Patents
Literature
574 results about "Stereo camera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
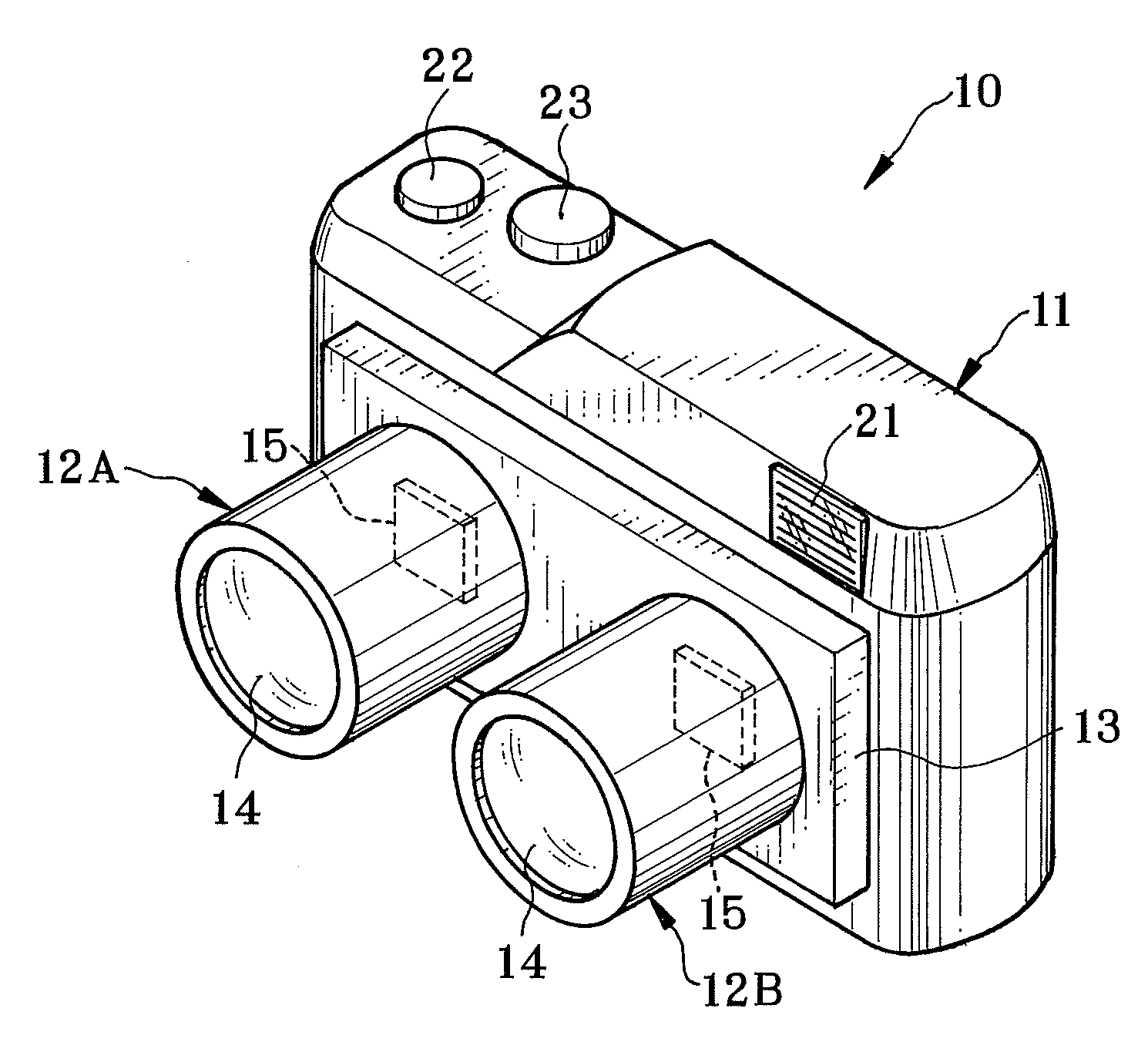
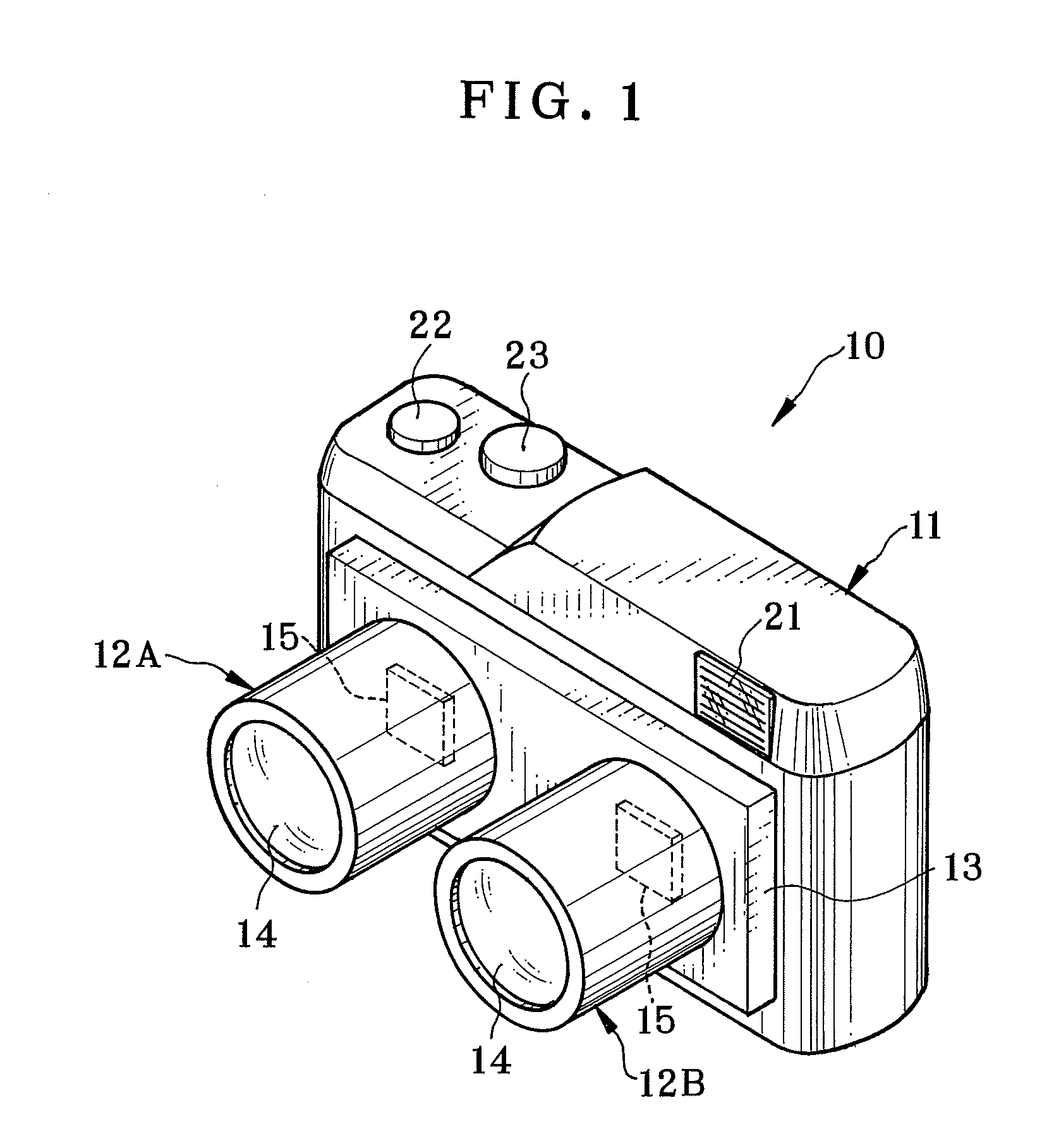
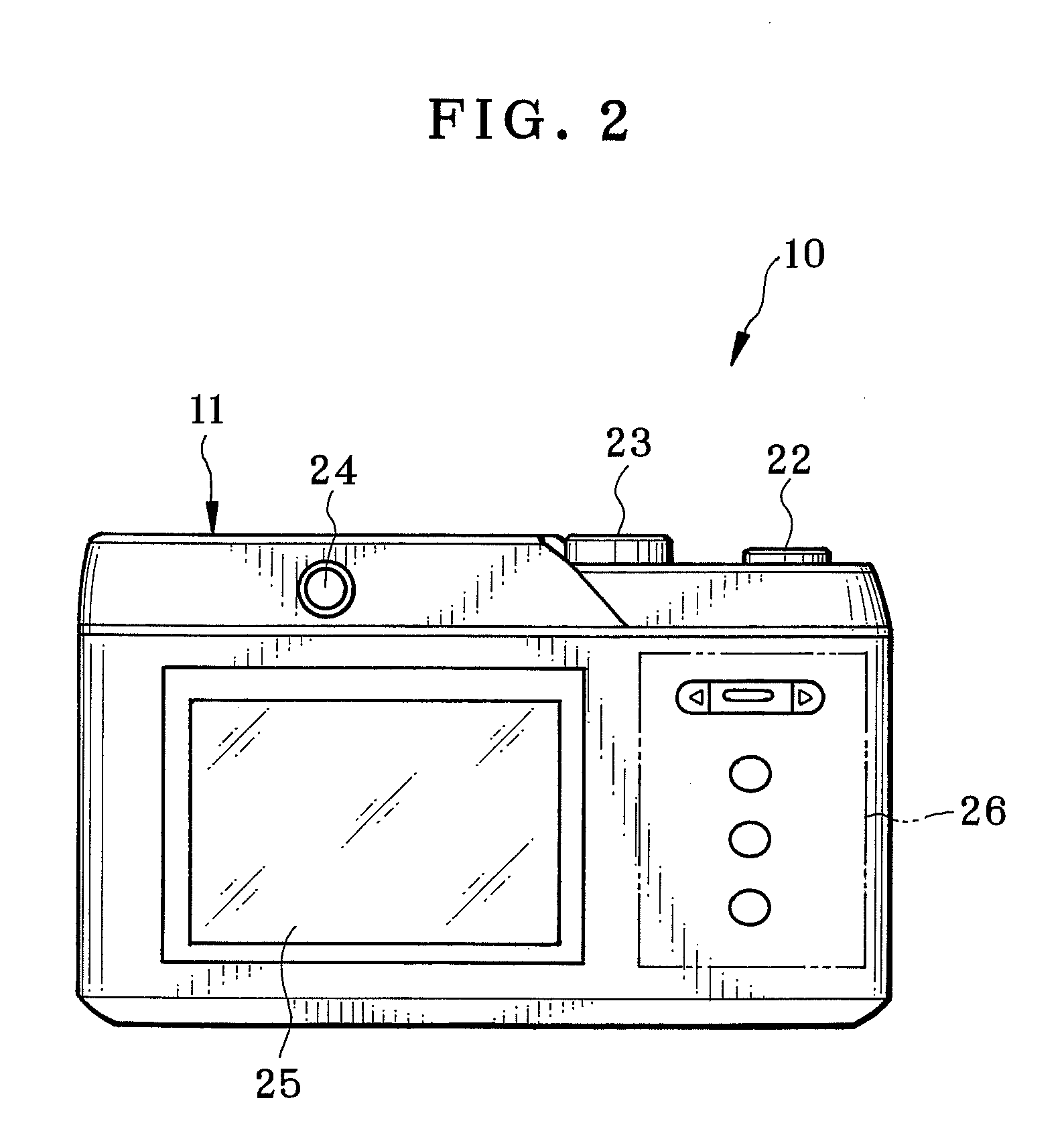
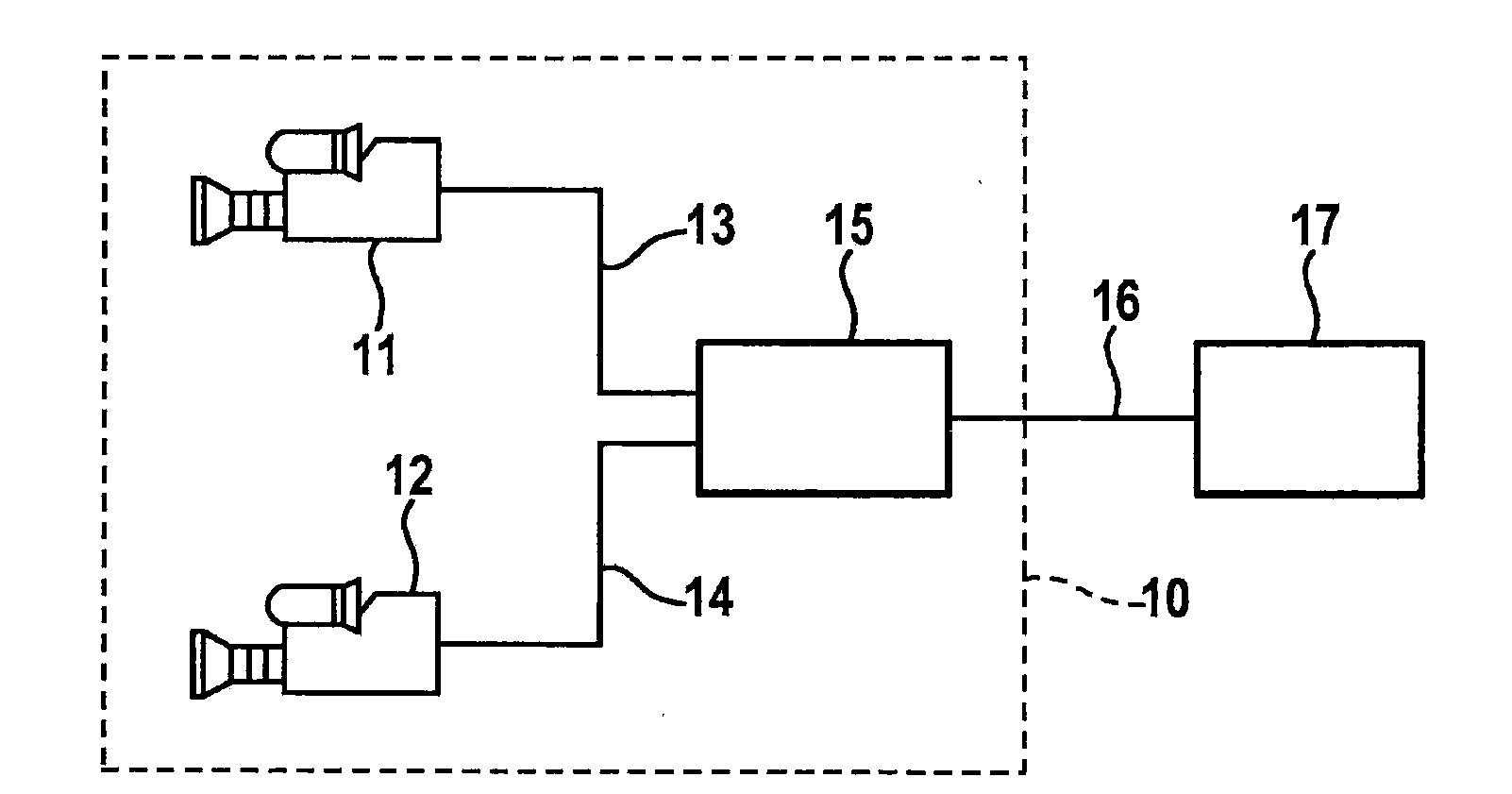
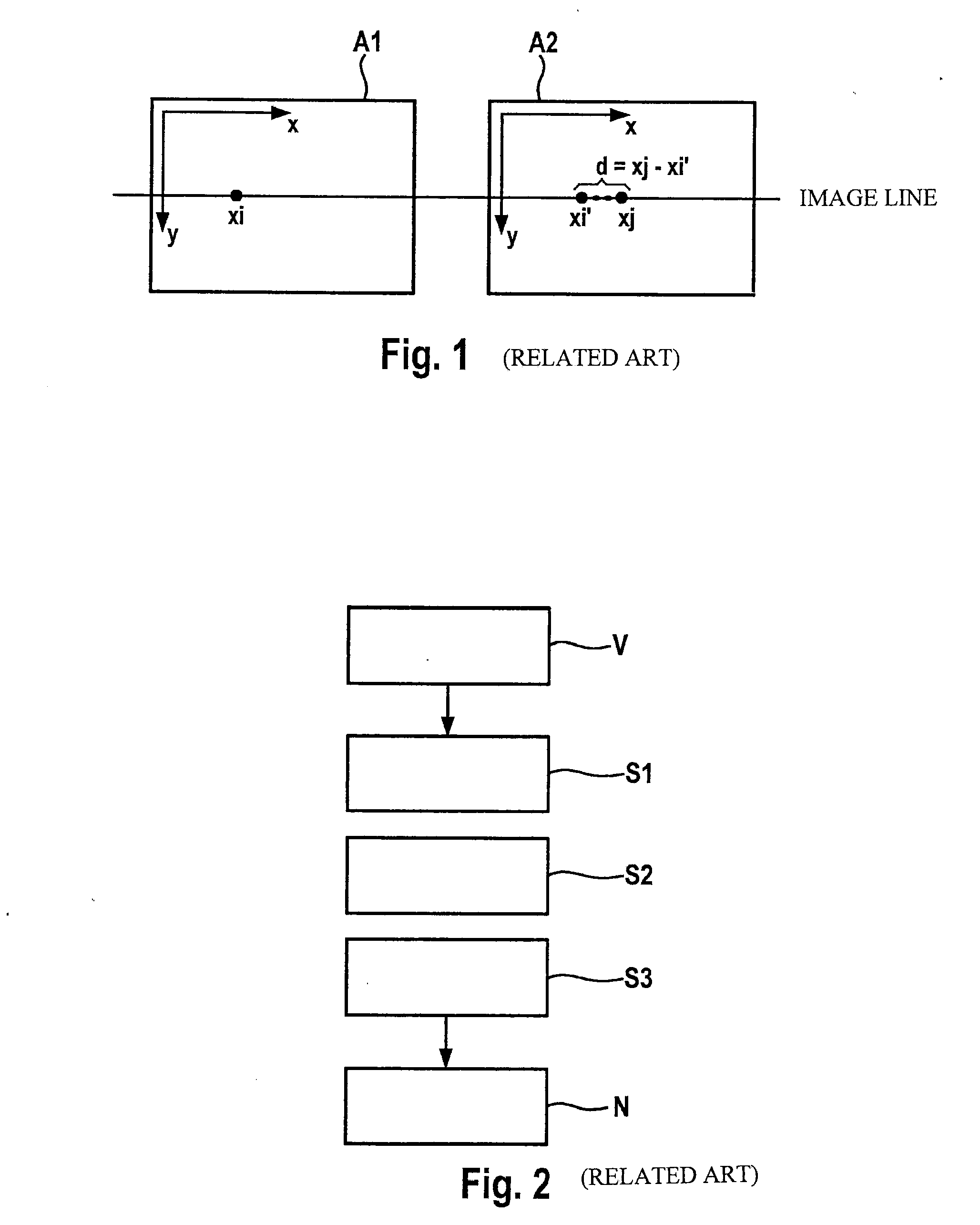
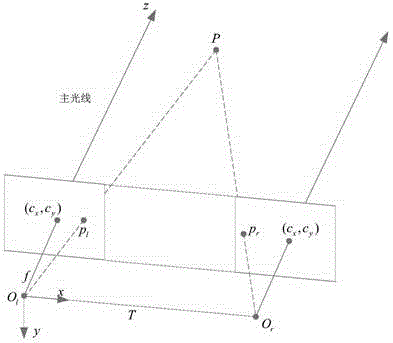
A stereo camera is a type of camera with two or more lenses with a separate image sensor or film frame for each lens. This allows the camera to simulate human binocular vision, and therefore gives it the ability to capture three-dimensional images, a process known as stereo photography. Stereo cameras may be used for making stereoviews and 3D pictures for movies, or for range imaging. The distance between the lenses in a typical stereo camera (the intra-axial distance) is about the distance between one's eyes (known as the intra-ocular distance) and is about 6.35 cm, though a longer base line (greater inter-camera distance) produces more extreme 3-dimensionality.
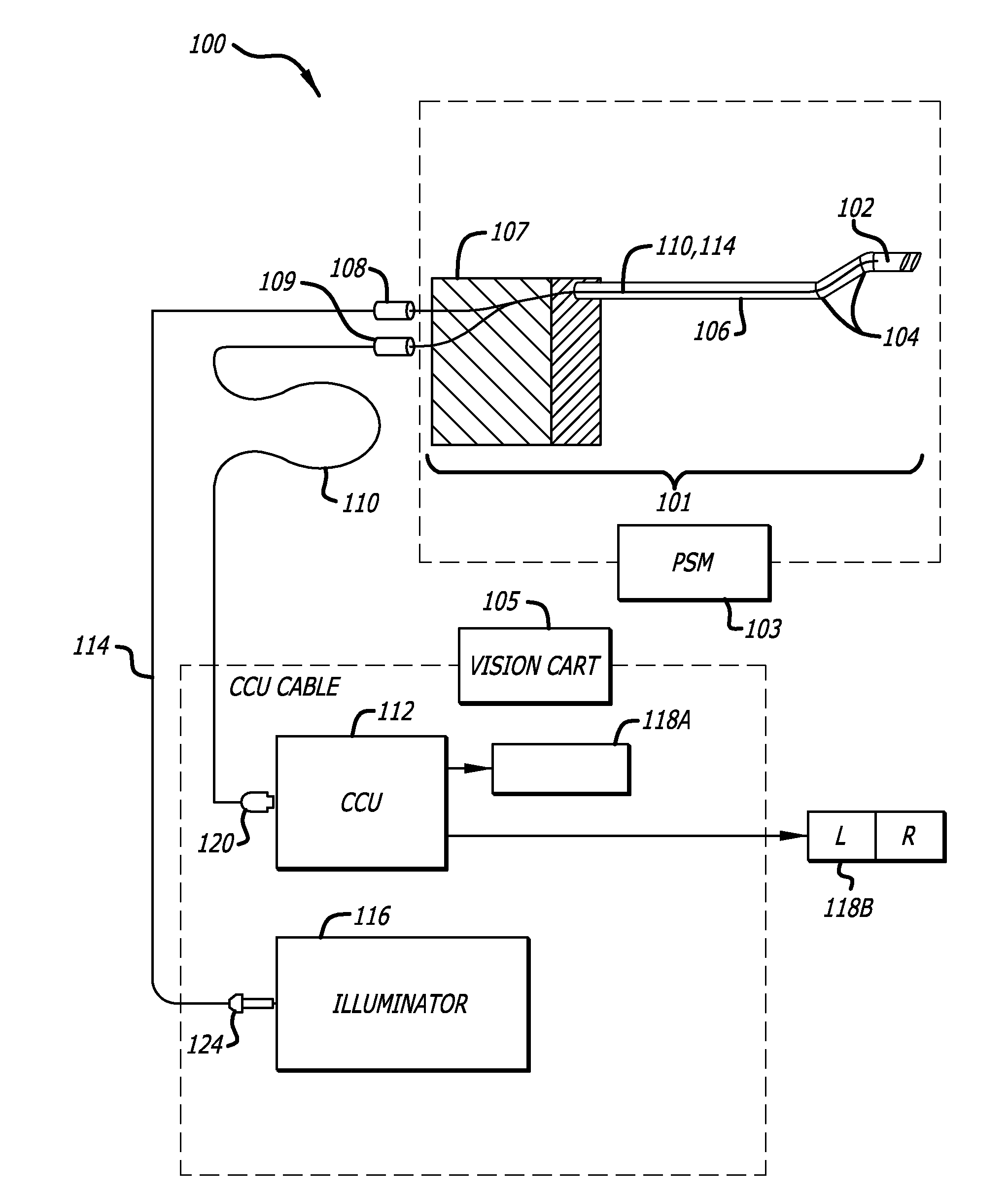
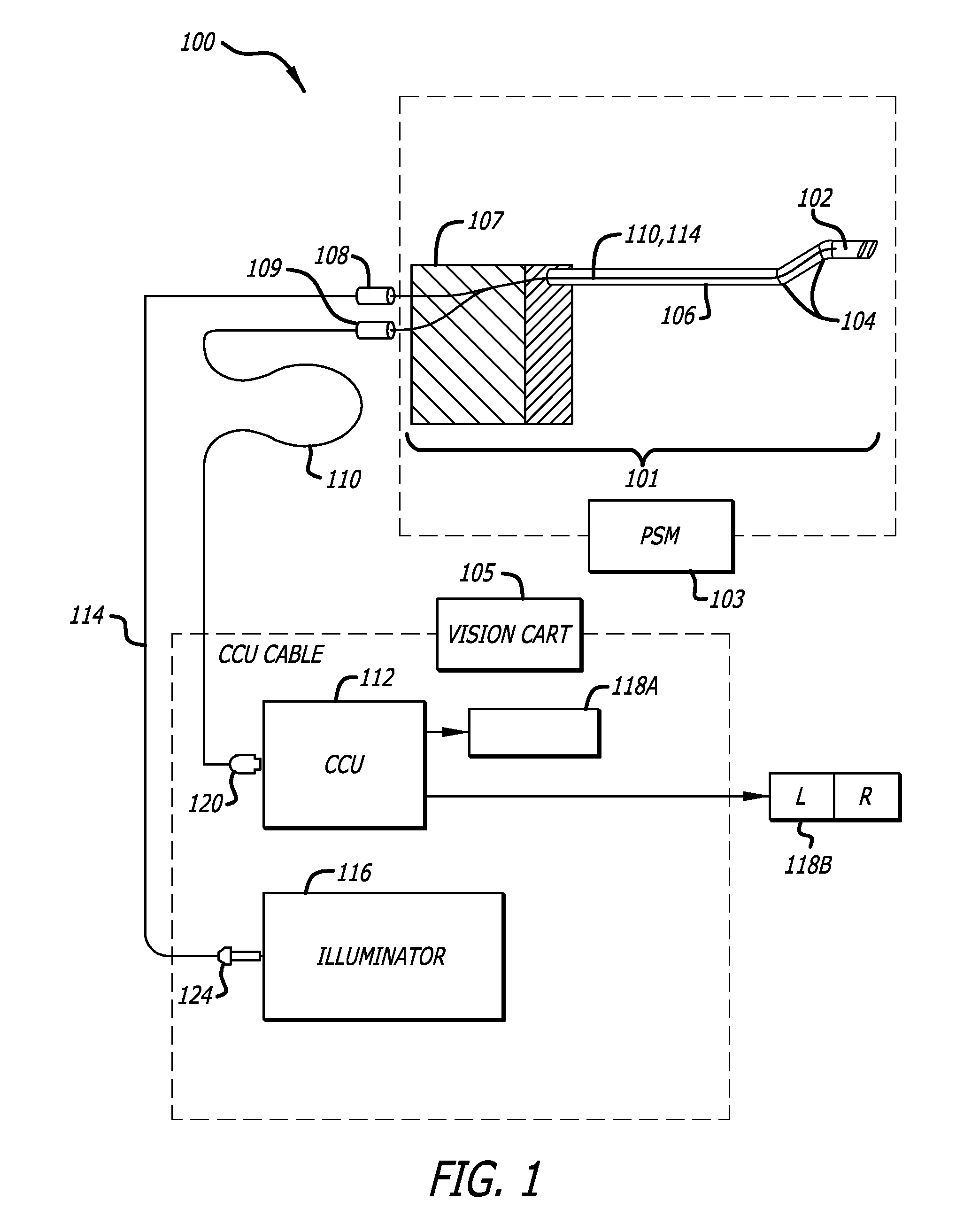
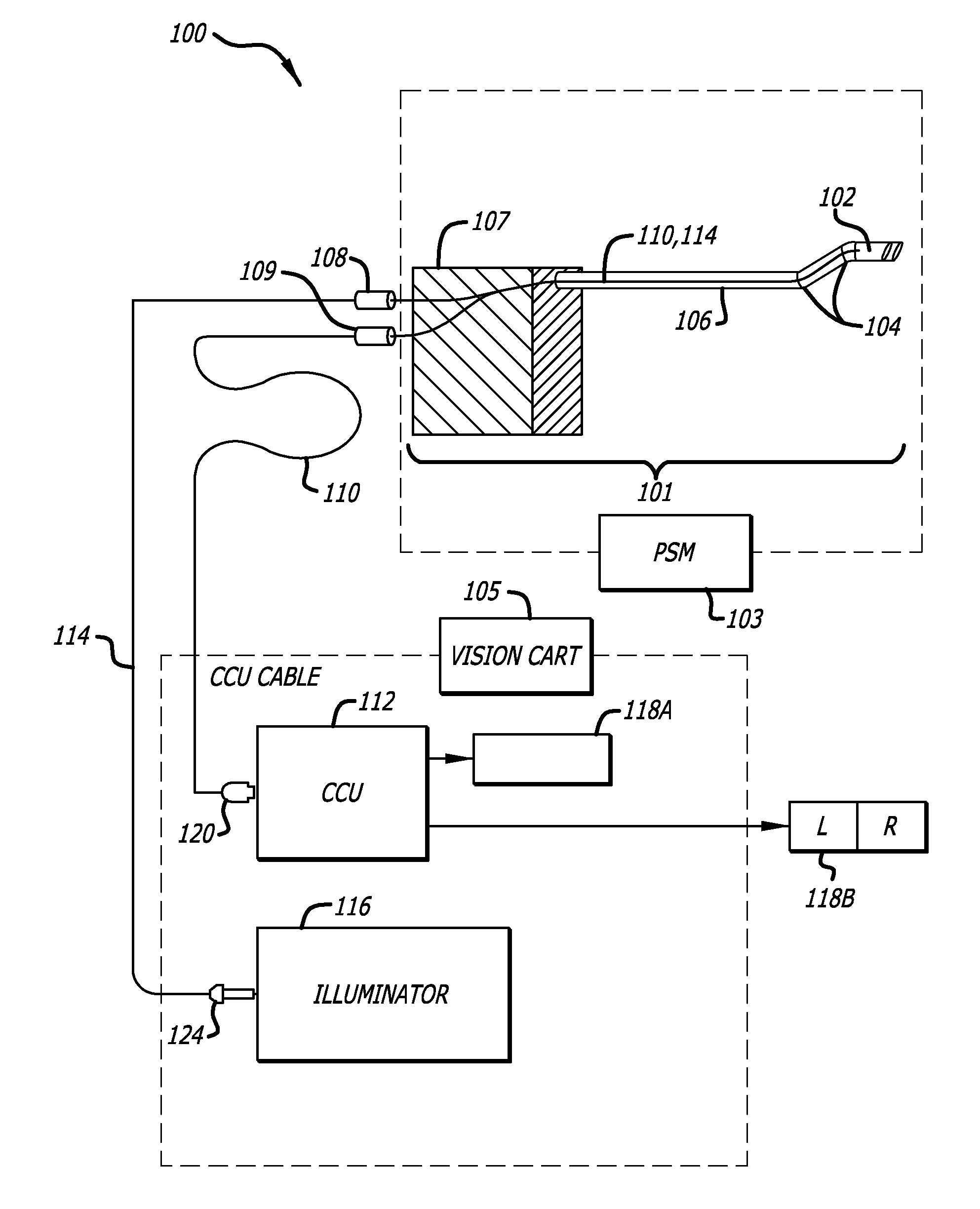
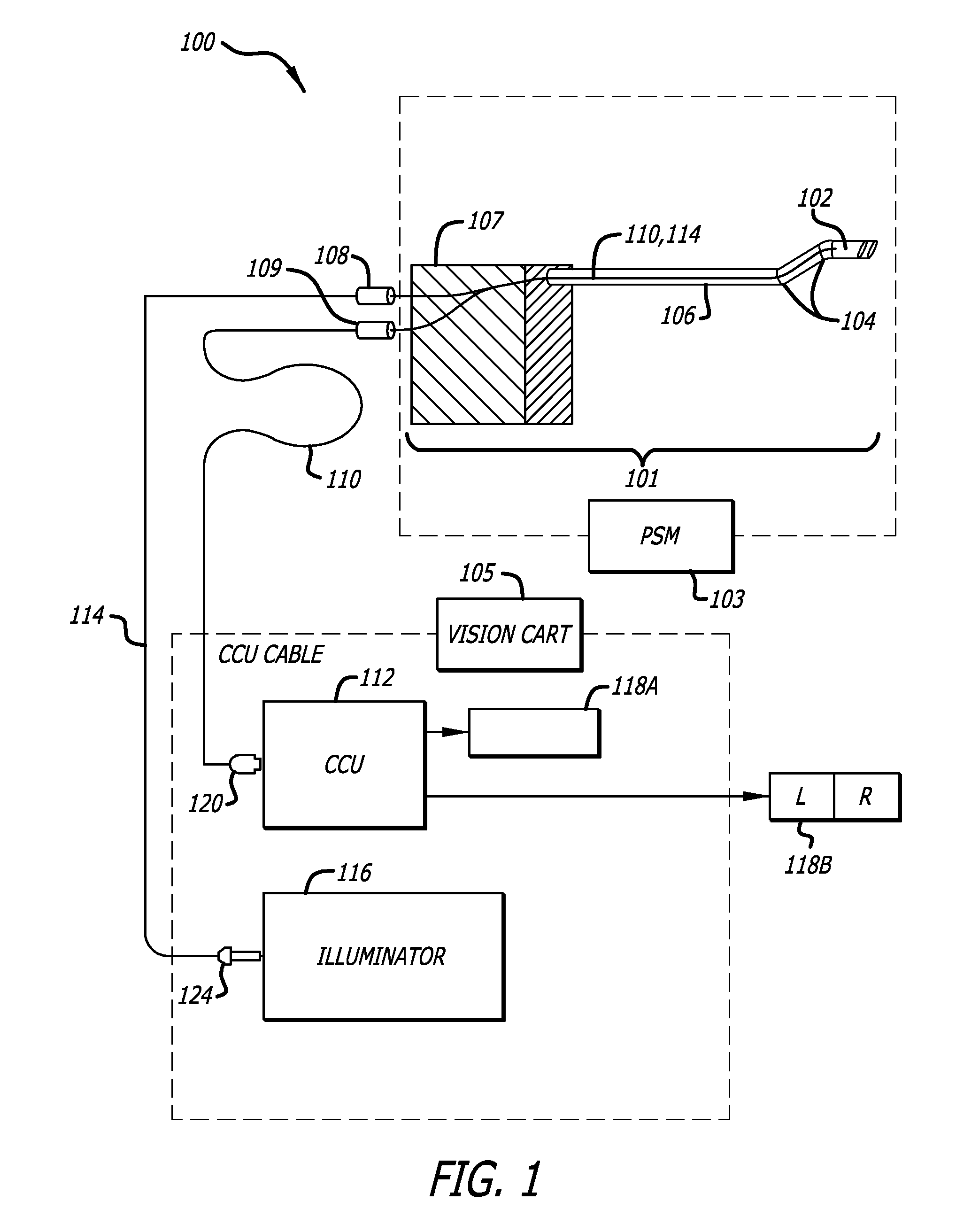
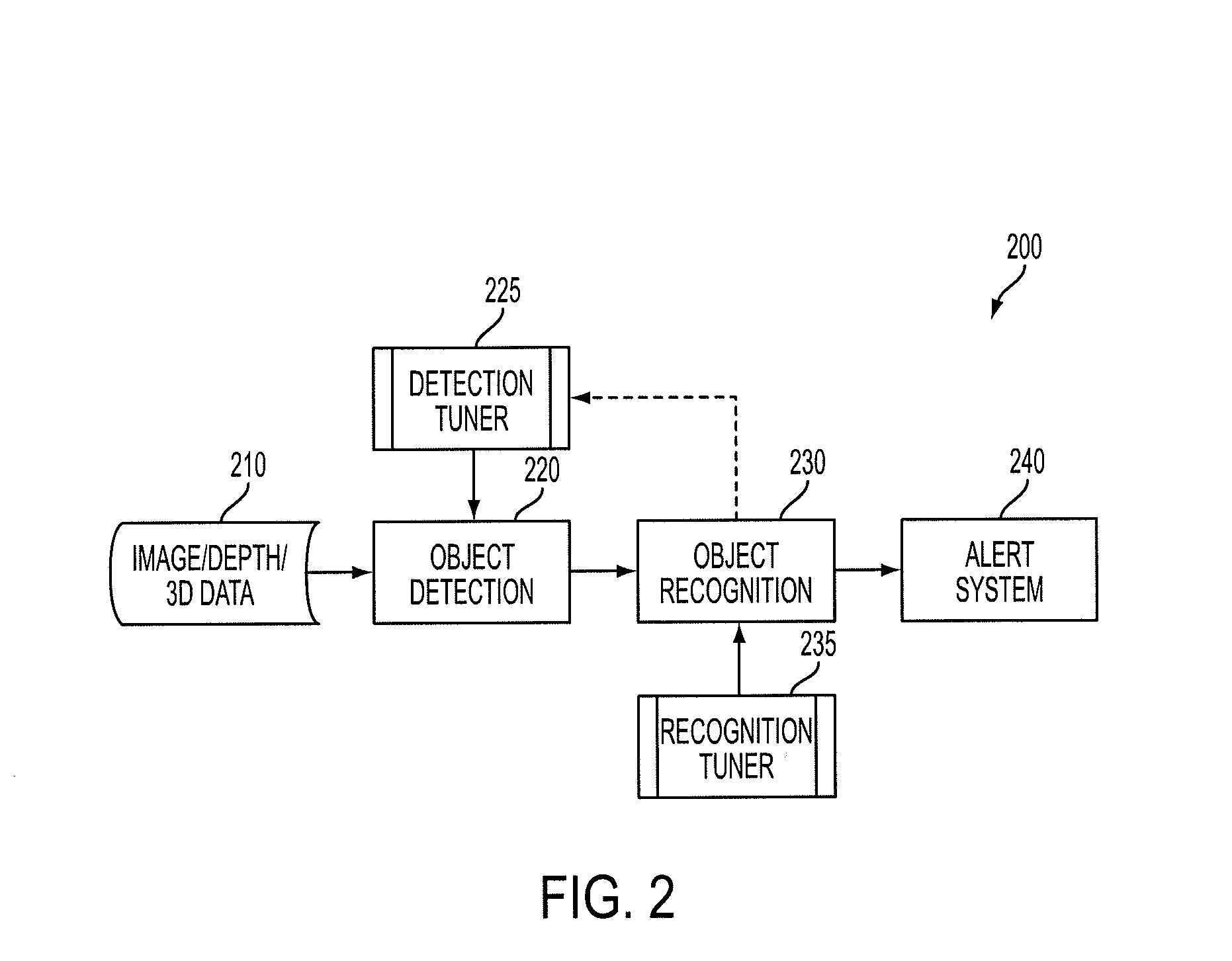
Hermetically sealed distal sensor endoscope
In one embodiment, an endoscopic camera for a robotic surgical system includes a stereo camera module mounted to a robotic arm of a patient side cart. The optical and electro-optic components of the camera module are hermetically sealed within a first housing. Signals from an electro-optic component travel through traces in a ceramic substrate forming one side of the hermetically sealed first housing. A second housing surrounds the first housing and optical fibers are dispersed between the housings to provide lighting in a body cavity. The camera module may be sterilized by an autoclave.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
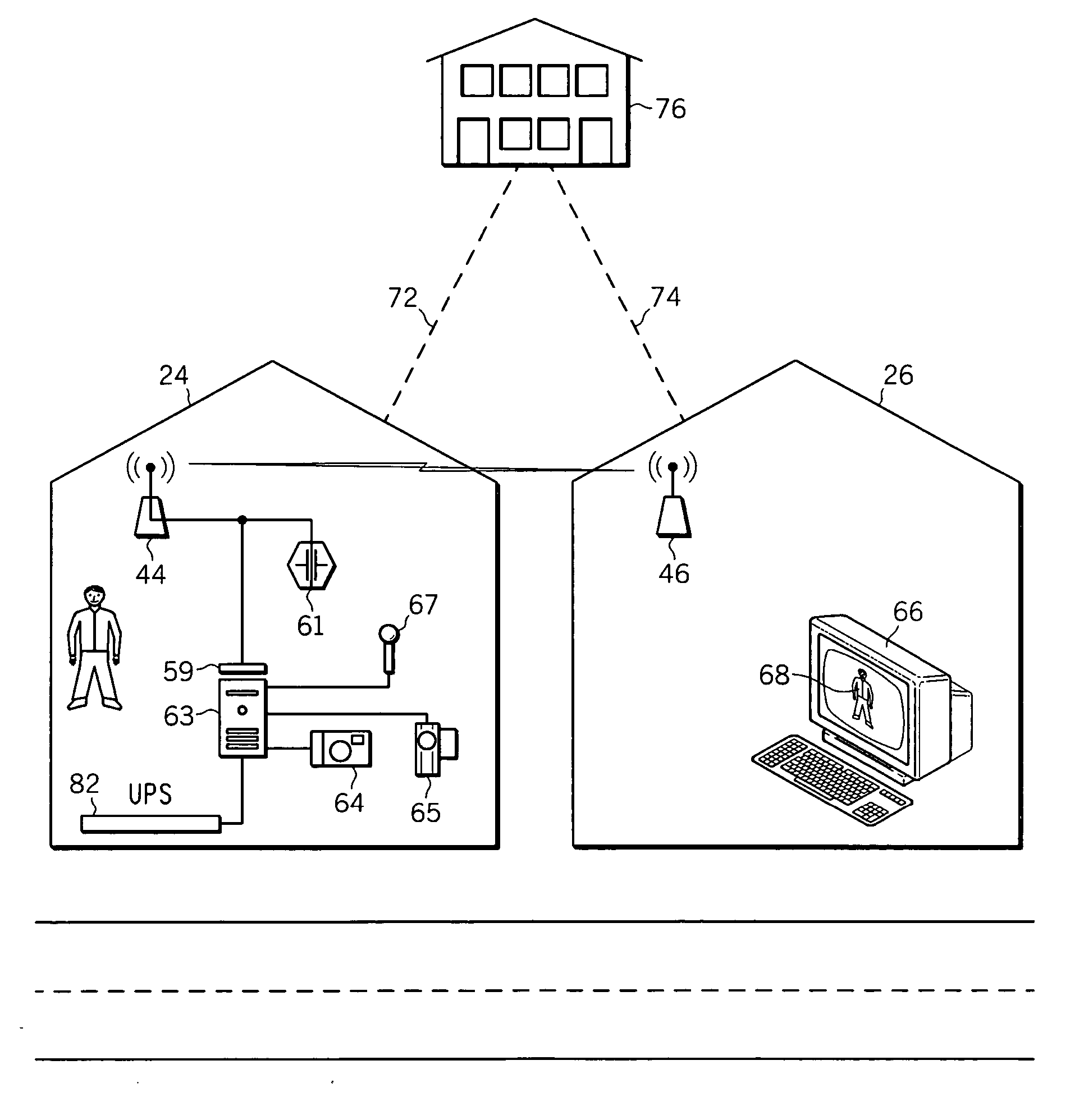
Home-monitoring system
InactiveUS20070090944A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexStereo cameraMonitoring system
A method and system for securing neighborhoods against crime. In one system, a short range wireless LAN technology, e.g., WiFi or WiMax, is employed to relay sensor information, including that from cameras, in real-time to a security server in a neighbor's house, which can significantly improve response time. The wireless LAN technology allows higher quality video to be captured by the on-site cameras, and relayed off-site in real-time, preserving the integrity of the data even if a burglar or intruder finds and destroys or steals the on-site security equipment. Modern IP monitoring may be employed to offer additional capabilities and reliability in these systems.
Owner:GENERAL INSTR CORP
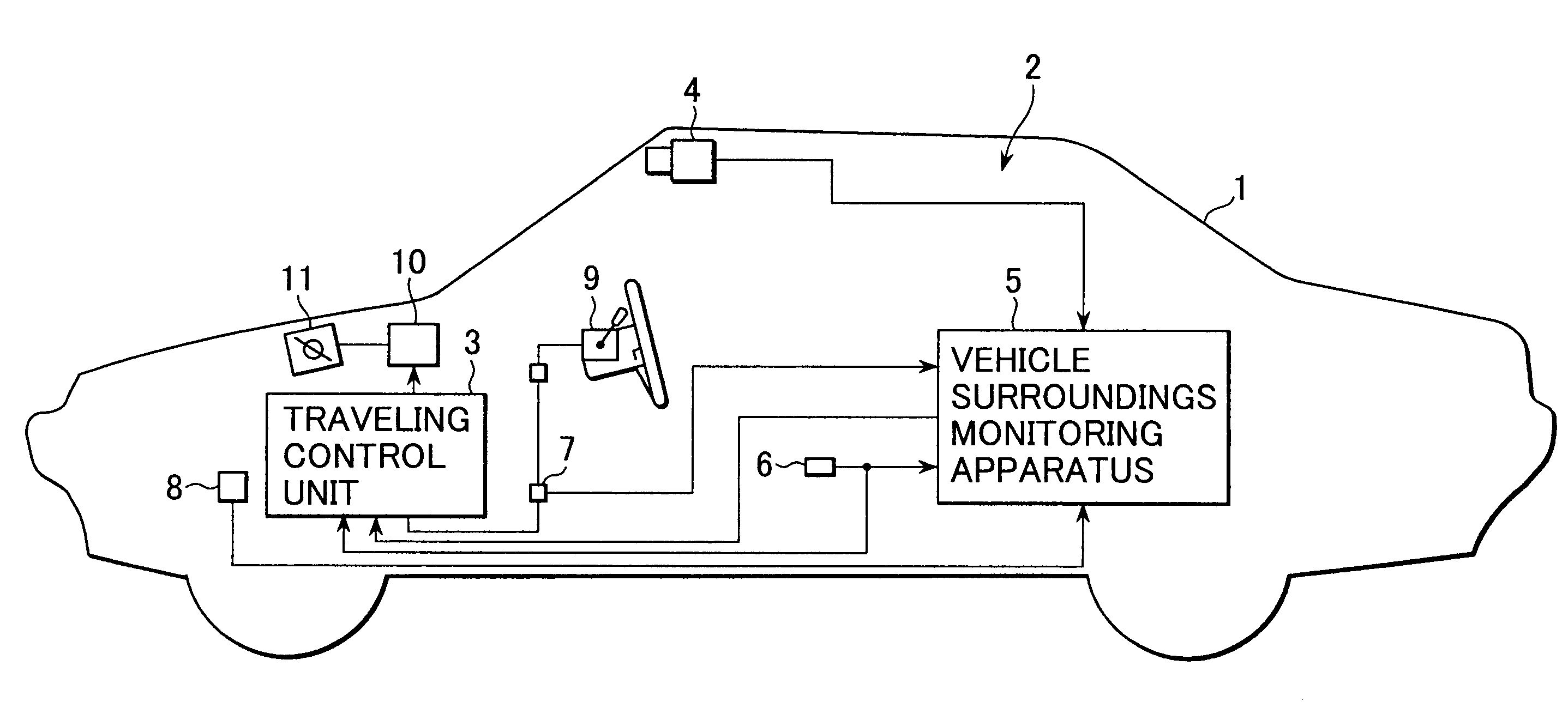
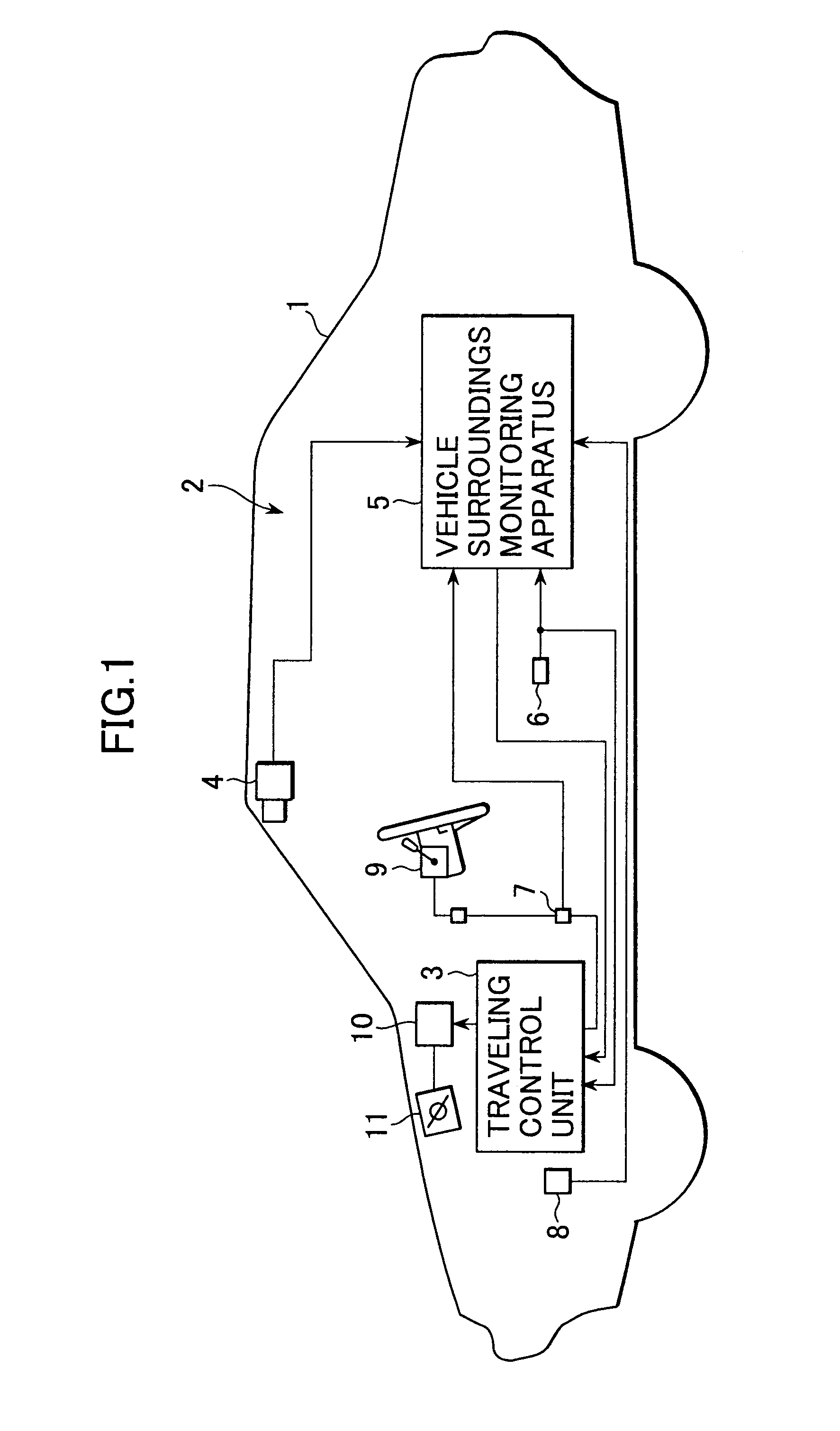
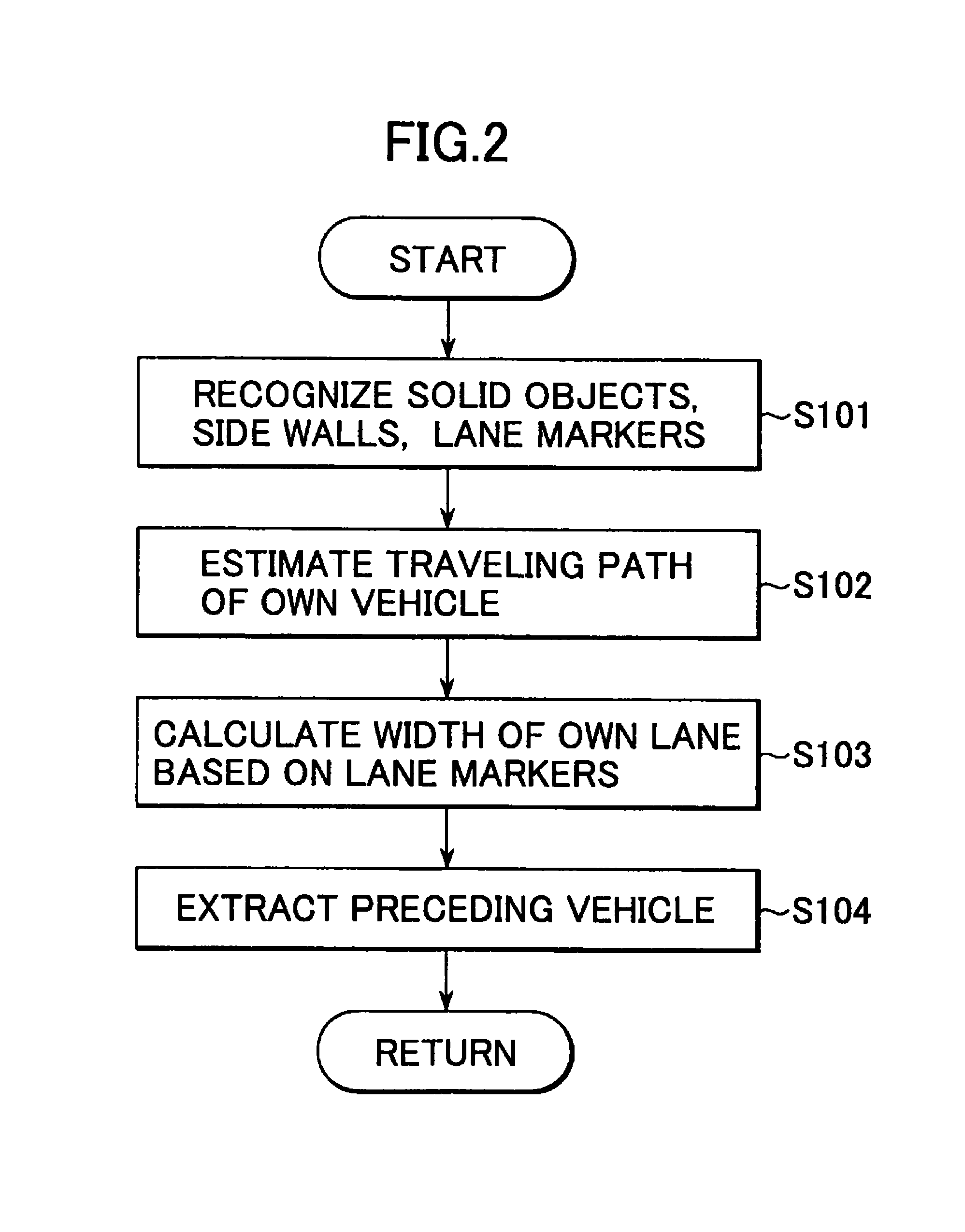
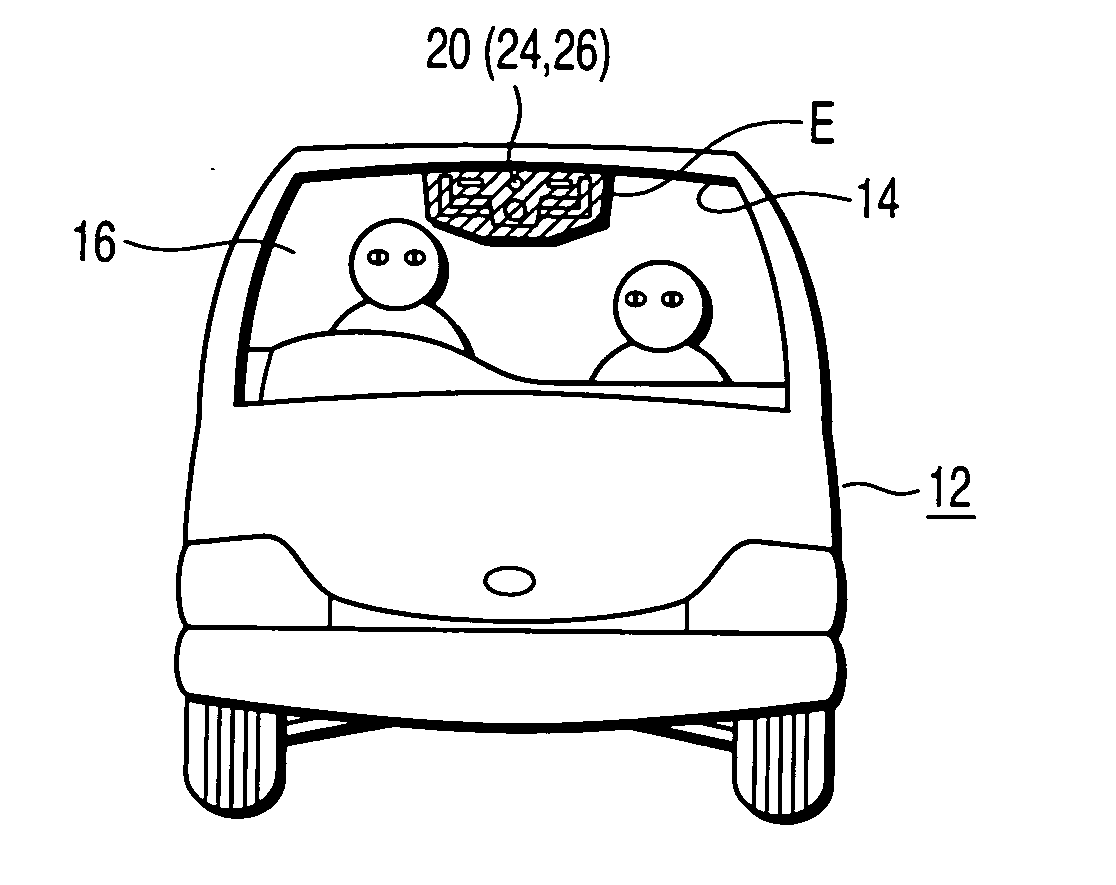
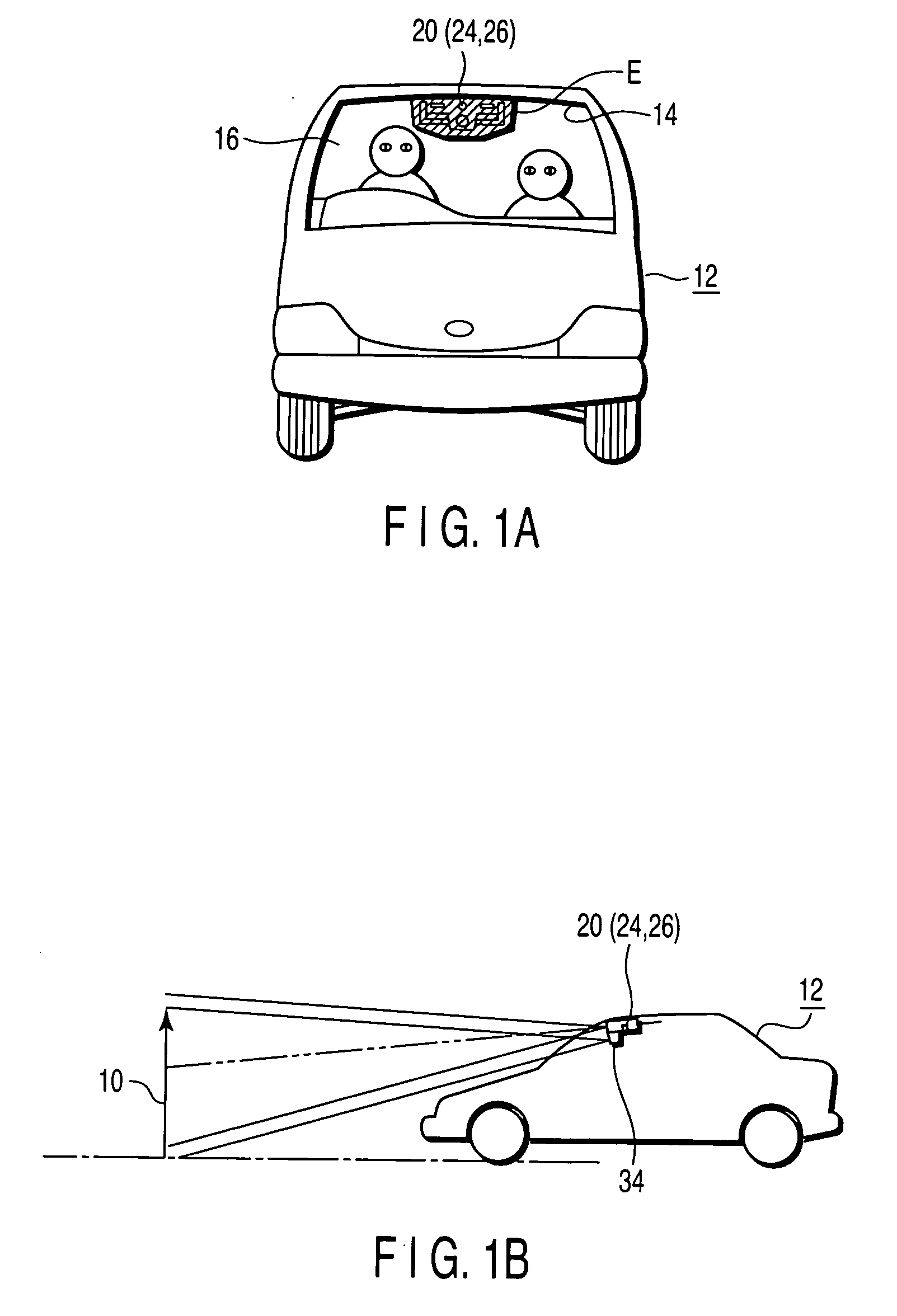
Vehicle surroundings monitoring apparatus and traveling control system incorporating the apparatus
ActiveUS7742864B2Smoothly and securely and quickly detectingVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsSteering wheelStereo camera
A vehicle surroundings monitoring apparatus inputs signals indicative of images from a stereoscopic camera, a vehicle speed, a steering wheel angle and a yaw rate and estimates a traveling path of an own vehicle according to vehicle forward information and traveling conditions of the own vehicle. The apparatus establishes a traveling region A according to this traveling path and further establishes a traveling region B based on at least either of the traveling region A and road information. It is judged whether a detected solid object is a preceding vehicle or a tentative preceding vehicle according to the state of existence of the object in the traveling regions A, B and the preceding vehicle is outputted to a traveling control unit.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
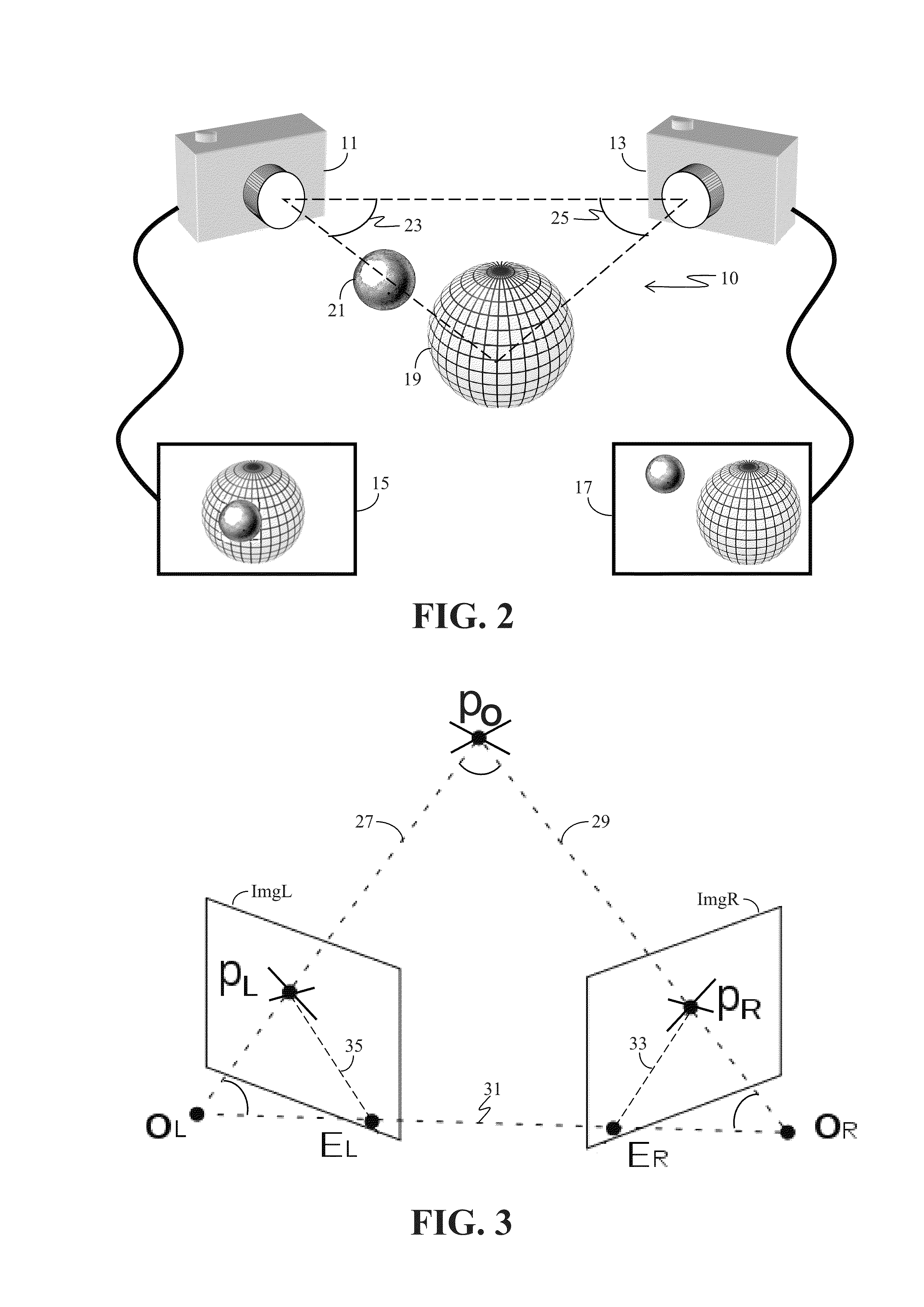
System and method for 3D photography and/or analysis of 3D images and/or display of 3D images
InactiveUS20050053274A1Generate efficientlySolve the real problemProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionScale model3d image
When 3D viewing means become much more available and common, it will be very sad that the many great movies that exist today will be able to be viewed in 3D only through limited and partial software attempts to recreate the 3D info. Films today are not filmed in 3D due to various problems, and mainly since a normal stereo camera could be very problematic when filming modern films, since for example it does not behave properly when zooming in or out is used, and it can cause many problems when filming for example smaller scale models for some special effects. For example, a larger zoom requires a correspondingly larger distance between the lenses, so that for example if a car is photographed at a zoom factor of 1:10, the correct right-left disparity will be achieved only if the lenses move to an inter-ocular distance of for example 65 cm instead of the normal 6.5 cm. The present invention tries to solve the above problems by using a 3D camera which can automatically adjust in a way that solves the zoom problem, and provides a solution also for filming smaller models. The angle between the two lenses is preferably changed according to the distance and position of the object that is at the center of focus, and changing the zoom affects automatically both the distance between the lenses and their angle, since changing merely the distance without changing the convergence angle would cause the two cameras to see completely different parts of the image. The patent also shows that similar methods can be used for example for a much better stereoscopic telescope with or without a varying zoom factor. In addition, the patent shows various ways to generate efficiently a 3D knowledge of the surrounding space, which can be used also for example in robots for various purposes, and also describes a few possible improvements in 3d viewing.
Owner:MAYER YARON +1
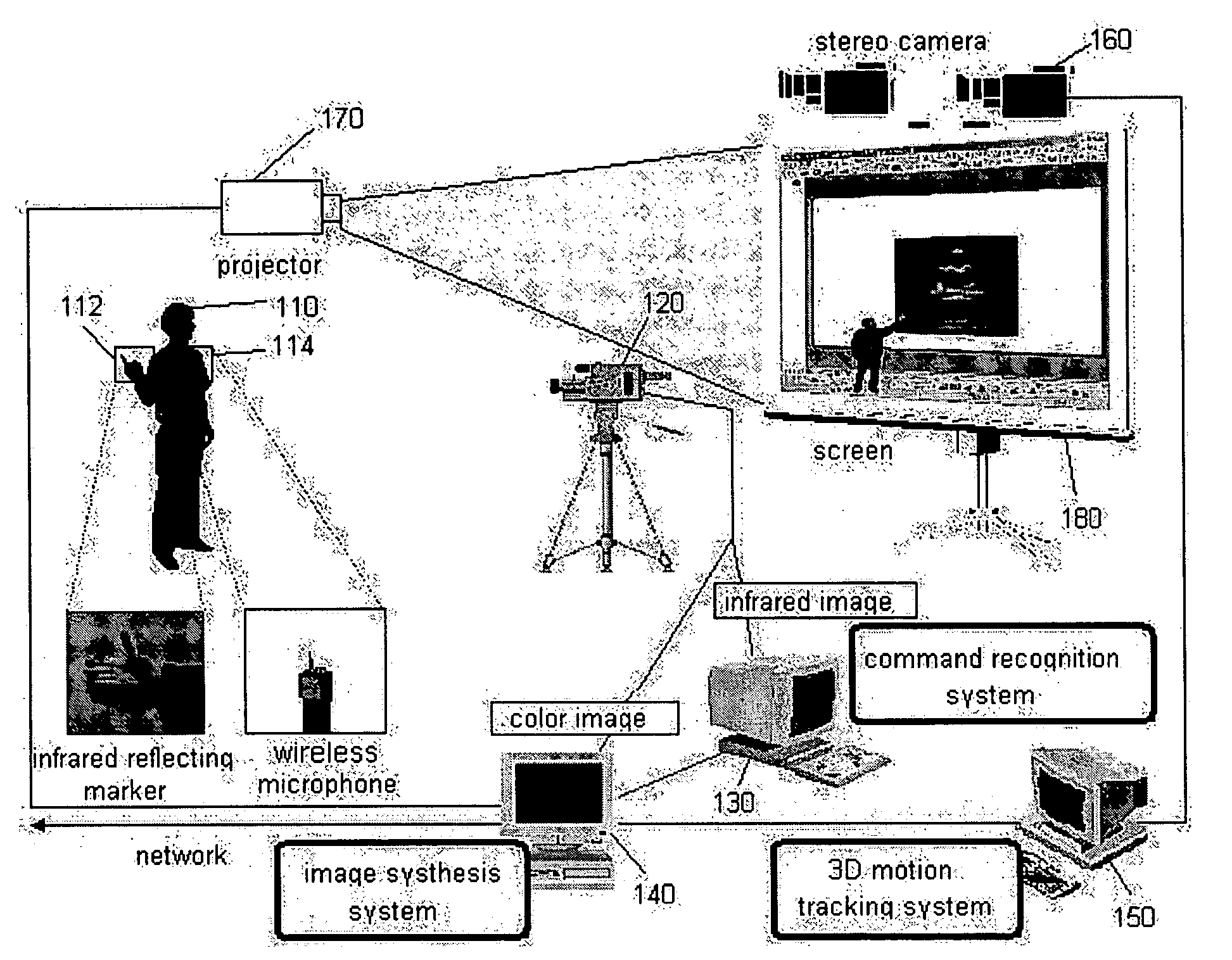
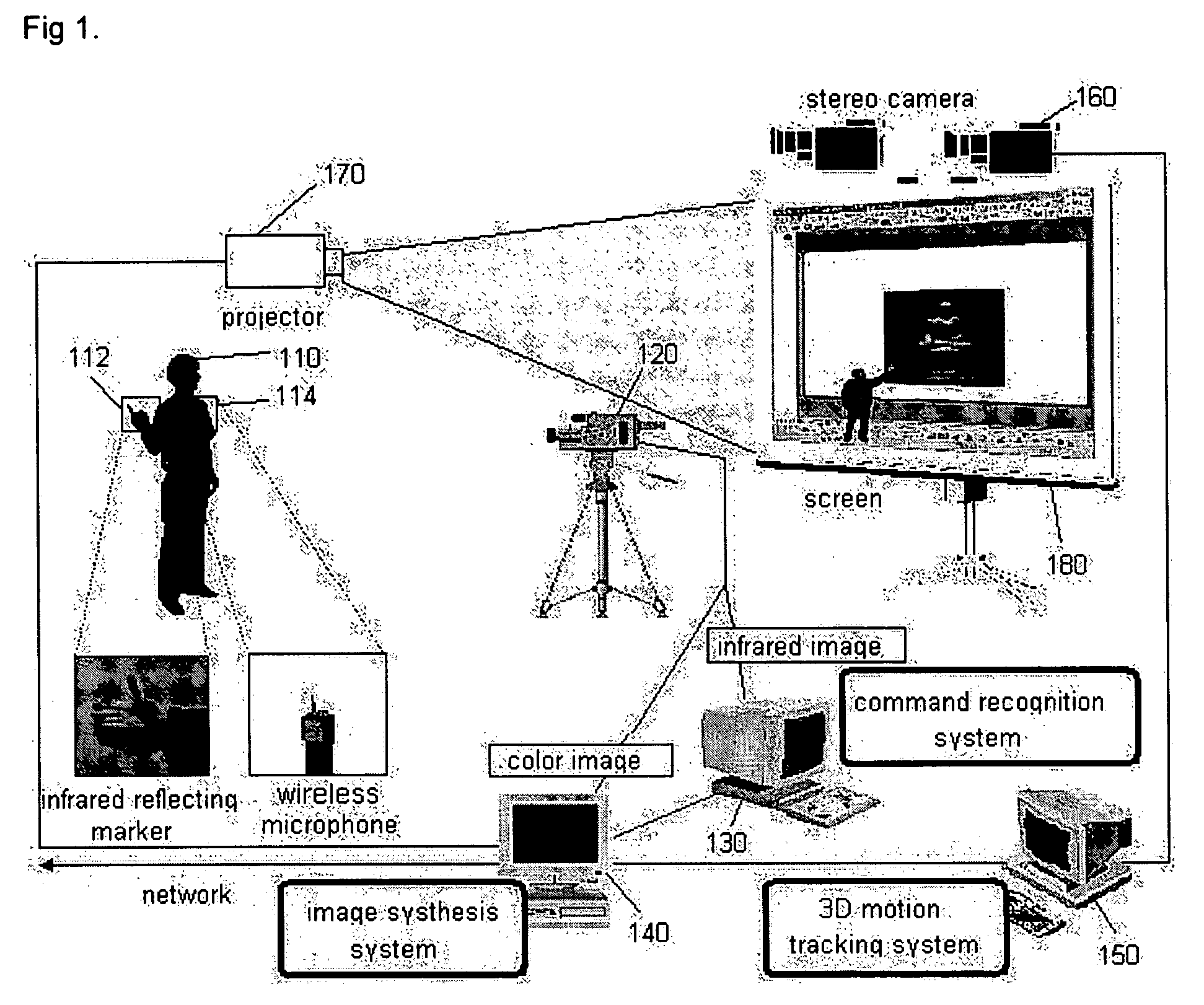
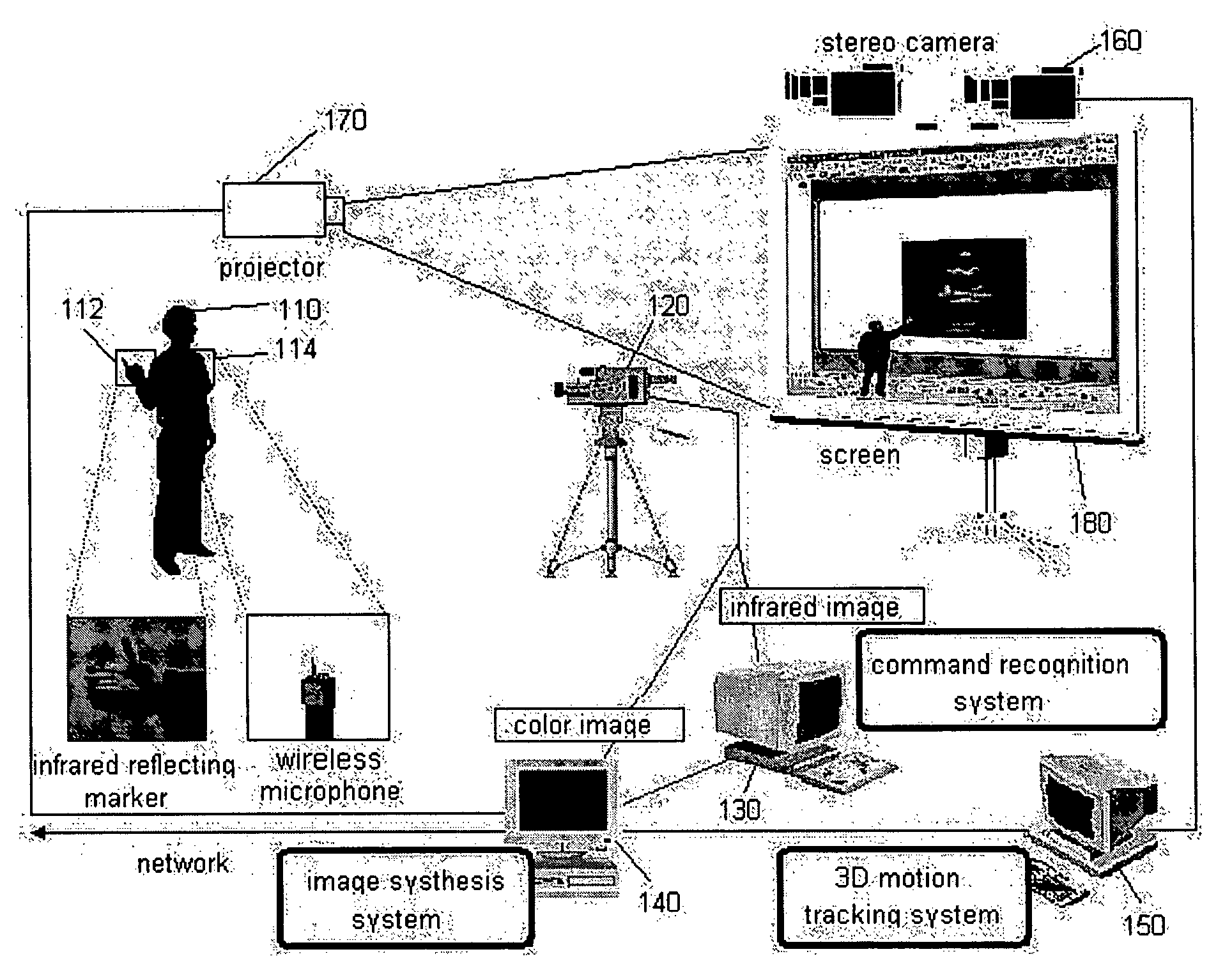
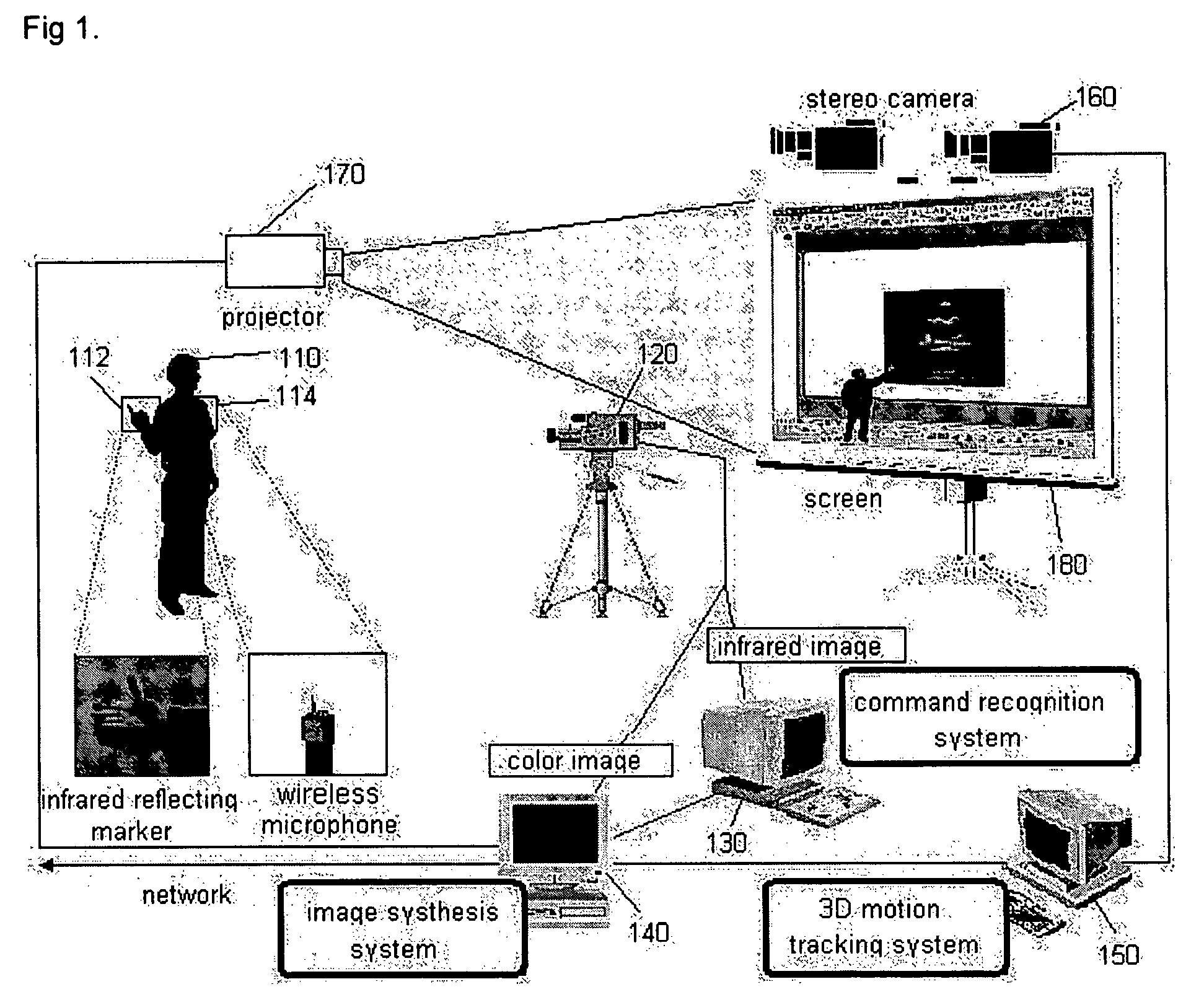
Interactive presentation system
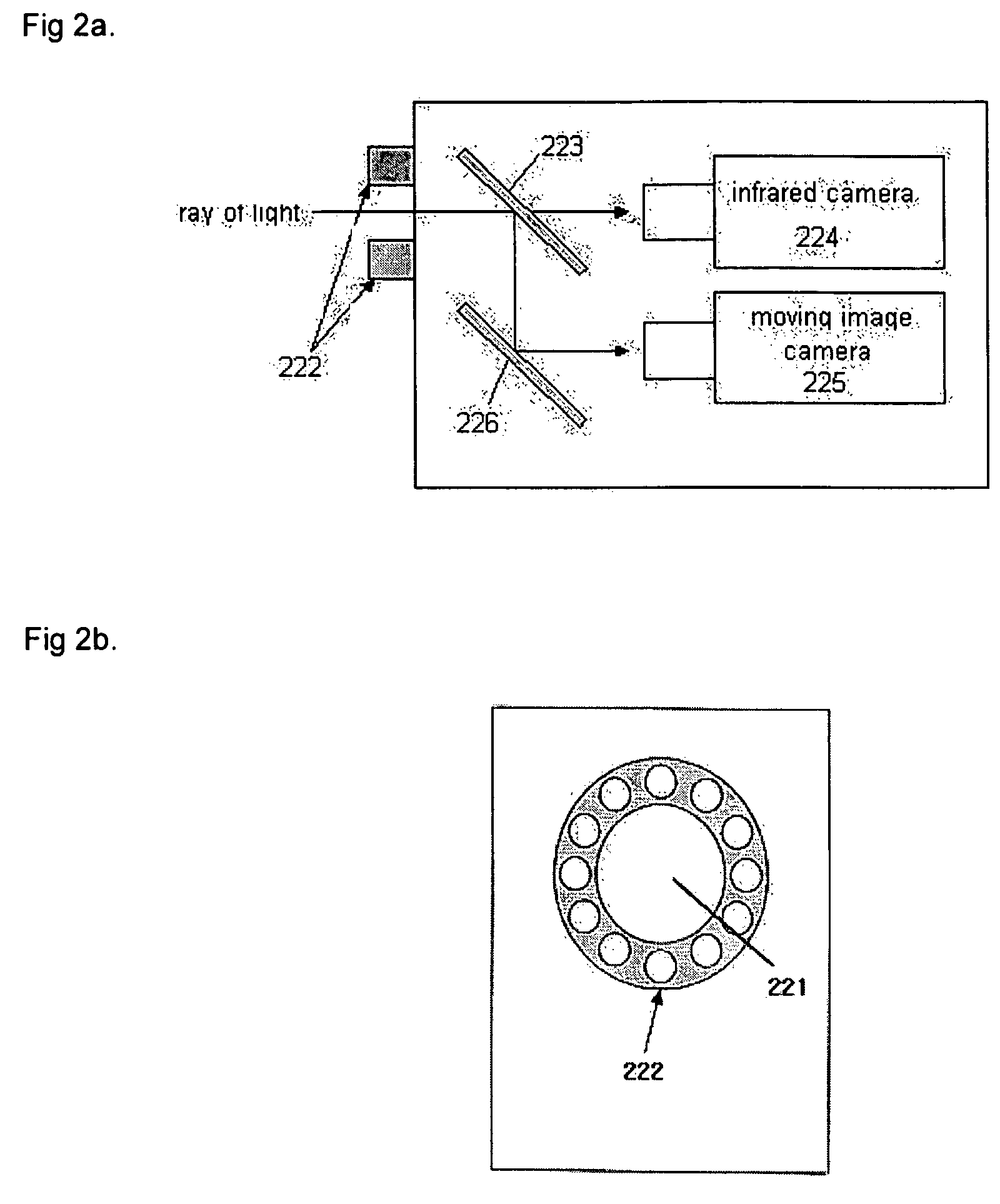
InactiveUS20050151850A1Effective spaceImprove image recognition rateTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsStereo camera3d image
The present invention discloses an interactive presentation system which allows a presenter to perform a presentation while having various interactions directly with presentation material images in real time through a gesture or / and voice. The interactive presentation system comprises: an active infrared camera; a command recognition system connected to the active infrared camera; and an image synthesis system connected to the active infrared camera and the command recognition system. The presentation system may further comprises a stereo camera set for properly synthesizing a presenter in a 3D image and a 3D motion system. By this configuration, it is possible to embody an interactive presentation system in which a command through a presenter's gesture or voice is processed in real time and the image of the presenter is synthesized in a presentation material screen in real time, and accordingly the audiovisual effect is maximized.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Hermetically sealed distal sensor endoscope
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
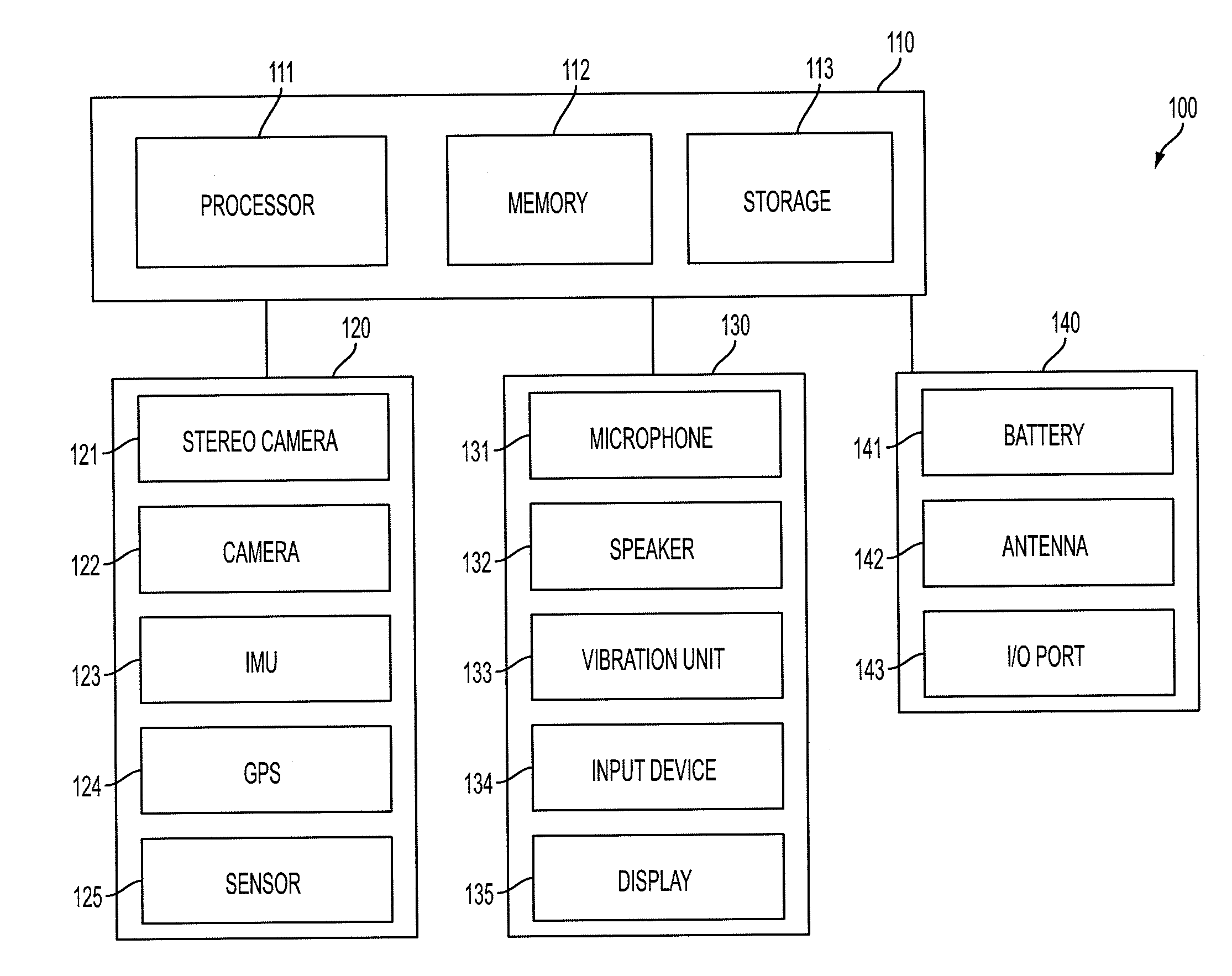
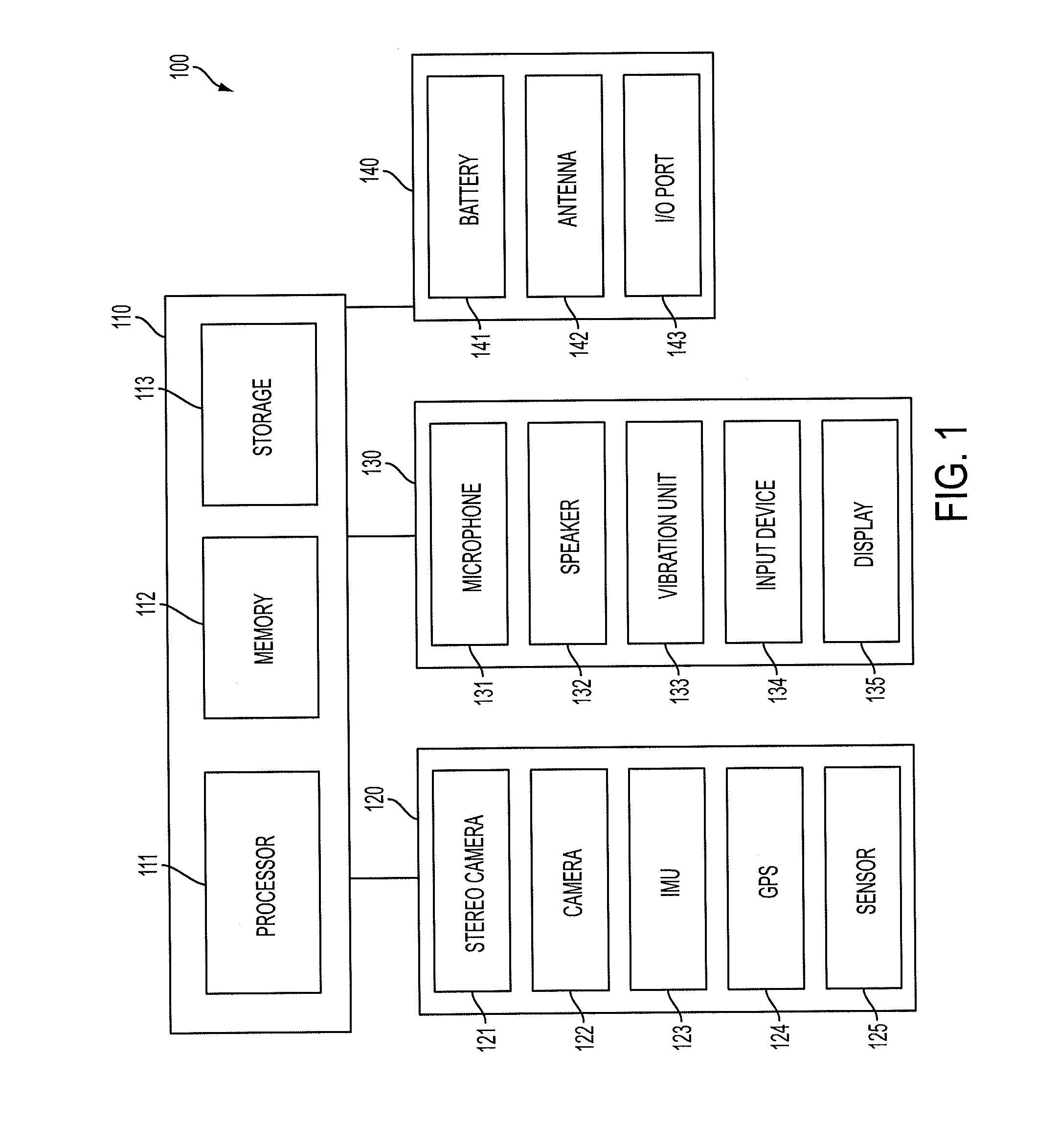
Smart necklace with stereo vision and onboard processing
ActiveUS20150201181A1Enhance environmental awarenessIncreased obstacle avoidanceInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementTouch PerceptionStereo camera
A wearable neck device for providing environmental awareness to a user, the wearable neck device includes a flexible tube. A first stereo pair of cameras is encased in a left portion of the flexible tube and a second stereo pair of cameras is encased in a right portion of the flexible tube. A vibration motor within the flexible tube provides haptic and audio feedback to the user. A processor in the flexible tube recognizes objects from the first stereo pair of cameras and the second stereo pair of cameras. The vibration motor provides haptic and audio feedback of the items or points of interest to the user.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
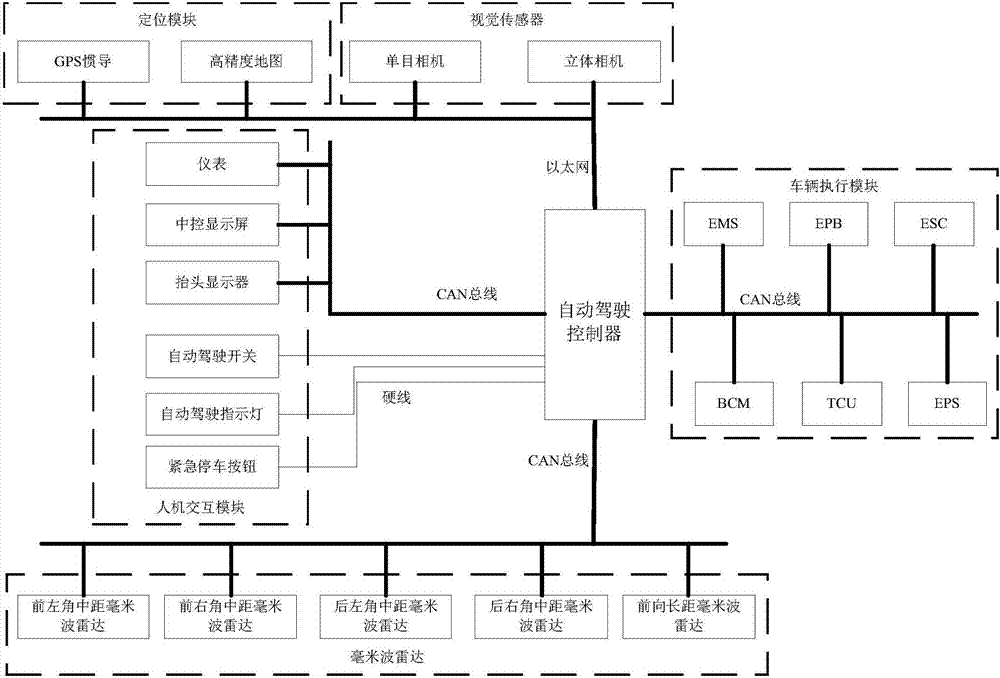
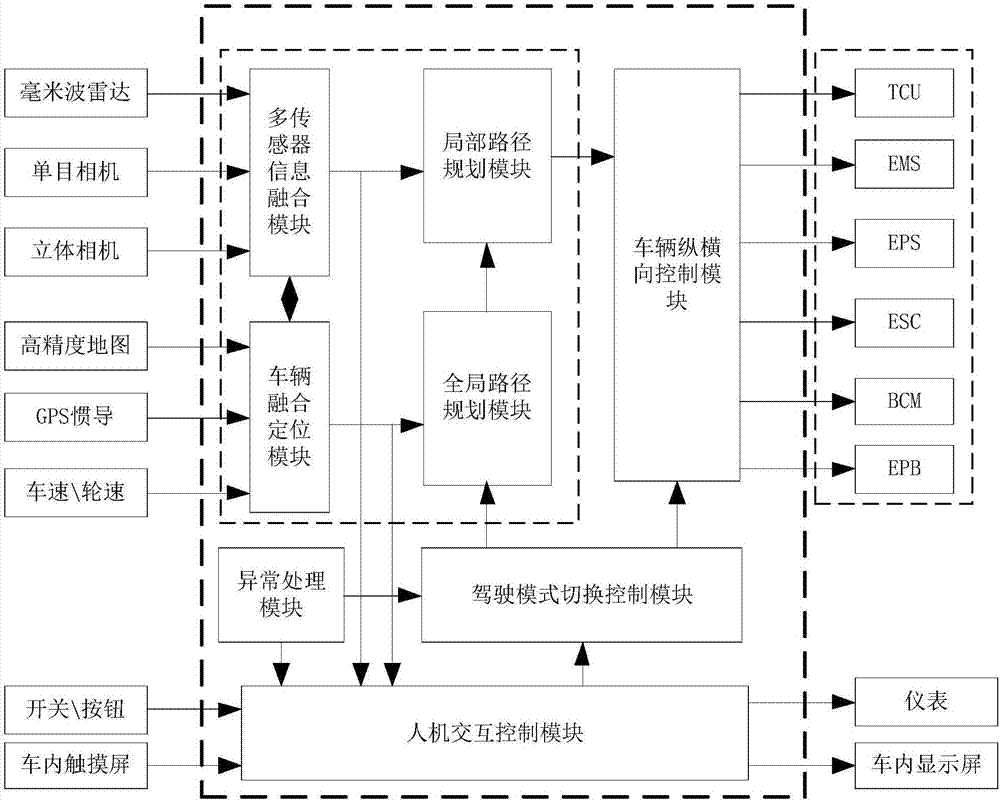
Automatic driving system based on highway
InactiveCN107031600ALow costEasy to integrateExternal condition input parametersStereo cameraPattern perception
The invention relates to the technical field of automatic driving, in particular to an automatic driving system based on a highway. The automatic driving system comprises a sensor, a positioning module, a man-machine interaction module, an automatic driving controller and a vehicle executing module. A traditional laser radar is replaced with a monocular camera, a stereo camera, a forward-direction long distance millimeter microwave radar and four-corner middle distance millimeter microwave radars which are arranged behind an inside-vehicle rearview mirror, at the center of a vehicle front bumper and on the two sides of the front bumper and a rear front bumper correspondingly. Multiple kinds of information in traffic sign road information and obstruction information are collected separately. The whole automatic driving system of perception fusion, path planning, decision planning, controlling and the like is integrated into an embedded type controller to achieve automatic driving. Compared with a traditional automatic driving system adopting the laser radar, the cost is low, and integration is easy. Perception precision is improved greatly, the system is high in integration level and small in size, the size of the automatic driving system is reduced greatly, the power consumption of the system is lowered, and mass production is easy.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR CORP HUBEI
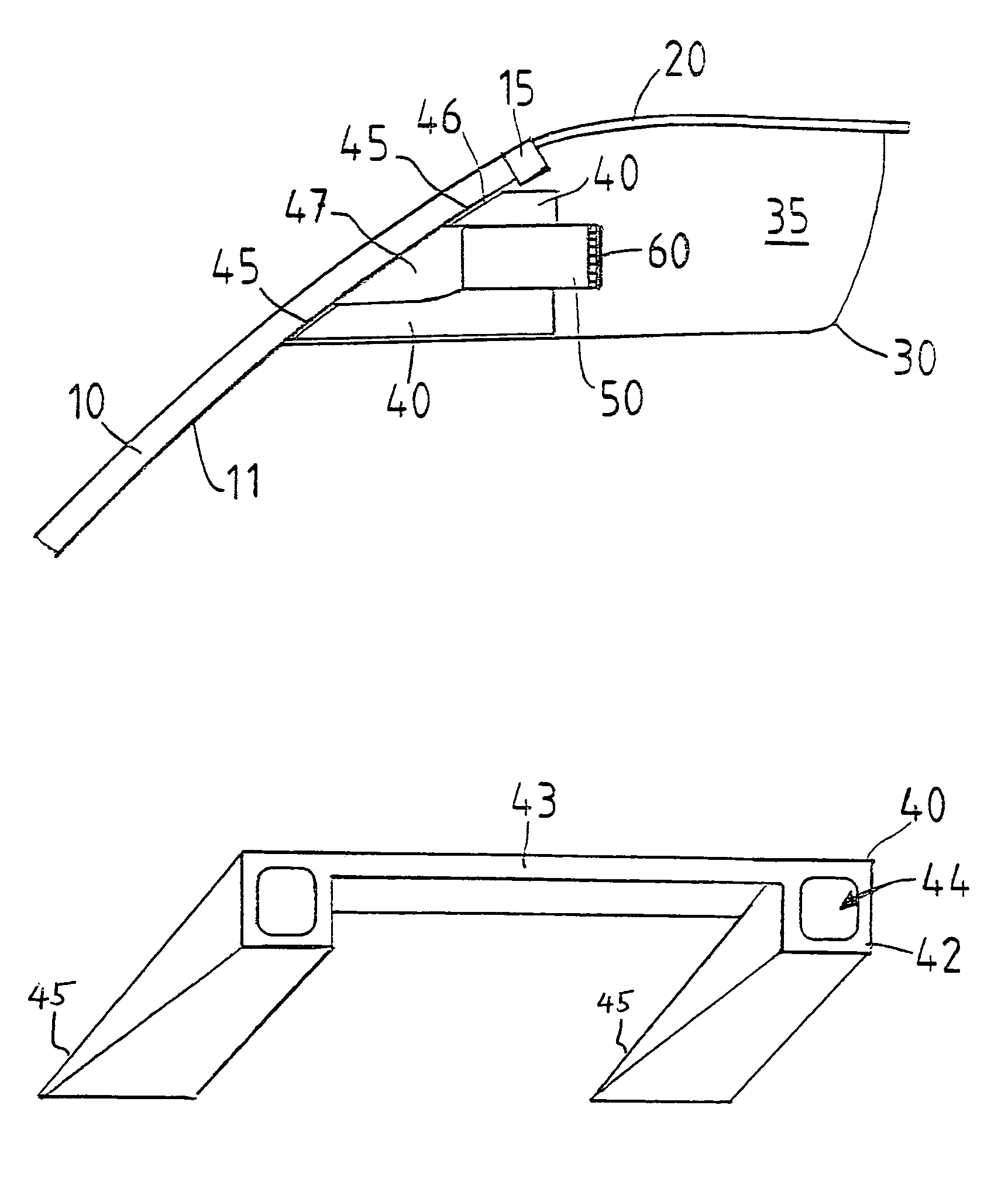
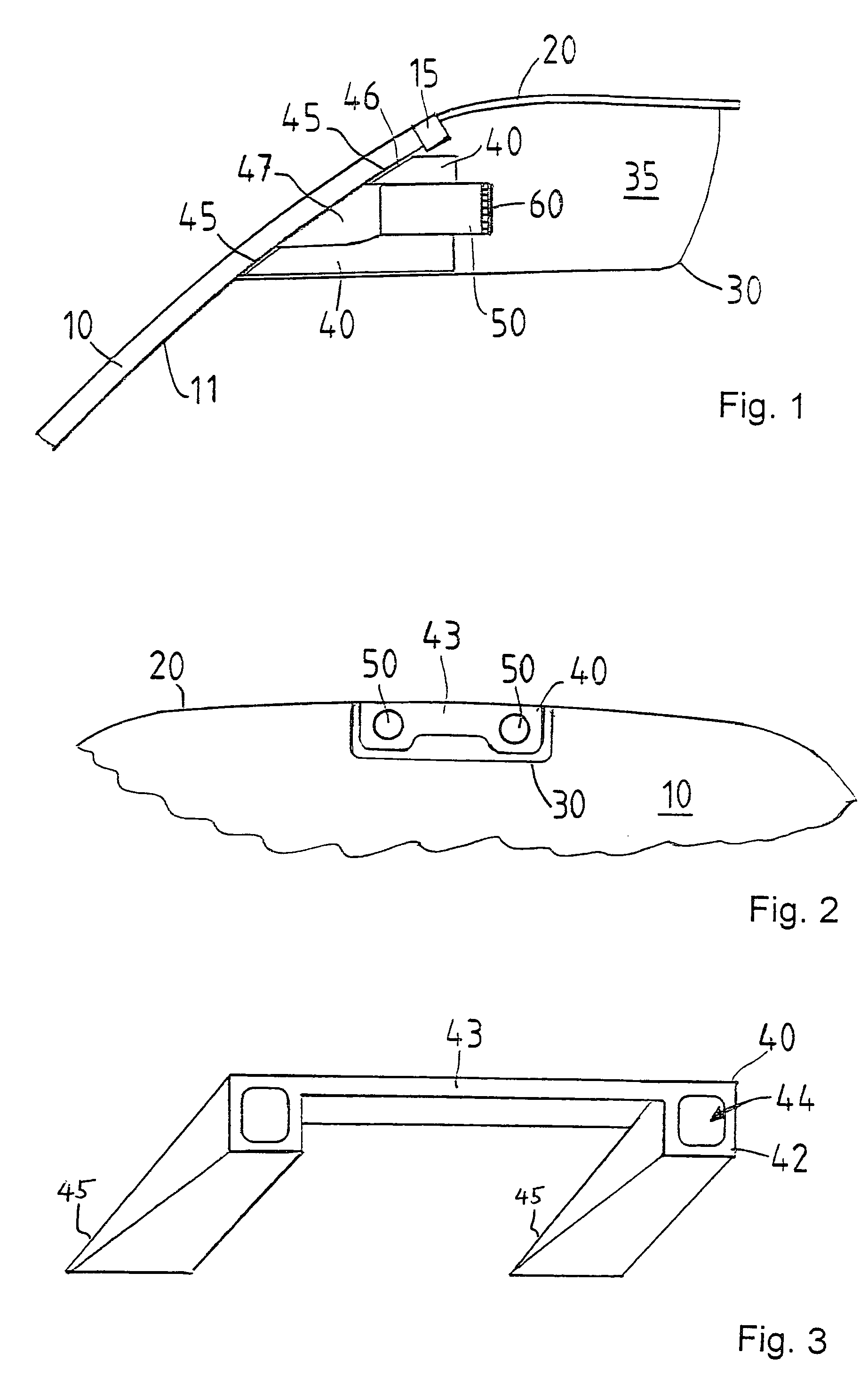
Stereoscopic image pickup apparatus and method of adjusting optical axis
InactiveUS20080239064A1Simple structureQuick correctionSteroscopic systemsFace detectionStereo camera
A stereoscopic camera includes first and second image pickup units, having respectively first and second optical axes, for photographing an object to form two image frames. Two angle adjusters make angle adjustment of the optical axes. An object detector detects a human face as a principal object in the two image frames. An arithmetic processor obtains a shift amount of the face between two image frames, and determines an axial correction angle according to the shift amount for the angle adjustment in consideration of the face. A checker checks whether the angle adjustment should be made for both optical axes or for one thereof. A controller operates at least one of the two angle adjusters according to the axial correction angle and in response to information from the checker, for positioning the face equally between the two image frames optically by adjusting the first and / or second optical axis.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
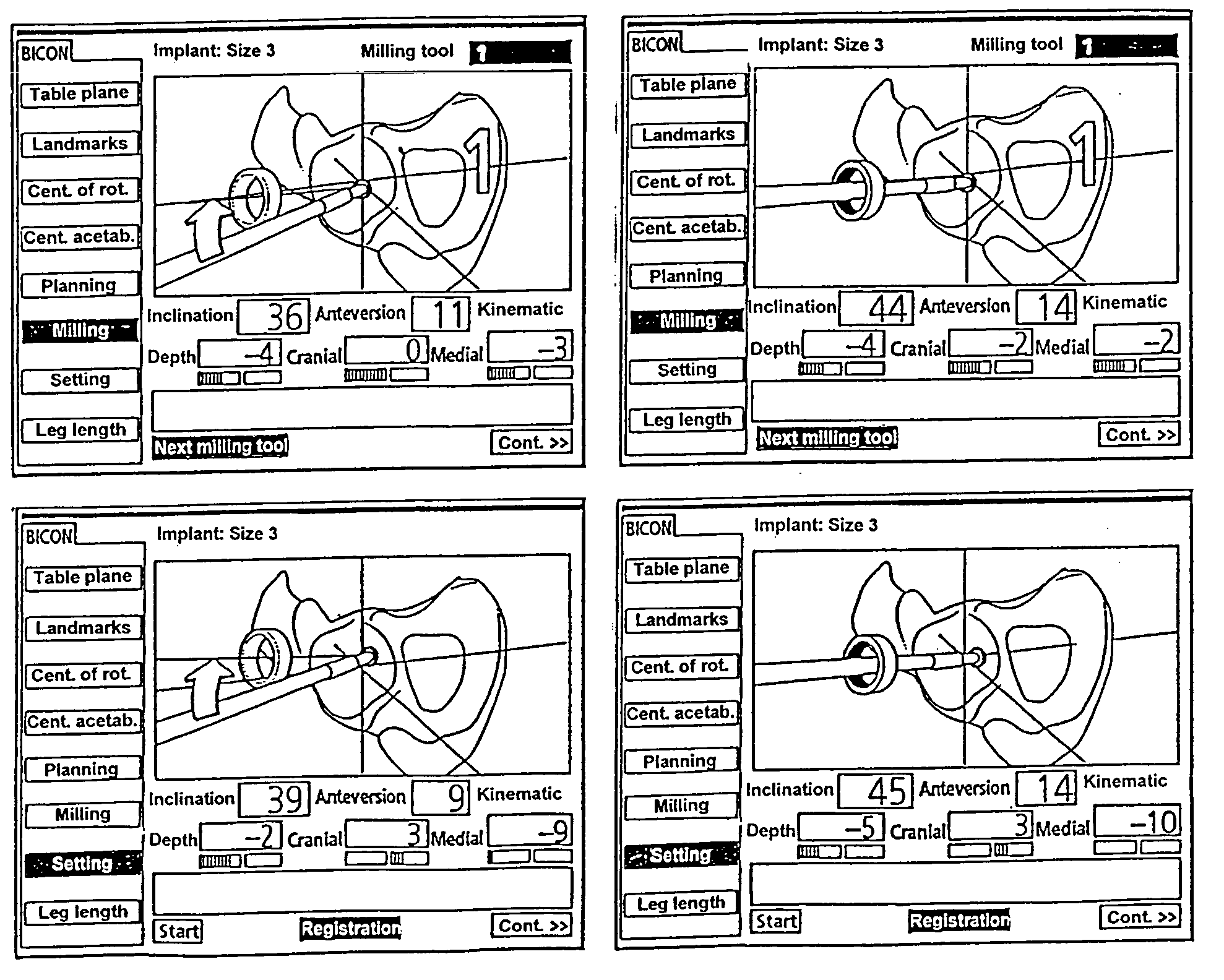
Method of determining the position of the articular point of a joint
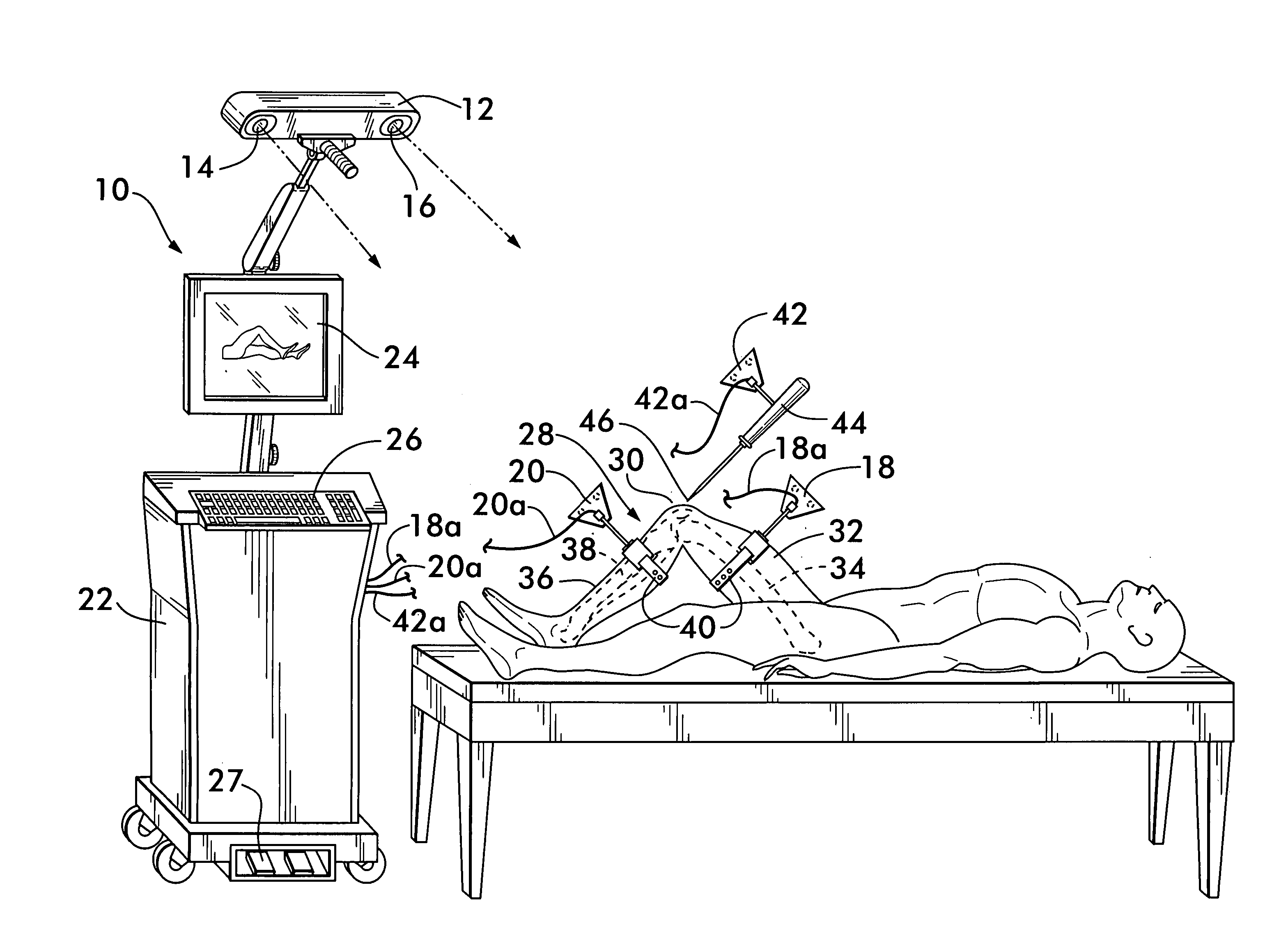
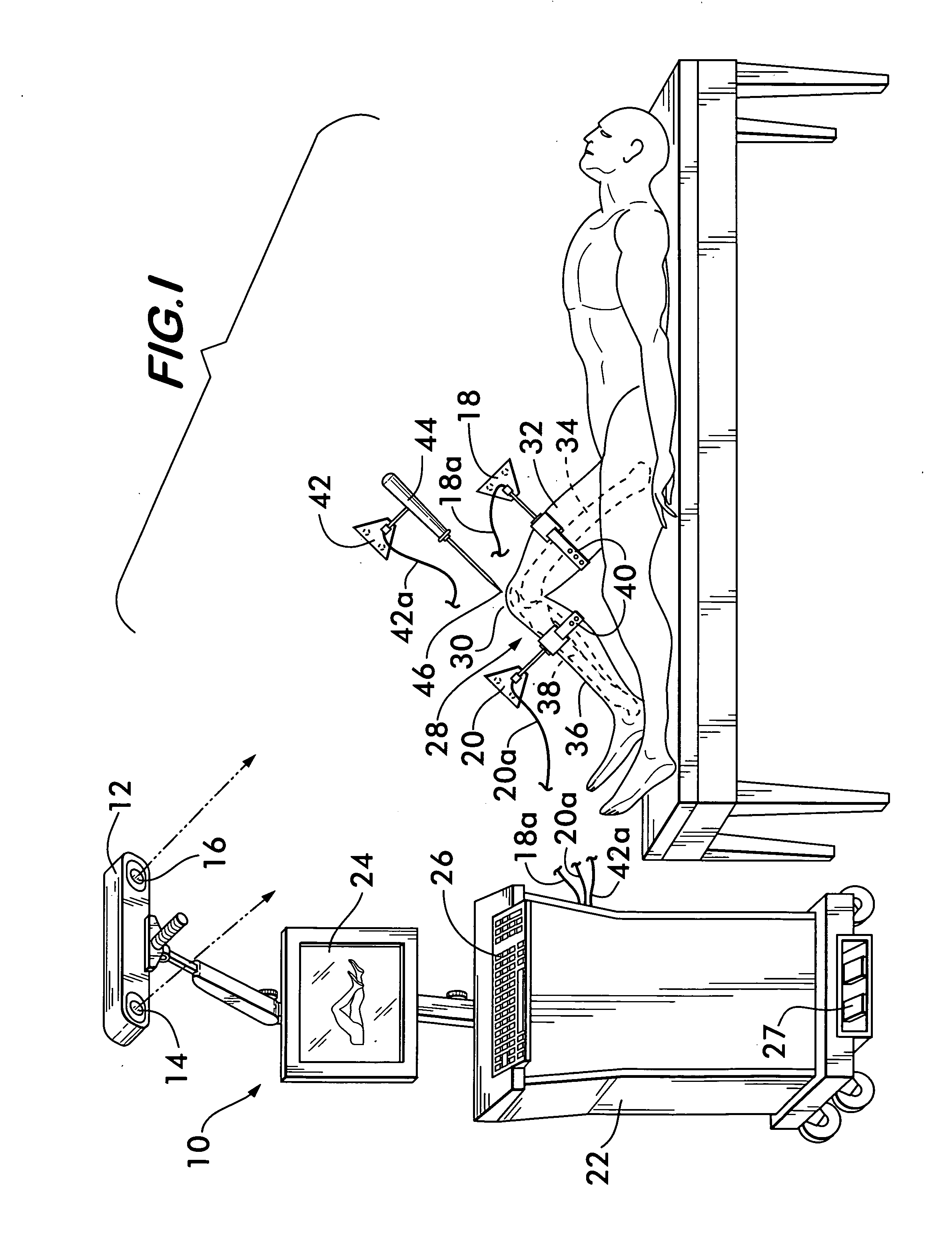
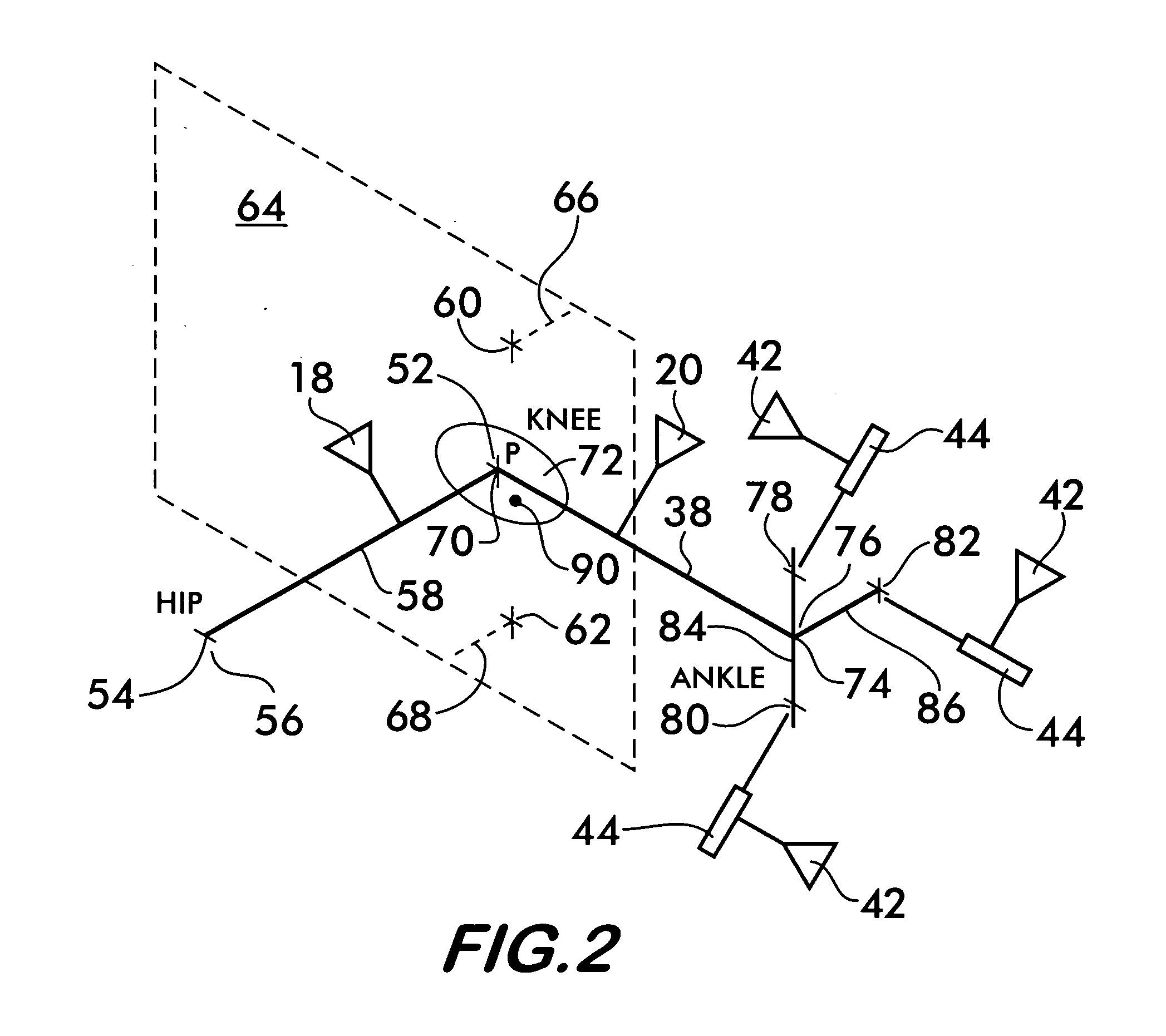
InactiveUS20060282023A1Surgical navigation systemsPerson identificationData processing systemKinematics
A non-invasive method for determining the articular point of a knee joint is disclosed. The method uses a surgical navigation system having stereoscopic cameras which track the positions of infrared emitting or reflecting markers attached to leg portions on either side of the knee joint. A movable marker is used to palpate known landmarks on the leg portions to determine their positions. The leg portions are moved to determine the trajectories of the landmarks relative to the joint. Positional information from the cameras is fed to a data processing system with resident software which uses the positional information and trajectories to mathematically determine the positions of the knee joint articular point according to the laws of kinematics.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
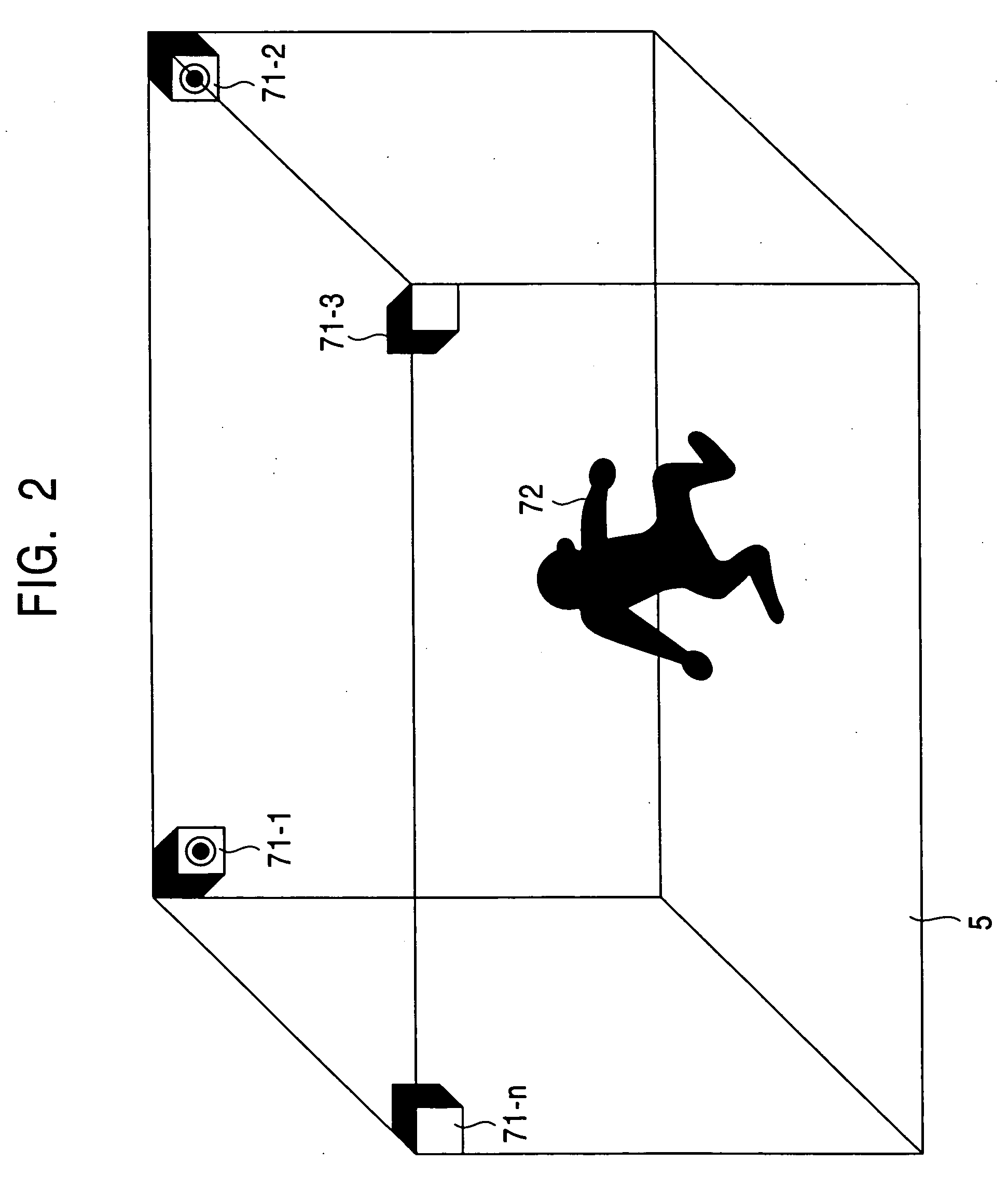
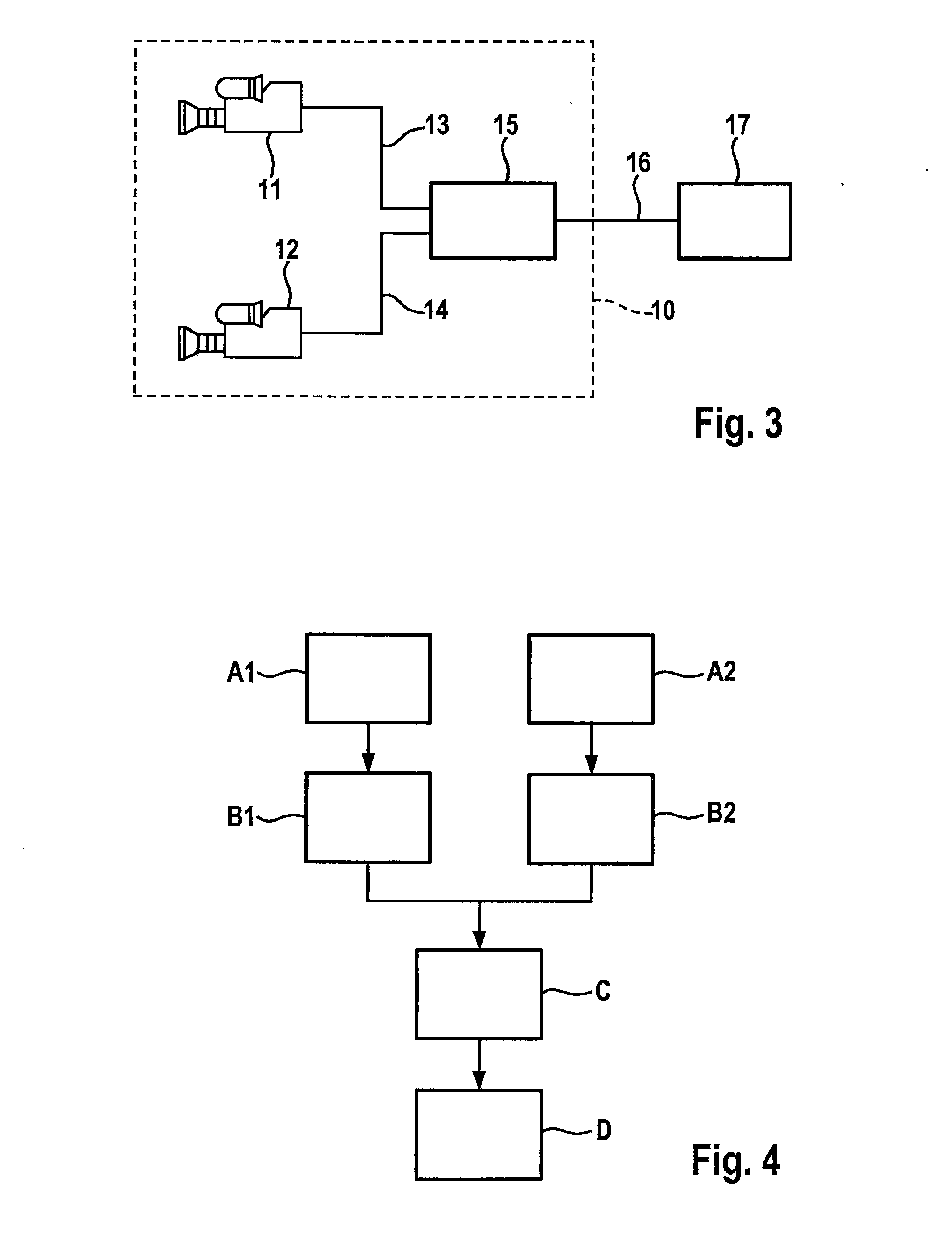
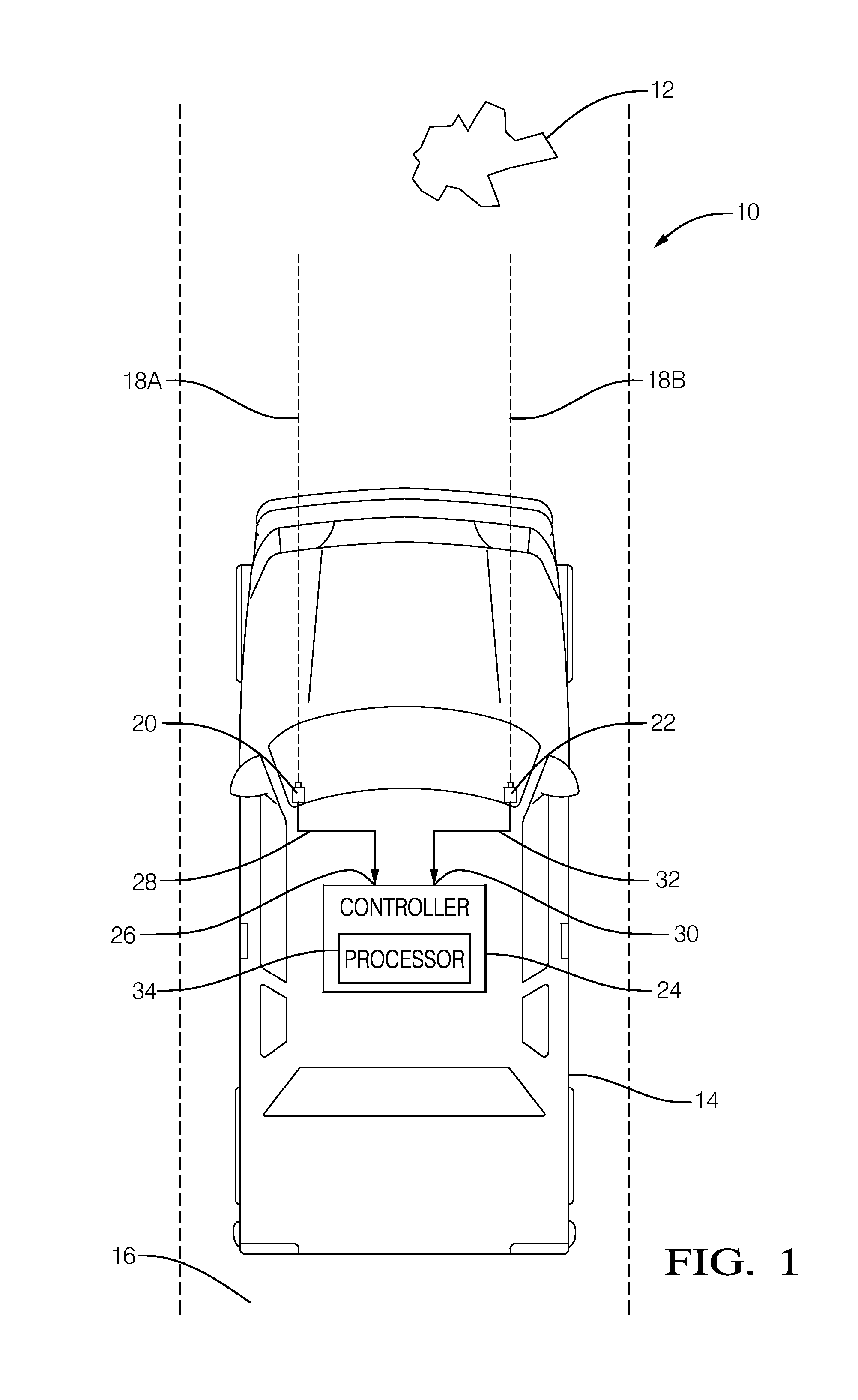
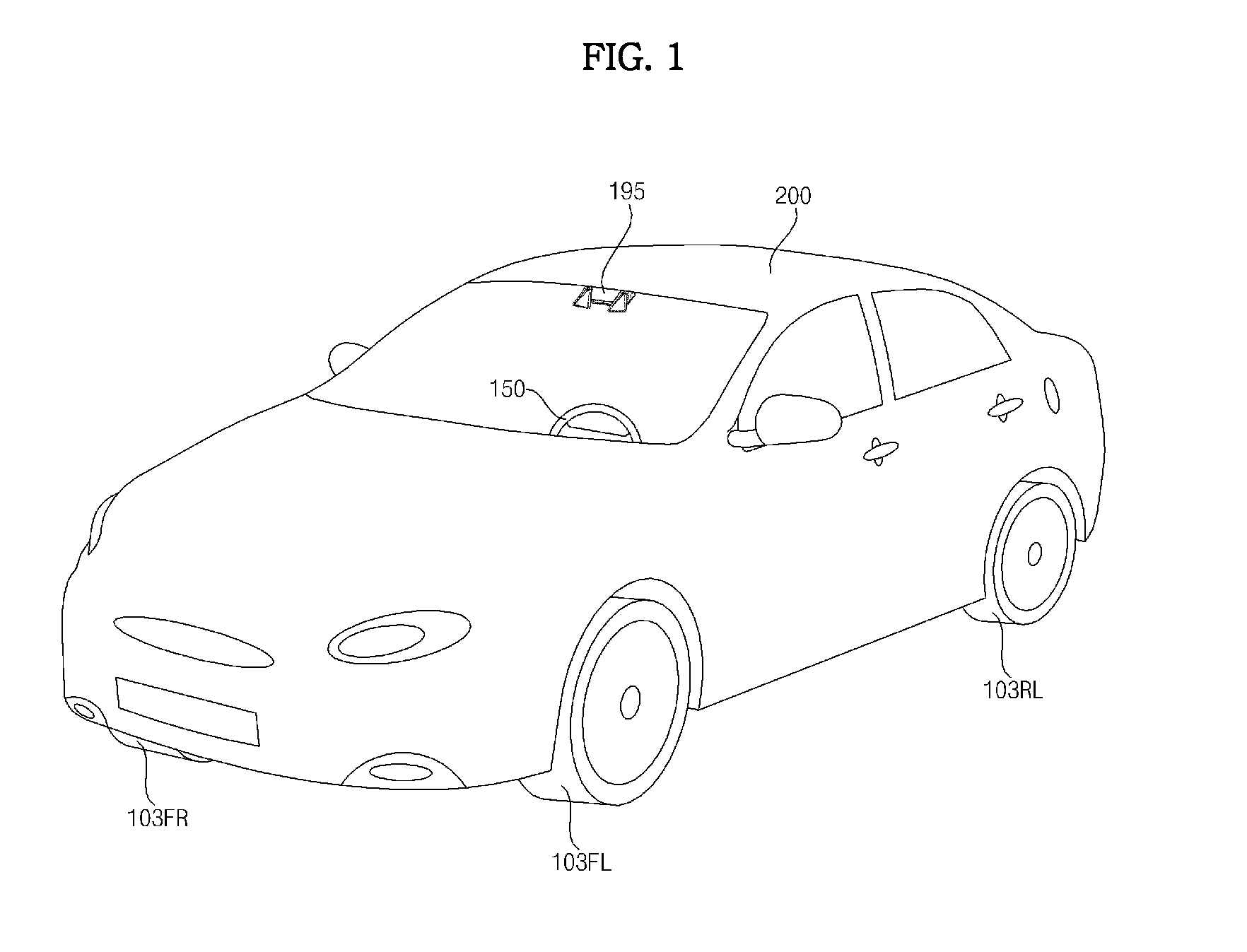
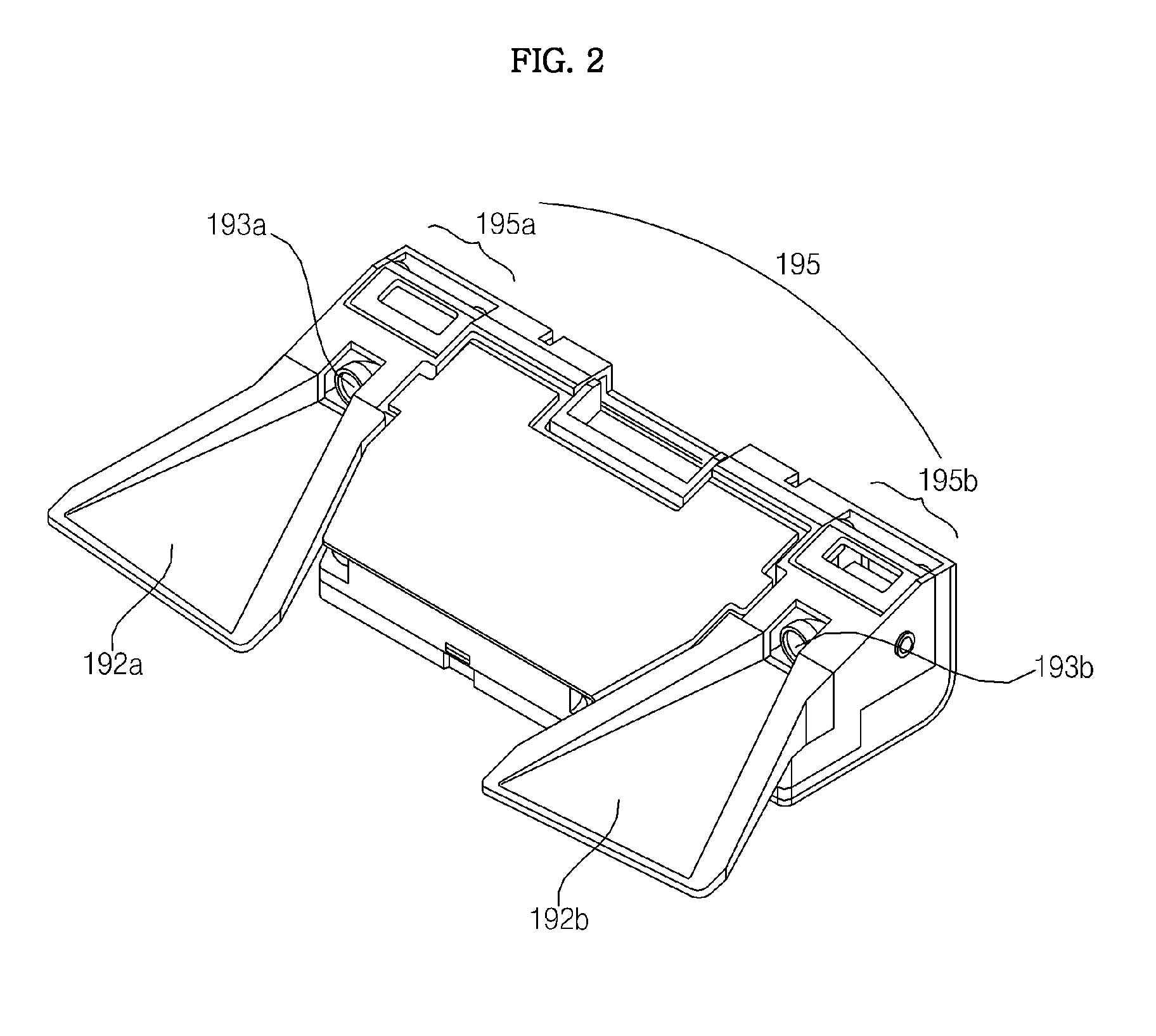
Stereo camera arrangement in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS7111996B2Rapid and simple and secure assemblyStable positionMachine supportsColor television detailsMobile vehicleStereo camera
A stereo camera system in a motor vehicle, in particular for classifying objects and determining distance. In order to ensure secure installation and precise positioning of the camera system, in particular fixing of its lateral position, the camera system is provided with at least two camera modules, and a mount, in which camera modules are installed at a specified lateral distance apart, the mount being cemented to the inside of the windshield.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
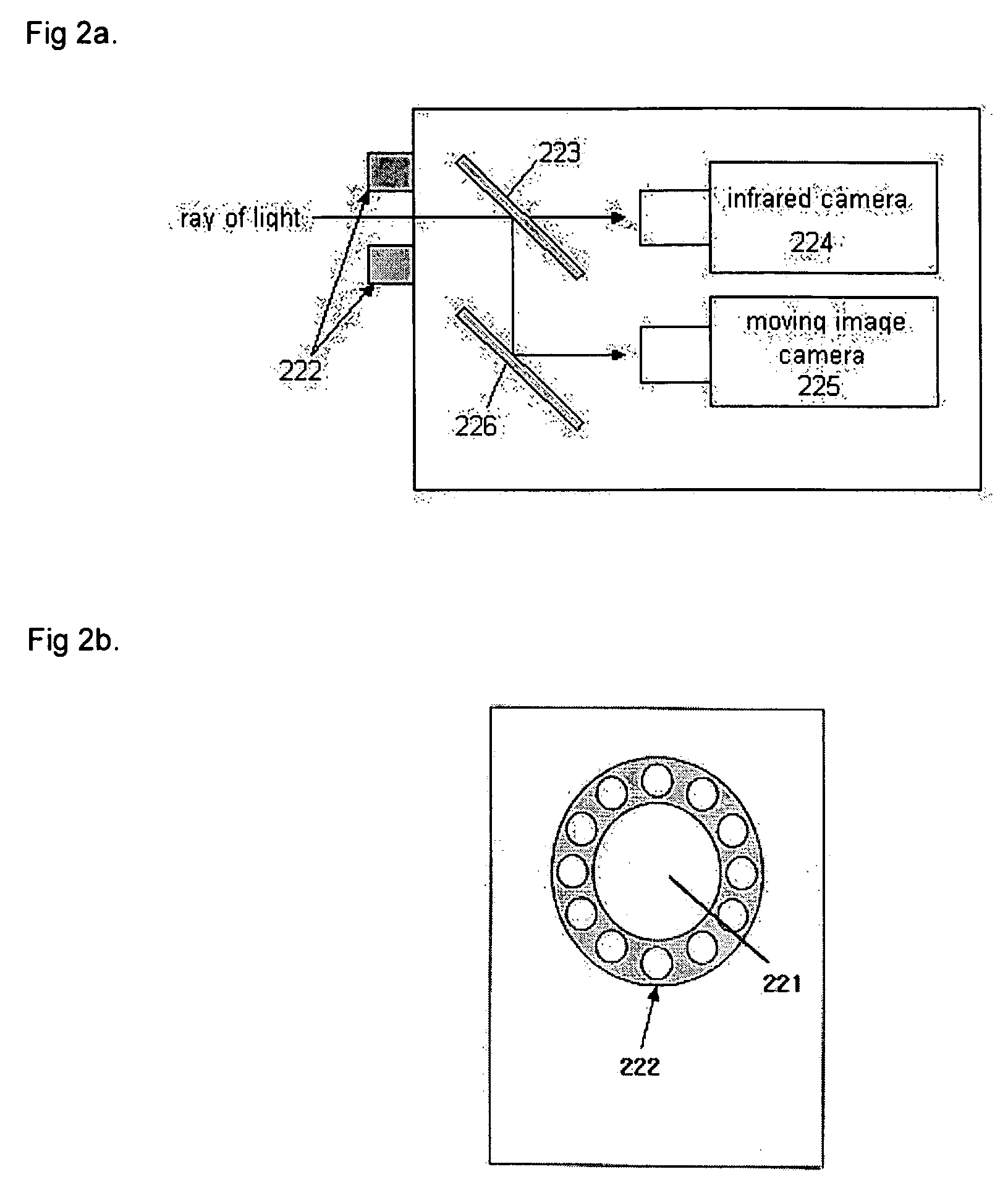
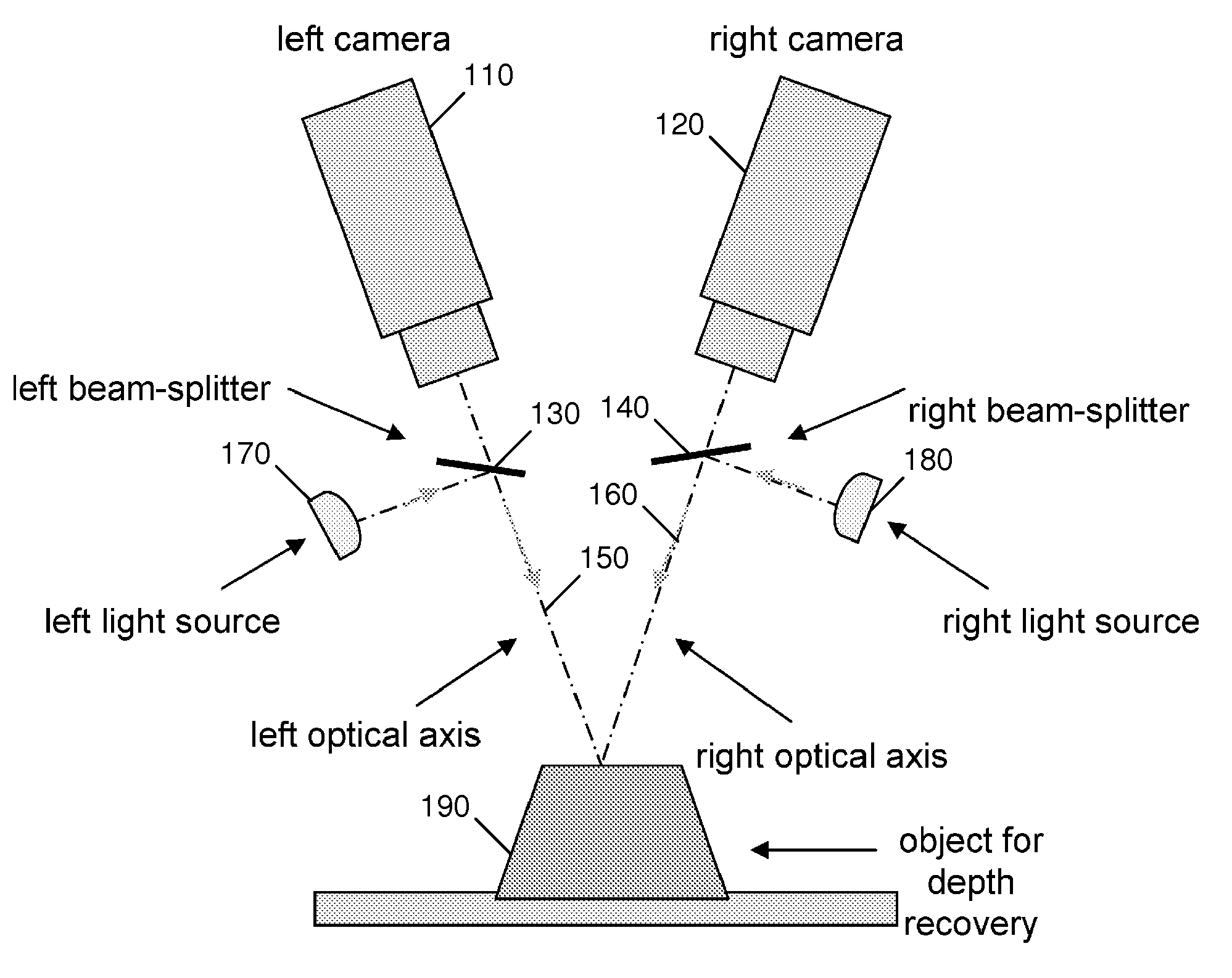
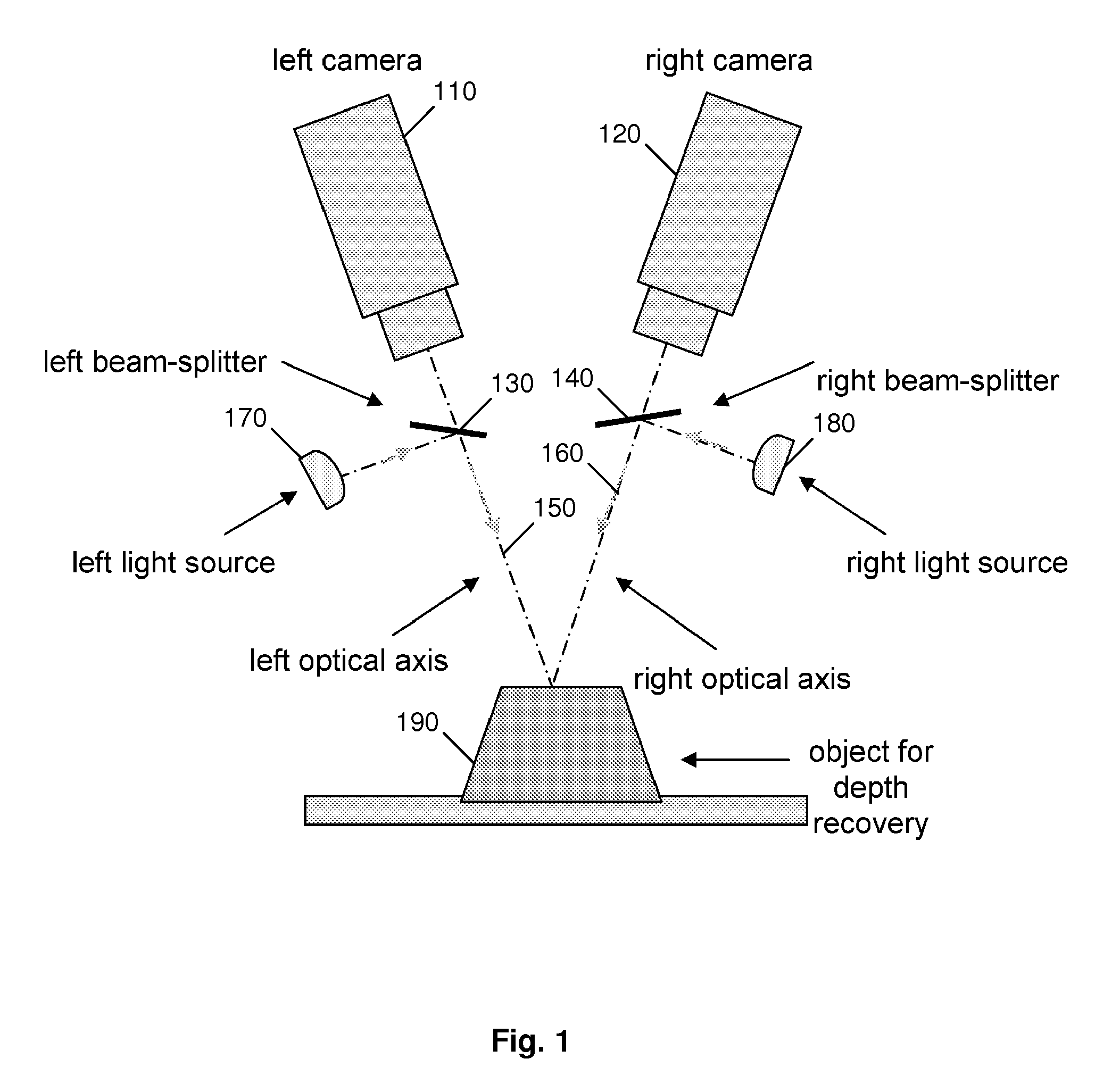
Fast Three Dimensional Recovery Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20080123937A1Easy to useSimple setup and calibration processImage enhancementImage analysisRecovery methodMetrology
The present invention comprises a method and an apparatus for three dimensional modeling to allow dense depth maps to be recovered, without previous knowledge of the surface reflectance, from only a single pair of stereo images. Several initial steps are performed for stereo and radiometric calibration and rectification for obtaining accurate results. The apparatus for the stereo images acquisition includes internal light sources, these are automatically commuted by a illumination control in order to fulfill the reciprocity property, a stereo camera head composed by the necessary optics to acquire the reciprocal stereo images and a compatible PC interface. The invention is faster than other systems since it requires only two images for obtaining a dense depth model of objects with an arbitrary surface reflectance distribution allowing the system to be used in a wide range of applications such as metrology, quality control, medical and dynamic three dimensional modeling.
Owner:PREFIXA VISION SYST DE C V
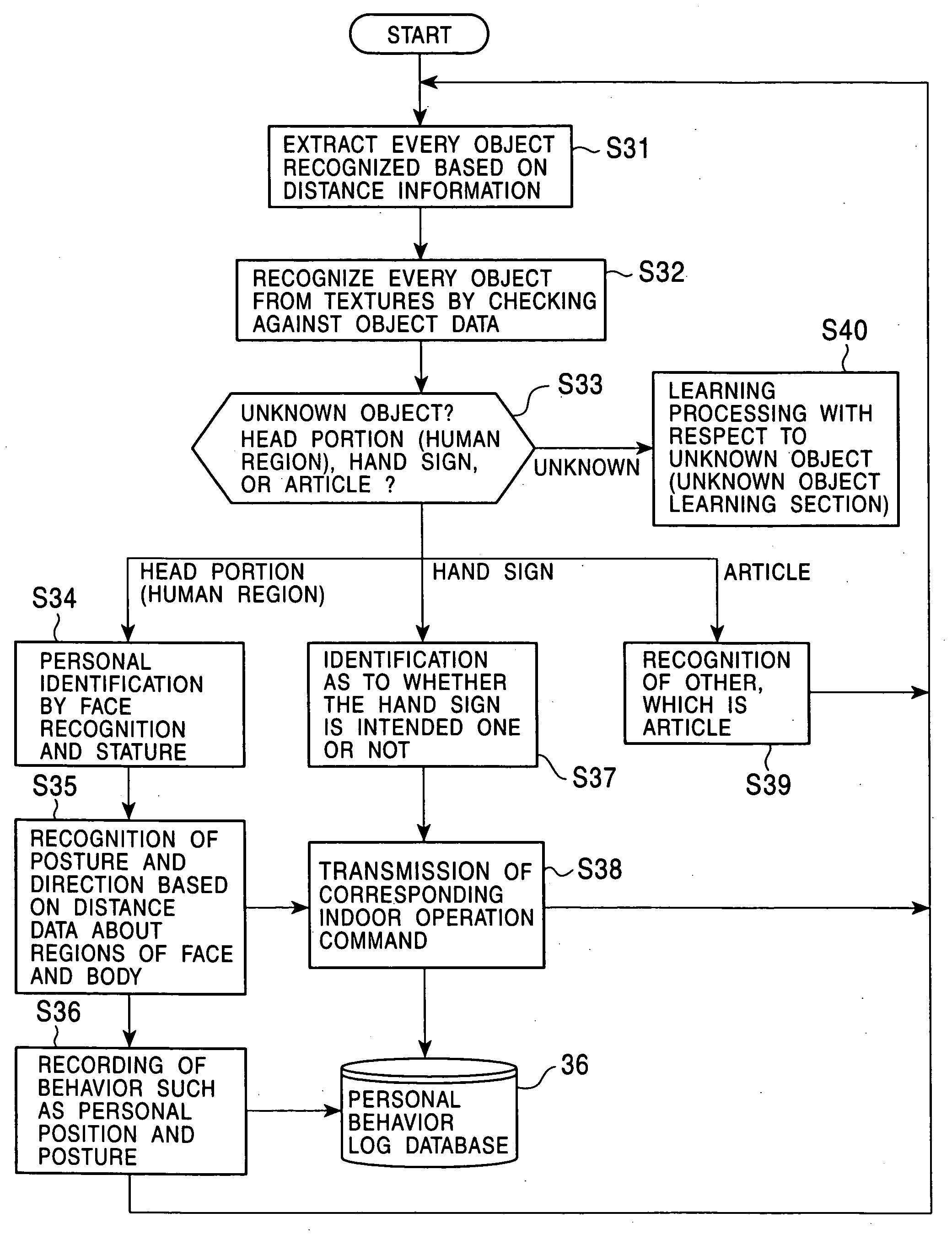
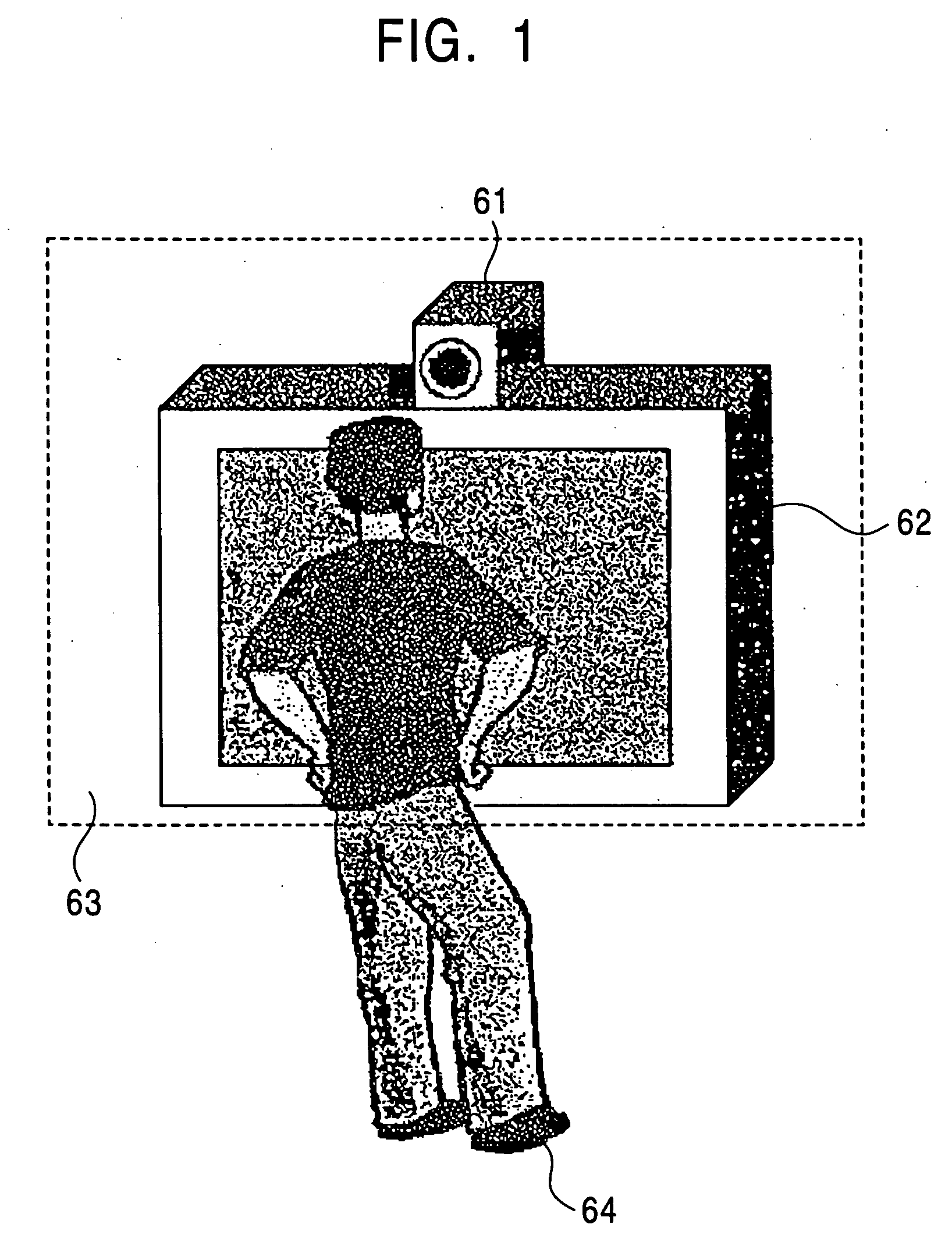
Interface apparatus
InactiveUS20060182346A1Easy to identifyInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual field lossColor image
An interface is provided that corresponds to an individual person without being restricted to a particular place within a room, by performing gesture recognition while identifying an individual person. A stereo camera (1) picks up an image of a user (4), and based on the image pickup output, an image processor 2 transmits a color image within a visual field and a distance image to an information integrated recognition device (3). The information integrated recognition device (3) identifies an individual by the face of the user (4), senses the position, and recognizes a significant gesture based on a hand sign of the user (4). The information integrated recognition device (3) executes a command corresponding the identified user (4) and performs operations of all devices (6) to be operated in the room (such as a TV set, an air conditioner, an electric fan, illumination, acoustic condition, and window opening / closing).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Object recognition apparatus
InactiveUS20060072914A1Improve reliabilityReduced space required for installationOptical rangefindersPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementStereo cameraIdentification device
The object recognition apparatus has an active range finder having a floodlight unit which floodlights a light onto a target object, and determines a distance up to a target object on the basis of a reflected light therefrom, a stereo camera to determine a distance up to the target object on the basis of image information from the target object, an object recognition unit which recognizes the target object on the basis of an output signal from the active range finder and an output signal from the stereo camera, and a fill light control unit which controls the floodlight unit to operate so as to irradiate a light floodlit by the floodlight unit as a fill light of the stereo camera.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
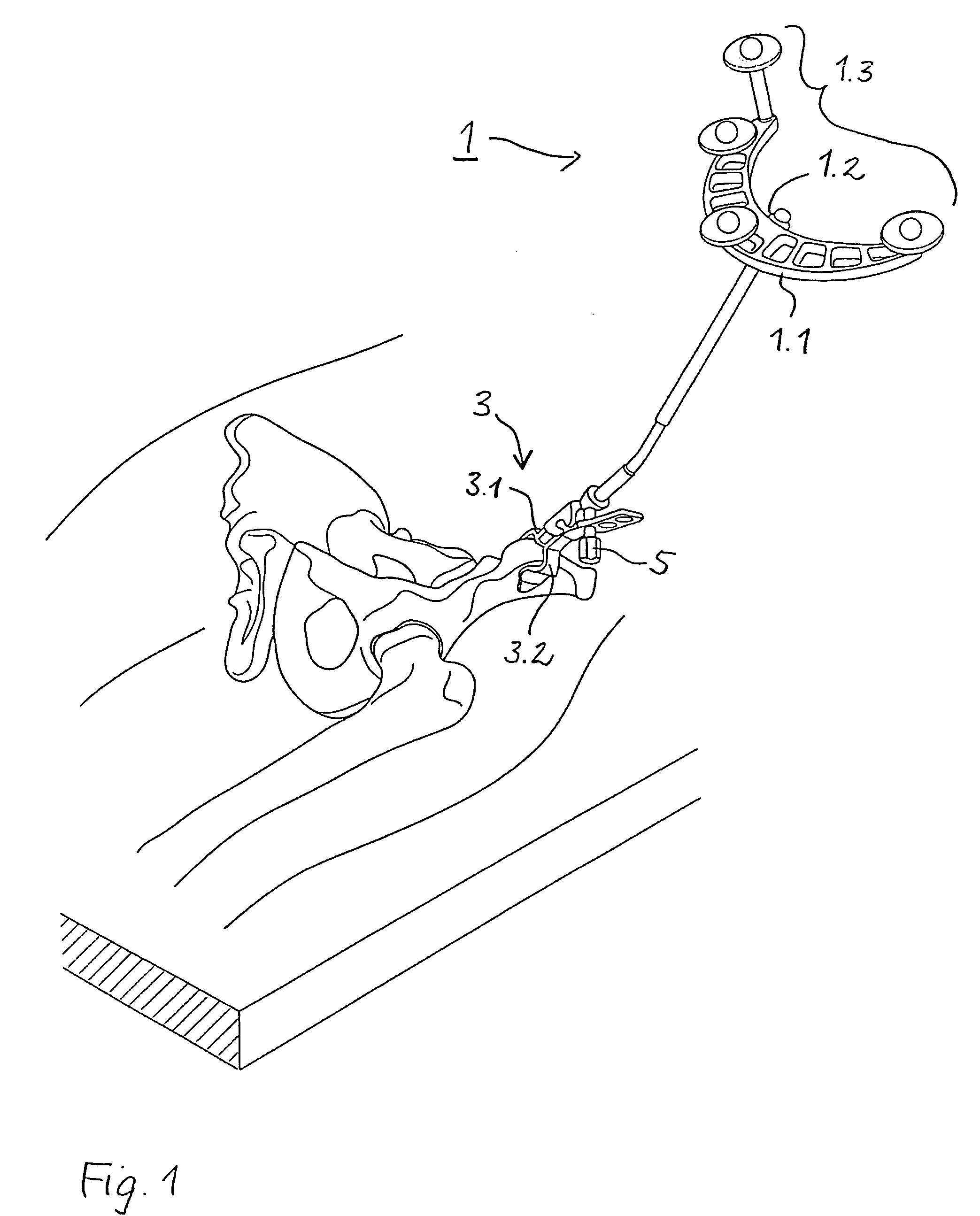
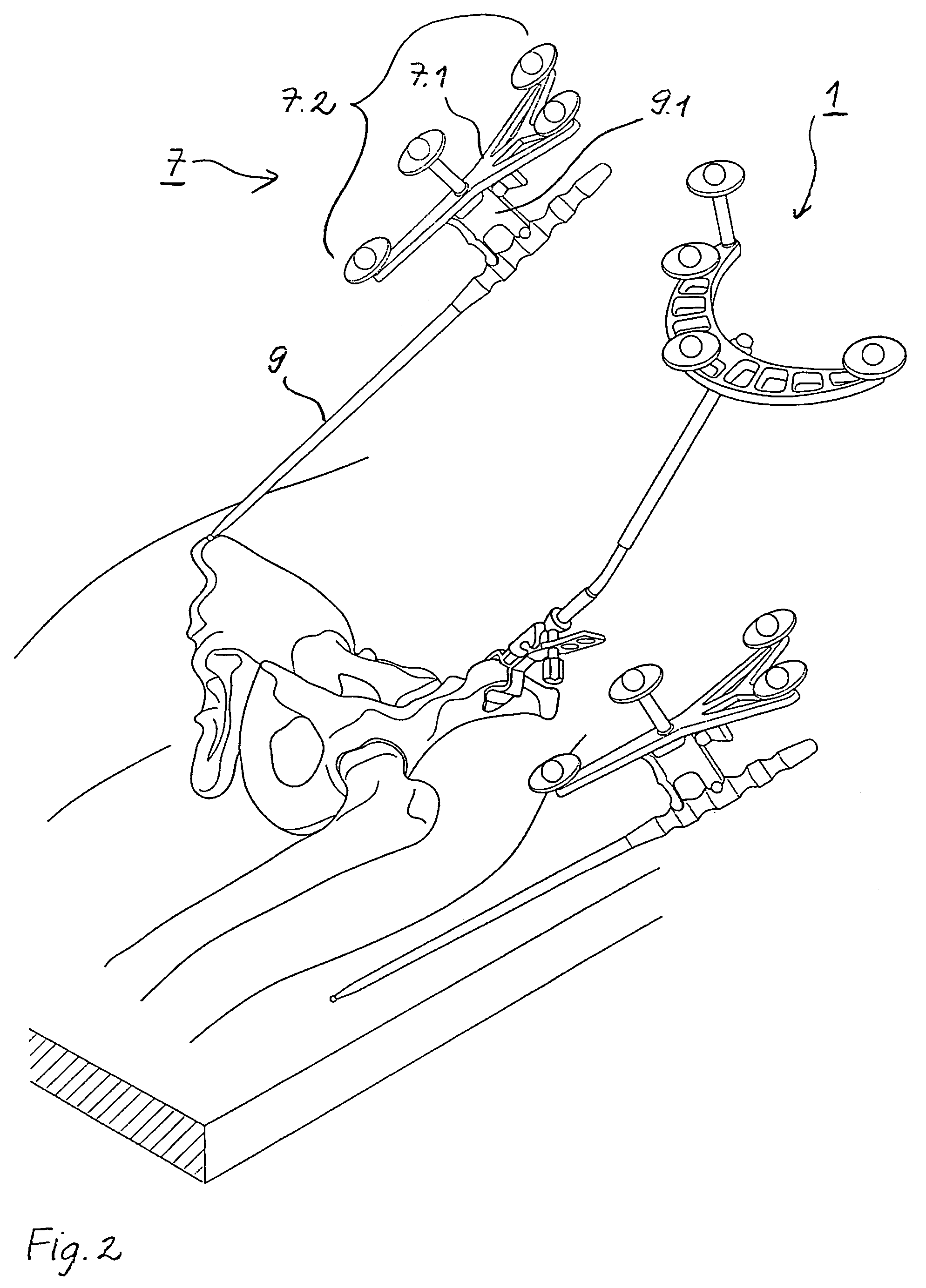
Arrangement for ascertaining function-determining geometric parameters of a joint of a vertebrate
InactiveUS20050182320A1Easy to operateReduce riskSurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceStereo cameraMeasurement point
Arrangement for ascertaining function-determining geometric parameters of a joint of a vertebrate, especially a hip or shoulder joint of a human being, in preparation for the installation of a joint replacement implant, especially a hip or shoulder socket or an associated stem implant, by means of an optical coordinate-measuring procedure, having a stereocamera or stereocamera arrangement for the spatial recording of optical transducer signals, a mobile multipoint transducer which is in the form of a movable sensor for sensing bony references in the joint region in order to determine the coordinates thereof, at least one bone-fixed multipoint transducer which is configured for rigid attachment, especially screwed or clamped attachment, (in a region sufficiently distant from the joint) to an extremity originating from the joint, especially close to the proximal end of a femur or a humerus, an interactive sequence controller for controlling the sequential registration and storage of a set of measurement point coordinates supplied by the mobile multipoint transducer and sets of measurement point coordinates recorded in a first plurality of positions of the bone-fixed multipoint transducer in a plurality of rotated positions of the extremity and their subsequent processing in accordance with a previously stored processing sequence, an evaluation unit for evaluating the sets of measurement point coordinates supplied by the multipoint transducers and recorded by the camera arrangement for the purpose of determining the geometric parameters, which comprises means for determining the transversal, vertical and sagittal body axes as well as means for carrying out an iterative procedure, especially an adjustment calculation in accordance with the least squares method, to determine the coordinates of the center of rotation of the joint, and an output unit, which is connected to the sequence controller and to the evaluation unit, for issuing manipulation proposals to an operating surgeon in accordance with the predetermined process sequence and in dependence upon the results of the determination of the geometric parameters, and for displaying the results of the evaluation.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
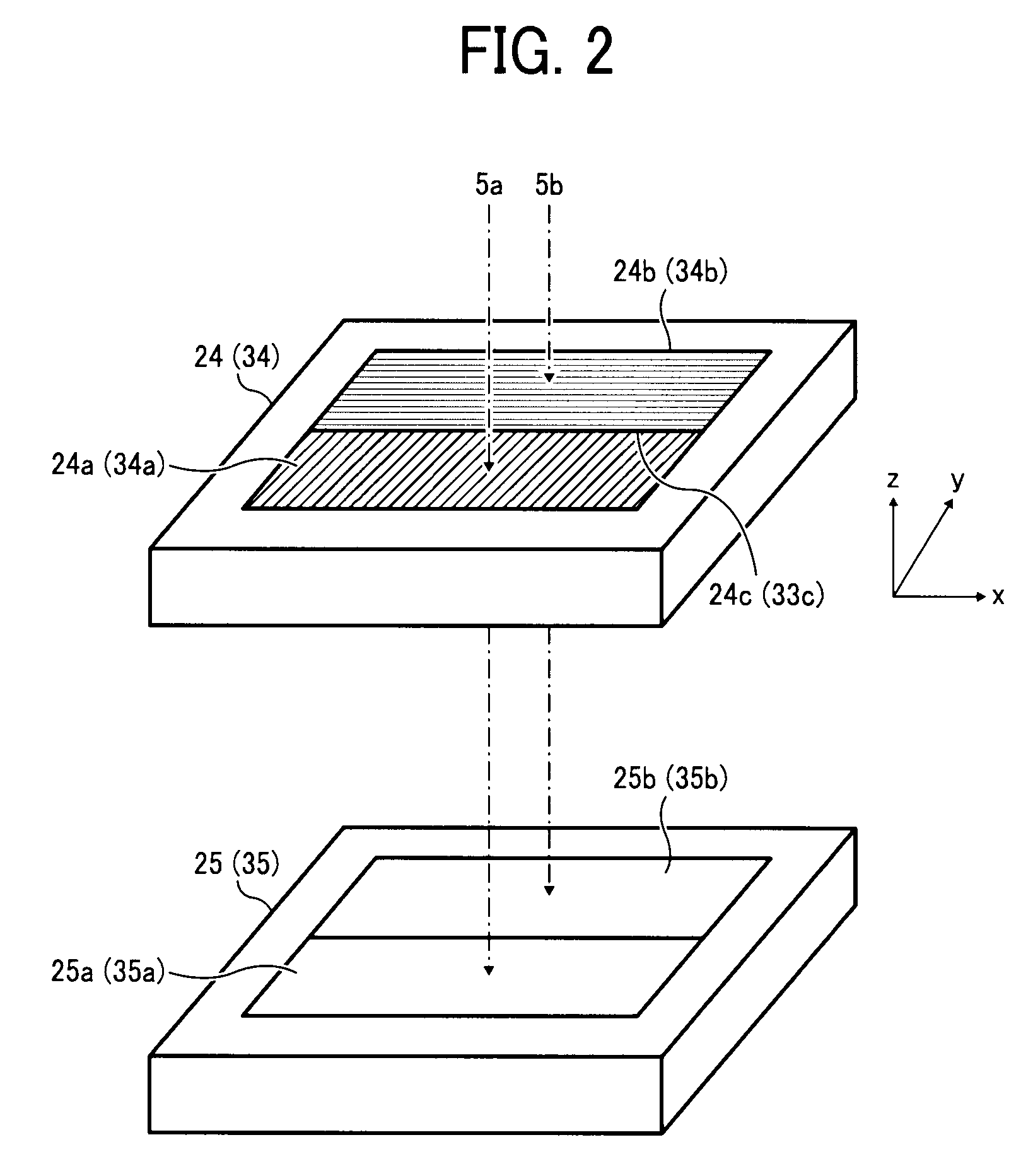
Image processing method for determining depth information from at least two input images recorded with the aid of a stereo camera system
InactiveUS20120127275A1Robust estimationEliminate the problemImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxGeometric property
An image processing method is described for determining depth information from at least two input images recorded by a stereo camera system, the depth information being determined from a disparity map taking into account geometric properties of the stereo camera system, characterized by the following method steps for ascertaining the disparity map: transforming the input images into signature images with the aid of a predefined operator, calculating costs based on the signature images with the aid of a parameter-free statistical rank correlation measure for ascertaining a cost range for predefined disparity levels in relation to at least one of the at least two input images, performing a correspondence analysis for each point of the cost range for the predefined disparity levels, the disparity to be determined corresponding to the lowest costs, and ascertaining the disparity map from the previously determined disparities.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
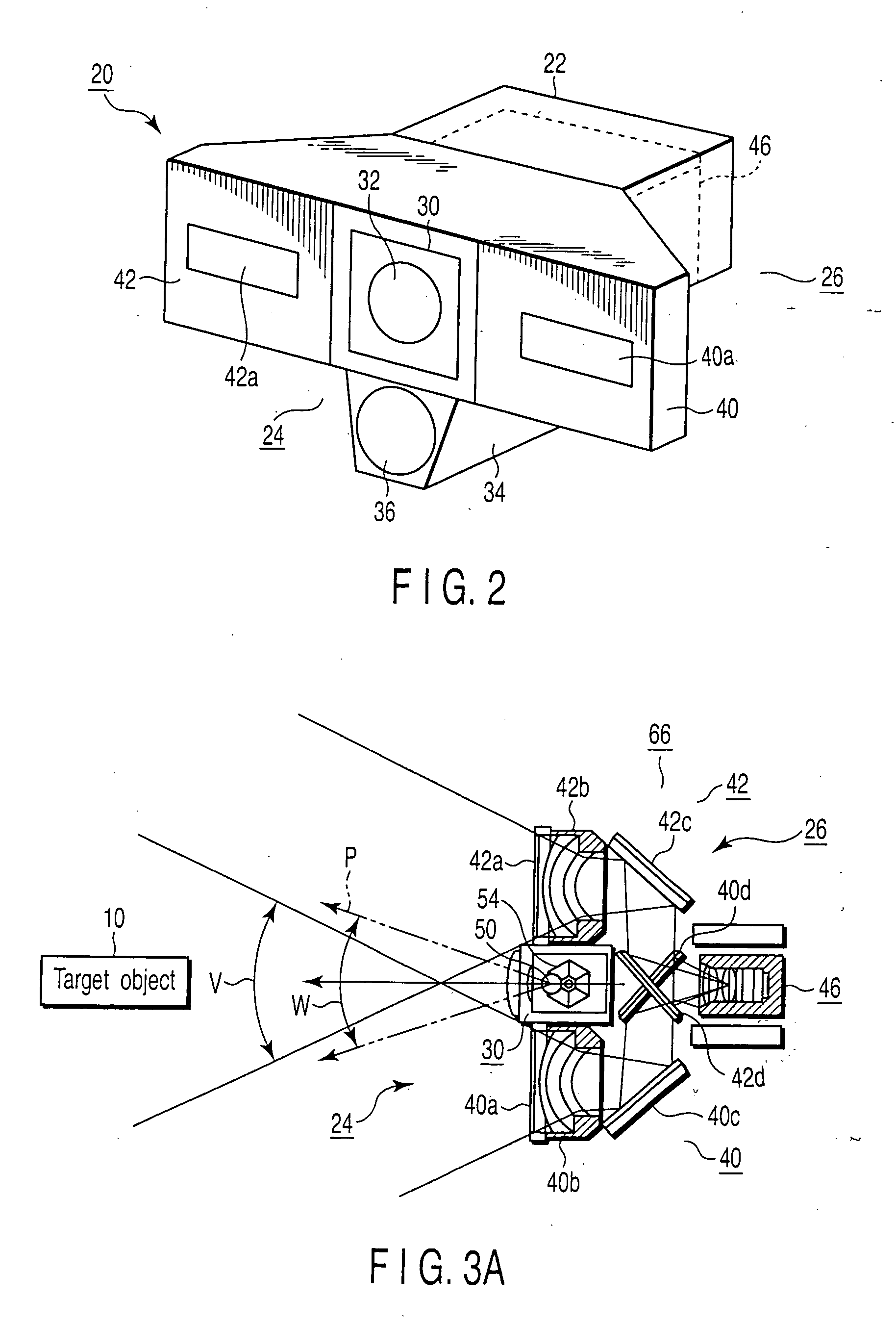
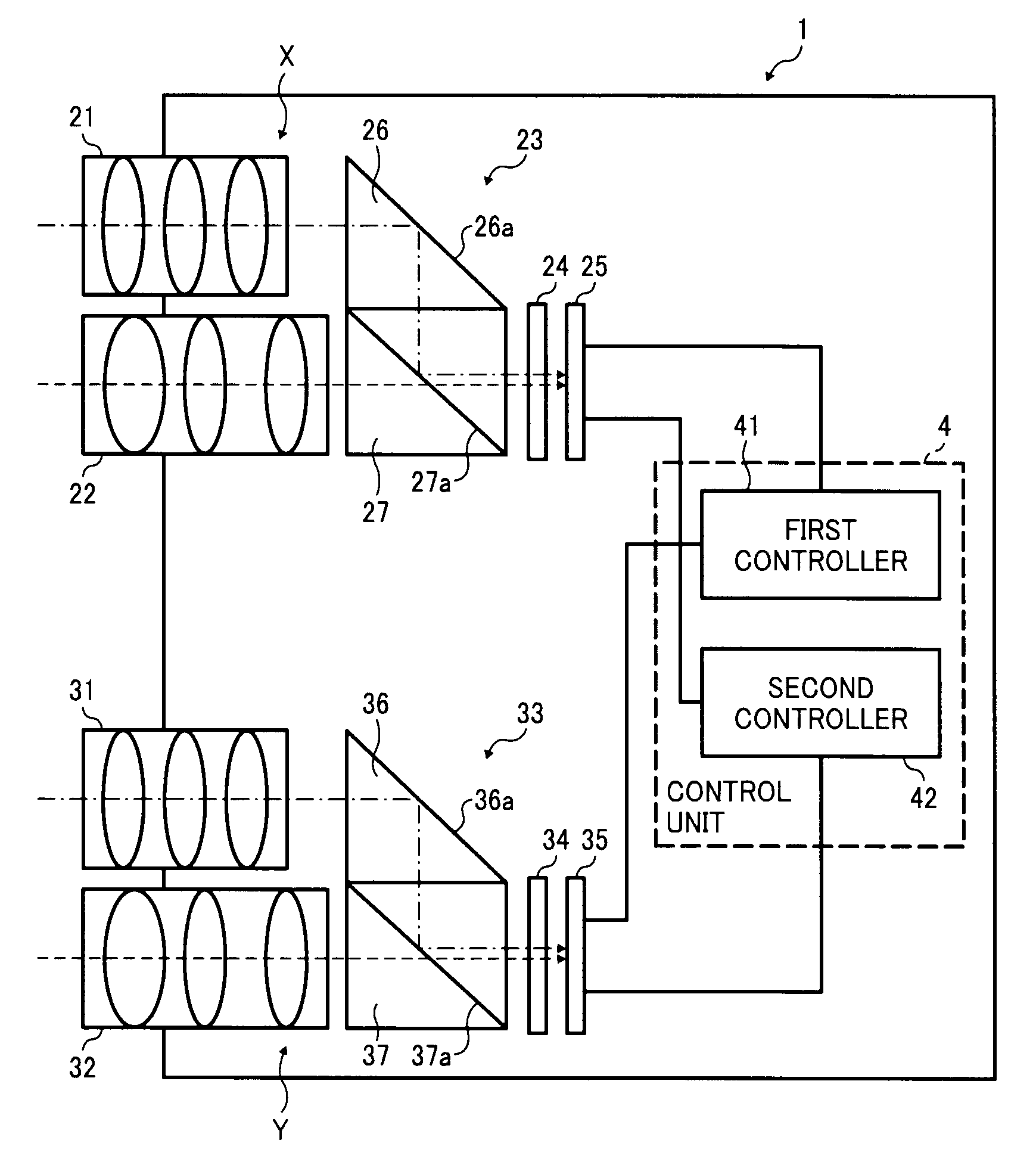
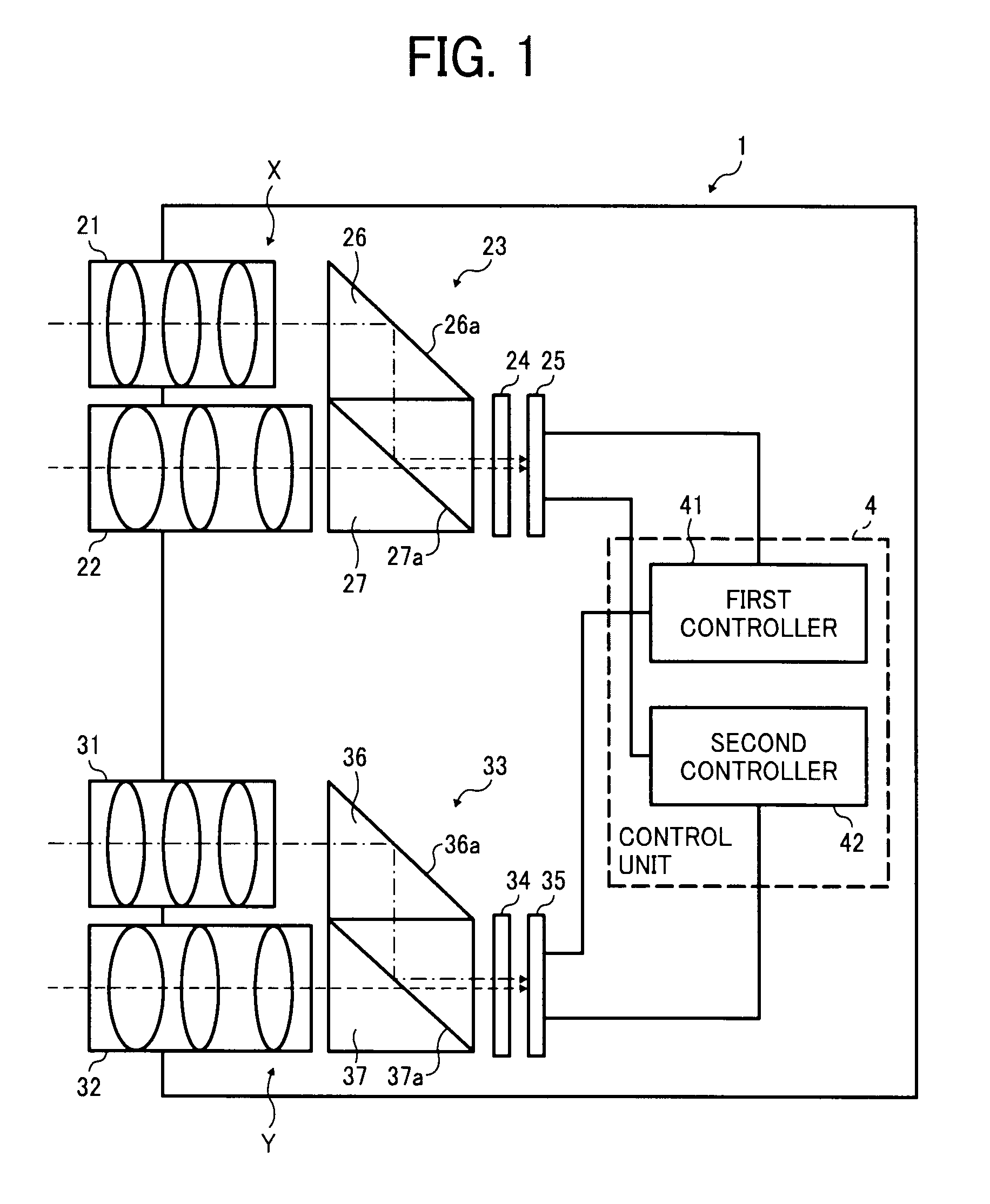
Stereo camera apparatus and vehicle-mountable monitoring apparatus using same
A stereo camera apparatus includes first and second image capturing units and a control unit. The first image capturing unit includes first and second lens units, a first light synthesis unit, a first area-divided filter, and a first image capturing element. The first light synthesis unit and the first area-divided filter guide S-polarized and P-polarized light components to the first image capturing element to detect S-polarized and P-polarized light component images. The second image capturing unit includes third and fourth lens units, a second light synthesis unit, a second area-divided filter, and a second image capturing element. The second light synthesis unit and the second area-divided filter guide S-polarized and P-polarized light components to the second image capturing element to detect S-polarized and P-polarized light component images. The control unit includes first and second controllers to compute three-dimensional data of object using the S-polarized and P-polarized light component images, respectively.
Owner:RICOH KK
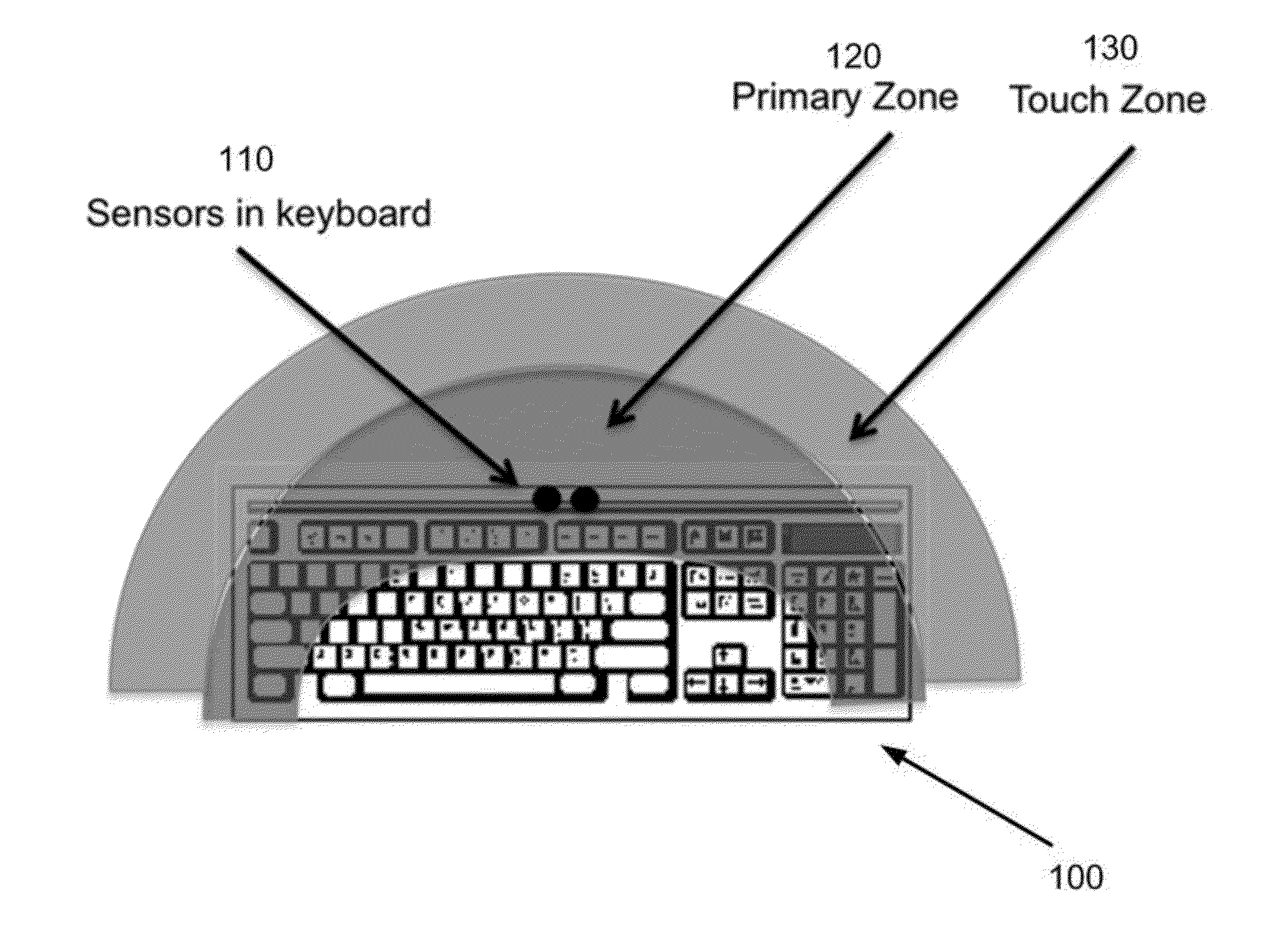
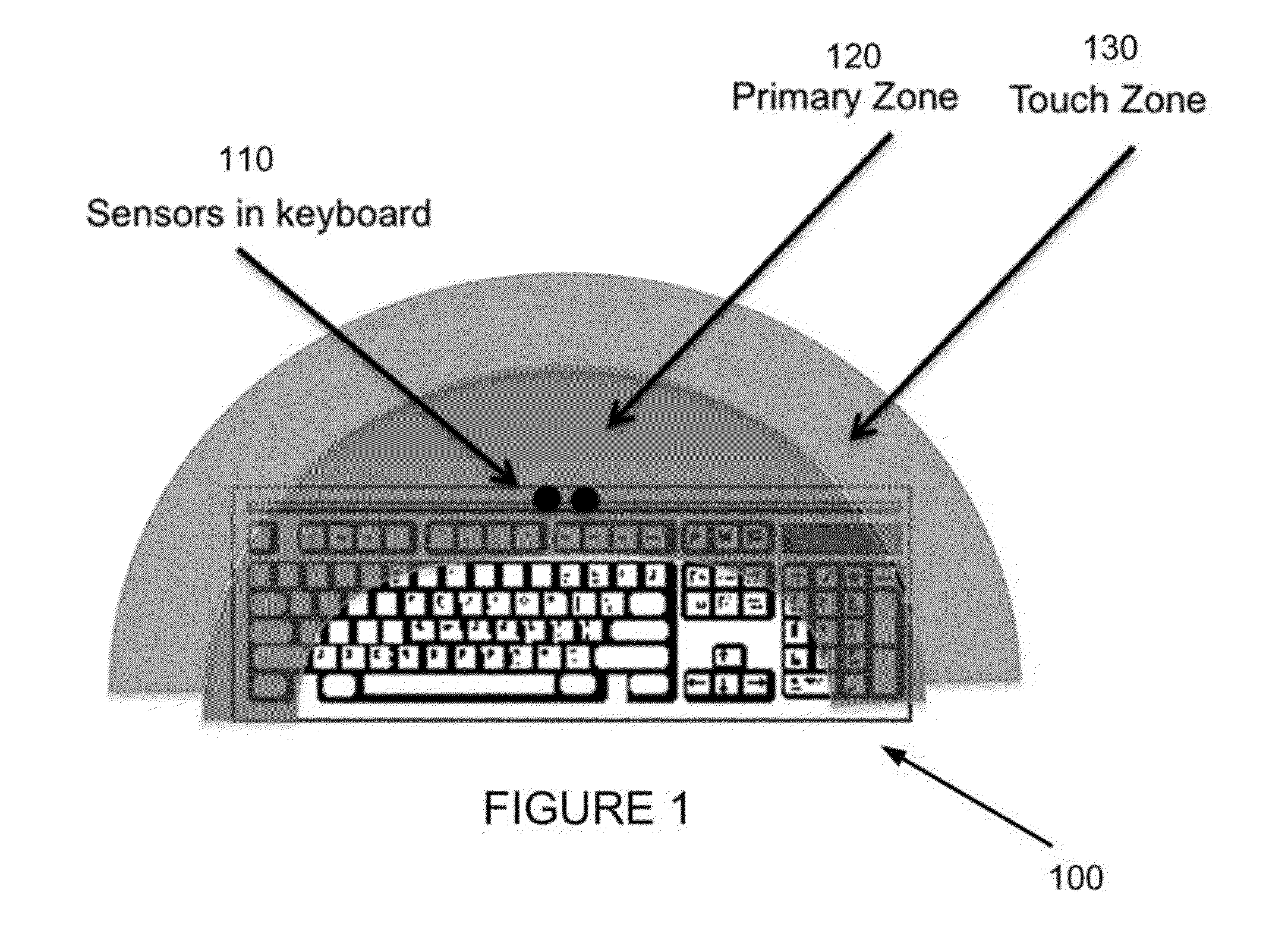
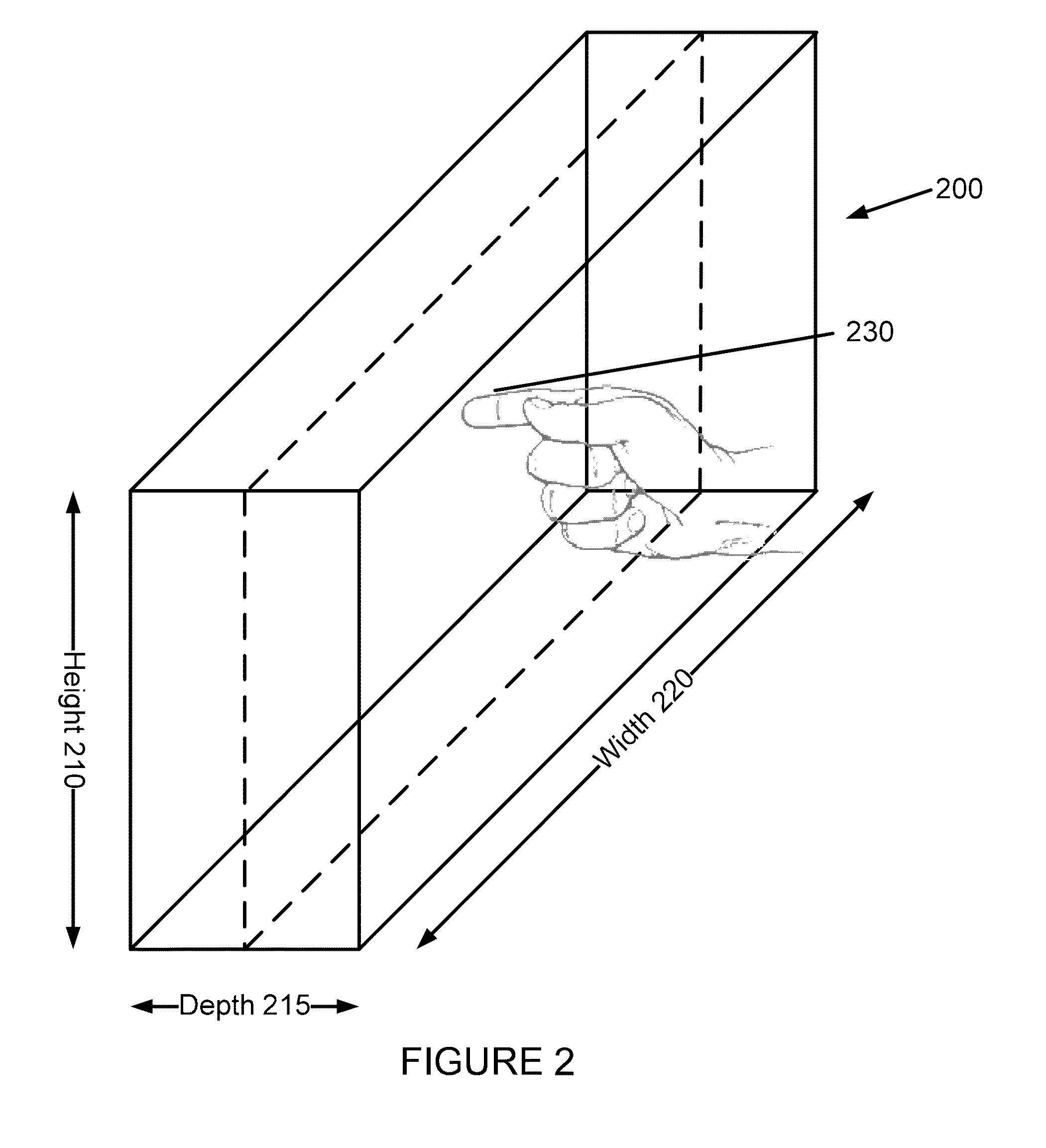
Gesture keyboard method and apparatus
ActiveUS8928590B1Wide field-of-viewComfortable to useInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingStereo cameraTyping
A gesture-enabled keyboard and method are defined. The gesture-enabled keyboard includes a keyboard housing including one or more keyboard keys for typing and a pair of stereo camera sensors mounted within the keyboard housing, a field of view of the pair of stereo camera sensors projecting substantially perpendicularly to the plane of the keyboard housing. A background of the field of view is updated when one or more alternative input devices are in use. A gesture region including a plurality of interaction zones and a virtual membrane defining a region of transition from one of the plurality of interaction zones to another of the plurality of interaction zones is defined within the field of view of the pair of stereo camera sensors. Gesture interaction is enabled when one or more gesture objects are positioned within the gesture region, and when one or more alternative input devices are not in use.
Owner:EDGE 3 TECH
Multi-eye image pickup apparatus and adjusting method
InactiveUS20090015689A1With balanceImprove the level ofTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsStereo cameraPhotoelectric conversion
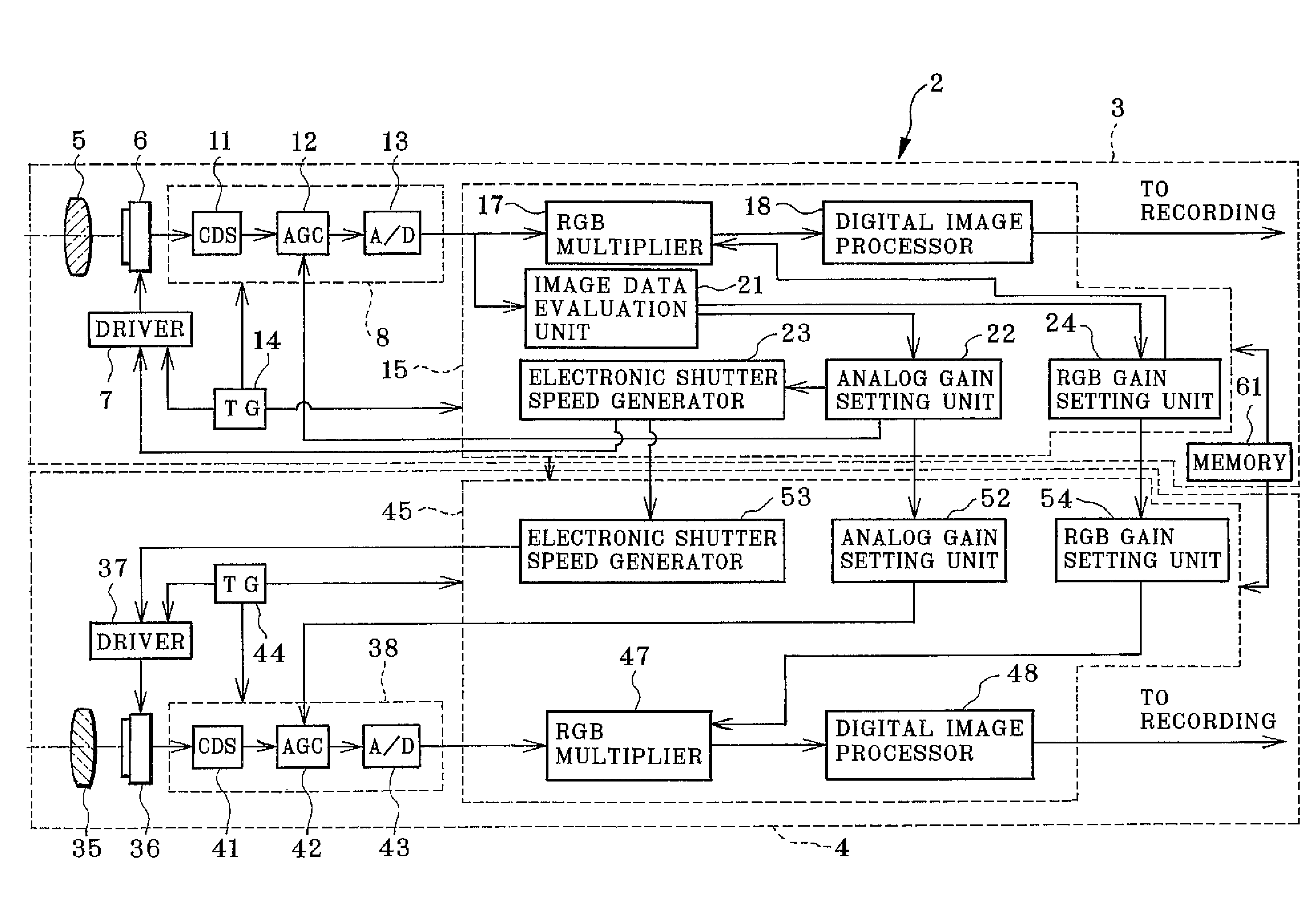
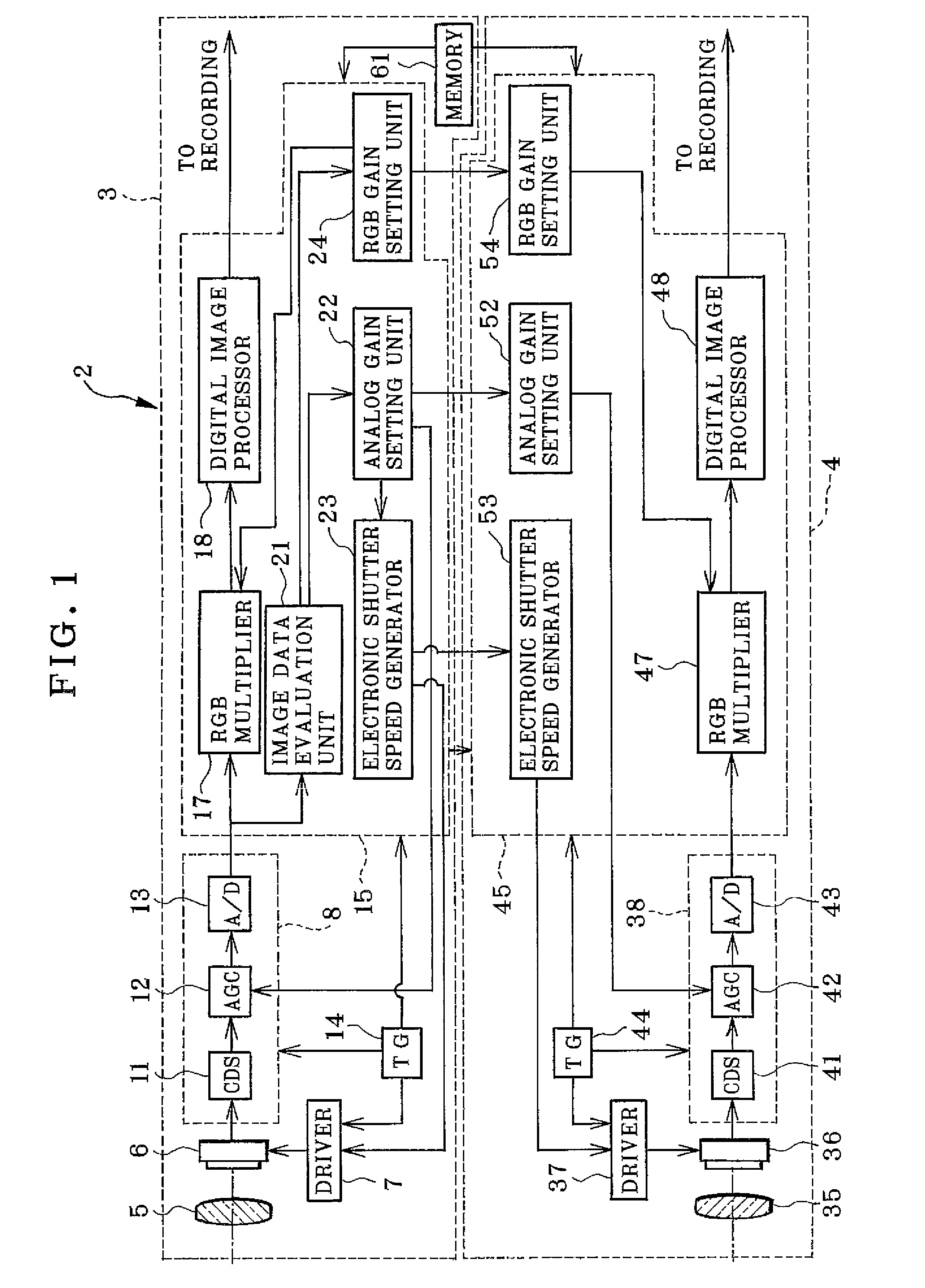
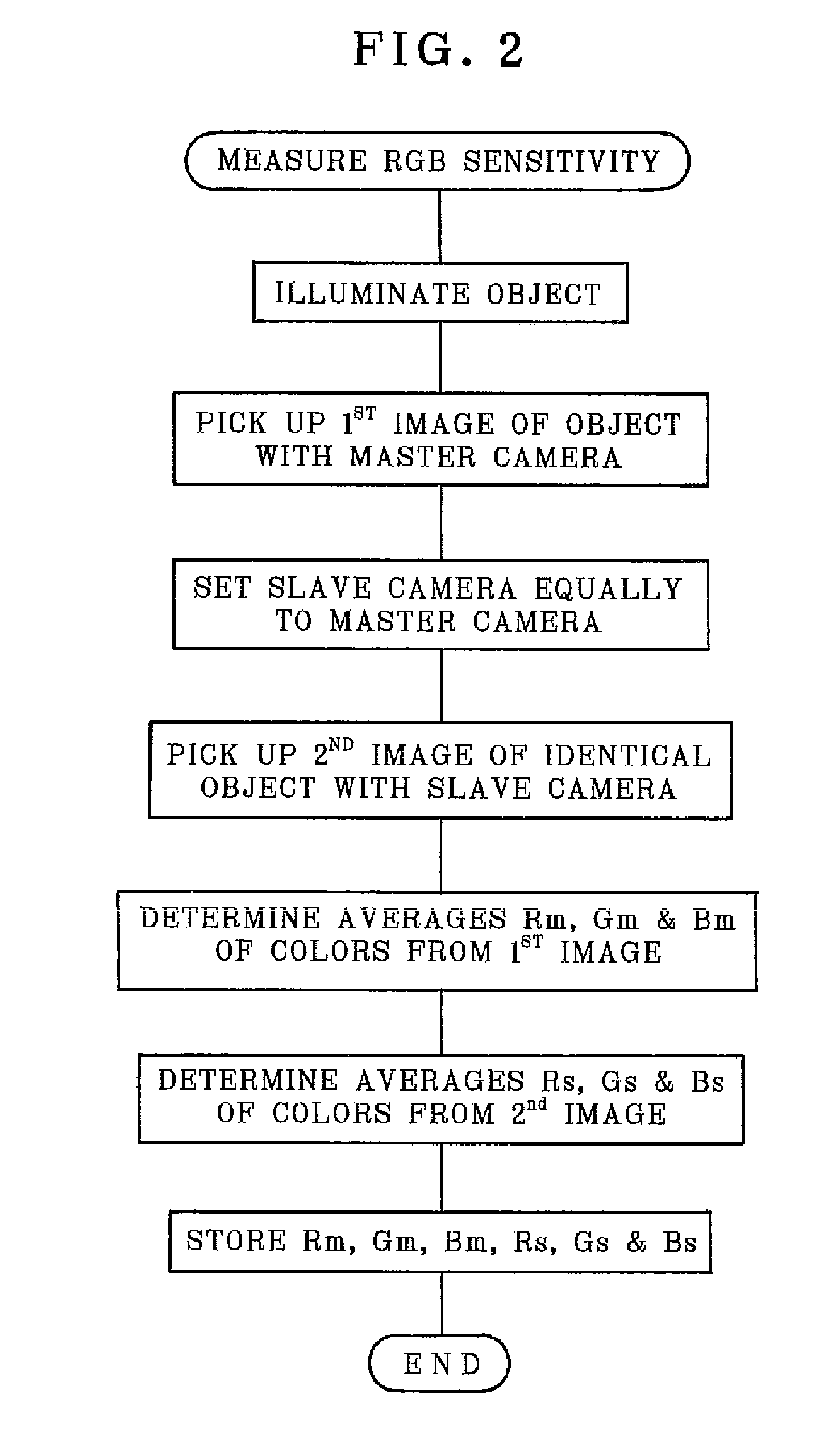
A stereoscopic camera includes a master camera for photoelectric conversion of object light to generate a first image signal with three color components G, R and B. A slave camera generates a second image signal. In an adjusting method, a first gain Dmr, Dmg and Dmb of the color components is determined according to the first image signal to correct a brightness level and white balance of the master camera, to adjust the first image signal by use thereof. A second gain Dsr, Dsg and Dsb of the color components is determined according to the first gain and color calibration information predetermined according to color sensitivity of the master and slave cameras in relation to the color components. The second image signal is adjusted by use thereof, for color matching between the first and second image signals to set equal the brightness level and the white balance.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Geodesic Distance Based Primitive Segmentation and Fitting for 3D Modeling of Non-Rigid Objects from 2D Images
ActiveUS20150317821A1Easy to operateDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementStereo cameraPoint cloud
A stereo camera system produces a stereo image pair of a cable harness, which is used to define a 3D point cloud of the cable harness at its current pose position. Pose information of specific parts of the cable harness are determined from the 3D point cloud, and the cable harness is then re-presented as a collection of primitive geometric shapes of known dimensions, whose positions and orientations follow the spatial position and orientation of the imaged cable harness. The length, position and number of geometric shapes are atomically determined from a 2D image segmentation of one of the images in the stereo image pair.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Interactive presentation system
InactiveUS7468742B2Effective spaceImprove image recognition rateTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsStereo camera3d image
The present invention discloses an interactive presentation system which allows a presenter to perform a presentation while having various interactions directly with presentation material images in real time through a gesture or / and voice. The interactive presentation system comprises: an active infrared camera; a command recognition system connected to the active infrared camera; and an image synthesis system connected to the active infrared camera and the command recognition system. The presentation system may further comprises a stereo camera set for properly synthesizing a presenter in a 3D image and a 3D motion system. By this configuration, it is possible to embody an interactive presentation system in which a command through a presenter's gesture or voice is processed in real time and the image of the presenter is synthesized in a presentation material screen in real time, and accordingly the audiovisual effect is maximized.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Volumetric sensor for mobile robotics
A volumetric sensor for mobile robot navigation to avoid obstacles in the robot's path includes a laser volumetric sensor on a platform with a laser and detector directed to a tiltable mirror in a cylinder that is rotatable through 360° by a motor, a rotatable cam in the cylinder tilts the mirror to provide a laser scan and distance measurements of obstacles near the robot. A stereo camera is held by the platform, that camera being rotatable by a motor to provide distance measurements to more remote objects.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
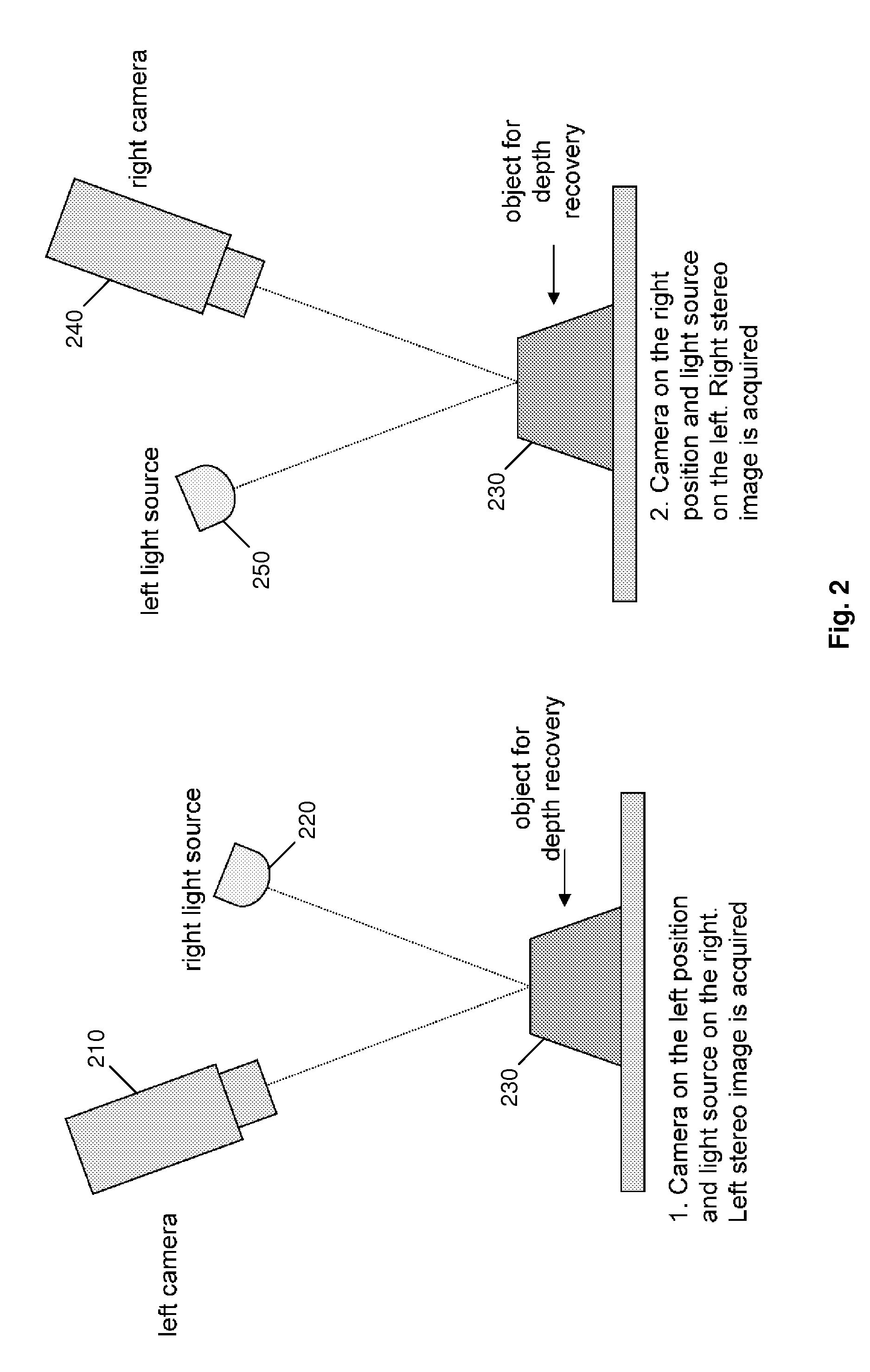
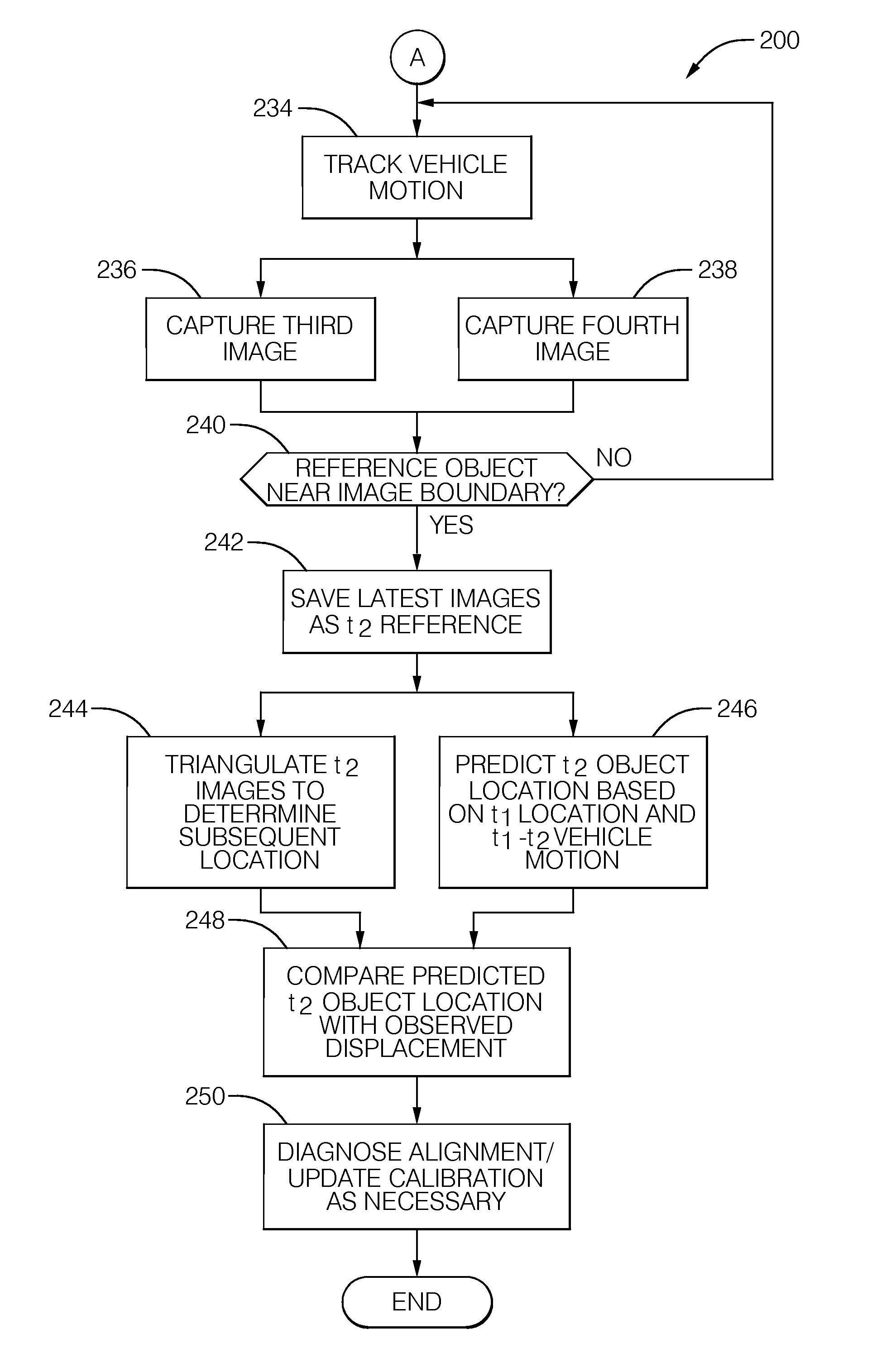
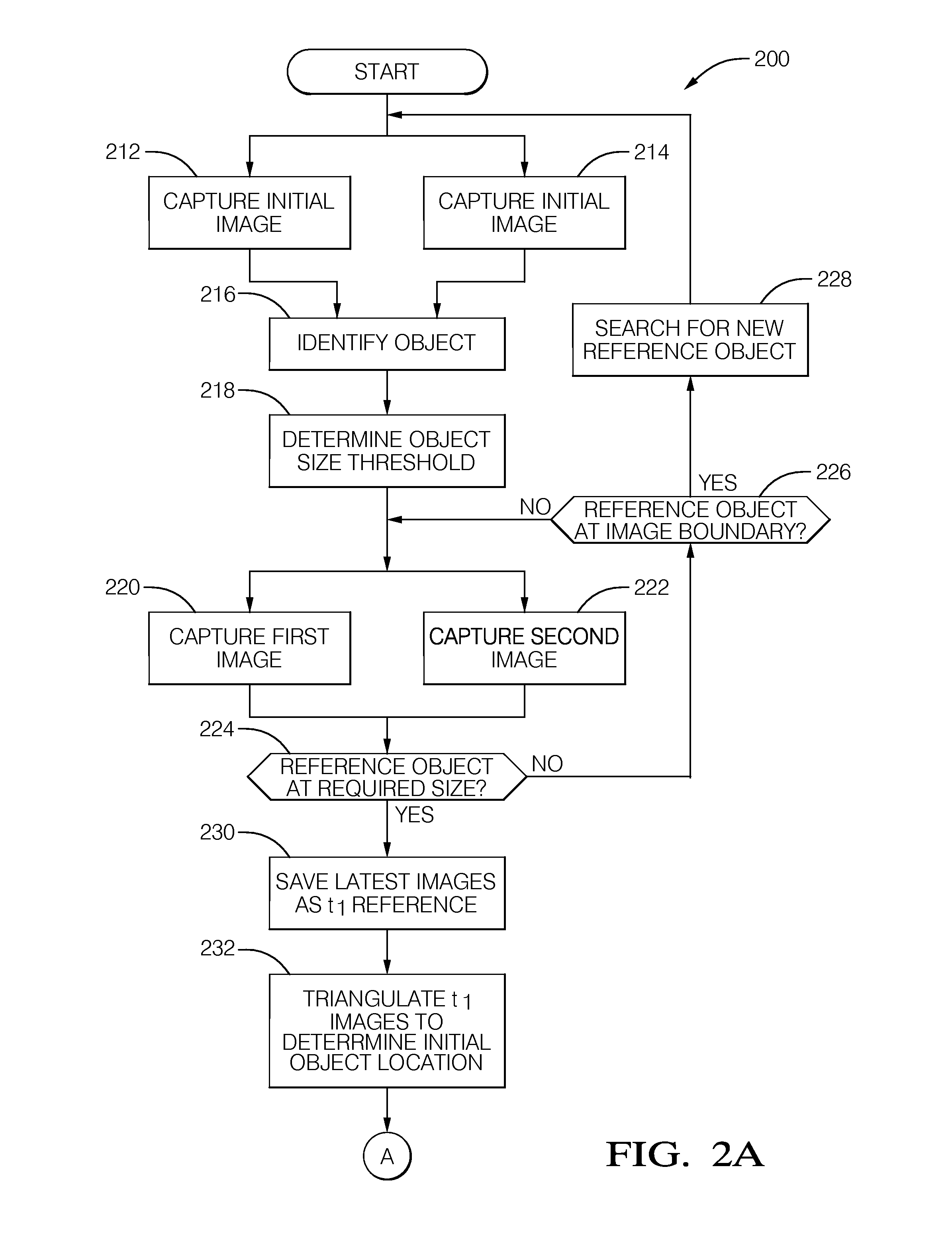
Stereoscopic camera object detection system and method of aligning the same
A system, controller, and method for aligning a stereo camera of a vehicle mounted object detection system that includes a first camera and a second camera mounted spaced apart on a vehicle. An image from each camera at two different times is used to determine an observed displacement of an object relative to the vehicle. A predicted displacement of the object relative to the vehicle is also determined using either a difference of vehicle position measured based on other vehicle measurements or GPS, or a difference of size of the object in images taken at the two different times. Alignment is provided by determining a triangulation correction based on a difference of the observed displacement and the predicted displacement to correct for misalignment of the cameras.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stereo camera and driver assistance apparatus and vehicle including the same
A stereo camera and a driver assistance apparatus and a vehicle including the same are disclosed. The stereo camera includes a first image sensor to sense an image corresponding to at least one exposure time, a second image sensor to sense images corresponding to a plurality of exposure times, and a processor to generate a disparity map and an RGB image based on the images acquired by the first and second image sensors. Consequently, it is possible to acquire the disparity map and the RGB image.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Object recognizing apparatus
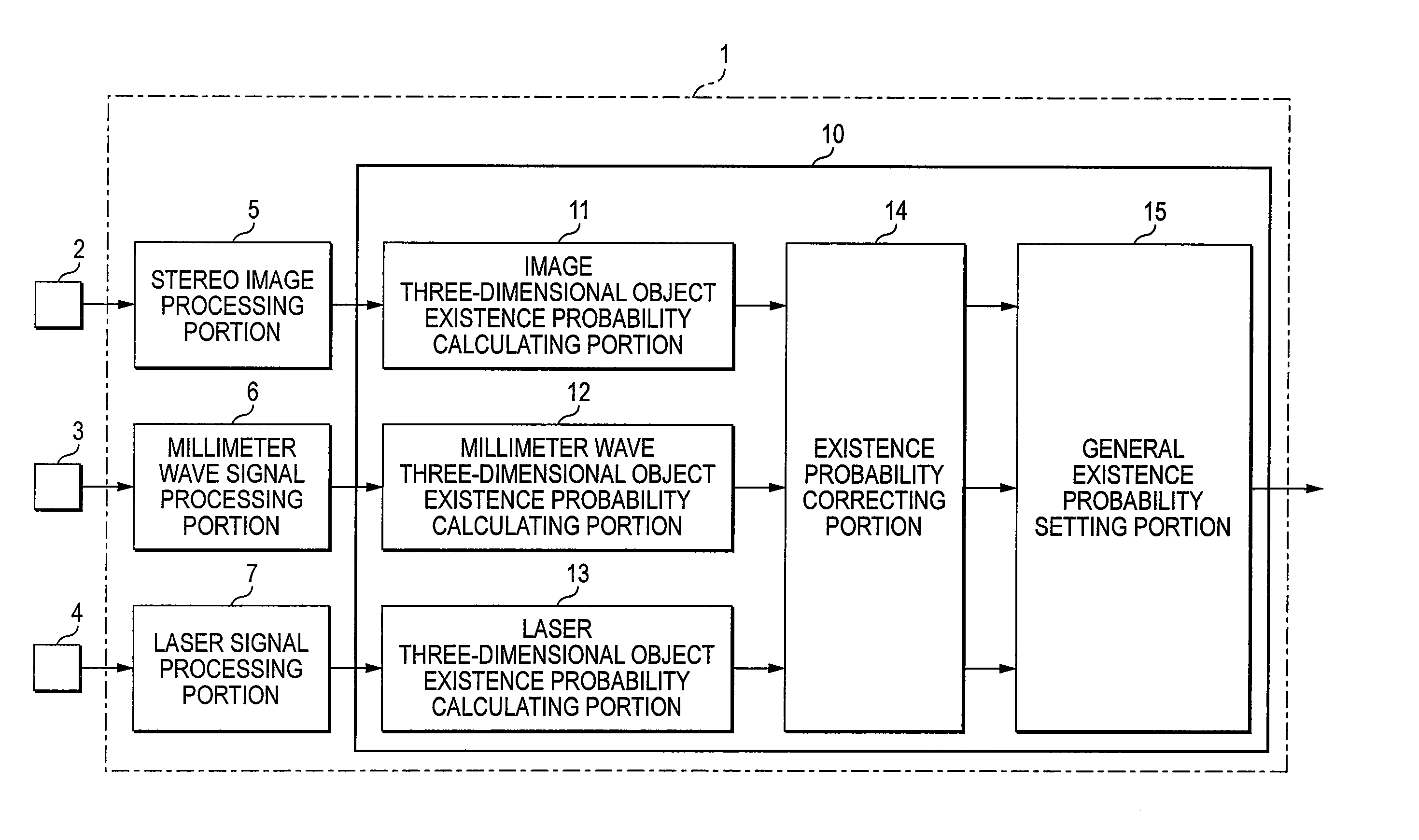
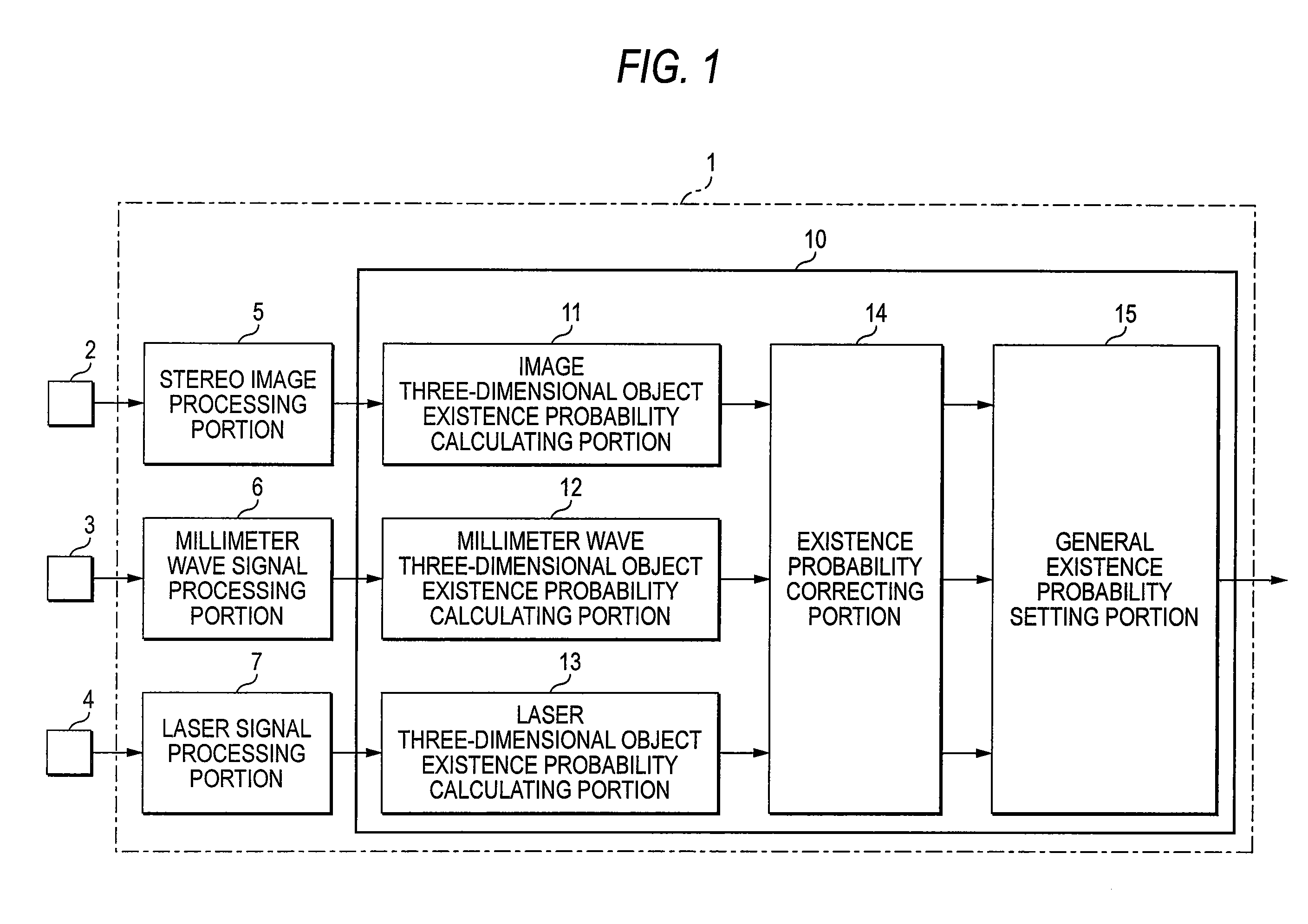
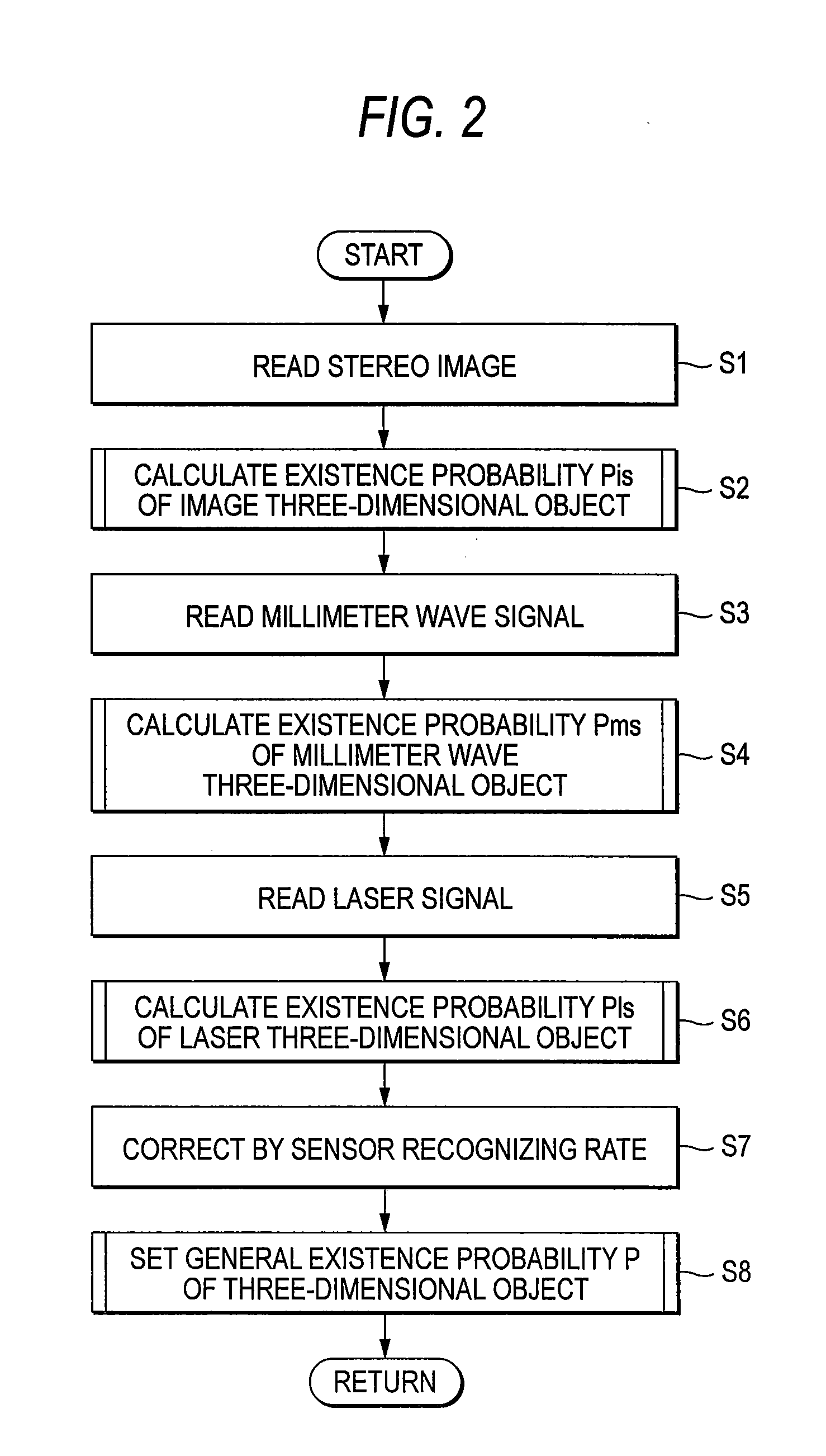
InactiveUS20070286475A1Digital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsObject basedStereo camera
An existence probability of an image object based on an image taken by a stereo camera 2 is calculated by an image object existence probability calculating portion 11, an existence probability of a millimeter wave object based on an output of a millimeter wave radar 3 is calculated by a millimeter wave object existence probability calculating portion 12, and an existence probability of a laser object based on an output of a laser radar 4 is calculated by a laser object existence probability calculating portion 13. Further, the respective existence probabilities of the image object, the millimeter wave object, the laser object are corrected based on recognizing rates of the respective recognizing sensors by an existence probability correcting portion 14, the existence probabilities after correction is fused as a fusion existence probability by a fusion existence probability calculating portion 15, thereby, a control of avoiding contact with a hazard or alarming or the like is made to be able to execute by a firm and optimum timing.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Stereoscopic camera and parallax self-adapting regulating method thereof
ActiveCN101424863APrecise adjustment of parallaxTelevision system detailsColor television detailsParallaxStereo camera
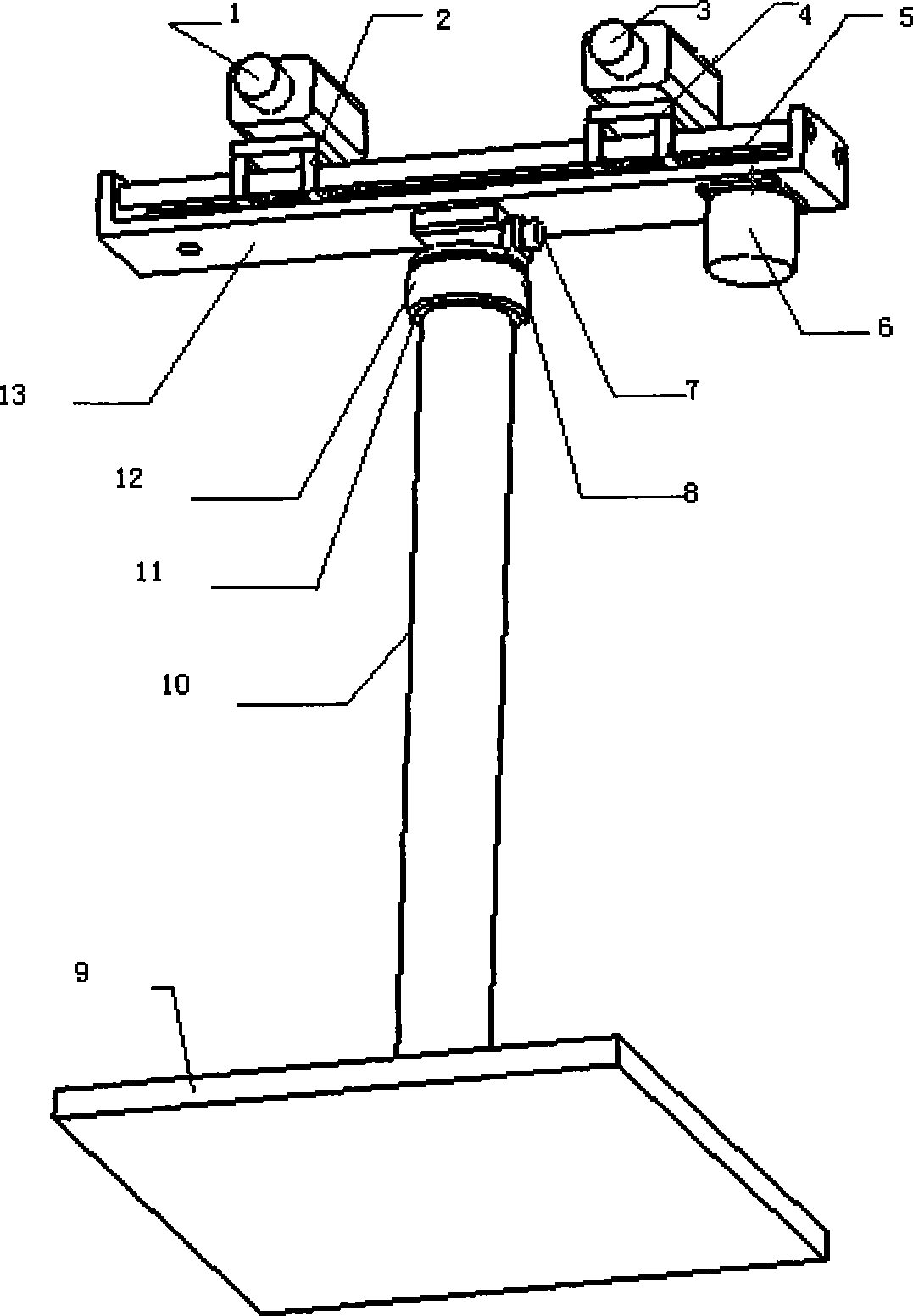
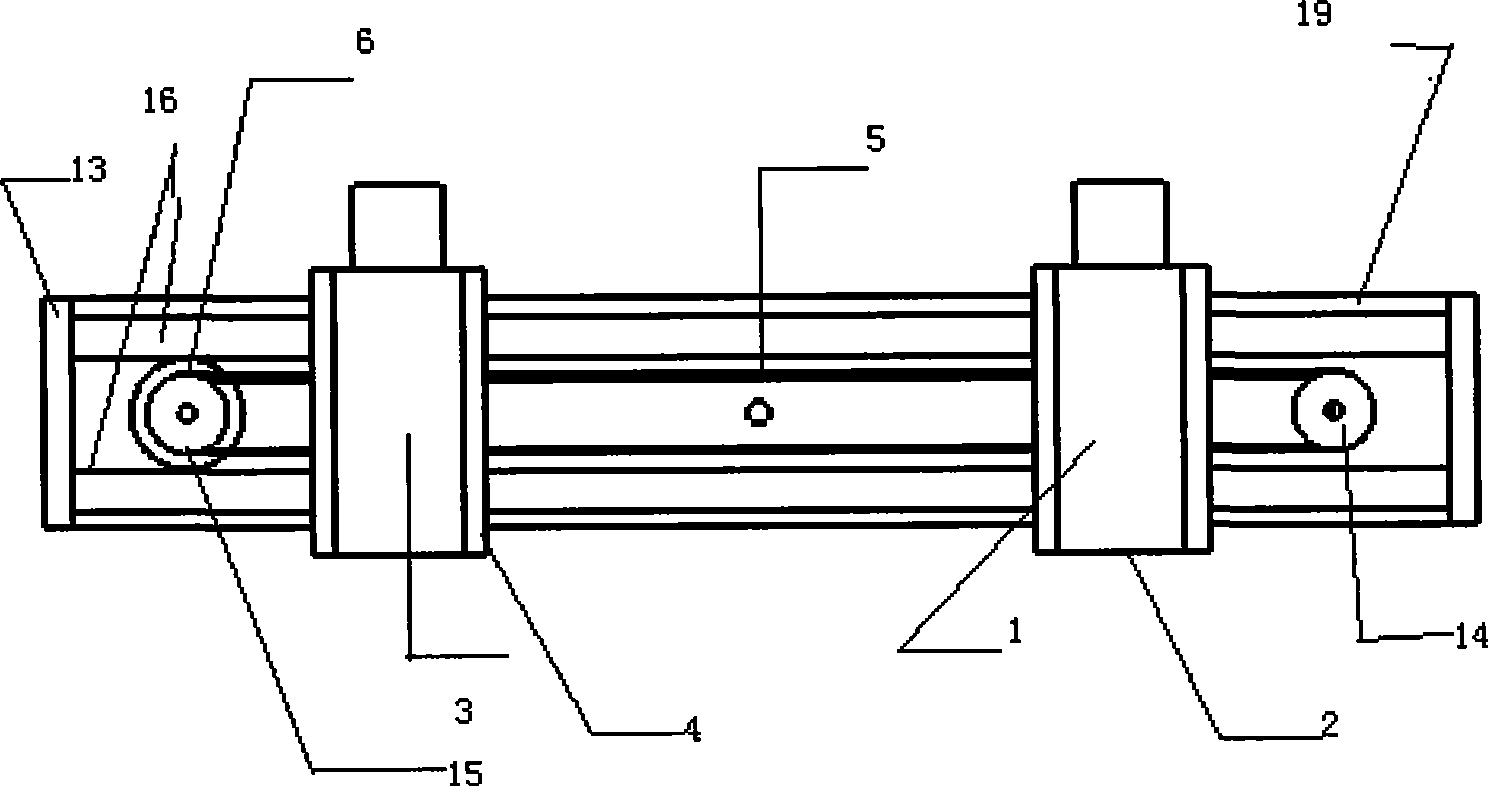
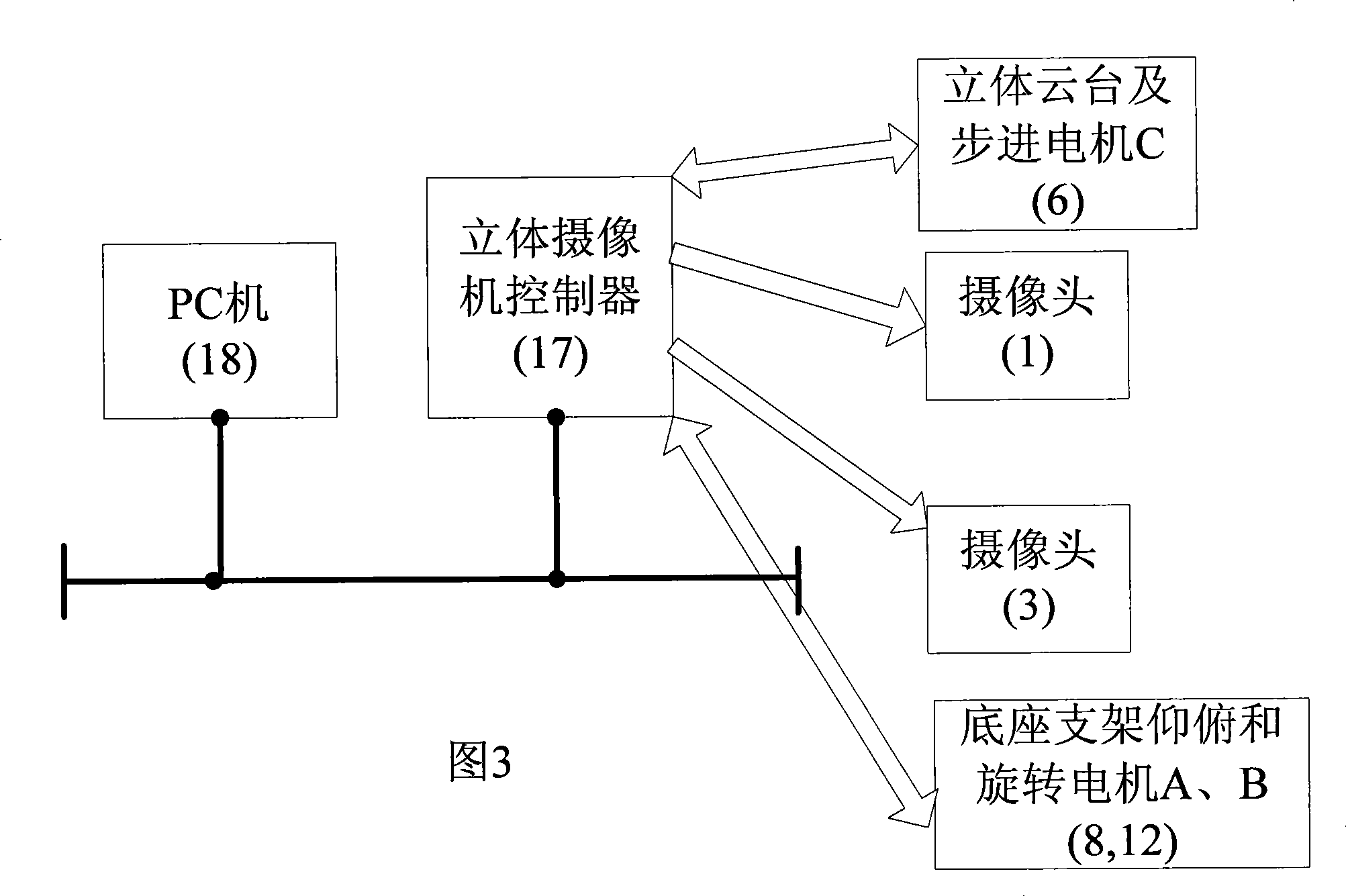
The invention relates to a stereo camera and a self-adapting parallax adjusting method. The camera is composed of two pick-up heads mounted on a machinery platform mechanism. The opposite and synchronous movement of the two pick-up heads on the control platform can be controlled through a stepper motor, thereby the parallax of the two pick-up heads is changed. Each pick-up head is provided with an electronic zooming device; the electronic zooming device can synchronously zoom under the control of a controller and control the stepper motor to accurately control the distance of the pick-up heads according to the control algorithm while the controller zooms, so that the focus of the pick-up heads is changed within a great extent; the parallax of an obtained stereo image can be always kept in the ideal state, thereby the problem of larger parallax change can not generate due to extensive zoom. The invention has the advantages of simple structure and cheap cost and can achieve the accurate and real-time adjustment of the parallax of the stereo camera within the larger zooming scope.
Owner:JIANGSU XINGHUA RUBBER BELT
Method and apparatus for estimating position
ActiveUS20150213617A1Cancel noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionStereo camera
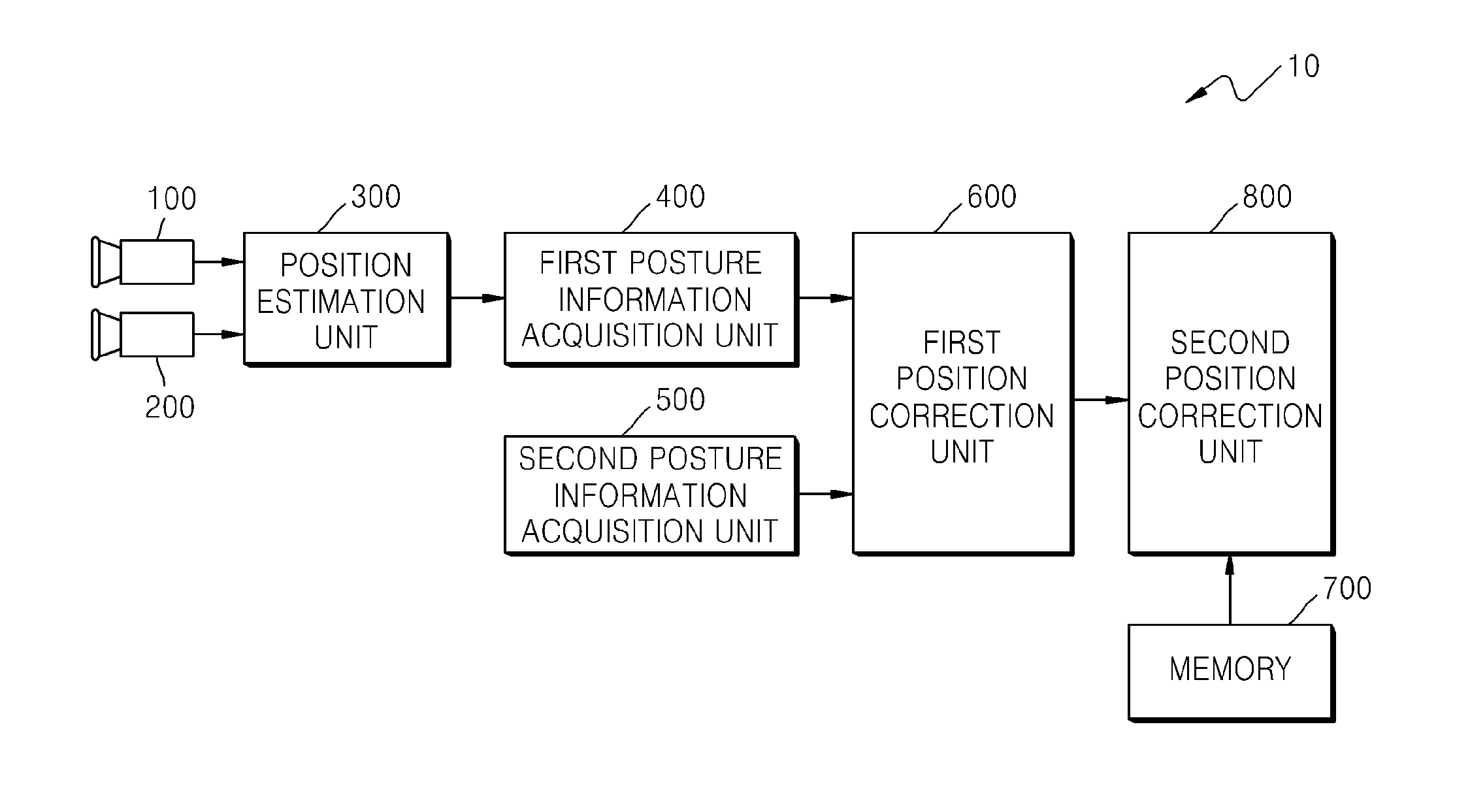
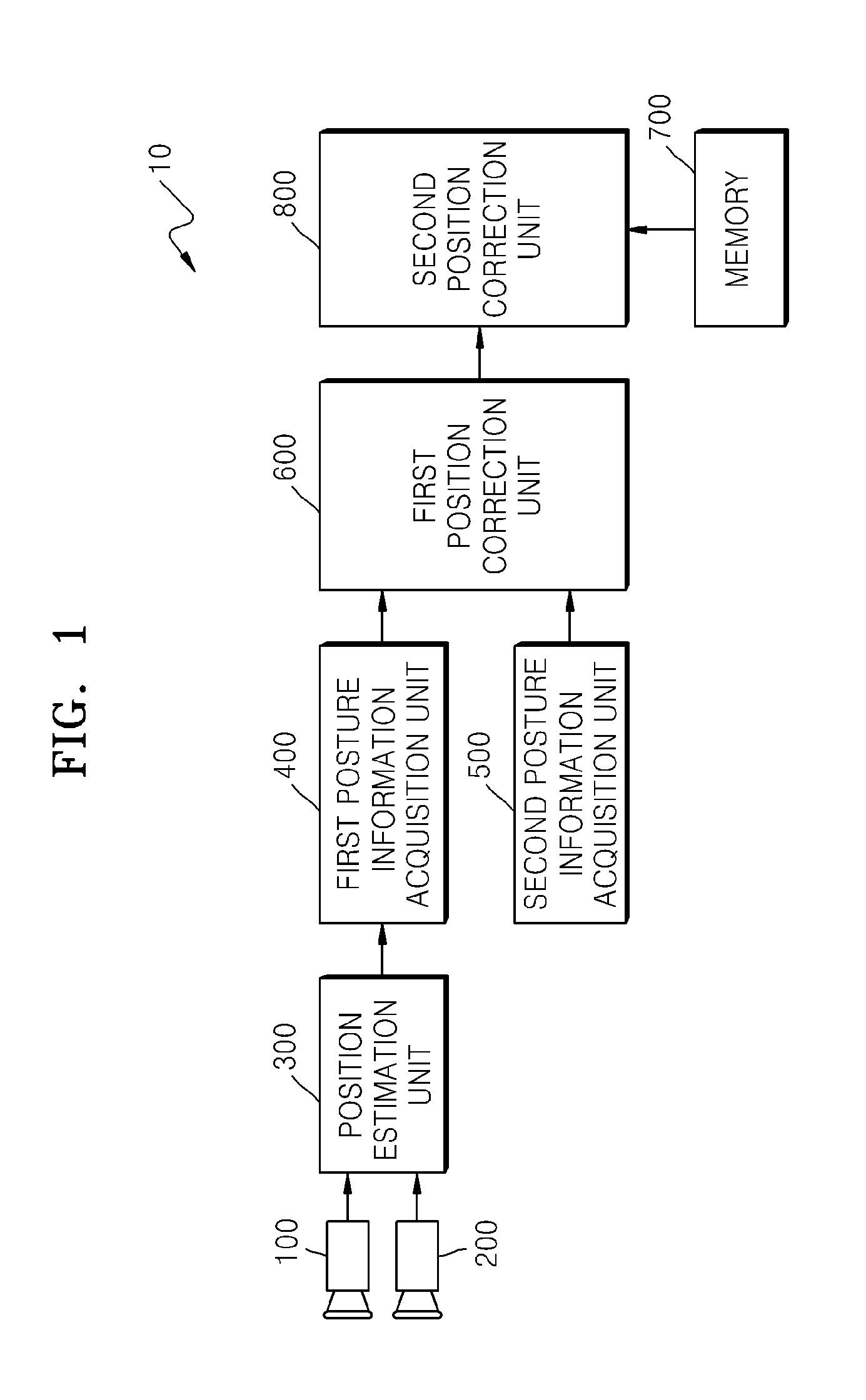
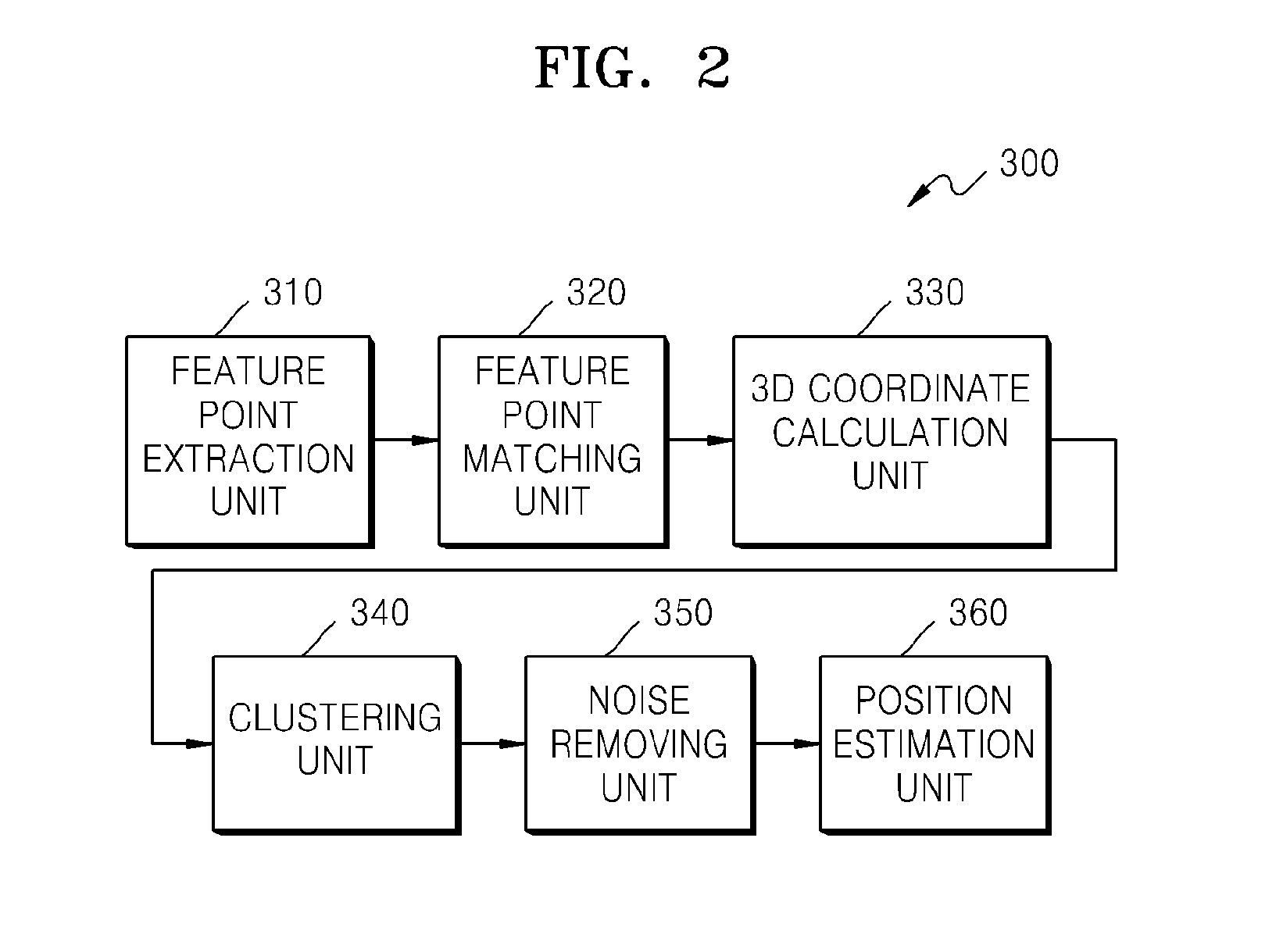
Provided is a position estimation apparatus including: a position estimation unit configured to estimate a position of a moving object driven on an arbitrary lane according to an image frame captured by a stereo camera provided in the moving object; a posture information acquisition unit configured to obtain first posture information of the moving object from the estimated position and second posture information of the moving object at a point of time of the stereo camera capturing the image frame; a position correction unit configured to calculate: a probability distribution for a current position of the moving object by using the first posture information and the second posture information, and configured to correct a first probability of the probability distribution for the current position as a corrected position of the moving object; and a composite probability distribution based on a probability of a lane section of the arbitrary lane from a lane probability distribution chart and the corrected position output from the first position correction unit and configured to re-correct a second probability of the composite probability distribution as a final position of the moving object.
Owner:HANWHA AEROSPACE CO LTD
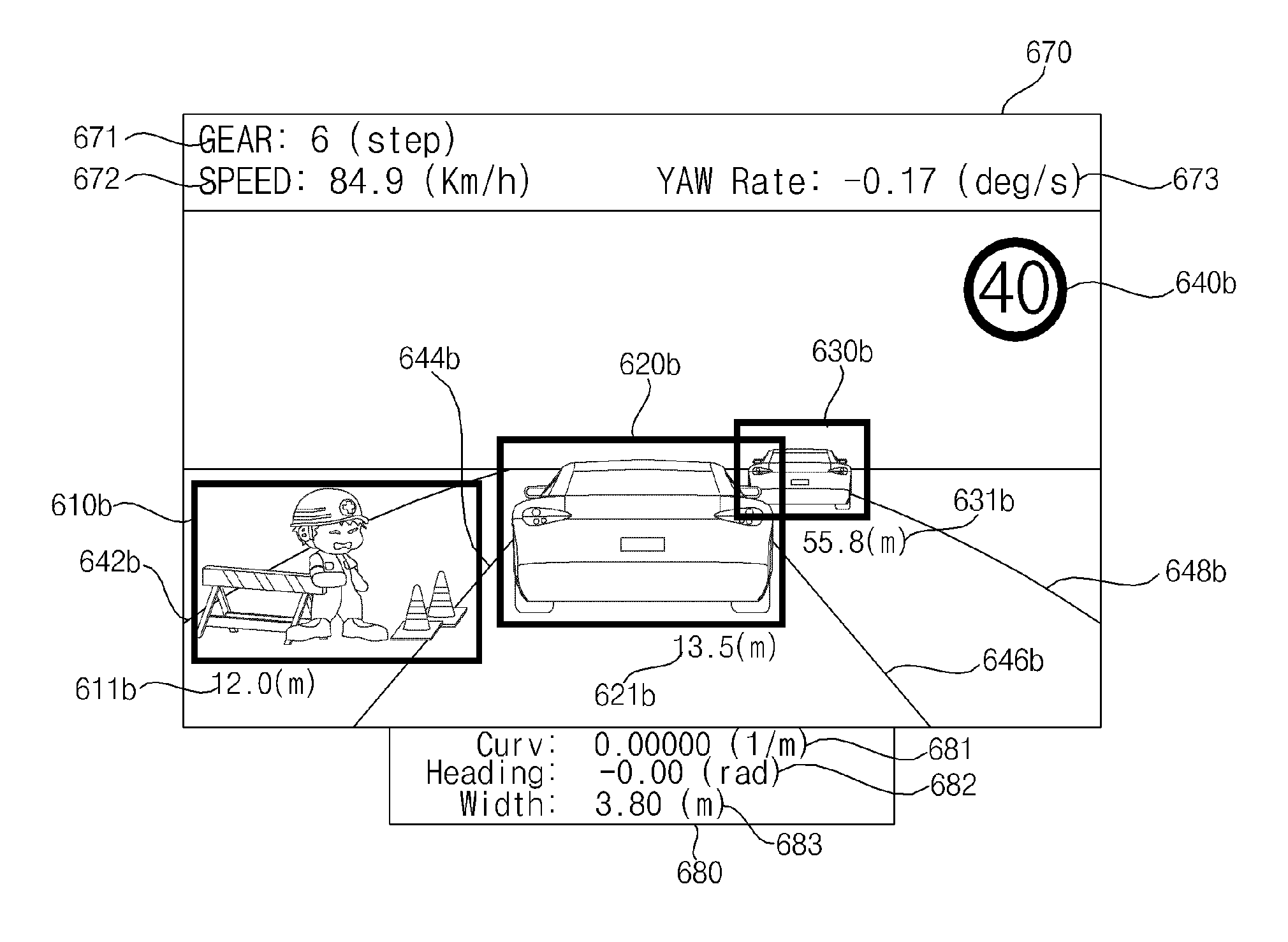
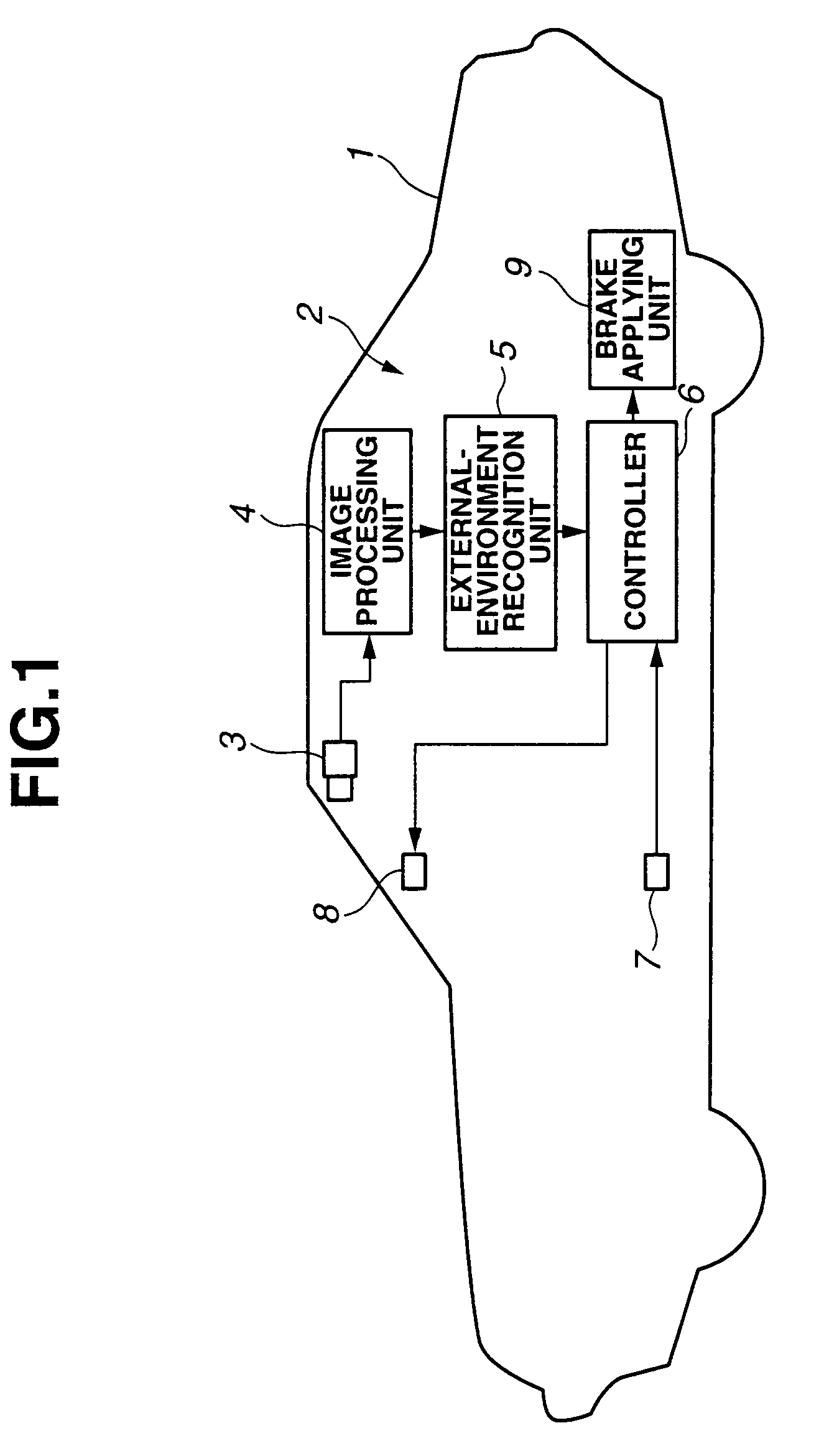
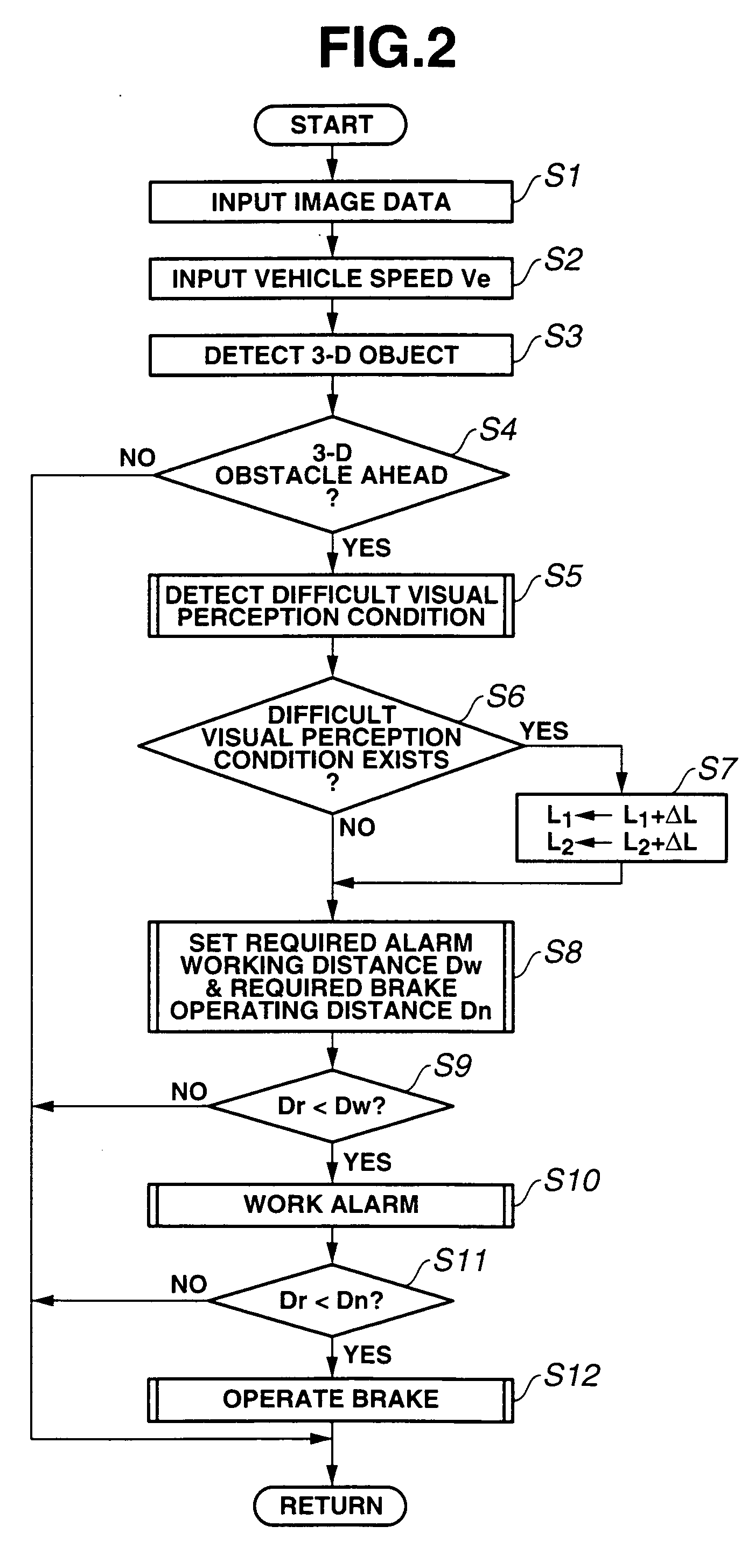
Vehicle driving assist system
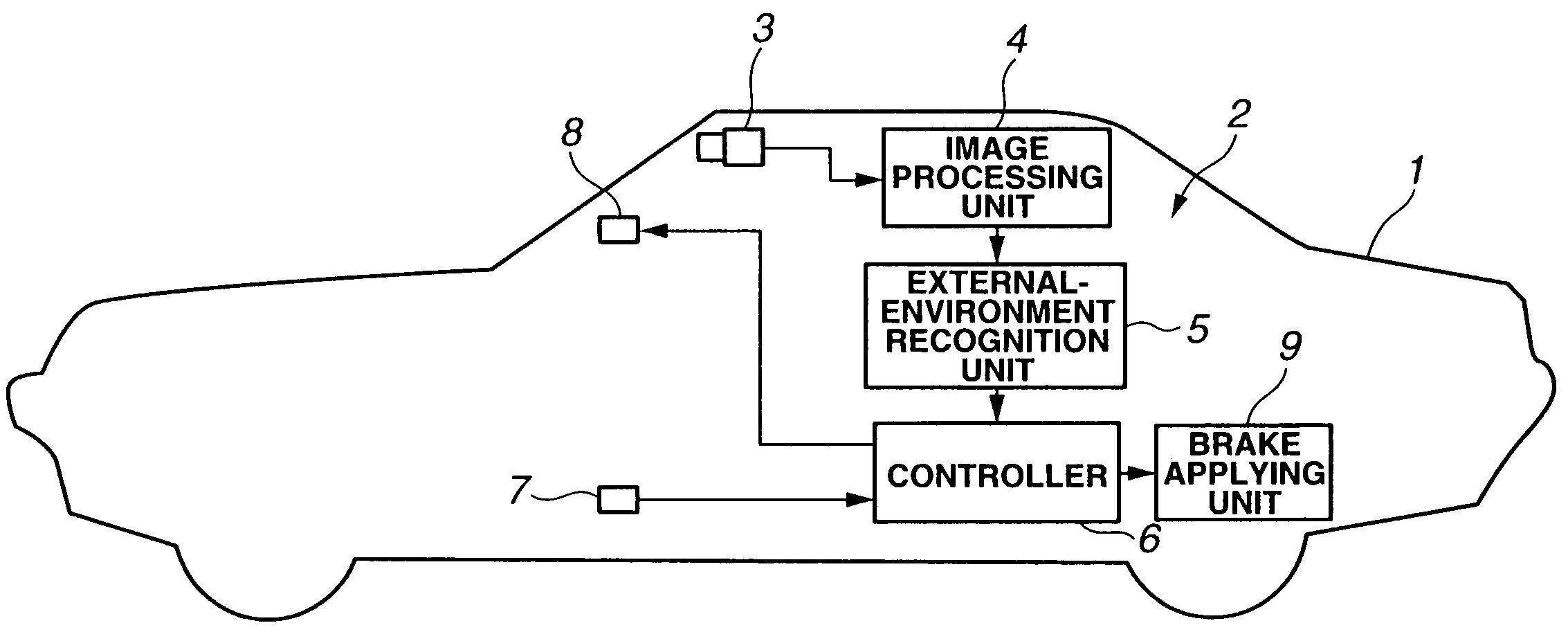
ActiveUS20050143887A1Decrease in perception abilityDigital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsStereo cameraVehicle driving
In a vehicle driving assist system, an external environment recognition unit detects a 3-D obstacle inhibiting the driving direction of the vehicle based on an image captured by a stereo camera and determines whether the image ahead of the vehicle is in a condition that makes visual perception of the 3-D obstacle difficult. A controller calculates a required alarm working distance between the vehicle and the 3D obstacle, at which an alarm unit is worked when the vehicle approaches the 3D obstacle, and a required brake operating distance, at which a brake is operated by a brake applying unit, based on a vehicle traveling speed. If it is determined that an external environment is in a condition that makes visual perception difficult, the required working and operating distances are extended by predetermined values to set the working and operating timings earlier.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
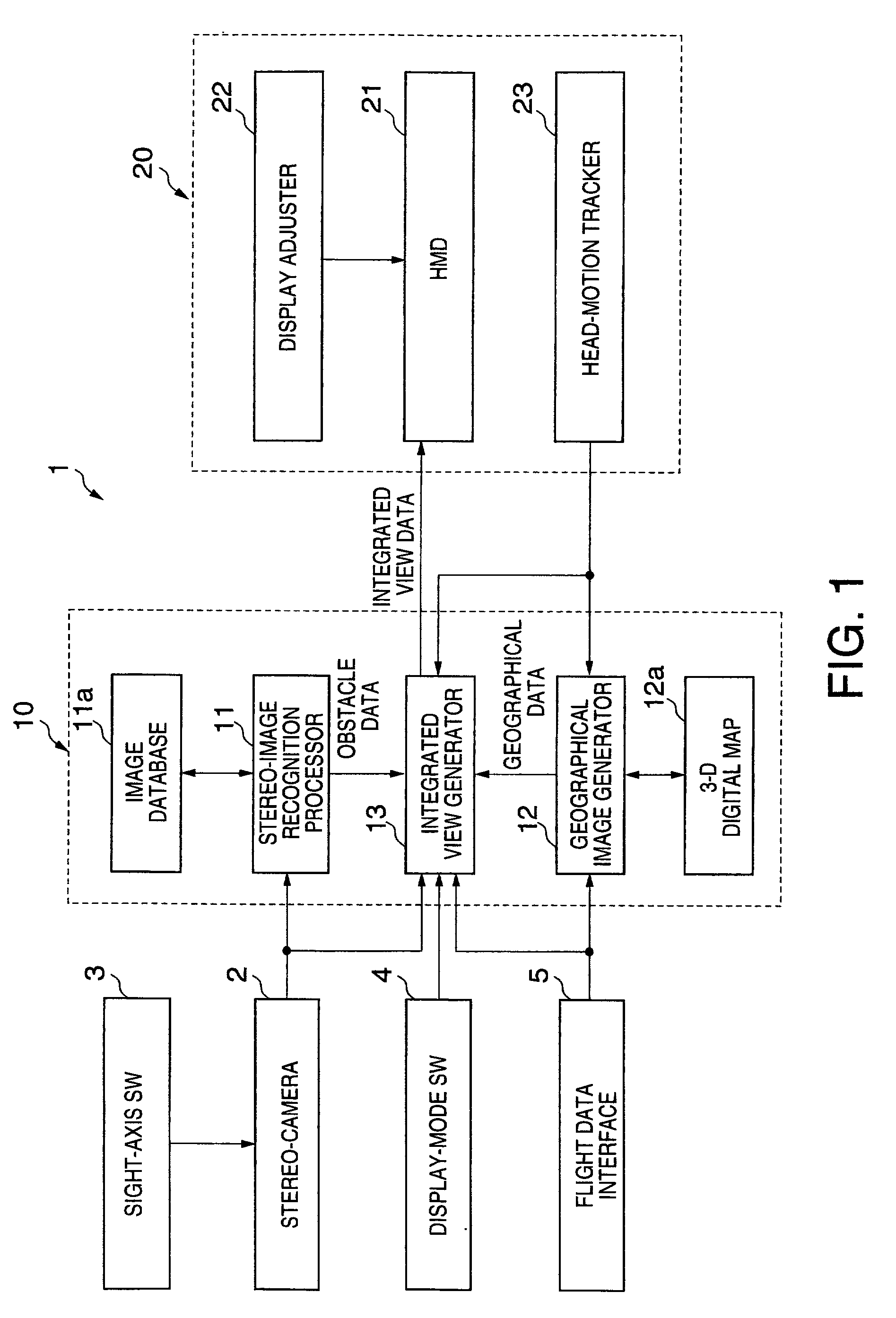
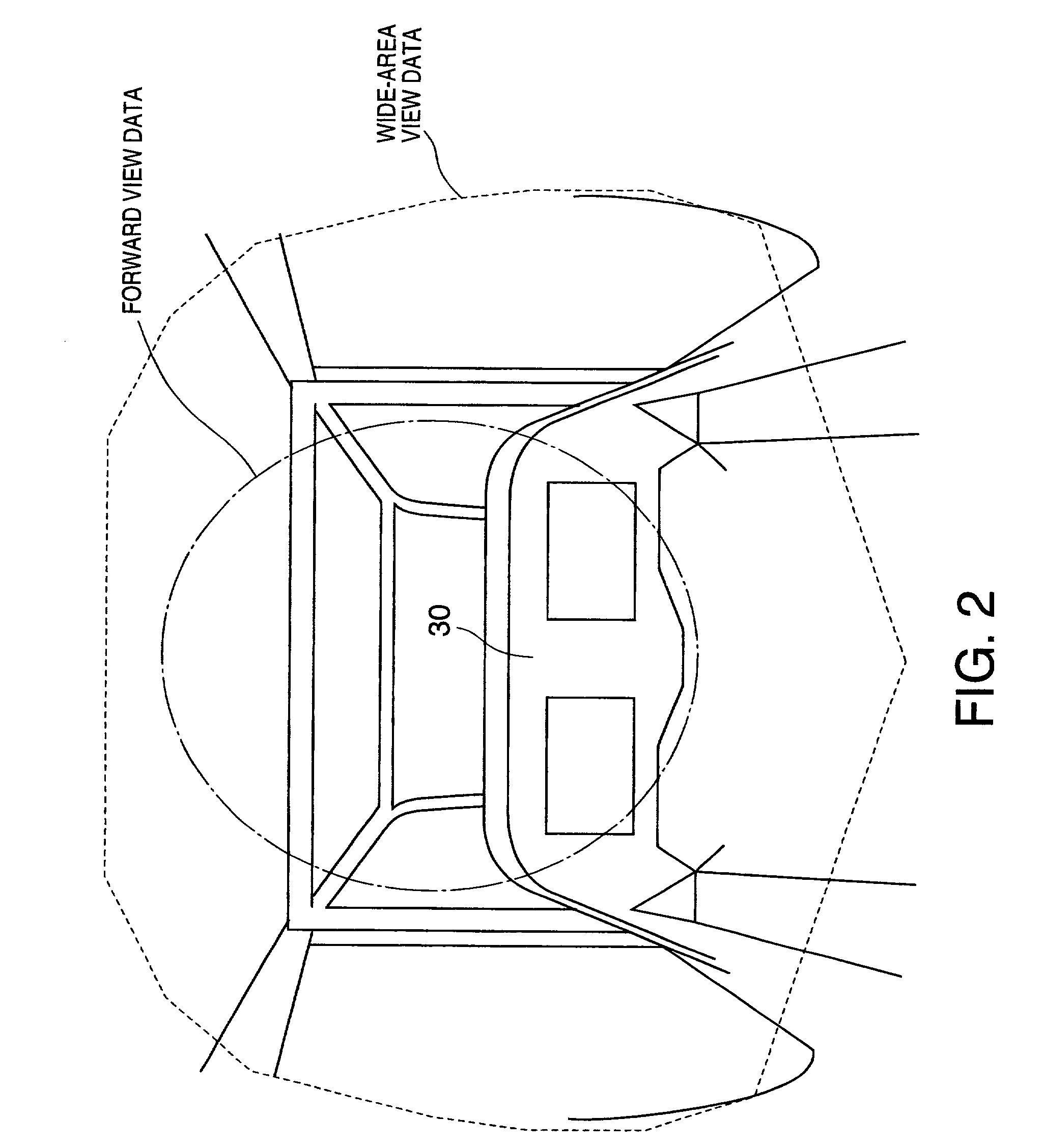
Integrated vision system
InactiveUS20010048763A1Aircraft componentsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementStereo cameraDisplay device
An integrated vision system is disclosed. Images of outside area are taken by at least one stereo-camera installed in a vehicle. A pair of images taken by the stereo-camera are processed by a stereo-image recognizer for recognition of objects that are obstacles to the front, thus generating obstacle data. Integrated view data including three-dimensional view data are generated by an integrated view data generator based on the pair of images and the obstacle data. The integrated view data are displayed by an integrated image display as visible images to crew on the vehicle.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Calibration method for relative attitude of binocular stereo camera and inertial measurement unit
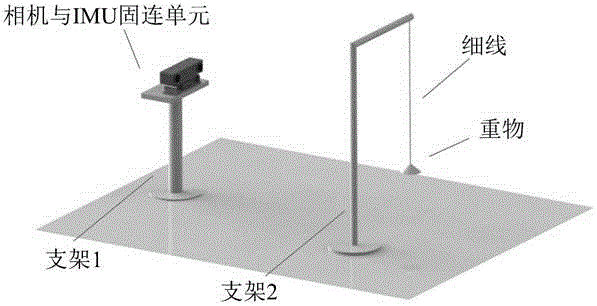
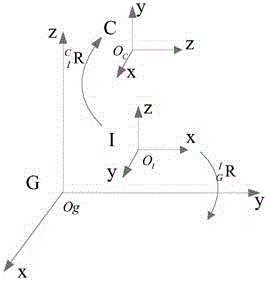
InactiveCN105606127AReduce mistakesImprove robustnessMeasurement devicesStereo cameraReference vector
The invention discloses a simple and feasible calibration method for the relative attitude of a binocular stereo camera and an inertial measurement unit on the basis of the absolute gravity direction. The method comprises the steps that a gravity direction vector serves as a reference vector, expressions of the gravity direction vector under a camera coordinate system and under an IMU coordinate system are solved respectively to obtain the expressions of the same vector under the two different coordinate systems, and then the attitude change relationship between the two coordinate systems can be solved; finally, precision verification is performed through reprojection errors, and application of the calibration method in a visual odometer is supplied. Experiments show that the relative attitude between the camera and the IMU can be accurately solved through the method. The method can be used for assisting in vision positioning of mobile robots and spherical robots.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com