Patents
Literature
87 results about "Fluid aspiration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
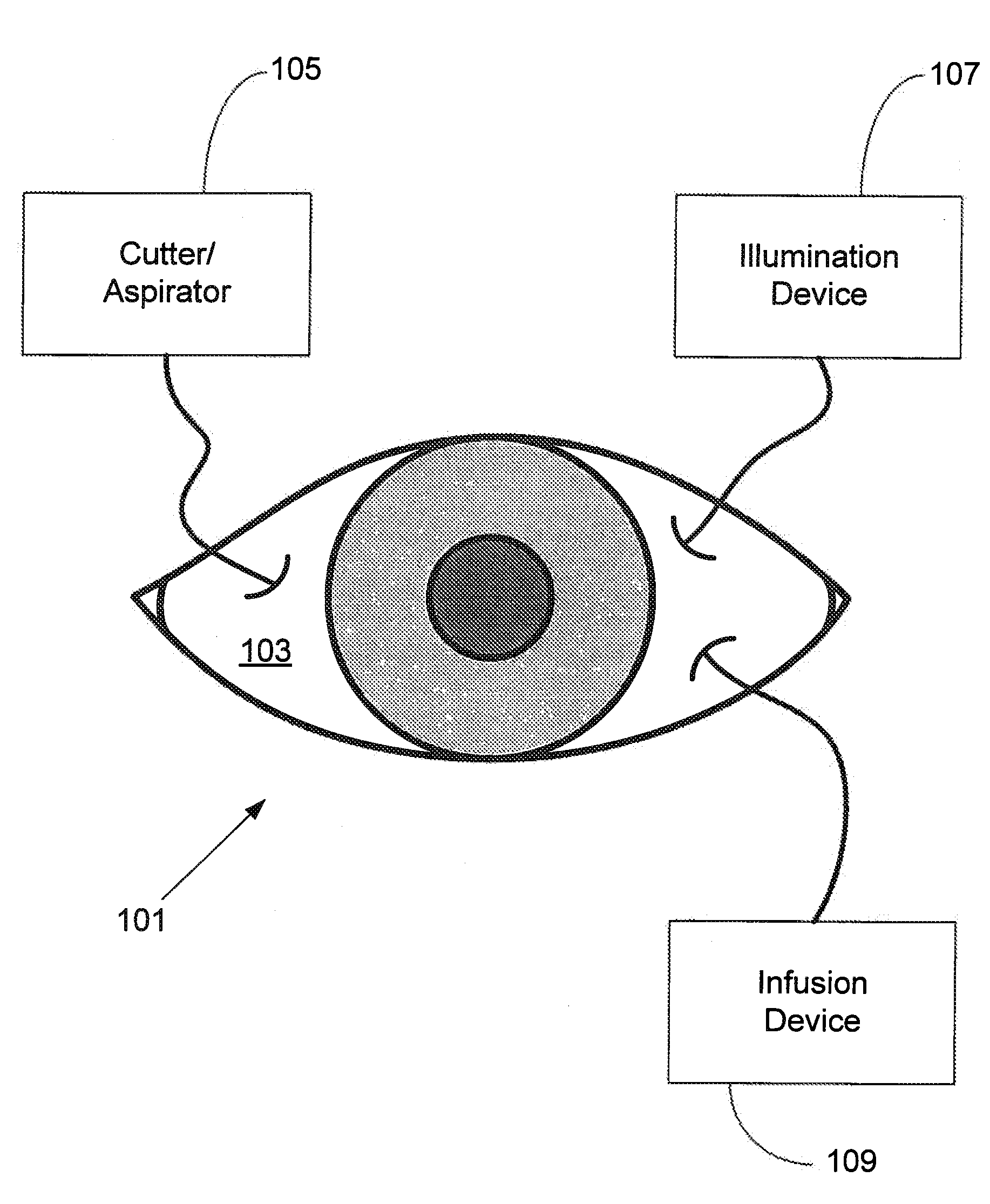
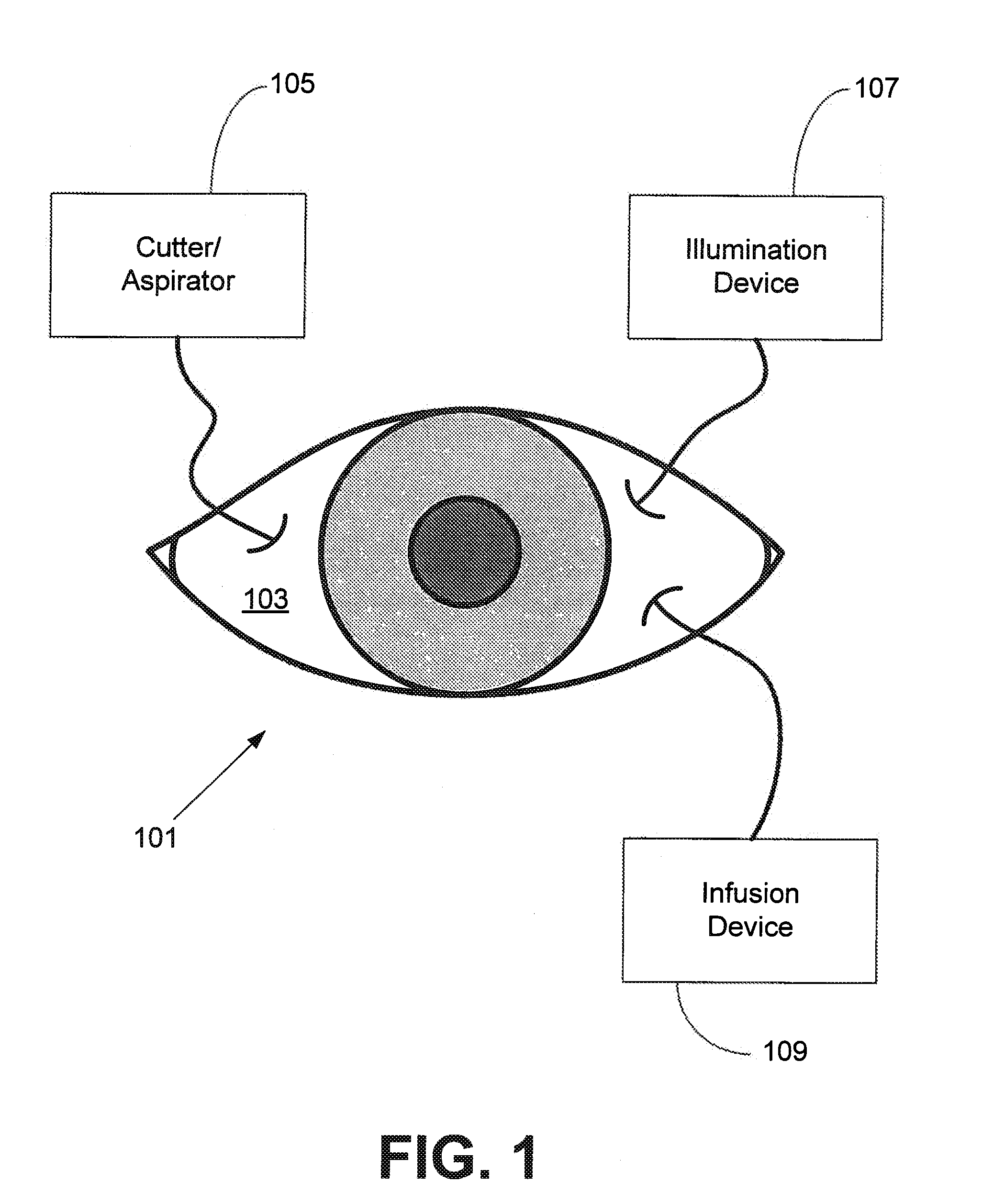
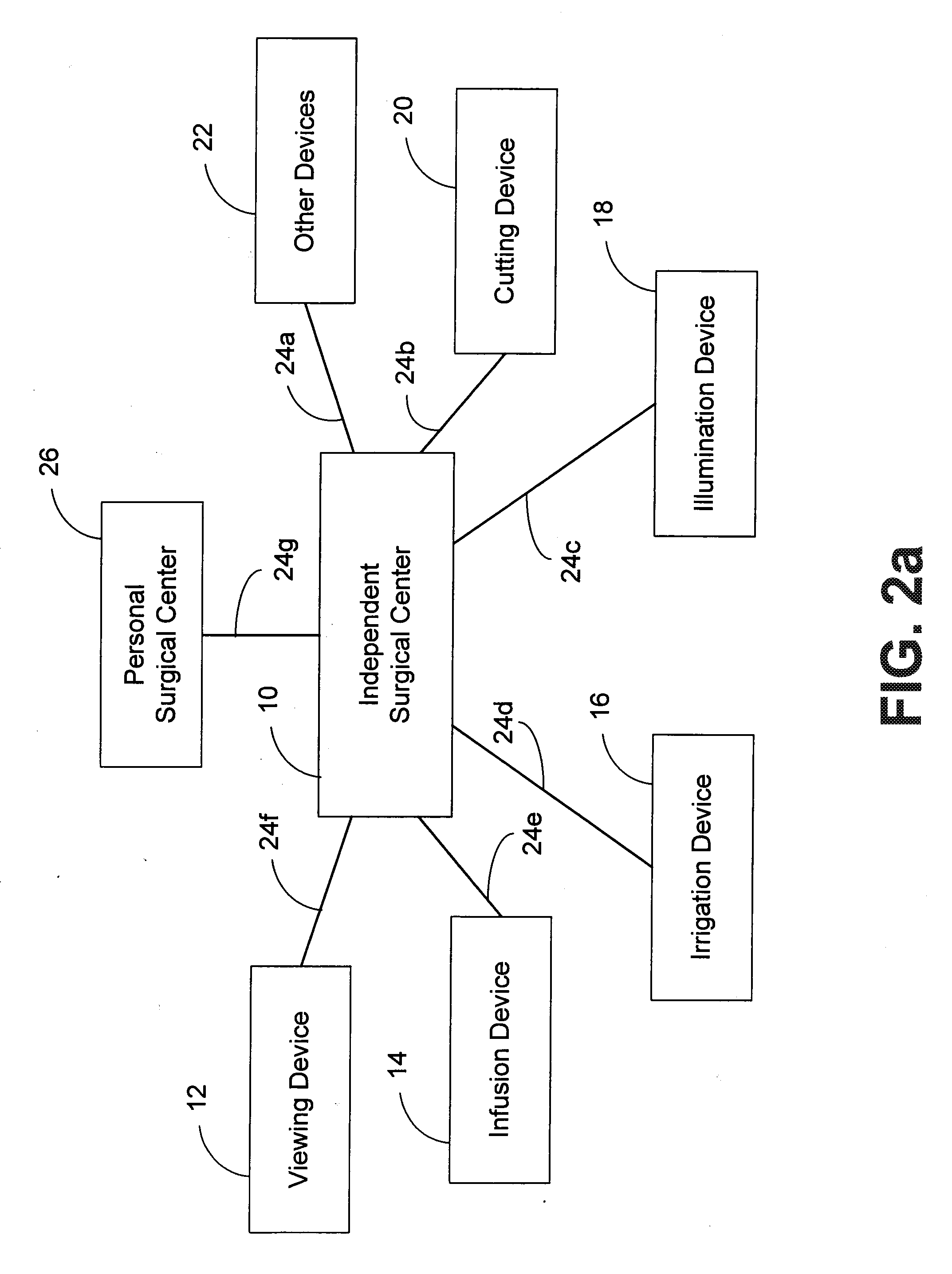
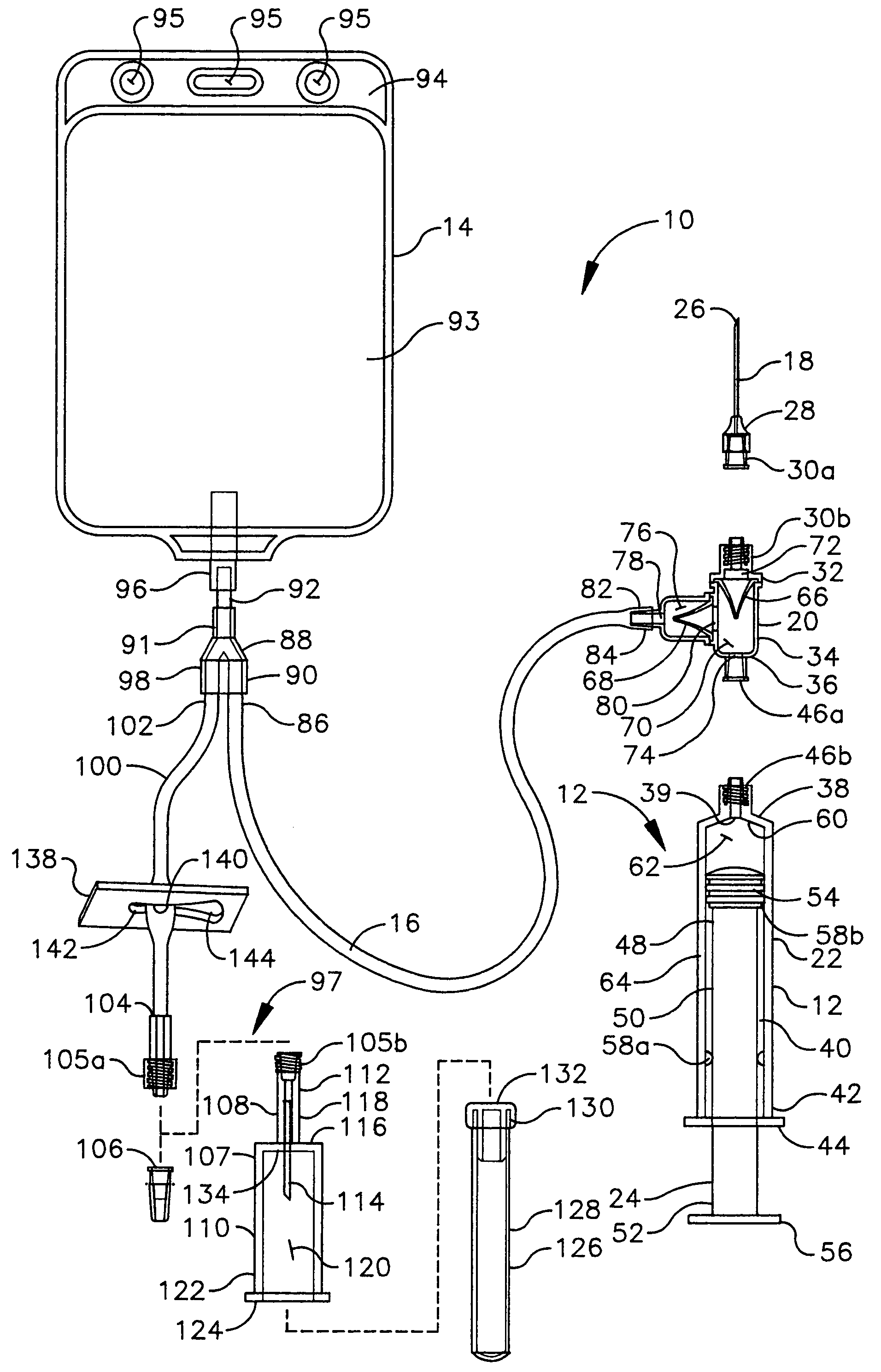
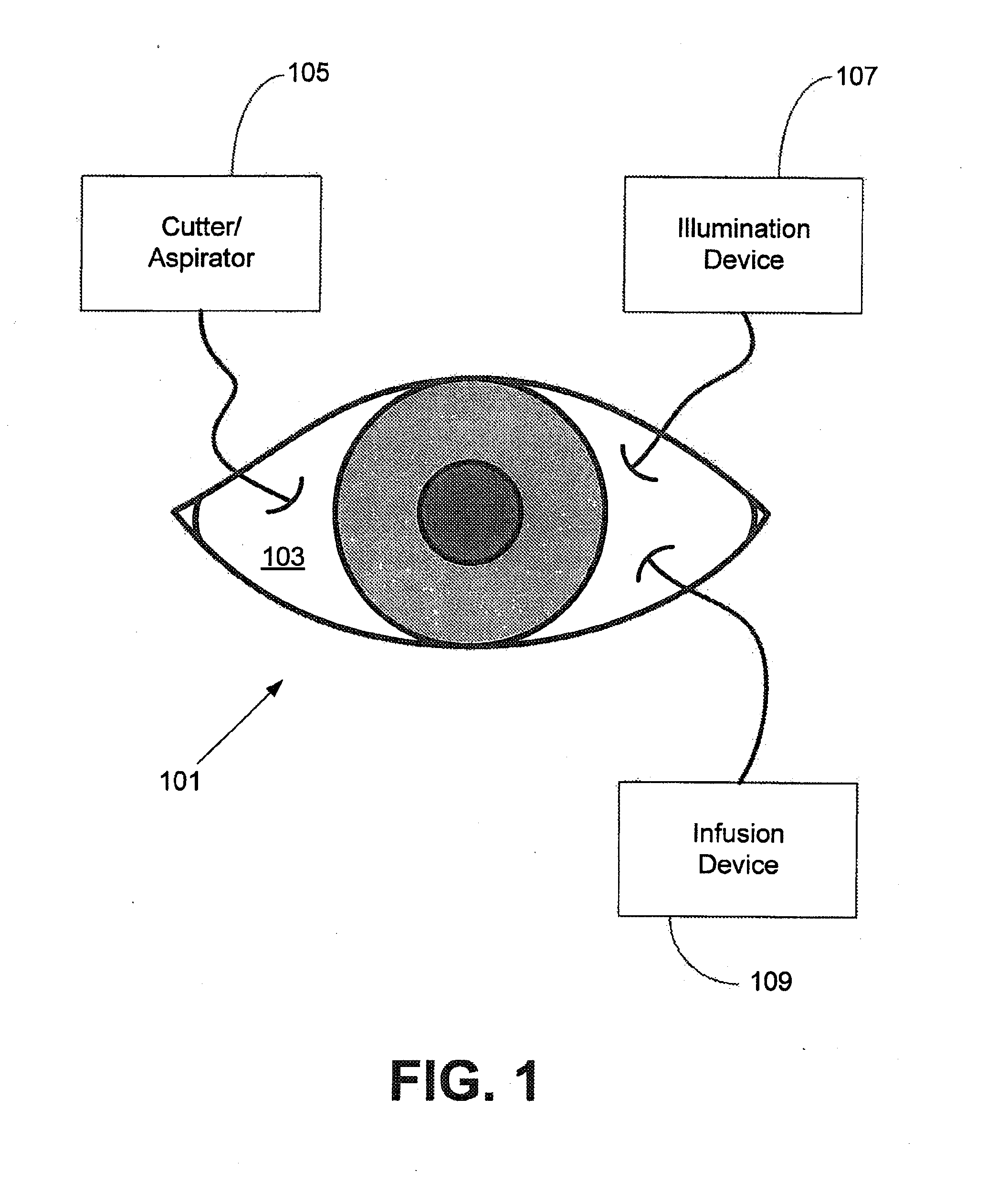
Independent Surgical Center
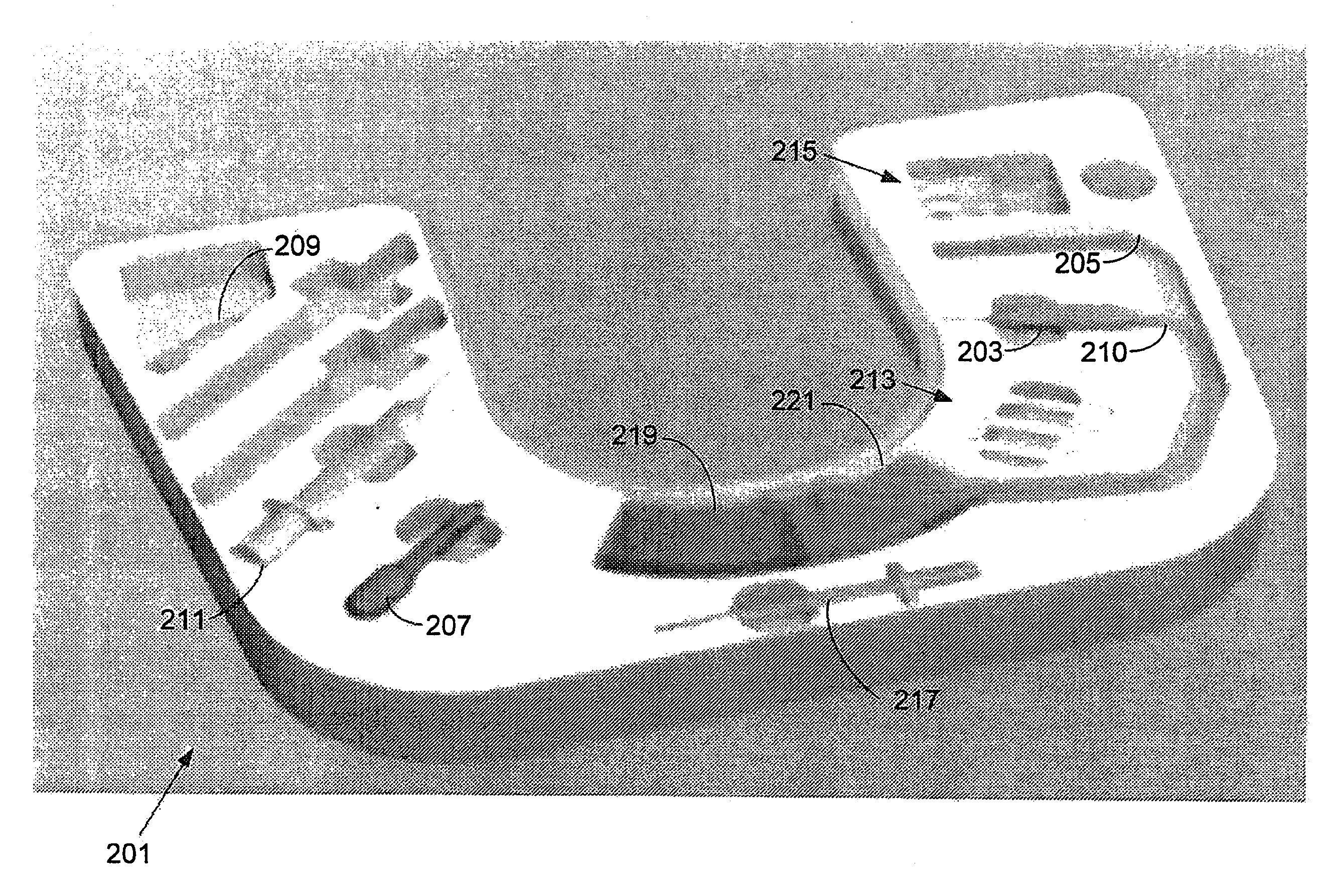
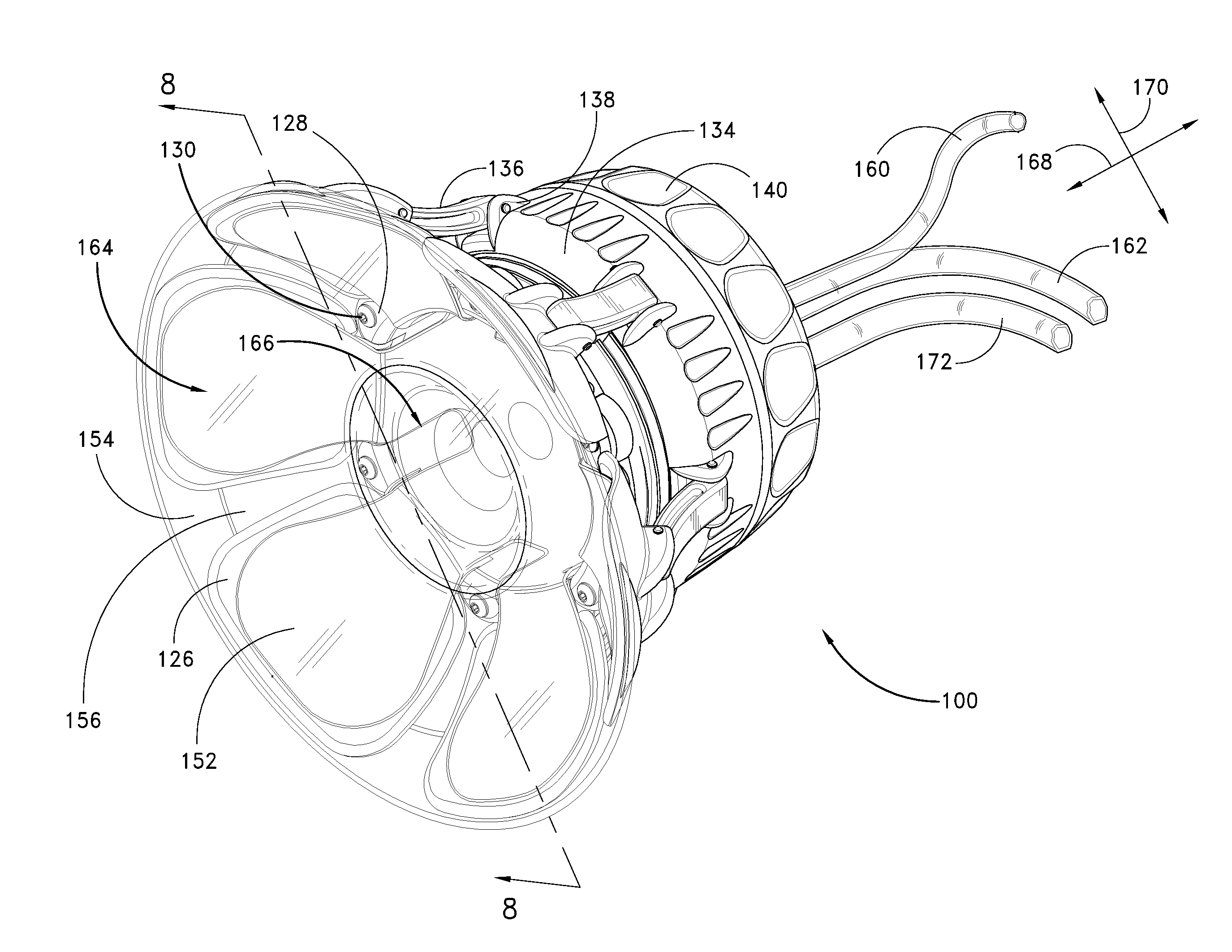
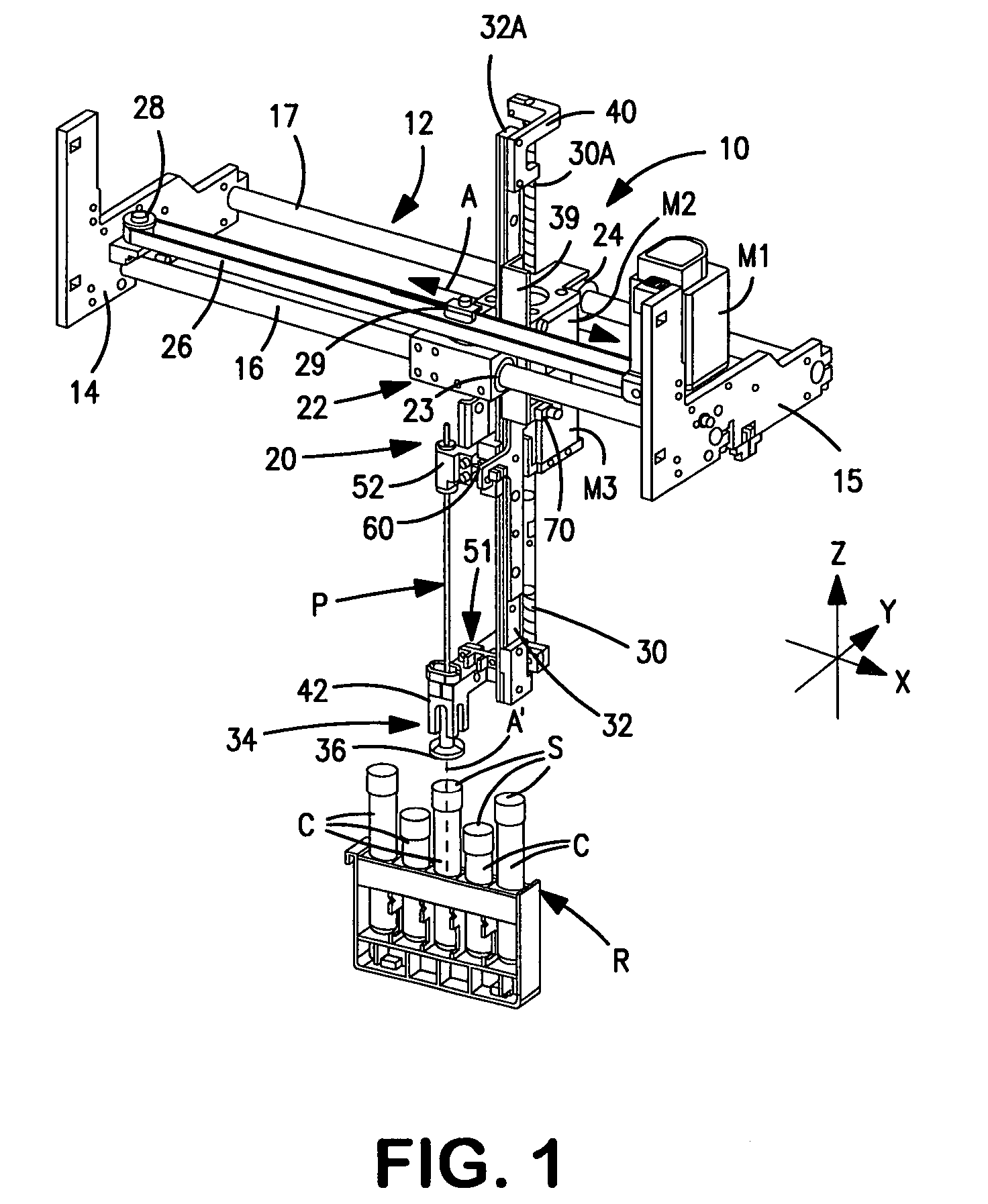
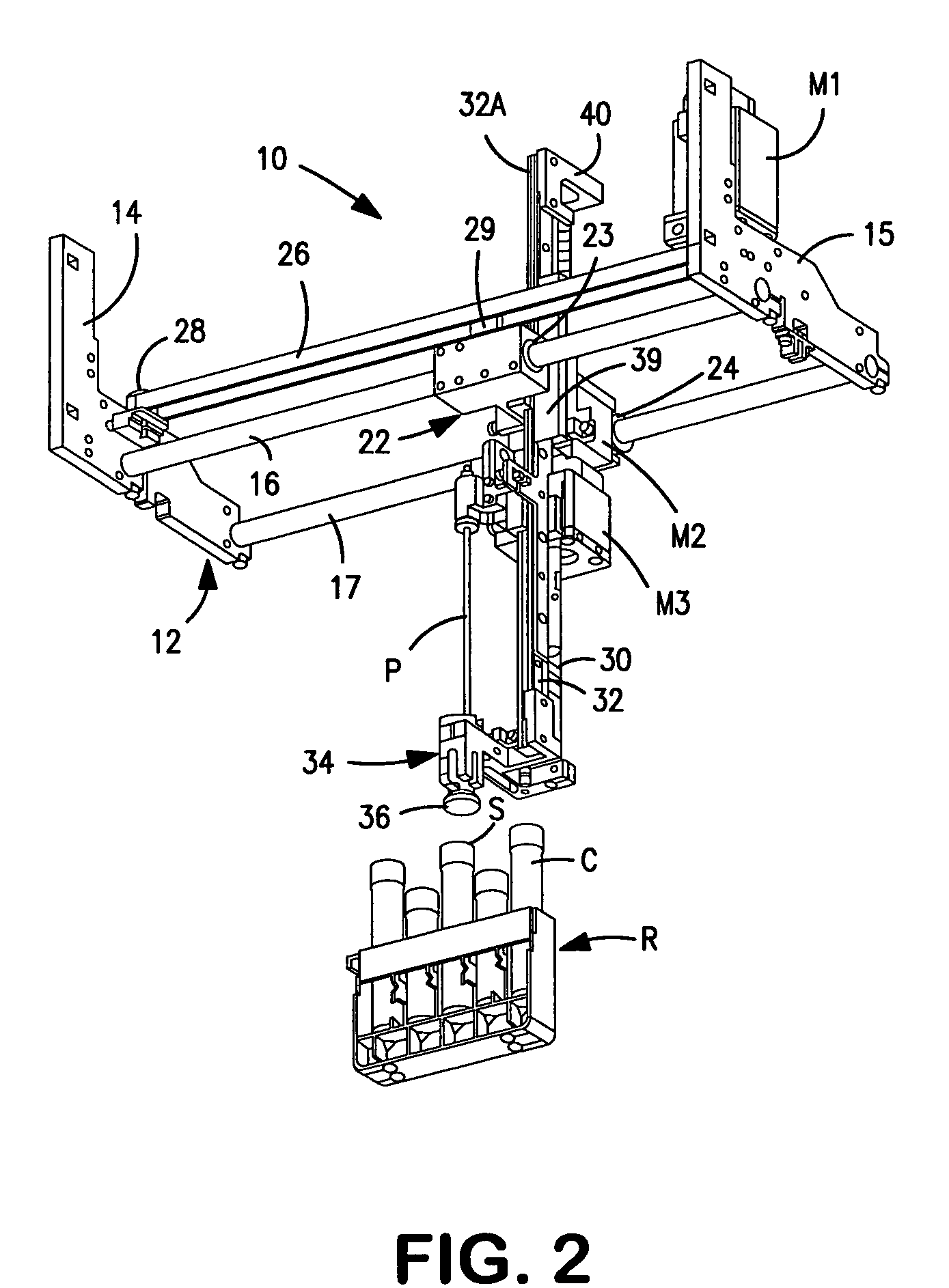
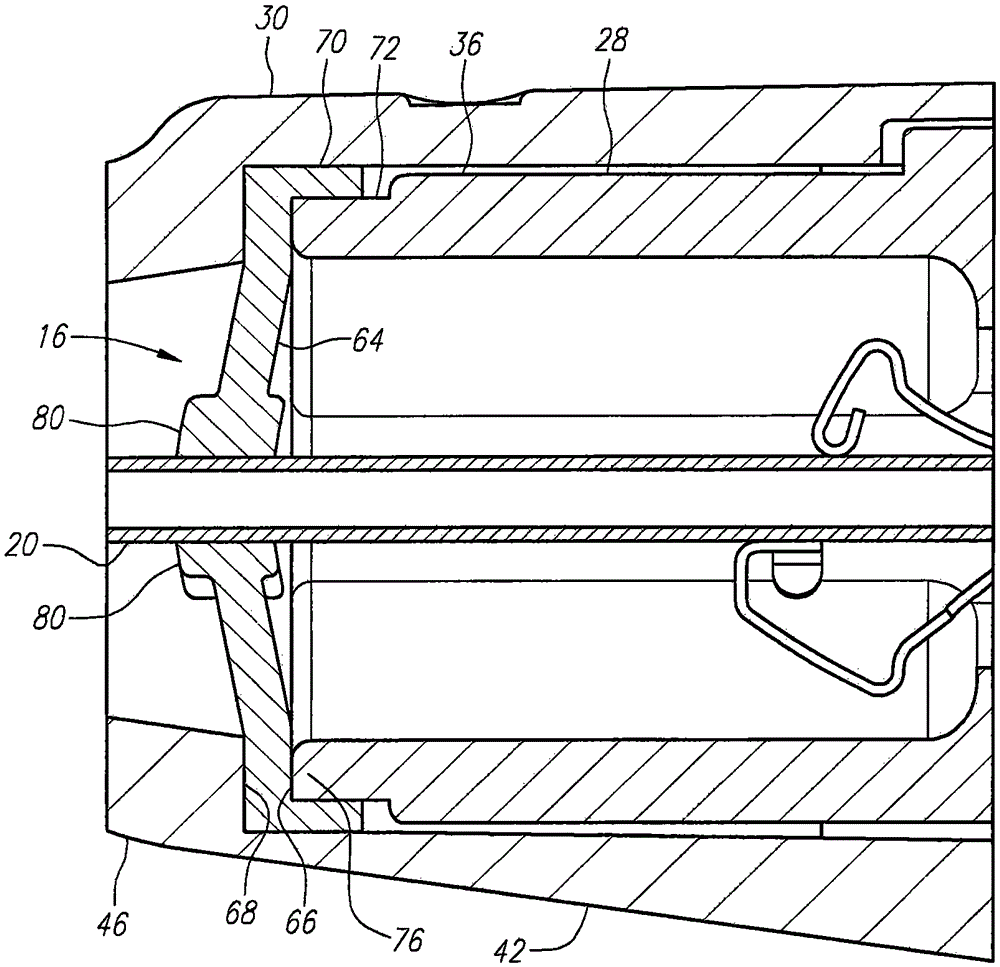
A biological tissue cutting and fluid aspiration system provides a plurality of surgical instruments operable independent of an external control console. In some embodiments, each surgical instrument may include all sensors and controls directly applicable to the surgical instrument, and may be used independently. In some embodiments, instruments communicate status information to each other, and adjust operating parameters based on the communications.
Owner:DOHENY EYE INST
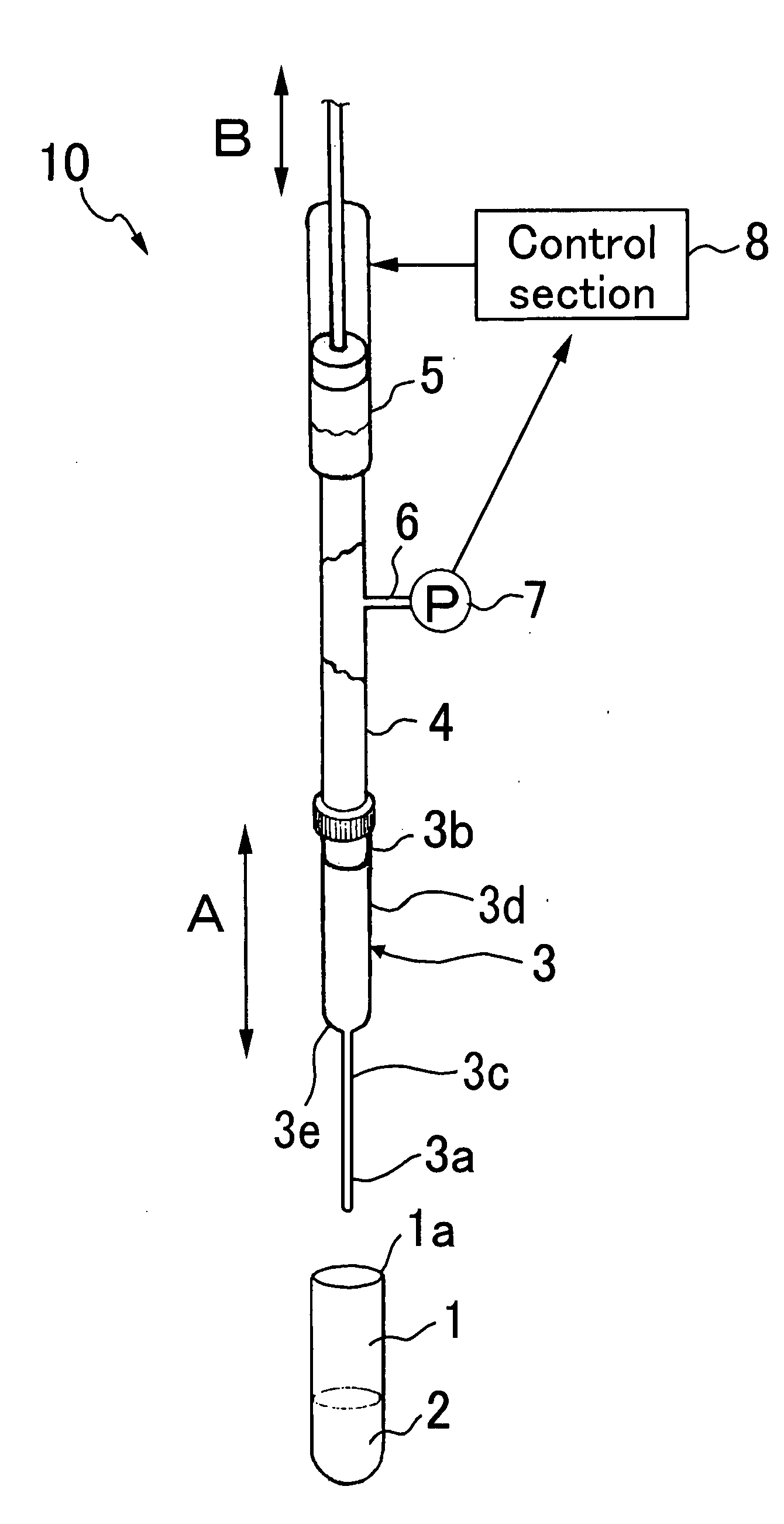
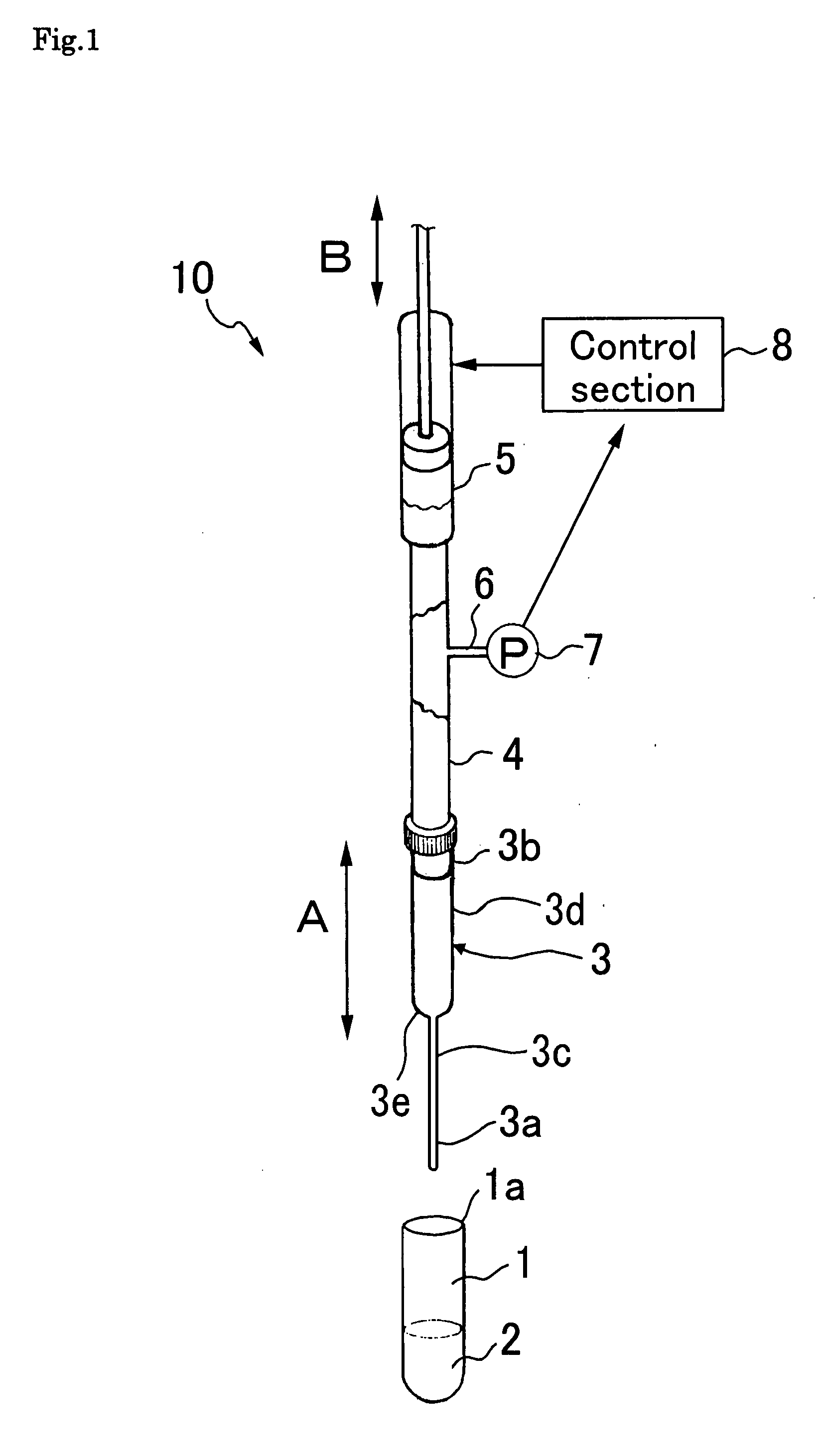
Fluid aspiration device
InactiveUS20050096627A1Preventing fluid communicationAvoid communicationMedical devicesPressure infusionBiomedical engineeringFluid aspiration
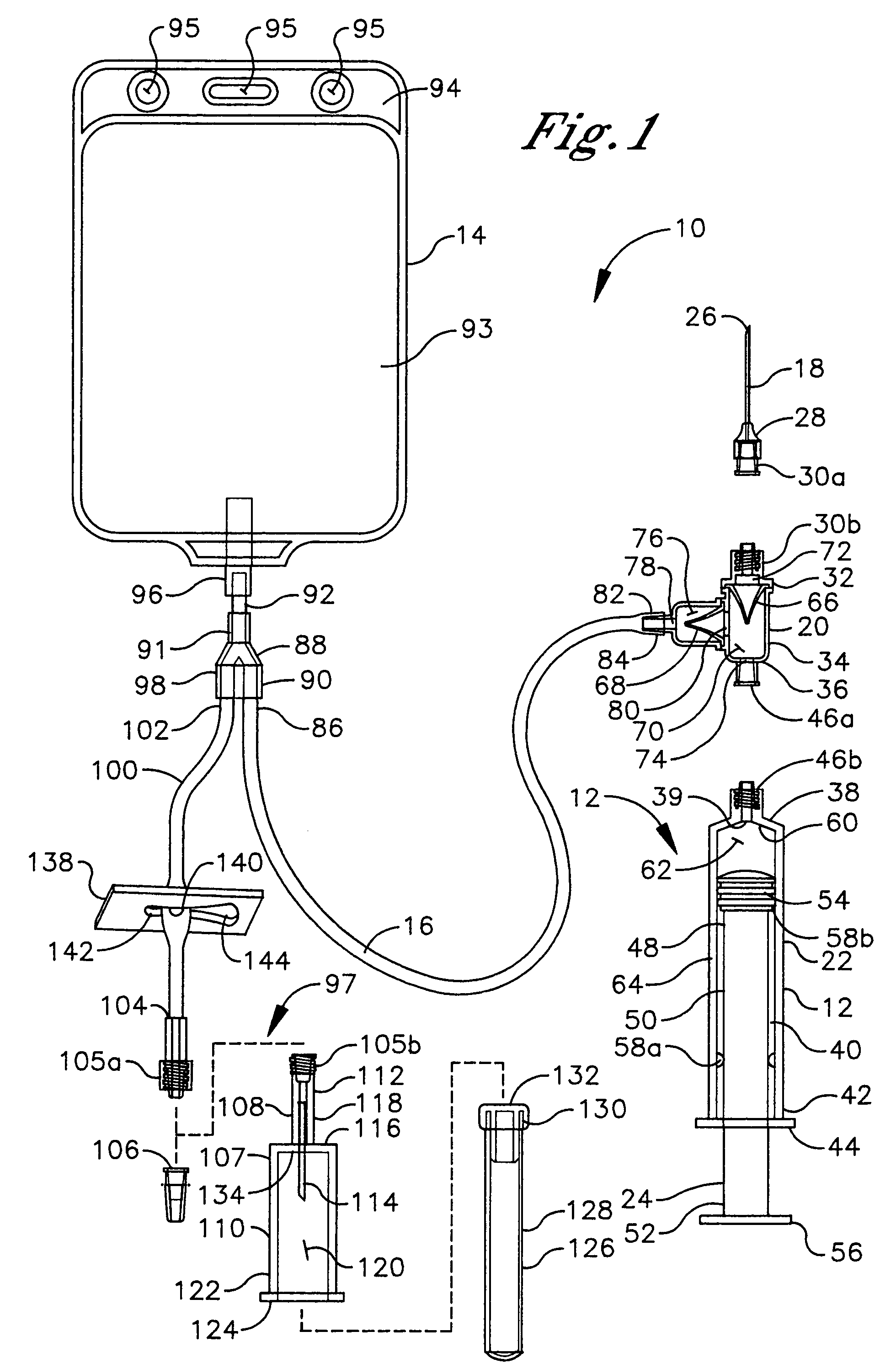
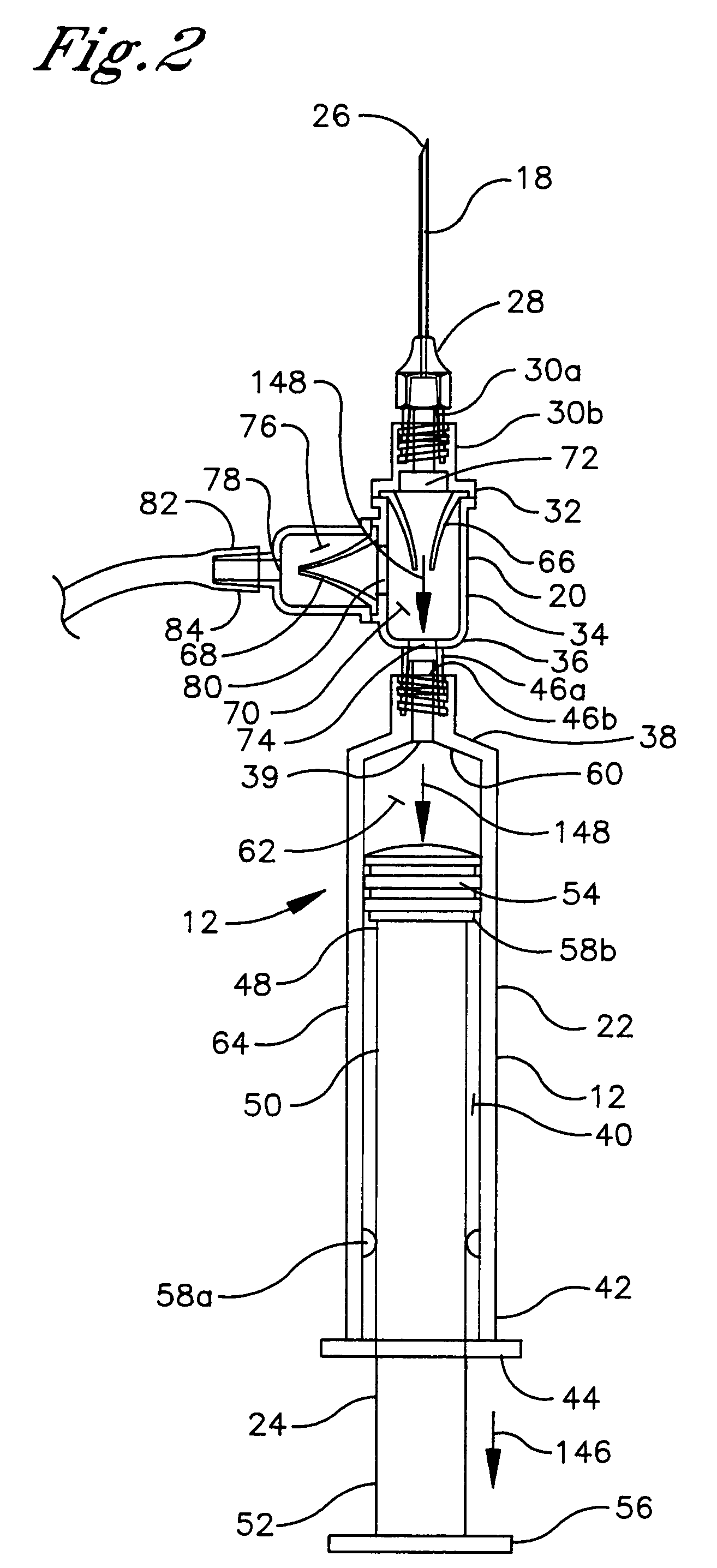
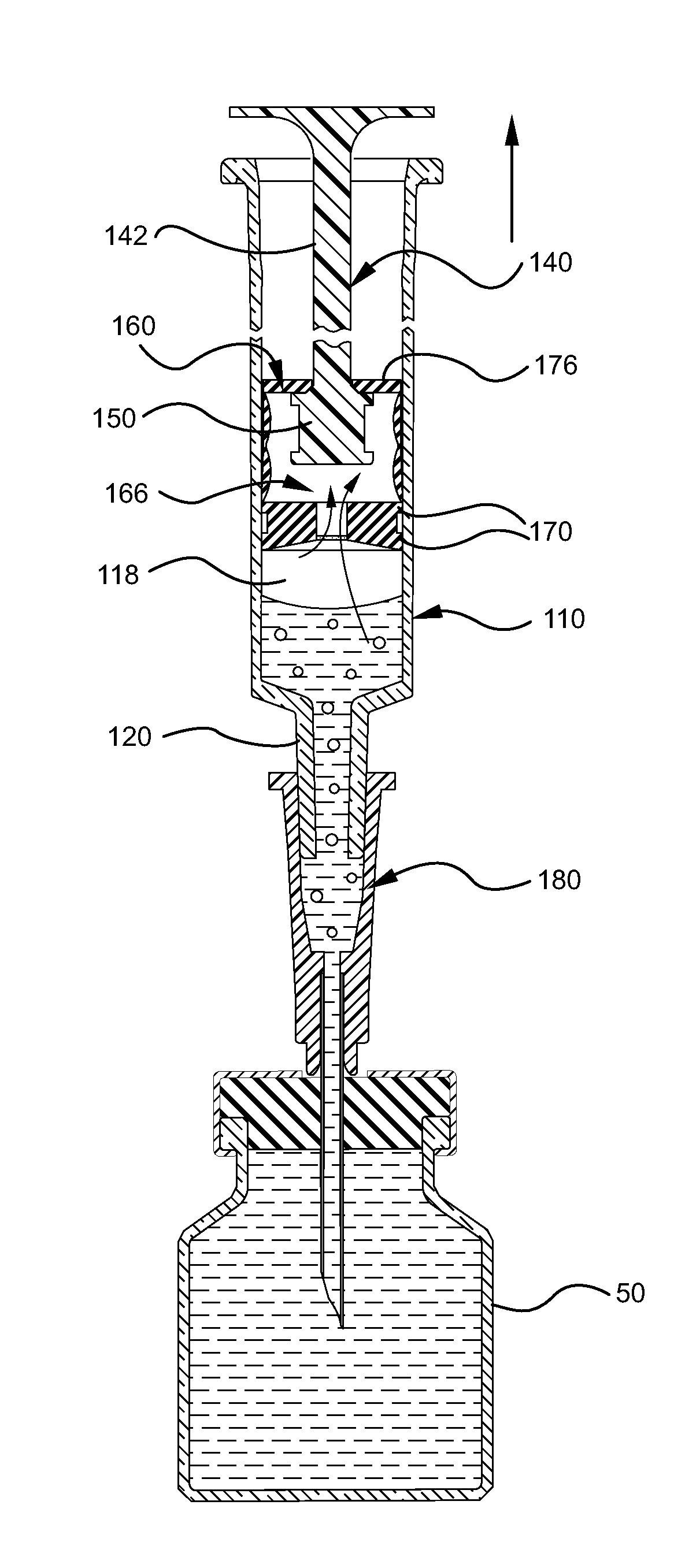
A fluid aspiration device is provided having a syringe, a disposal reservoir and a disposal fluid passageway. The syringe has a variable-volume fluid chamber and an aspiration fluid passageway between the fluid chamber and a region of the body containing a fluid for aspiration. An aspiration valve is positioned in the aspiration fluid passageway. The disposal fluid passageway is between the fluid chamber and disposal reservoir and has a disposal valve positioned therein. The fluid is aspirated by expanding the variable volume of the fluid chamber to draw the fluid through the open aspiration valve into the fluid chamber. The aspiration valve is closed and the variable volume of the fluid chamber is contracted to open the disposal valve and displace the fluid into the disposal reservoir. When aspiration is terminated, the fluid aspiration device is maintained intact and the intact device including the fluid is disposed.
Owner:BREG
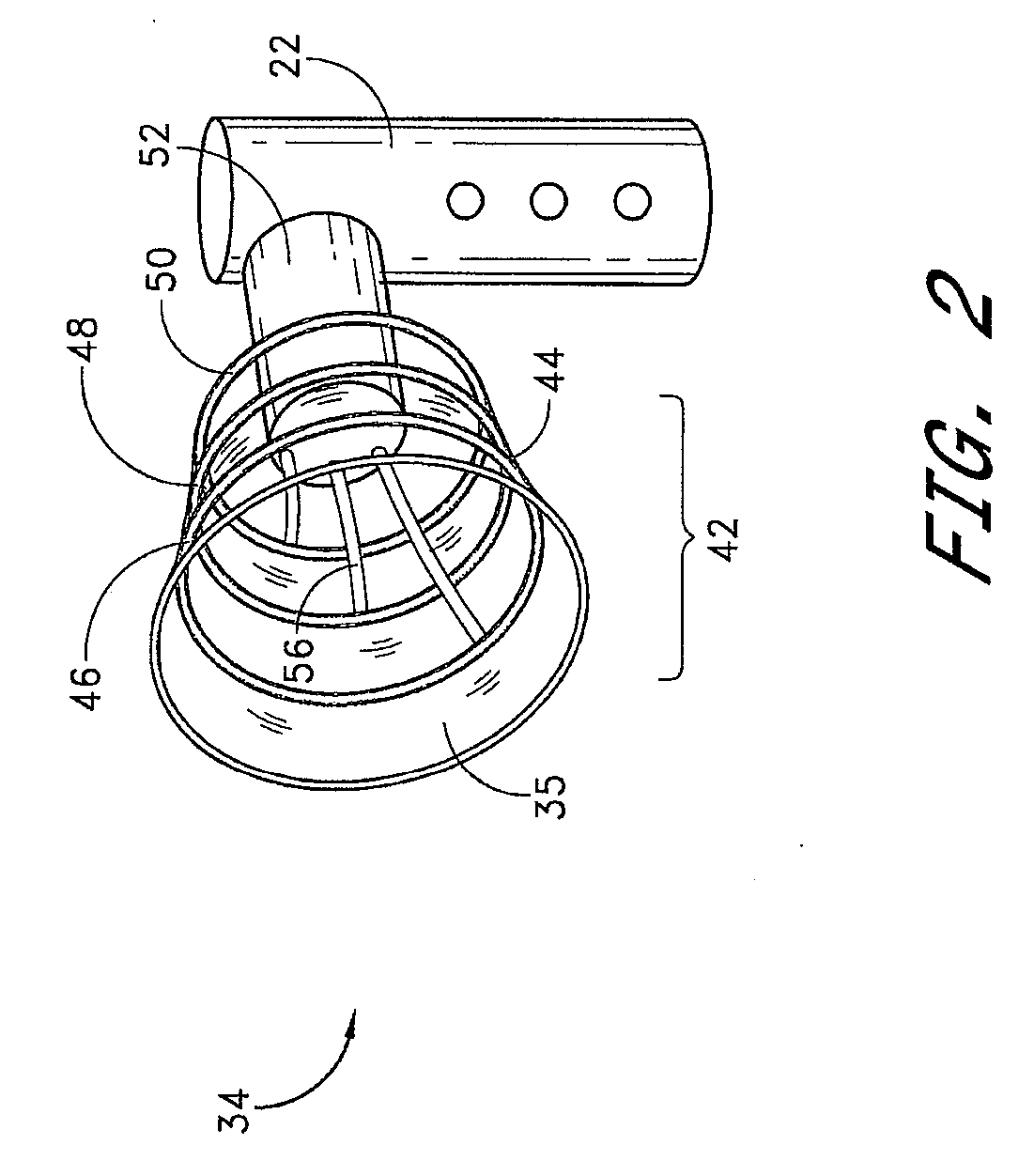
System, method and apparatus for electrosurgical instrument with movable suction sheath
ActiveUS8317786B2Surgical instruments for aspiration of substancesSuction devicesLeading edgeEngineering
An electrosurgical instrument having active and return electrodes with a movable suction sheath for variable fluid and debris removal during surgical procedures is disclosed. The suction apparatus has an outer sheath that is external to a shaft to provide a lumen. The sheath assembly is axially movable relative to the fluid aspiration element between first and second positions for treating the target site and fluid and debris removal, respectively. The first position positions the distal end of the shaft axially distal to a leading edge of the sheath assembly. The second position positions the distal leading edge of the sheath assembly axially adjacent to the end of the shaft. The fluid aspiration element comprises an inner lumen extending through the shaft, and at least one port extending radially through the shaft. The port is in communication with the inner lumen. A vacuum provides suction through the port and inner lumen.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
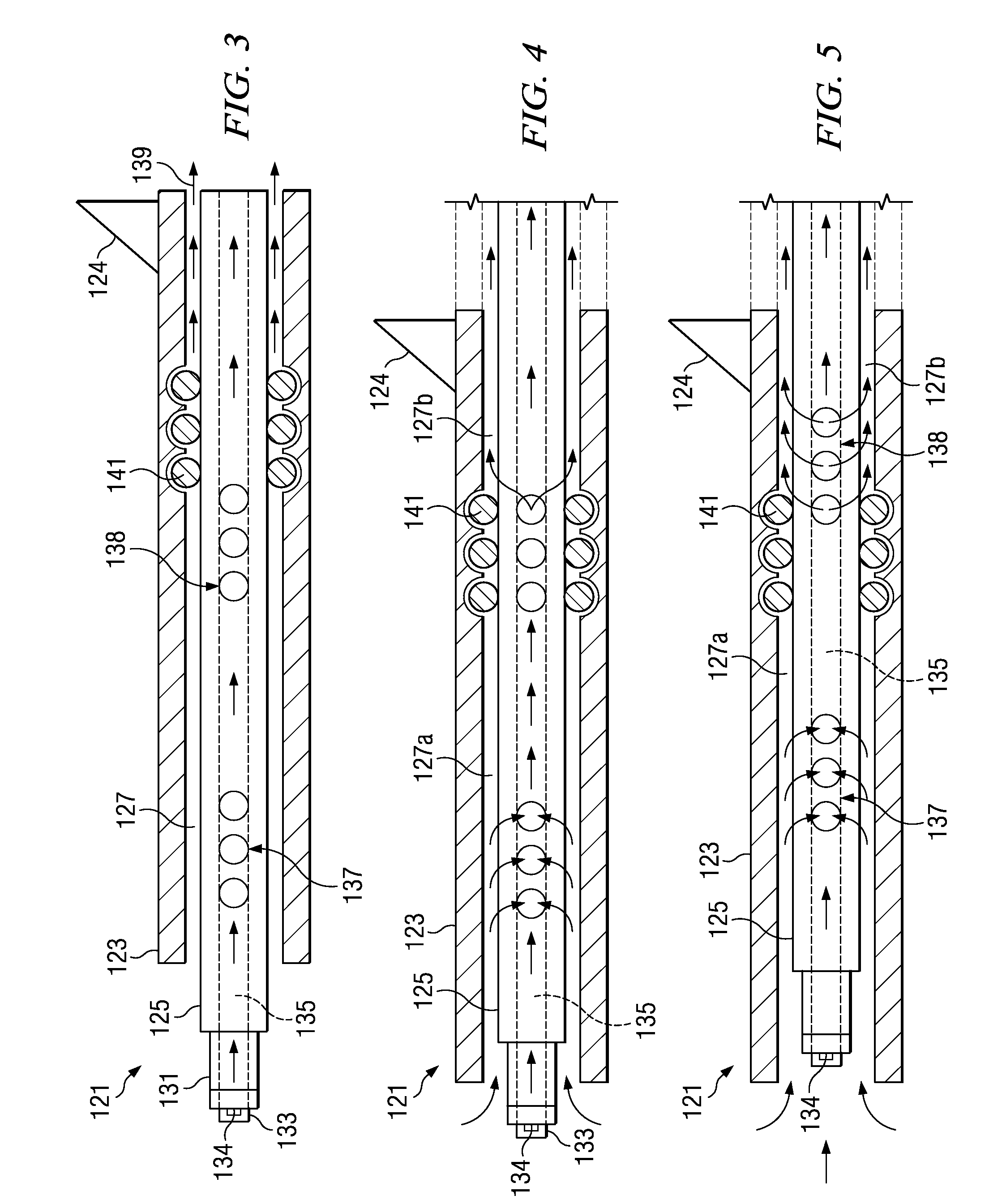
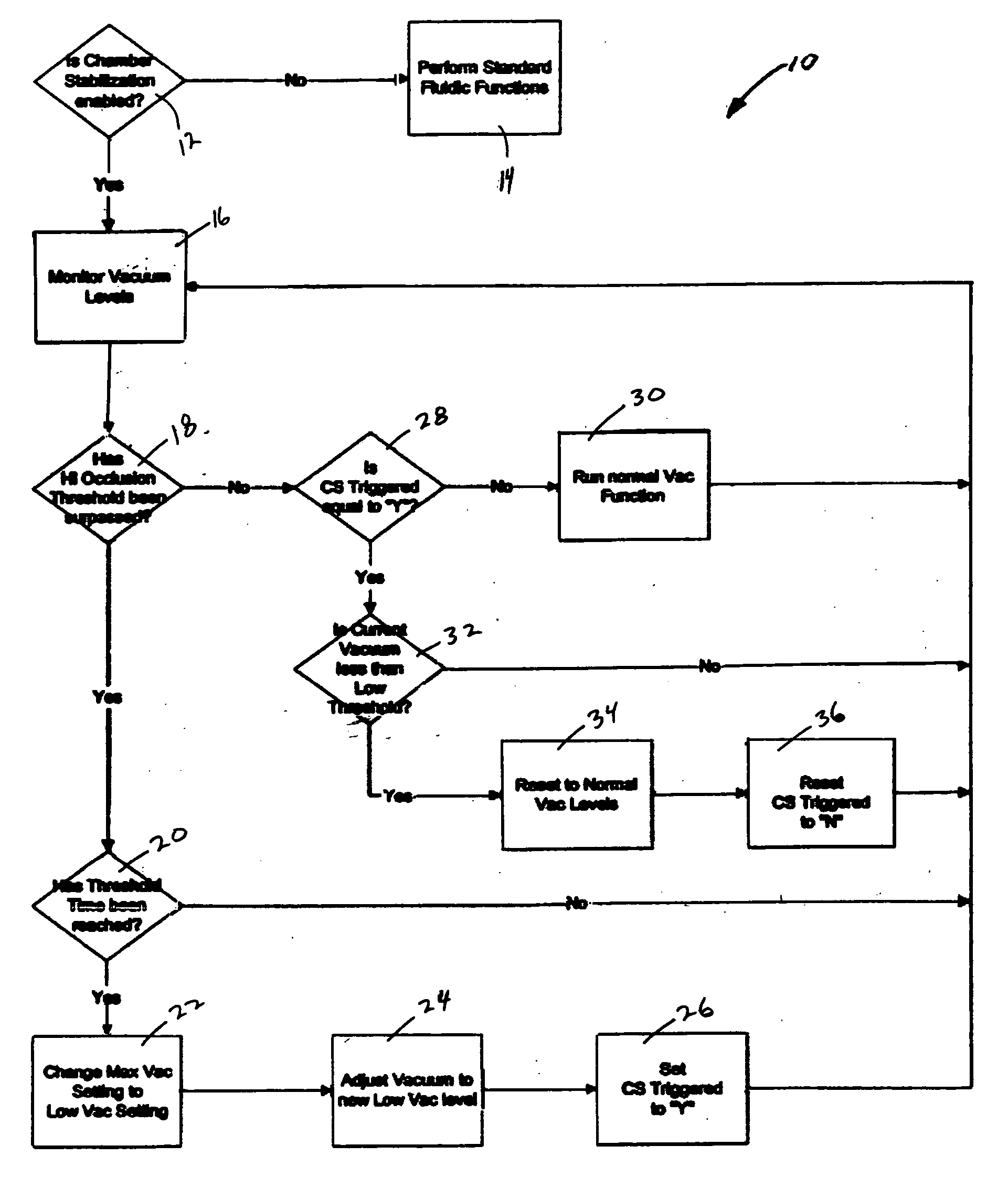
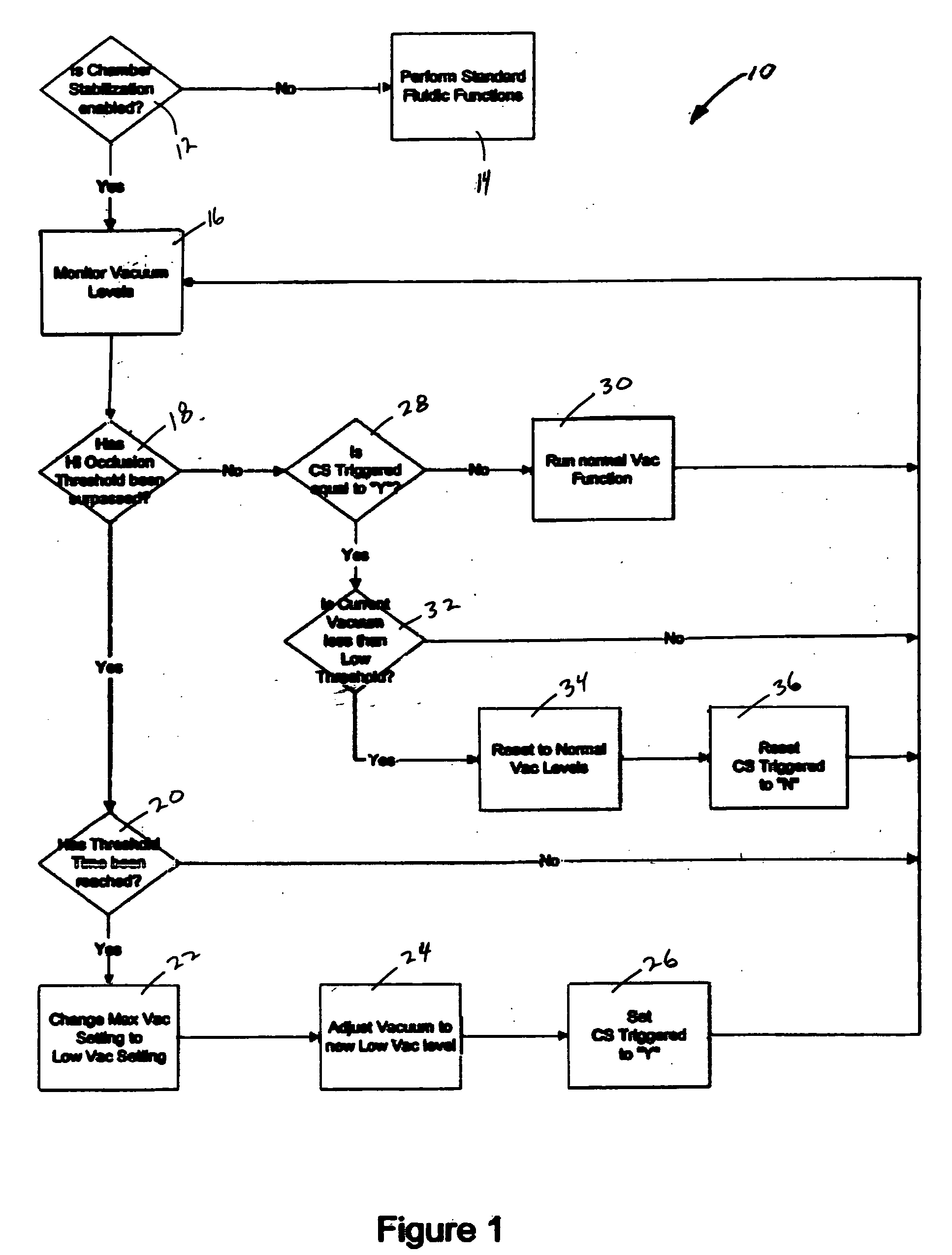
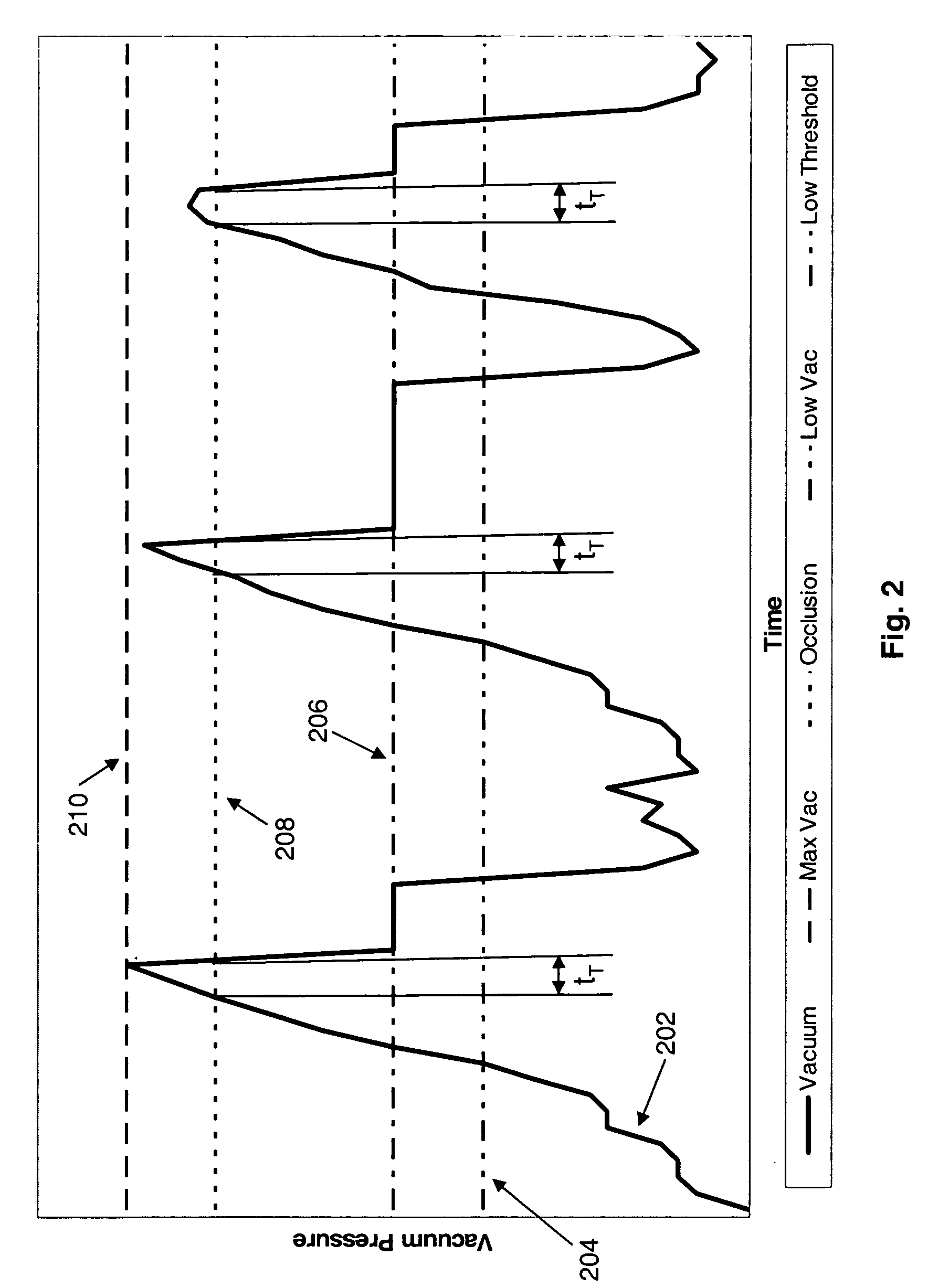
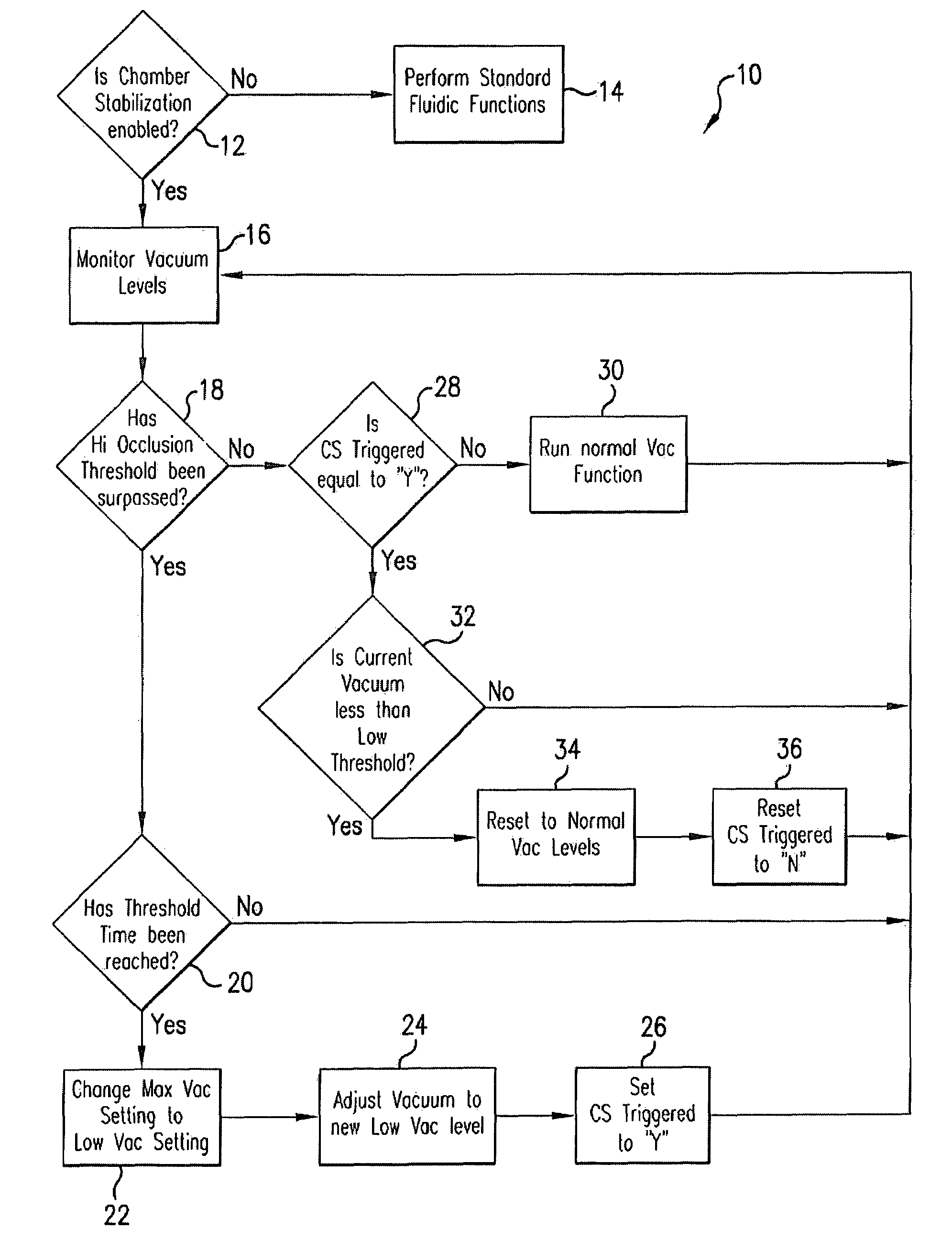
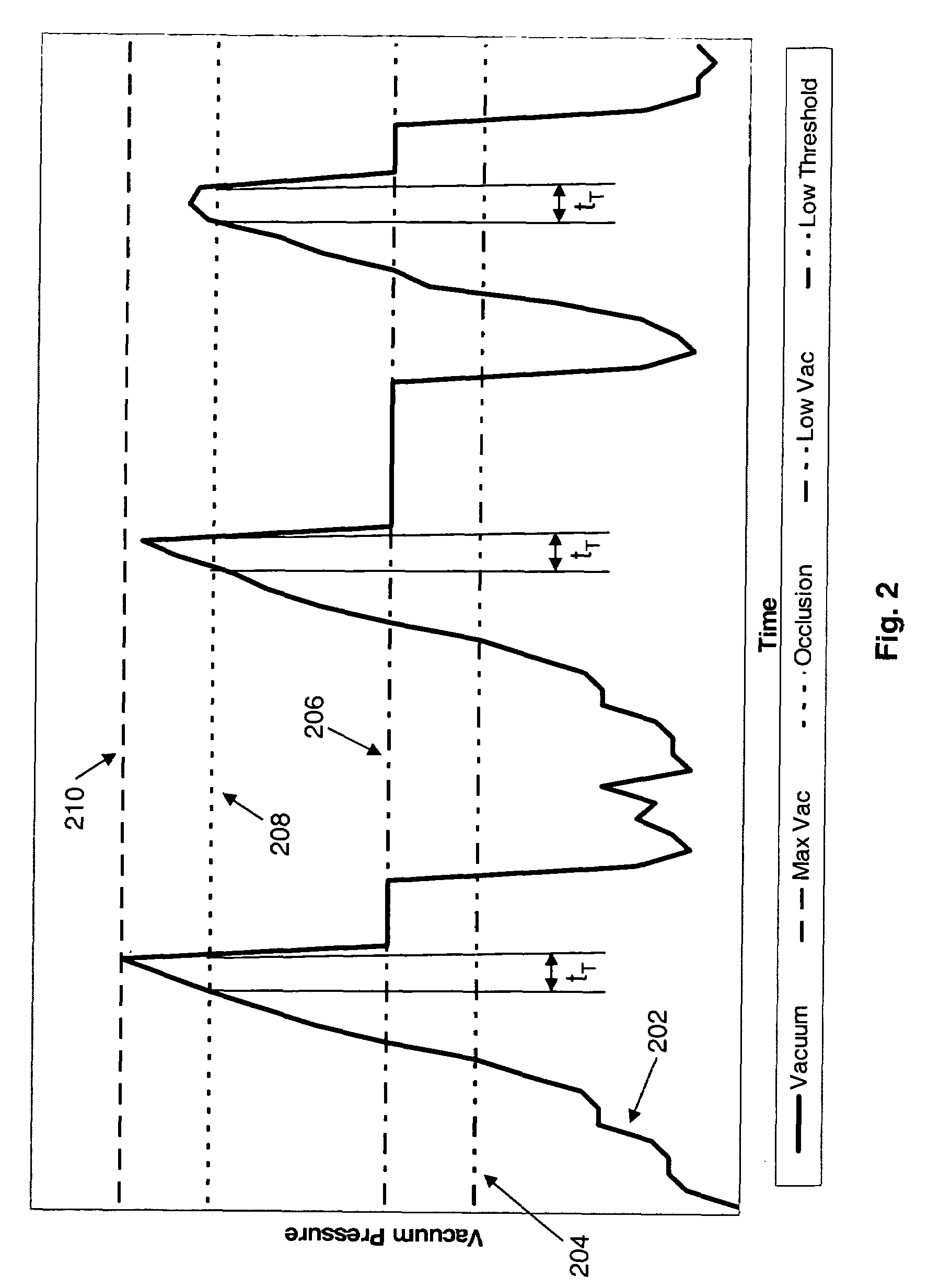
Application of vacuum as a method and mechanism for controlling eye chamber stability
A method for operating a surgical system including a control unit having a vacuum sensor and / or a flow rate sensor, the method including placing a handpiece in an operative relationship with an eye for a surgical procedure and thereafter supplying irrigation fluid to the handpiece while applying a vacuum to the handpiece to aspirate the irrigation fluid from the eye through the handpiece. During fluid aspiration, a vacuum level and / or flow rate is sensed which corresponds to an occlusion of the handpiece and from the sensed vacuum level and / or flow rate, a duration of the occlusion is determined. In response to the determined duration of occlusion, at least one of the handpiece parameters is varied.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
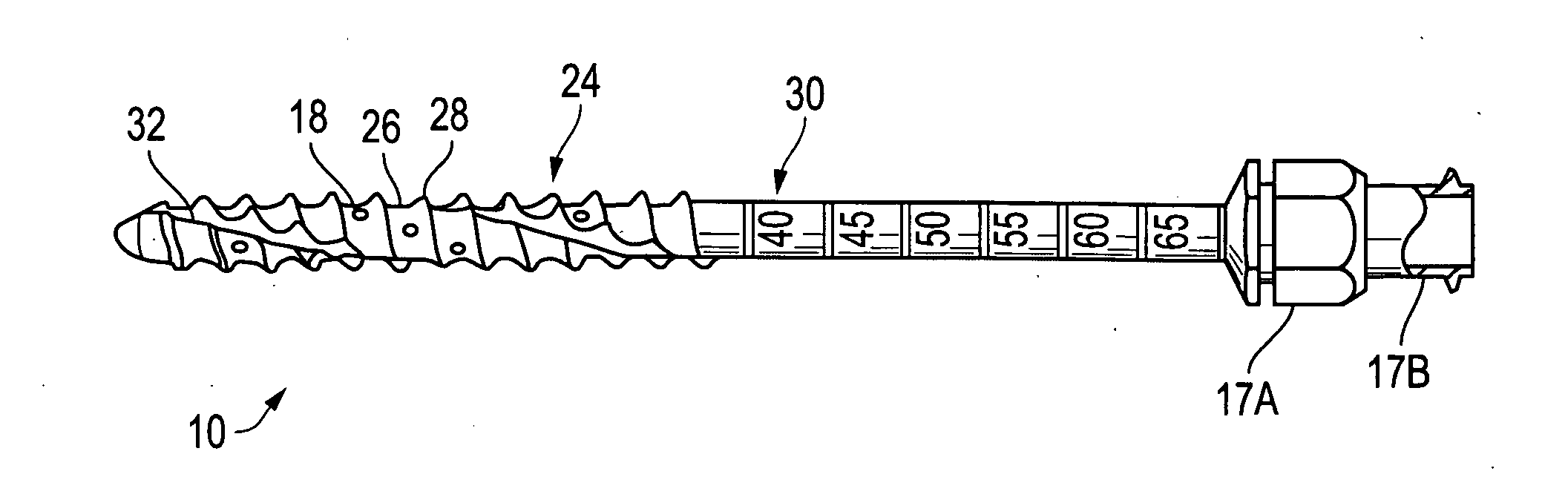
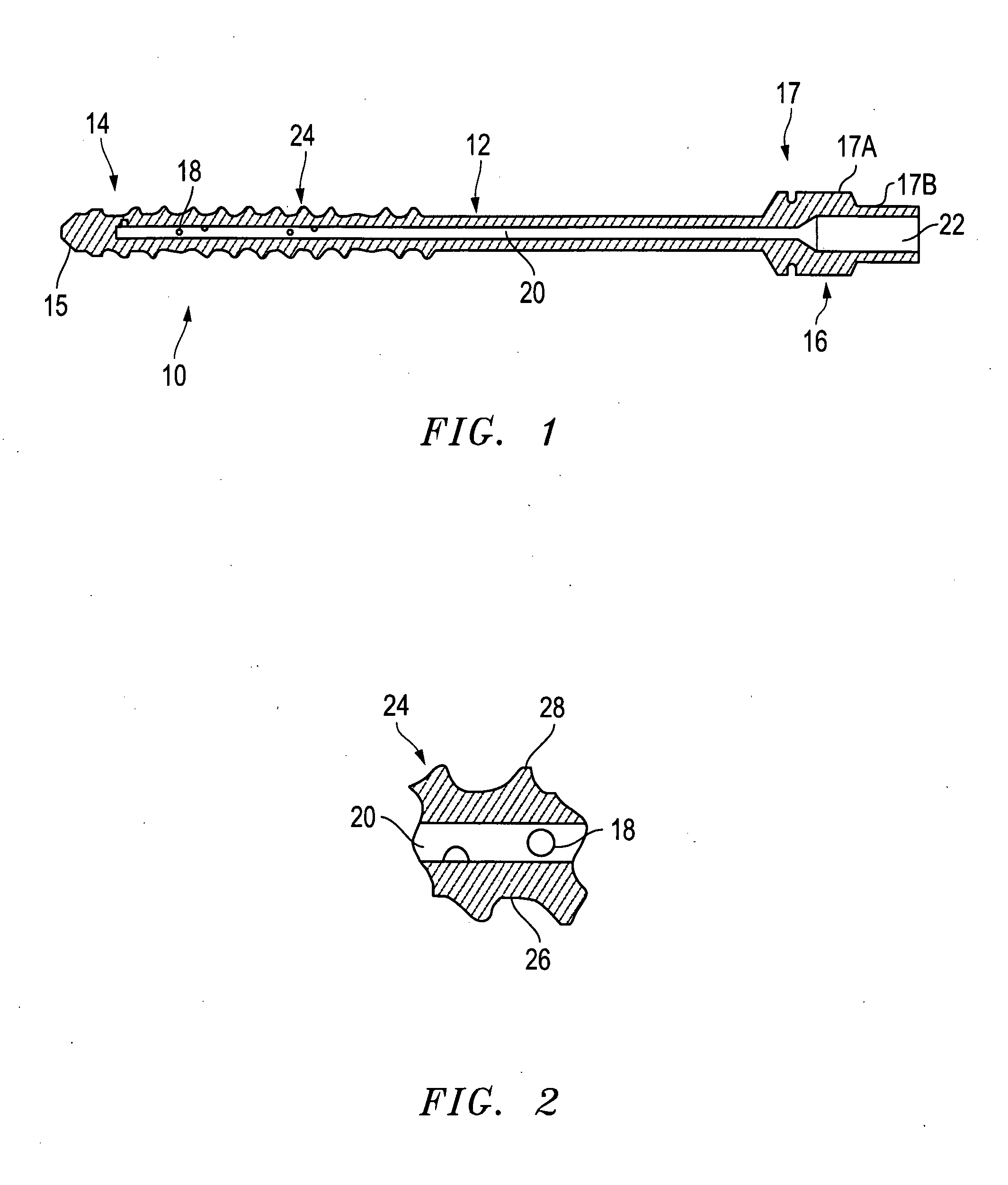
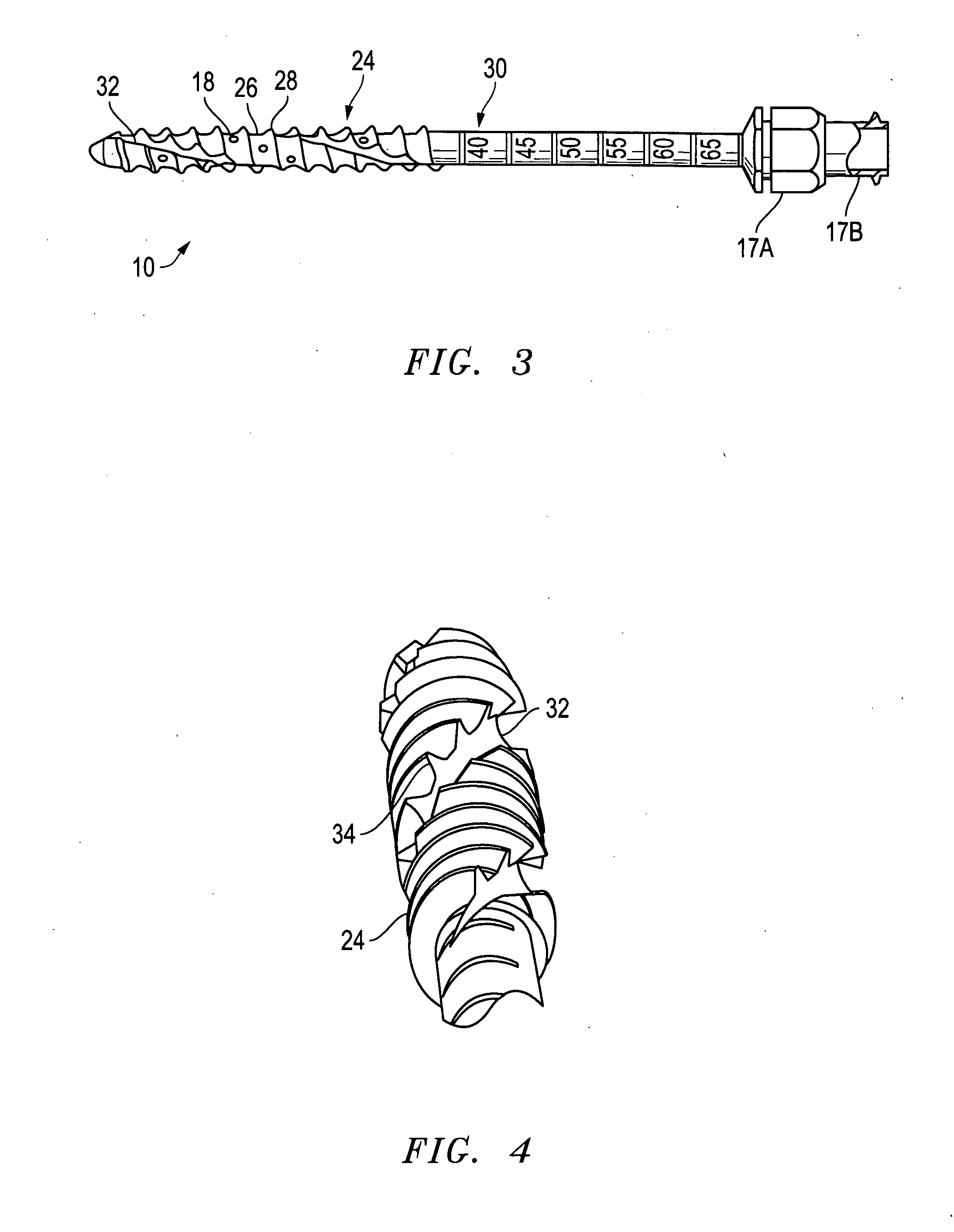
Distraction pins for fluid aspiration
InactiveUS20110112436A1Metal rolling stand detailsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAnatomyBiomedical engineering
A distraction pin for aspiration of a bone fluid and marrow. The pin includes an elongate metallic shaft of generally uniform diameter having a proximate end. The proximate end of the shaft includes an adaptor (attachment means) and a longitudinal bore extending from the distal end to the proximate end. The distal end of the shaft includes threading adapted for screwing the shaft into bone. The distal end also includes at least two fenestrations transverse to the longitudinal bore.
Owner:SPINESMITH PARTNERS
Use of fluid aspiration/dispensing tip as a microcentrifuge tube
InactiveUS20100015690A1Reduce errorsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluid aspirationFluid specimen
A fluid aspirating / dispensing member includes a sample cavity for sample acquisition and a sealable cavity that, once sealed, permits the separation of particles from the remainder of a fluid sample within the sample cavity after centrifugation or other separation means. The fluid aspirating / dispensing members, either individually or as part of an array, increase the efficiency of sample processing before analysis by a clinical analyzer.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
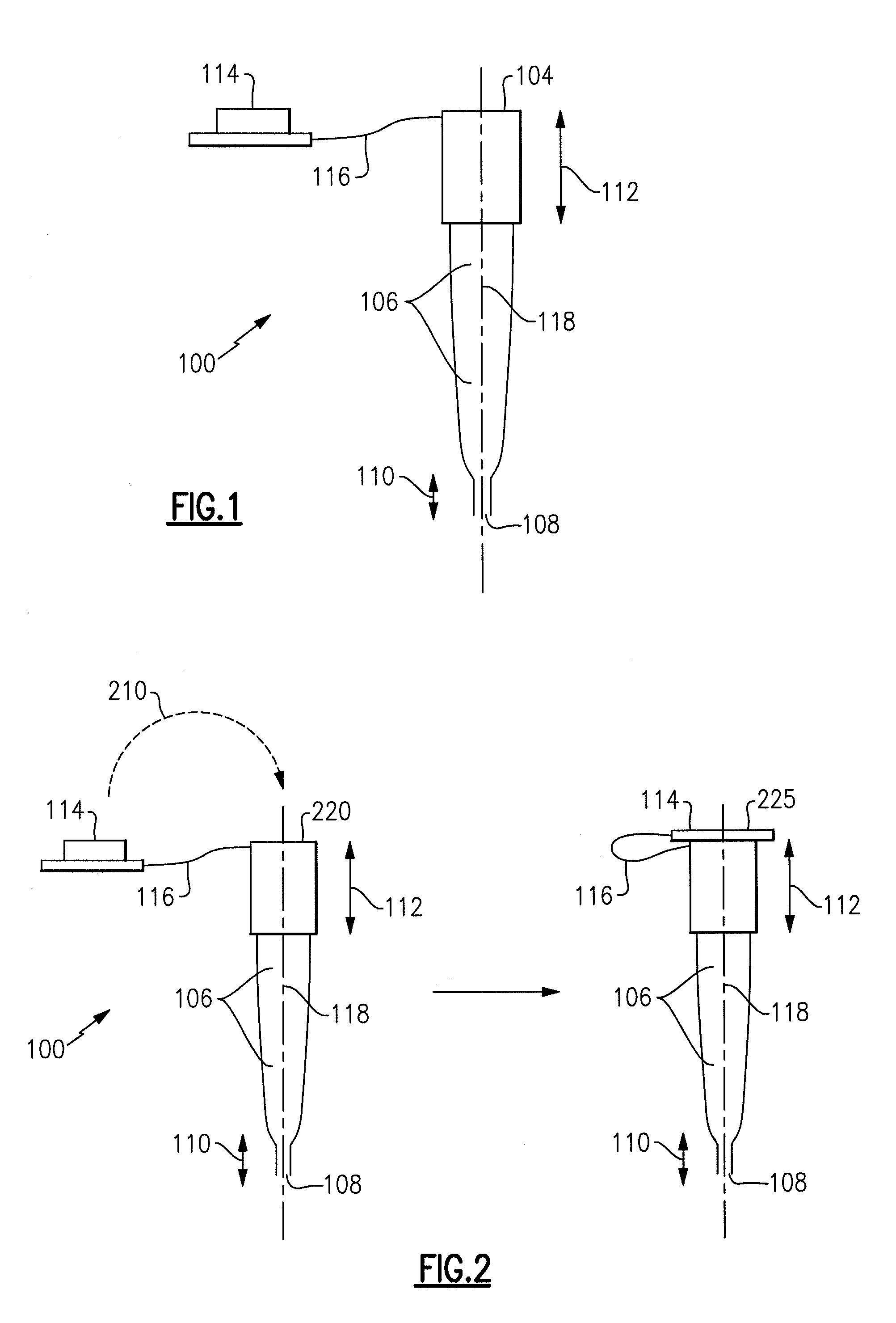
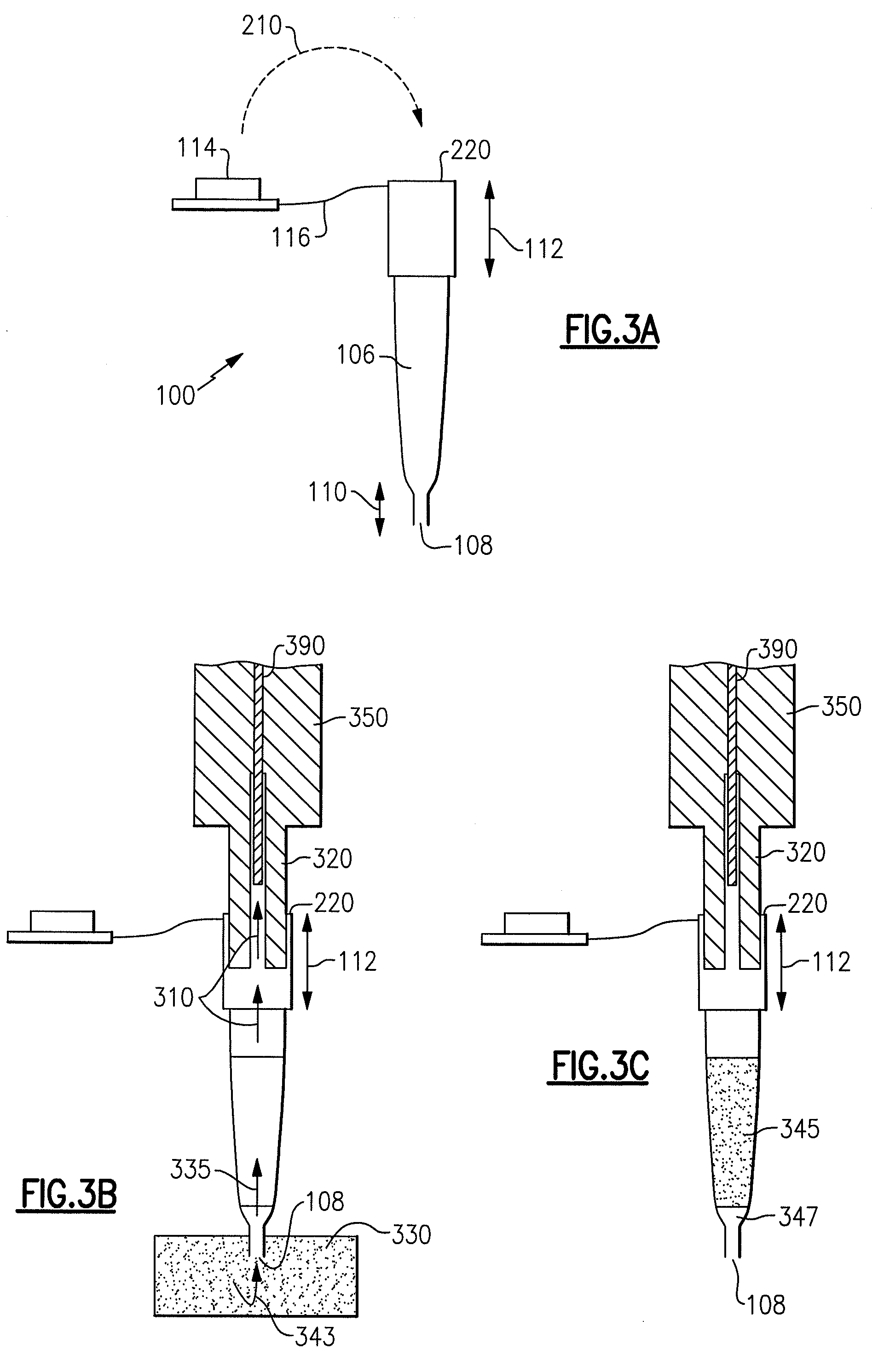
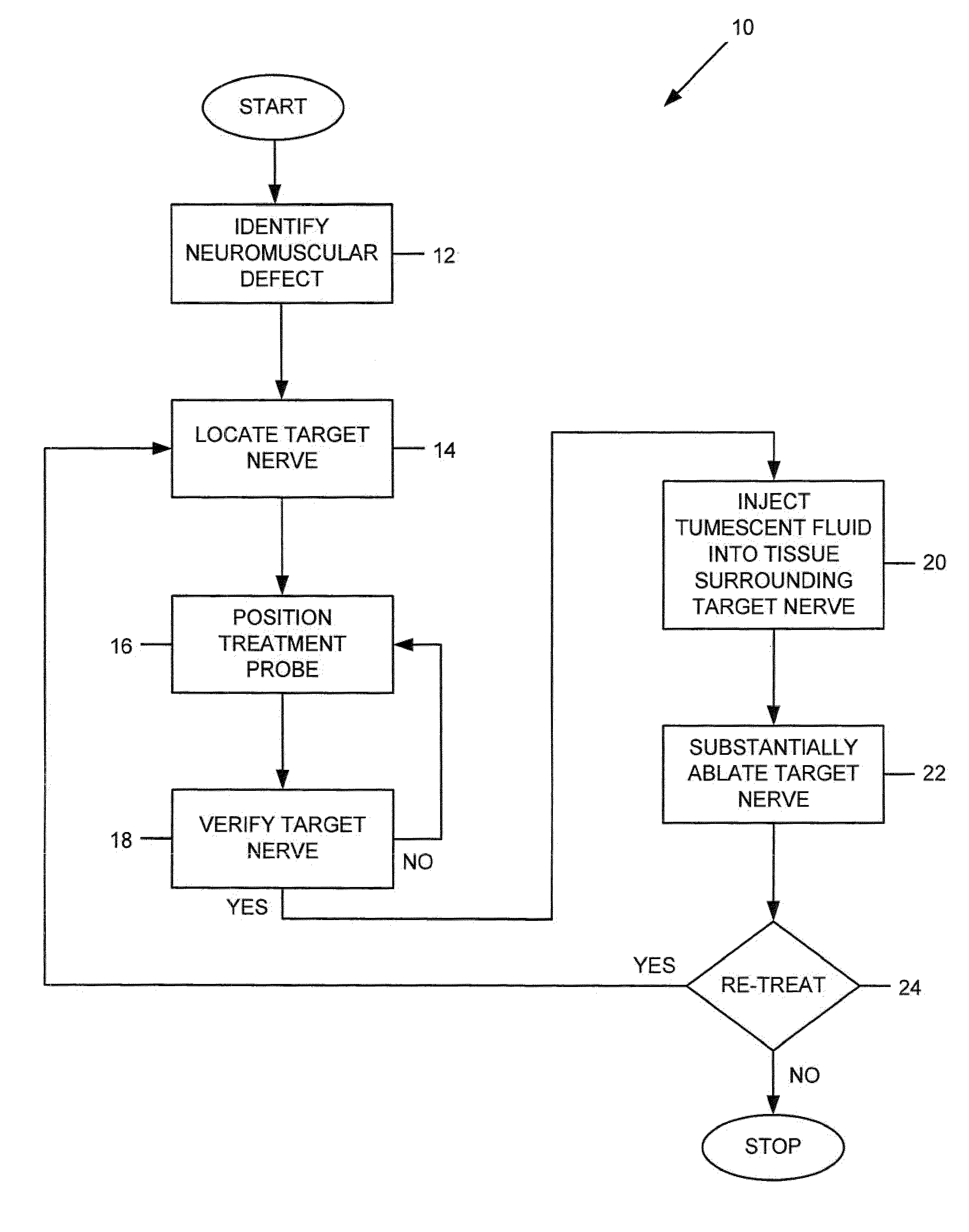
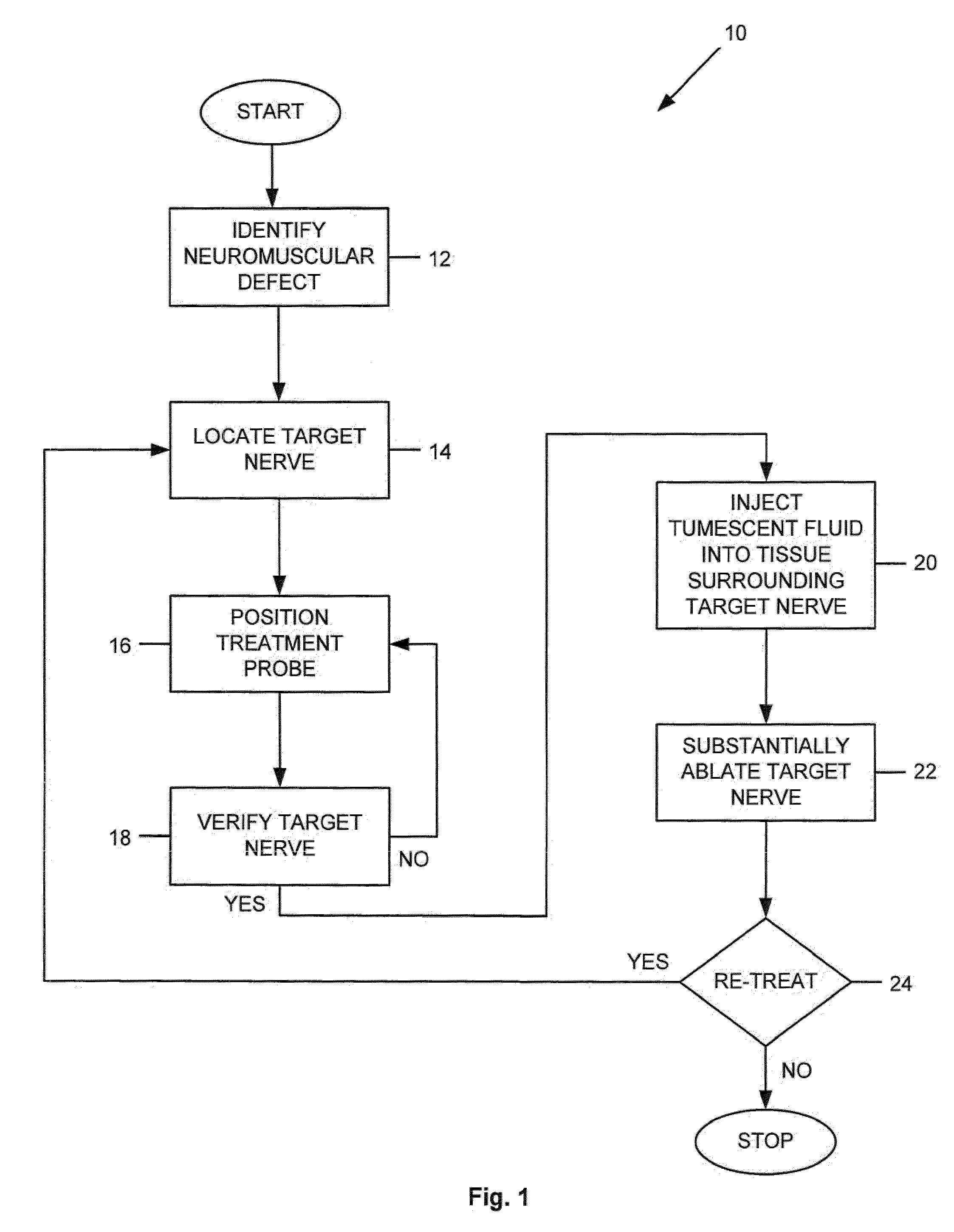
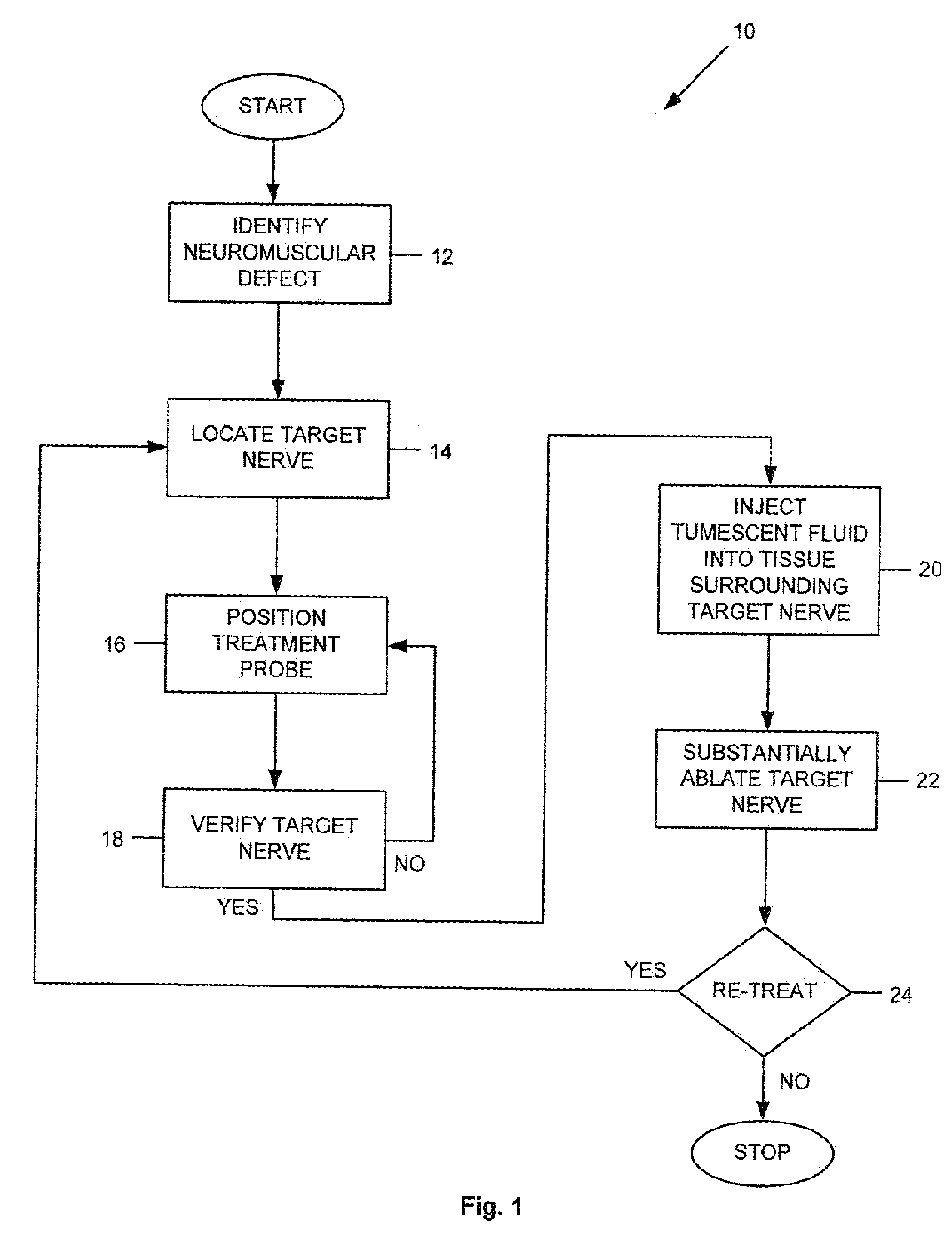
Apparatus and method for treating a neuromuscular defect
A method is provided for treating a neuromuscular defect in a subject. One step of the method includes locating a target nerve. After locating the target nerve, a treatment probe is provided. The treatment probe includes an elongated body member having a proximal end portion and a distal end portion. The distal end portion includes an energy delivery mechanism for stimulating or ablating the target nerve, a monitoring mechanism, and a fluid aspiration / delivery mechanism. Next, the target nerve is verified as an appropriate target for ablation by stimulating and then monitoring the target nerve via the energy delivery mechanism and the monitoring mechanism, respectively. After verifying the target nerve, a tumescent fluid is injected into the tissue surrounding the target nerve. An electric current is then delivered to the energy delivery mechanism to substantially ablate the target nerve.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
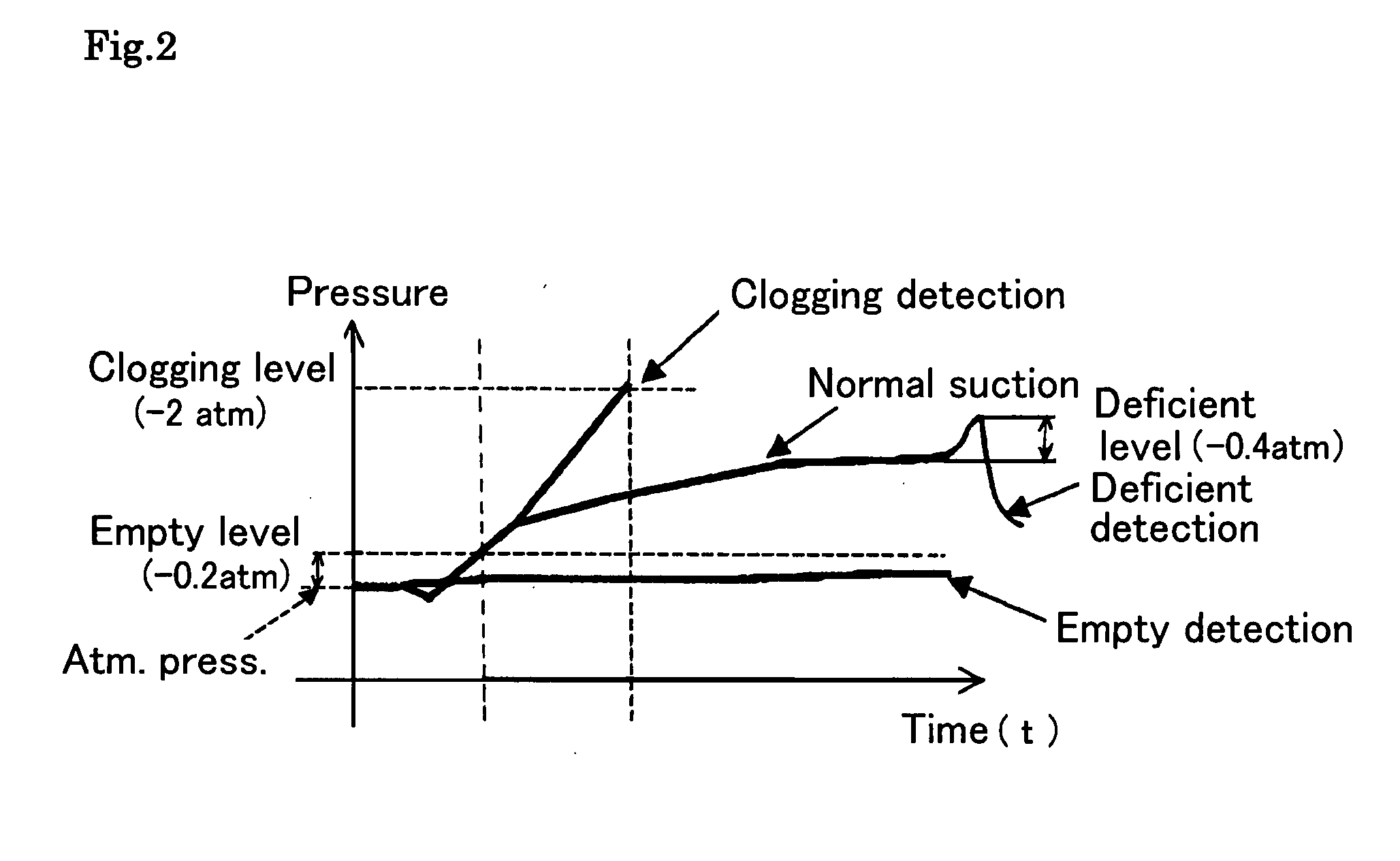
Differentiating Between Abnormal Sample Viscosities and Pipette Clogging During Aspiration
ActiveUS20090266149A1High viscosityMinimum sample volumeTesting/calibration apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansPipetteSample viscosity
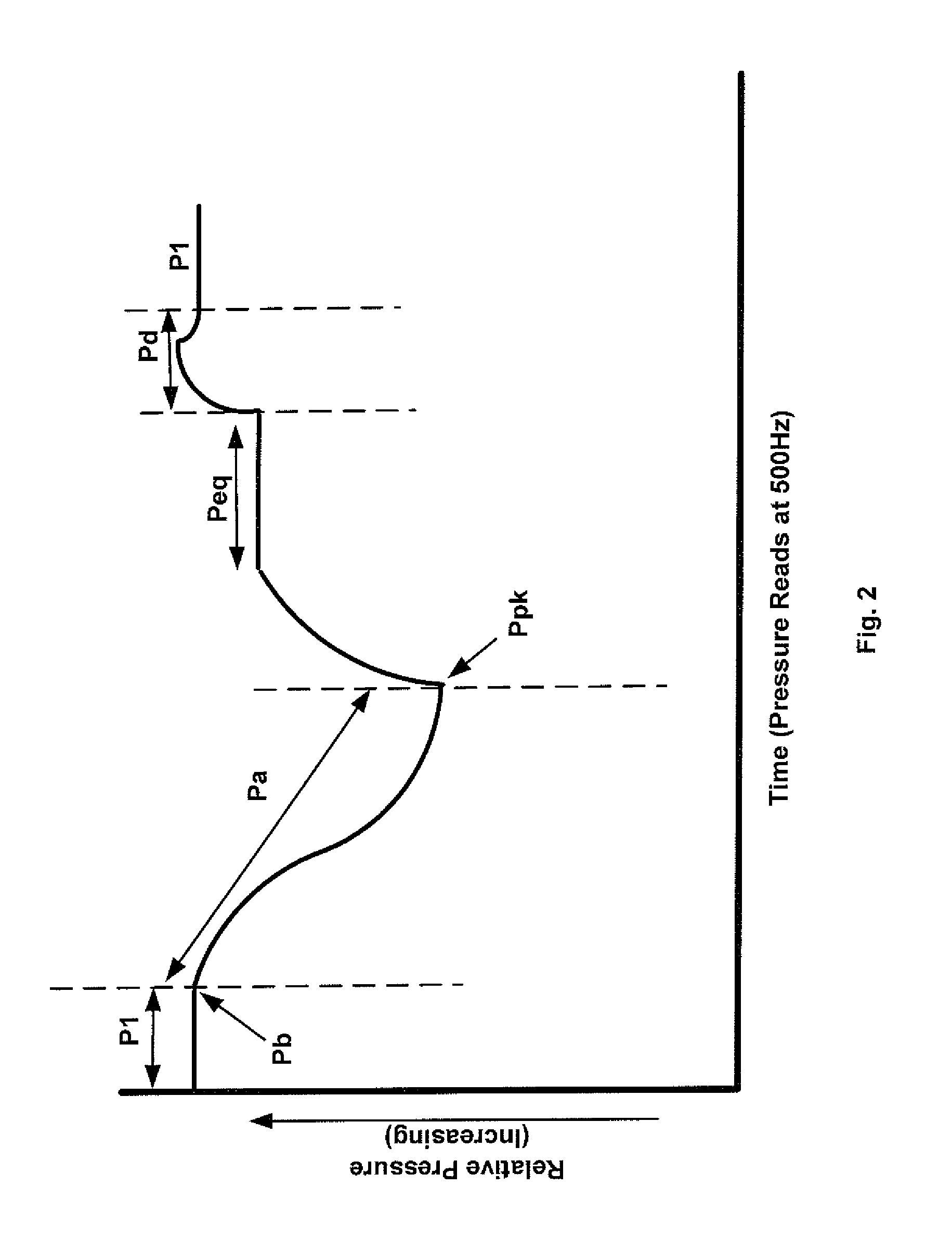
A method for differentiating between a liquid sample having clogs therein and a liquid sample having an abnormally elevated viscosity during a liquid aspiration process by relating the ratio between the maximum negative pressure during aspiration and an equilibrium pressure prior to dispensation to viscosity.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
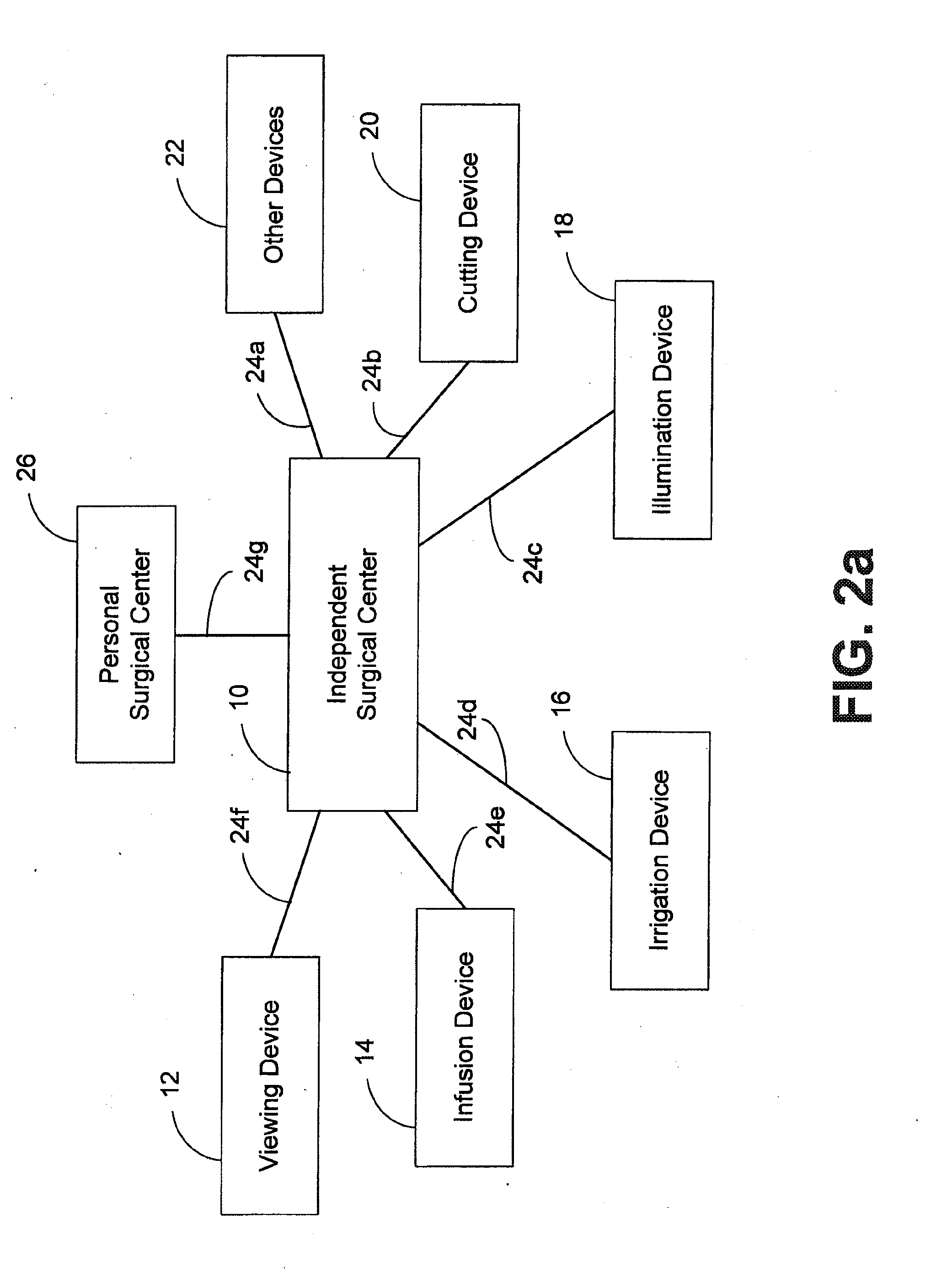
Independent surgical center
Owner:DOHENY EYE INST
Retrofittable aspiration prevention mechanism for patients
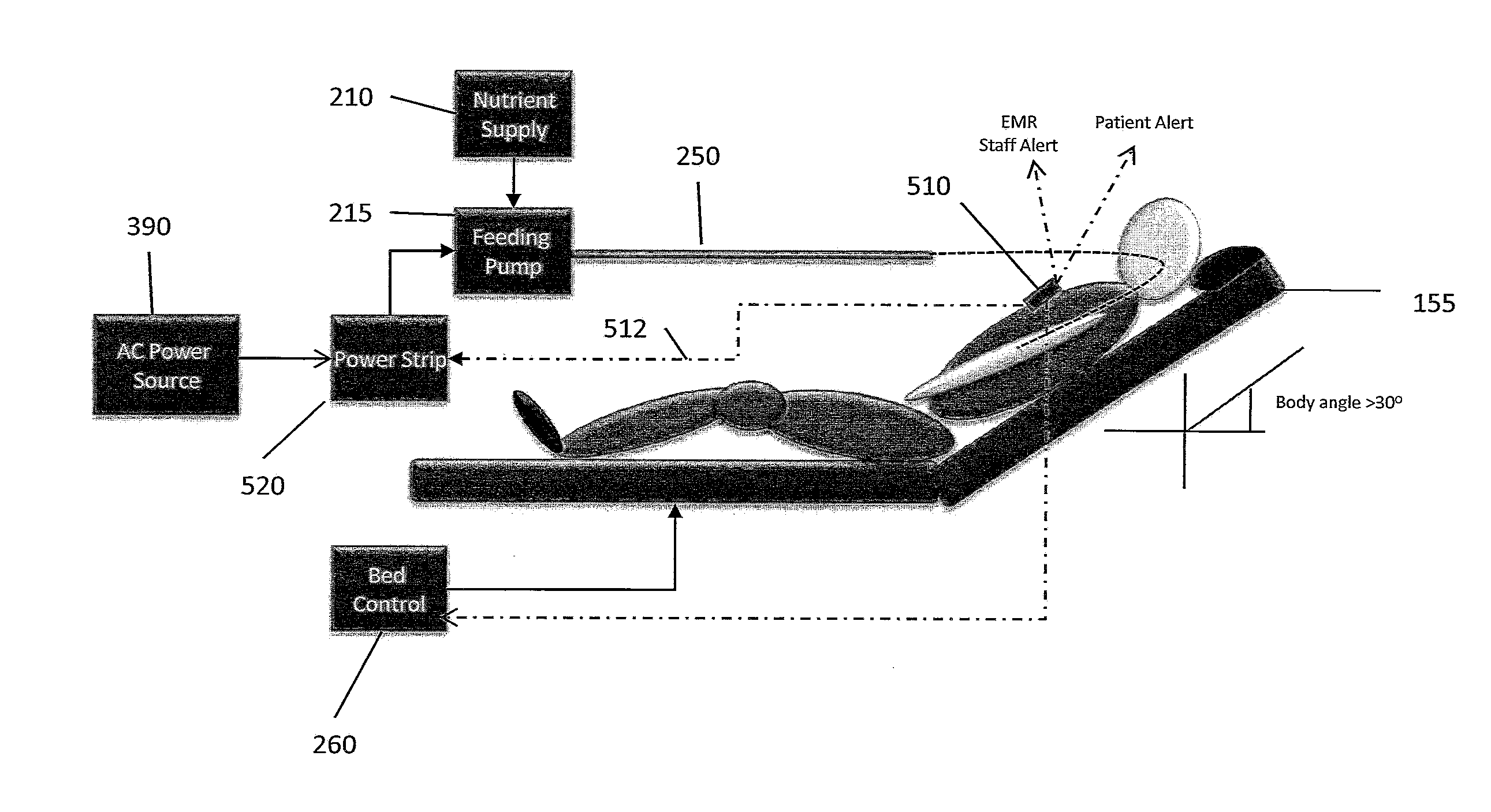
InactiveUS20120191038A1Reduce and eliminate problem of aspirationReduce eliminateInertial sensorsMedical devicesControl powerFeeding tube
A device is employed that can be retrofit onto existing feed pumps to remediate the problem of fluid aspiration in patients being fed through a feeding tube from the pump. In one embodiment the feeding pump is plugged into the device which is plugged into a power outlet. A patient angle sensor triggers power cutoff to the pump and stoppage of fluid flow. The angle sensor and operating program may be part of a smart phone. Power to the pump may be shut off due to a Bluetooth signal from the smart phone to a Bluetooth controlled power strip into which the pump is plugged to receive power.
Owner:GERBER ALLEN
Automated endoscope reprocessor connection integrity testing via liquid suction
A method detects proper connection of fixtures to a channel in an endoscope and proper flow through the channel during a cleaning or disinfection procedure. The endoscope has a first opening into one of its channels to which is connected a fixture and a second opening which is placed into a liquid. Negative pressure at the first opening draws an amount of liquid through the channel which is measured. If the channel is blocked insufficient liquid will flow an be measured. If the fixture is not connected properly air will leak in and insufficient liquid will flow an be measured.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Medical device including an air evacuation system
ActiveUS20110224612A1Preventing fluid communicationAvoid communicationInfusion syringesIntravenous devicesMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
Medical device assemblies capable of aspirating liquid into a syringe barrel or other medical devices while evacuating any air from the syringe are described. An exemplary medical device includes a syringe barrel, plunger rod and stopper assembly having an air permeable and liquid impermeable porous portion and structure for forming a vacuum within either the stopper or the plunger rod. Described is a medical device including a syringe barrel, plunger rod and stopper assembly having an air permeable and liquid impermeable porous portion and structure for forming a vacuum within chamber between the stopper and plunger rod wherein the plunger rod includes a sealing edge and is moveable relative to the stopper. Exemplary medical devices may include a vent for allowing air that permeates through the porous portion to escape to atmosphere. Methods for aspirating a syringe barrel with a liquid are also provided.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
System, method and apparatus for electrosurgical instrument with movable suction sheath
ActiveUS20110077643A1Minimal levelLarge levelSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesLeading edgeEngineering
An electrosurgical instrument having active and return electrodes with a movable suction sheath for variable fluid and debris removal during surgical procedures is disclosed. The suction apparatus has an outer sheath that is external to a shaft to provide a lumen. The sheath assembly is axially movable relative to the fluid aspiration element between first and second positions for treating the target site and fluid and debris removal, respectively. The first position positions the distal end of the shaft axially distal to a leading edge of the sheath assembly. The second position positions the distal leading edge of the sheath assembly axially adjacent to the end of the shaft. The fluid aspiration element comprises an inner lumen extending through the shaft, and at least one port extending radially through the shaft. The port is in communication with the inner lumen. A vacuum provides suction through the port and inner lumen.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Method and system for controllably administering fluid to a patient and/or for controllably withdrawing fluid from the patient
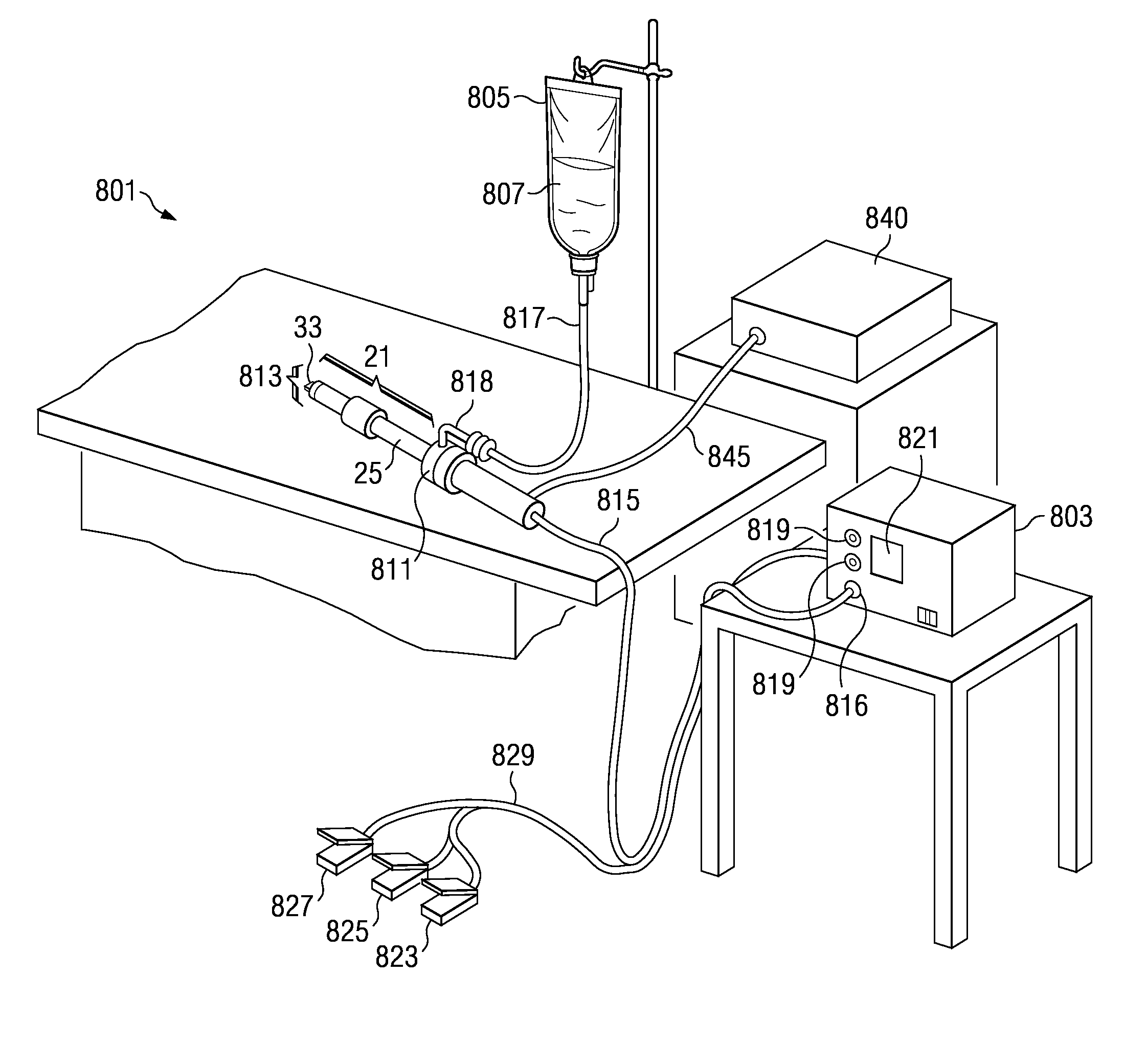
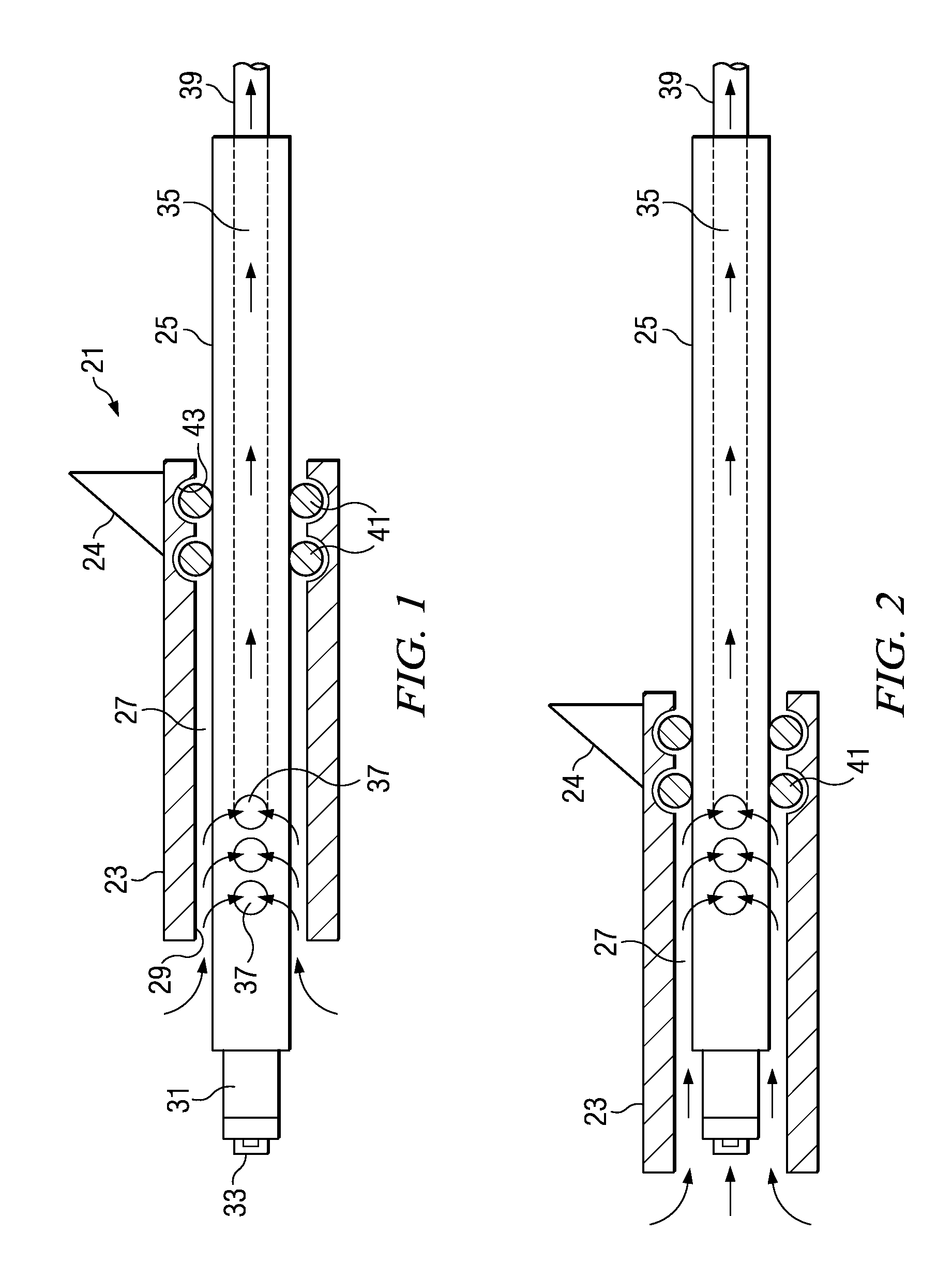
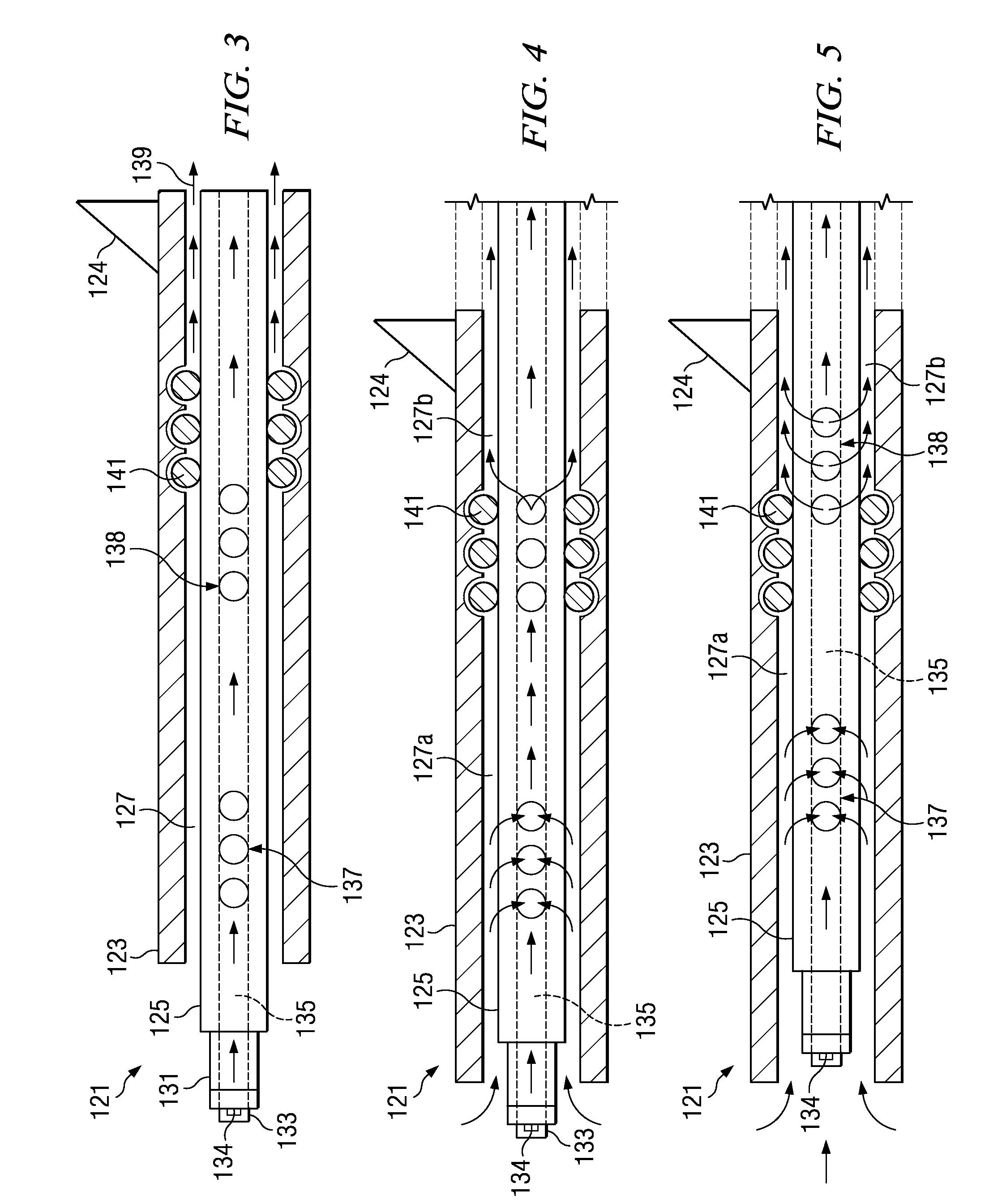
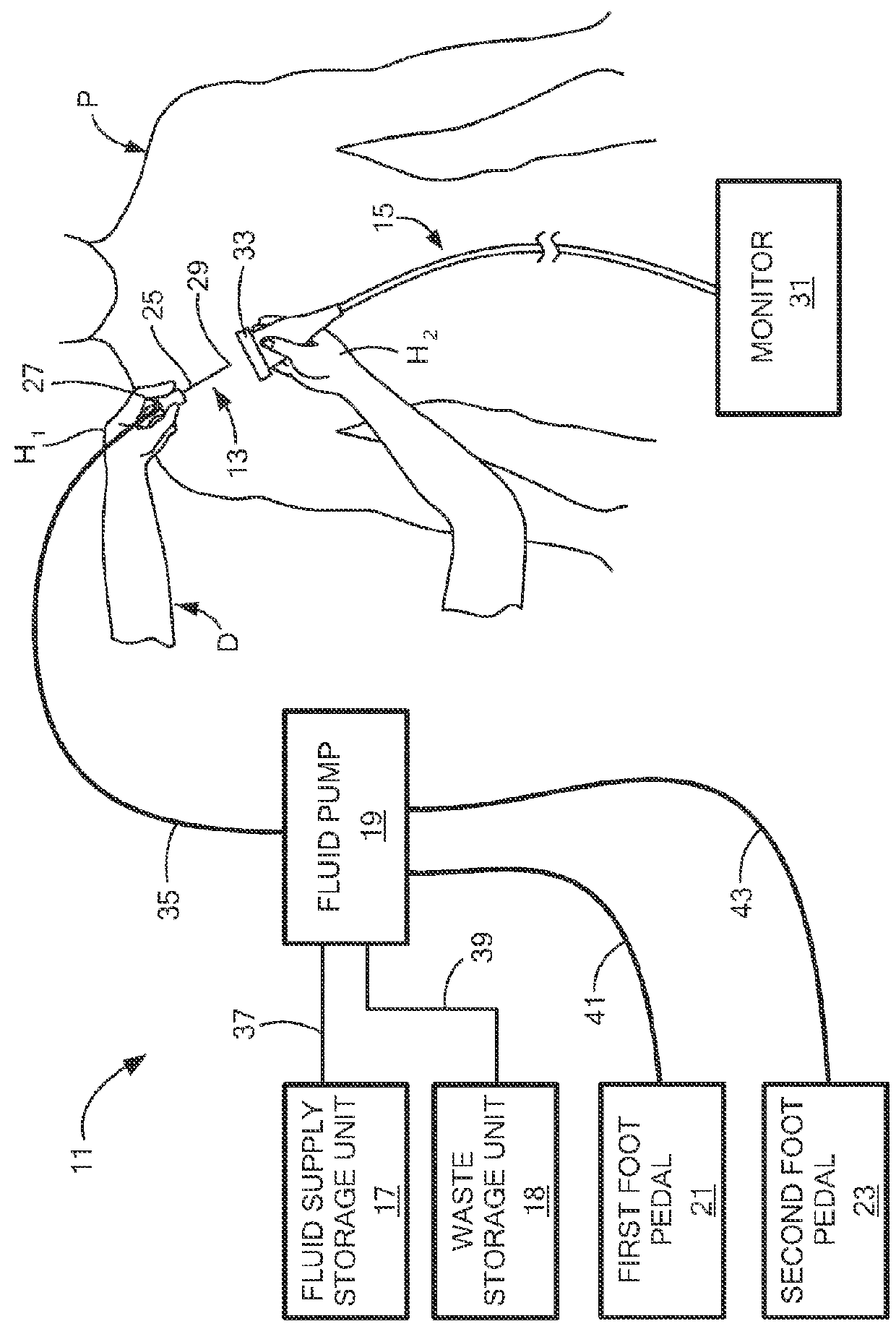
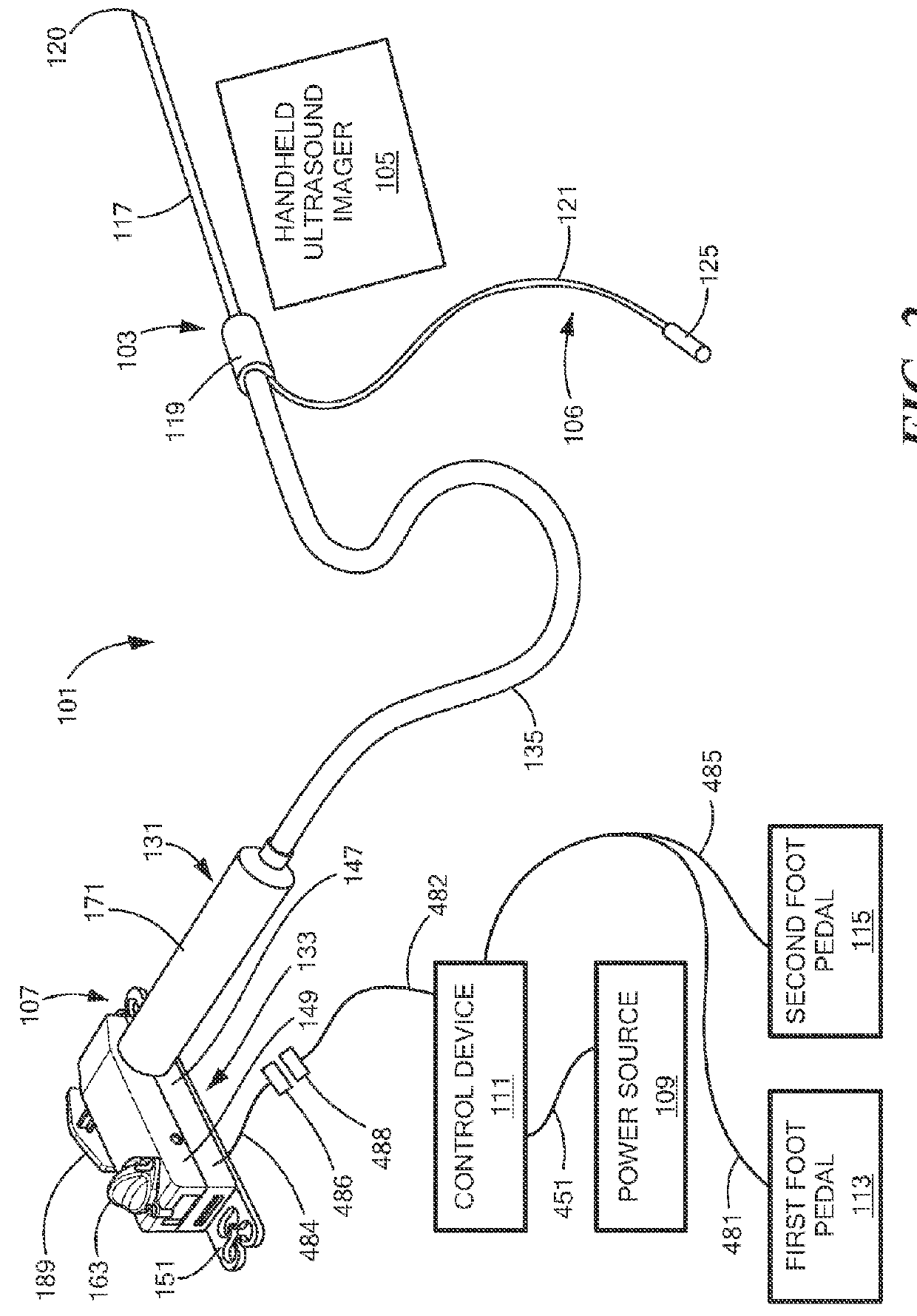
Method and system for controllably administering and / or withdrawing fluid from a patient. In one embodiment, the system may include a needle assembly, an ultrasound imager, a fluid supply storage unit, a waste storage unit, a fluid pump, and a foot pedal assembly. A syringe may serve as the fluid supply storage unit and the waste storage unit. The pump may include a bi-directional motor and a gear coupled to the motor. The gear may be engageable with a rack on the syringe plunger to drive the plunger either for fluid aspiration or infusion. Depression of one portion of the foot pedal assembly causes the motor to drive the gear in one direction, and depression of another portion of the foot pedal assembly causes the motor to drive the gear the other direction. The system may include a control device to keep pressure in the fluid path from exceeding a limit.
Owner:MEDOVATE LTD
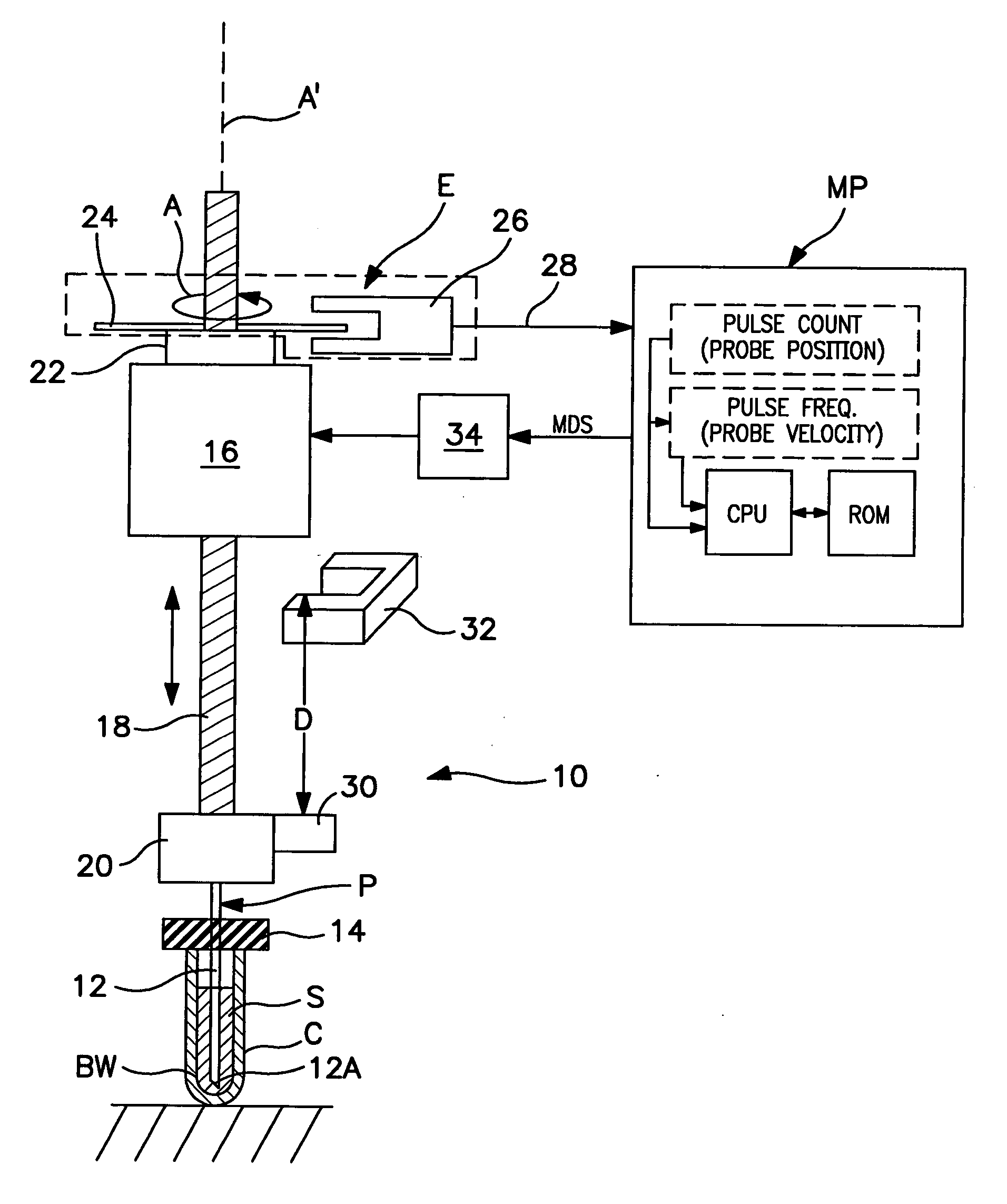
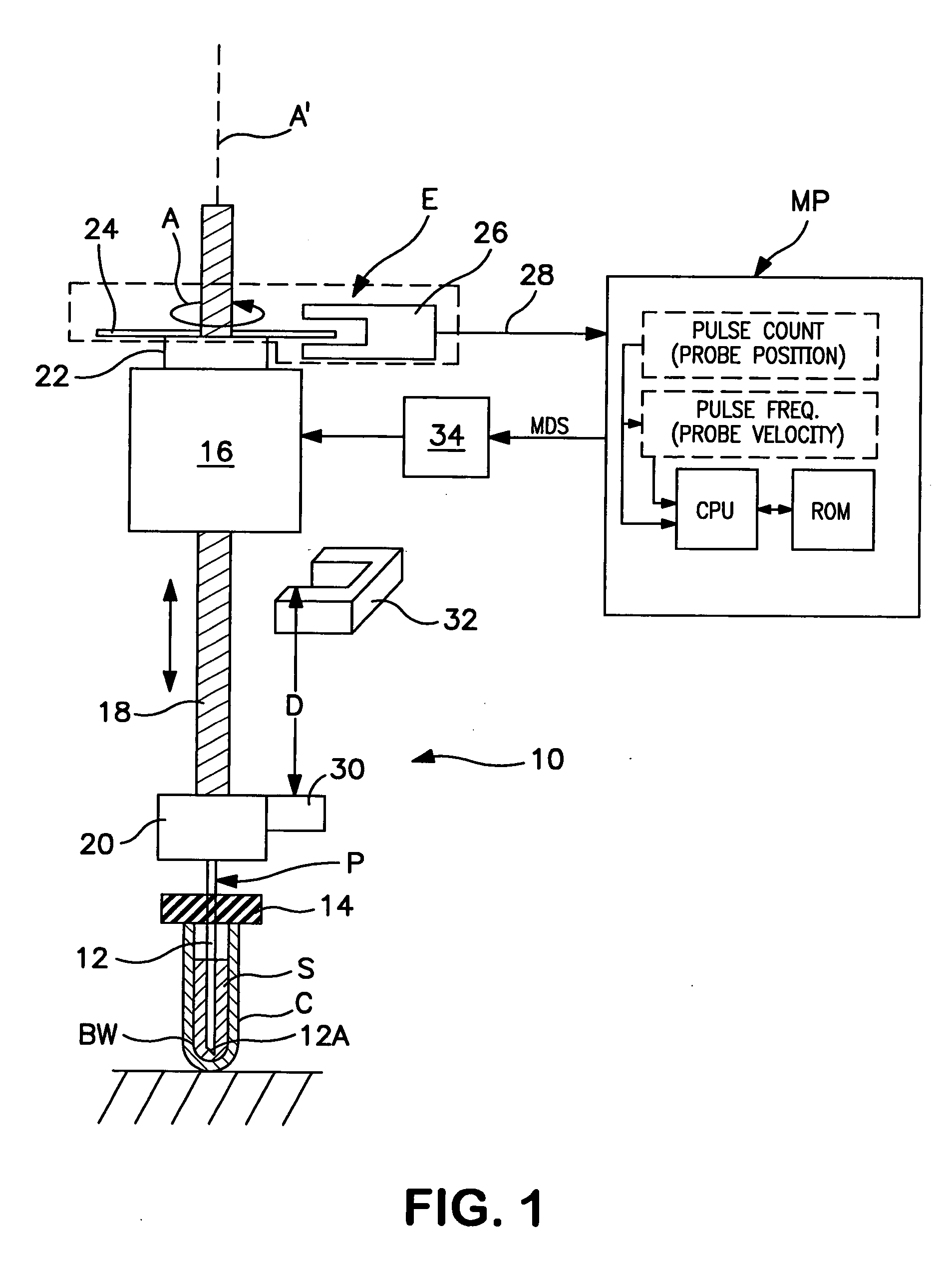
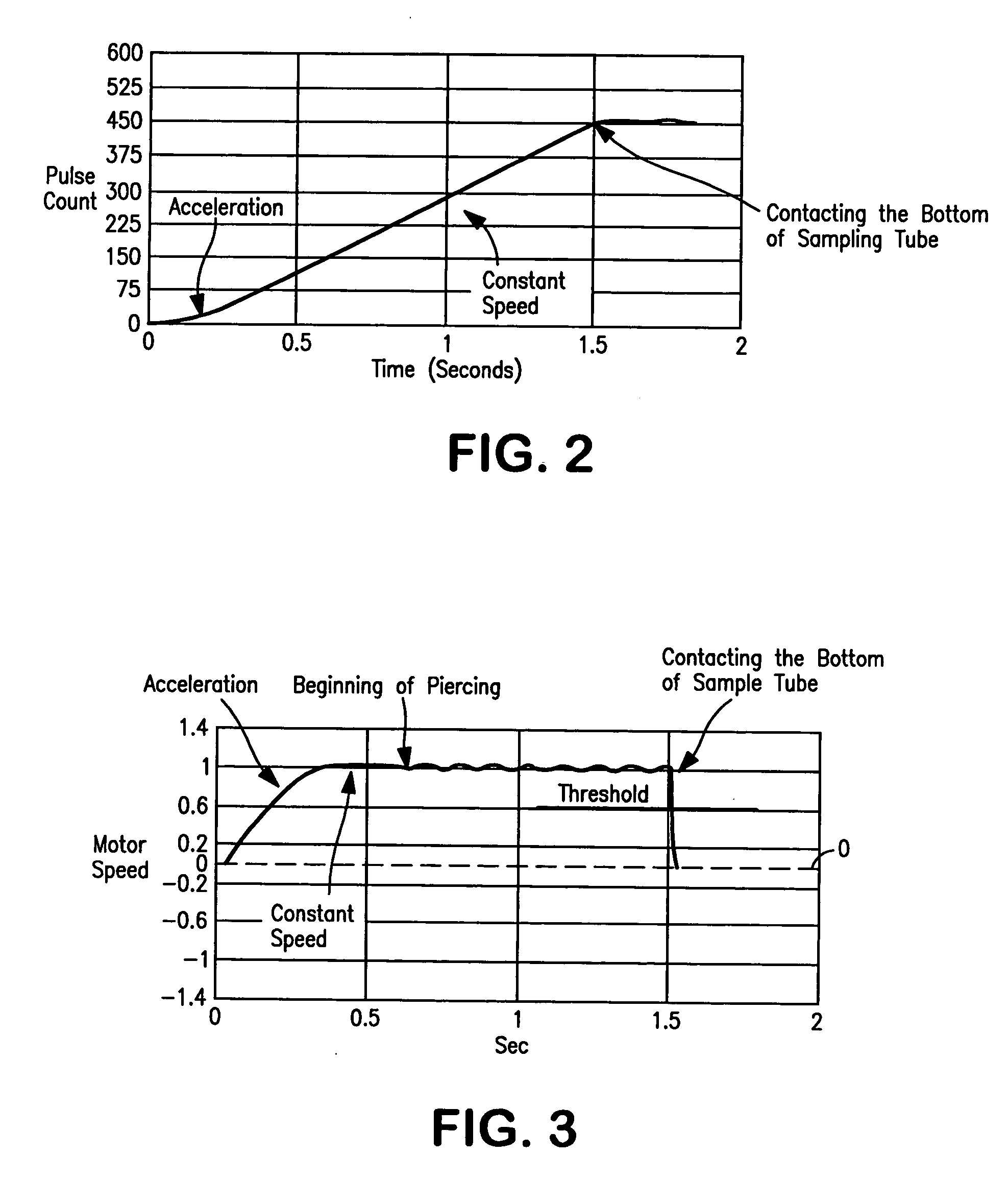
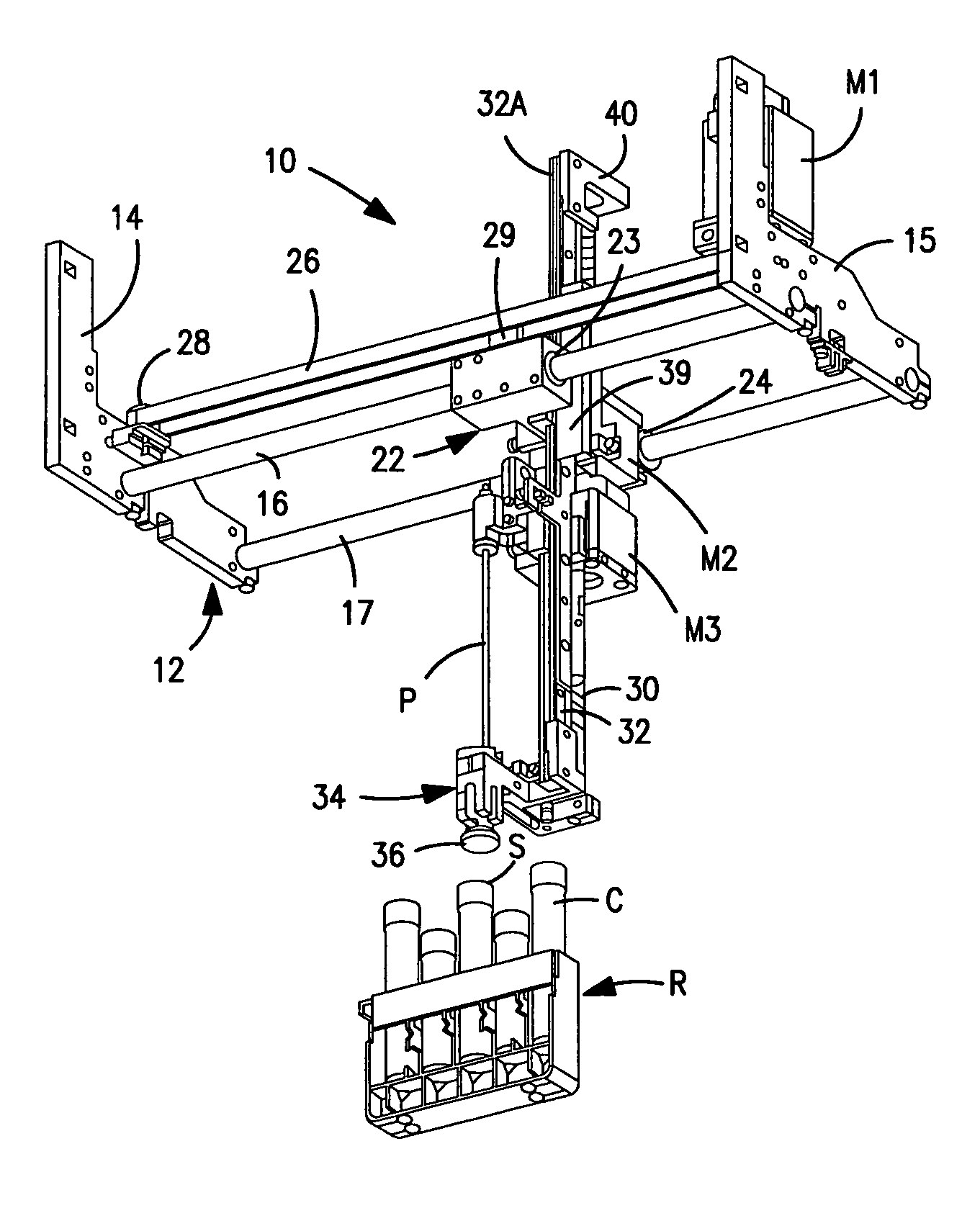
Method and apparatus for maximizing liquid aspiration from small vessels
Apparatus and method for aspirating liquid from a container, e.g., a test tube or other vessel, includes apparatus for sensing that an aspiration probe tip is contacting the inside bottom wall of the container, whereby a maximum volume of liquid can be aspirated from the container. According to the invention, an encoder is mounted on the driven member of a motor (e.g., on a rotatably-driven drive shaft or a nut of a stepper or D.C. motor, or on a linearly-driven shaft of a linear actuator) used to rectilinearly advance the probe tip into the container. Such encoder produces a series of pulses indicating the speed and / or linear position of the probe tip. A motor controller responds to a predetermined change in pattern of pulses from the encoder indicating that movement of the probe tip has been resisted by the vessel bottom, whereby further movement of the driven member and of the probe connected thereto is arrested, and the probe tip remains in contact with the vessel bottom.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
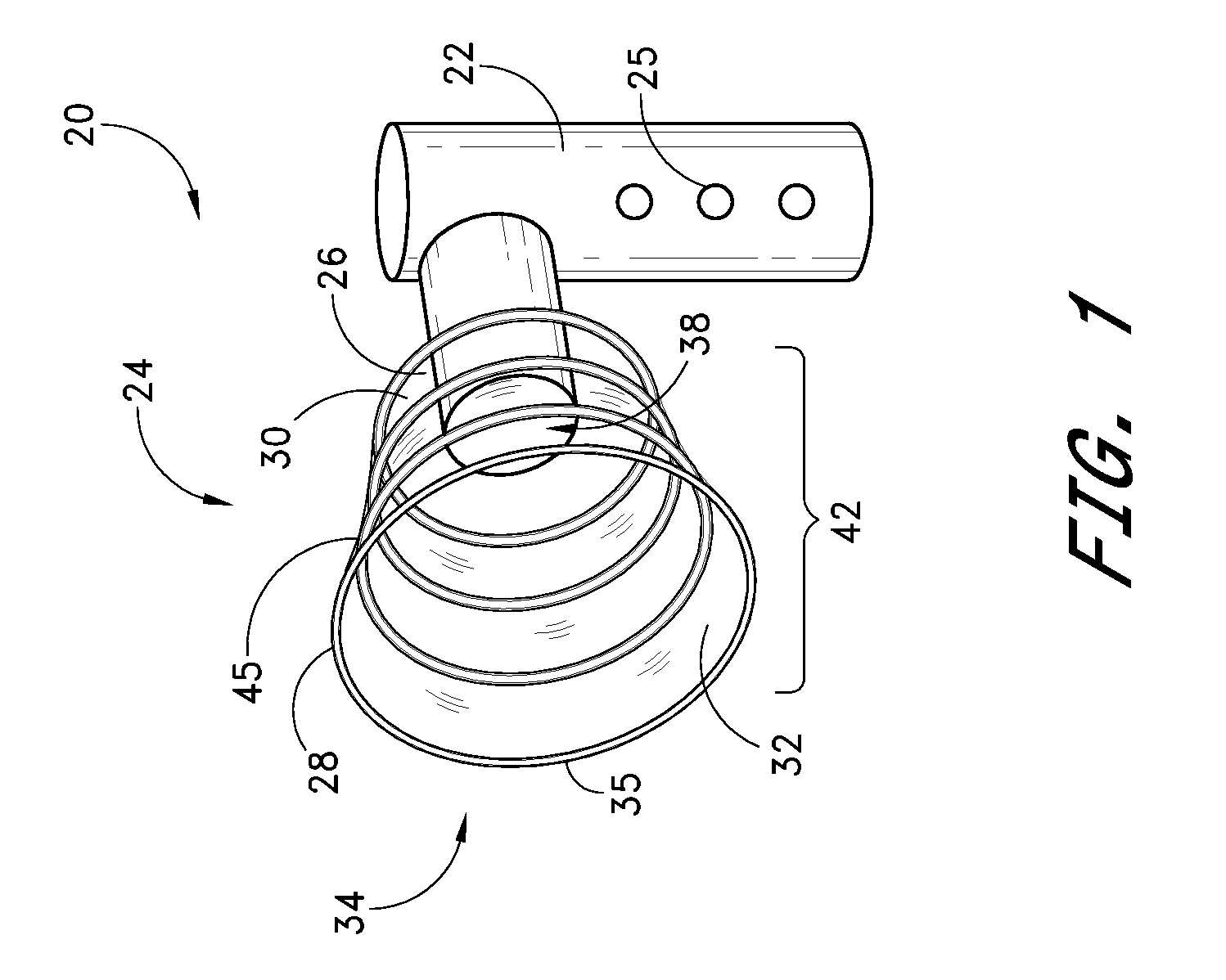
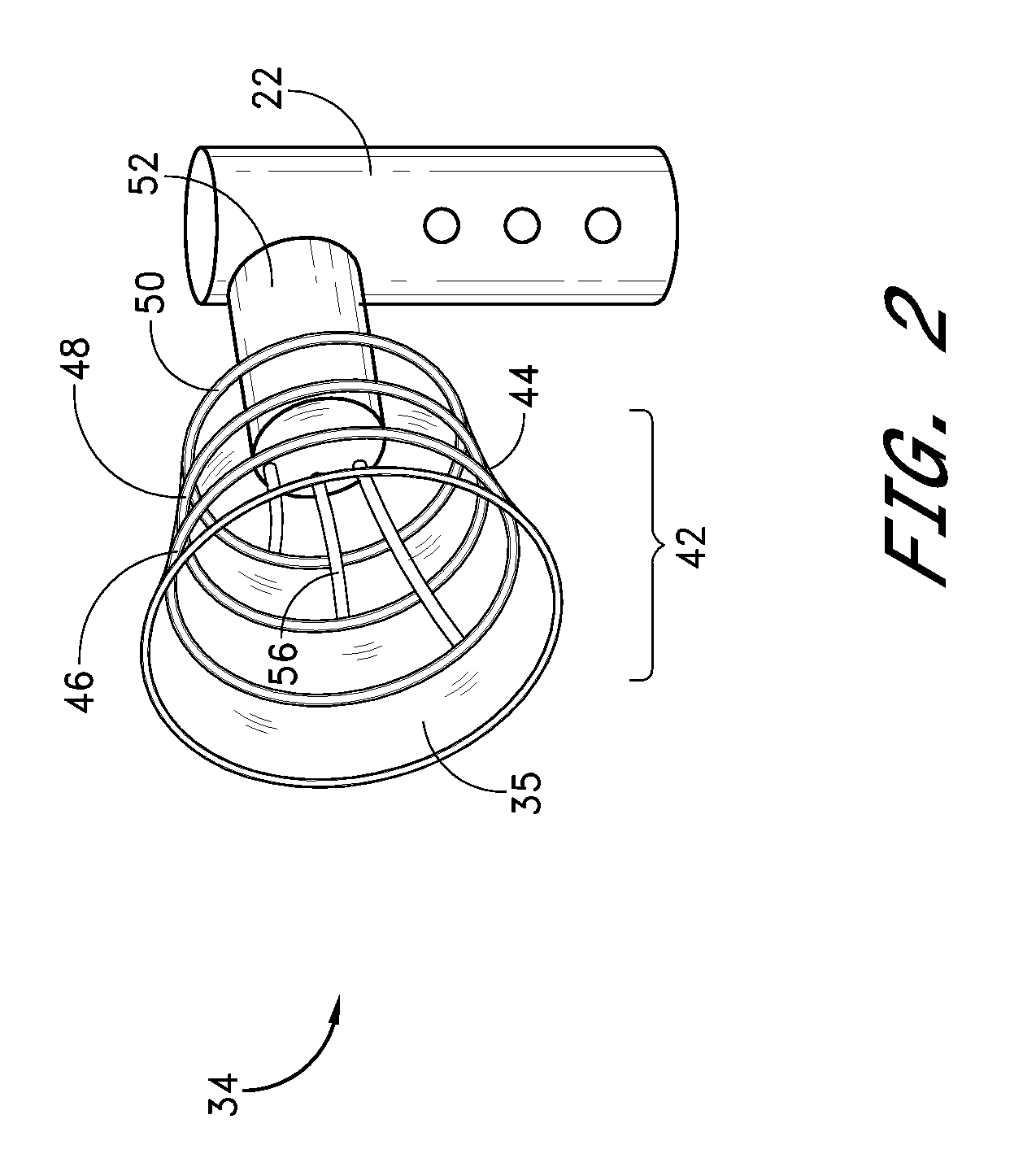
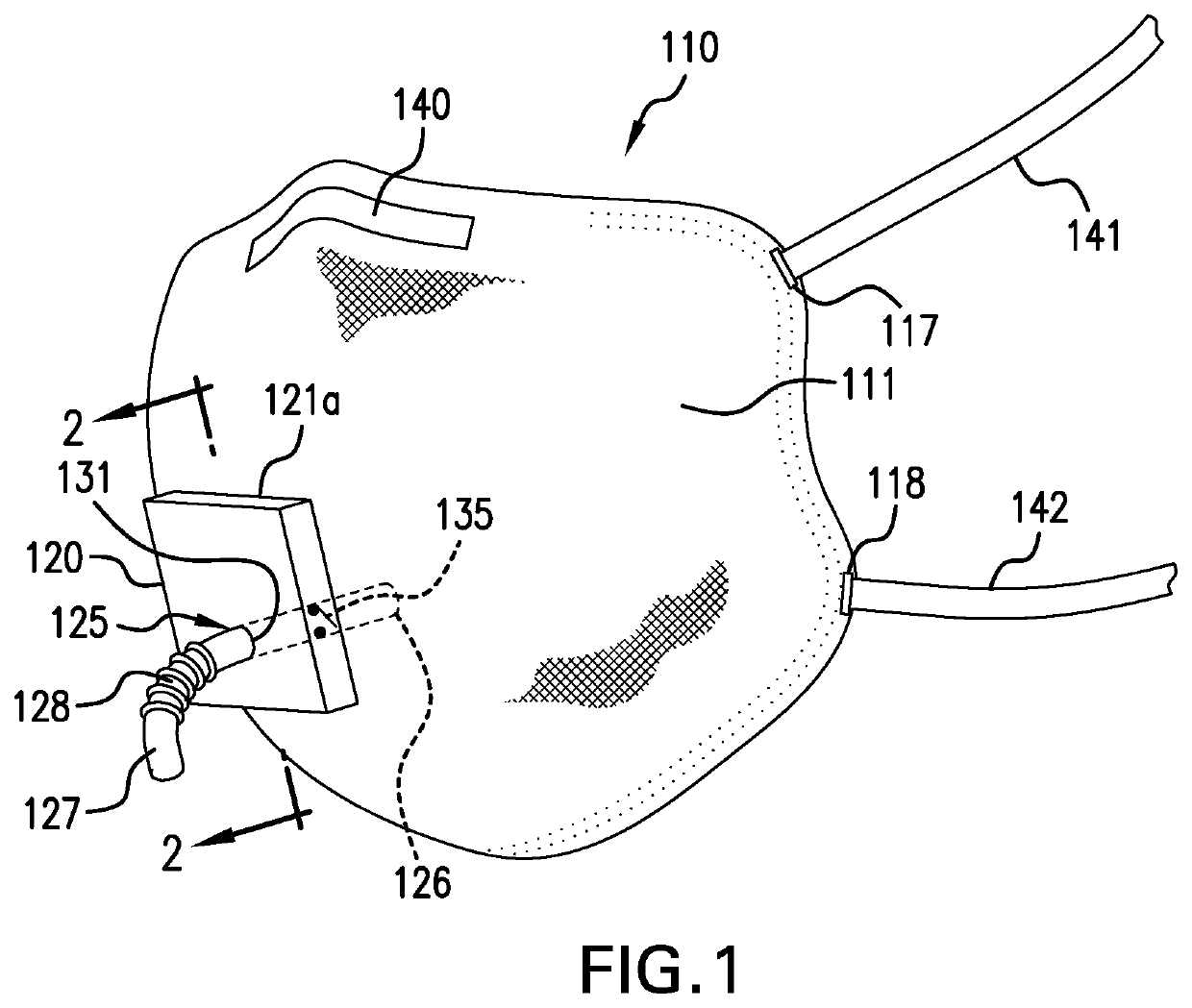
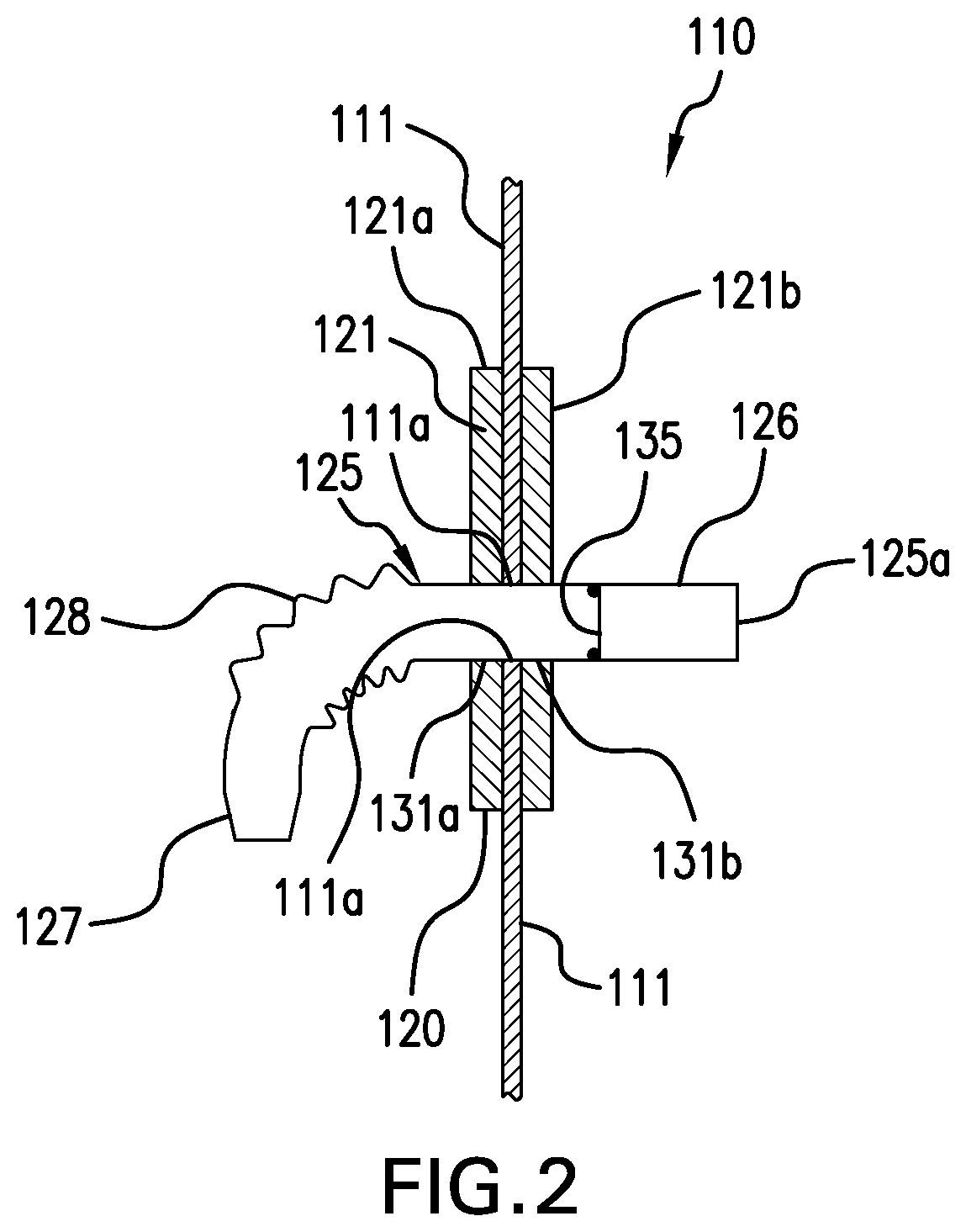
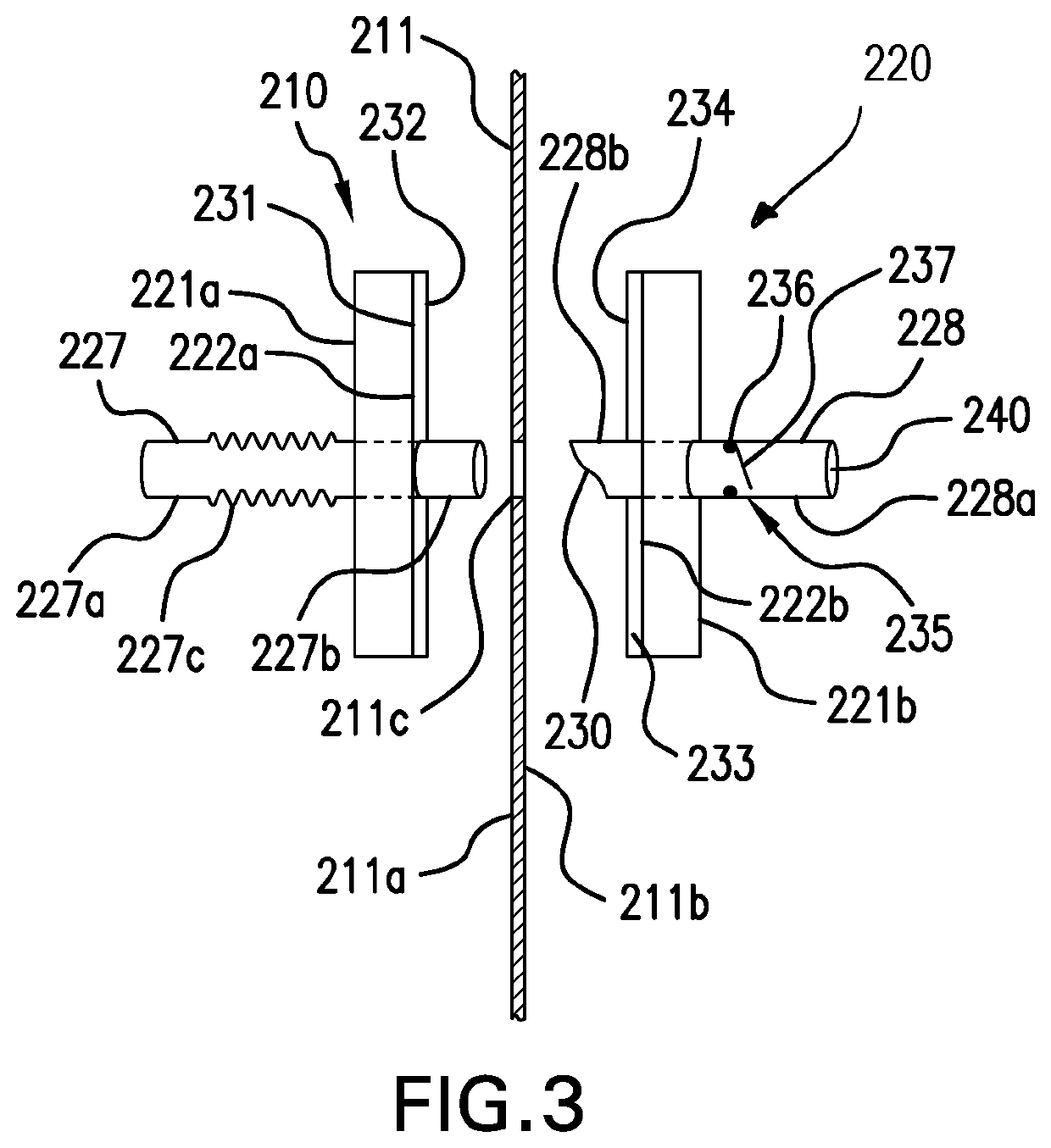
Disposable patient interface for intraductal fluid aspiration system
Disclosed is a disposable patient interface for an intraductal fluid aspiration system. The interface has a flexible tubular distal member for contacting the patient, and a proximal support portion forming a vacuum chamber therein. The support portion has a vacuum aperture for communication with a source of vacuum, and a retention structure for releasably mounting within a hand piece of an intraductal fluid aspiration system. The flexible member preferably has a low modulus of elasticity and a high tear strength, such that it can be stretched to fit over a rigid support without rupture.
Owner:HALO HEALTHCARE
Apparatus for aspirating liquids from sealed containers
ActiveUS7481978B2Easy constructionLess componentsWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringLinear actuator
Apparatus for aspirating liquid from a container, e.g., a test tube, having a puncturable stopper includes a pair of stepper motors that share a common linear actuator or drive member. One motor operates to axially advance the linear drive member (preferably a lead screw) to a position in which it serves to position a rigidly connected tube-detector / stripper member in engagement with the top of a stopper on a tube. Thereafter, the second motor operates to move along the surface of the same drive member to advance an aspiration probe through the engaged stopper and into a liquid aspirating position within the tube. Preferably, a linear guide rail, slidably-mounted on a frame that supports the liquid-aspirating apparatus, serves to guide both the movement of the aspiration probe and the linear drive member. As a result of the shared components, the apparatus is highly precise and reliable.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Dental suction arrangement
InactiveUS20180193120A1Effective absorptionEliminate the problemTeeth fillingCatheterEngineeringOral cavity
A dental suction arrangement which removes saliva and other fluids from a person's oral cavity. The suction arrangement includes a suction tube and an absorption body to be placed in the oral cavity. The suction tube includes a suction part which is arranged in the absorption body and which is equipped with a hole organs or elements communicating with the absorption body. The suction arrangement is made of elastically deformable material in order to adapt to the anatomical shape of the bottom of the mouth.
Owner:ASUM THOMAS
Needle Filter Apparatus
Disclosed is a disposable needle filter apparatus with a universal truncated syringe-receiving neck to enable the filtration of fluids / solutions aspirated into a needle-bearing syringe. The apparatus includes a needle seal stopper and needle stop to create a substantially airtight chamber to facilitate fluid aspiration through an enclosed filter and into the syringe. In an alternative embodiment, the filter apparatus includes an extended syringe-receiving neck configured to receive a specifically sized syringe / needle combination. In a further embodiment, the receiving neck is constructed as a modular unit to allow for interchangeable necks to accommodate different needle and syringe sizes with different cross-sectional diameters. In a yet further embodiment, the neck is constructed with stepped tapered segments of serially larger cross-sectional diameters to accommodate differently sized syringes. In a still further embodiment, the apparatus includes an accessory needle secured to the apparatus inlet.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS CORP
Method of Detecting Dispensed Quantity, and Liquid Suction Monitoring Dispensing Apparatus
ActiveUS20090211380A1Easy to detectImprove reliabilityTesting/calibration apparatusWithdrawing sample devicesPipetteEngineering
There are provided a method of detecting dispensed quantity in which without the need of detecting a surface of liquid accommodated in a container, a liquid quantity can be detected only by measuring pressure change; and a relevant liquid suction monitoring dispensing apparatus. There is provided a method of detecting dispensed quantity for detection of the quantity of liquid suctioned and discharged by a dispensing apparatus including a pipette tip, a liquid suctioning / discharging mechanism for the pipette tip, a pressure sensor capable of detecting the pressure within the pipette tip, and a lifting and lowering mechanism for the pipette tip, which method comprises: an insertion step for inserting a distal end of the pipette tip down to the deepest zone of a container accommodating liquid to be measured; a suction pressure measuring step for without moving of the pipette tip, while suctioning the liquid into the pipette tip at a predetermined suctioning rate, measuring any pressure change during the suctioning; and a suction detecting step for on the basis of pressure change measured, determining the state of suction. Further, there is provided a liquid suction monitoring dispensing apparatus capable of practicing this method.
Owner:UNIVERSAL BIO RESEARCH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for treating a neuromuscular defect
A method is provided for treating a neuromuscular defect in a subject. One step of the method includes locating a target nerve. After locating the target nerve, a treatment probe is provided. The treatment probe includes an elongated body member having a proximal end portion and a distal end portion. The distal end portion includes an energy delivery mechanism for stimulating or ablating the target nerve, a monitoring mechanism, and a fluid aspiration / delivery mechanism. Next, the target nerve is verified as an appropriate target for ablation by stimulating and then monitoring the target nerve via the energy delivery mechanism and the monitoring mechanism, respectively. After verifying the target nerve, a tumescent fluid is injected into the tissue surrounding the target nerve. An electric current is then delivered to the energy delivery mechanism to substantially ablate the target nerve.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
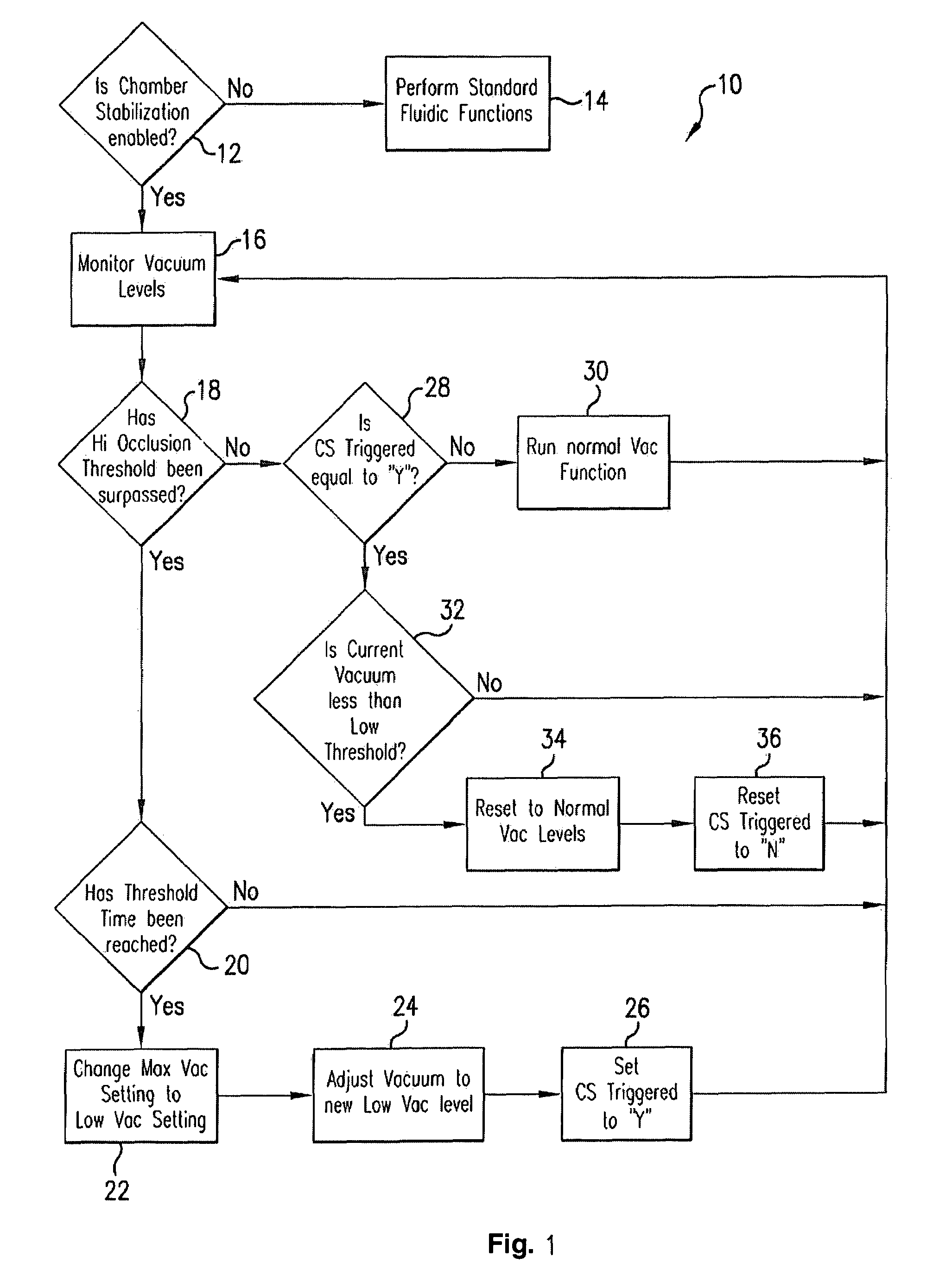
Application of vacuum as a method and mechanism for controlling eye chamber stability
A method for operating a surgical system including a control unit having a vacuum sensor and / or a flow rate sensor, the method including placing a handpiece in an operative relationship with an eye for a surgical procedure and thereafter supplying irrigation fluid to the handpiece while applying a vacuum to the handpiece to aspirate the irrigation fluid from the eye through the handpiece. During fluid aspiration, a vacuum level and / or flow rate is sensed which corresponds to an occlusion of the handpiece and from the sensed vacuum level and / or flow rate, a duration of the occlusion is determined. In response to the determined duration of occlusion, at least one of the handpiece parameters is varied.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Mask for drinking a beverage
ActiveUS10905905B1Avoid spendingMinimize spreadingBreathing filtersBreathing masksMedicineEngineering
A protective mask having a valve assembly that allow a user to drink a beverage while wearing the mask to maintain a safe environment by filtering contaminants, such as pathogens and particles from passing through the mask. The valve assembly may be provided on the mask or may be separately provided for attachment to a mask. The protective mask with the valve assembly has an attachment portion that allows common beverage straws to connect with the valve assembly to allow liquids to be draw through the mask by a user through a passageway. A check valve limits liquid flow in a single direction and actuates to open the valve when a user draws in liquid through the mouthpiece. The valve remains closed and blocks passage of inhaled or exhaled air, and blocks liquid flow in the direction opposite of the flow direction.
Owner:DETTORE ROBERT M
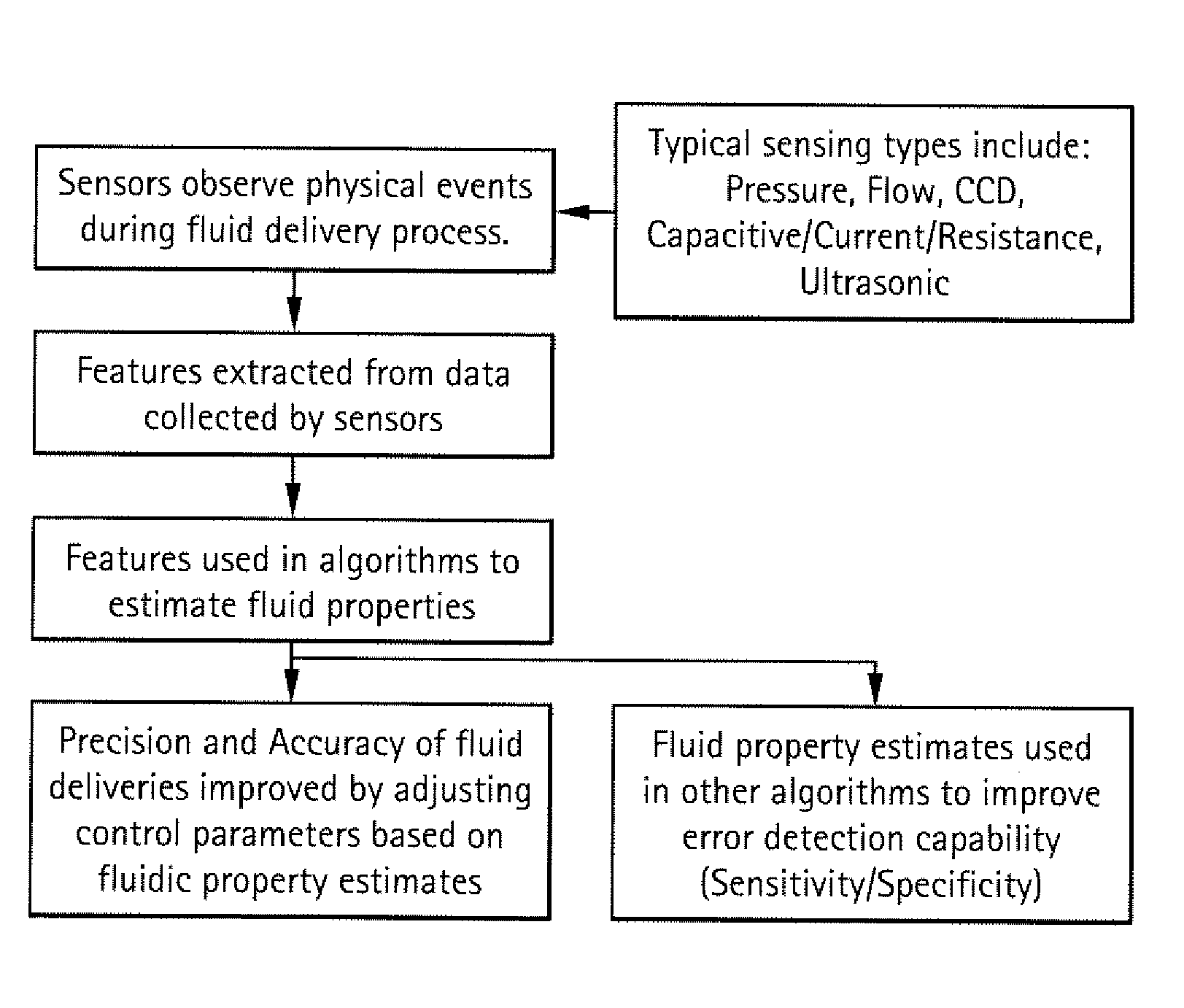
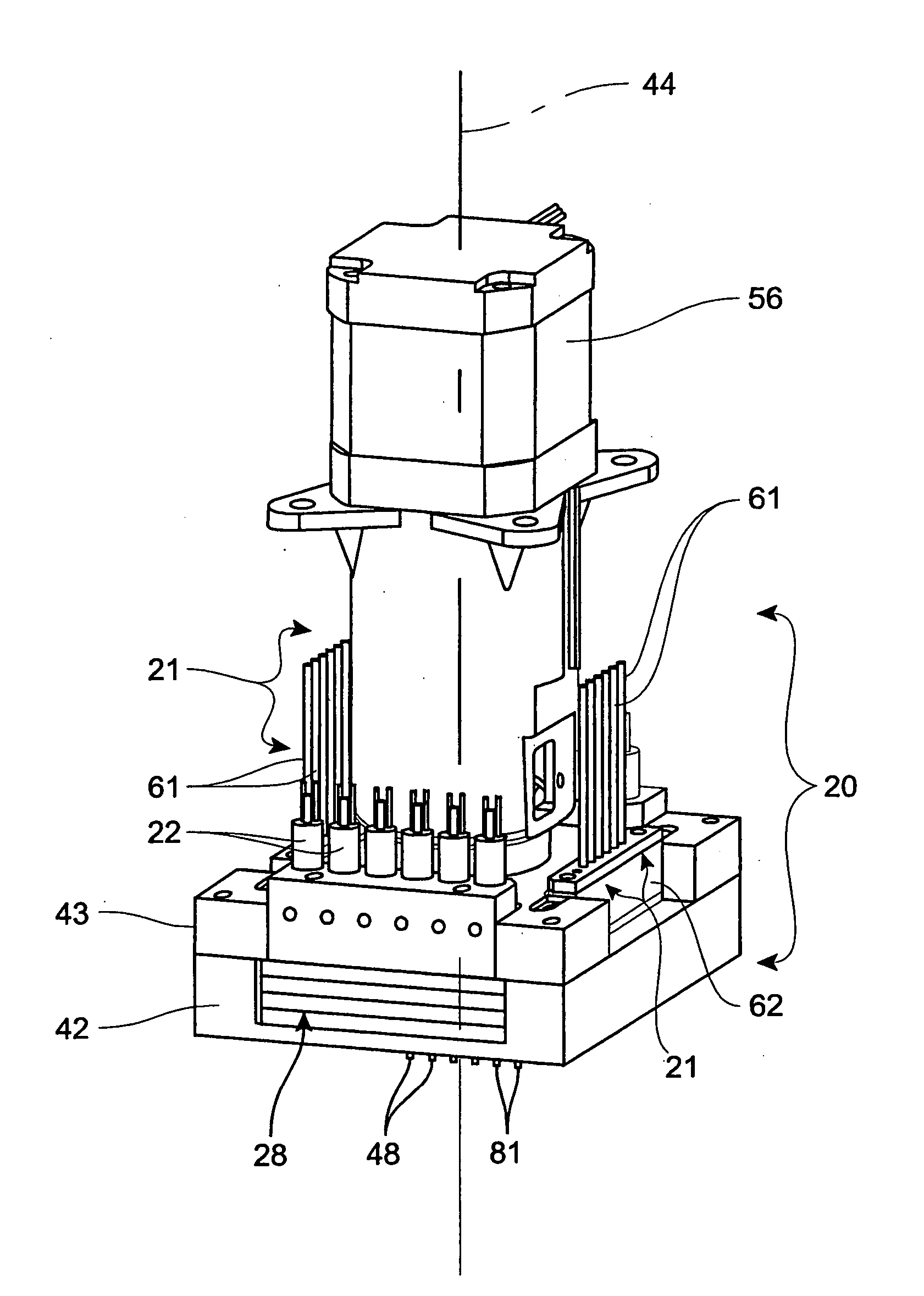
Estimating fluidic properties and using them to improve the precision/accuracy of metered fluids and to improve the sensitivity/specificity in detecting failure modes
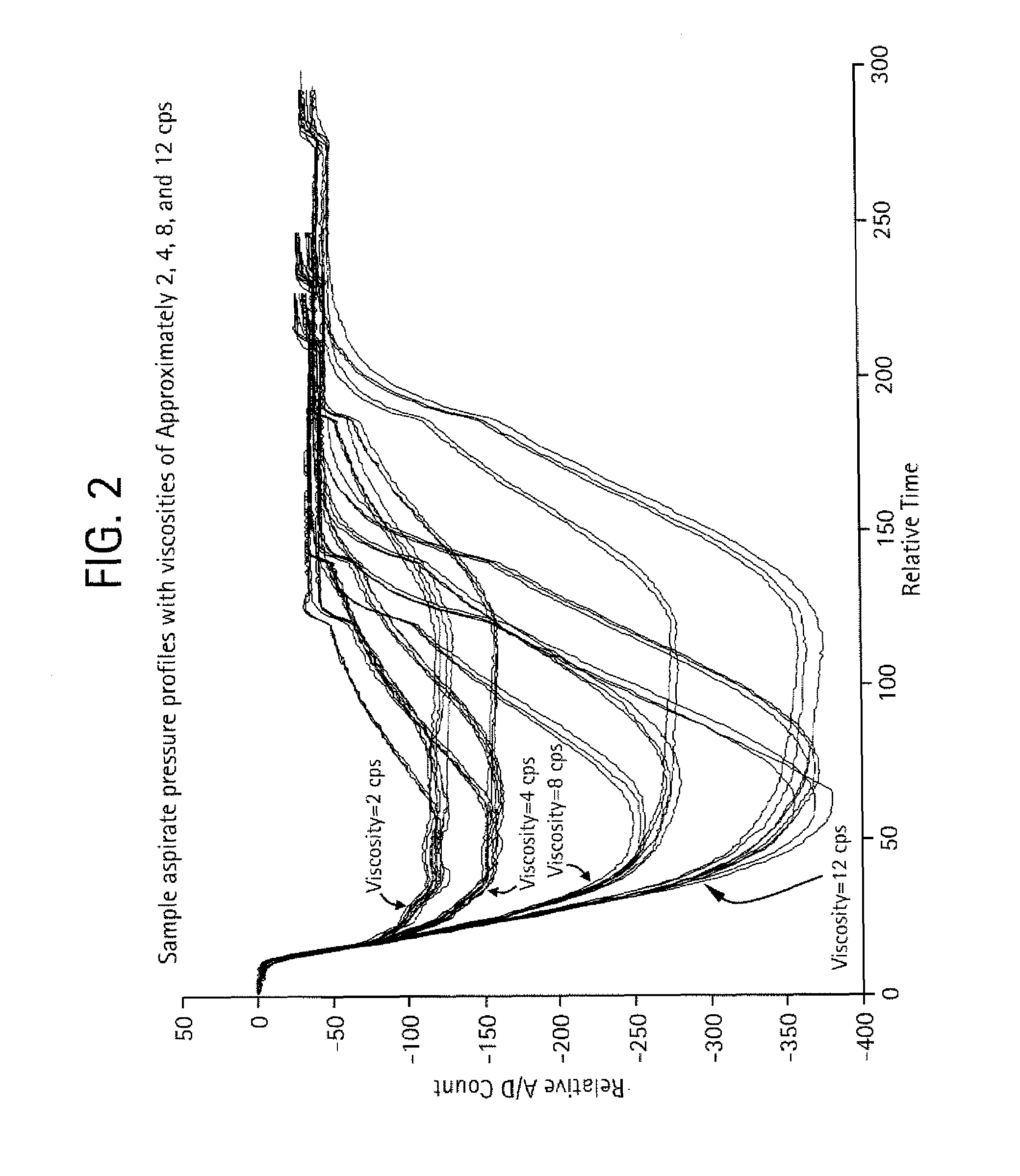
ActiveUS7634367B1Improve precisionImprove accuracyTesting/calibration apparatusDigital data processing detailsSensing dataViscosity
A method for improving the accuracy or precision of a metered fluid includes: estimating a fluidic property of the fluid being metered; and adjusting one or more control parameters based on the estimated property to improve the accuracy or precision of a metered fluid. Preferably, the estimating the property of the fluid being metered includes: monitoring a physical event during the metering operation to collect sensed data; extracting features from the sensed data; and using the features to estimate fluid properties. In another preferred embodiment, the estimated fluidic property is viscosity and the sensed data is a pressure profile during a fluid aspiration. In another preferred embodiment, the method includes a diagnostic analyzer which includes a metering probe having a hard probe or a probe having a disposable tip and wherein the fluid is a body fluid sample. Another method includes: estimating a fluidic property of the fluid being metered; and adjusting one or more control parameters or thresholds that determine when an error is flagged based on the estimated property to improve the detection of the failure.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Hybrid valve apparatus and method for fluid handling
InactiveUS20050129584A1Eliminate pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsEngineeringCatheter
Owner:BIONEX SOLUTIONS
Disposable patient interface for intraductal fluid aspiration system
Disclosed is a disposable patient interface for an intraductal fluid aspiration system. The interface has a flexible tubular distal member for contacting the patient, and a proximal support portion forming a vacuum chamber therein. The support portion has a vacuum aperture for communication with a source of vacuum, and a retention structure for releasably mounting within a hand piece of an intraductal fluid aspiration system. The flexible member preferably has a low modulus of elasticity and a high tear strength, such that it can be stretched to fit over a rigid support without rupture.
Owner:NEOMATRIX
Novel balloon expandable stent conveying system
ActiveCN102793598ASimple structureImprove handlingSurgeryProsthesisBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
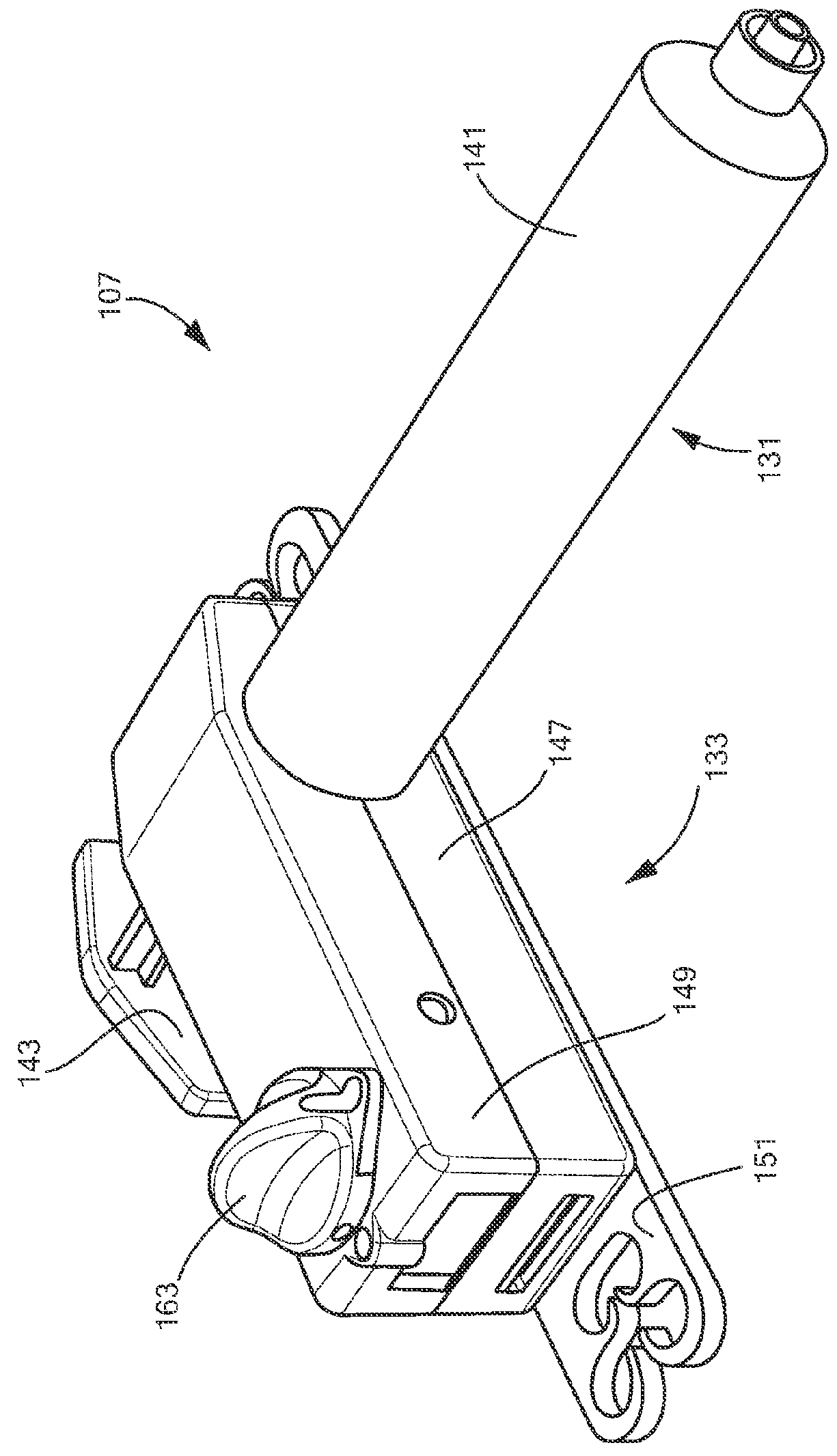
The invention discloses a novel balloon expandable stent conveying system which comprises a balloon, an inner tube, a far-end outer tube, a corrugated tube, a soft head and a stent pushing tube. The inner tube runs through an inner cavity of the far-end outer tube and an inner cavity of the balloon; a combination body of the soft head and the inner tube is placed and connected into the neck part of the far end of the balloon; the farthest end of the far-end outer tube is placed into the neck part of the near end of the balloon and is connected with the neck part of the near end of the balloon; the balloon is of a one-layer or multilayer structure; and at least one layer of the balloon is made of a material with a micropore structure. The stent conveying system disclosed by the invention has a simple structure, also has the functions of pre-expanding a narrow tube cavity and conveying a stent, has good operation and control performance and strong passing performance, is rapid and convenient to operate and is cost-saving. When adopting the ePTFE (expanded polytetrafluoroethylene) material with the micropore structure, the balloon does not need to be folded and is simple to process; and time of sucking liquid in the balloon is short, the blood supply of far-end blood vessels is high in recovery speed, the balloon is changed into a cylinder shape with a small diameter after the liquid is pumped out, and the blood vessels cannot be damaged or the stent shifting cannot be caused in the retracting process. The balloon with the double-layer structure has higher pressure resistance capacity.
Owner:吕文峰
Fluidic and electrical interface for microfluidic chips
ActiveUS20130313116A1Avoid spreadingEfficient separationSludge treatmentFixed microstructural devicesElectricityMeasurement device
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO THORNTON
Automated endoscope reprocessor connection integrity testing via liquid suction
A method detects proper connection of fixtures to a channel in an endoscope and proper flow through the channel during a cleaning or disinfection procedure. The endoscope has a first opening into one of its channels to which is connected a fixture and a second opening which is placed into a liquid. Negative pressure at the first opening draws an amount of liquid through the channel which is measured. If the channel is blocked insufficient liquid will flow an be measured. If the fixture is not connected properly air will leak in and insufficient liquid will flow can be measured.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Valved Catheter Assemblies And Related Methods
The invention relates to valved catheter assemblies and related methods. The valved catheter assemblies described herein provide several advantages, including low cracking pressure for fluid infusion, greater cracking pressure for fluid aspiration, and reduction or elimination of dead space. In some embodiments, a valve of the catheter assembly has a conical shape, which provides different cracking pressures for infusion and aspiration. Also in some embodiments, a valve of the catheter assembly may include peripheral slits that enable fluid to flow around the perimeter of the valve during infusion, which helps to flush out fluid from around the valve.
Owner:B BRAUN MELSUNGEN AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com