Patents
Literature
4257 results about "Biological tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biological tissue. Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected cells that perform a similar function within an organism. The study of tissue is known as histology, or, in connection with disease, histopathology. The classical tools for studying the tissues are the wax block, the tissue stain, and the optical microscope,...
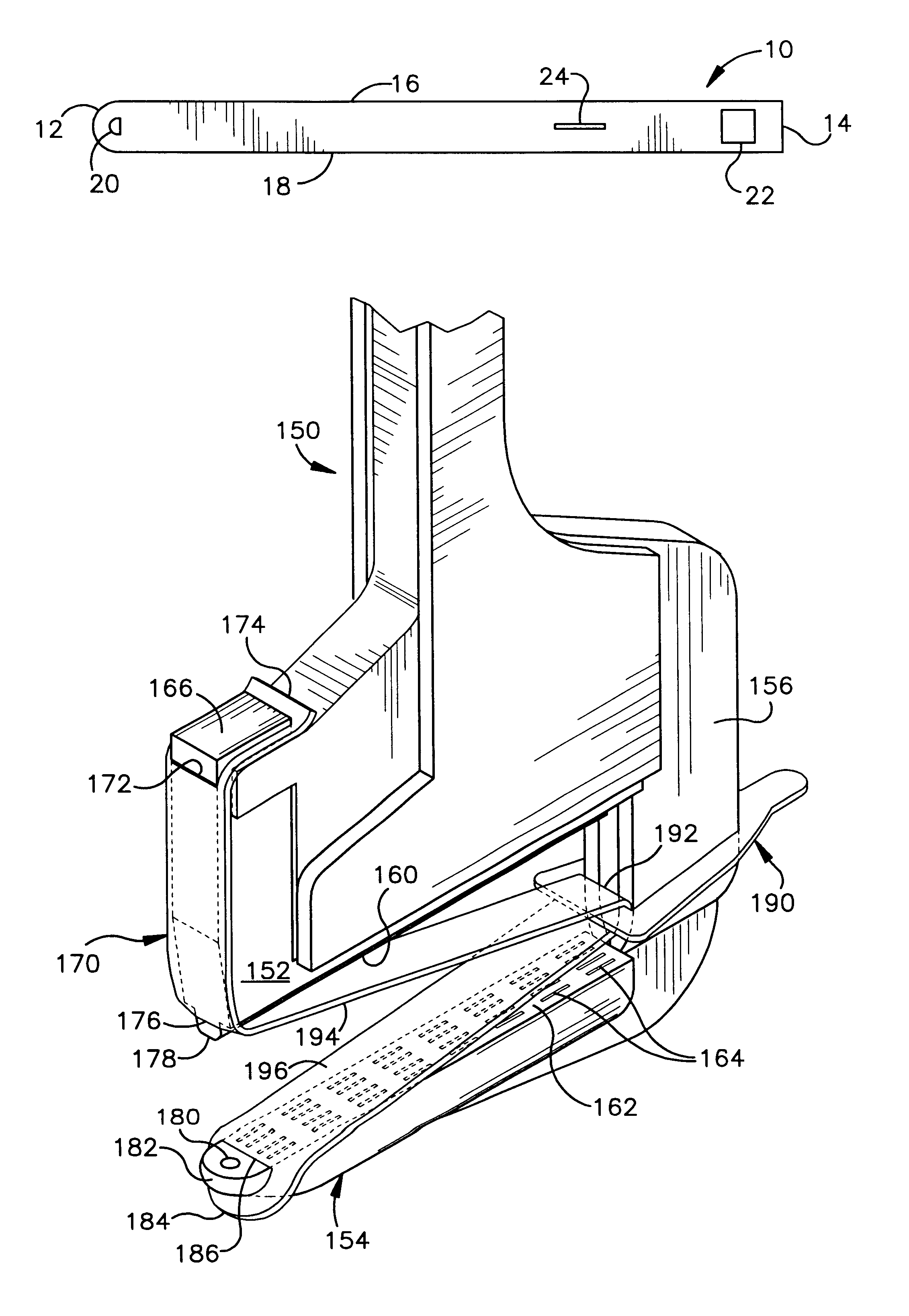
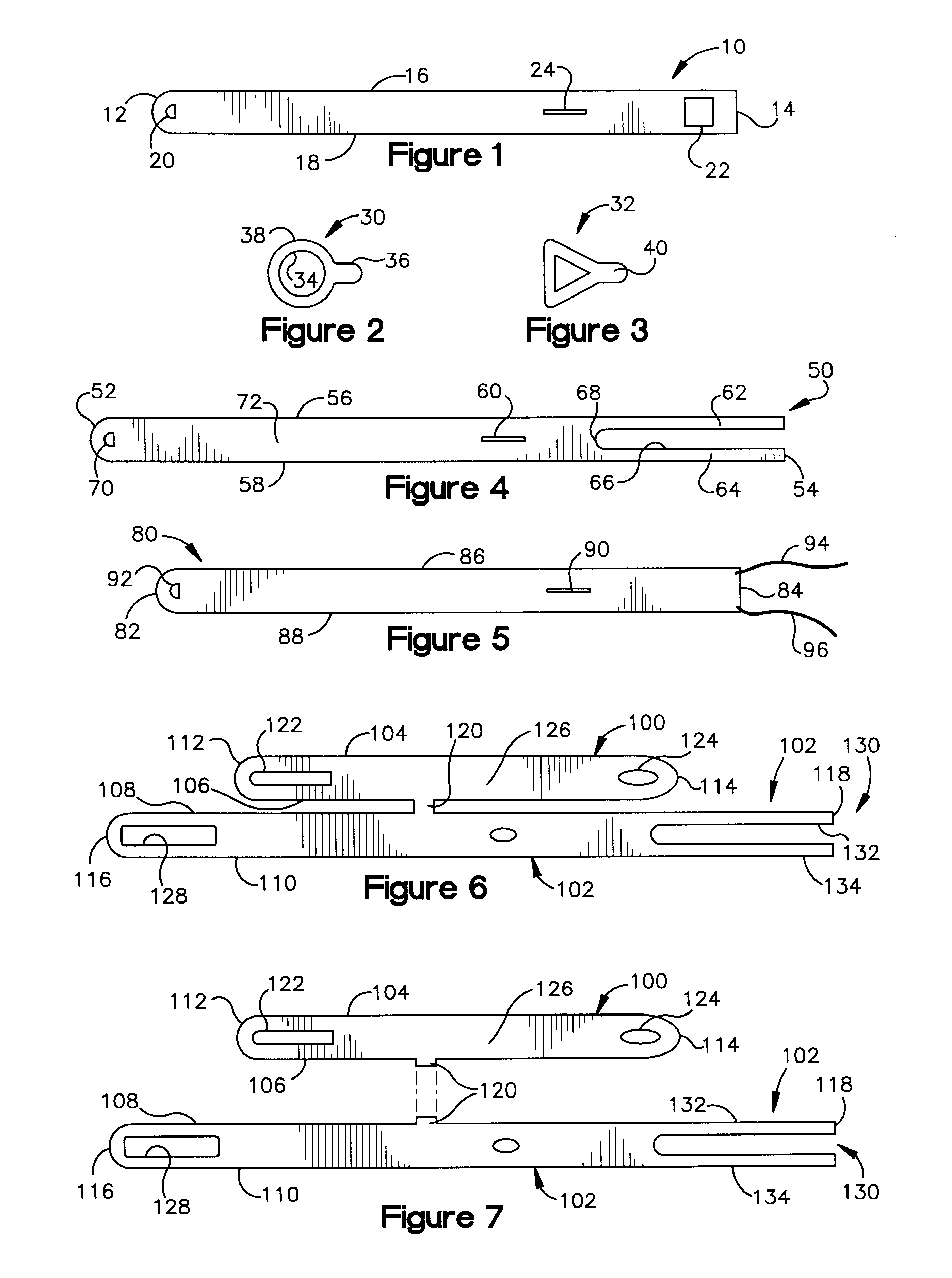
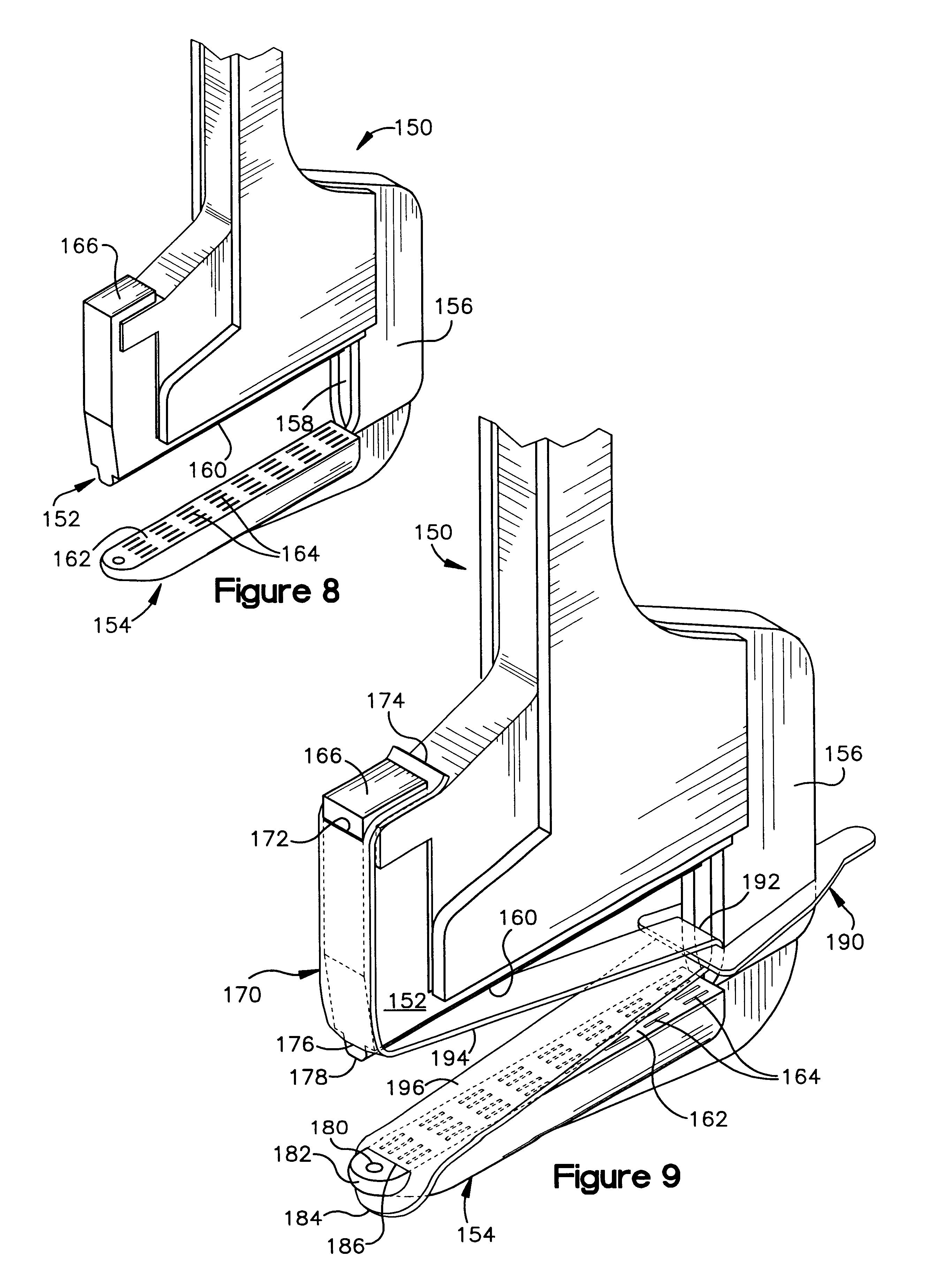
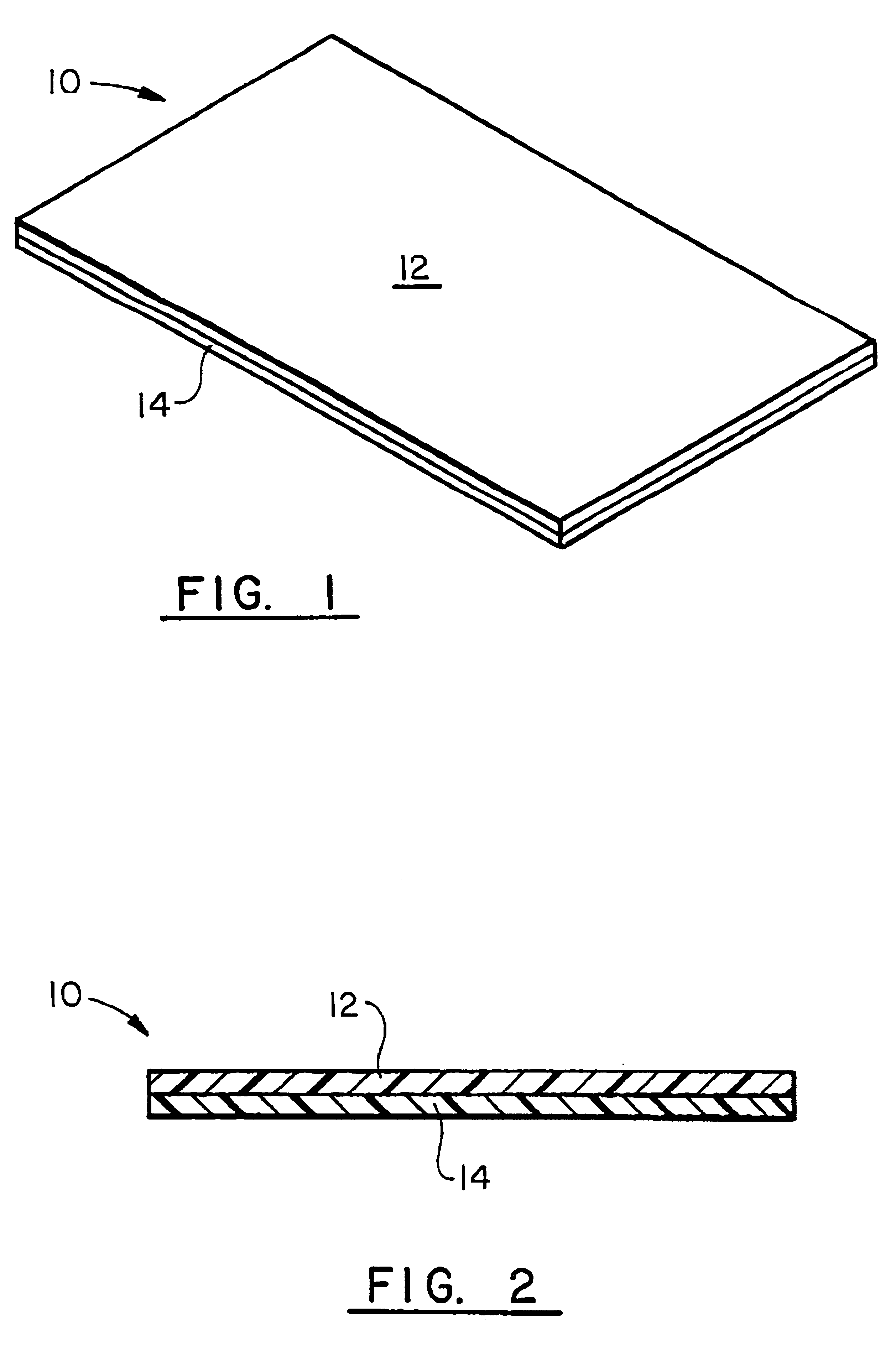
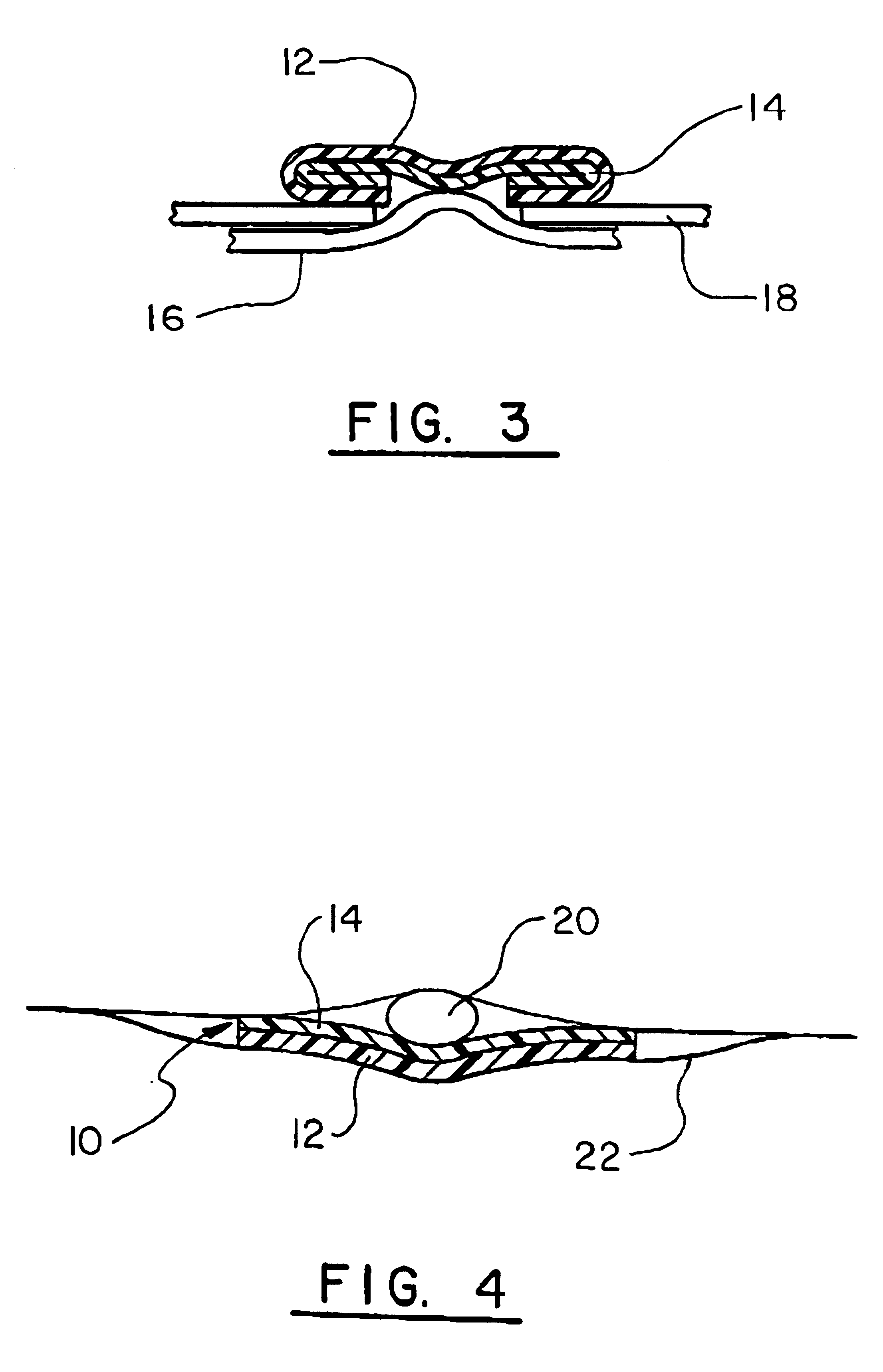
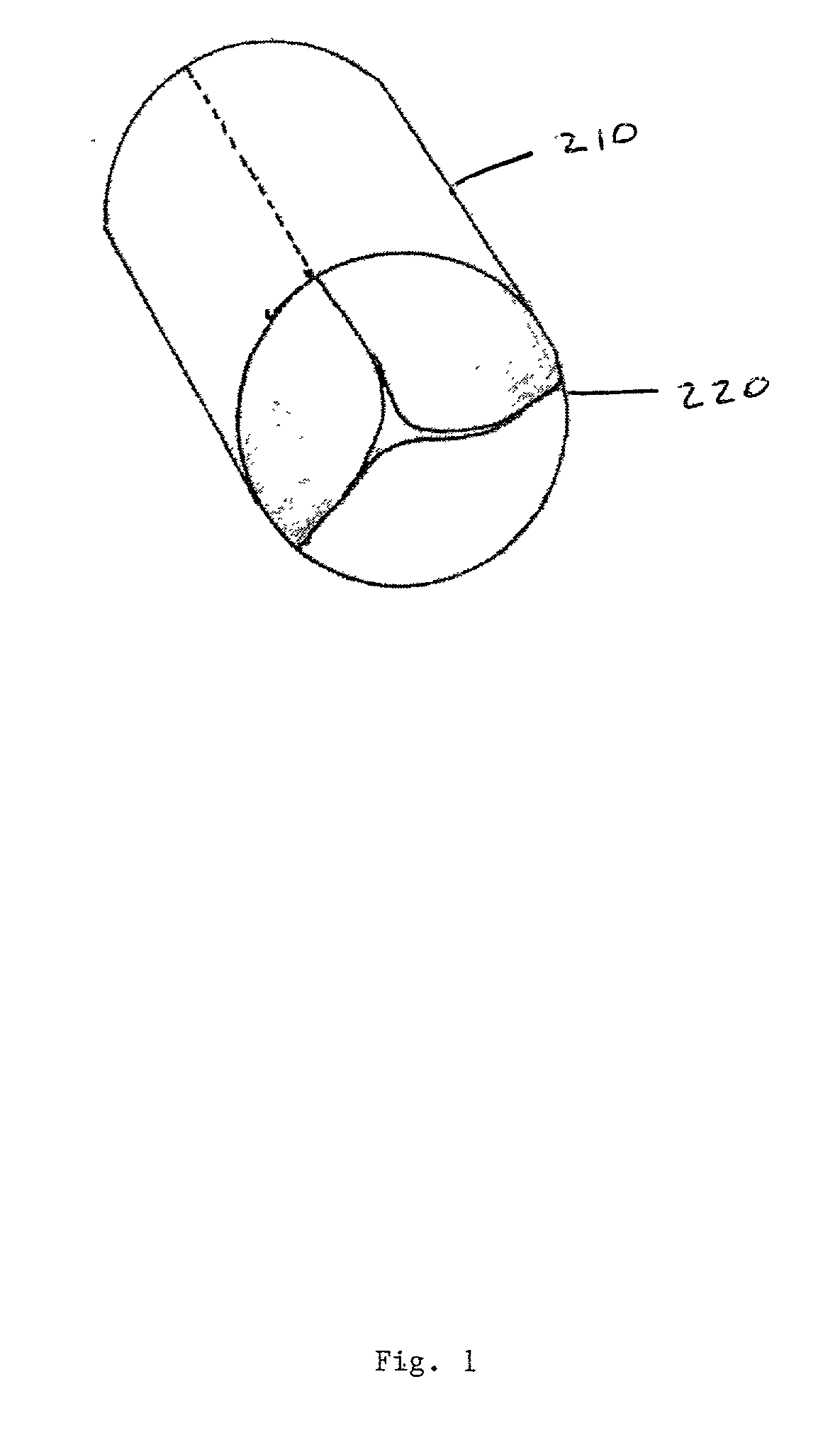
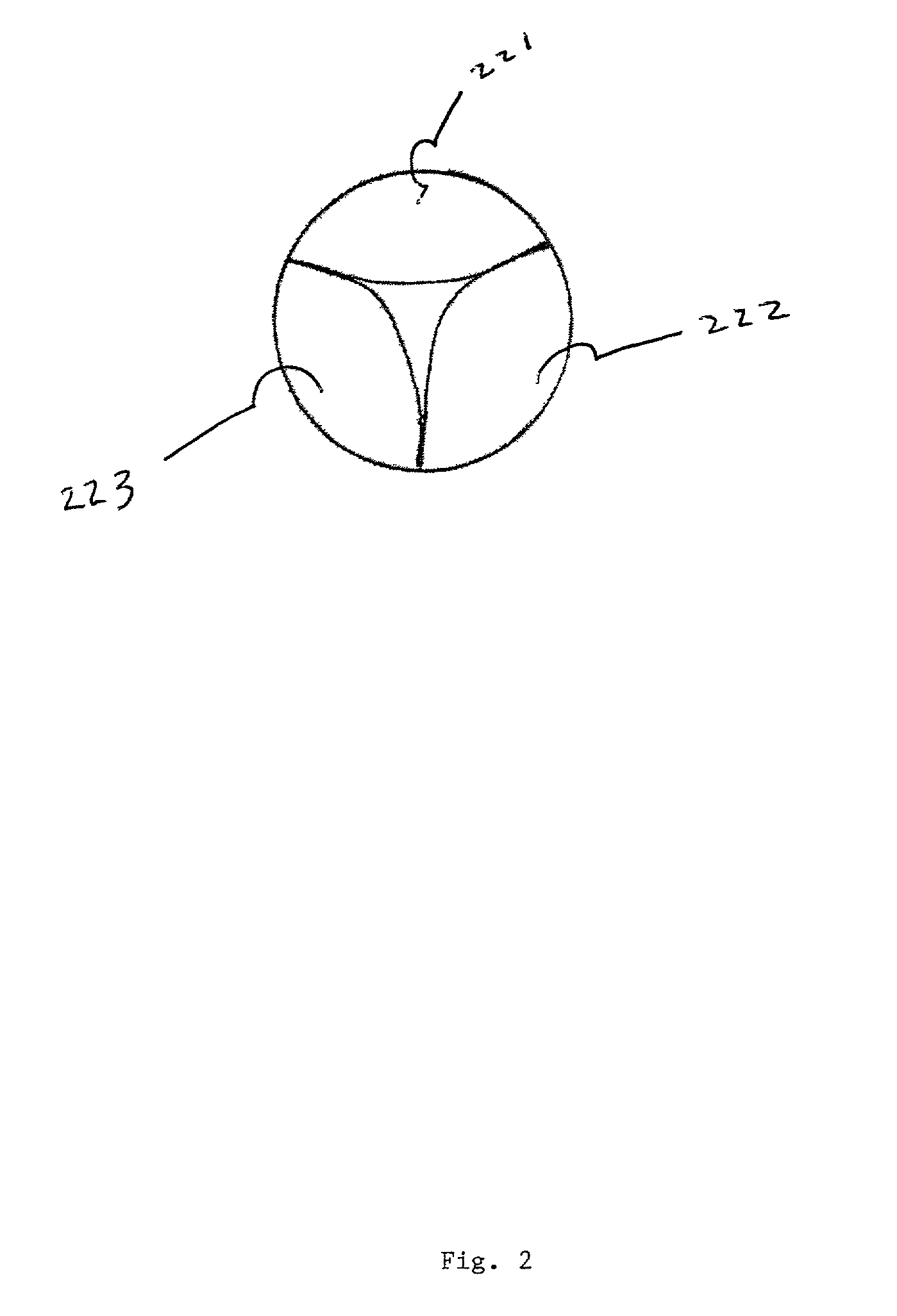
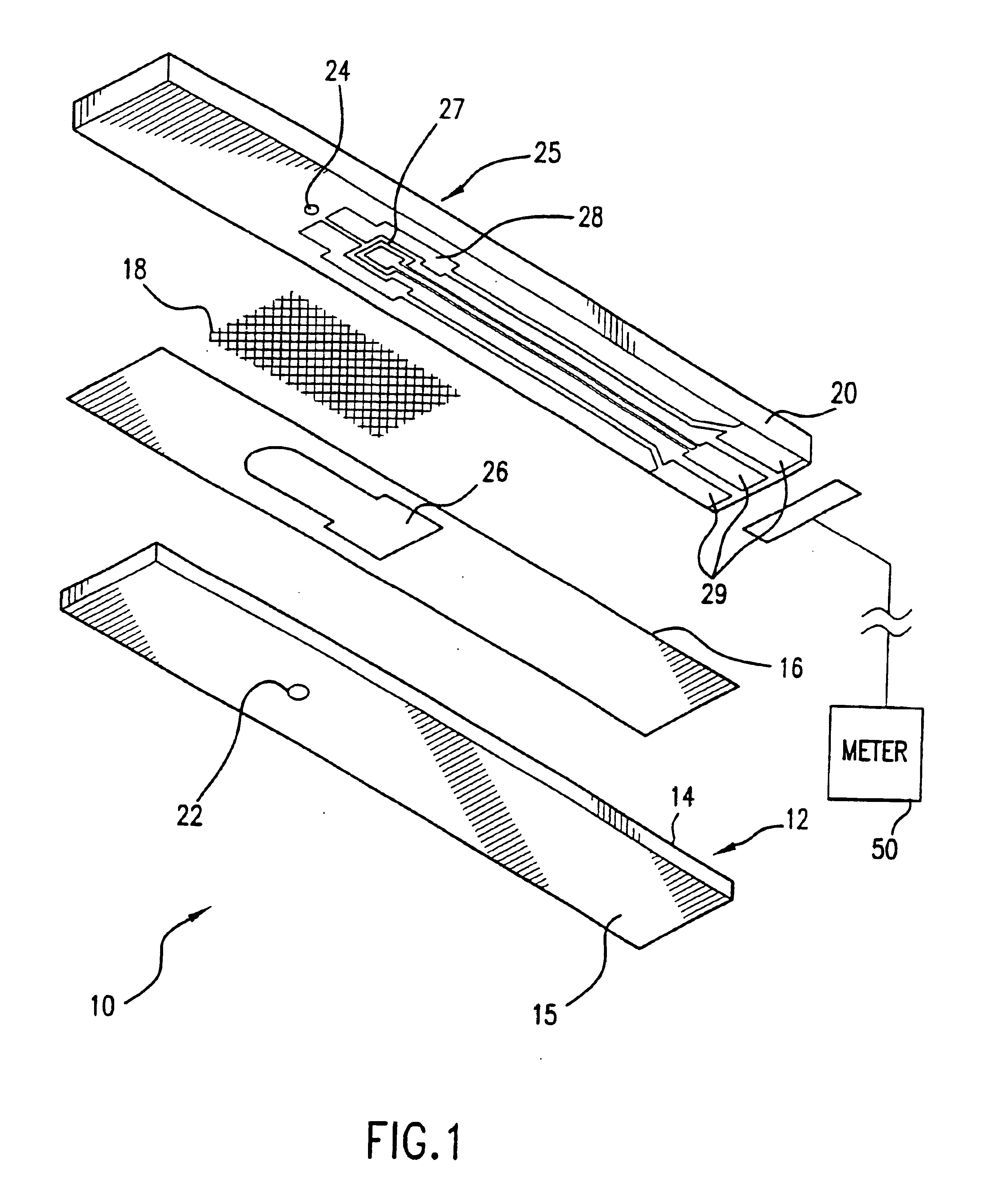
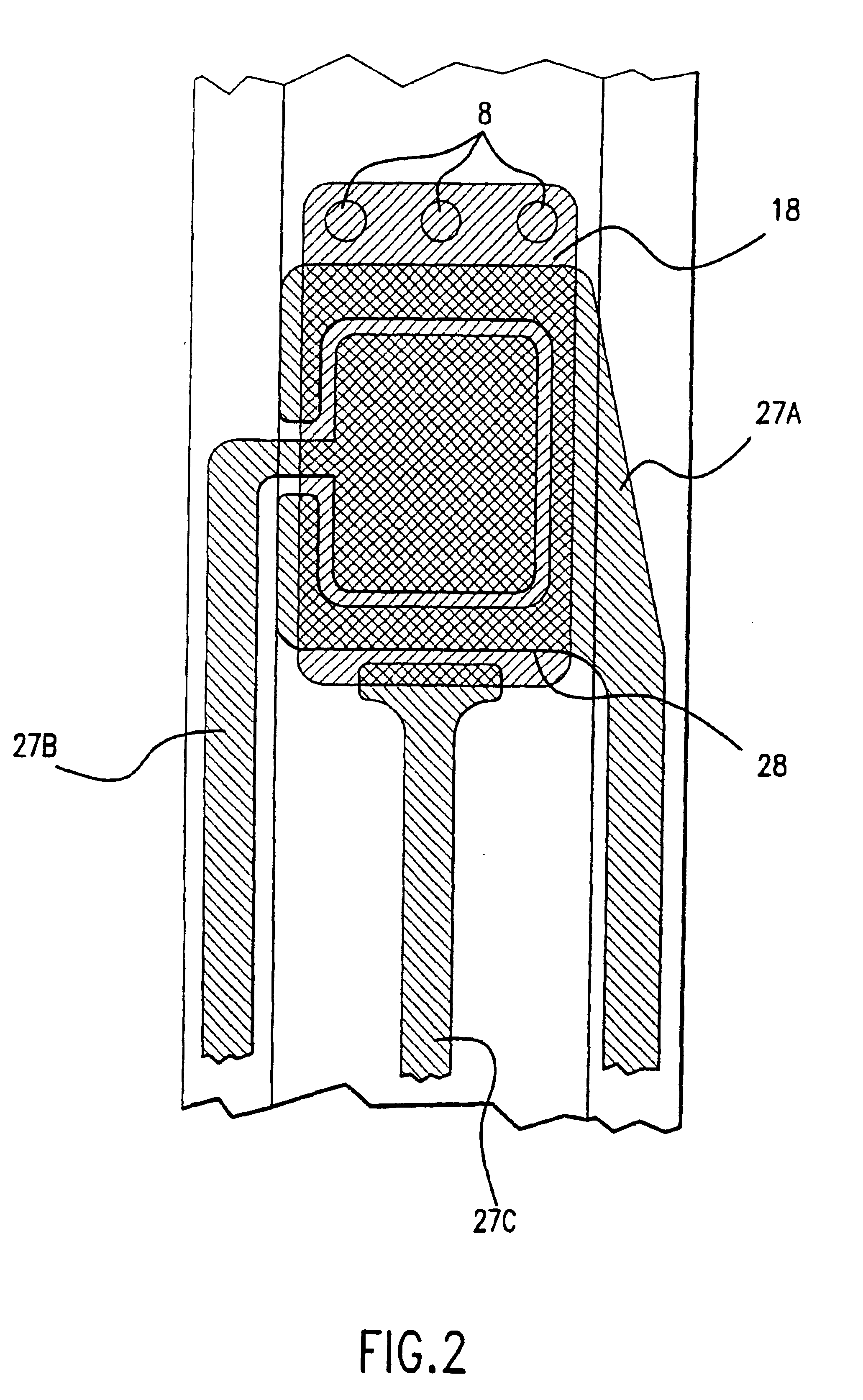
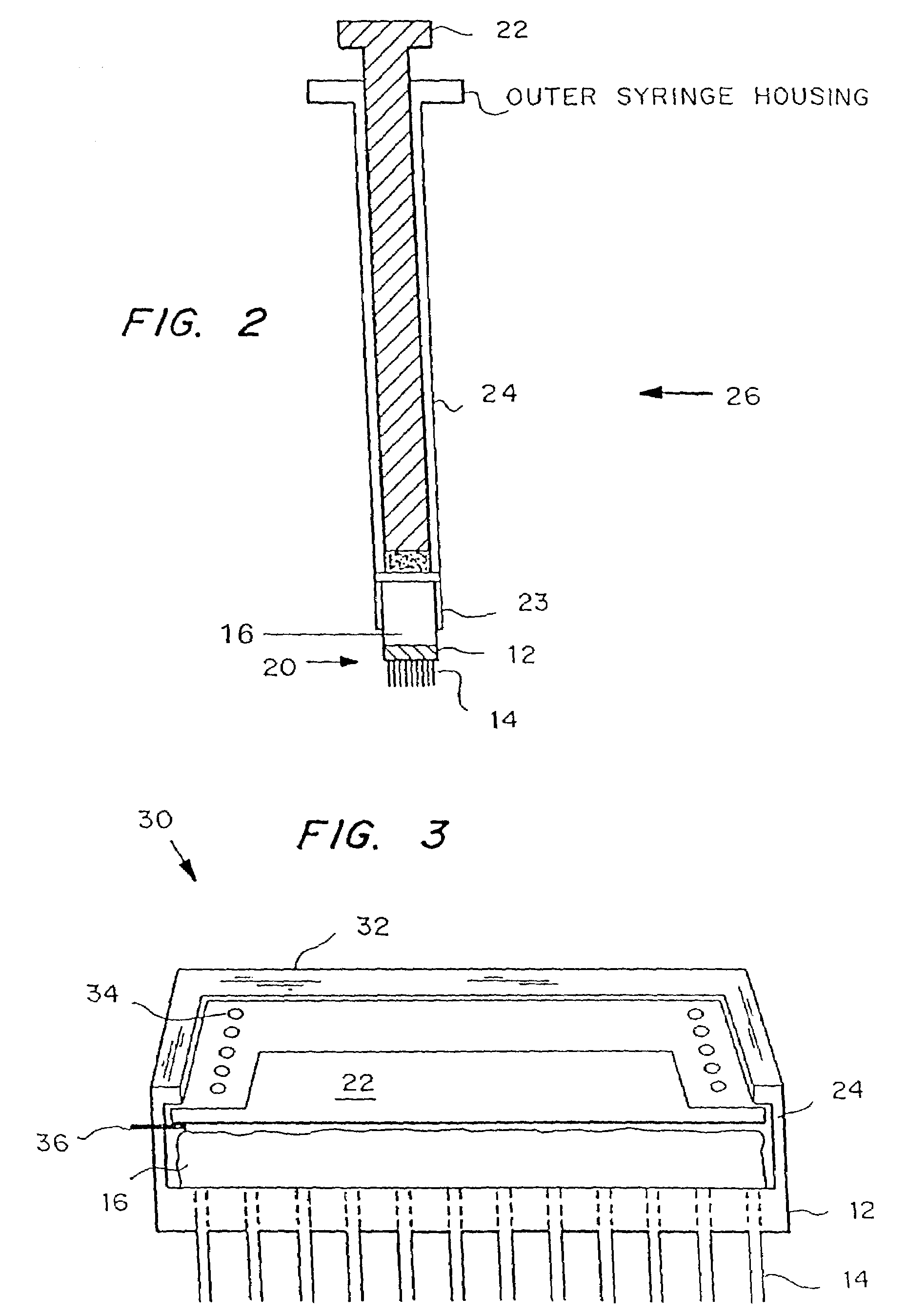
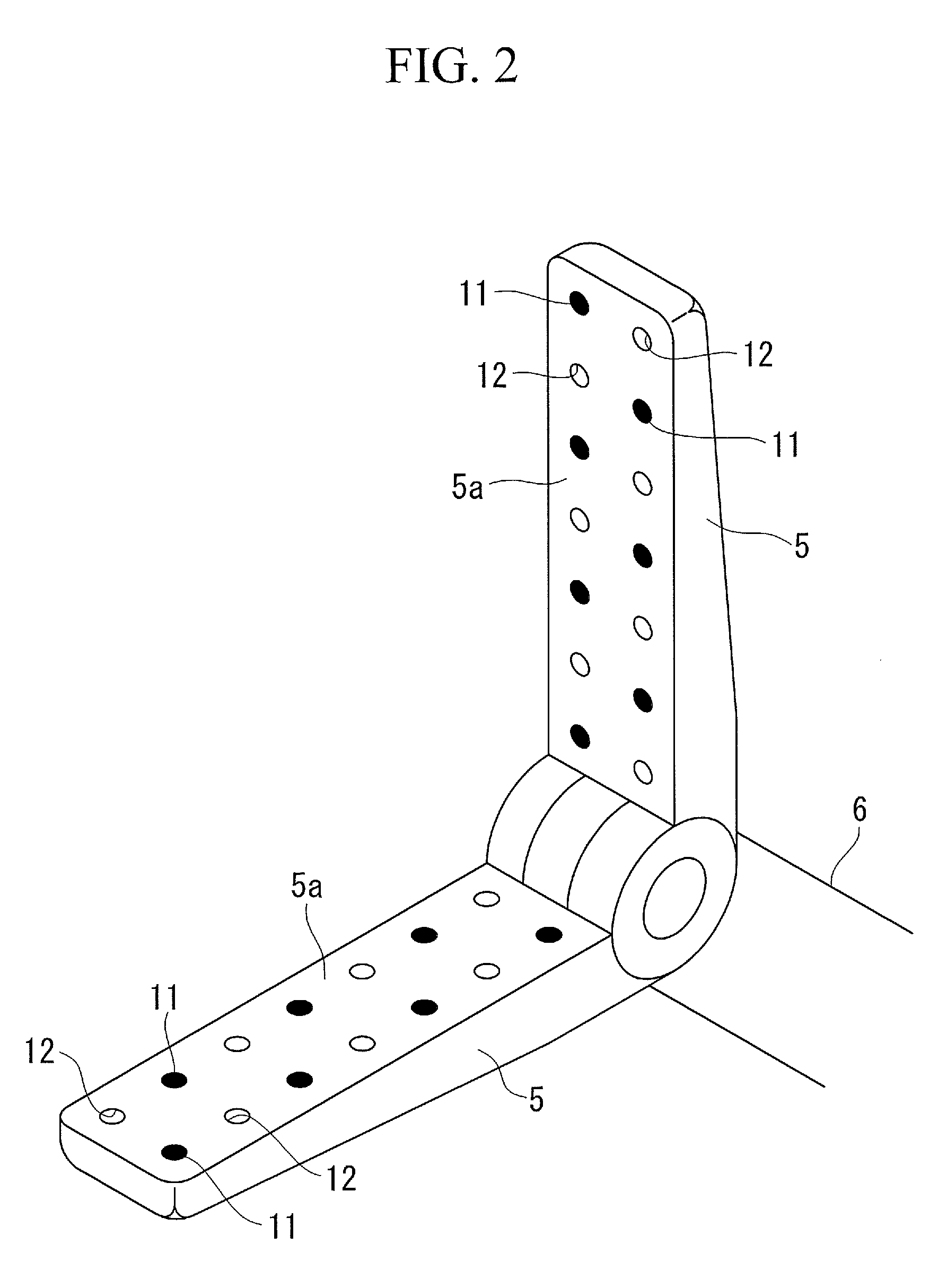
Biological tissue strip and system and method to seal tissue
A strip for use with a surgical stapler facilitates sealing tissue of a patient, such as the lungs, stomach, etc. The strip includes retaining elements near opposed ends of the strip for connecting to associated parts of a surgical stapler device. An aperture also extends through the strip at a location intermediate its opposed ends for receiving an alignment feature of the surgical stapler.In another aspect, a second elongated strip having retaining elements near opposed ends thereof may be utilized in conjunction with the strip and a surgical stapler to seal the patient's tissue. In addition, the strips may be connected together by a bridge of material to facilitate selection and use of appropriate strips.
Owner:GABBAY SHLOMO
Method of repairing inguinal hernias
A universal, surgical prosthesis for hernia repair is provided in the form of a foldable sheet. The prosthesis includes a barrier layer formed of a material adapted to prevent biological adherence thereto, such as polytetrafluoroethylene, and a second surface layer formed of a material adapted to promote biological tissue adherence thereto, such as polypropylene. The second surface may be formed of a series of spaced projections. The prosthesis is adapted to be manipulated into an operative position to exhibit an appropriate exterior when in the operative position. In this manner, the universal, surgical prosthesis can be utilized for a wide range of surgical procedures.
Owner:DAVOL
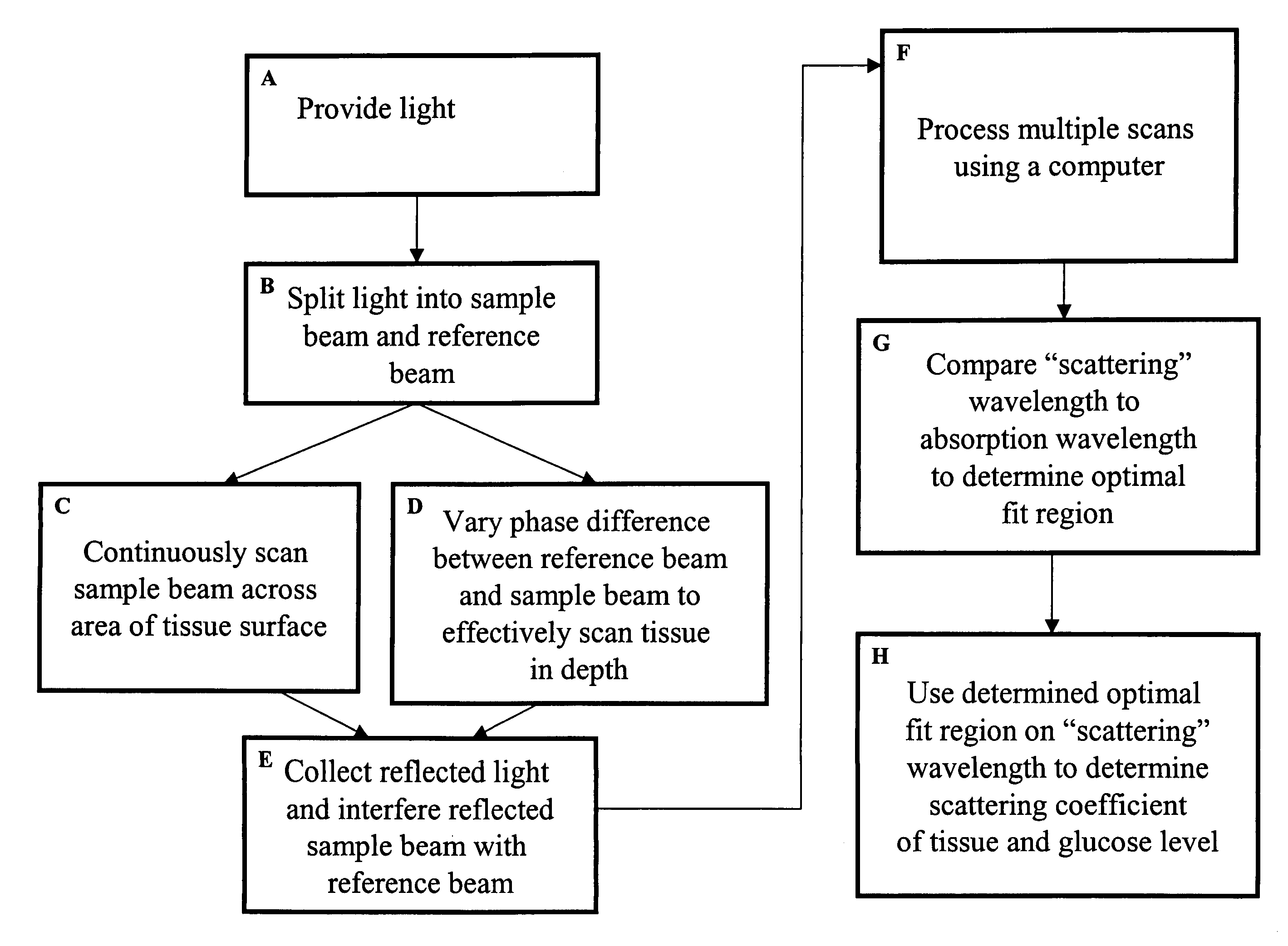
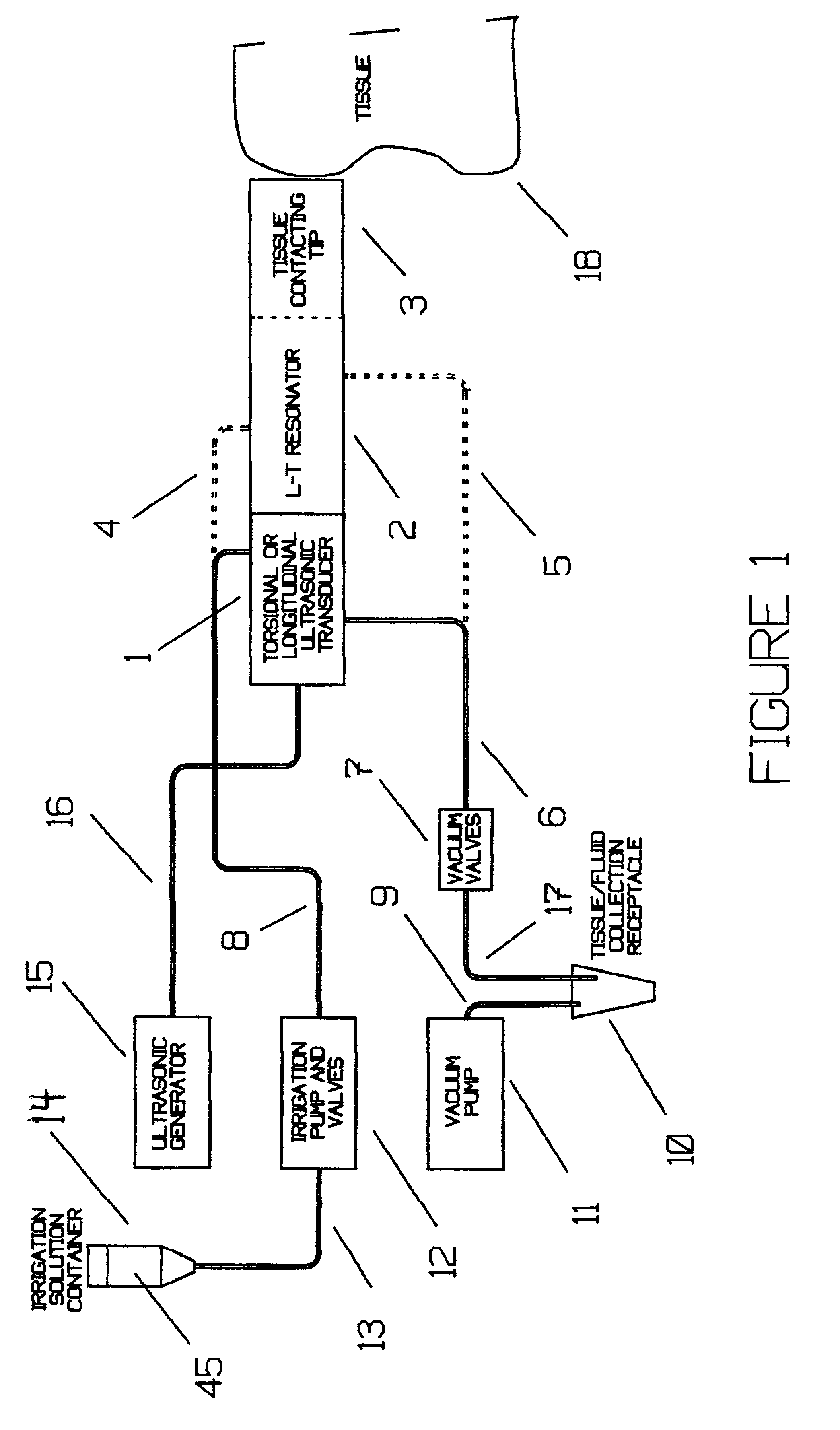
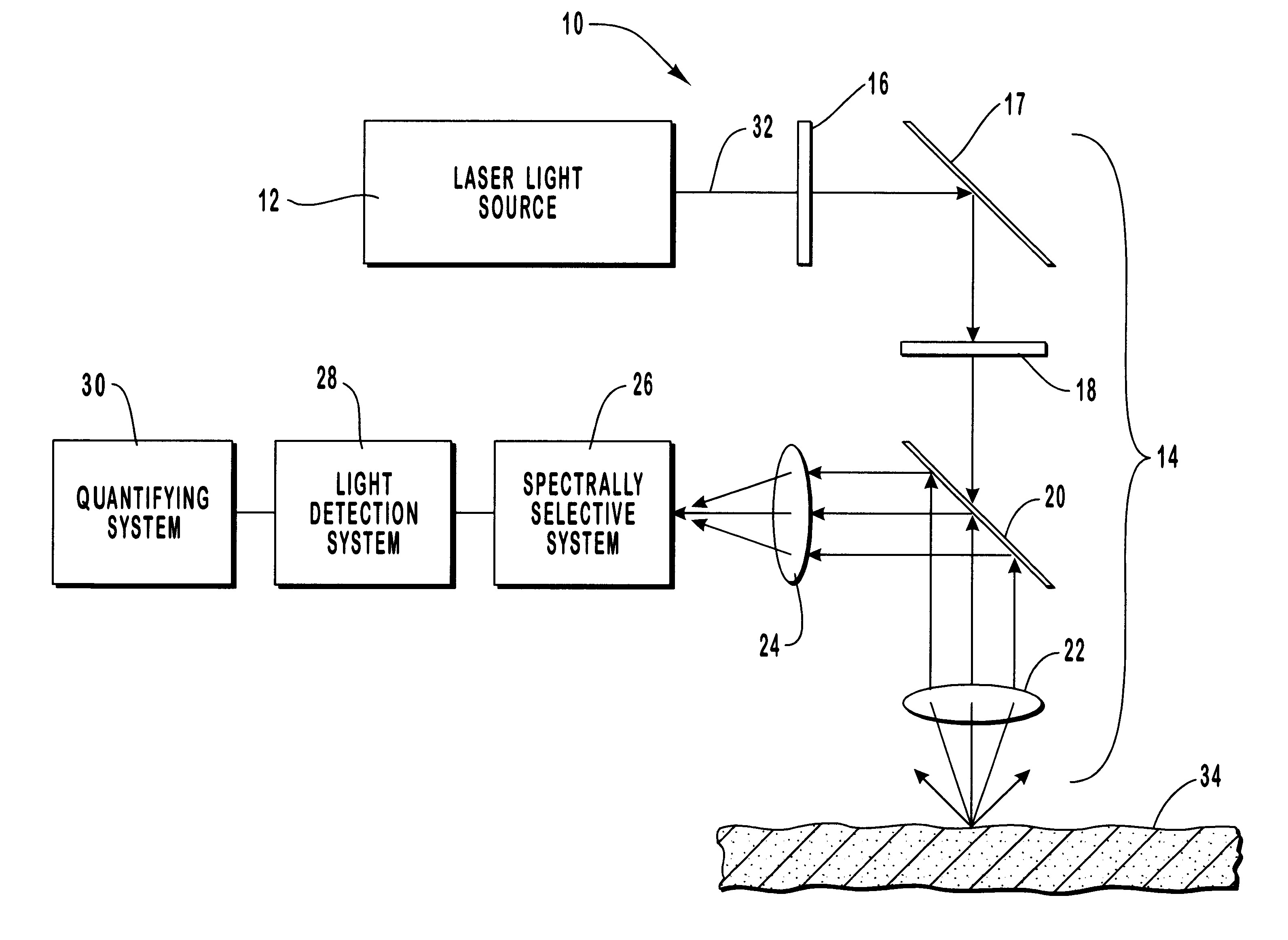
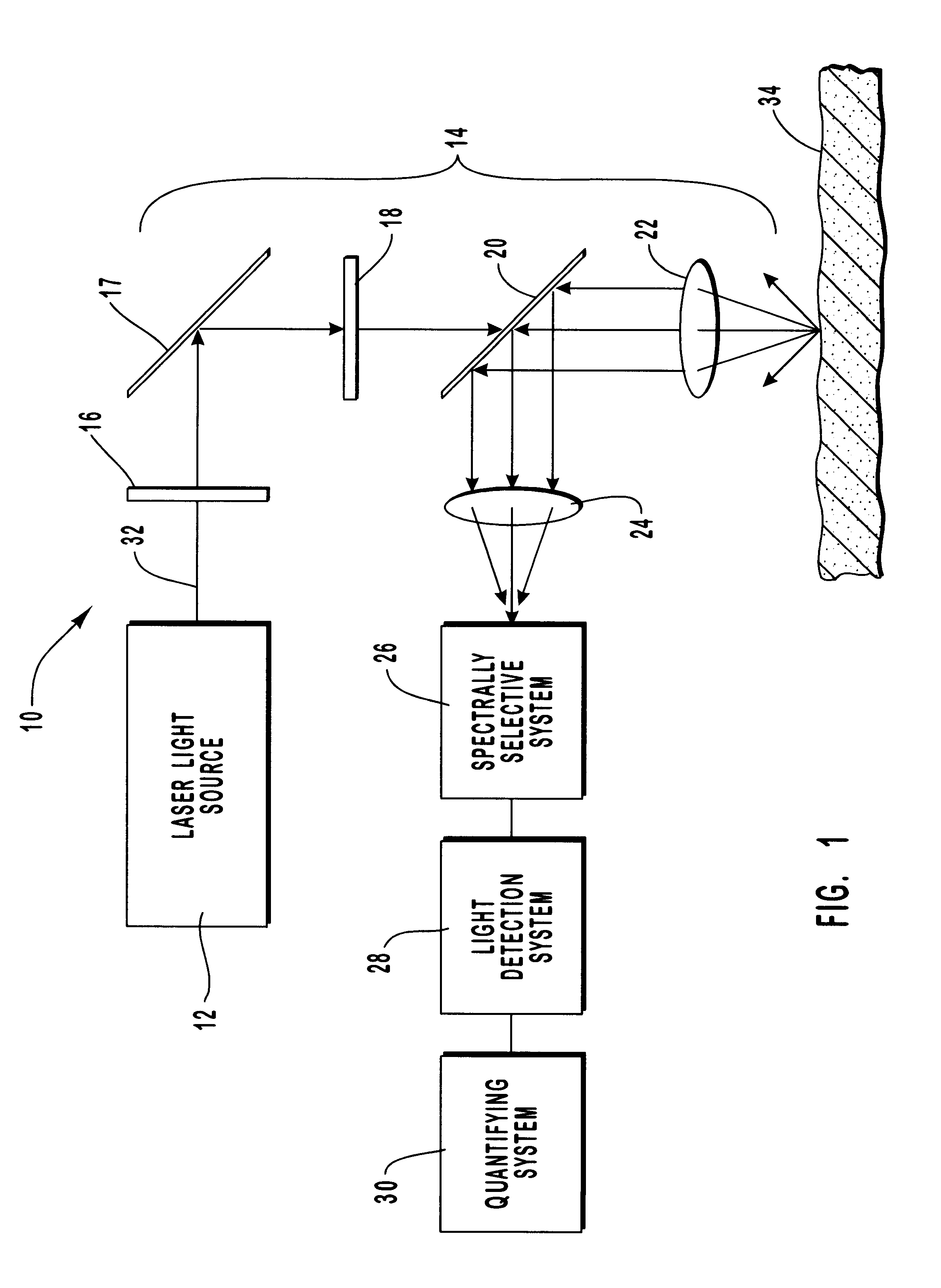
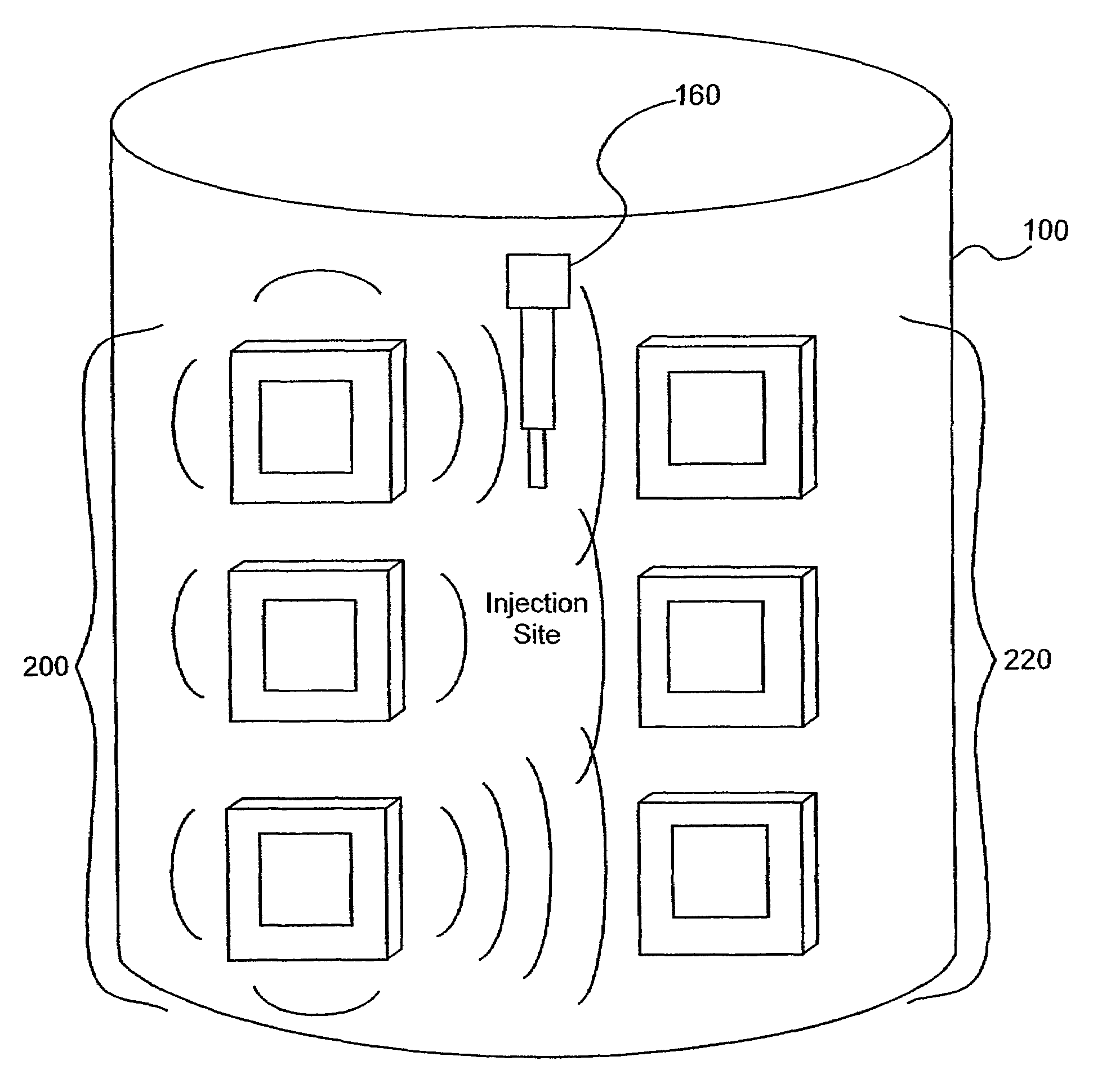
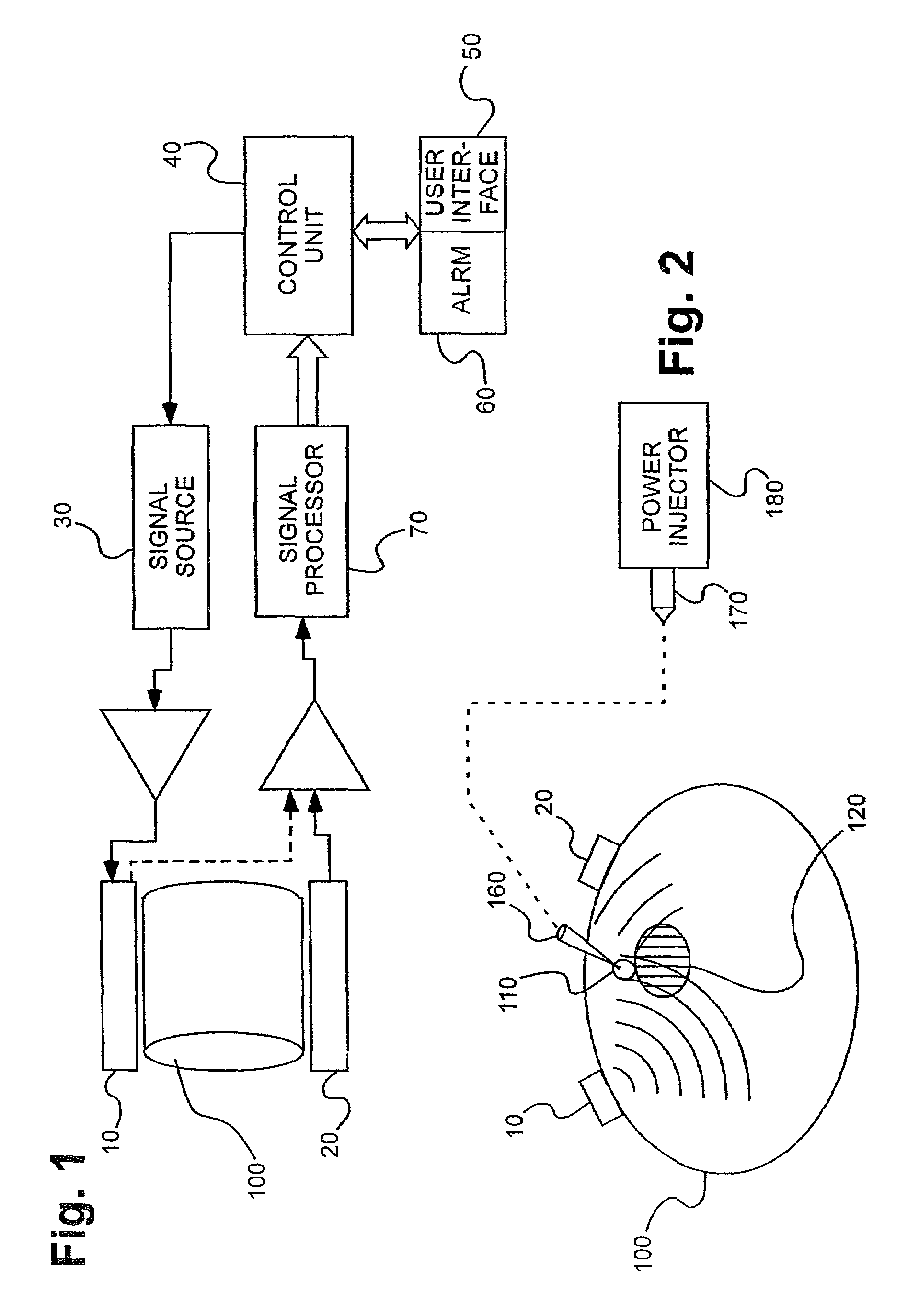
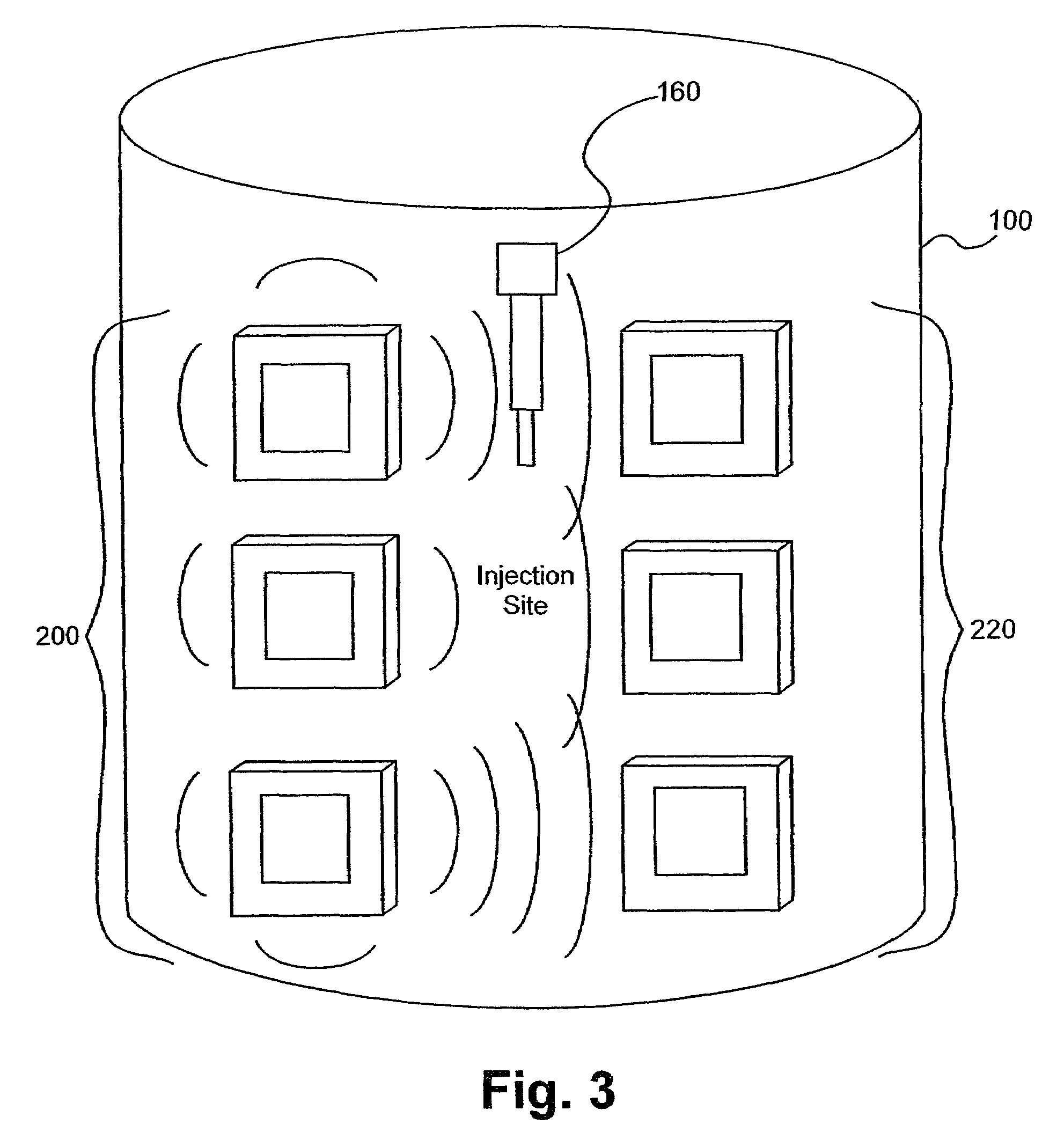
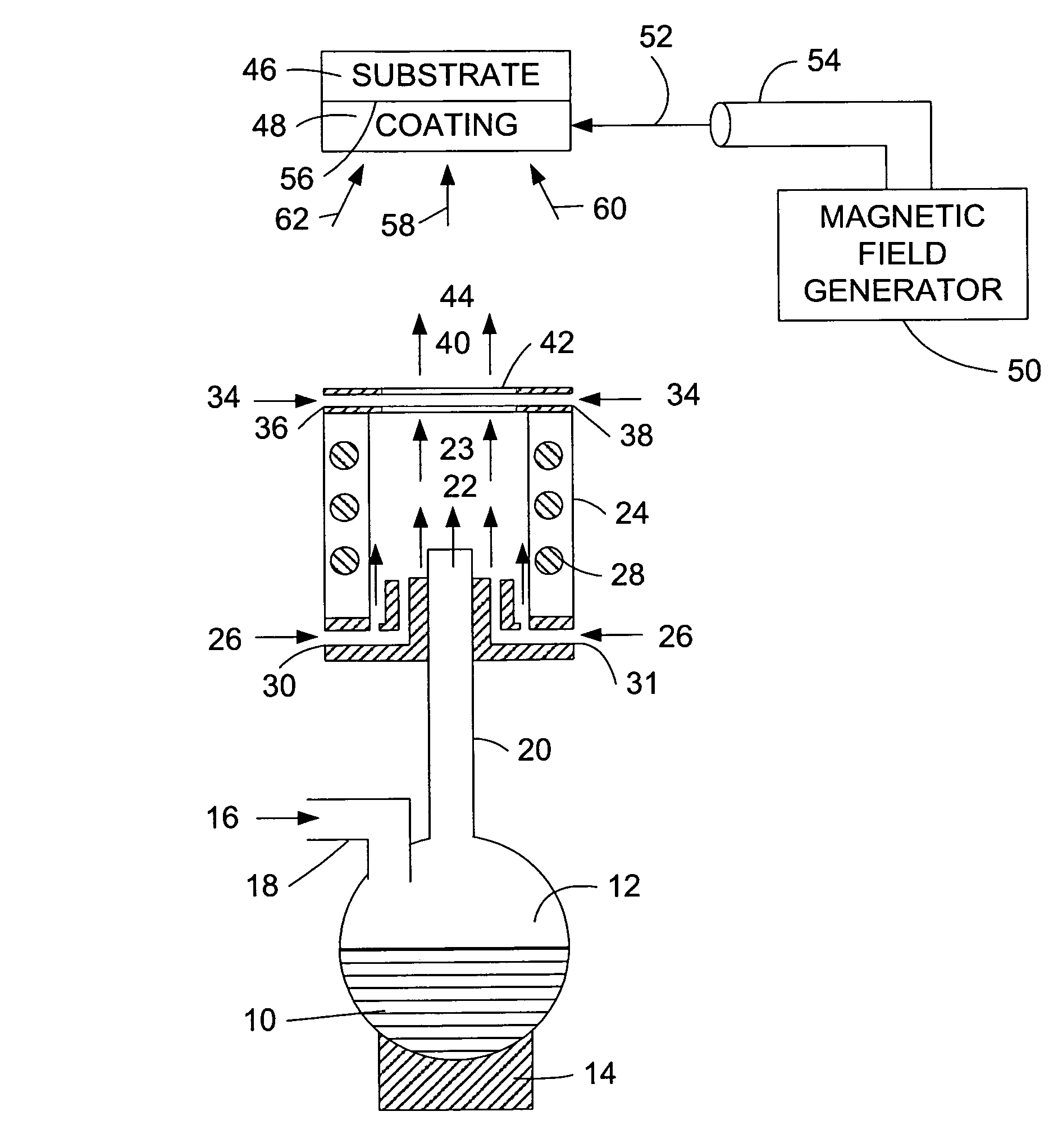
Method and apparatus for monitoring glucose levels in a biological tissue
ActiveUS7254429B2Convenient amountLow lightDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsContinuous scanningConcentrations glucose
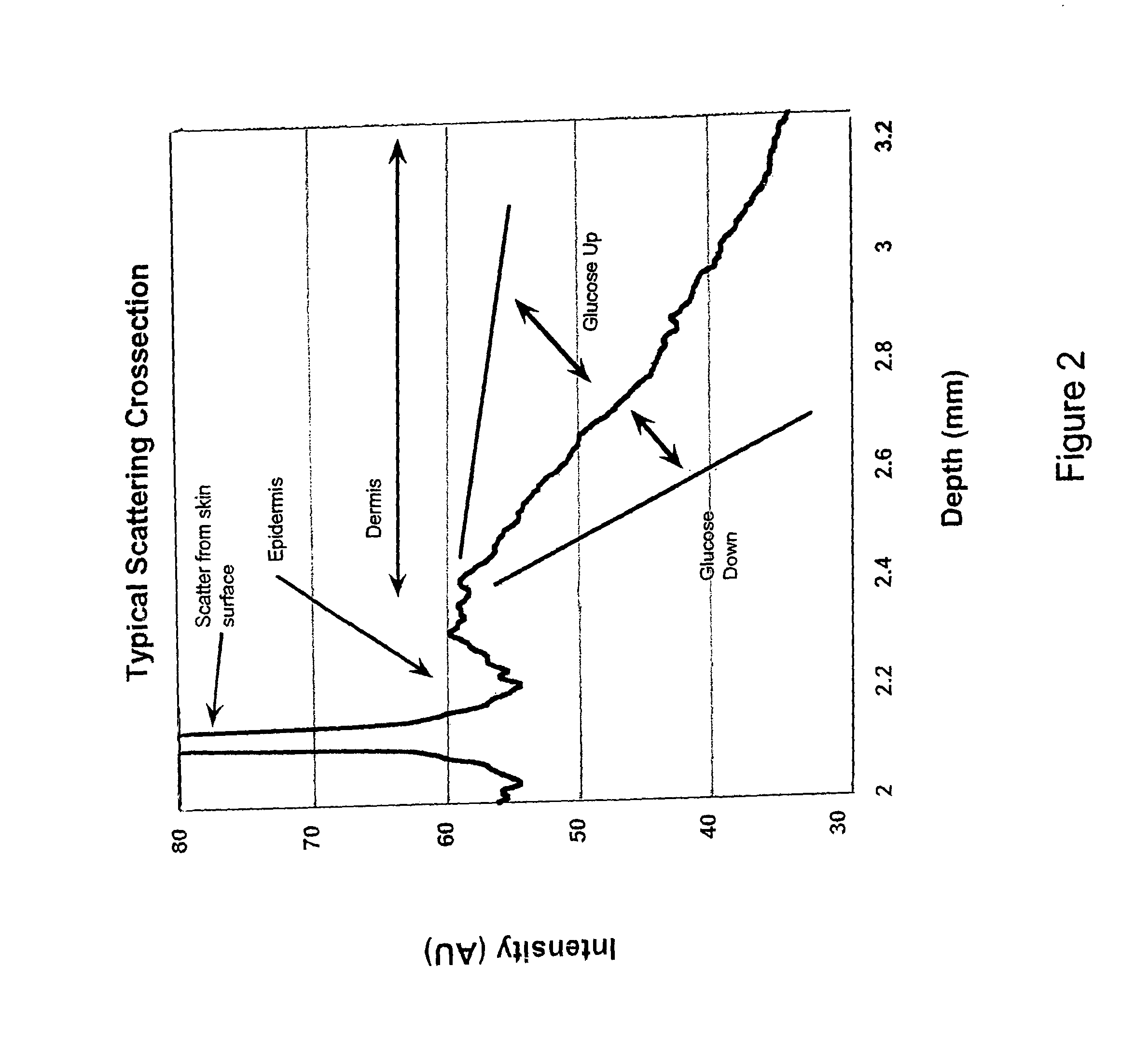
In accordance with the invention, a low coherence interferometer is used to non-invasively monitor the concentration of glucose in blood by shining a light over a surface area of human or animal tissue, continuously scanning the light over a two dimensional area of the surface, collecting the reflected light from within the tissue and constructively interfering this reflected light with light reflected along a reference path to scan the tissue in depth. Since the reflection spectrum is sensitive to glucose concentration at particular wavelengths, measurement and analysis of the reflected light provides a measure of the level of glucose in the blood. The measurement of glucose is taken from multiple depths within blood-profused tissue, and sensitivity is preferably enhanced by the use of multiple wavelengths. Noise or speckle associated with this technique is minimized by continuously scanning the illuminated tissue in area and depth.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Organism tissue suturing apparatus
InactiveUS8603110B2Easily inserted into tissueConvenience to workSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesBiological bodyOrganism
An organism tissue suturing apparatus for suturing a penetrated hole formed subcutaneously in a tissue membrane of an organism includes a body part having a predetermined length. The body part includes a rotary portion, disposed at a front end thereof, that can be inserted into the tissue of the organism from the hole, a needle member accommodated in a portion, inside the body part, rearward from the rotary position, and a pressing mechanism for advancing the needle member from a side surface of the body part and pressing the needle member into the rotary portion. The rotary portion has a needle member receiving portion for receiving essentially a front end of the needle member pressed into the rotary portion by the pressing mechanism, with the rotary portion disposed in the tissue of the organism. The needle member has a suturing thread of a duct for the suturing thread.
Owner:TERUMO KK
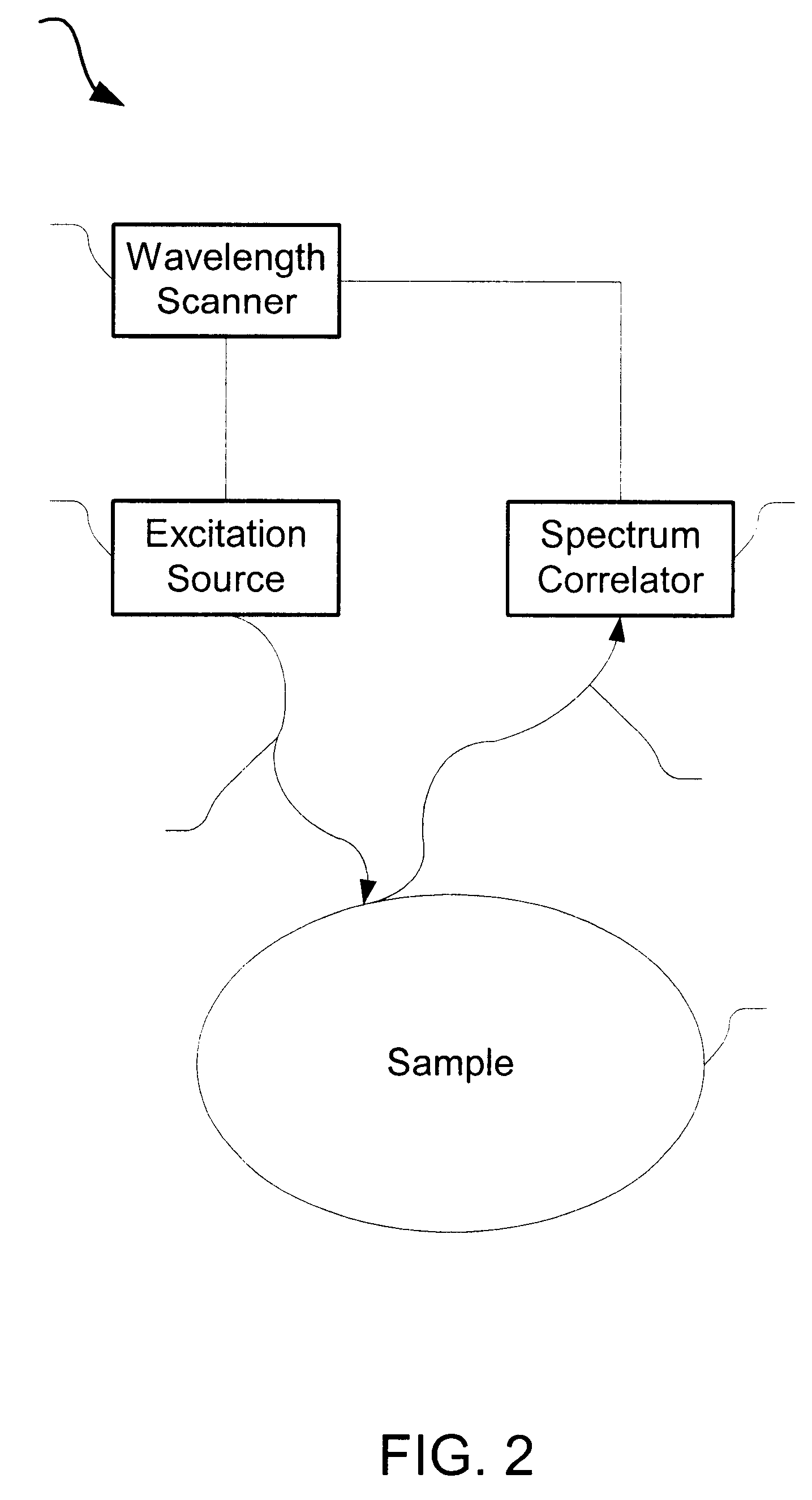
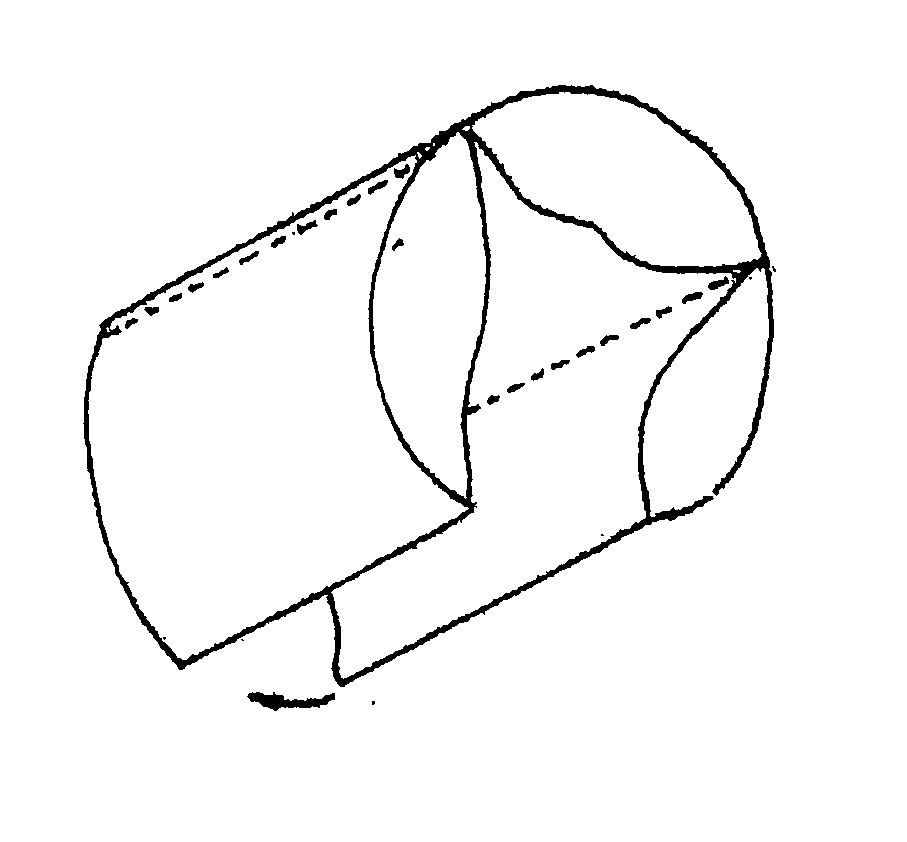
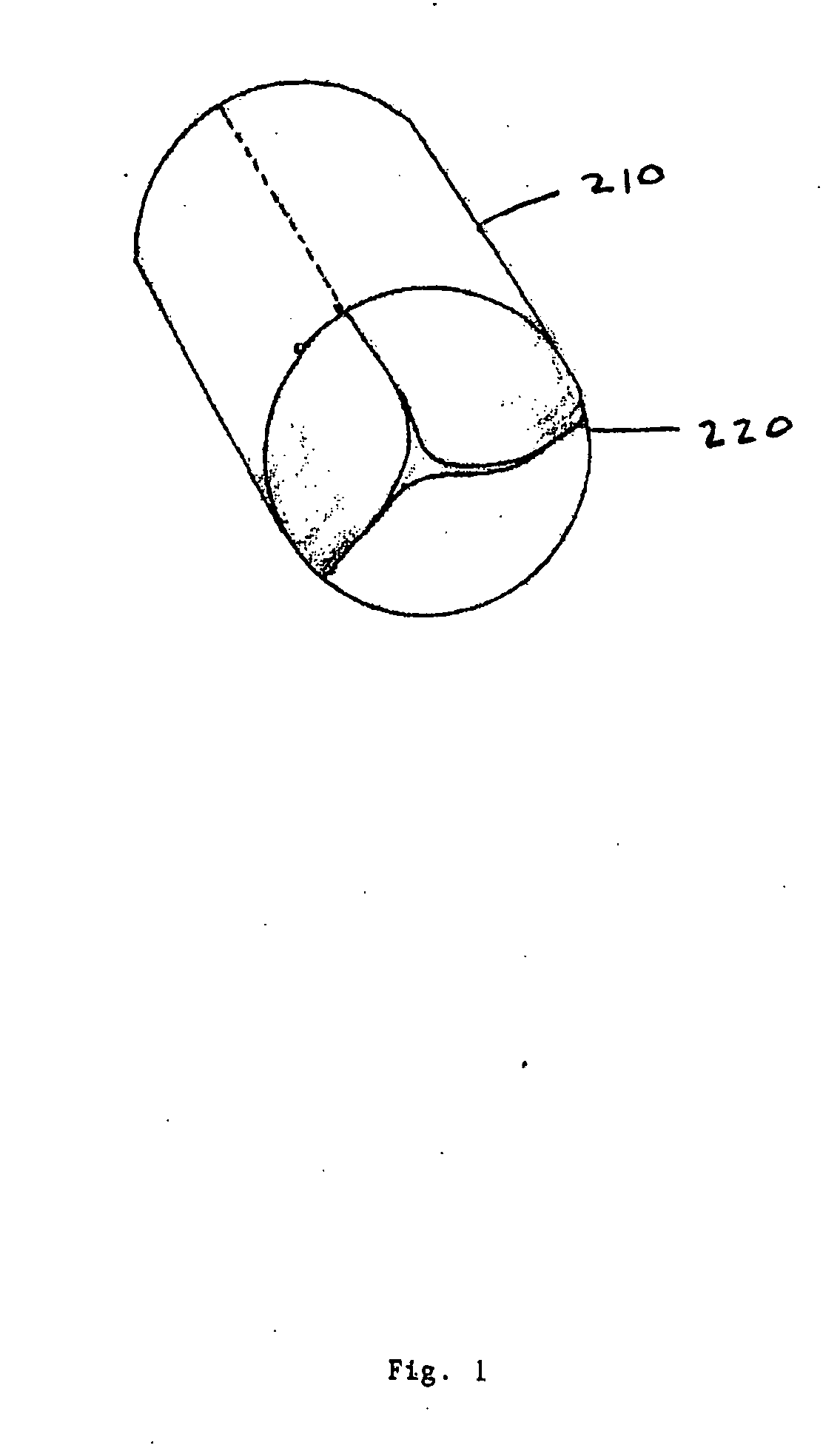
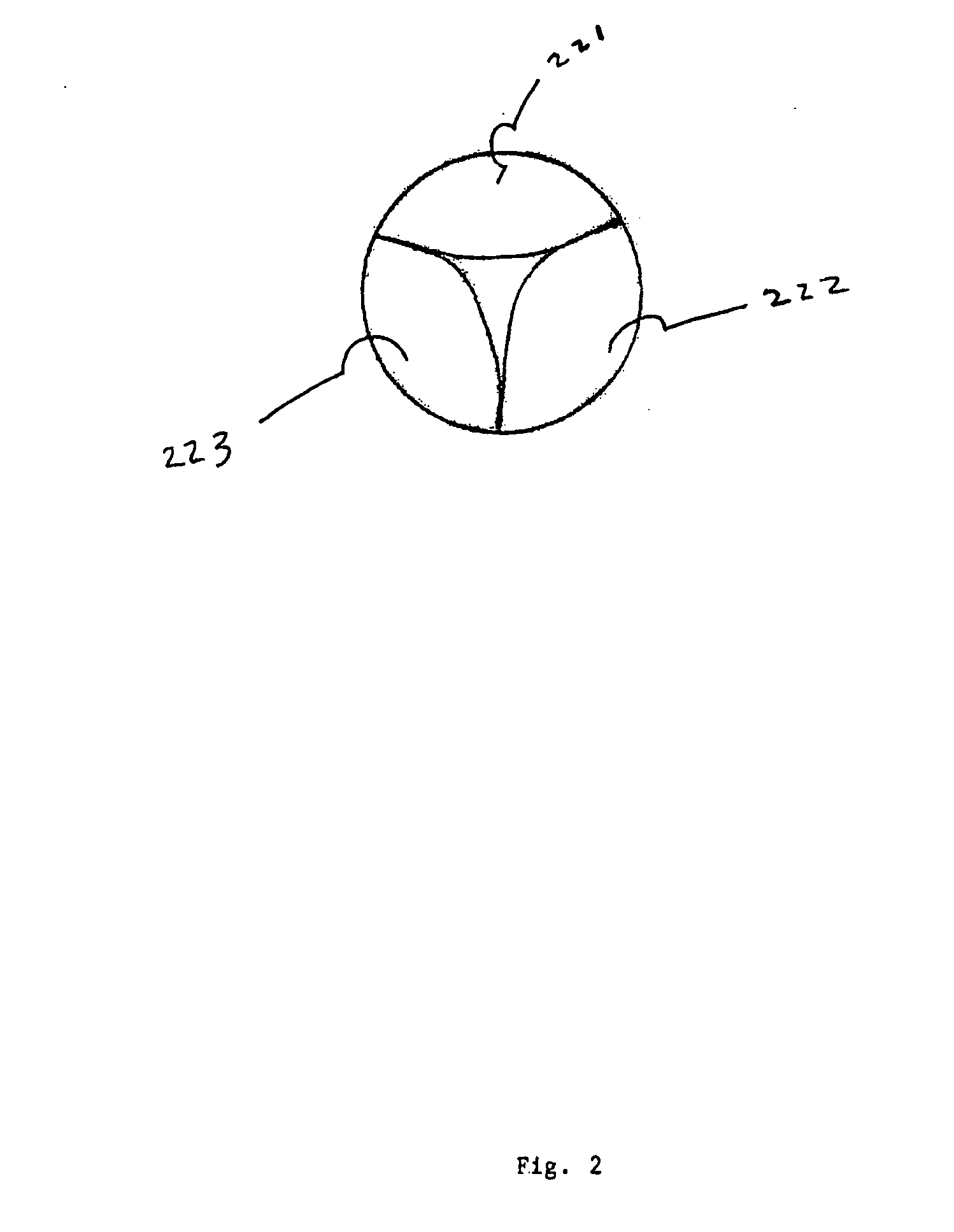
Method and devices for laser induced fluorescence attenuation spectroscopy
InactiveUSRE39672E1Large signal to noise ratioSurgeryScattering properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationSpectroscopy
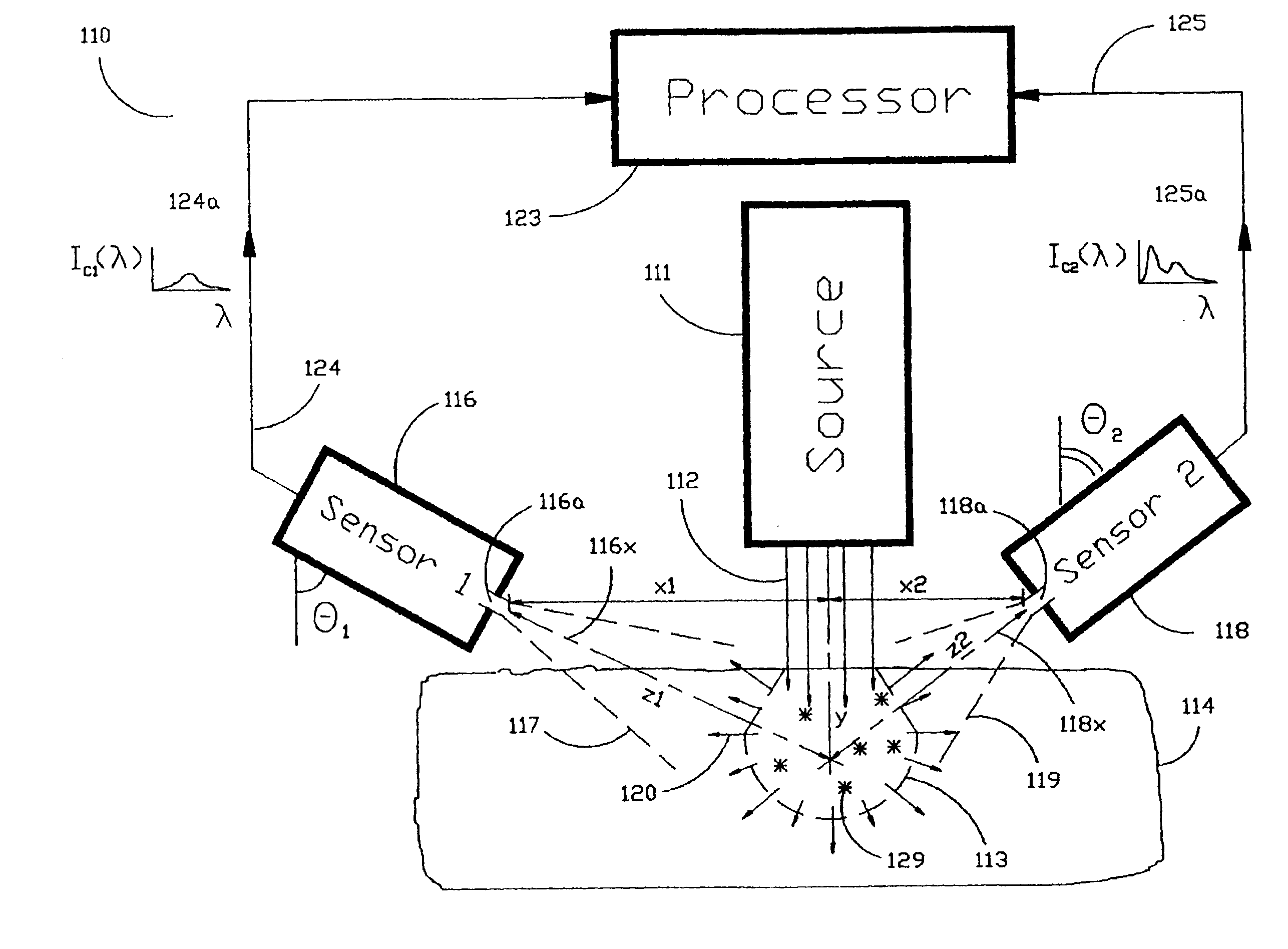
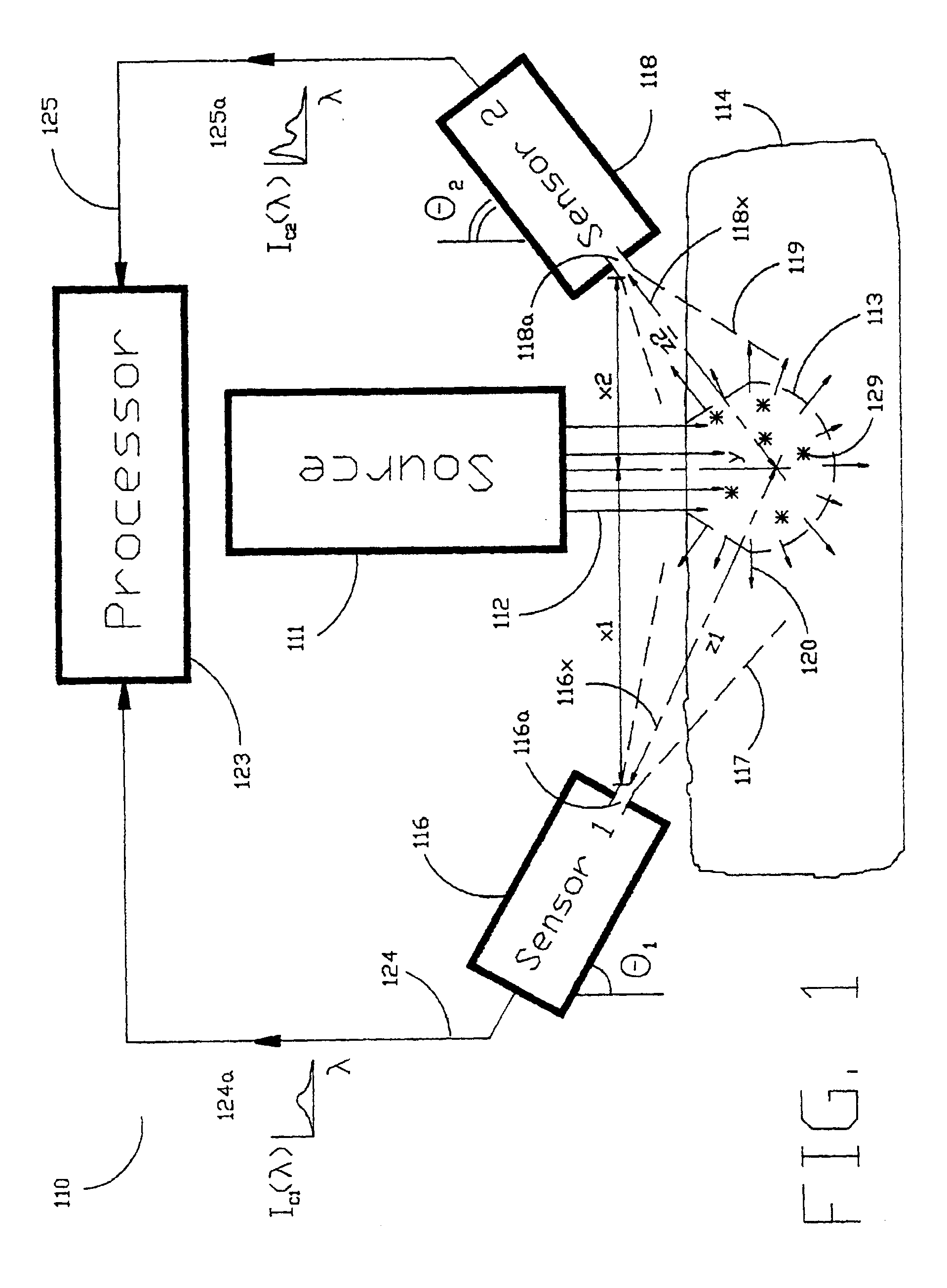
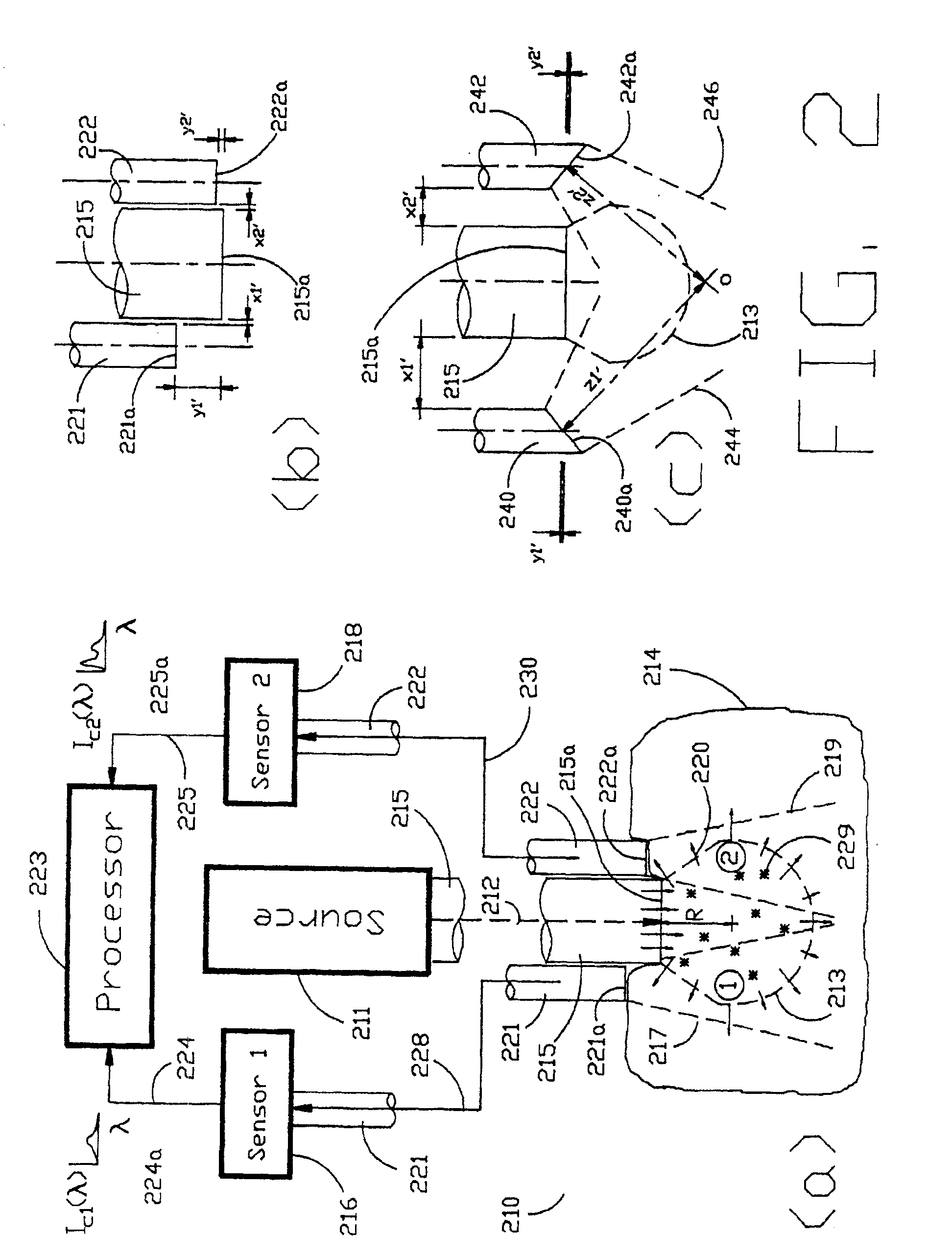
The Laser Induced Fluorescence Attenuation Spectroscopy (LIFAS) method and apparatus preferably include a source adapted to emit radiation that is directed at a sample volume in a sample to produce return light from the sample, such return light including modulated return light resulting from modulation by the sample, a first sensor, displaced by a first distance from the sample volume for monitoring the return light and generating a first signal indicative of the intensity of return light, a second sensor, displaced by a second distance from the sample volume, for monitoring the return light and generating a second signal indicative of the intensity of return light, and a processor associated with the first sensor and the second sensor and adapted to process the first and second signals so as to determine the modulation of the sample. The methods and devices of the inventions are particularly well-suited for determining the wavelength-dependent attenuation of a sample and using the attenuation to restore the intrinsic laser induced fluorescence of the sample. In turn, the attenuation and intrinsic laser induced fluorescence can be used to determined a characteristic of interest, such as the ischemic or hypoxic condition of biological tissue.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Percutaneously implantable replacement heart valve device and method of making same
The present invention comprises a percutaneously implantable replacement heart valve device and a method of making same. The replacement heart valve device comprises a stent member made of stainless steel or self-expanding nitinol, a biological tissue artificial valve means disposed within the inner space of the stent member. An implantation and delivery system having a central part which consists of a flexible hollow tube catheter that allows a metallic wire guide to be advanced inside it. The endovascular stented-valve is a glutaraldehyde fixed bovine pericardium which has two or three cusps that open distally to permit unidirectional blood flow. The present invention also comprises a novel method of making a replacement heart valve by taking a rectangular fragment of bovine pericardium treating, drying, folding and rehydrating it in such a way that forms a two- or three-leaflet / cusp valve with the leaflets / cusps formed by folding, thereby eliminating the extent of suturing required, providing improved durability and function.
Owner:COLIBRI HEART VALVE
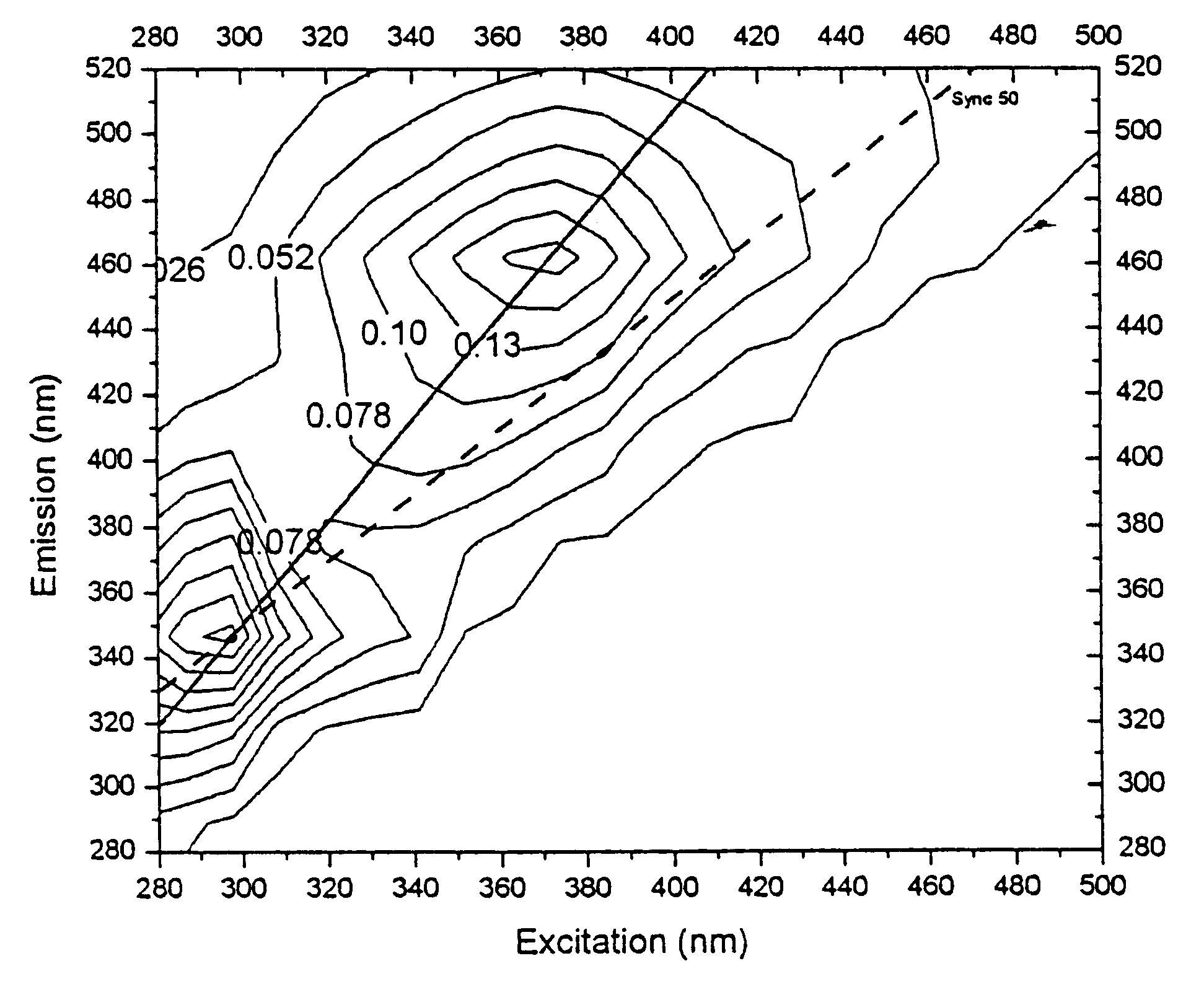
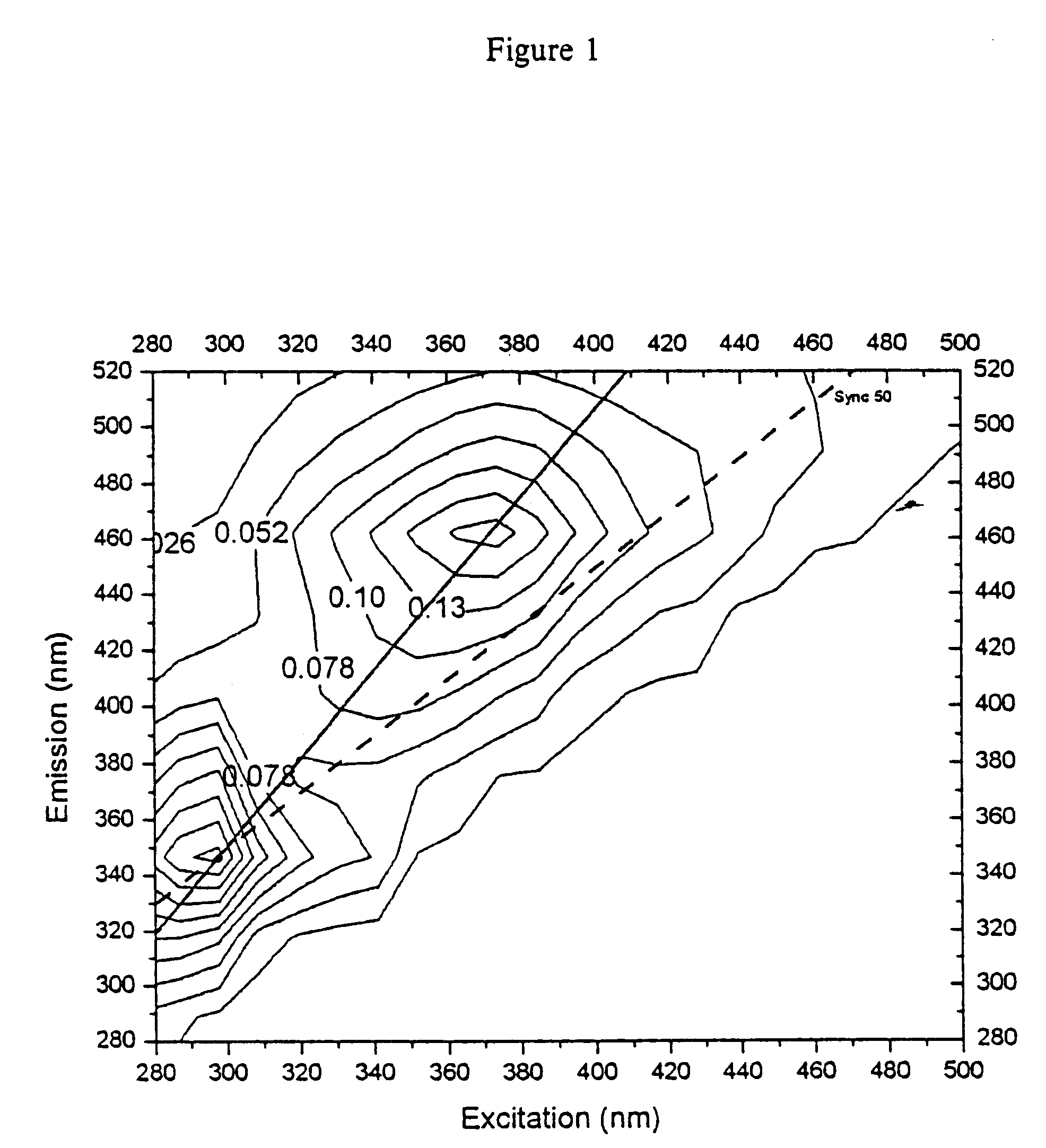
Asynchronous fluorescence scan
The present invention is directed to asynchronous scanning devices and methods of using asynchronous scanning to acquire fluorescence data from a sample, such as biological tissue, to facilitate diagnosis of the presence or absence of disease or other abnormality in the sample. The present invention is useful for biomedical diagnostics, chemical analysis or other evaluation of the target sample.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Percutaneously implantable replacement heart valve device and method of making same
The present invention comprises a percutaneously implantable replacement heart valve device and a method of making same. The replacement heart valve device comprises a stent member made of stainless steel or self-expanding nitinol, a biological tissue artificial valve means disposed within the inner space of the stent member. An implantation and delivery system having a central part which consists of a flexible hollow tube catheter that allows a metallic wire guide to be advanced inside it. The endovascular stented-valve is created from a glutaraldehyde fixed biocompatible tissue material which has two or three cusps that open distally to permit unidirectional blood flow. The present invention also comprises a novel method of making a replacement heart valve by taking a fragment of biocompatible tissue material and treating, drying, folding and rehydrating it in such a way that forms a two- or three-leaflet / cusp valve with the leaflets / cusps formed by folding, thereby eliminating the extent of suturing required, providing improved durability and function.
Owner:COLIBRI HEART VALVE
Surgical Cutting Guide
ActiveUS20080275452A1Prevent deviationComputer-aided planning/modellingNon-surgical orthopedic devicesEngineeringSurgical department
The present invention is directed to a surgical cutting guide for guiding a surgical instrument along a cutting path located on a biological tissue. The surgical guide includes a contact surface that conforms to a surface associated with the tissue and at least one guide for restricting movement of a surgical instrument in a first direction and for allowing the movement of the surgical instrument in a second direction along a cutting path across the surface of the tissue. The guide further contains a stop for restricting movement of the surgical instrument in the second direction along the cutting path. The stop is based at least, in part, on patient specific information.
Owner:CONFORMIS
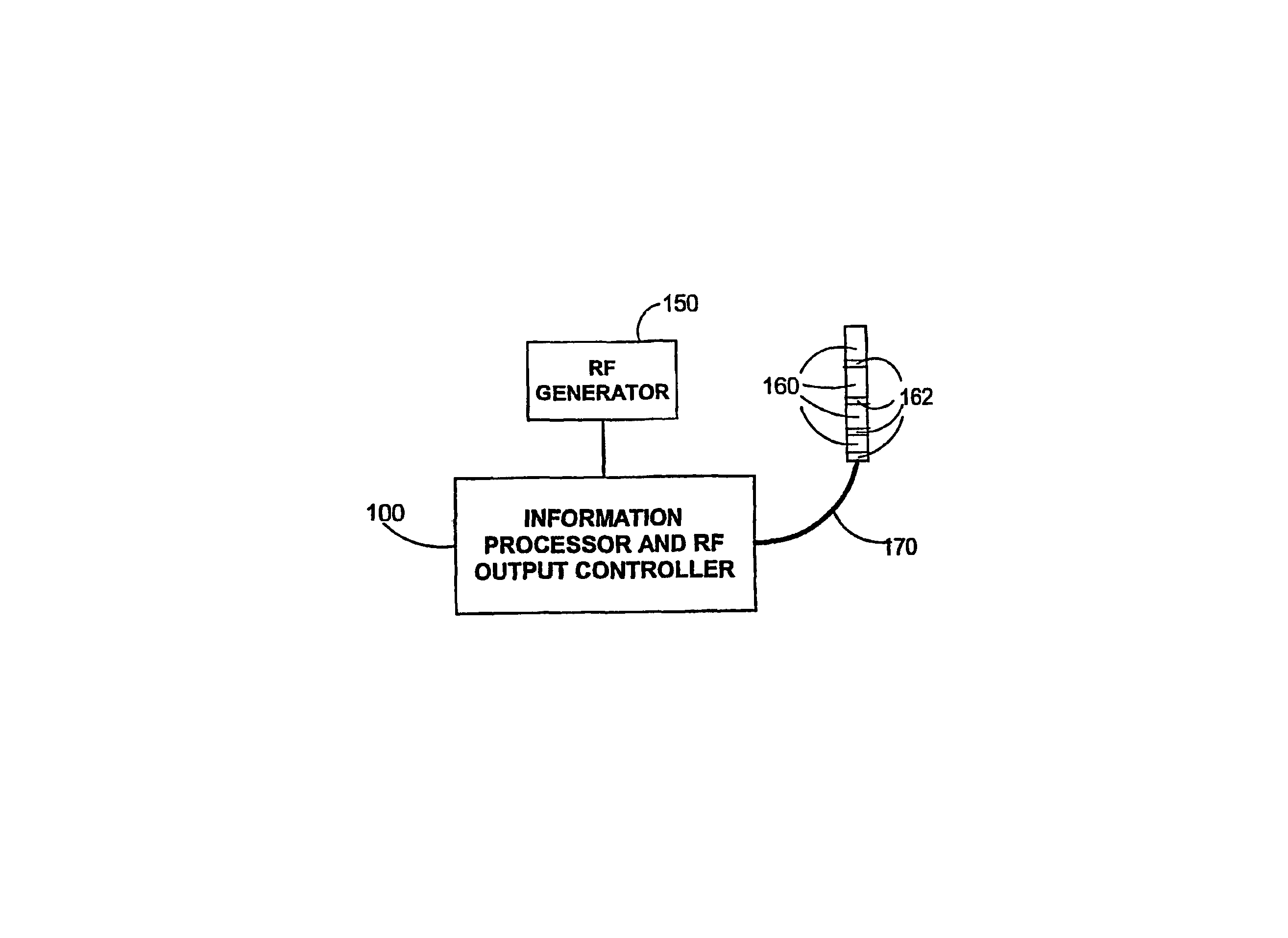
Multi-channel RF energy delivery with coagulum reduction
InactiveUS6936047B2Risk minimizationImprove efficiencySurgical instruments for heatingRf ablationCurrent sensor
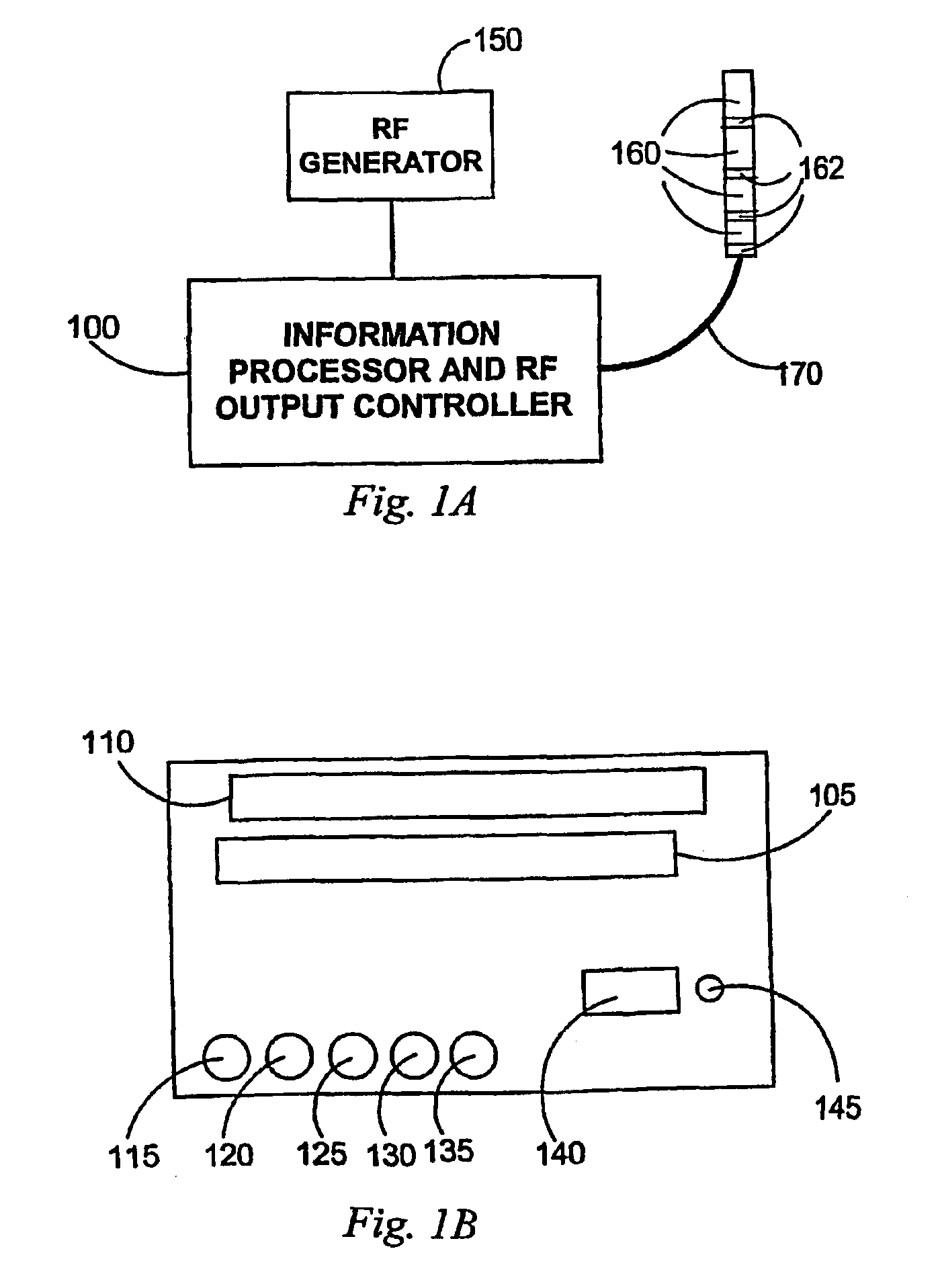
A system for efficient delivery of radio frequency (RF) energy to cardiac tissue with an ablation catheter used in catheter ablation, with new concepts regarding the interaction between RF energy and biological tissue. In addition, new insights into methods for coagulum reduction during RF ablation will be presented, and a quantitative model for ascertaining the propensity for coagulum formation during RF ablation will be introduced. Effective practical techniques a represented for multichannel simultaneous RF energy delivery with real-time calculation of the Coagulum Index, which estimates the probability of coagulum formation. This information is used in a feedback and control algorithm which effectively reduces the probability of coagulum formation during ablation. For each ablation channel, electrical coupling delivers an RF electrical current through an ablation electrode of the ablation catheter and a temperature sensor is positioned relative to the ablation electrode for measuring the temperature of cardiac tissue in contact with the ablation electrode. A current sensor is provided within each channel circuitry for measuring the current delivered through said electrical coupling and an information processor and RF output controller coupled to said temperature sensor and said current sensor for estimating the likelihood of coagulum formation. When this functionality is propagated simultaneously through multiple ablation channels, the resulting linear or curvilinear lesion is deeper with less gaps. Hence, the clinical result is improved due to improved lesion integrity.
Owner:SICHUAN JINJIANG ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
System and method for creating a stable optical interface
ActiveUS8219172B2High bandwidthReduce coherenceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRefractive indexLight beam
Owner:MASIMO CORP
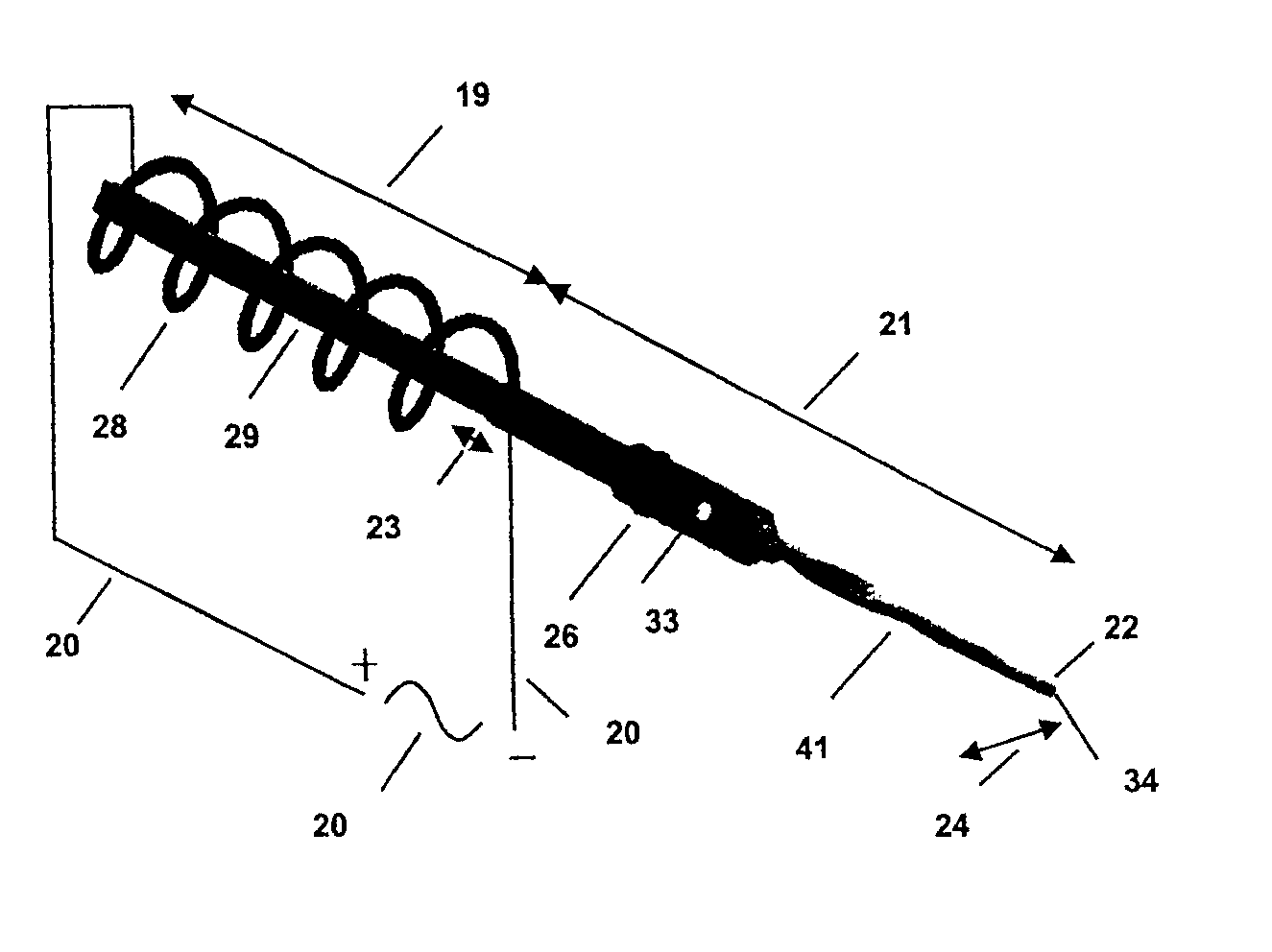
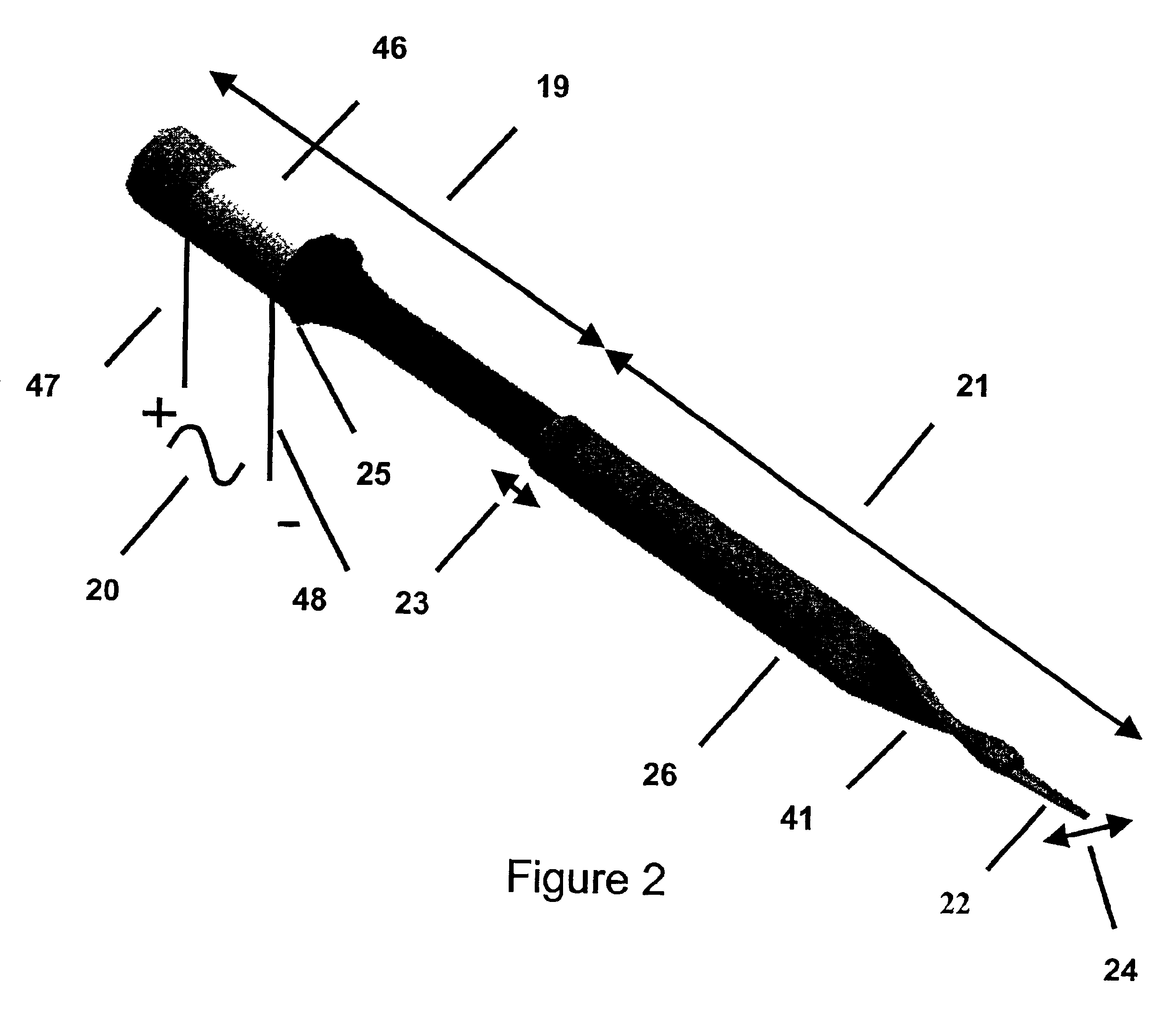
Longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic tissue dissection
An ultrasonic tissue dissection system providing combined longitudinal and torsional motion of tips, together with irrigation and aspiration, for improved cutting of resistant biological tissue. The system permits the use of common and inexpensive electro-mechanical transducers for the production of such motion through the use of longitudinal-torsional resonators.
Owner:WUCHINICH DAVID G
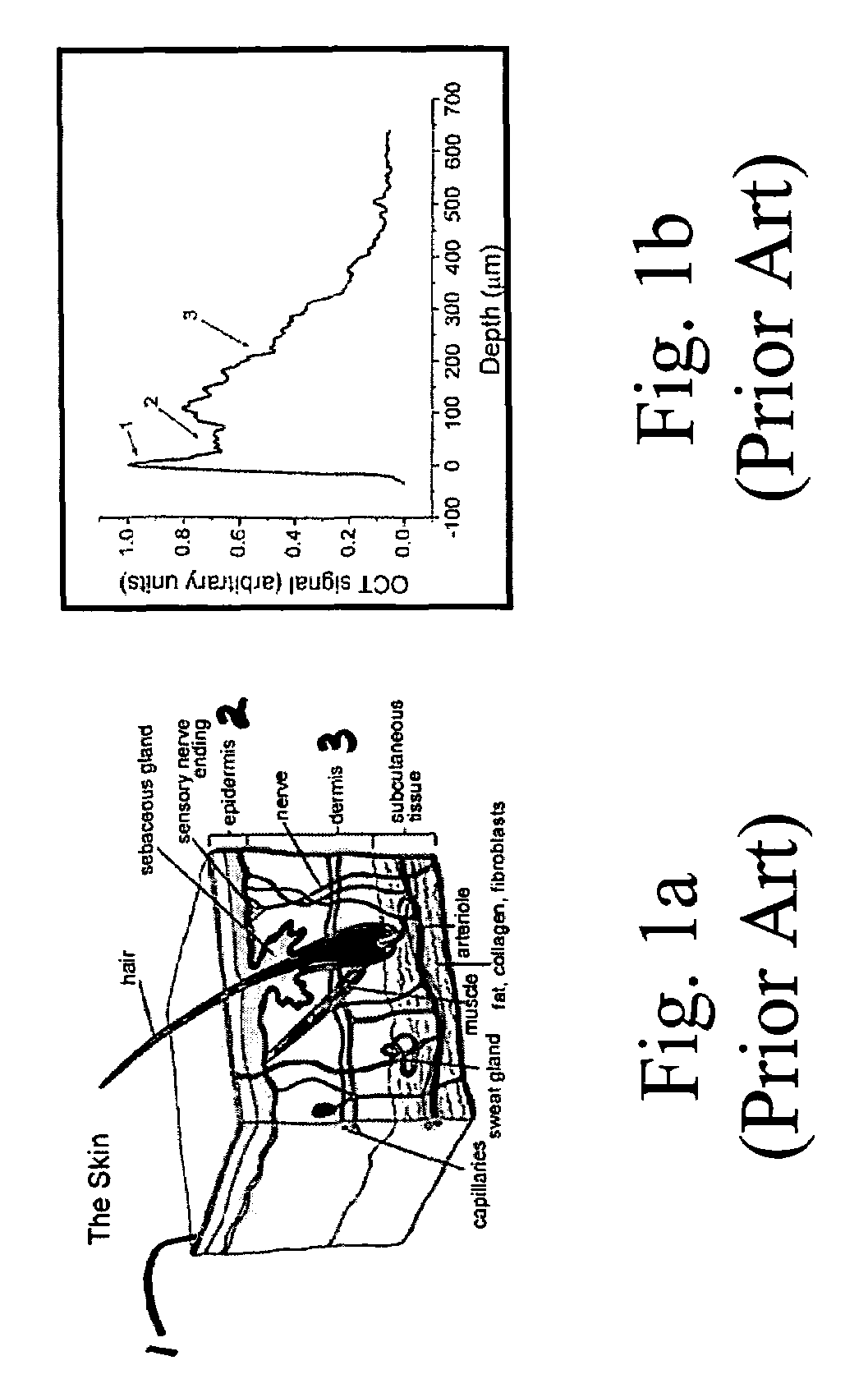
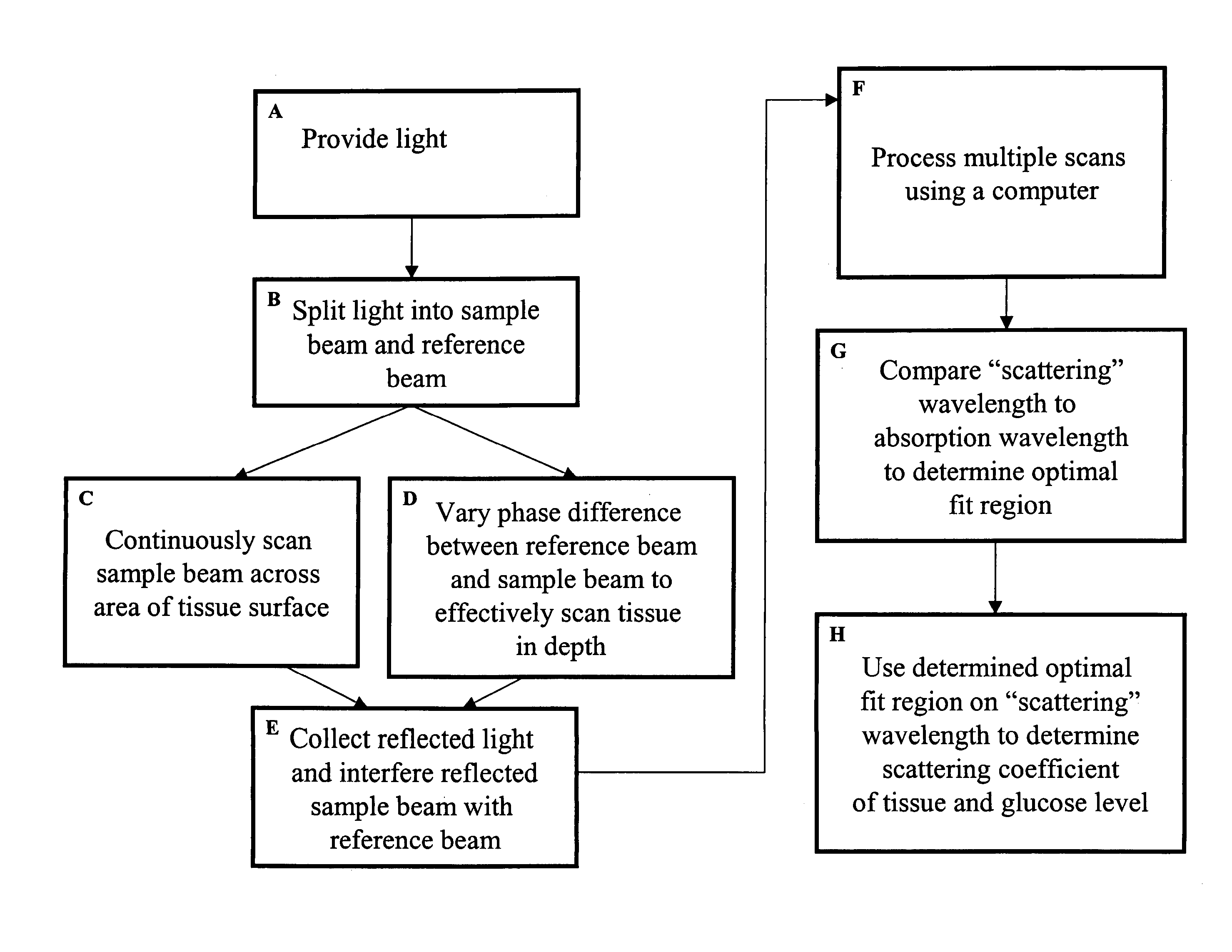
Methods for noninvasively measuring analyte levels in a subject
ActiveUS8036727B2Non-invasively measureNegligible effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalyteGlucose polymers
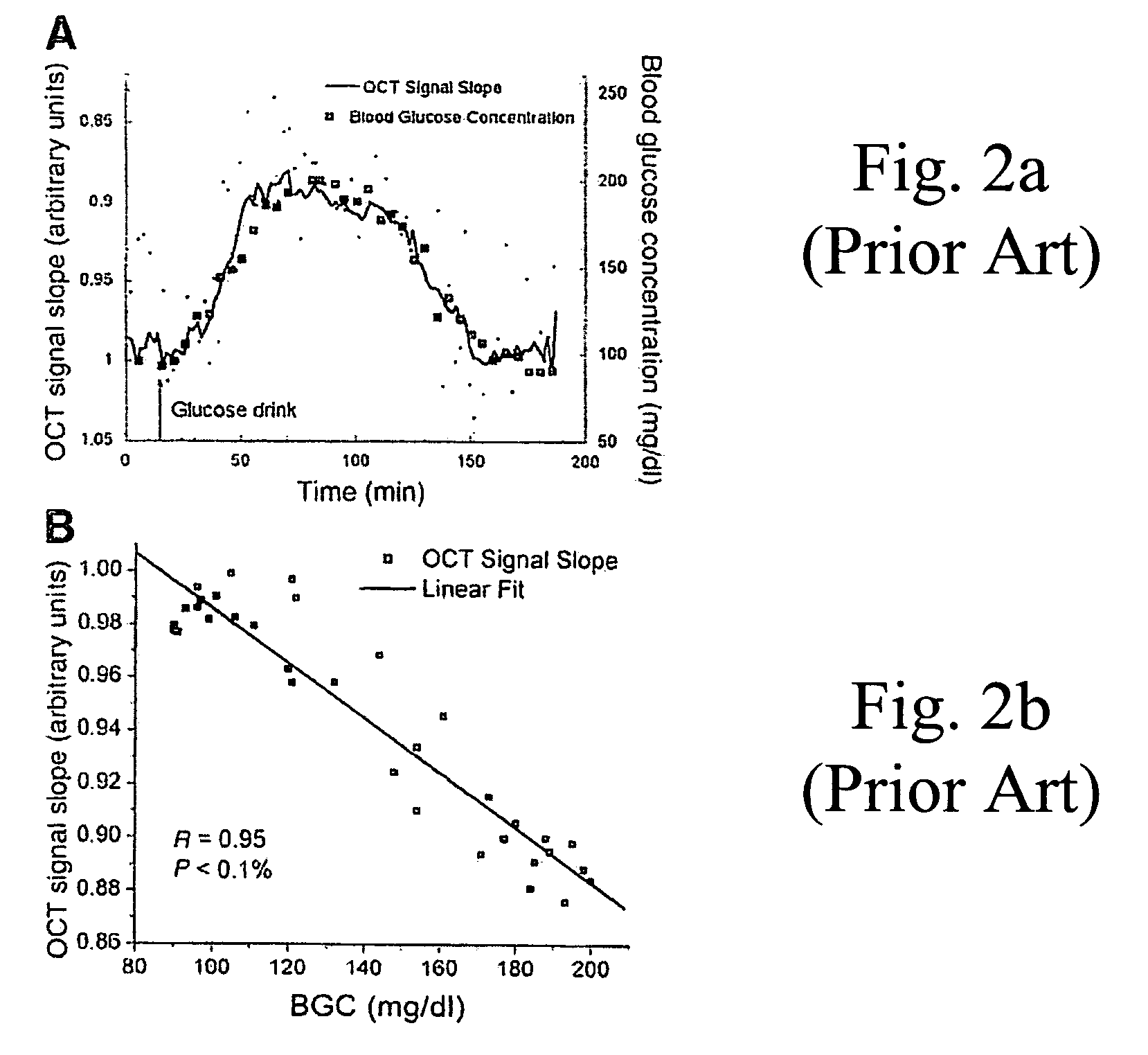
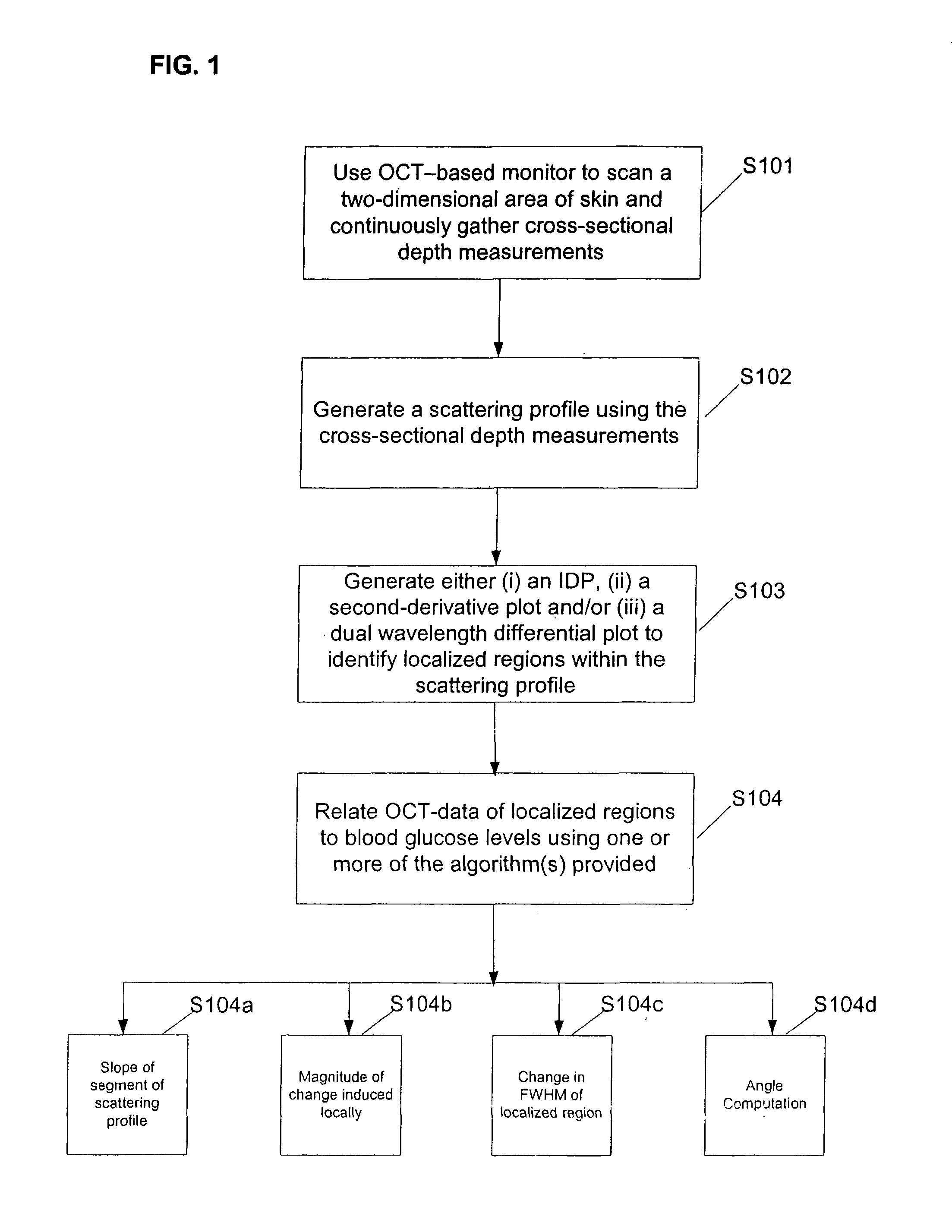
A method for noninvasively measuring analytes such as blood glucose levels includes using a non-imaging OCT-based system to scan a two-dimensional area of biological tissue and gather data continuously during the scanning. Structures within the tissue where measured-analyte-induced changes to the OCT data dominate over changes induced by other analytes are identified by focusing on highly localized regions of the data curve produced from the OCT scan which correspond to discontinuities in the OCT data curve. The data from these localized regions then can be related to measured analyte levels.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Expandable support device
A device for providing support for biological tissue is disclosed. The device can expand and be implanted in lieu of removed or otherwise missing bone, such as a vertebra, and / or soft tissue, such as a intervertebral disc. The device can be configured to radially expand in a single plane when the device is longitudinally contracted. Methods for using the device are also disclosed.
Owner:STOUT MEDICAL GROUP
Surgical treatment device
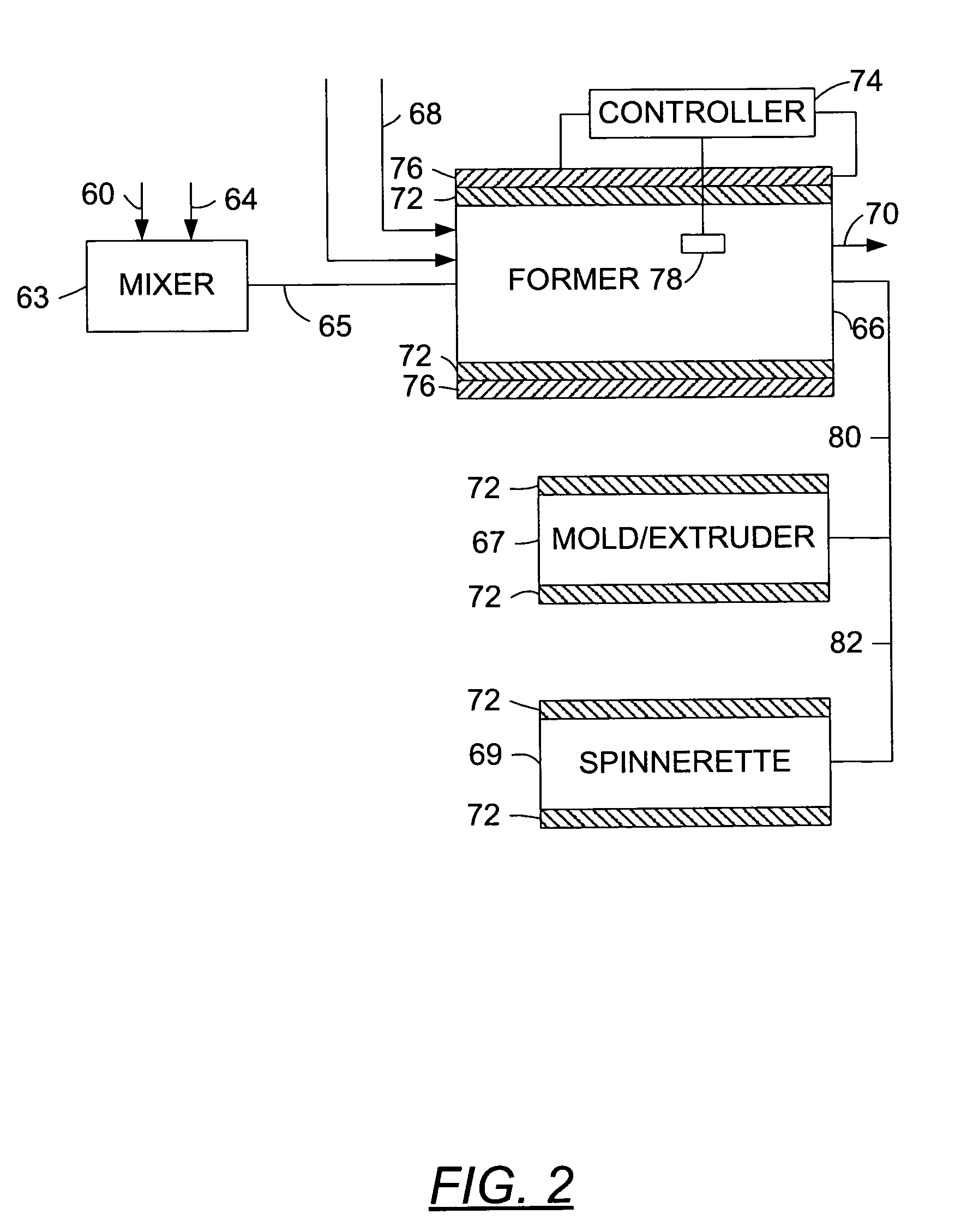
ActiveUS7101378B2Easily approachEffectively unfoldVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsExcision instrumentsSurgical treatmentEngineering
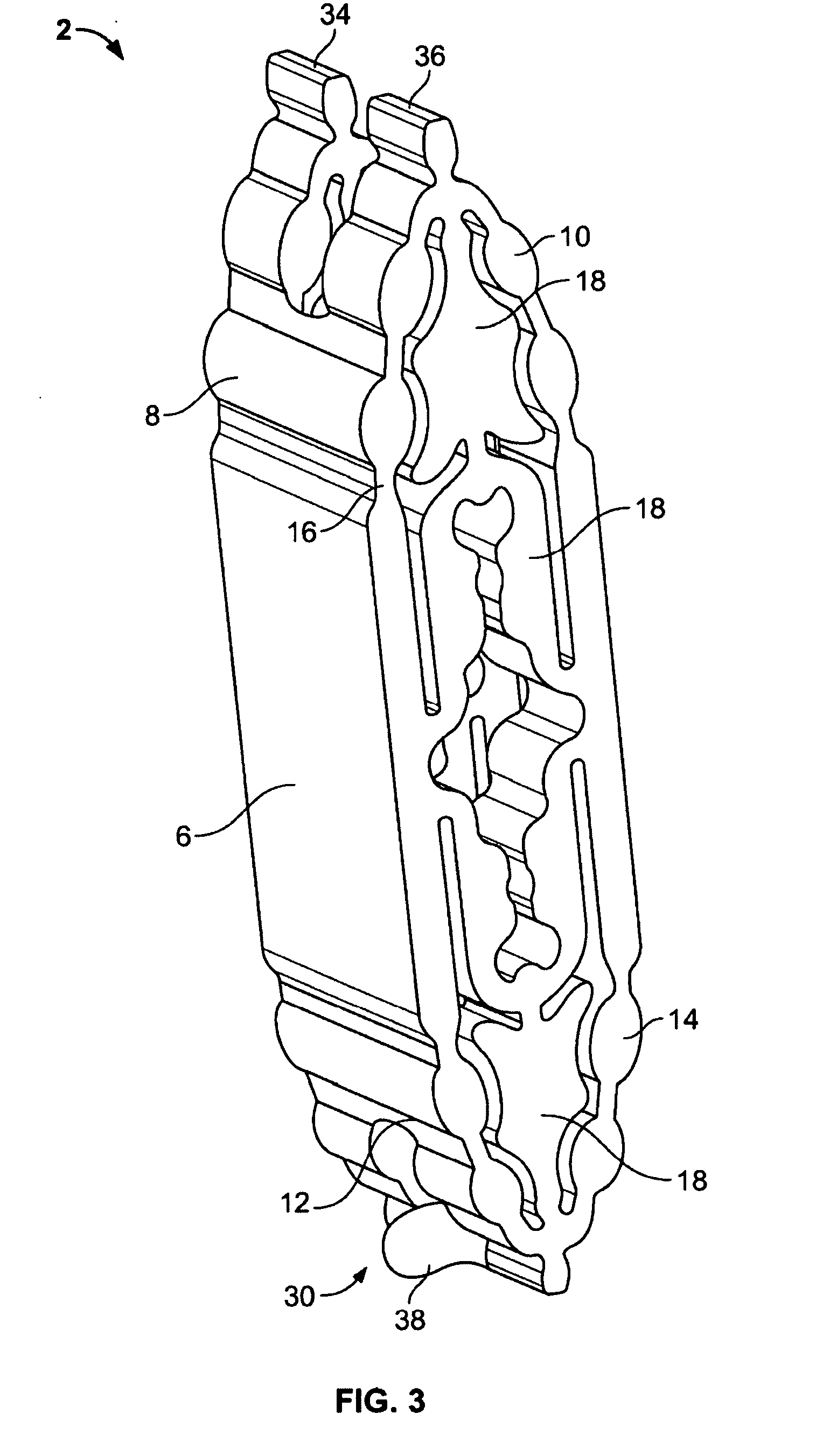
A biotissue excising instrument includes a tubular sheath inserted into a body, manipulator inserted into the sheath through leading end of the manipulator and having a loop portion that can be unfolded and contracted to accommodate biotissue to be excised. A slit is formed leading end the sheath to project and sink loop portion of the treatment portion so that manipulator is advanced or retreated to laterally project or sink the loop portion out of or into the or contract the loop portion, the sheath, and a treatment portion provided at thus excising the biotissue loop portion.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
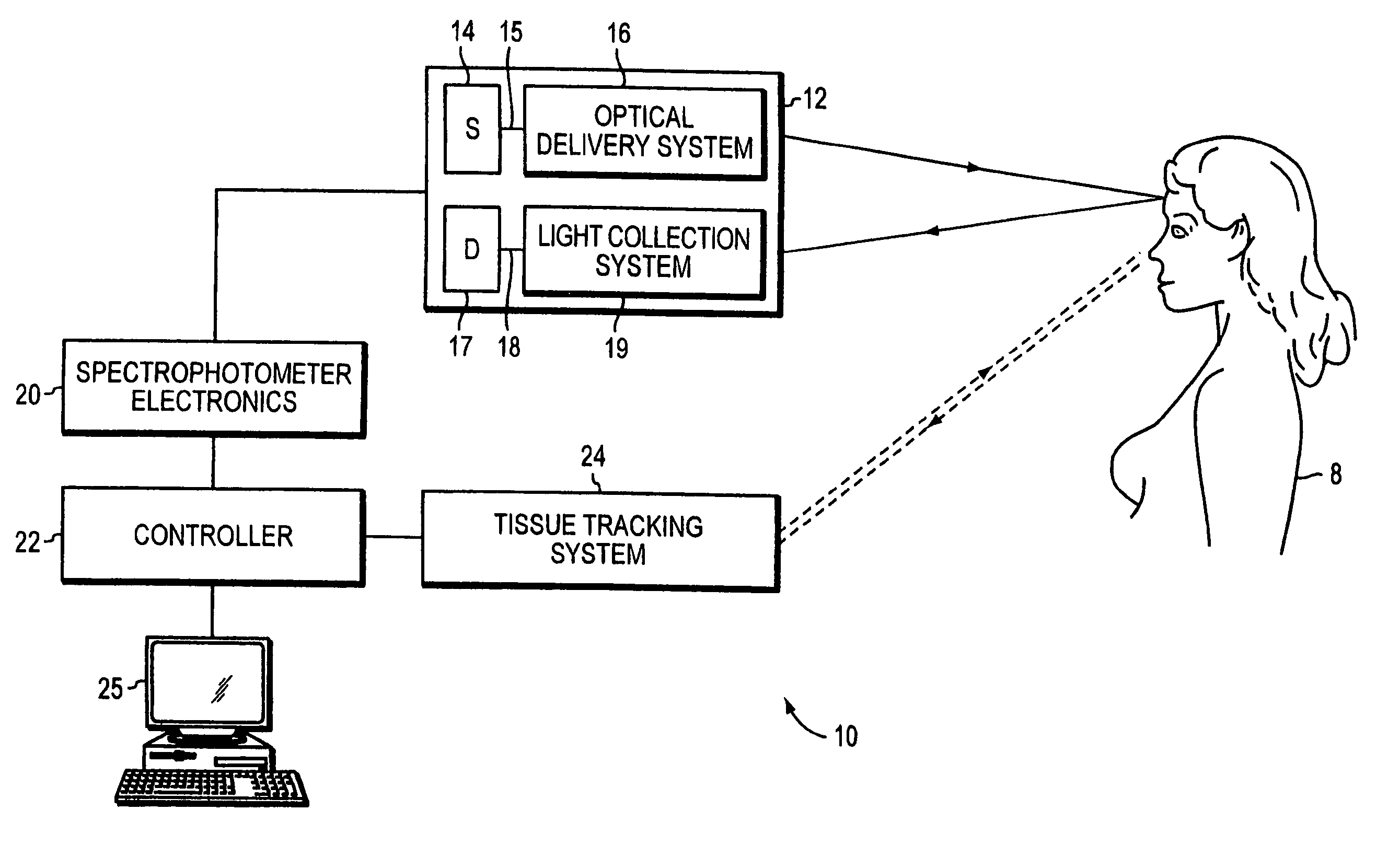
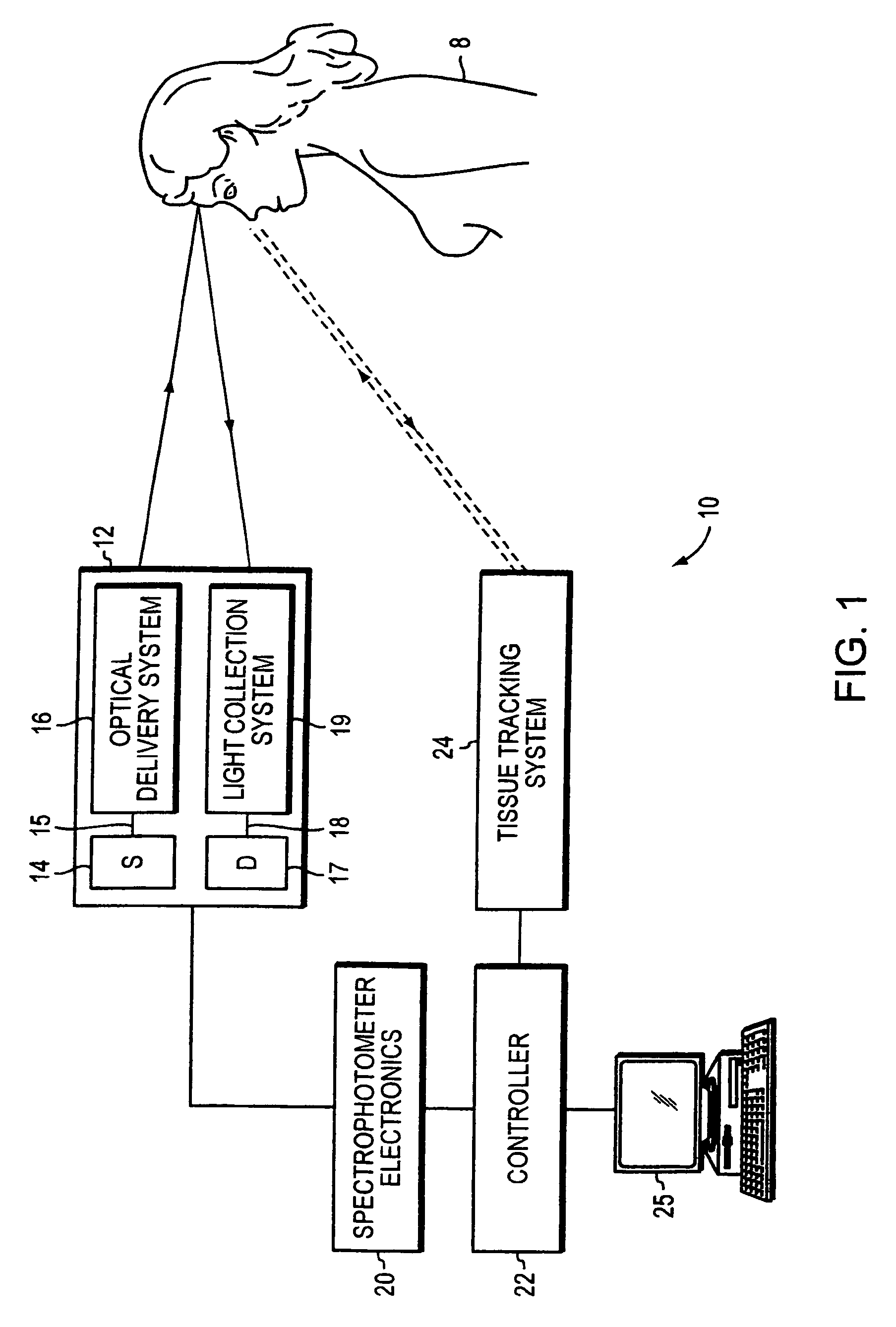
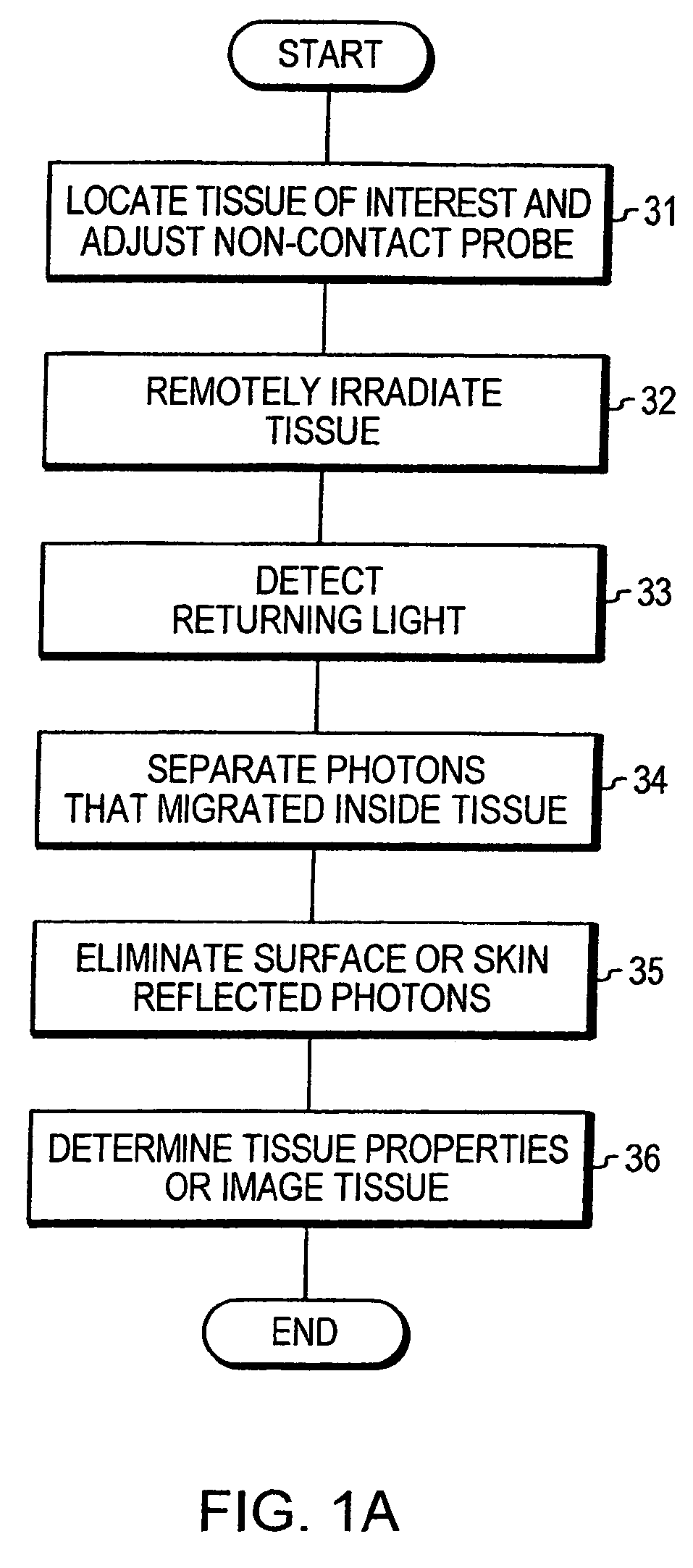
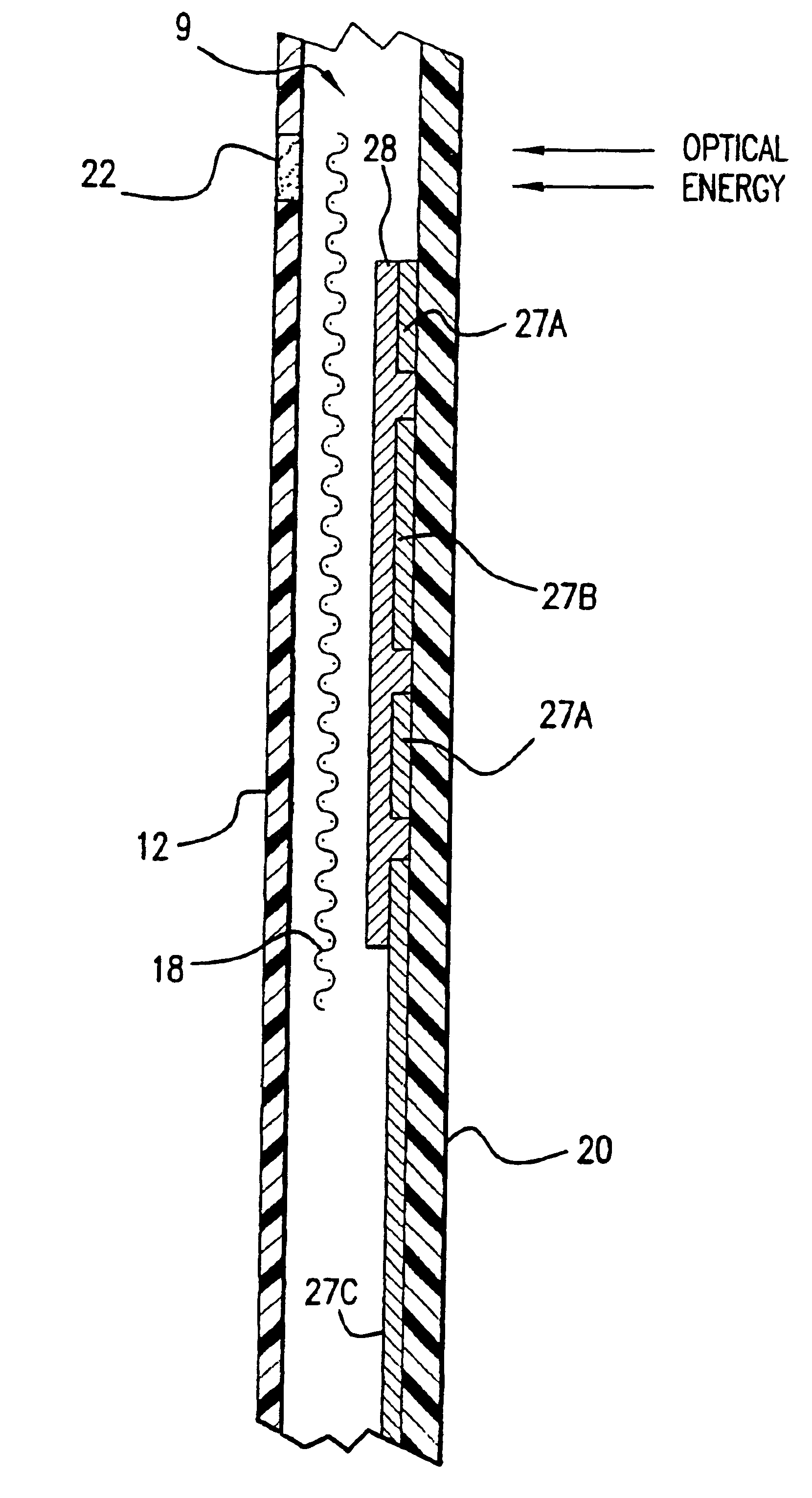
Optical examination of biological tissue using non-contact irradiation and detection
InactiveUS20060058683A1Avoid detectionCancel noiseDiagnostics using lightSensorsLight beamContact position
An optical system for examination of biological tissue includes a light source, a light detector, optics and electronics. The light source generates a light beam, transmitted to the biological tissue, spaced apart from the source. The light detector is located away (i.e., in a non-contact position) from the examined biological tissue and is constructed to detect light that has migrated in the examined tissue. The electronics controls the light source and the light detector, and a system separates the reflected photons (e.g., directly reflected or scattered from the surface or superficial photons) from the photons that have migrated in the examined tissue. The system prevents detection of the “noise” photons by the light detector or, after detection, eliminates the “noise” photons in the detected optical data used for tissue examination.
Owner:NONINVASIVE TECH
Integrated poration, harvesting and analysis device, and method therefor
An integrated device for poration of biological tissue, harvesting a biological fluid from the tissue, and analysis of the biological fluid. The device comprises a tissue-contacting layer having an electrically or optically heated probe to heat and conduct heat to the tissue to form at least one opening, such as a micropore to collect biological fluid from the opening, and a detecting layer responsive to the biological fluid to provide an indication of a characteristic of the biological fluid, such as the concentration of an analyte in interstitial fluid. In the embodiment in which, the probe comprises a photosensitizing assembly designed for the uniform application of a photosensitizing material, such as, for example, a dye or a pigment, to a tissue, e.g., the stratum comeum. In one embodiment, the photosensitizing assembly comprises photosensitizing material combined with a carrier, such as, for example, an adhesive or an ink, and the resulting combination is applied to a substrate, such as, for example, an inert polymeric substrate to form a photosensitizing assembly. In another embodiment, the photosensitizing assembly comprises photosensitizing material incorporated into a film-forming polymeric material.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP +1
Microneedle drug delivery device
InactiveUS7226439B2Minimal and no damage and pain and irritationAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical needlesIrritationMicro-needle
Simple microneedle devices for delivery of drugs across or into biological tissue are provided, which permit drug delivery at clinically relevant rates across or into skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The devices include a substrate to which a plurality of hollow microneedles are attached or integrated, and at least one reservoir, containing the drug, selectably in communication with the microneedles, wherein the volume or amount of drug to be delivered can be selectively altered. The reservoir can be formed of a deformable, preferably elastic, material. The device typically includes a means, such as a plunger, for compressing the reservoir to drive the drug from the reservoir through the microneedles. In one embodiment, the reservoir is a syringe or pump connected to the substrate.
Owner:VALERITAS LLC (US)
Method of treating glutaraldehyde-fixed pericardial tissue with a non-aqueous mixture of glycerol and a C1-C3 alcohol
A method of treating a biological tissue that enables dry storage of said tissue is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises contacting the biological tissue with a non-aqueous treatment solution comprising a polyhydric alcohol and a C1-C3 alcohol and removing a portion of the treatment solution from the solution-treated biological tissue. Also disclosed is biological tissue prepared using the above process and prosthetic devices made with such tissue.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and apparatus for temperature control of biologic tissue with simultaneous irradiation
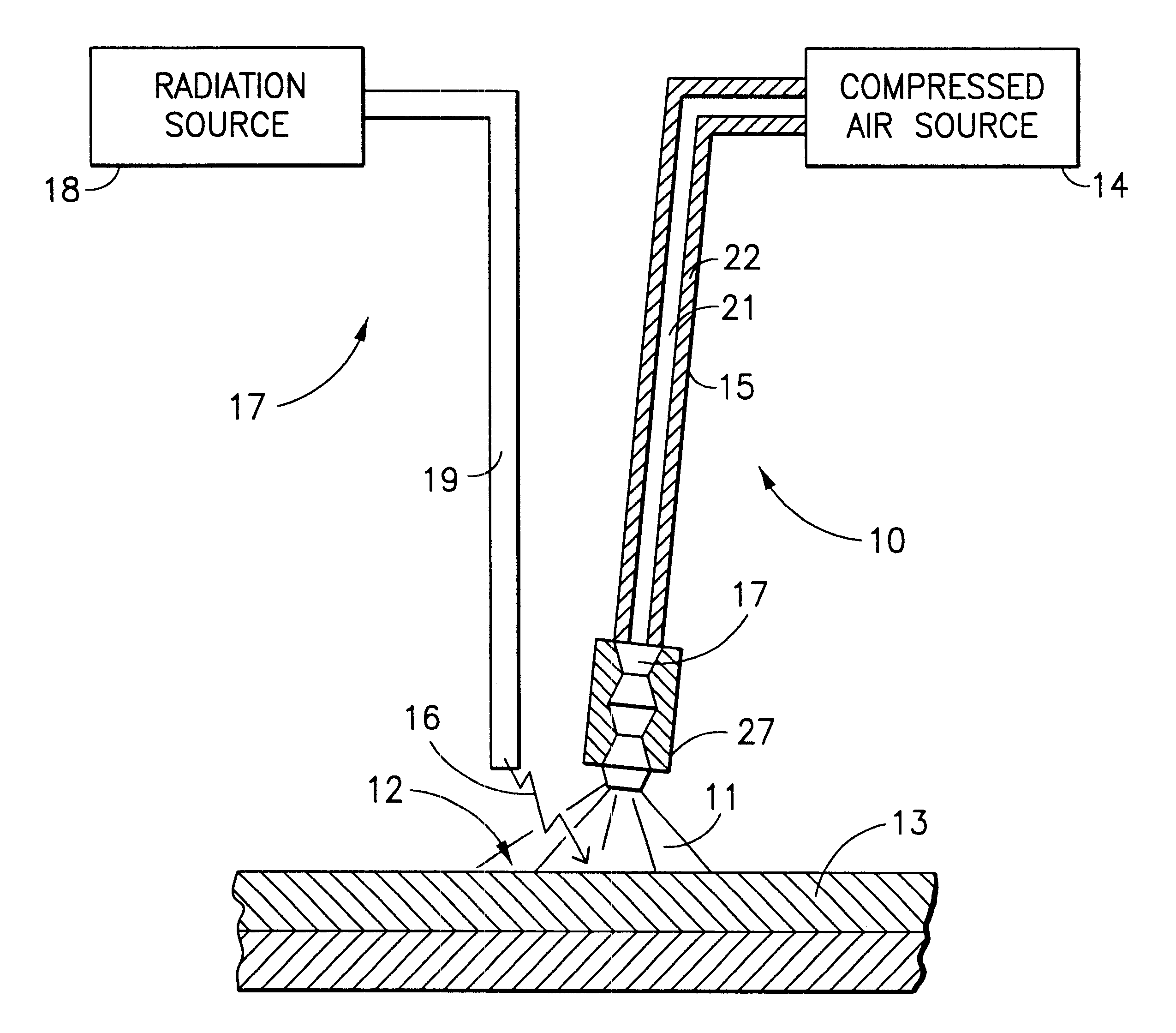
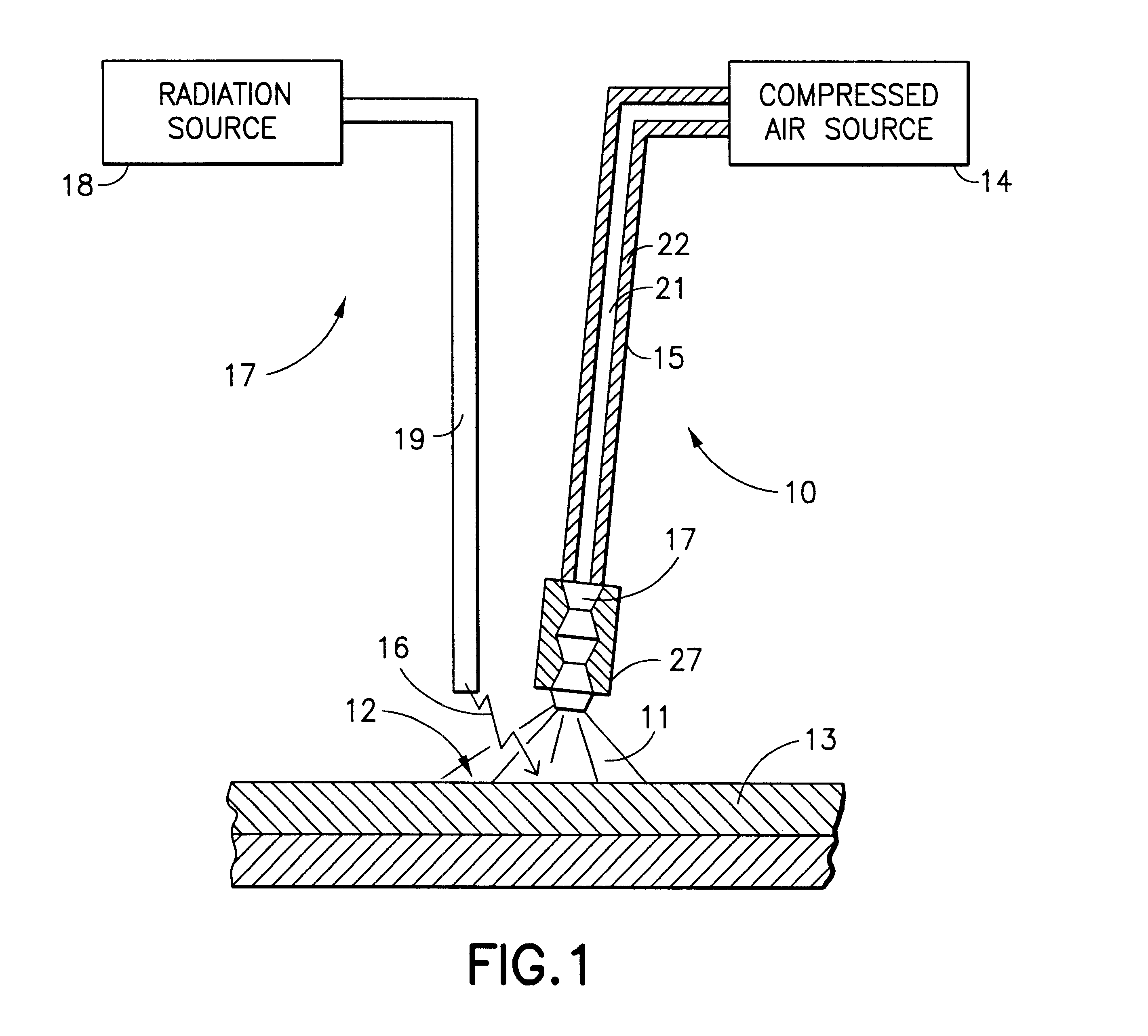
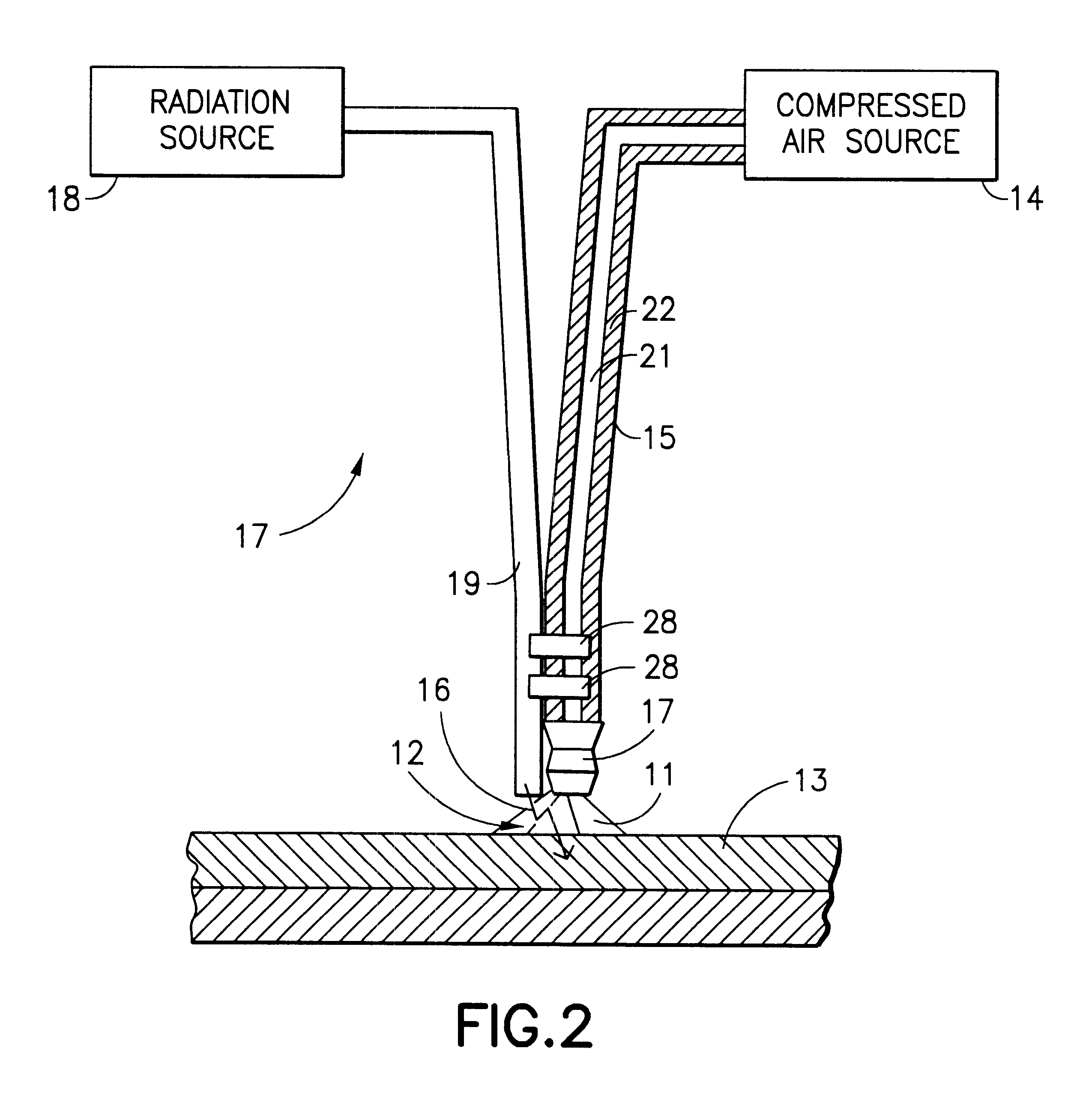
InactiveUS6475211B2Reduce usageLow costDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsTemperature controlTemperature modulation
A method and apparatus for treatment of the skin or other biologic tissue includes the ability to subject said skin or other tissue to temperature modulation and radiation, simultaneously. The apparatus that delivers warm or cold material to the treatment site to effect this modulation of temperature may be attached to the apparatus that delivers radiation or it may be a separate entity, that could be utilized with a variety of radiation generating equipment.
Owner:COOL LASER OPTICS
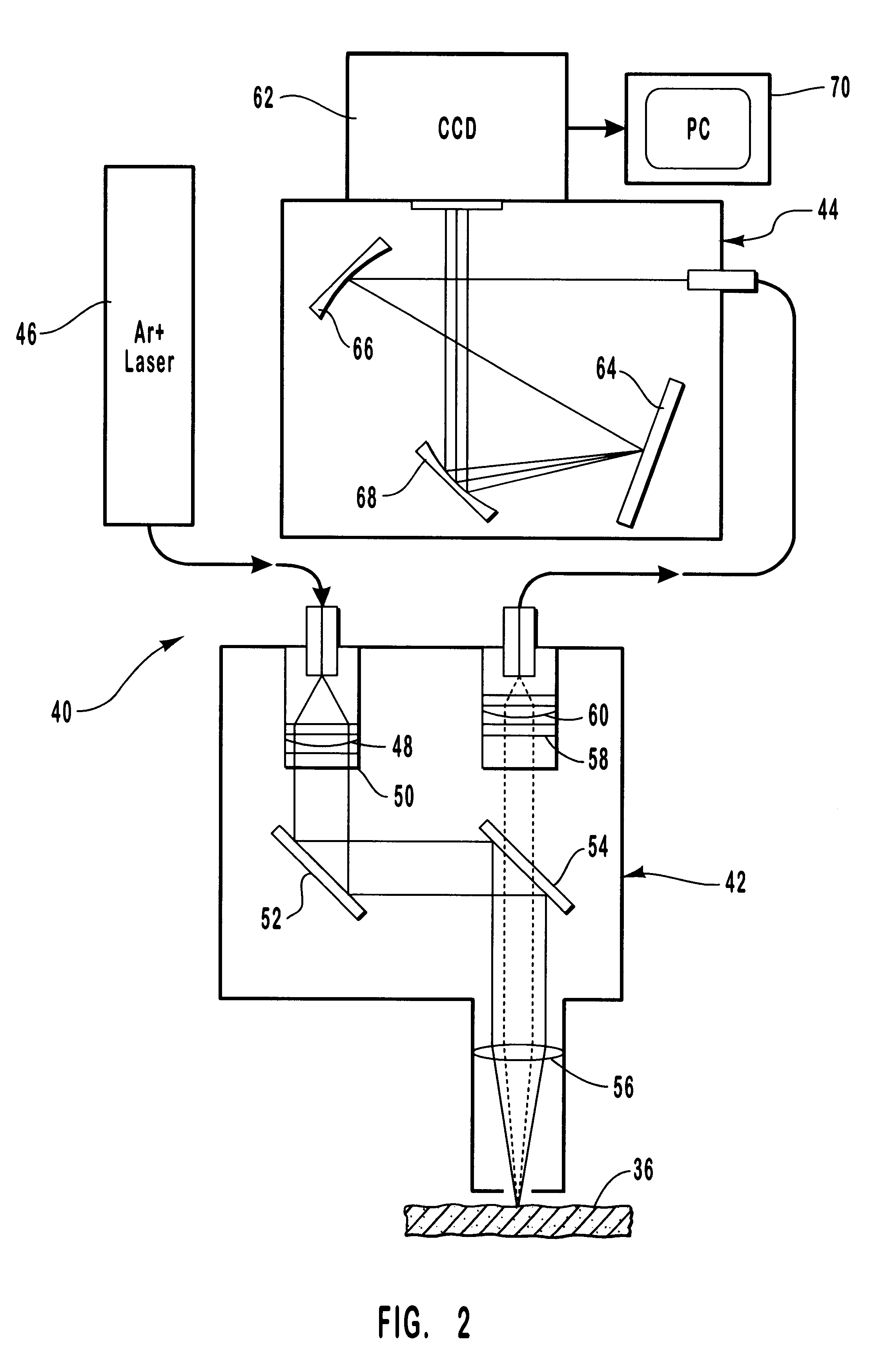
Method and apparatus for noninvasive measurement of carotenoids and related chemical substances in biological tissue
InactiveUS6205354B1Rapid and noninvasive and quantitative measurementRiskRadiation pyrometrySurgeryResonance Raman spectroscopyAntioxidant
A method and apparatus are provided for the determination of levels of carotenoids and similar chemical compounds in biological tissue such as living skin. The method and apparatus provide a noninvasive, rapid, accurate, and safe determination of carotenoid levels which in turn can provide diagnostic information regarding cancer risk, or can be a marker for conditions where carotenoids or other antioxidant compounds may provide diagnostic information. Such early diagnostic information allows for the possibility of preventative intervention. The method and apparatus utilize the technique of resonance Raman spectroscopy to measure the levels of carotenoids and similar substances in tissue. In this technique, laser light is directed upon the area of tissue which is of interest. A small fraction of the scattered light is scattered inelastically, producing the carotenoid Raman signal which is at a different frequency than the incident laser light, and the Raman signal is collected, filtered, and measured. The resulting Raman signal can be analyzed such that the background fluorescence signal is subtracted and the results displayed and compared with known calibration standards.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
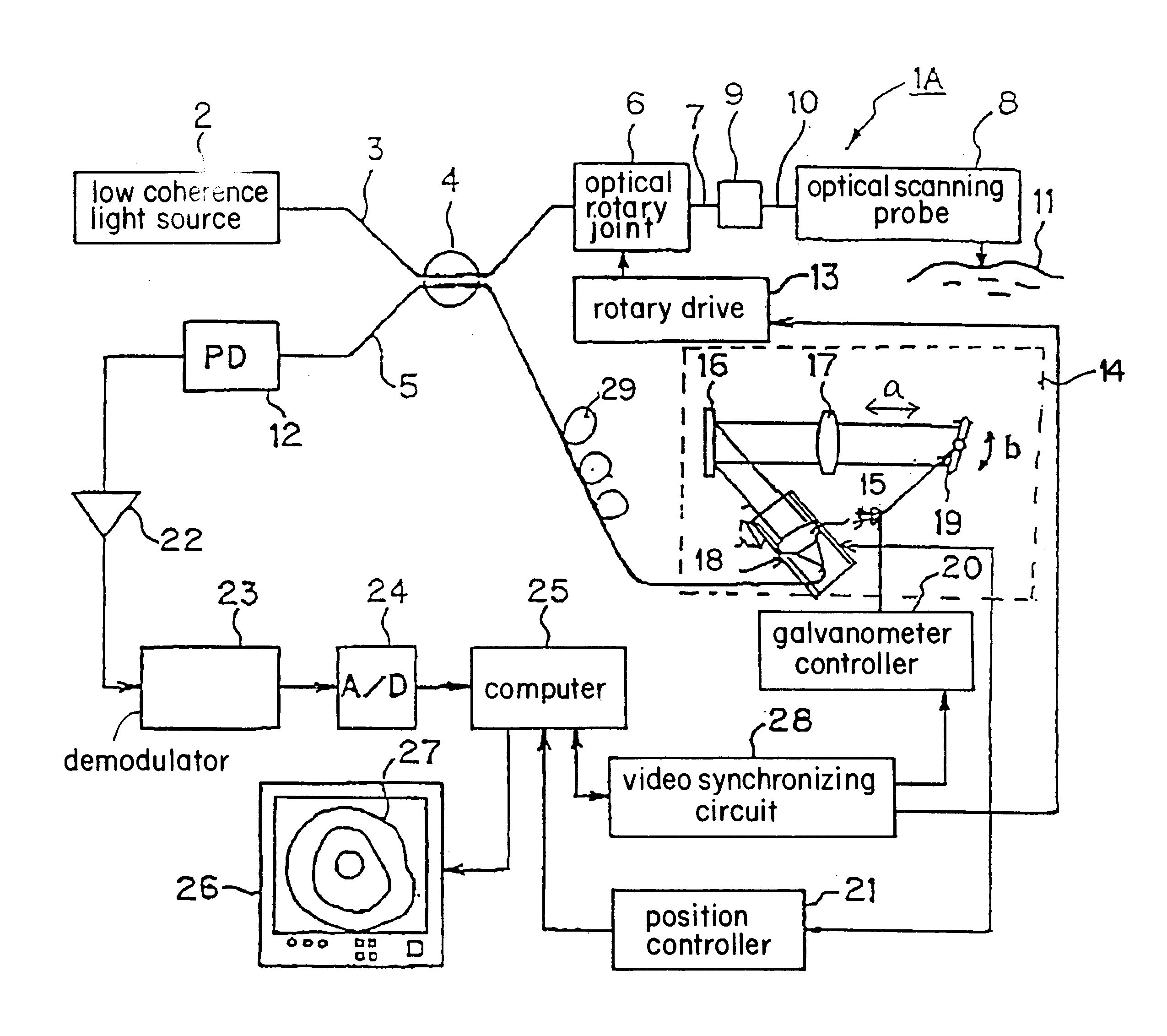
Optical imaging device
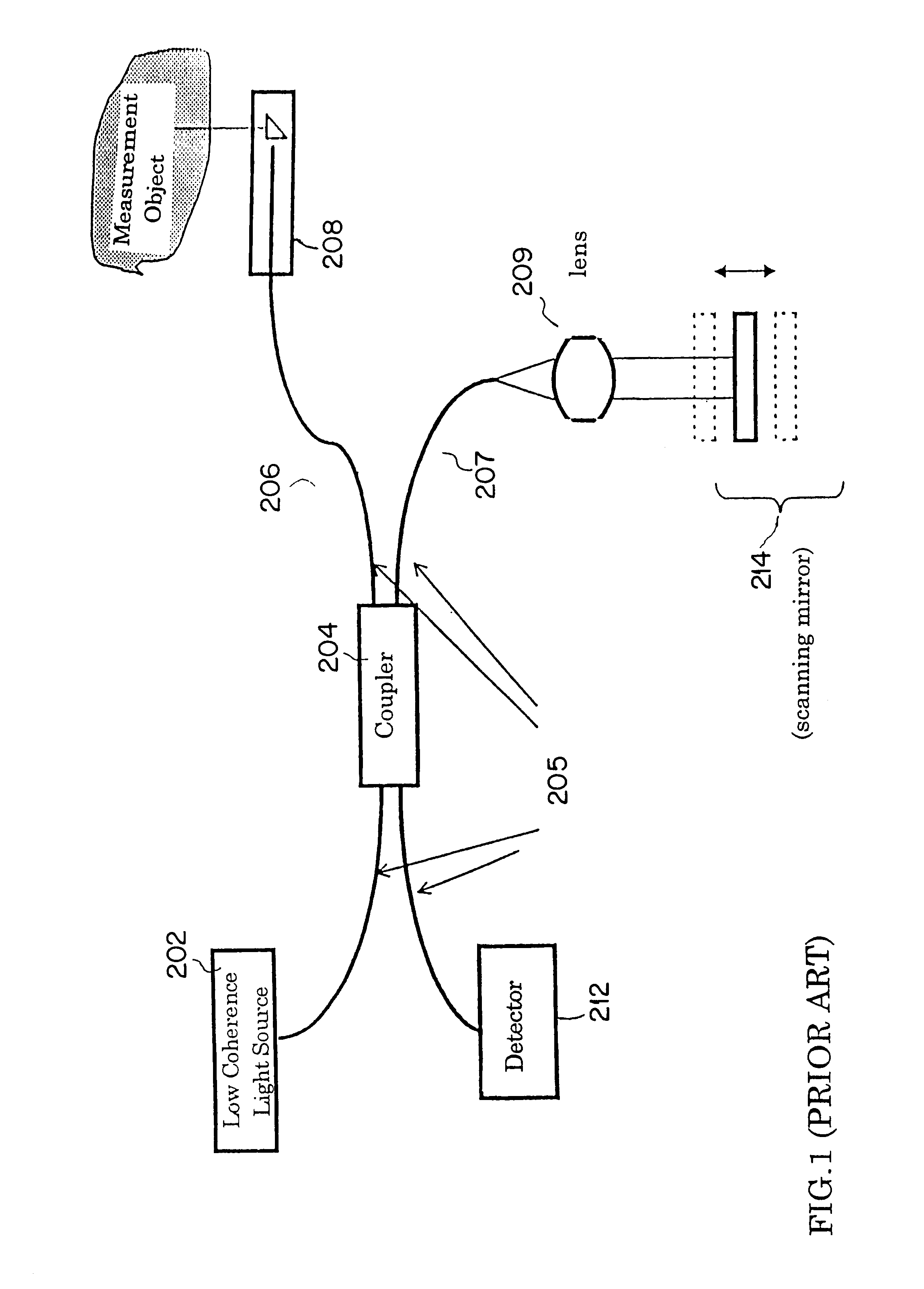
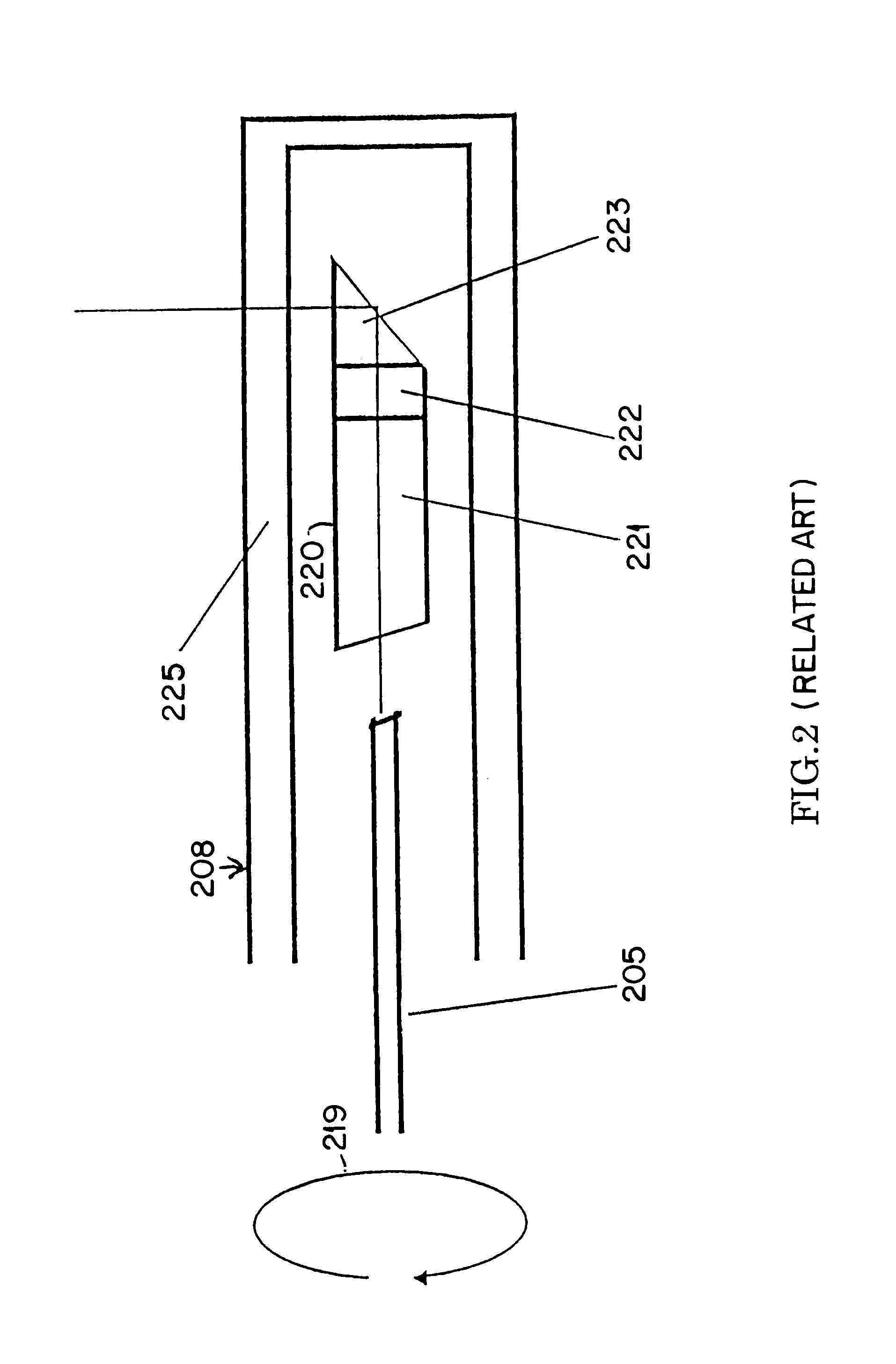
An Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) device irradiates a biological tissue with low coherence light, obtains a high resolution tomogram of the inside of the tissue by low-coherent interference with scattered light from the tissue, and is provided with an optical probe which includes an optical fiber having a flexible and thin insertion part for introducing the low coherent light. When the optical probe is inserted into a blood vessel or a patient's body cavity, the OCT enables the doctor to observe a high resolution tomogram. In a optical probe, generally, a fluctuation of a birefringence occurs depending on a bend of the optical fiber, and this an interference contrast varies depending on the condition of the insertion. The OCT of the present invention is provided with polarization compensation means such as a Faraday rotator on the side of the light emission of the optical probe, so that the OCT can obtain the stabilized interference output regardless of the state of the bend.
Owner:UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS OF CLEVELAND CLEVELAND +1
Multi-focal treatment of skin with acoustic energy
InactiveUS20080027328A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocal treatmentWavefront
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for applying acoustic energy to the skin. Acoustic waveguides with elements of varying thickness or shape are disclosed which deliver energy to more than one depth below a surface of the skin substantially simultaneously. The invention is especially useful with devices that focus ultrasound energy by condensing a propagating wavefront. The invention compensates for the mismatch in acoustic properties of the device's waveguide and the biological tissue that typically cause portions of the collapsing wavefront to lag behind other portions and, thereby, limit the focusing capabilities of acoustic treatment devices.
Owner:JULIA THERAPEUTICS
Microparticle coated medical device
A drug-loaded microparticle is applied to a medical device for subsequent application to biological tissues. A method of formulating a drug-loaded microparticle and applying it to the surface of a medical device, such as a stent, is disclosed. The drug-loaded microparticle is formulated by combining a drug with various chemical solutions. Specified sizes of the microparticles and amounts of drug(s) contained within the microparticles may be varied by altering the proportions of the chemicals / solutions. In addition to various drugs, therapeutic substances and radioactive isotopes may also be loaded into the microparticles. The drug-loaded microparticle are suspended in a polymer solution forming a polymer matrix. The polymer matrix may be applied to the entire surface or only selected portions of the medical device via dipping, spraying or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
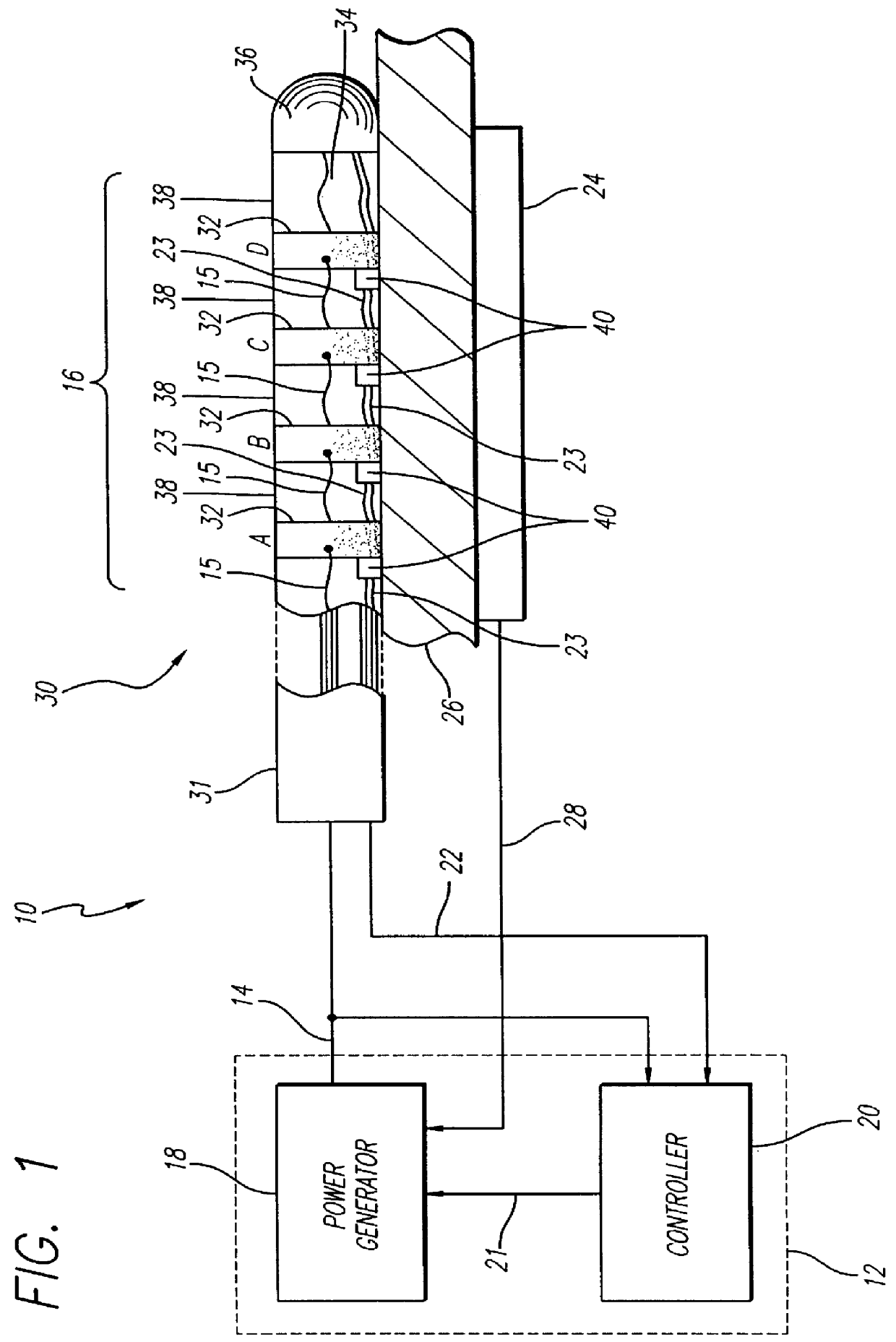
Electromagnetic sensors for biological tissue applications and methods for their use
ActiveUS7591792B2Improves signal couplingImproves resulting measurementElectrotherapyAntenna supports/mountingsMeasurement pointEngineering
Tissue sensors house one or more sensor elements. Each element has a housing mounted substrate and a superstrate with a planar antenna between. A transitional periphery (TP) of a superstrate outer surface interconnects a base to a plateau. At least some of the TP has a generally smooth transition. Plural elements are spaced by the housing. Alternately, the superstrate TP is flat, the housing extends to the outer superstrate surface and a shield surrounds the element. The housing is flush with or recessed below the superstrate and defines a TP between the housing and superstrate. A method converts a reference signal to complex form; plots it in a complex plane as a reference point (RP); converts a measurement signal to complex form; plots it in the complex plane as a measurement point (MP); determine a complex distance between the MP and the RP; and compares complex distance to a threshold.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
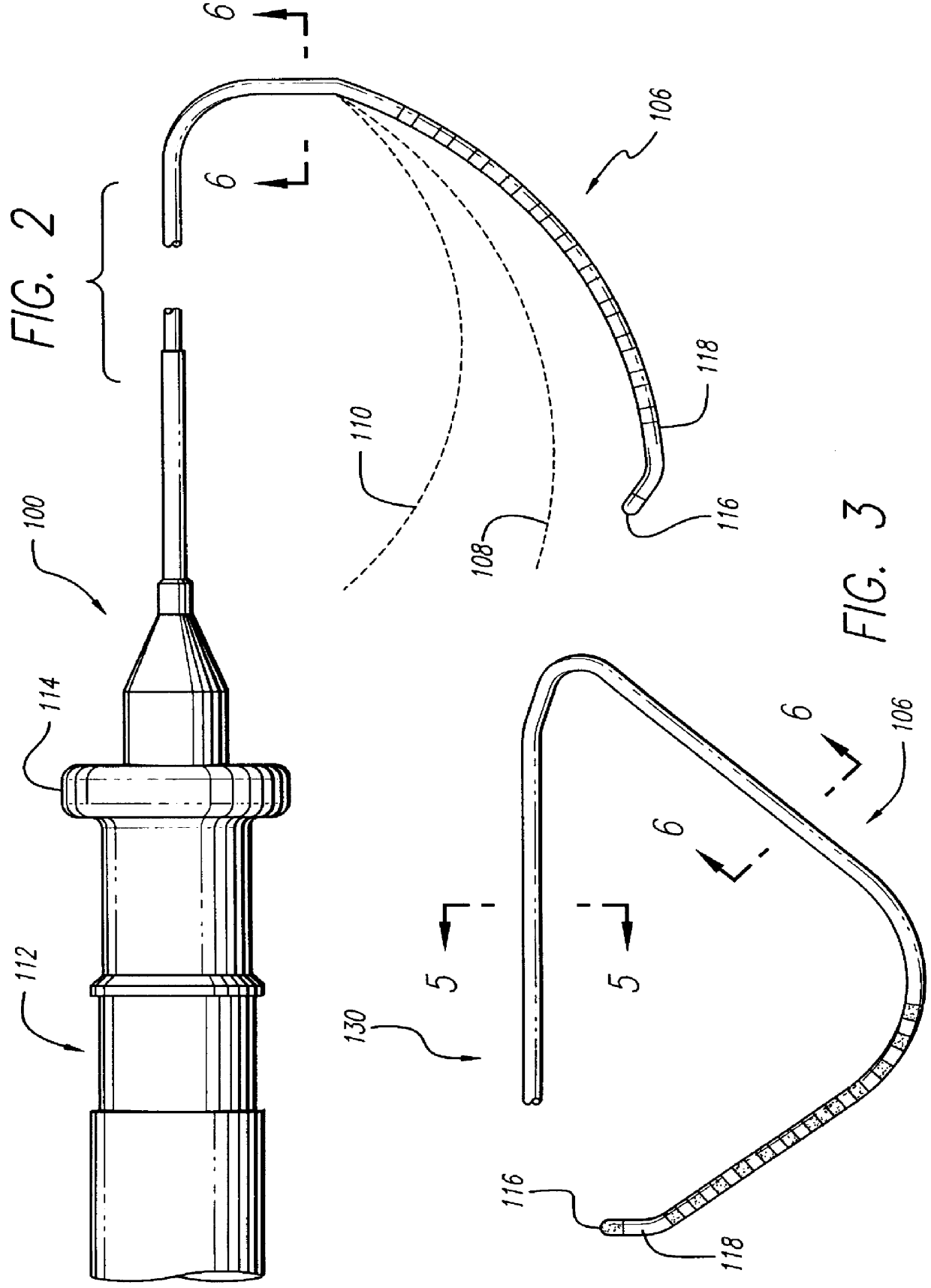
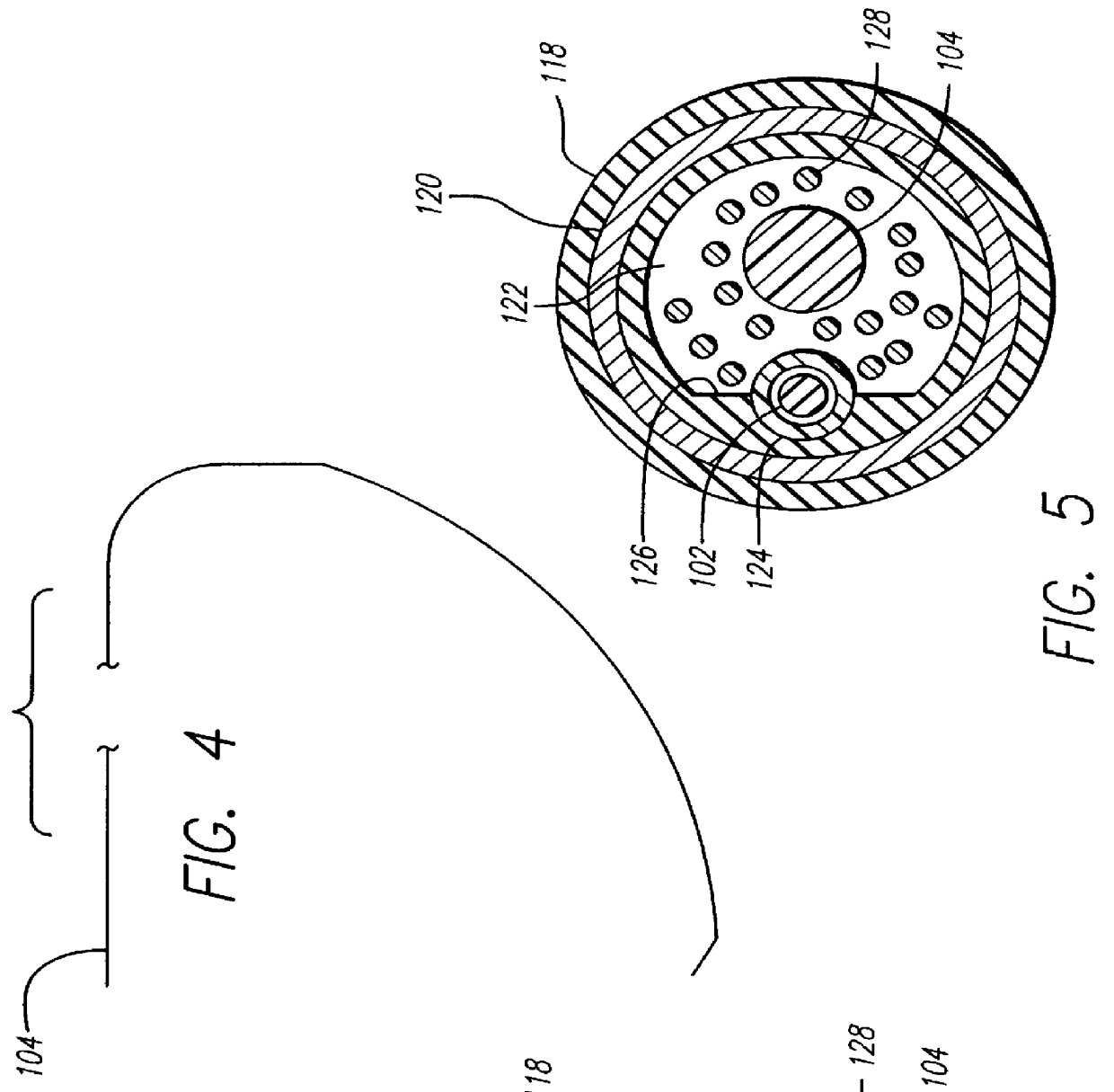
Steerable catheter with preformed distal shape and method for use
InactiveUS6096036AReduce curvatureTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsHeart chamberCurve shape
A catheter has a stylet formed of a shape-retentive and resilient material having a preformed curved shape at its distal end resulting in the catheter sheath having the preformed curved shape. The catheter sheath has a plurality of electrodes at its distal end for contacting selected biological tissue for imparting ablation energy thereto. The catheter sheath also has an axially mounted tendon for causing deflection of the distal end. The stylet material permits straightening the catheter sheath during insertion into the patient and advancing the electrodes to the target tissue. Upon removal of the straightening forces, such as by entry into a chamber of the heart, the stylet material resumes its preformed curved distal shape thereby forcing the catheter distal end with the electrodes into the same preformed curved shape. The operator may place the curved distal end into contact with the target tissue and axially move the tendon as desired to gain greater control over the bend in the distal end of the catheter sheath to adjust the radius of curvature of the distal end to obtain greater contact of the electrodes with the heart tissue. Preferably, the stylet is formed of nitinol.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
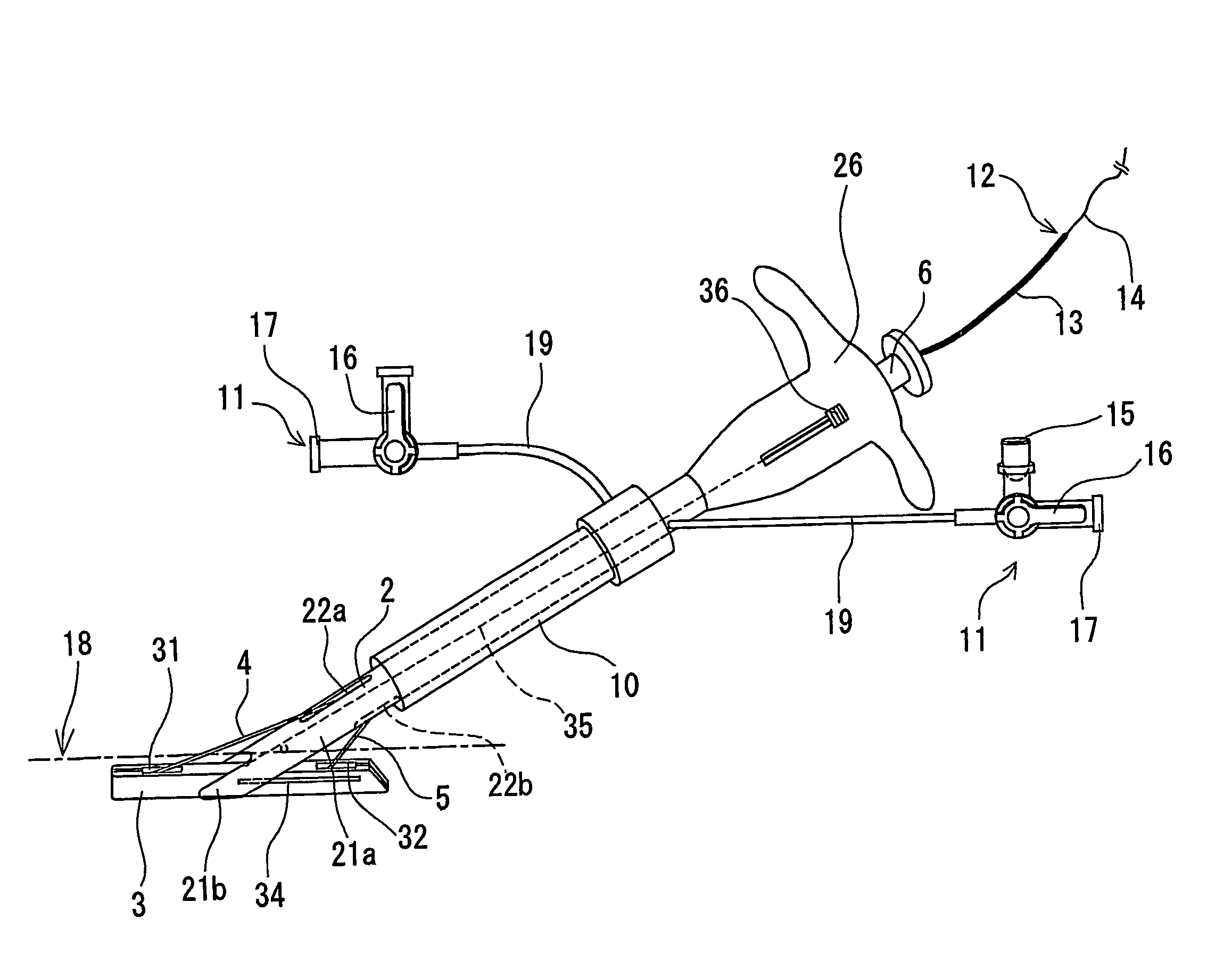
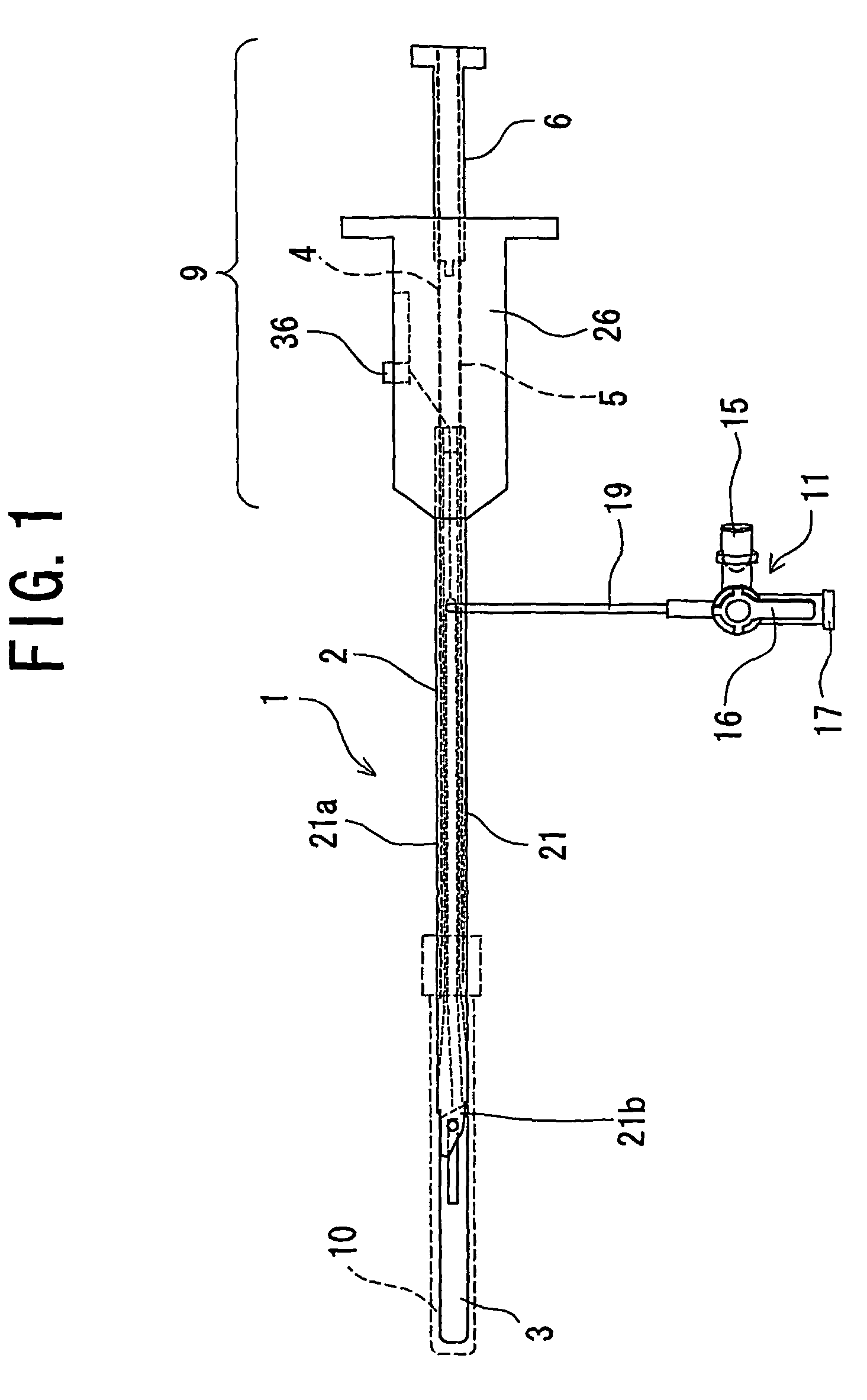
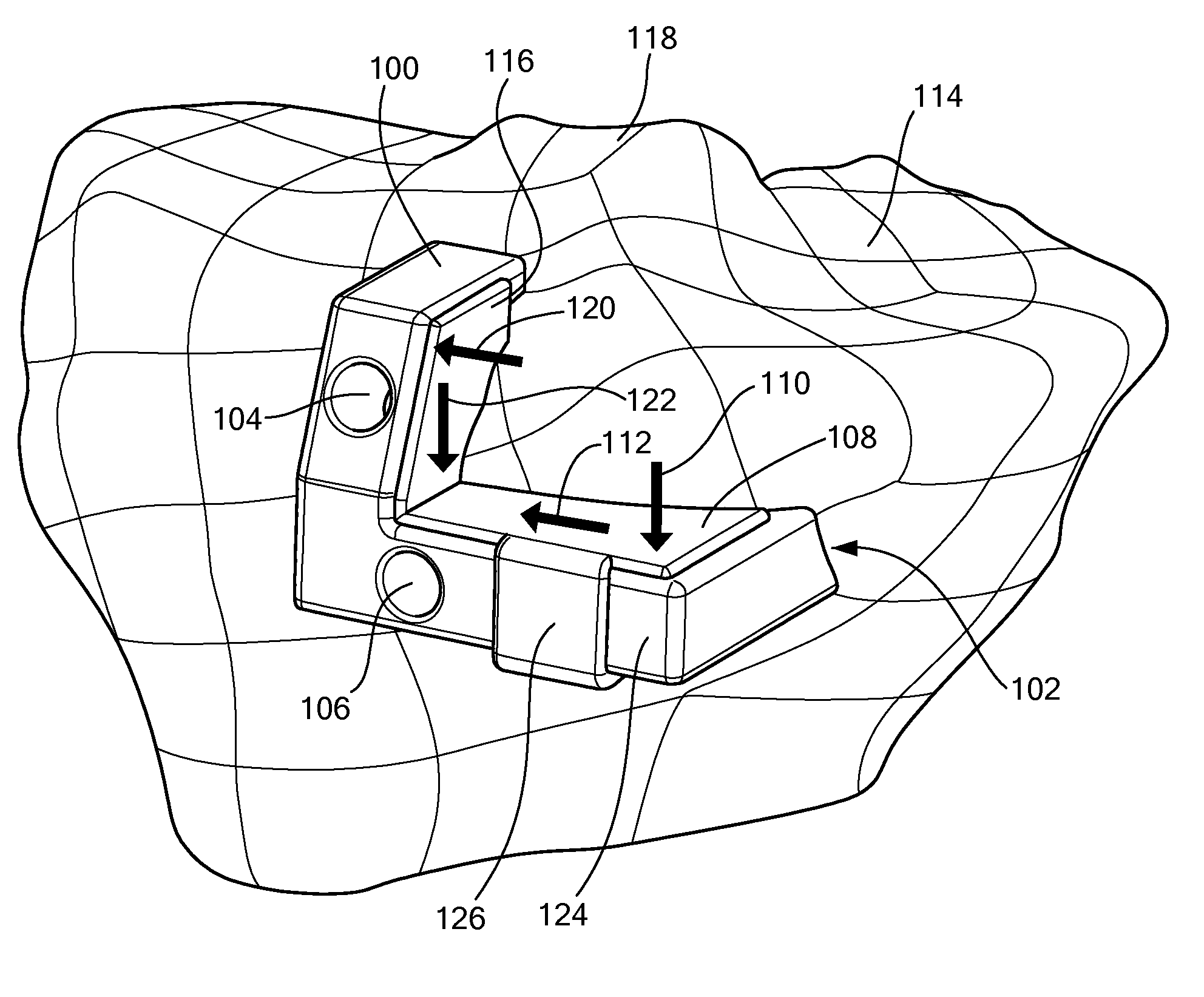
Biological-tissue joining apparatus
ActiveUS8460288B2Preventing inability to applyChiropractic devicesEye exercisersEnergy supplySupply energy
Regardless of the type of biological tissue, a sufficient joining force can be quickly obtained; the problem of an adhesive bonding biological tissue other than the target biological tissue can be prevented; and the adhesive can be prevented from becoming impossible to apply due to curing. There is provided a biological-tissue joining apparatus including an energy supplying part that clamps, with pressure, biological tissue to be joined and melts protein in the clamped biological tissue by supplying energy to the biological tissue; and an adhesive supplying part that supplies an adhesive to the biological tissue, wherein the adhesive supplying part includes a discharge port that discharges the adhesive to a contact surface of the energy supplying part in contact with the biological tissue.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
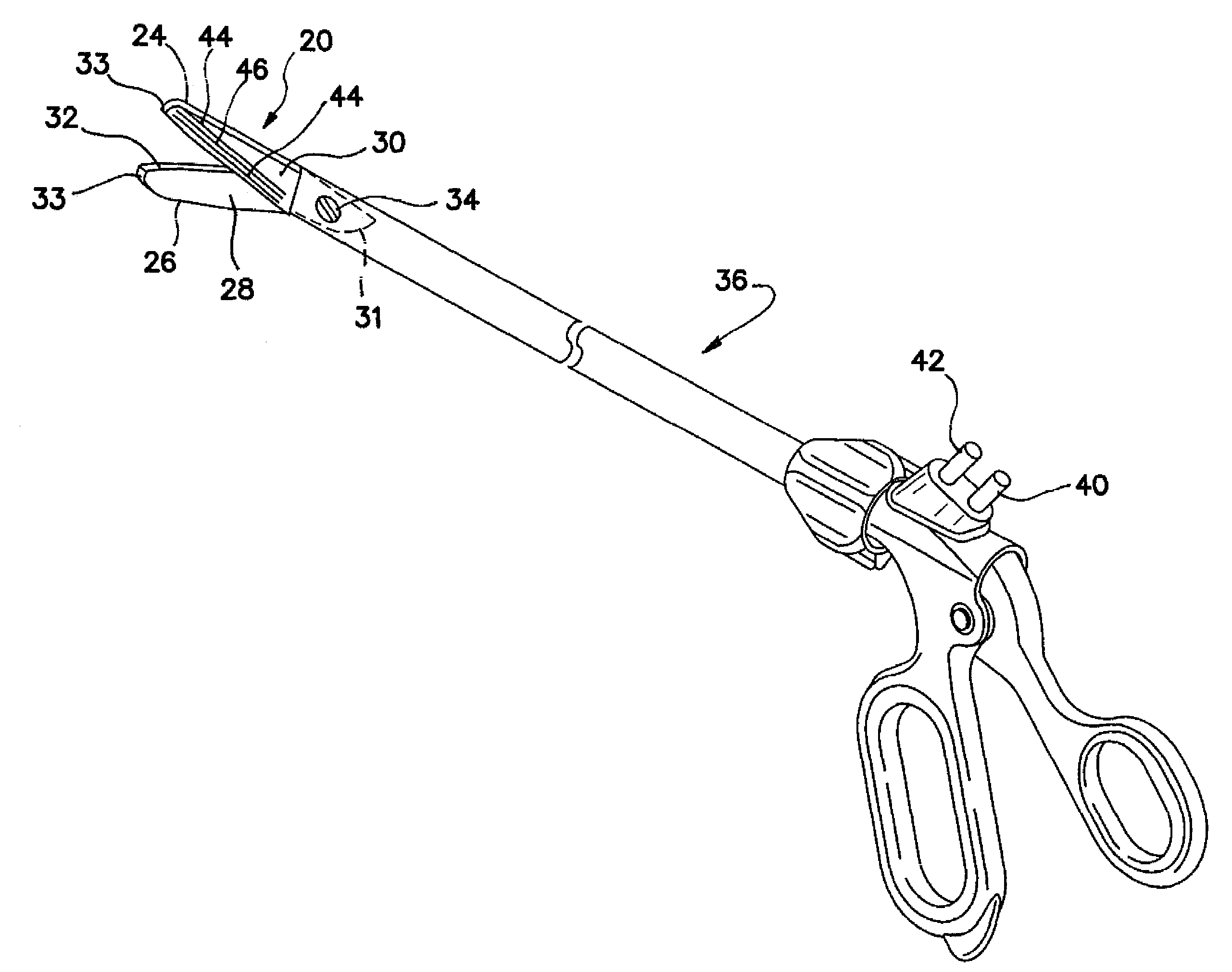
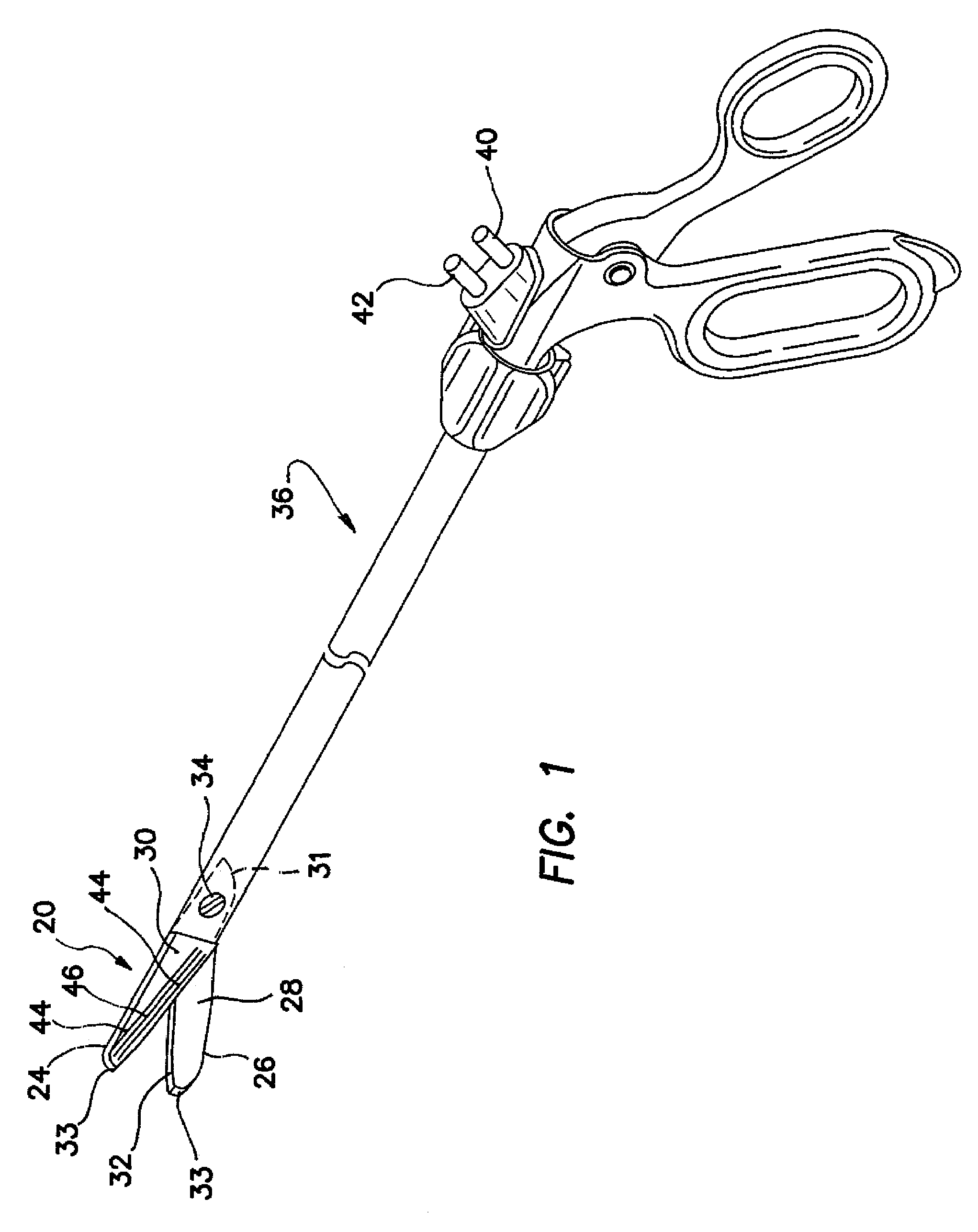
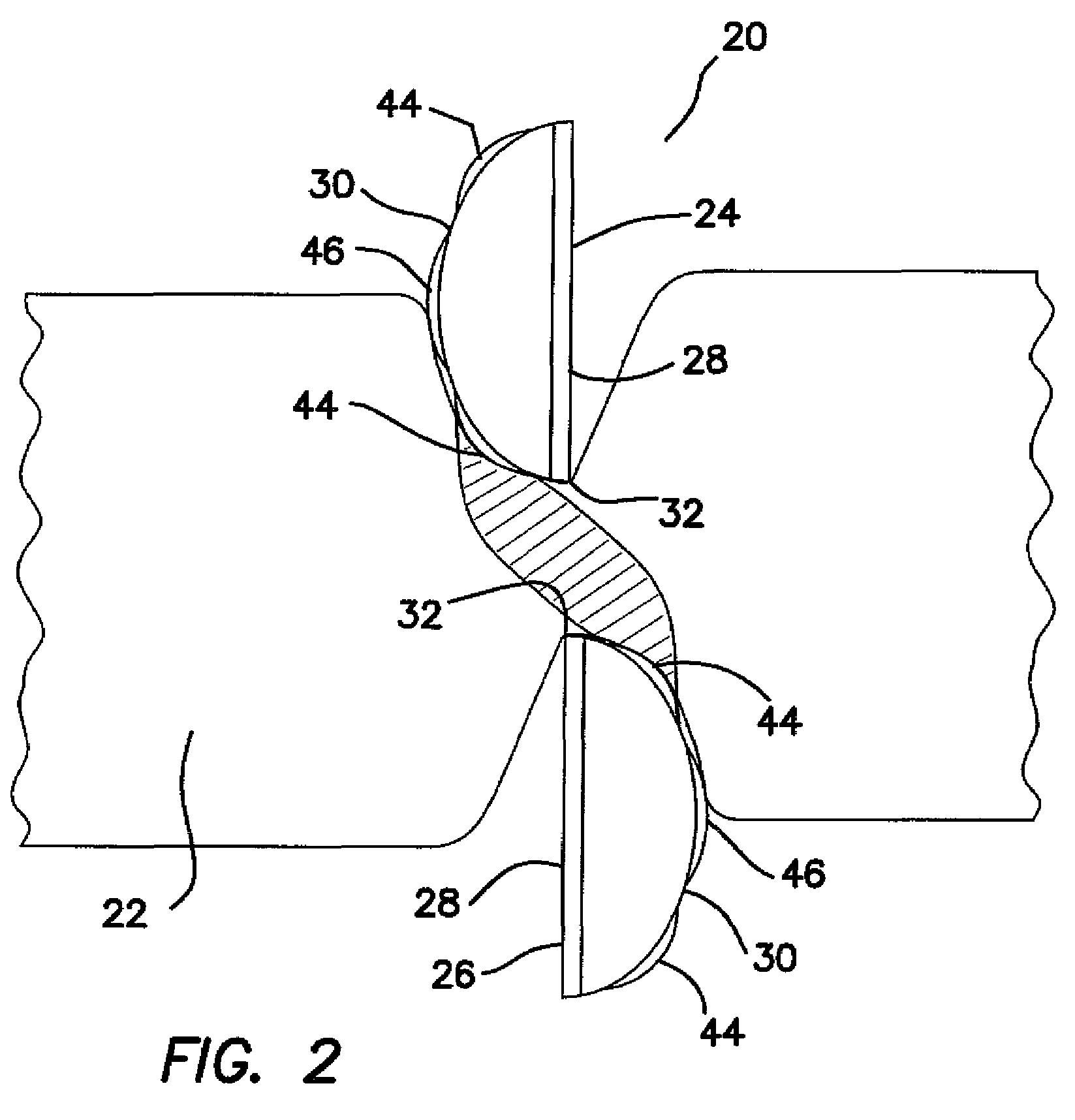
Bipolar electrosurgical scissors
ActiveUS7419490B2High dielectric strengthSurgical instrument detailsSurgical forcepsBipolar electrosurgeryElectrical polarity
Bipolar electrosurgical scissors for treating biological tissue include first and second scissor blades. A shearing surface and cutting edge of each blade is electrically neutral. The scissors include a pair of electrical connections for receiving electrical currents of opposing polarities. Each blade includes at least one first electrode and at least one second electrode positioned on a surface opposite the shearing surface The at least one first electrode on the first blade and the at least one second electrode on the second blade are coupled to the first electrical connection. The at least one second electrode on the first blade and the at least one first electrode on the second blade are coupled to the second electrical connection. In a first energized state, the electrical connections deliver electrical current only to the first electrodes. In a second energized state, the electrical connections deliver electrical current to all of the electrodes.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Protective assembly
An assembly for protecting biological tissue from the effects of heating. The assembly contains a conductor in contact with the biological tissue and forming an electrical circuit comprising the biological tissue. The assembly contains a device for modifying the impedance of the electrical circuit such that, at a frequency of from about 10 megahertz to about 150 megahertz, such impedance is at least about 0.5 ohms per centimeter of length of said conductor. The assembly also contains a device for limiting the flow of current through the biological tissue such that, when the assembly is exposed to an alternating current electromagnetic field at a frequency of 64 megahertz and a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla for 15 minutes, the temperature of the biological tissue does not exceed 42 degrees Celsius.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
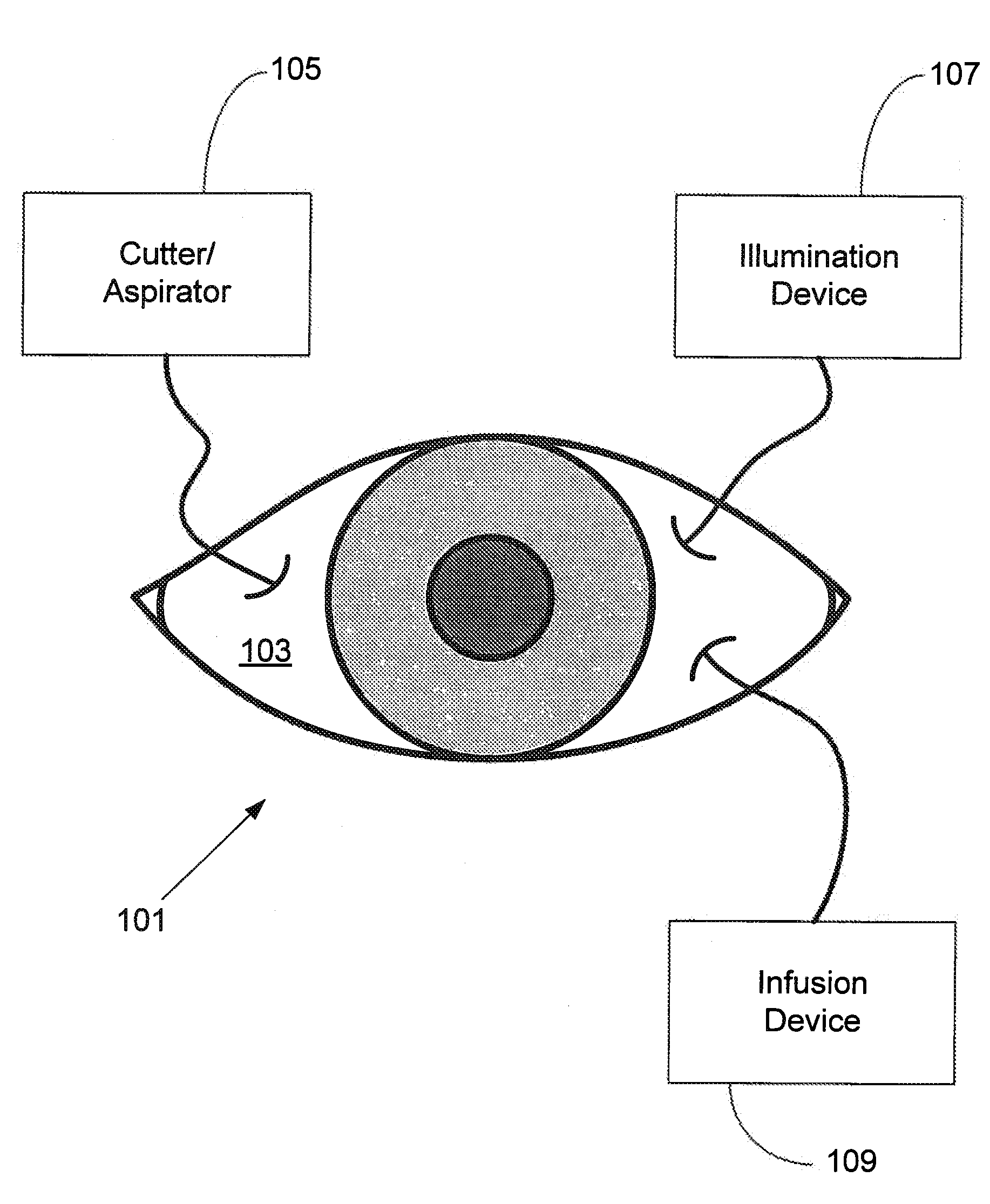
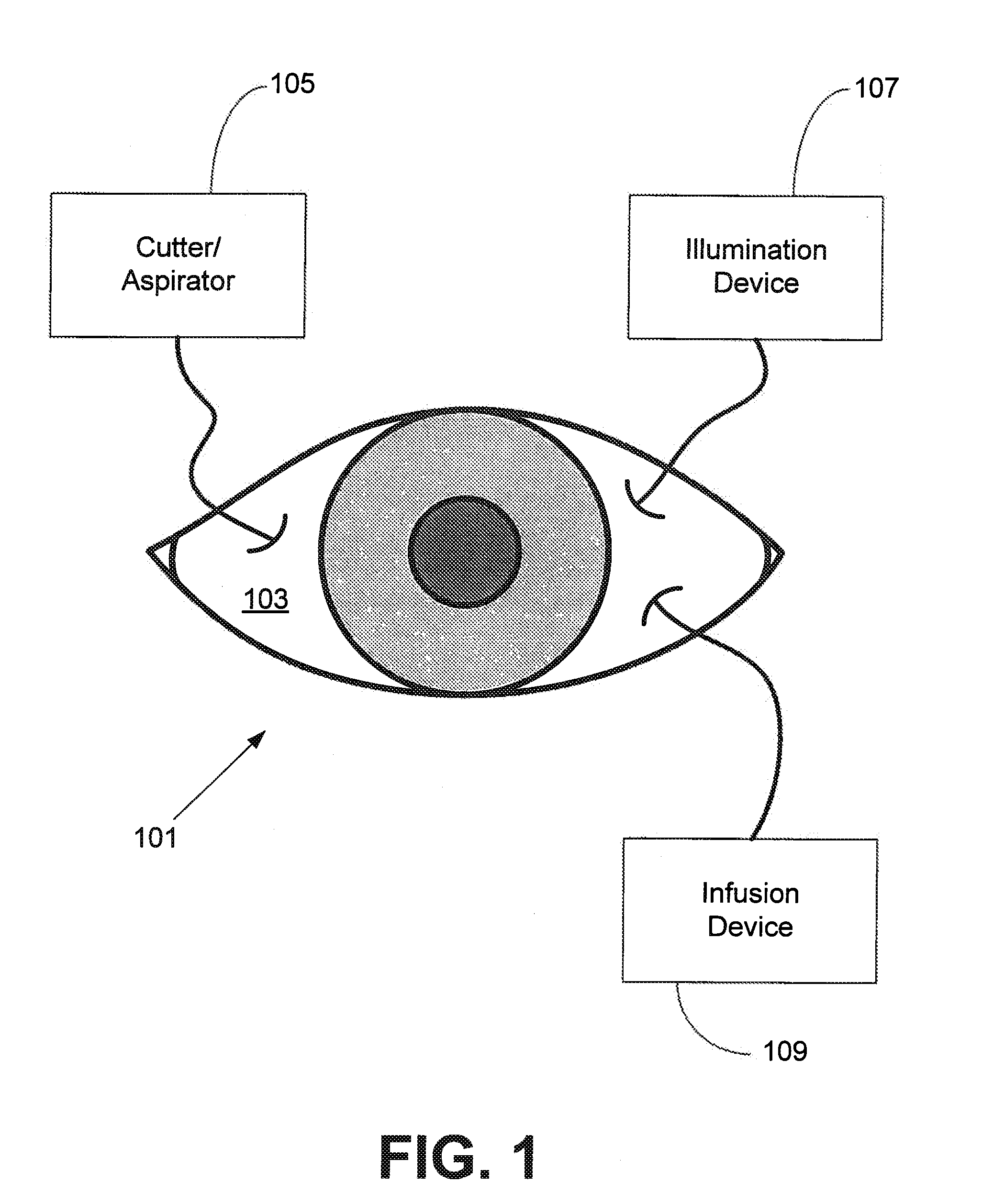
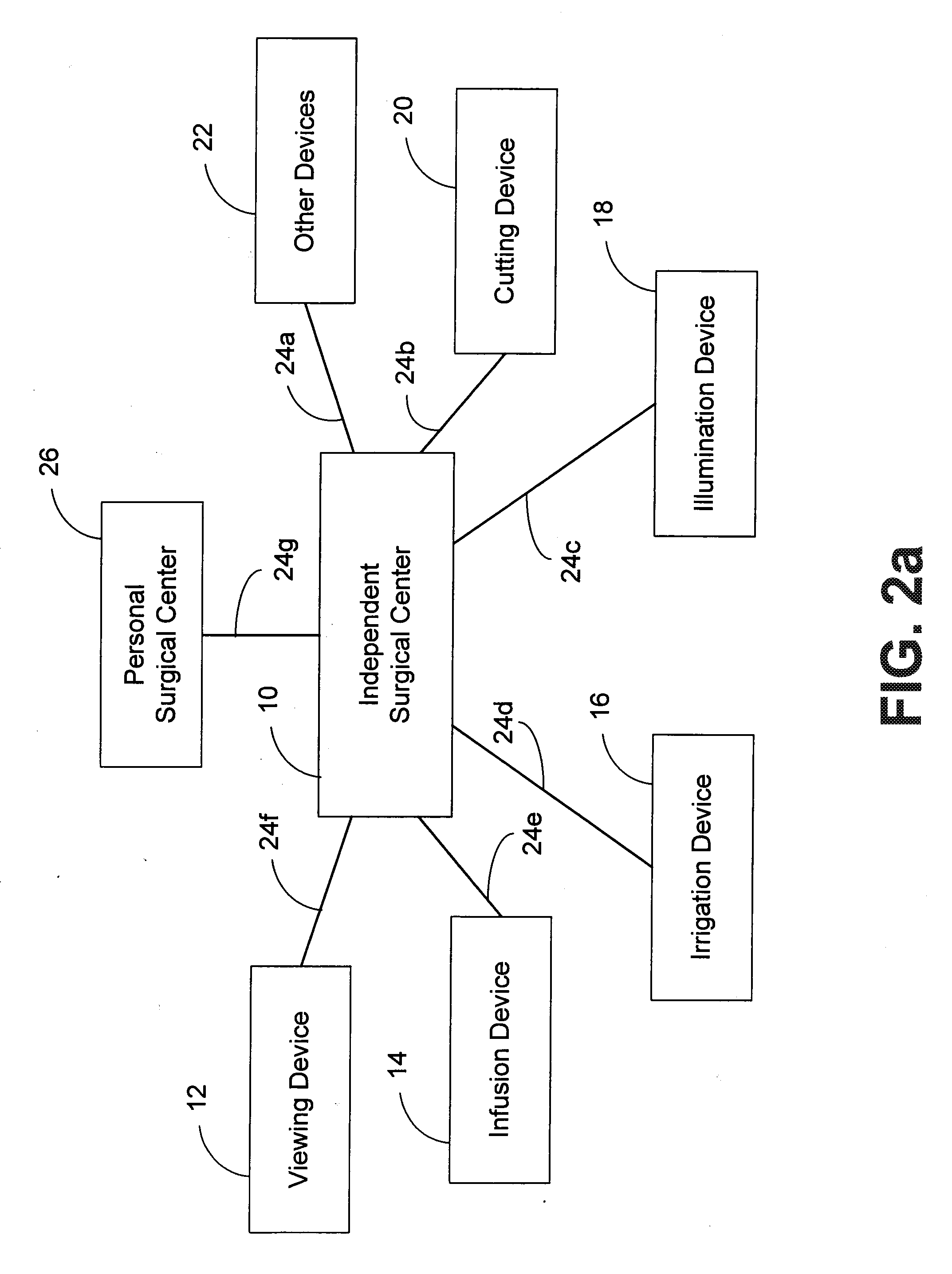
Independent Surgical Center
A biological tissue cutting and fluid aspiration system provides a plurality of surgical instruments operable independent of an external control console. In some embodiments, each surgical instrument may include all sensors and controls directly applicable to the surgical instrument, and may be used independently. In some embodiments, instruments communicate status information to each other, and adjust operating parameters based on the communications.
Owner:DOHENY EYE INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com