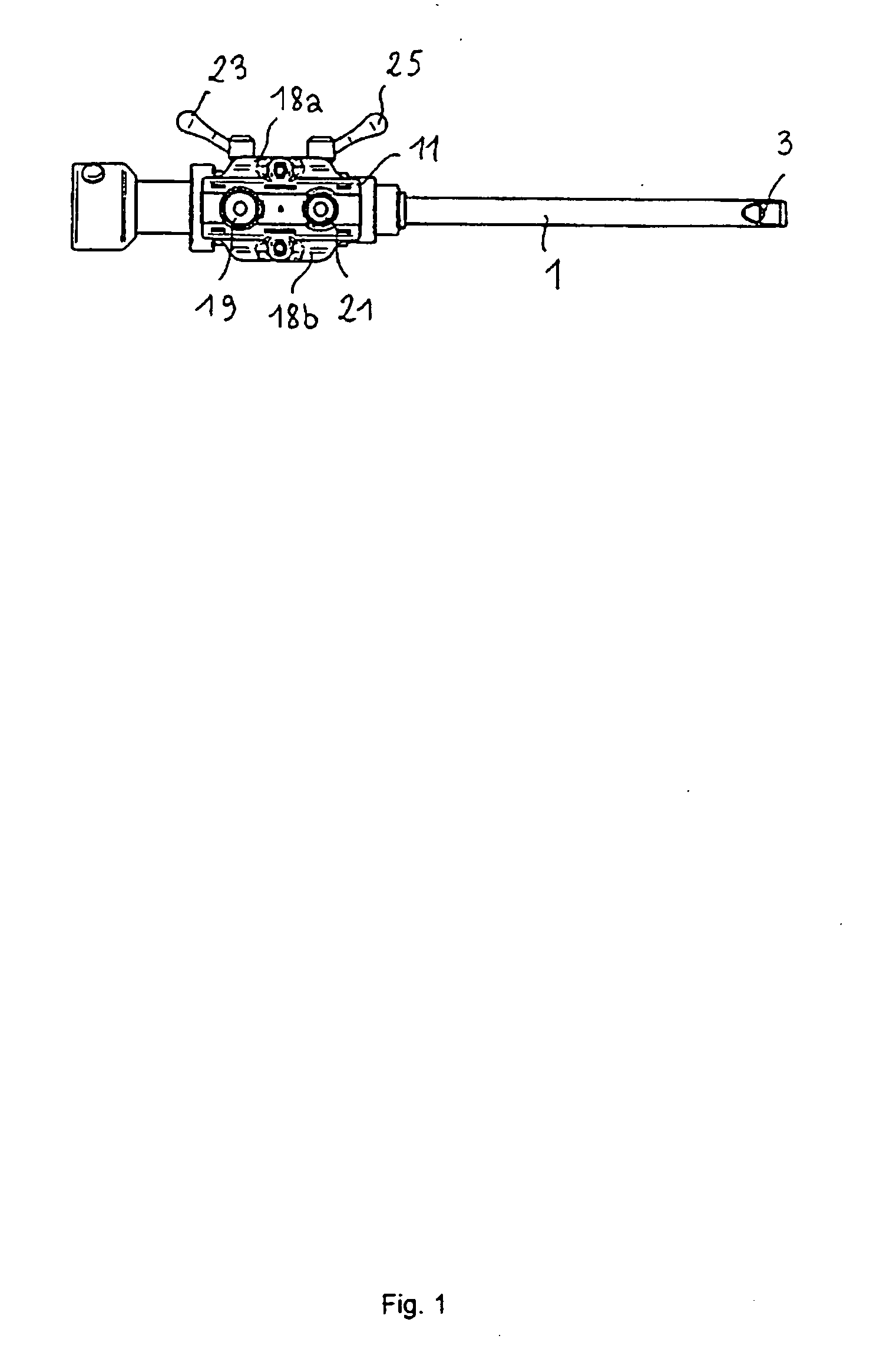Patents
Literature
64 results about "Aspiration fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
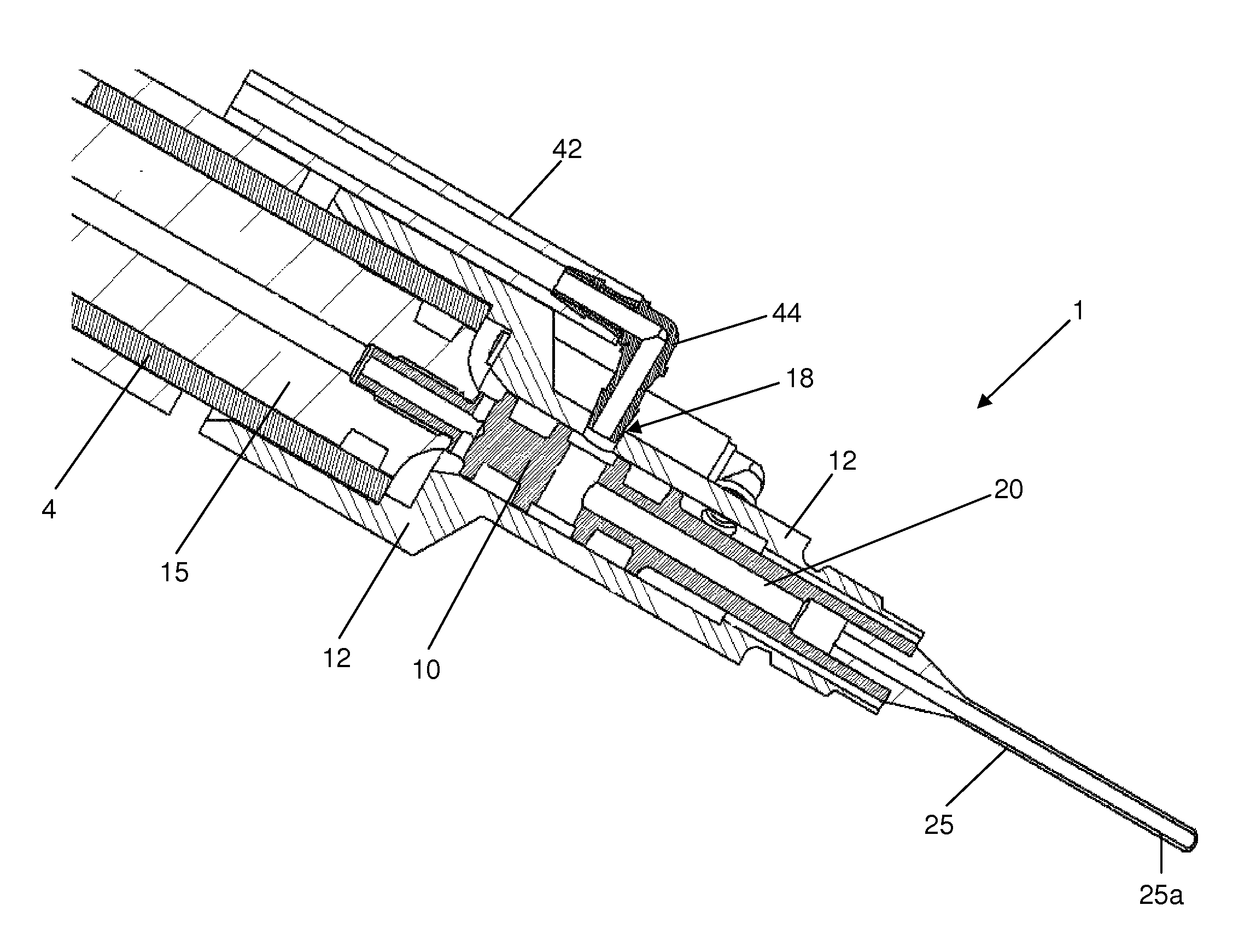
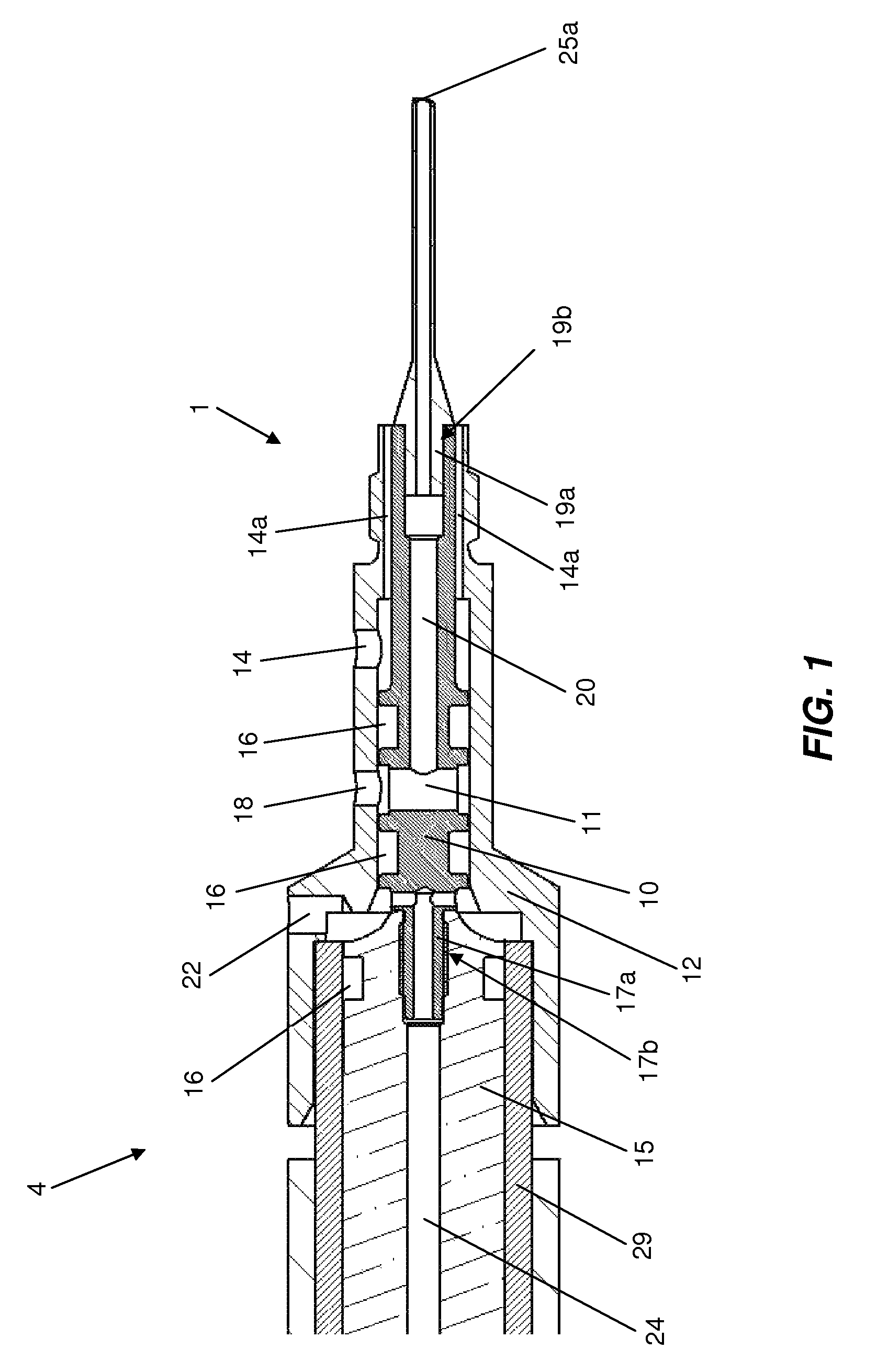
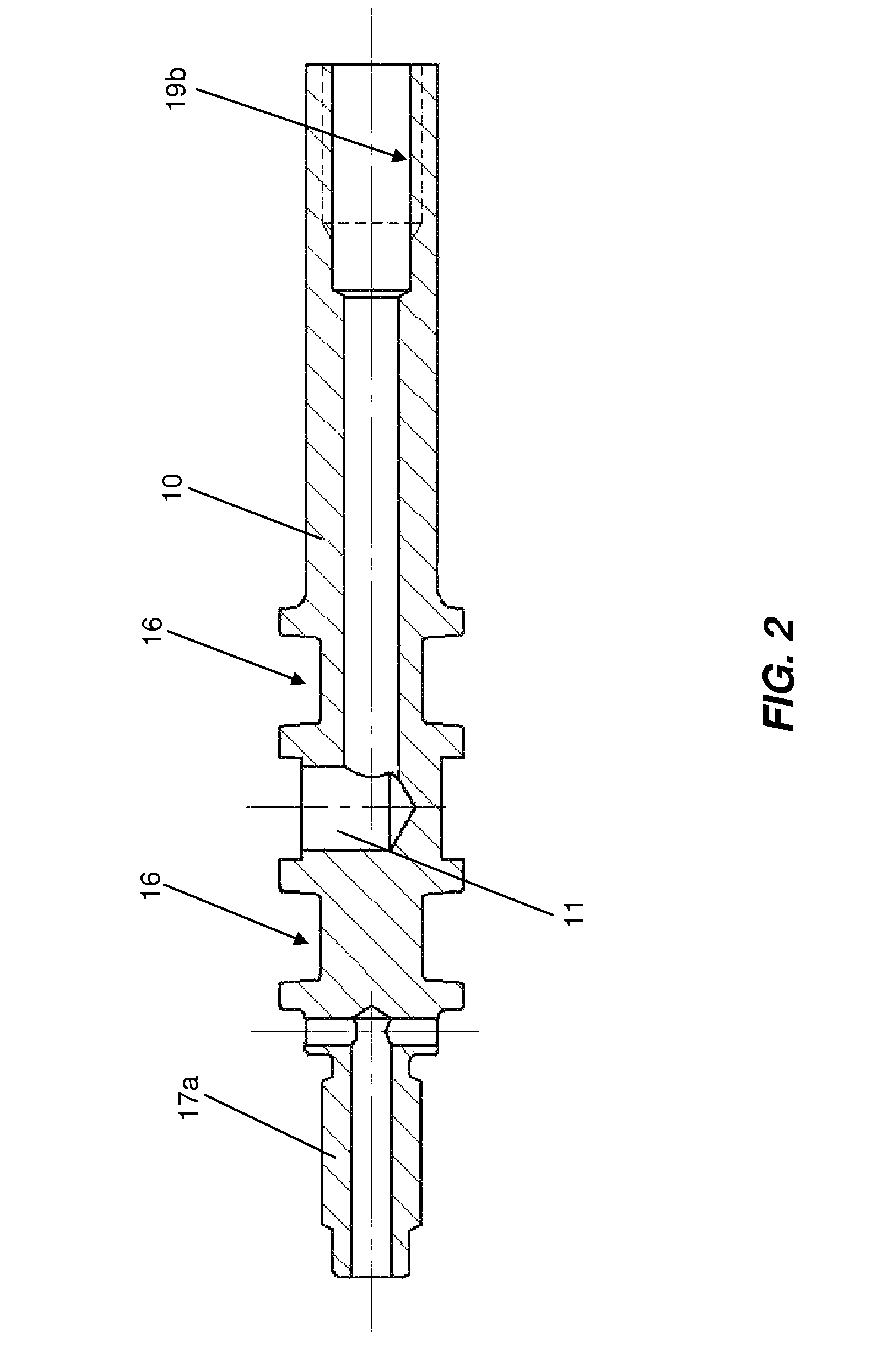
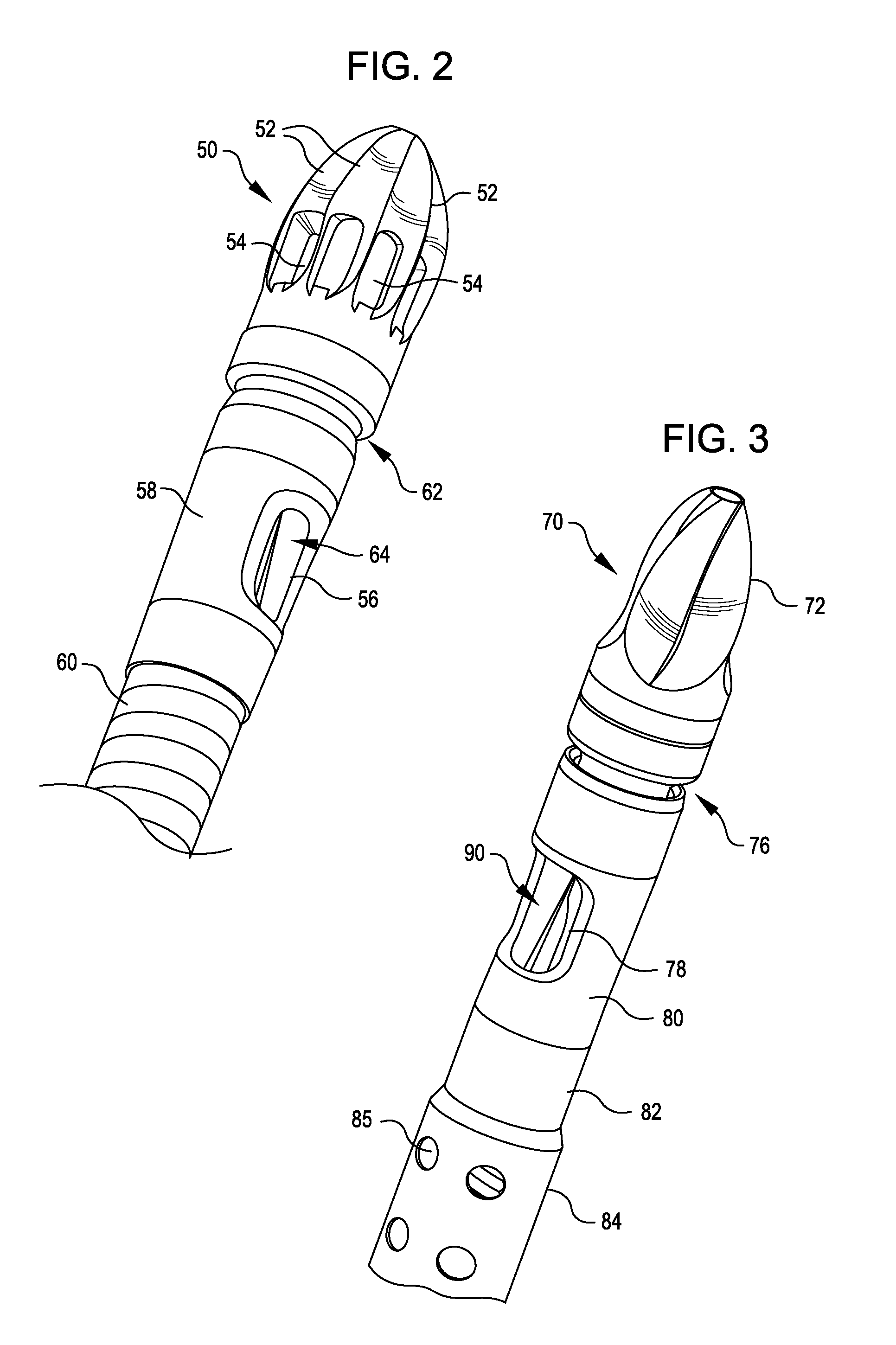
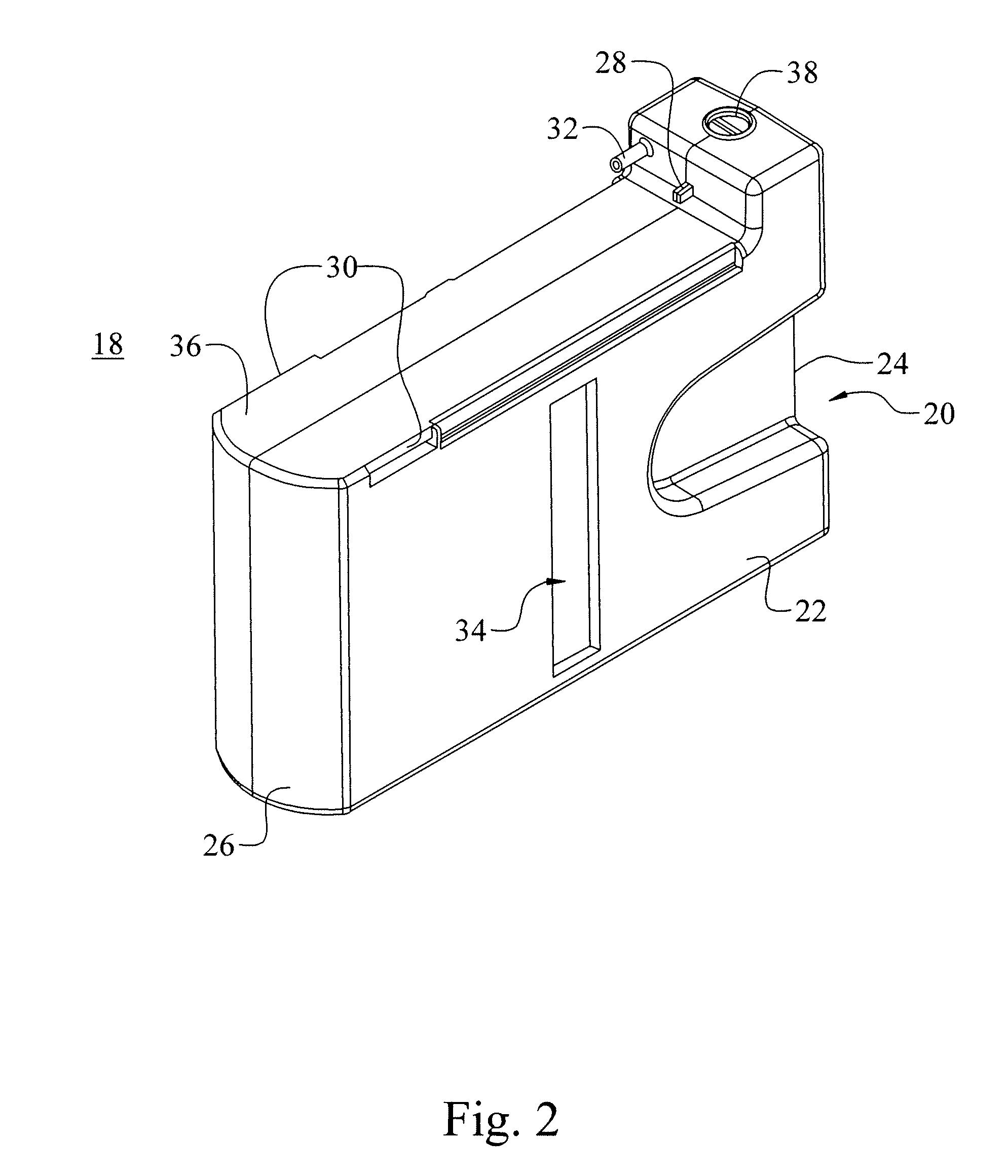
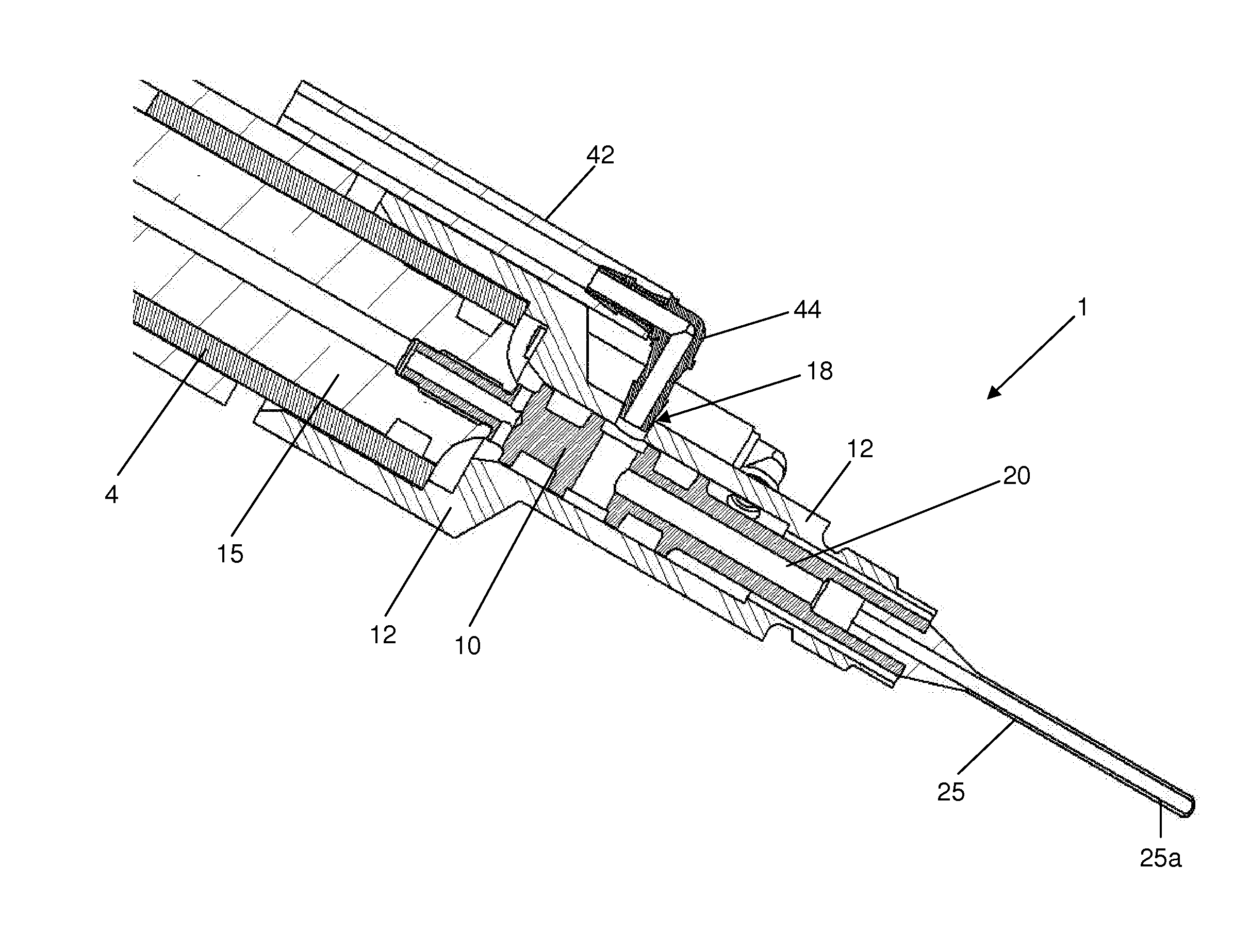
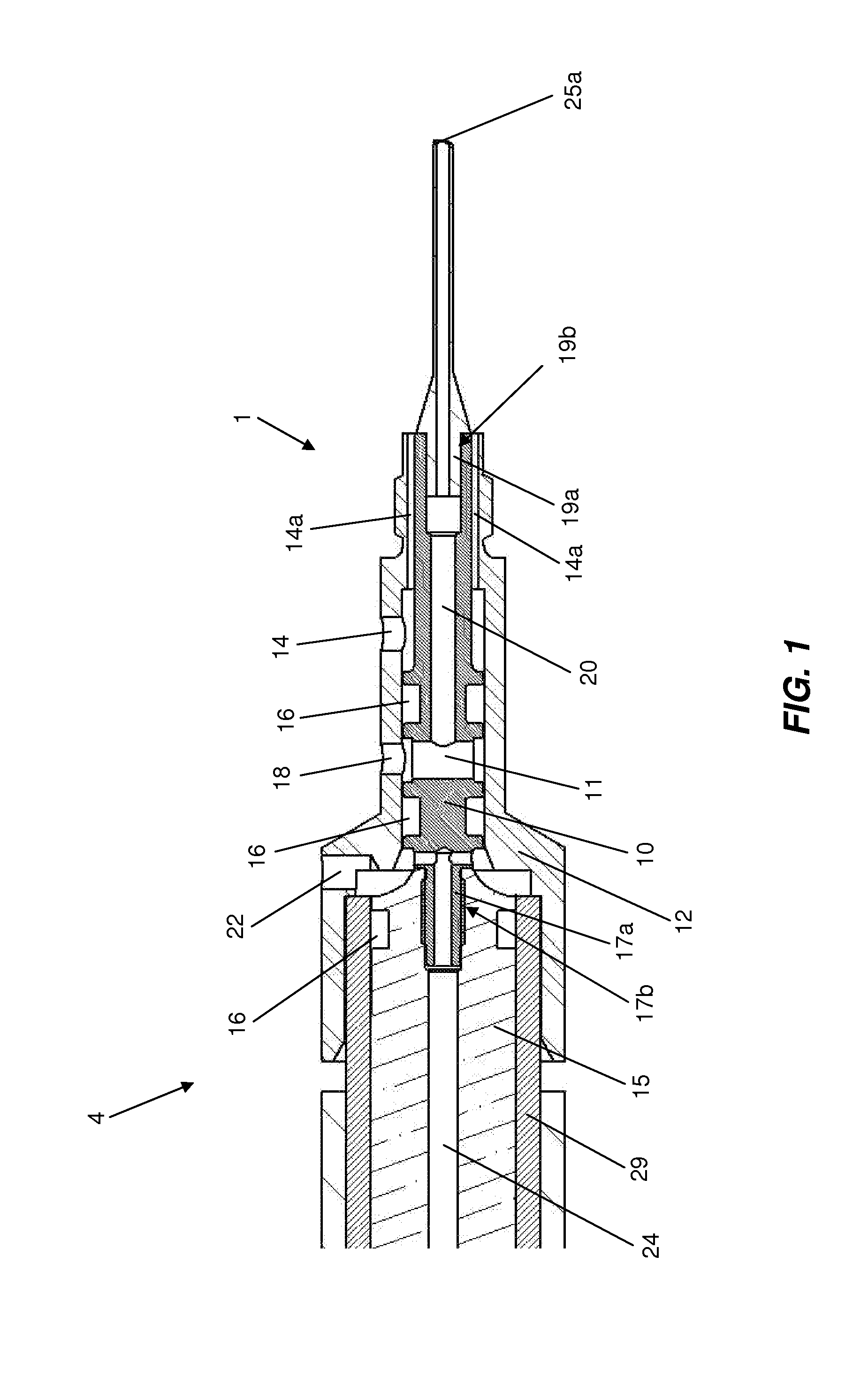
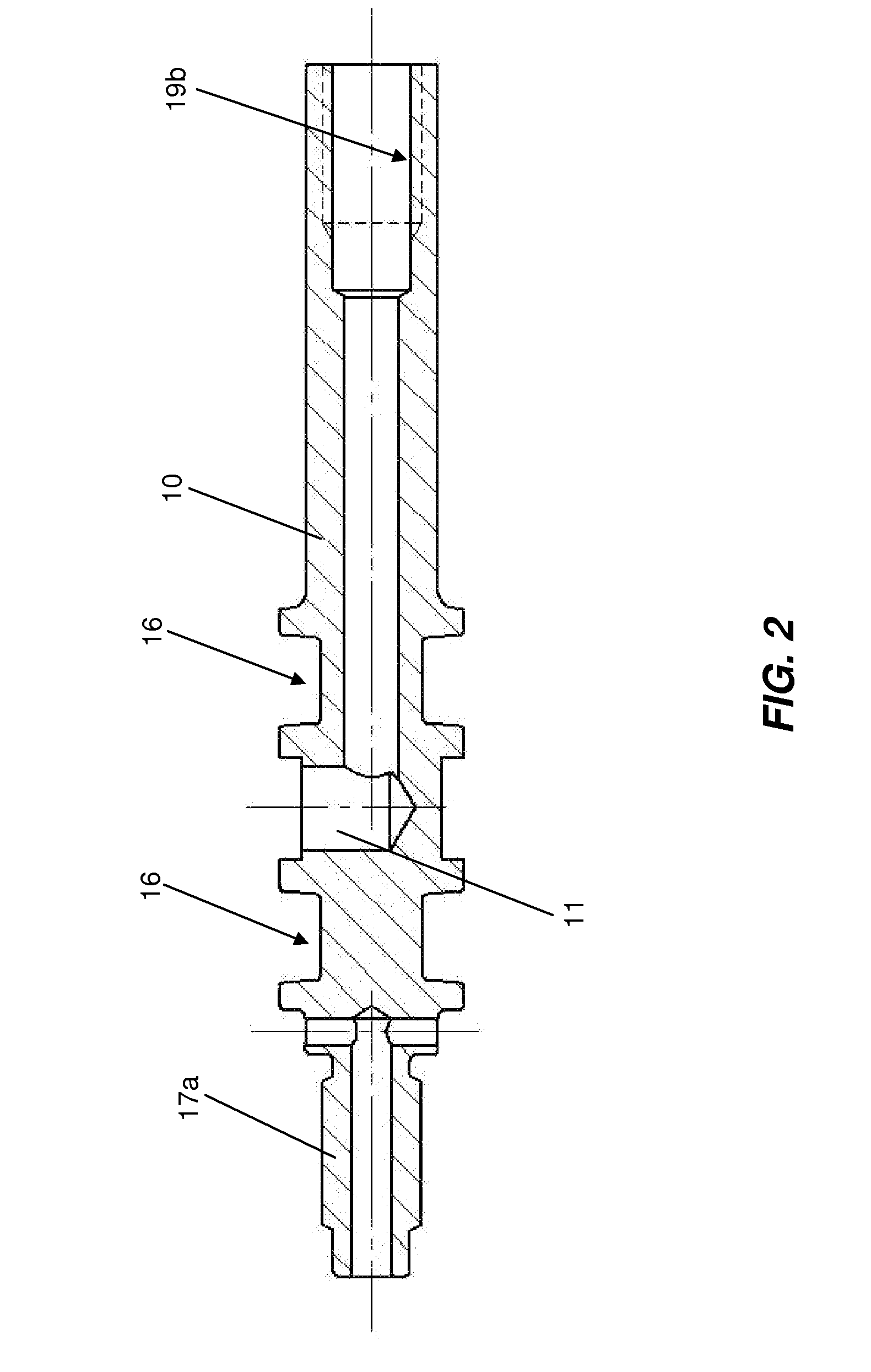
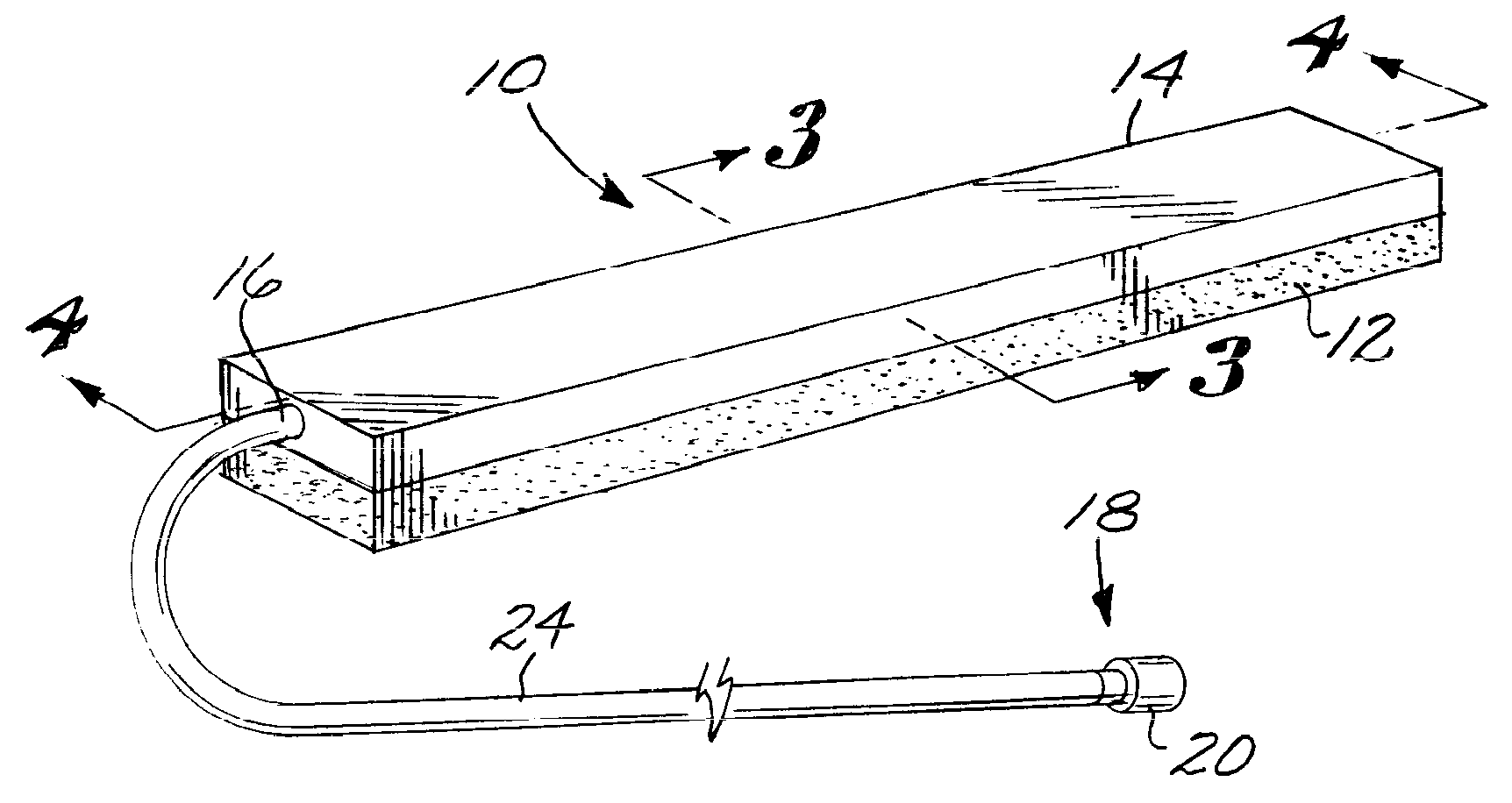
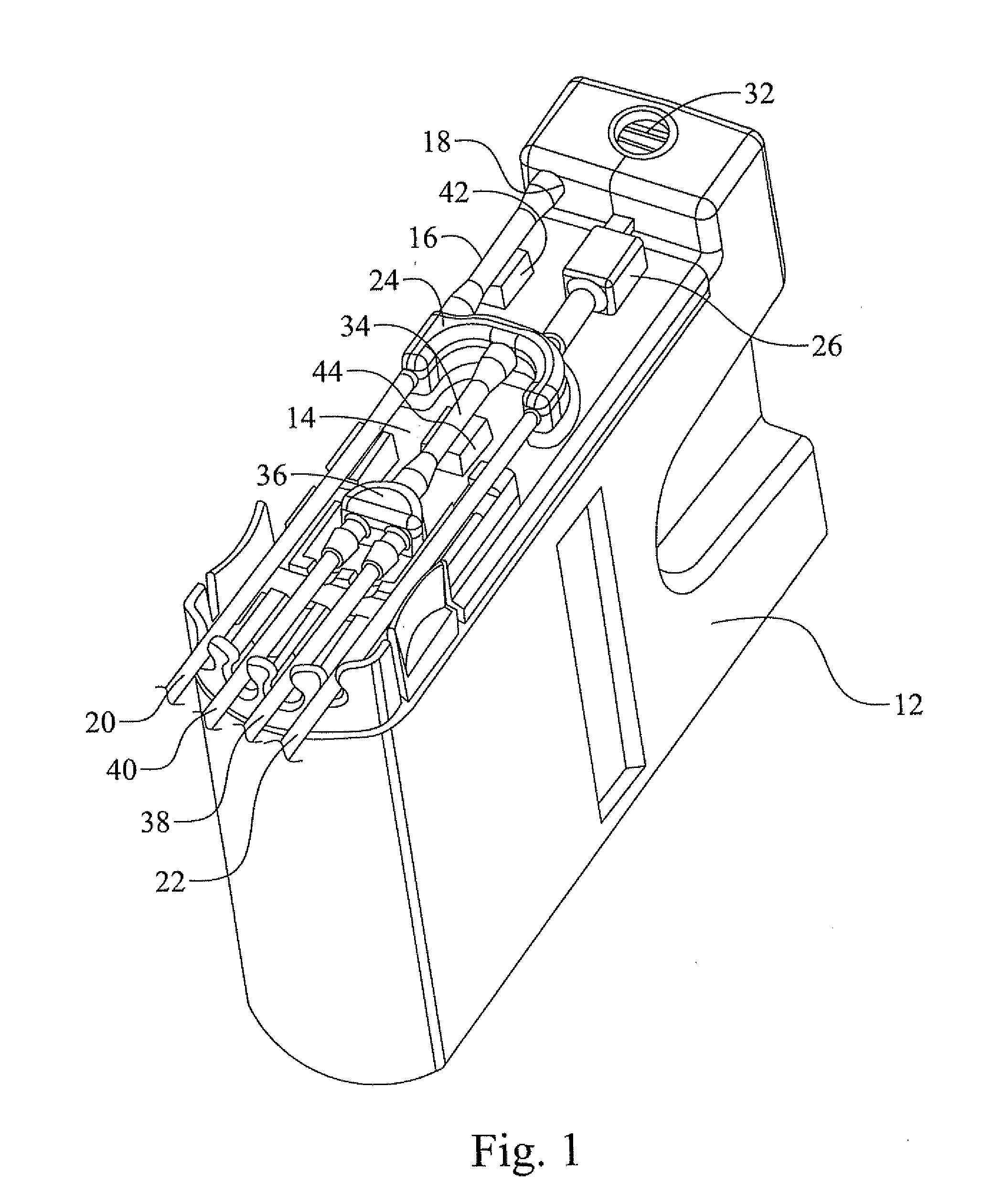
Removable adapter for phacoemulsification handpiece having irrigation and aspiration fluid paths
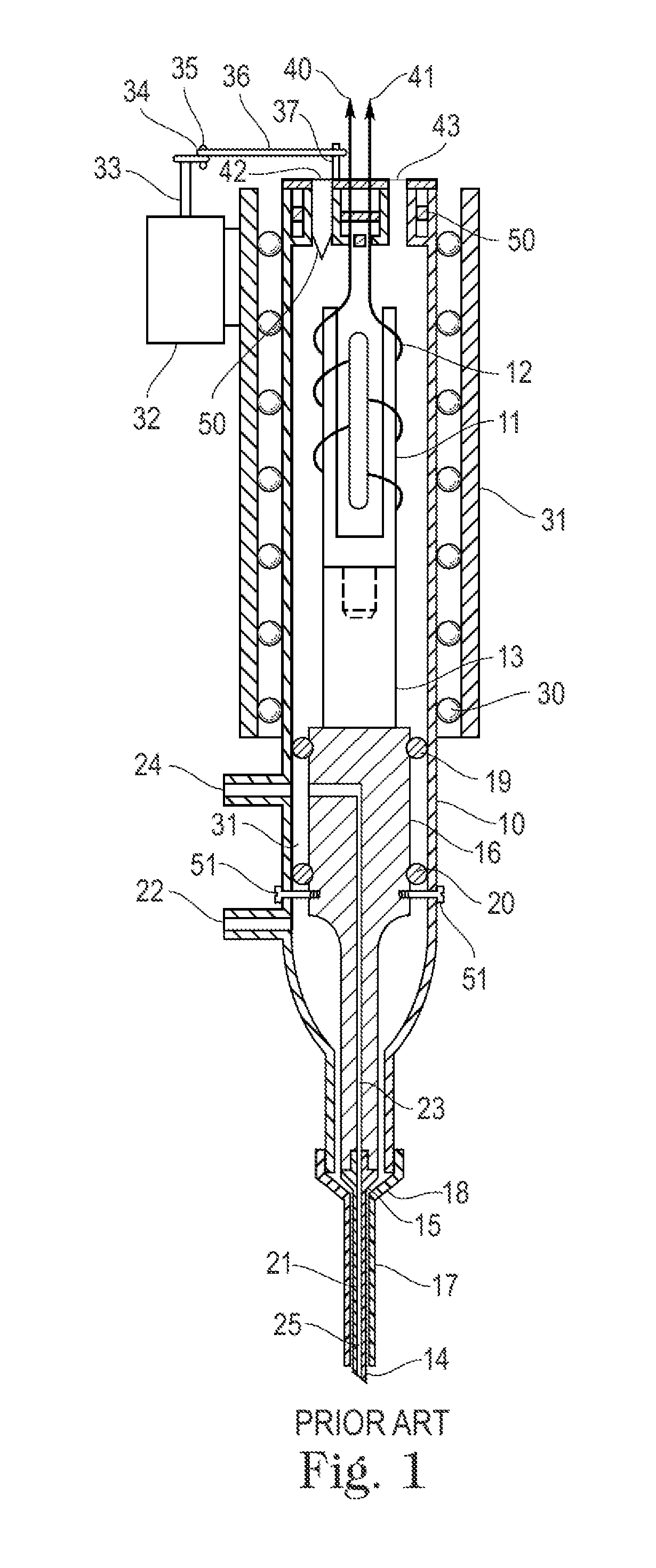
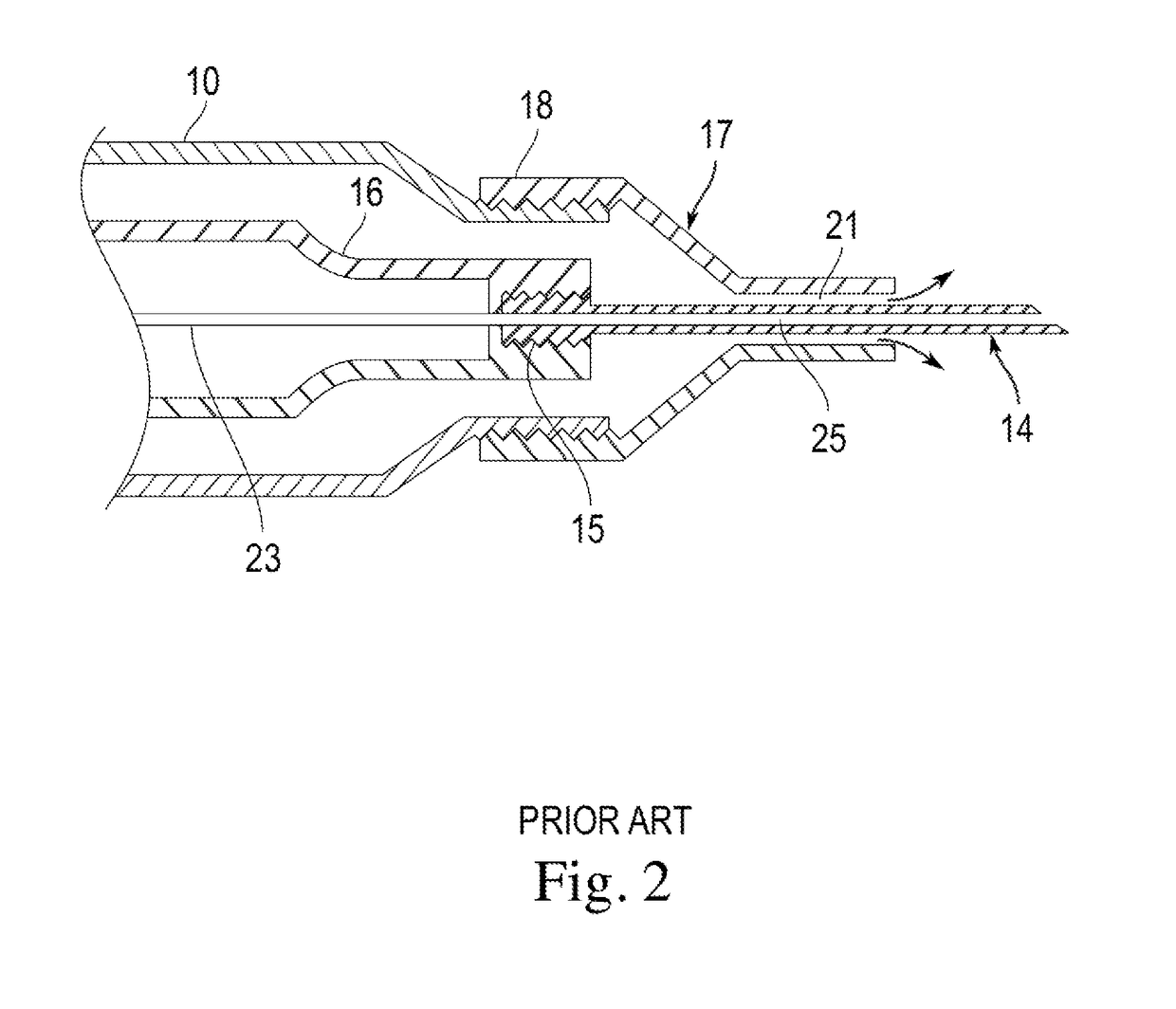
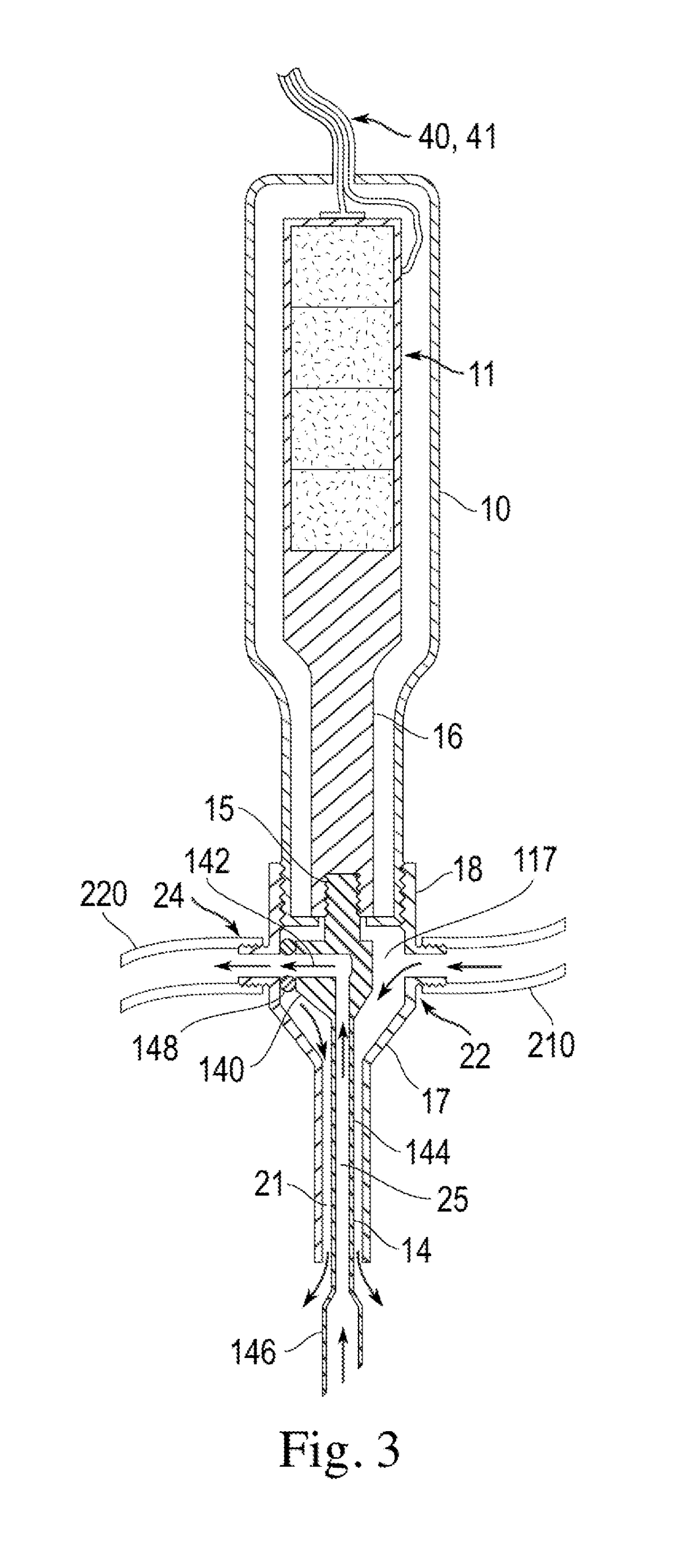
Current phacoemulsification handpieces require rigorous cleaning after each procedure because the aspiration and irrigation pathways for fluids are integral to the handpiece. According to the present invention, a removable horn extension and nosecone may be used with a phacoemulsification handpiece to allow for disposable fluid pathways exterior to the handpiece. This will reduce the cleaning time and effort, reduce cross-contamination, and increase the lifespan of the handpiece. Furthermore, the current invention allows different horn extensions to be used to excite different motions at the tip of the handpiece, depending on the preference of the surgeon.
Owner:ZEVEX
Interventional catheters incorporating an active aspiration system
ActiveUS20080103439A1Improve faultAssisted movementGuide wiresMedical devicesFree spaceCatheter device
An interventional catheter assembly comprises an operating head for removing obstructive material from a target site in a body lumen or cavity and at least one aspiration port located proximal to the operating head and penetrating the catheter assembly, the aspiration port being in communication with a sealed lumen that communicates with a vacuum system for withdrawing aspirate fluid and obstructive material from the target site. A rotatable member is positioned inside the catheter assembly at the site of the aspiration port and rotates during operation of the vacuum system. The rotatable member is provided with at least one upstanding bar that is sized to cooperate with the walls of the aspiration port and the inner surface of the catheter assembly to macerate debris that is drawn into the aspiration port.
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD
Interventional catheters incorporating an active aspiration system
ActiveUS20110118660A1Reduce amountHigh and consistent aspiration pressureGuide wiresExcision instrumentsCatheterTarget site
An interventional catheter assembly comprises an operating head for removing obstructive material from a target site in a body lumen or cavity and at least one aspiration port located proximal to the operating head and penetrating the catheter assembly, the aspiration port being in communication with a sealed lumen that communicates with a vacuum system for withdrawing aspirate fluid and obstructive material from the target site. The interventional catheter incorporates an elongated guidewire lumen bushing extending proximally from a distal region of the operating head to reduce the clearance between the guidewire and the internal surface of the guidewire lumen during operation of the interventional catheter. This feature restricts entry of fluid and debris into the guidewire lumen and promotes maintenance of consistent and high aspiration pressure and volume during operation of the aspiration system and interventional catheter assembly.
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD
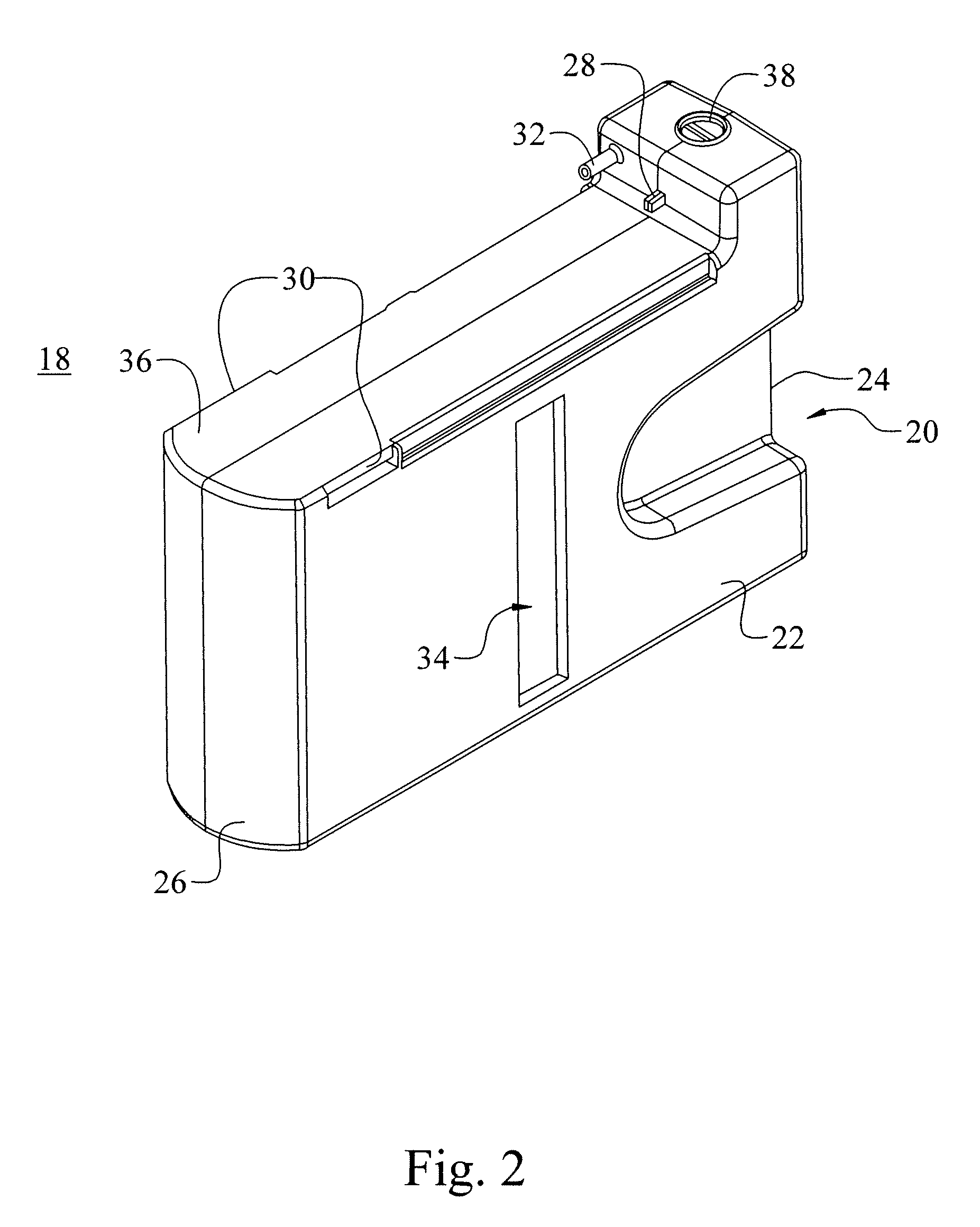
Combined peristaltic and vacuum aspiration cassette
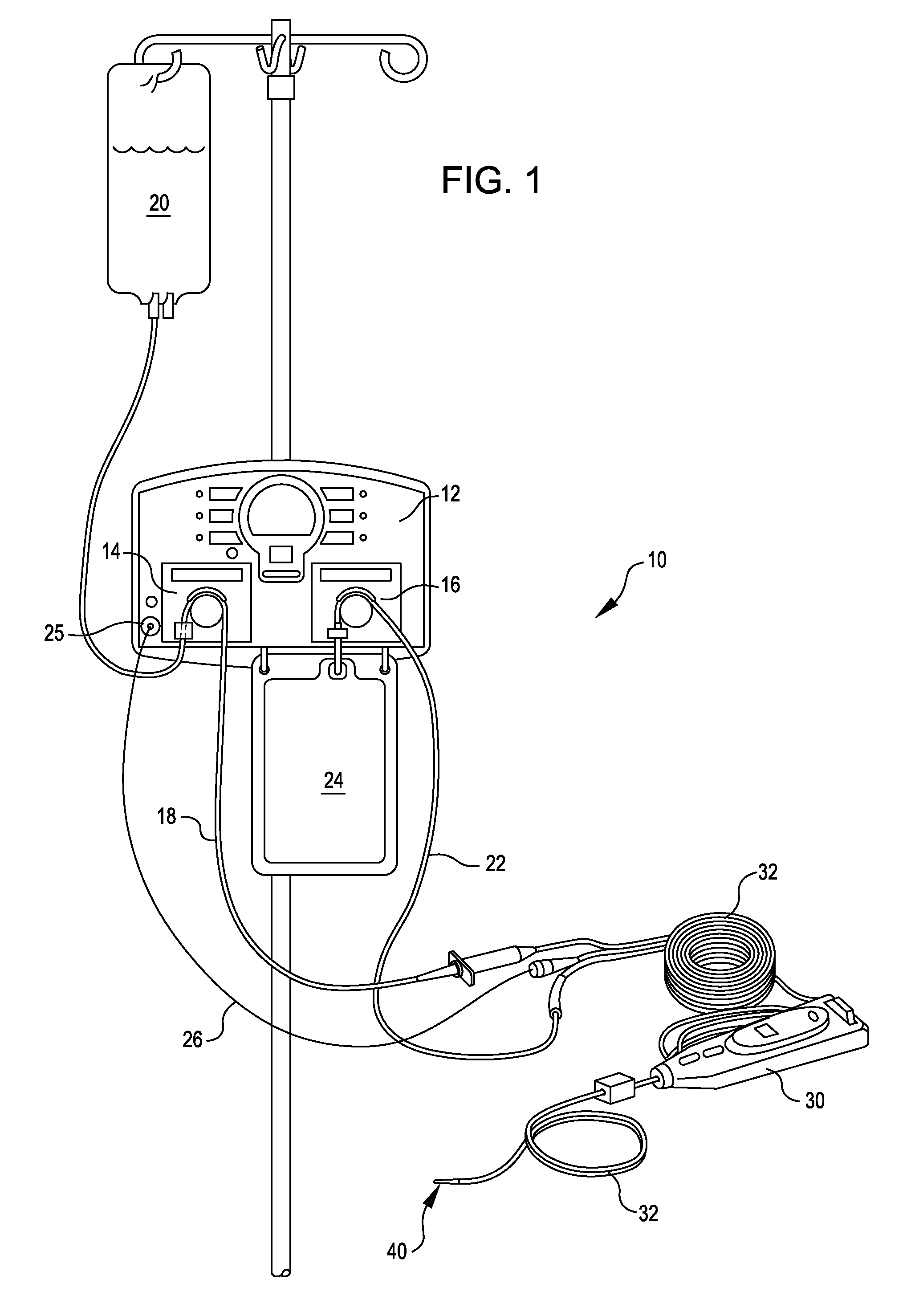
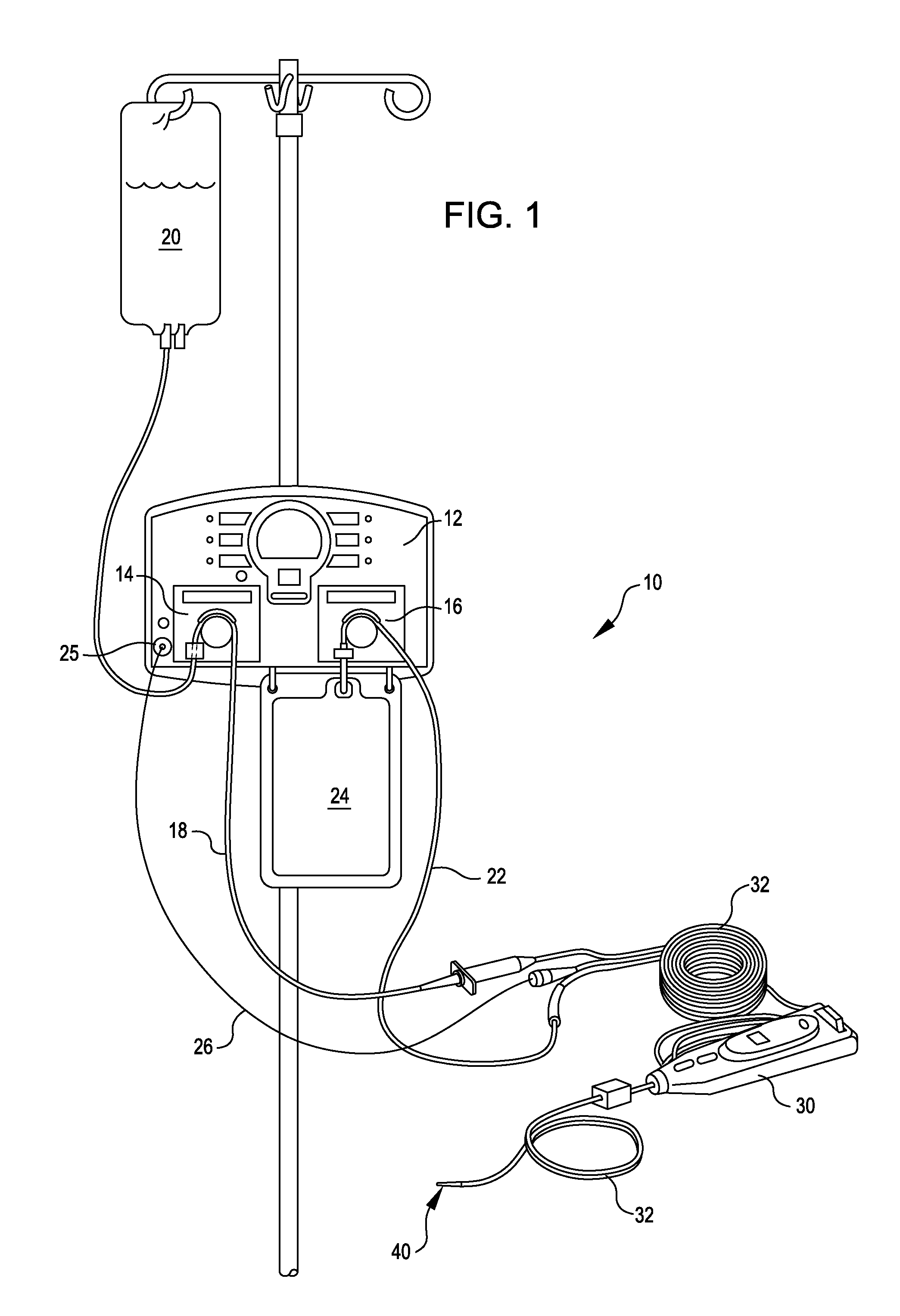
An aspiration collection cassette 10 includes a housing 12 for receiving aspiration fluids from a surgical site. An aspiration port 14 is attached to the housing 12 for connection to an aspiration tube 50 and for providing a passage way to an interior 22 of the housing 12. A vacuum port 16 is disposed in the housing 12 and communicates with the housing interior 22 for cooperation with a vacuum pump. A length of tubing 20 is connected to the housing 12 on each end, such that the tubing 20 will be placed between a peristaltic pump head and a backing plate.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
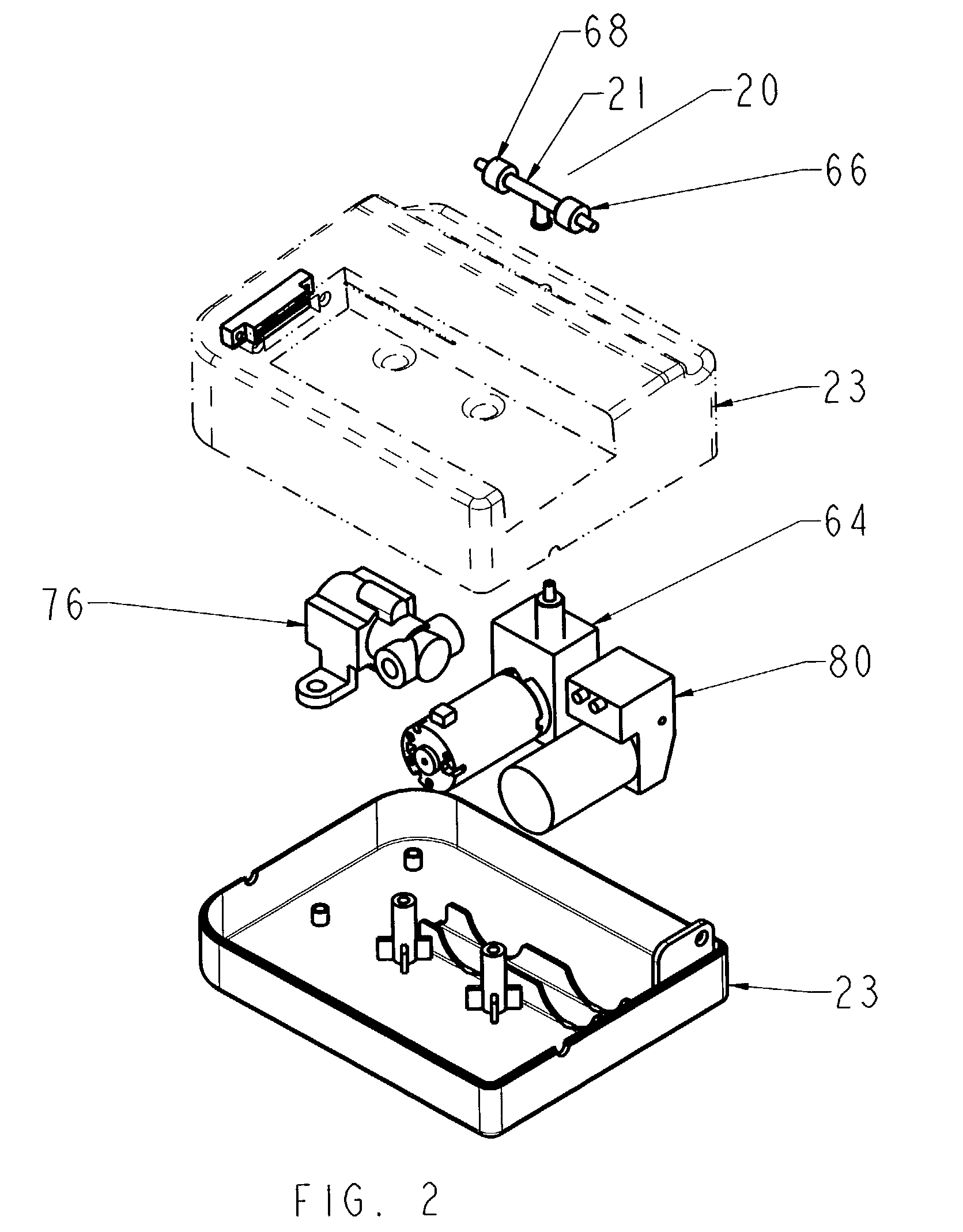
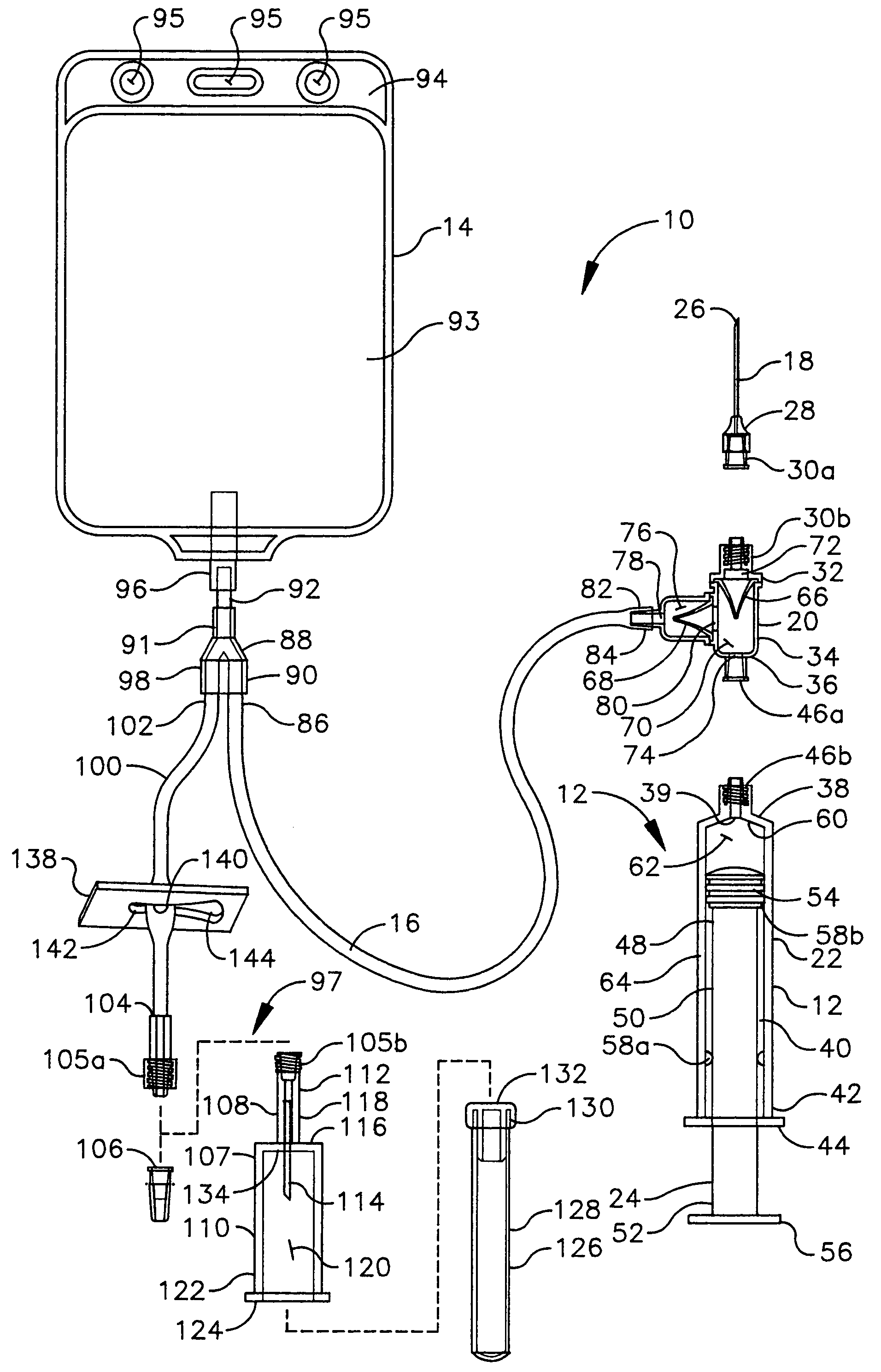
Interventional procedure drive and control system
InactiveUS20040059284A1Sufficiently compactSuppress fluctuationsIntravenous devicesSuction irrigation systemsReciprocating pumpSingle use
A pumping system for use in medical applications where liquids must be infused and aspirated from a mammalian patient, and whose economics are such that it is cost effective to simply dispose of it after a single use. The system features positive displacement pump(s) such as reciprocating pump(s) containing a damping mechanism to dampen out the peaks and valleys in the fluid pressure that is pumped, which is important for preventing cavitation. The system furthermore features a shut-off valve on the extraction side so that certain injected fluids such as contrast medium, are not immediately pumped out of the patient. In a preferred embodiment, the system also features means for independently controlling the fluid pressure / volume on the infusion and extraction sides, self-priming capability, a continuous fluid path, and visual air bubble detection, with viewports located at important points in the fluid path, such as at pumps and valves.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
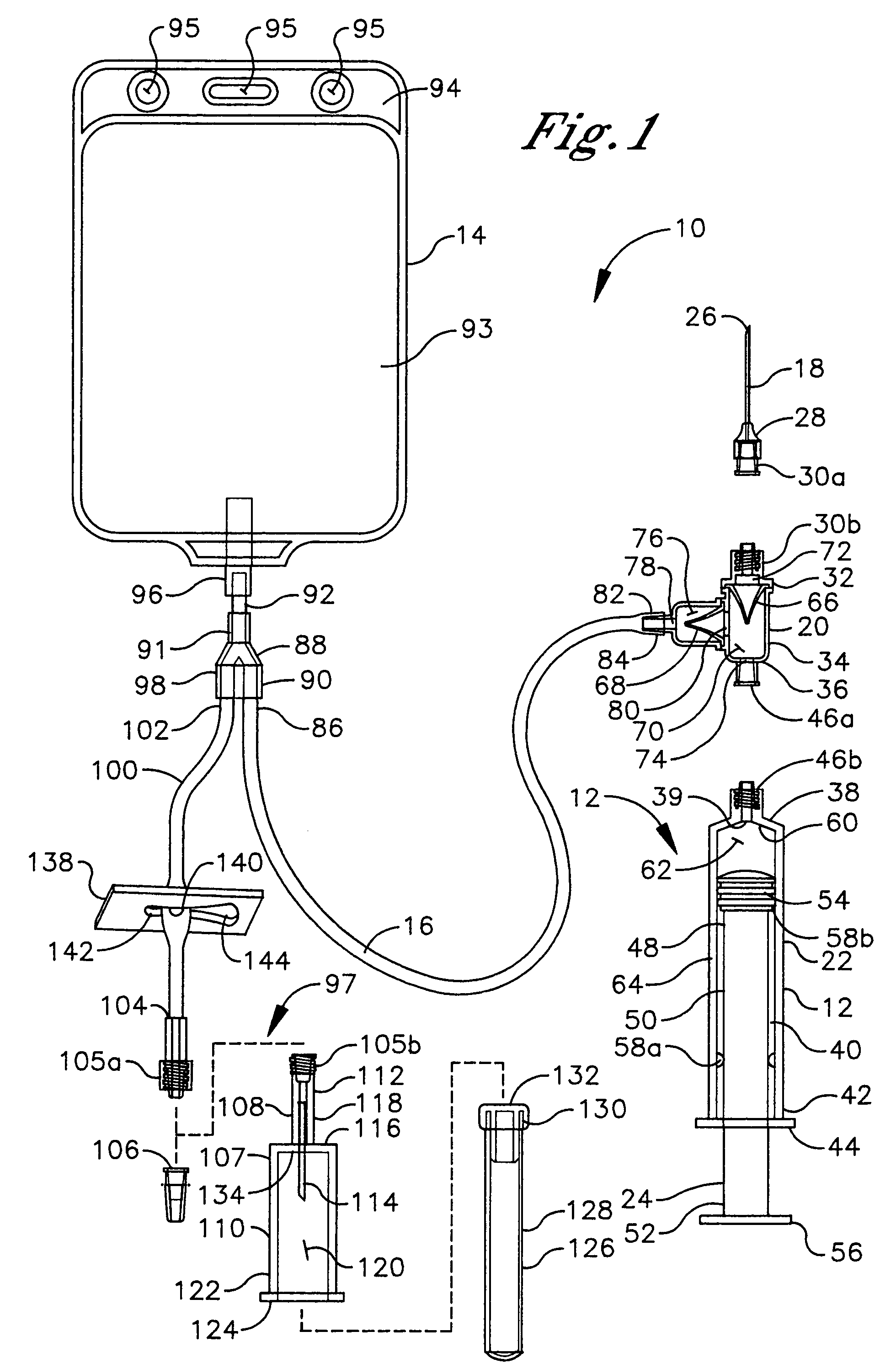
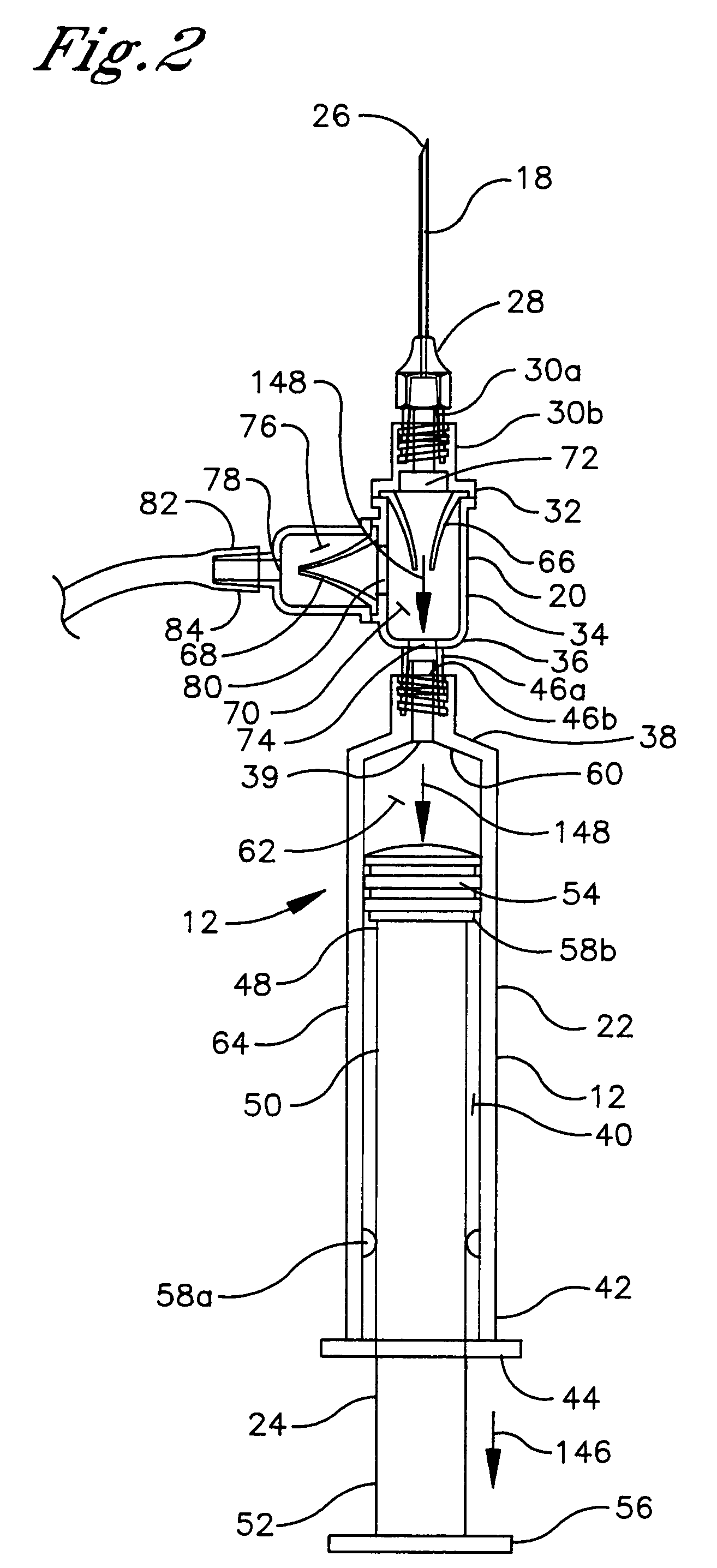
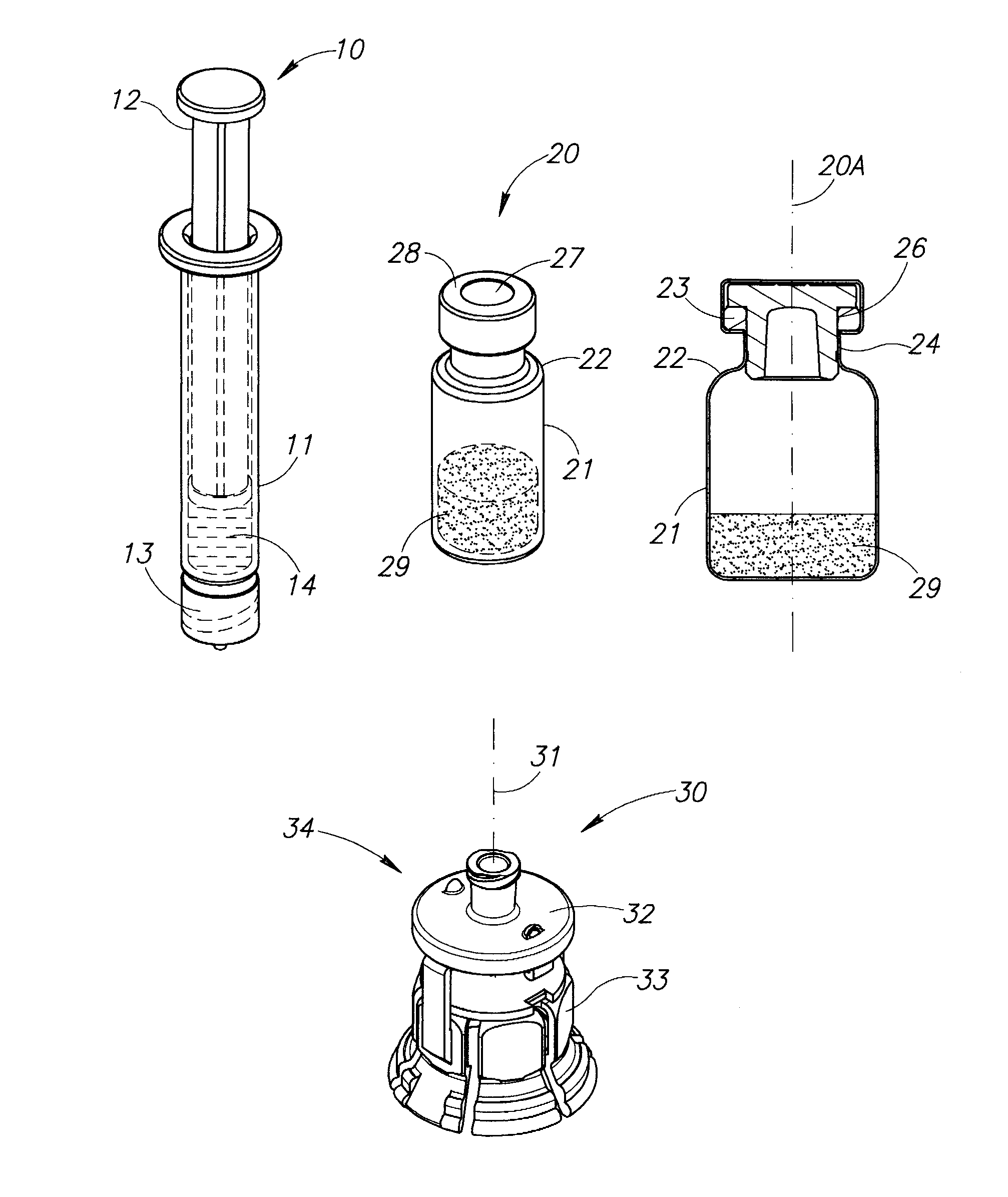
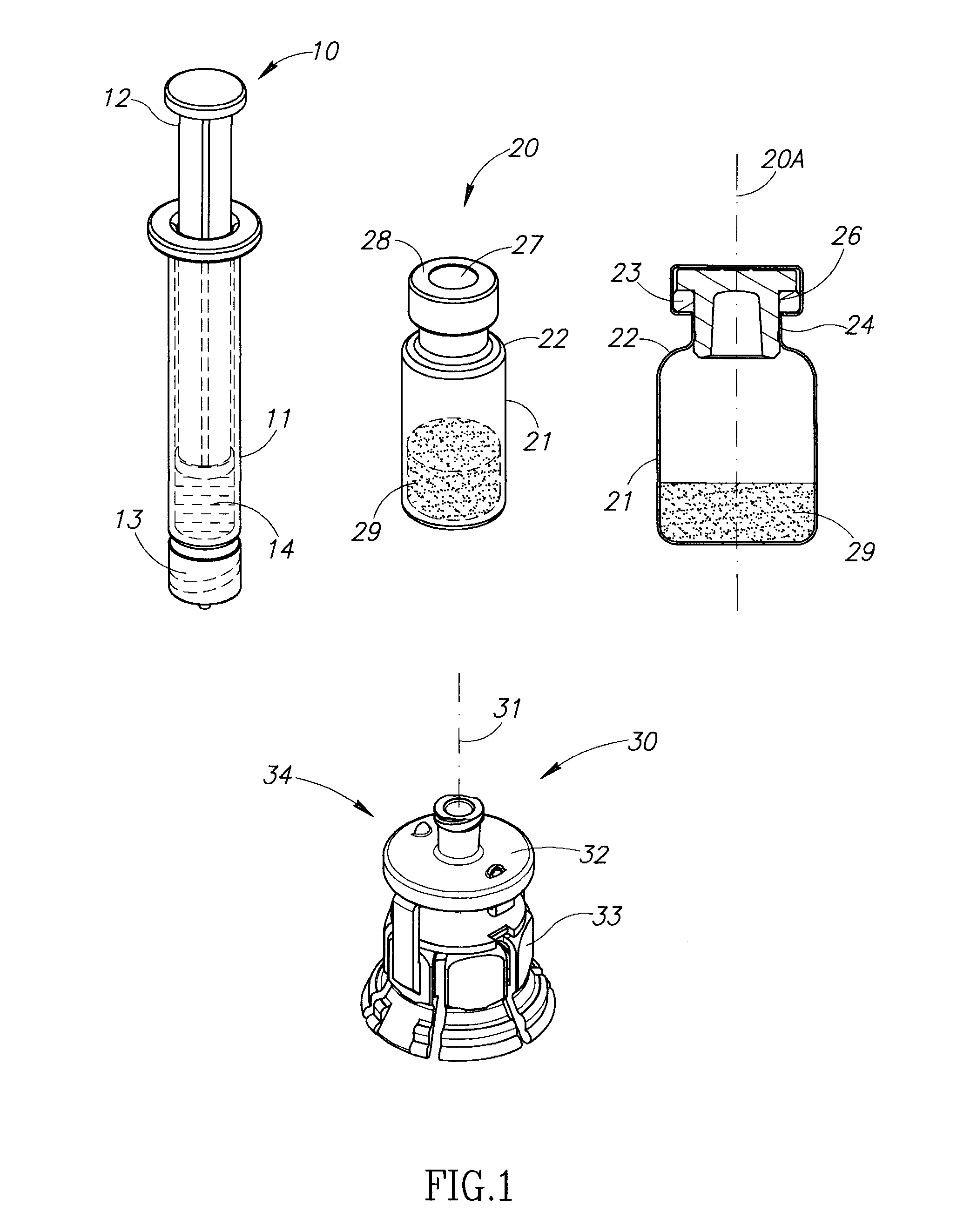
Fluid aspiration device
InactiveUS20050096627A1Preventing fluid communicationAvoid communicationMedical devicesPressure infusionBiomedical engineeringFluid aspiration
A fluid aspiration device is provided having a syringe, a disposal reservoir and a disposal fluid passageway. The syringe has a variable-volume fluid chamber and an aspiration fluid passageway between the fluid chamber and a region of the body containing a fluid for aspiration. An aspiration valve is positioned in the aspiration fluid passageway. The disposal fluid passageway is between the fluid chamber and disposal reservoir and has a disposal valve positioned therein. The fluid is aspirated by expanding the variable volume of the fluid chamber to draw the fluid through the open aspiration valve into the fluid chamber. The aspiration valve is closed and the variable volume of the fluid chamber is contracted to open the disposal valve and displace the fluid into the disposal reservoir. When aspiration is terminated, the fluid aspiration device is maintained intact and the intact device including the fluid is disposed.
Owner:BREG
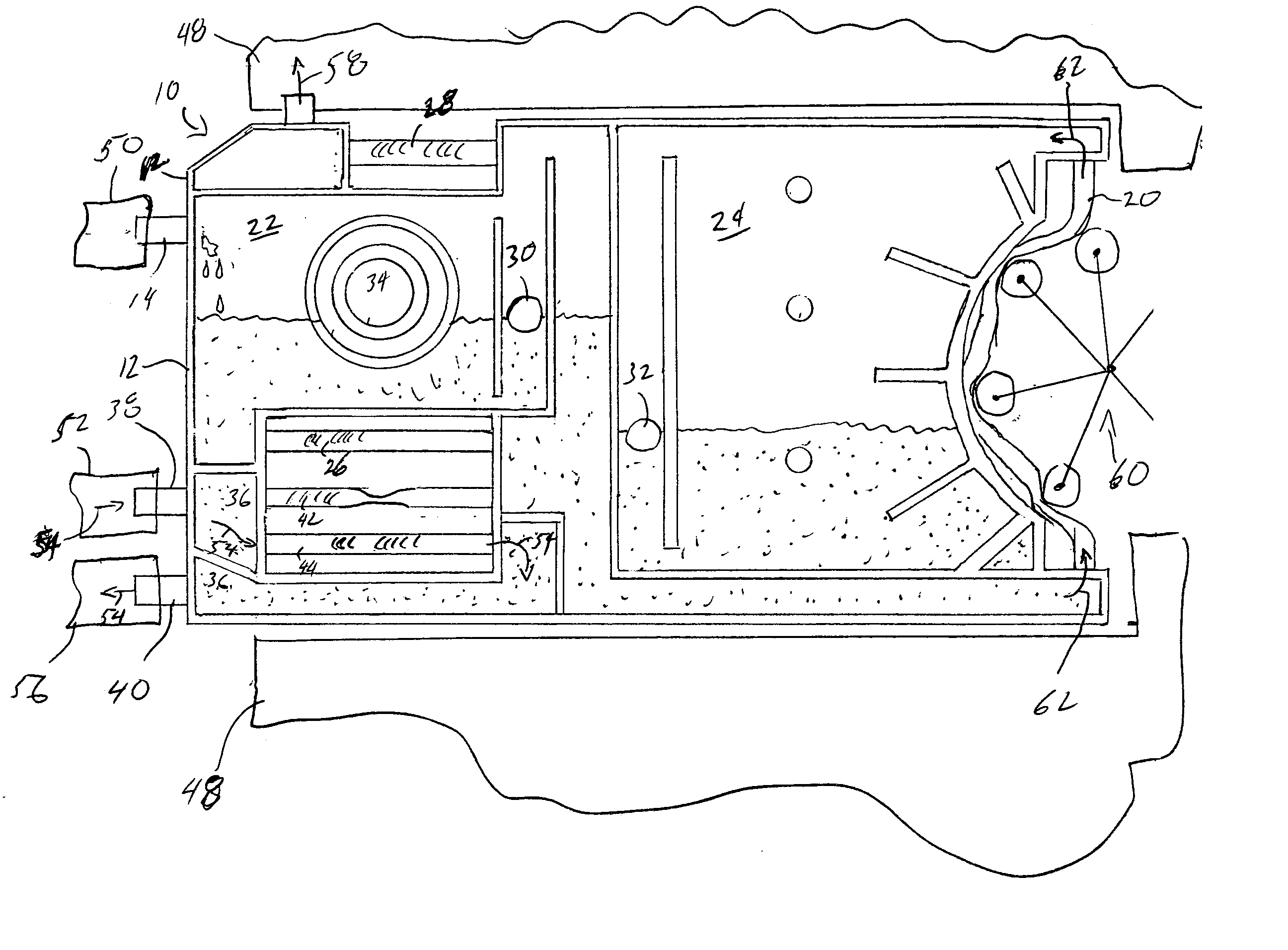
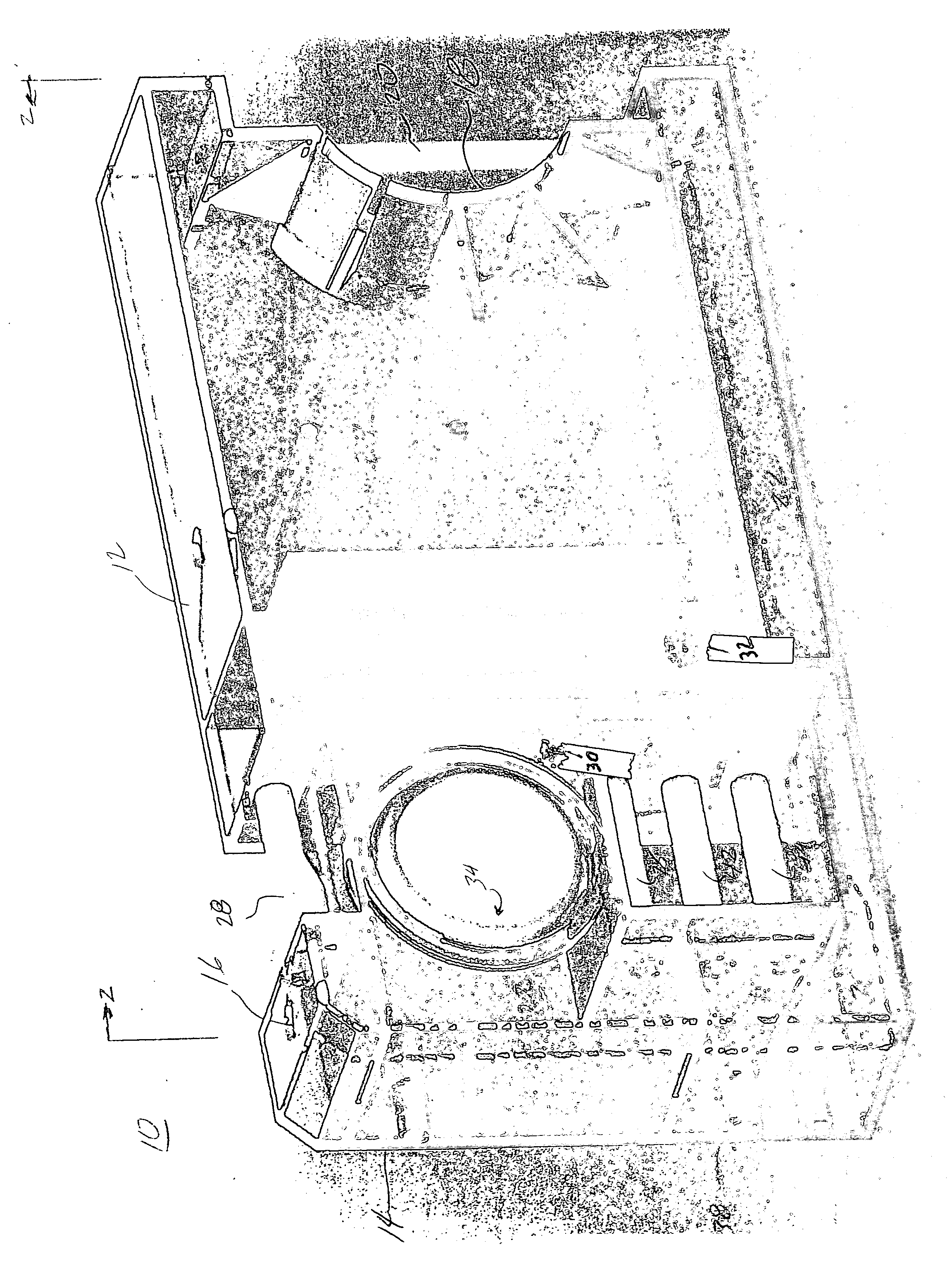
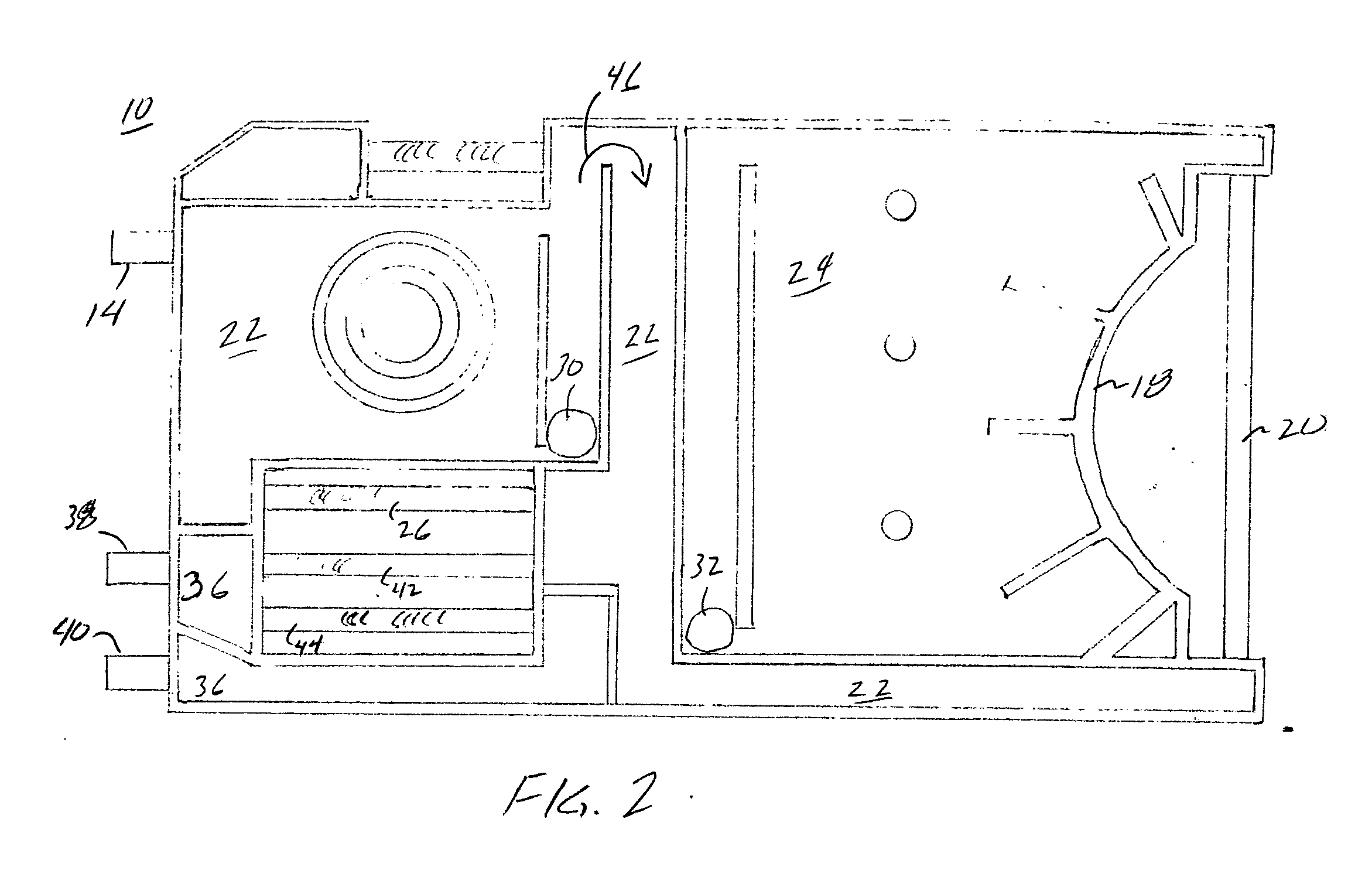
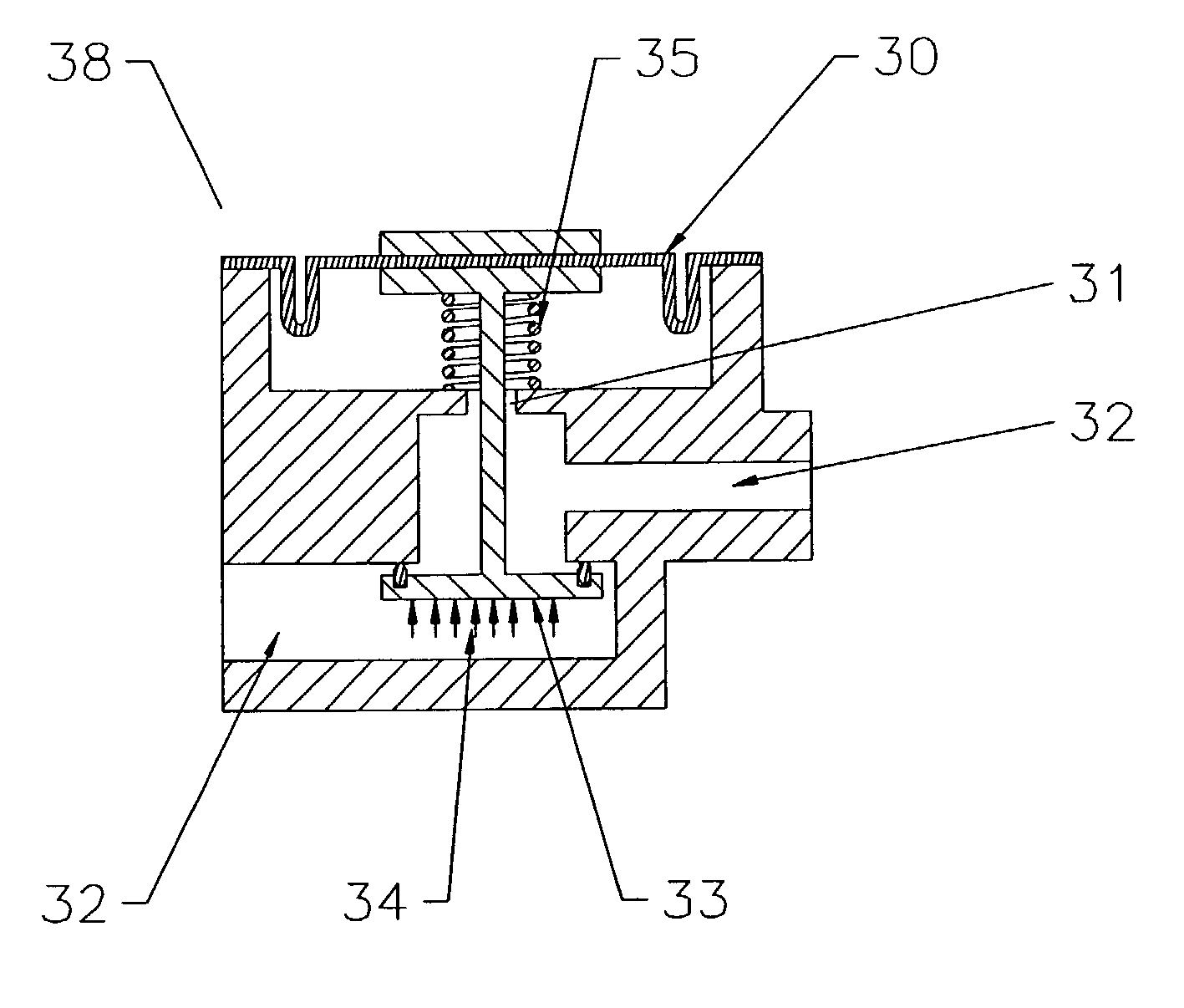
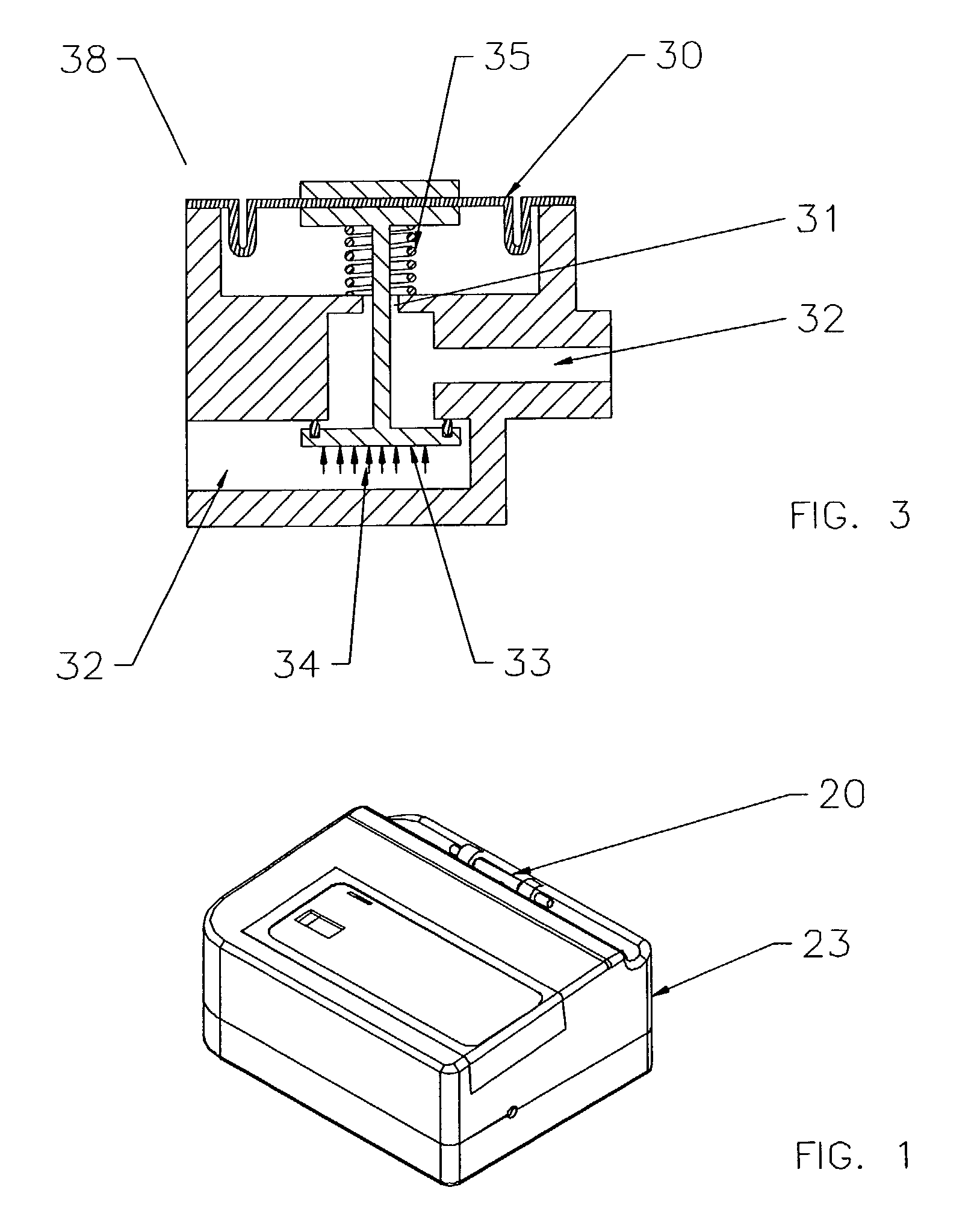
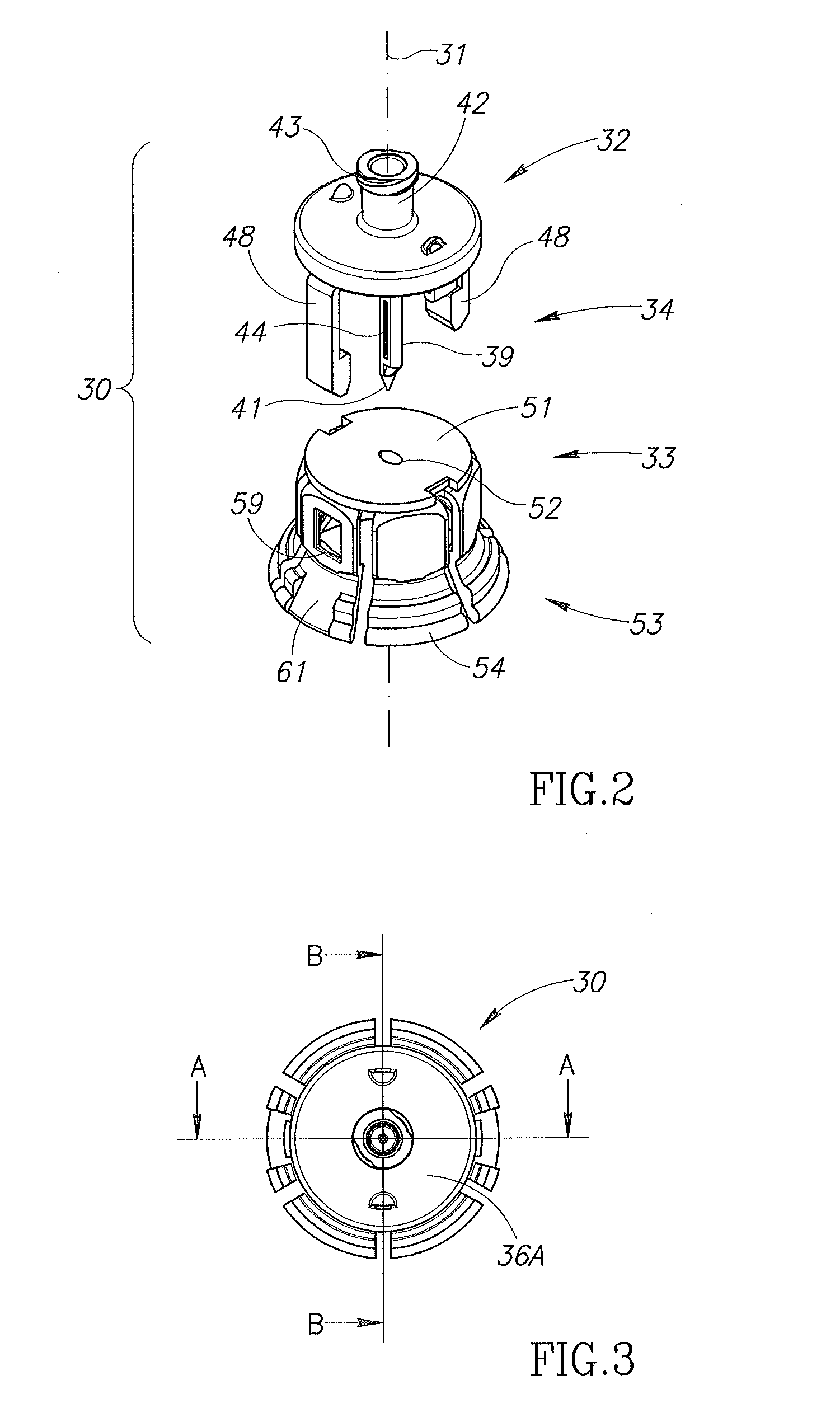
Ophthalmic Surgical Cassette and System
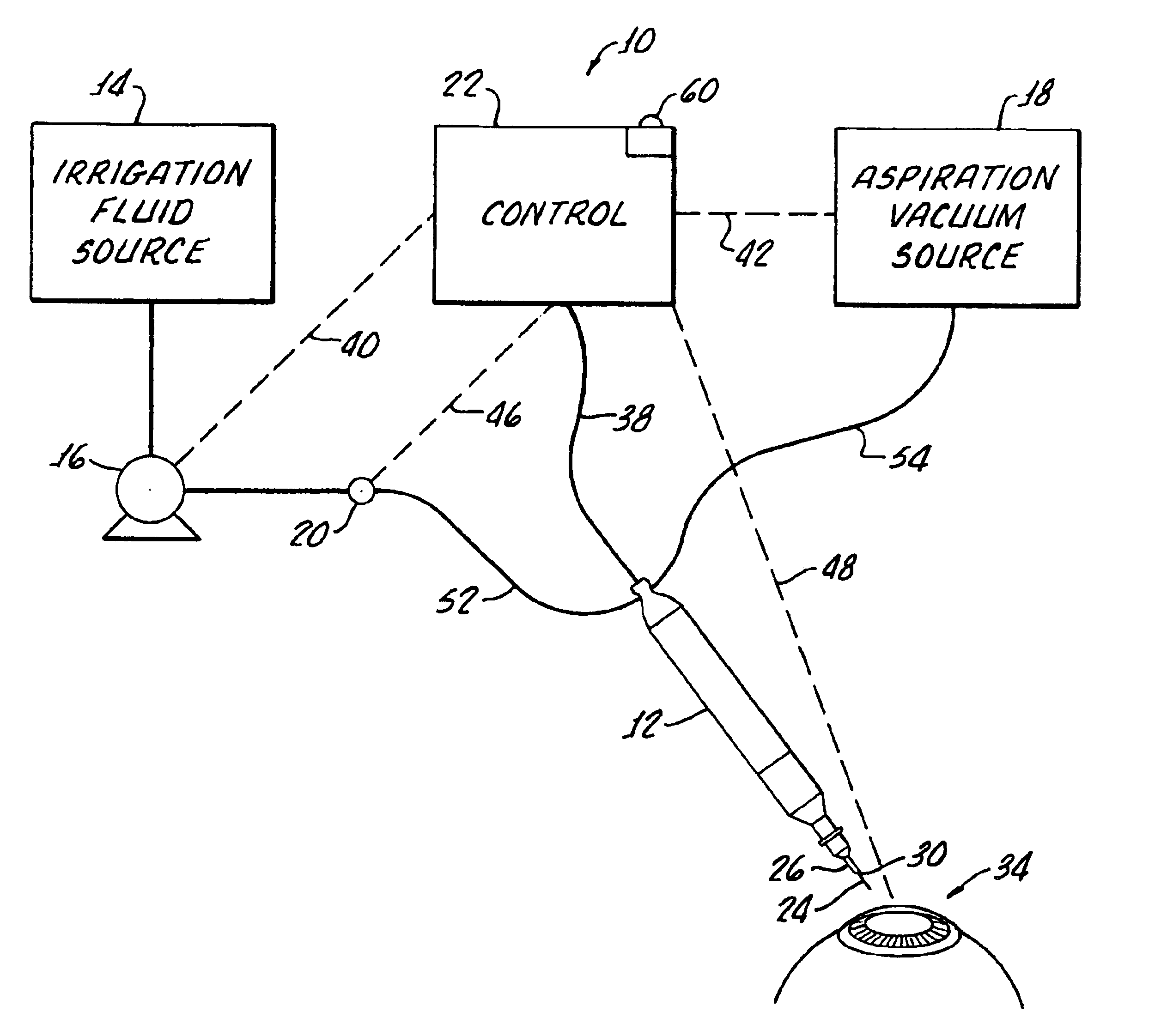
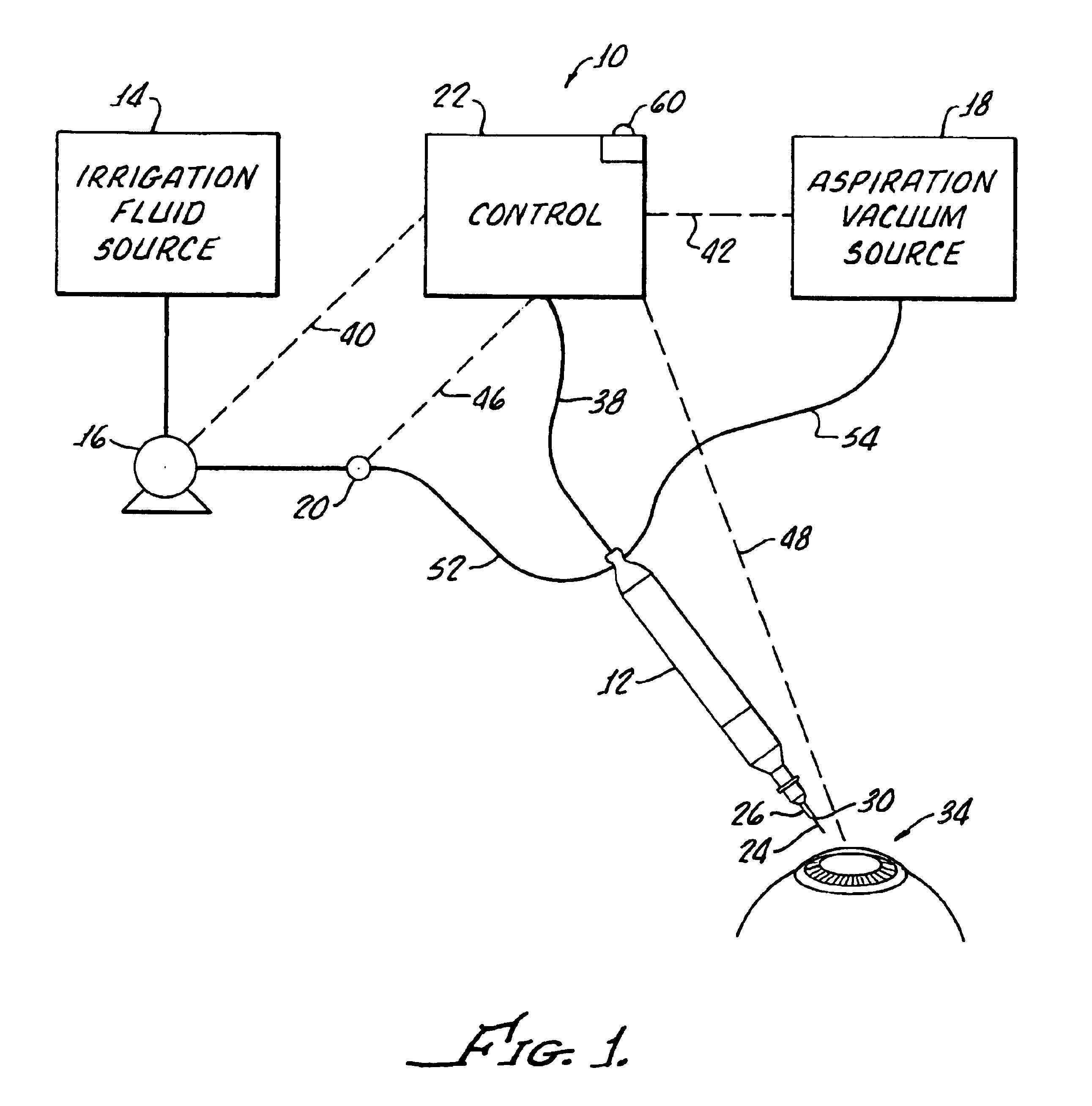
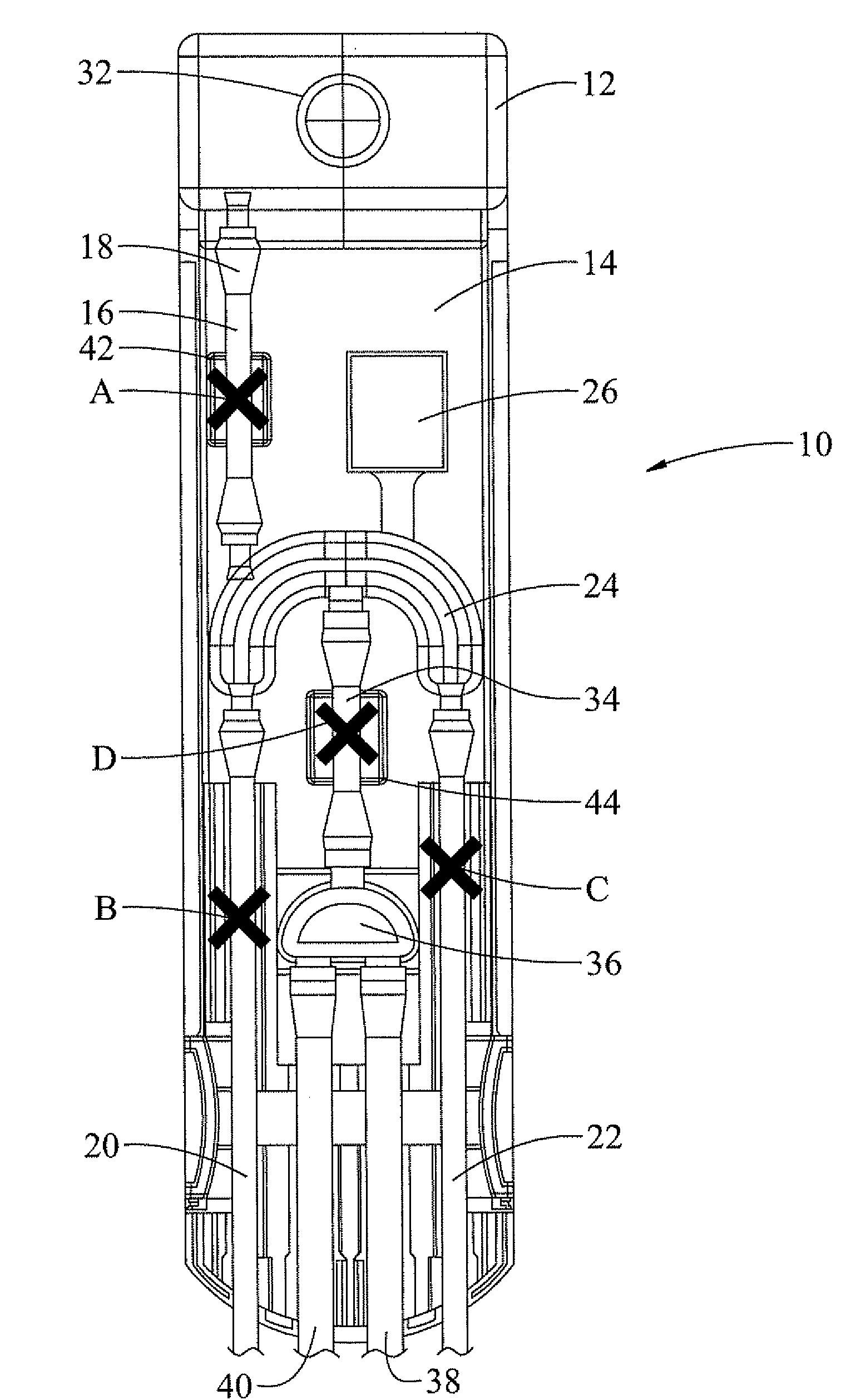
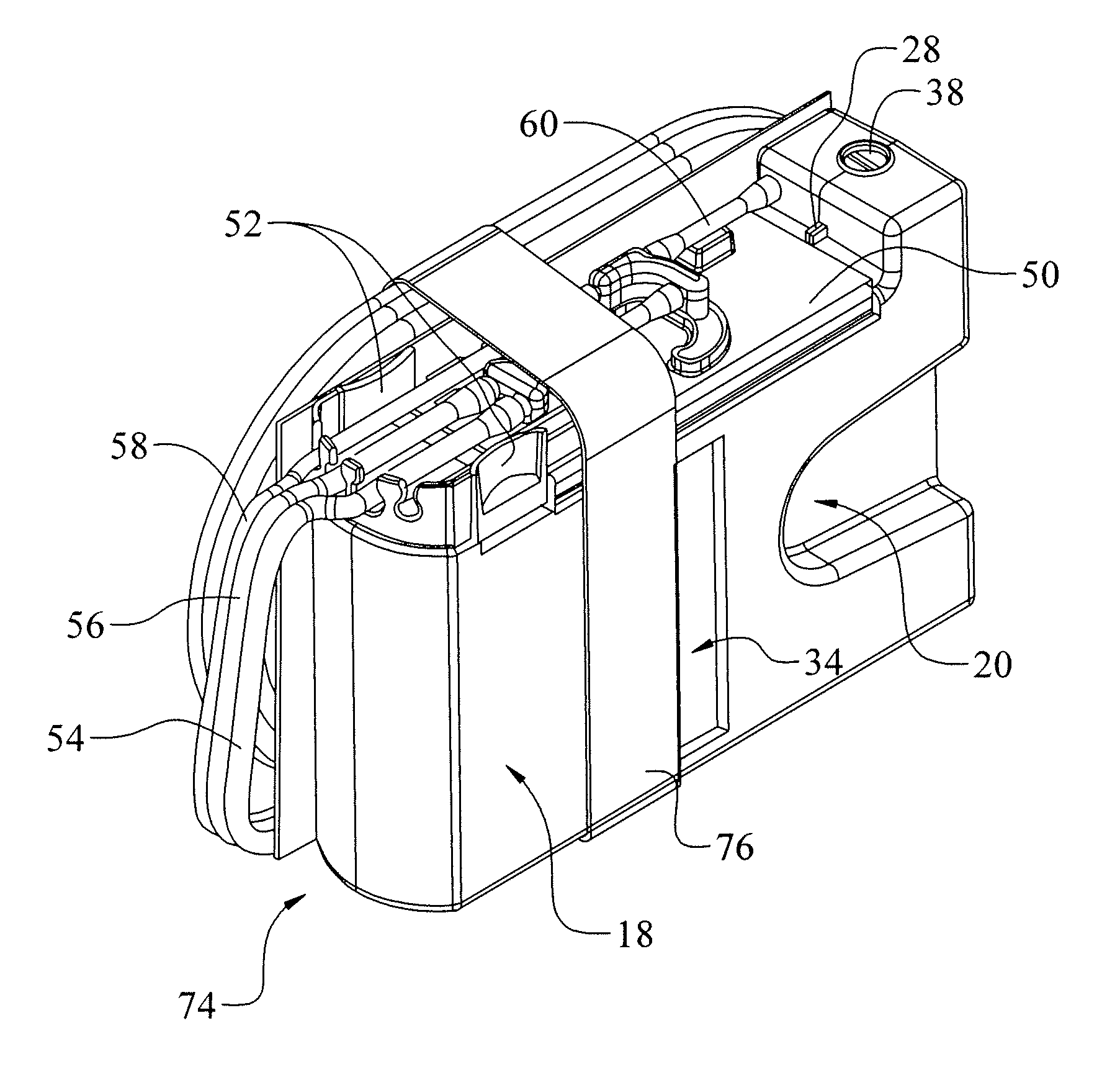
A cassette 74 for use with an ophthalmic surgical pump 16 for collecting aspirant fluid and tissue from a patient's eye includes a rigid walled container 18 having an interior volume 42. At least one tapered alignment slot 20 is formed in a side wall of the container 18 and extends from a back wall 24 towards a front wall 26. An irrigation and aspiration manifold base 50 is removeably attached to the container 18. An aspiration path 46 is formed within the container 18 for receiving the aspiration fluid and the tissue from the eye and directing the flow of fluid towards a front half of the container 18 before the fluid and tissue collects within a majority of the interior volume 42 of the container 18. A fluid level indicator 34 is formed on a wall 22 of the container 18, such that an associated photo-detector 86 of the pump 16 may determine a level of fluid in the container 18.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
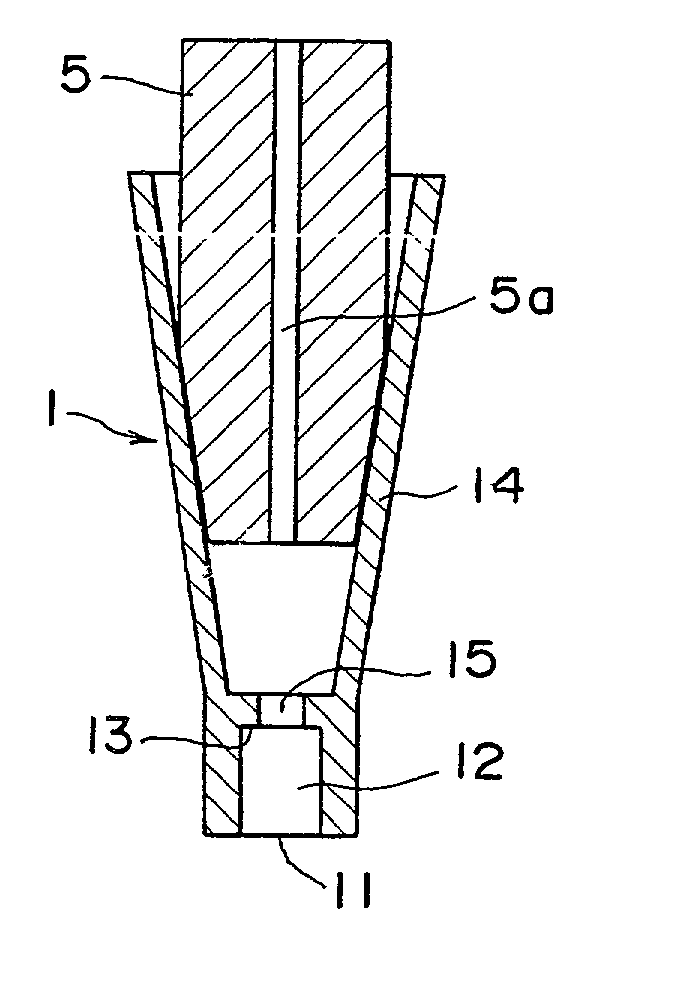
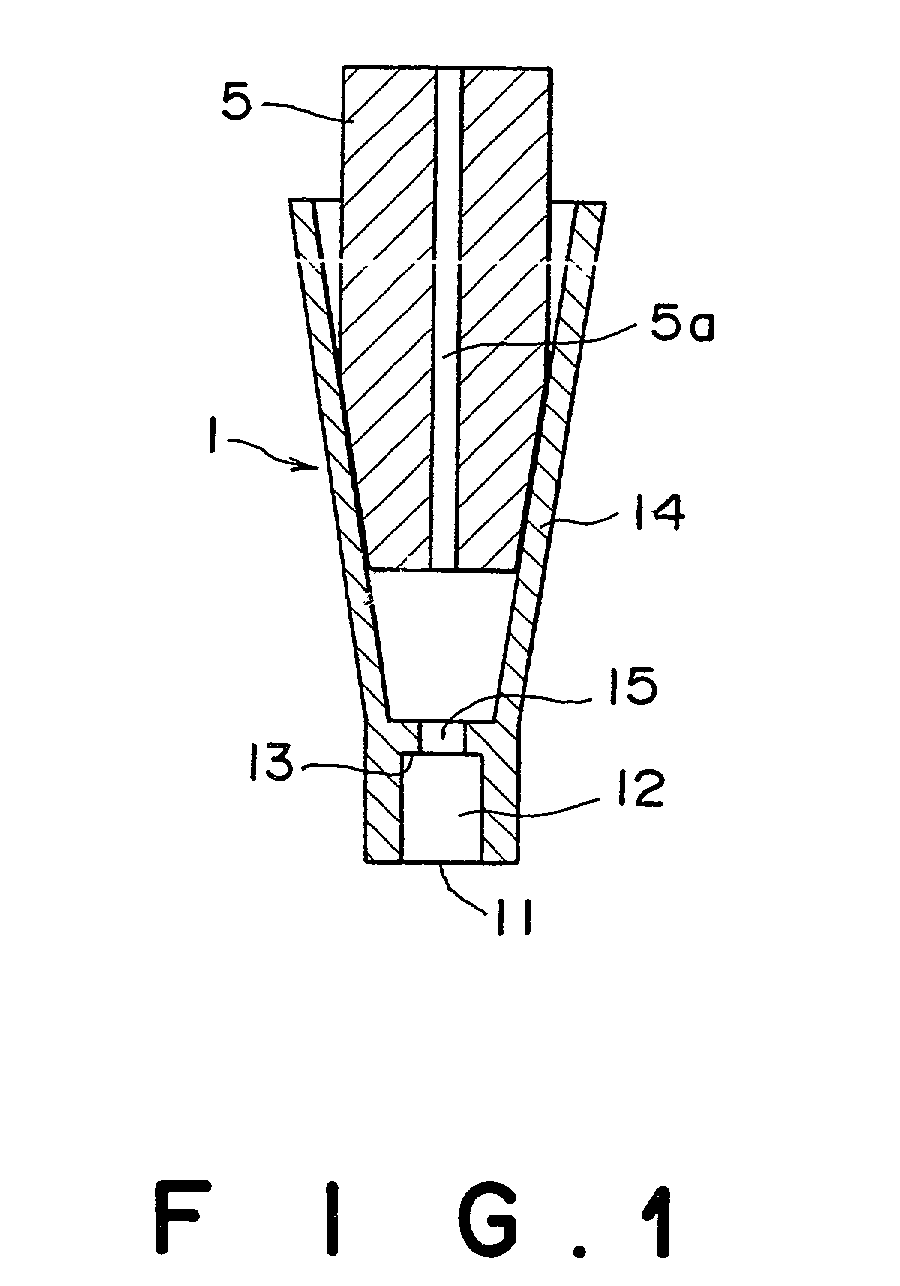
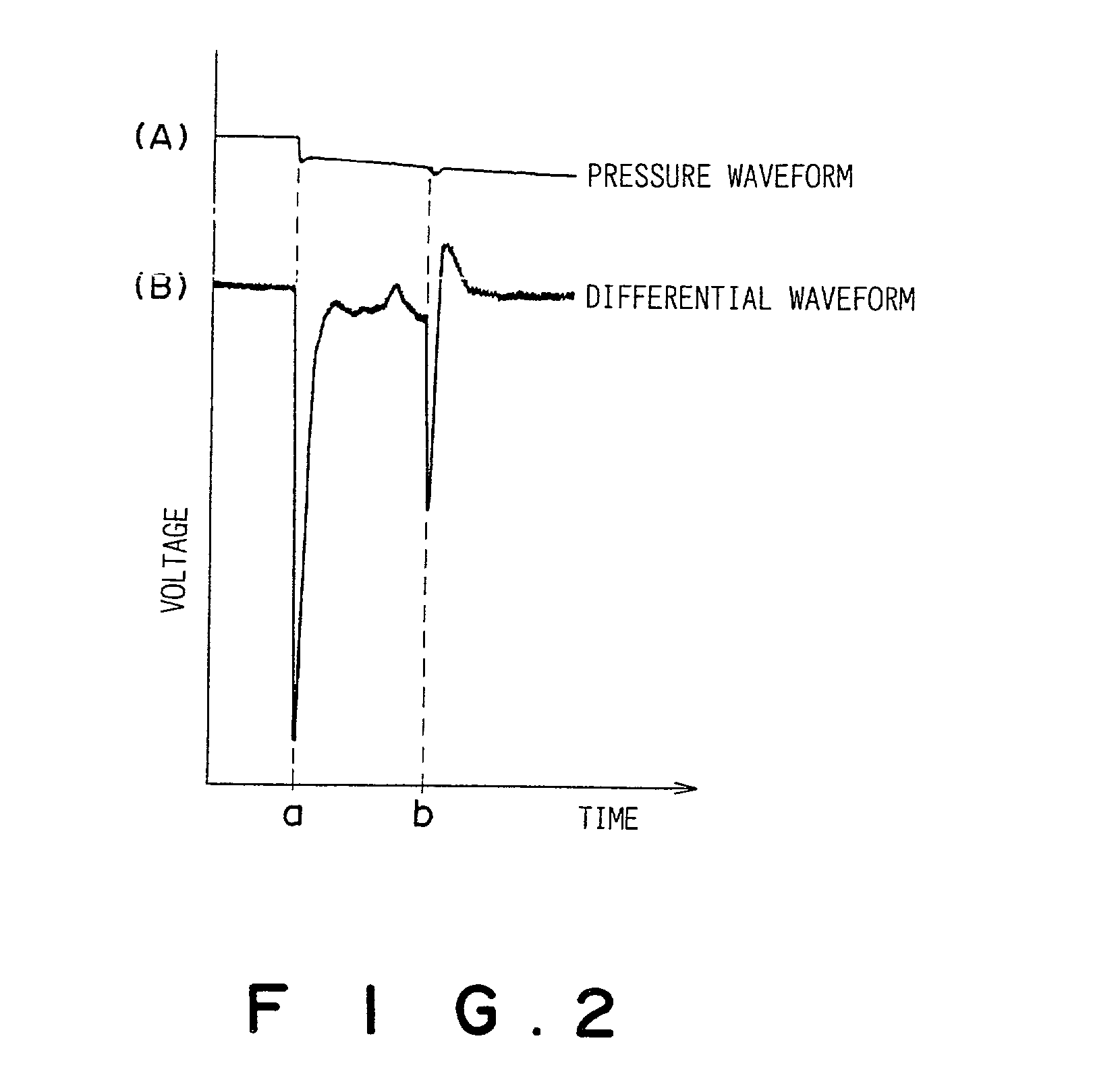
Quantitative suction tip and quantitative suction apparatus
InactiveUS20020037239A1Reduce impactImprove waterproof performanceAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSamplingEngineeringViscosity
A quantitative suction tip to be attached onto the tip of a suction nozzle 5 comprises a fixed volume chamber 12 with a predetermined volume. The fixed volume chamber 12 has a suction opening formed at a lower end thereof and a division wall 13 formed at an upper end thereof. The division wall 13 has a through hole 15 which has a smaller cross-sectional area than that of the fixed volume chamber 12. As a liquid fills the fixed volume chamber 12 and reaches the through hole 15, there is caused a change in the suction pressure which is detected to terminate a suction operation. Thus, a predetermined quantity of the liquid can be accurately drawn into the quantitative suction tip without being affected by e.g. the surface tension and viscosity of the drawn liquid or the wettability of the inner walls of the quantitative suction tip.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
Removable adapter for phacoemulsification handpiece having irrigation and aspiration fluid paths
Current phacoemulsification handpieces require rigorous cleaning after each procedure because the aspiration and irrigation pathways for fluids are integral to the handpiece. According to the present invention, a removable horn extension and nosecone may be used with a phacoemulsification handpiece to allow for disposable fluid pathways exterior to the handpiece. This will reduce the cleaning time and effort, reduce cross-contamination, and increase the lifespan of the handpiece. Furthermore, the current invention allows different horn extensions to be used to excite different motions at the tip of the handpiece, depending on the preference of the surgeon.
Owner:ZEVEX
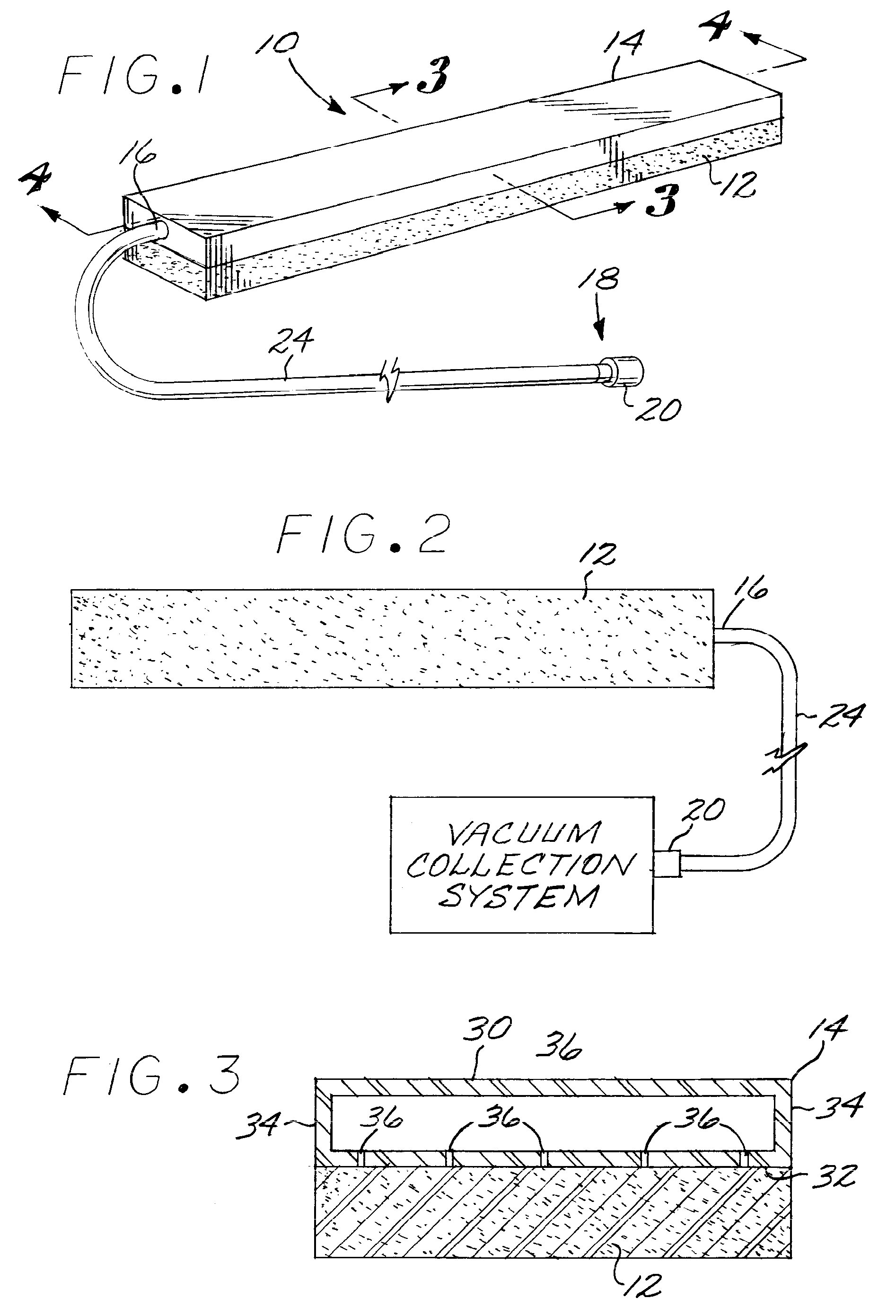
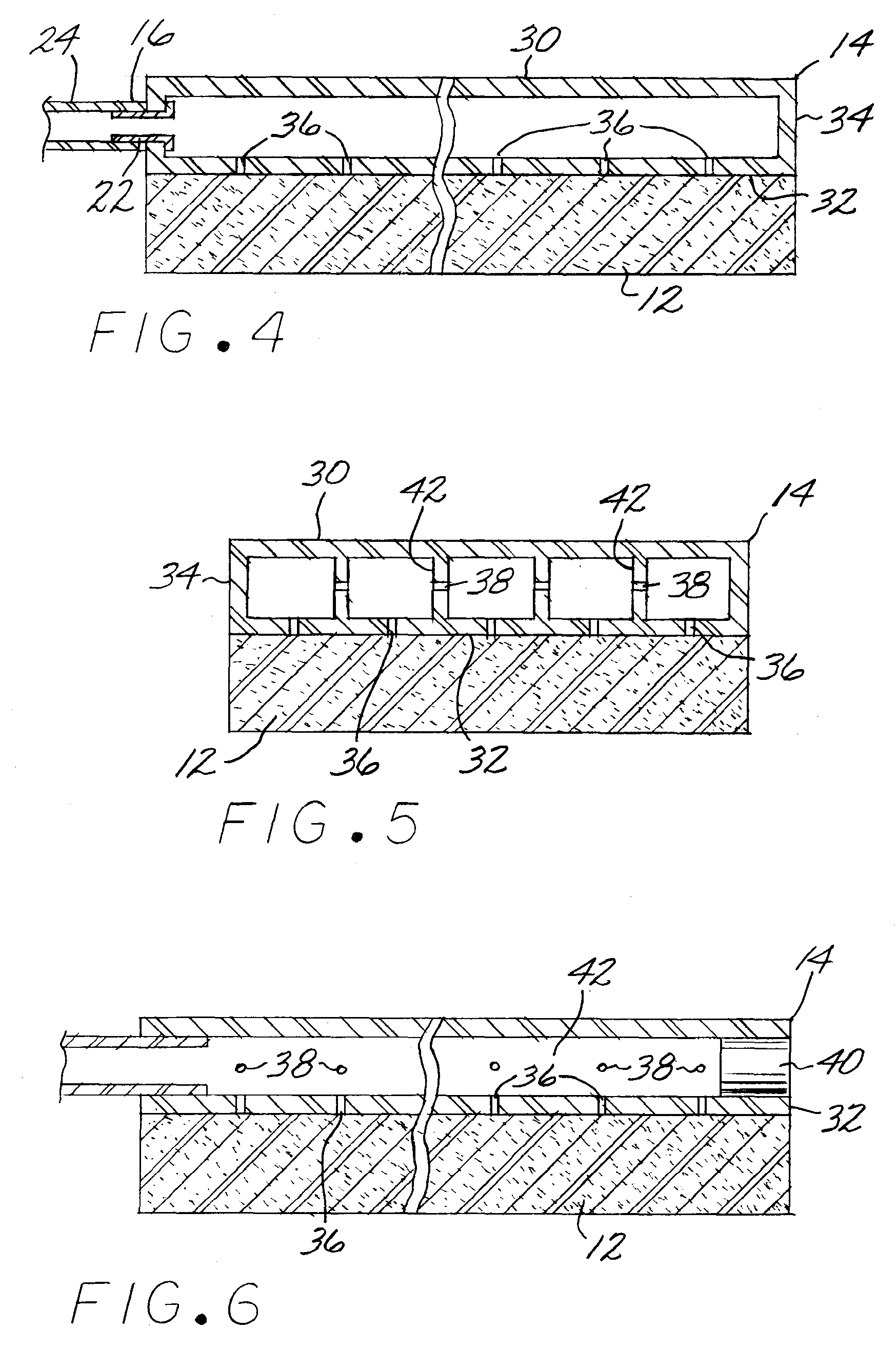
Liquid removal method and apparatus for surgical procedures
InactiveUS7901389B2Easy to repositionIncrease surface areaOperating tablesSuction nozzlesCollection systemEngineering
The present invention relates to an improved apparatus and method for aspirating liquids from surfaces particularly during medical procedures. Apparatus for removing liquid from a surface in the region of a medical procedure such as an operating room floor responsive to a drawn vacuum of preselected magnitude includes a plenum with an interior volume defined by an elongated box element with a plurality of supports member integral thereto or by an elongated tube, the plenum being perforated so as the exterior of the plenum is in direct liquid communication with the interior of the plenum, an absorptive wicking pad secured to the plenum so as to cover the perforations, an a vacuum conduit tube in direct vacuum communication with a vacuum collection system. A method of removal of liquids standing on surfaces such as operating room floors accomplished by positioning the disposable liquid removal apparatus with the exposed absorptive wicking pad down into the liquid, attaching the apparatus to a vacuum collection system, activating the system, and repositioning the apparatus as required.
Owner:AVEC SCI DESIGN CORP
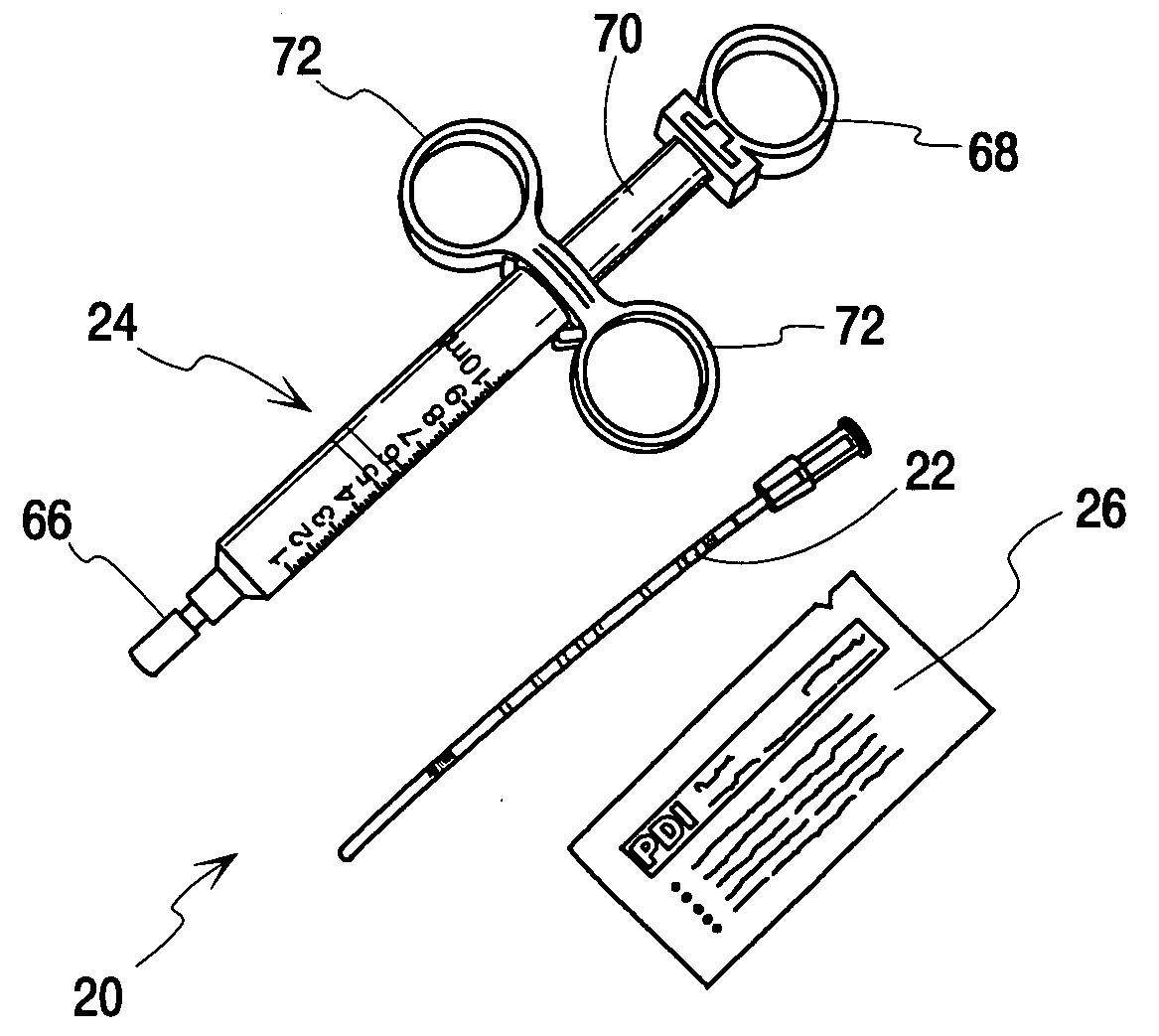
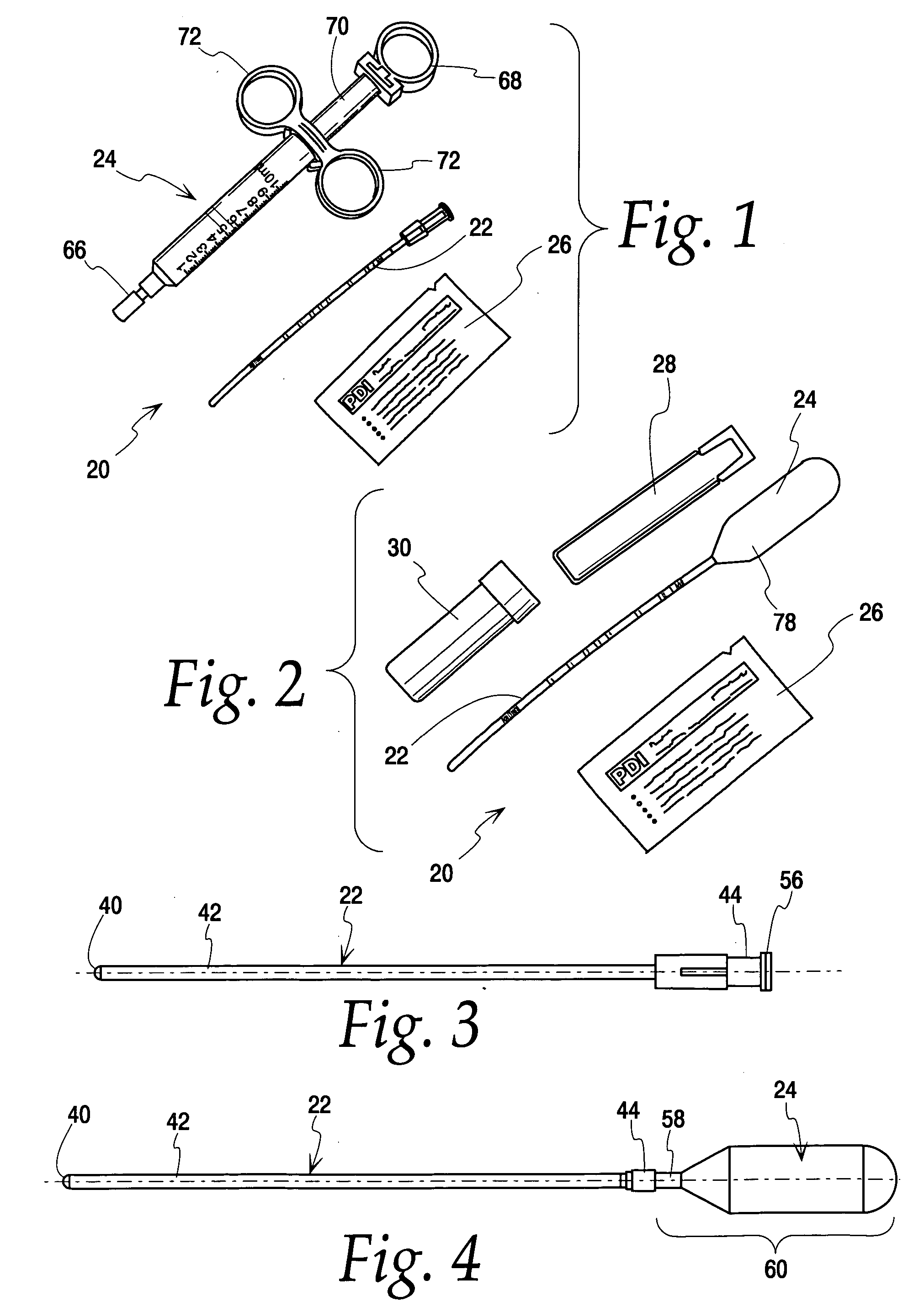
Methods and apparatus for nasal aspiration
Apparatus and methods for withdrawing nasopharyngeal fluid samples from a patient are disclosed. A kit including a catheter and a manual suction device is disclosed, wherein the catheter can be self-navigating and define aspiration holes through which aspiration fluid can be emitted and nasopharyngeal fluid samples can be withdrawn. The catheter may also include an insertion depth scale to ensure patient comfort and optimum sample quality. The methods for obtaining nasopharyngeal fluid samples include the steps of inserting the catheter into a patient's nasopharynx, and aspirating the nasal pharynx to withdraw a specimen.
Owner:WATERS KURT +1
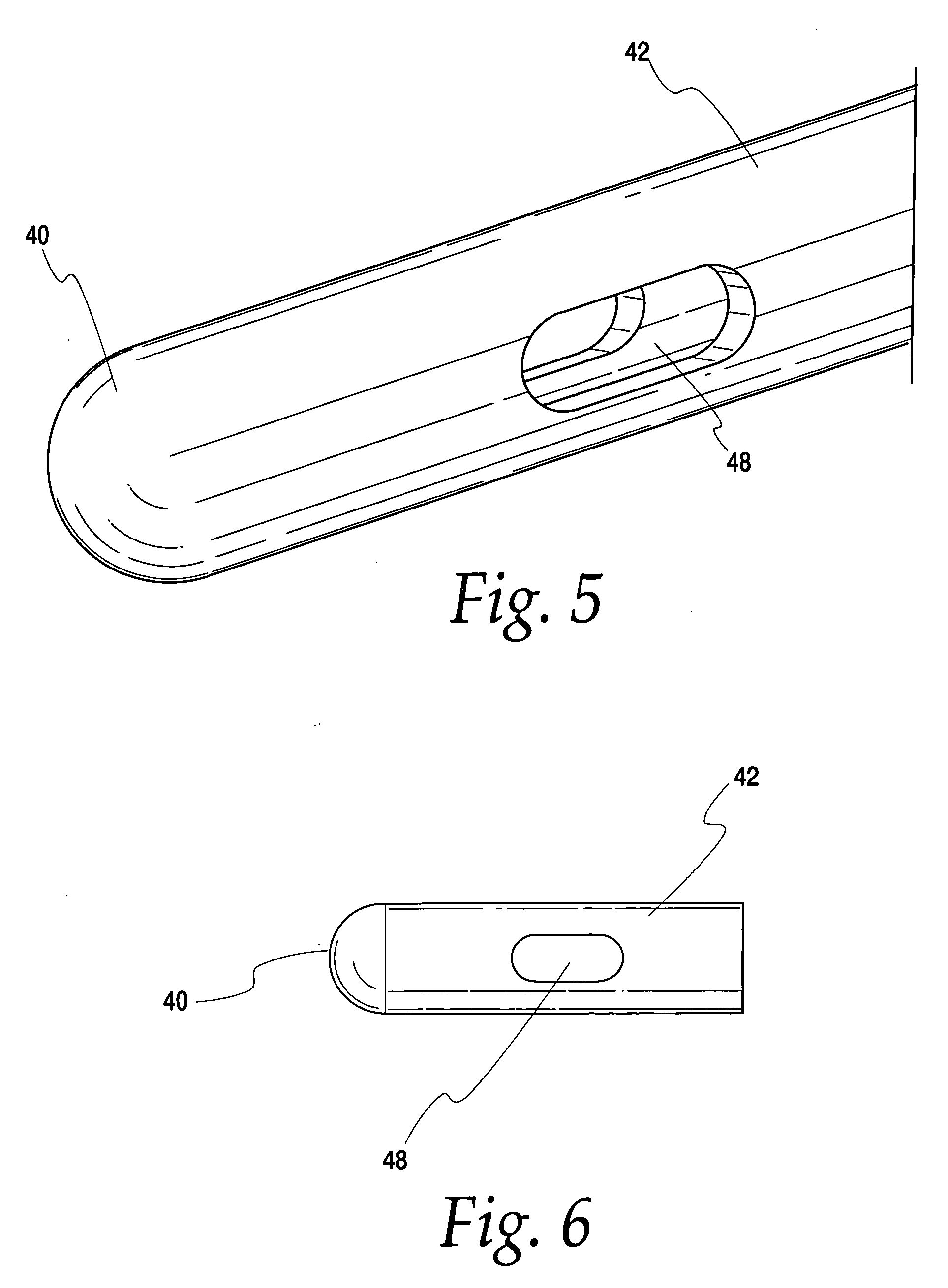
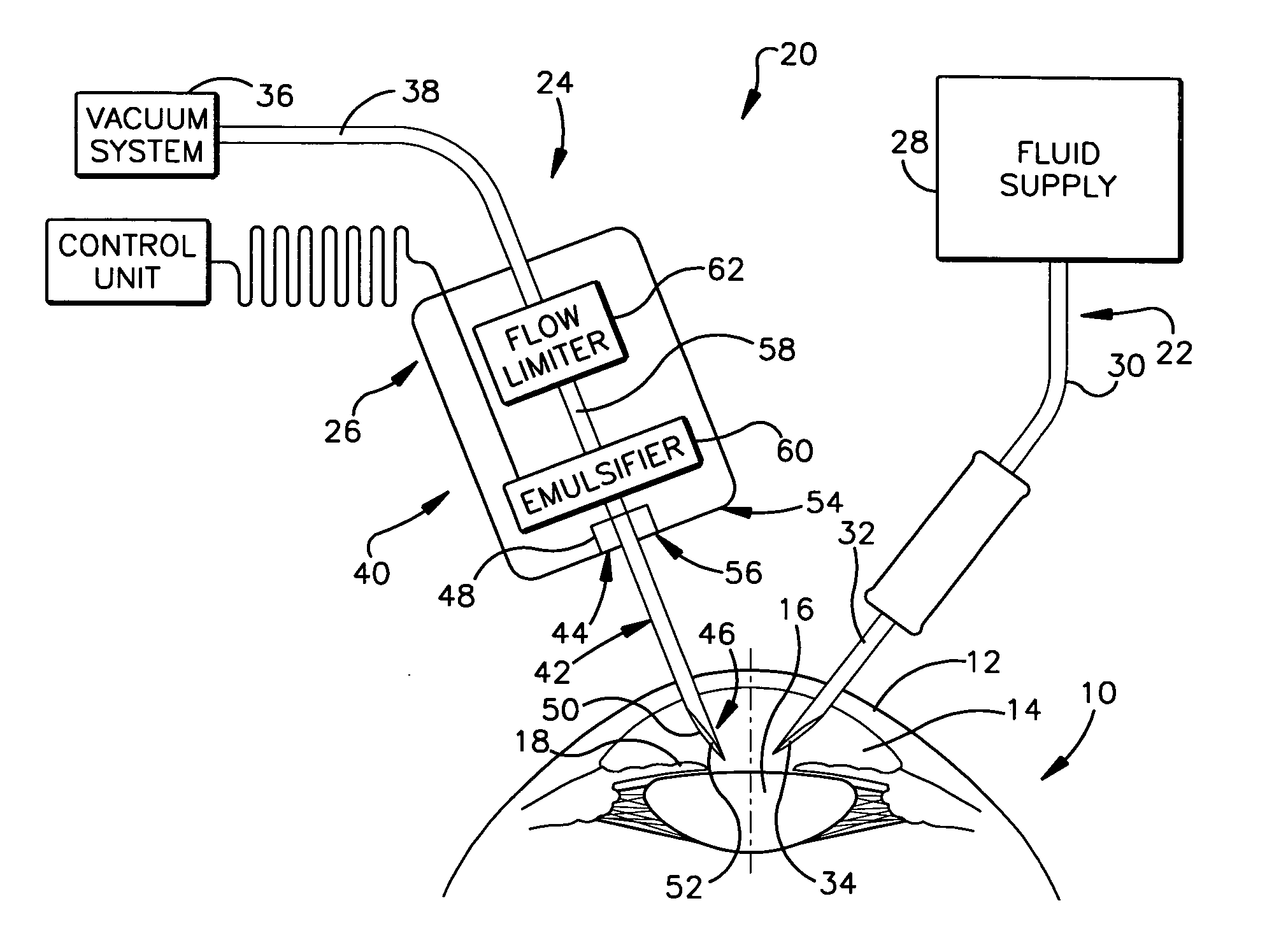
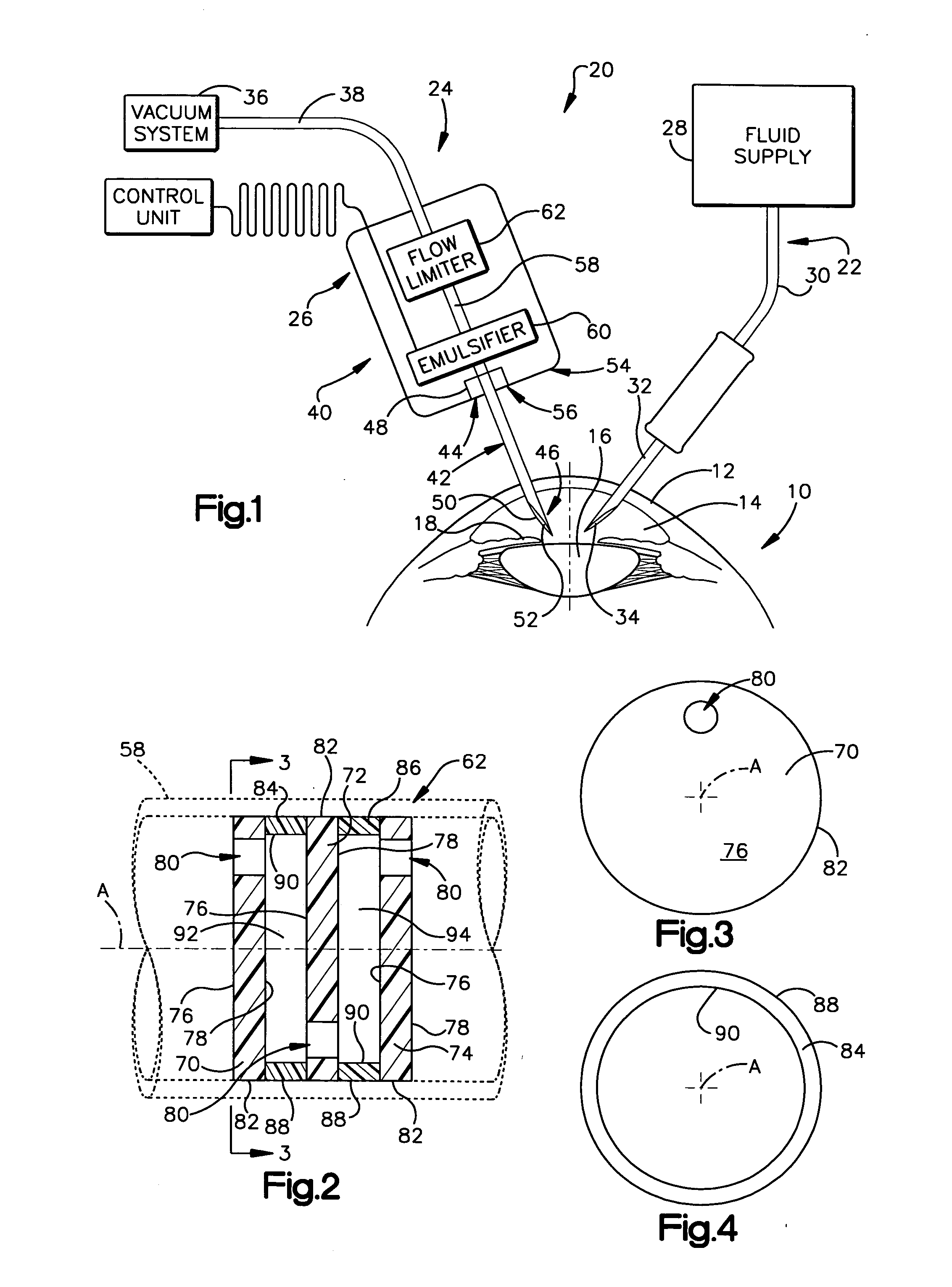
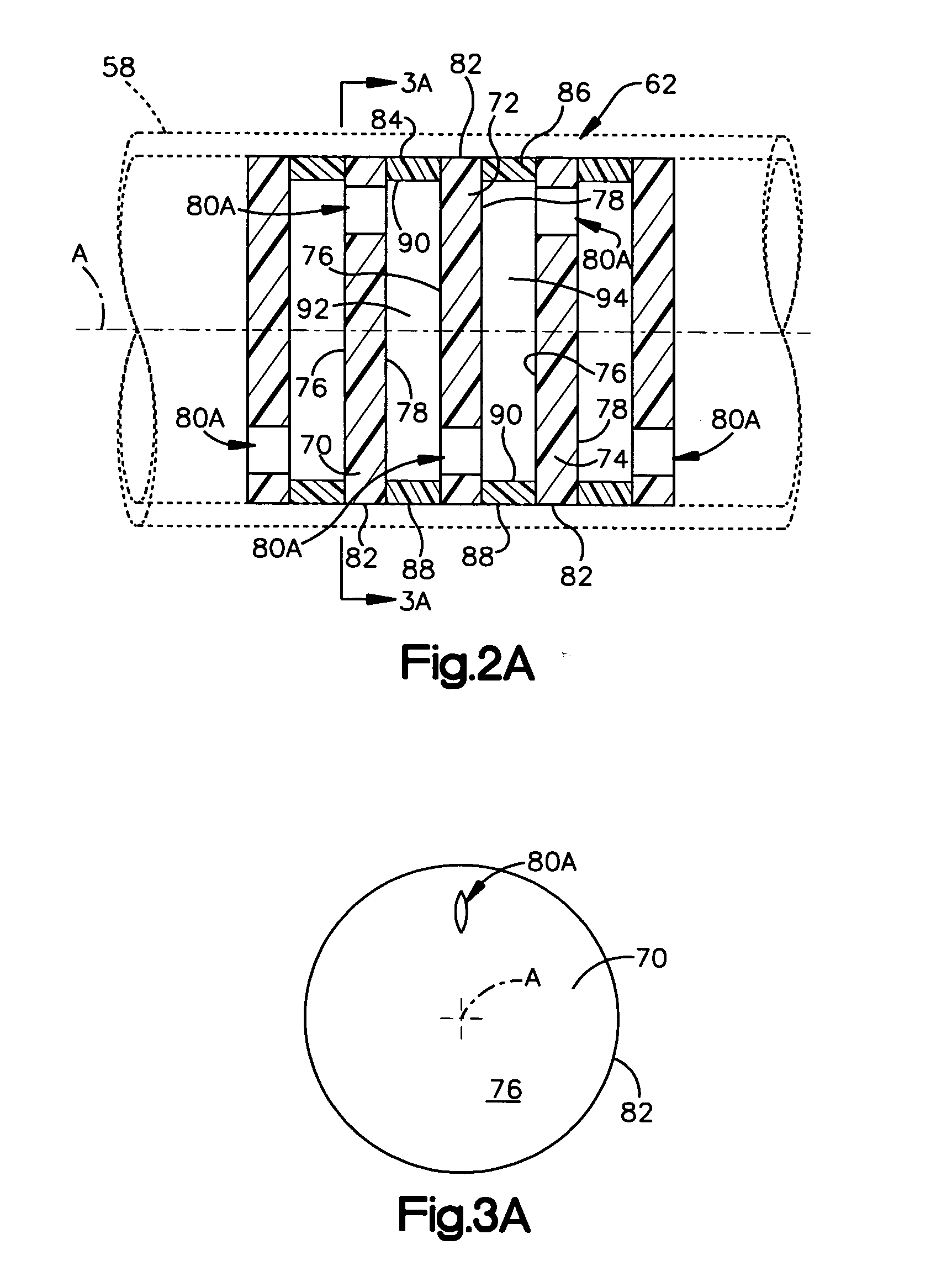
Device for controlling fluid flow in an aspiration system
A device for, when connected to a vacuum system, conducting aspiration fluid away from a surgical site includes a conduit having a portion adapted for insertion into the surgical site. The device also includes a flow limiter interposed between the vacuum system and the conduit and in fluid communication with the conduit. The flow limiter has at least two orifices arranged in series and a flow path interconnecting the at least two orifices. The flow path has a flow area that is greater than a flow area of each one of the at least two orifices. Aspiration fluid flows through the conduit and the flow limiter in response to a pressure drop between the surgical site and the vacuum system. The flow limiter produces a non-linear relationship between a rate of aspiration fluid flow and the pressure drop.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
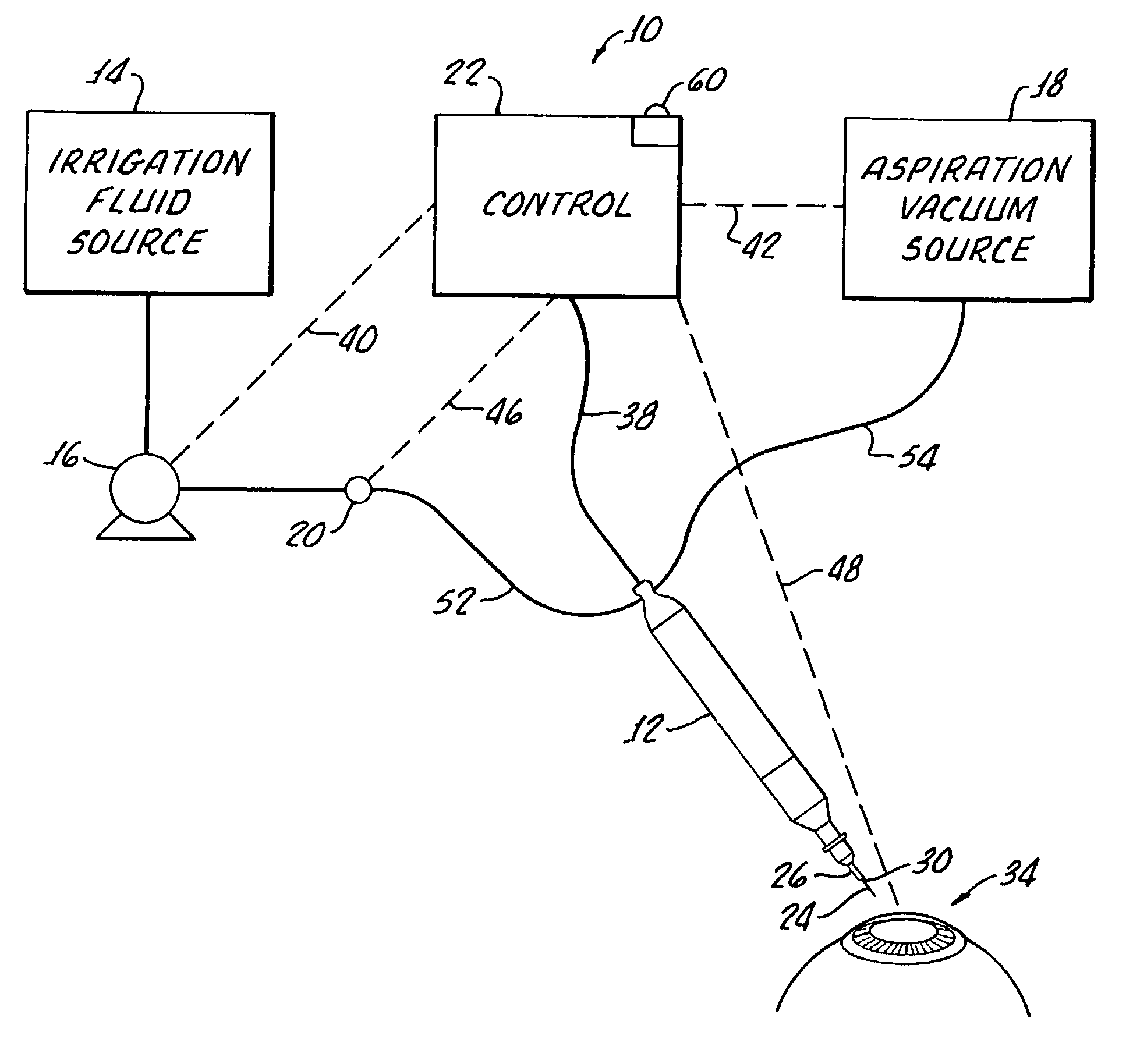
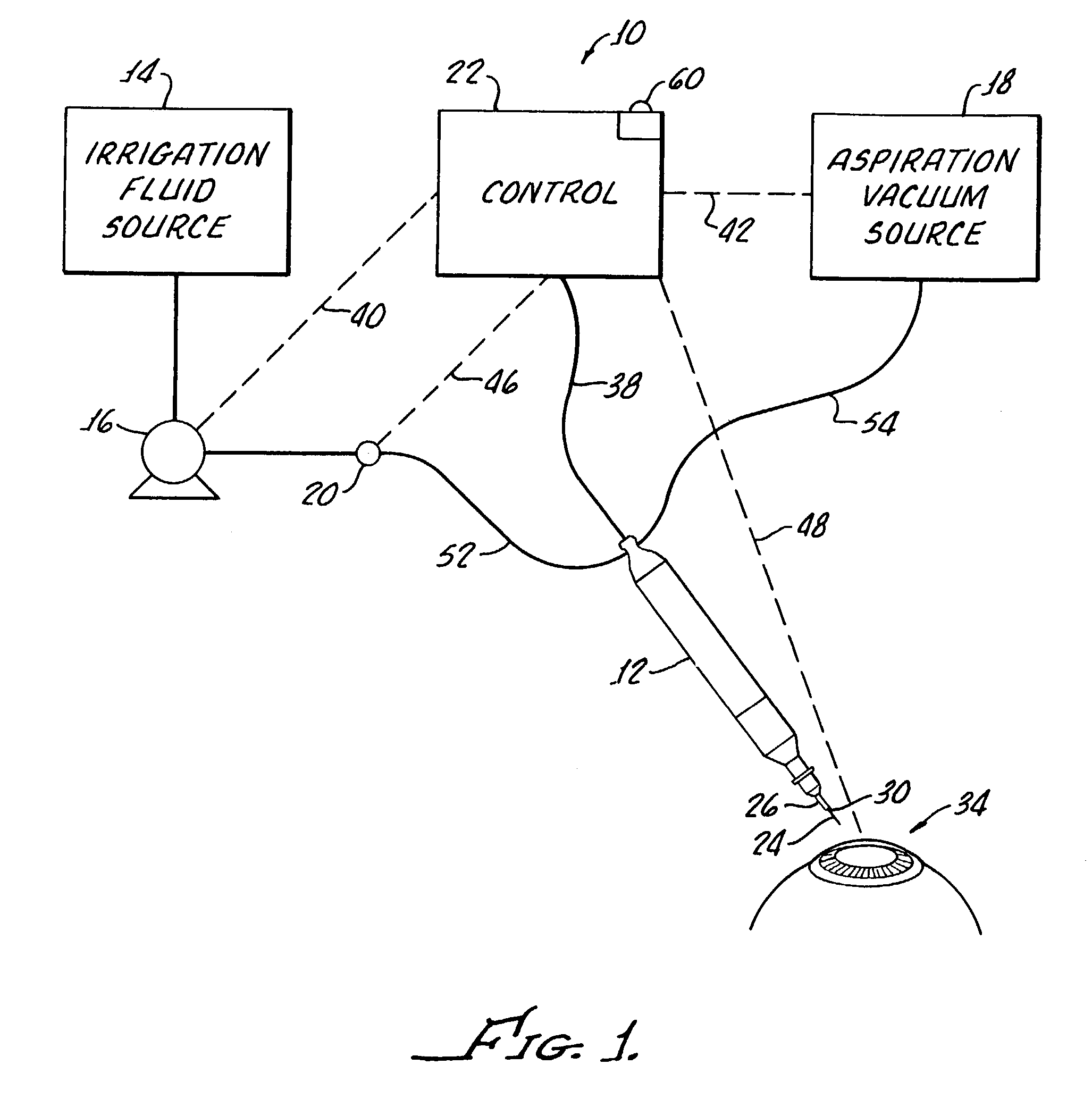
Method for controlling fluid flow to and from an eye during ophthalmic surgery
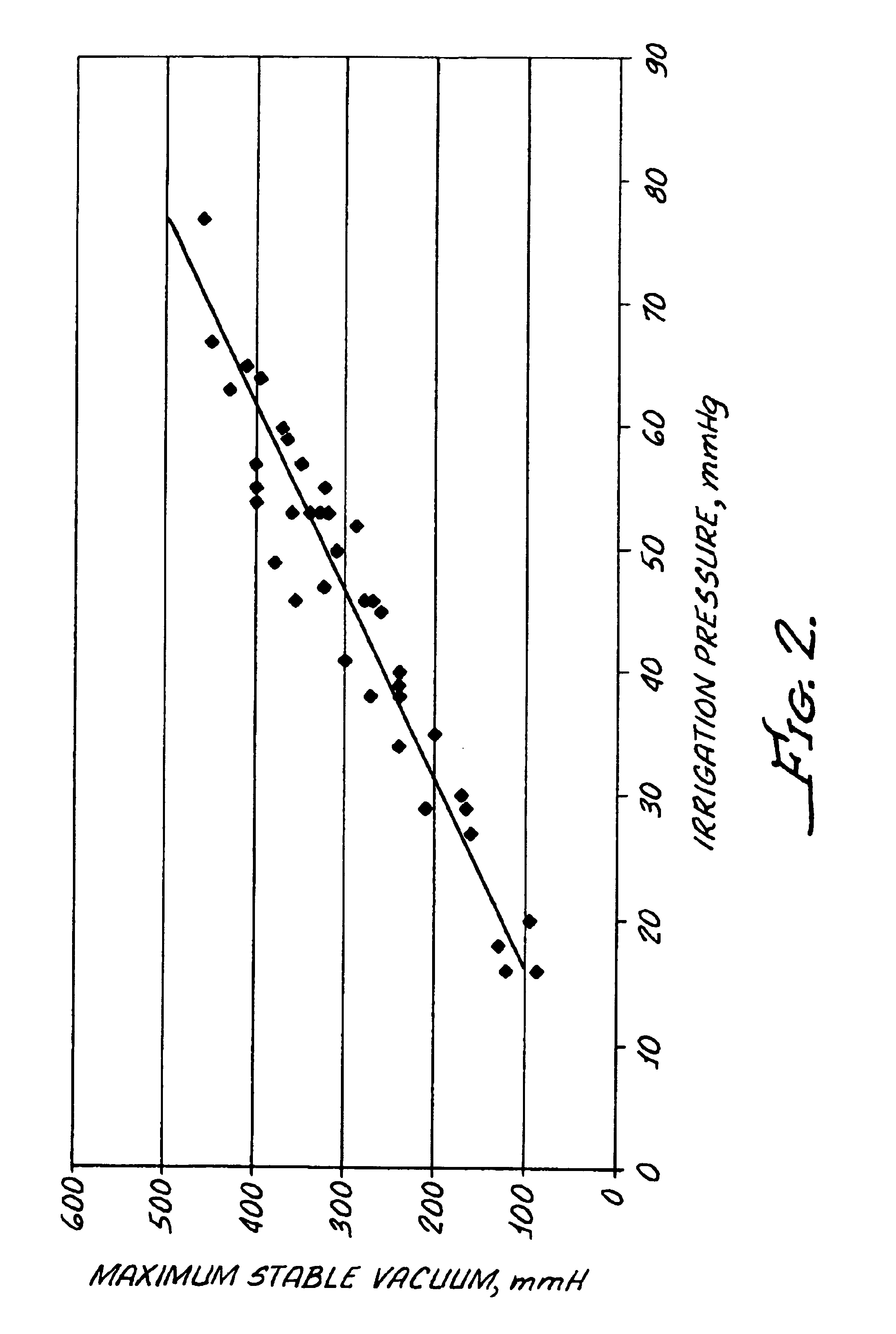
InactiveUS6899694B2Prevent crashChange leakage rateEye surgeryMedical devicesFluid controlOphthalmology
A method and apparatus provided for controlling fluid control to and from an eye or a phacoemulsification handpiece. The handpiece includes an ultrasonically driven, hollow, sleeved needle and the method includes inserting the needle and sleeve into an eye for phacoemulsification of eye tissue and introducing fluid into the eye through an annulus established between the sleeve and the needle. Aspiration of fragmented tissue and fluid from the eye is conducted through the hollow needle. An initial irrigation fluid pressure is determined and the irrigation fluid flow and aspiration fluid flow are adjusted based upon the initial determination. Thereafter continued determination of irrigation fluid pressure is utilized to continuously adjust irrigation fluid flow and / or aspiration fluid flow.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
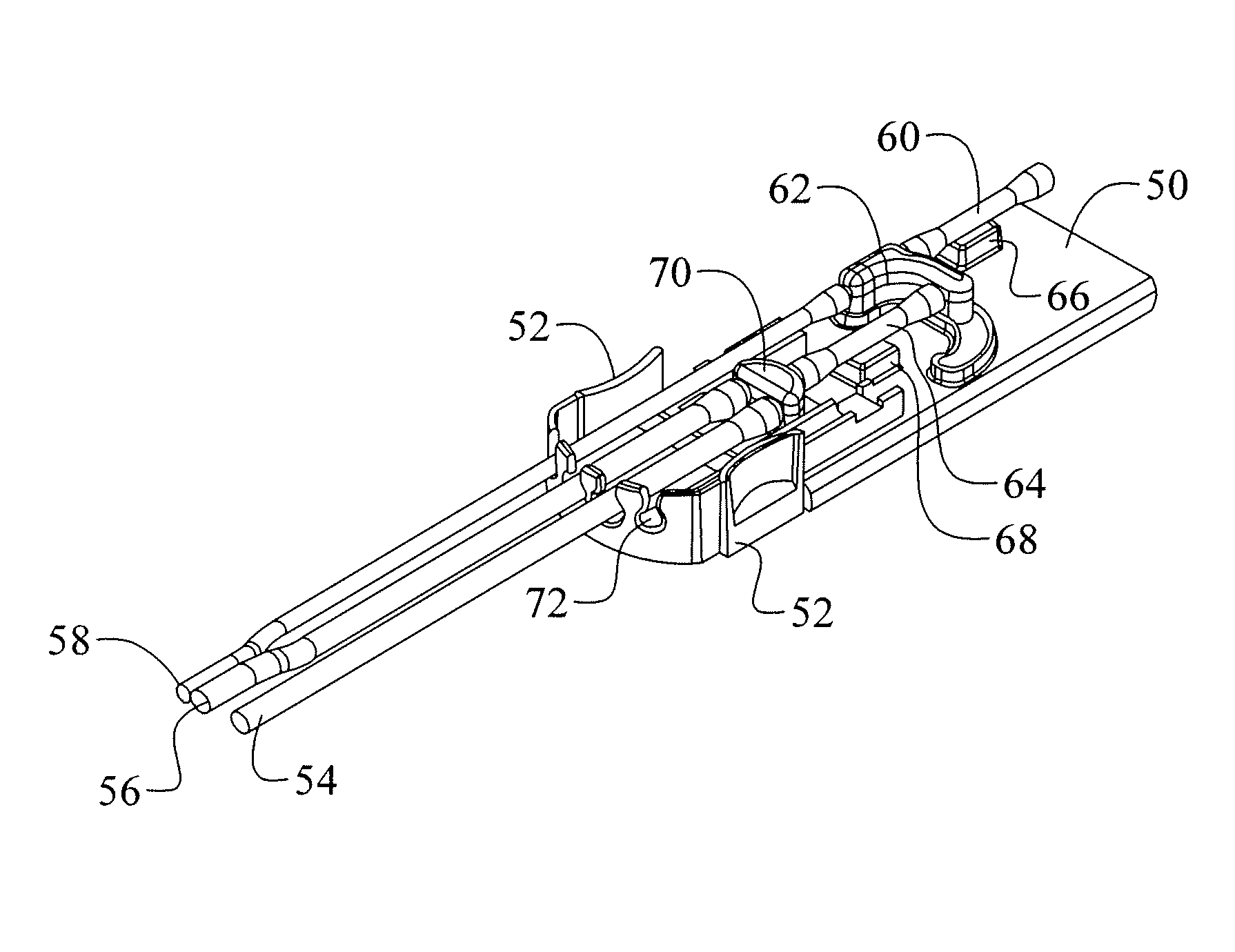
Ophthalmic surgical cassettes for ophthalmic surgery
An ophthalmic surgical cassette for collecting aspirant fluid and / or tissue during an ophthalmic surgical procedure. The ophthalmic surgical cassette includes a rigid walled container having an interior volume for collecting aspirant fluid and / or tissue and an aspiration manifold coupled to the rigid walled container. The aspiration manifold is connected to an aspiration tube in fluidic communication with the interior volume, a first aspiration line for coupling a first surgical handpiece, a second aspiration line for coupling a second surgical handpiece, and a reflux bulb in fluidic communication with the first and second aspiration lines.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Method for controlling fluid flow to and from an eye during ophthalmic surgery
InactiveUS7001356B2Prevent crashChange leakage rateEye surgeryMedical devicesFluid controlOphthalmology
A method and apparatus provided for controlling fluid control to and from an eye or a phacoemulsification handpiece. The handpiece includes an ultrasonically driven, hollow, sleeved needle and the method includes inserting the needle and sleeve into an eye for phacoemulsification of eye tissue and introducing fluid into the eye through an annulus established between the sleeve and the needle. Aspiration of fragmented tissue and fluid from the eye is conducted through the hollow needle. An initial irrigation fluid pressure is determined and the irrigation fluid flow and aspiration fluid flow are adjusted based upon the initial determination. Thereafter continued determination of irrigation fluid pressure is utilized to continuously adjust irrigation fluid flow and / or aspiration fluid flow.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
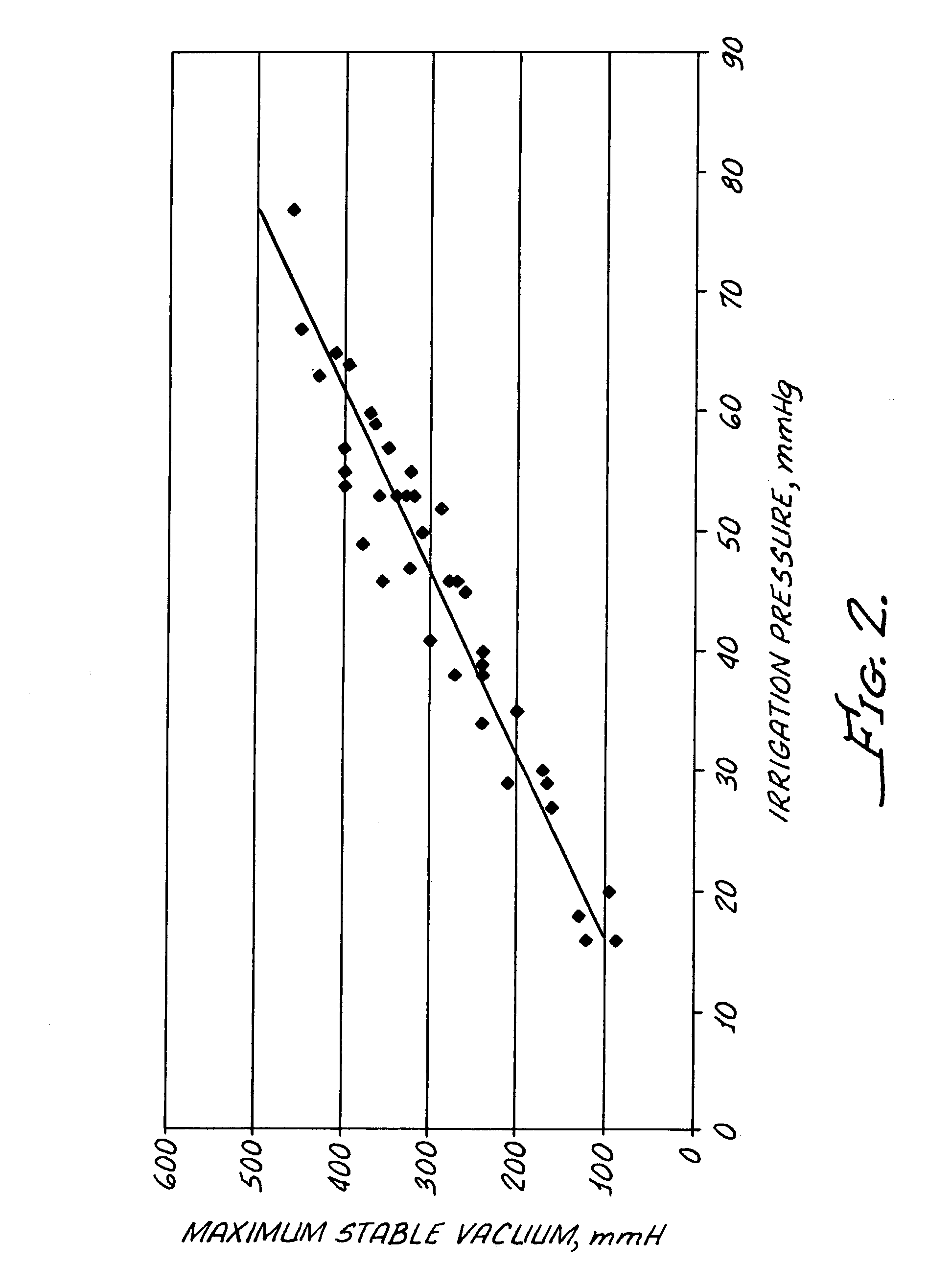
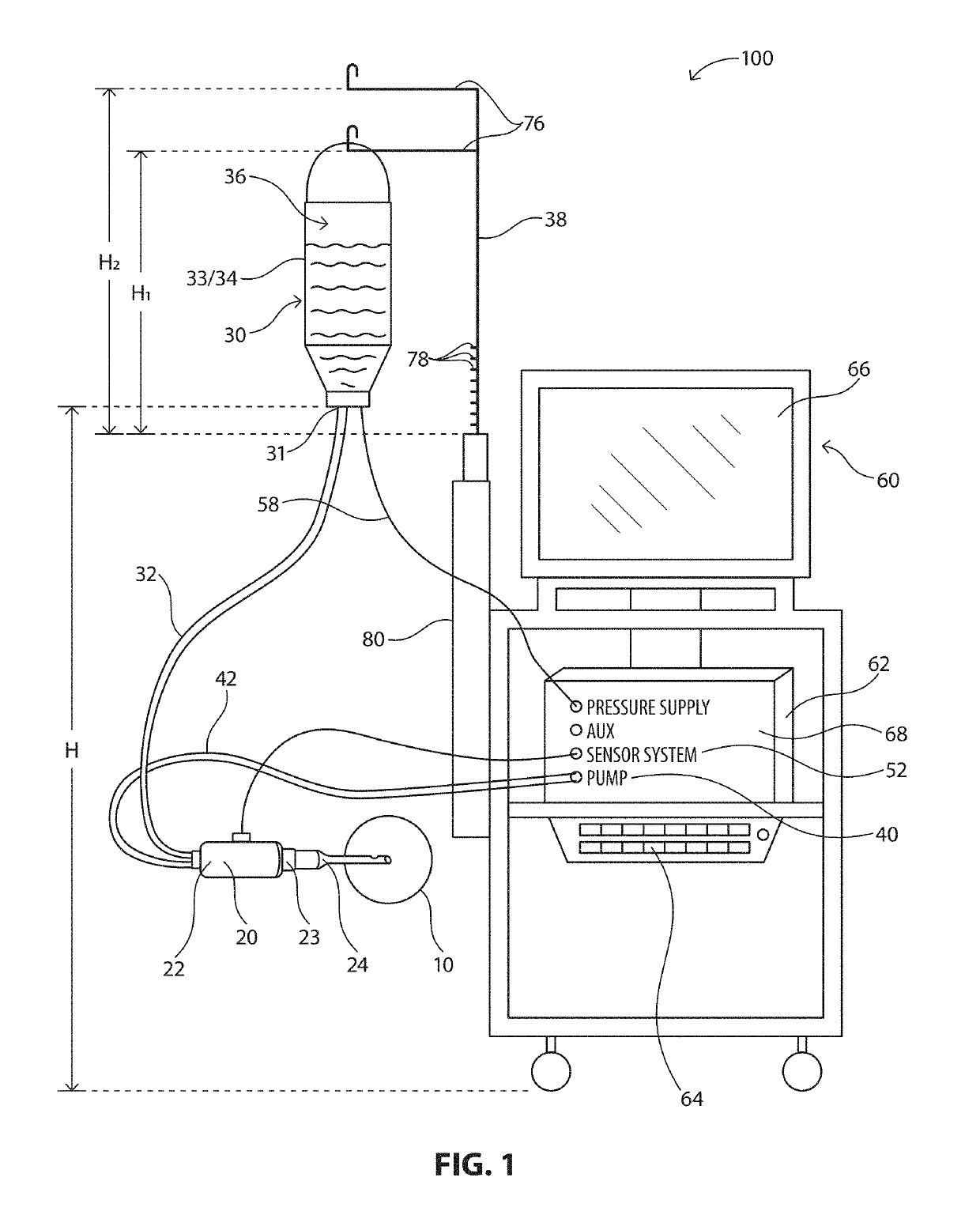
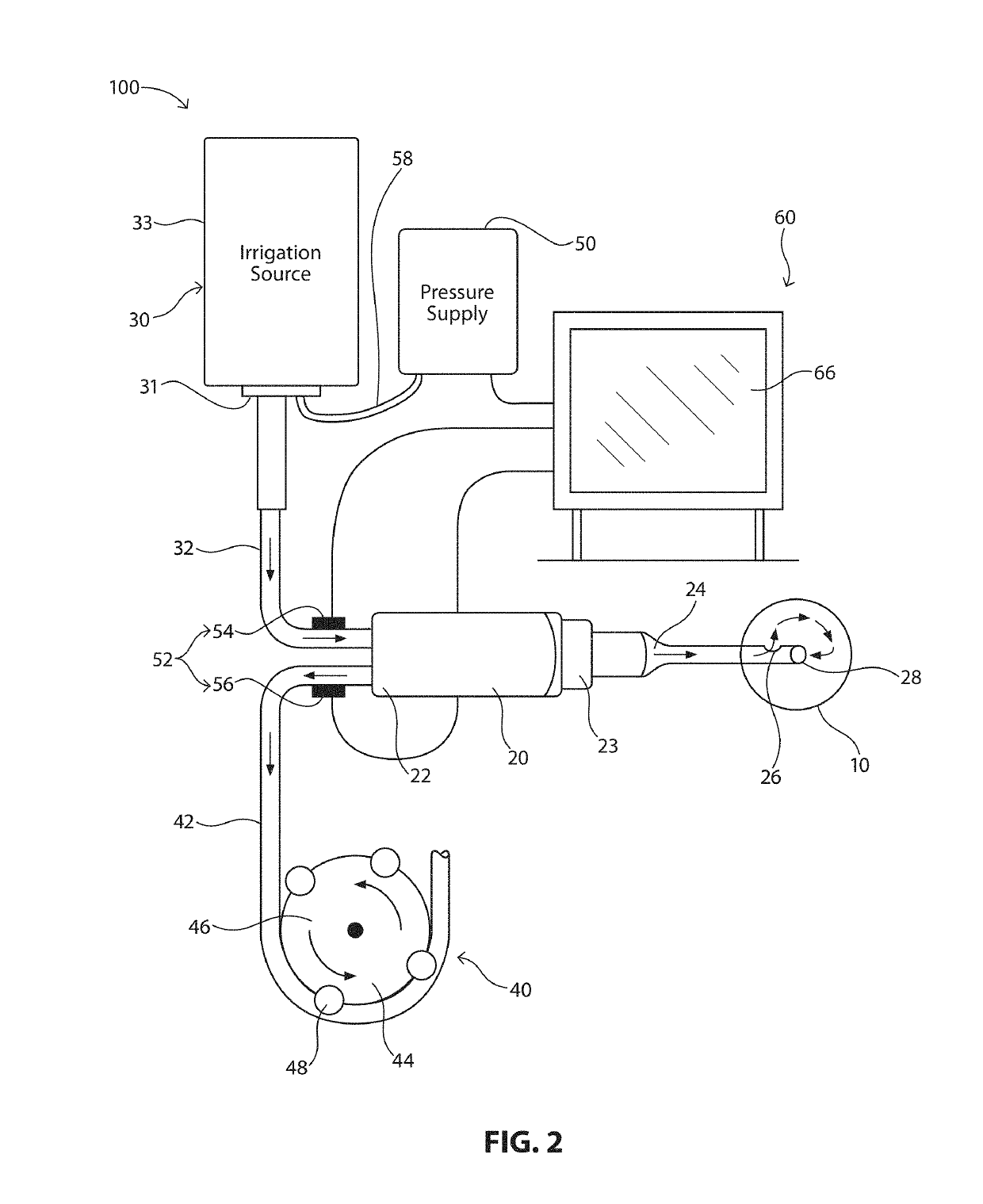
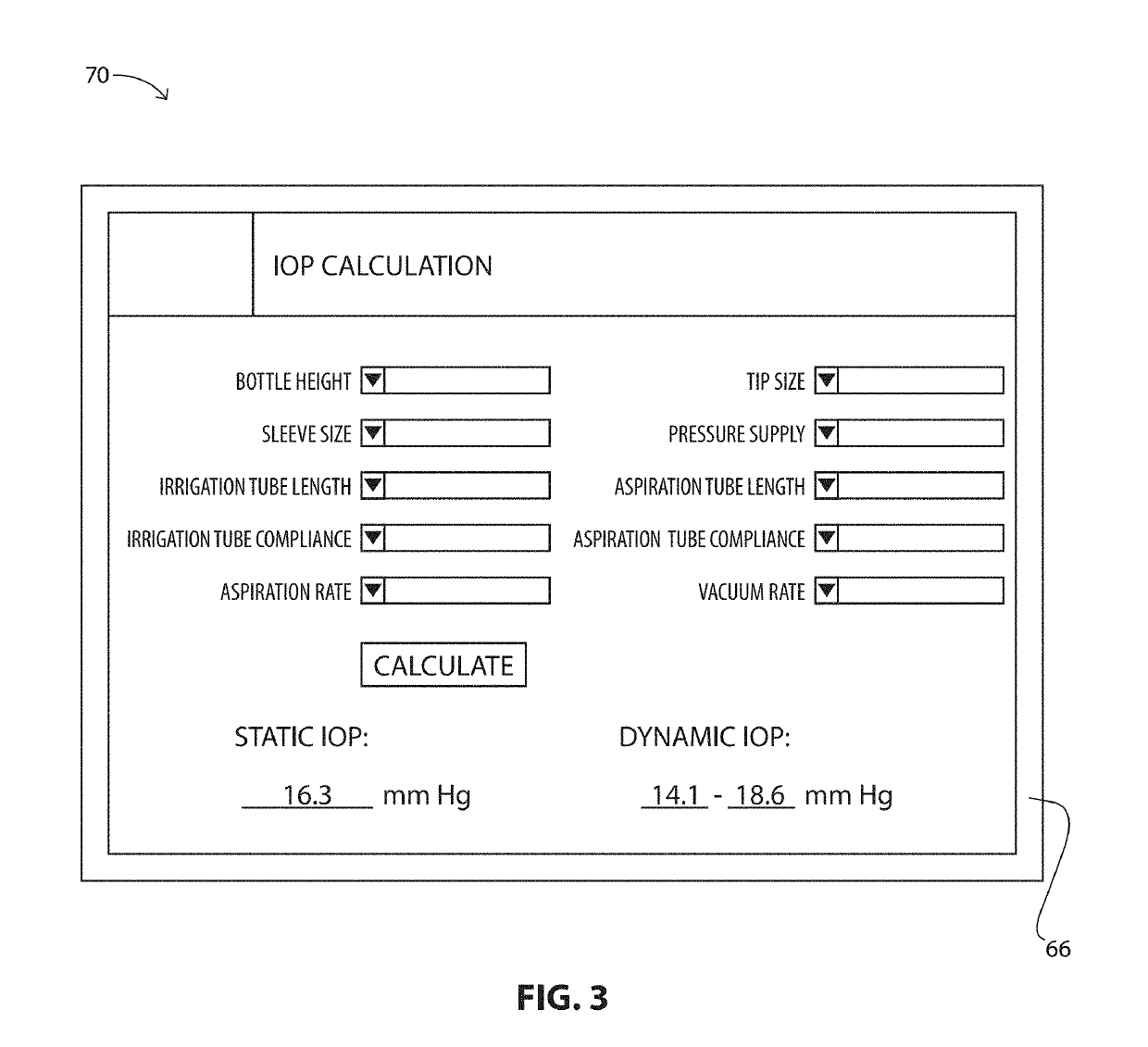
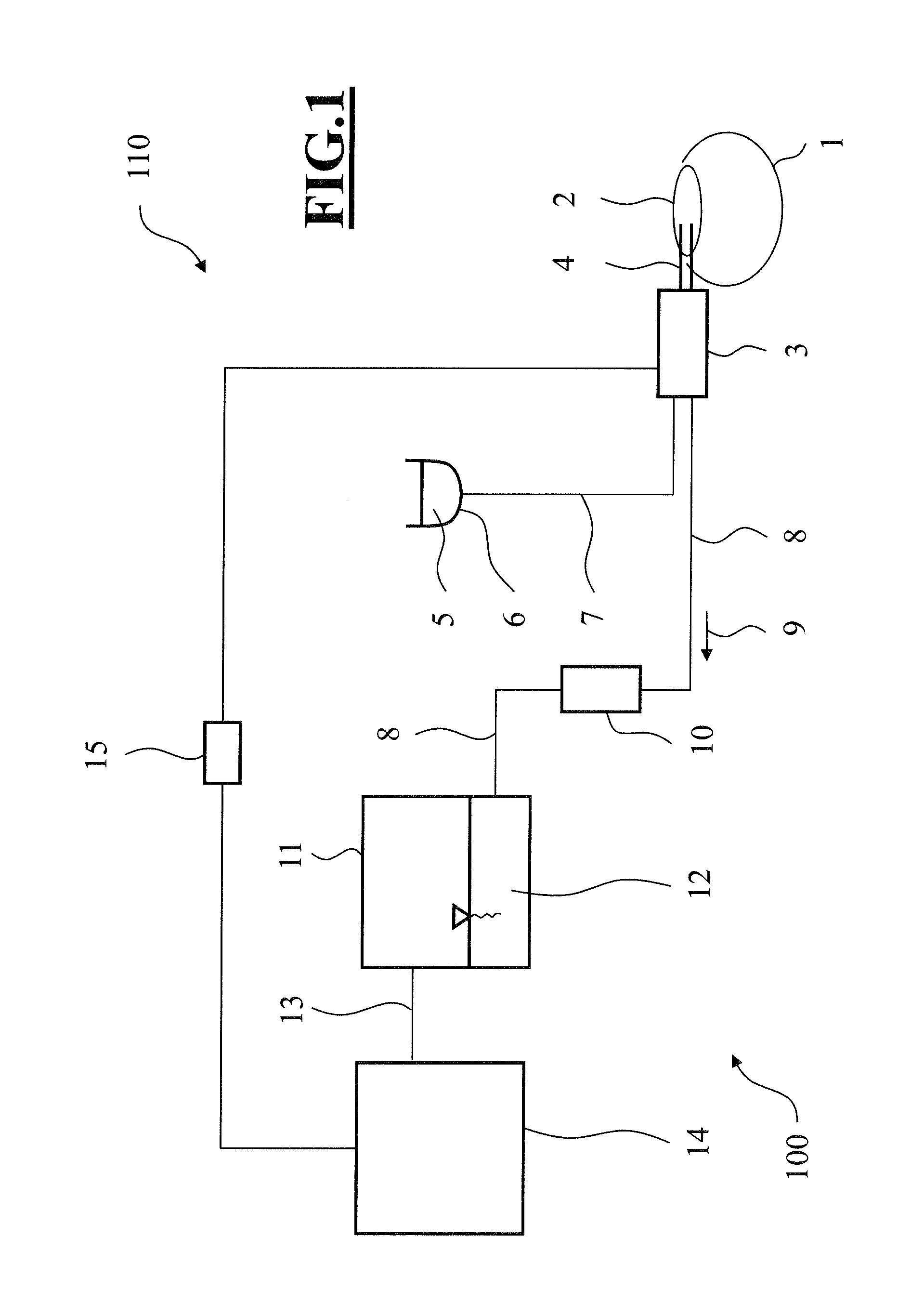
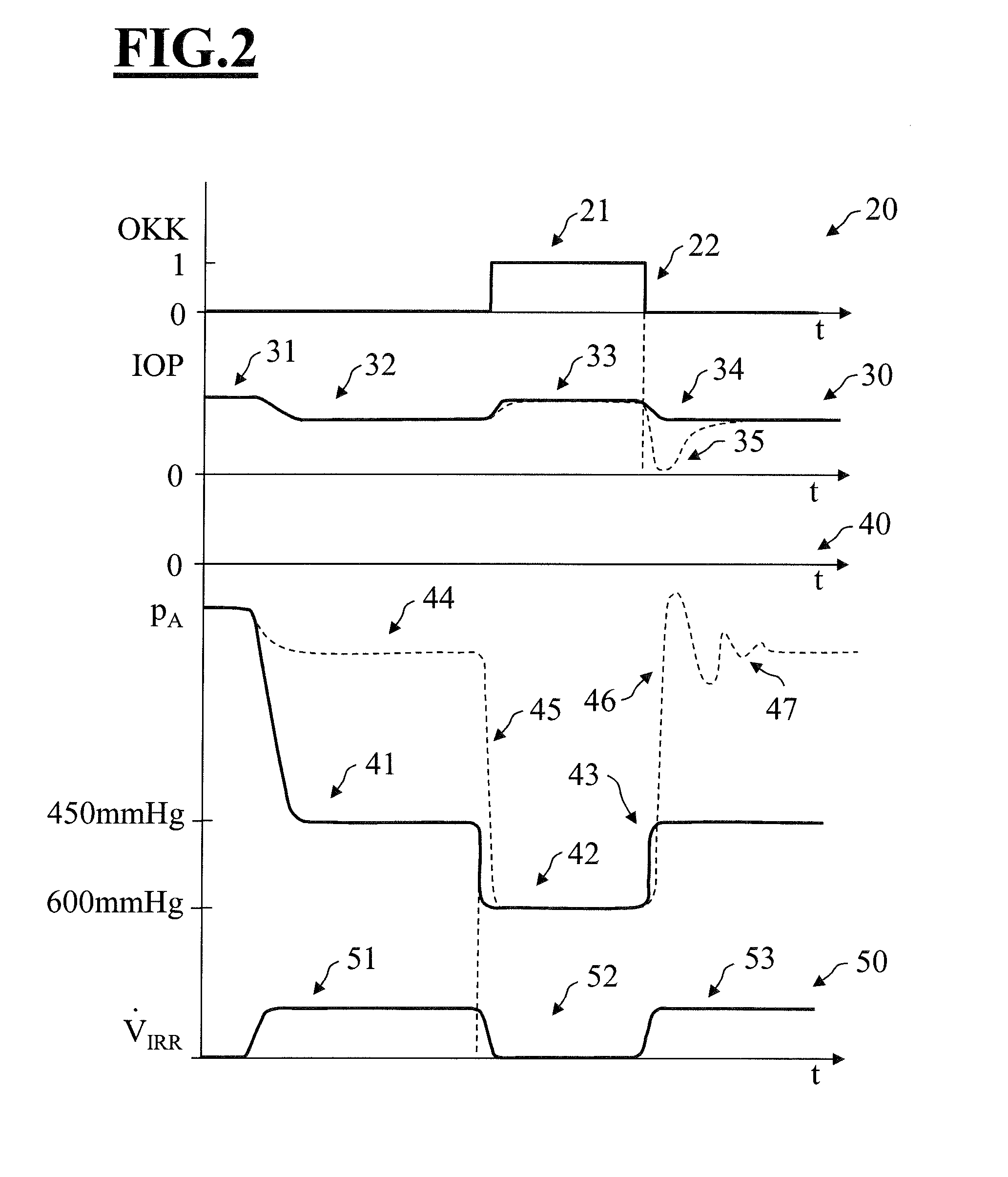
System, Apparatus and Method for Maintaining Anterior Chamber Intraoperative Intraocular Pressure
A system for detecting intraocular pressure events during phacoemulsification surgery having a surgical console, a handpiece having a proximal end being communicatively connected to an irrigation line and an aspiration line; a first sensor in communication with the aspiration line or the irrigation line for providing a first measurement value; and a second sensor in communication with the aspiration line for providing a second measurement value; and wherein at least one characteristic of the irrigation fluid or aspiration fluid in their respective lines is changed in accordance with the difference between the first measurement value and the second measurement value. A system for calibrating patient eye level and wound leakage; detecting occlusion or post occlusion surge; determining BSS usage or remaining in a container; and detecting a fluid line abnormality using a first sensor and a second sensor in different configurations and differences in first and second measurement values.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Telescopic female drug vial adapter
A telescopic female drug vial adapter including a spike component telescopically mounted on a skirt component for snap fit on and puncturing a drug vial in an actuated position. The telescopic female drug vial adapter is particularly suitable for implementation in a vented version to avoid wetting of its air filter during aspiration of liquid contents from a drug vial.
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES IL LTD
Ophthalmic surgical apparatus for phacoemulsification
InactiveUS20150196425A1Short operating timeSmall in intraocular pressureEye surgerySurgeryRotational axisLine tubing
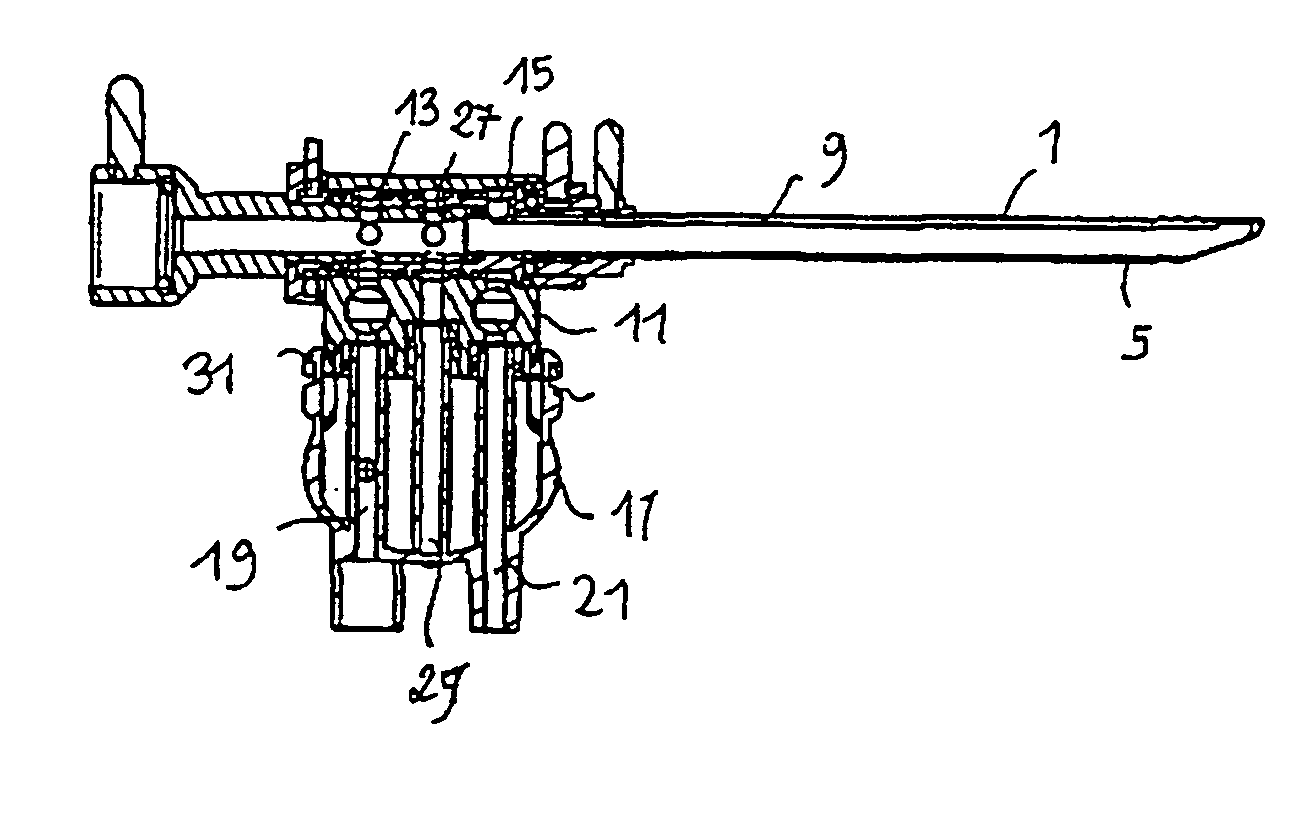
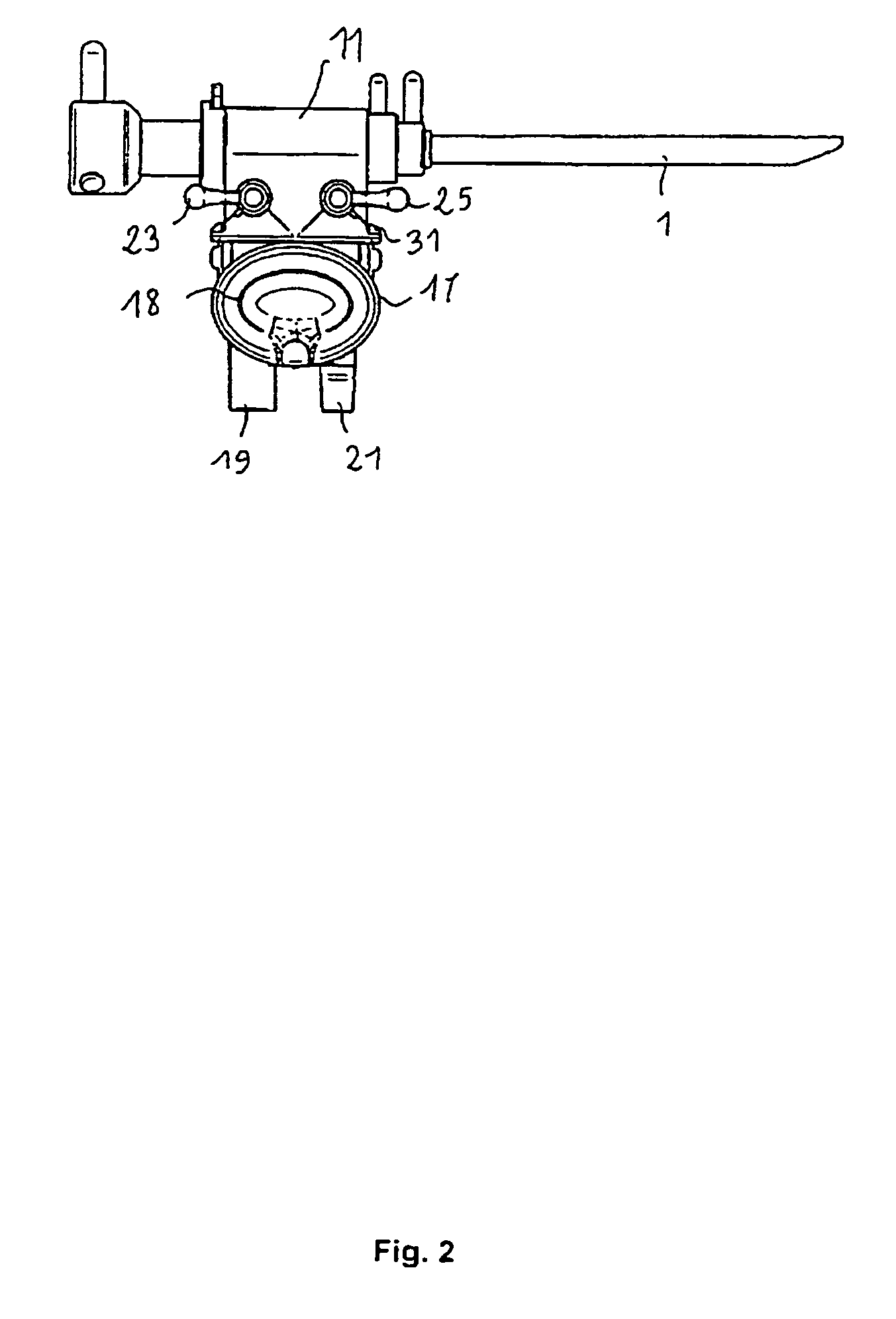
An ophthalmic surgical apparatus for phacoemulsification includes an aspiration line to transport an aspiration fluid and particles of an eye generated by phacoemulsification. A suction vacuum pump draws in the aspiration fluid and the particles of the eye via the aspiration line and a flow limiter adjustably limits the flow to a flow lying in a range of 5 milliliter to 100 milliliter per minute. The aspiration line defines an inner cross section and has an outer wall. The flow limiter is arranged upstream of the suction vacuum pump and has at least two press-on elements. The elements are each configured to contact engage the outer wall so as to cause the inner cross section to be reduced. The press-on elements are disposed mutually spaced so as to define a predetermined distance therebetween and are arranged to be rotatably movable in a rotational direction about a common rotational axis.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Modular liquid handling system
Integrated modular liquid handling systems are described. The modular liquid handling systems may be customized for use in a variety of applications, including sample processing, assays, diagnostic analyses, and separation of biomolecules. The liquid handling systems may include a variety of integrated modules that provide functions including dispensing of liquids, aspiration of liquids, sensing of liquid parameters, and detection of signals.
Owner:COUNSYL INC
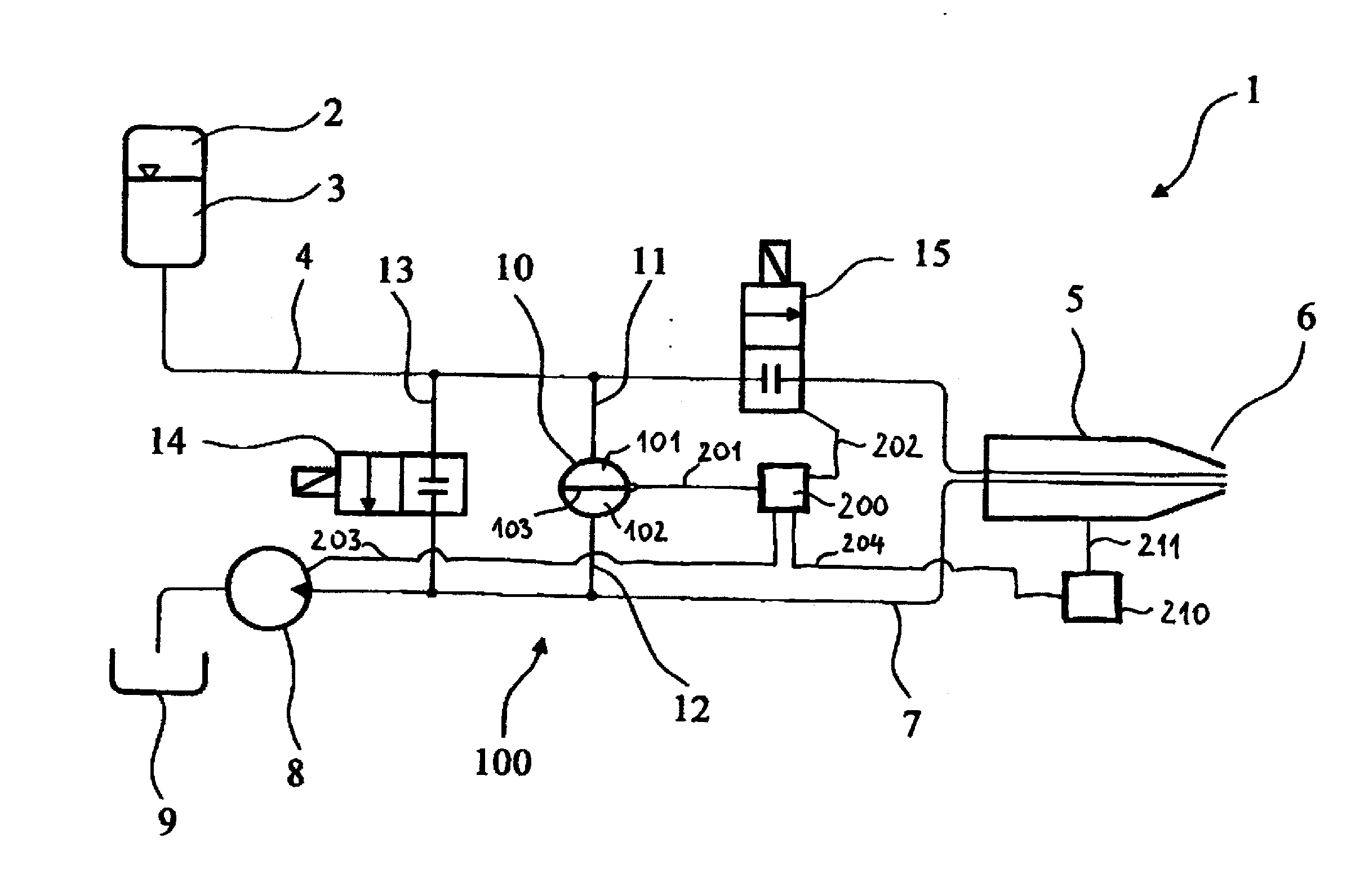
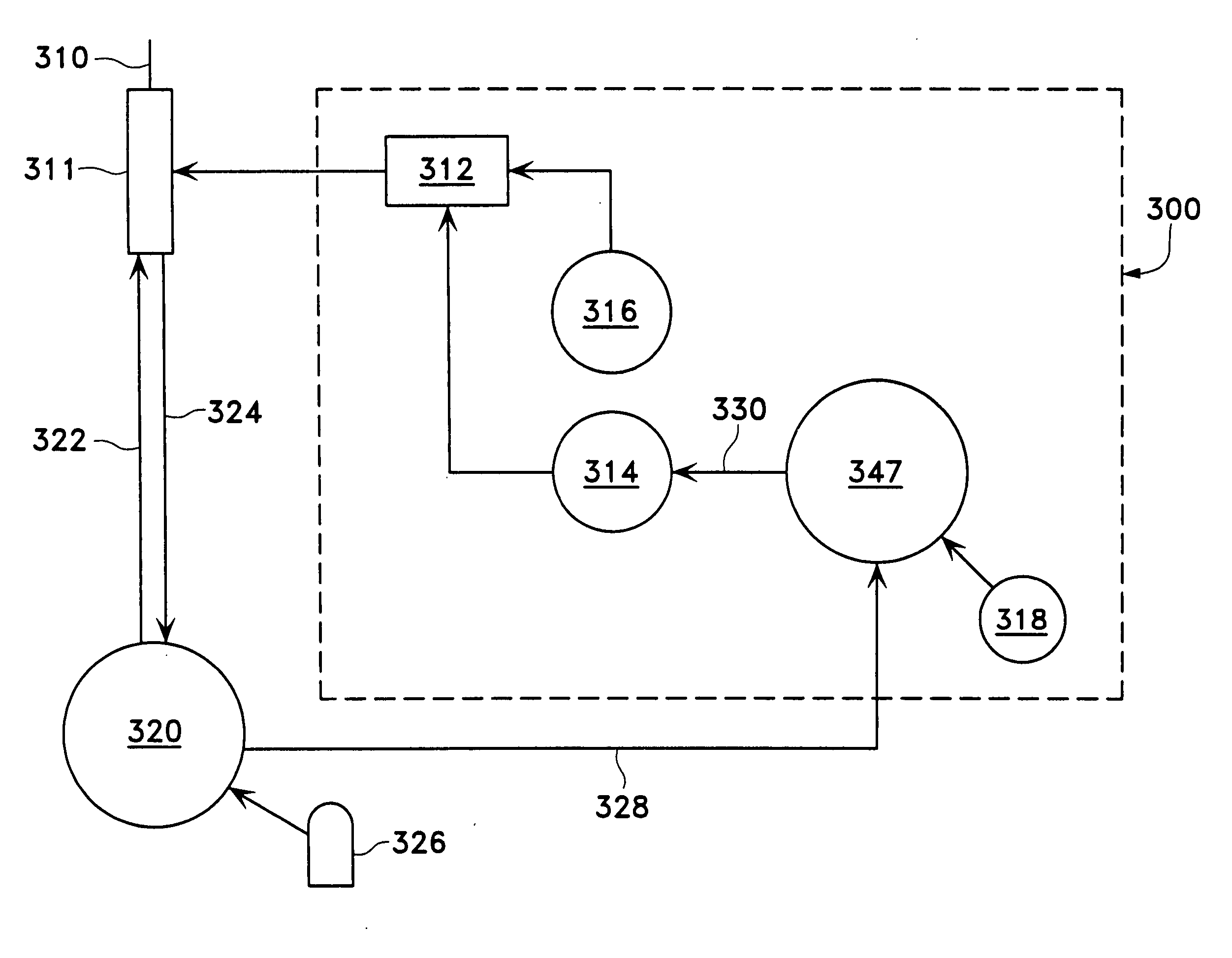
System and method for providing pressurized infusion and increasing operating room efficiency
ActiveUS20160367735A1Smooth fluid flowImproved pressurized deliveryEye surgeryEnemata/irrigatorsPeristaltic pumpOperating theatres
Apparatus, system and method for providing pressurized infusion of liquids and, more particularly, providing a stable and pressurized flow of fluid to the eye during surgery. Aspiration fluid may be received via an aspiration line at a first peristaltic pump, where aspiration fluid is transferred to a Venturi tank reservoir coupled to a second peristaltic pump. Fluid from a fluid source is provided via a third peristaltic pump to a pressurized infusion tank. A determination is made if the pressure in the pressurized infusion tank is at a predetermined level, where fluid may be transferred from the pressurized infusion tank to an irrigation line when pressure in the pressurized infusion tank is determined to be at the predetermined level. Alternate activation of a plurality of aspiration and irrigation lines are also provided.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Injection dosing method and dosing apparatus utilizing same
InactiveCN102579259AAvoid repeated puncture of liquid bottle rubber stopperEasy to operatePharmaceutical containersMedical packagingEngineeringBottle
The invention provides an injection dosing method and a dosing apparatus utilizing the same. The injection dosing method includes building a first passage between a liquid bottle and a negative pressure suction apparatus and a second passage between the liquid bottle and an injection ampoule. The negative pressure suction apparatus sucks air in the liquid bottle through the first passage so that negative pressure is formed inside the liquid bottle, the negative pressure in the liquid bottle is transmitted to the terminal of the second passage in the injection ampoule through the second terminal so that liquid medicine is sucked into the liquid bottle, and accordingly the dosing process is completed. The dosing apparatus comprises a double-passage puncture needle, a suction tube and the negative pressure suction apparatus, wherein the head of the double-passage puncture needle is provided with a liquid medicine inlet and an air suction hole, the other end of the puncture needle, exposed from a plug of the liquid bottle, is provided with a negative pressure connector and a suction tube connector, the air suction hole of the puncture needle is communicated with the negative pressure connector to form the first passage, the liquid medicine inlet and the suction tube connector of the puncture needle are communicated with the suction tube to form the second passage. By the aid of the dosing method and the dosing apparatus utilizing the same, operation can be simplified, and defects of puncturing the rubber plug of the liquid bottle repeatedly and operational complication in the prior art are avoided.
Owner:LANZHOU WENHE MEDICAL EQUIP RES & DEV CO LTD
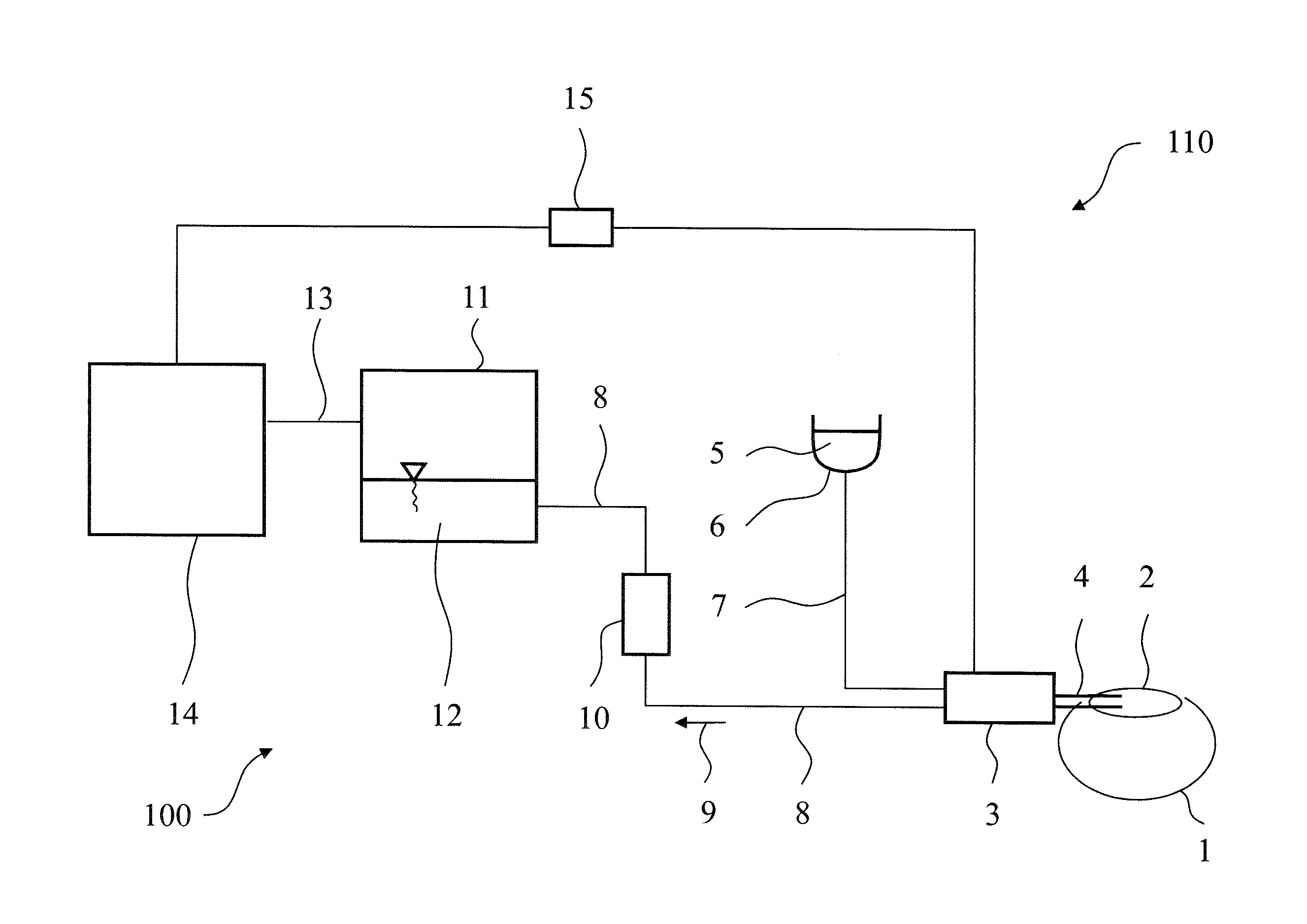
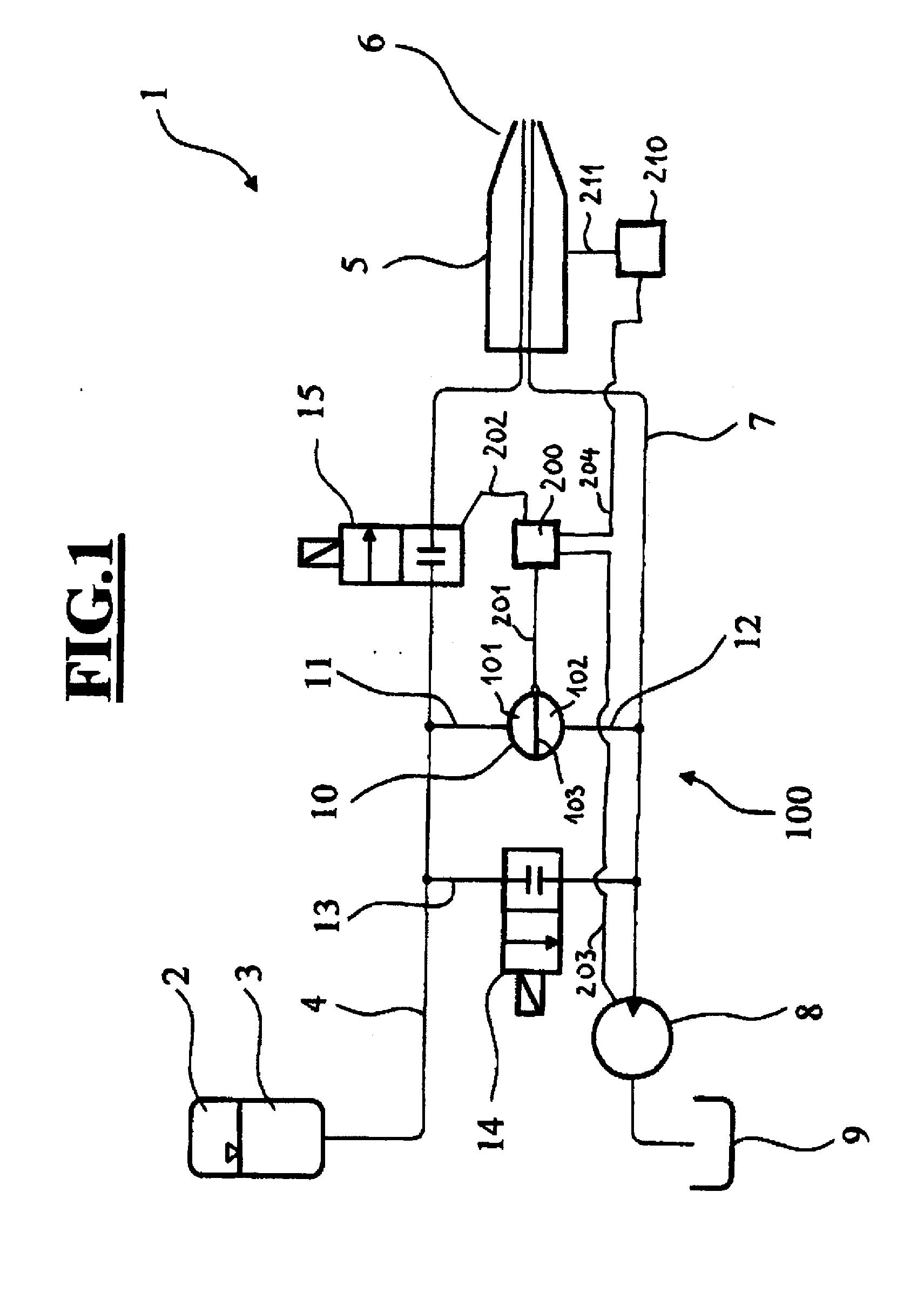
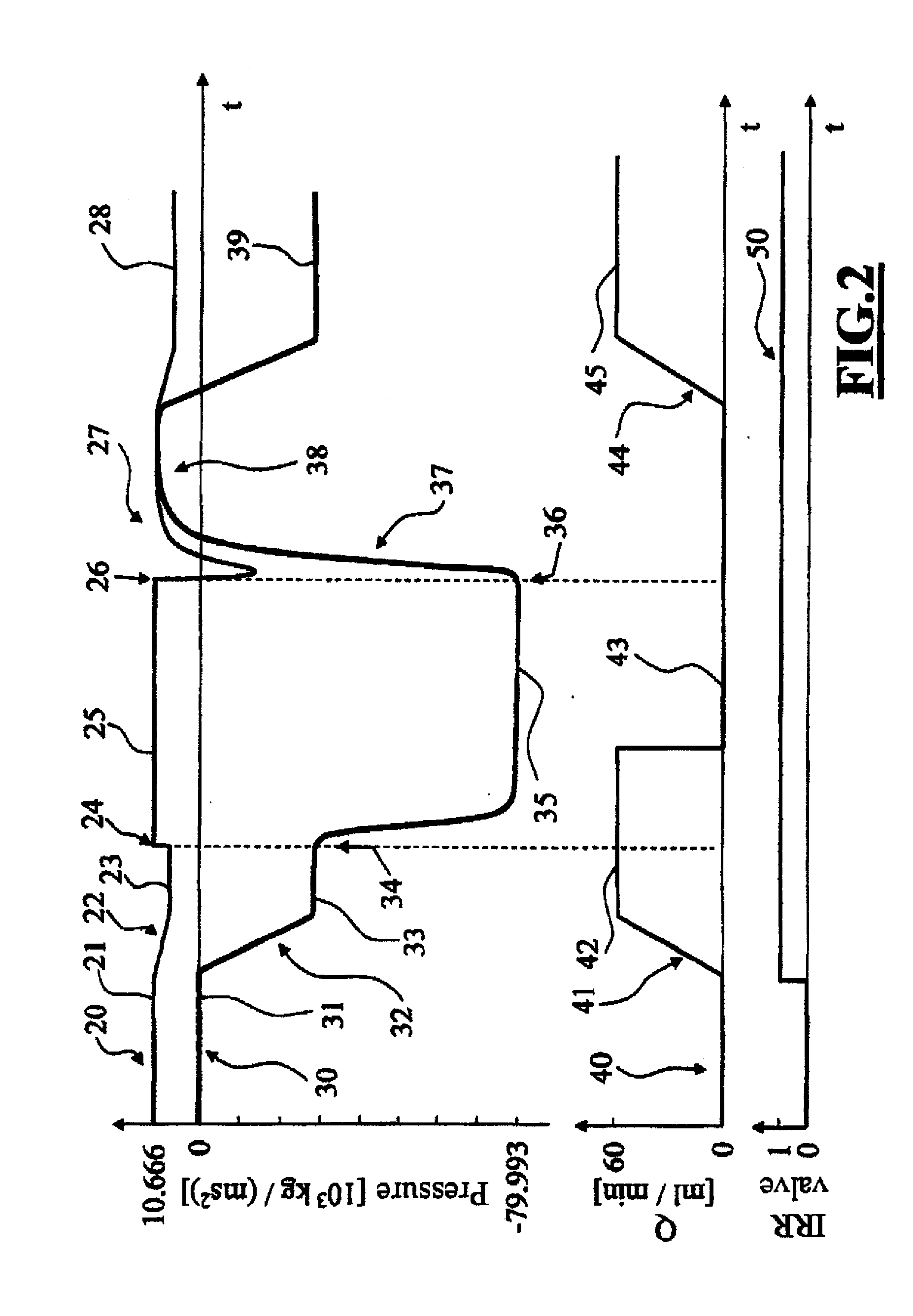
Ophthalmosurgical Measuring Device
InactiveUS20120232466A1Quick checkMinimal outlayEye surgeryEnemata/irrigatorsDifferential pressureEngineering
An ophthalmosurgical measuring device (100) has an irrigation line (4) through which irrigation fluid (3) can be transported and an aspiration line (7) through which aspiration fluid can be transported to a suction pump (8). The ophthalmosurgical measuring device also includes a sensor (10) with which a differential pressure between irrigation line (4) and aspiration line (7) can be detected.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
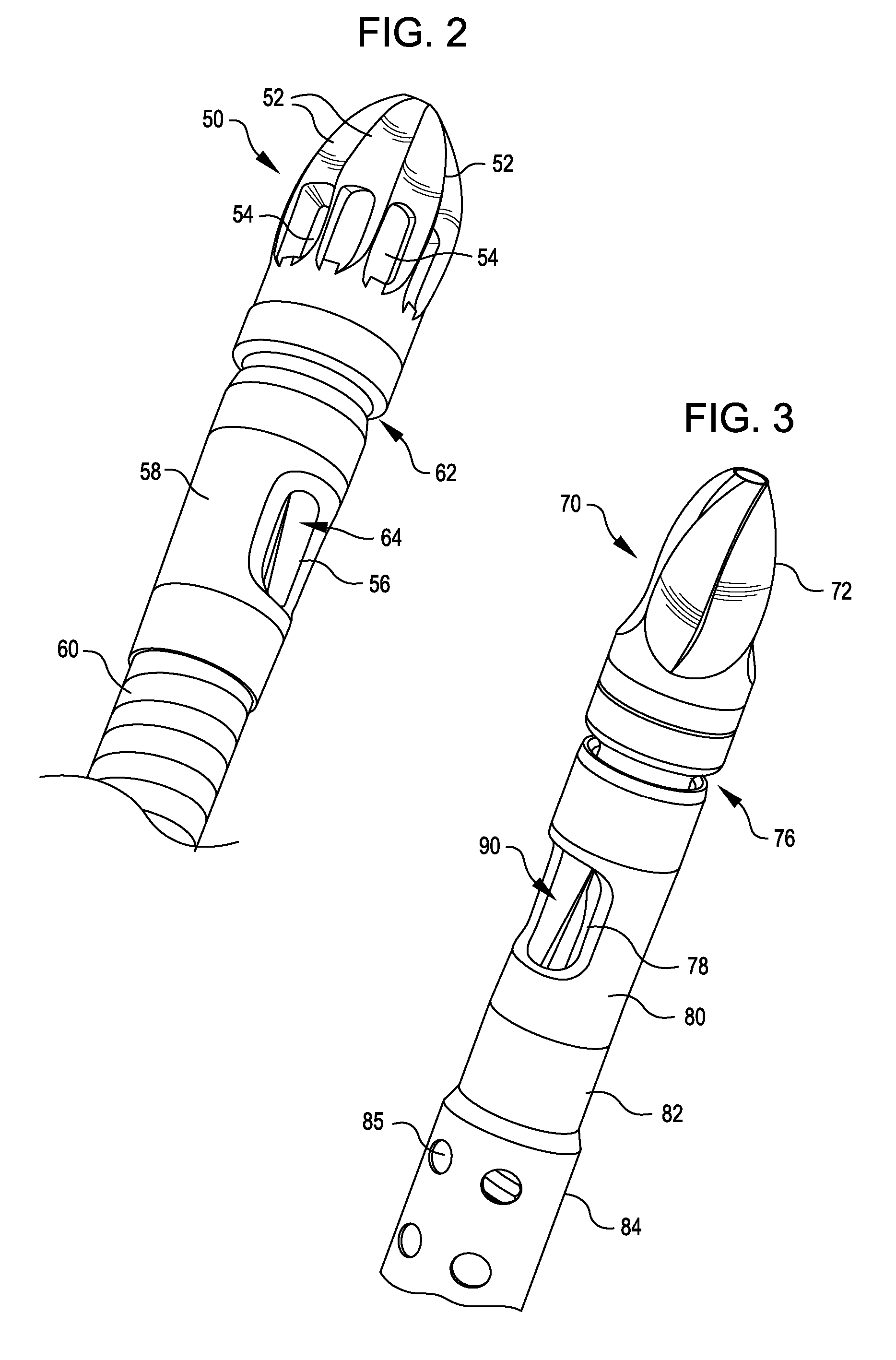
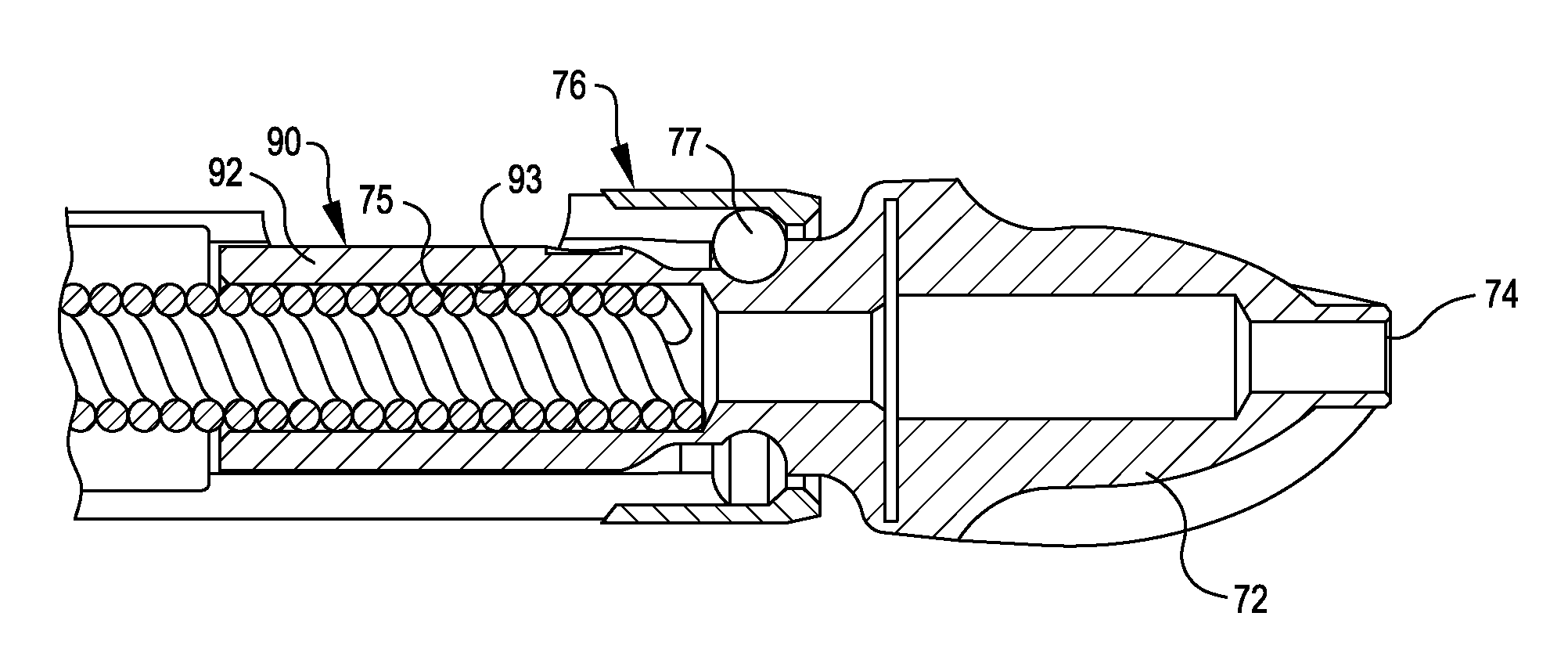
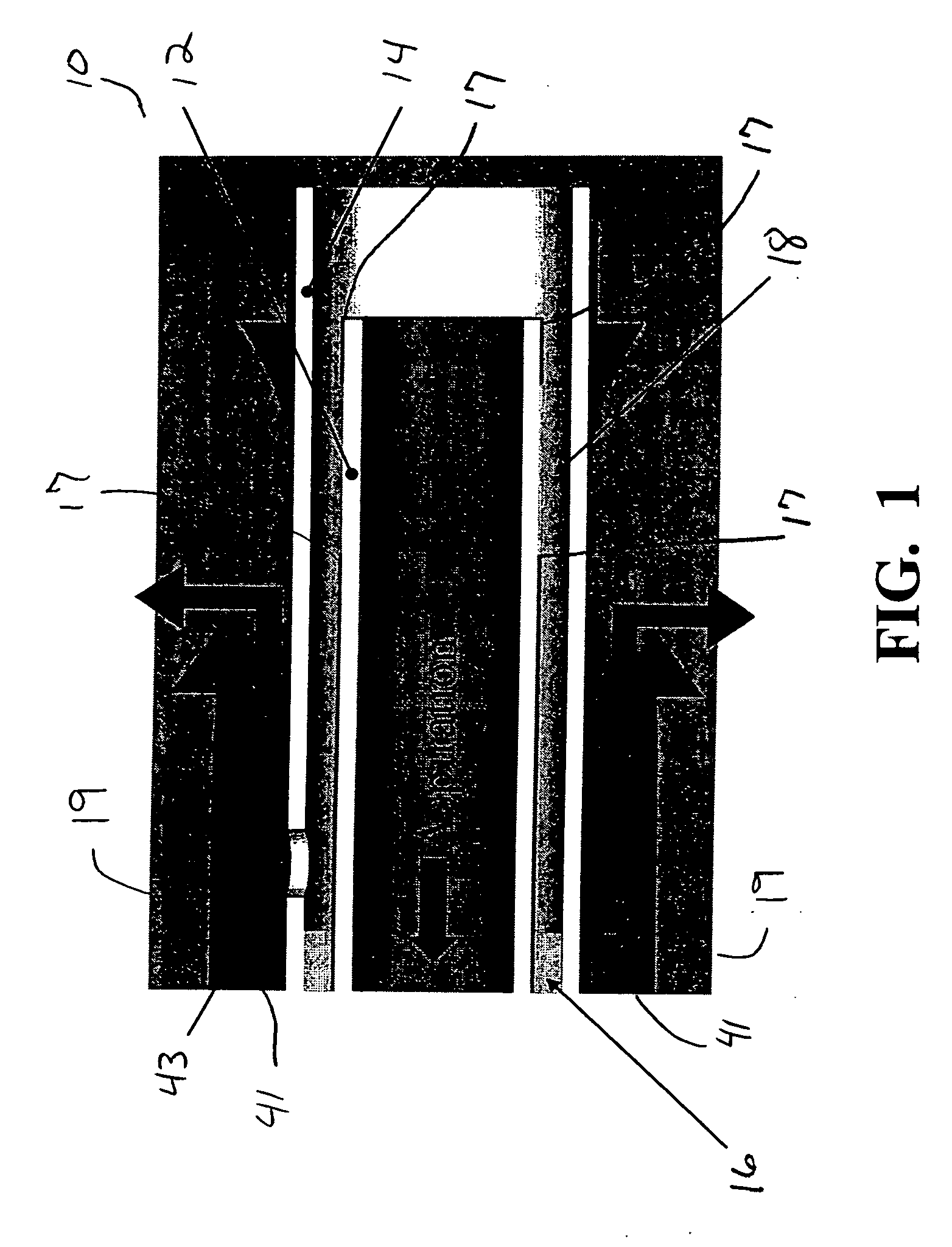
Surgical handpiece tip
A surgical handpiece having a tip with at least two coaxially spaced electrically conductive tubes. The tubes are separated by an electrical insulator. The interior of the inner tube is used for aspiration of liquefied tissue. The outer tube is surrounded by a soft irrigation sleeve that forms an irrigation fluid path. The distal portion of the interior tube terminates inside of the outer tube so as to form a boiling region. Surgical fluid from the irrigation fluid path can enter the boiling region through a hole or port in the outer tube. Electrical current is passed between the inner and outer tube to rapidly boil any surgical fluid in the boiling region. The boiling fluid rapidly expands out of the ring between the tube ends and forces hot fluid to contact the targeted tissue, thereby liquefying the tissue and allowing the tissue to be aspirated. Such a construction allows the boiling chamber to be self-priming and operate even if the outer tube is occluded with material.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method Suction Device and Related Method Thereof
ActiveUS20130131615A1Reduce incidence of obstructionUnclog easily and quicklySurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsMedical emergencyMedical treatment
A system or device for providing medical suction, particularly for intubating patients, wherein the system or device helps prevent clogging from solids dispersed in the liquid to be suctioned. This device will allow the user to effectively clear an airway or other region of the patient while minimizing the occurrence of clogs and providing for the effective and expedited unclogging of the device without the necessity of removing the device from the patient or requiring two hands to unclog.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Endoscopy system and a pressure transmitting connector for said system
ActiveUS20070185452A1Pressure in the joint to be always checkedInfusion syringesFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesFlexible endoscopeTransmission channel
The inventive endoscopy system includes a cannula for arranging an endoscope and forming, between said cannula and endoscope, an irrigation or aspiration channel for transporting an irrigation or aspiration fluid, respectively, a connection ring mounted around the cannula and provided with a connection channel connectable to the irrigation or aspiration channel, respectively and a connector which is mounted on the connection ring and includes a transport channel with the connection channel and a first pressure sensor for detecting pressure in the transport channel. The connection ring is provided with a bypass circuit connectable to the irrigation or aspiration channel, respectively and the connector including a dead channel connectable to the bypass circuit and a second pressure sensor for detecting pressure in the dead channel.
Owner:FUTURE MEDICAL SYST
Ophthalmosurgical measuring device
The invention relates to an ophthalmosurgical measuring device (100) having: an irrigation line (4) through which irrigation fluid (3) can be transported, an aspiration line (7) through which aspiration fluid can be transported to a suction pump (8), and a sensor (10) with which a differential pressure between irrigation line (4) and aspiration line (7) can be detected.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Ophthalmic surgical cassette and system
A cassette 74 for use with an ophthalmic surgical pump 16 for collecting aspirant fluid and tissue from a patient's eye includes a rigid walled container 18 having an interior volume 42. At least one tapered alignment slot 20 is formed in a side wall of the container 18 and extends from a back wall 24 towards a front wall 26. An irrigation and aspiration manifold base 50 is removeably attached to the container 18. An aspiration path 46 is formed within the container 18 for receiving the aspiration fluid and the tissue from the eye and directing the flow of fluid towards a front half of the container 18 before the fluid and tissue collects within a majority of the interior volume 42 of the container 18. A fluid level indicator 34 is formed on a wall 22 of the container 18, such that an associated photo-detector 86 of the pump 16 may determine a level of fluid in the container 18.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Aspiration Path Resistive Element
InactiveUS20120157943A1Reducing occlusion surgeConvenient lengthEye surgerySuction devicesSurgical siteEngineering
According to one exemplary aspect, this disclosure is directed to an aspiration system for a phacoemulsification surgical system. The system includes a pump and a flexible tubing configured to convey aspiration fluid from a hand piece to the pump. The flexible tubing includes a non-compliant, resistive element associated with the hand piece and disposed between the surgical site and the flexible tubing. The resistive element comprises a fluid pathway having substantially consistent nominal inner diameter and being configured to convey the aspiration fluid to the flexible tubing, the resistive element being formed in a compact orientation that provides a nonlinear fluid pathway length that is significantly greater than the axial length of the resistive element. The resistive element is structurally configured to provide occlusion surge resistance due to pressure changes resulting from occlusions in the aspiration path at the hand piece needle.
Owner:ALCON RES LTD
Surgical handpiece with disposable concentric lumen work tip
A surgical handpiece has a connecting body with a distal end and a work tip with a hub at a proximal end. The hub is detachably connected to the connecting body by a threaded connector. The work tip has an open operating end at a distal end. This opening leads an axial channel extending through the work tip from the operating end to the hub. A radial channel extends from the axial channel in the hub to the external surface of the hub. A sleeve surrounds and is spaced from the hub. This sleeve extends to the vicinity of the operating end of the work tip, and has a first external connector in the region of the radial channel of the hub. The sleeve also has a second external connector. A seal is provided for establishing a fluid connection between the radial channel of the hub and the second external connector of the sleeve. The first external connector of the sleeve is in fluid connection with an irrigation channel between the inner surface of the sleeve and the external surface of the work tip. This irrigation channel extends to the vicinity of the operating end of the work tip for delivery of irrigation fluid to that area. The irrigation channel is generally concentric with the axial channel in the hub. Aspiration fluid is withdrawn from the open operating end of the work tip, through the axial and radial channels of the hub, the seal and the second external connector of the sleeve to an aspiration pump.
Owner:SURGICAL DESIGN
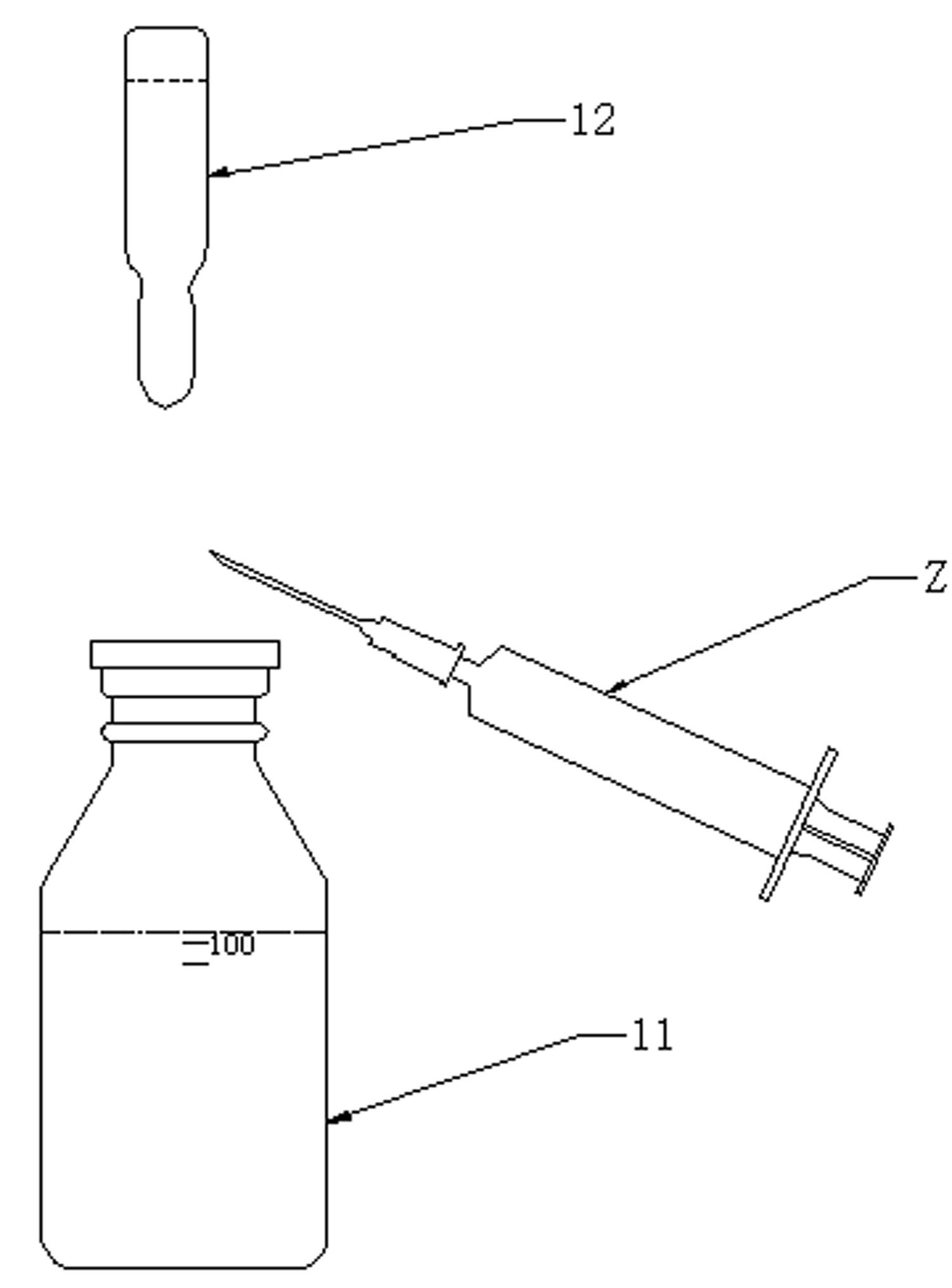
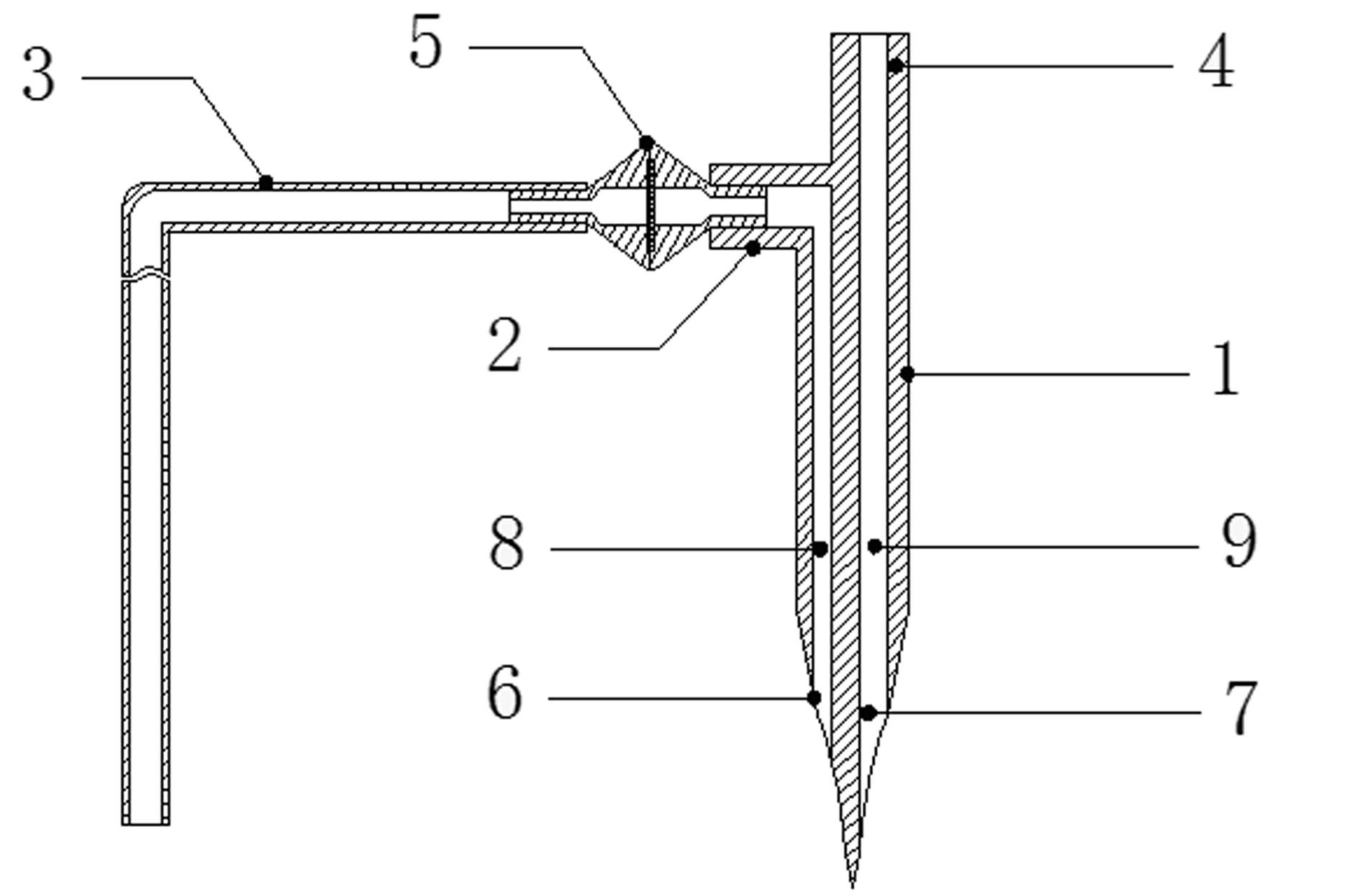
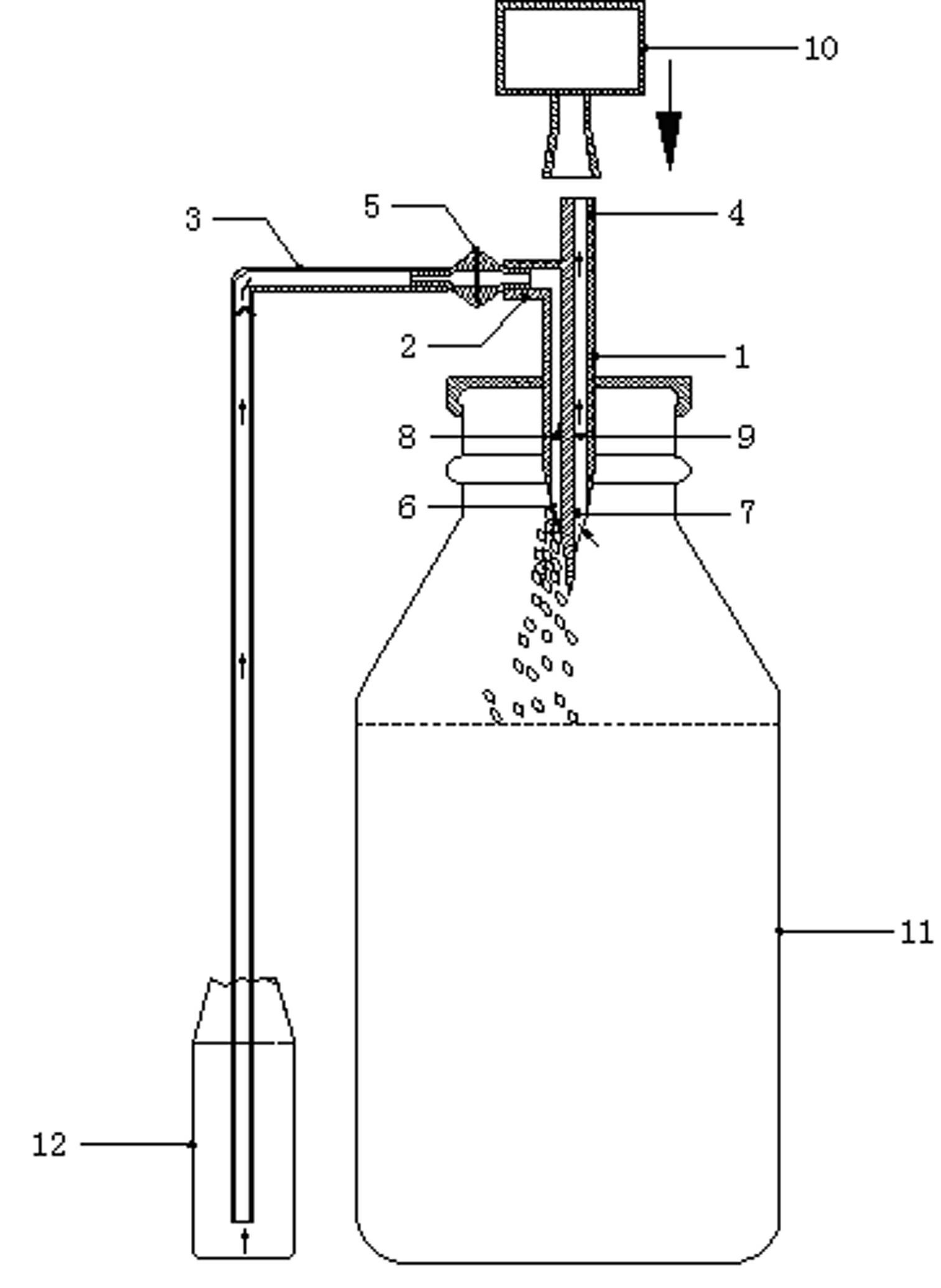
Disposable sterile precise automatic liquid suction dosing injection device
PendingCN114732726ARealize automatic suctionWill not affect each otherAutomatic syringesPharmaceutical containersMedicineEngineering
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com