Patents
Literature
2092results about "Inorganic pigment treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
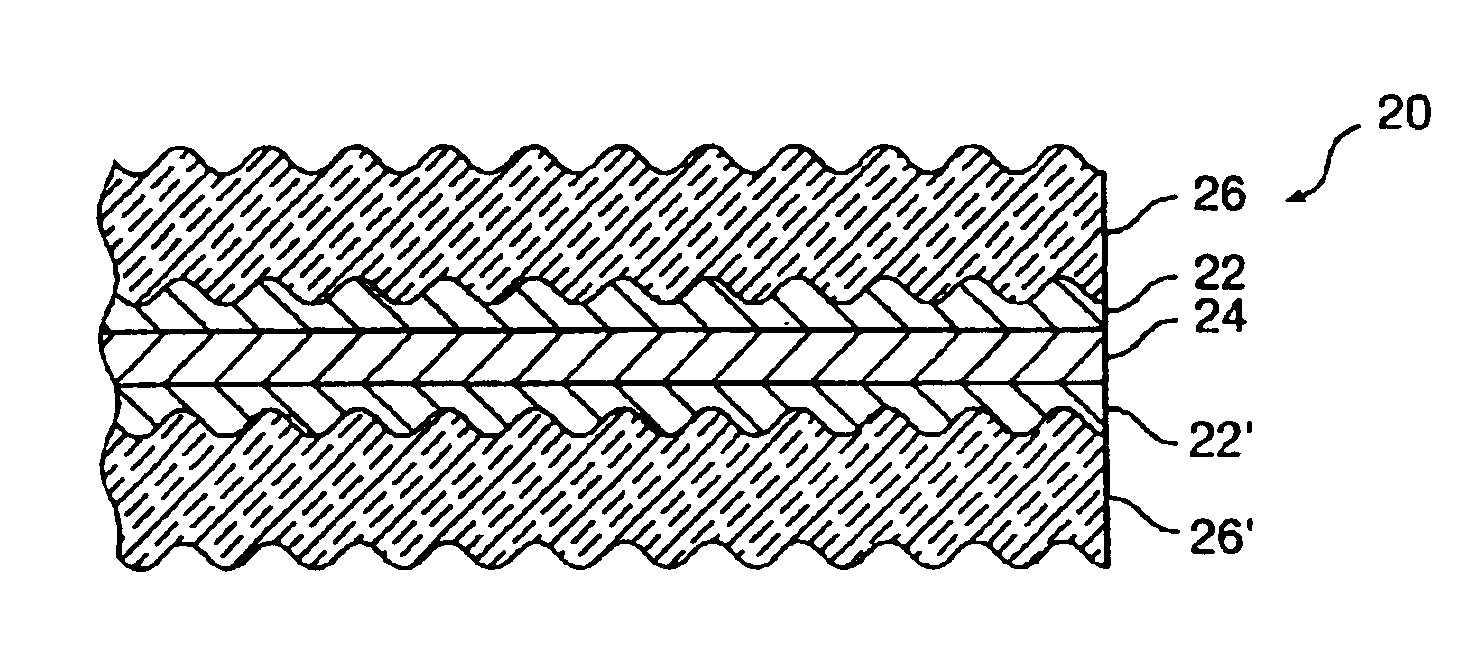
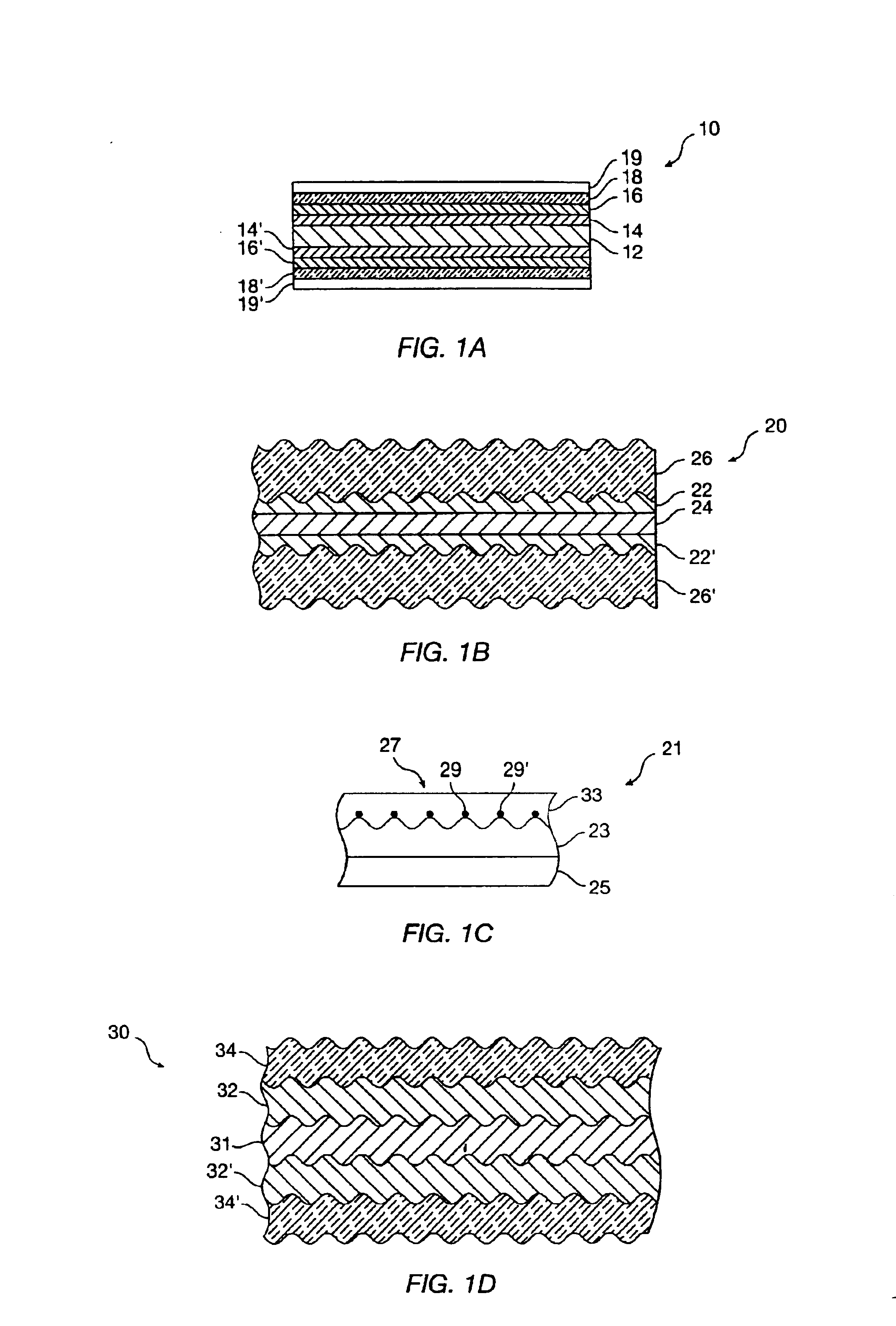
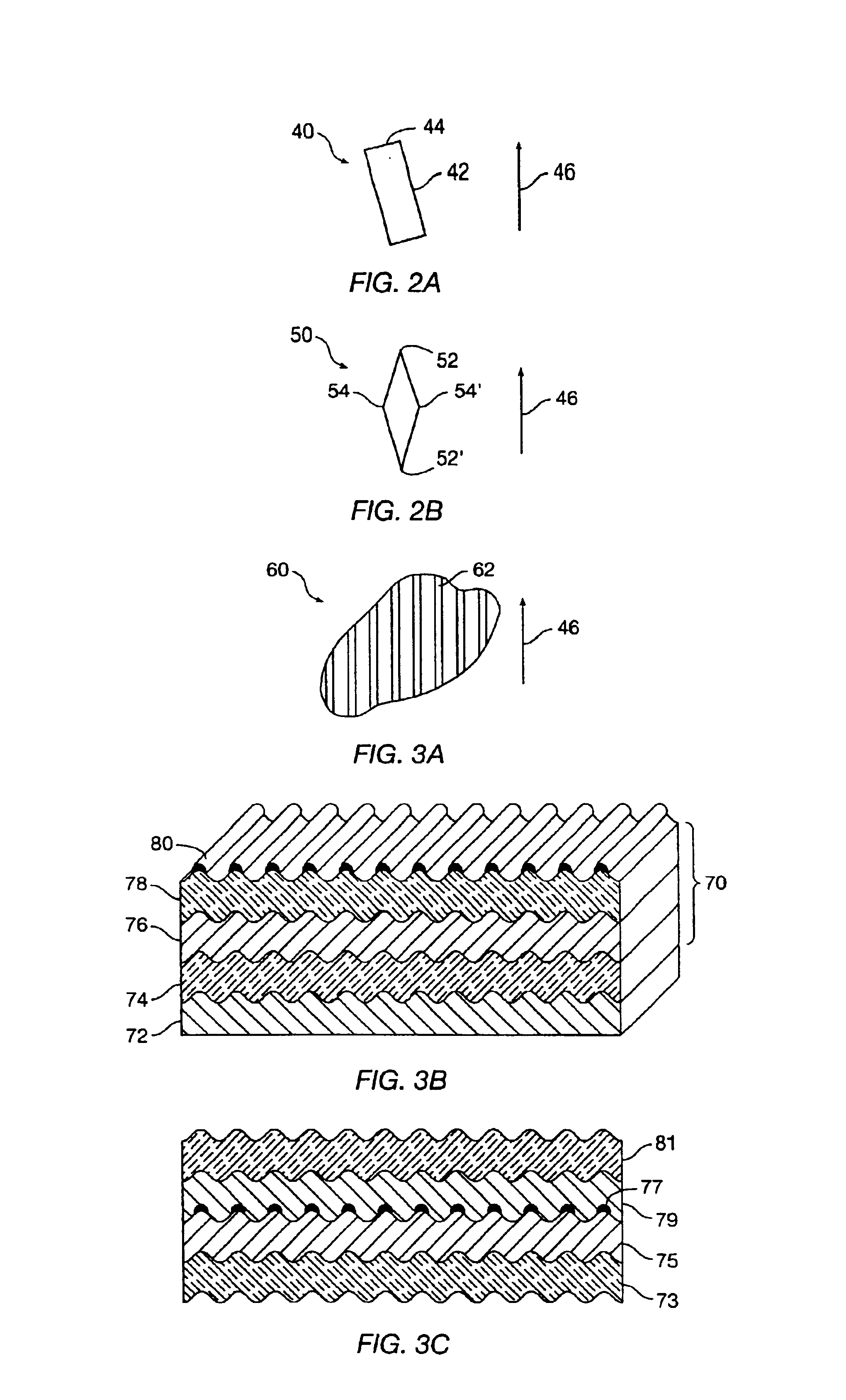
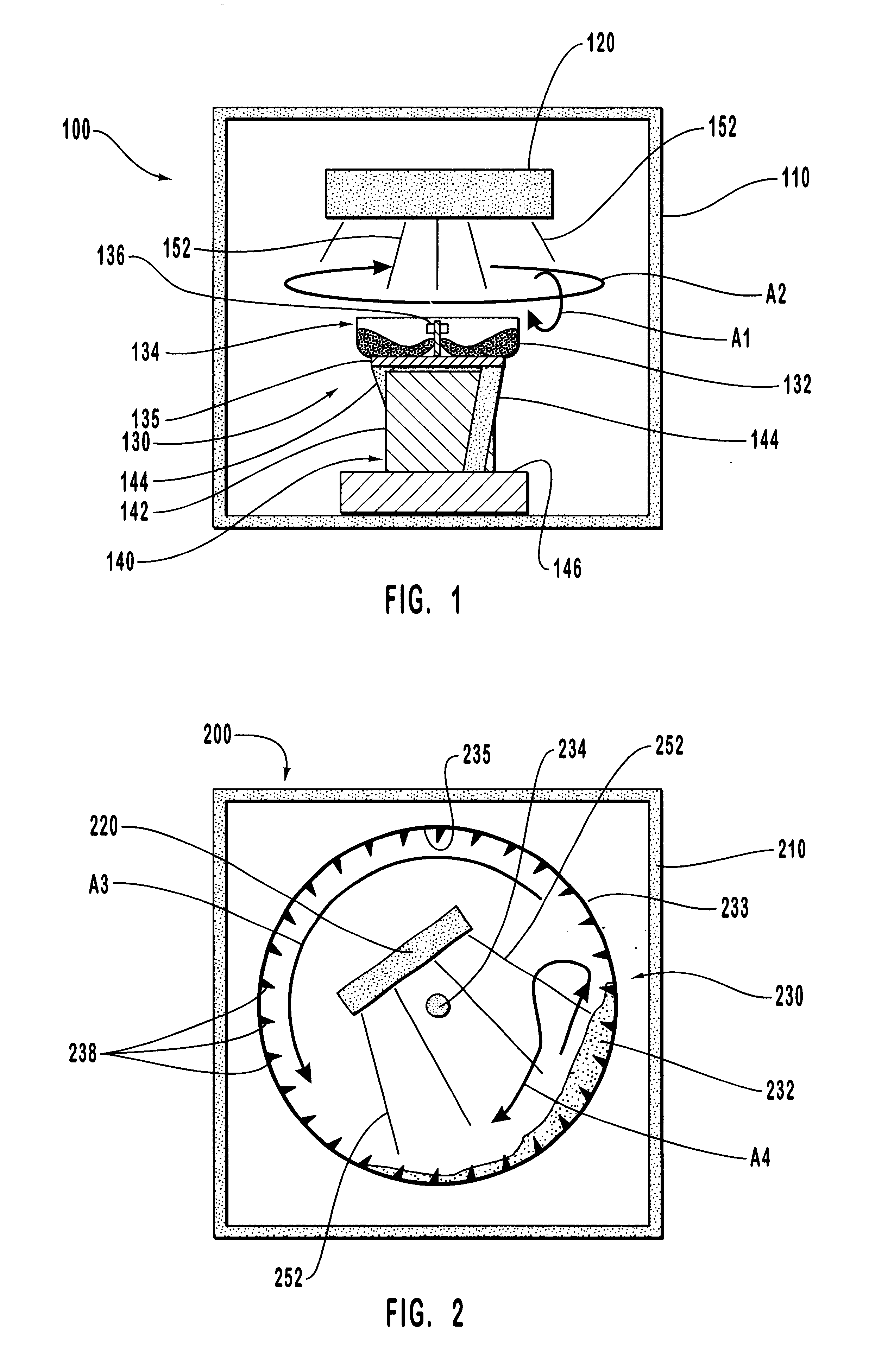
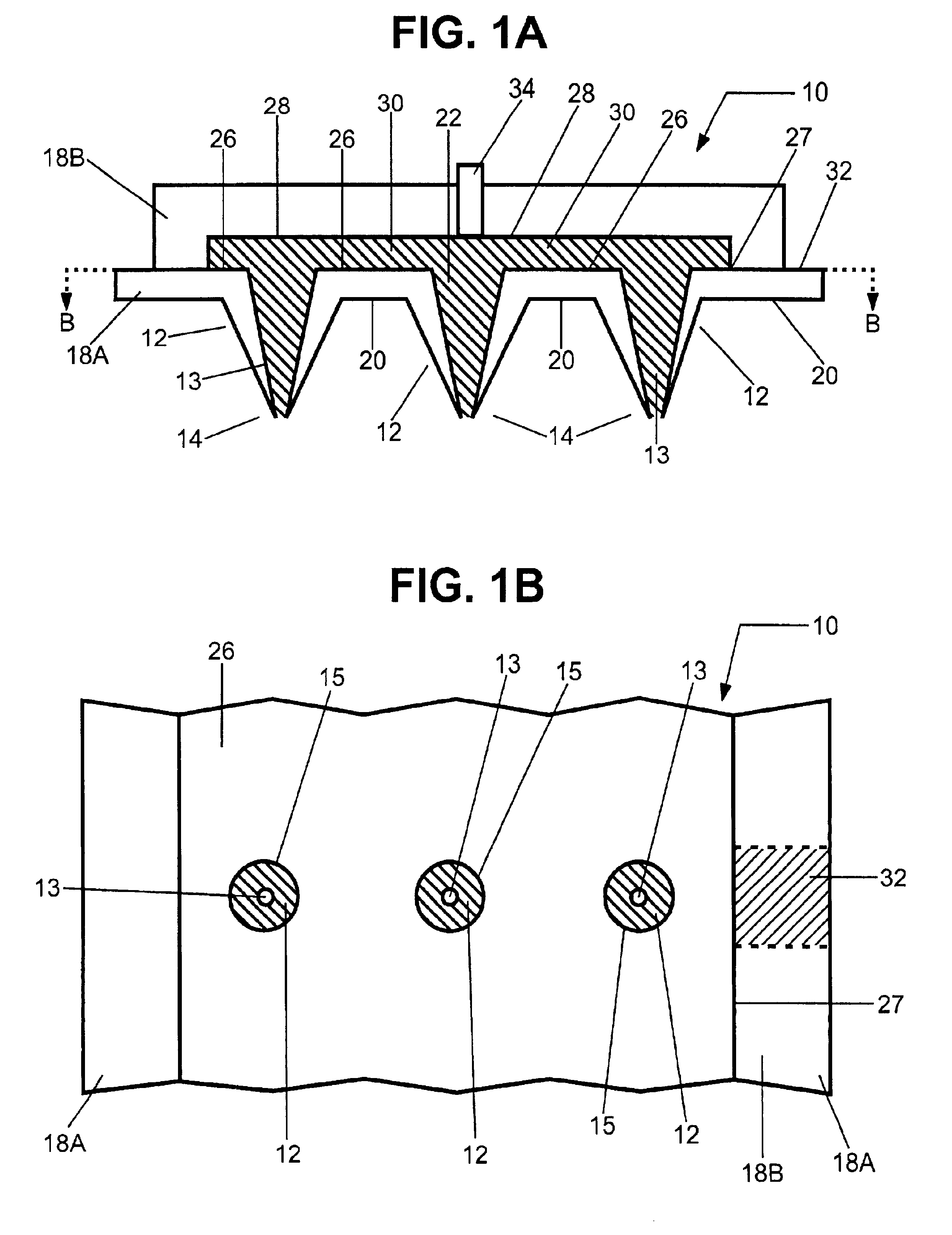
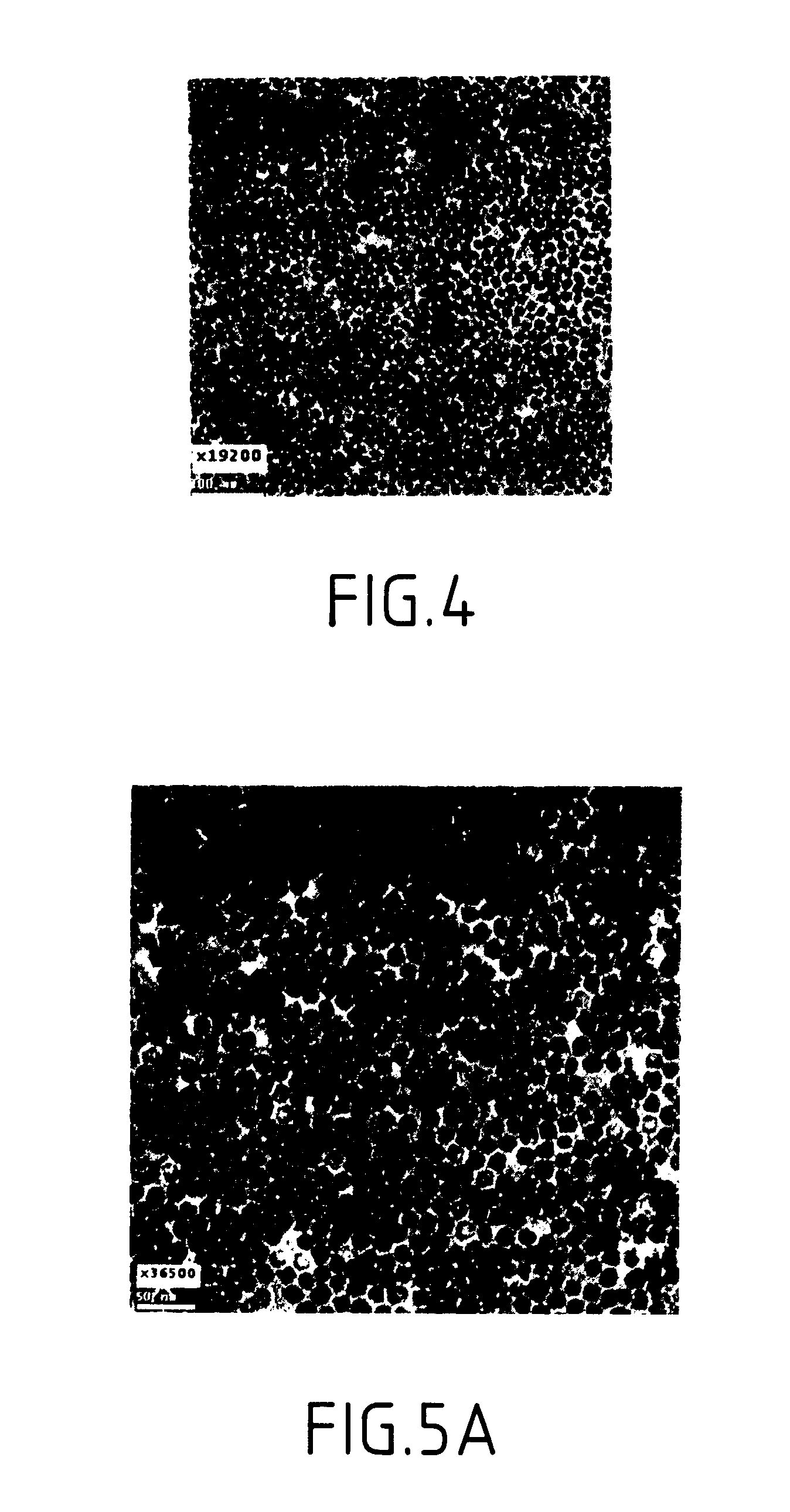
Alignable diffractive pigment flakes
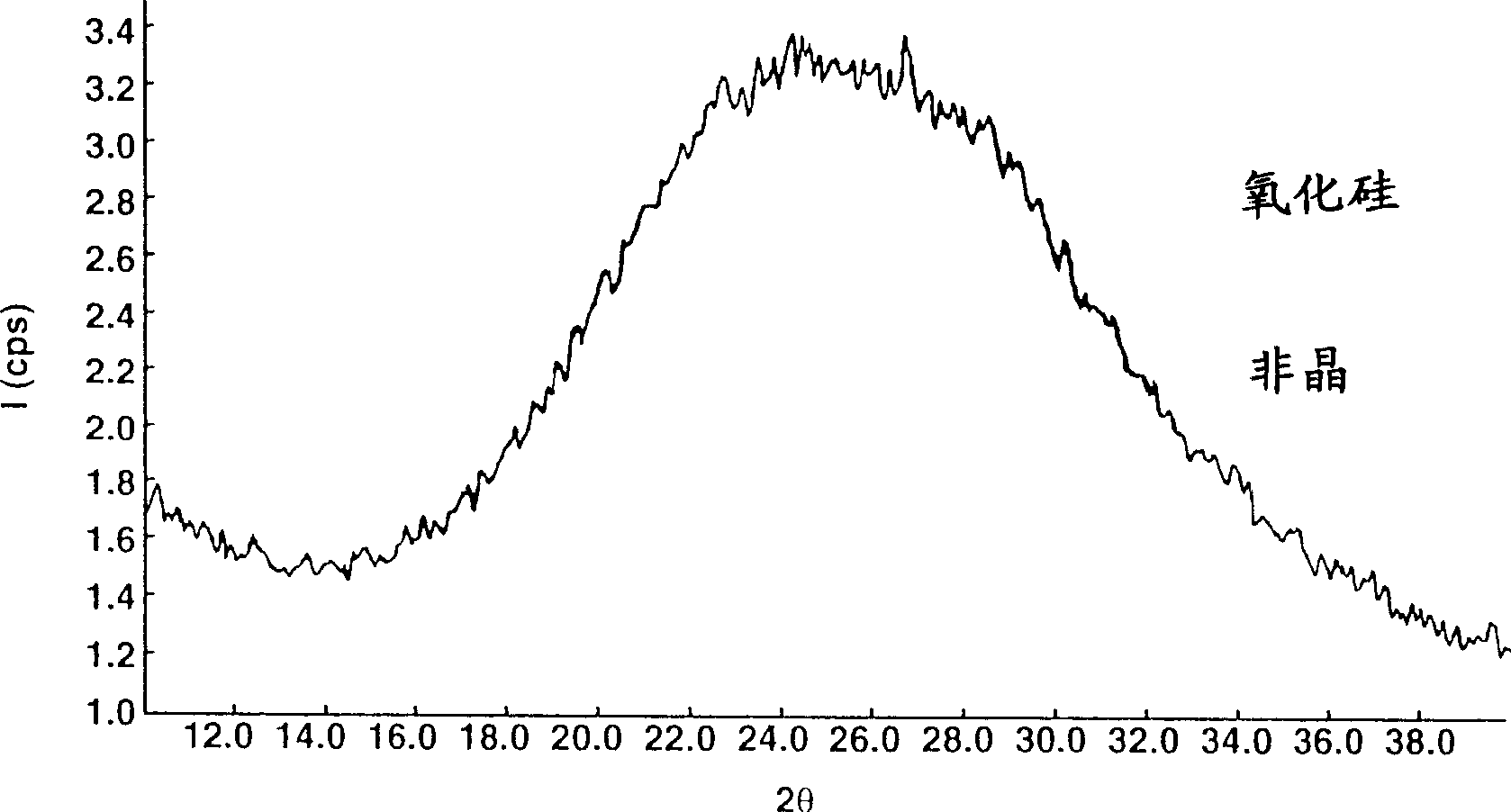
Diffractive pigment flakes are selectively aligned to form an image. In one embodiment, flakes having a magnetic layer are shaped to facilitate alignment in a magnetic field. In another embodiment, the flakes include a magnetically discontinuous layer. In a particular embodiment, deposition of nickel on a diffraction grating pattern produces magnetic needles along the grating pattern that allow magnetic alignment of the resulting diffractive pigment flakes. Color scans of test samples of magnetically aligned flakes show high differentiation between illumination parallel and perpendicular to the direction of alignment of the magnetic diffractive pigment flakes.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
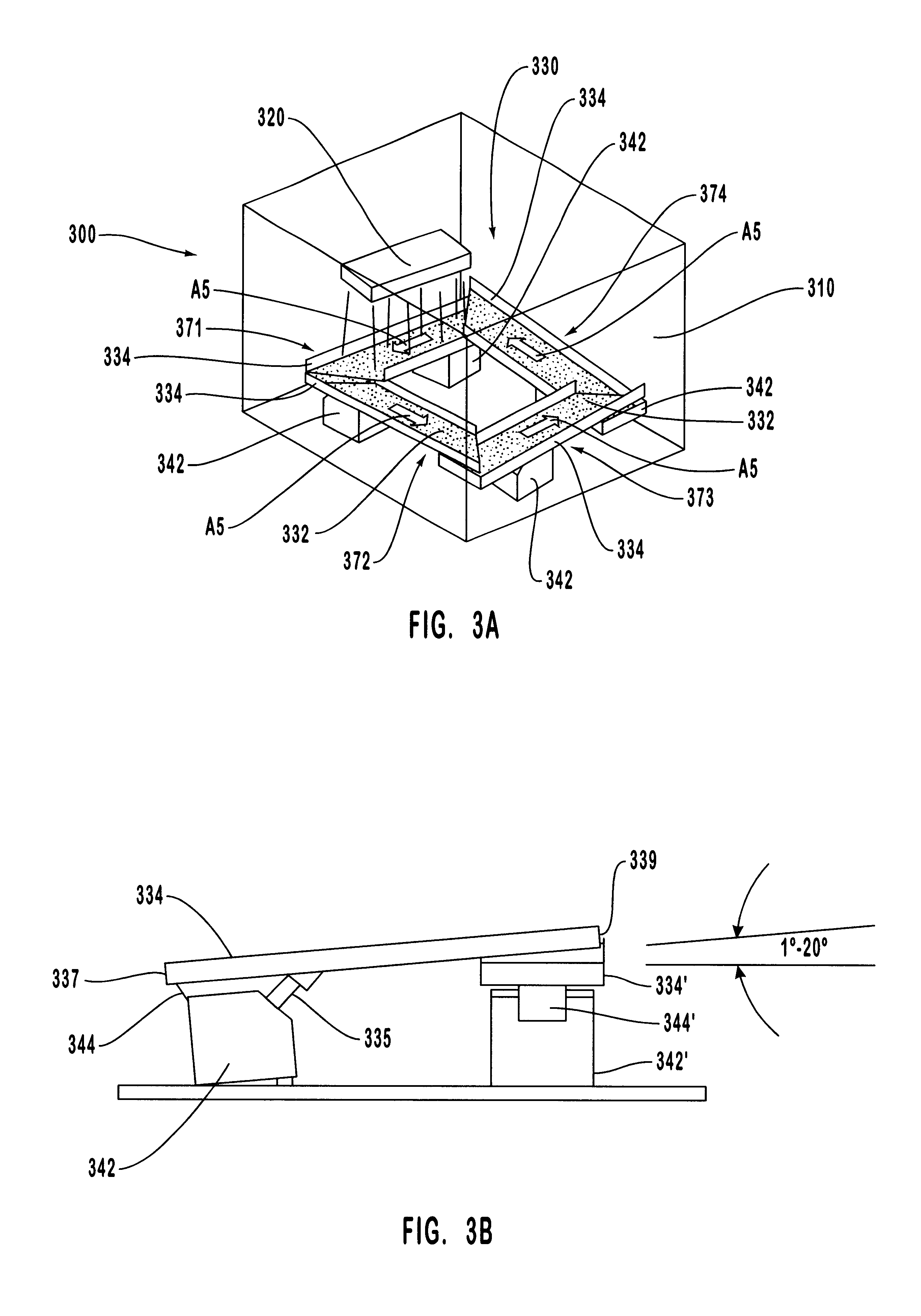
Methods and apparatus for producing enhanced interference pigments
InactiveUS6241858B1Interference be notGood effectElectric discharge heatingPigment preparation by PVD/CVD methodsGas phaseVaporization
Methods and apparatus are provided for uniformly depositing a coating material from a vaporization source onto a powdered substrate material to form a thin coalescence film of the coating material that smoothly replicates the surface microstructure of the substrate material. The coating material is uniformly deposited on the substrate material to form optical interference pigment particles. The thin film enhances the hiding power and color gamut of the substrate material. Physical vapor deposition processes are used for depositing the film on the substrate material. The apparatus and systems employed in forming the coated particles utilize vibrating bed coaters, vibrating conveyor coaters, or coating towers. These allow the powdered substrate material to be uniformly exposed to the coating material vapor during the coating process.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Use Of A Surface-Reacted Calcium Carbonate In Tissue Paper, Process To Prepare A Tissue Paper Product Of Improved Softness, And Resulting Improved Softness Tissue Paper Products
ActiveUS20120031576A1Good flexibilityNatural cellulose pulp/paperCoatings with pigmentsSurface responseTissue paper
The present invention related to the use of a surface-reacted natural calcium carbonate as filler in tissue paper products, to a process to prepare tissue paper products, and to a tissue paper product featuring an improved softness, wherein said surface-reacted natural calcium carbonate is the reaction product of a natural calcium carbonate with an acid and carbon dioxide, which is formed in situ by the acid treatment and / or supplied externally.
Owner:OMYA INT AG
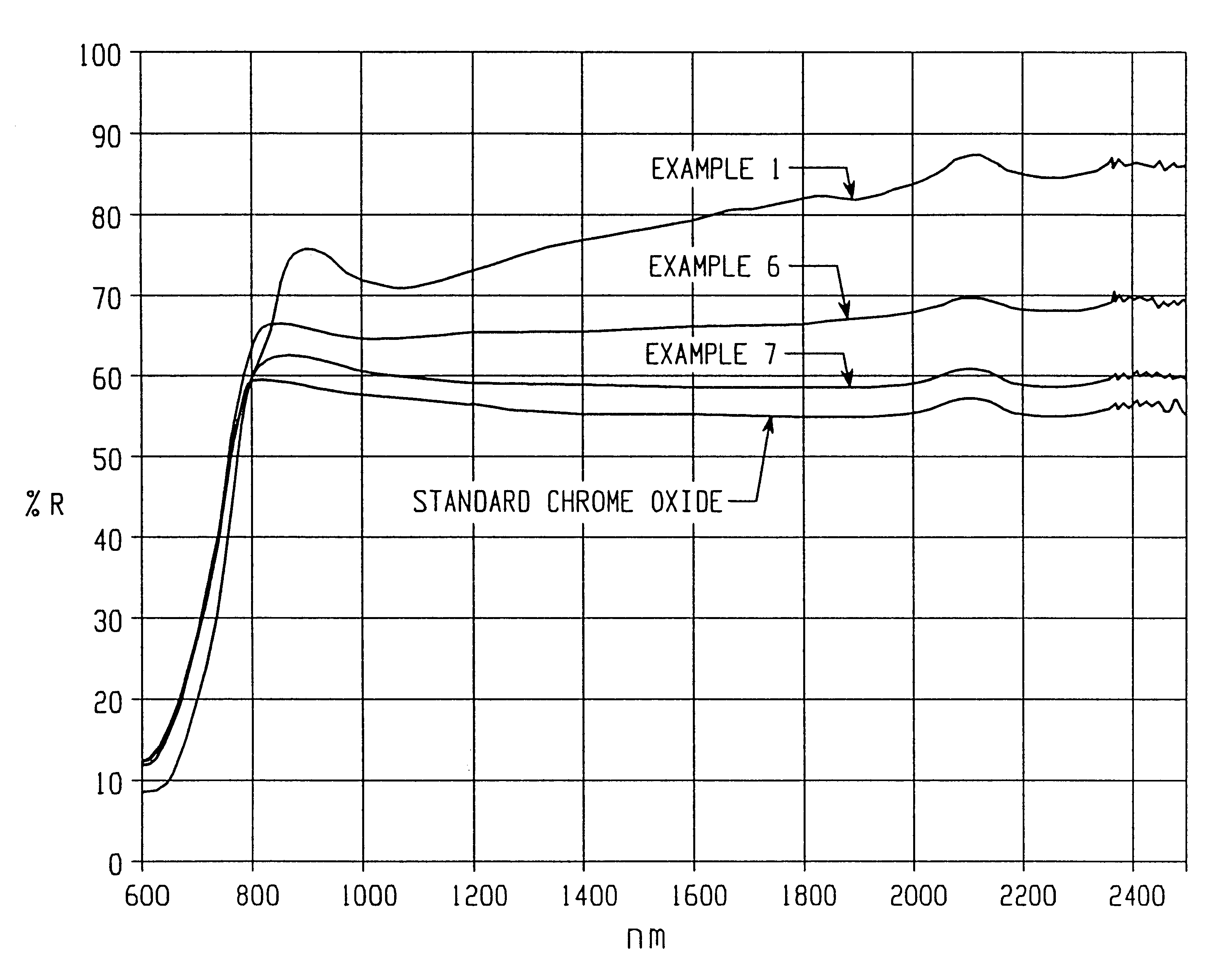
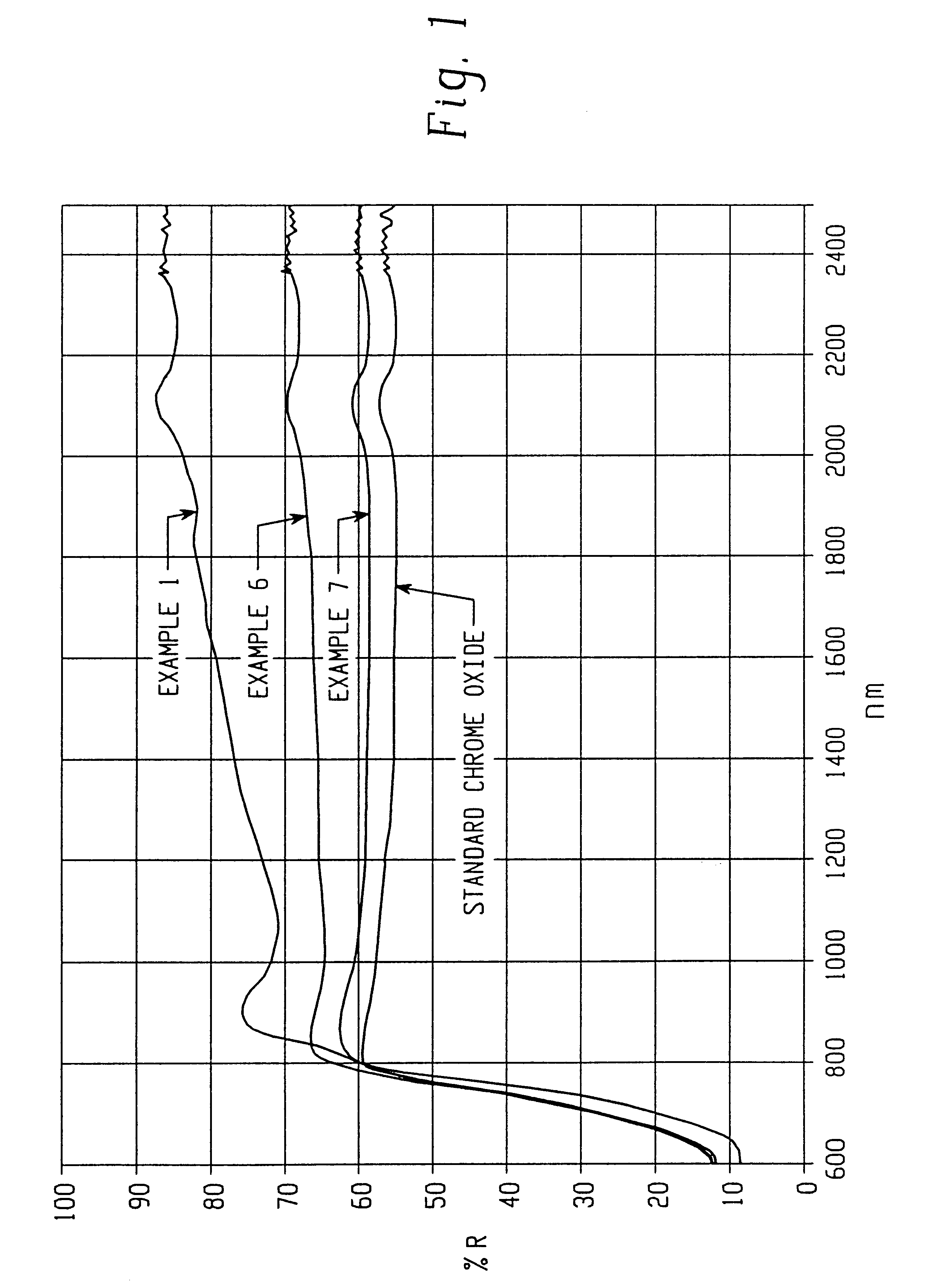
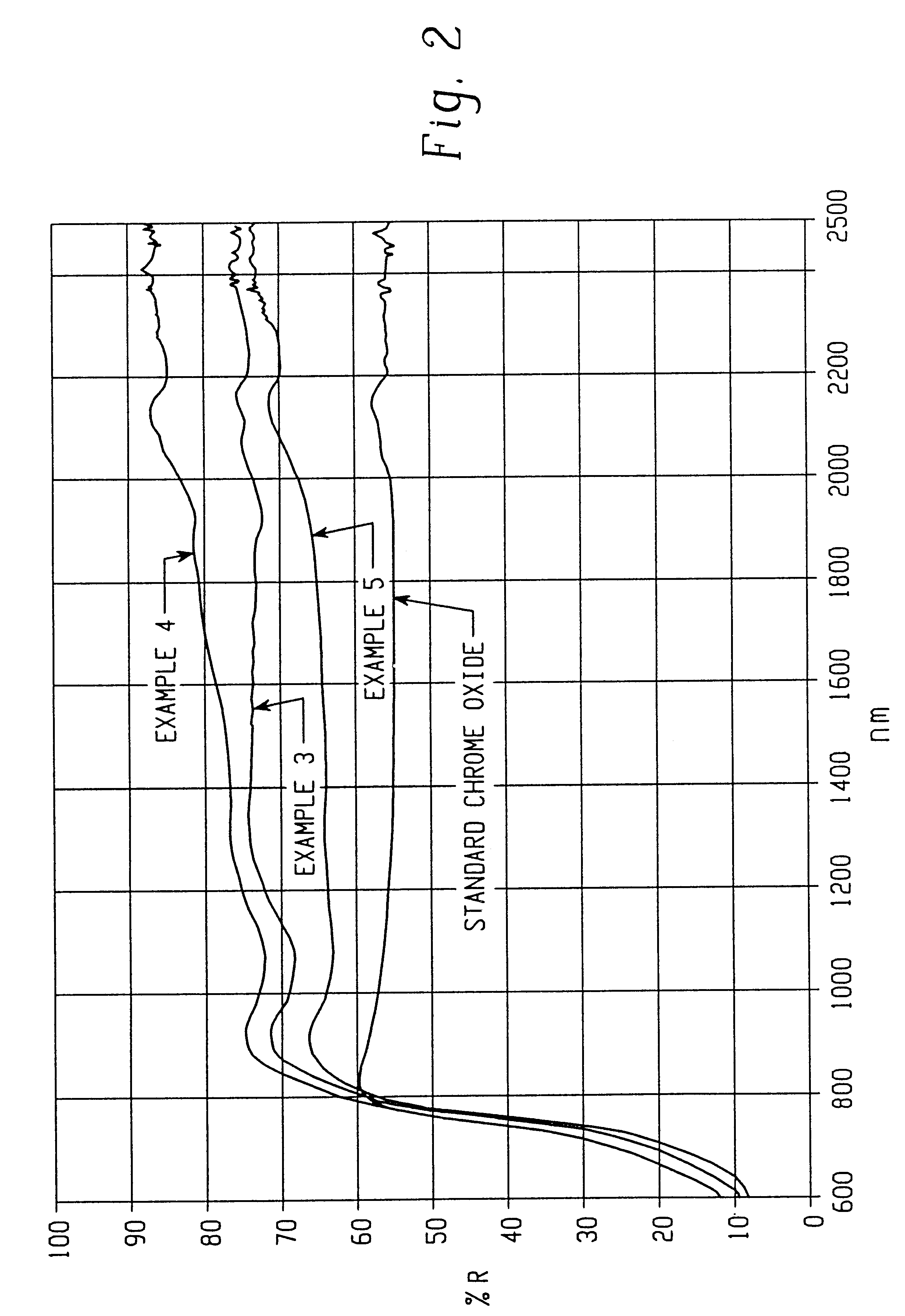
Infrared reflective color pigment
InactiveUS6454848B2Reduce heat buildupReduce energy costsInorganic pigment treatmentCoatingsIndiumCobalt
The present invention provides new solid solutions having a corundum-hematite crystalline structure which are useful as inorganic color pigments. Solid solutions according to the present invention include a host component having a corundum-hematite crystalline structure which contains as guest components one or more elements from the group consisting of aluminum, antimony, bismuth, boron, chrome, cobalt, gallium, indium, iron, lanthanum, lithium, magnesium, manganese, molybdenum, neodymium, nickel, niobium, silicon, tin, titanium, vanadium, and zinc. Solid solutions according to the present invention are formed by thoroughly mixing compounds, usually metal oxides or precursors thereof, which contain the host and guest components and then calcining the compounds to form the solid solutions having the corundum-hematite crystalline structure. Some of the new solid solutions according to the present invention exhibit relatively low Y CIE tri-stimulus values and relatively high near infrared reflectance.
Owner:FERRO CORP
Biological fluid constituent sampling and measurement devices and methods
A device for accessing biological fluid, sampling biological fluid constituents and determining the concentration of at least one target constituent within the accessed biological fluid is provided. The device has at least one micro-piercing member used to penetrate the skin to a selected depth and to access biological fluid, a constituent sampling means and a constituent measuring means. The constituent sampling means comprises a constituent transfer medium, such as a hydrophilic gel material, by which sampled constituents are transferred from the micro-piercing member to the measuring means. The measuring means includes an electrochemical cell having at least one porous electrode through which at least one sampled constituent is caused to enter into the electrochemical cell. Methods of sampling constituents within the skin and measuring the sampled constituents, as well as kits for practicing the invention are provided.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
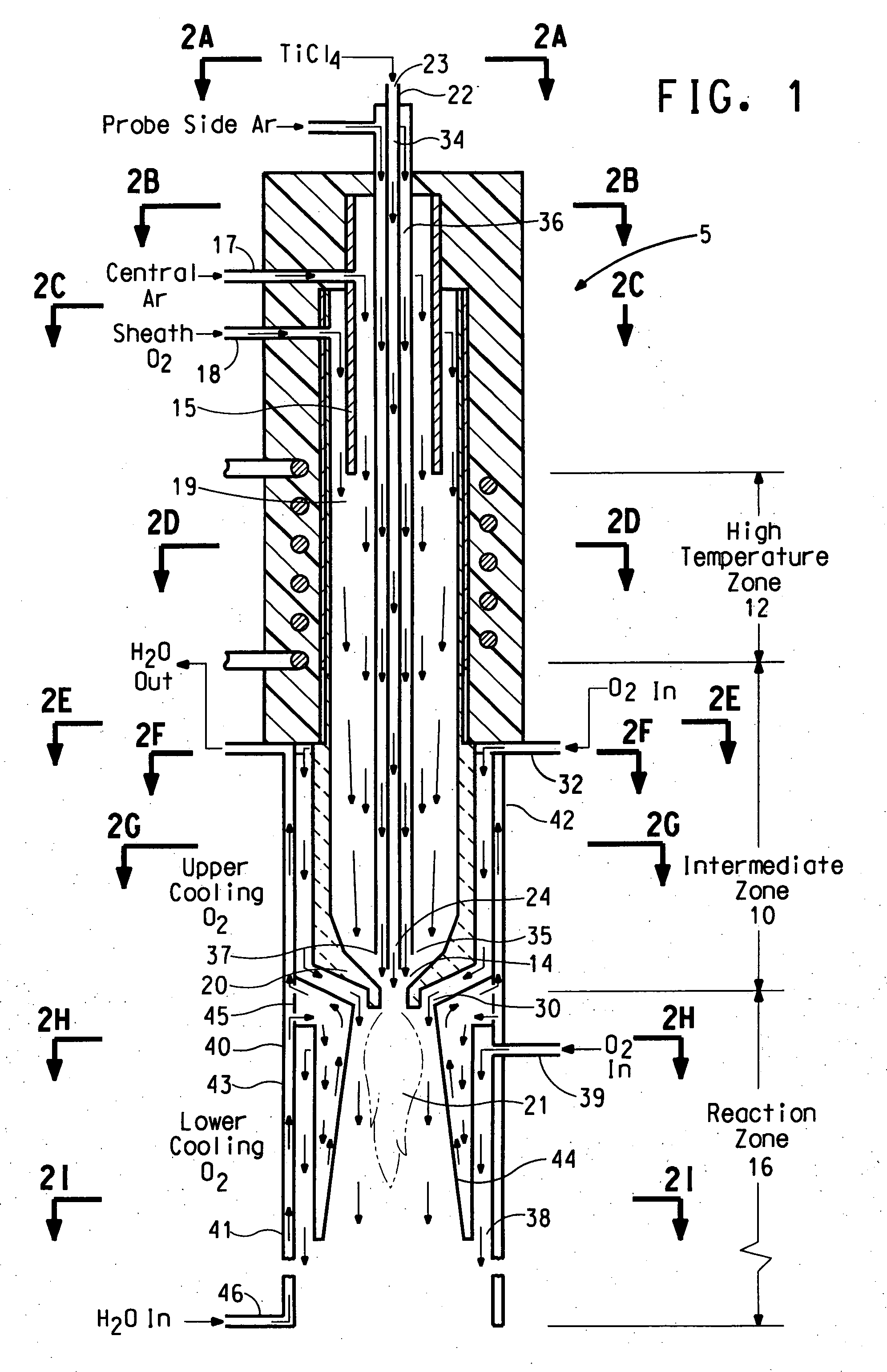
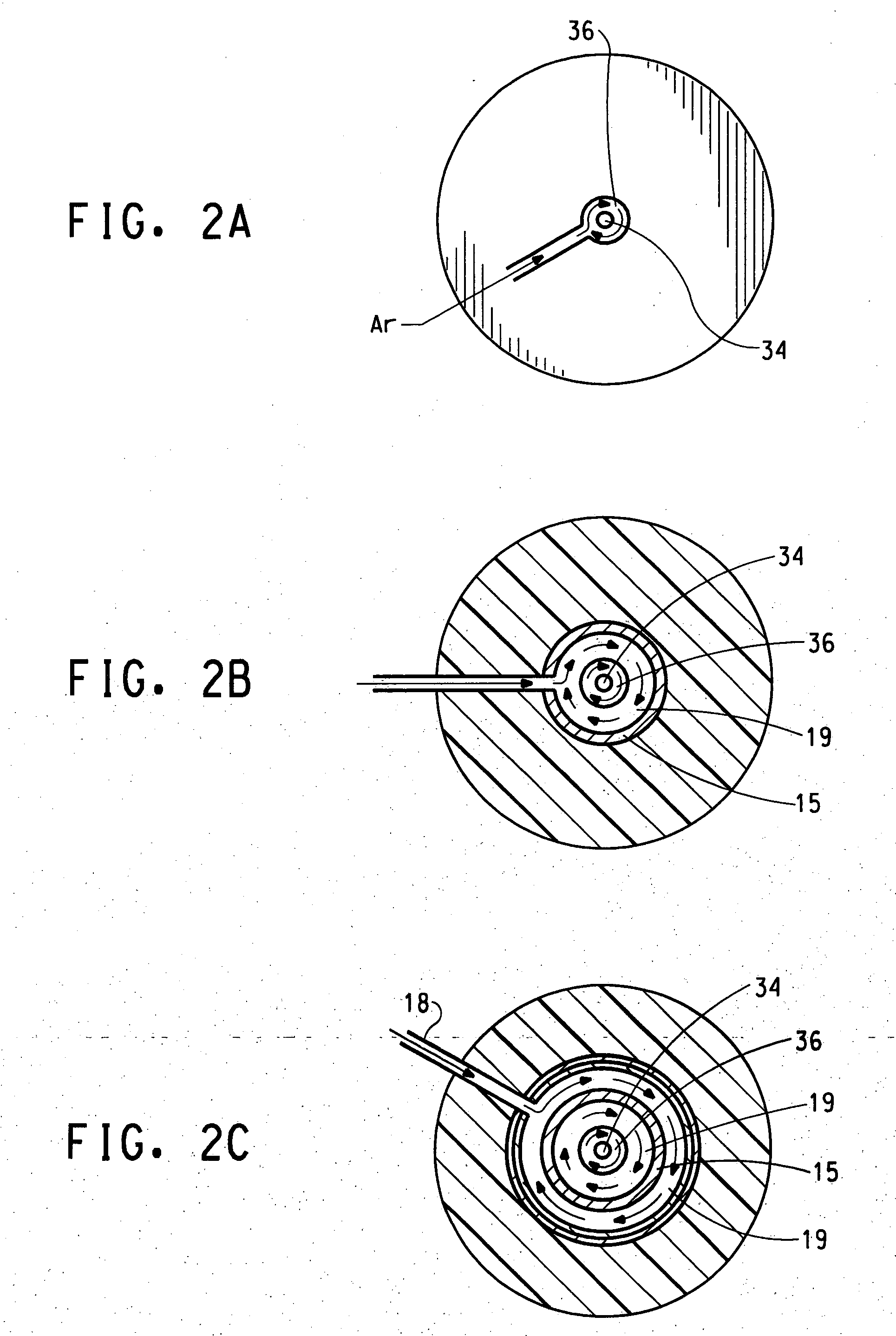
Process for making durable rutile titanium dioxide pigment by vapor phase deposition of surface treatment
The present invention relates to a process for making durable titanium dioxide pigment by vapor phase deposition of surface treatments on the titanium dioxide particle surface by reacting titanium tetrachloride vapor, an oxygen containing gas and aluminum chloride in a plug flow reactor to form a product stream containing titanium dioxide particles; and introducing silicon tetrachloride into the reactor at a point down stream of the point where the titanium tetrachloride and oxygen were contacted and where at least 97% of the titanium tetrachloride has been converted to titanium dioxide or where the reaction temperature is no greater than about 1200° C., and preferably not more than about 1100° C.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Solar heat-reflective roofing granules, solar heat-reflective shingles, and process for producing same
Solar-reflective roofing granules having improved solar heat-resistance are formed by coating colored mineral particles with a coating composition including titanium dioxide nanoparticles.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
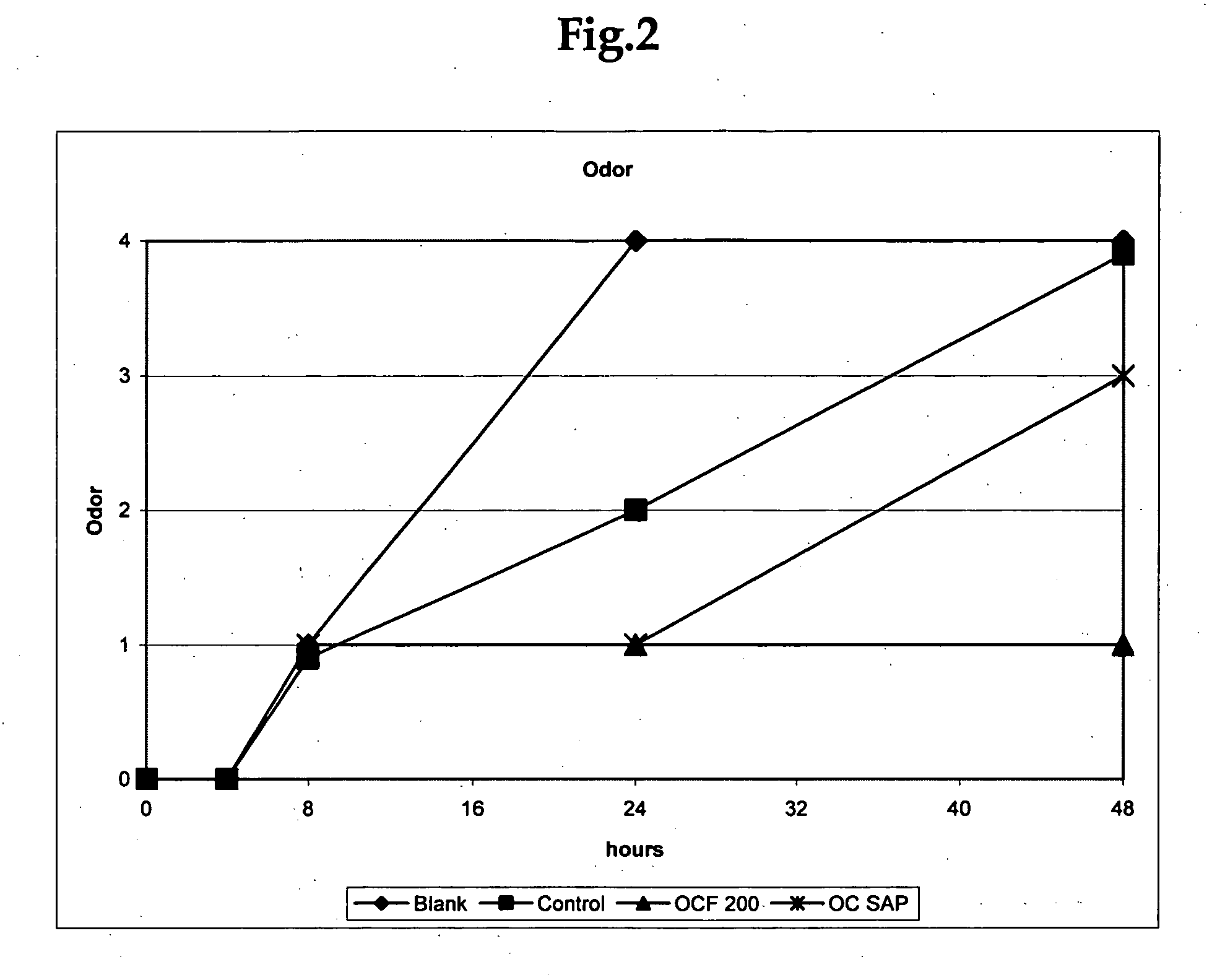
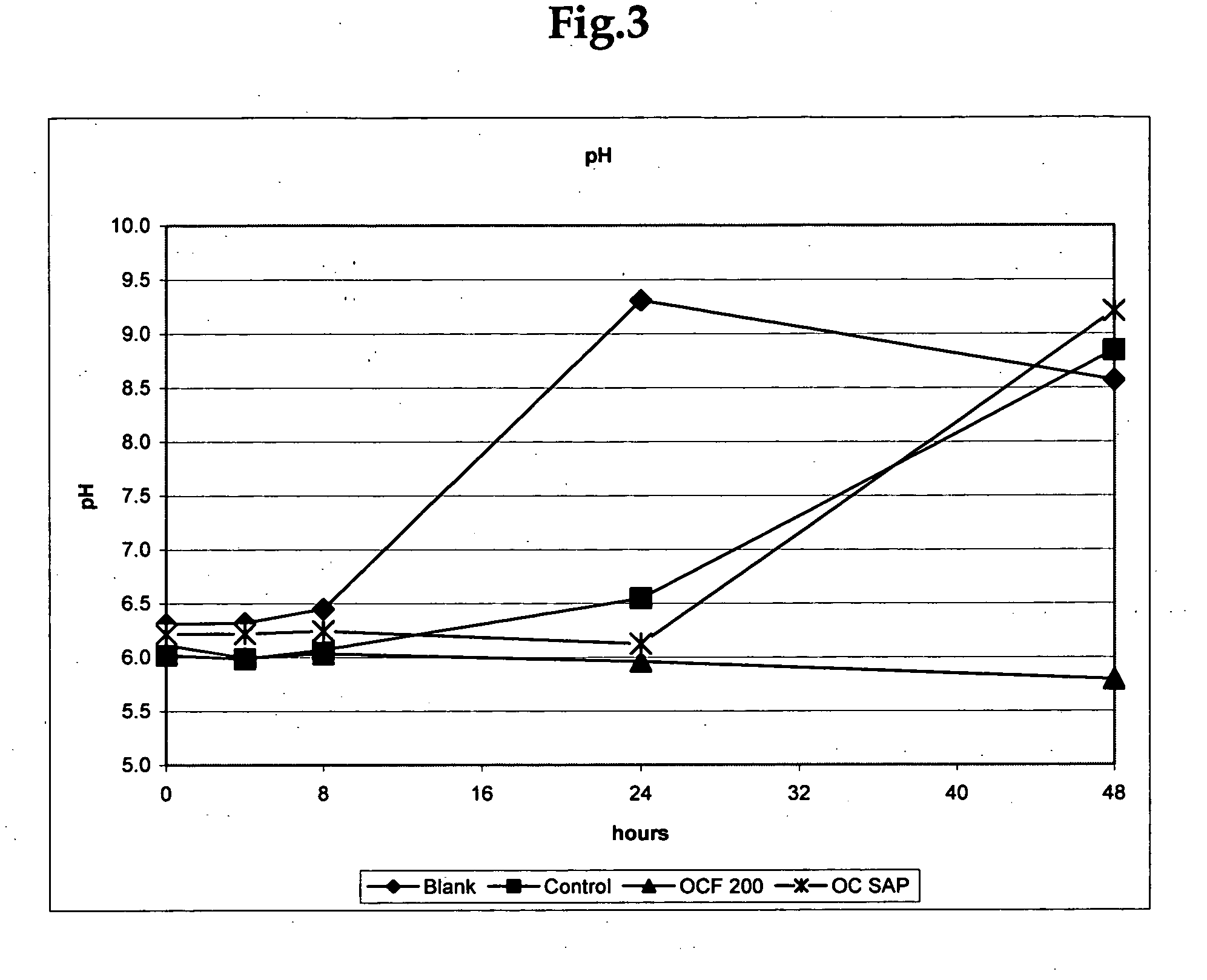
Cellulosic fibers with odor control characteristics
ActiveUS20070077428A1Avoid odorMaintain activityEngine sealsInorganic pigment treatmentBiotechnologyAmmonia production
An odor-inhibiting fiber having a cellulosic fiber and an odor-inhibiting formulation. The odor-inhibiting formulation may contain an odor-inhibiting agent, such as a biocide, an enzyme, a urease inhibitor. The odor-inhibiting formulation also may contain a liquid carrier such as a hydrophobic or hydrophilic organic liquid, or a mixture of a hydrophobic and hydrophilic organic liquid. The cellulosic fiber is impregnated with the odor-inhibiting formulation to produce fiber having odor-inhibiting characteristics. The resultant odor-inhibiting fiber is useful in making absorbent articles with odor-inhibiting characteristics. The fiber of the embodiments prevents odor by inhibiting bacteria growth and ammonia production, especially when used in an absorbent article such as a diaper or adult incontinence device.
Owner:RAYONIER PERFORMANCE FIBERS
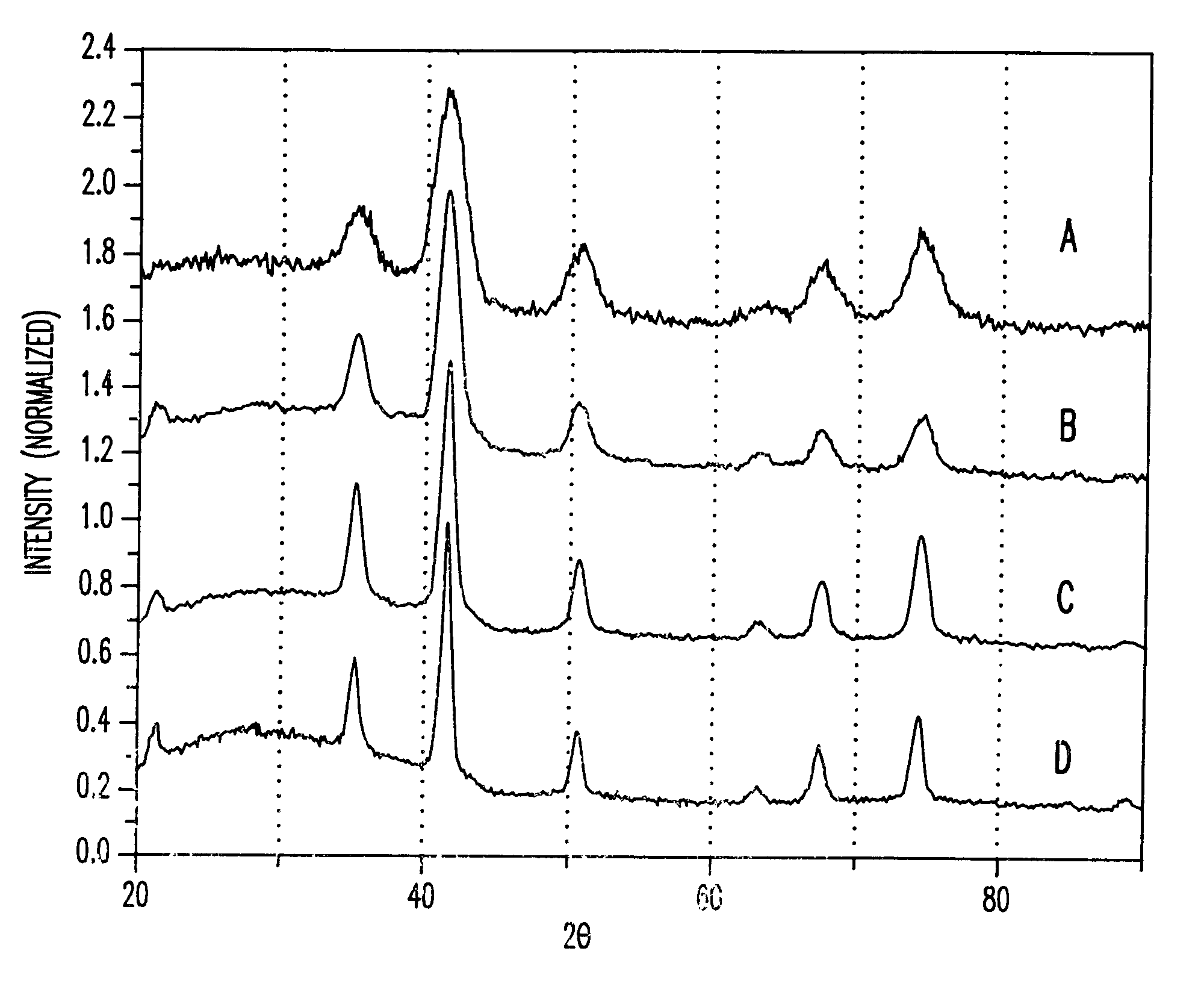
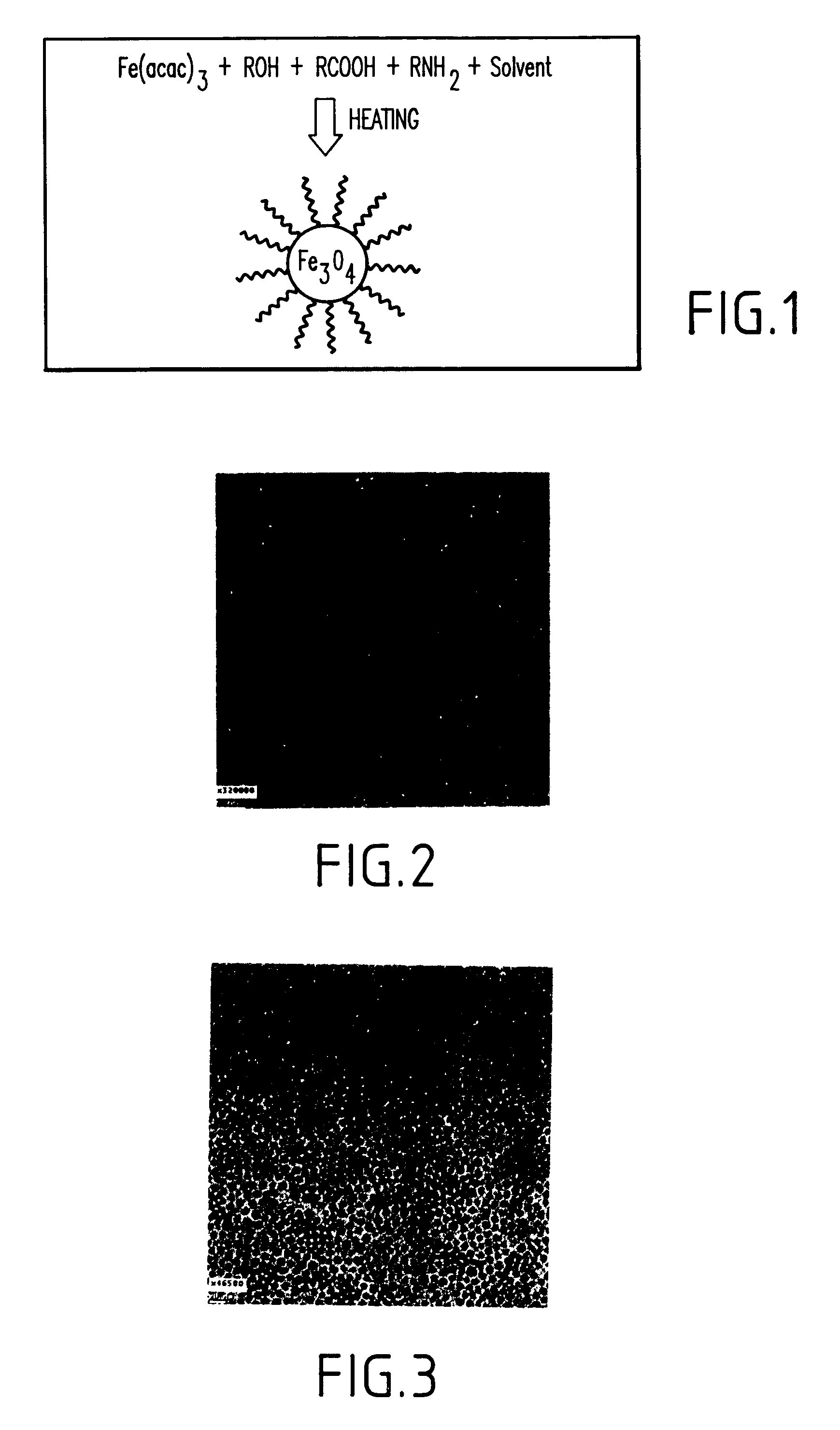
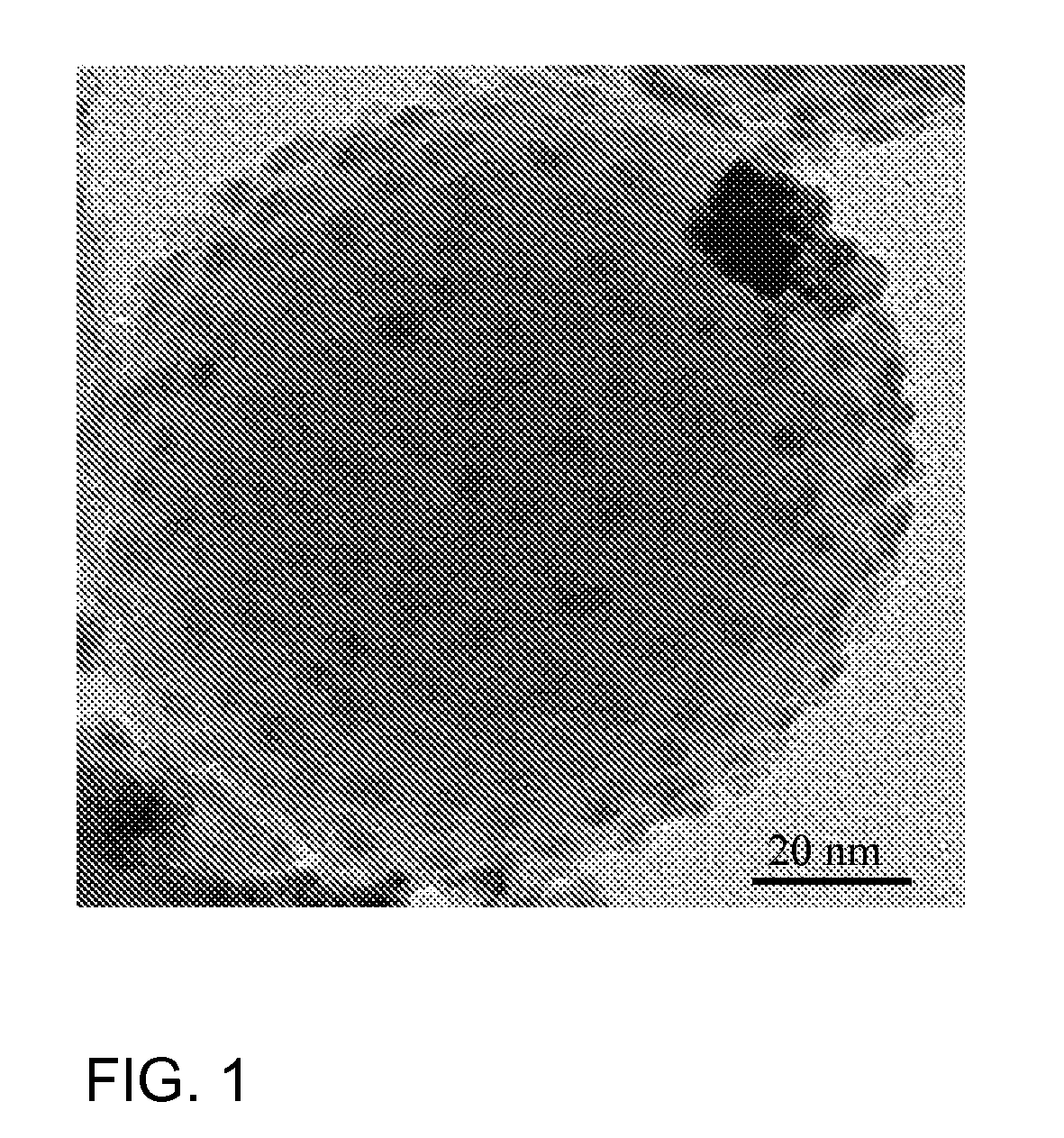
Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles and the process of forming Fe-based nanomaterials
InactiveUS6962685B2Small sizeNarrow size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismIron saltsMagnetite Nanoparticles
A method and structure for making magnetite nanoparticle materials by mixing iron salt with alcohol, carboxylic acid and amine in an organic solvent and heating the mixture to 200–360 C is described. The size of the particles can be controlled either by changing the iron salt to acid / amine ratio or by coating small nanoparticles with more iron oxide. Magnetite nanoparticles in the size ranging from 2 nm to 20 nm with a narrow size distribution are obtained with the invention. The invention can be readily extended to other iron oxide based nanoparticle materials, including M Fe2O4 (M=Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cr, Ti, Ba, Mg) nanomaterials, and iron oxide coated nanoparticle materials. The invention also leads to the synthesis of iron sulfide based nanoparticle materials by replacing alcohol with thiol in the reaction mixture. The magnetite nanoparticles can be oxidized to γ-Fe2O3, or α-Fe2O3, or can be reduced to bcc-Fe nanoparticles, while iron oxide based materials can be used to make binary iron based metallic nanoparticles, such as CoFe, NiFe, and FeCoSmx nanoparticles.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Alignable diffractive pigment flakes
Diffractive pigment flakes are selectively aligned to form an image. In one embodiment, flakes having a magnetic layer are shaped to facilitate alignment in a magnetic field. In another embodiment, the flakes include a magnetically discontinuous layer. In a particular embodiment, deposition of nickel on a diffraction grating pattern produces magnetic needles along the grating pattern that allow magnetic alignment of the resulting diffractive pigment flakes. Color scans of test samples of magnetically aligned flakes show high differentiation between illumination parallel and perpendicular to the direction of alignment of the magnetic diffractive pigment flakes.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
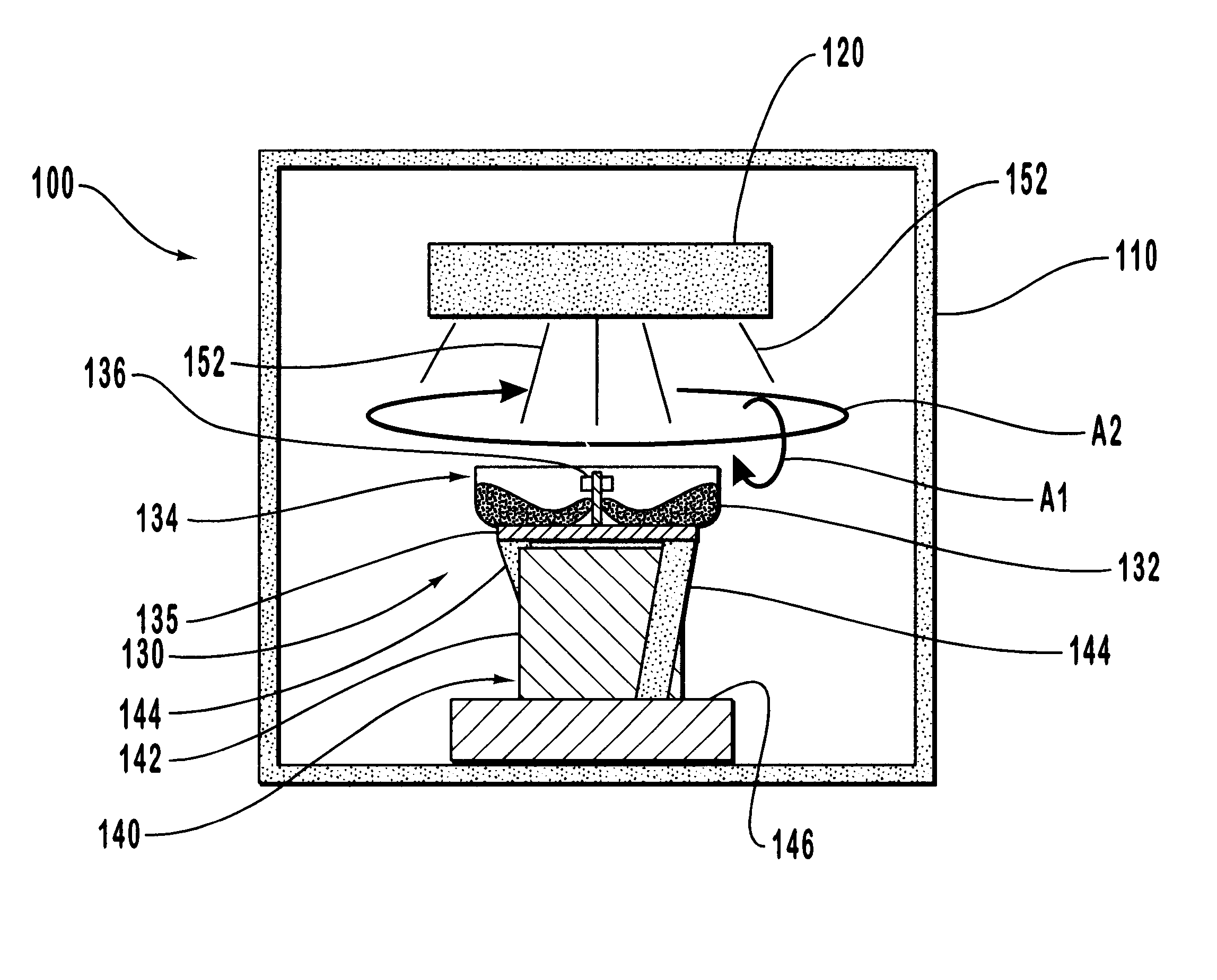
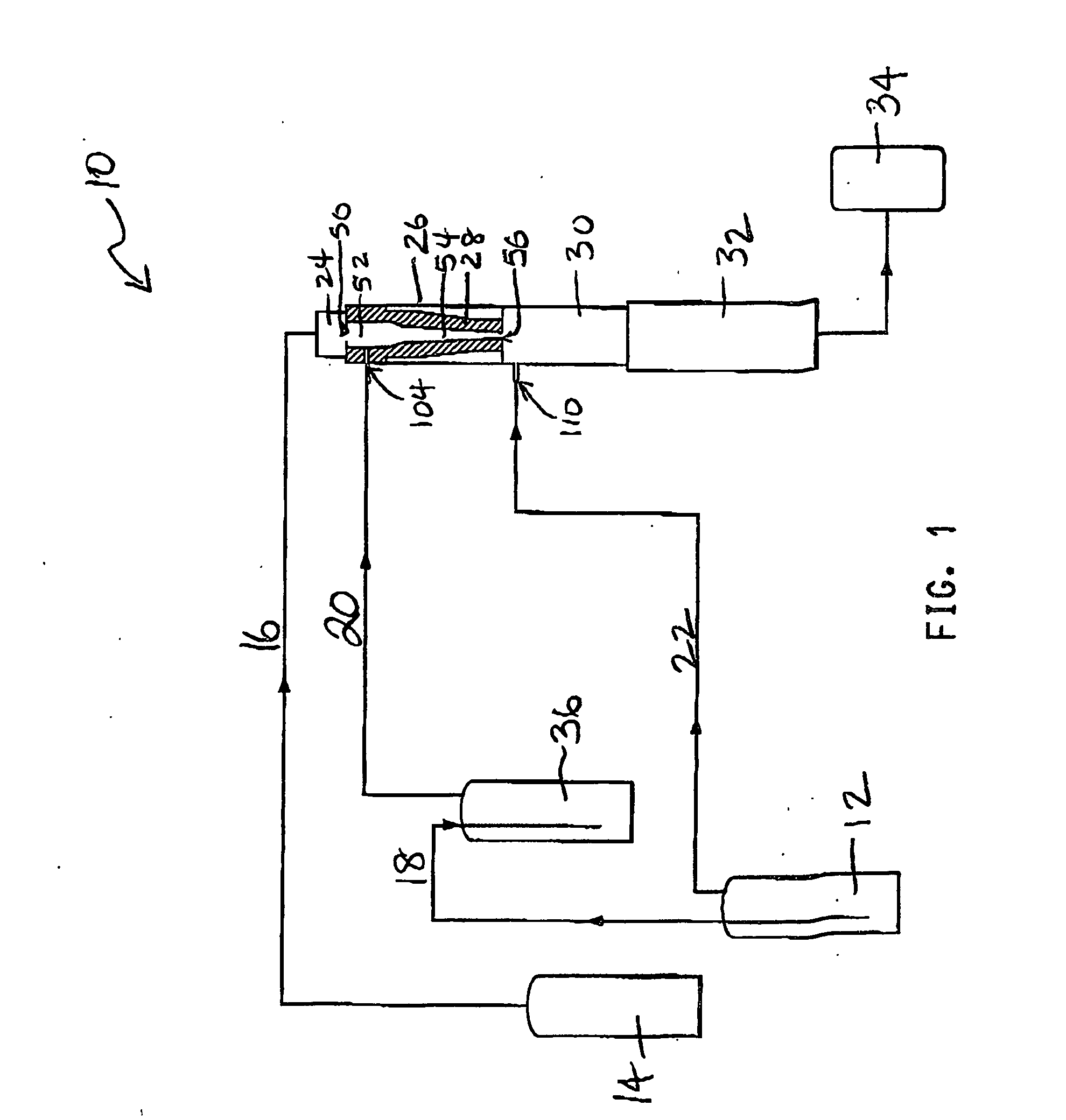
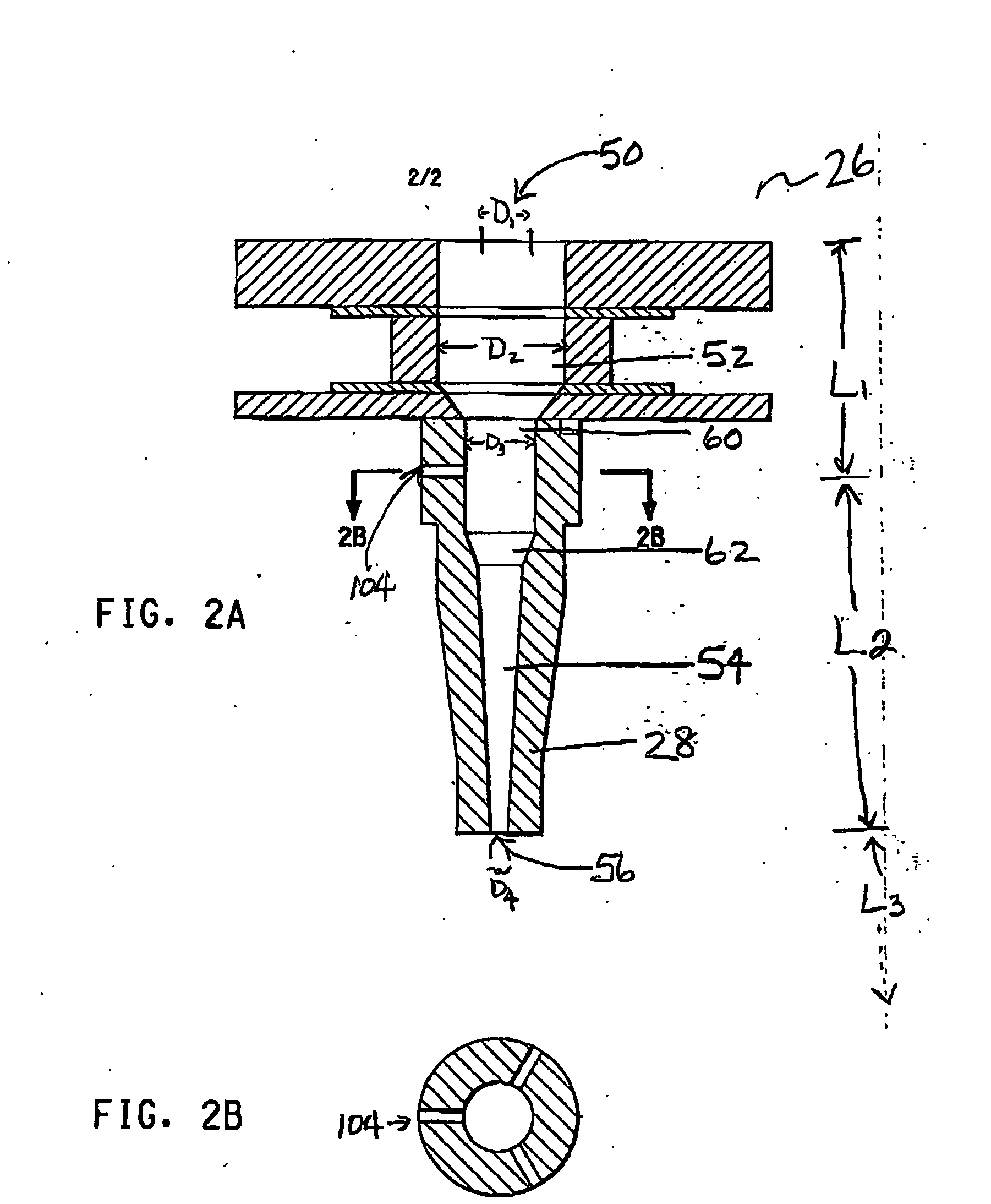
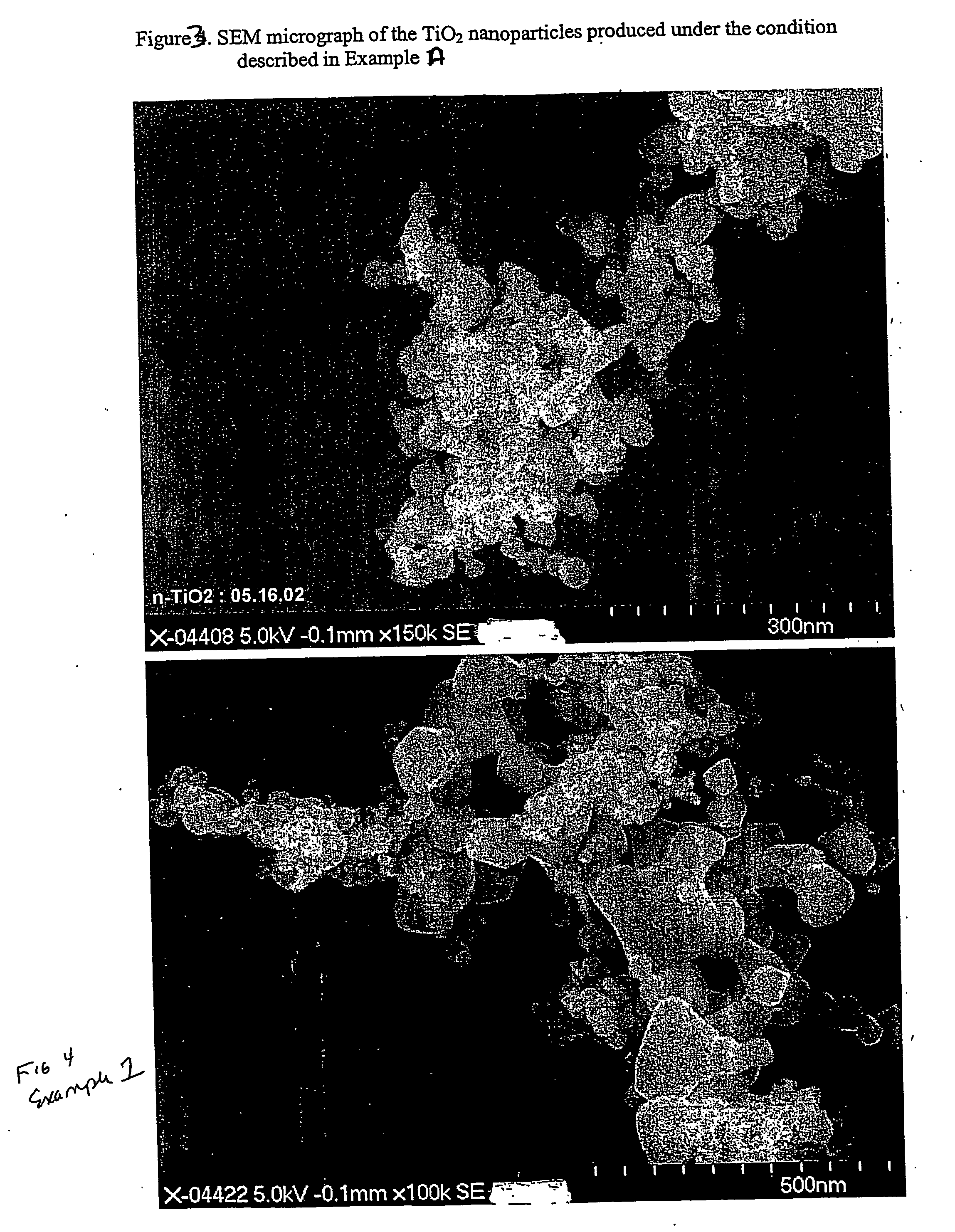
Method of producing nanoparticles using a evaporation-condensation process with a reaction chamber plasma reactor system
InactiveUS20060159596A1Reduce the temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleReaction zone
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the controlled synthesis of nanoparticles using a high temperature process. The reactor chamber includes a high temperature gas heated by means such as a plasma torch, and a reaction chamber. The homogenizer includes a region between the reactant inlets and the plasma (the spacer zone) to ensure that feeds from the reactant inlets are downstream of the recirculation zone induced by the high temperature gas. It also includes a region downstream of the reactant inlets that provides a nearly I dimensional (varying only in the axial direction) flow and concentration profile in the reaction zone to produce nanoparticles with narrow size distribution.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Raspberry-type metal oxide nanostructures coated with ceo2 nanoparticles for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP)
InactiveUS20120077419A1Efficient processCost-effective and convenient processMaterial nanotechnologySilicaCeo2 nanoparticlesWater soluble
Raspberry-type coated particles comprising a core selected from the group consisting of metal oxides of Si, Ti, Zr, Al, Zn and mixtures thereof with a core size of from 20 to 100 nm wherein the core is coated with CeCO2 particles having a particle size below 10 nm; process for preparing raspberry type coated particles comprising the steps of i) providing a mixture containing: a) core particles selected from the group of metal oxides of Si, Ti, Zr, Al, Zn and mixtures thereof, with a particle size of from 20 to 100 nm; b) a water soluble Ce-salt and c) water; ii) adding an organic or inorganic base to the mixture of step i) at temperatures of from 10 to 90° C. and iii) aging the mixture at temperatures of from 10 to 90° C.; and polishing agents containing the particles and their use for polishing surfaces.
Owner:BASF AG
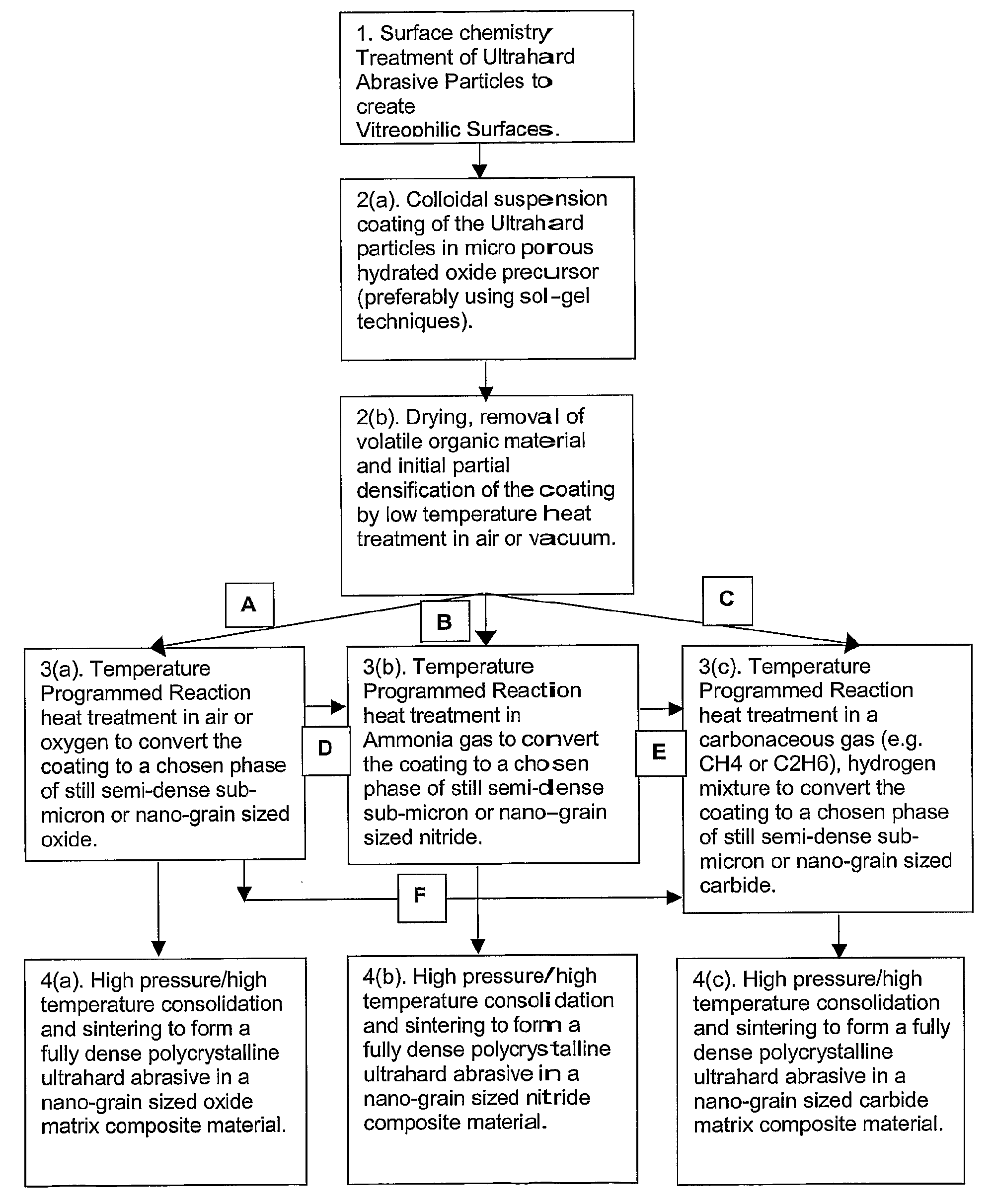
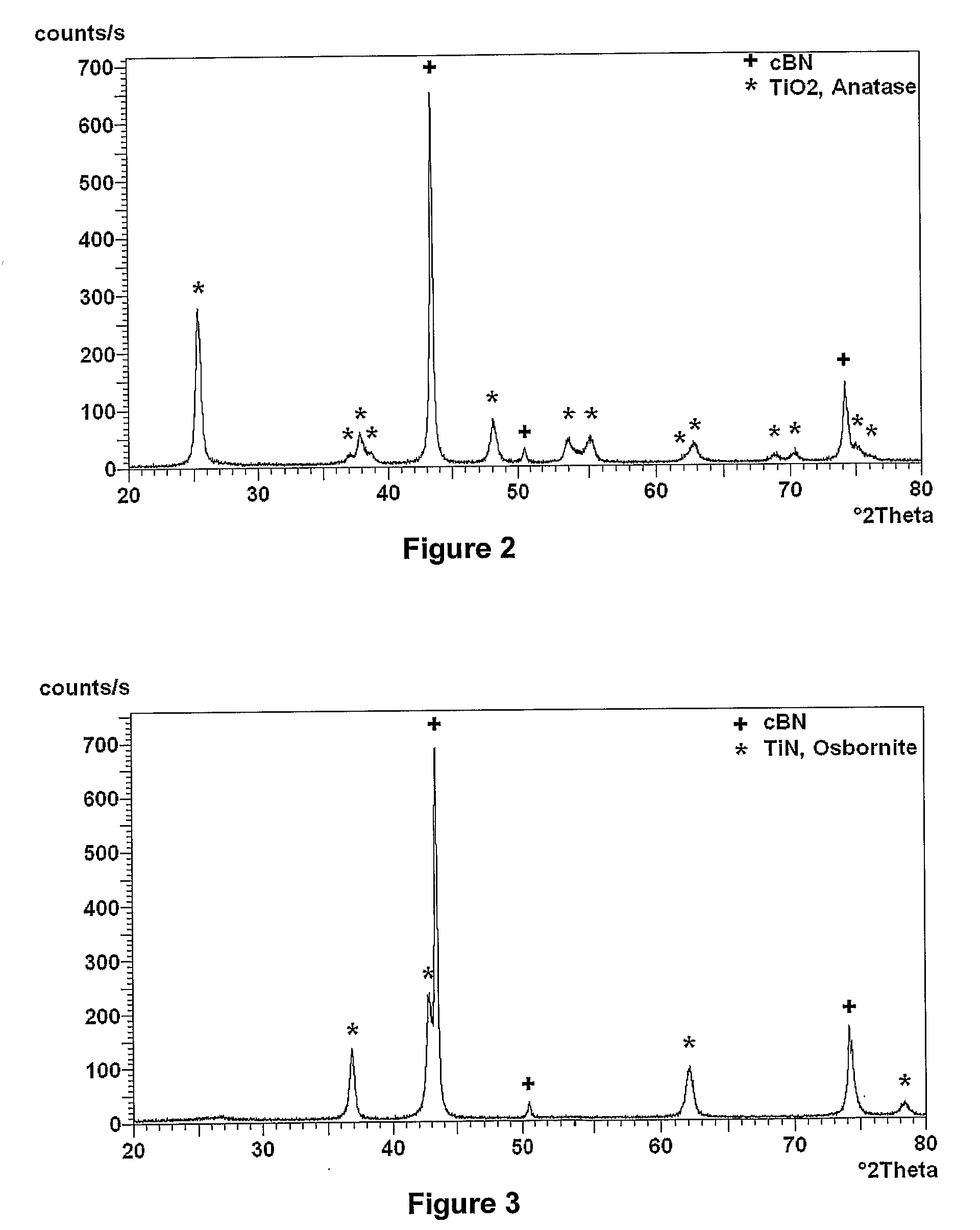
Polycrystalline Abrasive Materials and Method of Manufacture
ActiveUS20080115424A1Reduce the temperatureNanostructure manufactureOther chemical processesNitrogen oxidesNano size
A method of manufacturing polycrystalline abrasive elements consisting of micron, sub-micron or nano-sized ultrahard abrasives dispersed in micron, sub-micron or nano-sized matrix materials. A plurality of ultrahard abrasive particles having vitreophilic surfaces are coated with a matrix precursor material and then treated to render them suitable for sintering. The matrix precursor material can be converted to an oxide, nitride, carbide, oxynitride, oxycarbide, or carbonitride, or an elemental form thereof. The coated ultrahard abrasive particles are consolidated and sintcred at a pressure and temperature at which they are crystallographically or thermodynamically stable.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TRADE MARKS LTD +2
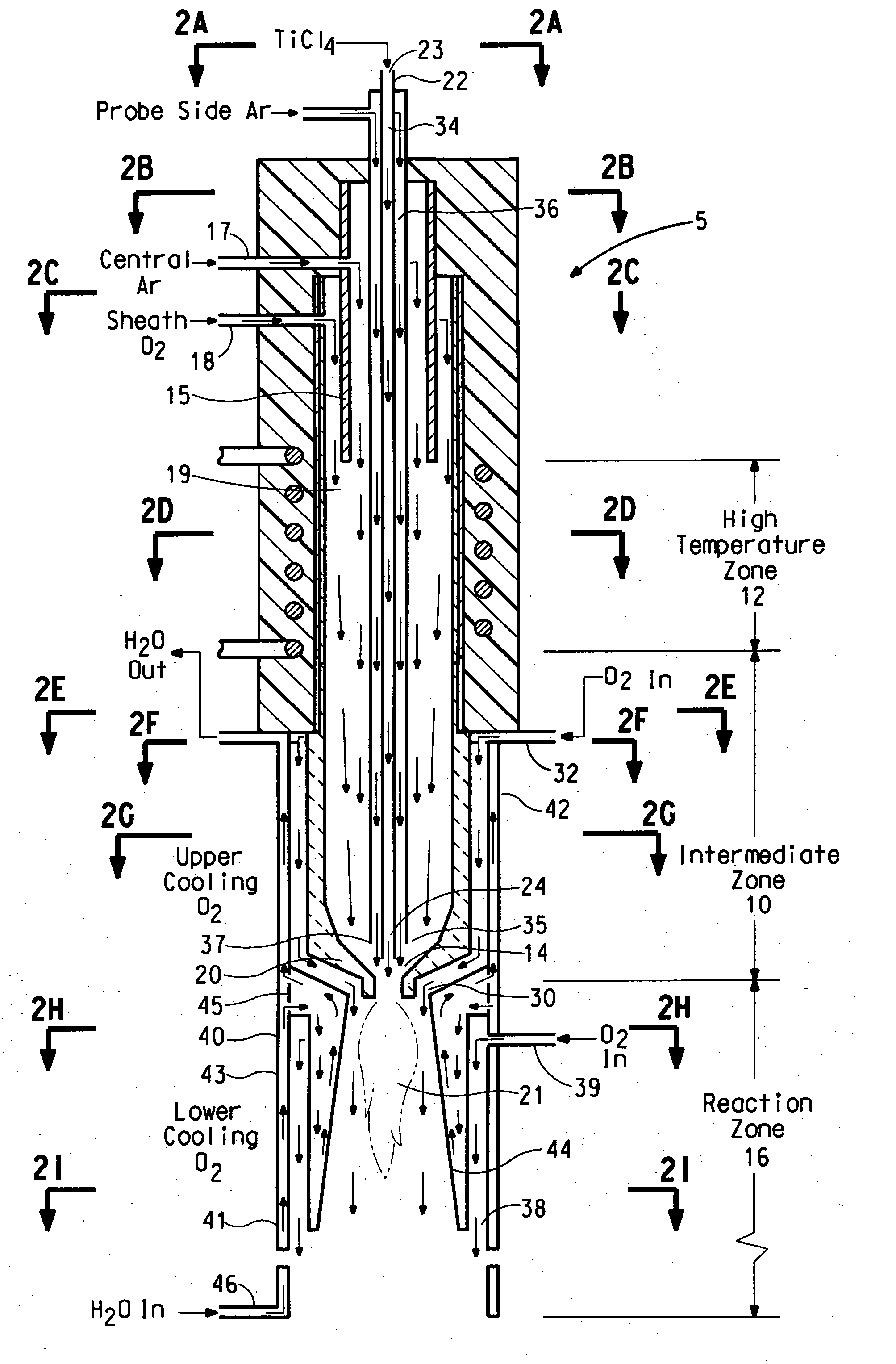
Apparatus for making metal oxide nanopowder
InactiveUS20070292321A1Reduce decreaseEliminate coarse tailMaterial nanotechnologyOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideReaction zoneCooling fluid
There is described an apparatus for making metal oxide particles which are substantially free of coarse tail from an oxidizing agent and a metal reactant in a flow reactor. The apparatus can be a concentric tubular flow reactor comprising a substantially funnel-shaped reactant contacting region located adjacent to a reaction zone which is able to direct a flow of a hot oxidizing agent towards a flow of the metal reactant to form a reaction stream which flows downstream into a reaction zone, whereby the hot oxidizing agent of the reaction stream is able to surround the flow of metal reactant sufficient to prevent the metal reactant from contacting the wall of the reactant contacting region and forming scale on the wall. A cooling fluid conduit being able to direct a flow of a cooling fluid into the reaction zone to flow coaxially with the reaction stream and to form a fluid curtain between the reaction stream and a baffle, which defines at least a portion of the reaction zone, while the metal reactant and hot oxidizing agent within the reaction stream react to form the metal oxide nanopowder prevents scale from forming on the baffle.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
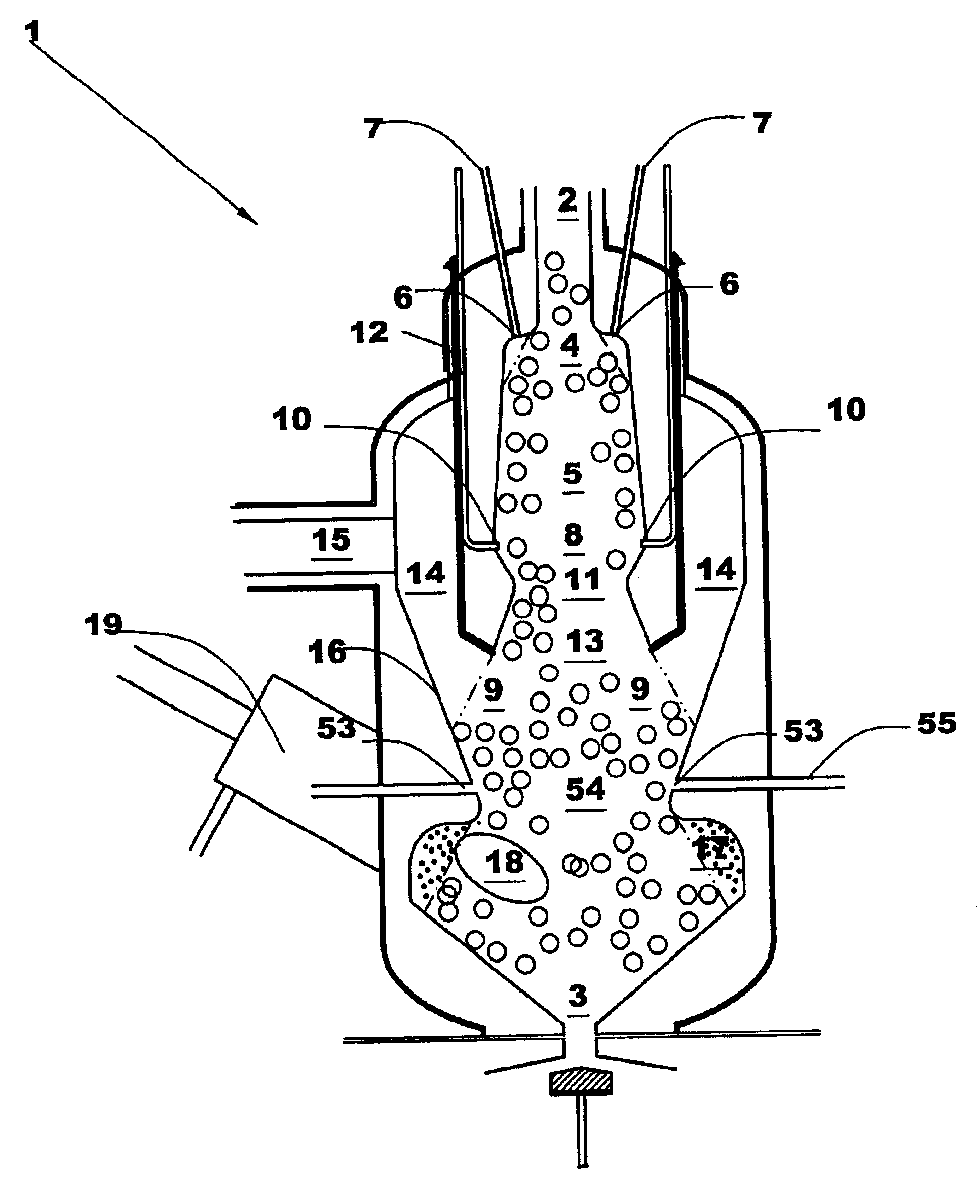
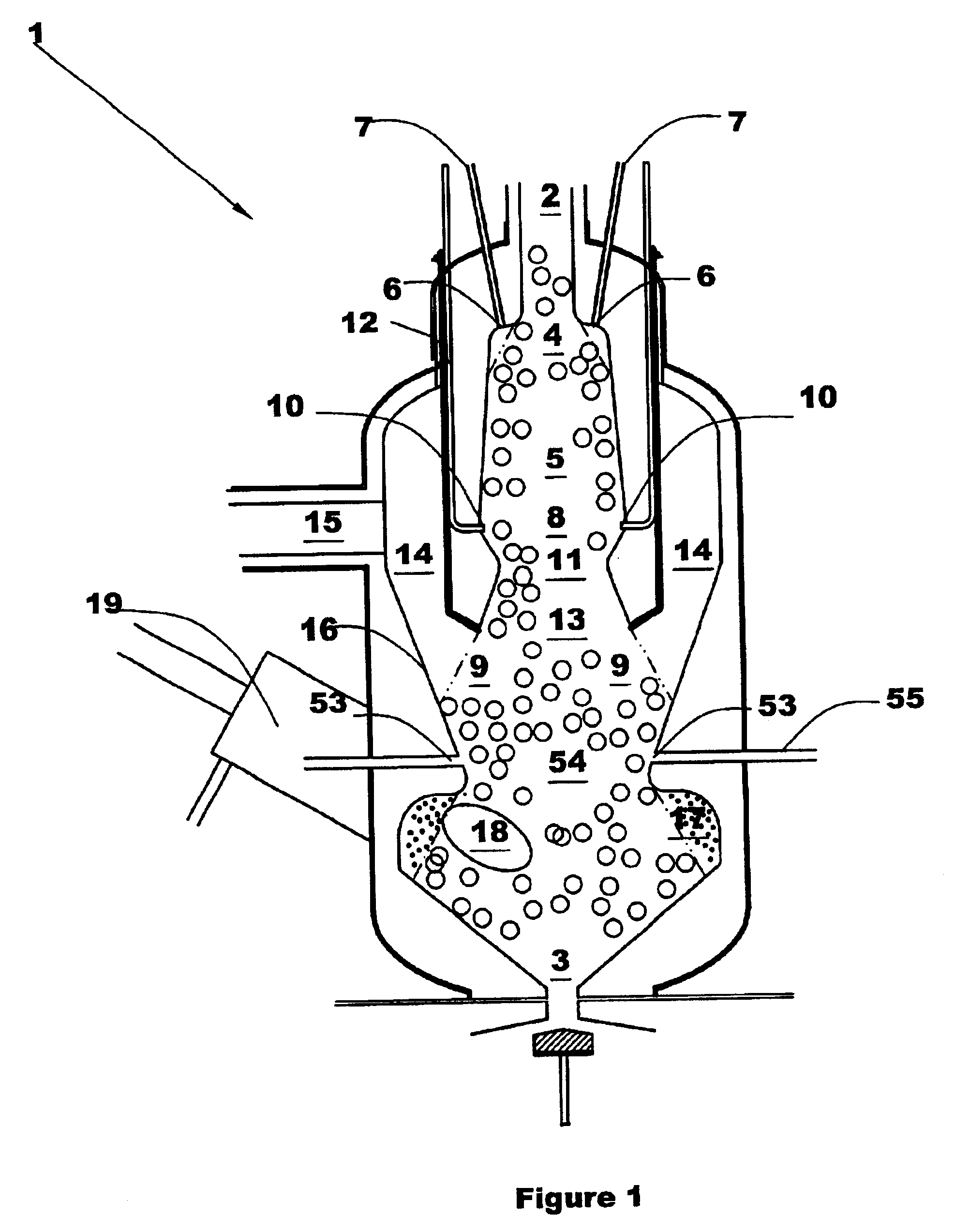
Multi-faceted gasifier and related methods
InactiveUS6960234B2Increased hydrogen productionImprove overall plant economicsLiquid degasificationCoke ovensActivated carbonInjection port
A gasifier is disclosed combining a fixed bed gasification section where coarse fuel is gasified and an entrained flow gasification section where fine fuel is gasified. The fixed bed section includes upper and lower sections. Coarse fuel is devolatilized in the upper fixed bed section and subjected to elevated temperatures sufficient to crack and destroy tars and oils in the effluent gases. The entrained flow gasification section is disposed in a lower plenum adjacent the lower fixed bed section. A plurality of injection ports are configured to introduce oxygen, steam, or air into different sections of the gasifier to control temperature and operating conditions. Activated carbon may be formed in the upper fixed bed section and in the entrained flow section. The activated carbon may be used as a sorbent to remove pollutants from the effluent gases. The gasifier may be used with various coarse and fine fuel feedstocks.
Owner:EMERY ENERGY
Changing surface properties by functionalized nanoparticles
InactiveUS20100178512A1Strong and durable adhesionMaterial nanotechnologyPretreated surfacesFunctionalized nanoparticlesUltraviolet
A process for modifying the surface of an inorganic or organic substrate with strongly adherent nanoparticles is described, providing to the surface modified substrate durable effects like hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, electrical conductivity, magnetic properties, flame retardance, color, adhesion, roughness, scratch resistance, UV-absorbance, antimicrobial properties, antifouling properties, antiprotein properties, antistatic properties, antifog properties, release properties. In this process, an optional first step a) a low-temperature plasma, ozonization, high energy irradiation, corona discharge or a flame is caused to act on the inorganic or organic substrate, and in a second step b) one or more defined nanoparticles or mixtures of defined nanoparticles with monomers, containing at least one ethylenically unsaturated group, or solutions, suspensions or emulsions of the afore-mentioned substances, are applied, preferably at normal pressure, to the inorganic or organic substrate. In a third step c) suitable methods are applied to dry or cure those afore-mentioned substances and, optionally, in a fourth step d) a further coating is applied on the substrate so pretreated.
Owner:CIBA CORP
Cationic mixed-oxide dispersion, coating pigment and ink-absorbing medium
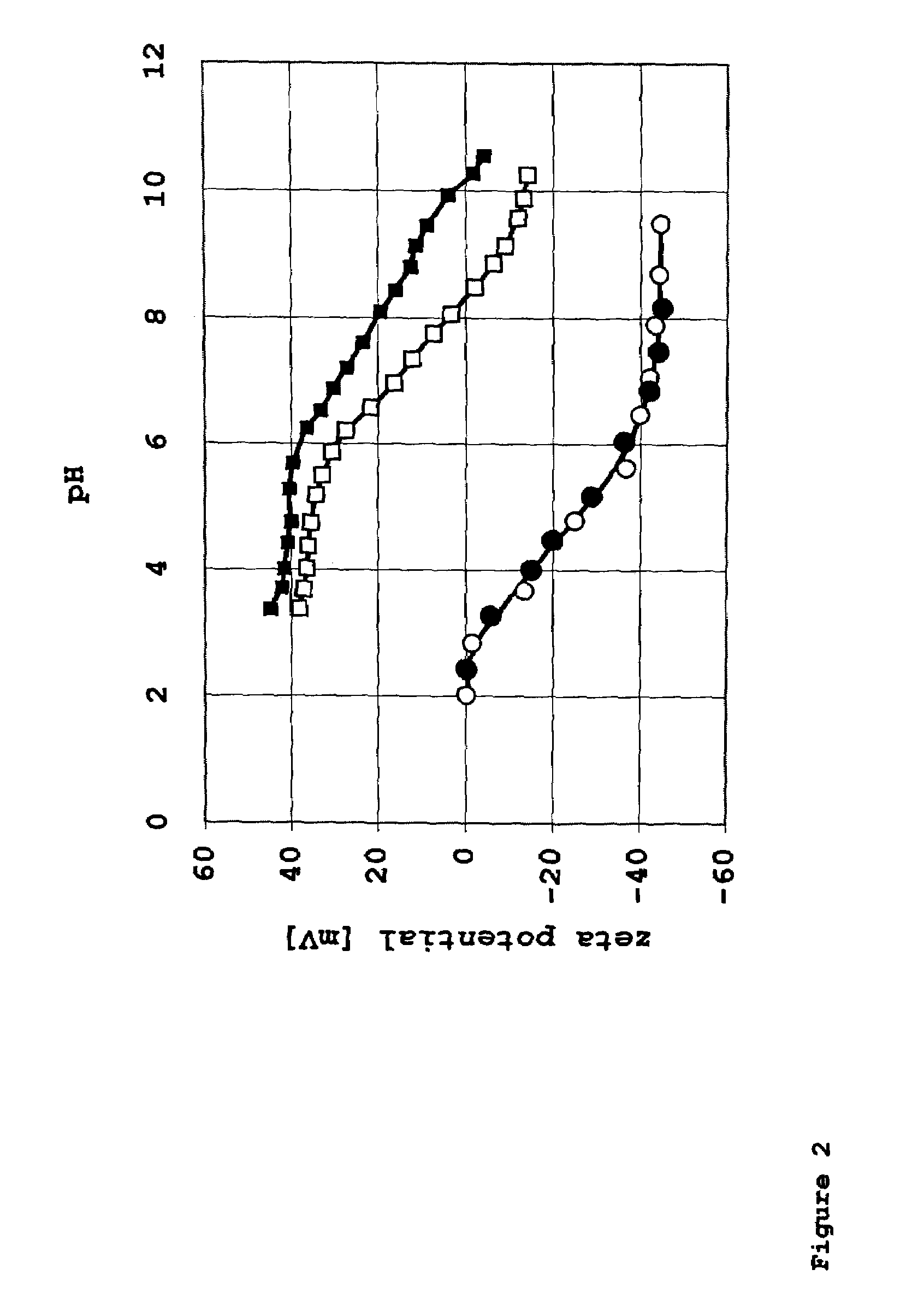
InactiveUS7015270B2Avoid large quantitiesHigh glossCoatings with pigmentsInorganic pigment treatmentZeta potentialMixed oxide
A stable, aqueous dispersion, which includes:silicon dioxide mixed-oxide particles dispersed in at least one water-soluble cationic polymer having a mass average molar mass of less than 100,000 g / mol, said mixed-oxide including aluminum oxide or titanium dioxide,wherein said particles are produced by flame hydrolysis,wherein said particles have a BET specific surface area of 5 to 600 m2 / g and a negative zeta potential,and wherein the dispersion has a positive zeta potential.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Phosphate film-coated powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101045828AUniform particlesParticle size distribution andNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOther chemical processesDepolymerizationDouble decker
This invention relates to a method of preparing envelope powder. The shattering, depolymerization and coating processed at same time, and solid phase acid-base reaction participate the method. This envelope powder possess double-decker or three-layer structure, inner core is composed by oxide or hydrate or inorganic oxysalt, crust composed by inorganic oxysalt, envelope by aluminum phosphate or boron phosphate. This low cost powder be able to used as fortifier, power stuff, colorant and so on, applied to plastic, rubber, ceramics, dope, binder and paper, set foundation for popularization of ultramicro and nanometer powder.
Owner:张义纲 +1
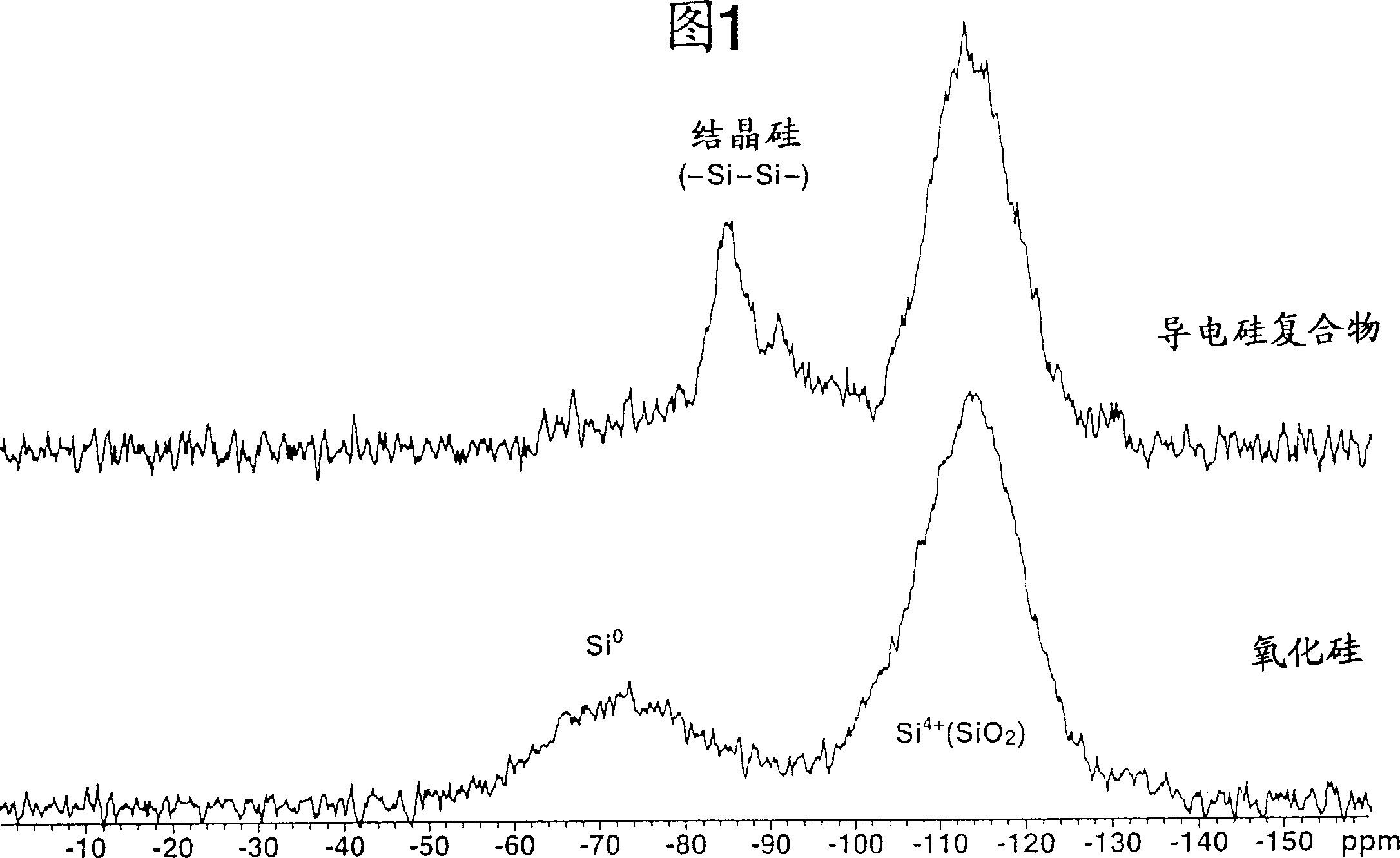
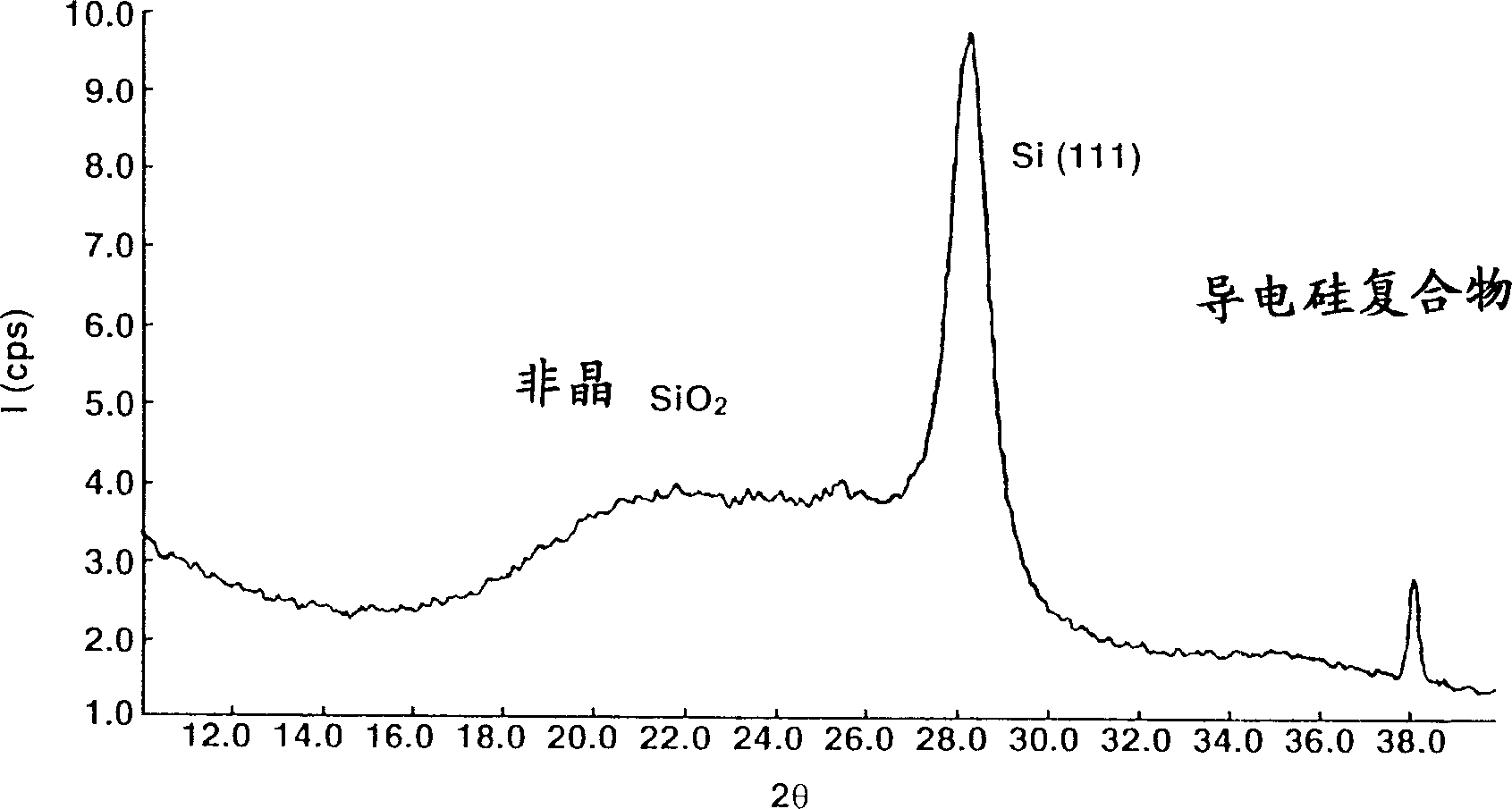
Conductive silicon compound, its preparation and negative electrode material of non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveCN1513922AImprove cycle performanceAvoid defectsMaterial nanotechnologyInorganic pigment treatmentSilicon dioxideSilicon
A conductive silicon composite in which particles having a structure in which crystallites of silicon are dispersed in silicon dioxide are coated on their surfaces with carbon affords satisfactory cycle performance when used as the negative electrode material in a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Methods for producing enhanced interference pigments
InactiveUS6524381B1Enhancement in electron generation rateIncrease deposition rateElectric discharge heatingPigment preparation by PVD/CVD methodsGas phaseVaporization
Methods and apparatus are provided for uniformly depositing a coating material from a vaporization source onto a powdered substrate material to form a thin coalescence film of the coating material that smoothly replicates the surface microstructure of the substrate material. The coating material is uniformly deposited on the substrate material to form optical interference pigment particles. The thin film enhances the hiding power and color gamut of the substrate material. Physical vapor deposition processes are used for depositing the film on the substrate material. The apparatus and systems employed in forming the coated particles utilize vibrating bed coaters, vibrating conveyor coaters, or coating towers. These allow the powdered substrate material to be uniformly exposed to the coating material vapor during the coating process.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Carbon-coated metal oxide nanoparticles
InactiveUS6843919B2Effective airborne decontaminationProvide protectionMaterial nanotechnologySolid sorbent liquid separationMetal oxide nanoparticlesToxin
Composites for destroying chemical and biological agents such as toxins and bacteria, and methods of preparing and using those composites are provided. According to the invention, the substance to be destroyed is contacted with the inventive composites which comprise finely divided metal oxide nanoparticles at least partially coated with carbon. Advantageously, the composites exclude water while not excluding the target compound or adsorbates. The desired metal oxide nanoparticles can be pressed into pellets for use when a powder is not feasible. Preferred metal oxide nanoparticles include MgO, SrO, BaO, CaO, TiO2, ZrO2, FeO, V2O3, V2O5, Mn2O3, Fe2O3, NiO, CuO, Al2O3, SiO2, ZnO, Ag2O, and mixtures thereof.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Ceramic materials, abrasive particles, abrasive articles, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030126802A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityOxide formationOther chemical processesInorganic pigment treatmentGlass-ceramicMaterials science
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Process for preparing modified pigments
A process for preparing a modified pigment having attached at least one organic group is described. This process comprises the step of reacting a dried mixture comprising a pigment having attached at least one reactive group and a modifying agent. The dried mixture is reacted under high intensity mixing conditions for a time and temperature sufficient to form the modified pigment.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Method for preparing core-shell silicon dioxide coated nano calcium carbonate
InactiveCN101225245AImprove acid resistanceImprove qualityInorganic pigment treatmentCarbonizationHydrolysis
The invention provides a preparation method for core-shell type silicon dioxide-coated nanometer calcium carbonate, which comprises following steps: adding silicate in calcium carbonate suspension pulp; stirring and mixing using emulsion pump; introducing kiln gas with CO2 for carbonization until the pH is 6.5 to 7.0; heating to 60 to 90 DEG C; adding coating agent for coating treatment; the product is obtained after the coated pulp is filtered and the filter cake is dried. The preparation method for core-shell type silicon dioxide-coated nanometer calcium carbonate has the advantages of improving the acid resistance of nanometer calcium carbonate since silica sol precipitated through hydrolysis is coated on the surface of nanometer calcium carbonate, improving dispersion of the product in polymer due to surface treatment using coupling agent and organic acid, good acid resistance and dispersion, greatly improving physical and chemical properties, and felicitating industrial production with simple operation.
Owner:上海卓越纳米新材料股份有限公司
Method of making amorphous materials and ceramics
InactiveUS20030110709A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityEliminates and minimizes heat transferWood working apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusCeramicAbrasive
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Aqueous dispersion of water-insoluble-colorant-containing particle and preparation process thereof, water-insoluble-colorant-containing particle and preparation process thereof, and ink
InactiveUS6921433B2Good colorHigh transparencyLiquid surface applicatorsInorganic pigment treatmentWater insolublePeak value
An embodiment of the invention relates to an aqueous dispersion containing pigment-containing particles. The dispersion is an aqueous dispersion comprising particles containing a water-insoluble colorant dispersed in a water-containing medium, wherein the light-scattering intensity of the dispersion is at most 30,000 cps when the absorbance peak value of the dispersion in a visible region is regarded as 1.
Owner:CANON KK
Abrasive particles, abrasive articles, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030115805A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityOxide formationOther chemical processesInorganic pigment treatmentAbrasive
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Nano-zinc oxide coated sericite powder composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104017393AImproves UV resistanceImprove antibacterial propertiesCosmetic preparationsInorganic pigment treatmentCalcium hydroxideOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a sericite / nano-zinc oxide composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is characterized in that the surface of sericite powder is coated with nano-zinc oxide. The preparation method comprises the following step: adding calcium hydroxide or calcium oxide into a mixed system of the sericite powder and zinc sulfate solution so as to directly obtain the nano-zinc oxide coated sericite powder composite material. According to the method, the sericite which is taken as a base material is a natural mineral, so that the raw material is easily available, free of pollution and low in cost; the preparation process is simple, safe, reliable and easy to control; the obtained composite material is stable in quality, and has the good dispersibility in an organic solvent and also has the excellent ultraviolet resistance and the excellent antibacterial and deodorant performance. Thus, the composite material can be applied to the field of coatings, cosmetics and the like. The method has a good potential application value in the field of synthesis of the composite material or other related sciences.
Owner:ANHUI HENGHAO SCI & TECH
Controllable filler prefloculation using a dual polymer system
ActiveUS8088213B2Inorganic pigment treatmentReinforcing agents additionPolymer chemistryAqueous dispersion
A method of preparing a stable dispersion of flocculated filler particles for use in papermaking processes comprises sequential addition of a first flocculating agent to an aqueous dispersion of filler particles followed by shearing of the dispersion, followed by addition of a second flocculating agent to the dispersion and further shearing of the resultant filler flocs to the desired particle size resulting in shear resistant filler flocs with a defined and controllable size distribution. In addition, a neutralizing coagulant can be added to the dispersion to partially or completely neutralize the charge of the filler before the first flocculating agent is added.
Owner:NALCO CO
Method of preparing electric conductive adhesive by chemical plating silver on graphite powder surface
InactiveCN1919933AEase of mass productionLow resistivityInorganic pigment treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical platingSilver plate
The invention discloses a chemical silver plating preparing conducting resin method on the graphite powder surface in the chemical silver plating and micro-electronics connection material technique domain, which comprises the following steps: oxidizing the graphite powder in the air at 600-650DEG C; putting the dispersant, reducer and stabilizing agent in de-ionized water for reduced liquid; adding in graphite powder to stir; putting the silver nitrate in the de-ionized water; adding in ammonia and sodium hydroxide to get argentamine; putting the reduced liquid in the argentamine liquid to finish chemical silver plating on the graphite powder surface; filtering; separating and washing; drying in vacuum to get silver coated graphite powder.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com