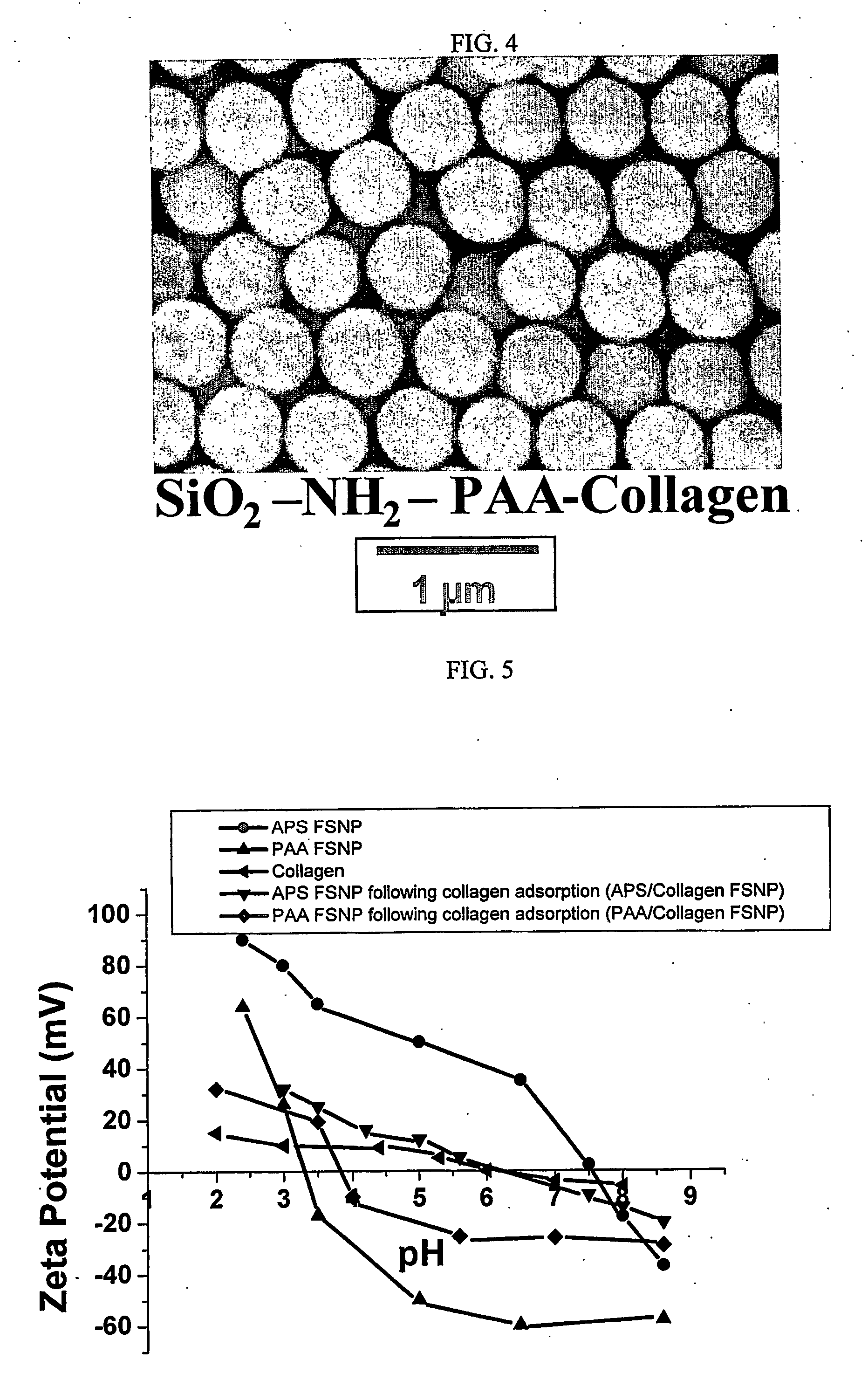
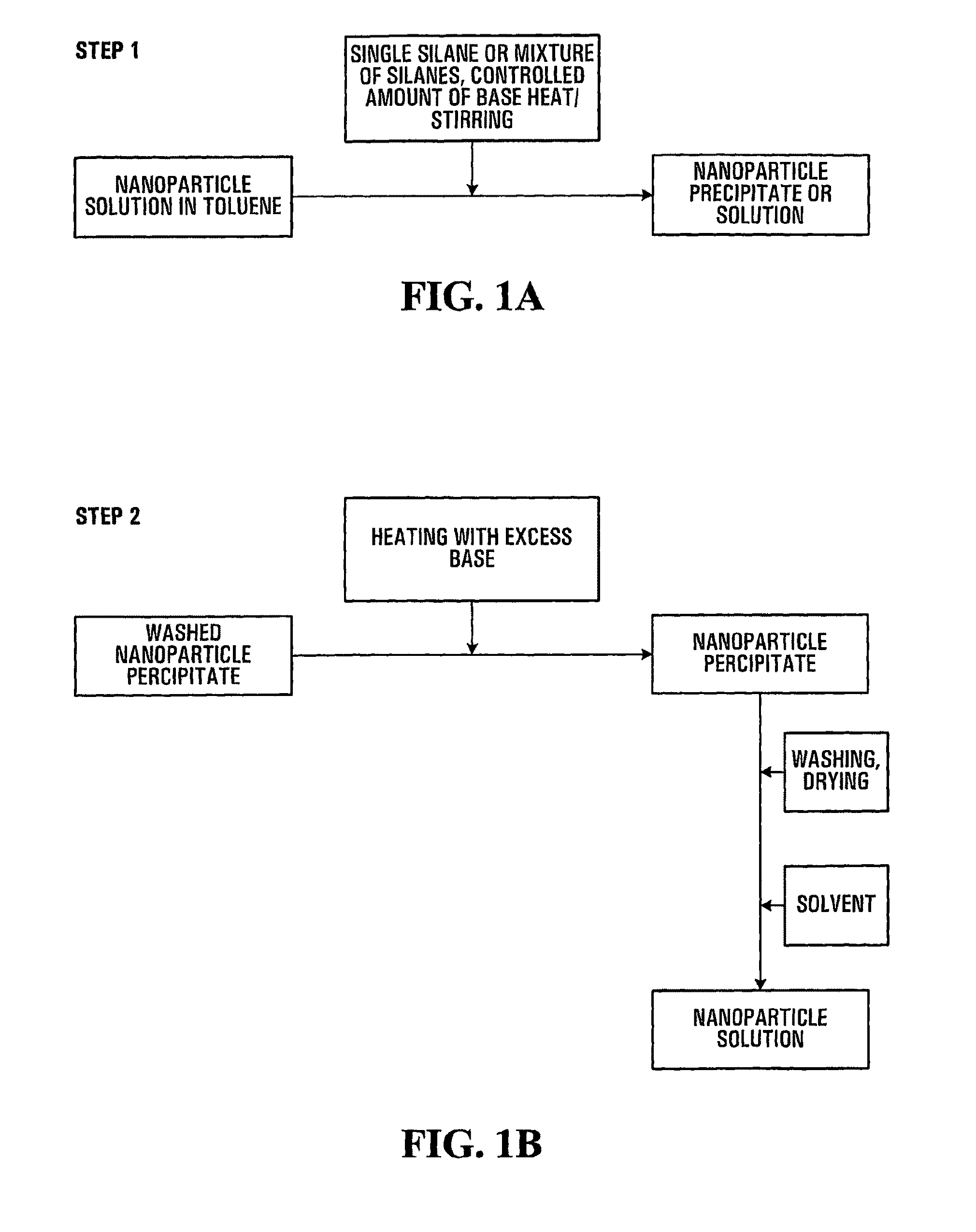
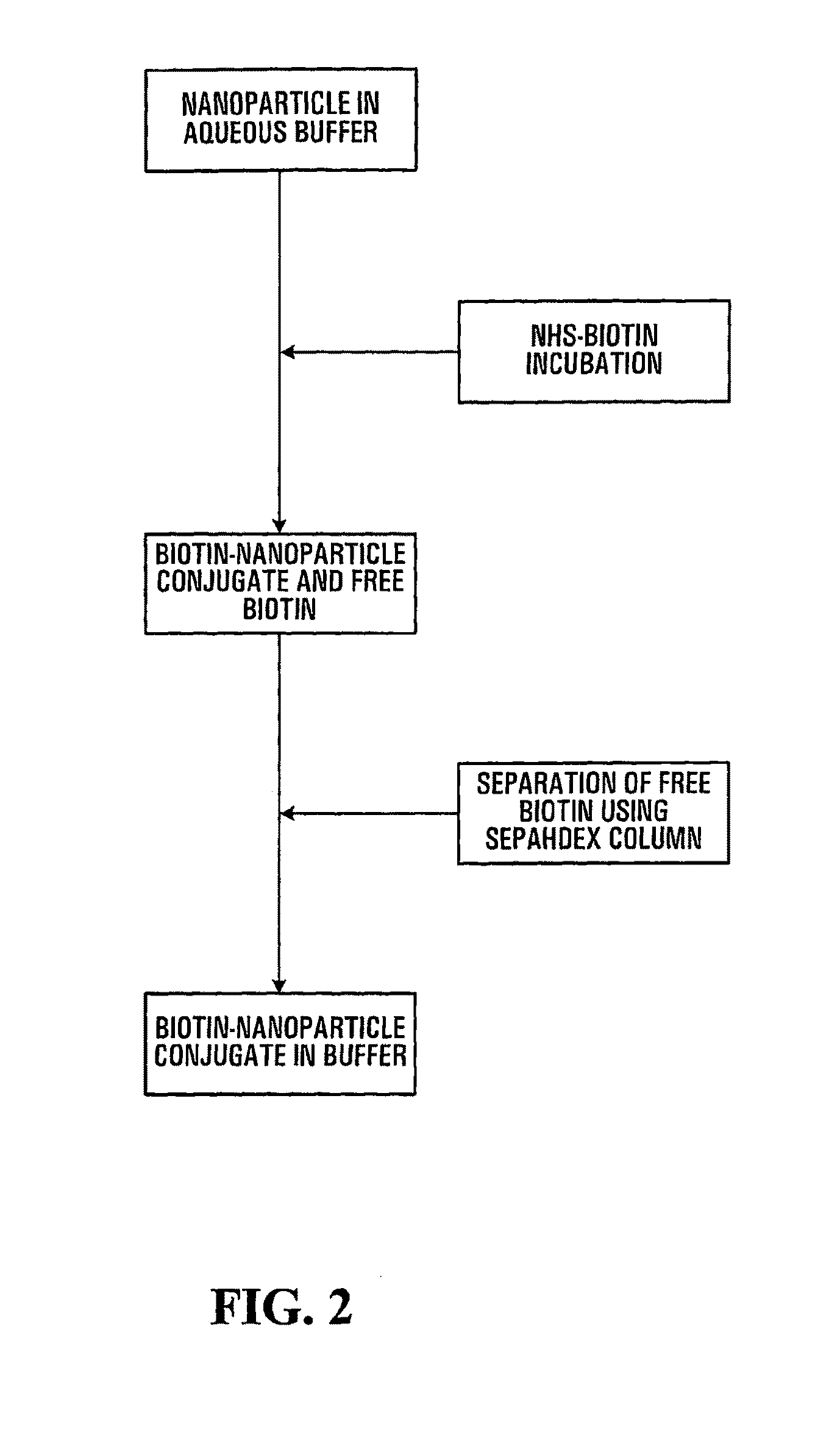
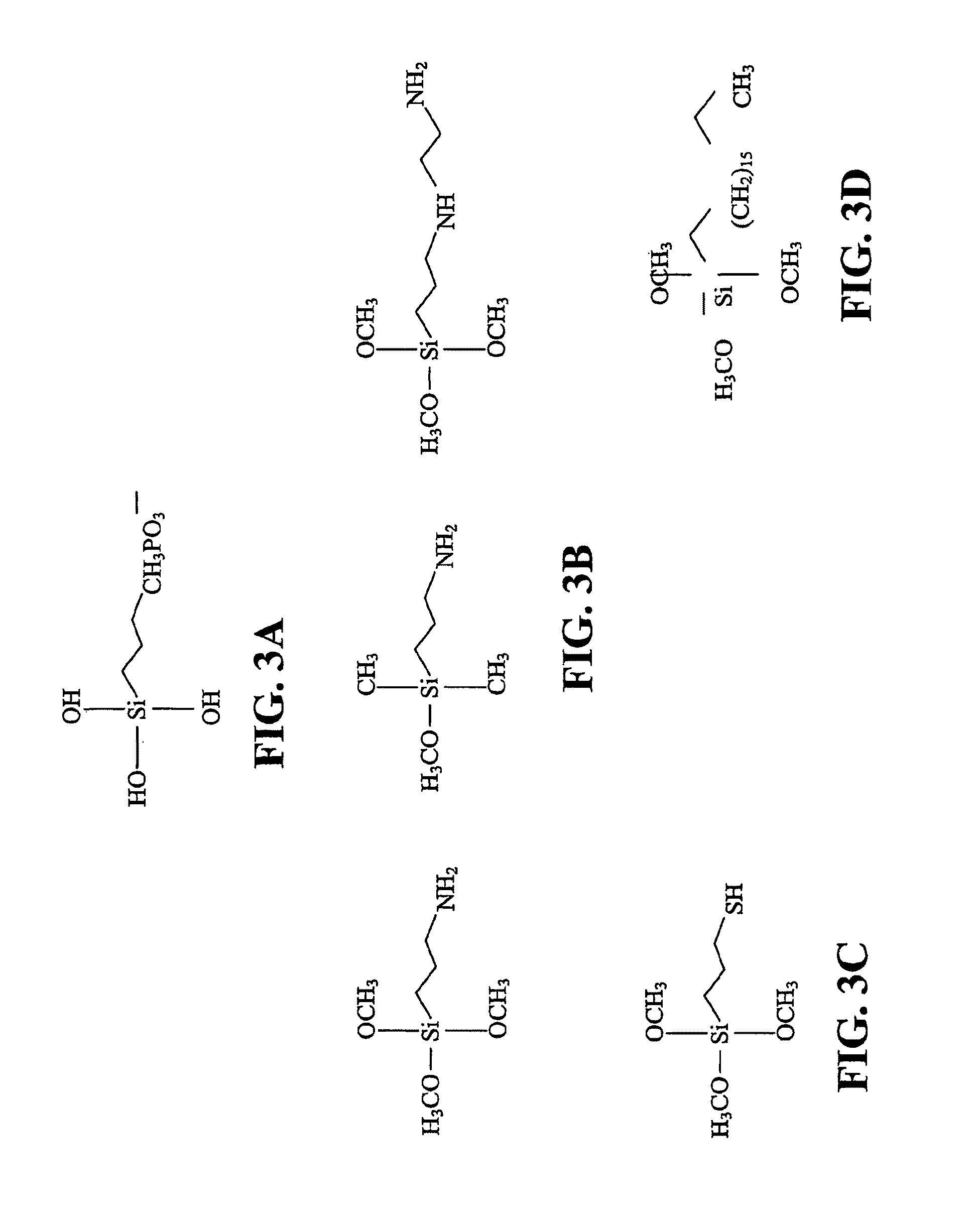
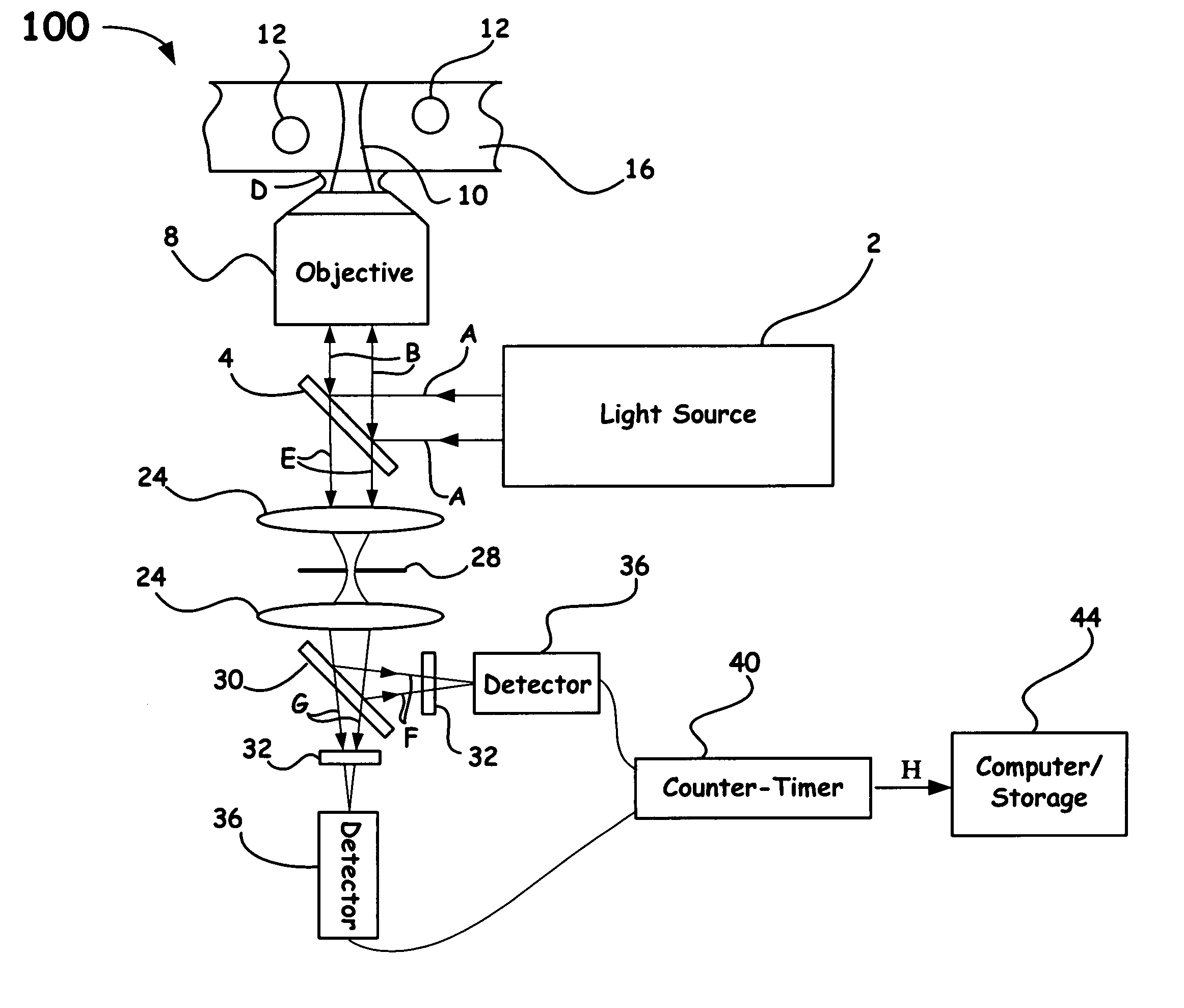
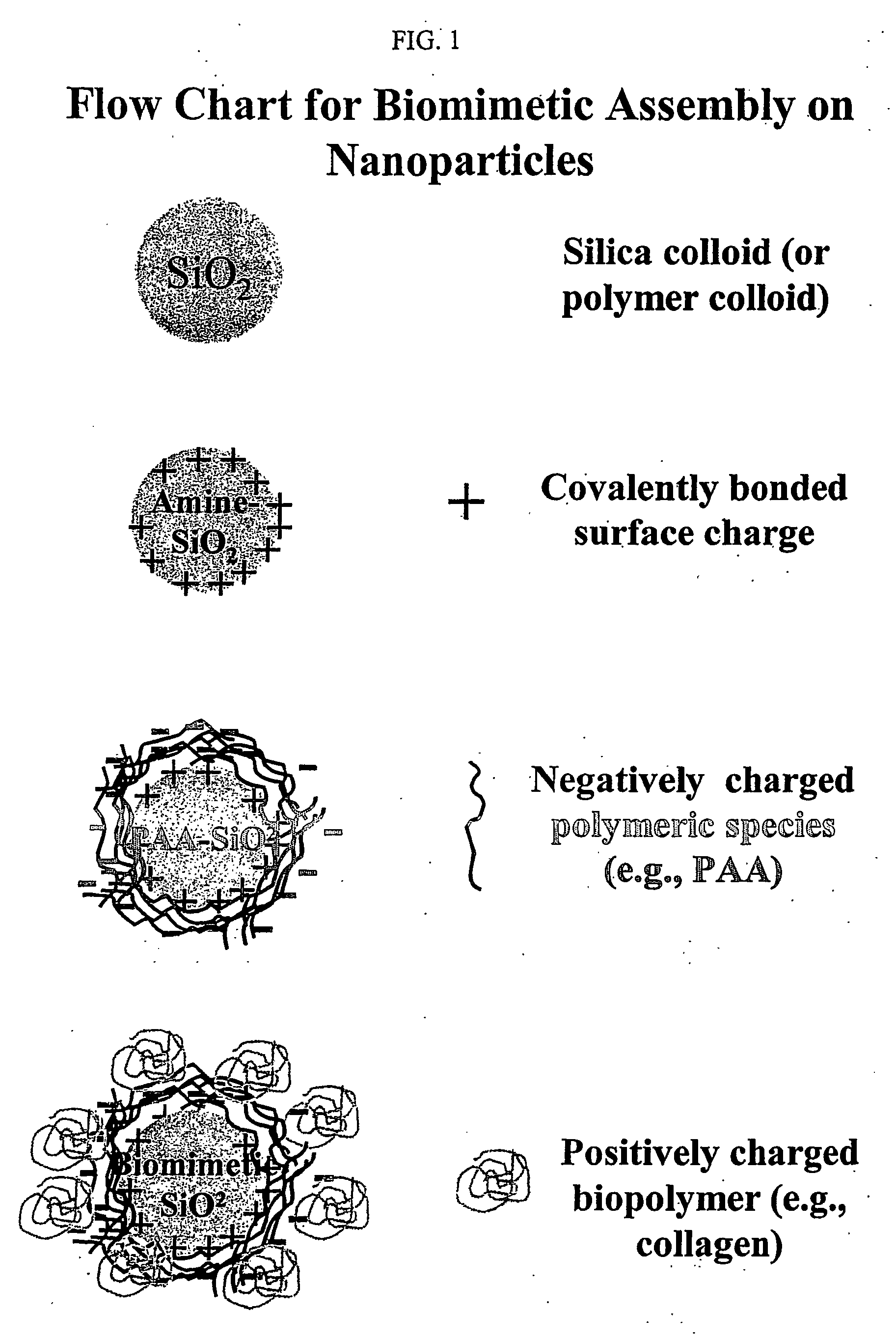Patents
Literature
194 results about "Functionalized nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Absorbent articles comprising nanoparticles
Owner:NANO MET ZERO
Stabilized and chemically functionalized nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060177376A1Improve protectionMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsFunctionalized nanoparticlesQuantum dot
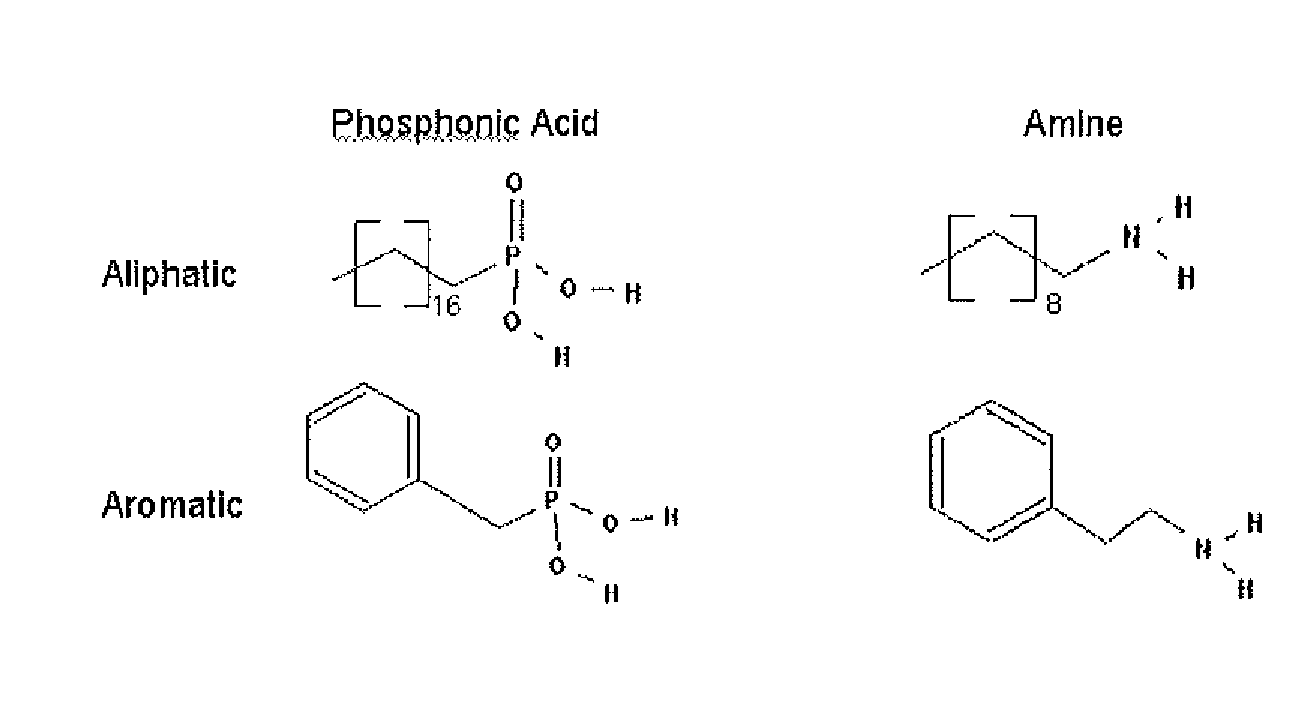
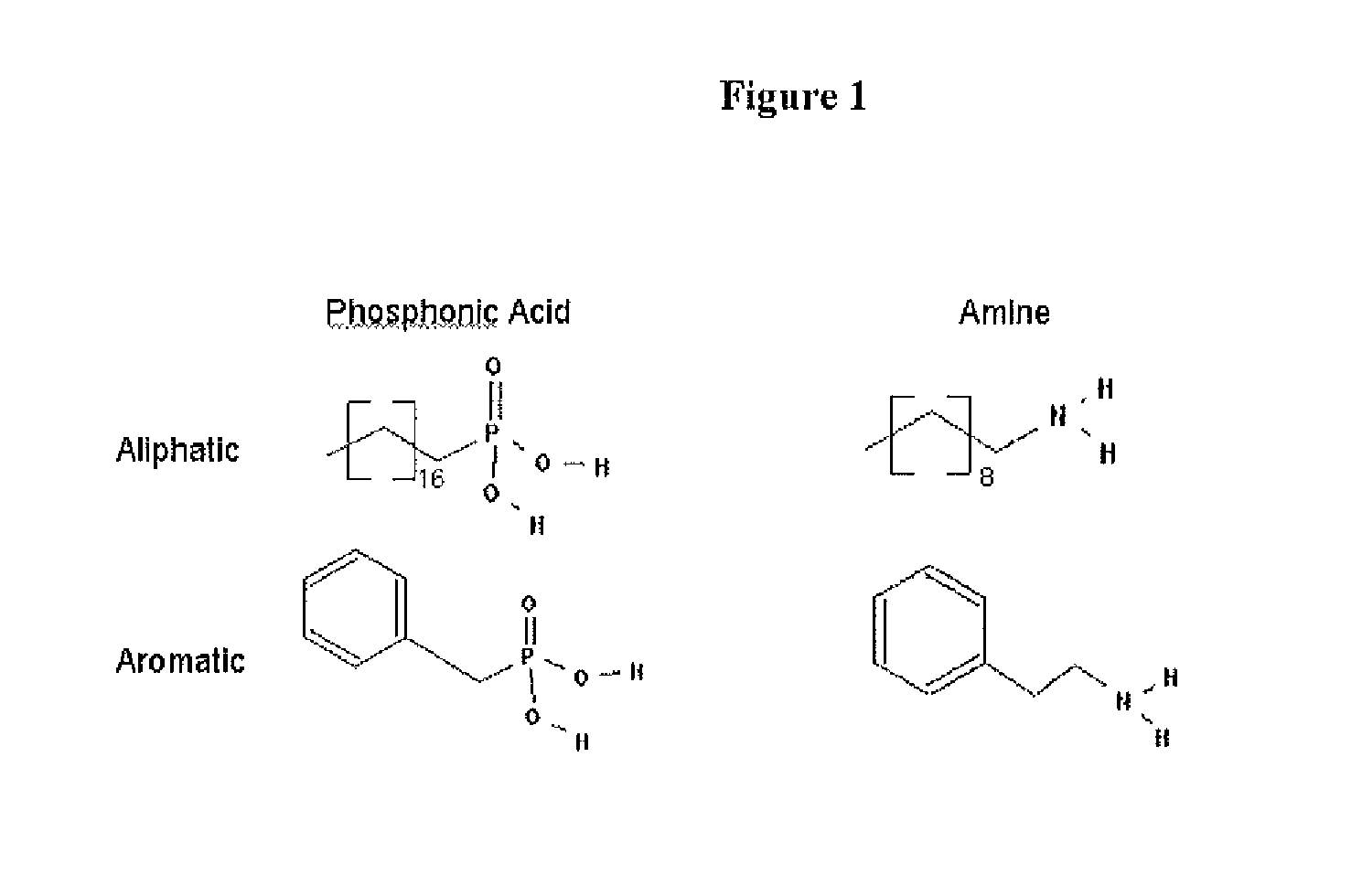
Dendronization of nano-scale surfaces with focal point reactive dendrons to produce stabilized chemically functionalized nano-particles having quantum dot dimensions.
Owner:DENDRITIC NANO TECH INC
Functionalized nanoparticles and method
ActiveUS20100283014A1Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor materialsChemical reaction
A nanoparticle including an inorganic core comprising at least one metal and / or at least one semi-conductor compound comprising at least one metal includes a coating or shell disposed over at least a portion of a surface of the core. The coating can include one or more layers. Each layer of the coating can comprise a metal and / or at least one semiconductor compound. The nanoparticle further includes a ligand attached to a surface of the coating. The ligand is represented by the formula: X-Sp-Z, wherein X represents, e.g., a primary amine group, a secondary amine group, a urea, a thiourea, an imidizole group, an amide group, a phosphonic or arsonic acid group, a phosphinic or arsinic acid group, a phosphate or arsenate group, a phosphine or arsine oxide group; Sp represents a spacer group, such as a group capable of allowing a transfer of charge or an insulating group; and Z represents: (i) reactive group capable of communicating specific chemical properties to the nanocrystal as well as provide specific chemical reactivity to the surface of the nanocrystal, and / or (ii) a group that is cyclic, halogenated, or polar a-protic. In certain embodiments, at least two chemically distinct ligands are attached to an surface of the coating, wherein the at least two ligands (I and II) are represented by the formula: X-Sp-Z. In ligand (I) X represents a phosphonic, phosphinic, or phosphategroup and in ligand (II) X represents a primary or secondary amine, or an imidizole, or an amide; In both ligands (I) and (II) Sp, which can be the same or different in the two compounds, represents a spacer group, such as a group capable of allowing a transfer of charge or an insulating group; Z, which can be the same or different in the two compounds, is a group chosen from among groups capable of communicating specific chemical properties to the nanoparticle as well as provide specific chemical reactivity to the surface of the nanoparticle. In preferred embodiments, the nanoparticle includes a core comprising a semiconductor material.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Changing surface properties by functionalized nanoparticles
InactiveUS20100178512A1Strong and durable adhesionMaterial nanotechnologyPretreated surfacesFunctionalized nanoparticlesUltraviolet
A process for modifying the surface of an inorganic or organic substrate with strongly adherent nanoparticles is described, providing to the surface modified substrate durable effects like hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, electrical conductivity, magnetic properties, flame retardance, color, adhesion, roughness, scratch resistance, UV-absorbance, antimicrobial properties, antifouling properties, antiprotein properties, antistatic properties, antifog properties, release properties. In this process, an optional first step a) a low-temperature plasma, ozonization, high energy irradiation, corona discharge or a flame is caused to act on the inorganic or organic substrate, and in a second step b) one or more defined nanoparticles or mixtures of defined nanoparticles with monomers, containing at least one ethylenically unsaturated group, or solutions, suspensions or emulsions of the afore-mentioned substances, are applied, preferably at normal pressure, to the inorganic or organic substrate. In a third step c) suitable methods are applied to dry or cure those afore-mentioned substances and, optionally, in a fourth step d) a further coating is applied on the substrate so pretreated.
Owner:CIBA CORP
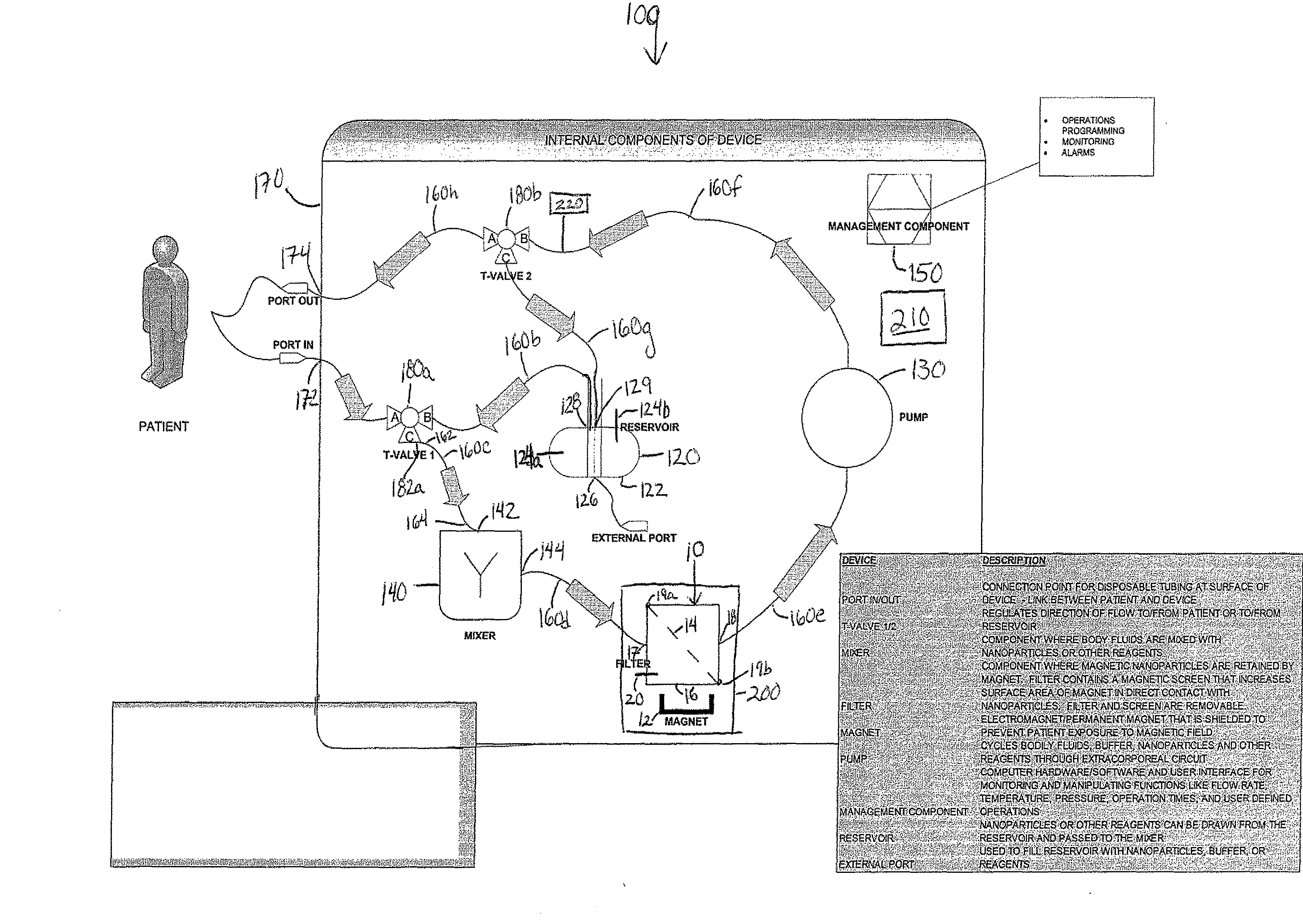
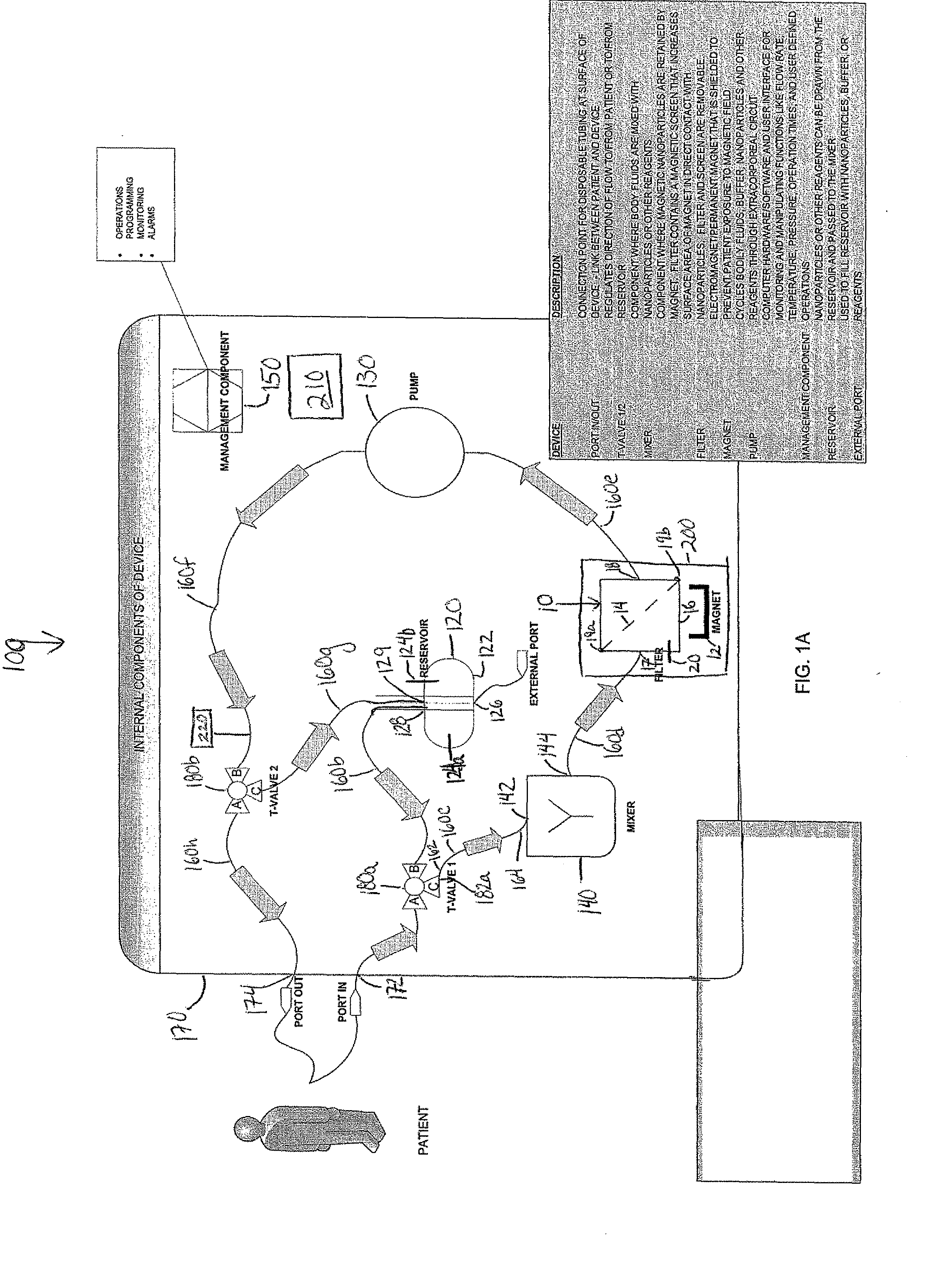
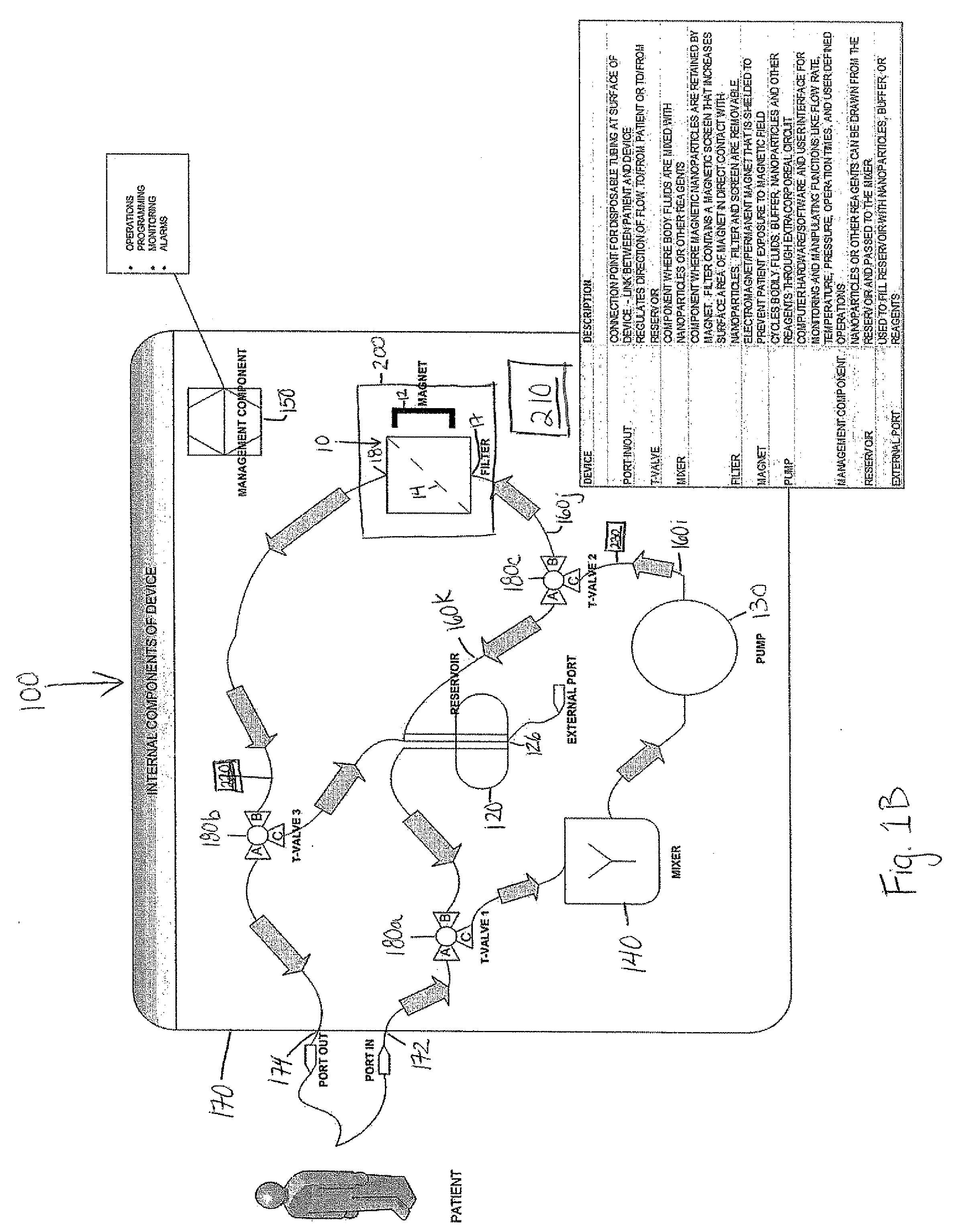
Device and method of using superparamagnetic nanoparticles in treatment and removal of cells
InactiveUS20110098623A1Simple methodAntibacterial agentsOther blood circulation devicesCancer cellFunctionalized nanoparticles
Methods and devices for selectively removing from a subject a target cell, pathogen, or virus expressing a binding partner on its surface are presented. In one embodiment, the device contains an excorporeal circuit, which includes, at least, a magnetic filter comprising a magnet and a removable, magnetizable substrate capable of capturing magnetic nanomaterials; and a pump in fluid communication with the magnetic filter, wherein the pump moves fluid through the excorporeal circuit. The magnet is capable of generating a magnetic field sufficient to capture magnetic nanomaterials in the magnetic field. In a preferred embodiment, the target cells are cancer cells and / or cells infected with pathogenic agents. The devices may be designed for extracorporeal or in vivo uses. Functionalized superparamagnetic nanoparticles are either mixed ex vivo with a biological fluid from the patient or injected into the patient. Then the biological fluid, which includes the nanoparticles is transported to the magnetic filter to remove any nanoparticles that are complexed to the target cells, pathogens, or virus, and any free nanoparticles. Optionally, the functionalized nanoparticles contain and deliver a therapeutic agent. In one embodiment, the therapeutic agent is released when the nanoparticle binds to the target cells, pathogens, or virus.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
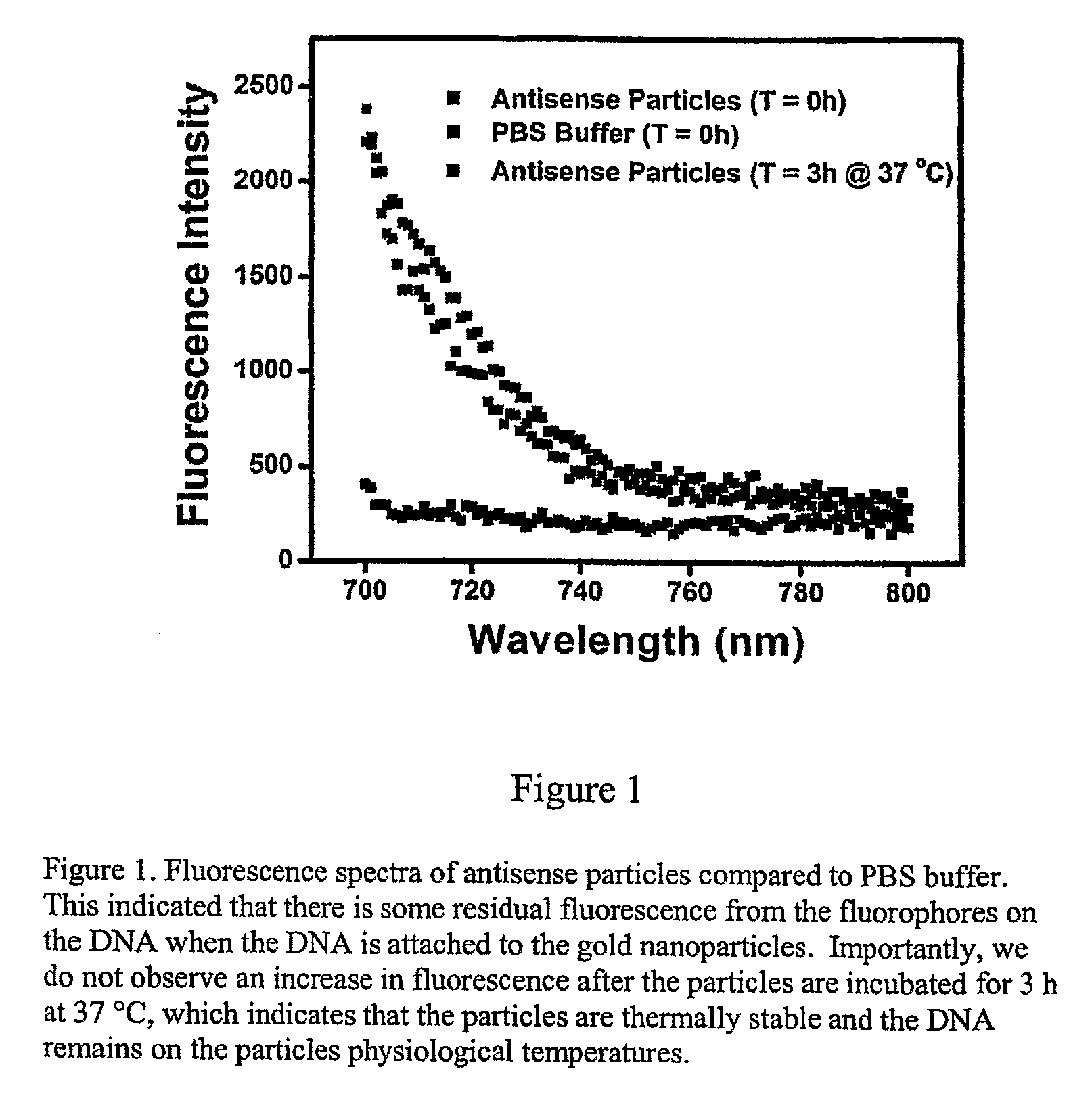
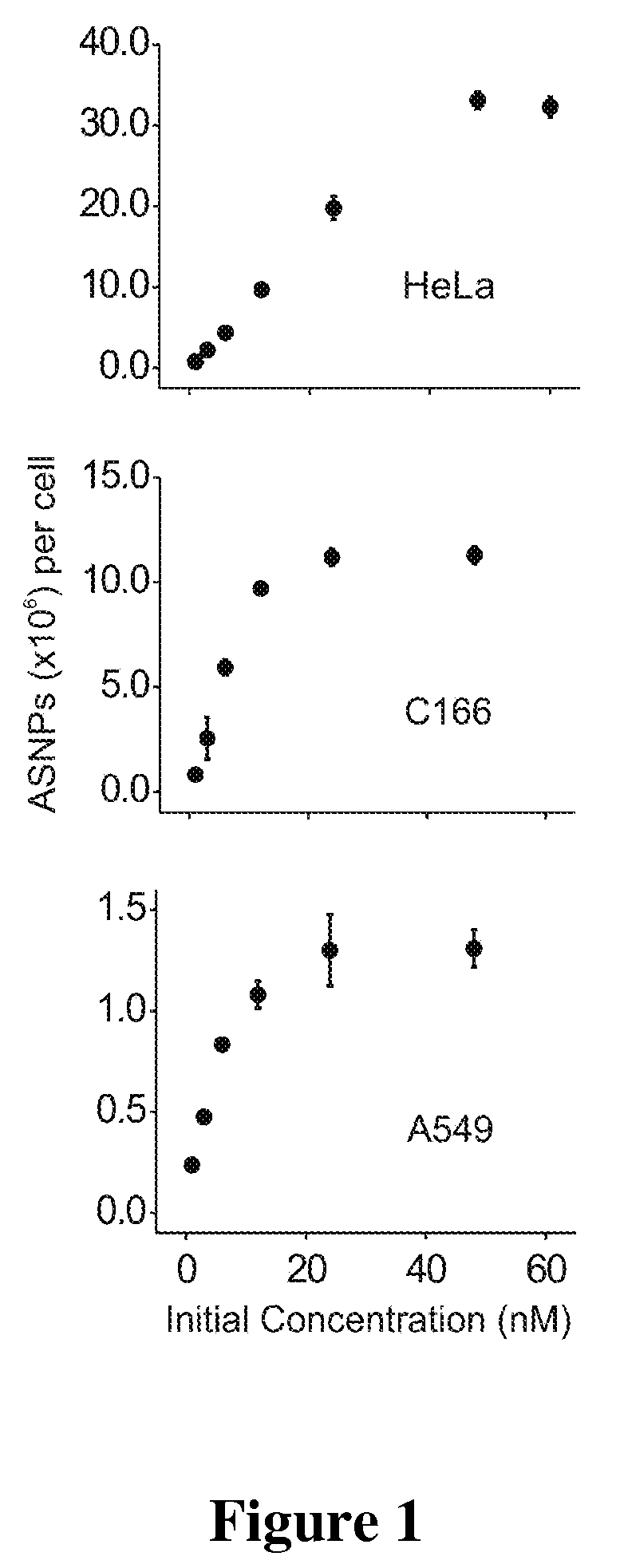
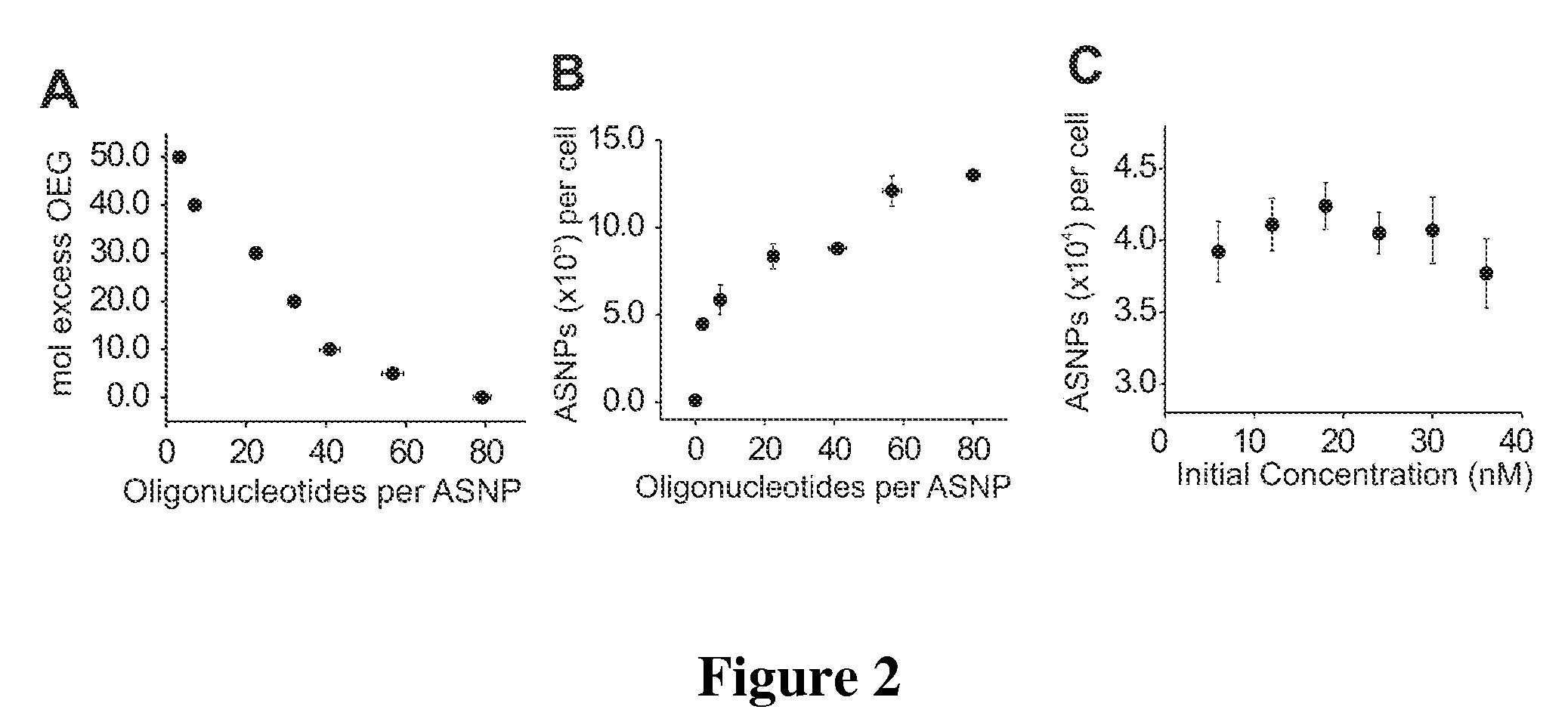
Nucleic Acid Functionalized Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Applications
ActiveUS20090209629A1High bonding strengthImprove the immunityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryFunctionalized nanoparticlesGene expression
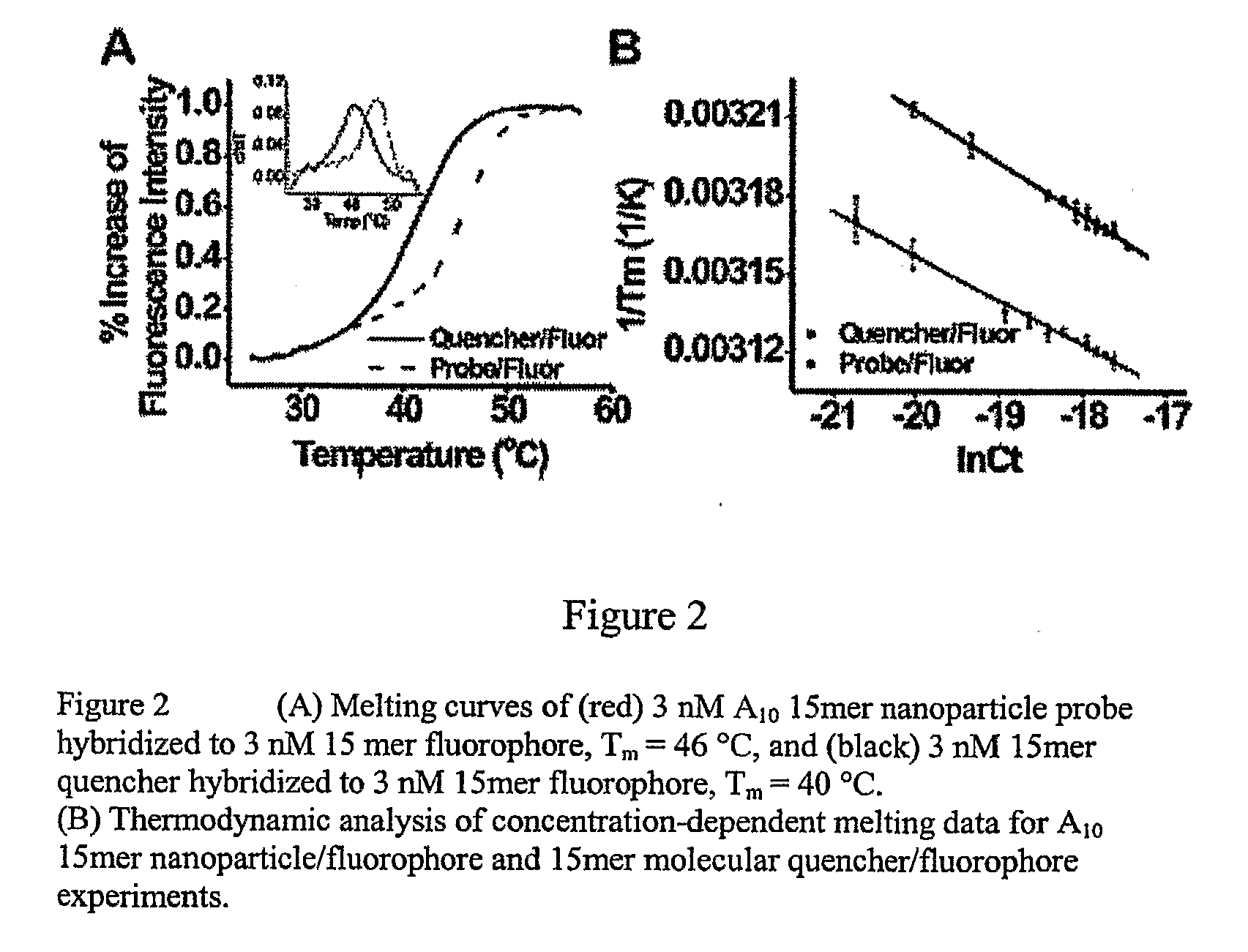
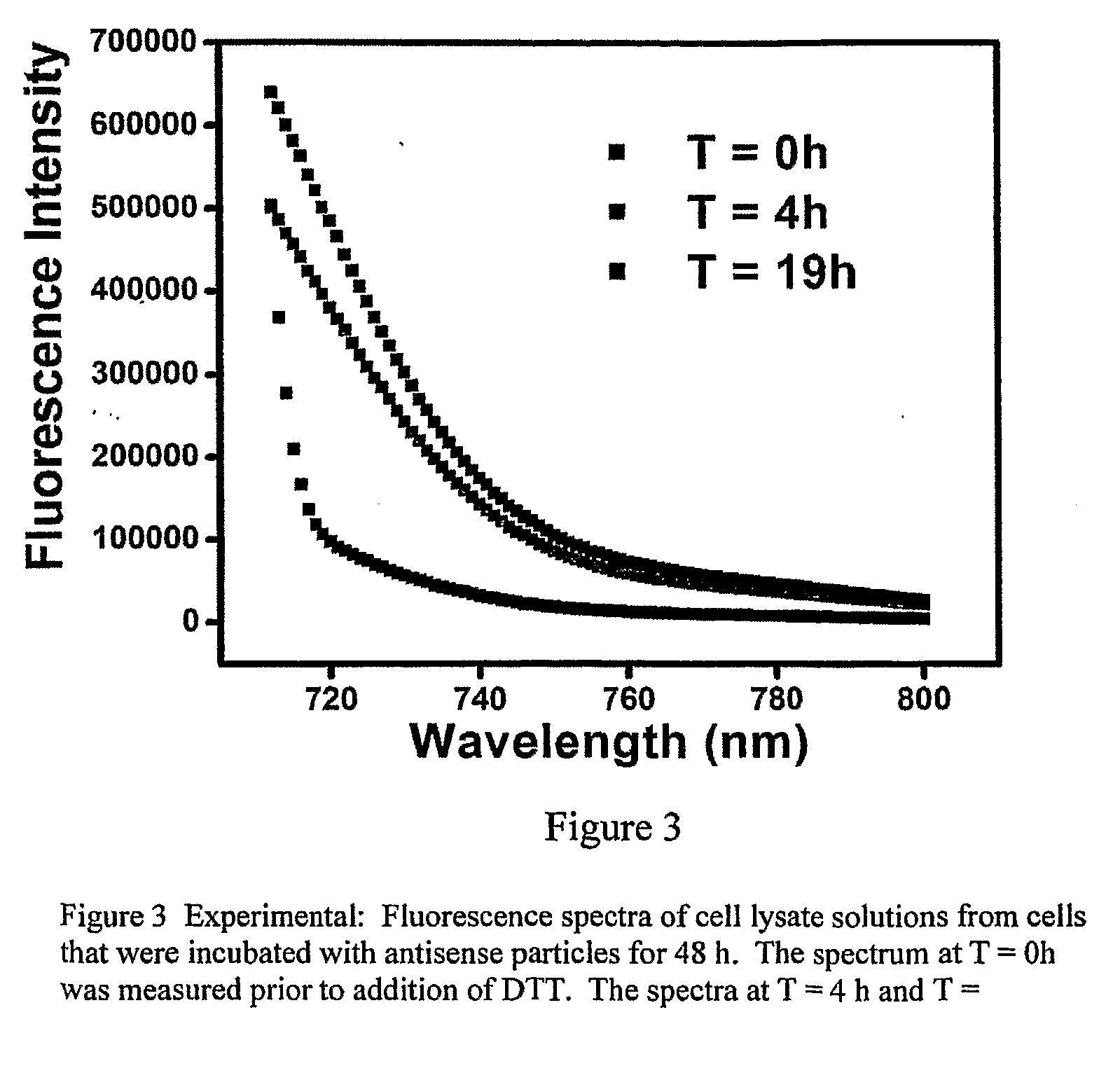
Materials and methods for regulating gene expression using nanoparticles functionalized with antisense oligonucleotides are provided.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Biommetic hierarchies using functionalized nanoparticles as building blocks
InactiveUS20070026069A1Improve responseAccurate thicknessPowder deliveryBiocideFunctionalized nanoparticlesVolumetric Mass Density
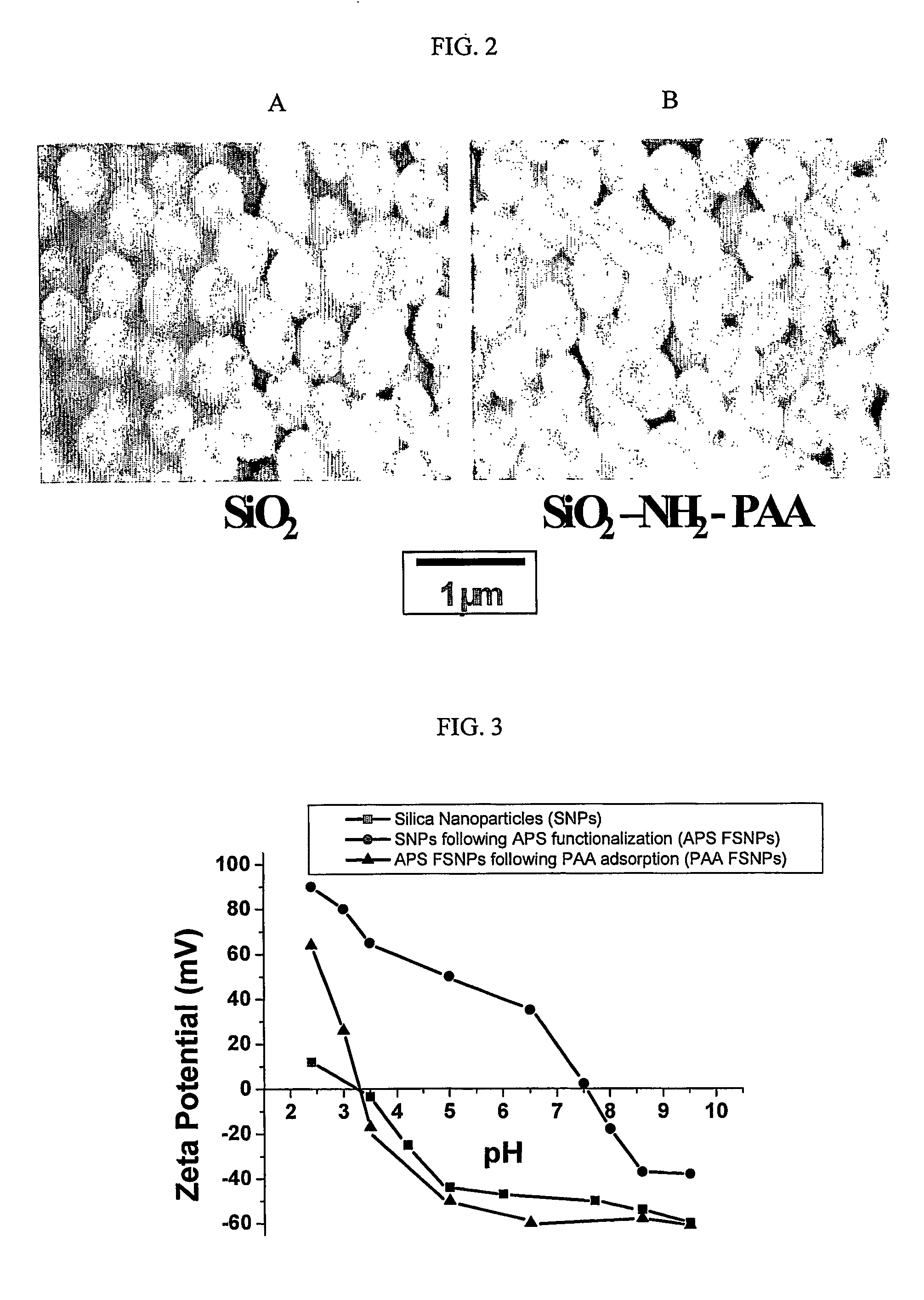
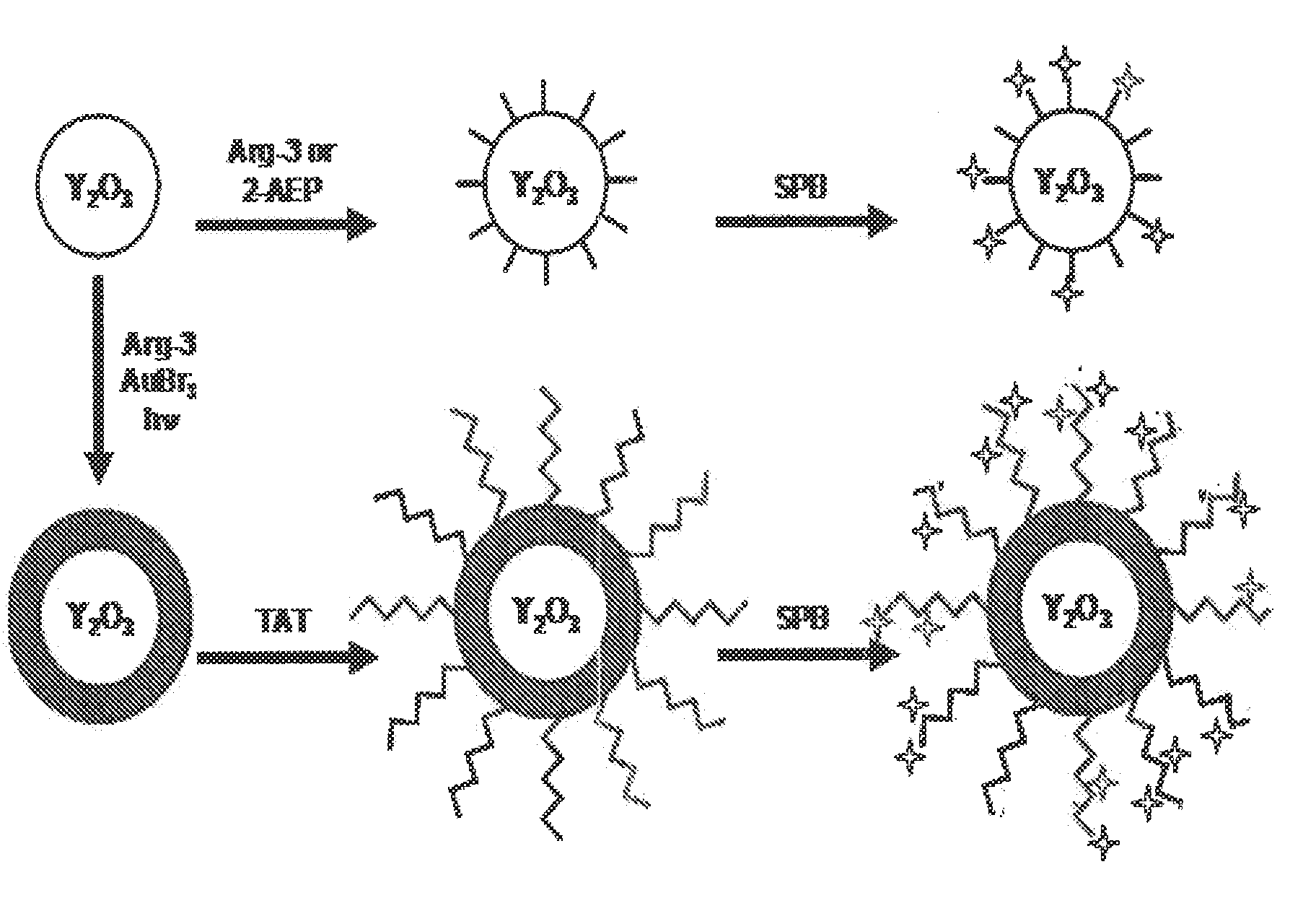
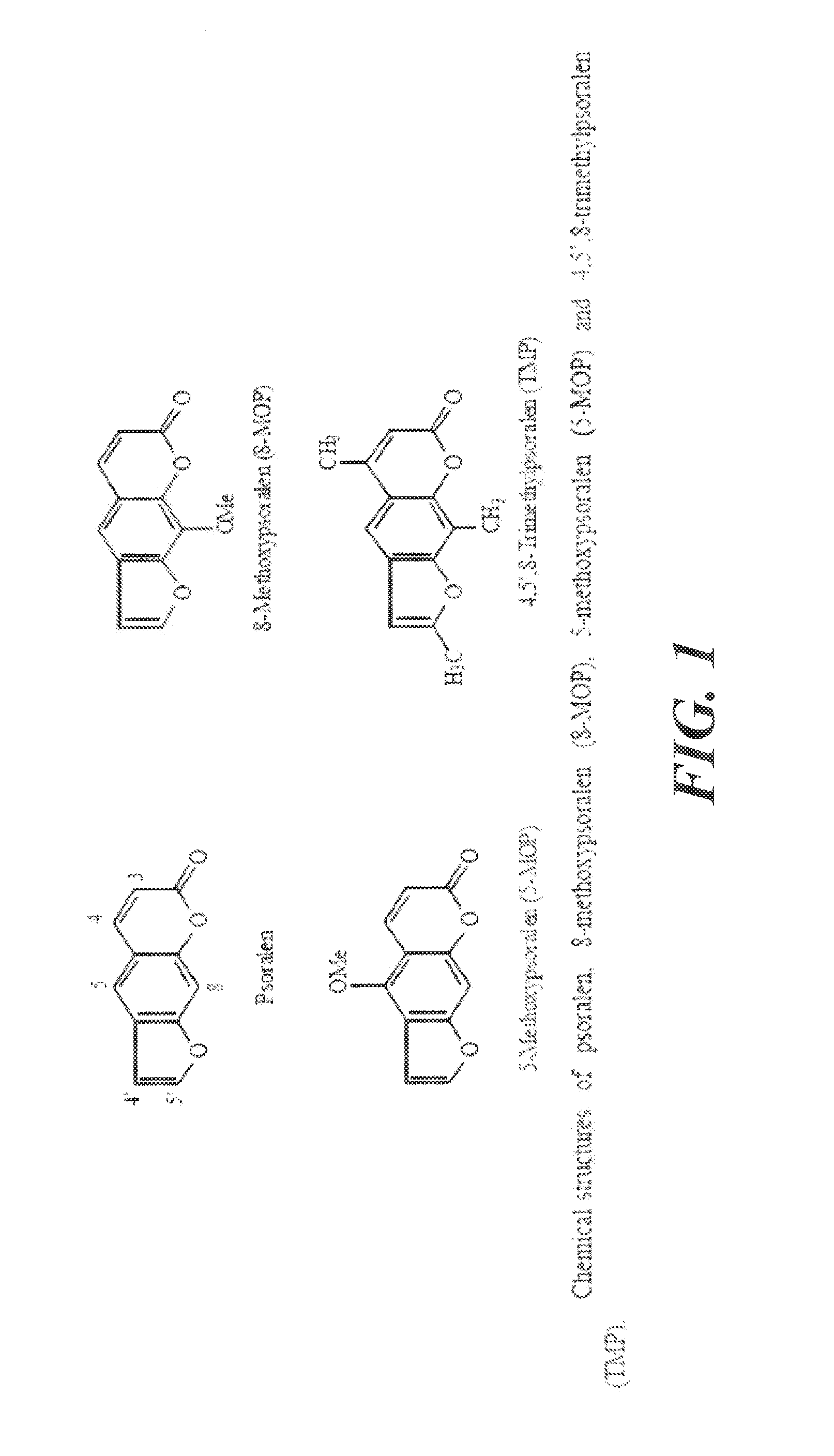
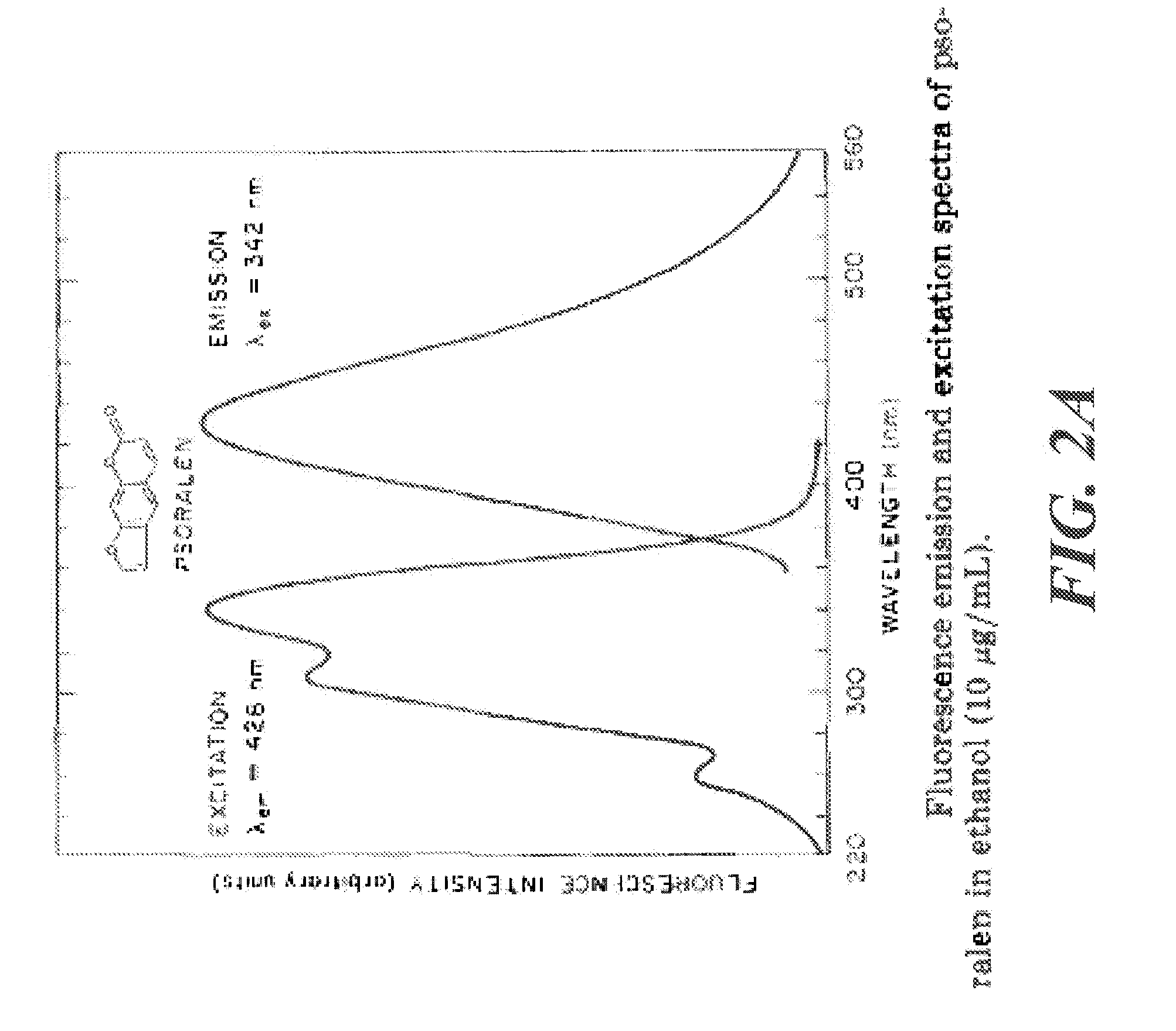
The invention provides a three-dimensional construct including a polymeric matrix and a nanoparticle as shown in FIG. 1 having a diameter of about 5 nm to about 10 microns, wherein the nanoparticle is (a) coated with at least two monomolecular layers each carrying biological information and (b) dispersed in the polymeric matrix at a density of at least 0.01 vol %. The invention further provides a method of presenting biological information to a cell or a tissue and thereby affecting at least one parameter of the cell or the tissue, the method involves providing the three-dimensional construct and contacting it with the cell or the tissue to present the biological information and thereby affecting at least one characteristic of the cell or the tissue. In certain embodiments, the diameter, the biological information and the density are selected to affect at least one characteristic of the cell or the tissue.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Directed Assembly of Carbon Nanotubes and Nanoparticles Using Nanotemplates With Nanotrenches
ActiveUS20090087622A1Material nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureFunctionalized nanoparticlesElectrophoresis
The present invention provides methods and tools for directed assembly of nanoelements across a large area using a nanosubstrate. The nanosubstrate has a substrate layer, an adhesive layer, a conductive layer, and an insulating layer that is interrupted by one or more nanotrenches or nanowells having a width of at least 20 nm. The nanosubstrate allows the rapid assembly of linear assemblies and arrays of single walled carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles by DC electrophoresis. The density of nanoelements assembled can be controlled by varying the voltage and trench size. Functionalized nanoparticles can be assembled into arrays useful, e.g., as biosensors.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method of forming stable functionalized nanoparticles
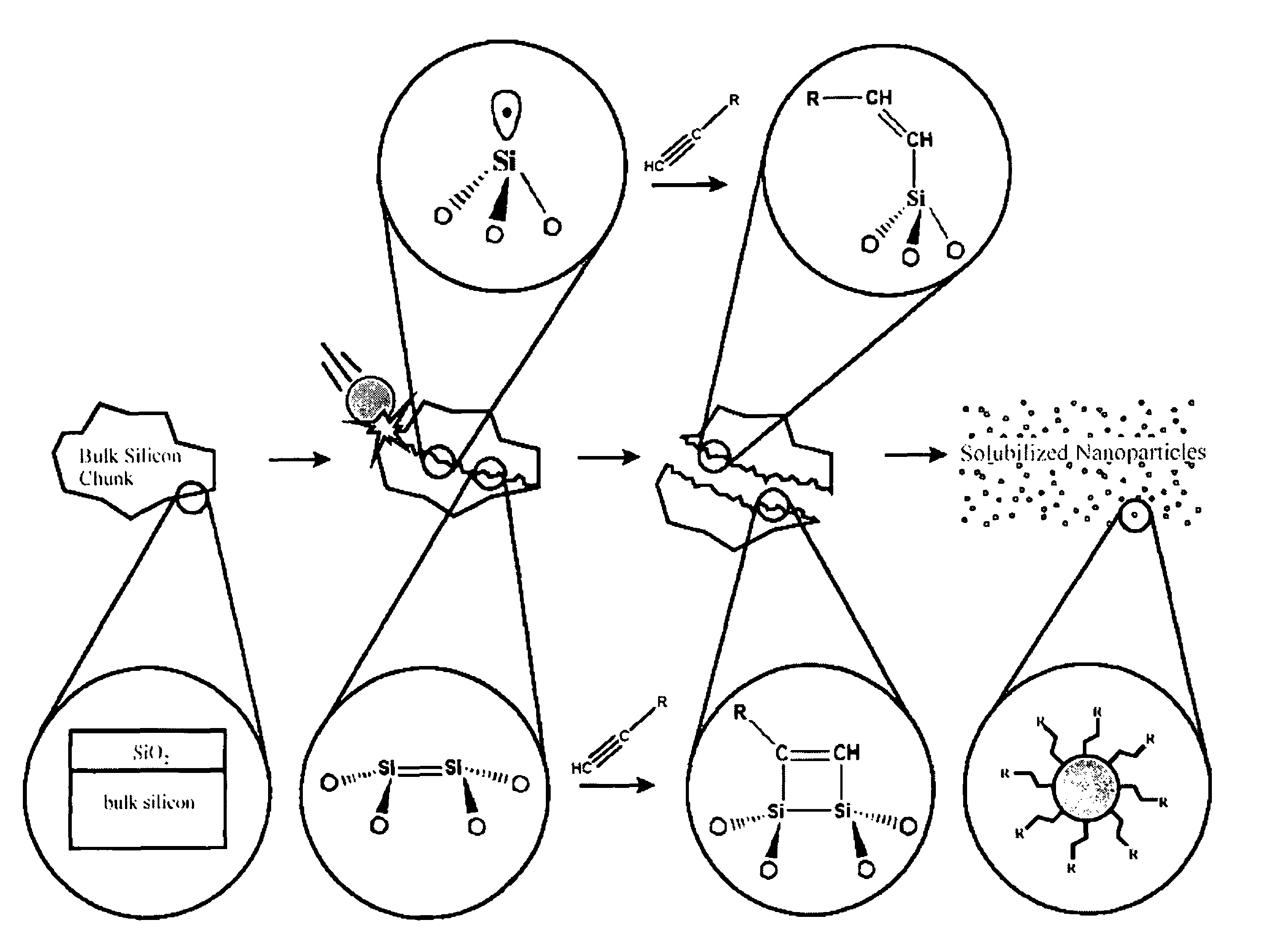
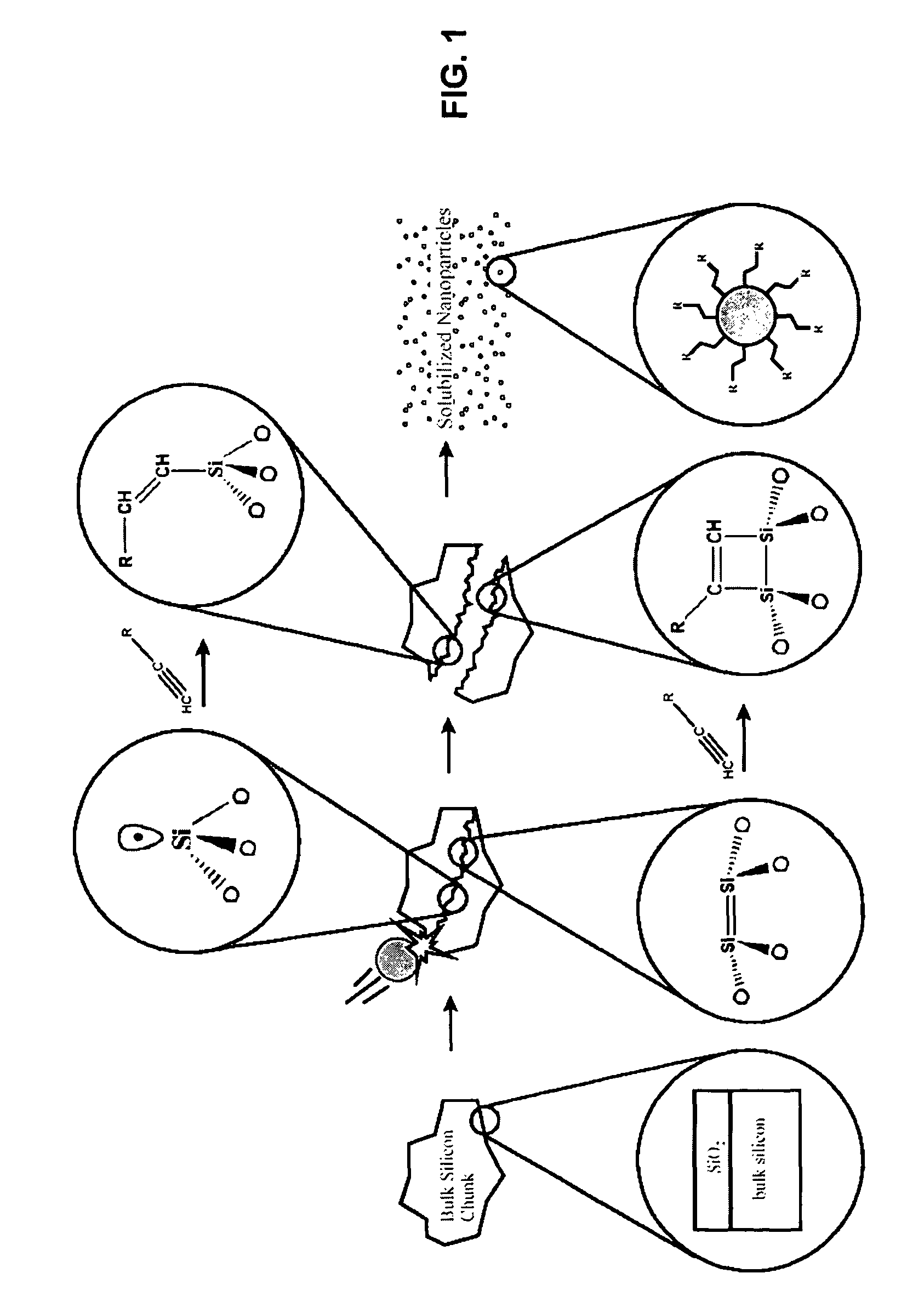
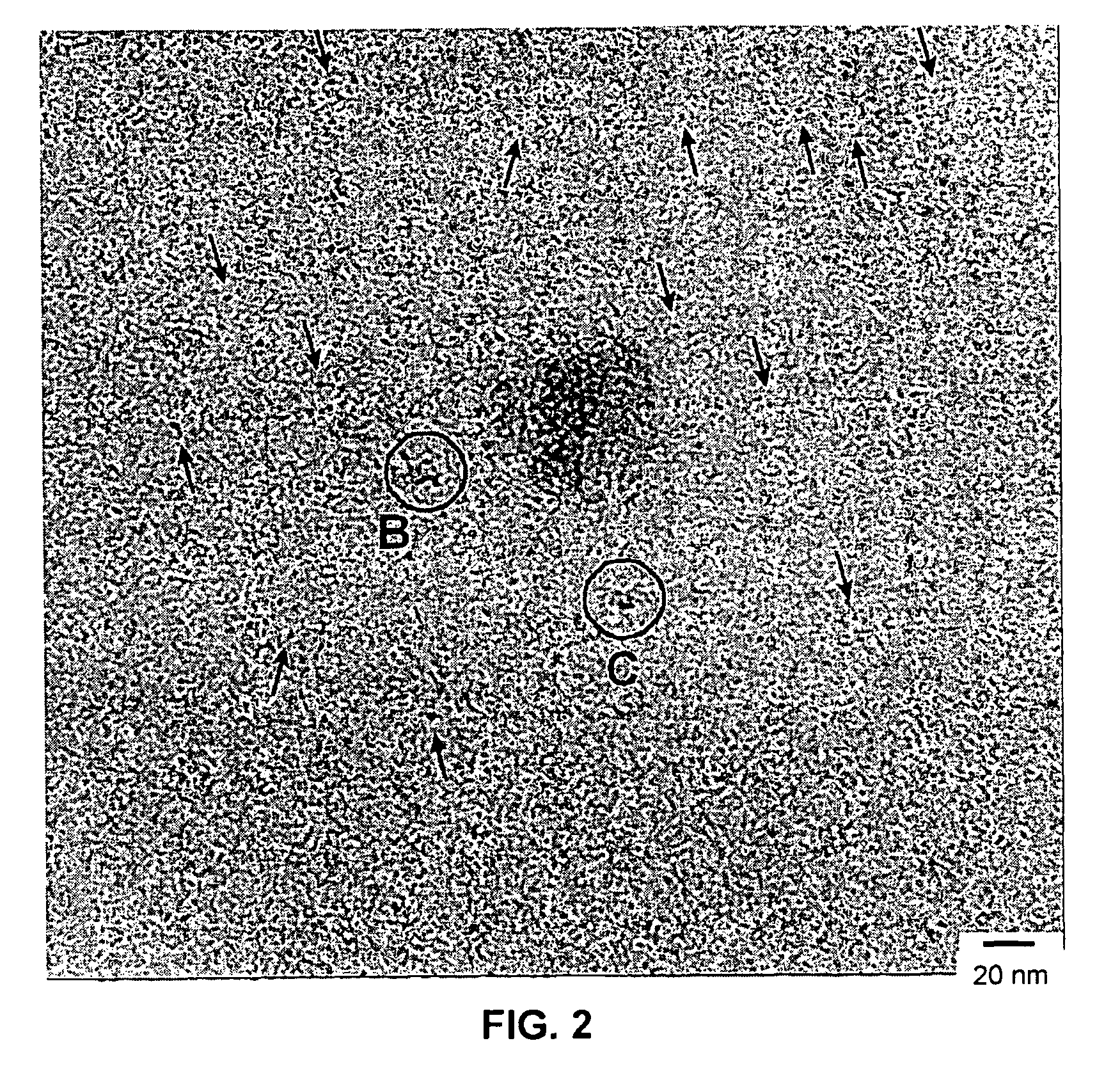
ActiveUS7883995B2Stable and functionalized nanoparticlesStable functionalized nanoparticlesMaterial nanotechnologySiliconHigh energyFunctionalized nanoparticles
A novel top-down procedure for synthesis of stable passivated nanoparticles uses a one-step mechanochemical process to form and passivate the nanoparticles. High-energy ball milling (HEBM) can advantageously be used to mechanically reduce the size of material to nanoparticles. When the reduction of size occurs in a reactive medium, the passivation of the nanoparticles occurs as the nanoparticles are formed. This results in stable passivated silicon nanoparticles. This procedure can be used, for example in the synthesis of stable alkyl- or alkenyl-passivated silicon and germanium nanoparticles. The covalent bonds between the silicon or germanium and the carbon in the reactive medium create very stable nanoparticles.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Nucleic Acid Functionalized Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Applications
InactiveUS20080306016A1Enhance cellular uptakeIncreased cellular uptakeOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryFunctionalized nanoparticlesBiology
Materials and Methods for modulating cellular uptake of functionalized nanoparticles are provided. Also provided are materials and methods for modulating the effectiveness of a therapeutic agent with a functionalized nanoparticle.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Light-emitting nanoparticle compositions
InactiveUS20050123760A1Material nanotechnologySolid-state devicesLuminophoreFunctionalized nanoparticles
Light-emitting chromophores (lumophores) that emit different colored light may be covalently attached to a nanoparticle core such as a silsequioxane. The light emission profile of the resulting lumophore-functionalized nanoparticle is the sum of the light emission of all of the lumophores attached to the nanoparticle. In some embodiments, the lumophore-functionalized nanoparticle is white light-emitting.
Owner:CAMMACK J KEVIN +3
Polysaccharide-functionalized nanoparticle, drug delivery system for controlled release comprising the same and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20070053870A1Extend posting timeEffective and stablePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsControlled releaseFunctionalized nanoparticles
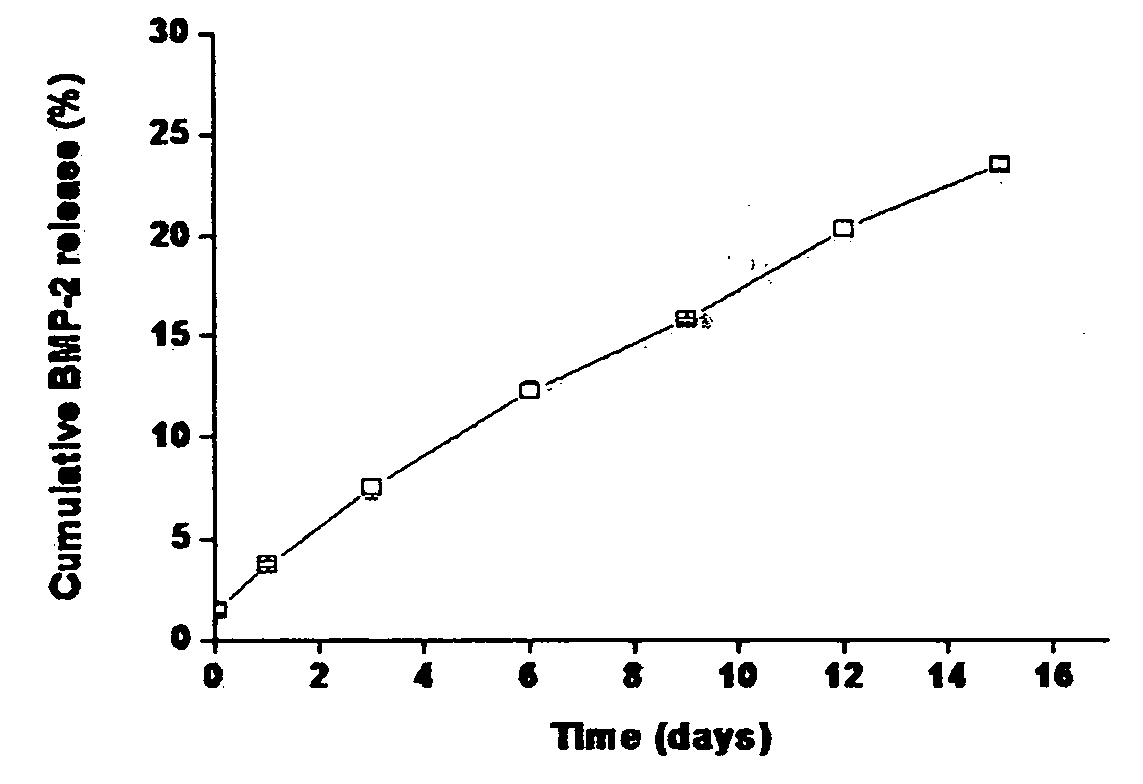
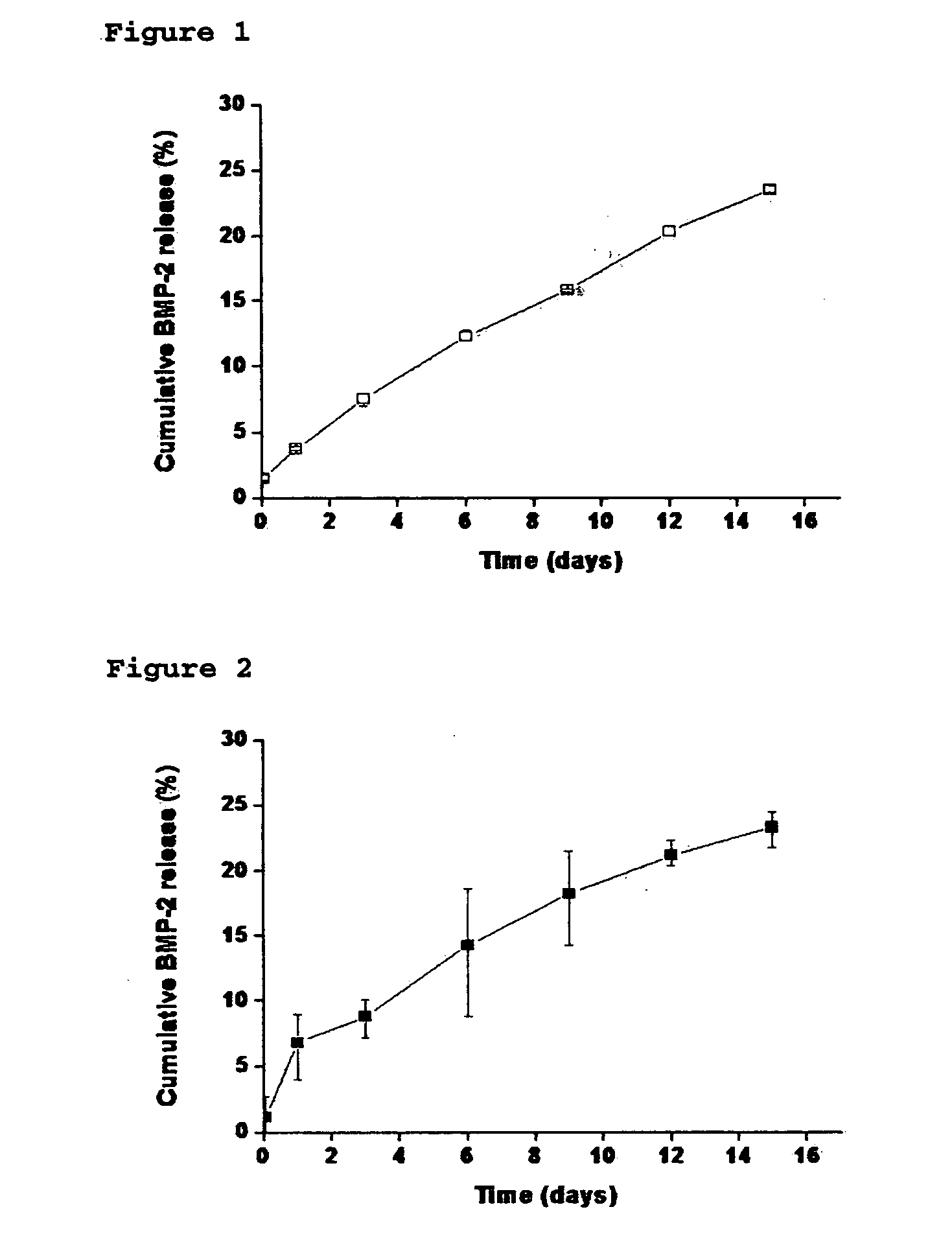
The present invention provides a polysaccharide-functionalized nanoparticle, a drug delivery system for controlled release comprising the nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof. In particular, the nanoparticle of the present invention comprises a core of a biodegradable polymer, an outer hydrogel layer of a biocompatible polymer emulsifier and a polysaccharide physically bound to the core and the hydrogel layer, thus enabling to significantly enhance stability and controlled release of a protein drug such as a growth factor.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
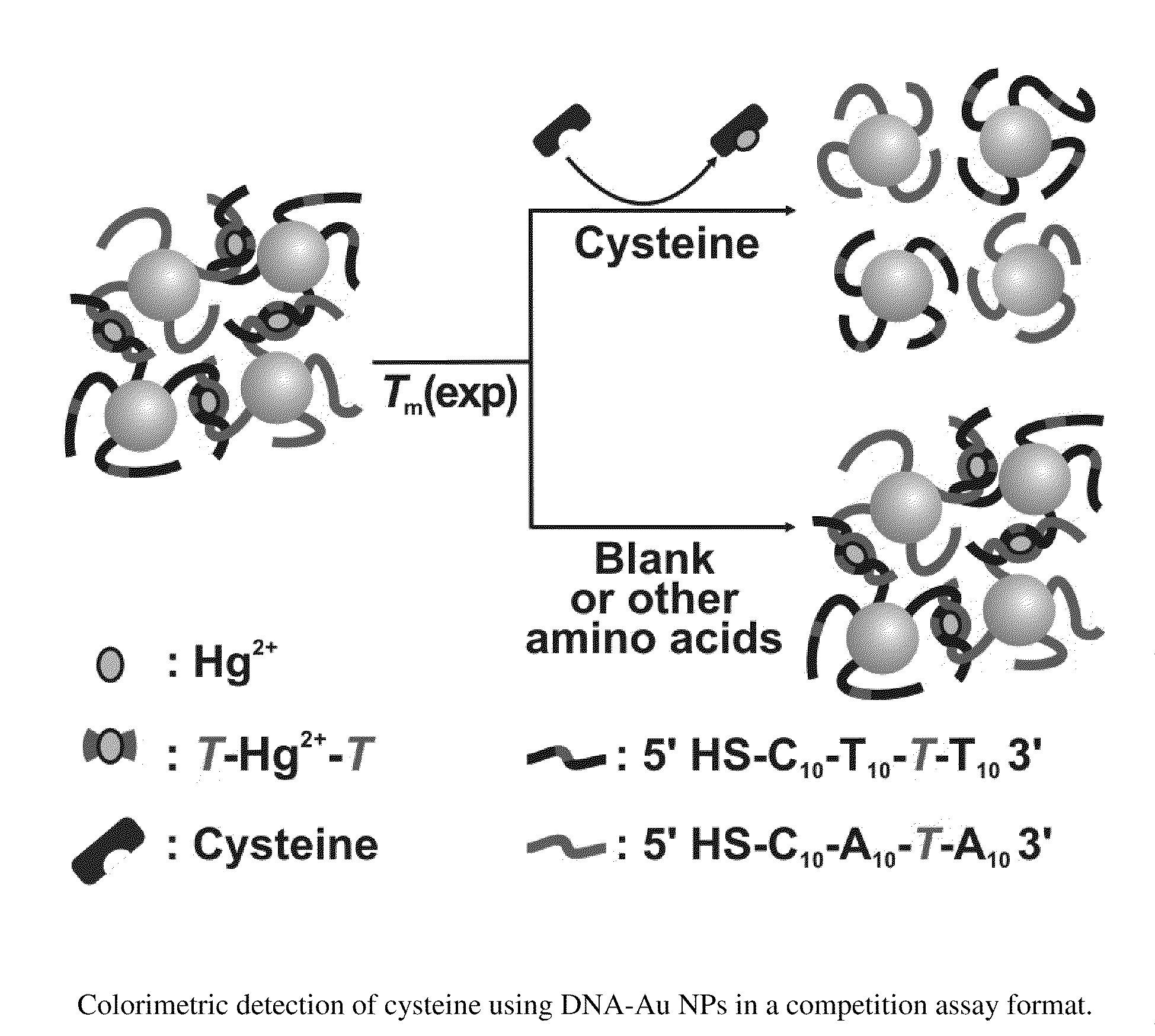
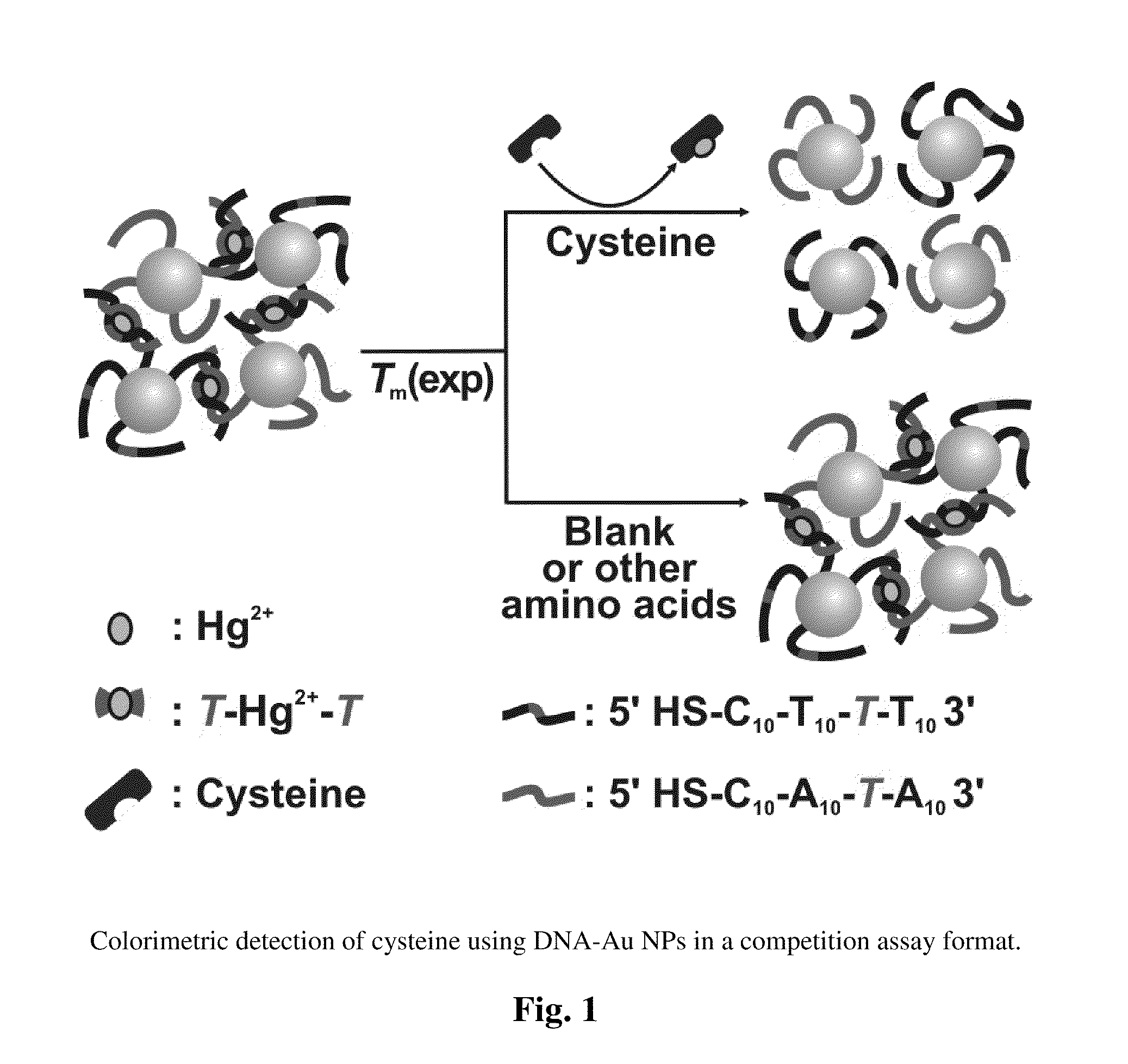
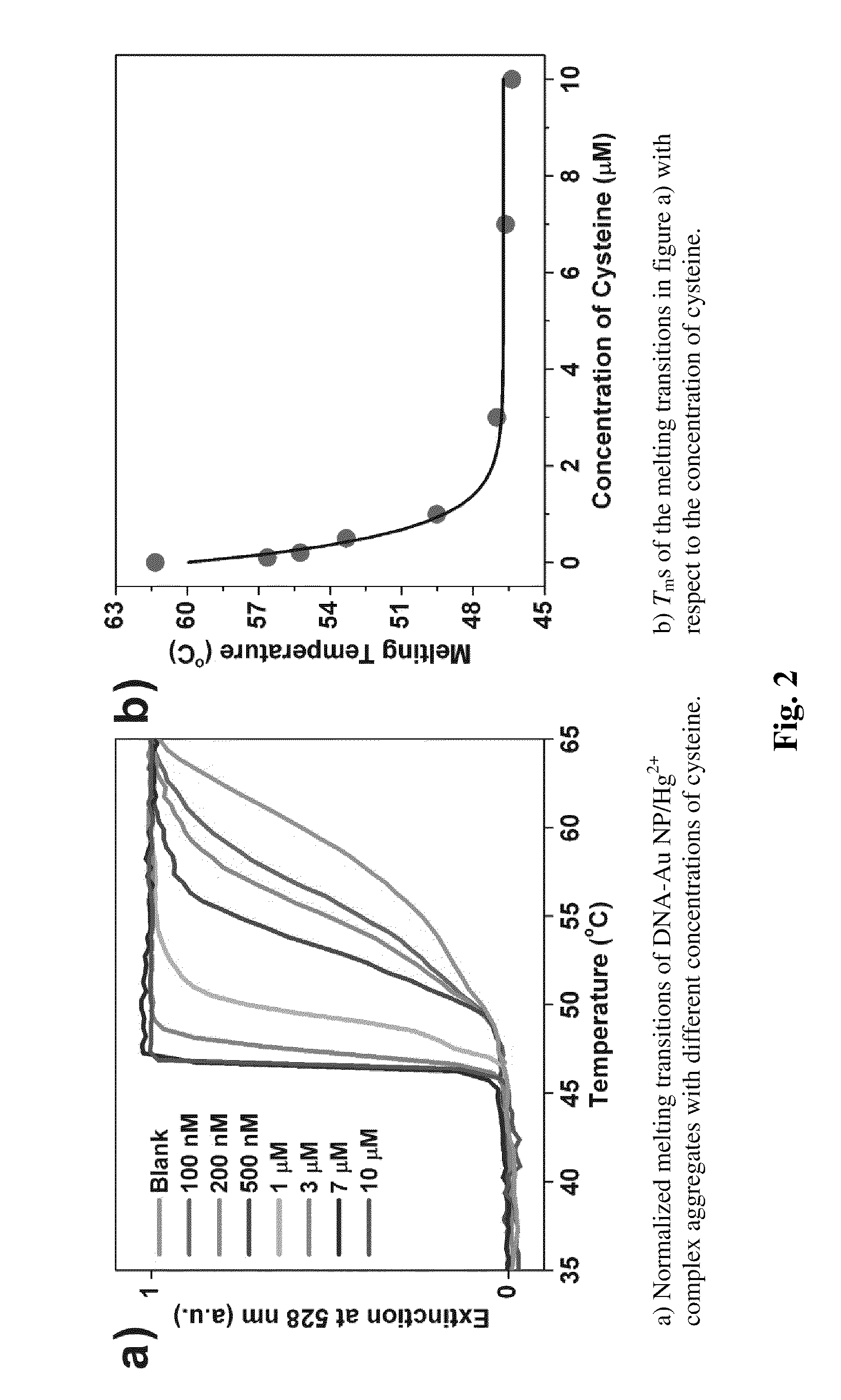
Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Detection Of Cysteine
InactiveUS20100021894A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingFunctionalized nanoparticlesOligonucleotide
The invention provides methods to detect cysteine which employ oligonucleotide functionalized nanoparticles.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Nanocomposites and methods for synthesis and use thereof
InactiveUS7556743B2Liquid crystal compositionsSynthetic resin layered productsSynthesis methodsFunctionalized nanoparticles
Nanocomposite compositions and methods of synthesis of the compositions are described. In particular, liquid crystal-functionalized nanoparticles, liquid crystal-templated nanoparticles, nanocomposite compositions including the nanoparticles, and composite compositions including the nanocomposites are detailed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Metal Nanoparticles functionalized with rationally designed coatings and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100255311A1Material nanotechnologyNanomagnetismFunctionalized nanoparticlesPolyethylene glycol
The present invention provides a composition and method for functionalizing nanoparticles that enables them to undergo reversible aggregation / deaggregation. The aggregation properties of this new system are reversible and readily monitored by optical absorbance measurements with the possibility of electrical and / or magnetic monitoring as well. The outer portion of the coating material is functionalized with polyethylene glycol (PEG) entities that facilitate biocompatibility and stability both in solution and in the solid state. Also provided are nanoparticles functionalized with rationally designed free radical initiators to effect tailored polymer growth from the surface. These systems may be used for a broad variety of applications, including biosensing with real-time feedback.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
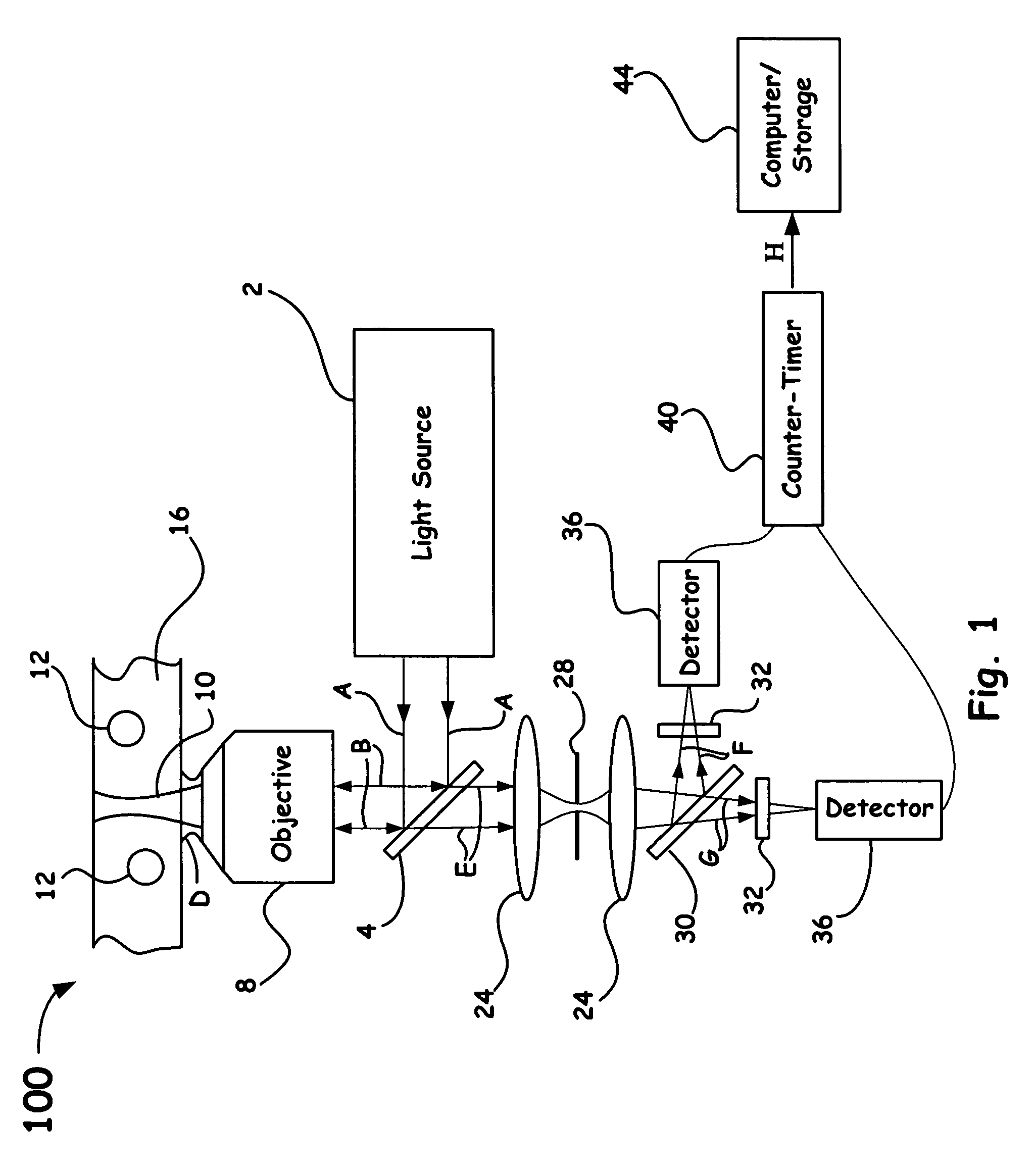
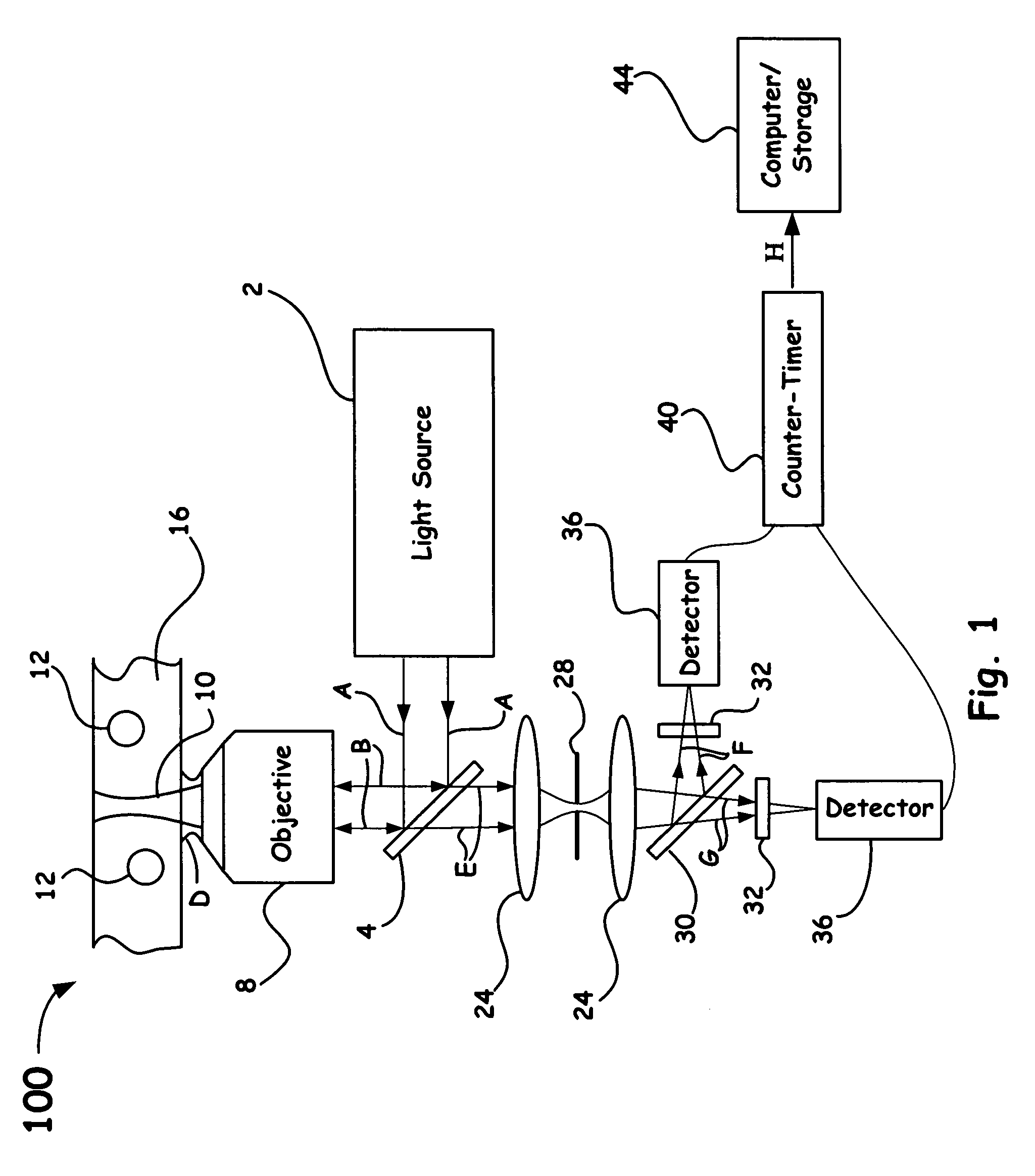
Nanosensors based on functionalized nanoparticles and surface enhanced raman scattering
ActiveUS7301624B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFunctionalized nanoparticlesSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
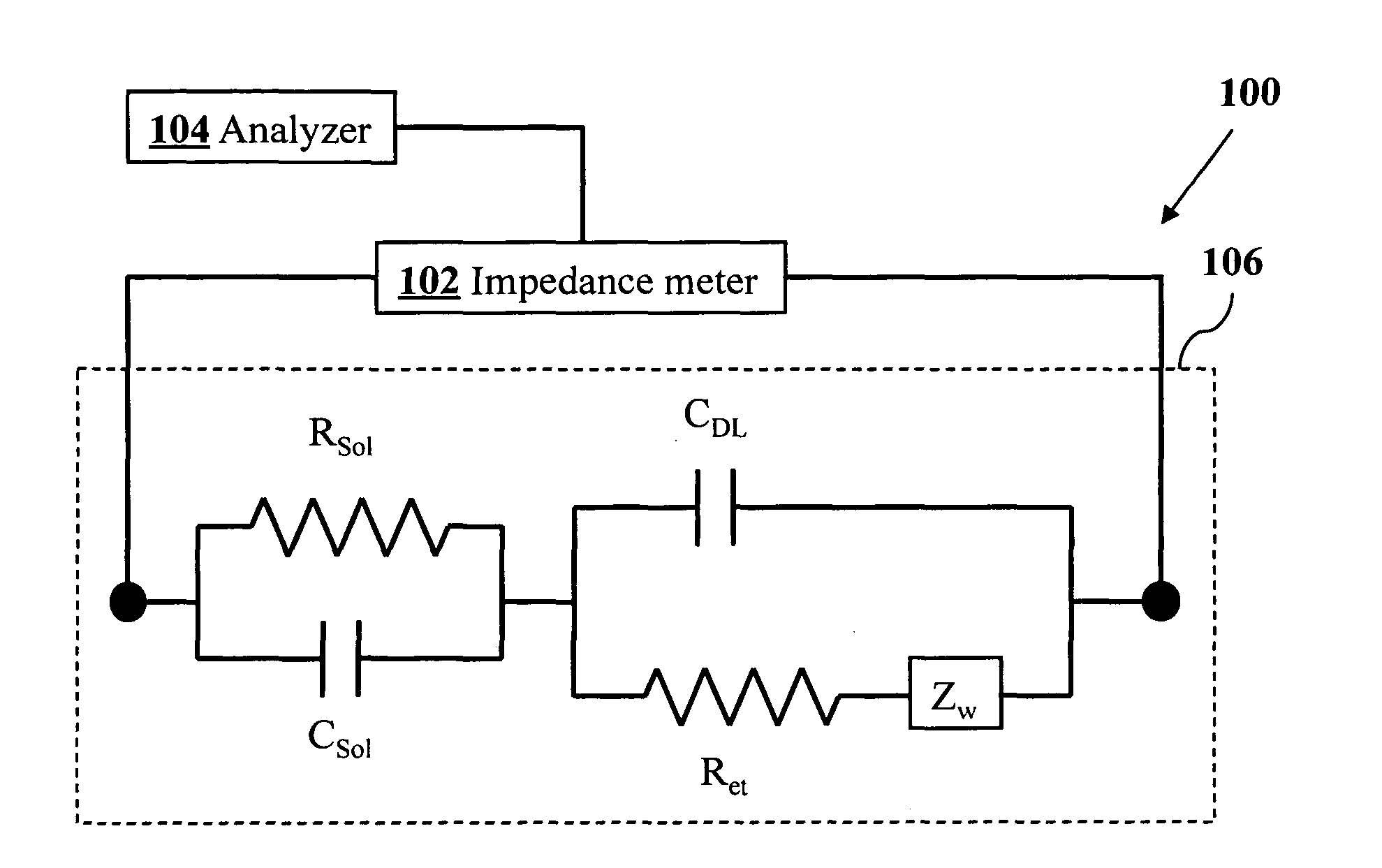
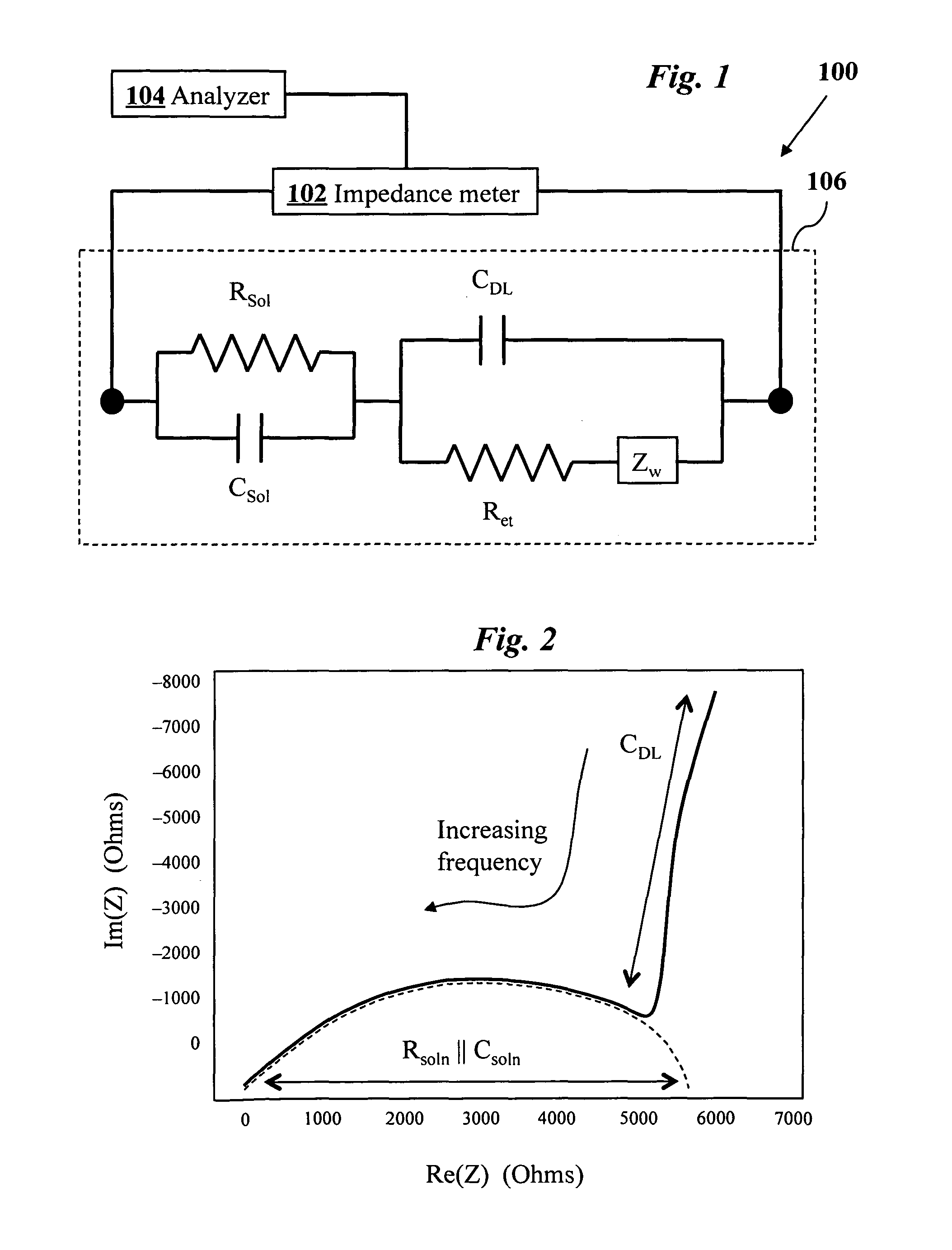
Impedimetric sensors using dielectric nanoparticles
InactiveUS20120037515A1High sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceFunctionalized nanoparticlesSpectroscopy
A method for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy uses interdigitated electrodes functionalized with a first species and nanoparticles functionalized with a second species that preferentially attaches to the first species. The nanoparticles are composed of a material with a dielectric constant (k value) greater than 2. The chemically functionalized electrodes are then exposed to a solution containing the chemically functionalized nanoparticles which then become immobilized on the electrodes through the attachment of the first species to the second species. The impedance spectrum is measured and an amount of the first species is then determined from the measured spectrum. Because the high-k dielectric nanoparticles increase the double-layer capacitive impedance, the sensitivity of determining the amount of the first species attached to the second species is enhanced.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV
Precision-guided nanoparticle systems for drug delivery
InactiveUS20100260676A1Diagnose and treat diseaseAccurate guidePowder deliveryBiocideDiseaseFunctionalized nanoparticles
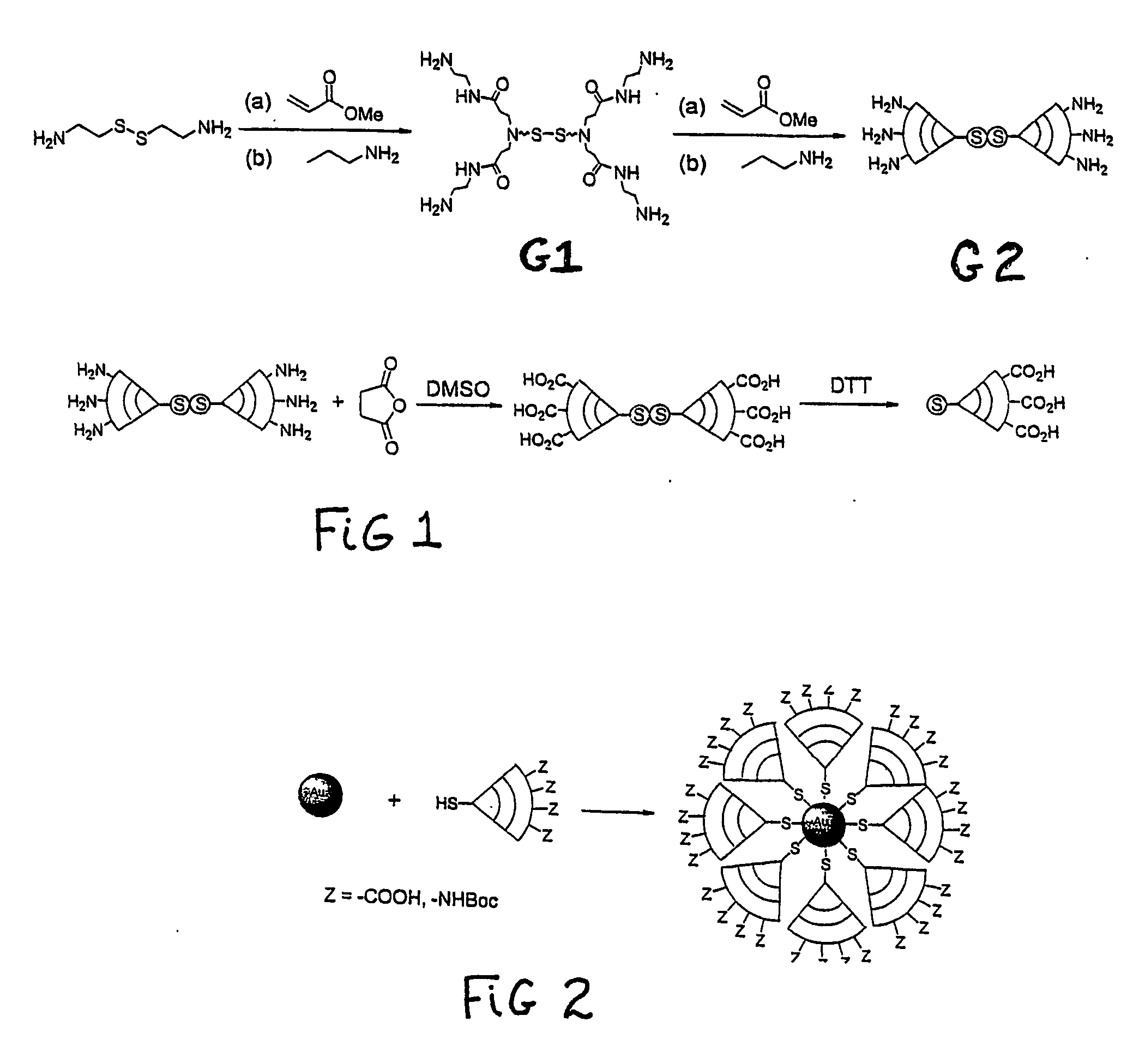
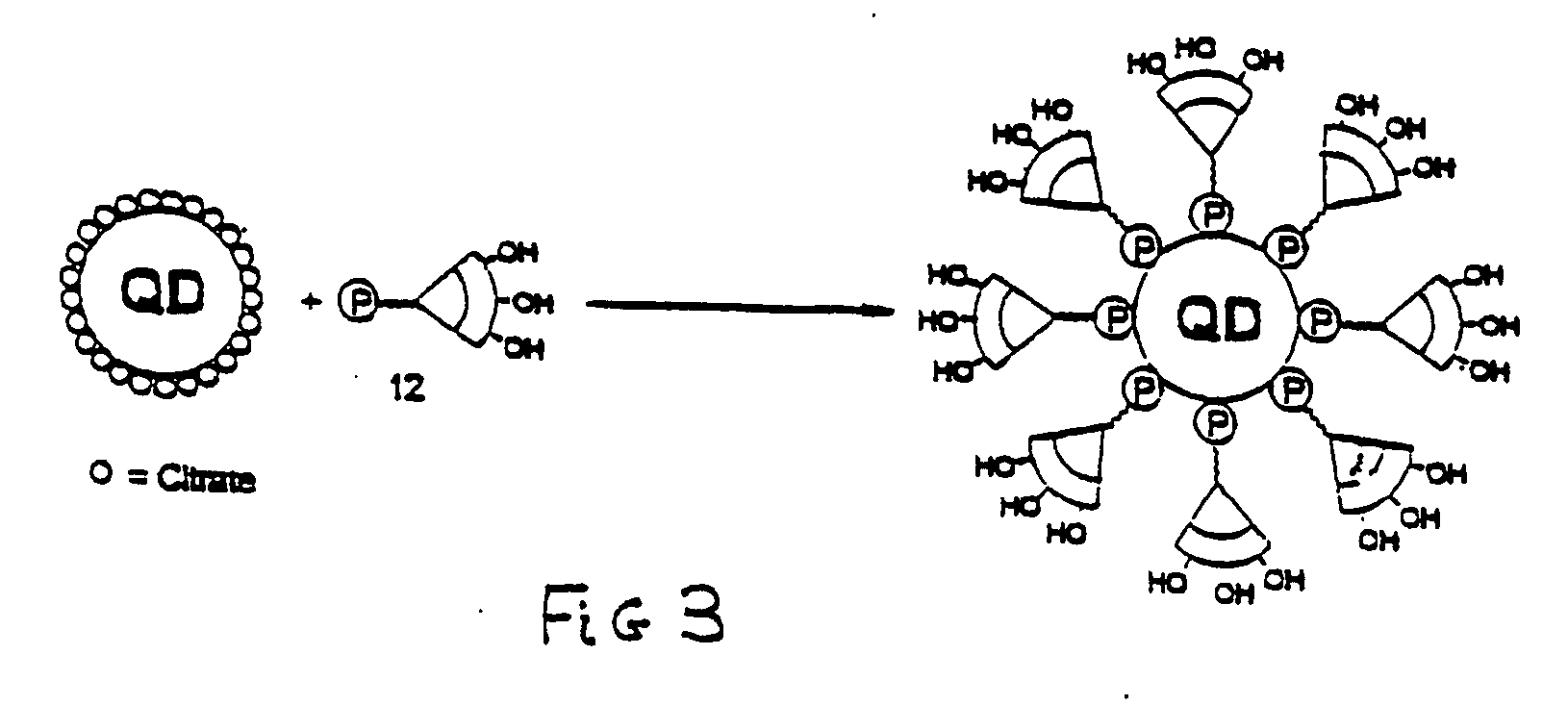
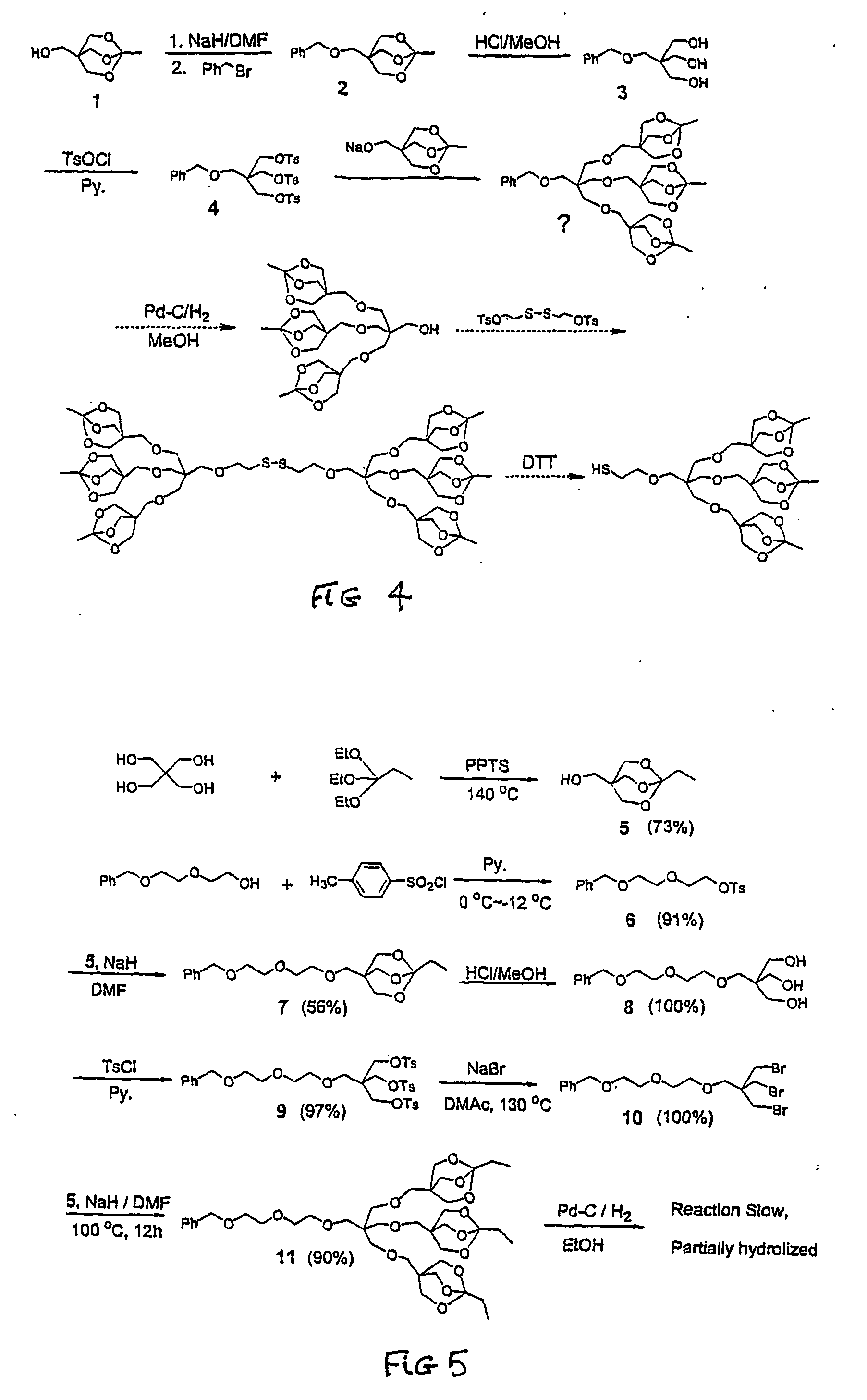
A method of preparing multifunctionalized nanoparticles involves using a modular system of half-linkers to attach functional moieties that serve to deliver the nanoparticles to a desired target, exert an effect at the target, or track the nanoparticles within a cell or an animal. The modular chemistry of the half-linker system permits the custom design and synthesis of functionalized nanoparticles bearing multiple groups and therefore results in precise delivery to desired cell types and intracellular locations. The functionalized nanoparticles can be used to treat or diagnose a variety of medical conditions, including neoplastic diseases, infectious diseases, and chronic diseases.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Functionalized metal-coated energy converting nanoparticles, methods for production thereof and methods for use
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Superhydrophobic inorganic organic nano composite polymeric coating material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101824278AWide range of usesReduce resistancePretreated surfacesSpecial surfacesChemical reactionFunctionalized nanoparticles
The invention discloses a superhydrophobic inorganic organic nano composite polymeric coating material and a preparation method thereof. The coating material is prepared from 30 to 98 mass percent of thermosetting polymeric precursor and 10 to 70 mass percent of surface functionalized nanoparticle under the action of 0 to 5 mass percent curing agent, wherein the obtained surface water contact angle and rolling angle of the material are 120 to 180 DEG and 1 to 20 DEG respectively; and a falling water drop which is spherical can bounce up and can freely roll on the surface. The method has the characteristic of simple preparation process by using the chemical reaction between organic groups on the surfaces of the polymeric precursor and the modified nanoparticle in the solution. The coating material has the functions of stain resistance, dust prevention and self cleaning.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods of making a curable composition having low coefficient of thermal expansion and an integrated circuit and a curable composition and integrated circuit made there from
InactiveUS20060199301A1Low compositionMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFunctionalized nanoparticlesThermal expansion
Disclosed is a method for making a low CTE curable composition. In one embodiment, the method comprises mixing together (i) from 0.1 to 60.0% by weight of a nanoparticle composition and (ii) from 20.0 to 90.0% by weight of a curable binder to provide a premixture, based on the total weight of the premixture, and subjecting the premixture to high shear forces until the nanoparticle composition (i) is sufficiently dispersed in the curable binder (ii) to provide a curable composition. It has been found that the nanoparticle composition (i) must be at least one of (a) a strongly functionalized nanoparticle composition having no more than 25 mole % functionalization, (b) a weakly functionalized nanoparticle composition having from 1 to 100 mole % functionalization, (c) a nonfunctionalized nanoparticle composition, or (d) mixtures thereof.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods for Preparing and Functionalizing Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070212542A1Reduce eliminateAvoid problemsMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsCombustionFunctionalized nanoparticles
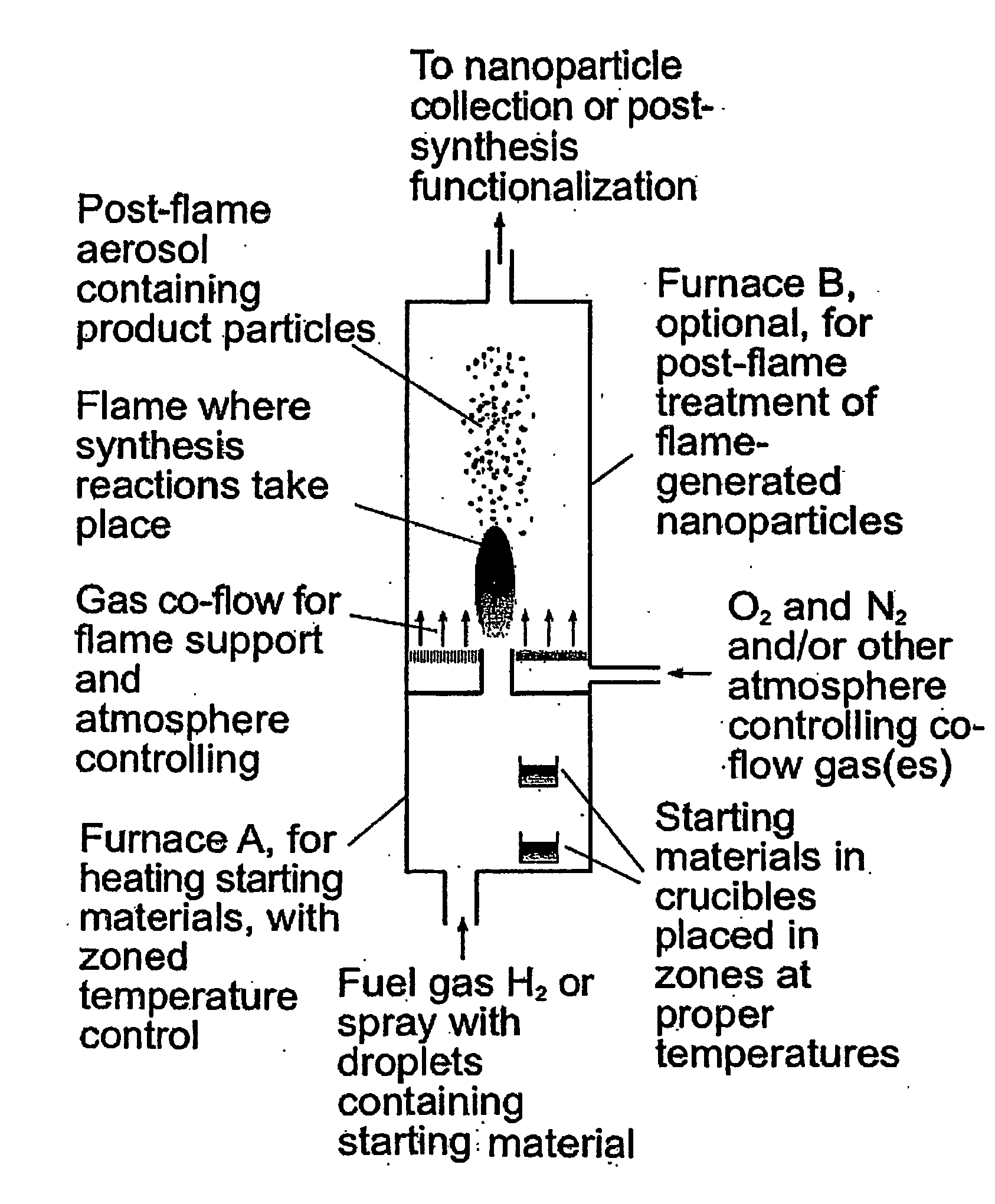
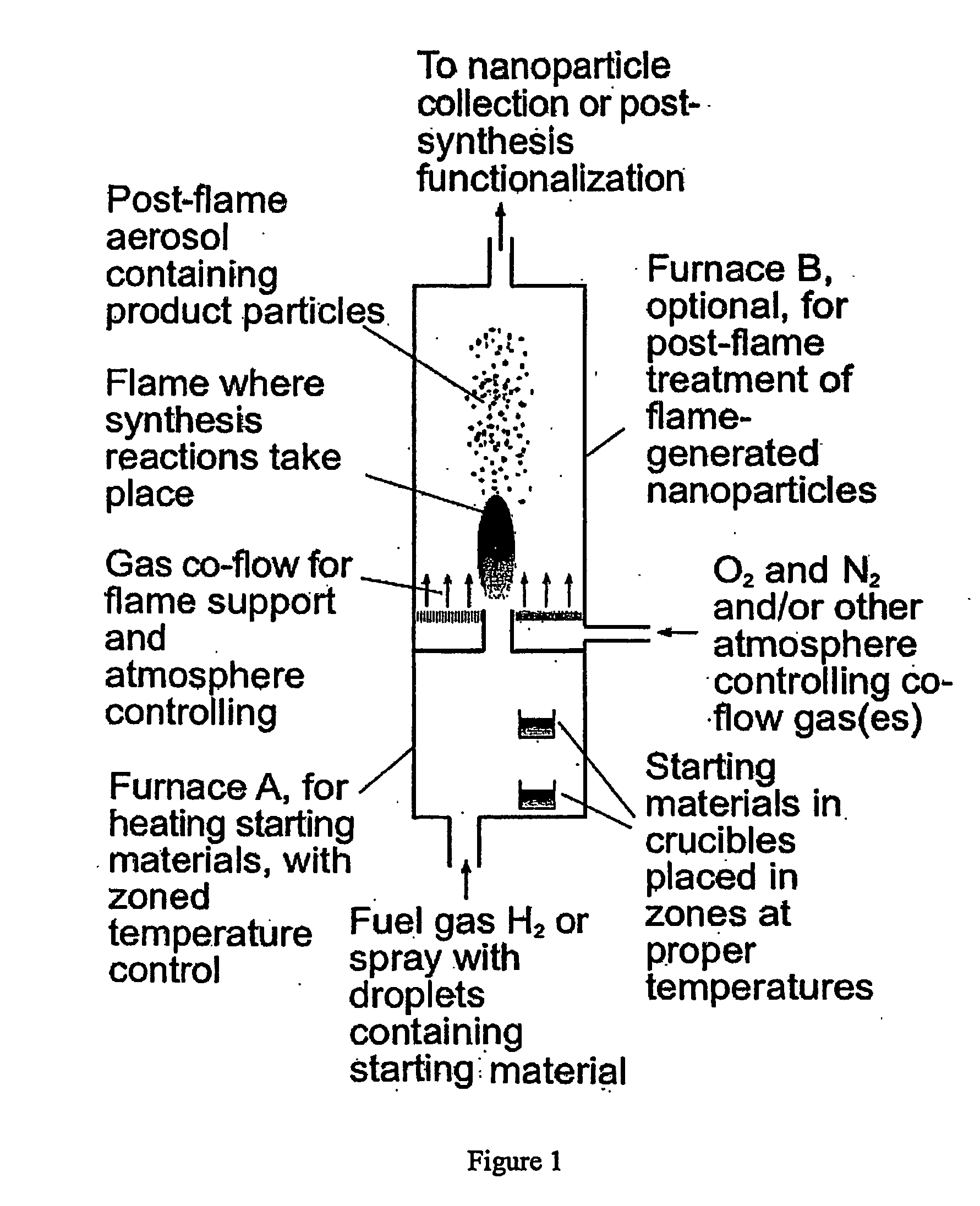
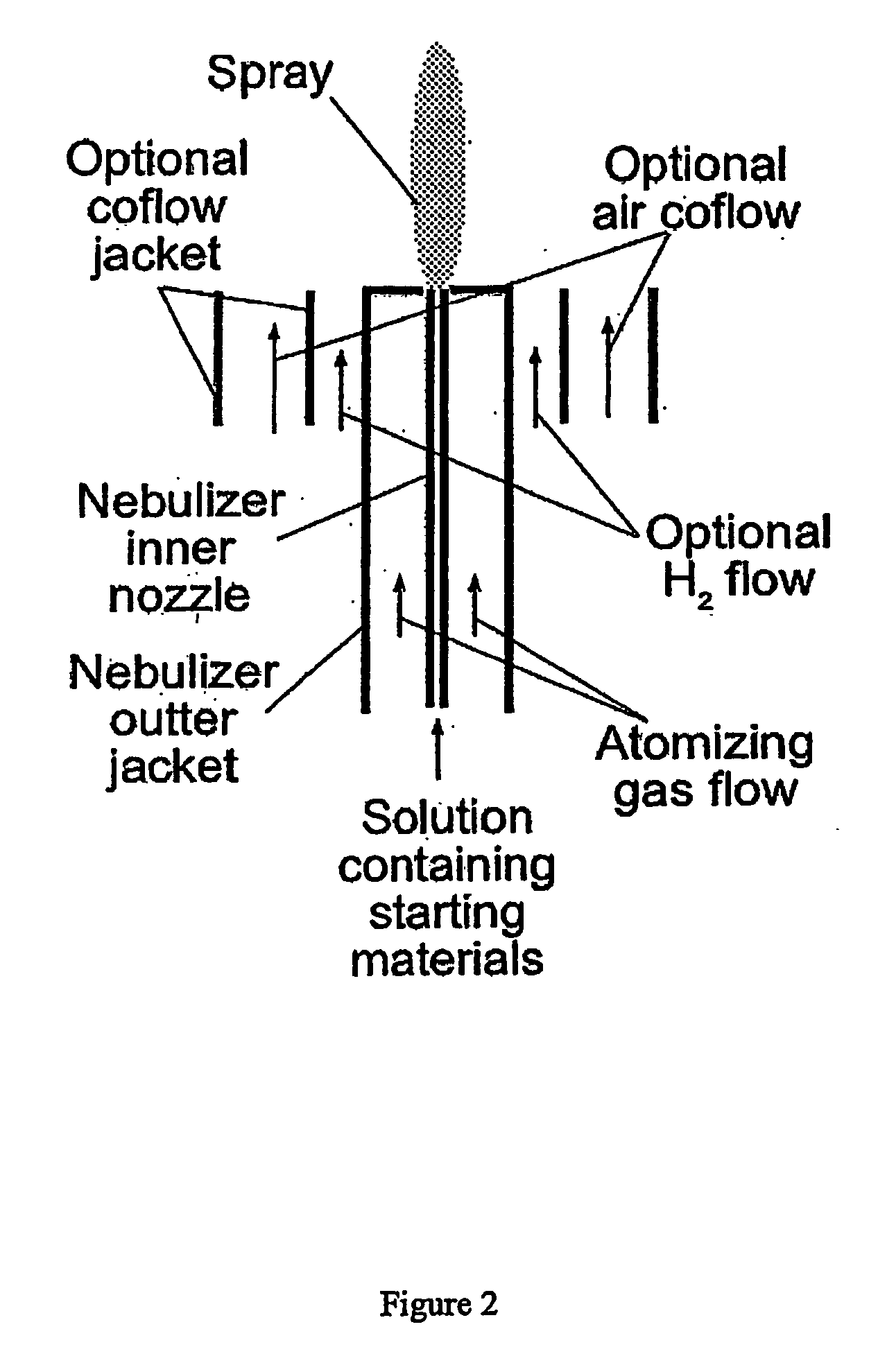
Fluorescent or phosphorescent nanoparticles, fluorescent or phosphorescent magnetic nanoparticles, combustion-based methods for their synthesis, and methods to functionalize them are described. The methods provided by the invention are simplified, efficient and cost effective as compared to prior art methods. The resulting fluorescent or phosphorescent nanoparticles have reduced tendency toward aggregation, and diminished need for postmanufacturing processing steps. The particles may be manufactured with combinations of lanthanides so as to absorb and emit light over a variety of wavelengths.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Polyvalent polynucleotide nanoparticle conjugates as delivery vehicles for a chemotherapeutic agent
InactiveUS20120244230A1Strong cytotoxicityPowder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsDelivery vehicleFunctionalized nanoparticles
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods of delivering a chemotherapeutic agent via a polynueleotide-functionalized nanoparticle (PN-NP).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
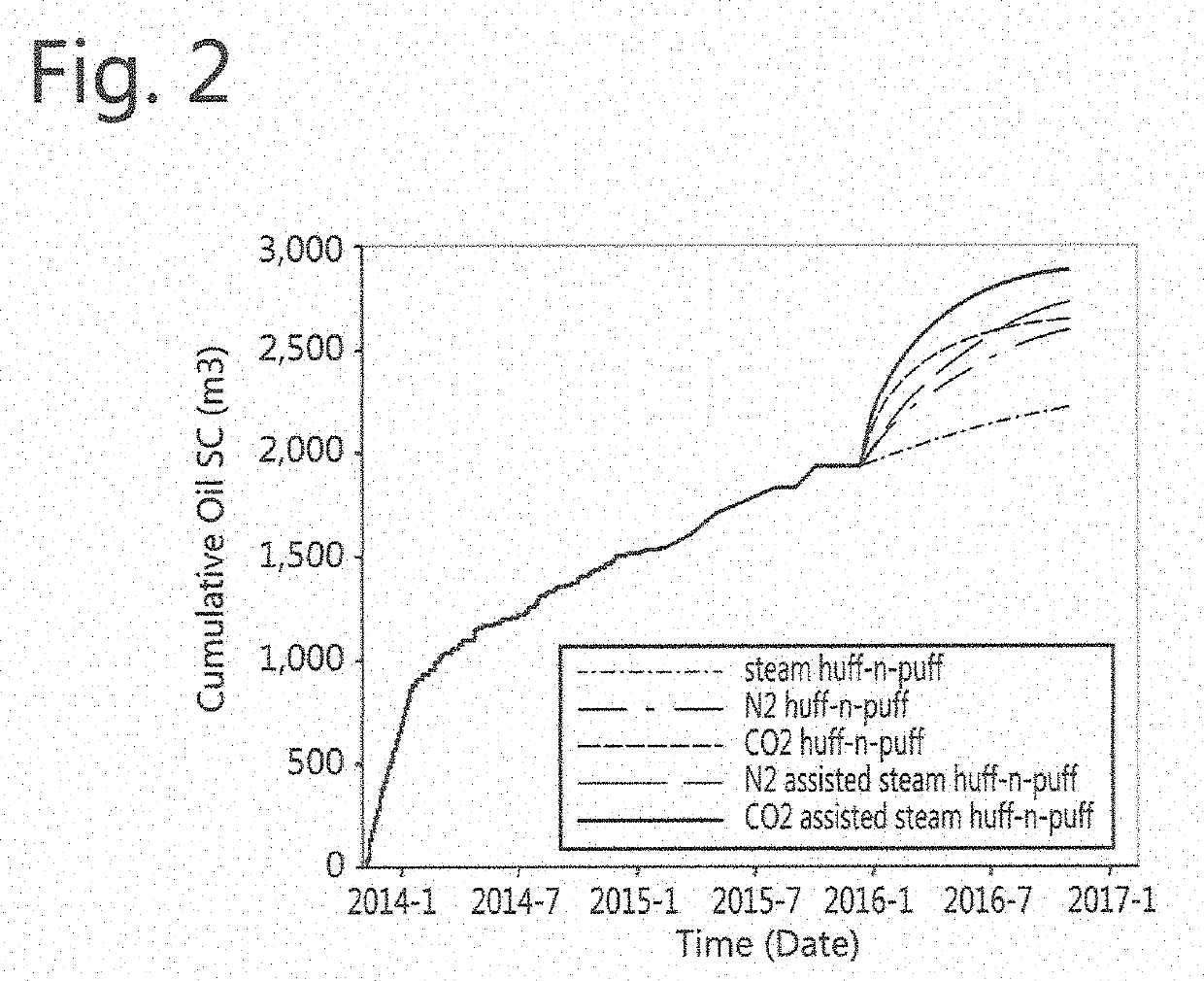
Using gases and hydrocarbon recovery fluids containing nanoparticles to enhance hydrocarbon recovery
A process of stimulating hydrocarbon recovery is described and claimed. This process includes introducing a gas, a liquified gas or a vaporized liquified gas, into an underground formation containing hydrocarbons such as crude oil and gas, permitting said gas to be absorbed by said hydrocarbons, and withdrawing said hydrocarbons containing the gas therein, wherein a pill of Hydrocarbon Recovery Fluid comprising surface functionalized nanoparticles is inserted into the underground formation containing hydrocarbons before, during or after the introduction of the gas, liquified gas or a vaporized liquified gas.
Owner:MESSER IND USA INC +1
Composite comprising polysaccharide-functionalized nanoparticle and hydrogel matrix, a drug delivery system and a bone defect replacement matrix for sustained release comprising the same, and the preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20070248675A1Powder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsFunctionalized nanoparticlesUnit mass
The present invention relates to a nanoparticle-protein-hydrogel composite comprising (1) a polysaccharide-functionalized nanoparticle comprising a core composed of a biodegradable polymer, a hydrogel surface layer composed of a biocompatible polymer emulsifier, and a polysaccharide physically bound to the core and / or the hydrogel layer; (2) a protein forming a specific binding with the polysaccharide; and (3) a hydrogel matrix composed of a biocompatible polymer as a matrix for the nanoparticle. The present also relates to a drug delivery system and a bone defect replacement matrix comprising the composite for sustained release, and the preparation method thereof. Further, the present invention also provides a method for controlling the release rate of a protein drug by changing the content of the polysaccharide in a unit mass of the nanoparticle and / or by changing the content of the nanoparticle in a unit mass of the composite.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Copolymers containing nanoparticles
The invention provides copolymers of ethylenically unsaturated monomers and of ethylenically functionalized nanoparticles in the form of their aqueous polymer dispersions or water-redispersible polymer powders, obtainable by means of free-radically initiated polymerization in an aqueous medium and, if desired, subsequent drying of the resultant polymer dispersion, ofA) one or more monomers from the group consisting of vinyl esters, (meth)acrylic esters, vinylaromatics, olef ins, 1,3-dienes, vinyl ethers and vinyl halides and, if desired, further monomers copolymerizable therewith, in the presence ofB) at least one particle P having an average diameter of ≦1000 nm, which is functionalized with ethylenically unsaturated, free-radically polymerizable groups, characterized in thatB2) particles P used are one or more from the group of metal oxides and semimetal oxides, and / orB2) particles P used are silicone resins composed of repeating units of the general formula [R4(p+Z)SiO(4−p−Z) / 2] (II), where for at least 20 mol % of the respective silicone resin p+z=0, 1 or 3,and where B1) and B2) are each functionalized with one or more α-organosilanes of the general formula (R1O)3−(R2)nSi—(CR32)—X (I), where X is a radical having 2 to 20 hydrocarbon atoms and containing an ethylenically unsaturated group.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Water-soluble, surface-functionalized nanoparticle for bioconjugation via universal silane coupling
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Nanosensors based on functionalized nanoparticles and Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering
ActiveUS20060050268A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFunctionalized nanoparticlesSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) is a vibrational spectroscopic technique that utilizes metal surfaces to provide enhanced signals of several orders of magnitude. When molecules of interest are attached to designed metal nanoparticles, a SERS signal is attainable with single molecule detection limits. This provides an ultrasensitive means of detecting the presence of molecules. By using selective chemistries, metal nanoparticles can be functionalized to provide a unique signal upon analyte binding. Moreover, by using measurement techniques, such as, ratiometric received SERS spectra, such metal nanoparticles can be used to monitor dynamic processes in addition to static binding events. Accordingly, such nanoparticles can be used as nanosensors for a wide range of chemicals in fluid, gaseous and solid form, environmental sensors for pH, ion concentration, temperature, etc., and biological sensors for proteins, DNA, RNA, etc.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Methods of forming nano-coatings for improved adhesion between first level interconnects and epoxy under-fills in microelectronic packages and structures formed thereby
InactiveUS20090065932A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEpoxyFunctionalized nanoparticles
Methods and associated structures of forming microelectronic devices are described. Those methods may include coating an interconnect structure disposed on a die with a layer of functionalized nanoparticles, wherein the functionalized nanoparticles are dispersed in a solvent, heating the layer of functionalized nanoparticles to drive off a portion of the solvent, and applying an underfill on the coated interconnect structure.
Owner:INTEL CORP
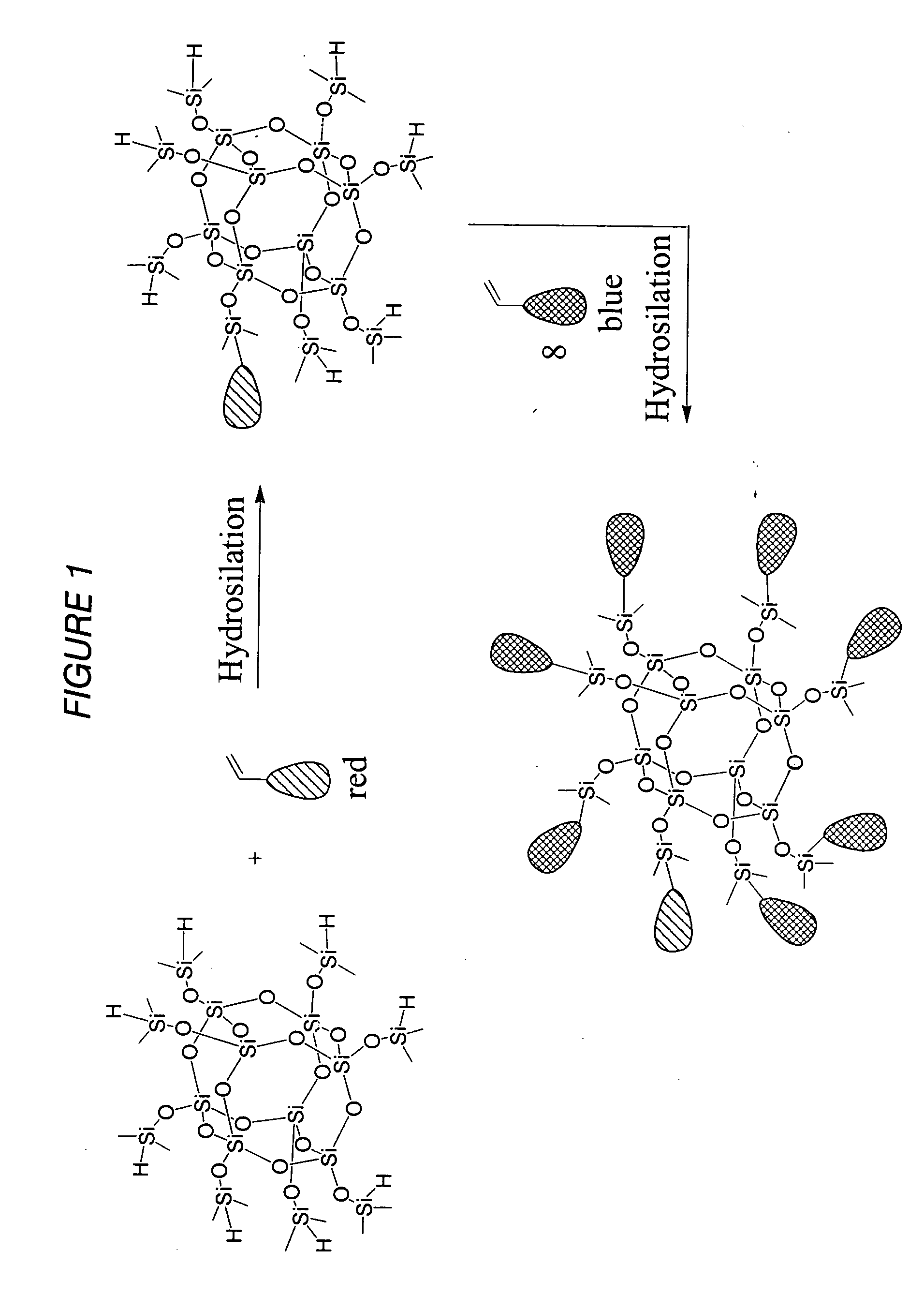
Well-defined nanosized building blocks for organic/inorganic nanocomposites
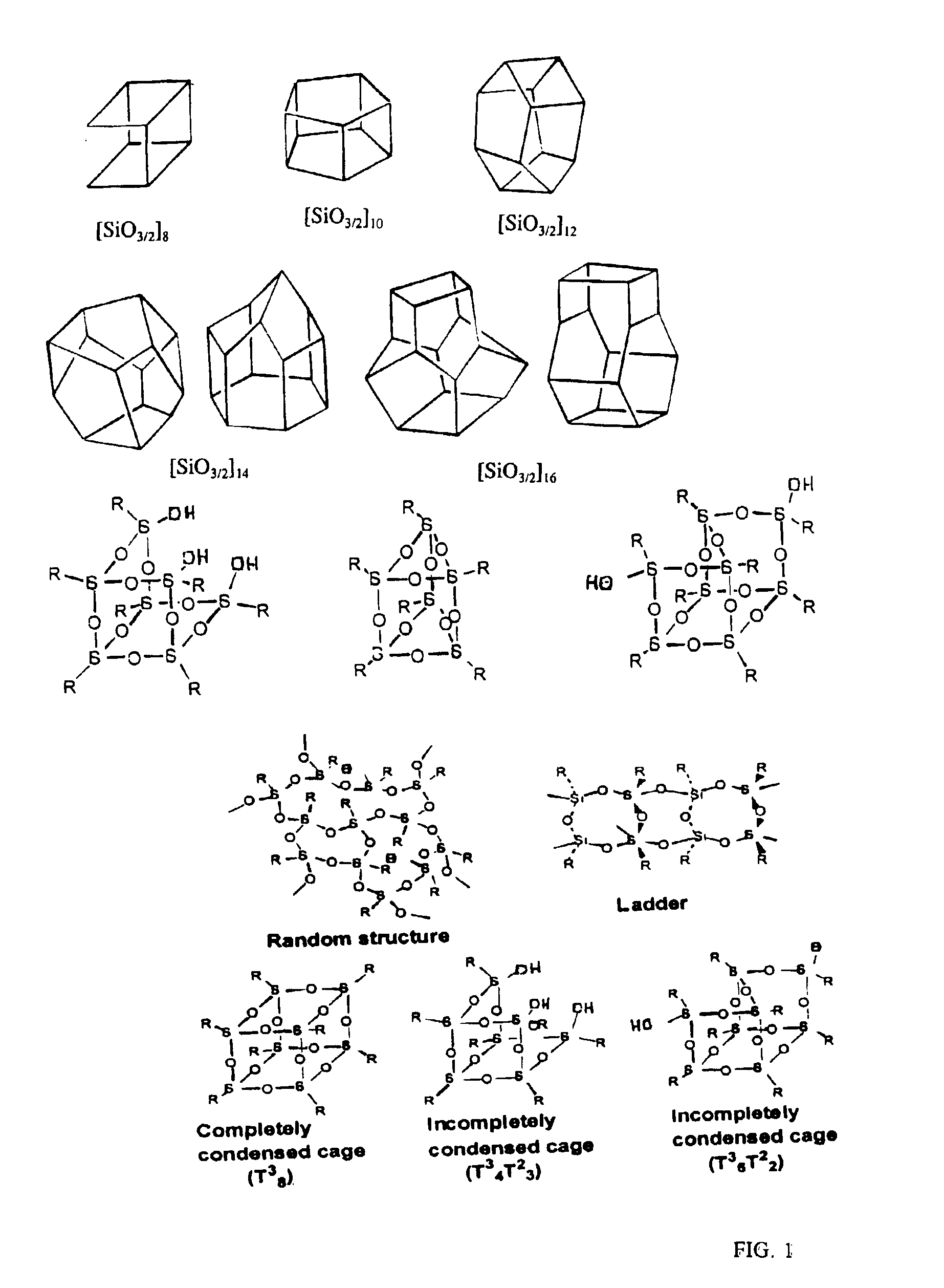
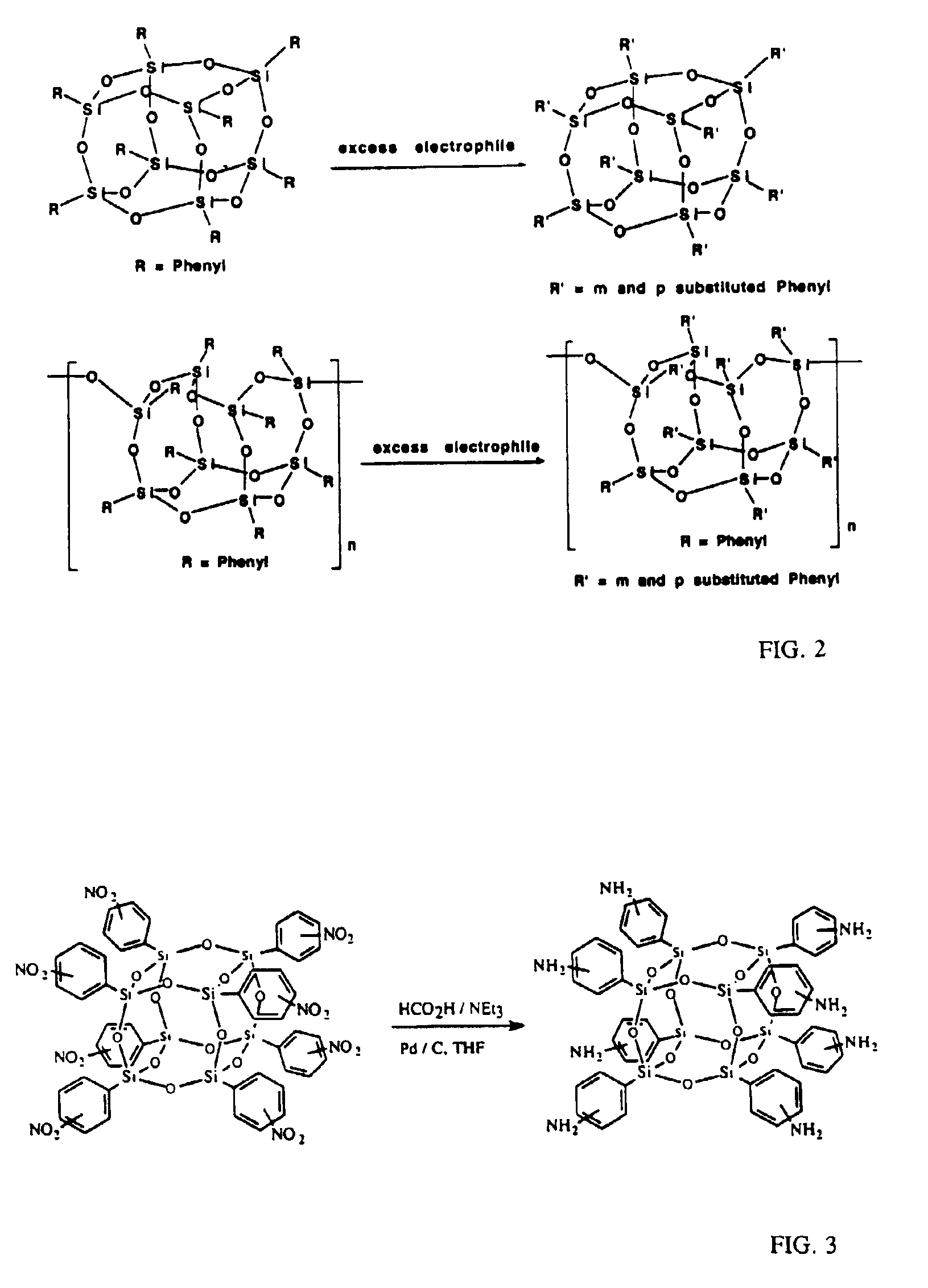
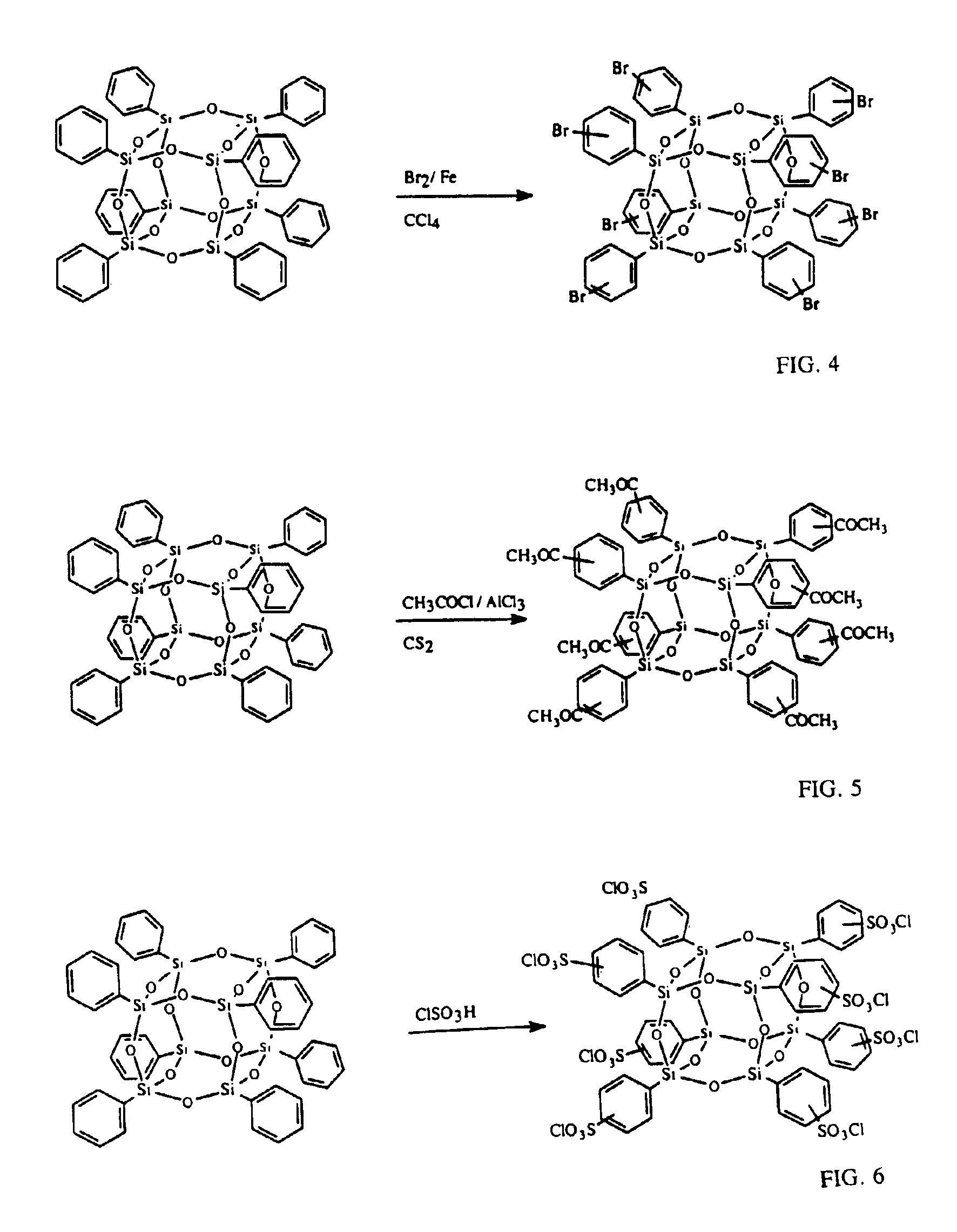
Functionalized silsesquioxanes containing from 6 to 24 silicon atoms and minimally about 67 mol percent RSiO3 / 2 moieties where R is a phenyl group bearing a chemically reactive functional group are highly suitable for use as nanoparticles in producing highly ordered nanocomposites of many types, containing a high proportion of interphase. The nanocomposites have unusual physicochemical properties due to the use of uniform, highly functionalized nanoparticles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com