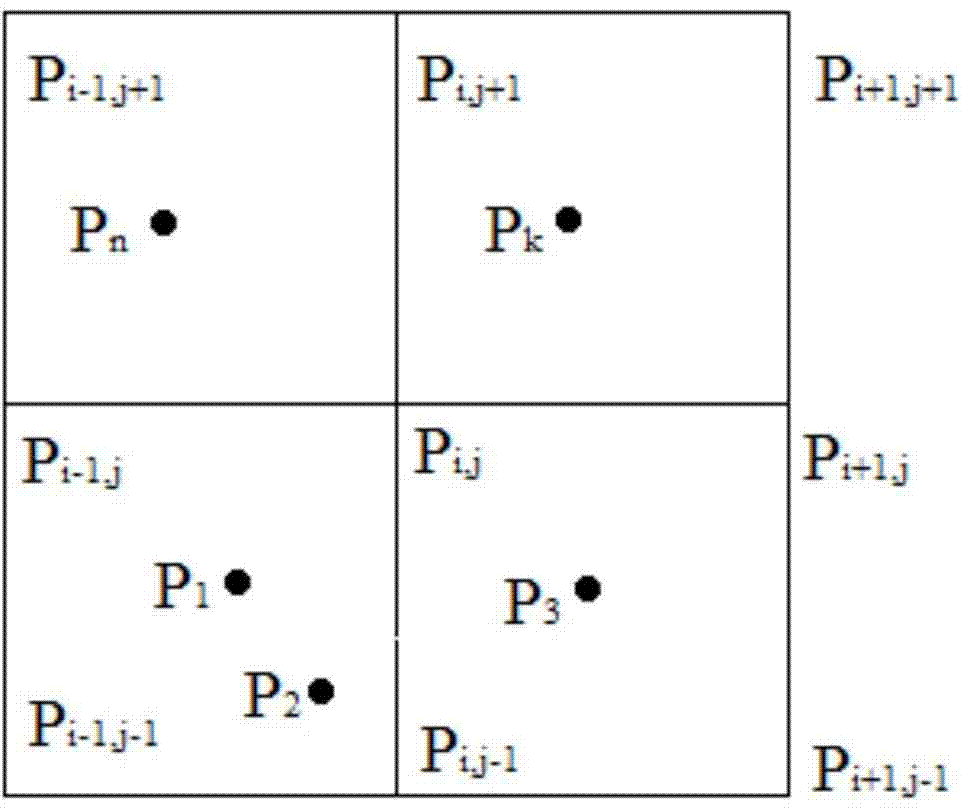
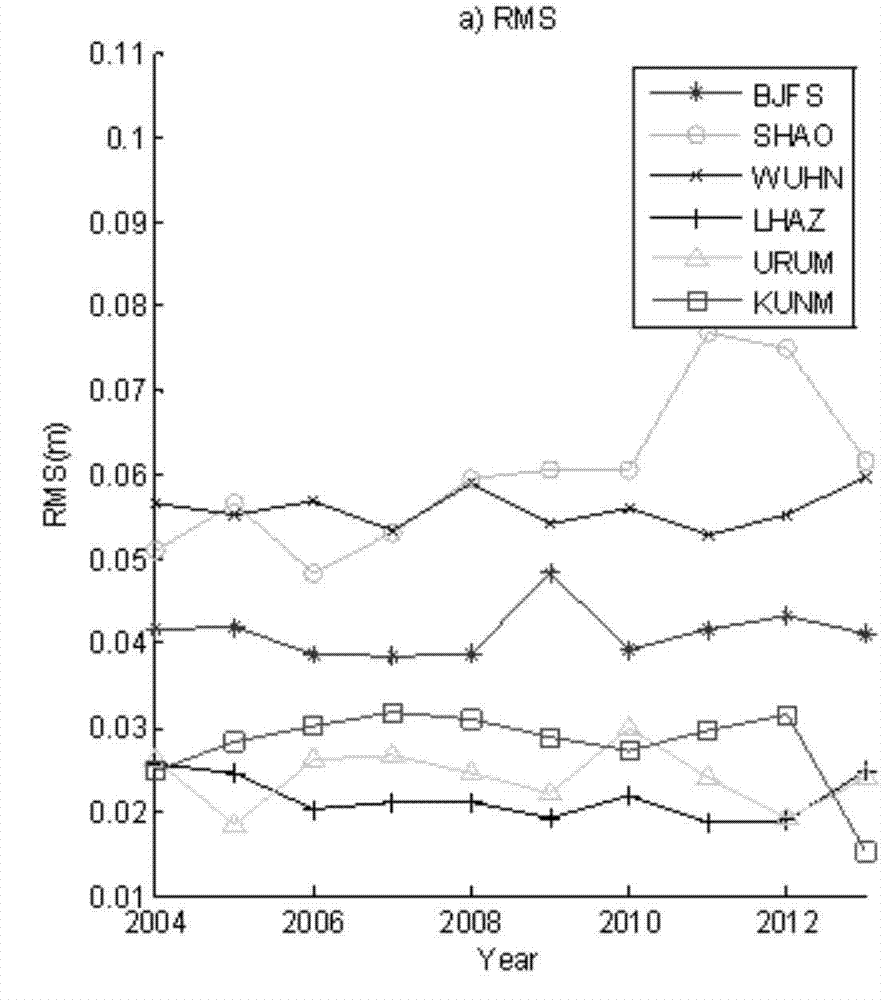
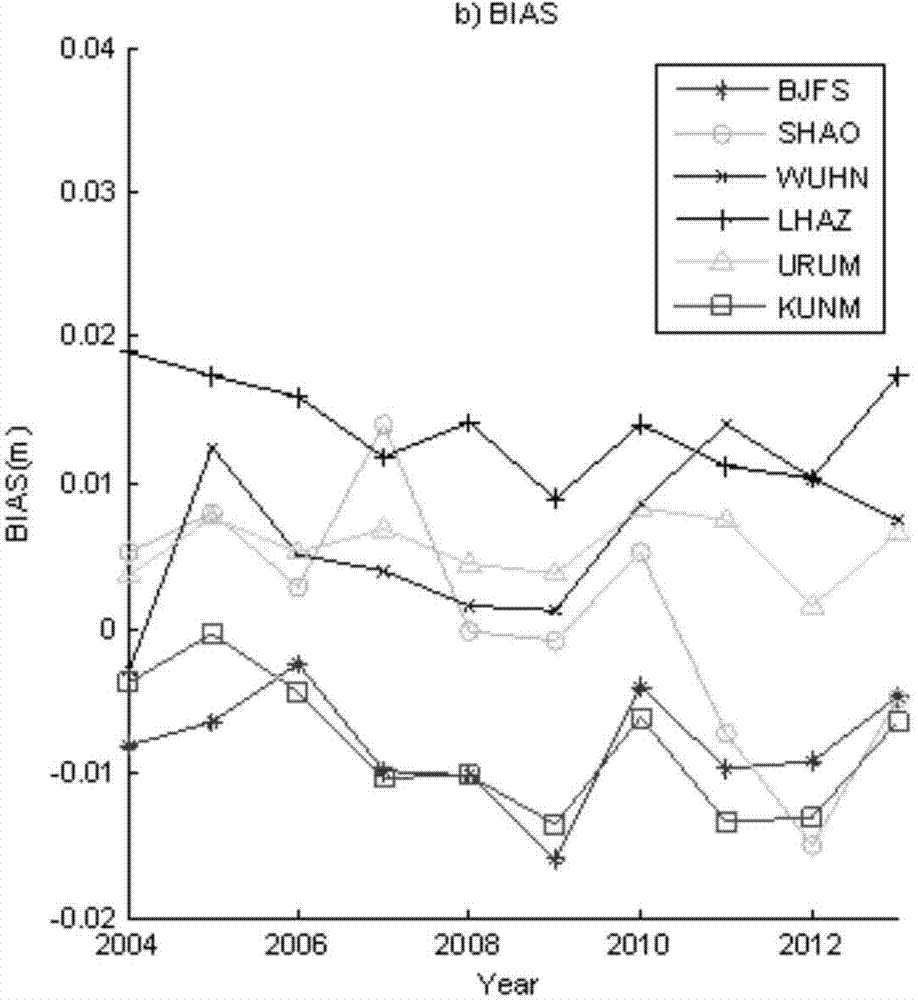
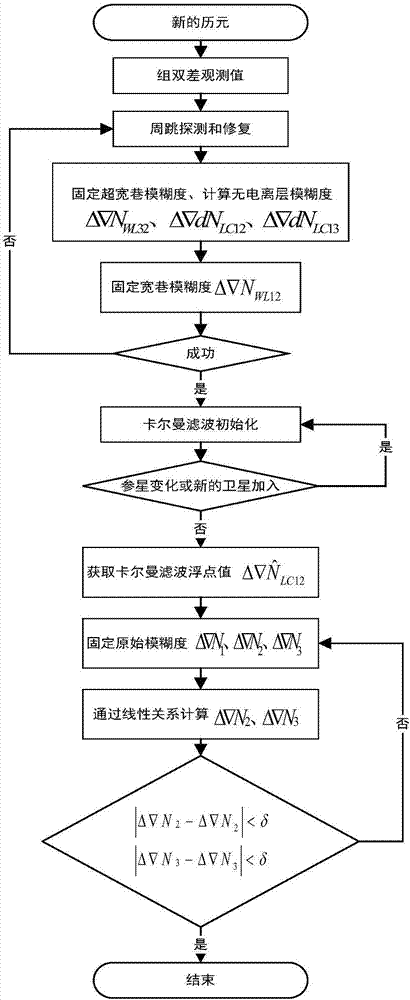
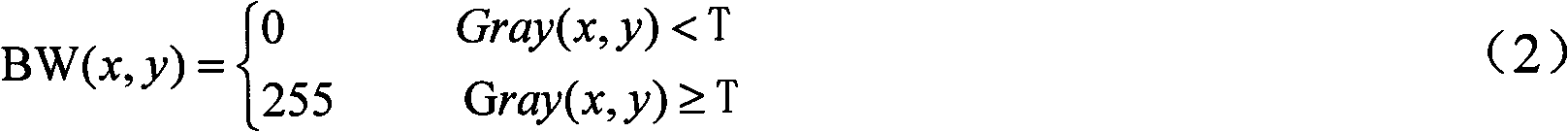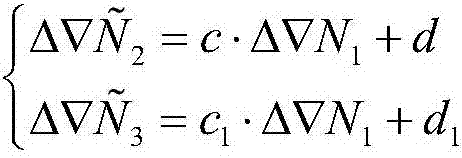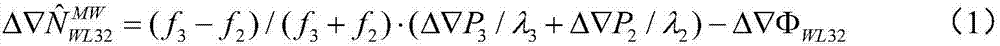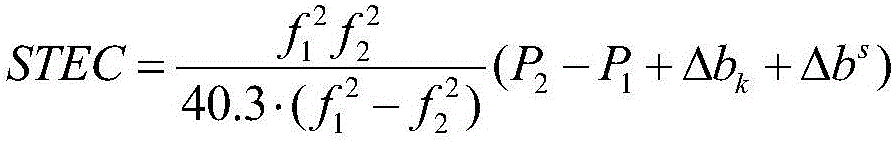Patents
Literature
494 results about "Zenith" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
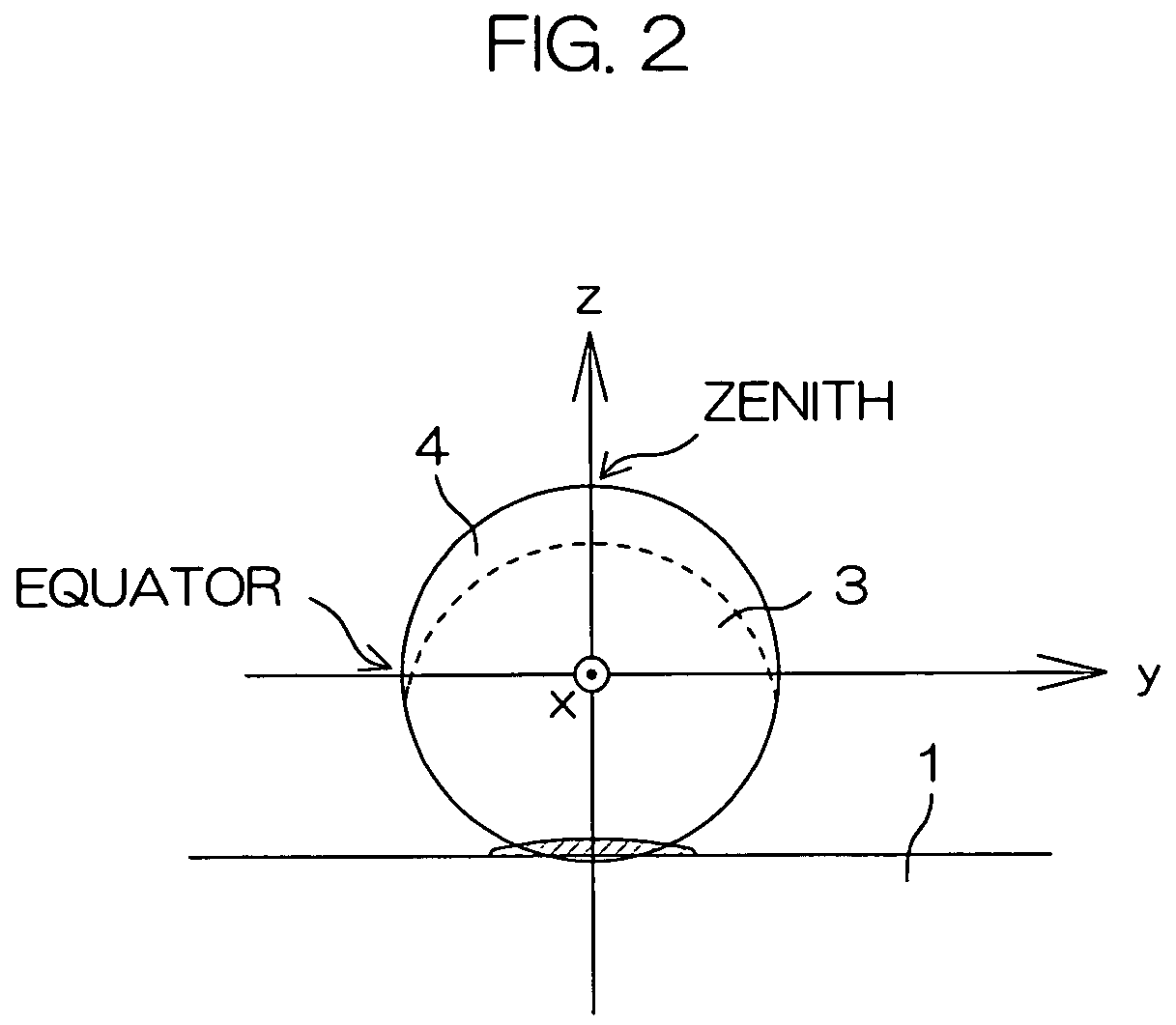
The zenith is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the imaginary celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction opposite to the apparent gravitational force at that location. The opposite direction, i.e. the direction in which gravity pulls, is toward the nadir. The zenith is the "highest" point on the celestial sphere.
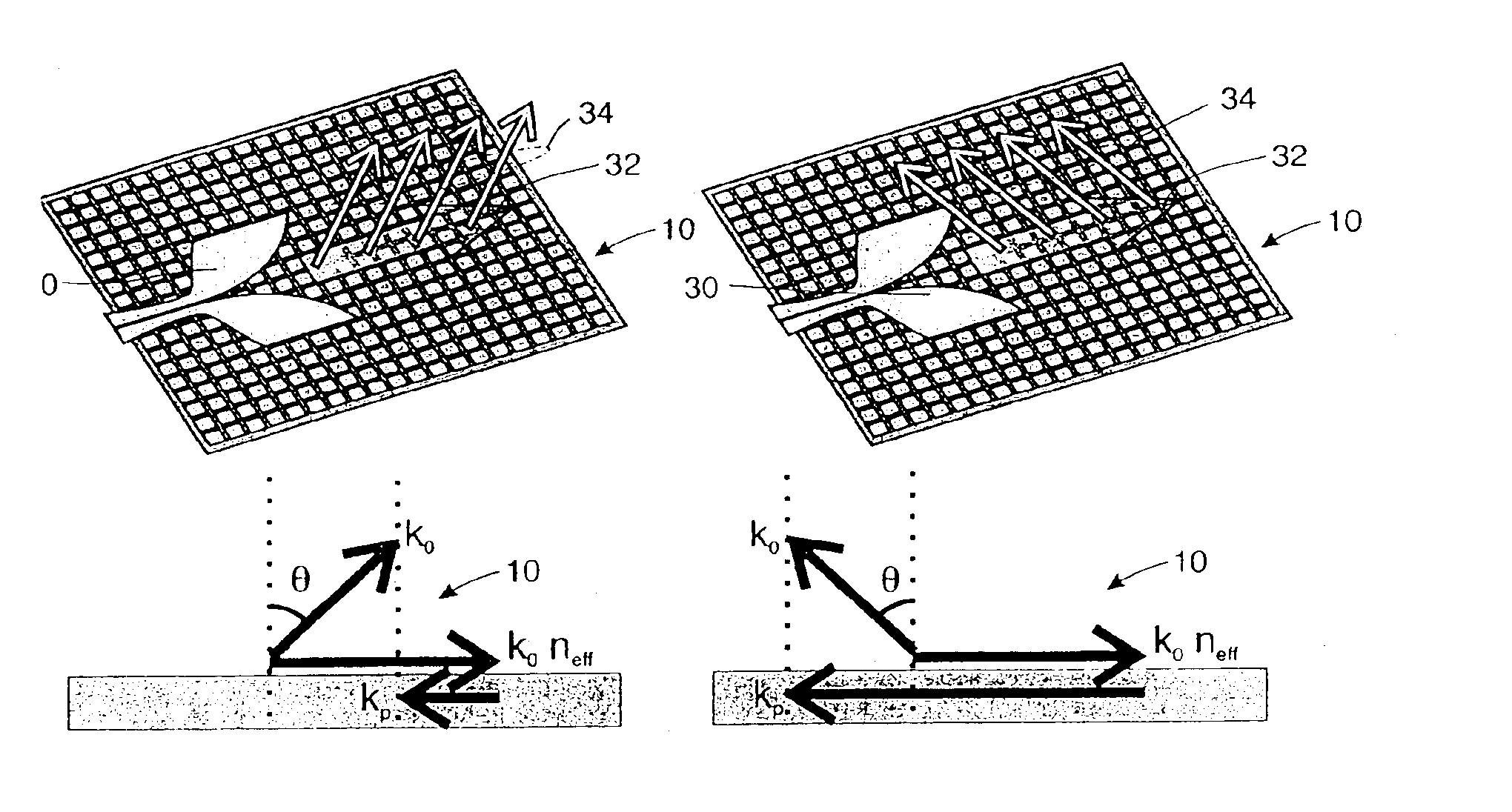
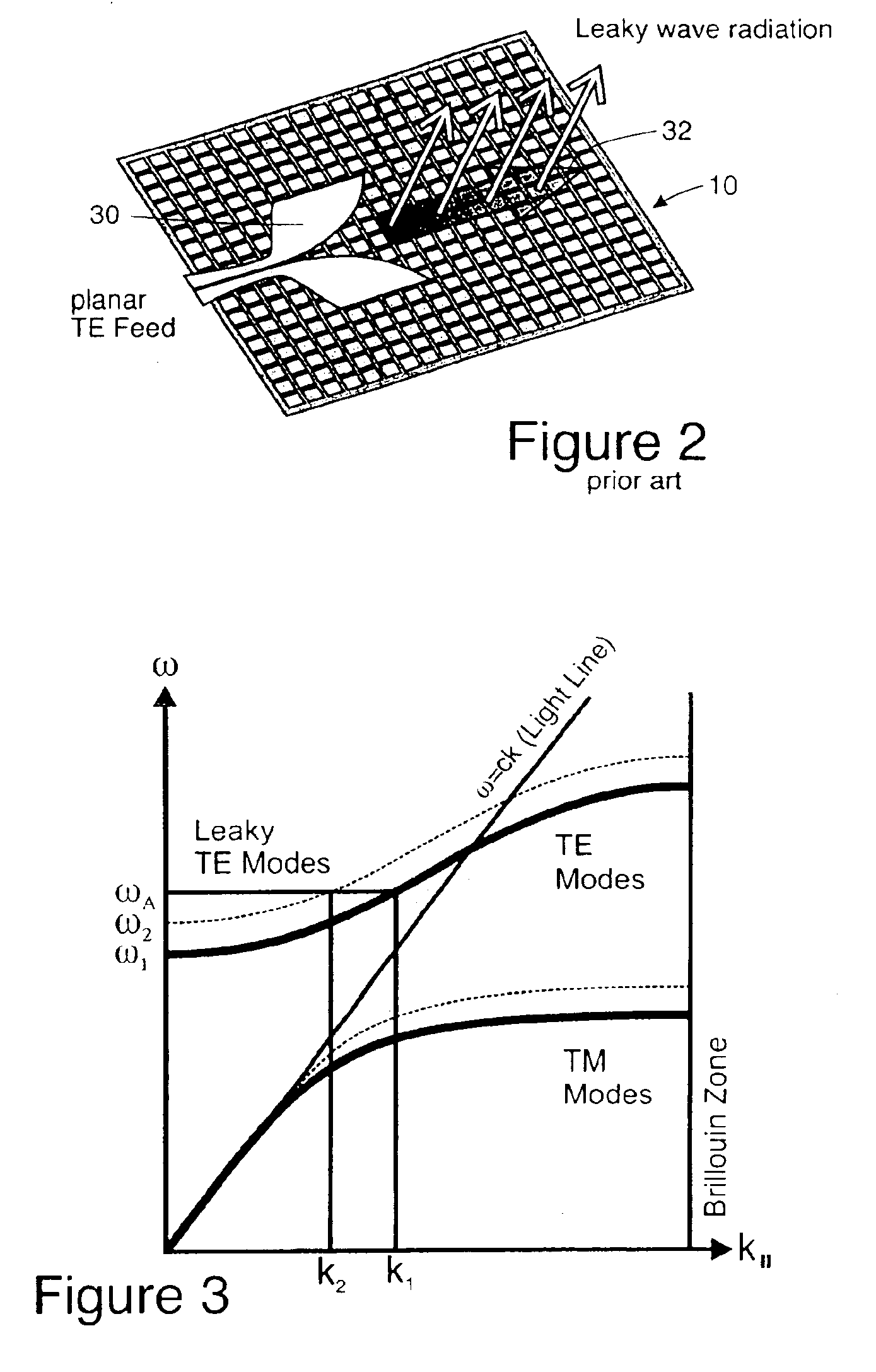
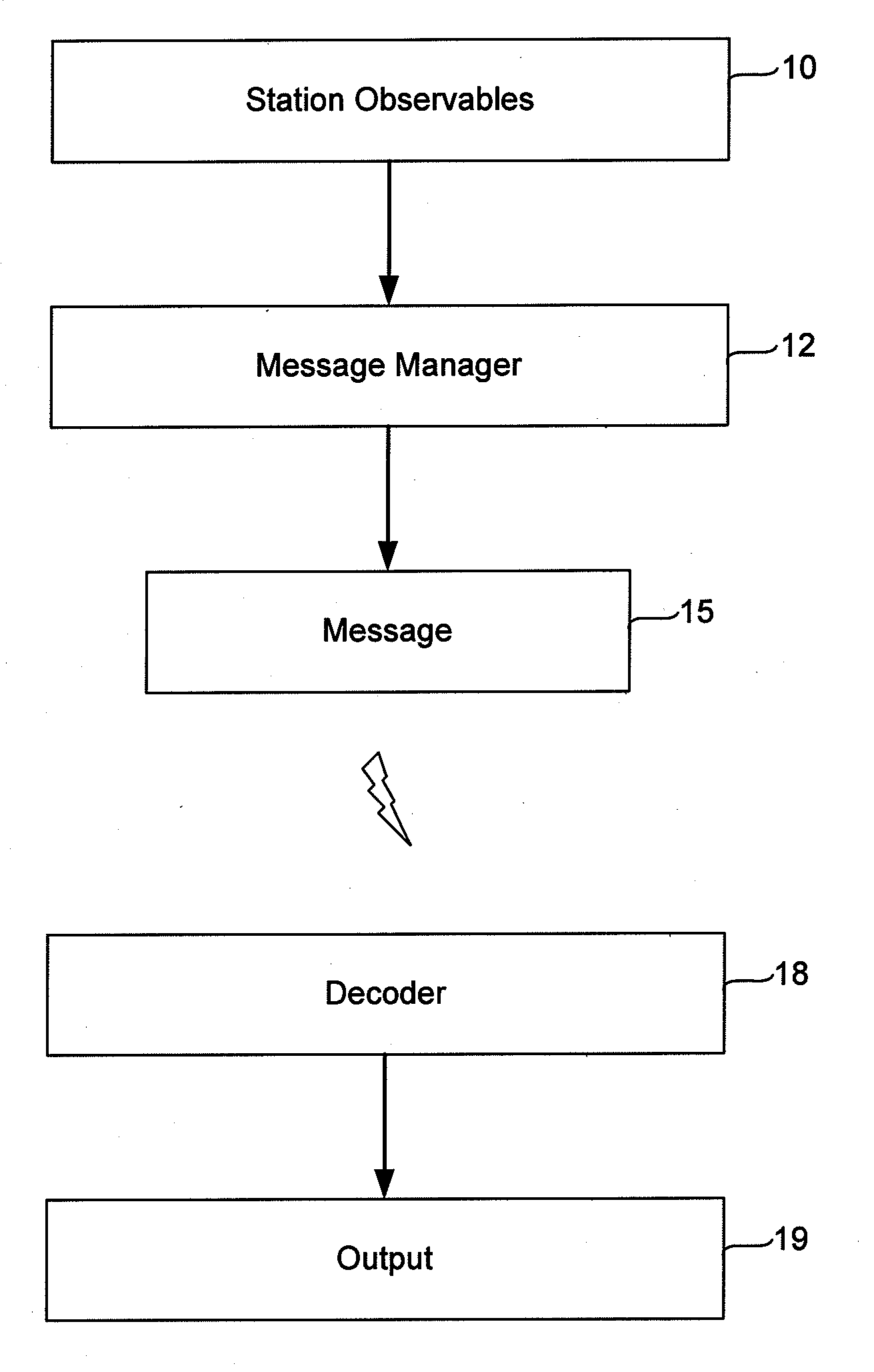
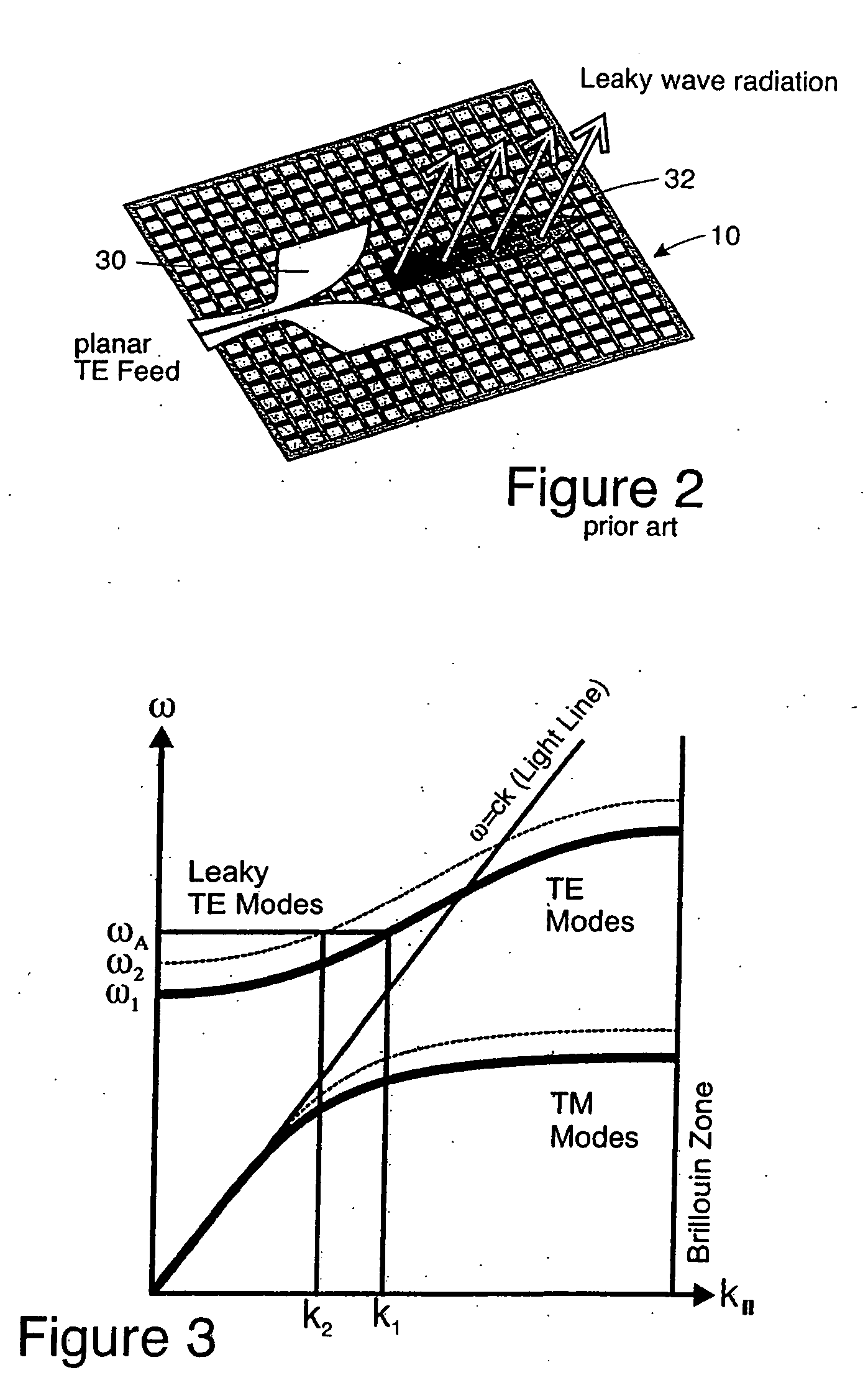
Steerable leaky wave antenna capable of both forward and backward radiation
ActiveUS7071888B2Individually energised antenna arraysElectrically short antennasHorizonBeam steering
Leaky wave antenna beam steering that is capable of steering in a backward direction, as well as further down toward the horizon in the forward direction than was previously possible, and also directly toward zenith. The disclosed antenna and method involve applying a non-uniform impedance function across a tunable impedance surface in order to obtain such leaky wave beam steering.
Owner:HRL LAB
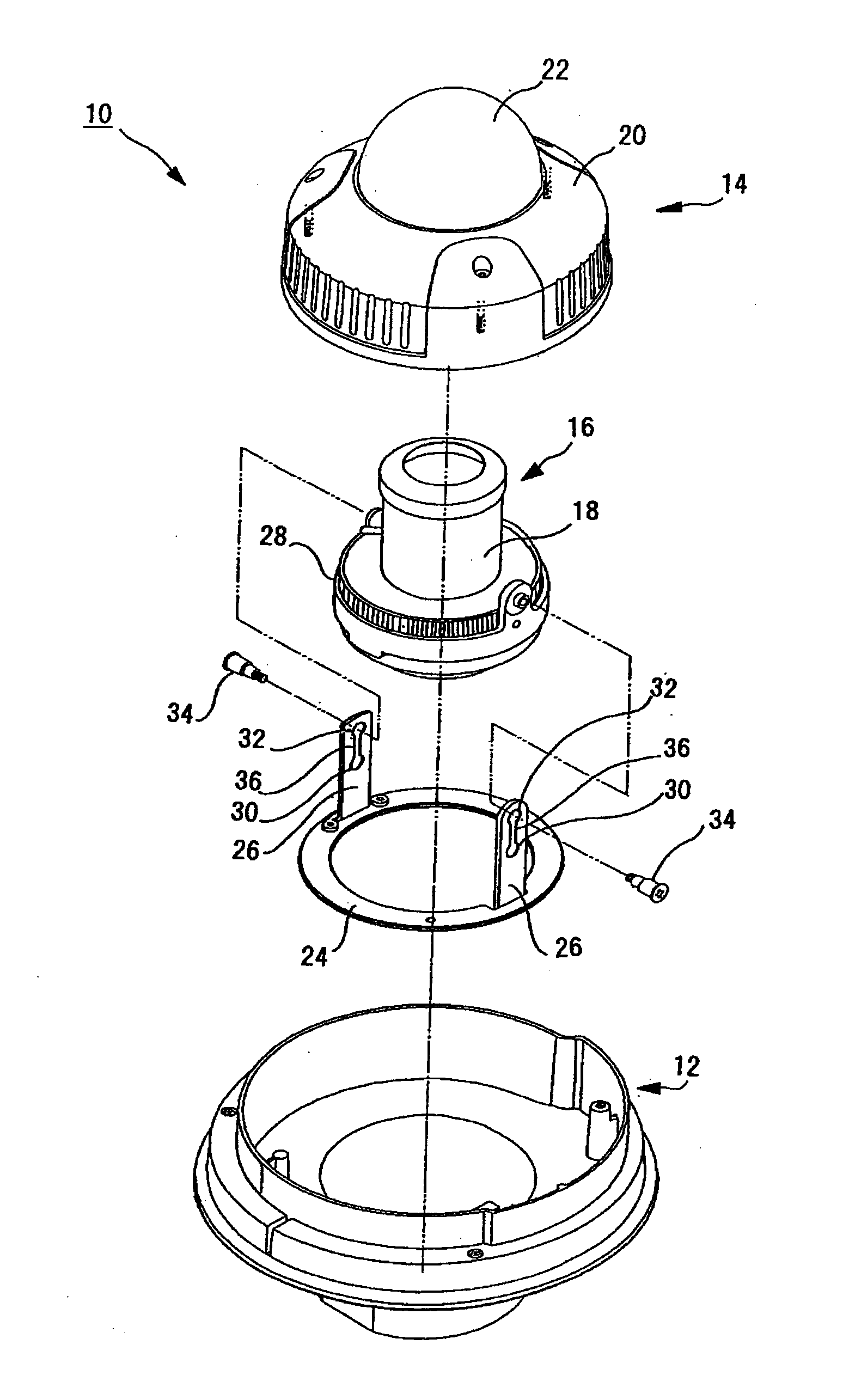
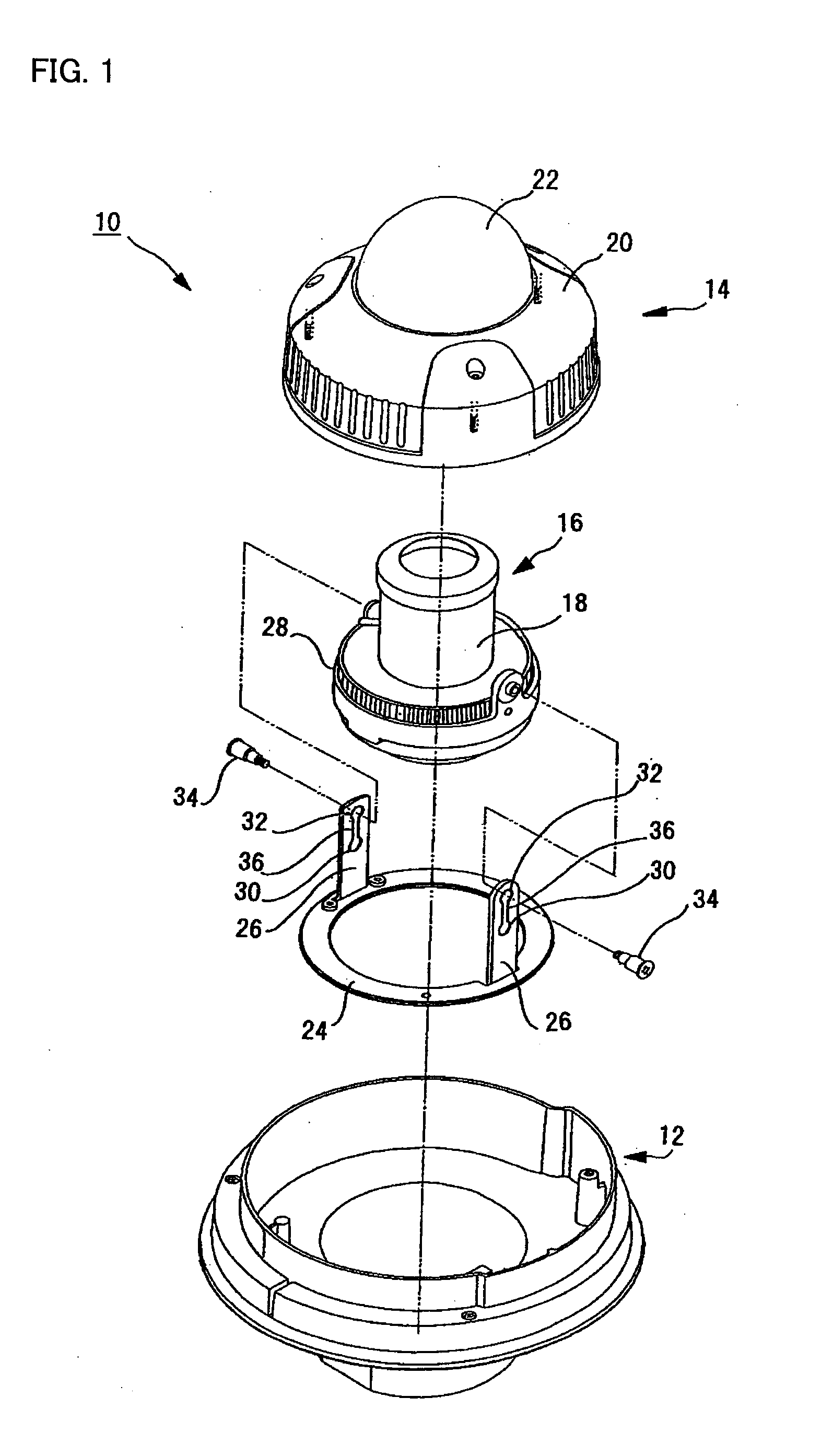
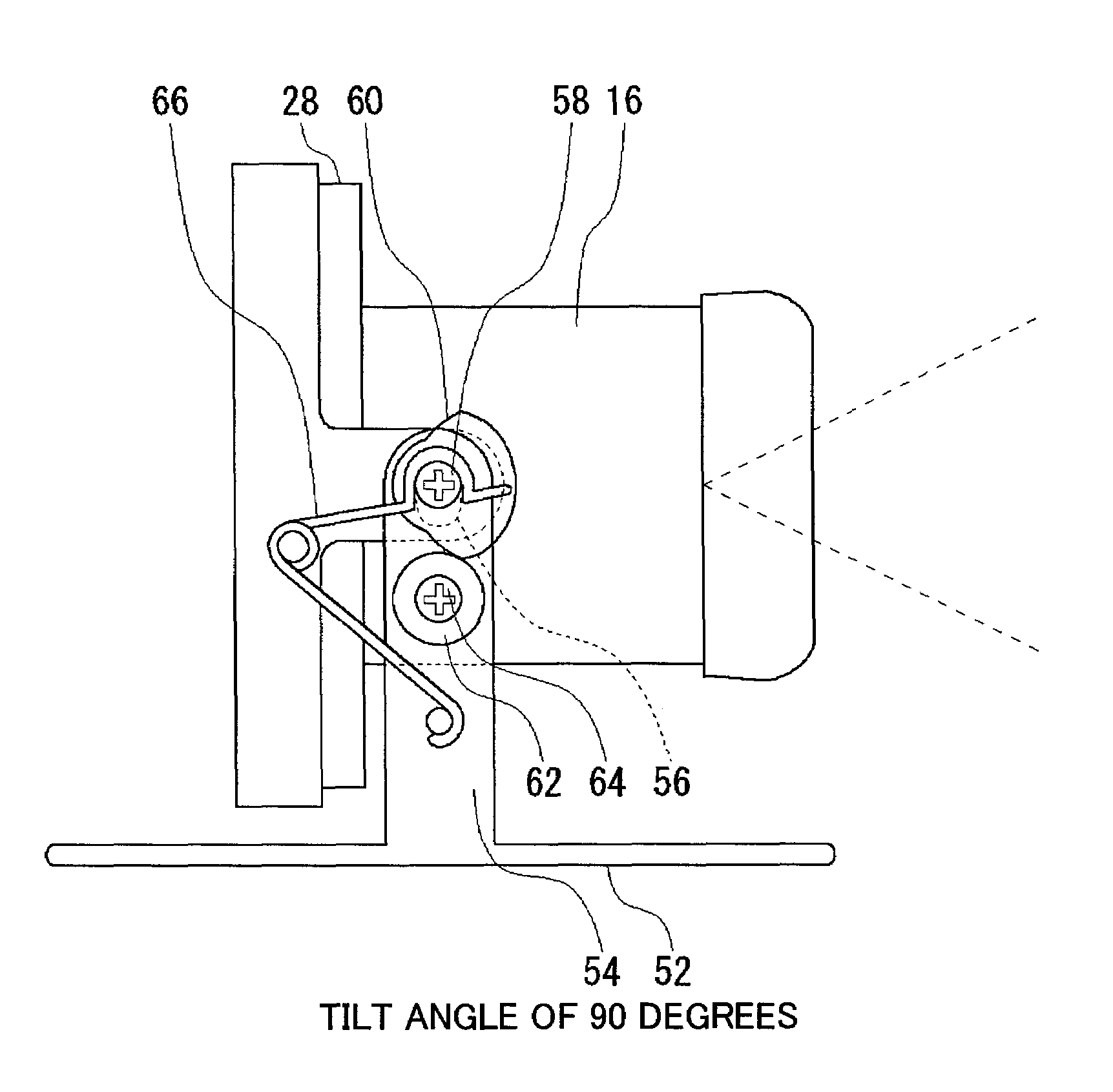
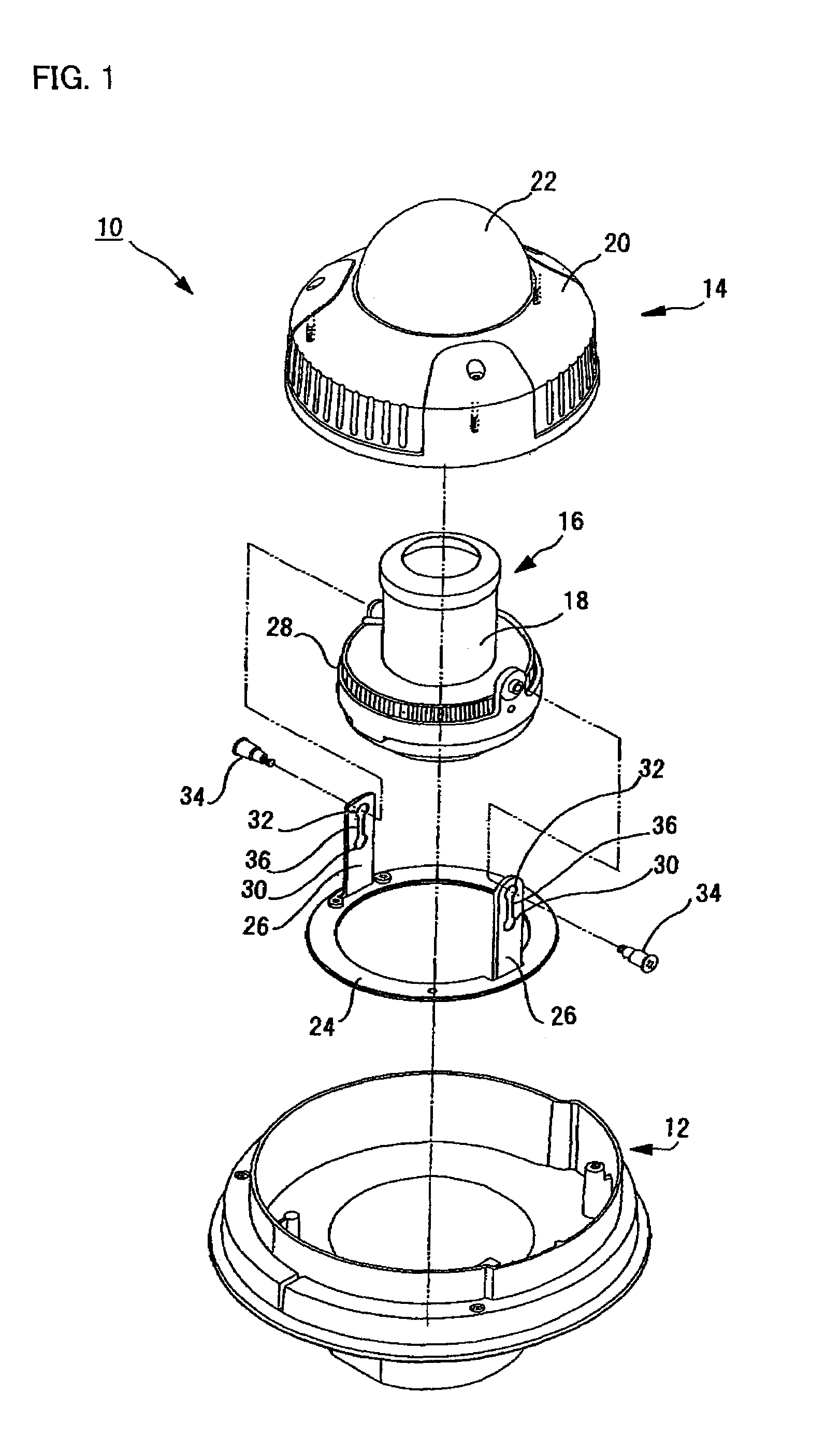
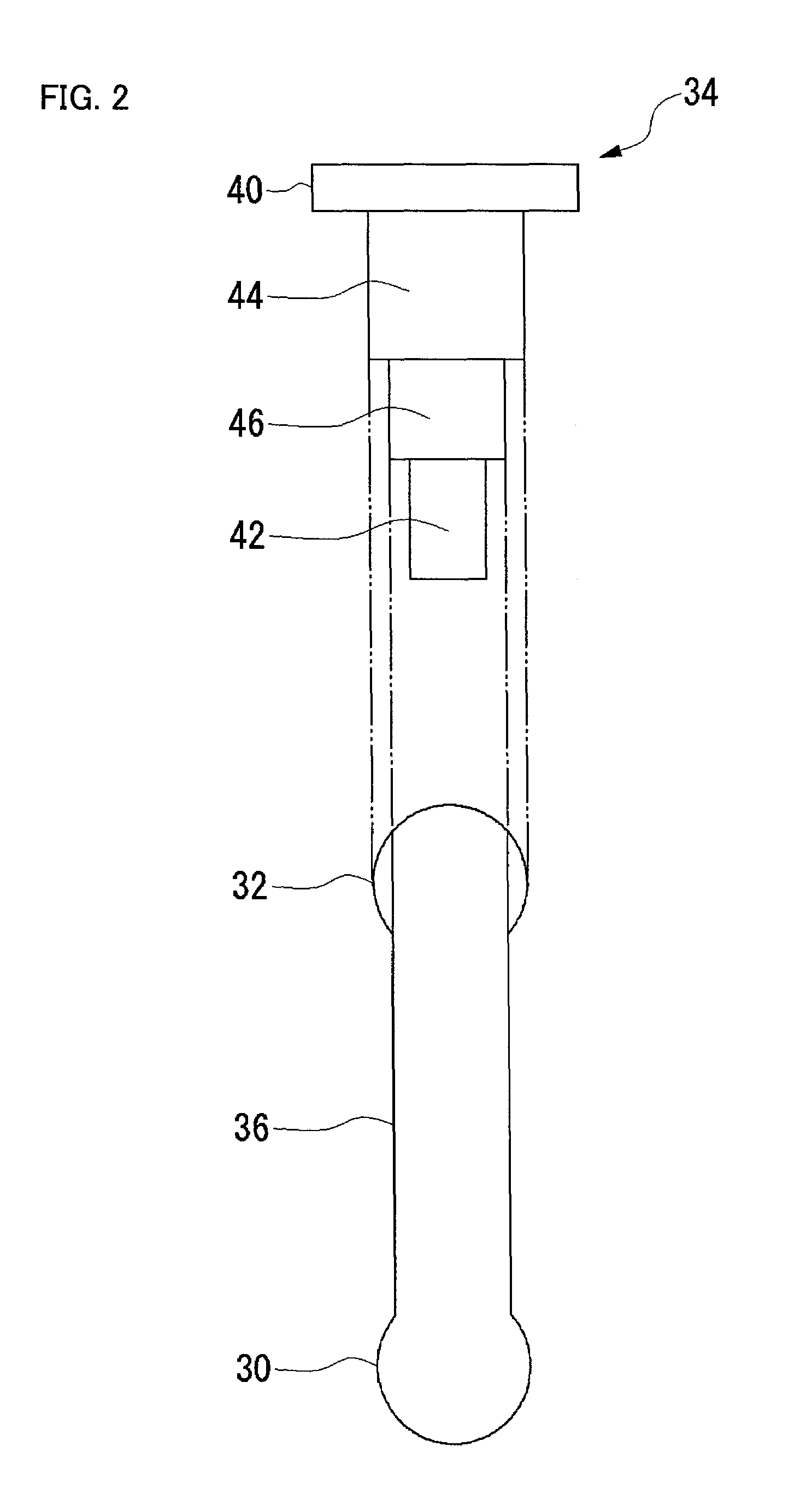
Dome Type Camera
InactiveUS20080231699A1Enhance the imageTelevision system detailsPrintersElevation angleCentre of rotation
A lens (16) is rotatably provided inside a dome cover (22). The lens (16) is supported so that the center of rotation can be moved from the center of a dome to a position apart therefrom in the zenith direction. A lens moving mechanism for moving the lens (16) according to a rotation in the tilt direction of the lens (16) may be provided. The lens moving mechanism may be a cam structure. The cam structure is set so that the rotation axis of the lens (16) is held at the center of the dome in a predetermined center hold angle range corresponding to the direction of an elevation angle, and that the rotation axis of the lens (16) is moved from the center of the dome in the zenith direction at angles lower than the center hold angle range. Good images can be obtained even when shooting in the direction of a depression angle.
Owner:PANASONIC I PRO SENSING SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Real-time precise orbit determining method of short orbit arc low earth orbit (LEO) navigation satellite
ActiveCN107153209AError Effect CompensationLow priceSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteData center
The invention discloses a real-time precise orbit determining method of a short orbit arc low earth orbit (LEO) navigation satellite. The method is characterized in that four or more ground receivers are used for tracking navigation signals of a plurality of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) navigation satellites and LEO navigation satellites, and transmitting the navigation signals to a data center in real time. The method comprises the following steps: I, acquiring and preprocessing observing data; II, performing precise time synchronization on the receivers; III, calculating tropospheric delay in an LEO gazing direction by using tropospheric delay in a vertical direction and a projection function; IV, correcting hardware delay of the receivers to build an LEO determining geometric observing equation; V, solving an LEO precise orbit and a precise clock error through a dynamical model and the geometric equation of the LEO; VI, distributing the LEO precise orbit and the precise clock error in real time. By adopting the method, the problem of need of post-processing due to incapability of calculating the precise orbit of a low earth orbit satellite can be solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Continuous Tracking Counter for Enabling Cycle-slip Free Messages in a Network of Global Navigation System Satellite Receivers
ActiveUS20100085253A1Smooth bandwidth utilizationGuaranteed usageCode conversionSatellite radio beaconingHigh elevationSatellite tracking
A method of communicating satellite tracking information among a network of global navigation satellite system receivers is described. The method includes determining at a first GNSS receiver which satellites in a constellation of satellites have been continuously tracked over a preceding selected time period, and for each such satellite determining its elevation with respect to the zenith. Only the elevation value for the lowest satellite in the set of satellites for which all satellites of higher elevation values have been continuously tracked over the selected time period is then transmitted to the second GNSS receiver. That receiver can then reconstruct the set of satellites which have been continuously tracked.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
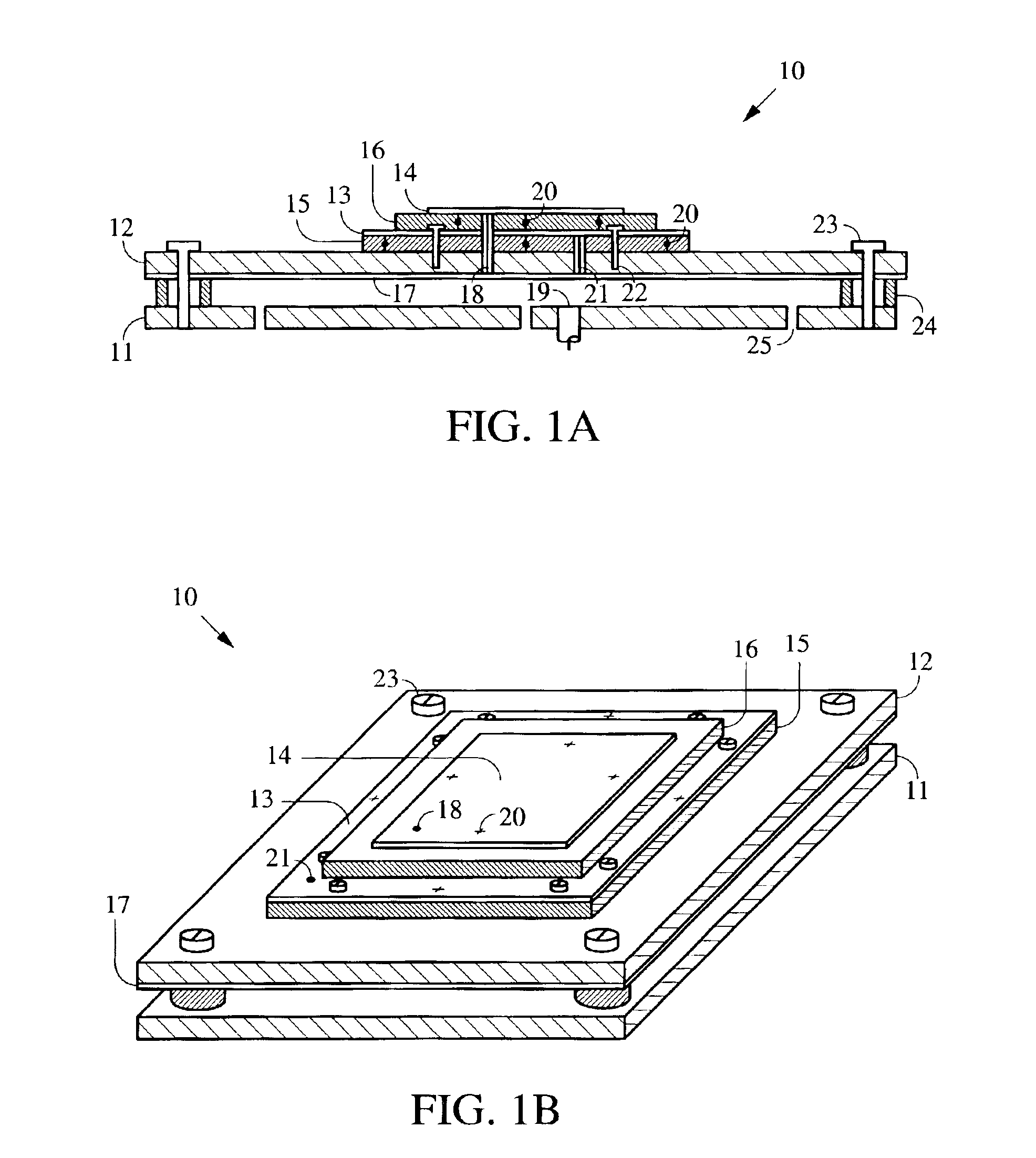
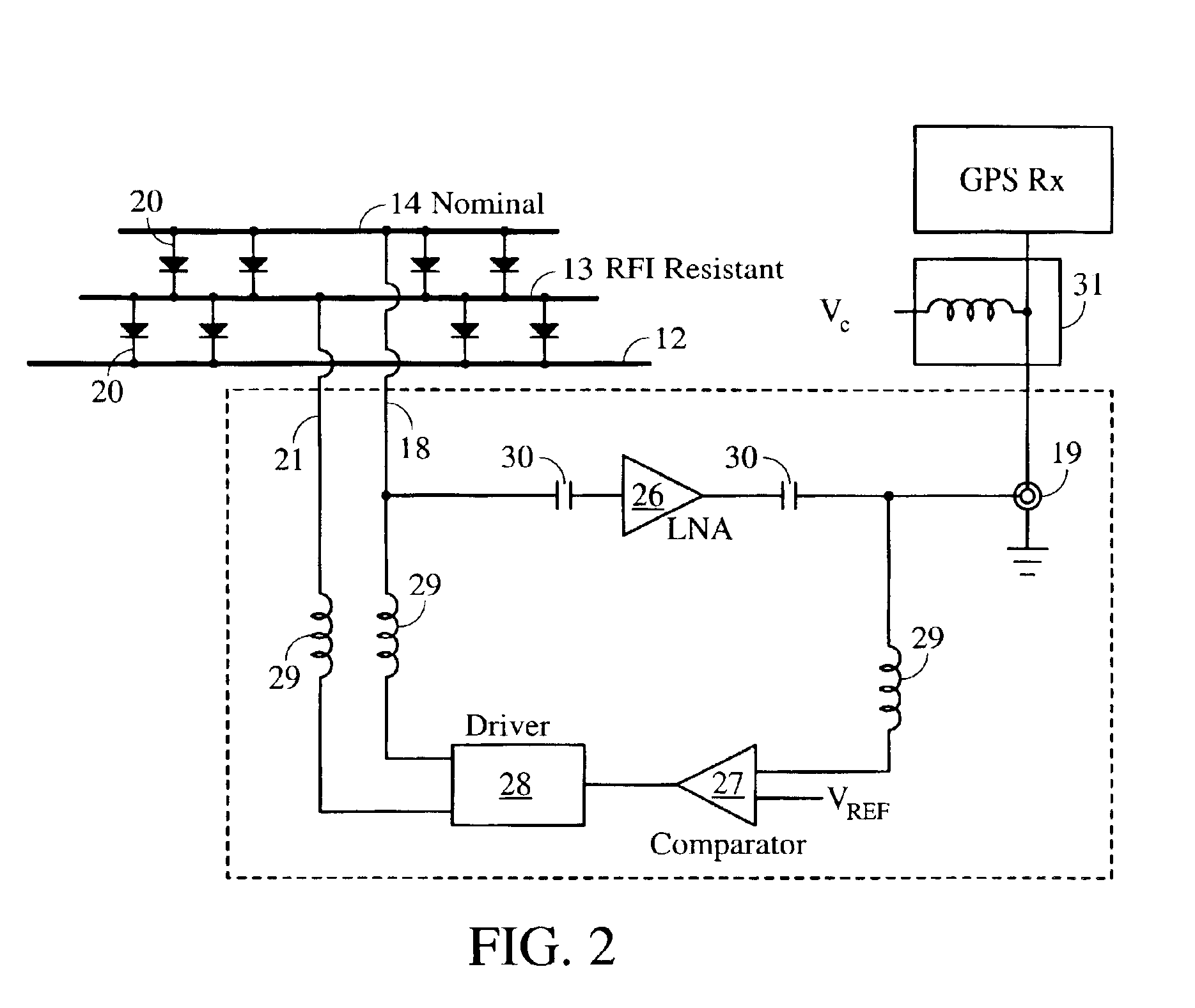
Dual-element microstrip patch antenna for mitigating radio frequency interference
InactiveUS6930639B2High sensitivityLess sensitivitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaHorizon
Method and apparatus for reducing radio frequency interference (RFI) using a dual-element patch antenna [10]. The antenna possesses two antenna elements [13, 14] having distinct radiation patterns. Either element may be independently selected using a DC bias voltage. Diodes [20] connected to the elements serve to disable one element when the other is selected. In one selected mode, a nominal radiation pattern provides a broad, hemispherical shaped sensitivity that is designed for acquiring and tracking all navigation satellites above the horizon. This nominal radiation pattern, however, is susceptible to interference that is present near or below the horizon. The second selectable radiation pattern of the dual-element antenna has comparatively higher gain toward zenith, and lower gain at and below the horizon to mitigate interference. This combination of features is packaged in a single antenna unit that can be a direct replacement for existing antennas. The dual-element antenna unit has a low vertical profile and is suitable for mounting on high-speed moving vehicles.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
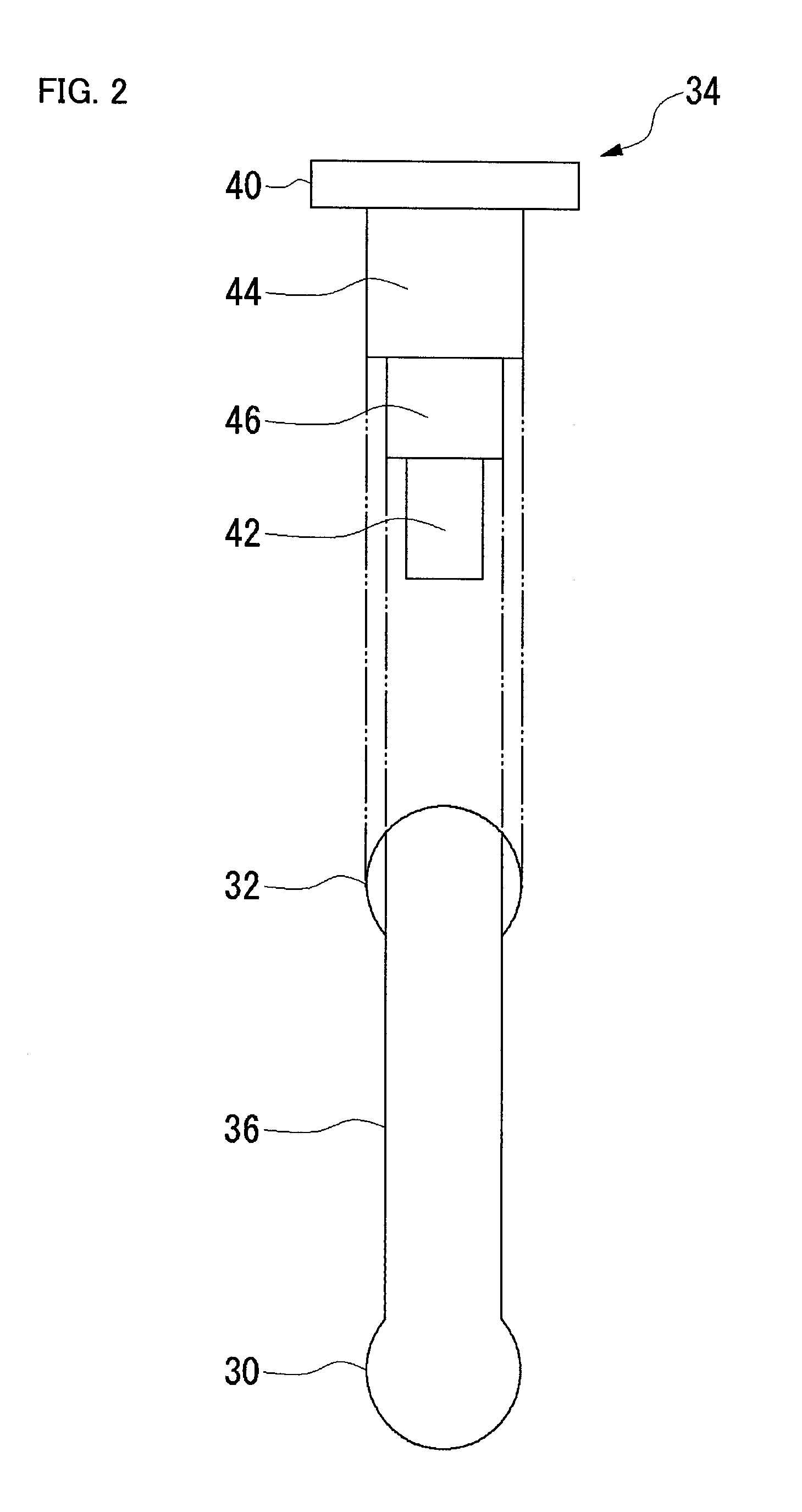
Dome type camera
The lens moving mechanism may be a cam structure. The cam structure is set so that the rotation axis of the lens is held at the center of the dome in a predetermined center hold angle range corresponding to the direction of an elevation angle, and that the rotation axis of the lens is moved from the center of the dome in the zenith direction at angles lower than the center hold angle range. Good images can be obtained even when shooting in the direction of a depression angle.
Owner:PANASONIC I PRO SENSING SOLUTIONS CO LTD
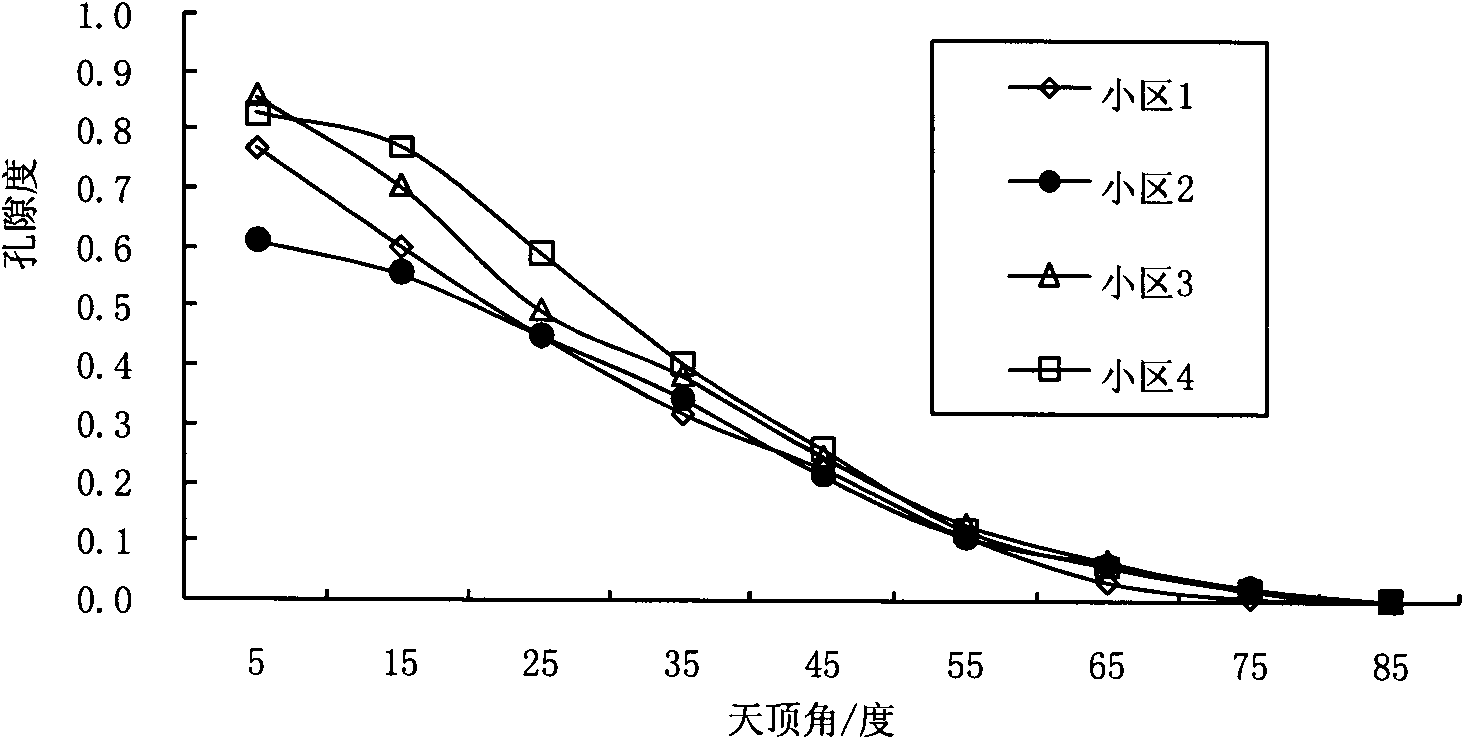
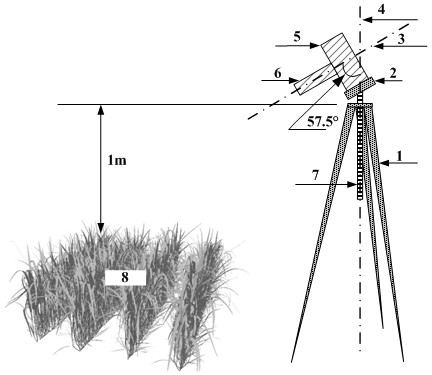
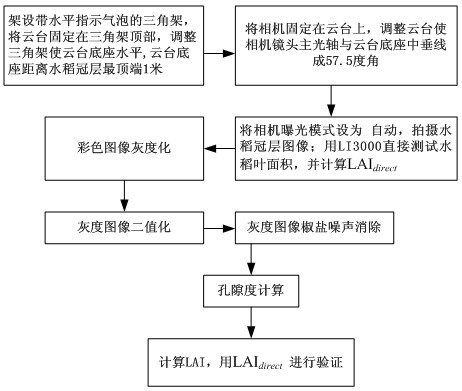
Method for obtaining leaf area index and average leaf inclination of rice canopy by using hemisphere photographic process
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the leaf area index and the average leaf inclination of rice canopy by using a hemisphere photographic process. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting a hemisphere image of rice canopy from bottom to top inside the rice canopy by using a digital hemisphere shooting system based on a fisheye lens; after performing gray conversion and binaryzation on the hemisphere image, obtaining the canopy porosity under the zenith angle at a viewing angle of 57 degrees, and calculating the rice canopies LAI and ALIA under the condition of the single zenith angle at the viewing angle of 57 degrees based on the Beer-Lambert law and a poisson model as well as the two characteristics of the blade projection function of the rice canopy; simulating the leaf inclination distribution of the rice canopy by an elliptic function and optimizing the rice canopies LAI and ALIA calculated by using the single-angle method so as to rapidly acquire the rice canopies LAI and ALIA. The rice canopies LAI and ALIA can be obtained in real time without picking up rice blade outdoors for destructive artificial measurement, and basic parameters for monitoring the rice growth in real time and remotely estimating the yield of rice are provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Scanning Electron Microscope System, Pattern Measurement Method Using Same, and Scanning Electron Microscope
ActiveUS20160379798A1High aspect ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectron microscopeCalibration curve
In order to allow detecting backscattered electrons (BSEs) generated from the bottom of a hole for determining whether a hole with a super high aspect ratio is opened or for inspecting and measuring the ratio of the top diameter to the bottom diameter of a hole, which are typified in 3D-NAND processes of opening a hole, a primary electron beam accelerated at a high accelerating voltage is applied to a sample. Backscattered electrons (BSEs) at a low angle (e.g. a zenith angle of five degrees or more) are detected. Thus, the bottom of a hole is observed using “penetrating BSEs” having been emitted from the bottom of the hole and penetrated the side wall. Using the characteristics in which a penetrating distance is relatively prolonged through a deep hole and the amount of penetrating BSEs is decreased to cause a dark image, a calibration curve expressing the relationship between a hole depth and the brightness is given to measure the hole depth.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
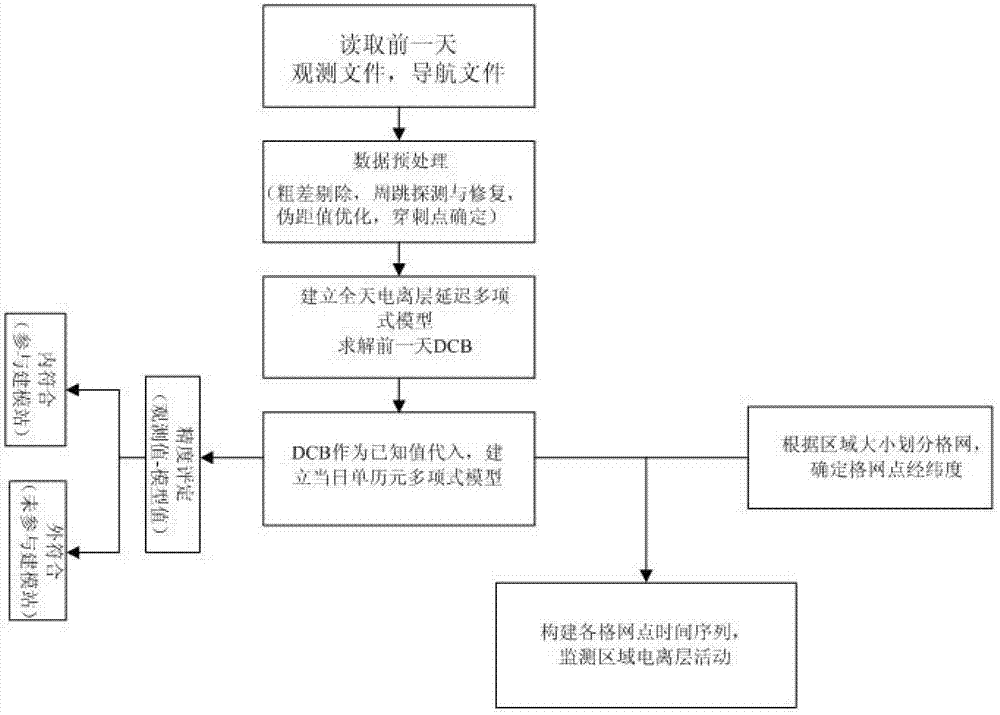
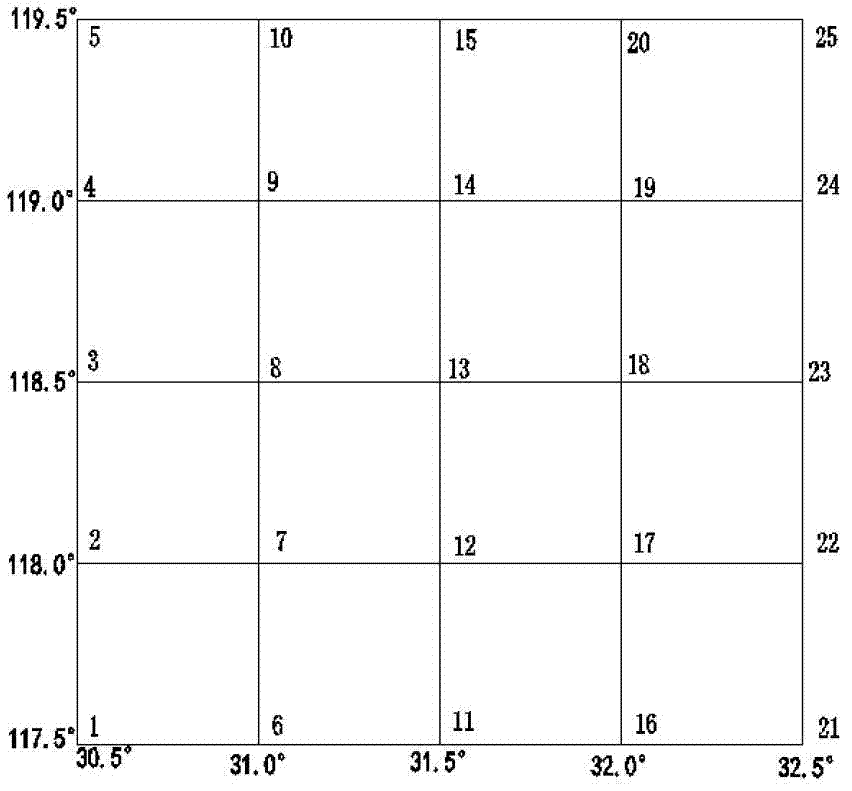
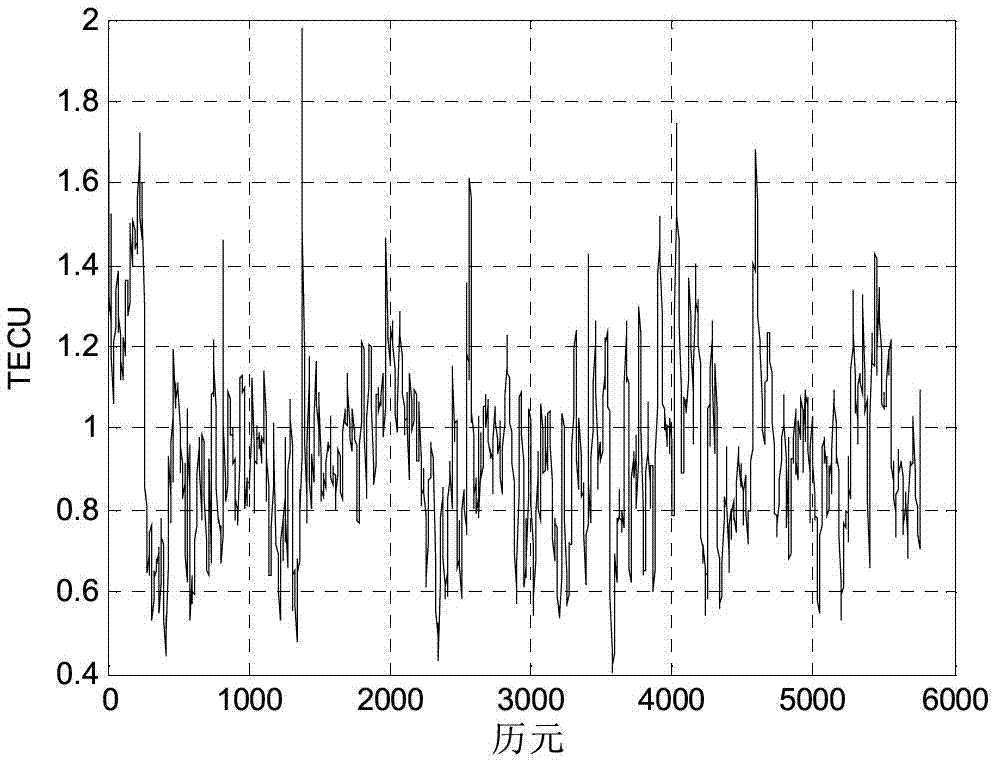
Gridding real-time monitoring method for total electron content of ionized layer
InactiveCN103197340AMonitoring changes in total electron contentExcellent internal coincidence accuracyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentIonosphereIonospheric total electron content
The invention discloses a gridding real-time monitoring method for total electron content of an ionized layer. The gridding real-time monitoring method for the total electron content of the ionized layer comprises the steps of firstly using data of a plurality of reference stations in a continuous operation reference station network to build a whole day ionized layer delay polynomial model, and resolving a receiver hardware delay of the day before and a satellite hardware delay of the day before; and then using the receiver hardware delay of the day before and the satellite hardware delay of the day before to correct the total content of electron concentration of the ionized layer on a satellite propagation path on the day of monitoring according to a characteristic that the receiver hardware delay and the satellite hardware delay are stable, and building a single epoch multi-station polynomial model to monitor changes of the total electron content of the ionized layer in the zenith direction of a grid point after gridding in real time. Experiment results of all epochs in a whole day indicate that inner coincidence precision of the gridding real-time monitoring method for the total electron content of the ionized layer is averagely superior to 1TECU, and outer coincidence precision of the gridding real-time monitoring method for the total electron content of the ionized layer is averagely 1TECU.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
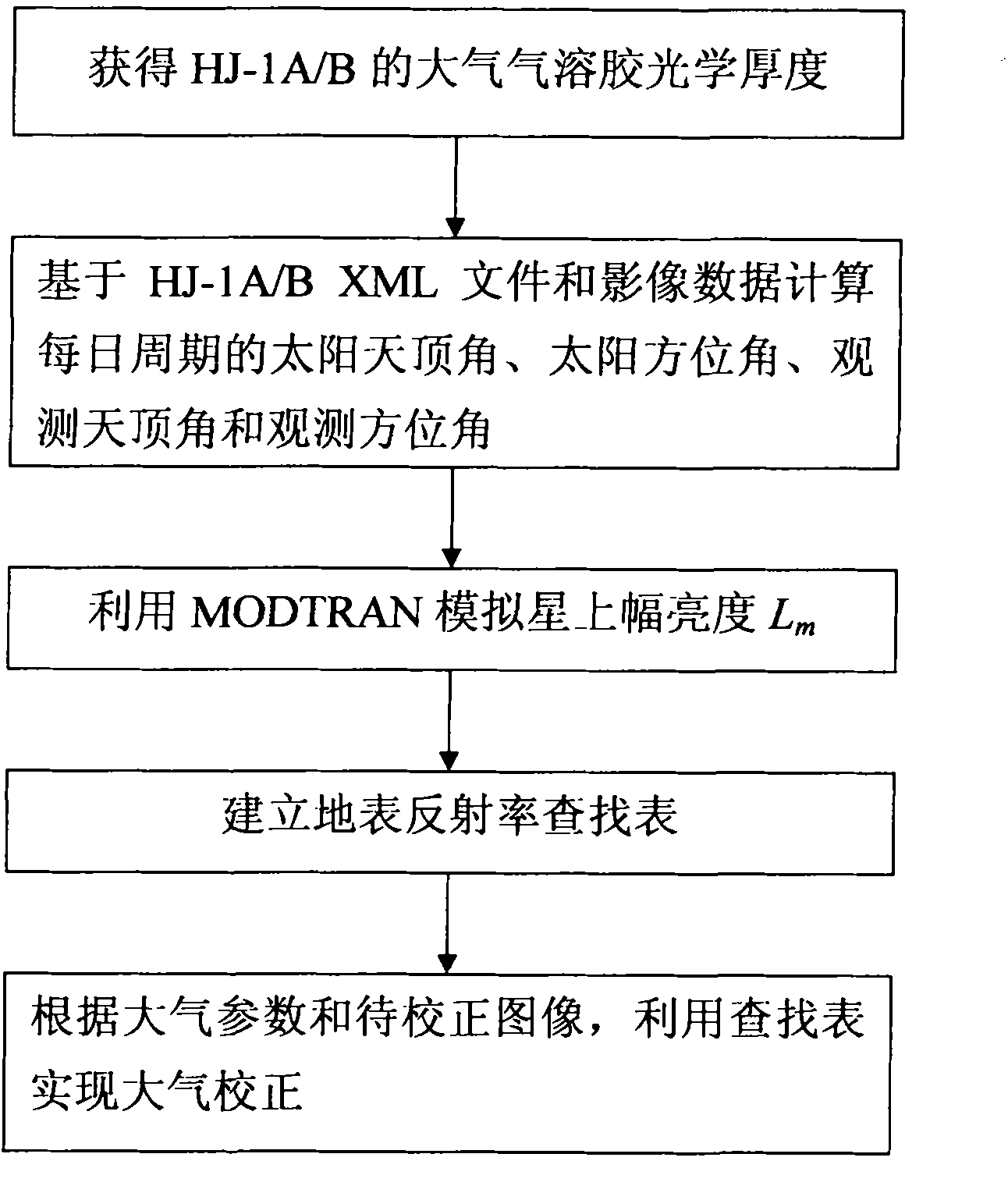
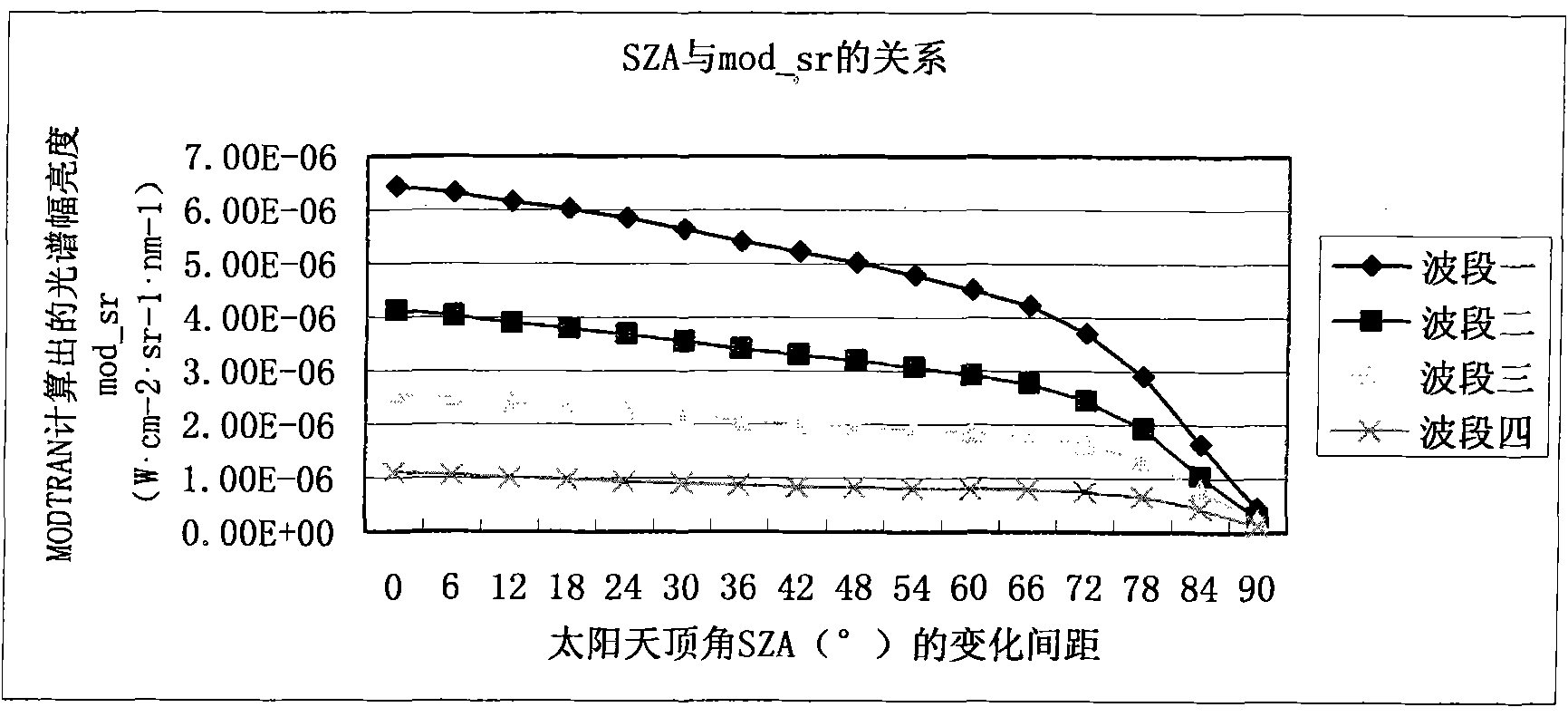
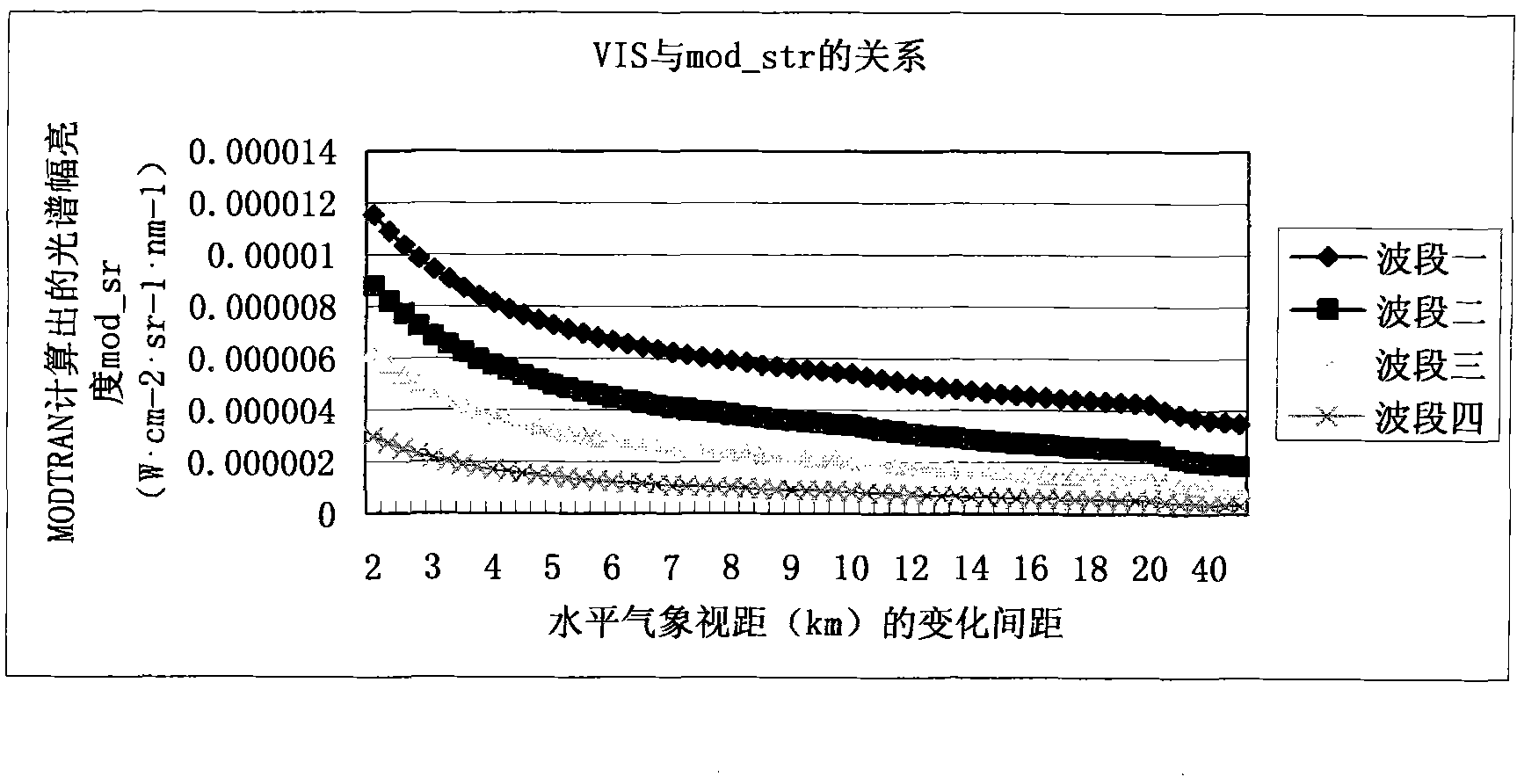
Method and device for calculating reflectivity of earth surface
InactiveCN102338871AImprove accuracyEliminate AbsorbencyWave based measurement systemsMiddle infraredExtensible markup
The invention relates to a method and a device for calculating the reflectivity of an earth surface, which are used for HJ-1A / B satellites. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring the optical thickness of atmospheric aerosol by using middle-infrared bands of an HJ-1B charge coupled device (CCD) and an infrared camera on the basis of a dark target method, and acquiring the optical thickness of the atmospheric aerosol by using an HJ-1A large-width quick revisit characteristic on the basis of an invariant target method; 2) calculating a solar zenith angle and a solar azimuth angle and observing the zenith angle and the azimuth angle on the basis of an HJ-1A / binary extensible markup language (BXML) file and image data; 3) simulating radiance Lm on a star through moderate resolution atmospheric transmission (MODTRAN) on the basis of parameters acquired in the steps 1) and 2); 4) establishing an earth surface reflectivity lookup table through the step 3); and 5) calibrating the atmosphere by using the lookup table according to an atmospheric parameter and an image to be calibrated. By the method and the device, the absorbing and scattering performance of the atmosphere on a remote sensing image can be effectively eliminated, the reflectivity of an earth surface target can be recovered, the bottleneck of industry application is eliminated, and the application range of environment disaster reduction moonlet data is further expanded.
Owner:曹春香 +2
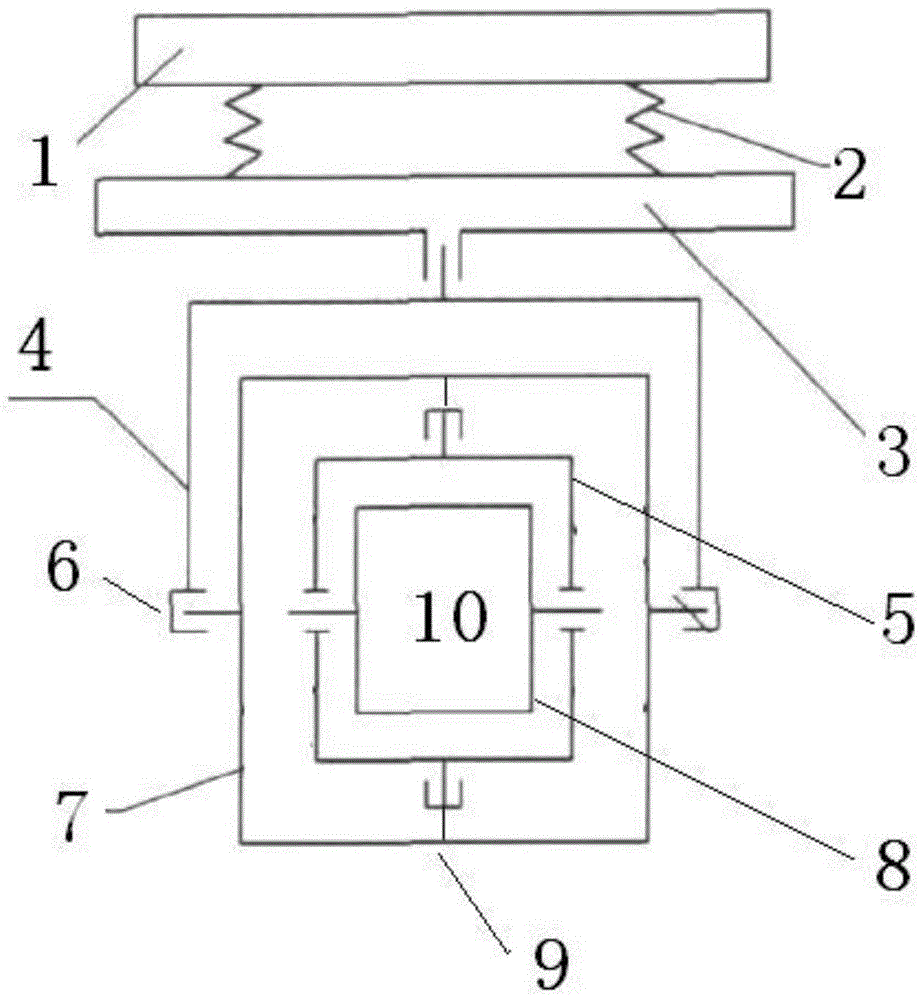
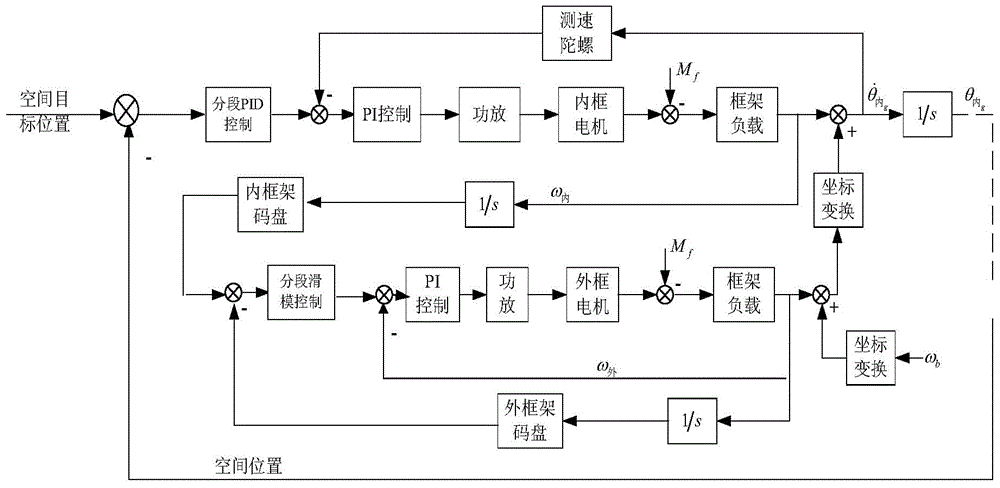
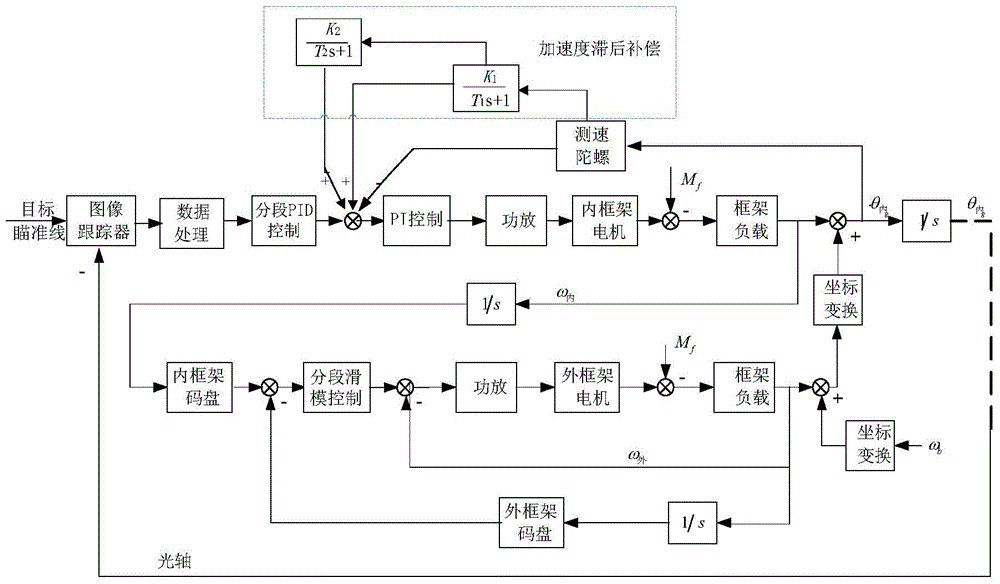
Servo control method and system of two-axis four-frame optoelectronic pod
The invention belongs to the servo control technique of an airborne optoelectronic pod, particularly relates to a platform stabilizing technique and a high-precision optoelectronic tracking control technique of a two-axis four-frame optoelectronic pod, and provides a servo control method and system of the two-axis four-frame optoelectronic pod. The inner-outer frame linkage platform stabilization control technique is designed firstly to enable the pod to have good platform stability, the platform stabilization control technique can guarantee that an inner direction frame and an inner pitching frame to be perpendicular to each other constantly, geometry restraining coupling of the pot frames is reduced, and the optoelectronic pod is enabled to have good platform stability during zenith pass; on the basis, the inner-outer frame linkage optoelectronic tracking control technique is designed as well, and finally high-precision and high-stability optoelectronic tracking control of the optoelectronic pod is realized. The method and system serving as the key servo control technique applicable to the two-axis four-frame optoelectronic pod has good application prospect and brings high economic benefits and military benefits.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
Method for interactively playing panoramic video stream on CAVE projection system
InactiveCN101852980ASolve the problem that the panoramic video stream cannot be interactively played directly on the CAVE projection systemSimple methodTelevision system detailsColor television detailsProjection screenVirtual camera
The invention discloses a method for interactively playing a panoramic video stream on a CAVE projection system, which belongs to the technical field of digital media. A conventional 360-degree panoramic video browser does not support the interactive play of the panoramic video stream on the CAVE projection system. The method comprises the following steps of: mapping panoramic picture images onto a 3D sphere as textures, splitting a 360-degree all-round spherical view field into six sub-areas, and shooting a front sub-area, a rear sub-area, a left sub-area, a right sub-area and a zenith sub-area respectively by using five different virtual cameras to obtain the pictures on each projection screen of the CAVE projection system respectively. The method has the advantage of the capacity of solving the problem that the panoramic video stream cannot be interactively played on the CAVE projection system, simplicity, practicability, no need of expensive special equipment, real-time interaction capacity, relatively lower implementation cost and convenient popularization and application.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
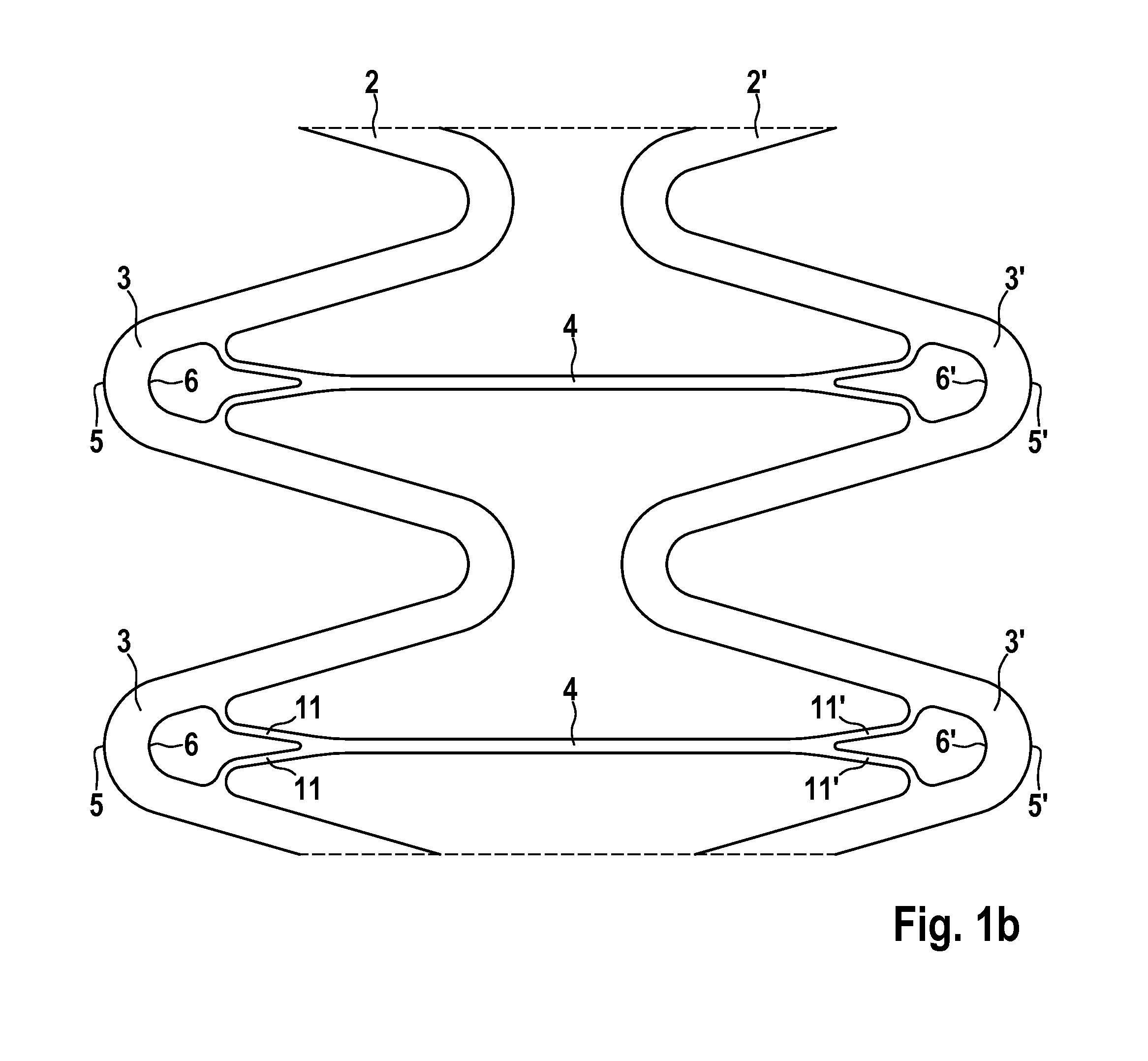
Stent having improved stent design
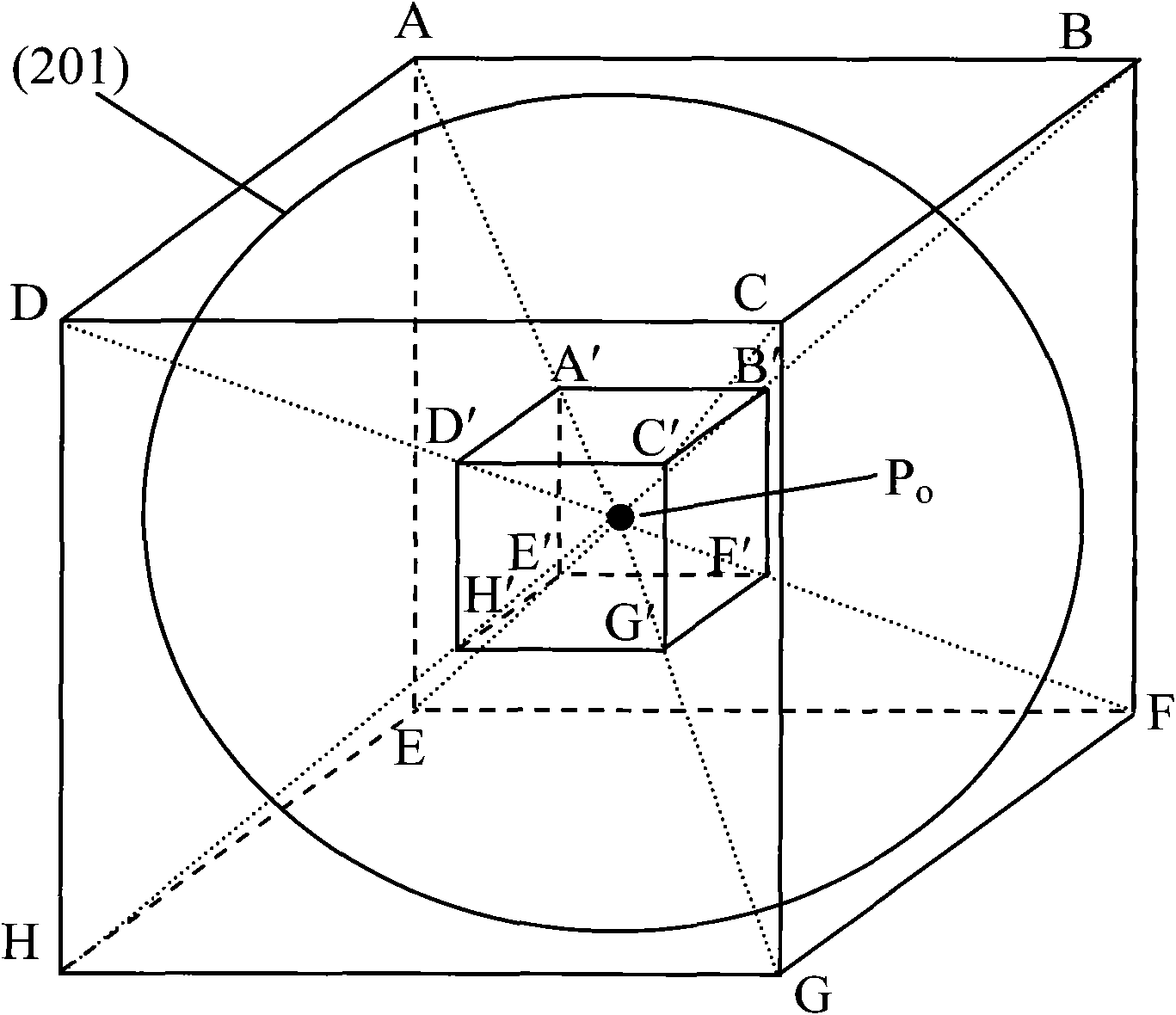
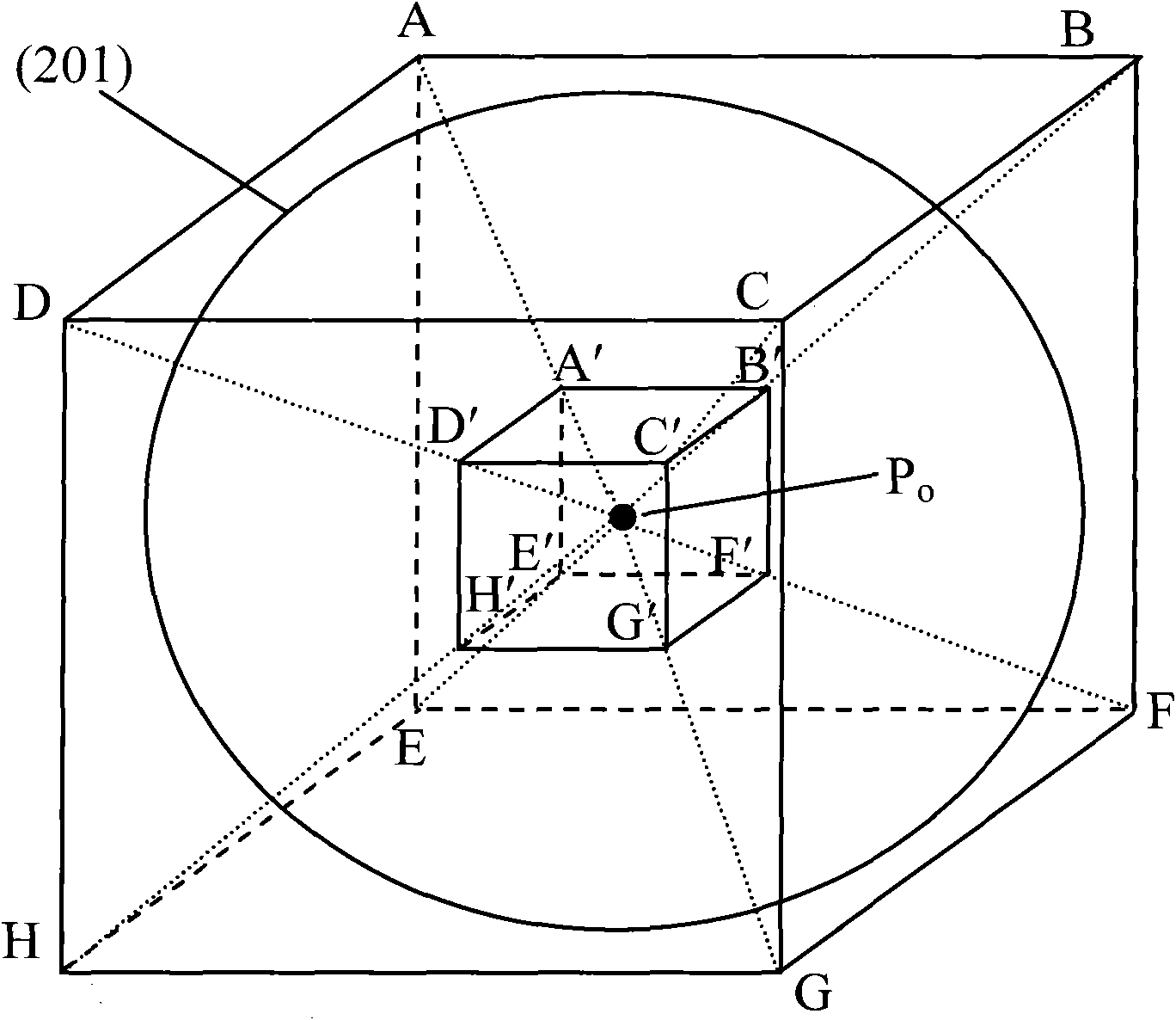
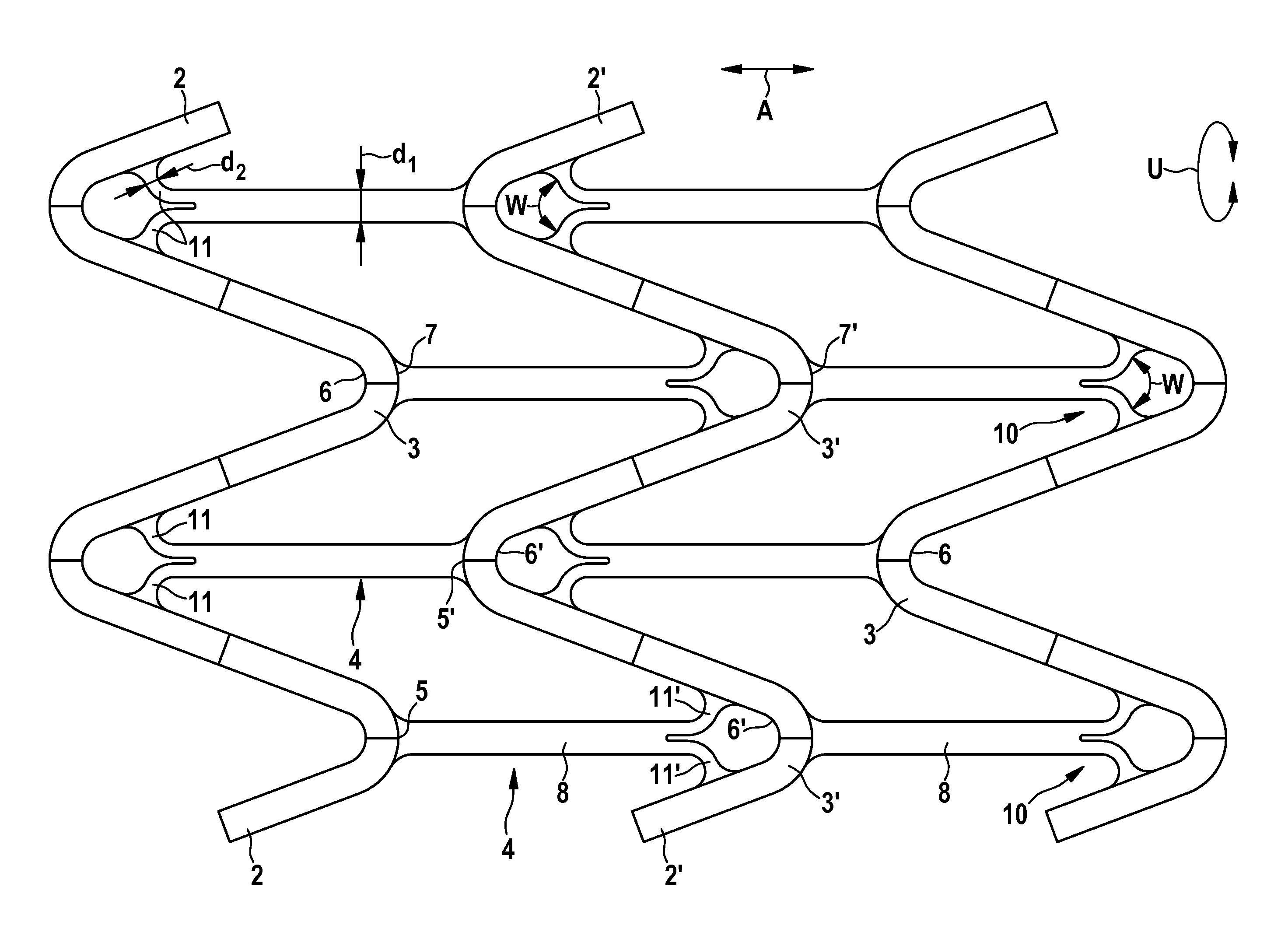
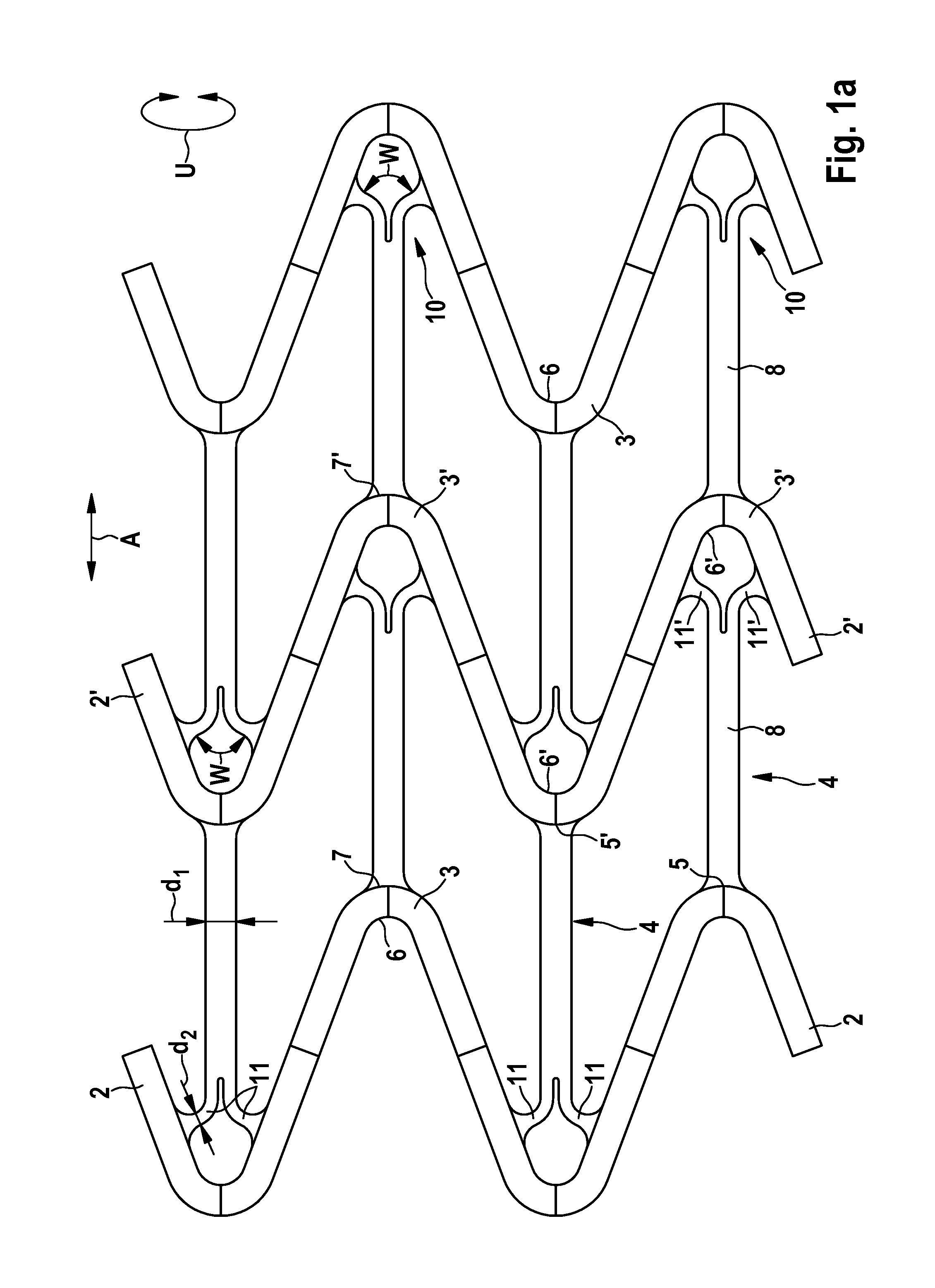
A stent is provided having a base body circumscribing a cylindrical shape and radially expandable from a contracted starting position into a dilated support position, including a plurality of meander-shaped struts disposed in the circumferential direction and arrayed on one another in the axial direction, each strut being meander-shaped in its coarse structure and made of a flexible material, and at least one axial connector in the axial direction, connecting the meander-shaped struts of two axially adjacent meandering curves, wherein the at least one axial connector connects the inside radius of a zenith point of a first meandering curve with a second meandering curve, characterized in that the at least one axial connector at the inside radius of the zenith point of the first meandering curve has an at least double-arm structure.
Owner:BIOTRONIK AG
Non-horizontalization free established station for total station and project measurement method of non-horizontalization free established station
The invention discloses a non-horizontalization free established station for a total station and a project measurement method of the non-horizontalization free established station. The invention belongs to the technical field of project measurement. The non-horizontalization free established station for the total station and the project measurement method are characterized in that (1) the total station is in a non-horizontal working gesture; the total station is operated to measure a slope distance, a horizontal angle and a zenith distance of at least thee geodetic datums; (2), according to the obtained measurement information of geodetic datums, a three-dimensional geodetic coordinate and gesture information of a total station point are obtained by using the method of non-horizontalization free established station for the total station; (3) the total station measures a point to be tested by the non-horizontal working gesture, and obtains the three-dimensional geodetic coordinate of the point to be tested through the measurement method of a non-horizontalization project of the total station. The invention solves technical problems of establishing a station, lofting and measuring only after flattening the total station in advance during project measurement, realizes the non-horizontalization free established station for the total station and project measurement of the non-horizontalization free established station; operation is simple; efficiency of field lofting and measuring works can be obviously improved.
Owner:JIANGXI EVERBRIGHT MEASUREMENT & CONTROL TECH CO LTD
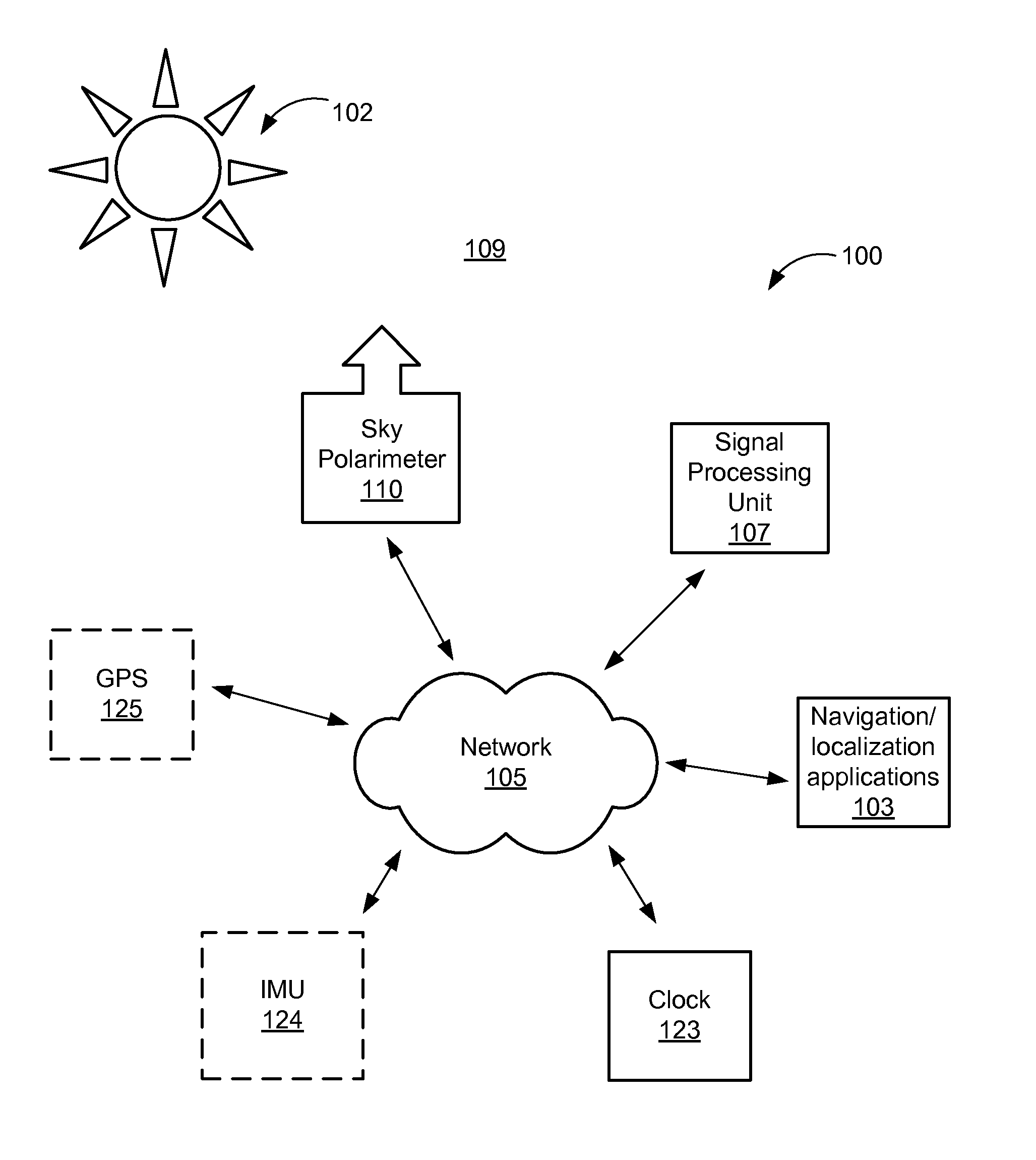
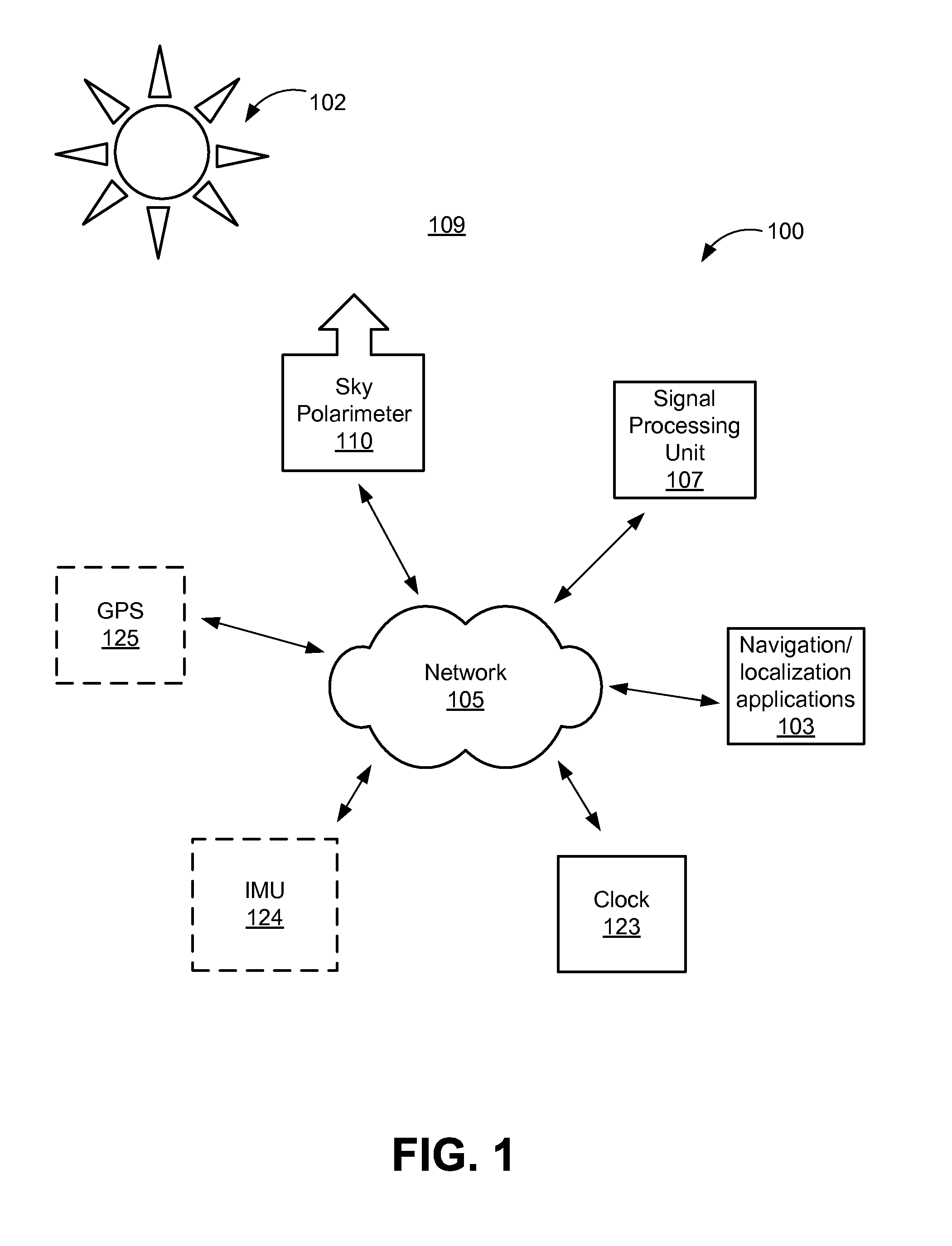
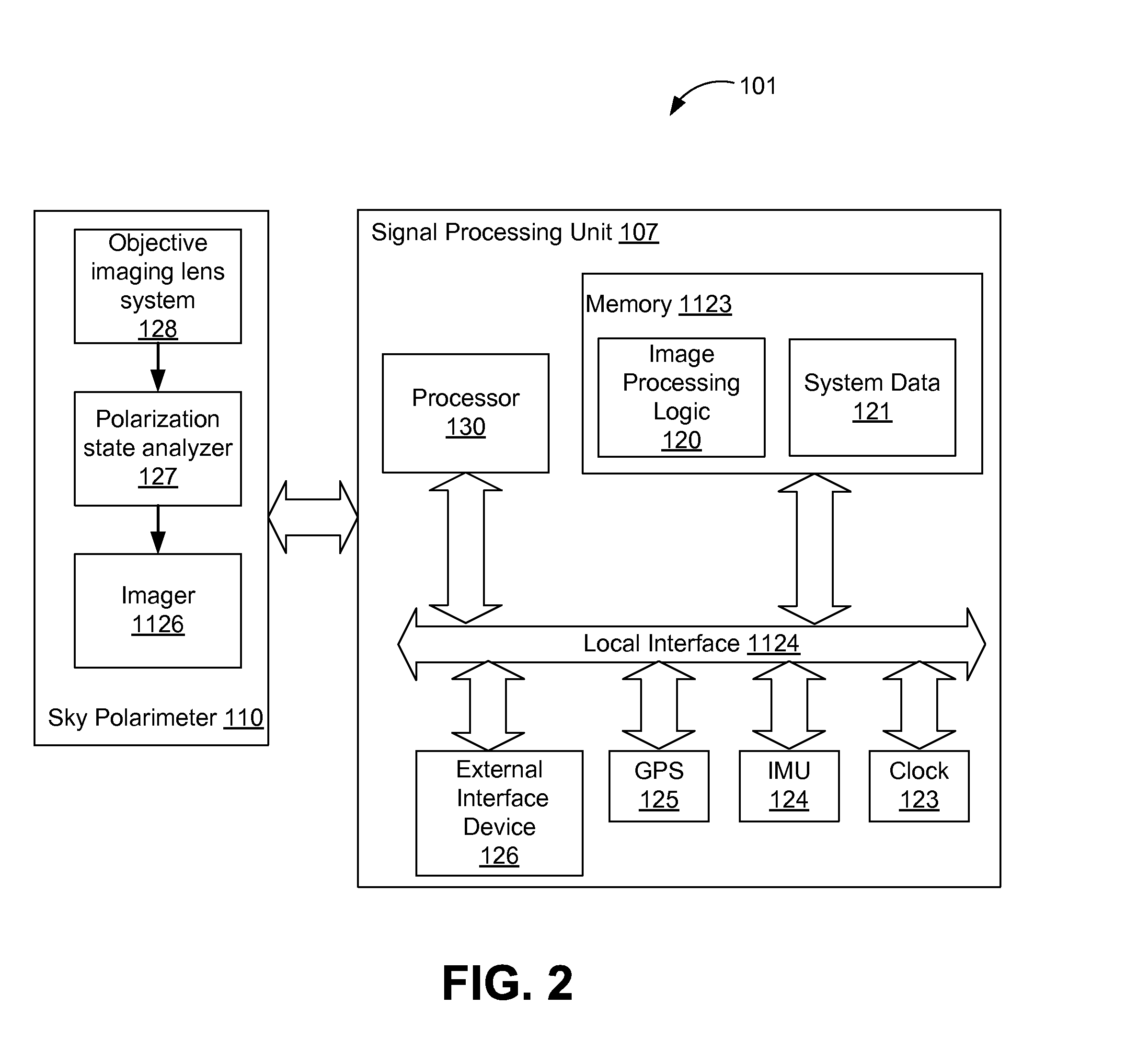
Sky Polarization and Sun Sensor System and Method
A system for determining a new orientation and / or position of an object comprises a sky polarimeter configured to record image data of the sky, a signal processing unit, and logic configured to receive and store in memory the image data received from the sky polarimeter. The logic calculates the Stokes parameters (S0, S1, S2,), DoLP, and AoP from the image data, detects obscurants and filters the obscurants (such as clouds and trees) from the image data to produce a filtered image. The logic is further configured to find the Sun and zenith in the filtered image, and to determine the roll, pitch, yaw, latitude and longitude of the object using the filtered image. A method for determining a new position / orientation of an object comprises recording raw image data using a sky polarimeter, calculating S0, S1, S2, DoLP, and AoP from the image data, detecting obscurants and filtering the obscurants from the image data to produce a filtered image, obtaining last known position / orientation data of the object, finding the Sun and zenith in the filtered image, and determining the roll, pitch, yaw, latitude and longitude of the object using the filtered image.
Owner:POLARIS SENSOR TECH
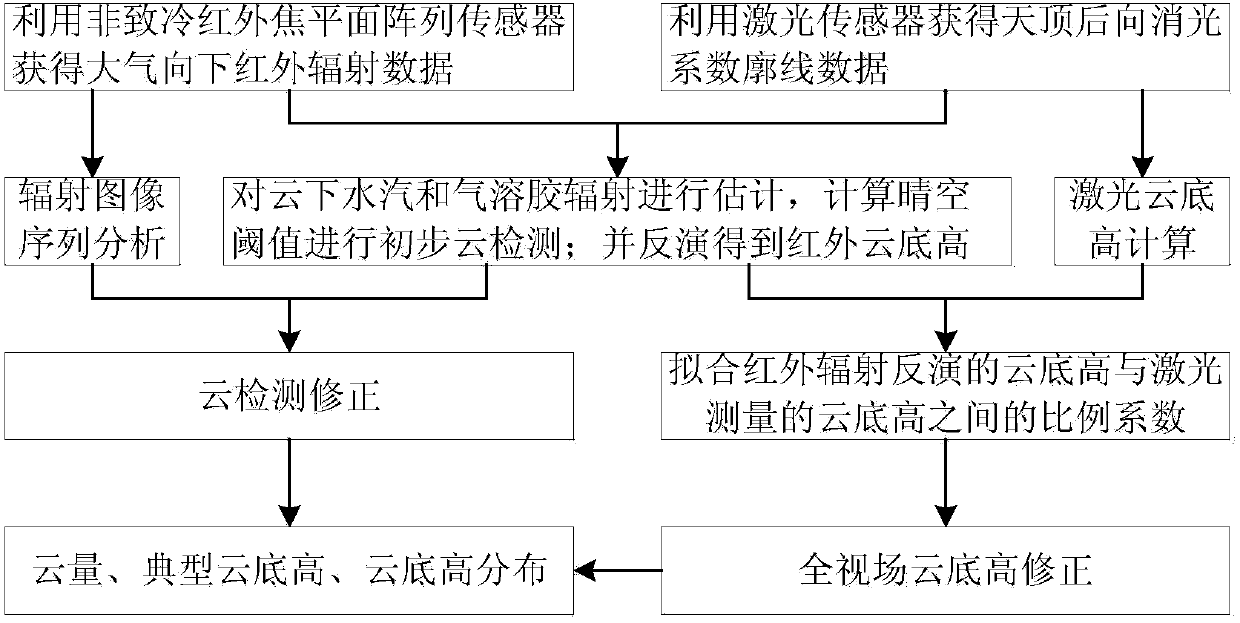
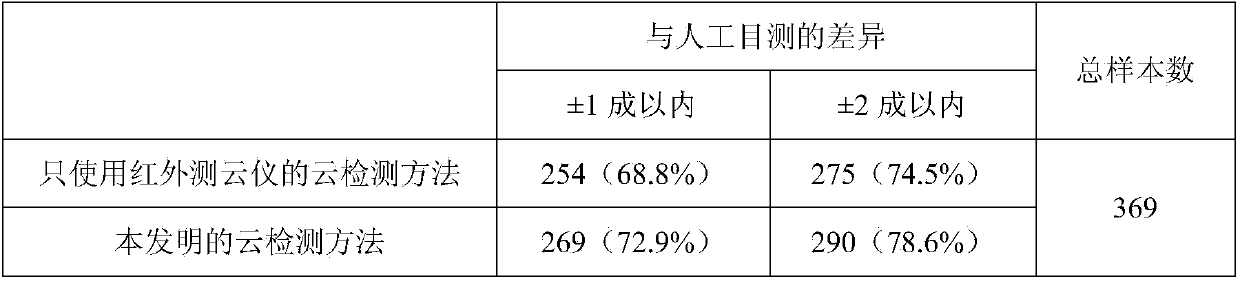
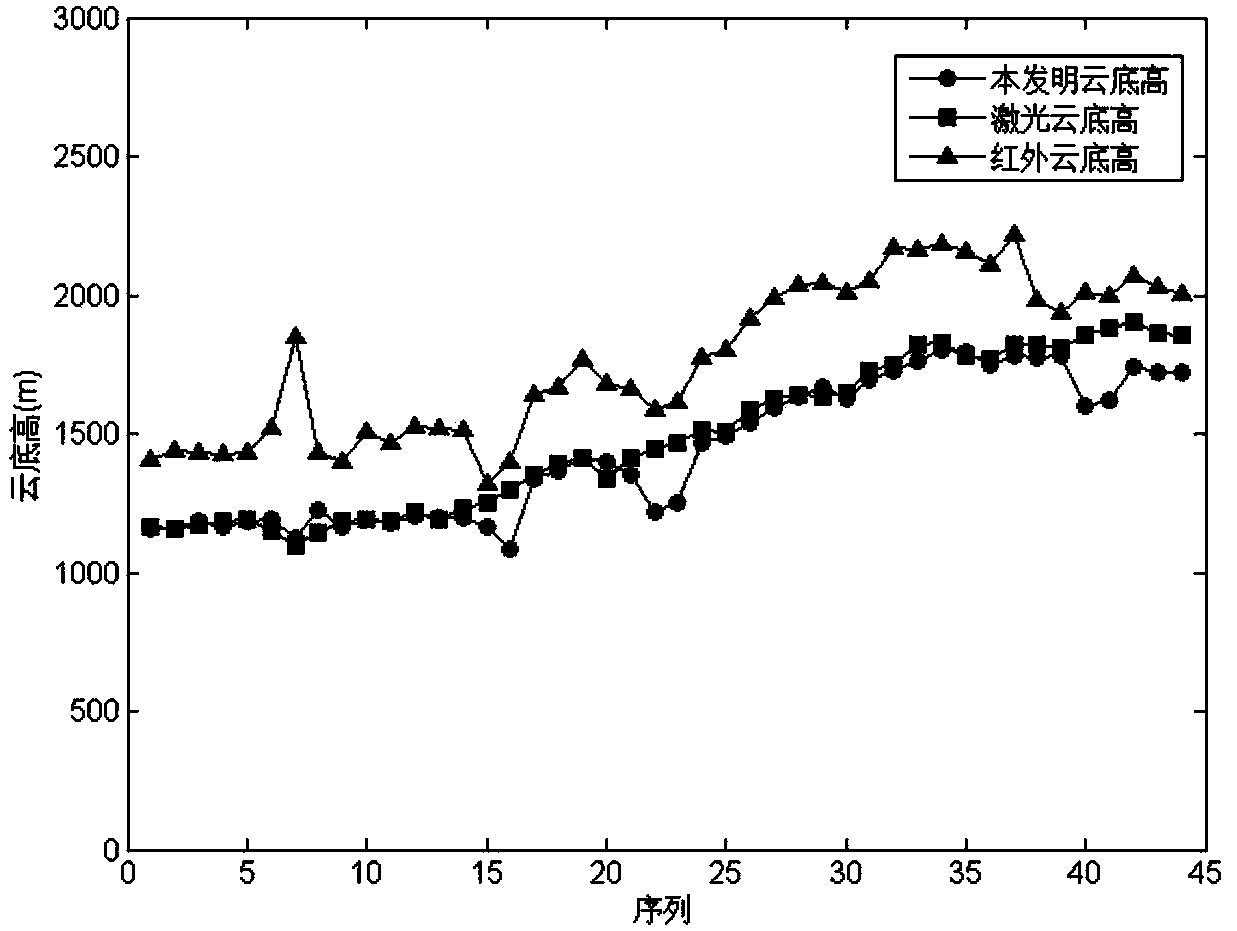
Foundation cloud measuring method combining infrared and lasers
InactiveCN104181612AEasy to detectAccurate estimateElectromagnetic wave reradiationSpecial data processing applicationsExtinctionWater vapor
A foundation cloud measuring method combining infrared and lasers comprises the following steps that (1) atmosphere downward infrared radiation data are obtained through an uncooled infrared focal planar array sensor, zenith backward extinction coefficient profile data are obtained through a laser sensor, and the obtaining time of the atmosphere downward infrared radiation data is synchronous with the obtaining time of the zenith backward extinction coefficient profile data; (2) water vapor and aerosol radiation under cloud are estimated by combining the data, clear sky threshold values calculated through a radiation transmission pattern are used for conducting initial cloud detection, it is assumed that the cloud is a black body, and the cloud base height is obtained through inversion; (3) sequence analysis is conducted on infrared radiation images with high time resolution, the clear sky threshold values are combined to conduct further cloud detection, and the cloud cover is calculated; (4) proportionality coefficients between the cloud base height obtained through the infrared radiation inversion and the cloud base height obtained through laser measurement are fitted; (5) the cloud base height of a whole view field is corrected, and the typical cloud base heights of every ten minutes are obtained through calculation.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
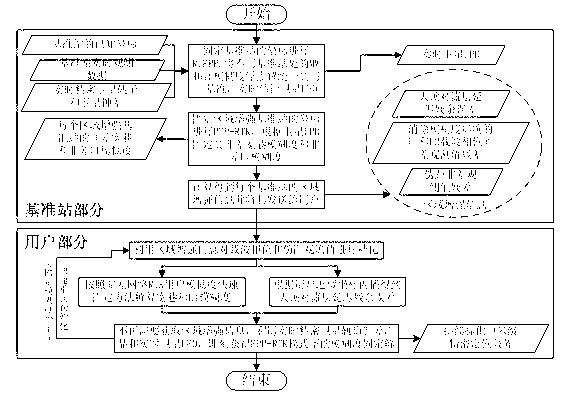
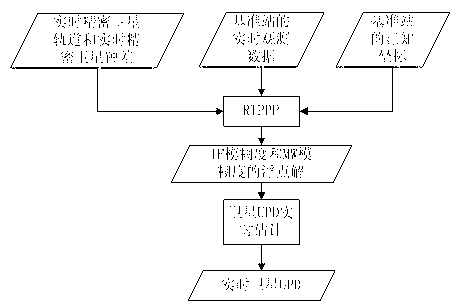
Area enhanced precision positioning service method suitable for large-scale users
InactiveCN103344978ASolve the burden of real-time data communicationIncrease the number ofSatellite radio beaconingTroposphereReal-time data
The invention discloses an area enhanced precision positioning service method suitable for large-scale users. According to the technical scheme, the method includes the steps that after the users effectively fix wide-lane ambiguity and L1 ambiguity of at least four satellites in a zero difference network RTK processing mode, area enhanced information of surrounding base stations does not need to be acquired, at this moment ambiguity fixed results and zenith troposphere delay residual errors acquired by interpolation are used as known truth values, received satellite UPD information is combined, and an ambiguity fixed solution in a PP-RTK mode can be immediately acquired without initialization. Due to the fact that satellite UPD, real-time satellite orbits and real-time satellite clock errors are only related to the satellites, and short-term forecast lasting tens of seconds to a few minutes can be conducted, the information can be broadcasted to the users through the communication satellites in a broadcast mode, and then real-time data communication burdens among the users and the base stations can be greatly reduced. Once user ambiguity is firstly fixed, the number of the users simultaneously serviced by an area enhanced system is no longer restricted at this moment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
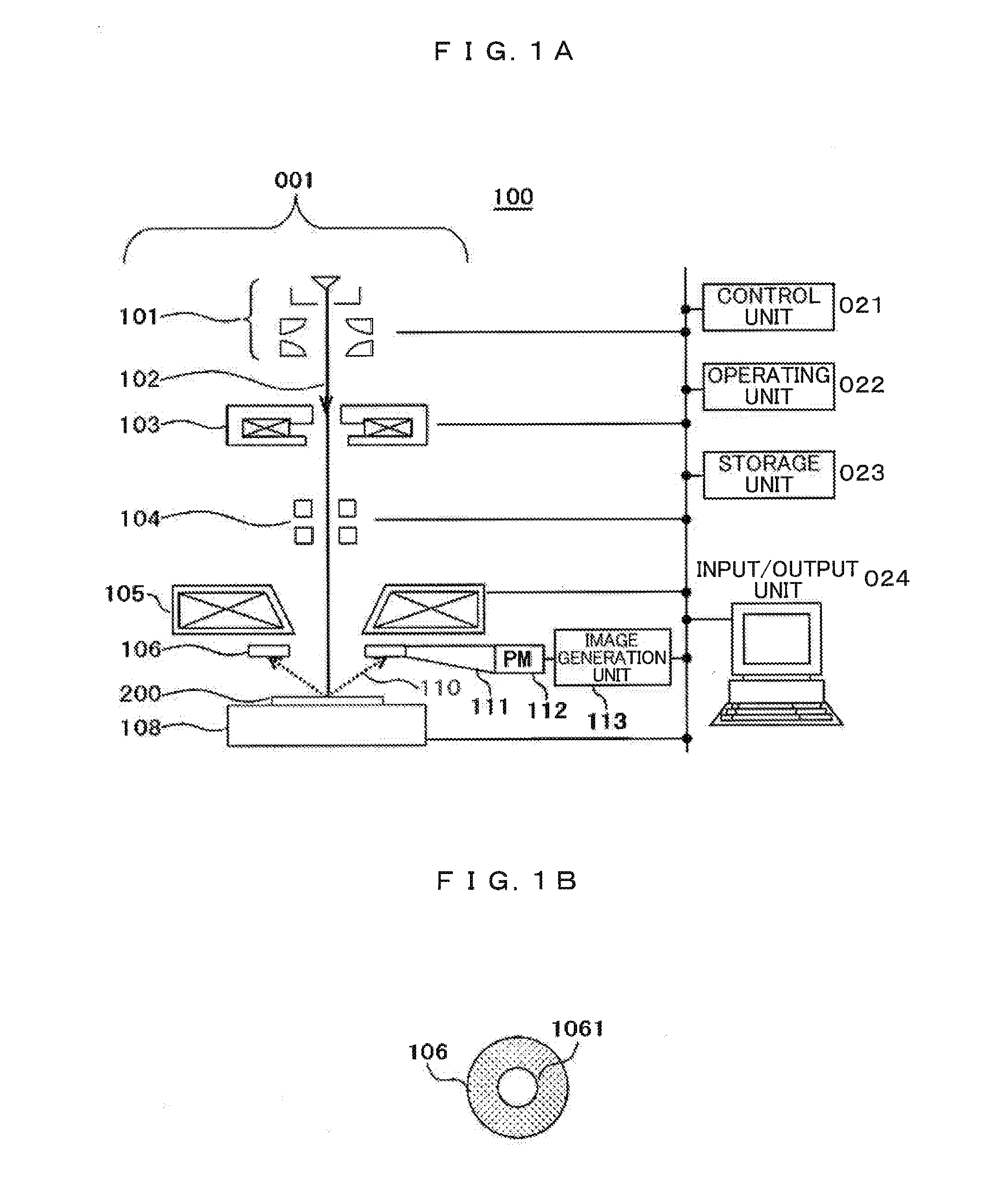
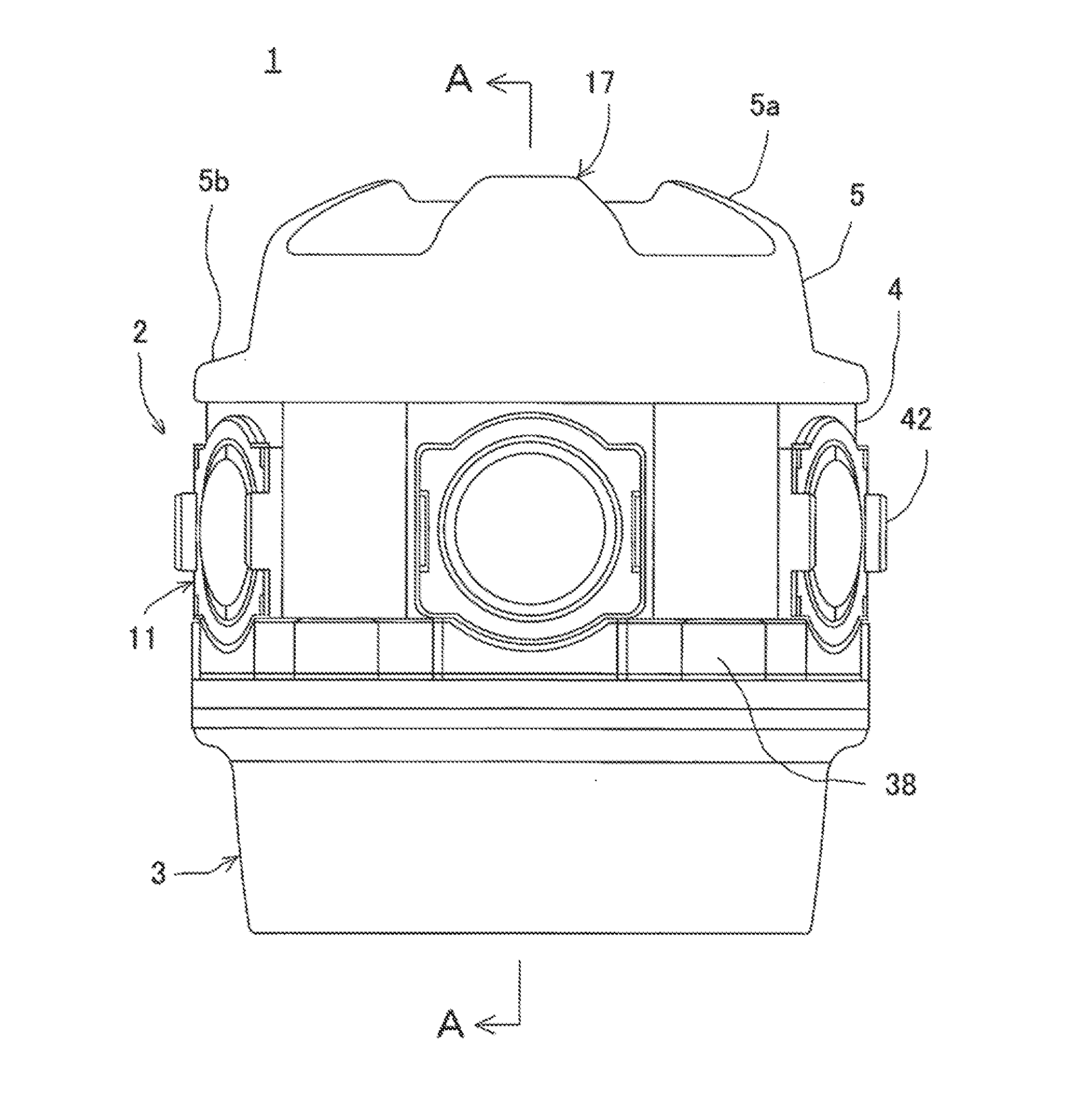
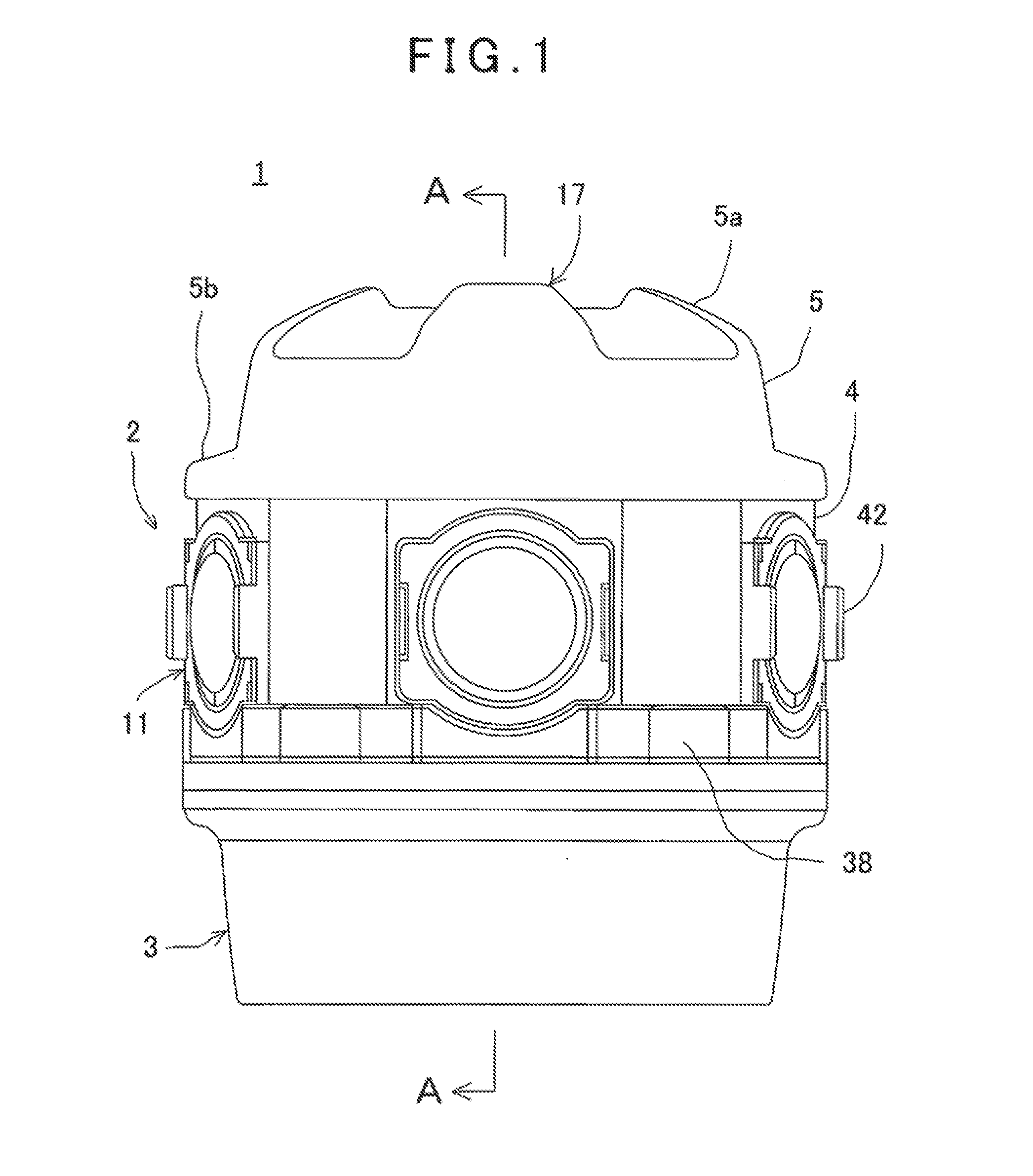
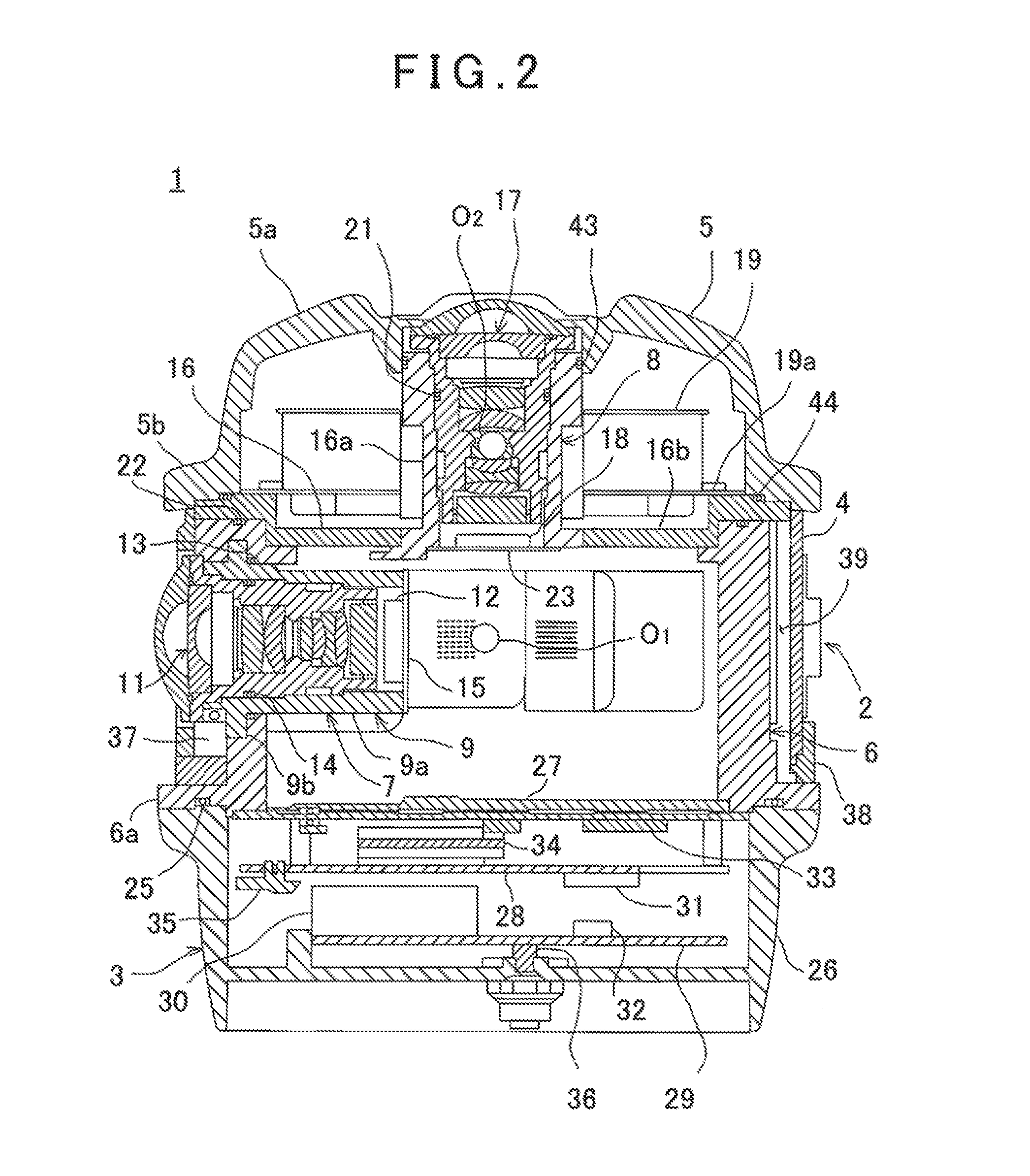
Omnidirectional Camera
ActiveUS20140160274A1Prevent deviationReduce measurementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOmnidirectional antennaComputer vision
An omnidirectional camera comprises a camera mounting frame 6 of cylindrical hollow body, a plurality of horizontal camera units 7 each of which is provided on a horizontal plane orthogonal to a center line of the camera mounting frame 6 and adapted to acquire an image in a horizontal direction, a vertical camera unit 8 provided so as to coincide with the center line of the camera mounting frame 6 and adapted to acquire an image in a zenith direction, and a ring-like GPS antenna 19 provided so as to surround the vertical camera unit 8.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Modeling method and device for zenith tropospheric delay as well as measuring method and device
ActiveCN104777488AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingTroposphereLongitude
The invention provides a modeling method for zenith tropospheric delay. The modeling method comprises the following steps: S11, obtaining a zenith tropospheric delay amount actually measured in each observation station; S12, calculating an annular mean value ZTDh of the zenith tropospheric delay amount corresponding to the observation station, fitting based on ZTDh to obtain an elevation correction coefficient beta and an annular mean delay amount ZTD0 naturalized to an ellipsoidal surface, corresponding to the observation station, and obtaining a single-day delay amount ZTD0(doy) after elevation correction, corresponding to the observation station according to the beta; S13, fitting based on ZTD0(doy) to obtain a period constant term A0, amplitude and initial phases A1 and d1 of an annual periodic term as well as amplitude and initial phases A2 and d2 of a semi-annual periodic term, corresponding to the observation station; S14, building a latitude and longitude grid function model based on the Chinese mainland area, and calculating based on the parameters A0, A1, d1, A2 and d2 corresponding to the observation station to obtain A0, A1, d1, A2 and d2 corresponding to each grid point in the grid function model. The modeling method is suitable for the Chinese mainland area, the precision is remarkably improved, and the overall service level of a satellite navigation positioning system of the Chinese mainland area can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Rapid ambiguity determination method among network RTK reference stations of big-dipper three-frequency signal
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Steerable leaky wave antenna capable of both forward and backward radiation
ActiveUS20060187126A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsHorizonBeam steering
Leaky wave antenna beam steering that is capable of steering in a backward direction, as well as further down toward the horizon in the forward direction than was previously possible, and also directly toward zenith. The disclosed antenna and method involve applying a non-uniform impedance function across a tunable impedance surface in order to obtain such leaky wave beam steering.
Owner:HRL LAB
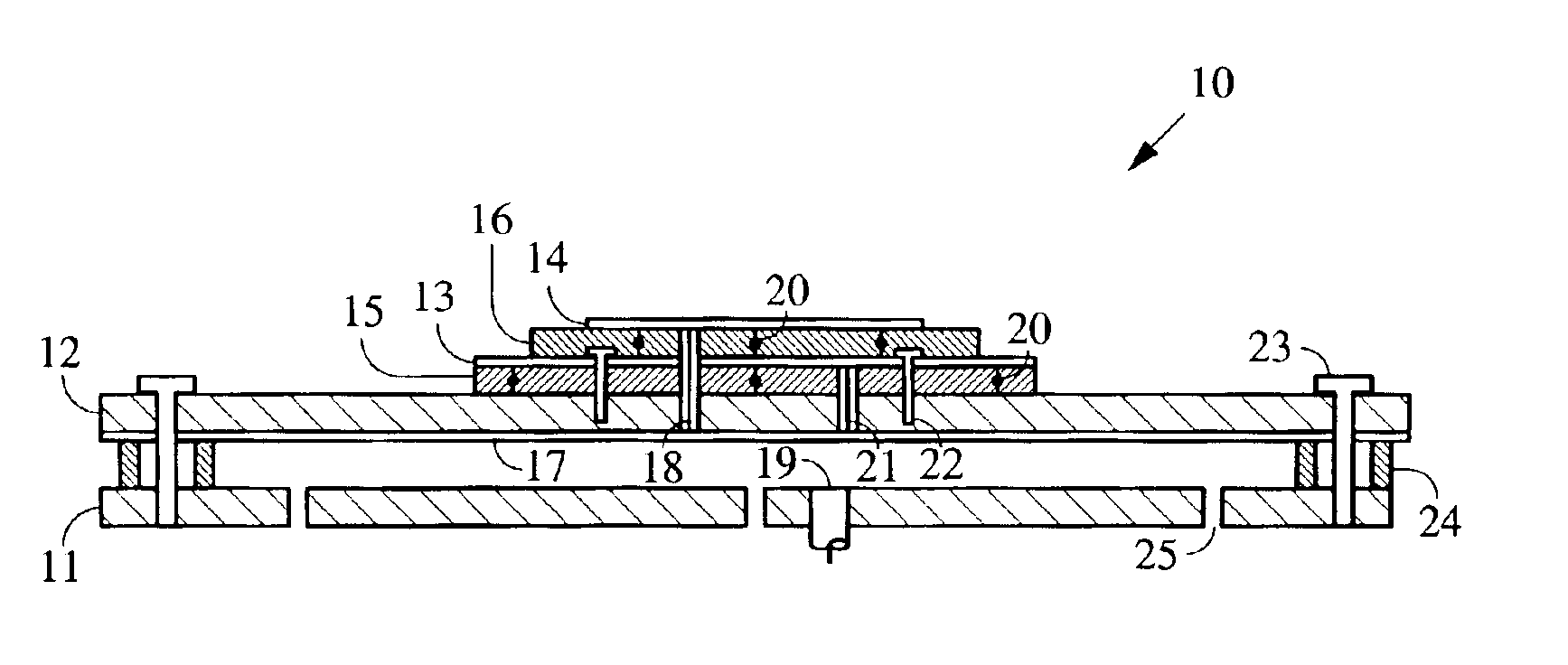
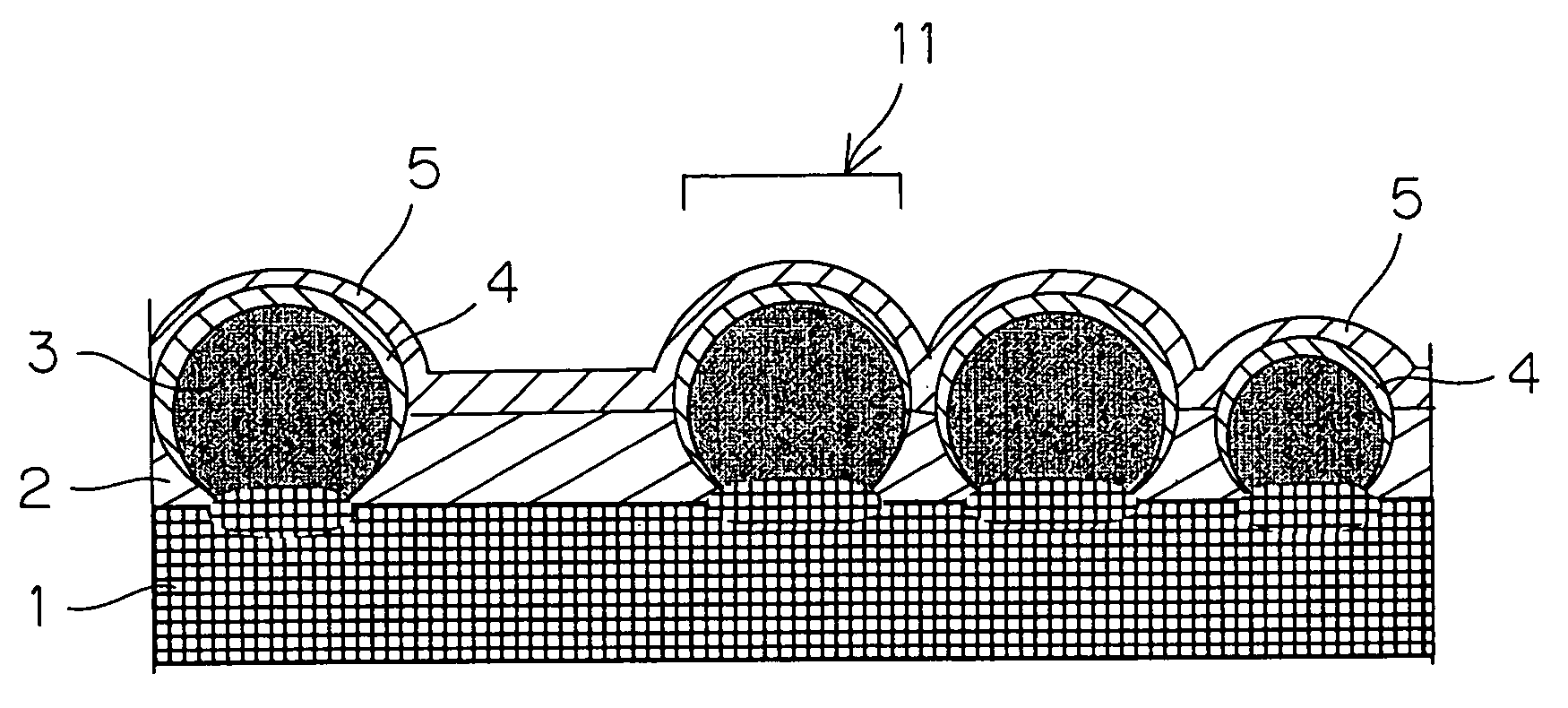
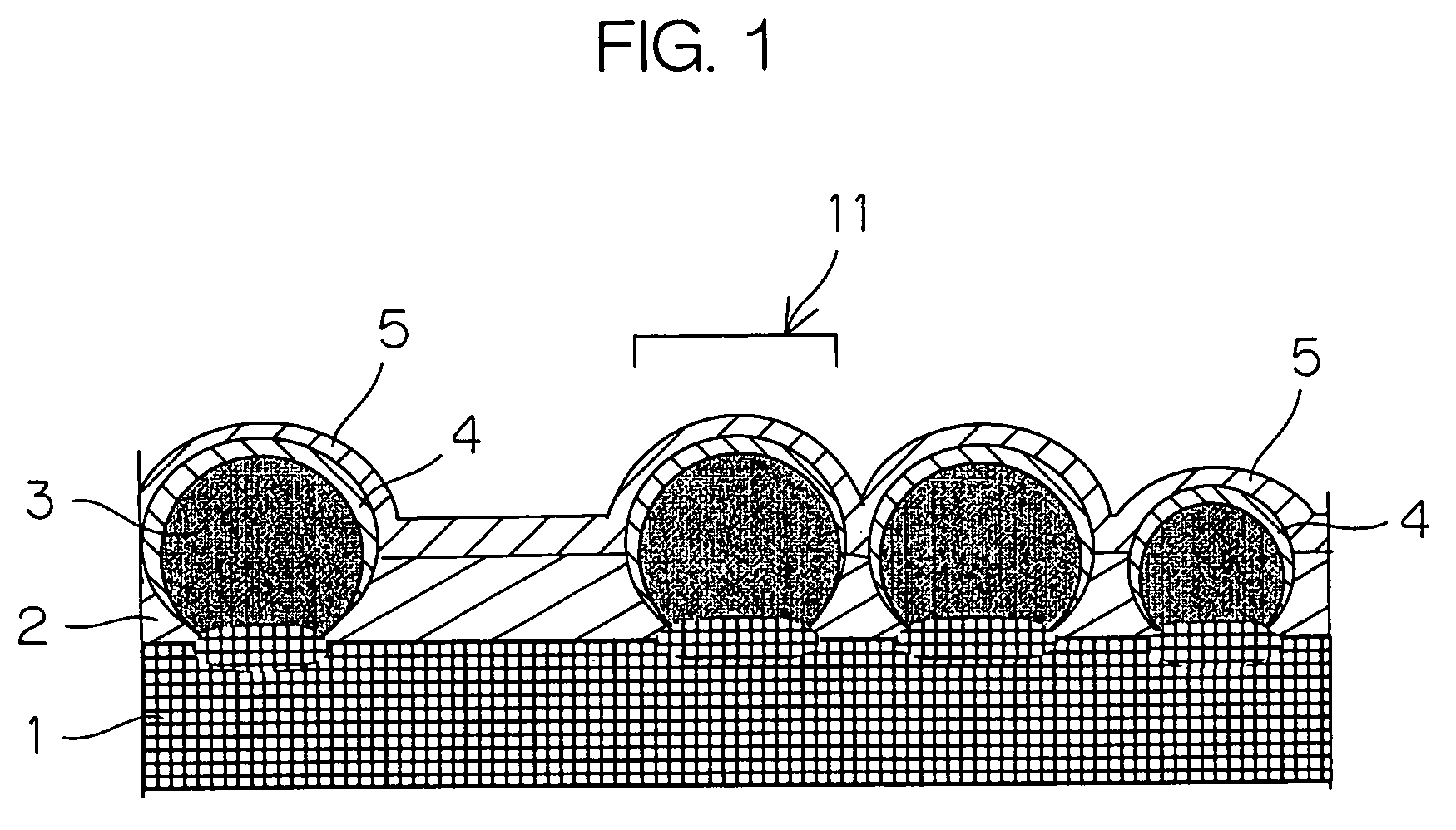
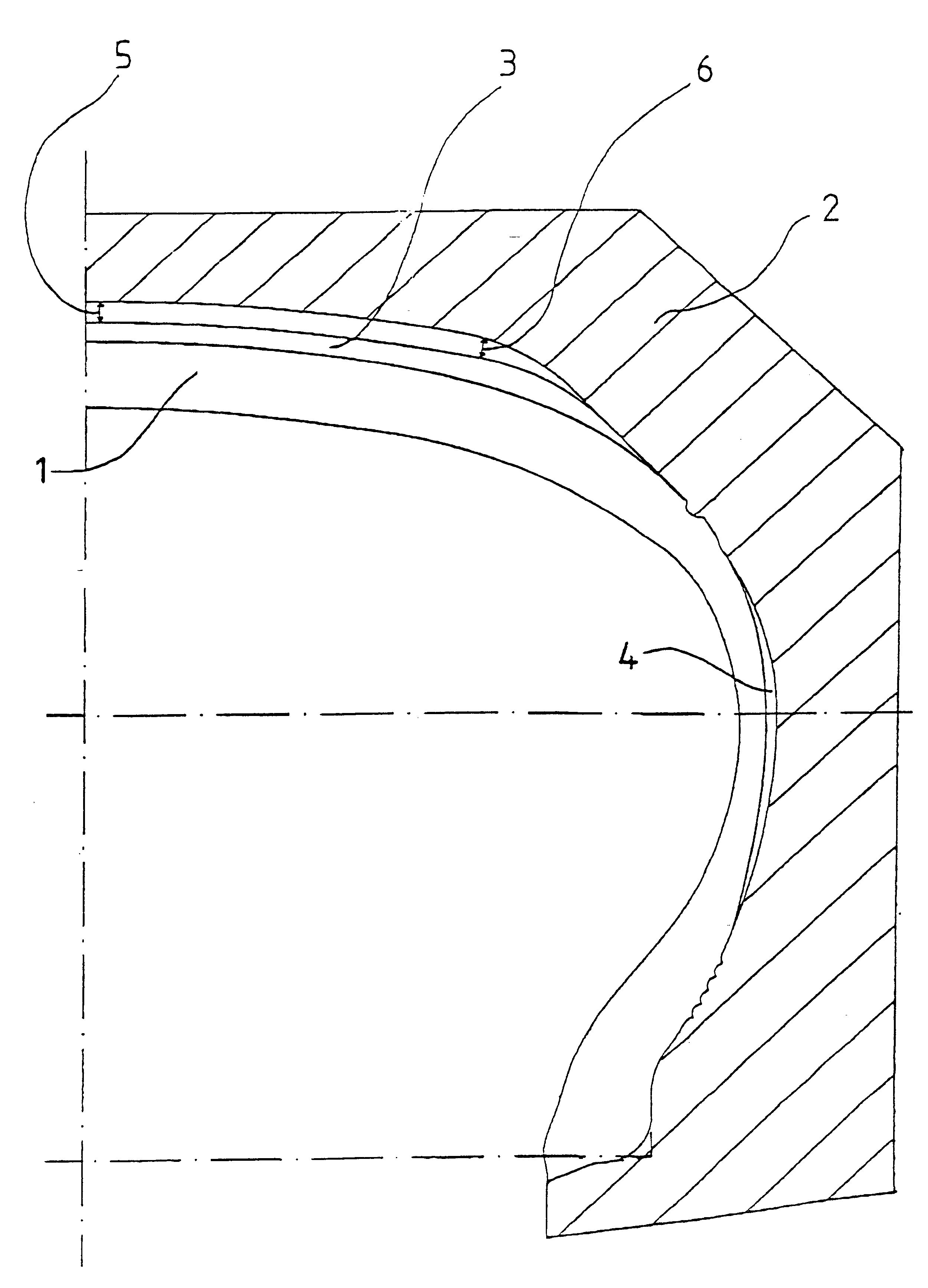
Photoelectric conversion device and method of manufacturing the device
InactiveUS7402747B2Improve conversion efficiencyReliable formingStrutsPV power plantsPhotoelectric conversionConcentration gradient
There is disclosed a photoelectric conversion device comprising a substrate 1 serving as a lower electrode; first conductivity-type crystalline semiconductor particles 3 deposited on the substrate; second conductivity-type semiconductor layers 4 formed on the crystalline semiconductor particles 3; an insulator layer 2 formed among the crystalline semiconductor particles; and an upper electrode layer 5 formed on the second conductivity-type semiconductor layers 4, wherein the second conductivity-type semiconductor layers 4 each have a smaller thickness at or below an equator of each of the crystalline semiconductor particles than at a zenith region thereof, and the second conductivity-type semiconductor layers 4 include an impurity element with a concentration gradient decreasing with proximity to the crystalline semiconductor particles.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Laser radar system for measuring Raman spectra of atmospheric water and fluorescence spectra of aerosols
ActiveCN105675576AGuaranteed normal transmissionRealize simultaneous measurementRaman/scattering spectroscopyLaser detailsRadar systemsFluorescence spectra
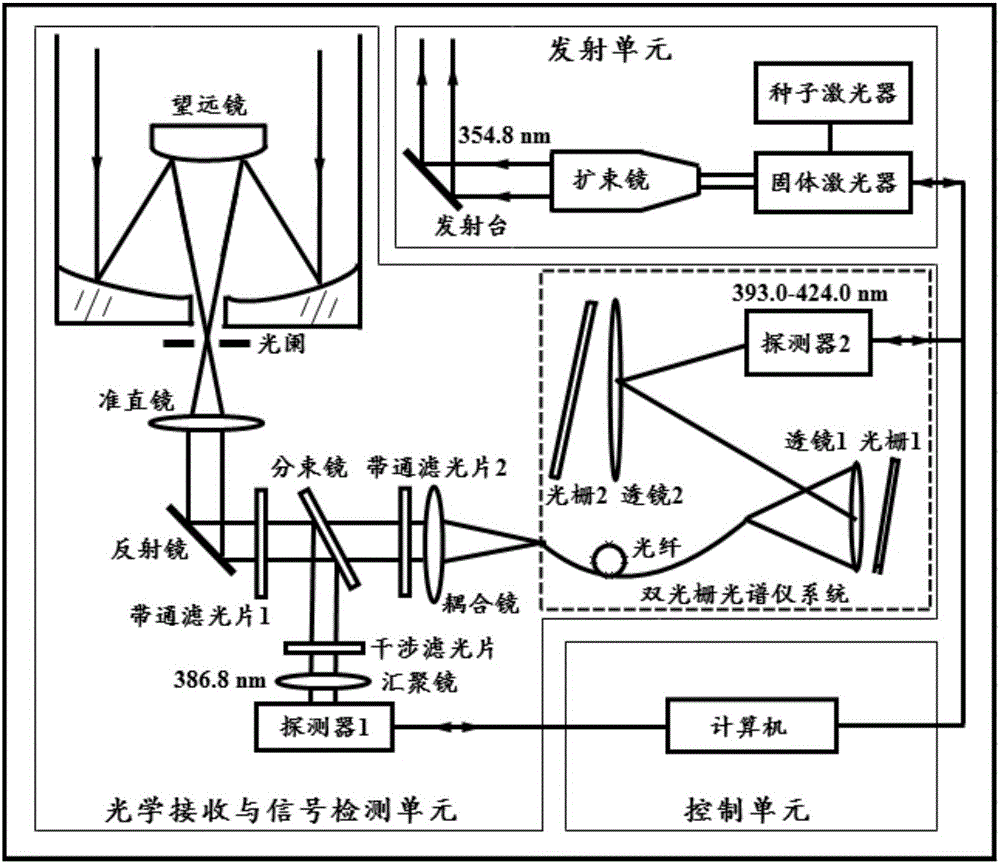
The invention discloses a laser radar system for measuring Raman spectra of atmospheric water and fluorescence spectra of aerosols.The system consists of a transmitting unit, an optical receiving and signal detection unit and a control unit.The transmitting unit adopts a seed injected solid laser to output ultraviolet laser with the narrow linewidth of 354.8 nm and guide the ultraviolet laser to the zenith.The optical receiving and signal detection unit collects backward scattering light from atmospheric substances, produces inhabitation superior to 15 orders of magnitude to nearby light of 354.8 nm and distinguishes and records signal light in the spectrum band range of 393.0-424.0 nm at the spectral precision of 0.8 nm.The control unit guarantees the orderly work of the whole radar system.Under the radiation of ultraviolet laser with the wave length of 354.8 nm, the vibrational-rotational Raman spectrum regions of gas-state, liquid-state and solid-state water sequentially correspond to the ranges of 395-409 nm, 396-410 nm and 401-418 nm.The laser radar system can simultaneously record the Raman spectra produced by the three states of water and fluorescence spectra of produced by aerosol particles and achieve simultaneous detection of the atmospheric water, aerosols and other substances.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and device for determining global ionized layer grid model
InactiveCN106405589ASolve the problem that simple fusion cannot be performedSatellite radio beaconingSpace environmentSpherical harmonics
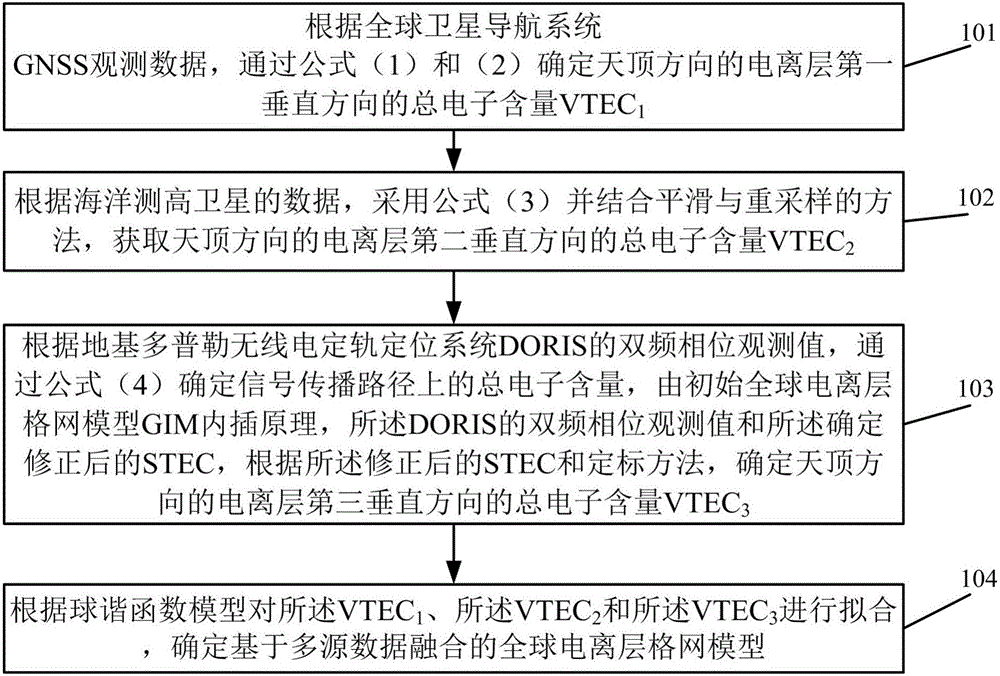
The invention provides a method and device for determining a global ionized layer grid model, belongs to the field of global navigation systems and space environment monitoring, and is used for solving the problems that systematic bias exists among various ionized layer data, and the various ionized layer data cannot be fused in a simple manner. The method includes determining an ionized layer VTEC1 in a zenith direction through formulae (1) and (2) according to GNSS observed data; adopting a formula (3) and combined with a smooth and resampling method to obtain an ionized layer VTEC2 in the zenith direction according to data of ocean height-measuring satellites; according to a double-frequency phase observed value of a DORIS, determining STEC<bias> through a formula (4), through a GIM interpolation principle, the double-frequency phase observed value of the DORIS and the STEC<bias>, determining corrected STEC, and determining an ionized layer VTEC3 in the zenith direction according to the corrected STEC and a calibration method; and performing fitting on the ionized layers VTEC1, VTEC2 and VTEC3 according to a spherical harmonics model, and determining the global ionized layer grid model based on multi-source data fusion.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
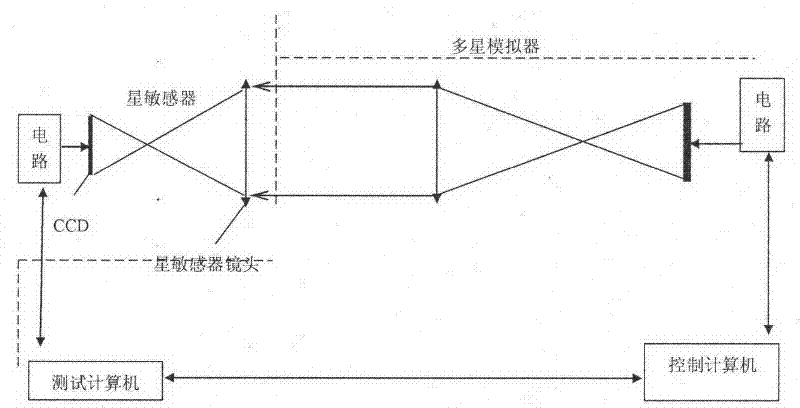
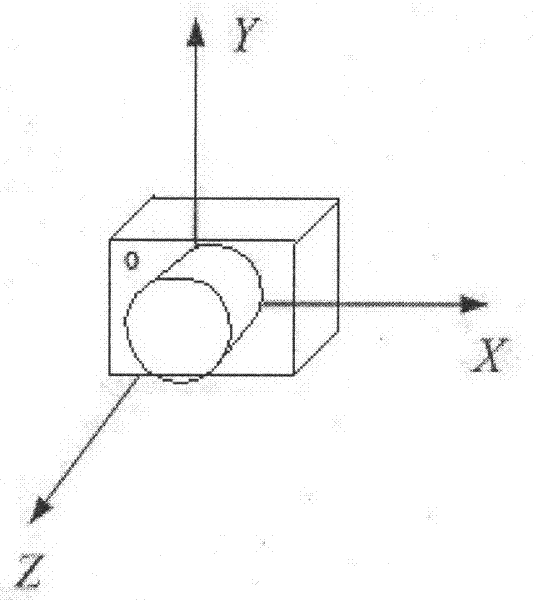
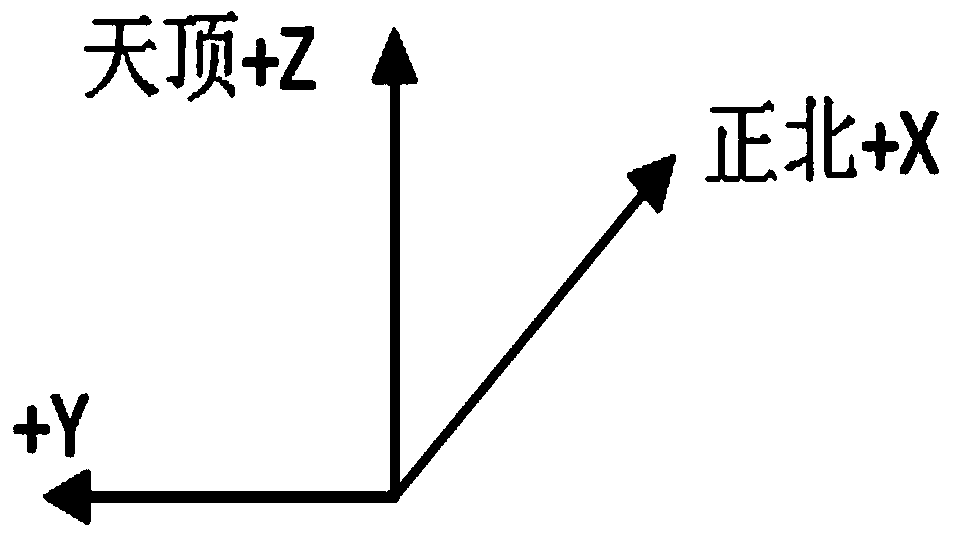
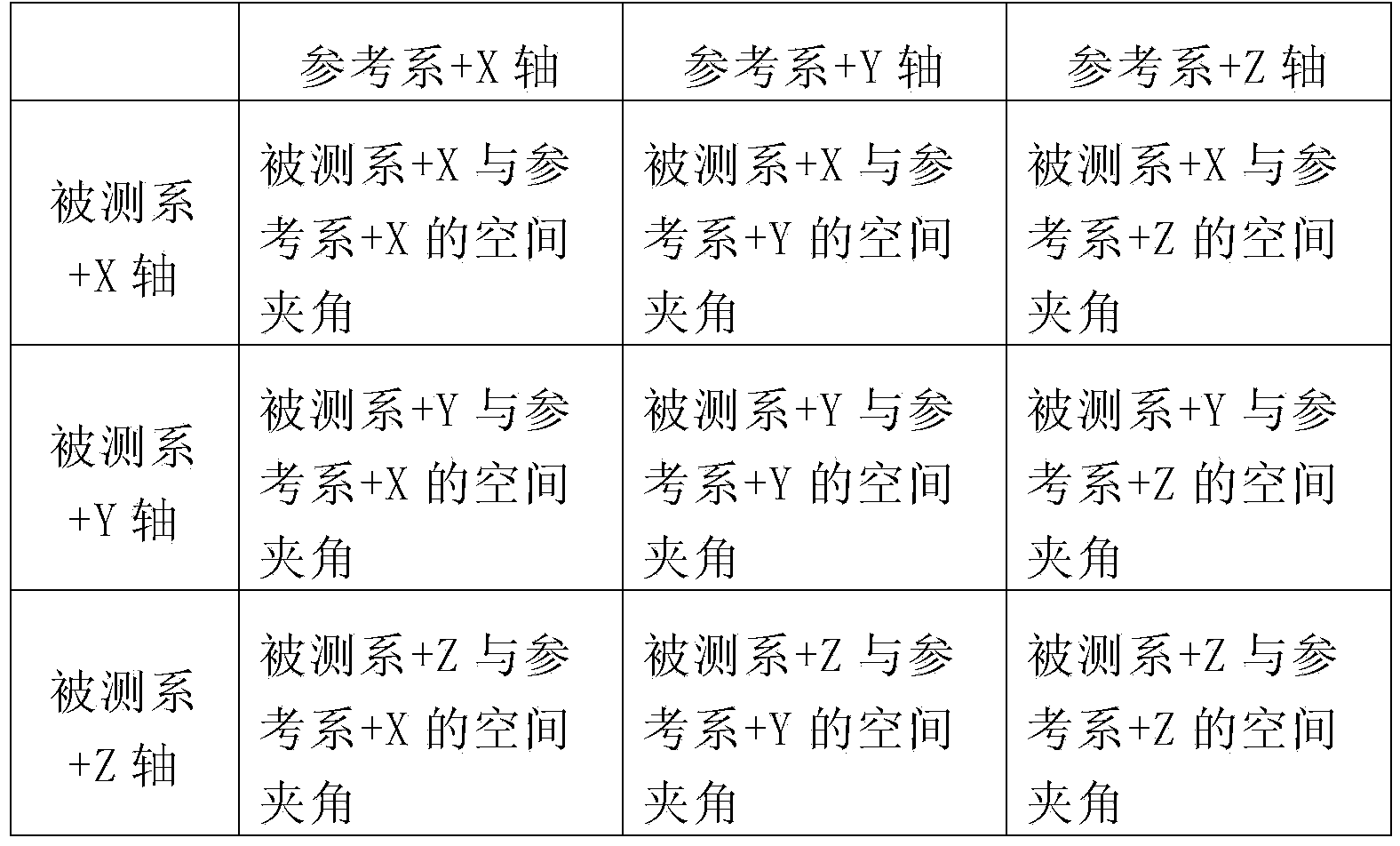
A ground test method for star sensor
The invention provides a ground testing method of a star sensor. The method comprises the following steps of: adjusting the star sensor by using a theodolite so that the Z axis of the star sensor points to true north and the Y axis of the star sensor vertically faces towards zenith; receiving a quaternion of the star sensor under an inertial coordinate system; converting the posture of the star sensor into a quaternion under a WGS84 coordinate system; converting the quaternion under the WGS84 coordinate system of the star sensor into a three-axis Euler angle; continuously operating the star sensor for 30 minutes, storing the difference between a roll angle and the local longitude and the difference between a drift angle and the local latitude in real time, and counting precisions of the roll angle and the drift angle; and storing the difference between a pitch angle and the local longitude in real time, and counting the precision of the pitch angle. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the testing process is simple; any special equipment is unnecessary; the method is not only used for testing the precision of the three-axis Euler angle of the star sensor but also used for completely testing the three-axis polarity of the star sensor; and in addition, only when the time precision satisfies requirements, the method is also used for testing the absolute longitude of the star sensor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Process for producing a pneumatic tire
InactiveUS6406575B1Reducing cord forceGood effectTyresTyre tread bands/patternsInternal pressureVulcanization
Process for producing a pneumatic tire that includes an inner liner of a layer that is as air-impermeable as possible, at least one carcass ply provided with strength supports, horn profiles, bead cores, sidewalls, a belt assembly, and a tread. The process includes building-up a partial tire in a production part A, where the partial tire includes at least a carcass body that includes the at least one carcass ply provided with the strength supports, bead reinforcements and cores, core fillers and horn profiles, and an undertread, and shaping and at least partially vulcanizing the partial tire under an internal pressure in a vulcanization mold in a first vulcanization procedure. The process also includes determining a cross-sectional contour for a completed tire and an amount of surface and strength supports to be added to the partial tire prior to a production part B, and building-up the partial tire in the production part B by adding remaining tire components to produce a complete tire. Further, the process includes vulcanizing the complete tire in the vulcanization mold, thereby bonding the partial tire to the remaining tire components. While vulcanizing the complete tire, a residual elevation produced by internal pressure is applied, whereby the complete tire is molded to its final contour. The residual elevation in shoulder areas of the completed tire is greater than or equal to the residual elevation in a zenith area.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AG
GNSS maneuvering satellite orbit determination method with additional clock error model constraint
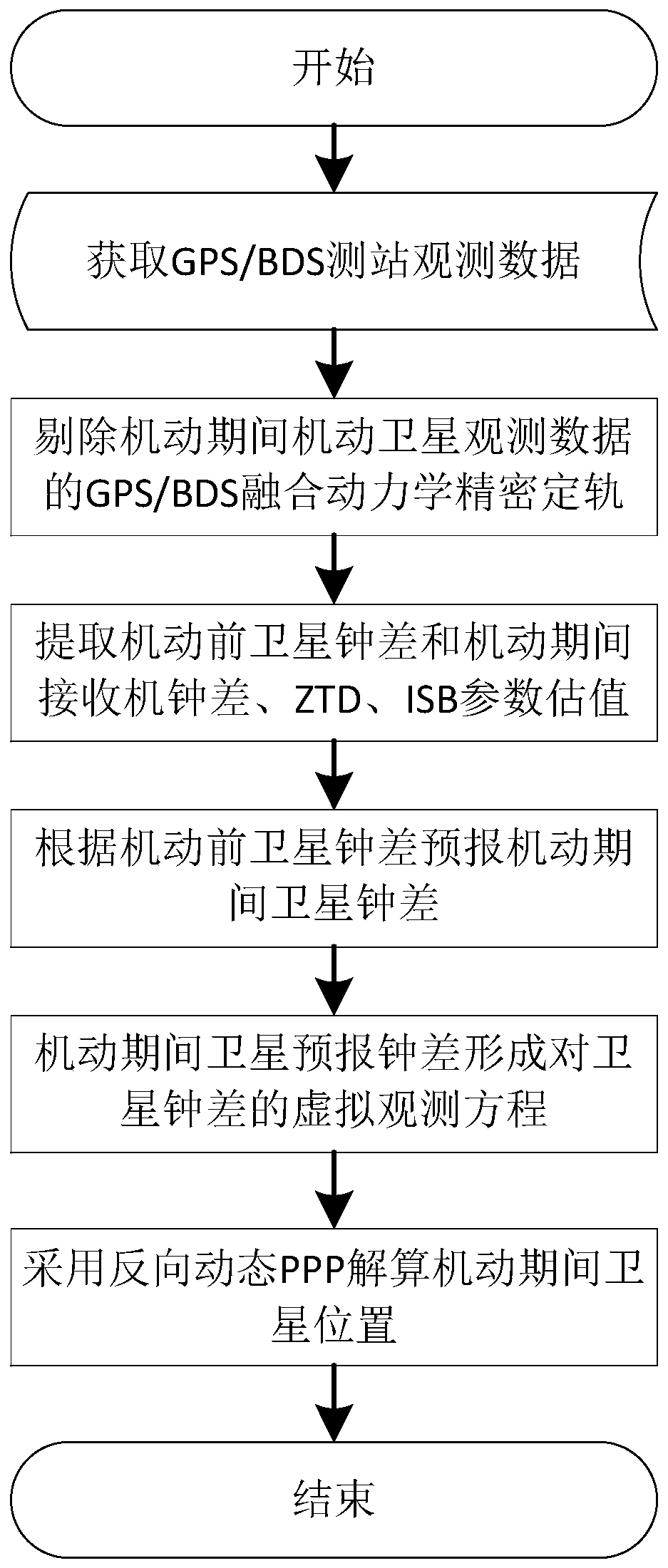
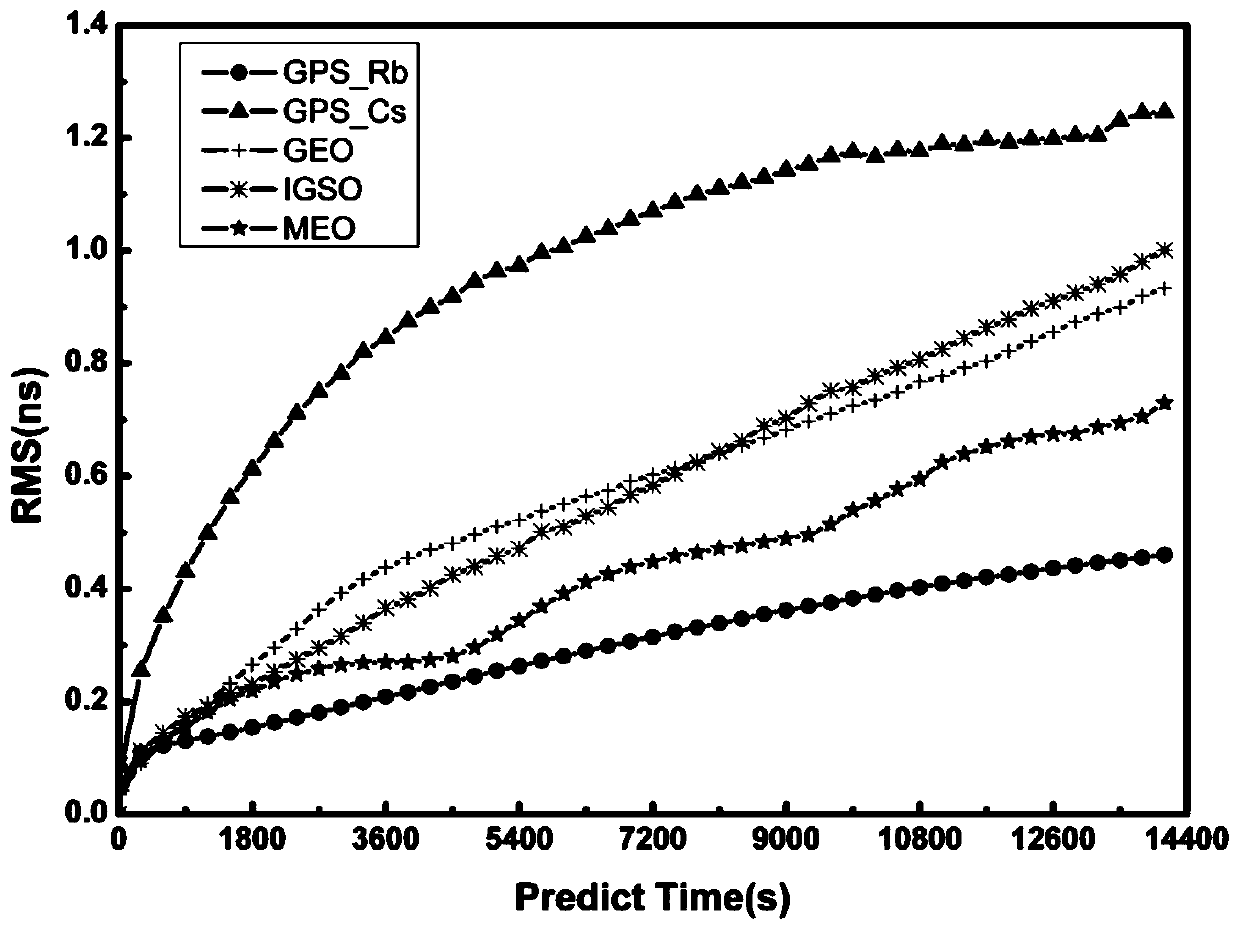
ActiveCN110231037AAvoid certain effectsImproving the Accuracy of Track Radial Orbit DeterminationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingObservation dataAmbiguity
The invention discloses a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) maneuvering satellite orbit determination method with additional clock error model constraint, comprising the steps of: acquiring observation data of an observation station; 2) eliminating observation data after maneuvering, and performing dynamic precision orbit determination calculation on arc sections before and during maneuvering; 3) extracting estimation values of a satellite clock error before maneuvering, an ambiguity, a receiver clock error during maneuvering, a ZTD (Zenith Tropospheric Delay) and an ISB (Inter-SystemBias) parameter; 4) establishing a clock error forecasting model based on the estimation value of the satellite clock error before maneuvering; 5) fixing the receiver clock error, the ambiguity without cycle slip, the ZTD and the ISB parameter, adding constraint of the clock error forecasting model, and performing orbit determination calculation on a satellite orbit during maneuvering by adoptinga reverse dynamic precision single-point positioning method; and 6) iteratively solving position parameters of the maneuvering satellite at the current epoch until the position parameters are converged, and performing solving at the next epoch. According to the GNSS maneuvering satellite orbit determination method of the invention, through introduction of the satellite clock error forecasting model constraint, the correlation between satellite orbit radial direction and the satellite clock error can be greatly weakened, and the orbit radial direction orbit determination precision of the maneuvering satellite is effectively improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method of acquiring leaf area index (LAI) of rice canopy by using common digital camera
ActiveCN102331244AAvoid destructive manual measurementsReal-time accessUsing optical meansPorosityVertical plane
The invention discloses a method of acquiring LAIs of a rice canopy by using a common digital camera. According to the method, a common digital camera is employed to shoot a picture of a rice canopy above the rice canopy with primary optic axis of the lens of the camera and a vertical plane of the rice canopy forming an angle of 57.5 degrees; gray scale conversion, binaryzation and noise cancellation are carried out on the obtained picture of the rice canopy, and porosity of the rice canopy at a visual angle and zenith angle of 57.5 degrees is directly extracted from the processed picture; LAIs of the rice canopy are directly calculated based on the relationship between the LAI of the rice canopy and porosity of the rice canopy at a visual angle and zenith angle of 57.5 degrees. The advantages of the invention are as follows expensive imported special-purpose equipment is not employed; field plucking of rice leaves for destructive manual measurement is avoided; real time and rapid acquisition of LAIs of the rice canopy is realized, thereby providing fundamental parameters for real time monitoring of growth vigor of rice and for rice yield estimation through remote sensing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for measuring posture angle of base cubic mirror based on gyro theodolite
InactiveCN104266649AAvoid mutual aimingAvoid occlusionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsClassical mechanicsMeasurement precision
The invention discloses a method for measuring the posture angle matrix of a base cubic mirror, relative to a geodetic coordinate system based on a gyro theodolite. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, measuring any two adjacent side surfaces of the base cubic mirror in an alignment manner by the gyro theodolite and an electronic theodolite respectively to obtain the azimuth angle and zenith distance of the gyro theodolite in the alignment direction and the zenith distance of the electronic theodolite in the alignment direction; secondly, calculating through a vertical relationship between the two surfaces to obtain the azimuth angle of the electronic theodolite in the alignment direction; finally, obtaining the posture angle matrix of the base cubic mirror, relative to the geodetic coordinate system. According to the method, one gyro theodolite is omitted, so that the cost is reduced; meanwhile, the mutual alignment between a general theodolite and the gyro theodolite is avoided, so that the measurement precision and efficiency are improved, and the light path shielding during mutual alignment under the complicated working condition is prevented.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Device and method for calibrating plumb aligner
The invention discloses a device for calibrating a plumb aligner. An upright column is provided with a plumb aligner holding cabin and an operating platform which are connected with a laser mirror cabin through a supporting column; the laser mirror cabin is connected with a fine adjusting cabin through a supporting column; the fine adjusting cabin is provided with a rough adjusting head; and the rough adjusting head is provided with a plurality of rough adjusting bolts. The invention provides the device and a method for calibrating the plumb aligner, which are used for calibrating a sight axis and a laser optical axis by taking a vertical axis and a zenith / nadir sighting mark (or remote fixed sighting mark) of the plumb aligner calibrated by a water level as dynamic bench marks. In the calibration process, the calibrated plumb aligner always keeps the leveling state during use, the target seeking task is completely finished by the zenith / nadir sighting mark, and therefore, the influence of included target seeking of the plumb aligner in the traditional method on the indeterminacy of a calibration result is greatly reduced. In addition, fewer adjustment times, shorter adjustment time, higher correction precision and more convenience for operation are realized.
Owner:宜昌市计量检定测试所 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com