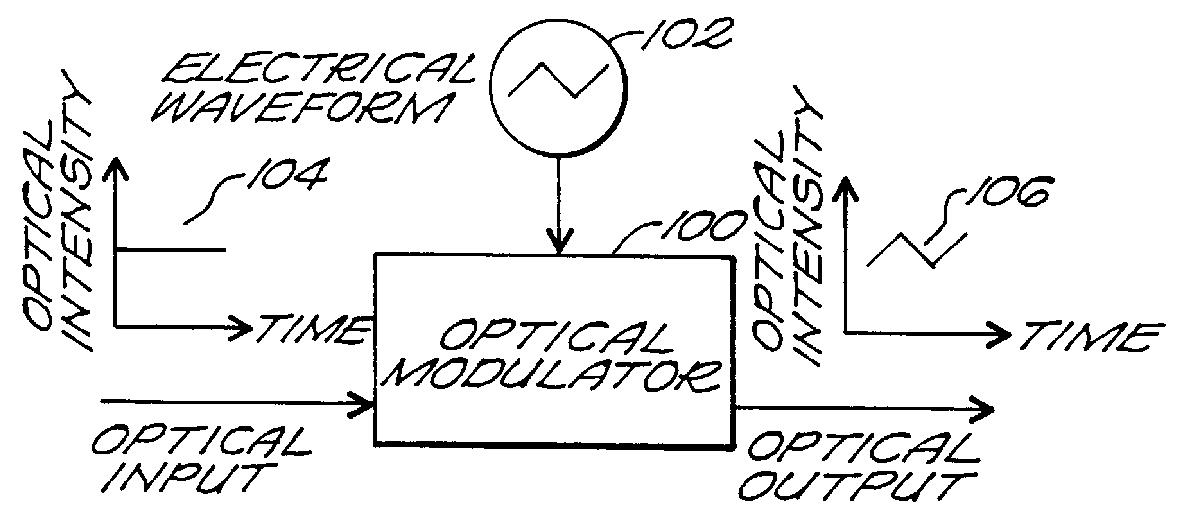
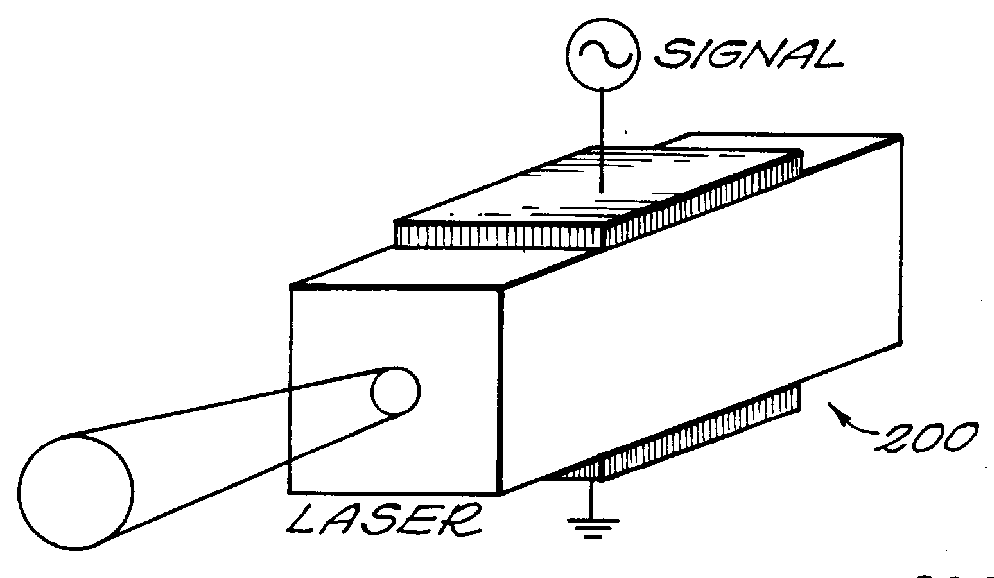
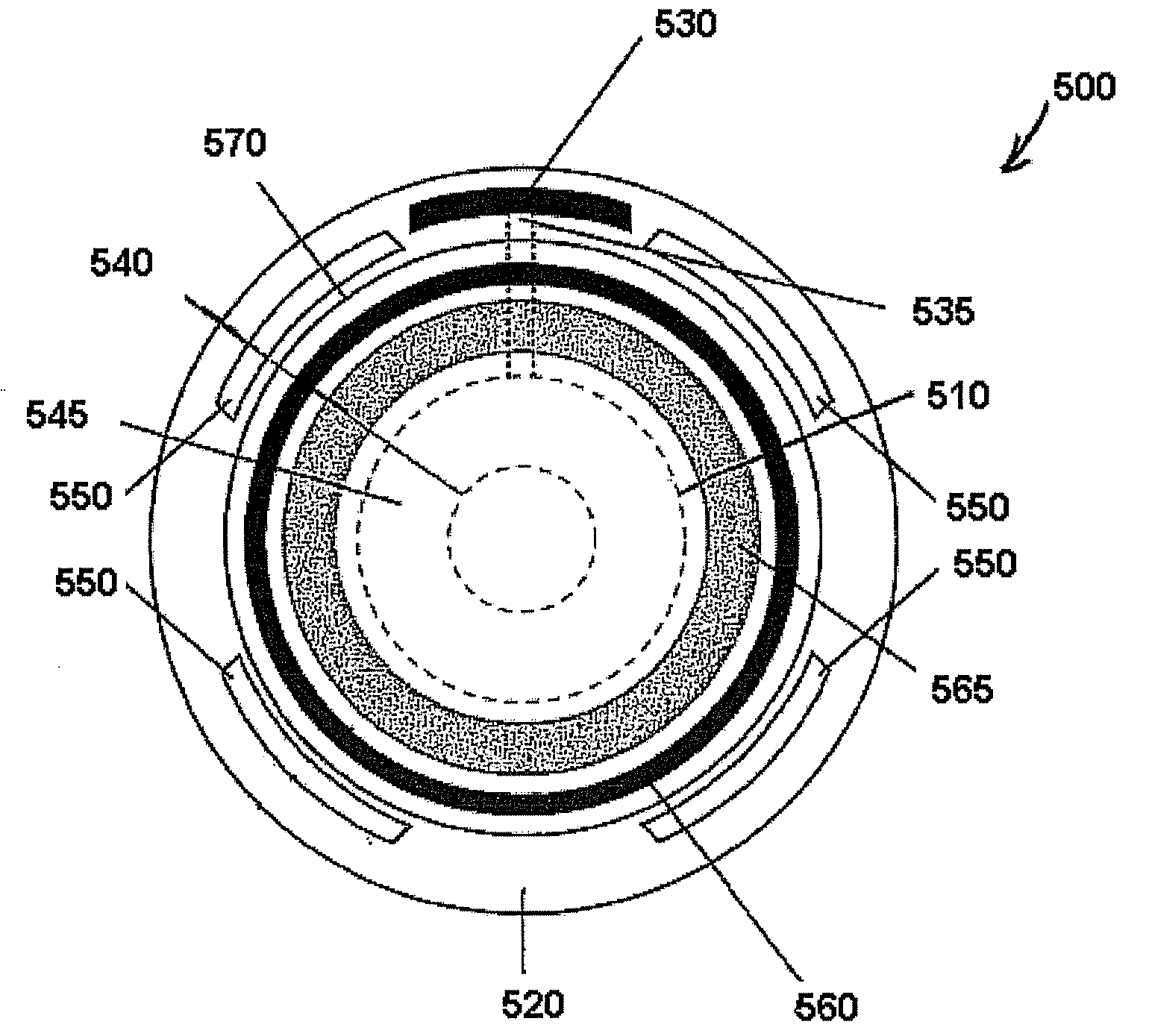
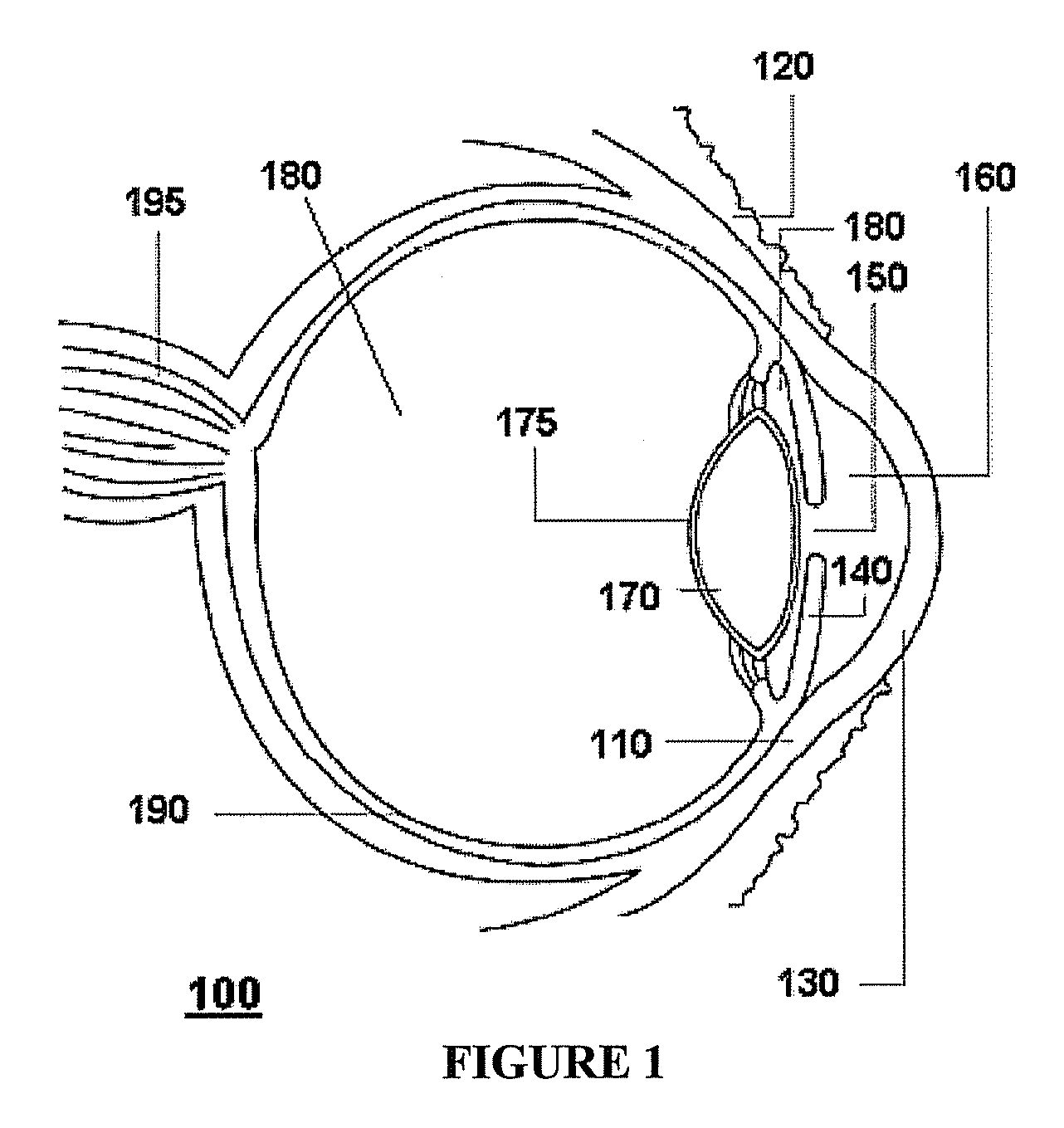
Patents
Literature
6296 results about "Optical power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical power (also referred to as dioptric power, refractive power, focusing power, or convergence power) is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length of the device: P = 1/f. High optical power corresponds to short focal length. The SI unit for optical power is the inverse metre (m⁻¹), which is commonly called the dioptre.
Dynamic surface annealing using addressable laser array with pyrometry feedback
Apparatus for dynamic surface annealing of a semiconductor wafer includes a source of laser radiation emitting at a laser wavelength and comprising an array of lasers arranged in rows and columns, the optical power of each the laser being individual adjustable and optics for focusing the radiation from the array of lasers into a narrow line beam in a workpiece plane corresponding to a workpiece surface, whereby the optics images respective columns of the laser array onto respective sections of the narrow line beam. A pyrometer sensor is provided that is sensitive to a pyrometer wavelength. An optical element in an optical path of the optics is tuned to divert radiation emanating from the workpiece plane to the pyrometry sensor. As a result, the optics images each of the respective section of the narrow line beam onto a corresponding portion of the pyrometer sensor. The apparatus further includes a controller responsive to the pyrometry sensor and coupled to adjust individual optical outputs of respective columns of the laser array in accordance with outputs of corresponding portions of the pyrometry sensor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Resonator modulators and wavelength routing switches
InactiveUS6052495ASmall sizeImprove responseCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsClosed loopRefractive index
The invention provides an optical switch and modulator which uses a closed loop optical resonator. The optical resonator is a dielectric cavity whose primary function is to store optical power. Various structures are possible, and a particularly advantageous one is a ring shaped cavity. The wavelength response at the output port of a ring resonator side coupled to two waveguides is determined by the details of the resonator, and the coupling between the resonator and the waveguides. By coupling to adjacent resonators, the modulator response can be improved over that of a single resonator. One such improvement is in modulator efficiency, which is defined as the ratio of the change in optical intensity at the output, to a change in absorption in the ring waveguides. Absorption is used for switching and modulation without incurring significant optical attenuation. Another improvement involves making the resonance insensitive to small deviations in wavelength or index change. The latter improves fabrication tolerances and compensates for possible drift of the signal wavelength. Collectively, the behavior of multiple coupled resonators yields higher order responses.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
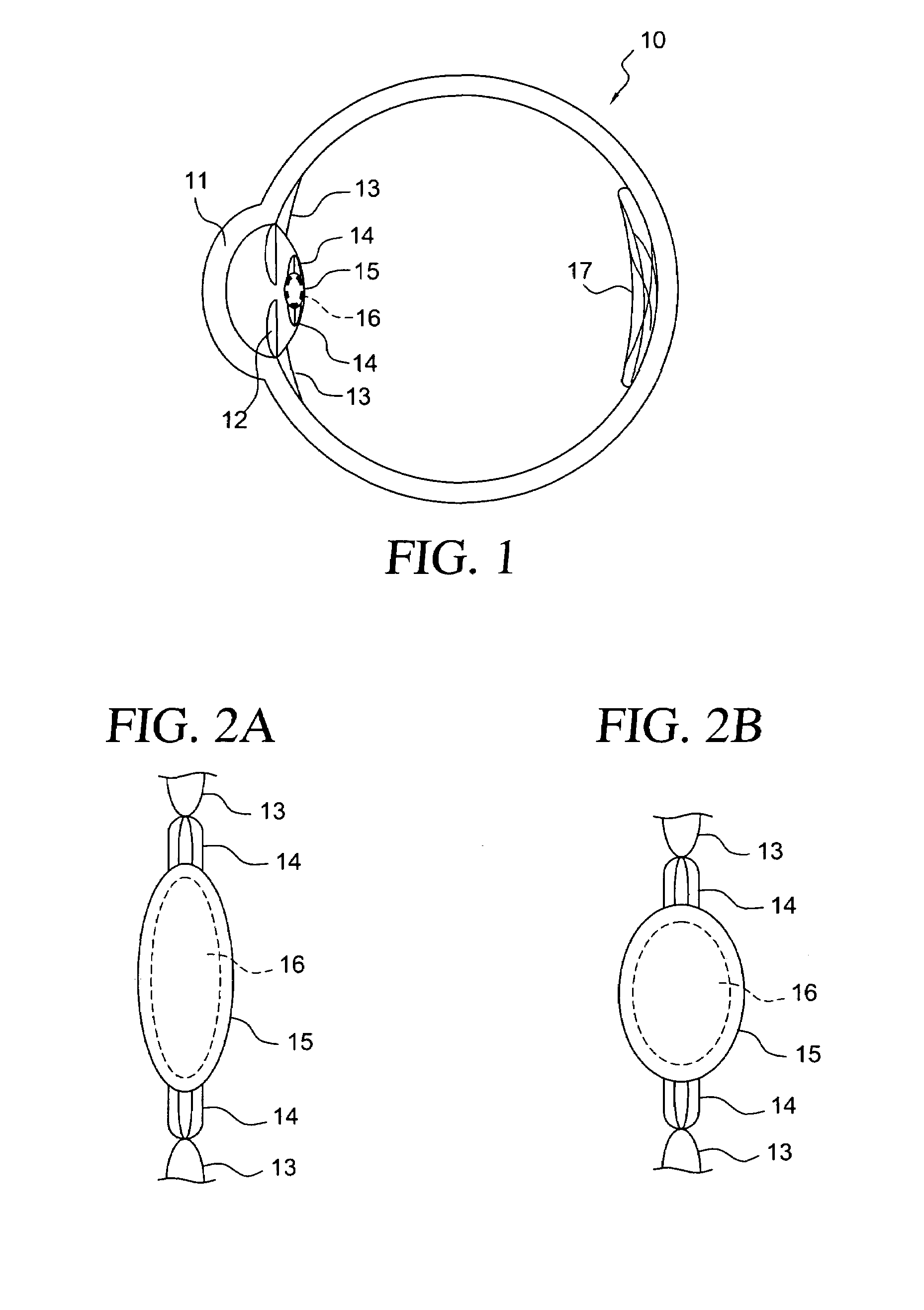
Ophthalmic dynamic aperture
ActiveUS20090033863A1Increase heightAdd depthSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensCorneal inlayDynamic aperture
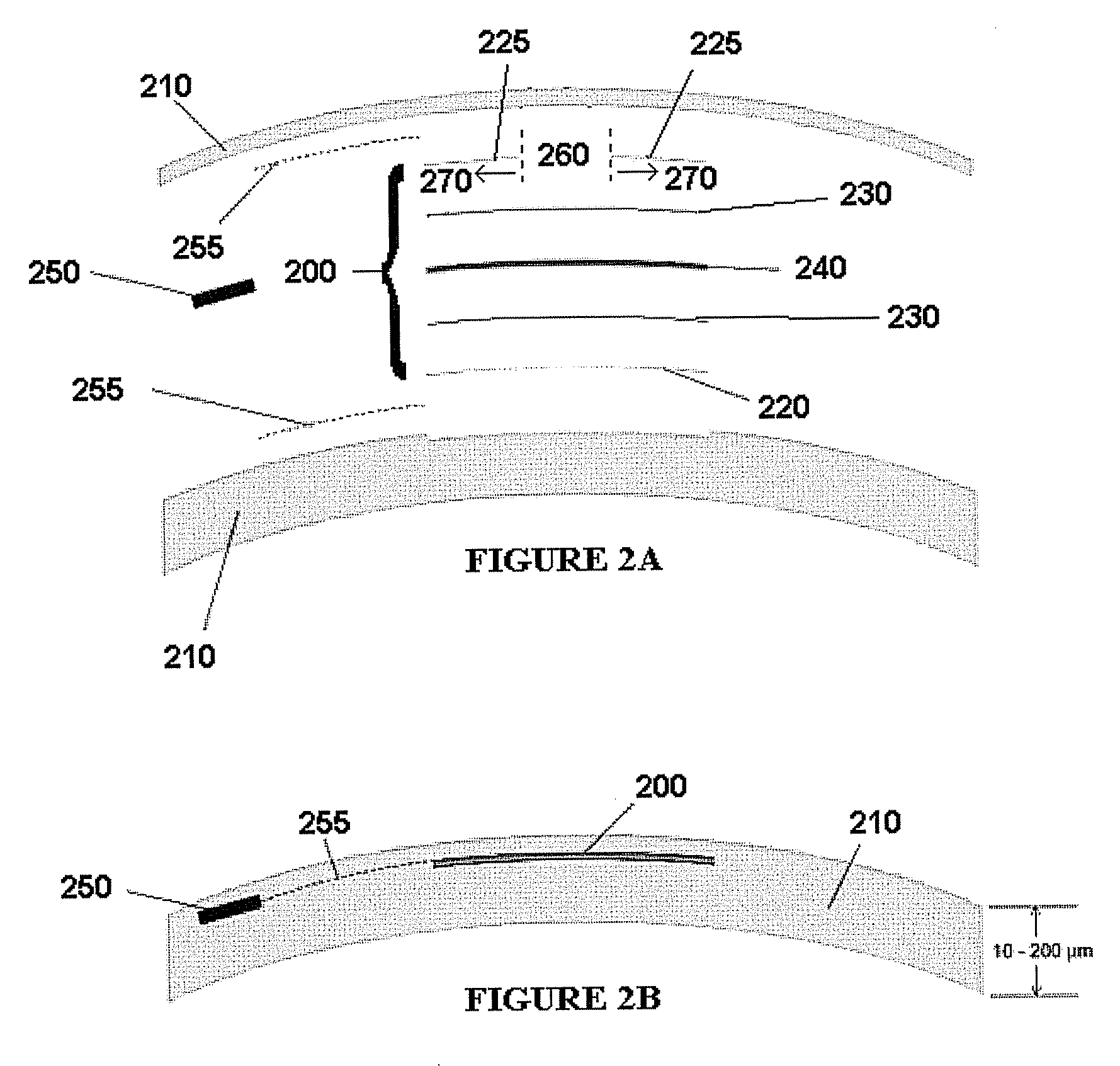
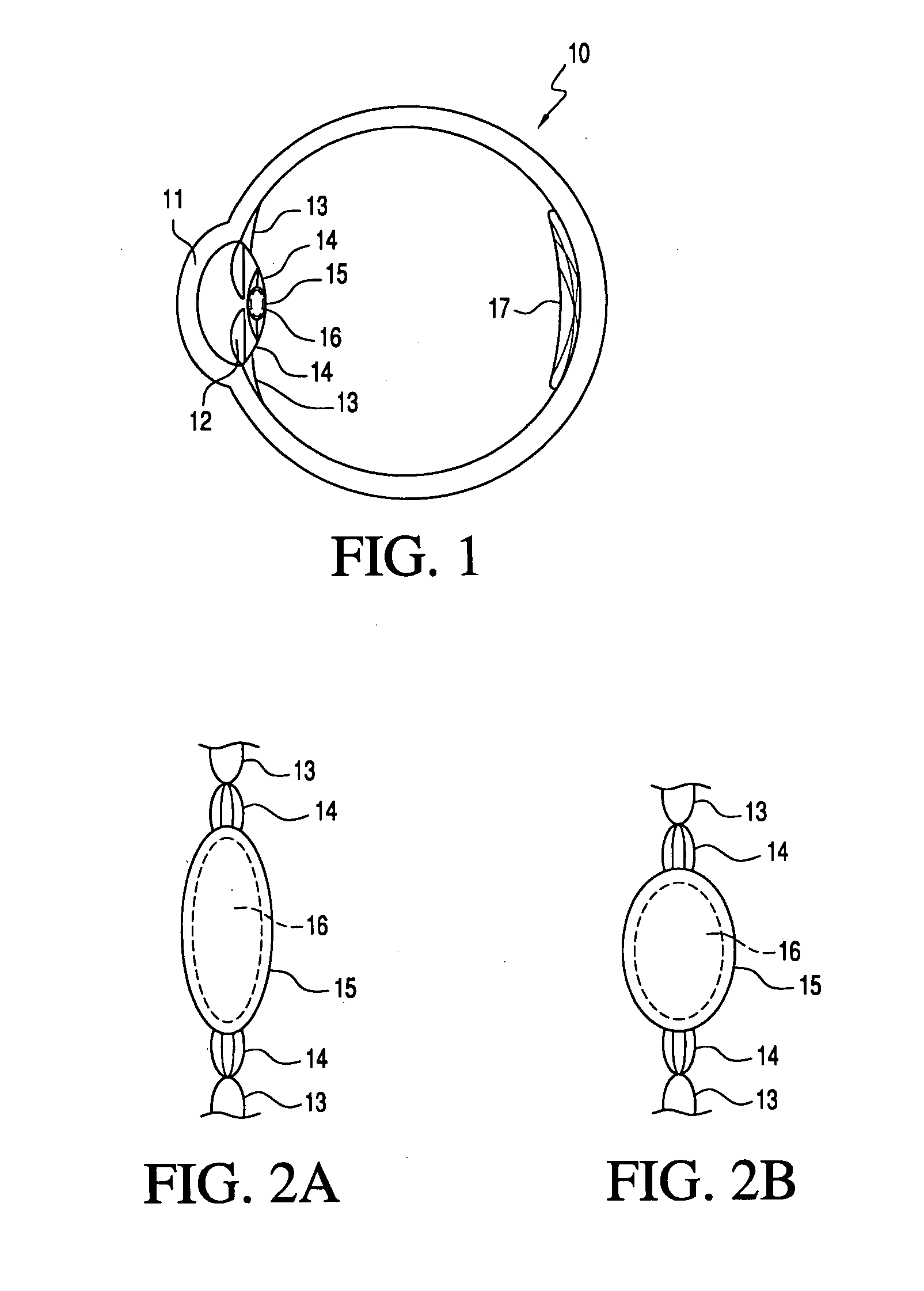
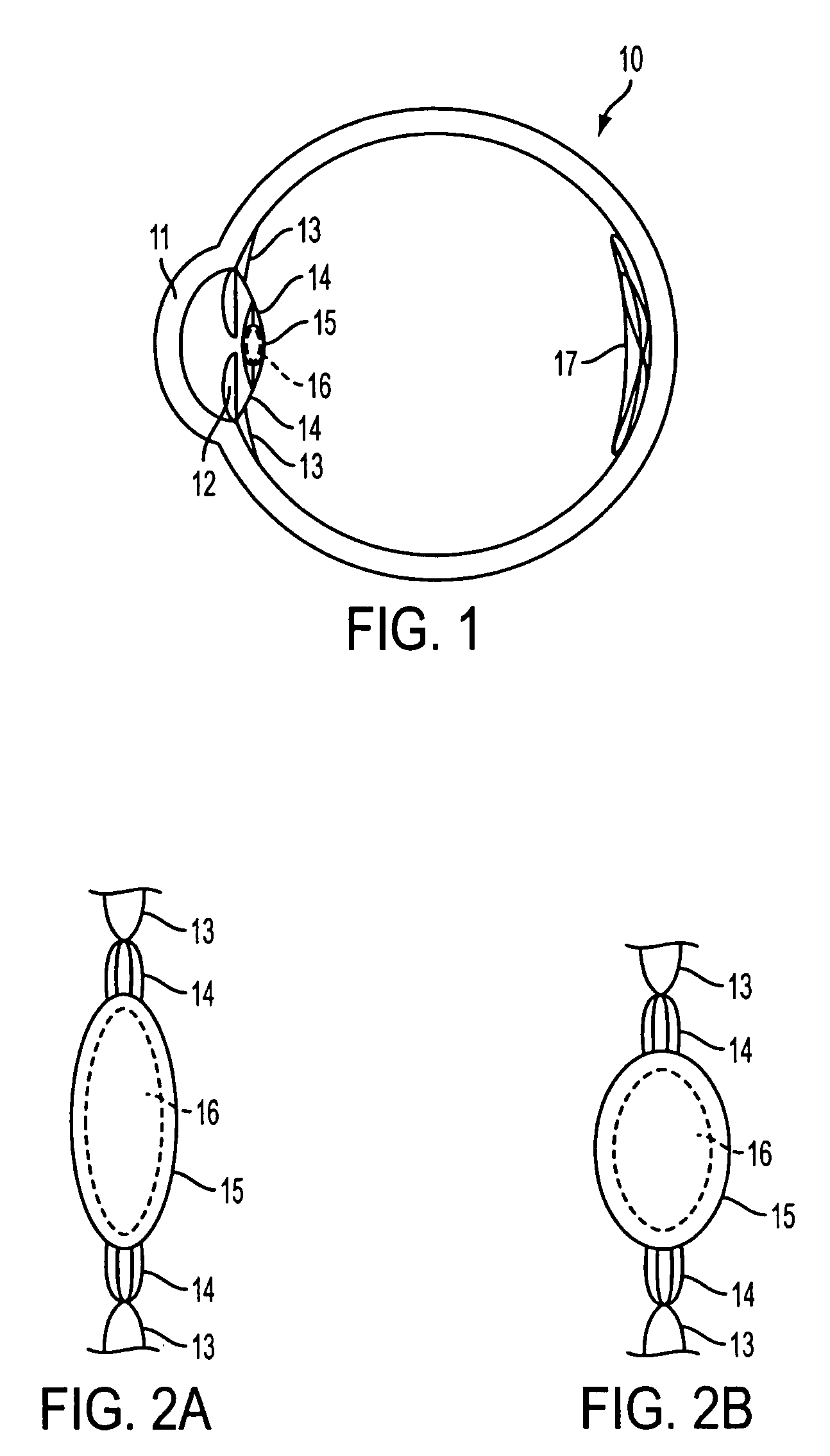
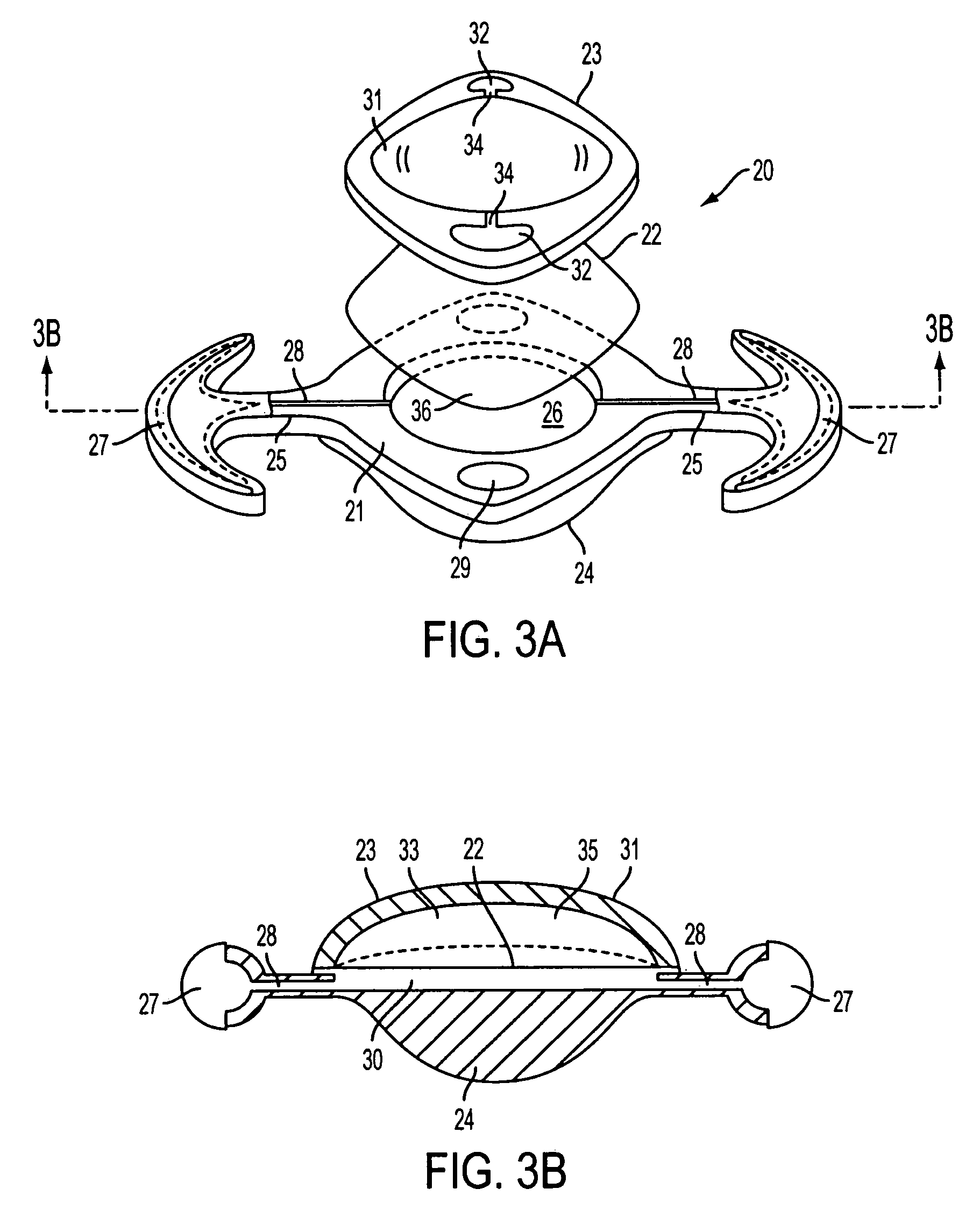
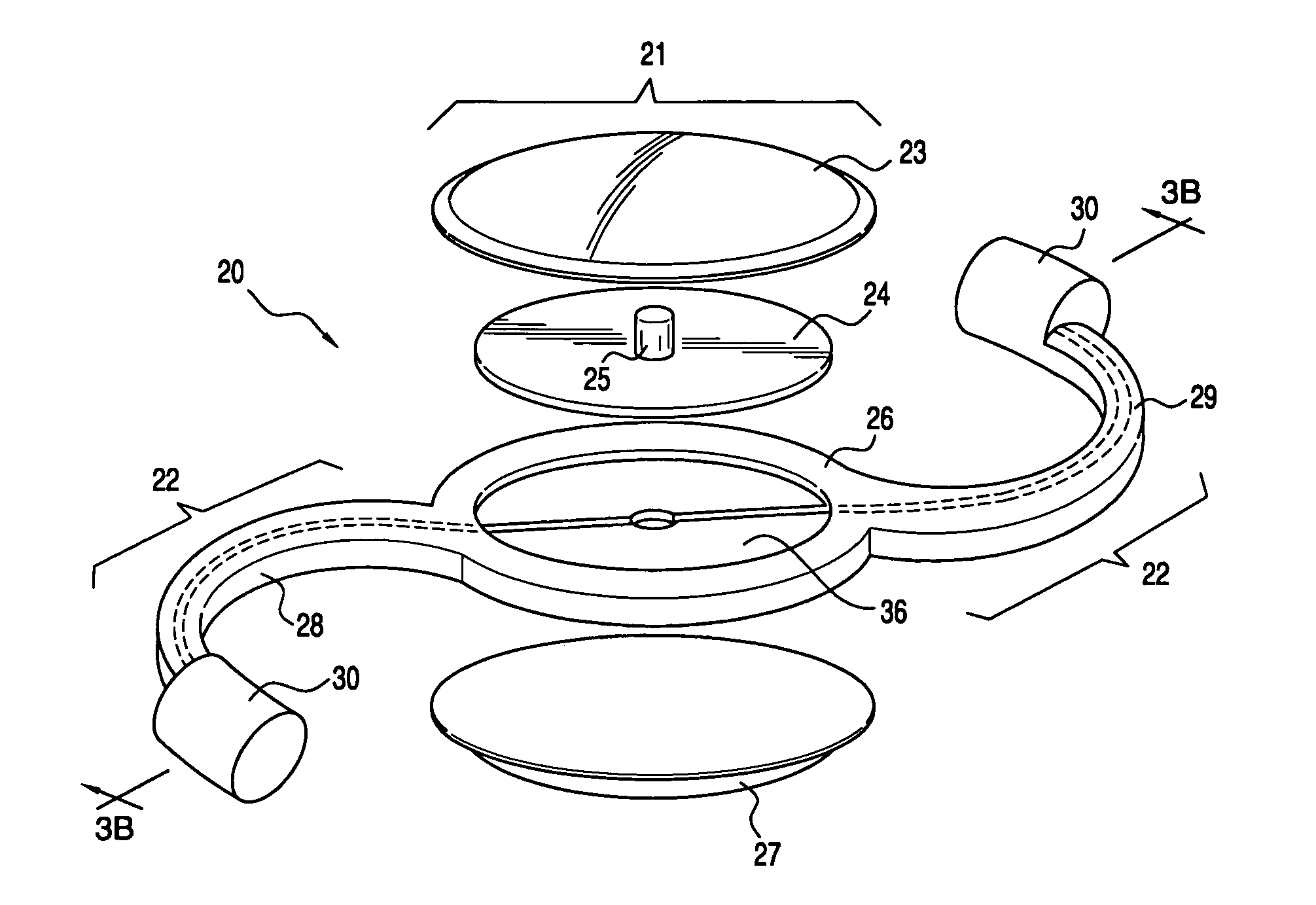
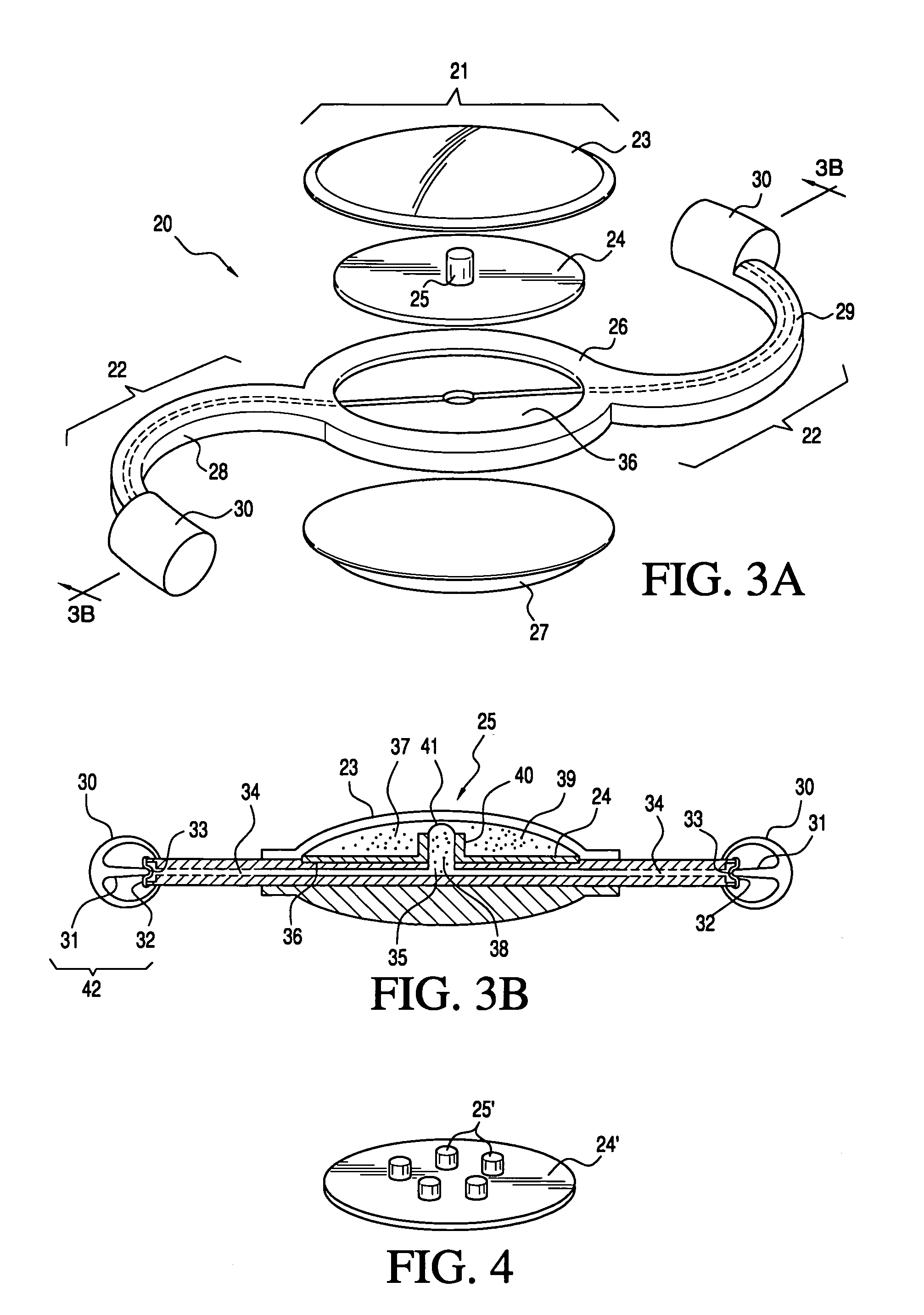
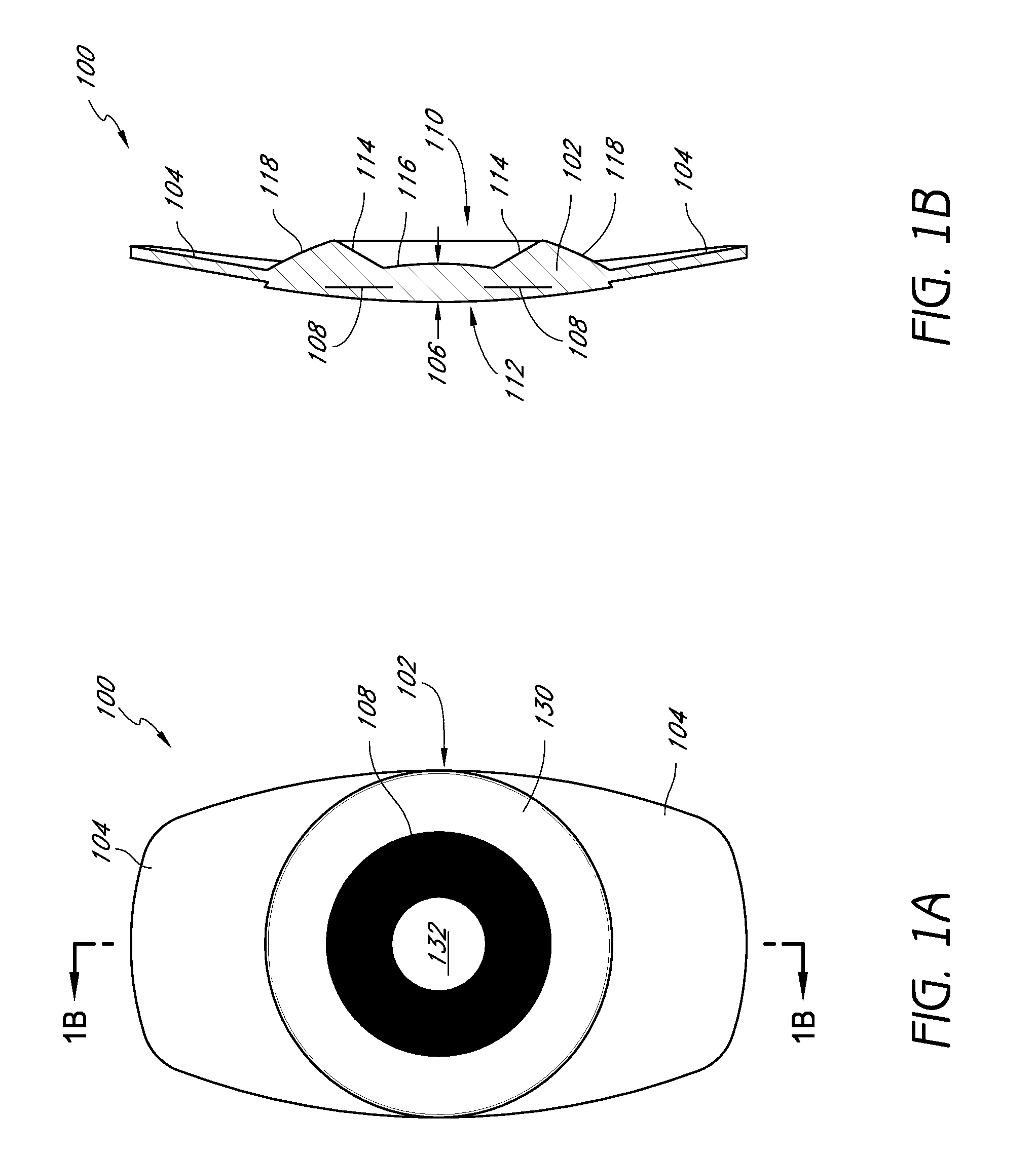
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an electro-active element having a dynamic aperture. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may be used in a non-focusing ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, a contact lens, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may also be used in a focusing or non-focusing device such as an intraocular optic, an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a contact lens which may or may not have an optical power. By changing the diameter of dynamic aperture either increased depth of field or increased light reaching the retina may be achieved.
Owner:E VISION LLC +1
Wearable display system
InactiveUS20060098293A1Large field of viewBrighter imagePolarising elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPhysicsOptical power
A wearable display system, such as a Head Mounted Display, having a display engine producing light, preferably linearly polarized light, which defines a synthetic image that is relayed to a wire grid polarizing combiner which overlays the synthetic image onto a real image of an object of the outside world, and wherein the real image is contemporaneously viewed through the wire grid polarizing combiner by the wearer of the system. The wire grid polarizing combiner can be curved in at least one axis, and preferably two axis such that optical power is added to the wire grid polarizing combiner.
Owner:CONCURRENT TECH
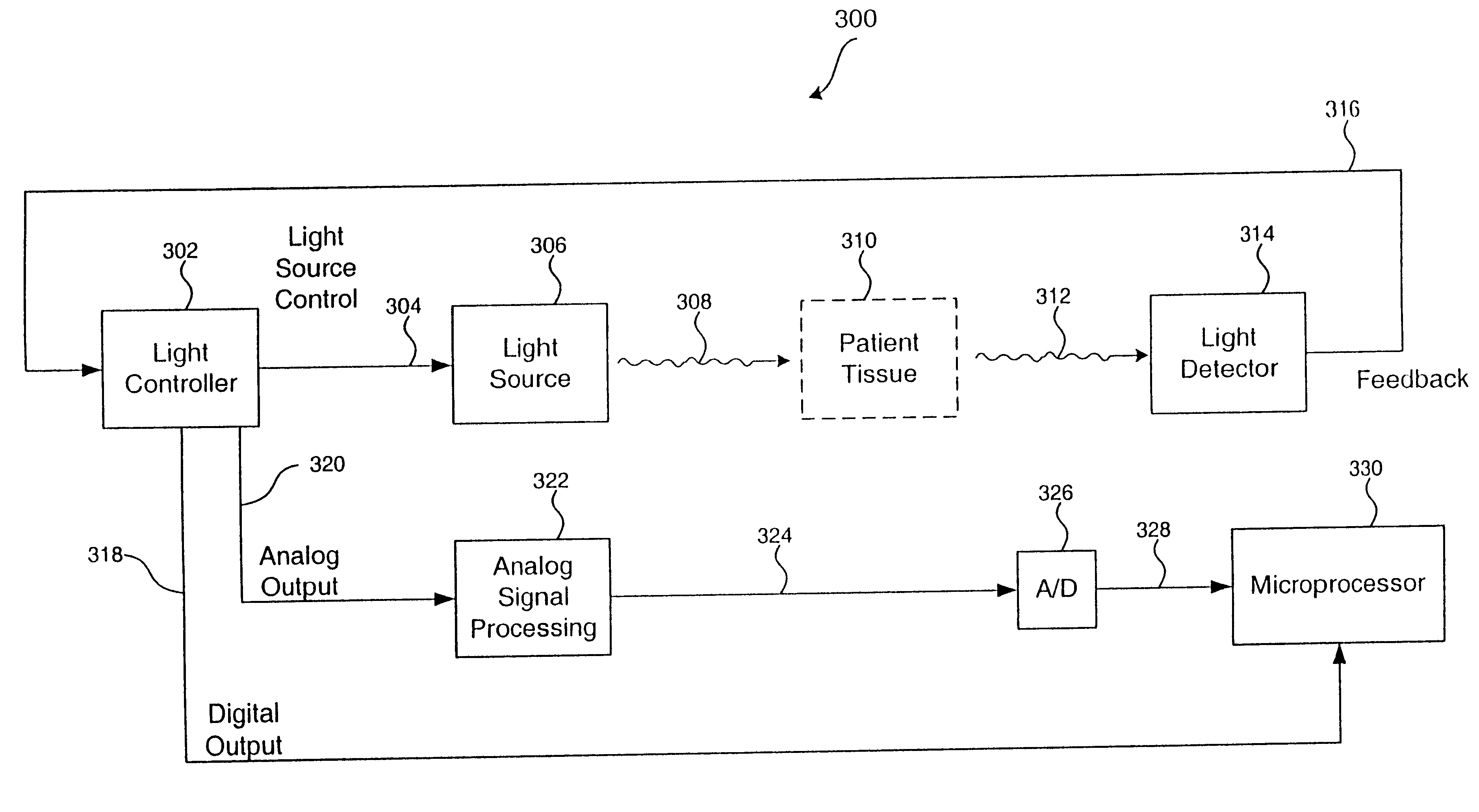
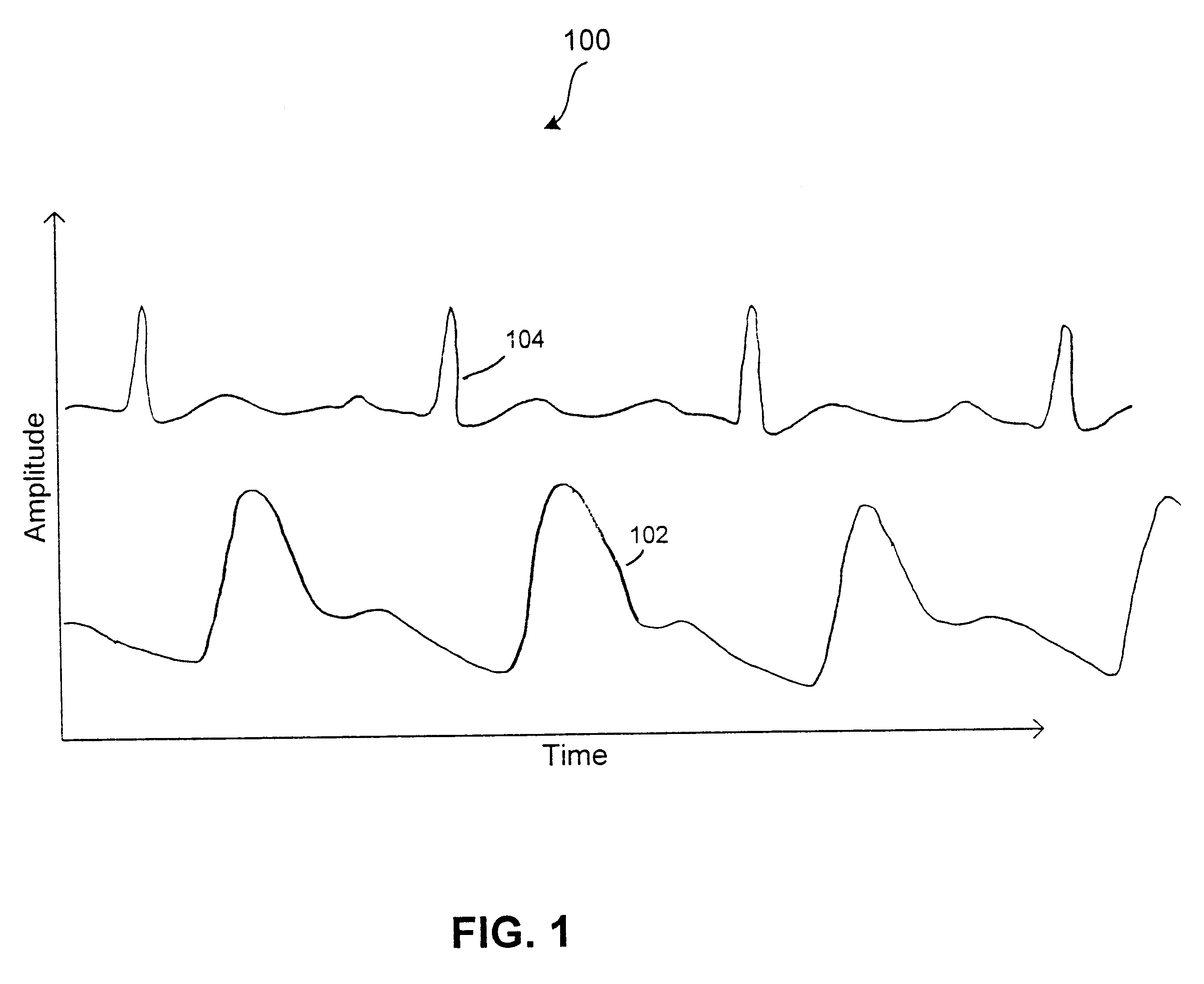
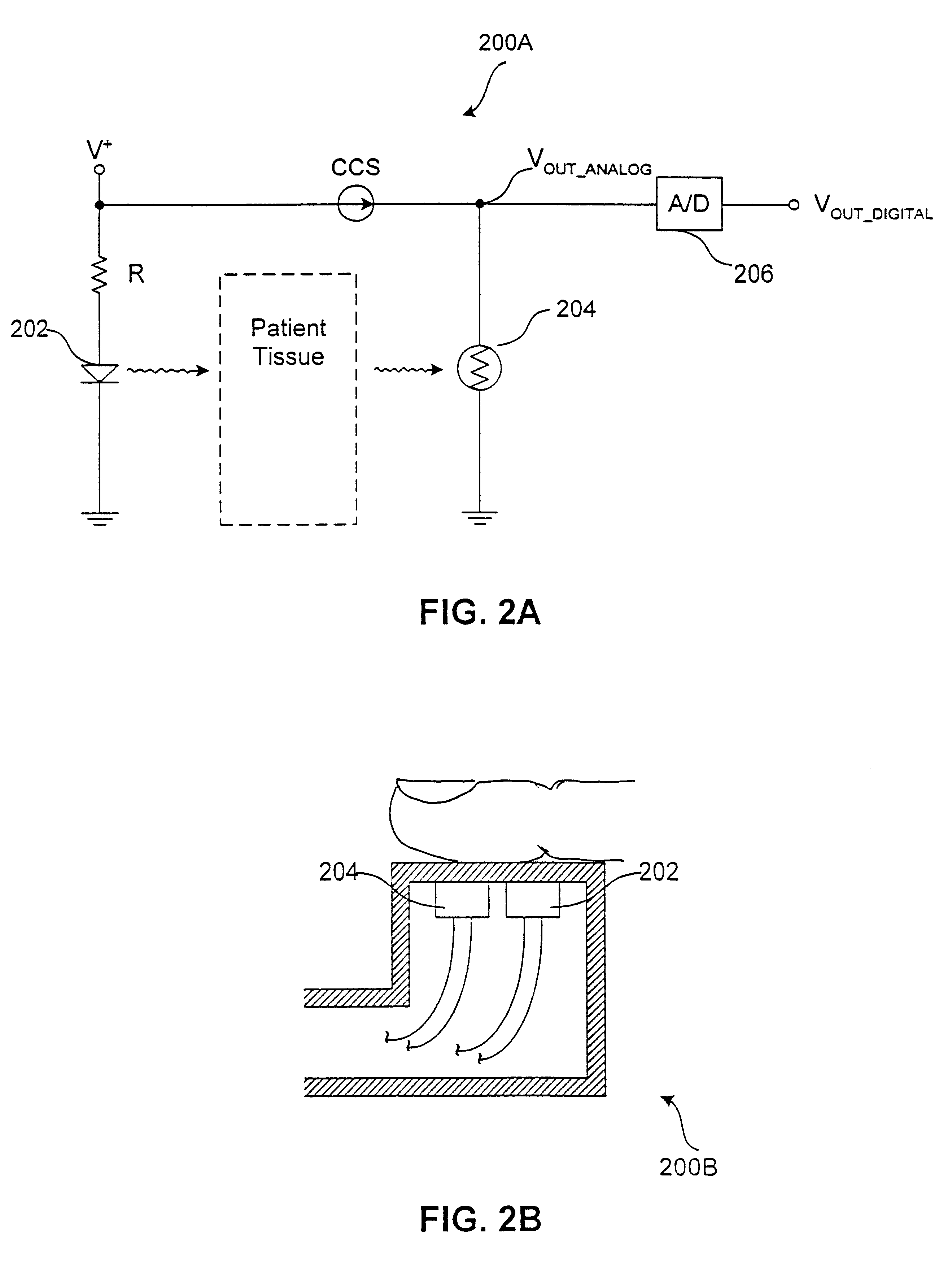
Methods and devices for vascular plethysmography via modulation of source intensity
A time-varying modulating signal is used as a plethysmography signal, rather than a time-varying detected optical power. The time-varying detected optical power is used (e.g., in a feedback loop) to adjust the source intensity. Light is transmitted from a light source, wherein an intensity of the transmitted light is based on a light control signal. A portion of the light transmitted from the light source is received at a light detector, the portion having an associated detected light intensity. A feedback signal is produced based the portion of light received at the light detector, the feedback signal indicative of the detected light intensity. The feedback signal is compared to a reference signal to produce a comparison signal. The light control signal is then adjusted based on the comparison signal, wherein at least one of the comparison signal and the light control signal is representative of volume changes in blood vessels.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
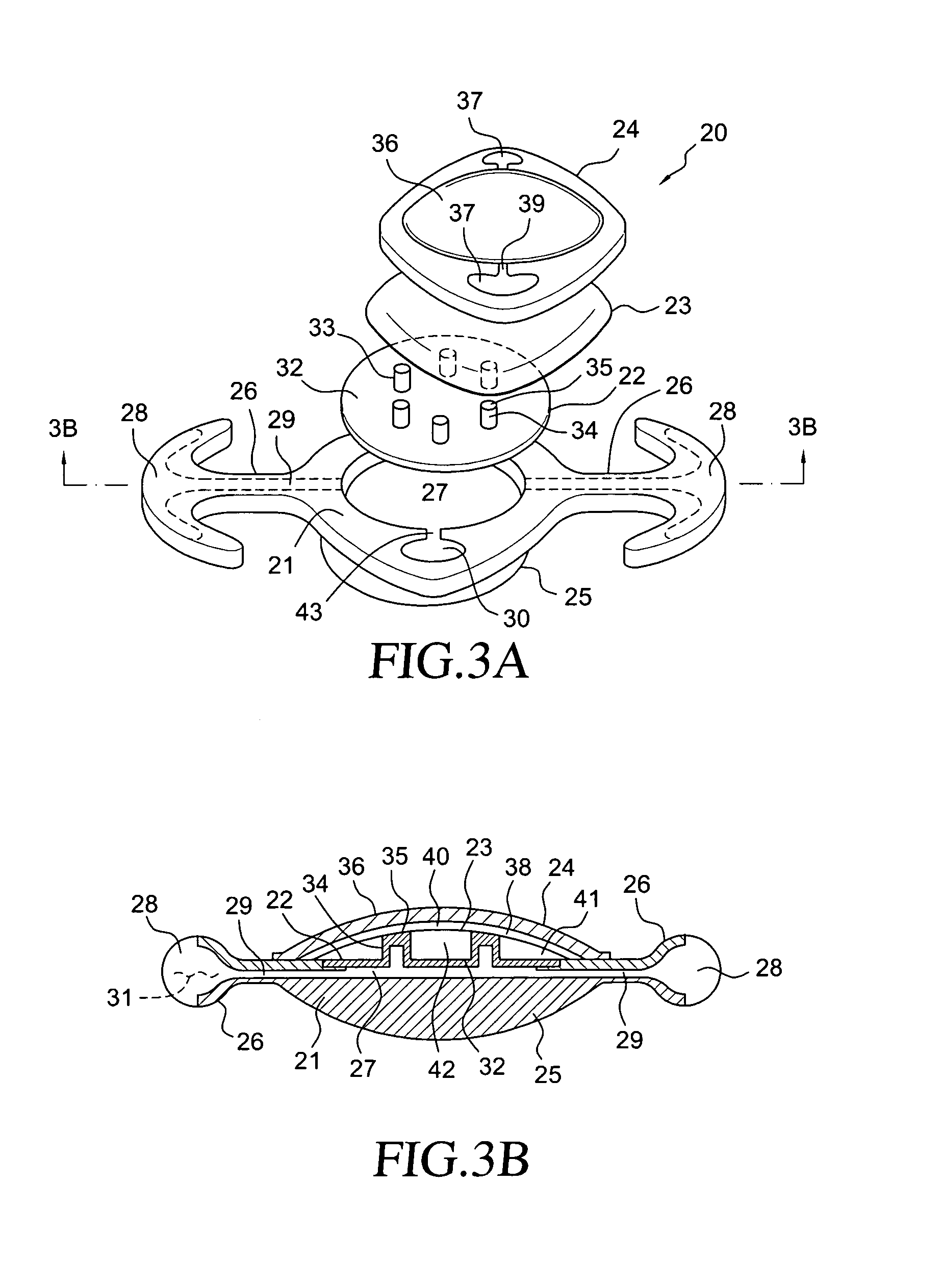
Accommodating intraocular lens system utilizing direct force transfer from zonules and method of use
InactiveUS20070088433A1Efficiently manipulatedEnhancing resistance to migrationIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical power
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided having optical parameters that are altered in-situ, wherein an optic portion of the lens includes a lens piston that alters the shape of a lens element of the lens to alter the optical power of the lens, responsive to forces applied to a haptic portion to the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles. Forces applied to the haptic portion are transferred hydraulically to cause the lens to become more or less accommodated. The haptic portion is retained in a fixed unaccommodated state during an initial healing period following implantation to facilitate affixation of the haptic portion to the capsule.
Owner:POWERVISION
Accommodating intraocular lens system and method
ActiveUS7122053B2Great motionEfficiently manipulatedIntraocular lensOptical partsIntraocular lensRelative Volume
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided that having optical parameters that are altered in-situ using forces applied by the ciliary muscles, in which a lens body carries an actuator separating two fluid-filled chambers having either the same index of diffraction or different indices of refraction, actuation of the actuator changing the relative volumes of fluid within an optic element of the lens and altering the optical power of the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
High intensity photocuring system
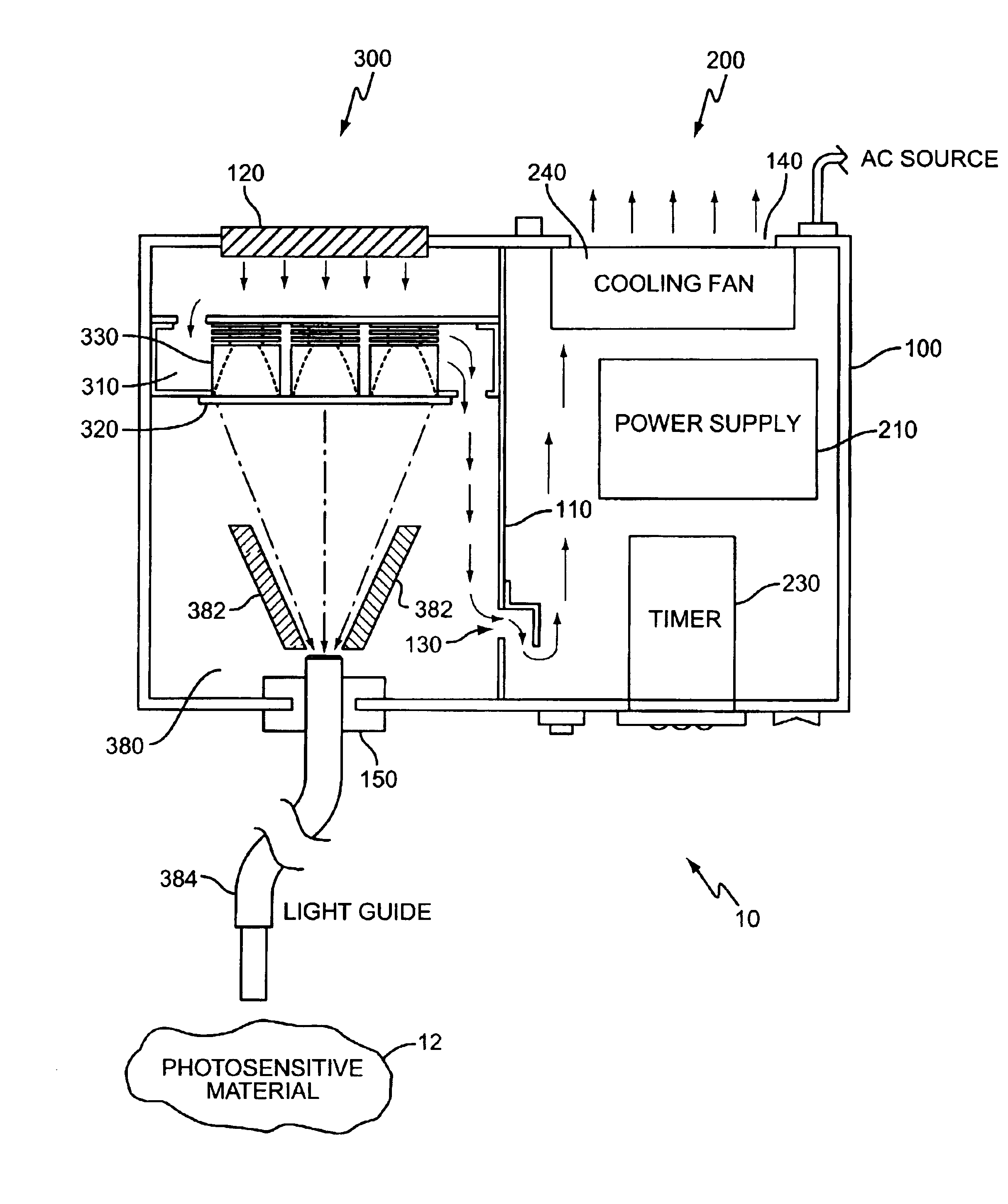
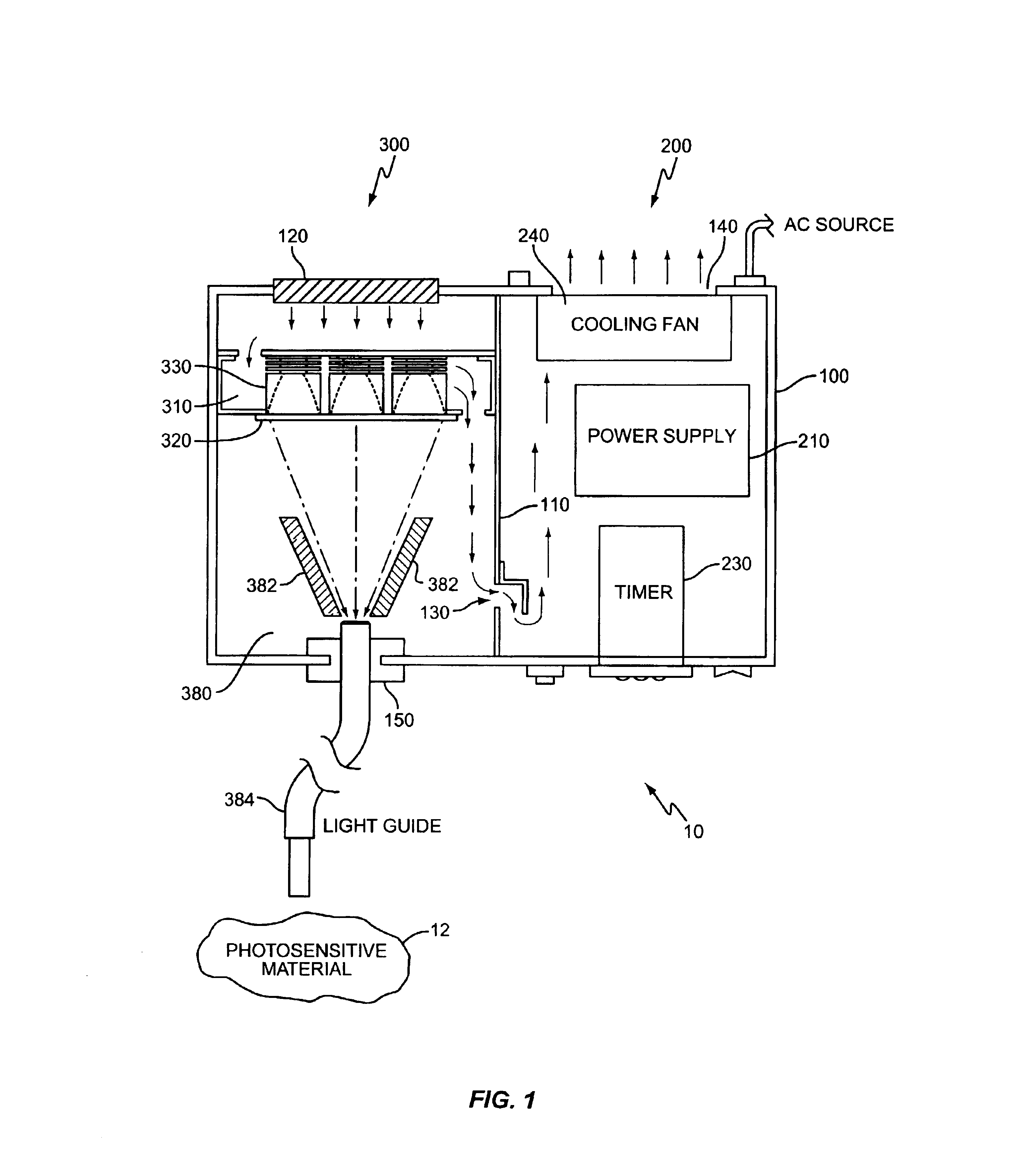
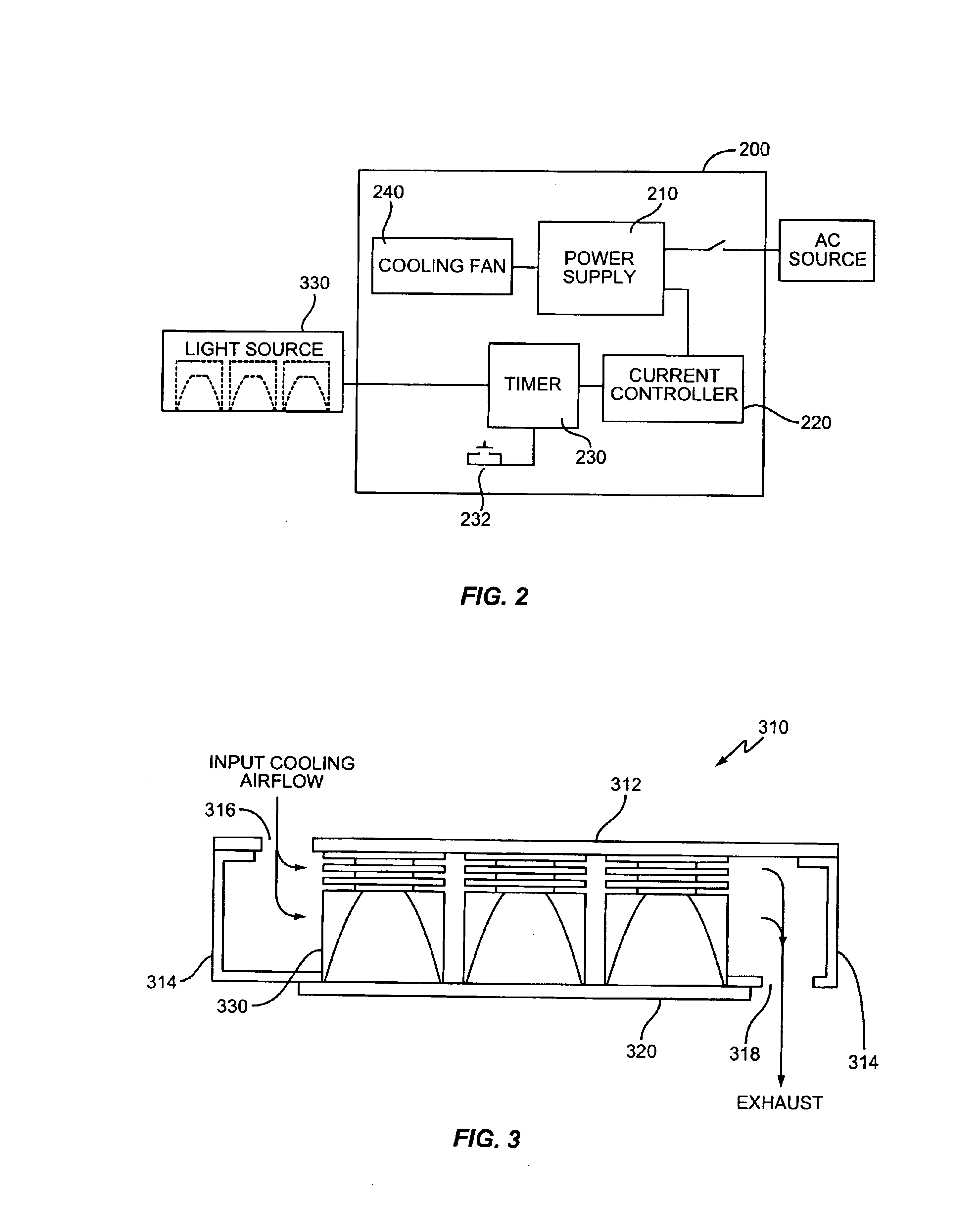
A method and apparatus for curing photosensitive materials uses LEDs and an optical concentrator to generate high optical power intensities. An LED array, comprising a plurality of LED assemblies, generates collimated light. A collection lens functions as an optical concentrator and focuses the collimated light to a desired spot size at a desired location. The LED assemblies may be at least partially disposed in a cooling plenum, where the cooling plenum is at least partially defined by the collection lens. Each LED assembly within the LED array may be detachably coupled to a mounting surface, enabling easy replacement of individual LED assemblies within the LED array. The photocuring assembly may also include a redirecting assembly disposed between the collection lens and the desired location that may further concentrate the light at the desired location. The photocuring assembly may include more than one of the above features.
Owner:SMD SOFTWARE
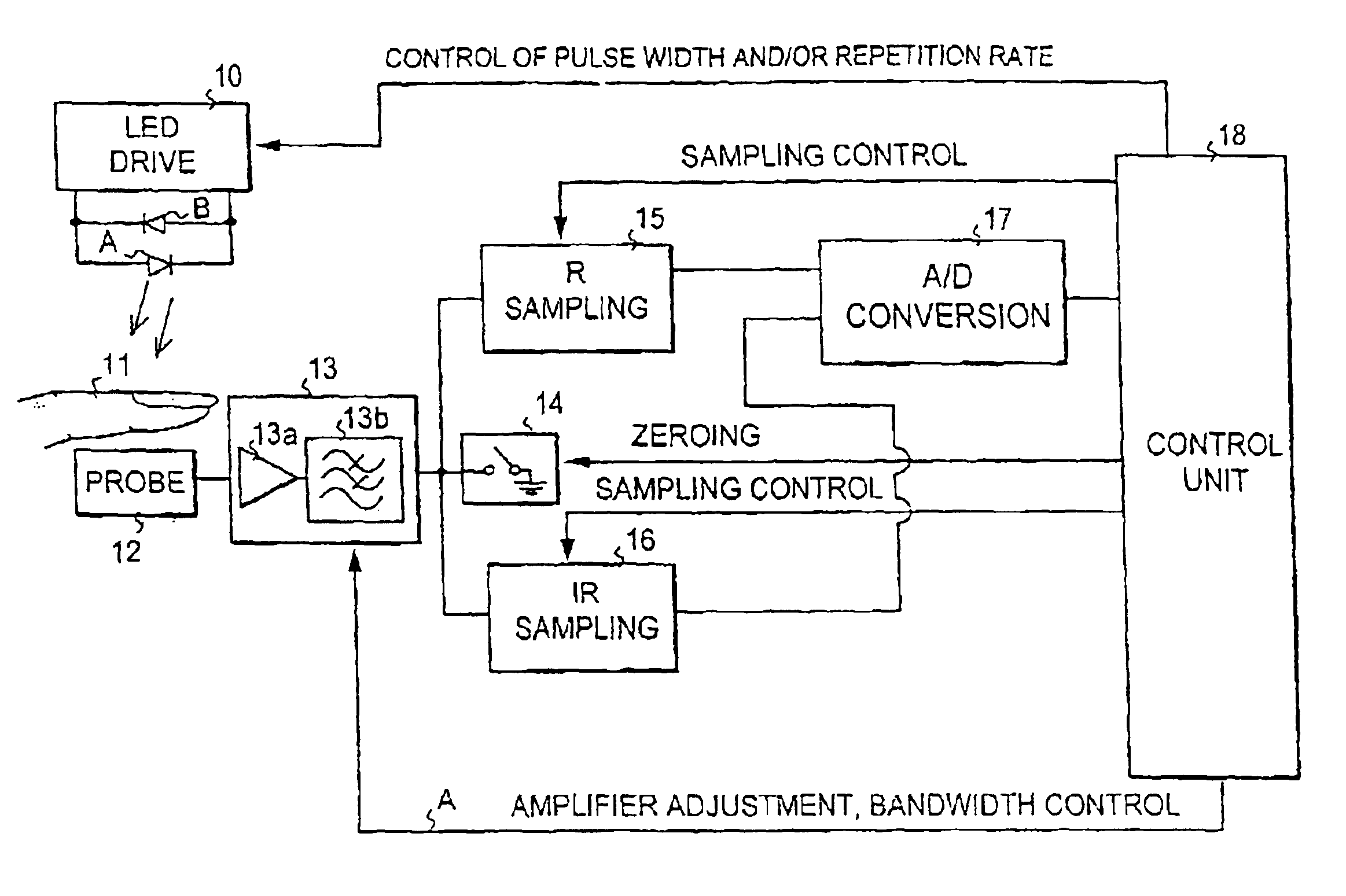
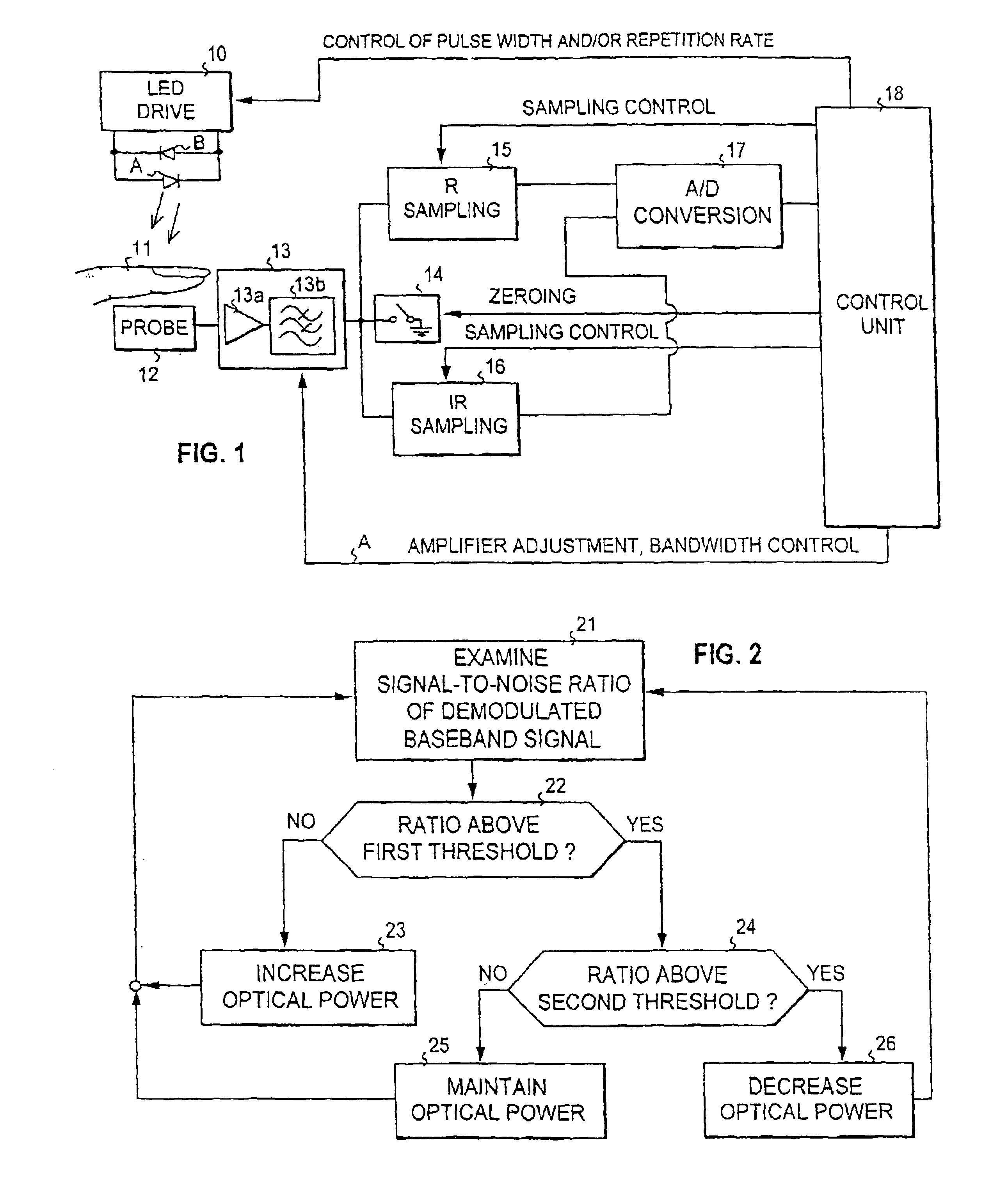
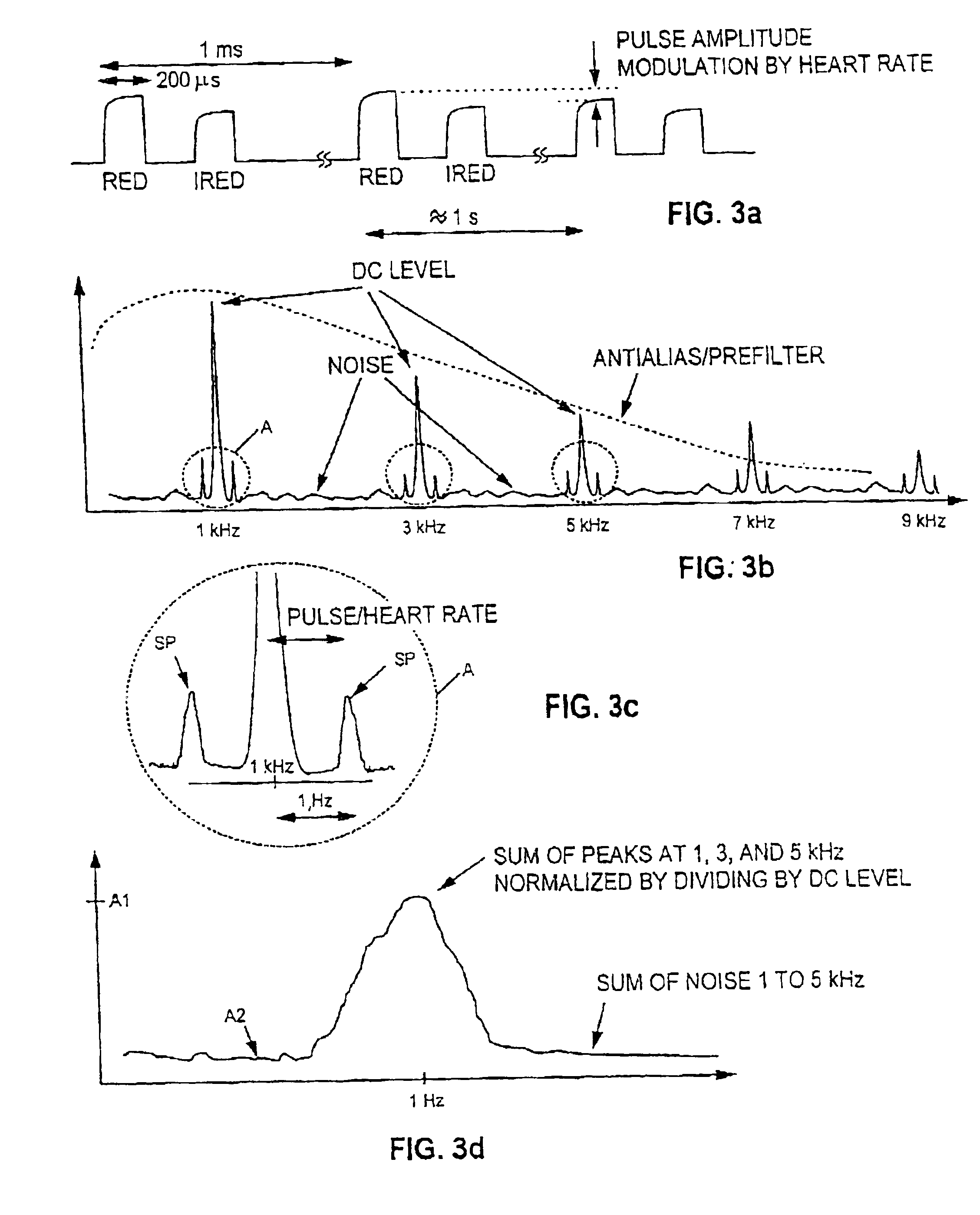
Pulse oximeter
InactiveUS6912413B2Improve performanceMinimize powerDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood oxygenationPulse oximetry
The invention relates to pulsed oximeters used to measure blood oxygenation. The current trend towards mobile oximeters has brought the problem of how to minimize power consumption without compromising on the performance of the device. To tackle this problem, the present invention provides a method for controlling optical power in a pulse oximeter. The signal-to-noise ratio of the received baseband signal is monitored, and the duty cycle of the driving pulses is controlled in dependence on the monitored signal-to-noise ratio, preferably so that the optical power is minimized within the confines of a predetermined lower threshold set for the signal-to-noise ratio. In this way the optical power is made dependent on the perfusion level of the subject, whereby the power can be controlled to a level which does not exceed that needed for the subject.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
Microscope with tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction lens enabling multiple focal plan imaging
An apparatus, system and method for microscopy. The apparatus, system and method includes a stage configured to receive an item; a tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction (TAG) lens having a first aspect positioned to image the received item, wherein the first aspect of the TAG lens is configured to have an optical power profile in accordance with an operational frequency of the TAG lens; one or more lenses configured to magnify an image of the received item at a viewing point; and at least one pulsed light source configured to illuminate the received item and to pulse at one or more points within the optical power profile of the TAG lens.
Owner:MITUTOYO OPTICS MFG AMERICA CORP +1
Fiber array unit with integrated optical power monitor
A technique for monitoring optical power in a fiber array unit having a plurality of optical transmission waveguides terminating at an edge thereof for carrying optical signals to and / or from a PLC. A tapping filter is placed within a slit formed in the substrate and interrupting the transmission channels, thereby tapping at least some of the optical power from the channels and directing the tapped optical power toward respective photodetector channels for detection, while allowing other optical power to continue transmission in the at least one channel of the fiber array unit.
Owner:ZHU HAI BEN JIA TECH CO LTD +1
Lens system and method for power adjustment
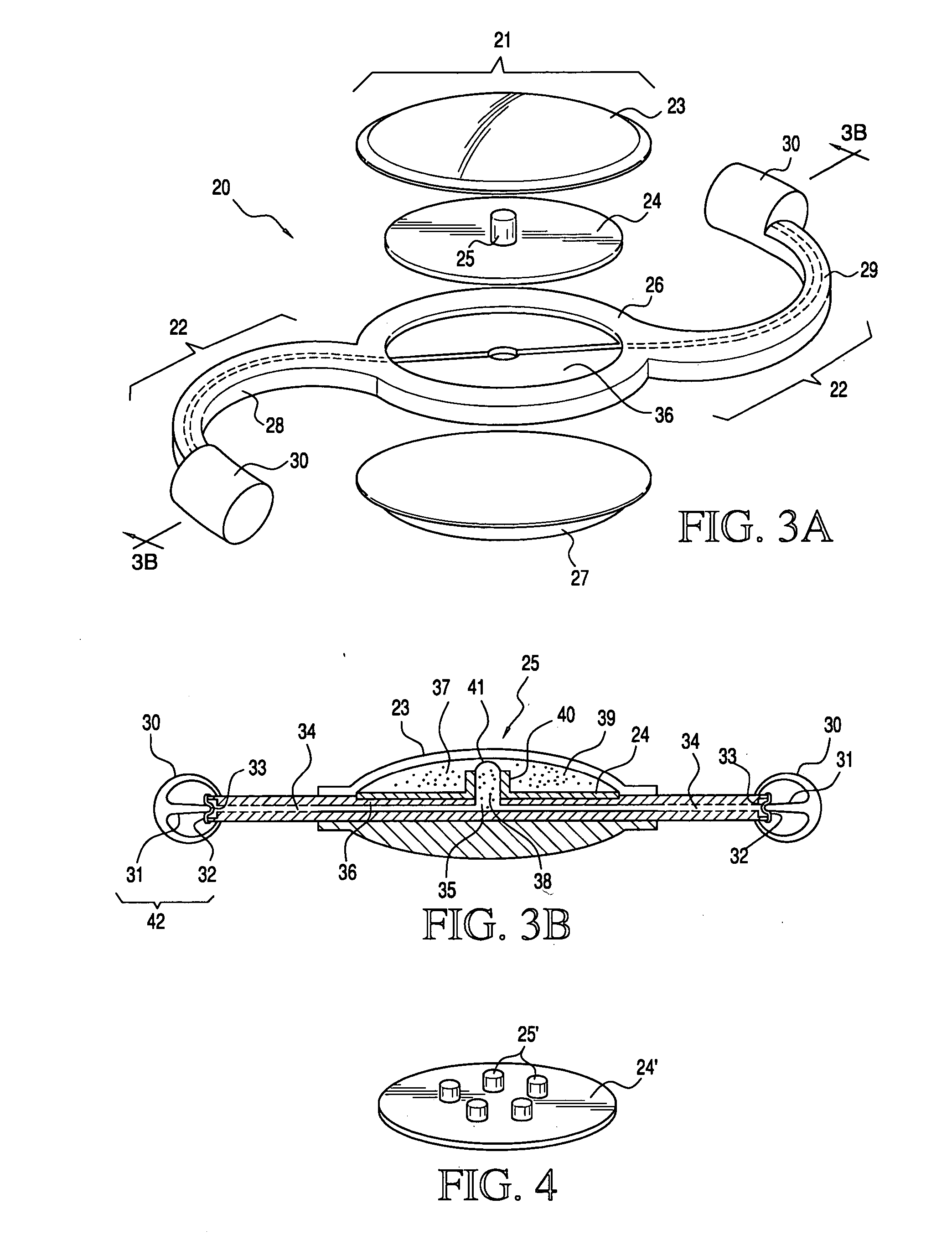
A lens is provided that having optical parameters that may be adjusted in-situ, and is particularly useful as an IOL for use in cataract patients that require an adjustment in the optical power of the lens post-implantation. In one embodiment, the lens body carries an array of interior fluid-filled cells in which fluid is controllably moved upon application of energy from an external source to move a fluid media into or out of the cells to thereby alter the lens surface shape.
Owner:ALCON INC
Imaging device and digital camera using the imaging device
InactiveUS20040008271A1Solve the thickerLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical power
An imaging device has a zoom lens system having a plurality of lens units and forming an optical image of an object so as to continuously optically zoom by varying distances between the lens unit; and an image sensor converting the optical image formed by the zoom lens system to an electric signal. The zoom lens system has from an object side, a first lens unit being overall negative and including a reflecting surface that bends a luminous flux substantially 90 degrees; and a second lens unit disposed with a variable air distance from the first lens unit, and having an optical power, and wherein at least one lens element made of resin is included in the entire lens system.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
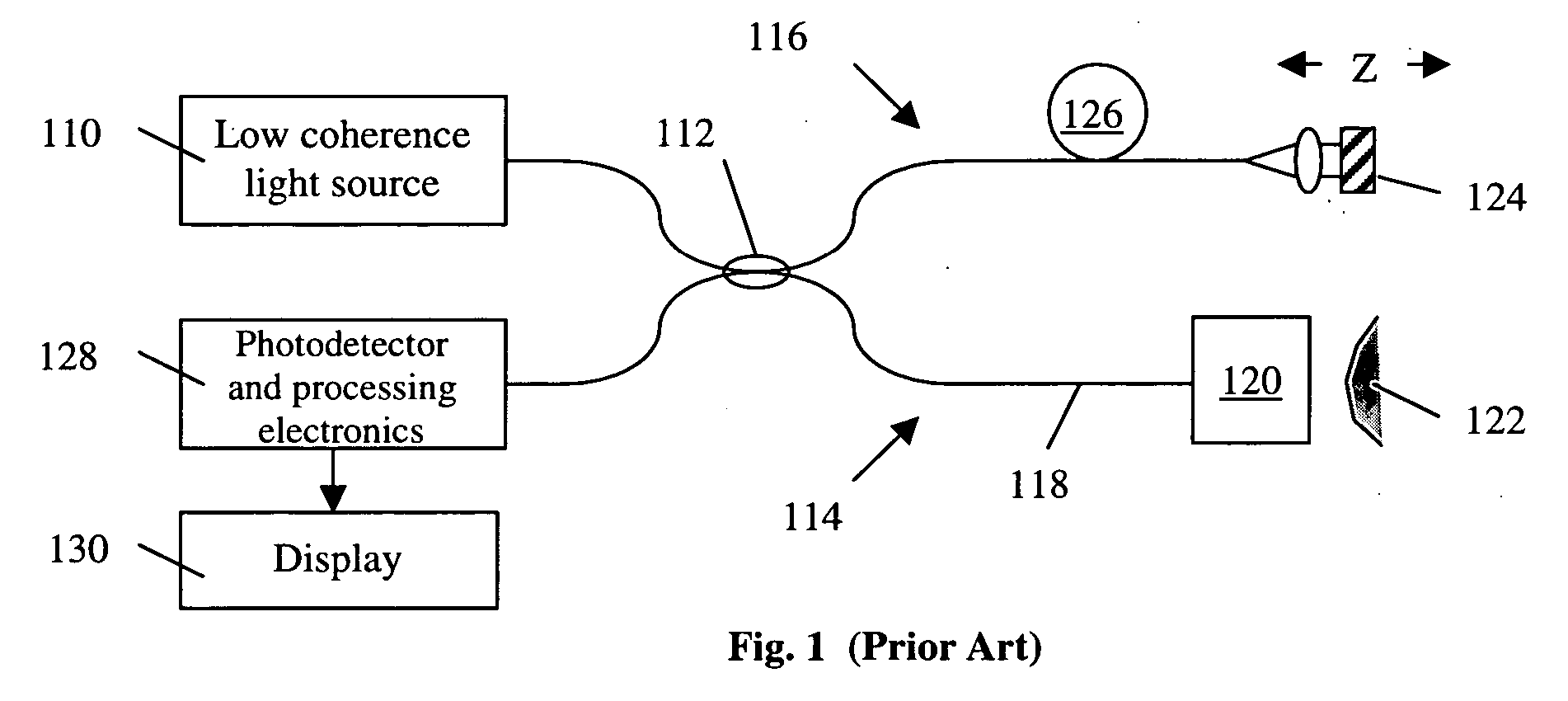
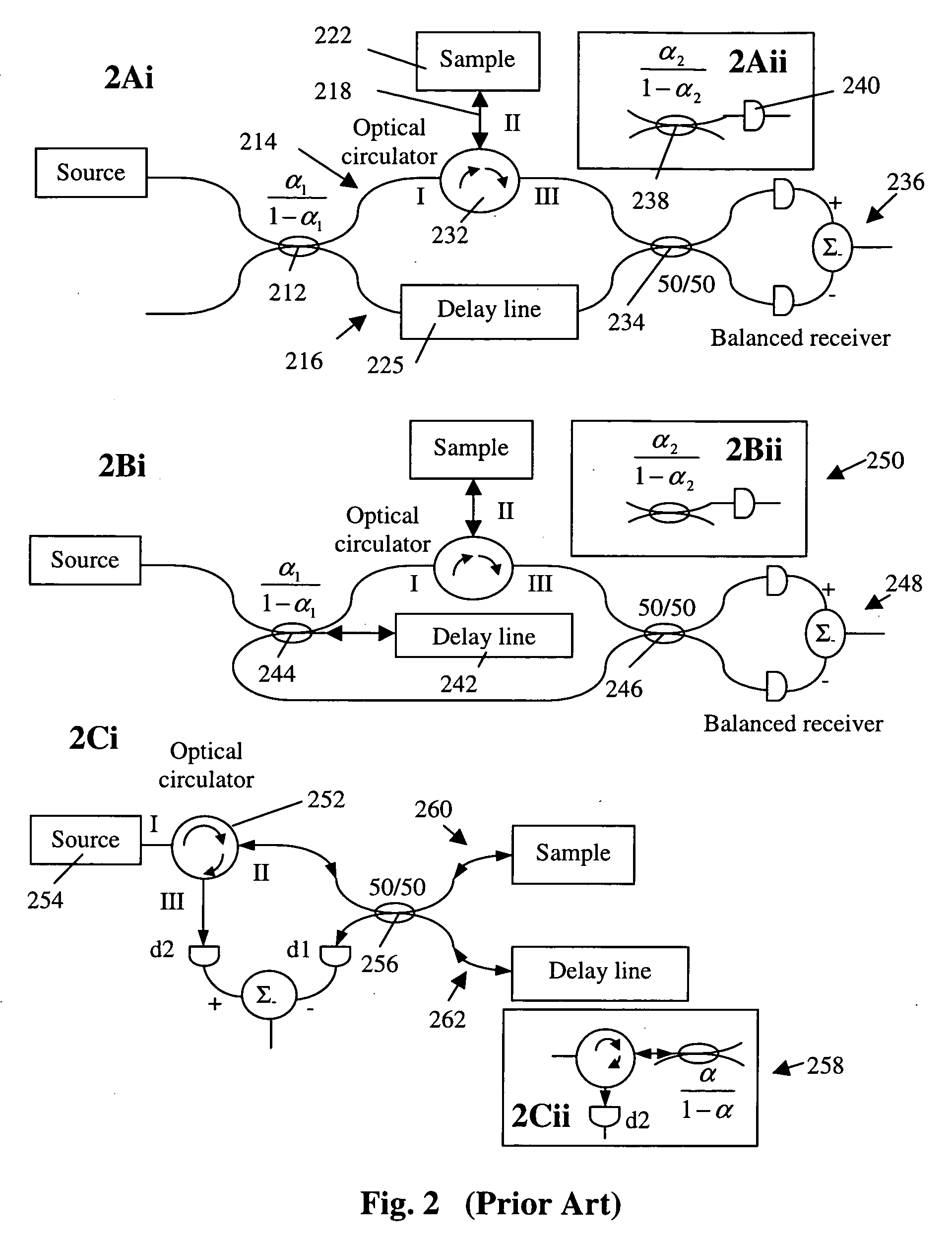
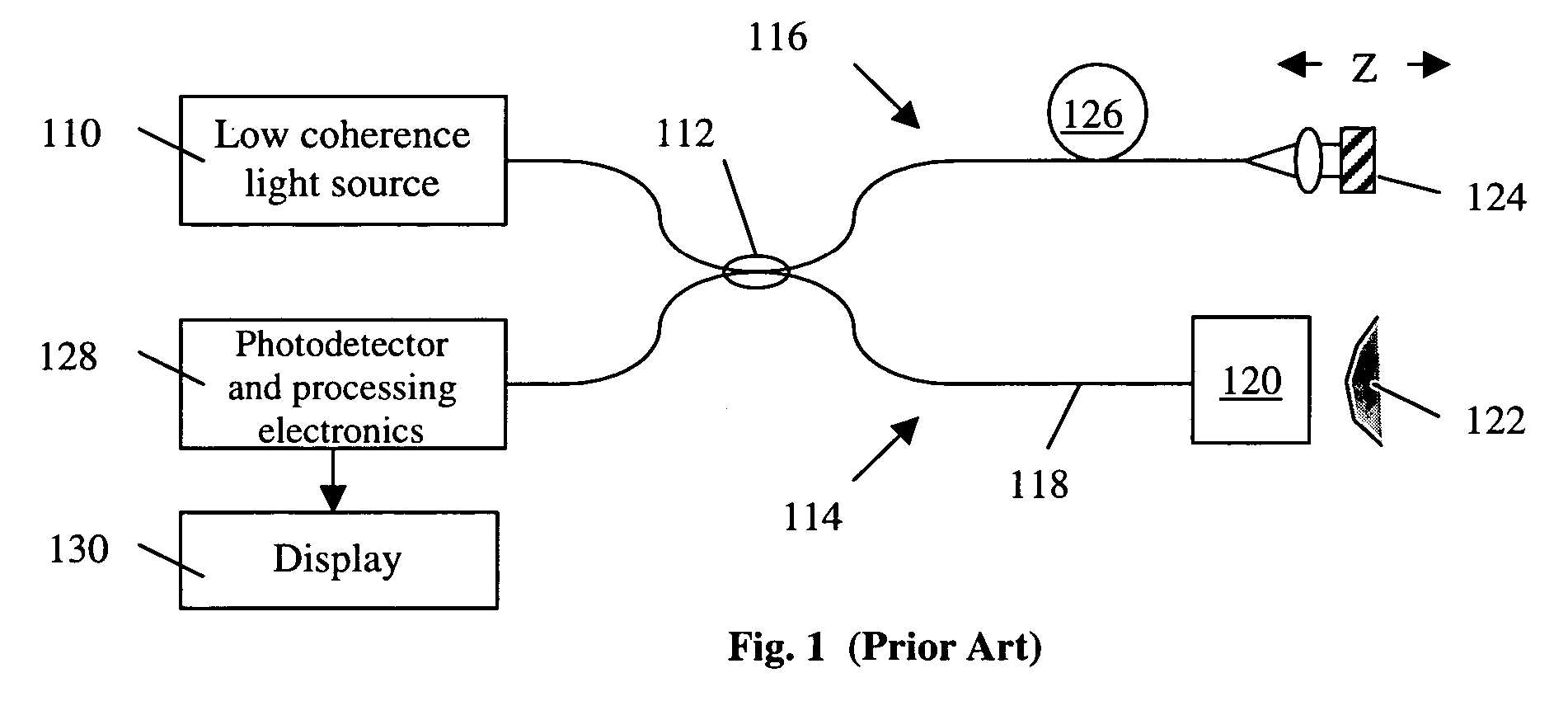
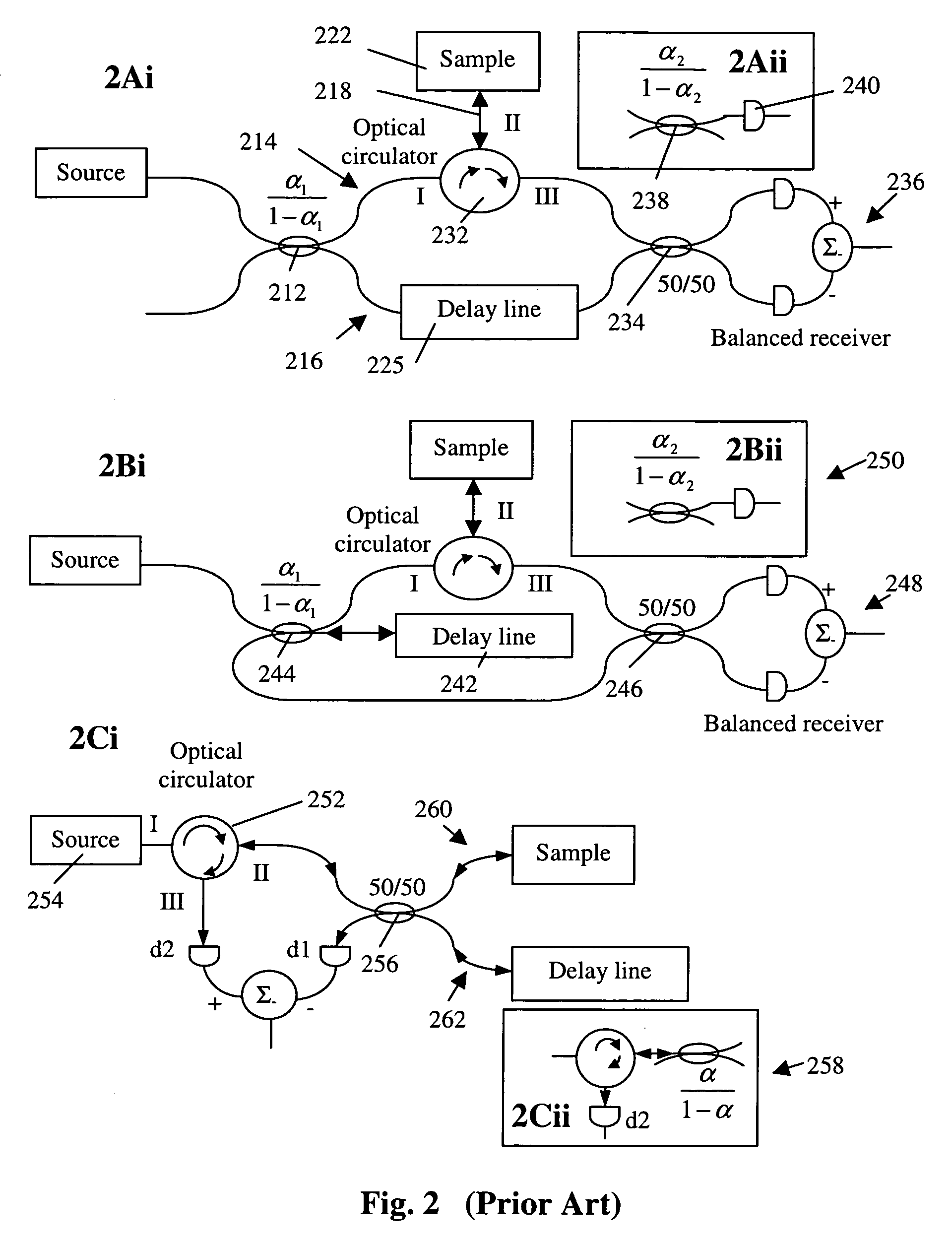
Simple high efficiency optical coherence domain reflectometer design
ActiveUS20050213103A1Reduce system costLow costReflectometers dealing with polarizationInterferometersBeam splitterDetector array
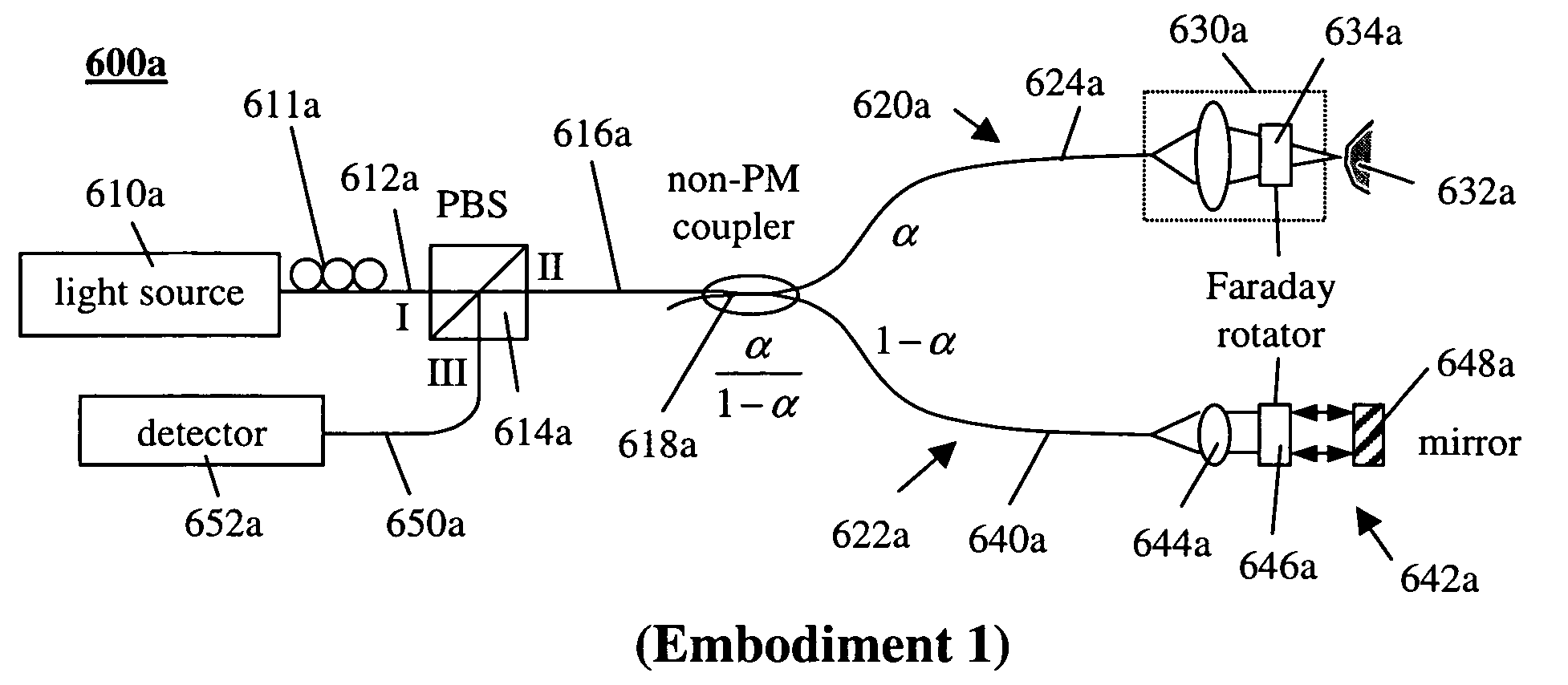
The present invention discloses simple and yet highly efficient configurations of optical coherence domain reflectometry systems. The combined use of a polarizing beam splitter with one or two polarization manipulator(s) that rotate the returned light wave polarization to an orthogonal direction, enables one to achieve high optical power delivery efficiency as well as fixed or predetermined output polarization state of the interfering light waves reaching a detector or detector array, which is especially beneficial for spectral domain optical coherence tomography. In addition, the system can be made insensitive to polarization fading resulting from the birefringence change in the sample and reference arms. Dispersion matching can also be easily achieved between the sample and the reference arm for high resolution longitudinal scanning.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
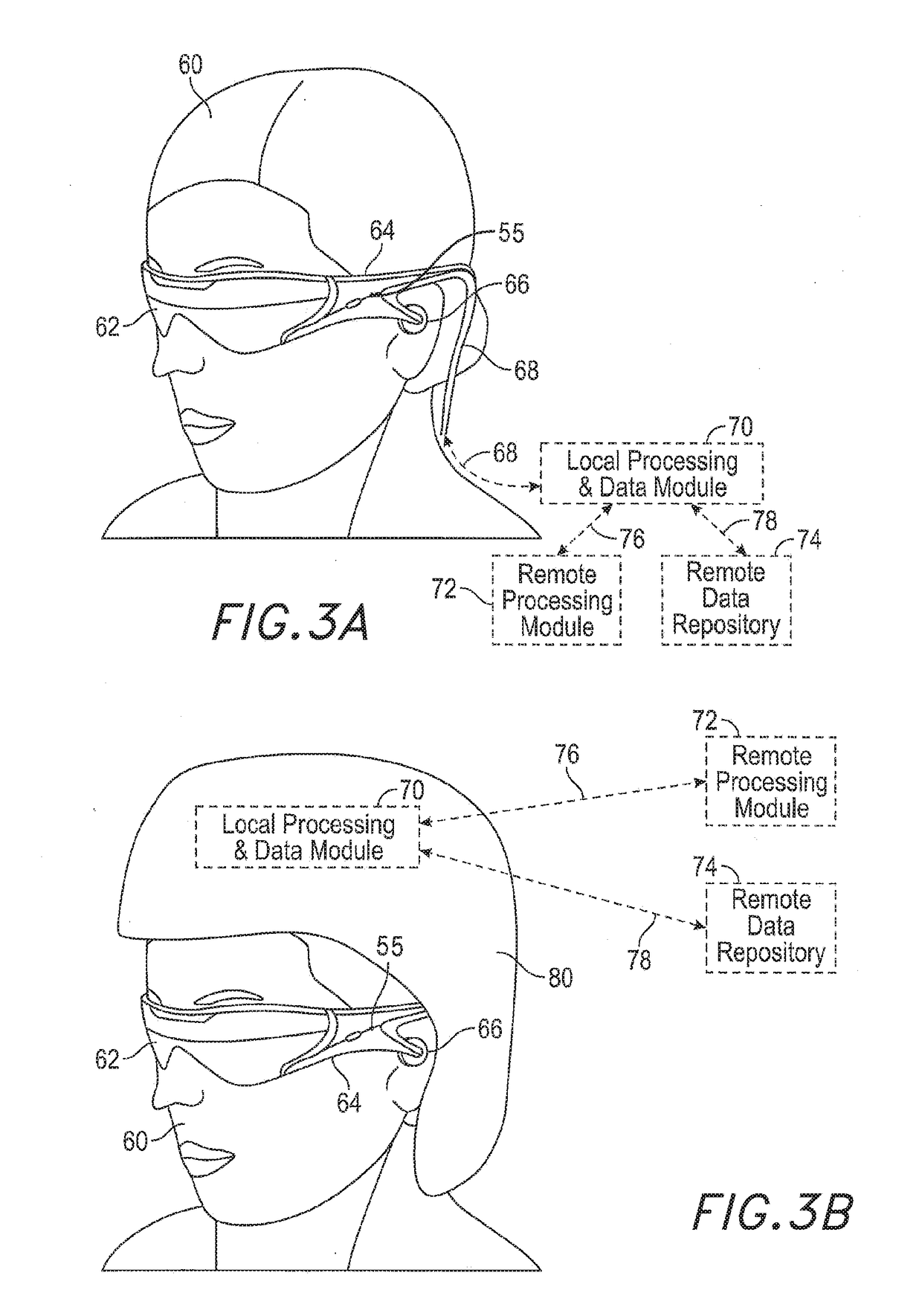
Light field processor system
A wearable ophthalmic device is disclosed. The device may include an outward facing head-mounted light field camera to receive light from a user's surroundings and to generate numerical light field image data. The device may also include a light field processor to access the numerical light field image data, to obtain an optical prescription for an eye of the user, and to computationally introduce an amount of positive or negative optical power to the numerical light field image data based on the optical prescription to generate modified numerical light field image data. The device may also include a head-mounted light field display to generate a physical light field corresponding to the modified numerical light field image data.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
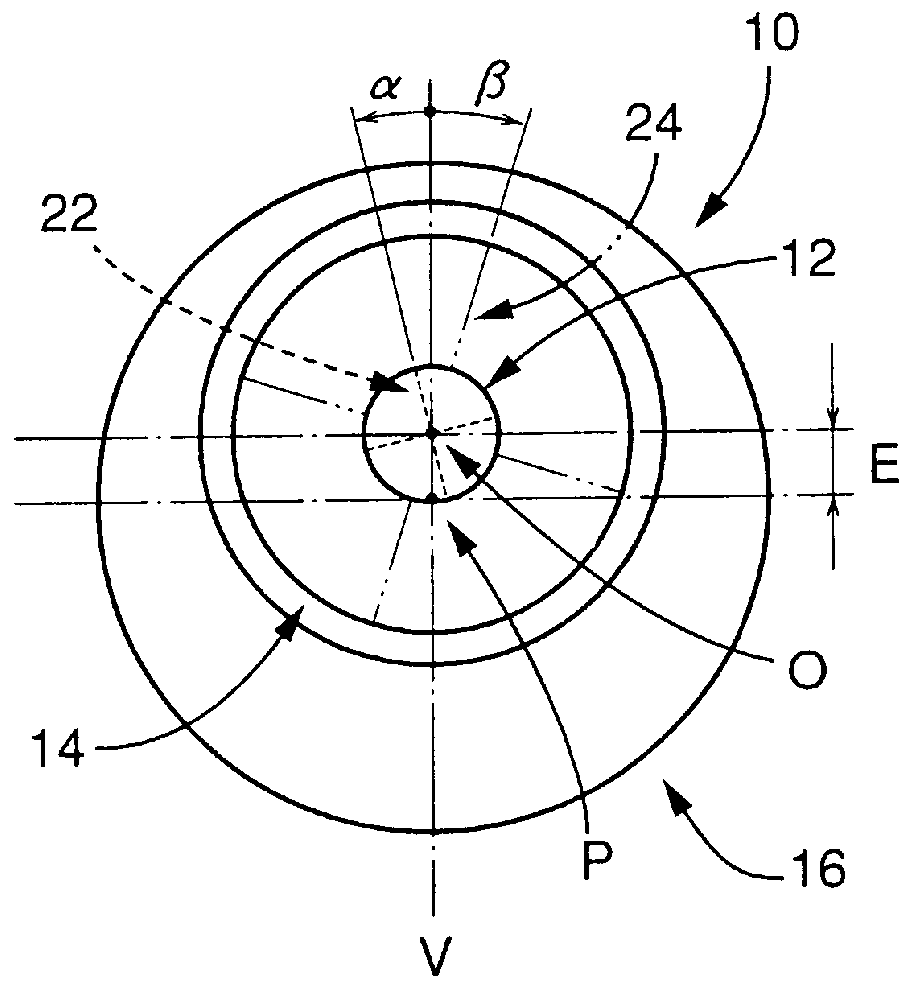
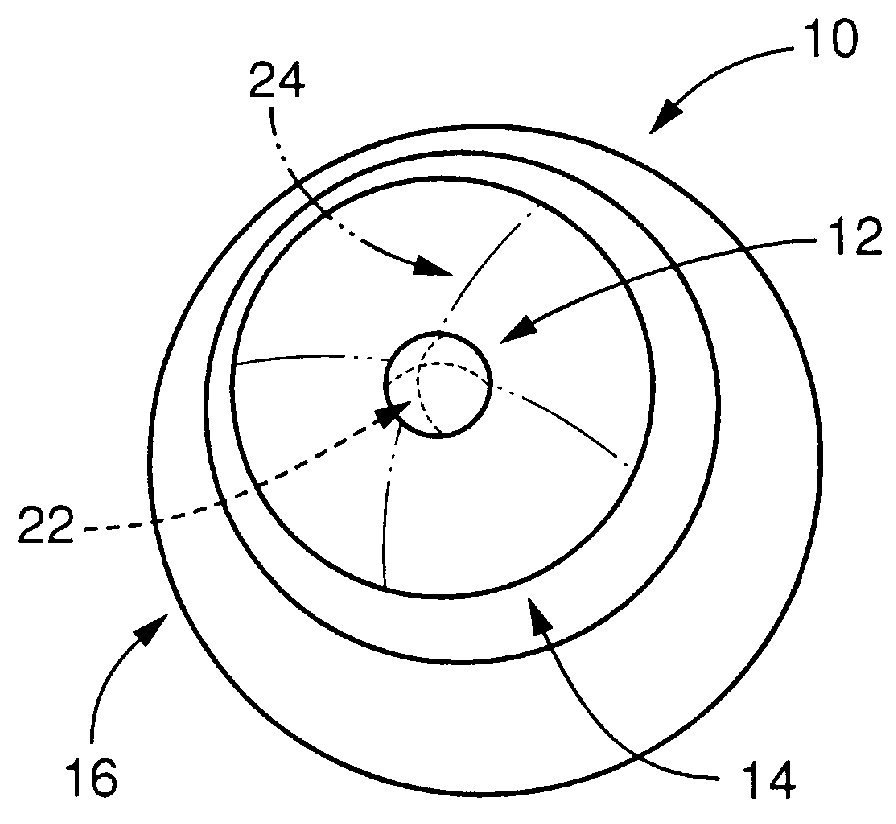
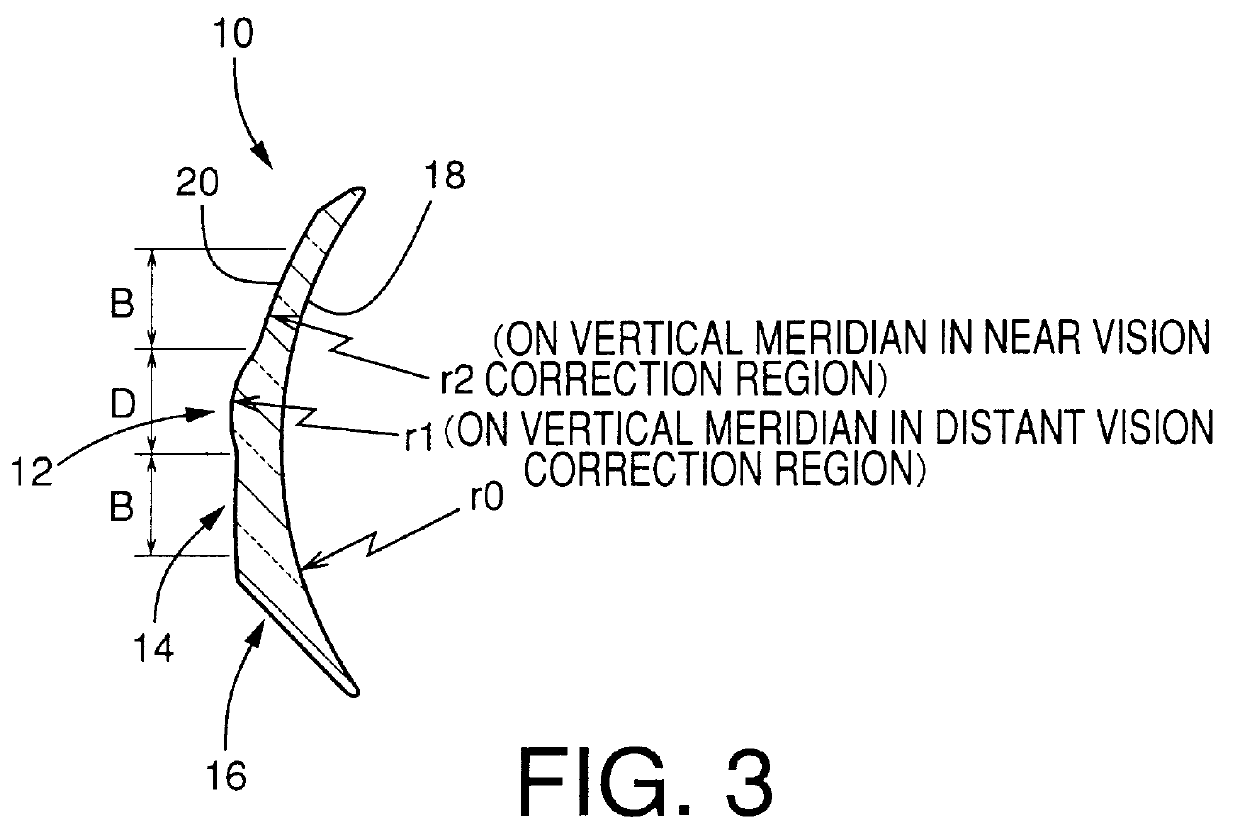
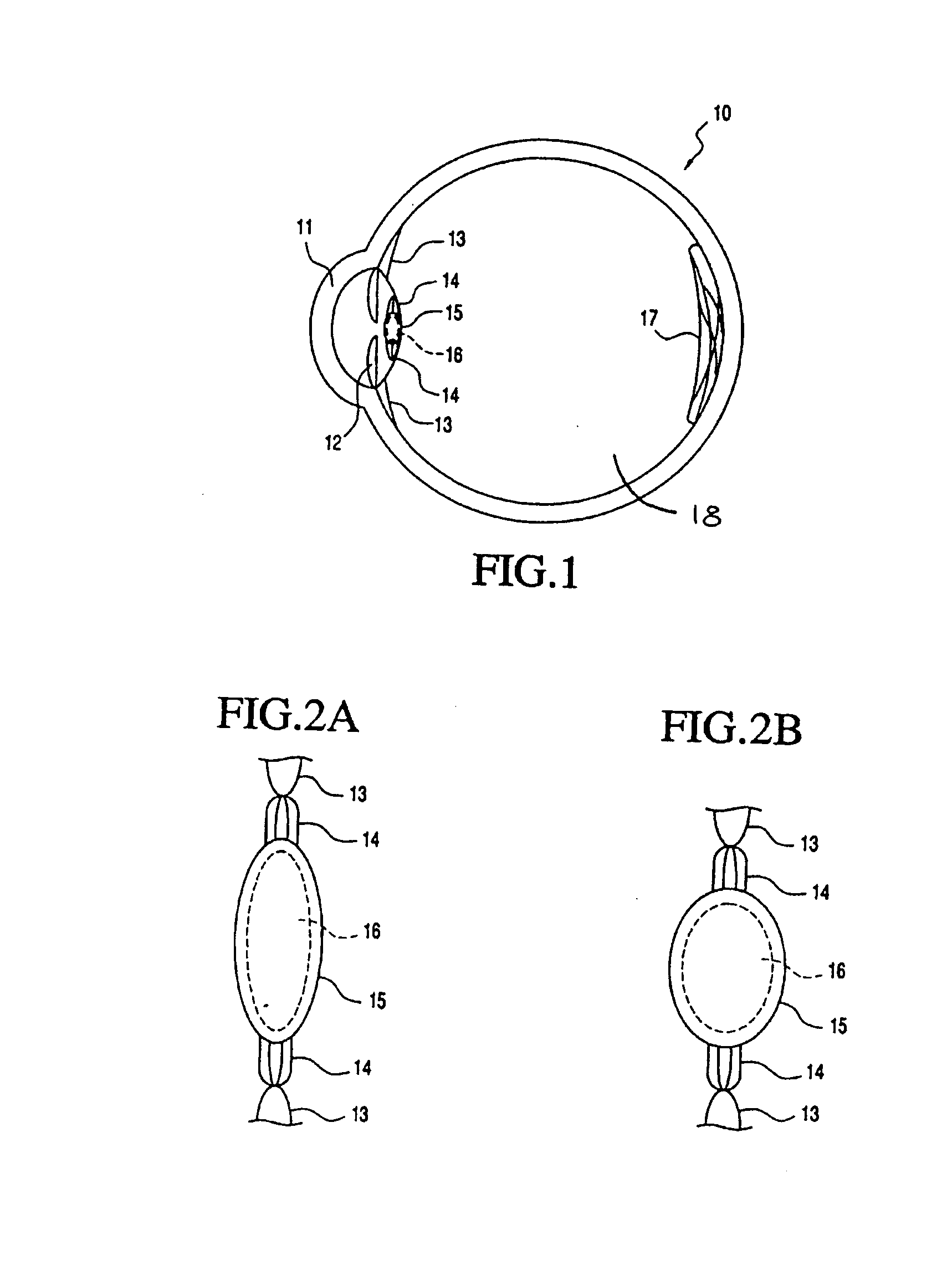
Toric multifocal lens having different astigmatism corrective optical powers in respective vision correction regions, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6142625AEasy to produceImprove stabilitySpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsOptical powerStigmatism
A toric multifocal lens including a plurality of vision correction regions having centers on a common optical center axis, the plurality of vision correction regions providing respective different values of a spherical optical power, each of the plurality of vision correction regions having an optical power for correction of astigmatism, wherein the improvement comprises: at least one of a cylindrical optical power and a cylindrical axis orientation which determine the optical power for correction of astigmatism being different in at least two different vision correction regions of the plurality of vision correction regions, so that the at least two different vision correction regions have respective different values of the optical power for correction of astigmatism.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Accommodating intraocular lens system and method
ActiveUS7261737B2Efficiently manipulatedAltering the optical parametersIntraocular lensOptical partsIntraocular lensOptical power
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided having optical parameters that are altered in-situ, wherein an optic portion of the lens includes a lens piston that alters the shape of a lens element of the lens to alter the optical power of the lens, responsive to forces applied to a haptic portion to the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles. Forces applied to the haptic portion are concentrated by the lens piston to provide a greater dynamic range, and may be further augmented by the use of haptic pistons disposed in the haptic portion of the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
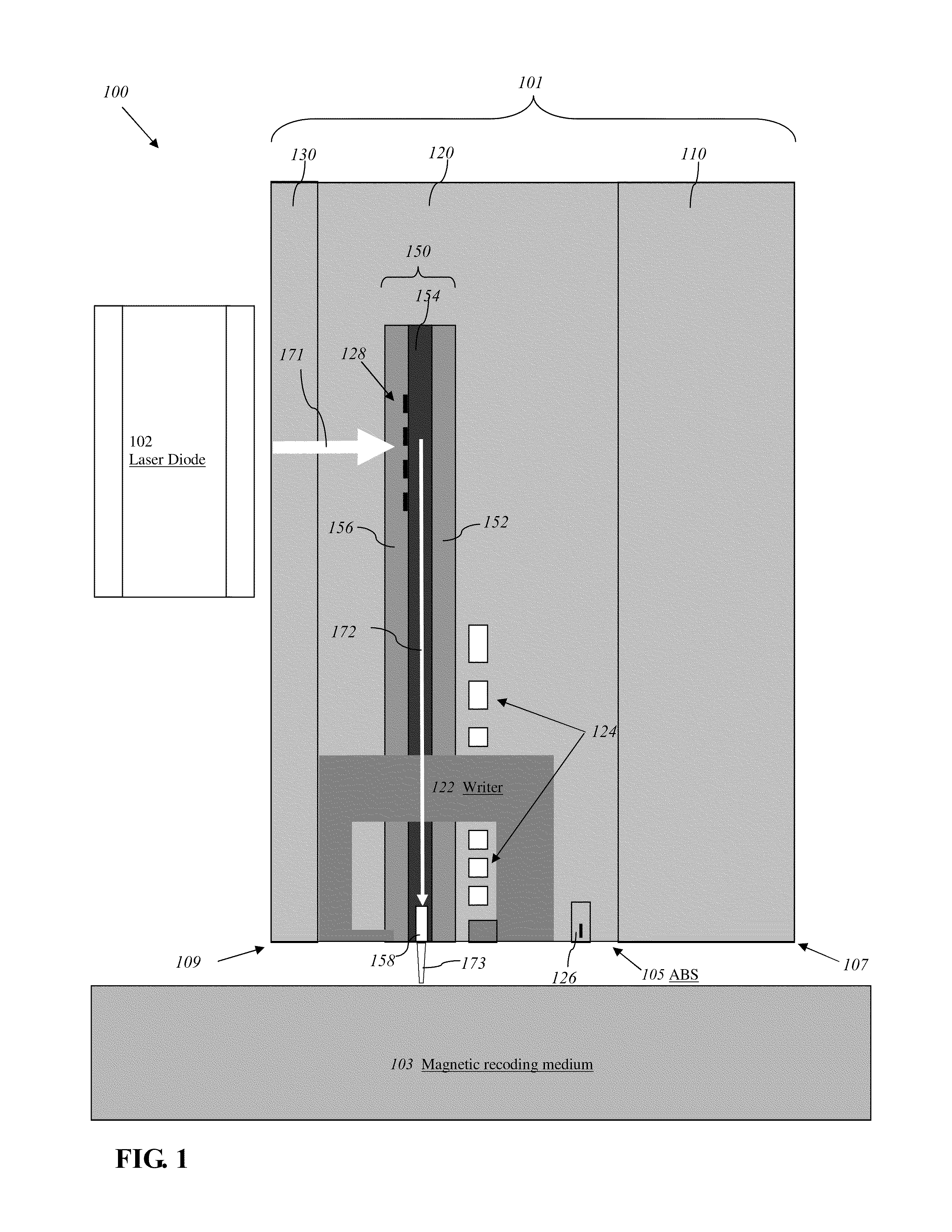
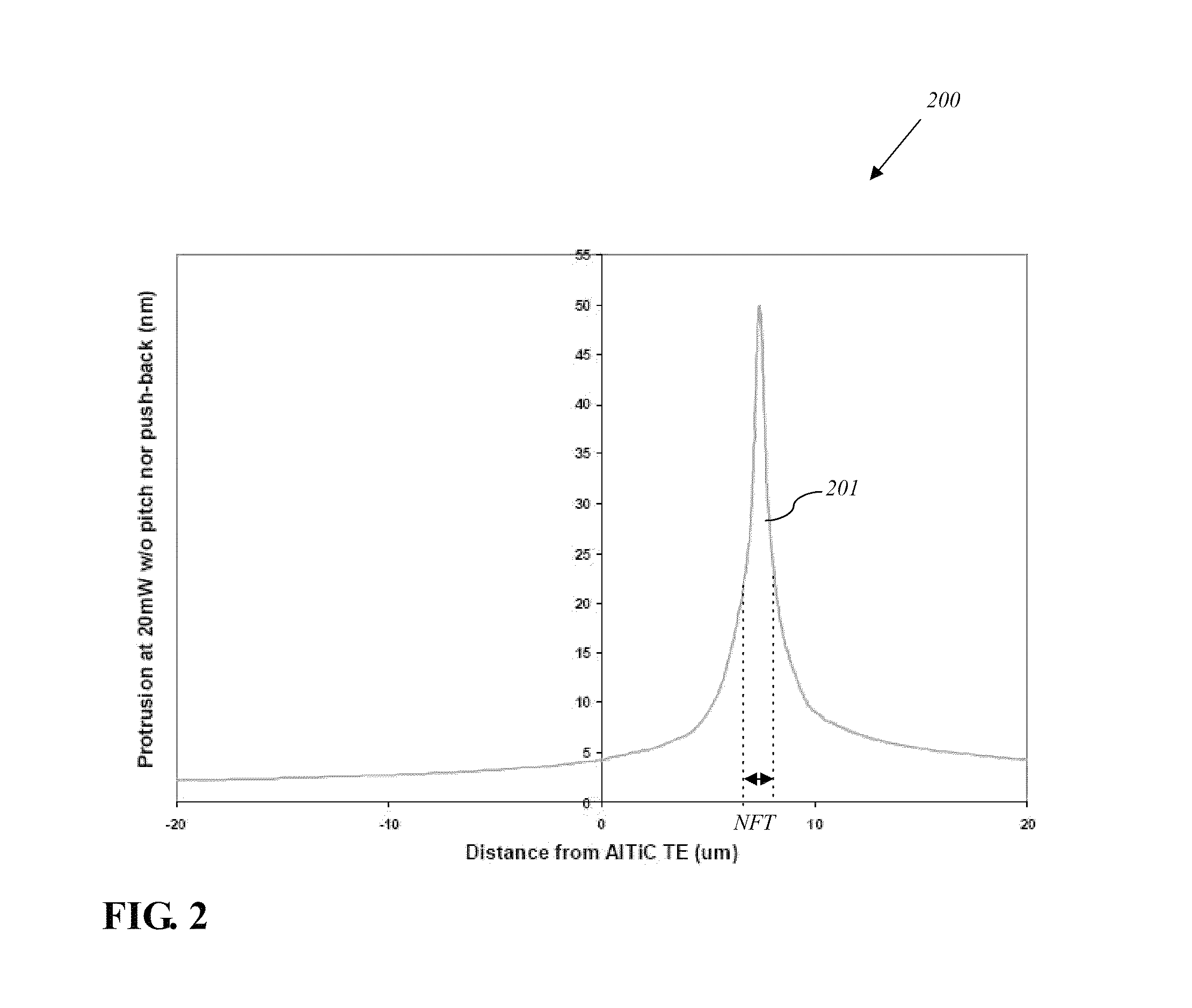
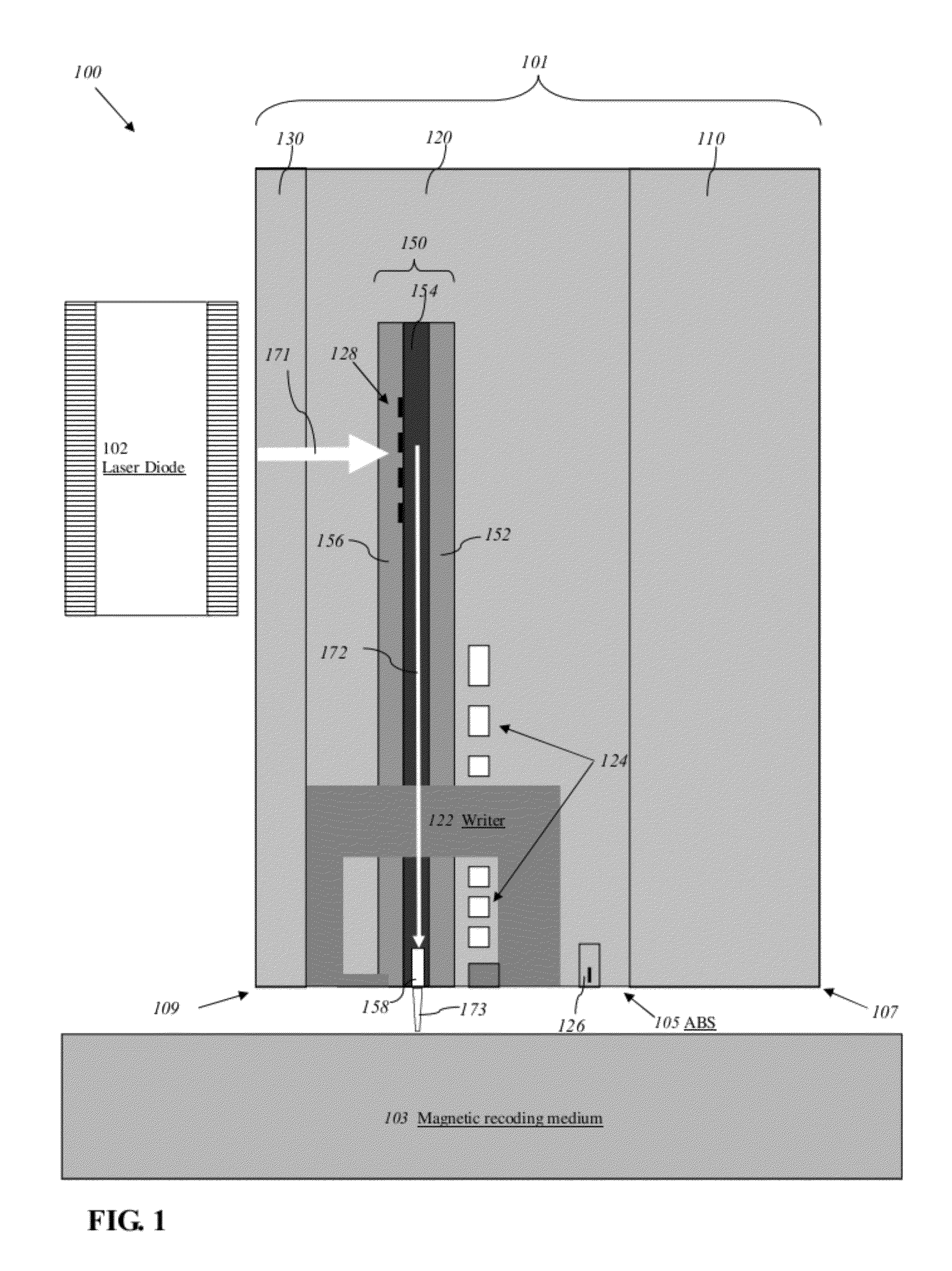
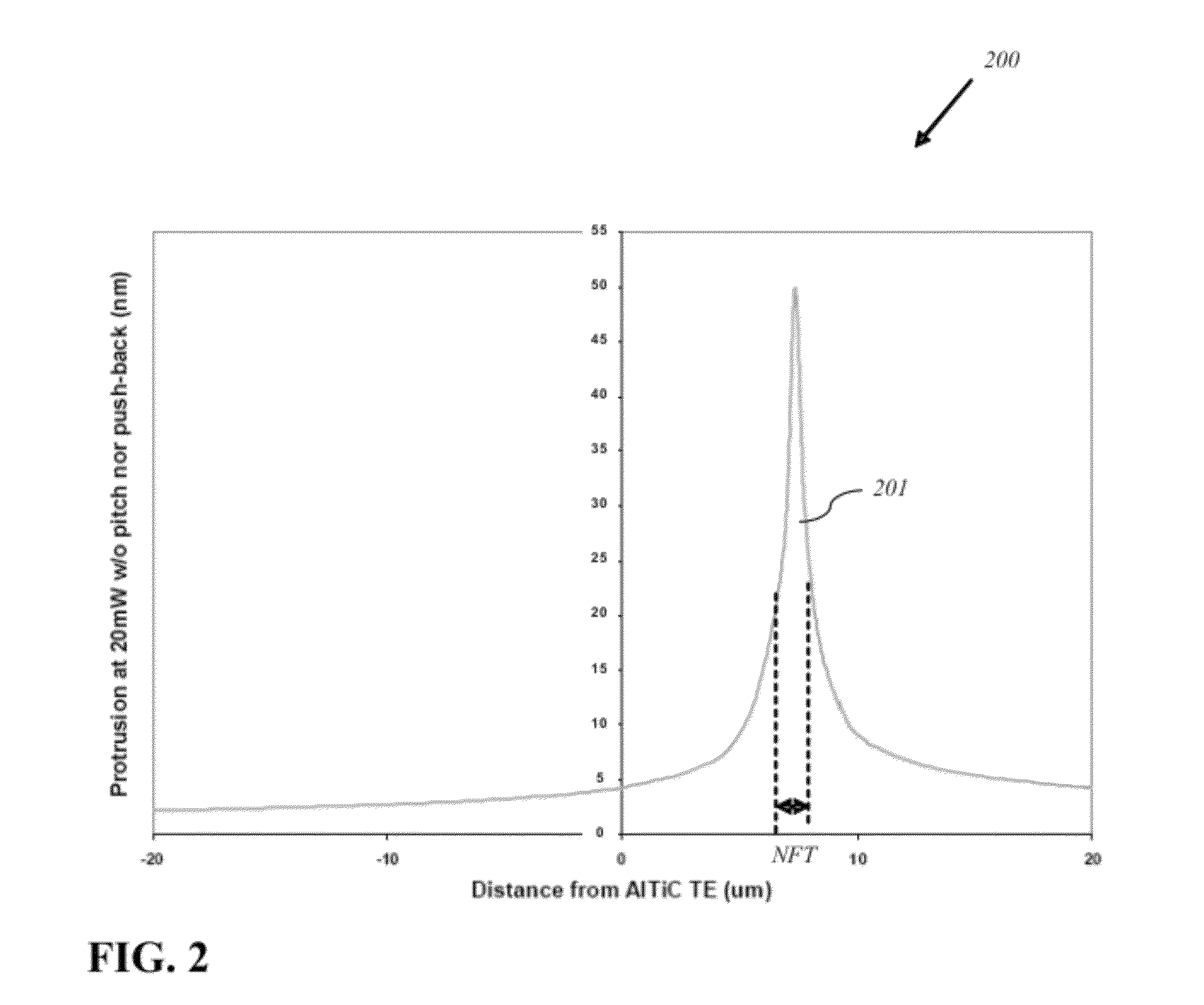
Reducing thermal protrusion of a near field transducer in an energy assisted magnetic recording head
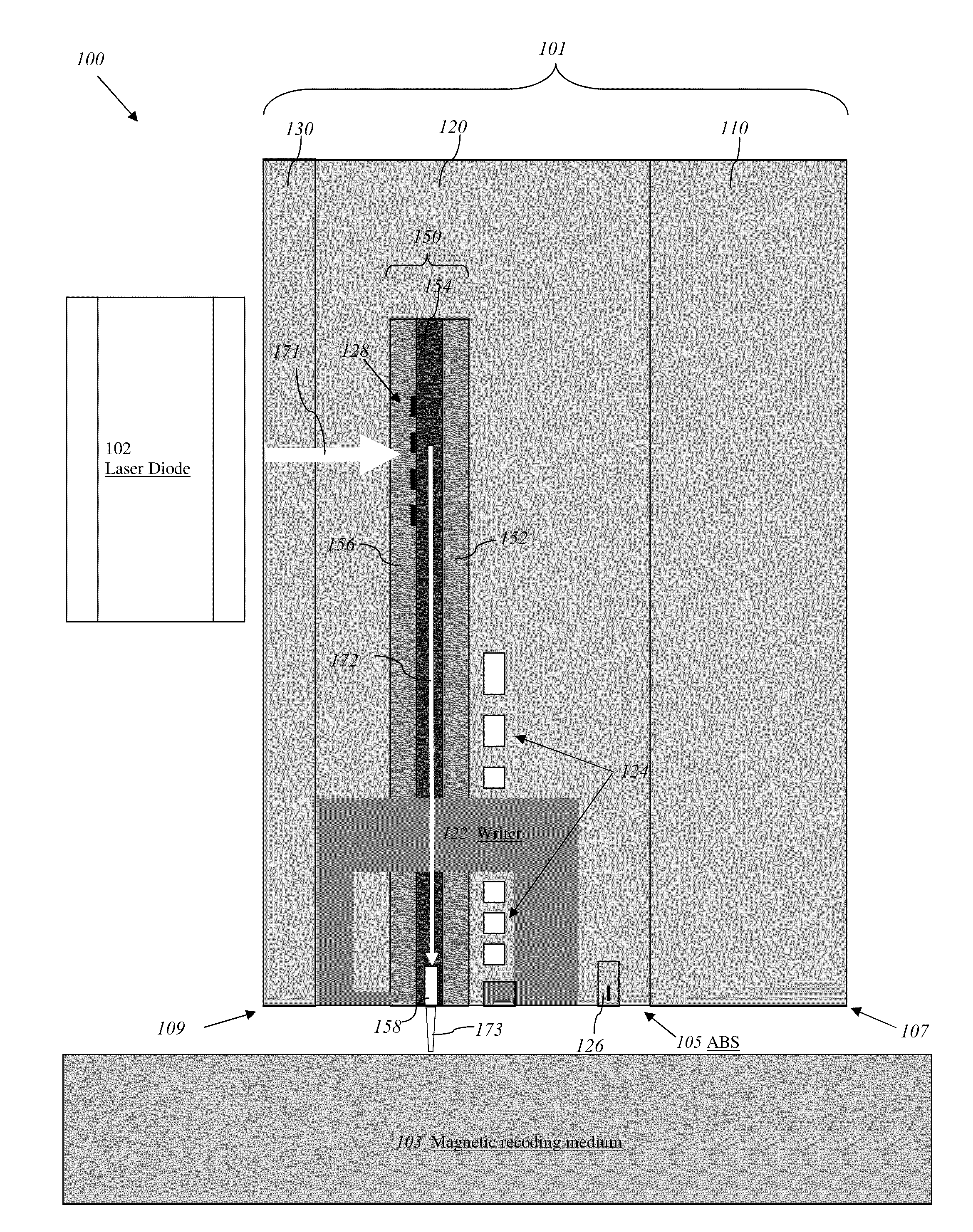
ActiveUS8077418B1Preventing protrusion-related damageImprove reliabilityCombination recordingElectrical transducersTransducerOptical power
Methods of fabricating an energy-assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) head to compensate for a heat-induced protrusion of a near field transducer formed therein are disclosed. The methods can include applying optical power to the near field transducer to generate heat therein. The near field transducer protrudes beyond an air bearing surface of the EAMR head by the generated heat. The methods can further include removing a protruded portion of the near field transducer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
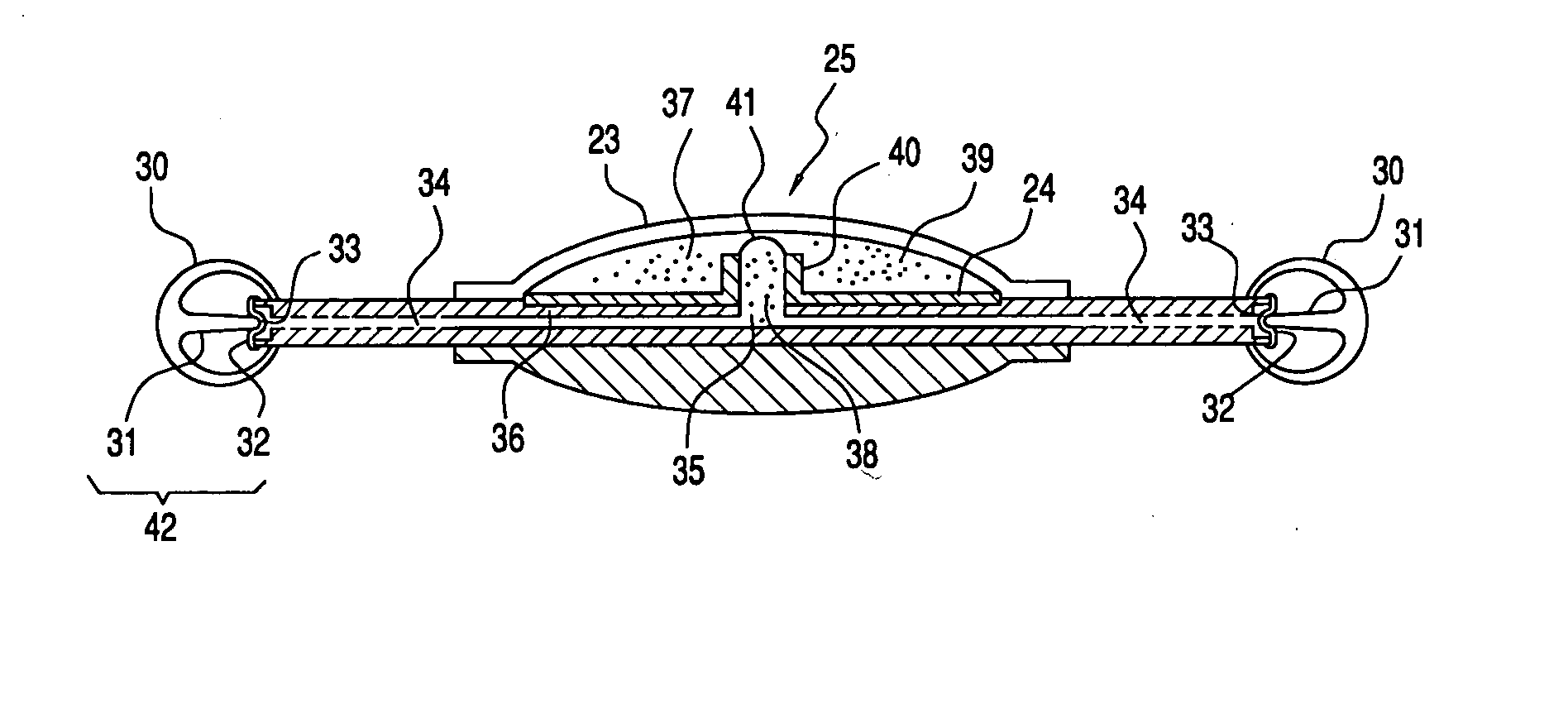
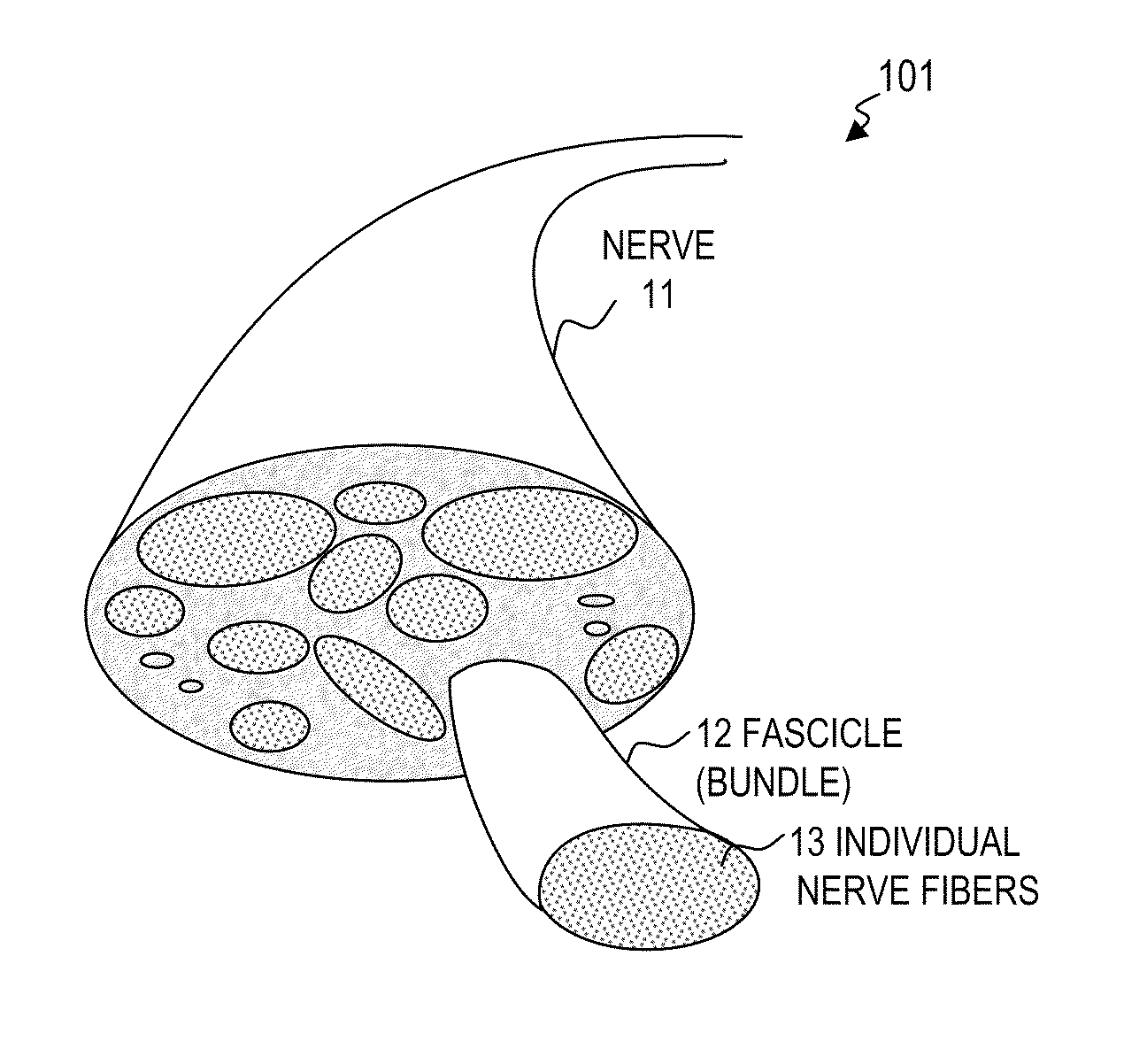
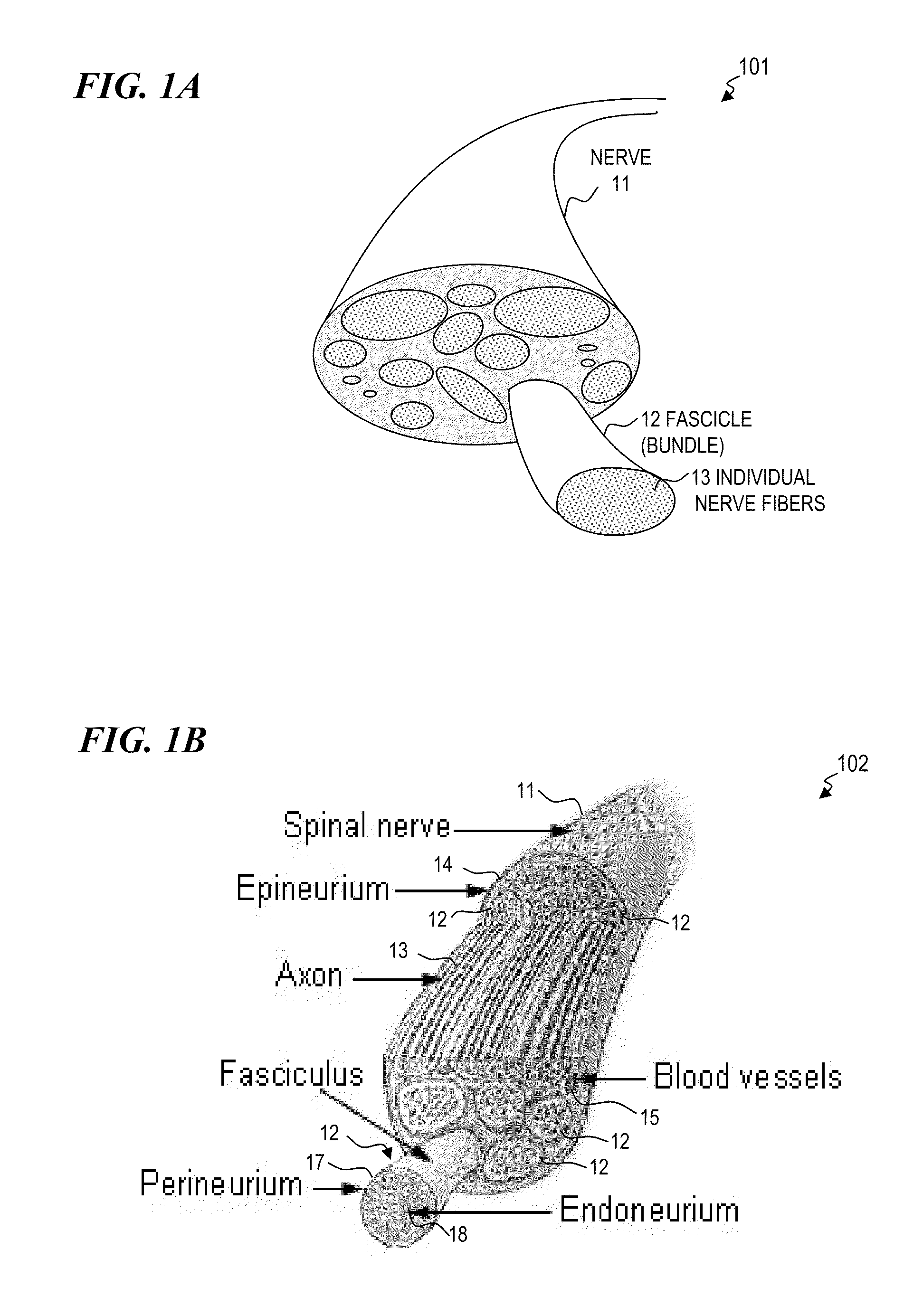
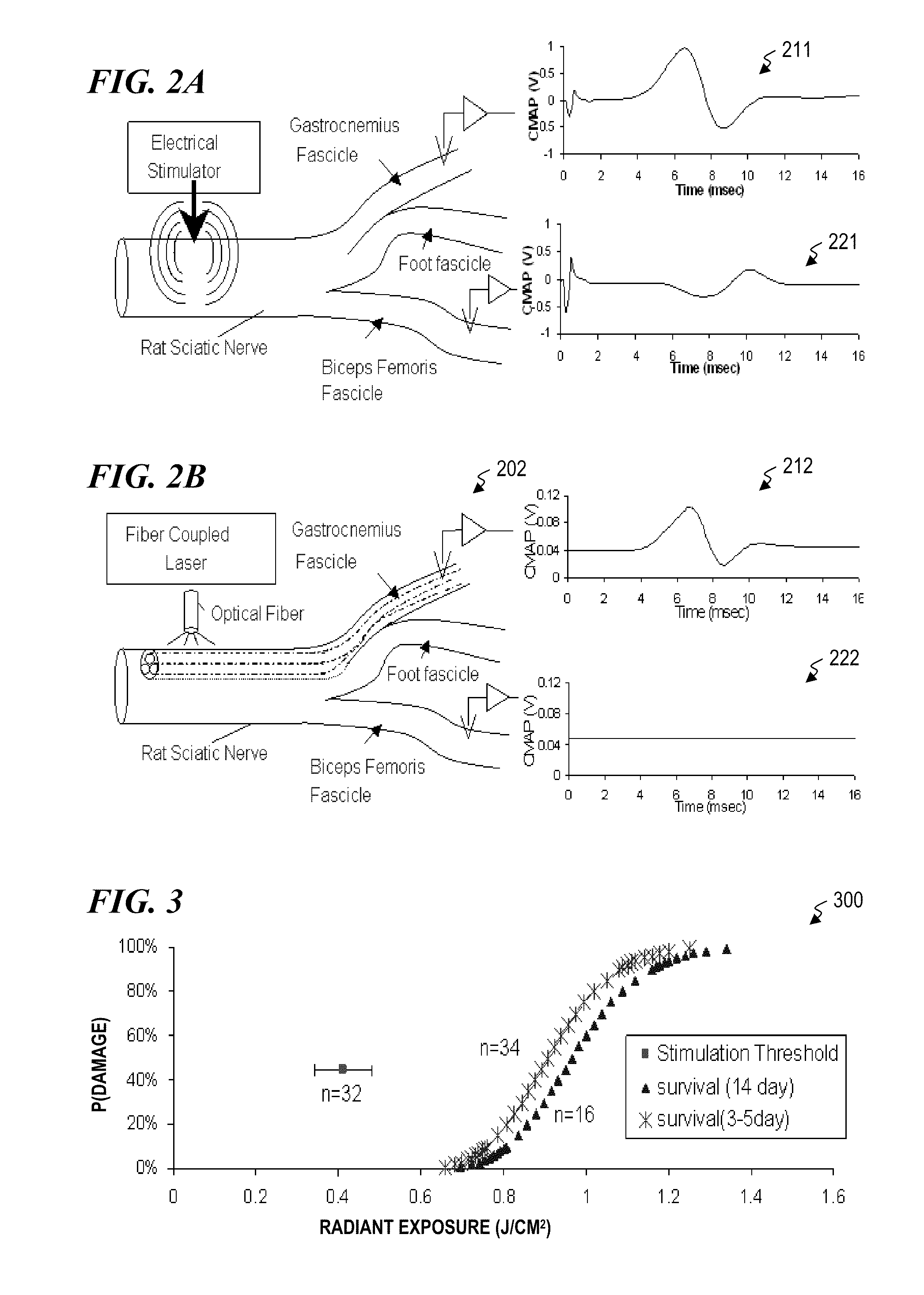
Nerve stimulator and method using simultaneous electrical and optical signals
ActiveUS20100114190A1Reduce amountLower Level RequirementsInternal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsEngineeringAction potential
An apparatus and method for stimulating animal tissue (for example to trigger a nerve action potential (NAP) signal in a human patient) by application of both electrical and optical signals for treatment and diagnosis purposes. The application of an electrical signal before or simultaneously to the application of a NAP-triggering optical signal allows the use of a lower amount of optical power or energy than would otherwise be needed if an optical signal alone was used for the same purpose and effectiveness. The application of the electrical signal may precondition the nerve tissue such that a lower-power optical signal can be used to trigger the desired NAP, which otherwise would take a higher-power optical signal were the electric signal not applied. Some embodiments include an implanted nerve interface having a plurality of closely spaced electrodes placed transversely and / or longitudinally to the nerve and a plurality of optical emitters.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
Accommodating intraocular lens having peripherally actuated deflectable surface and method
ActiveUS7217288B2Efficiently manipulatedThe surface is moreIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical axis
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided in which a deflectable lens element is anchored to a substrate along its optical axis to define a fluid filled space. Fluid-filled haptics disposed in fluid communication with the space vary the fluid volume in the space responsive to forces applied by the ciliary muscles, thereby causing the periphery of the lens element to deflect relative to the substrate and changing the optical power of the intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
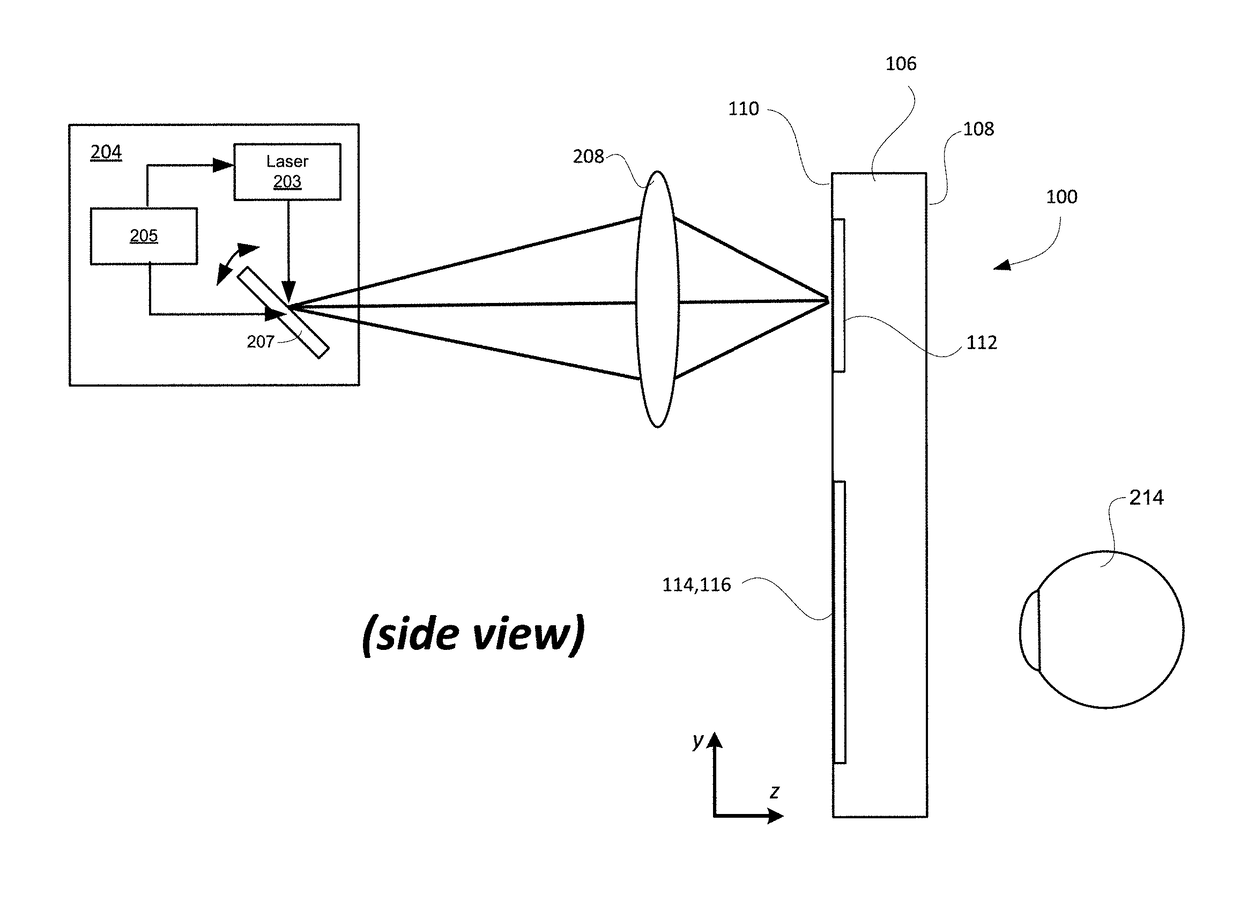
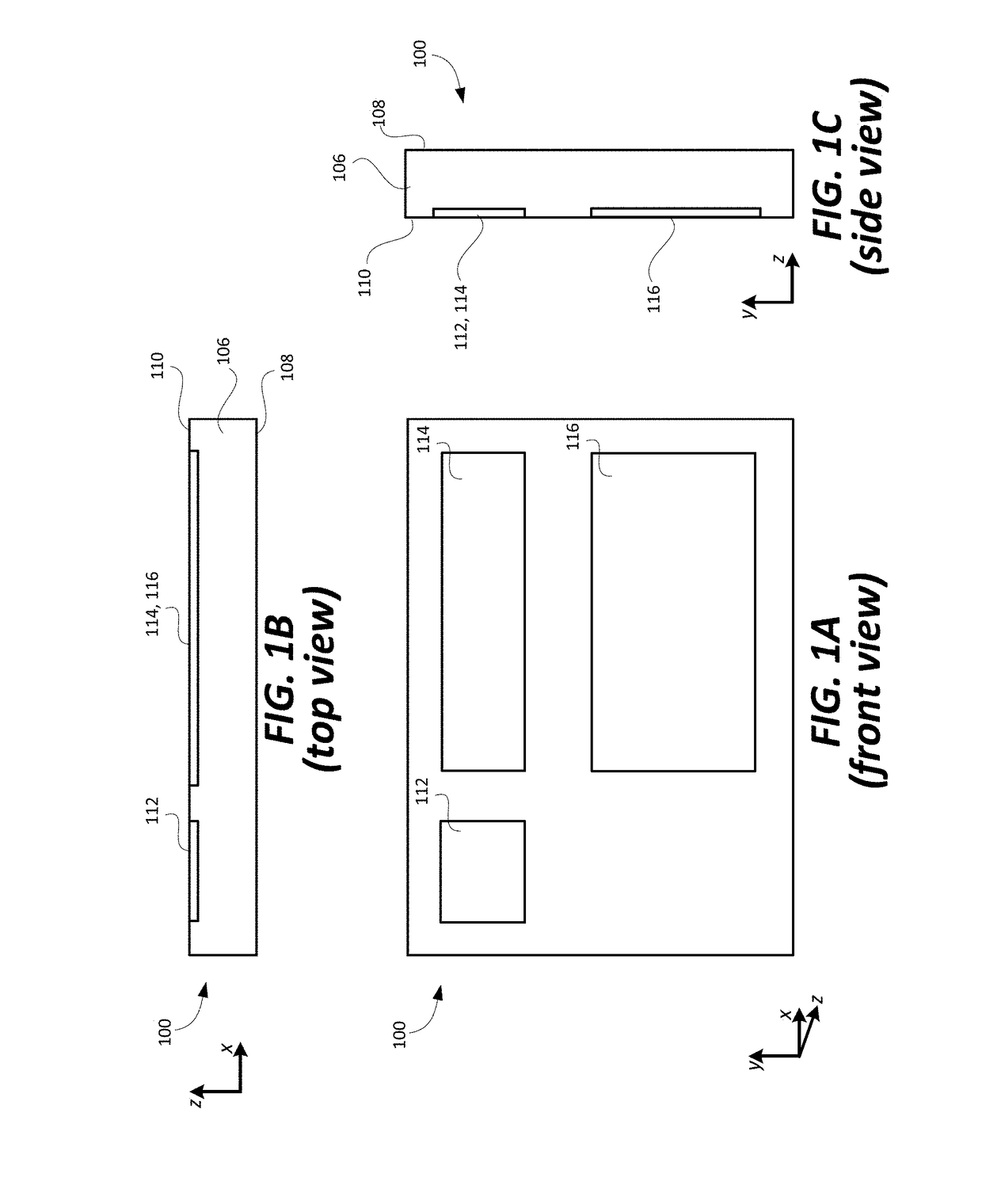
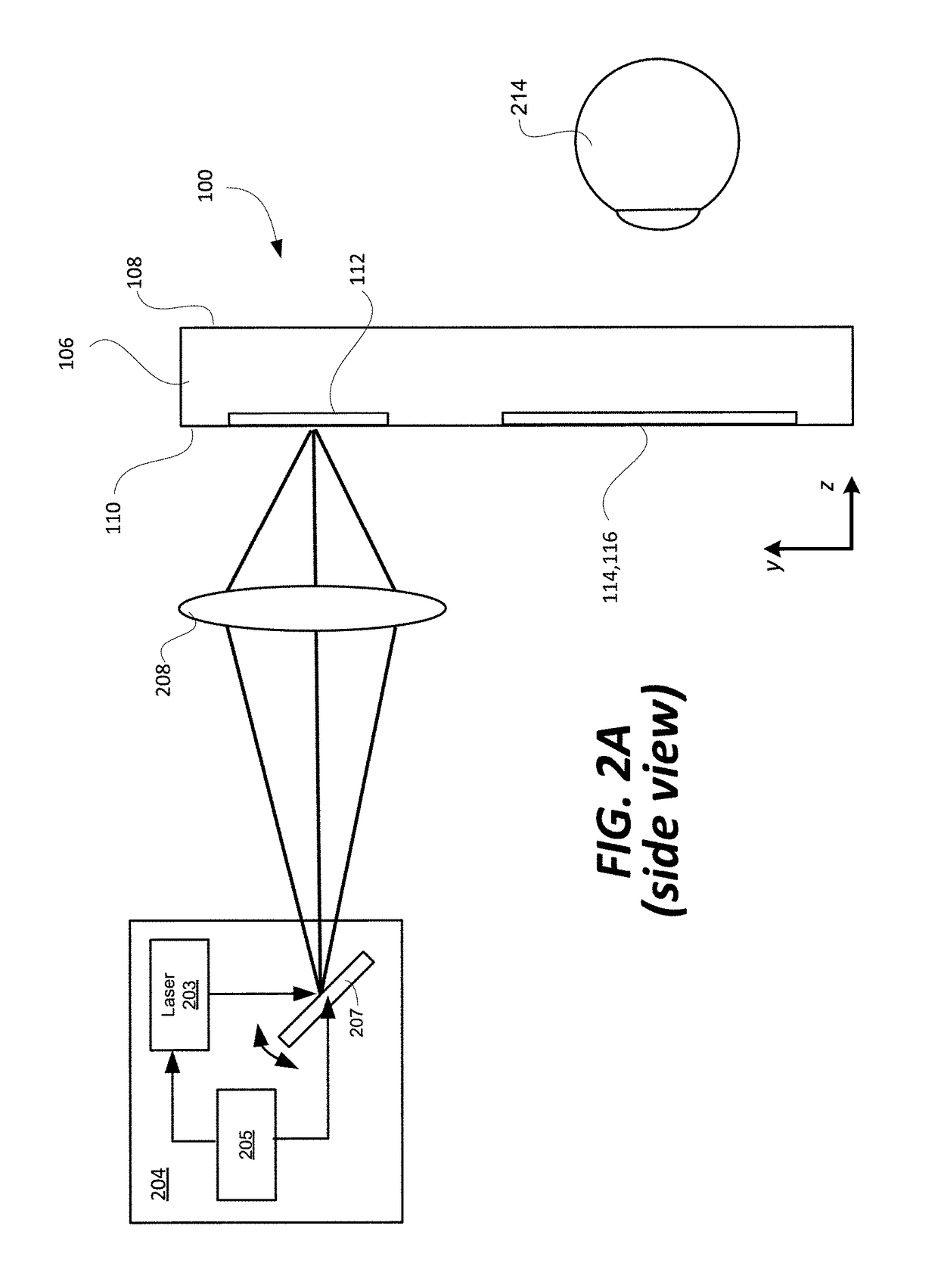
Compact optical system with improved illumination
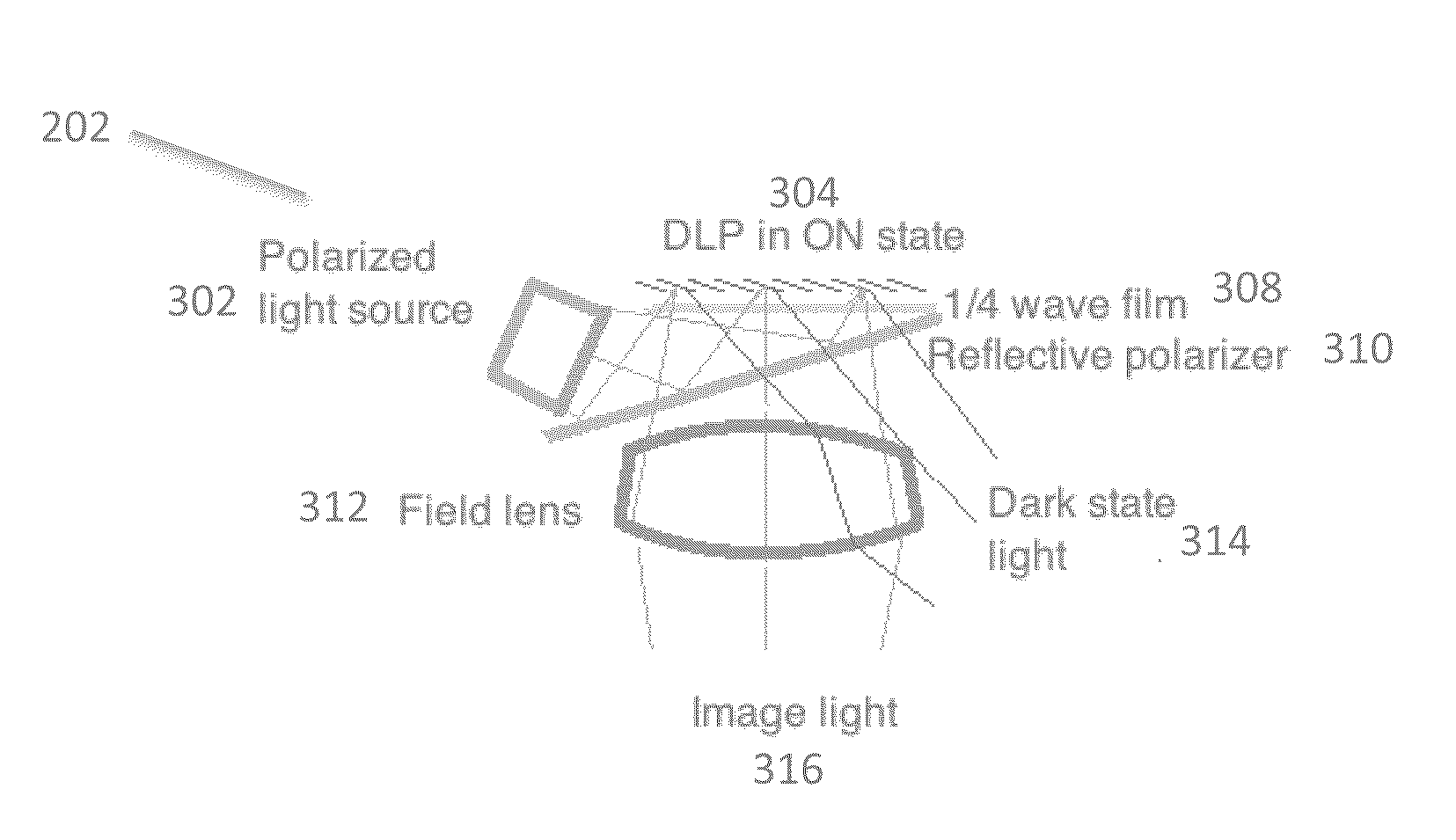
ActiveUS20160216517A1Increase contrastLow costElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesOptical powerDisplay device
A compact optical system with improved contrast for a head-worn computer includes a light source including a lens with positive optical power positioned within the head-worn computer and adapted to project converging illuminating light towards a partially reflective partially transmissive surface wherein the illuminating light forms a spot with an area smaller than the light source on the partially reflective partially transmissive surface prior to being reflected as diverging illuminating light that passes through a field lens and towards a reflective display. The illuminating light reflects off a surface of the reflective display, forming diverging image light which is transmitted through the field lens and then through the partially reflective partially transmissive surface to a lower display optical system adapted to present the image light to an eye of a user wearing the head-worn computer.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
Energy assisted magnetic recording head having a near field transducer with reduced thermal protrusion
ActiveUS8208350B1Preventing protrusion-related damageImprove reliabilityCombination recordingElectrical transducersLeading edgeTransducer
An energy assisted magnetic recording head comprises a slider having a leading edge, a trailing edge, and an air bearing surface (ABS), and a near field transducer (NFT) disposed in the slider and having a distal end proximate the ABS. The distal end is recessed from the ABS when no optical power is applied to the NFT, and is co-planar with the ABS when a predetermined amount of optical power is applied to the NFT. A portion of the slider surrounding the distal end forms a concave surface having a continuously varying slope when no optical power is applied to the NFT, and a flat surface coplanar with the ABS and the distal end when the predetermined amount of optical power is applied to the NFT. Applying optical power comprises coupling light into a waveguide formed in the head and directing the coupled light to the NFT via the waveguide.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Accommodating intraocular lens system having spherical aberration compensation and method
ActiveUS20070106377A1Small internal volumeIncrease the internal volumeIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical power
An accommodating intraocular lens includes an optic portion, a haptic portion. The optic portion of the lens includes an actuator that deflects a lens element to alter the optical power of the lens responsive to forces applied to the haptic portion of the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles and a secondary deflection mechanism. Movement of the lens element by the actuator causes the lens element to deform and the secondary deflection mechanism causes the lens to further deform.
Owner:ALCON INC
Advanced electro-active optic device
Optical devices having a dynamic aperture and / or an apodization mask are provided. The aperture and / or mask may be provided by one or more electro-active elements, and may be used in an ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power.
Owner:EA3TECH LLC +1
Ballistic reticle for projectile weapon aiming systems and method of aiming
ActiveUS20050229468A1Good compensationCompensation effectSighting devicesHorizontal axisOptical power
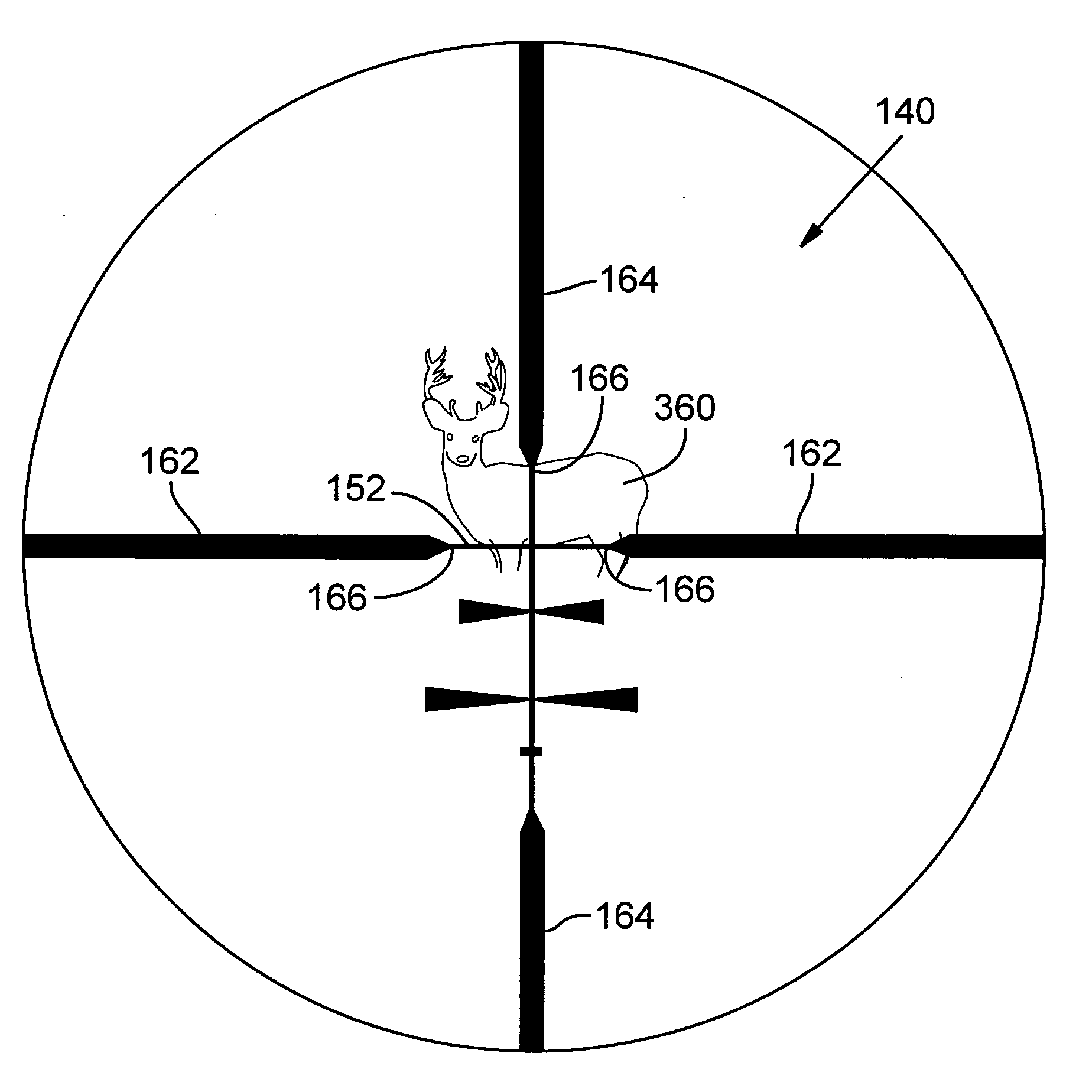
A reticle of a projectile weapon aiming system such as a riflescope includes a primary aiming mark adapted to be sighted-in at a first selected range and further includes a plurality of secondary aiming marks spaced apart below the primary aiming mark. The secondary aiming marks are positioned to compensate for ballistic drop at preselected incremental ranges beyond the first selected range, for a selected group of ammunition having similar ballistic characteristics. Angles subtended by adjacent aiming marks of the reticle can be adjusted by changing the optical power of the riflescope, to thereby compensate for ballistic characteristics of different ammunition. In some embodiments, the reticle includes a set of windage aiming marks spaced apart along at least one secondary horizontal axis intersecting a selected one of the secondary aiming marks, to facilitate compensation for the effect of crosswinds on the trajectory of the projectile.
Owner:LEUPOLD & STEVENS
Simple high efficiency optical coherence domain reflectometer design
ActiveUS7126693B2Improve efficiencySimple configurationReflectometers dealing with polarizationInterferometersBeam splitterDetector array
The present invention discloses simple and yet highly efficient configurations of optical coherence domain reflectometry systems. The combined use of a polarizing beam splitter with one or two polarization manipulator(s) that rotate the returned light wave polarization to an orthogonal direction, enables one to achieve high optical power delivery efficiency as well as fixed or predetermined output polarization state of the interfering light waves reaching a detector or detector array, which is especially beneficial for spectral domain optical coherence tomography. In addition, the system can be made insensitive to polarization fading resulting from the birefringence change in the sample and reference arms. Dispersion matching can also be easily achieved between the sample and the reference arm for high resolution longitudinal scanning.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
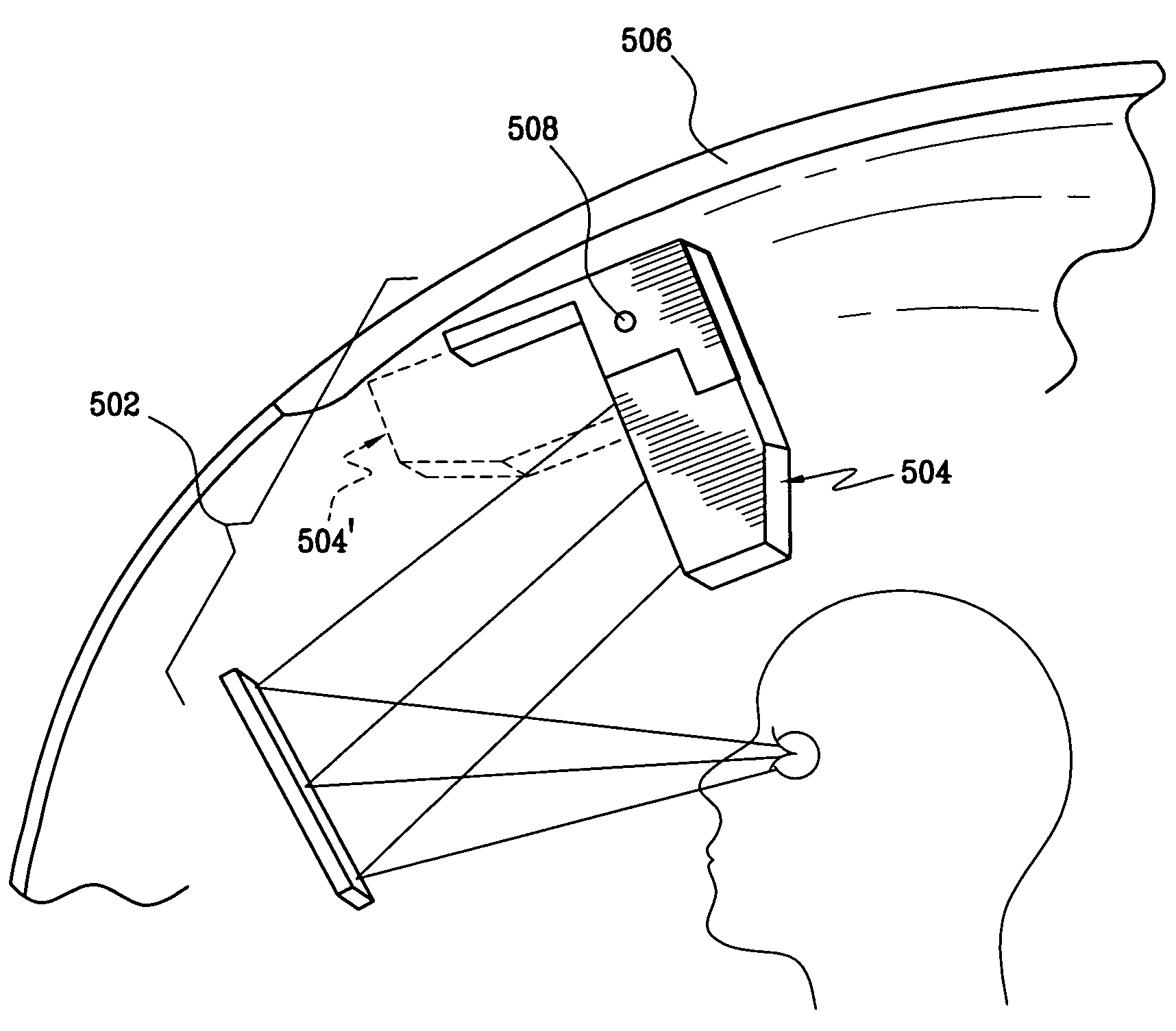
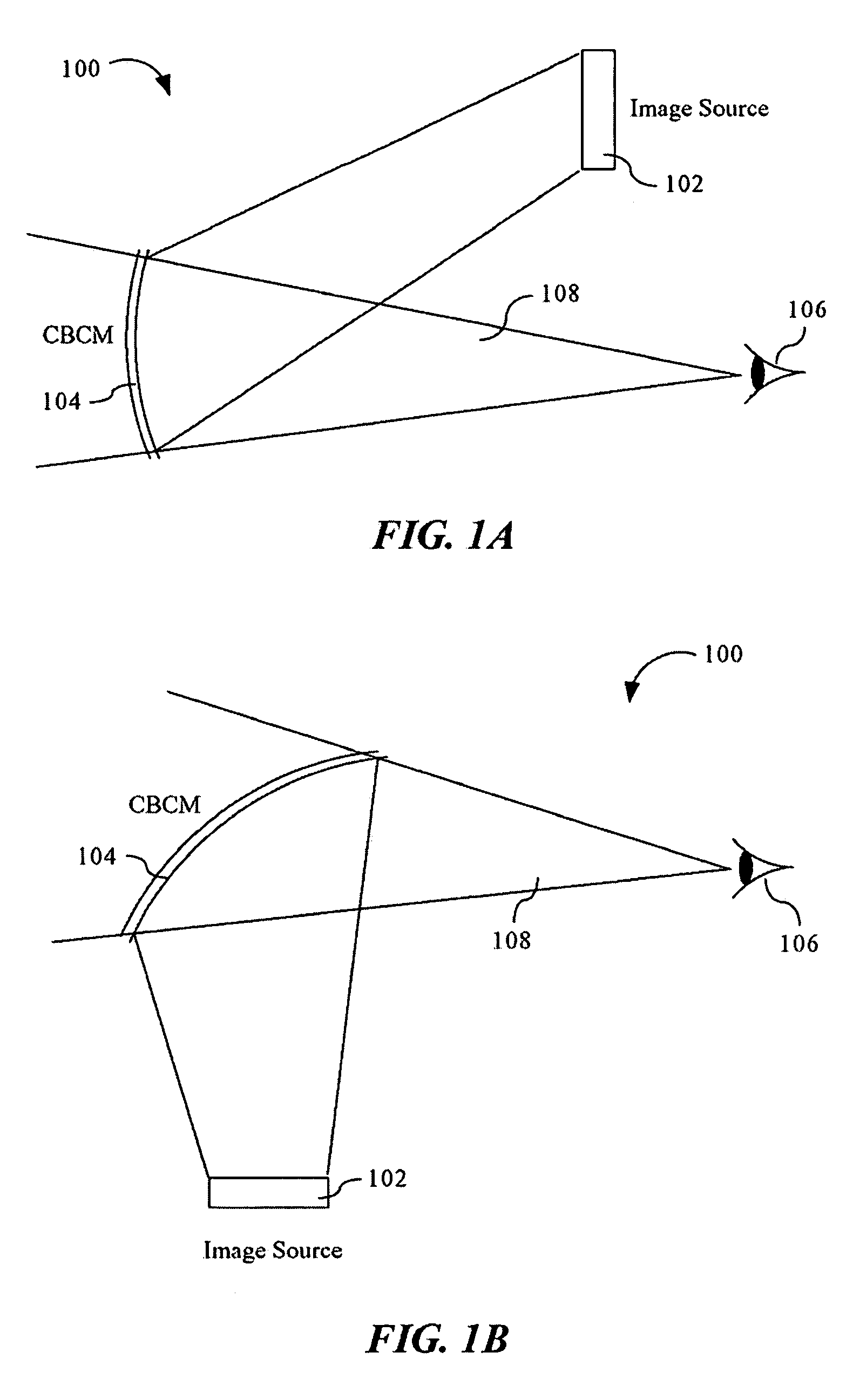
Advanced compact head up display
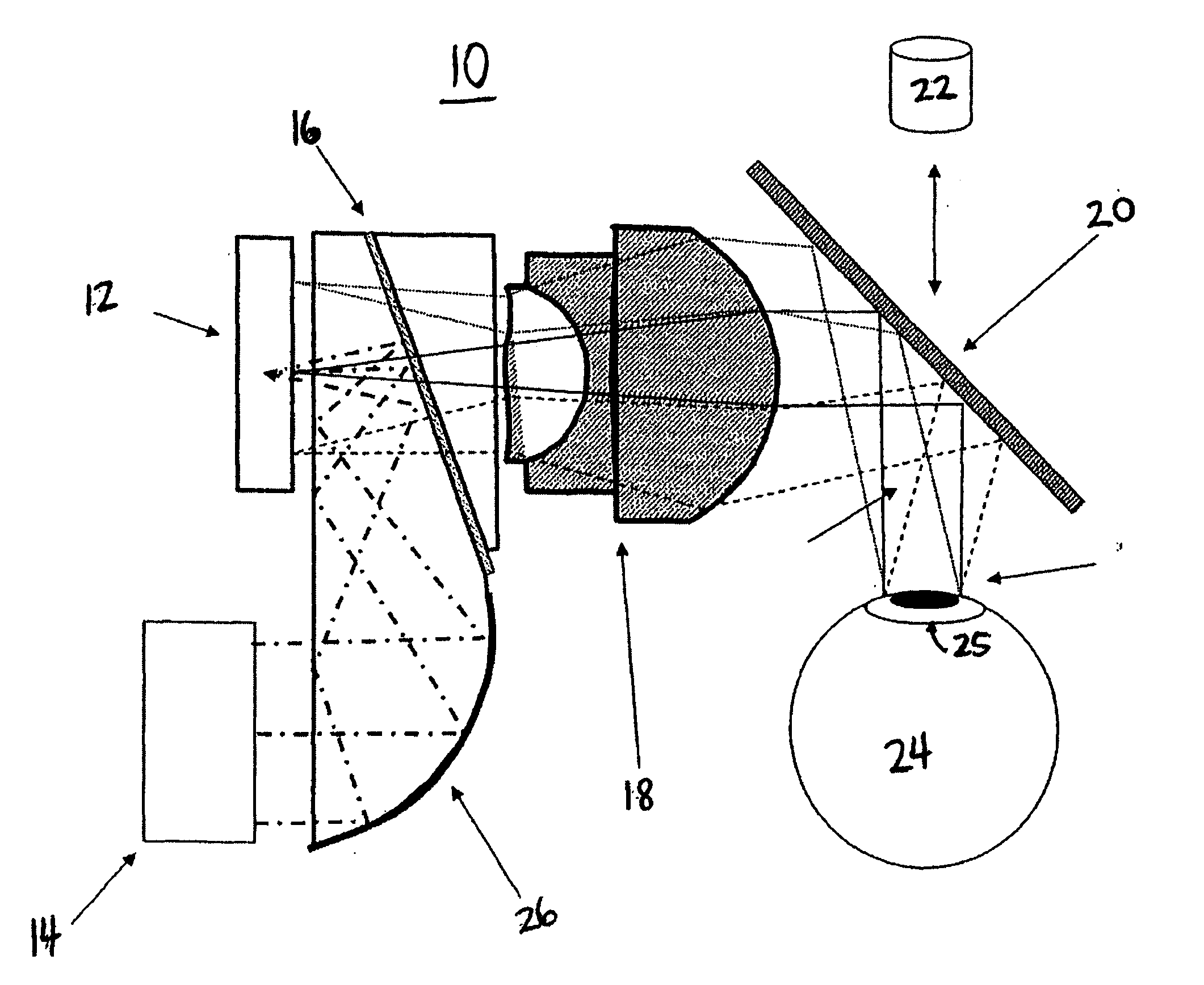
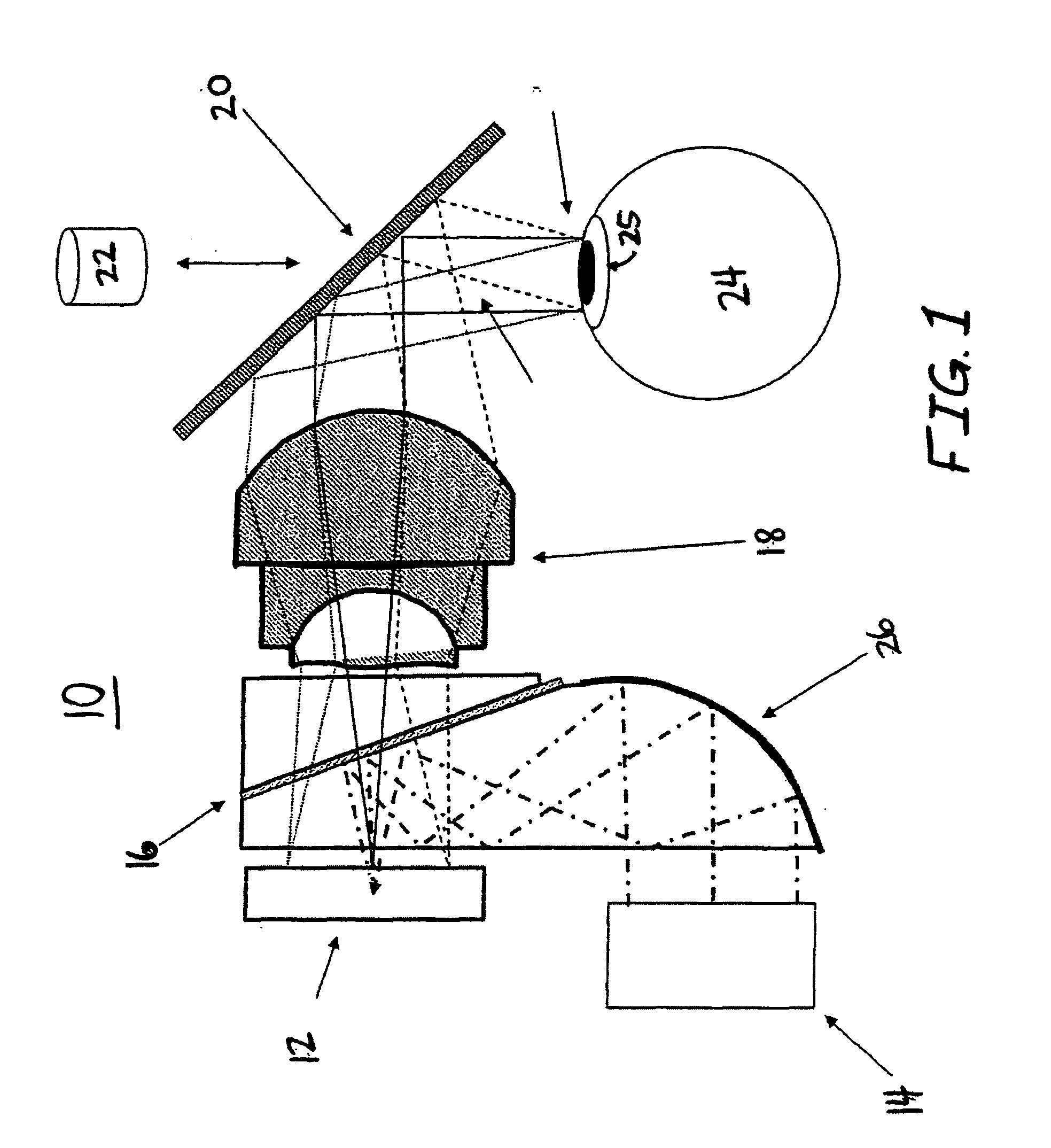
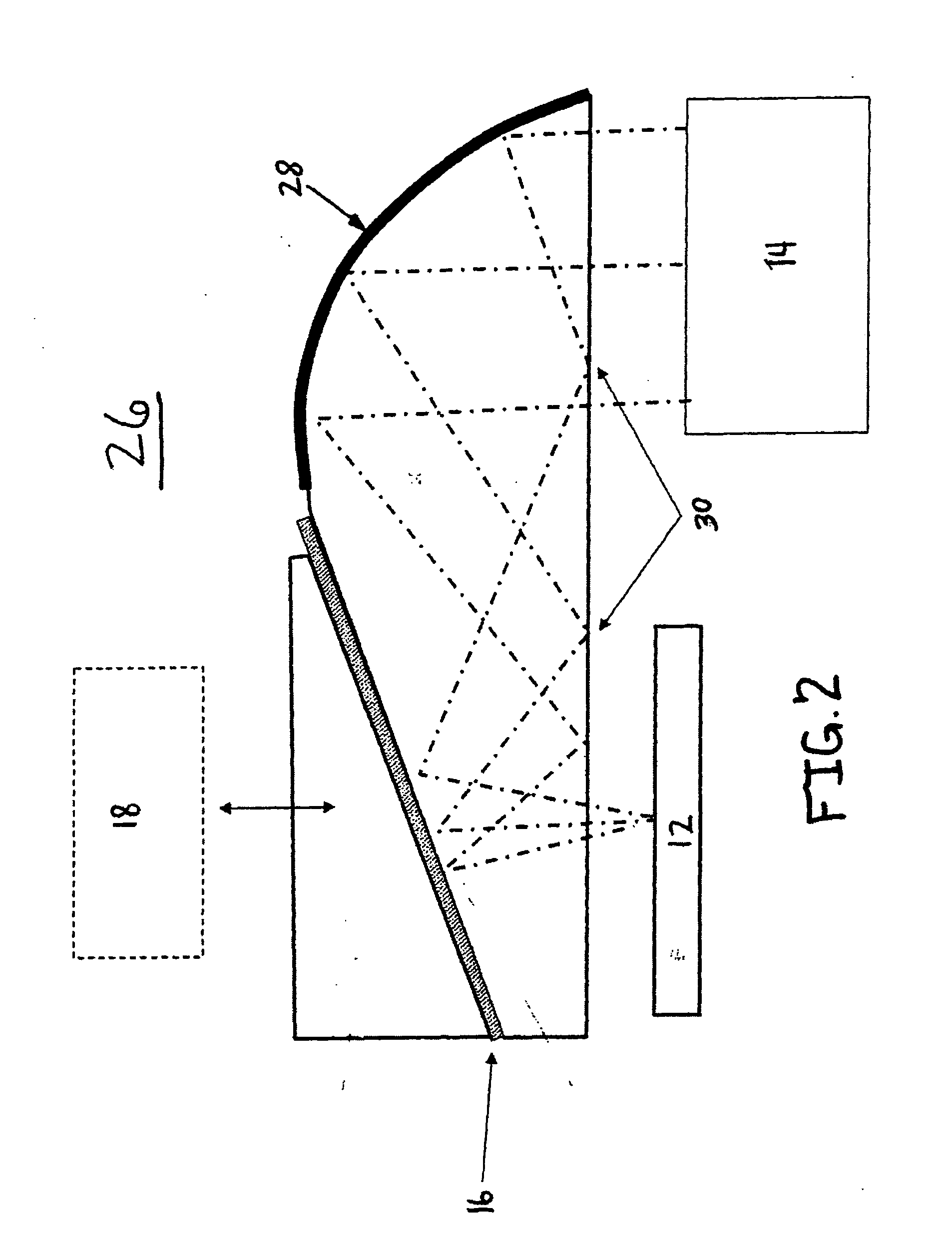
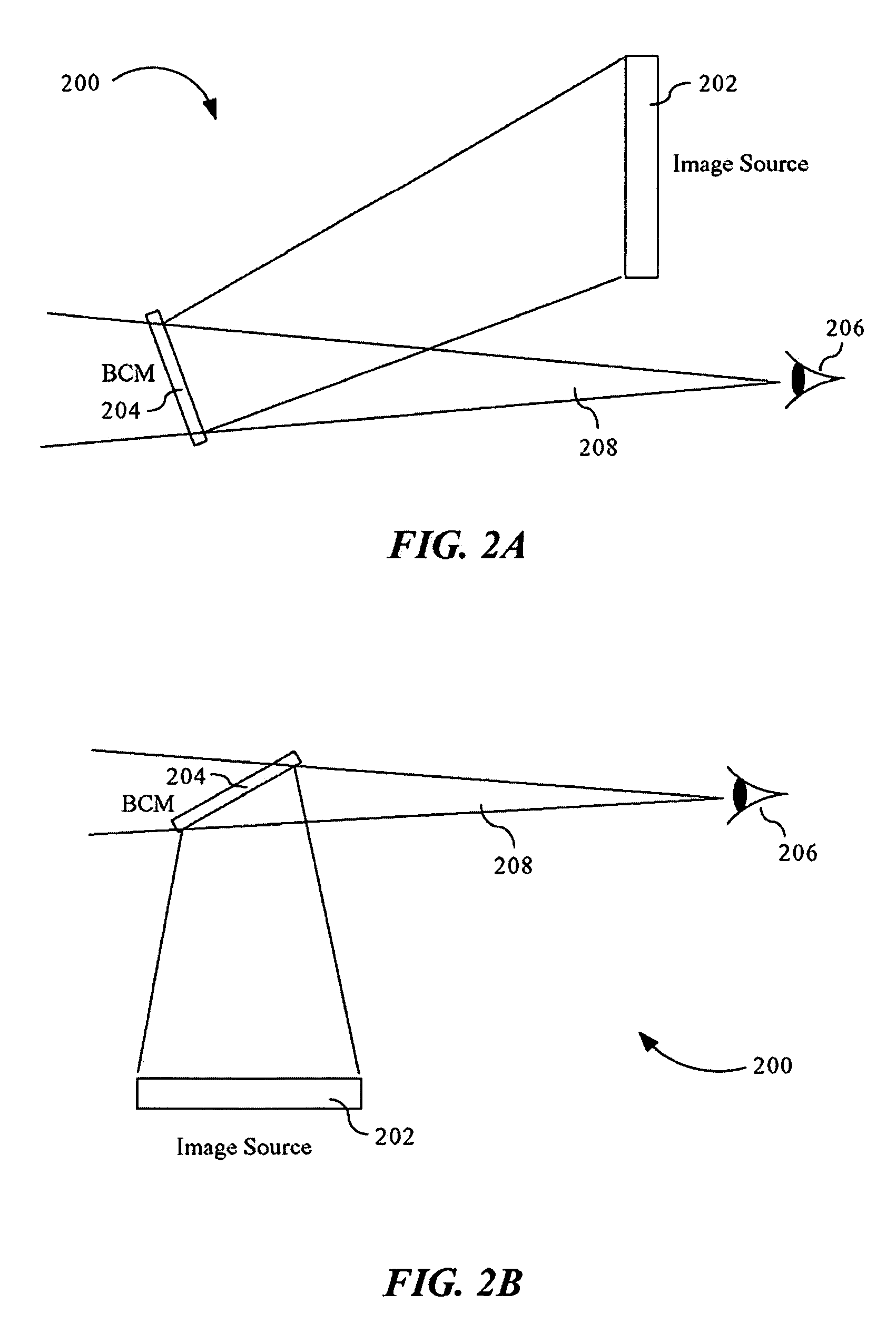
ActiveUS7095562B1Simplifies optical systemMinimize aberrationLighting support devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsHead-up displayDashboard
A head up display system for a vehicle that includes a compact image source for projecting an image. The compact image source may be foldable up toward or into a cockpit ceiling of the vehicle, be positioned within a dashboard of the vehicle, or located at another suitable position. A combiner reflects the projected image with optical power toward an observer for observation. The combiner is positioned so that the observer, in a line of sight, may see a visual exterior view of an outside scene through the combiner and the projected image in the combiner. In a preferred embodiment, the image source includes an illumination system that includes a high power light emitting diode (LED) array assembly. A Fresnel lens array is operatively associated with the LED array assembly for receiving light produced by the LED and providing a nearly collimated light output. A spatial light modulator receives the nearly collimated light output. The preferred combiner is a meniscus combiner that includes a meniscus lens; a multi-layer dichroic coating formed on a first surface of the meniscus lens; and, an anti-reflection coating formed on a second, opposite surface of the meniscus lens. The meniscus combiner preferably utilizes a non-symmetric aspheric meniscus lens.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Waveguide-Based Displays With Exit Pupil Expander
ActiveUS20170299860A1Good optical performanceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesHead-up displayExit pupil
A near eye or heads up display system includes a scan beam projector engine, an optical waveguide, and an exit pupil expander (EPE) optically coupled between the scan beam projector engine and the optical waveguide. The EPE improves the optical performance of the display system. The EPE could include a diffusive optical element, diffractive optical element, micro-lens array (MLA), or relay of aspherical lenses. A dual MLA EPE may have cells that prevent cross-talk between adjacent pixels. A dual MLA EPE may have a non-periodic lens array. The optical power of one MLA may be different from the other MLA.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
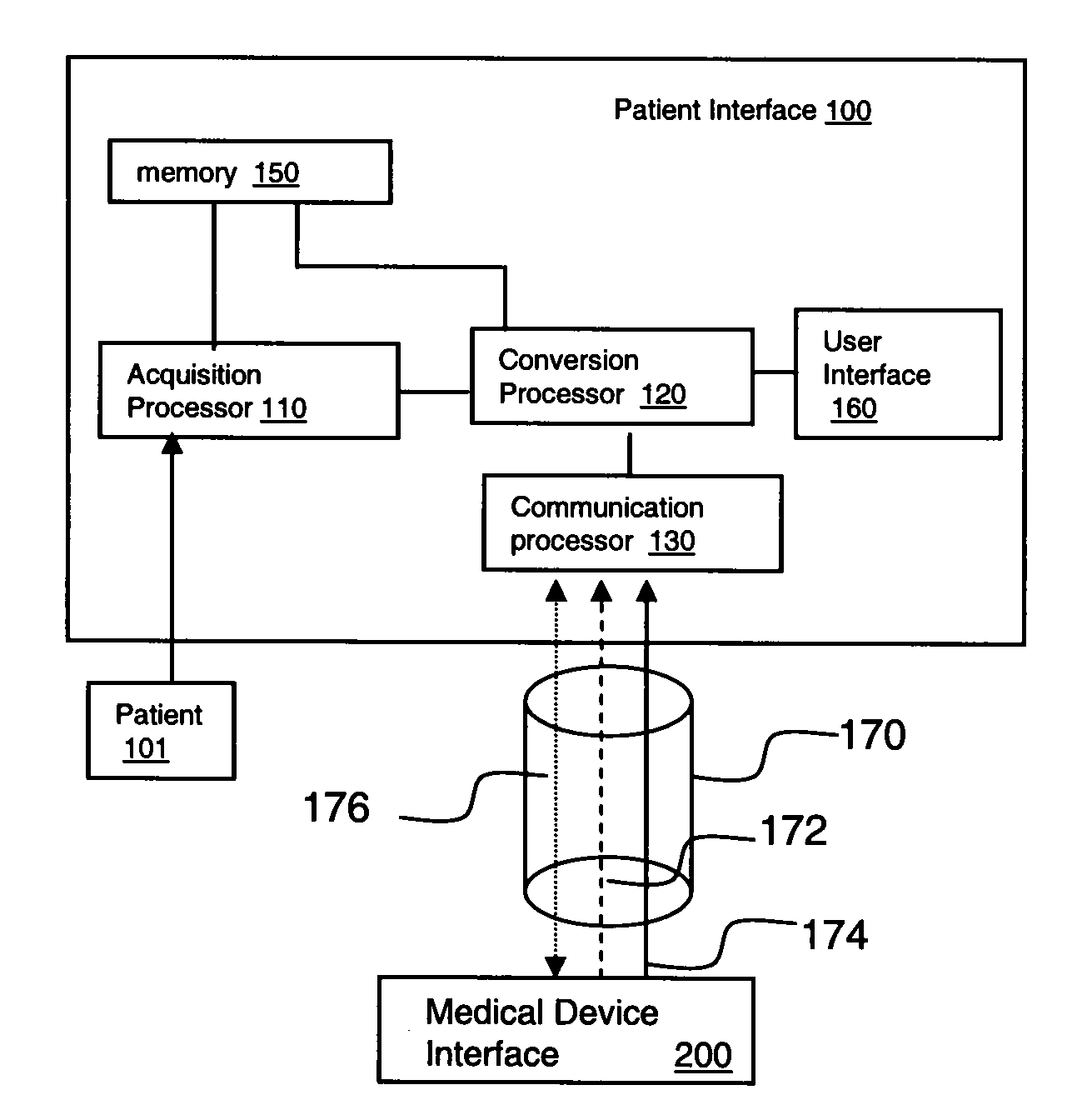
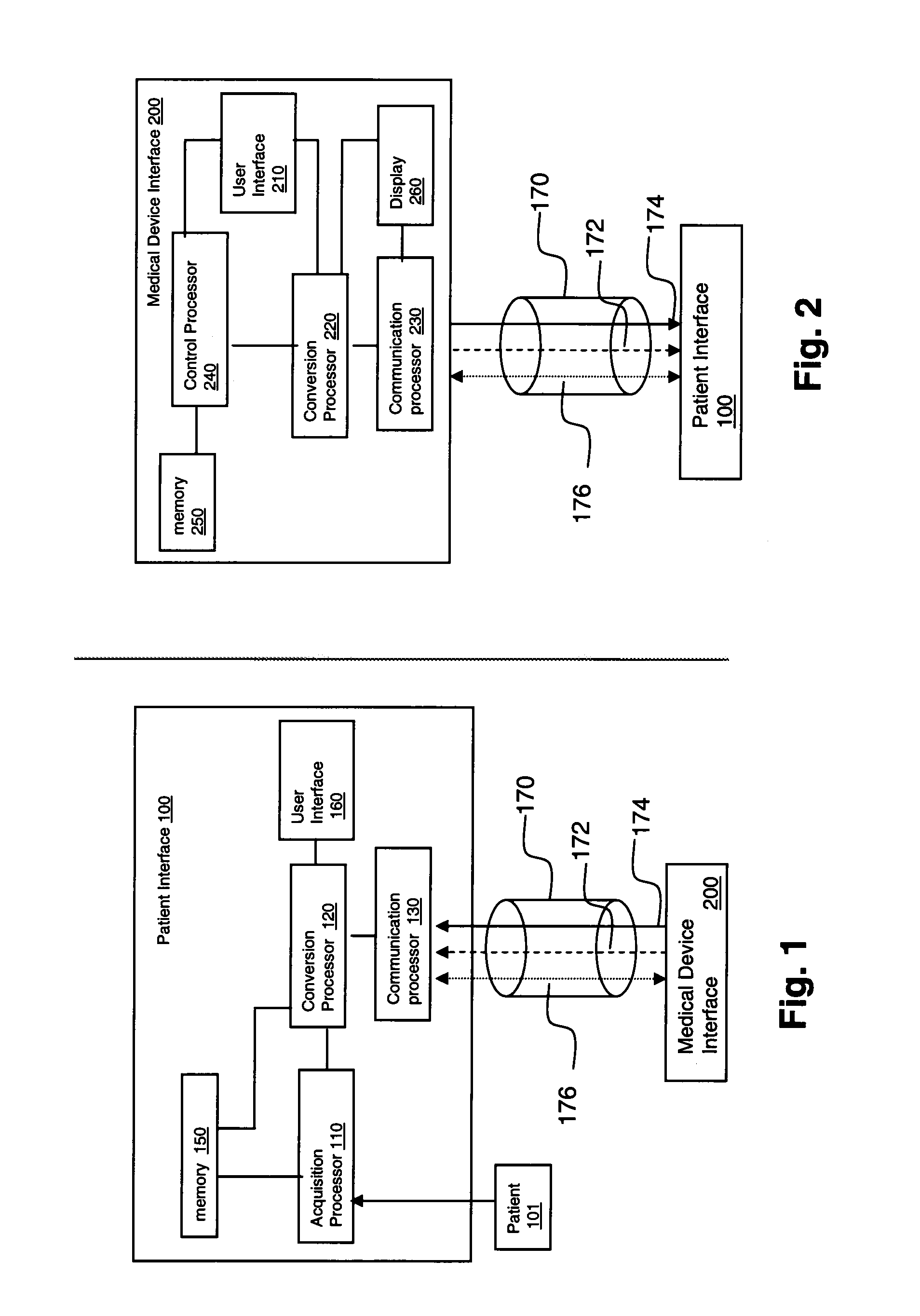
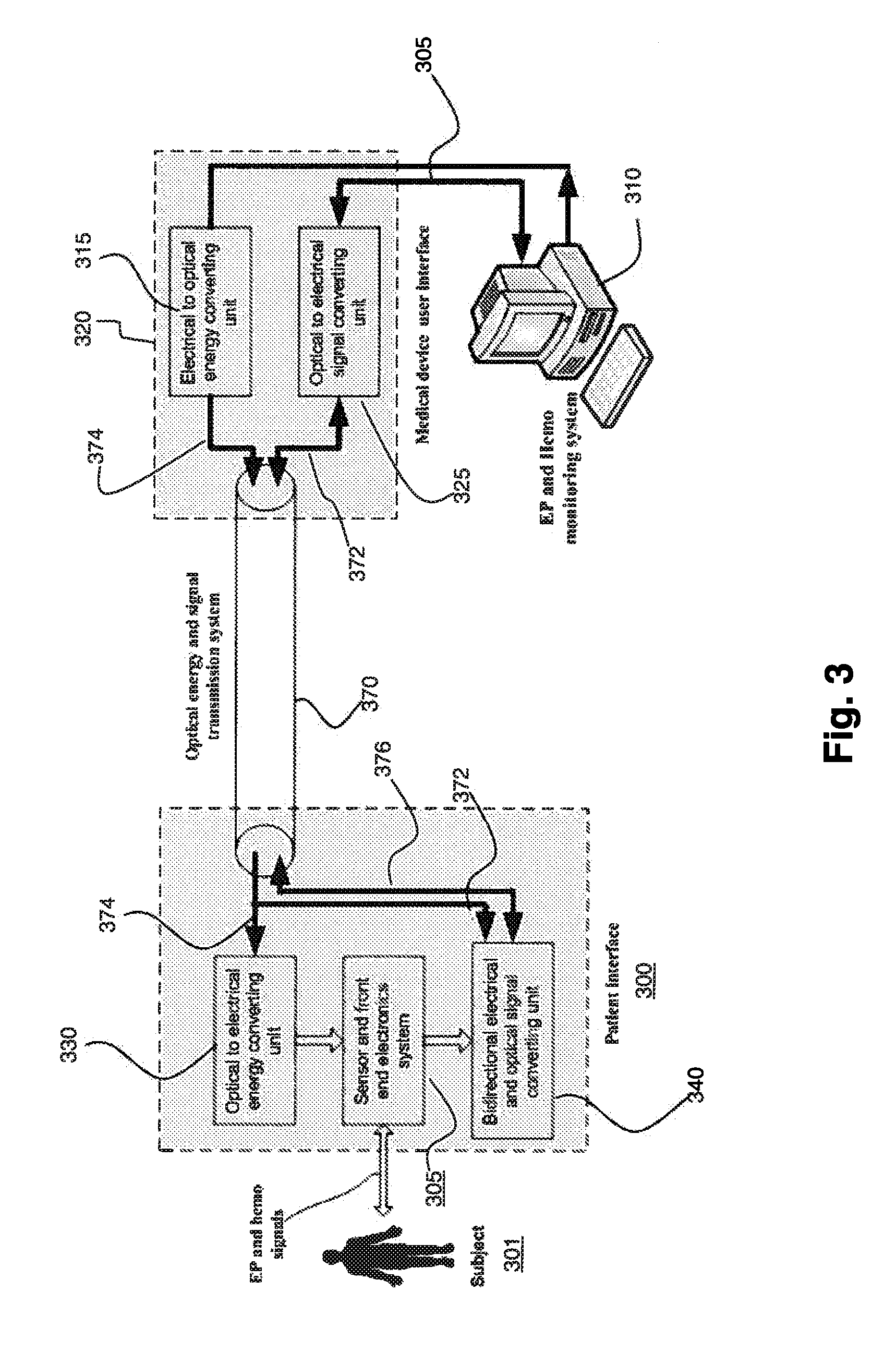
System for Processing Patient Monitoring Power and Data Signals
ActiveUS20090110148A1Radiation diagnosis data transmissionPatient positioning for diagnosticsControl signalData signal
A device interface selectively acquires patient physiological parameter data. An acquisition processor acquires physiological data from a patient. A communication processor is coupled to an optical communication pathway for receiving a plurality of optical signals from a source. A conversion processor is electrically coupled to the acquisition processor and communication processor and converts a first optical power signal at a first frequency and received via the optical communication pathway using the communication processor, to a first electrical signal for providing power to said device 1interface. The conversion processor converts an optical control signal at a second frequency different from the first frequency and received via the optical communication pathway using the communication processor, to a second electrical signal for providing control data to the acquisition processor directing the acquisition processor to acquire at least one physiological parameter from a patient.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Masked intraocular implants and lenses
ActiveUS20110040376A1Improve eyesightIncrease depth of focusOptical articlesIntraocular lensMedicineOptical power
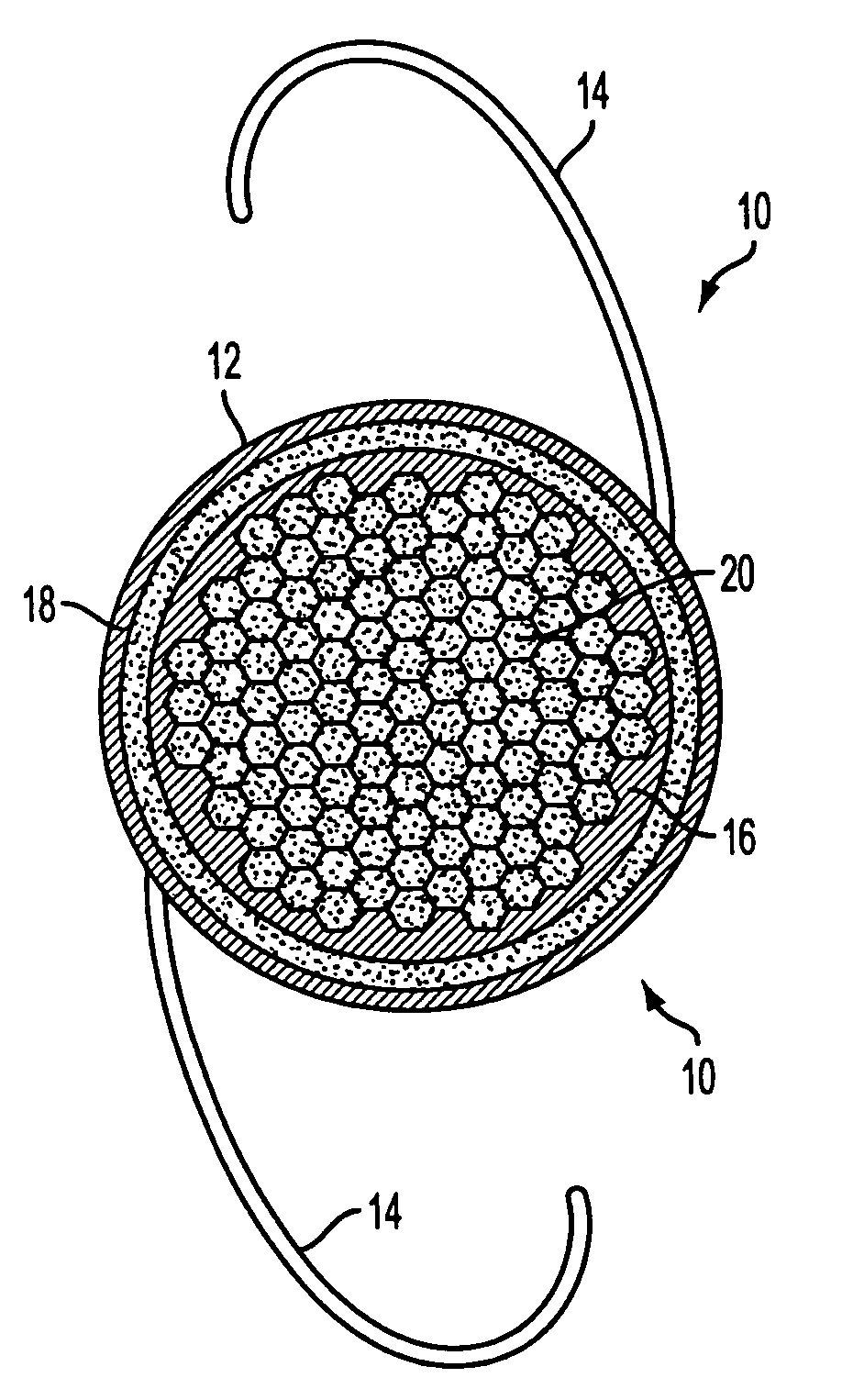
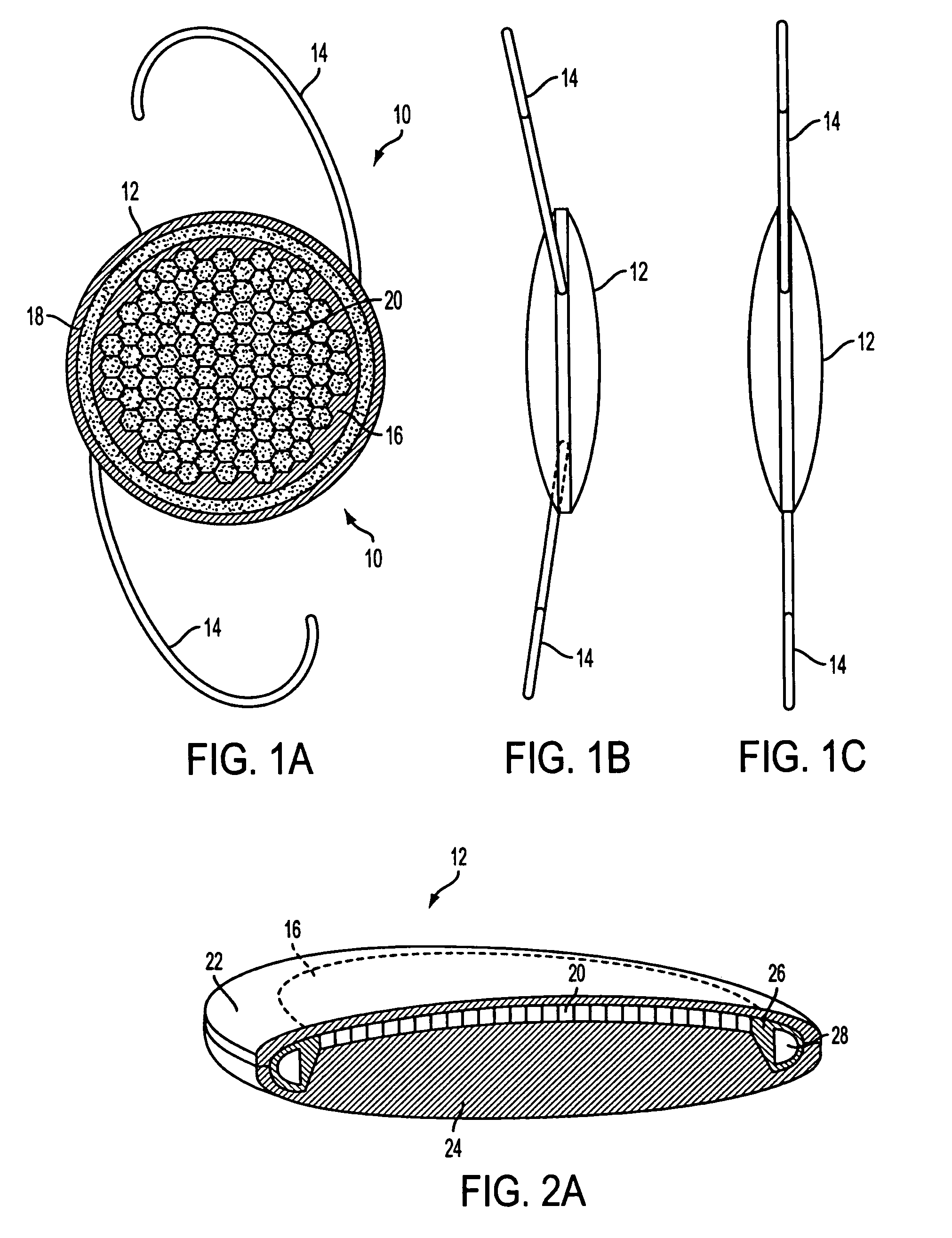
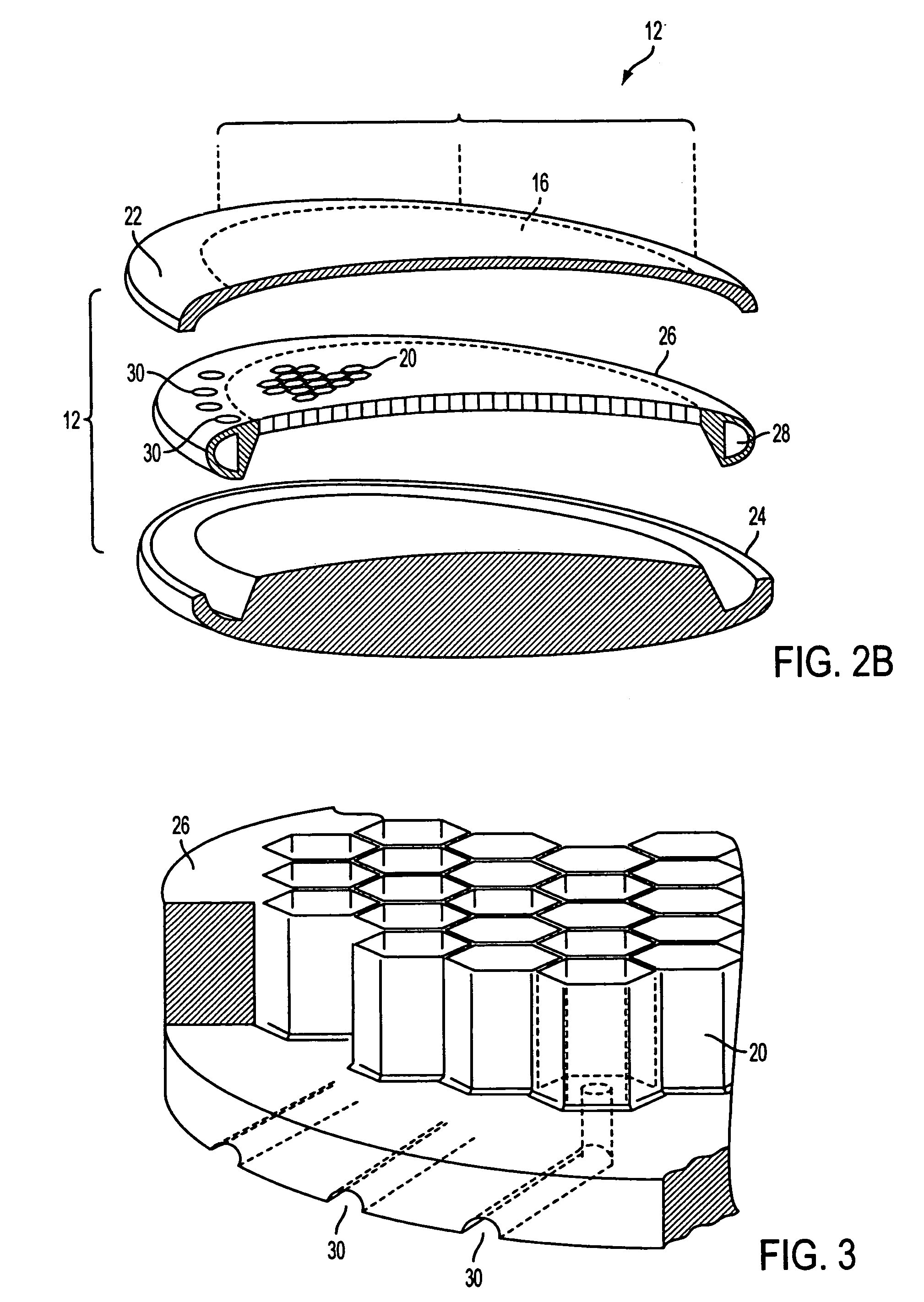
Intraocular implants and methods of making intraocular implants are provided. The intraocular implants can improve the vision of a patient, such as by increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. In particular, the intraocular implants can include a mask having an annular portion with a relatively low visible light transmission surrounding a relatively high transmission central portion such as a clear lens or aperture. This construct is adapted to provide an annular mask with a small aperture for light to pass through to the retina to increase depth of focus. The intraocular implant may have an optical power for refractive correction. The intraocular implant may be implanted in any location along the optical pathway in the eye, e.g., as an implant in the anterior or posterior chamber.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com