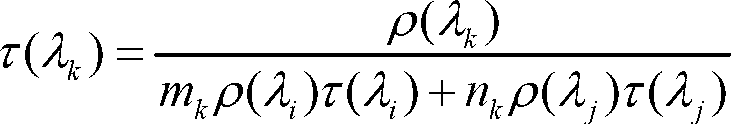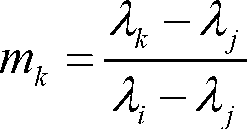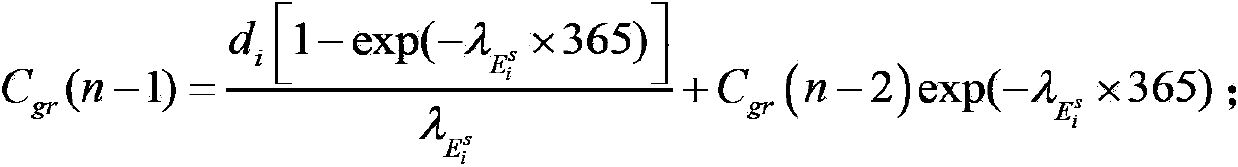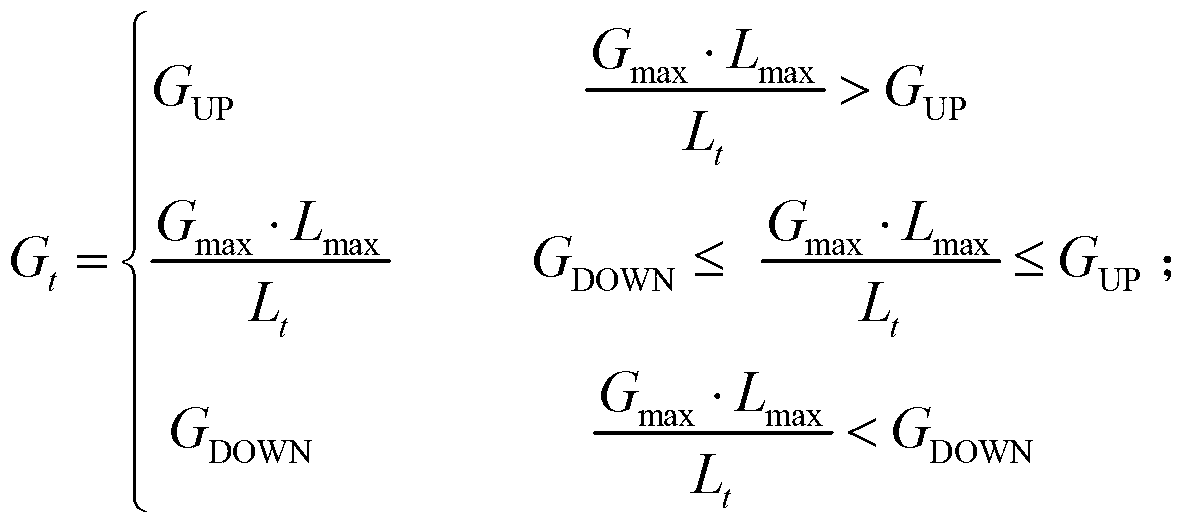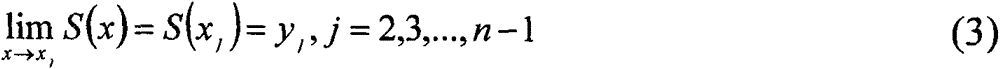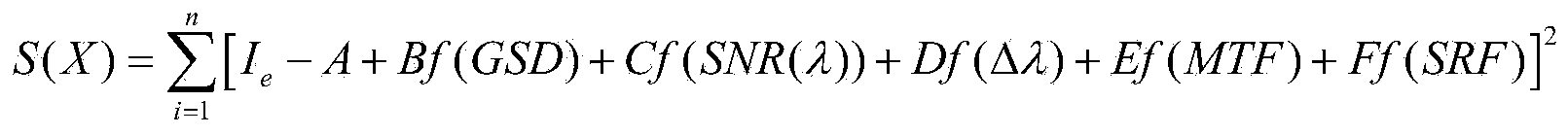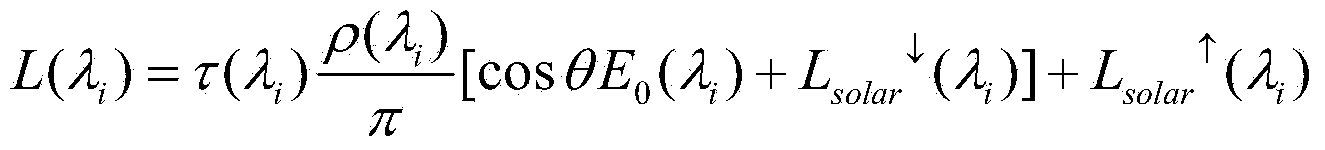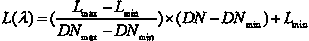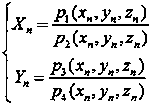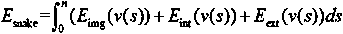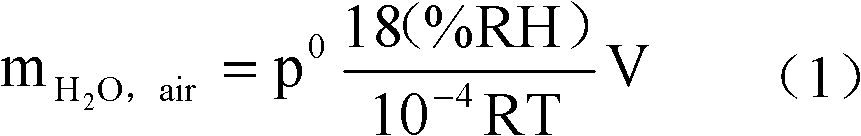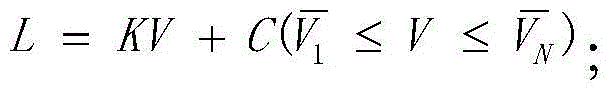Patents
Literature
204 results about "Atmospheric radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
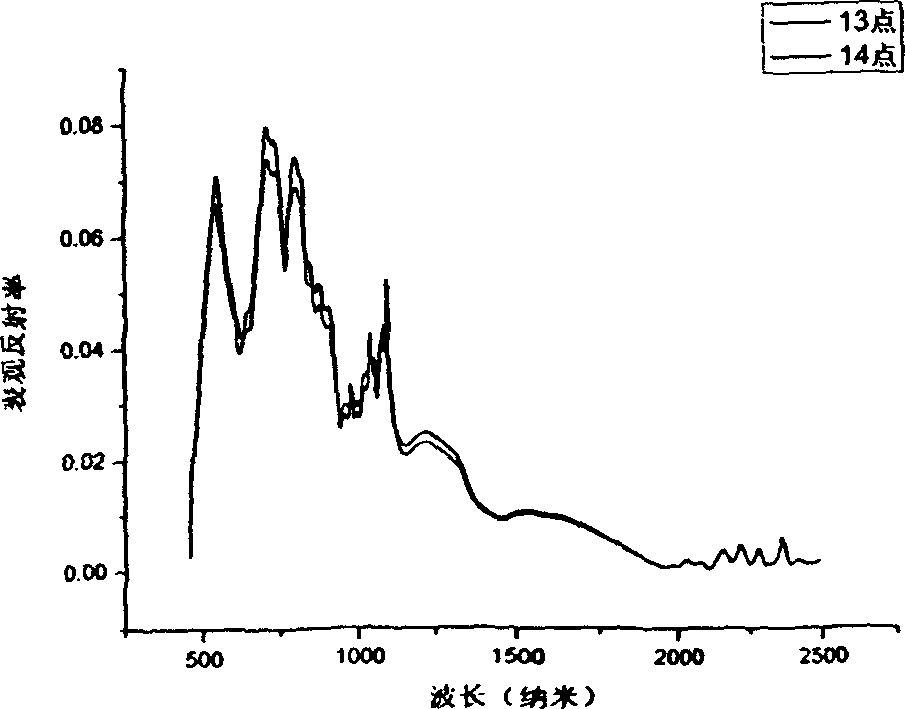
Atmospheric radiation is radiation that passes through the Earth's atmosphere and might circulate within it. Not all of the energy from the sun actually reaches the Earth's surface, and that which does might change in behavior by moving through the atmosphere.
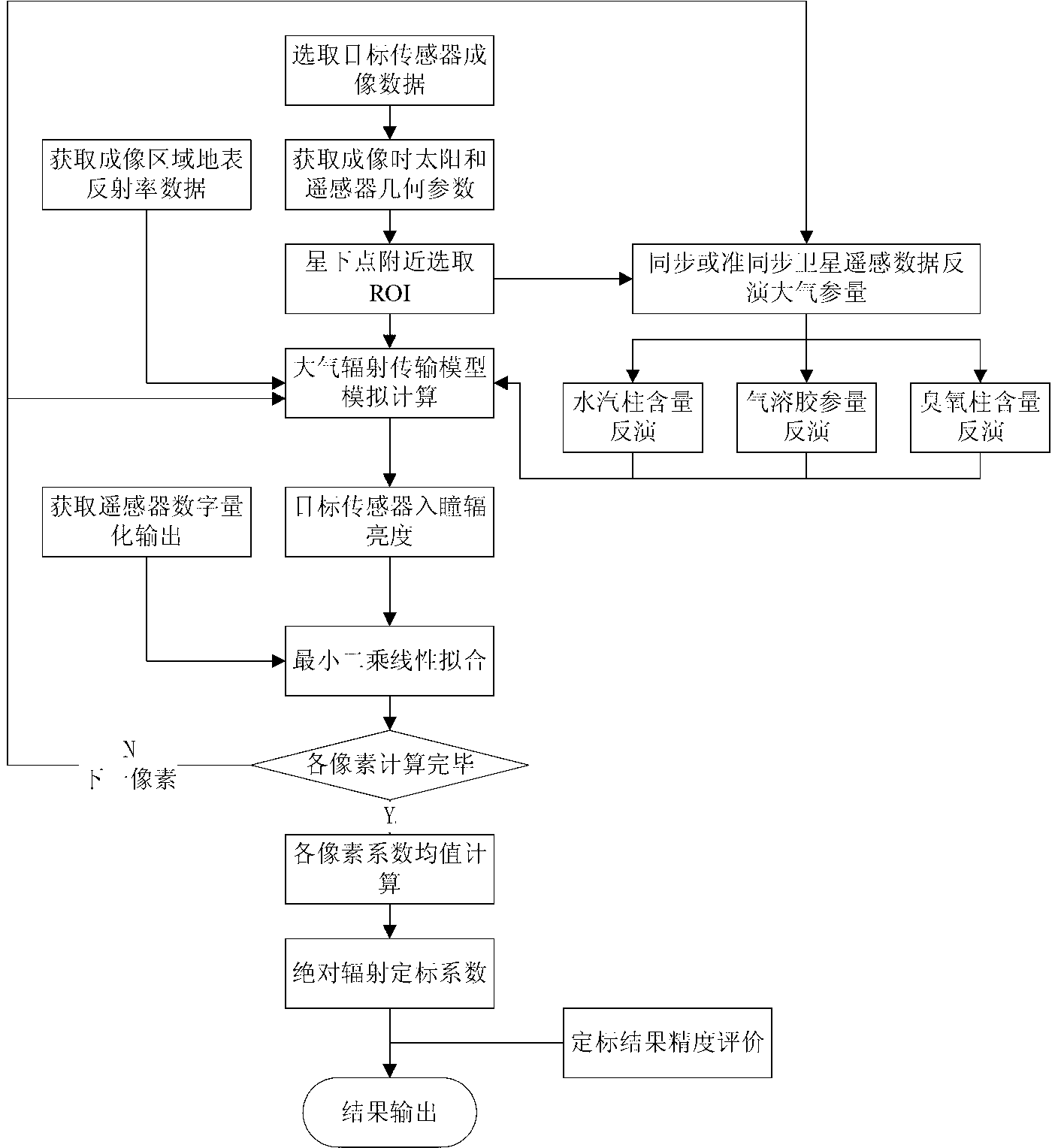
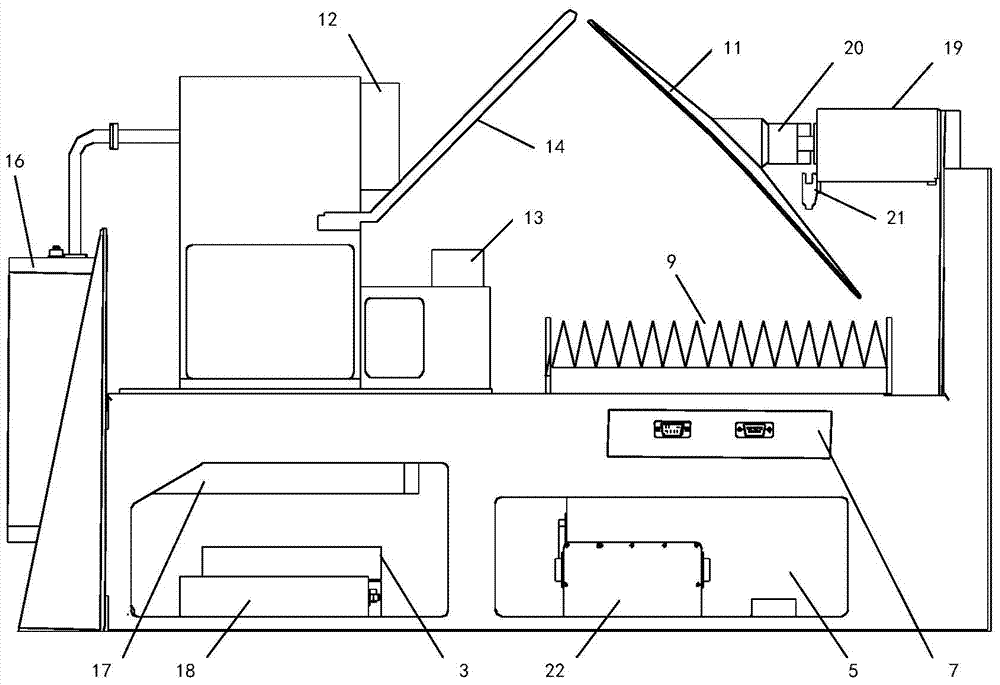
Satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval
InactiveCN103018736ASimulation is accurateAccurate entrance pupil radianceWave based measurement systemsMeteorological satelliteEntrance pupil
The invention discloses a satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval. The method includes nine steps. A surface reflectance is obtained through ground synchronous actual measurement during satellite crossing or historical data, imaging time and observation geometry parameters are obtained through remote sensing data head files, atmospheric parameters during imaging of synchronous crossing meteorological satellite sensors or related load retrieval remote sensors are utilized, the entrance pupil radiance of the remote sensors is calculated by an atmospheric radiation transmission model according to retrieval results of the atmospheric parameters, a calibration coefficient is calculated through a radiation calibration model, and thereby the on-orbit radiation calibration for a satellite-borne remote sensor is achieved. The satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on the atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval is a pixel-level calibration method and has the advantages that the accuracy is high, the costs are low, simultaneously, the high frequency calibration can be achieved, historical remote sensing data can be calibrated, and the method has a wide application prospect to remote sensing data processing methods and application technical fields.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Daytime land radiation fog remote sensing monitoring method based on object-oriented classification
InactiveCN103926634AAvoid the status quo that is difficult to detectPlay a supporting roleInstrumentsFeature parameterSpectral signature
The invention provides a daytime land radiation fog remote sensing monitoring method based on object-oriented classification. The method comprises the steps of selecting EOS / MODIS satellite remote sensing data with the highest spatial resolution being 250 m, constructing cloud and fog feature parameters through the combination of atmospheric radiation transmission model simulation and statistic of a large number of the EOS / MODIS satellite remote sensing data, and selecting a suitable remote sensing image partitioning algorithm to conduct image partitioning on the cloud and fog feature parameters; calculating spectral signatures, textural features, geometrical features and cloud and fog feature parameter feature values of homogeneous units obtained through partitioning one by one, training the attributes of the homogeneous units constructed after the image partitioning on the basis of ground actual measurement meteorological observation data and by the adoption of a decision tree classification algorithm, and constructing the daytime land radiation fog remote sensing monitoring method for fog detection. According to the daytime land radiation fog remote sensing monitoring method, the problem that low clouds and fog are hard to distinguish due to the similarity of spectra and textures can be effectively avoided.
Owner:CHANGJIANG RIVER SCI RES INST CHANGJIANG WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
Atmosphere correction method of airosol optical thickness of aeronautical high-spectrum remote-sensing inversion boundary layer
A method for inverting optical thickness of boundary layer aerosol includes picking up boundary layer aerosol optical thickness data from atmosphere transmission spectrum by utilizing transmission and radiation principle of atmosphere, obtaining expression reflectivity by carrying out reinterpolation for atmosphere and aerosol modes in boundary layer, thus realizing inversion of calculation for boundary layer aerosol optical thickness . The atmospheric calibration can be carried out based on result calculated out by above method.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
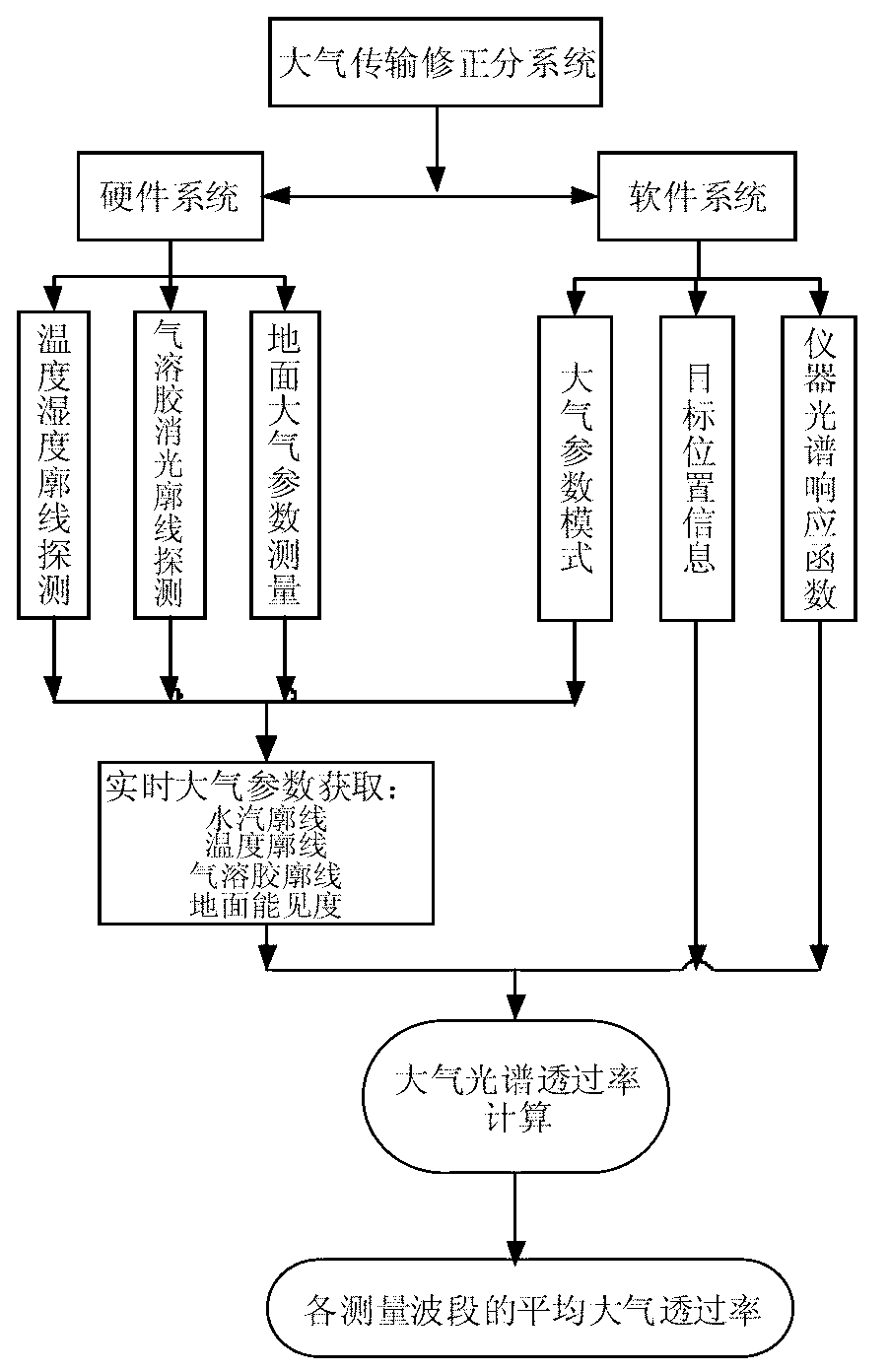
Atmospheric radiation transmission correction system and correction method
ActiveCN103278479AImprove calculation accuracyImprove real-time performanceTransmissivity measurementsMicrowave radiometerCorrection method
The invention discloses an atmospheric radiation transmission correction system and a correction method. The atmospheric radiation transmission correction system comprises a temperature and humidity profile detection system, an aerosol profile detection system, a ground atmospheric parameter measurement system and a general control computer, wherein the temperature and humidity profile detection system comprises a ground microwave radiometer; a signal output terminal of the ground microwave radiometer is connected with a first computer; the n aerosol profile detection system comprises a micro pulse laser radar; a signal output terminal of the micro pulse laser radar is connected with a second computer; the ground atmospheric parameter measurement system comprises an automatic weather station, a visibility meter and a rain sensor, signal output terminals of the automatic weather station, the visibility meter and the rain sensor are co-accessed a third computer; each computer is connected to a router through network cables; the general control computer is provided with anamospheric optical parameter control software and an atmospheric transmittance calculation software to calculate an average transmittance of various wave bands of a measuring device. The correction system and the correction method have high calculation speed and good stability and real-time performance.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
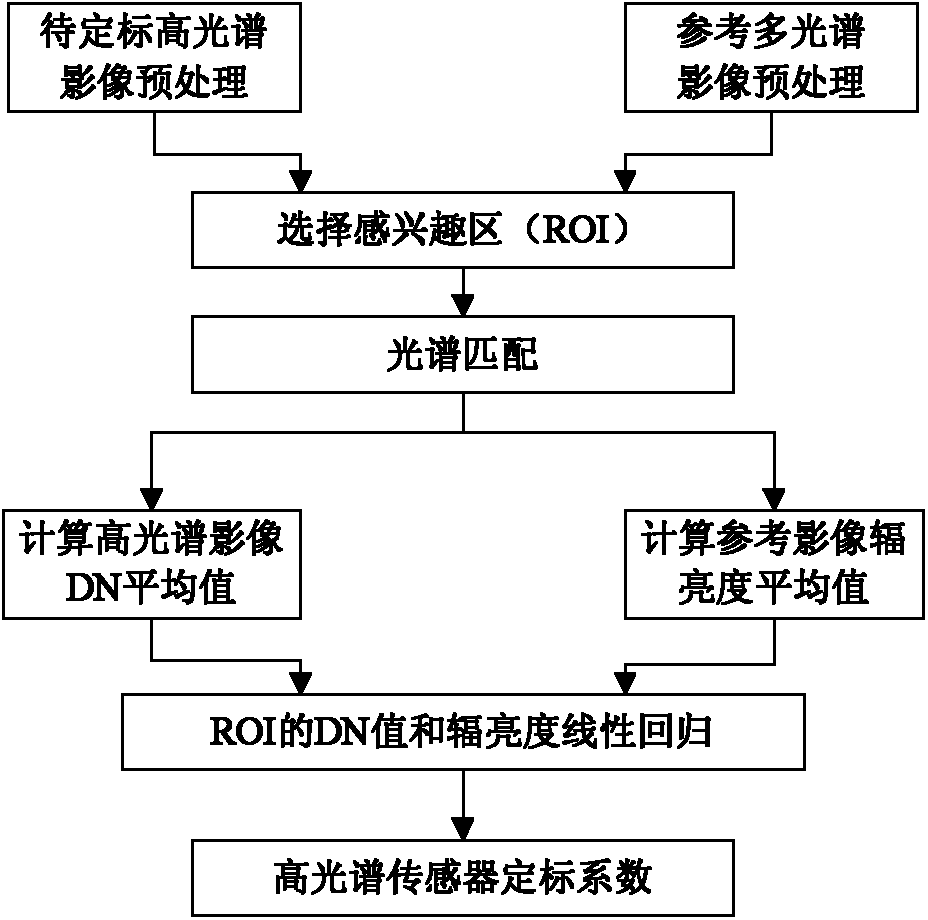
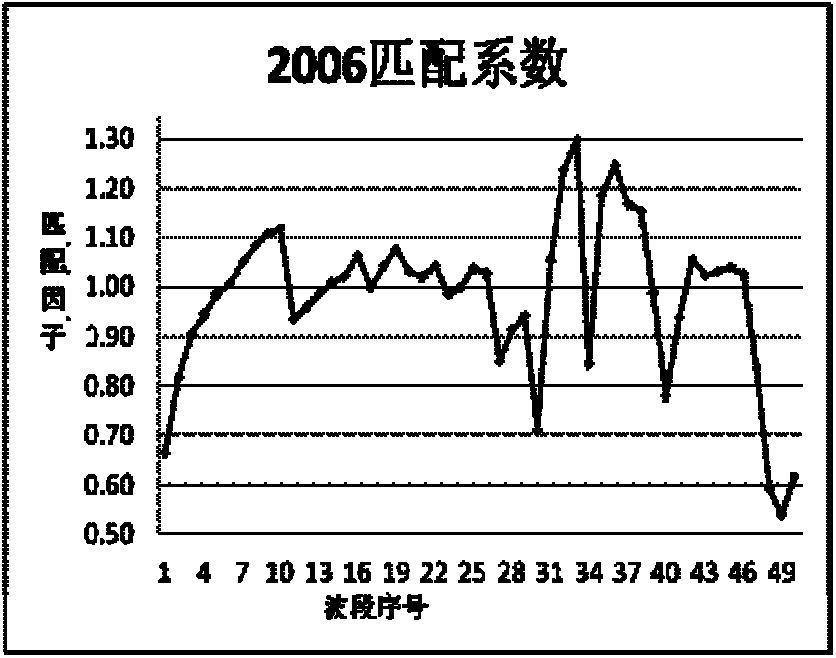
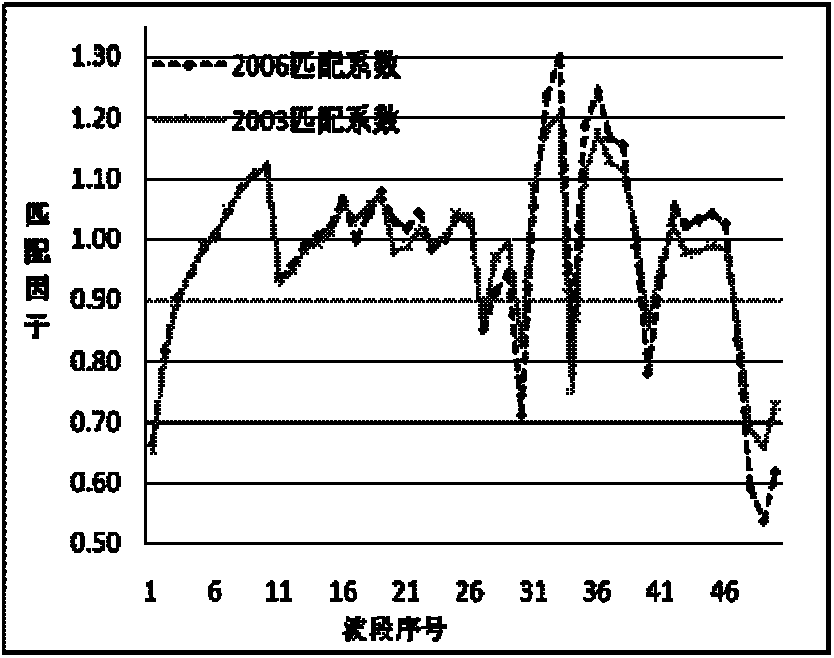
A cross-radiation calibration method for hyperspectral sensors based on multispectral sensors
InactiveCN102279393AAchieving Cross Radiation CalibrationReduce mistakesWave based measurement systemsLightnessEntrance pupil
The invention discloses a cross radiometric calibration method of a hyper-spectral sensor based on a multi-spectral sensor. The method is used for solving the cross radiometric calibration problem of the hyper-spectral sensor without a matched reference hyper-spectral image. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting cloudless hyper-spectral image data; selecting a multi-spectral reference image according to the hyper-spectral data; selecting a uniform ground object on the image as an interesting region; performing geometric precise correction of the two images; calculating entrance pupil radiances of various types of wave bands of the two sensors by using an atmospheric radiation transmission model; solving spectrum matching factors of various types of corresponding wave bands according to a certain rule; solving the entrance pupil radiances of the various types of wave bands of the hyper-spectral sensor by using the spectrum matching factors and the multi-spectral data; and linearly fitting pixel DN (Digital Number) values in the interesting region of the hyper-spectral image to be calibrated and the radiances of corresponding pixels of the multi-spectral reference image after being corrected through the spectrum matching factors to obtain calibration coefficients of the various types of wave bands of the hyper-spectral sensor. The method has the advantages of good stability, high reliability, high precision and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
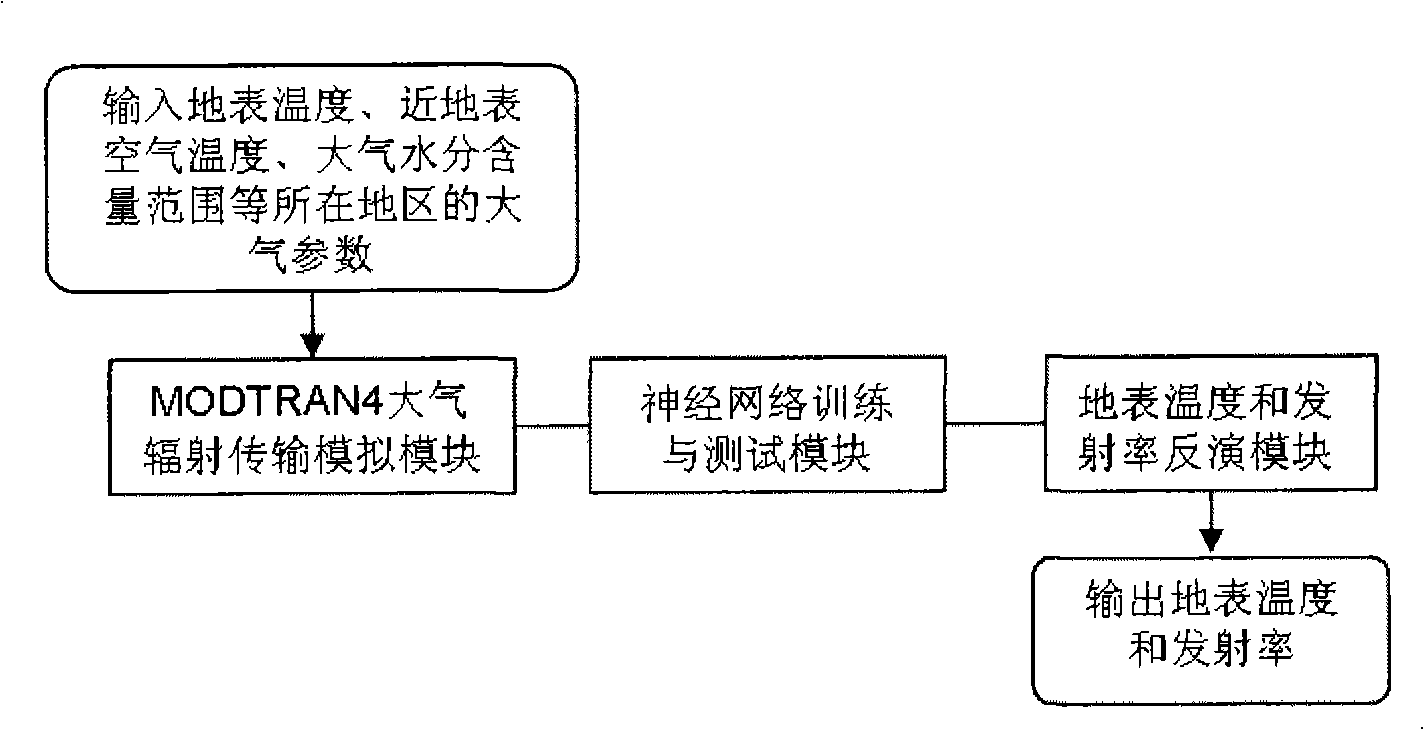
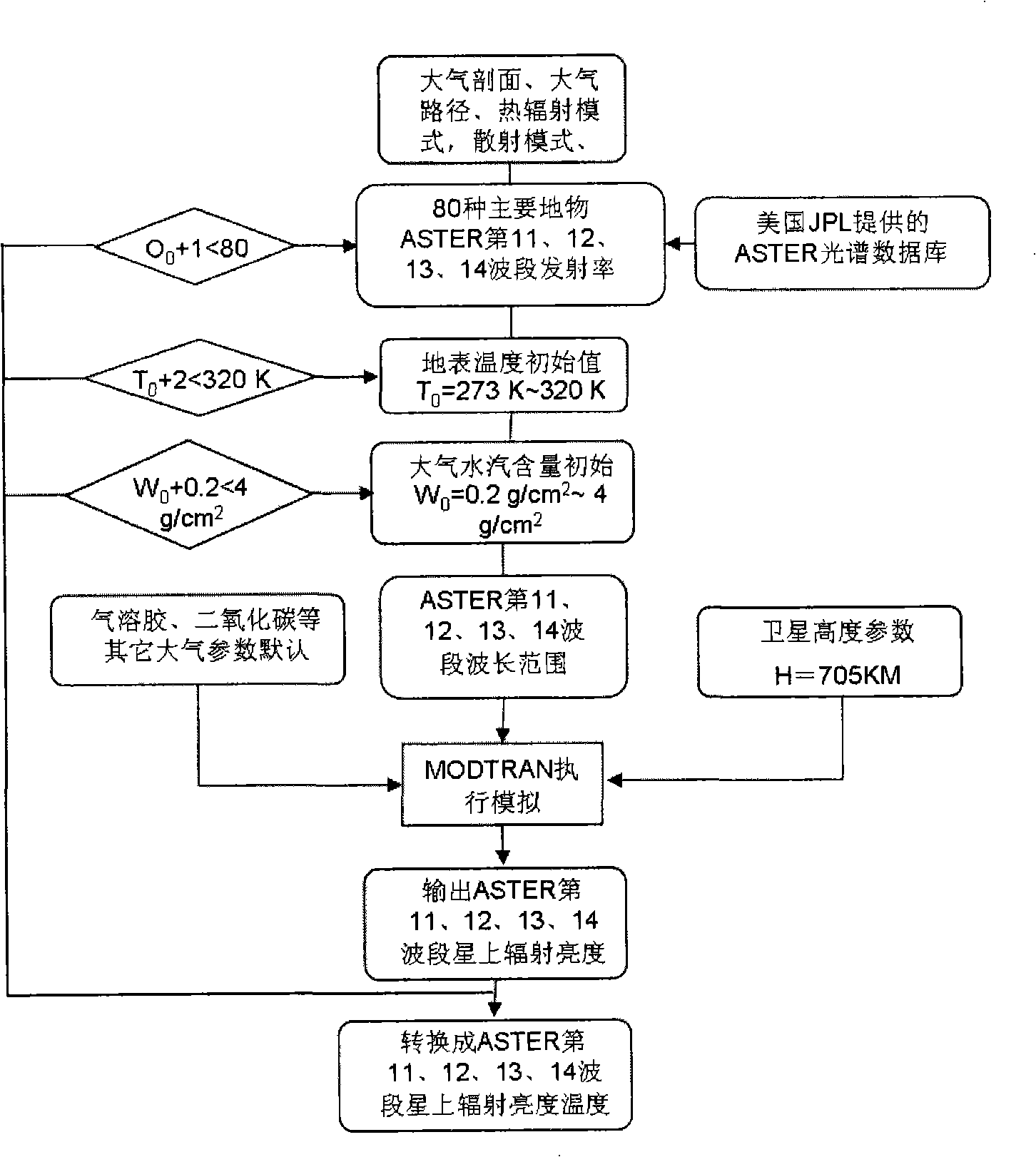
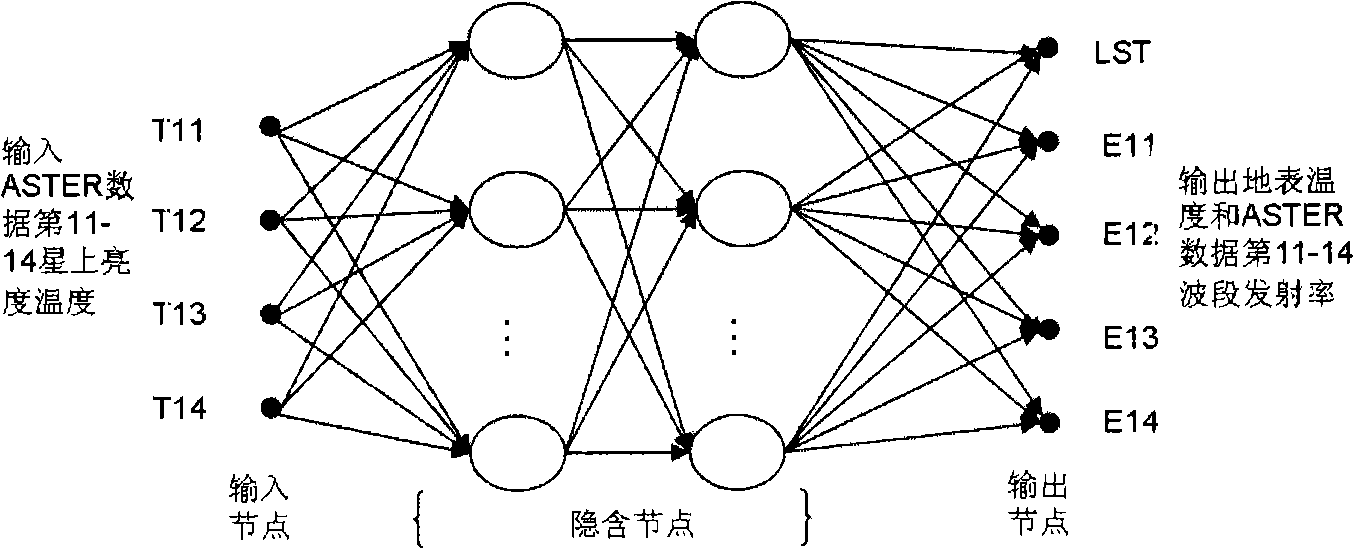
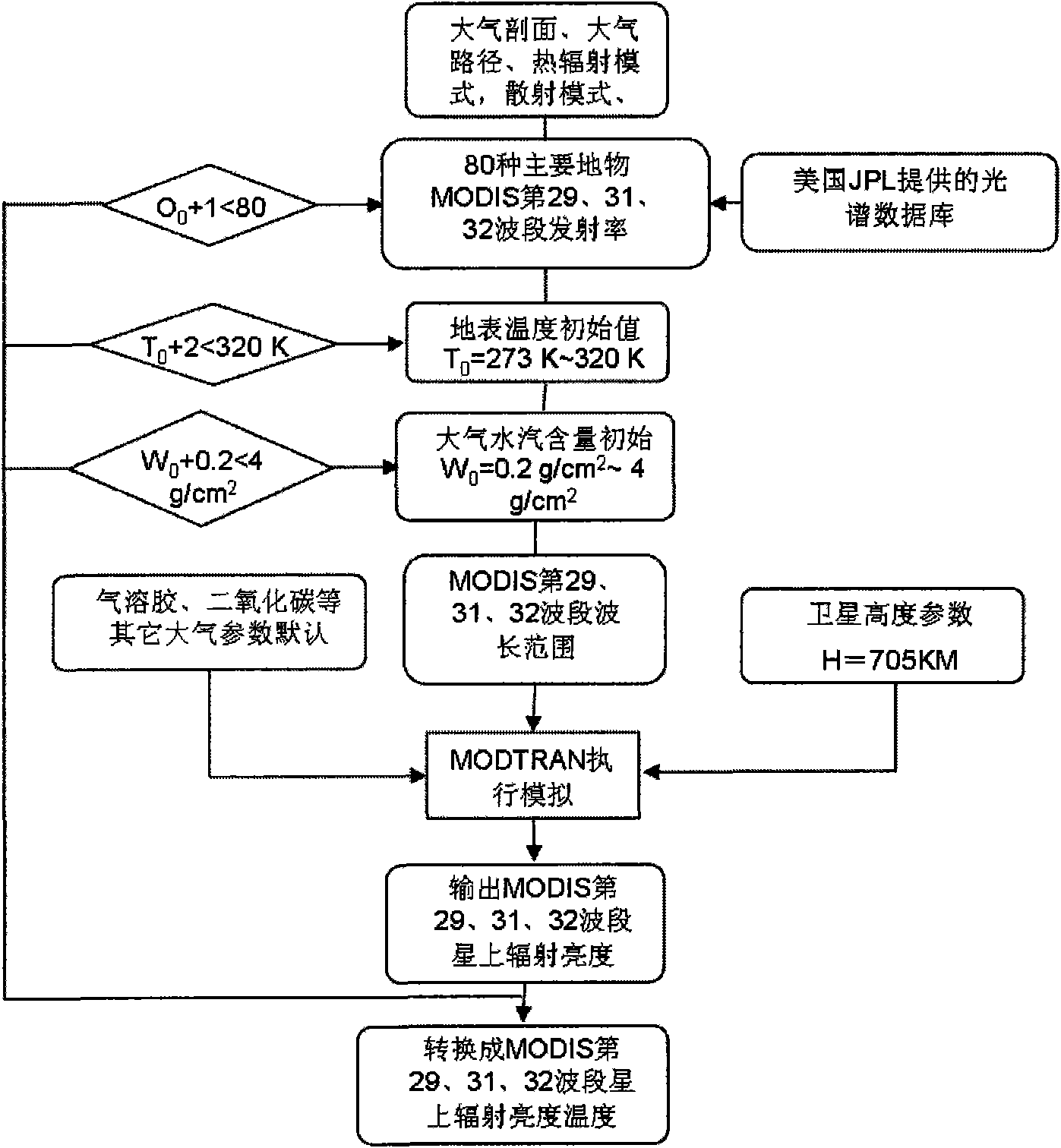
Method for ground surface temperature and emissivity inversion by remote sensing data ASTER
InactiveCN101295022AReduce unknownsImprove inversion accuracyBiological neural network modelsElectromagnetic wave reradiationData setEarth surface
The invention relates to a method for inverting surface temperature and emissivity from remote sensing data ASTER, comprising three steps: step one: a training and testing database is established by utilizing that an atmospherical radiation transmission simulating software carries out positive simulation aiming at the areas and seasons of the 11th, 12th, 13th and 15th thermal infrared wave bands of the obtained thermal sensing data ASTER and an atmospherical model; step two: a neural network is utilized for carrying out repeated training and test to a training and testing data set; step three: inversion calculation is carried out to the ASTER actual image data, and actual earth surface verification and application analysis are carried out. The products obtained by the method have high precision, especially when the surrounding atmospherical changes greatly.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
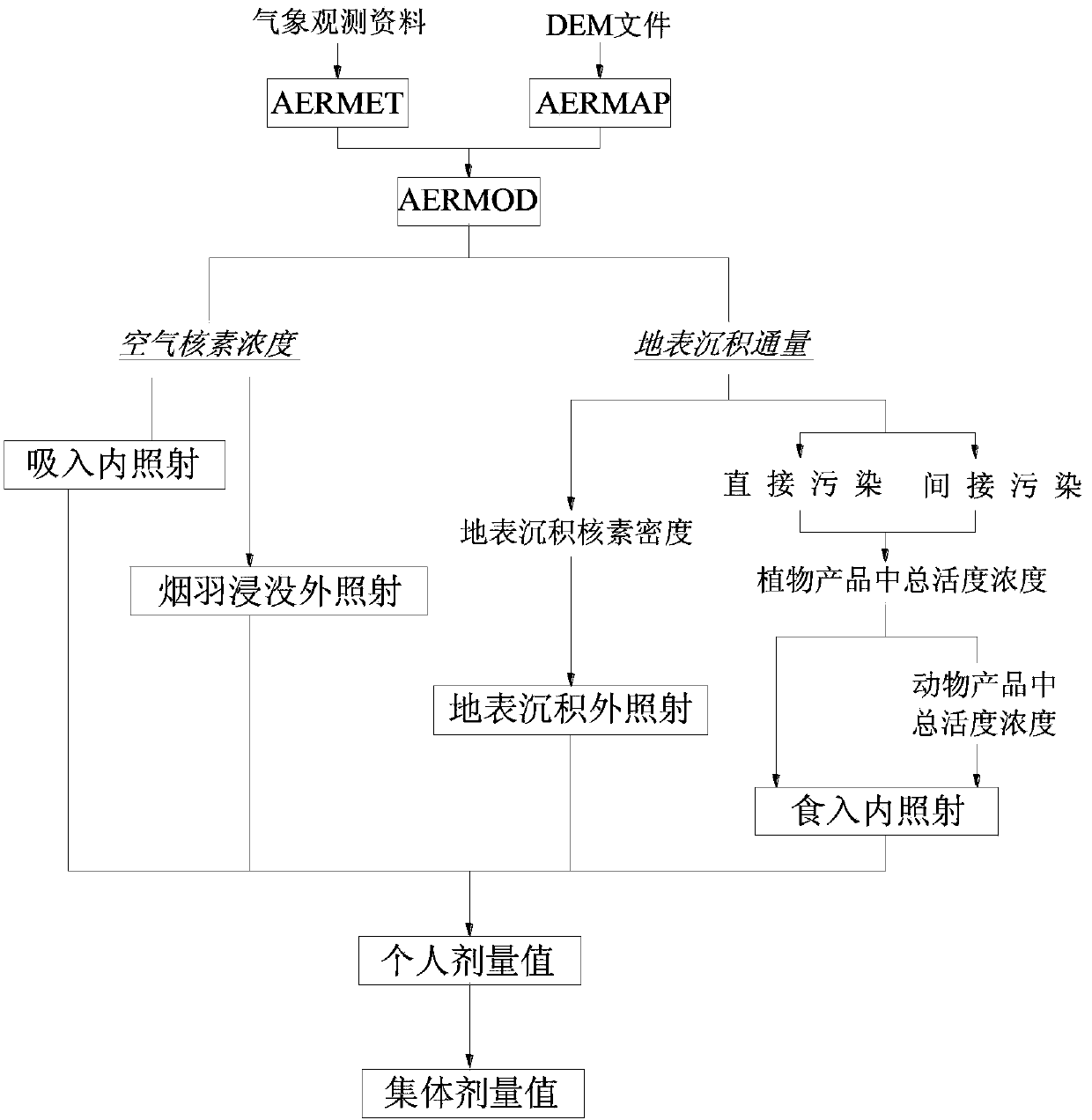
Method for comprehensive evaluation of uranium mining and milling atmospheric radiation environment
InactiveCN104424388ASolve the problem that cannot be calculated at the same timeRealize local multi-source prediction functionSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationTerrainEarth surface
The invention provides a method for comprehensive evaluation of uranium mining and milling atmospheric radiation environment. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating atmosphere; pretreating terrain; calculating atmospheric diffusion; determining breathed internal radiation dose; determining eaten internal radiation dose; determining dose of external radiation deposited on earth surface; determining dose of external radiation immersed in smoke plume; determining public individual dose; determining public group dose and the like. The method disclosed by the invention has the functional characteristics of being scientific, accurate, rapid and comprehensive, and is suitable for prediction and evaluation on influences of the national uranium mining and milling atmospheric radiation environment; by using the method, the calculation results can preferably satisfy the actual relocation diffusion rules of atmospheric pollutants, and the environmental influences and public dose calculation are more scientific and reasonable.
Owner:THE FOURTH INST OF NUCLEAR ENG OF CNNC
High-resolution remote sensing data atmospheric correction method
ActiveCN102955154AHigh precisionImprove usabilityWave based measurement systemsSensing dataUsability
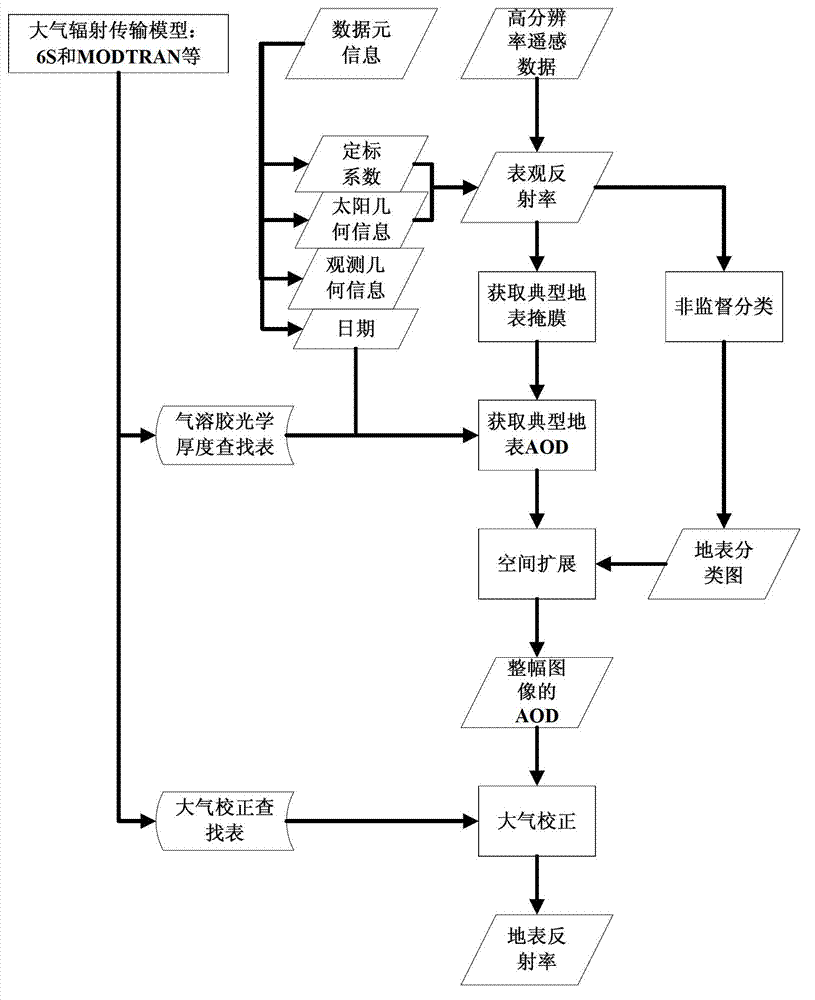
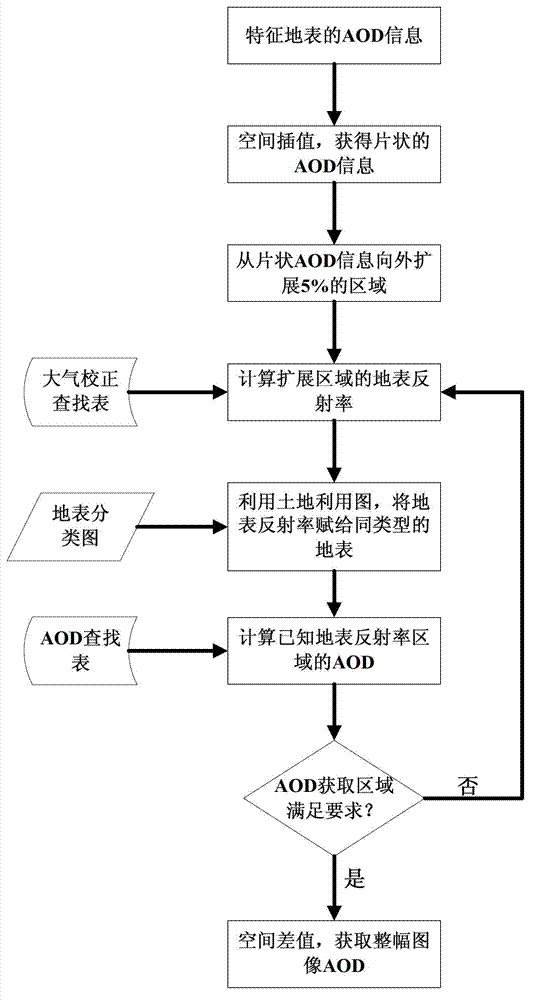
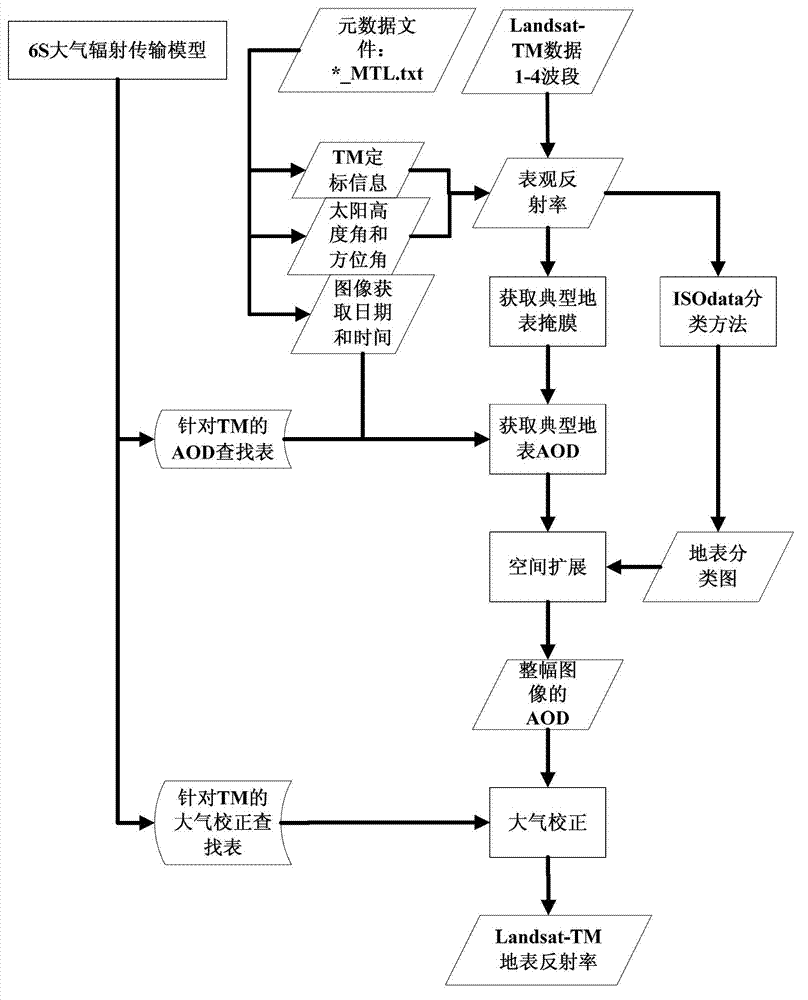
The invention discloses a high-resolution remote sensing data atmospheric correction method comprising the following steps of: S1, obtaining related information from data element information; S2, calculating the apparent reflectance of the typical land surface; S3, obtaining a mask of the typical land surface; S4, building an AOD (Aerosol Optical Depth) inversion correction lookup table by utilizing an atmospheric radiation transmission model; S5, calculating the AOD of the typical land surface; S6, obtaining a land surface classification chart; S7, forming the AOD of an whole image through a spatial expansion method; and S8, executing atmospheric correction on the high-resolution remote sensing data according to the AOD of the whole image and the atmospheric correction lookup table to get the land surface reflectance of the high-resolution remote sensing data. In the method, the high-resolution satellite remote sensing data is used for obtaining the AOD of the whole image, the accuracy and usability of the atmospheric correction are improved, and automation of the whole flow from AOD to atmospheric correction is realized.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
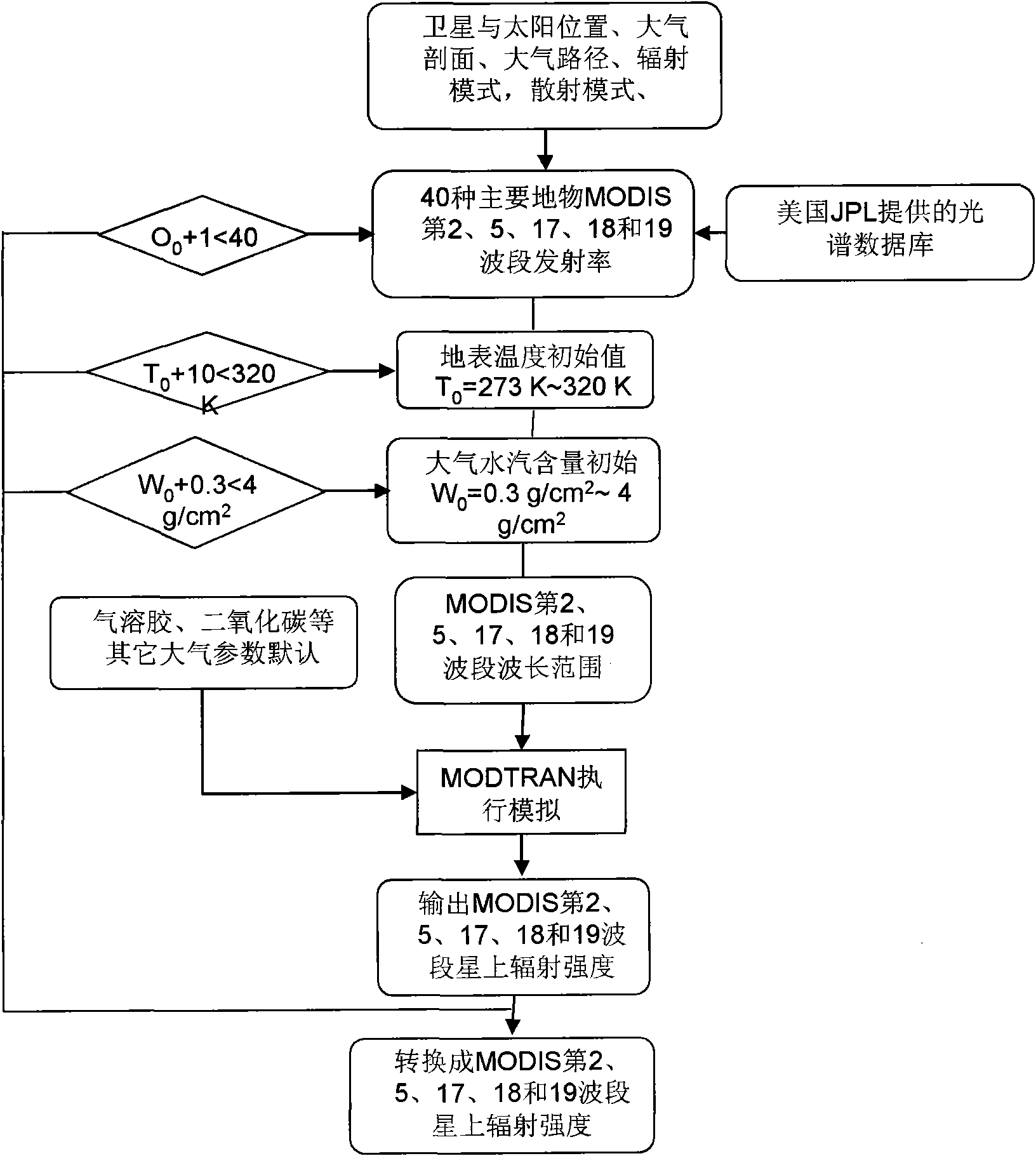
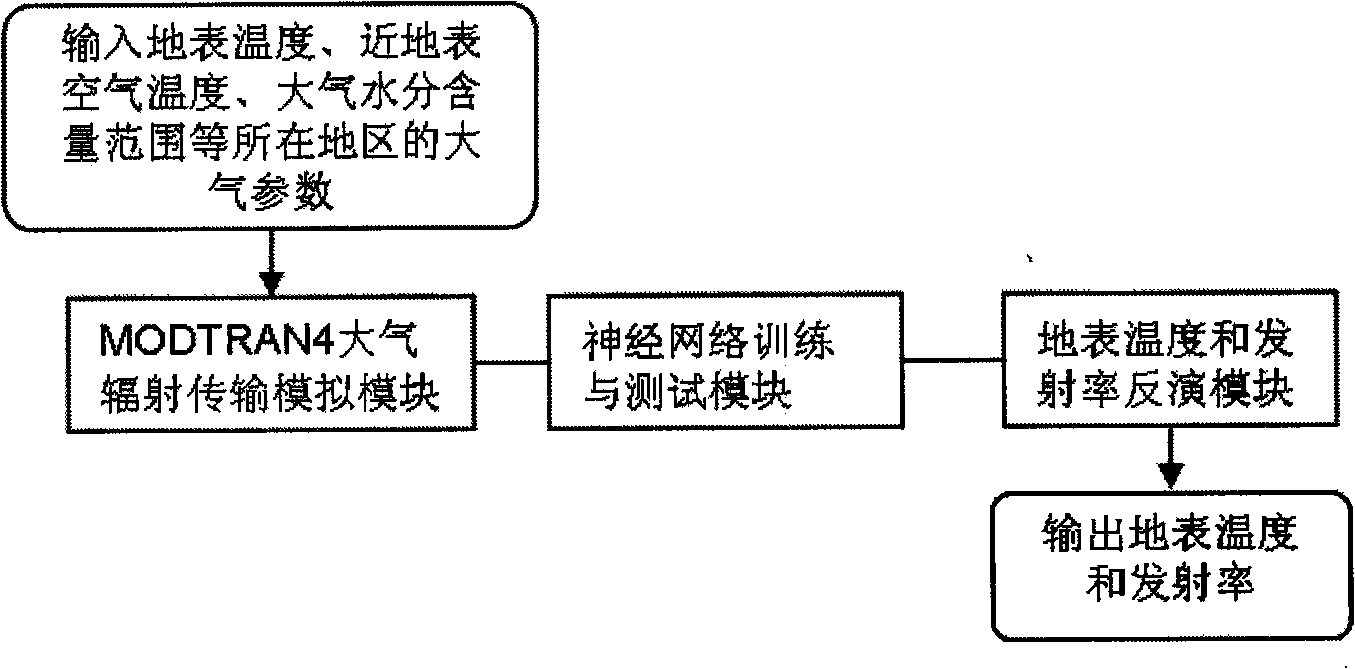
Method for estimating temperature of near-surface air from MODIS data
InactiveCN101634711ATo overcome the shortcomings of insufficient information for estimating near-surface air temperatureReduce unknownsElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationData setDisaster monitoring
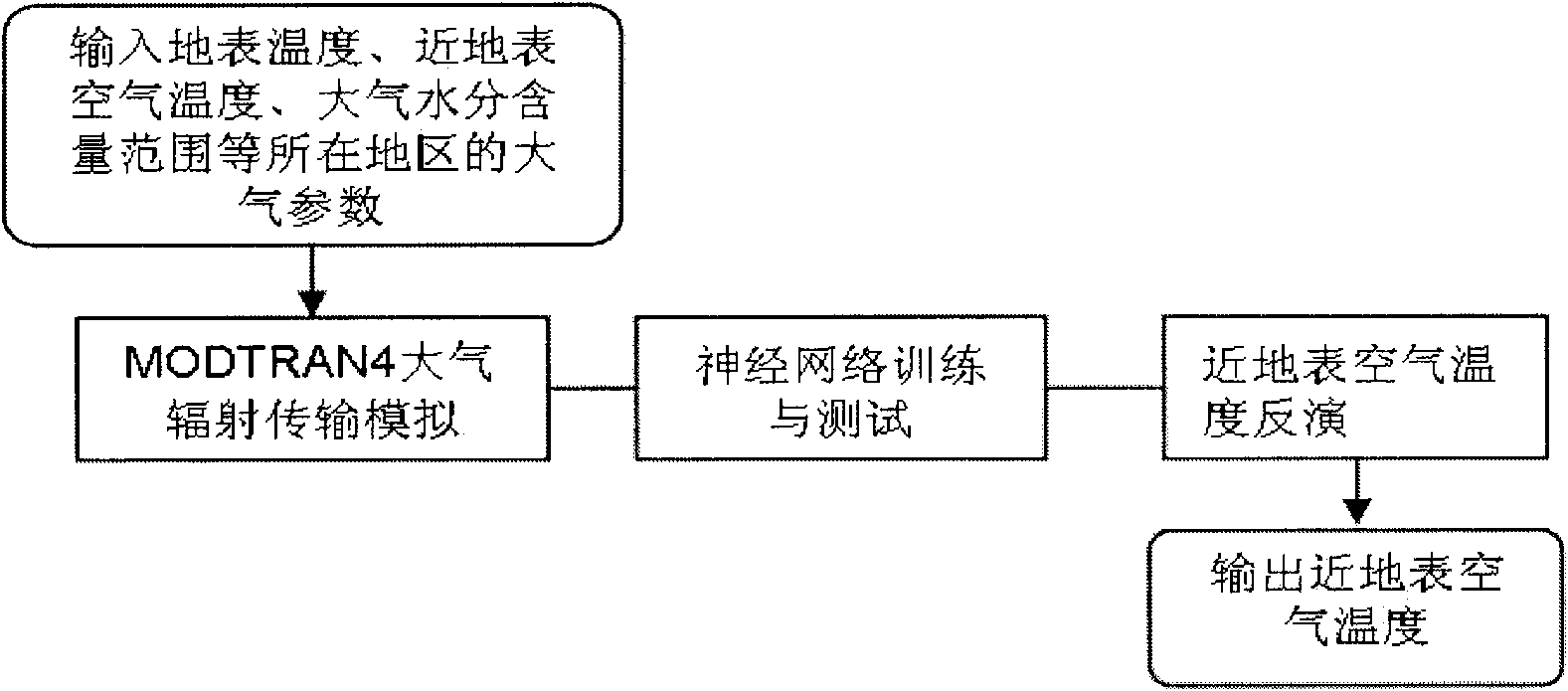
The invention relates to a method for estimating the temperature of near-surface air near from MODIS data, which can be used for remote sensing application departments, i.e. weather, environmental monitoring, land management, agricultural monitoring, disaster monitoring, and the like. The method comprises three steps: step1: utilizing the near-surface temperature and the emission rate of each pixel of a MODIS data product and the water vapour content value of atmosphere as priori knowledge and input parameters of atmosphere radiation transmission module simulation software MODTRAN4, carrying out forward direction simulation in different areas and seasons aiming at a 29th thermal infrared band, a 31st thermal infrared band and a 32nd thermal infrared band of each pixel of the obtained remote sensing data MODIS and establishing a training and testing database; step2: utilizing a neural network to repeatedly training and testing a training and testing dataset; step3: carrying out back calculation for practical image data of the MODIS to obtain the temperature distribution condition of the air near the earth's surface of an objective area of the earth's surface. The method can be usedfor weather prognosis, the environmental monitoring, the agricultural monitoring, the disaster monitoring, and the like.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
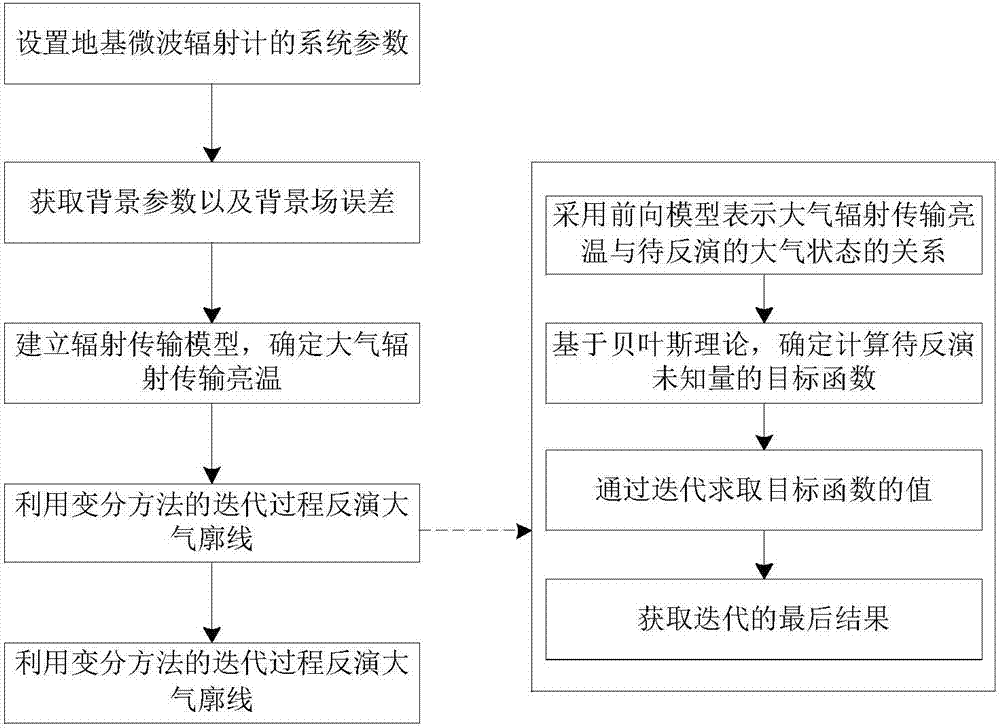
Atmosphere profile inversion method based on foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer
InactiveCN103792538AAdaptableAccurate calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationBrightness temperatureMicrowave radiometer
The invention provides an atmosphere profile inversion method based on a foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer, and belongs to the technical field of microwave remote sensing. The atmosphere profile inversion method based on the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer comprises the following steps of setting system parameters of the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer, acquiring background parameters and background field errors, establishing a radiation transfer model, determining atmospheric radiation transmission brightness temperature, and inverting an atmosphere profile by using the iterative process of a variational method. Through the utilization of the atmosphere profile inversion method based on the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer, the accurately inverted atmosphere profile can be obtained through the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer, and the atmosphere profile inversion method is especially suitable for multi-channel radiometers and detection situations of insufficient prior data, enables a large amount of frequency band information provided by the foundation hyperspectral microwave radiometer to be used completely, and has strong adaptability and small detection errors.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
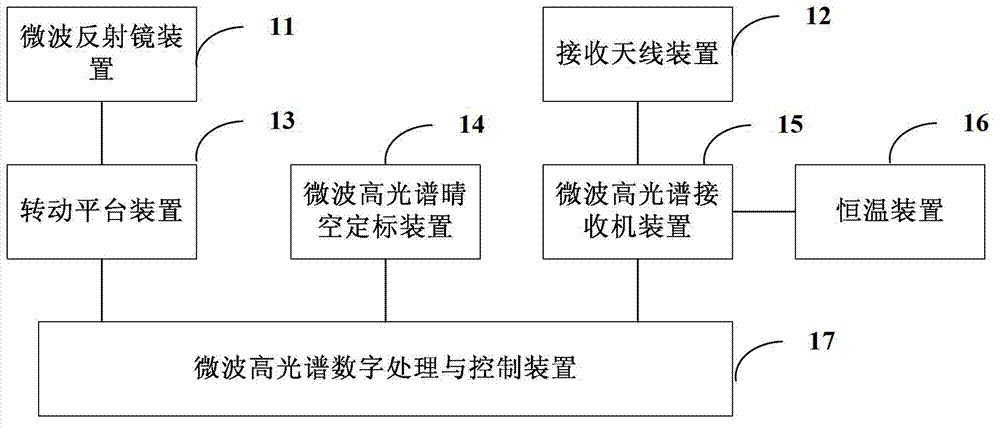
Microwave high spectrum radiometer
The invention provides a microwave high spectrum radiometer. A rotatable platform is used to adjust a rotation angle of a microwave reflector device to change working wave beam directing of a receiving antenna device to realize measuring of atmospheric radiation spectrum. Incident microwave energy is reflected in the receiving antenna device through the microwave reflector device, and directing of the antenna wave beam is changed by rotating the microwave reflector device by 360 degrees. Elevation of the antenna wave beam can be accurately measured by an elevation positioner, and when a computer or a remote computer issues a series of observation instructions of the microwave radiometer, the rotatable platform device instructs the microwave reflector device to rotate to a specified elevation and an azimuth. A microwave high spectrum digital processing and control device enables a microwave high spectrum receiver device to be arranged into a needed passage, simultaneously orders the microwave high spectrum receiver device to start to observe the sky, and then transmits observed data to the computer or the remote computer to be inverted into meteorological parameter curves.
Owner:BEIJING KUNQI ELECTRONICS SYST
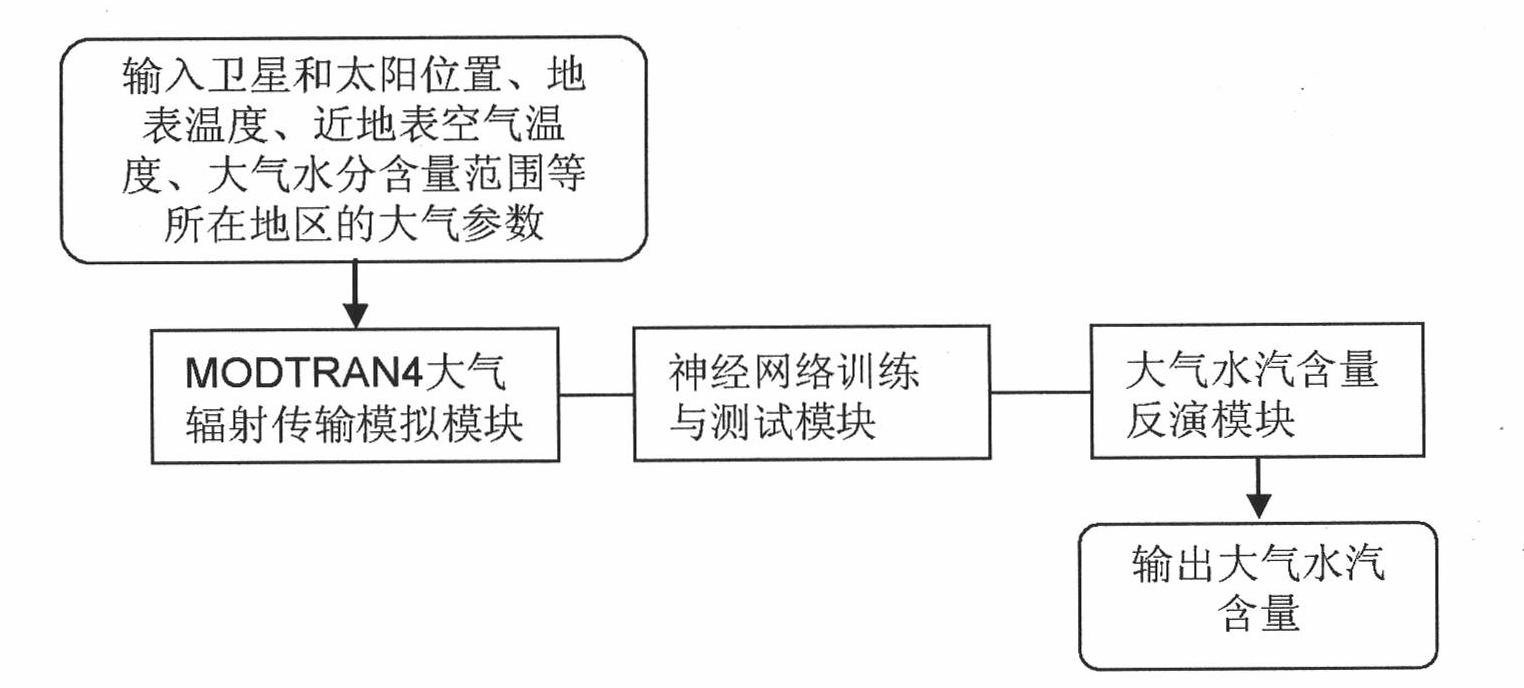
Method for inverting atmospheric water vapor content from MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data
InactiveCN101936877AReduce unknownsReduce computing timeMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological neural network modelsData setDisaster monitoring
The invention relates to a method for inverting atmospheric water vapor content from MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data, which can be applied to the remote sensing application departments, such as meteorology, environment monitoring, land management, crop condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and the like. The method comprises the following three steps of: (1) performing forward simulation to the second, fifth, seventeenth, eighteenth and nineteenth near-infrared bands of acquired remote sensing MODIS data in given areas and seasons and an atmospheric model by using atmospheric radiation transmission simulation software MODTRAN, and establishing a training and test database; (2) repeatedly training and testing the training and test data set by using a neural network; and (3) performing inversion calculation to the MODIS actual image data, and performing actual earth surface verification and application analysis. The atmospheric water vapor inversed product has high precision, strong practicability and relatively simple operation. The method can be applied to the departments of weather forecast, environment monitoring, crop condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and the like.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
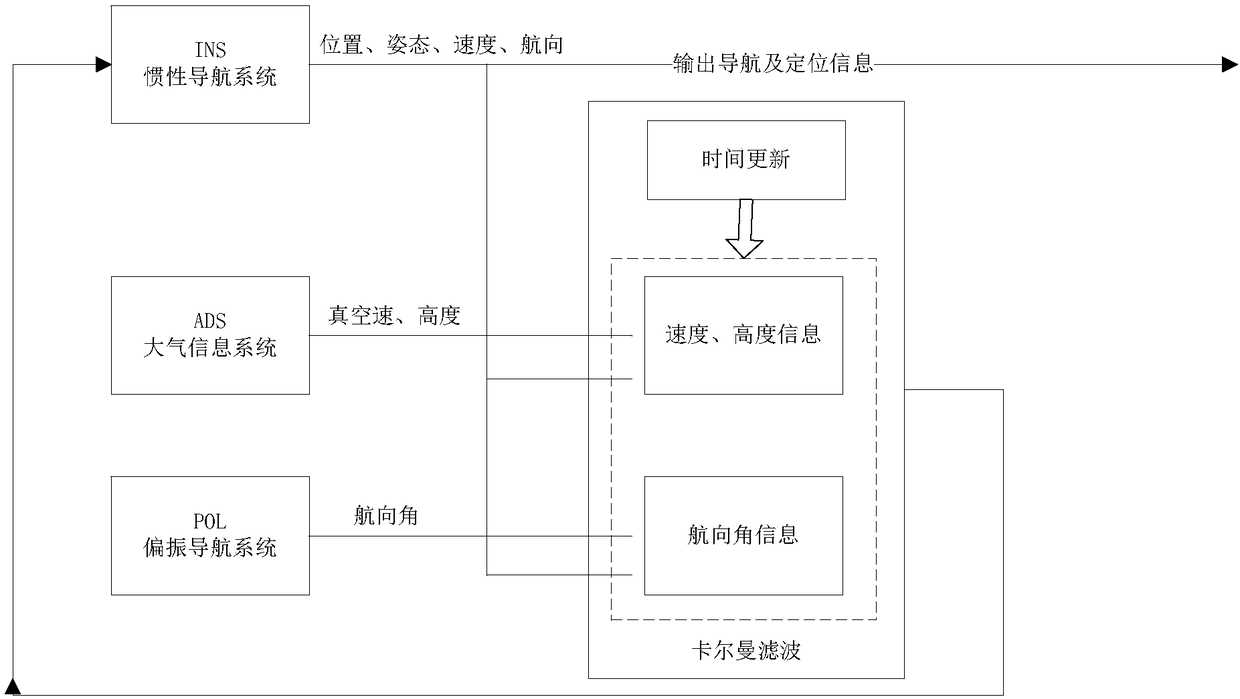
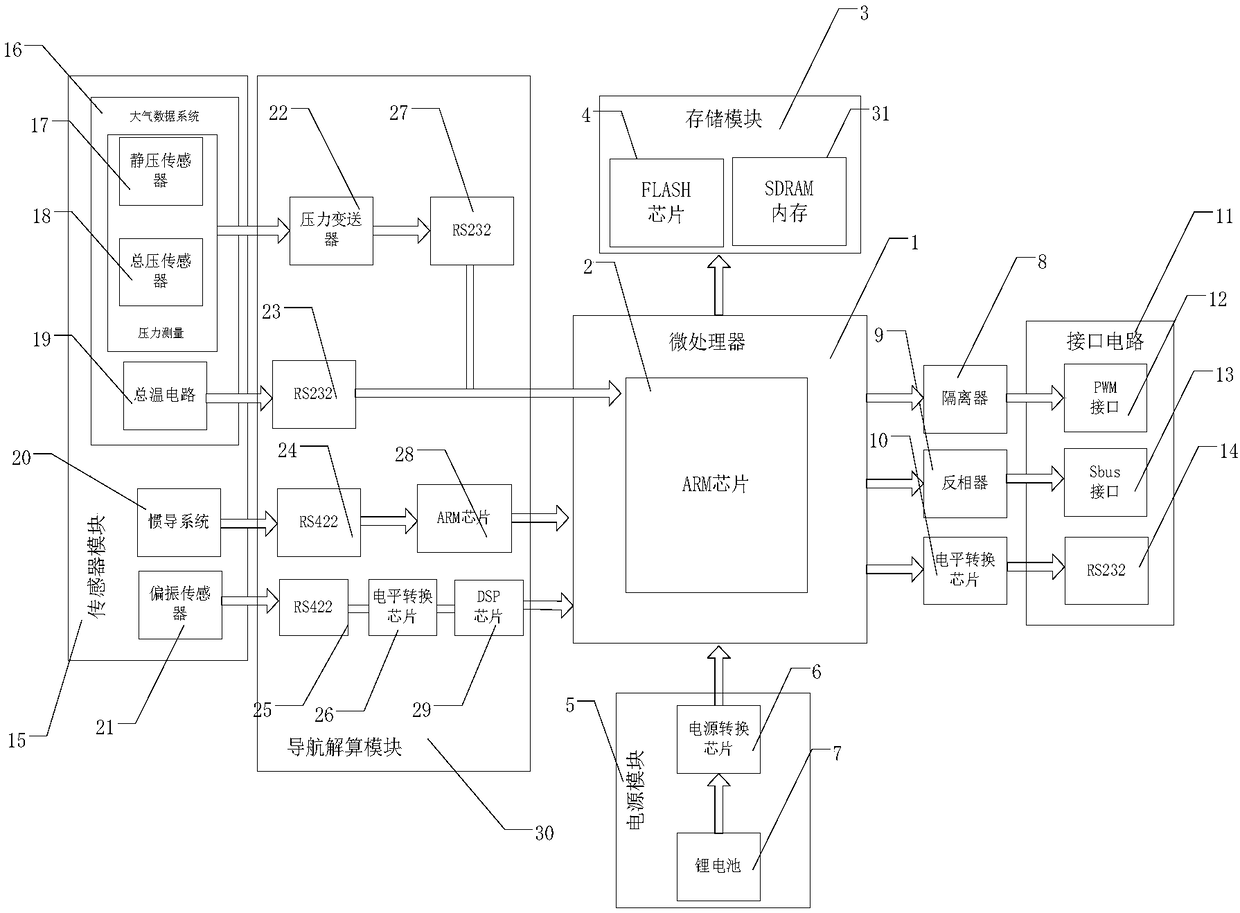
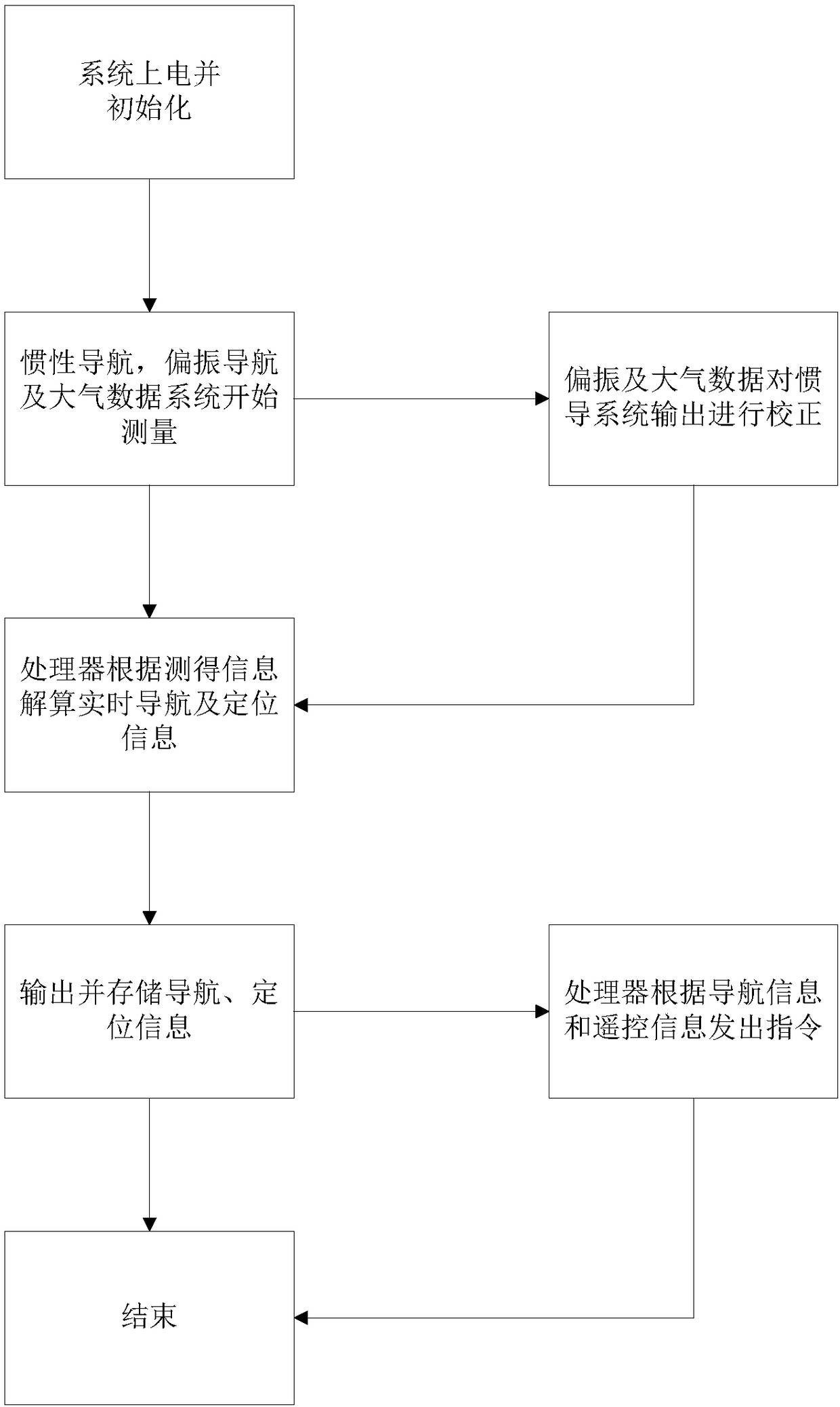
Bionic polarization/inertial/atmospheric data integrated navigation system
ActiveCN108303081AIncrease autonomyImprove reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsWork flowData system
The invention relates to a bionic polarization / inertial / atmospheric data integrated navigation system. The system consists of a navigation sensor, a solving module, an interface circuit, a microprocessor, a storage module and a power supply module. The sensor is composed of a biomimetic polarization sensor, an inertial measurement unit and an atmospheric data system. Specifically, the bionic polarization sensor includes an optical camera, a motor, a polarizing device and other components, and the atmospheric data system is composed of a pitot-static sensor, a pitot-static pipeline and a totaltemperature circuit. The work flow includes that: the sensor module collects the polarized light information, atmospheric static pressure, full pressure and other data in the atmospheric environment,and transmits the data to the solving module, and the processor determines whether the sensor works reliably, selects a working mode, and works out the course angle, true airspeed, height and other information for compensation correction of the attitude and speed of the navigation system, and stores and outputs navigation parameters. The integrated navigation system provided by the invention has the advantages of flexible navigation mode, strong autonomy, small volume and the like, and has interference suppression, fault detection and system reconstruction functions.
Owner:郭晓宇
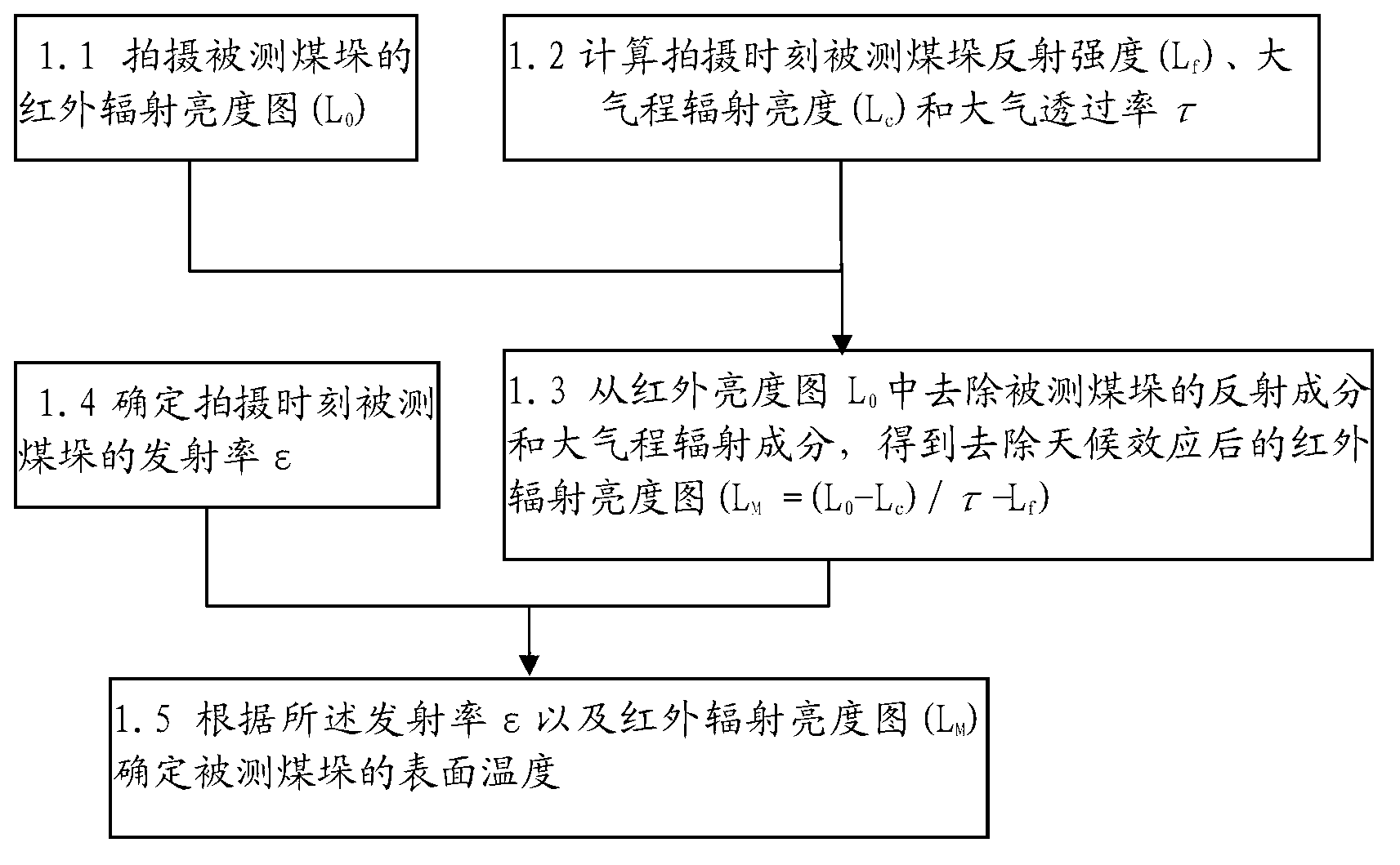
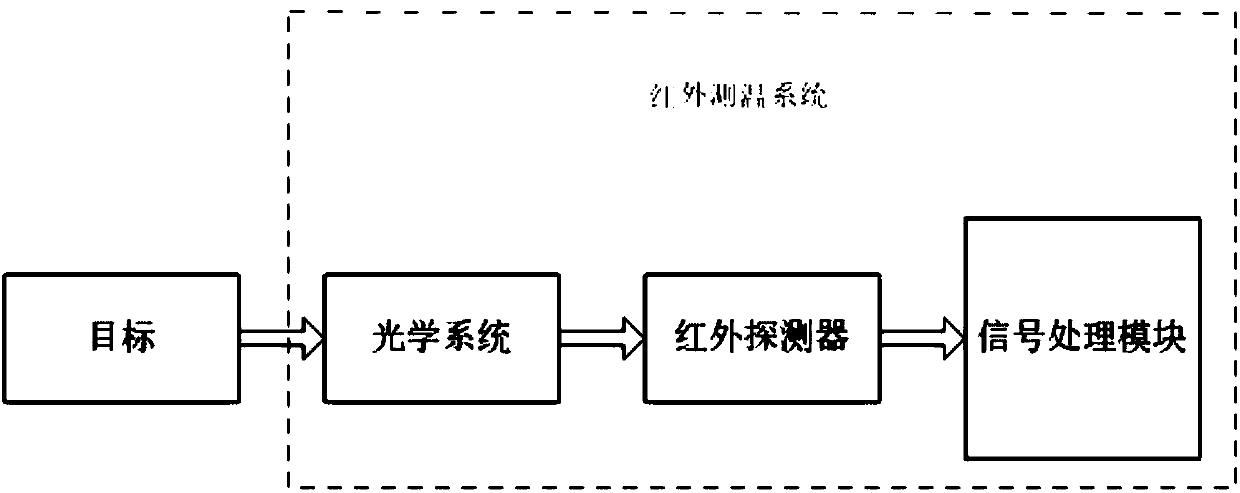
Method and system for conducting remote infrared temperature measurement on coal pile surfaces
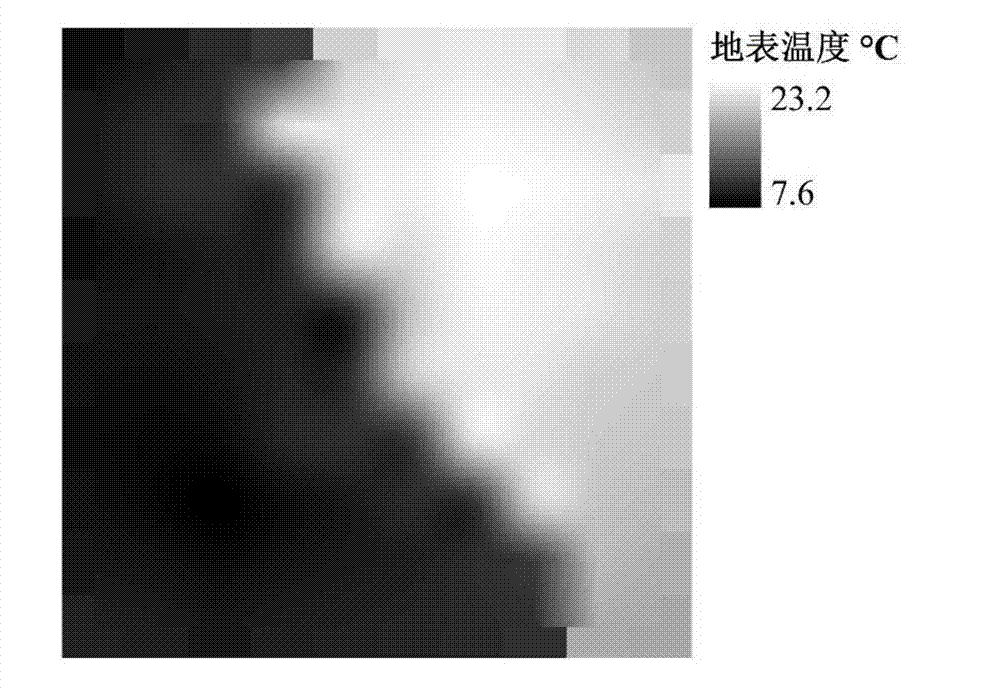
The invention provides a method and a system for conducting remote infrared temperature measurement on coal pile surfaces. The method comprises steps of 1.1 photographing an infrared radiance image of a coal pile to be measured; 1.2 calculating reflected intensity, atmosphere radiance and atmospheric transmittance of the coal pile to be measured at the photographing moment; 1.3 removing reflection components and atmospheric radiation components of the coal pile to be measured from the infrared radiance image in accordance with results of the step 1.2 and obtaining an infrared radiance image after weather effect removal; 1.4 determining emissivity data of the coal pile to be measured at the photographing moment; and 1.5 determining the surface temperature of the coal pile in accordance with the emissivity data and the infrared radiance image after weather effect removal. By the aid of the method, the accuracy of coal pile temperature measurement is improved.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD +2
Superglacial moraine covering type glacier identification method based on optical and thermal infrared remote sensing images
InactiveCN103500325AAccurate identificationEasy to distinguishCharacter and pattern recognitionThermal infrared remote sensingData space
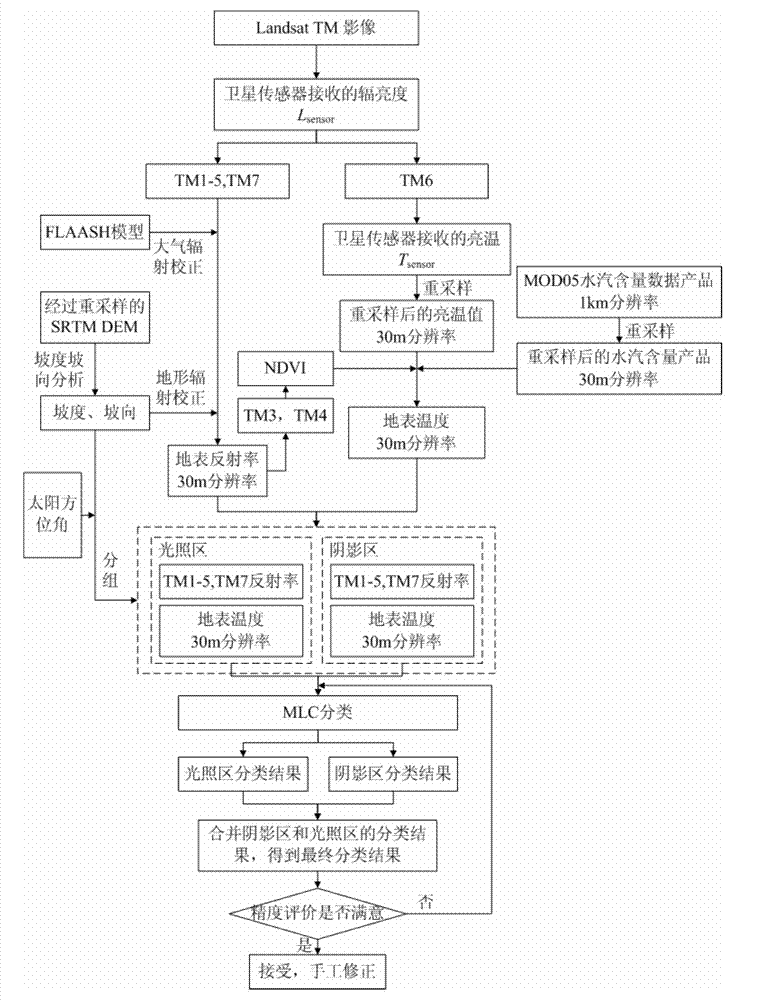
The invention relates to a superglacial moraine covering type glacier identification method based on optical and thermal infrared remote sensing images, and belongs to the field of remote sensing geoscience application. According to the method, the thermal infrared wave band and the optical wave band of Landsat TM / ETM and remote sensing images are utilized, the data of a DEM (dynamic effect model) and the like is combined for carrying out identification on the superglacial moraine covering type glacier, firstly, the topical wave band of the TM / ETM images is subjected to atmosphere radiation correction and topography radiation correction, the thermal infrared wave band is used for carrying out ground surface temperature inversion, in addition, the normalization is carried out, then, the illumination region and the shade region are distinguished, and finally, a maximum likelihood method is utilized for respectively classifying the illumination region and the shade region of the images to obtain the types of ice, superglacial moraine covering type glacier, ice and rock debris mixed regions, shade, rock and the like. Compared with a traditional method, the superglacial moraine covering type glacier identification has the advantages that the thermal infrared waveband is introduced, the identification on the superglacial moraine covering type glacier is more accurate and efficient, and the results obtained by adopting the method provided by the invention are more reasonable in the aspect of data space resolution ratio resampling.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Real-time telemetry system and method of greenhouse gas column concentration
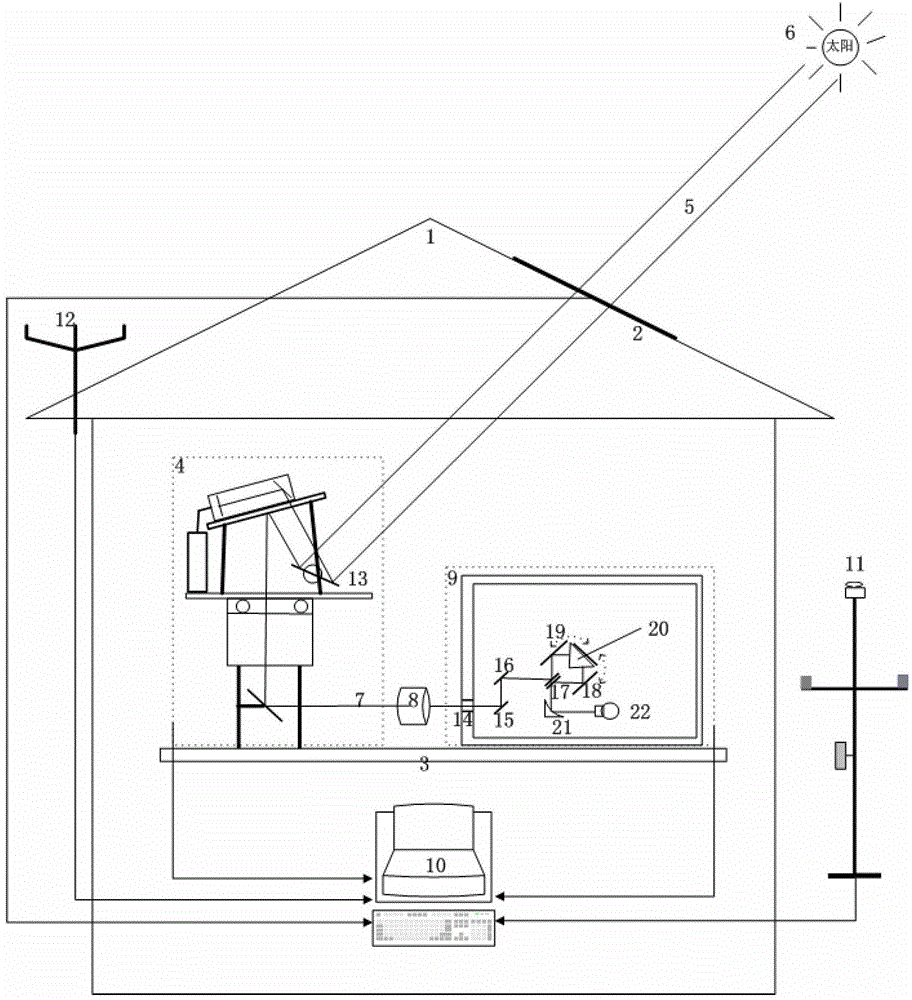
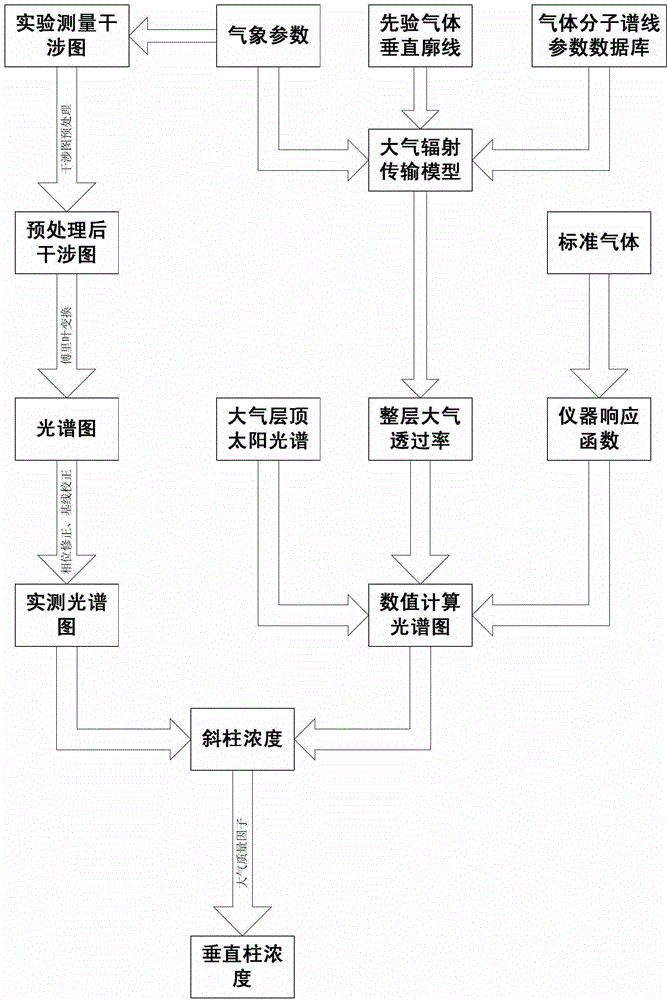
ActiveCN102944530AFast Online TelemetryEasy Online TelemetryColor/spectral properties measurementsFollow-the-sunEngineering
The invention discloses a real-time telemetry system and a real-time telemetry method of greenhouse gas column concentration. The real-time telemetry system comprises a fixed station building and a sun follower, wherein the station building is provided with an automatic sunroof; the sun follower is installed on a fixed platform in the station building and used for receiving sunlight from the sunroof, thereby automatically following the sun; emergent light of the sun follower passes through a sample tank to enter an infrared spectrometer, and an output end of the infrared spectrometer is connected with a computer; a micro weather station and a wireless data transmission antenna are installed outside the station building and connected to the corresponding input end of the computer; measured spectra and numerical simulation calculated spectra based on an atmospheric radiation transmission model are obtained simultaneously; and the greenhouse gas column concentration of various kinds is obtained in real time by using a nonlinear least-squares iteration method. According to the real-time telemetry system and the real-time telemetry method, the defects of the greenhouse gas three-dimensional high space-time resolution measurement technology are overcome, calibration data can be provided for airborne and satellite telemetry, and local long-term greenhouse gas observation results can be provided.
Owner:合肥中科环境监测技术国家工程实验室有限公司
Method and device for performing vegetation parameter remote sensing retrieval in neural network system
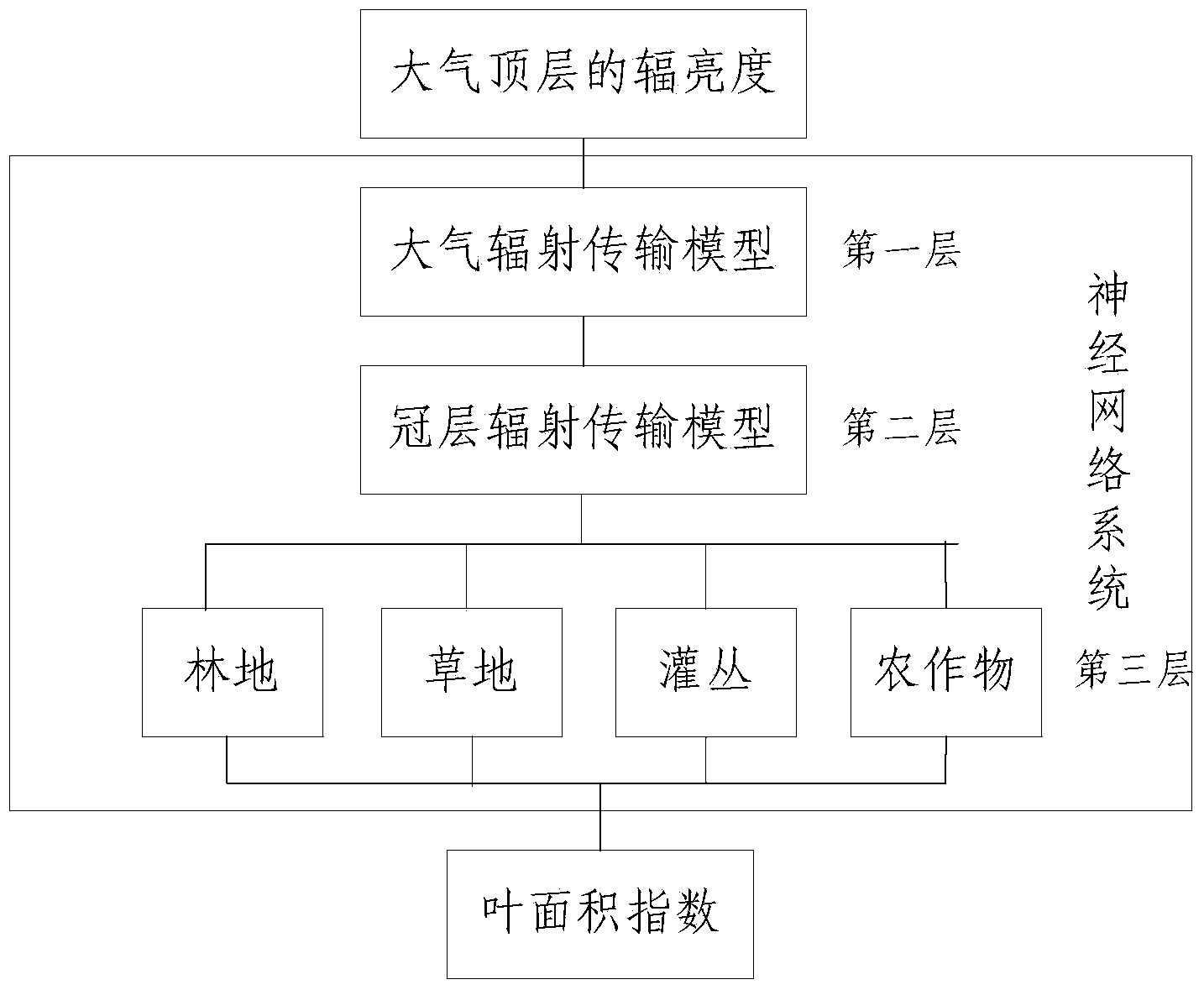
ActiveCN103529439AStrong simulationThe result is accurateBiological neural network modelsElectromagnetic wave reradiationSensing dataVegetation
The invention provides a method and device for performing vegetation parameter remote sensing retrieval in a neural network system. The method comprises the steps as follows: training data sets between vegetation parameters and earth surface reflectance of different types of earth surfaces are obtained according to simulation models of earth surface reflectance of different types of earth surfaces; a neutral network between the vegetation parameters and earth surface reflectance of different types of earth surfaces is established; training data sets between earth surface reflectance and apparent reflectance under different meteorological conditions are obtained according to atmospheric radiation models; a neutral network between the earth surface reflectance and the apparent reflectance under different atmospheric conditions is established; multiple neutral networks are combined to form a neural network system; and remote sensing data obtained after radiometric calibration or atmospheric correction is subjected to vegetation parameter remote sensing retrieval in the neural network system. According to the method and the device, multiple different neutral networks can be combined to form the neural network system, compared with the prior art, the data analog capability is stronger, and an obtained result is more accurate.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
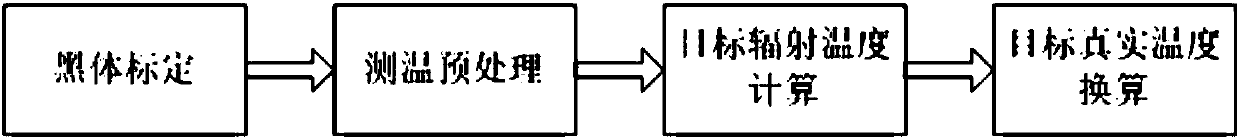
Method for improving temperature measurement precision of thermal infrared imager
InactiveCN107741276AImprove temperature measurement accuracyImprove conversionRadiation pyrometryBlack bodyRadiation temperature
The invention relates to a method for improving the temperature measurement precision of a thermal infrared imager. The method comprises the steps that a high-precision black body is adopted to calibrate the thermal infrared imager, wherein the calibration aims to test the whole system to find the relation between the temperature of the black body and the gray value of an image and describe the relation with a lookup table; the radiation temperature of an object is calculated by using the gray value of the image; the radiation temperature is converted into the real temperature. Compared with atraditional fitted curve black body calibration temperature measurement method, in the method, the black body calibration is conducted by using the difference value lookup table, the temperature measurement pretreatment is adde, the conversion of the radiation temperature is added, and the real temperature value of the target object is obtained; meanwhile, the influences of target reflected radiation, backgrounds and atmospheric radiation on the temperature measurement are reduced, and the temperature measurement precision is improved. The method is suitable for the application field where temperature measurement and detection are conducted by using an infrared detector in electrical equipment detection, fire situation detection, petroleum pipeline detection and the like.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
On-track space camera gain regulating method
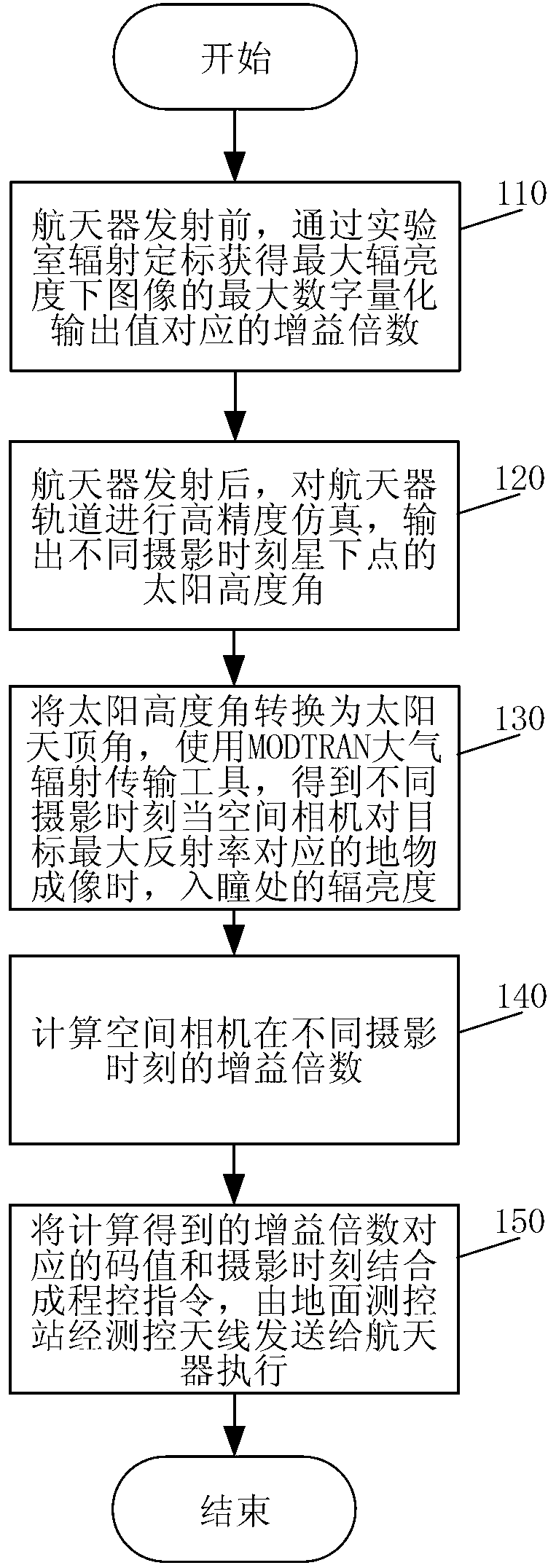
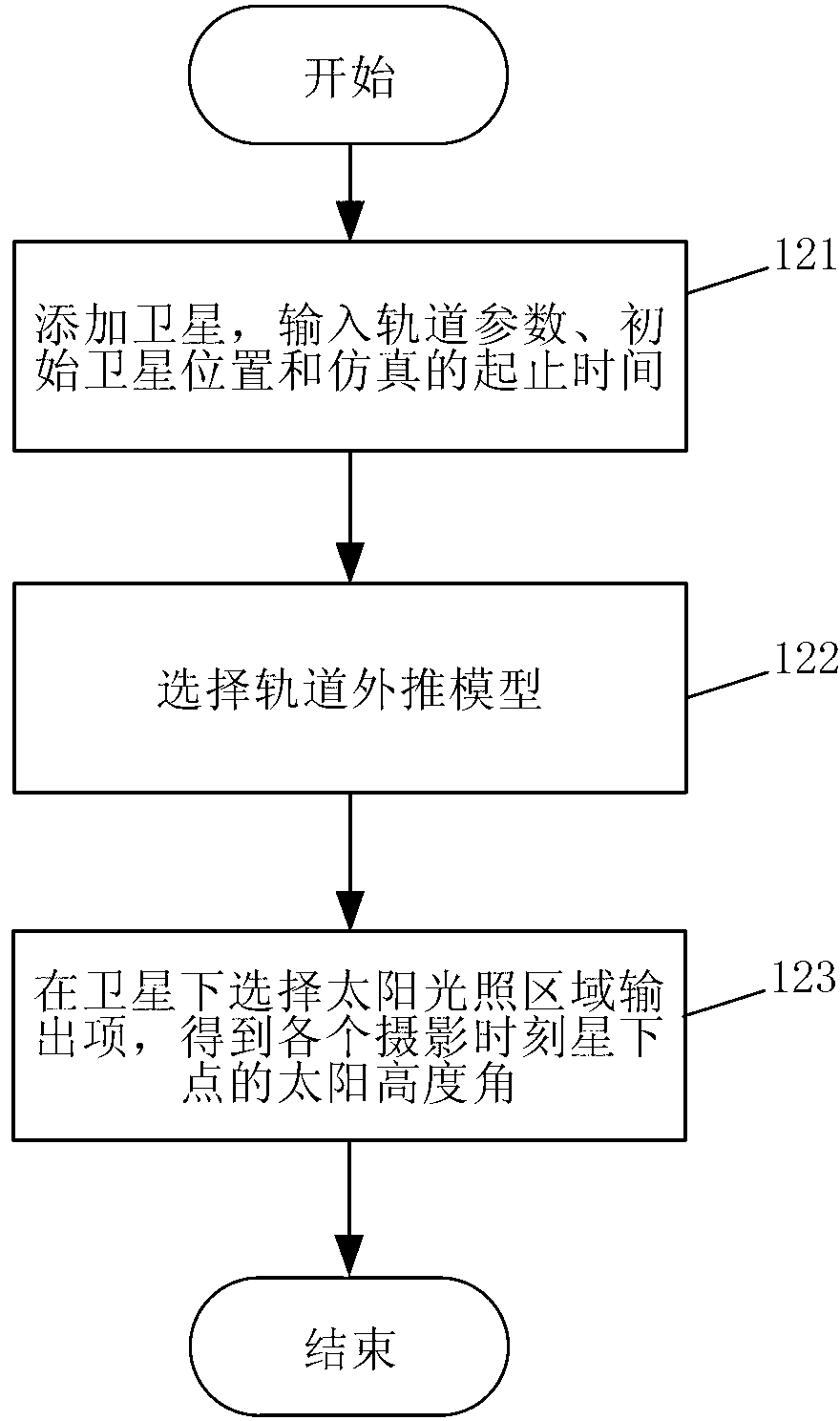
ActiveCN103322982ASolve the darkSolve the image level is not richPicture taking arrangementsEarth observationEngineering
The invention discloses an on-track space camera gain regulating method, which relates to an on-track gain regulating method of a space camera for earth observation, and aims to the solve the problems that at present, a space camera adopts a fixed gain so as to lead to overall dimming of part of images, poor image gradation, low signal to noise ratio and the like. The regulating method comprises the following steps of: before a spacecraft is launched, acquiring a gain factor corresponding to the maximal digital quantification output value of images under maximal radiance through laboratory radiometric calibration; after the spacecraft is launched, simulating the track of the spacecraft with high accuracy, and outputting the solar altitude of sub-satellite points at different shooting time; converting the solar altitude into the solar zenith angle, thereby obtaining the radiance of an entrance pupil part by an MODTRAN atmospheric radiation transfer tool when the space camera forms images of a ground feature corresponding to the maximal object reflectivity at different time; calculating gain factors of the space camera at different shooting time; combining the code values corresponding to the gain factors obtained through calculation with the shooting time into a program control instruction, and sending the program control instruction from a ground measurement and control station to the spacecraft to execute through a measurement and control antenna.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Shadow extraction method facing ecological environment parameter remote sensing inversion
ActiveCN108051371AEasy to distinguishEasy to operateMaterial analysis by optical meansInformation spaceEcological environment
The invention discloses a shadow extraction method facing ecological environment parameter remote sensing inversion. The method comprises the following steps of performing radiometric calibration andatmospheric radiation correction on an original remote sensing image to obtain a remote sensing image result map; calculating a vegetation index, and calculating a shadow index according to the obtained vegetation index so as to obtain a shadow index information space distribution map; performing enhanced algorithm treatment of an image on the remote sensing image result map, and collecting the picture element sample of a shadow as a sample area at random; statistically calculating cumulative frequency and statistical variable, which change from small to big, of a shadow index number value corresponding to the sample area, and setting up the range of a threshold; according to the obtained range of the threshold, making and extracting a two-value mask pattern of shadow information, enablingthe made two-value mask pattern and the remote sensing image result map to be subjected to space superposition, and performing wave band product calculation to quickly extract an accurate space distribution map of shadow information in a remote sensing image. The shadow extraction method is simple and flexible in operational process and easy to popularize and apply, and improves the accuracy of ecological environment parameter information remote sensing inversion.
Owner:河北省科学院地理科学研究所
Method for inverting urban atmospheric aerosol optical depth on basis of MODIS data
InactiveCN104019753AOptical thickness inversion method is easy to implementEffective monitoringWave based measurement systemsUsing optical meansMicrometerMathematical model
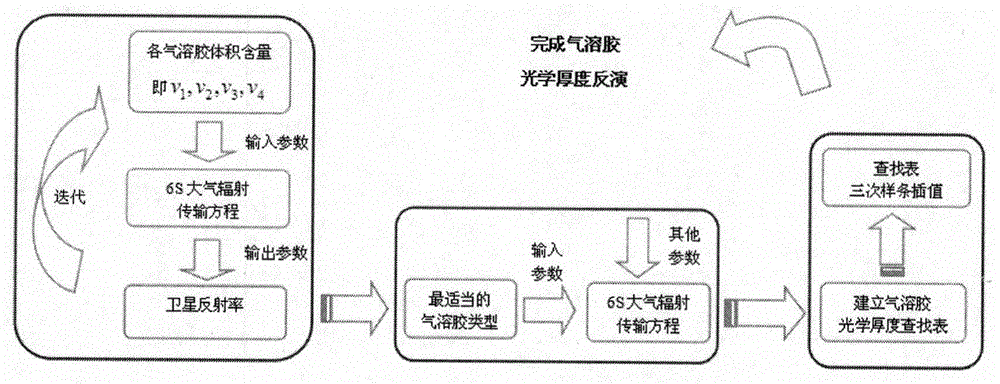
The invention discloses a method for inverting the urban atmospheric aerosol optical depth on the basis of MODIS data. The method includes the steps (1), a mathematical model is established according to a 6S atmospheric radiation transmission equation, the volume ratio concentration of four basic aerosols including the dust aerosol, the water-soluble aerosol, the maritime aerosol and the soot aerosol is calculated, and customized aerosol types are obtained; (2), according to the relation among the surface reflectance of a 2.1-micrometer channel, the surface reflectance of a red channel and the surface reflectance of a blue channel in the MODIS data, an estimated value of the surface reflectance of the red channel and an estimated value of the surface reflectance of the blue channel are obtained; (3), an aerosol optical depth lookup table of the red channel and an aerosol optical depth lookup table of the blue channel are built respectively according to the 6S atmospheric radiation transmission equation and the aerosol types in the step (1); (4) spline interpolation is carried out on data in the lookup tables three times, the aerosol optical depth under the appointed surface reflectance is obtained, and inversion of the atmospheric aerosol optical depth is finished. The method for inverting the urban atmospheric aerosol optical depth is easy to implement, high in inversion accuracy and capable of being effectively used for urban aerosol monitoring.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Hyperspectral-imager index optimization method based on remote-sensing application
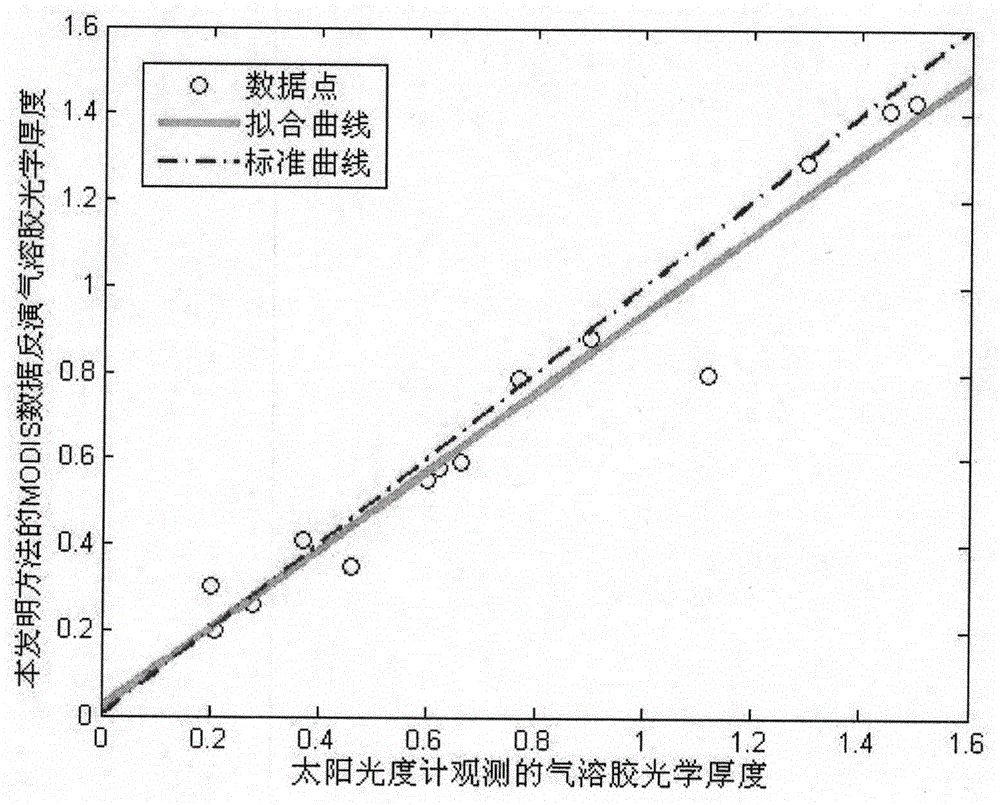
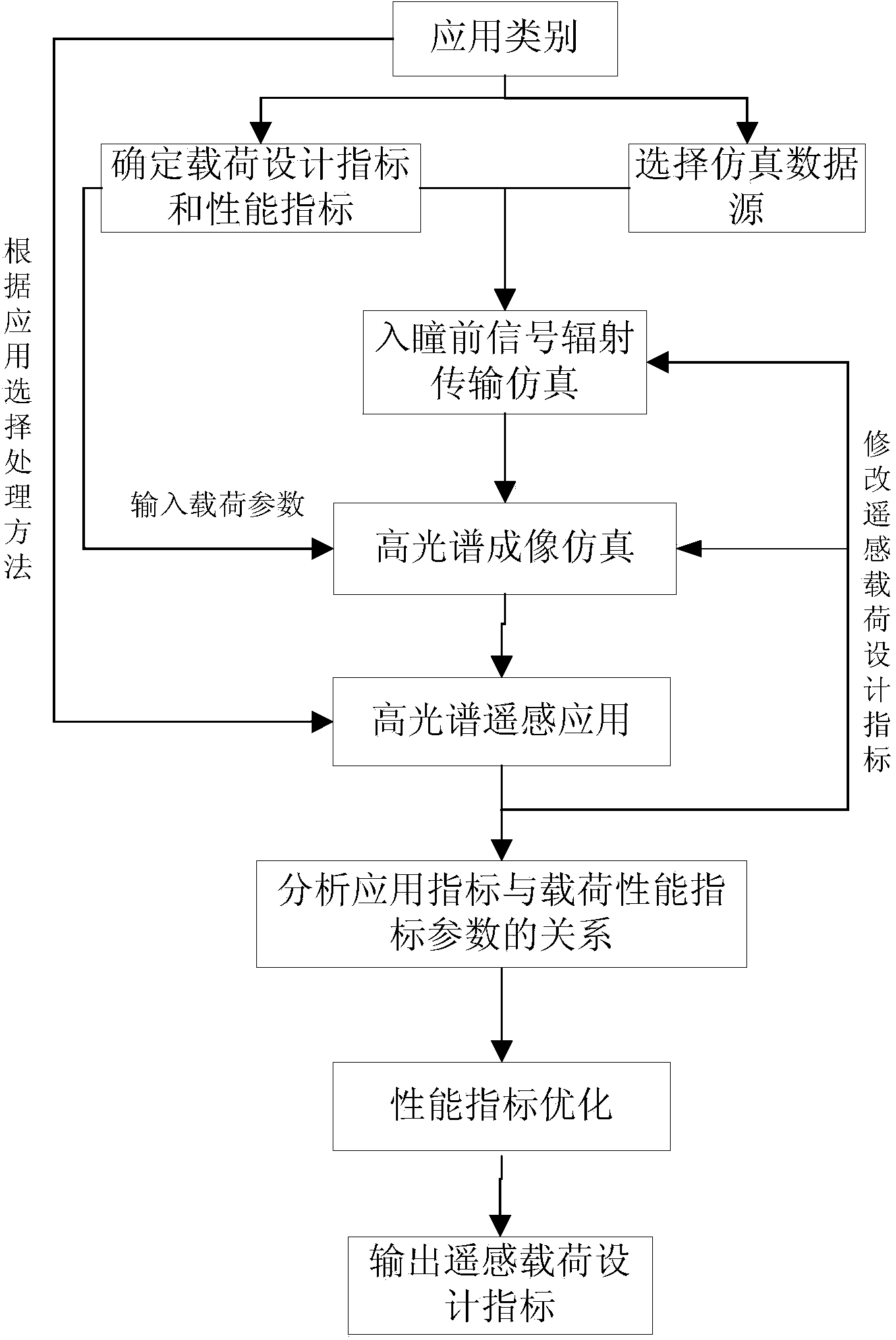
ActiveCN103776532ATightly boundEstimated Application AbilitySpectrum investigationParallel computingRemote sensing application
Disclosed is a hyperspectral-imager index optimization method based on remote-sensing application. Firstly, a hyperspectral data application objective is determined and according to the application objective and load design index requirements, hyperspectral load performance index parameters and design index parameters are preset; then an atmospheric radiation transmission model is used to perform hyperspectral signal simulation before pupil entrance of a remote sensing load; then according to a push-broom hyperspectral imaging principle, a hyperspectral imaging simulation model is established so that imaging simulation of the hyperspectral load at a space dimension and a spectral dimension is realized and hyperspectral imaging data and hyperspectral load performance index parameter values are obtained and a hyperspectral data processing method is used to obtain an application result and the relation between an application effect index and a load performance index is established; and at last, an optimization index is determined through a least square method. The hyperspectral-imager index optimization method based on the remote-sensing application introduces a remote-sensing application index into a load index optimization design and considers hyperspectral load index optimization from an application angle so that a reliable and effective means is provided to hyperspectral load design and hyperspectral data application performance evaluation.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
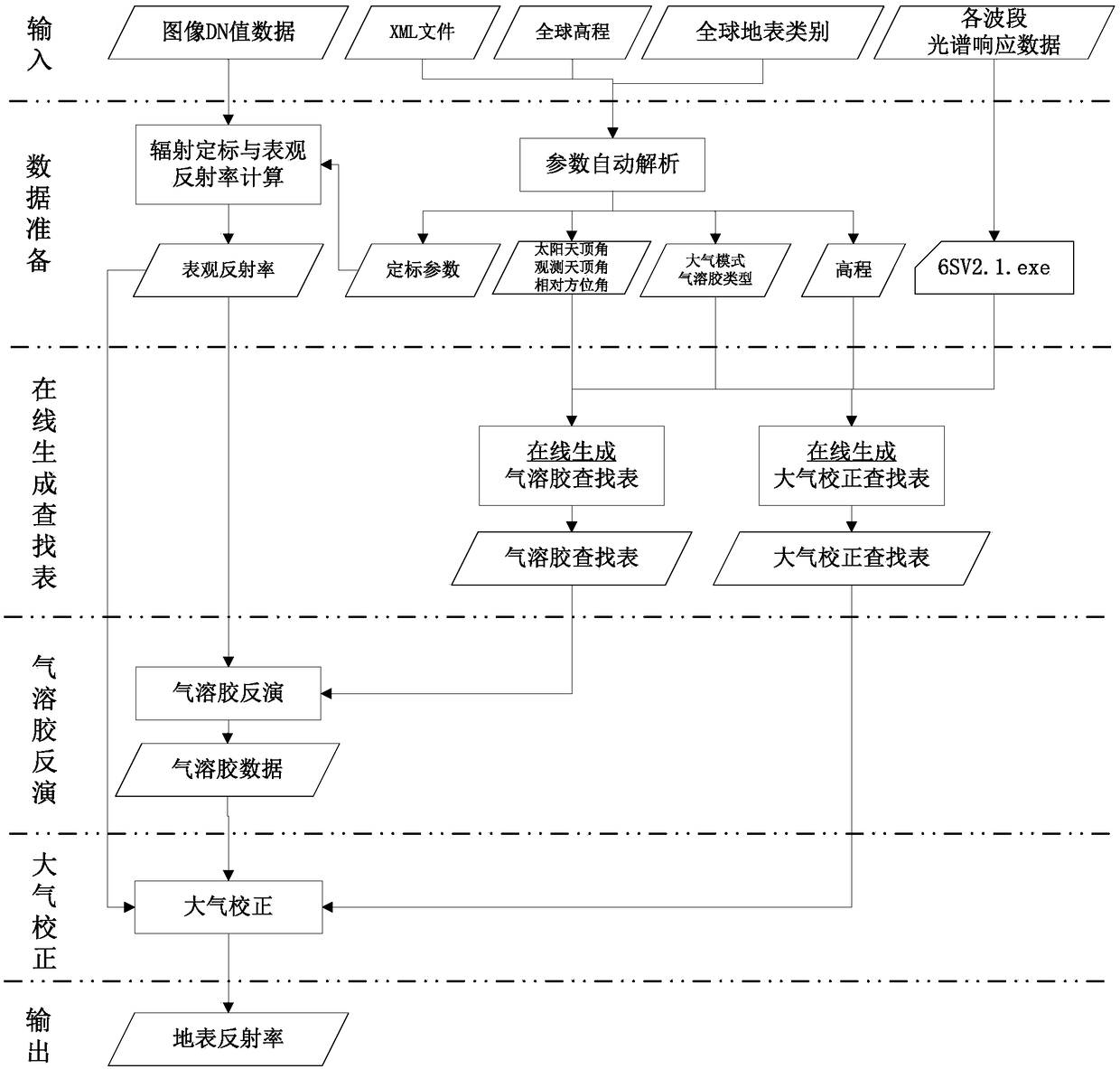
Pixel-by-pixel atmospheric correction method for calculating look-up table online
ActiveCN108256186AHigh degree of automationImprove stabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsGeosynchronous satelliteAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses a remote-sensing image pixel-by-pixel atmospheric correction method based on a 6S atmospheric radiation transmission software package online calculation. The method comprises the steps that a 6S online parallel computing look-up table is utilized, the look-up table for different aerosol optical thicknesses of a remote-sensing image under different imaging geometry and atmospheric modes is generated, aerosol distribution data is obtained onteh basis of the look-up table, a look-up table of atmospheric correction coefficients is generated, and pixel-by-pixel atmospheric correction is conducted on the basis of the look-up table. Accordingly, the problems that for a traditional method of building the look-up table offline, the application range is limited, the table building amount is large, and pixel-by-pixel multi-dimensional interpolation is complex are solved, and high stability and applicability are achieved for high-resolution remote-sensing image atmosphericcorrection obtained by the Gaofen-4 geosynchronous satellites any time all day.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
The Changjiang River drainage basin information extracting and spatial coding method
ActiveCN107491758AClear spaceClarify administrative powerMaterial analysis by optical meansScene recognitionClassification methodsSpatial encoding
The invention provides the Changjiang River drainage basin information extracting and spatial coding method which comprises the following steps of (1), performing high resolution remote sensing image atmosphere correction based on an atmosphere radiation transmission model; (2), performing high resolution remote sensing image geographical correction based on a rational function model; (3), performing high resolution remote sensing image data embedding processing based on a Snake model; (4), performing high resolution remote sensing image data fusion processing based on wavelet transformation; (5), performing extraction based on object-oriented water body time-space information; and (6), performing water body information spatial coding based on a hierarchical classification method. The Changjiang River drainage basin information extracting and spatial coding method has advantages of 1), effectively realizing real-time monitoring and management for water environment and resource of the Changjiang River drainage basin; 2), supplying a scientific basis for the Changjiang River economic band development strategy, area ecology environment protection and planning; and 3), realizing suitability for spatial extraction and management of water body information in other drainage basins.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for determining water content and moisture absorption mass increase rate of atmospheric particles
InactiveCN102749260AAids in obtaining hygroscopic propertiesWithdrawing sample devicesWeighing by absorbing componentParticulatesFiltration membrane
The invention relates to a method for determining water content and moisture absorption mass increase rate of atmospheric particles. The process comprises that: 1) an atmospheric sample passes through a filtration membrane, particles in the atmosphere are collected on the filtration membrane, and sampling is stopped after a predetermined time to obtain a sample membrane adsorbed with the atmospheric particles in a sampling time; 2) the sample membrane is subjected to dry gas purging, water content of the purged moisture is quantitatively determined; and 3) gases with different humidity are repeatedly introduced to the sample membrane to carry out moisture absorption culture, weights of the filtration membrane before and after moisture absorption are weighed, and mass increase rate of the atmospheric sample under different humidity conditions is calculated. The present invention further discloses an apparatus for performing the method. With the present invention, base data is provided for dust-haze formation mechanism, air quality, atmospheric chemistry model development research and the like, and important effects are provided for researches of cloud water chemistry and physics, artificial influence on weather, atmospheric radiation and climate, and the like.
Owner:INST OF ATMOSPHERIC PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY SCI
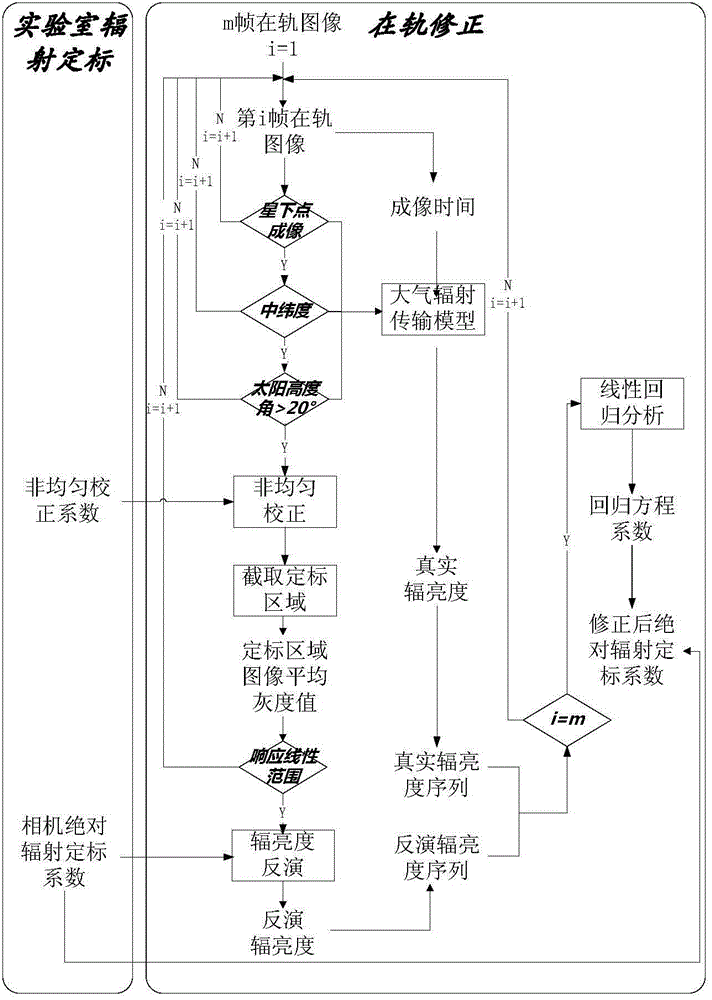
Solar blind ultraviolet remote sensing camera absolute radiometric calibration coefficient in-orbit correction method
ActiveCN104977024ARadiation calibration accuracy cannot be guaranteedMeet the high-frequency on-orbit calibration requirementsMeasurement devicesUltravioletLinear regression
The present invention relates to a solar blind ultraviolet camera absolute radiometric calibration equation coefficient in-orbit correction method, wherein a camera is subjected to laboratory absolute radiometric calibration to obtain the absolute radiometric calibration coefficient and the non-uniformity correction coefficient of the camera, the atmosphere background radiation value calculated based on the atmosphere radiation transmission model can be considered as the true background radiance when the camera in-orbit operating meets a certain constraint of the imaging mode, the location and the illumination condition, the background radiance is inverted according to the laboratory absolute radiometric calibration coefficient and the image local gray mean, and a linear regression method is used to analyze the inverted radiance value and the true radiance value so as to achieve the in-orbit correction of the calibration equation coefficient. According to the present invention, according to the solar blind ultraviolet spectrum atmosphere background radiation characteristic, the high-frequency and operational in-orbit absolute radiometric calibration of the solar blind ultraviolet spectrum remote sensor can be supported, and the blank of the in-orbit absolute radiometric calibration method of the domestic camera at the spectrum is filled.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
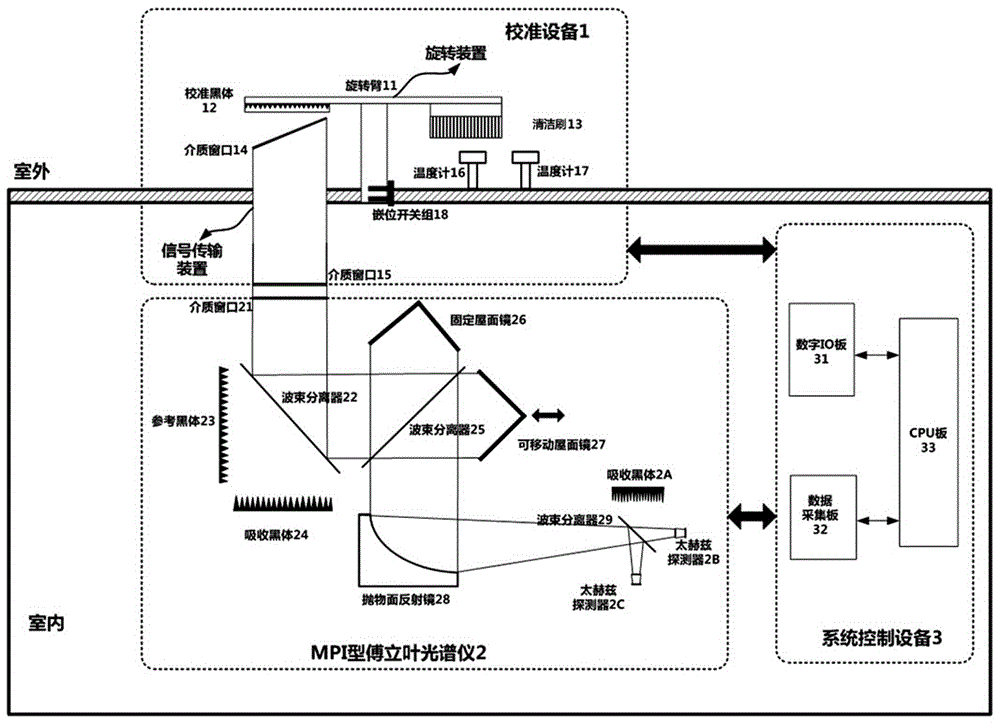
Automatic terahertz atmosphere characteristic measuring system and calibration method thereof
InactiveCN106813779AImproving the signal-to-noise ratio of observational calibration dataIncrease the amount of lightInterferometric spectrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansBlack bodyLow frequency band
The invention discloses an automatic terahertz atmosphere characteristic measuring system and a calibration method thereof; the system comprises a calibration signal source, a calibration device, a terahertz spectrometer and a system control device; the calibration signal source is a double-temperature calibration signal source based on nature ambient temperature, i.e., a passive work mode can effectively simplify the calibration device and improve the system calibration precision, thus ensuring the system to carry out long term consistent unmanned works; the terahertz spectrometer is a dual-frequency band overlapping ultra wide band MPI type terahertz Fourier spectrometer, and employs a two-port input and two-port output mode; a black body calibration signal source or an atmosphere radiation signal source and a built in reference blackbody signal source are inputted so as to form interference fringes under an interferometer effect; the interference fringes are outputted to two detectors with different detection frequency band ranges yet overlapping on the low frequency band; the two detectors respectively singly receive and output interference fringe electric signals, and the signals are corrected, accumulated and averaged in a frequency domain, thus improving the overlapping frequency band observation calibration data signal to noise ratio.
Owner:ZIJINSHAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
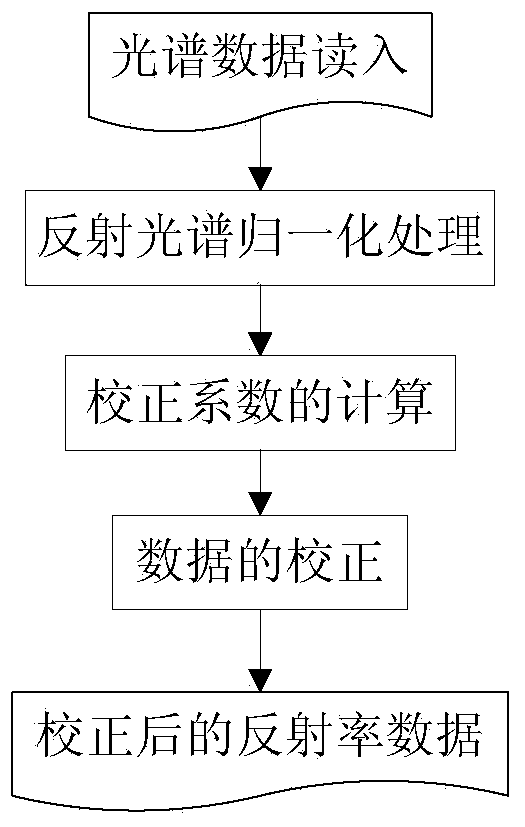
Spectral correction method of imaging spectrum reflectivity data
InactiveCN103592235AReduce leak rateReduce mistakesColor/spectral properties measurementsMineral identificationAtmospheric radiative transfer codes
A spectral correction method of imaging spectrum reflectivity data comprises the following steps: 1, reading in the spectrum data; 2, normalizing a reflection spectrum; 3, calculating a correction coefficient; and 4, correcting the data. The method can be used for correcting the imaging spectrum reflectivity data generated after the spectral reconstruction by utilizing an atmospheric radiative transfer model in order to reduce the error and reduce the information extraction leakage rate. The method has a practical value and a wide application prospect in the hyperspectral remote-sensing mineral identification field.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
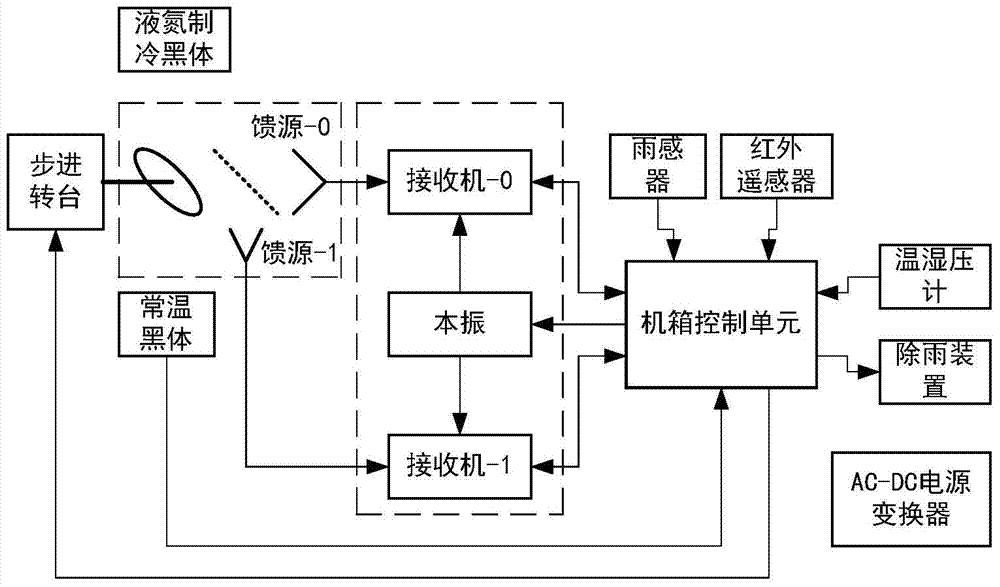
Multi-channel microwave radiation measuring device
InactiveCN103616567AReduce complexityReduce volumeElectromagentic field characteristicsBlack bodyConnection control
The invention relates to a multi-channel microwave radiation measuring device. The multi-channel microwave radiation measuring device is characterized by comprising an antenna portion adapted to the K frequency band and the V frequency band, a receiving device and a microwave black body radiation source, wherein the receiving device and the microwave black body radiation source are connected with the K frequency band and the V frequency band. A feed source of the K frequency band of the antenna portion and a feed source of the V frequency band of the antenna portion are connected with a K frequency band receiver and a V frequency band receiver, and the output end of the K frequency band receiver and the output end of the V frequency band receiver are connected with a controlling unit. The two receivers share the same local oscillator. The microwave black body radiation source comprises a normal-temperature black body radiation source and a liquid nitrogen refrigeration black body radiation source, the normal-temperature black body radiation source and the liquid nitrogen refrigeration black body radiation source are arranged symmetrically about a rotary shaft of the reflective face of an antenna, and the pyramids of black bodies respectively face the rotary shaft. The multi-channel microwave radiation measuring device has the advantages of being capable of working under the condition of unattended operation for a long time, having the capability of continuously detecting the intensity spectrum of atmospheric radiation at a sensitive frequency band, and being capable of being used for continuous real-time monitoring on the atmospheric humidity and temperature profile.
Owner:CNGC INST NO 206 OF CHINA ARMS IND GRP
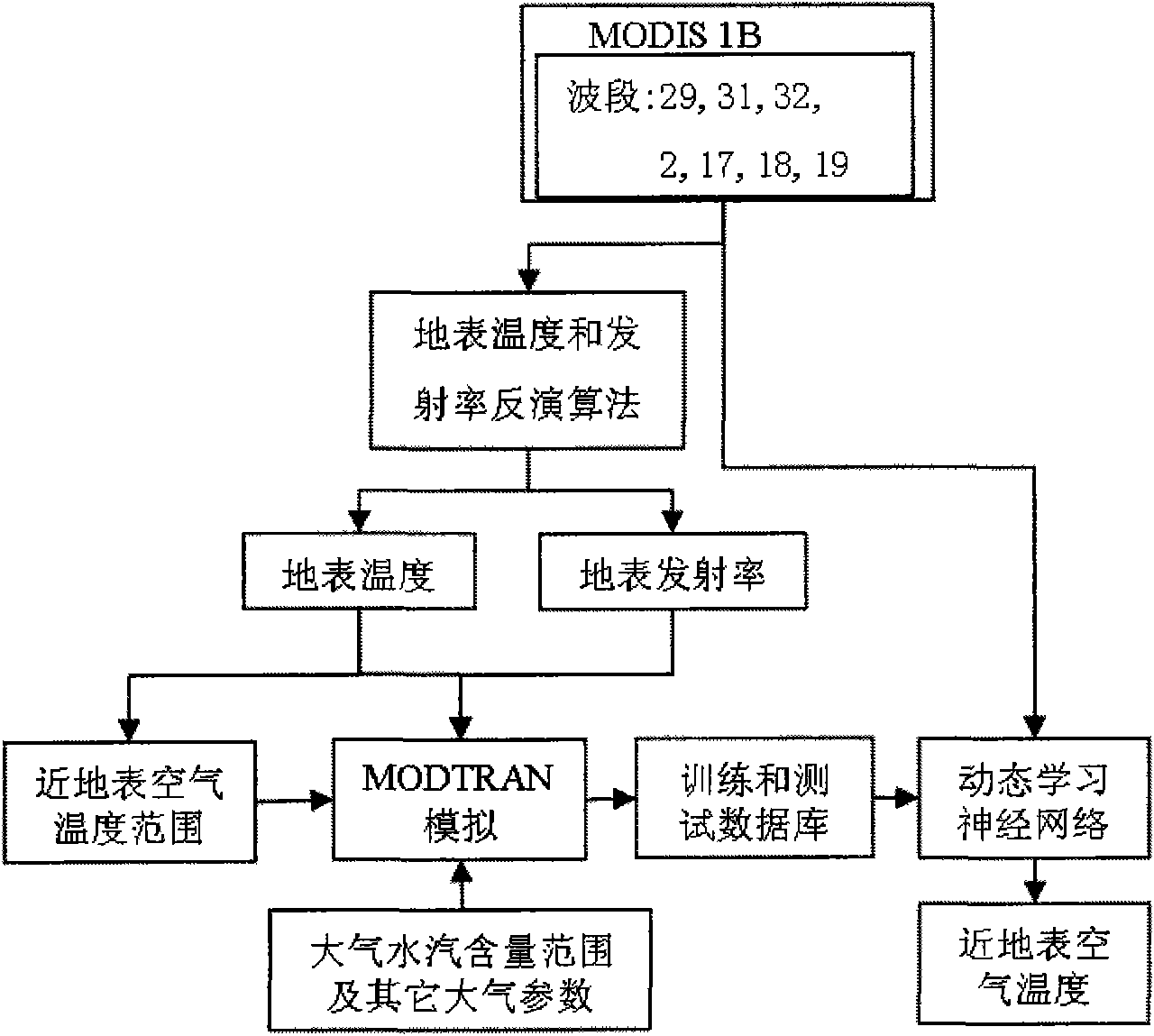
Method for inversing surface temperature and emissivity from MODIS data
InactiveCN101655564AReduce unknownsReduce computing timeBiological neural network modelsElectromagnetic wave reradiationData setEmissivity
A method for inversing surface temperature and emissivity from a remote sensing MODIS data comprises the steps of forward simulating by utilizing an atmospheric radiation transferring simulation software MODTRAN4 aiming at the atmospheric model, the region and the season of the 29th, 31st and 32nd thermal infrared bands of the received remote sensing MODIS data to create a training and testing database, retraining and retesting the training and testing database by using a neural network, back calculating an actual MODIS image data, verifying the actual ground surface and analyzing the application. The surface temperature and the emissivity received by the invention have the advantages of high precision, wide application range and simple operation.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com