Patents
Literature
2166 results about "DC bias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
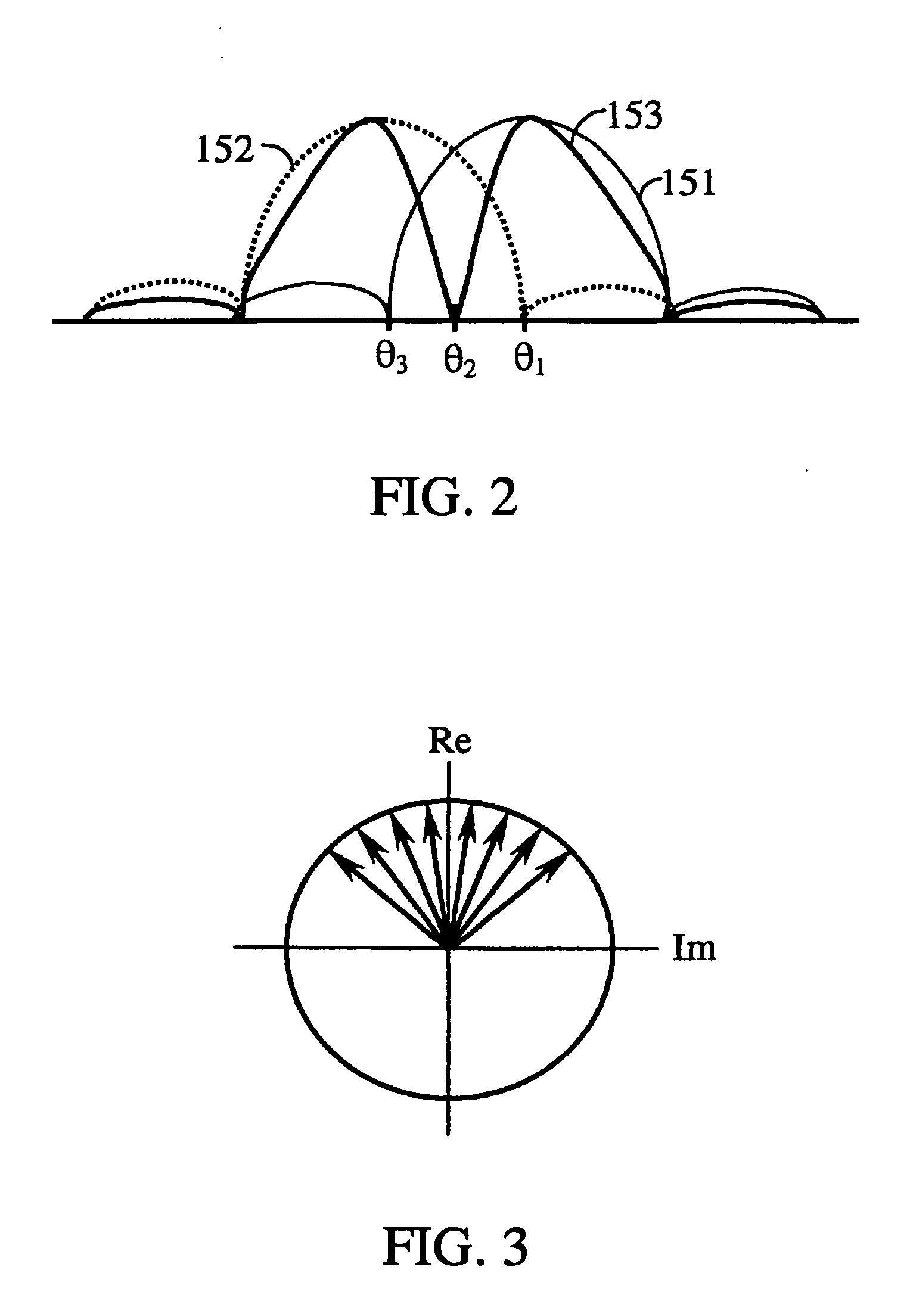
When describing a periodic function in the time domain, the DC bias, DC component, DC offset, or DC coefficient is the mean amplitude of the waveform. If the mean amplitude is zero, there is no DC bias. A waveform with no DC bias is known as a DC balanced or DC free waveform.
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
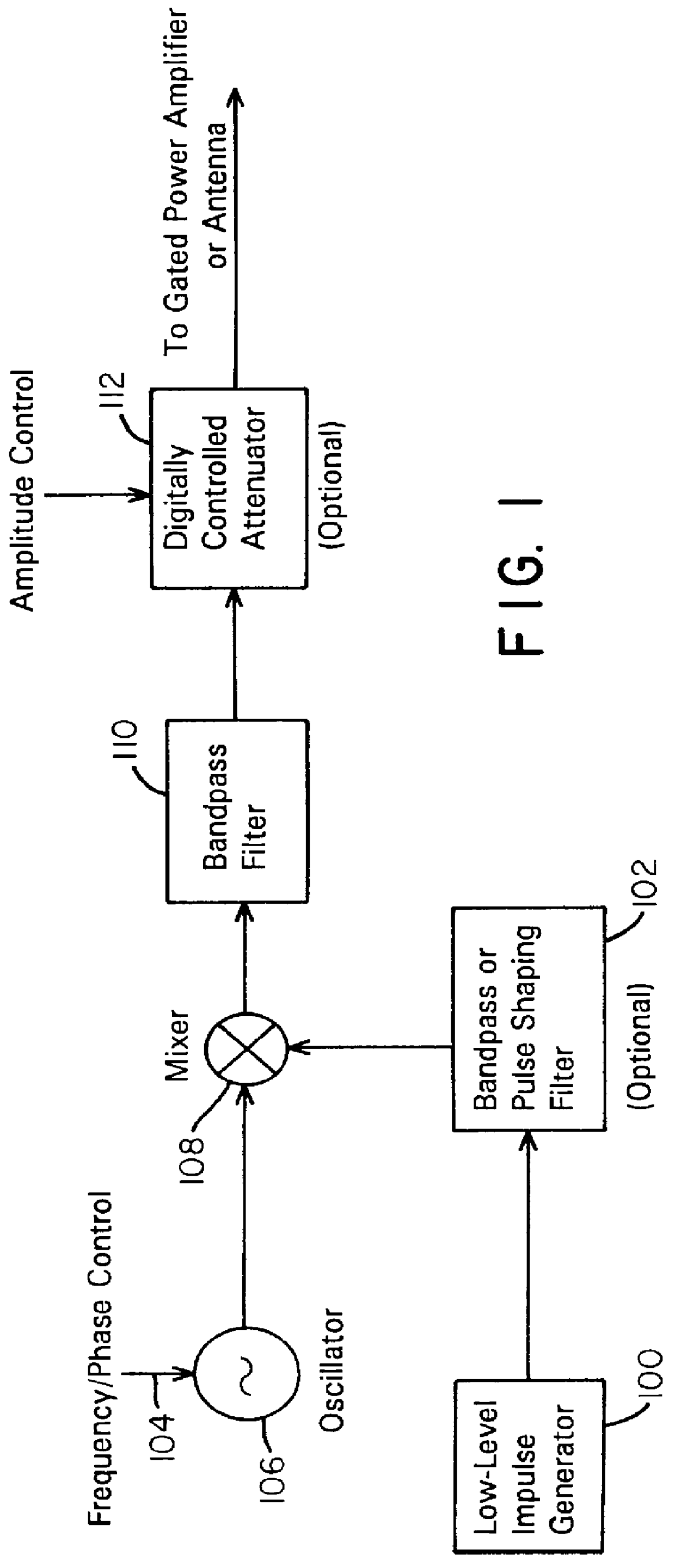
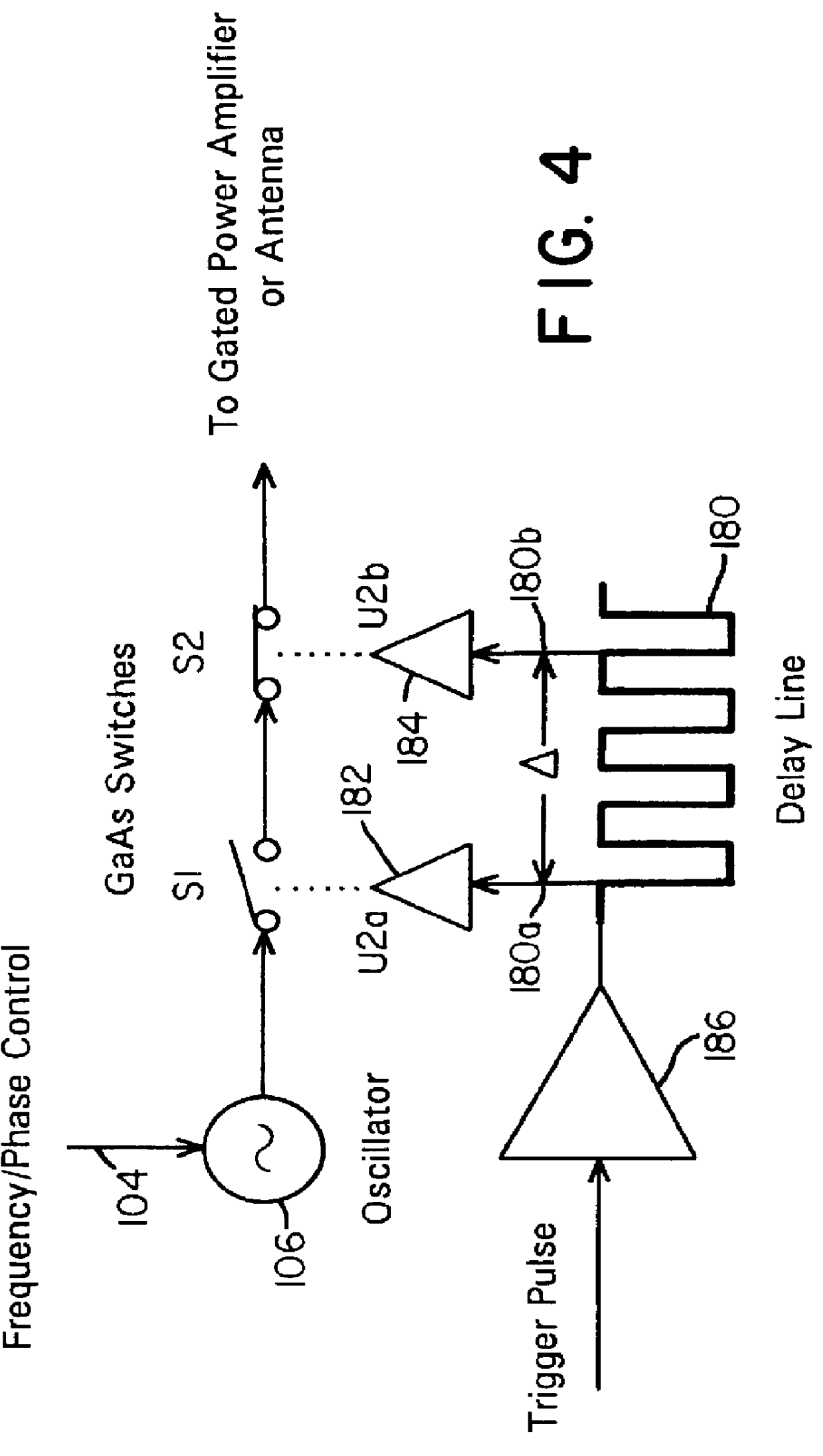
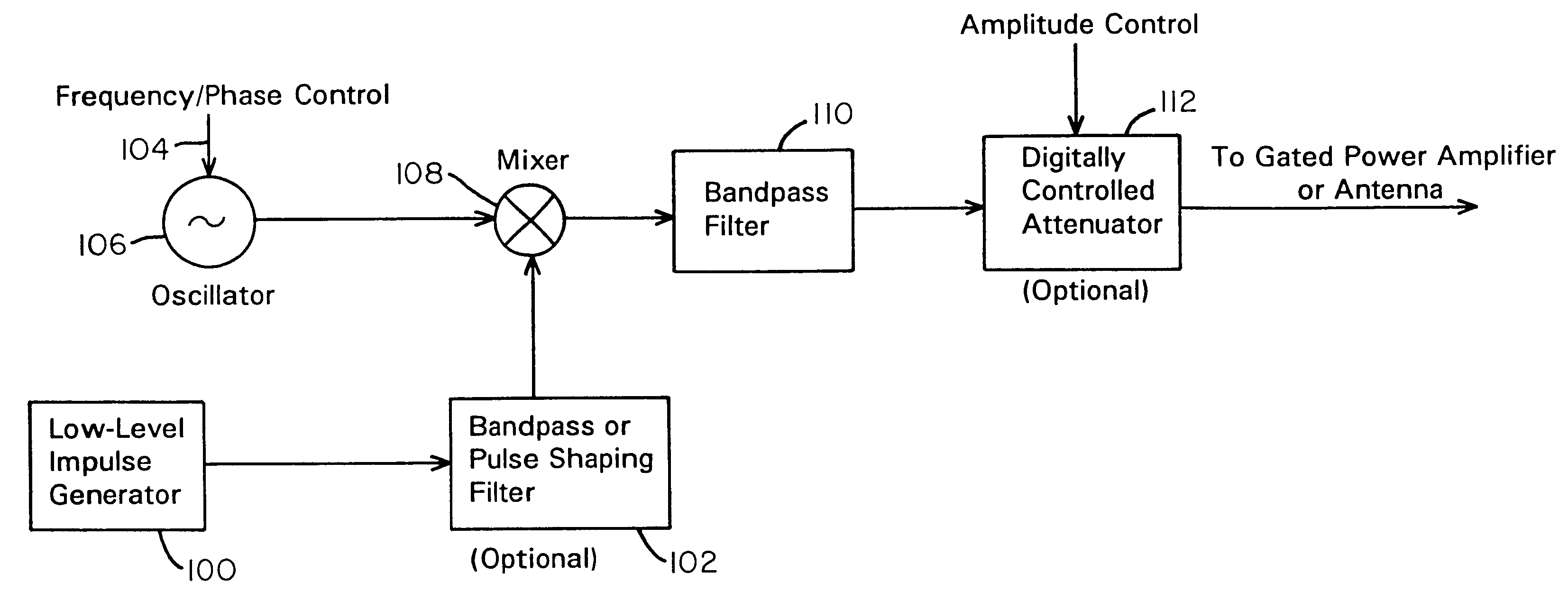
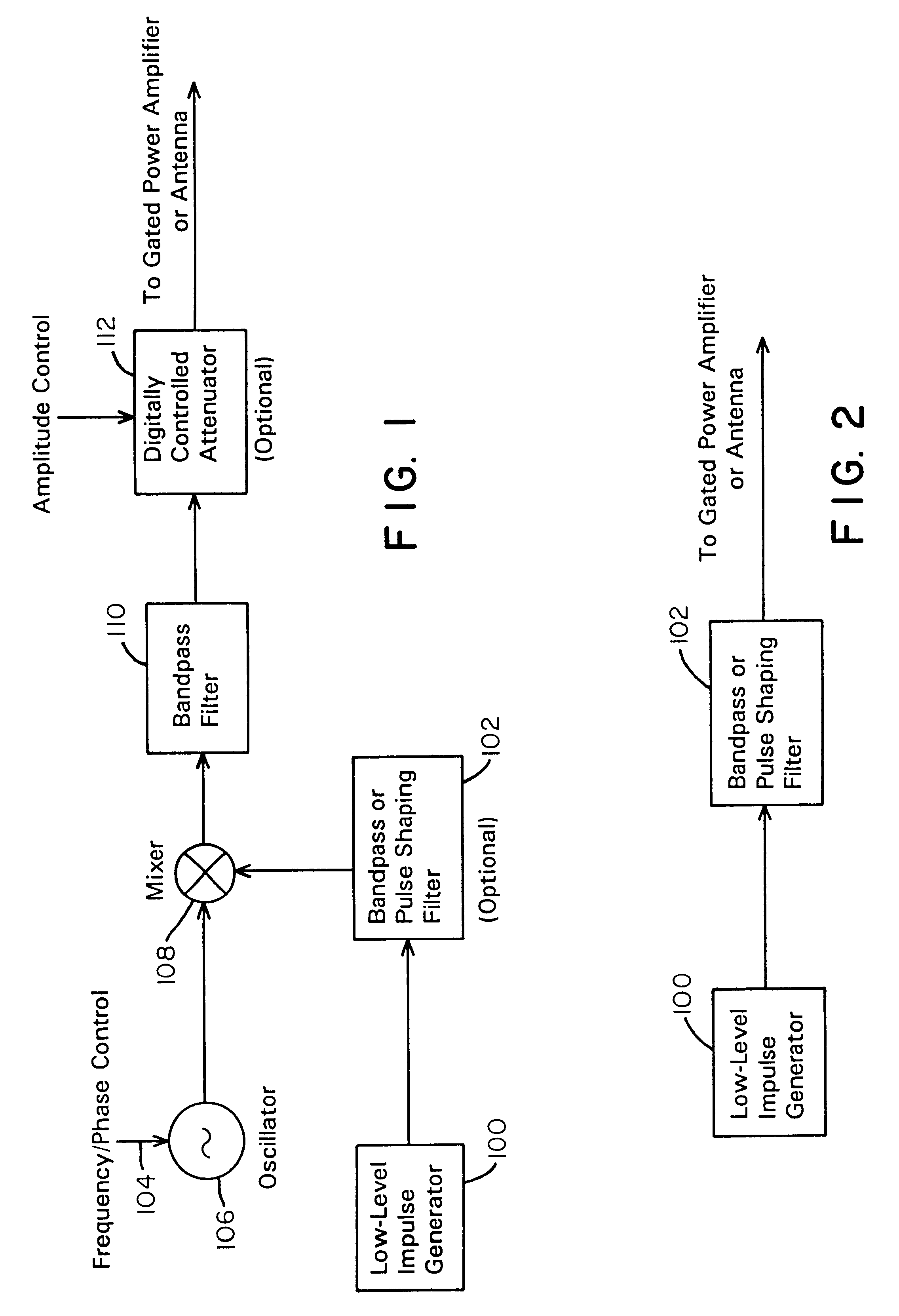
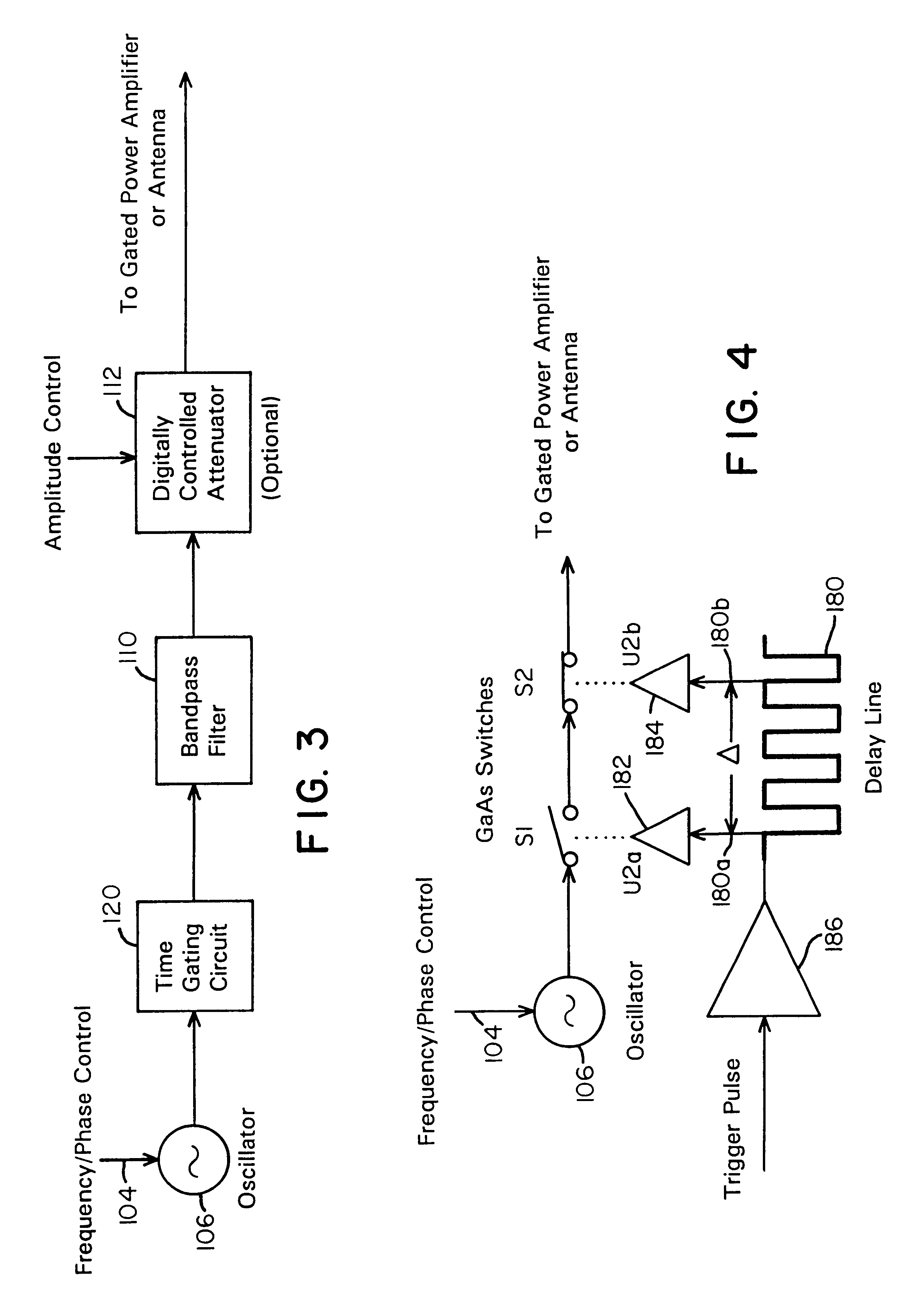
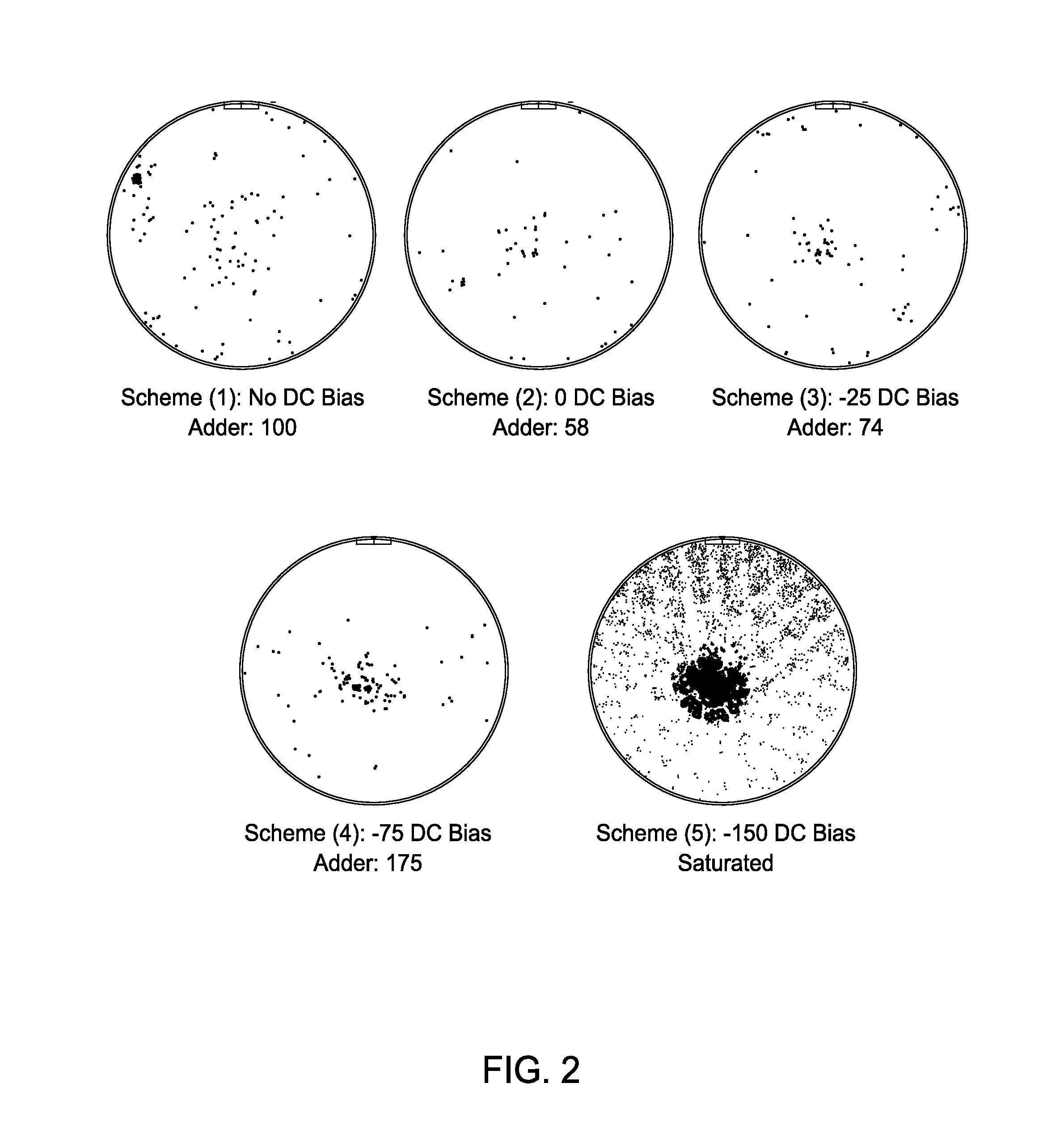
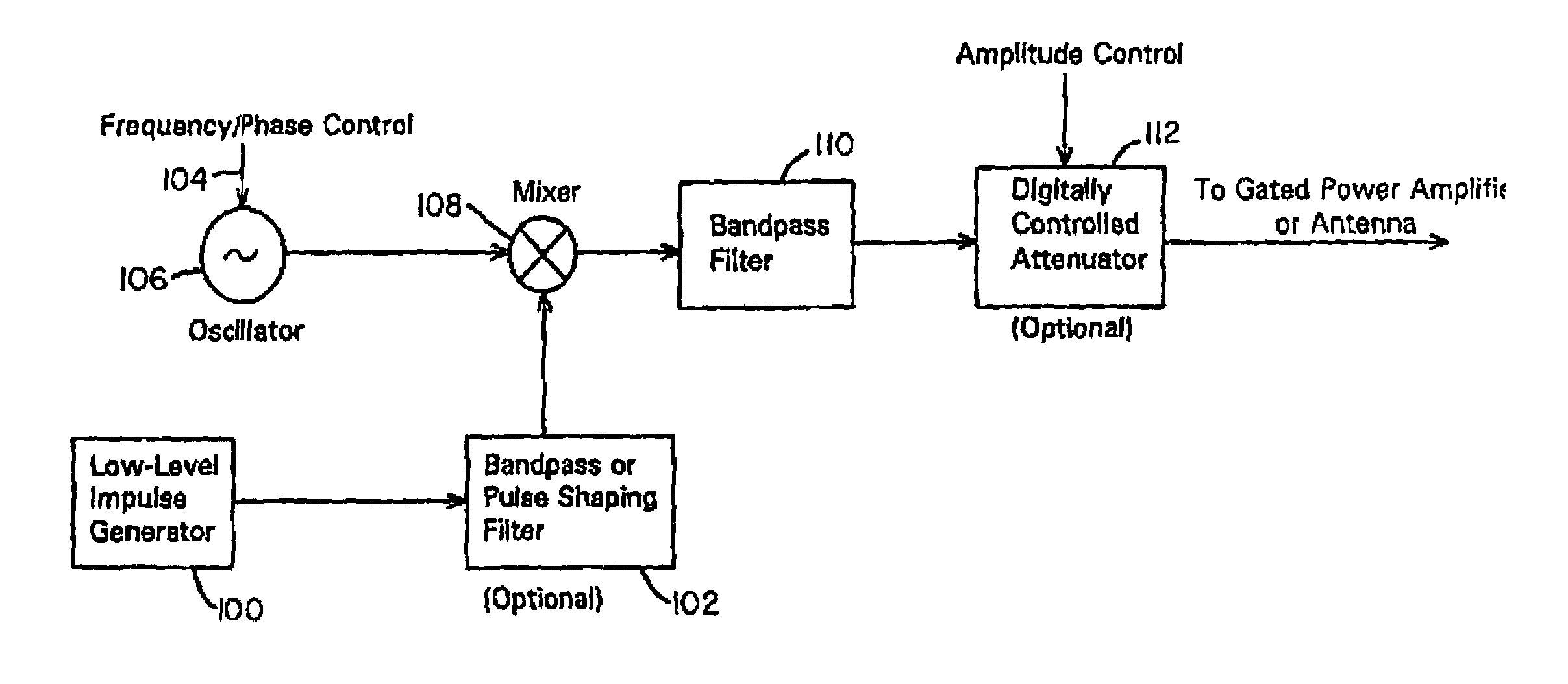
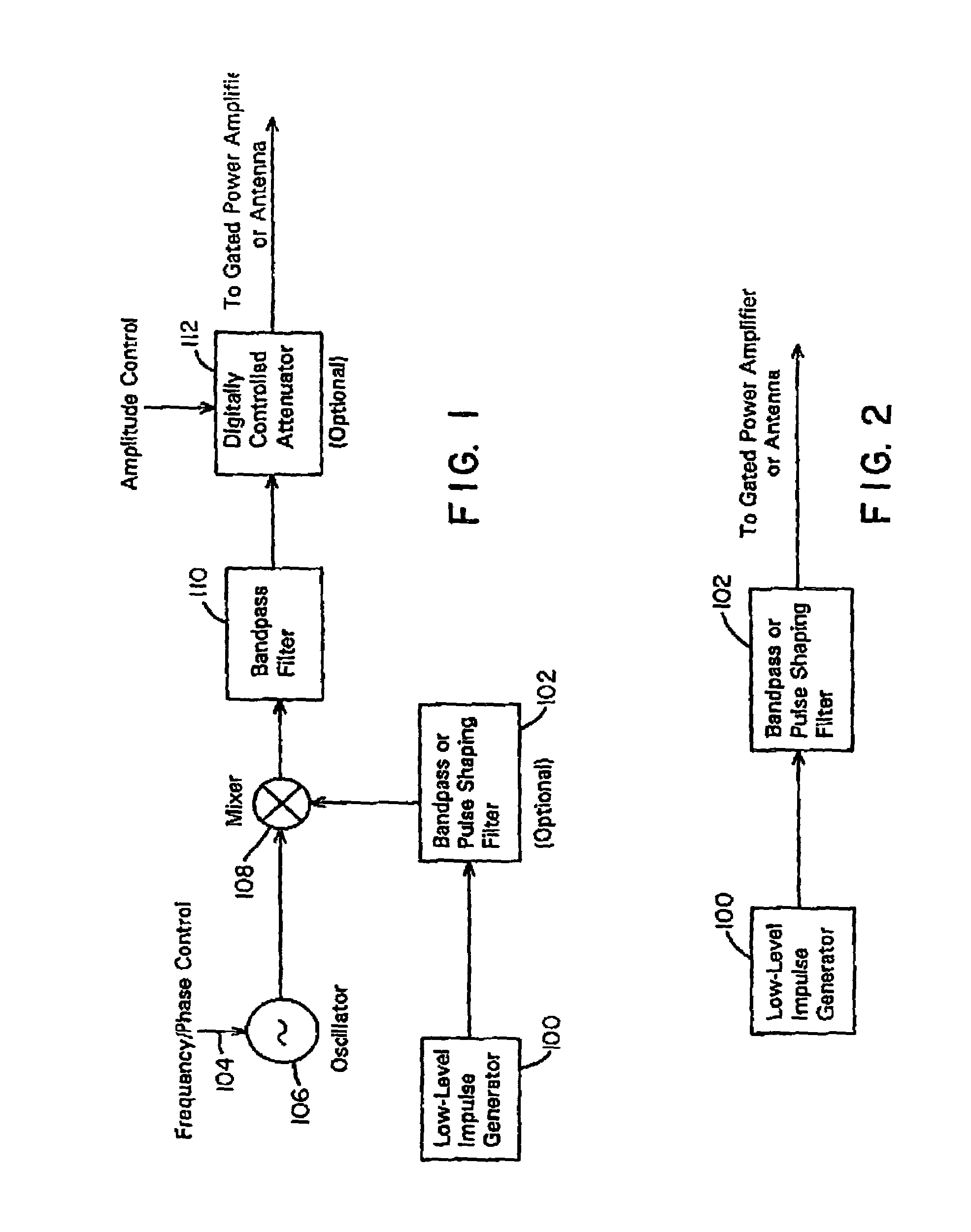
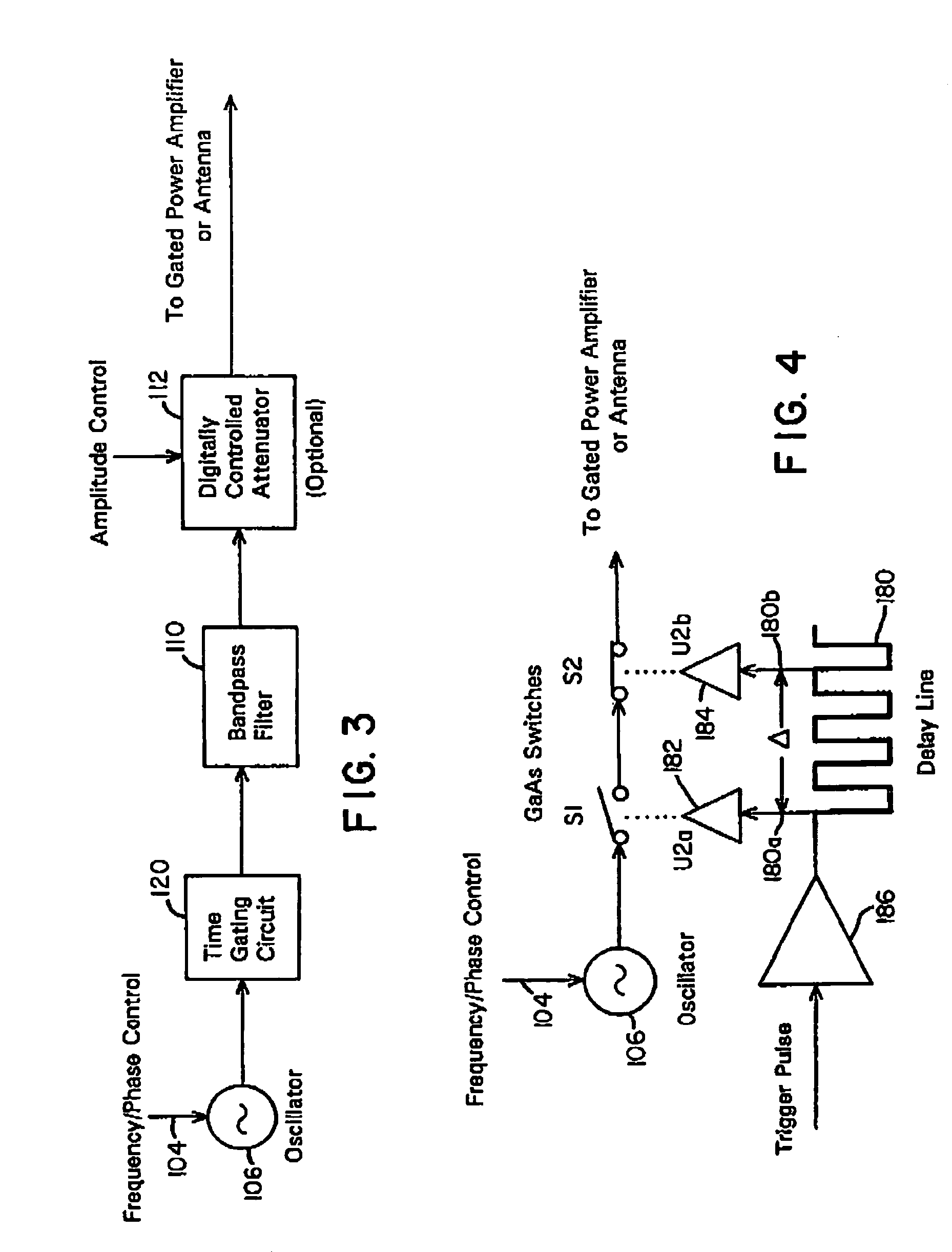
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Ultra wideband data transmission system and method
InactiveUS6690741B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationBandpass filteringExtensibility
A data-modulated ultra wideband transmitter that modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Coupling circuit arrangement for data communication over power lines
InactiveUS20050069321A1Effective preventionSave design spaceElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl signalData signal
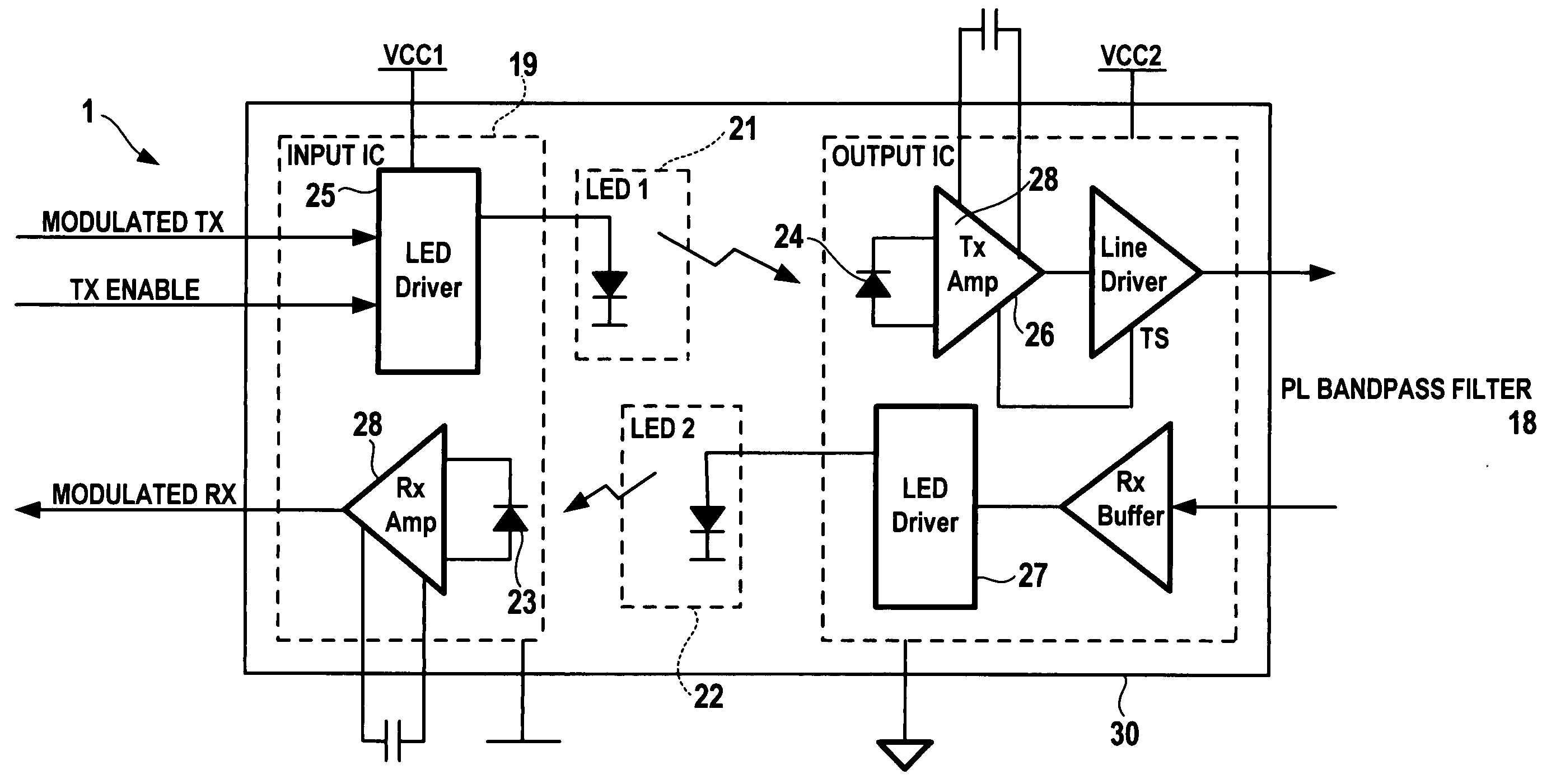
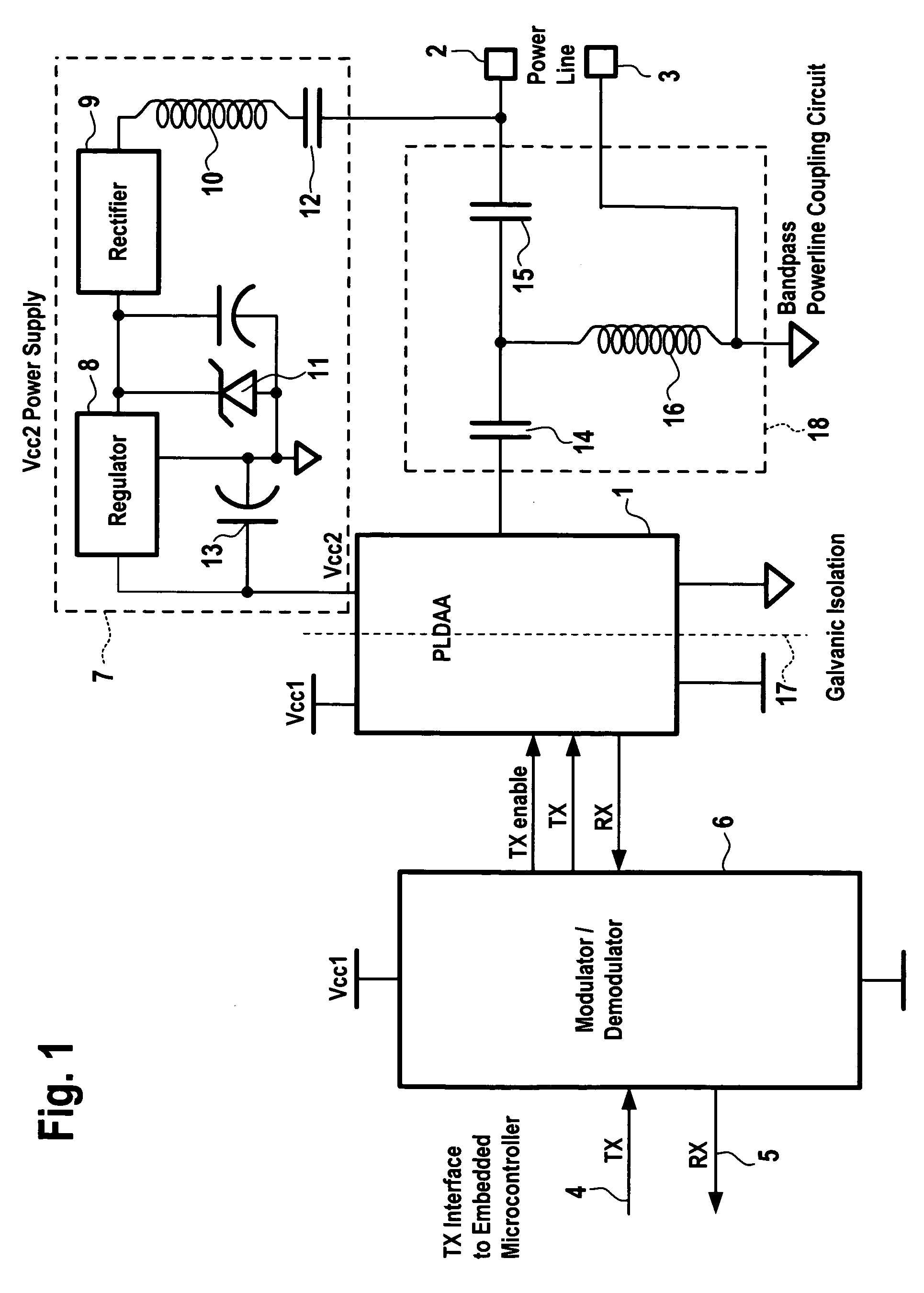
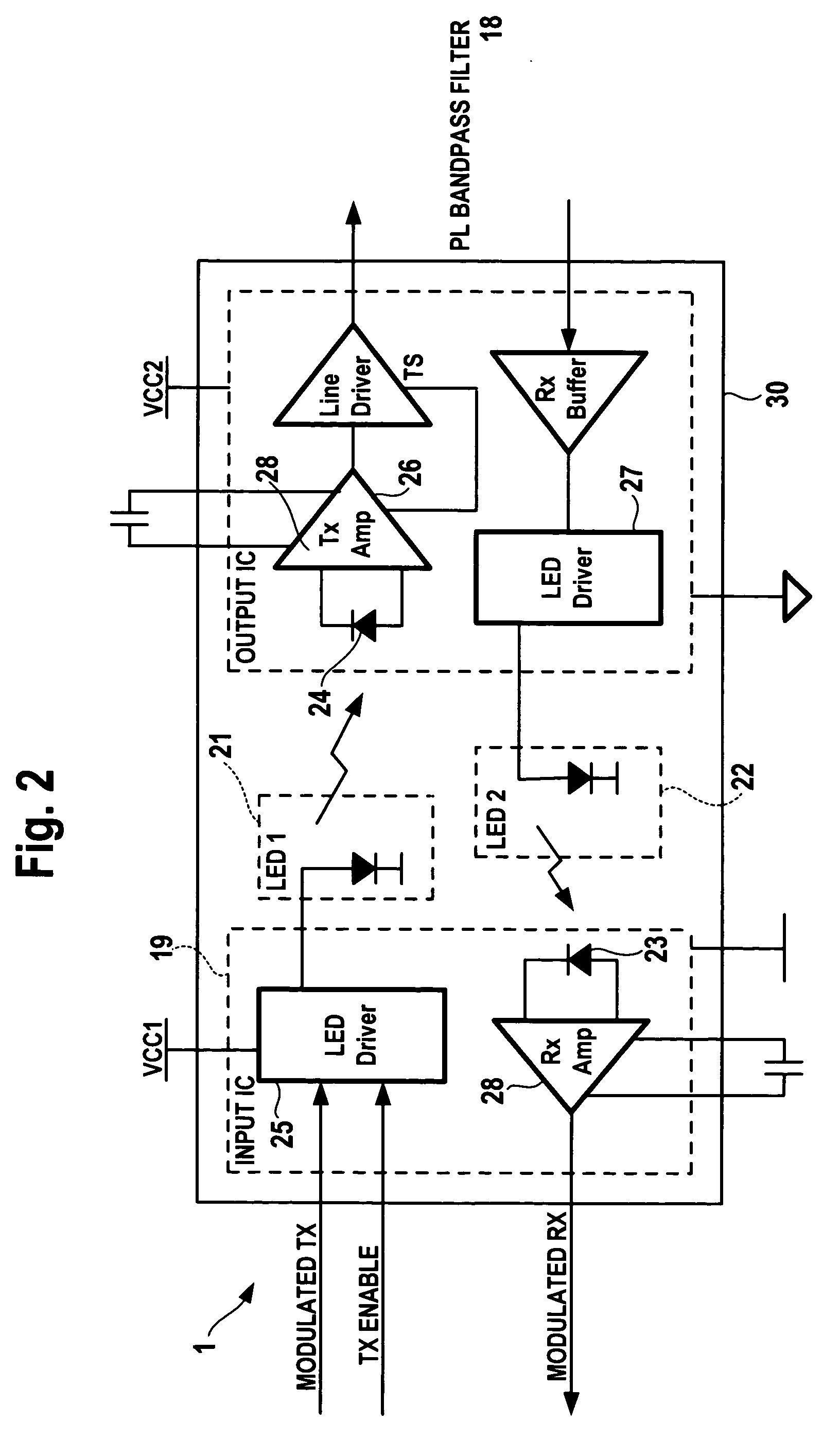
A coupling circuit arrangement for data communication over a power line comprises a modulator / demodulator circuit for modulating data signals for transmission over the power line, and for demodulating signals which have been transmitted over the power line into data signals, a power supply circuit, and isolation means for providing galvanic isolation from the power line. The isolation means comprises light emitting elements and light detecting elements, which are arranged between the modulator / demodulator circuit and the power line. The isolation means may also be used to transmit a digital control signal which indicates the status of the power supply circuit or an over-temperature condition, or which is a transmit enable signal. The digital control signal may be encoded in the analog data signal by a digital shift in the DC bias level or by a complete removal of the DC biasing signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Semiconductor polysilicon component and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6838308B2Improve responseTransistorPolycrystalline material growthOptoelectronicsGlass structure
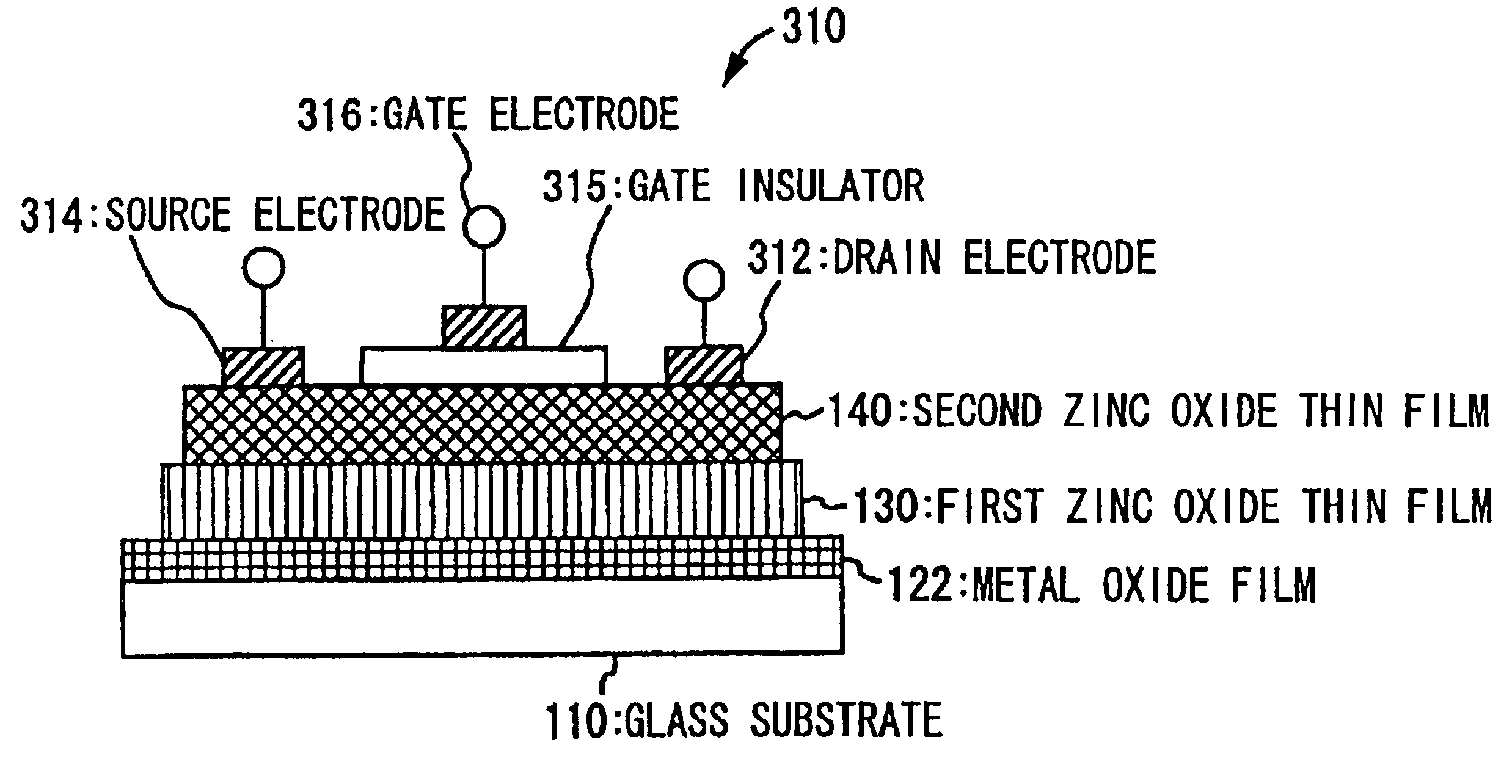
On a transparent substrate, by use of, for instance, vapor deposition, an Al film is formed. Subsequently, with a DC-bias applied on a surface of the Al film, a first zinc oxide thin film is formed by use of a sputtering method. On a surface of the first zinc oxide thin film, according to an atmospheric MO-CVD method, a second zinc oxide thin film is formed. When the second zinc oxide thin film deposited by use of an MO-CVD method is formed on the first zinc oxide thin film having a-axis orientation, the second zinc oxide thin film becomes to have the a-axis orientation. Since the Al thin film, owing to heat during the deposition by use of the MO-CVD method, is absorbed in the first zinc oxide thin film, the transparency is improved. As a result, a sample having a ZnO / ZnO / Al / glass structure becomes high in the transparency as a whole.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD +1
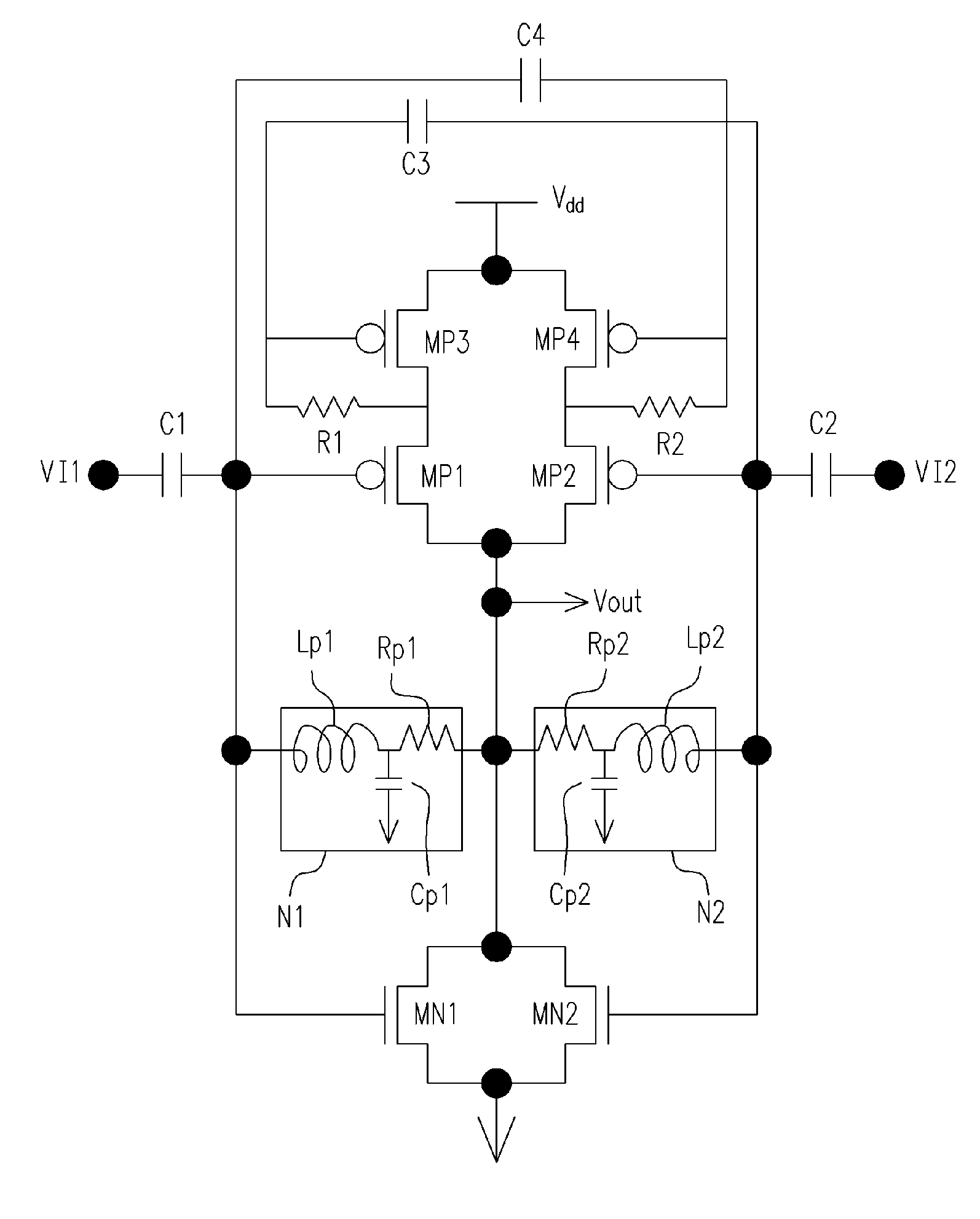
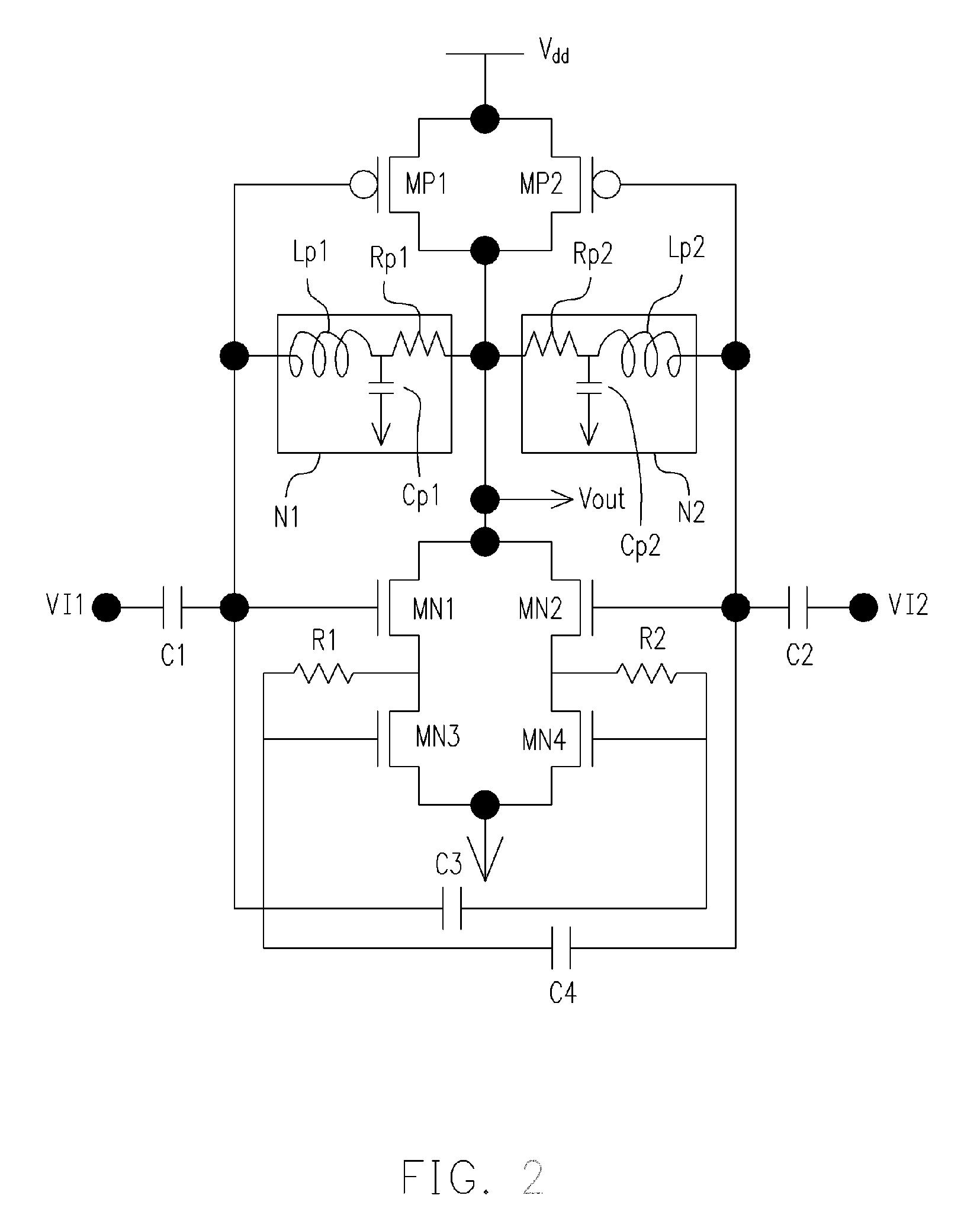
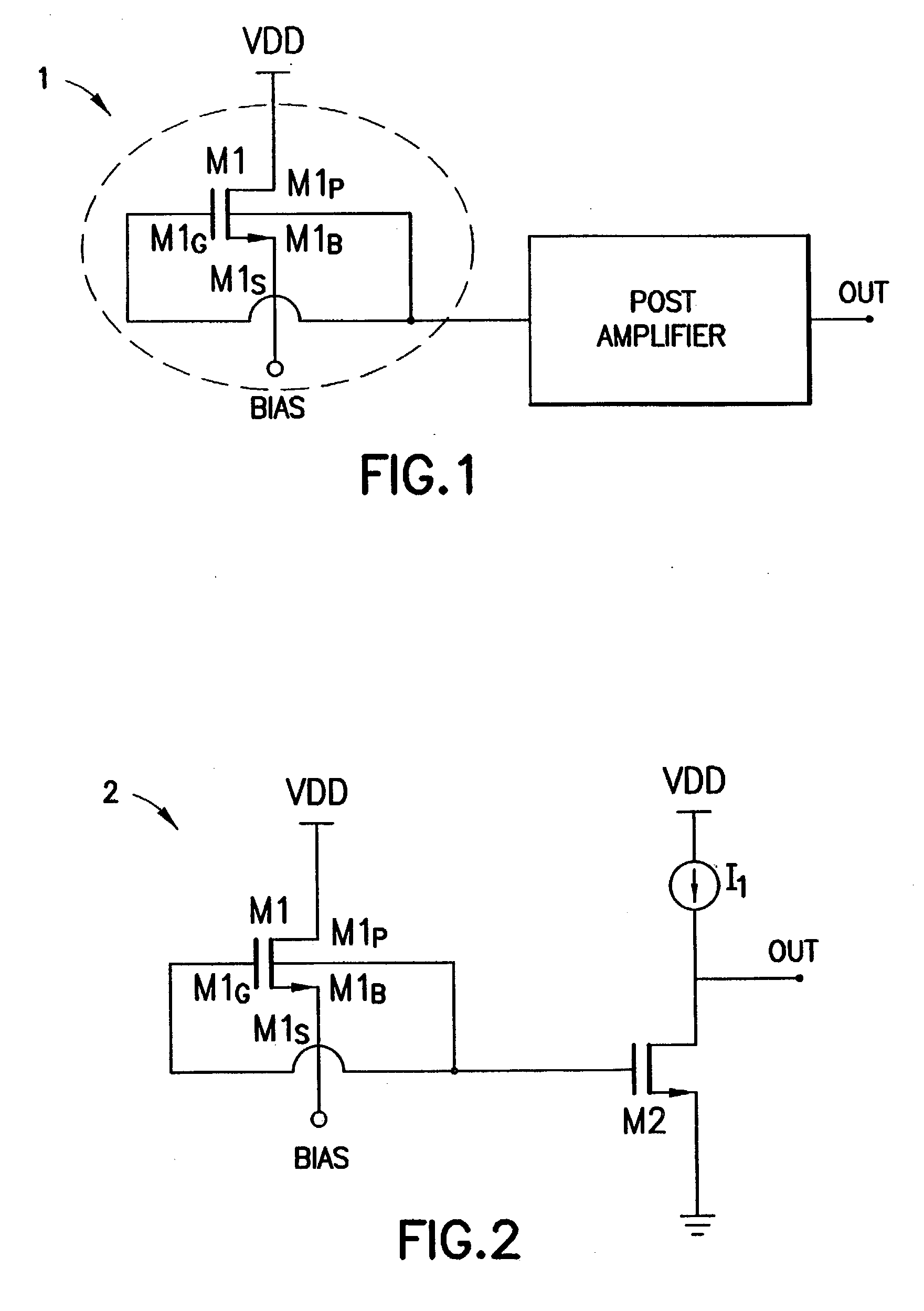
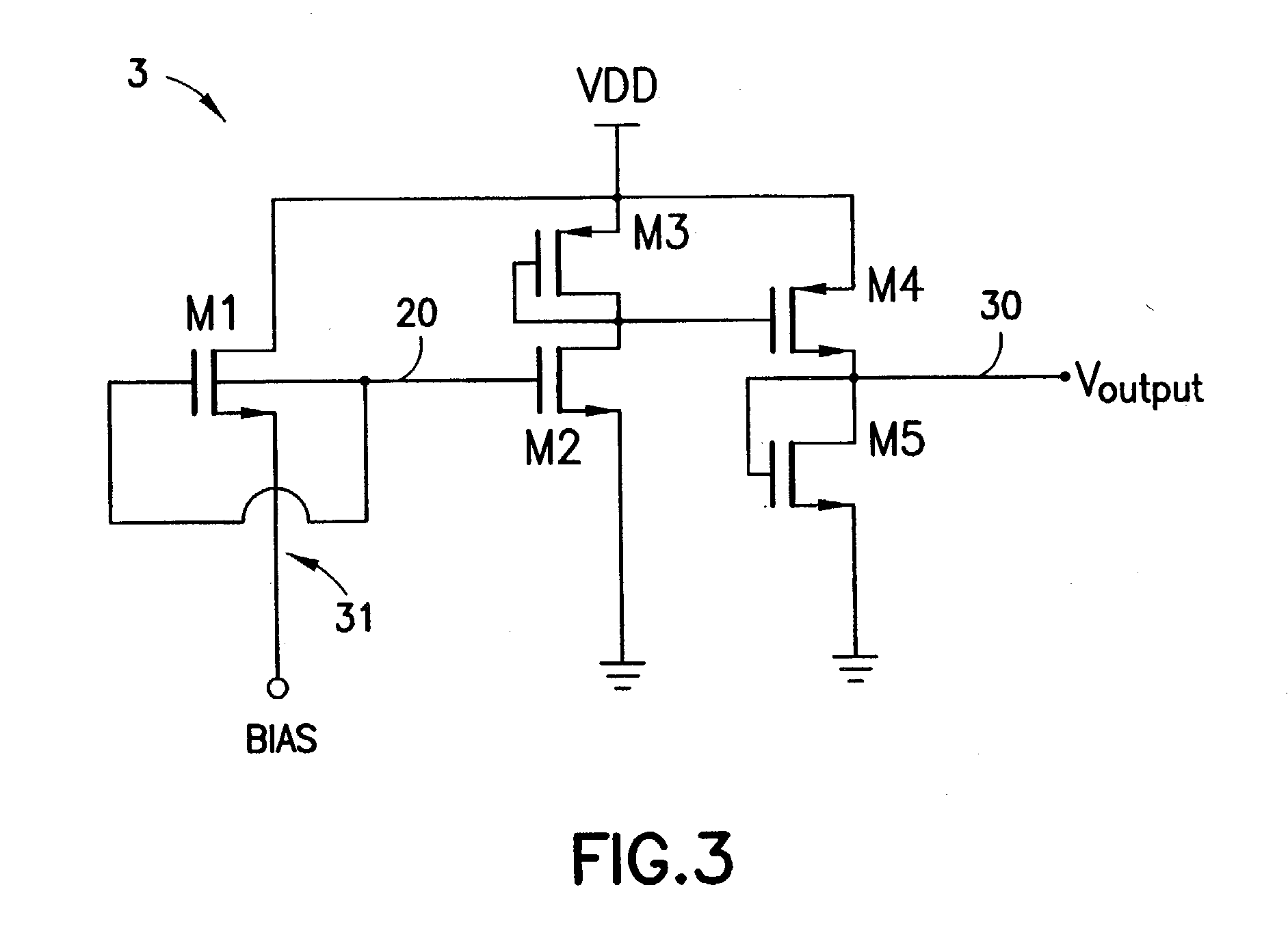
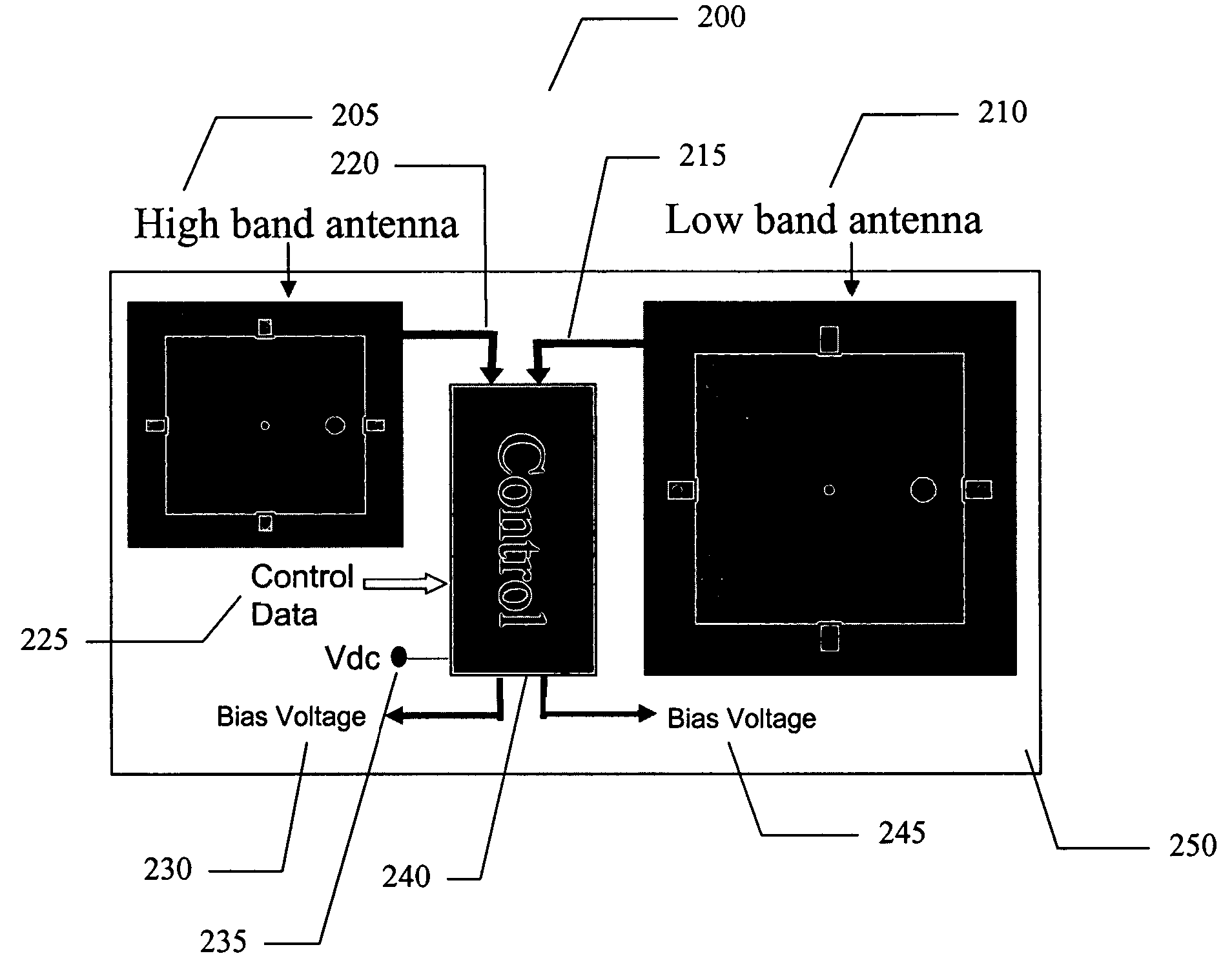
Self dc-bias high frequency logic gate, high frequency NAND gate and high frequency nor gate
InactiveUS20060197557A1Electric power will not be wastedNot to wasteReliability increasing modificationsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsNOR gateNAND gate
A self DC-bias high frequency logic gate is disclosed. The logic gate comprises at least one input terminal and one output terminal for performing Boolean operation on the high frequency input signals. The logic gate is characterized in that each transistor is coupled to an impedance matching network. The impedance matching network comprises a first terminal and a second terminal. Wherein, the first terminal is coupled to a gate of the transistor, and the second terminal is coupled to a drain of the transistor for providing an operation voltage to the transistor. When a gate of an N-type transistor and a gate of a P-type transistor are coupled with each other, and a drain of the N-type transistor and a drain of the P-type transistor are also coupled with each other, a common impedance matching network is shared with both the N-type transistor and the P-type transistor.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
Remote Plasma Atomic Layer Deposition Apparatus and Method Using Dc Bias
InactiveUS20090011150A1Prevent direct shockElectric discharge tubesFrom chemically reactive gasesRemote plasmaProduct gas
A conventional plasma applied ALD apparatus has a problem in that physical shock is directly imposed on a substrate and a thin film thereby damaging the thin film. Further, many reports have said that since an apparatus for controlling plasma energy is not arranged well, the thin film is not formed uniformly due to plasma nonuniformity. Therefore, there is provided a remote plasma atomic layer deposition apparatus using a DC bias comprising: a reaction chamber having an inner space; a substrate supporting body on which a substrate on which a thin film is to be formed is loaded arranged at one side of the inner space of the reaction chamber; a remote plasma generating unit arranged outside of the reaction chamber to supply a remote plasma into the inner space of the reaction chamber; a DC bias unit controlling energy of the remote plasma; and a source gas supply unit supplying a source gas for forming the thin film into the reaction chamber.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
Reflect array antennas having monolithic sub-arrays with improved DC bias current paths
ActiveUS20070090997A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsHeat spreaderActive array
Embodiments of active array antennas are generally described herein. Other embodiments may be described and claimed. In some embodiments, a reflect array antenna includes an array of rectangular monolithic sub-array modules arranged in a non-uniform pattern to leave a plurality of rectangular gaps in the pattern. A DC feed pin located within each gap may provide DC bias current to the sub-array modules. The sub-array modules may be mounted on a heat sink in the non-uniform pattern. The heat sink may have holes aligned with the gaps to allow passage of the DC feed pins. In some embodiments, an array cooling assembly may be coupled to the back of the heat sink to cool the reflect array antenna with a coolant.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Apparatus for generating remote plasma
ActiveUS20100096367A1Eliminate chargeImprove film qualityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaPulsed DC
Provided is an apparatus for generating remote plasma, which can improve thin-film quality by preventing an arc at a bias electrode. The apparatus includes a radio frequency (RF) electrode installed inside an upper portion of a chamber, a bias electrode installed apart from the RF electrode, and including a plurality of through holes through which plasma passes, wherein a bias power is supplied to the bias electrode, a plasma generating unit formed between the RF electrode and the bias electrode, wherein a plasma gas is supplied to the plasma generating unit, and a ground electrode installed under and spaced apart from the bias electrode, and including plasma through holes corresponding to the through holes of the bias electrode, wherein a pulsed DC bias of a second voltage level, which has a first voltage level periodically, is applied to the bias electrode.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
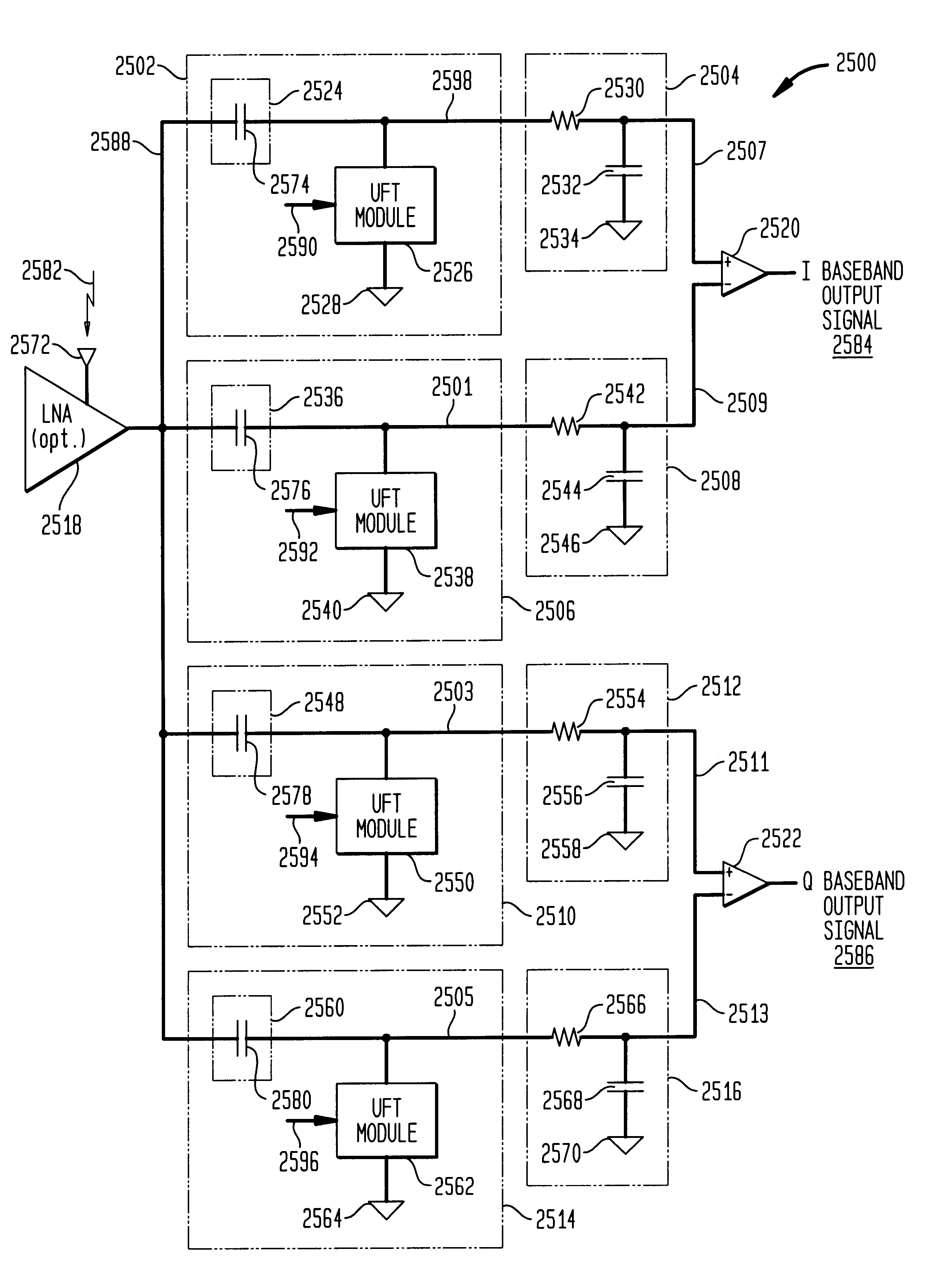
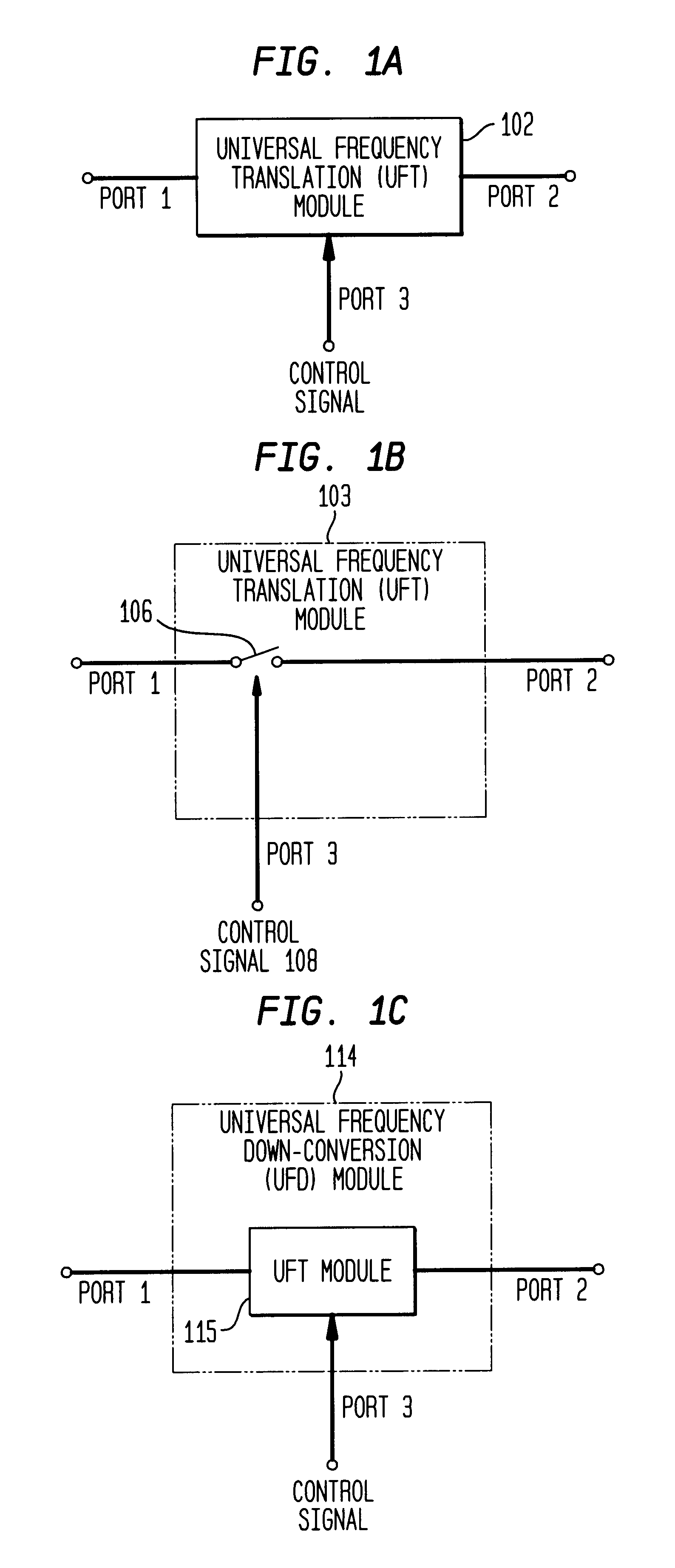
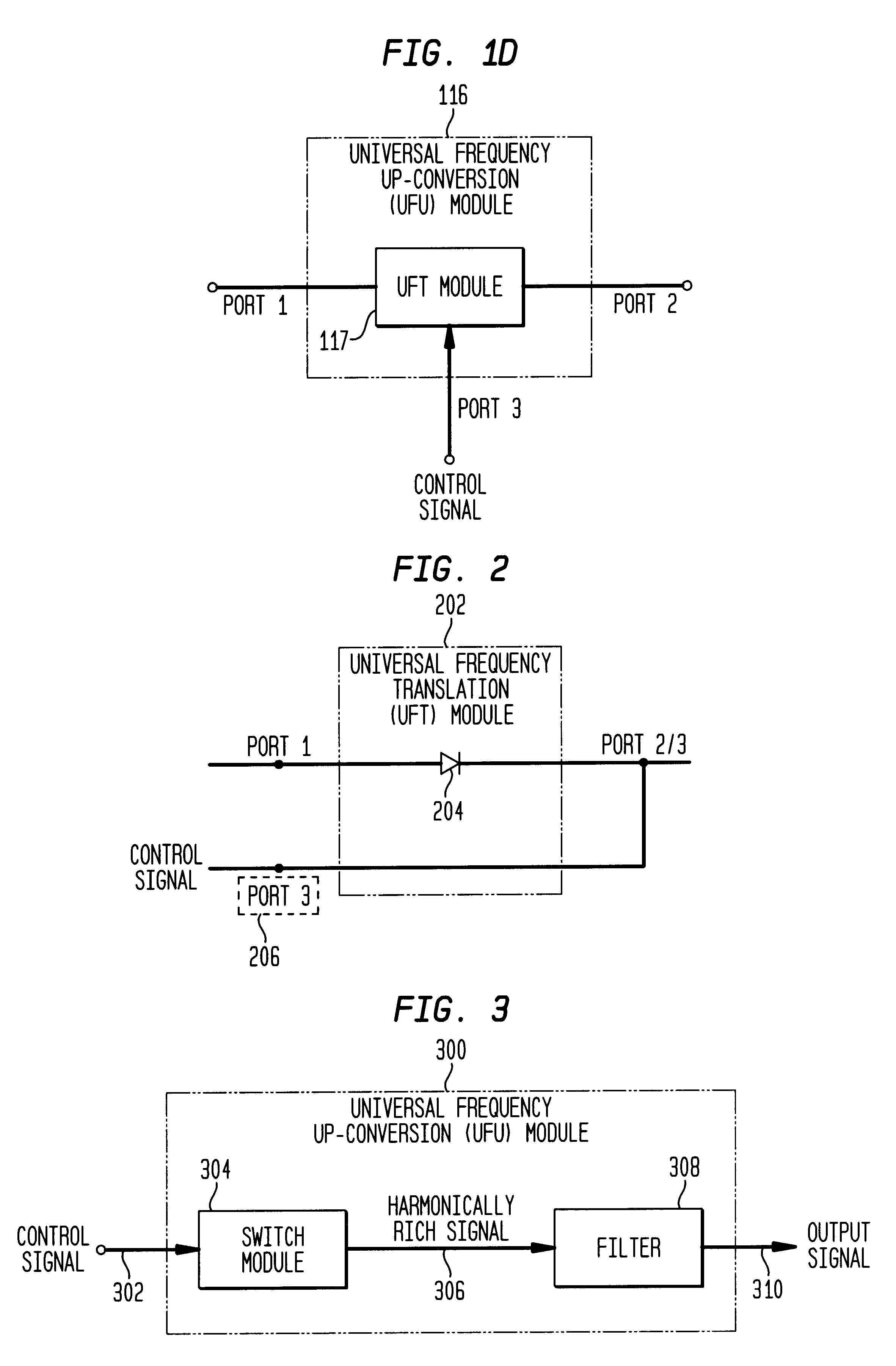
DC offset, re-radiation, and I/Q solutions using universal frequency translation technology
InactiveUS6879817B1Reduce voltageImprove dynamic rangeModulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionEngineeringDynamic range
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
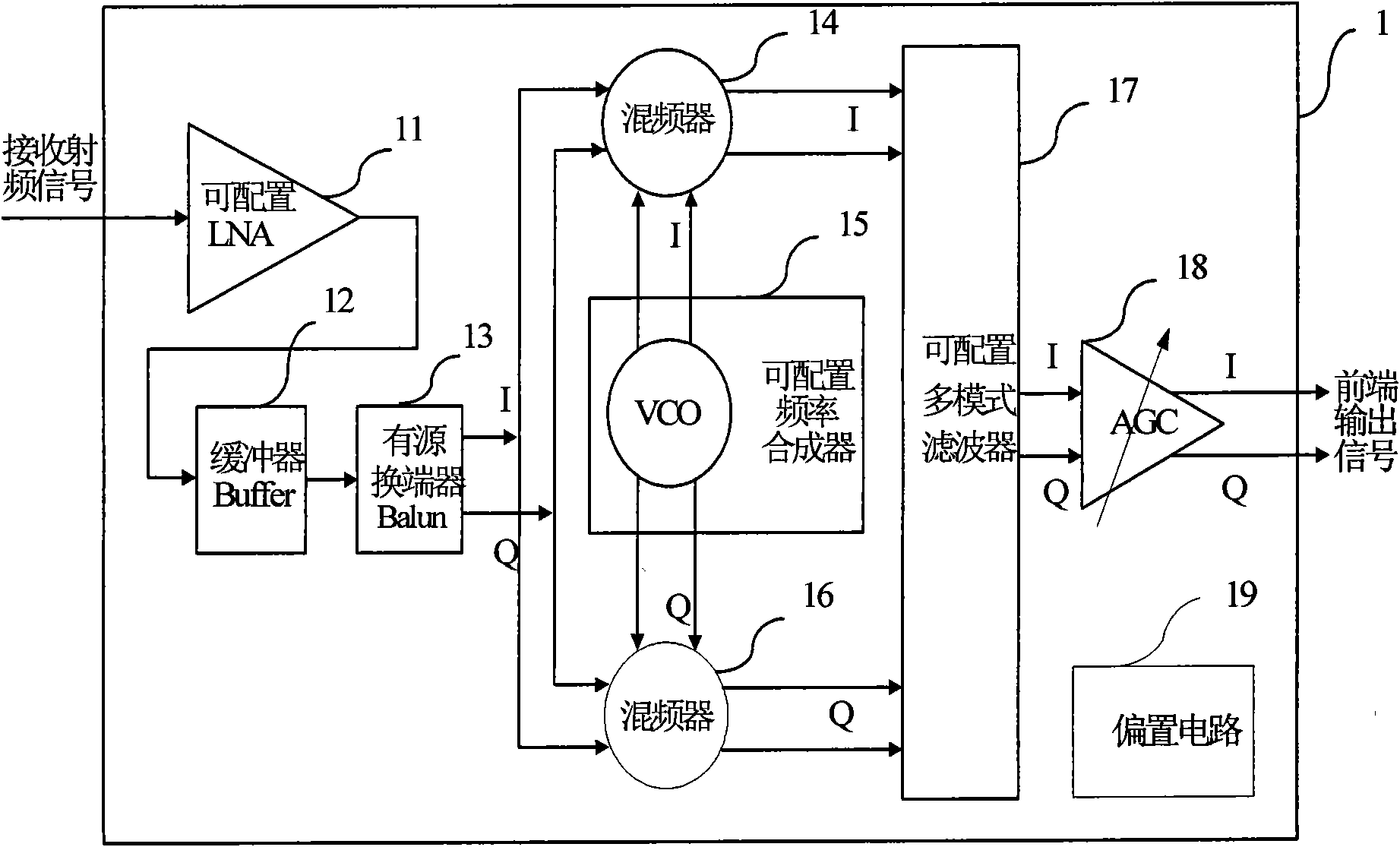
Method for constructing radio frequency front end of multi-mode multi-band satellite navigation receiver and module thereof
InactiveCN102096079ASimple and reliable compositionReduce common mode noiseBeacon systems using radio wavesSatellite radio beaconingMulti bandDifferential signaling
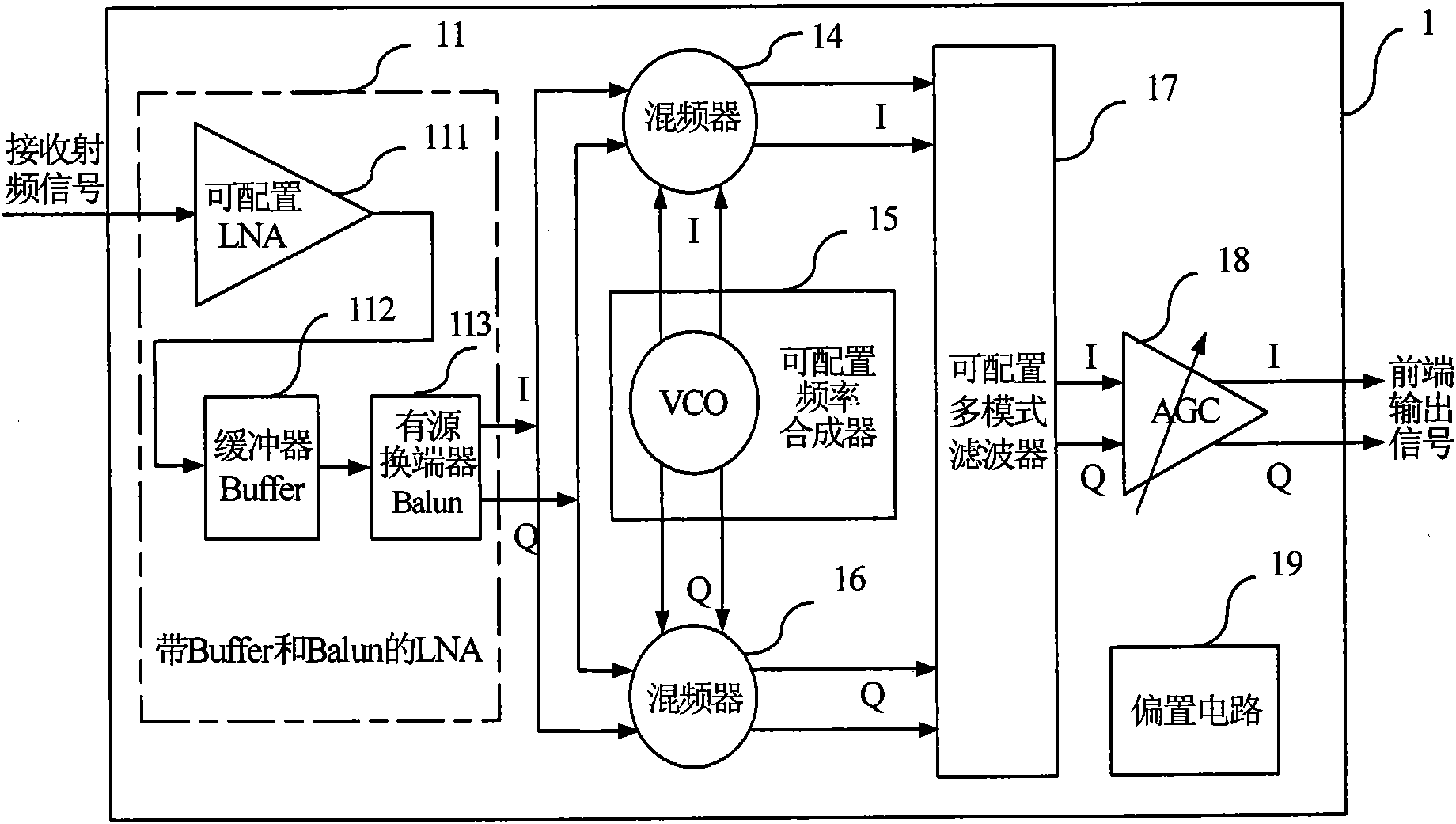
The invention discloses a configurable multi-mode multi-band satellite navigation receiving method and a radio frequency front end module constructed by the method. The front end module can receive signals of satellite navigation and positioning systems such as a global positioning system (GPS), the Big Dipper, a Galileo positioning system and a global navigation satellite system (Glonass), and comprises a configurable low-noise amplifier (LNA) with a buffer and an active balun, a folding passive mixer with a configurable frequency synthesizer, a configurable multi-mode filter, an automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier, a direct-current bias circuit, and a multi-mode multi-band program controlled and coded on-off control word from a receiving system. The radio frequency front end module can meet the requirement of multi-band multi-mode work through the control word programmed by the receiving system, has a simple and reliable structure, does not need complicated time division multiplexing control system and off-chip module, has low cost and high flexibility, and improves the noise performance of the radio frequency front end of the whole receiver and multi-mode multi-band signal processing capacity; and a one-channel signal is input into the module, and the module outputs a two-channel differential signal. The receiver can be used for receiving and processing multi-mode satellite navigation signals asynchronously, and receiving and processing satellite navigation signals with the required mode in different time intervals according to the requirement.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
Particle generation suppresspr by DC bias modulation
Embodiments of the present disclosure generally relate to an apparatus and method for reducing particle generation in a processing chamber. In one embodiment, the methods generally includes generating a plasma between a powered top electrode and a grounded bottom electrode, wherein the top electrode is parallel to the bottom electrode, and applying a constant zero DC bias voltage to the powered top electrode during a film deposition process to minimize the electrical potential difference between the powered top electrode and the plasma and / or the electrical potential difference between the grounded bottom electrode and the plasma. Minimizing the electrical potential difference between the plasma and the electrodes reduces particle generation because the acceleration of the ions in the sheath region of the electrodes is reduced and the collision force of the ions with the protective coating layer on the electrodes is minimized. Therefore, particle generation on the substrate surface is reduced.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Ultra-wideband receiver and transmitter
InactiveUS7209523B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPulse demodulatorExtensibilityBandpass filtering
A waveform-adaptive ultra-wideband (UWB) transmitter and noise-tracking UWB receiver for use in communications, object detection and radar applications. In one embodiment, the output of an oscillator is gated by a low-level impulse generator either directly or through an optional filter. In a special case of that embodiment wherein the oscillator is zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, the low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The low-level impulse signal can be generated digitally. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry data, or may be used in object detection or ranging applications. The power amplifier may be gated to provide a power-efficient UWB transmitter. The UWB transmitter exhibits well defined and controllable spectral characteristics. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Controllable nanomechanical memory element
A memory device includes a mechanical element that exhibits distinct bistable states under amplitude modulation. The states are dynamically bistable or multi-stable with the application of a drive signal of a given frequency. The natural resonance of the element in conjunction with a hysteretic effect produces distinct states over a specific frequency range. Devices with multiple elements that respond to different frequency ranges provided on a common contact are formed with improved density. The devices may be excited and read with magnetomotive, capacitive, piezoelectric and / or optical methods. The devices may be planar oriented or out of plane oriented to permit three dimensional memory structures. DC biases may be used to shift frequency responses to permit an alternate method for differentiating states of the element.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
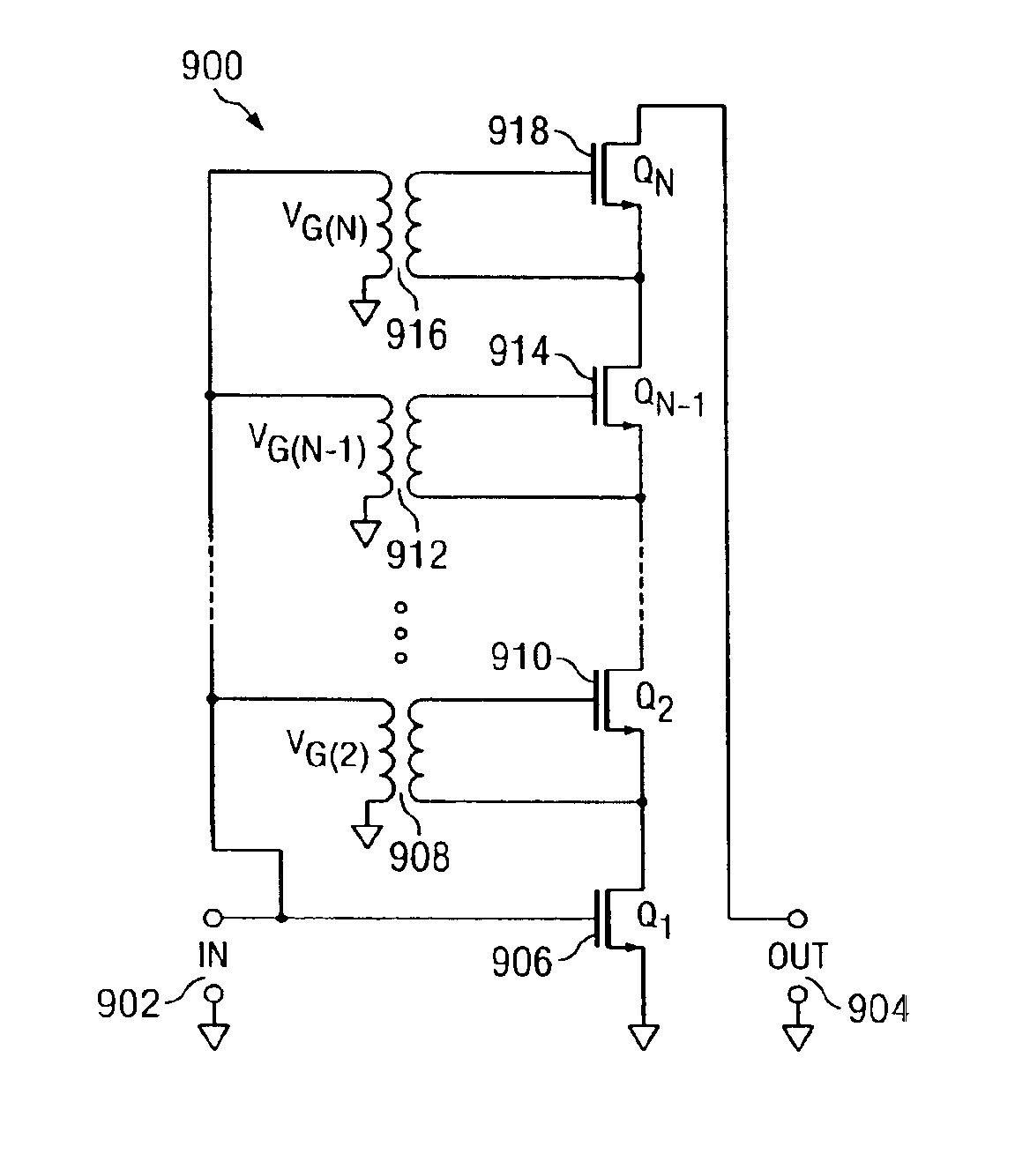
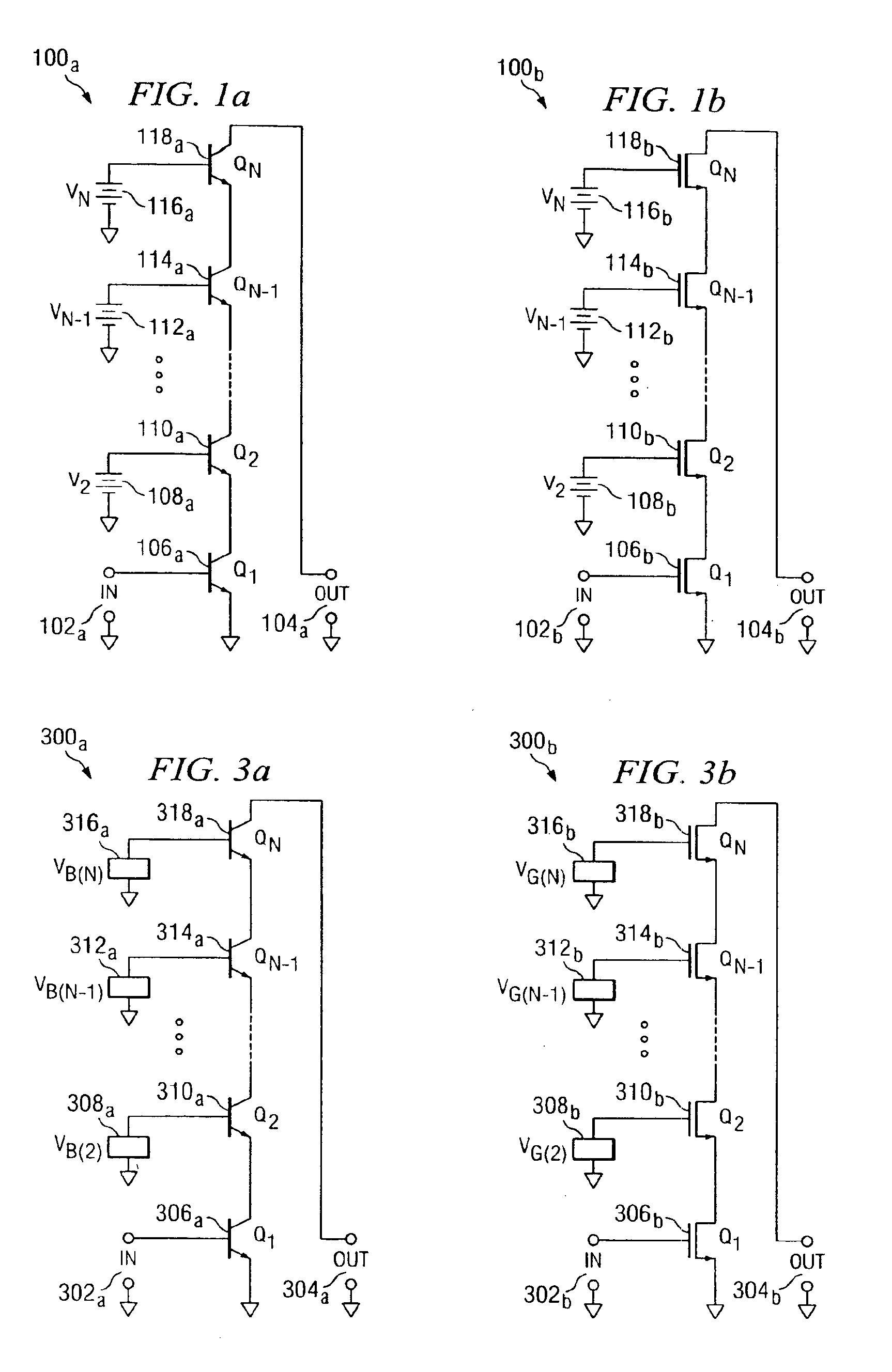
Multi-cascode transistors
InactiveUS6888396B2Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceMOSFETCascode
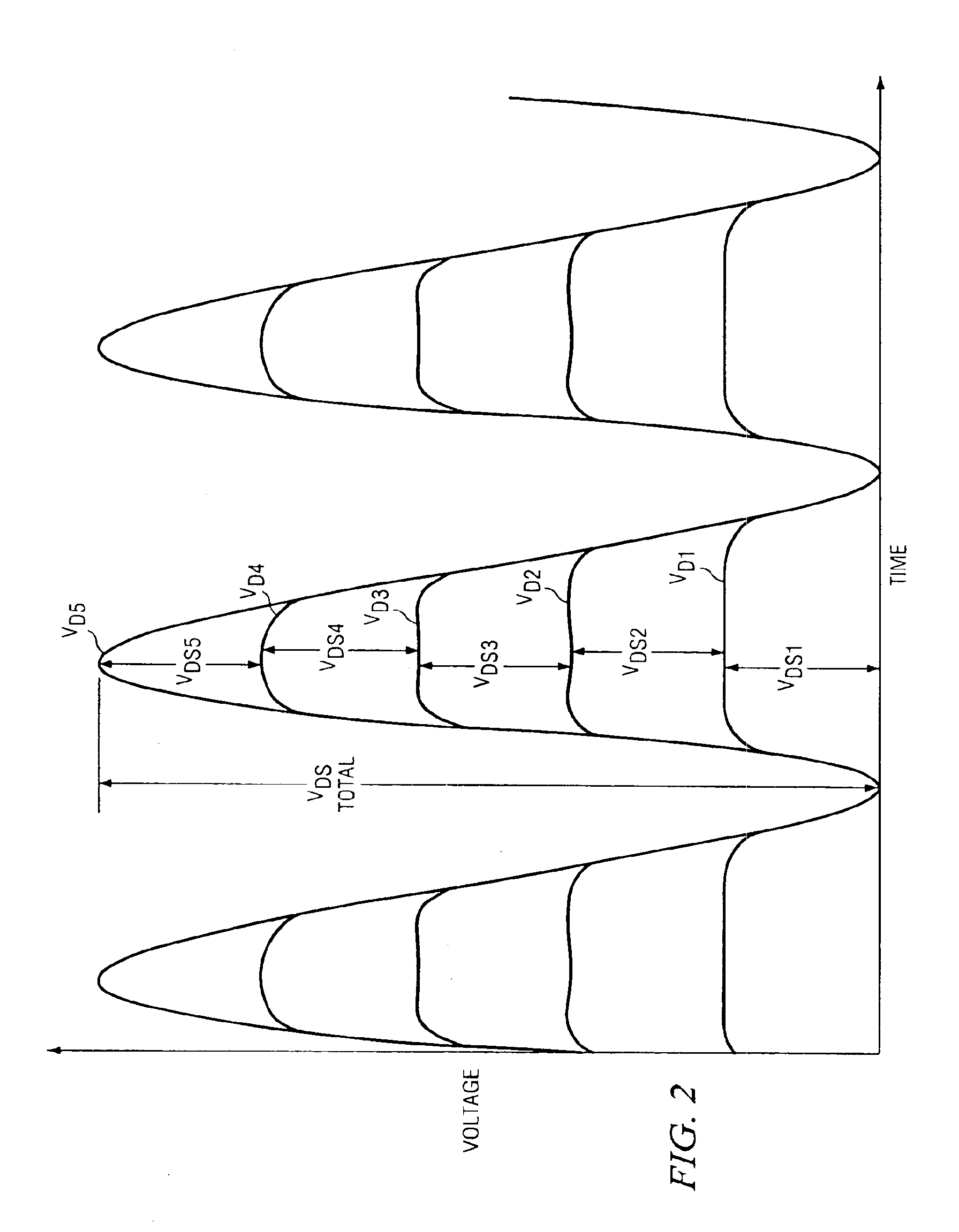
A cascode circuit with improved withstand voltage is provided. The cascode circuit includes three or more transistors, such as MOSFET transistors. Each transistor has a control terminal, such as a gate, and two conduction terminals, such as a drain and a source. The conduction terminals are coupled in series between two output terminals, such as where the drain of each transistor is coupled to the source of another transistor. A signal input is provided to the gate for the first transistor. Two or more control voltage sources, such as DC bias voltages, are provided to the gate of the remaining transistors. The DC bias voltages are selected so as to maintain the voltage across each transistor to a level below a breakdown voltage level.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Pulse and OFDMD double-data modulation method
InactiveCN101710890AFlexible configurationIncrease transfer rateMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalPeak value
The invention discloses a double-data modulation method of pulse and OFDM. An optical spectrum of a single chip white light LED is formed by exciting fluorescent powder of yellow color or red-green color and the like by a blue light, and the shape of the whole optical spectrum has two relative independent peak values, wherein the responding speed of the blue light is higher than that of a warm color light. The invention can be used for transmitting data by pulse modulation of the blue light and can be used as a carrier wave for the warm color light OFDM modulation, thus a double channel high-speed data transmission is realized. In addition, the blue light can be used as a reference simultaneously for OFDM symbol synchronization, direct current offset estimation and channel estimation.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
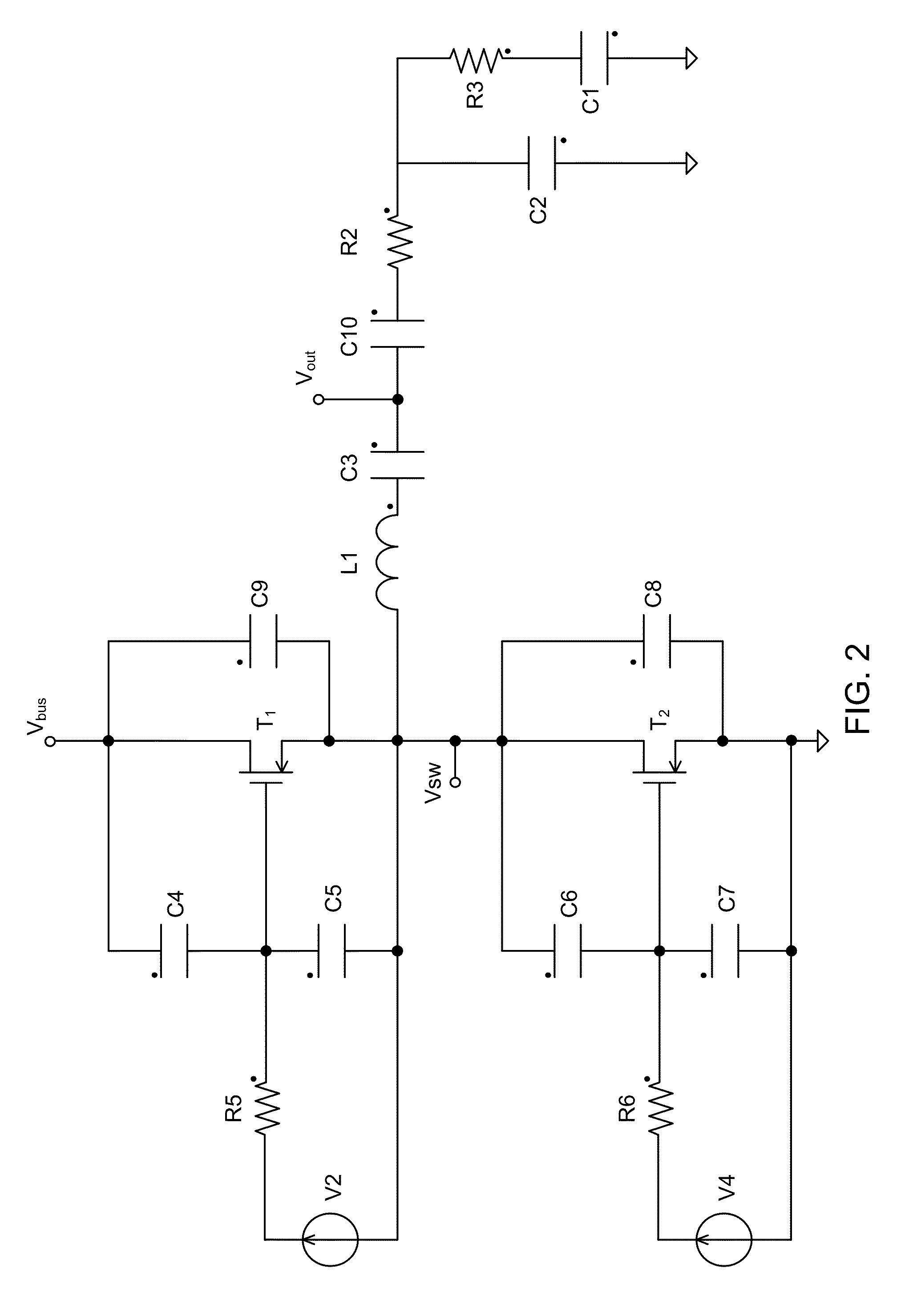
Synchronous commutation dc-dc converter
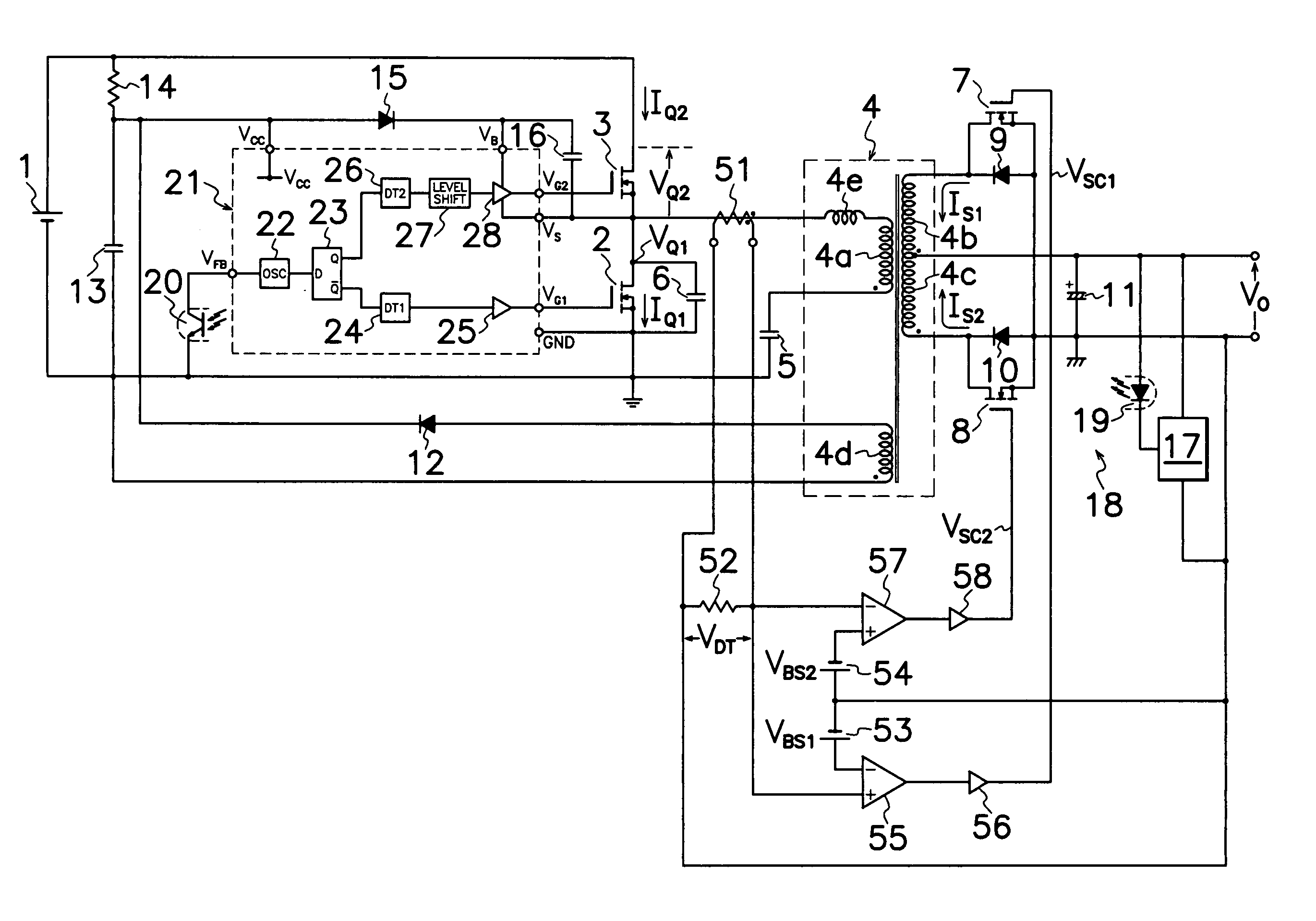
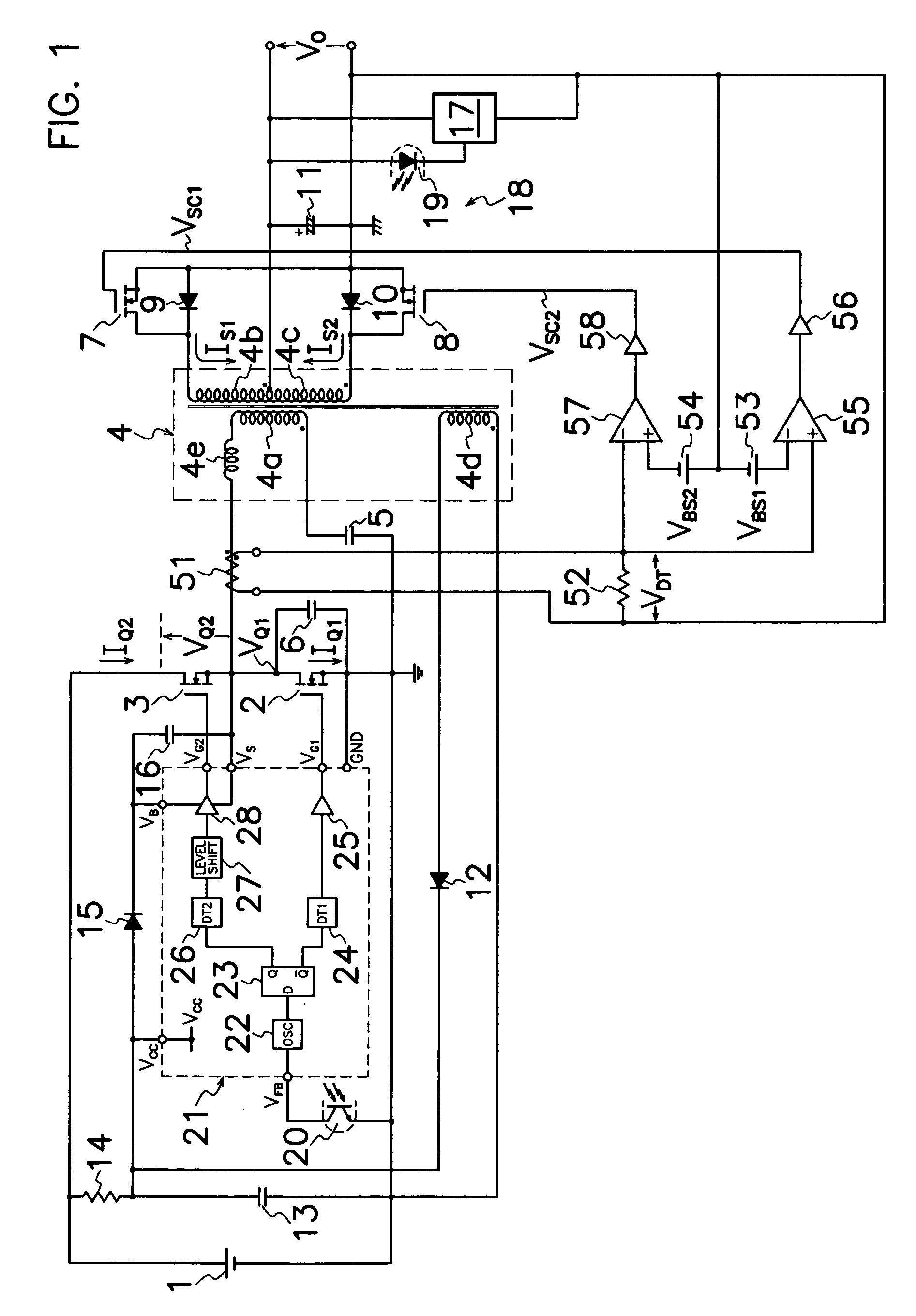
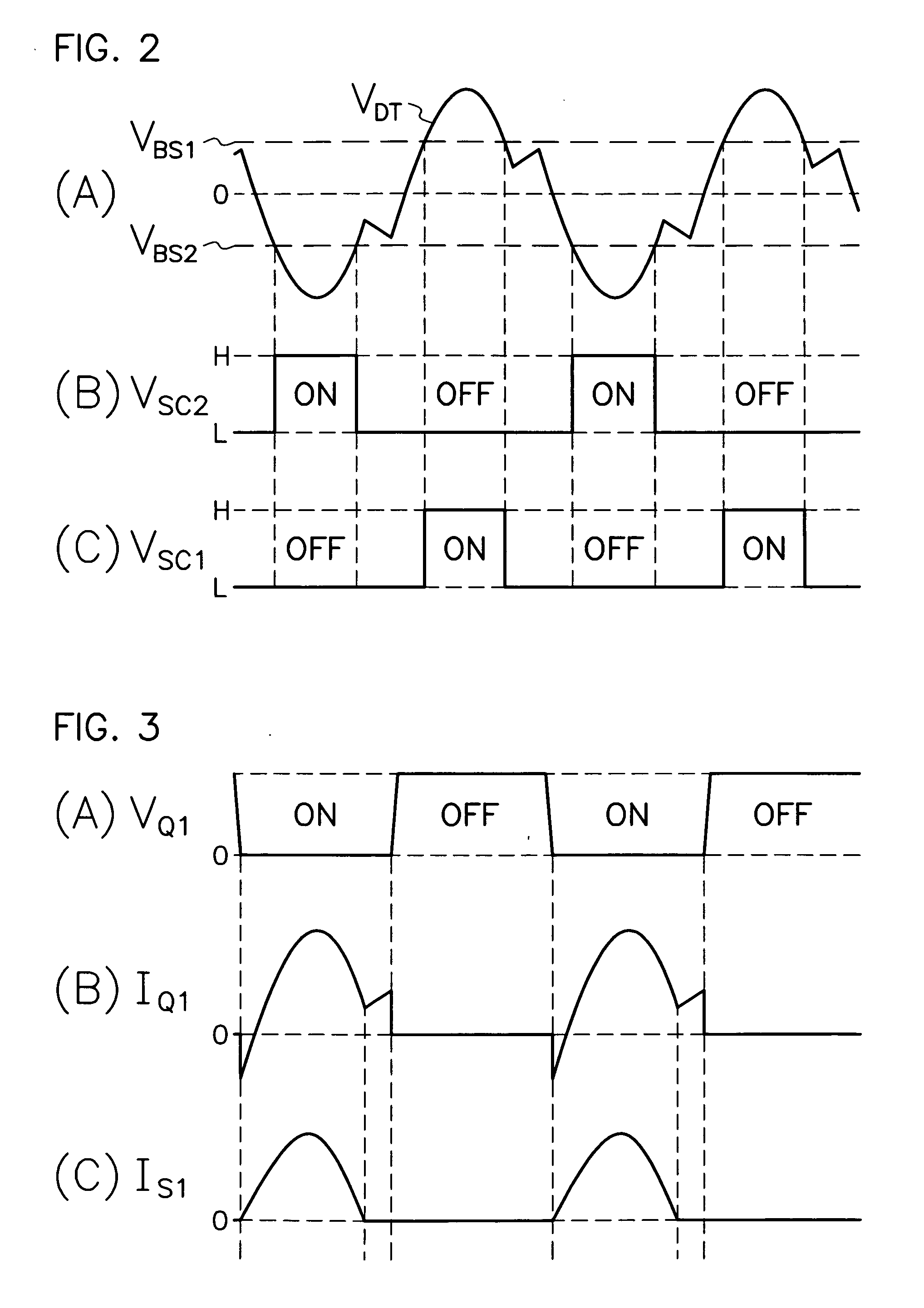
InactiveUS20070008757A1Avoid power outagesImprove conversion efficiencyAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterExcitation current
A DC-DC converter of synchronous rectification type is provided which comprises: a current detector (51) for discerning electric current (IQ1, IQ2) flowing through a primary side circuit; first and second DC biasing power supplies (53, 54) for producing a bias voltage (VBS1, VBS2) higher than voltage corresponding to excitation current through transformer (4); and first and second comparators (55, 57) for activating first and second rectifying MOS-FET (7, 8) when current detector (51) produces the detection voltage (VDT) over bias voltage (VBS1, VBS2) of first and second DC biasing power supplies (53, 54). As each of first and second rectifying MOS-FETs (7, 8) in secondary side circuit is driven synchronously with electric current (IQ1, IQ2) flowing through the primary side circuit except excitation current component through transformer (4), the converter can minimize switching loss in each rectifying MOS-FET (7, 8) in secondary side circuit to improve conversion efficiency.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
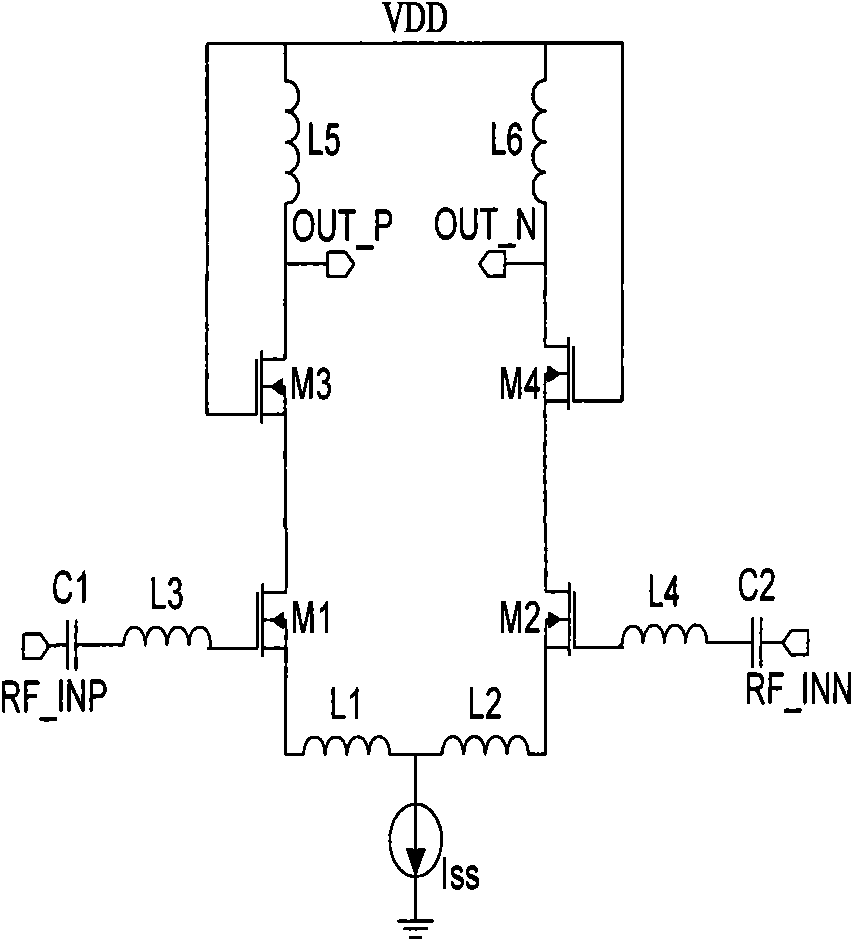
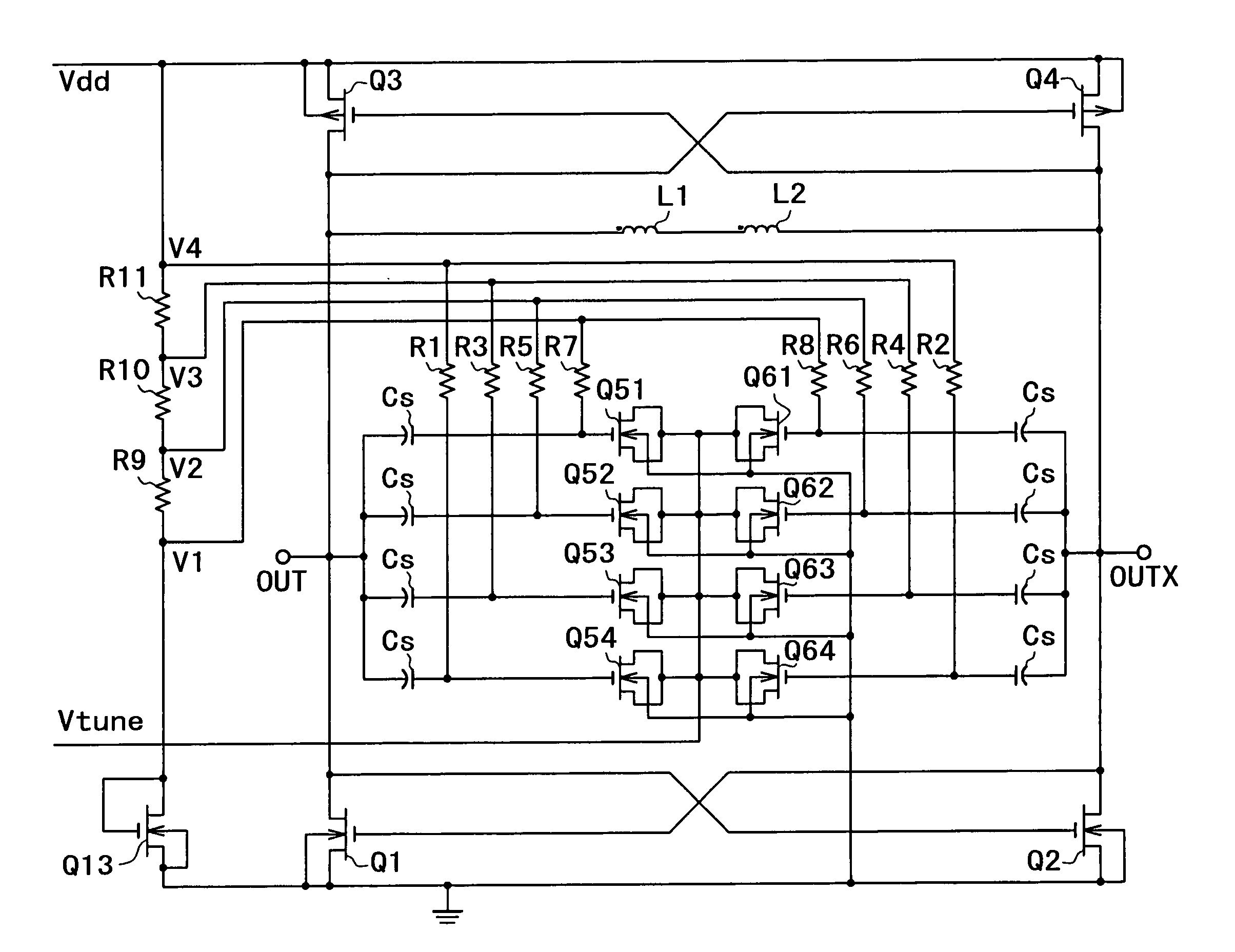
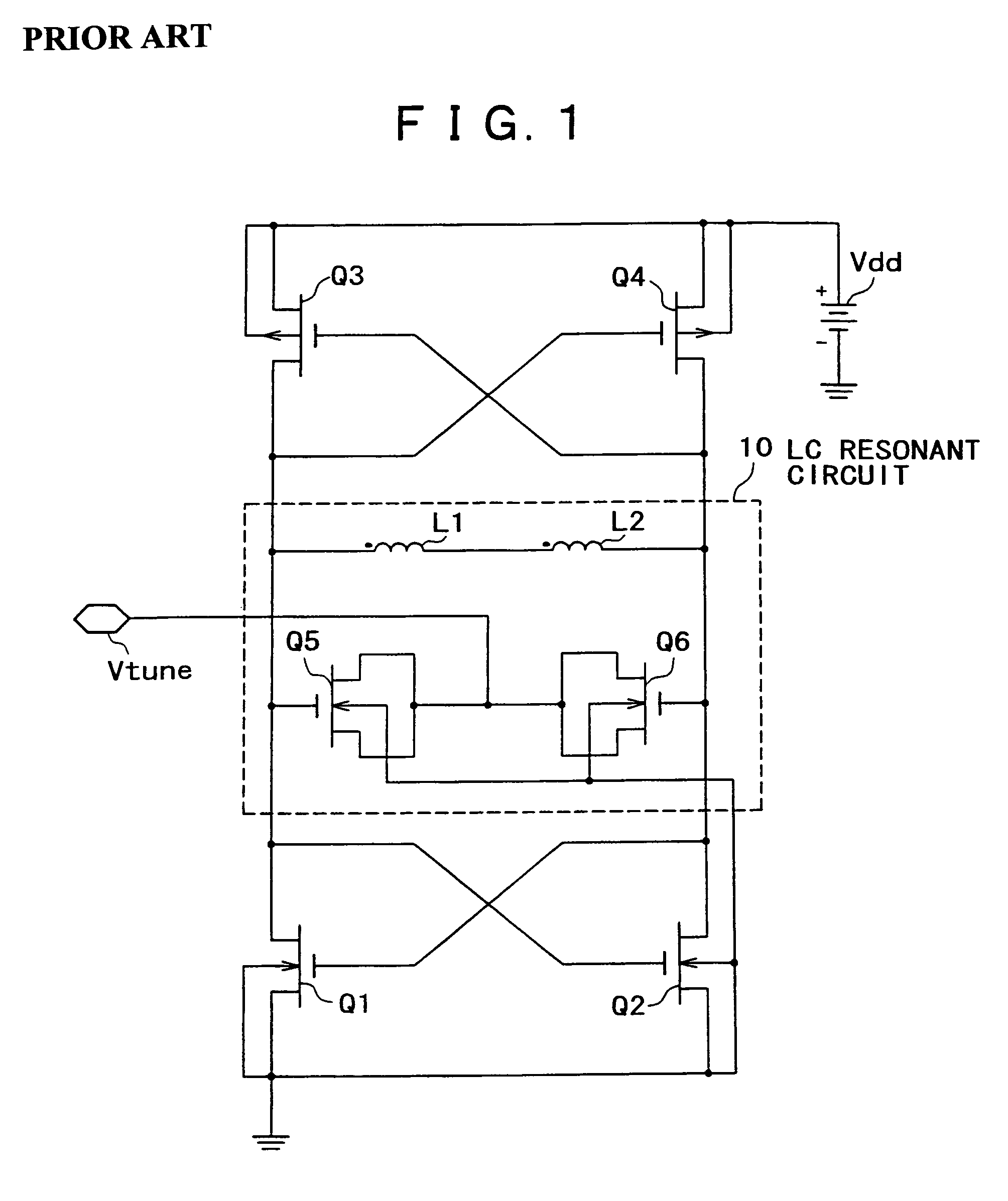
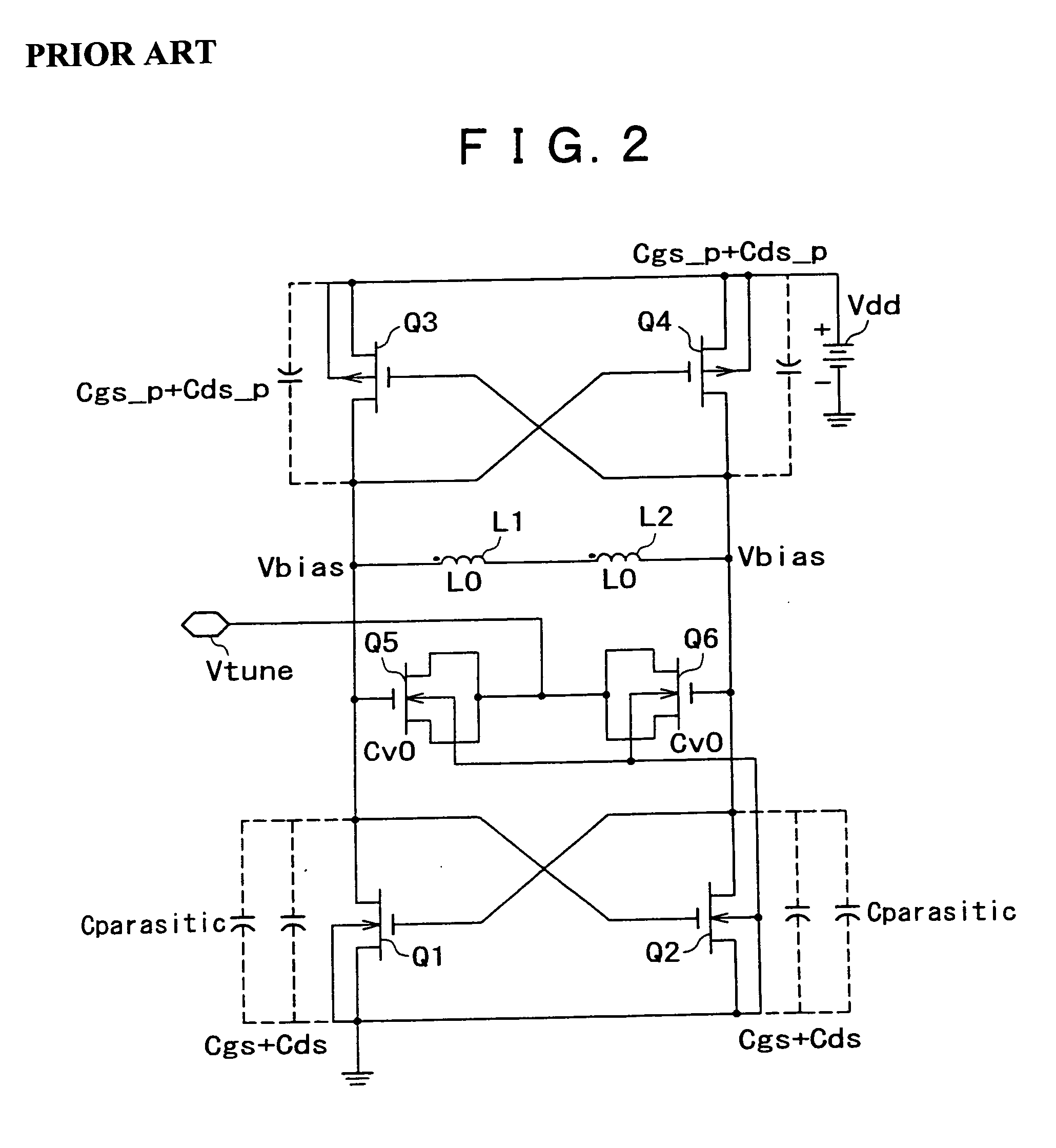
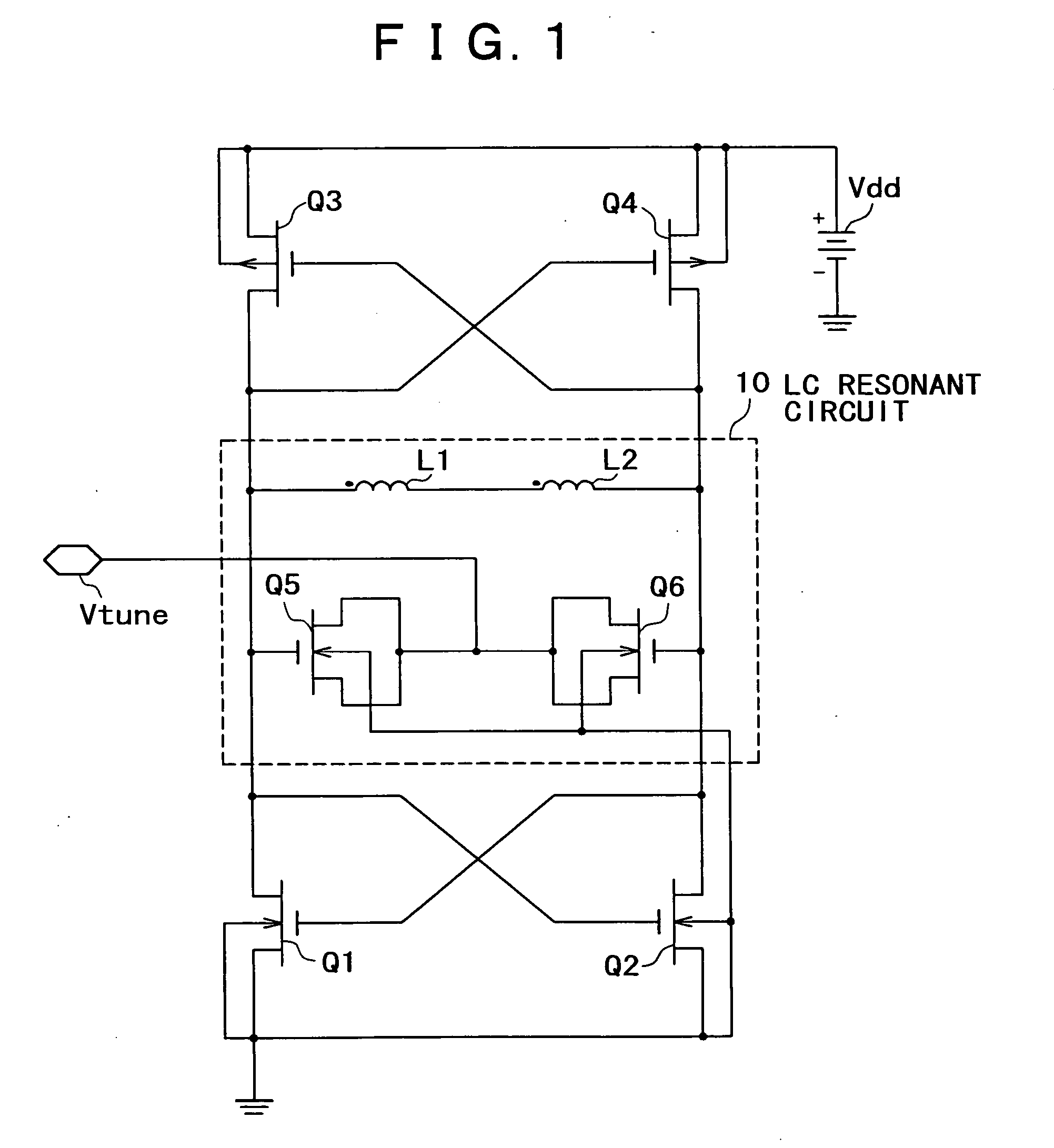
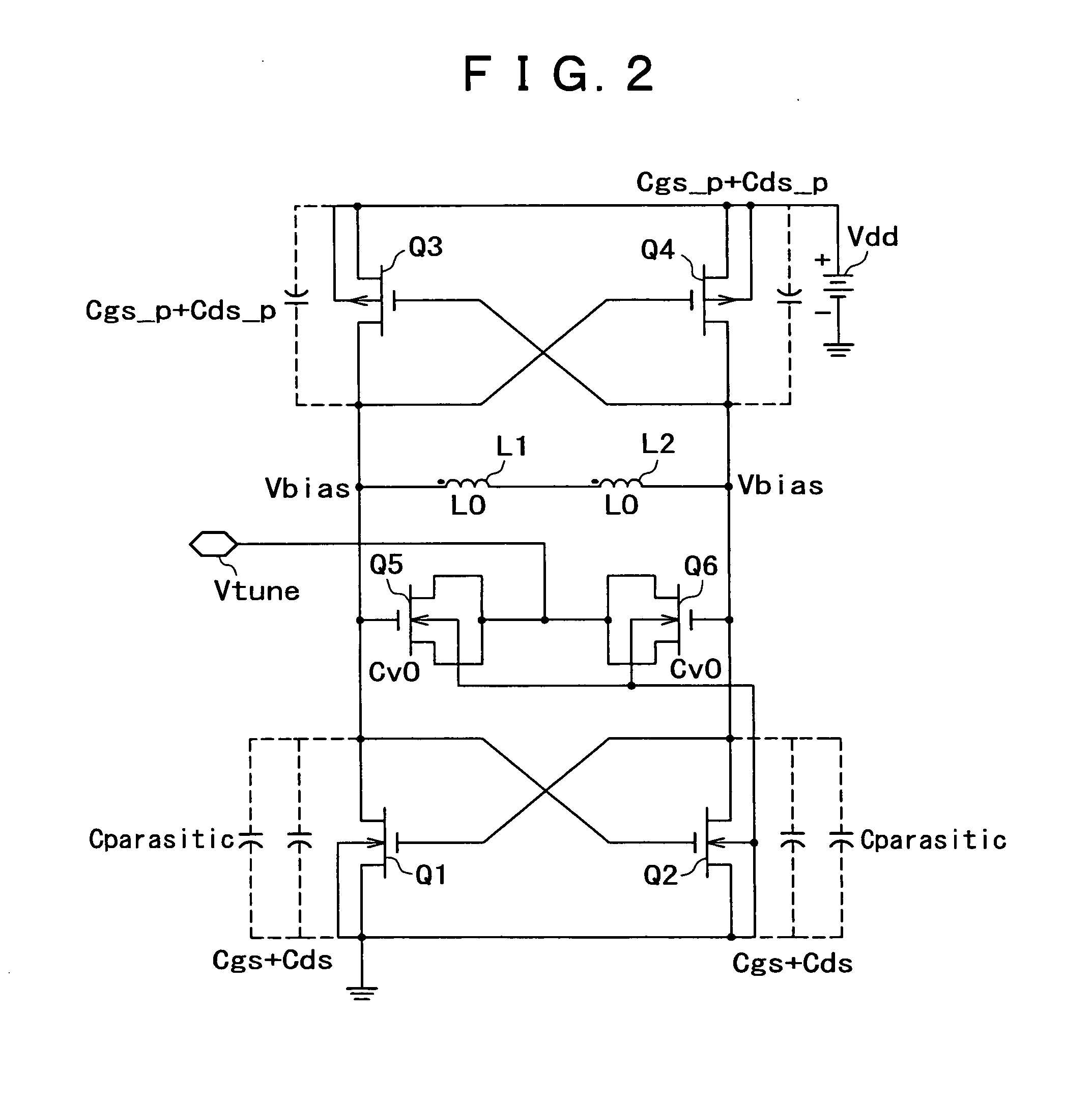
Resonant circuit and a voltage-controlled oscillator
InactiveUS7183870B2Improve phase noiseSimple compositionAngle modulation by variable impedenceAngle modulation detailsCapacitanceVoltage generator
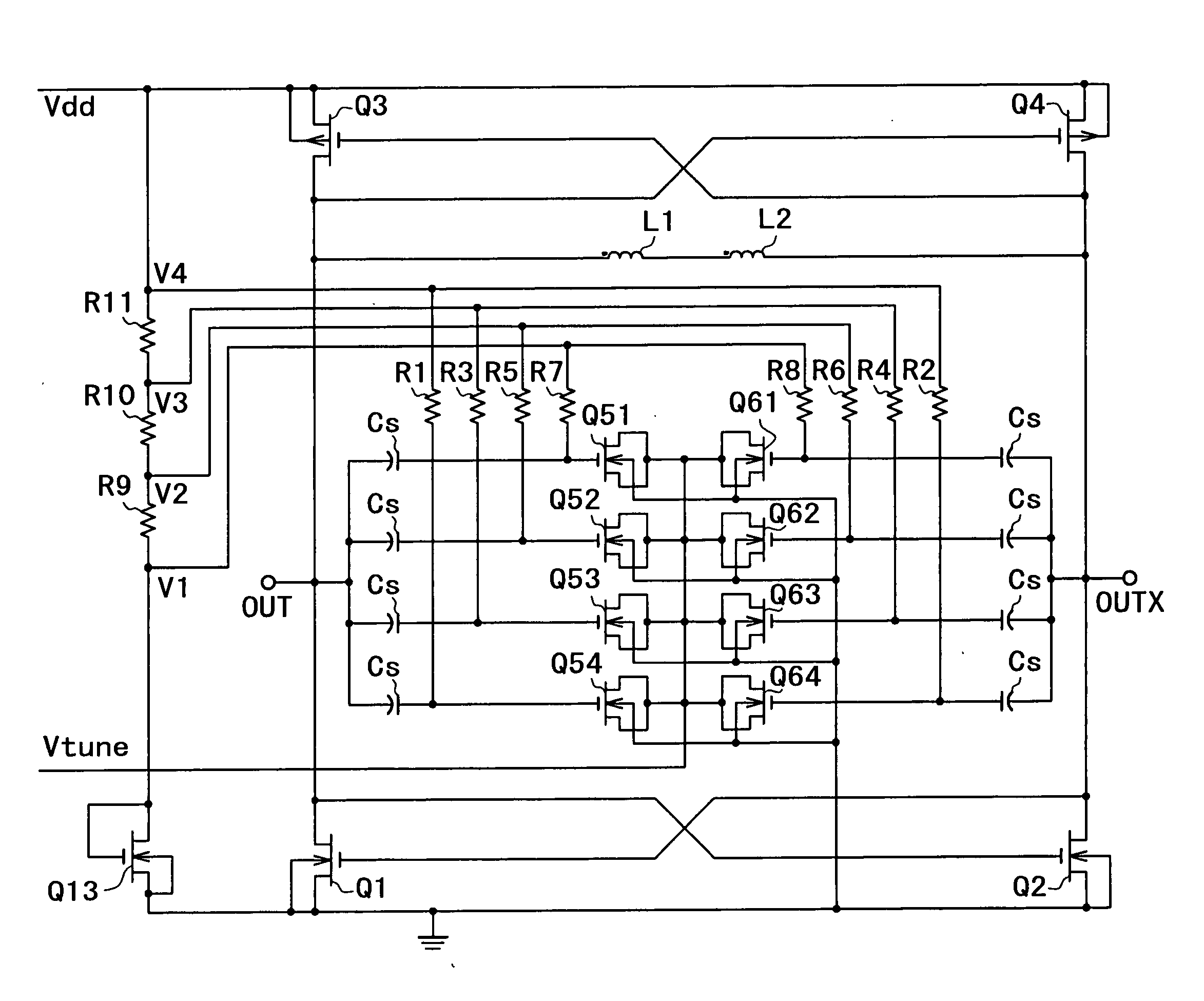
A voltage-controlled oscillator comprising a resonant circuit and MOS transistors which constitute a negative resistance circuit of a differential structure. The resonant circuit consists of an inductance element and a MOS variable capacitance element connected in parallel therewith. The MOS variable capacitance element is divided into plural pairs connected in parallel with each other. A voltage division circuit generates staircase different-step DC bias voltages to be applied respectively to the gates of the plural divided MOS transistors. The divided MOS variable capacitance elements have a common terminal to which a common control voltage is applied. The resonant circuit is capable of reducing a load on the control voltage generator and improving the characteristics of the voltage-controlled oscillator.
Owner:SONY MOBILE COMM INC
Integrated photodetector for VCSEL feedback control
InactiveUS20030109142A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling light guidesDriver circuitPhotovoltaic detectors
An integrated photodetector means for controlling the output of a light source, where the control means is a photodetector formed on a silicon-on-insulator substrate. The integrated photodetector senses the optical power from the light source and provides an electrical feedback signal which can be used to adjust the DC bias levels of the light source control driver circuit. The approach readily lends itself to large arrays of light sources bonded to silicon-on-sapphire driver circuits and is especially suitable for controlling light sources such as VCSELs in arrays such as are found in communications systems.
Owner:PEREGRINE SEMICONDUCTOR
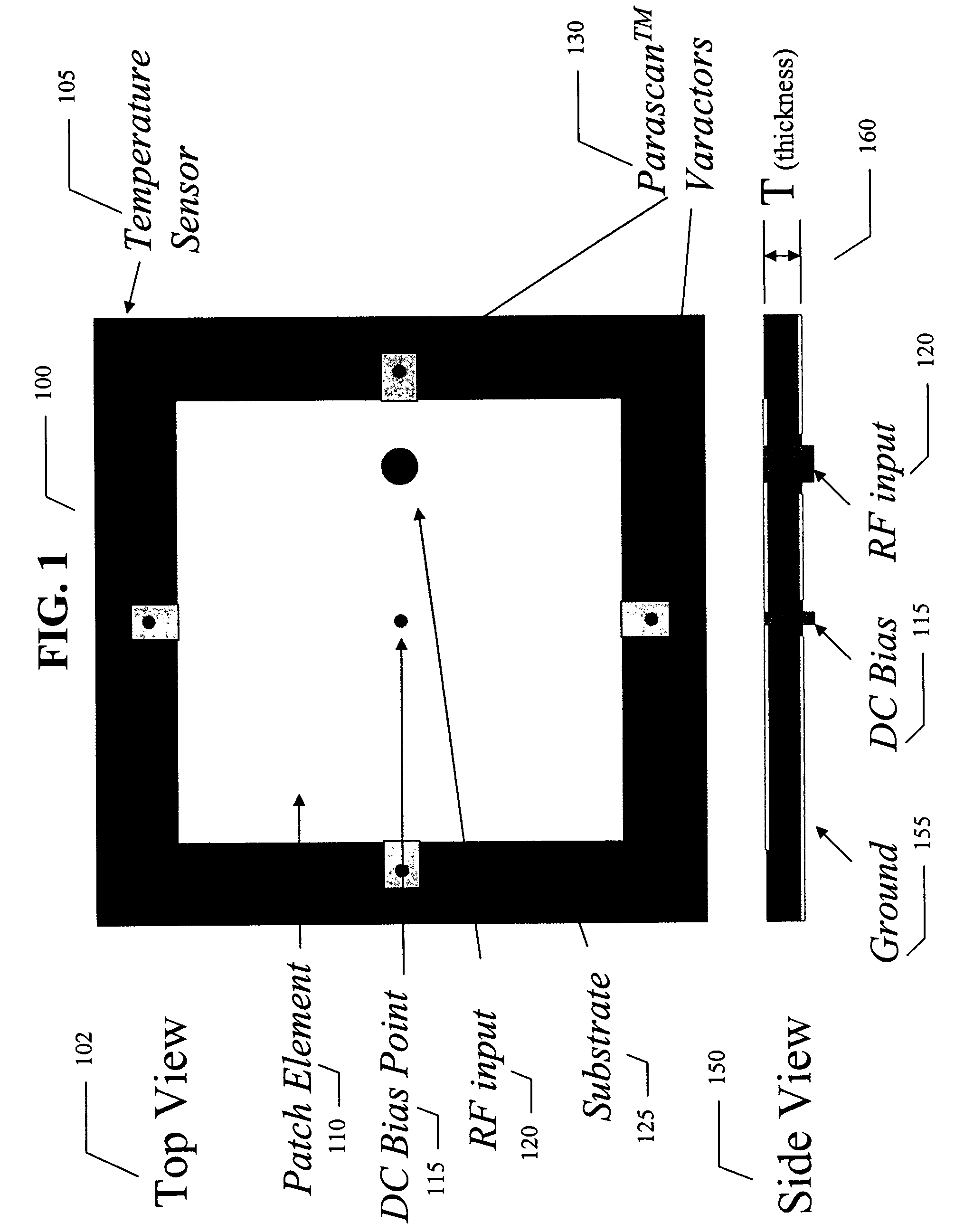
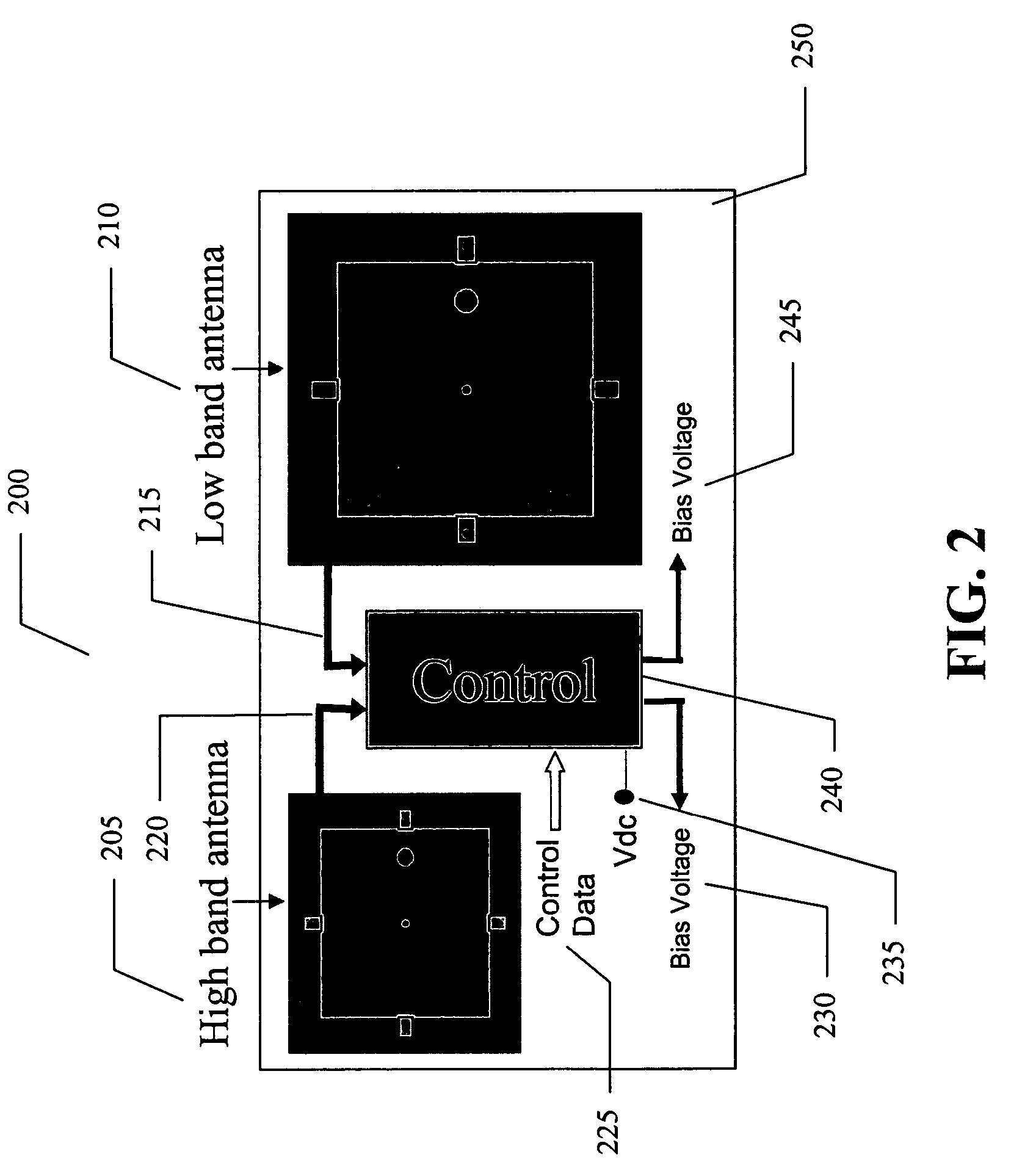
Electronically tunable quad-band antennas for handset applications
An electronically tunable quad-band antenna which includes a tunable high band antenna tuned by at least one tunable varactor associated therewith; the tunable high band antenna further includes a substrate, a patch element on said substrate, at least one voltage tunable varactor associated with the patch element, a DC bias point on the patch element, an RF input on the patch element, and a temperature sensor associated with the high band pass antenna. Also included in a preferred embodiment of the electronically tunable quad-band antenna of the present invention is a tunable low band antenna tuned by at least one tunable varactor associated therewith, the tunable low band antenna further including a substrate, a patch element on said substrate, at least one voltage tunable varactor associated with said patch element, a DC bias point on said patch element, an RF input on said patch element, and a temperature sensor associated with said low band pass antenna.Also included is a controller receiving control data, and receiving output information from said low band antenna and output information from said high band antenna and controlling a first bias voltage for biasing the at least one voltage tunable varactor associated with the high band antenna and a second bias voltage for biasing the at least one voltage tunable varactor associated with the low band antenna. The bias voltages can be provided by a DC to DC converter regulator.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Composite magnetic body, and magnetic element and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6888435B2Solve the real problemImprove featuresTransformers/inductances casingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInductanceMetal
The present invention provides a composite magnetic body containing metallic magnetic powder and thermosetting resin and having a packing ratio of the metallic magnetic powder of 65 vol % to 90 vol % and an electrical resistivity of at least 104 Ω·cm. When a coil is embedded in this composite magnetic body, a miniature magnetic element can be obtained that has a high inductance value and is excellent in DC bias characteristics.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
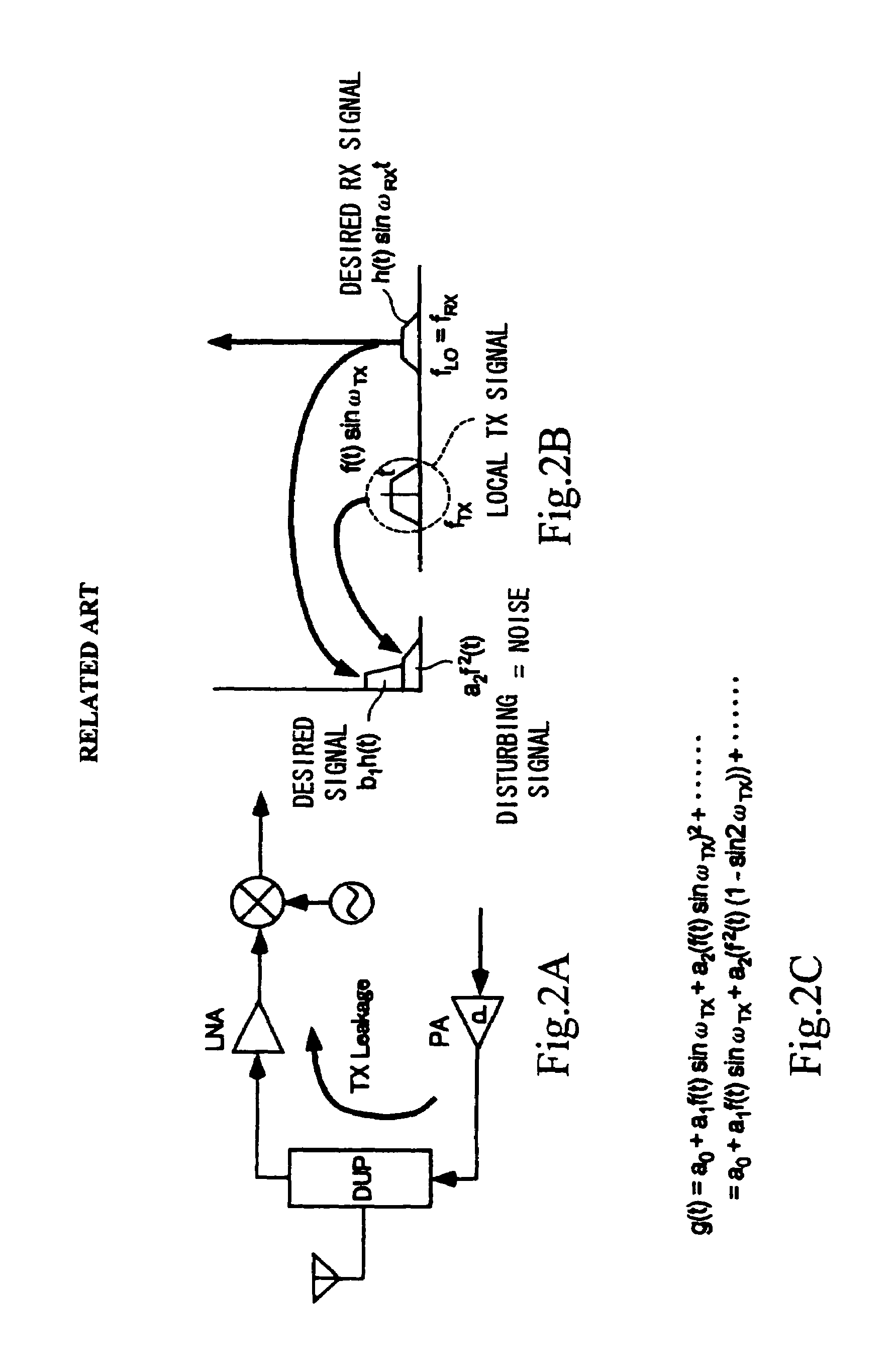
Cancellation system for frequency reuse in microwave communications
InactiveUS6882868B1Good than fifty percent transmit efficiencyWeakening rangeRadio wave finder detailsSpatial transmit diversityNonlinear distortionFrequency reuse
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
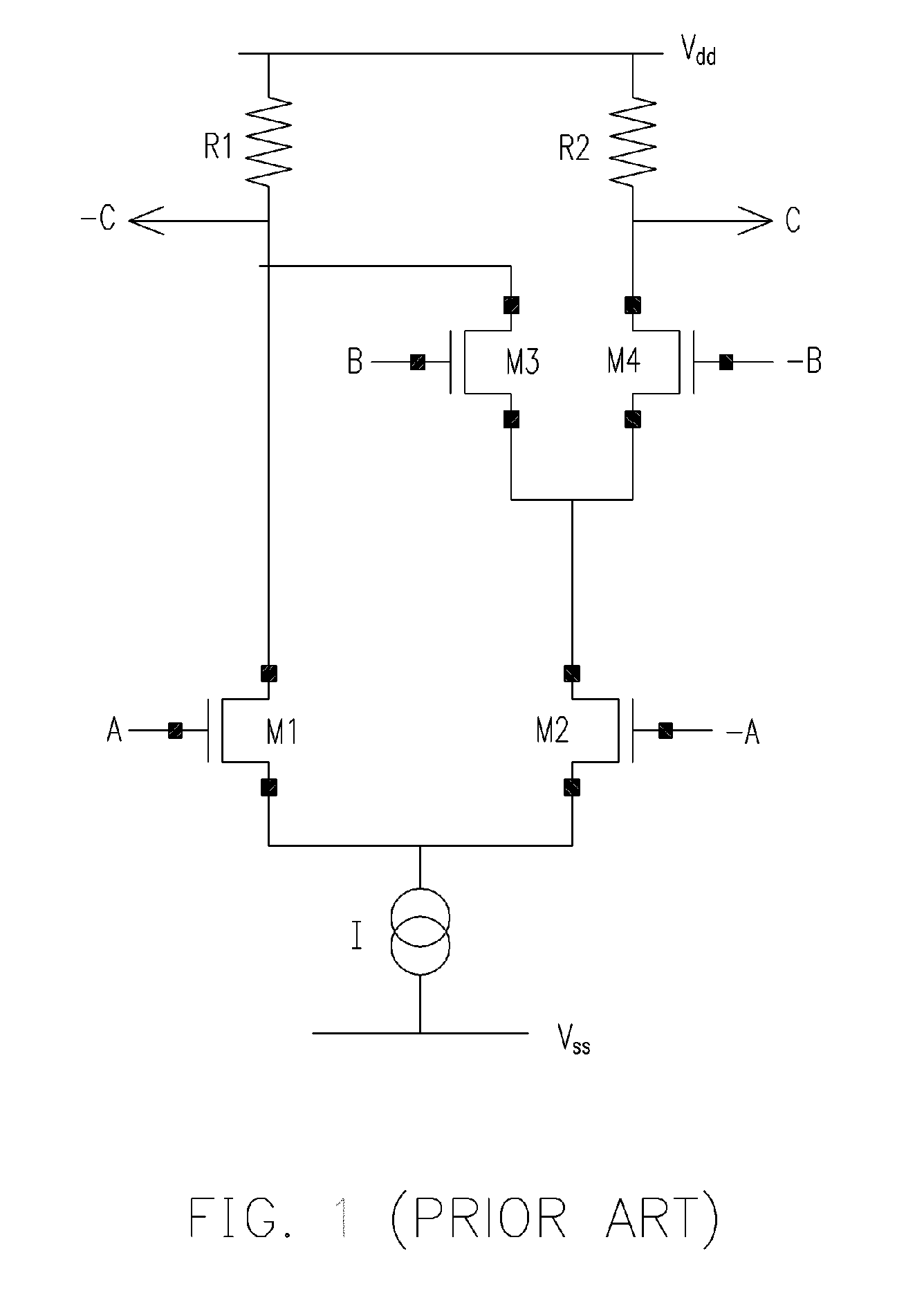
Bias circuit for transconductance amplifier
InactiveUS6023196AModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationSignificant errorVoltage reference
In low-voltage circuits, there is often insufficient voltage to use a current source to bias a transconductance amplifier stage. This is particularly true in mixers where a switching circuit must be stacked on top of the transconductance input stage. One way around this problem is to get "double-duty" out of the input differential pair, using it both for gain stage and for DC bias. This is done by AC coupling in a high-frequency input signal, while using a low-frequency, DC-coupled circuit to establish the proper bias level. One common technique is to use a simple current mirror scheme to establish the DC level. Proper biasing using this technique requires good matching of resistance. In some implementations of transconductance amplifiers, particularly those that use inductors as degeneration elements, series resistance of the inductor and interconnect resistance can cause significant errors in the bias current. This invention addresses that problem by using an operational amplifier with a current-sensing resistor and a low-frequency feedback loop to compensate automatically for any resistance errors. The operational amplifier drives the feedback voltage (generated in accordance with the sensed voltage at the current-sensing resistor and applied to one input of the operational amplifier) towards a reference voltage that is applied to the other input of the operational amplifier to bias the transistor(s) in the transconductance amplifier for desired operating conditions.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Cancellation system for frequency reuse in microwave communications
InactiveUS20050239406A1Weakening rangeKeep shapeRadio wave finder detailsSpatial transmit diversityNonlinear distortionAntenna impedance
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Transflective liquid crystal display with reduced flicker
InactiveUS20060007194A1Reduce flickerFacilitating dynamic useCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A method of reducing visible flicker in a transflective display device, having a plurality of pixels, each pixel comprising a transmissive sub-pixel and a reflective sub-pixel, is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: driving the pixels with an alternating voltage; determining a first desired compensation voltage for the transmissive sub-pixels and a second desired compensation voltage for the reflective sub-pixels; deriving a common compensation voltage from said first desired compensation voltage and said second desired compensation voltage; and applying said common compensation voltage to both the transmissive and the reflective sub-pixels. Thus, the flicker resulting from a DC bias of the driving voltage is substantially reduced. In a preferred embodiment, the method further comprises the steps of: determining a lowest available frame frequency setting for which any remaining flicker is invisible; and setting a frame frequency at which the display is driven to said lowest available frame frequency. According to another embodiment, a backlight is manually controlled and the common compensation voltage is derived as a function of a mode of operation of the backlight. A transflective display device implementing the above methods is also disclosed.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Photon method and system for realizing microwave down-conversion and phase shift by using integrated devices
ActiveCN107846254AImprove performanceRealize functionPhotonic quantum communicationElectromagnetic transmittersBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
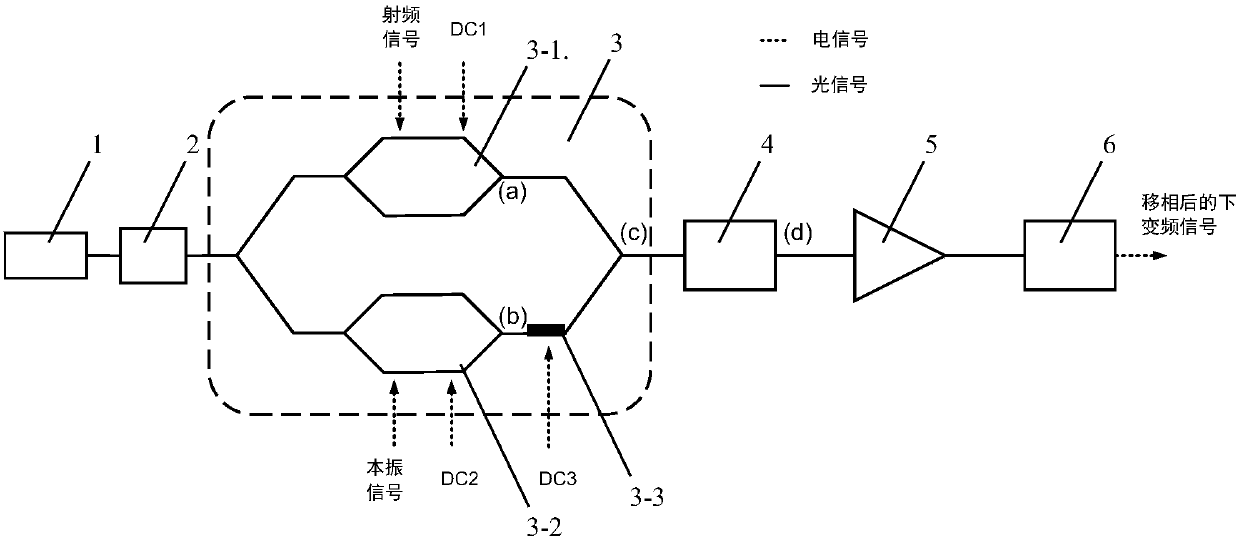
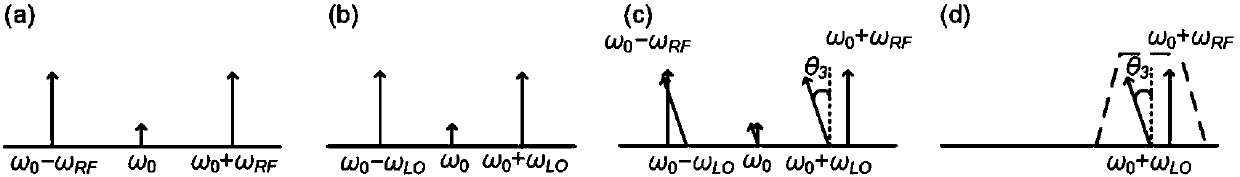
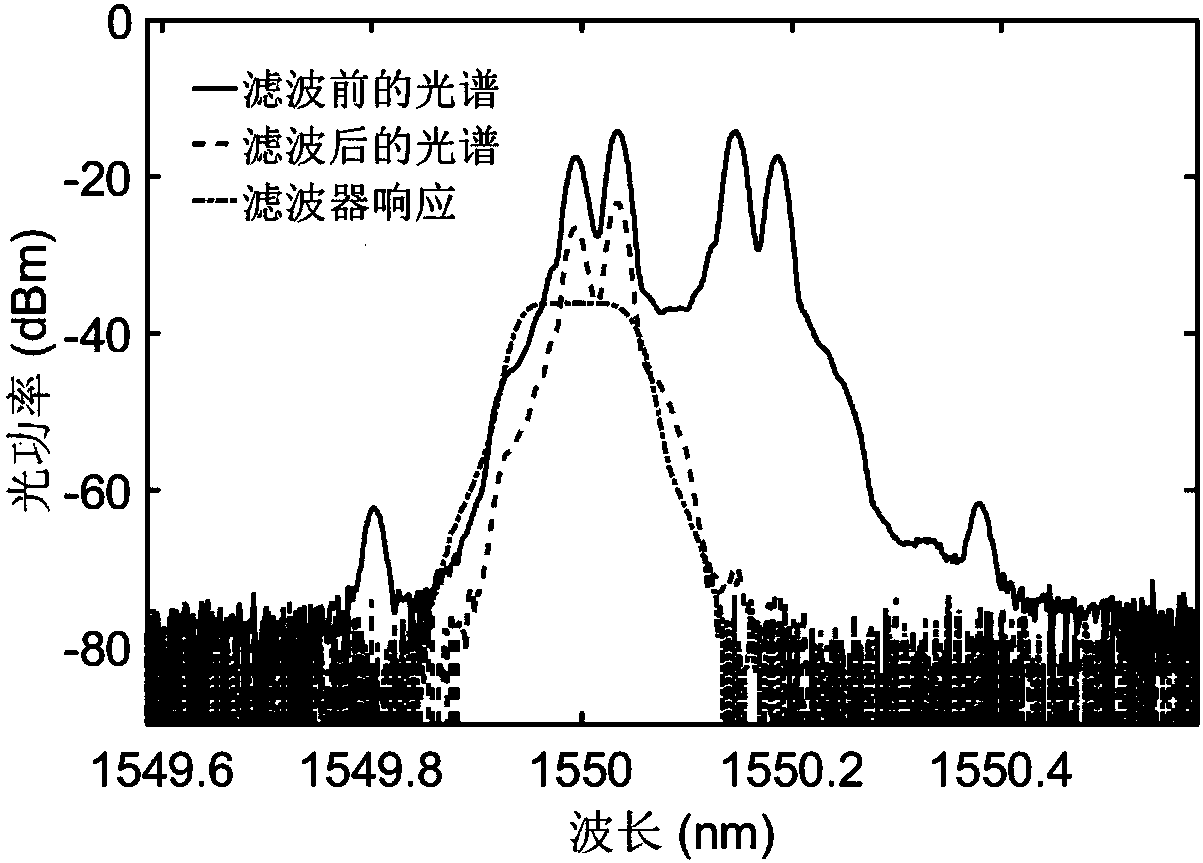
The invention provides a photon method and system for realizing microwave down-conversion and phase shift by using integrated devices, and belongs to the field of microwave photonics. Firstly, opticalcarriers generated by a laser are input to a double-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator after passing through a polarization controller, a radio frequency signal is modulated by an upper arm sub-modulator, and carrier suppression double-sideband modulation is realized by DC bias; a local oscillator signal is modulated by a lower arm sub-modulator, and the carrier suppression double-sideband modulation is realized by the DC bias; the DC bias of a main intensity modulator is used for changing the phase difference between the radio frequency optical signal and the local oscillator optical signal. A-1 order optical sideband is filtered from an output carrier suppression double-sideband modulation optical signal by an optical bandpass filter, a +1 order optical sideband is retained, and the useless optical sideband is suppressed below the noise floor. Then, power amplification is performed on the optical signal to compensate the insertion loss of modulator and the filter. At last, a down-conversion signal subjected to phase shift is obtained by performing beat frequency by using a photodetector. A very pure frequency spectrum signal is output, and the performance of an integrated functionlink of down-conversion and phase shift is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Resonant circuit and a voltage-controlled oscillator
InactiveUS20050030116A1Improve phase noiseSimple compositionAngle modulation by variable impedenceOscillations generatorsCapacitanceVoltage generator
A voltage-controlled oscillator comprising a resonant circuit and MOS transistors which constitute a negative resistance circuit of a differential structure. The resonant circuit consists of an inductance element and a MOS variable capacitance element connected in parallel therewith. The MOS variable capacitance element is divided into plural pairs connected in parallel with each other. A voltage division circuit generates staircase different-step DC bias voltages to be applied respectively to the gates of the plural divided MOS transistors. The divided MOS variable capacitance elements have a common terminal to which a common control voltage is applied. The resonant circuit is capable of reducing a load on the control voltage generator and improving the characteristics of the voltage-controlled oscillator.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM JAPAN INC
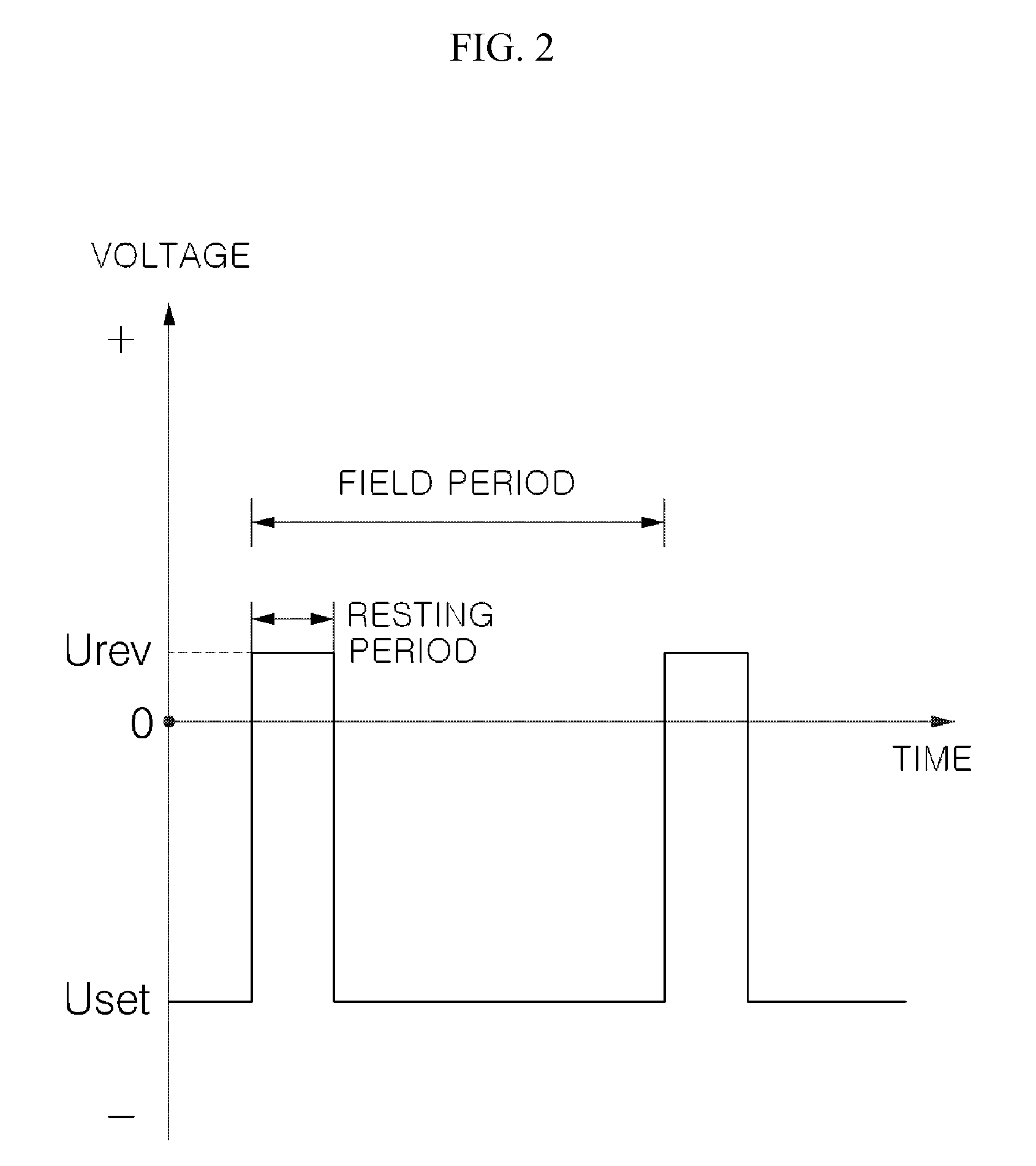
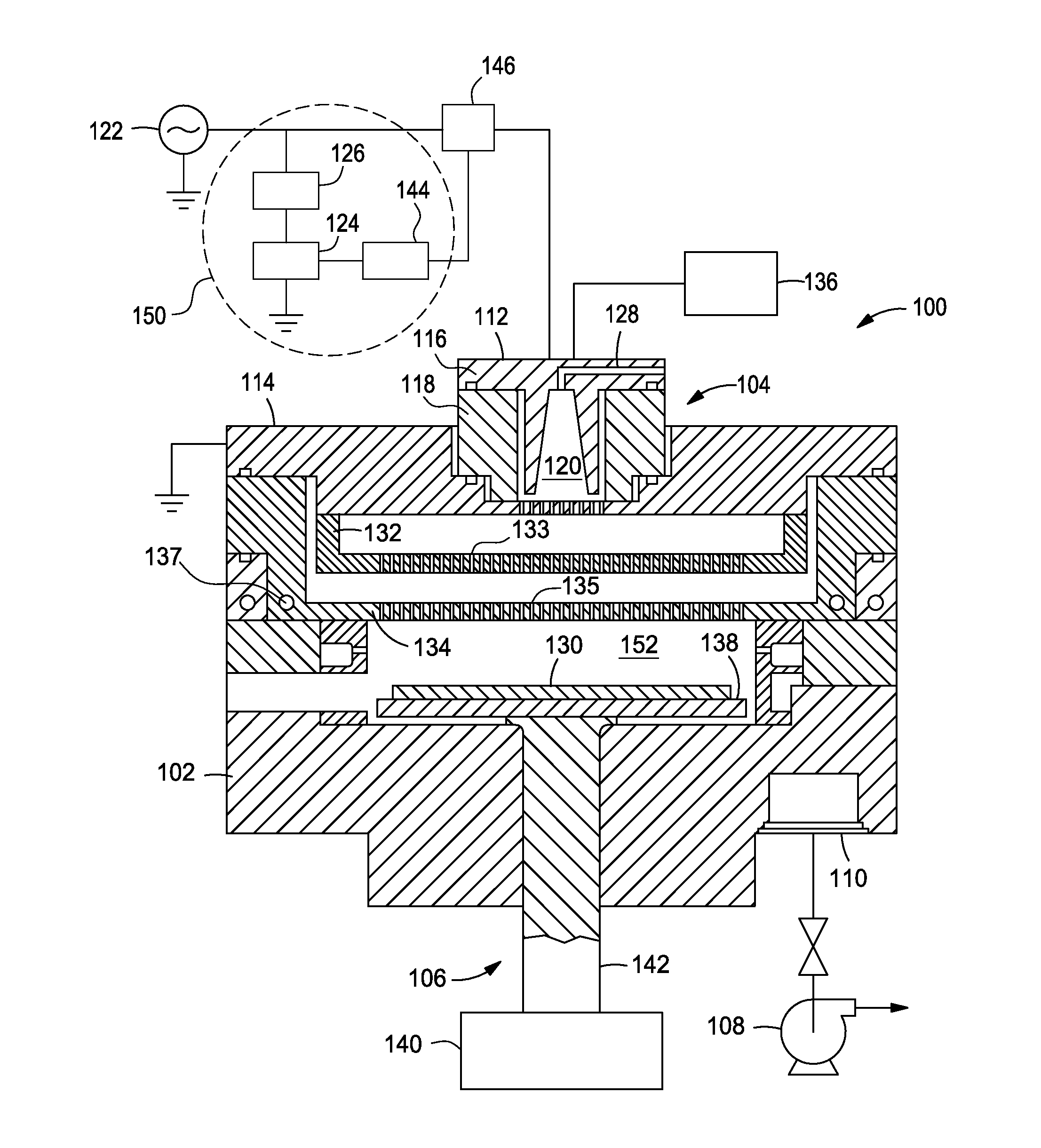
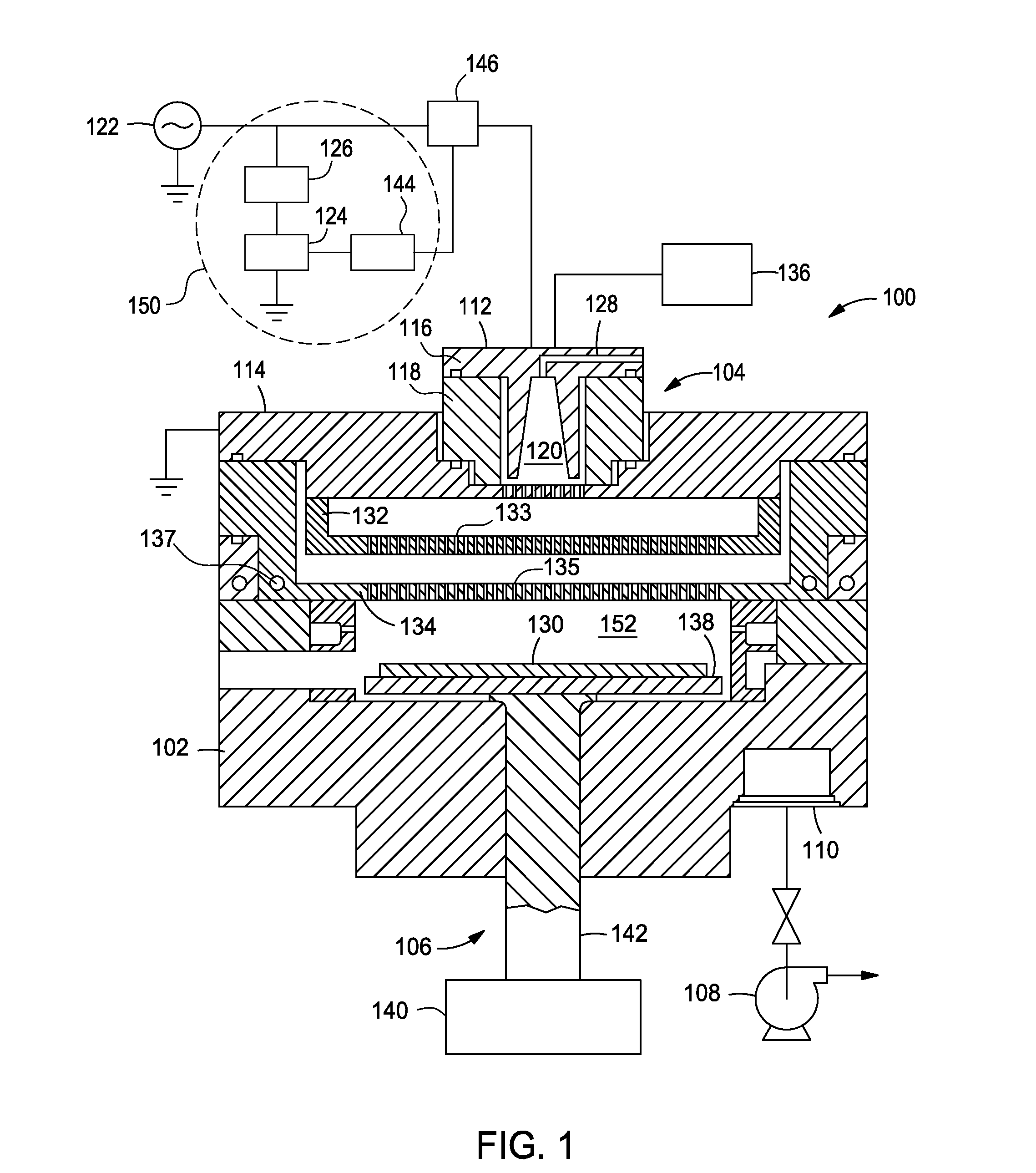
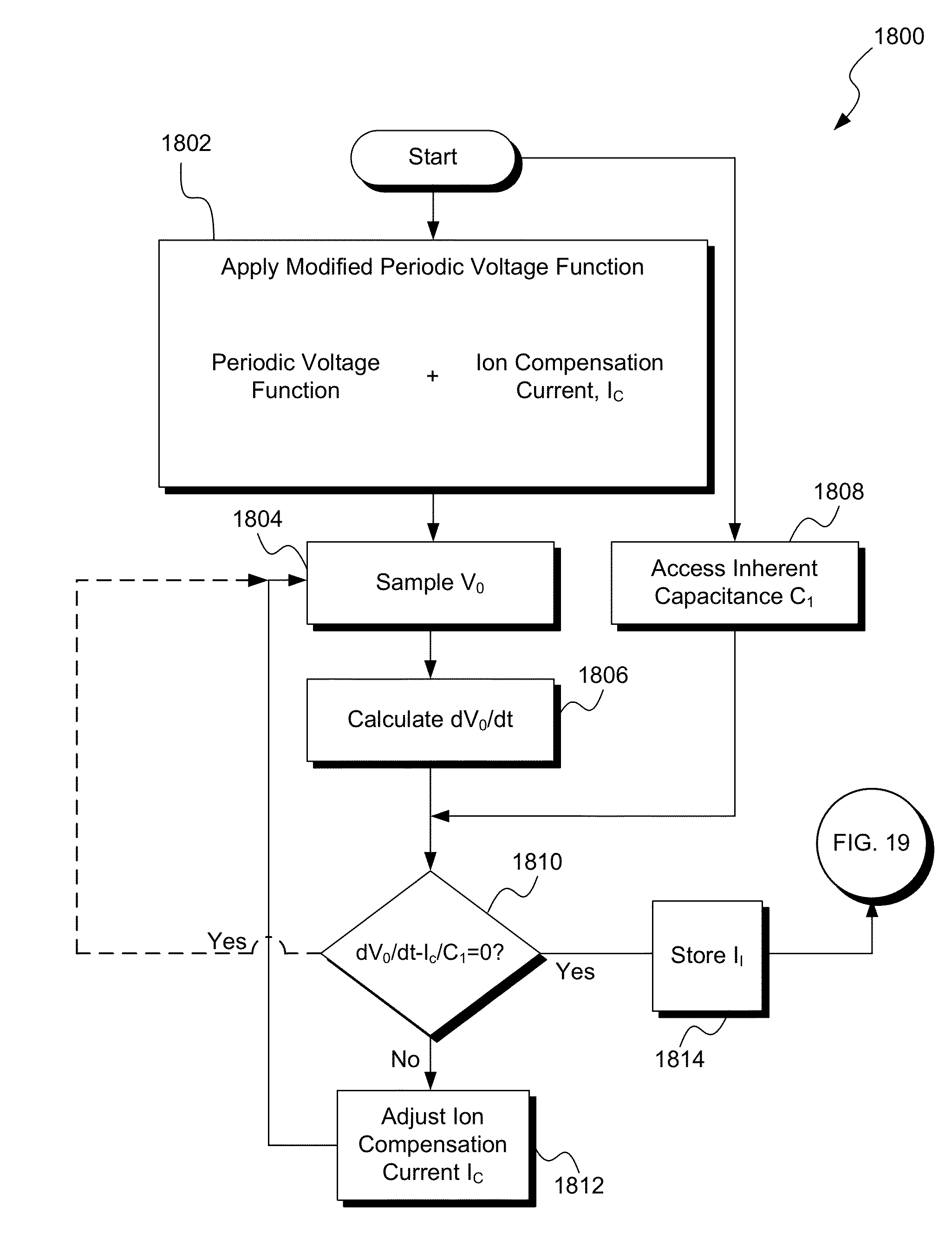
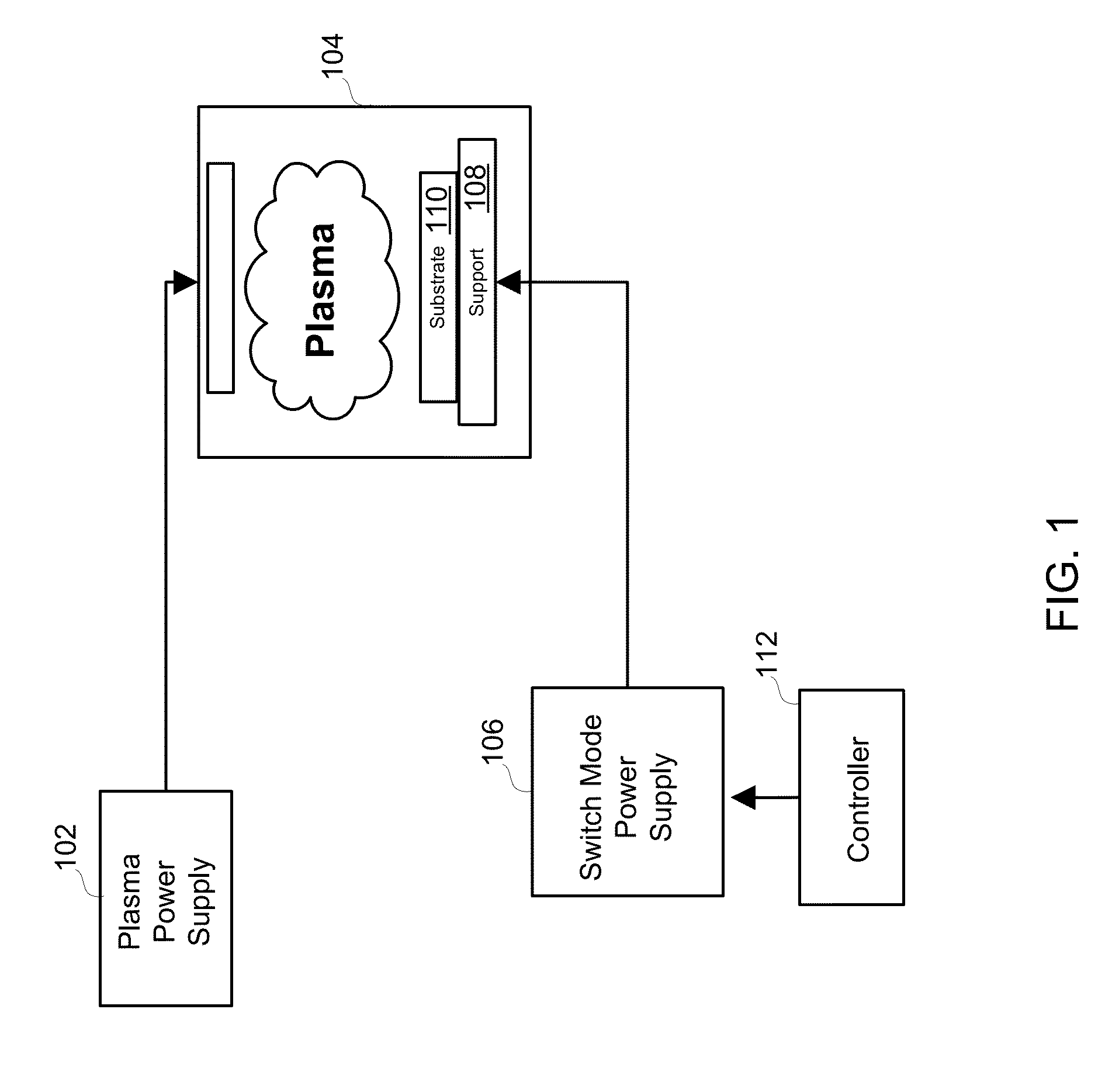
Wide dynamic range ion energy bias control; fast ion energy switching; ion energy control and a pulsed bias supply; and a virtual front panel
This disclosure describes systems, methods, and apparatus for operating a plasma processing chamber. In particular, a periodic voltage function combined with an ion current compensation can be provided as a bias to a substrate support as a modified periodic voltage function. This in turn effects a DC bias on the surface of the substrate that controls an ion energy of ions incident on a surface of the substrate. A peak-to-peak voltage of the periodic voltage function can control the ion energy, while the ion current compensation can control a width of an ion energy distribution function of the ions. Measuring the modified periodic voltage function can provide a means to calculate an ion current in the plasma and a sheath capacitance of the plasma sheath. The ion energy distribution function can be tailored and multiple ion energy peaks can be generated, both via control of the modified periodic voltage function.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
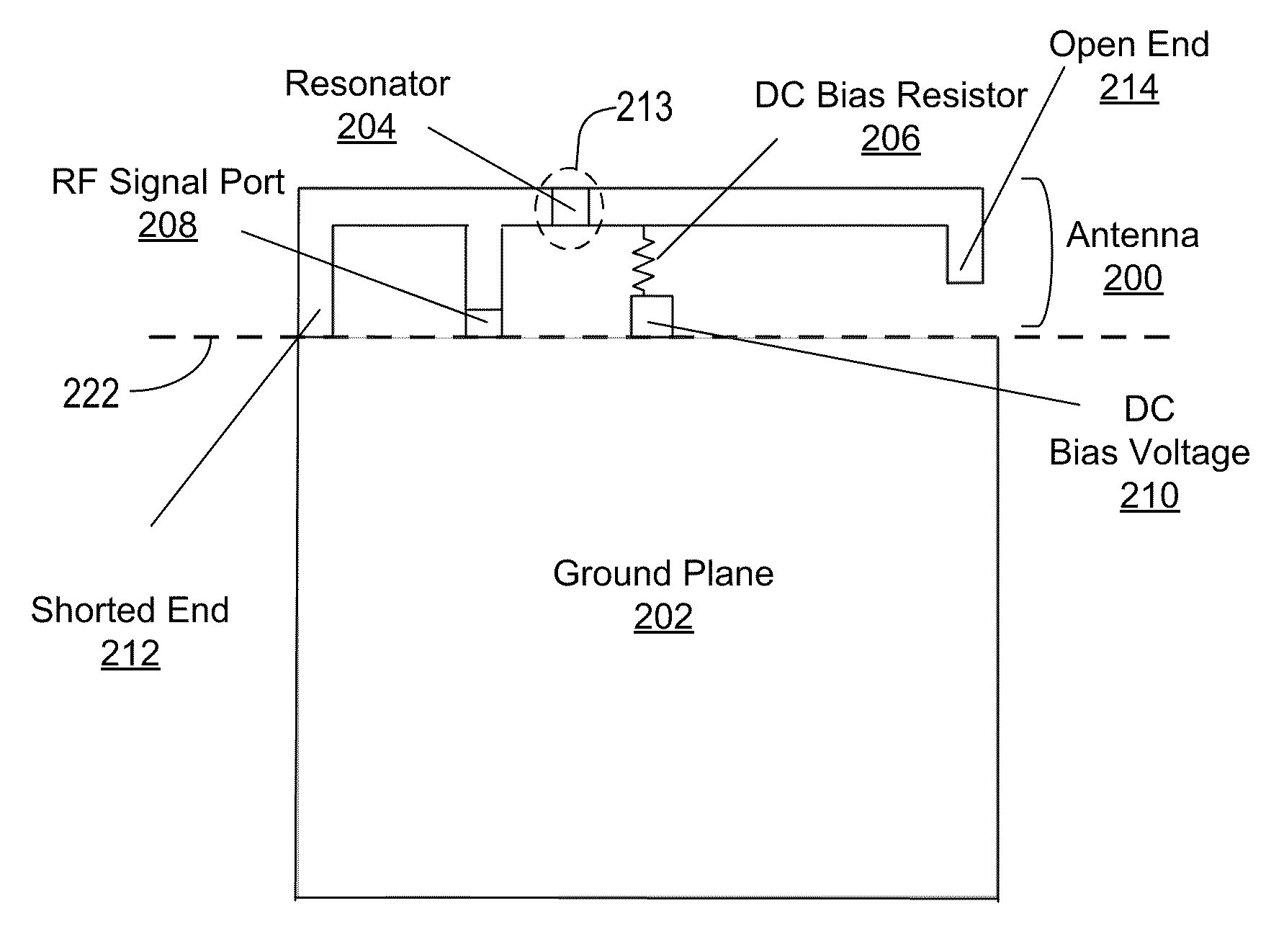
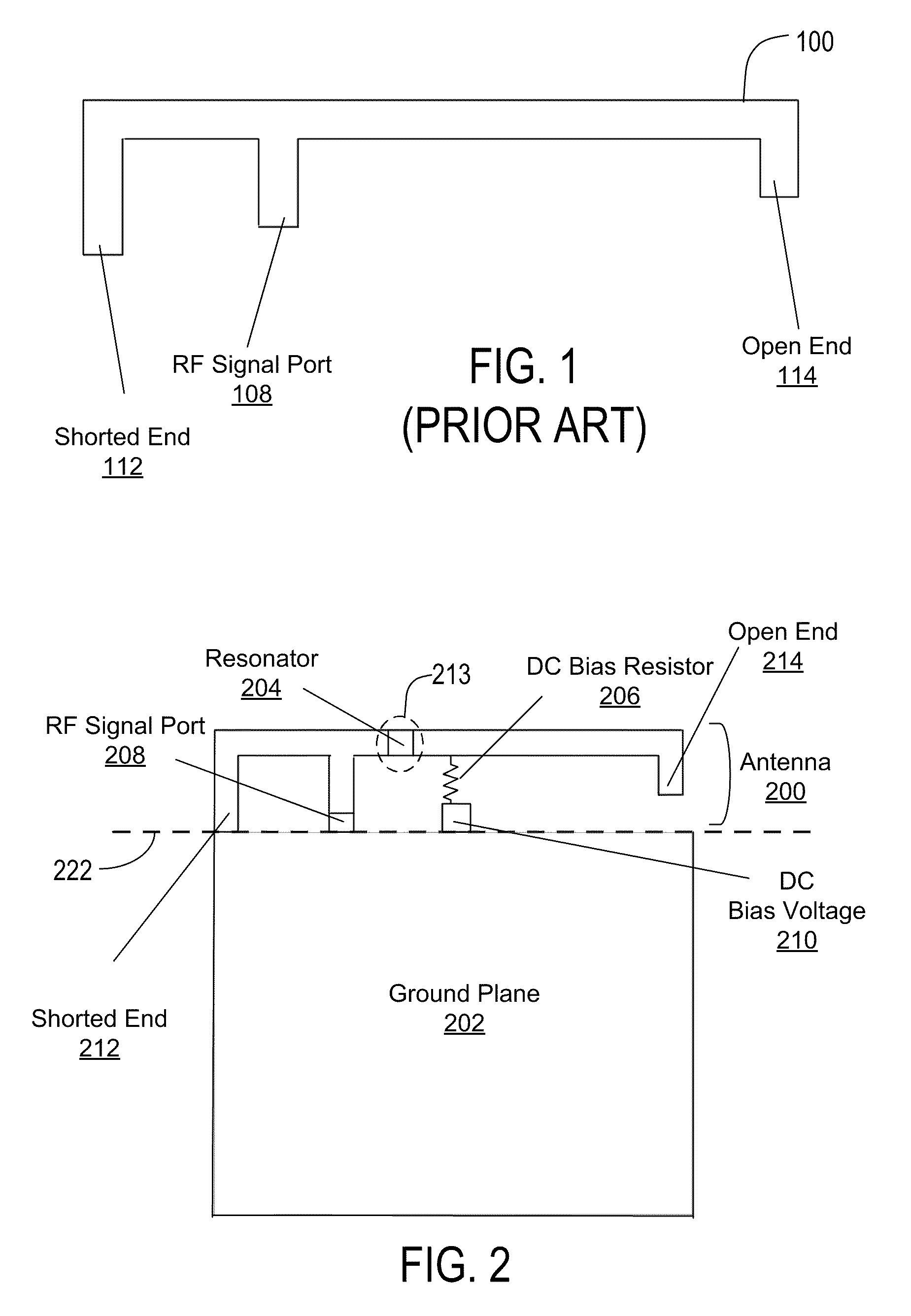
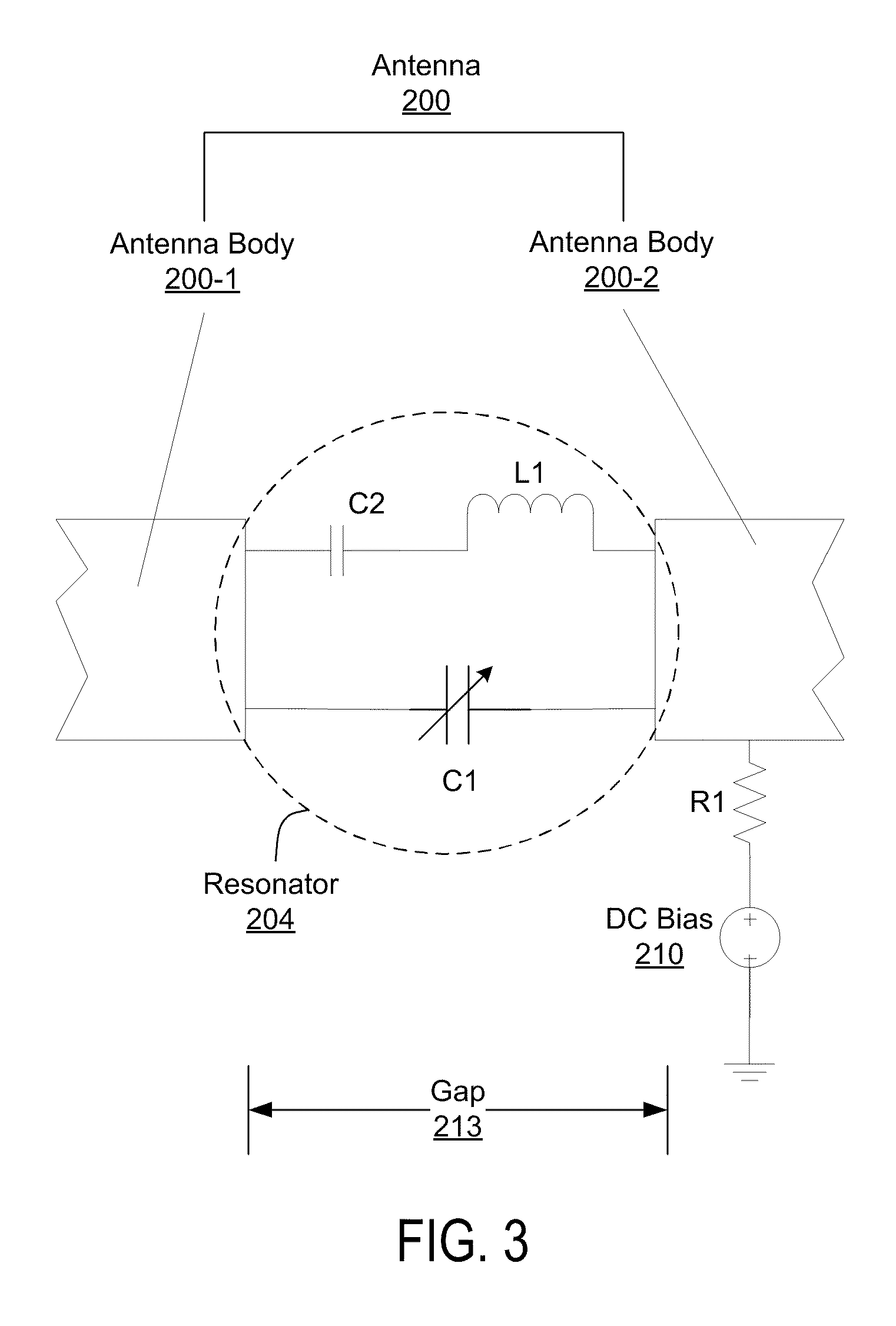
Tunable dual-band antenna using lc resonator
InactiveUS20100053007A1Easily incorporated into cell phoneEasily other wireless deviceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceLc resonator
An Inverted-F antenna (IFA) includes a tunable parallel LC resonator physically inserted between two antenna bodies of the IFA structure. The LC resonator is comprised of a tunable capacitor C1 connected in parallel with a combination of a DC blocking capacitor C2 and an inductor L1 connected in series to each other. A DC bias voltage is applied to the tunable capacitor C1 through a DC bias resistor R1, in order to adjust the capacitance of the tunable capacitor C1. The IFA exhibits dual band characteristics, and its resonant frequencies and bandwidths may be turned by adjusting the capacitance of the tunable capacitor C1. The tunable capacitor C1 may be a BST capacitor.
Owner:AGILE RF
On-chip frequency degradation compensation
ActiveUS20050140418A1Electrical testingElectric pulse generatorFrequency compensationElectrical and Electronics engineering
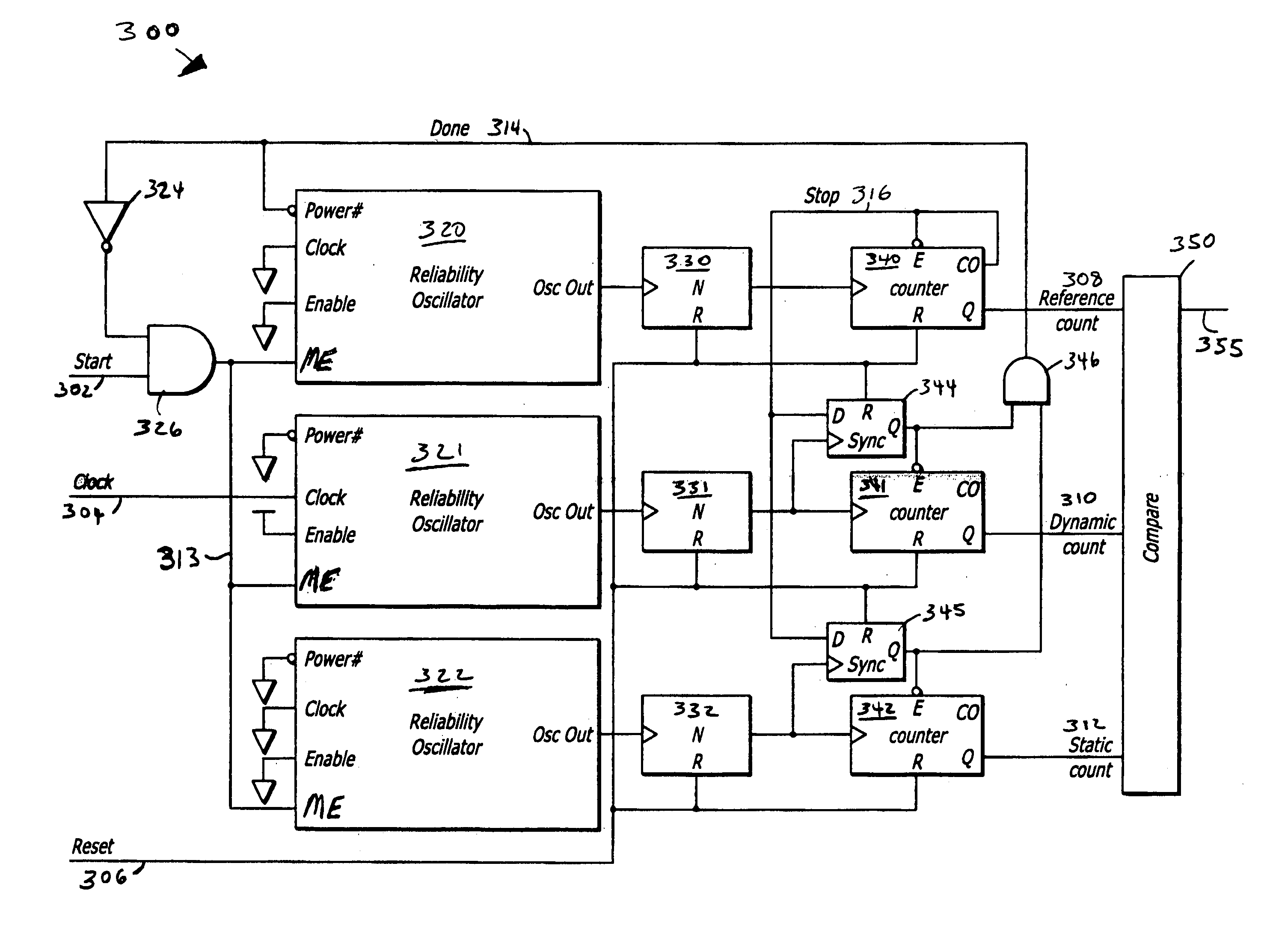
Embodiments of the invention include a trio of reliability oscillators. In one embodiment, an on-chip frequency compensation circuit includes a selectively enabled reliability oscillator to generate a reference oscillating signal, a clocked reliability oscillator to generate an AC degraded oscillating signal, and a static reliability oscillator to generate a DC bias degraded oscillating signal. A compare circuit coupled to the reliability oscillators compares the oscillating signals and generates a frequency compensation signal if the comparison determines that there is frequency degradation greater than a predetermined threshold.
Owner:INTEL CORP
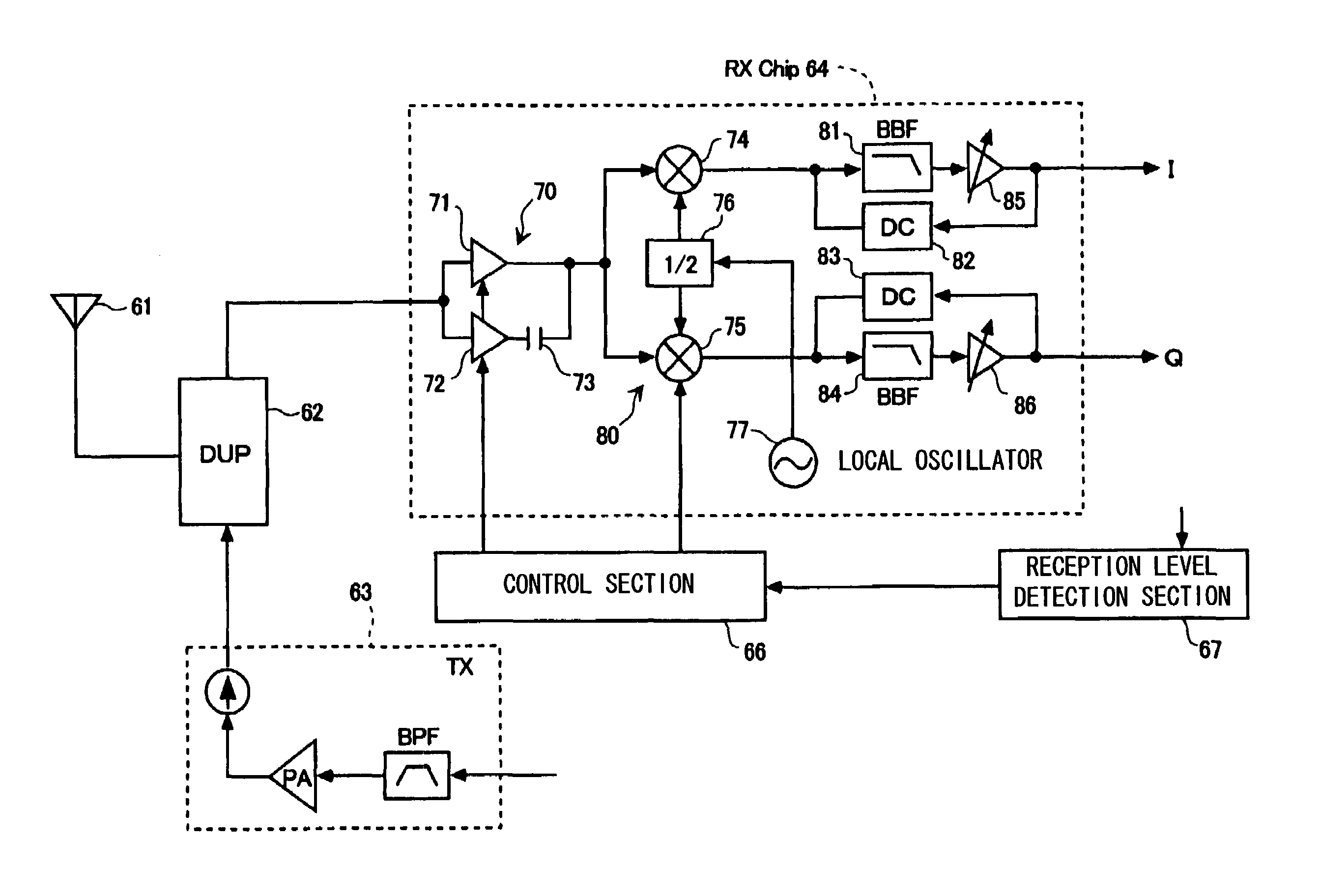
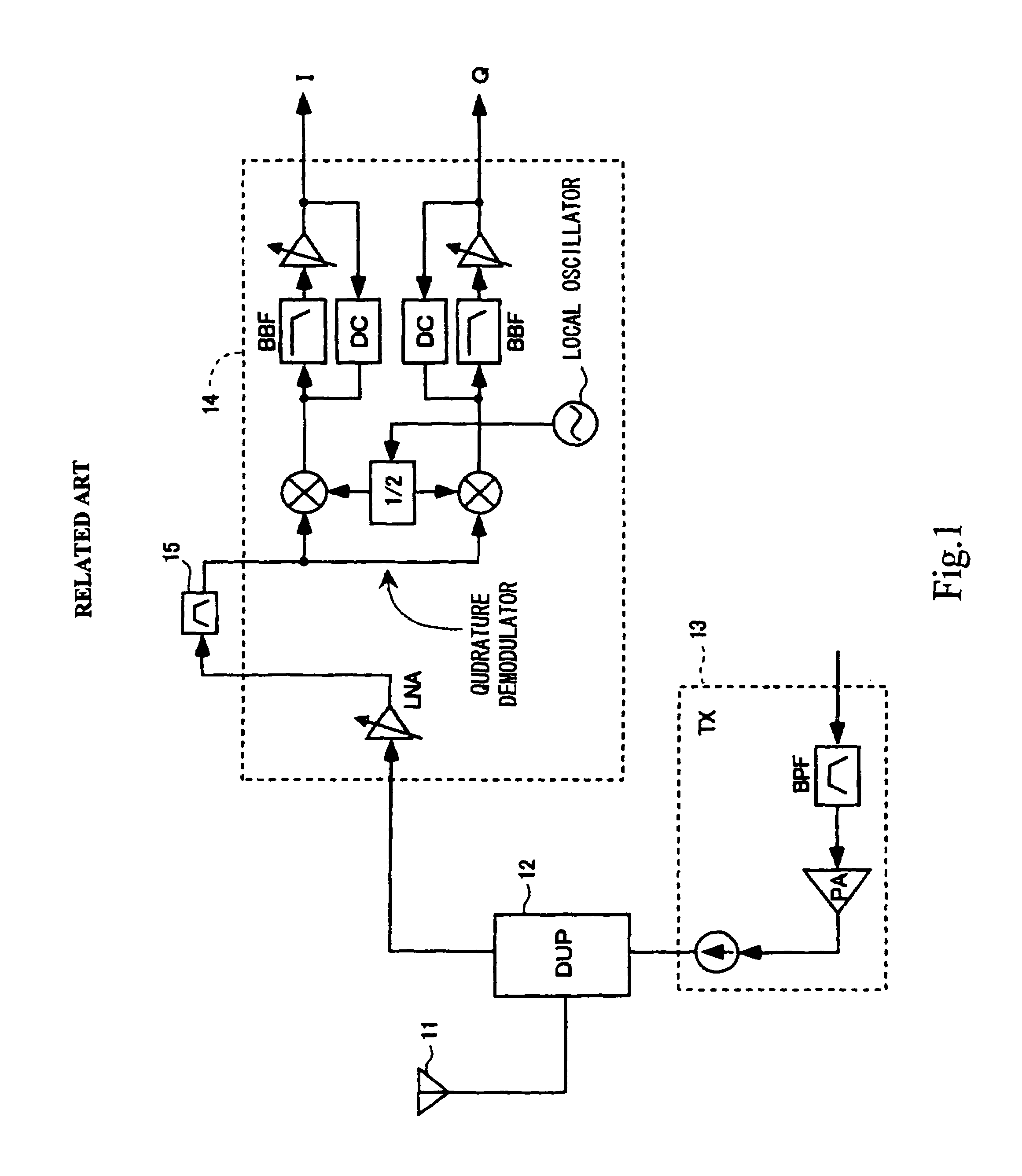
Receiver circuit and radio communication terminal apparatus
ActiveUS7221919B2Reduce power consumptionReduce areaGain controlDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
There are provided, as a low noise amplifier (70) a low noise amplifier (71) with a low gain and a low noise amplifier (72) with a high gain, selectively operable under control of a bias current, and an output from the low noise amplifier (72) and a quadrature demodulator (80) are connected with a serial capacitance (73) and also an output from the low noise amplifier (71) and the quadrature demodulator (80) are serially connected. A control section (66) controls a reception circuit so that the low noise amplifier (71) operates when a reception signal level is high and the low noise amplifier (72) operates when the reception signal level is low. When the low noise amplifier (72) operates, a DC bias current thereof is made flow separately from a DC bias current of the quadrature demodulator (80), and, when the low noise amplifier (71) operates, a DC bias current thereof is shared with the quadrature demodulator.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com