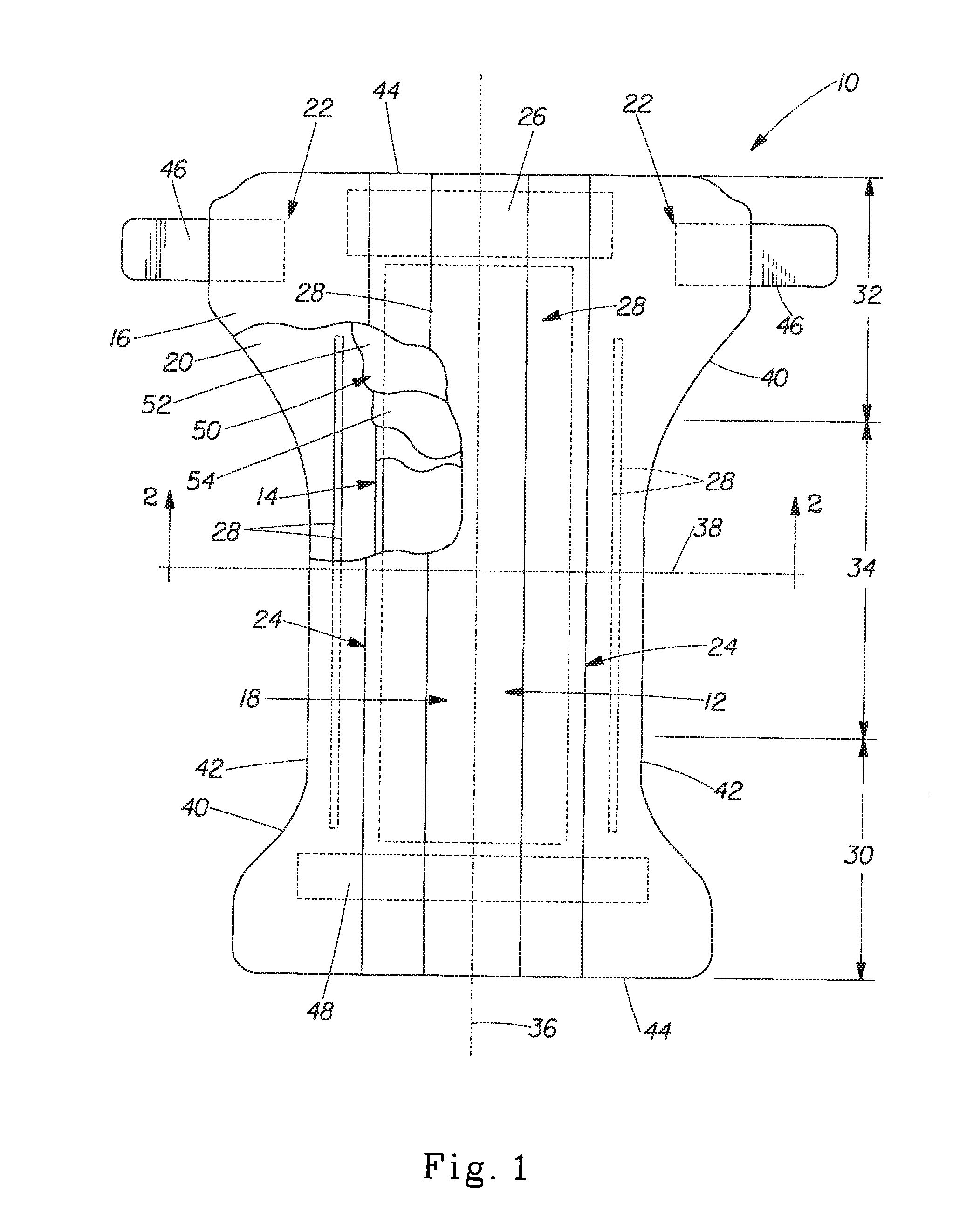
Cellulose fibers (/ˈsɛljʊloʊs, -loʊz/) are fibers made with ethers or esters of cellulose, which can be obtained from the bark, wood or leaves of plants, or from other plant-based material. In addition to cellulose, the fibers may also contain hemicellulose and lignin, with different percentages of these components altering the mechanical properties of the fibers.
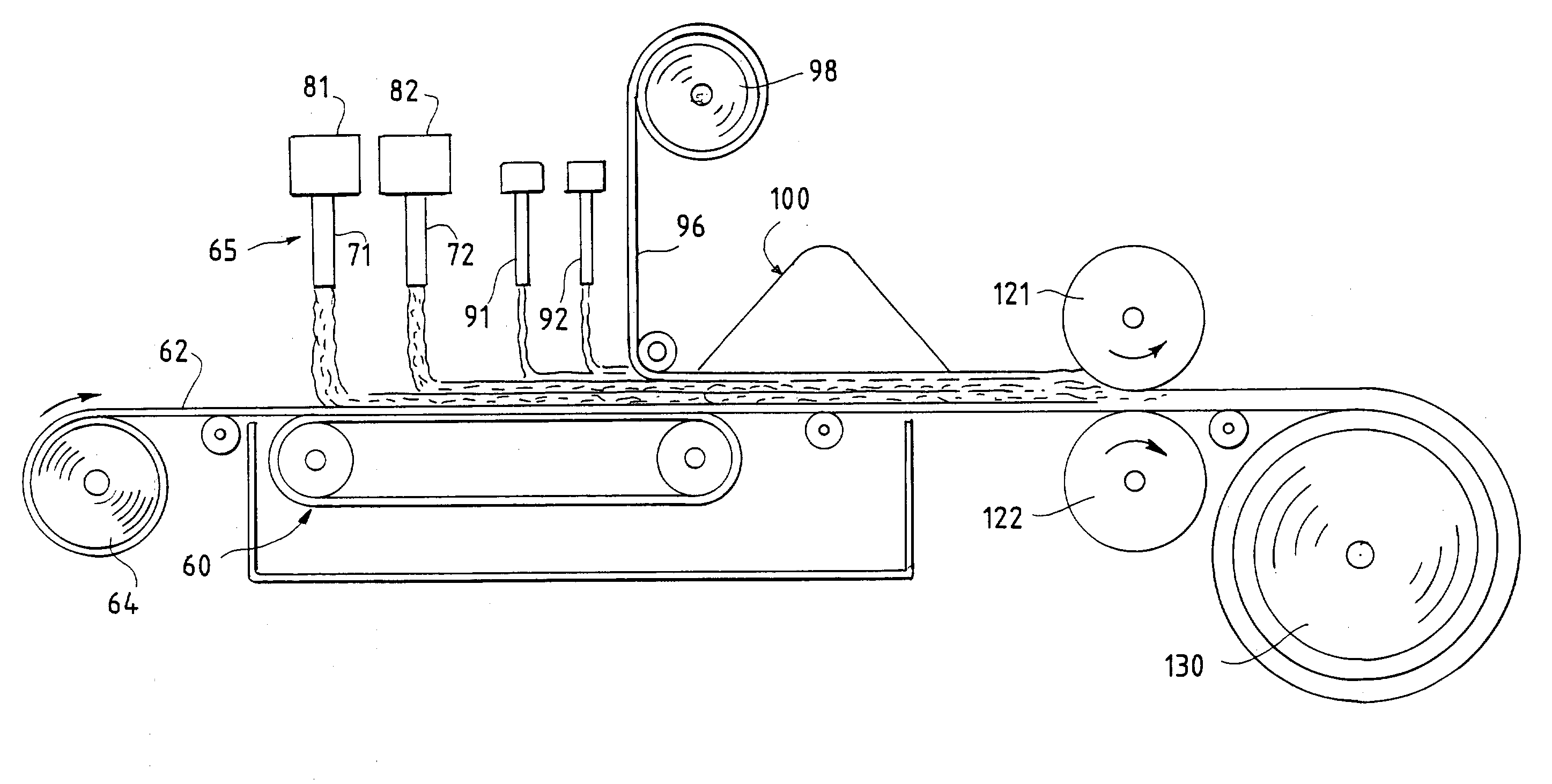
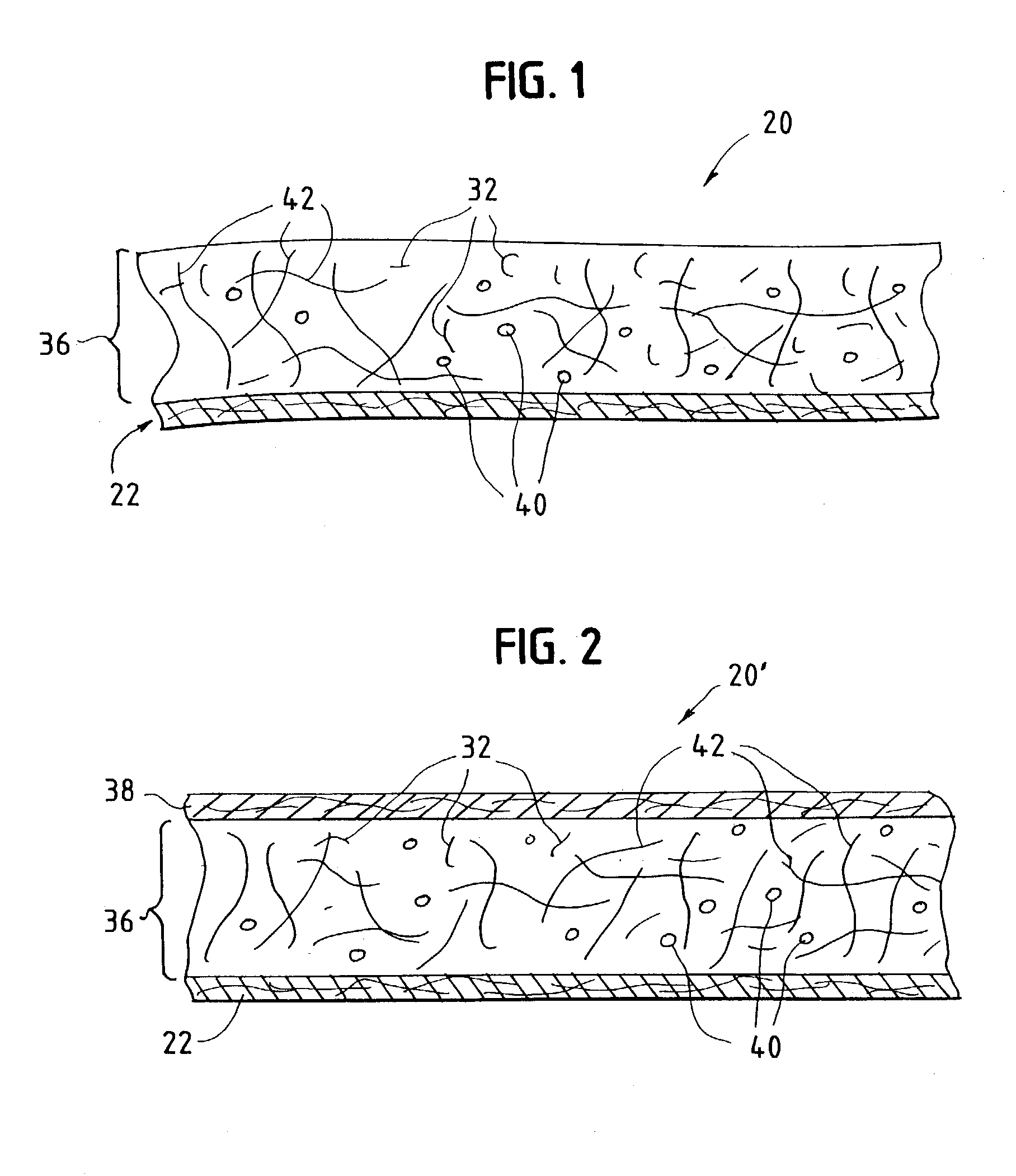
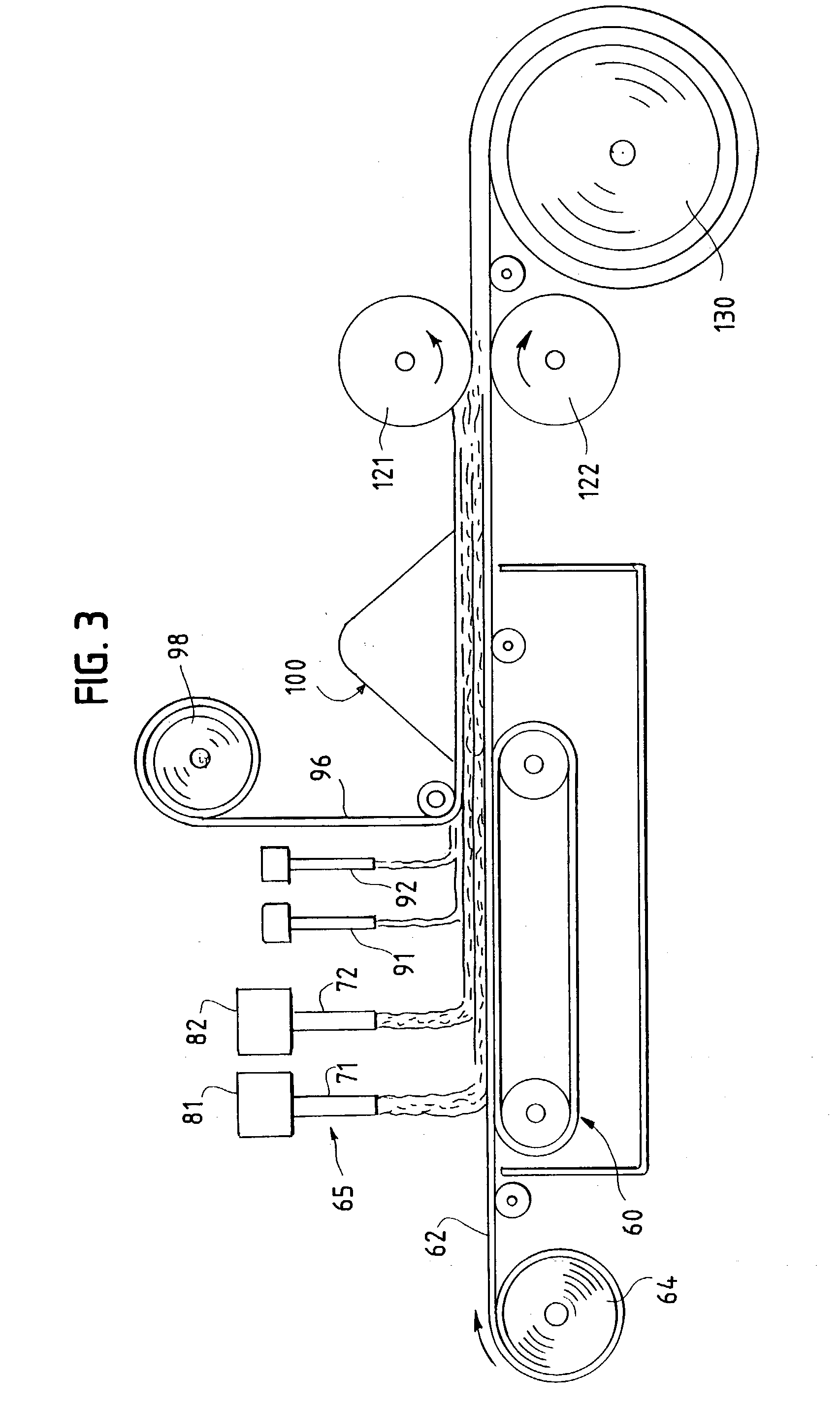
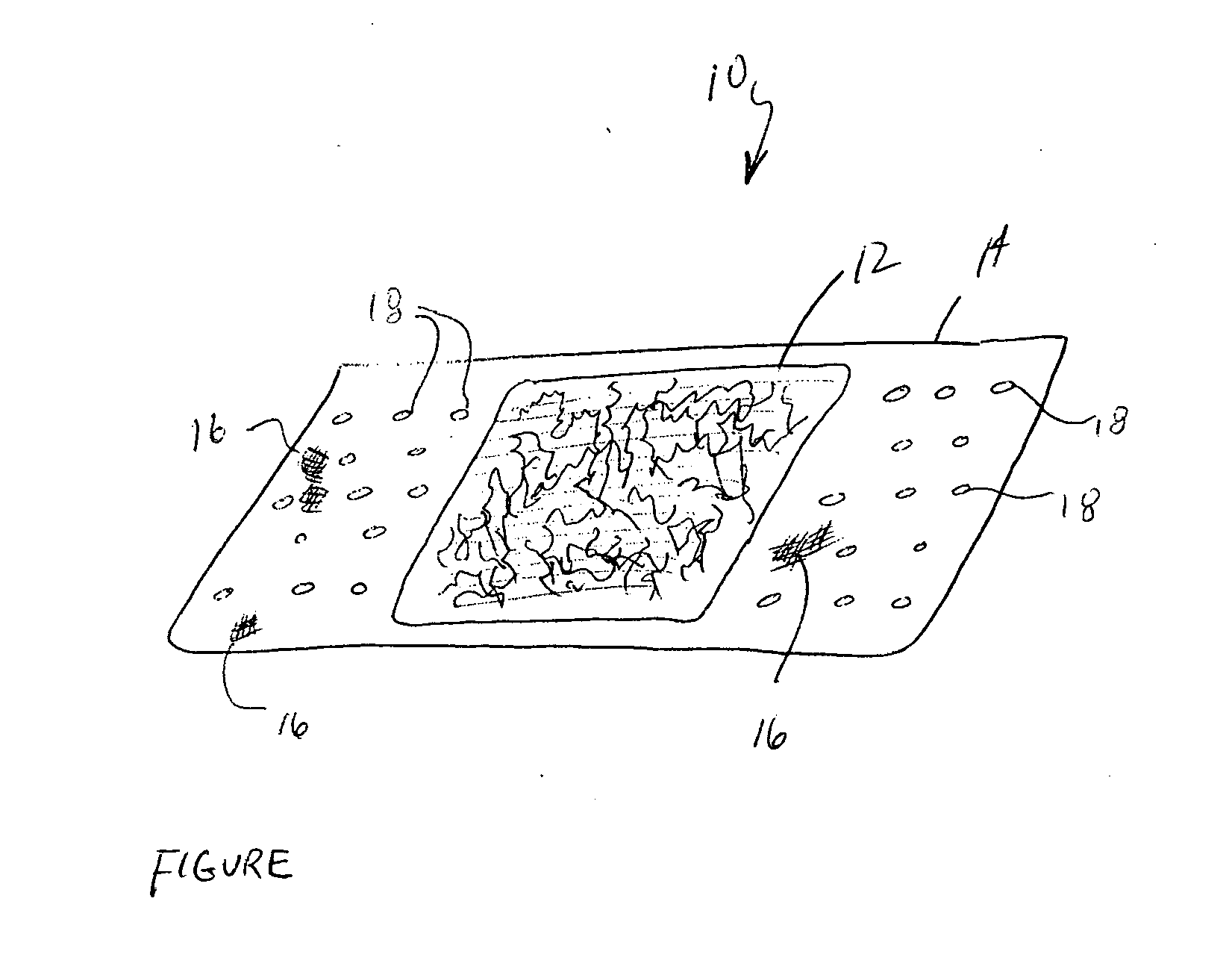
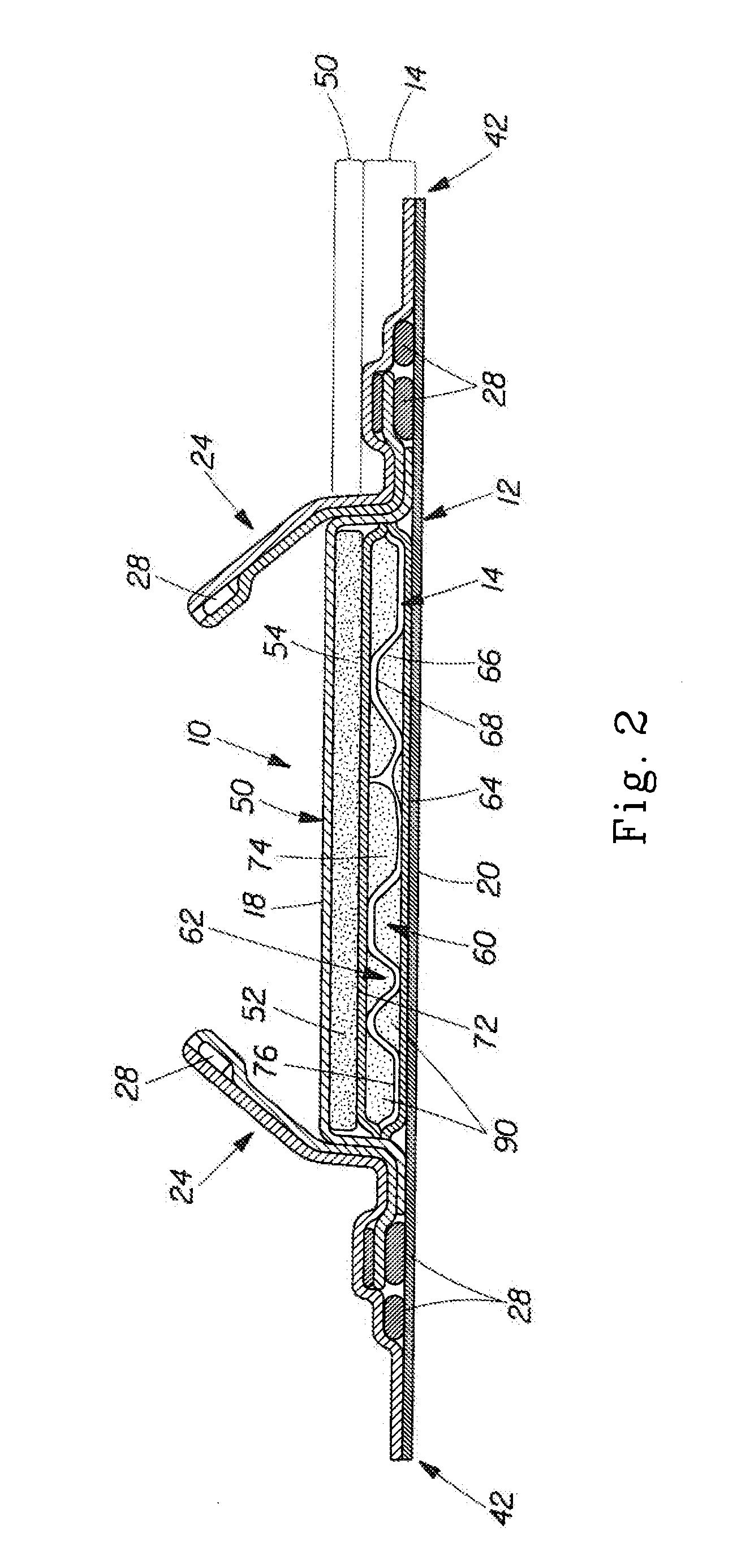
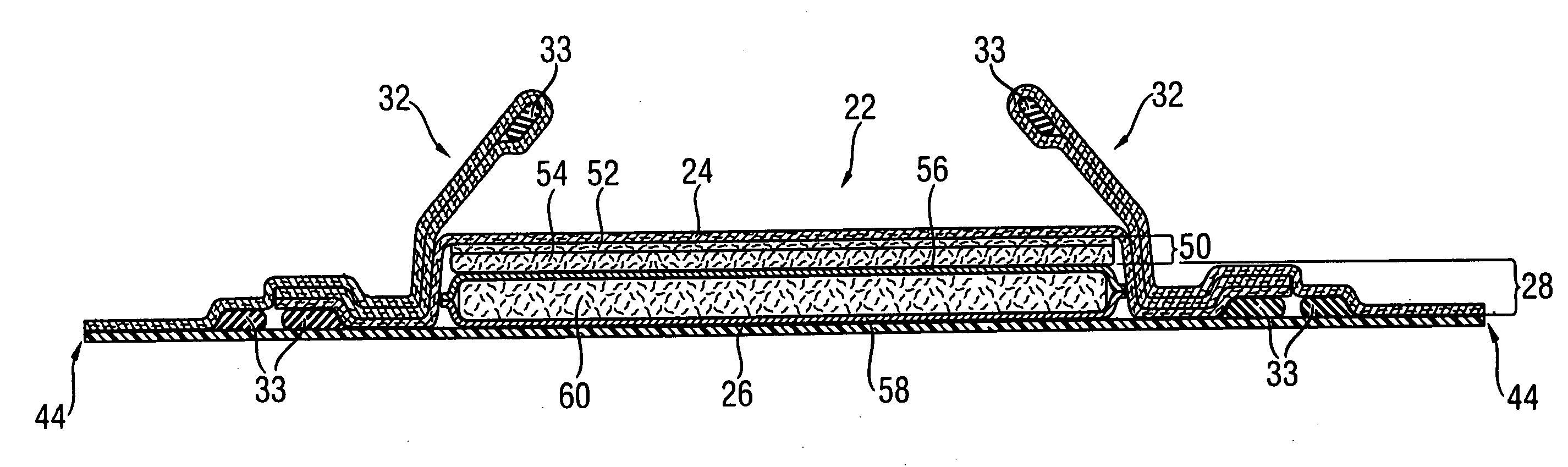
Absorbent material incorporating synthetic fibers and process for making the material
InactiveUS20030084983A1Reduce leakageWidespread acceptanceLayered productsBaby linensPolymer scienceHigh density
A process is provided for making a soft, high density, absorbent material with improved characteristics. A web is formed from material that includes a mixture of cellulosic fibers and synthetic polymer fibers. Then, the web is preferably compacted and embossed at an elevated temperature to further increase the web density and preferably to also create liquid-stable bonds between the synthetic polymer fibers and the cellulosic fibers in spaced-apart regions of the web.
Owner:EAM
Agents and devices for providing blood clotting functions to wounds
InactiveUS20070190110A1Promote healingShorten the timePhysical treatmentAntithrombogenic treatmentNitrogen dioxideMedicine
Hemostatic agents and devices are made from oxidized cellulose fiber, the oxidized cellulose having a carboxylation content increased by the action of nitrogen dioxide on virgin cellulose fiber. A composition may be incorporated into the oxidized cellulose fiber to cause a pharmacological effect on a wound to which the hemostatic agents and devices are applied. When applied, the oxidized cellulose fiber causes blood emanating from the wound to clot. The oxidized cellulose fiber can either be resorbed into the wound or removed from the wound after healing. A hemostatic bandage includes a pad of unwoven oxidized cellulose fibers mounted on a substrate. Methods of arresting a flow of blood emanating from a wound using such devices are also disclosed. Methods of fabricating oxidized cellulose are also disclosed.
Owner:PAMEIJER CORNELIS H +1
Process for making unitary fibrous structure comprising randomly distributed cellulosic fibers and non-randomly distributed synthetic fibers
InactiveUS7067038B2High densityNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer scienceRepeat pattern
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Disposable Absorbent Article With Improved Acquisition System
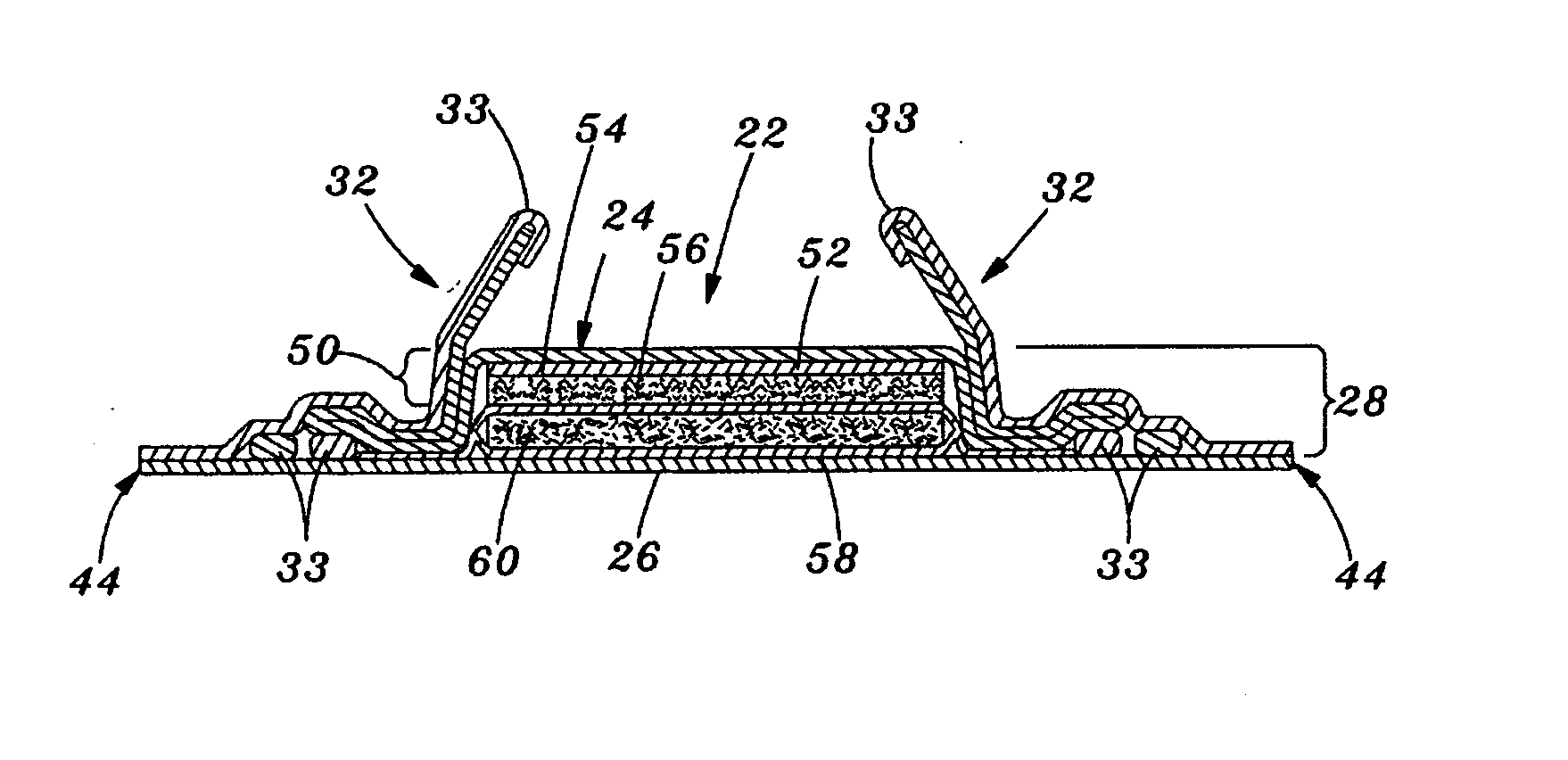
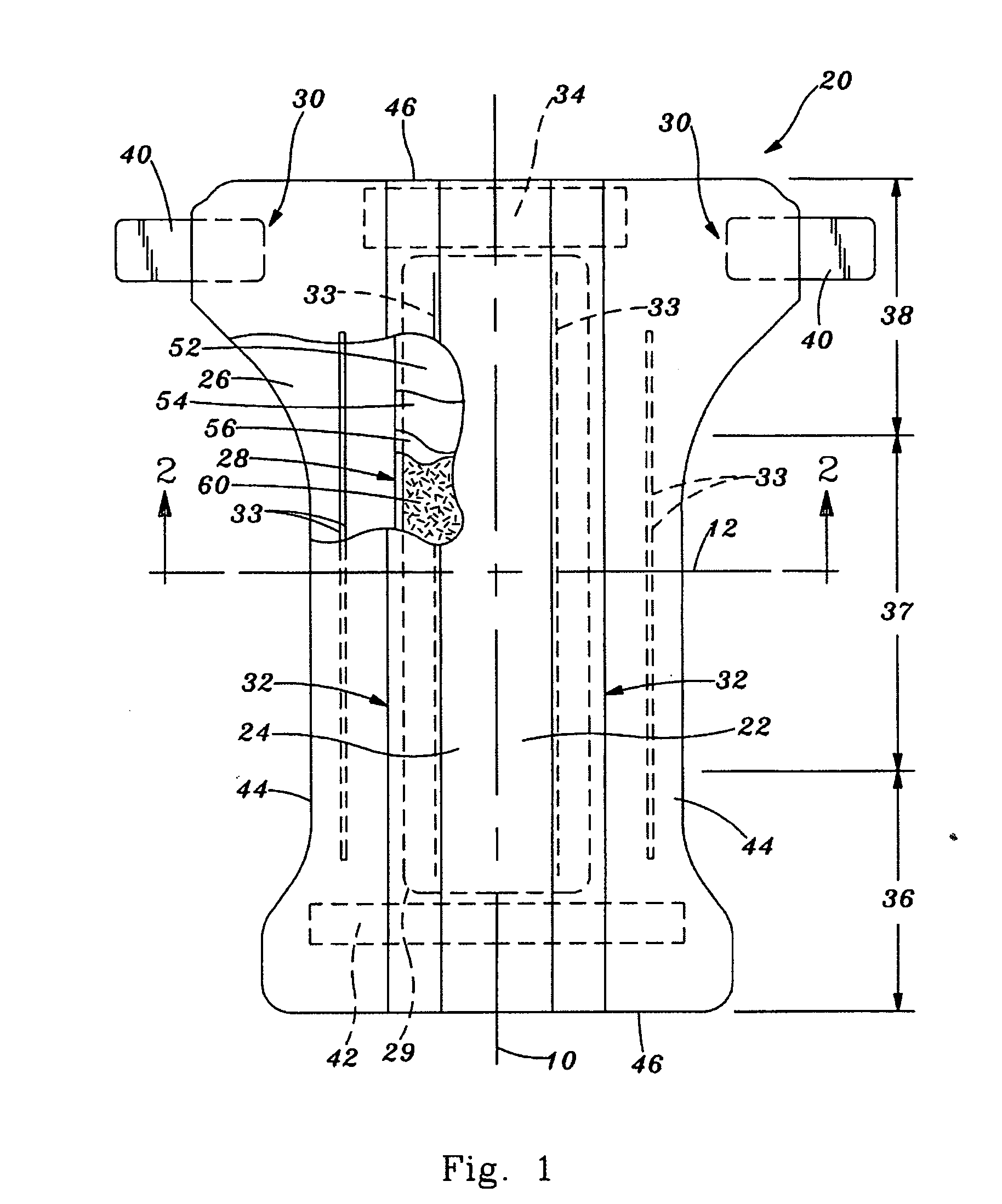
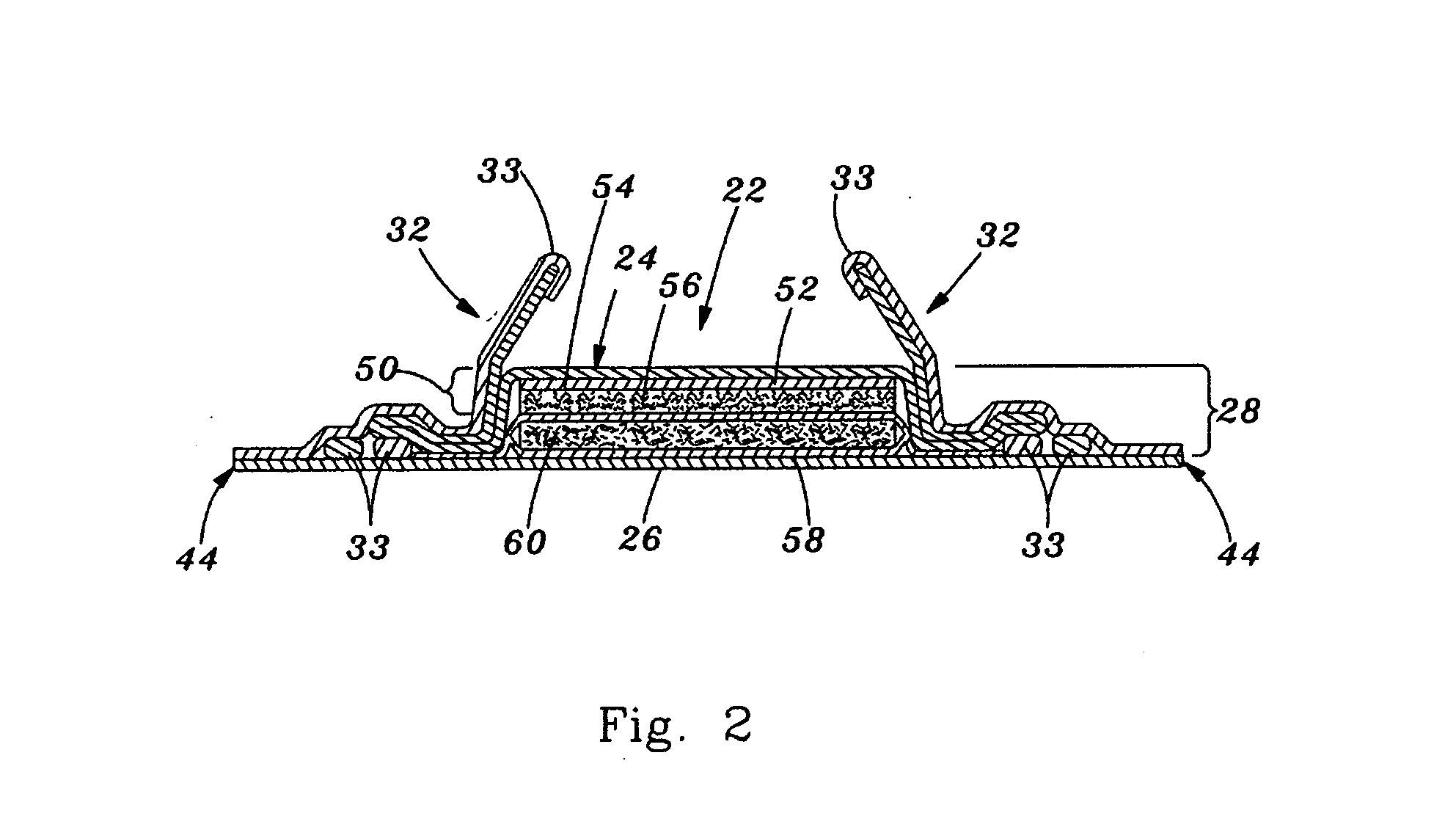
A disposable absorbent article comprising a chassis including a topsheet and a backsheet, a substantially cellulose free absorbent core located between the topsheet and the backsheet and having a wearer facing side oriented toward a wearer when the article is being worn and an opposed garment facing side, and a liquid acquisition system disposed between the liquid permeable topsheet and the wearer facing side of the absorbent core comprising chemically cross-linked cellulosic fibers.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Fluid acquisition layer
A liquid acquisition material for use in an absorbent article. The liquid acquisition material having first fibers and second fibers. The first fibers are chemically cross-linked cellulose fibers and the second fibers are selected from the group consisting of: polyethylene, polypropylene, polyester, rayon, lyocell, and mixtures thereof. The liquid acquisition material has a total dry weight, the first fibers have a first dry weight, and the second fibers have a second dry weight. The first dry weight is from 30 to 95 percent of the total dry weight and the second dry weight is from 5 to 70 percent of the total dry weight.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
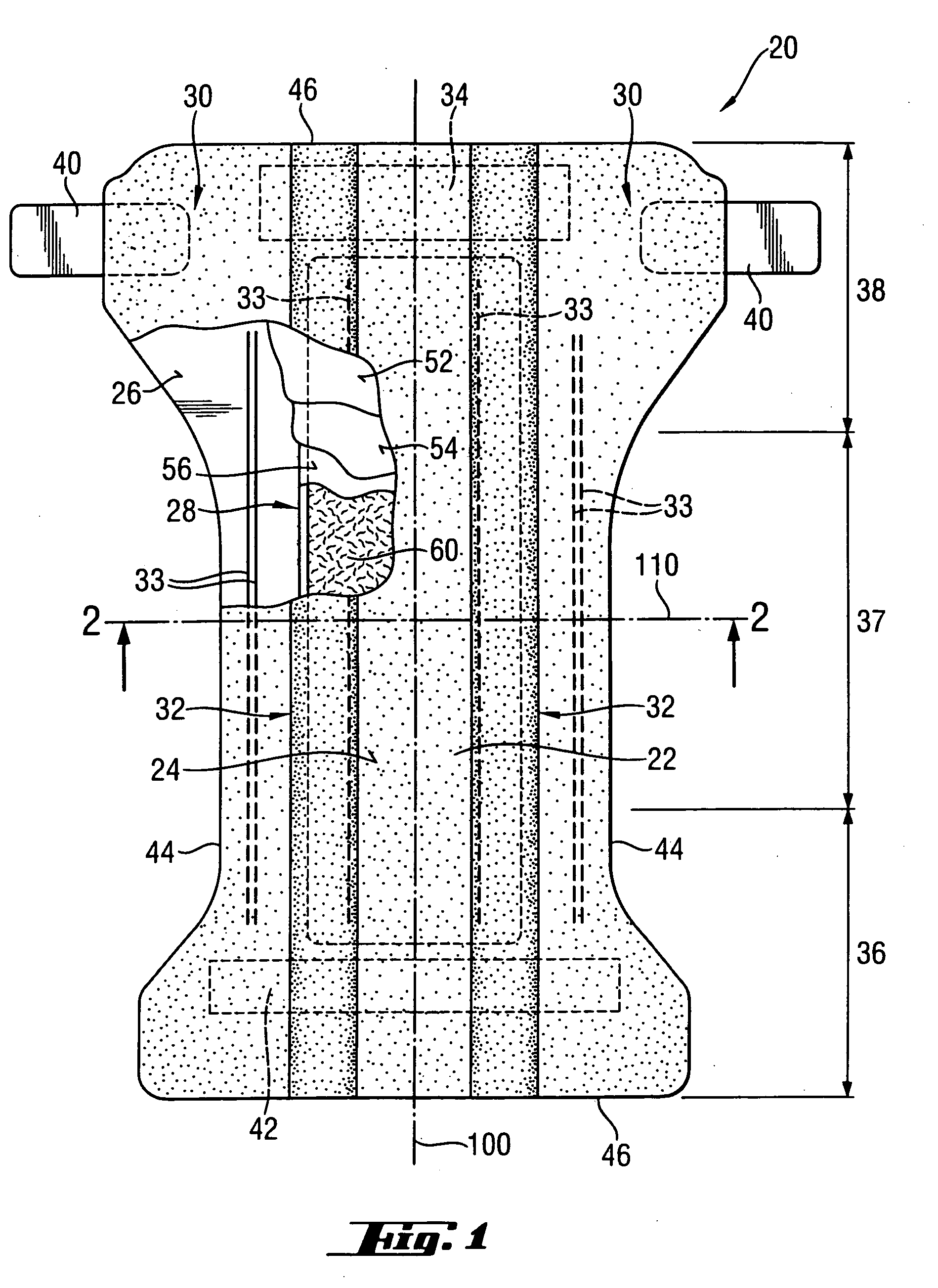
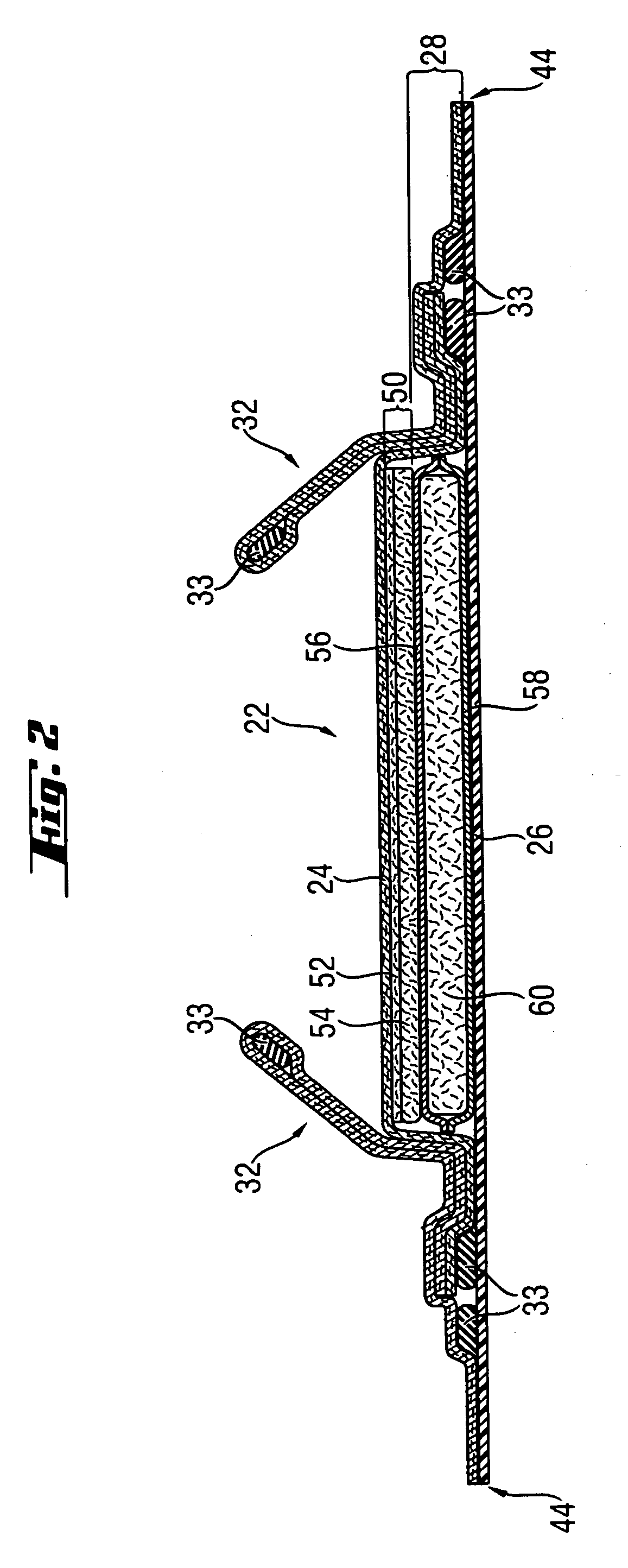
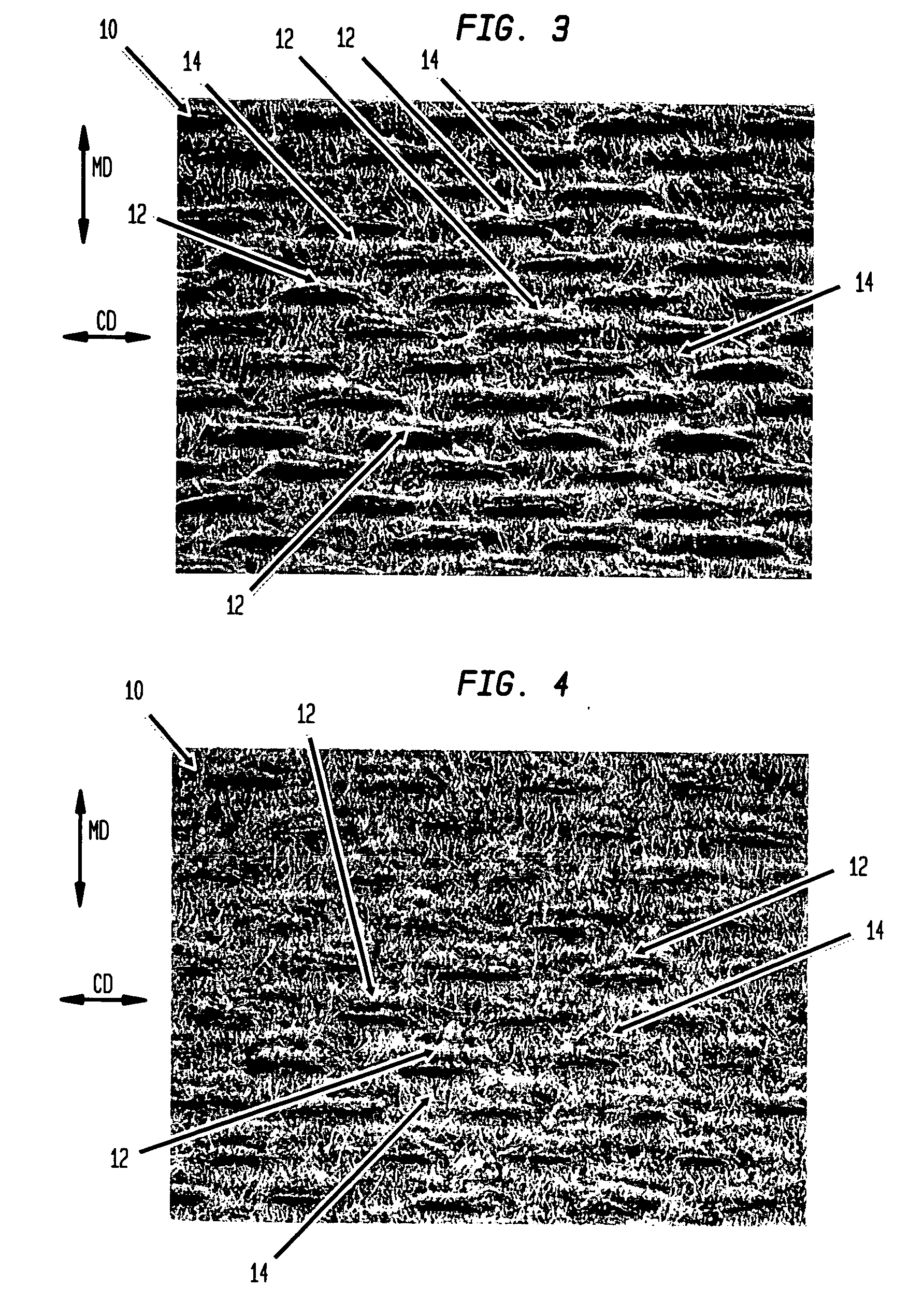
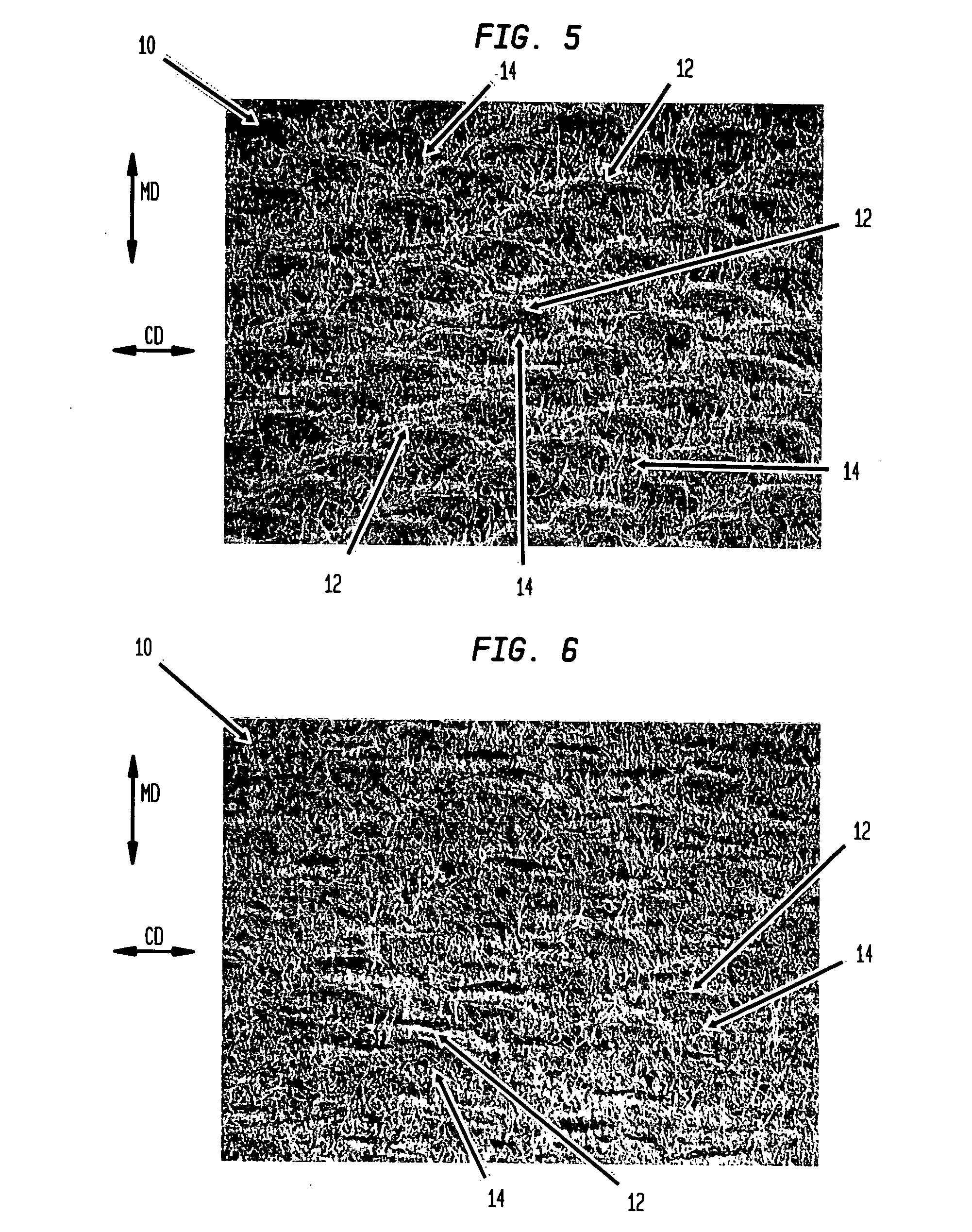
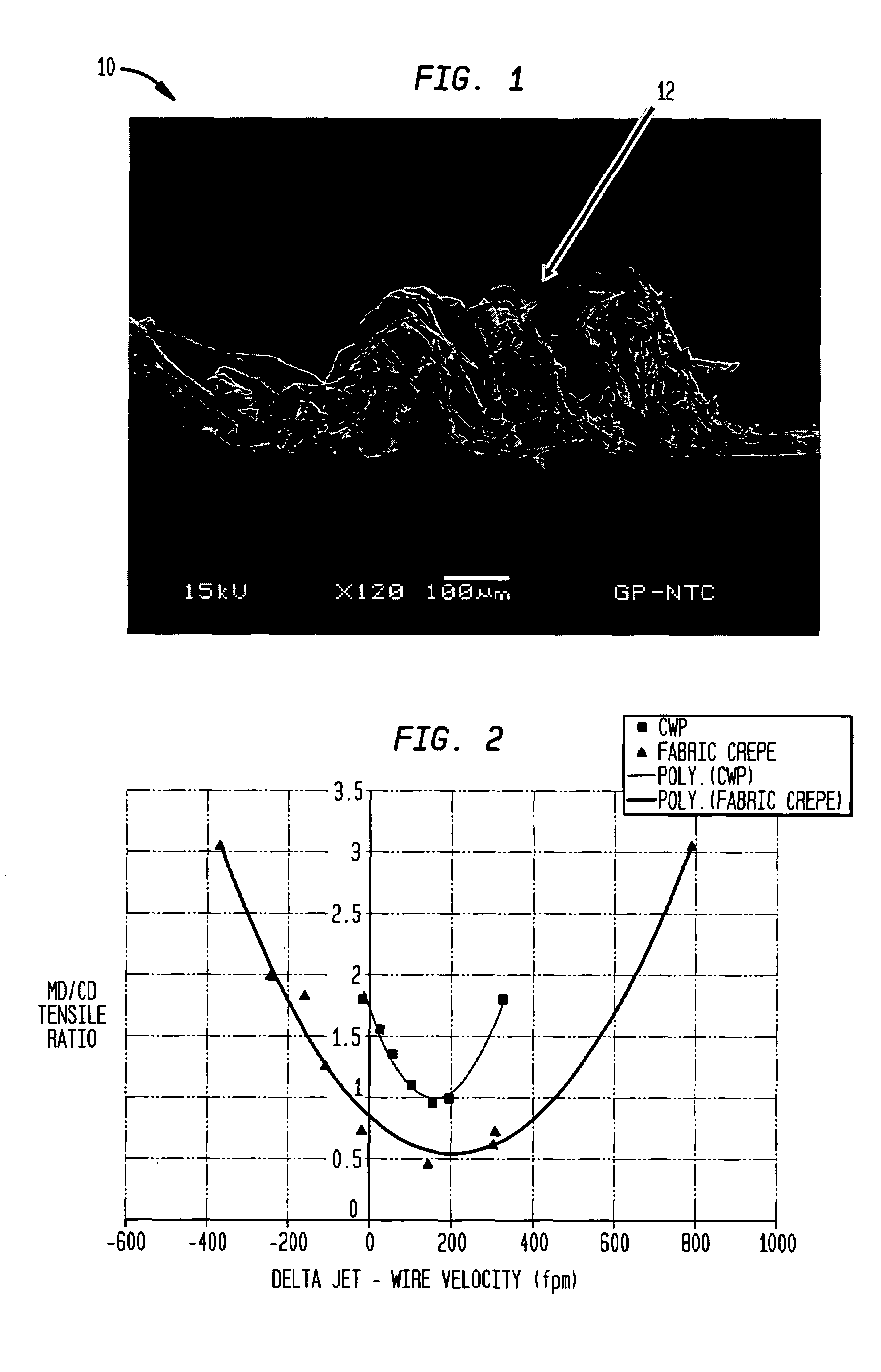
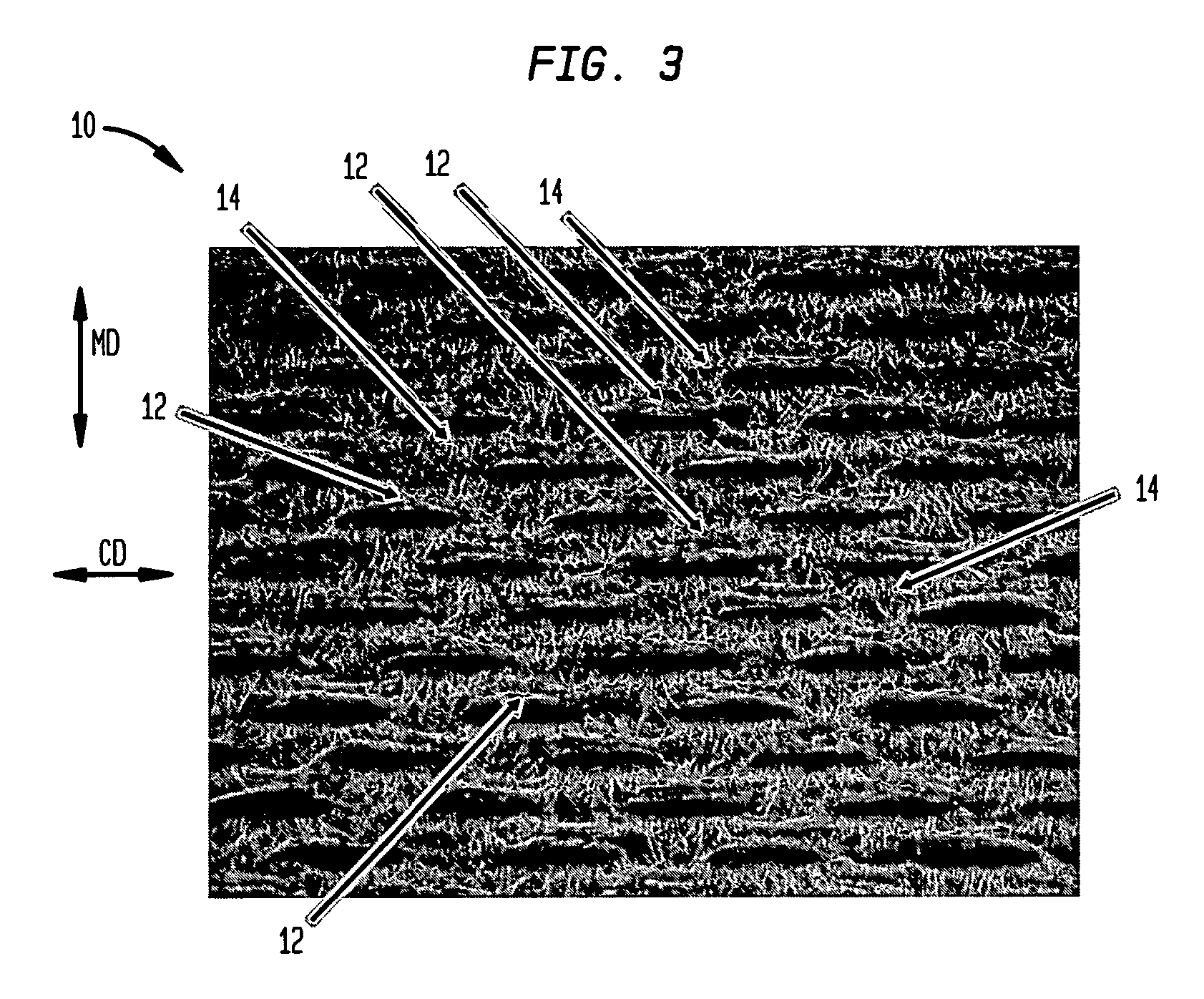
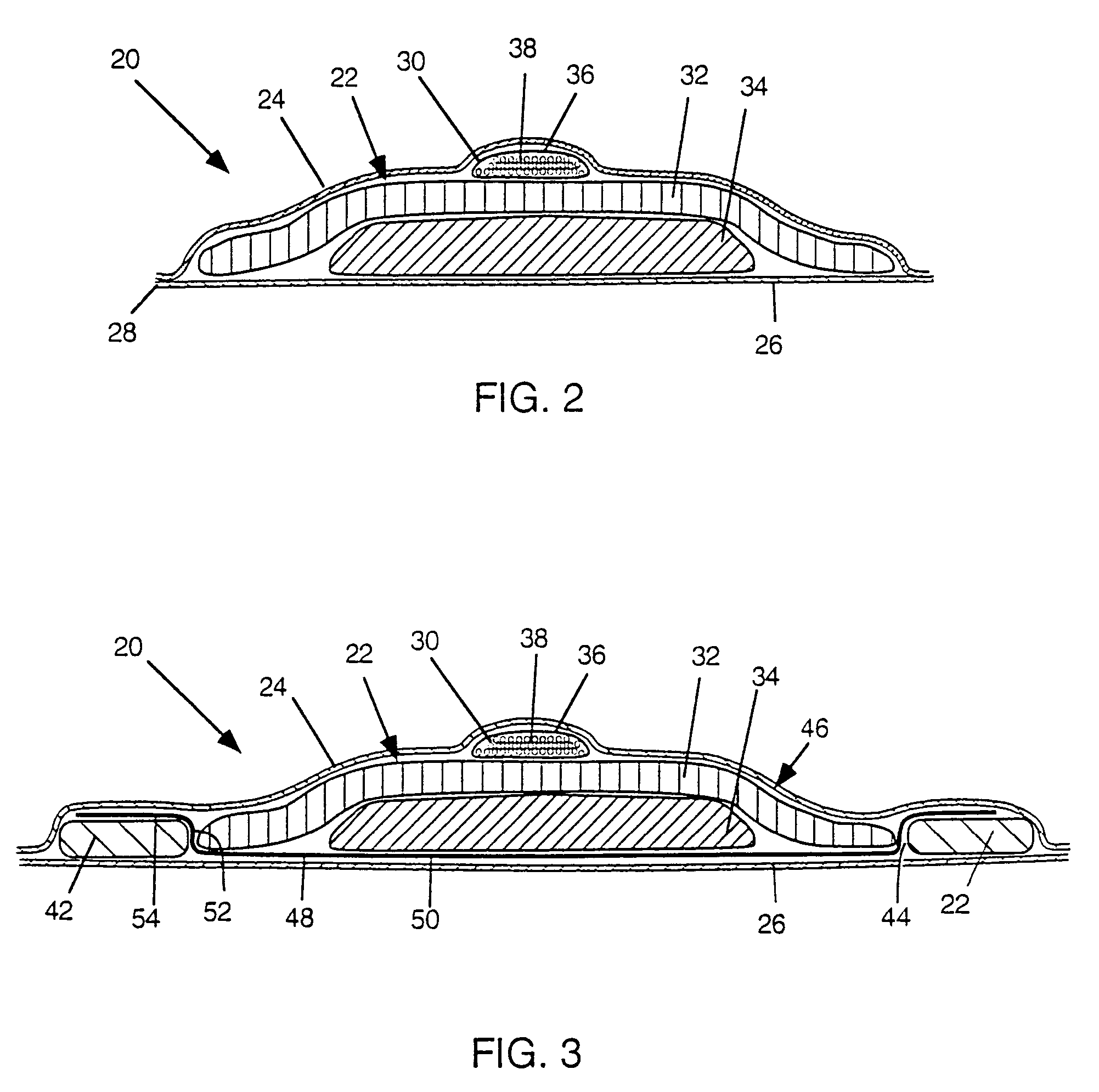
Wet-pressed tissue and towel products with elevated CD stretch and low tensile ratios made with a high solids fabric crepe process
ActiveUS20050241786A1The implementation process is simpleNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationMedicineCellulose fiber
An absorbent sheet of cellulosic fibers includes a mixture of hardwood fibers and softwood fibers arranged in a reticulum having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking regions whose fiber orientation is biased along the machine direction between pileated regions interconnected thereby, wherein the sheet exhibits a % CD stretch which is at least about 2.75 times the dry tensile ratio of the sheet. Tensile ratios of from about 0.4 to about 4 are readily achieved.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Process for forming micro-fiber cellulosic nonwoven webs from a cellulose solution by melt blown technology and the products made thereby
InactiveUS20050056956A1Artificial filament washing/dryingLoose filtering material filtersNon solventEngineering
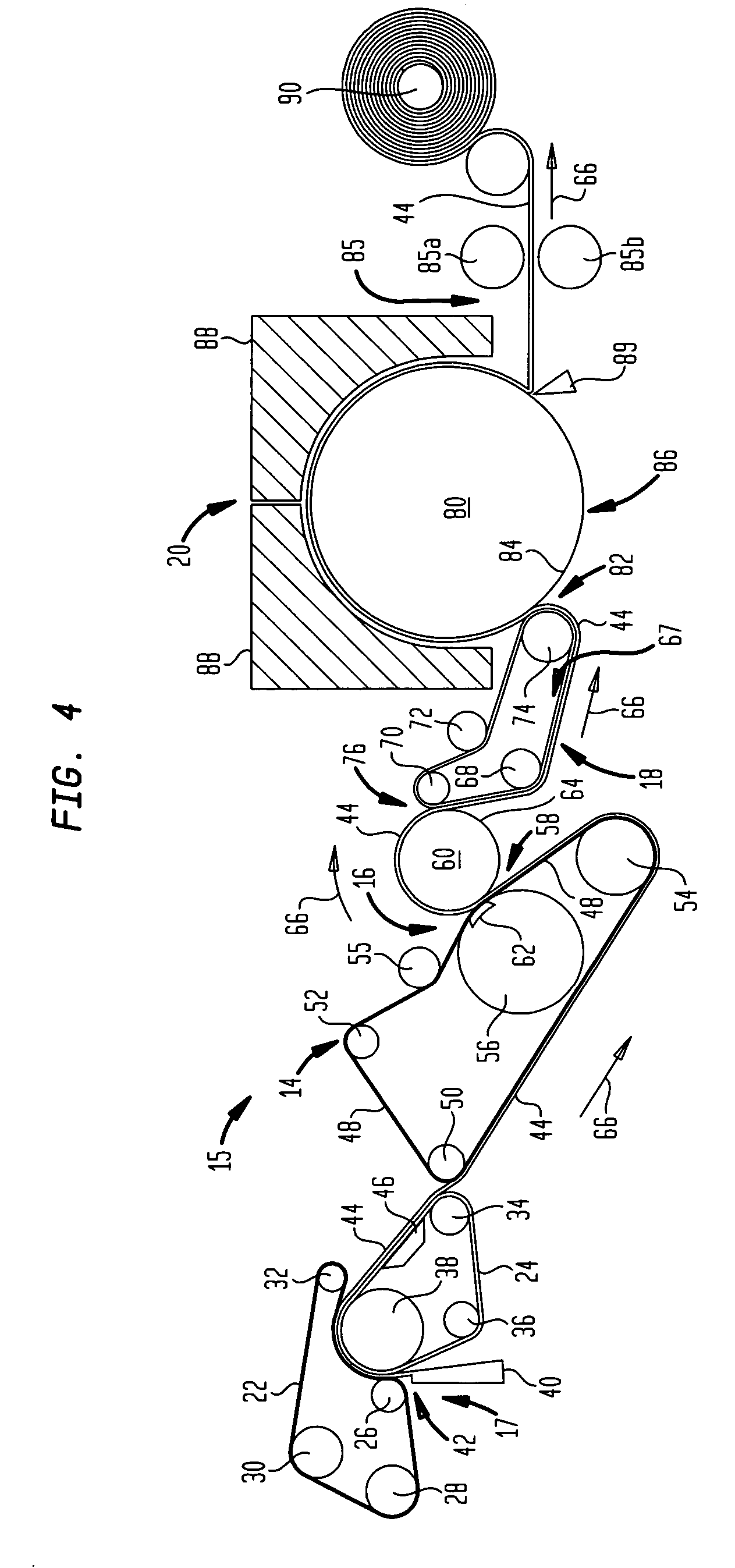
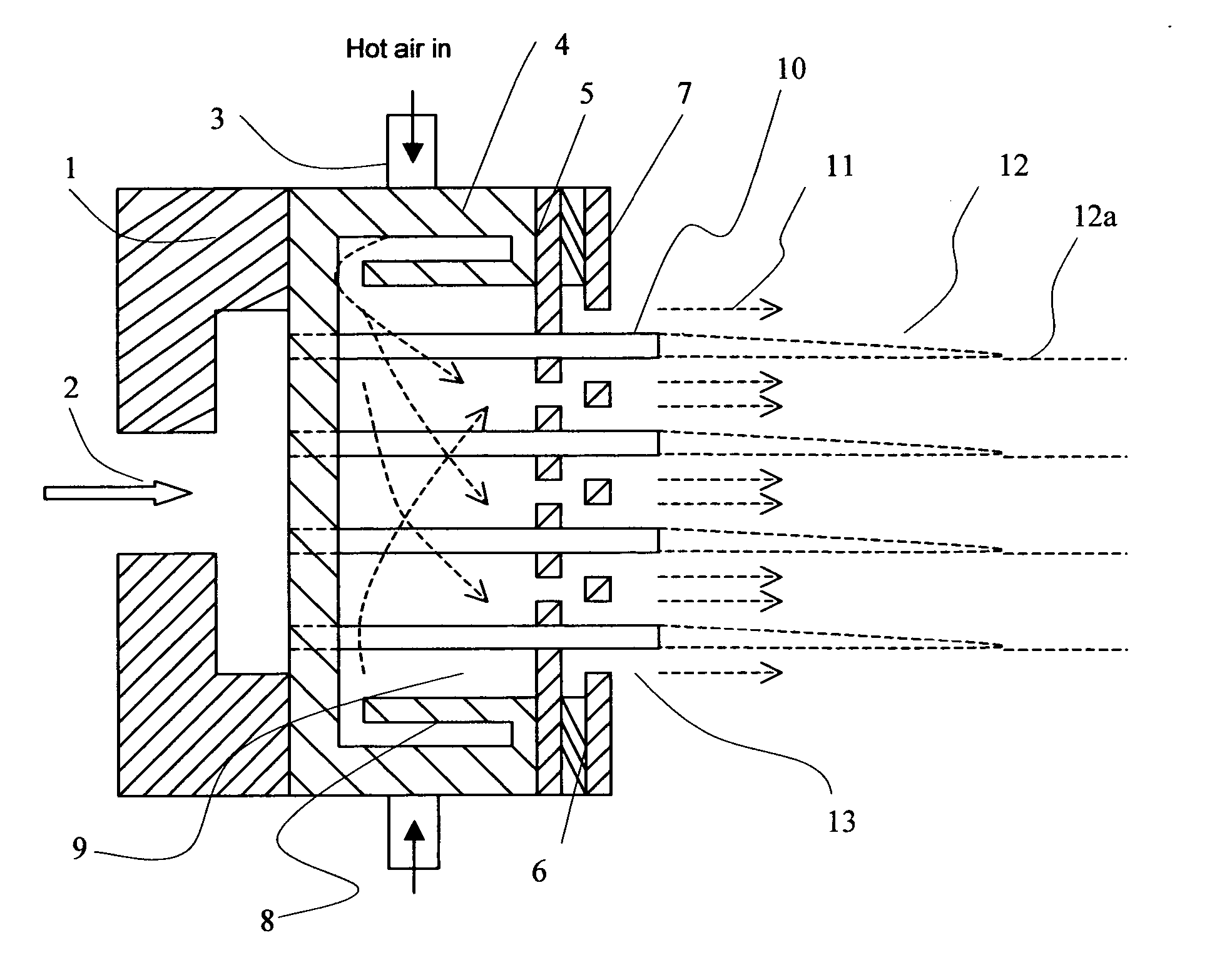
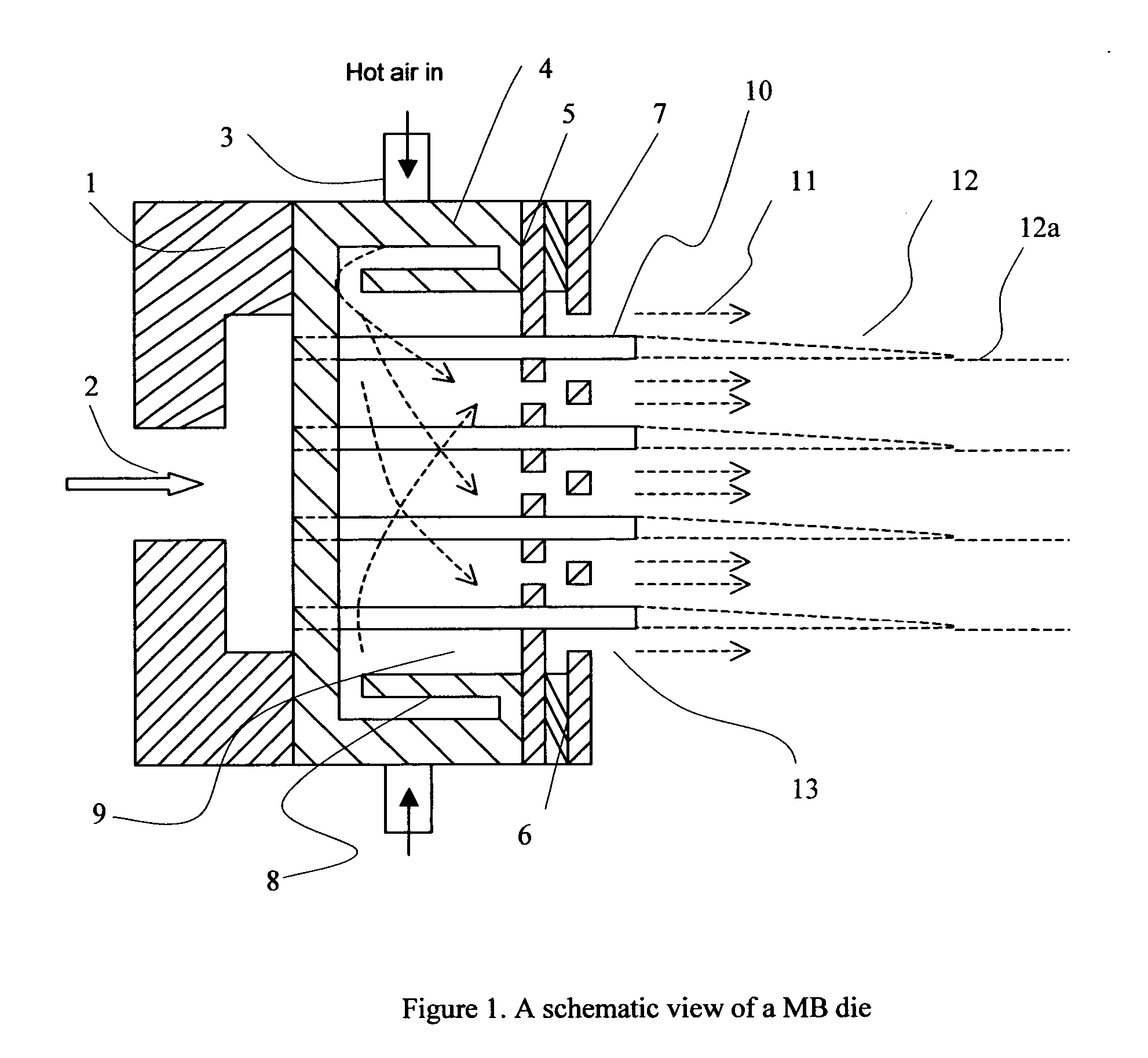
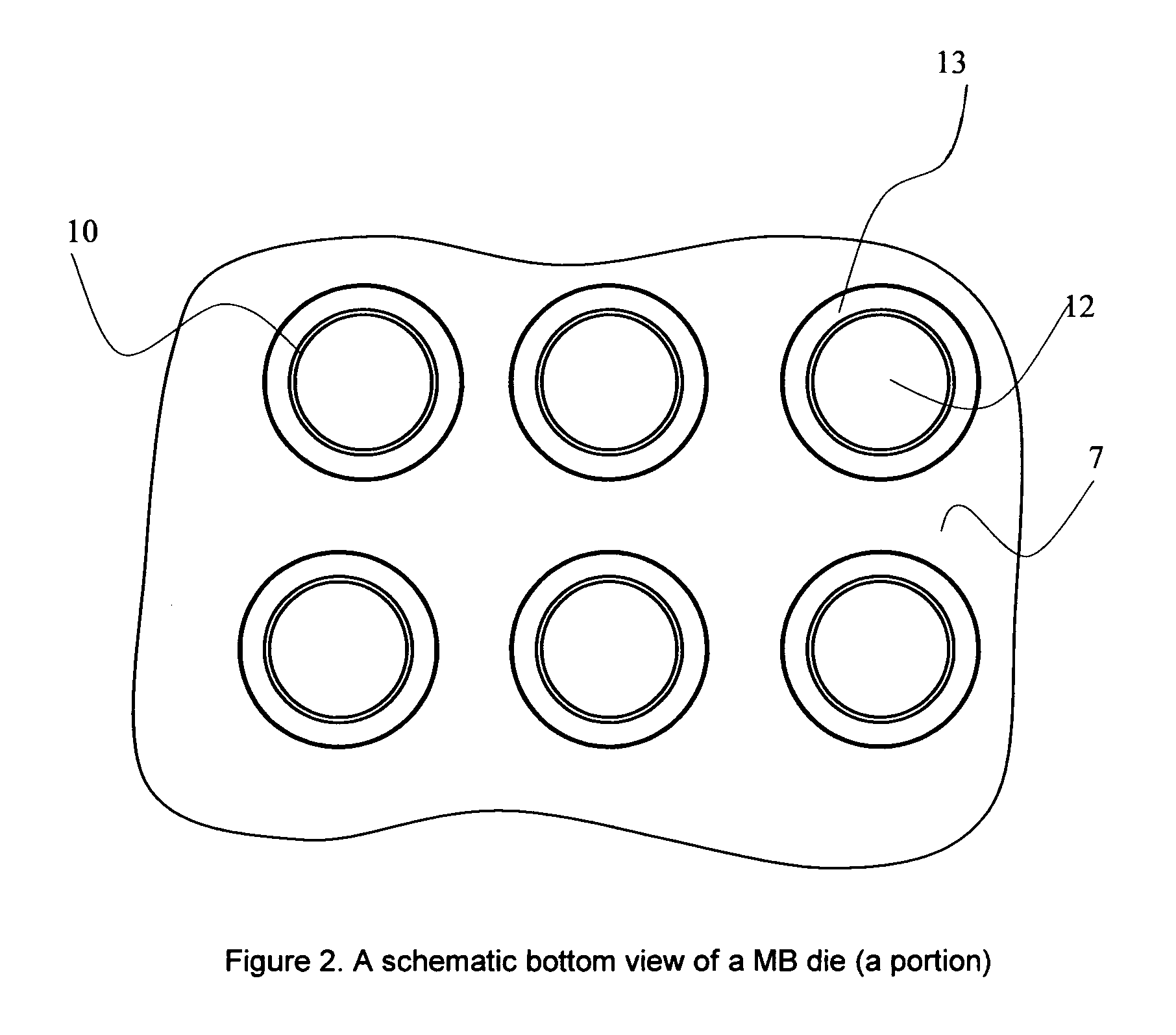
This invention relates to a process of melt blowing a cellulose solution through a concentric melt blown die with multiple rows of spinning nozzles to form cellulosic microfiber webs with different web structures. The process comprises the steps of (a) extruding a cellulose solution (dope) through a melt blown spinneret with multiple rows of spinning nozzles; (b) drawing each individual extrudate filament to fine fiber diameter by its own air jet; (c) coagulating and entangling the fine fibers with a series of pressured hydro needling jets of recycling solution of the mixture of cellulose solvent and non-solvent in the spin-line; (d) collecting the stream of microfibers, air and needling jets on a moving collecting surface to form cellulosic fiber web; (e) hydro-entangling the said pre-bonded web downstream with at least one set of hydro needling jets of recycling solvent / non-solvent solution for forming well bonded nonwoven web; (f) regenerating the fine fibers in at least one bath for at least 5 seconds; (g) further regenerating and washing the fine fibers in another bath for at least 5 seconds; (h) pinching the well bonded melt blown cellulosic nonwoven with pressure rollers to remove major portions of the non-solvent; (i) drying the nonwoven web by heat, or vacuum or both, and (j) winding the nonwoven web into rolls.
Owner:BIAX FIBERFILM CORP
Dust filter bag including a highly porous backing material ply
InactiveUS6706086B2Simple and cost-effective productionCleaning filter meansCombination devicesBursting strengthCellulose fiber
A dust filter bag having a highly porous backing material ply and a method for producing the dust filter bag. The dust filter bag includes at least one filter material ply and at least one backing material ply, the backing material ply possessing an air permeability of at least 900 l / m<2 >x s, a burst strength of at least 70 kPa, a rupture strength longitudinally better than 10 and transversely better than 3 N, a flexural rigidity longitudinally better than 0.5 cN cm<2 >and transversely better than 0.25 cN cm<2>, a basis weight of 30-80 g / m<2 >and a droplet sink-in time of less than 10 minimum. The dust filter bag can be produced by the following steps: mixing fibers including cellulose fibers and fusible fibers into a homogenous fiber mix, processing the fiber mix into a fiber web by wet laying, drying the fiber web, curing the dried fiber web by thermofusion into a backing material ply, processing the backing material ply with a filter material ply into a raw bag, and finishing the raw bag into a dust filter bag.
Owner:NEENAH GESSNER GMBH
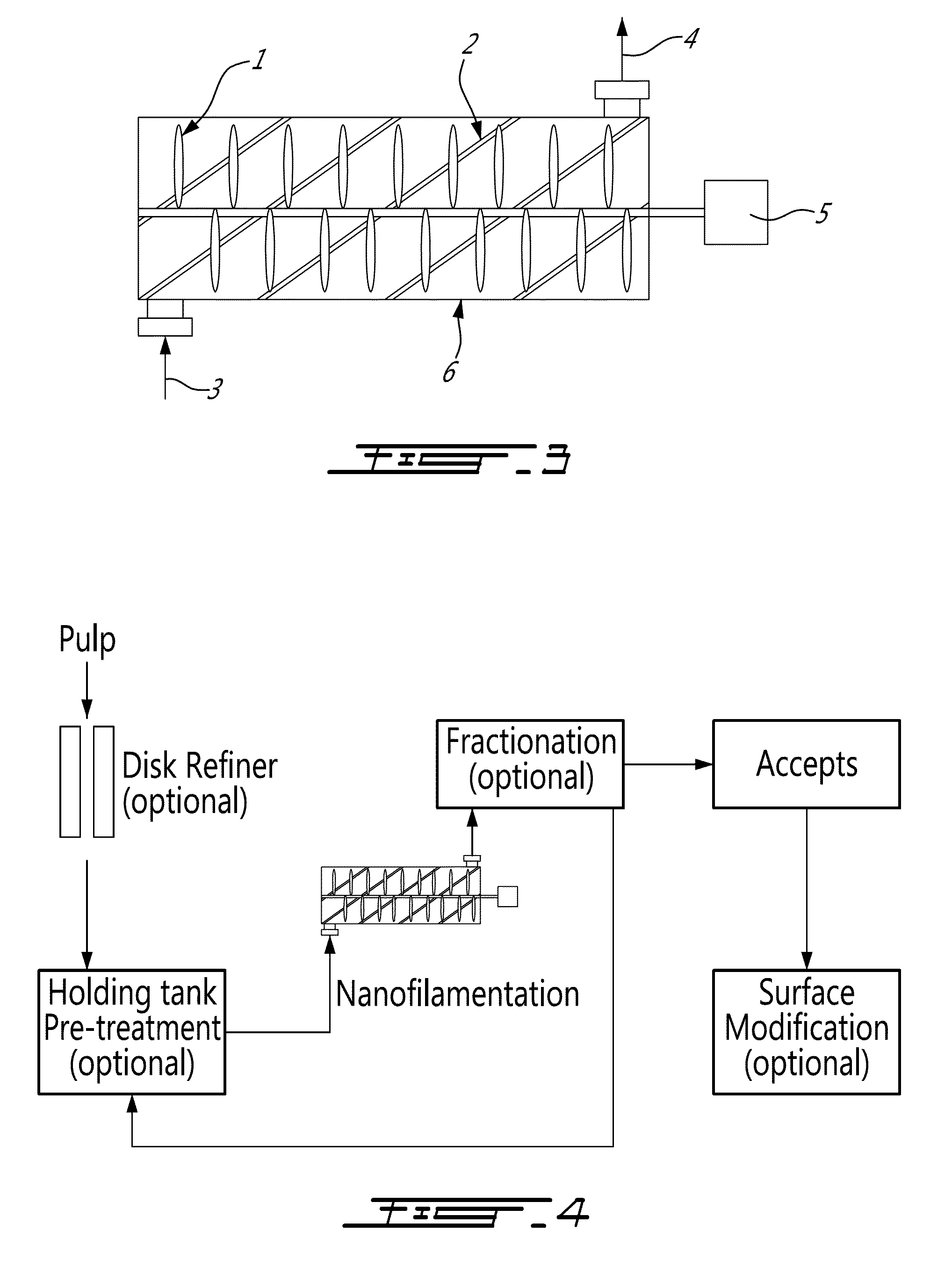
Method and apparatus for manufacturing microfibrillated cellulose fiber
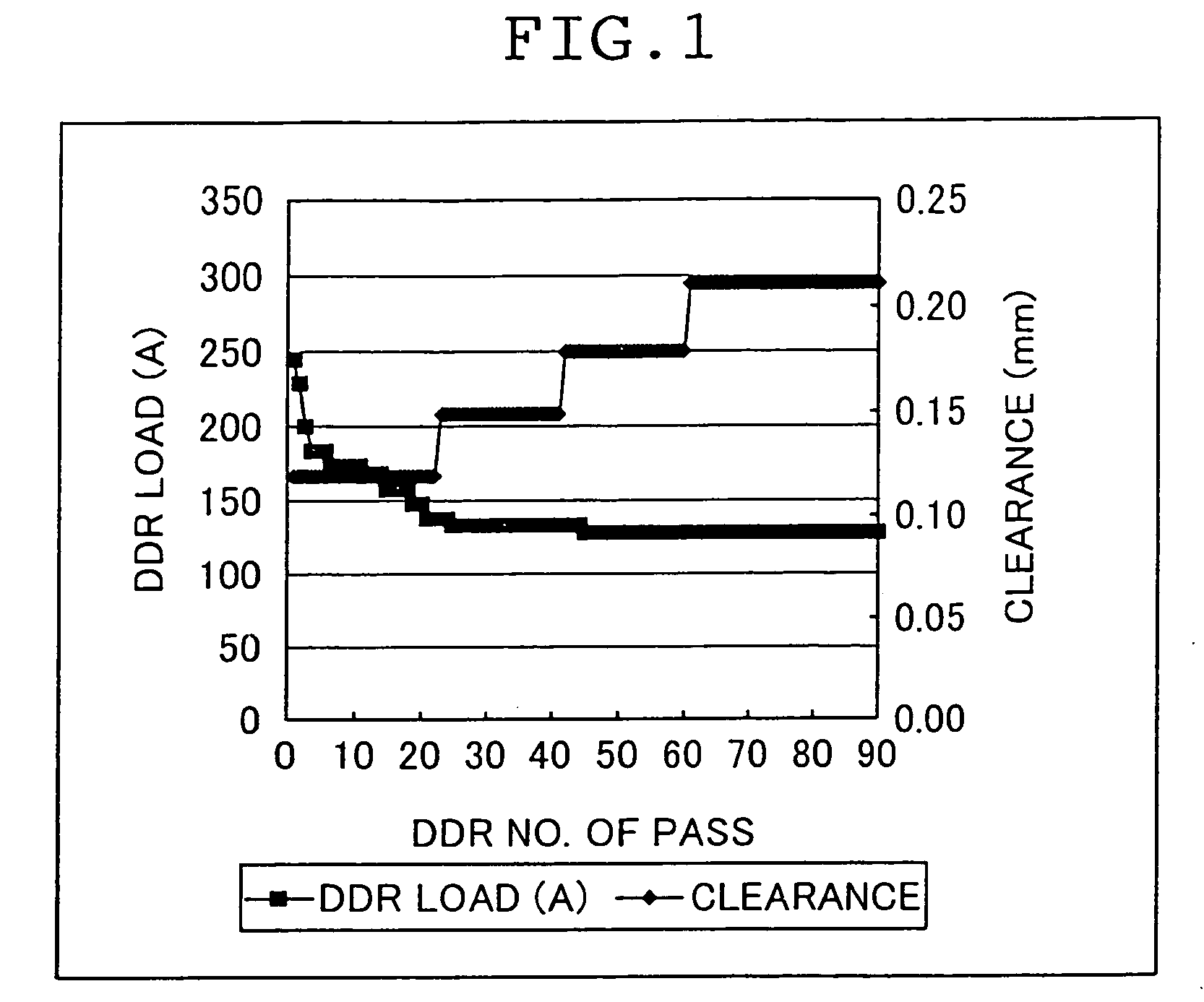
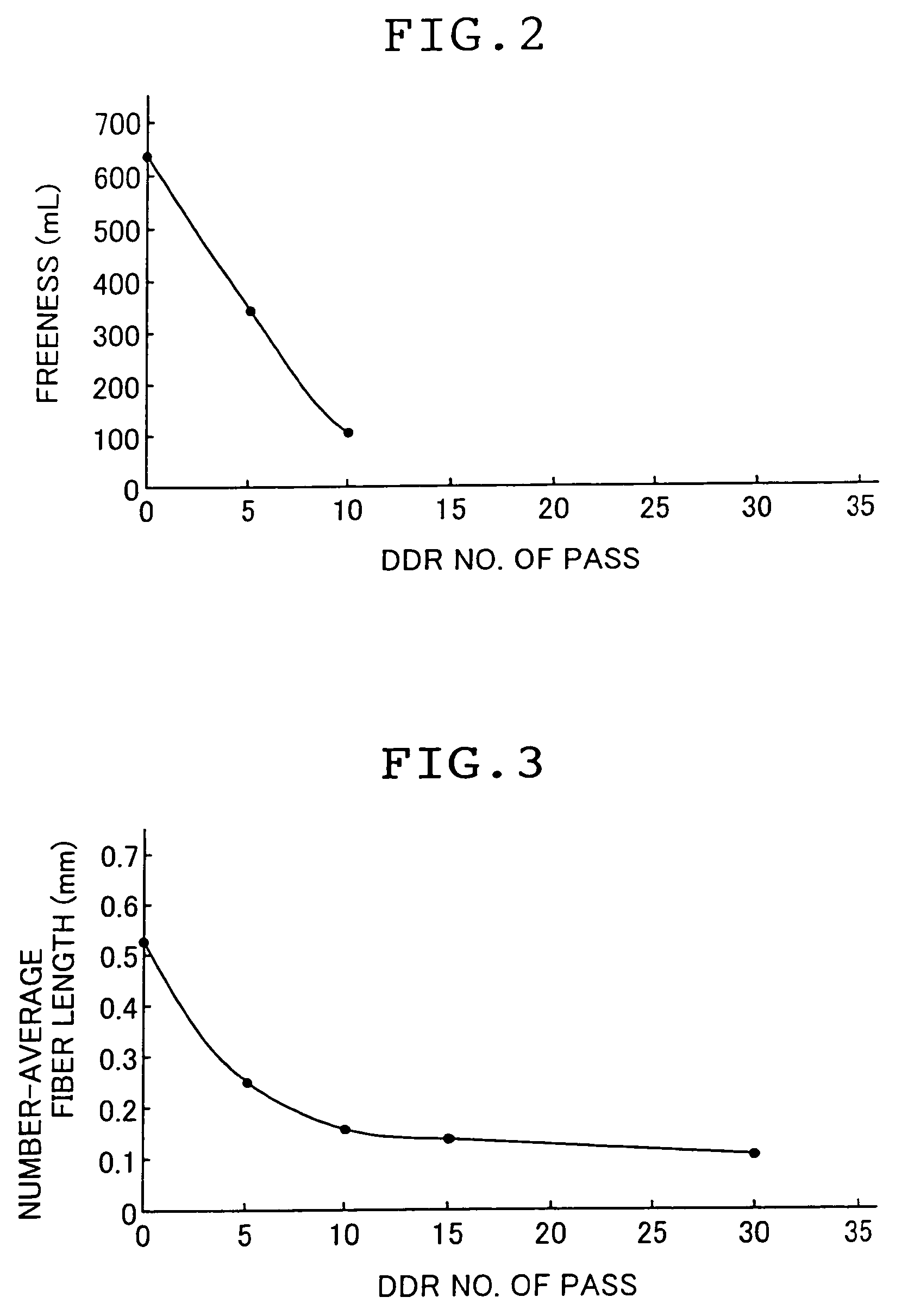
ActiveUS7381294B2Efficient and stable productionQuality improvementNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulose fiberSlurry
A method for producing a microfibrillated cellulose, which comprises subjecting a slurry containing a pulp having a solids concentration of 1 to 6 wt % to the treatment with a disc refiner repeatedly ten times or more, to thereby prepare a microfibrillated cellulose having a number average fiber length or 0.2 mm or less and an amount of water hold of 10 mL / g or more, the amount representing the volume of water capable of being held by a unit weight of the cellulose fiber. The method allows the production of a microfibrillated cellulose having high quality with stability and with good efficiency.
Owner:DSG INT LTD
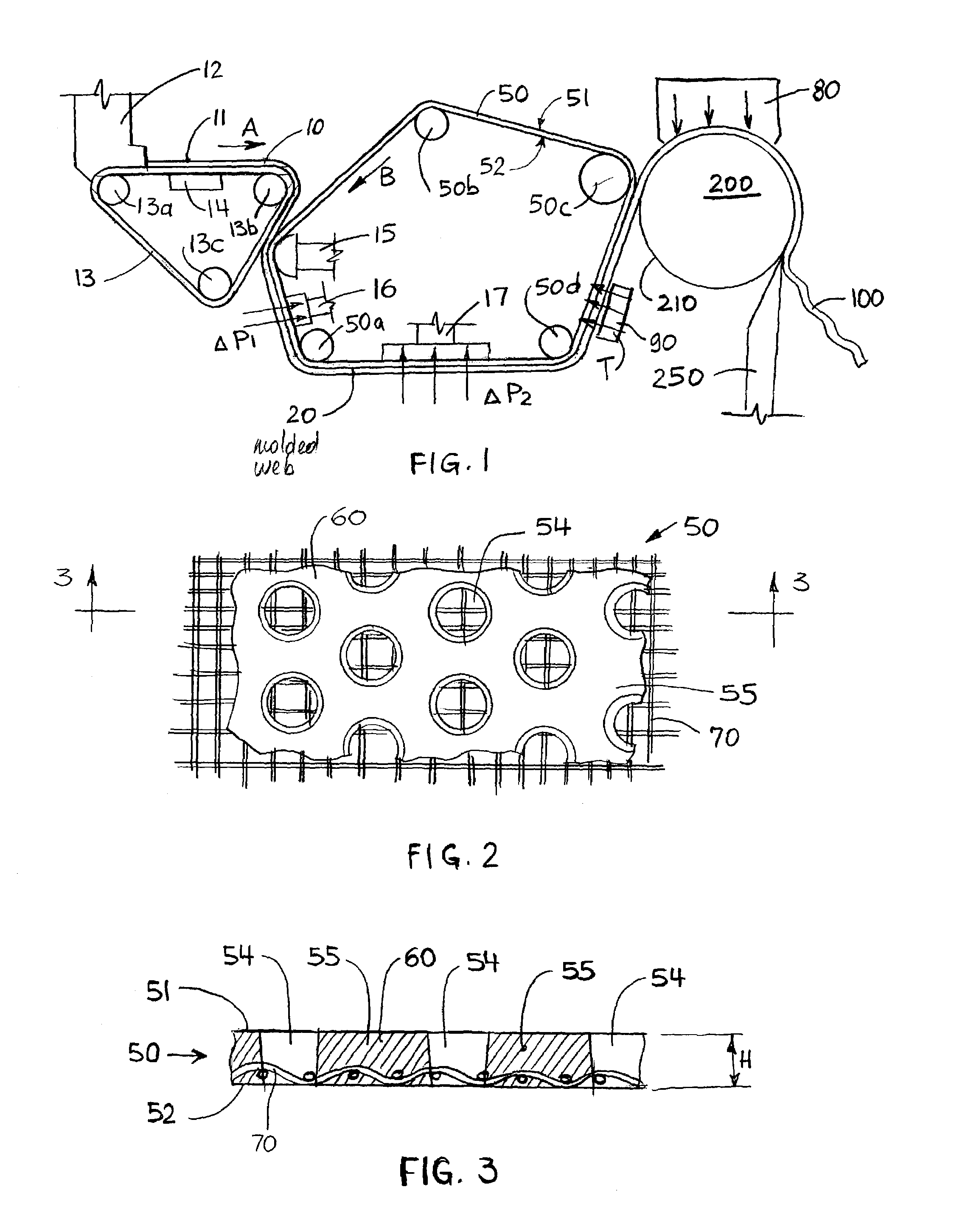
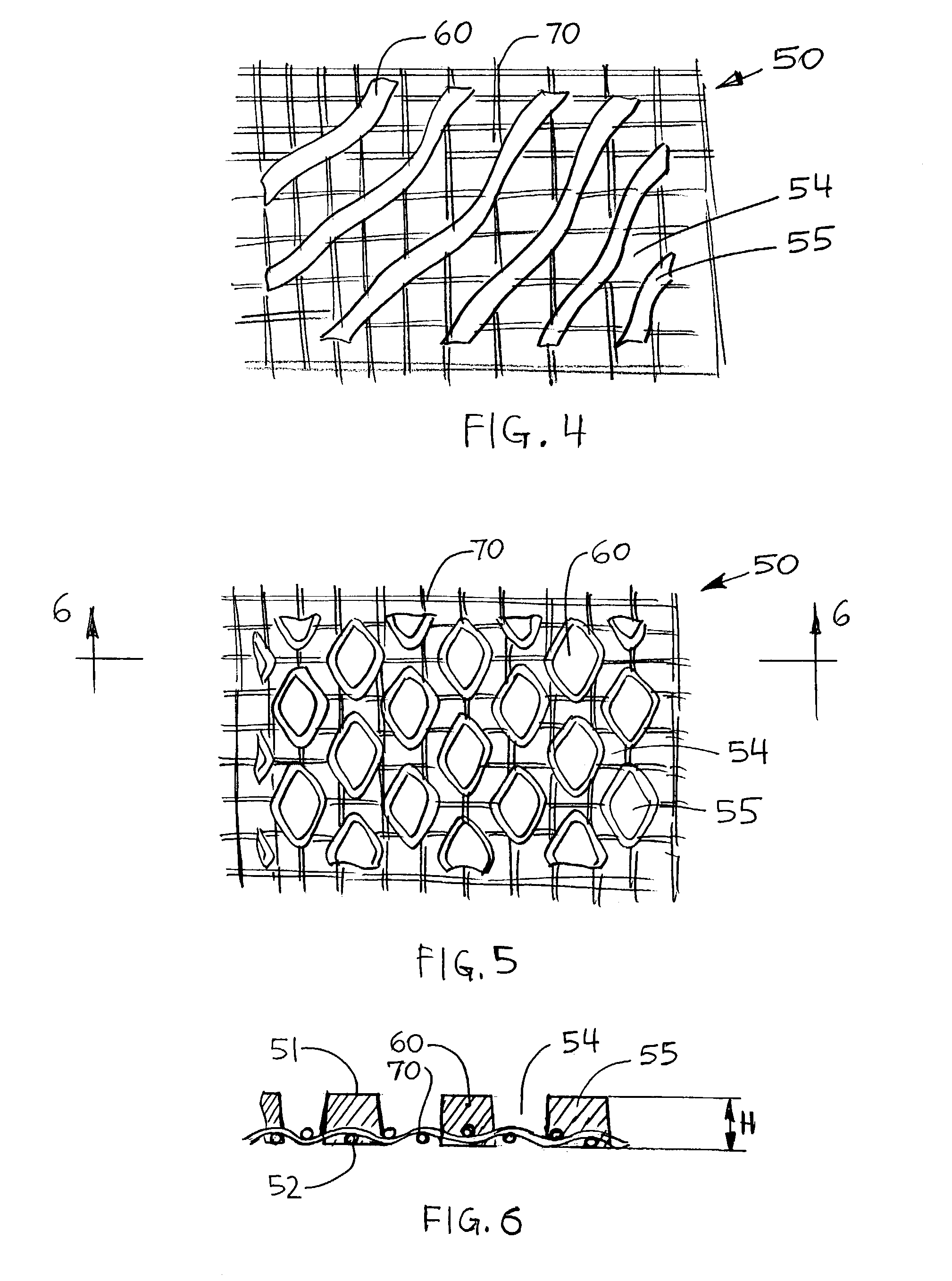
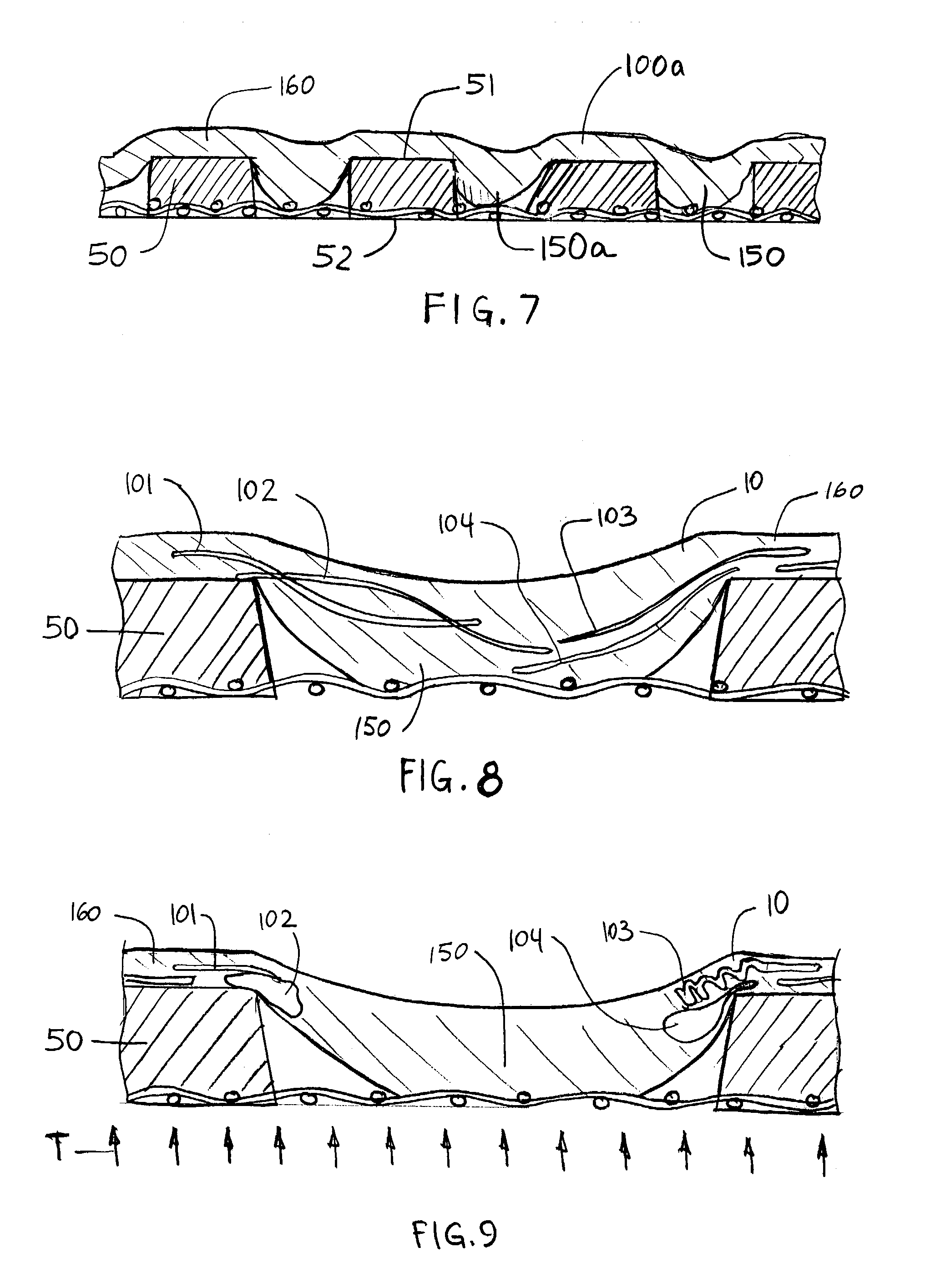
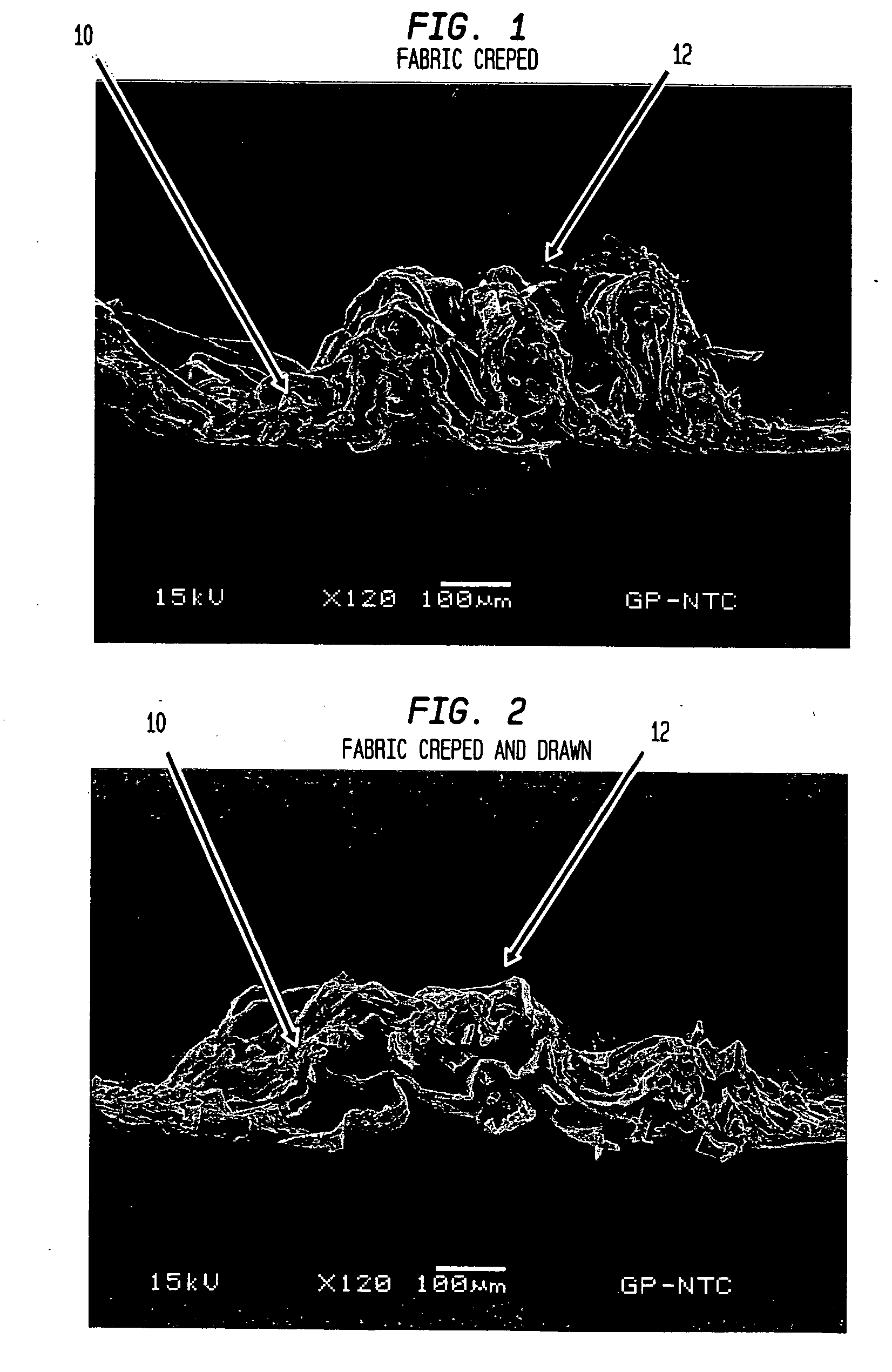
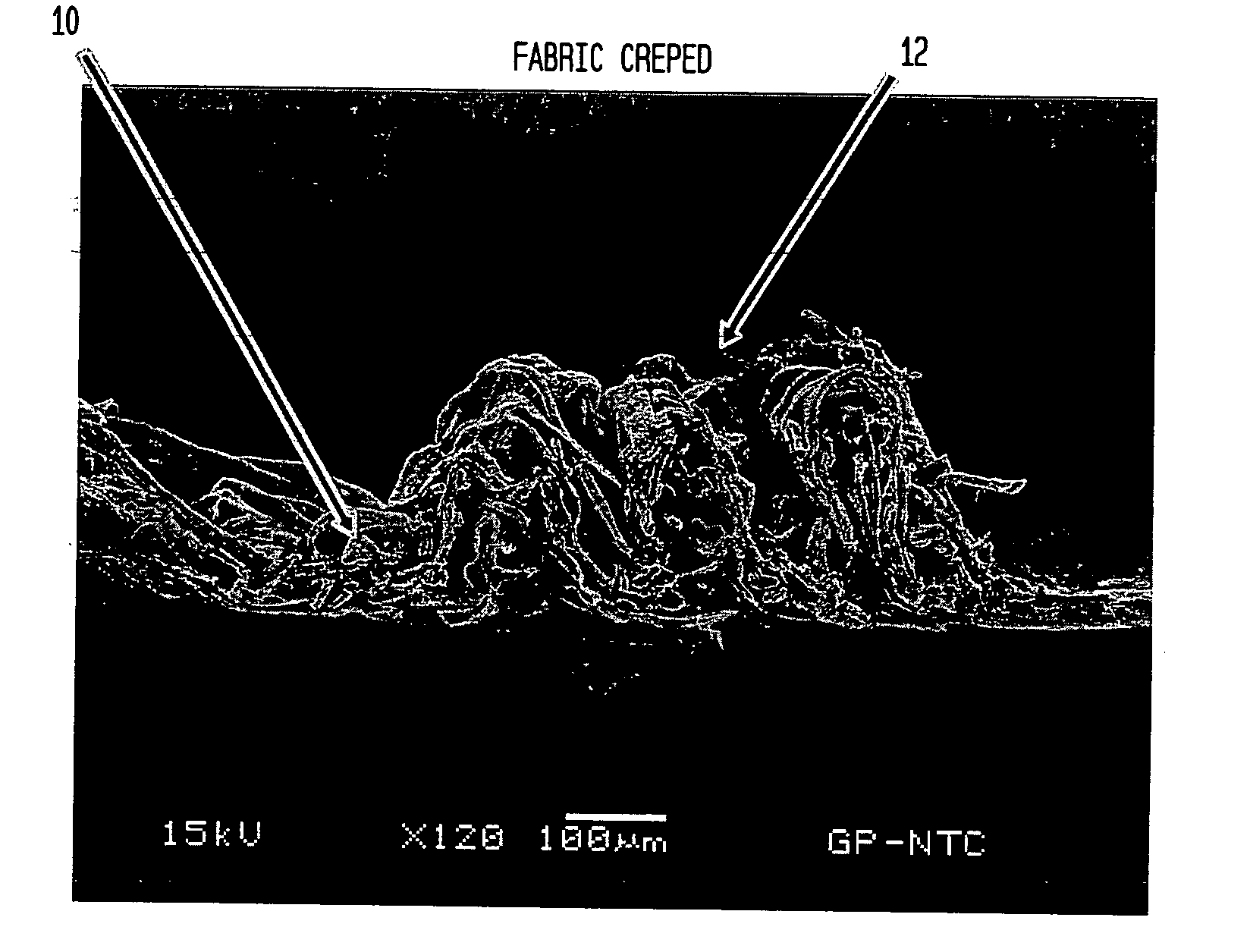
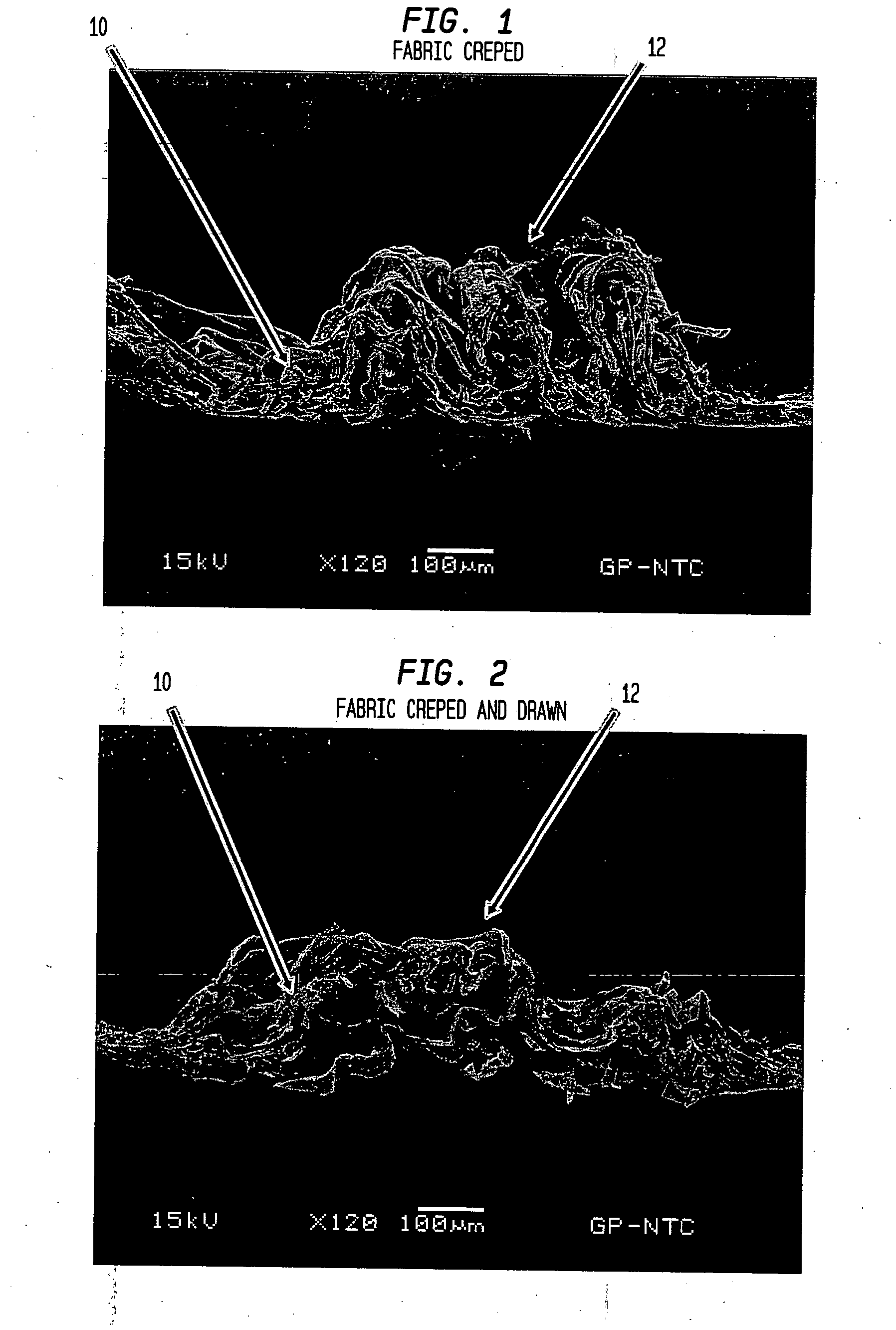
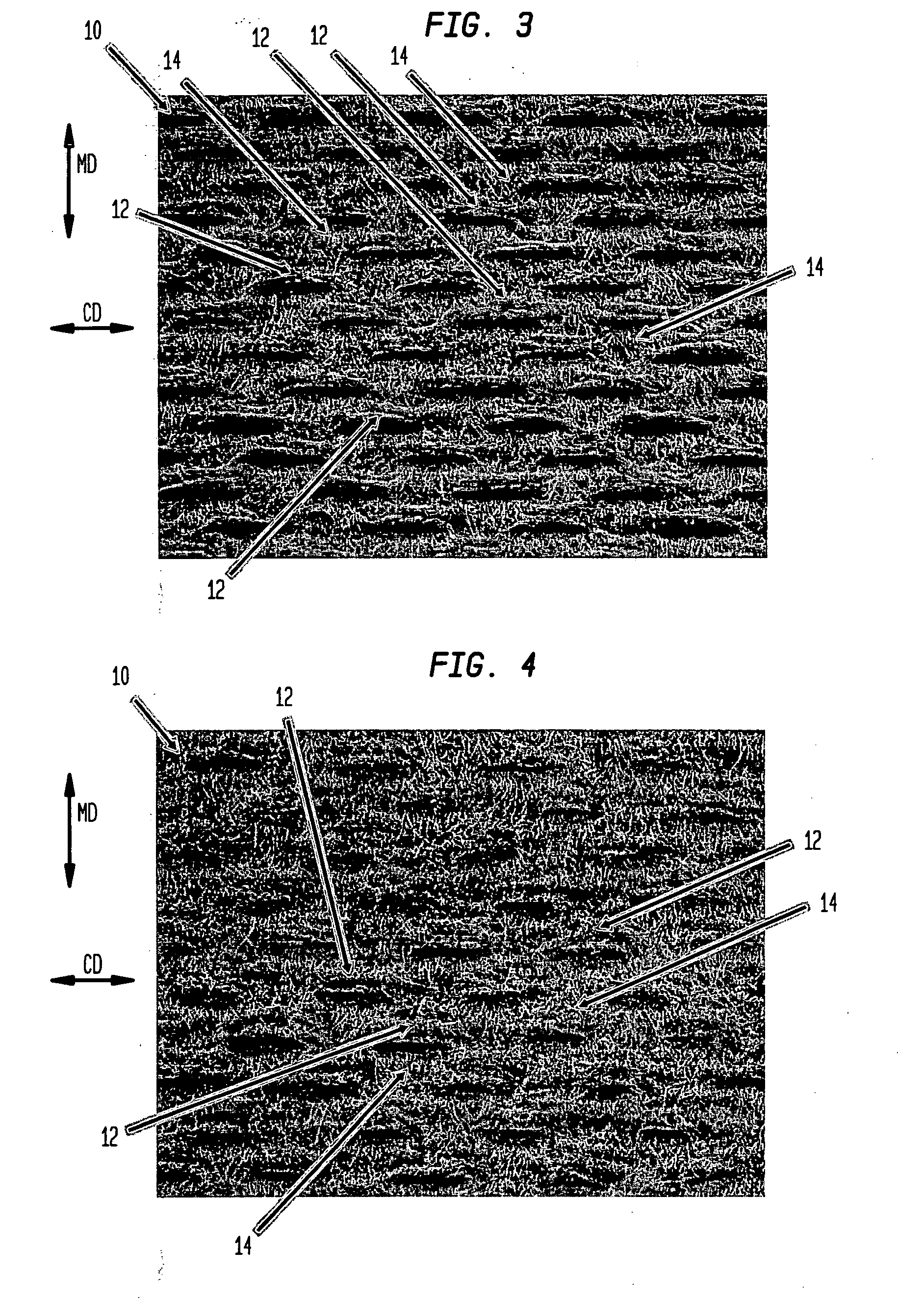
Fabric crepe and in fabric drying process for producing absorbent sheet
ActiveUS20050241787A1Decrease sidednessReduced areaNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulose fiberPulp and paper industry
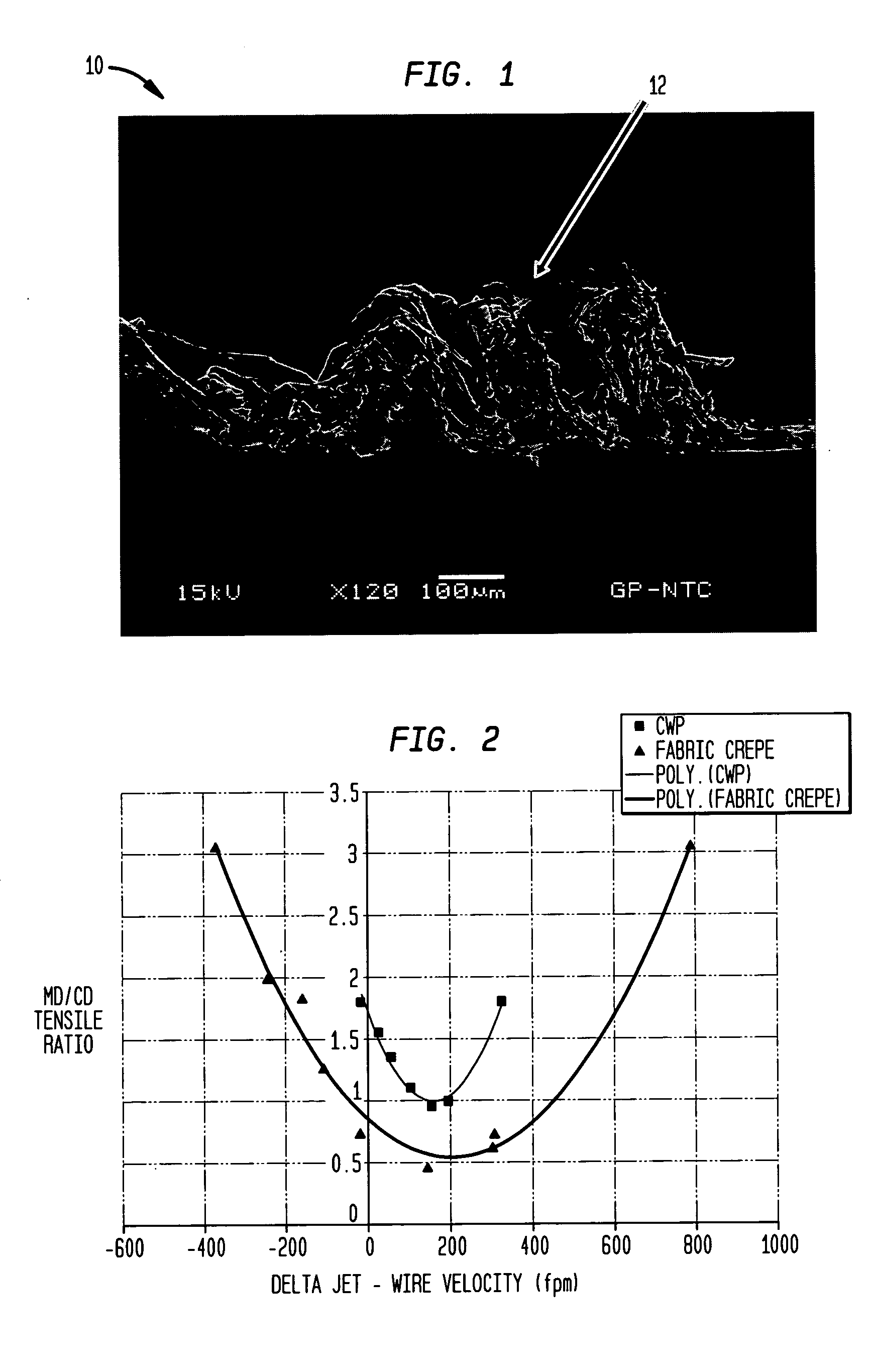
A method of making a cellulosic web includes: forming a nascent web from a papermaking furnish, the nascent web having a generally random distribution of papermaking fiber; b) transferring the web having a generally random distribution of papermaking fiber to a translating transfer surface moving at a first speed; drying the web to a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent including compactively dewatering the web prior to or concurrently with transfer to the transfer surface; fabric-creping the web from the transfer surface at a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent utilizing a creping fabric with a patterned creping surface, the fabric creping step occurring under pressure in a fabric creping nip defined between the transfer surface and the creping fabric wherein the fabric is traveling at a second speed slower than the speed of said transfer surface, the fabric pattern, nip parameters, velocity delta and web consistency being selected such that the web is creped from the transfer surface and redistributed on the creping fabric such that the web has a plurality of fiber-enriched regions arranged in a pattern corresponding to the patterned creping surface of the fabric, optionally drying the wet web while it is held in the creping fabric. Preferably, the formed web is characterized in that its void volume increases upon drawing.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Wet-pressed tissue and towel products with elevated CD stretch and low tensile ratios made with a high solids fabric crepe process
An absorbent sheet of cellulosic fibers includes a mixture of hardwood fibers and softwood fibers arranged in a reticulum having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking regions whose fiber orientation is biased along the machine direction between pileated regions interconnected thereby, wherein the sheet exhibits a % CD stretch which is at least about 2.75 times the dry tensile ratio of the sheet. Tensile ratios of from about 0.4 to about 4 are readily achieved.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Recyclable printing mechanism and related method
InactiveUS20050030554A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsCardboardCellulose fiber
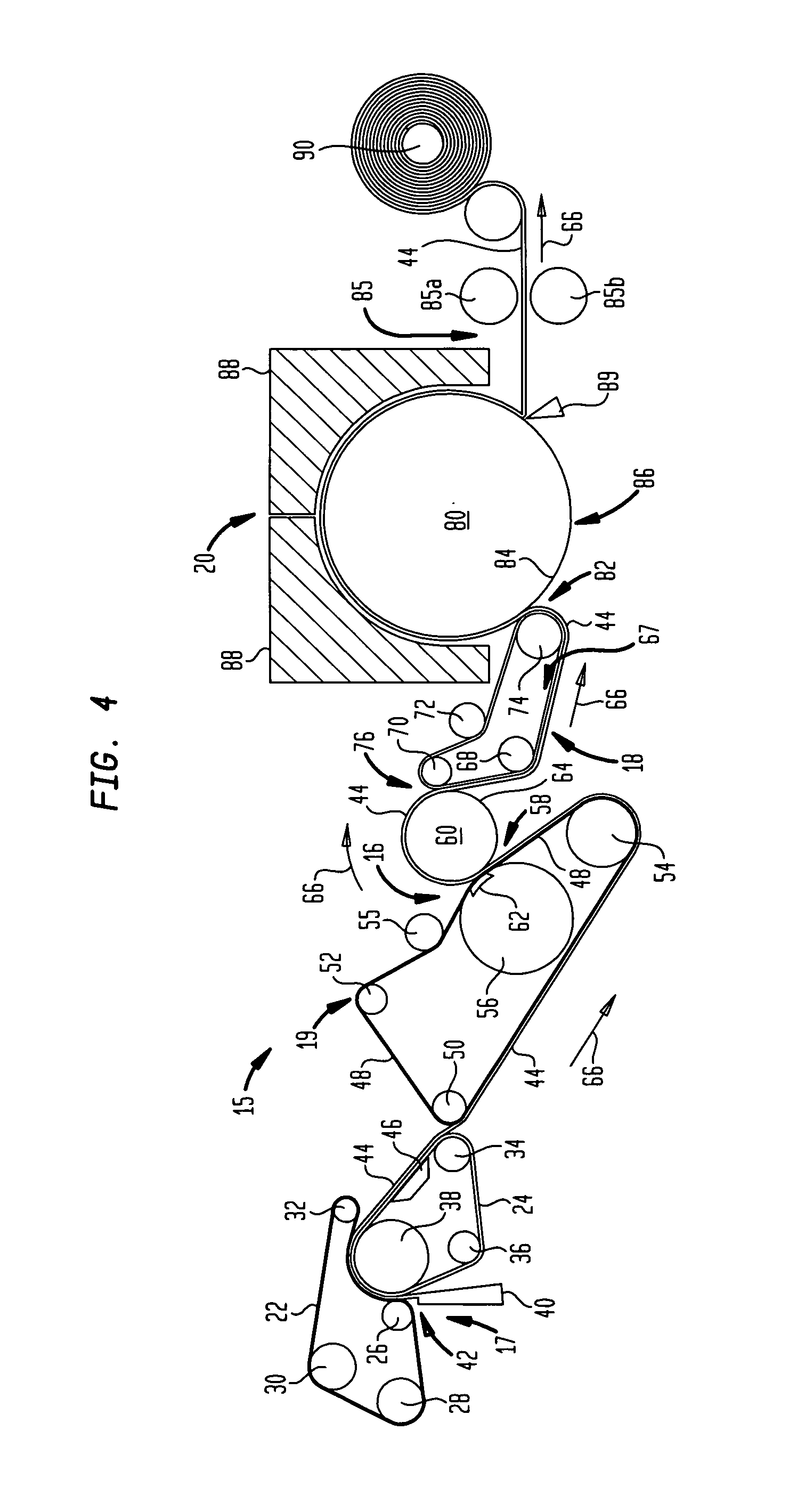
An embodiment of a printing apparatus is provided as including a chassis, a print engine supported by the chassis, and a casing of a cardboard material comprising cellulose fiber attached to the chassis and surrounding the print engine when attached to the chassis. A business method for recycling or refurbishing a recyclable printing mechanism is also provided.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
High Softness, High Durability Bath Tissue Incorporating High Lignin Eucalyptus Fiber
ActiveUS20130029106A1Less-wet lintOffsetting costsCellulosic pulp after-treatmentNon-fibrous pulp additionCellulose fiberMaterials science
A cellulosic tissue includes cellulosic fibers selected from the group consisting of chemically pulped fibers and mechanically pulped fibers, the cellulosic fibers have from about 10% to about 50% by weight eucalyptus fibers having a lignin content of at least about 20% by weight, and from about 3% to about 10% by weight regenerated cellulosic microfibers.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
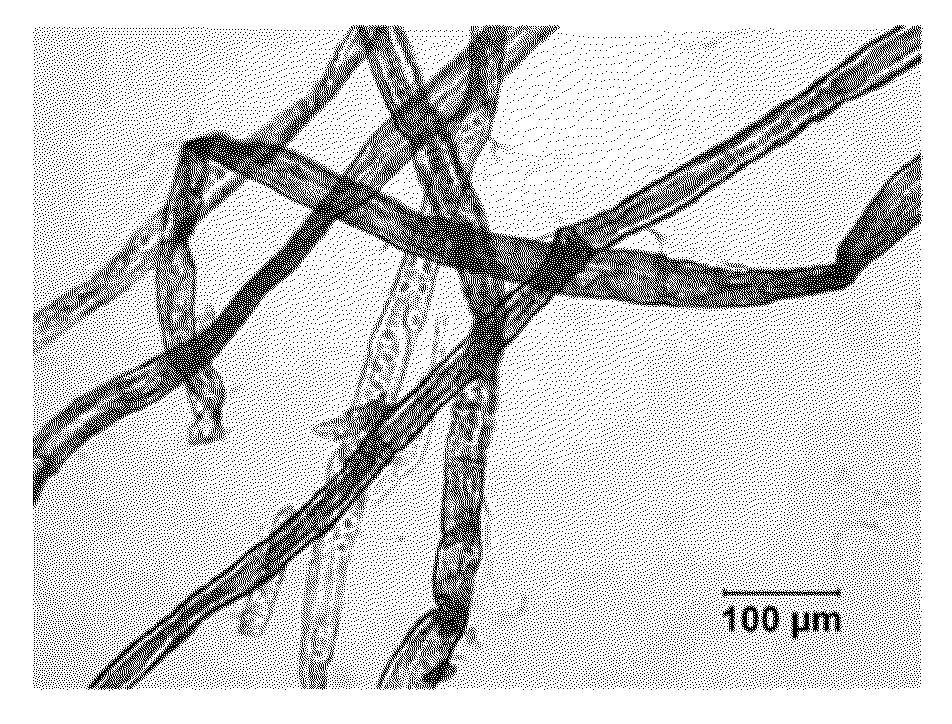
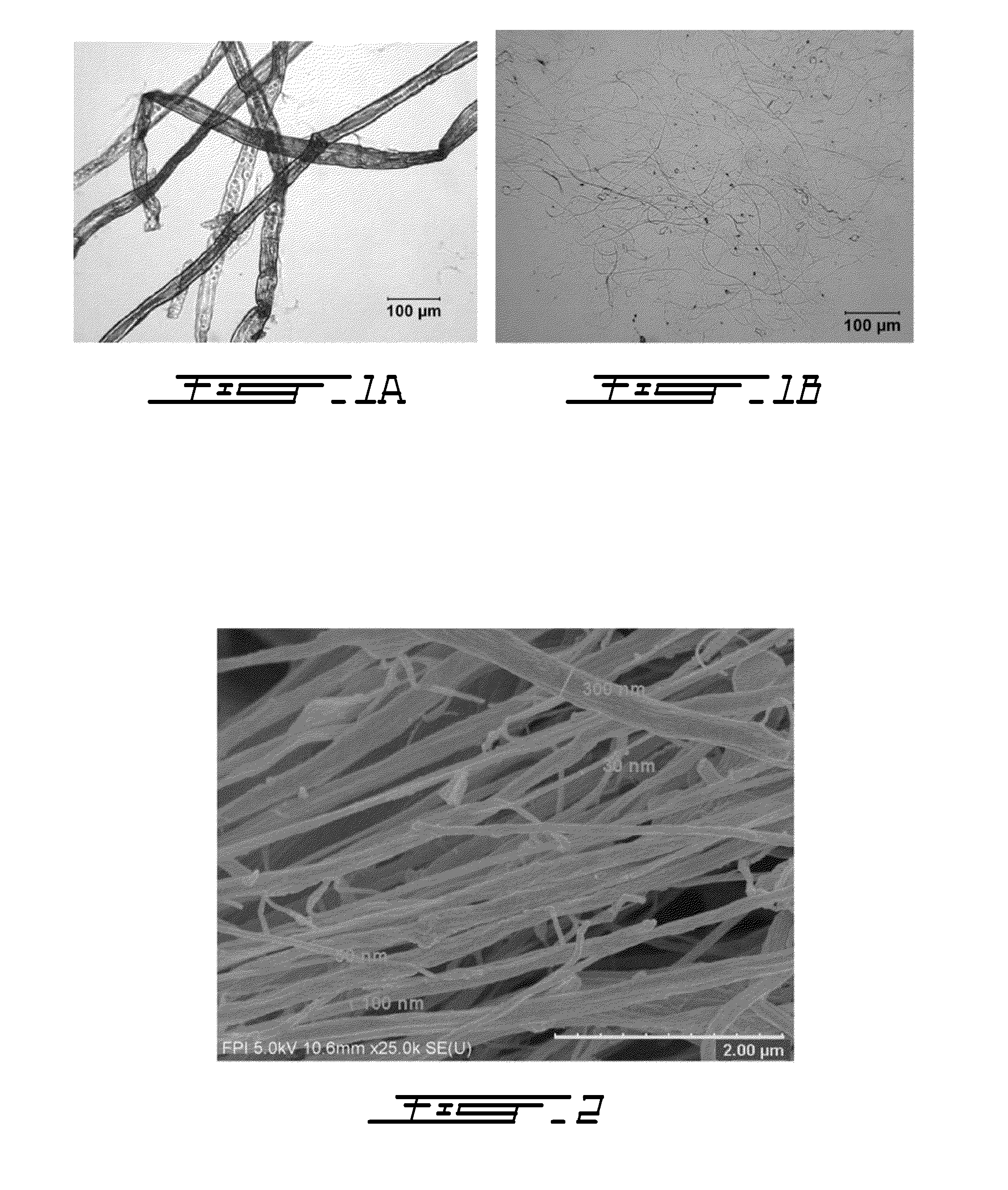
Cellulose nanofilaments and method to produce same
ActiveUS20110277947A1Improve strength propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer sciencePaperboard
Cellulose nanofilaments from cellulose fibers, a method and a device to produce them are disclosed. The nanofilaments are fine filaments with widths in the sub-micron range and lengths up to a couple of millimeters. These nanofilaments are made from natural fibers from wood and other plants. The surface of the nanofilaments can be modified to carry anionic, cationic, polar, hydrophobic or other functional groups. Addition of these nanofilaments to papermaking furnishes substantially improves the wet-web strength and dry sheet strength much better than existing natural and synthetic polymers. The cellulose nanofilaments produced by the present invention are excellent additives for reinforcement of paper and paperboard products and composite materials, and can be used to produce superabsorbent materials.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
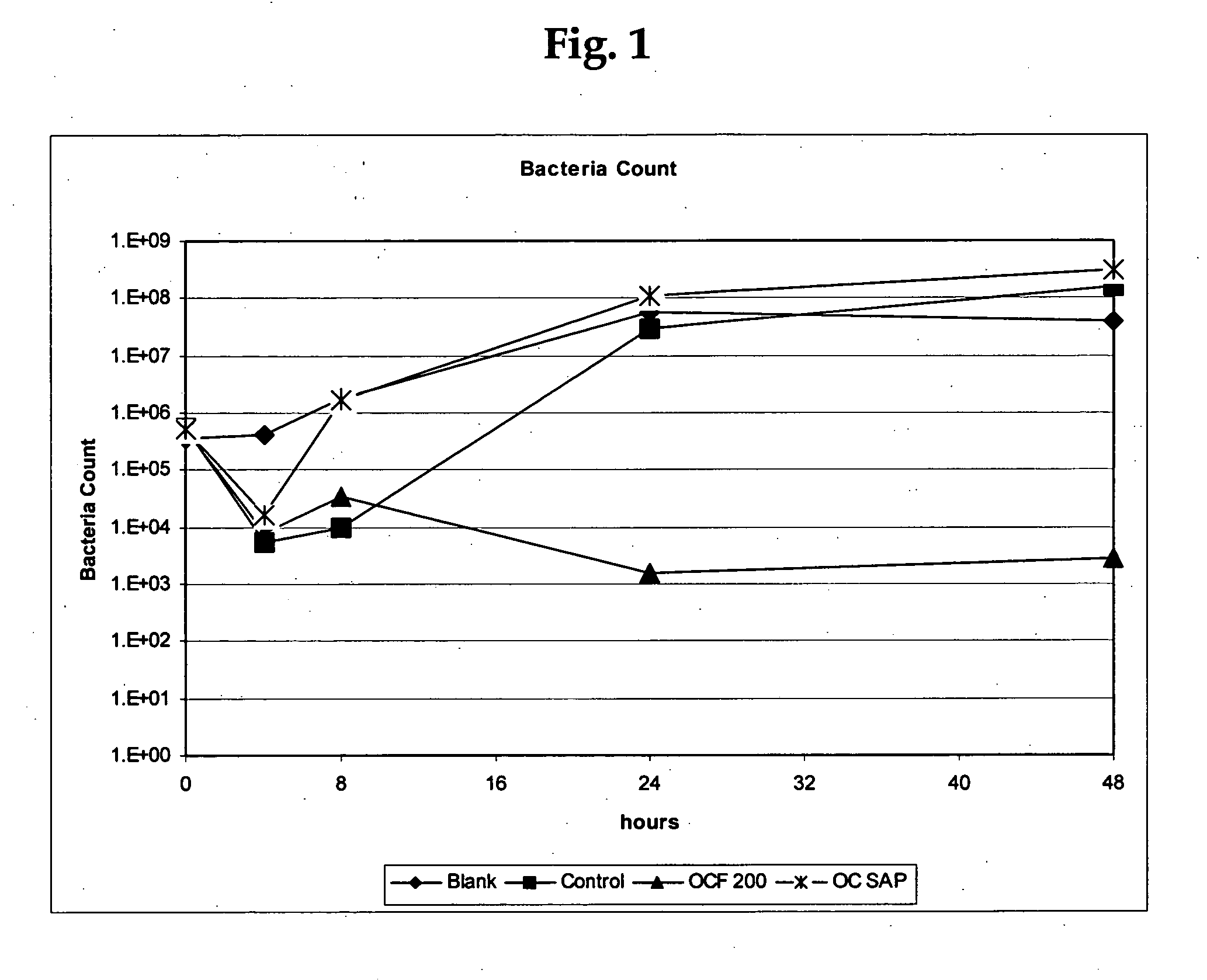
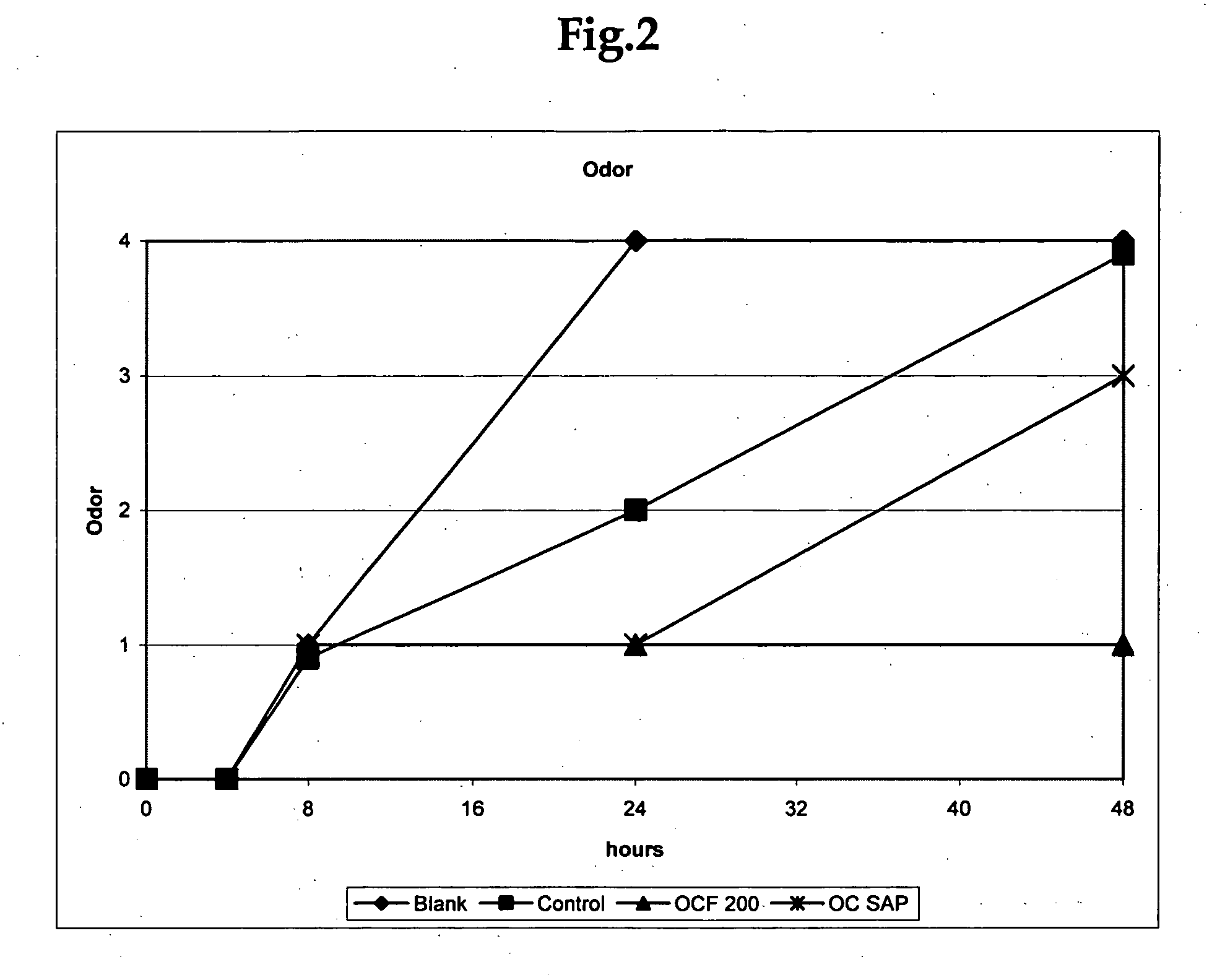
Cellulosic fibers with odor control characteristics
ActiveUS20070077428A1Avoid odorMaintain activityEngine sealsInorganic pigment treatmentBiotechnologyAmmonia production
An odor-inhibiting fiber having a cellulosic fiber and an odor-inhibiting formulation. The odor-inhibiting formulation may contain an odor-inhibiting agent, such as a biocide, an enzyme, a urease inhibitor. The odor-inhibiting formulation also may contain a liquid carrier such as a hydrophobic or hydrophilic organic liquid, or a mixture of a hydrophobic and hydrophilic organic liquid. The cellulosic fiber is impregnated with the odor-inhibiting formulation to produce fiber having odor-inhibiting characteristics. The resultant odor-inhibiting fiber is useful in making absorbent articles with odor-inhibiting characteristics. The fiber of the embodiments prevents odor by inhibiting bacteria growth and ammonia production, especially when used in an absorbent article such as a diaper or adult incontinence device.
Owner:RAYONIER PERFORMANCE FIBERS
Panel, Use of a Panel, Method for Manufacturing a Panel and a Prepreg
InactiveUS20100323187A1Improve light fastnessSpecial ornamental structuresWood working apparatusSurface layerWear resistant
Described are panels including a surface layer on a substrate. The surface layer includes a) cellulose fibers, b) at least one binder and (c) wear resistant particles. The use of different panels and a method for manufacturing is also described.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
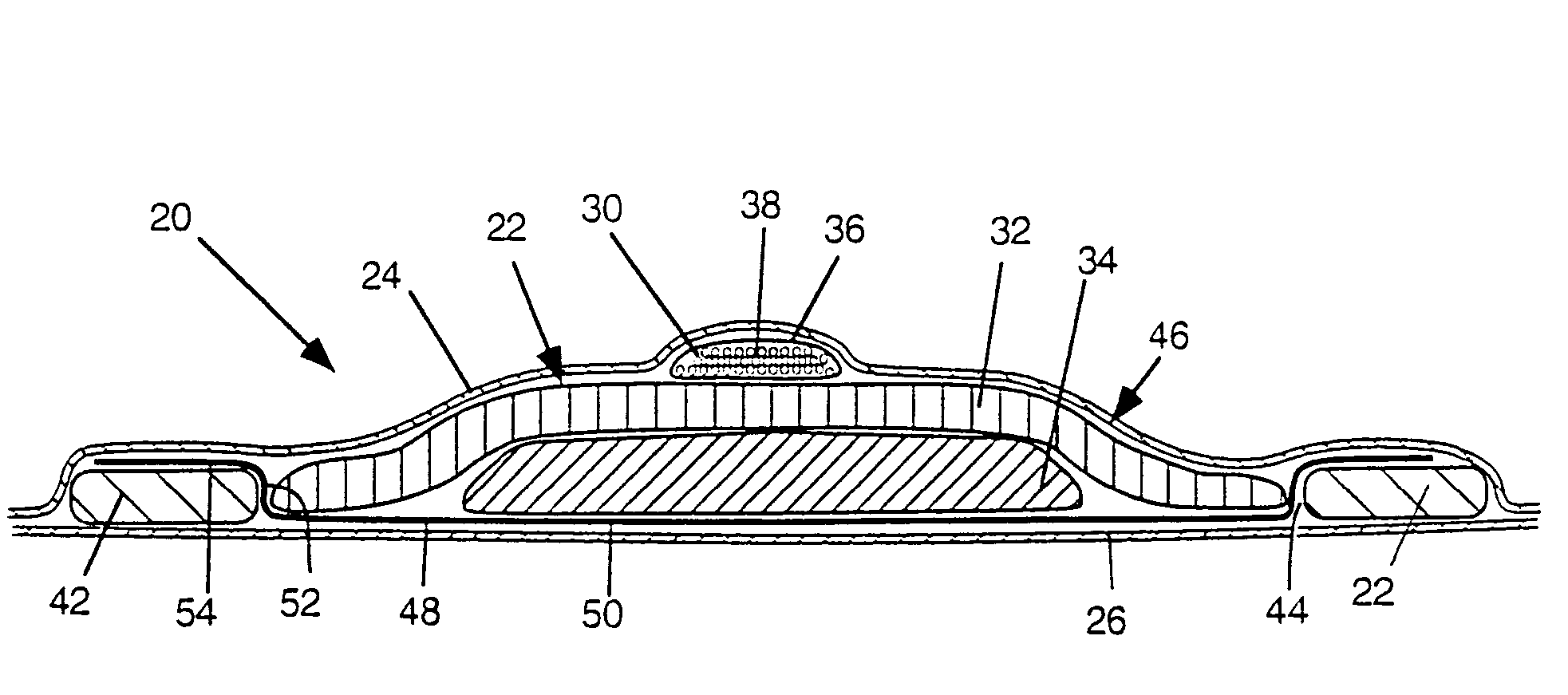
Flexible absorbent article with improved body fit
An absorbent article that has a thin, conformable absorbent core where the core has at least two layers, each including a different superabsorbent material, and each being typically substantially free of cellulosic fibres, is described. The absorbent article has a Circular Bend Flexibility of less than about 15 N. The core includes a storage layer and an acquisition / storage layer each a specific basis capacity of and absorption efficiency.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
High aspect ratio cellulose nanofilaments and method for their production
ActiveUS20130017394A1High consistency refiningIncrease surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyFinely-divided cellulose conservationMicrometerPaperboard
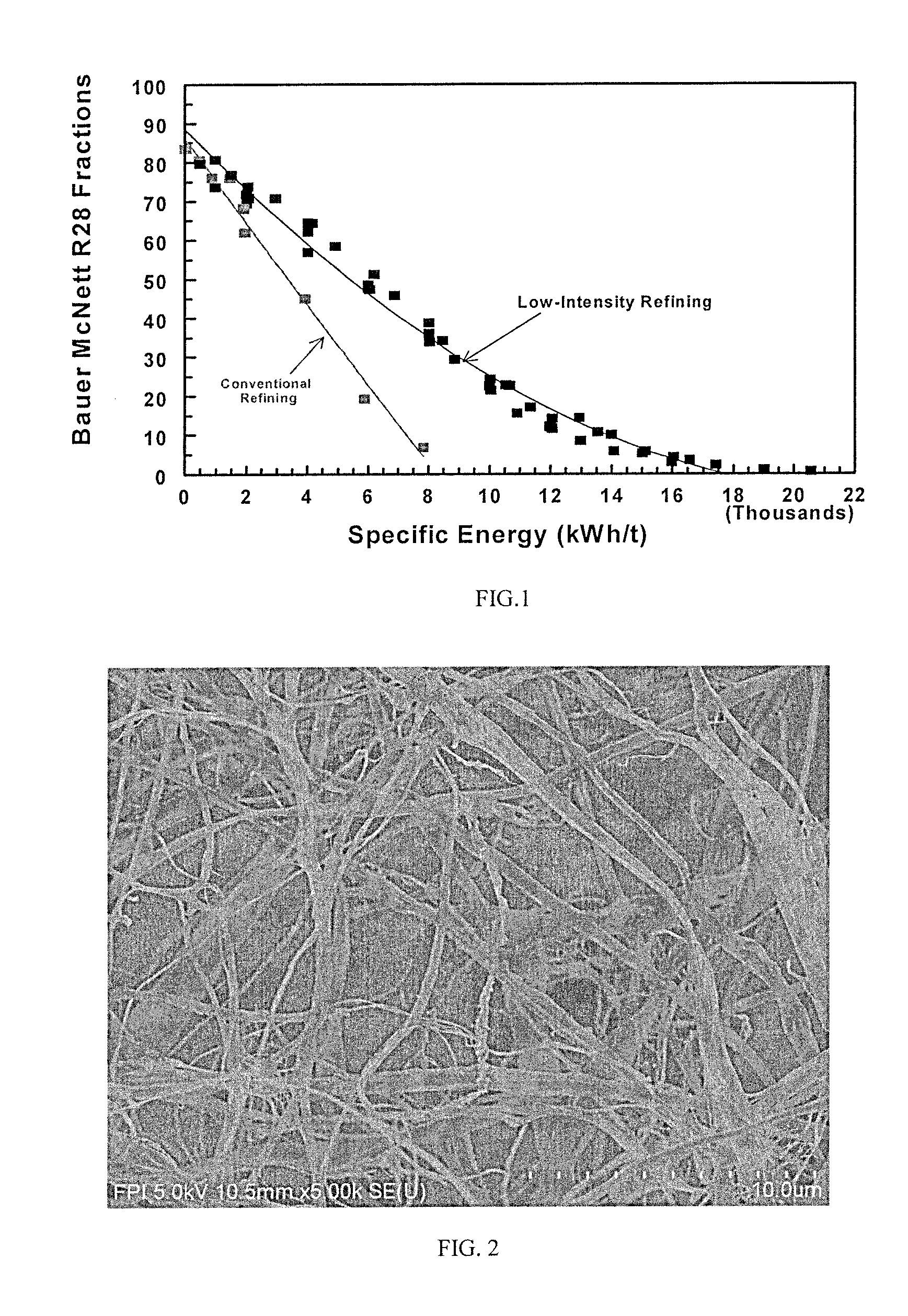
A method to produce on a commercial scale, high aspect ratio cellulose nanofilaments (CNF) from natural lignocellulosic fibers comprises a multi-pass high consistency refining (HCR) of chemical or mechanical fibers using combinations of refining intensity and specific energy. The CNF produced represents a mixture of fine filaments with widths in the submicron and lengths from tens of micrometers to few millimeters. The product has a population of free filaments and filaments bound to the fiber core from which they were produced. The proportion of free and bound filaments is governed in large part by total specific energy applied to the pulp in the refiner, and differs from other cellulose fibrillar materials by their higher aspect ratio and the preserved degree of polymerization (DP) of cellulose, and are excellent additives for the reinforcement of paper, tissue, paperboard and the like. They display exceptional strengthening power for never-dried paper webs.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Moving bed biomass fractionation system and method
InactiveUS20080029233A1Improve production yieldIncrease pressureWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsDigestersChemical reactionFiltration
Countercurrent extraction of lignocellulosic biomass such as trees, grasses, shrubs, and agricultural residues or waste involves the separation of cellulose fibers from other constituents, for subsequent use in the manufacture of paper, plastics, ethanol, and other industrial chemicals. Systems and methods involve continuous, multiple processing steps that may include chemical reactions with mixing at elevated temperature and / or pressure, efficient reagent or solvent utilization, filtration at elevated temperature and / or pressure, controlled discharge of liquid and solid products, and energy recuperation.
Owner:PUREVISION TECH
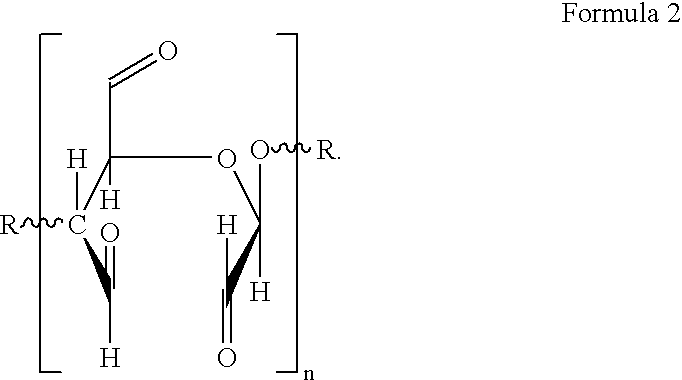
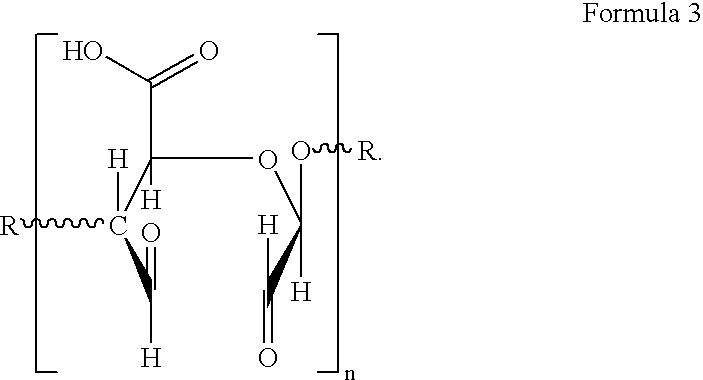
Oxidized polymeric carbohydrates and products made thereof
The present invention relates to a polysaccharide having functional groups, wherein said groups are aldehyde groups formed at positions C2 and / or C3 as well as at position C6 of the anhydroglucose units of the polysaccharide chain. Preferably the polysaccharide is a cellulosic fibrous material whose primary and secondary hydroxyl groups of the cellulose are oxidized into aldehyde groups at least in part by means of TEMPO oxidation and periodate oxidation.The invention also concerns a paper or nonwoven comprising the above polysaccharide. According to the invention a relative wet strength of more than 10% can be achieved.
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
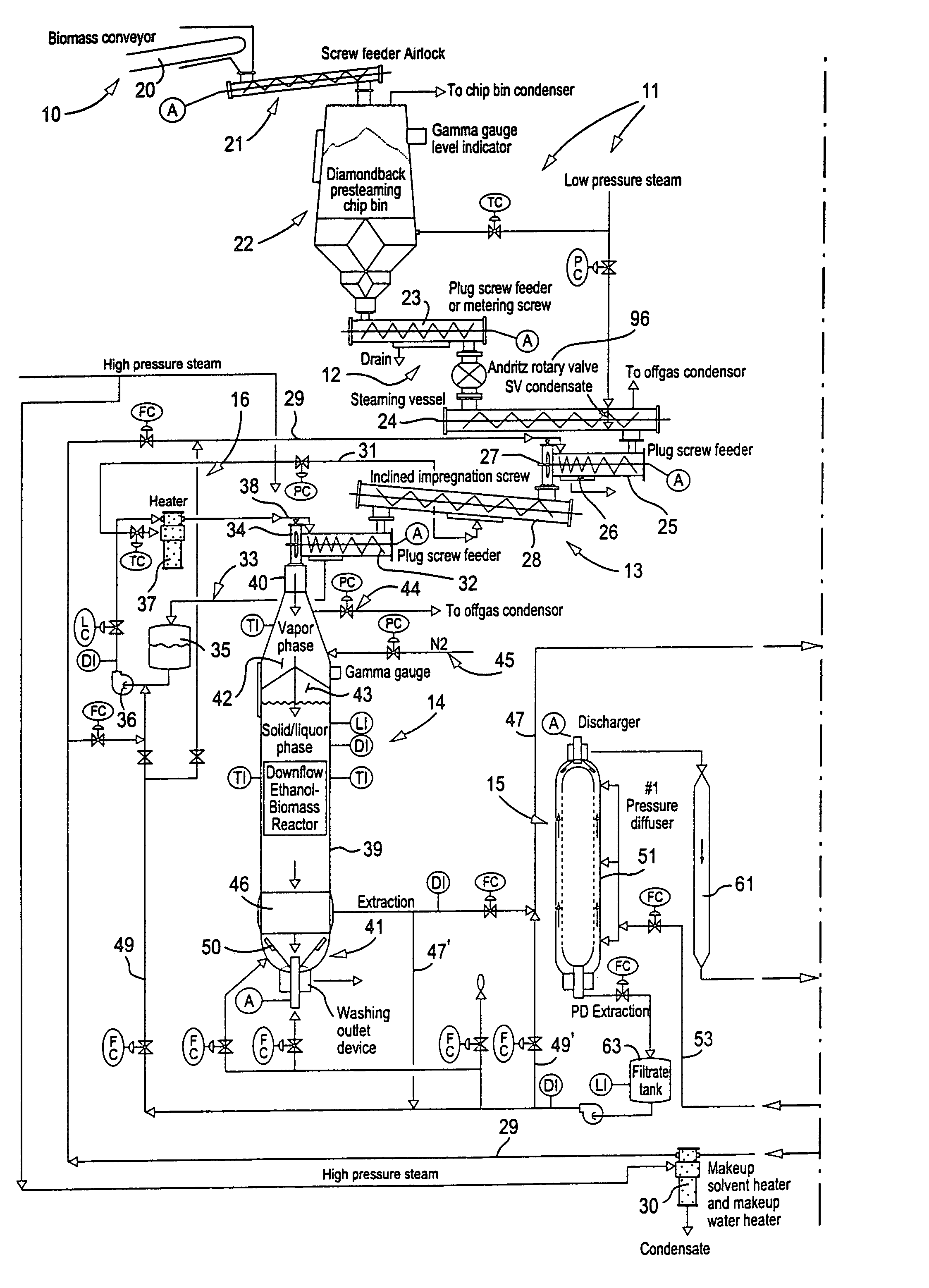
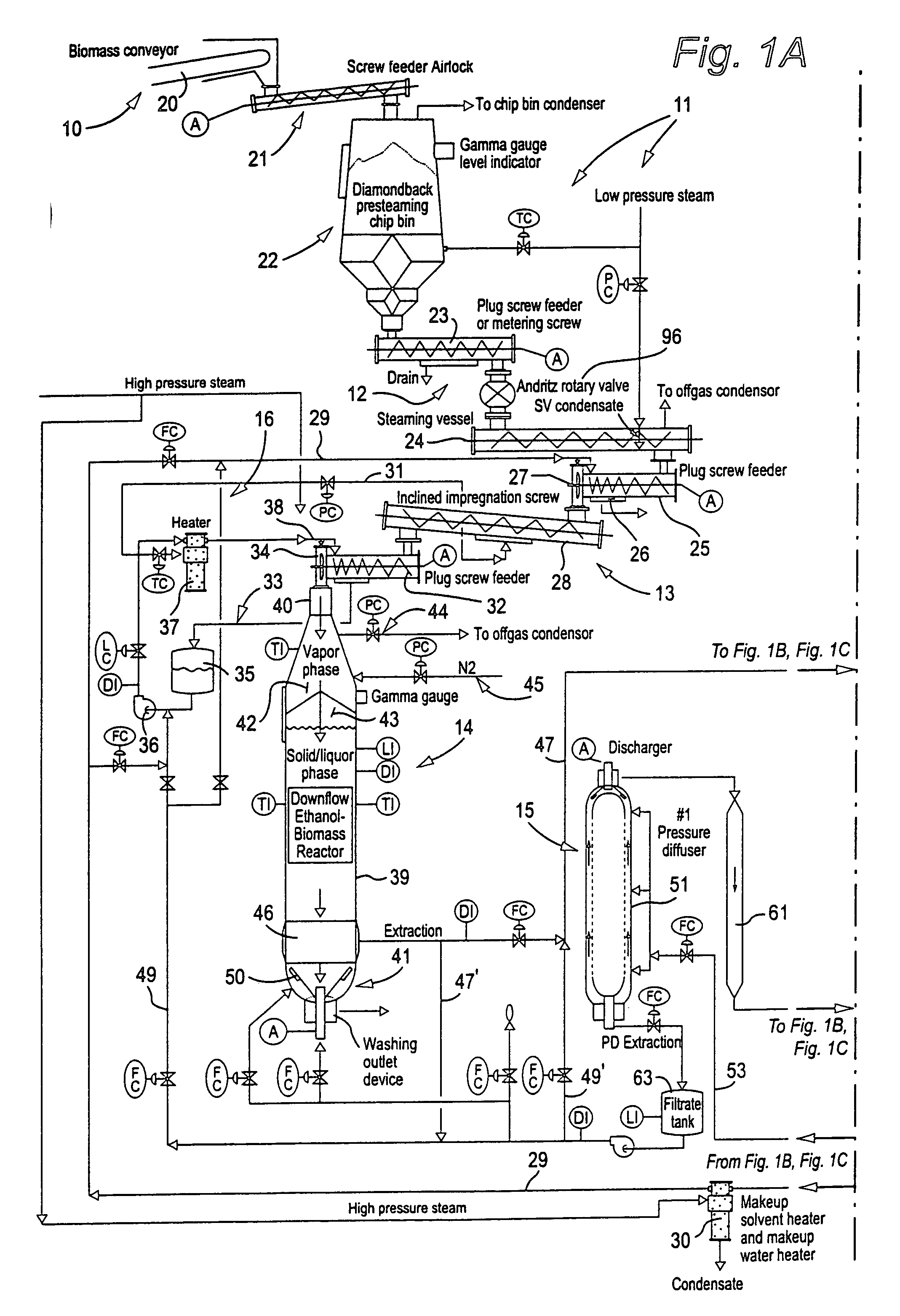
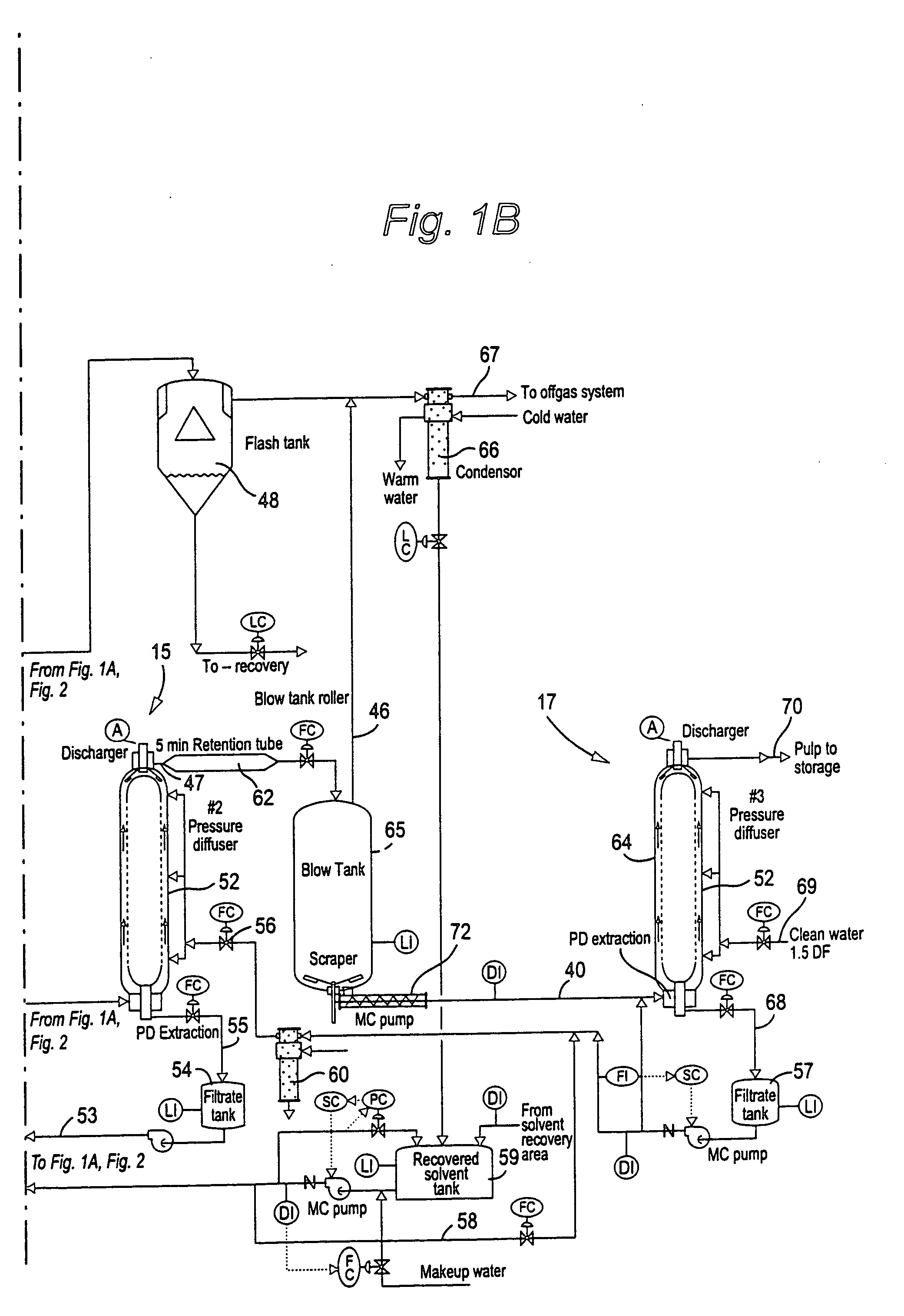
Solvent pulping of biomass
InactiveUS20040060673A1Pretreatment with water/steamWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsCellulose fiberChemistry
An apparatus and process for solvent pulping of cellulose-containing biomass utilizes at least one steaming vessel, a plug screw feeder or compression screw device, at least one super-atmospheric impregnation vessel, a solvent delignification reactor capable of operating at a pressure of 350 psig or more, and a solvent containing line for introducing solvent-containing liquor at the plug screw feeder outlet or compression screw device outlet. The process and system can also include at least one series connected pressure diffuser and optionally a retention tube downstream of each pressure diffuser to provide sufficient retention time to substantially preclude re-deposition of lignin on the cellulose fibers of the biomass, a blow tank connected to the last of the pressure diffusers and retention tubes, and vessels for multistage alcohol washing. The method steams the biomass and impregnates it with solvent to produce an aqueous slurry of biomass and solvent, delignifies the particulate biomass in the slurry, removes solvent while continuing delignification of the biomass in the slurry and while substantially precluding re-deposition of lignin on the cellulose of the biomass, reduces the pressure of the slurry; and then washes the slurry.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Dispersible nonwoven wipe material
ActiveUS20120144611A1High wet and dry strengthGood dispersionBoard cleaning devicesSpecial paperMedicineSubject matter
The presently disclosed subject matter relates to a dispersible, nonwoven multistrata wipe material that is stable in a wetting liquid and flushable in use. More particularly, the presently disclosed subject matter relates to multilayered structures including, but not limited to, two, three, or four layers to form the dispersible nonwoven wipe material. The layers contain combinations of cellulosic and noncellulosic fibers, and optionally a binder or additive.
Owner:GLATFELTER CORP
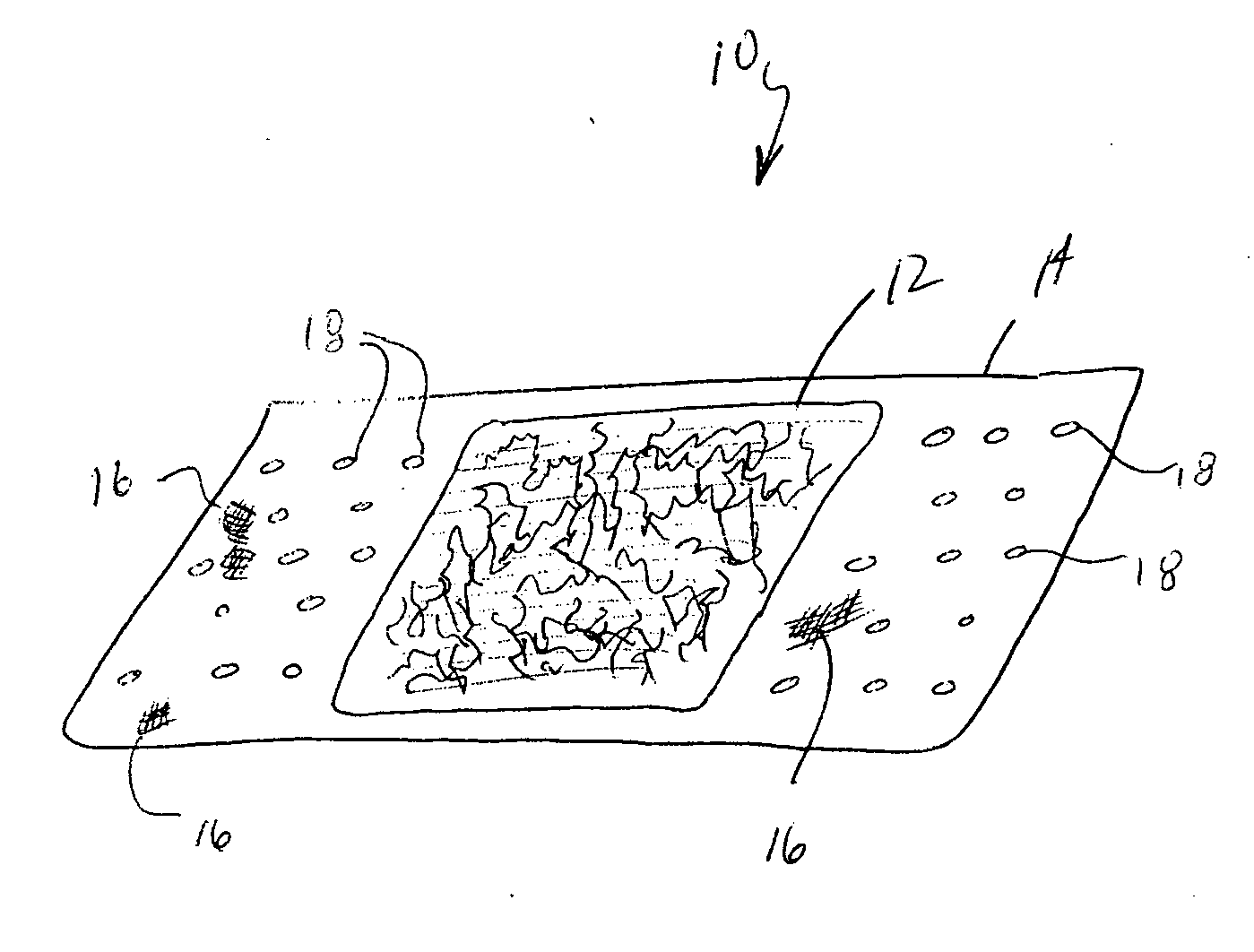
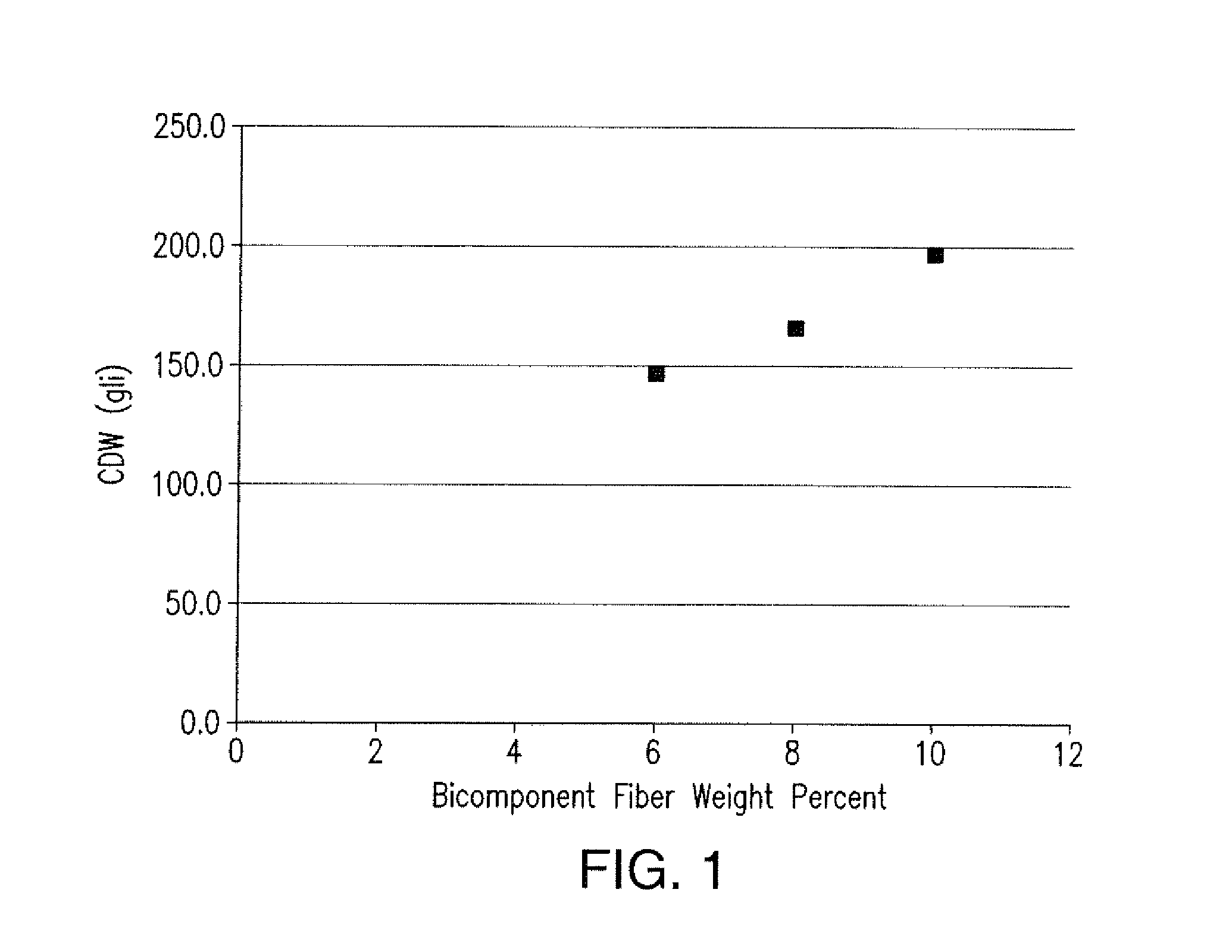
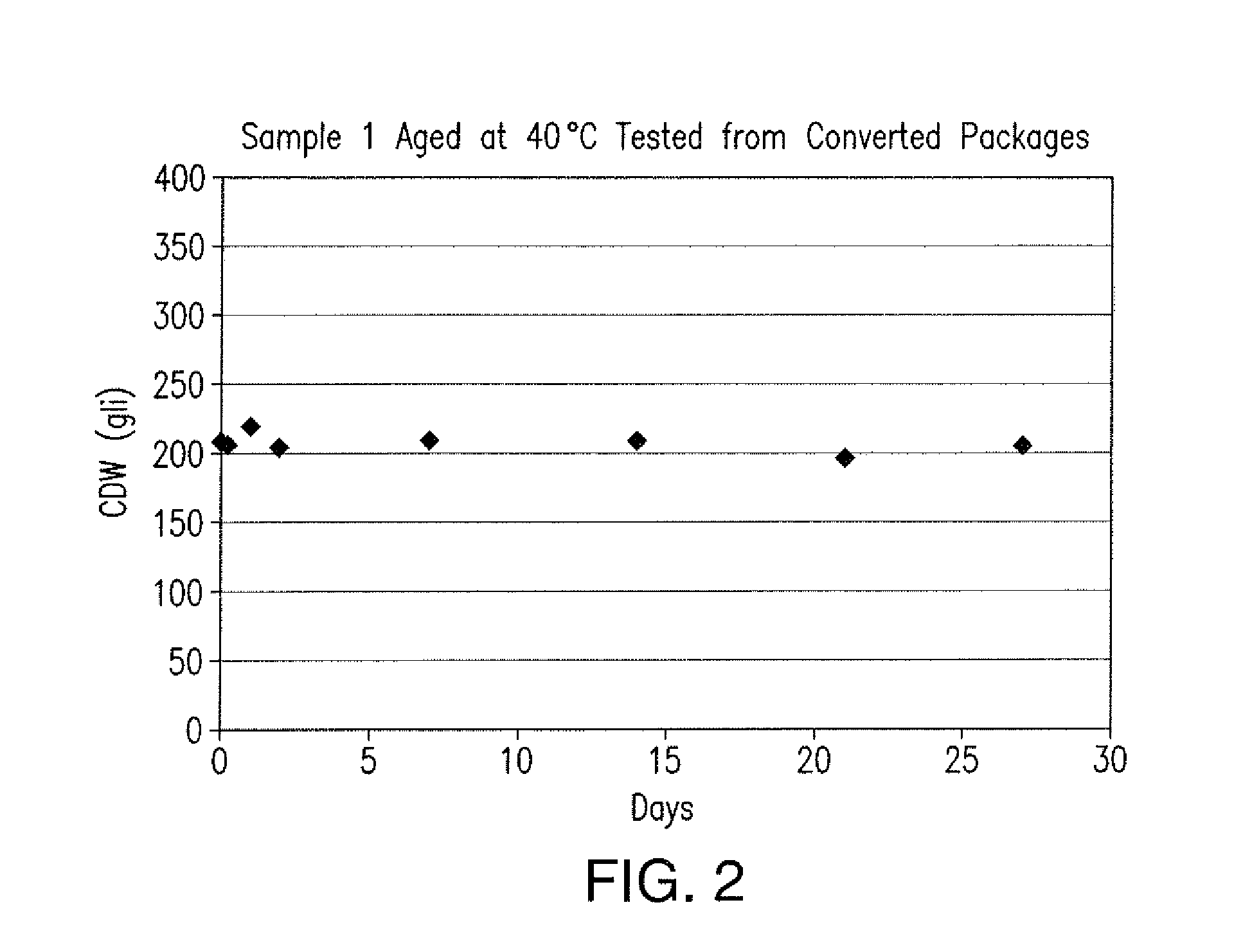
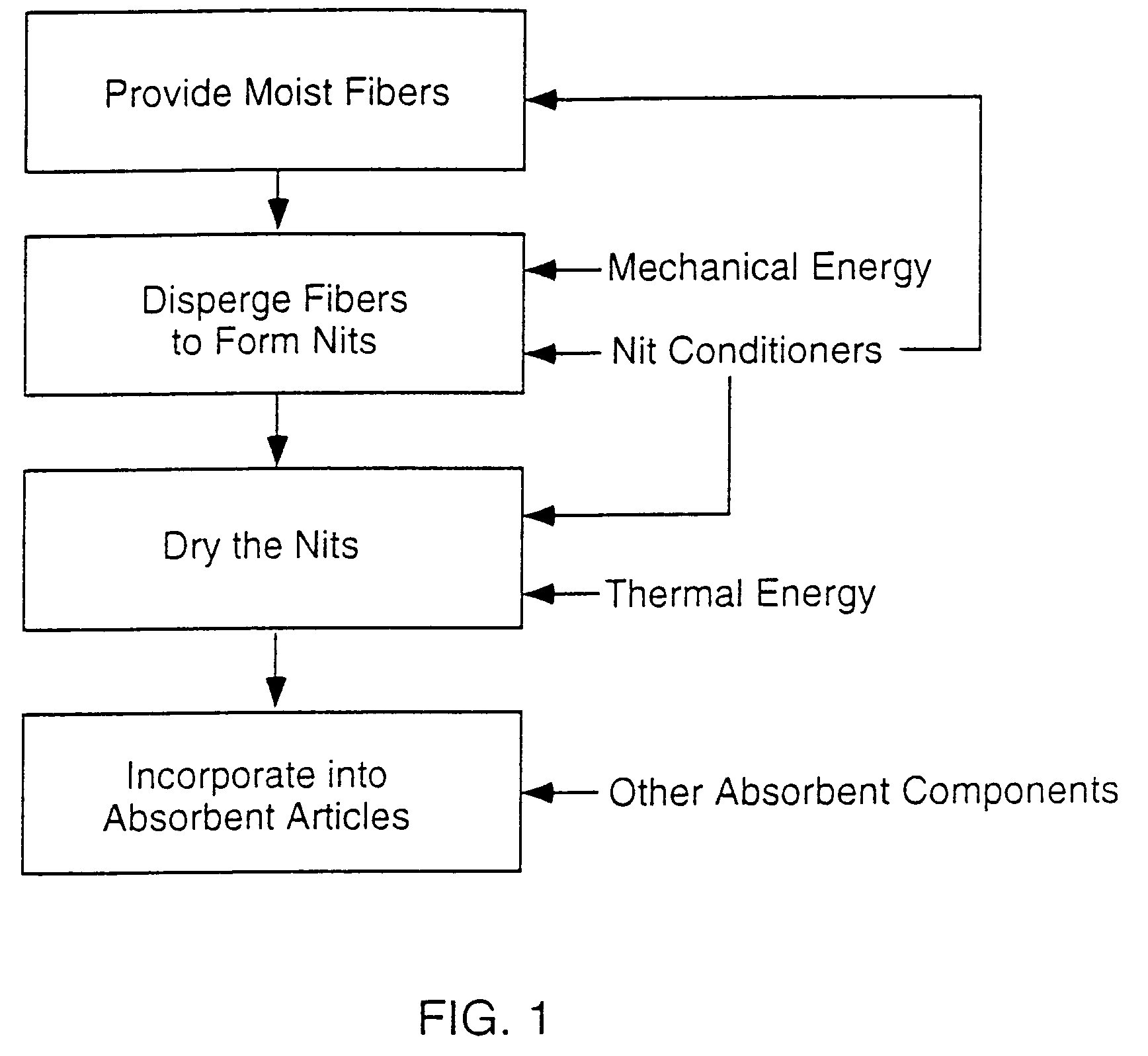
Absorbent articles with nits and free-flowing particles
Absorbent articles comprising fibrous nits and other free-flowing particles are disclosed. In one embodiment, an absorbent article is disclosed comprising free-flowing particles in a central portion which, in conjunction with other absorbent members, provides excellent body fit and good fluid handling performance. In another embodiment, good leakage control is provided by the combined effect of good intake and fluid handling performance of fibrous nits coupled with a wicking barrier between the nits and the longitudinal sides of the articles. An optional central rising member can further enhance the topography of the article when compressed by urging the portion comprising nits to deflect vertically upward.Methods of preparing cellulosic nits and incorporating them into absorbent articles are also described.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Absorbent sheet
InactiveUS20080008860A1Increase in sizeDecrease sidednessNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulose fiberPulp and paper industry
A method of making a cellulosic web includes: forming a nascent web from a papermaking furnish, the nascent web having a generally random distribution of papermaking fiber; b) transferring the web having a generally random distribution of papermaking fiber to a translating transfer surface moving at a first speed; drying the web to a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent including compactively dewatering the web prior to or concurrently with transfer to the transfer surface; fabric-creping the web from the transfer surface at a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent utilizing a creping fabric with a patterned creping surface, the fabric creping step occurring under pressure in a fabric creping nip defined between the transfer surface and the creping fabric wherein the fabric is traveling at a second speed slower than the speed of said transfer surface, the fabric pattern, nip parameters, velocity delta and web consistency being selected such that the web is creped from the transfer surface and redistributed on the creping fabric such that the web has a plurality of fiber-enriched regions arranged in a pattern corresponding to the patterned creping surface of the fabric, optionally drying the wet web while it is held in the creping fabric. Preferably, the formed web is characterized in that its void volume increases upon drawing.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
High basis weight TAD towel prepared from coarse furnish
ActiveUS8080130B2Low costGood flexibilityNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulose fiberCalipers
Kitchen roll toweling having surprising softness, absorbency and bulk is formed from a furnish comprising long cellulosic fiber having: (i) average weight-weighted fiber length of at least 2.5 mm; coarseness at least 15.5 mg / 100 mm; and a Canadian Standard freeness of at least 600 ml combined with (ii) short cellulosic fiber having an average weight-weighted fiber length of at most 1.9 mm having a Canadian Standard freeness of at least 500 ml in a weight ratio of short fiber to long fiber of at least 0.25 to 1.0 to form a nascent web having a consistency in the range from about 10% to about 35% which is rush transferred from one fabric to another at a speed differential of at least about 15%; and creping the web from a Yankee dryer while controlling the real crepe to at most 3% and thereafter converting the web to form a two ply product having a basis weight of at least 29 lb / rm and caliper of at least 220 mils / 8 sheets.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Multi-ply absorbent paper product having impressed pattern
A multi-ply tissue includes a first cellulosic embossed ply having an emboss pattern applied over a portion of its surface and a second cellulosic embossed ply of tissue. The first ply is contact laminated to the second ply so that the primary adhesion between the plies of tissue is the result of contact between cellulosic fibers. The first and second plies contact one another in contact-areas, with the contact areas between the first and second plies defining compliant voids. The contact areas between the first ply and the second ply are elongated and / or rounded contact areas. A method of forming a multi-ply tissue involves conveying a base sheet through a nip between an impression roll and a pattern roll to produce an embossed base sheet having a back side possessing projections, applying adhesive to the back side of the embossed base sheet at spaced apart locations, and applying a flat backing sheet to the back side of the embossed base sheet so that the backing sheet adheres to the back side of the embossed base sheet at said spaced apart locations. A method of producing an embossed tissue involves successively conveying a base sheet through a nip between a first impression roll and a pattern roll, and conveying the base sheet through another nip between the pattern roll and a second impression roll, wherein the second impression roll is made of rubber having a lower hardness than the rubber from which the first impression roll is made.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Soft and strong webs from highly refined cellulosic fibres
InactiveUS20040144510A1Fully softenedNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPolymer scienceWater soluble
Soft and strong cellulose-based fibrous web, comprises a) cellulosic fibres having a freeness value of more than 26° SR measured according to DIN-ISO 5267 / 1 (March 1999), b) a water-soluble cationic polymer, c) a water-soluble anionic polymer, and d) a cationic surfactant-based softener. The webs are prepared by refining cellulosic fibres to a degree of freeness of more than 26° SR measured according to DIN-ISO 5267 / 1, adding at least one water-soluble anionic polymer and water-soluble cationic polymer to the refined cellulosic fibres, adding a cationic surfactant-based softener to the cellulosic fibres obtained thereby, and wet-laying and dewatering the celulosic fibres obtained thereby.
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
Process for production of paper or board
ActiveUS9605382B2Improve propertiesReinforcing agents additionPaper/cardboardCardboardPulp and paper industry
Owner:KEMIRA OY
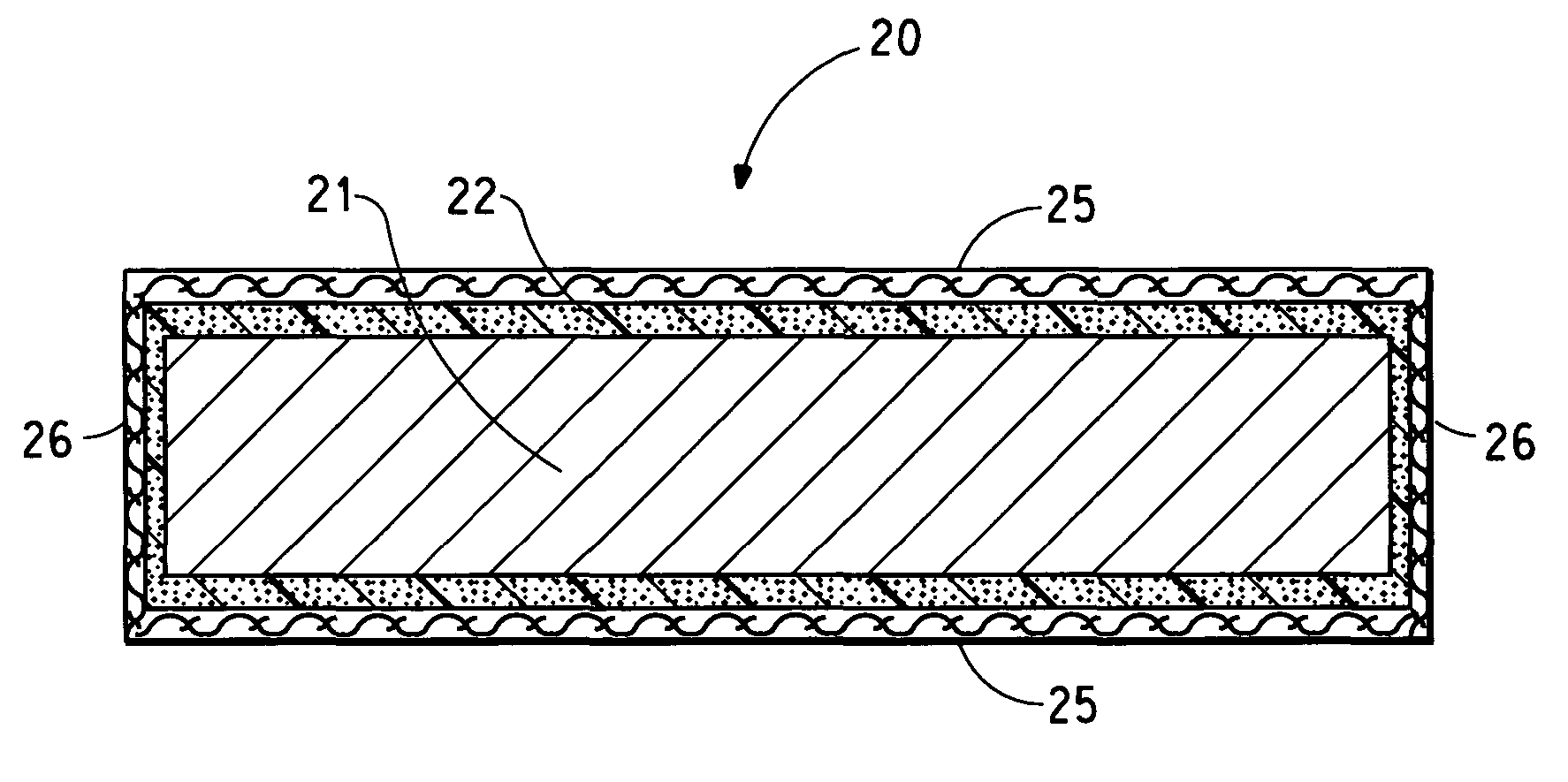
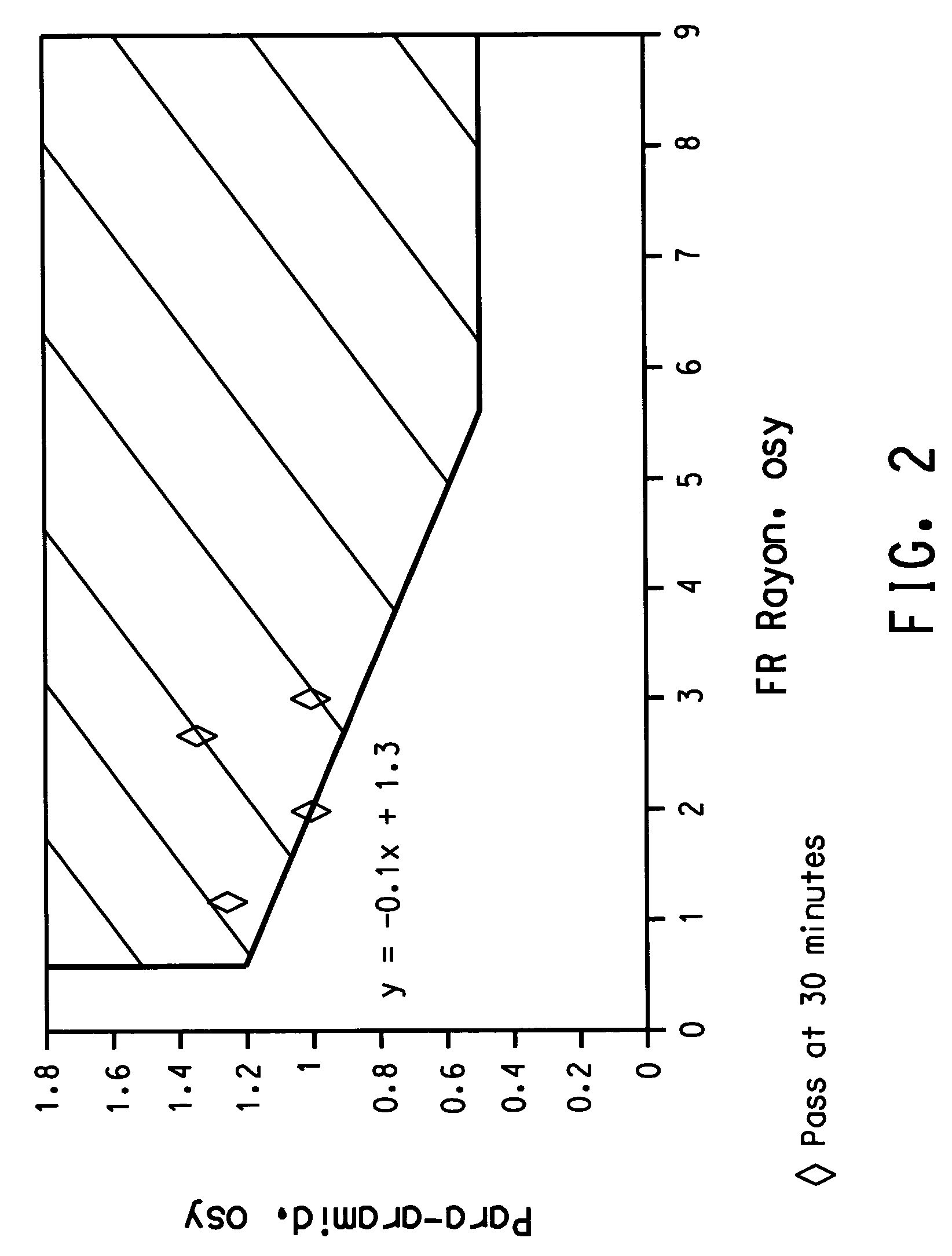
Fire resistant fabric composite, process for fire-blocking a mattress and mattress set, and a mattress and mattress set fire-blocked thereby
This invention relates to a fabric composite for use in fire-blocking a mattress, a fire-blocked mattress set, and a process for fire-blocking mattresses; the fabric composite comprising, in order, (a) sacrificial outer ticking, (b) sacrificial cushioning material, and (c) fire-blocking fabric, the fire-blocking fabric being a single layer of nonwoven fabric comprising at least 0.5 ounces per square yard (17 grams per square meter) of a cellulose fiber that retains at least 10 percent of its fiber weight when heated in air to 700 C at a rate of 20 degrees C. per minute, and at least 0.5 ounces per square yard (17 grams per square meter) of a heat-resistant fiber. Mattress sets fire-blocked with this fabric composite have a peak heat release rate of less than 150 kilowatts within 30 minutes, preferably less that 150 kilowatts within 60 minutes, and a total heat release of less than 25 megajoules within 10 minutes when tested according to Technical Bulletin 603 of the State of California.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Absorbent, nonwoven material exhibiting z-direction density gradient
InactiveUS20100318047A1Inhibition releaseMaintain integrityPersonal careCellulosic plastic layered productsAbsorbent materialVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to an absorbent material that can be used as an absorbent core in absorbent articles such as sanitary napkins, pantiliners, incontinence products, disposable diapers, etc. The material of the present invention is a nonwoven sheet, consisting of cellulosic fibers, optionally superabsorbent polymeric material, containing no binders, latexes, etc, relying on hydrogen bonding to produce the necessary structure. The material contains density gradients which direct fluid into the material and distribute it providing more effective fluid transport and efficient utilization of storage capacity. The material consists of two regions. In the first region, the material has a low-density stratum adjacent to one surface, overlaying at least one higher density stratum adjacent to the opposite surface of the sheet. These strata create a density gradient in the thickness direction (Z-direction) of the sheet. The second region consists of a fluid distribution structure that has a higher density than at least the lower density of the strata comprising the first region. The fluid distribution structure is in direct fluid communication with the adjacent strata in the first region, along their boundaries.
Owner:EAM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com