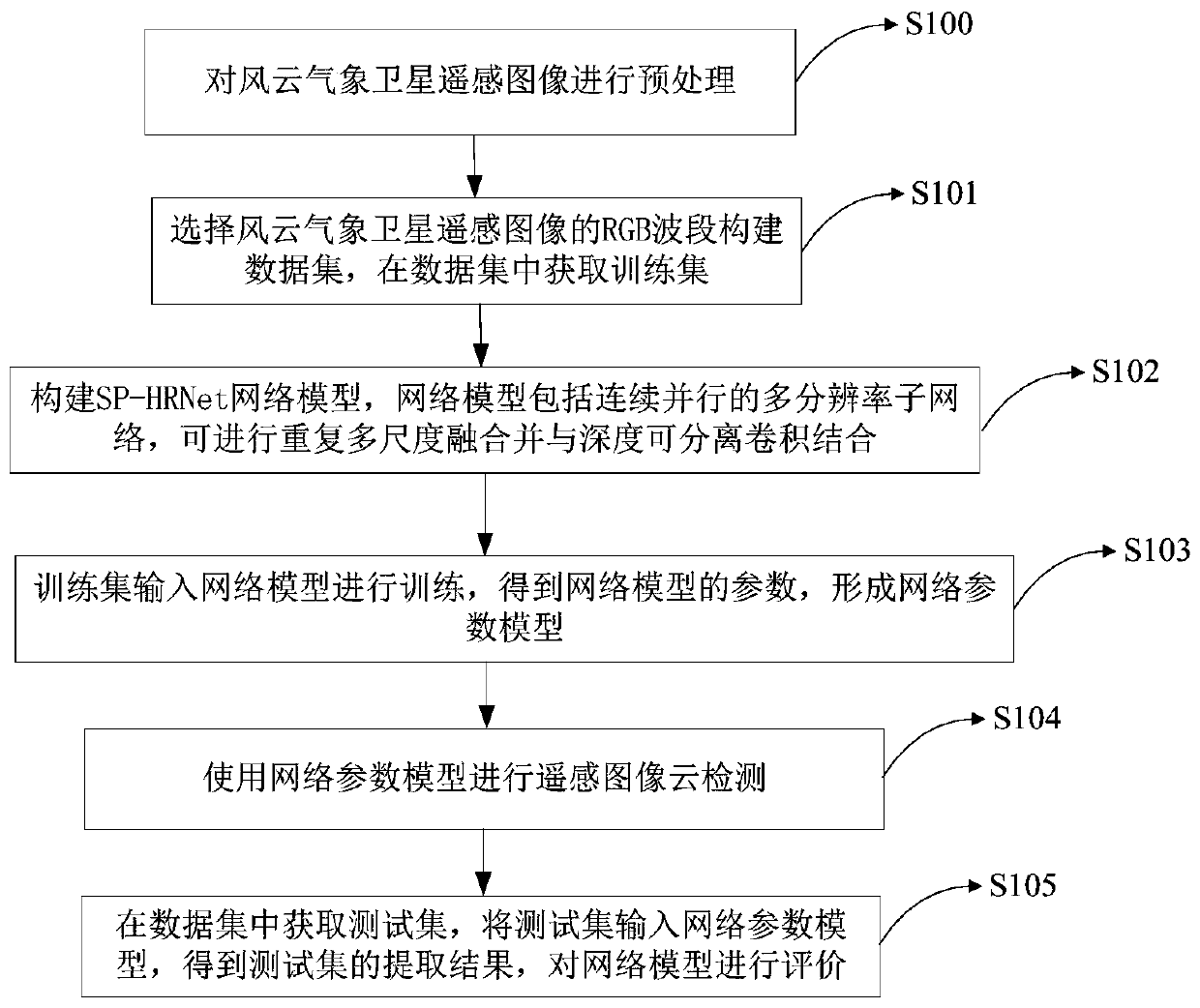
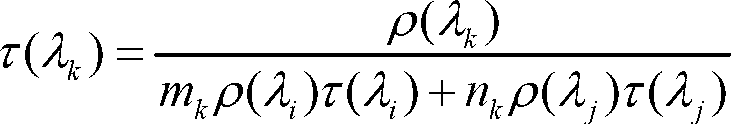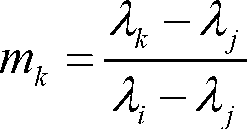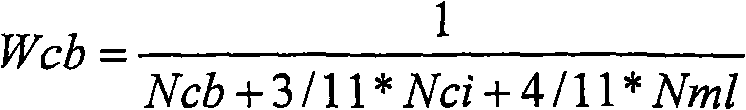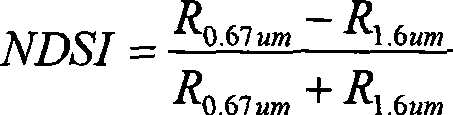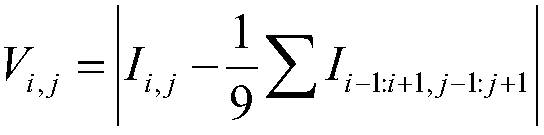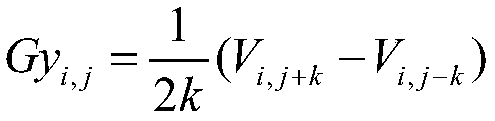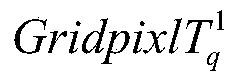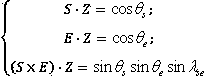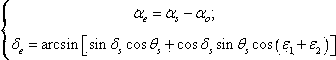Patents
Literature
189 results about "Meteorological satellite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Meteorological satellite - a satellite that transmits frequent picture of the earth below. weather satellite. artificial satellite, orbiter, satellite - man-made equipment that orbits around the earth or the moon.
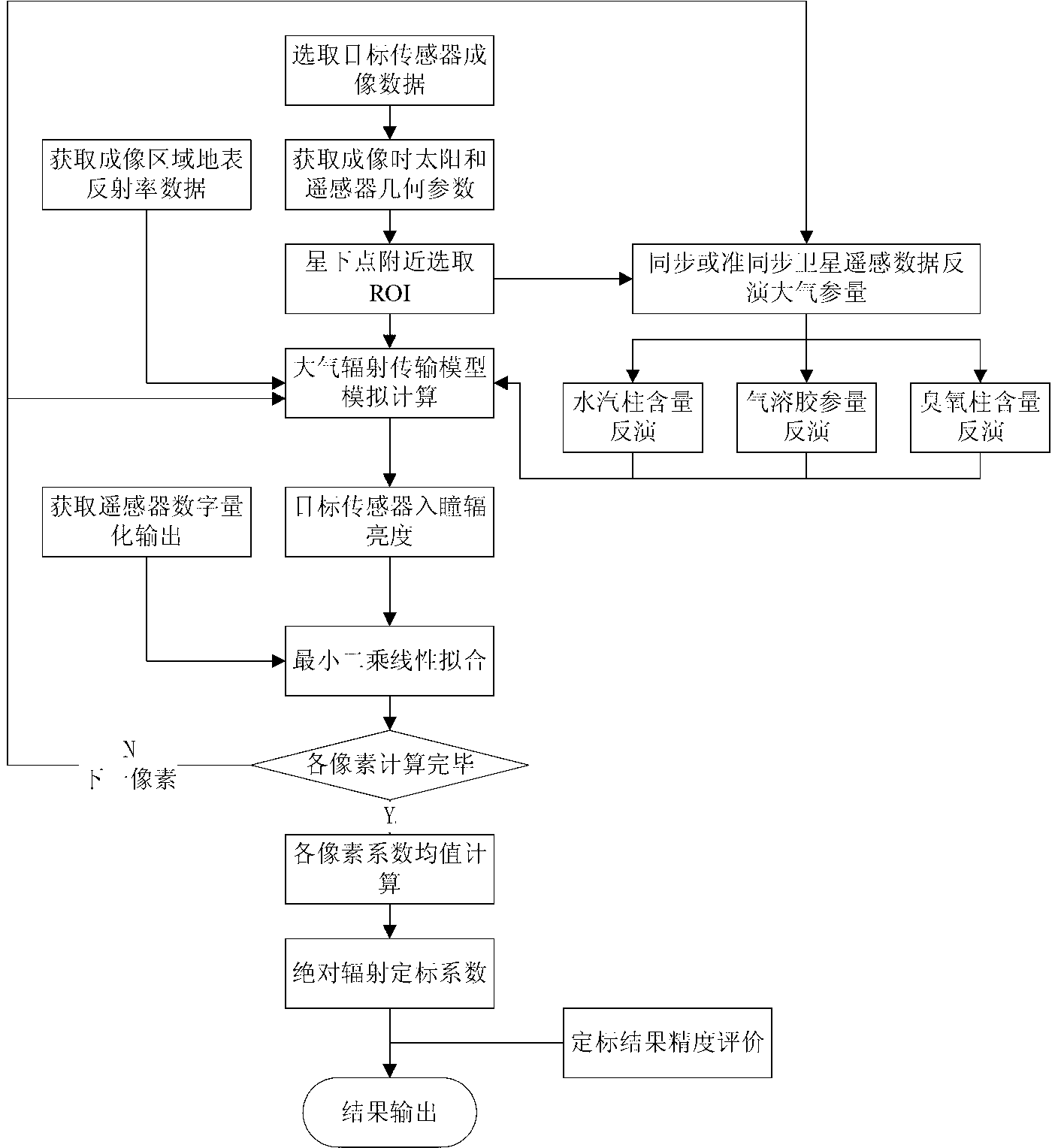
Satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval
InactiveCN103018736ASimulation is accurateAccurate entrance pupil radianceWave based measurement systemsMeteorological satelliteEntrance pupil
The invention discloses a satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval. The method includes nine steps. A surface reflectance is obtained through ground synchronous actual measurement during satellite crossing or historical data, imaging time and observation geometry parameters are obtained through remote sensing data head files, atmospheric parameters during imaging of synchronous crossing meteorological satellite sensors or related load retrieval remote sensors are utilized, the entrance pupil radiance of the remote sensors is calculated by an atmospheric radiation transmission model according to retrieval results of the atmospheric parameters, a calibration coefficient is calculated through a radiation calibration model, and thereby the on-orbit radiation calibration for a satellite-borne remote sensor is achieved. The satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on the atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval is a pixel-level calibration method and has the advantages that the accuracy is high, the costs are low, simultaneously, the high frequency calibration can be achieved, historical remote sensing data can be calibrated, and the method has a wide application prospect to remote sensing data processing methods and application technical fields.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
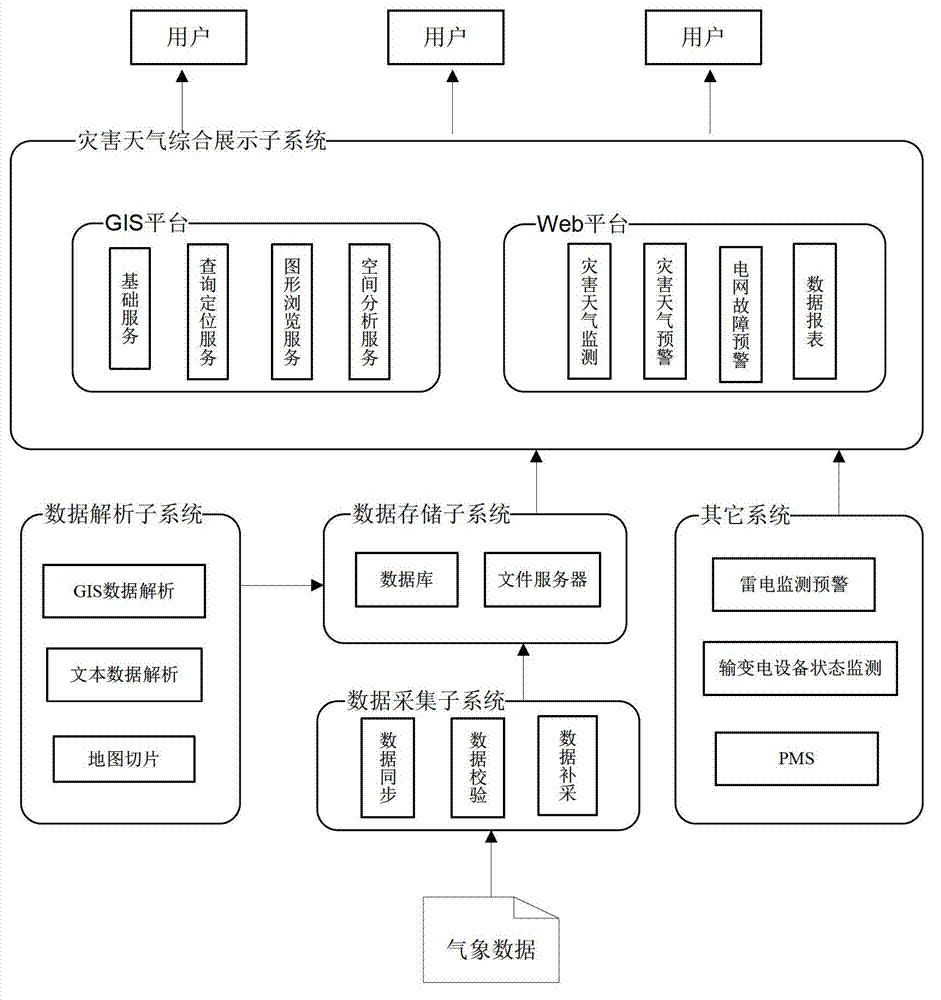
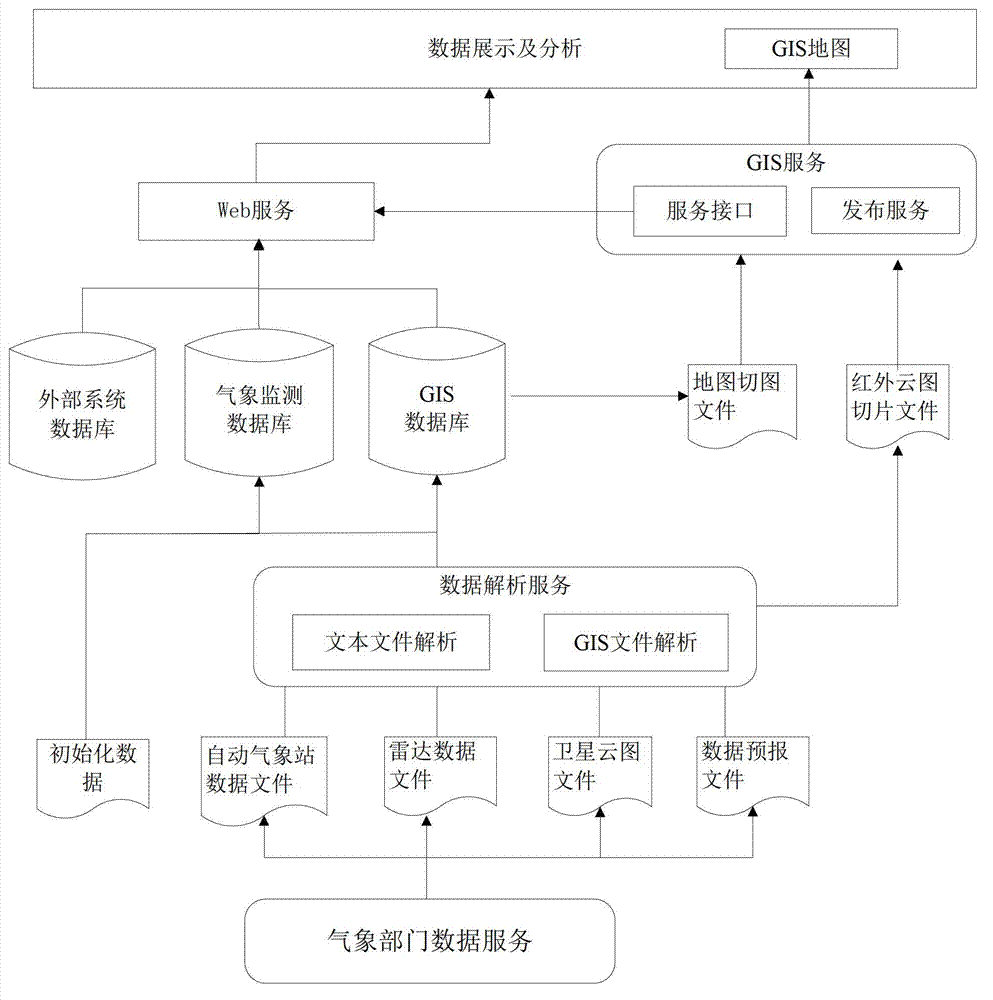
Grid meteorological disaster monitoring and early warning system
ActiveCN103033855ARapid positioningTo achieve the purpose of accurate early warningIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesDisaster monitoringOriginal data
The invention discloses a grid meteorological disaster monitoring and early warning system which comprises a data collection subsystem, a data analysis subsystem, a data storage subsystem and a disaster weather comprehensive display subsystem, wherein the data collection subsystem is responsible for completing a collection task of original meteorological monitoring data. The original meteorological monitoring data is composed of automatic meteorological station data, Doppler radar data, meteorological satellite data and value forecasting data. The data analysis subsystem is responsible for analysis of original meteorological data, cutting a satellite cloud picture, and finally storing processed data into the data storage subsystem. The data storage subsystem is responsible for storing original data of data of various stages and types, including original data, a relational data, a vector data and a picture, the original data is received from a meteorological department, the relational data is analyzed by the data analysis subsystem, the vector data is analyzed by the data analysis subsystem, and the picture is processed by the data analysis subsystem. The disaster weather comprehensive display subsystem is responsible for system function display. The grid meteorological disaster monitoring and early warning system can accurately position grid facilities which are affected by disaster weather.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Global three-dimensional atmosphere data analysis and management method
ActiveCN106547840AAchieve unified integrationReliable data supportSpecial data processing applicationsMeteorological satelliteInstrumentation
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +1
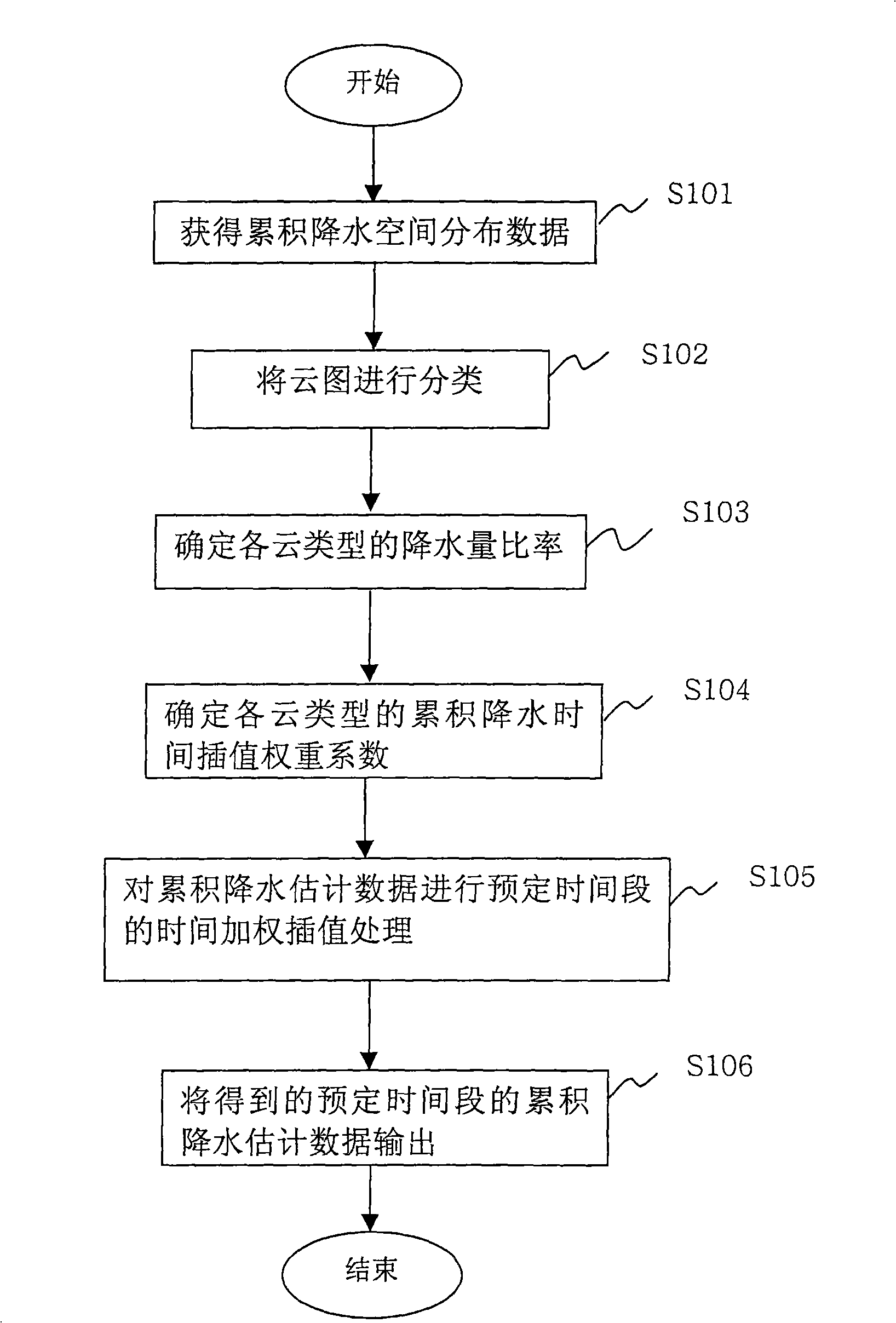
High resolution precipitation data processing method
InactiveCN101349767ARainfall/precipitation gaugesWeather condition predictionImage resolutionEvaluation data
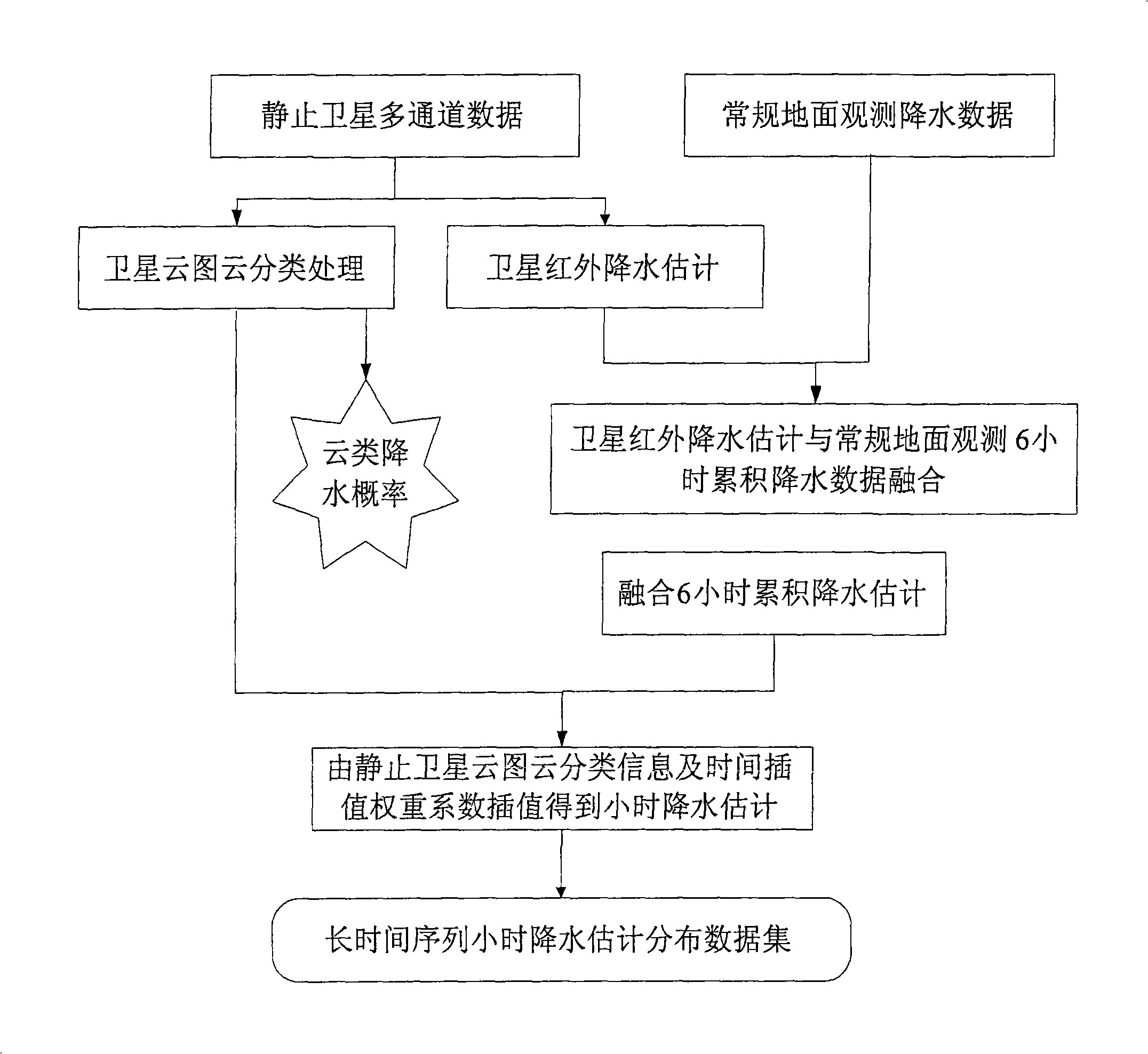
The invention relates to a precipitation data processing method which uses temporal interpolation to treat detected accumulated precipitation, based on the could picture detected per hour by geostationary meteorological satellite and cloud classification information to attain high resolution. The method comprises the steps of: attaining accumulation precipitation spatial distribution data; classifying could pictures; finding the precipitation rate of each could type; determining the accumulation precipitation temporal interpolation weight factor of each could type; processing temporal weight interpolation of each hour for the accumulation precipitation evaluation data; and outputting the accumulated precipitation evaluation data of each hour. The invention can improve the time resolution of precipitation evaluation data treatment.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT
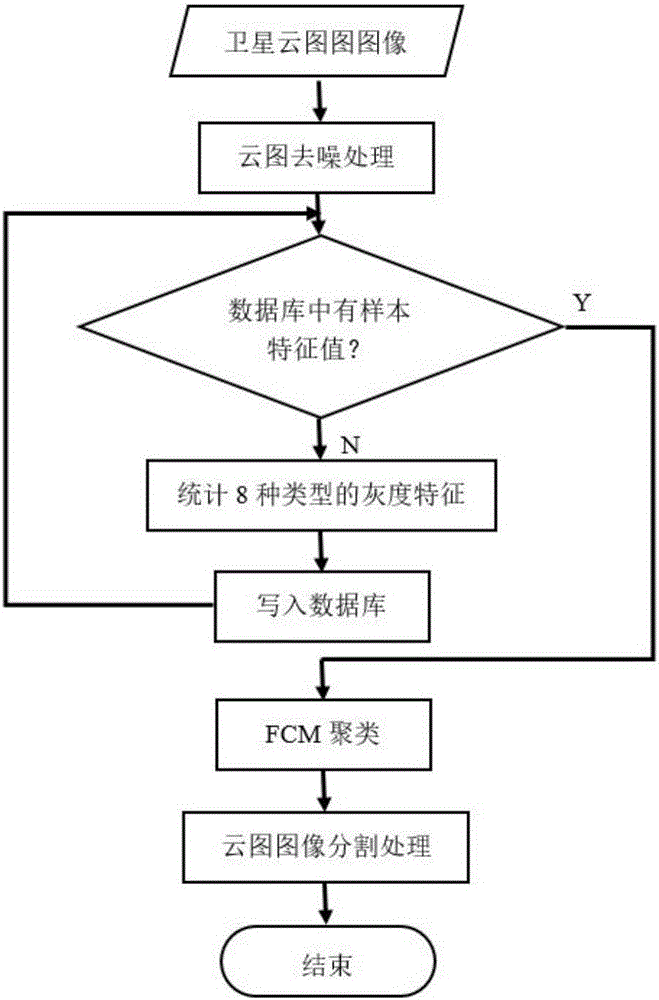
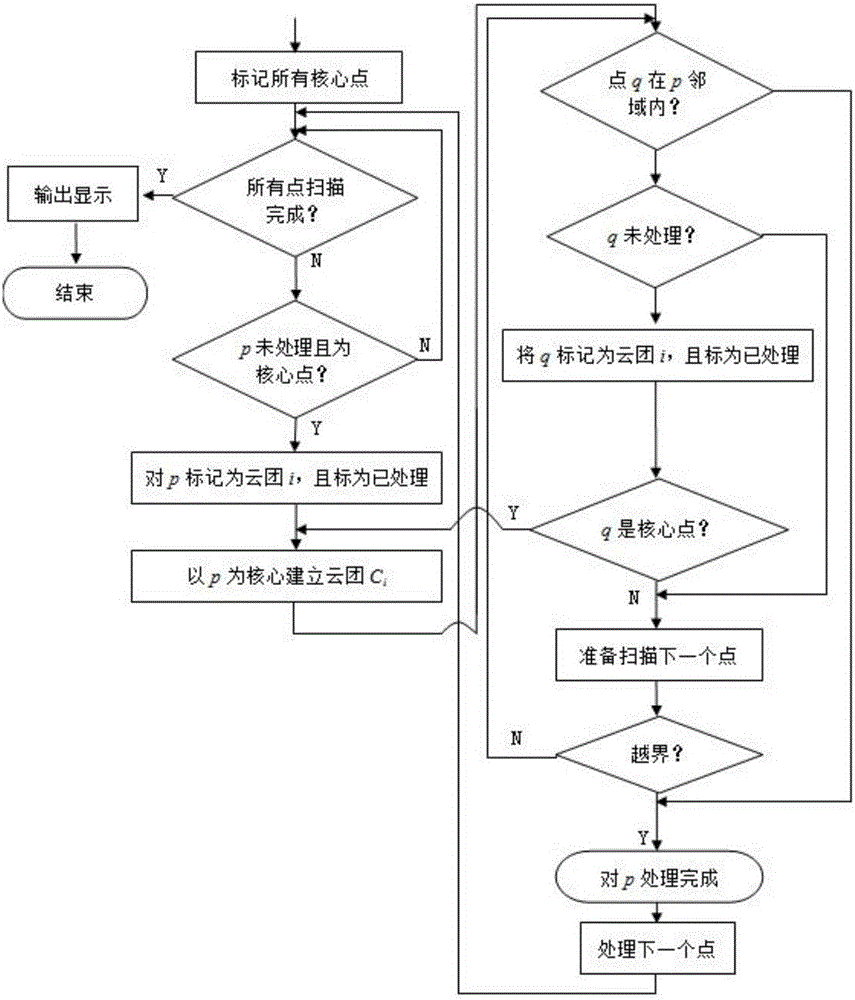
Secondary clustering segmentation method for satellite cloud picture
InactiveCN103034858AIntegrity guaranteedImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionKnowledge extractionMeteorological satellite
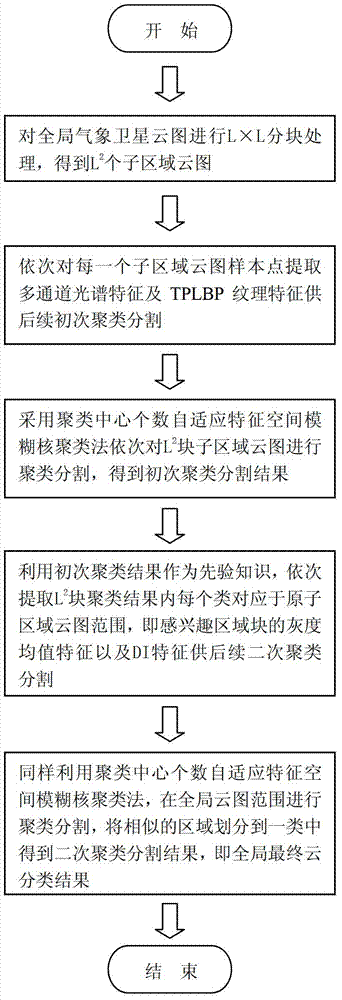
The invention discloses a secondary clustering segmentation method for a satellite cloud picture. According to the secondary clustering segmentation method for the satellite cloud picture, firstly, block processing is carried out to the whole wide-range satellite could picture; secondly, corresponding multi-channel spectral features and three-patch length between perpendiculars (TPLBP) textural features are sequentially extracted from each of sample points of each sub regional could picture for fine initial kernel clustering segmentation so as to obtain multiple sub regional could picture segmentation results; and at last, secondary kernel clustering segmentation is carried out to the global cloud picture on the basis of the initial kernel clustering segmentation results by utilization of the initial kernel clustering segmentation results as prior knowledge to extract a variety of grayscale average features and density indicator features of the initial kernel clustering segmentation results in a corresponding original sub regional cloud picture range so as to ensure integrity of cloud classification. The secondary clustering segmentation method for the satellite cloud picture has the advantages of being high in precision and robustness, and capable of identifying cloud classification in a fine mode according to huge and complicated geographical information, ocean information, atmospheric information and other information which are contained in the wide-range meteorological satellite cloud picture.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
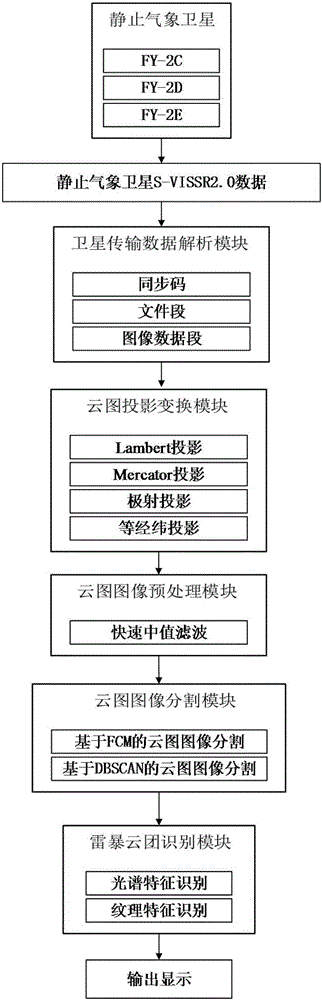
Thunderstorm cloud cluster identification method and system for meteorological satellite cloud picture
InactiveCN106023177ASolve the problem of object recognitionImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisOriginal dataThunderstorm
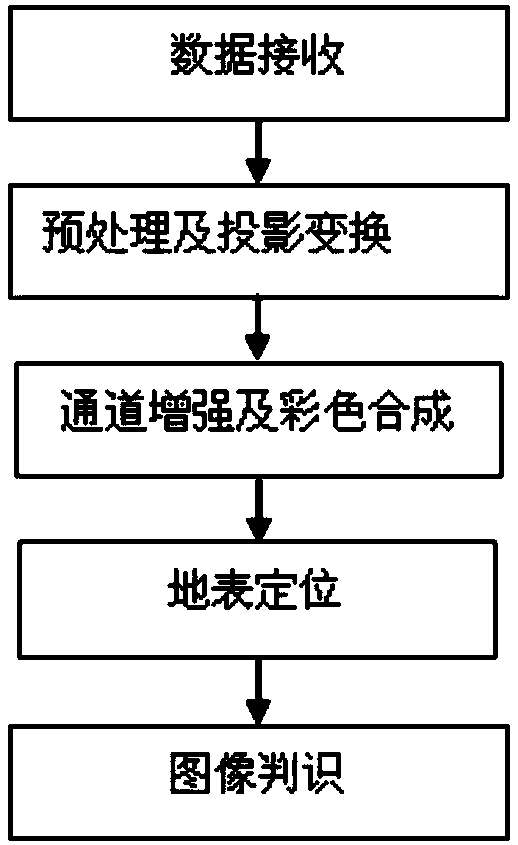
The invention discloses a thunderstorm cloud cluster identification method and system for a meteorological satellite cloud picture. The method and system performs disc picture data analysis, projection transformation, median filtering, multiple image segmentation, and thunderstorm cloud cluster automatic identification on satellite original data, performs spectrum characteristic analysis and texture characteristic analysis on the basis of cloud cluster clustering to finally obtain the coverage, the intensity, and the motion locus of the thunderstorm cloud cluster. The invention further provides a thunderstorm cloud cluster identification system for a meteorological satellite cloud picture so as to systematically, efficiently, and automatically execute the above method, rapidly process and respond to meteorological satellite cloud picture data at each time level and continuous time sections, identify the thunderstorm cloud clusters, track the development and change of the thunderstorm cloud cluster, and provide valid technical support for prediction and early warning of meteorological disasters.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
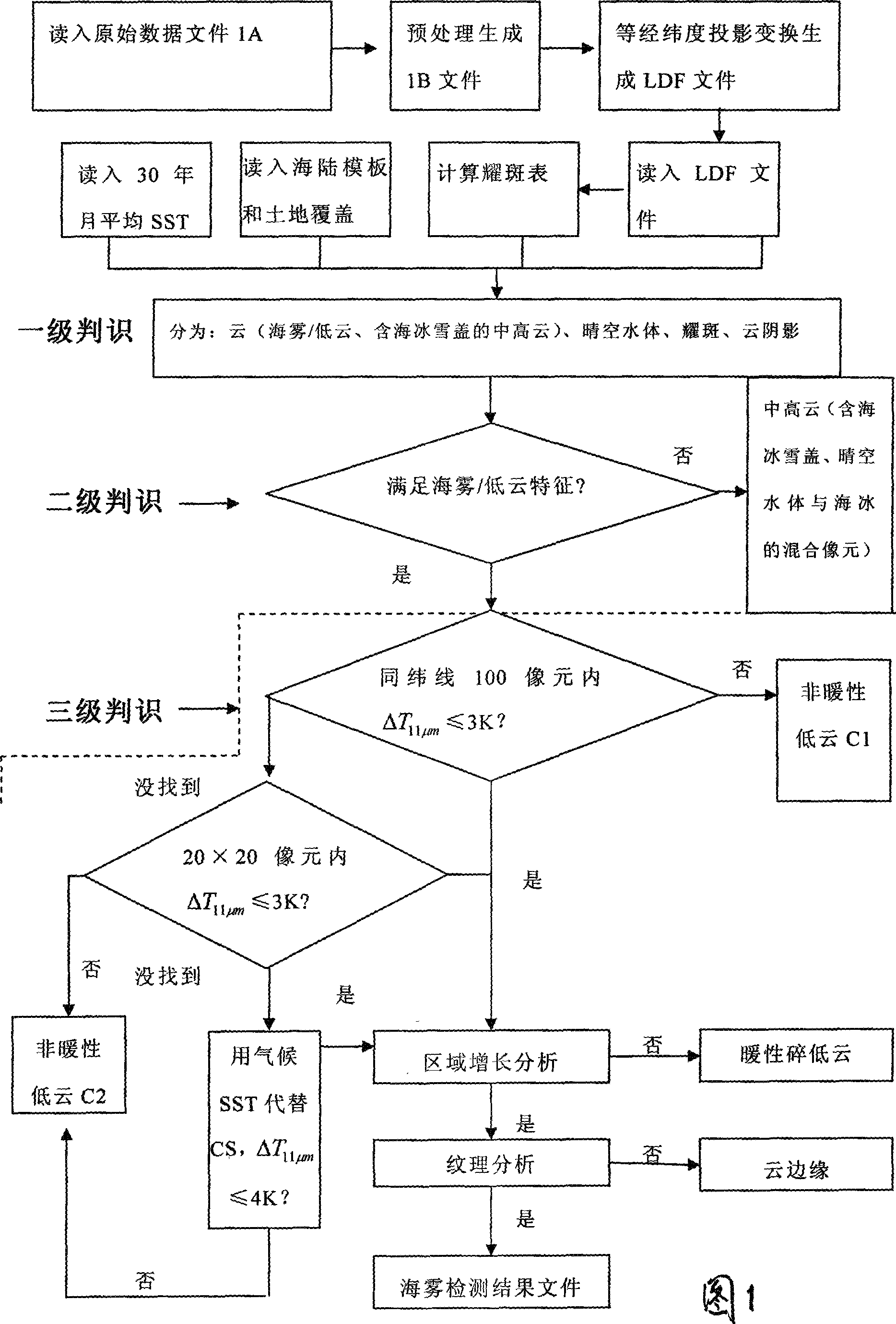
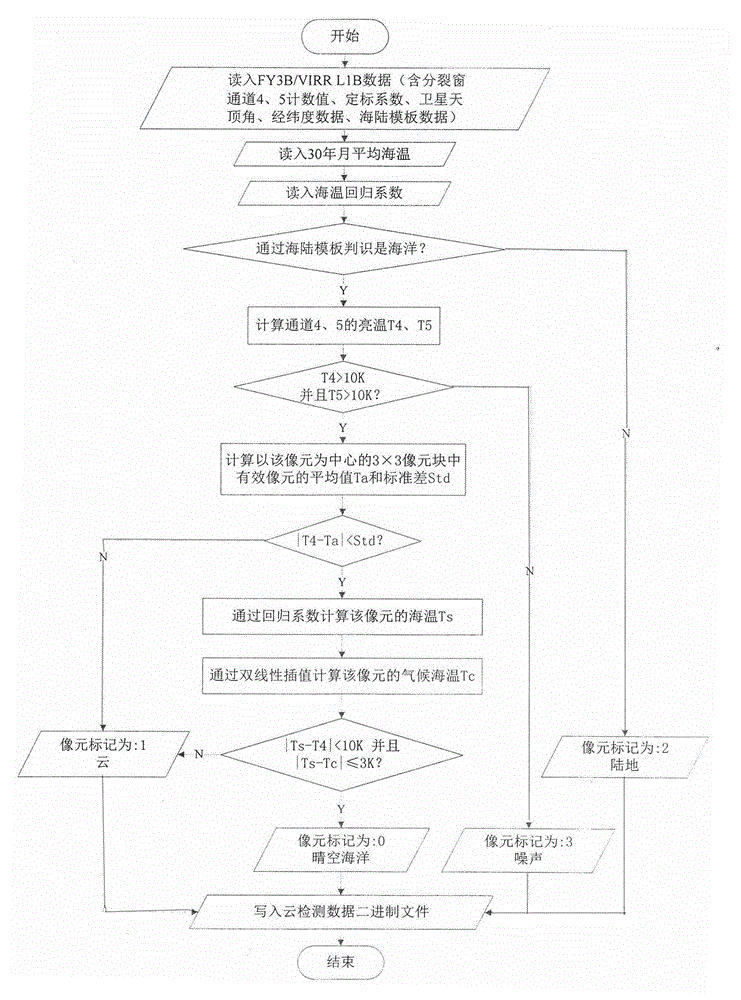
Daytime and nighttime sea fog detecting method based on polarorbiting meteorological satellite remote sense
InactiveCN101452078ARealize real-time monitoringElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationOriginal dataMeteorological satellite
The present invention relates to a method for detecting sea fog at daytime and night with polar-orbiting meteorological satellite. The polar-orbiting satellite information is used. The original data file is read into. The medium-high cloud, the clear-air water, the solar flare water, the cloud shadow areas, the sea-ice-snow sheets, non-warm low clouds, warm broken low clouds and wind edges are respectively filtered with a three-stage determining method through comprehensively using the multi-channel optical spectrum information, NDVI index, NDSI index and average month SST in thirty years. The sea fog arrangement areas are obtained and the file comprising sea fog detecting result is generated. Namely the image display can be executed on a microcomputer with GRADS drawing software. The method according to the invention separates the sea fog from low cloud thereby realizing the real-time monitoring of sea fog. Effective meteorological information with real time monitoring is provided for the safe flying over sea surface, marine traffic transportation, seaport and coasting airport operation.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +1
High reflection film of silicon carbide reflection mirror within visible light wave range, and its production method
InactiveCN101315435AReduce weightLower launch costsMirrorsVacuum evaporation coatingHigh energyHigh energy laser
The invention relates to a high reflective film for a silicon carbide reflecting mirror in the visible light wave band and the preparation method thereof. At present, the reflection factor of the surface of a reflecting mirror in a specific wavelength range is a key index in order to meet the design requirements of equipment such as large space telescopes, large terrestrial telescopes, early-warning satellites, explorer satellites, reconnaissance satellites, meteorological satellites, high energy lasers and laser radars. A reflecting mirror body in a complex shape is prepared by adopting the reactive sintering method, basic mechanical treatment and surface treatment are performed to the reflecting mirror, and then the following steps are adopted: firstly, the surface of the reflecting mirror is cleaned; secondly, filming treatment is performed with a magnetic control sputtering apparatus; and thirdly, the reflecting film layer is fine-finished. The invention is applied to the preparation method for the reflecting film of the silicon carbide reflecting mirror in the visible light wave band with the reflection factor larger than 97 percent.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
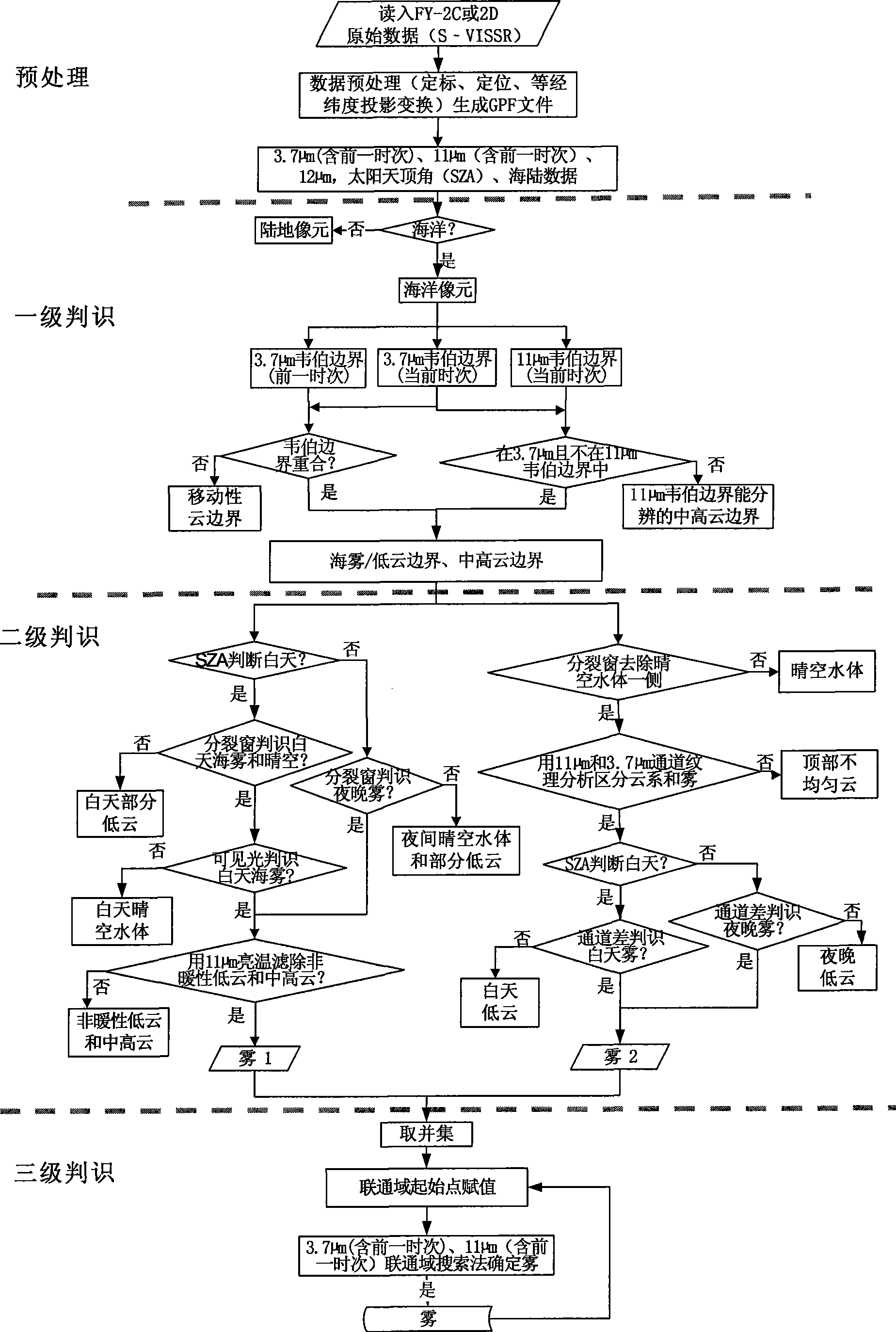
Detection method for remote sensing day and night sea fog by stationary weather satellite
InactiveCN101464521AReal-timeRealize dynamic trackingElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationSplit windowData file
The invention relates to a detection method of sea fog remotely sensed by stationary meteorological satellites in the daytime and at night. The detection method comprises the following steps: firstly receiving and processing a data file S-VISSR by utilizing the number of the stationary meteorological satellites and obtaining a GPF document containing 5 channel data after being projected through calibration and location, data amendment, latitude and longitude projection and other pretreatments; then extracting sea fog information by utilizing 4 channel data in the GPF document, 2 split window channels in a long wave infrared window region, 1 intermediate infrared channel of 3.7 Mu m and 1 visible light channel of 0.67 Mu m according to the kinematic characteristics and the spectral characteristics of the sea fog; and firstly filtering a movable cloud boundary and a medium-high cloud boundary and then filtering water body in clear sky and partial low clouds by adopting the tertiary judging method, and finally determining a sea fog region by utilizing the region growing method. The invention not only achieves the real-time monitoring of the sea fog in a wide ocean plane and the dynamic track of the sea fog region, but also provides an important basis for the shot forecast of the sea fog, thereby obtaining sea fog real-time monitoring images per hour at least.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +1
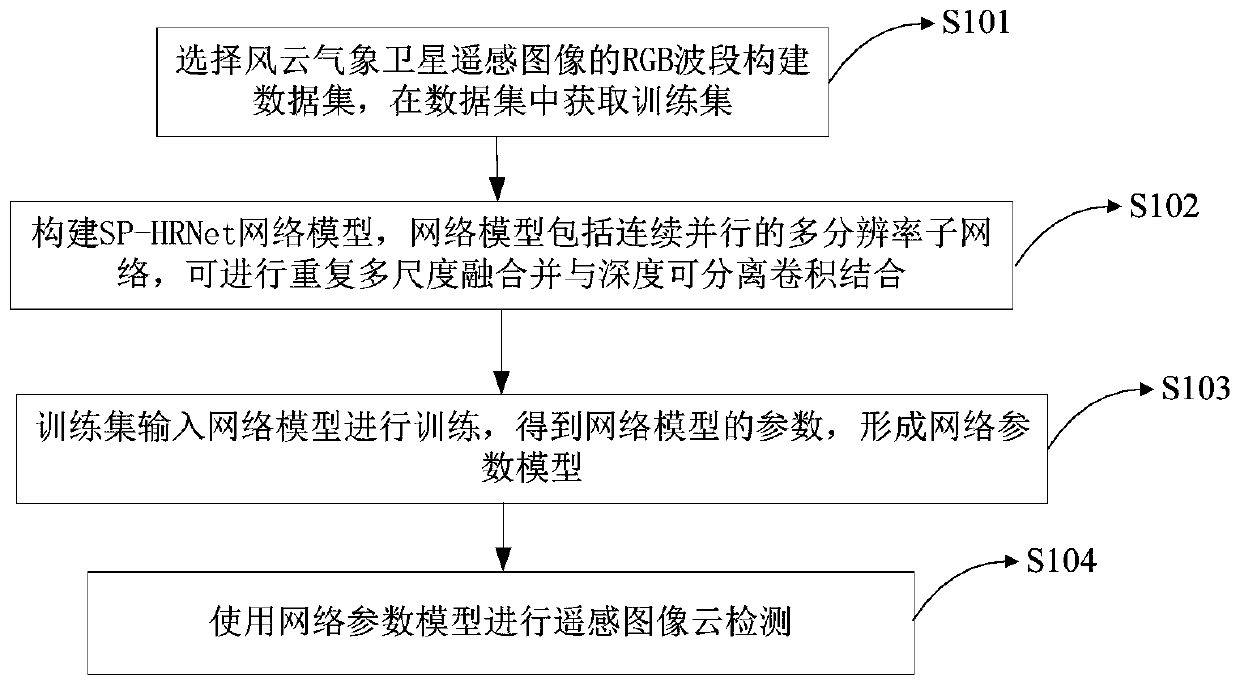
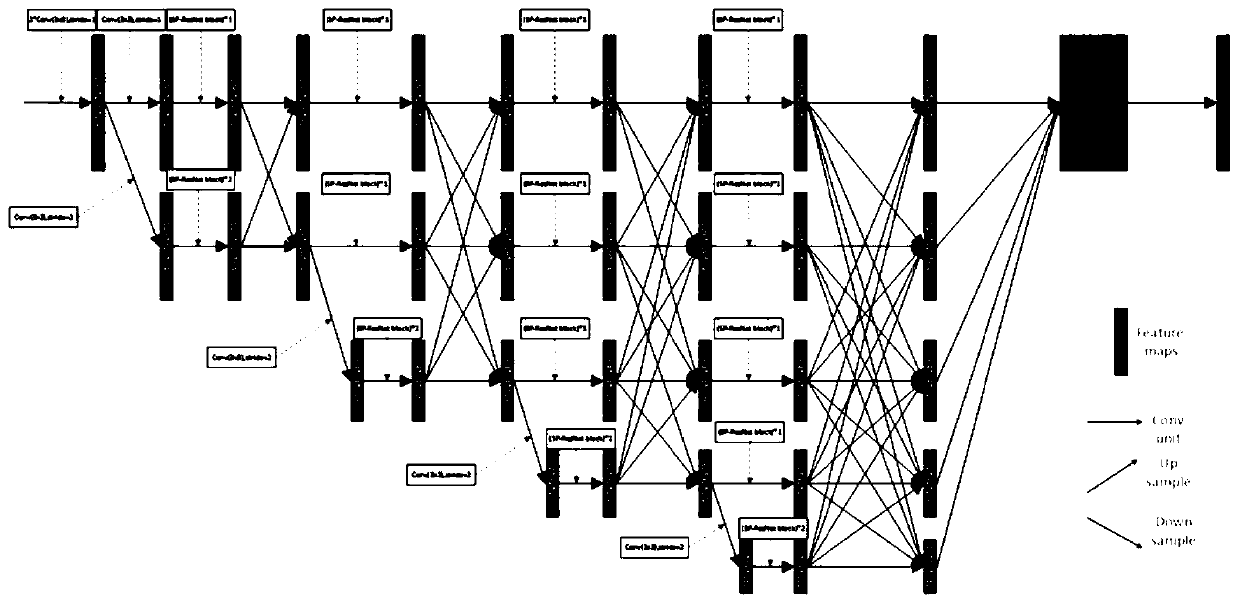
Remote sensing image cloud detection method and device based on full convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111274865AHigh precisionImprove the extraction effectScene recognitionNeural architecturesData setEngineering
The invention relates to the field of remote sensing detection, in particular to a remote sensing image cloud detection method and device based on a full convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps of selecting an RGB waveband of a wind cloud meteorological satellite remote sensing image to construct a data set, and obtaining a training set in the data set; constructing an SP-HRNet network model, wherein the network model comprises a continuous and parallel multi-resolution sub-network, a repeated multi-scale fusion module and a depth separable convolution combination module;inputting the training set into a network model for training to obtain parameters of the network model, and forming a network parameter model; and performing remote sensing image cloud detection by using the network parameter model. According to the method and the device, the sub-networks with multiple resolutions can be kept all the time, so that information is not lost in the feature extractionprocess of the image, the network depth is deepened, the depth separable convolution is combined, the feature extraction capability of the network is improved, the detail information of a detection result is enriched, and the cloud detection precision is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for typhoon monitoring and evaluation of monitoring precision based on multi-source satellite data
ActiveCN106443830AAchieve positioningRealize monitoringInstrumentsScatterometerMeteorological satellite
The invention provides a method for typhoon monitoring and evaluation of the monitoring precision based on multi-source satellite data, belongs to the technical field, and solves the problem of limitation of a single satellite data source in the practical application in the prior art. The method for typhoon monitoring and evaluation of the monitoring precision based on the multi-source satellite data includes: (1) typhoon information data acquisition: obtaining typhoon visible light or infrared image information data by employing a Fengyun geostationary meteorological satellite, and obtaining typhoon microwave scattering data by employing a microwave scatterometer of an ocean satellite; (2) information data standardization processing: performing cloud atlas grayscale information extraction on a read base data source of visible light or infrared images of a Fengyun geostationary meteorological satellite partition map, performing geo-statistical interpolation on the microwave scattering data of the ocean satellite to obtain a final regional wind field map; and (3) typhoon center interpretation: determining the typhoon center. According to the method, accurate typhoon information is obtained by employing mutual confirmation and mutual supplementation of different satellite data.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
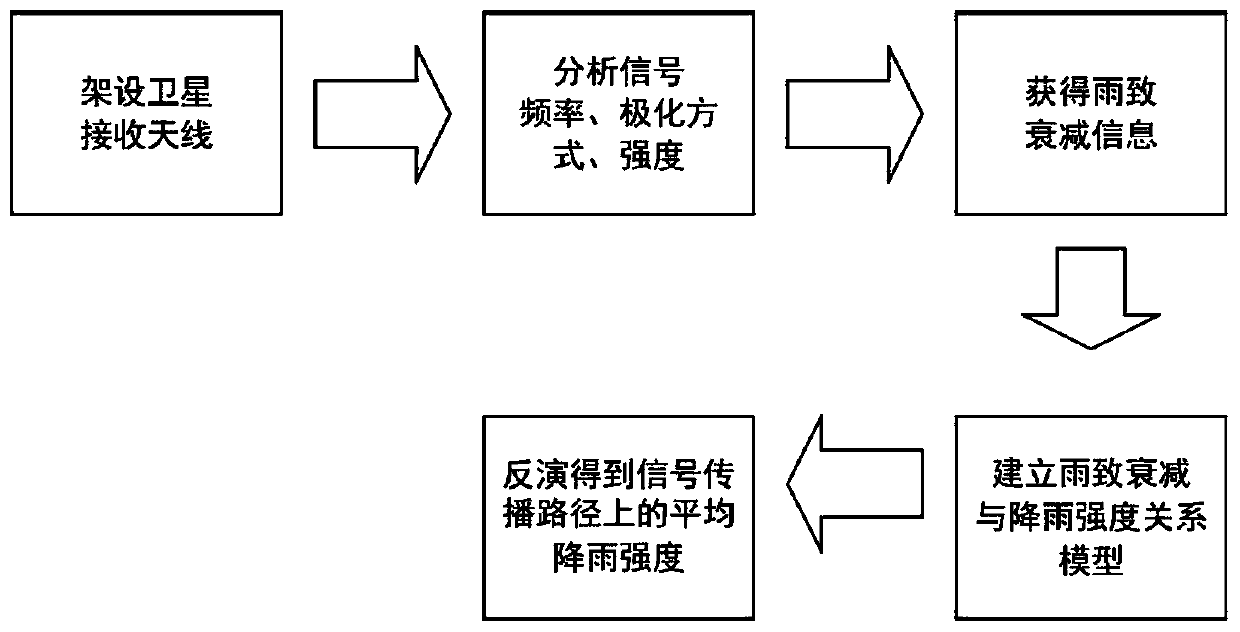
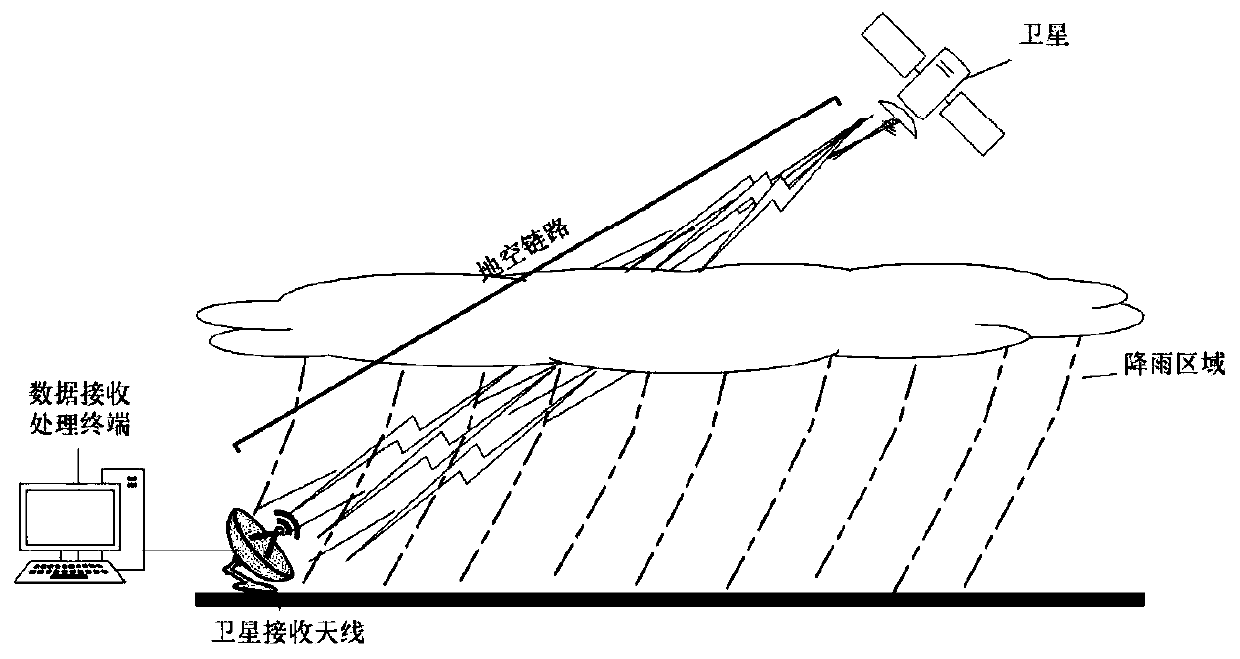
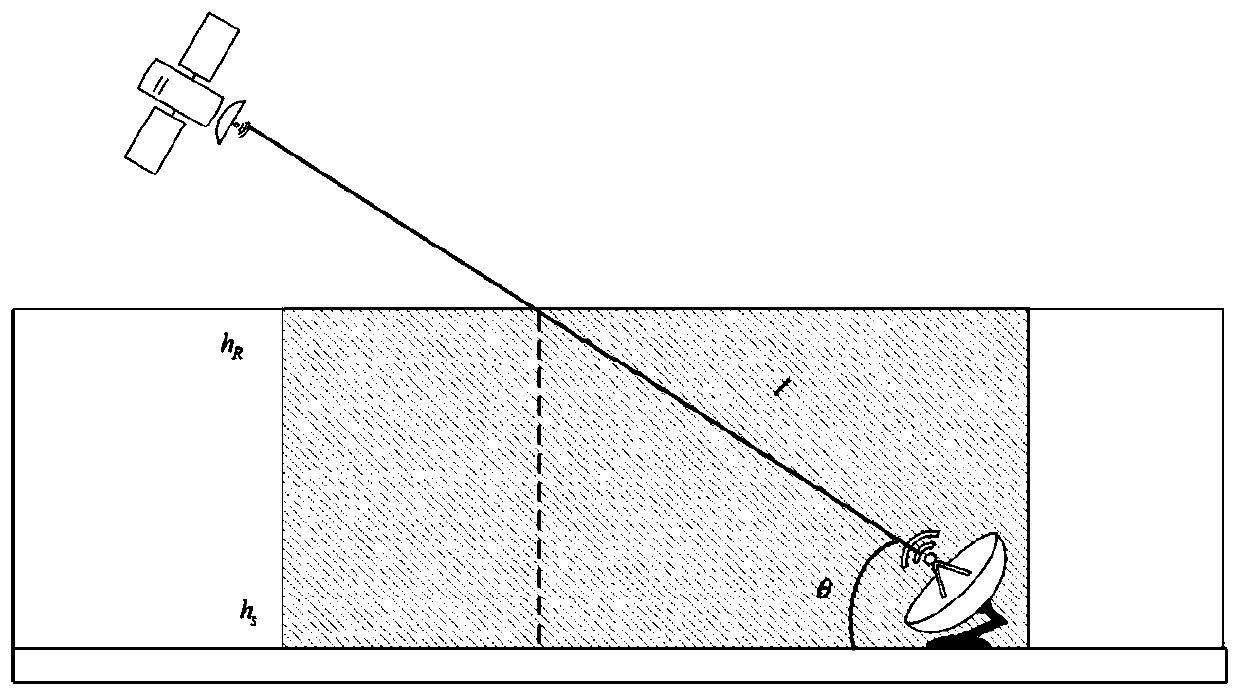
Rainfall intensity measuring method based on satellite-ground link attenuation effect
ActiveCN110031916AIncrease the number ofWidely distributedRainfall/precipitation gaugesSatellite radio beaconingWeather radarMeasurement point
The invention discloses a rainfall intensity measuring method based on a satellite-ground link attenuation effect. Attenuation characteristics generated when satellite communication signals pass through a rain area are used, and the average rainfall intensity of a satellite-ground link in a propagation path in the rain area is measured; the rainfall intensity measuring method comprises the following steps that firstly, a satellite signal receiving antenna is set up on the ground, the frequency and a polarization method of the satellite signals are determined, and the signal intensity is recorded by a satellite receiver; then rain-caused signal attenuation quantity is extracted according to changes of the signal intensity in rainy weather and non-rainy weather; and finally a relationship between rain-caused attenuation and the rainfall intensity are used for inversion to obtain the average rainfall intensity in the propagation path. The rainfall intensity measuring method based on the satellite-ground link attenuation effect has the characteristics that measuring points are many, the covered range is wide, the temporal-spatial resolution is high, the erection and maintenance costs are low and the like, areas with erected satellite antennae can be used for measuring the rainfall intensity, and the deficiencies that the temporal-spatial resolution of a meteorological satellite islow, scanning of a weather radar has a blind area, rain gauge stations are sparse and the like can be overcome.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
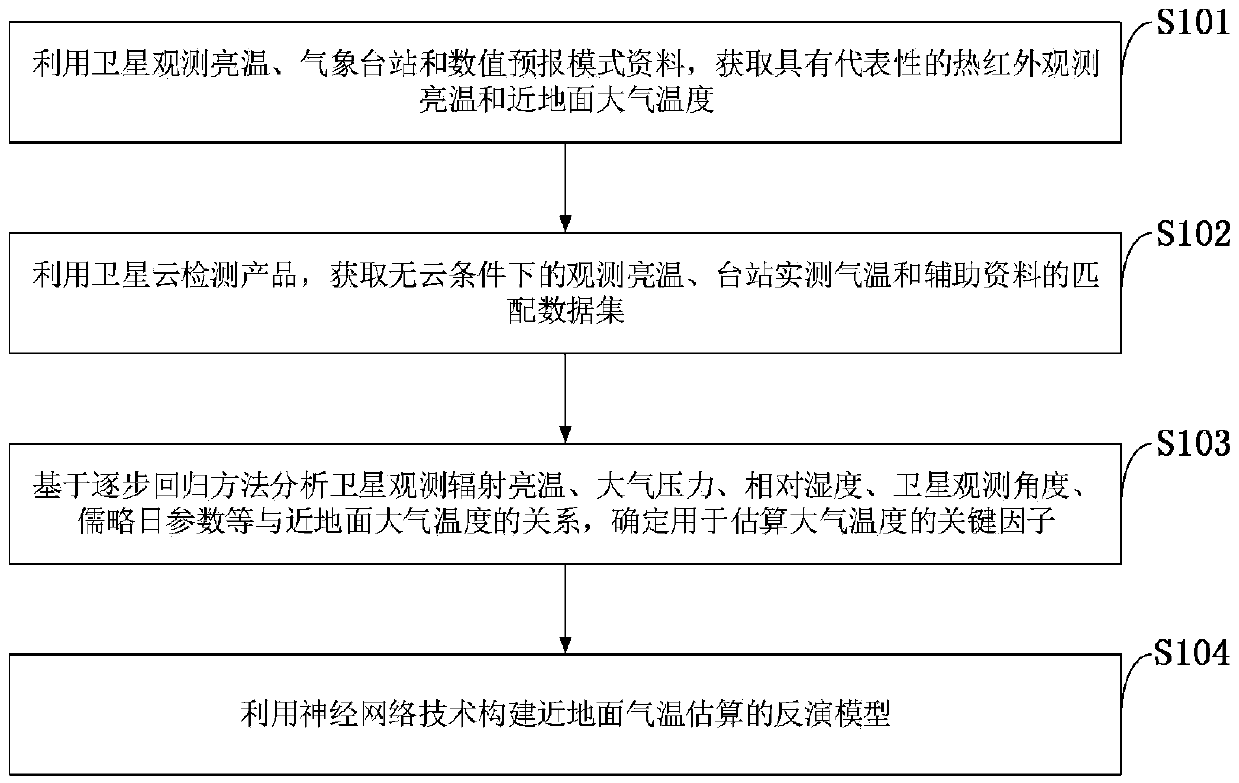
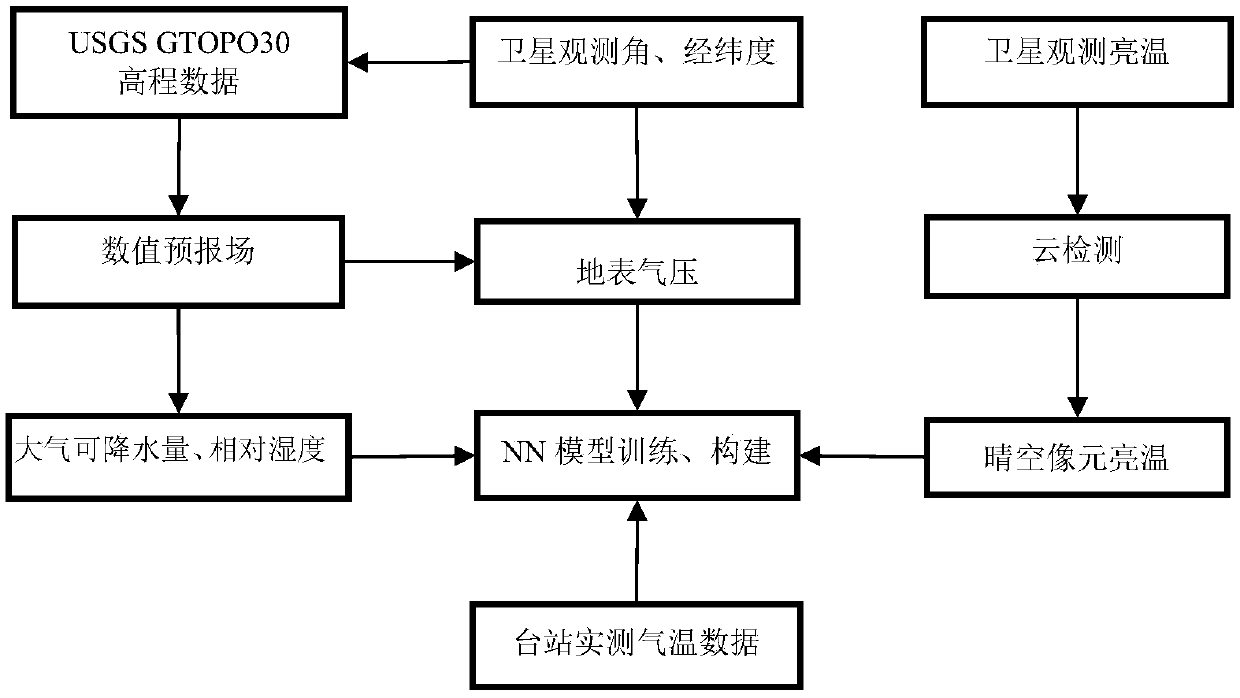
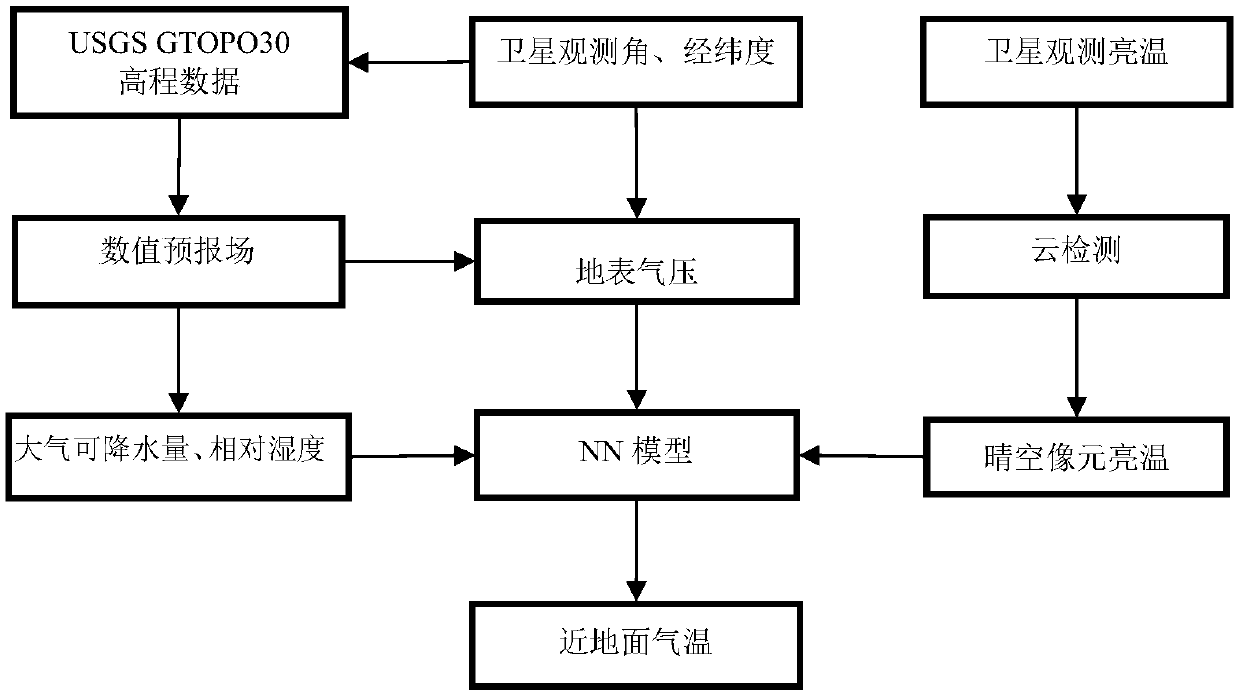
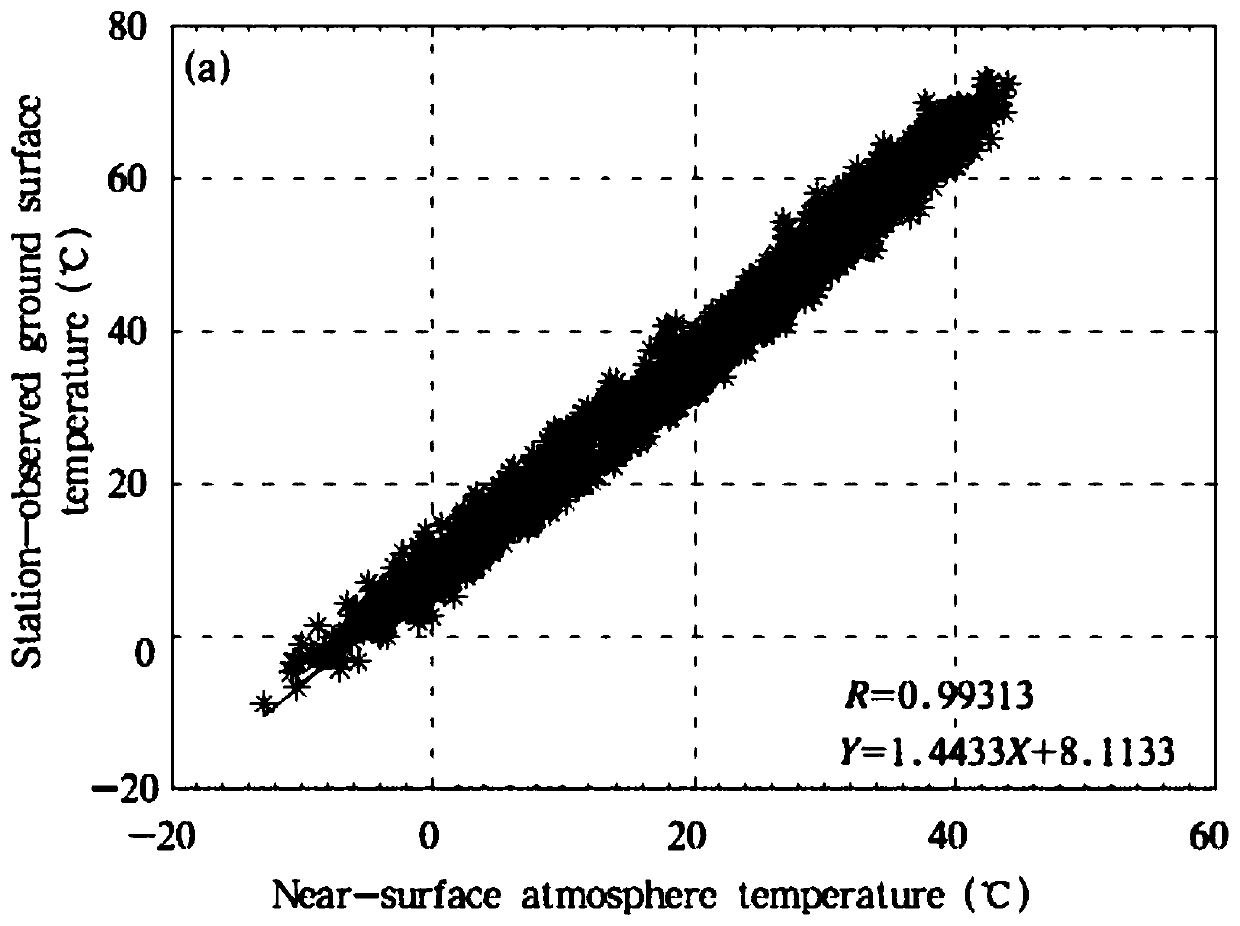
Method for estimating near-surface atmospheric temperature by thermal infrared data of geostationary meteorological satellite
ActiveCN109580003AGood precisionImprove applicabilityRadiation pyrometrySatellite radio beaconingData setAtmospheric temperature
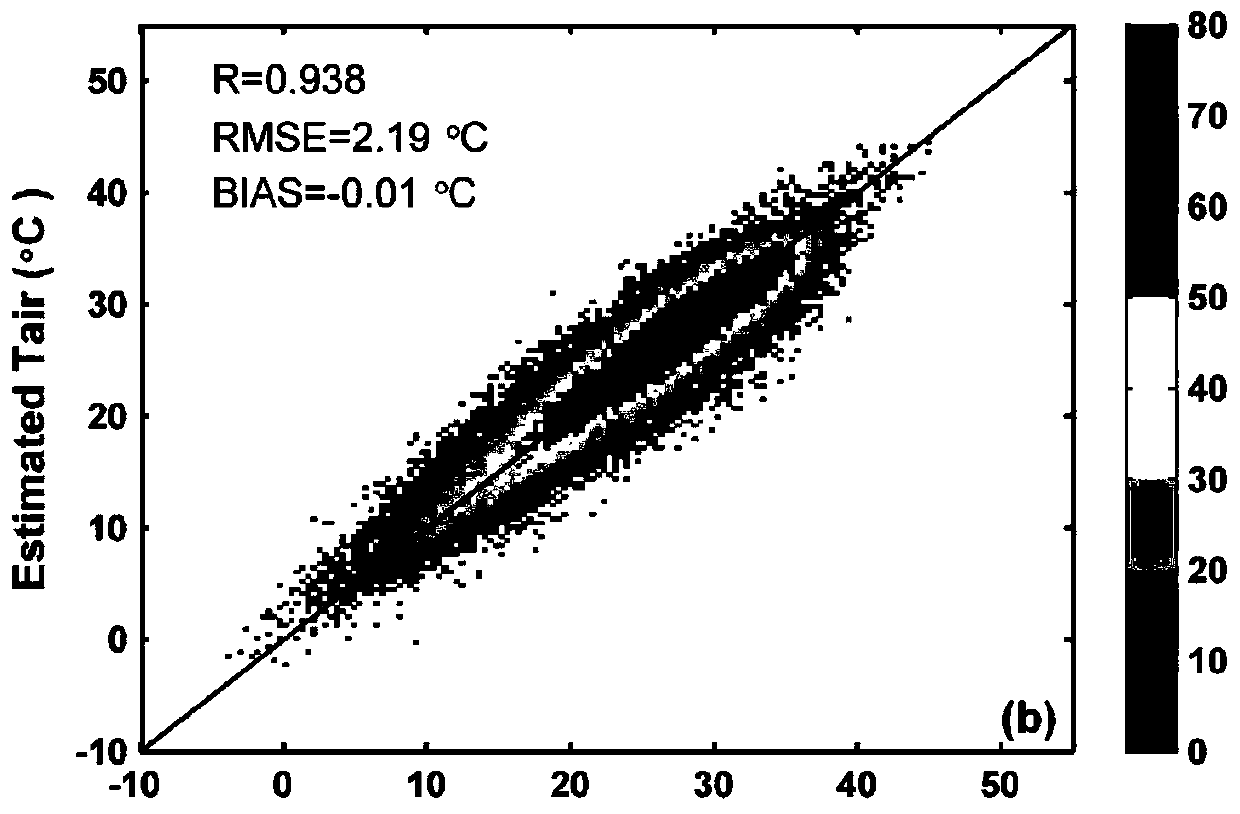
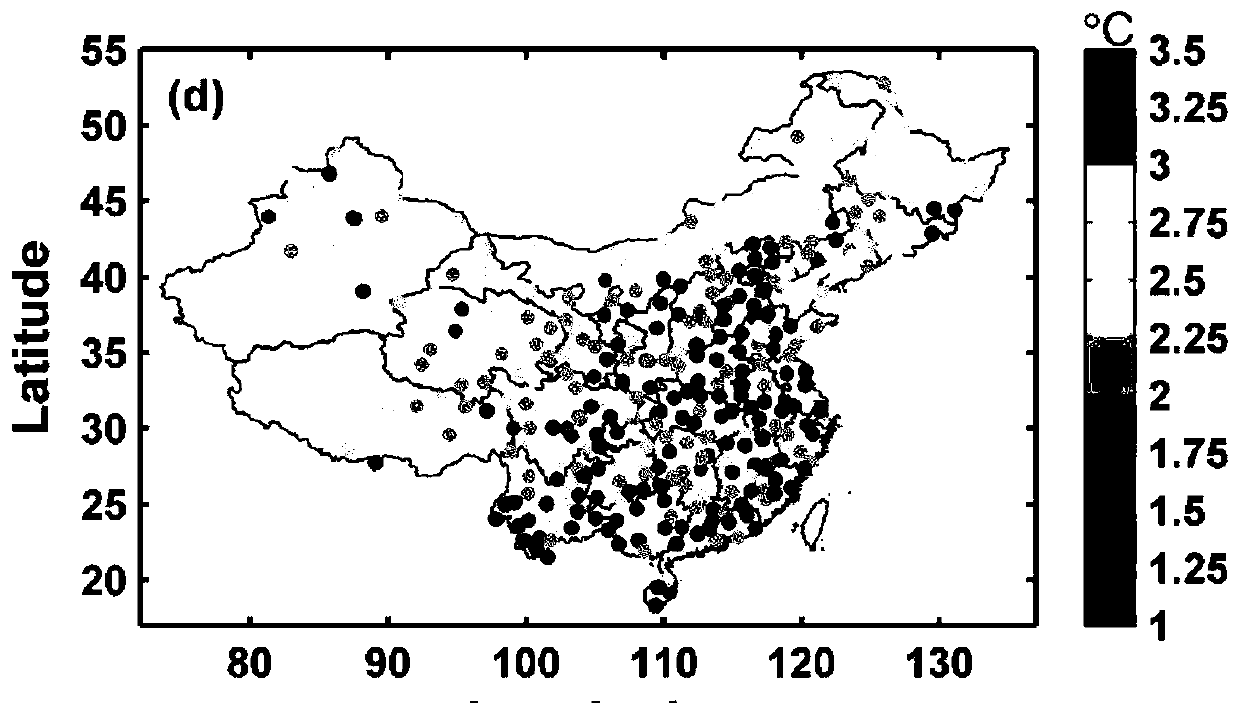
The invention belongs to the technical field of atmospheric remote sensing, and discloses a method for estimating a near-surface atmospheric temperature by using thermal infrared data of a geostationary meteorological satellite. The satellite is used for observing brightness temperature, meteorological station and numerical prediction model data to obtain a representative thermal infrared observation brightness temperature and near-surface atmospheric temperature; satellite cloud detection products are used for obtaining matched data sets for the observation brightness temperature, the stationactually measured temperature and auxiliary data under cloudless conditions; based on a stepwise regression method, the relationship between the radiation temperature of satellite observation, atmospheric pressure, relative humidity, a satellite observation angle, Julian daily parameters and the like and near-surface atmospheric temperature is analyzed, and key factors used for estimating the atmospheric temperature are determined; and a inversion model of near-surface temperature estimation is constructed by using a neural network technology. The method can realize the purpose of inversion of the near-surface atmospheric temperature under the clear sky condition of the thermal infrared data of the stationary meteorological satellite.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
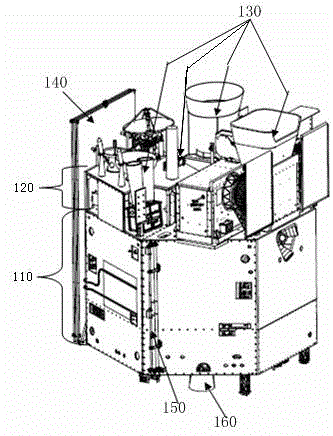
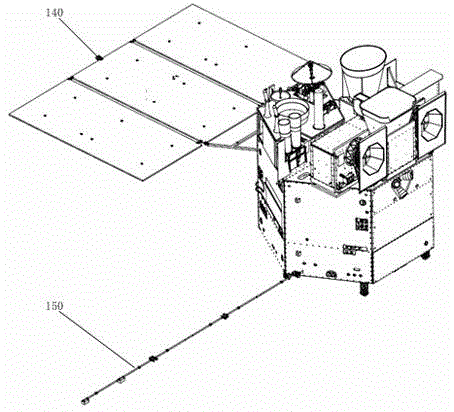
Geostationary orbit meteorological satellite
InactiveCN104698509ARealize the demand for multi-payload simultaneous star installationMeet the needs of multi-purpose missions on one starInstrumentsSolar batteryMeteorological satellite
The invention discloses a geostationary orbit meteorological satellite which mainly comprises a propulsion service capsule, an antenna capsule, an effective load, a solar battery array, a magnetometer stretching mechanism and an apogee engine. The propulsion service capsule comprises a top plate opposite to the ground, side plates and a bottom plate; the antenna capsule is arranged on the top plate; the effective load is arranged on the top plate; the solar battery array is connected with the side plates; the magnetometer stretching mechanism is connected with the side plates; the apogee engine is connected on a bearing cylinder inside the propulsion service capsule through a support. Tile layout of a six-sided cylinder structure and multiple large-volume storage tanks is designed, and a domestic gap in this field is filled; requirements that multiple loads are installed in the satellite simultaneously are met, the task that one satellite for multiple purposes is satisfied, development cost is lowered, and compared with similar meteorological satellites launched at the same time in European and American countries, the geostationary orbit meteorological satellite has the advantages of advancement and flexible extensibility capacity.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
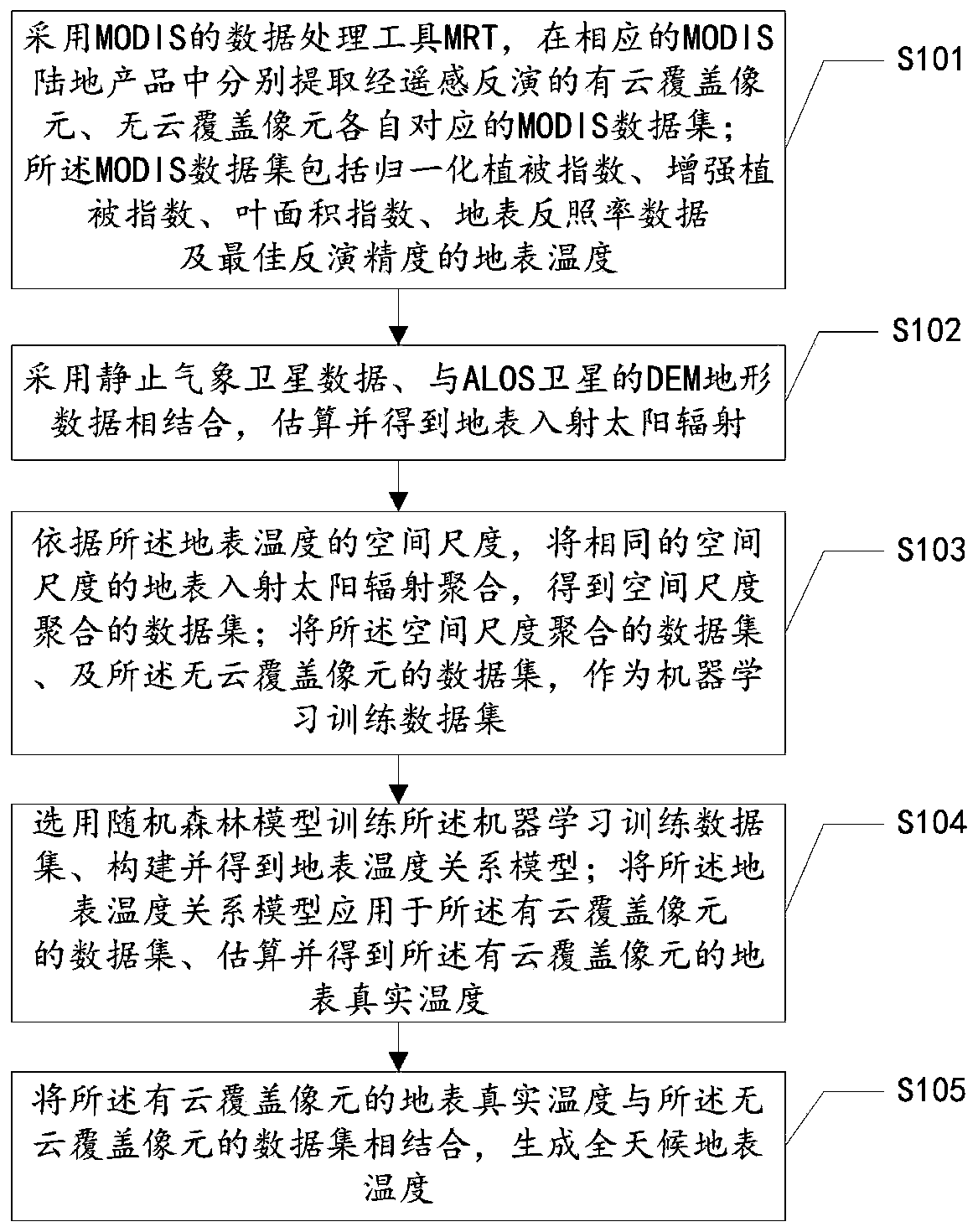
All-weather surface temperature generation method and device based on machine learning
ActiveCN110516816ASolve the problem with a large number of empty missing value regionsRadiation pyrometryMachine learningThermal infrared remote sensingData set
The invention discloses an all-weather surface temperature generation method and device based on machine learning. The method comprises: extracting an MODIS data set subjected to remote sensing inversion through an MODIS tool MRT; combining static meteorological satellite data with DEM topographic data of the ALOS satellite, and estimating and obtaining surface incident solar radiation; performingspatial aggregation on data sets with the same spatial scale, and taking the data sets and the MODIS data set as a machine learning training data set; constructing a surface temperature relation model through a random forest model; estimating the real temperature of the earth surface with the cloud coverage pixels; and combining the real earth surface temperature of the cloud-covered pixel with the data set of the cloudless-covered pixel to generate the all-weather earth surface temperature. According to the method, the problems that current thermal infrared remote sensing is easily influenced by cloud and mist, and a large number of blank value-lacking areas exist in surface temperature products are solved, cloud condition surface temperature estimation is achieved, and an important basis is provided for all-weather surface temperature product generation.
Owner:INST OF MOUNTAIN HAZARDS & ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
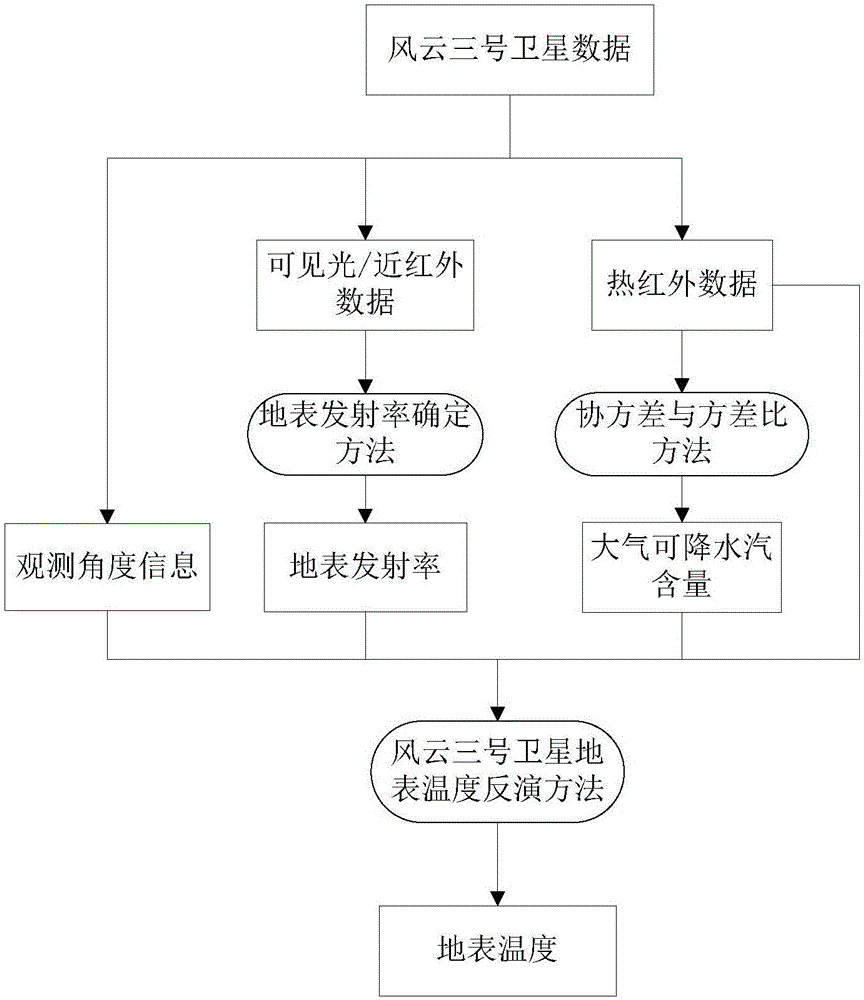
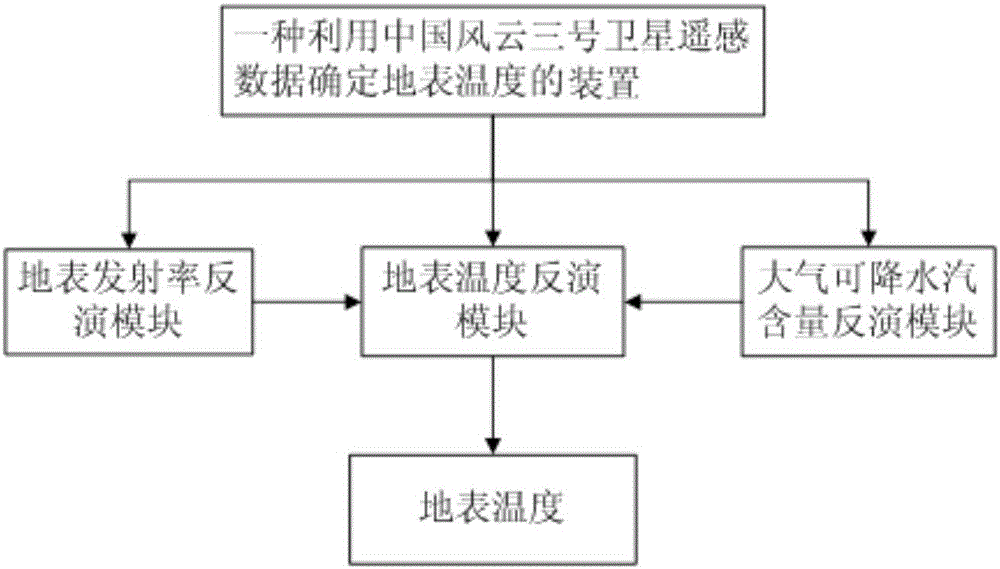
Method and device for determining ground surface temperature by utilizing remote sensing data of FY-3 meteorological satellite of China
InactiveCN106778516ARealize remote sensing inversion of surface temperatureRealization of remote sensing inversionRadiation pyrometryScene recognitionCovarianceMeteorological satellite
The invention discloses a method and device for determining ground surface temperature by utilizing remote sensing data of FY-3 meteorological satellite of China. The method comprises the following steps of: (A) obtaining a ground surface emissivity by utilizing visible light and near-infrared channel data of the FY-3 meteorological satellite of China and combining a developmental ground surface emissivity determination method; (B) determining an atmosphere precipitable water content by utilizing thermal infrared channel data of the FY-3 meteorological satellite of China and combining a developmental covariance to variance ratio; and (C) directly inverting the ground surface temperature from the thermal infrared channel data observed by the FY-3 meteorological satellite by utilizing the ground surface emissivity obtained in the step (A) and the atmosphere precipitable water content obtained in the step (B) and combining a developmental ground surface temperature remote sensing inversion method. According to the method and device disclosed by the invention, the quantitative remote sensing inversion carried out on the ground surface temperature through data of the FY-3 meteorological satellite of China is realized.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
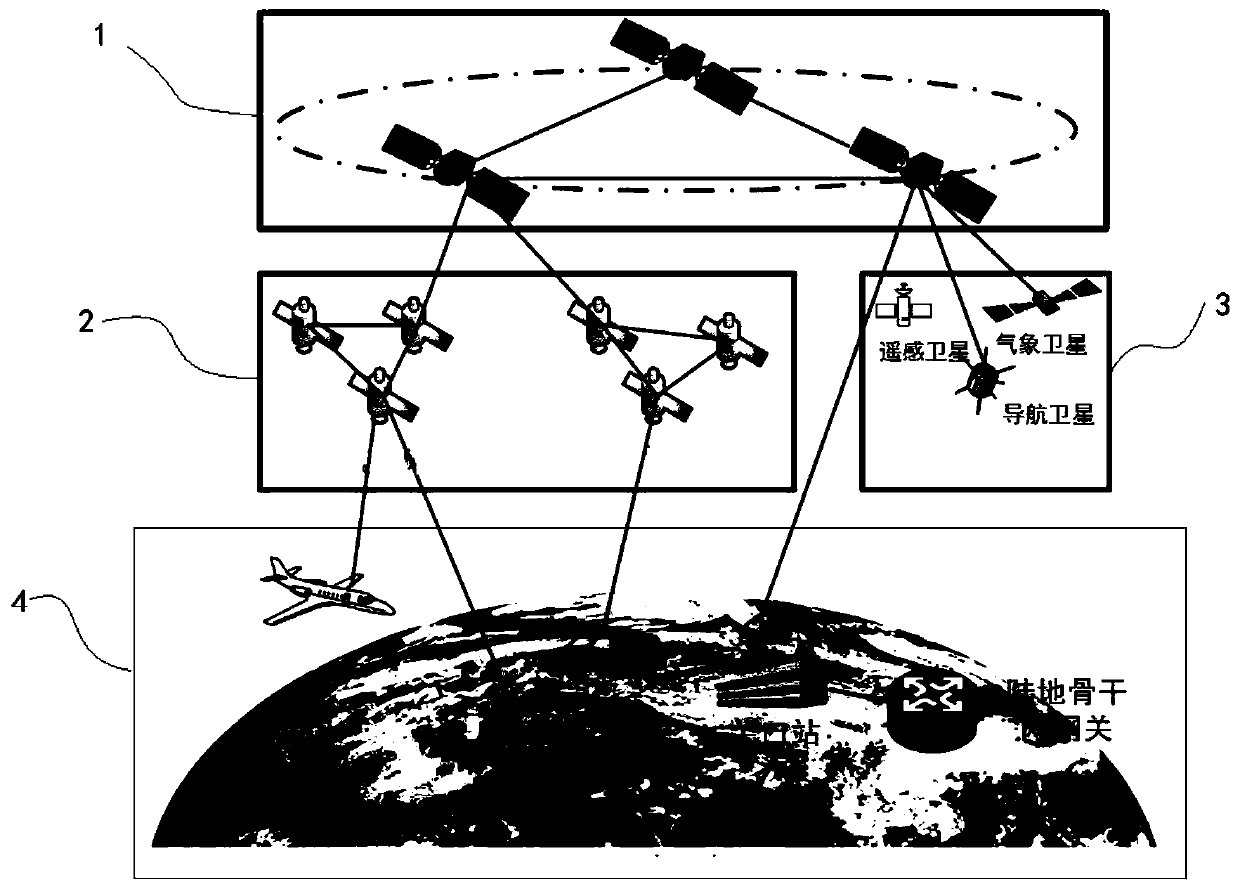
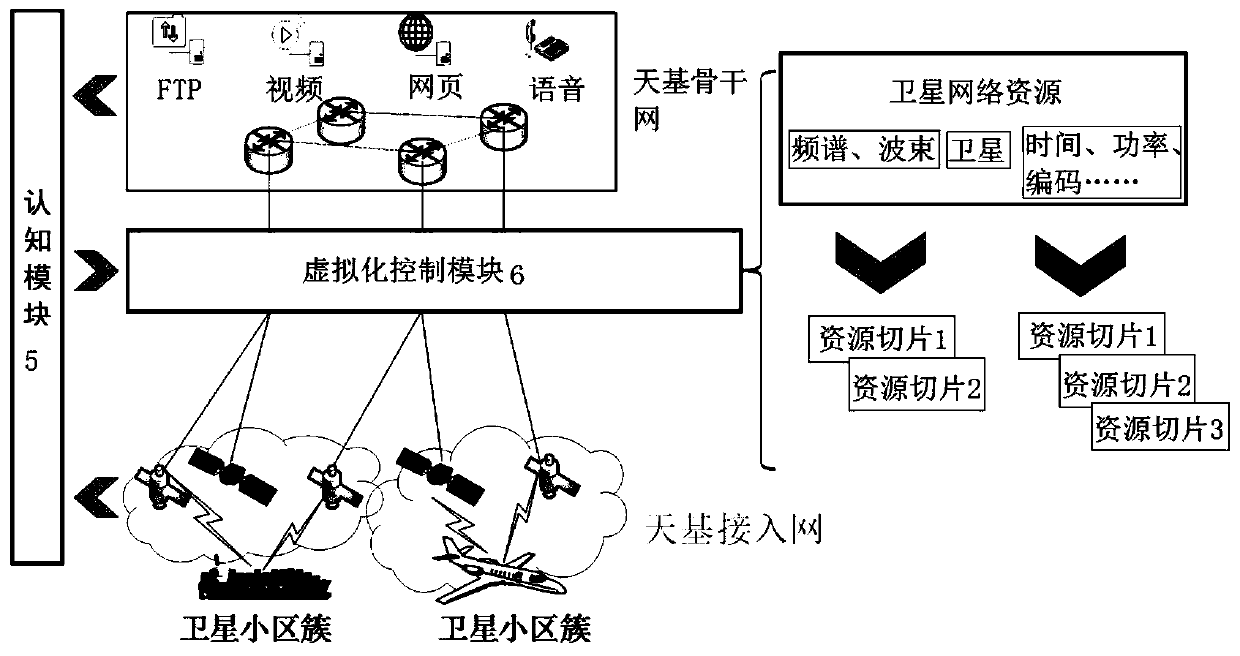
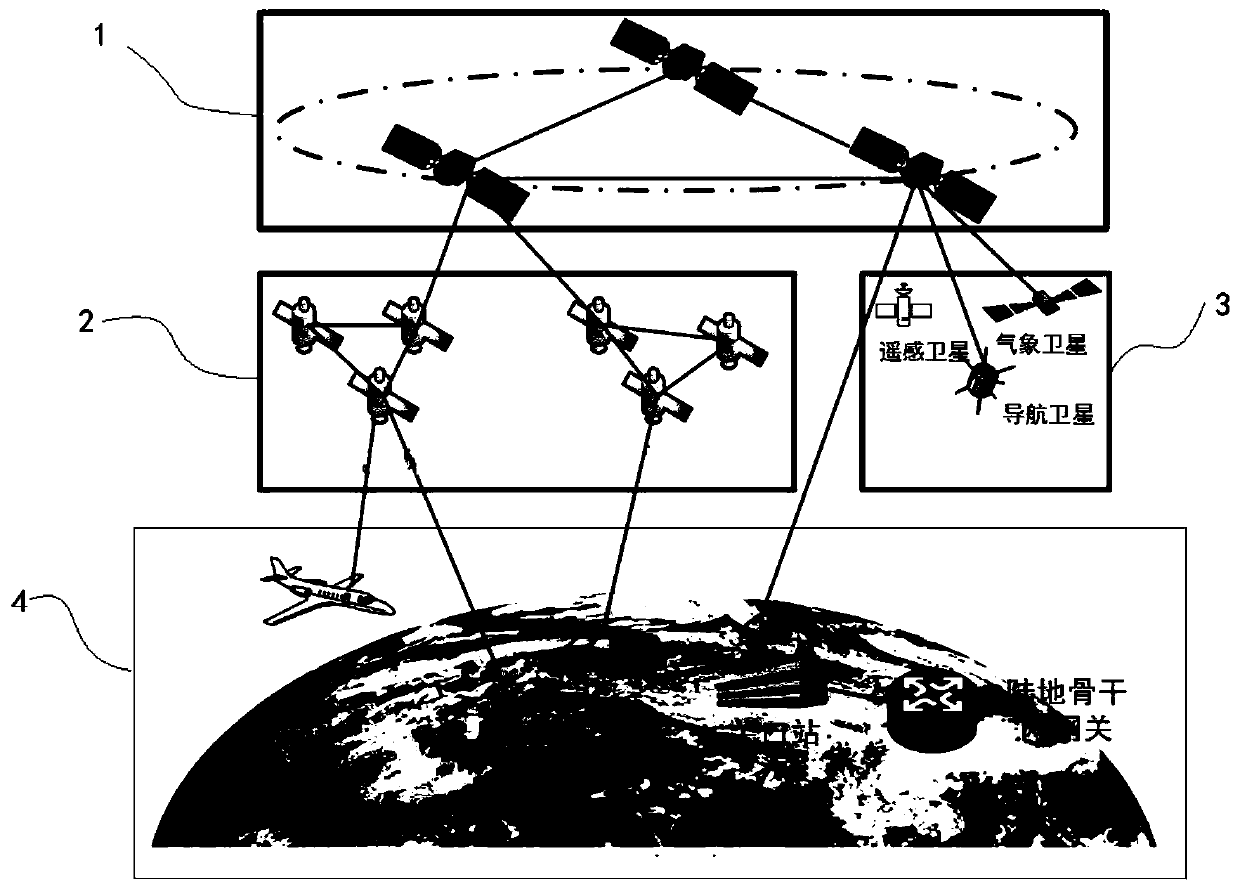
Satellite network architecture with network reconstruction capability
ActiveCN110012558ARealize integrated utilizationHas flexible refactoring capabilitiesNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionAccess networkInformation networks
The invention provides a satellite network architecture with a network reconstruction capability. The architecture comprises a space-based network and a land backbone network, the space-based networkcomprises a space-based backbone network, a space-based access network and a space-based sensing network, wherein the space-based backbone network is mainly composed of geosynchronous orbit satellites, the space-based access network is mainly composed of low-orbit satellite constellations, and the space-based sensing network is mainly composed of any one or any combination of remote sensing satellites, meteorological satellites and navigation satellites. The method has the beneficial effects that the architecture design problem of a space-based information network for joint networking and fusion utilization of high, medium and low orbit satellites and cooperative work of communication, navigation and remote sensing satellites is solved, integrated utilization of various satellite resourcesin the existing space is realized, and a hybrid heterogeneous satellite network architecture with a satellite network flexible reconstruction function is built.
Owner:亚太卫星宽带通信(深圳)有限公司
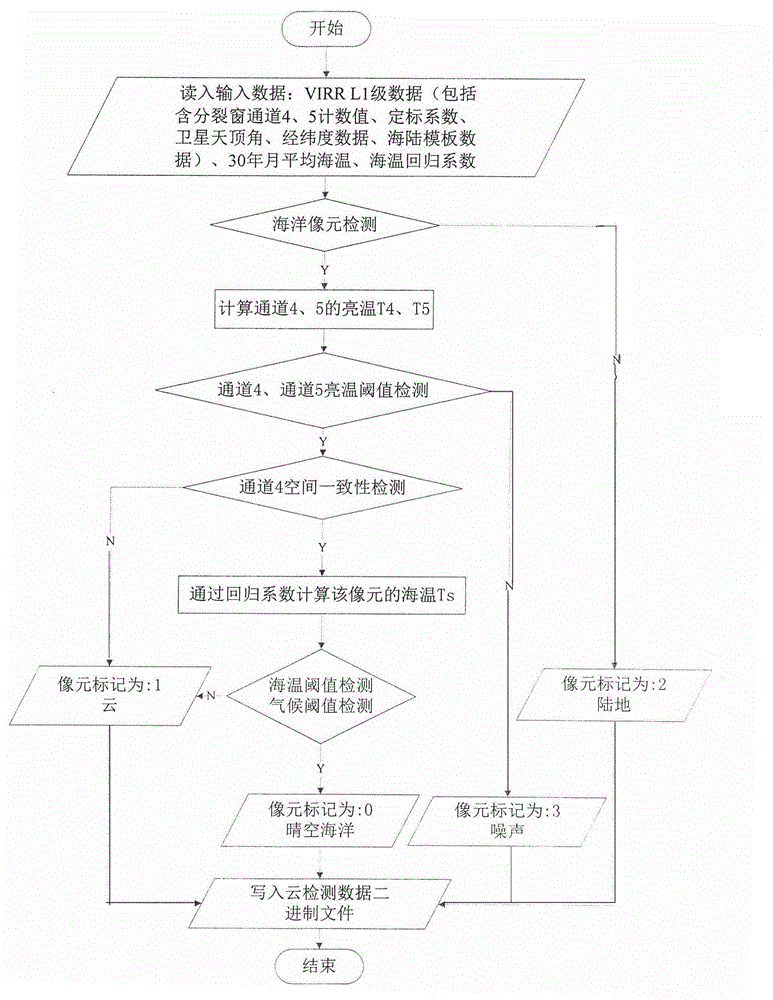
Processing method for detecting clouds on sea by polar orbit meteorological satellite visible and infrared radiometer (VIRR)
InactiveCN104820250AImprove accuracyIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesSplit windowData set
The invention relates to a processing method for detecting clouds on sea by polar orbit meteorological satellite visible and infrared radiometer (VIRR), which belongs to the field of meteorological remote sensing technology. According to the processing method, firstly first-grade observation data of the polar orbit meteorological satellite visible and infrared radiometer (VIRR) after positioning and scaling and corresponding sea-and-land template information are identified, thereby obtaining sea observation data; for sea image elements, information such as split window brightness temperature, brightness temperature difference, satellite zenith angle and sea temperature regression coefficient is used for performing sea surface temperature inversion; according to the characteristic of the VIRR instrument, statistical analysis is performed based on a matching data set of a long time sequence, and a temperature threshold is set; when the observed brightness temperature and the inversed sea temperature or the inversed sea temperature and the climatic sea temperature of the sea image element exceed a preset threshold, a fact that the sea image element is the image element with a cloud is determined. Compared with the prior art, the temperature threshold is set by means of the clinic change rule of the sea surface temperature and long-time sequence statistical information of the satellite detecting instrument VIRR; quantitative calculation or judgment for cloudy or sunny is performed on a target; and accuracy for detecting the clouds on the sea is improved.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT
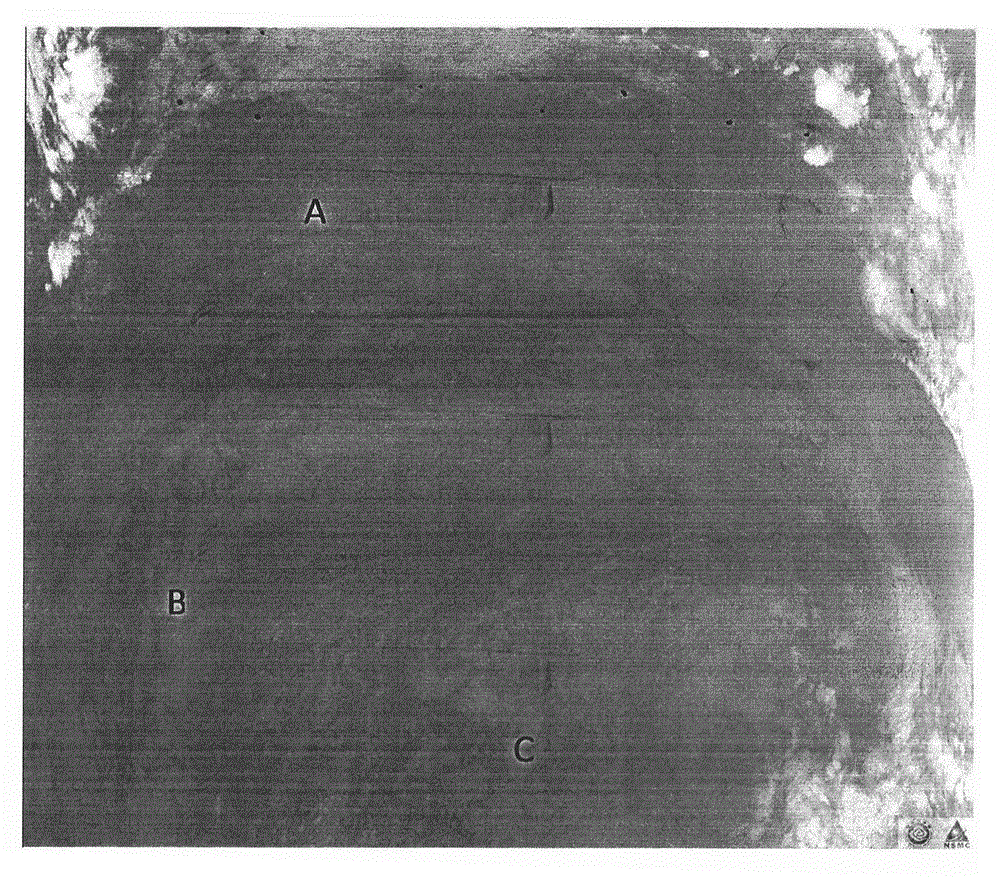
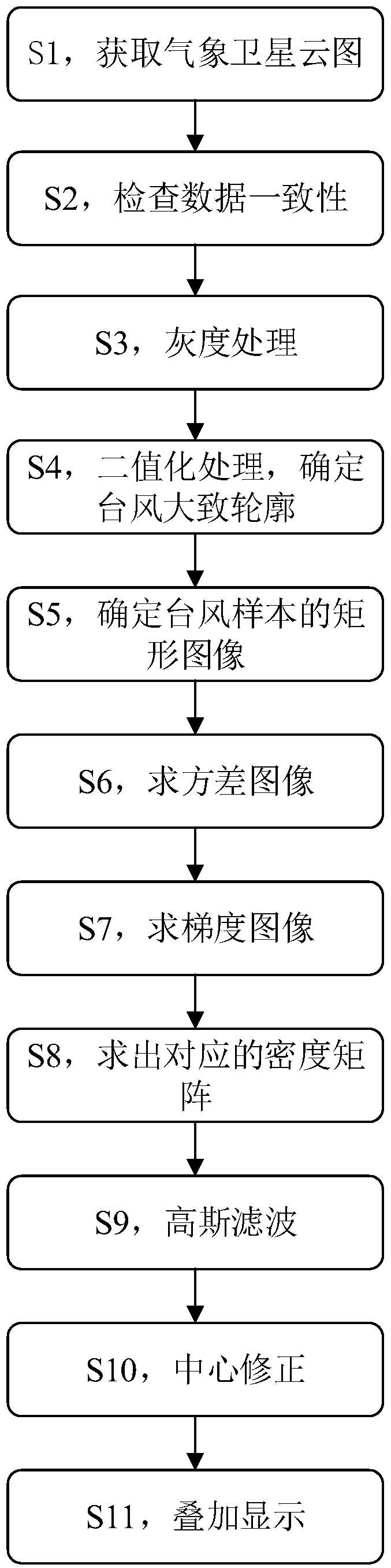
Typhoon positioning detection method based on Himawari meteorological satellite
InactiveCN109164513AImprove detection accuracyImprove real-time performanceWeather condition predictionICT adaptationCloud atlasAtmospheric sciences
The invention provides a typhoon positioning detection method based on a Himawari meteorological satellite. A meteorological satellite cloud atlas in 0.64-micron short-wave infrared window frequency band is adopted, the detection precision is higher, and the instantaneity is good; since the form of the typhoon is highly irregular at the beginning and the end of the typhoon, a detected center location and a CMA optimal path are large in deviation; and when the typhoon forms obvious eye of wind or is at a mature stage, the detection method has high accuracy on the centralized positioning of thetyphoon.
Owner:湖北河海科技发展有限公司
Near-surface air temperature inversion method
ActiveCN104657935AAvoid interferenceImplement combined applicationImage data processing detailsTerrainOriginal data
The invention discloses a near-surface air temperature inversion method comprising the following steps: establishing an original data record set of an unmanned weather station; constructing a first sub-pattern learning set and a first sub-pattern validation set; and acquiring a second sub-pattern to a fth sub-pattern, performing near-surface air temperature inversion to acquire a near-surface air temperature inversion image map of a target zone, and performing error correction to acquire a corrected near-surface air temperature inversion image map. According to the near-surface air temperature inversion method disclosed by the invention, the near-surface air temperature inversion is performed by collecting actually-measured air temperature of the unmanned weather station, collecting meteorological satellite data, DEM data and astronomy and calendar rules and also adopting a super nonlinear algorithm, and the near-surface air temperature inversion image map is then calculated by using a high-performance computer. Results show that the near-surface air temperature inversion method disclosed by the invention is relatively high in pattern accuracy, high in result reliability and strong in generalization ability, and ensures that the interferences of clouds, terrains and the like can be overcome; and a constructed CPU+GPU heterogeneously-cooperative parallel computer ensures that the computation speed can be increased by more than 1000 times, so that the near-surface air temperature inversion method is convenient for large-area application and computing capacity expansion.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF METEOROLOGICAL DISASTER REDUCING RES +1
Precipitation intensity estimation method based on deep learning
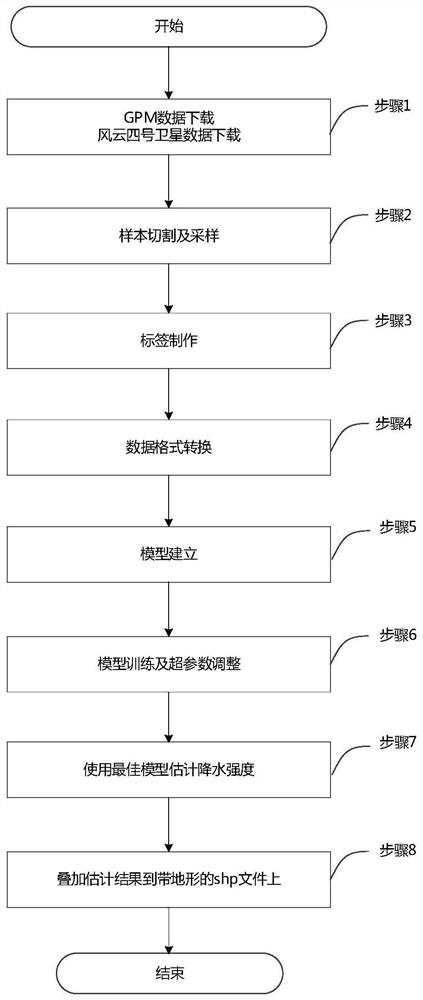
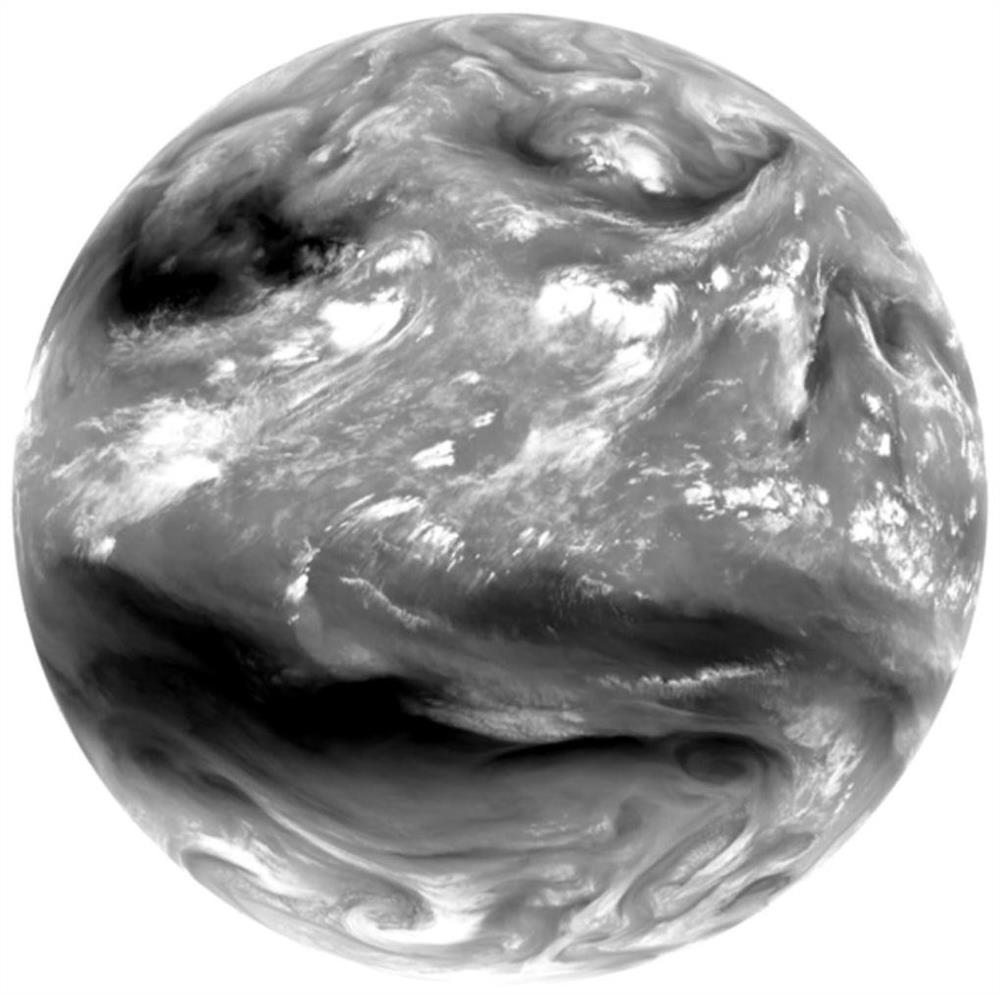
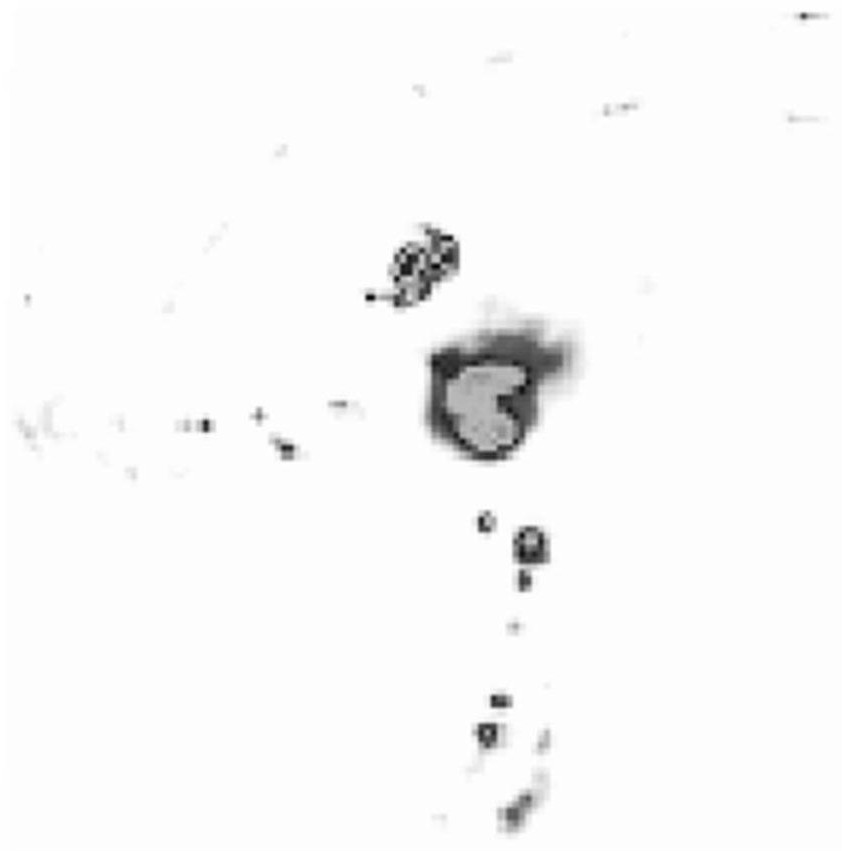
ActiveCN111983732AEasy to divideHigh strengthRainfall/precipitation gaugesImage resolutionAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a precipitation intensity estimation method based on deep learning. The method comprises: acquiring meteorological satellite data and precipitation data respectively; accordingto the acquired meteorological satellite data, cutting a required estimation region out from the meteorological satellite data, correcting and storing the estimation region in an array form; according to the obtained rainfall data, resampling to a required spatial resolution, and classifying the rainfall data to obtain rainfall intensity labels of different levels; converting the rainfall intensity label into single-channel images with only background and different levels of rainfall intensity, cutting the single-channel images into different sizes, and respectively taking the single-channelimages as input and labels of a rainfall intensity estimation model; establishing a precipitation intensity estimation model based on deep learning; training to obtain an optimal model; testing new meteorological satellite data, and generating a complete rainfall intensity estimation result; and superposing the generated rainfall intensity estimation result to the shp terrain file. According to the method, the corresponding rainfall intensity can be accurately estimated, and high-precision rainfall intensity estimation is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Near-surface air temperature estimation method under cloud conditions
ActiveCN109871637AThe method is simpleImprove spatial resolutionSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationTemporal informationData set
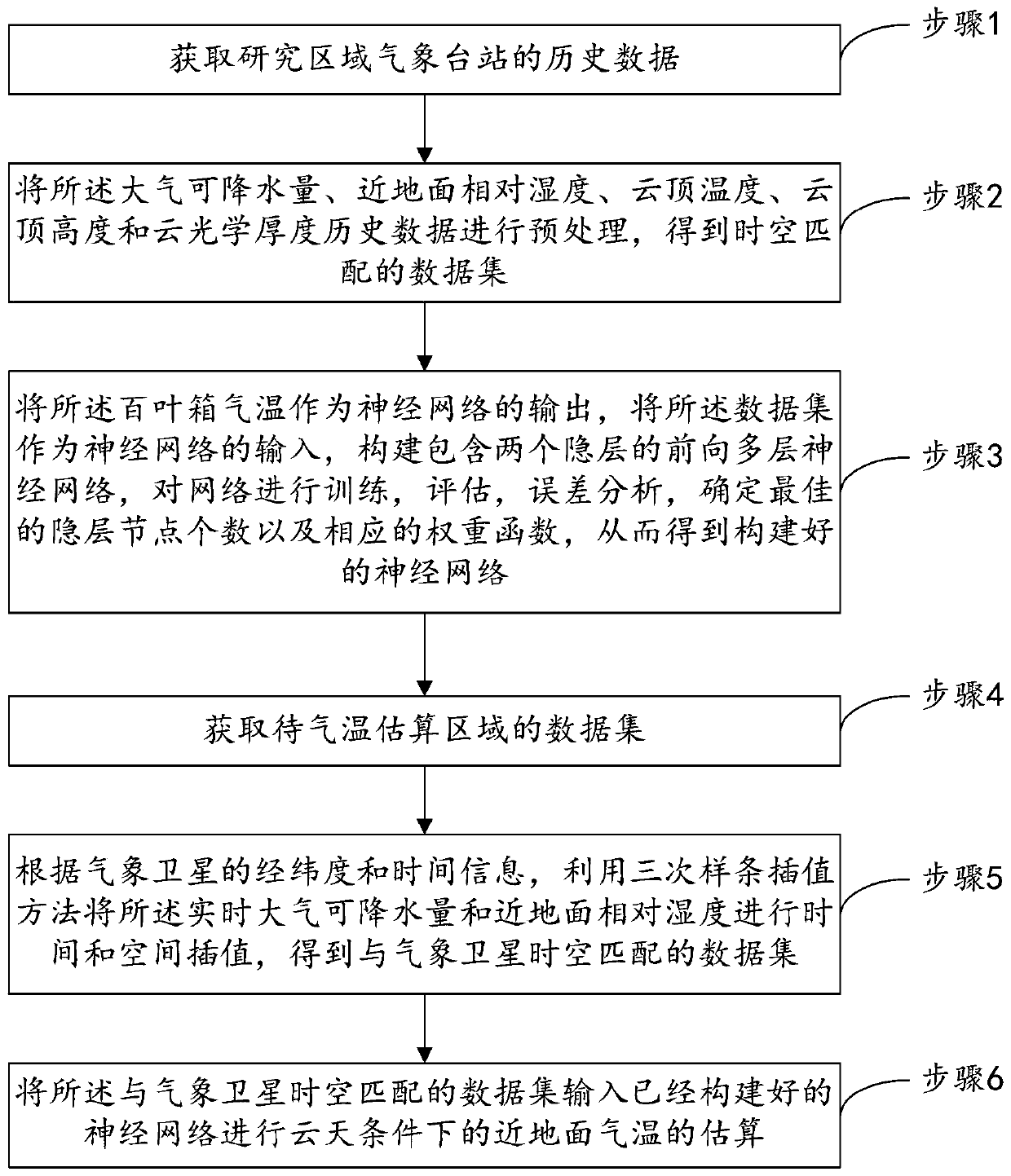
The invention provides a satellite remote sensing data-based near-surface air temperature estimation method under cloud conditions. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring historical data of a meteorological station in a research area; (2) preprocessing the historical data of the atmospheric precipitation, the relative humidity near the ground, the cloud top temperature, the cloudtop height and the cloud optical thickness to obtain a spatio-temporal matching data set; (3) taking the temperature of the instrument shelter as the output of a neural network, taking the data set asthe input of the neural network, and constructing the neural network; (4) obtaining a data set of an area to be subjected to air temperature estimation; (5) carrying out time and space interpolationby utilizing a cubic spline interpolation method according to the latitude, longitude and time information of the meteorological satellite to obtain a data set matched with the space-time of the meteorological satellite; And (6) inputting the data set matched with the space-time space of the meteorological satellite into the constructed neural network to estimate the near-surface air temperature under the cloud day condition. The method is simple and easy to implement and high in precision.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
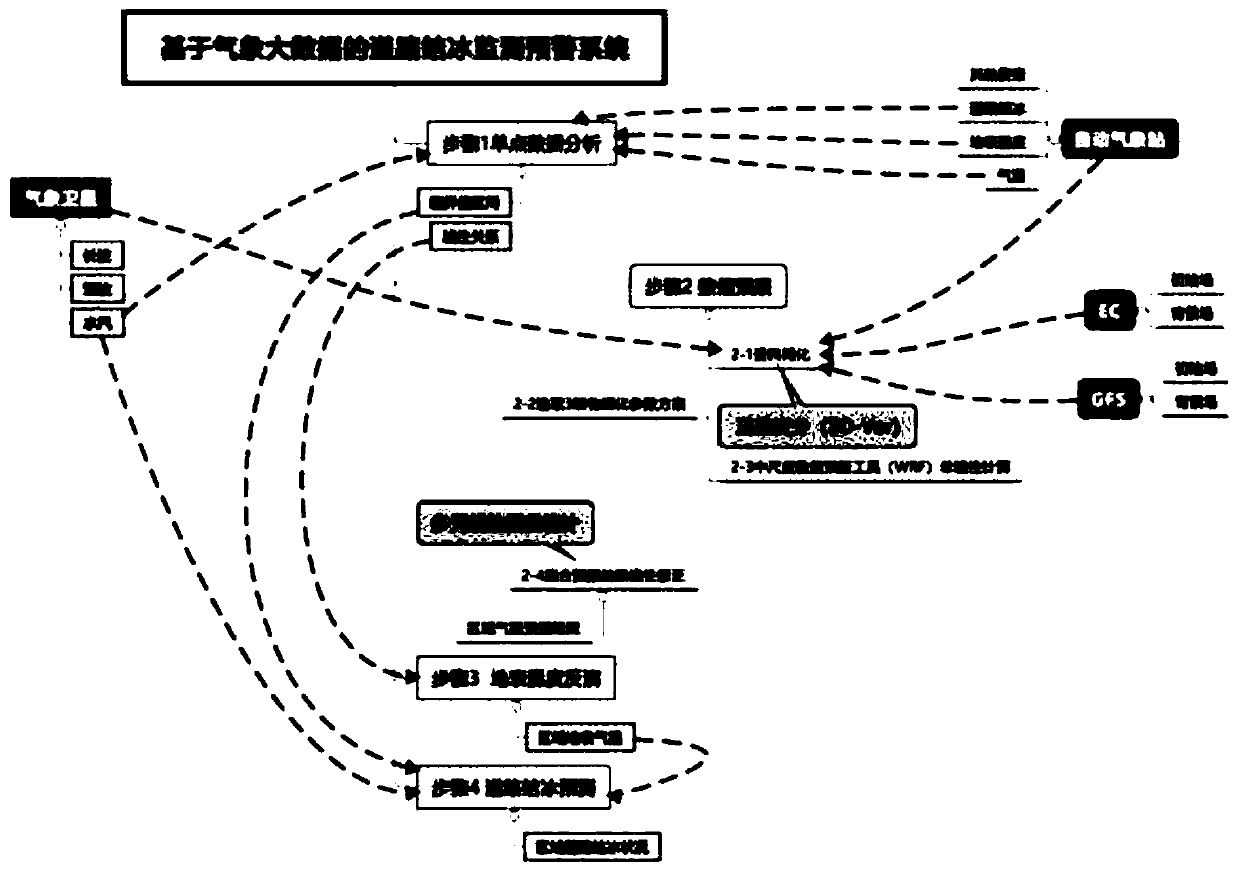
High-precision monitoring and early-warning system for regional road icing based on meteorological big data
The invention discloses a high-precision monitoring and early-warning system for regional road icing based on meteorological big data. The high-precision monitoring and early-warning system compriseshardware operating environment construction, live data collection and analysis, mesoscale numerical forecasting tool nonlinear calculation, temperature ensemble forecast result linear correction, regional ground surface temperature inversion and regional road icing condition early warning. The high-precision monitoring and early-warning system has the beneficial effects that the high-precision monitoring and early-warning system introduces data of a meteorological satellite, expands the dimension of meteorological observation data, participates in data assimilation of a numerical forecasting mode, and indirectly improves the precision of forecast results; the numerical mode ensemble forecasting is introduced, a sliding training period is adopted when the forecast results are collected, a weight coefficient changes with time, and the precision is improved; and by utilizing various kinds of representative sites, the high-precision monitoring and early-warning system explores relationships among temperature, ground surface temperature and water vapor in different geographical environments through linear analysis, and improves the forecasting precision of regional road icing conditionsfrom point to surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGWANG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
Forest fire monitoring method and system of power transmission line
The invention discloses a forest fire monitoring method and a forest fire monitoring system of a power transmission line. The method comprises the steps of (1) building a basic database on a server, storing and updating latitude and longitude coordinates (obtained according to data received and measured by a meteorological satellite) of a fire point, latitude and longitude coordinates of the power transmission line and a distance threshold in real time; (2) calculating the distances between the fire point and the power transmission line according to the latitude and longitude coordinates of the fire point and the latitude and longitude coordinates of the power transmission line; (3) pushing alarm information to a mobile terminal; and (4) receiving alarm information by the mobile terminal and reminding a worker of examining. According to the forest fire monitoring method and system of the power transmission line, power transmission line operation and maintenance staff can quickly obtain the forest fire condition of the power transmission line and make a response.
Owner:STATE GRID HUNAN ELECTRIC POWER +2
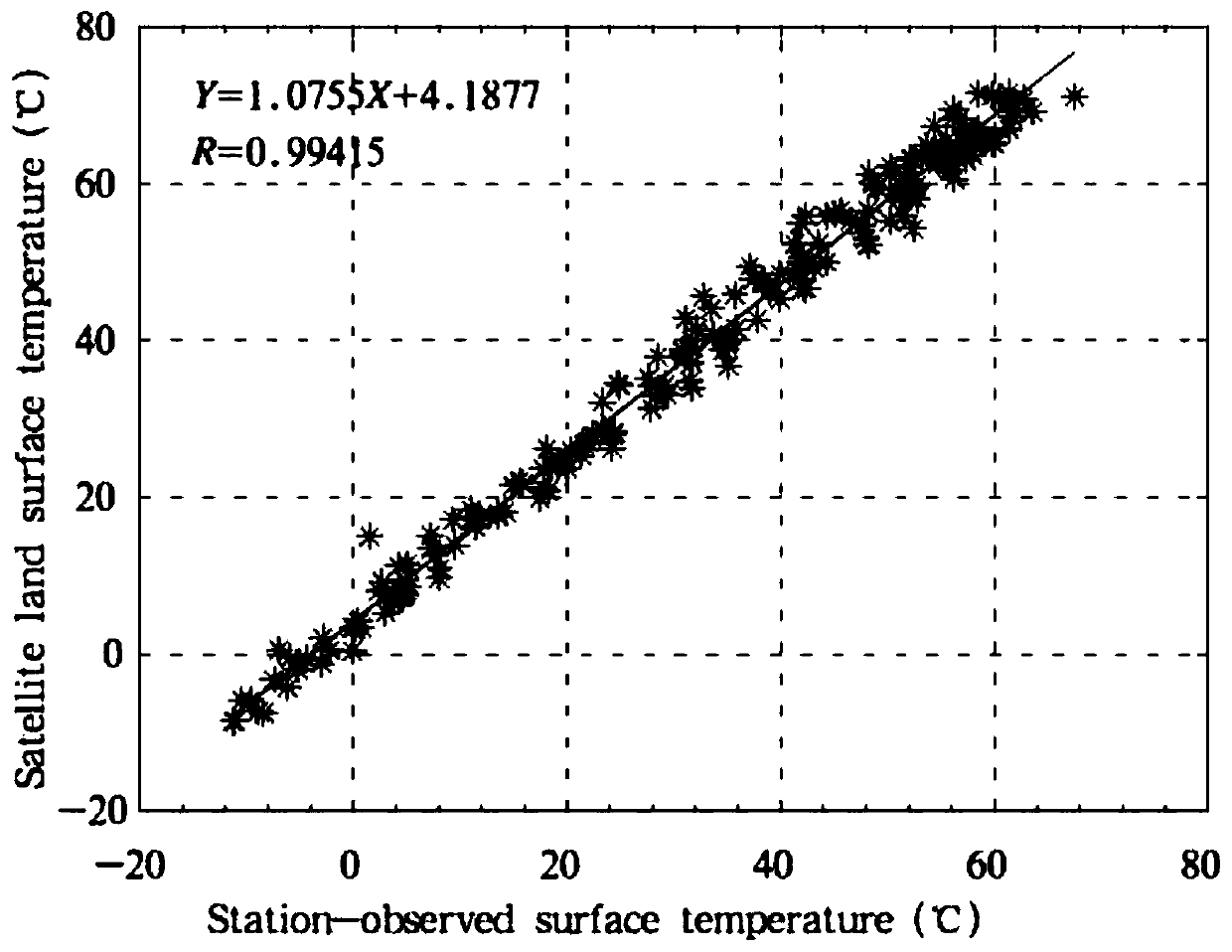
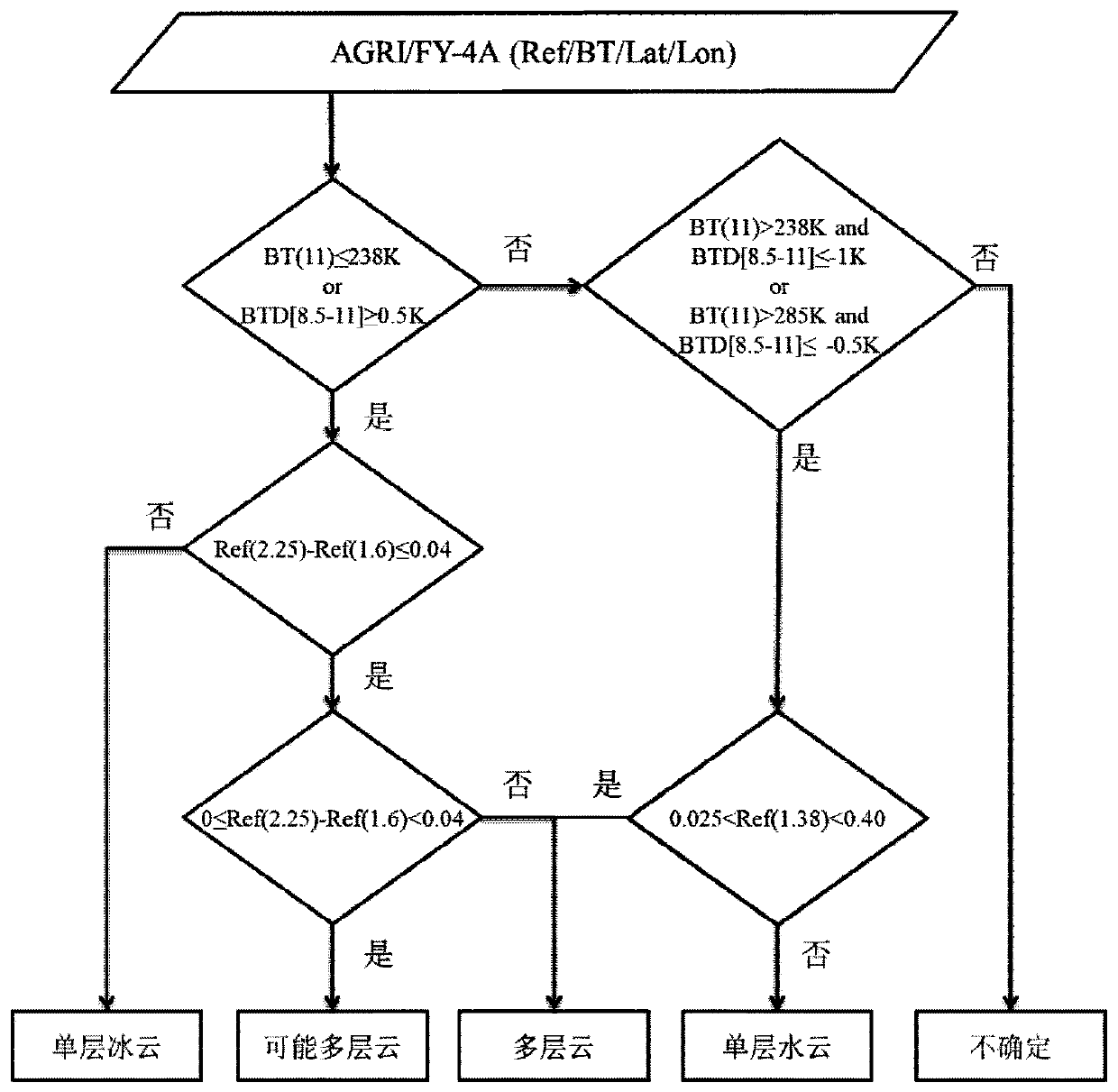
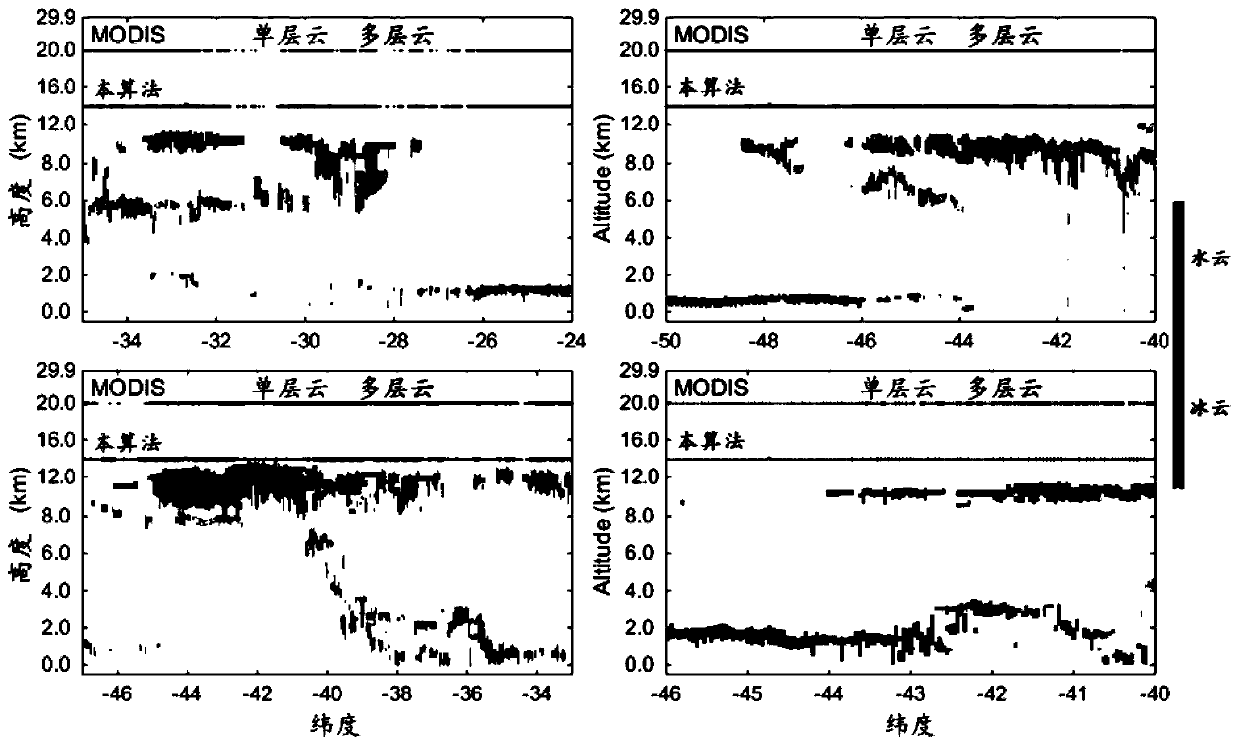
Multilayer cloud inversion method for multi-channel scanning imaging radiometer of FengYun 4A meteorological satellite
ActiveCN109946235AAccurate multilayer cloud detection resultsEfficient multilayer cloud detection resultsMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiometerMeteorological satellite
The invention discloses a multilayer cloud inversion method for a multi-channel scanning imaging radiometer of a FengYun 4A meteorological satellite, and fills the blank in the algorithm domestically.Unique design characteristics of a spectral channel of a domestic satellite radiometer (AGRI) are taken into full consideration, a multilayer cloud model is established on theoretical basis of rapidradiation transmission simulation, sensitivity of different short-wave infrared channels (1.6 and 2.25 micron) to different phase clouds is analyzed, and it is discovered for the first time that the two channels can be used to identification of the cloud phase. According to the model, it is provided that penetration of the short-wave infrared channels is high in different cloud optical thicknesses, and lower-layer water cloud information can penetrate the upper layer and extracted by satellite observation. The infrared channels are combined to identify the cloud top phase, and the brand new multilayer cloud (upper ice cloud and lower water cloud) identification algorithm via the radiometer is provided. A multilayer cloud result of the algorithm is verified by using the accurate active spaceborne laser radar CALIOP, and is highly accurate. The unique design characteristics of the spectral channel of the domestic imager are fully considered, the method is applied to a new generator of domestic imager AGRI, and can be used to provide more accurate and efficient multilayer cloud detection results for applications in future.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Automatic assimilation method for multi-source thermal infrared wave band data of polar-orbit meteorological satellite
InactiveCN1790051ASolve the assimilation preprocessing problemComparableElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationNatural satelliteOriginal data
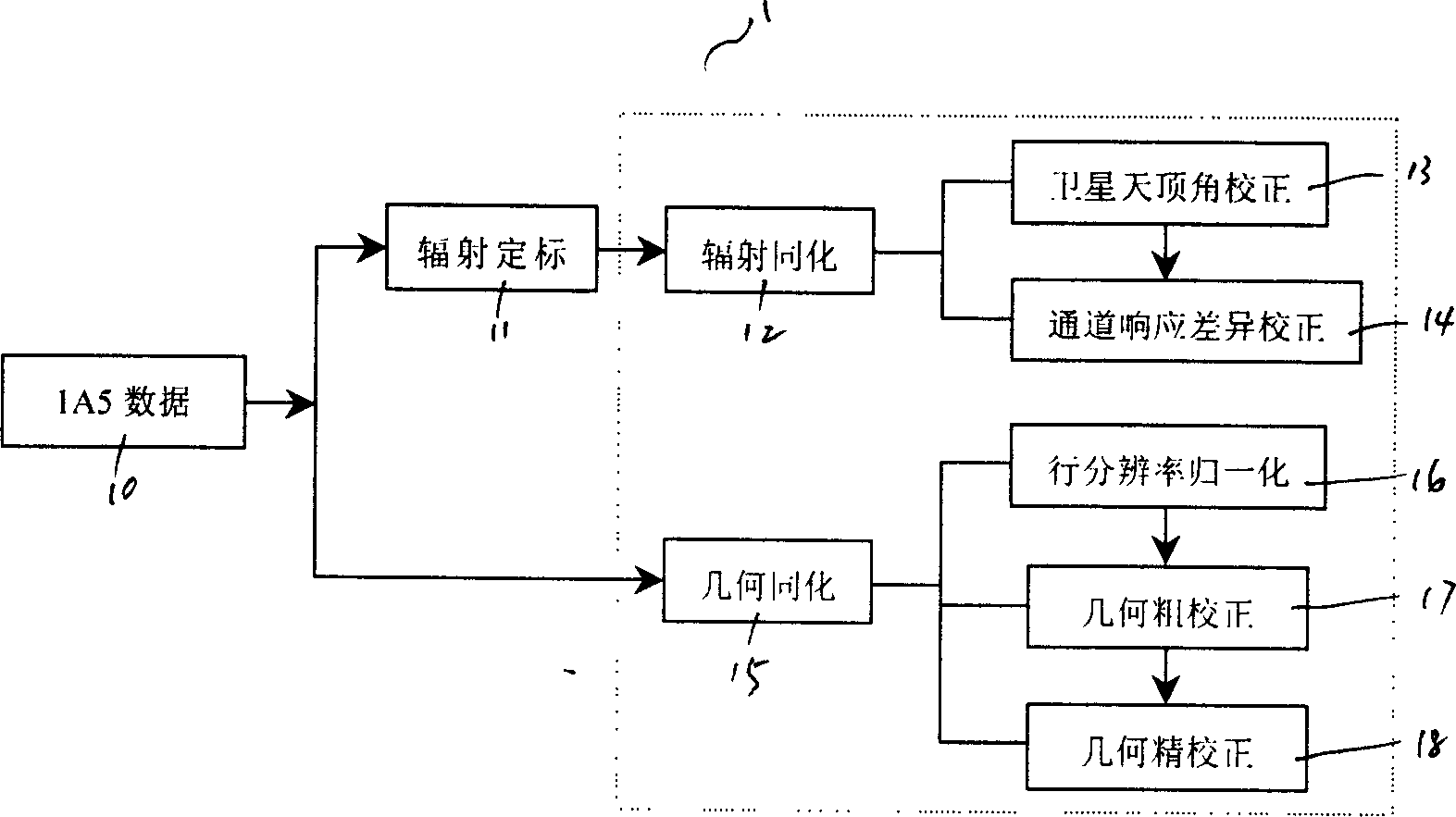
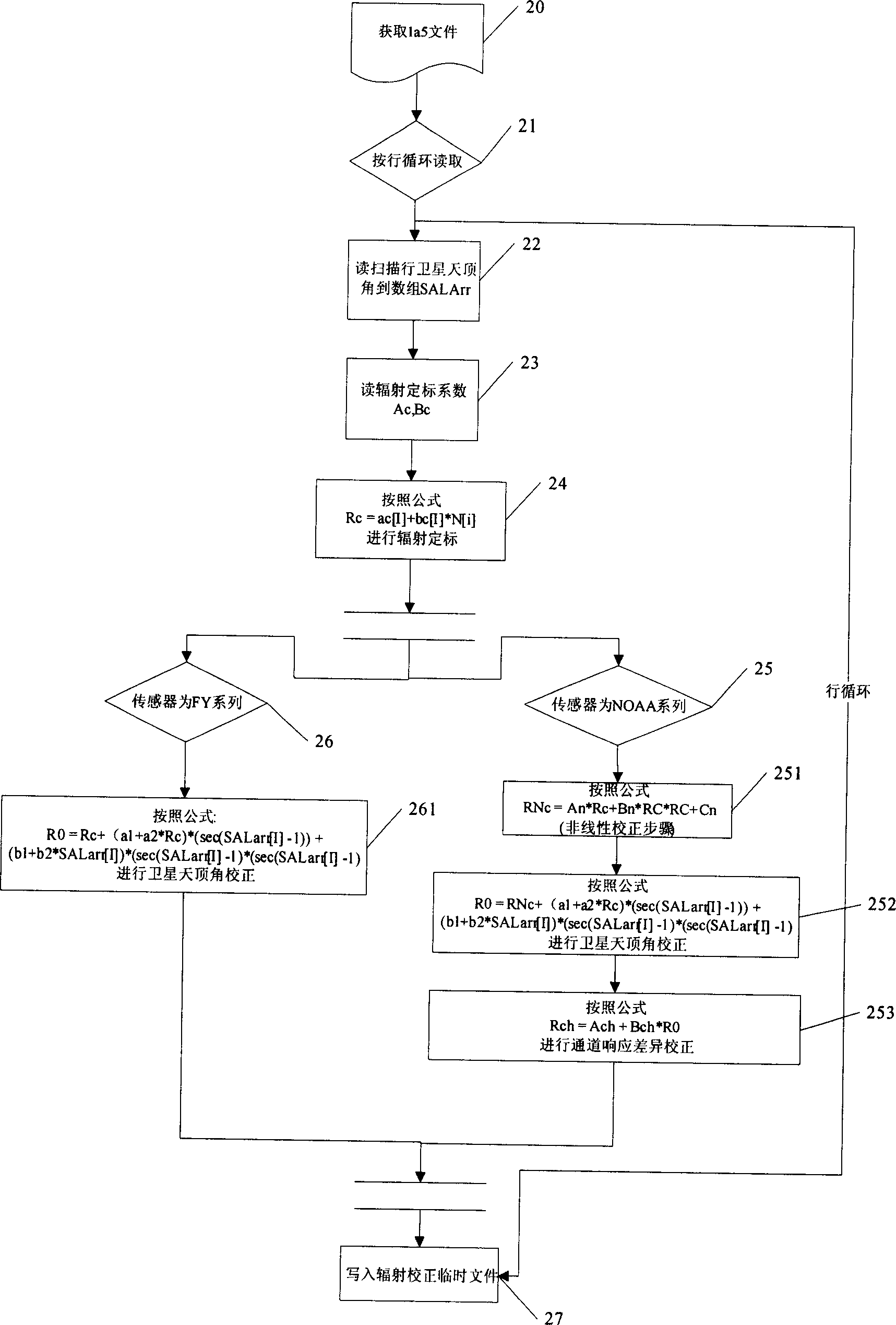
The invention discloses a thermal-infrared band data automatic disposal method of multi-source polar orbit meteorological satellite with radiating assimilation subcourse and geometrical assimilation subcourse, which is characterized by the following: scaling the primitive data by radiation then correcting through satellite zenith angle; finishing radiation assimilation after correcting corresponding channel difference; accomplishing geometrical assimilation through distinguishability normalization, standard space projection transformation and image translation; finishing self-judgment of the same name pixel point through relative matching; reaching direct comparison of different satellite detecting radiation values without artificial operation; improving the precision of geometrical position for multi-source data; paving the base of data disposal and appliance of polar orbit satellite remote sensing data.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Determination method for attitudes of spinning stabilized meteorological satellite based on coarse-fine attitude relation model
InactiveCN103438886AHigh precisionImprove applicabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsNatural satelliteRelational model
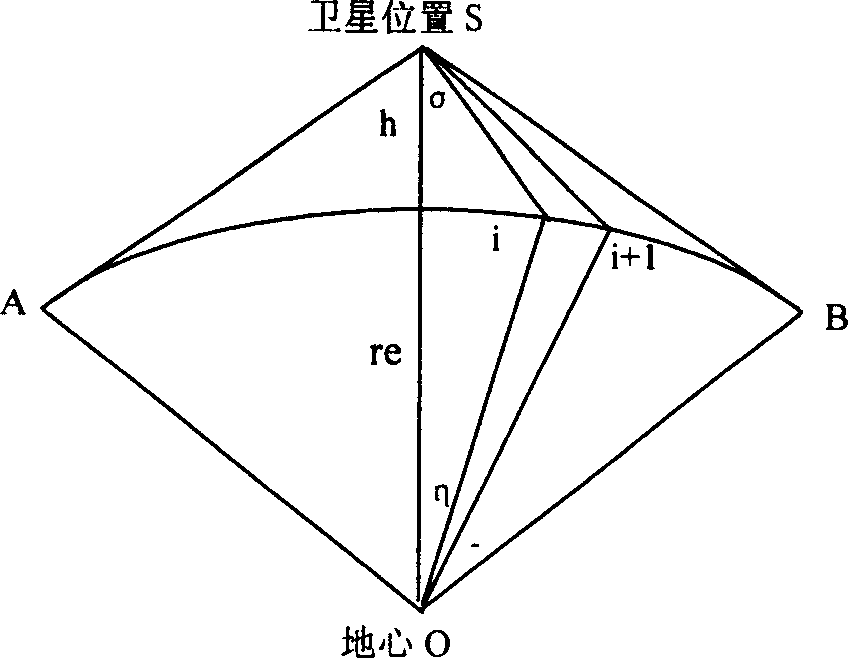
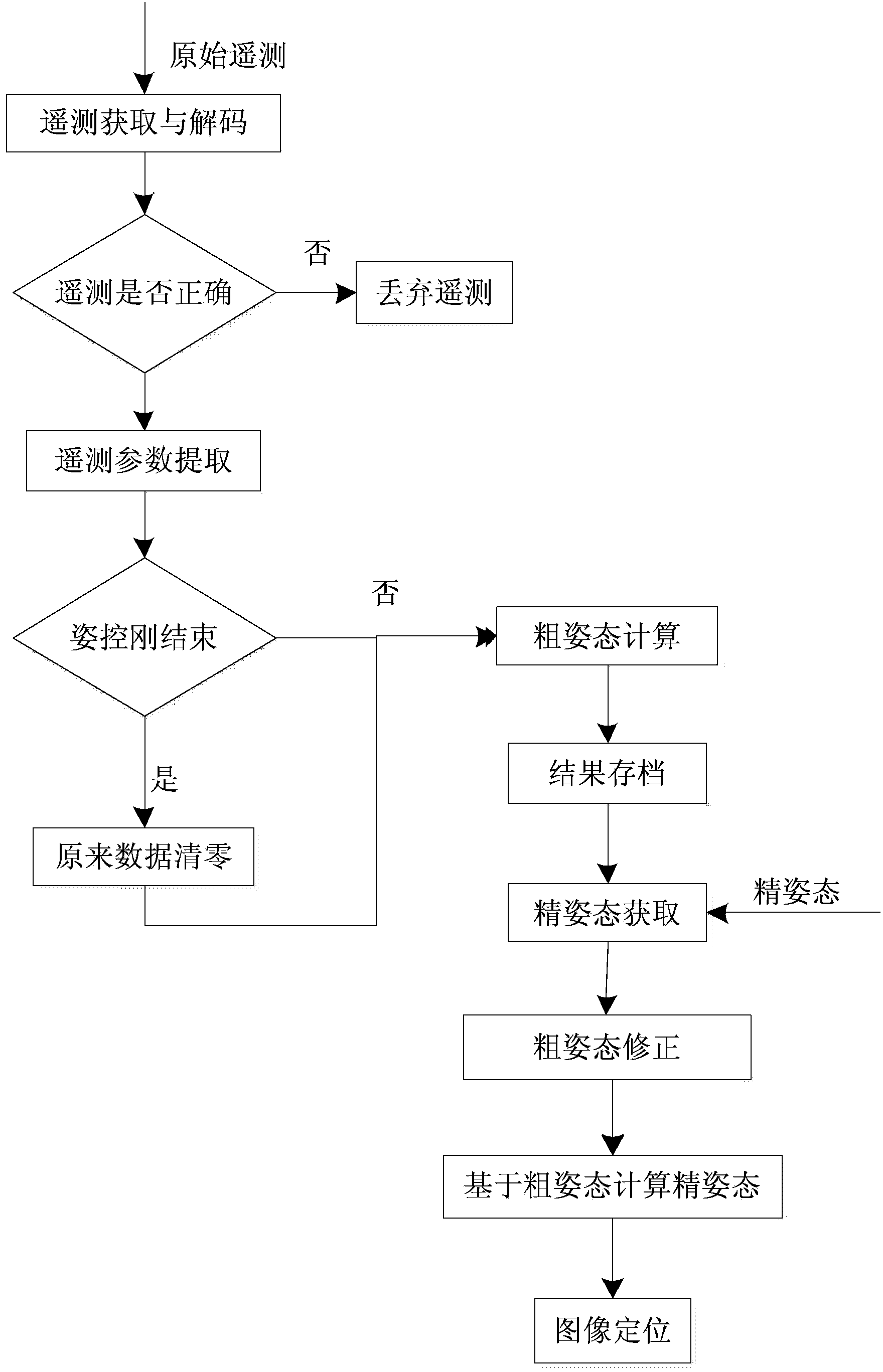
The invention relates to a determination method for attitudes of a spinning stabilized meteorological satellite based on a coarse-fine attitude relation model. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that 1: the coarse attitude of the satellite is calculated; 2: a random error in the coarse attitude of the satellite is eliminated; and 3: the coarse attitude is modified by utilizing the coarse-fine attitude relation model. The method has the benefits that 1, the precision is high, and a calculated fine attitude result is basically consistent with the practical fine attitude of the satellite; 2, the applicability is high, and the fine attitude of the satellite can be calculated by the method to achieve accurate positioning of an observation cloud picture when the fine attitude cannot be obtained within 24h after attitude orbit control of the satellite or in an area observation mode; and 3, a processing procedure is distinct, the operand is not great, and implementation is facilitated.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT
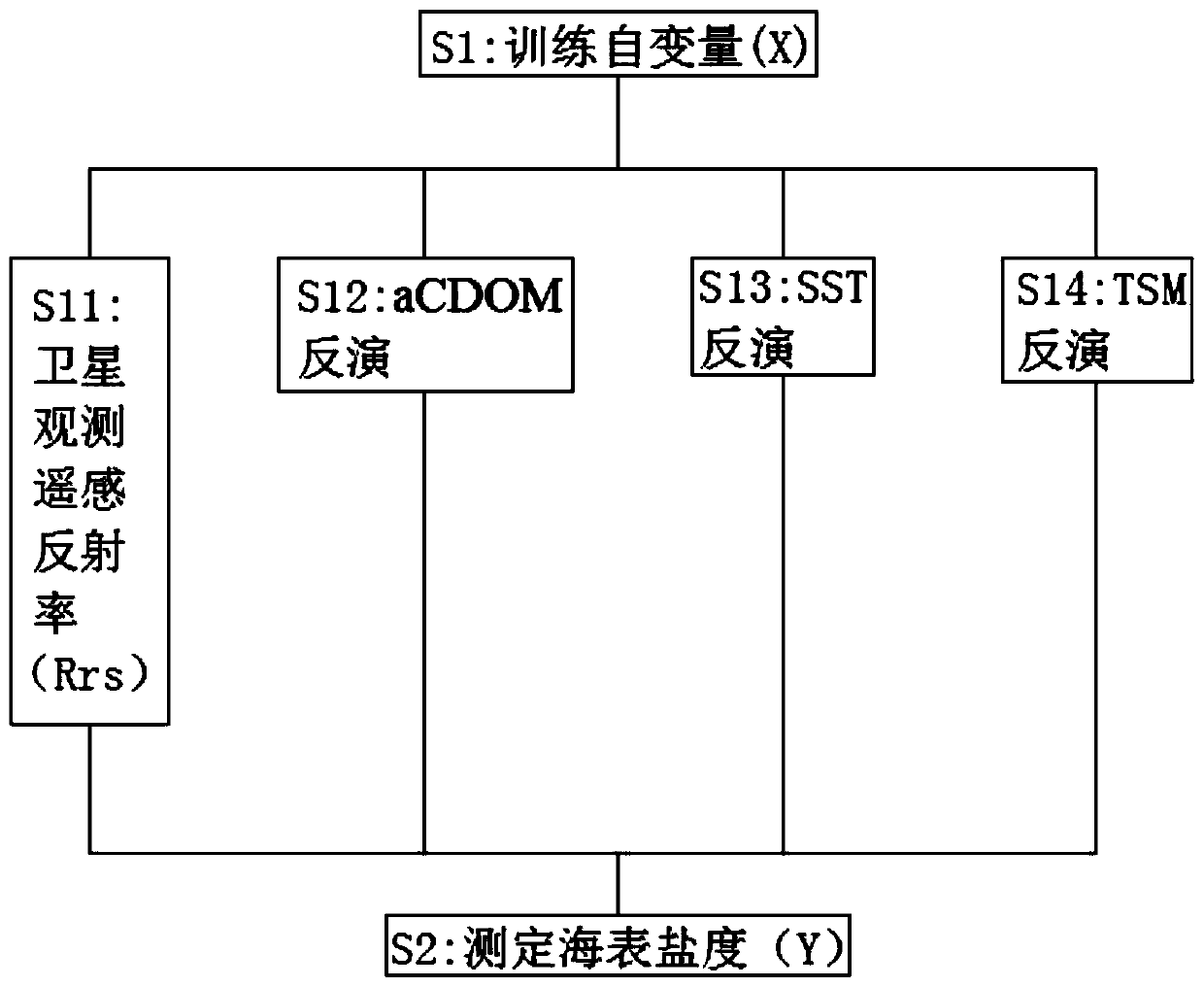
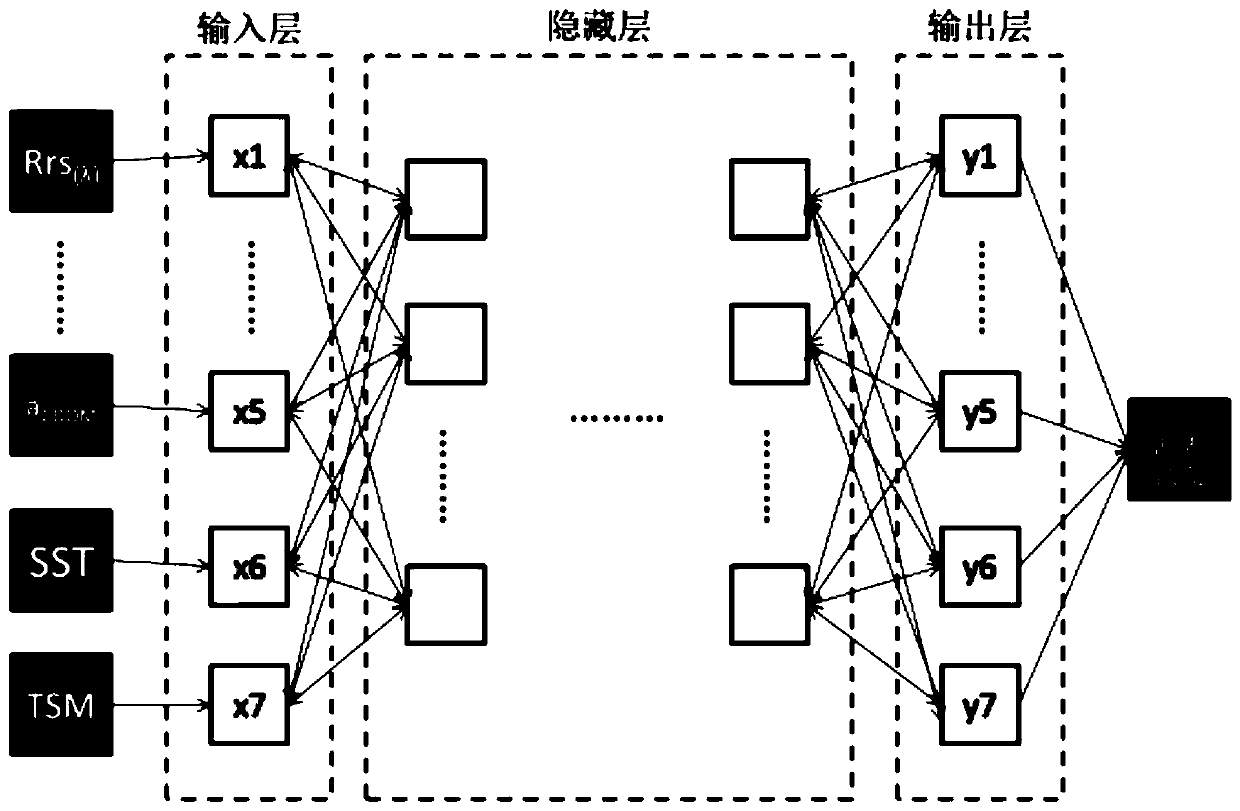
Sea surface salinity inversion algorithm based on wind cloud meteorological satellite
PendingCN110909491ADesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesHidden layerTemporal resolution
Owner:山西大地新亚科技有限公司
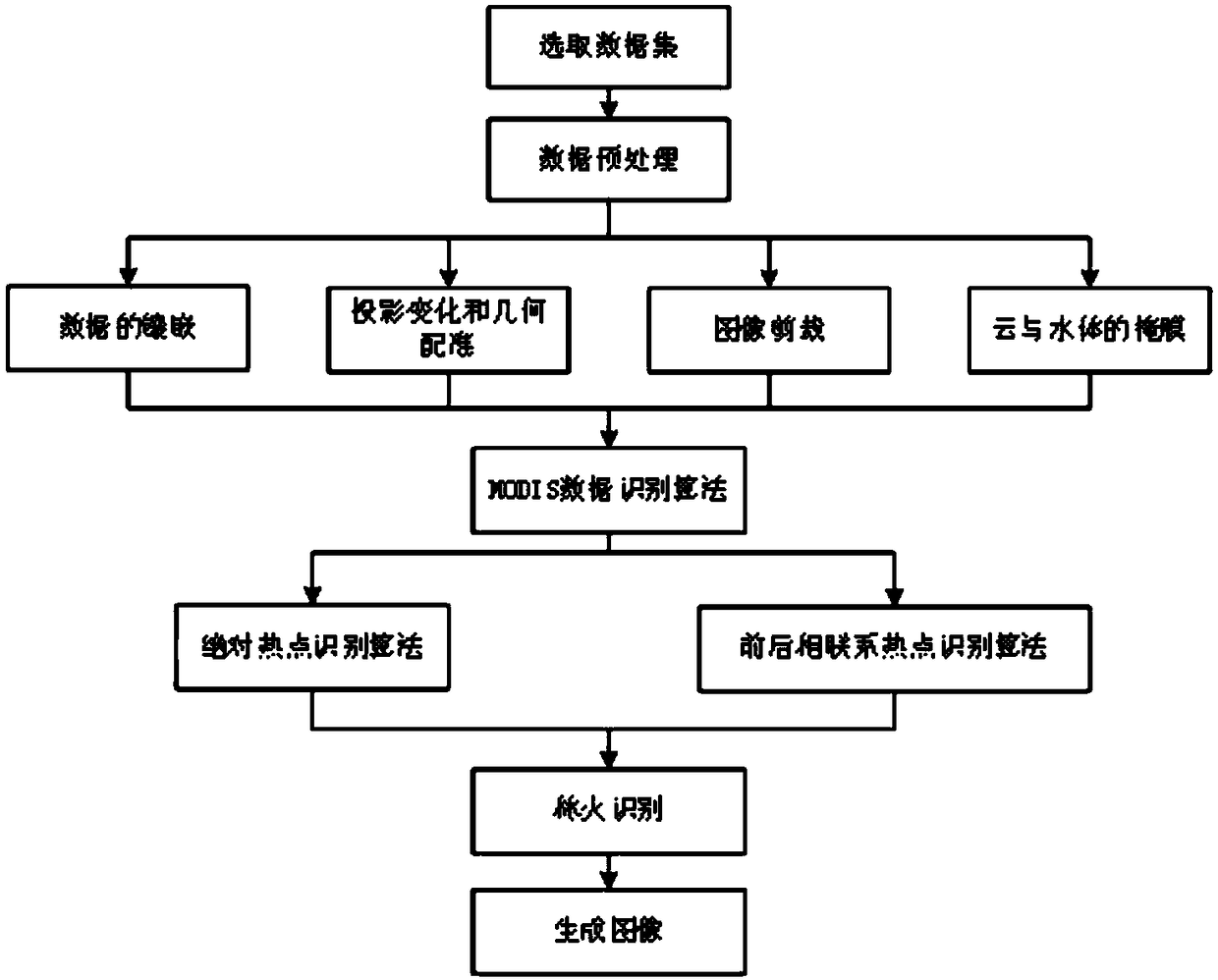
Forest fire identification method based on MODIS data
InactiveCN108898049AUpdate and understand in timeImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisData setFire - disasters
The invention relates to a forest fire identification method based on MODIS data. The method includes the following steps: selecting a data set; performing data preprocessing; using the absolute hot spot identification algorithm and the forward-backward association identification algorithm to identify forest fires according to MODIS data; and generating an identified forest fire remote sensing image. Meteorological satellite monitoring can timely detect early fires and extinguish the fires as soon as possible, can be used to monitor the trend and expansion of the forest fires, and can track and monitor serious forest fire disasters.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
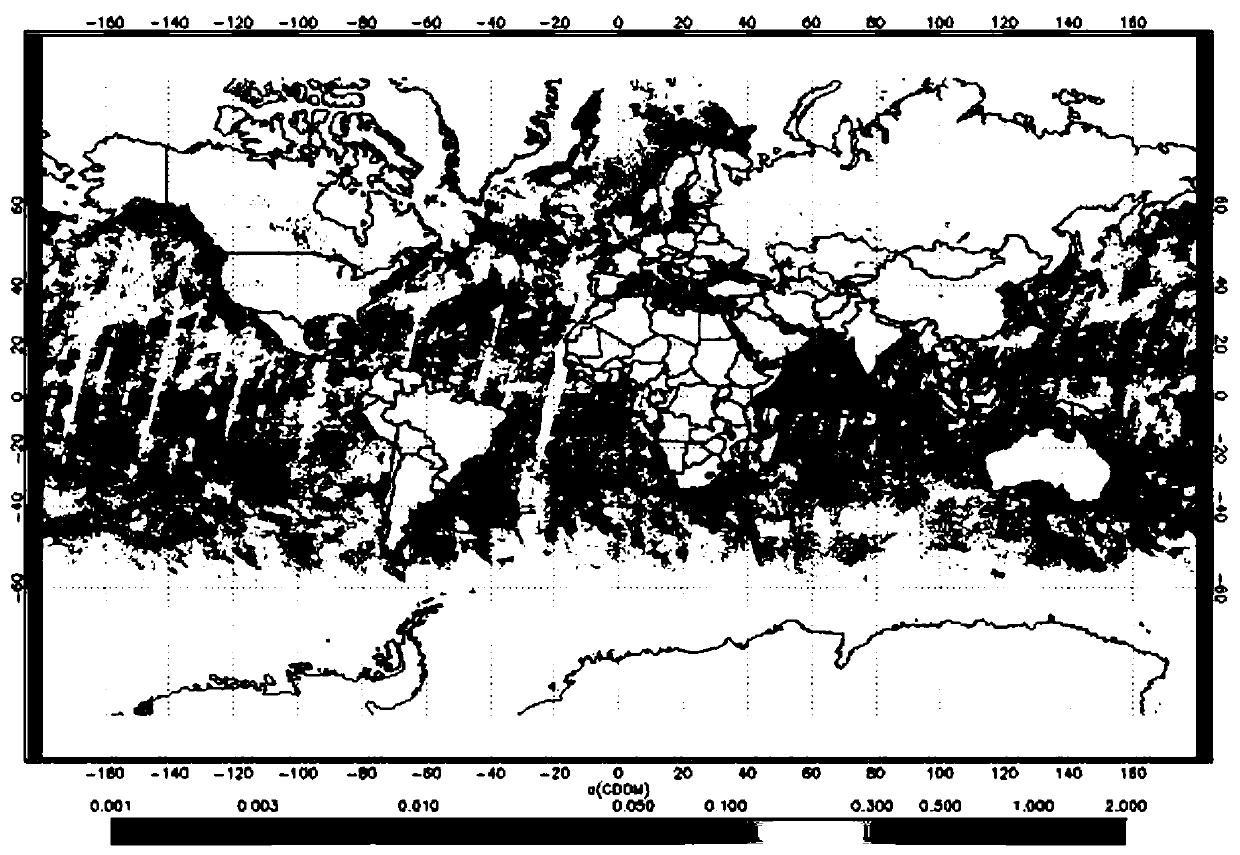
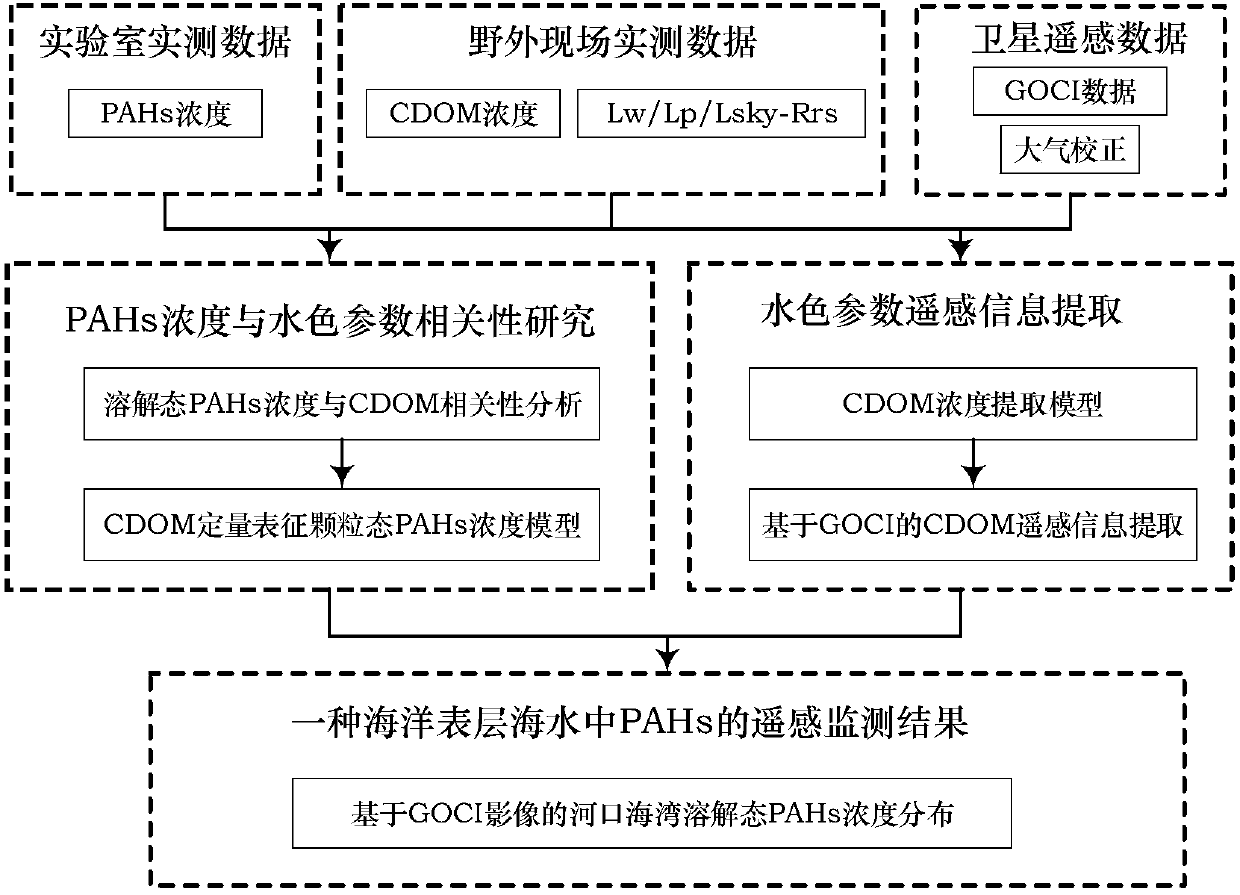
Method for monitoring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface seawater by means of remote sensing
ActiveCN107044985AImprove the level of monitoring technologyReduce health risksOptically investigating flaws/contaminationOffshore waterSurface water
The invention discloses a method for monitoring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface seawater by means of remote sensing. According to the method, the large-area distribution of the remote sensing inversion concentration of the dissolved PAHs in the surface water of estuaries and bays is obtained by establishing a content algorithm model for quantitatively expressing the dissolved PAHs of the ocean by using water color parameters such as chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) concentration of the estuaries and the bays, and applying the content algorithm model to images of a geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI) of a first geostationary meteorological satellite sensor on the world. After the method is adopted, the contamination status of the PAHs in offshore waters can be monitored by means of remote sensing; the method is mainly used for monitoring the distribution characteristics of marine pollutants in ways of large area and high frequency. The remote sensing-based monitoring model for monitoring the distribution situation of the PAHs in the surface water of estuaries and the bay is proposed based on analysis of measured data and is applied to satellite data of the GOCI, and remote sensing monitoring of the PAHs concentration is realized in virtue of the remote component CDOM in the seawater.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com