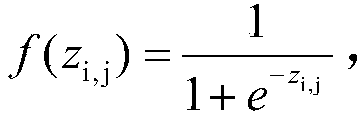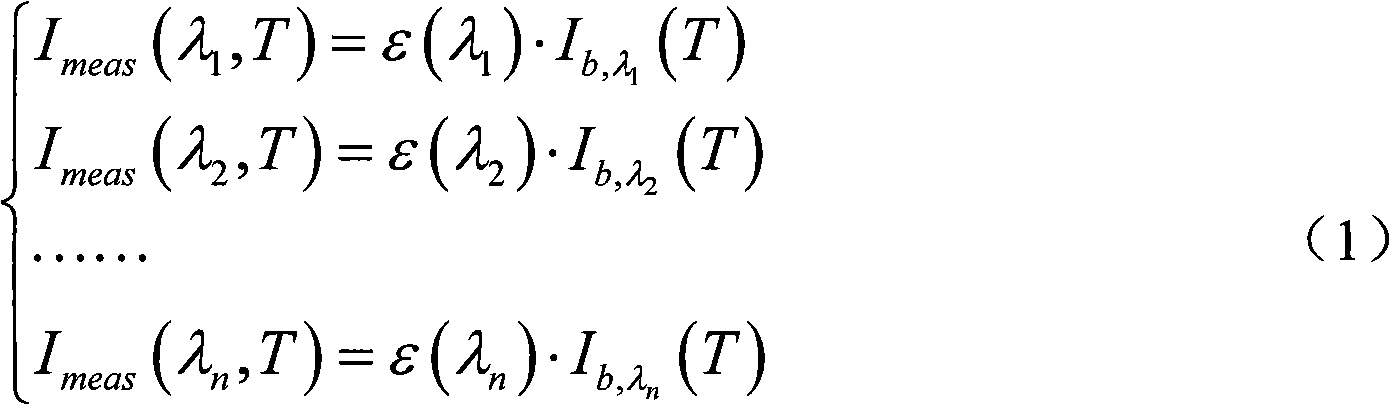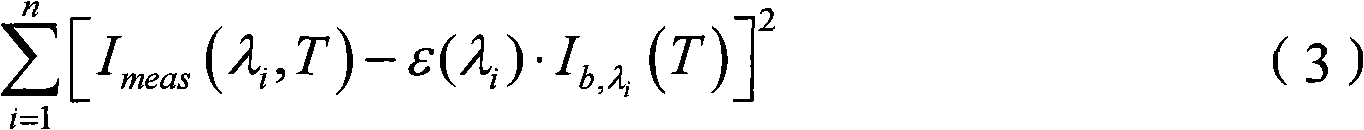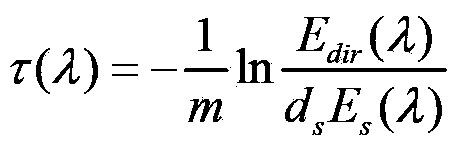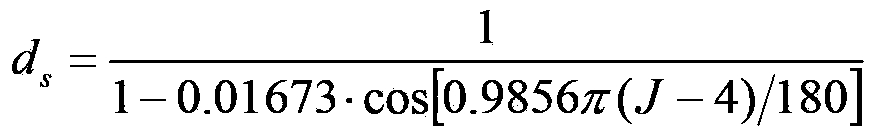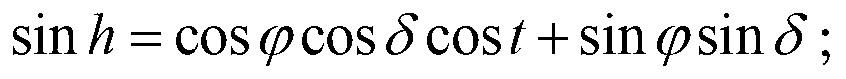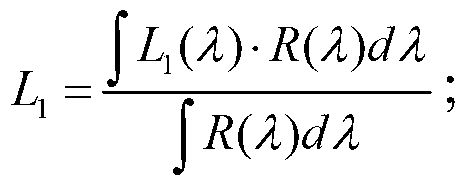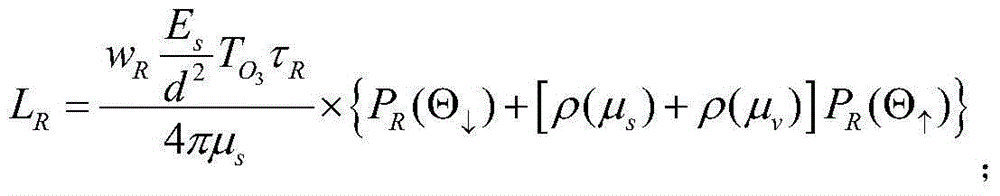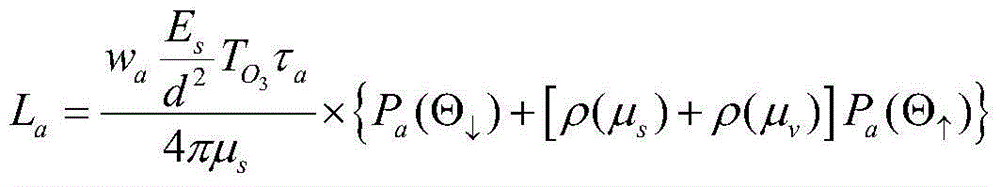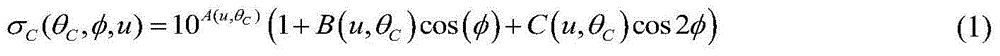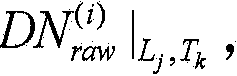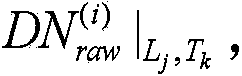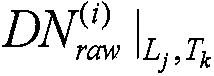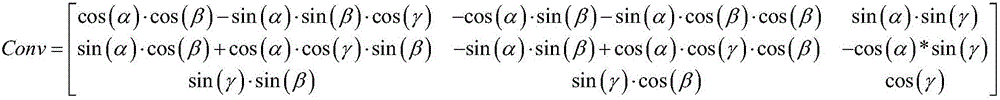Patents
Literature
307 results about "Radiometric calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiometric calibration is a general term used in science and technology for any set of calibration techniques in support of the measurement of electromagnetic radiation and atomic particle radiation. These can be for instance, in the field of Radiometry or the measurement of ionising radiation radiated from a source.
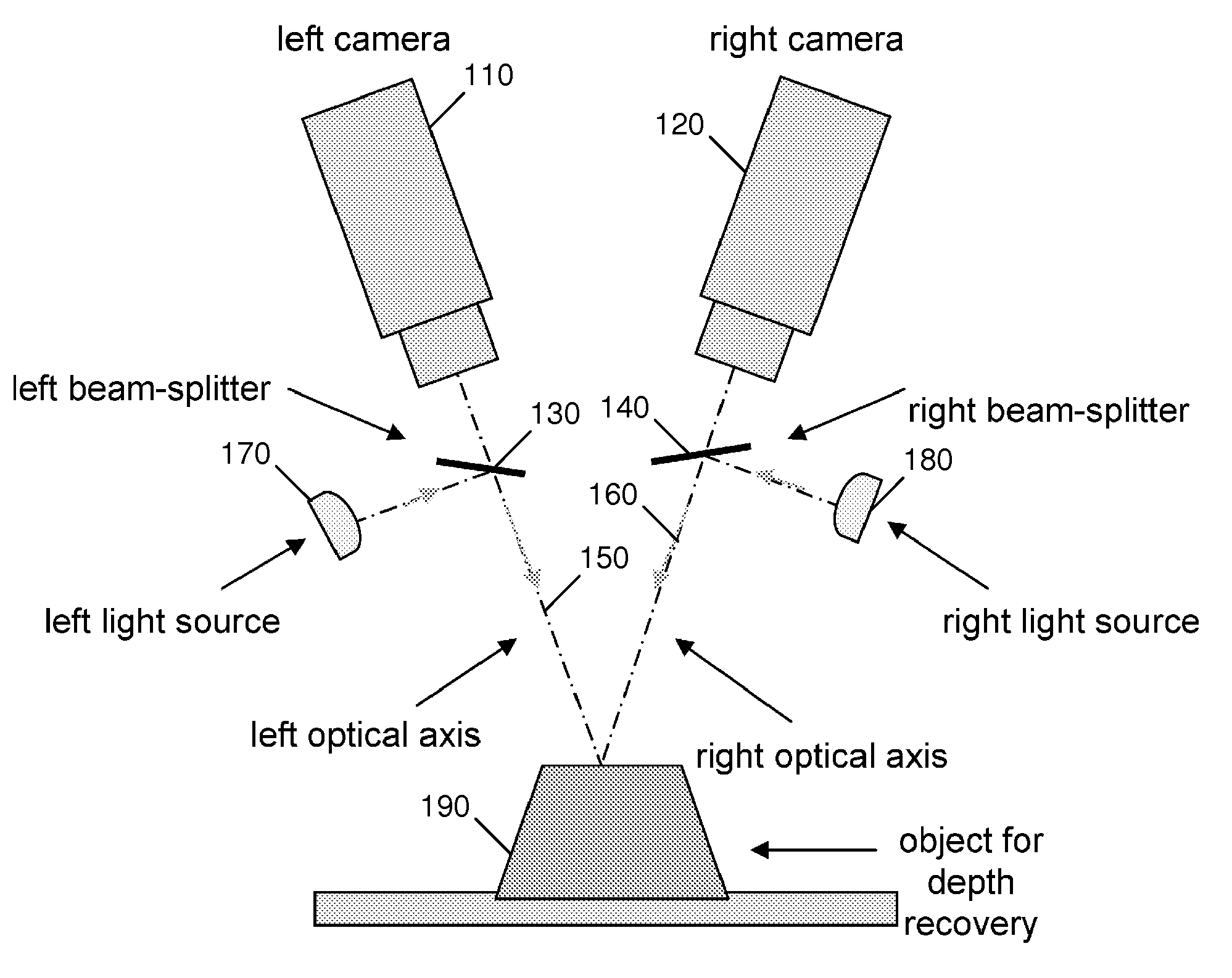
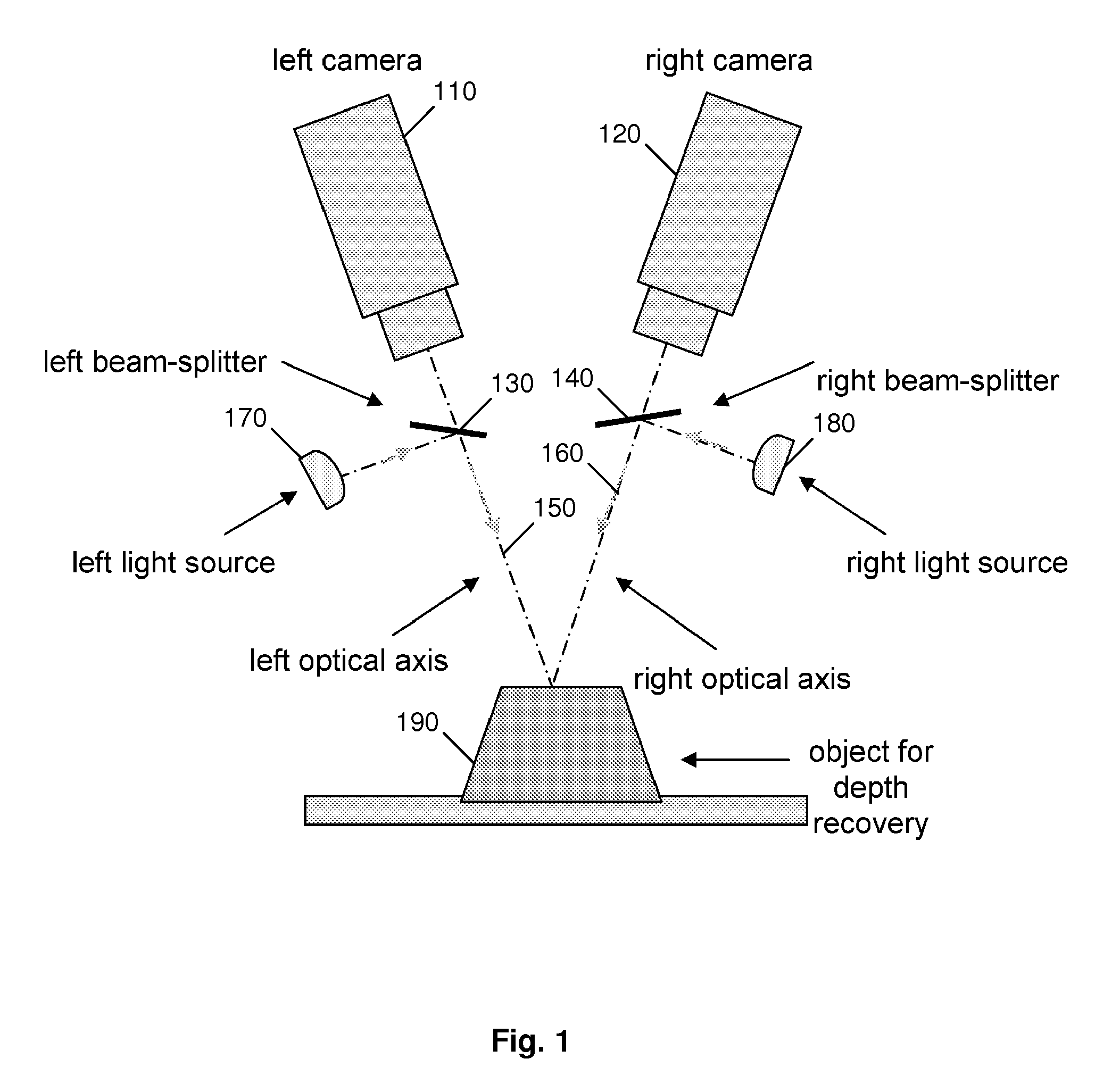
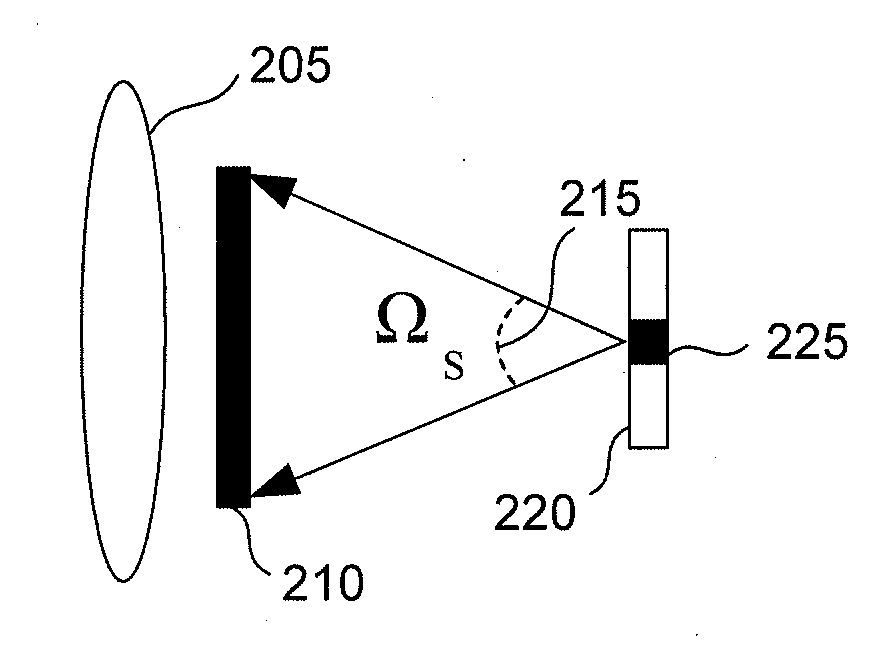
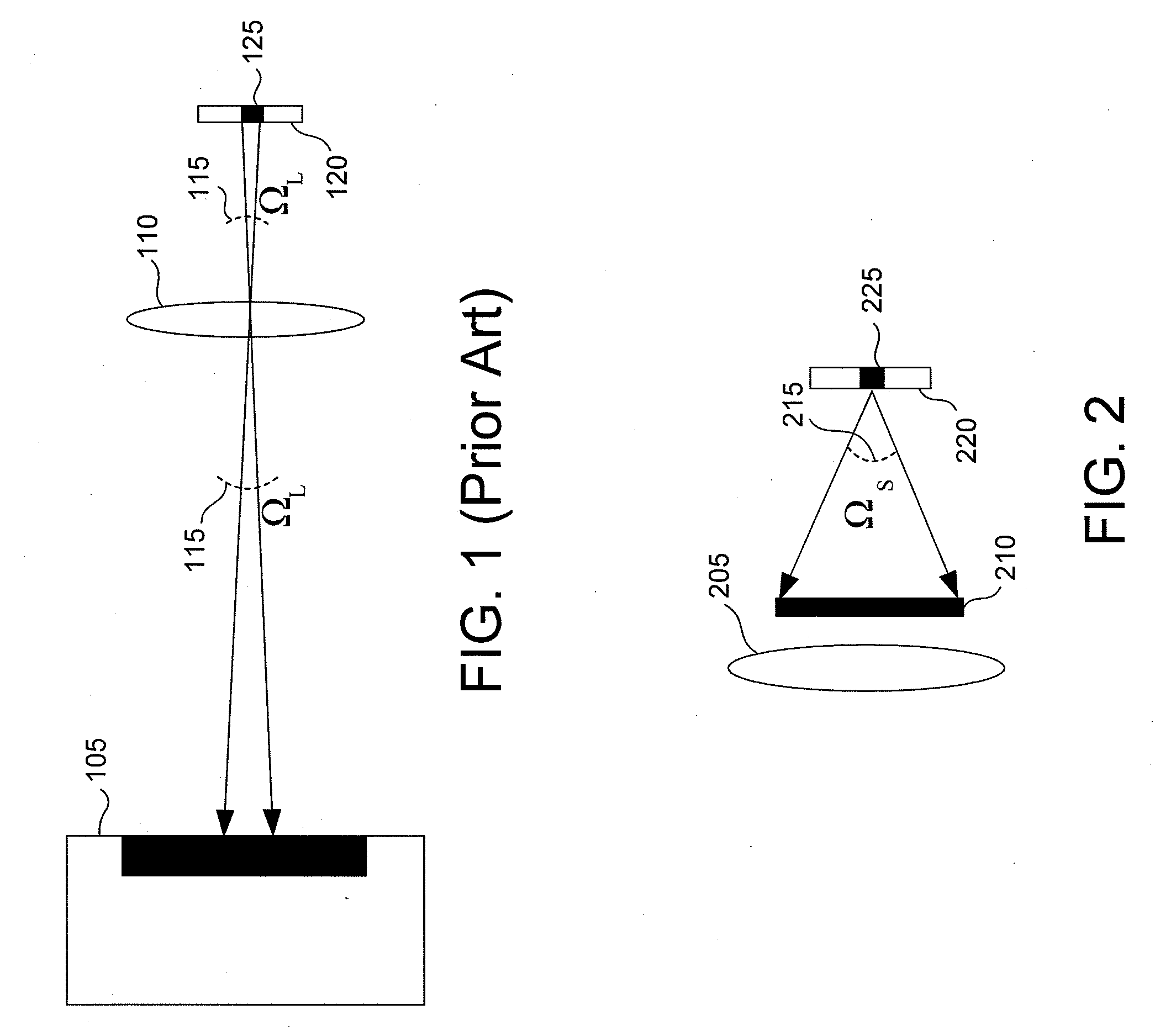
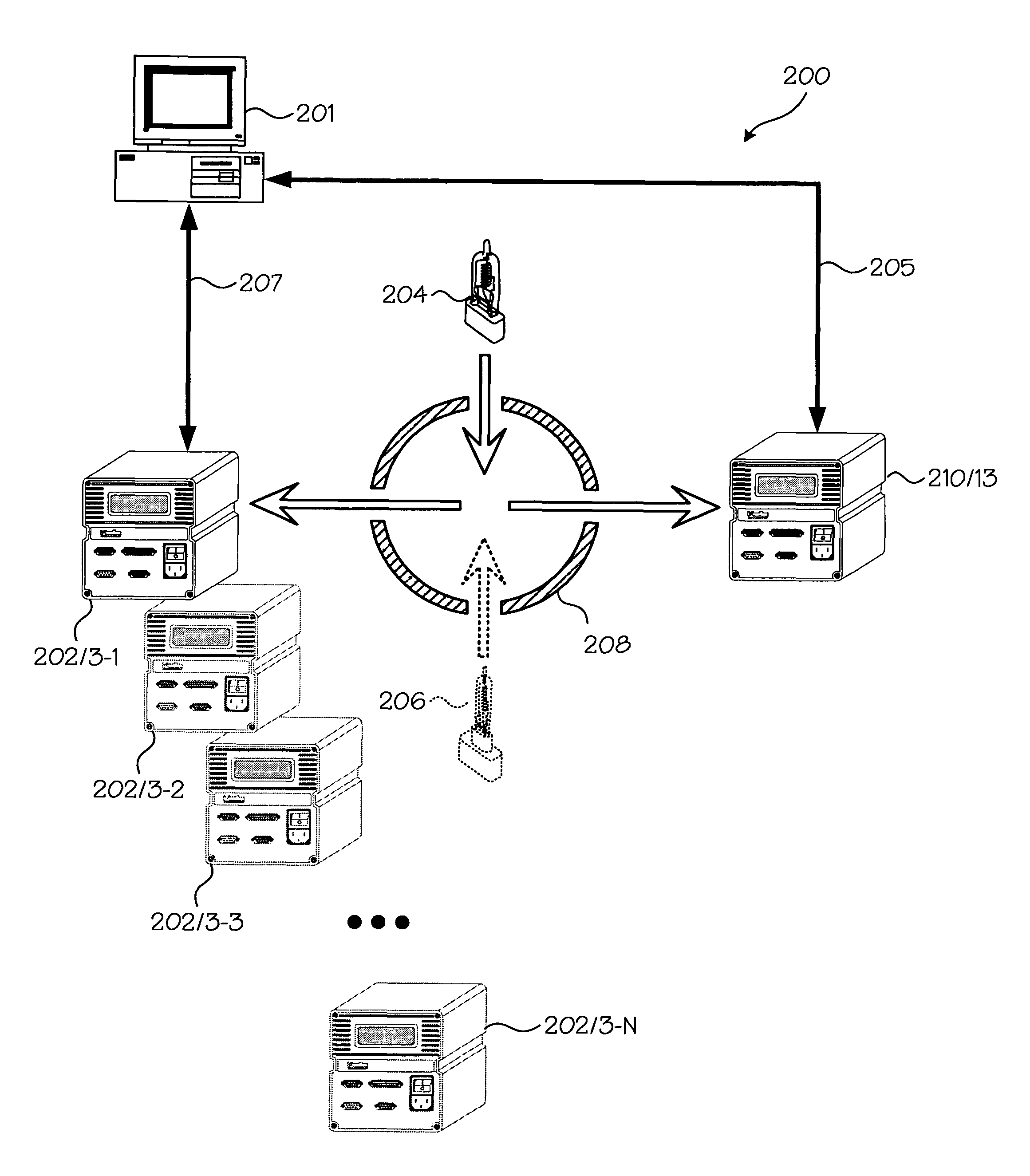
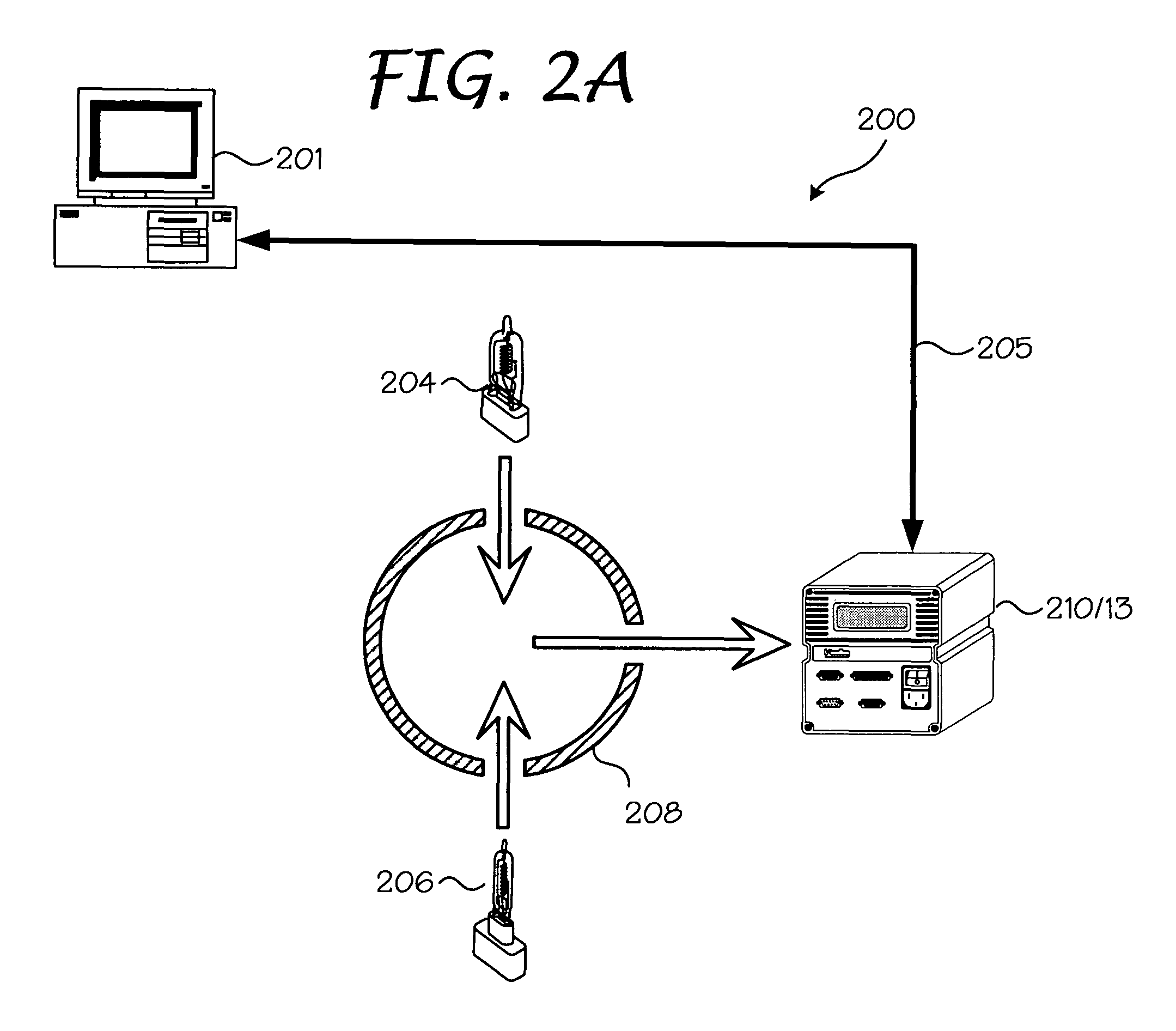
Fast Three Dimensional Recovery Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20080123937A1Easy to useSimple setup and calibration processImage enhancementImage analysisRecovery methodMetrology
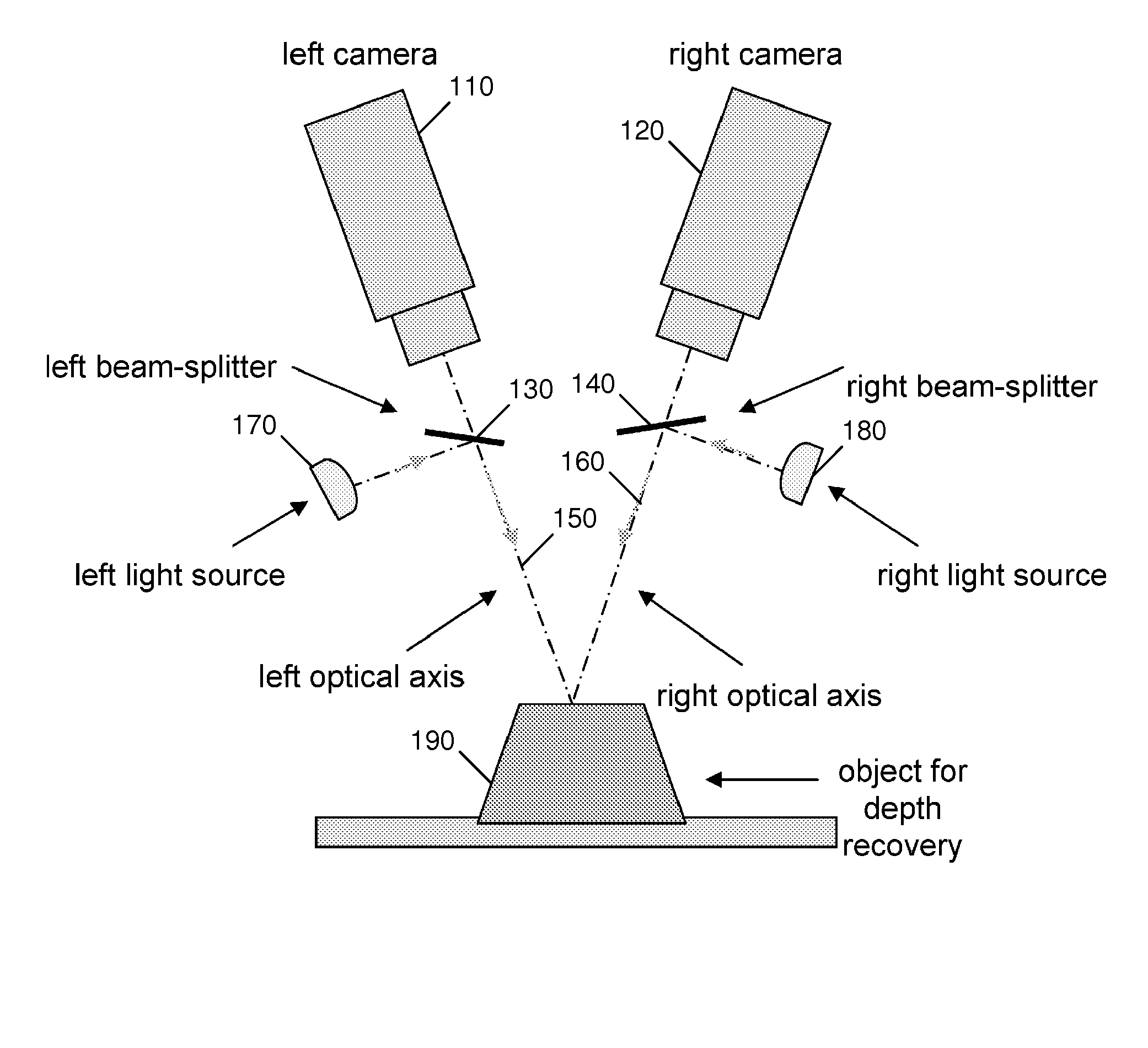
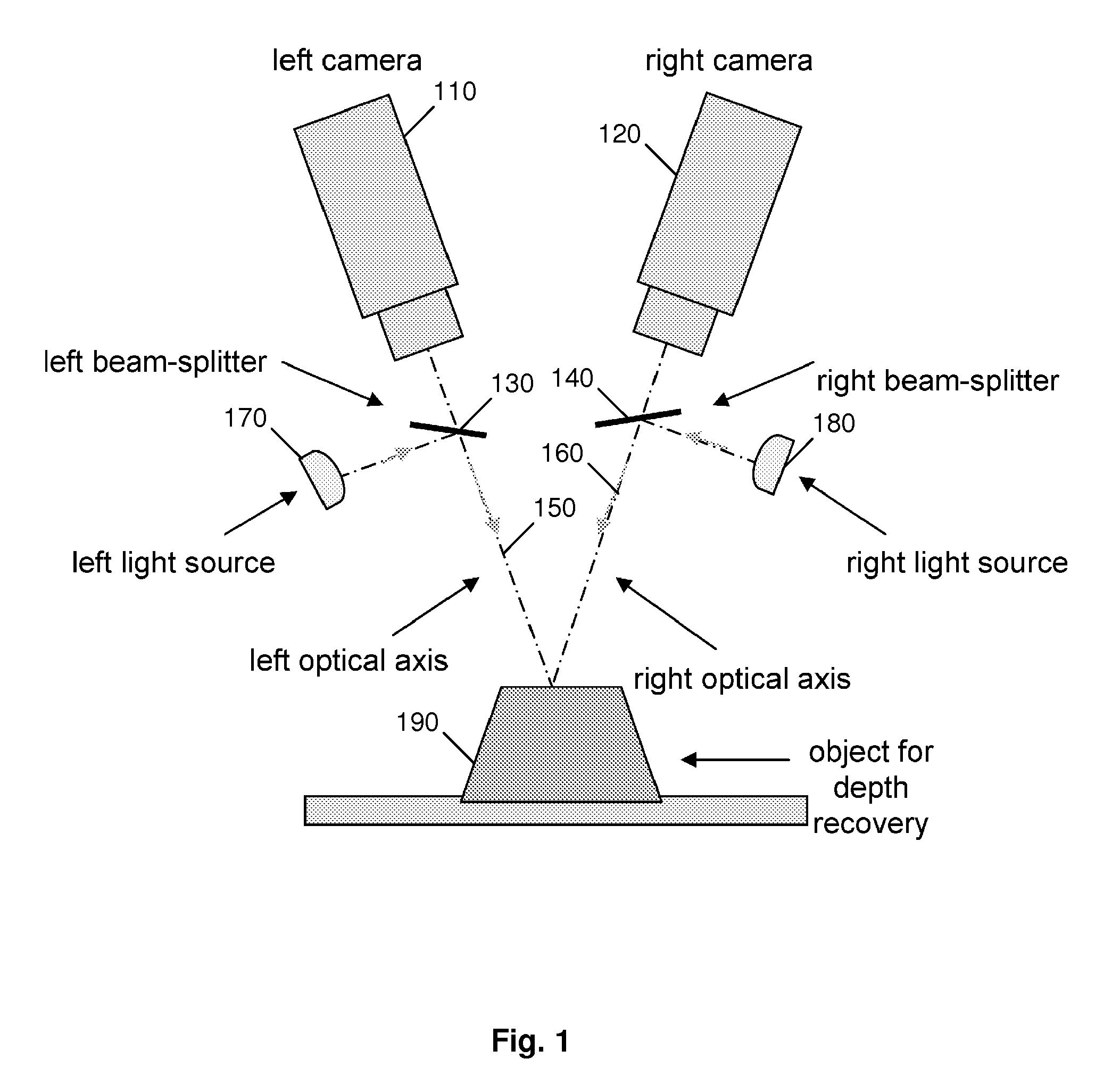
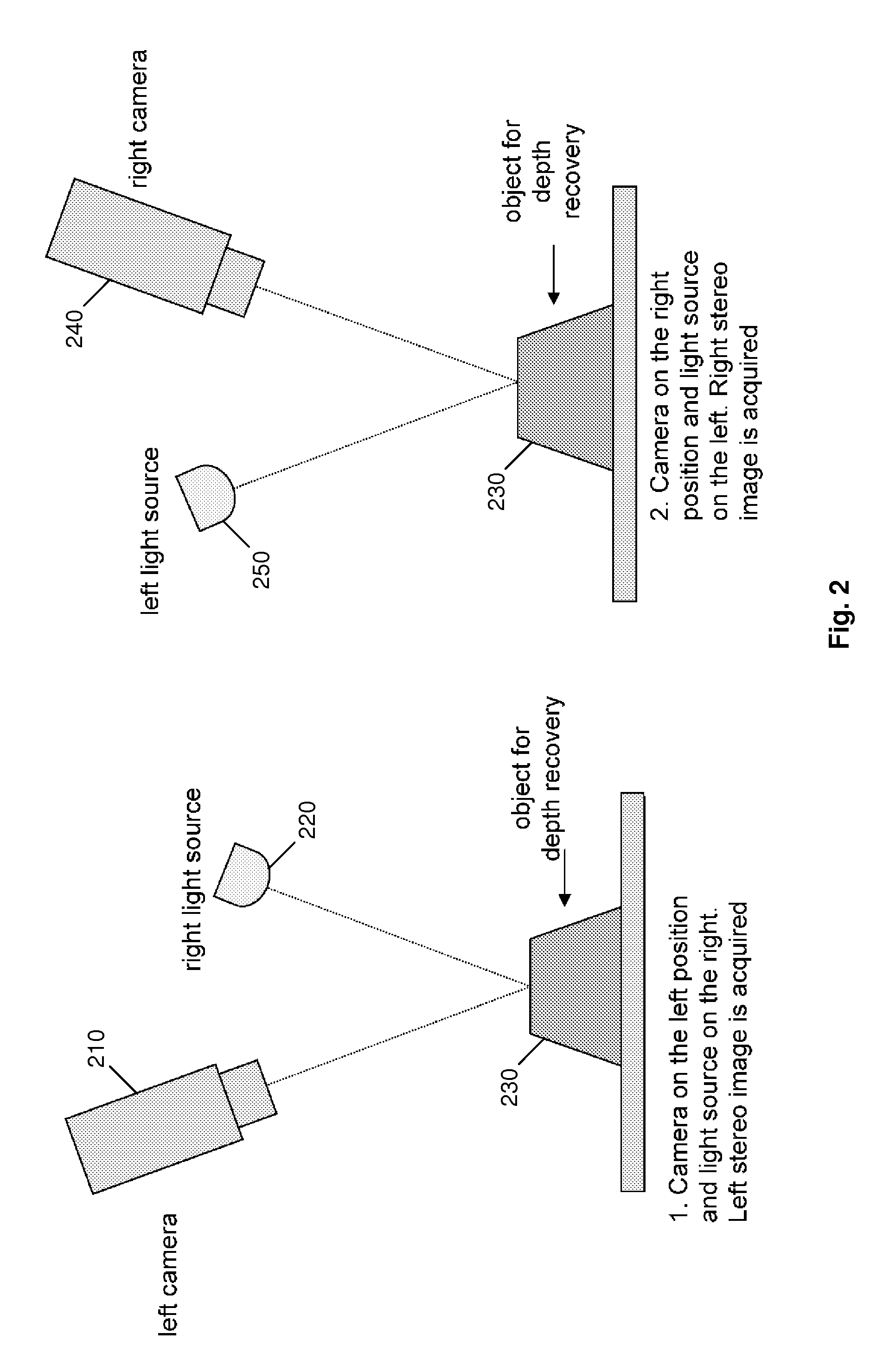
The present invention comprises a method and an apparatus for three dimensional modeling to allow dense depth maps to be recovered, without previous knowledge of the surface reflectance, from only a single pair of stereo images. Several initial steps are performed for stereo and radiometric calibration and rectification for obtaining accurate results. The apparatus for the stereo images acquisition includes internal light sources, these are automatically commuted by a illumination control in order to fulfill the reciprocity property, a stereo camera head composed by the necessary optics to acquire the reciprocal stereo images and a compatible PC interface. The invention is faster than other systems since it requires only two images for obtaining a dense depth model of objects with an arbitrary surface reflectance distribution allowing the system to be used in a wide range of applications such as metrology, quality control, medical and dynamic three dimensional modeling.
Owner:PREFIXA VISION SYST DE C V
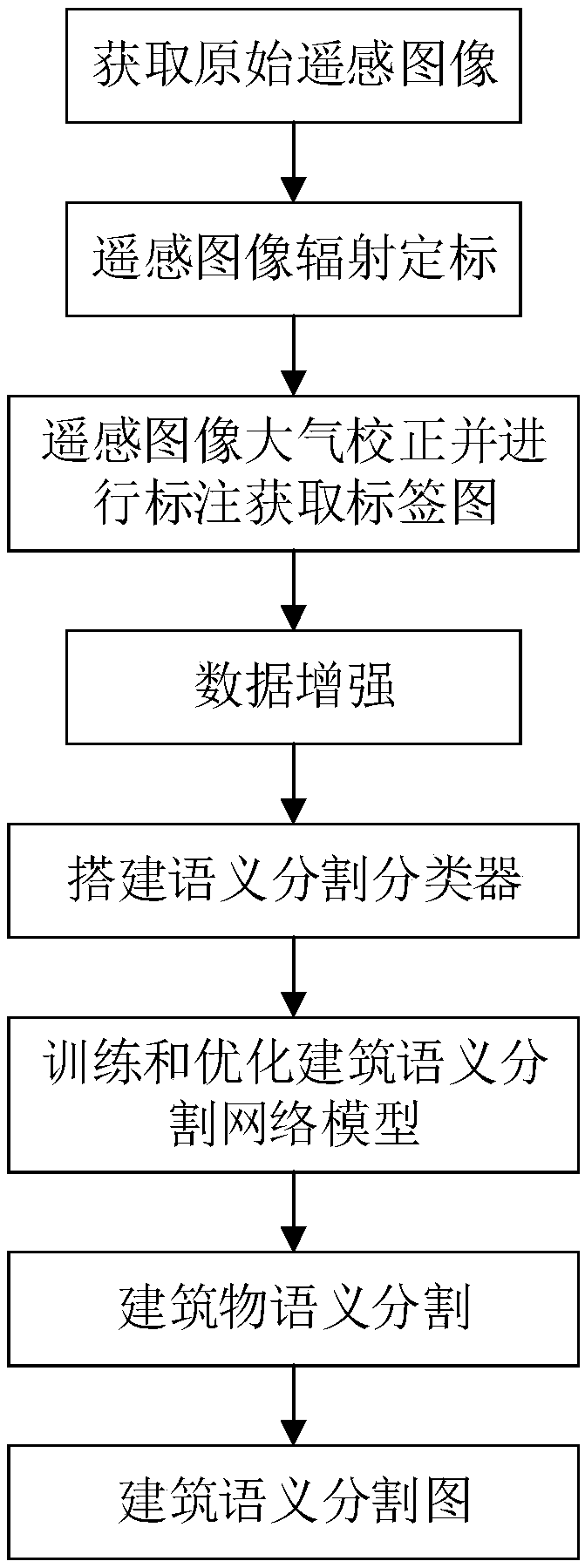
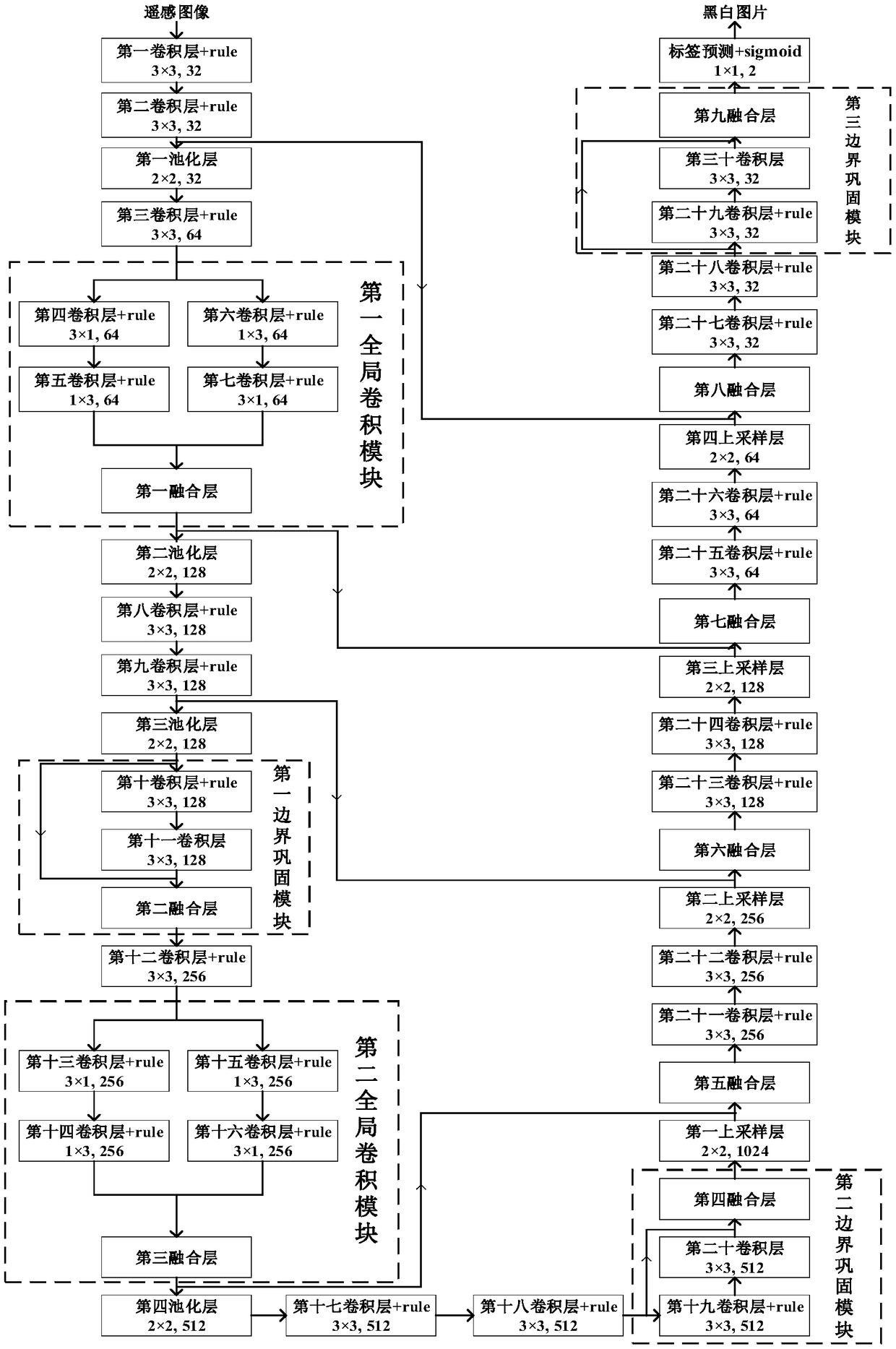
A method of building remote sensing image recognition based on convolution neural network
InactiveCN109389051AHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setNetwork model
The invention discloses a building remote sensing image identification method based on a convolution neural network, comprising the following steps: acquiring an original remote sensing image; Radiometric calibration of the original remote sensing image; Atmospheric correction is carried out on the radiometric calibrated remote sensing image, and the atmospheric calibrated remote sensing image islabeled. The atmospheric corrected remote sensing image and the label map are randomly segmented and then the data are enhanced to form a data set. A semantic segmentation classifier is built to get the network model of architectural semantic segmentation. The atmospheric corrected remote sensing image is sent to the building semantic segmentation network module for building semantic segmentation,and the building semantic segmentation map is obtained. The technical scheme of the invention improves the accuracy of building and non-building classification of remote sensing images, and solves the problems of object classification and pixel position determination in the building semantic segmentation network model of remote sensing images restrict each other.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
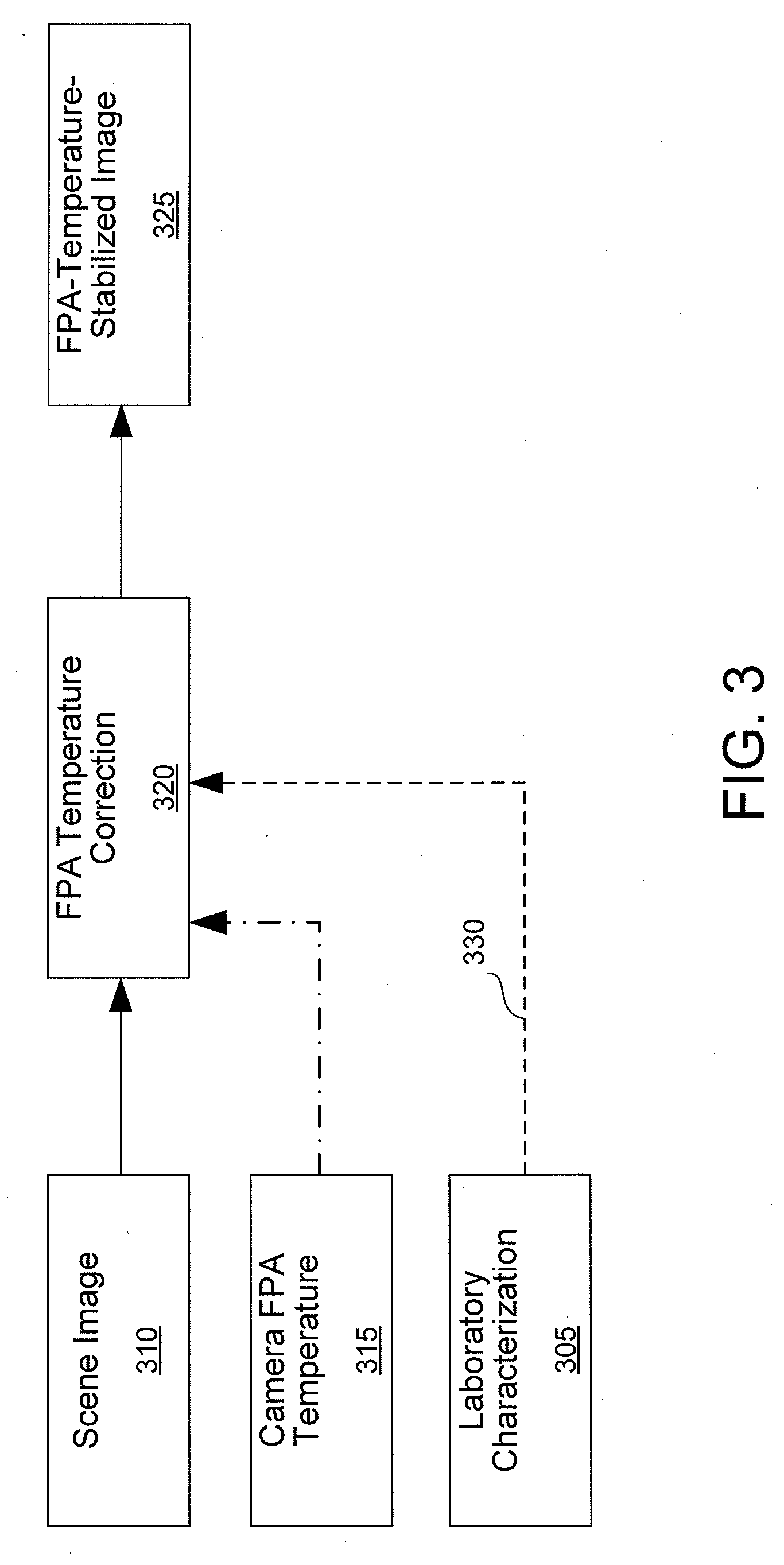
Thermal infrared imaging system and associated methods for radiometric calibration
InactiveUS20090272888A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermodynamicsResponsivity
A thermal infrared (IR) imaging system and associated calibration methods are described. In various illustrative embodiments, techniques are provided for the stabilization and radiometric calibration of a thermal IR imager without stabilization of the device's focal-plane-array (FPA) temperature. In one embodiment, a scene image is corrected for FPA temperature to produce a FPA-temperature-stabilized image, to which radiometric calibration can optionally be added through additional calculations and prior device characterization. In another embodiment, the internal shutter of the thermal IR imager is used as an equivalent external blackbody source to cancel the FPA-temperature-dependent offset from a scene image Radiometric calibration can be included through additional calculations and prior device characterization. In some embodiments, these techniques are combined to correct for dependence on FPA temperature of both the imager's responsivity and its zero-radiance-scene offset.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
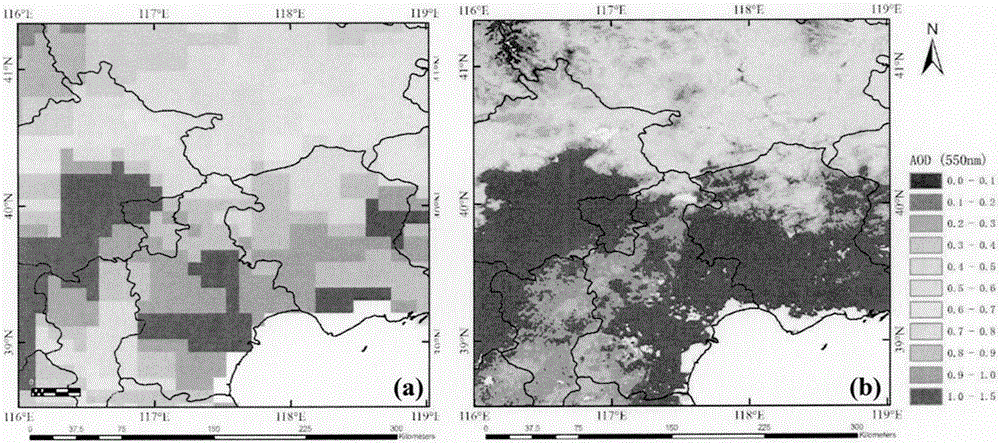
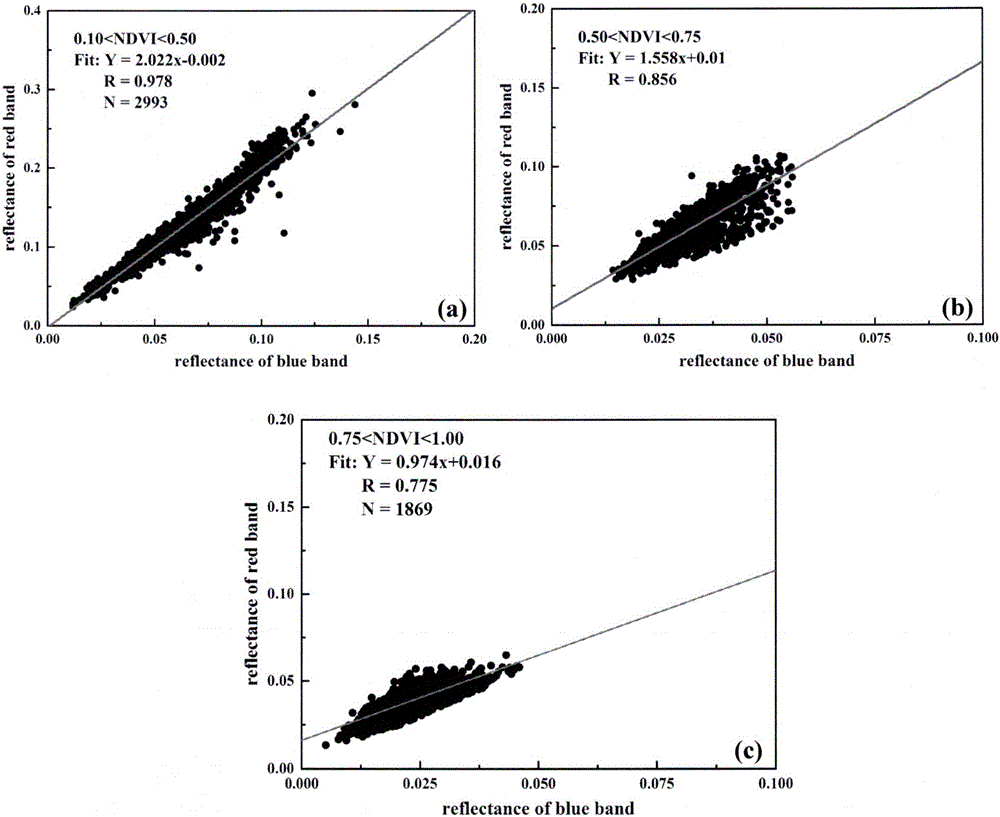
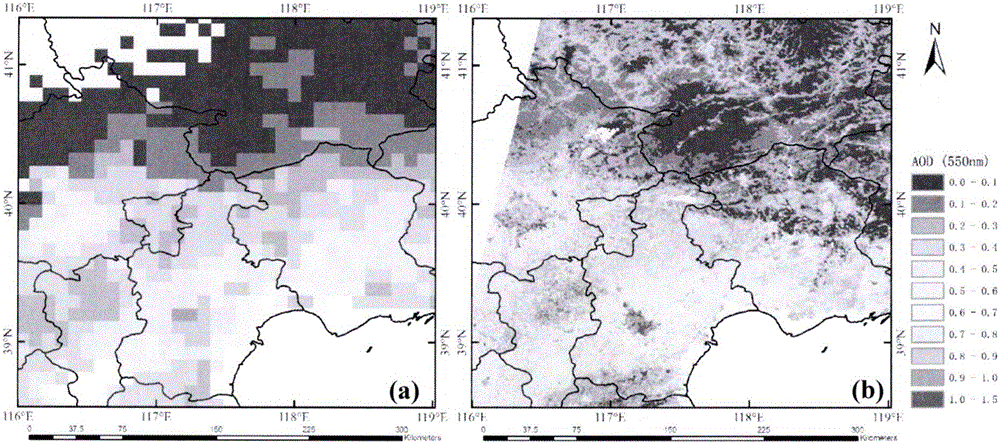
Retrieval method for aerosol optical thickness based on high resolution satellite image data
InactiveCN106407656AImproving the Accuracy of Optical Depth InversionIncrease spaceParticle suspension analysisInformaticsRadiation transferPollution
The invention discloses a retrieval method for an aerosol optical thickness based on high resolution satellite image data. The retrieval method specifically comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a lookup table according to a 6S radiation transfer model; 2) carrying out high resolution data preprocessing, comprising radiometric calibration, geometric correction and cloud detection, acquiring original apparent reflectance and observation angle information, and acquiring atmospheric parameters according to the observation angle information and the lookup table; 3) calculating the normalized differential vegetation index of each pixel, and determining a red-blue wave band relation corresponding to each pixel according to the vegetation index and priori knowledge provided by the invention; and 4) inverting the aerosol optical thickness according to the satellite observed apparent reflectance, the atmospheric parameters and the red-blue wave band relation. According to the remote sensing retrieval method for the aerosol optical thickness disclosed by the invention, aerosol monitoring can be carried out on high solution satellites effectively, and a data source can be provided for regional and urban atmospheric environment and pollution.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Calibration of a radiometric optical monitoring system used for fault detection and process monitoring
ActiveUS8125633B2Accurate measurementFacilitates quantitative comparisonsEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryPrimary standardMonitoring system
Owner:VERITY INSTR
System for measuring normal spectral emissivity of high-temperature material
ActiveCN102042993ASimple designLess interference with radiometric measurementsSpectrum investigationMaterial thermal analysisData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses a system for measuring the normal spectral emissivity of a high-temperature material, comprising a vacuum heating unit, a water cooling sleeve unit, an optical fiber sensor measurement unit and a data acquisition and analysis unit, wherein a test sample is arranged on the upper part of the vacuum heating unit, and the vacuum heating unit performs radiant heating on the lower surface of the test sample; the water cooling sleeve unit is sleeved on the upper part of the test sample, and the upper surface of the test sample is placed in a constant-temperature cold environment; the optical fiber sensor measurement unit is arranged above the test sample to measure the normal spectral radiant intensity of the upper surface of the test sample; and the data acquisition and analysis unit is connected with the optical fiber sensor measurement unit and is used for calculating the normal spectral emissivity through a multi-spectrum inversion algorithm according to the measured normal spectral radiant intensity. The invention realizes material normal spectral emissivity measurement in a spectrum range of 0.4-1.7mum and a temperature range of 600-1,500 DEG C without on-line radiometric calibration, is accurate and reliable to realize the technology, and overcomes limitations on high price, complicated structure, high difficulty in technical implementation and other applications of the conventional spectral emissivity device.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
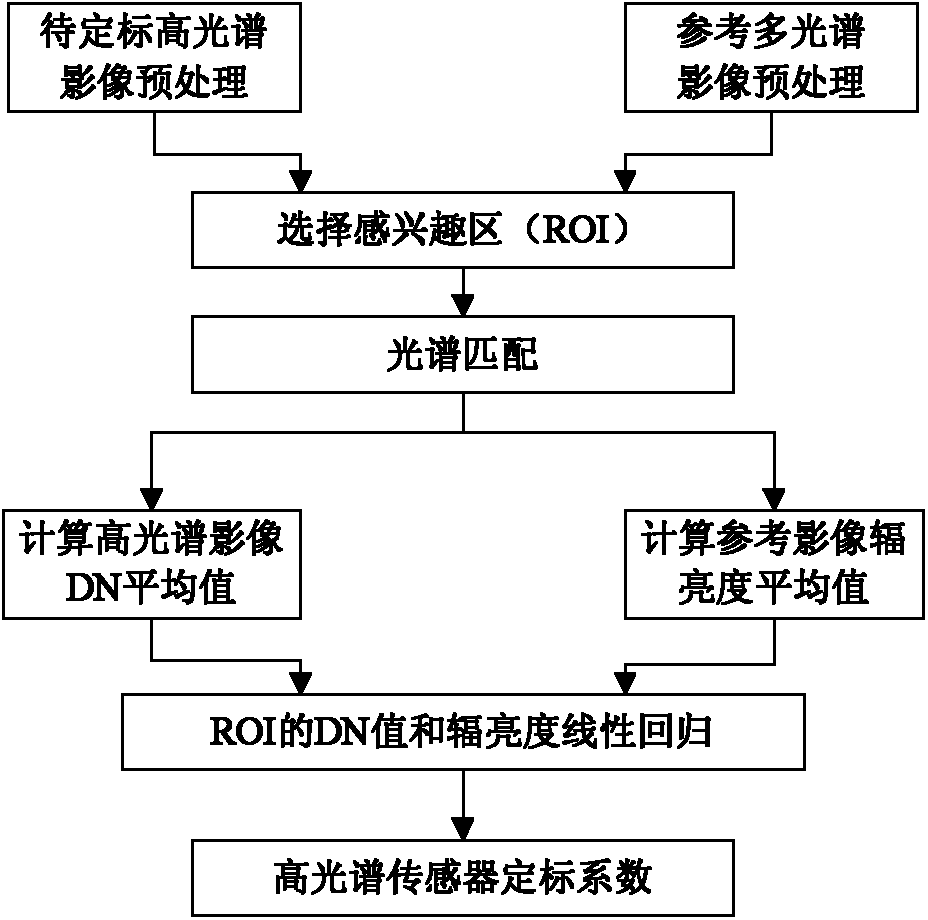
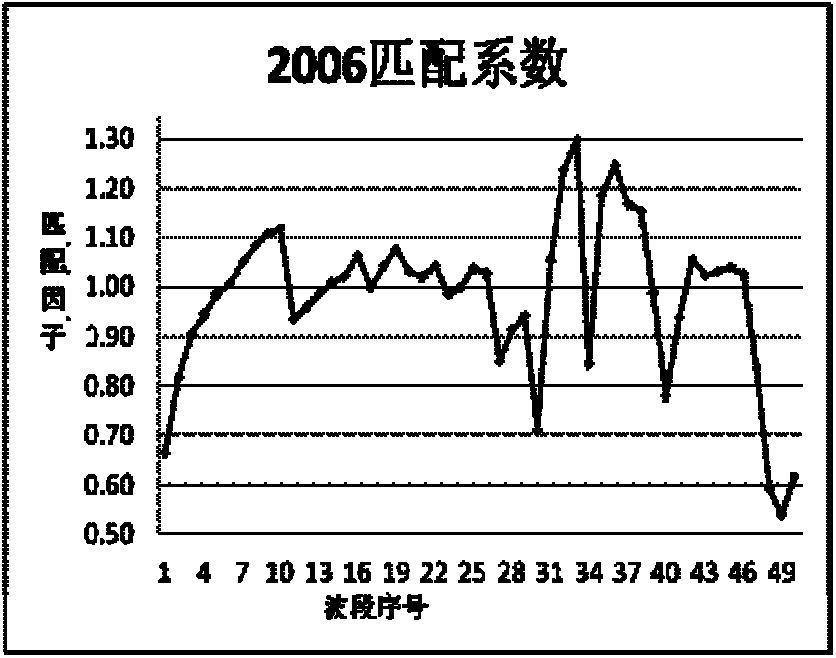
A cross-radiation calibration method for hyperspectral sensors based on multispectral sensors
InactiveCN102279393AAchieving Cross Radiation CalibrationReduce mistakesWave based measurement systemsLightnessEntrance pupil
The invention discloses a cross radiometric calibration method of a hyper-spectral sensor based on a multi-spectral sensor. The method is used for solving the cross radiometric calibration problem of the hyper-spectral sensor without a matched reference hyper-spectral image. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting cloudless hyper-spectral image data; selecting a multi-spectral reference image according to the hyper-spectral data; selecting a uniform ground object on the image as an interesting region; performing geometric precise correction of the two images; calculating entrance pupil radiances of various types of wave bands of the two sensors by using an atmospheric radiation transmission model; solving spectrum matching factors of various types of corresponding wave bands according to a certain rule; solving the entrance pupil radiances of the various types of wave bands of the hyper-spectral sensor by using the spectrum matching factors and the multi-spectral data; and linearly fitting pixel DN (Digital Number) values in the interesting region of the hyper-spectral image to be calibrated and the radiances of corresponding pixels of the multi-spectral reference image after being corrected through the spectrum matching factors to obtain calibration coefficients of the various types of wave bands of the hyper-spectral sensor. The method has the advantages of good stability, high reliability, high precision and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Thermal imager utilizing improved radiometric calibration technique
A thermal imaging apparatus comprises a thermal image camera having a lens and a display. The camera further includes a focal plane array located behind the lens for converting imaging radiation to produce an image signal for further processing. A shutter mechanism is operative to selectively inhibit exposure of the focal plane array to the imaging radiation such that the focal plane array produces a reference signal. Processing circuitry is operative to receive the image signal and produce a corresponding thermal image on the display. The processing circuitry is further operative to utilize the image signal and the reference signal to derive temperature information.
Owner:RAYTEK
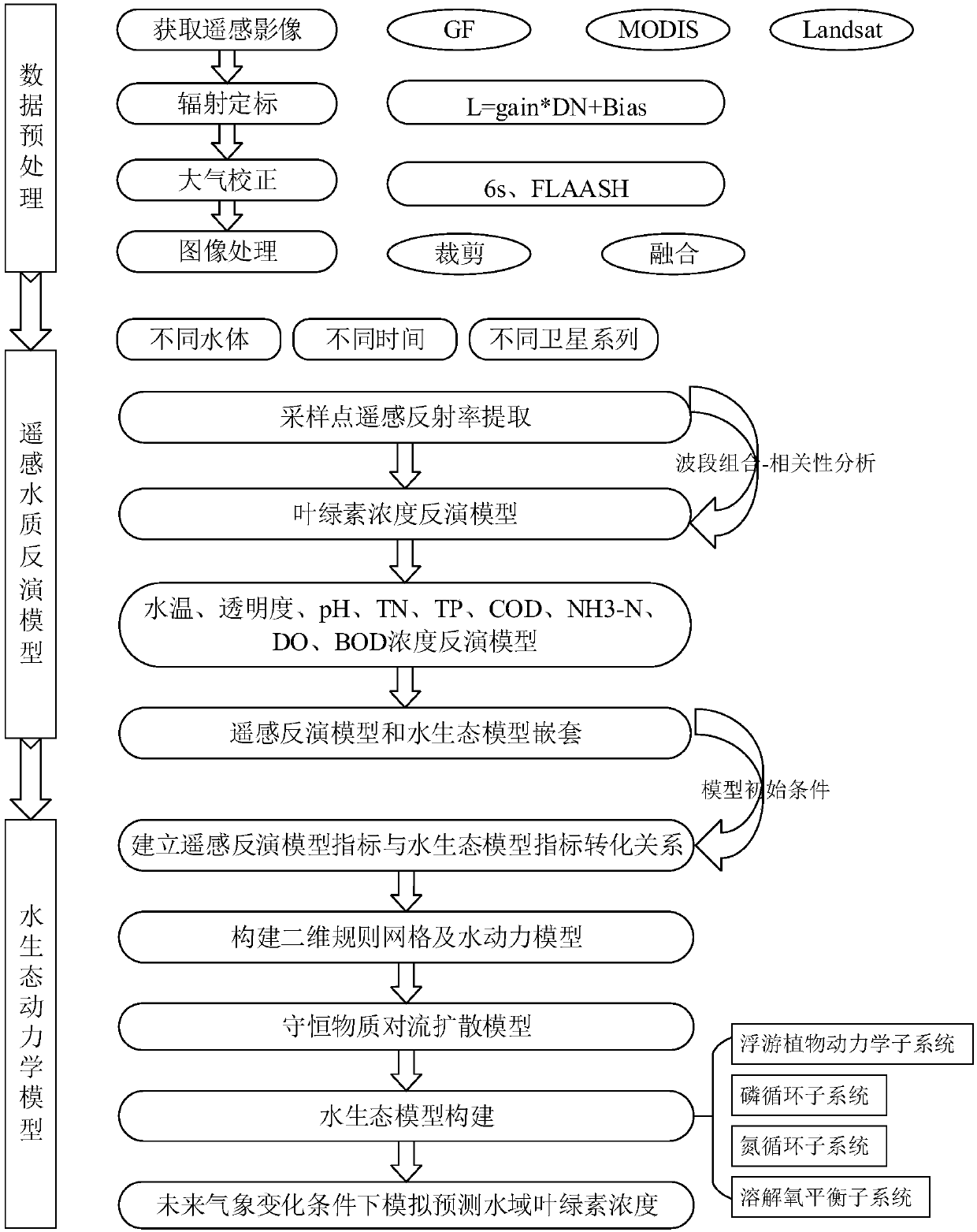
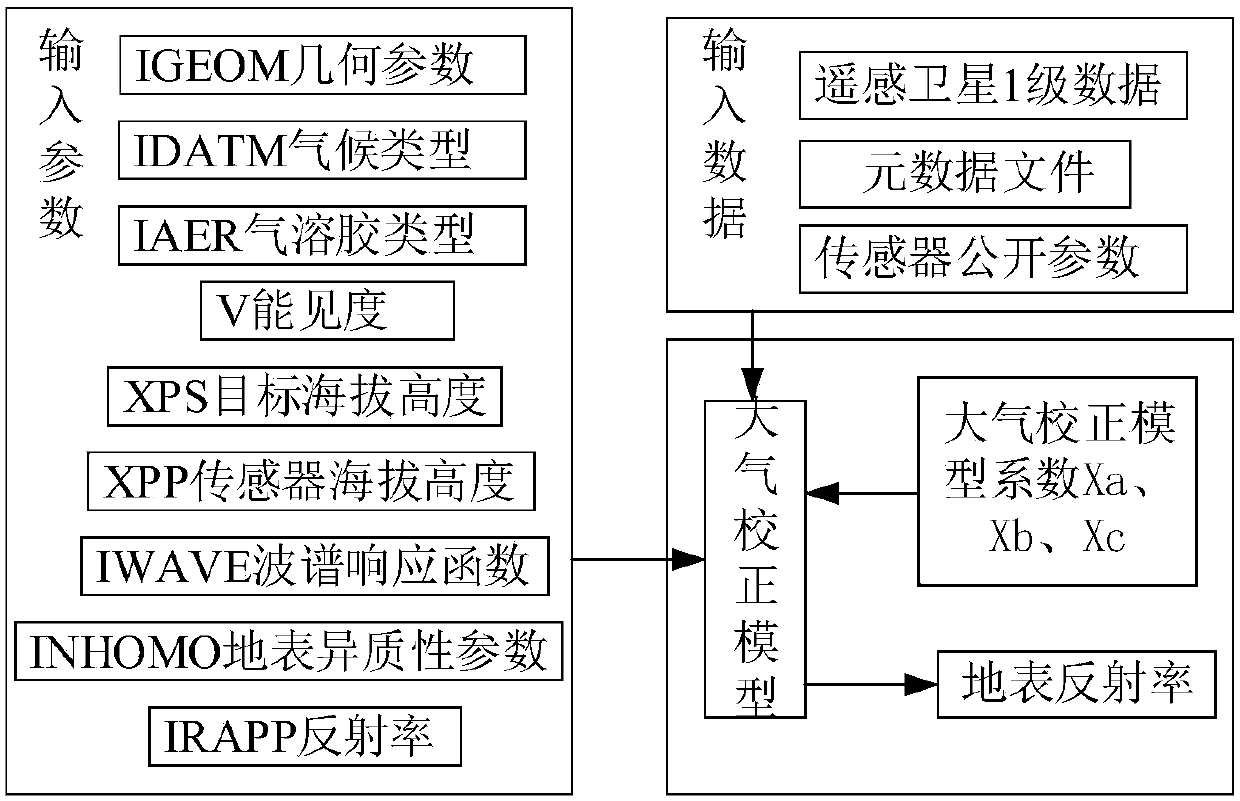
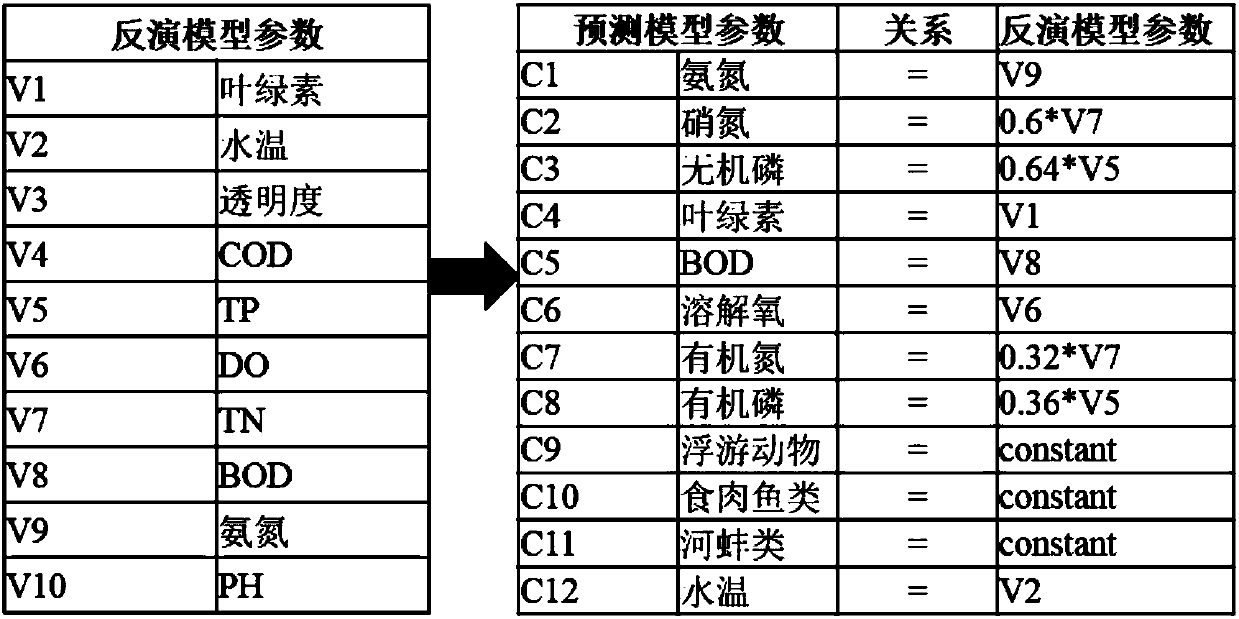
Chlorophyll calculating method based on remote-sensing images and water ecological model
ActiveCN108038351AComprehensiveImprove applicabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSystems biologyWater qualityAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses a chlorophyll calculating method based on remote-sensing images and a water ecological model. The method comprises the steps of 1, based on remote-sensing image data, data preprocessing like radiometric calibration, atmospheric correction and image cropping and fusing is conducted; 2, a remote-sensing water quality inversion model is constructed, and respective inversion ofindexes like water temperature and chlorophyll concentration is achieved; 3, various index concentrations and future weather change which are obtained through inversion of the remote-sensing images are regarded as input conditions of the water ecological model, and the chlorophyll concentration dynamic change process of a water area environment is simulated within a future duration caused by change like nutritive substance conversion and algae growth and death under a future weather change condition. The chlorophyll calculating method is applicable to water environment monitoring and predicting, and has popularity and high calculation precision, chlorophyll concentration prediction and simulation of a large area of a drainage basin are achieved in real time under the condition of the limited monitoring site, and an integrated chlorophyll concentration predicting system integrating the remote-sensing images and the water ecological model can be formed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
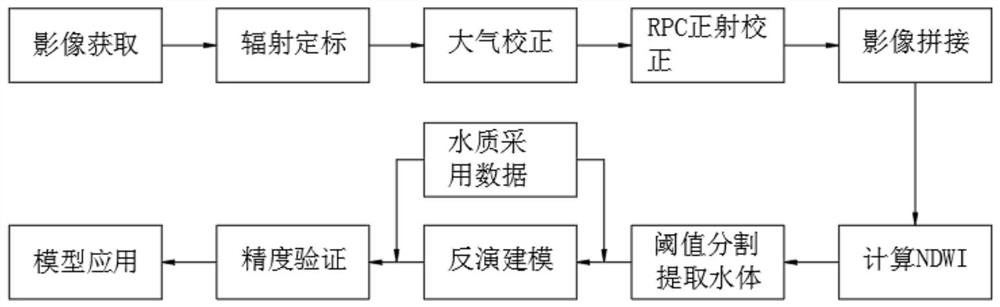
River and lake water quality monitoring method based on high-resolution satellite images
InactiveCN112051222ARealize water quality assessmentWide range of monitoringMethod using image detector and image signal processingScattering properties measurementsWater qualityAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses a river and lake water quality monitoring method based on high-resolution satellite images. The river and lake water quality monitoring method comprises satellite image radiometric calibration, atmospheric correction, RPC orthographic correction, image splicing, automatic water body extraction, water quality quantitative inversion modeling, water quality quantitative inversion model precision verification and water quality quantitative inversion model application. The invention relates to the technical field of inland water environment remote sensing science, in particular to a river and lake water quality monitoring method based on a high-resolution satellite image, which has the advantages of wide monitoring range, high speed, low cost and convenience in long-termdynamic monitoring by utilizing a remote sensing technology. A multiple linear regression model between different water quality parameter concentrations and image waveband reflectivity is establishedby combining sampling data of a water quality monitoring station and representation of various substances in a water body on a remote sensing image, and a relative error and an absolute error of themodel are calculated according to an inversion result, so as to promote the model, and water quality evaluation of the whole river and even a water area with a larger range is achieved.
Owner:山东锋士信息技术有限公司
Remote sensing inversion method and system for land cloud optical thickness
InactiveCN104535979AImplement extractionGood inversion resultElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationImaging dataBrightness perception
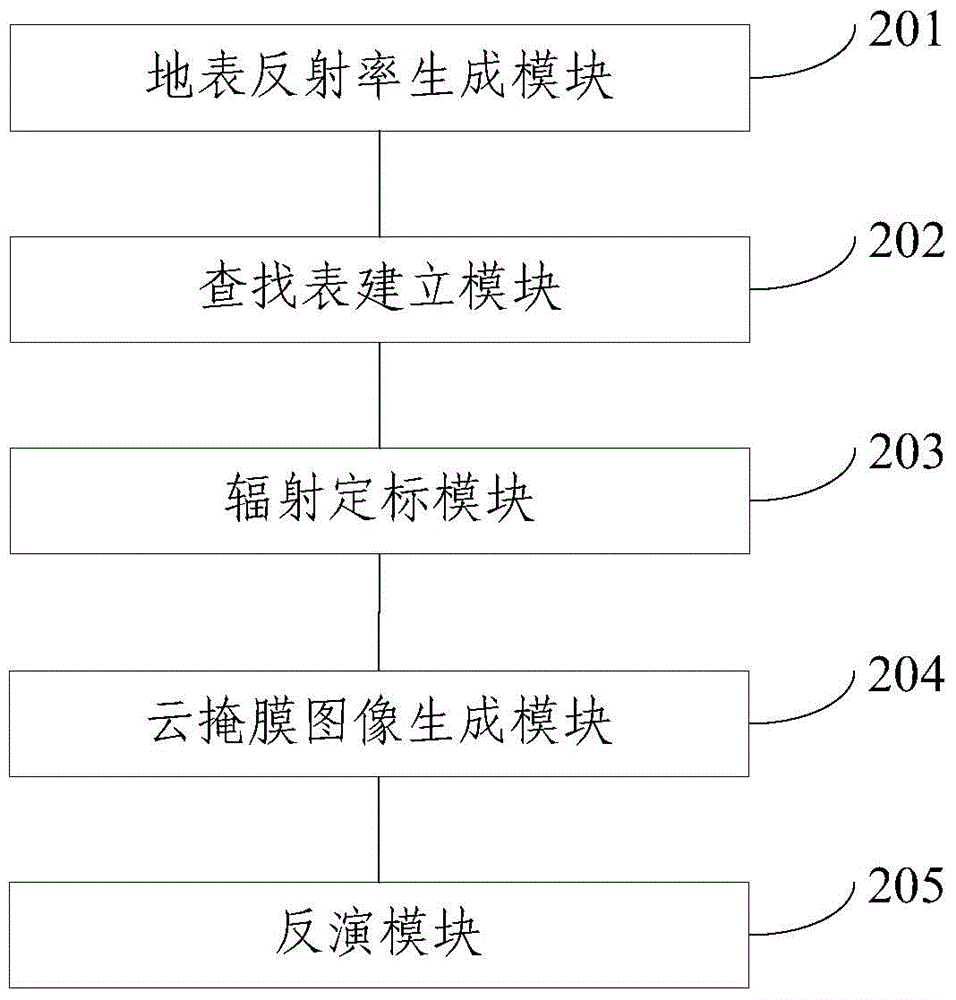
The invention provides a remote sensing inversion method and system for the land cloud optical thickness. The remote sensing inversion method comprises the steps that visible light images of a land are obtained, and the surface reflectance of the visible light images is generated; a lockup table is established through a radiation transmission module according to preset parameters; radiometric calibration is conducted on the visible light images, and the on-star irradiance of the visible light images is obtained through transformation; cloud mask images are generated through the visible light images with the combination of multi-spectral image data; the on-star irradiance of cloud coverage pixels in the cloud mask images are inverted into the cloud optical thickness through the lockup table according to the surface reflectance and the on-star irradiance of the visible light images. According to the remote sensing inversion method and system for the land cloud optical thickness, the cloud optical thickness at the daytime can be rapidly and accurately extracted based on the extraction precision of the cloud mask images, the method and system are independent from specific sensors and satellites, and good inversion results are obtained under the situation of the high-brightness ground surface with the underlying surfaces such as ice and snow.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
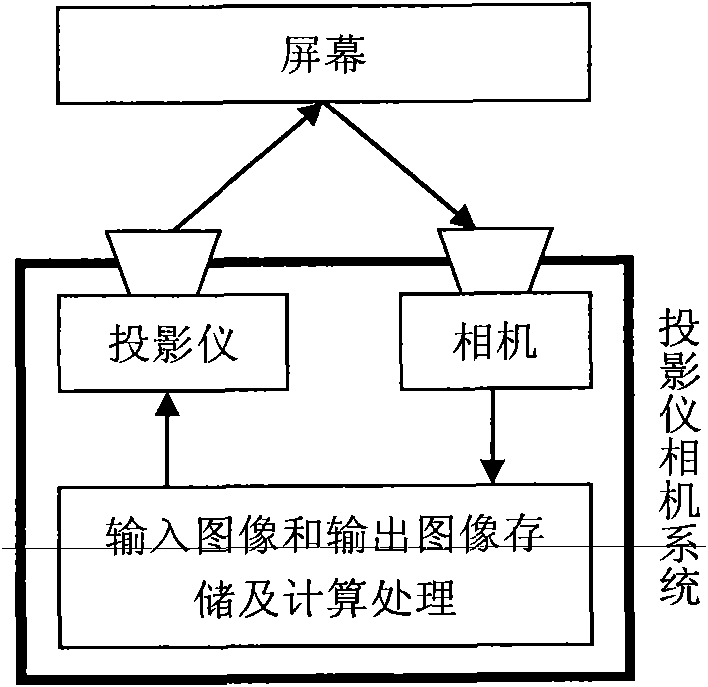
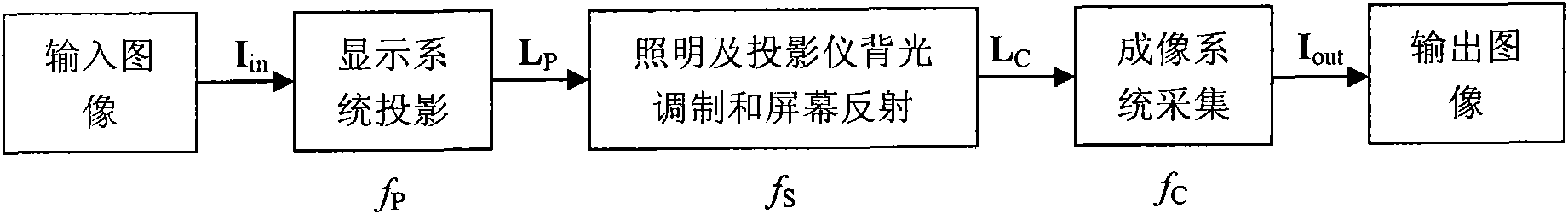
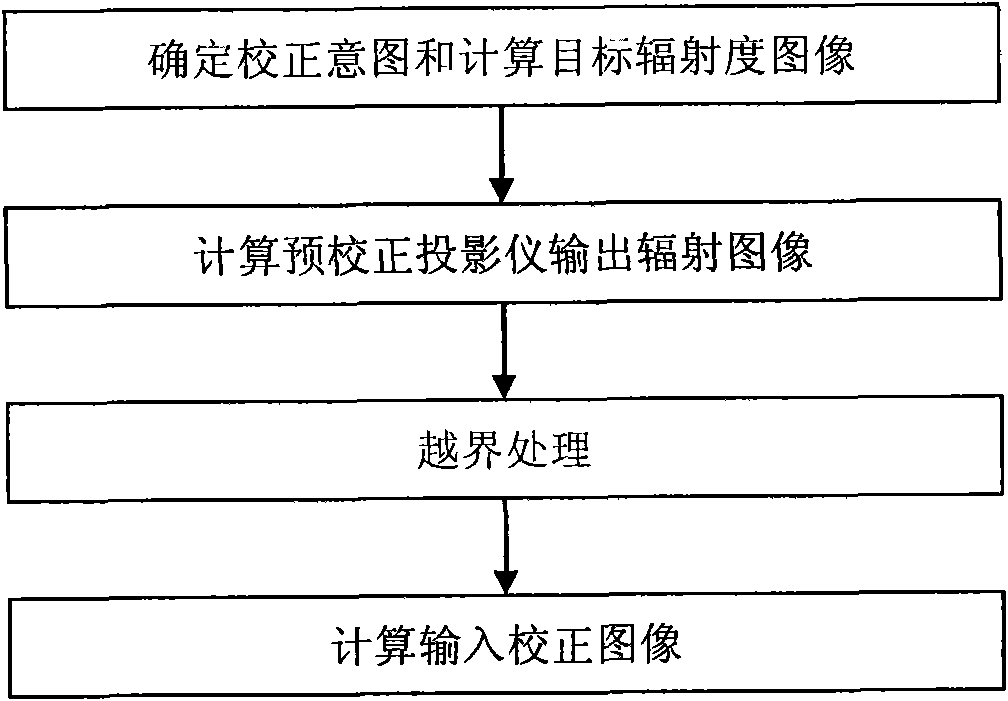
Correction method of color distortion of projected display images
InactiveCN101860761AFunction increaseQuality assurancePicture reproducers using projection devicesCorrection methodRadiometric calibration
The invention discloses a correction method of color distortion of projected display images. The correction of color distortion of images is divided into three simple steps, such as geometrical mapping, radiometric calibration and input images computation of correction of color distortion to ensure that the process of correction has low operation complexity and is suitable for low-end microprocessors, thereby reducing the operation cost. The invention provides two correction purposes for choice expands the application range of the method and increases the projected display function. Meanwhile, by the treatment of a cross-border step, the corrected images effectively compensate the color distortion on screen and simultaneously ensure the robustness of the method. Moreover, adaptive adjustment can be realized in the process of cross-border treatment according to image contents and overall surface characteristics so as to ensure the quality of the corrected output images, thereby achieving the purposes of comprehensively considering cost, functions and performance in product development, and being favorable for promoting the expansion of the projected display from high-end applications to low-end consumption electronic applications.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
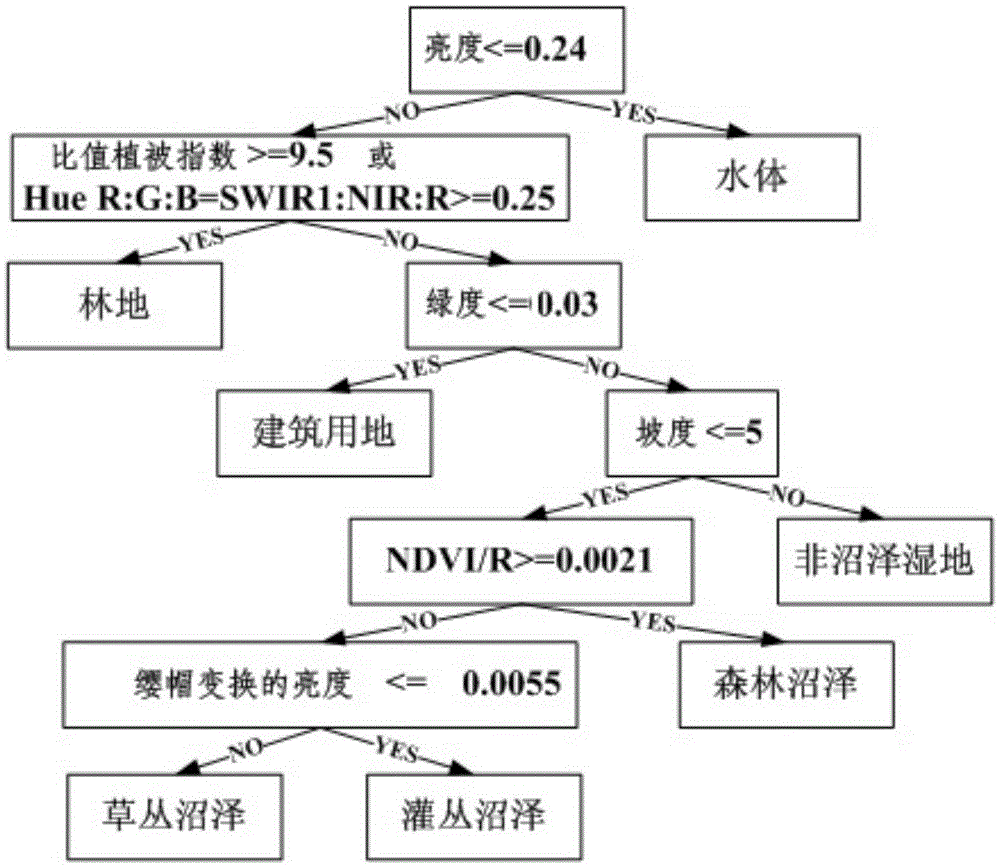
Marsh wetland mapping method based on object-oriented random forest classification method and medium-resolution remote sensing image
InactiveCN105404753AHigh precisionMeeting cartographic needsGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsMarshImage resolution
The present invention relates to a marsh wetland mapping method based on an object-oriented random forest classification method and a medium-resolution remote sensing image. The purpose of the present invention is to solve the technical problem that a current remote sensing classification method can not accurately extract spatial information of a tussock marsh, a shrub marsh and a forest marsh only by using of spectral information. The marsh wetland mapping method provided by the present invention comprises: carrying out radiometric calibration, atmospheric correction, ortho-rectification, accurate geometric correction and projective conversion by using Landsat-80LI data; processing the data by using eCognition 8.6 software; removing non-marsh wetland objects from marsh wetland objects; setting an index threshold region to separate the tussock marsh, the shrub marsh and the forest marsh; and then mapping a thematic marsh wetland map in ArcGIS 10.0 software. The marsh wetland mapping method provided by the present invention is high in accuracy. The marsh wetland mapping method provided by the present invention is applied to marsh wetland mapping.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
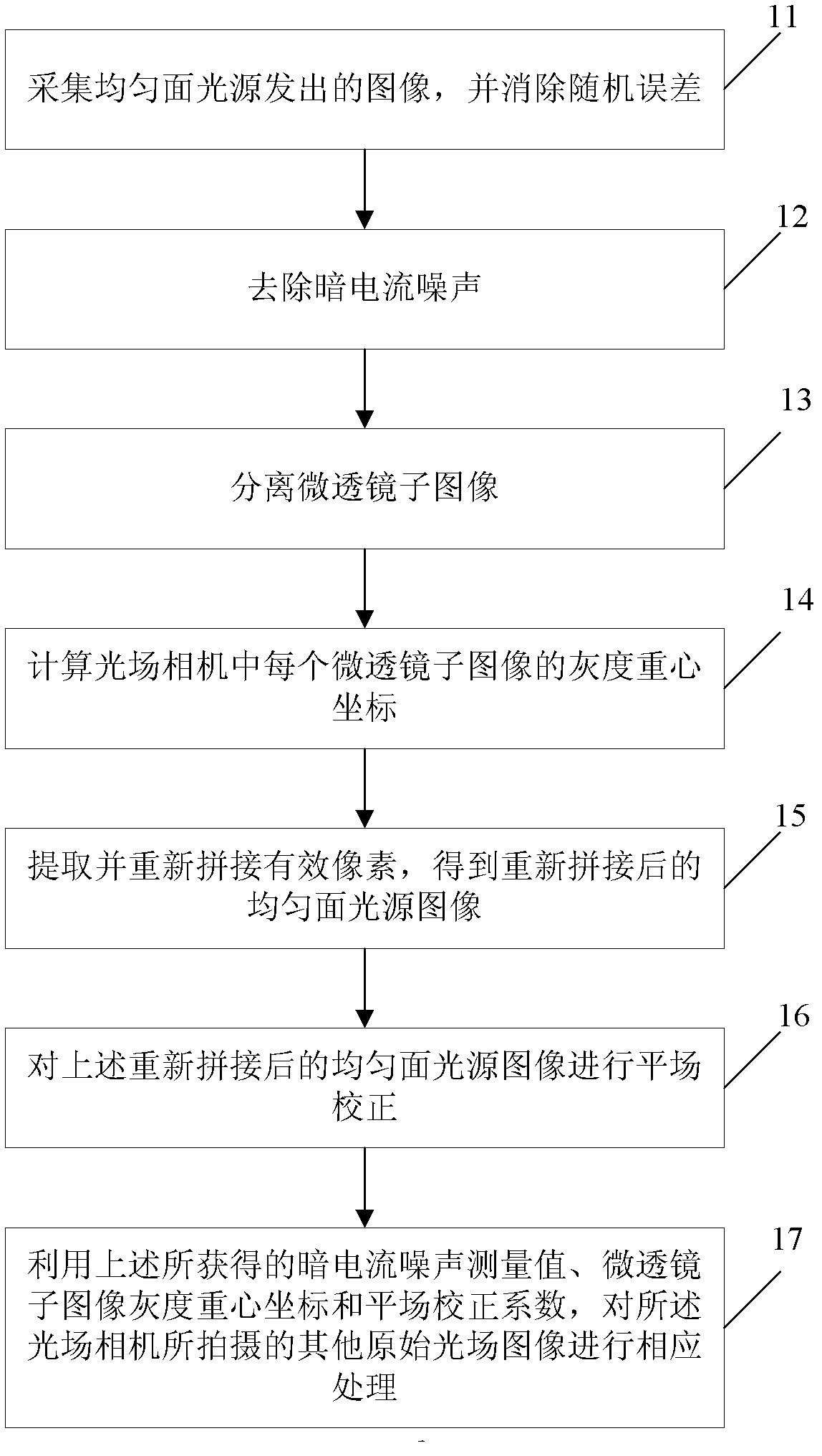
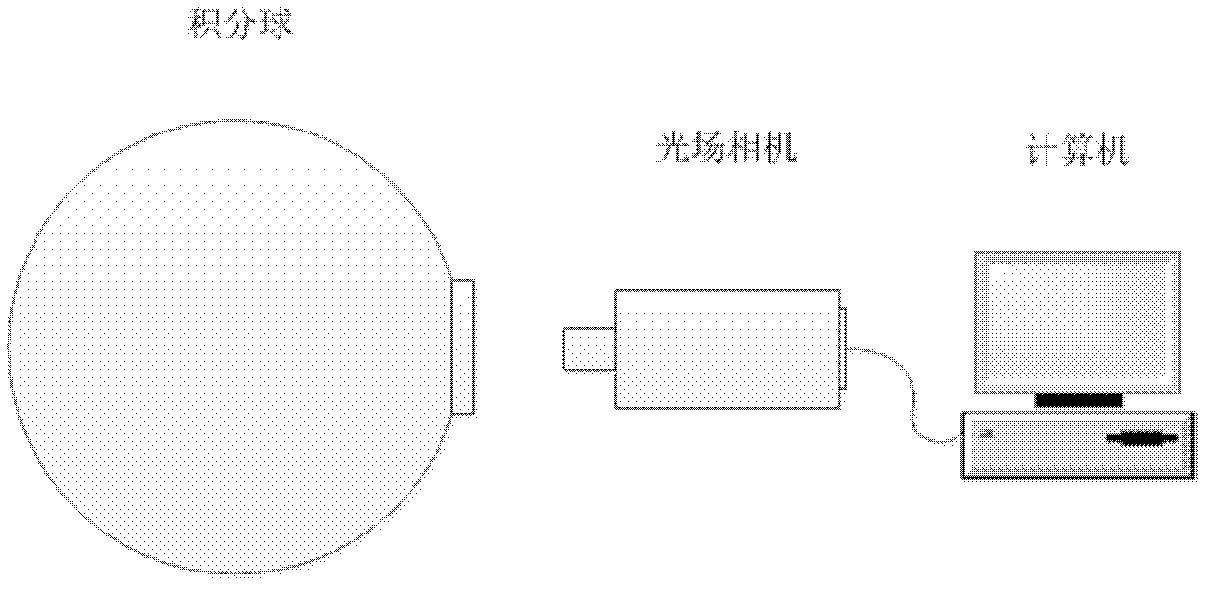
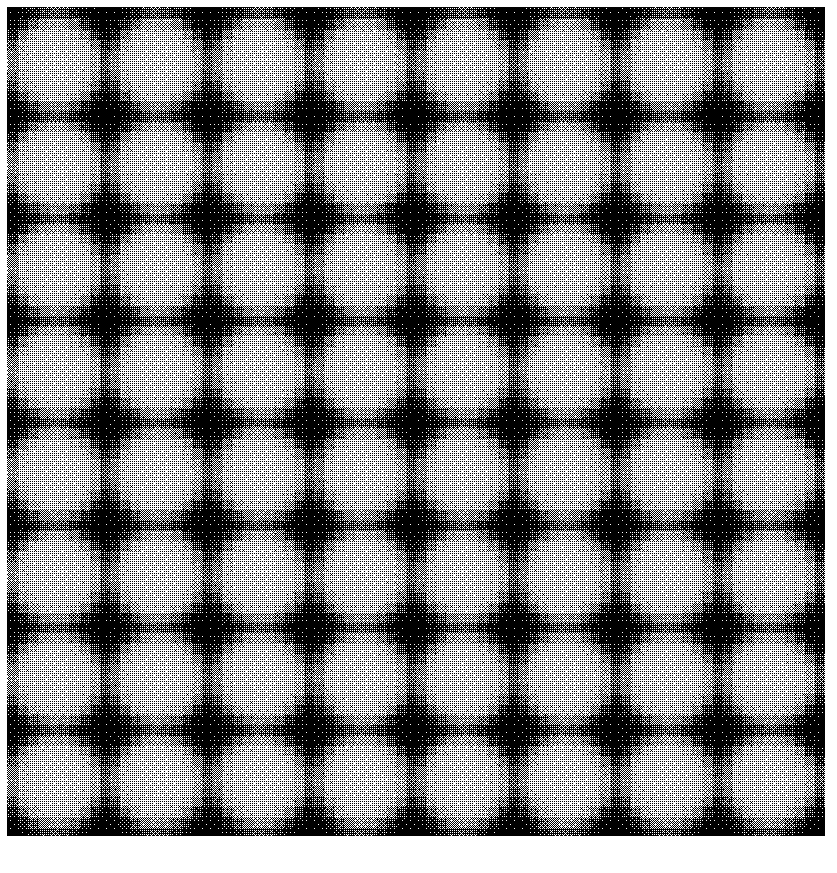
Relative radiometric calibration method for light field camera
InactiveCN102663732AEliminate Grayscale UncertaintyEliminate dark current noiseImage analysisPower flowLight-field camera
The embodiment of the invention discloses a relative radiometric calibration method for light field camera, which comprises the steps of: carrying out calibration processing of images emitted from an uniform area light source by a light field camera to obtain measurement values of dark current noise, grey centroid coordinates of subimages of microlens, and flat-field correction coefficients; and processing other original light field images shot by the light field camera correspondingly by utilizing the measurement values of dark current noise, the grey centroid coordinates of subimages of microlens, and the flat field correction coefficients to obtain light filed images after relative radiometric calibration processing. The method of the invention can eliminate dark current noise in light field camera system, remove invalid pixels between subimages of microlens, and correct the problem of pixel response nonuniformity caused by various factors, thereby improving the performance of the light field camera.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
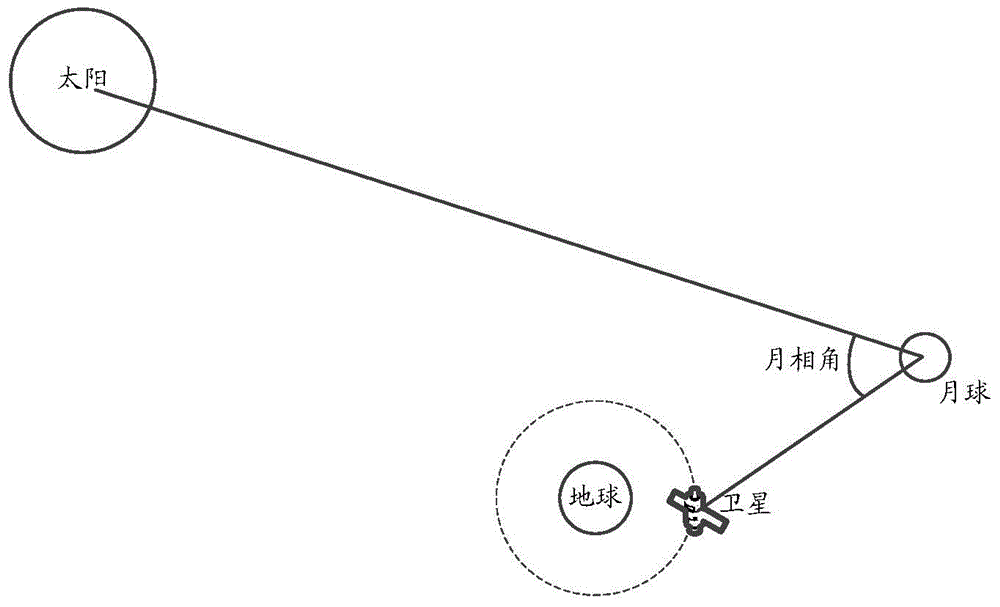
Method for absolutely radiometric calibration of low orbit earth observation satellite with moon as reference
ActiveCN104462776ALong-term stabilitySave calibration costImage analysisMeasurement devicesStart timeAngular velocity
The invention provides a method for absolutely radiometric calibration of a low orbit earth observation satellite with moon as reference. The method comprises the following steps that the time during which the low orbit earth observation satellite can observe the moon is primarily determined through a satellite tool kit; the starting time of moon imaging, the ending time of moon imaging, the camera exposure time, the satellite attitude angle during imaging, the pitching angular velocity and the like are determined; according to the parameters, moon imaging is conducted, so that an image of moon is obtained; the image of the moon is analyzed through a ROLO absolutely radiometric calibration model, and absolutely radiometric calibration coefficients are obtained. By the adoption of the method, an onboard calibration device and an operating mechanism are not needed, a special ground reference source is not needed, the long-term stability of moon and the attitude maneuver capacity of the satellite are fully utilized, and the image of moon is obtained and used as a reference source.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Relative radiometric correction method for star-load TDICCD camera
ActiveCN101226639ASolve the problem of different nonlinearity of light intensity responseSolve for uniformityImage analysisWave based measurement systemsCalibration coefficientLinear fitting
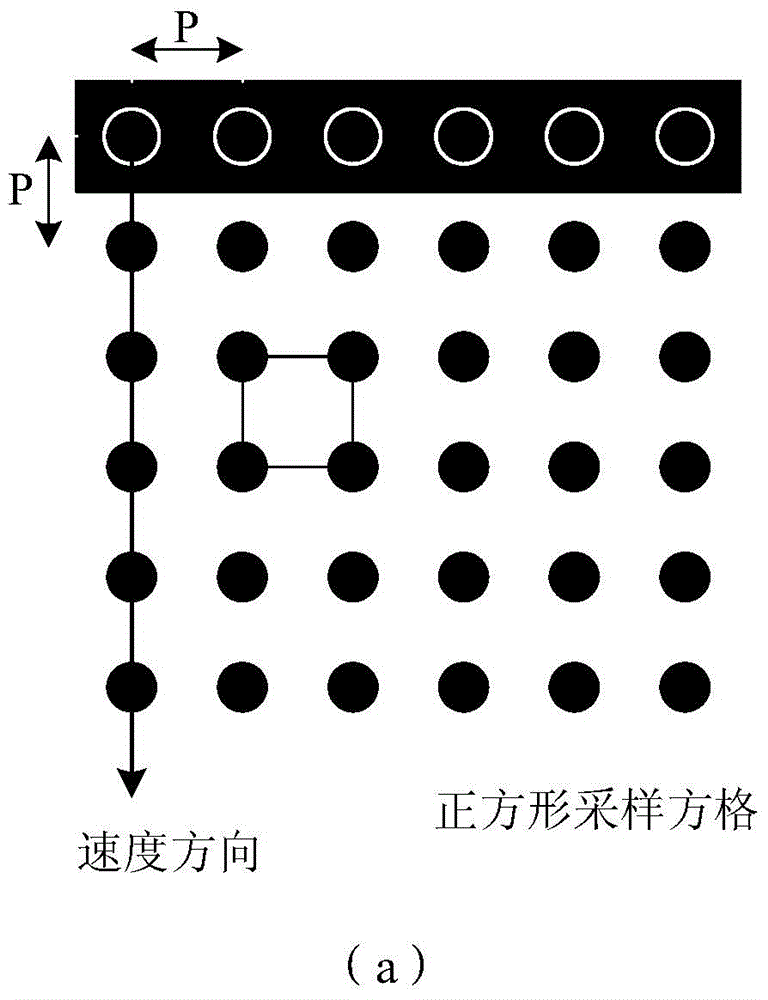
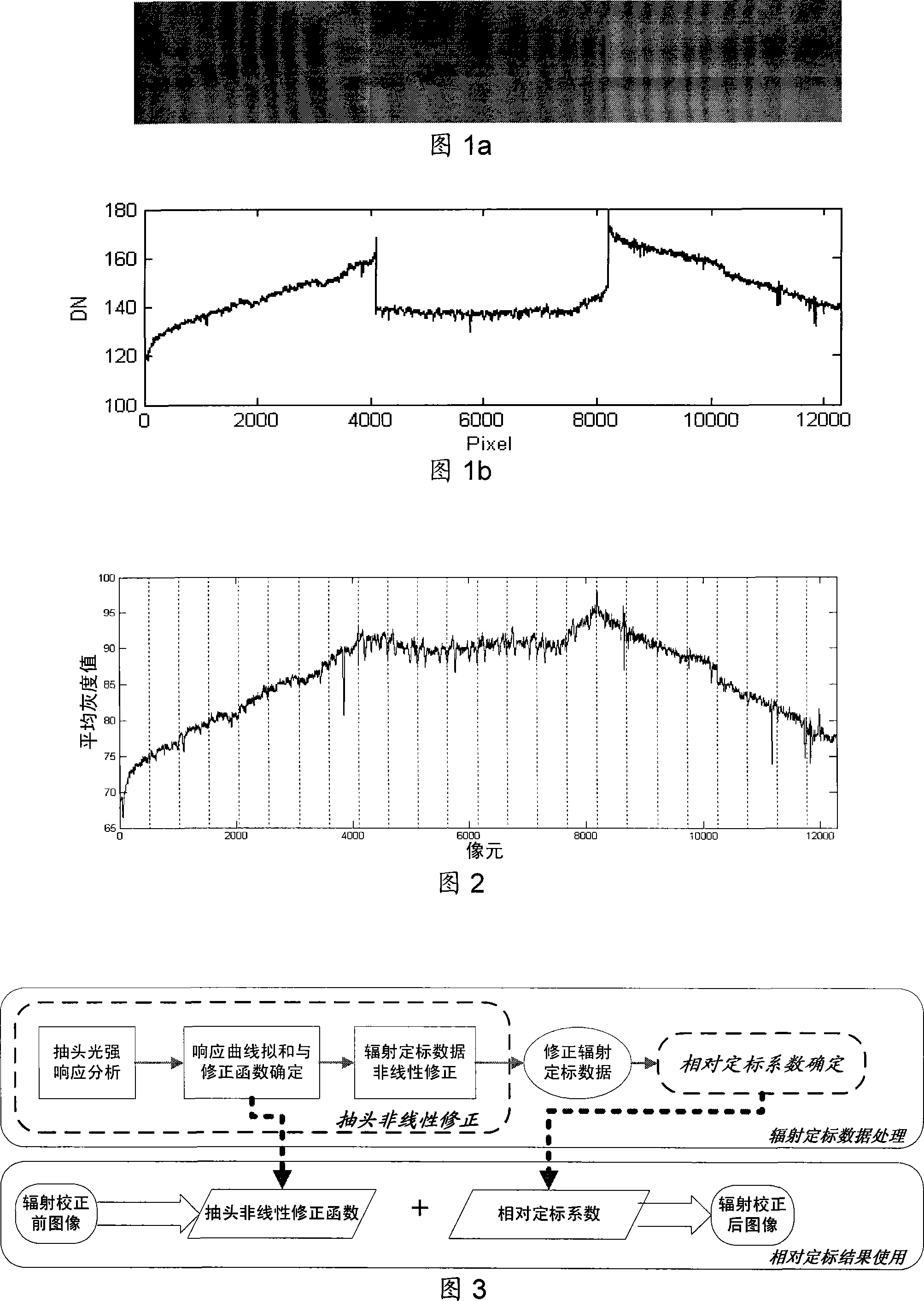
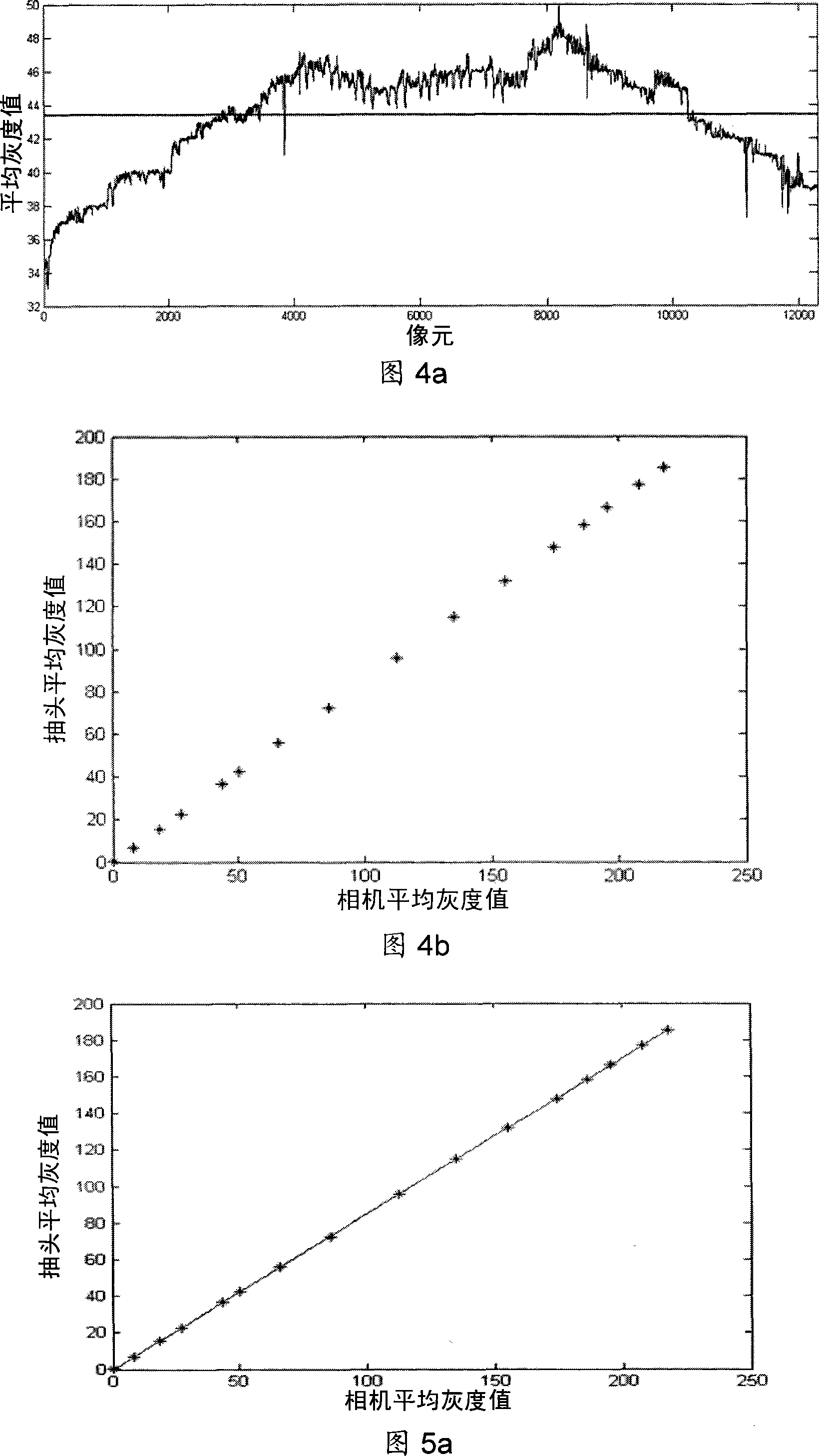
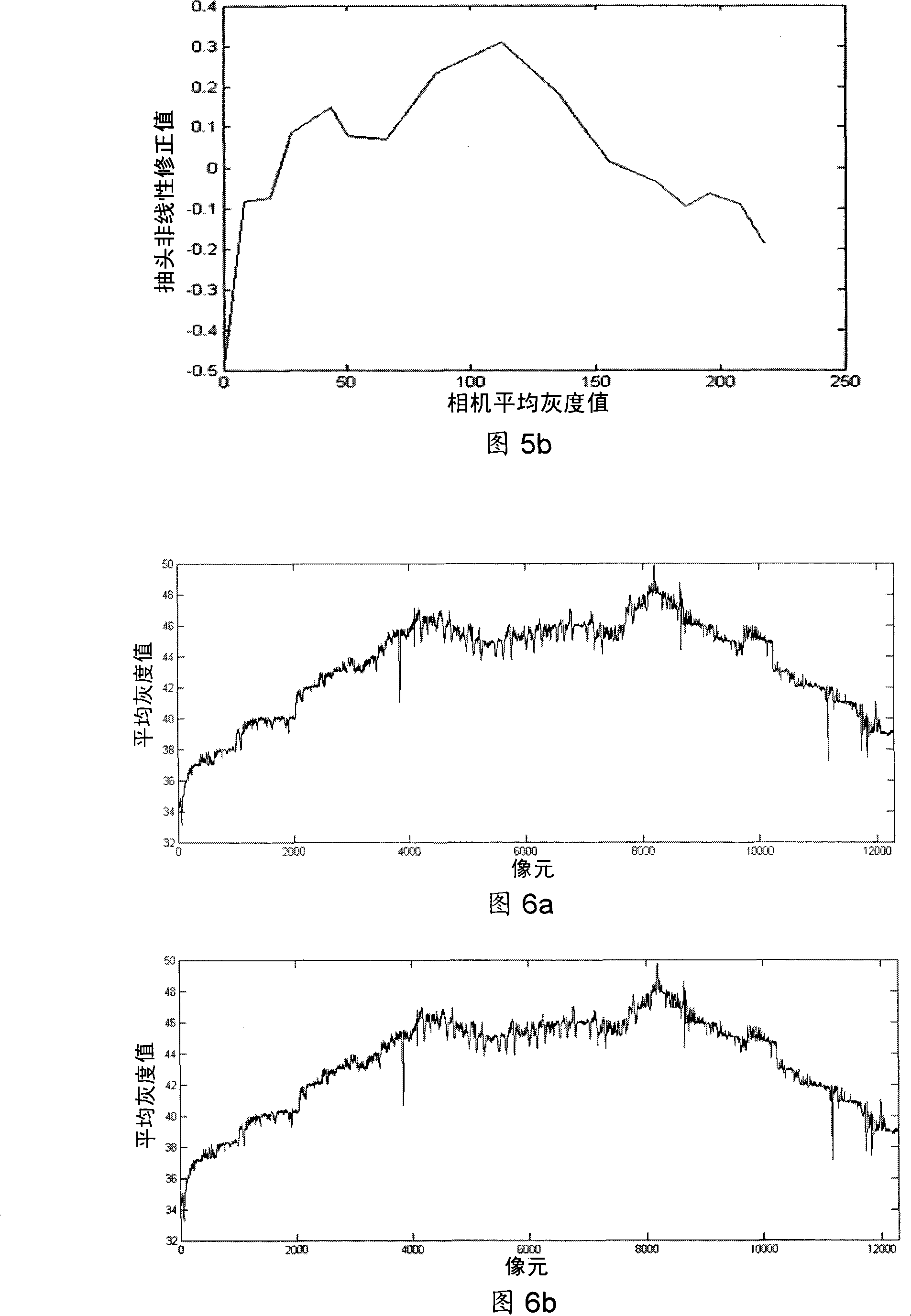
Disclosed is a relative radiometric correction method for the satellite-borne TDICCD camera. The steps comprises (1) analyzing the response output of a tapping under different light intensities and acquiring a scatter diagram of tapping light intensity response, (2) carrying out linear fitting to the scatter diagram of tapping light intensity response, then carrying out linear interpolation to the scatter diagram to obtain an interpolation curve, subtracting the interpolation curve of each tapping from respective fitting line to obtain a non-linear modified function of the tapping to light intensity, (3) using the non-linear modified function to carry out non-linear modification one after another to tapping of radiometric calibration data, and obtaining modified radiometric calibration data, (4) processing the modified radiometric calibration data and obtaining a modified inter- calibration coefficient, (5) carrying out radiation homogeneousness correction to arbitrary image produced by TDICCD via using the non-linear modified function and the modified inter- calibration coefficient. The invention resolves the problem that non-linear response to light intensity of the tapping can not be corrected in existing radiometric calibration method, and can increase relative radiometric calibration accuracy.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
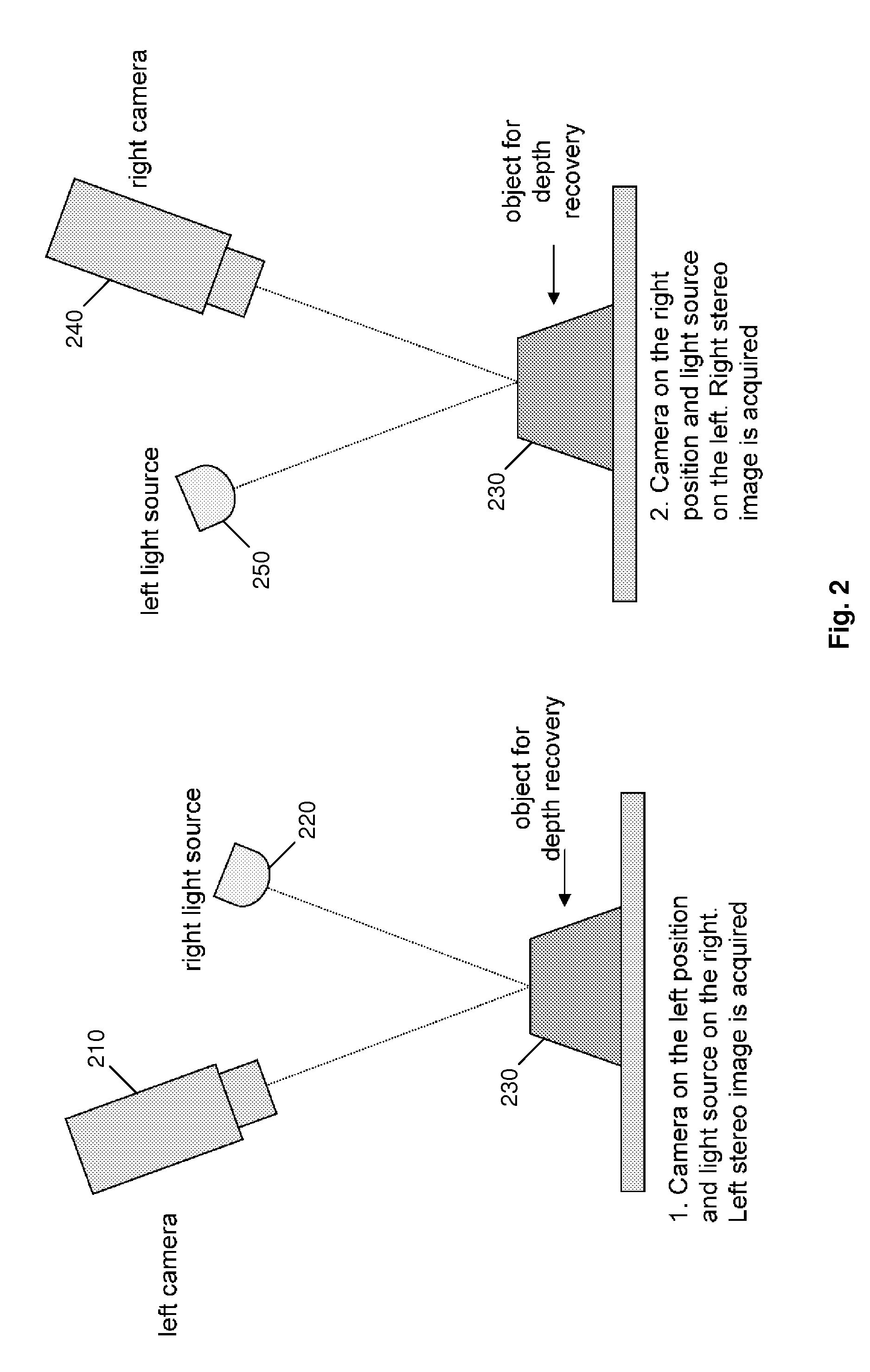
Fast three dimensional recovery method and apparatus
InactiveUS7769205B2Easy to useSimple setup and calibration processImage enhancementImage analysisRecovery methodMetrology
The present invention comprises a method and an apparatus for three dimensional modeling to allow dense depth maps to be recovered, without previous knowledge of the surface reflectance, from only a single pair of stereo images. Several initial steps are performed for stereo and radiometric calibration and rectification for obtaining accurate results. The apparatus for the stereo images acquisition includes internal light sources, these are automatically commuted by a illumination control in order to fulfill the reciprocity property, a stereo camera head composed by the necessary optics to acquire the reciprocal stereo images and a compatible PC interface. The invention is faster than other systems since it requires only two images for obtaining a dense depth model of objects with an arbitrary surface reflectance distribution allowing the system to be used in a wide range of applications such as metrology, quality control, medical and dynamic three dimensional modeling.
Owner:PREFIXA VISION SYST DE C V
Infrared spectral radiometric calibration system
InactiveCN101008584AAbility to measure with high precisionImprove stabilityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingSpectral responsivity
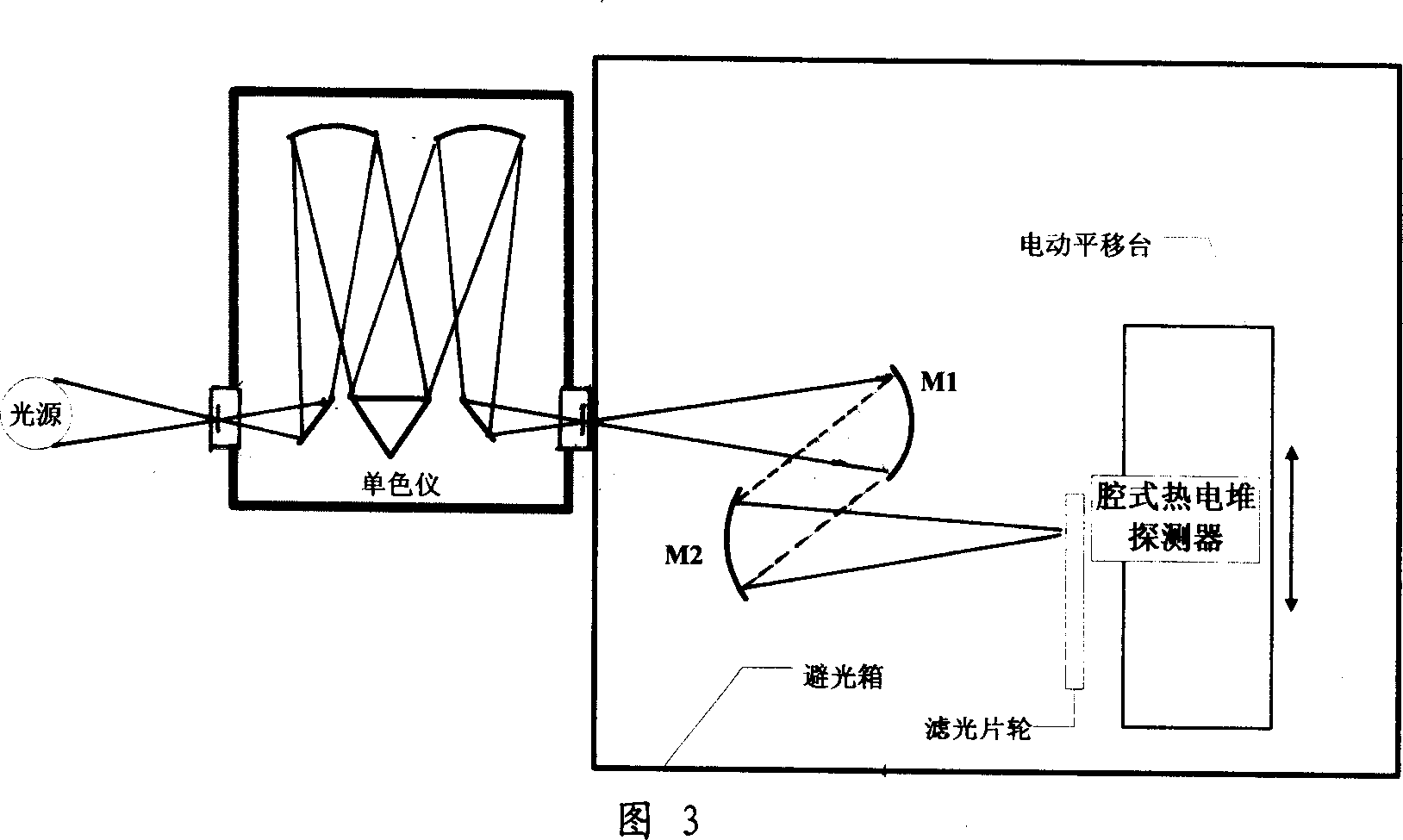
This invention discloses one infrared light spectrum scaling system based on detector, wherein, the light source and single color device incidence seam are fixed with wave trop device; the single color device inside is fixed with grating from exit seam into light shield box through two axis arc lens and filter slices to detector and scaling detector. This invention adopts Newport company infrared light source and Acton Research single color machine to realize light spectrum response test volume of 1 mum-12 mum.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
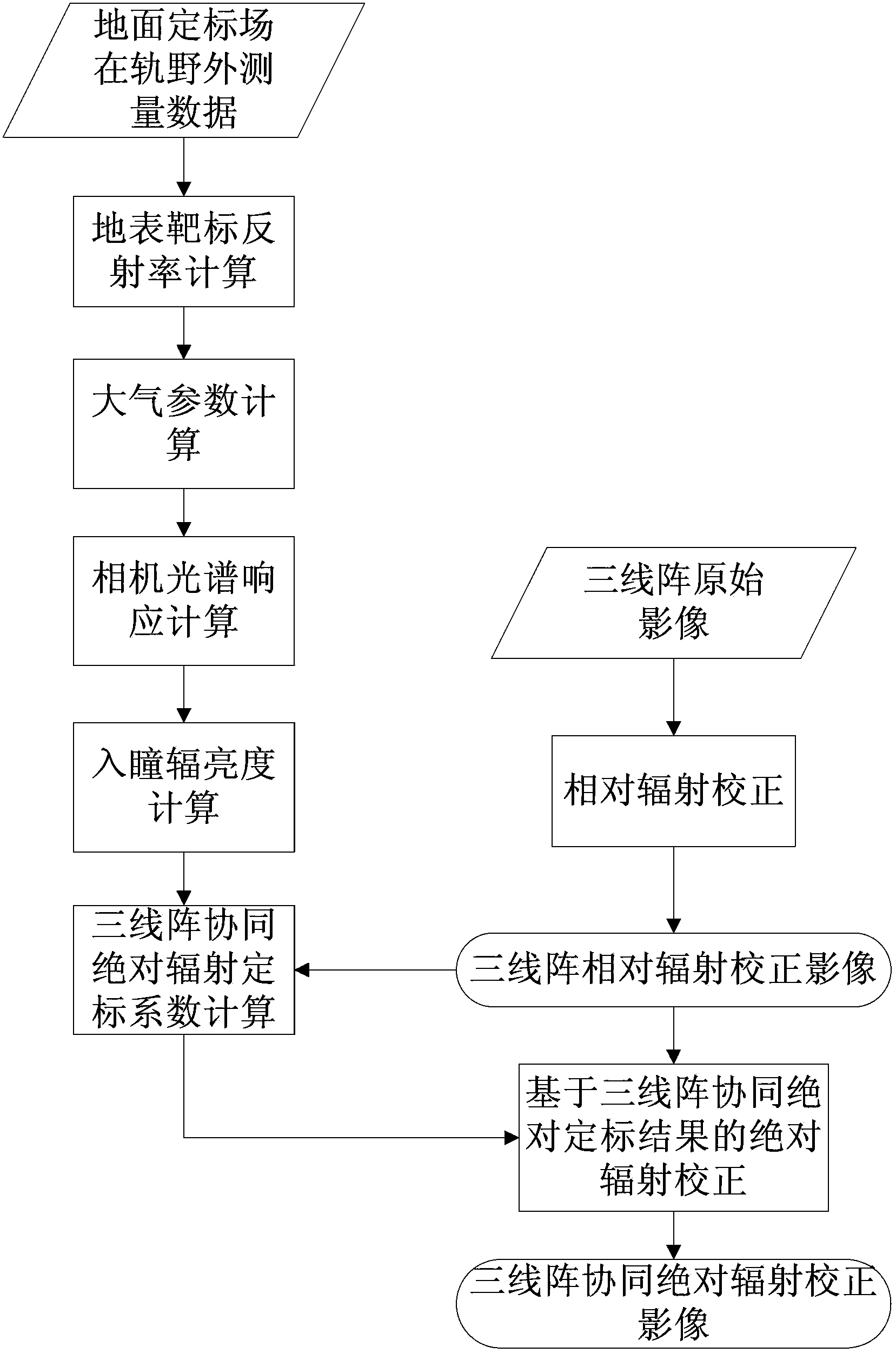
Three-line-array camera image collaborative absolute radiometric calibration and compensation method
ActiveCN103438900ATruly reflect the actual spectral characteristicsReflect the actual spectral characteristicsMeasurement devicesSpectral responseCorrection method
The invention discloses a three-line-array camera image collaborative absolute radiometric calibration and compensation method. The three-line-array camera image collaborative absolute radiometric calibration and compensation method comprises following steps: 1) respective relative radiometric calibration of three-line-ray camera images; 2) calculation of ground target reflectivity; 3) calculation of atmosphere parameters; 4) respective spectral response calculation of the three-line-ray camera; 5) respective entrance pupil radiance calculation of the three-line-array camera; 6) calculation of three-line-array collaborative absolute radiometric calibration coefficients; and 7) absolute radiometric correction based on the three-line-array collaborative absolute radiometric calibration coefficients. According to the three-line-array camera image collaborative absolute radiometric calibration and compensation method, an unified model is constructed based on the radiation response relationship of front sight, fore sight and back sight images of the three-line-array camera, so that actual spectral characteristics of the ground target are reflected by the radiation response of three-line-array imagines, and the foundation for photogrammetric stereoplotting and remote sensing quantitative application is provided.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
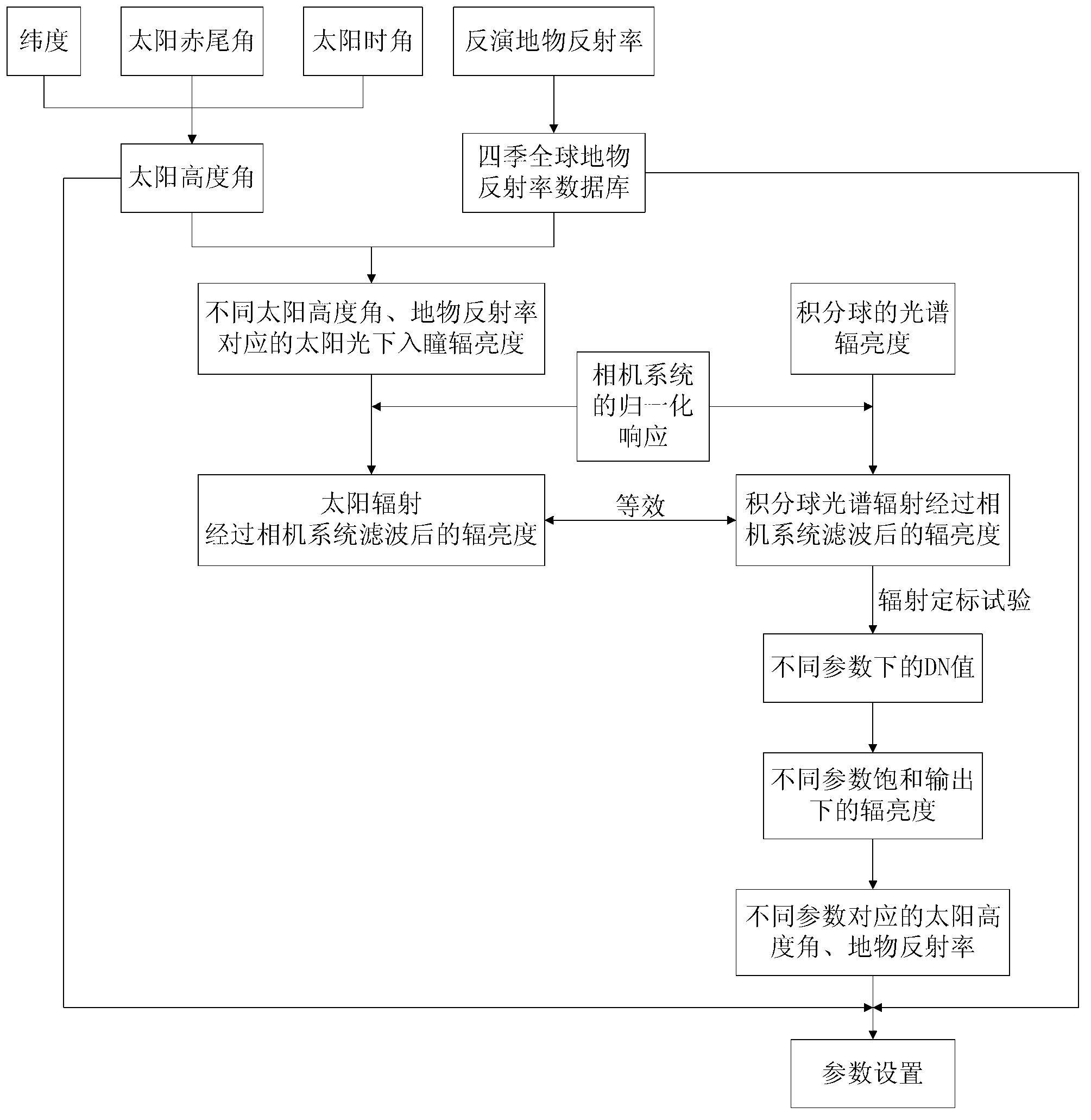
Method for on-orbit optimization of imaging parameters of TDI CCD camera
ActiveCN103322981AImprove impactImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsPicture taking arrangementsImaging conditionImaging quality
The invention discloses a method for on-orbit optimization of imaging parameters of a TDI CCD camera. The method is suitable for different imaging conditions. The method comprises the following steps of 1, aiming at a season change, building a global ground feature reflectivity database by an acquired satellite image, 2, making solar spectral radiance and integrating sphere spectral radiance equivalent by normalized responsibility of a camera system, and acquiring a relationship between a camera system output and apparent radiance according to a radiometric calibration test result, and 3, by the global ground feature reflectivity database and a solar altitude change, acquiring a camera parameter arrangement suggestion by the above computed result. Aiming at different ground feature objects and imaging conditions, the method can realize real time calculation of TDI integration class and gain and provide the calculation result for a user. The method guarantees accuracy, real-time performances and reliability of on-orbit parameter arrangement and improves on-orbit imaging performances and image quality of an optical remote sensor.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
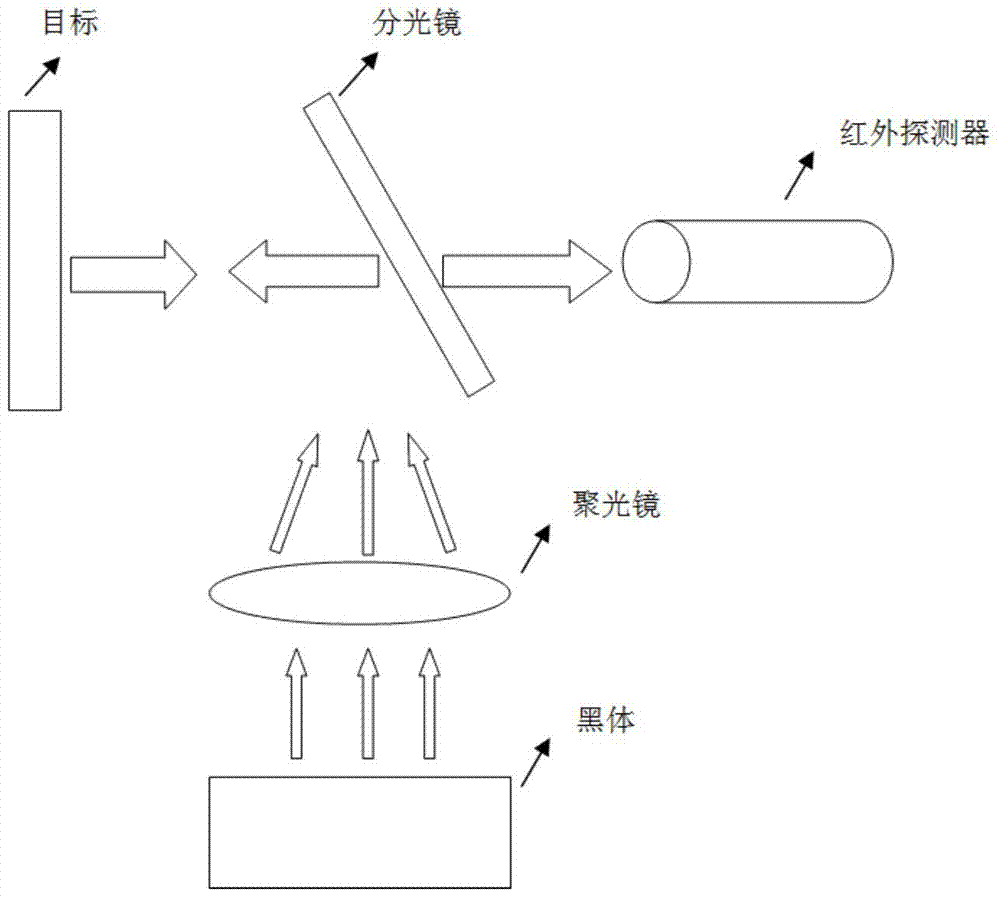
Site target emissivity measuring system and method based on environmental radiation change
InactiveCN104266762ARadiation characteristics do not changeDoes not change the temperature fieldPyrometry using electric radation detectorsEmissivityOptical axis
The invention discloses a site target emissivity measuring system and method based on the environmental radiation change. The system comprises a target, a spectroscope and an infrared detector, wherein the target, the spectroscope and the infrared detector are sequentially arranged in the optical path direction and located on the same optical axis. The system further comprises a black body and a collecting lens. Radiation light of the black body converges on the spectroscope through the collecting lens, is reflected to the target through the spectroscope, acts on the target, then is reflected to the spectroscope and reaches the detector. The method includes the steps that firstly, radiometric calibration is conducted on the infrared detector; a system response function is established with the radiation of the black body serving as the standard; an output response value V1 of the infrared detector is measured under the condition of the environmental radiation intensity Vs1; an output response value V2 of the infrared detector is measured when the condition is changed into the environmental radiation intensity Vs2; according to the output response values measured under the two different radiation intensity conditions of the infrared detector, the reflectivity and the emissivity of the target are calculated. According to the system and method, necessary parameters are provided for infrared radiation non-contact accurate temperature measurement.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
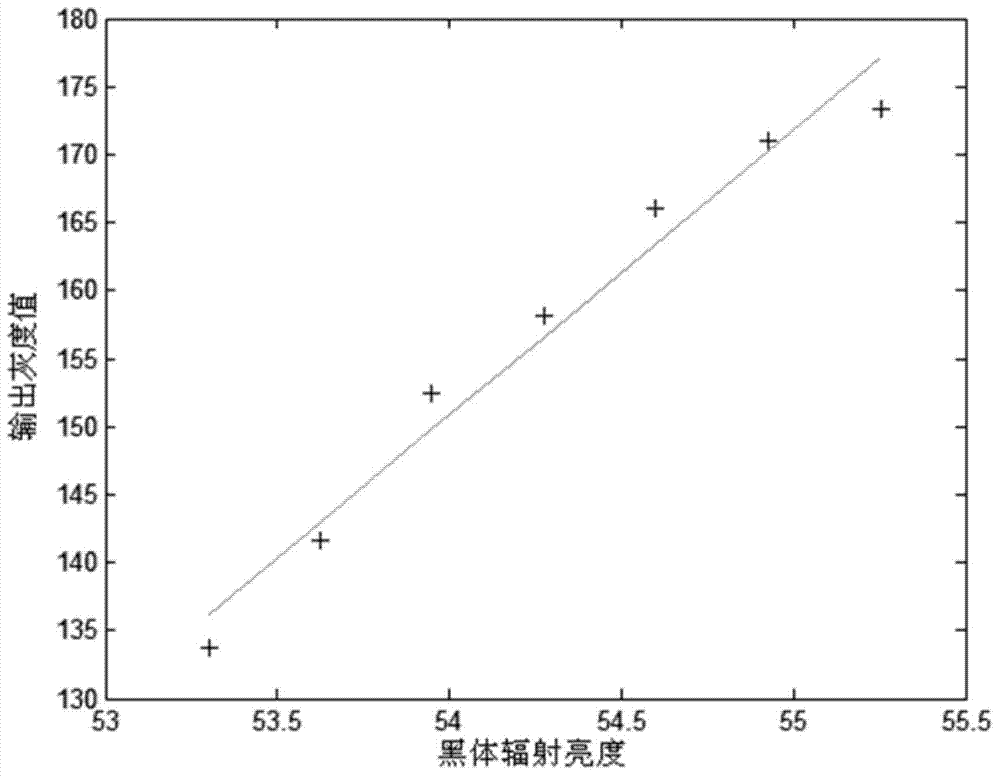
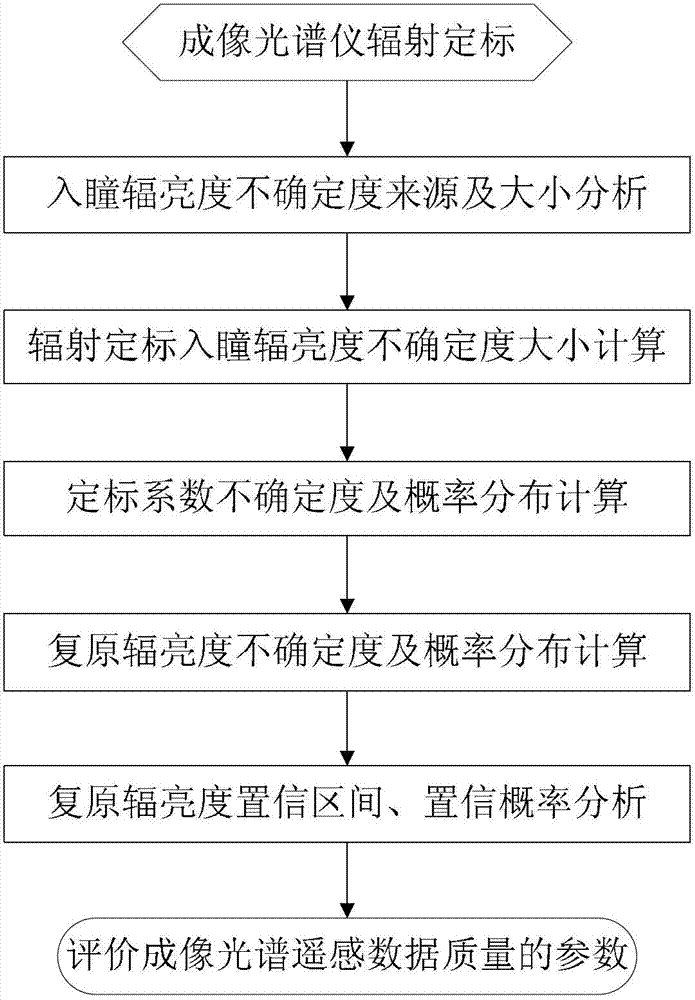
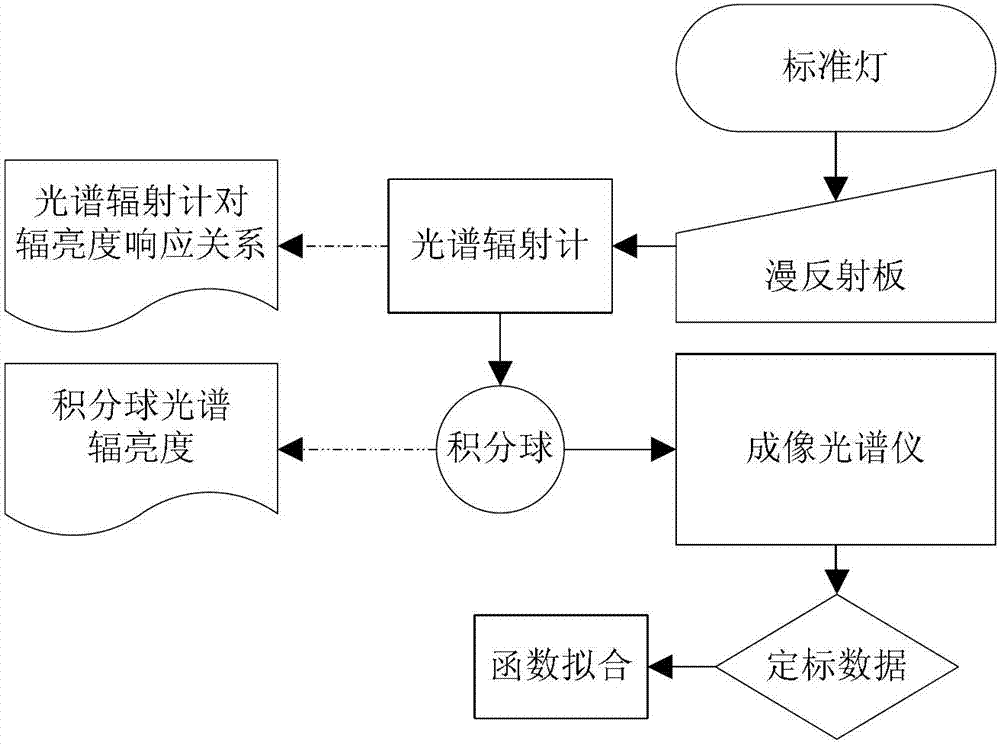
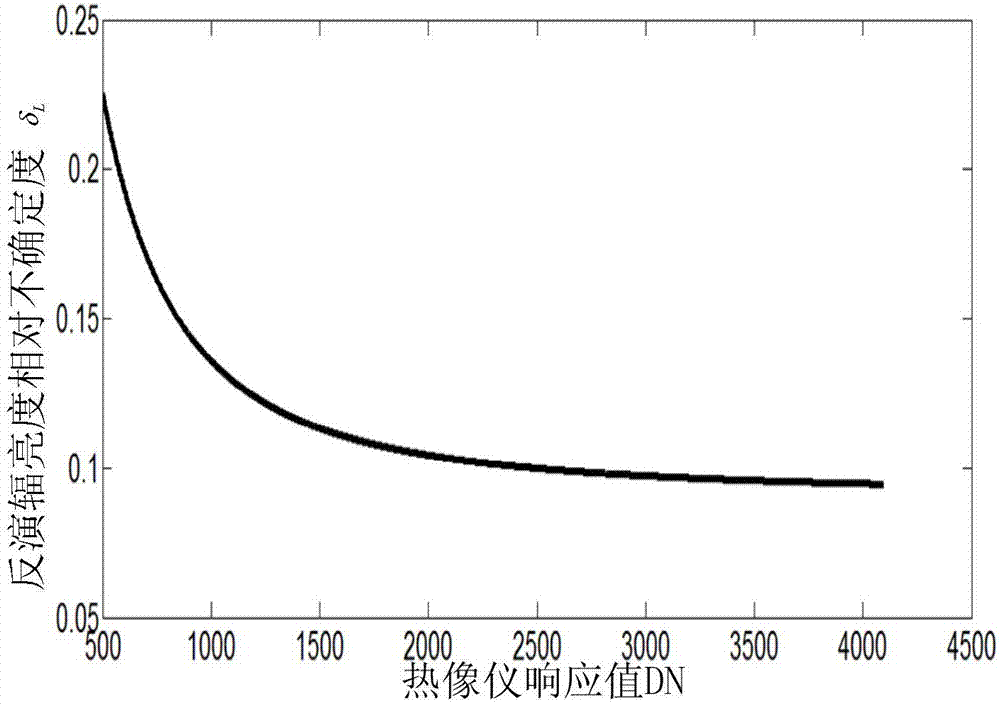
Impact analysis method of imaging spectrometer radiometric calibration precision on data quality
ActiveCN102879094ARich evaluation methodsEffective evaluationSpectrum investigationSensing dataData simulation
An impact analysis method of imaging spectrometer radiometric calibration precision on data quality includes six steps. Uncertainty of entrance pupil radiance in an imaging spectrometer radiometric calibration process is computed by analyzing uncertainty origins impacting the entrance pupil radiance in a laboratory radiometric calibration process and uncertainty of each impact quantity, probability distribution of the entrance pupil radiance is obtained by the central limit theorem, further the uncertainties of calibration coefficients and the probability distribution form of the calibration coefficients are obtained by computing of two-dimensional random variables and function probability distribution, and finally uncertainty and probability distribution of recovery radiance are obtained. The method can be used for analyzing impacts of the radiometric calibration precision on the imaging spectrometer remote sensing data quality, so that precision of remote sensing data simulation is improved beneficially, and the remote sensing data quality can be more effectively evaluated in a remote sensing process.
Owner:青岛唯实空间数据科技有限公司
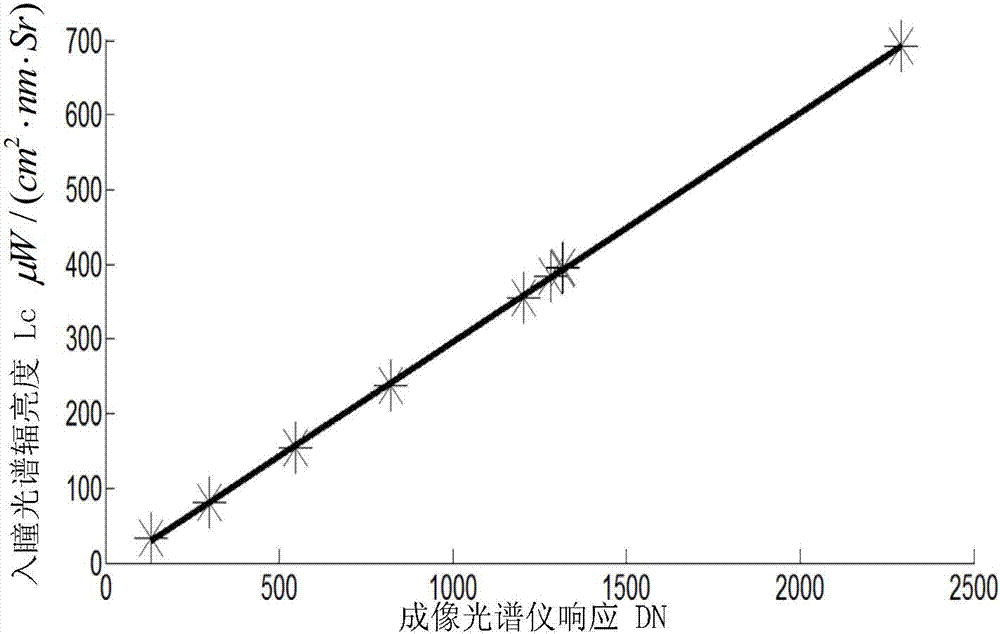
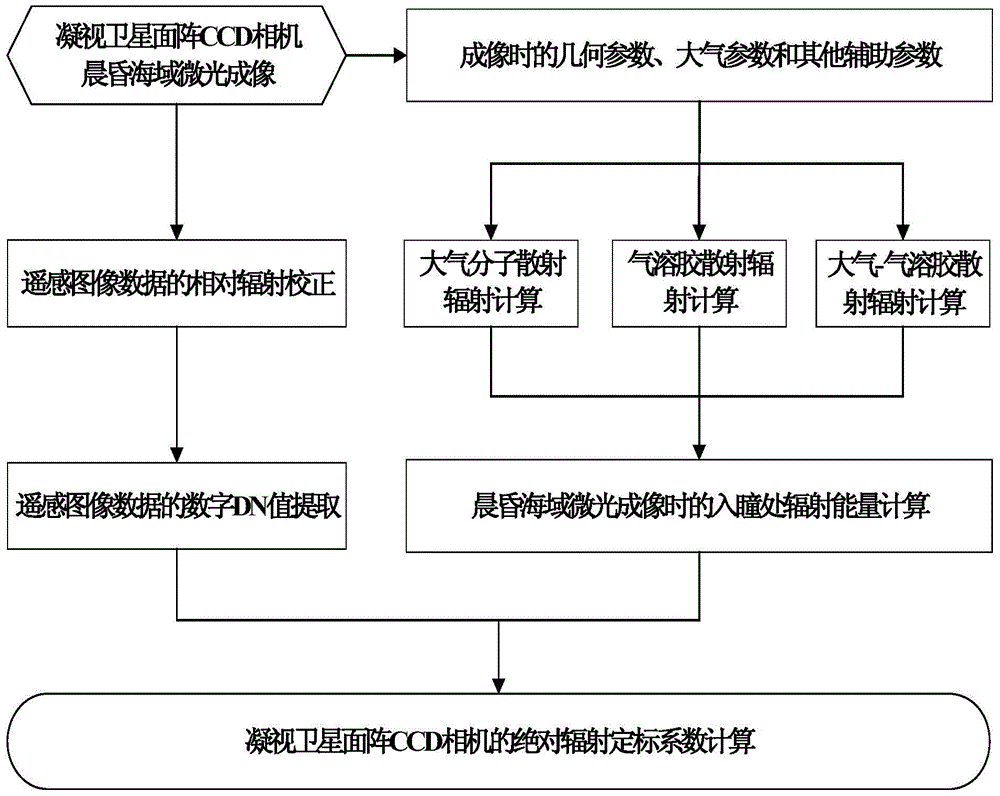
Absolute radiometric calibration method for satellite staring planar array CCD camera
The invention relates to an absolute radiometric calibration method for a satellite staring planar array CCD camera. The absolute radiometric calibration method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a linear quantitative relationship between digital DN value information after relative radiometric calibration for remote sensing image data of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera and radiation energy information at entrance pupil of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera, and a radiation energy model at the entrance pupil of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera in sea imaging; then calculating to obtain radiation energy L at the entrance pupil of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera in low light level imaging of the sea area at morning or nightfall and acquire a sample average value of all probing digital DN values of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera after the relative radiometric calibration to be used as an average digital DN value DNR of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera probing units; and finally performing linear fitting on the above L and DNR and calculating to obtain an absolute radiometric calibration coefficient. The absolute radiometric calibration method overcomes the technical problem of no absolute radiometric calibration method for in-orbit operation of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
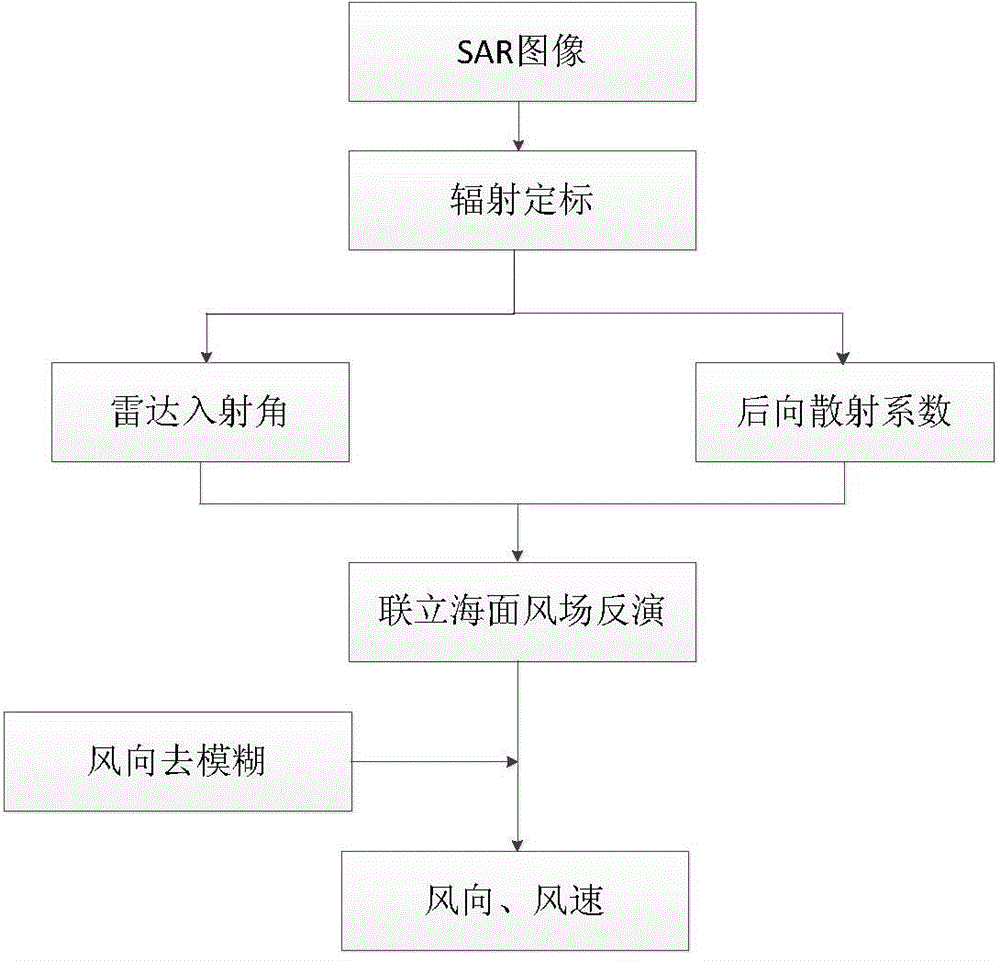
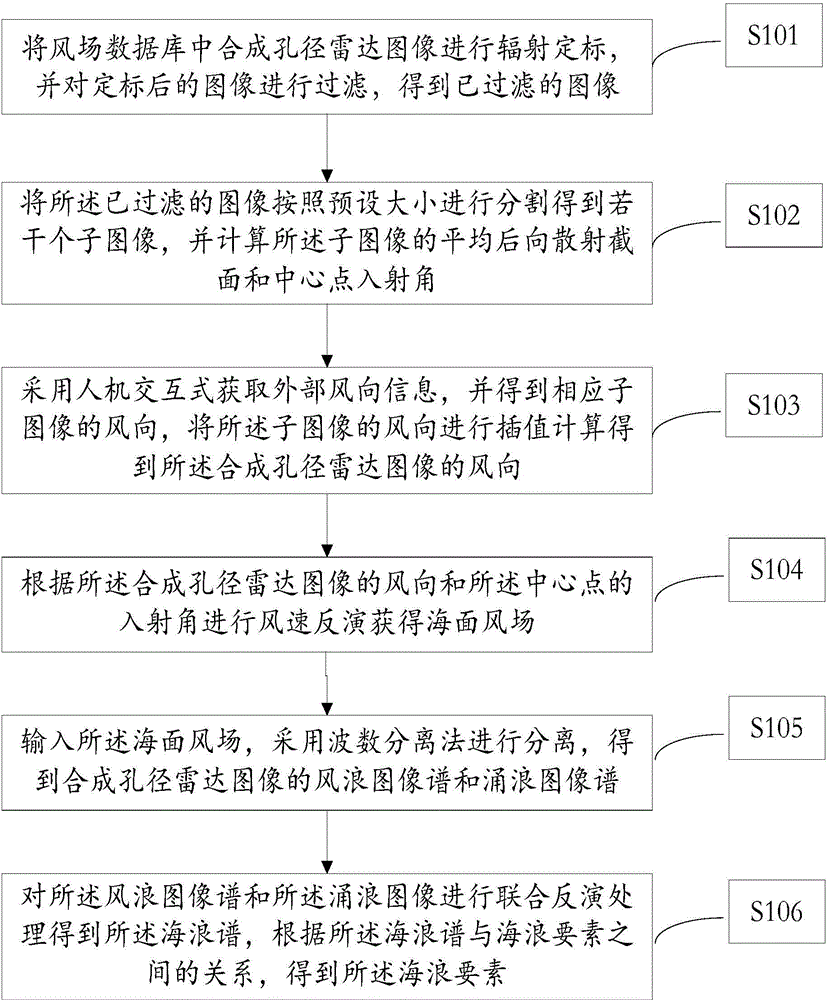
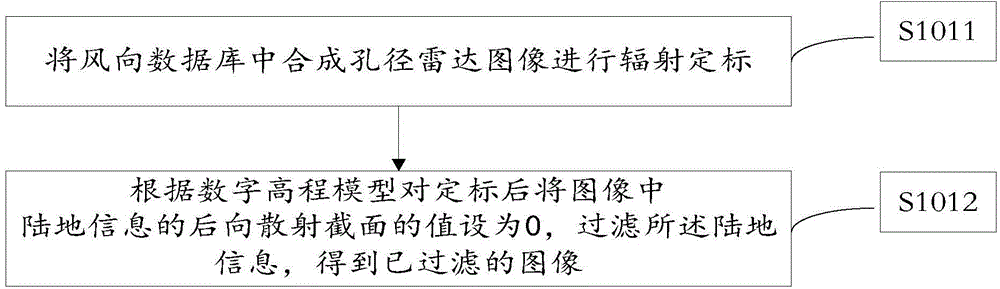
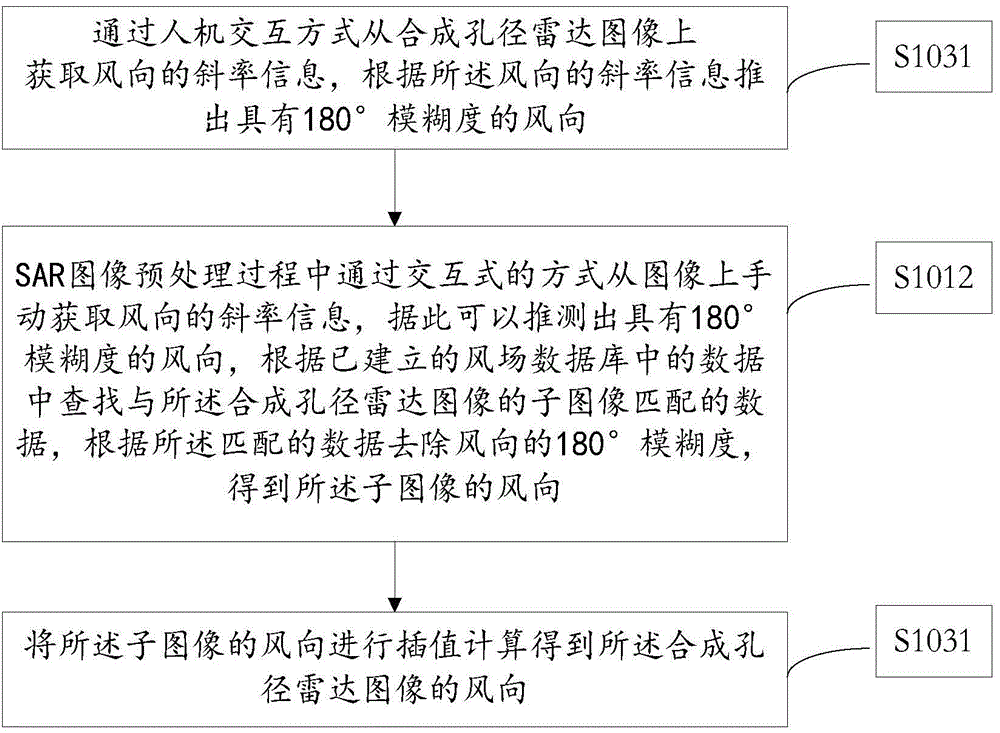
Ocean wind-field retrieval method of double-frequency coplanar synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
The invention discloses an ocean wind-field retrieval method of a double-frequency coplanar synthetic aperture radar (SAR), relates to the technical field of remote sensing, and aims at developing a new ocean wind-field retrieval method according to the ocean detection characteristics of the double-frequency coplanar SAR. The method comprises the steps of performing radiometric calibration for an SAR image to obtain the calibrated SAR image; analyzing calculating backscattering coefficients through L-waveband and C-waveband geophysical model functions; then performing simultaneous restructuring for the L-waveband and C-waveband geophysical model functions to obtain the minimum cost functions; directly solving to obtain the ocean wind speed and wind direction; removing fuzzy wind direction. With the adoption of the method, the problem that the SAR ocean wind-field retrieval method depends on the background field wind direction data and wind stripes can be effectively solved, high-precision ocean wind speed and wind direction can be inverted directly through the back scattering of the radar, and therefore, the support is provided to the service application of the SAR ocean wind-filed detection.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for carrying out relative radiometric calibration on CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) image
ActiveCN104580944AThe level of DN value is consistentEliminate chromatic aberrationTelevision system detailsImage enhancementRadianceCcd camera
The invention provides a method for carrying out relative radiometric calibration on a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) image, which is used for carrying out relative radiometric calibration on an original image obtained through push broom of a one-dimensional CCD camera. The method comprises the following steps of step A testing radiometric calibration data (formula) of each detection unit of the one-dimensional CCD camera under different integrating sphere output radiances Lj and different integral times Tk by utilizing an integrating sphere method; step B computing a relative radiometric calibration coefficient of each detection unit by the radiometric calibration data (formula) of each detection unit of the one-dimensional CCD camera under different energy levels Lj and different integral times Tk through an improved relative radiometric calibration model through; and step C carrying out radiation intensity calibration on each pixel in the original image by utilizing the relative radiometric calibration coefficient of each detection unit corresponding to a pixel so as to obtain an image after relative radiometric calibration. According to the method, the problem of obvious chromatic aberration of a splicing image of the interior of the same flight strip and an adjacent flight strip, which is caused by the difference between the integral times during processing of an airway array CCD image, is avoided.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
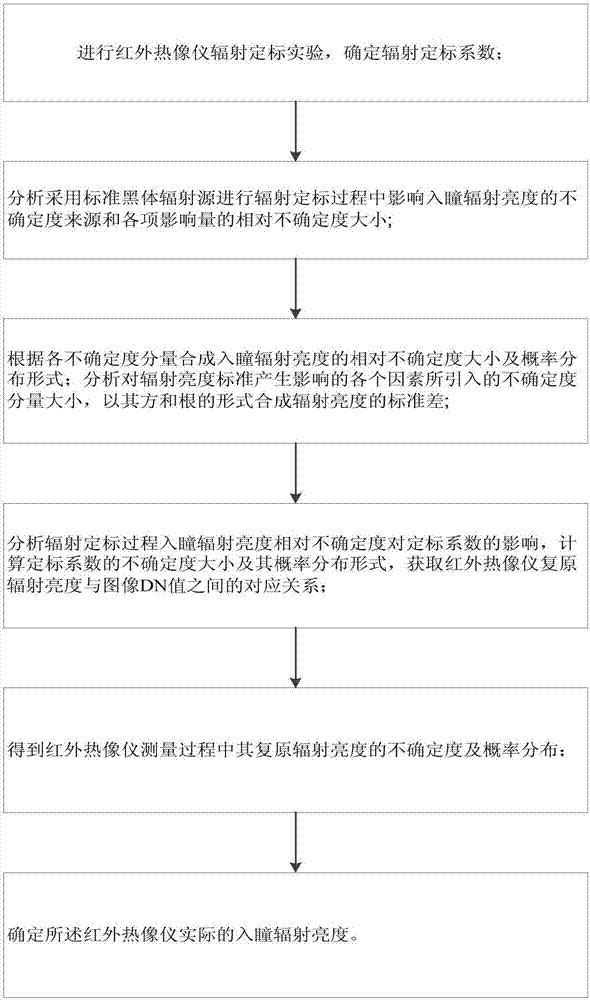
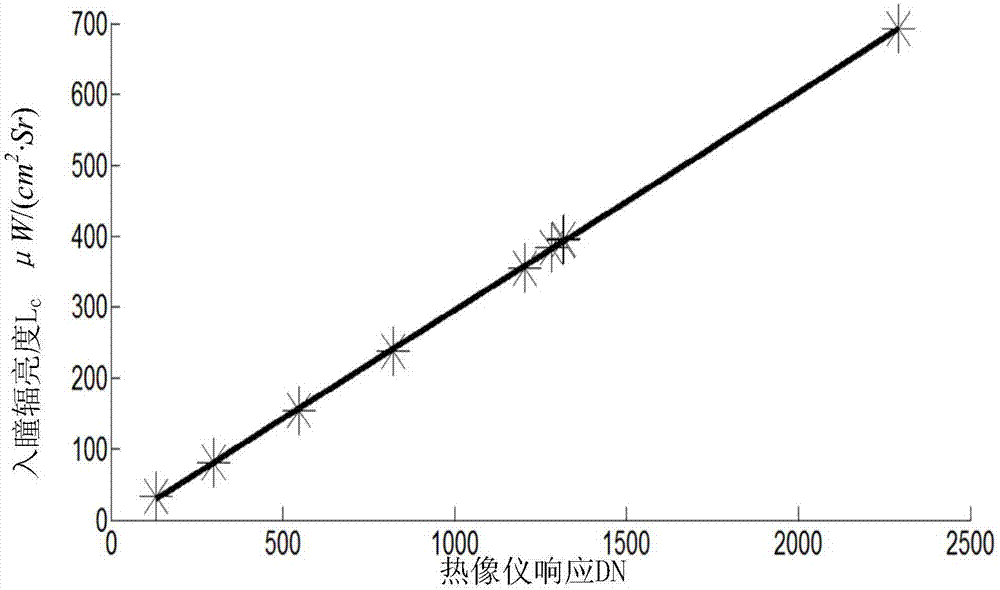
Thermal imager radiation calibration accuracy analysis method
The invention discloses a thermal imager radiation calibration accuracy analysis method. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) an infrared thermal imager radiometric calibration experiment is performed, and a radiometric calibration coefficient is determined; (2) the sources of uncertainties influencing entrance pupil radiance in a process when a standard blackbody radiation source isadopted to perform radiometric calibration, and the relative uncertainty magnitudes of influence quantities are analyzed; (3) the relative uncertainty magnitude and probability distribution form of the entrance pupil radiance are synthesized, the magnitudes of introduced uncertainty components are analyzed, and the standard deviation of the radiance is synthesized; (4) the uncertainties and probability distribution form of the radiometric coefficient are calculated, a corresponding relation between the recovered radiance and DN value of a thermal imager is obtained; (5) the uncertainty and probability distribution of the recovered radiance of the thermal imager are obtained; and (6) the actual entrance pupil radiance of the thermal infrared imager is determined. The thermal imager radiation calibration accuracy analysis method of the invention is used for evaluating the reliability of the radiance measurement of the infrared thermal imager, and can improve calibration accuracy and improve data quality.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
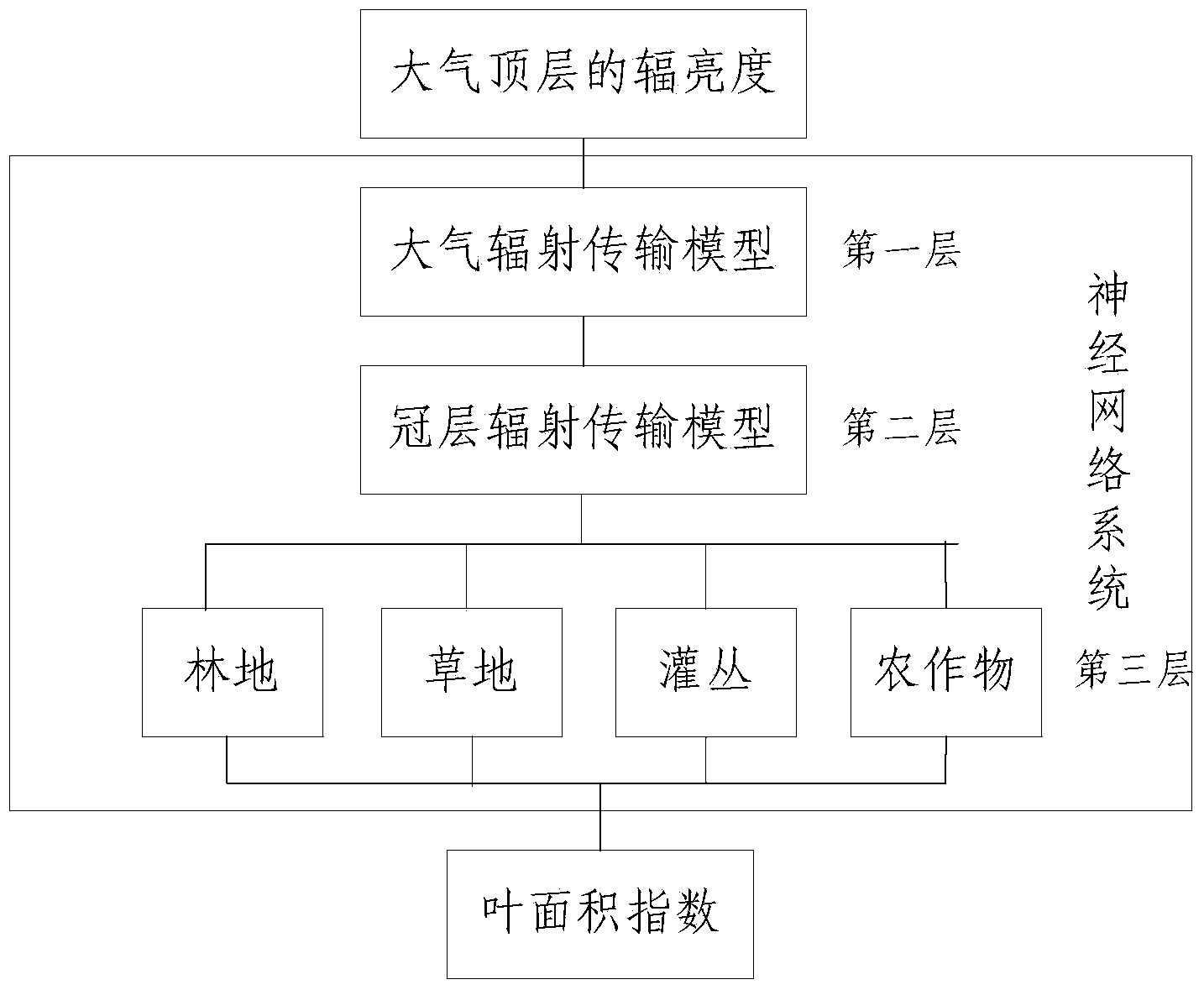
Method and device for performing vegetation parameter remote sensing retrieval in neural network system
ActiveCN103529439AStrong simulationThe result is accurateBiological neural network modelsElectromagnetic wave reradiationSensing dataVegetation
The invention provides a method and device for performing vegetation parameter remote sensing retrieval in a neural network system. The method comprises the steps as follows: training data sets between vegetation parameters and earth surface reflectance of different types of earth surfaces are obtained according to simulation models of earth surface reflectance of different types of earth surfaces; a neutral network between the vegetation parameters and earth surface reflectance of different types of earth surfaces is established; training data sets between earth surface reflectance and apparent reflectance under different meteorological conditions are obtained according to atmospheric radiation models; a neutral network between the earth surface reflectance and the apparent reflectance under different atmospheric conditions is established; multiple neutral networks are combined to form a neural network system; and remote sensing data obtained after radiometric calibration or atmospheric correction is subjected to vegetation parameter remote sensing retrieval in the neural network system. According to the method and the device, multiple different neutral networks can be combined to form the neural network system, compared with the prior art, the data analog capability is stronger, and an obtained result is more accurate.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
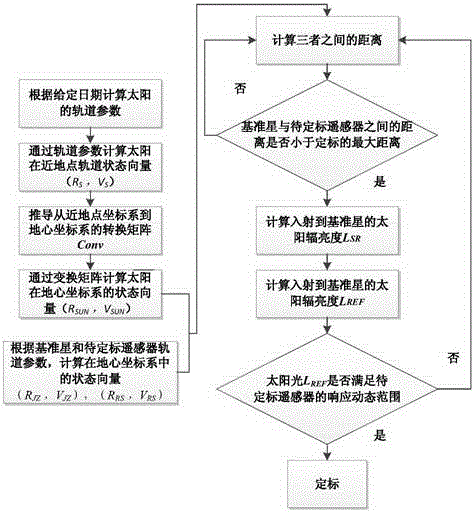
Radiometric calibration method based on on-orbit benchmark satellite
ActiveCN106643796AImprove calibration accuracyGet rid of featuresMeasurement devicesLink modelAbsolute calibration
Aimed at the current situation of poor on-orbit absolute radiometric calibration precision, the invention provides an on-orbit absolute radiometric calibration method based on a benchmark satellite. Sunlight with appropriate intensity is reflected onto a to-be-calibrated remote sensor by a diffuse reflection plate on a benchmark satellite, the influence of atmospheric conditions on a radiation transfer path is got rid of, an accurate apparent radiance is obtained, and thereby an accurate absolute calibration coefficient is obtained. In the invention, the sun, the benchmark satellite and the to-be-calibrated remote sensor are integrated into a geocentric coordinate system, so that the distance between each two of the three and the incidence angle and emergence angle of sunlight on the surface of the diffuse reflection plate on the benchmark satellite can be conveniently obtained, a radiation transfer link model from the sun to the benchmark satellite and to the to-be-calibrated remote sensor is created, and finally, calibration is complete.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Radiometric Calibration
InactiveUS20070257188A1Improve image qualityPrecise positioningRadiation pyrometryCalibration apparatusLength wavePyramid
A calibration load is provided for calibrating a signal in a range of wavelengths or of a single known wavelength. In one embodiment, the load comprises a calibration surface including an emissive material, the calibration surface having relief features, such as pyramids or wedges, that have a dimension that is substantially the same as or less than the shortest wavelength of the range of wavelengths or the single known wavelength that has to be calibrated.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Joint inversion method of sea surface wind field and sea waves
InactiveCN104036108AAvoid duplicate typingAccurate and efficient feedbackSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarSea waves
The invention discloses a joint inversion method of a sea surface wind field and sea waves. The joint inversion method of the sea surface wind field and the sea waves includes: performing radiometric calibration and filtration on a synthetic aperture radar image in a wind field database, splitting the image after being filtered into a plurality of subsidiary images according to preset size, and respectively calculating back scattering sections and central point incidence angles of the subsidiary images; using a man-machine interactive method to obtain external wind direction information, and obtaining the wind directions corresponding to the subsidiary images and obtaining the wind direction of the synthetic aperture radar image through interpolation calculation; processing the wind direction of the synthetic aperture radar image and the central point incidence angles so as to obtain spectrum of the sea waves, and obtaining parameters of the sea waves according to a relation between the spectrum of the sea waves and the parameters of the sea waves. The joint inversion method of the sea surface wind field and the sea waves achieves the purpose of avoiding repeating input operations of external information, can accurately and efficiently feed back the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) sea surface wind field, guarantees that the wind filed and the sea waves have the same spatial resolution, and improves accuracy of an inversion result.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com