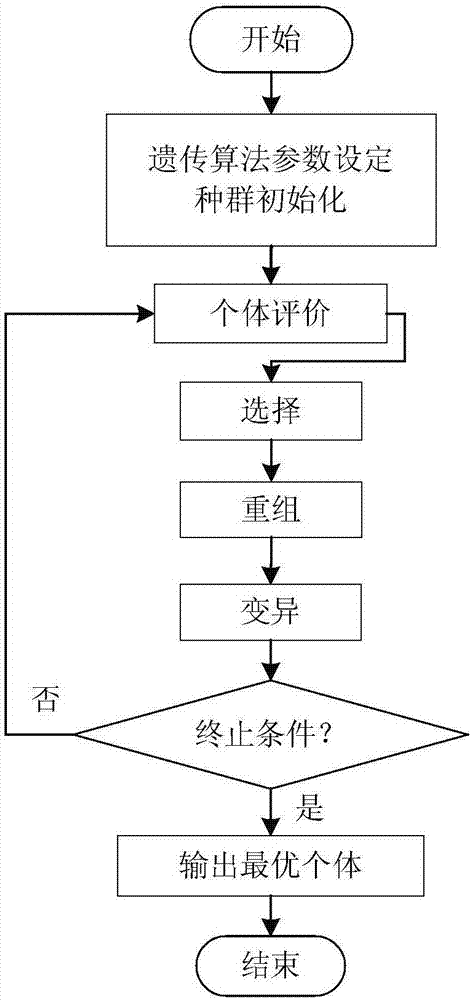
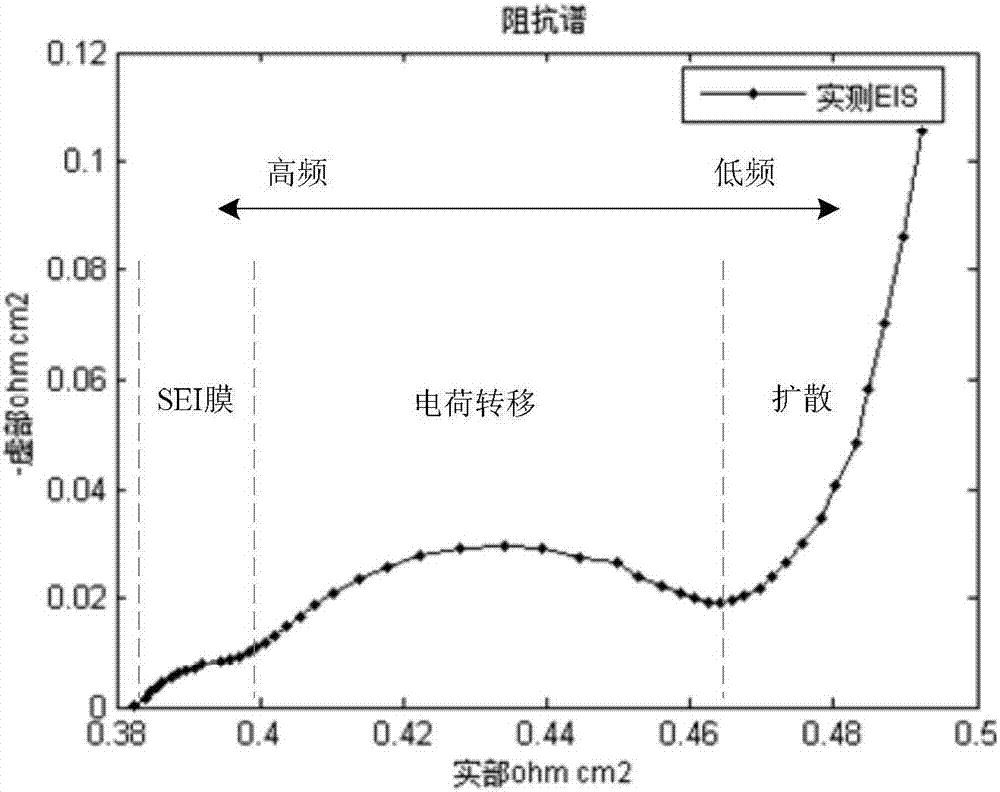
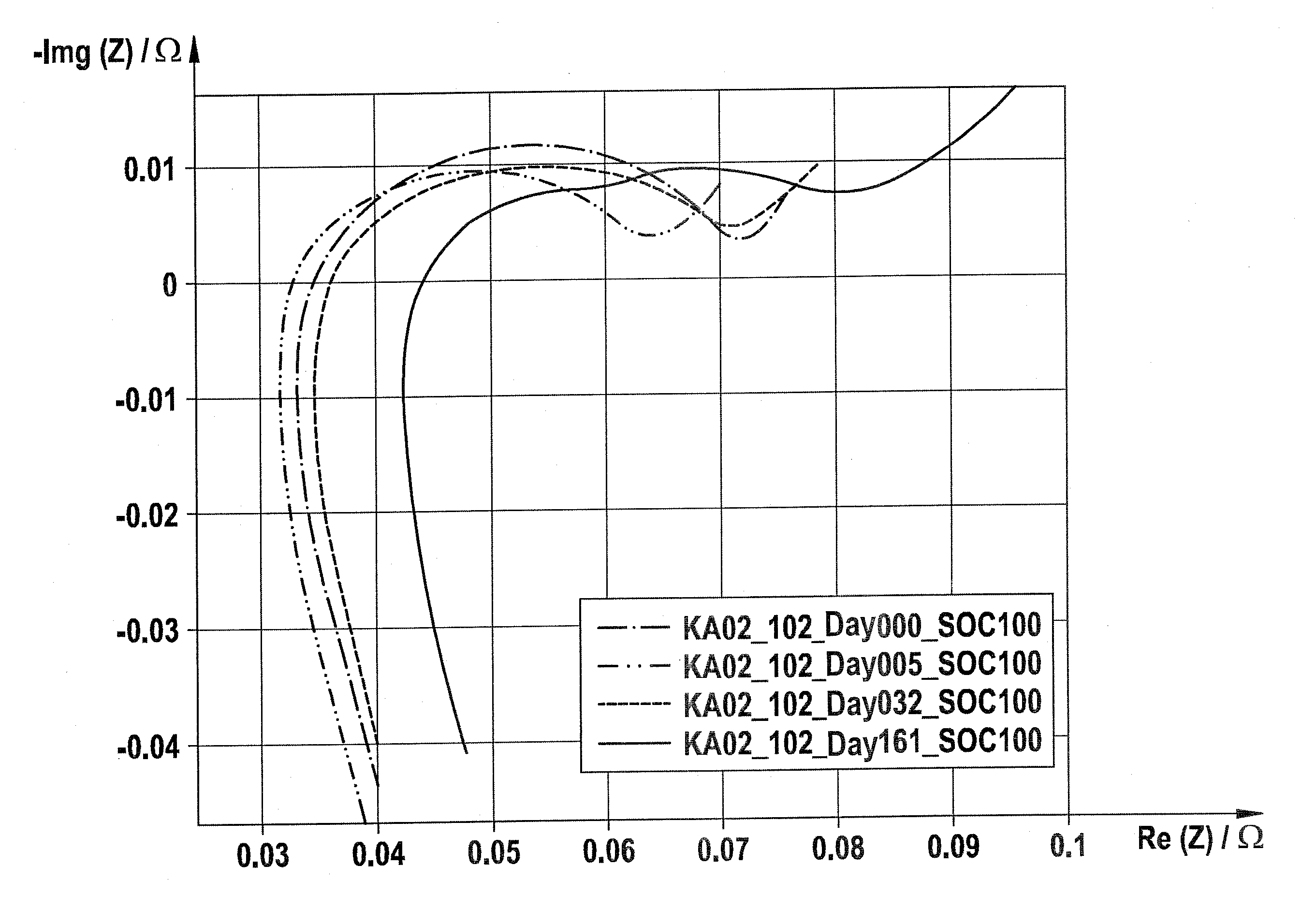
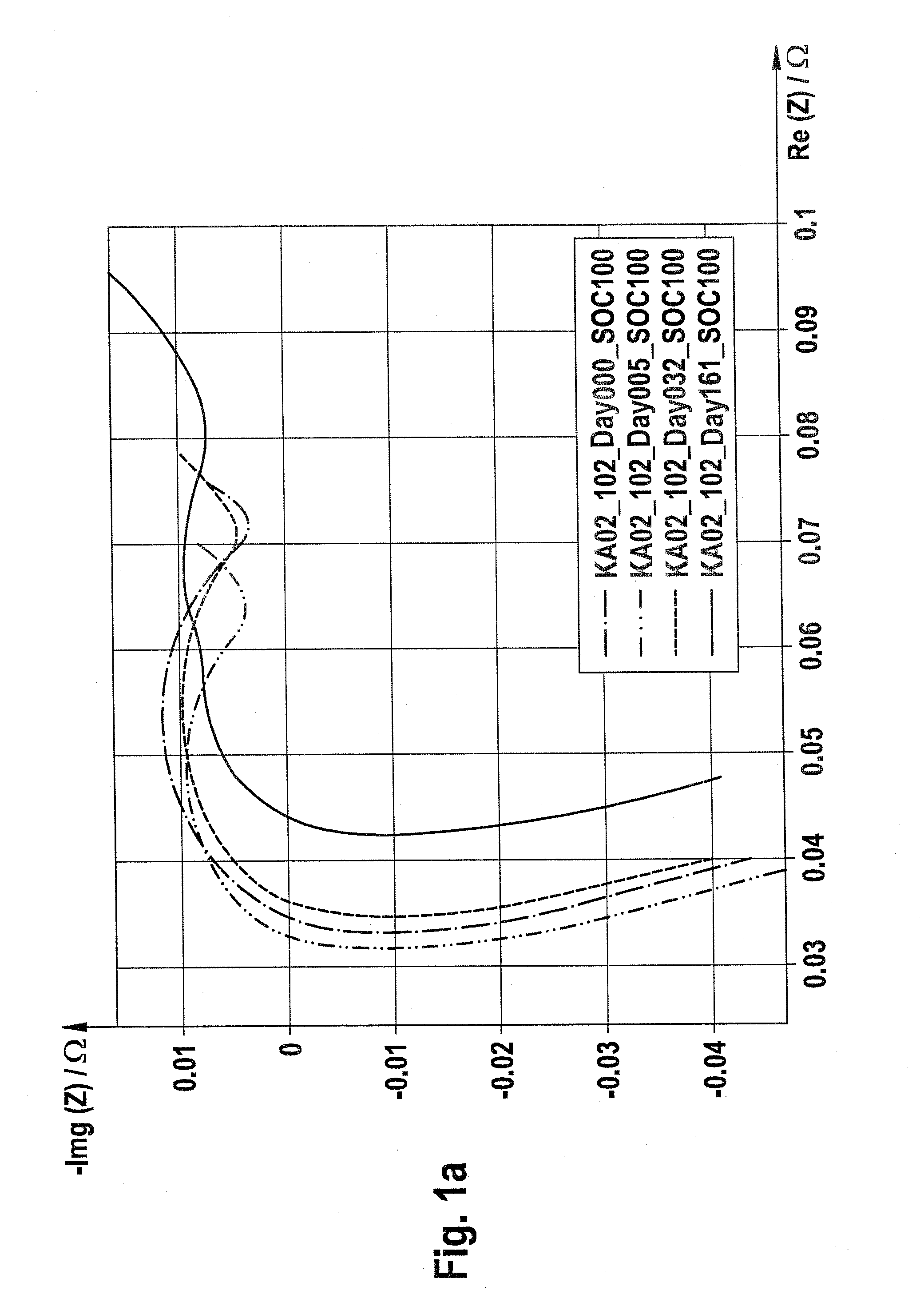
Patents
Literature
430 results about "Impedance spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
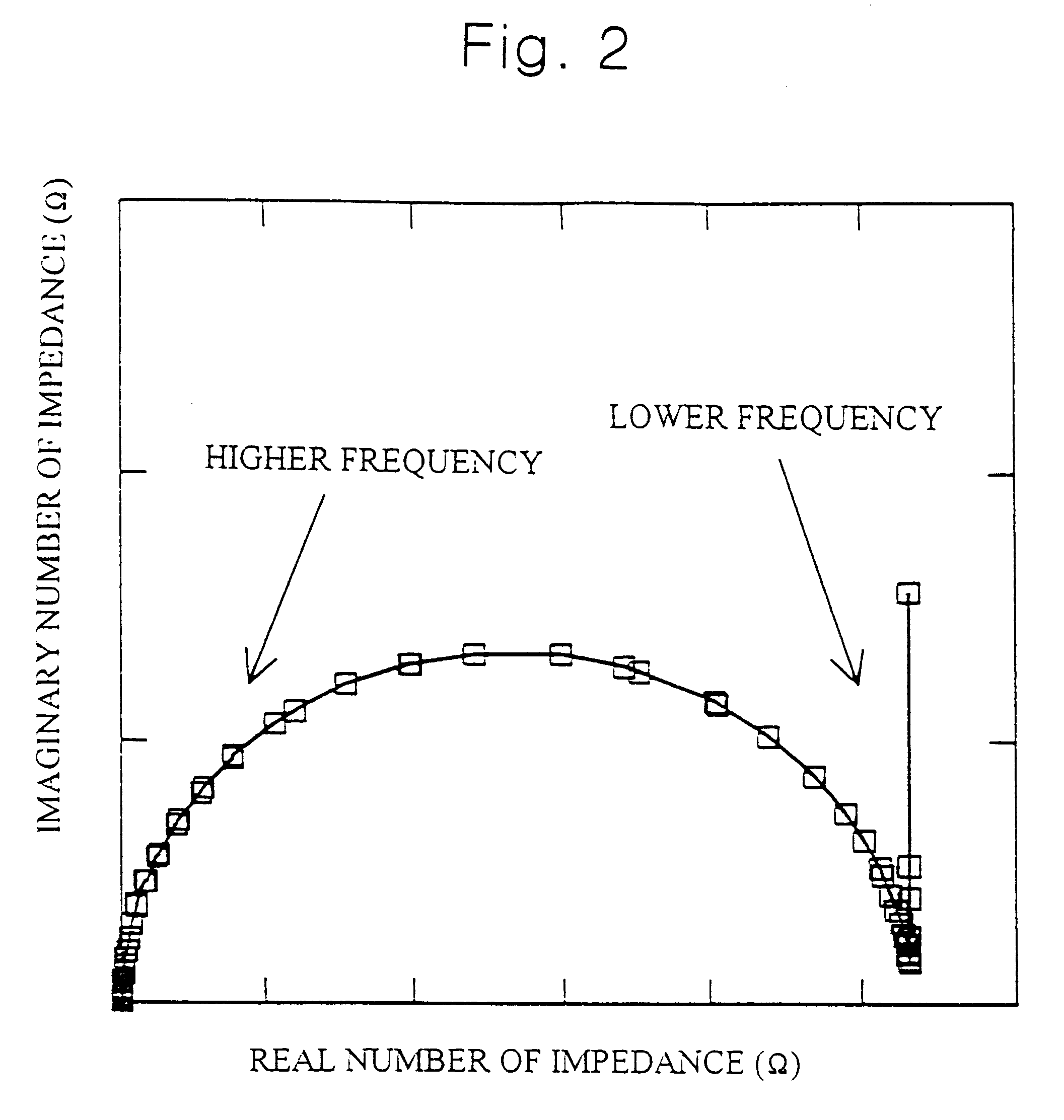
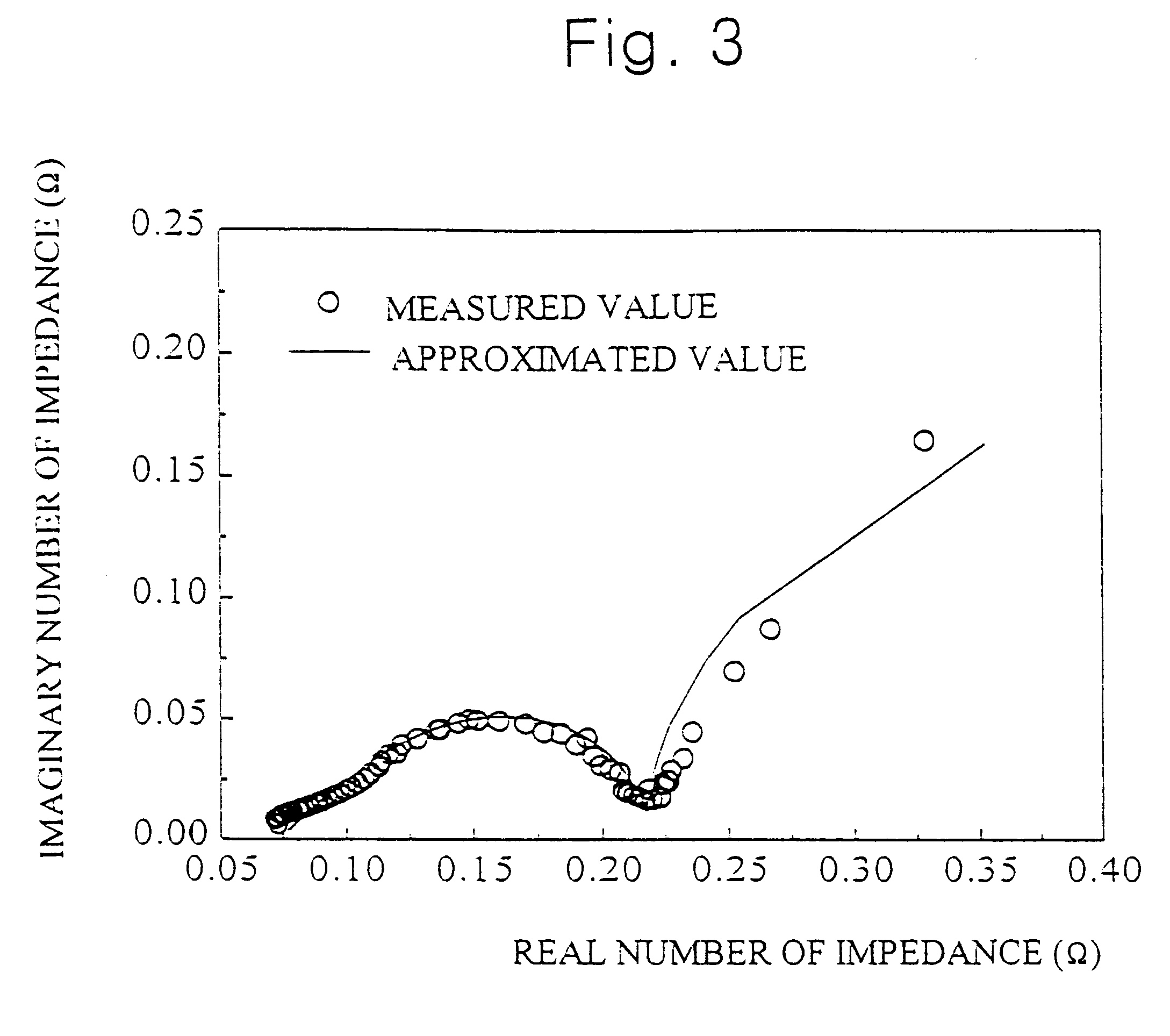
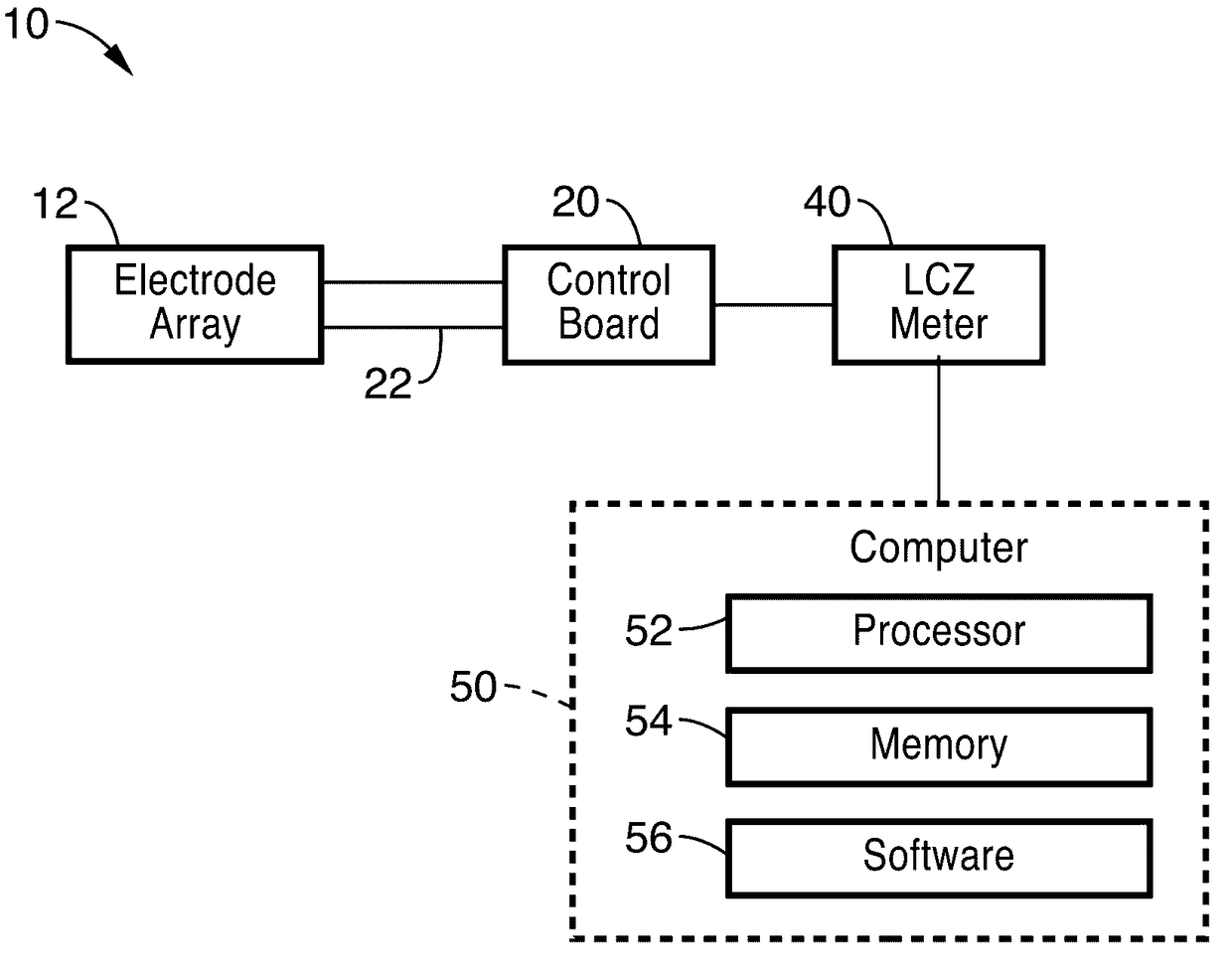
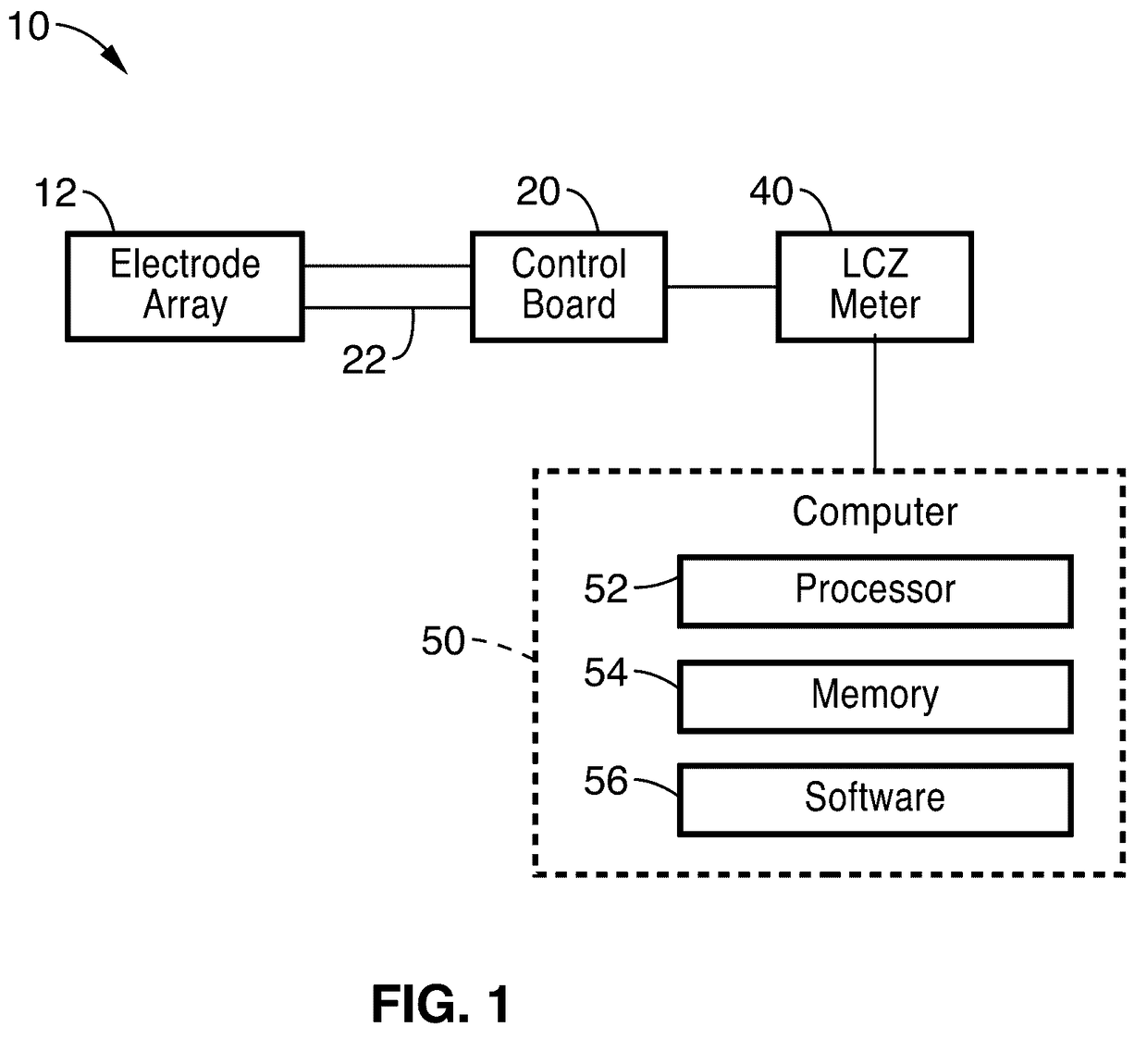
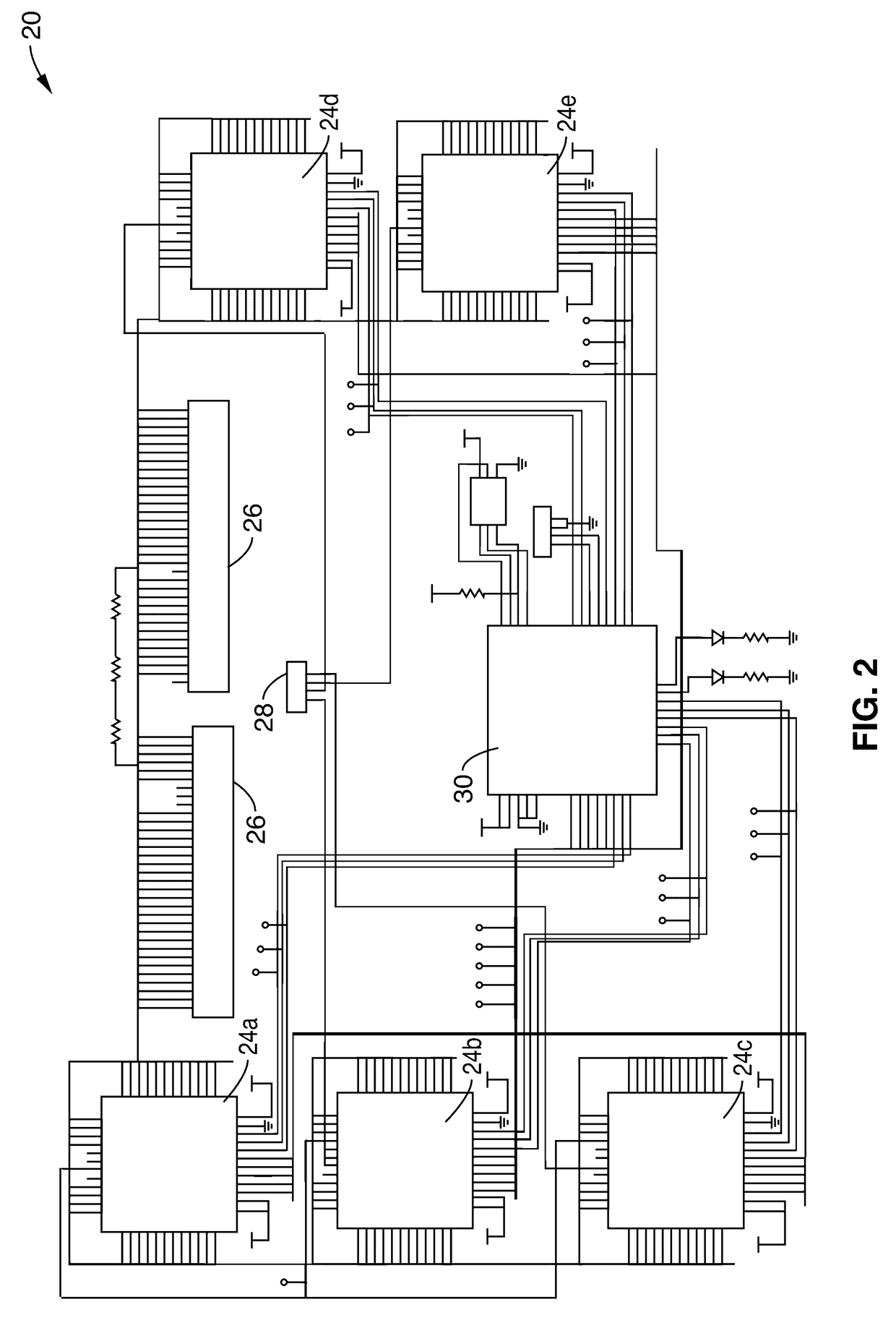
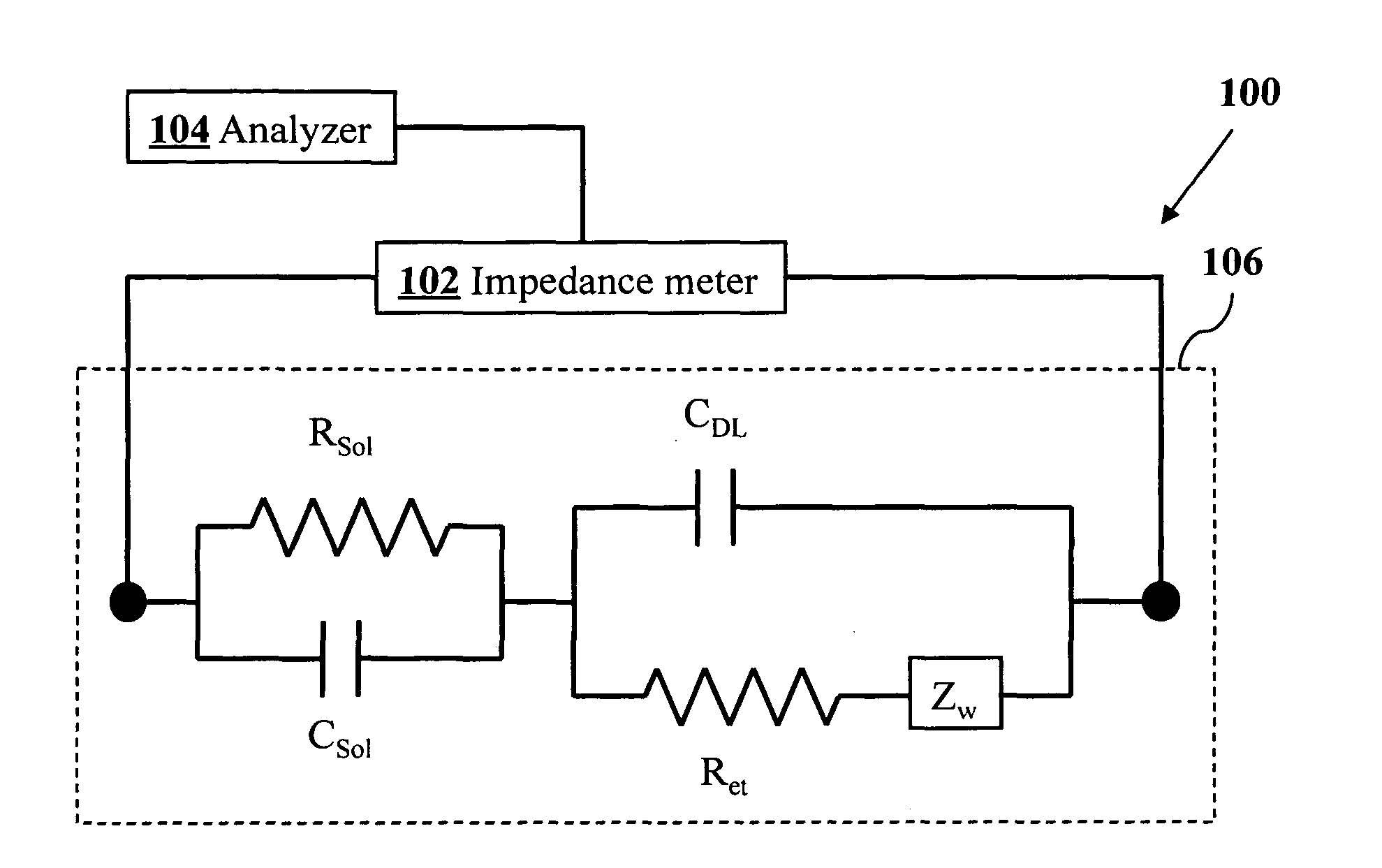
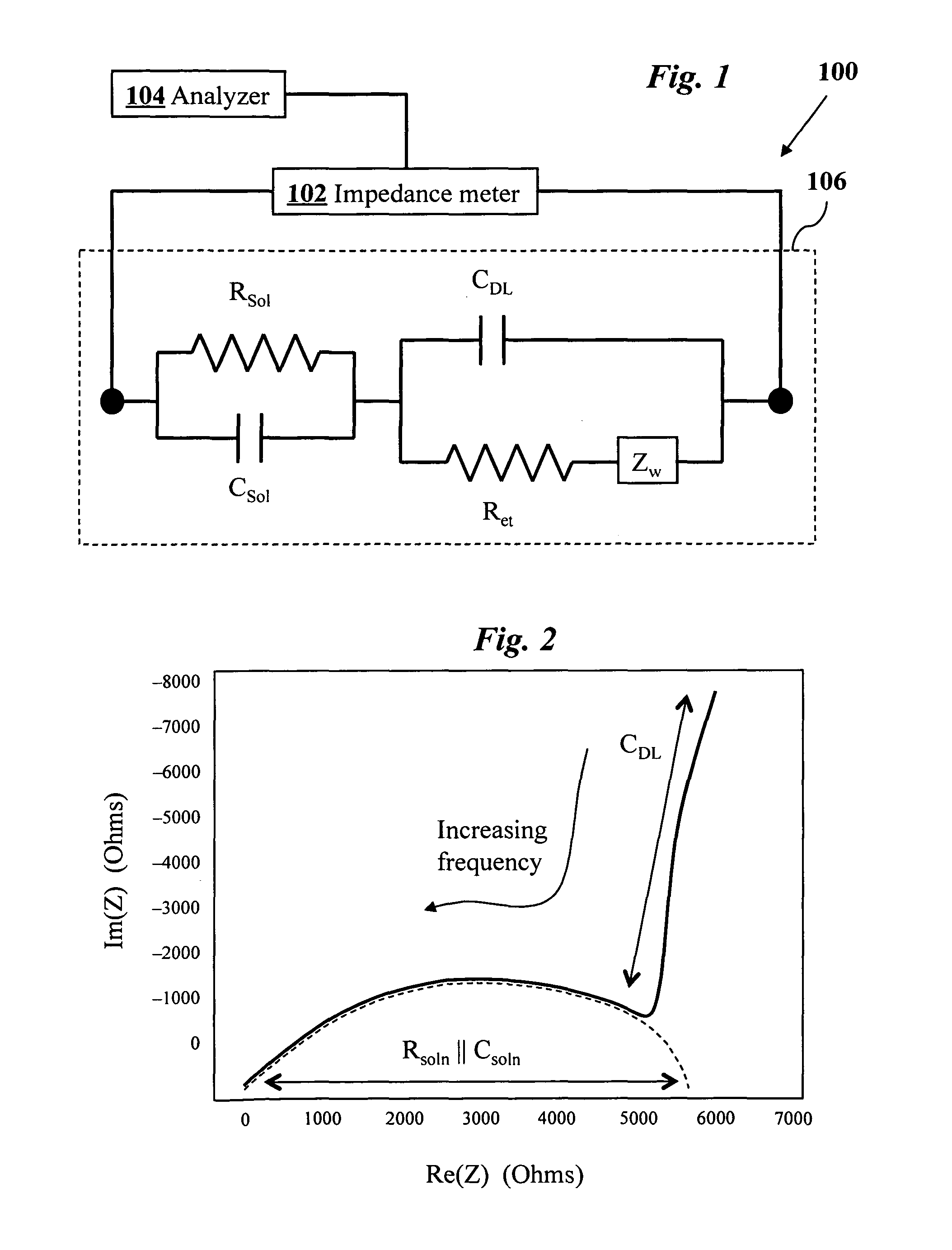
Impedance spectrometer. Device consisting of a high current potentiostat or galvanostat for carrying out accelerated corrosion tests by using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy.
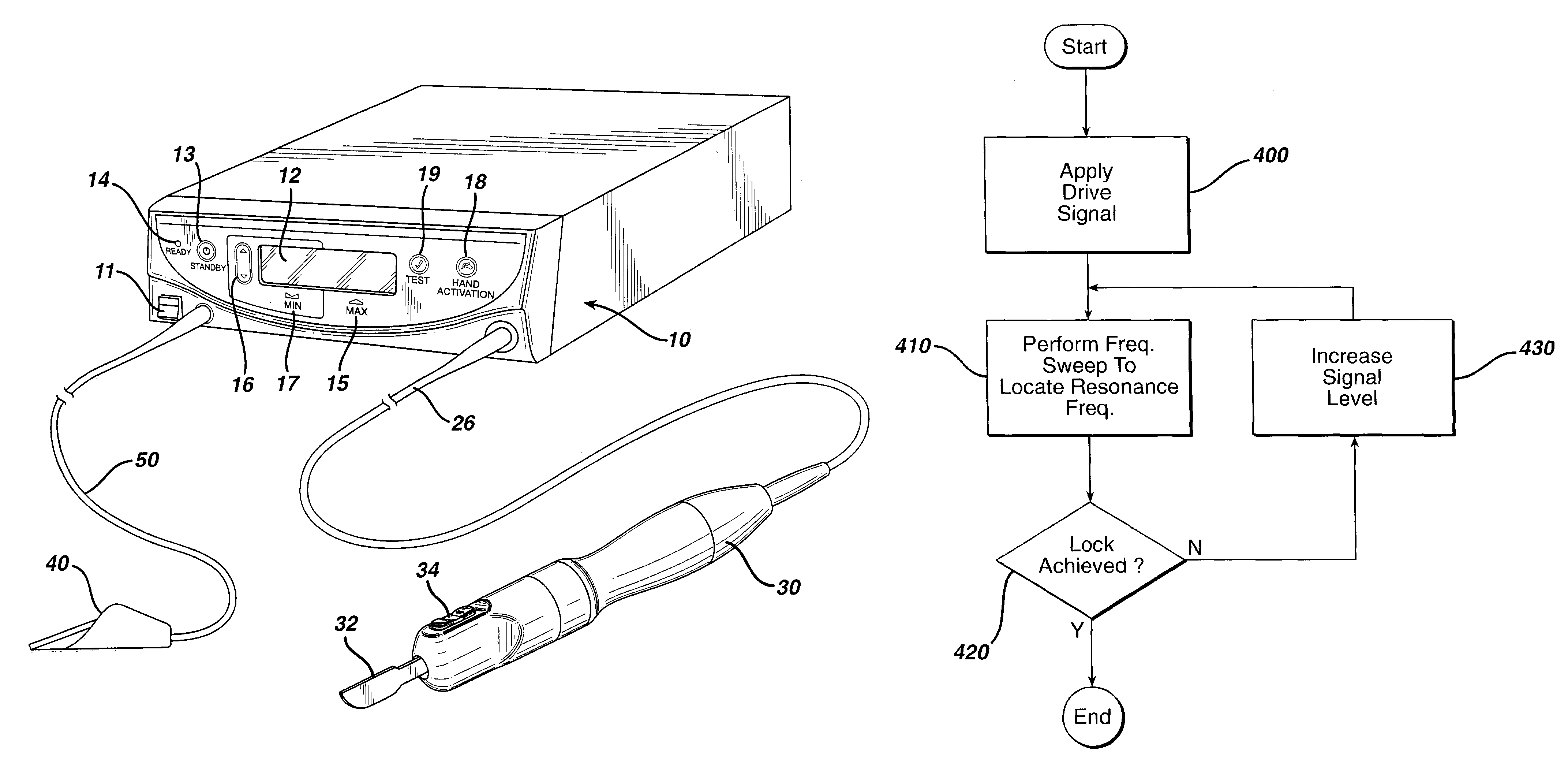
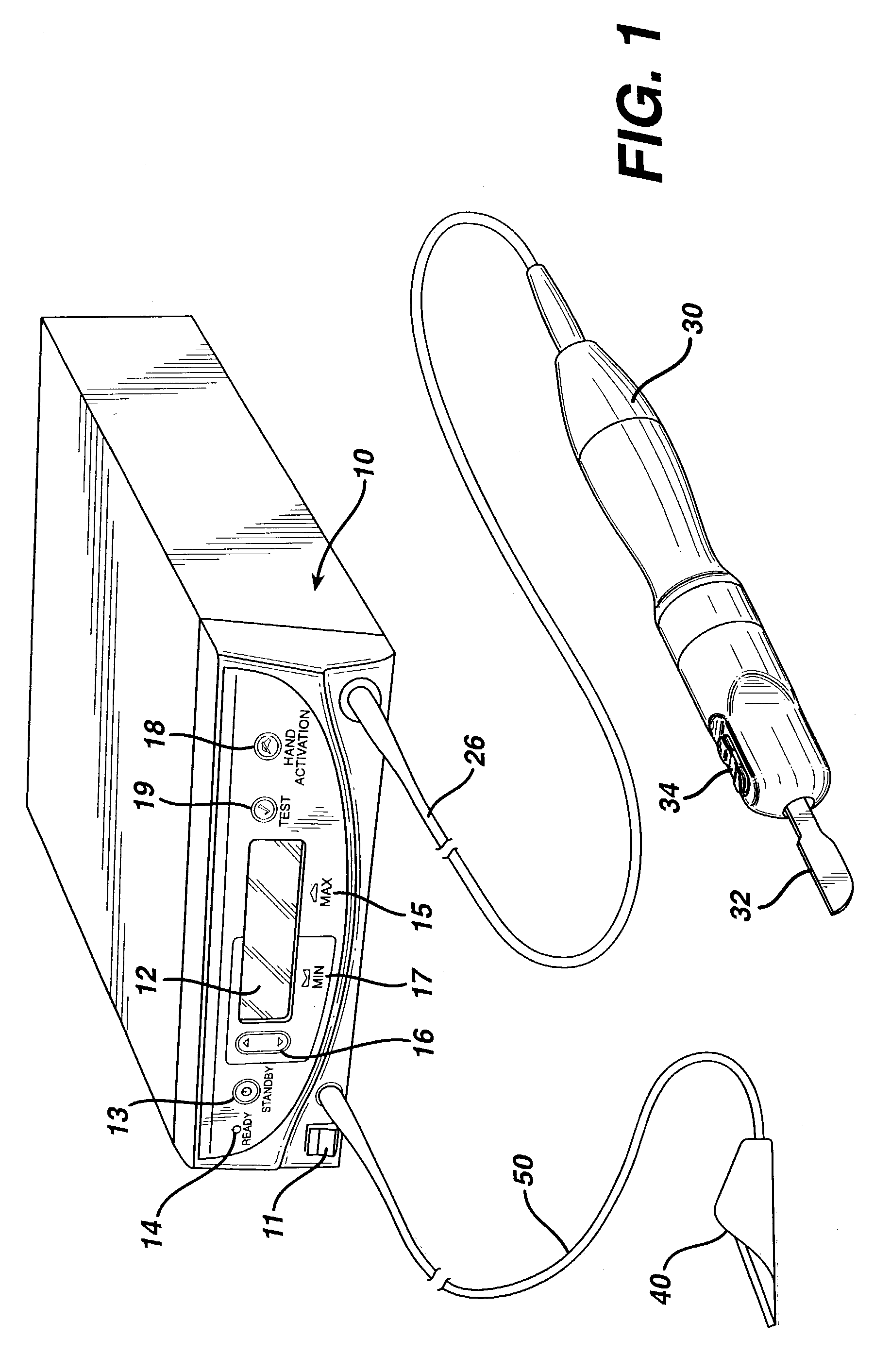
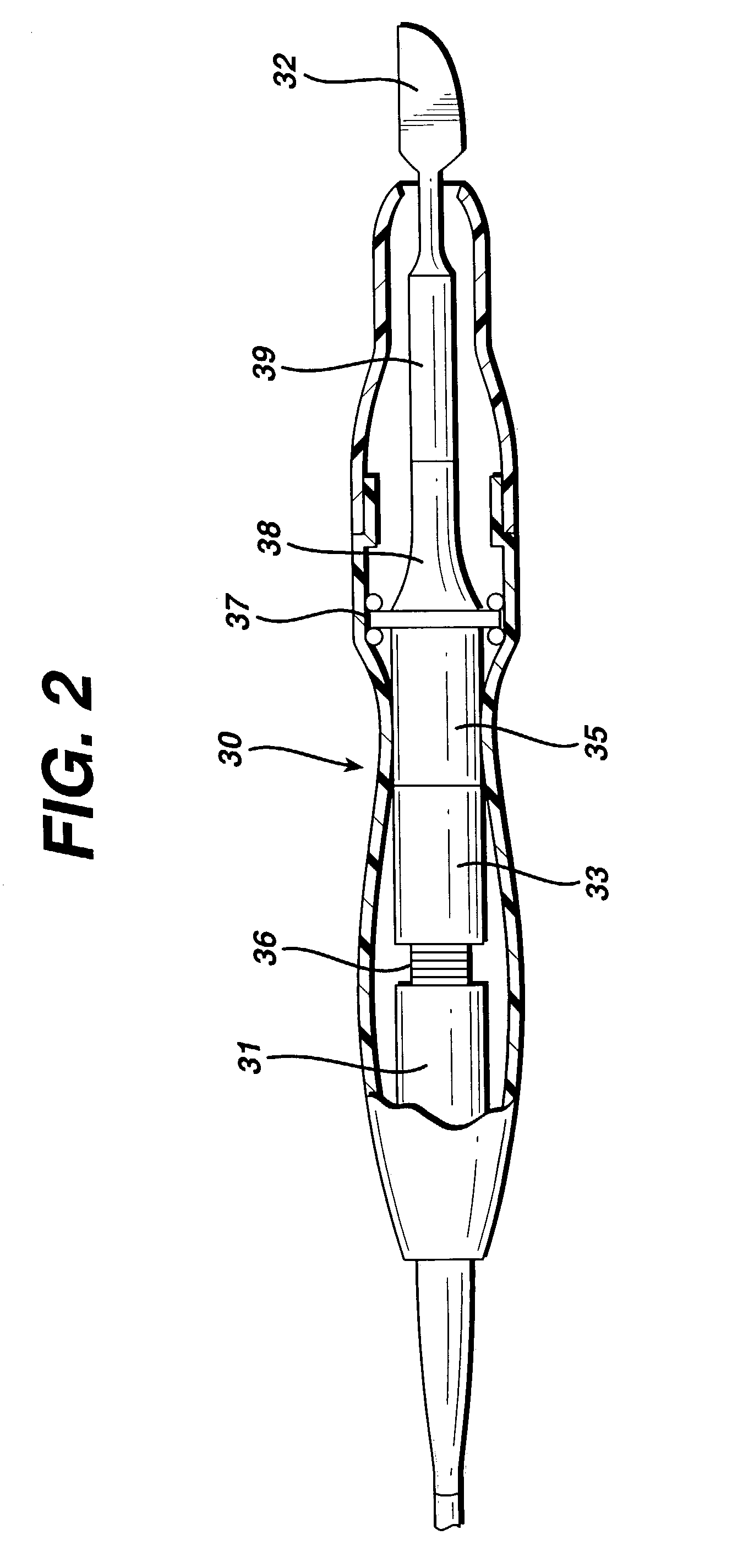
Method for driving an ultrasonic system to improve acquisition of blade resonance frequency at startup
InactiveUS7179271B2Increase load capacityImprove abilitiesSurgeryElectrical measurementsDriving currentResonance
The ability of an ultrasonic system to sweep and lock onto a resonance frequency of a blade subjected to a heavy load at startup is improved by applying a high drive voltage or a high drive current while systematically increasing the level of the applied signal. Increasing the drive signal to the hand piece results in an improved and more pronounced “impedance spectrum.” That is, under load, the increased drive signal causes the maximum phase margin to become higher and the minimum / maximum impedance magnitude to become more pronounced. Increasing the excitation drive signal to the hand piece / blade at startup significantly alleviates the limiting factors associated with ultrasonic generators, which results in an increase of the maximum load capability at startup.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
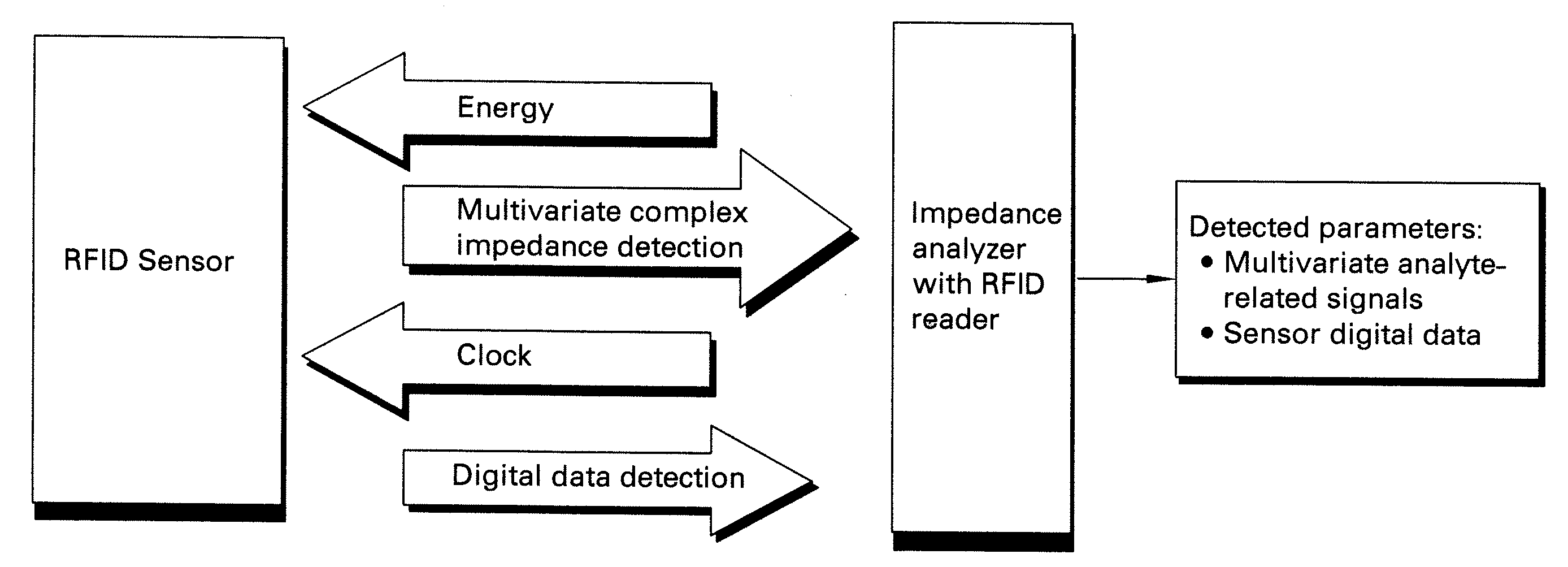
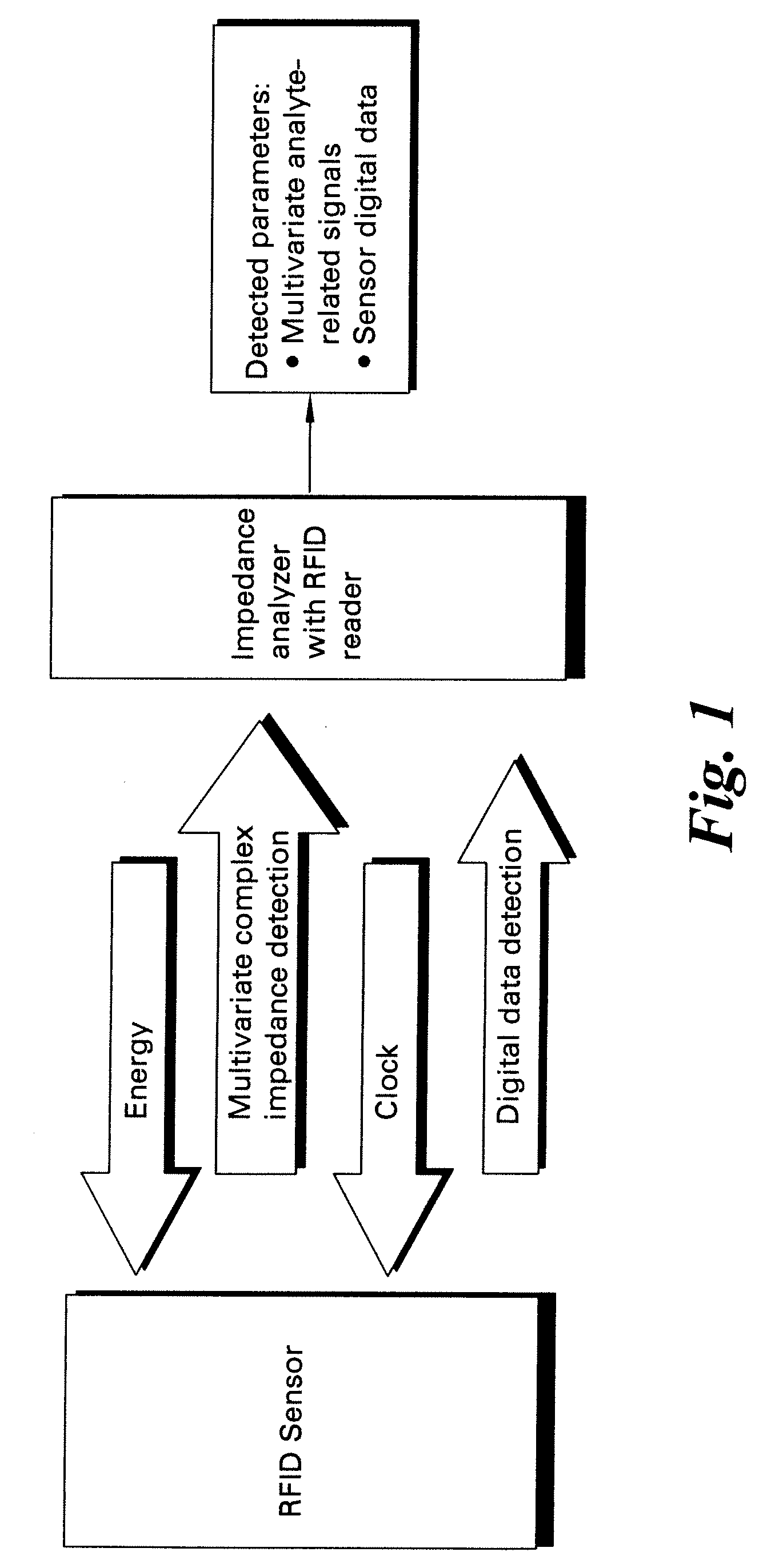
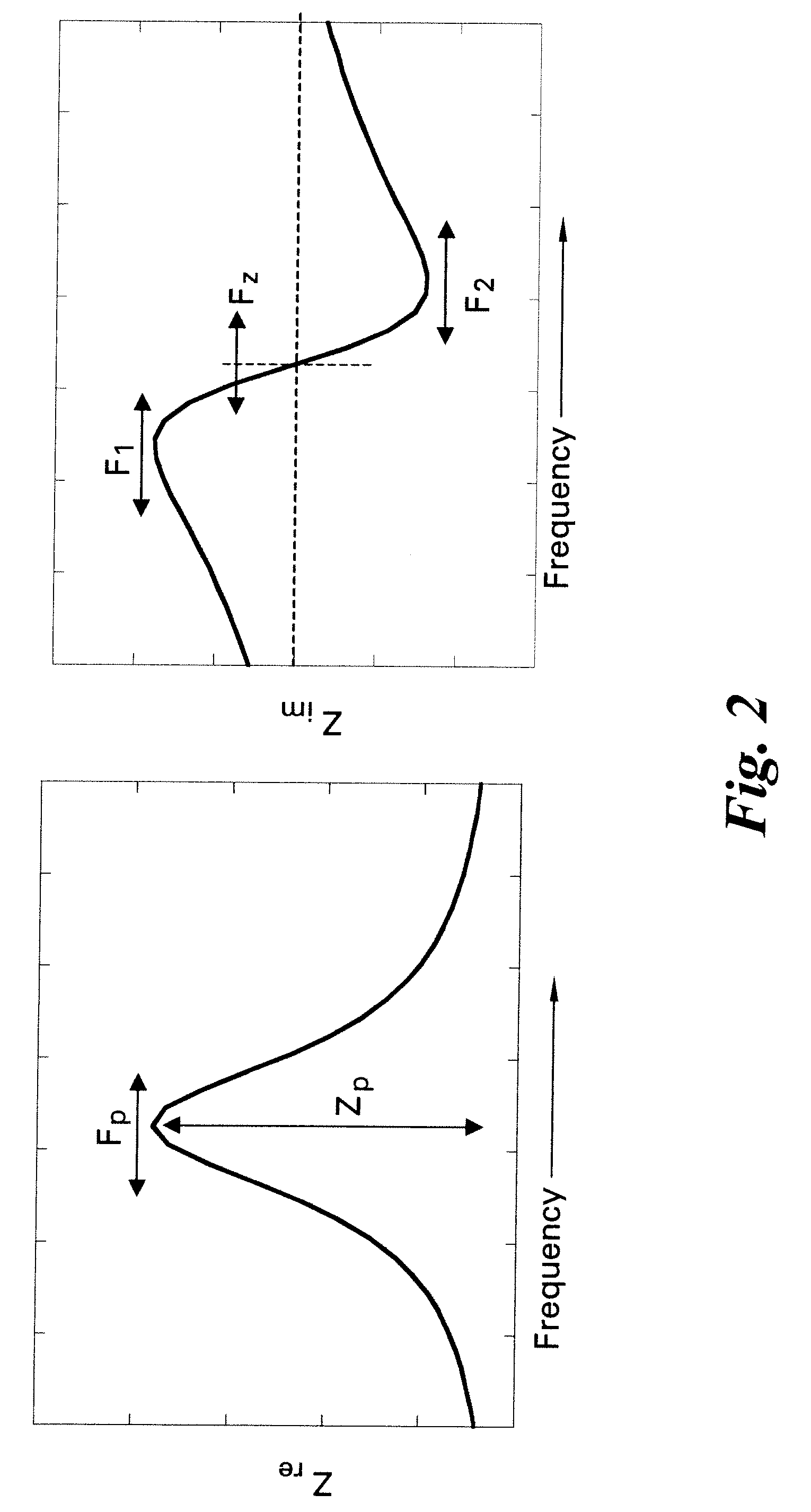
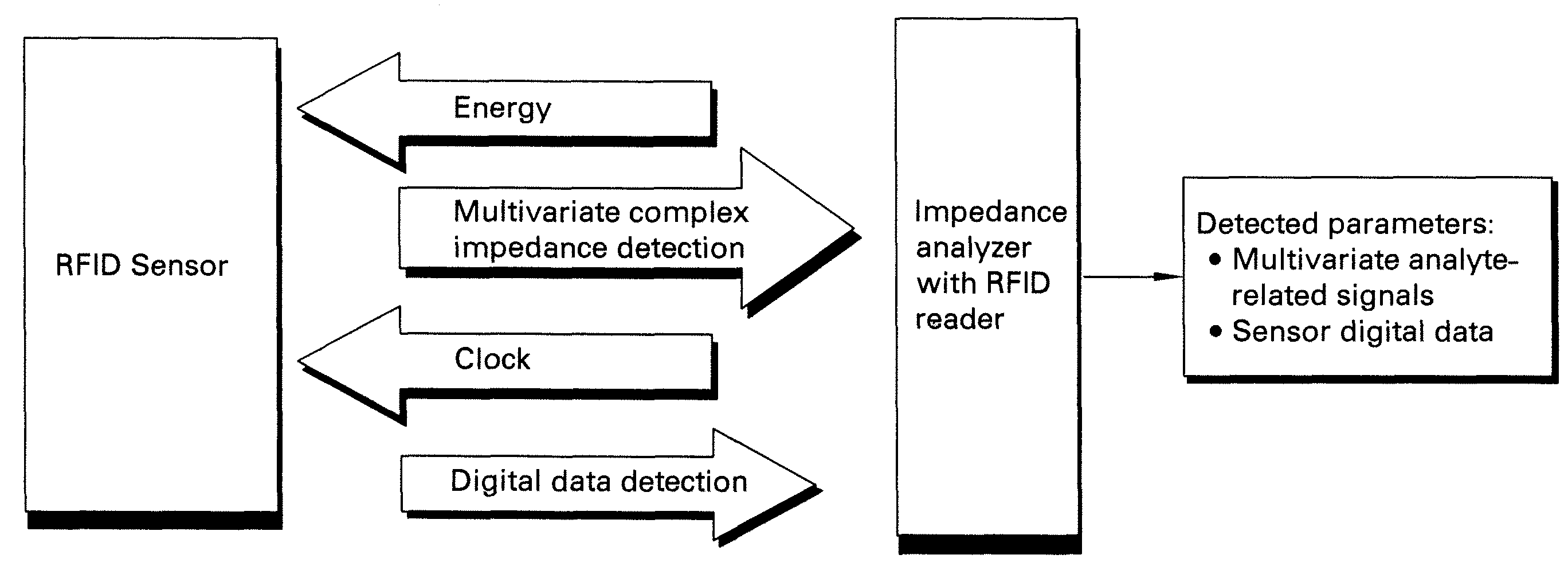
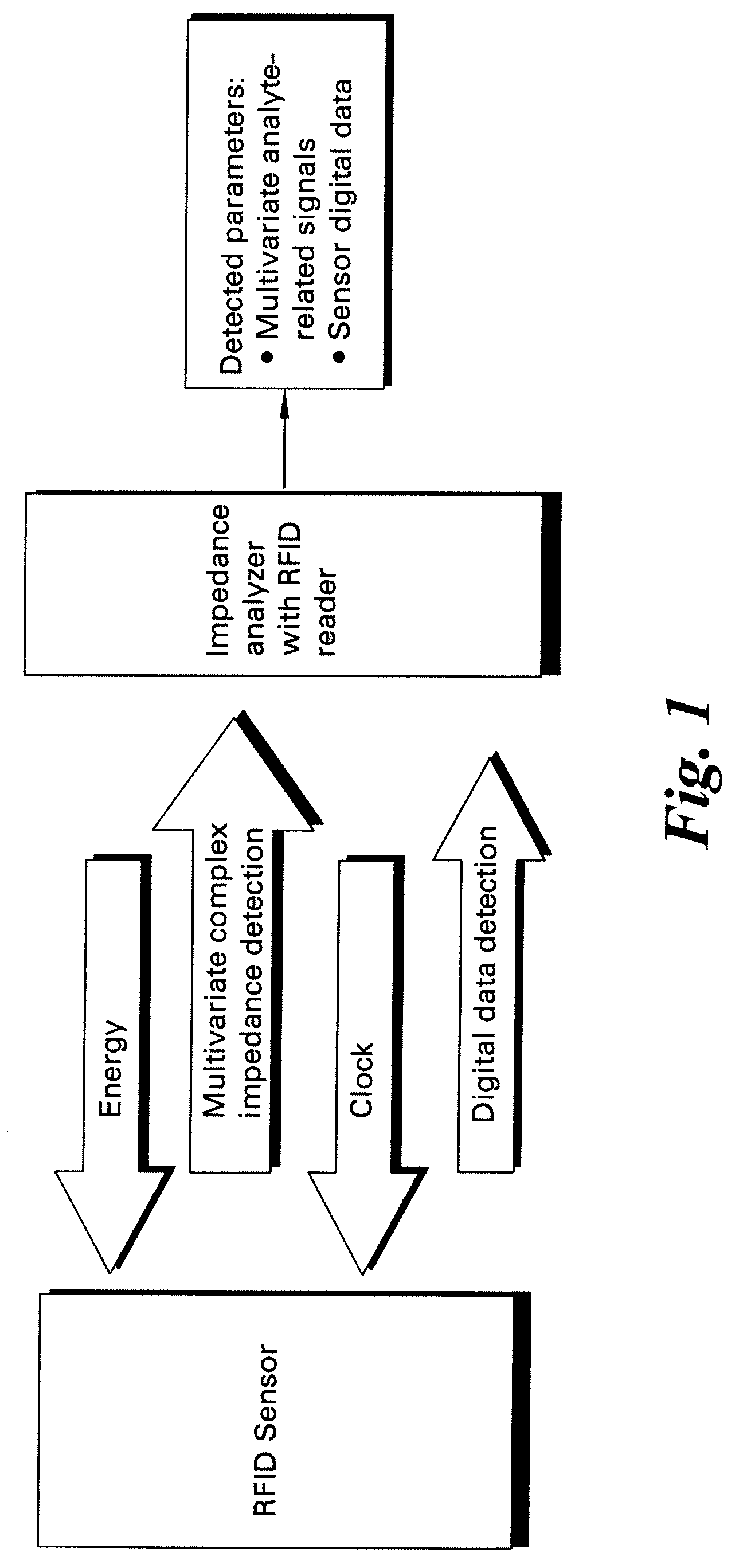
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors
ActiveUS20090278685A1Testing sensing arrangementsGas analyser calibrationMemory chipComplex impedance spectra
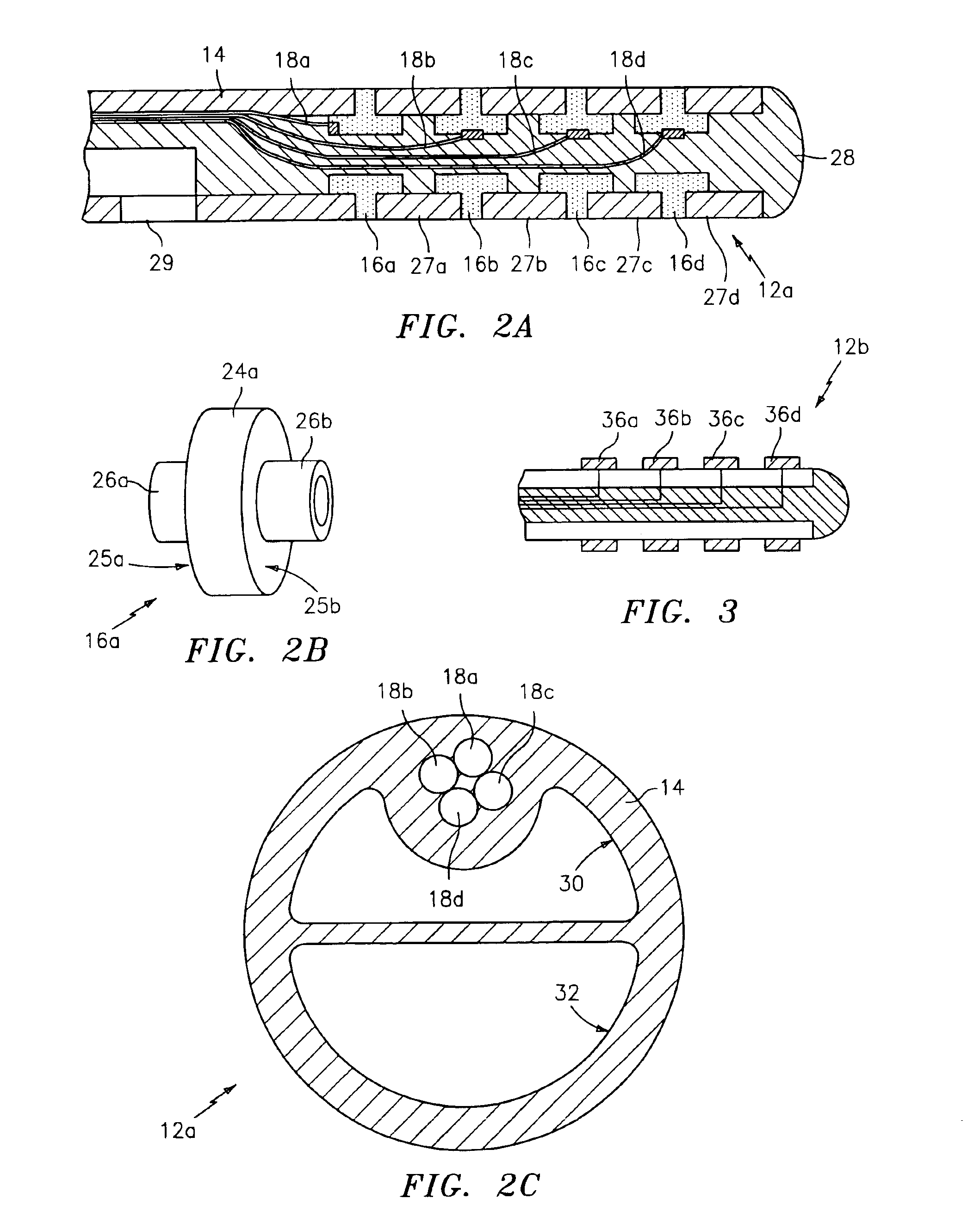
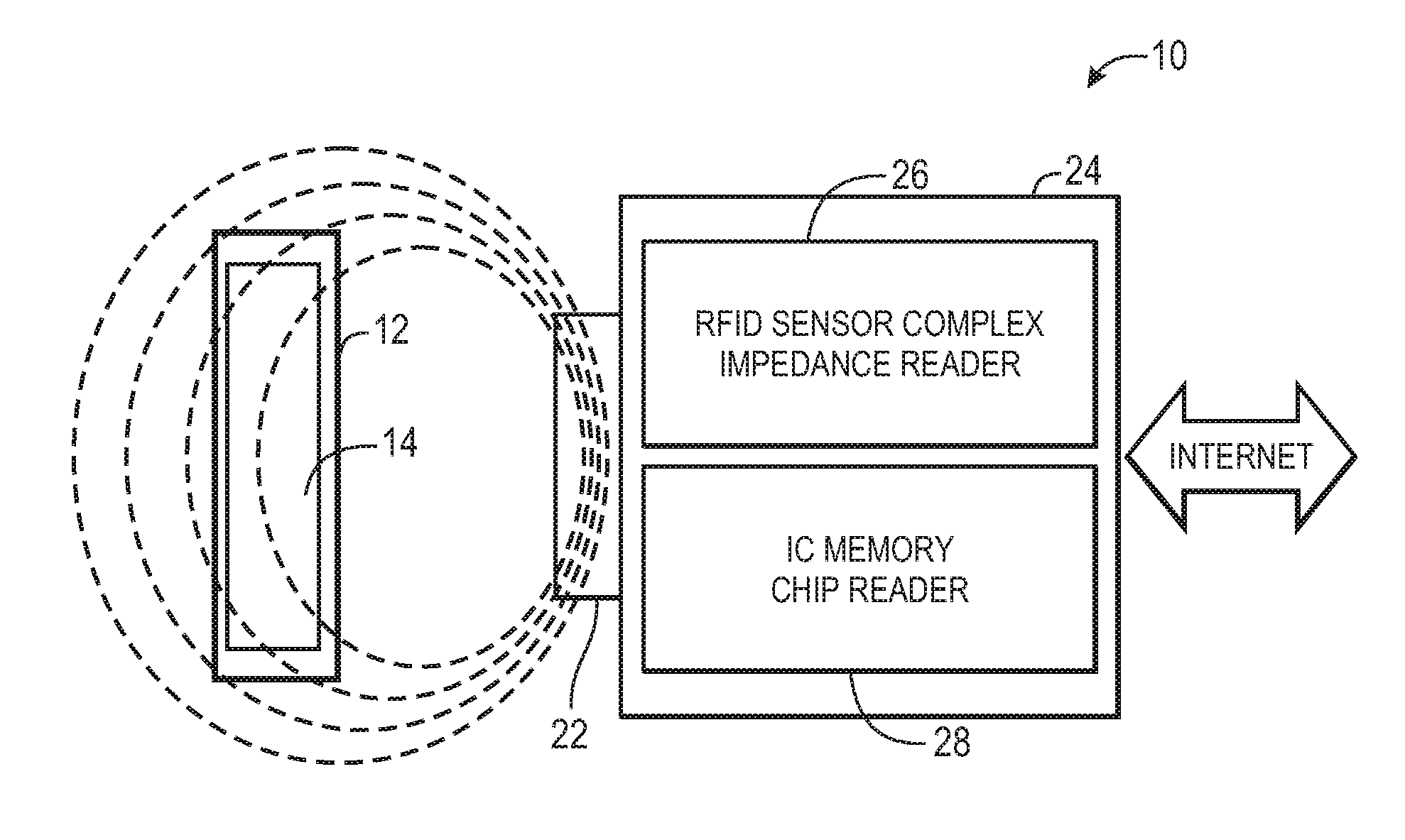
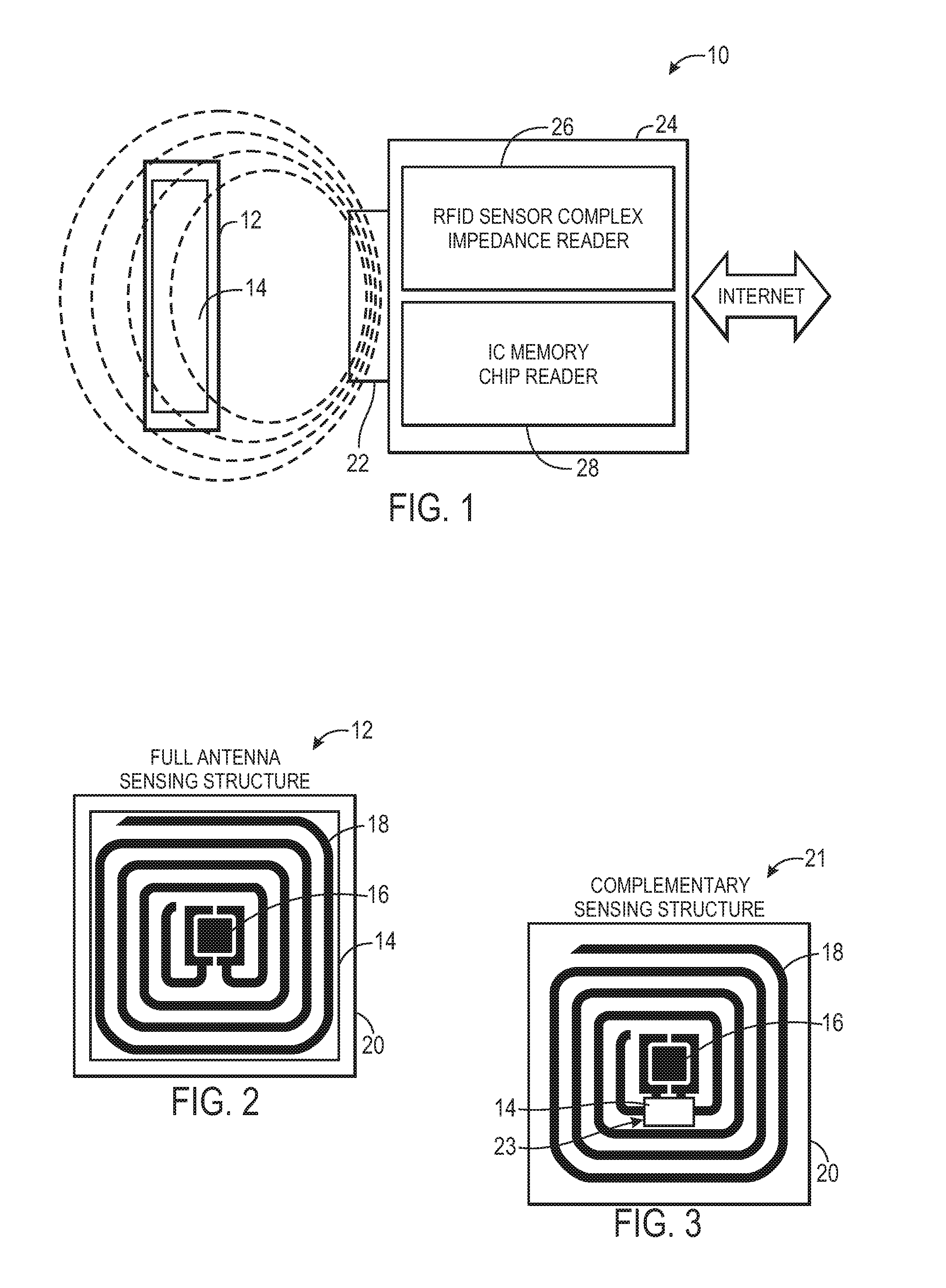
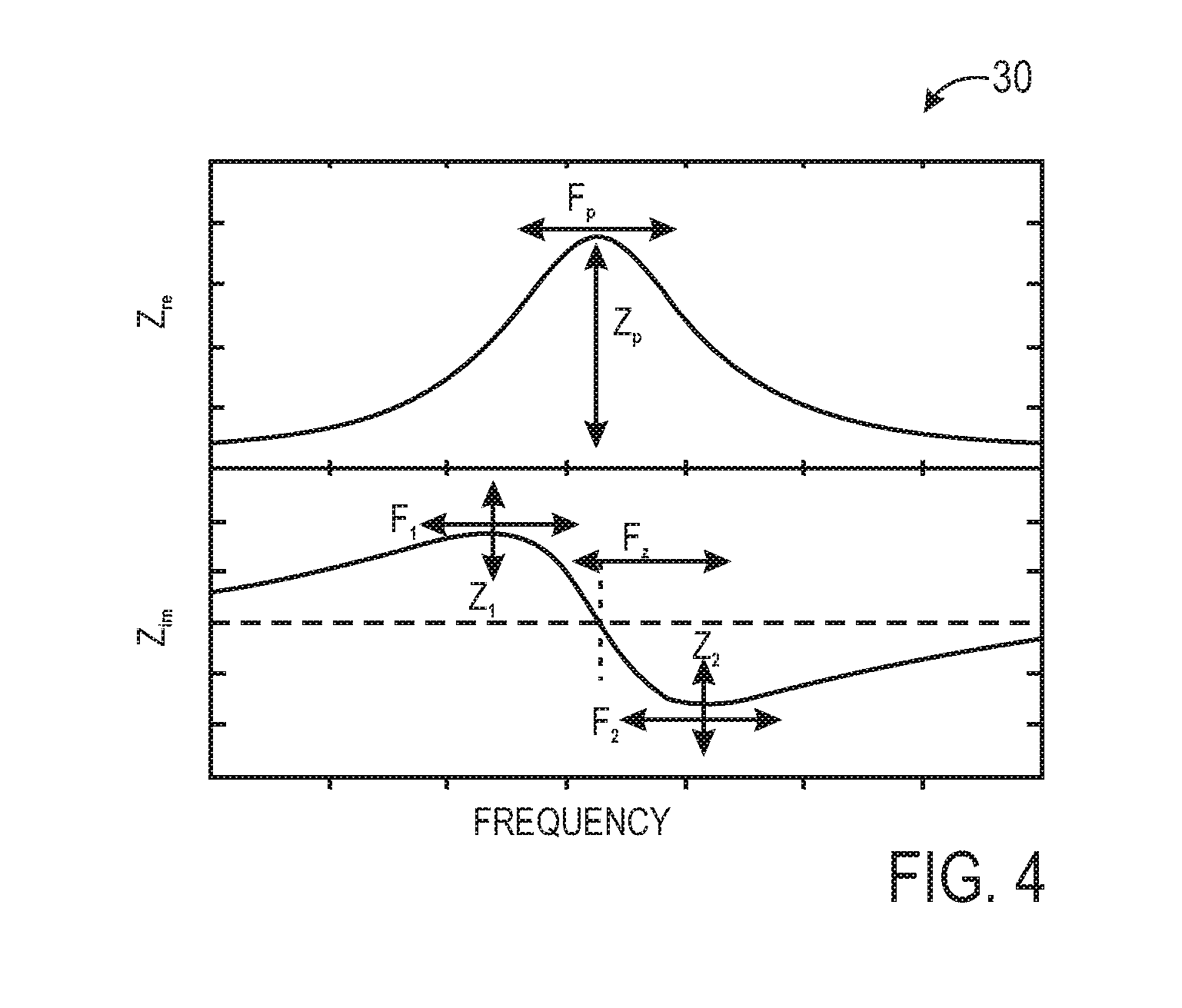
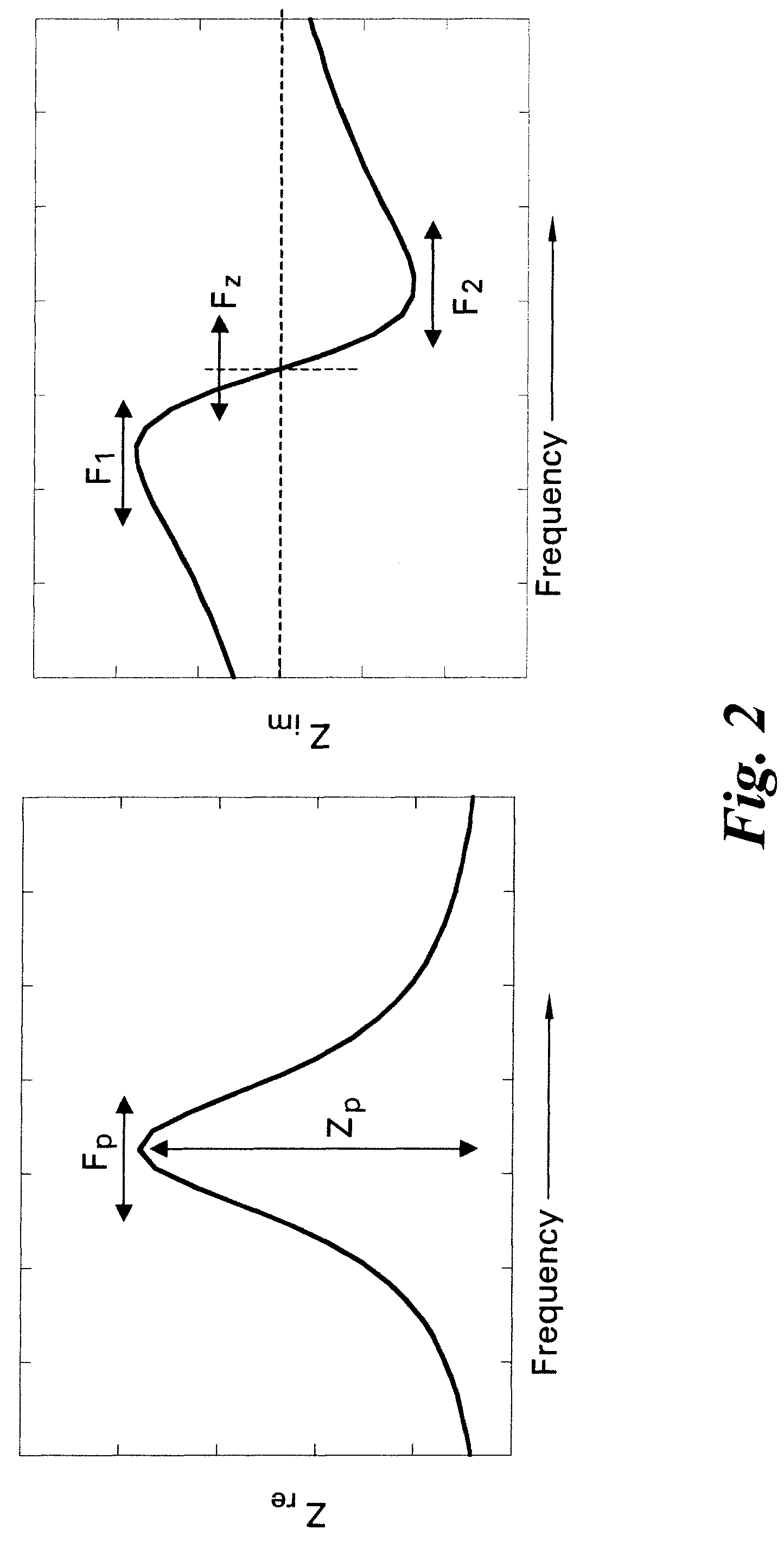
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors used in manufacturing and monitoring systems are provided. The methods include measuring impedance of an RFID sensor antenna, relating the measurement of impedance to one or more parameters (such as physical, chemical and biological properties), computing one or more analytical fit coefficients, and storing the one or more analytical fit coefficients on a memory chip of the RFID sensor. Measuring impedance of the RFID sensor may comprise measuring complex impedance which involves measuring complex impedance spectrum, phase angle and magnitude of the impedance, at least one of frequency of the maximum of the real part of the complex impedance, magnitude of the real part of the complex impedance, zero-reactance frequency, resonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance, and antiresonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a sensing film wherein analytical fit coefficients are stored on the memory chip to allow calibration of the RFID sensor. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a complementary sensor attached to the antenna where the complementary sensor in a pre-calibrated fashion predictably affects the impedance of the antenna.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
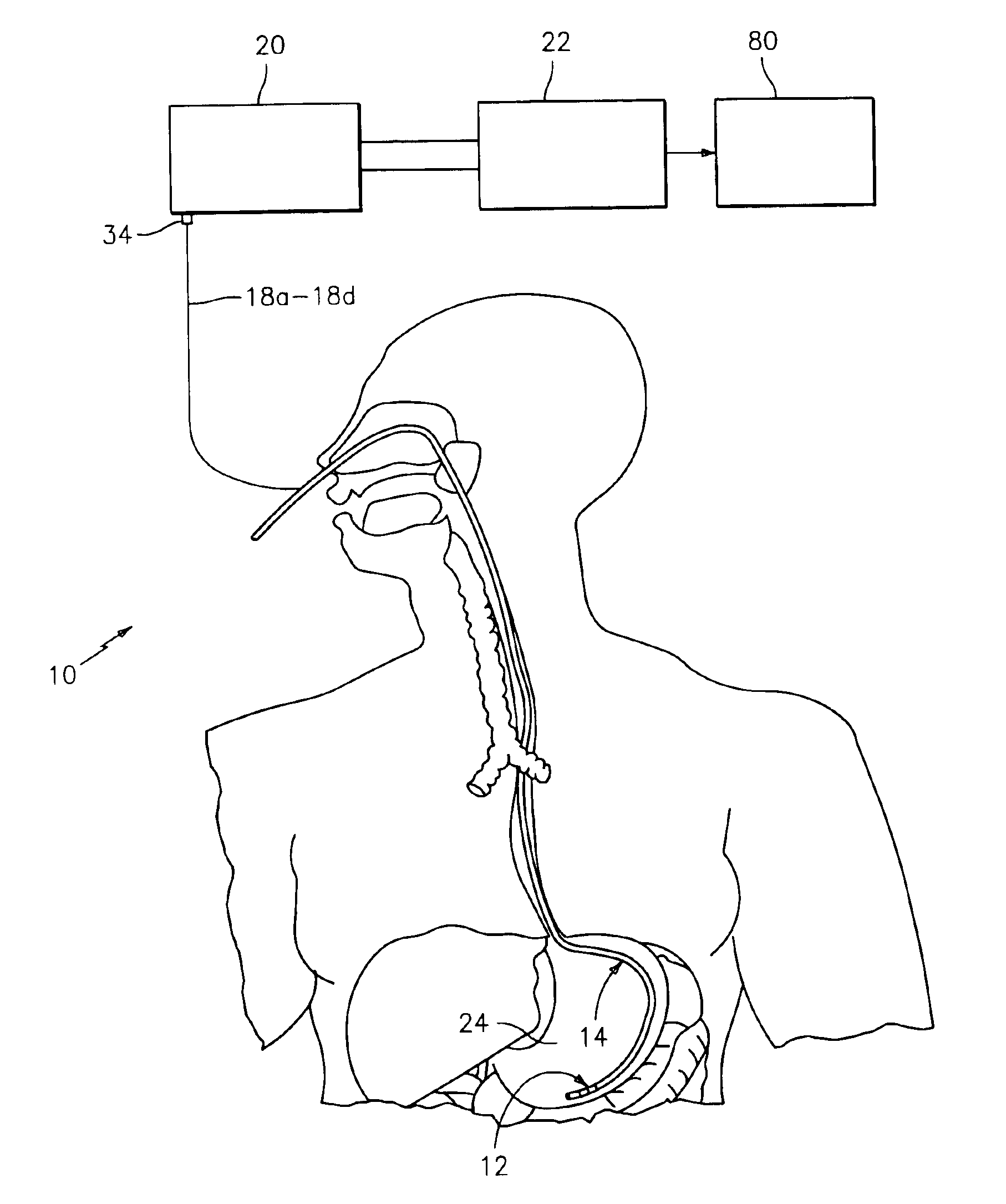
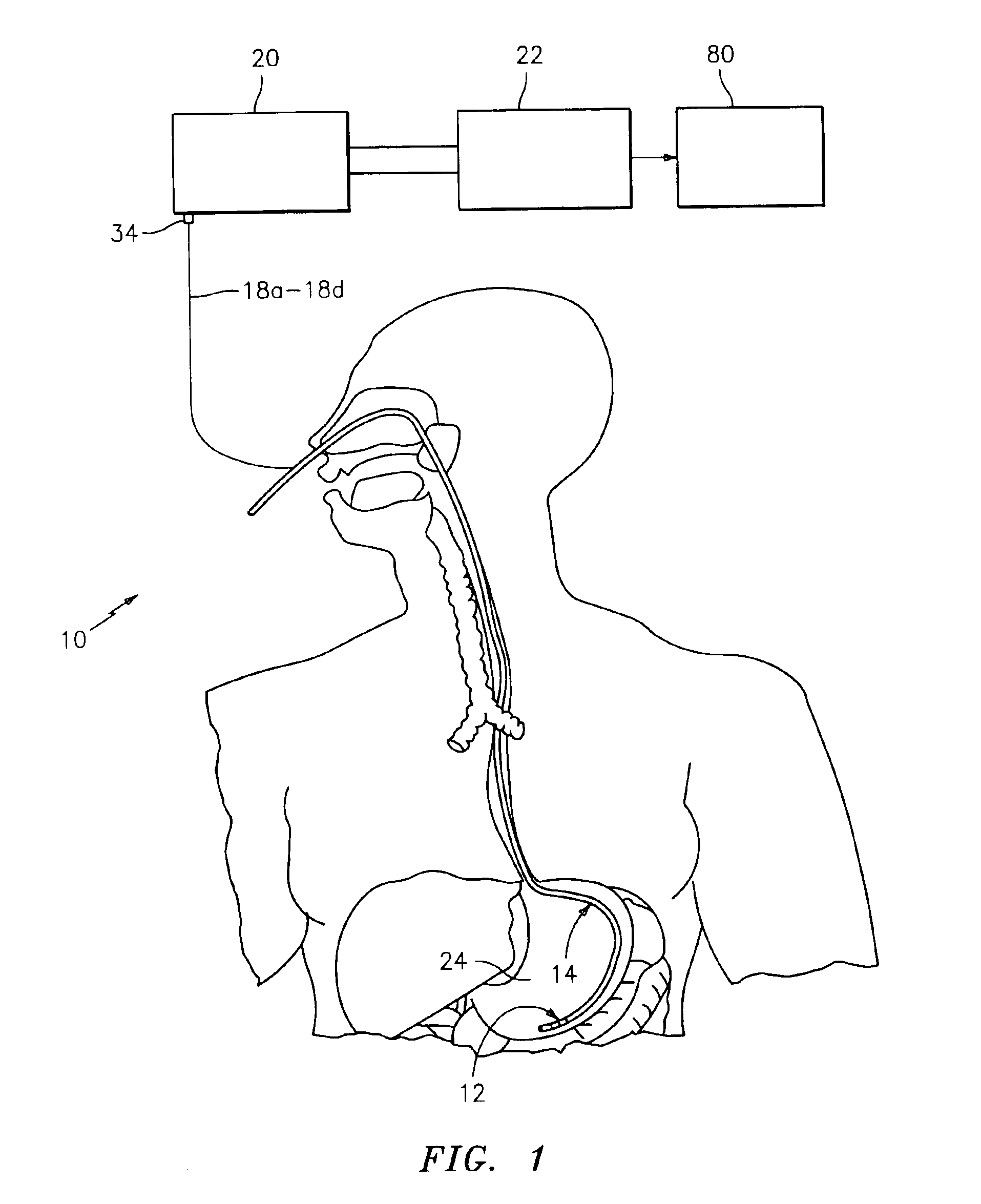
Impedance spectroscopy system and catheter for ischemic mucosal damage monitoring in hollow viscous organs
InactiveUS6882879B2ElectrocardiographyDevices for locating reflex pointsSpectroscopyImpedance spectrum
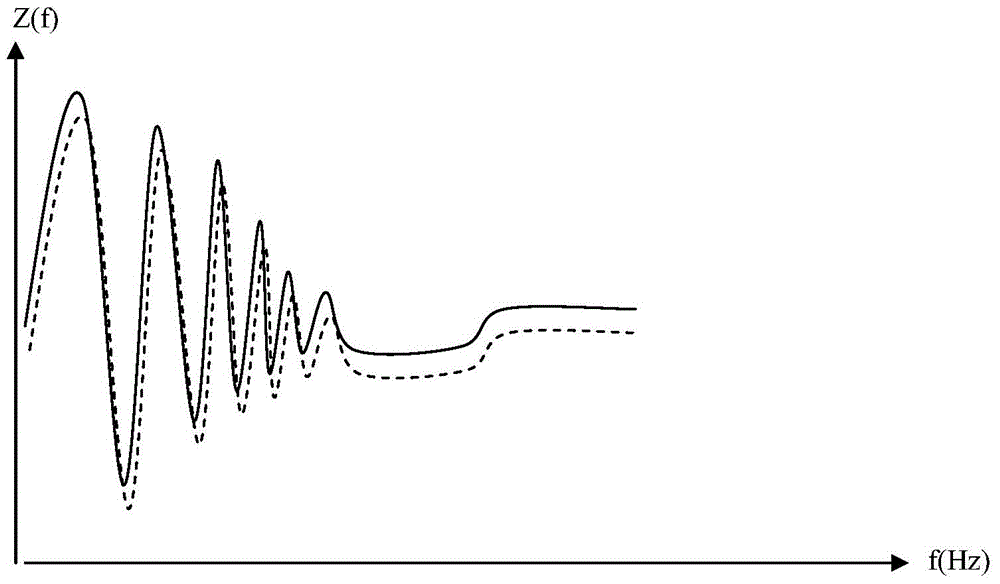
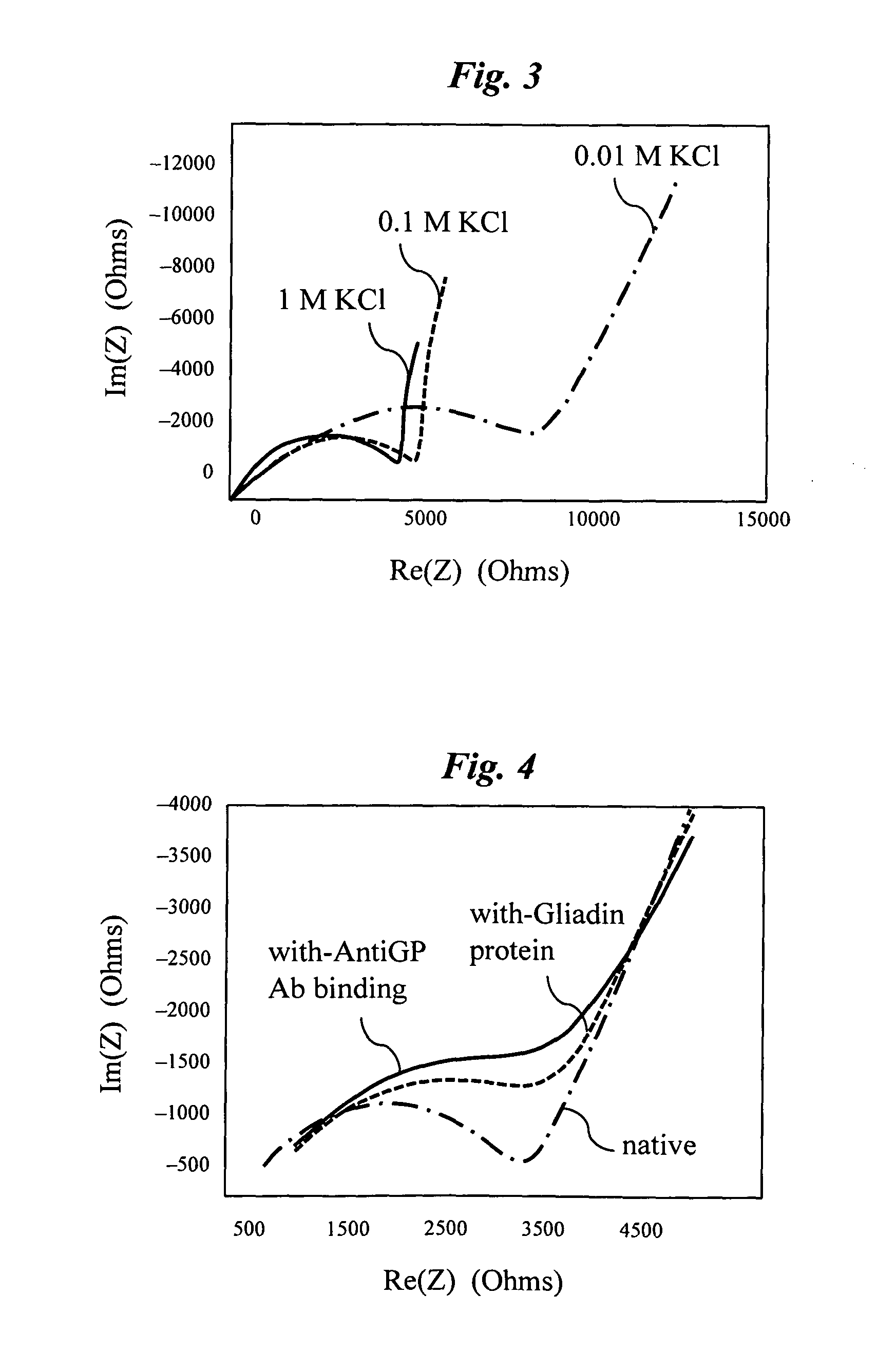
An impedance spectroscopy system for monitoring ischemic mucosal damage in hollow viscous organs comprises a sensor catheter and an impedance spectrometer for electrically driving the catheter to obtain a complex tissue impedance spectrum. Once the catheter is in place in one of a patient's hollow viscous organs, the impedance spectrometer obtains the complex impedance spectrum by causing two electrodes in the tip of the catheter to inject a current into the mucosal tissue at different frequencies, while two other electrodes measure the resulting voltages. A pattern recognition system is then used to analyze the complex impedance spectrum and to quantify the severity of the mucosal injury. Alternatively, the complex impedance spectrum can be appropriately plotted against the spectrum of normal tissue, allowing for a visual comparison by trained personnel.
Owner:CRITICAL PERFUSION
Highly selective chemical and biological sensors
ActiveUS20120116683A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceBiological testingHigh concentrationPrincipal component analysis
Methods and sensors for selective fluid sensing are provided. Each sensor includes a resonant inductor-capacitor-resistor (LCR) sensor that is coated with a sensing material. In order to collect data, an impedance spectrum is acquired over a relatively narrow frequency range, such as the resonant frequency range of the LCR circuit. A multivariate signature may be calculated from the acquired spectrum to discern the presence of certain fluids and / or fluid mixtures. The presence of fluids is detected by measuring the changes in dielectric, dimensional, resistance, charge transfer, and other changes in the properties of the materials employed by observing the changes in the resonant electronic properties of the circuit. By using a mathematical procedure, such as principal components analysis (PCA) and others, multiple fluids and mixtures can be detected in the presence of one another, even in a high humidity environment or an environment wherein one or more fluids has a substantially higher concentration (e.g. 10×, 1,000,000×) compared to other components in the mixture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors
ActiveUS7911345B2Testing sensing arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMemory chipComplex impedance spectra
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors used in manufacturing and monitoring systems are provided. The methods include measuring impedance of an RFID sensor antenna, relating the measurement of impedance to one or more parameters (such as physical, chemical and biological properties), computing one or more analytical fit coefficients, and storing the one or more analytical fit coefficients on a memory chip of the RFID sensor. Measuring impedance of the RFID sensor may comprise measuring complex impedance which involves measuring complex impedance spectrum, phase angle and magnitude of the impedance, at least one of frequency of the maximum of the real part of the complex impedance, magnitude of the real part of the complex impedance, zero-reactance frequency, resonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance, and antiresonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a sensing film wherein analytical fit coefficients are stored on the memory chip to allow calibration of the RFID sensor. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a complementary sensor attached to the antenna where the complementary sensor in a pre-calibrated fashion predictably affects the impedance of the antenna.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
Method of and apparatus for measuring battery capacity by impedance spectrum analysis
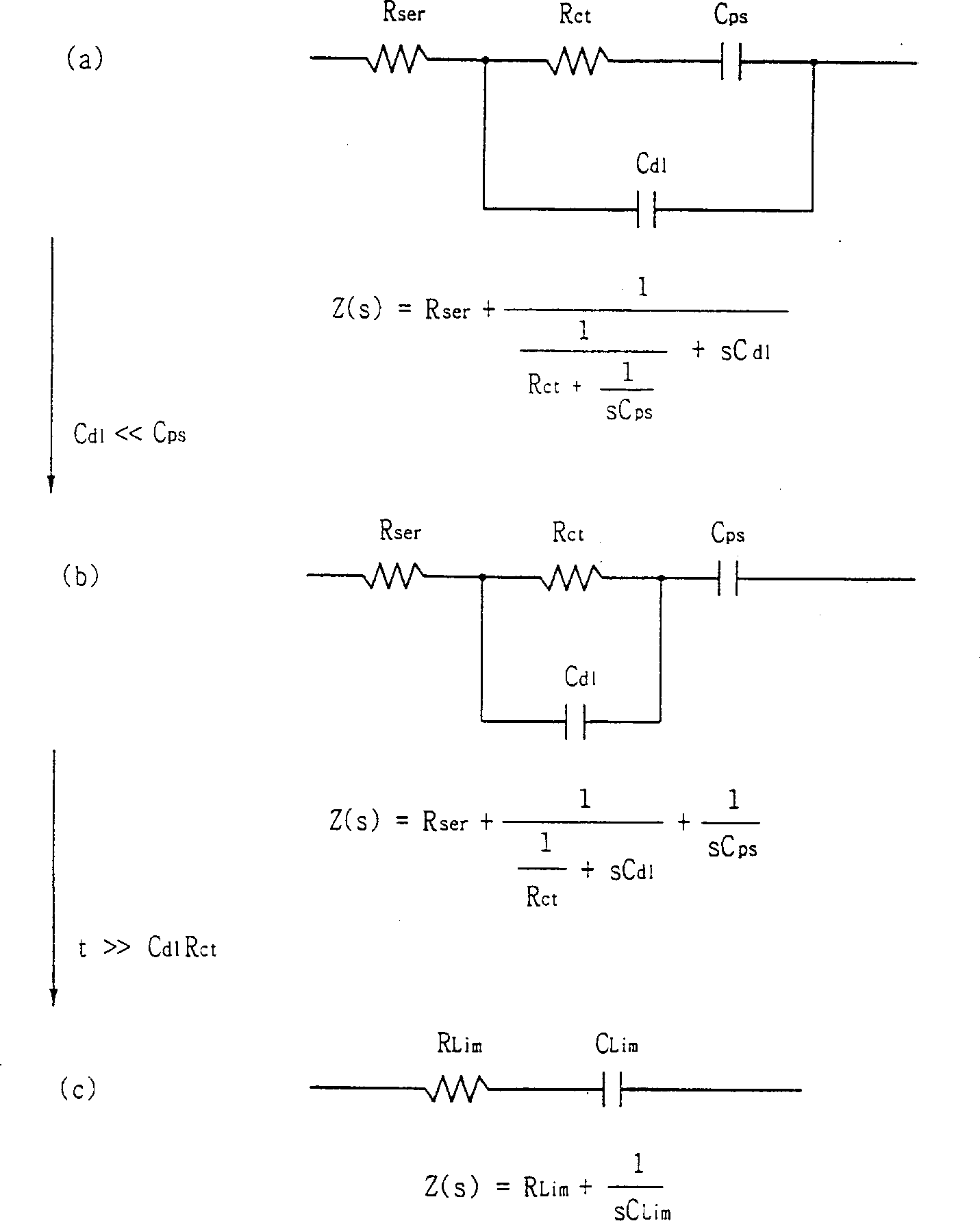
InactiveUS6208147B1Less timeGood efficiency and reliabilityResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringCharacteristic impedance
Provided with a method of measuring battery capacity by impedance spectrum analysis, which is to measure a characteristic impedance spectrum of primary and secondary batteries and determine the battery capacity the method including the steps of: (1) measuring the characteristic impedance spectrum of a battery in a predetermined frequency region; (2) determining a parameter from the measured impedance spectrum; (3) monitoring in advance the correlation between the determined parameter and the battery capacity measured by a real-time discharge technique; and (4) determining the battery capacity from the characteristic impedance spectrum of a battery having an unknown capacity based on the monitored correlation.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Sensing system and method
System includes a sensor operably coupled to a device body. The sensor includes a sensing region and at least one resonant inductor-capacitor-resistor (LCR) circuit. The sensing region is configured to be placed in operational contact with an industrial fluid. The at least one resonant LCR circuit is configured to generate an electrical stimulus that is applied to the industrial fluid via electrodes at the sensing region. The device body includes one or more processors configured to receive an electrical signal from the sensor that is representative of a resonant impedance spectral response of the sensing region in operational contact with the industrial fluid responsive to the electrical stimulus. The one or more processors are further configured to analyze the resonant impedance spectral response and determine both a water concentration in the industrial fluid and an aging level of the industrial fluid based on the resonant impedance spectral response.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for testing battery impedance spectroscopy
InactiveCN1967270AImprove measurement efficiencyAccurate measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingFrequency spectrumTest battery
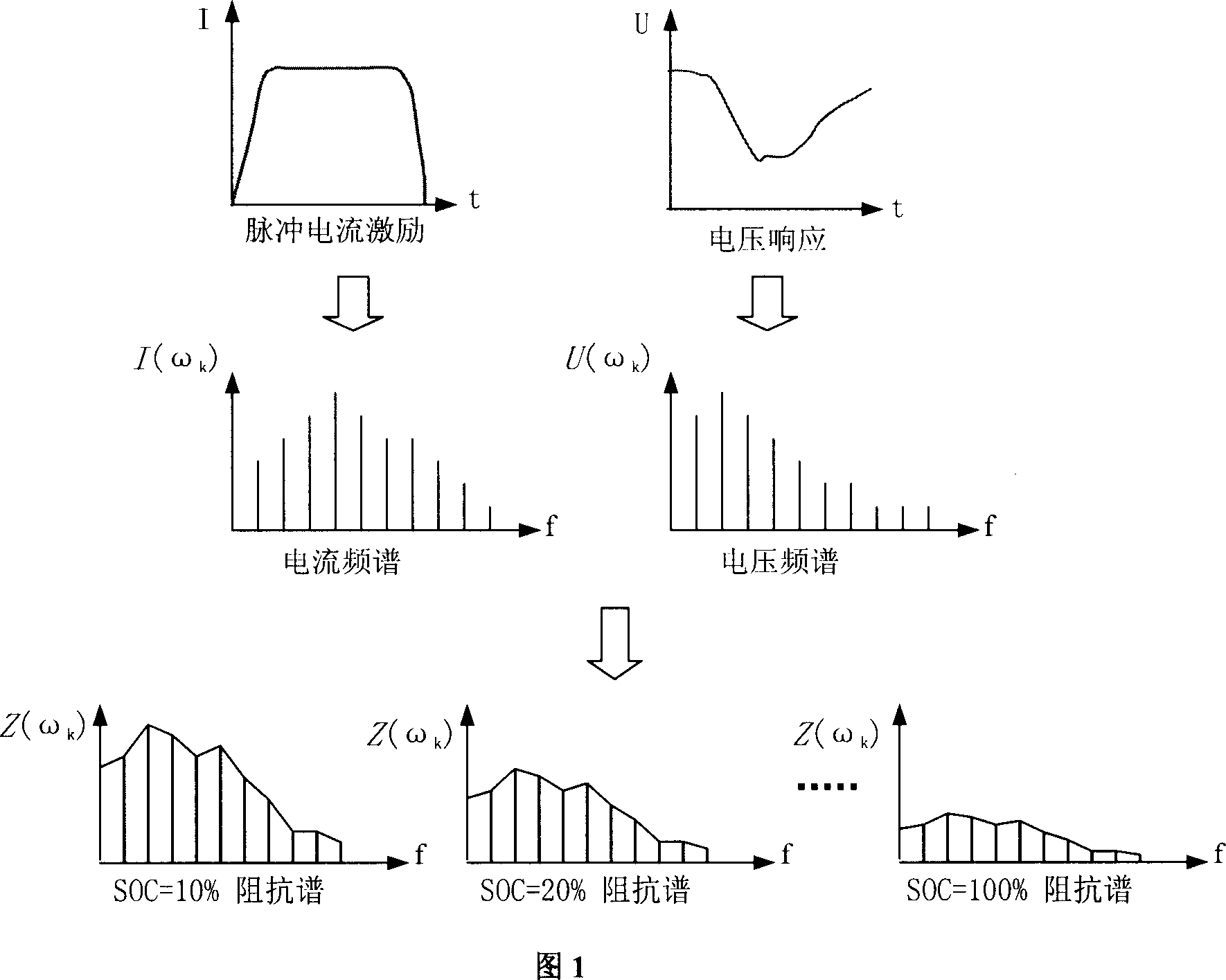
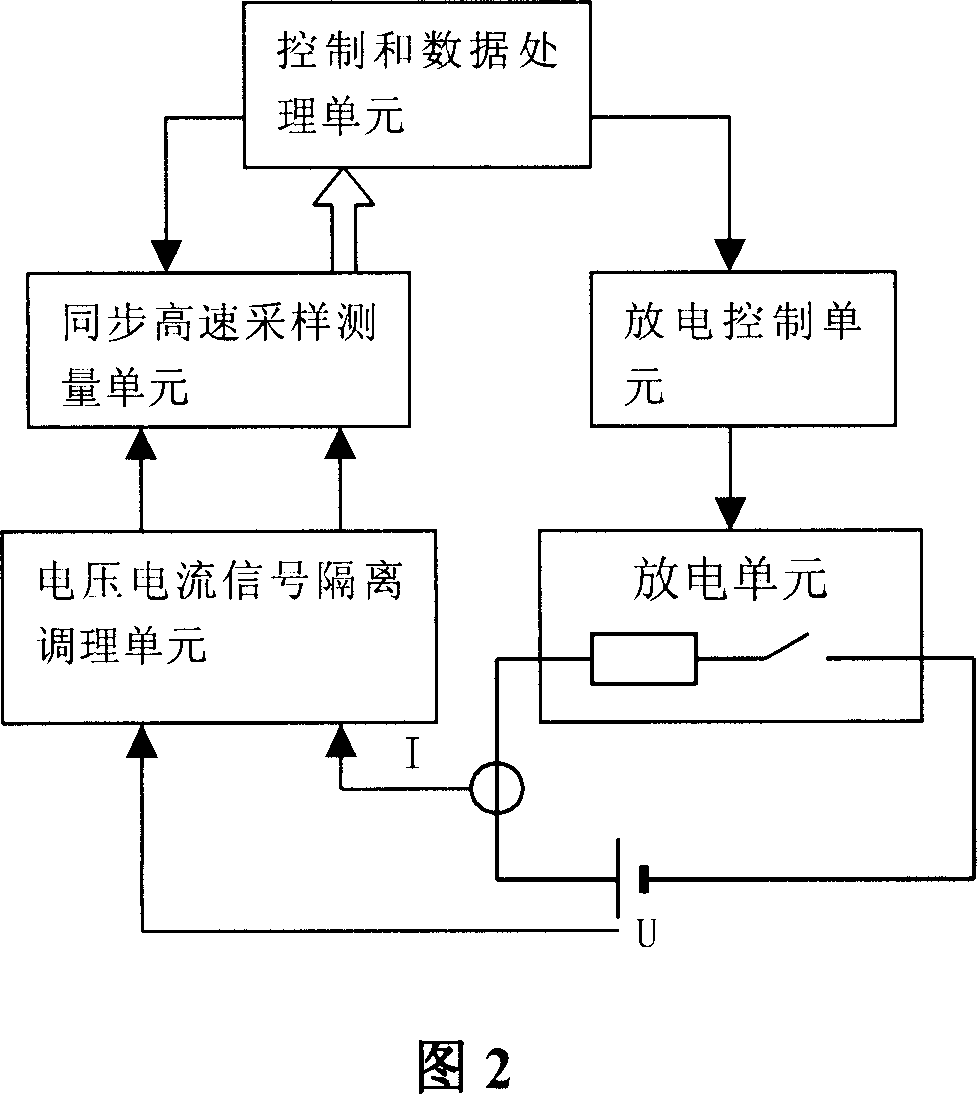
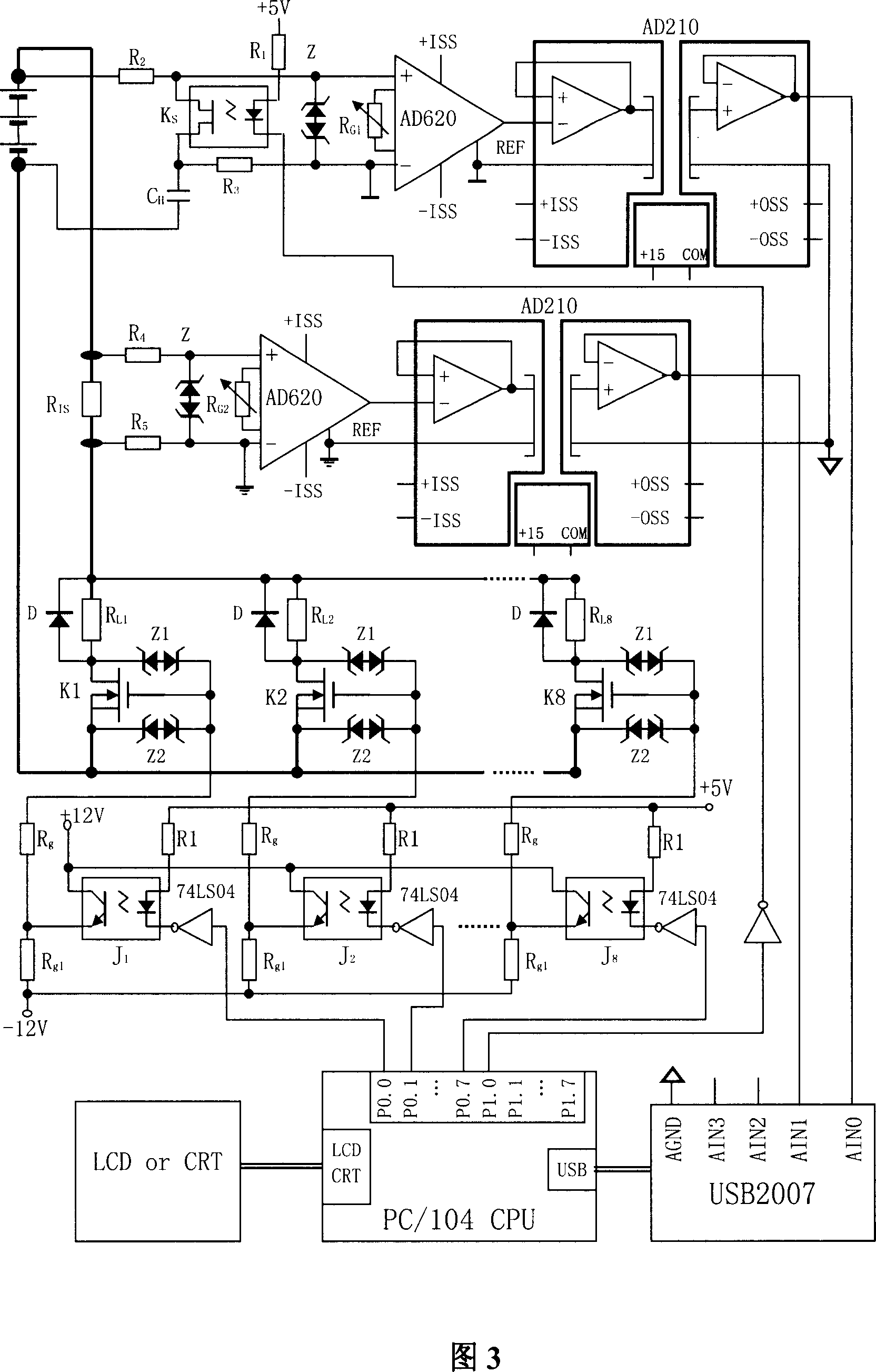
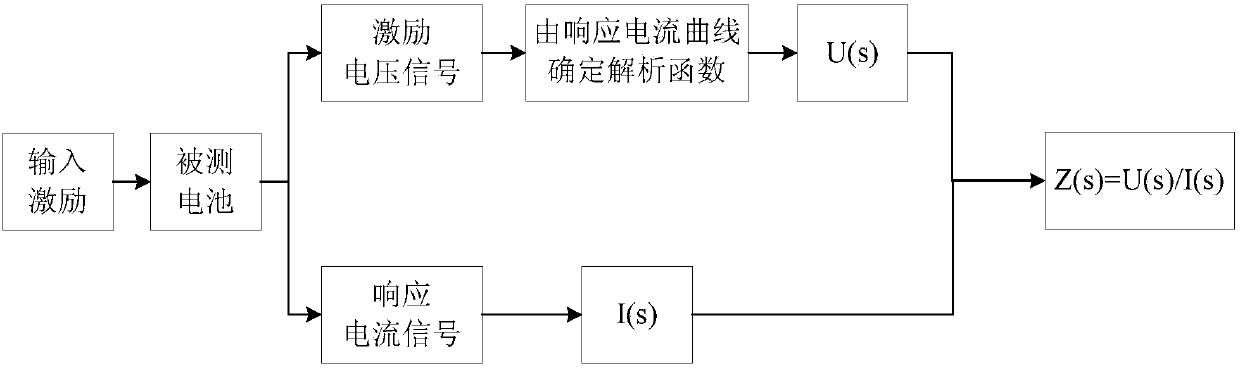
The invention relates to the battery impedance spectroscopy testing technology. The invention provides a battery impedance spectroscopy testing method, which imposes the current incentive I(t) on the battery, and through synchronous measurement of current incentive I(t) and terminal voltage response U(t), calculates the amplitude spectrum I(Omegak), U(Omegak) and phase spectrum phiI(Omegak), phiU(Omegak) of current incentive I(t) and terminal voltage response U(t) under a variety of frequencies, and according to the spectrum of I and U, calculates the battery inner impedance Z0(Omegak)=U(Omegak) / I(Omegak) under a variety of frequencies, resulting in the complete spectra of battery inner impedance. The invention also provides a battery impedance spectroscopy testing system, including the control and data processing module, the high-speed synchronous sampling and measurement module, the voltage and current signal isolation and modulating module, the discharge control module, the controllable discharge module. Using the method and system in this invention, it can quickly complete the battery impedance spectrum measurement and analysis in a short time, greatly increasing the measurement efficiency.
Owner:BEIHUA UNIV +1
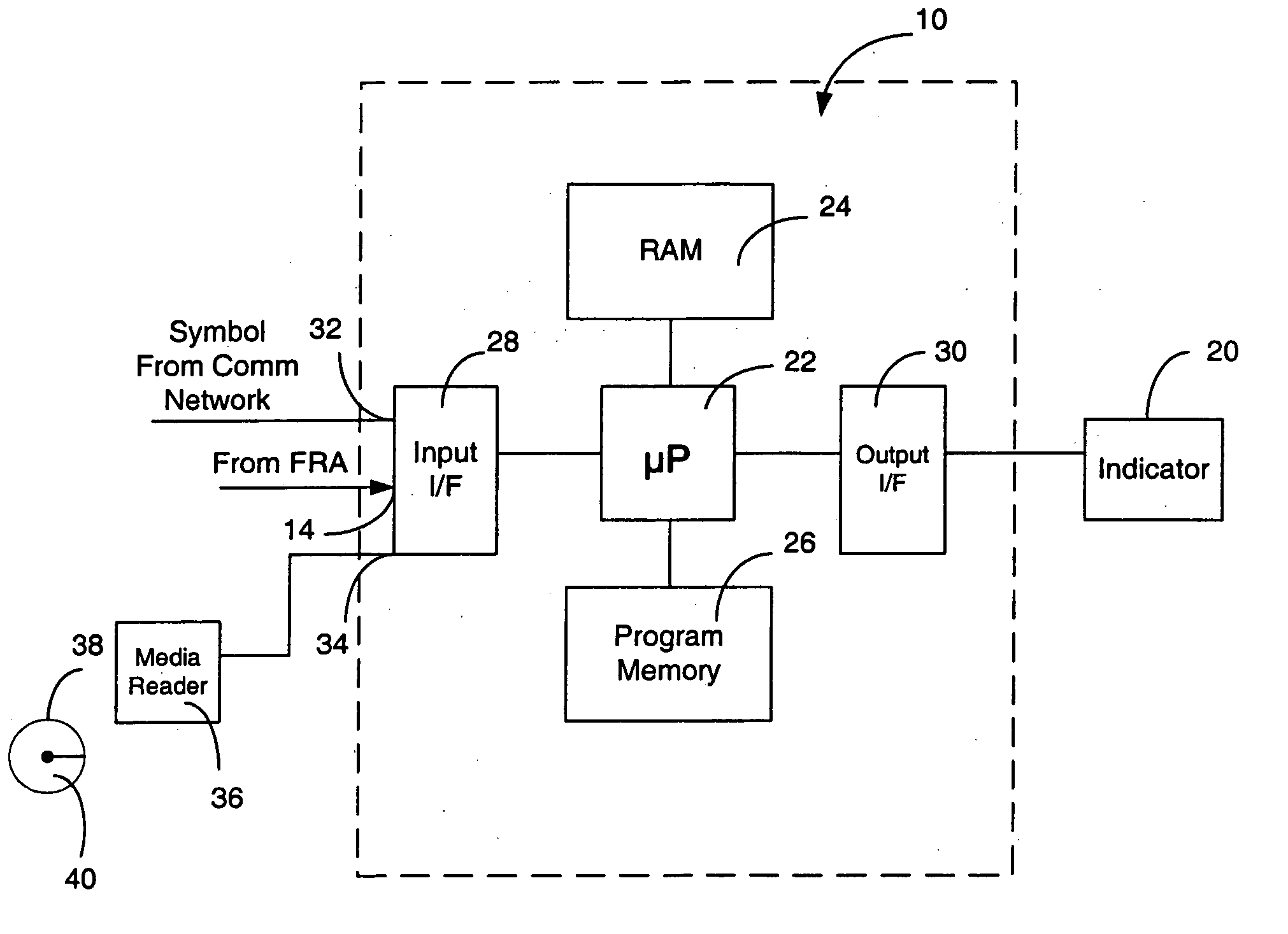
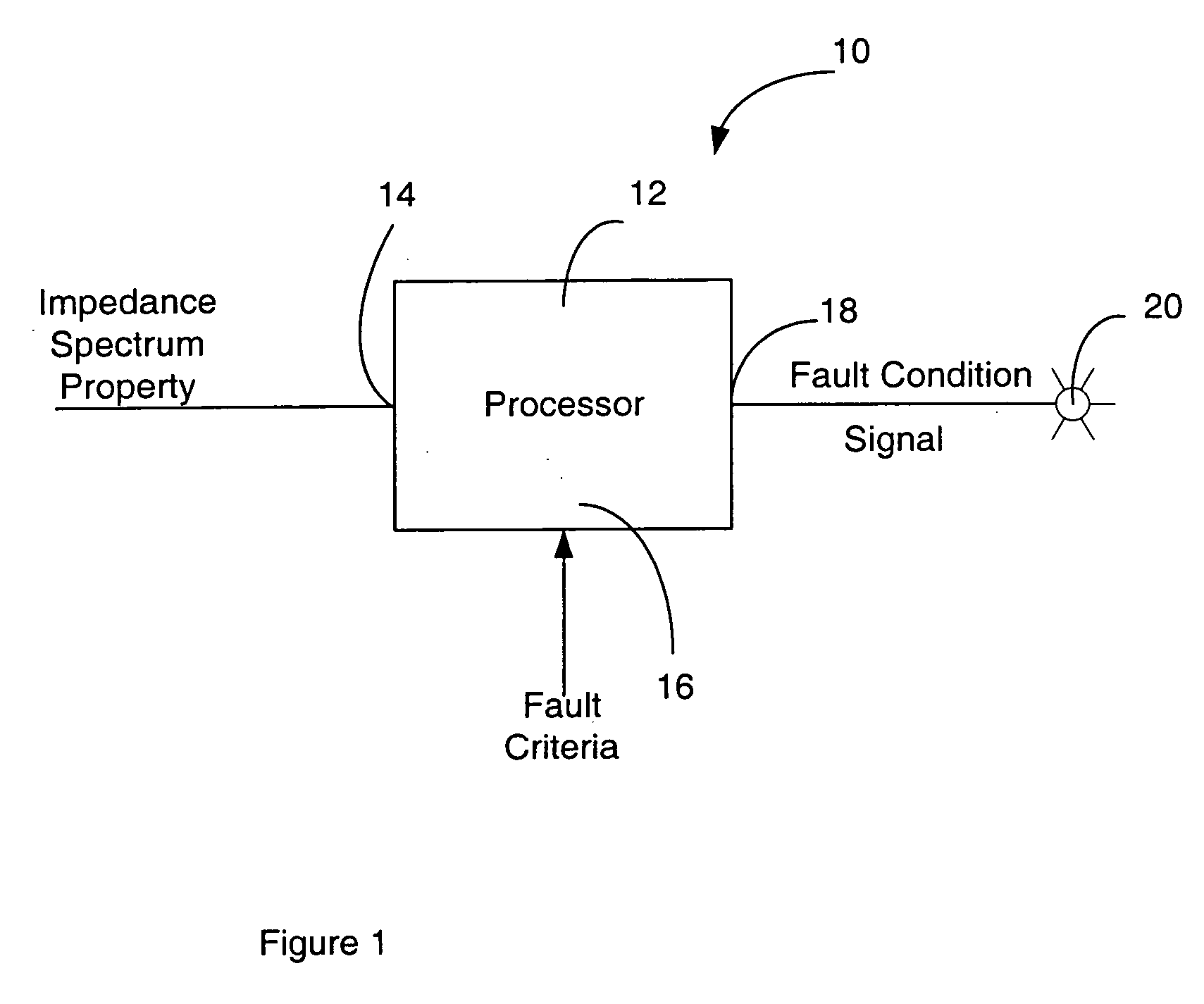
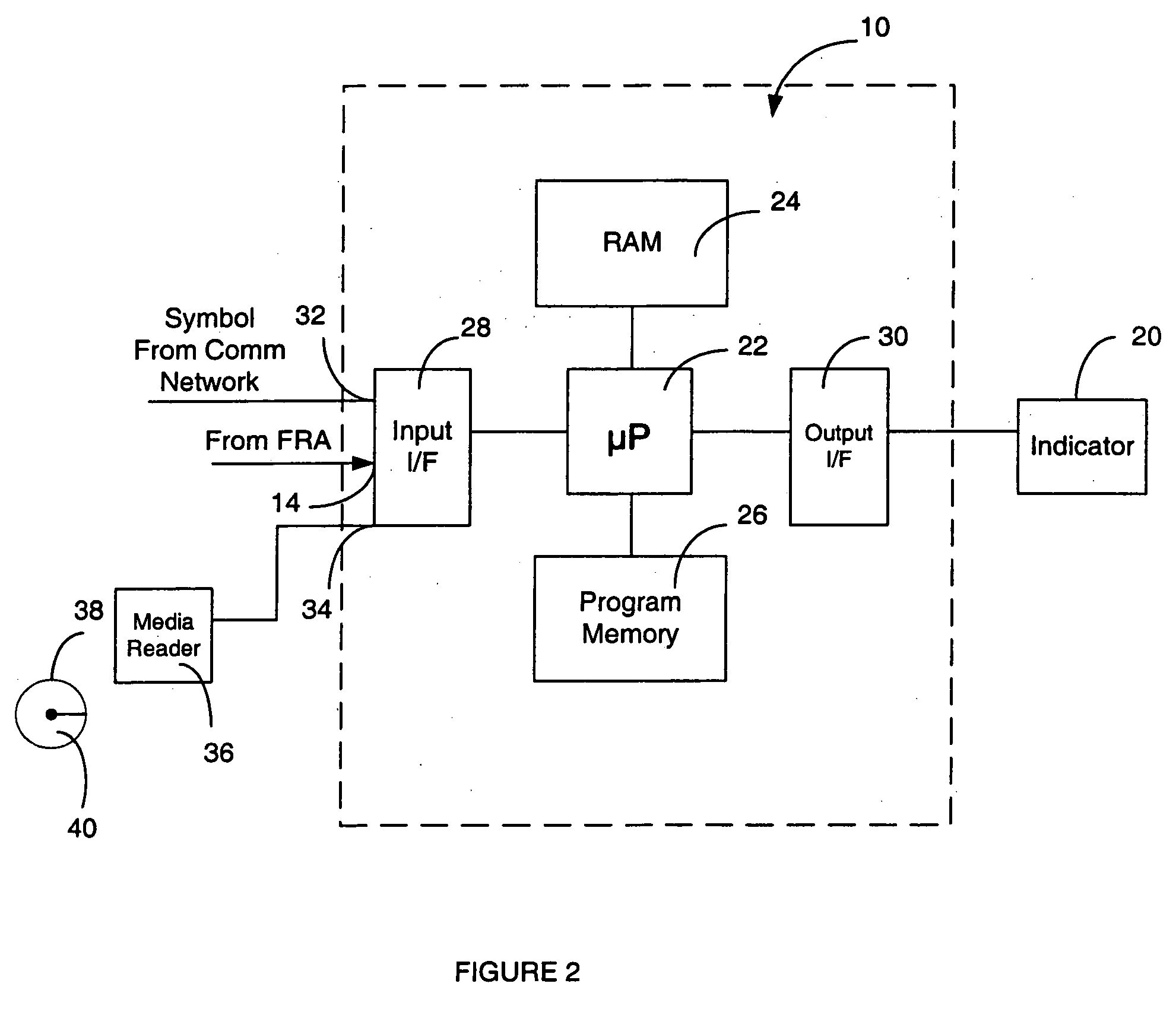
Methods and apparatus for indicating a fault condition in fuel cells and fuel cell components
An apparatus and methods for detecting and identifying faults in a fuel cell are disclosed. An impedance spectrum relating to the fuel cell is compared with fault criteria to identify fault conditions in the fuel cell. A time-varying current is drawn from the fuel cell at a selected frequency and the impedance of the fuel cell at the frequency is measured. This may optionally be repeated at a range of frequencies or at combinations of frequencies to provide an impedance spectrum across the range of frequencies. The fault criteria identify one or more fault conditions that may be identified by comparing the measured impedance spectrum to the fault conditions.
Owner:GREENLIGHT POWER TECH
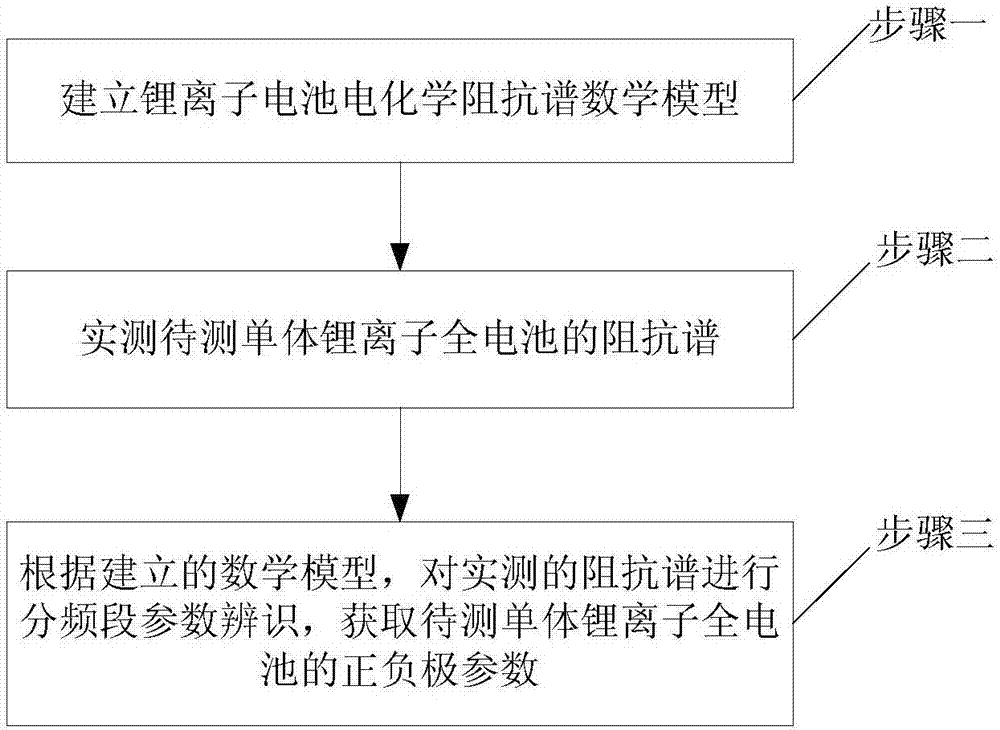
Parameter obtaining method of single lithium ion full battery
The invention provides a parameter obtaining method of a single lithium ion full battery, and belongs to the field of new energy research. The method comprises the following steps that 1) a mathematical electrochemical impedance spectrum model of the lithium ion battery is established; 2) an electrochemical impedance spectrum of the single lithium ion full battery to be measured is measured actually; and 3) according to the established mathematical model, parameters of the actually measured electrochemical impedance spectrum are identified according to frequency ranges, and anode and cathode parameters of the single lithium ion full battery to be measured are obtained. Aimed at the defect that parameters cannot be identified effectively when a present semi-battery model is used for a full battery, characteristics of the electrochemical impedance spectrum of the lithium ion battery are combined, a manner of parameter identification according to the frequency ranges is used, and anode and cathode model parameters of the lithium ion full battery can be obtained rapidly and accurately. The method of the invention can be used for gaining mechanism analysis, SOC estimation and life prediction of the lithium ion battery.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for determining an aging condition of a battery cell by means of impedance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20120019253A1Without effortWithout expenseSpectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceSpectroscopyEngineering
The invention relates to a method for determining an aging condition of a battery cell. The method has the following steps of a) providing a battery cell, b) recording an impedance spectrum of the battery cell, c) determining an evaluation quantity based on the measured impedance spectrum, and d) determining an aging condition of the battery cell based on a comparison of the evaluation quantity to a reference value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
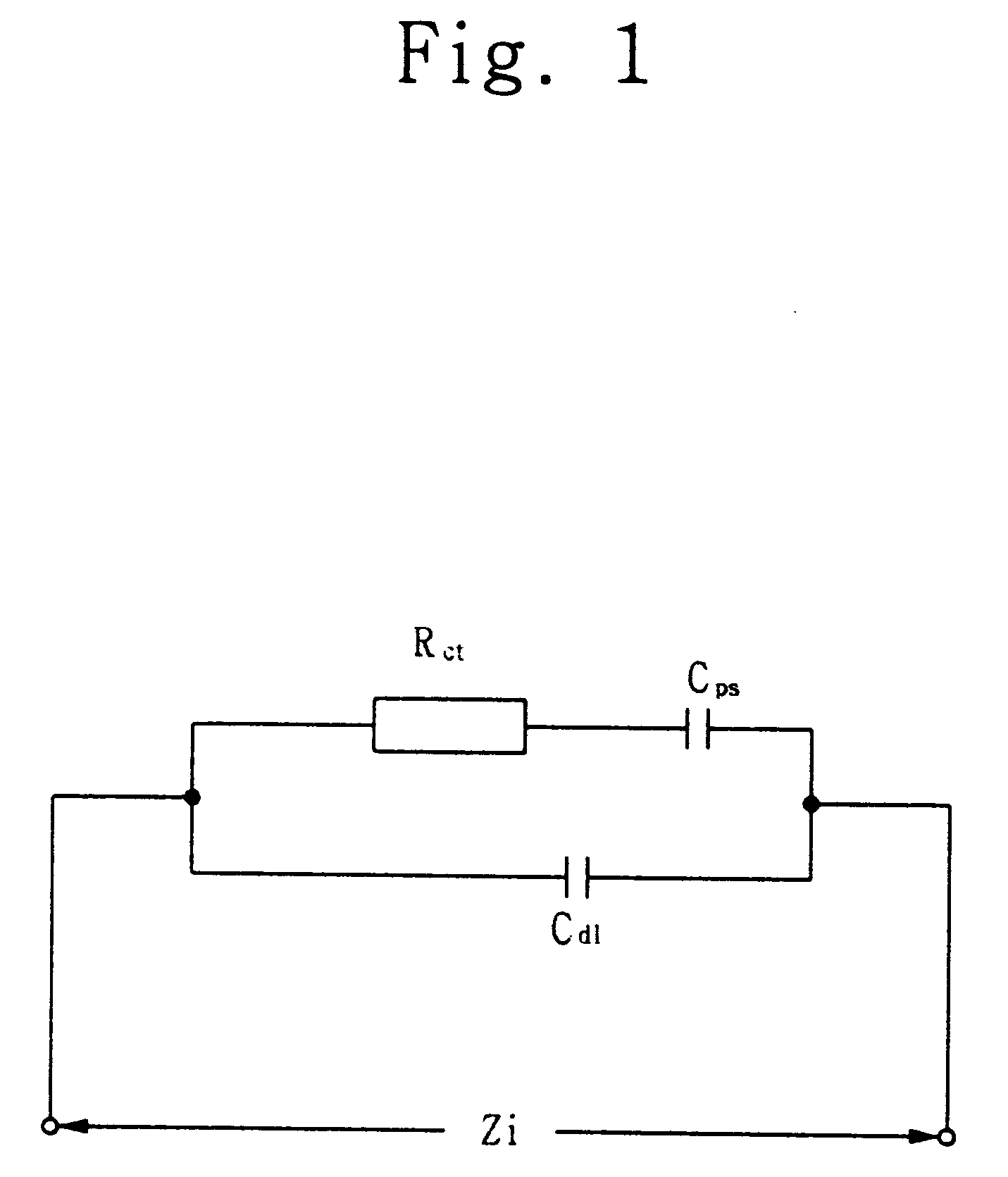
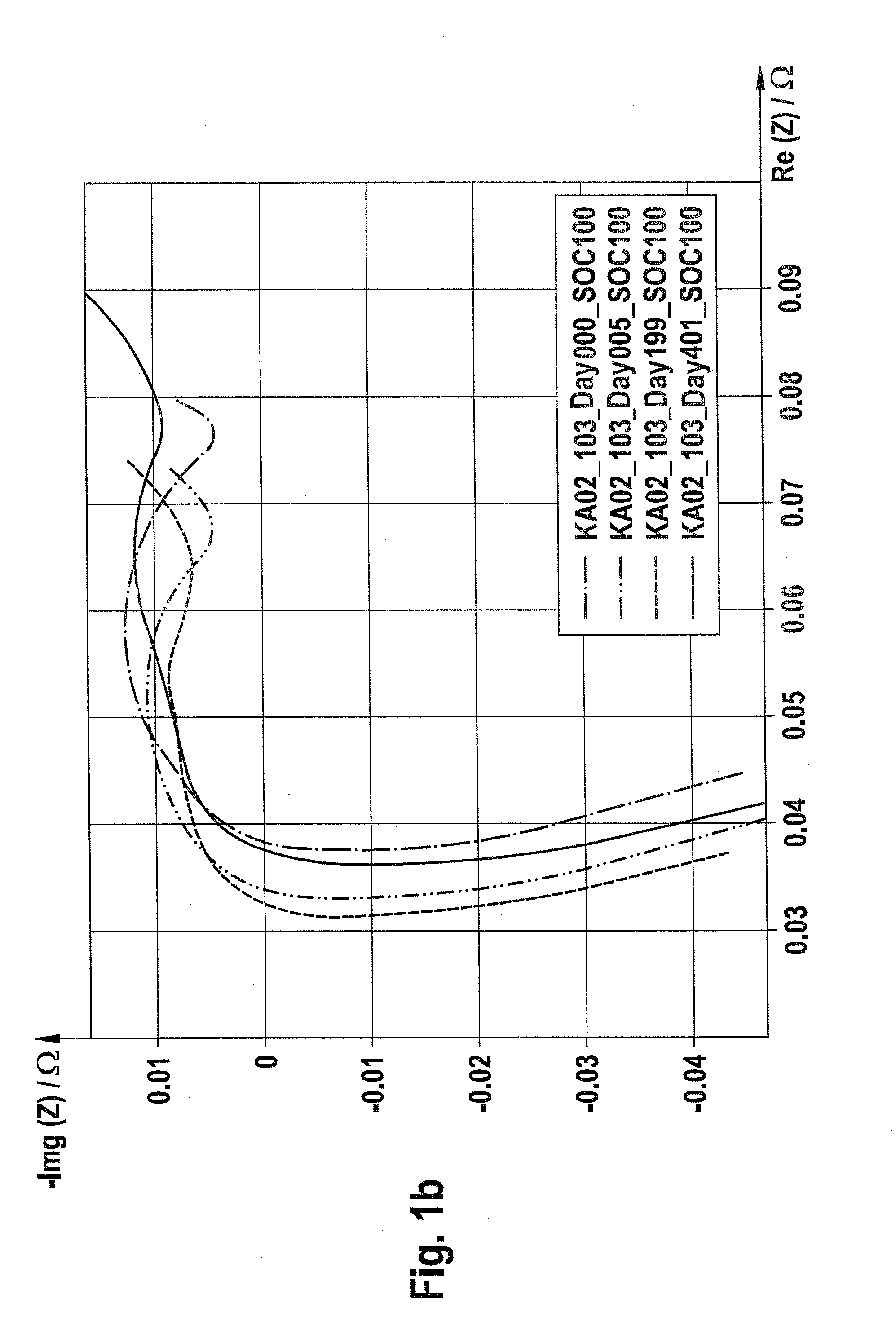
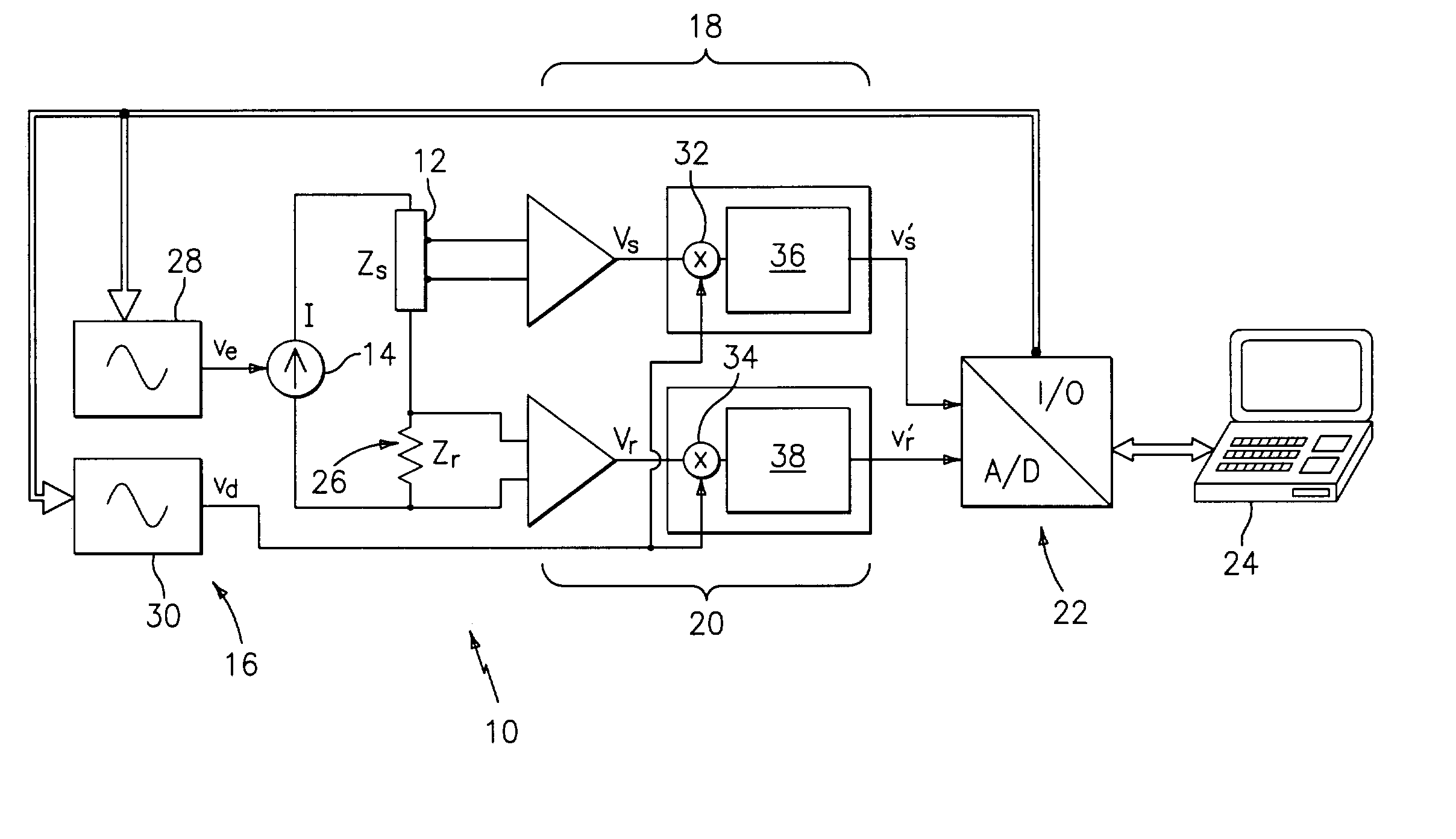
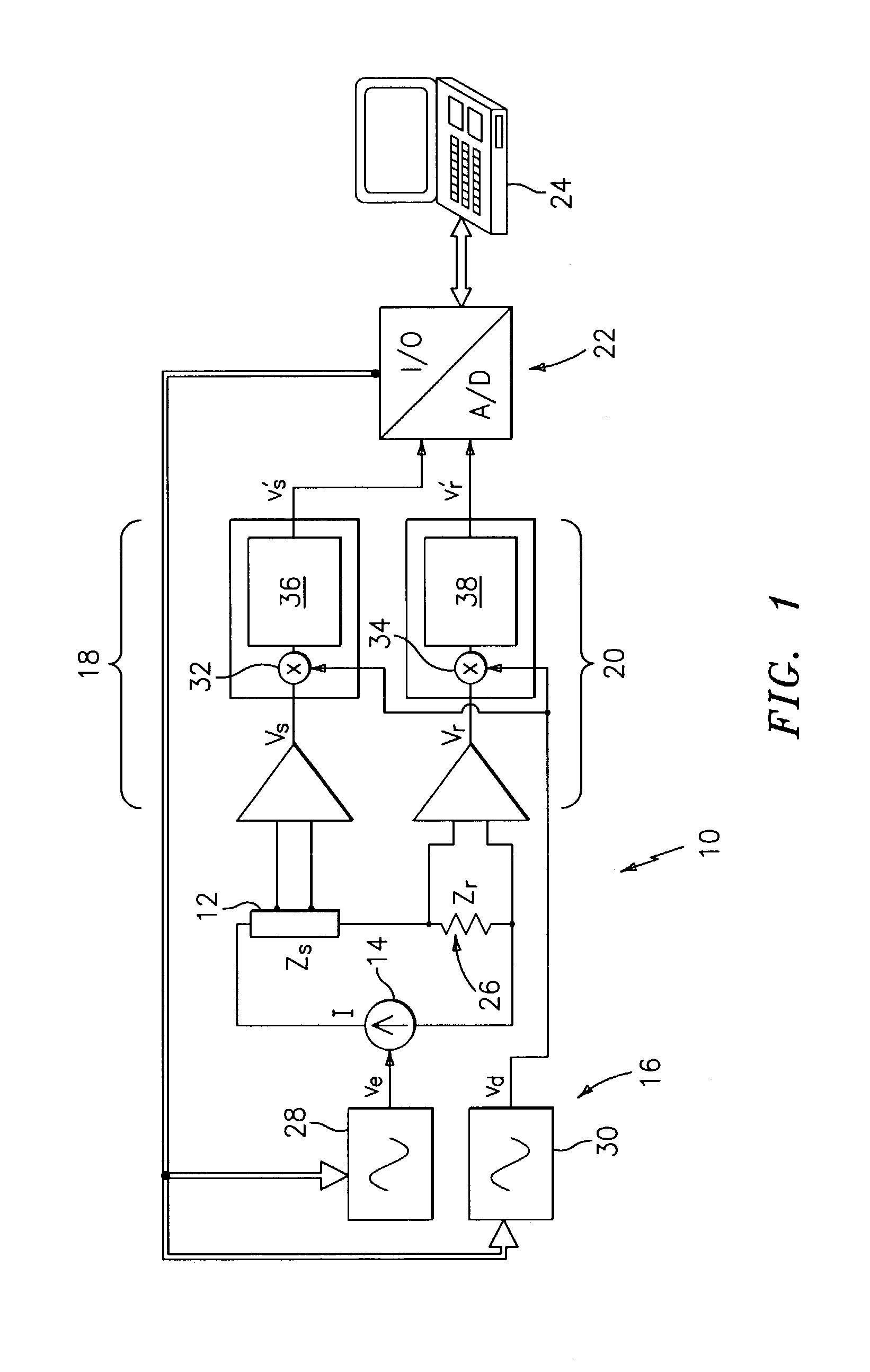
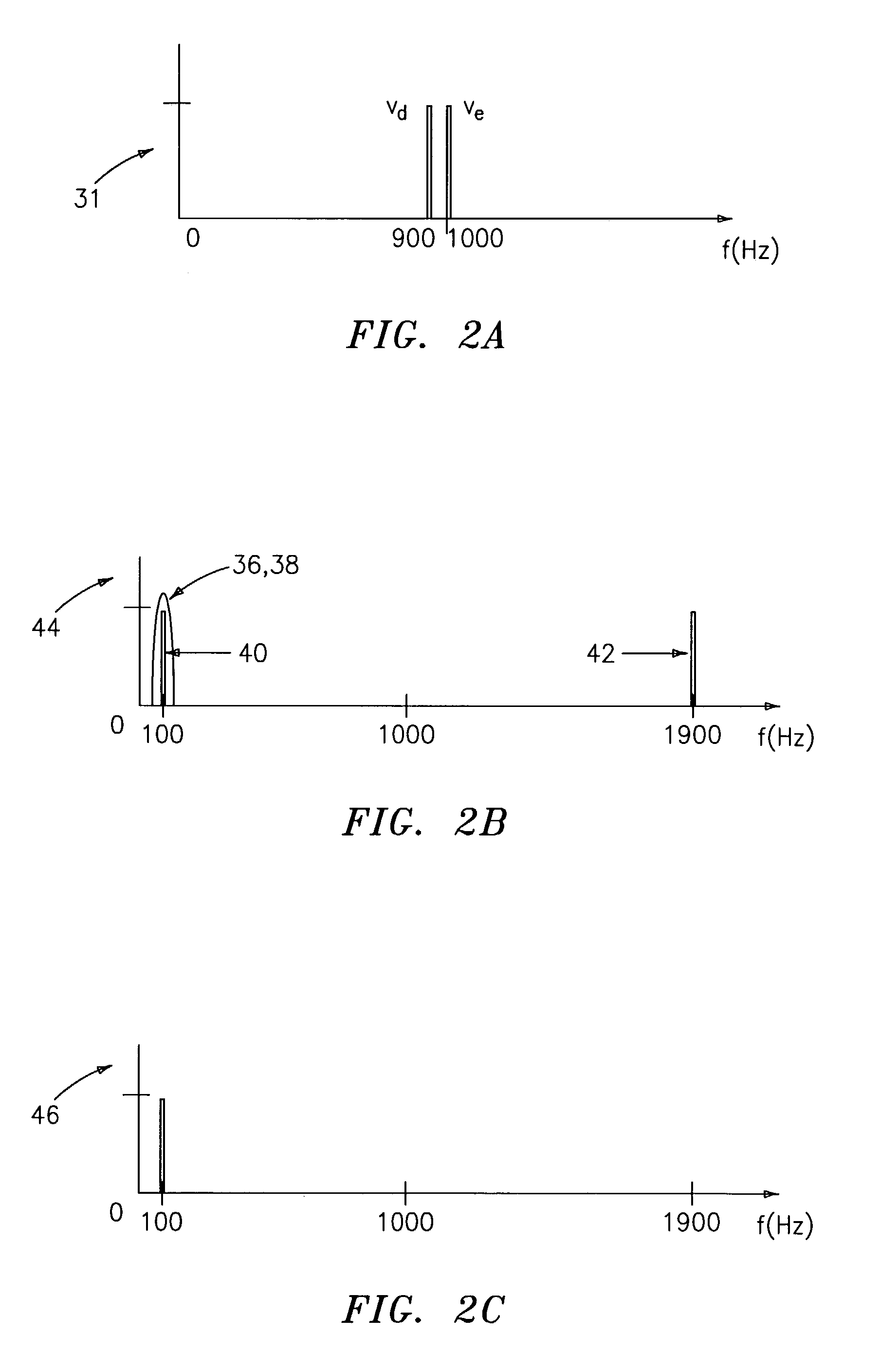
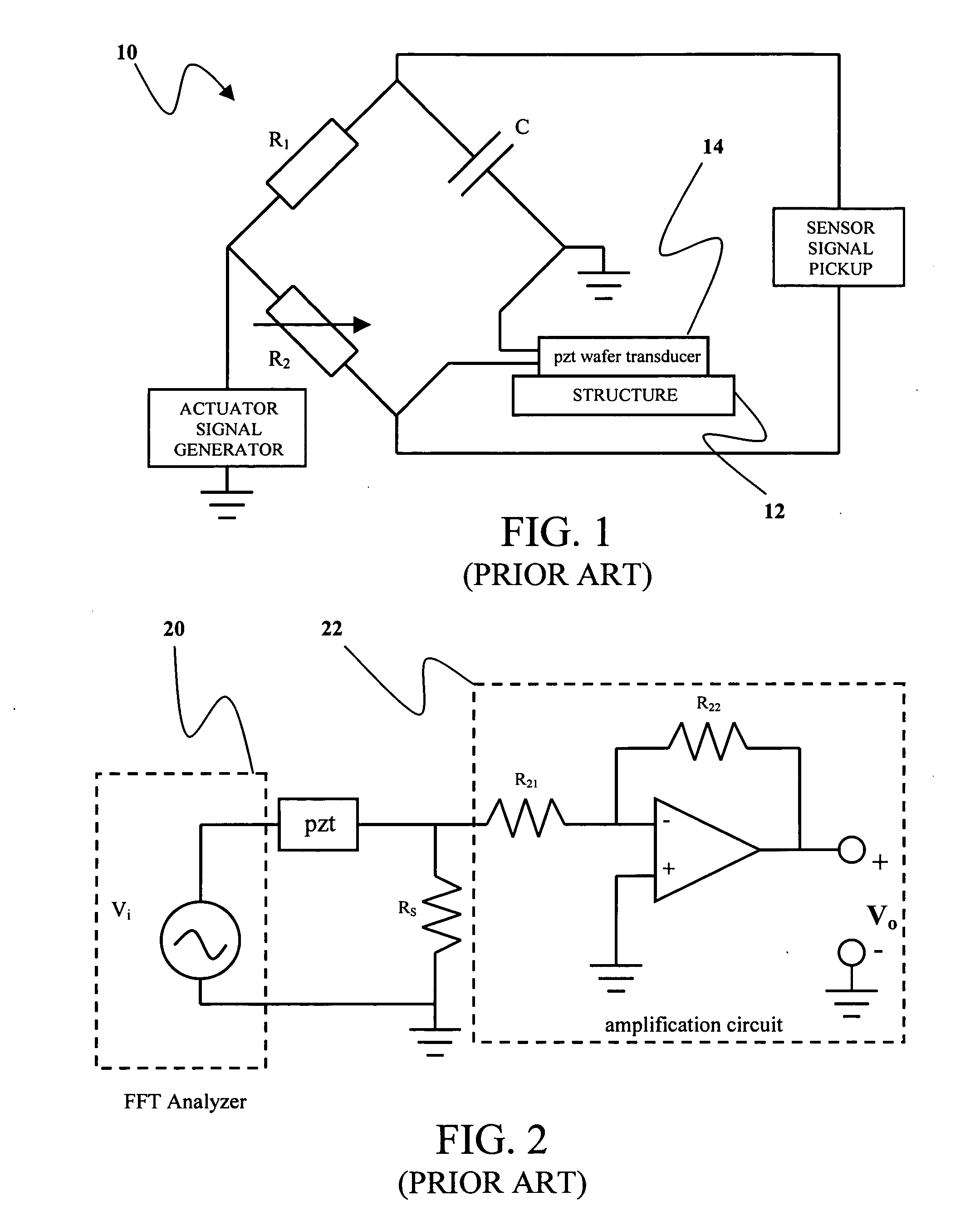
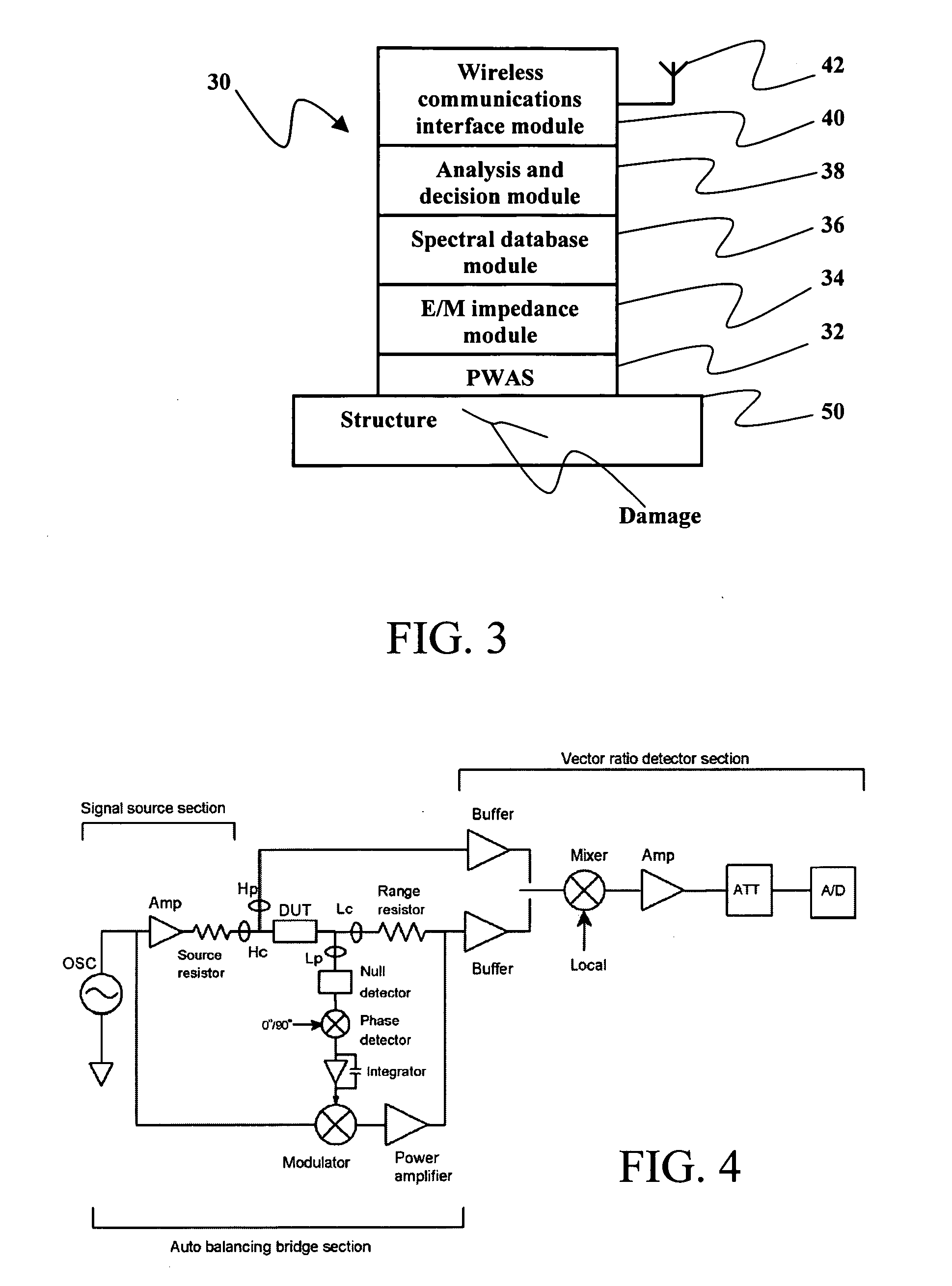
Complex impedance spectrometer using parallel demodulation and digital conversion
ActiveUS6970738B1Accurate measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceDiagnostic recording/measuringImpedance spectrumCurrent generator
A spectrometer for measuring the complex impedance spectrum of tissue comprises: a multi-frequency excitation current generator; a demodulation signal generator; two identical amplification / demodulation circuits; an A / D converter; and a microprocessor for signal processing. In use, the current generator excites the tissue sample and a series-connected reference impedance. The voltages generated in the tissue and reference are measured, demodulated, and digitized in parallel using the demodulation signal generator, the two amplification / demodulation circuits, and the A / D converter. Demodulation is done using the same demodulation signal generated at a frequency with a preset difference from the excitation signal, which allows measurements to be made at a low frequency independent of the excitation frequency. The microprocessor then calculates the complex impedance spectrum in relation to the reference signal. Because the measurements are relative, they are independent of both the excitation current amplitude of the phase of the excitation and demodulation signals.
Owner:CRITICAL PERFUSION
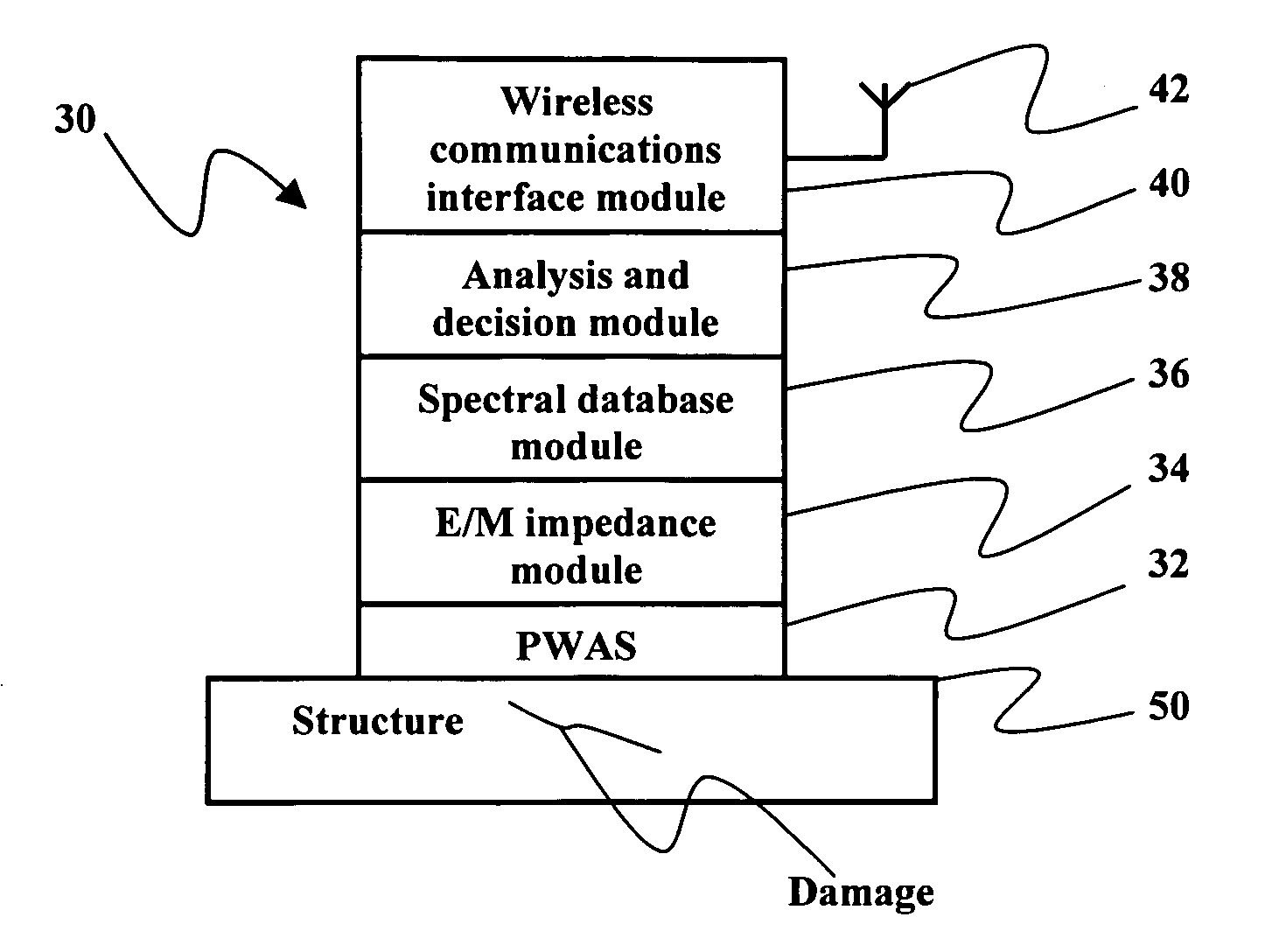
Self-processing integrated damage assessment sensor for structural health monitoring
ActiveUS20050114045A1Easy to useAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementStructural health monitoringSelf processing
A small, lightweight, portable, and inexpensive self-processing integrated damage assessment sensor (SPIDAS) that may be temporarily or permanently attached to a structure for structural health monitoring is provided. The SPIDAS device employs an electromechanical impedance measuring method to directly measure the high-frequency local impedance spectrum of the structure, process the electromechanical impedance data, and issue structural health reports that the device may transmit over a wireless connection.
Owner:SOUTH CAROLINA UNIV OF
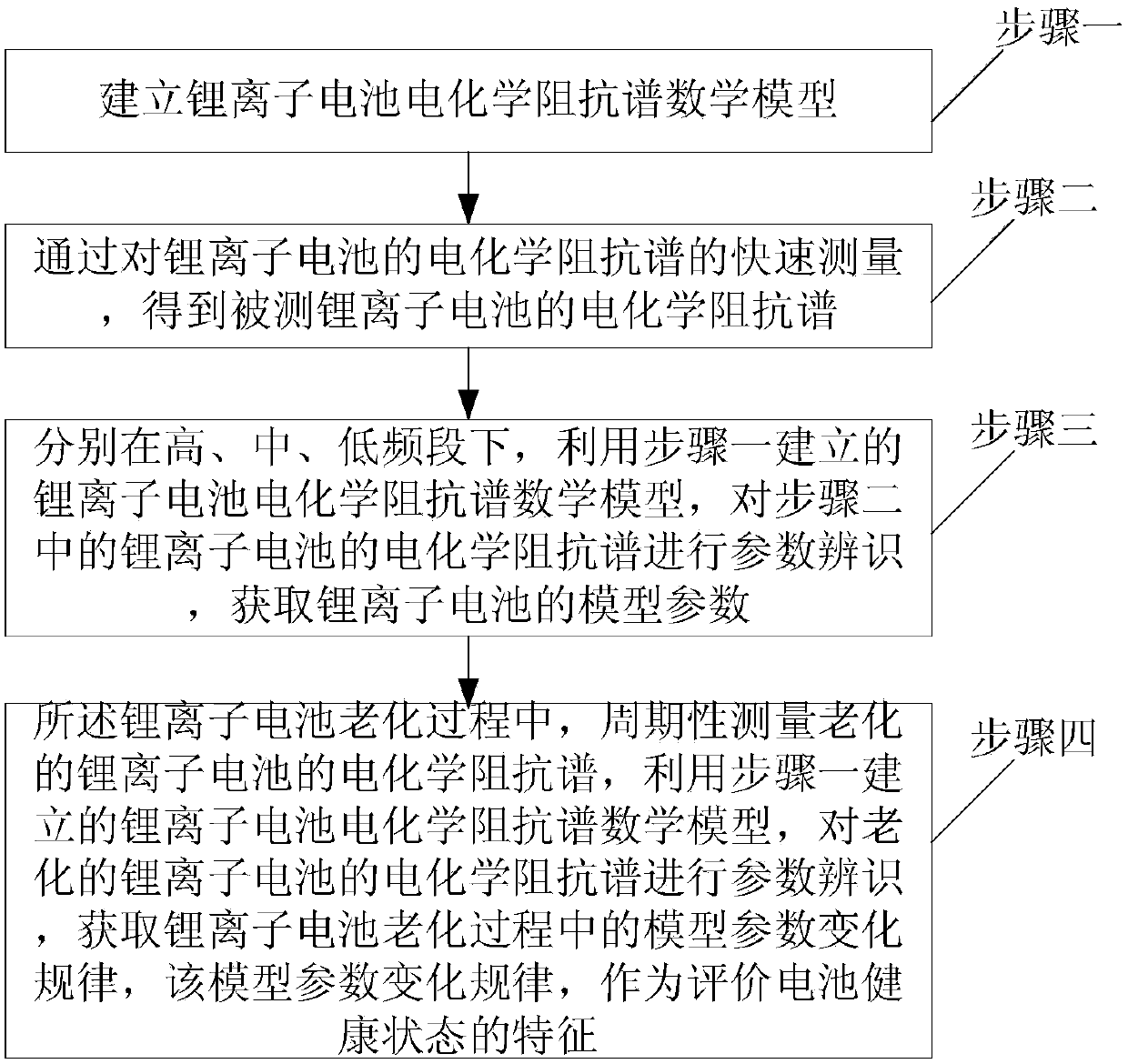
Lithium ion battery internal health feature extraction method based on impedance spectrum
A lithium ion battery internal health feature extraction method based on an impedance spectrum, and relates to the new energy research field; an existing method uses an EIS to analyze and estimate a SOH, wherein the EIS is long in measuring time, and cannot realize online measurements; the lithium ion battery internal health feature extraction method comprises the following steps: building a lithium ion battery electrochemistry impedance spectrum mathematics model; fast measuring a lithium ion battery electrochemistry impedance spectrum, and obtaining the lithium ion battery electrochemistry impedance spectrum; using the lithium ion battery electrochemistry impedance spectrum mathematics model to identify the lithium ion battery electrochemistry impedance spectrum parameters respectively under high, medium and low frequency stages, thus obtaining the lithium ion battery model parameters; periodically measuring the electrochemistry impedance spectrum of the aged lithium ion battery, using the lithium ion battery electrochemistry impedance spectrum mathematics model to identify the lithium ion battery electrochemistry impedance spectrum parameters of the aged lithium ion battery, thus obtaining the model parameter changing rules in the lithium ion battery aging process, and serving as the features that evaluate the battery health states. The lithium ion battery internal health feature extraction method is used for evaluating the battery health states.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
An online proton exchange membrane fuel cell fault diagnosis method based on an impedance spectrum
ActiveCN109726452AEasy fault detectionImprove reliabilityElectrical testingComplex mathematical operationsSupport vector machineDiagnosis methods
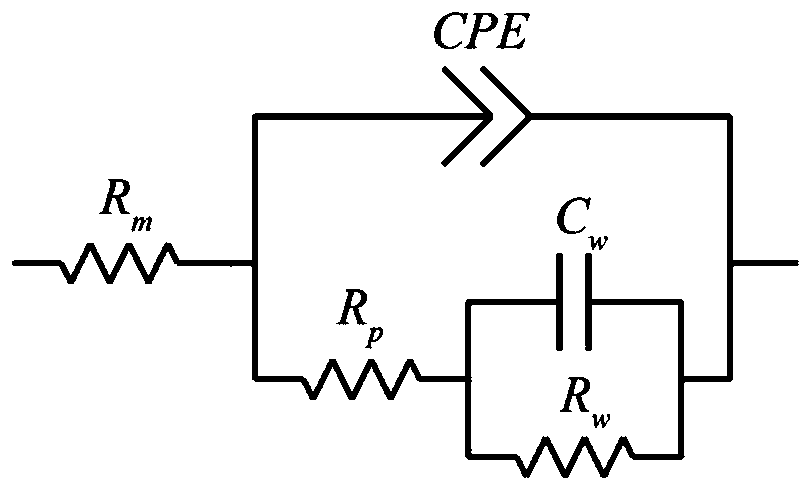
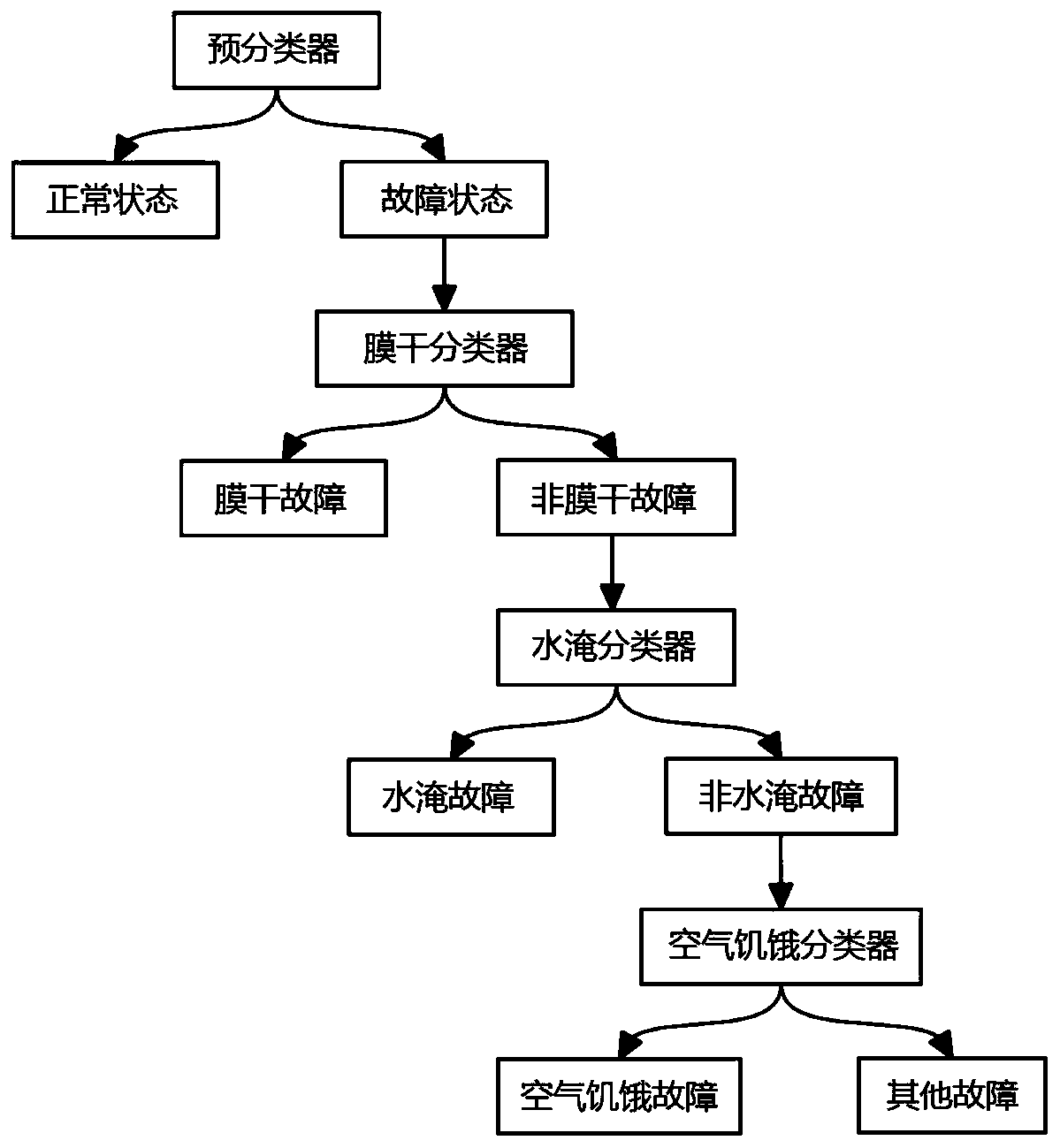
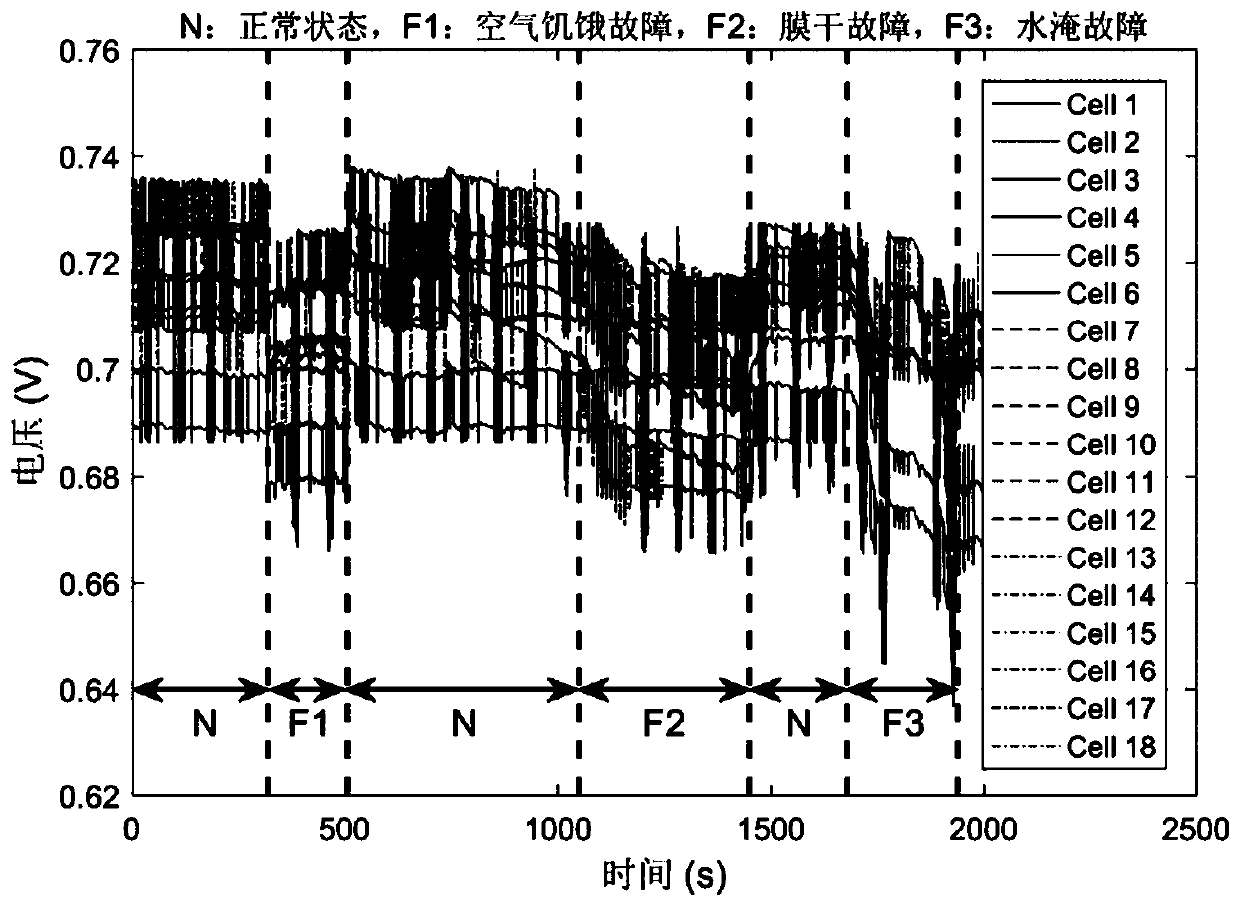
The invention discloses an online proton exchange membrane fuel cell fault diagnosis method based on an impedance spectrum. The method includes: Firstly, establishing an electrochemical equivalent circuit model of the proton exchange membrane fuel cell; performing measuring to obtain an electrochemical impedance spectrum of the proton exchange membrane fuel cell; fitting and solving parameters inthe electrochemical equivalent circuit model by using an electrochemical impedance spectrum; and then selecting a part of parameters as classification characteristics, carrying out classification processing on the proton exchange membrane fuel cells by using a fault diagnosis algorithm based on a binary tree support vector machine, and diagnosing faults such as membrane dryness, water logging andair starvation which easily occur in the proton exchange membrane fuel cells. The problem that fault detection is difficult in the operation process of the proton exchange membrane fuel cell is solved, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy technology is applied to on-line operation monitoring and fault diagnosis of the fuel cell, and the reliability and durability of the cell can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and apparatus for sensing the internal temperature of an electrochemical device
ActiveUS20140372055A1Improve accuracy and reliabilityImprove battery safetyElectric devicesThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical batteryEngineering
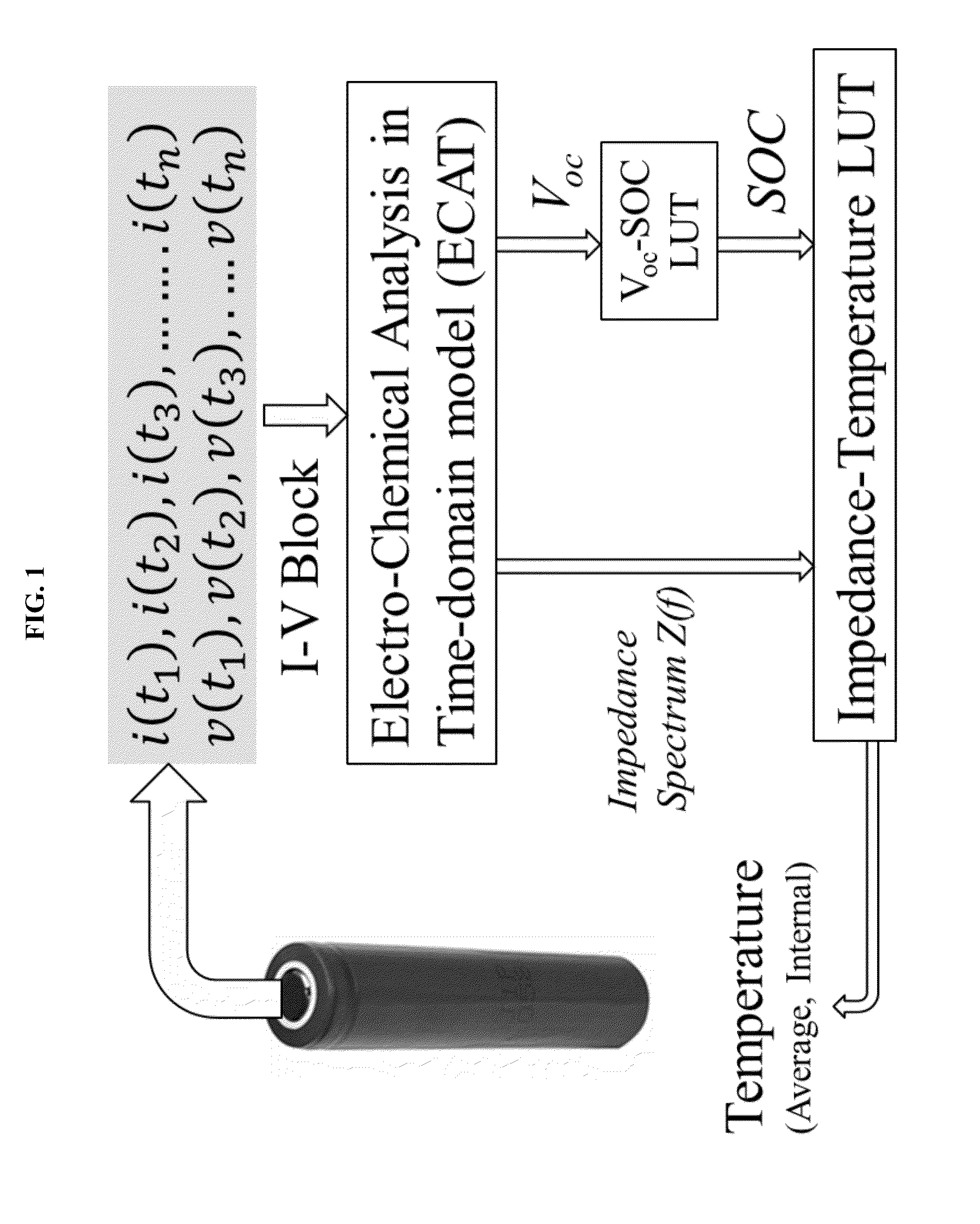
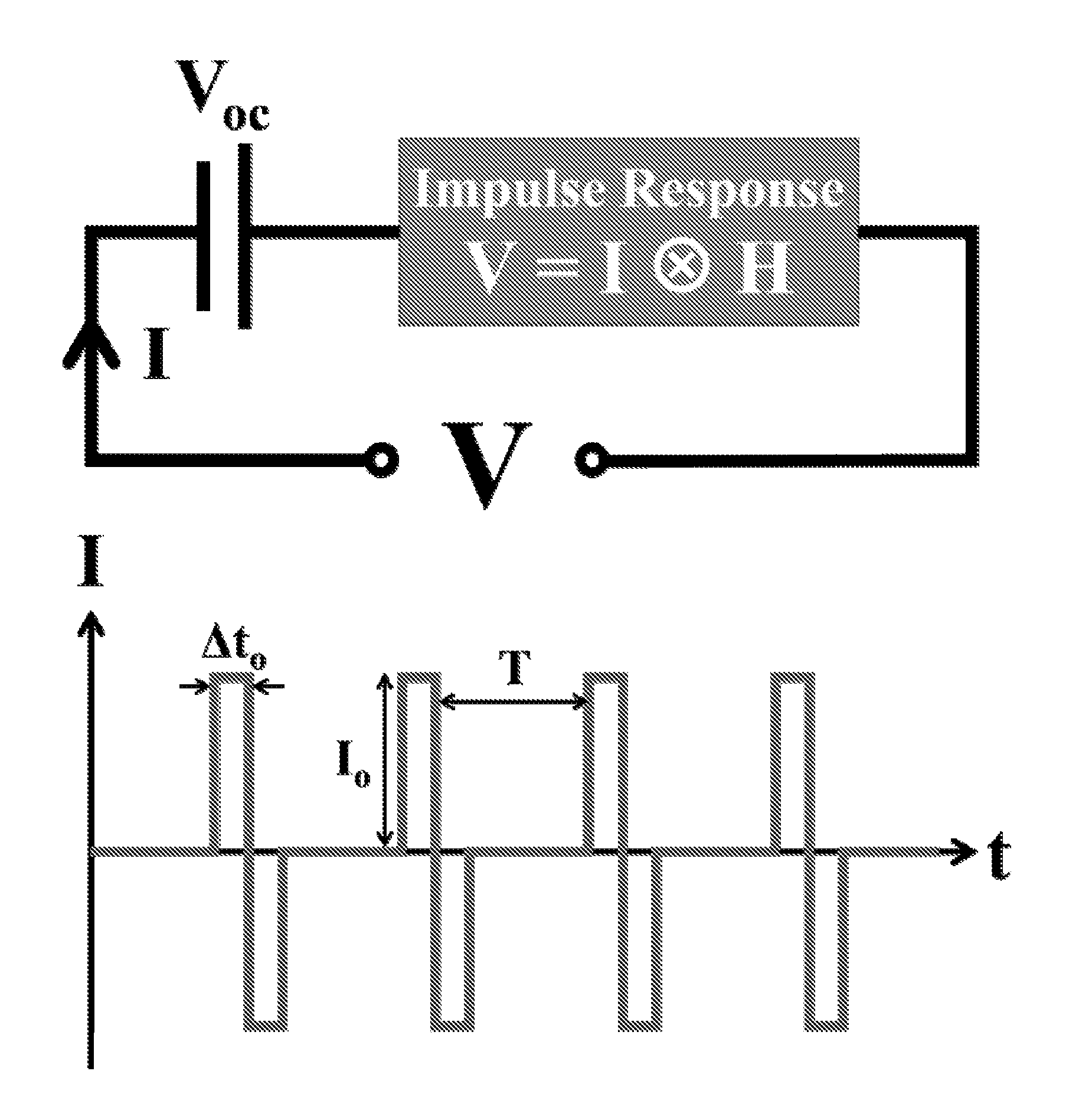
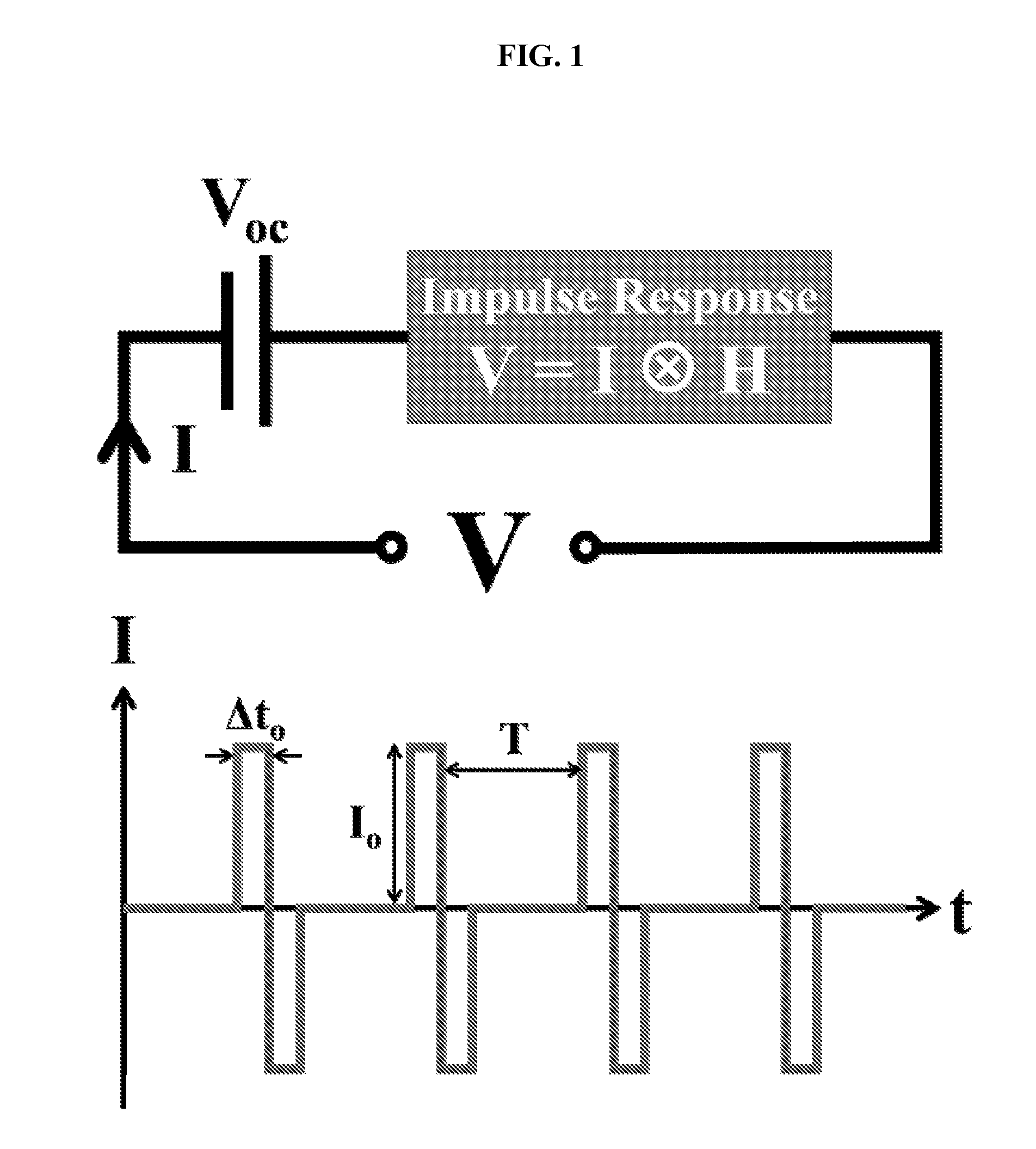
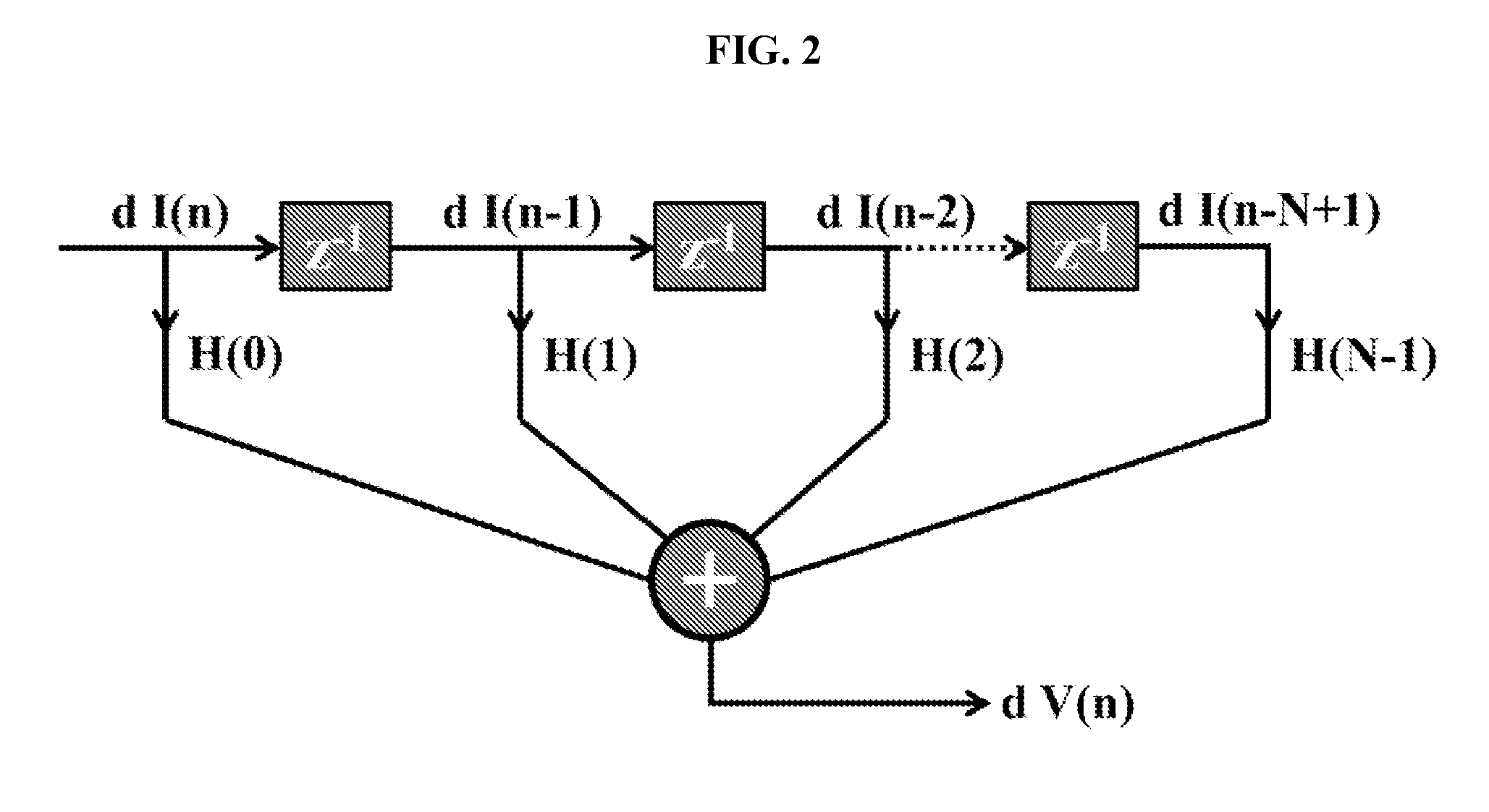
The internal temperature of an electrochemical device may be probed without a thermocouple, infrared detector, or other auxiliary device to measure temperature. Some methods include exciting an electrochemical device with a driving profile; acquiring voltage and current data from the electrochemical device, in response to the driving profile; calculating an impulse response from the current and voltage data; calculating an impedance spectrum of the electrochemical device from the impulse response; calculating a state-of-charge of the electrochemical device; and then estimating internal temperature of the electrochemical device based on a temperature-impedance-state-of-charge relationship. The electrochemical device may be a battery, fuel cell, electrolytic cell, or capacitor, for example. The procedure is useful for on-line applications which benefit from real-time temperature sensing capabilities during operations. These methods may be readily implemented as part of a device management and safety system.
Owner:HRL LAB
Methods and apparatus for monitoring wound healing using impedance spectroscopy
ActiveUS20170156658A1Inhibition formationMonitor progression of wound healingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsWound healingMedicine
Methods and apparatus for real-time, quantifiable monitoring of high-risk areas of biological tissue are described. The methods and apparatus use impedance spectroscopy to detect subtle changes in tissue health.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cable fault detection and aging analysis method
The invention discloses a cable fault detection and aging analysis method. According to the insulation resistance oscillation theory of the frequency domain, the cable fault detection and aging analysis method is characterized in that a fault location model is established by analyzing the oscillation characteristics of frequency domain impedance on the basis of oscillation wave spectrum analysis of the frequency domain impedance acquired by a non-destructive test system or a destructive test system, and then test oscillation impedance spectrum defect is compared with an internal simulation curve, so that long-distance accurate fault location can be realized, and the fault types can be also effectively distinguished. Compared with the prior art, the method not only is capable of realizing accurate multipoint positioning of faults, but also is capable of carrying out fault type recognition and insulation aging state analysis; in the whole detection and analysis processes, artificial experience is hardly depended; the method is suitable for a cable with the length of 1m-1,000km, and is especially suitable for a cable with the length of more than hundreds of kilometers.
Owner:GAUSS ELECTRONICS TECH
Method for sensor reader calibration
ActiveUS20140028327A1Mitigate for environmental parameterReduce the environmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDiagnostic recording/measuringLoad circuitResonance
In one embodiment a method for sensor reader calibration comprising: performing a calibration of a sensor reader wherein the calibration comprises open circuit calibration, a short circuit calibration, and a load circuit calibration, or any combination thereof in any succession; enabling connection of a pickup coil to the sensor reader to measure a sensor response; and applying a baseline correction to the sensor response, wherein the baseline correction is obtained utilizing measurements from the calibration step. In a further embodiment, a method for sensor response calibration incorporating environmental correction comprising: measuring a first resonance impedance spectrum of the sensor with a first applied power to the pickup coil; measuring a second resonance impedance spectrum of the sensor with a second applied power to the pickup coil; and applying a correction to the sensor response corresponding to the respective measured first and second resonance impedance spectrum to mitigate for environmental parameters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
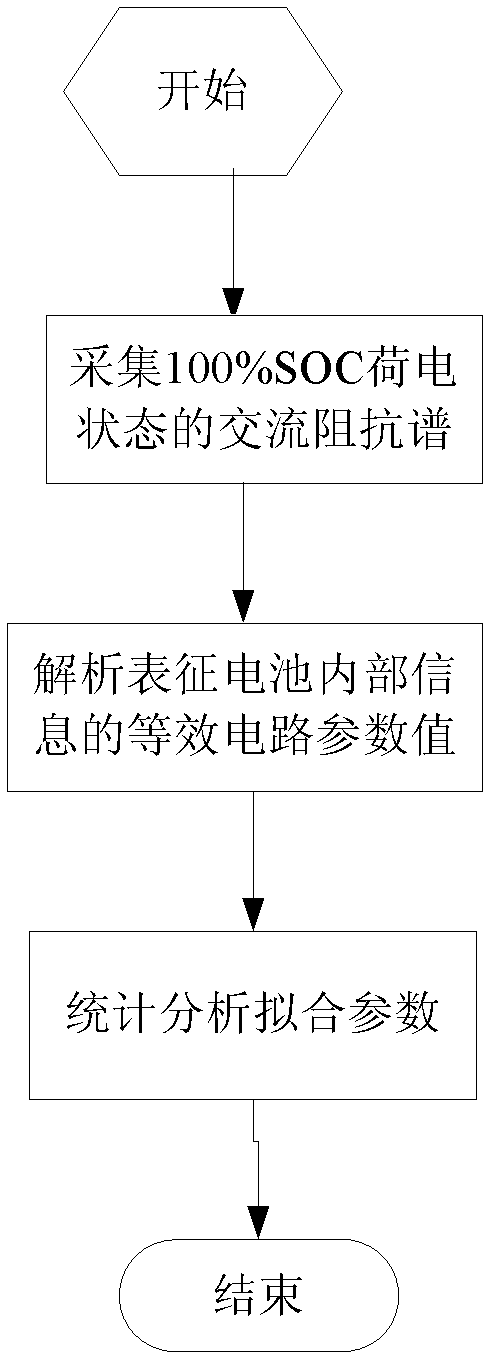
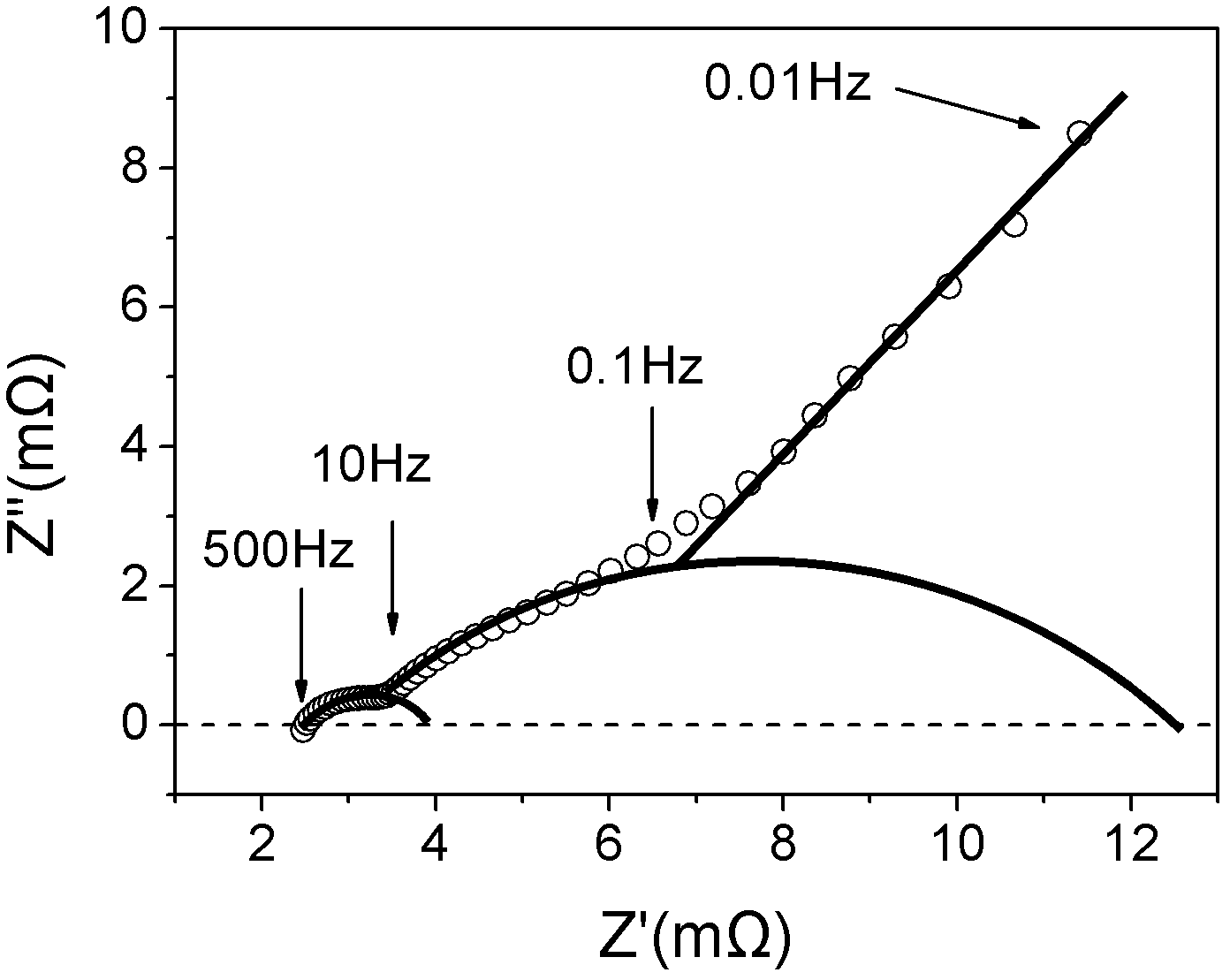
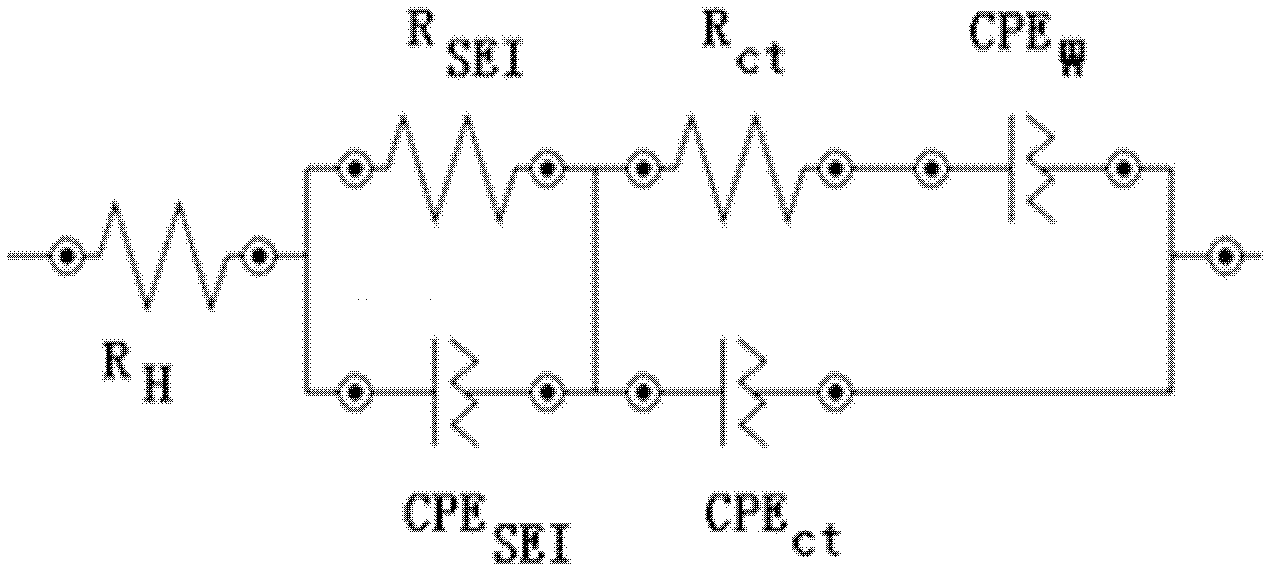
Battery sorting method based on alternating-current impedance spectrum
ActiveCN102553838AAccurate reflection of healthAccurately reflects electrolyte concentrationSortingLithiumElectrical battery
The invention relates to a lithium ion secondary battery, in particular to a sorting method based on an alternating-current impedance spectrum. The method comprises the steps of (1) acquiring the alternating-current impedance spectrum; (2) analyzing equivalent-circuit parameters; and (3) conducting statistic analysis on the equivalent-circuit parameters. In the method provided by the invention, an electrode structure inside a battery system can be detected without damaging a battery, the inner information such as health condition of the battery, the electrolyte concentration, diaphragms and SEI (Solid Electrolyte Interface) membranes are accurately reflected; and according to the information, the coefficient of concordance is calculated by utilizing the principle of statistics, so that the consistency of the inner structure of the sorted battery can be ensured sufficiently, the differences of the sorted batteries are reduced obviously, and the defects of a sorting method in prior arts can be overcome.
Owner:许昌许继电科储能技术有限公司
Double-pulse technique for on-line diagnostics of electrochemical systems
InactiveUS20140372054A1Electrical testingSpecial data processing applicationsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)State of charge
Owner:HRL LAB
Method and apparatus for measuring battery capacity
Provided with a method of measuring battery capacity using parameters obtained from a voltage response signal of a current waveform or an impedance spectrum generated thereof where the method includes the steps of: measuring voltage response signals based on a current waveform applied to a primary or secondary battery; obtaining parameters of an equivalent circuit composed of model parameters such as resistors, capacitors and transmission lines either directly from voltage response or after its conversion to frequency dependent impedance; and determining the unknown battery capacity from the voltage response characteristics based on a correlation between the measured capacity and the model parameters, which correlation is previously determined by a real-time discharge method, thereby takes a shorter time than a real-time discharge method and delivering efficiency and reliability in determining model parameters of an equivalent circuit which are in close correlation with the charge / discharge condition of the battery.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring biological tissue multi-frequency impedance
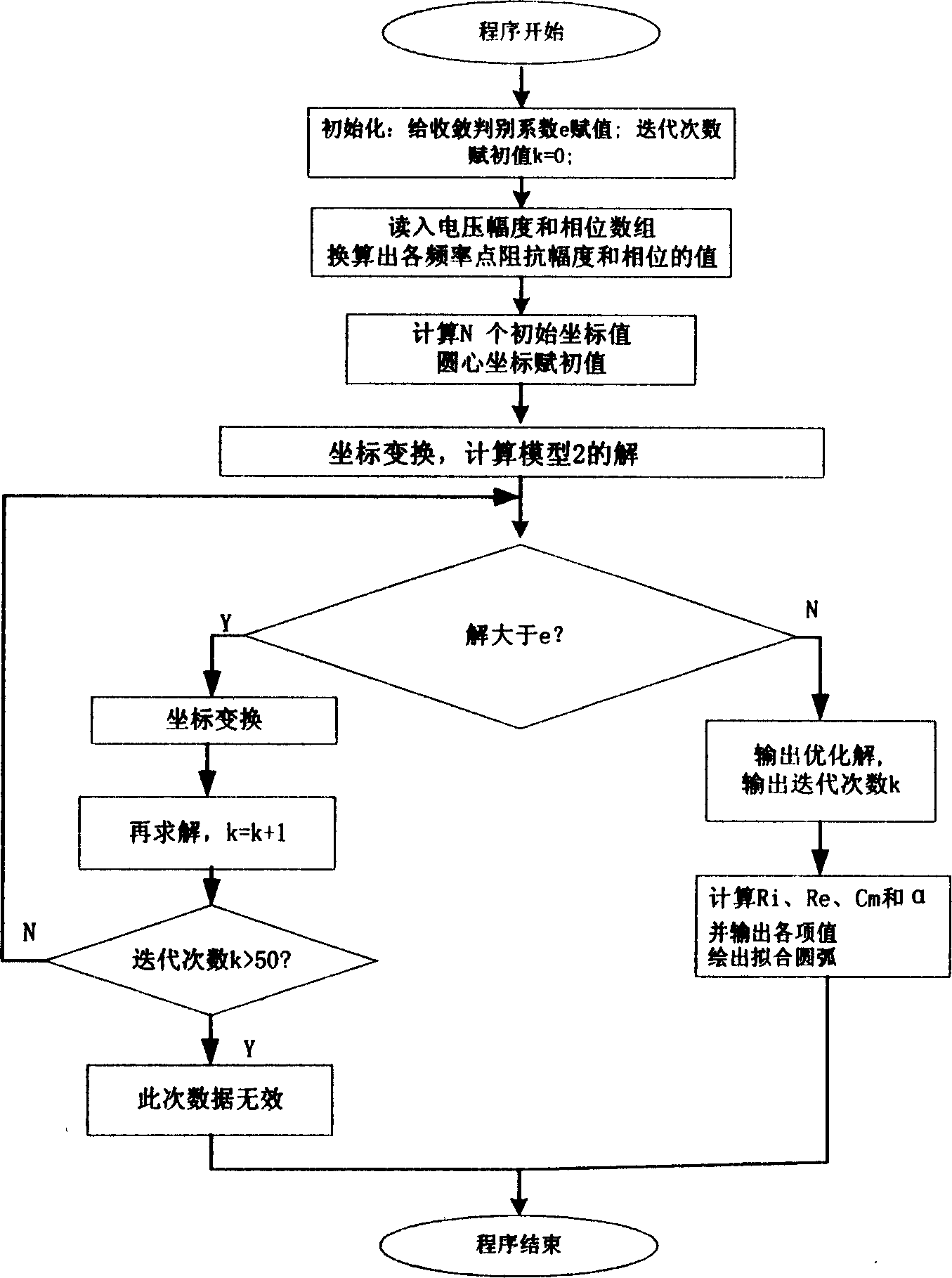
InactiveCN1543912AAccurate extractionFast convergenceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMicrocontrollerSerial line
The invention discloses biological tissue multiple frequency impedance measuring method and measuring apparatus thereof, wherein the linear transformation iterate method of curve fitting is first applied to the extraction of biological tissue impedance model parameter, which can realize accurate matching only through limited frequencies. The measuring apparatus includes a single chip machine for data acquisition, a direct digital frequency synthesizer, a voltage control constant-current source, a current electrode, a voltage measurement and reference signal magnification and filtering circuit, an amplitude discrimination device, a shaping and phase detector, a PC and an isolated serial line interface.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
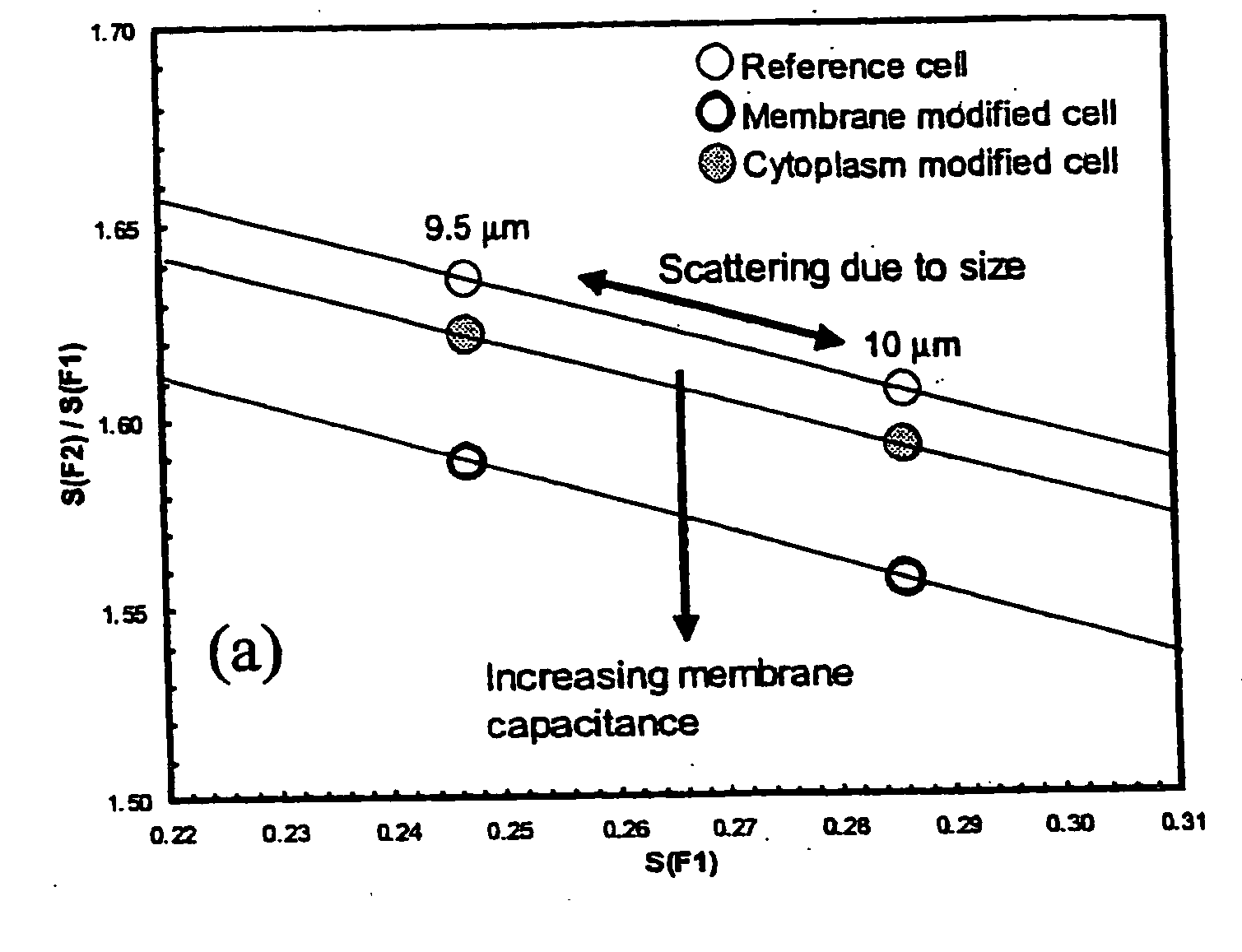
System for simultaneous representation of single cell Young's modulus and cell membrane specific capacitance
ActiveCN104251810AReliable methodReliable wayResistance/reactance/impedenceIndividual particle analysisCapacitanceFrequency spectrum
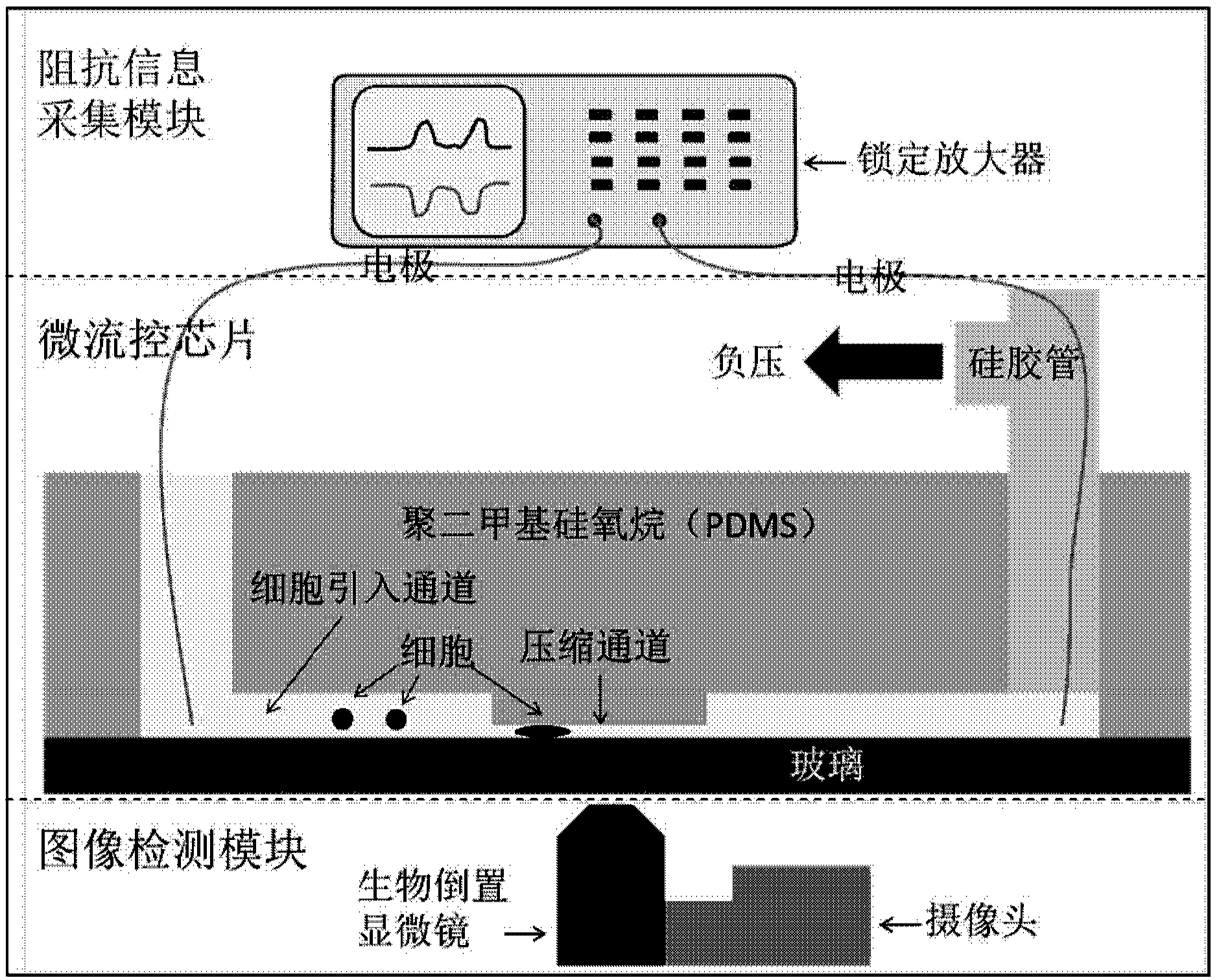
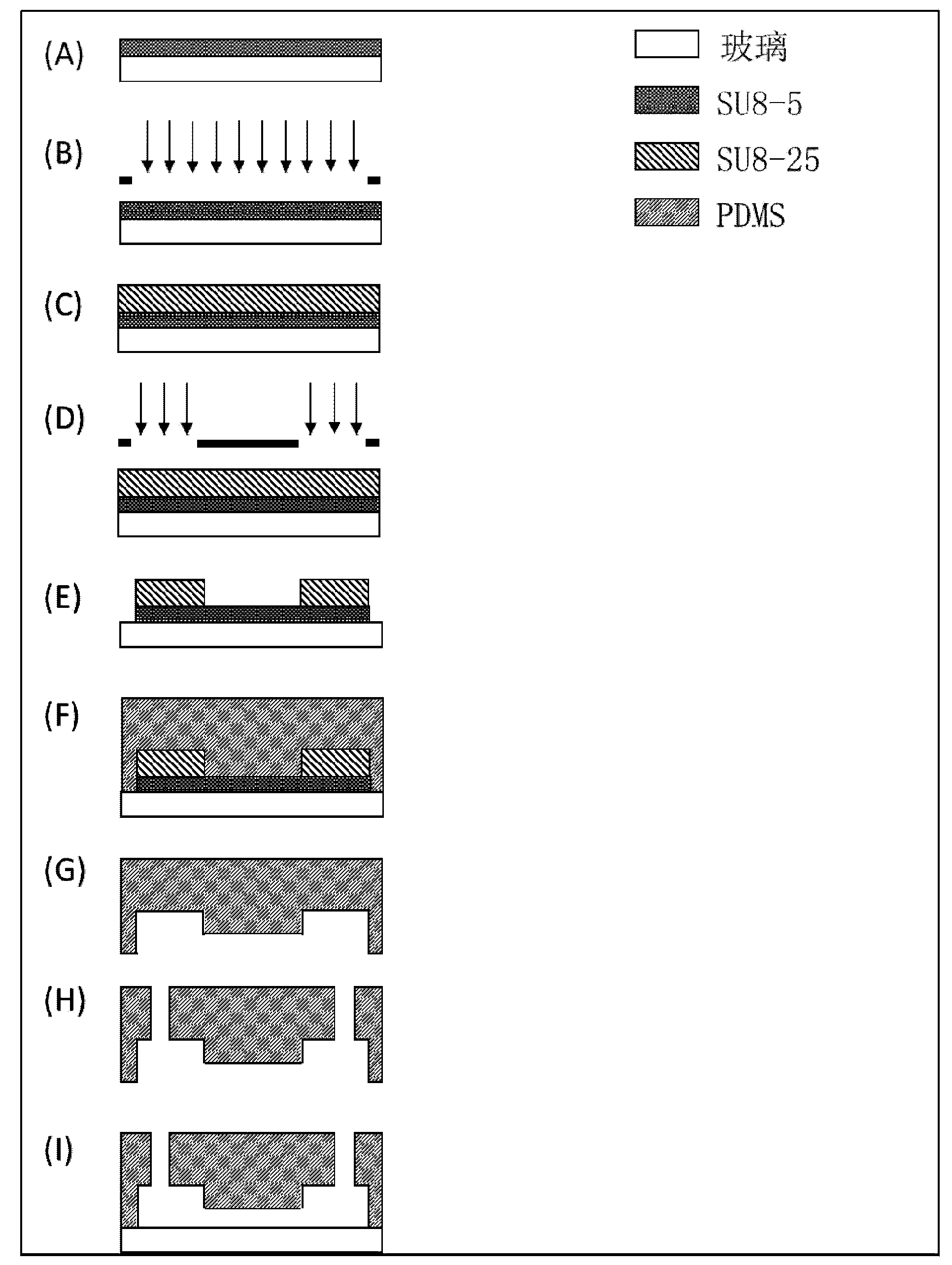
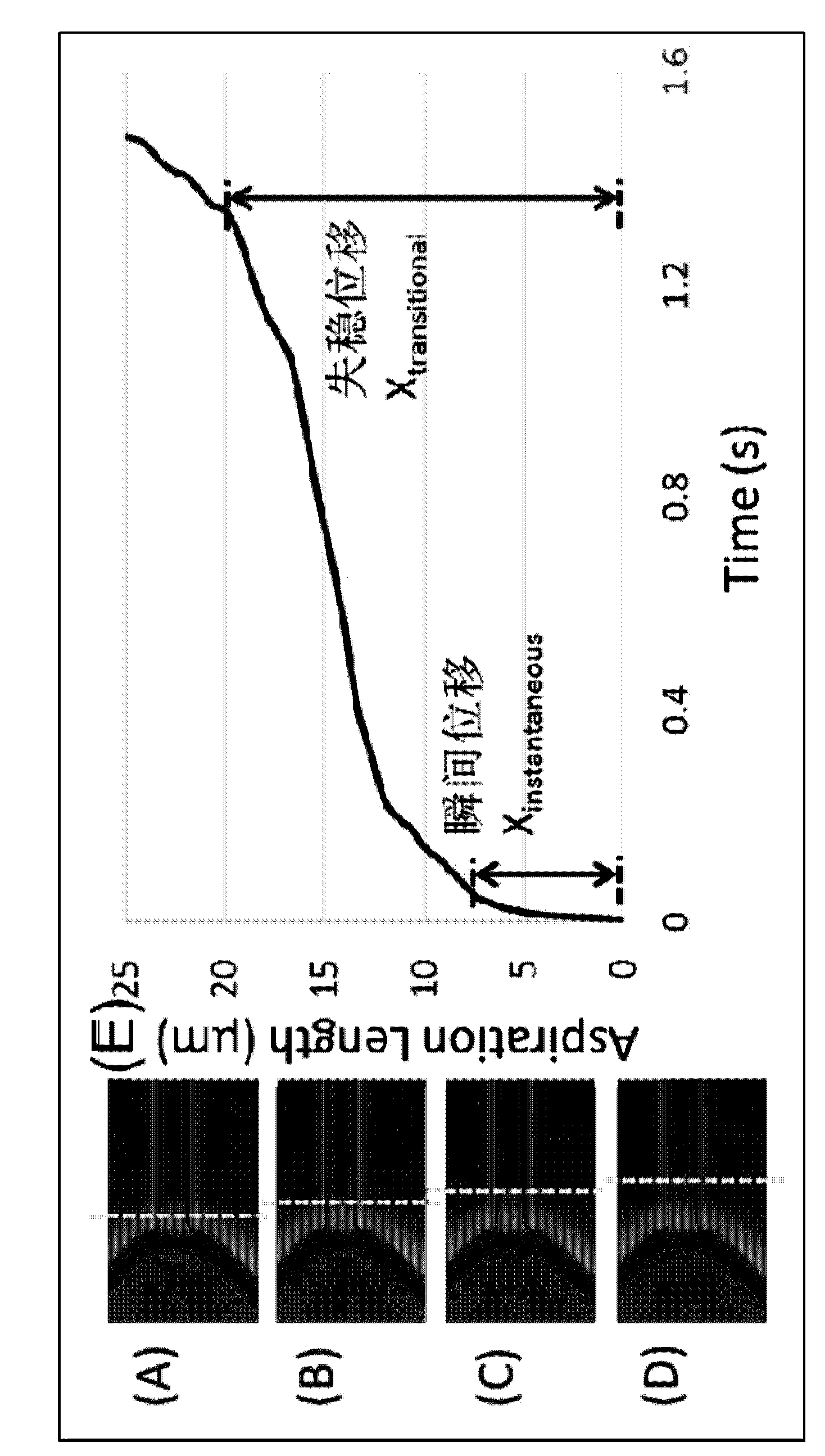
The invention provides a system for simultaneous representation of single cell Young's modulus and cell membrane specific capacitance based on a microfluidic technology. The system makes a cell equivalent to an isotropic super-viscoelastic body, based on ABAQUS mechanical simulation, the relation between the displacement generated by instantaneous entrance of the cell front end into a compression channel, and the cell size, the Young's modulus, the pressure intensity, and geometric parameters of the compression channel, and the Young's modulus of the cell can be calculated. In addition, the invention also puts forward an equivalent electrical model for the cell to pass through the compression channel, the relation between the cell membrane capacitance, cytoplasm resistance, cell and compression channel wall leakage resistance, electrical parameters of the compression channel itself, and the impedance spectrum can be obtained, the impedance change caused by passing of the cell through the compression channel is converted to cell membrane specific capacitance, so that the cell membrane specific capacitance of the single cell can be calculated, thus realizing synchronous measurement of the single cell Young's modulus and cell membrane specific capacitance.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of detecting system function by measuring frequency response
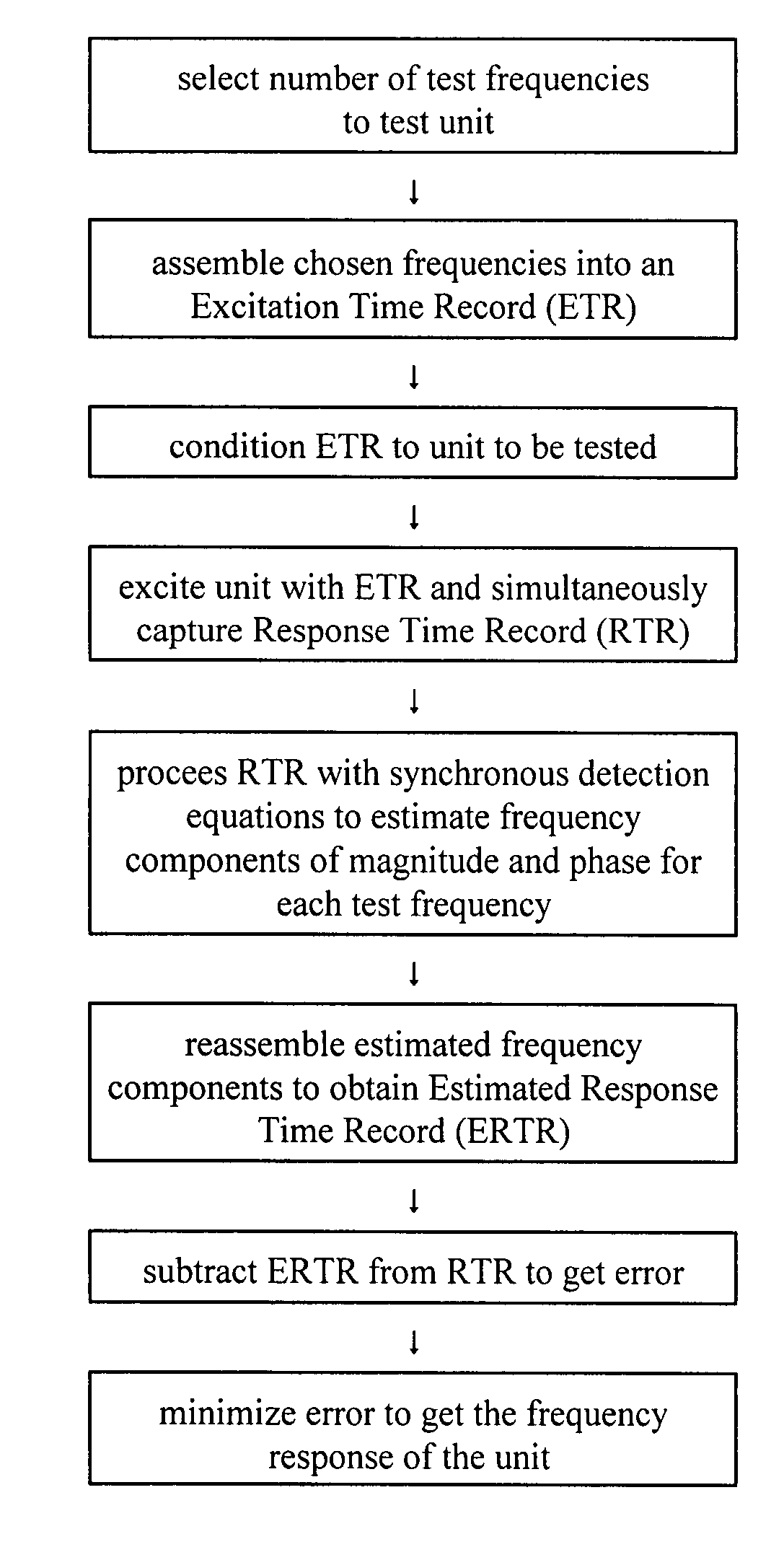
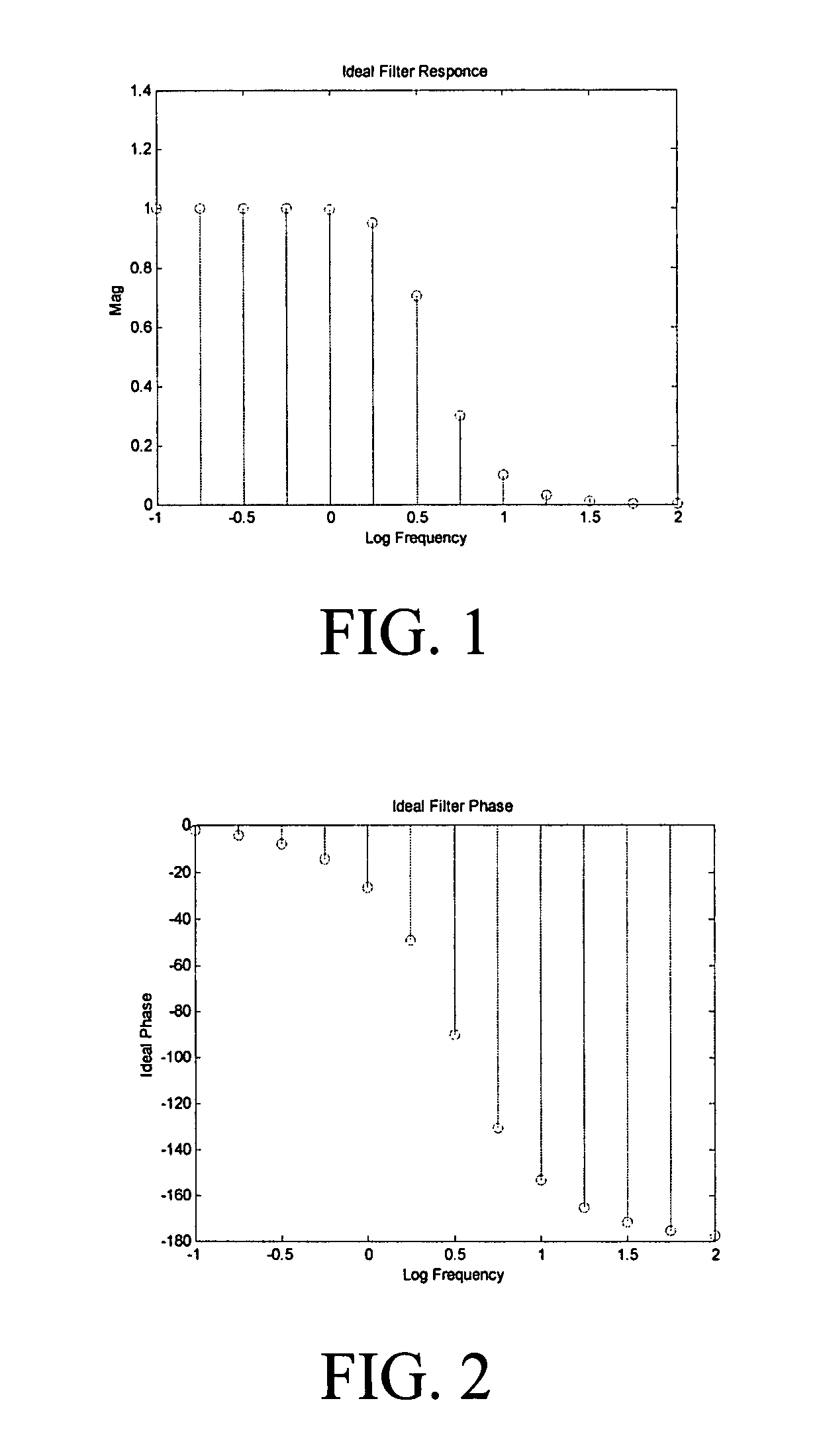
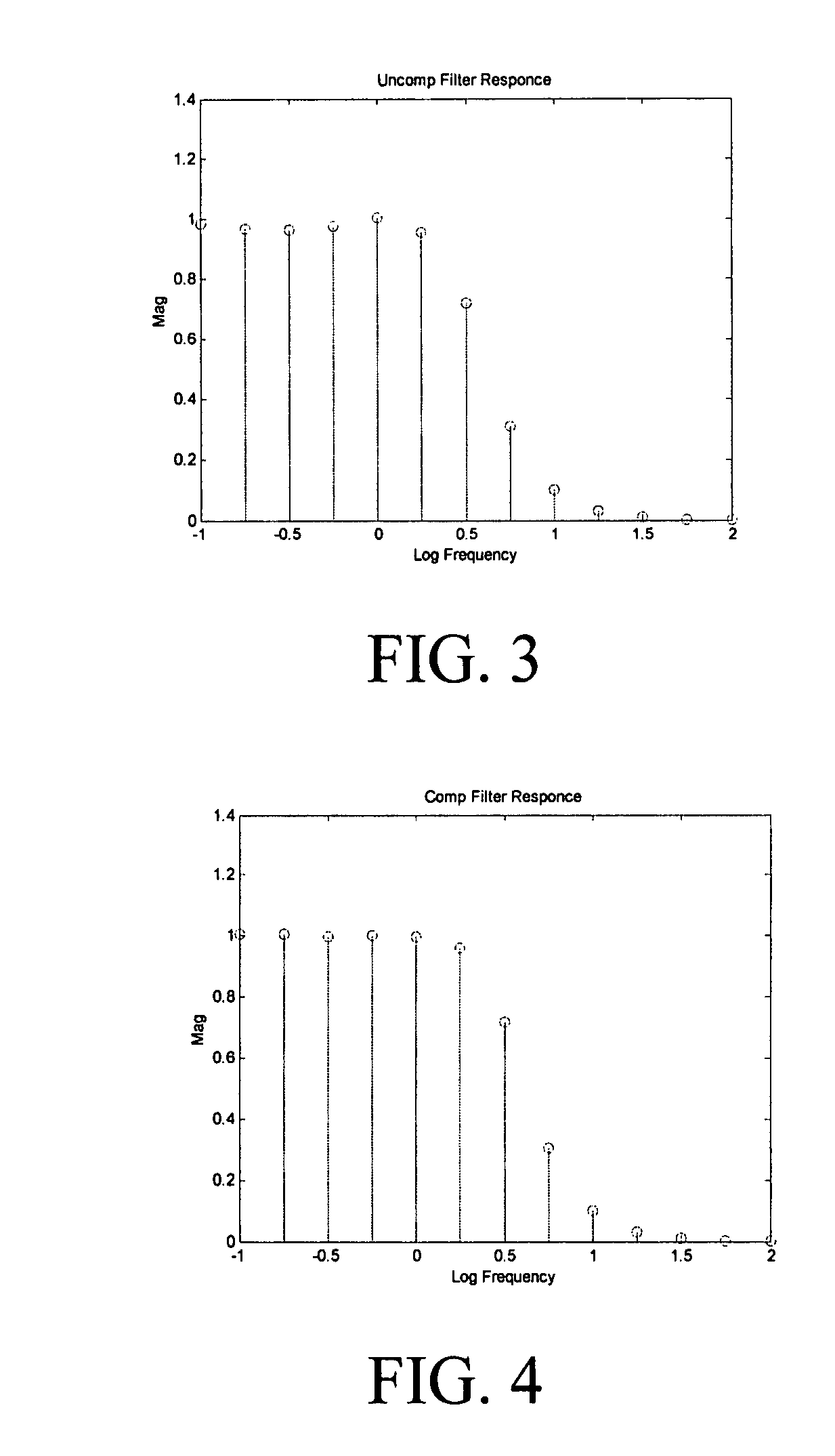
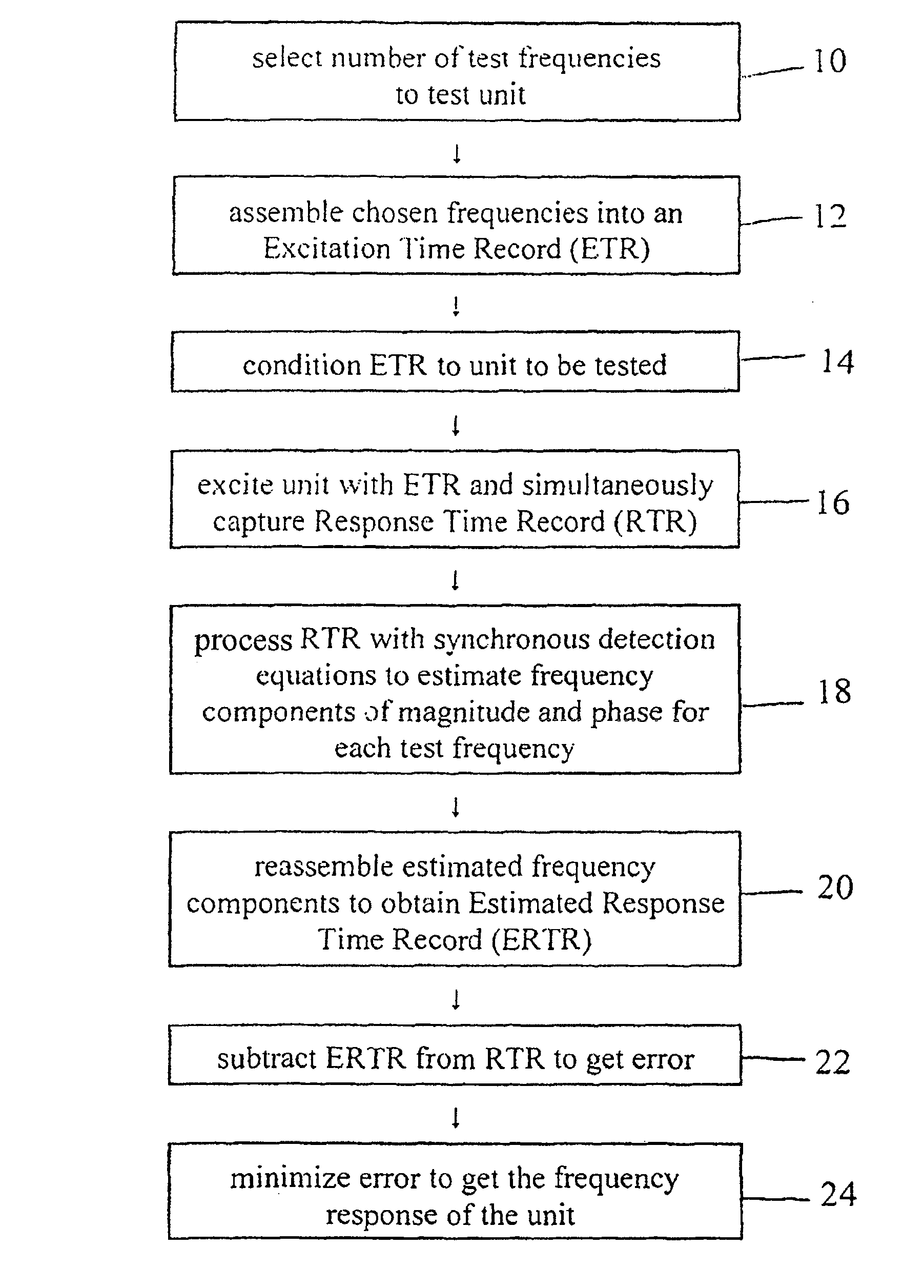
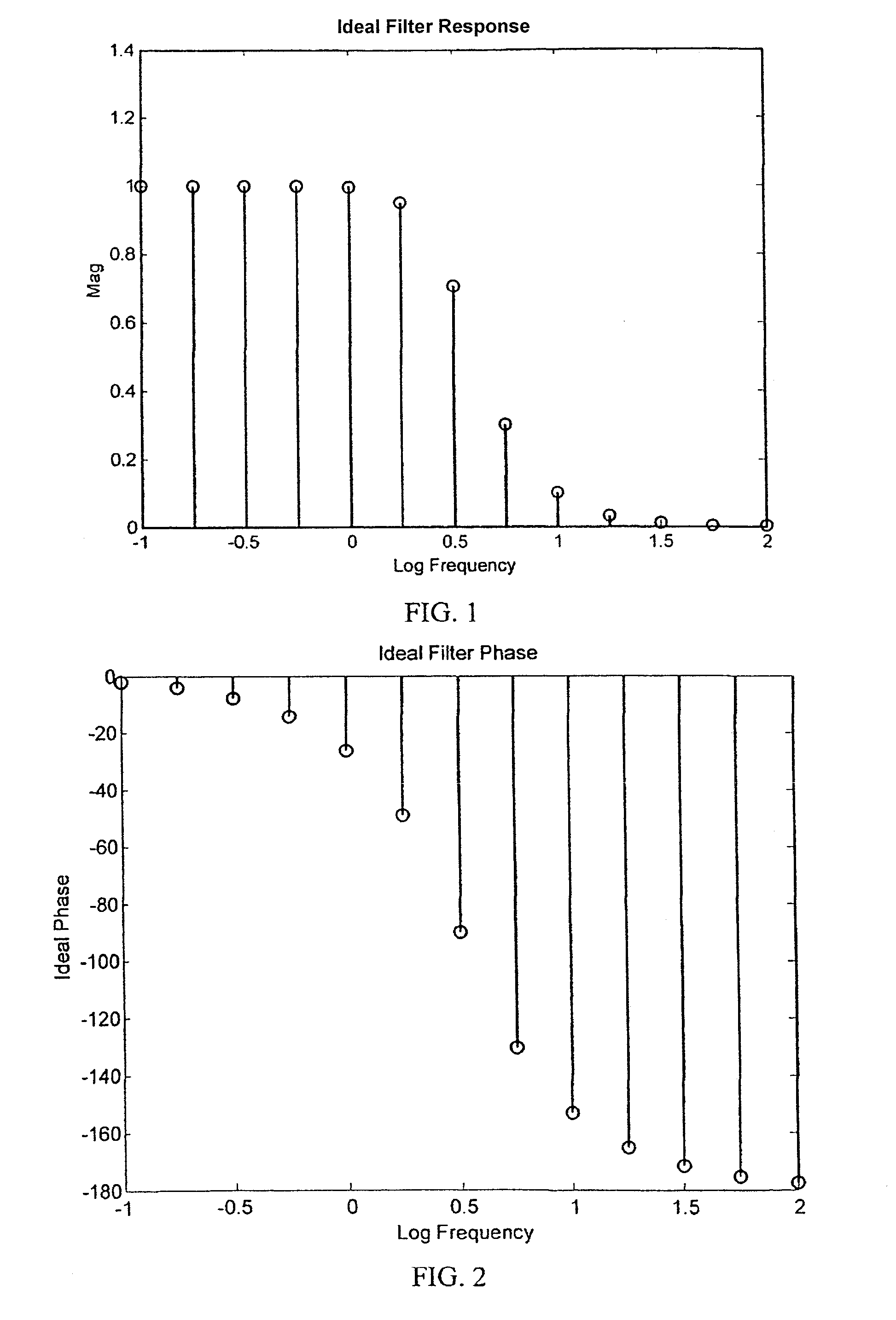
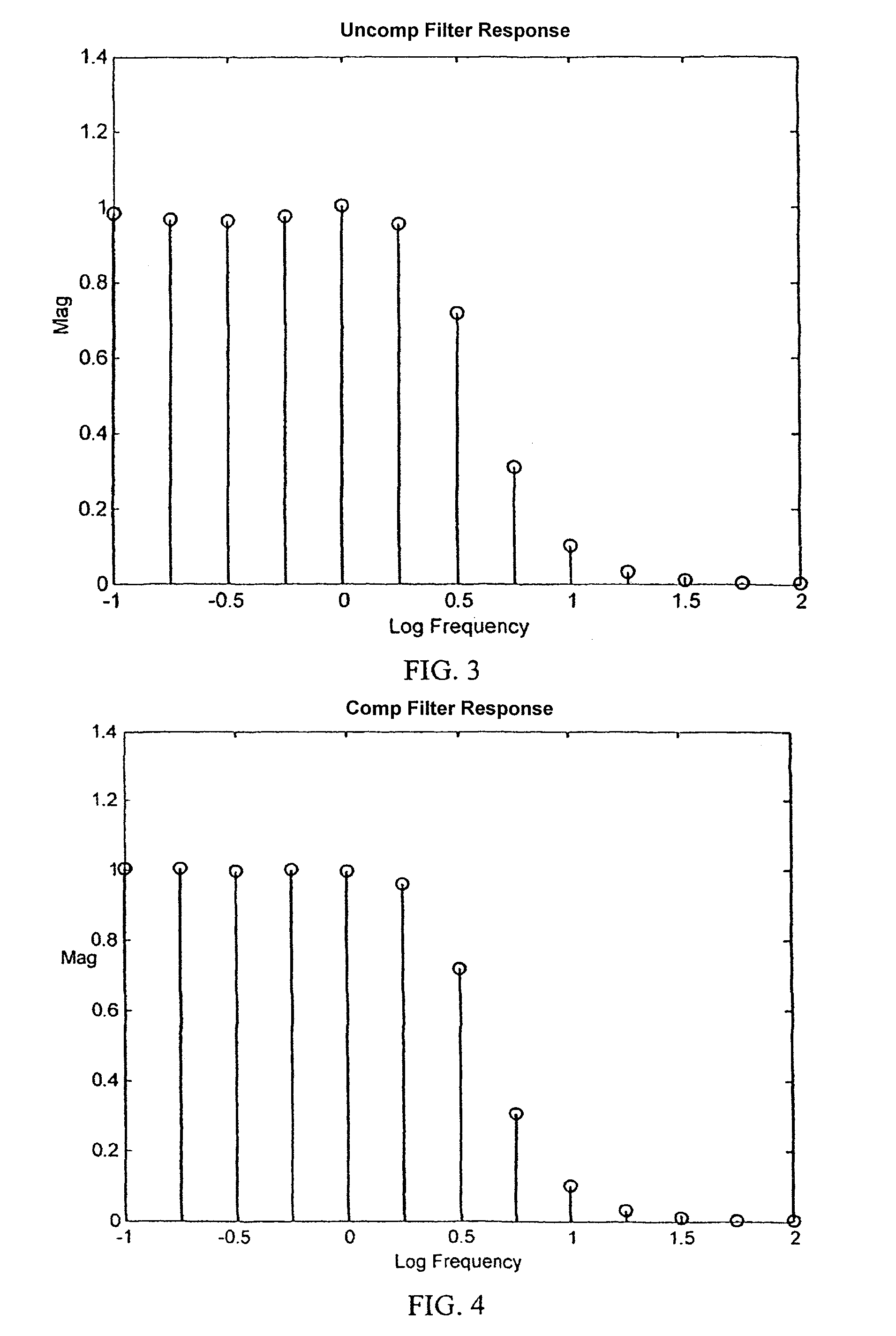
ActiveUS7395163B1Shorten test timeError minimizationResistance/reactance/impedenceError detection/correctionTest batteryTime profile
Real time battery impedance spectrum is acquired using one time record, Compensated Synchronous Detection (CSD). This parallel method enables battery diagnostics. The excitation current to a test battery is a sum of equal amplitude sin waves of a few frequencies spread over range of interest. The time profile of this signal has duration that is a few periods of the lowest frequency. The voltage response of the battery, average deleted, is the impedance of the battery in the time domain. Since the excitation frequencies are known, synchronous detection processes the time record and each component, both magnitude and phase, is obtained. For compensation, the components, except the one of interest, are reassembled in the time domain. The resulting signal is subtracted from the original signal and the component of interest is synchronously detected. This process is repeated for each component.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Impedimetric sensors using dielectric nanoparticles
InactiveUS20120037515A1High sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceFunctionalized nanoparticlesSpectroscopy
A method for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy uses interdigitated electrodes functionalized with a first species and nanoparticles functionalized with a second species that preferentially attaches to the first species. The nanoparticles are composed of a material with a dielectric constant (k value) greater than 2. The chemically functionalized electrodes are then exposed to a solution containing the chemically functionalized nanoparticles which then become immobilized on the electrodes through the attachment of the first species to the second species. The impedance spectrum is measured and an amount of the first species is then determined from the measured spectrum. Because the high-k dielectric nanoparticles increase the double-layer capacitive impedance, the sensitivity of determining the amount of the first species attached to the second species is enhanced.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy system and methods for determining spatial locations of defects
InactiveUS7088115B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectroscopyImpedance spectrum
A method and apparatus for determining spatial locations of defects in a material are described. The method includes providing a plurality of electrodes in contact with a material, applying a sinusoidal voltage to a select number of the electrodes at a predetermined frequency, determining gain and phase angle measurements at other of the electrodes in response to applying the sinusoidal voltage to the select number of electrodes, determining impedance values from the gain and phase angle measurements, computing an impedance spectrum for an area of the material from the determined impedance values, and comparing the computed impedance spectrum with a known impedance spectrum to identify spatial locations of defects in the material.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Peak power prediction method for power battery
ActiveCN104267354APredicting short-term peak output powerPredicted Peak Power Output CapabilityElectric devicesElectrical testingPower batteryReference model
The invention discloses a peak power prediction method for a power battery, relates to a peak power prediction technology for the power battery, and aims to improve the peak power prediction accuracy for the power battery. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following two parts: A, parameter online estimation based on a simplified electrochemical impedance spectrum equivalent circuit model and fractional order combined kalman filtering; B, a battery peak power prediction method based on decomposition of zero-state response and zero-input response. According to the invention, the simplified impedance spectrum model comprising a fractional order component is selected as a reference model for the battery peak power prediction, so that the peak power prediction method based on the model not only can accurately predict short-time peak output power of the battery, but also can accurately predict the peak power output capacity of the battery within a longer time period. The peak power prediction method is suitable for online peak power prediction of an electric car.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of detecting system function by measuring frequency response
ActiveUS8150643B1Shorten test timeLoss of accuracyResistance/reactance/impedenceError detection/correctionTime profileOctave
Real-time battery impedance spectrum is acquired using a one-time record. Fast Summation Transformation (FST) is a parallel method of acquiring a real-time battery impedance spectrum using a one-time record that enables battery diagnostics. An excitation current to a battery is a sum of equal amplitude sine waves of frequencies that are octave harmonics spread over a range of interest. A sample frequency is also octave and harmonically related to all frequencies in the sum. The time profile of this signal has a duration that is a few periods of the lowest frequency. The voltage response of the battery, average deleted, is the impedance of the battery in the time domain. Since the excitation frequencies are known and octave and harmonically related, a simple algorithm, FST, processes the time record by rectifying relative to the sine and cosine of each frequency. Another algorithm yields real and imaginary components for each frequency.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Method for discrimination of particles in a flow cytometer
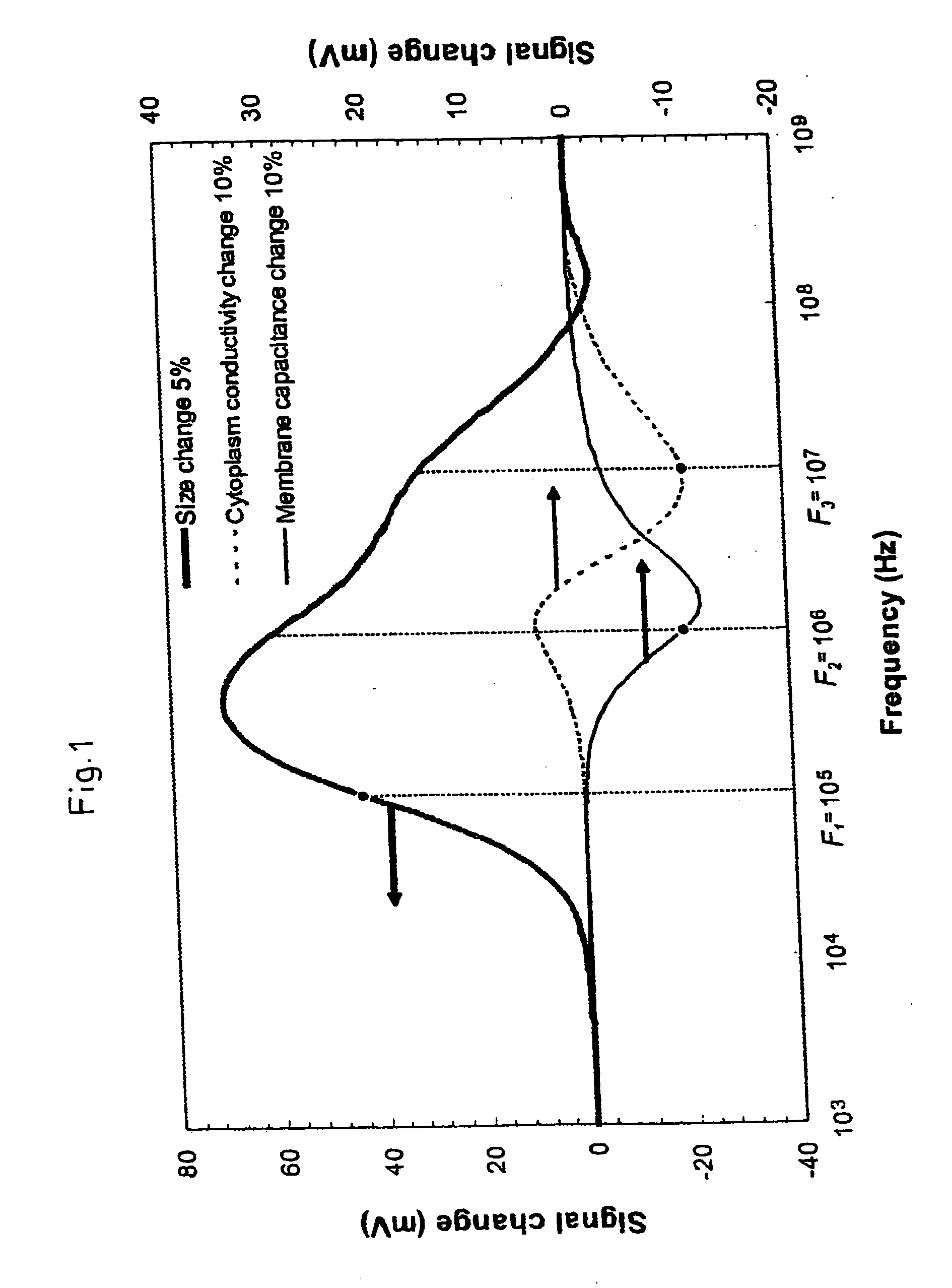
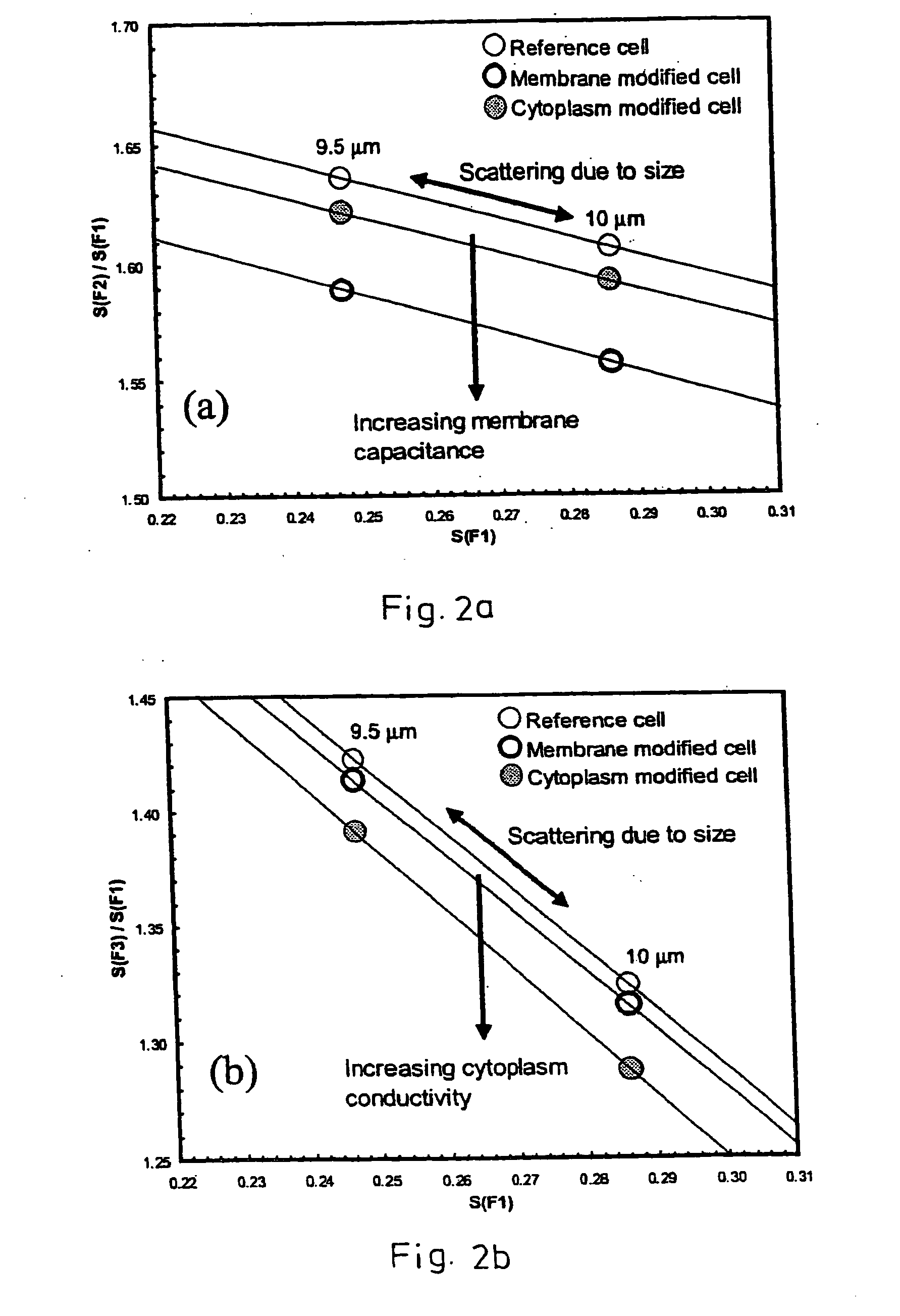
InactiveUS20050114041A1Short timeLaboratory glasswaresIndividual particle analysisPhysicsCapacitance
A method for discrimination of particles, preferably biological cells, in a measurement channel having a liquid for transporting the particles by impedance spectroscopy. Pairs of measurement and reference electrodes are arranged in the measurement channel. During movement of a particle through the pair of measurement electrodes, the pairs of measurement and reference electrodes are admitted with same input signals having different frequencies. Measurement values at the measurement and reference electrodes are compared to determine particle specific values for the particle being moved through the measurement channel. The particle specific values for the different frequencies are normalized to a particle specific basic value at a basic frequency; and then the normalized particle specific values are compared with corresponding values of at least one reference particle at the same different frequencies. The comparison shows changes in the capacitance or in the conductance of the particle, which are used in discriminating the particle.
Owner:LEISTER PROCESS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com