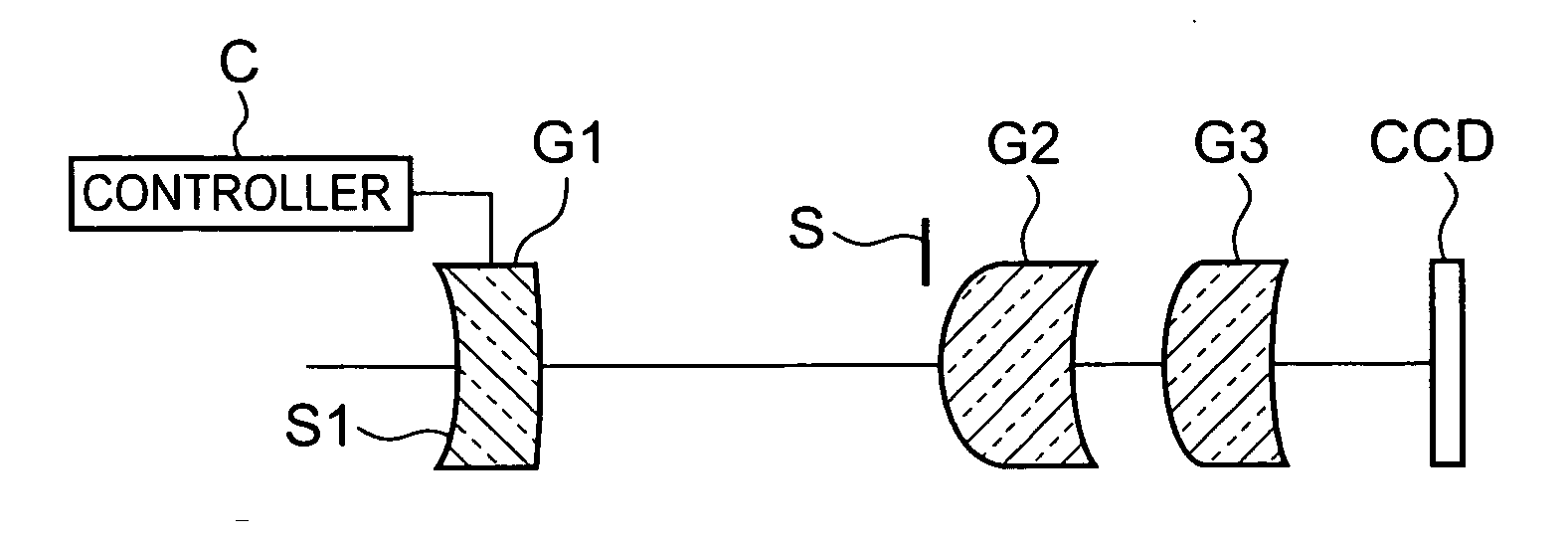
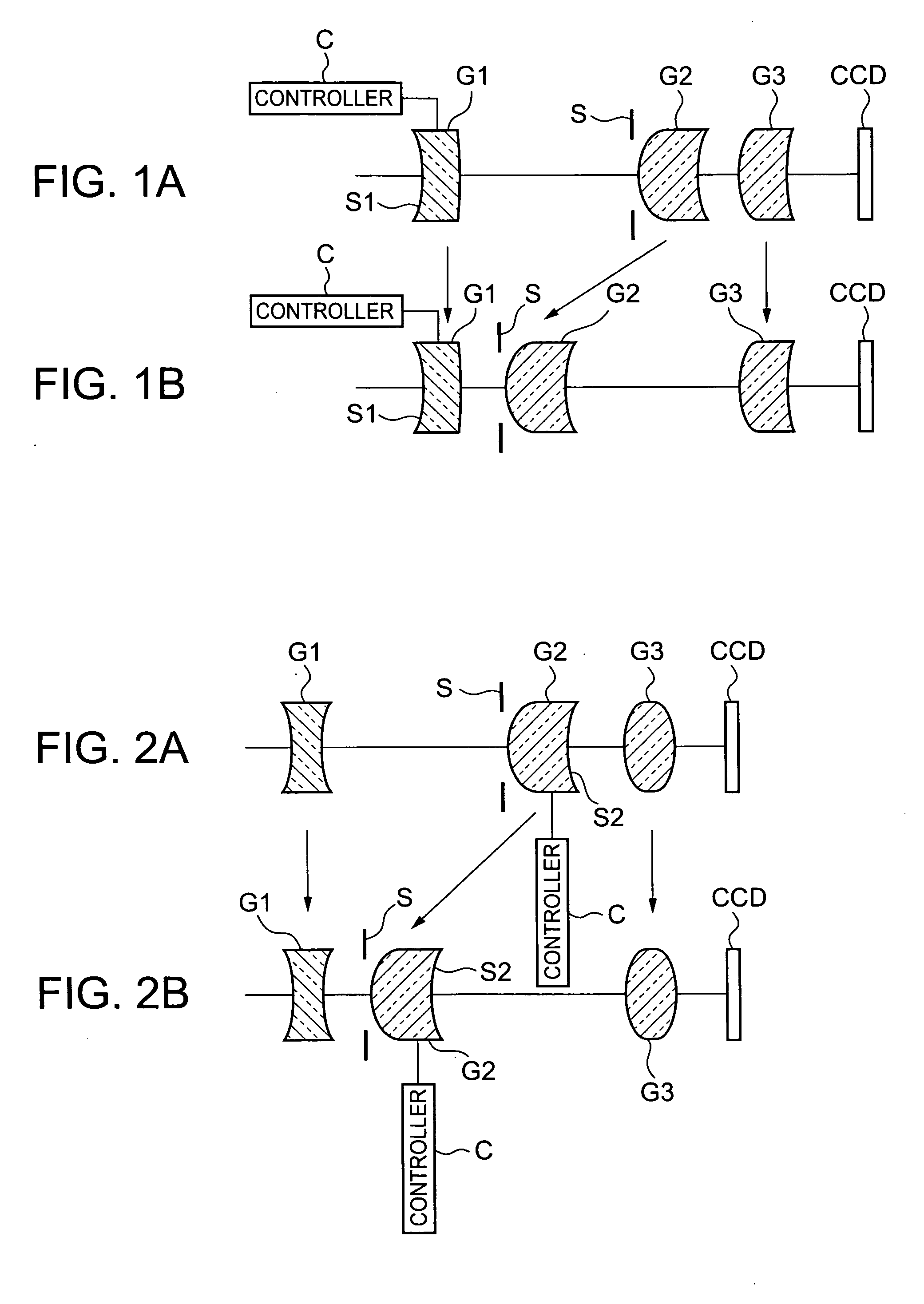
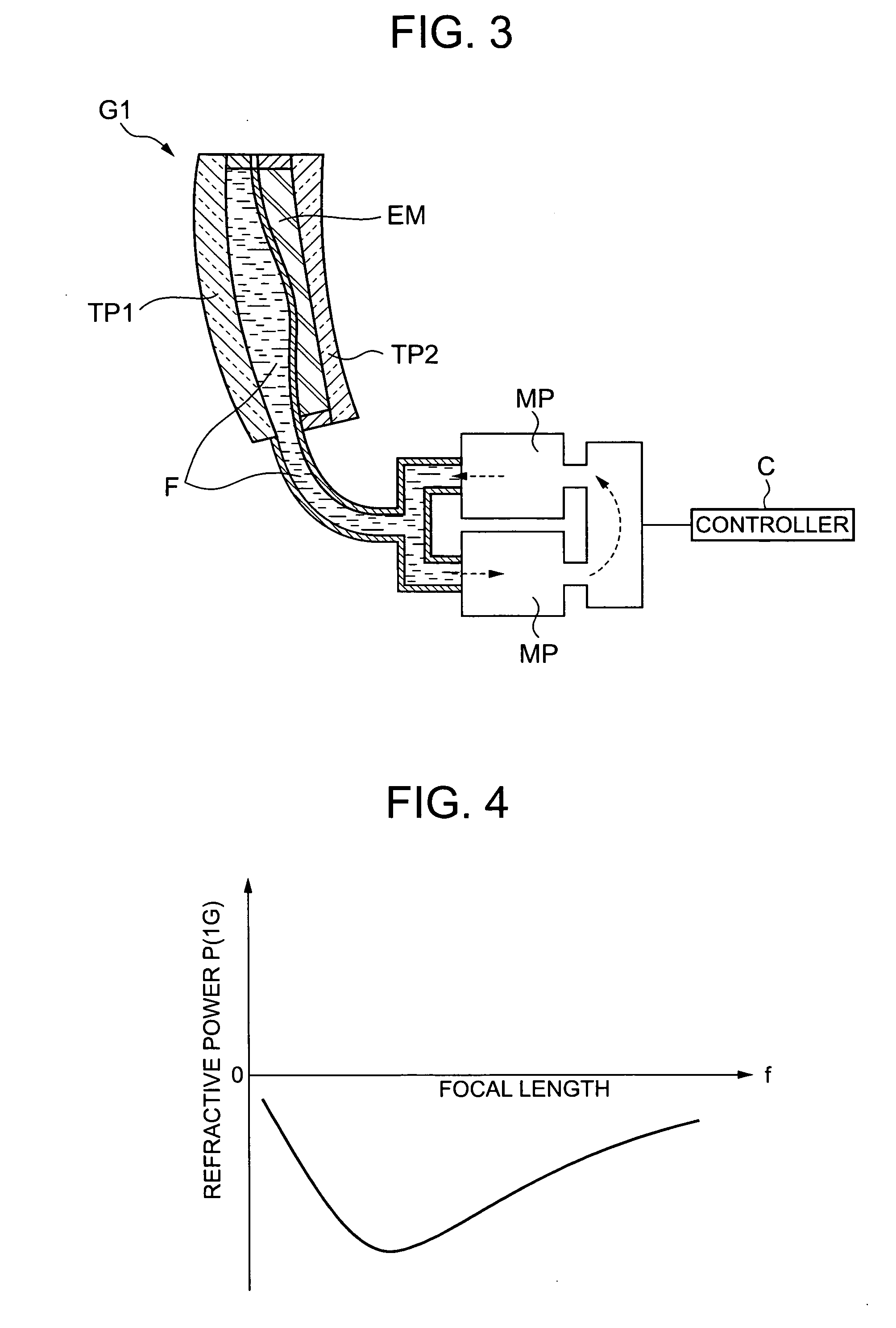
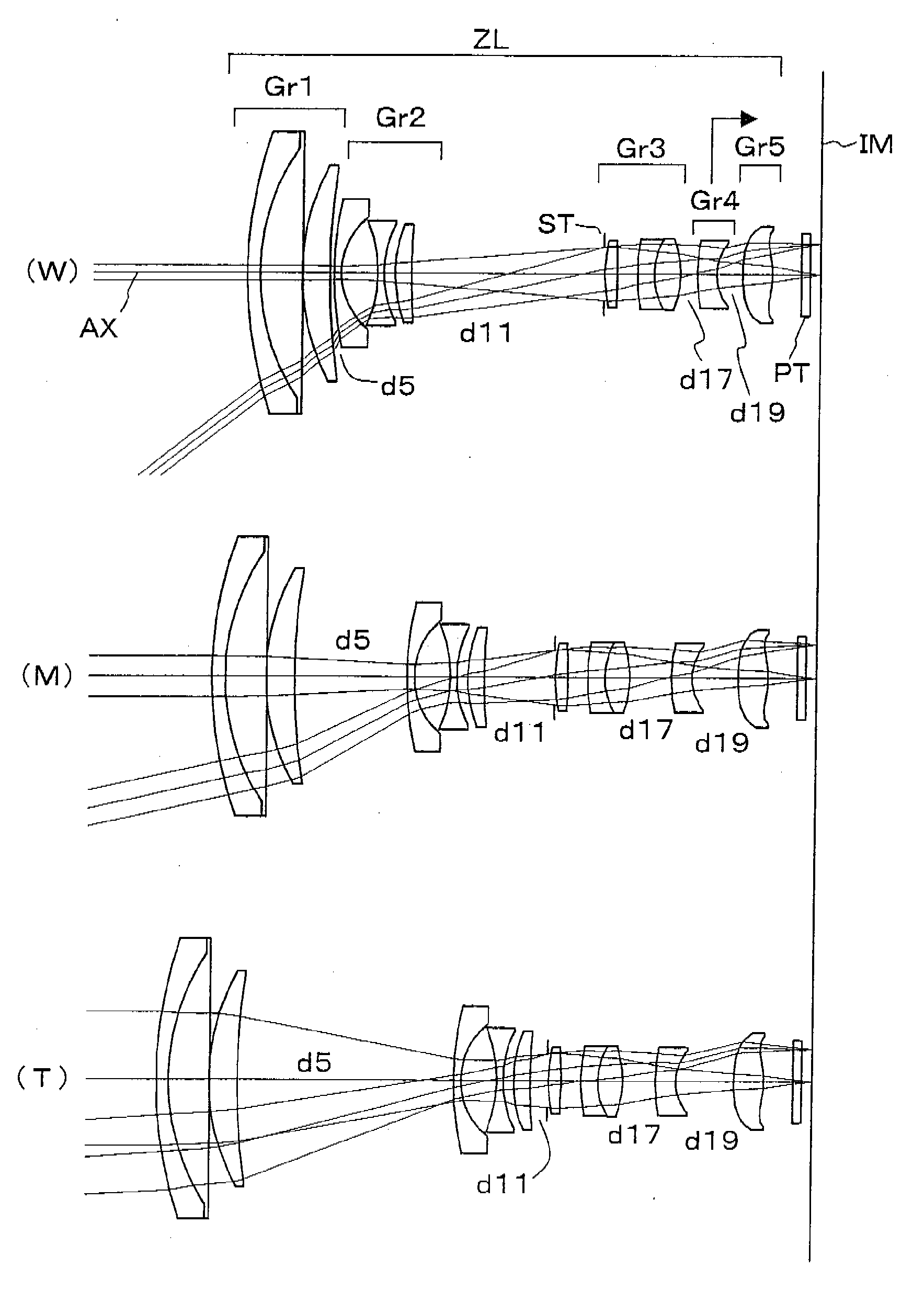
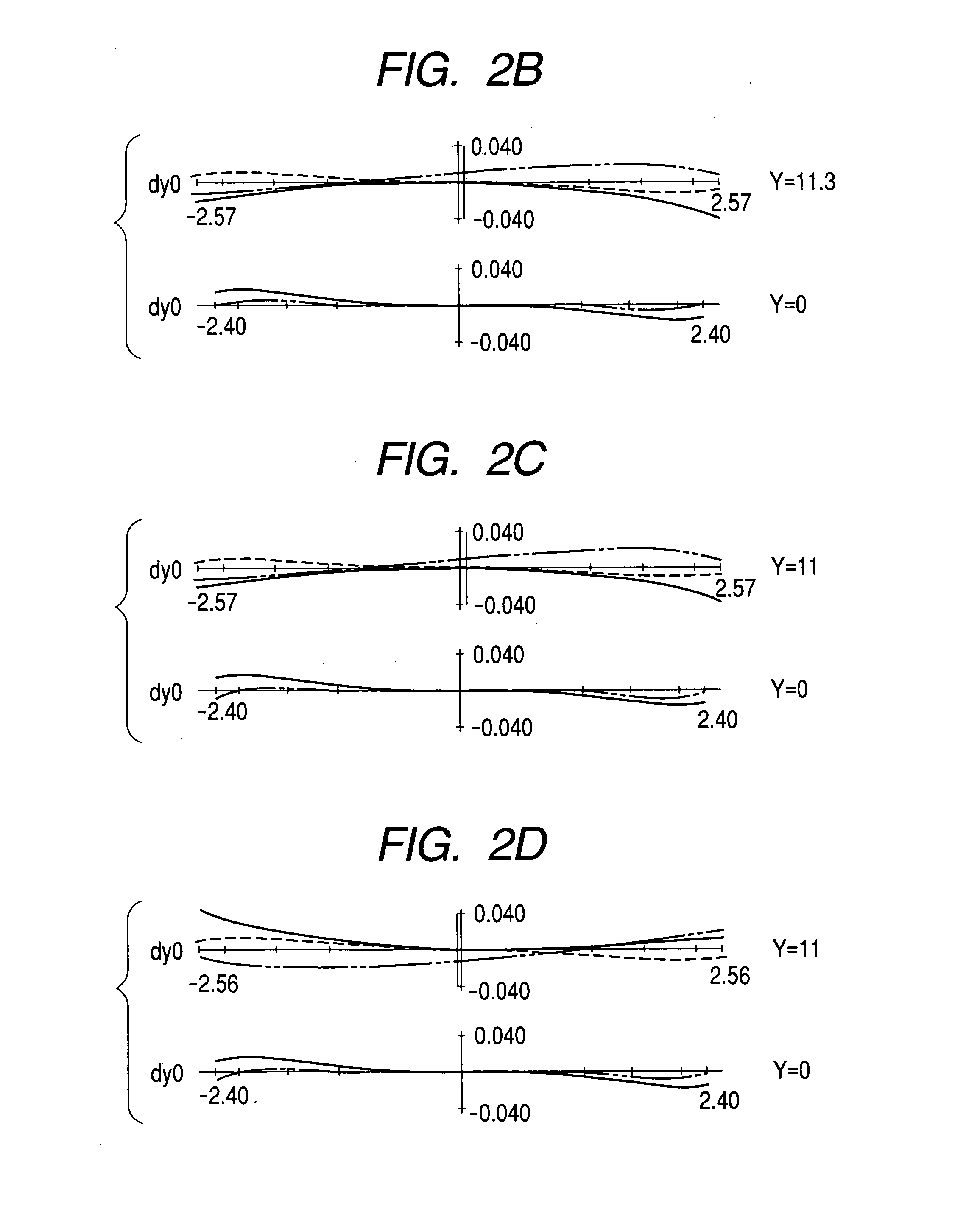
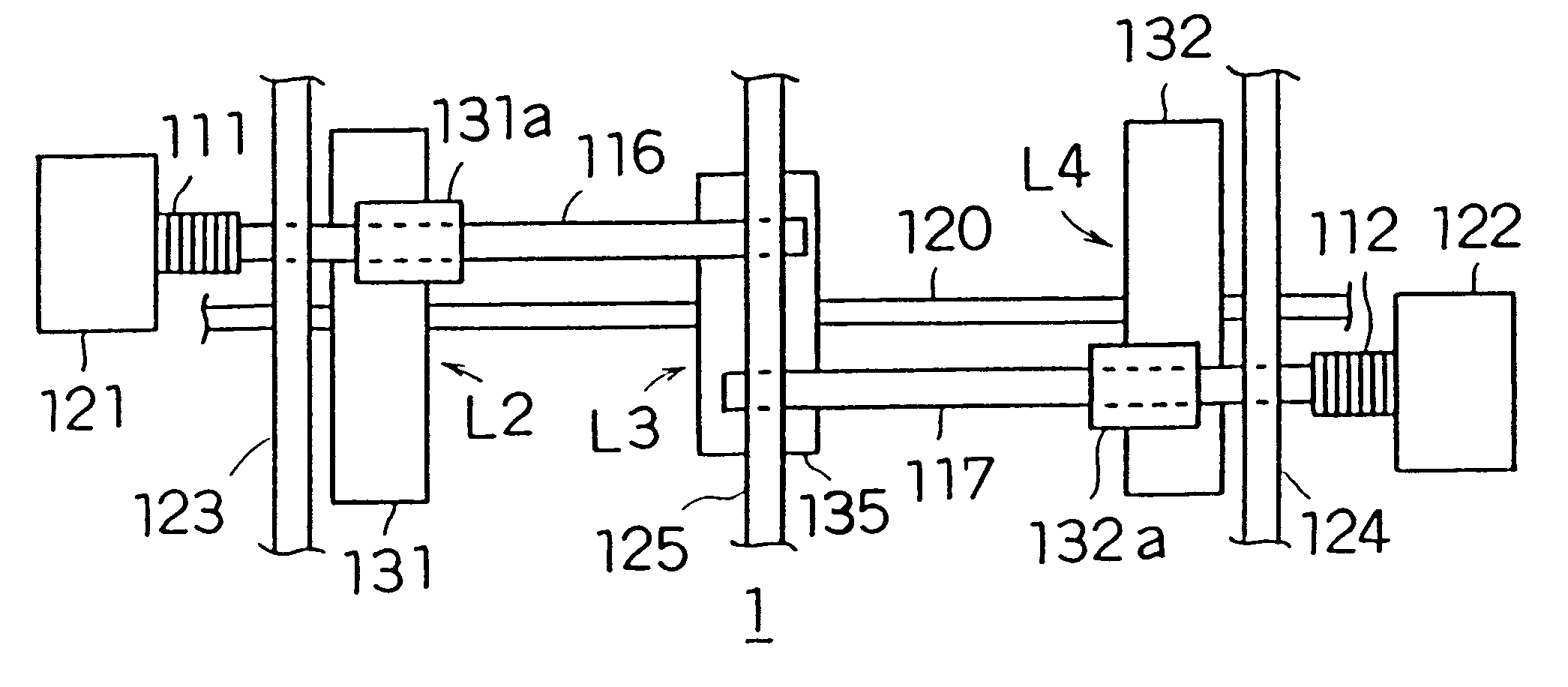
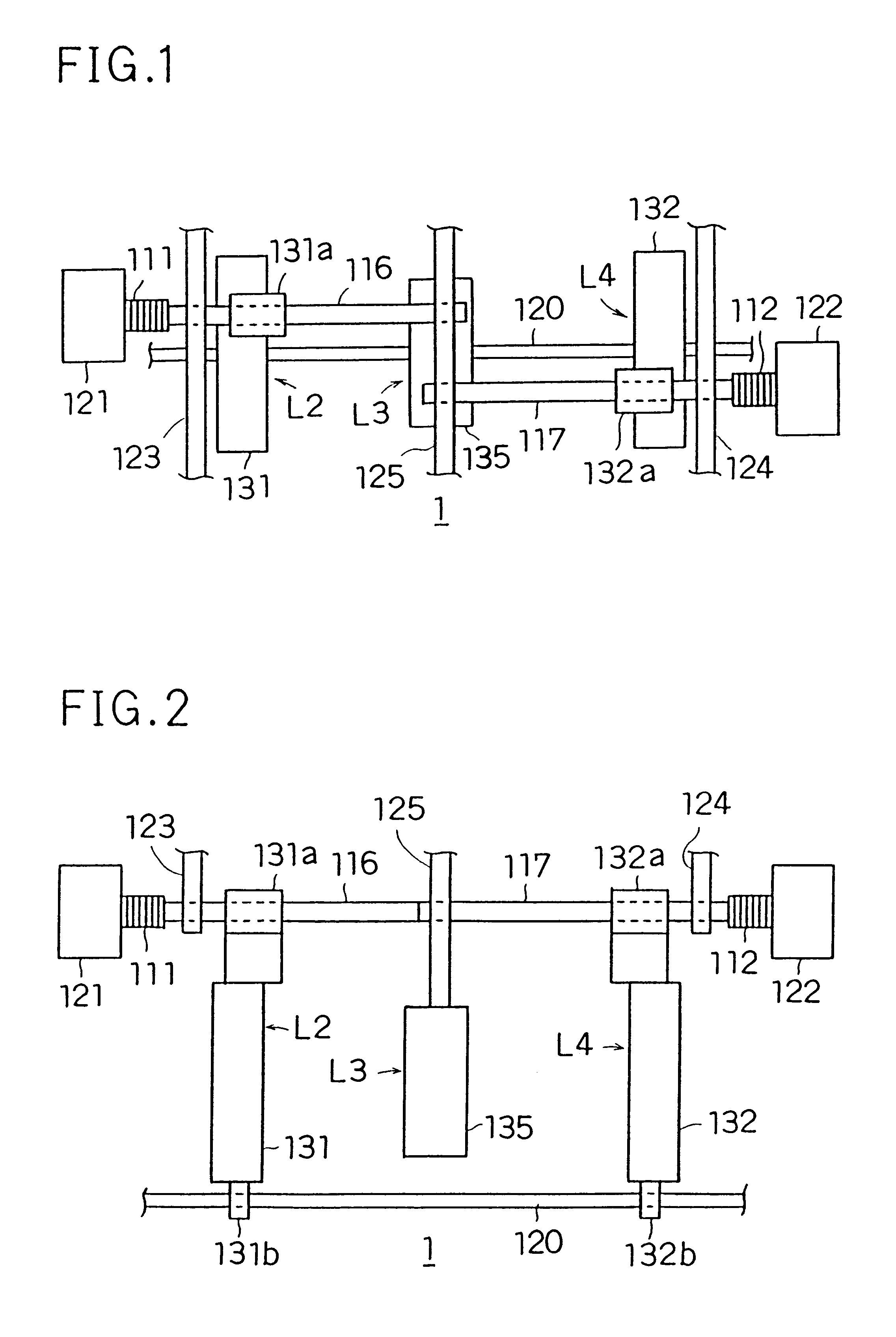
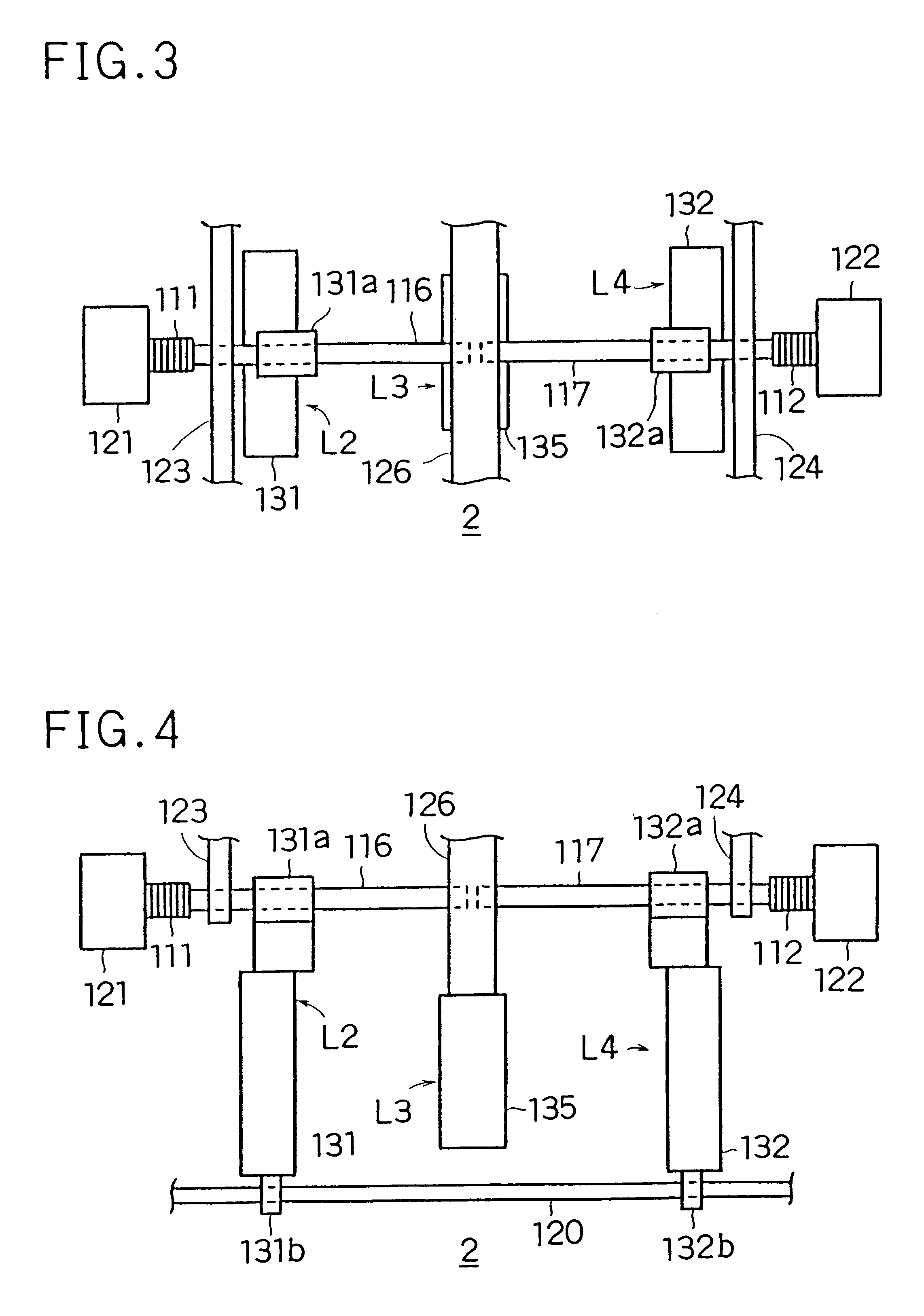
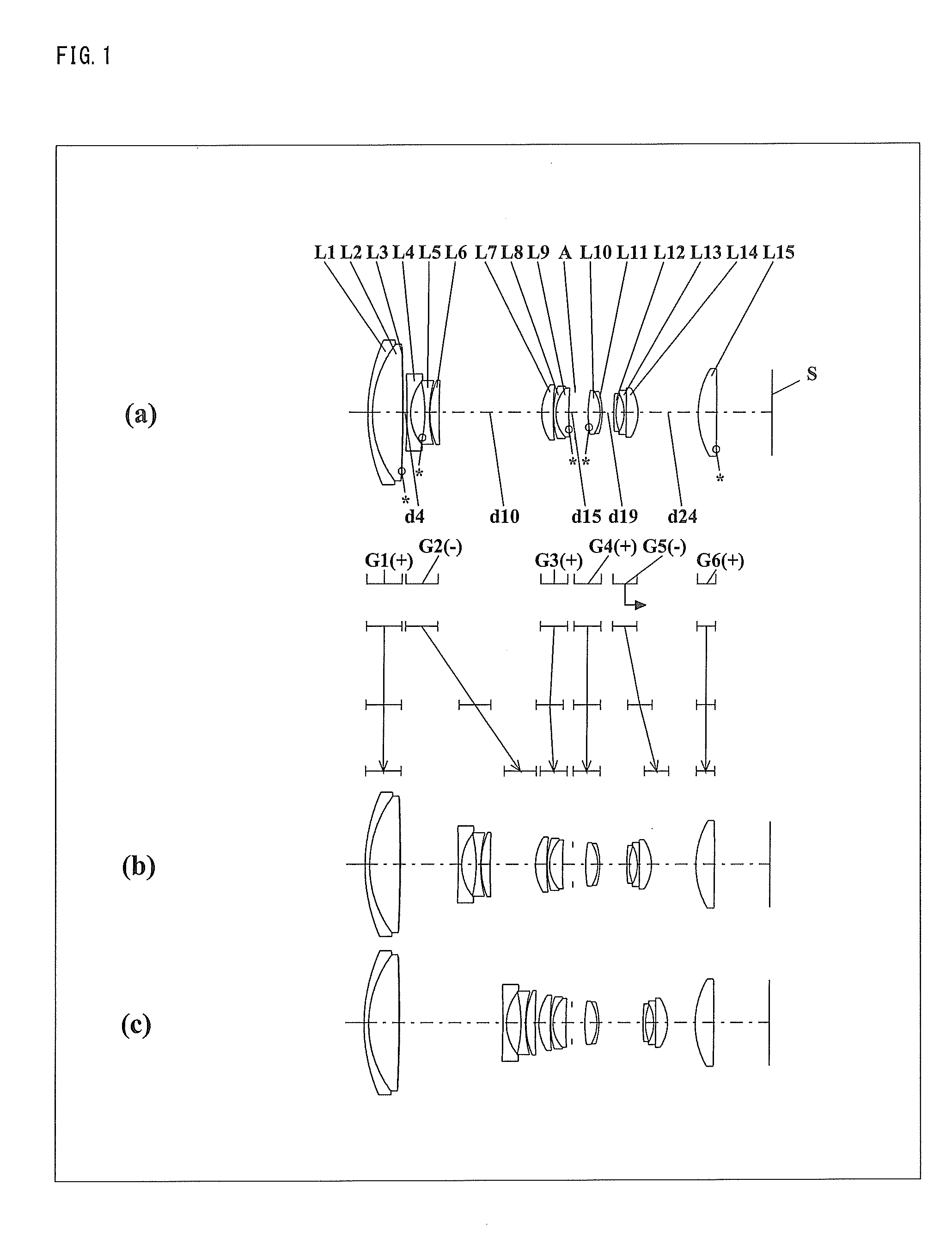
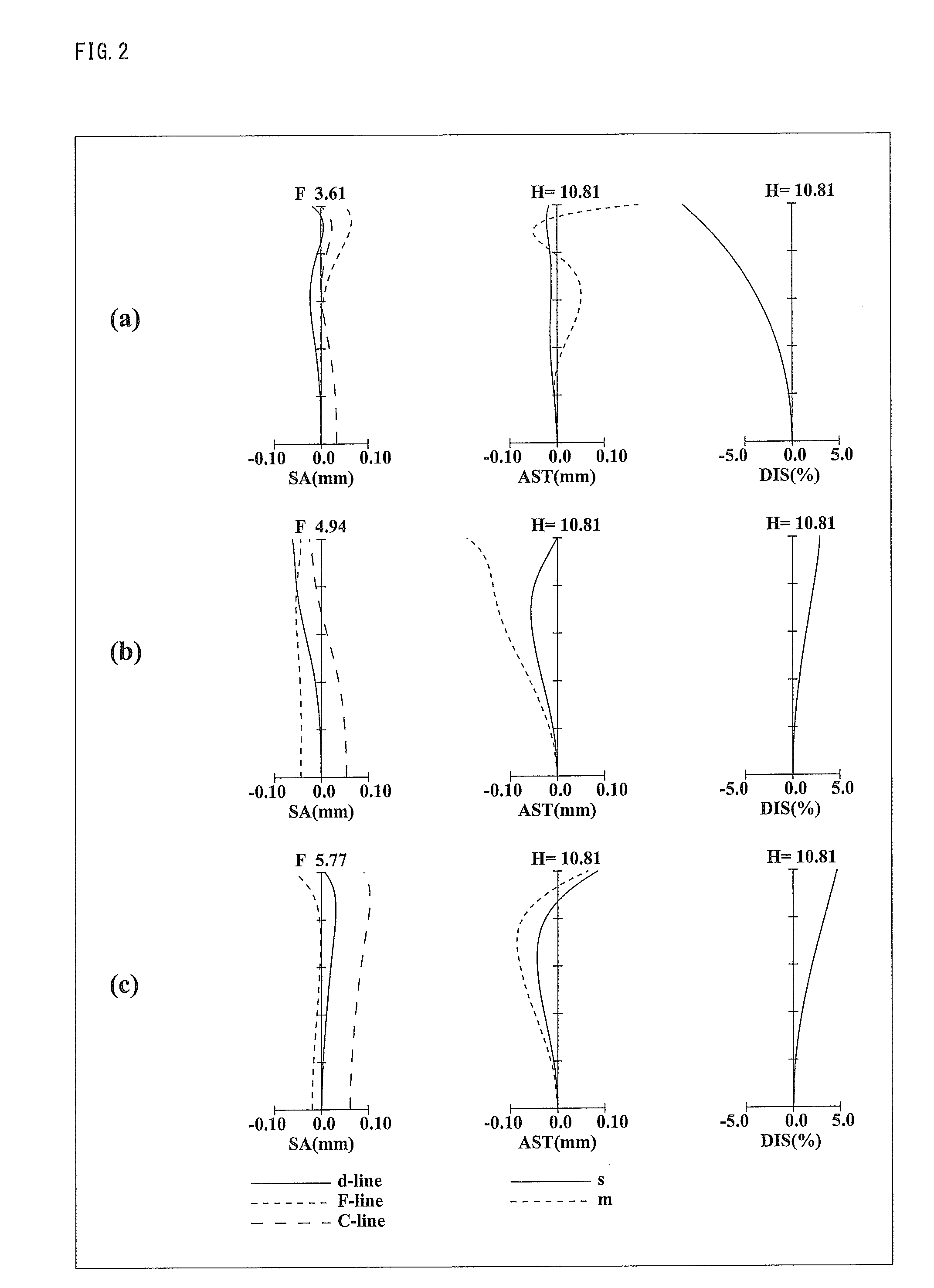
Patents
Literature
5852 results about "Zoom lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length (and thus angle of view) can be varied, as opposed to a fixed focal length (FFL) lens (see prime lens). A true zoom lens, also called a parfocal lens, is one that maintains focus when its focal length changes.. Most consumer zoom lenses do not maintain perfect focus, but are still parfocal designs.
Autonomous electro-optical framing camera system with constant ground resolution, unmanned airborne vehicle therefor, and methods of use
InactiveUS6130705AReduce vibrationIncrease flexibilityTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCamera imageImage resolution
An aerial reconnaissance system generates imagery of a scene that meets resolution or field of view objectives automatically and autonomously. In one embodiment, a passive method of automatically calculating range to the target from a sequence of airborne reconnaissance camera images is used. Range information is use for controlling the adjustment of a zoom lens to yield frame-to-frame target imagery that has a desired, e.g., constant, ground resolution or field of view at the center of the image despite rapid and significant aircraft altitude and attitude changes. Image to image digital correlation is used to determine the displacement of the target at the focal plane. Camera frame rate and aircraft INS / GPS information is used to accurately determine the frame to frame distance (baseline). The calculated range to target is then used to drive a zoom lens servo mechanism to the proper focal length to yield the desired resolution or field of view for the next image. The method may be performed based on parameters other than range, such as aircraft height and stand off distance.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
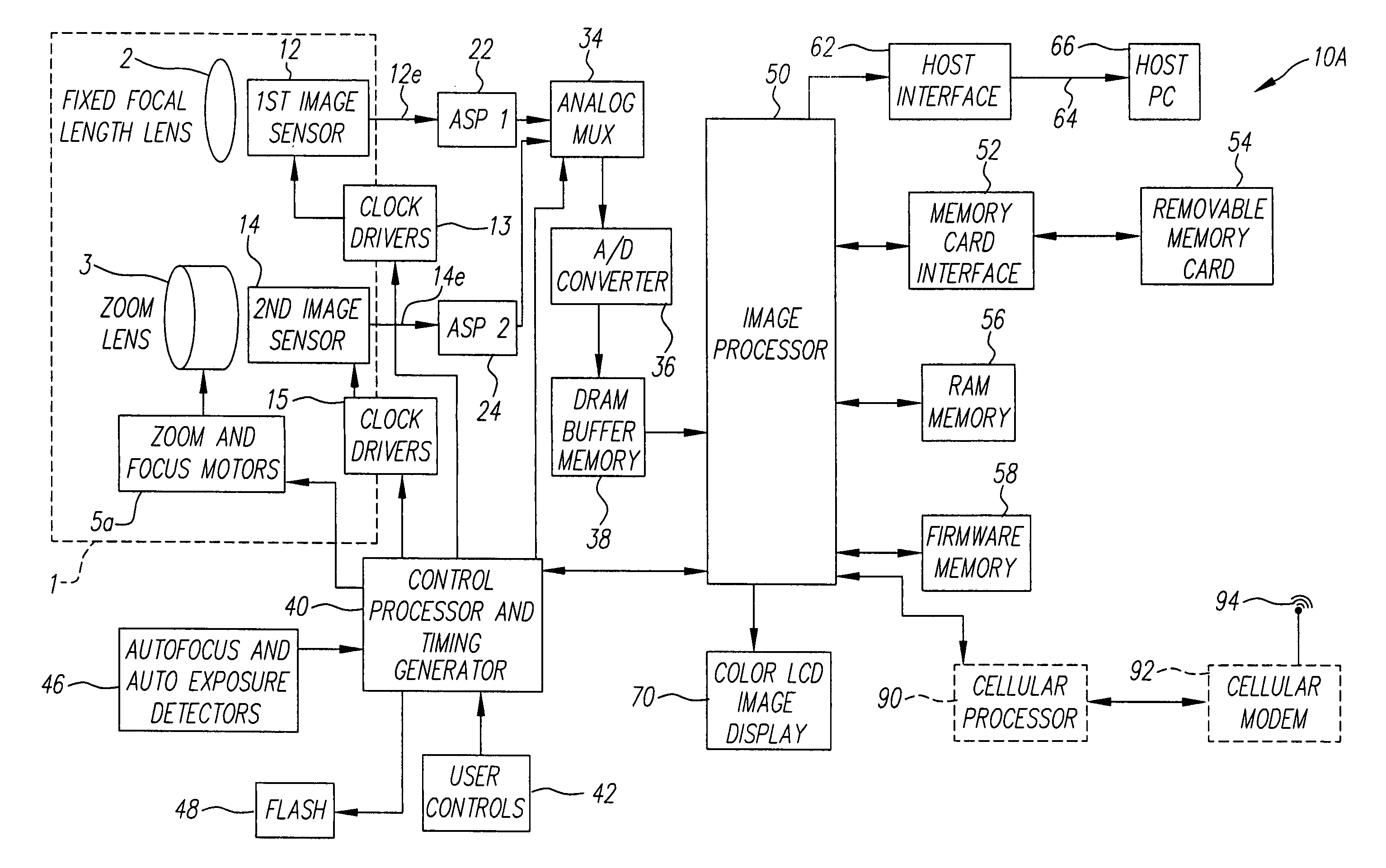
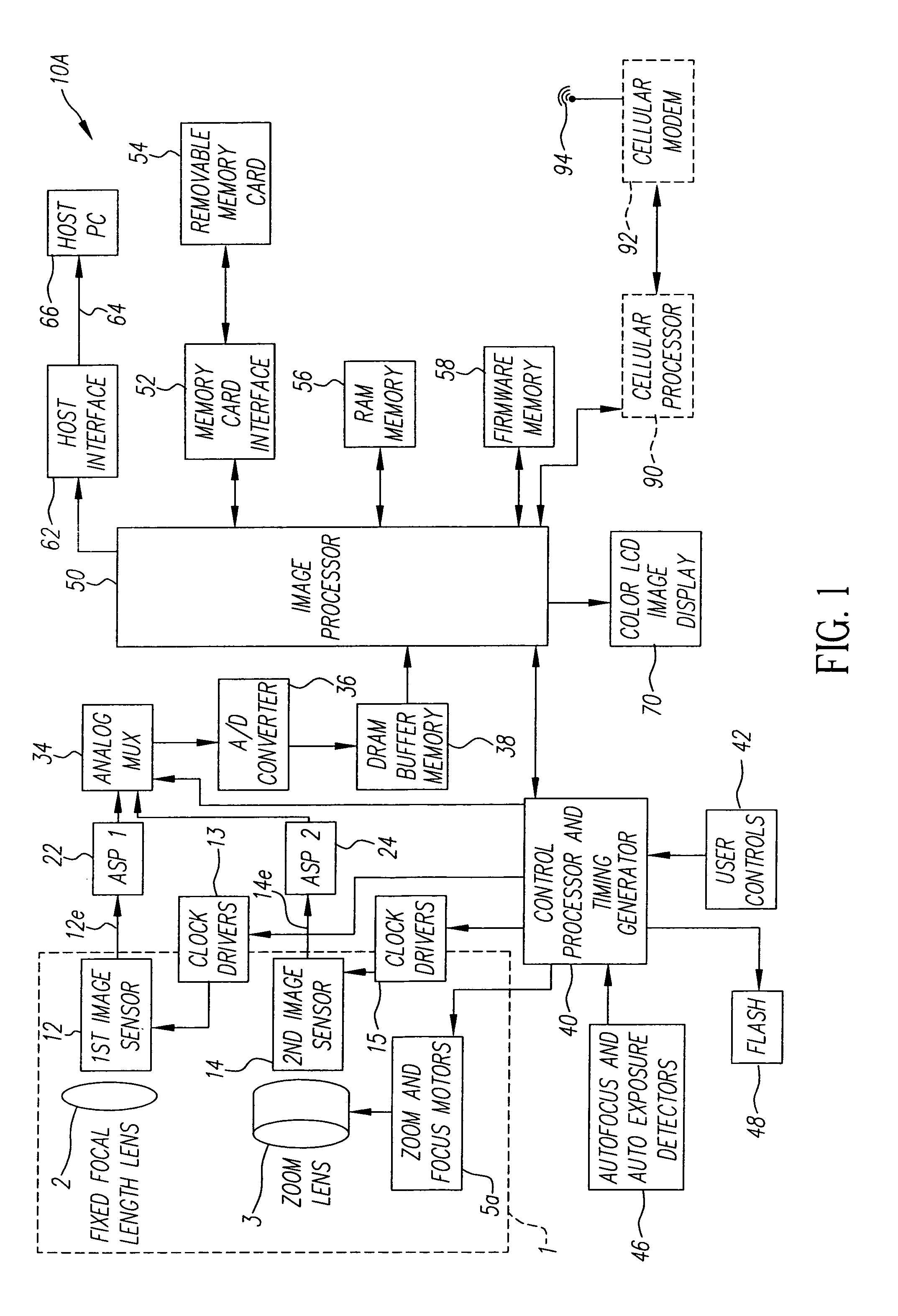
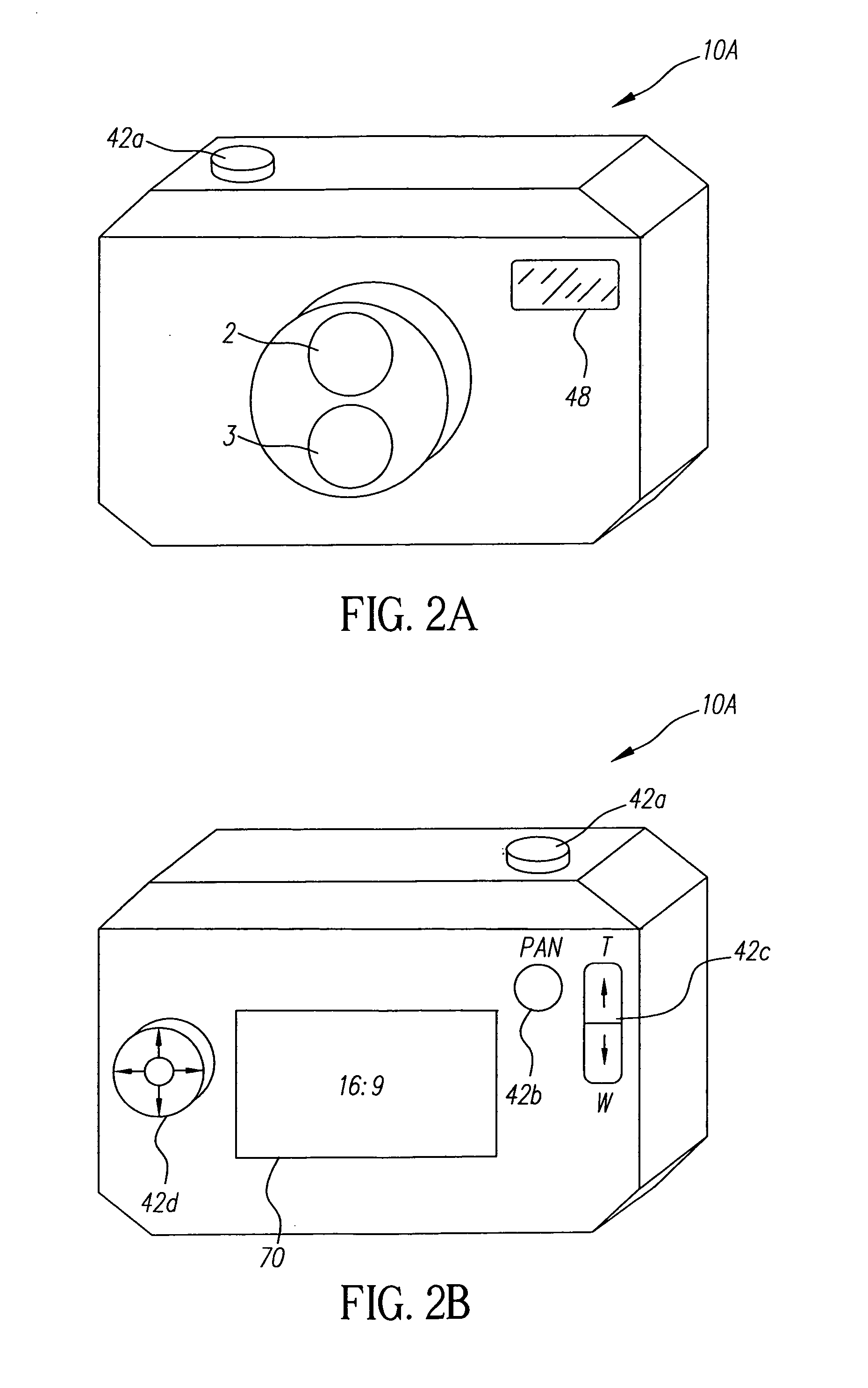
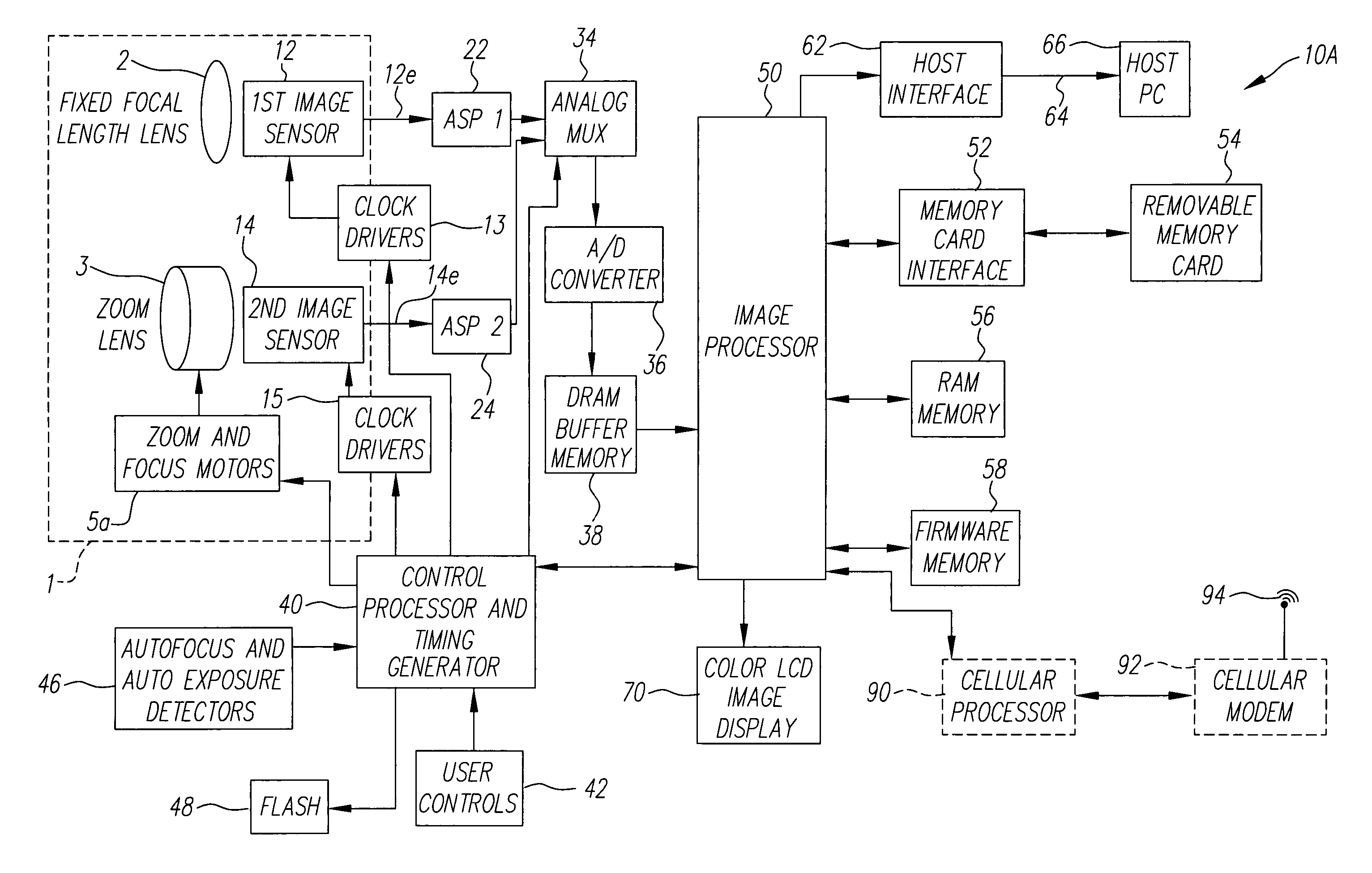
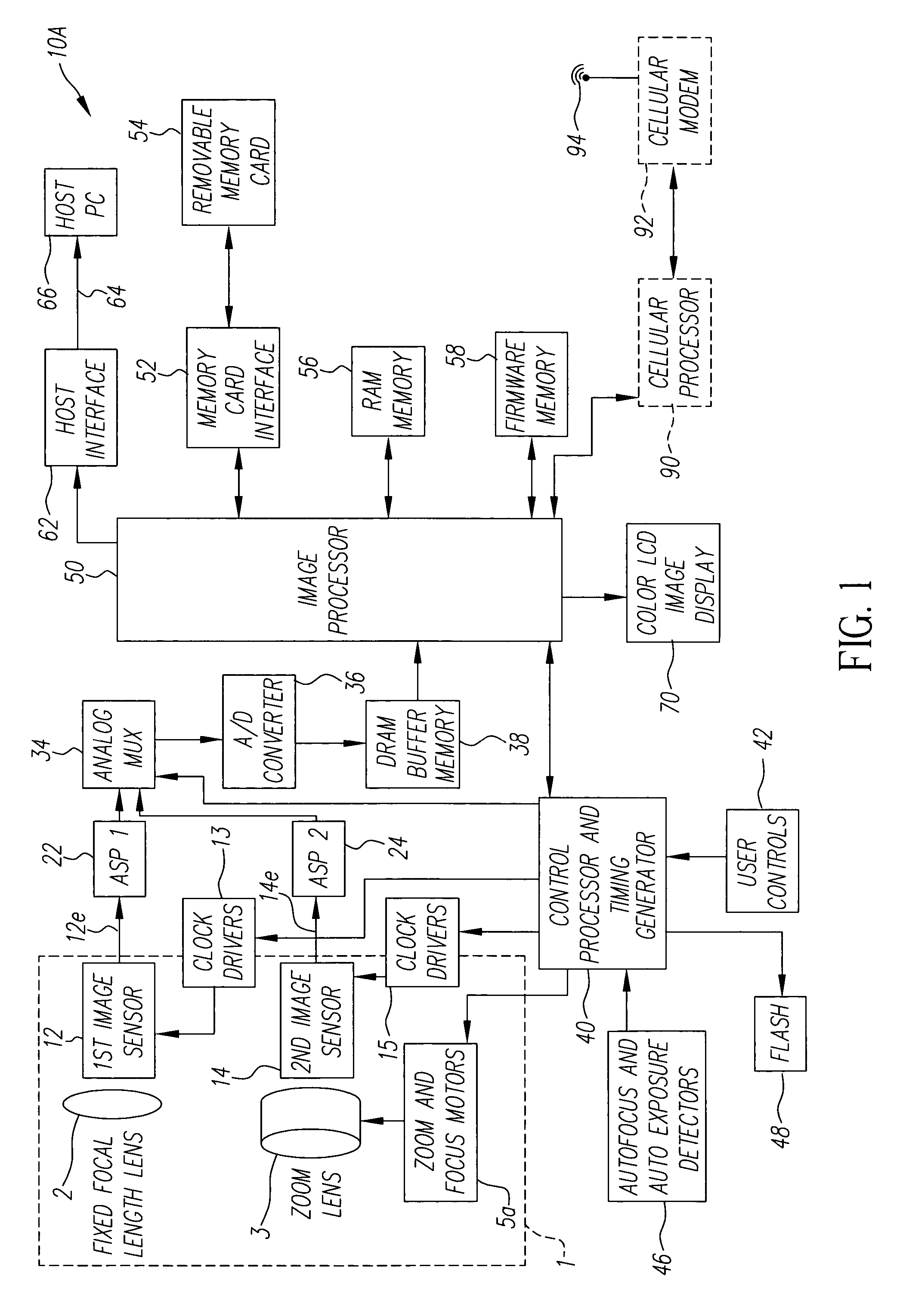
Digital camera using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide an extended zoom range
ActiveUS7206136B2Increase the zoom rangeIncreasing size and costTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsCamera lensZoom lens
A digital camera includes a first image sensor, a first wide angle lens for forming a first image of a scene on the first image sensor; a second image sensor, a zoom lens for forming a second image of the same scene on the second image sensor, a control element for selecting either a first sensor output from the first image sensor or a second sensor output from the second image sensor, and a processing section for producing the output image from the selected sensor output. In one variation of this embodiment, the first lens is also a zoom lens, where the maximum focal length of the first lens is less than or equal to the minimum focal length of the second zoom lens.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Imaging device and digital camera using the imaging device
InactiveUS20040008271A1Solve the thickerLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical power
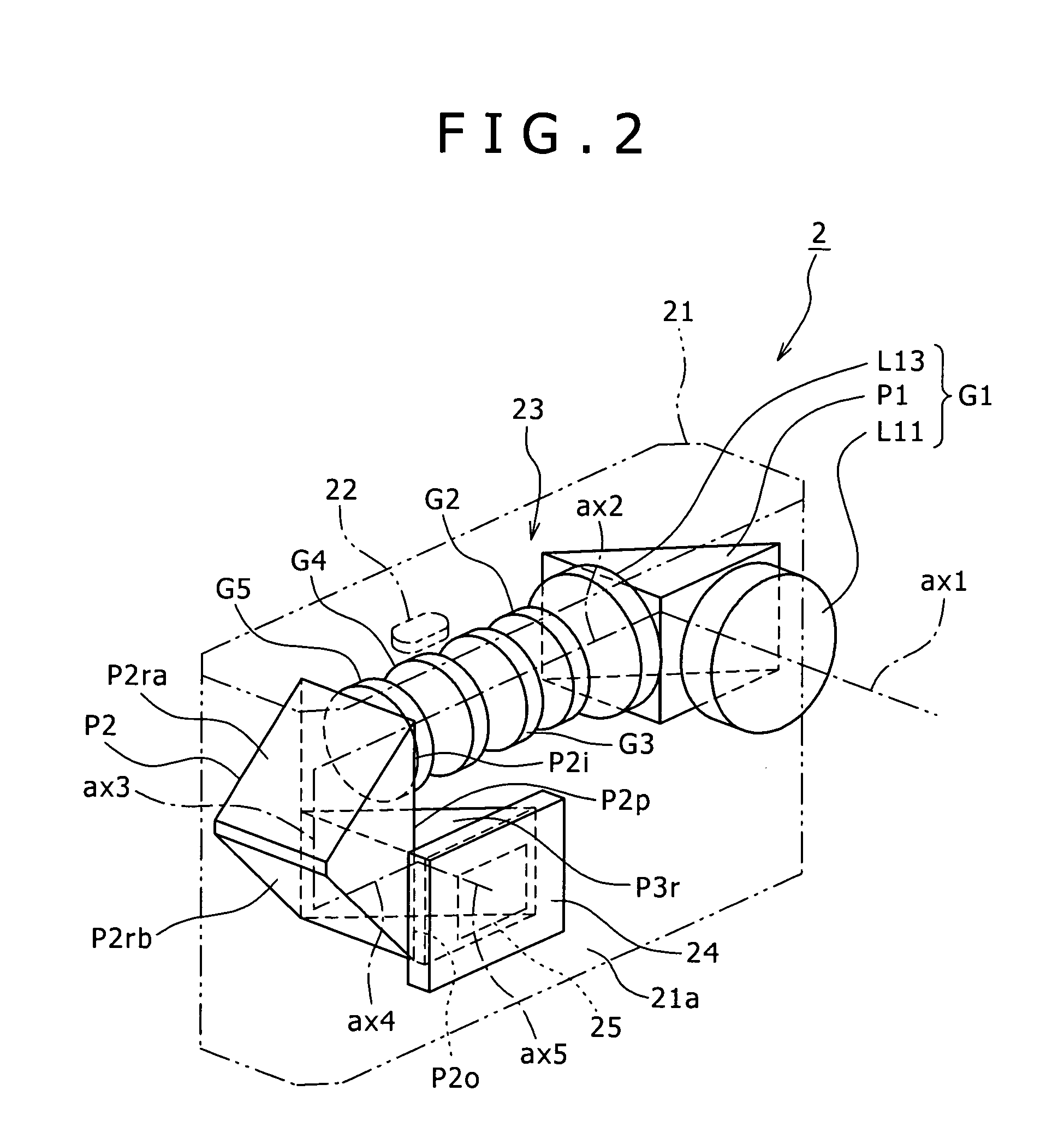
An imaging device has a zoom lens system having a plurality of lens units and forming an optical image of an object so as to continuously optically zoom by varying distances between the lens unit; and an image sensor converting the optical image formed by the zoom lens system to an electric signal. The zoom lens system has from an object side, a first lens unit being overall negative and including a reflecting surface that bends a luminous flux substantially 90 degrees; and a second lens unit disposed with a variable air distance from the first lens unit, and having an optical power, and wherein at least one lens element made of resin is included in the entire lens system.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
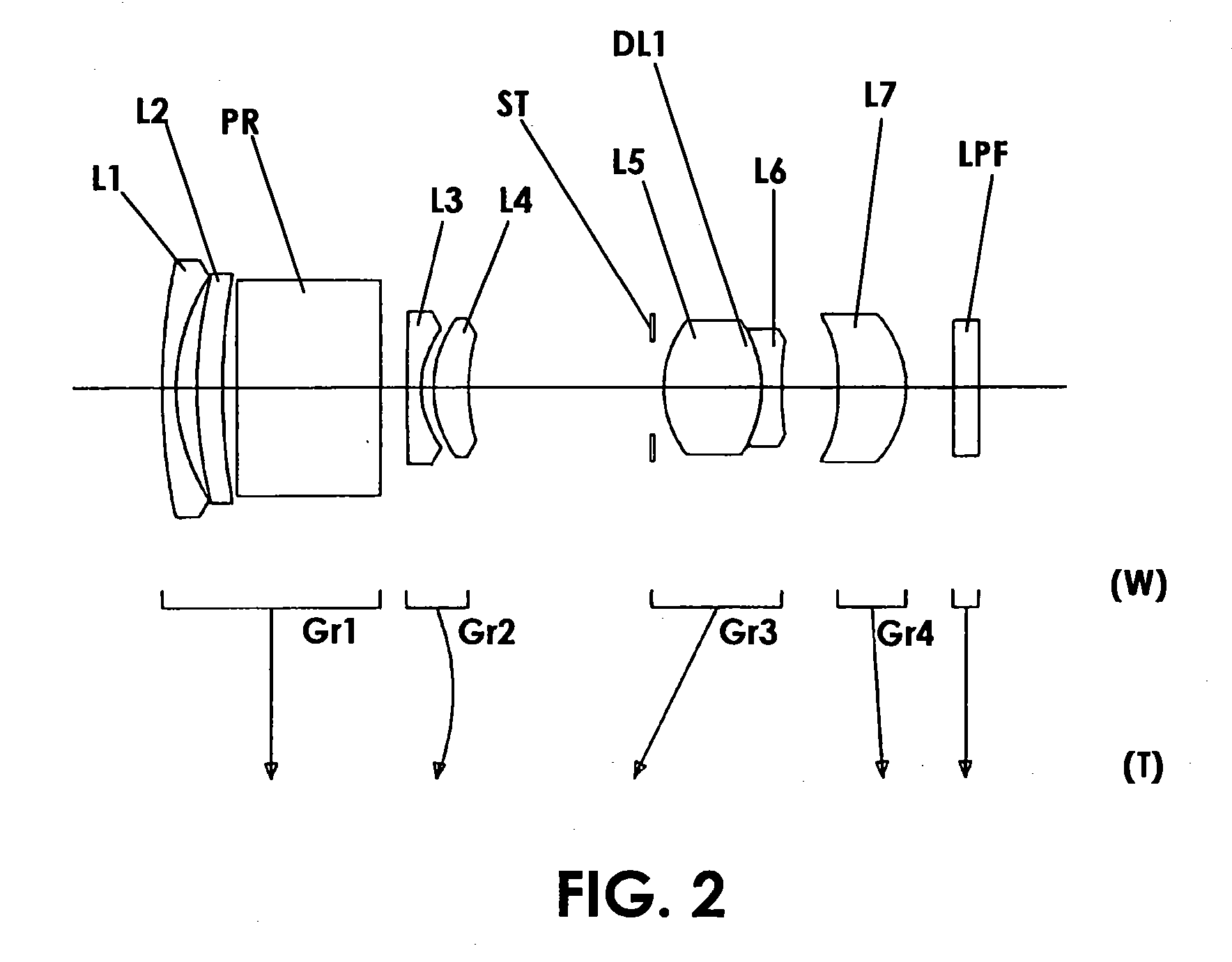
Zoom lens and photographing apparatus having the same
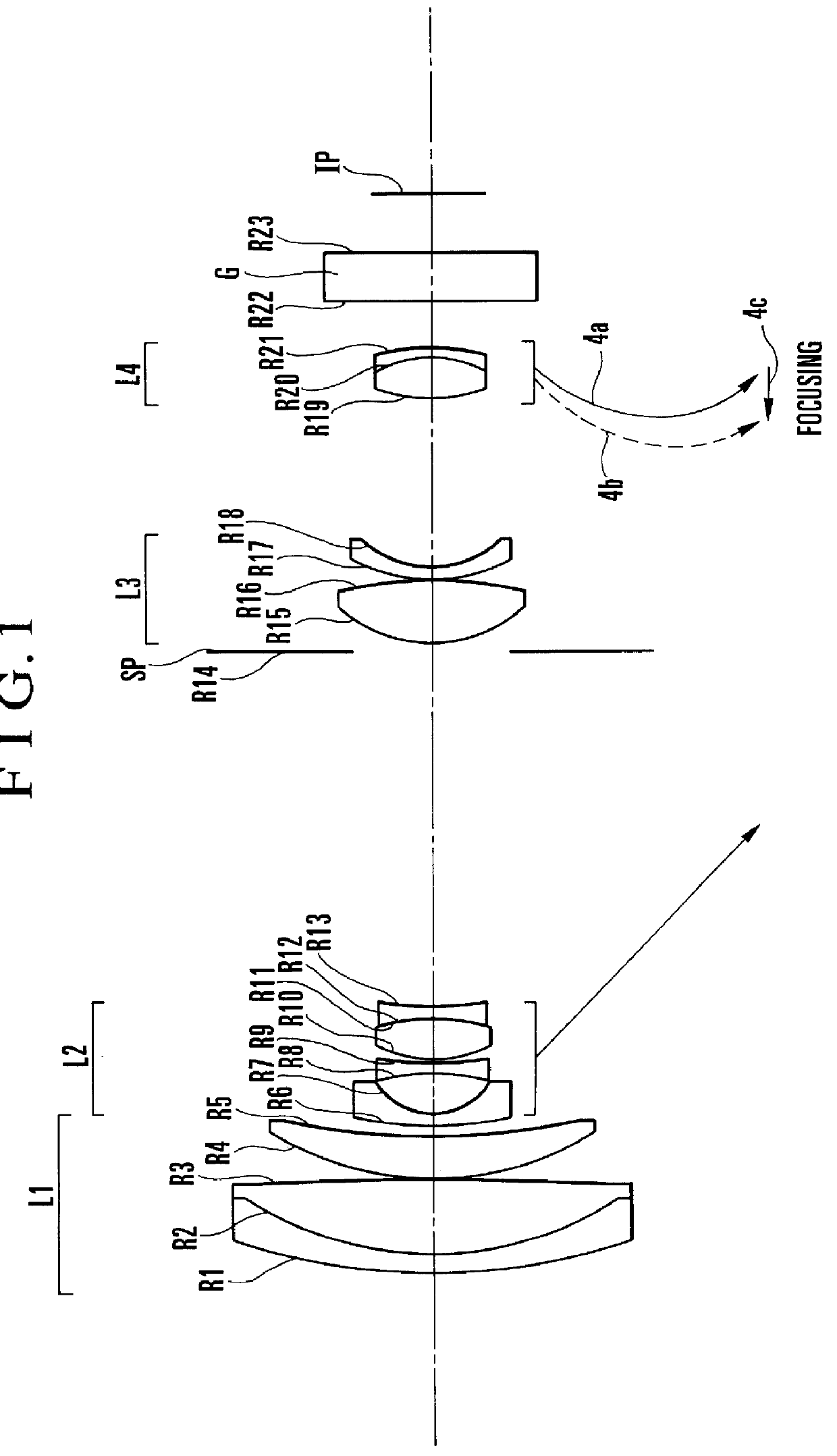
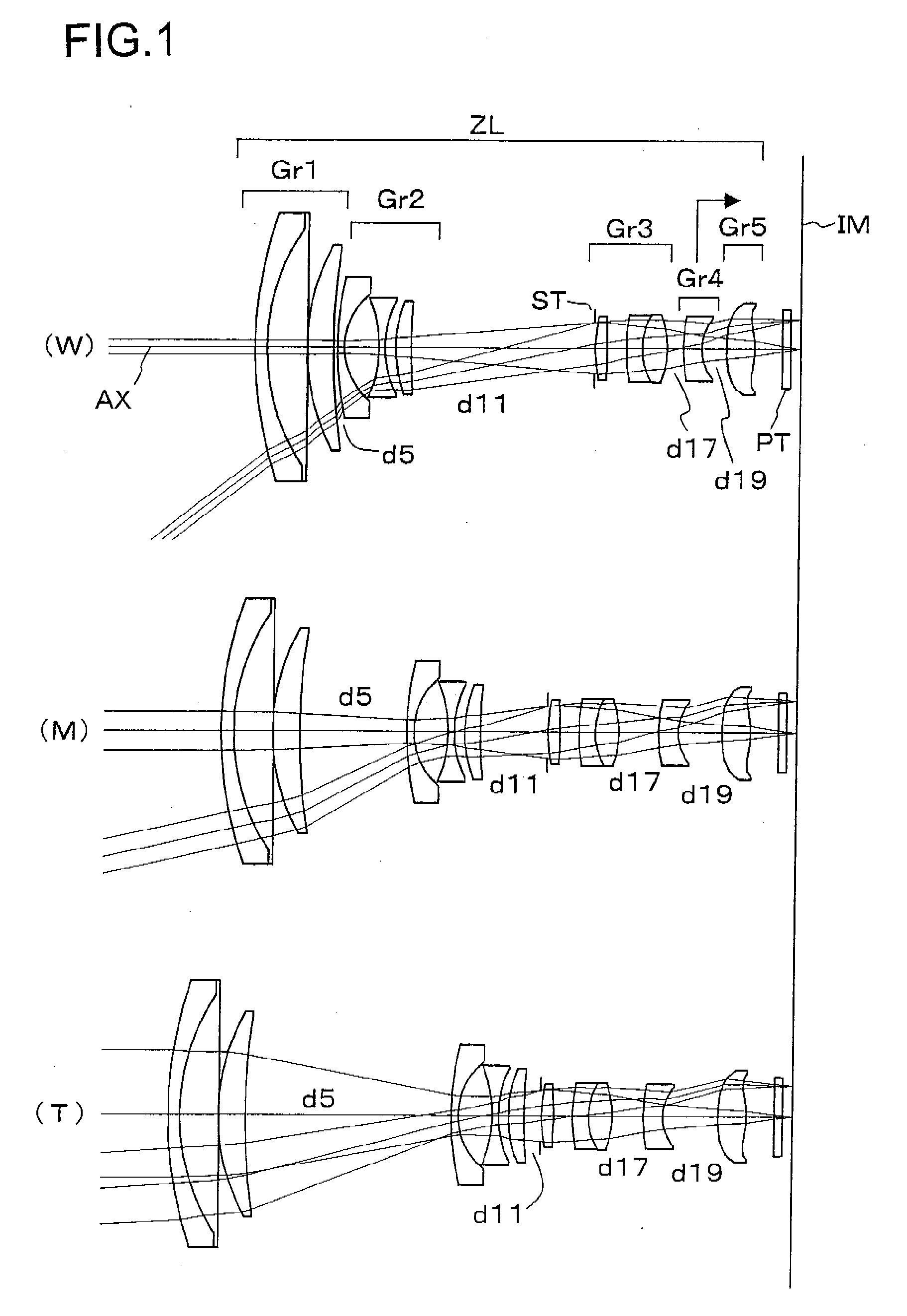
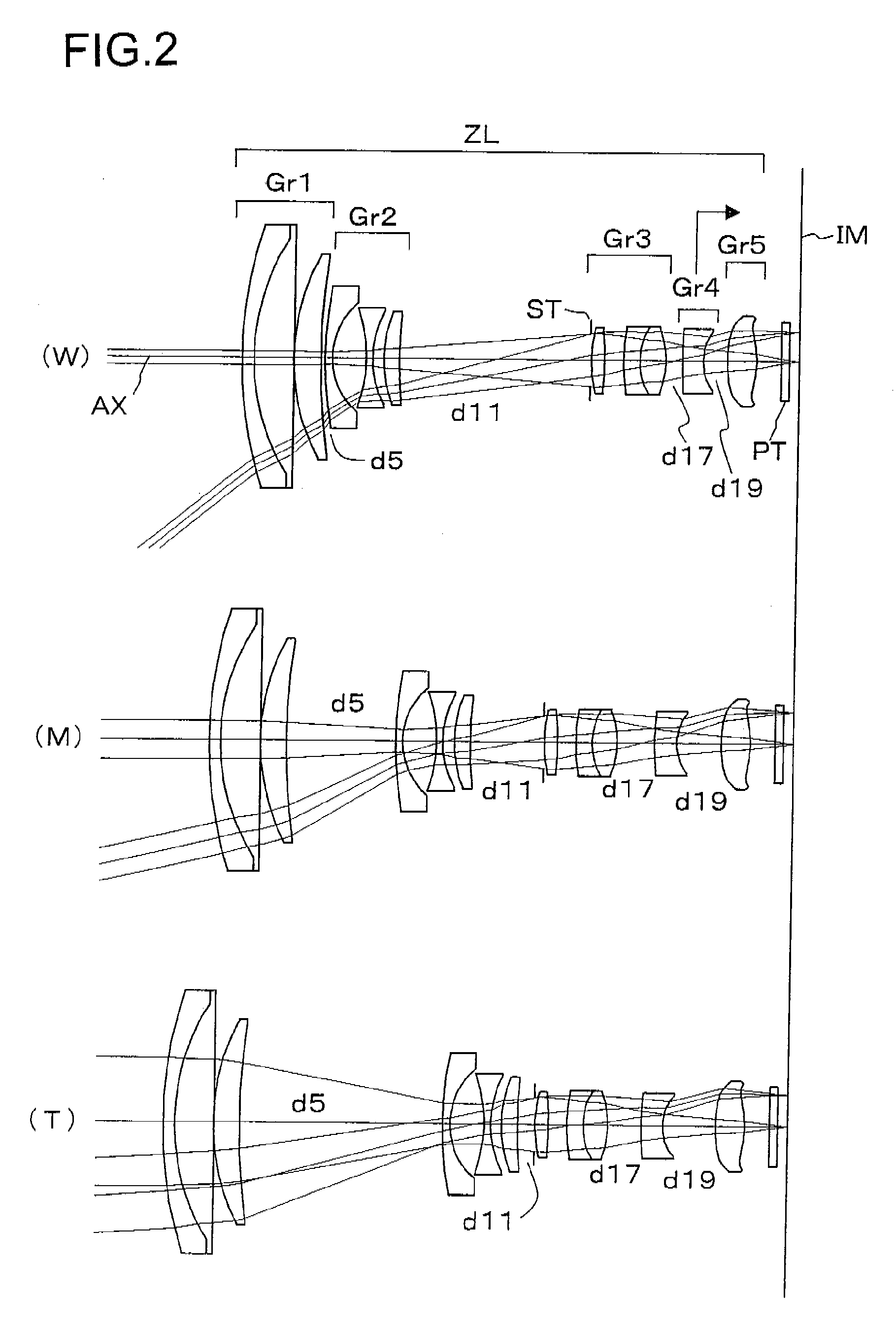
A zoom lens, includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens unit of negative refractive power, the first lens unit having an aspherical lens of negative refractive power, a stop, a second lens unit of positive refractive power, the second lens unit having an aspherical lens of positive refractive power, and a third lens unit of positive refractive power, wherein, during zooming from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end, the second lens unit and the stop move in unison toward the object side, and the first lens unit so moves as to compensate for a shift of an image plane resulting from the zooming.
Owner:CANON KK
Distortion free image capture system and method
InactiveUS20020041383A1Low costImprove distortionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementOphthalmologyDistortion free
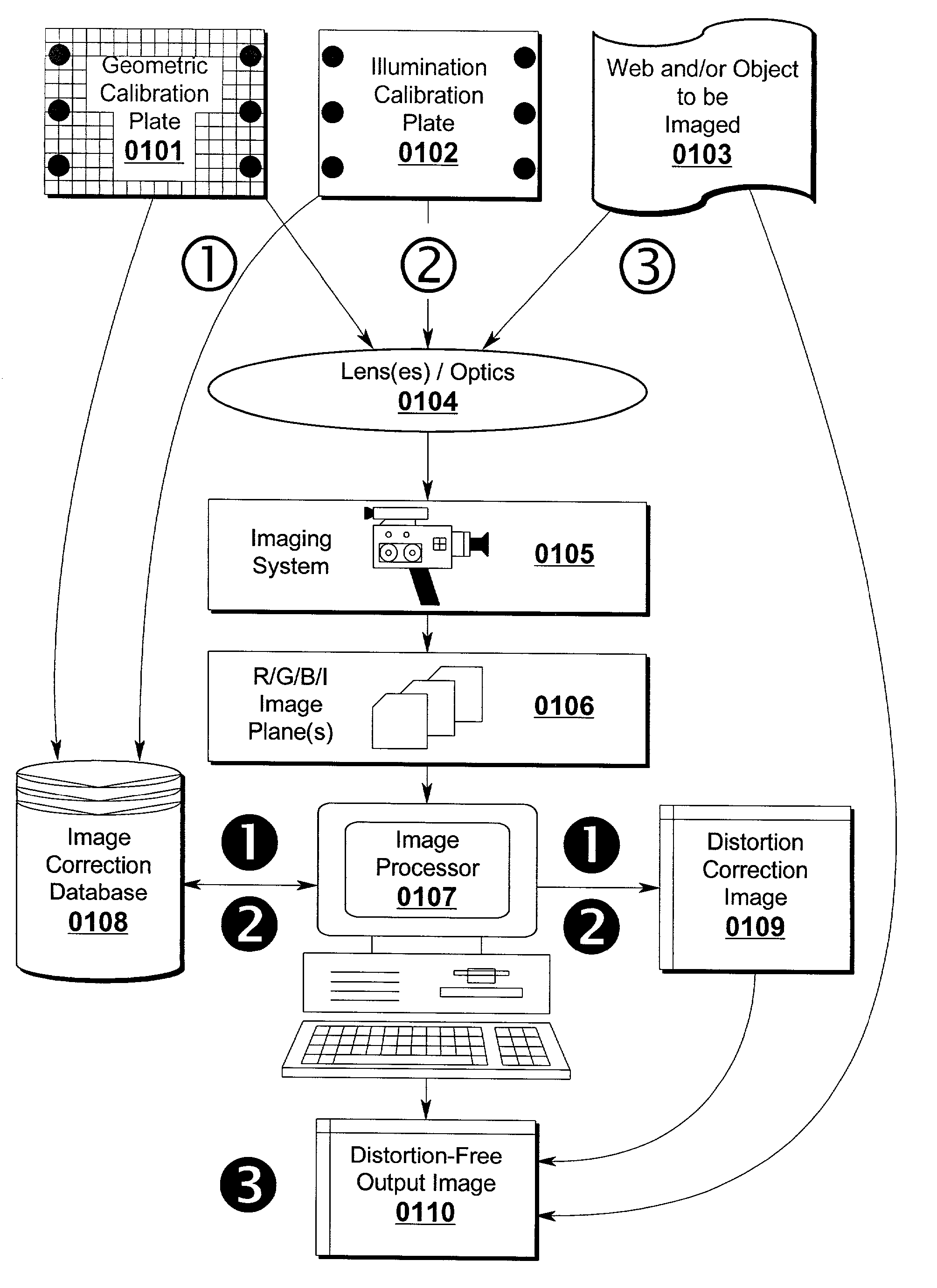
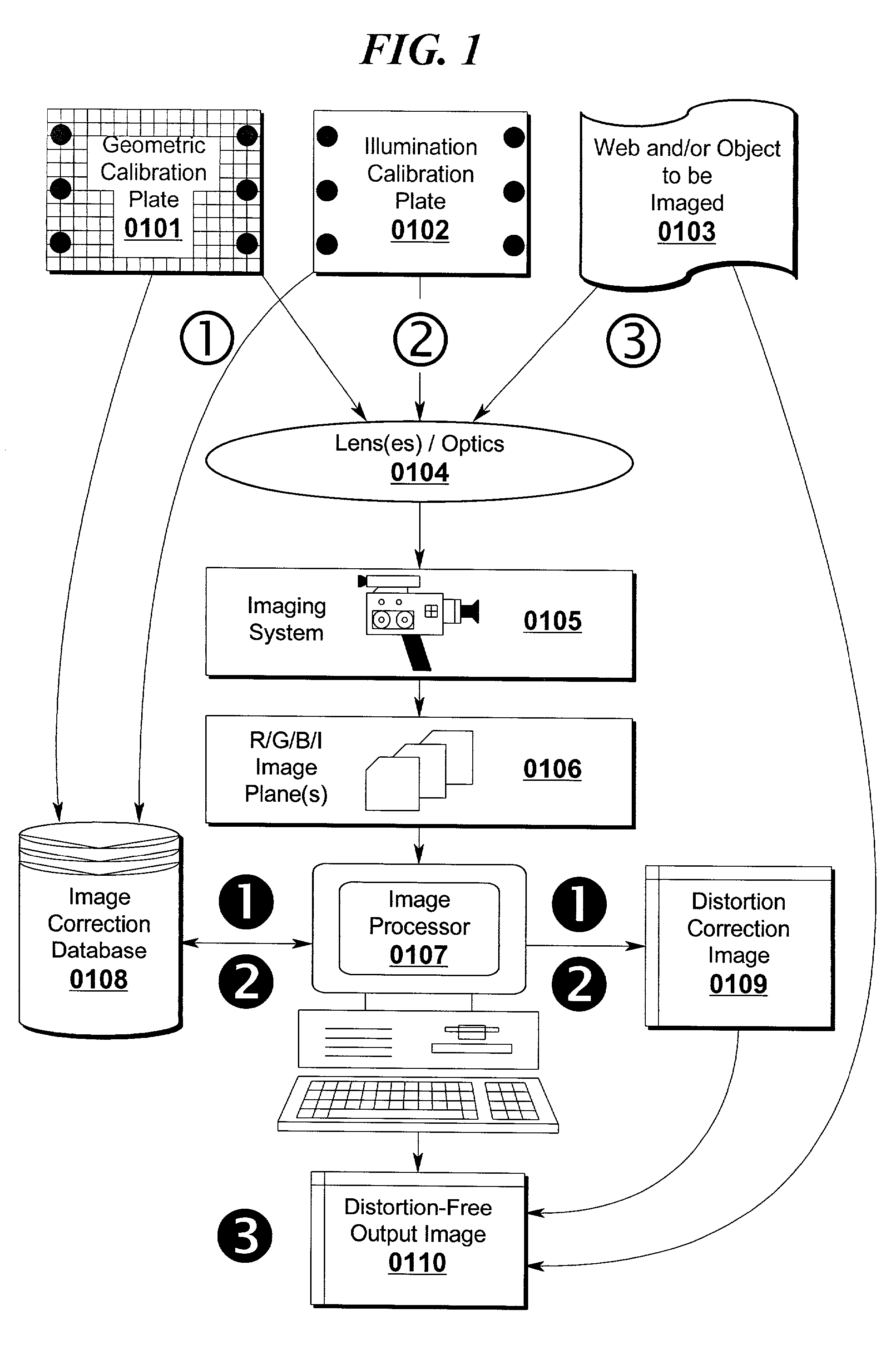
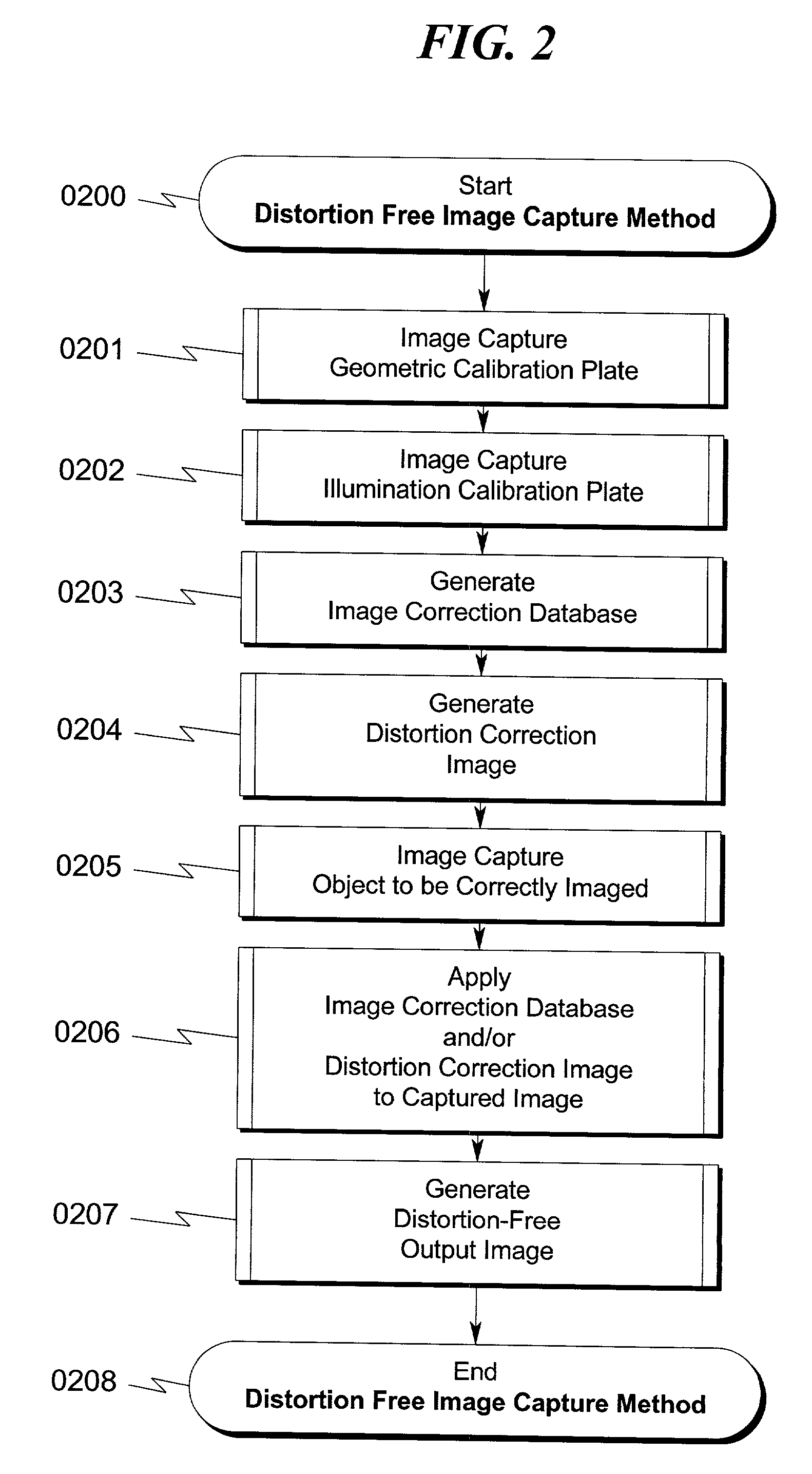
A system and method for correcting distortions that occur in image capture systems is disclosed. The present invention in some preferred embodiments includes provisions to correct or change magnification differences for all causes including position errors in zoom lens positioning mechanisms as well as those caused by chromatic aberration, CCD alignment errors, lens distortion off center variations, pincushion / barrel lens distortion, magnification distortions, camera and lens misalignment errors, and lighting variations (including flash-to-flash illumination variations). A significant feature of the present invention in contrast with the prior art is that with the use of a movable calibration plate in the present invention it is possible to image capture both the calibration plate and the input object image in a single image capture, thus permitting simultaneous compensation for a variety of lighting and illumination variations not possible with the prior art.
Owner:LEWIS JR CLARENCE A +1
Image capturing apparatus
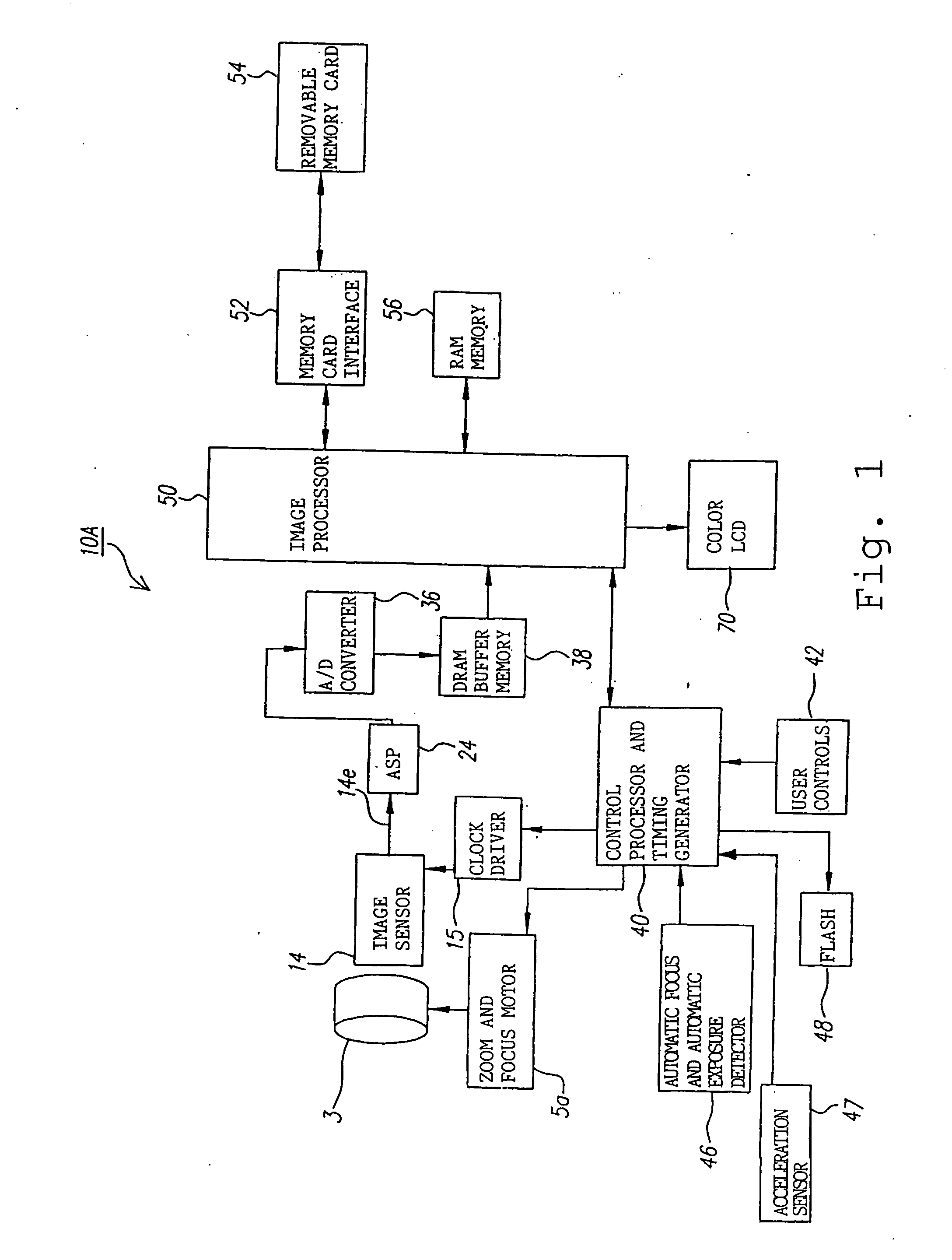
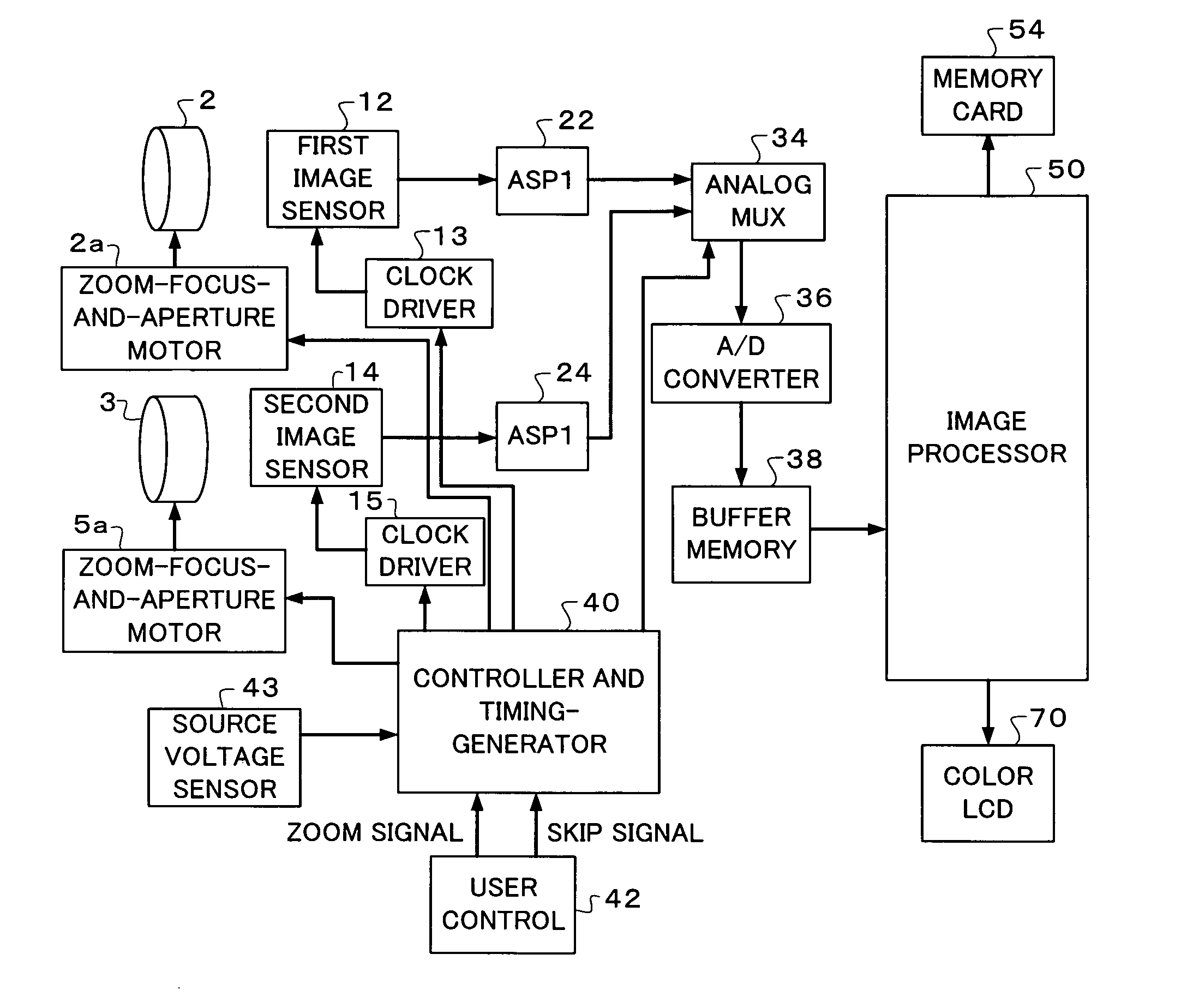
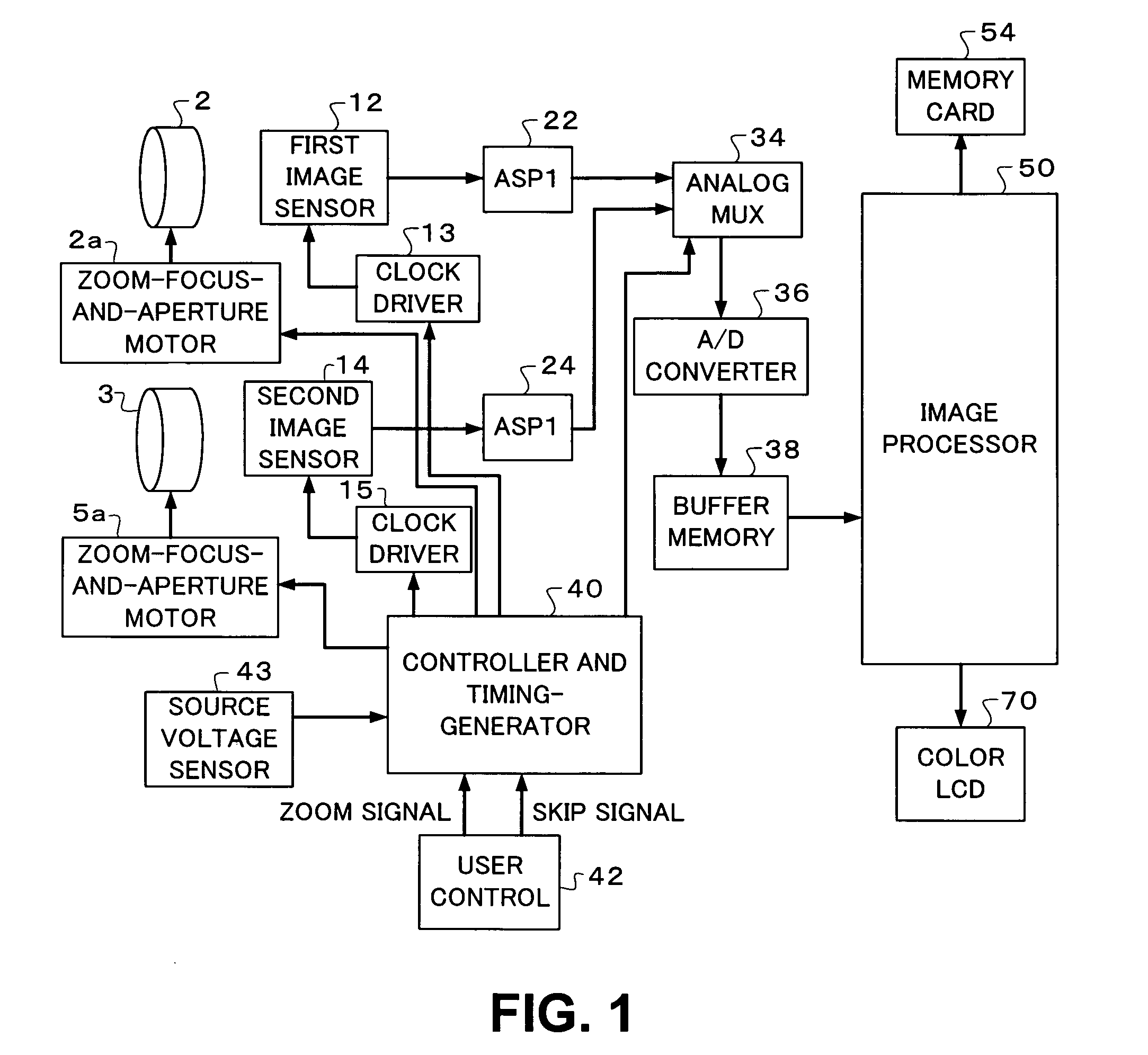
InactiveUS20070025714A1Easy to handleInappropriate exposureTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsImaging conditionTiming generator
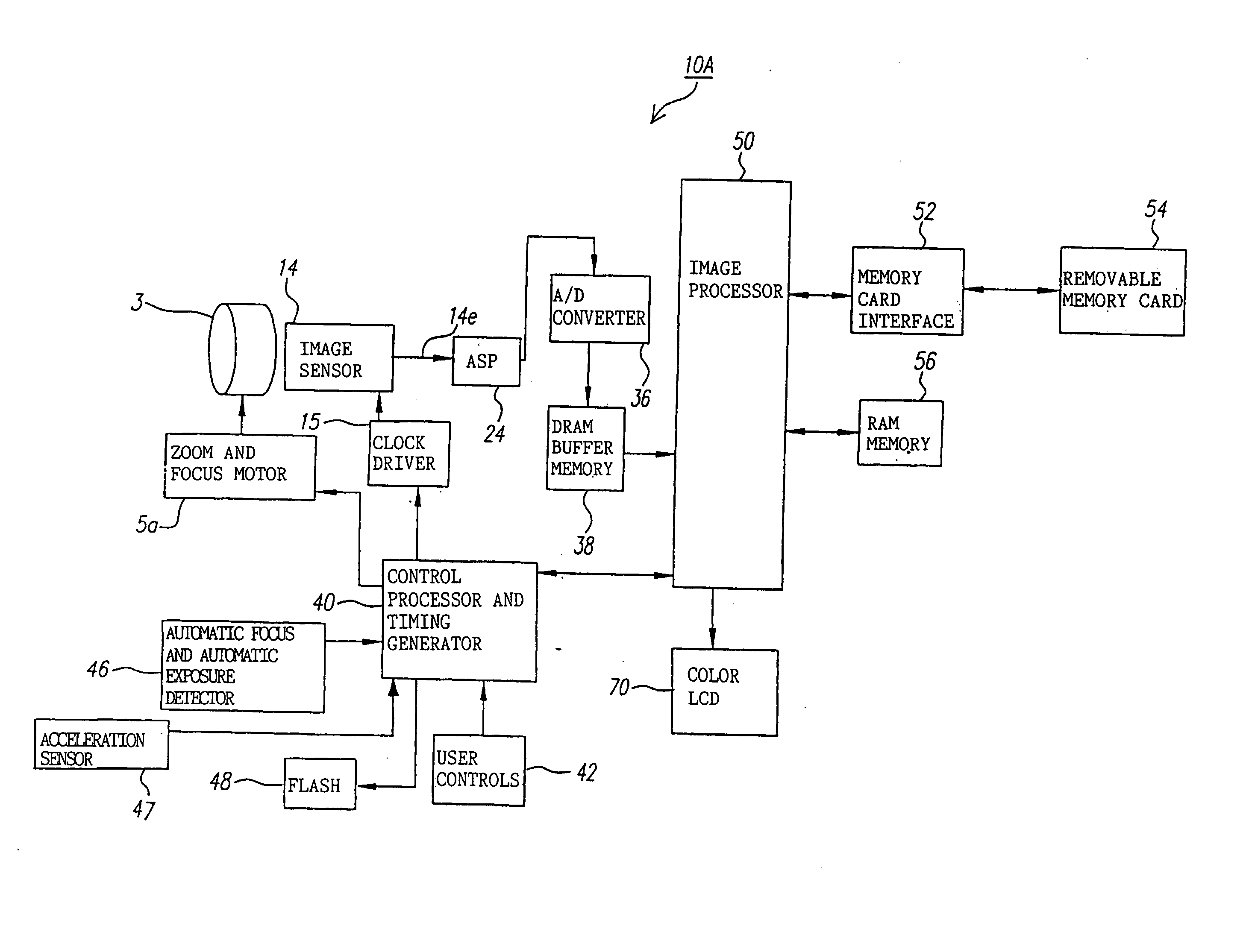
In a digital camera, control operations, such as an AF (automatic focusing) operation which is performed immediately after zooming or panning of the camera, can be performed quickly in an appropriate manner. When a zoom lens 3 is driven to zoom “up”(“in”), a control processor and timing generator 40 uses, of imaging conditions data, such as distance measuring data and photometering data, which are obtained at a wide viewing angle before zooming up, a portion of the imaging conditions data corresponding to a “tele” (telephoto) viewing angle after zooming up, to thereby perform AF, AE, and / or AWB operations after zooming up. When the user pans the camera to shift the viewing angle out of the range of the original wide viewing angle, the data of an area of the image plane of the wide viewing angle closest to the image plane of a new post-panning viewing angle is reused. In a digital camera having a plurality of image capturing optical systems which are switched in response to a zoom position, data obtained by the pre-switching image capturing optical system is reused by a selected post-switching image capturing optical system.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
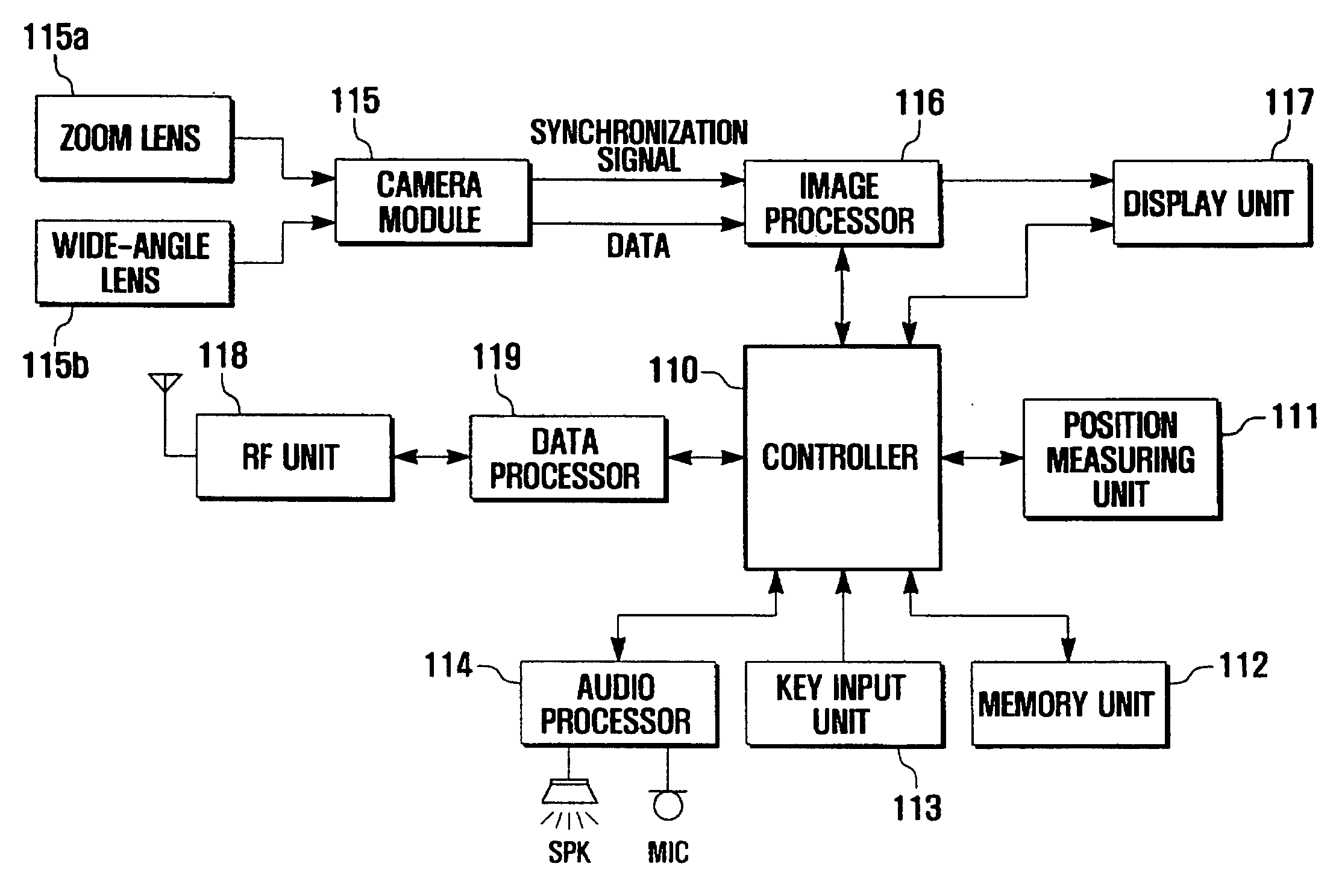
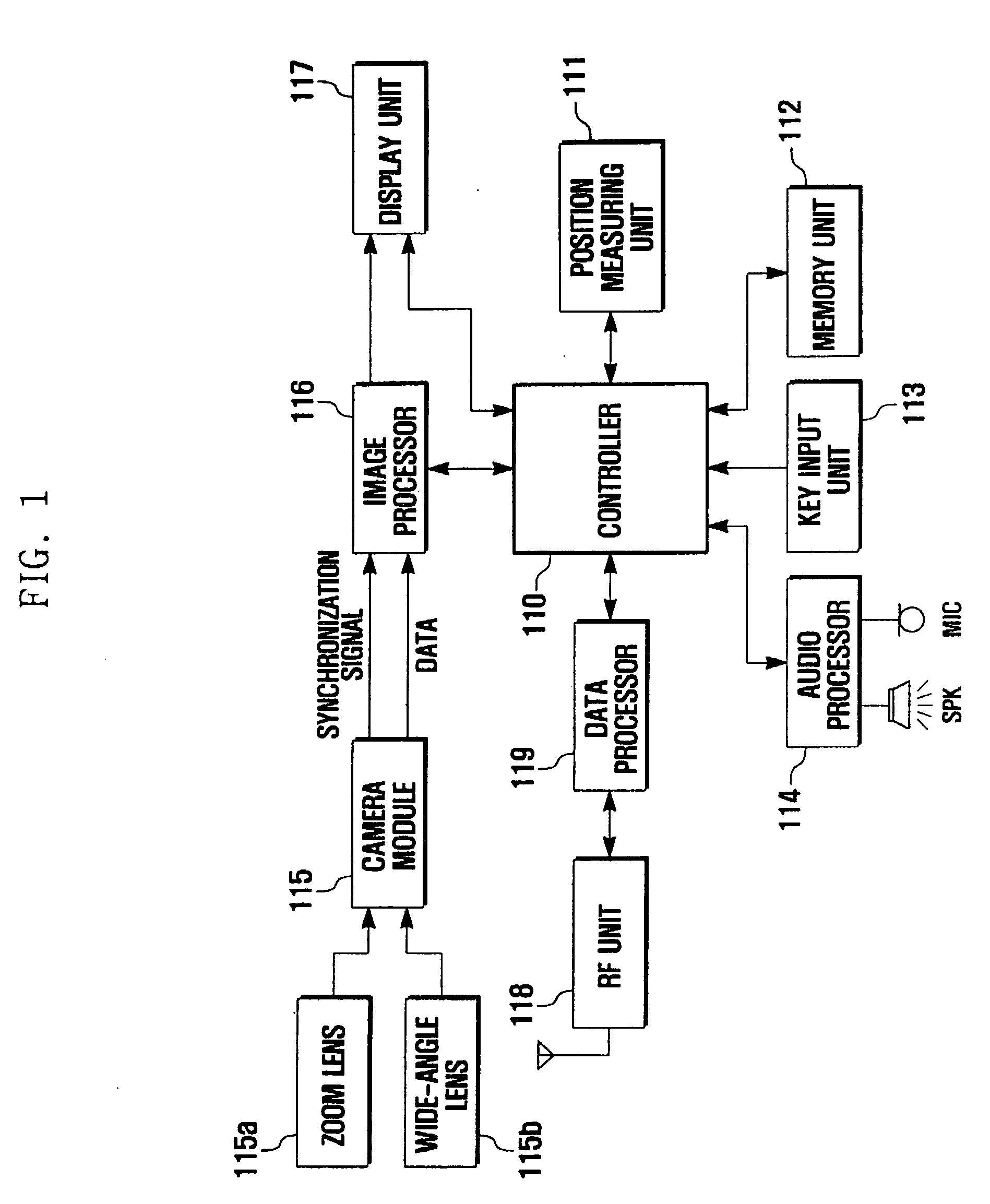
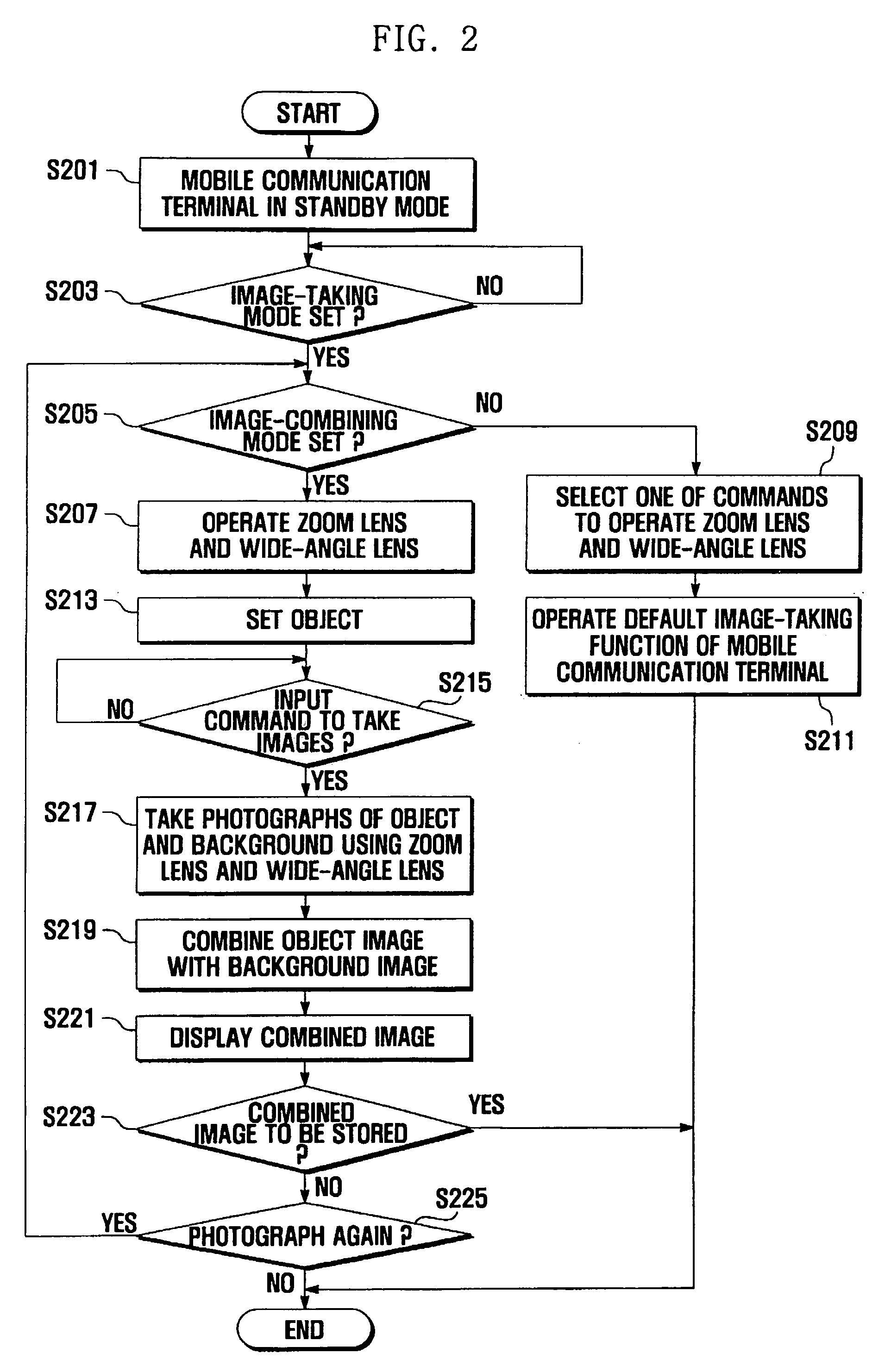
Method and apparatus for taking images using mobile communication terminal with plurality of camera lenses
InactiveUS20070285550A1Television system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensVisual perception
Provided are a method and apparatus for taking images using a mobile communication terminal with a plurality of camera lenses, that can visually emphasize the shape of an object by photographing a specific object and its surrounding background using a zoom lens and a wide-angle lens, respectively, and combining the photographed images. The method includes setting the mobile communication terminal to an image-taking mode, entering into an image-combining mode, operating the plurality of camera lenses, setting an object, taking images using the plurality of camera lenses, and combining together the images obtained using the plurality of lenses. The method and apparatus enables visual emphasis of a specific object in an entire image by photographing the specific object with a zoom lens and a background containing the object with a wide-angle lens, and then combining the photographed images so as to display the specific object at a higher magnification ratio than that of the background.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
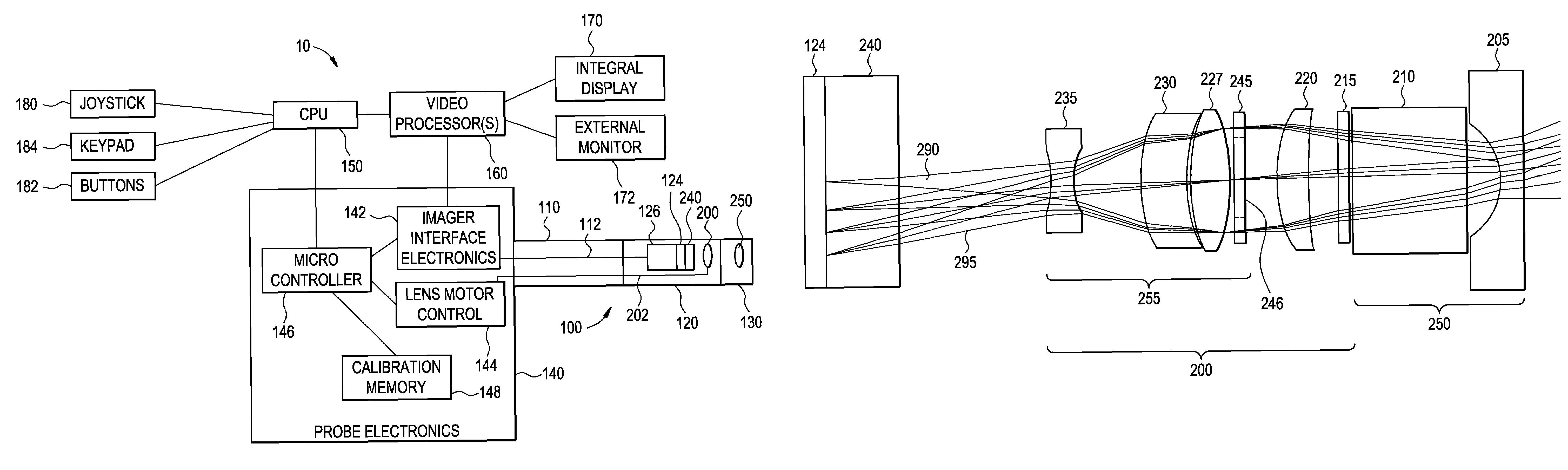
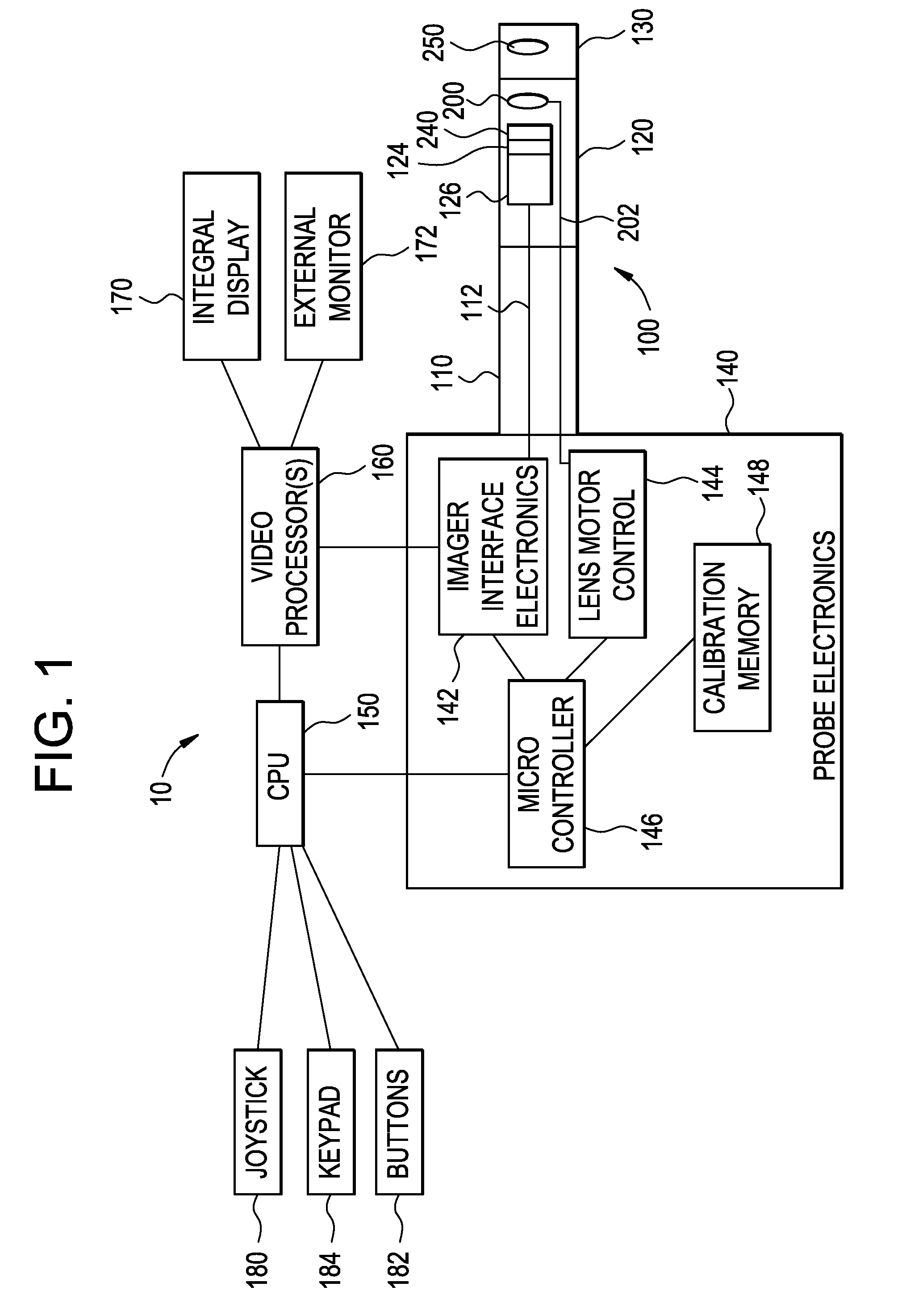
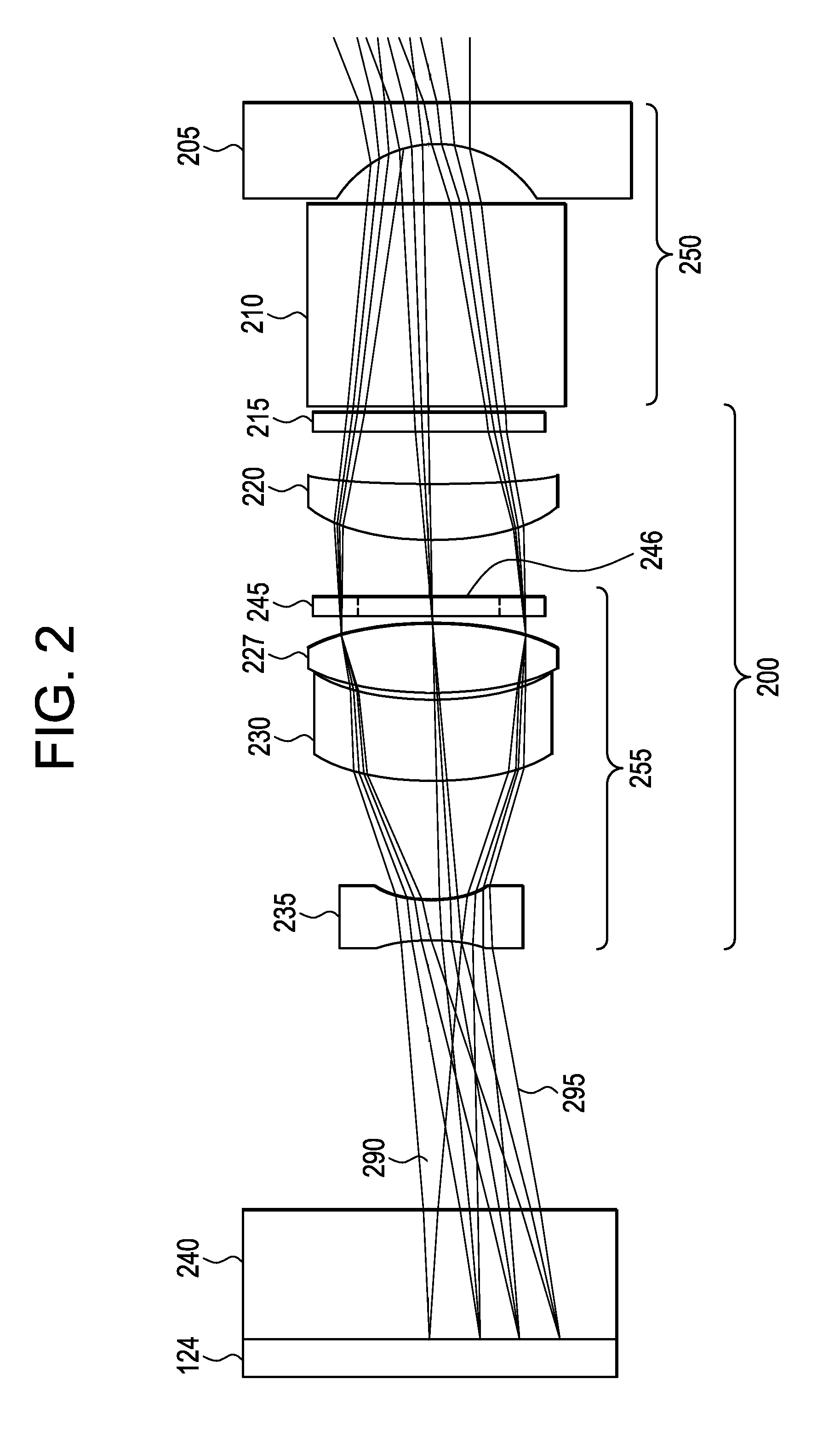
System for providing zoom, focus and aperture control in a video inspection device
An optical system for a remote video inspection device including an elongated probe for inspection of target objects, comprising: an imager located distally within the probe, wherein the imager receives an image of the target object; a focus lens group located within the probe, the focus lens group comprising a variable aperture and at least one focus lens; a zoom lens group located within the probe, the zoom lens group comprising at least one zoom lens, wherein the movement of the zoom lens group in relation to the imager changes the magnification of the image; a tip lens located further from the imager than the focus lens group and the zoom lens group, wherein the distance between the tip lens and the imager is fixed; wherein a first movement of the focus lens group proportional to the movement of the zoom lens group provides an initial image focus, and a second movement of the focus lens group independent of the movement of the zoom lens provides a final image focus and proportional changes to the size of the variable aperture.
Owner:GE INSPECTION TECH LP
Digital camera with dual optical systems
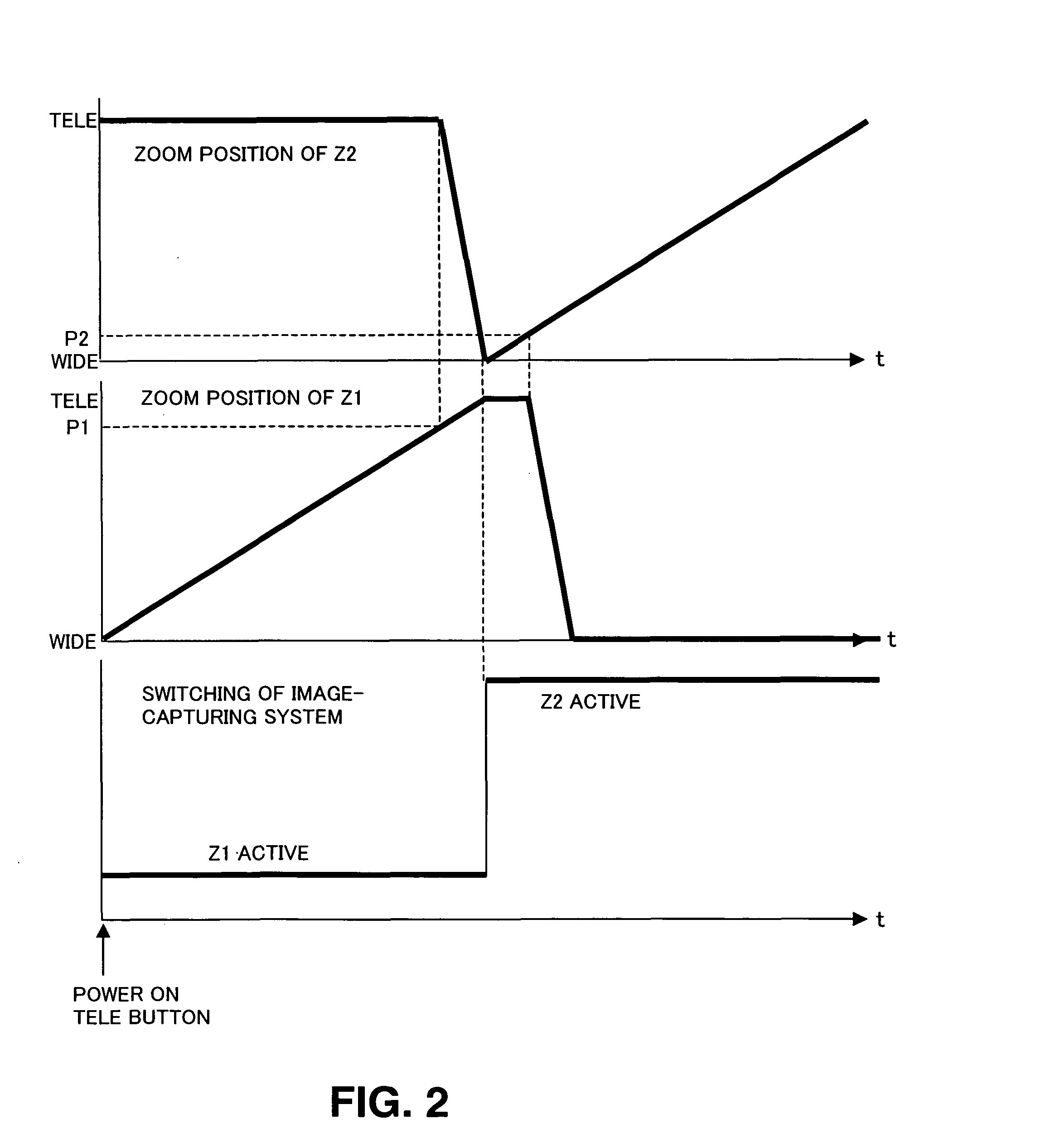
ActiveUS7738016B2Easy to switchTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensTiming generator
A digital camera has a first optical system having a wide zoom lens and a second optical system for a telephotography zoom lens. In an initial state where power is active, a controller and timing-generator controls the wide zoom lens so as to be situated at a wide position and the telephotography zoom lens so as to be situated at a telephotograph position. When zoom-in is effected, the wide zoom lens is actuated, and the telephotography zoom lens is maintained at the telephotograph position. When a zoom position of the wide zoom lens has reached a threshold zoom position set to a wider angle of view than that achieved at the telephotograph position, the telephotography zoom lens starts being actuated toward the wide position. When the zoom lens has reached the telephotograph position, an image signal is switched from the wide zoom lens to the telephotography zoom lens, and the selected image signal is output.
Owner:APPLE INC
Moving object monitoring surveillance apparatus for detecting, tracking and identifying a moving object by zooming in on a detected flesh color
ActiveUS7355627B2Enhance the imageWide range of fieldsTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage databaseZoom lens
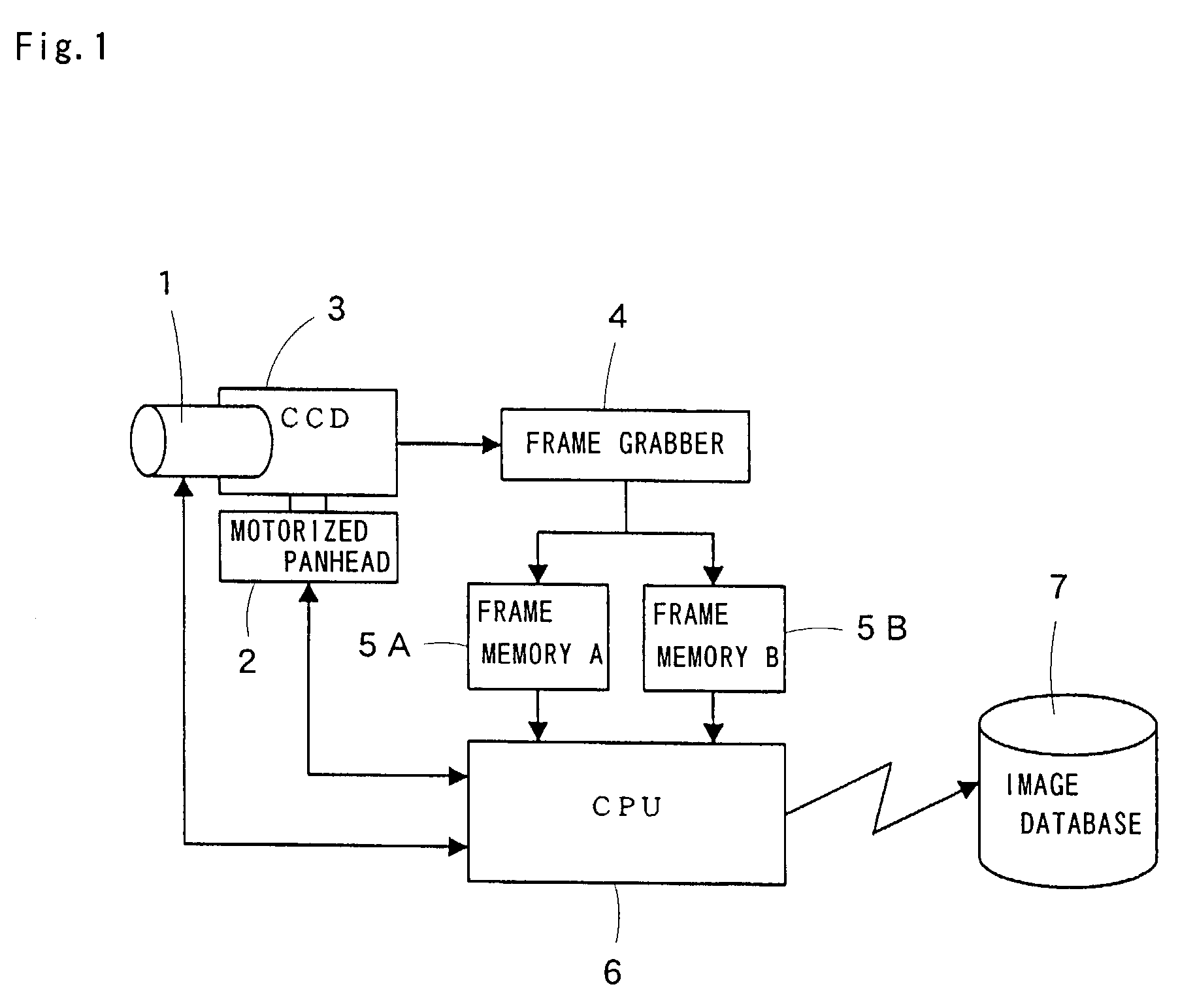
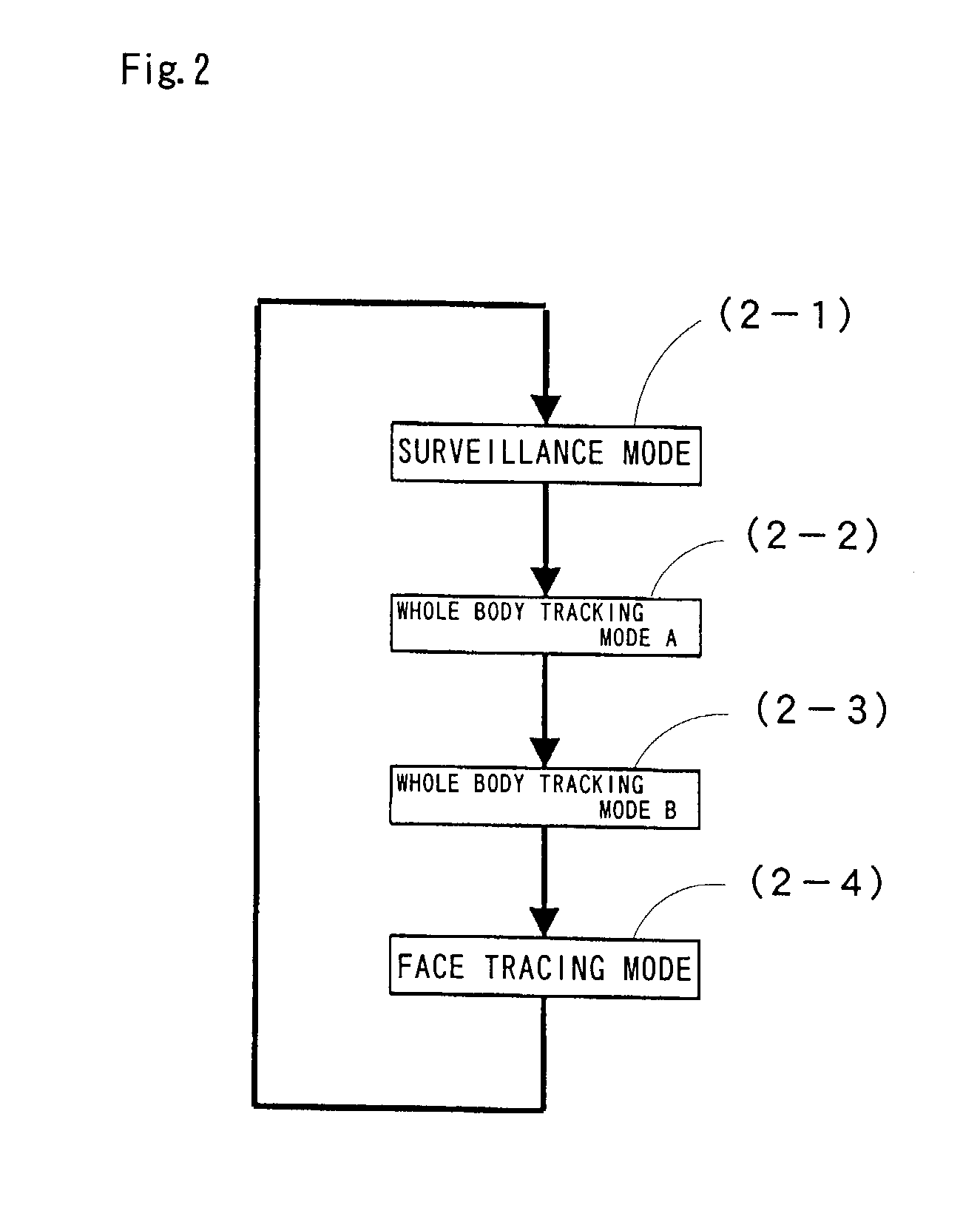
A moving object monitoring surveillance apparatus that controls a camera using a motorized panhead and a motorized zoom lens to identify correctly a moving object, particularly, a person is disclosed. The apparatus includes a video device acquiring information of the image of a moving object as a video signal, a panhead for panning and tilting the video device, a frame grabber for extracting, frame by frame, a still image from the video signal output from the video device and binarizing the still image into frame data, a plurality of frame memories for alternately storing the binarized frame data, a CPU for controlling the operation of the panhead and for processing the frame data, and an image database for storing the processed data. The video device sequentially monitors at least one single surveillance area. The CPU compares frame data with immediately prior frame data to determine a difference therebetween, tracks coordinates corresponding to the difference if the difference is detected, and detects and expands a particular color.
Owner:NIPPON MICRO SYST
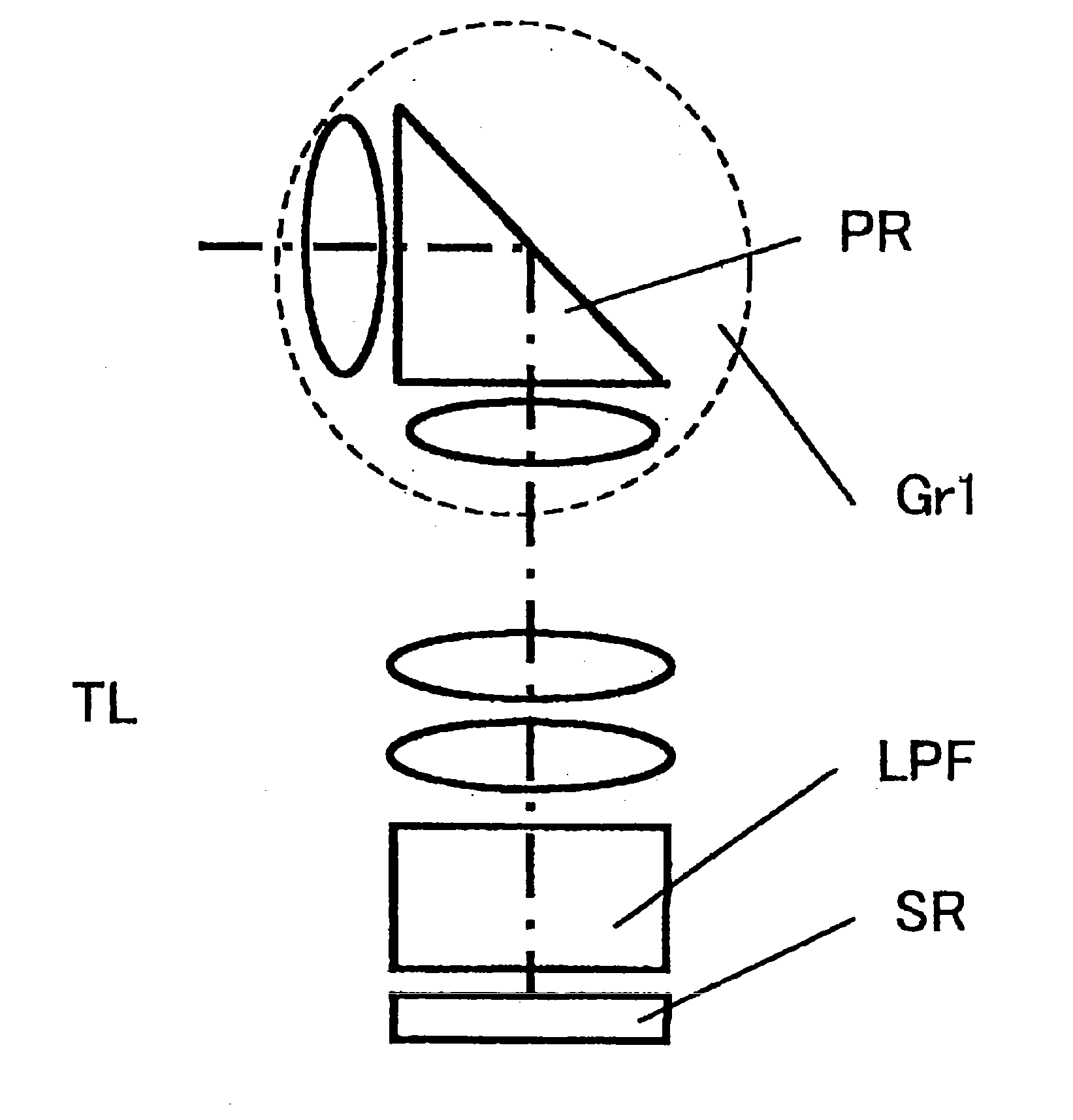
Image capture apparatus and zoom lens
InactiveUS20070126911A1High quality imagingImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsPrismsOptical axisPrism
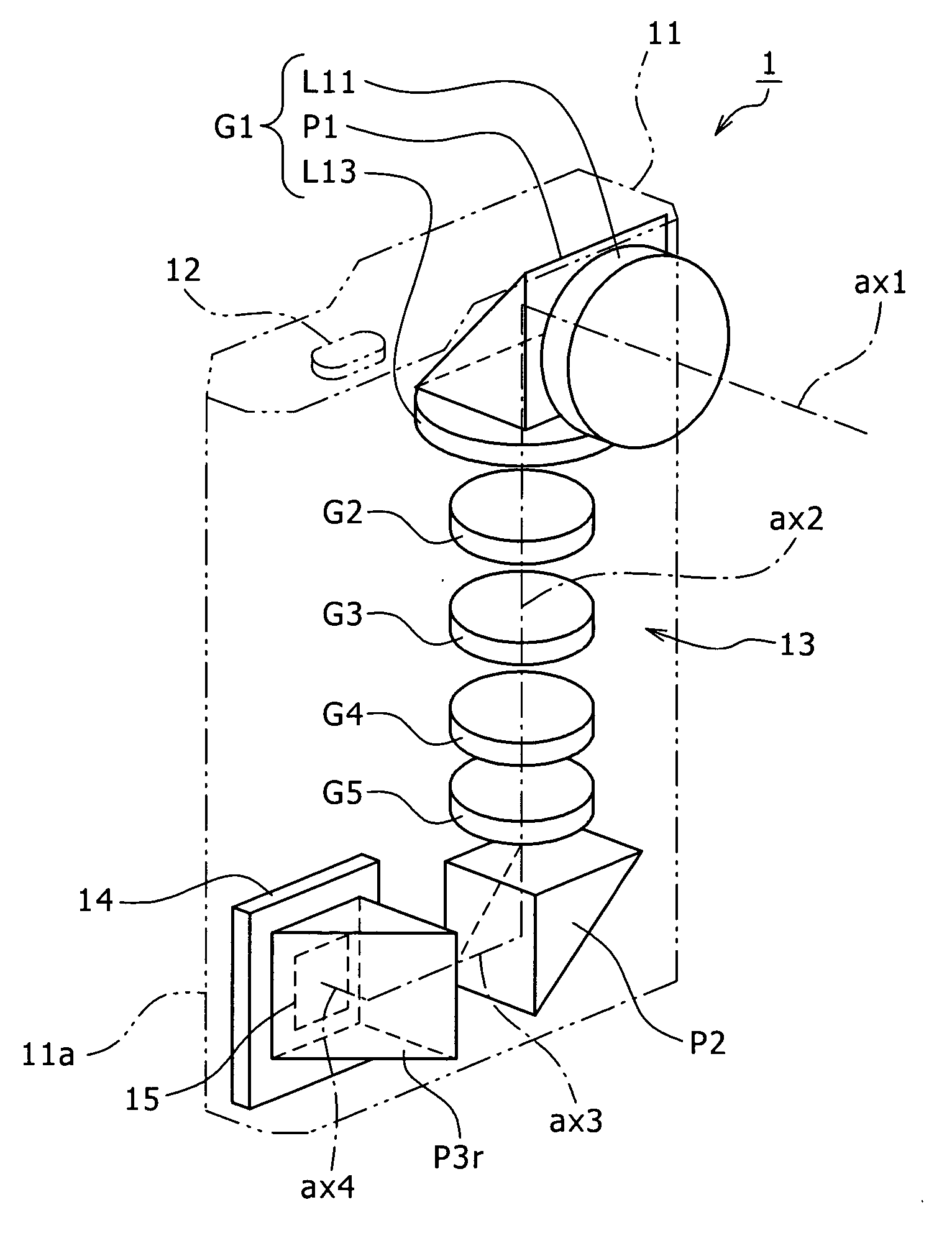
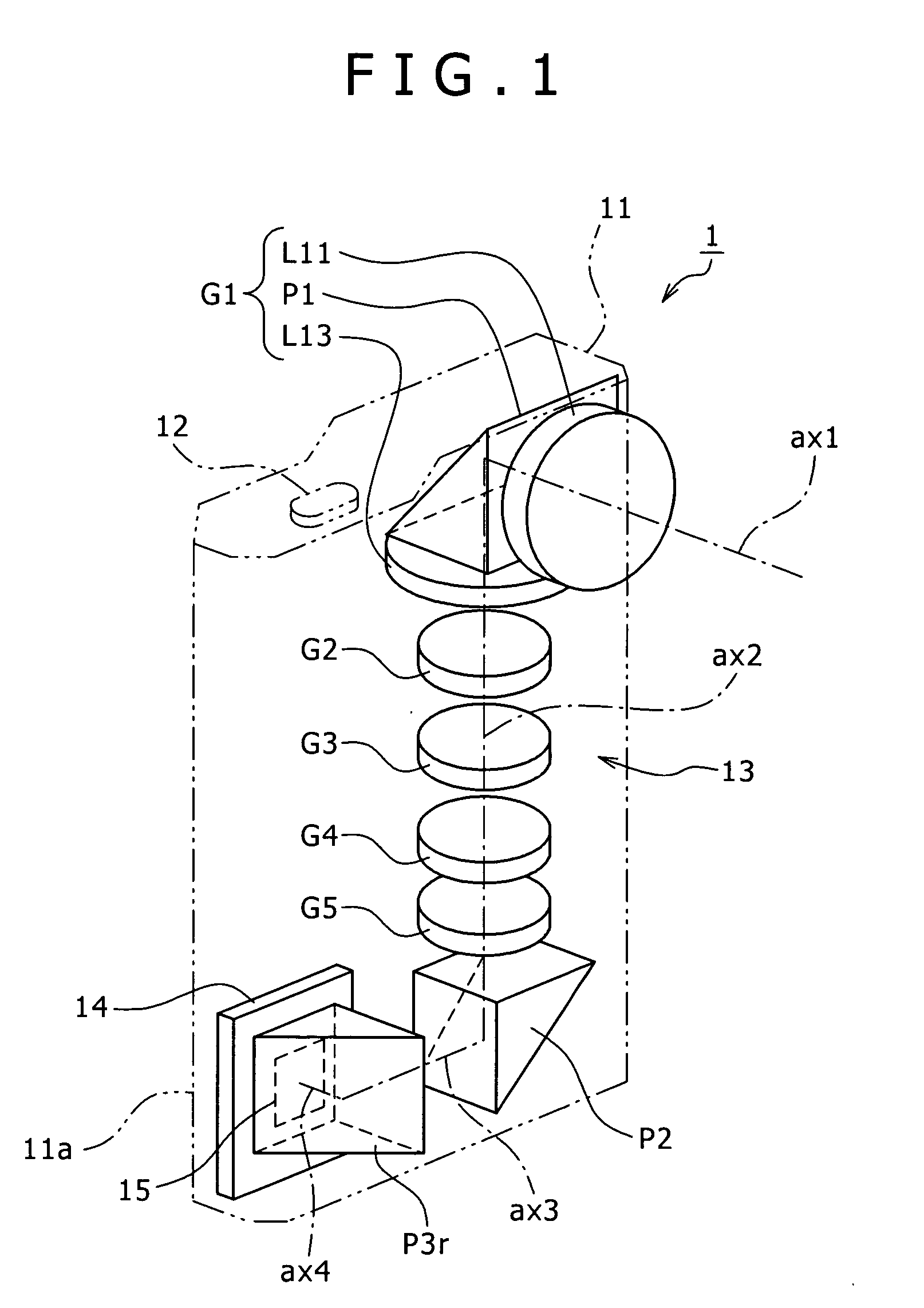
An image capture apparatus includes: a zoom lens arranged in a housing and including fixed lens groups, movable lens groups and at least three prisms; and an imager device arranged in the housing. The zoom lens includes: a fixed first lens group including a negative lens group having a first optical axis, a first prism approximately perpendicularly folding an optical axis, and a positive lens group having a second optical axis folded by the first prism; movable lens groups and at least one fixed lens group arranged along the second optical axis to perform a zooming action, an image plane position correcting action and a focusing action; and a second prism arranged on an image side relative to a movable lens group that is a closest to the image side among the plurality of movable lens groups for approximately perpendicularly folding the optical axis.
Owner:SONY CORP
Wavefront coding zoom lens imaging systems
InactiveUS6911638B2Quality improvementFast imagingPhotometry using reference valueBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsImaging processingOphthalmology
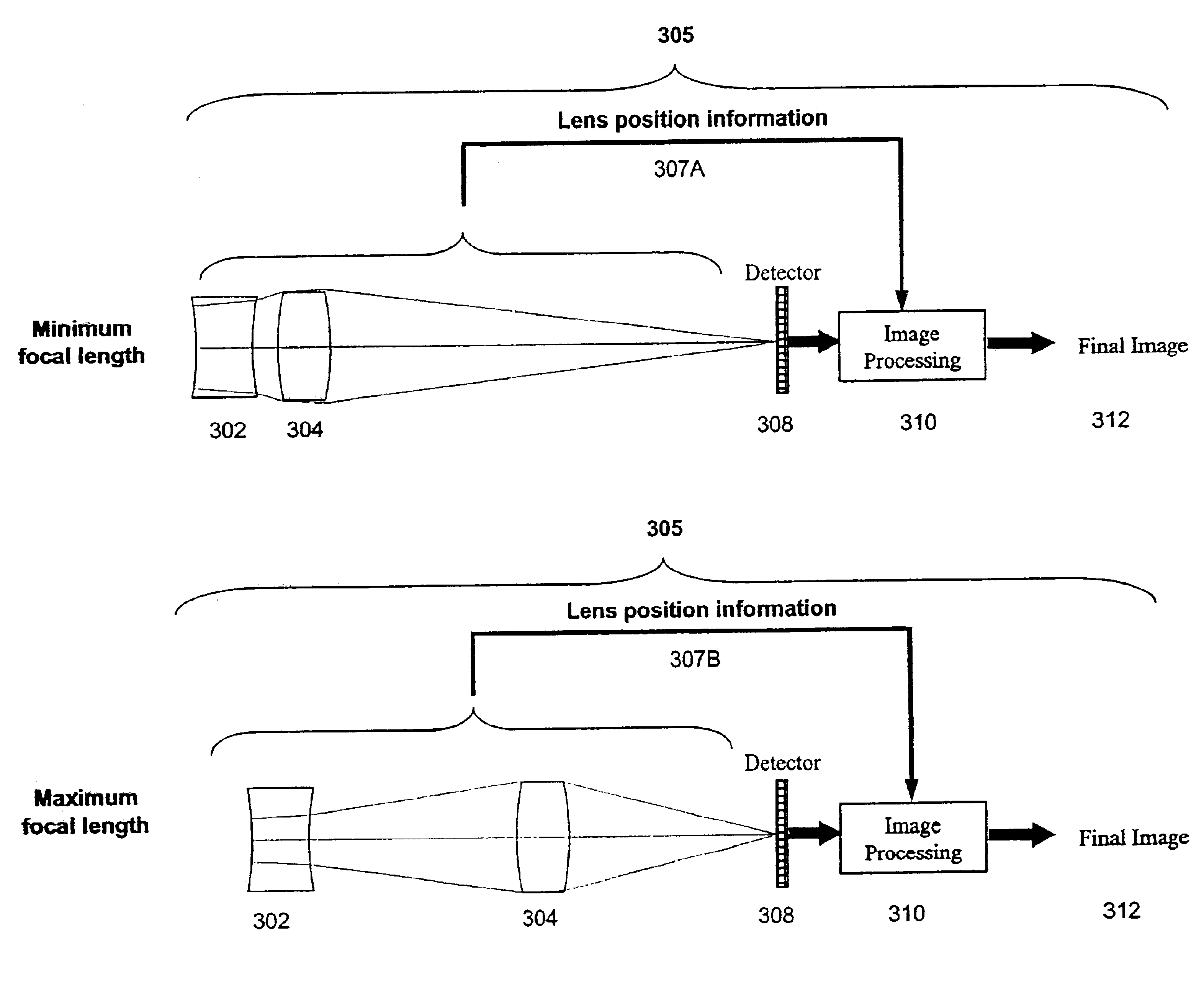
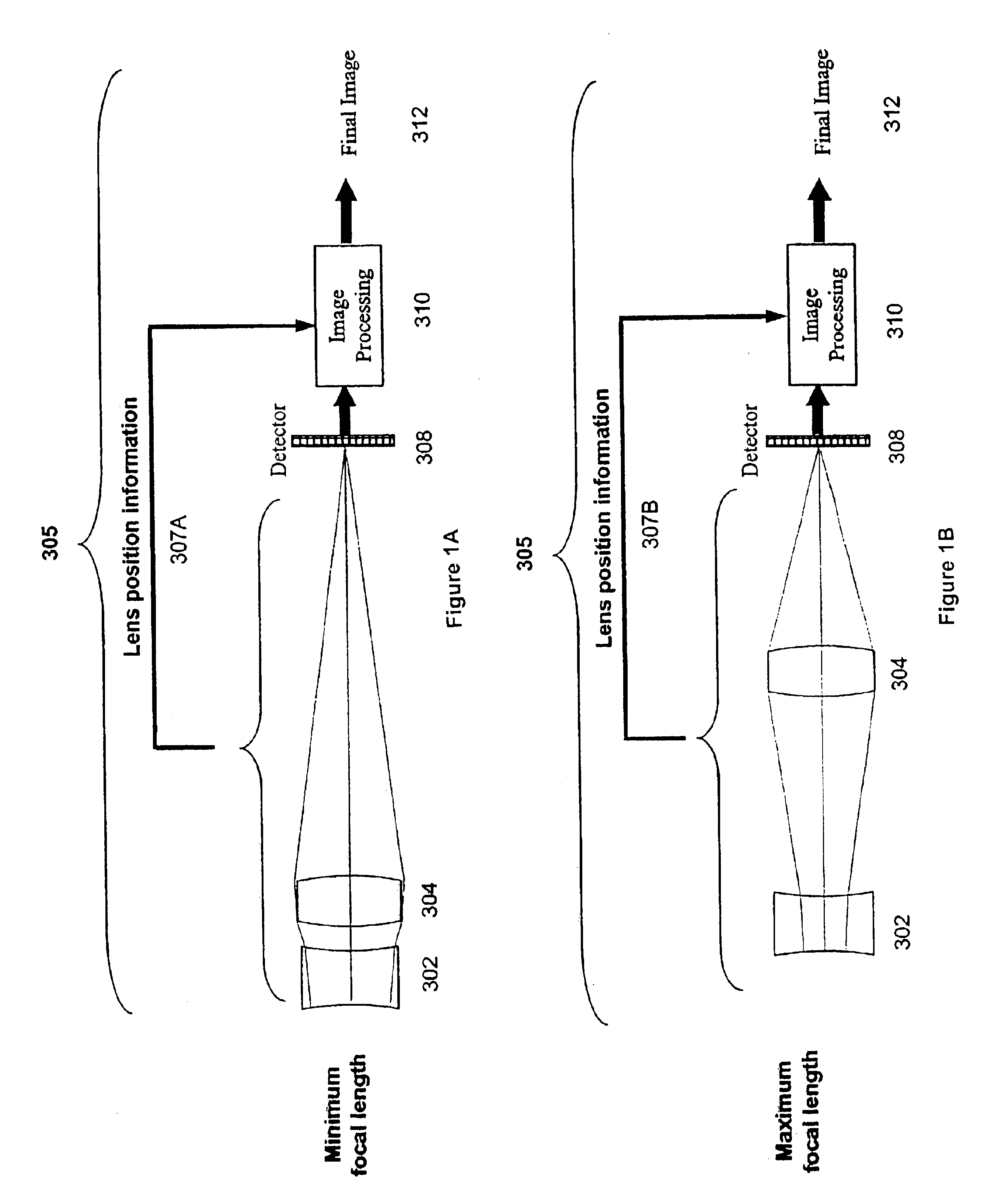
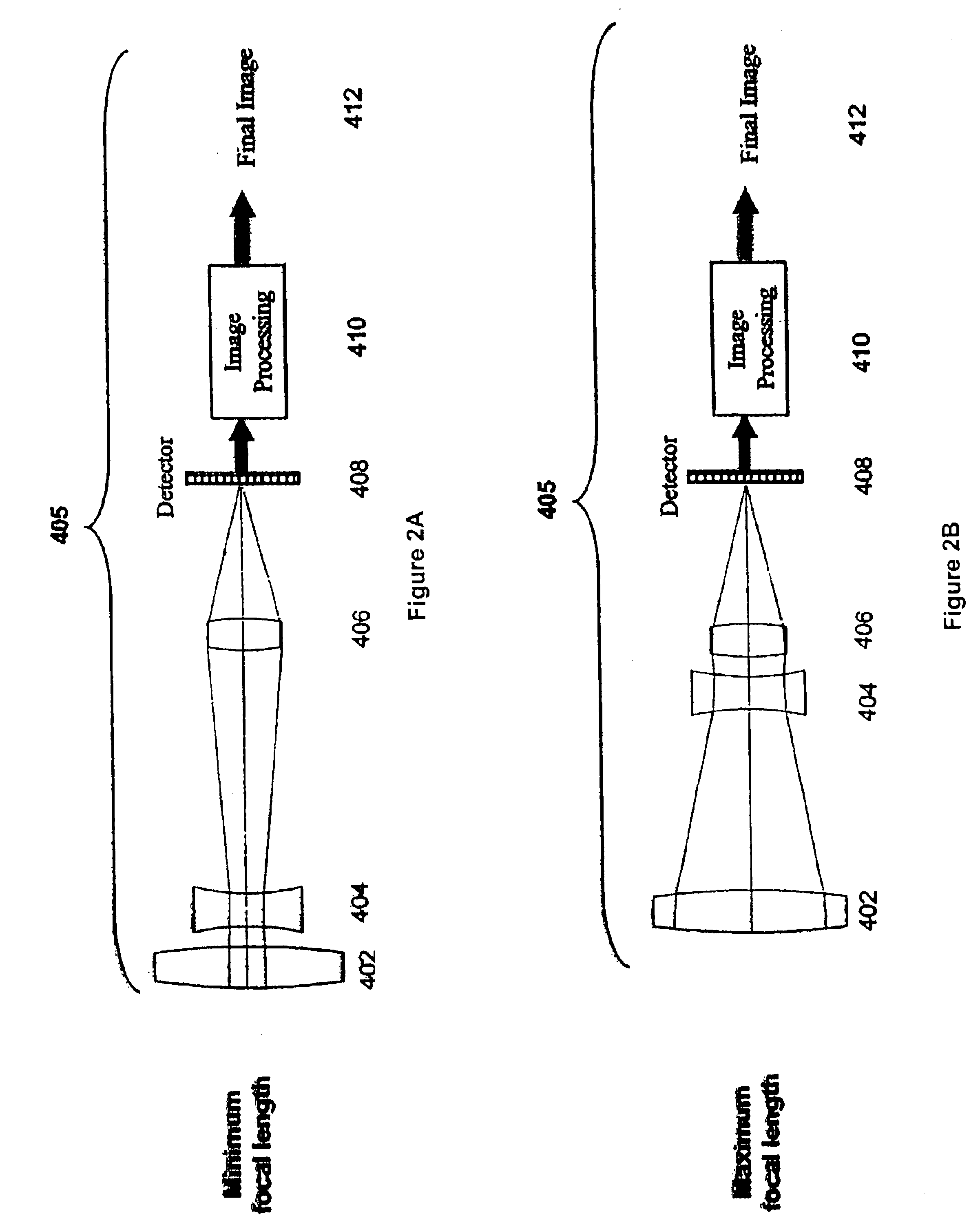
A wide-angle zoom lens with as few as two plastic elements codes the wavefront produced by the imaging system such that the imaging system is substantially invariant to aberrations related to misfocus. Signal processing is used to decode the wavefront to form the final image. A first type of zoom lens configuration uses as few as two lens elements. In this type, image processing may be modified to take into account the positioning of the lenses.
Owner:COLORADO UNIV OF RGT
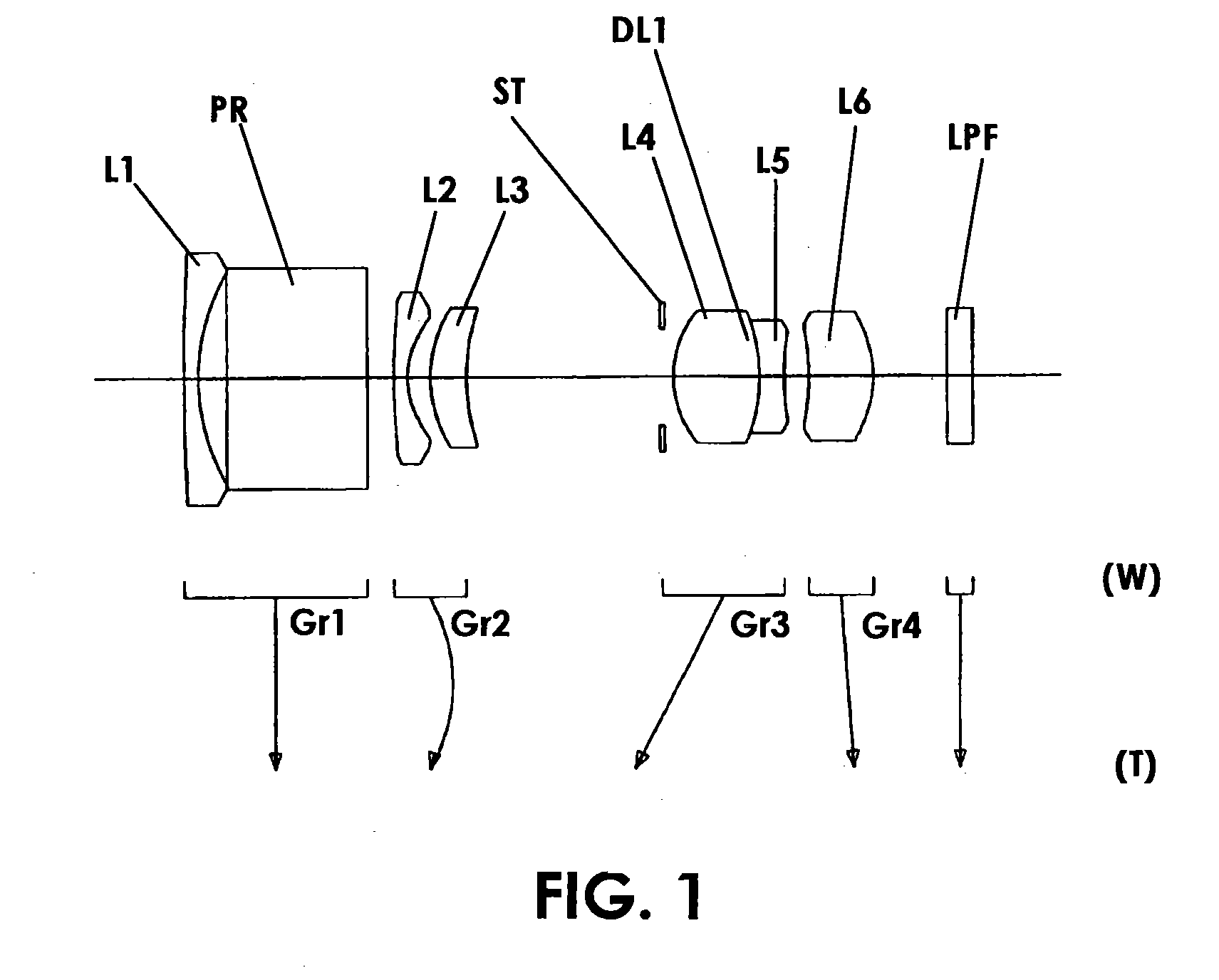
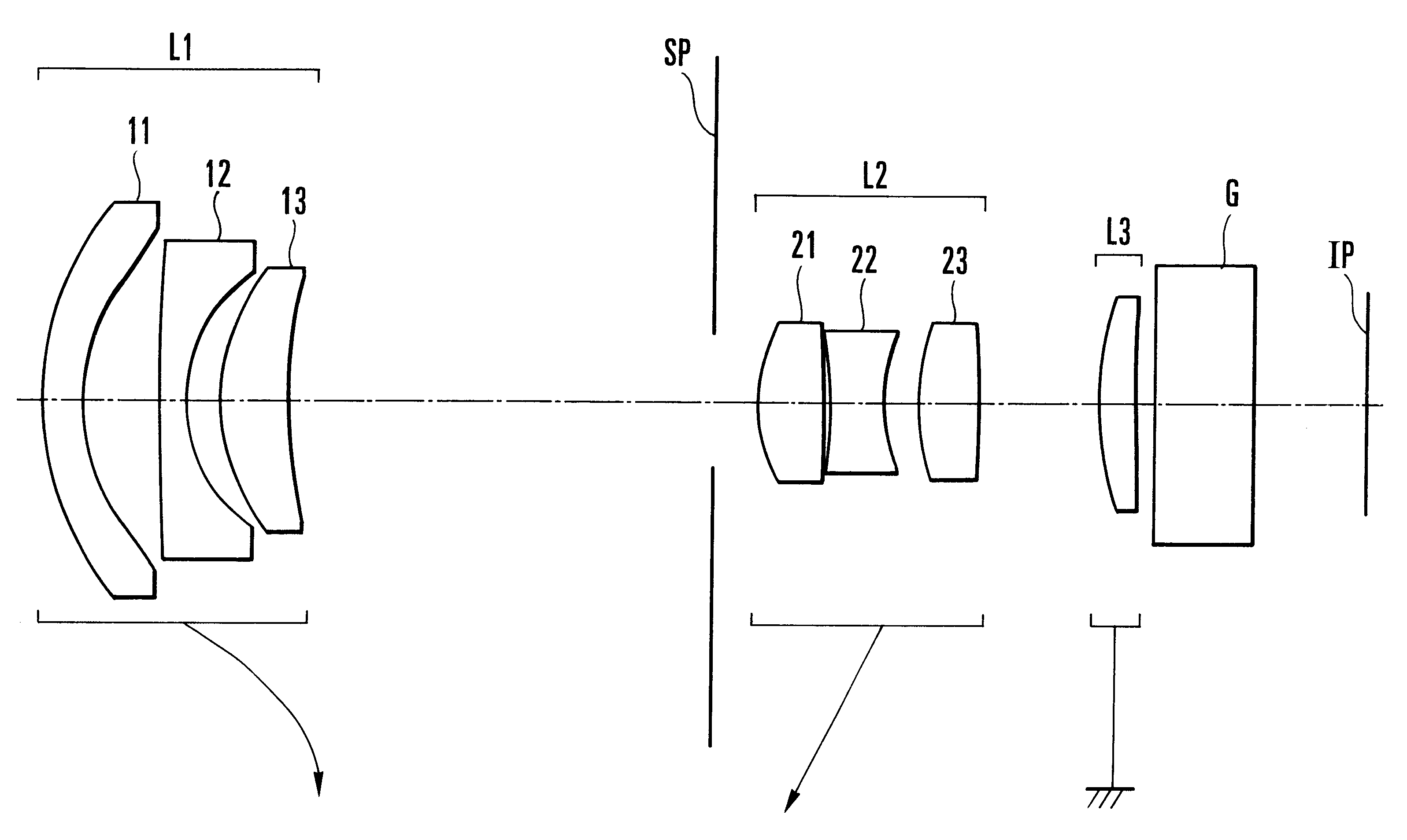
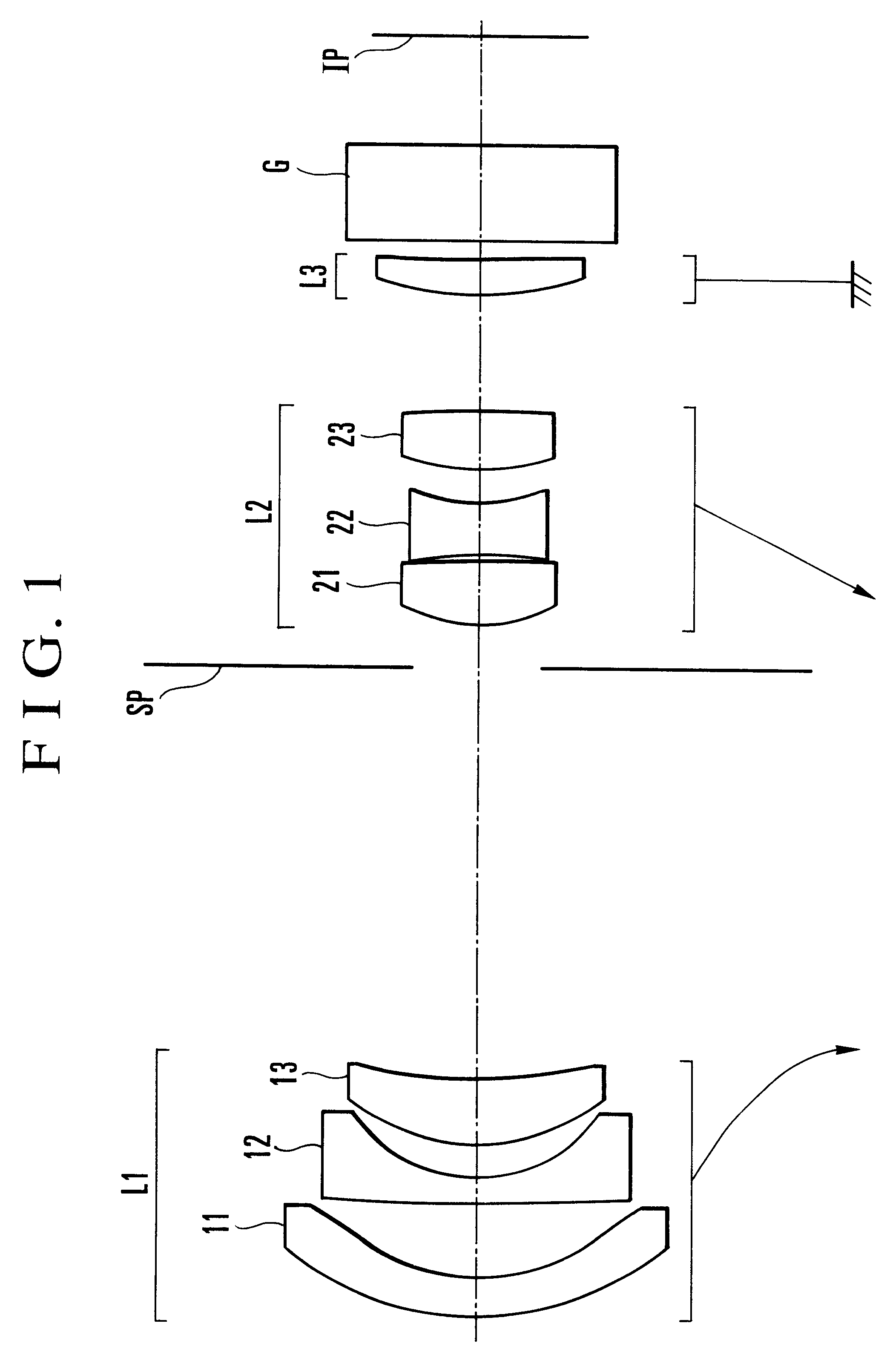
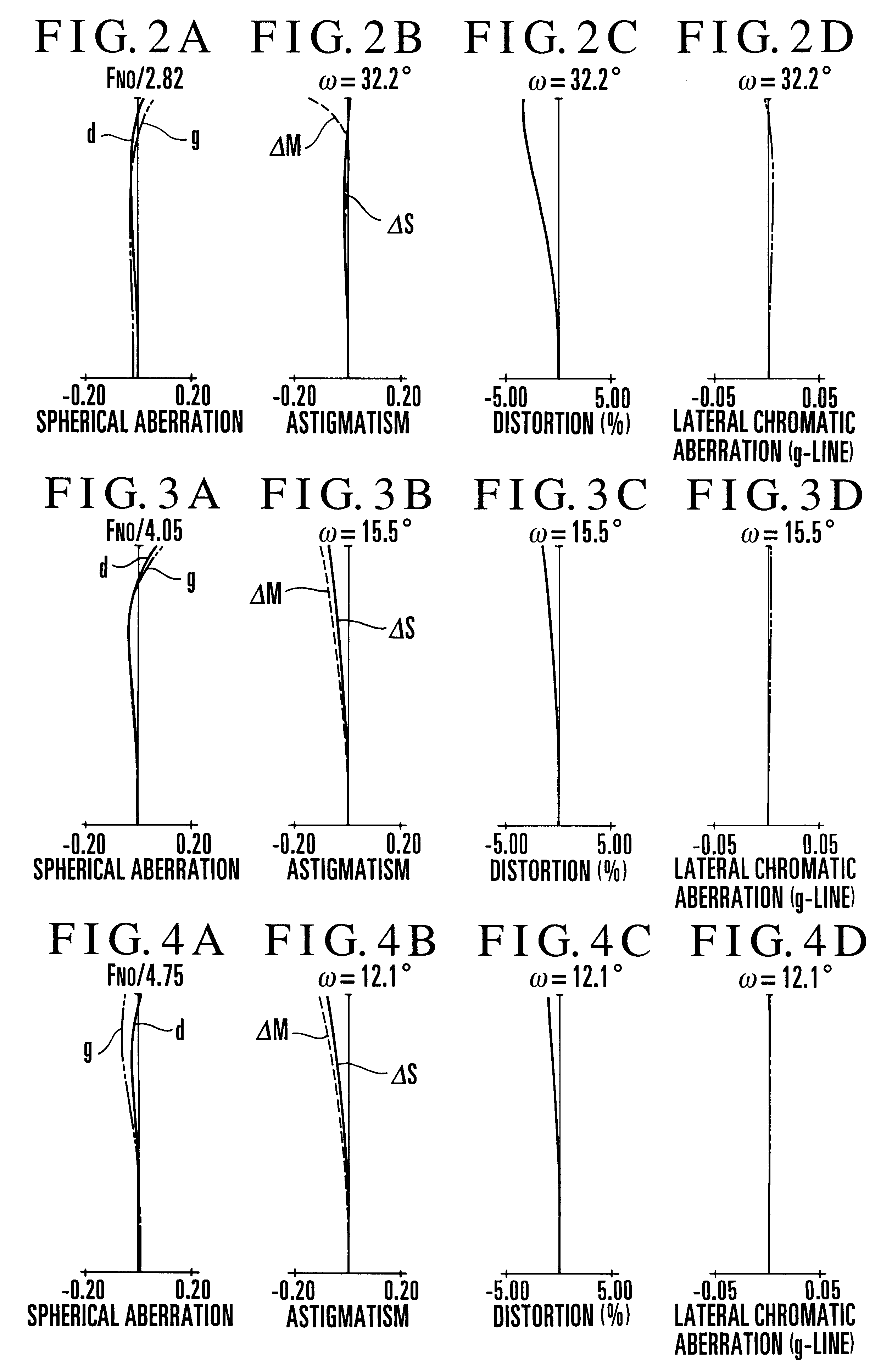
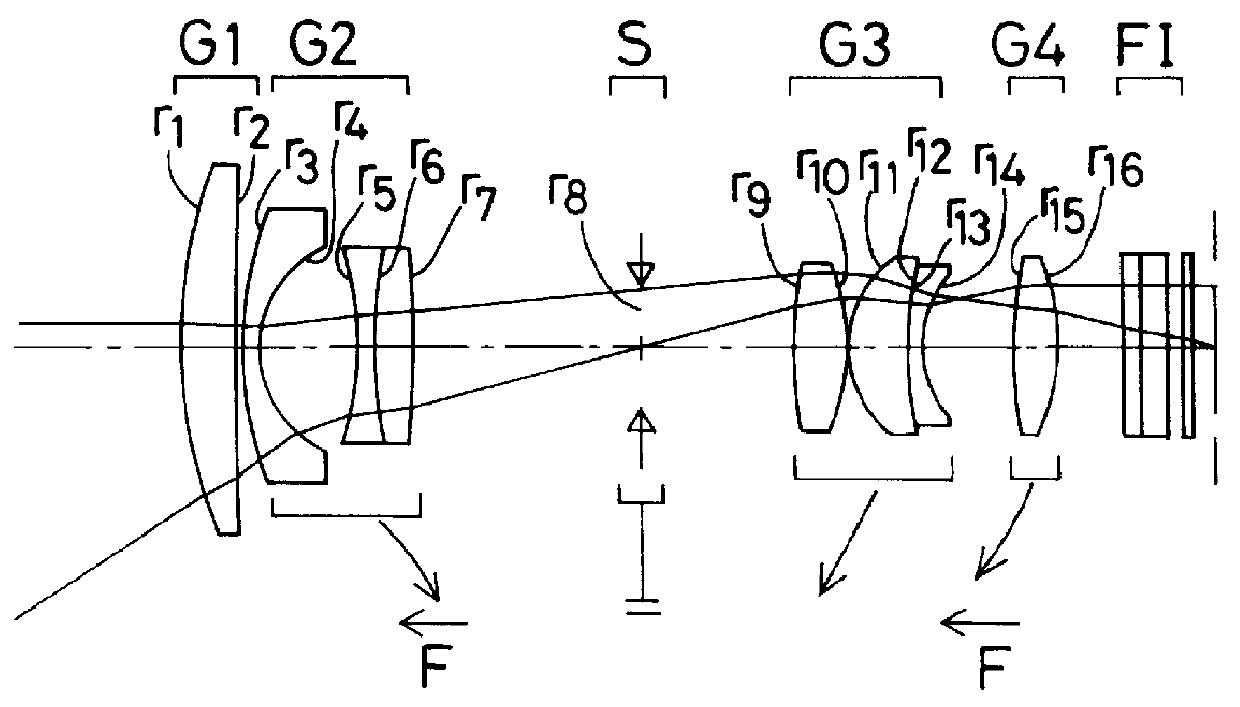
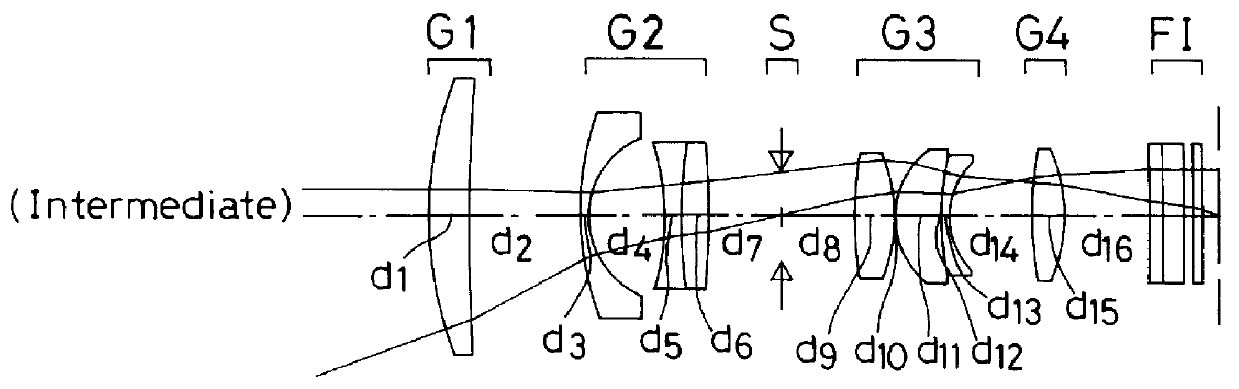
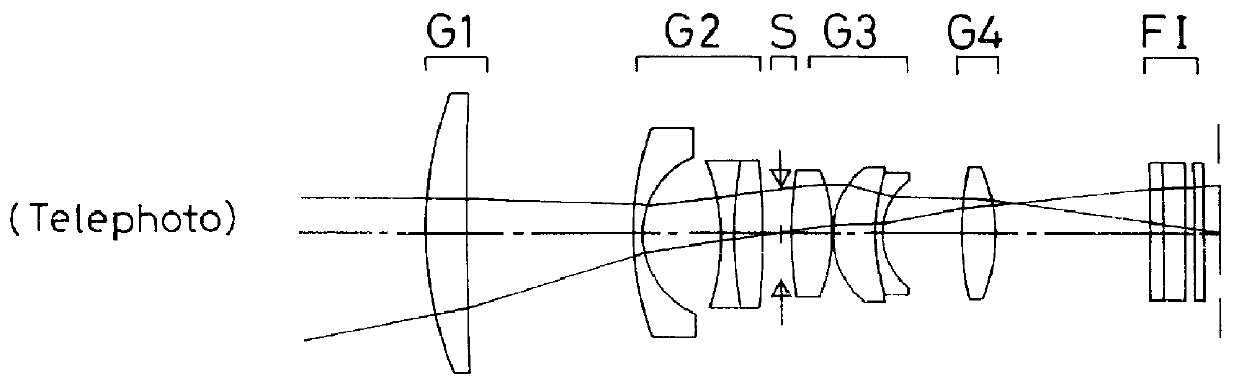
Zoom lens system
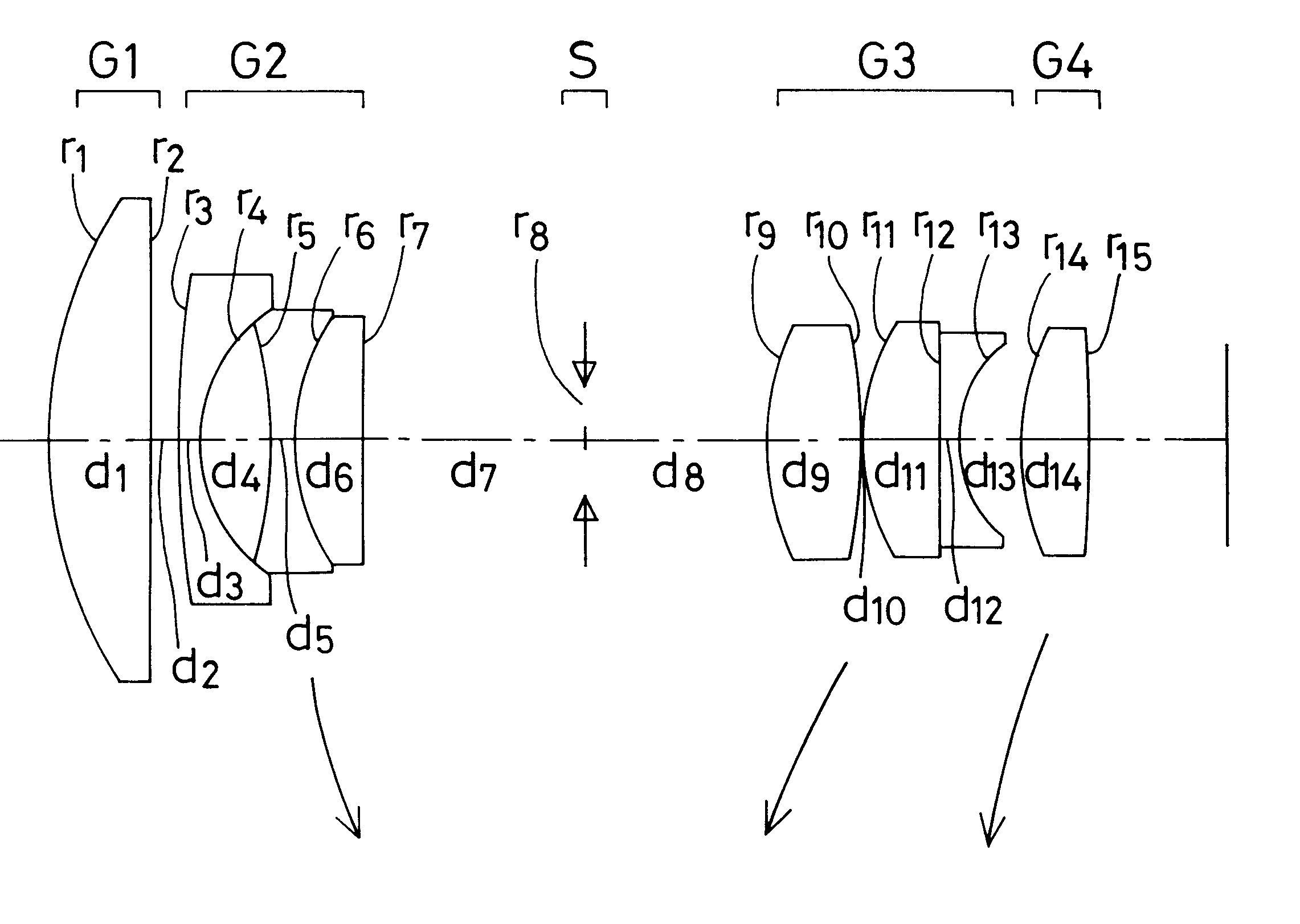
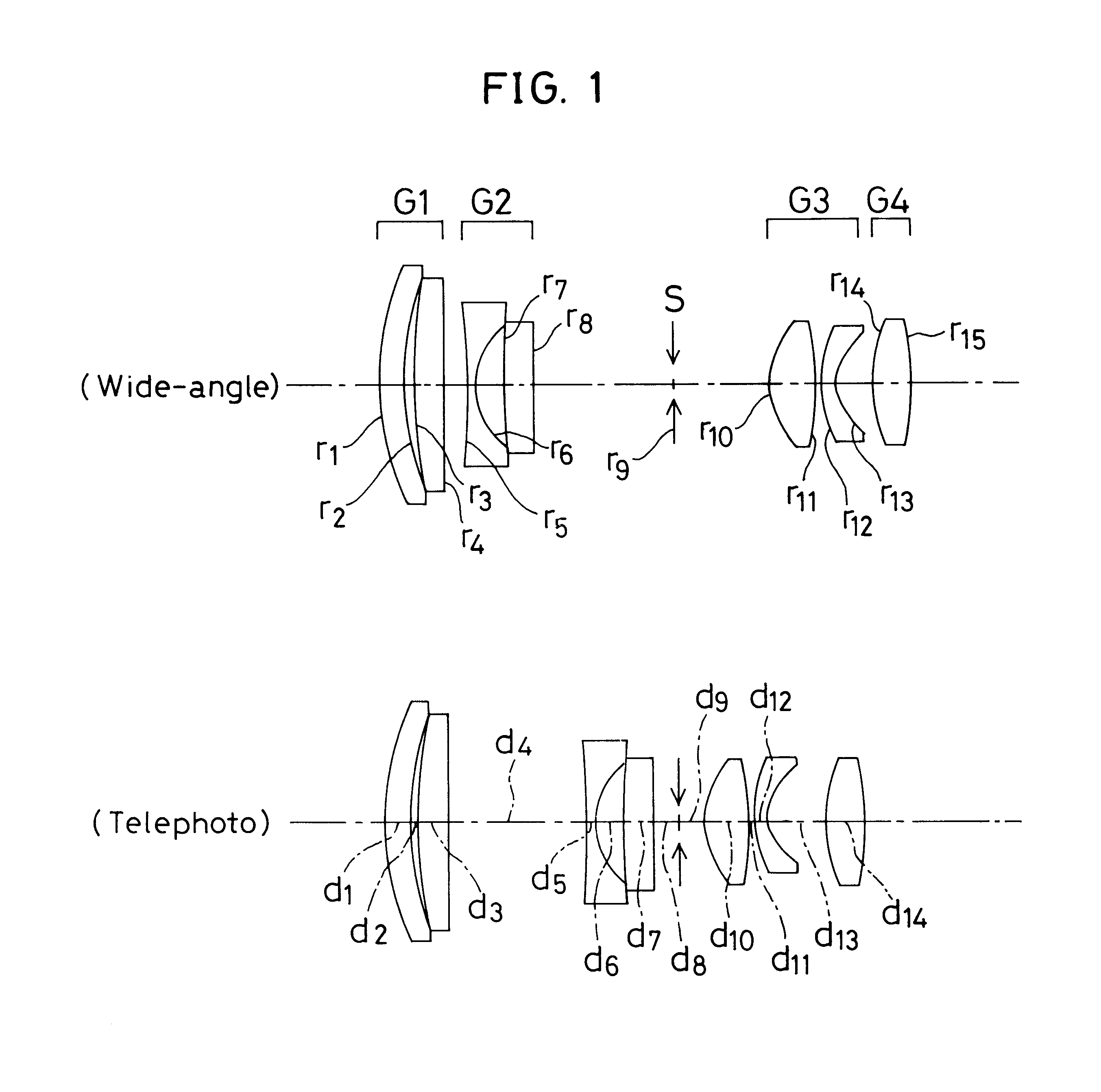
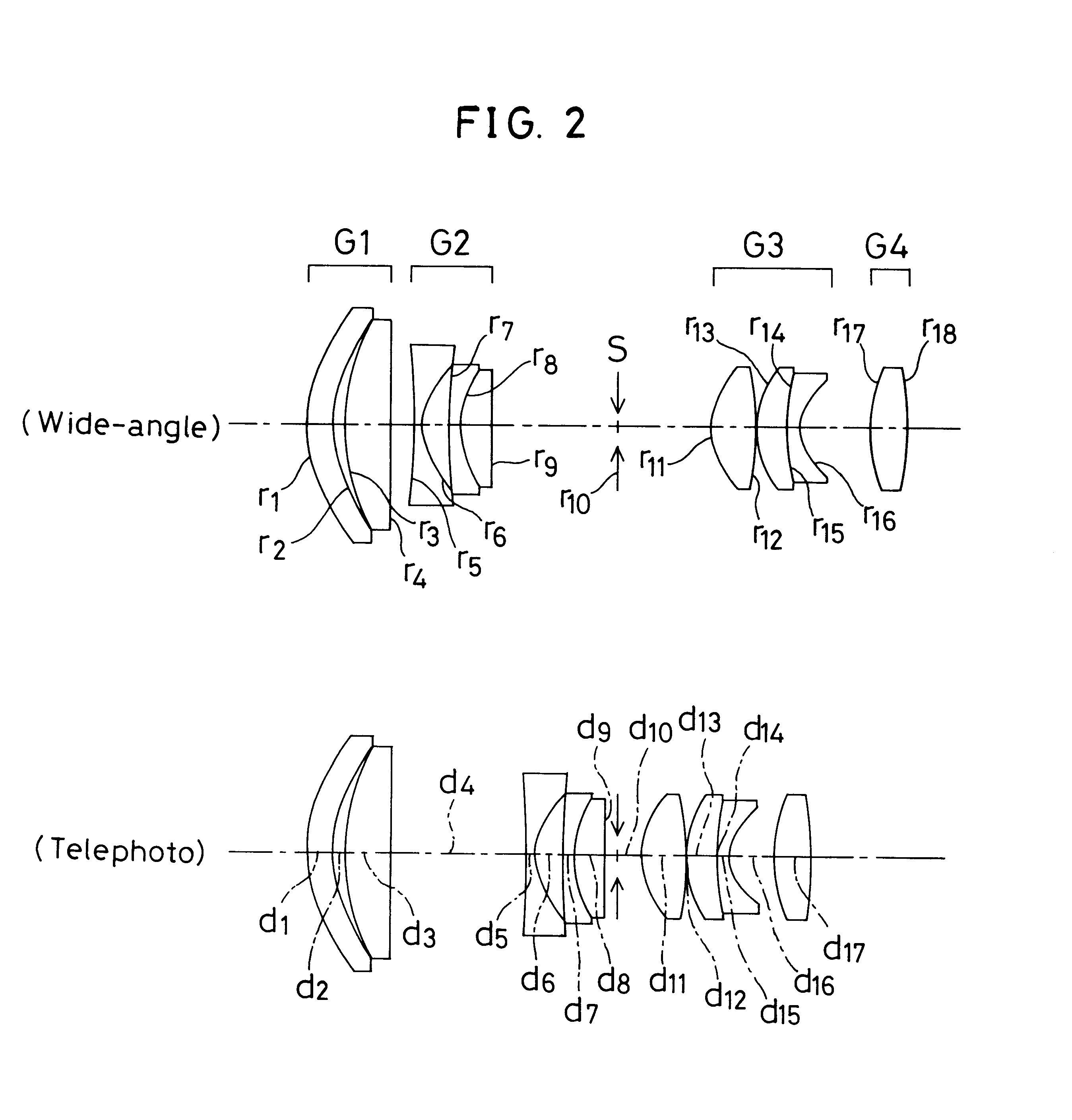
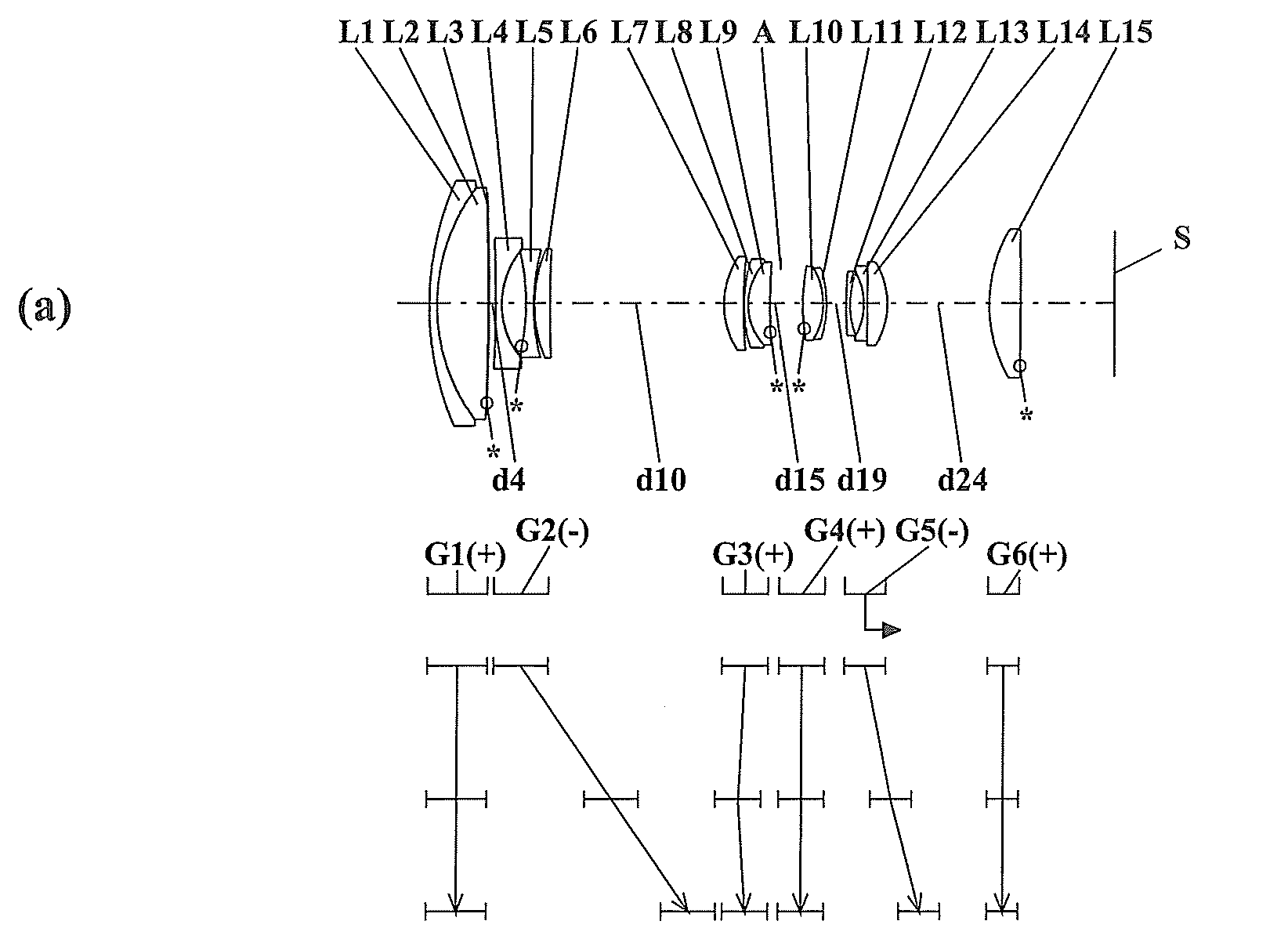
The invention provides a zoom lens system which achieves a wide angle of field, has a simplified construction, and is suitable for use on video cameras. The zoom lens system comprises, in order from an object side thereof, a first lens group G1 having positive refracting power, a second lens group G2 having negative refracting power, a third lens group G3 having positive refracting power, and a fourth lens group G4 having positive refracting power. The second lens group G2 moves toward an image side thereof while the third G3 and fourth G4 lens groups move constantly toward the object side for zooming from a wide-angle end thereof to a telephoto end thereof. The first lens group G1 consists only of a positive single lens.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
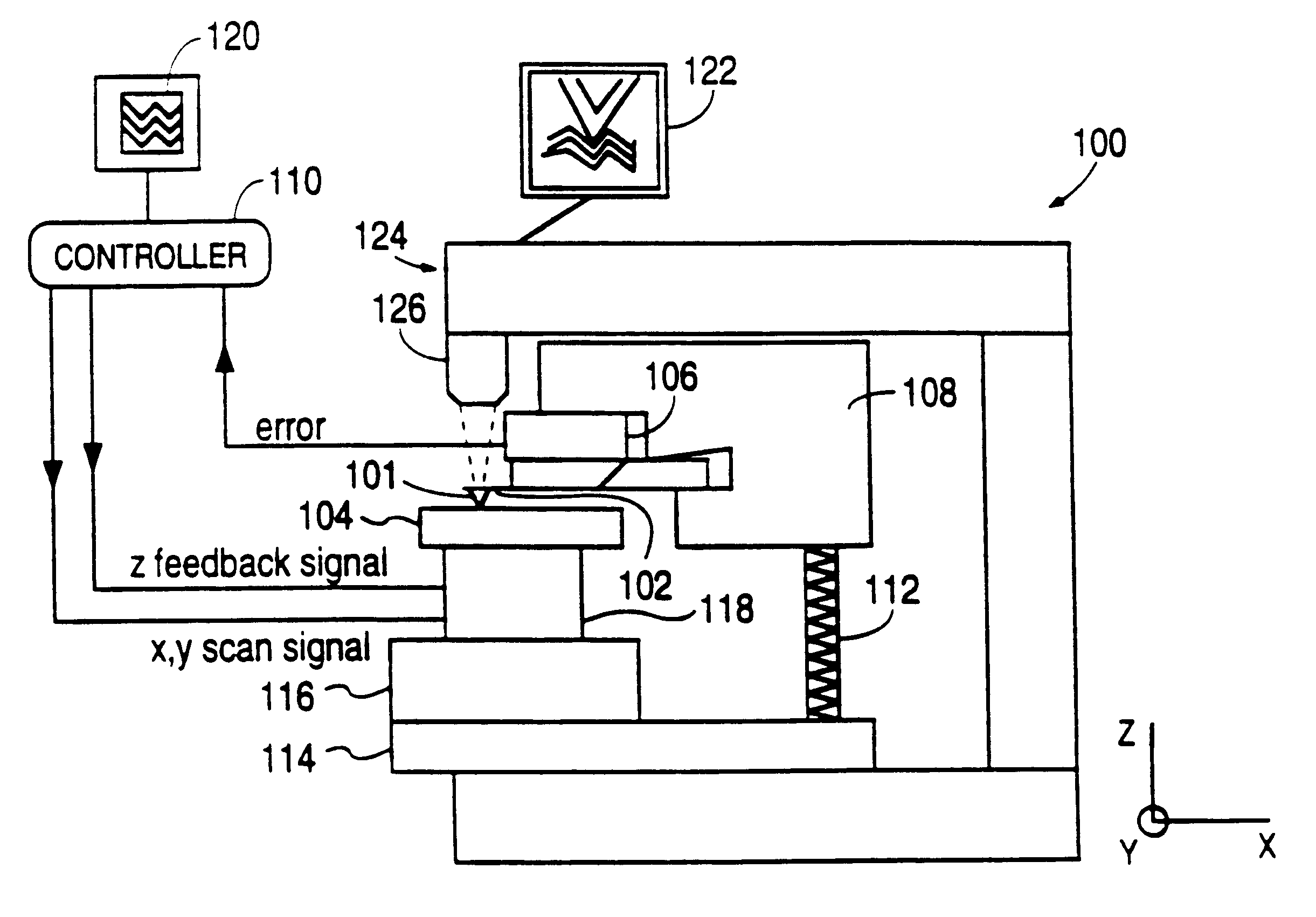
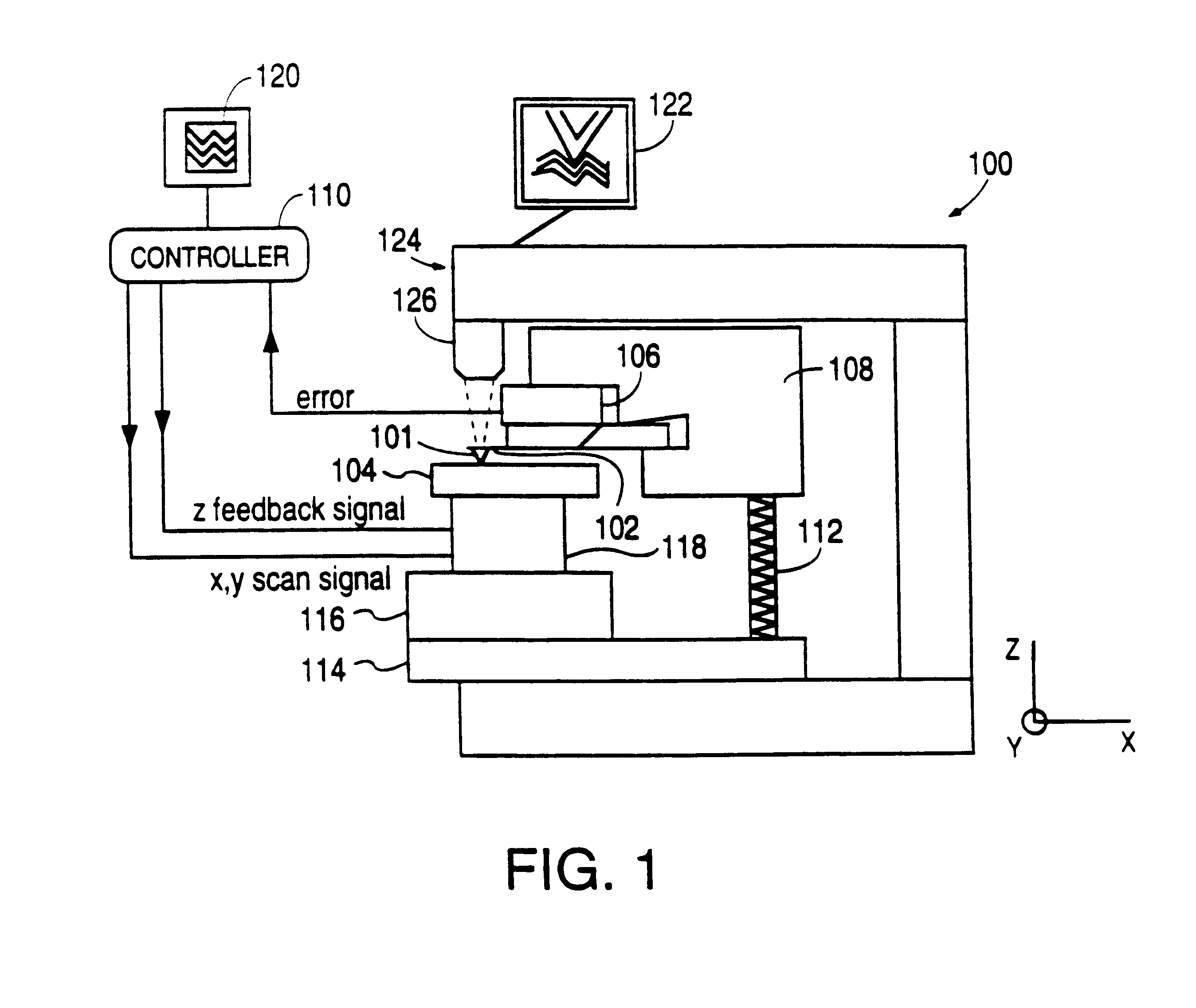
Scanning probe microscope with scan correction
An optical system for a scanning probe microscope provides both an optical on-axis view and an optical oblique view of the sample by means of two optical paths each providing an image to a CCD camera via an auto-zoom lens. A shutter alternately blocks the image of either view from reaching the auto-zoom lens. The CCD camera provides the optical image to a video display which also displays the scanning probe image, thus eliminating the need for eyepieces and allowing easy viewing of both the optical and scanning probe images simultaneously.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Digital camera using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide an extended zoom range
InactiveUS20060275025A1Increase the zoom rangeIncreasing size and costTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsRadiologyNuclear medicine
A digital camera includes a first image sensor, a first wide angle lens for forming a first image of a scene on the first image sensor; a second image sensor, a zoom lens for forming a second image of the same scene on the second image sensor, a control element for selecting either a first sensor output from the first image sensor or a second sensor output from the second image sensor, and a processing section for producing the output image from the selected sensor output. In one variation of this embodiment, the first lens is also a zoom lens, where the maximum focal length of the first lens is less than or equal to the minimum focal length of the second zoom lens.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Compact high performance zoom lens system
A compact high performance objective zoom lens system is disclosed that provides optimum optical performance over the entire zoom focal length range at focus distances from close to infinity. The system comprises, from object space to image space, one focusing objective lens group (comprising a focus lens group and a stationary lens group) and three zoom lens groups aligned on the optical axis. The focus lens group and the zoom lens groups are axially movable along the optical axis for focusing and zooming. In one embodiment, the system has a focal length zoom region from about 19 mm to 90 mm, an aperture of F / 2.7 and substantially the same optical performance as high quality fixed objective lenses of the same range. The performance characteristics of this system makes it suitable for use with both film and electronic detector cameras.
Owner:COURTLAND CAPITAL MARKET SERVICES LLC +1
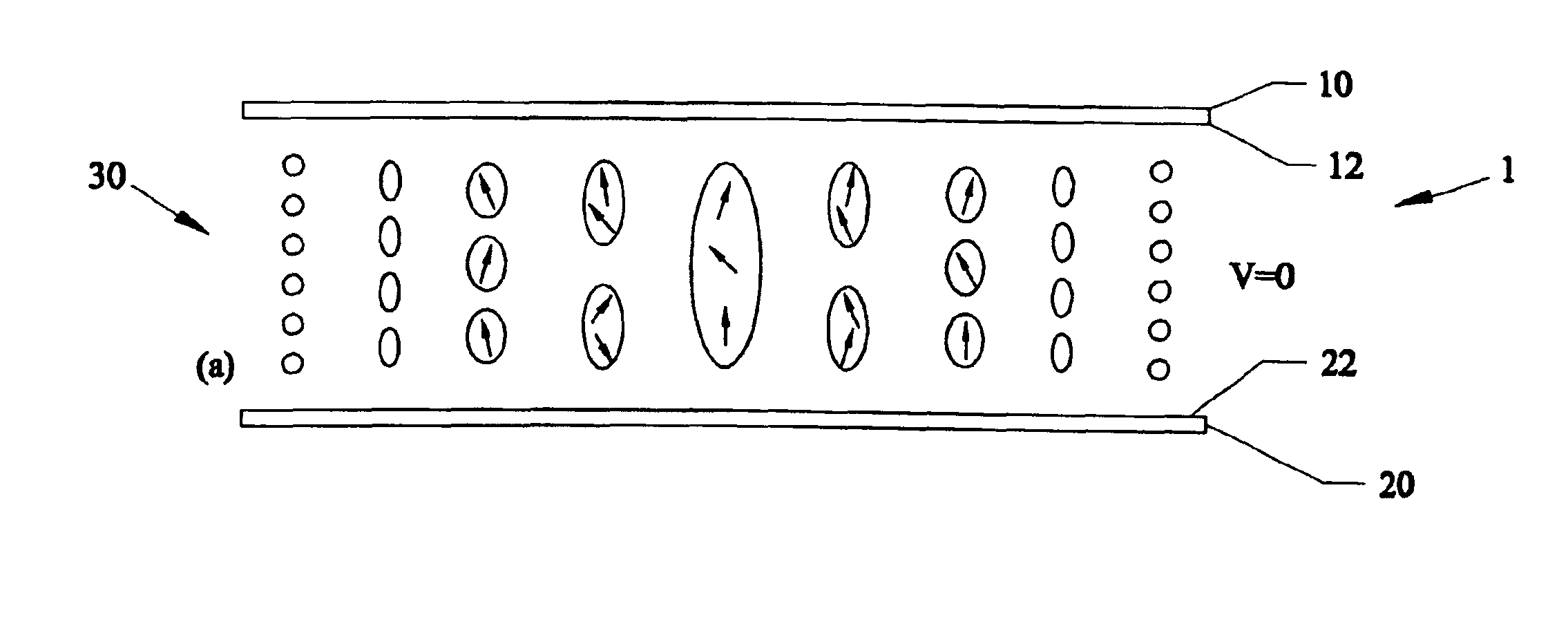
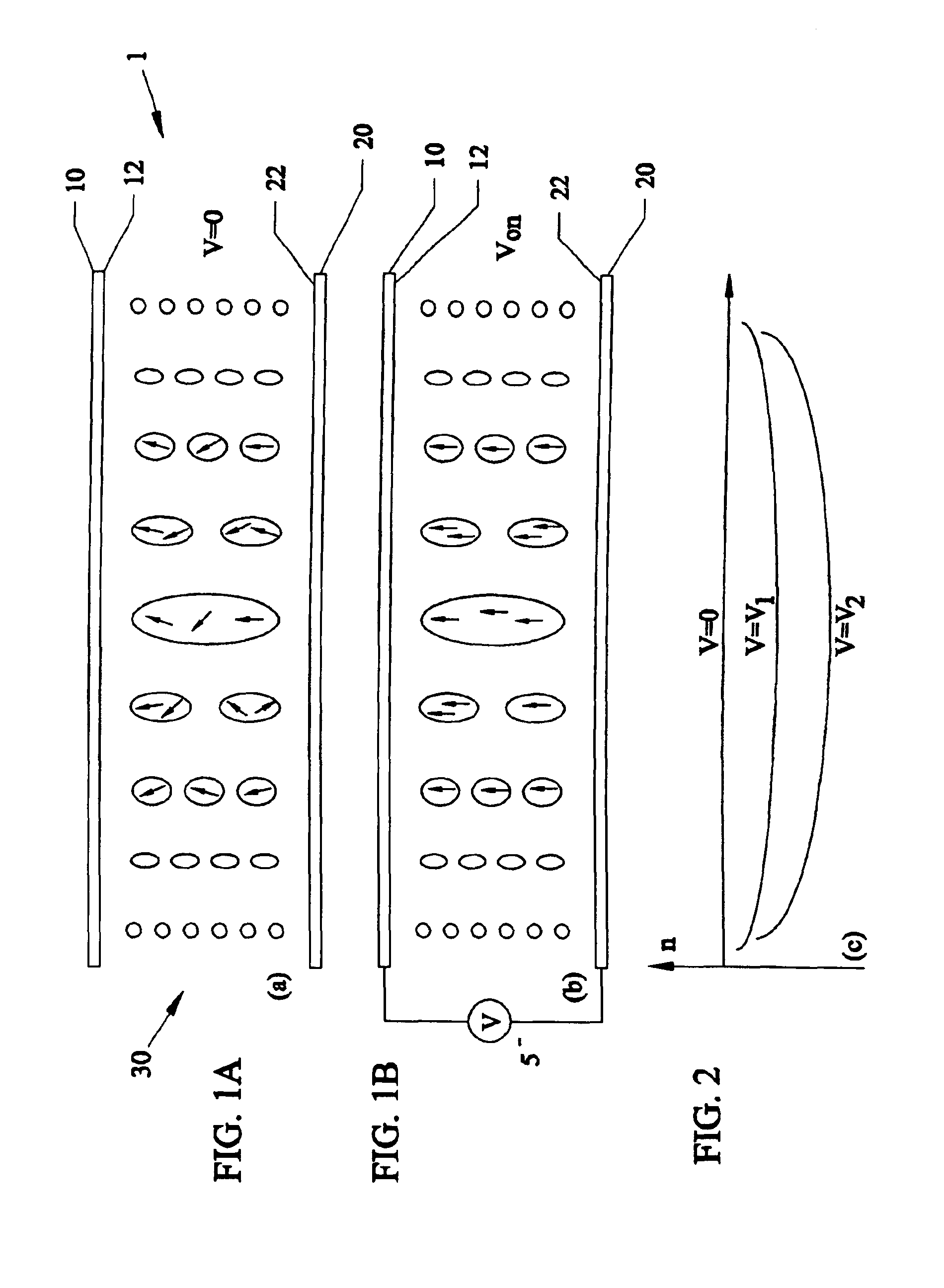
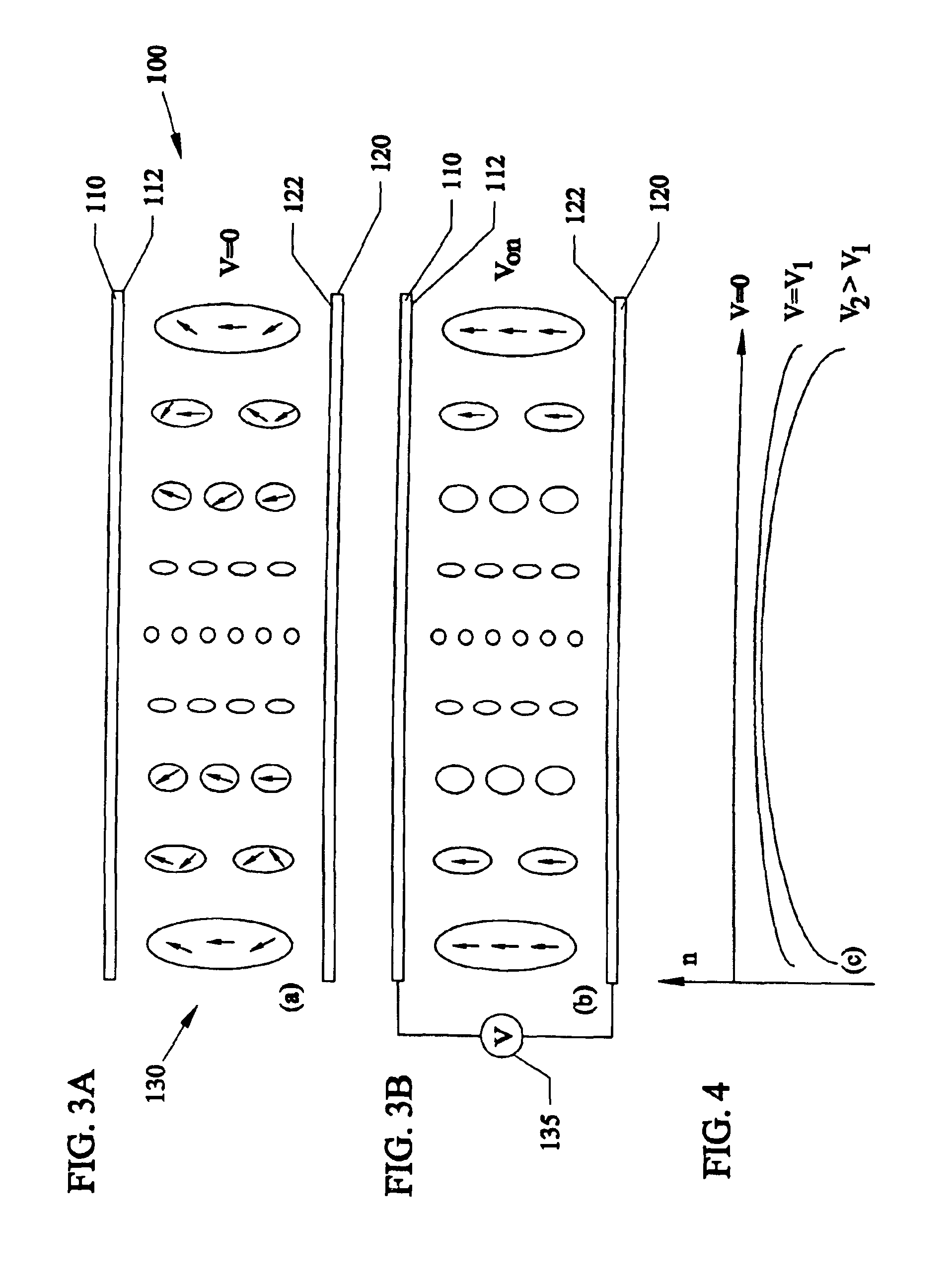
Tunable electronic lens and prisms using inhomogeneous nano scale liquid crystal droplets
InactiveUS6864951B1Simple manufacturing processLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsCamera lensFresnel lens
Using inhomogeneous sized liquid crystal (LC) droplets for lens and prisms. For forming a positive lens, the LC droplet size can gradually increase from the center to the side edges. For forming a negative lens, the LC droplet size can gradually decrease from the center to the side edges. The lens can be created by Ultra Violet light exposure to patterns. The lens can be tuned by applying voltage to the droplets. The inhomogeneous droplets can also be used in Fresnel lens and prisms. Applications of the invention can be used for eyeglasses, arrays, camera type zoom lenses and beam steering applications.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
System and method for zoom lens calibration and method using same
Using marks of known dimensions and size, and spacing, a zoom lens may be calibrated in either or both the X and Y spatial directions. A system comprising an image capture device, positioning means, position encoder means, operator interface, and processing unit permits this method to be advantageously applied to a wide variety of web inspection / control functions, including but not limited to initial web registration, multiple color ink registration, lateral web positioning, repeat length calculations, image capture synchronization, thermal / mechanical differential compensation, and accurate registration of objects within an image to other objects within an image or to a mechanical reference on a machine. Since the Zoom Calibration method permits a system to be constructed with both wide / variable field of view and accurate distance measurement positioning and calibration, all of the web inspection / control functions traditionally used in the web printing industry may be implemented with a single inspection / control system using a multitasking approach with the same inspection / control hardware. This permits rapid implementation of old and new web inspection / control functions at a greatly reduced cost as compared to traditional fixed lens systems, as well as permitting a degree of automation, remote access, diagnostic control, quality assurance, and product quality control heretofore not possible with conventional web inspection / control systems.
Owner:CC1
Zoom lens and optical apparatus using the same
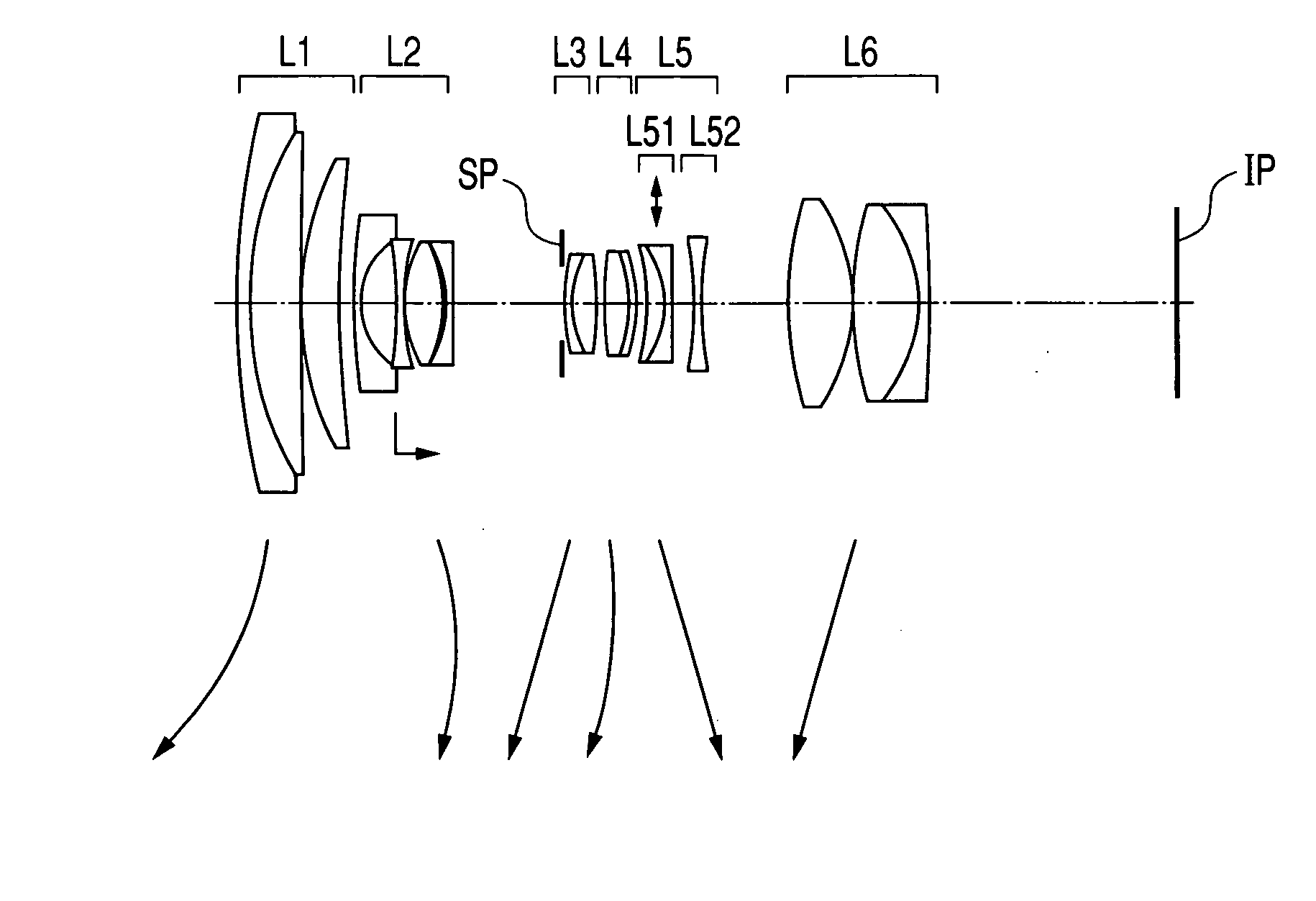
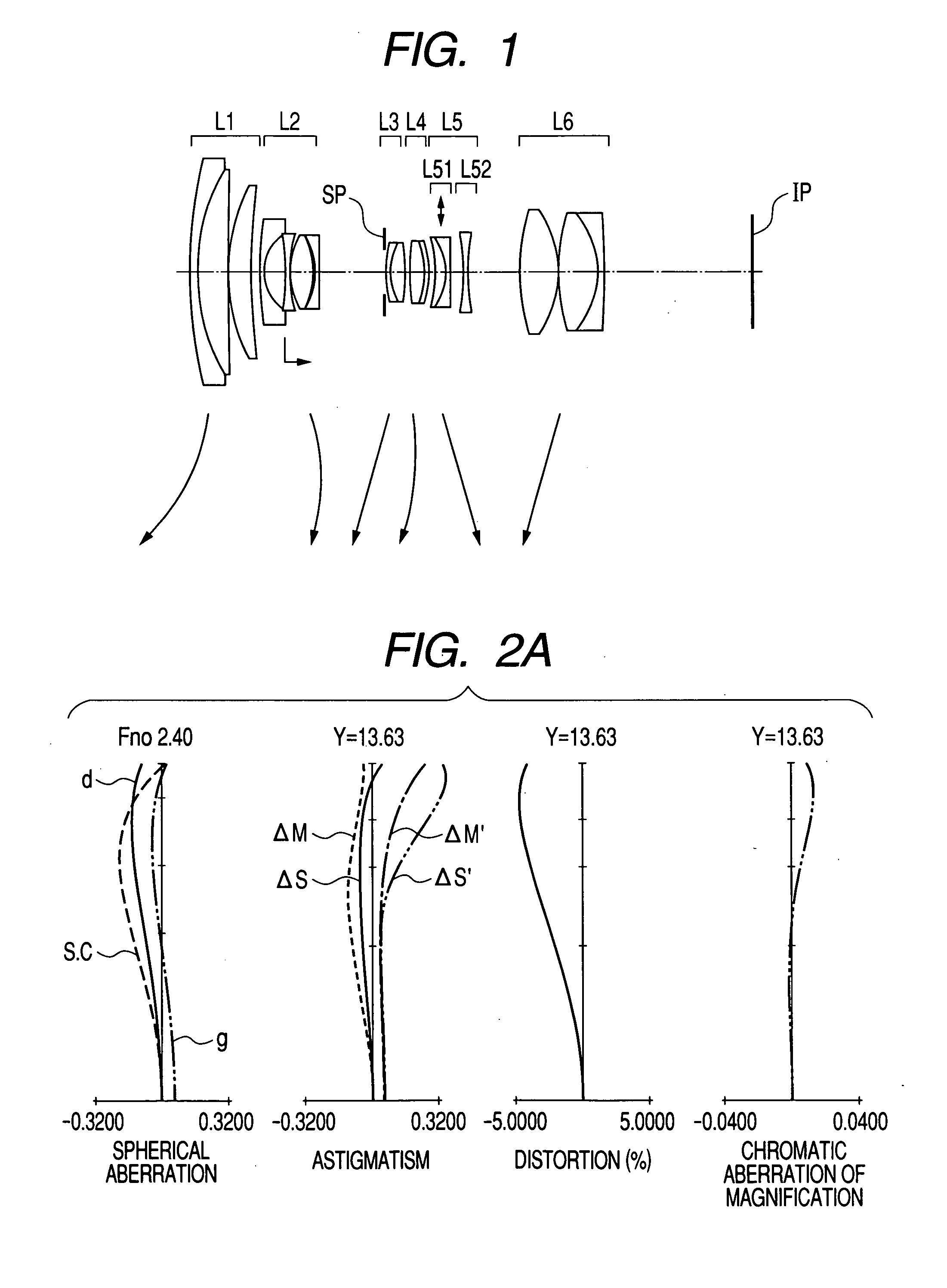
A zoom lens includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens unit of positive refractive power, a second lens unit of negative refractive power, a third lens unit of positive refractive power and a fourth lens unit of positive refractive power, zooming from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end being effected by moving the second lens unit toward the image side, and shifting of an image plane due to zooming being compensated for by moving the fourth lens unit, wherein the second lens unit consists of four separate single lenses including three negative lenses and one positive lens, and the third lens unit has at least one positive lens both surfaces of which are aspherical.
Owner:CANON KK
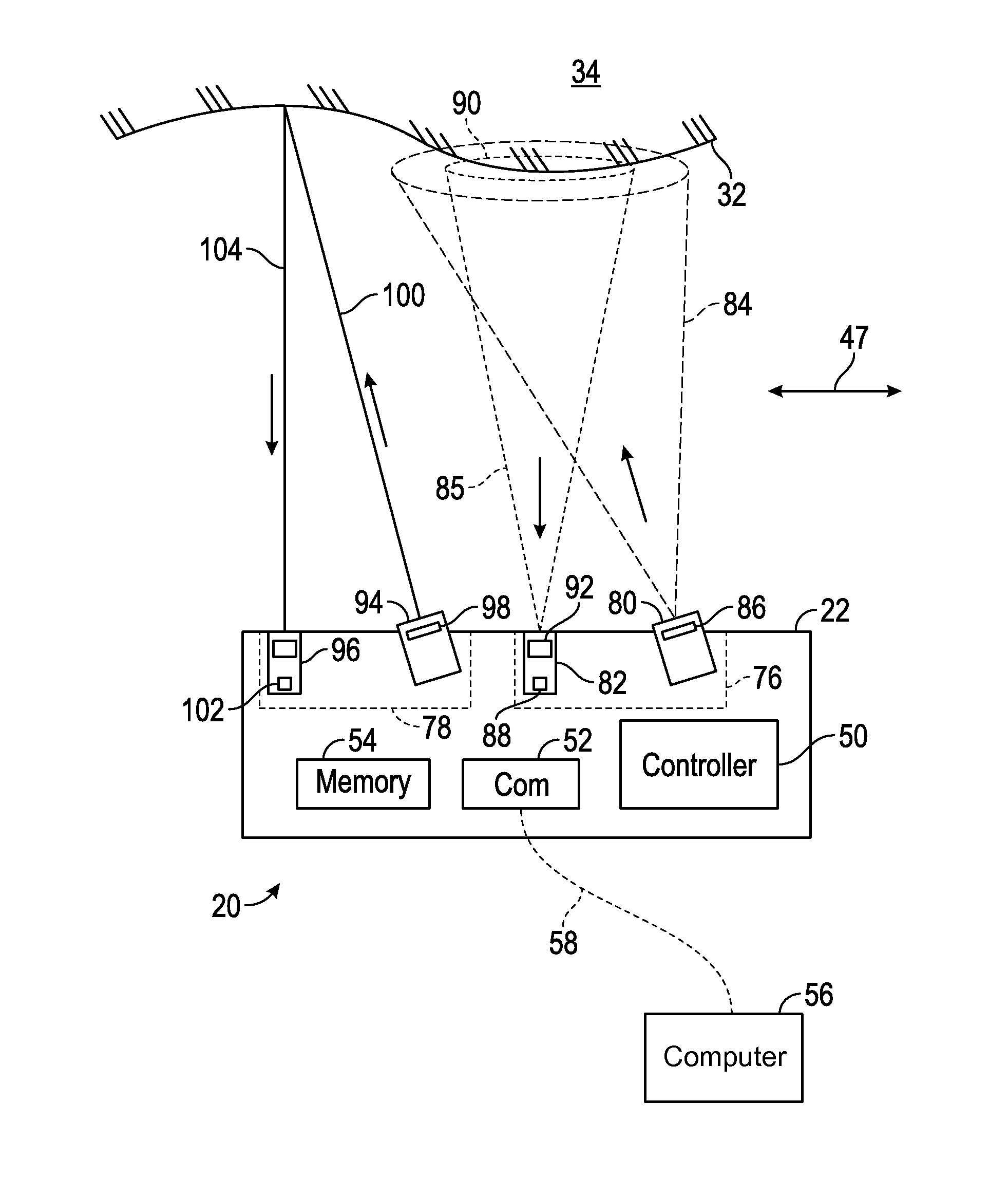
Triangulation scanner having motorized elements
InactiveUS20150015701A1Television system detailsColor television detailsTriangulationComputer science
A 3D triangulation scanner includes a projector, a camera, and a processor. At least one of the projector and the camera has a zoom lens and a motorized zoom adjustment mechanism. The processor is responsive to executable instructions that uses triangulation calculations to calculate 3D coordinates of points on a surface that are based at least in part on a baseline length, an orientation of the projector and the camera, a position of a corresponding source point on an illuminated pattern source of the projector, and a position of a corresponding image point on a photosensitive array of the camera. The 3D coordinates of the points are calculated at one time and at another time, at least one of the projector FOV being wider at the one time than at the another time or the camera FOV being wider at the one time than at the another time.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus incorporating the same
ActiveUS20120092777A1High zoom ratioRelatively small amount of movementLensOptical axisImaging equipment
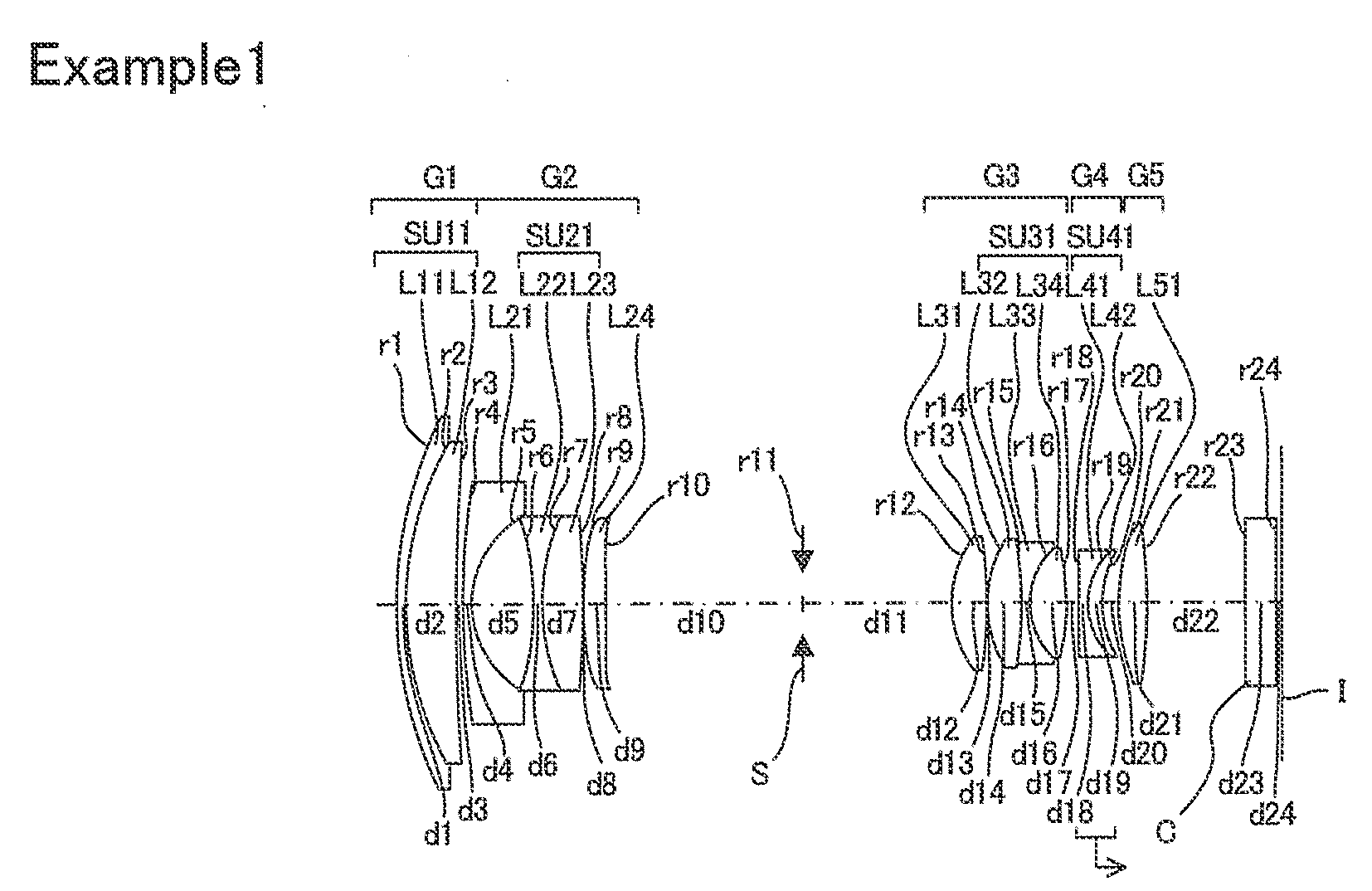
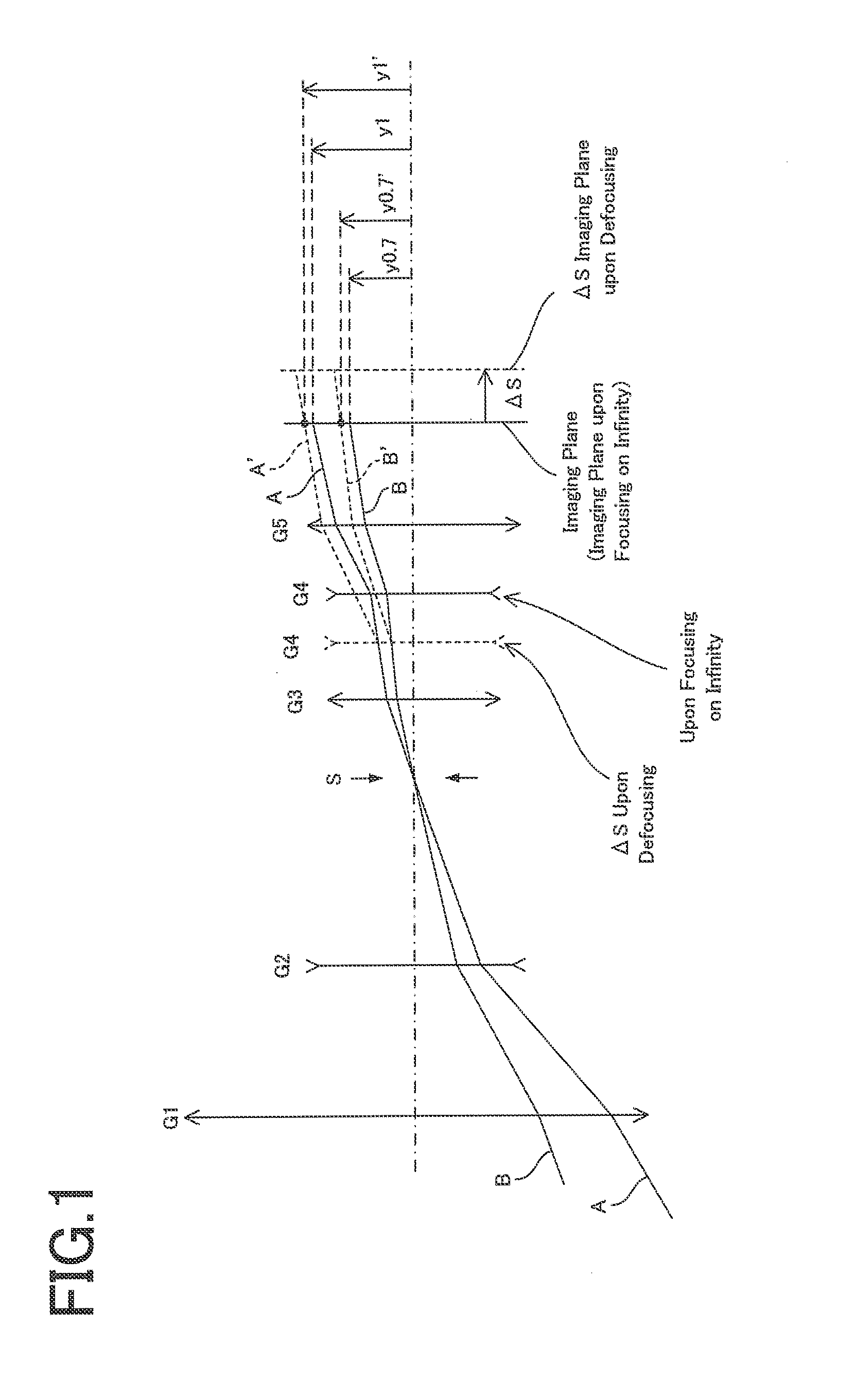
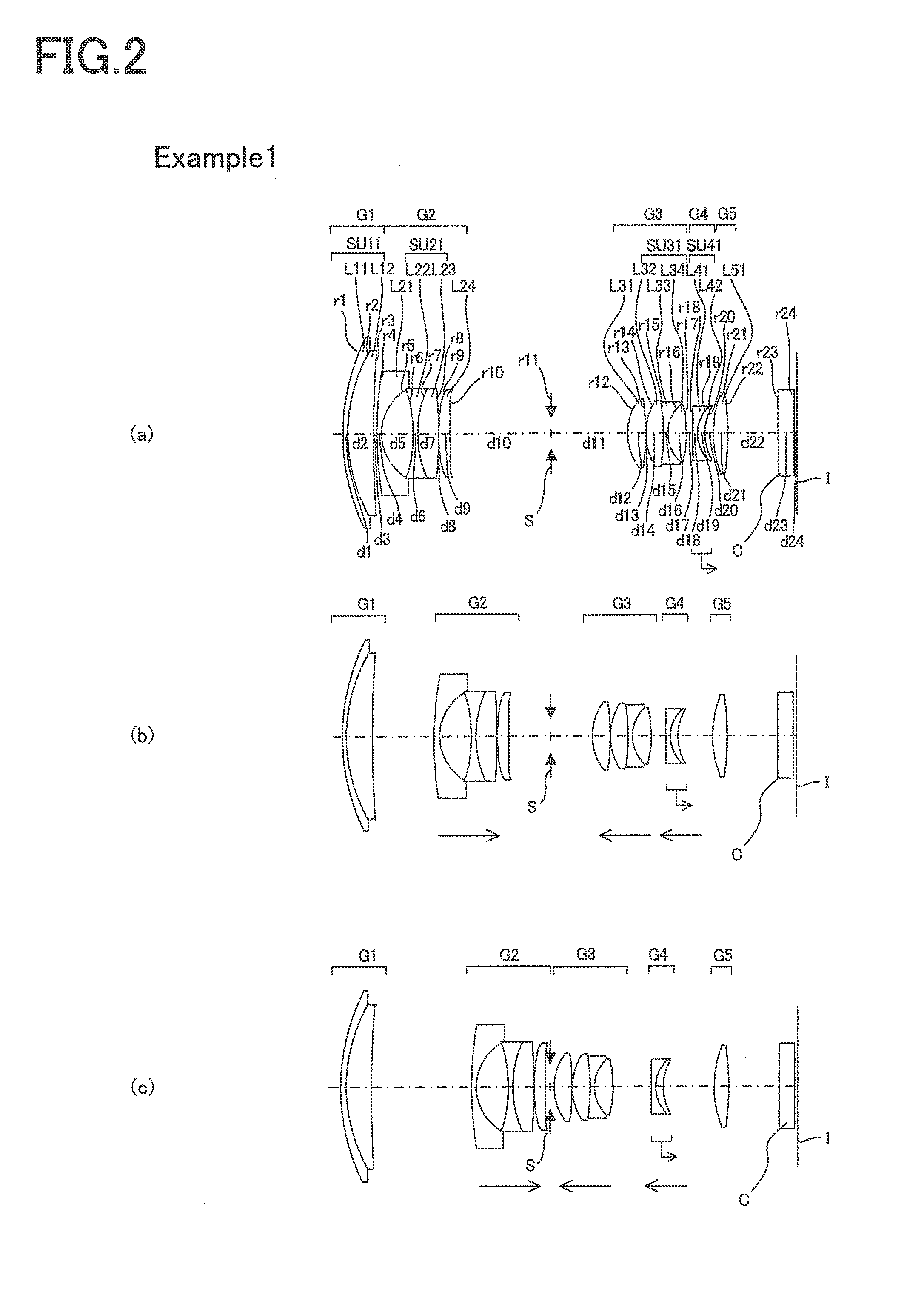
A zoom lens comprising, in order from an object side thereof, a first lens group of positive refracting power, a second lens group of negative refracting power, an aperture stop, a third lens group of positive refracting power, a fourth lens group of negative refracting power, and a fifth lens group of positive refracting power. Upon zooming from the wide-angle end to the telephoto end, at least the first lens group and the aperture stop remain fixed in position, the second and third lens groups move in the optical axis direction, and the separation between each of the lens groups and the aperture stop changes. Upon focusing from a focusing-on-infinity state to a close-range-focusing state, the fourth lens group moves in the optical axis direction, with satisfaction of the following:−0.36<f4 / f1<−0.05 (1A),where f1 and f4 are the focal lengths of the first and fourth lens groups, respectively.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
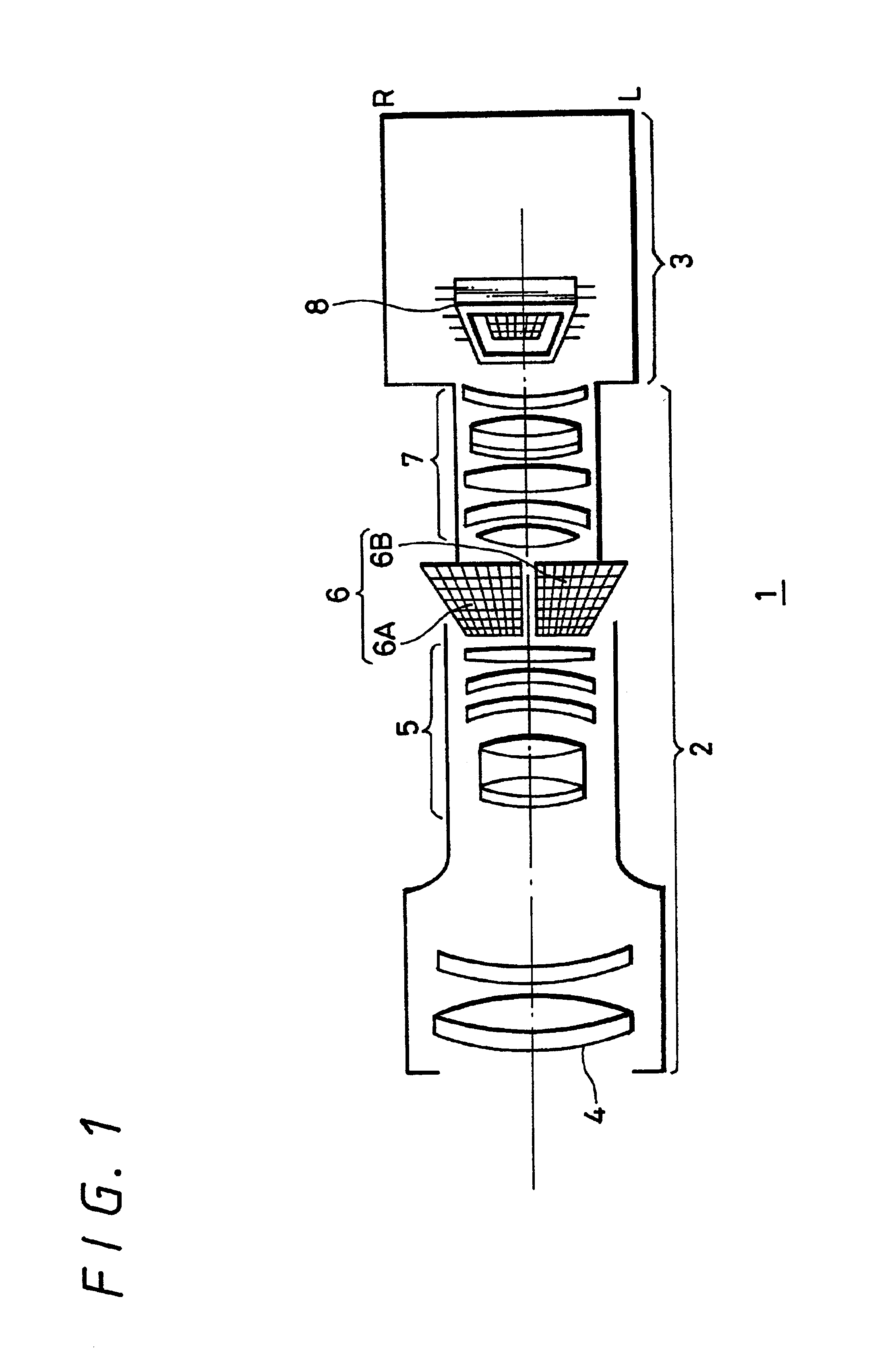
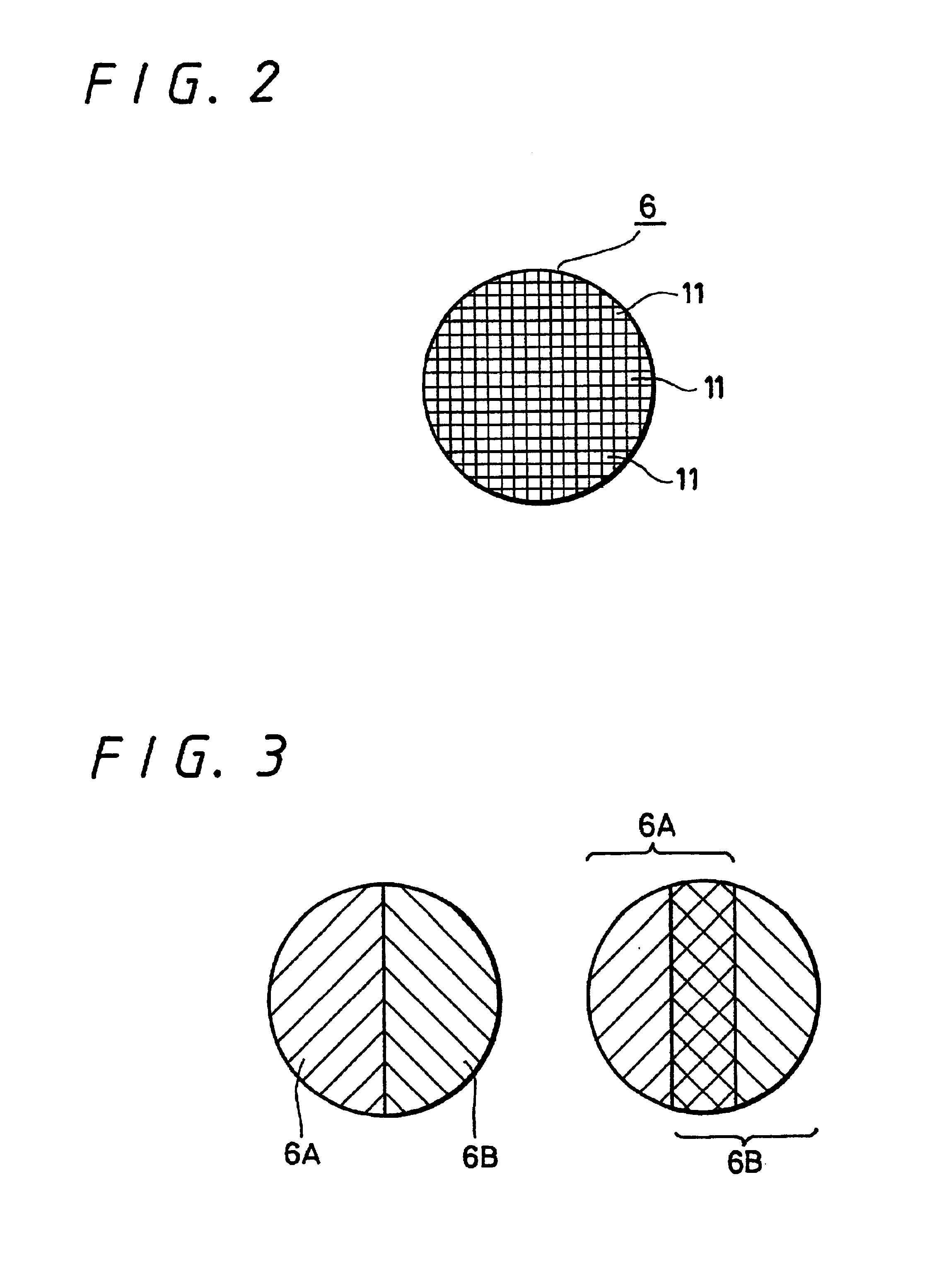
Stereoscopic zoom lens with shutter arranged between first and second lens groups
InactiveUS7019780B1Quick switchTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensComputer science
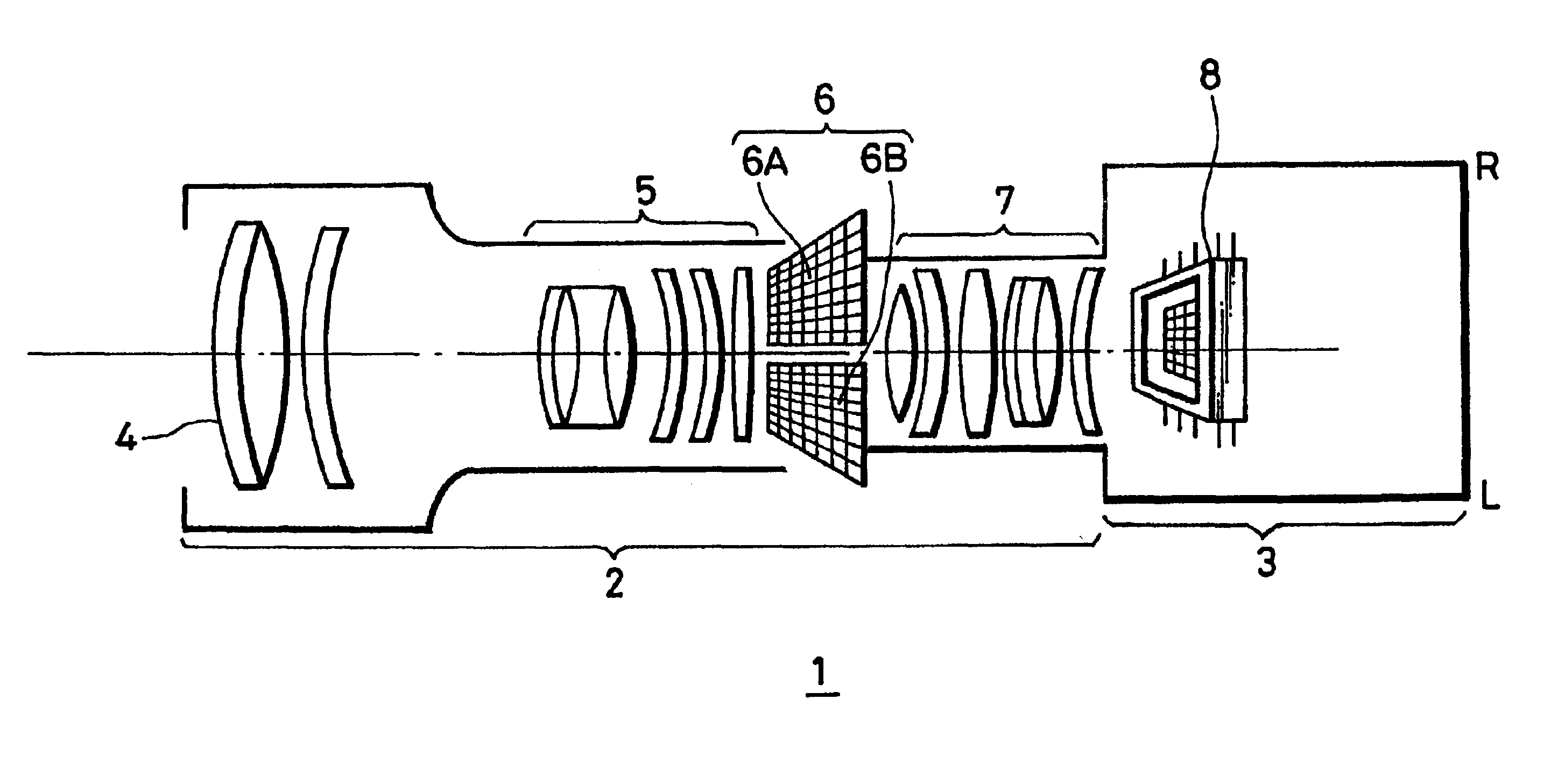
A lens unit and a camera capable of achieving stereoscopic television function and zoom function at the same time. More specifically, a lens unit (2) and a camera (1) each including at least a zoom lens (4), light quantity adjusting device (6 or 20), an electronic optical shutter provided on a stage of the zoom lens (4), and an optical shutter driving portion for controlling the electronic optical shutter (6) to open (6A, 6B) in a predetermined pattern.
Owner:SONY CORP
Zoom lens system
The invention provides a zoom lens system that is reduced in terms of both size and cost. The zoom lens system comprises a first positive lens group G1, a second negative lens group G2, a stop S, a third positive lens group G3 and a fourth positive lens group G4. During zooming from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end of the system, while the first lens group G1 remains fixed, the second lens group G2 moves from an object side to an image plane side of the system, the third lens group G3 moves from the image plane side to the object side, and the fourth lens group G4 moves to keep an image plane at a constant position. The first lens group G1 is made up of a negative meniscus lens convex on an object side and a double-convex lens, the second lens group G2 is made up of a double-concave lens and a positive meniscus lens convex on an object side thereof, with an aspherical surface being used for a surface of the positive meniscus lens that is located on an image side thereof, the third lens group G3 is made up of a double-convex lens and a negative meniscus lens convex on an object side thereof, with an aspherical surface being used for a surface of the double-convex lens that is located on an object side thereof, and the fourth lens group G4 is made up of one double-convex lens.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Image quality mapper for progressive eyeglasses
An instrument and method for optical testing of an eyeglass lens, including progressive addition lenses, to obtain image quality measurements includes an illumination system for presenting a beam of light to a test lens, a test lens positioning system for rotating the test lens so that different areas on the lens are illuminated, a zoom lens for focusing the beam at a constant effective focal length, a detection system for recording and measuring image quality of the test lens, and an alignment boom for conveying the zoom lens and the detection system such that the optical axis remains aligned with the beam existing the test lens. The instrument is fully automated and capable of obtaining measurements of the power, astigmatism, prism and modulation transfer function at various locations on the surface of the lens.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Zoom lens
InactiveUS20050200973A1Reduce the numberSimplify the movement mechanismLensElectrical polarityZoom lens
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Zoom lens and image sensing apparatus
A zoom lens for forming an optical image of an object on a sensing surface of an image sensor at a variable magnification has first, second, third, fourth and fifth lens groups with positive-negative-positive-negative-positive zoom arrangement. Between the second lens group and the fourth lens group, an optical aperture stop is located. The fourth lens group is composed of one negative lens element having at least one aspherical surface and having a paraxial radius of curvature of an image side surface smaller than a paraxial radius of curvature of an object side surface, and satisfies conditional formula -1.15<f4 / √{square root over (fw.ft)}<-0.5 (where f4 represents a focal length of the fourth lens group, fw represents a focal length of an entire system at a wide-angle end, and ft represents a focal length of the entire system at a telephoto end).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Zoom lens system and image pickup apparatus having the same
Disclosed is a compact zoom lens system having a image stabilizing function. This zoom lens system is provided with a plurality of lens units of which the interval between adjacent ones is changed during zooming. Shake correction is effected by a part of a lens unit of negative optical power of the plurality of lens units. Specifically, the lens unit of negative optical power is comprised of two lens components of negative optical power, and one of these two lens components is moved so as to have a component in a direction perpendicular to an optical axis to thereby change the imaging position of the zoom lens system.
Owner:CANON KK
Driving device
A plurality of movable lenses included in a zoom lens system are driven individually by piezoelectric actuators provided one for each lens. Two driving rods are arranged at different positions along the same line in such a way that neither of the driving rods reaches into the driving stroke of the lens driven by the other. Each driving rod has a piezoelectric actuator provided at its end farther from the other. Alternatively, a plurality of piezoelectric actuators are fixed to a single base block having a groove or a surface level difference to restrict propagation of vibration between the piezoelectric actuators. A graduated member having N-pole and S-pole regions formed alternatively thereon with a predetermined pitch is fixed, parallel to the driving rods, to the driving device itself. A magnetic resistance sensor is attached to each lens frame so as to face the graduated member. Based on the outputs of the sensors, the positions of the individual lenses are detected.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Self-zooming camera
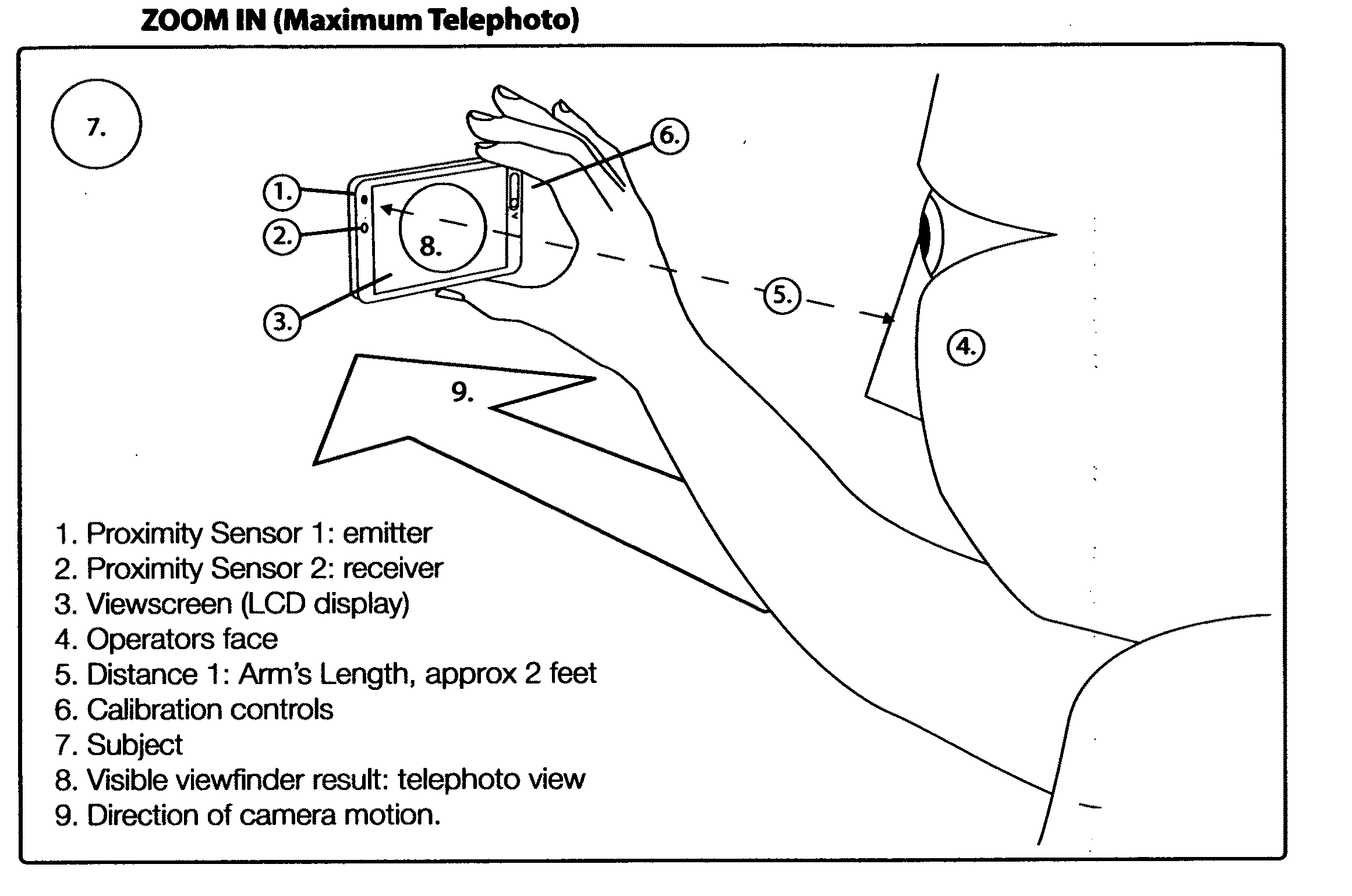
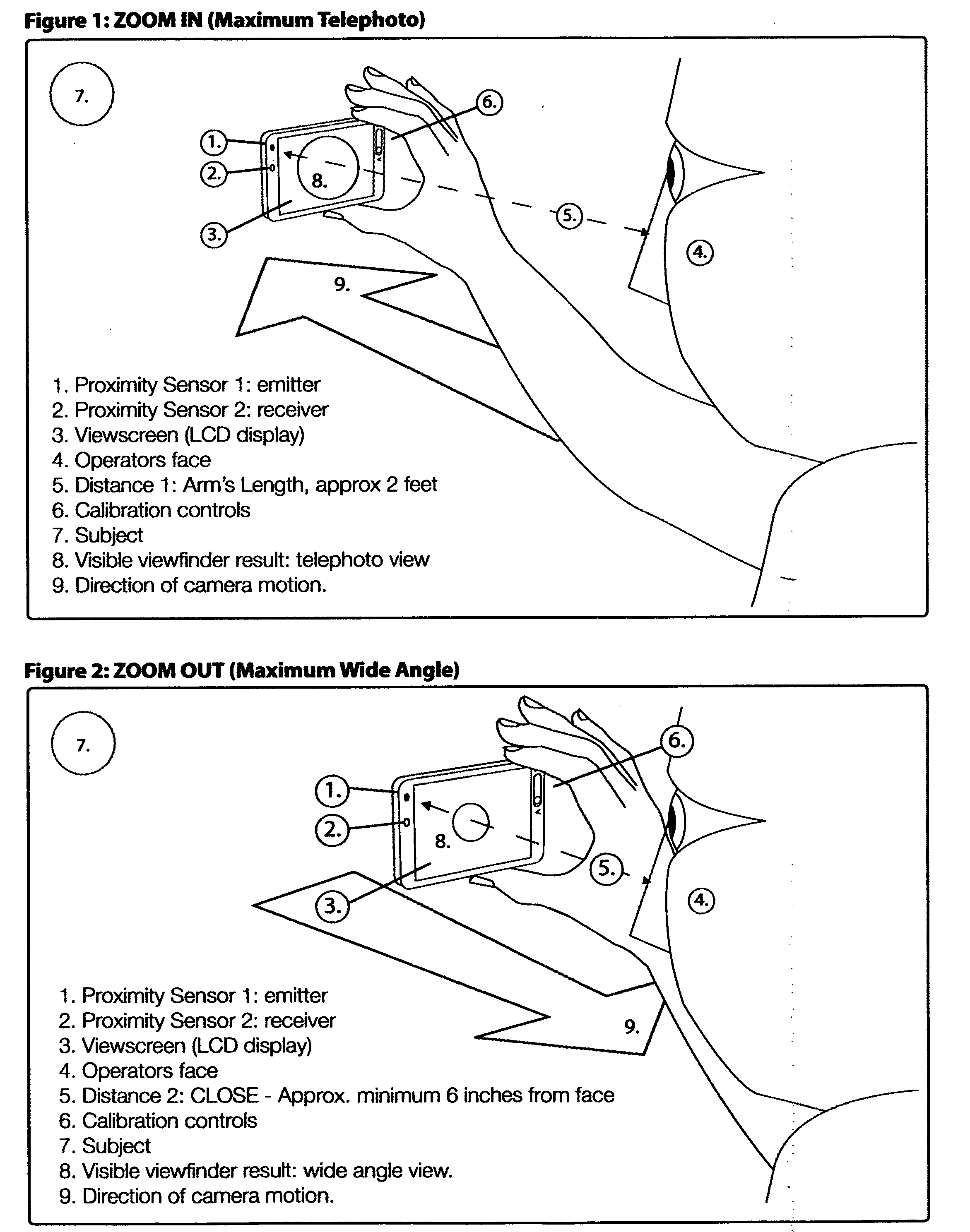
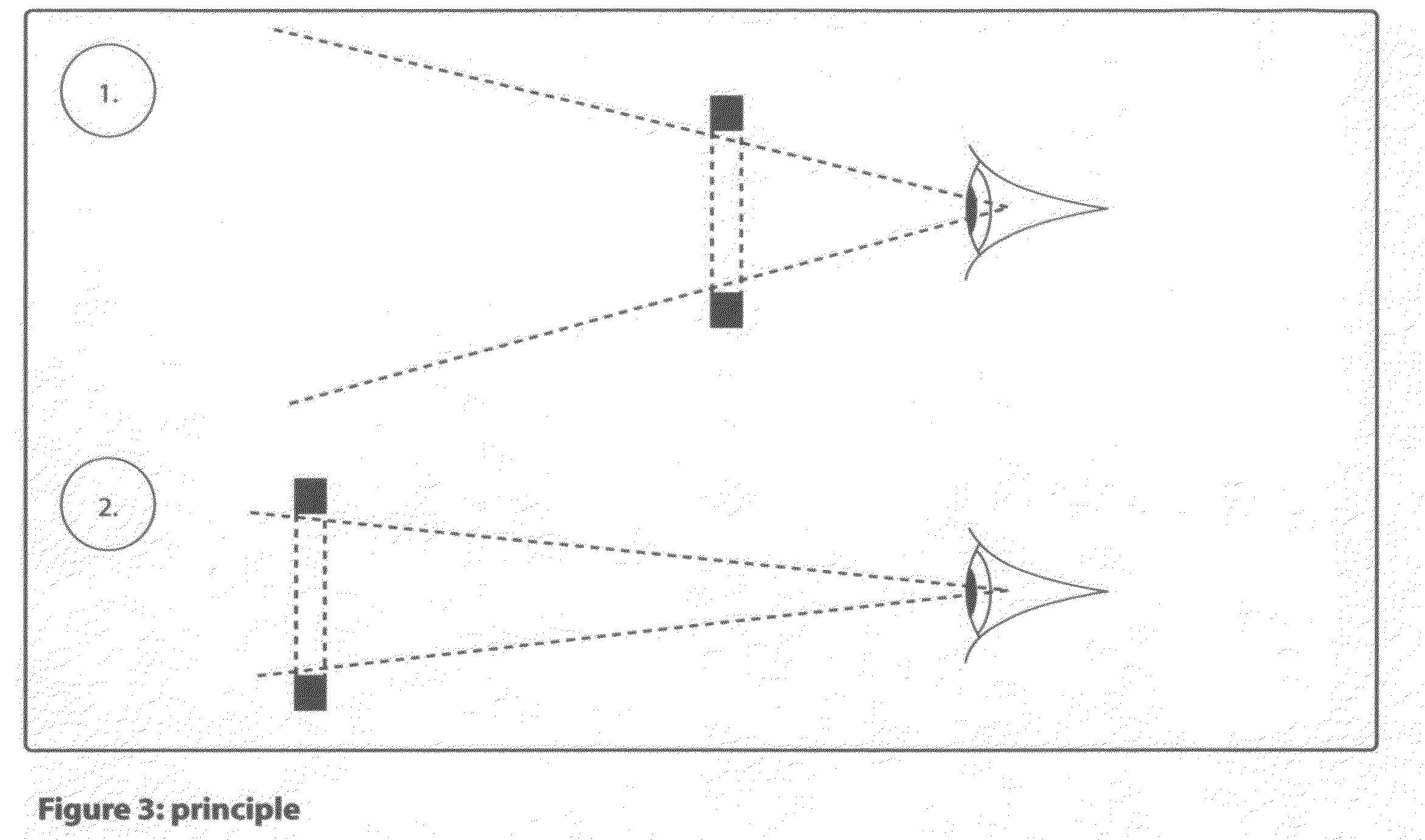
The Self-Zooming Camera uses proximity detectors and / or motion detectors in the camera to detect the position of the camera / recording device relative to the operator's eye or face. At closest viewable distance to the face (approx. 6 inches), the zoom lens operates at it's widest angle or user-specified widest angle setting. At furthest extent from the face (arm's length, approximately 2 feet), the camera zooms to its longest telephoto extent or user-specified longest zoom setting.The Self-Zooming Camera allows simple and creative zoom operation of a camera, video recorder or mobile device with camera without using buttons or zoom / focus pulling—replacing traditional controls with intuitive gesture or camera motion.
Owner:DAVIES JOHN ANDREW
Zoom Lens System, Interchangeable Lens Apparatus and Camera System
InactiveUS20120050603A1High zoom ratioLess aberration fluctuationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisOptical power
A zoom lens system comprising a plurality of lens units, wherein a lens unit located closest to an object side has positive optical power, among lens units located on the image side relative to an aperture diaphragm, a lens unit having negative optical power is at least one focusing lens unit which moves along an optical axis in focusing, an image blur compensating lens unit is provided, which moves in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis, in order to optically compensate image blur, the image blur compensating lens unit and the at least one focusing lens unit are arranged adjacent to each other, and the condition: 0.1<(T1+T2) / H<2.0 (T1 is an axial thickness of the lens unit located closest to the object side, T2 is an axial thickness of a lens unit located having one air space toward the image side from the lens unit located closest to the object side, H is an image height) is satisfied; an interchangeable lens apparatus; and a camera system are provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com