Patents
Literature
28027results about How to "Good adhesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
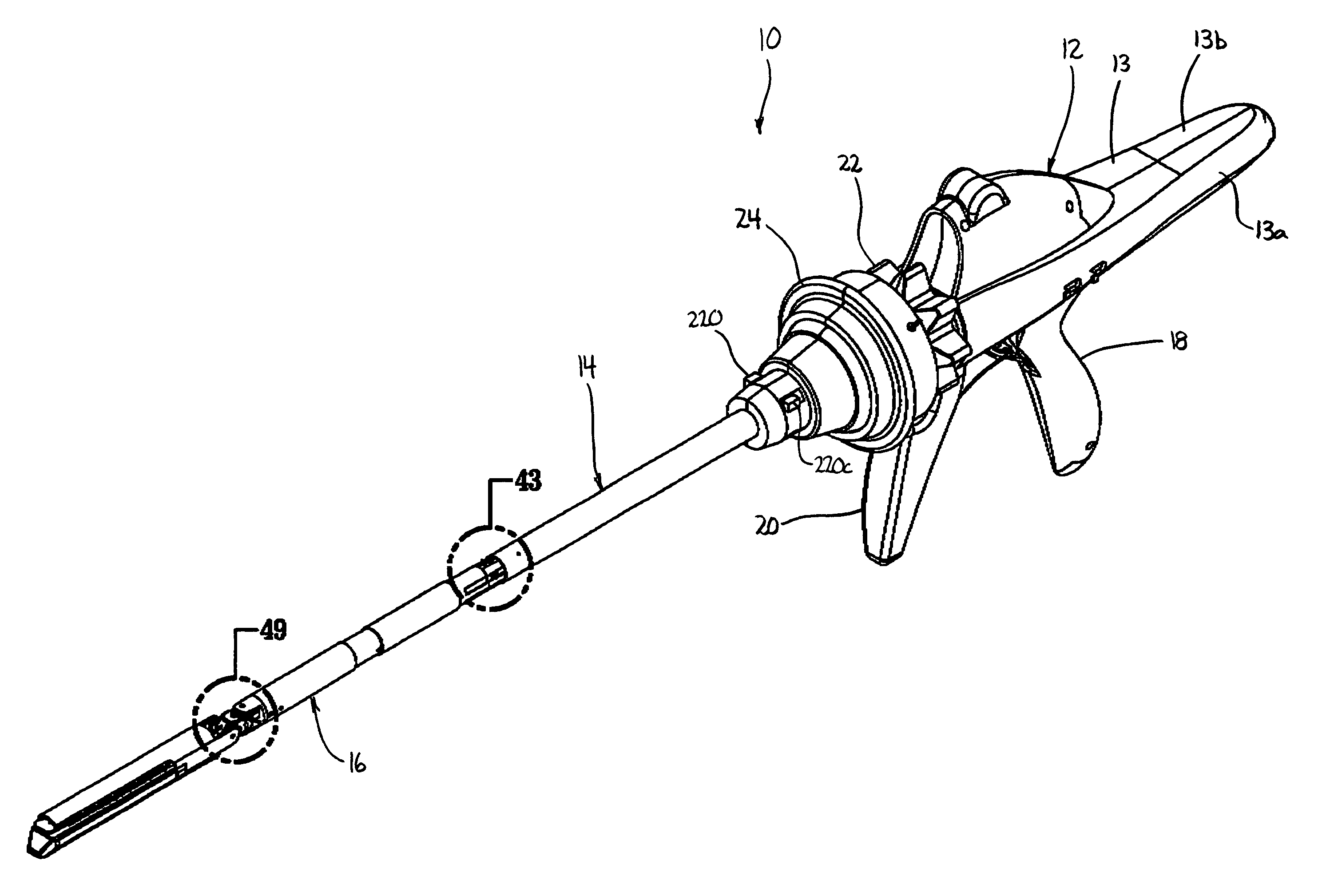
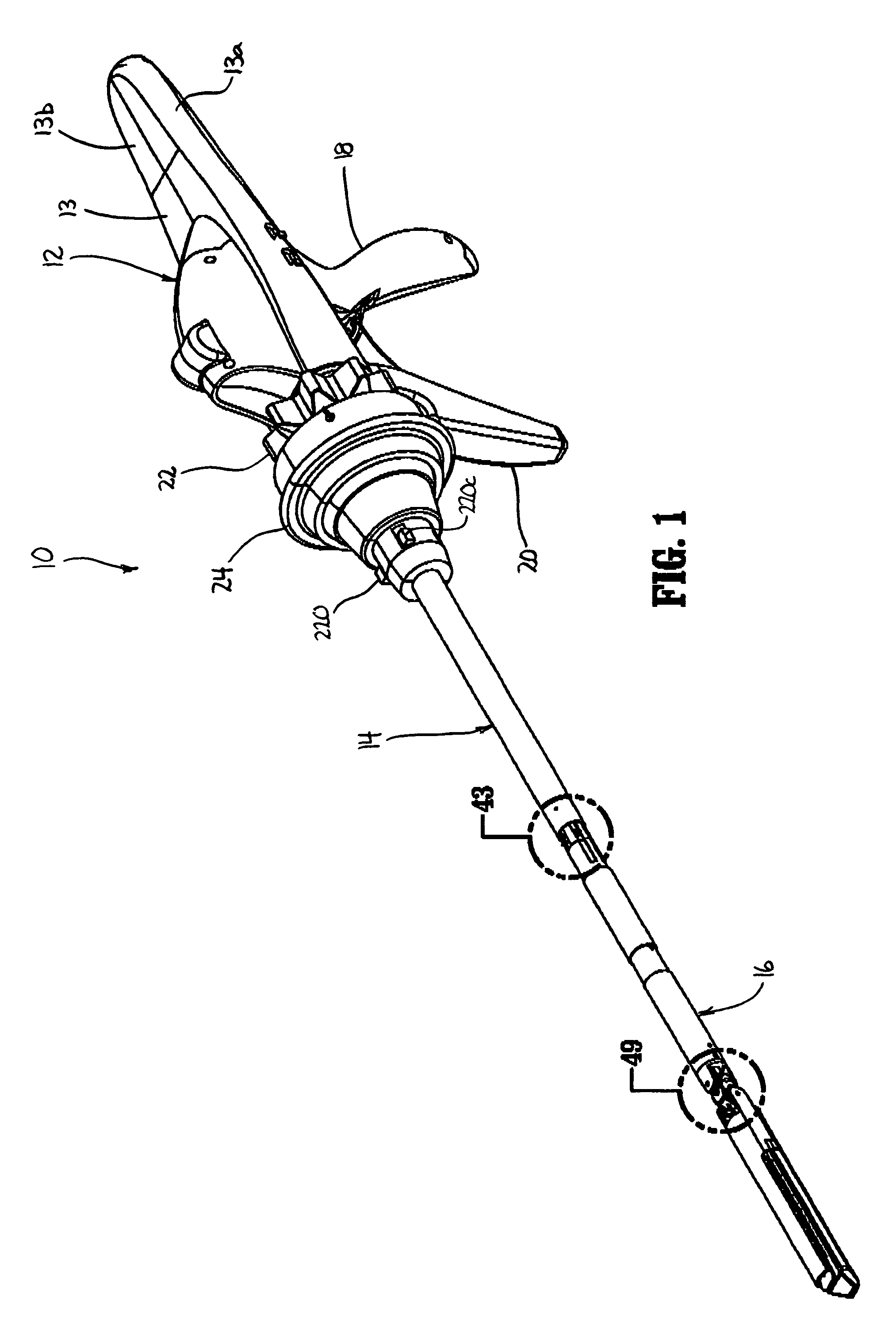
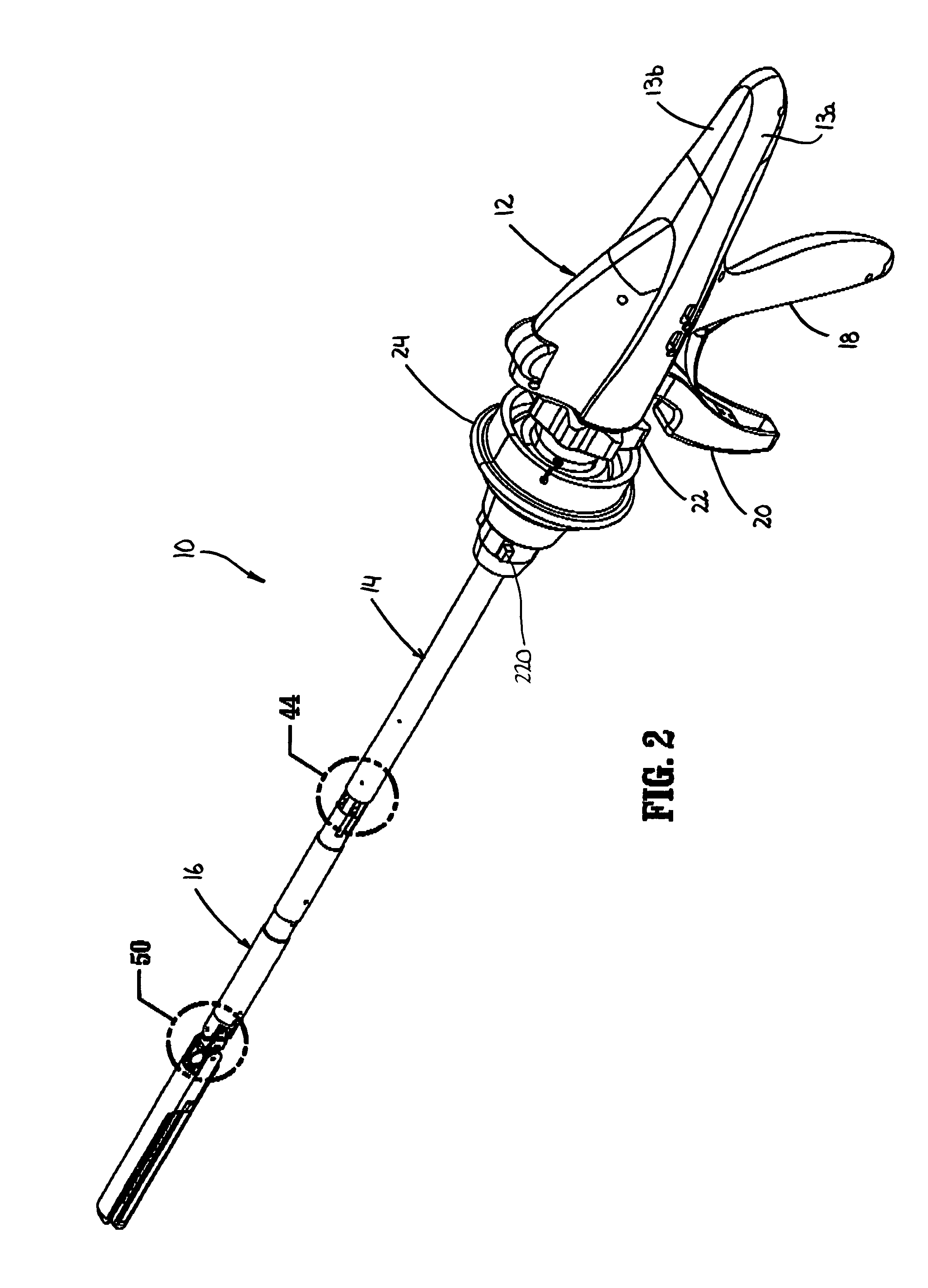
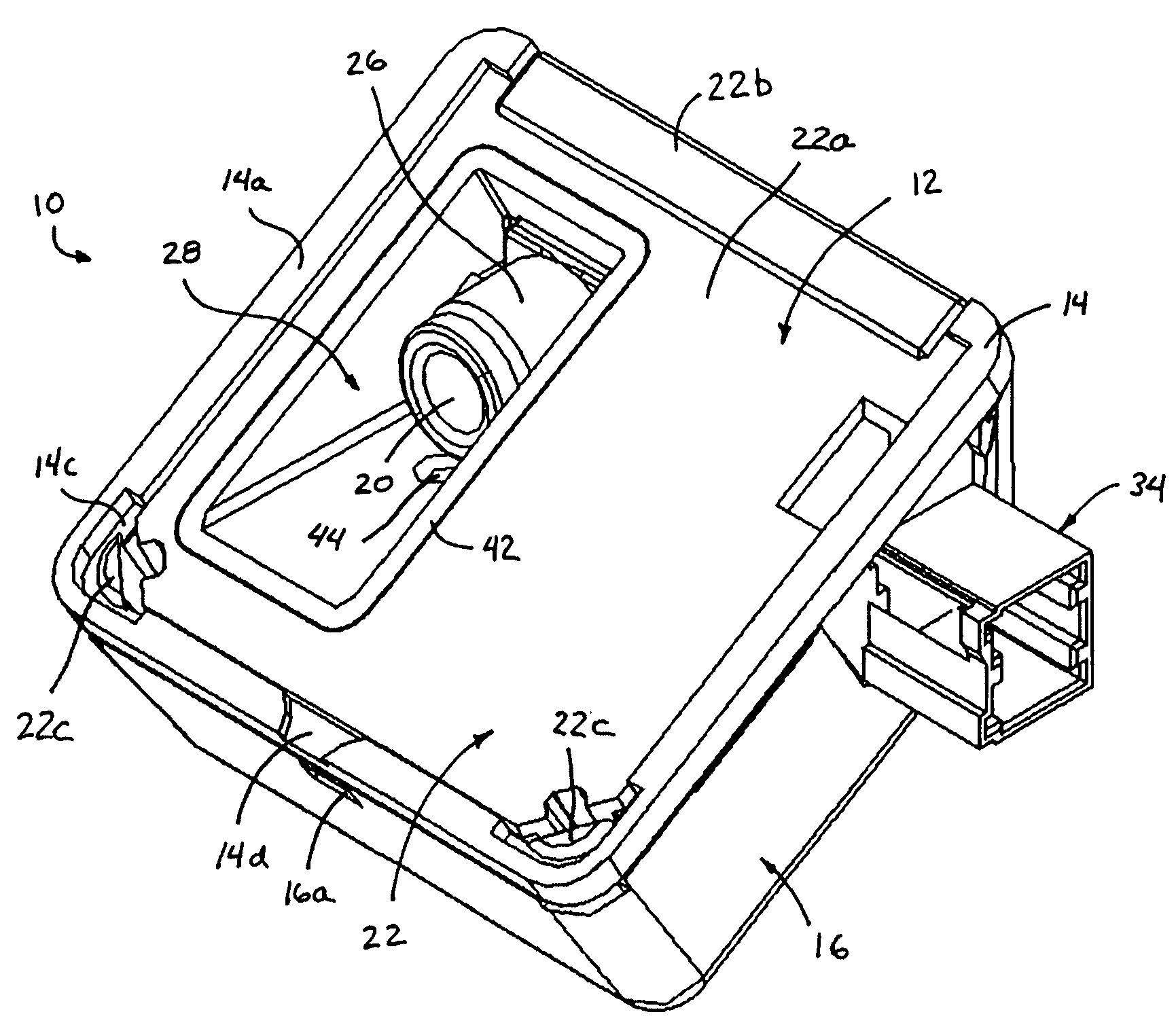
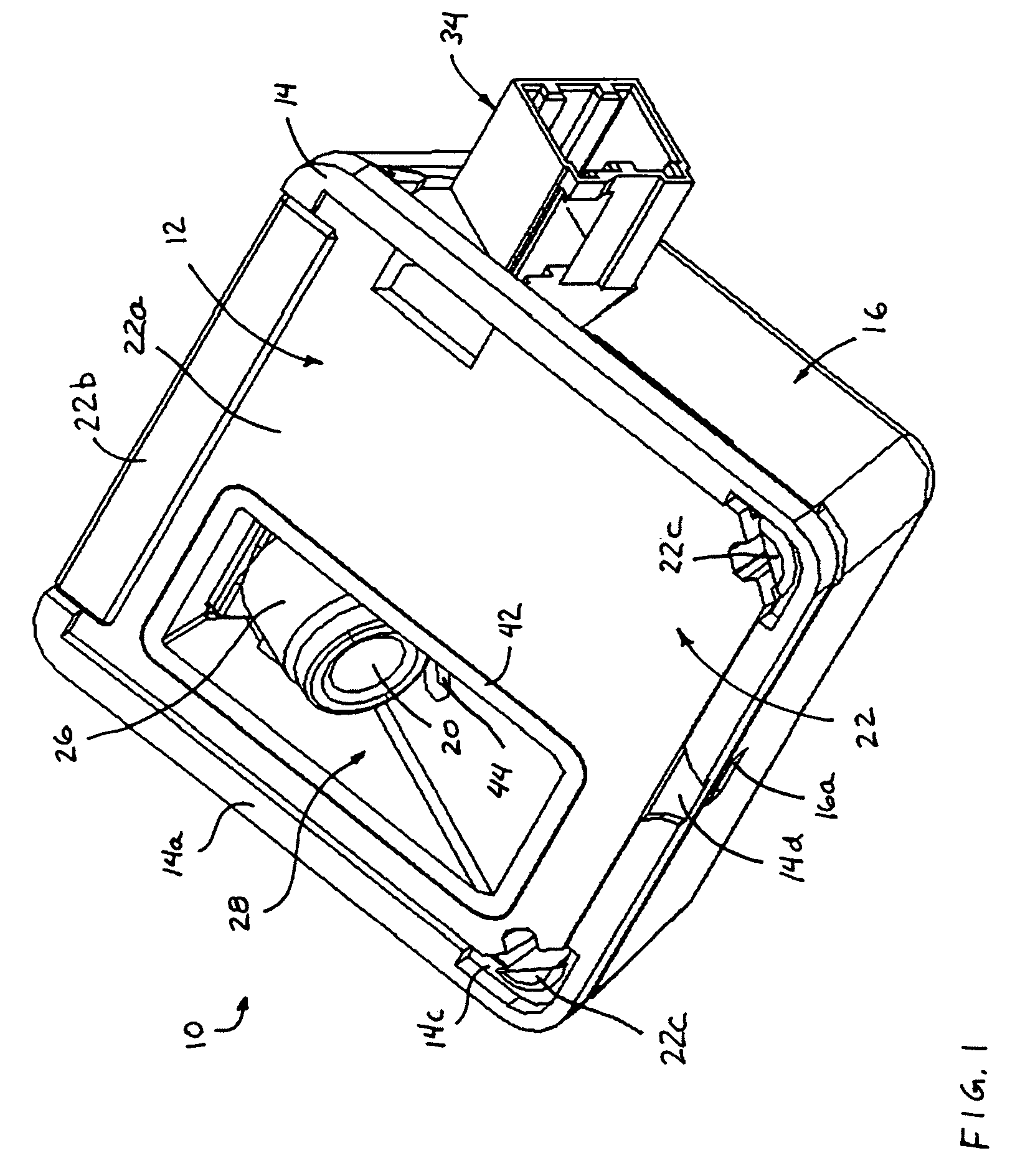
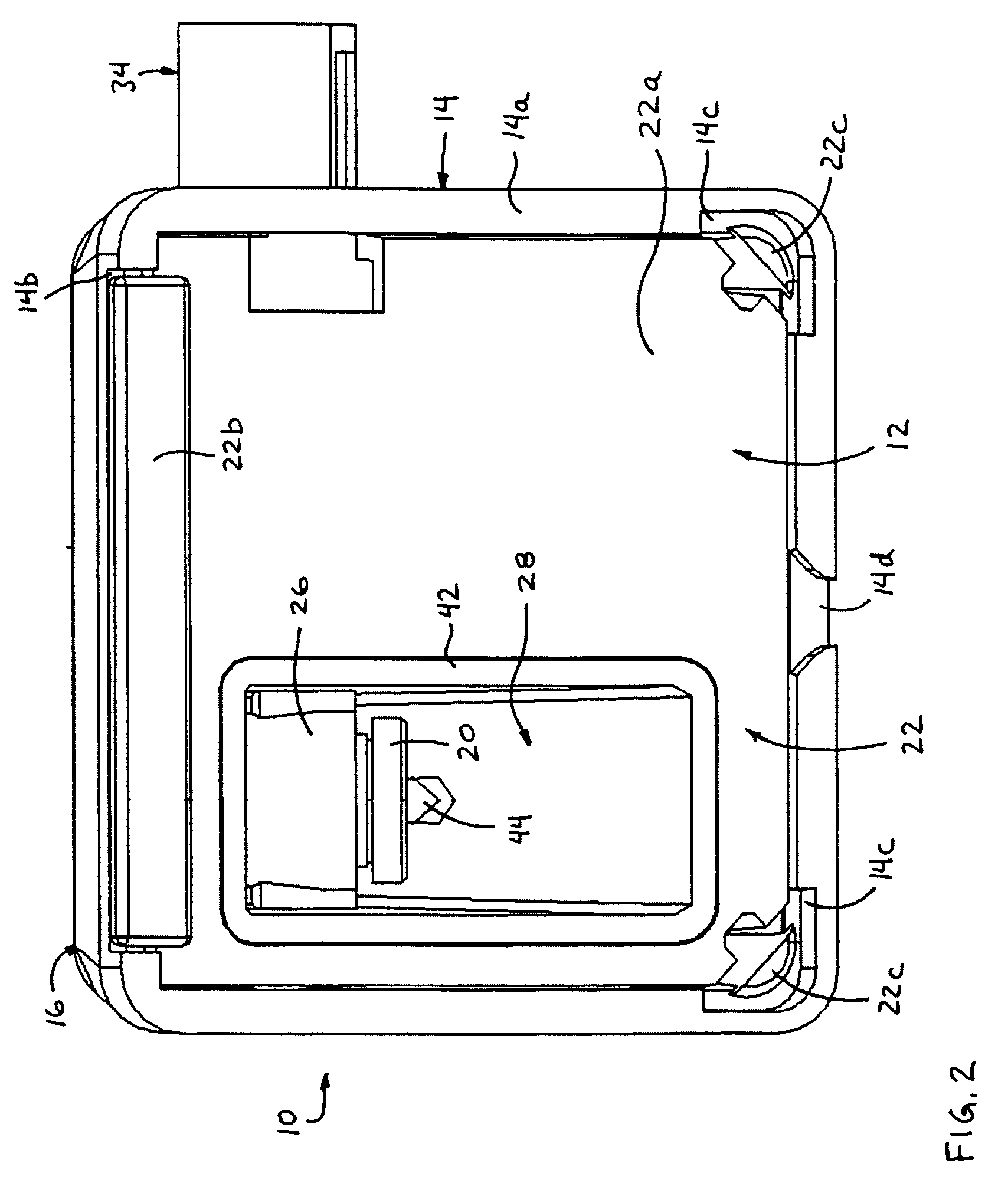
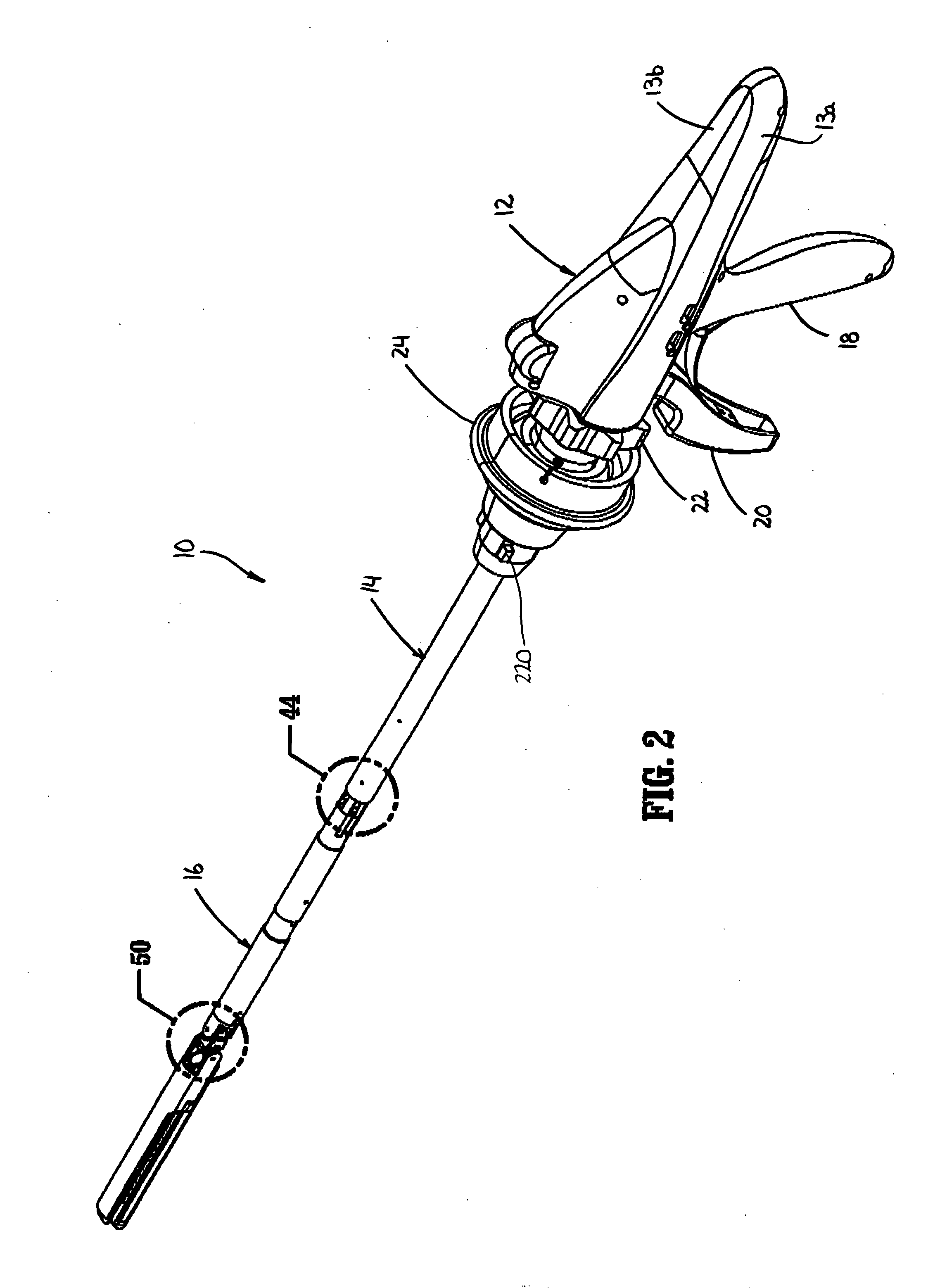
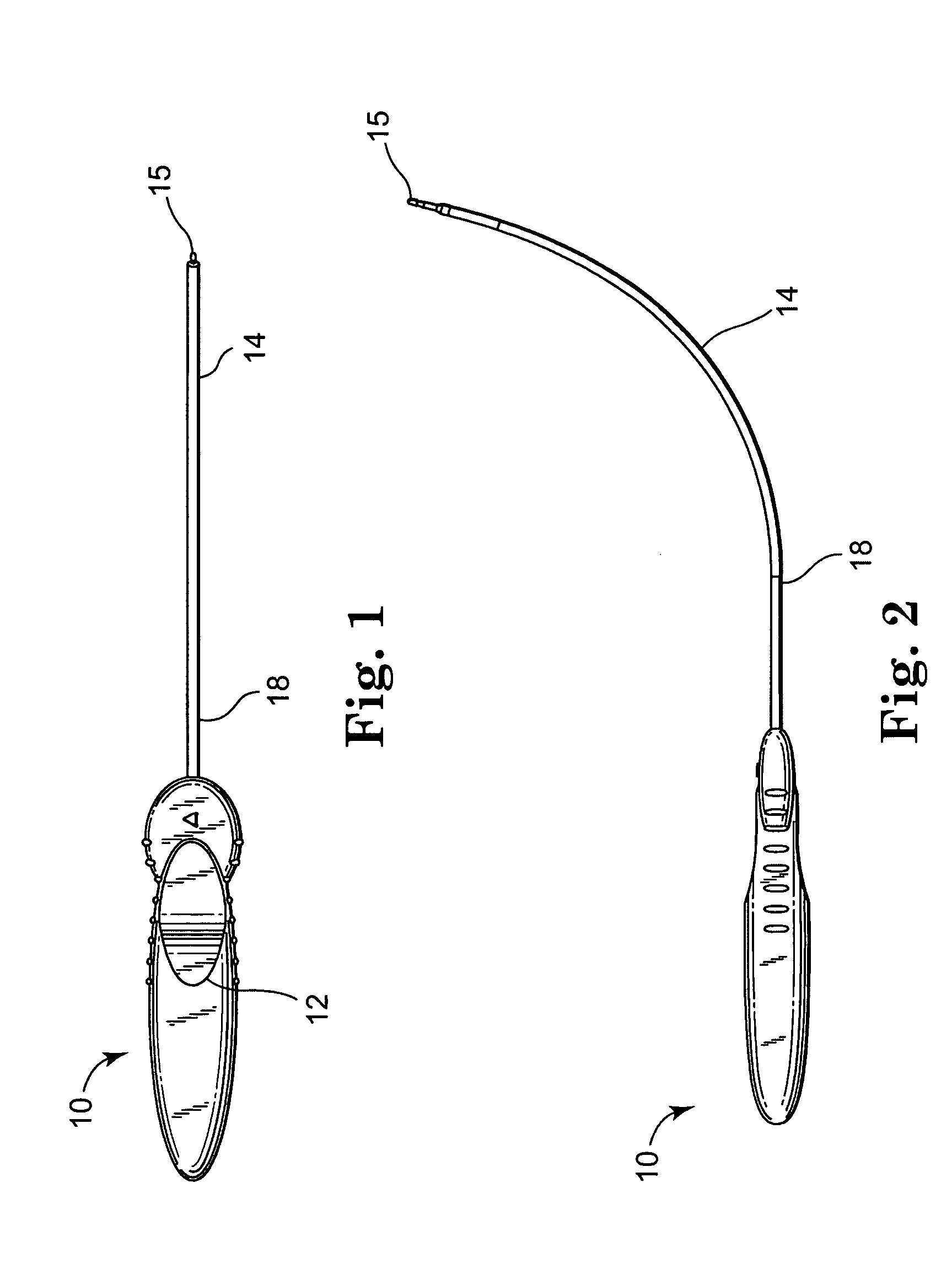
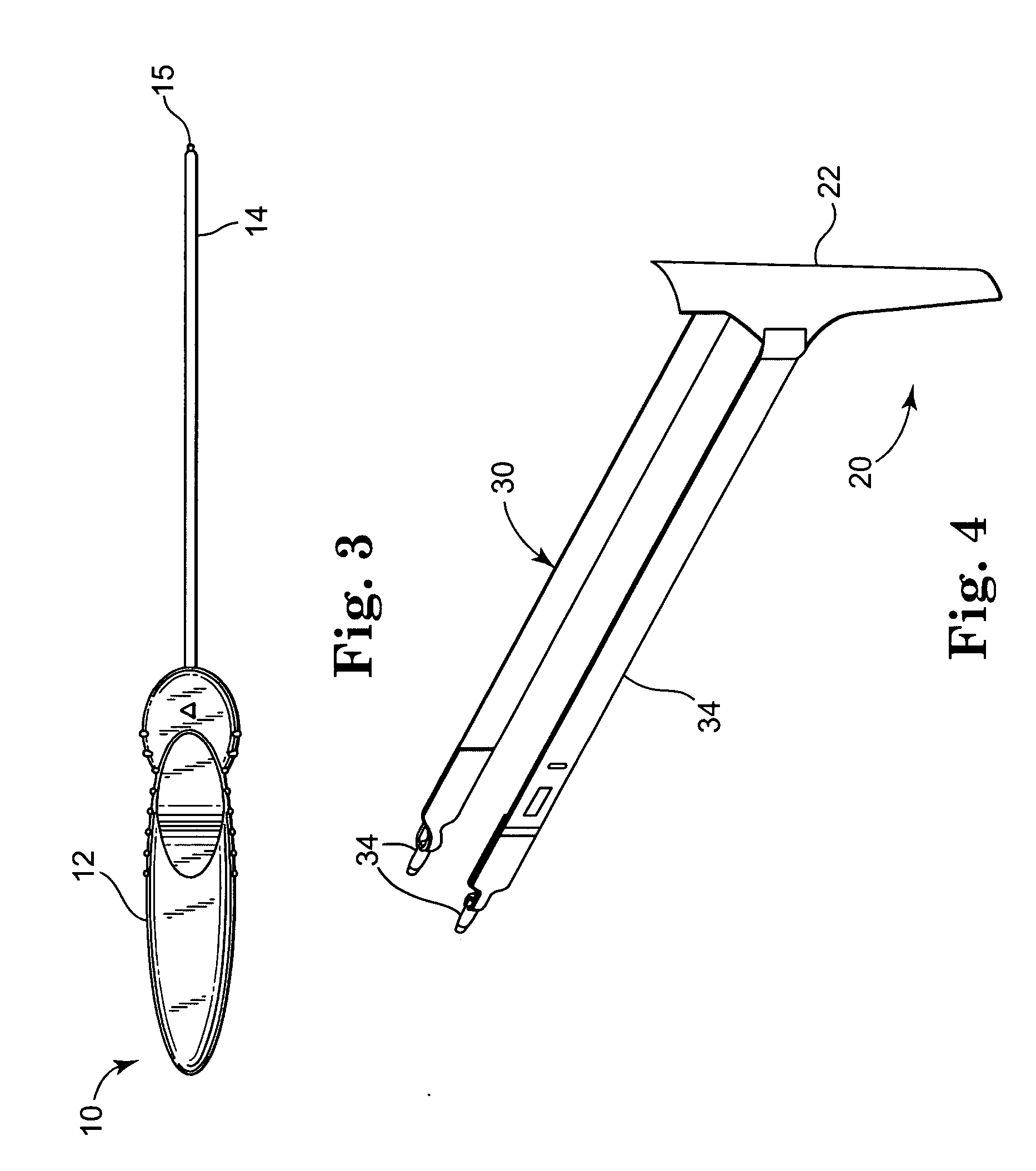
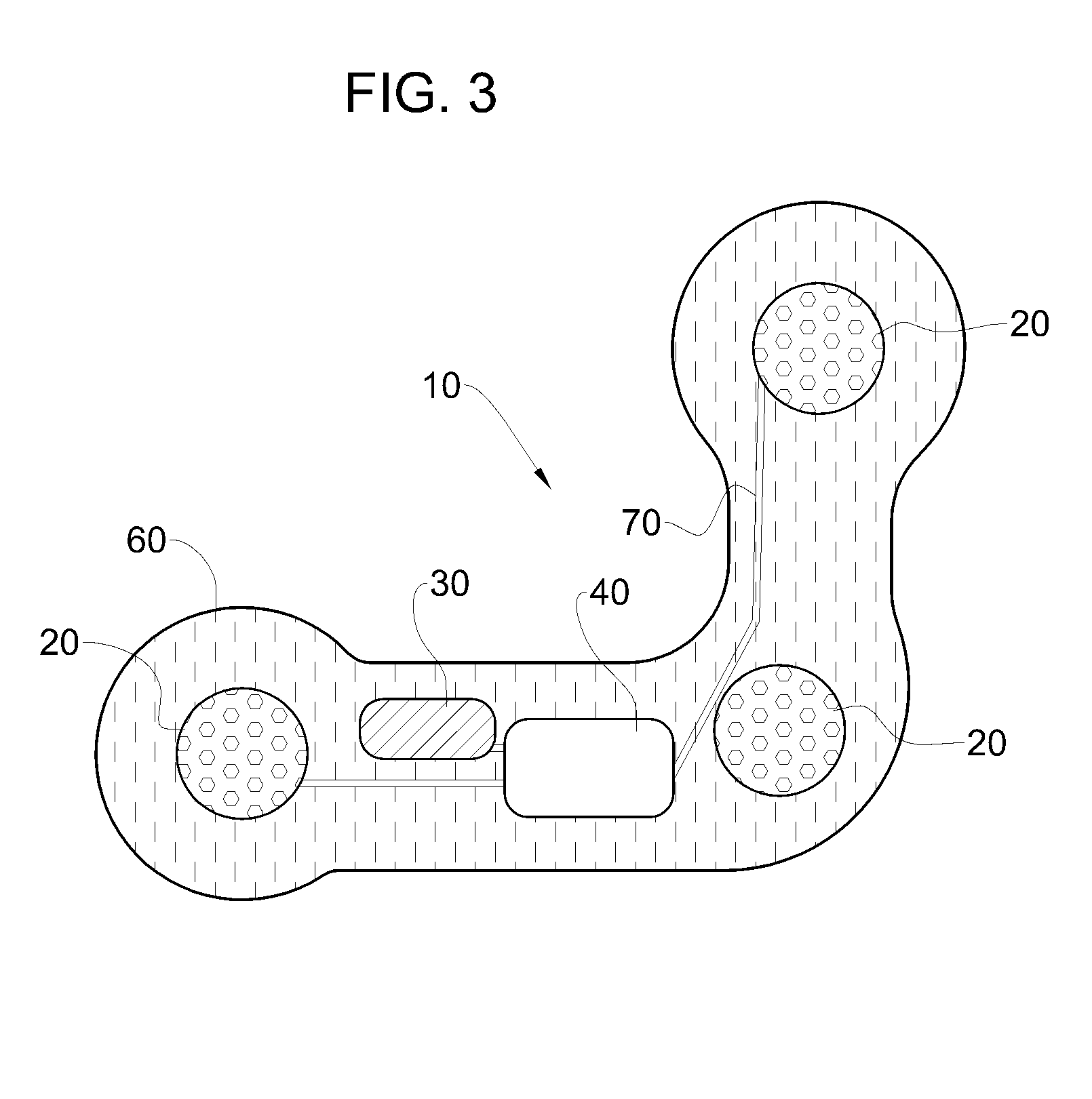
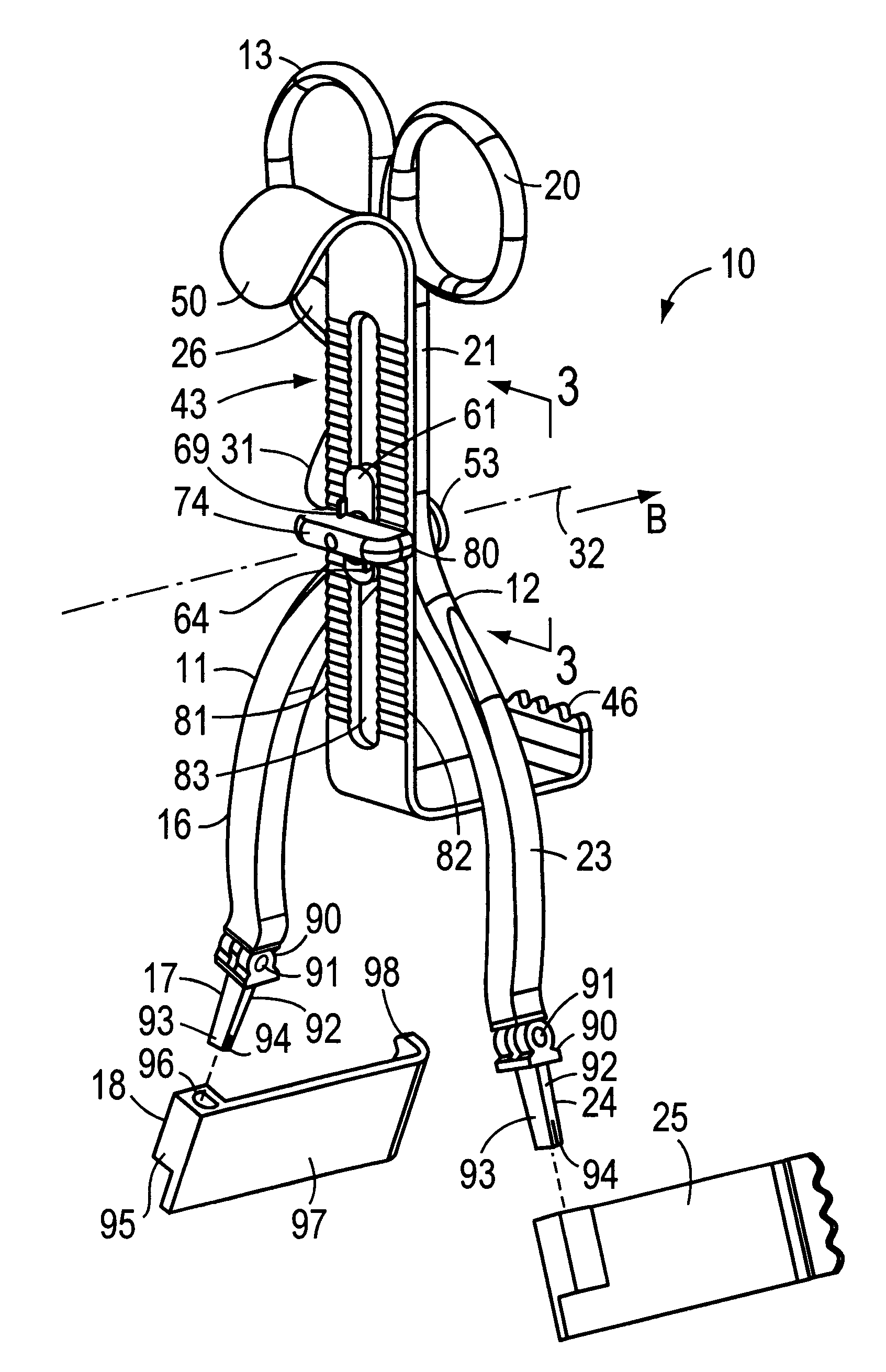
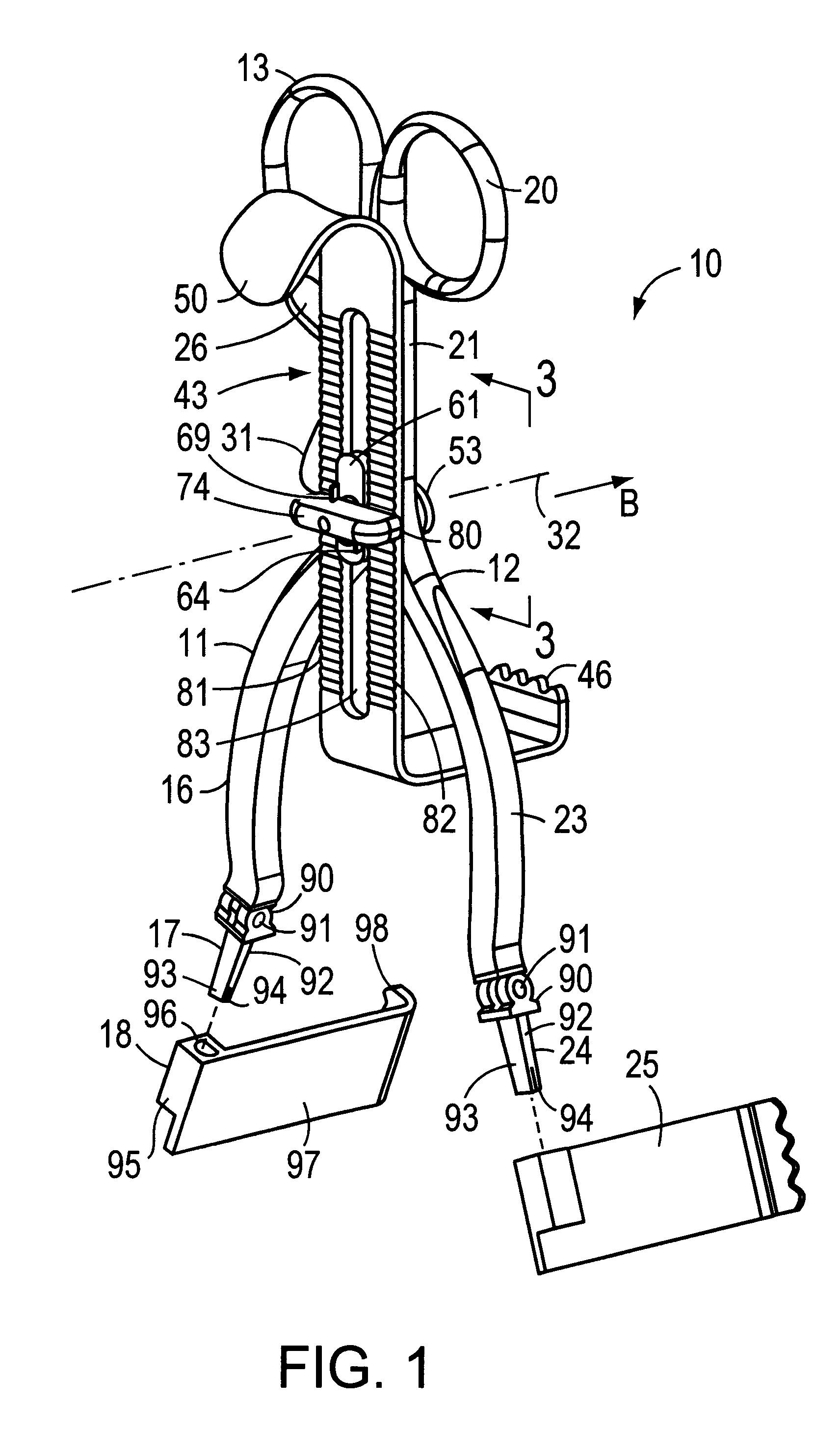
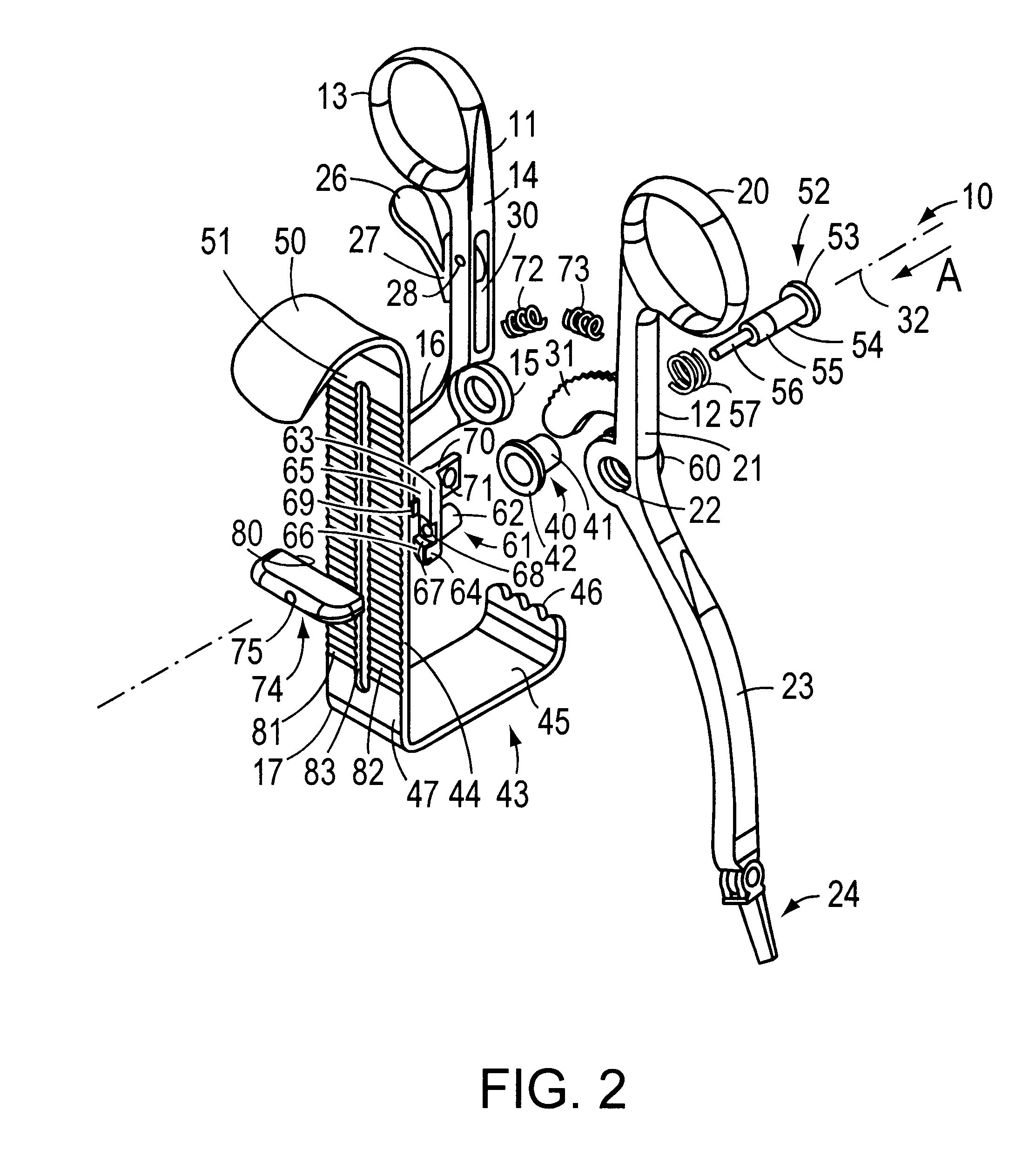
Surgical stapling device
ActiveUS7159750B2Easy to operatePositioning is simple and fastSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringActuator
A surgical device is disclosed which includes a handle portion, a central body portion and a Simple Use Loading Unit (“SULU”) [SULU]. The SULU includes a proximal body portion, an intermediate pivot member and a tool assembly. The intermediate pivot member is pivotally secured to the proximal body portion about a first pivot axis and the tool assembly is pivotally secured to the intermediate pivot member about a second pivot axis which is orthogonal to the first pivot axis. The SULU includes a plurality of articulation links which are operably connected to the tool assembly by non-rigid links. The articulation links are adapted to releasably engage articulation links positioned in the central body portion. The body portion articulation links are connected to an articulation actuator which is supported for omni-directional movement to effect articulation of the tool assembly about the first and second axes. The handle portion includes a spindle and barrel assembly drive mechanism for advancing and retracting a drive member positioned in the tool assembly. In one embodiment, the tool assembly includes a cartridge assembly having a plurality of staples and an anvil assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electronic cigarette
InactiveUS20050016550A1Efficient disseminationGood adhesionTobacco preparationCigar manufactureInhalationEngineering
An electronic cigarette is provided. The electronic cigarette includes a casing having an inhalation hole and a substantially cylindrical configuration, ejection means (first ejection means) provided in the casing and at least one ejection head. Pressure in a cavity filled with a liquid flavor generating medium is changed by driving an actuator to eject the flavor generating medium as droplets from a nozzle in communication with the cavity. Control means provided in the casing controls the driving of the ejection means.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
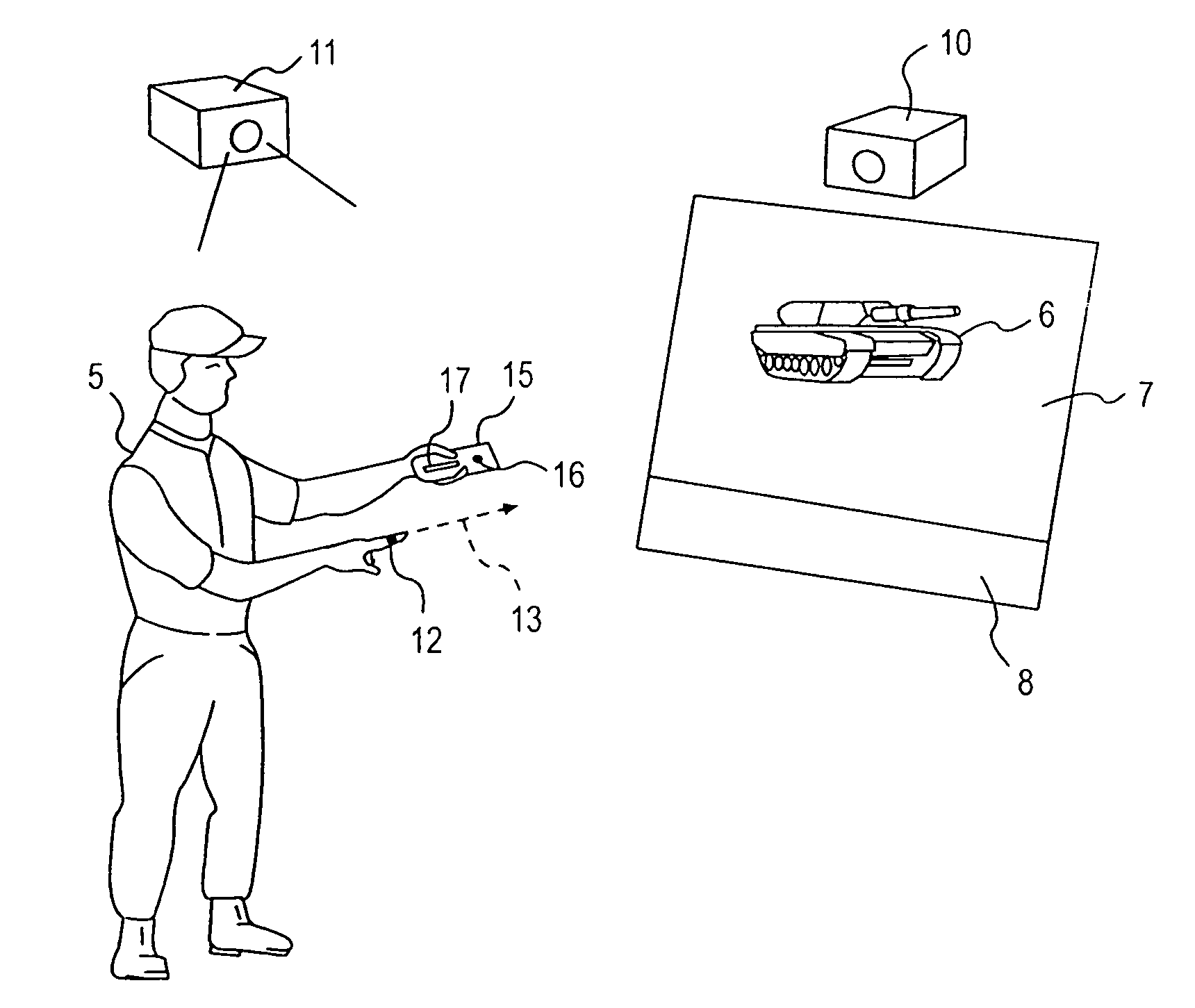
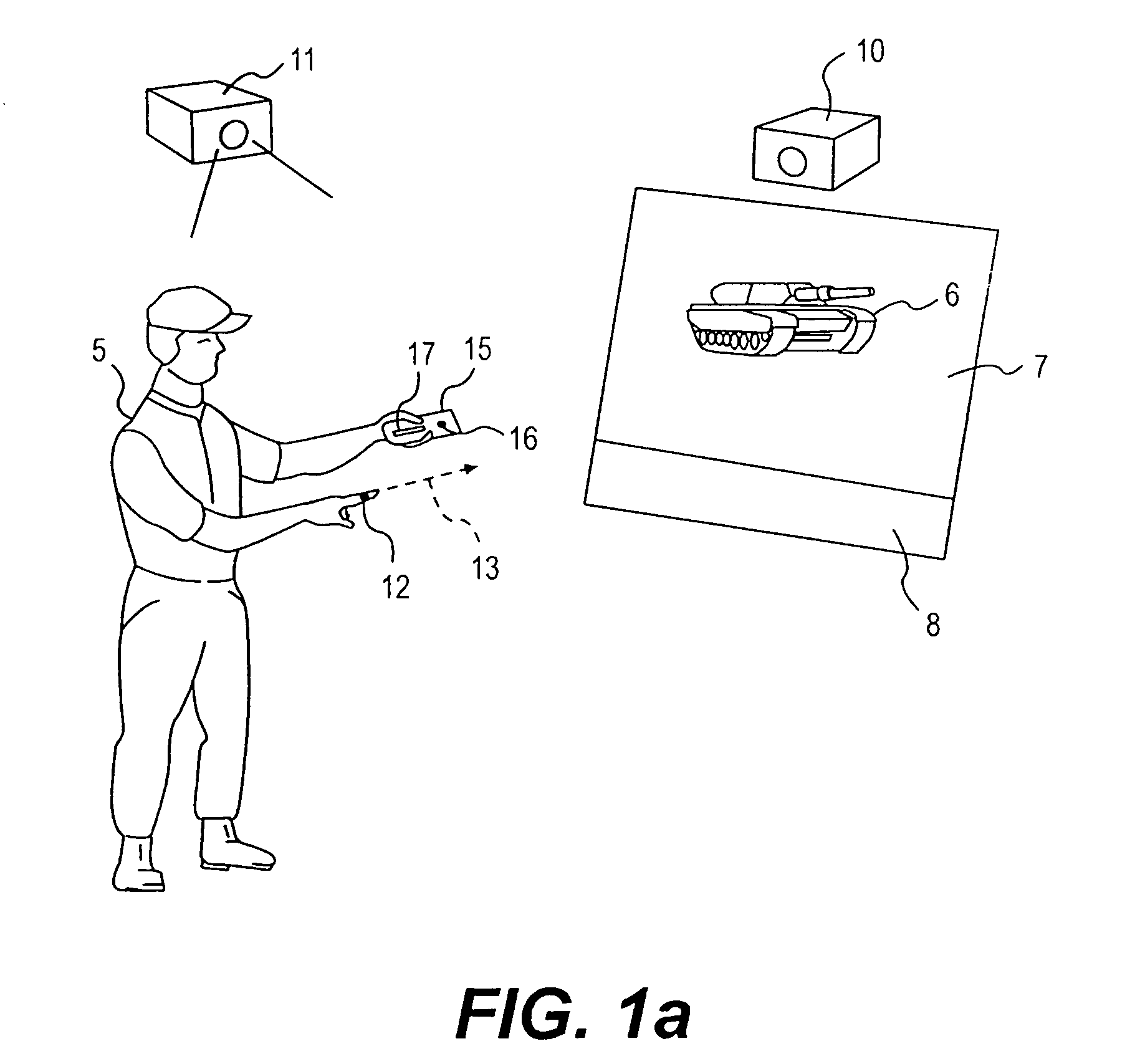
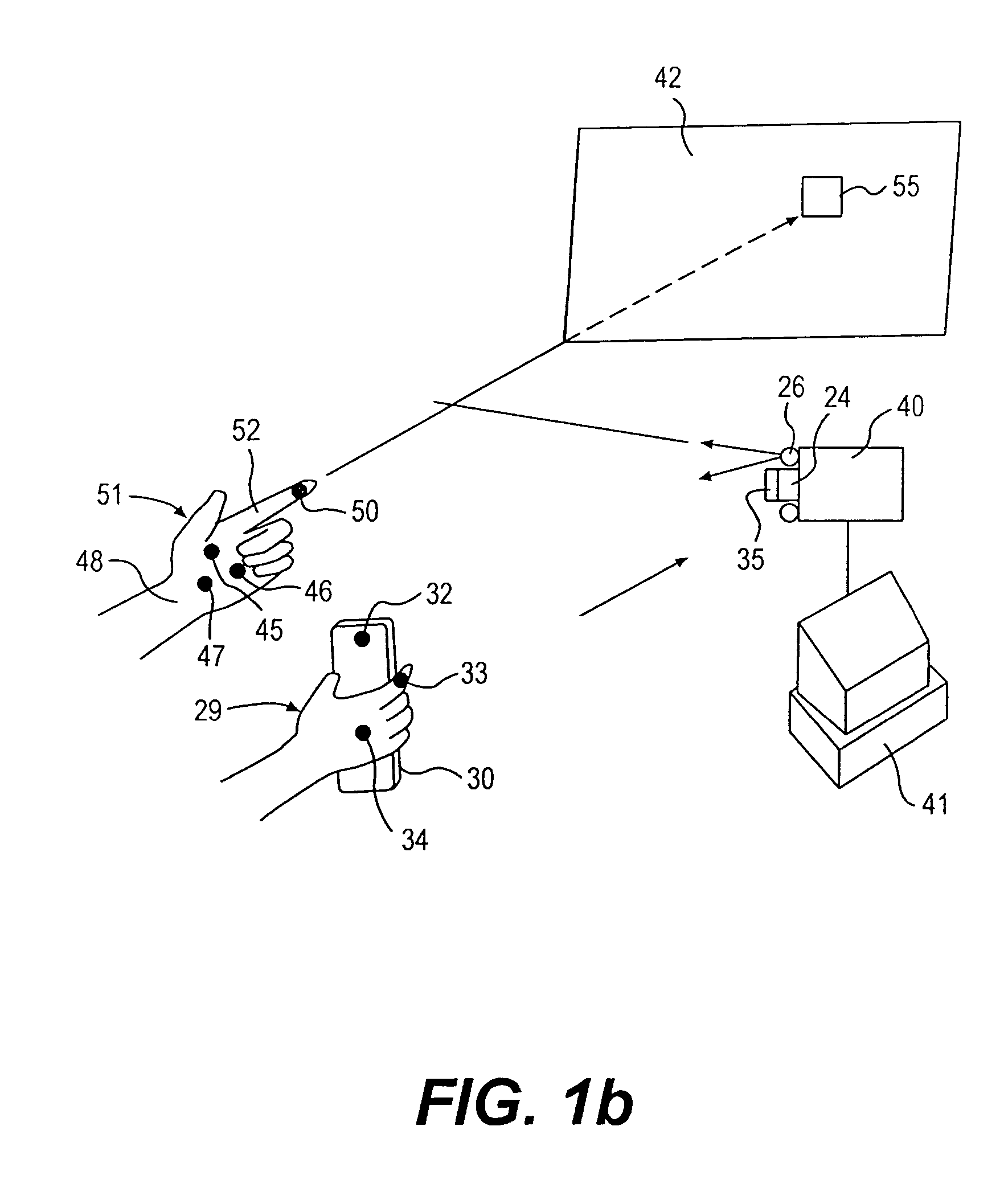
Man machine interfaces and applications
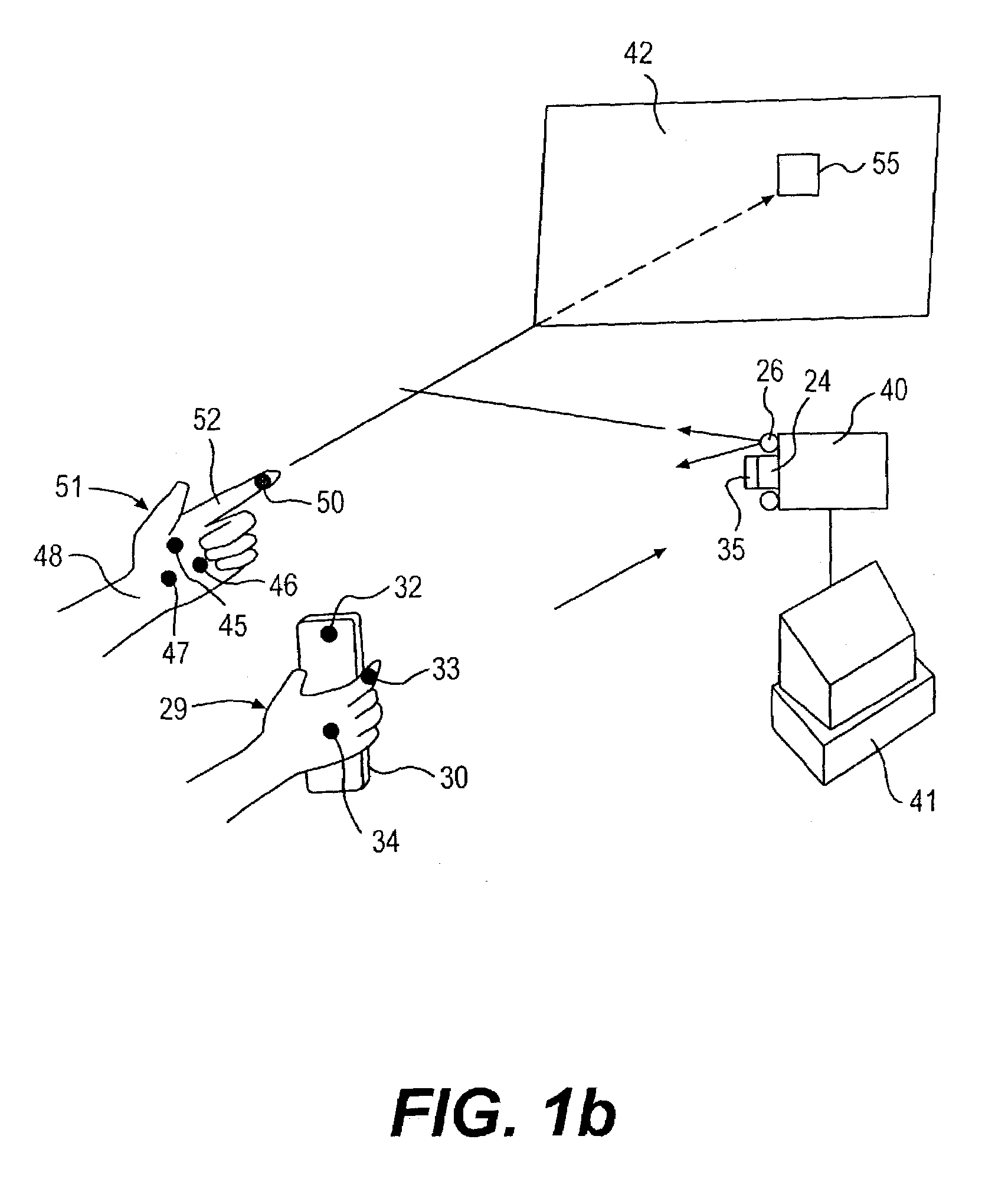
InactiveUS7042440B2Avoid carpal tunnel syndromeImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrophonic musical instrumentsComputer Aided DesignHuman–machine interface
Affordable methods and apparatus are disclosed for inputting position, attitude (orientation) or other object characteristic data to computers for the purpose of Computer Aided Design, Painting, Medicine, Teaching, Gaming, Toys, Simulations, Aids to the disabled, and internet or other experiences. Preferred embodiments of the invention utilize electro-optical sensors, and particularly TV Cameras, providing optically inputted data from specialized datum's on objects and / or natural features of objects. Objects can be both static and in motion, from which individual datum positions and movements can be derived, also with respect to other objects both fixed and moving. Real-time photogrammetry is preferably used to determine relationships of portions of one or more datums with respect to a plurality of cameras or a single camera processed by a conventional PC.
Owner:PRYOR TIMOTHY R +1
Removable adapter for phacoemulsification handpiece having irrigation and aspiration fluid paths
Current phacoemulsification handpieces require rigorous cleaning after each procedure because the aspiration and irrigation pathways for fluids are integral to the handpiece. According to the present invention, a removable horn extension and nosecone may be used with a phacoemulsification handpiece to allow for disposable fluid pathways exterior to the handpiece. This will reduce the cleaning time and effort, reduce cross-contamination, and increase the lifespan of the handpiece. Furthermore, the current invention allows different horn extensions to be used to excite different motions at the tip of the handpiece, depending on the preference of the surgeon.
Owner:ZEVEX
Accessory module for vehicle
ActiveUS7480149B2Good adhesionEasy to assembleCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical signallingEngineeringElectrical connector
An accessory module is mountable to an interior surface of a vehicle windshield and includes a mounting element securable to an interior surface of a windshield of a vehicle, and an accessory support having a base portion attachable to the mounting element. The accessory support includes an accessory holding element configured to hold an accessory, at least one circuitry holding element configured to hold a printed circuit board at the accessory support, and an electrical connector for electrically connecting the printed circuit board and the accessory to an electrical source of the vehicle. The base portion, the accessory holding element and the circuitry holding element are integrally molded together so that the accessory support comprises a unitarily molded accessory support. The accessory module includes a cover portion attachable to the accessory support to substantially encompass the accessory and the printed circuit board within the accessory module.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS INC
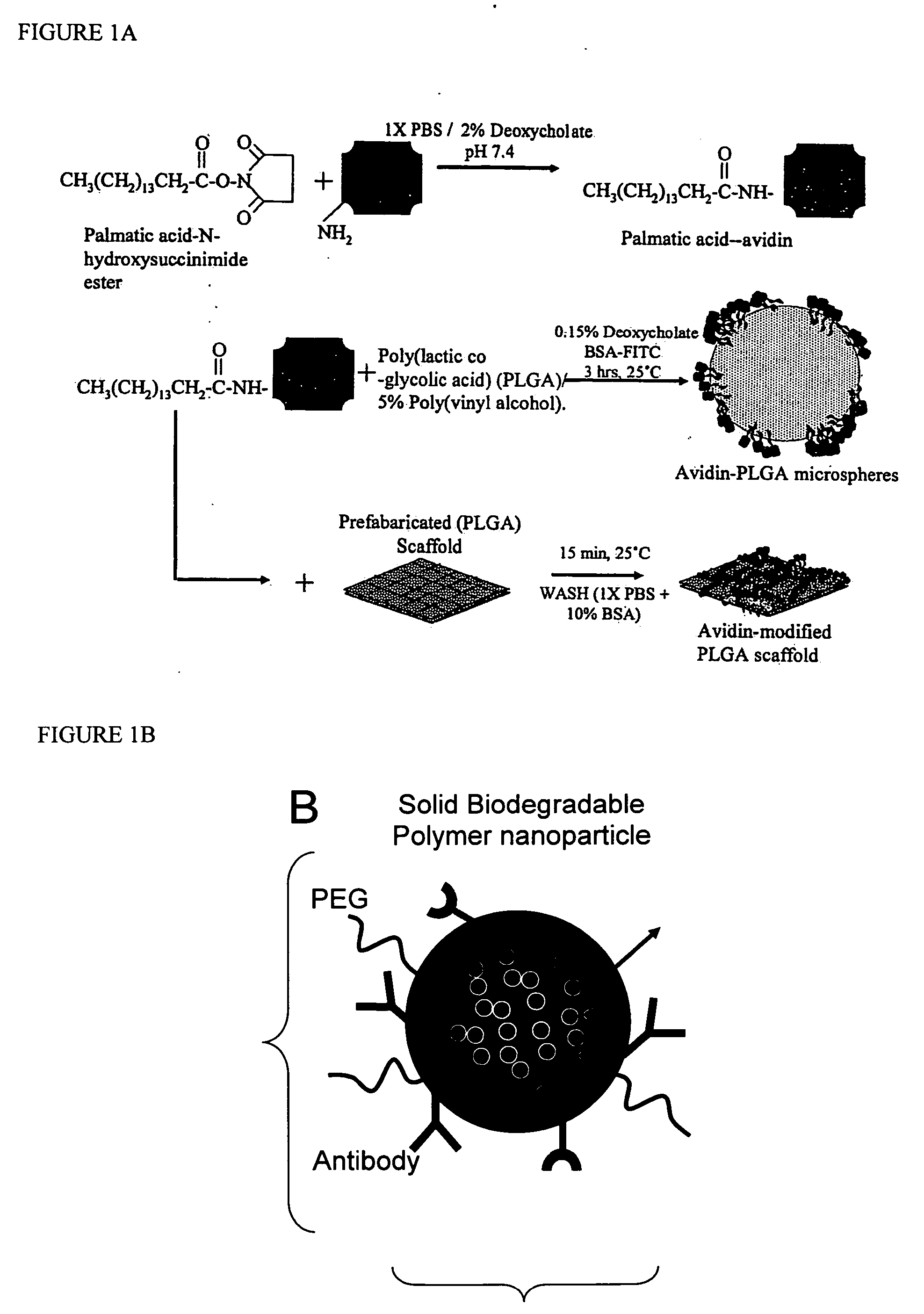
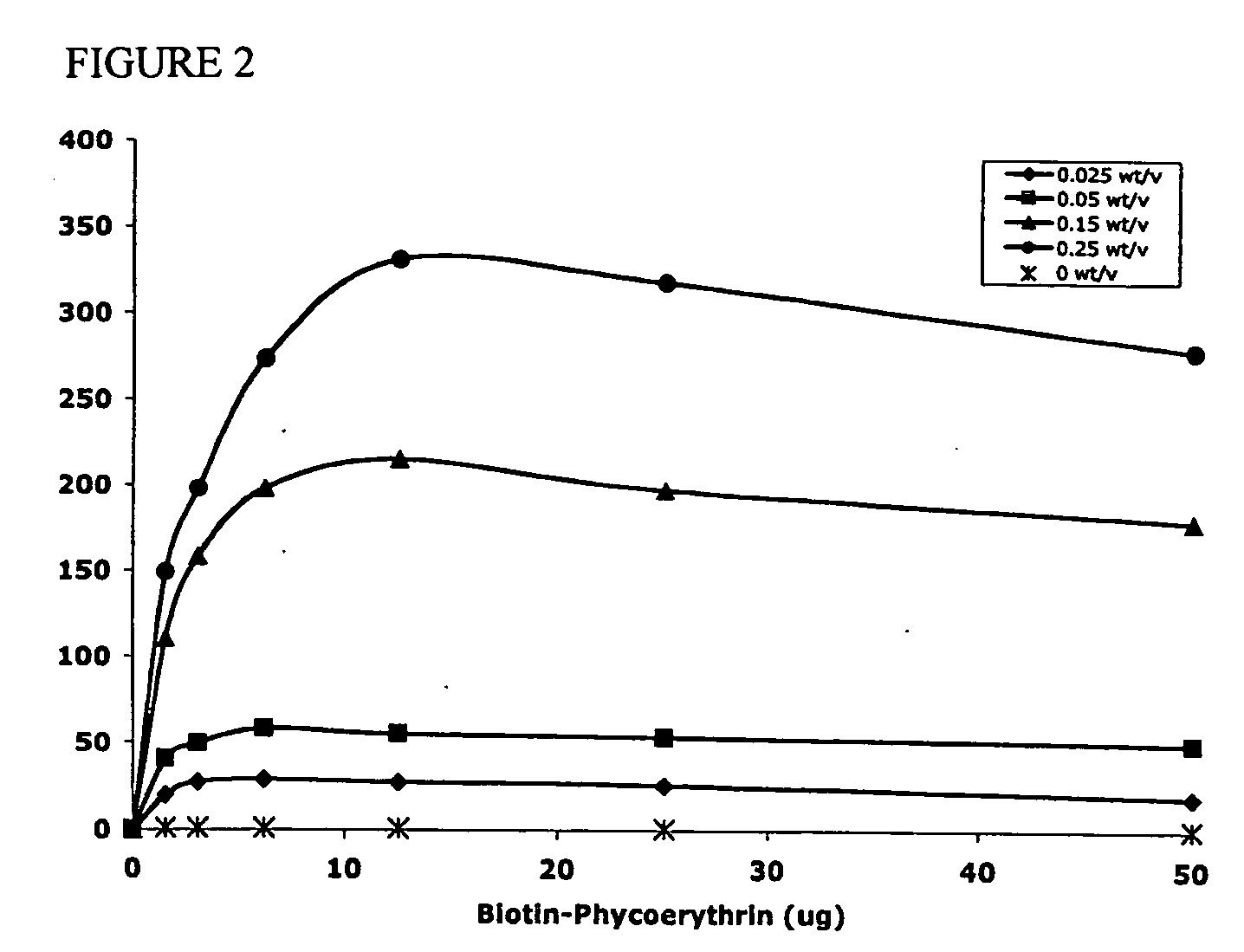
Targeted and high density drug loaded polymeric materials
ActiveUS20060002852A1Increase molecular densityHigh densityPowder deliveryBiocideAntigenWound dressing
Polymeric delivery devices have been developed which combine high loading / high density of molecules to be delivered with the option of targeting. As used herein, “high density” refers to microparticles having a high density of ligands or coupling agents, which is in the range of 1000-10,000,000, more preferably between 10,000 and 1,000,000 ligands per square micron of microparticle surface area. A general method for incorporating molecules into the surface of biocompatible polymers using materials with an HLB of less than 10, more preferably less than 5, such as fatty acids, has been developed. Because of its ease, generality and flexibility, this method has widespread utility in modifying the surface of polymeric materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering, as well other other fields. Targeted polymeric microparticles have also been developed which encapsulate therapeutic compounds such as drugs, cellular materials or components, and antigens, and have targeting ligands directly bound to the microparticle surface. Preferred applications include use in tissue engineering matrices, wound dressings, bone repair or regeneration materials, and other applications where the microparticles are retained at the site of application or implantation. Another preferred application is in the use of microparticles to deliver anti-proliferative agents to the lining of blood vessels following angioplasty, transplantation or bypass surgery to prevent or decrease restenosis, and in cancer therapy. In still another application, the microparticles are used to treat or prevent macular degeneration when administered to the eye, where agents such as complement inhibitors are administered.
Owner:YALE UNIV
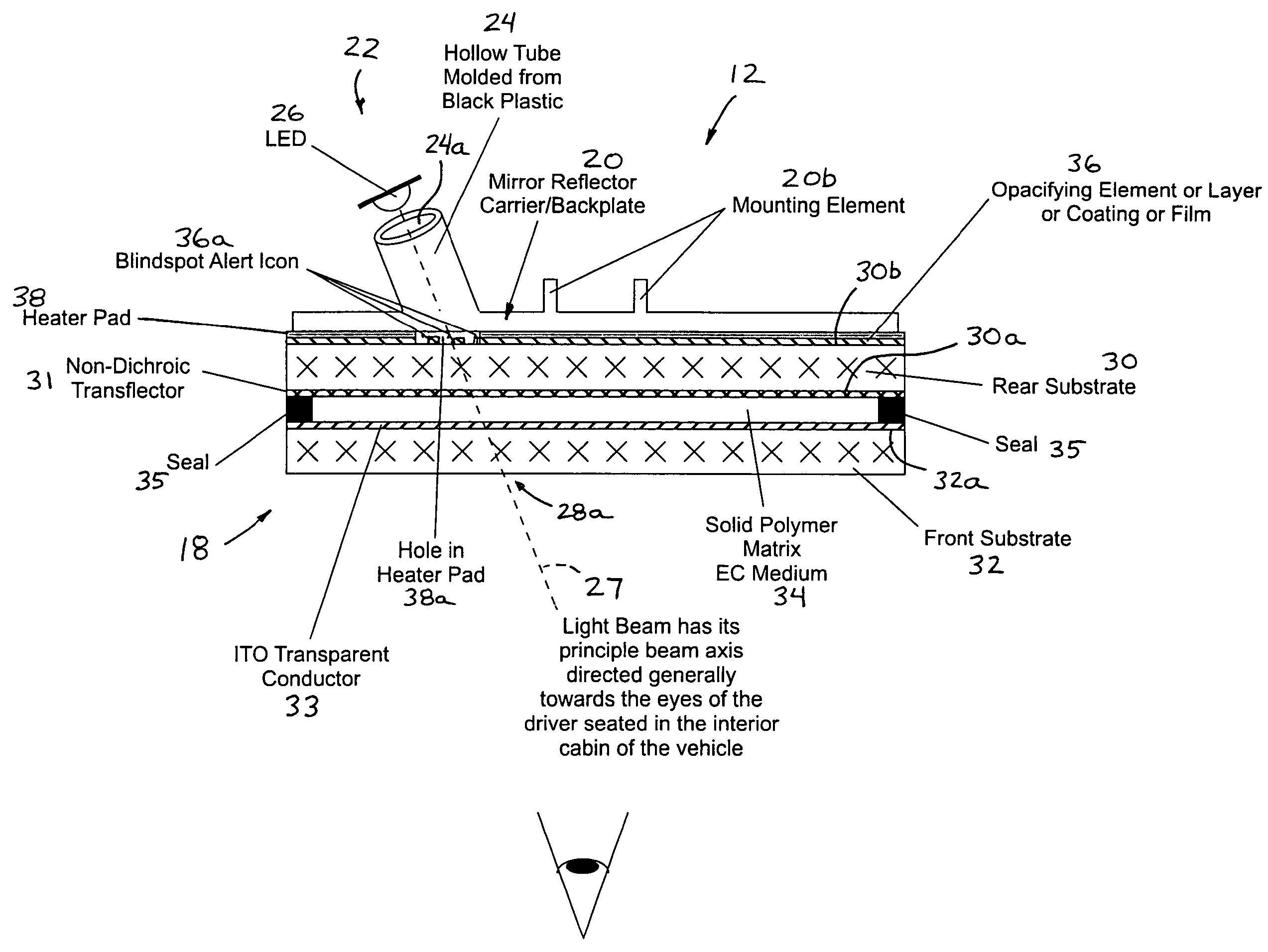
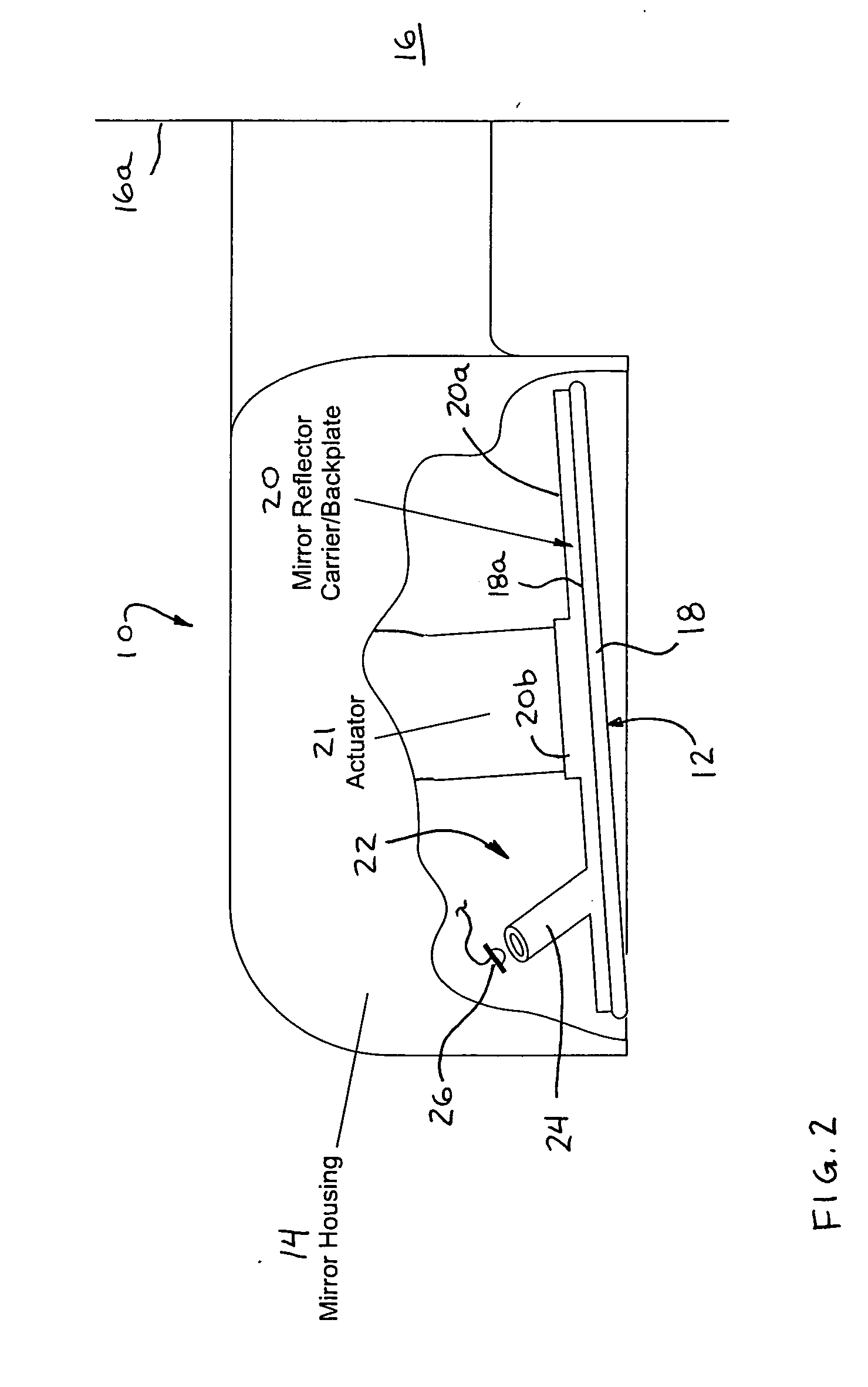
Display device for exterior rearview mirror
InactiveUS7581859B2Good adhesionEasy to assembleOptical signallingOptical viewingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
An exterior mirror sub-assembly includes a reflective element, a back plate, and a display element having a light source that is activatable to emit light. The display element attaches to a display receiving portion of the back plate and the light source is activatable to emit light through the display receiving portion. The display receiving portion may be configured to orient the display element at a predetermined angle so that light exiting the display element when the light source is activated may be directed (a) generally away from the vehicle when the mirror assembly is mounted to the vehicle so as to be principally viewed by drivers of other vehicles or (b) generally toward the driver of the vehicle when the mirror assembly is mounted to the vehicle so as to be principally viewed by the driver of the host vehicle.
Owner:MAGNA MIRRORS OF AMERICA INC
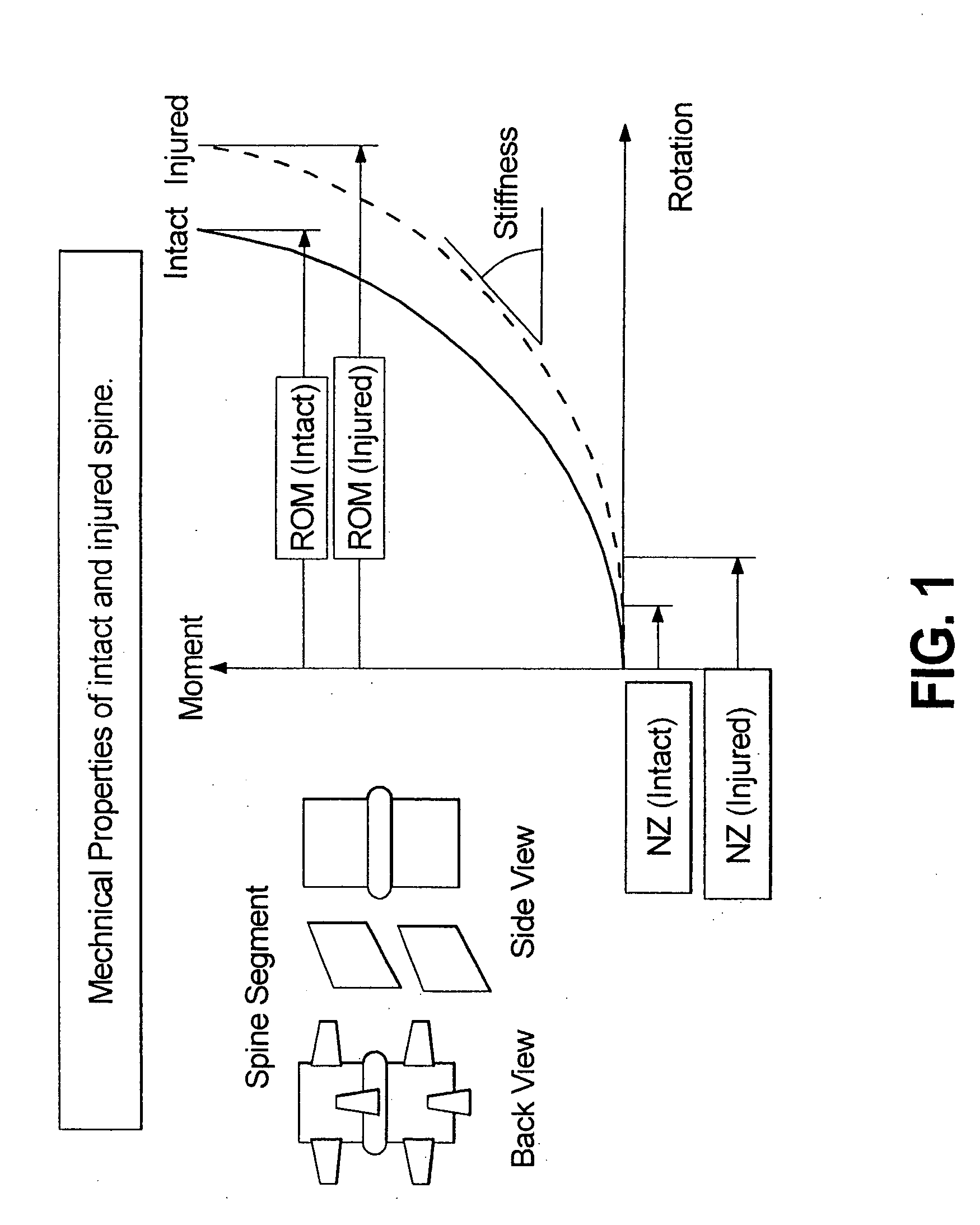
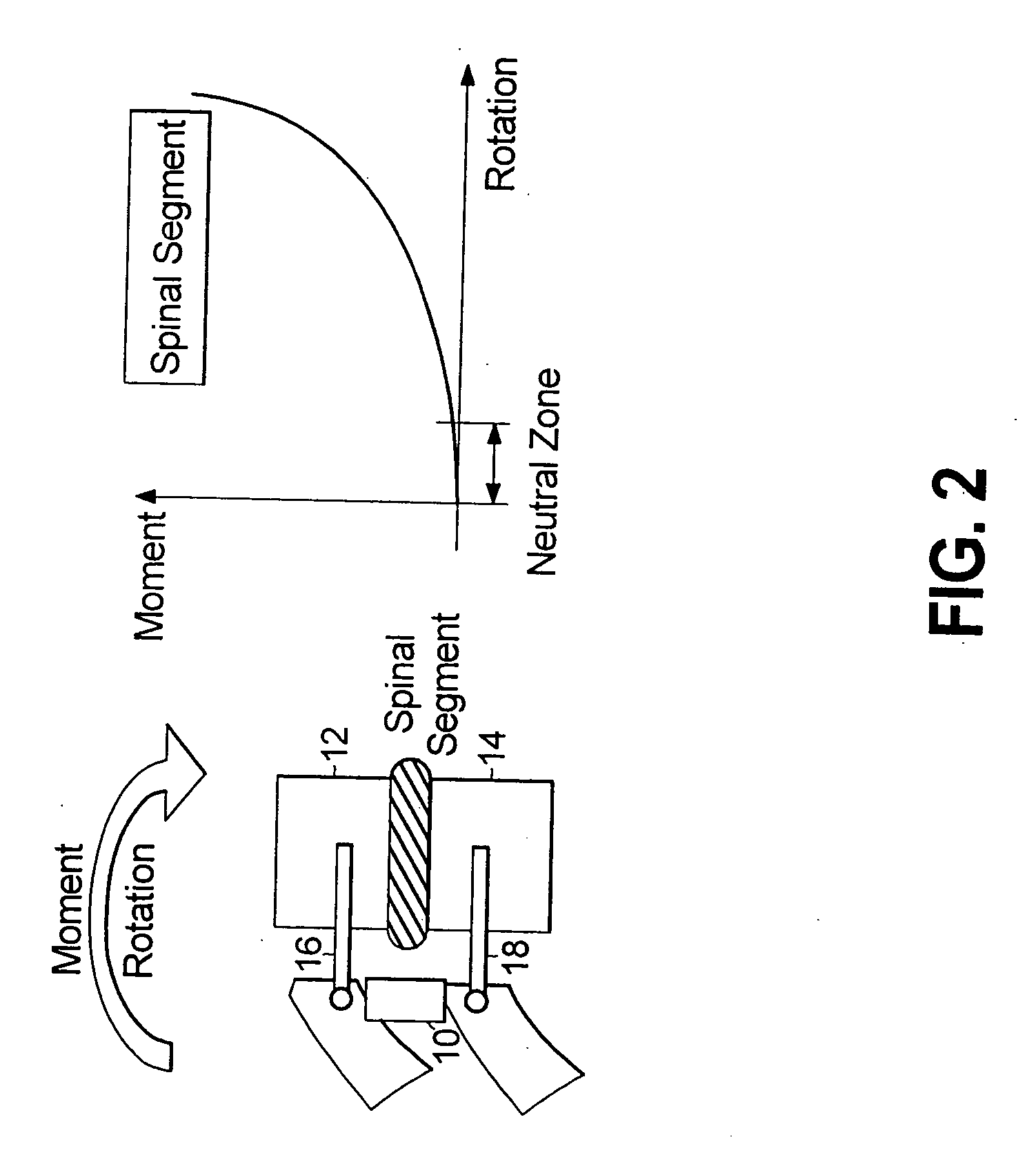
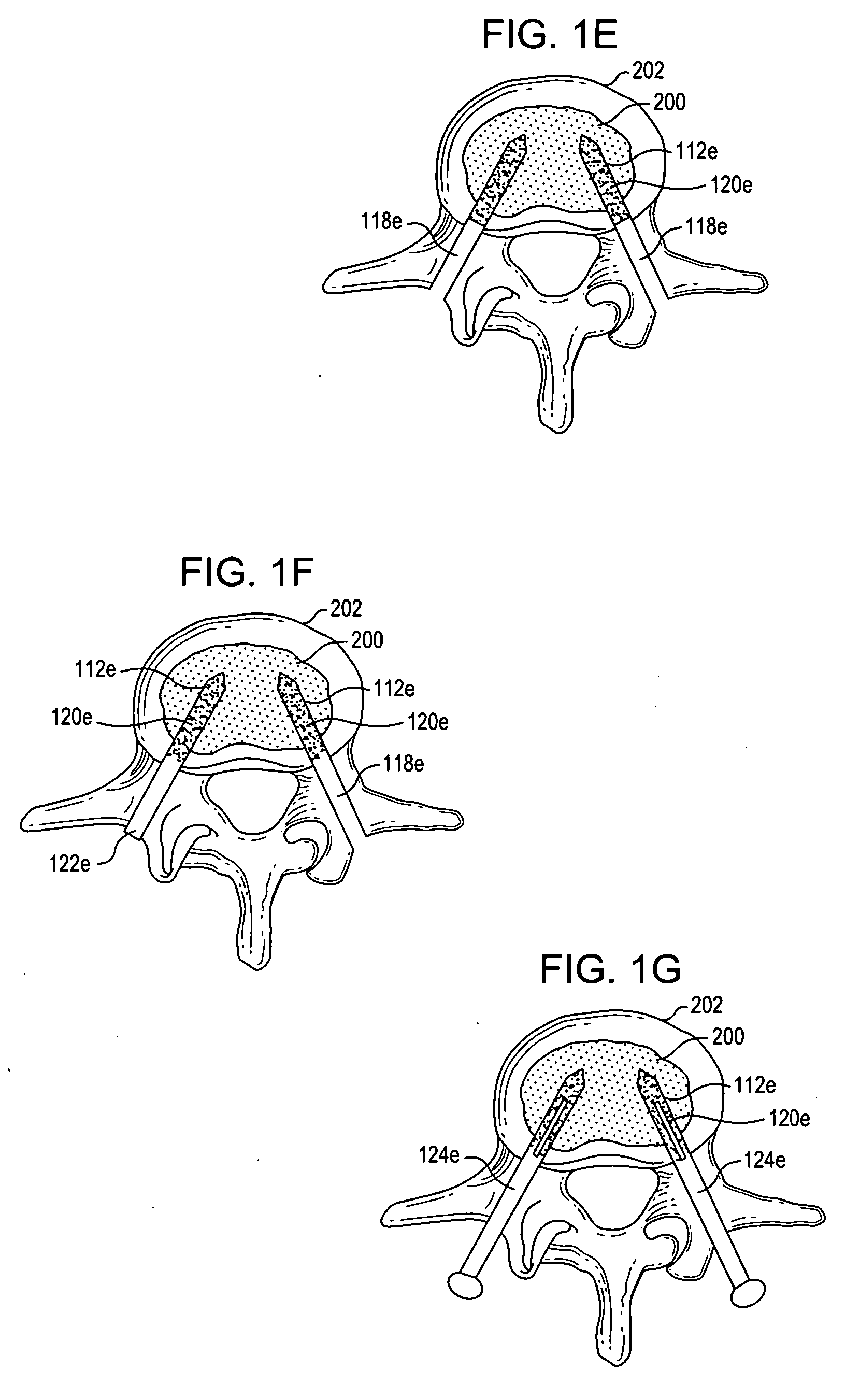
Systems and methods for spine stabilization including a dynamic junction
InactiveUS20050182401A1Easy to installImprove clinical outcomesSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisRotational freedomUniversal joint
Spinal stabilization devices, systems and methods are provided that include at least one pedicle screw and at least one mechanism that supports three degrees of rotational freedom relative to the pedicle screw. The mechanism may include a universal joint mechanism or a ball and socket mechanism. In the case of the ball and socket mechanism, at least one spherical element is mounted with respect to the at least one pedicle screw and a socket member cooperates with the spherical element. The spherical element and the socket member cooperate to define a dynamic junction that allows the socket member to move relative to the ball element while remaining engaged therewith. The dynamic junction is advantageously incorporated into a spinal stabilization system that includes additional pedicle screw(s), spherical element(s) and socket member(s). The spinal stabilization system may incorporate dynamic stabilizing member(s) to so as to provide clinically efficacious results.
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
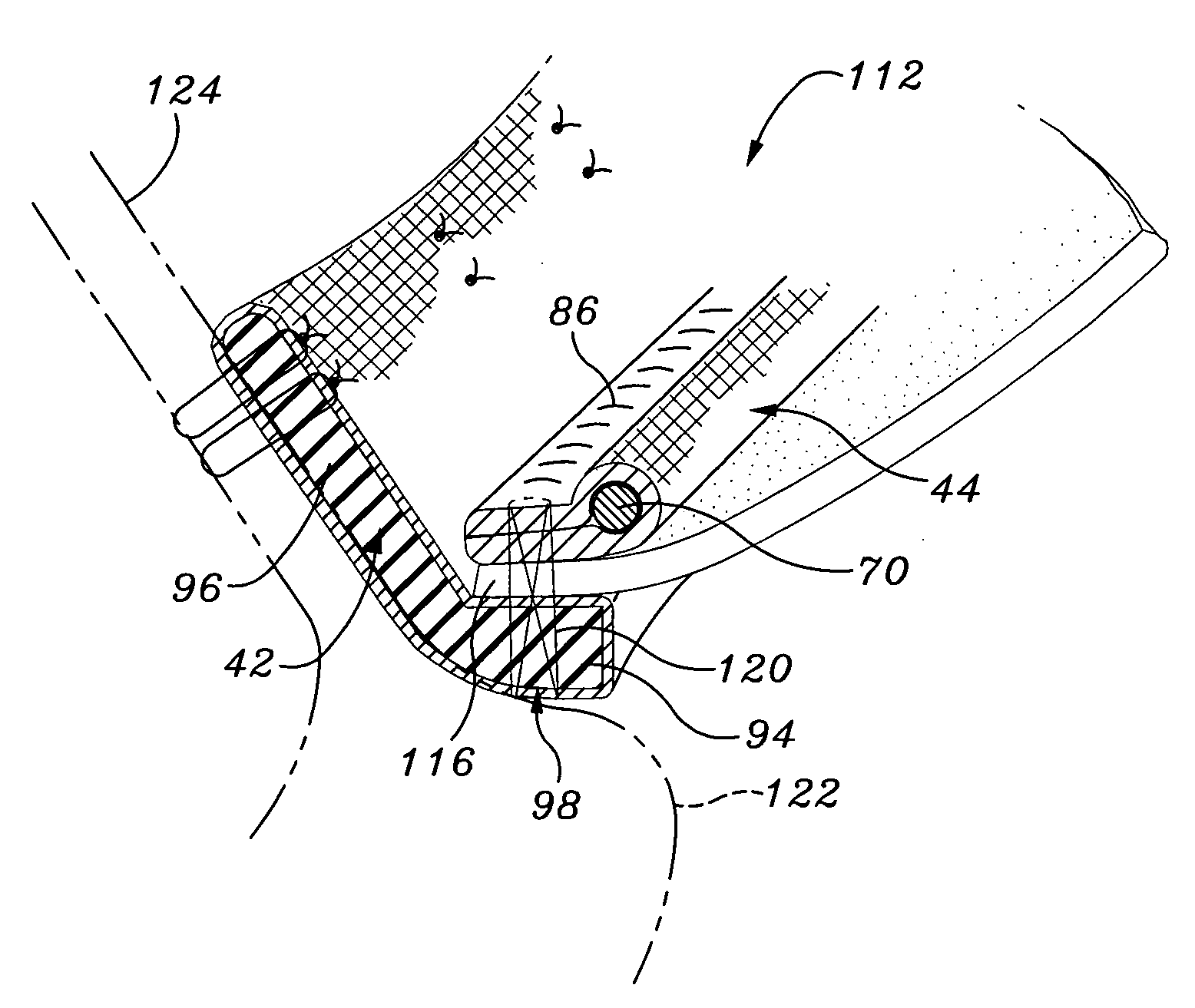
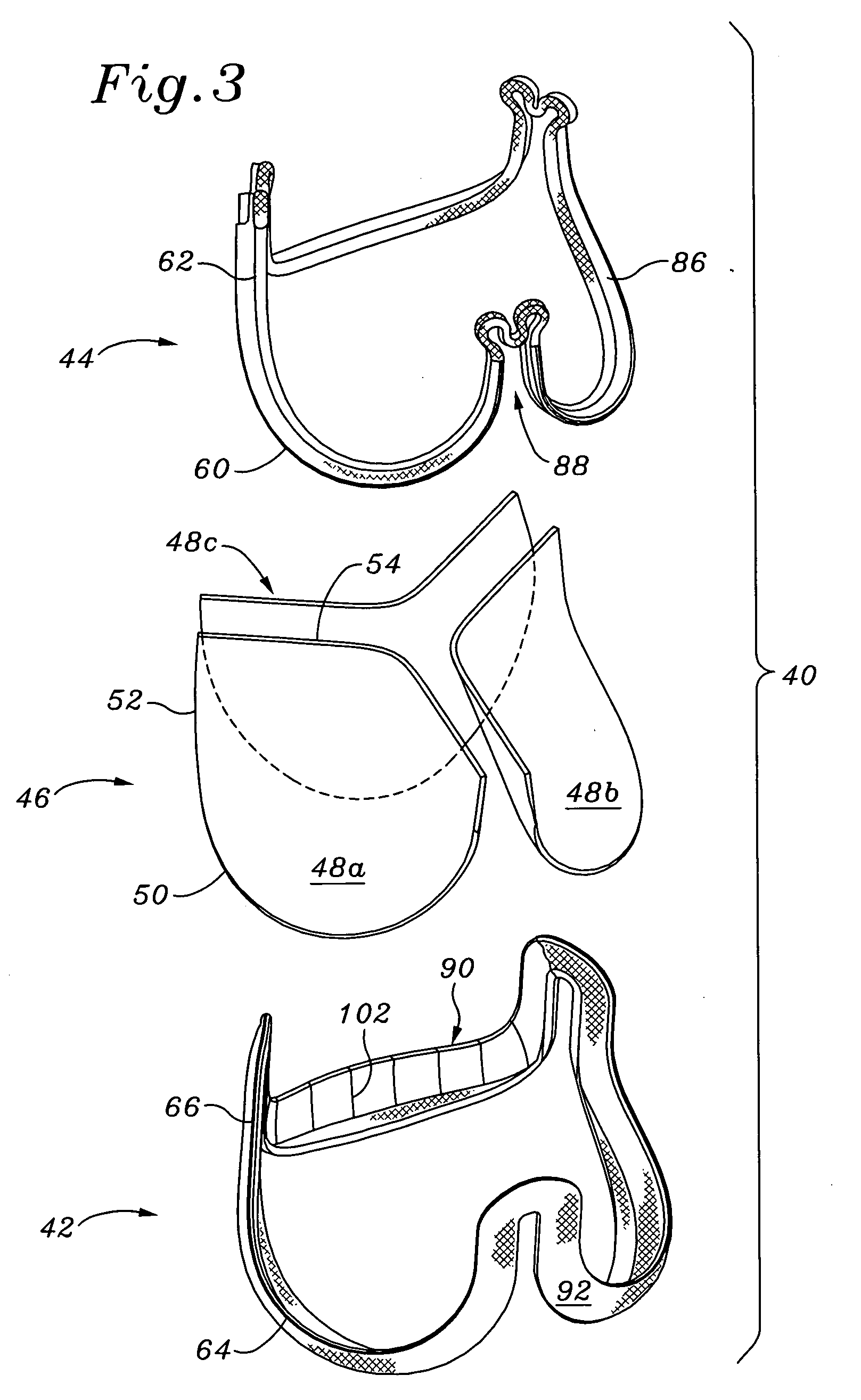
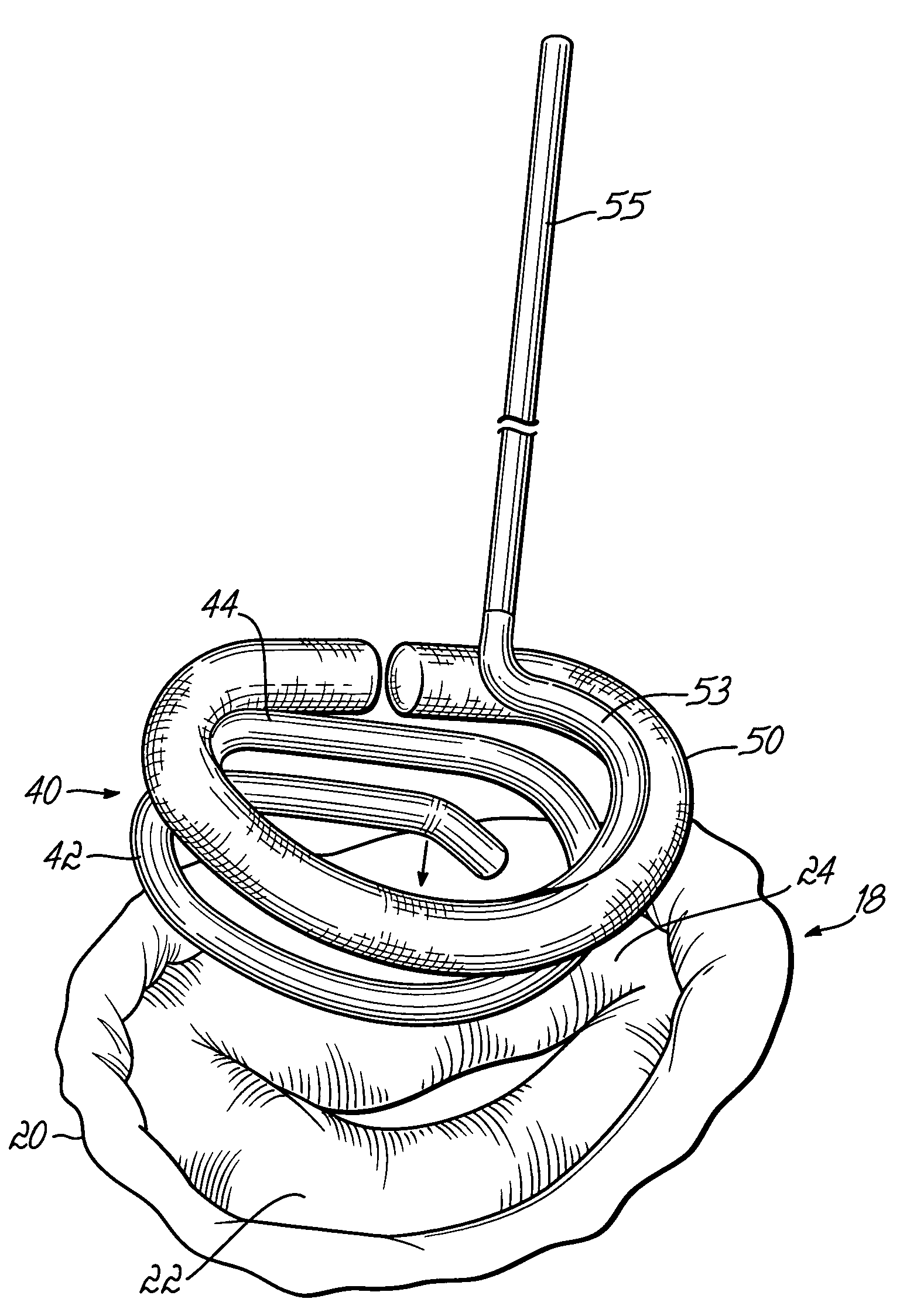
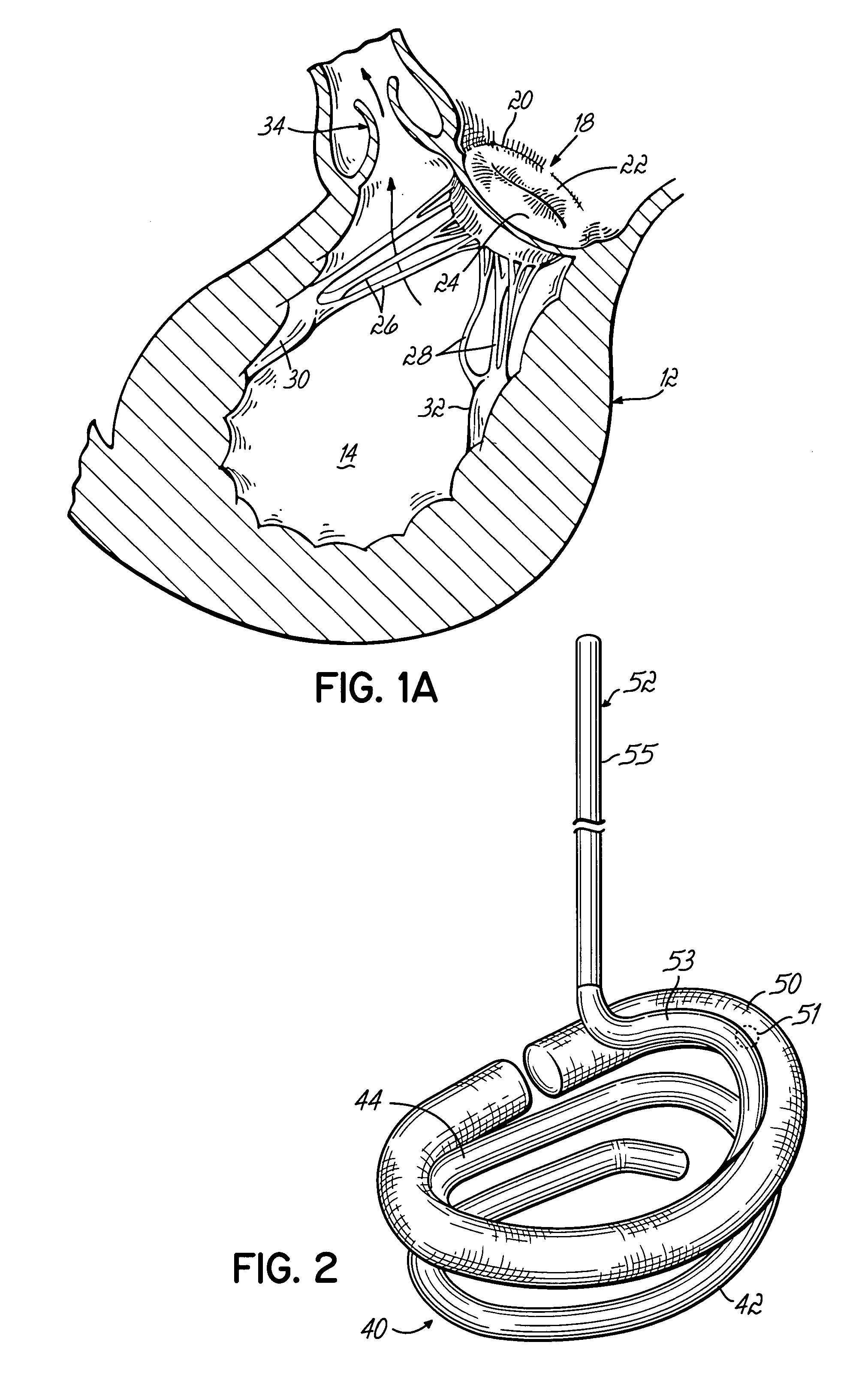
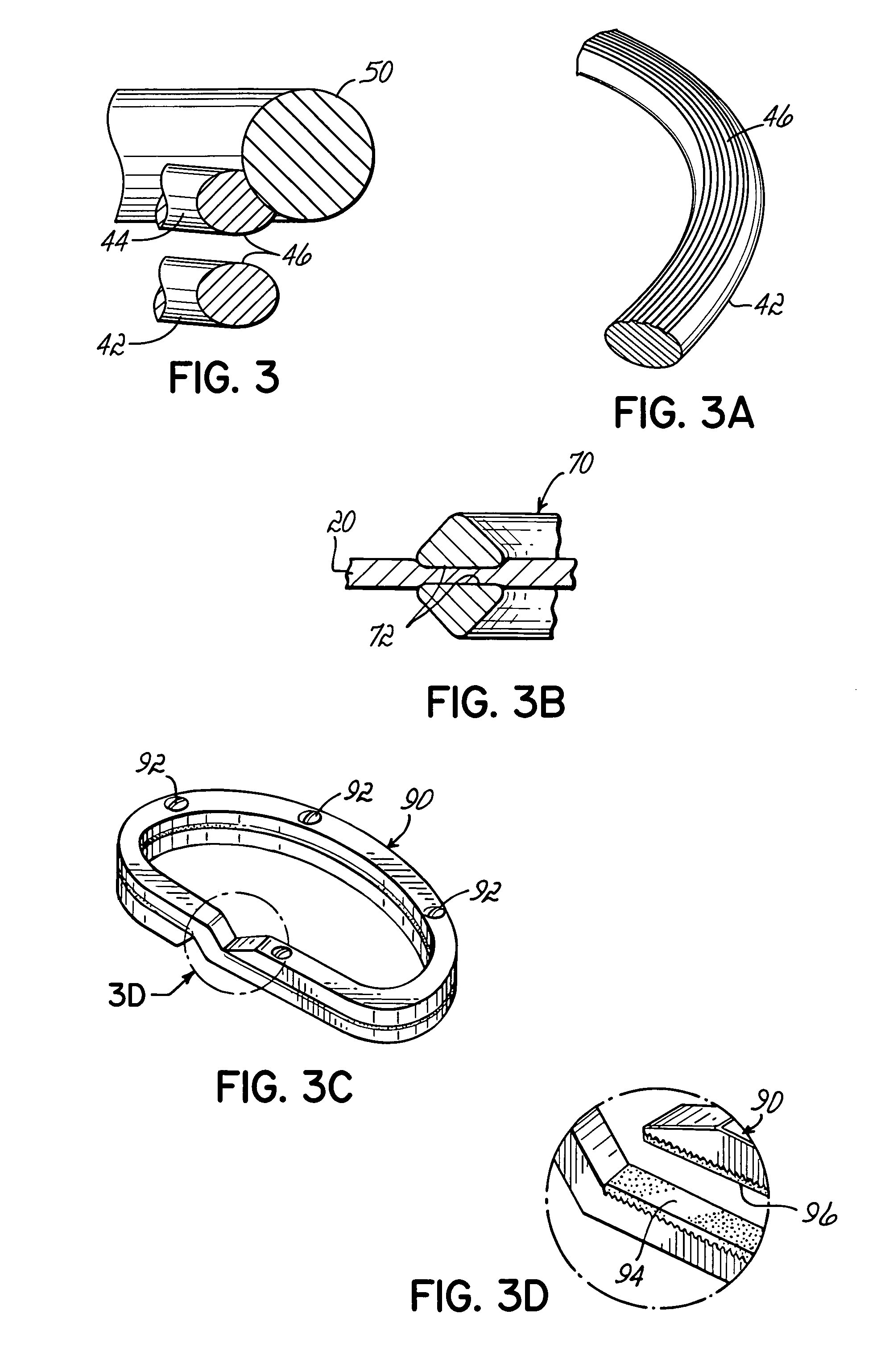
Highly flexible heart valve connecting band
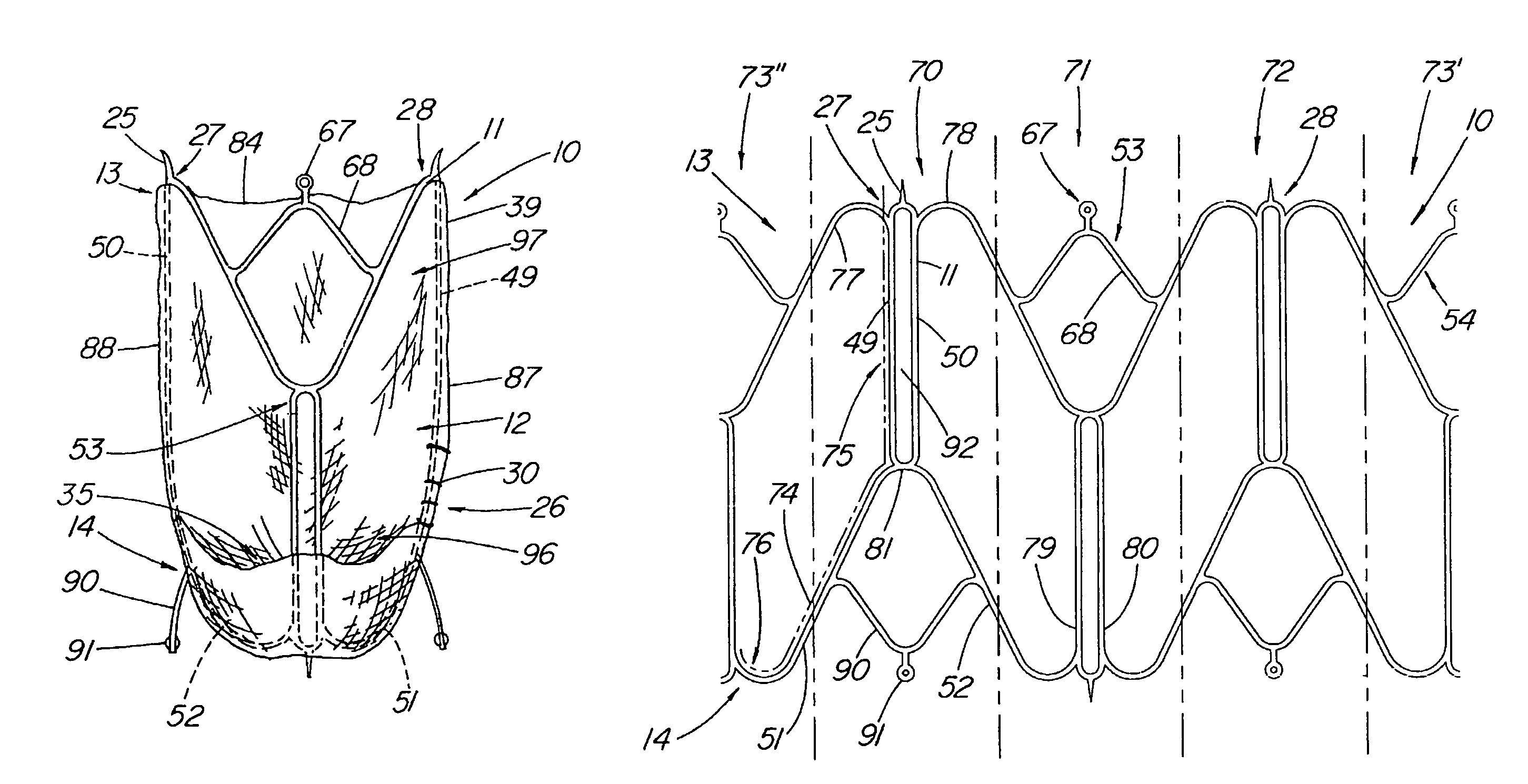
ActiveUS20060229719A1Facilitates supra-annular attachmentIncrease flexibilityHeart valvesInsertion stentTissues types
A connecting band for a highly flexible tissue-type heart valve having a stent with cusps and commissures that are permitted to move radially. The connecting band follows the cusps and commissures and extends outwardly. The valve is connected to the natural tissue along the undulating connecting band using conventional techniques, such as sutures. The connecting band may be a cloth-covered inner suture-permeable member and attaches to the underside of the valve at the cusps to provide support to the stent and to the outer side of the valve at the commissures. The connecting band includes commissure portions defining generally axial gaps that help permit flexing of the valve. The inner member may include one or more slits along the cusps to enhance flexibility. The inner member may further include a continuous outwardly projecting sewing ridge around its periphery which includes a series of ribs separated by grooves around the inflow edge of the cusps. The sewing ridge enables supra-annular implant of a valve constructed with the connecting band.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Surgical stapling device
ActiveUS20050006432A1Facilitates selective operationEasy to operateSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringActuator
A surgical device is disclosed which includes a handle portion, a central body portion and a SULU. The SULU includes a proximal body portion, an intermediate pivot member and a tool assembly. The intermediate pivot member is pivotally secured to the proximal body portion about a first pivot axis and the tool assembly is pivotally secured to the intermediate pivot member about a second pivot axis which is orthogonal to the first pivot axis. The SULU includes a plurality of articulation links which are operably connected to the tool assembly by non-rigid links. The articulation links are adapted to releasably engage articulation links positioned in the central body portion. The body portion articulation links are connected to an articulation actuator which is supported for omni-directional movement to effect articulation of the tool assembly about the first and second axes. The handle portion includes a spindle and barrel assembly drive mechanism for advancing and retracting a drive member positioned in the tool assembly. In one embodiment, the tool assembly includes a cartridge assembly having a plurality of staples and an anvil assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Work holding mechanism
ActiveUS7748760B2Improve shipping speedVacuum operationGripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Artificial valve prosthesis with improved flow dynamics
ActiveUS7618447B2Easy to removeMore turbulent flowVenous valvesBlood vesselsVenous ValvesProsthetic valve
An expandable venous valve having a support structure that configured to enlarge the area adjacent to the valve structure such that the flow patterns of retrograde flow are modified in a way that facilitates the flushing of the pockets at the base of the valve area to prevent stagnation of bodily fluid, which in the venous system, can lead to thrombus formation. The enlarged pocket areas can be created by forming an artificial sinus adjacent the valve structure in an unsupported section of vessel wall between two support frame section or the support frame can comprise an expanded-diameter intermediate or proximal section that forms an artificial sinus adjacent the valve structure. In another group of embodiments, the attachment pathway between opposing leaflets and the support frame and / or vessel wall comprises a proximal portion that places the leaflets in extended contact with one another and a distal portion forms a large angle with respect to the adjacent walls such that a large pocket is created at the base of the leaflets. In one embodiment, the attachment pathway extends distally along a pair of substantially parallel longitudinal attachment struts to create an extended leaflet contact area, then angles circumferentially and distally from the former along distal attachment struts to define the bottom edge of the leaflets.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Surgical implant devices and systems including a sheath member
InactiveUS20050177156A1Easy to installImprove clinical outcomesSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAnatomical structuresSpinal column
A surgical implant is provided that includes first and second abutment surfaces between which are positioned a force imparting mechanism. A sheath is positioned between the first and second abutment surfaces, and surrounds the force imparting mechanism. The sheath is fabricated from a material that accommodates relative movement of the abutment members, while exhibiting substantially inert behavior relative to surrounding anatomical structures. The sheath is generally fabricated from expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, a copolymer of polycarbonate and a urethane, or a blend of a polycarbonate and a urethane. The force imparting member may include one or more springs, e.g., a pair of nested springs. The surgical implant may be a dynamic spine stabilizing member that is advantageously incorporated into a spine stabilization system to offer clinically efficacious results.
Owner:RACHIOTEK
Annuloplasty instrument
InactiveUS7077861B2Easy to insertReliable and more easily accomplishedBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsBiomedical engineeringVALVE PORT
A device for repairing a heart valve comprises an implantation instrument. The implantation instrument comprises a first support ring, and a second support ring connected to said first support ring to form a coiled configuration. The first support ring is configured to abut one side of the valve and the second support ring is configured to abut an opposite side of the valve to thereby trap a portion of the valve tissue therebetween. The device further comprises an annuloplasty implant adapted to be attached to the heart valve annulus in order to reshape the annulus and allow the leaflets to open and close properly. The annuloplasty implant is connected to the implantation instrument for insertion to the annulus.
Owner:MEDTENTIA INT LTD OY
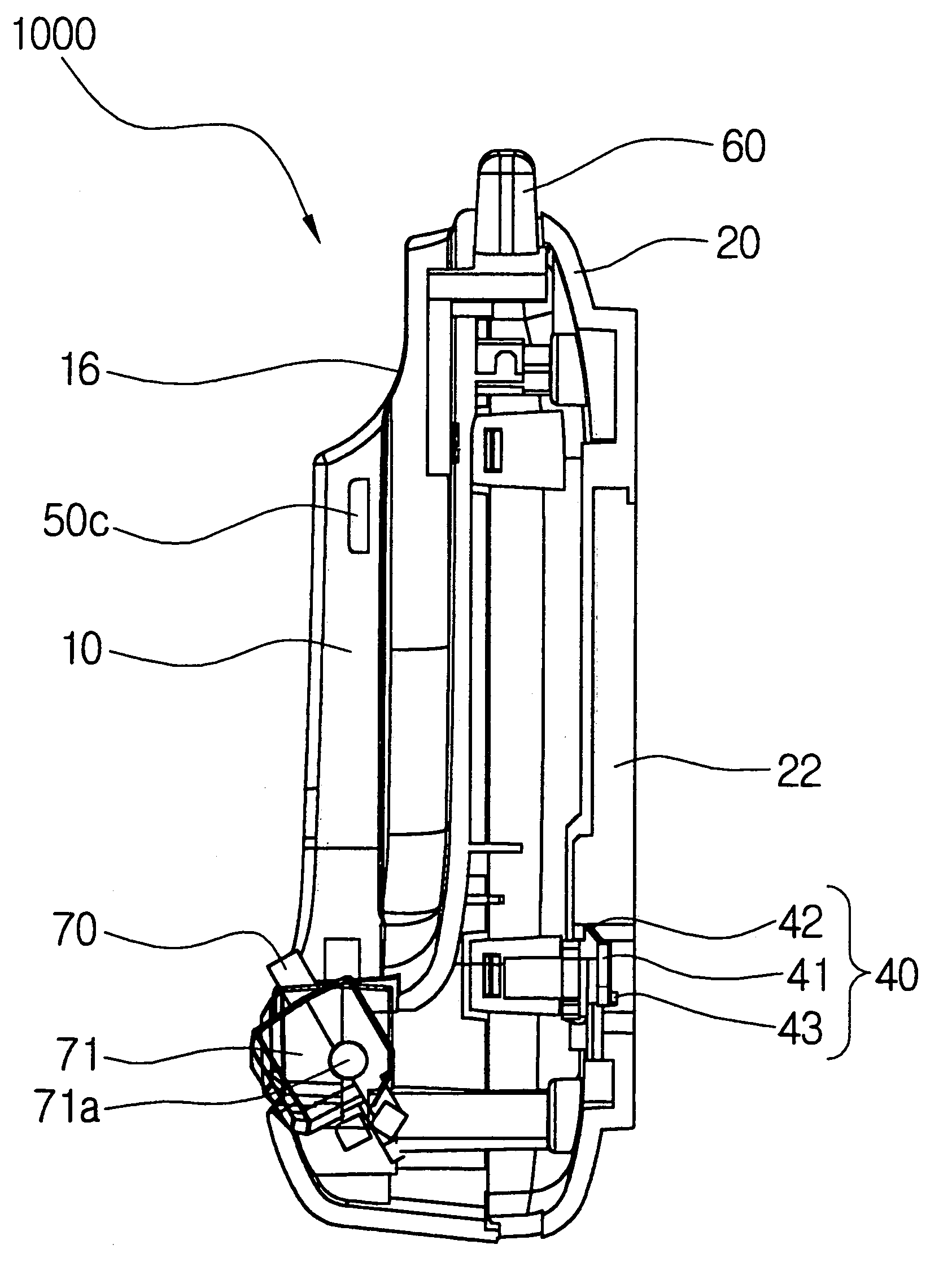
Portable charger for mobile phone
InactiveUS7166987B2Easy to carryGood adhesionTravelling carriersHoldersCapacitanceElectrical battery
Owner:R F TECH
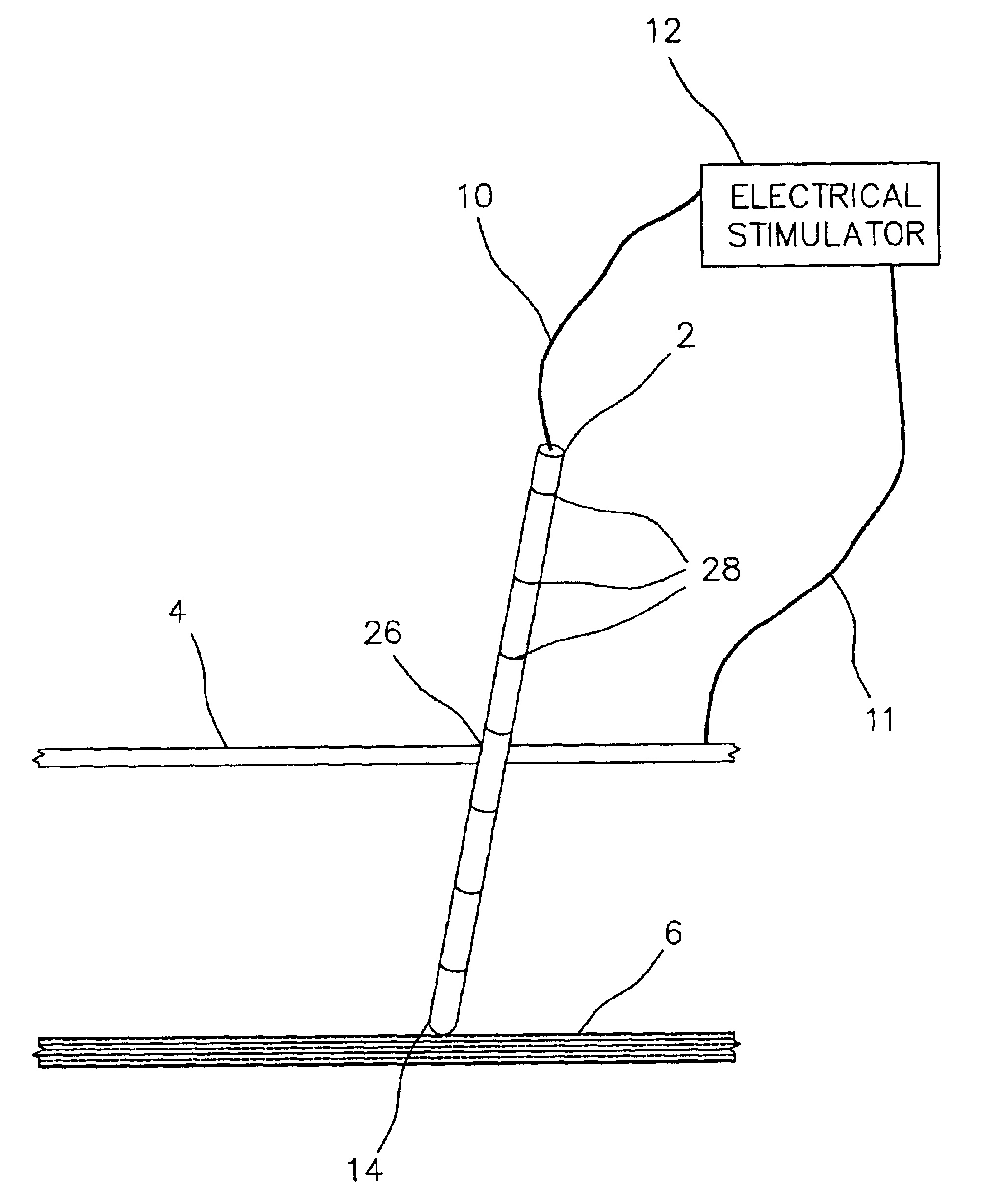
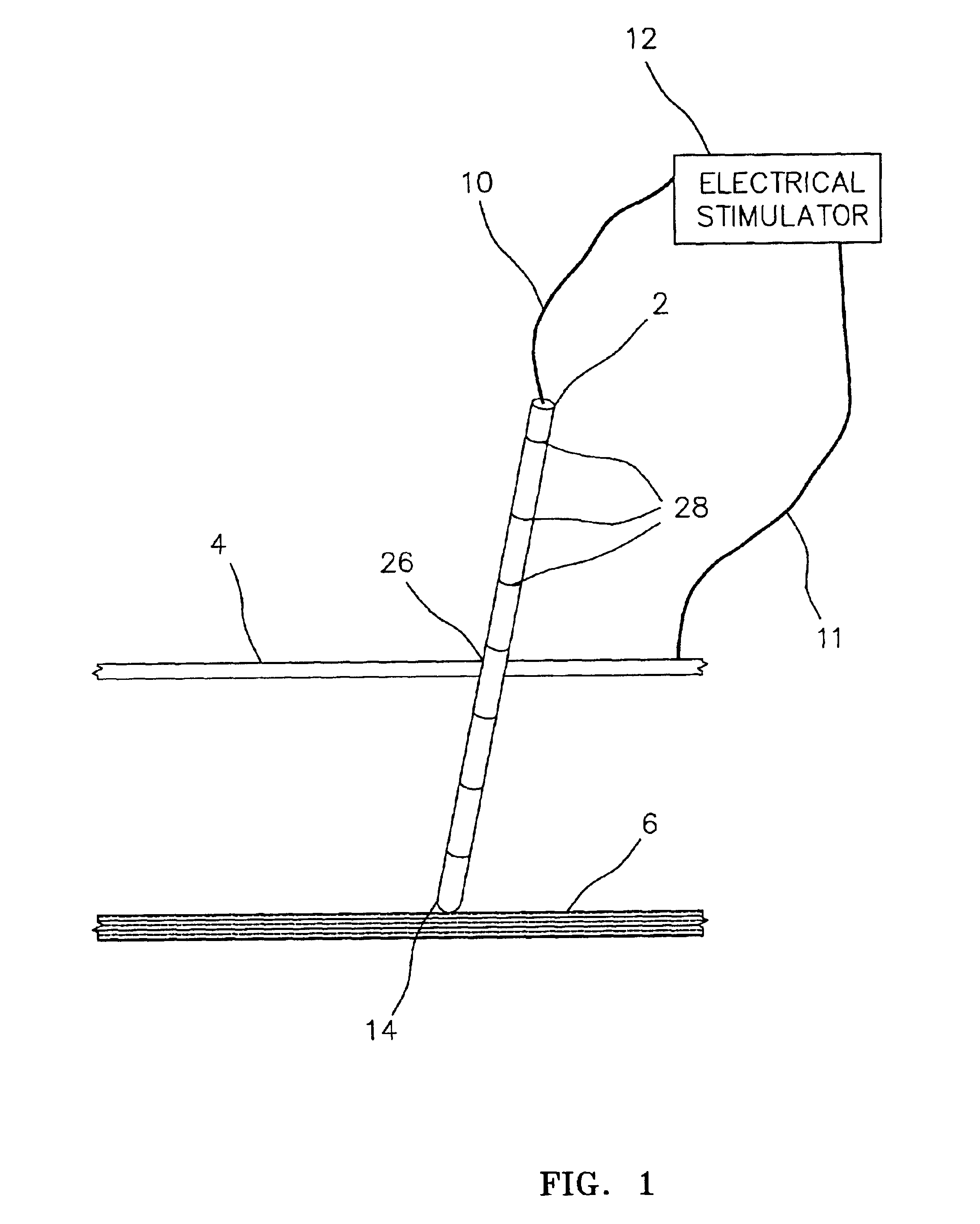
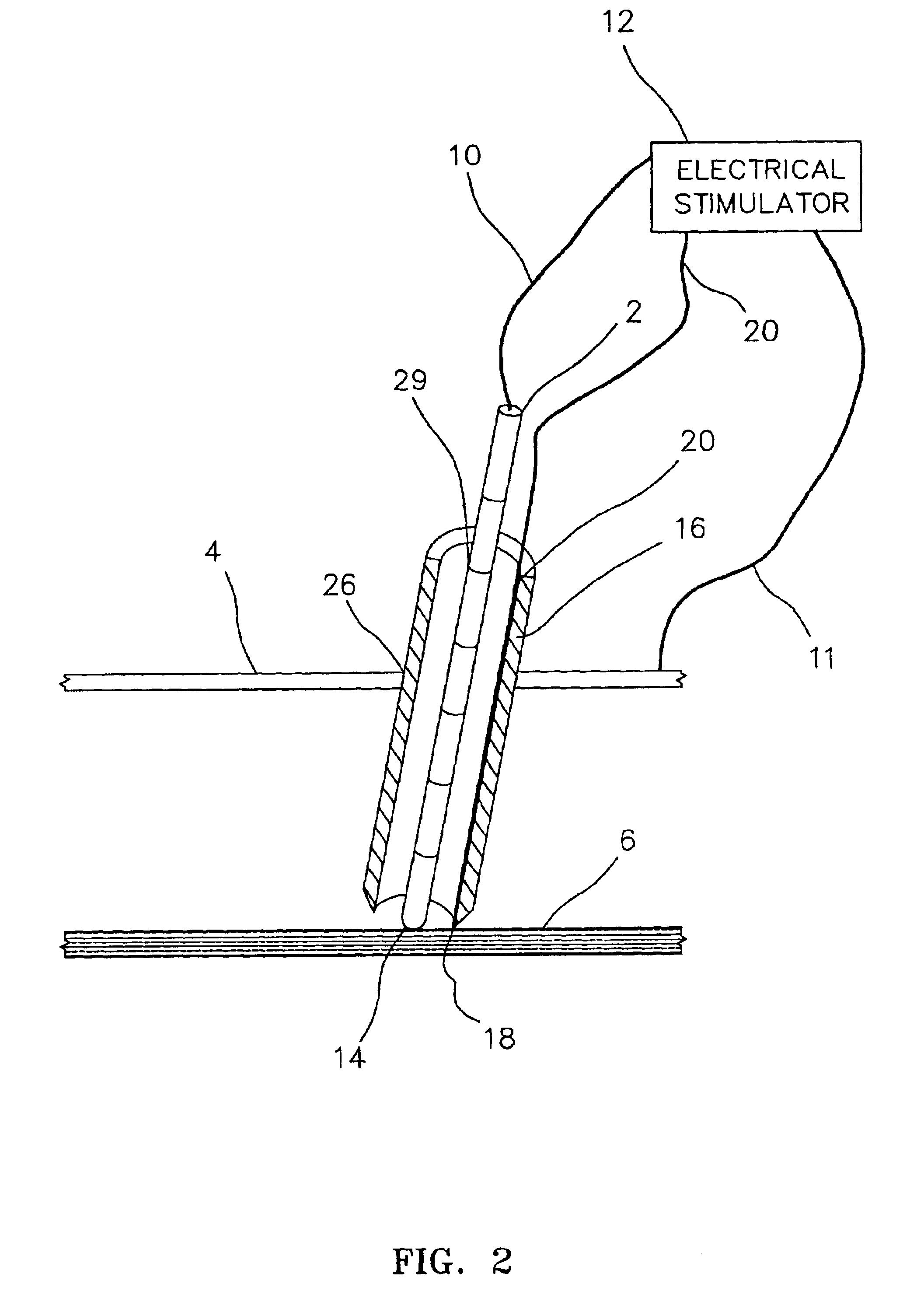
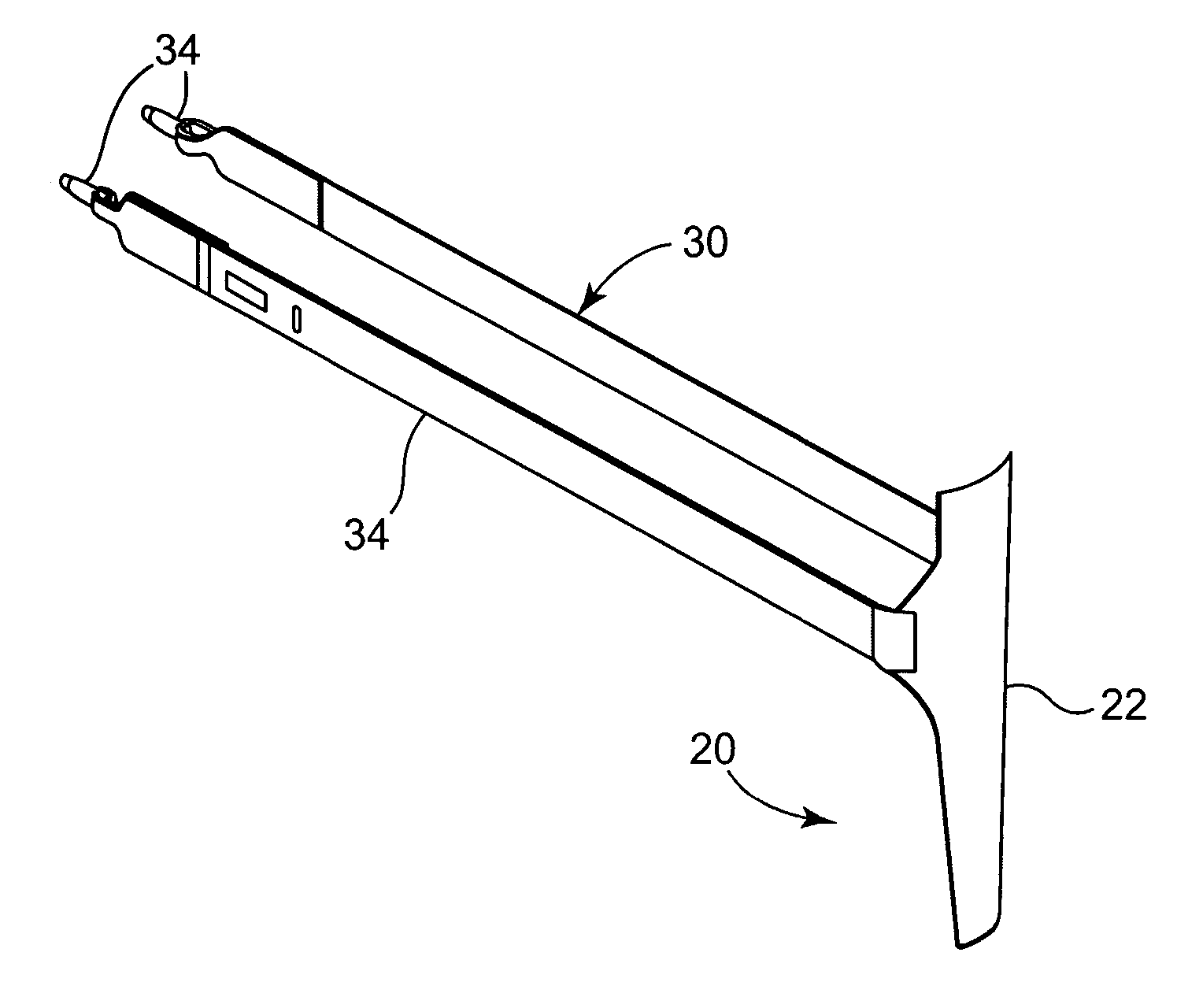
Electrically sensing and stimulating system for placement of a nerve stimulator or sensor
InactiveUS6829508B2Easy to installLongerSpinal electrodesSurgical needlesSurgical departmentSurgical procedures
An electrically sensing and stimulating outer sheath for ensuring accurate surgical placement of a microsensor or a microstimulator near a nerve in living tissue is disclosed. The electrically sensing outer sheath may also be used to verify the function of the microstimulator or microsensor during surgical placement but before the outer sheath is removed. In the event that the microstimulator is not optimally placed near the nerve, or if the microstimulator is malfunctioning, this can be determined prior to removal of the outer sheath, thus reducing the possibility of nerve or tissue damage that might be incurred during a separate operation to remove the microstimulator.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Method and apparatus for treating pelvic organ prolapse
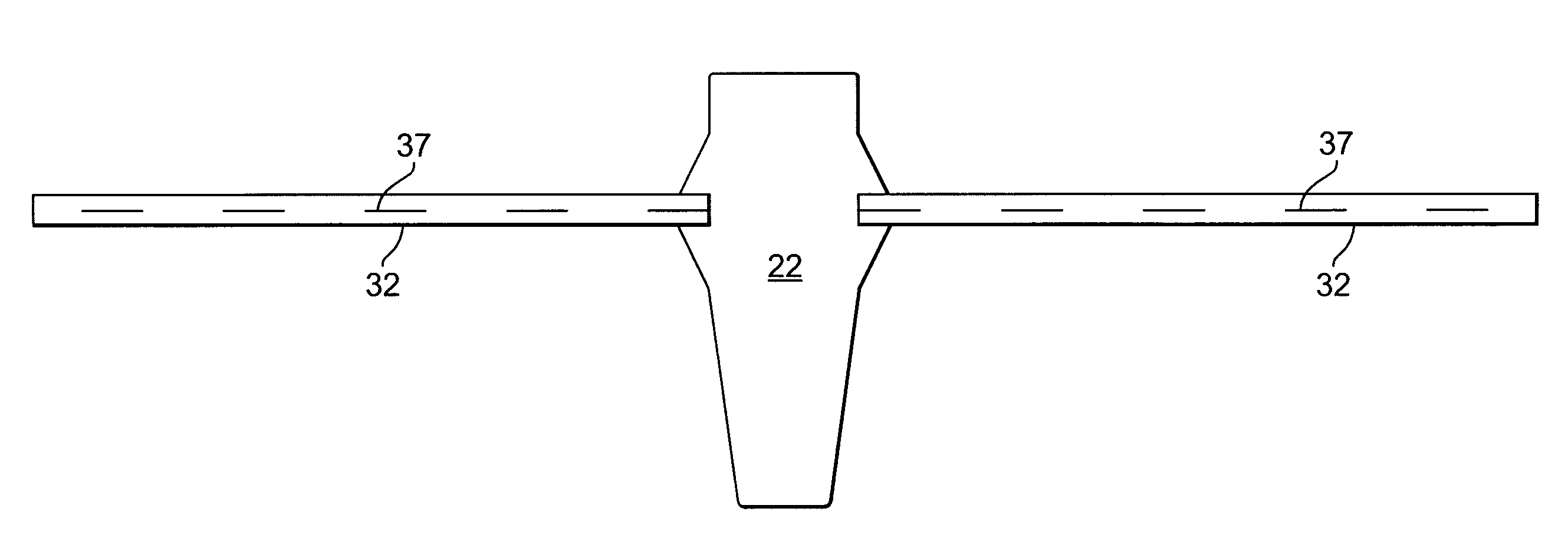
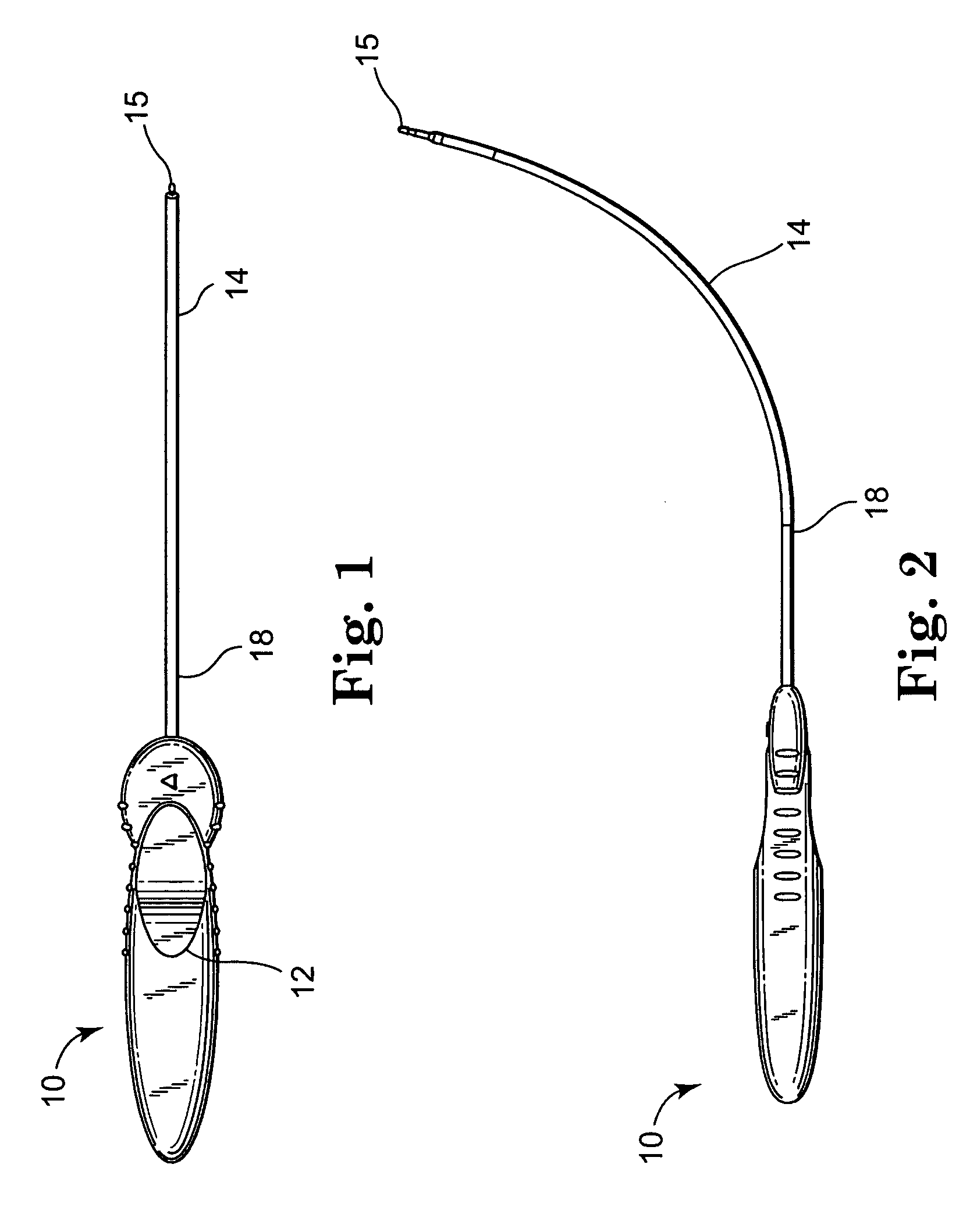
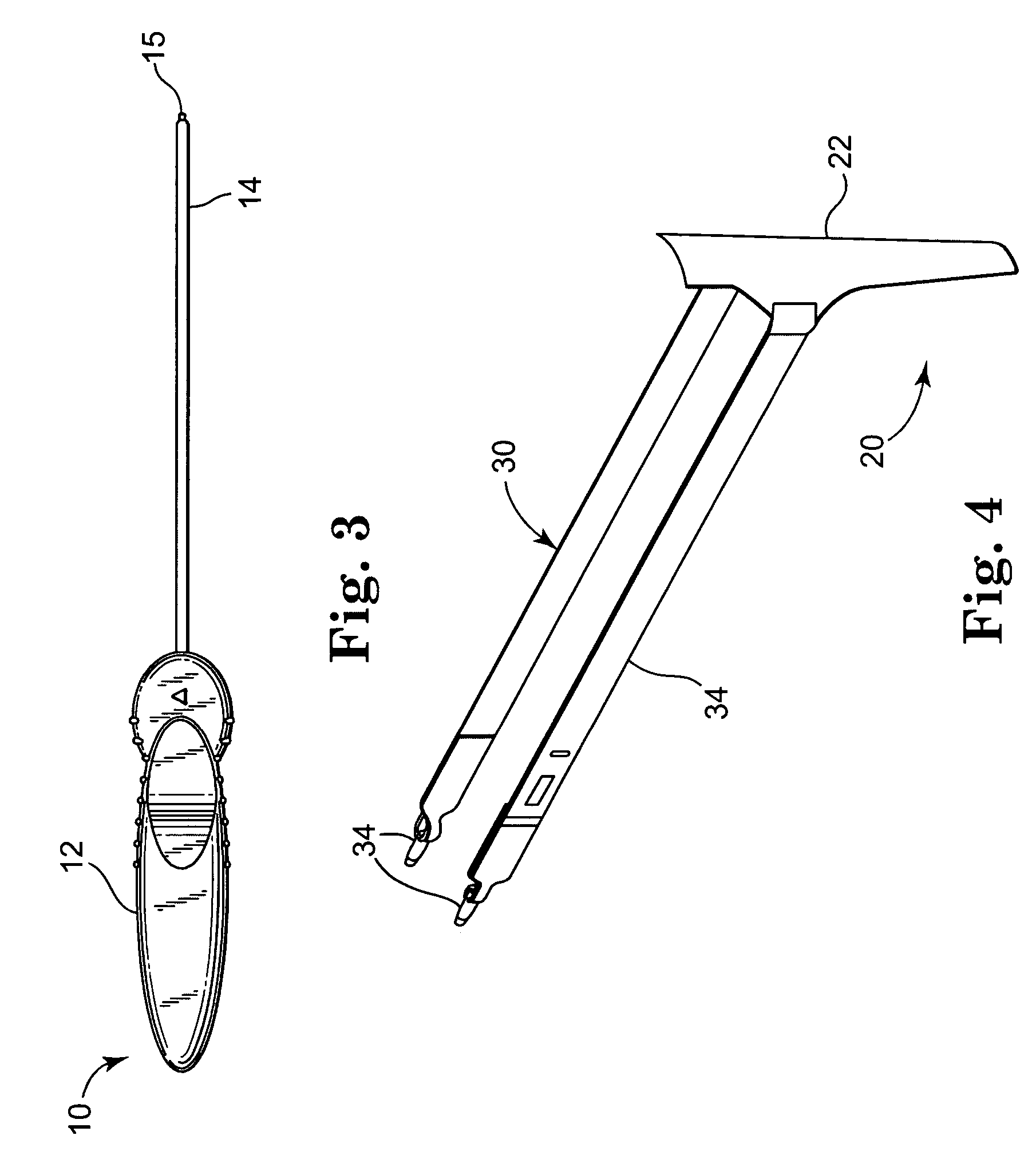
ActiveUS20050245787A1Convenient for operatorsEasy to operateSuture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesFirst pathwayIschial spine
A method of treating pelvic organ prolapse is provided. The method generally includes the steps of establishing a first pathway between the external perirectal region of the patient to the region of the ischial spine in tissue on one side of the prolapsed organ, followed by establishing a second pathway in tissue on the contralateral side of the prolapsed organ. A support member, which includes a central support portion and two end portions, is positioned in a position to reposition said prolapsed organ in said organ's anatomically correct location. The end portions of the support member are introduced through the respective tissue pathways, followed by adjustment of the end portions so that the support member is located in a therapeutic relationship to the prolapsed organ that is to be supported. An apparatus and kit for said treatment is further provided.
Owner:ASTORA WOMENS HEALTH
Heart monitoring body patch and system
InactiveUS20090062670A1Good adhesionEasily attached to patientElectrocardiographySensorsTransceiverHeart monitoring
Provided is a diagnostic patch system for monitoring and storing patient information, which includes sensors, a data storage unit, and a transceiver. Each of the sensors is attached to a skin to detect a patient data. The data storage unit is configured to store stream of the detected patient data from the plurality of sensors. The transceiver, connected with the sensors and the data storage unit, communicates the stream of the patient data with an analyzer, and the analyzer is configured to process and analyze the stream of the patient data. Two or more diagnostic patch systems can communicate with each other.
Owner:BIOSEVEN
Sterile control unit with a sensor screen
InactiveUS20110235168A1Direct contact guaranteeGood adhesionDiagnosticsSurgical drapesSurgical microscopeIdentification device
The present invention relates to a control unit for an item of medical equipment, particularly a surgical microscope, for controlling equipment functions, comprising a sensor-screen having a sensor-screen surface for displaying image material, the sensor-screen being configured to be operated in contactless manner via a recognition device and to accommodate a sterile transparent control surface in front of the sensor-screen surface.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS (SCHWEIZ) AG
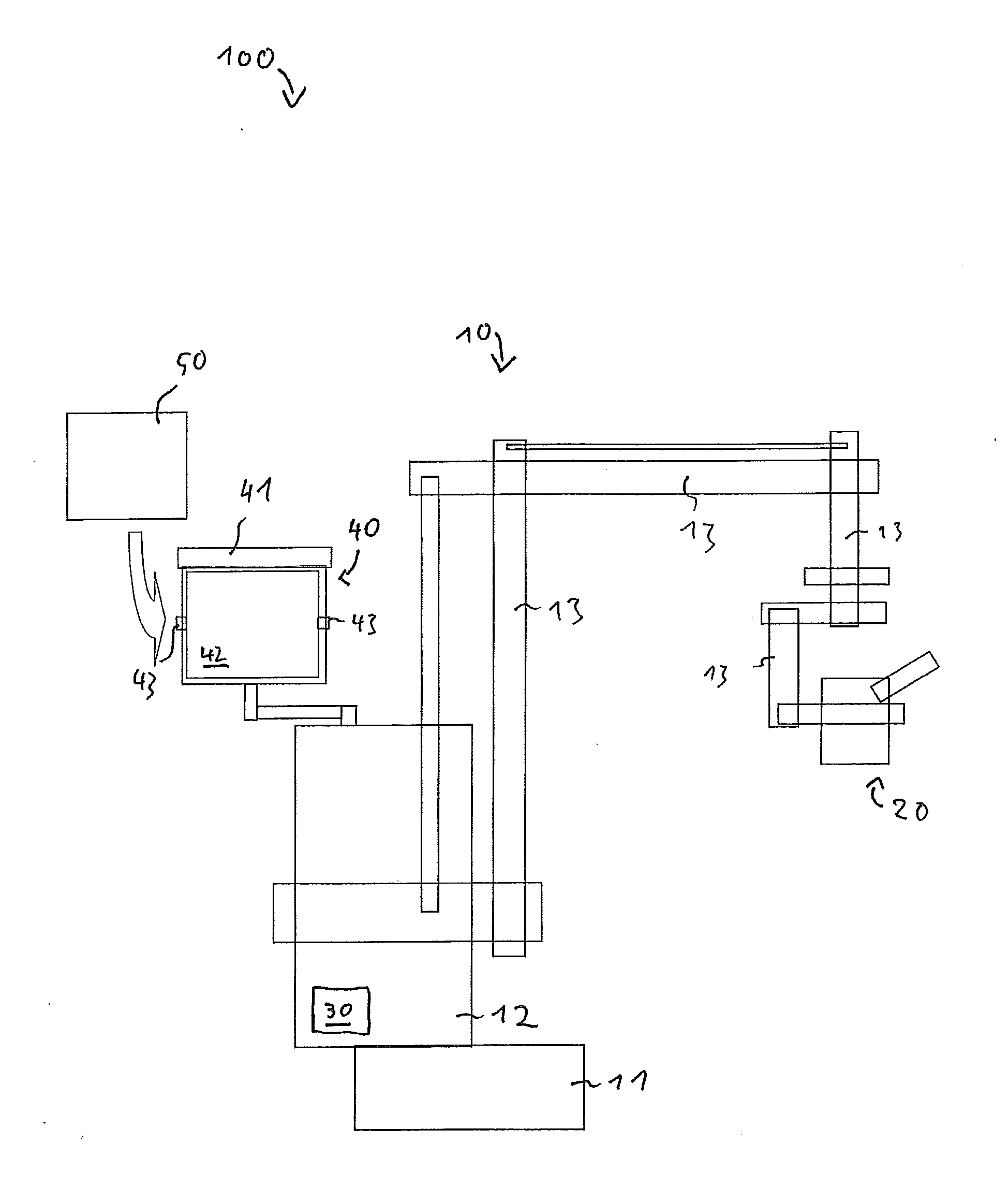
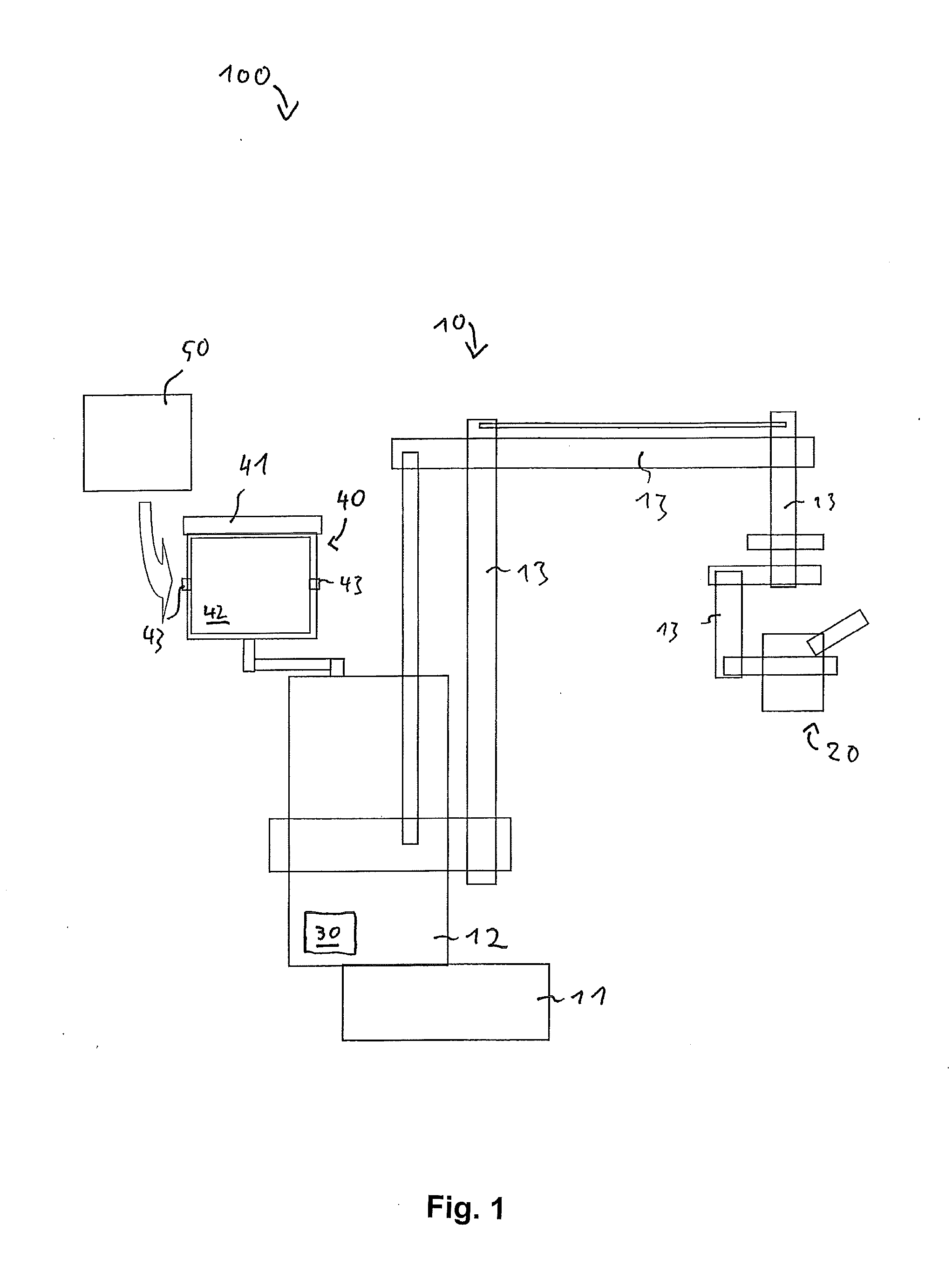
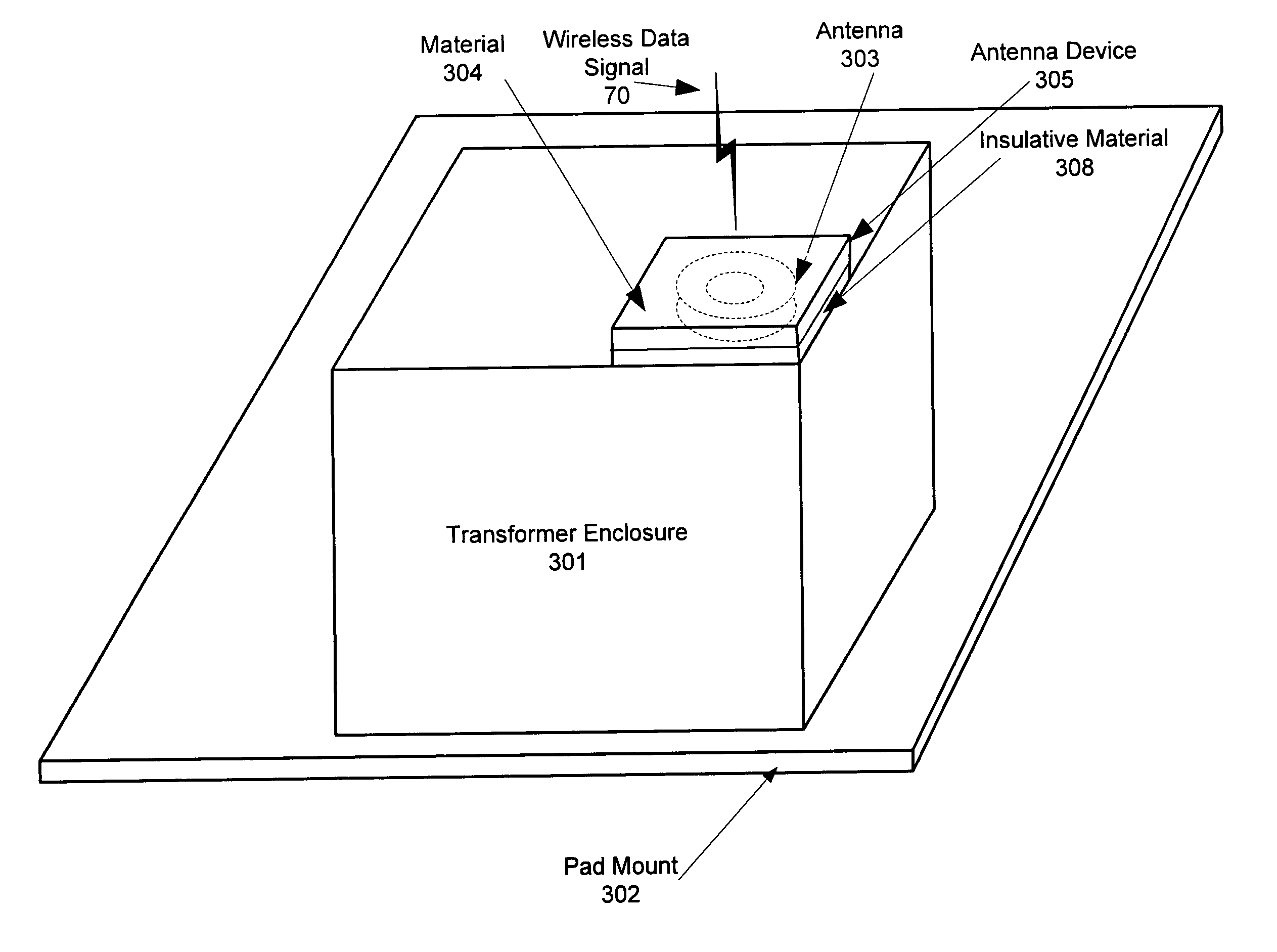
Transformer antenna device and method of using the same
InactiveUS7113134B1Good adhesionAvoid accessAntenna supports/mountingsProtective material radiating elementsElectricityElectrical conductor
The invention contemplates an antenna device, system and method of installing the antenna device for receiving a wireless signal at a pad mounted electrical transformer. The novel device includes an antenna capable of communicating the wireless signal and a material located around the antenna. The material facilitates attachment to the pad mounted electrical transformer as well as preventing access to the antenna. The antenna may be covered by or embedded within the material. The material may be emissive and / or insulative. In addition, the device may include a conductor that passes through an enclosure of the pad mounted transformer. The conductor may be communicatively coupled to a first communication device that provides communication to a customer premise that is electrically coupled to the pad mounted electrical transformer.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
Display device for exterior rearview mirror
InactiveUS20070058257A1Good adhesionEasy to assembleMirrorsOptical signallingDriver/operatorDisplay device
An exterior mirror sub-assembly includes a reflective element, a back plate, and a display element having a light source that is activatable to emit light. The display element attaches to a display receiving portion of the back plate and the light source is activatable to emit light through the display receiving portion. The display receiving portion may be configured to orient the display element at a predetermined angle so that light exiting the display element when the light source is activated may be directed (a) generally away from the vehicle when the mirror assembly is mounted to the vehicle so as to be principally viewed by drivers of other vehicles or (b) generally toward the driver of the vehicle when the mirror assembly is mounted to the vehicle so as to be principally viewed by the driver of the host vehicle.
Owner:MAGNA MIRRORS OF AMERICA INC
Interactive video based games using objects sensed by TV cameras
InactiveUS20060033713A1High costLow possible cost and complexityInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionStereo photogrammetryStereo cameras
A method and apparatus for interactive TV camera based games in which position or orientation of points on a player or of an object held by a player are determined and used to control a video display. Both single camera and stereo camera pair based embodiments are disclosed, preferably using stereo photogrammetry where multi-degree of freedom information is desired. Large video displays, preferably life-size may be used where utmost realism of the game experience is desired.
Owner:MOTION GAMES
Method and apparatus for treating pelvic organ prolapse
ActiveUS7500945B2Less riskEasy to operateSuture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesFirst pathwayIschial spine
A method of treating pelvic organ prolapse is provided. The method generally includes the steps of establishing a first pathway between the external perirectal region of the patient to the region of the ischial spine in tissue on one side of the prolapsed organ, followed by establishing a second pathway in tissue on the contralateral side of the prolapsed organ. A support member, which includes a central support portion and two end portions, is positioned in a position to reposition said prolapsed organ in said organ's anatomically correct location. The end portions of the support member are introduced through the respective tissue pathways, followed by adjustment of the end portions so that the support member is located in a therapeutic relationship to the prolapsed organ that is to be supported. An apparatus and kit for said treatment is further provided.
Owner:ASTORA WOMENS HEALTH
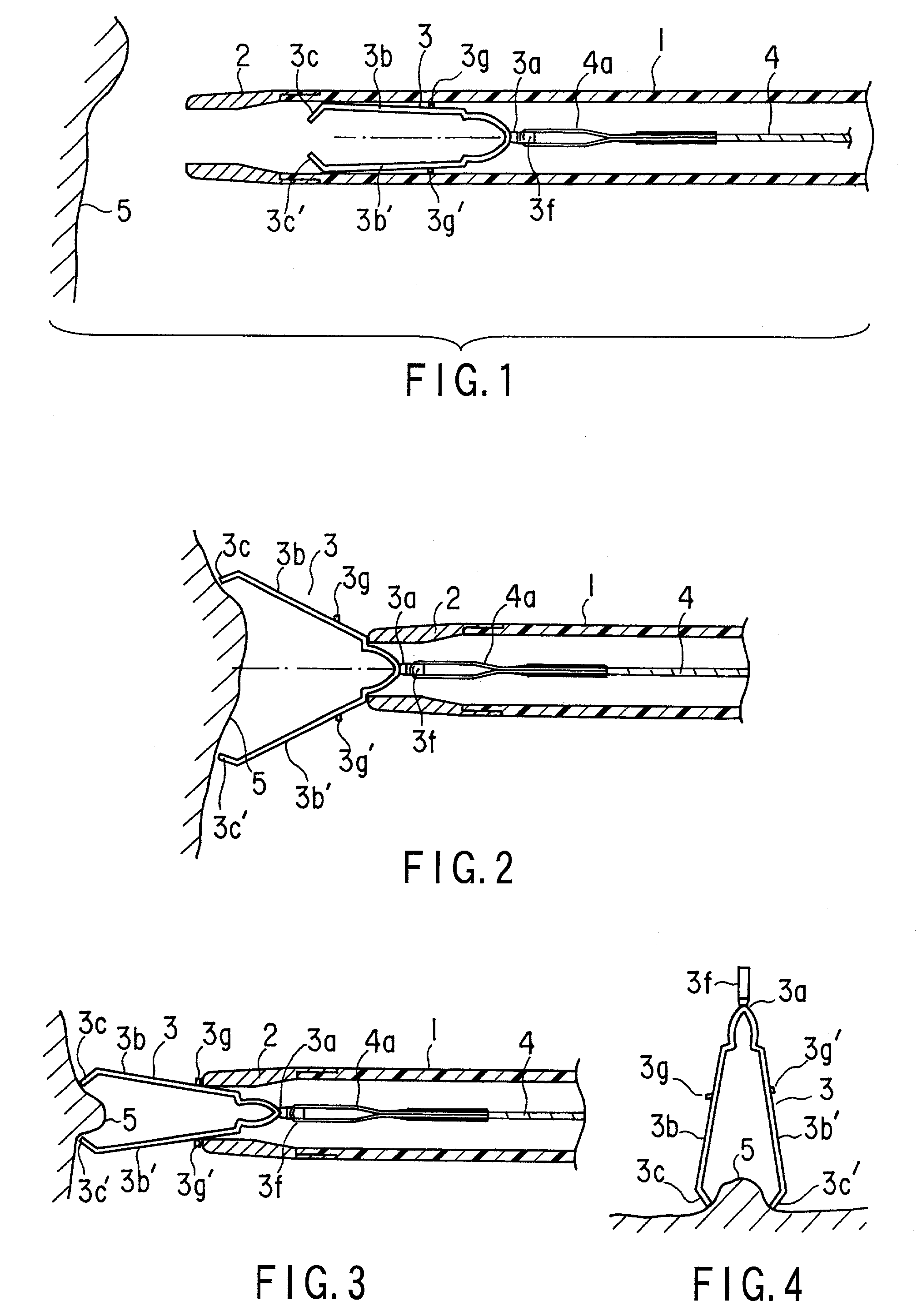
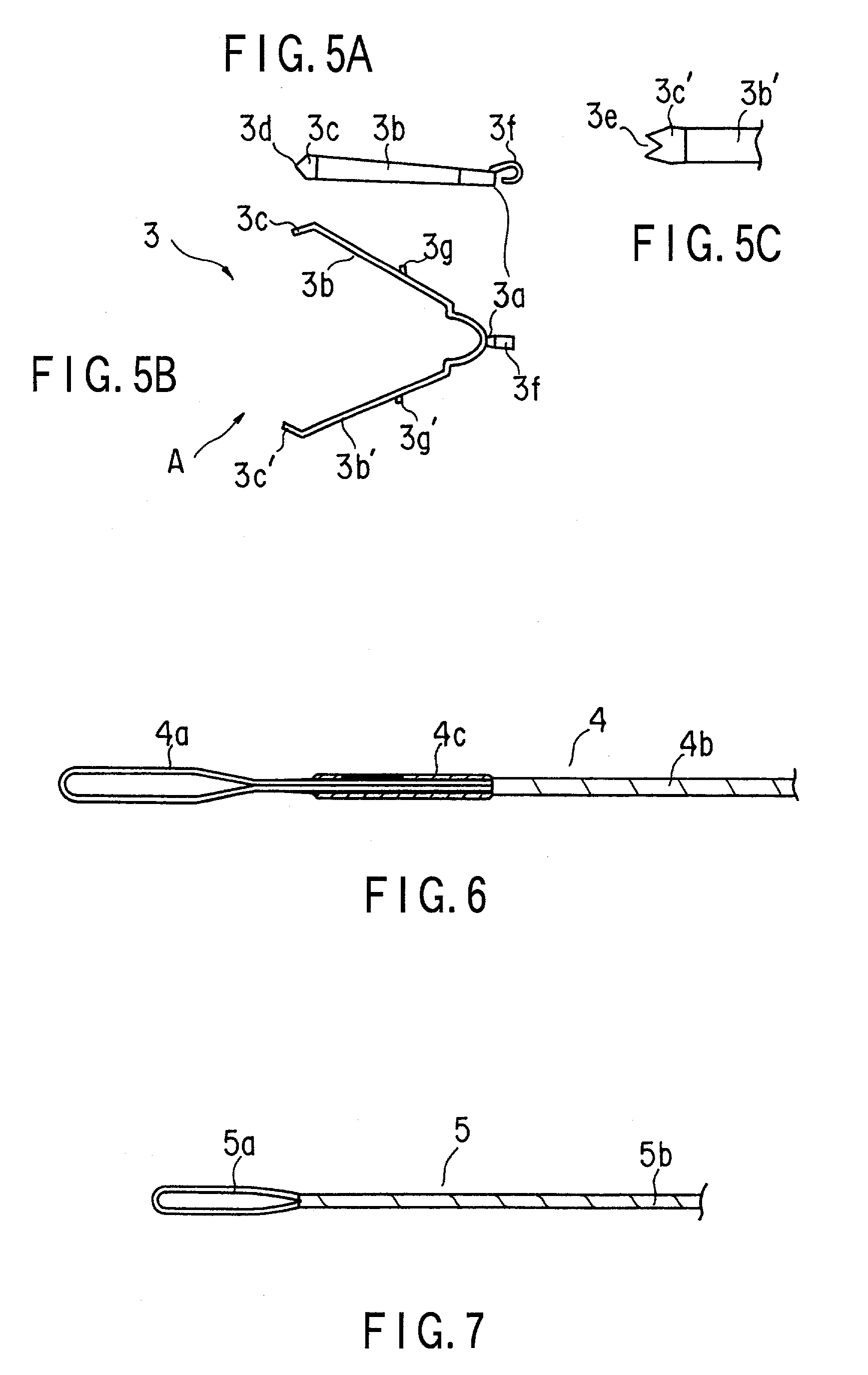
Apparatus for ligating living tissues
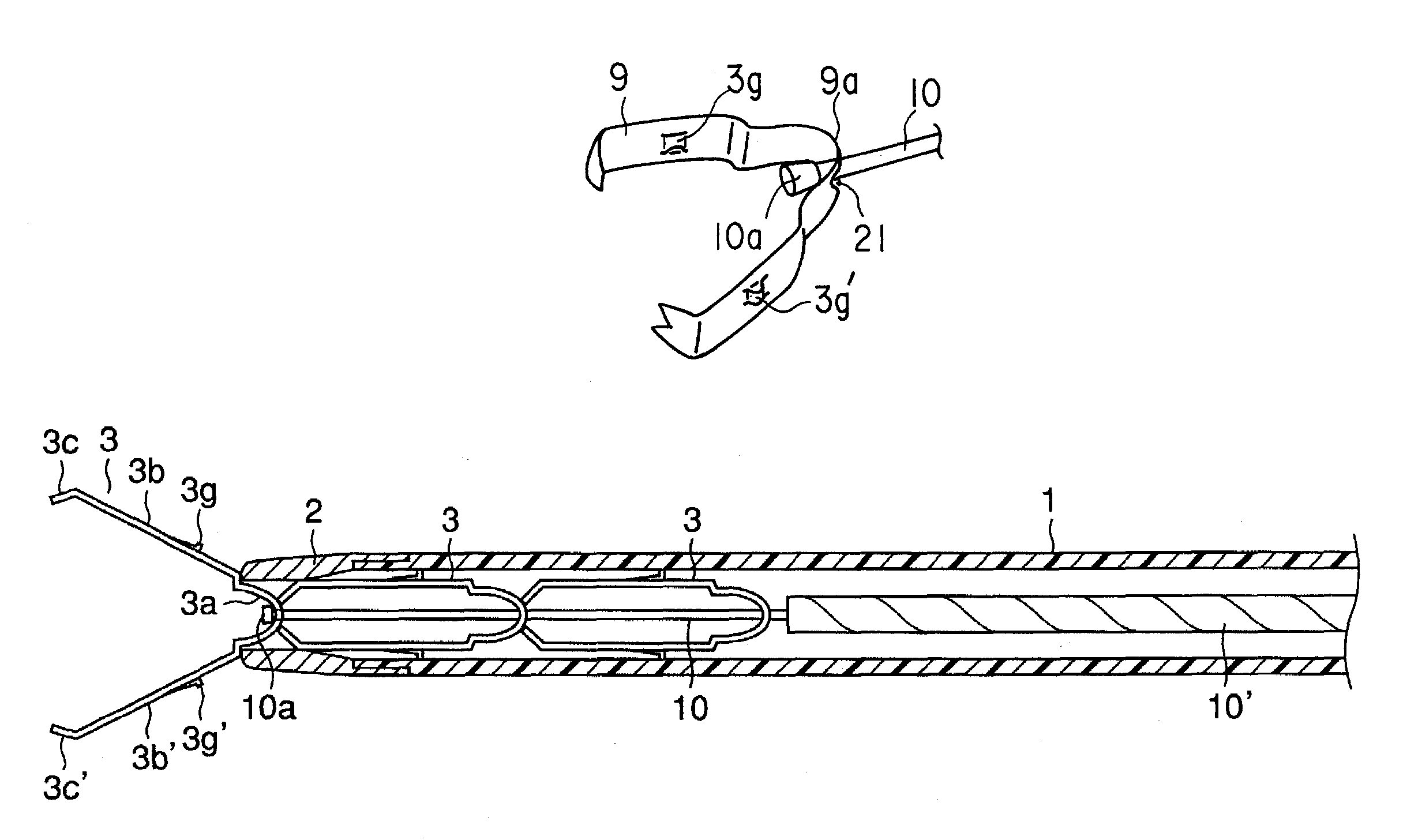
InactiveUS7223271B2Reduce component countReduce manufacturing costStaplesNailsEngineeringLiving body
A ligating apparatus includes an introducing tube which can be inserted in a living body cavity, a manipulating wire inserted in the introducing tube in such a manner that the manipulating wire can freely advance or retreat, a clip which is directly joined to a tip end of the manipulating wire, which has a holding portion formed in a tip end of an arm portion extending from the base end, and which has an extending / opening property, and engaging structure disposed in at least one of the base end of the clip and the tip end of the manipulating wire, wherein at least one of the engaging means is deformed and releases engaging of the clip and the manipulating wire, when the clip engages with the tip end of the introducing tube, and a force for detaching the base end of the clip from the tip end of the manipulating wire is applied.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP +1
Methods and devices for improved bonding of devices to bone
InactiveUS20060079895A1Improve interface strengthSufficient supportSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisImplanted deviceSoft tissue
The present invention is directed to improving bonding between orthopedic devices, particularly vertebral devices, and bone. The present invention provides various methods and devices employing mechanical and bio-fixation modalities for such attachment. As provided herein, the initial mechanical attachment of a device to bone is sufficiently stable to ensure that the implanted device is relatively immobile (or alternatively microscopic motion is promoted), facilitating bone and soft tissue in-growth and the eventual bio-fixation of the device.
Owner:FACET SOLUTIONS
Method of sealing two plates with the formation of an ohmic contact therebetween
InactiveUS20070072391A1Reduce depthBudget is reducedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsOhmic contact
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Tissue retractor adapted for the attachment of an auxiliary element
A tissue retractor with an adjustable center claw. The retractor includes two pivoted retractor arms. An axially and angularly displaceable, spring biased clamping mechanism is positioned on the pivot axis. In a mounting position, a elongated clamping element aligns with a slot in the center claw. When the center claw is positioned and the clamp moves to its clamping position, the elongated clamping member clamps the center claw in position. The counterfacing surfaces of the center claw and the clamping member are toothed to provide a positive one-way ratchet clamp.
Owner:LAB ENG & MFG
Electro-optic window incorporating a discrete photovoltaic device and apparatus for making same
InactiveUS6045643ALimited amountSimple designStatic indicating devicesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesElectricityResistor
An electro-optic window is provided which is powered solely by at least one discrete photovoltaic cell within an electro-optic window. The electro-optic window has front and back spaced-apart glass elements sealably bonded together in a spaced-apart relationship and defining a chamber filled with an electro-optic material. The front glass element has a transparent conductive layer on the face of the front glass element confronting the rear glass element and the rear glass element has a transparent conductive layer on the face confronting the front glass element. The seal is generally disposed along the perimeter of three edges of both glass elements and some distance in from the remaining (fourth) edge. The photovoltaic assembly is electrically connected to the two transparent conductive layers and is placed on the outer perimeter along this fourth edge with the photon-absorbing side of all the photovoltaic cells within the photovoltaic assembly facing in one direction ("out" the window). When light impinges on the photovoltaic cell a current is created which darkens the electro-optic material in proportion to the amount of impinging light. By choosing the relative area of the photovoltaic assembly to produce the correct current for the electro-optically active window area, the darkening of the electro-optic portion can be directly and accurately controlled without the need for any circuit, wires or shorting resistors. In addition, an apparatus for making an electro-optic window having two members capable of securing and holding two glass elements in a spaced-apart and parallel relationship is provided. The glass elements may be secured by vacuum-applying members or simple clips. The glass elements may be held in a spaced-apart and parallel relationship by a hydraulic mechanism or by simple spacers placed between the securing members.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
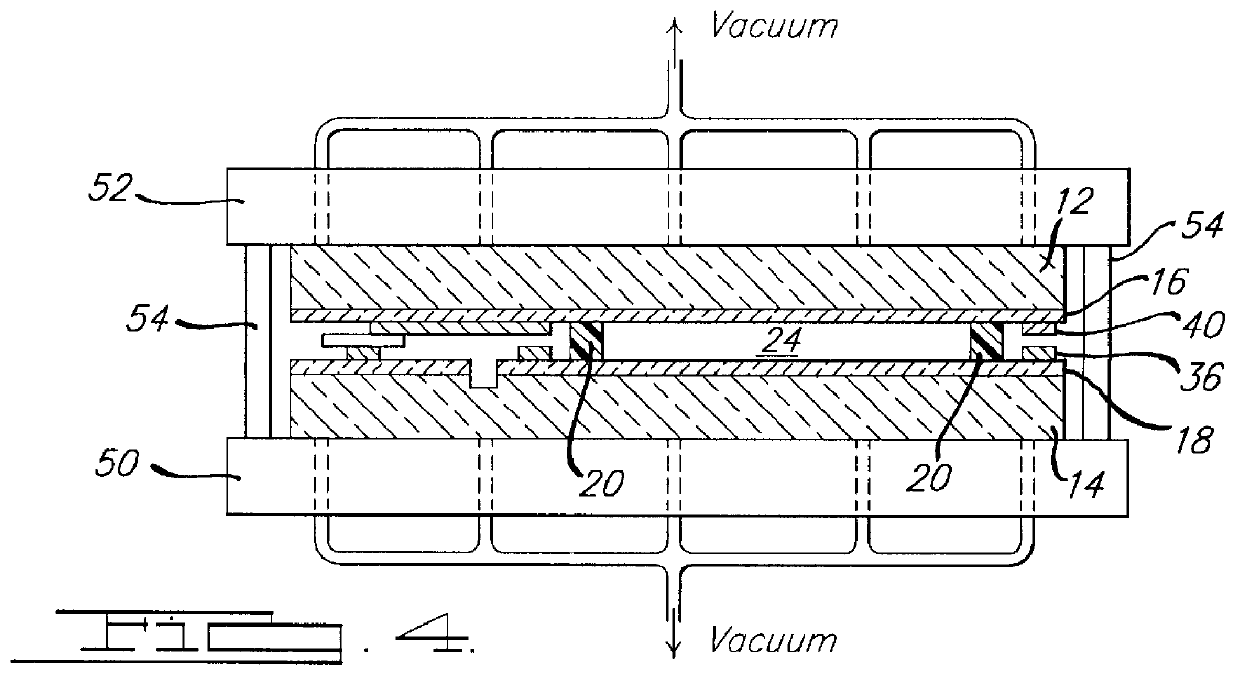
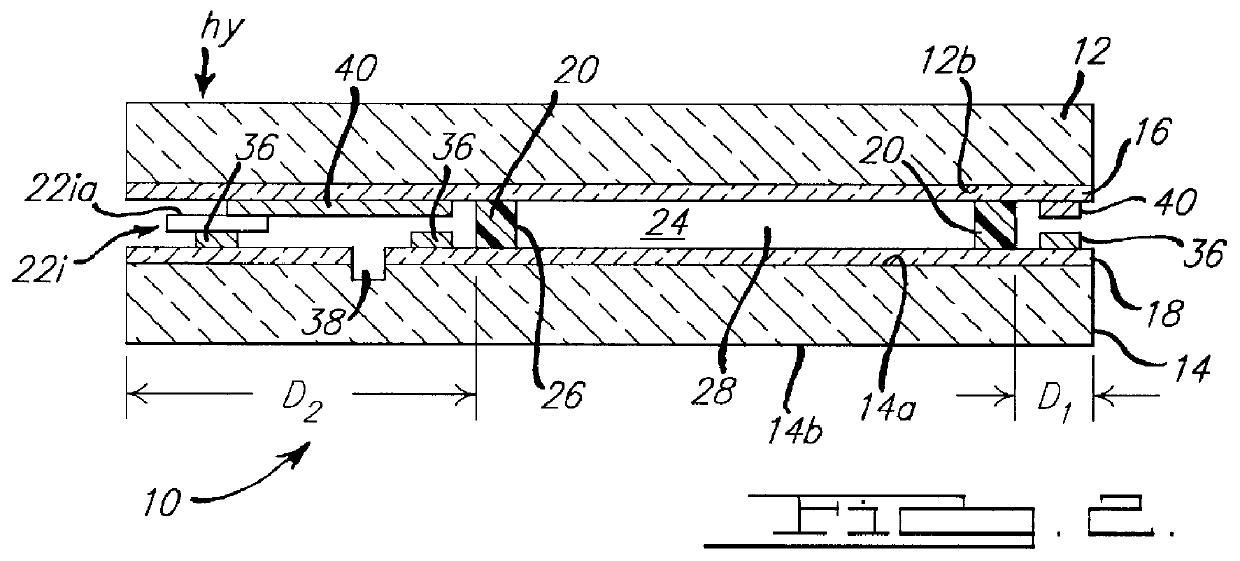
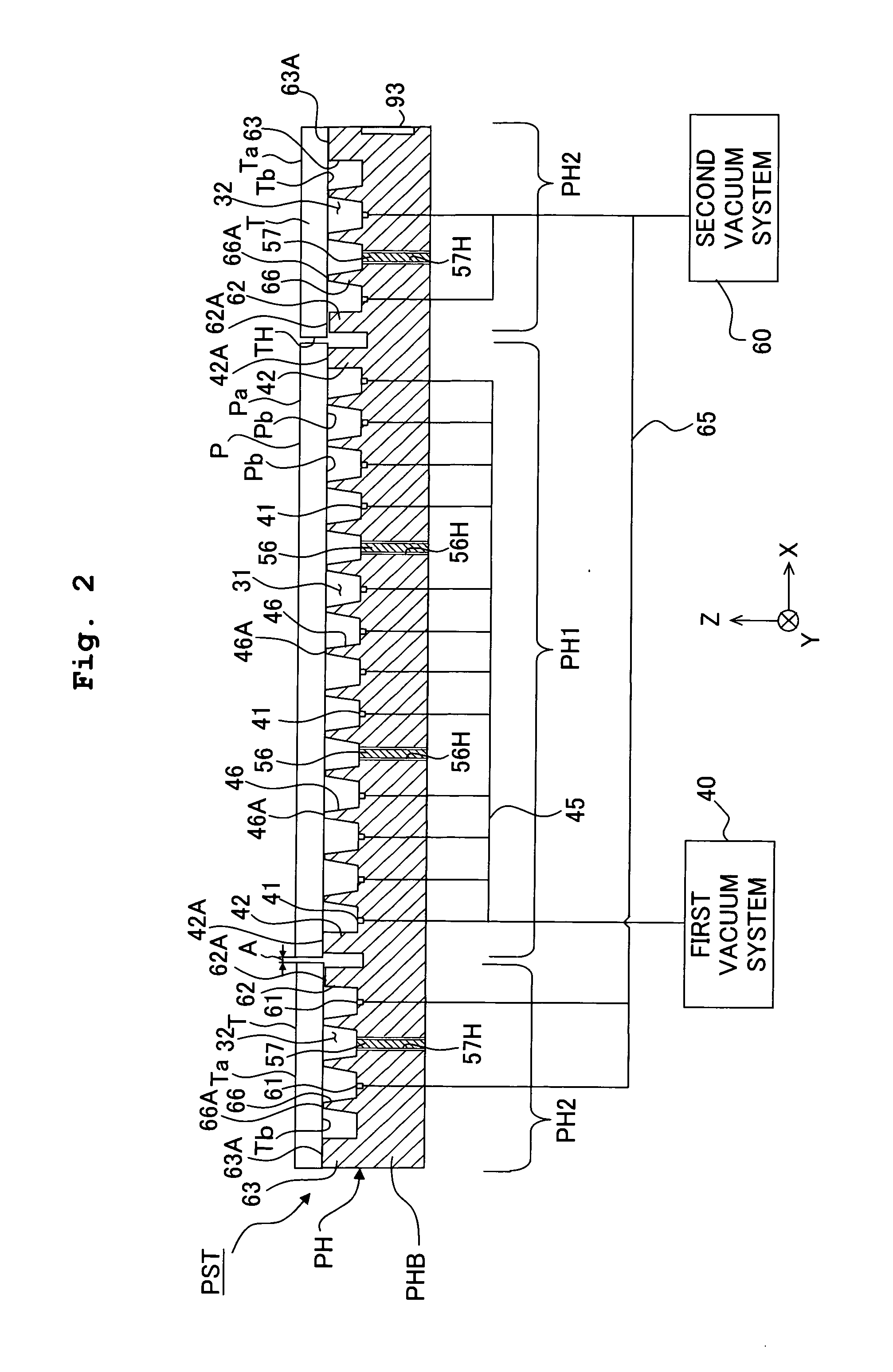
Substrate holding unit, exposure apparatus having same, exposure method, method for producing device, and liquid repellent plate
InactiveUS20070177125A1Good adhesionEasy detachmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringExposure
A substrate holder includes a base; a first holding portion which is formed on the base and which attracts and holds a substrate; and a second holding portion which is formed on the base and which attracts and holds a plate member in the vicinity of the substrate attracted and held by the first holding portion. In an exposure apparatus including such a substrate holder, the plate can be exchanged easily, thereby making the maintenance of the apparatus easy. Consequently, such an exposure apparatus is suitable for immersion exposure.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Solvent-free expansion type fire-proof epoxy coating and its preparation method
The invention discloses the inflatable fire-resisting paint, comprising A and B. The A comprises epoxide resin, modified resin, catalyst, foamable agent, fire retarding agent, fluxing agent, color filler and smog inhibiting agent, and the B comprises color filler, curing agent and auxiliary agent. The fire-resisting paint has the advantages of good heat-insulating property, adhesion force and intensity. The coating has good water resistance, acid- alkali resistance, corrosion resistance and tenacity, and is not easy to drop. The paint can be used in rolled steel and aluminum products, especially the fireproof situation of oil factories.
Owner:MARINE CHEM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com