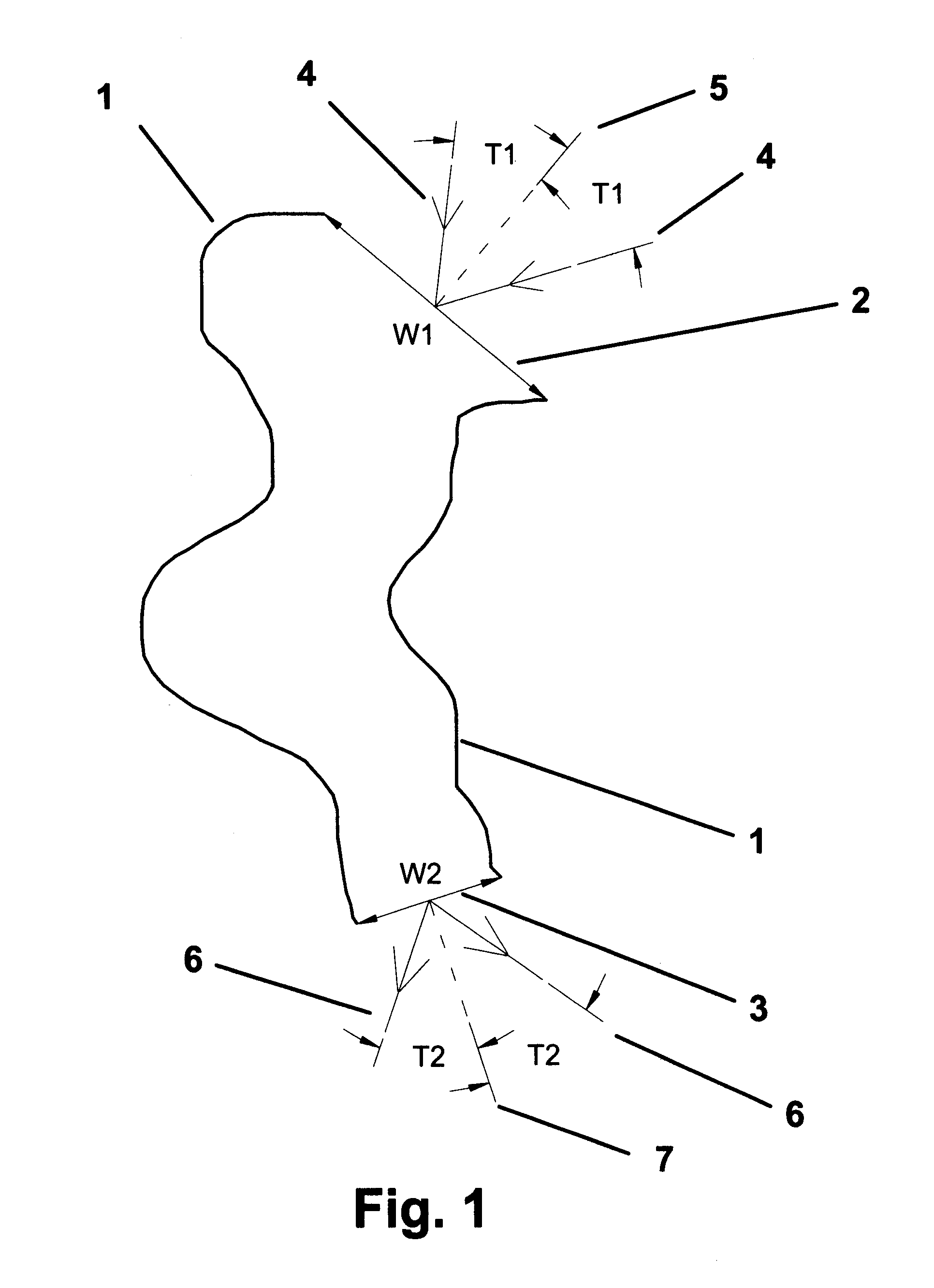
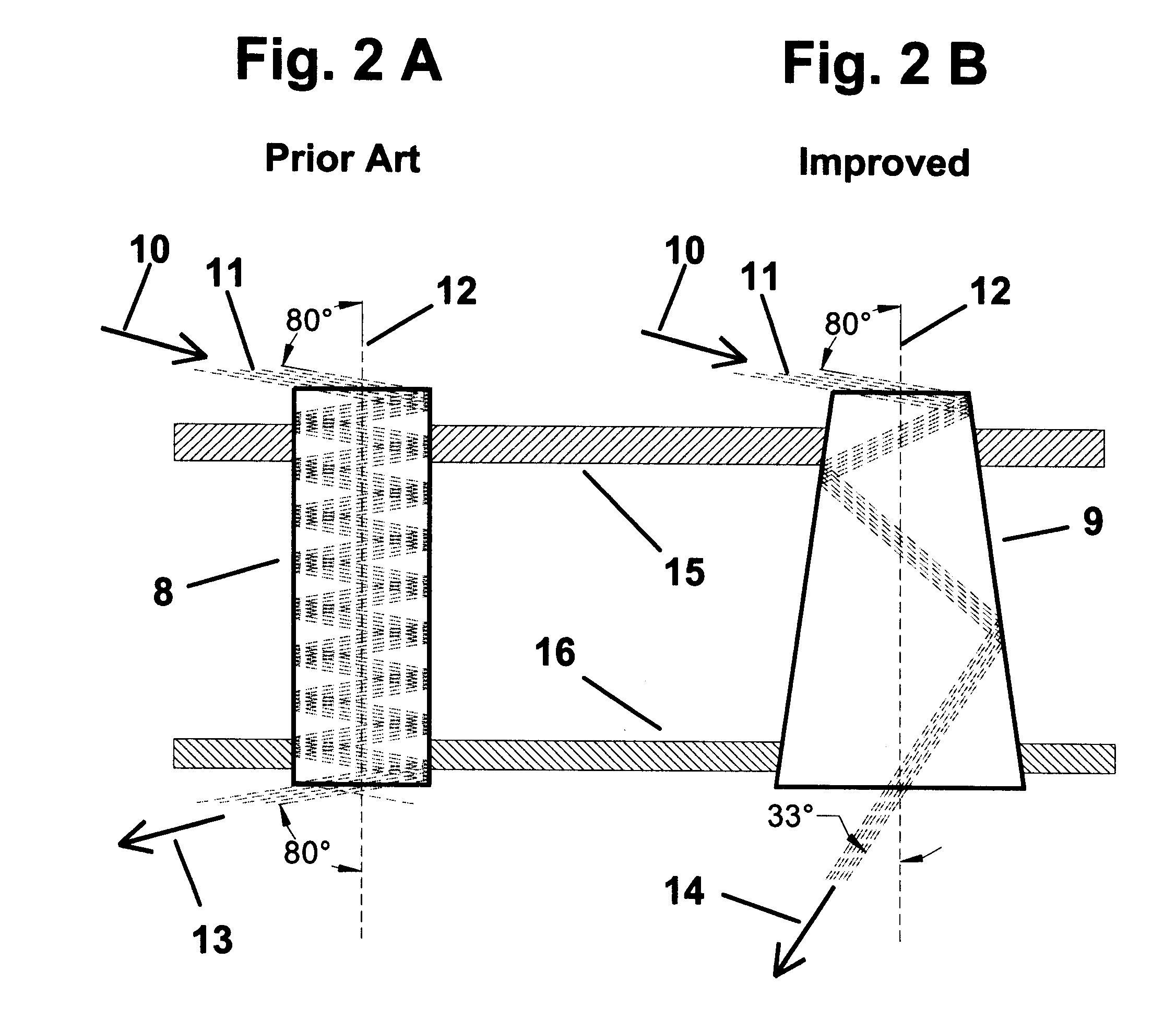
Patents
Literature
3260 results about "Luminous flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In photometry, luminous flux or luminous power is the measure of the perceived power of light. It differs from radiant flux, the measure of the total power of electromagnetic radiation (including infrared, ultraviolet, and visible light), in that luminous flux is adjusted to reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light.
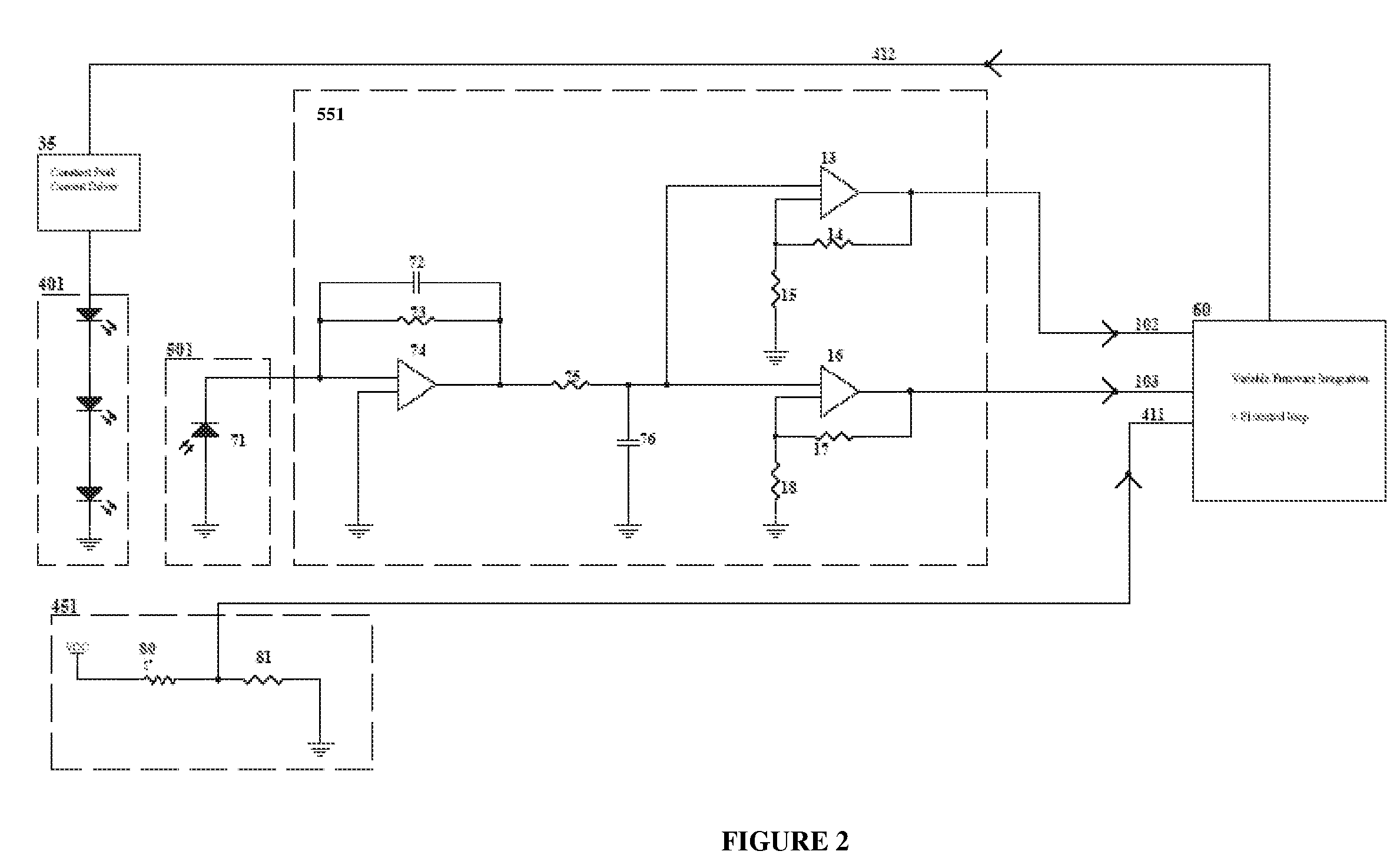
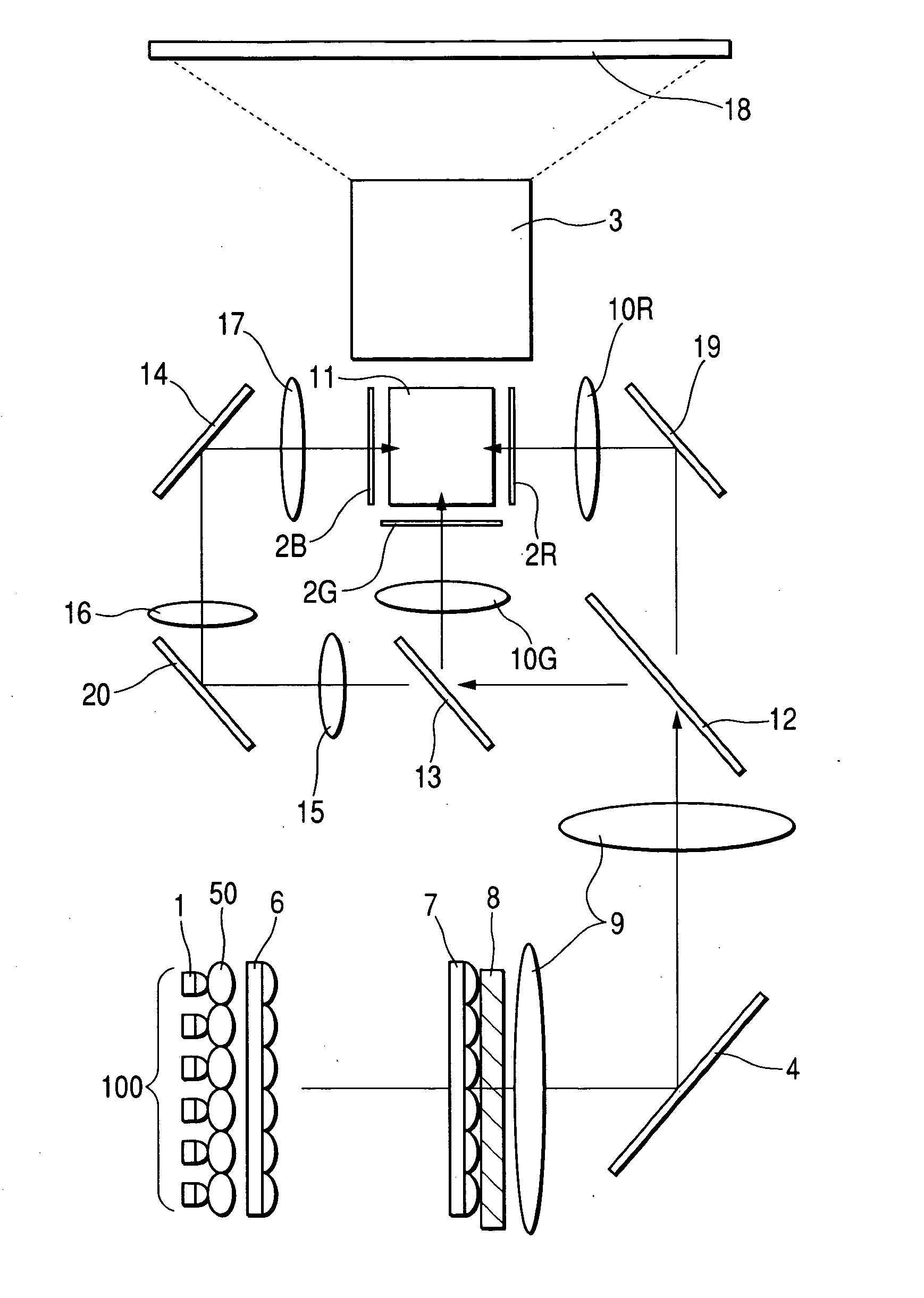
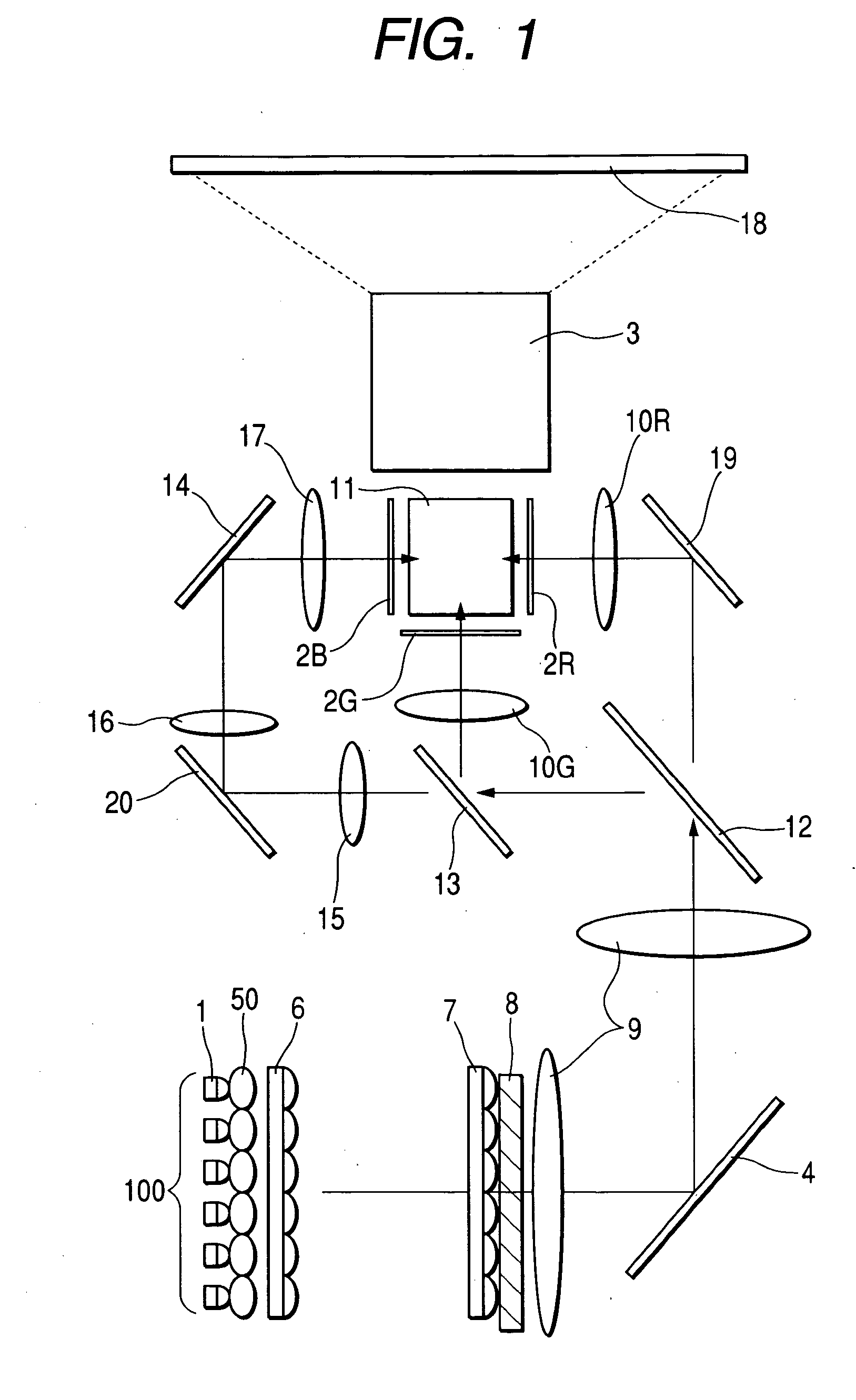
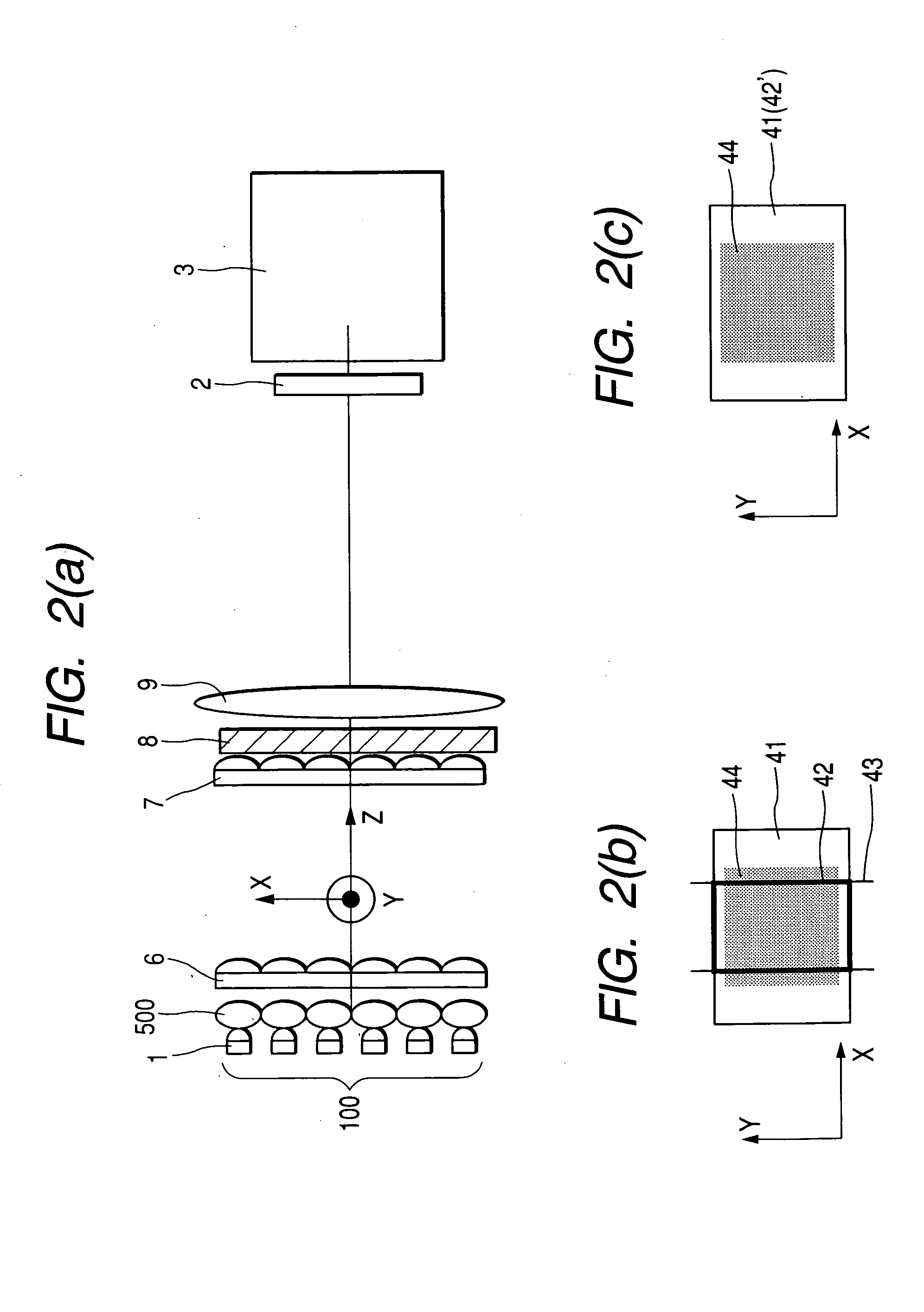
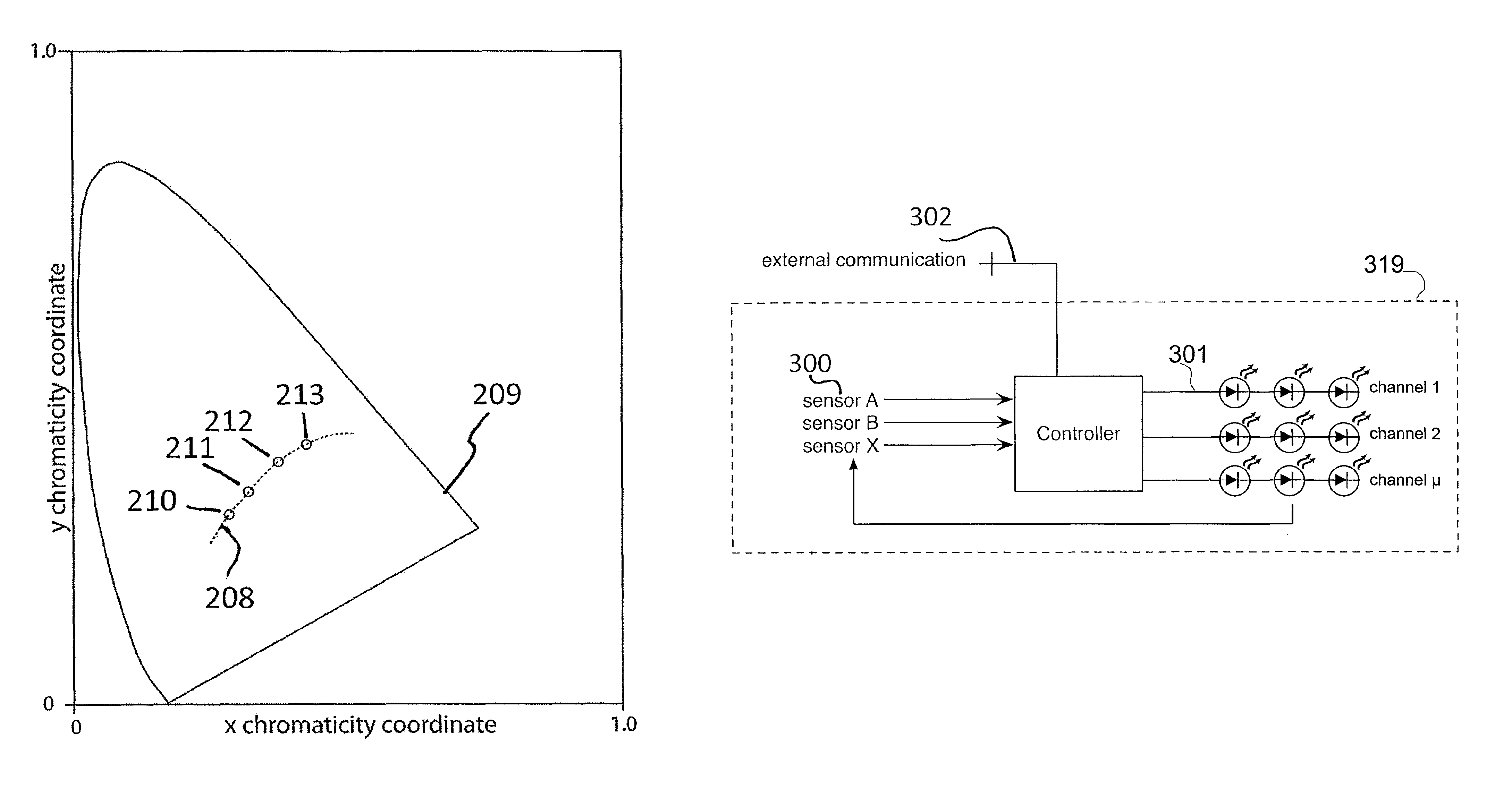
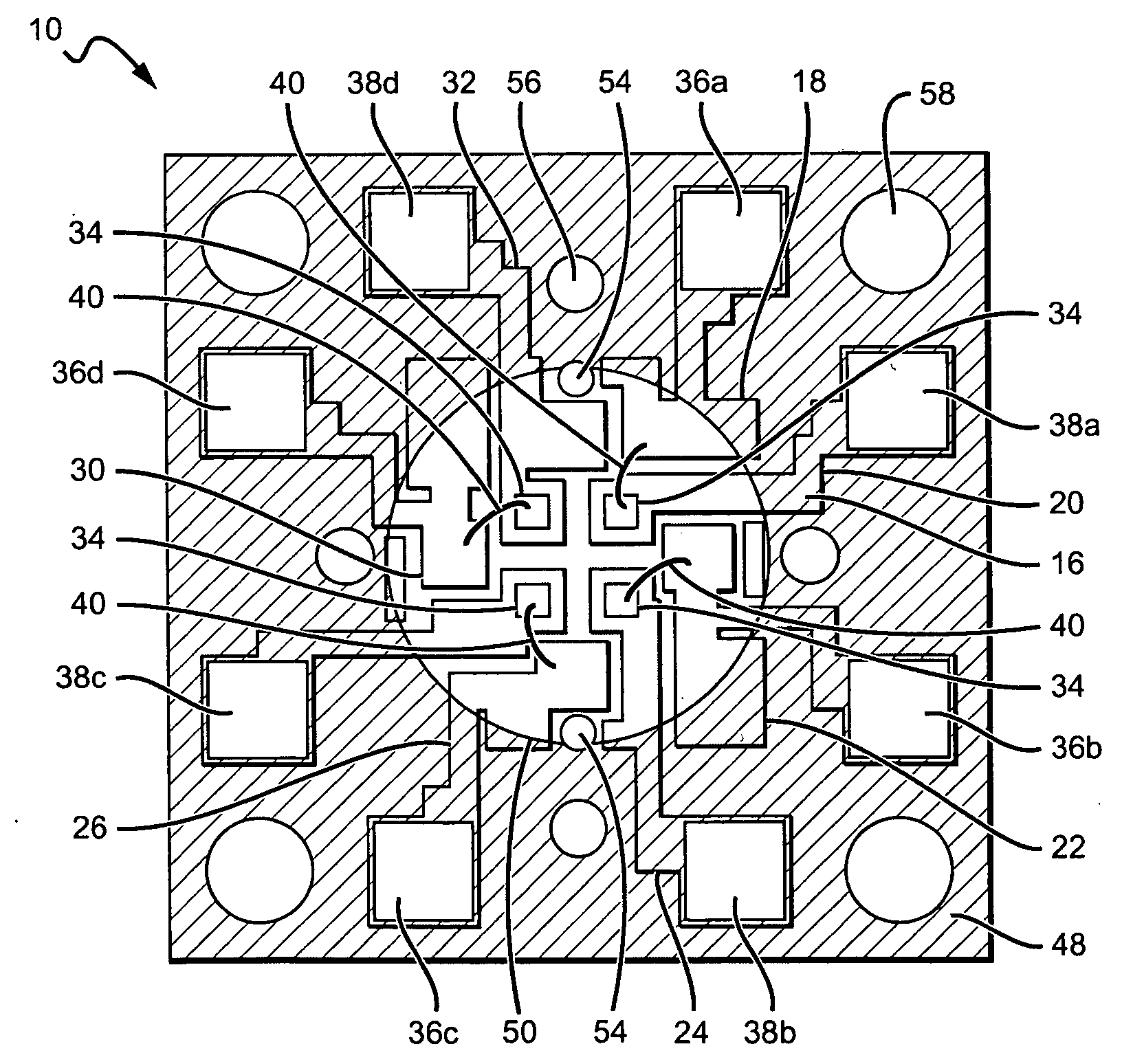
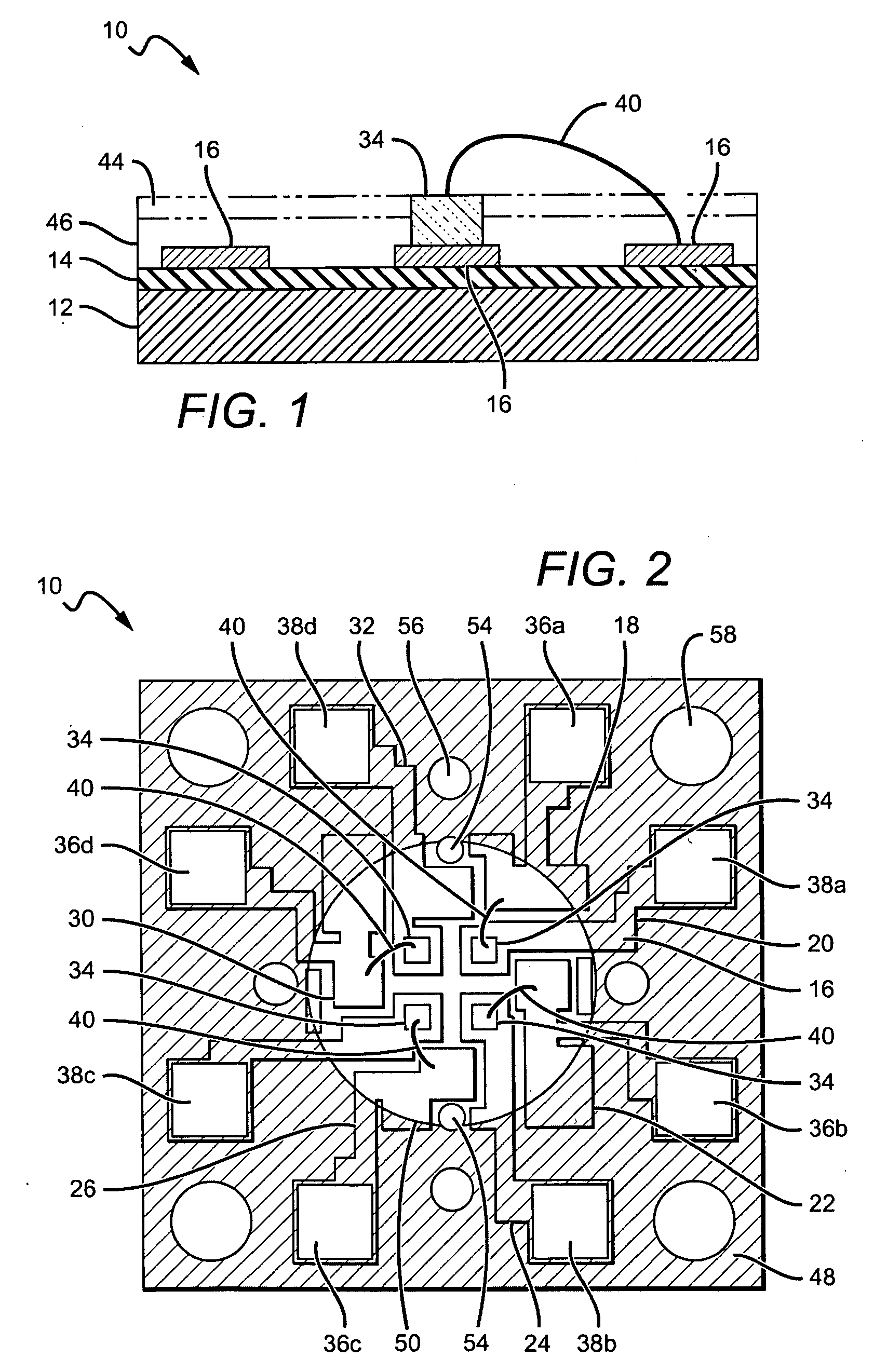
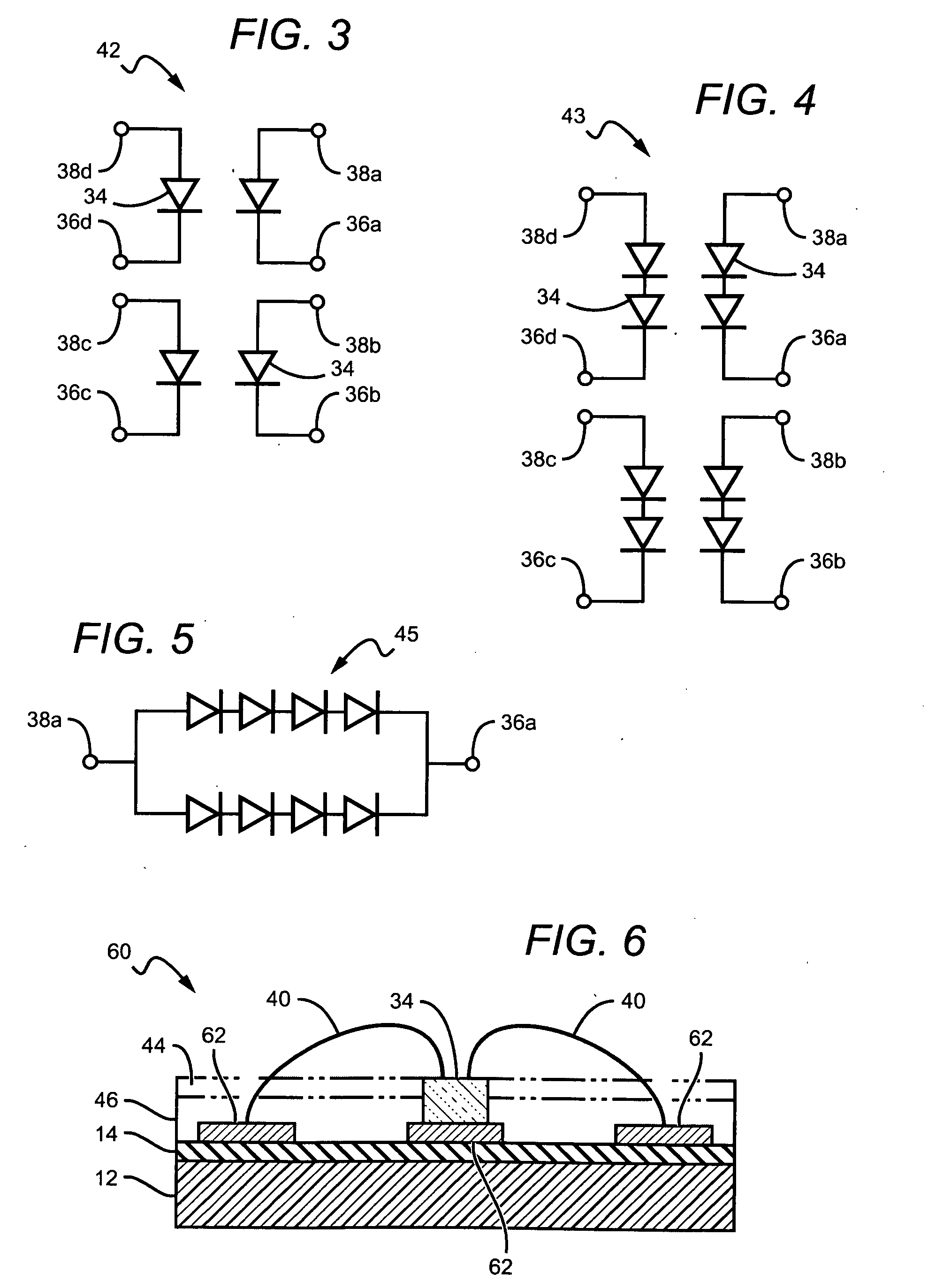
Digitally controlled luminaire system
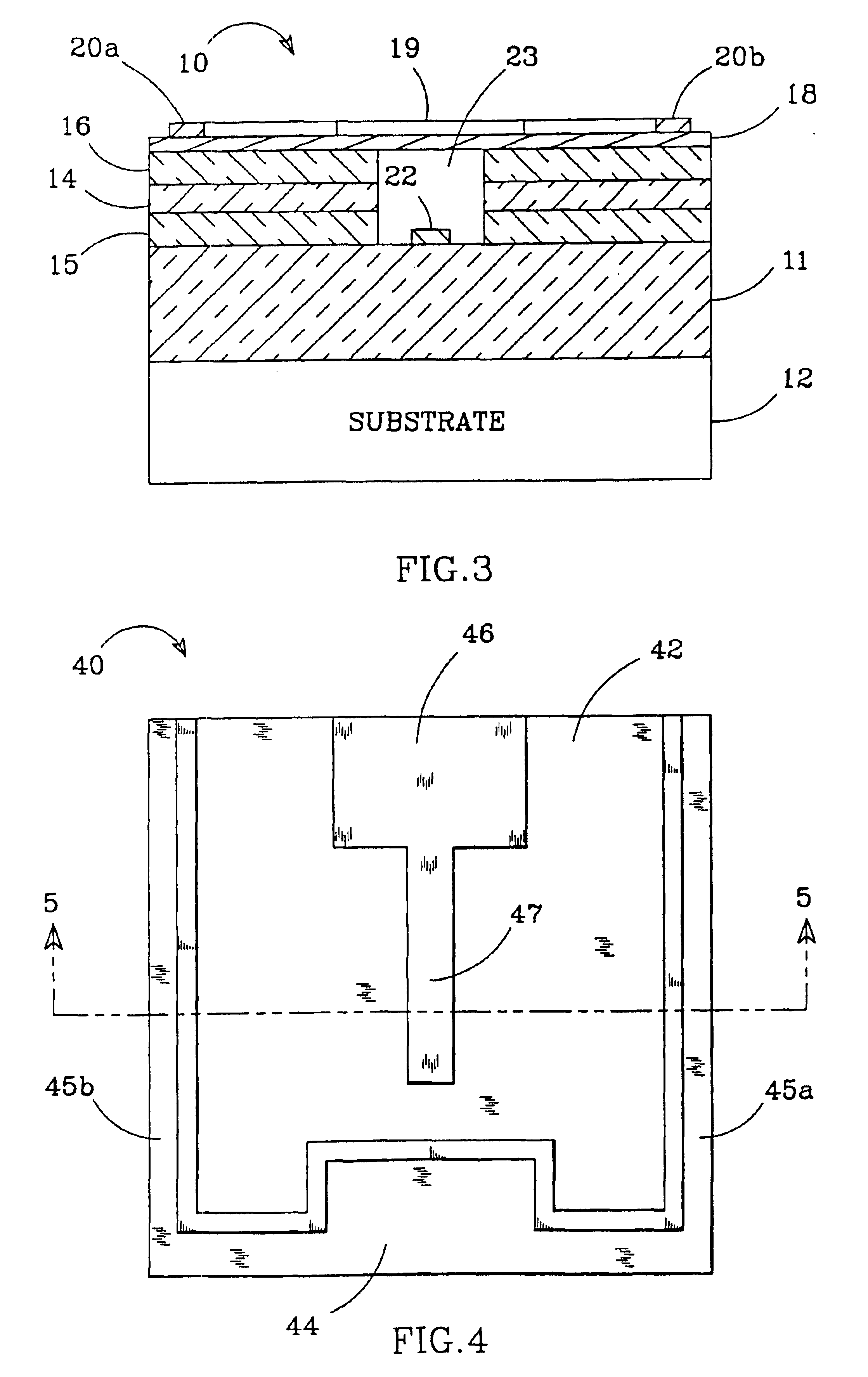
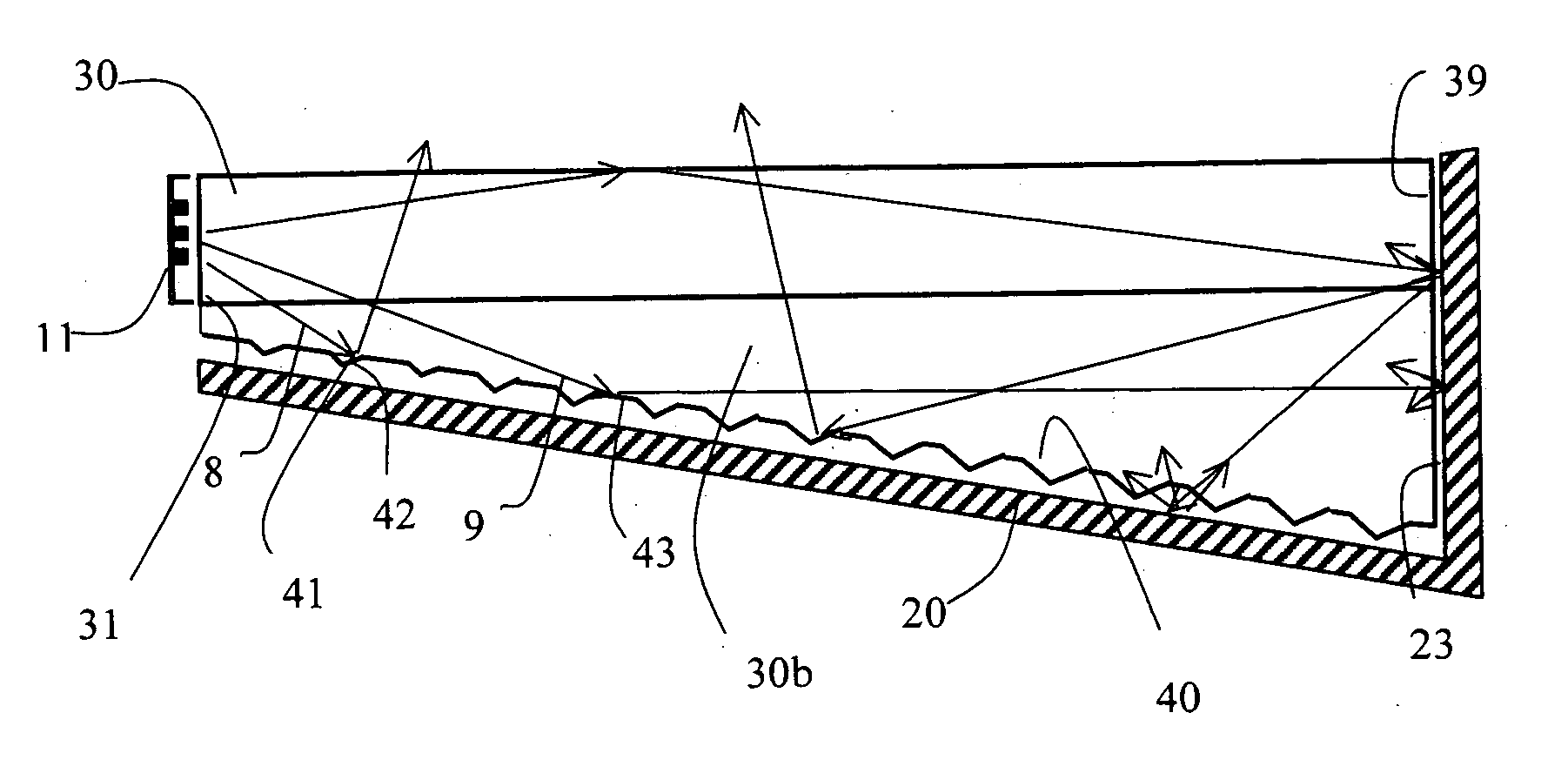
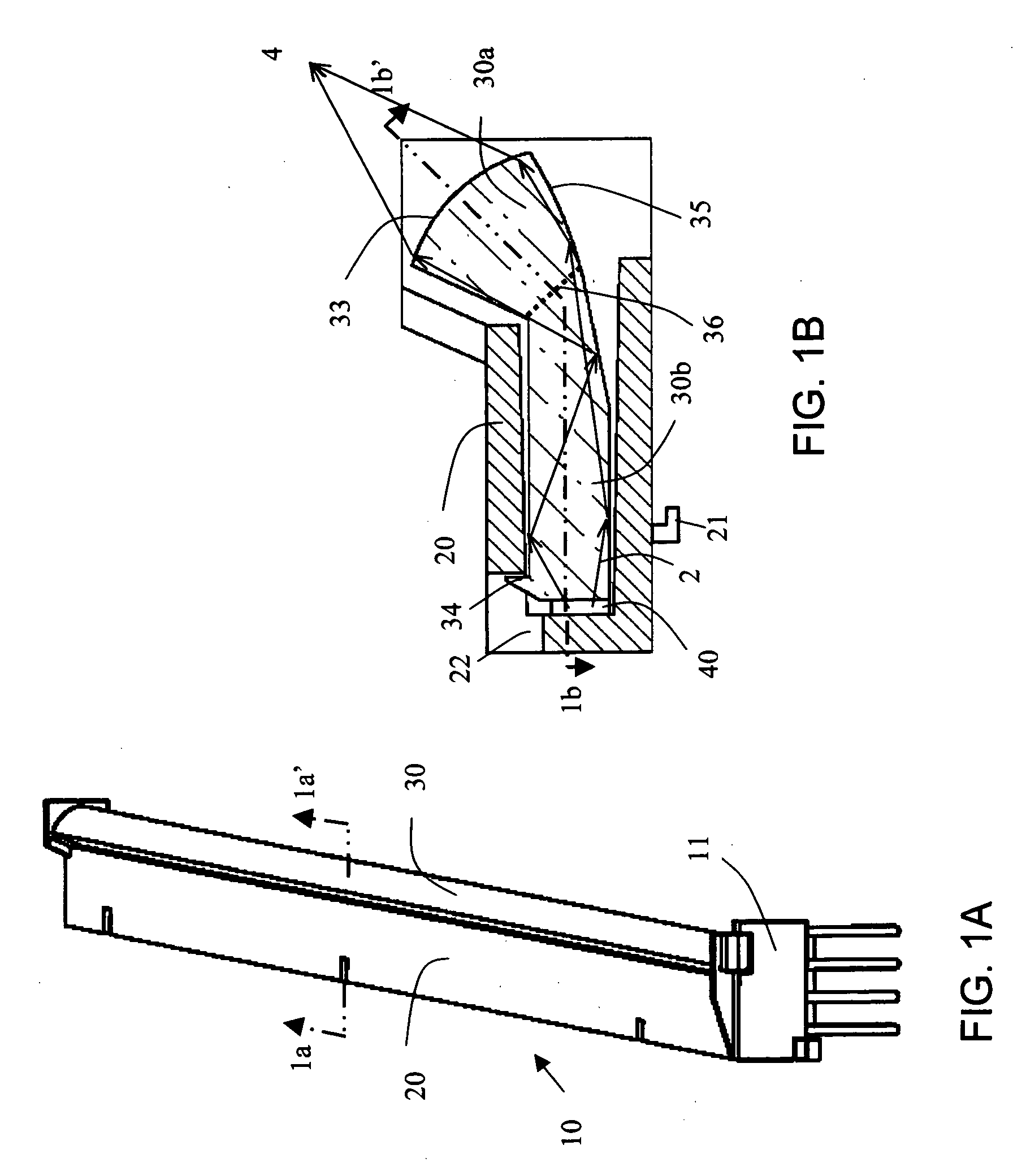
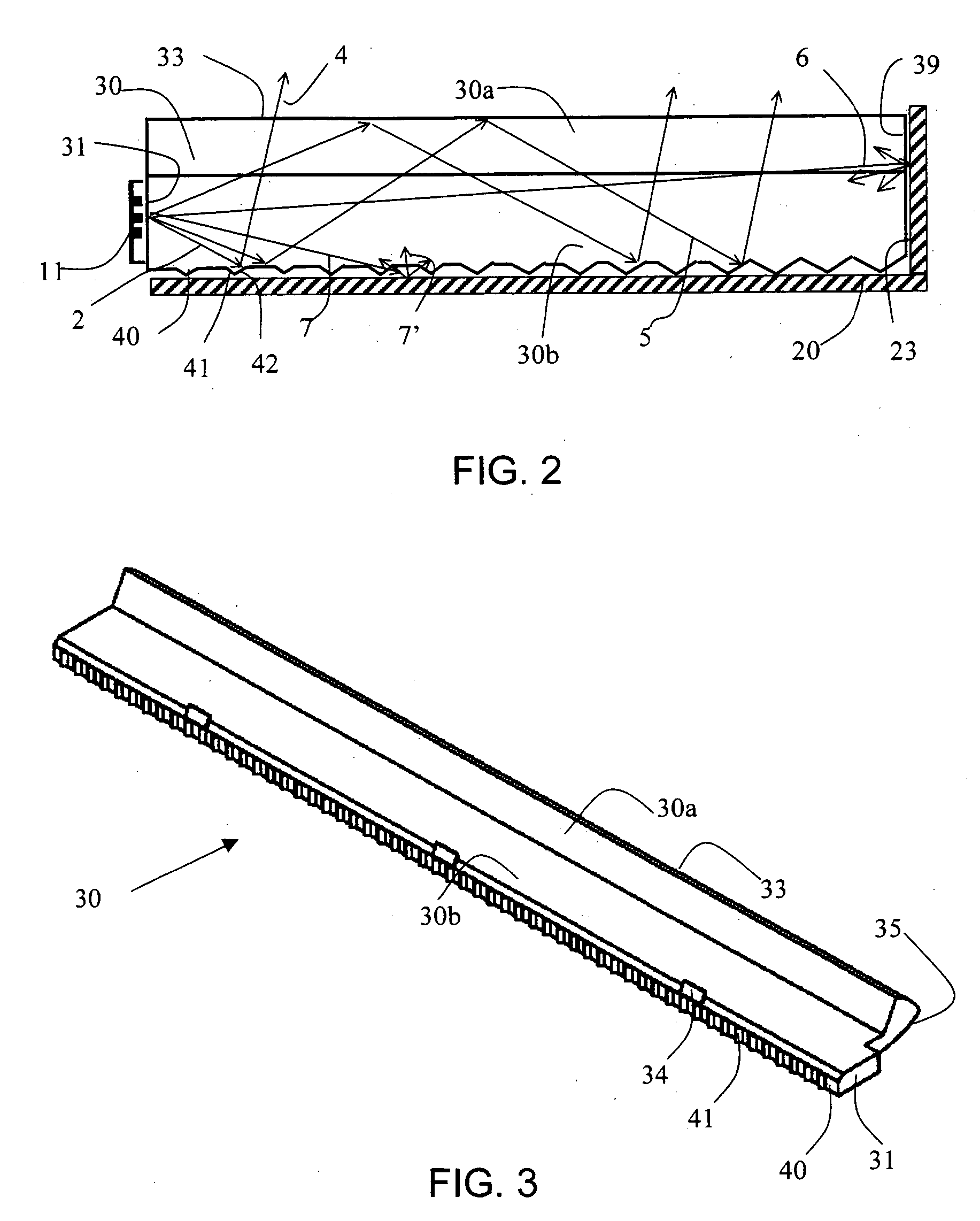
InactiveUS20070040512A1Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsJunction temperatureEngineering
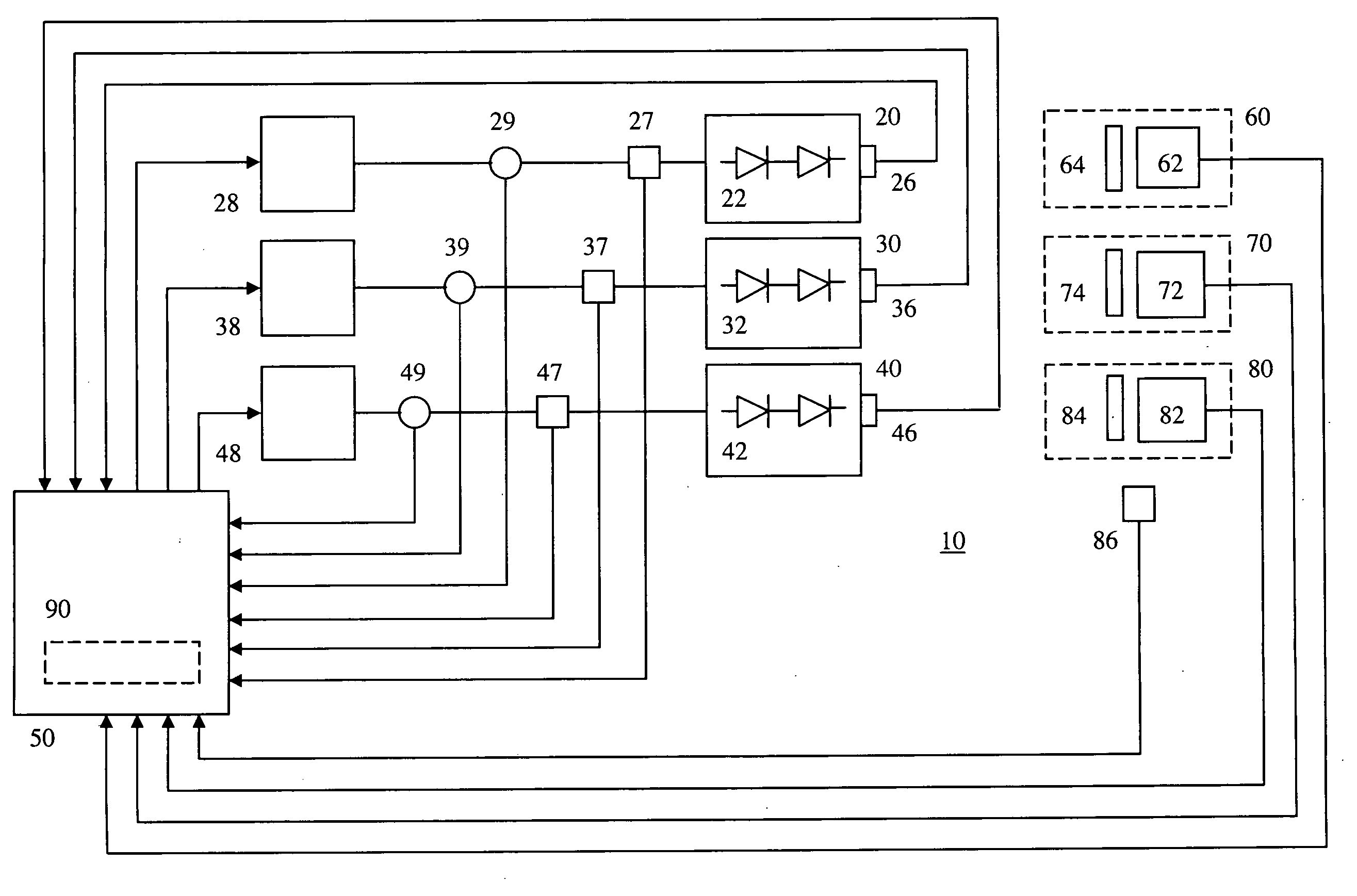
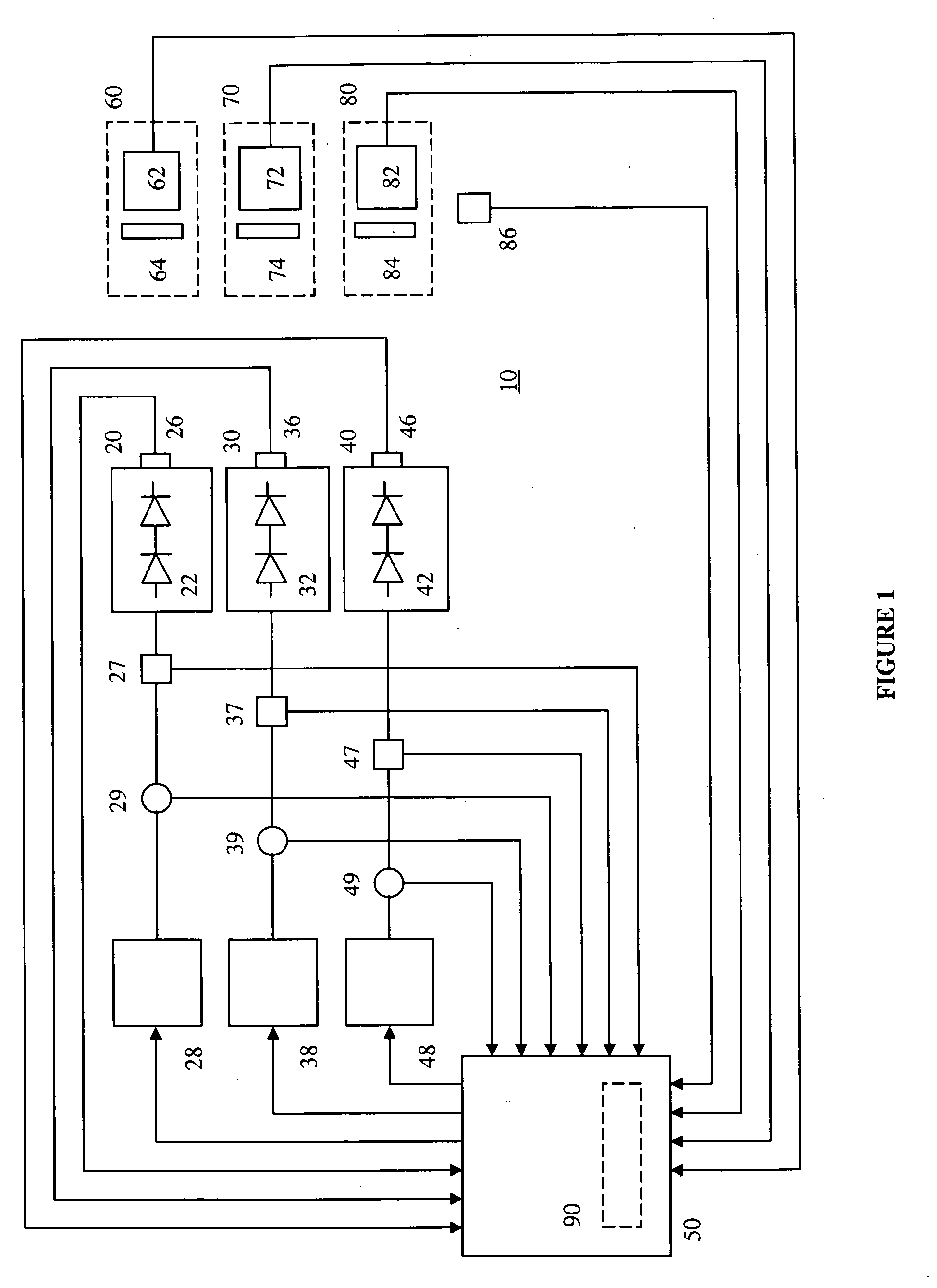
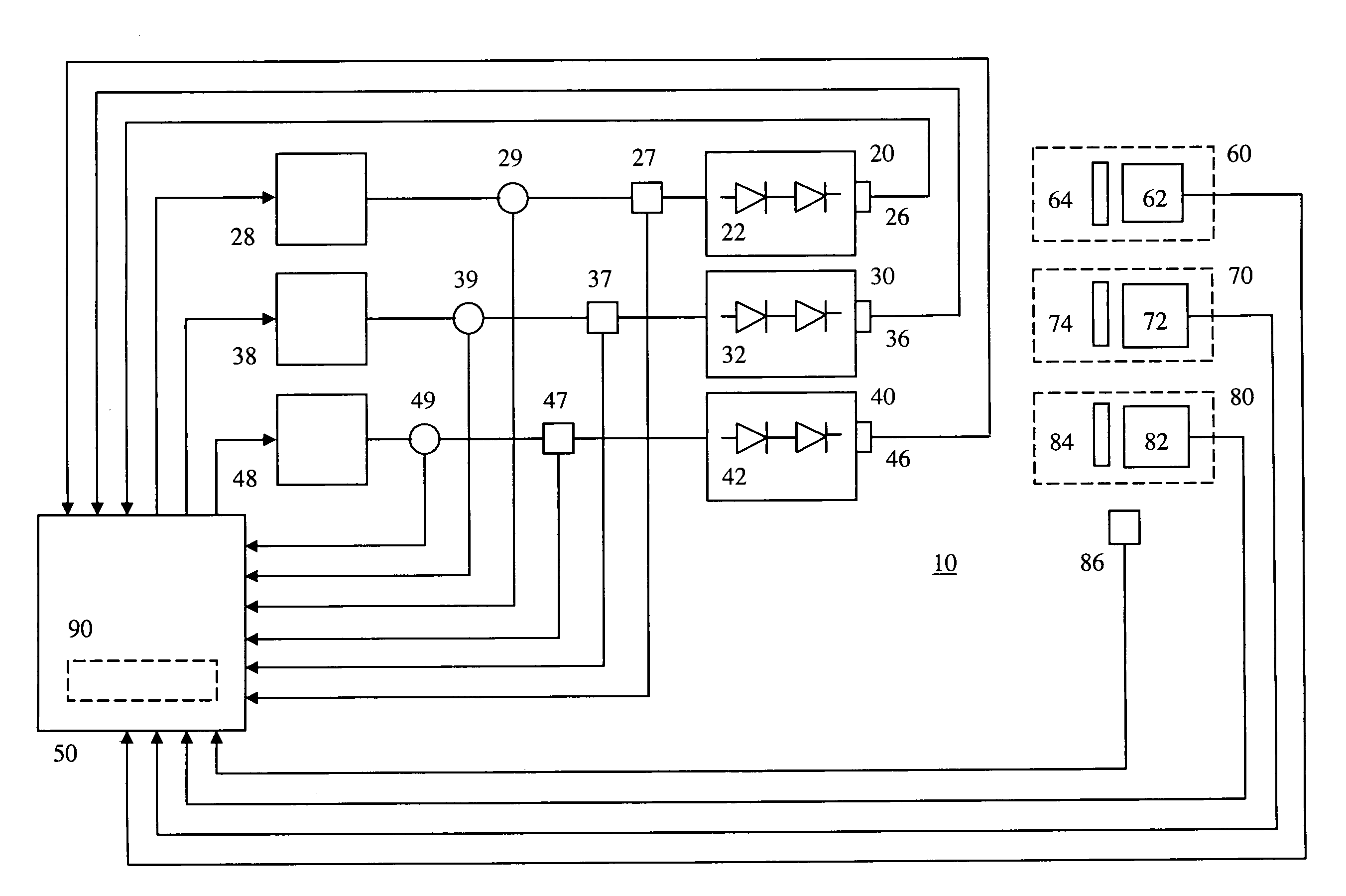
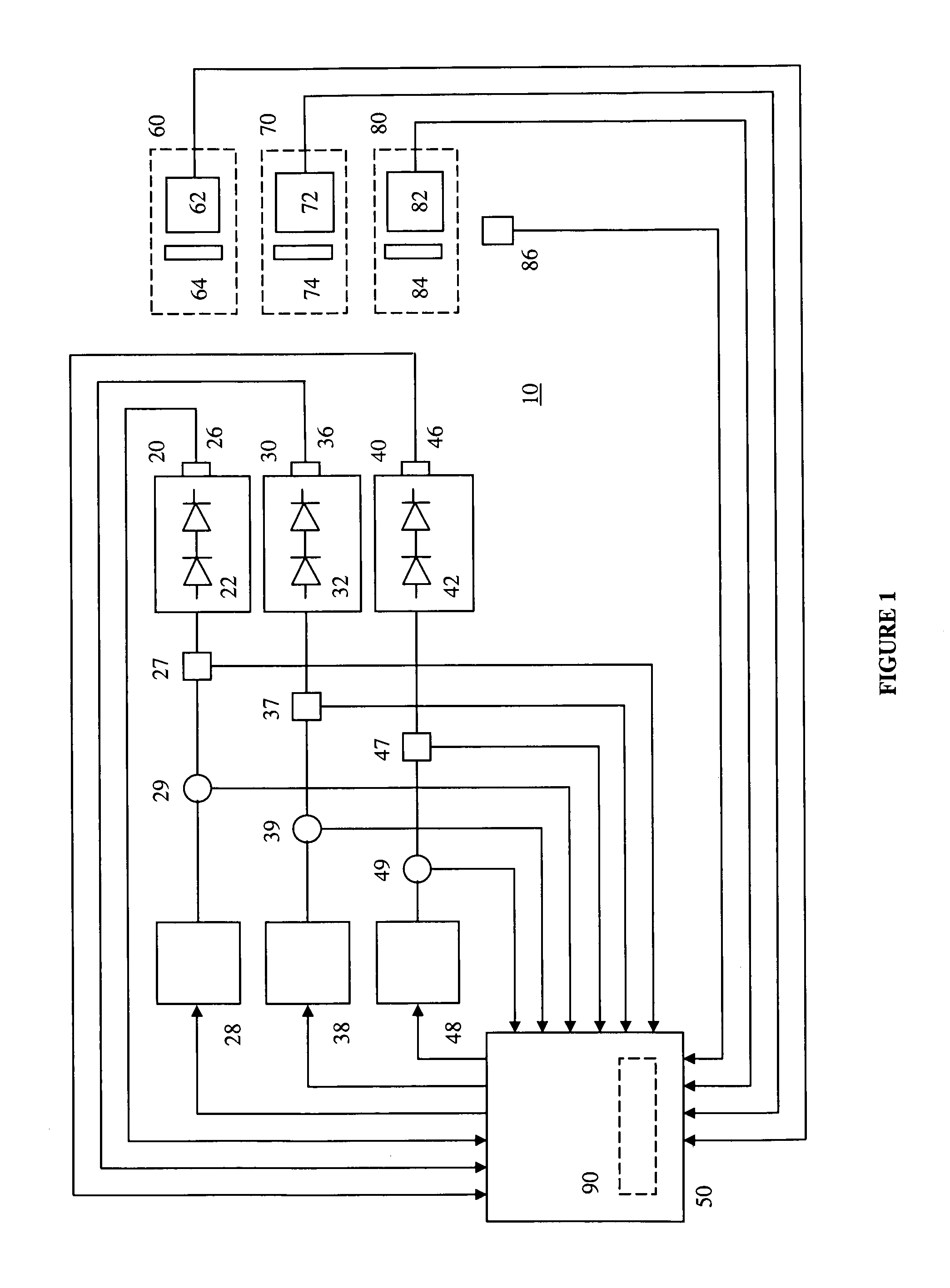
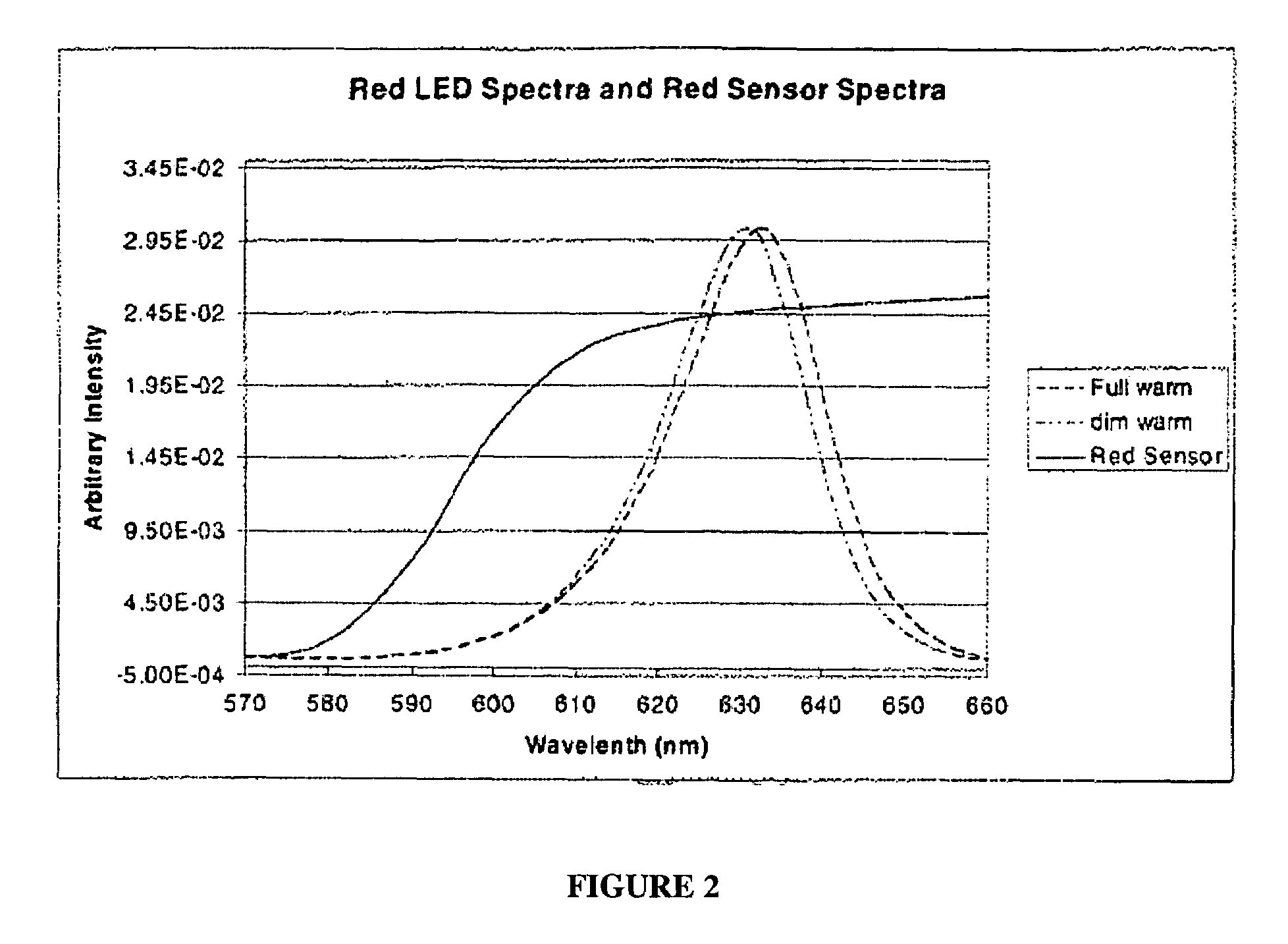
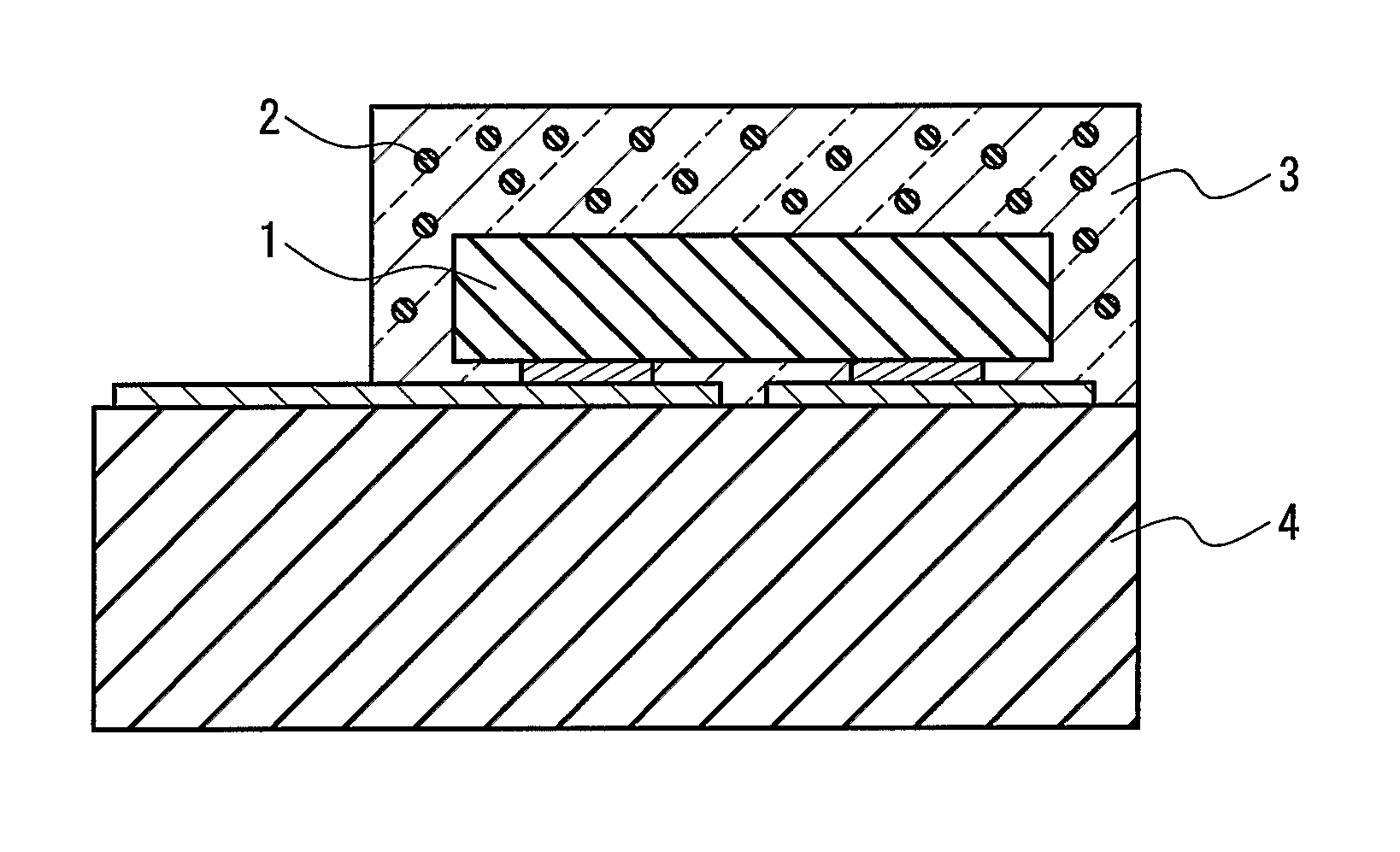
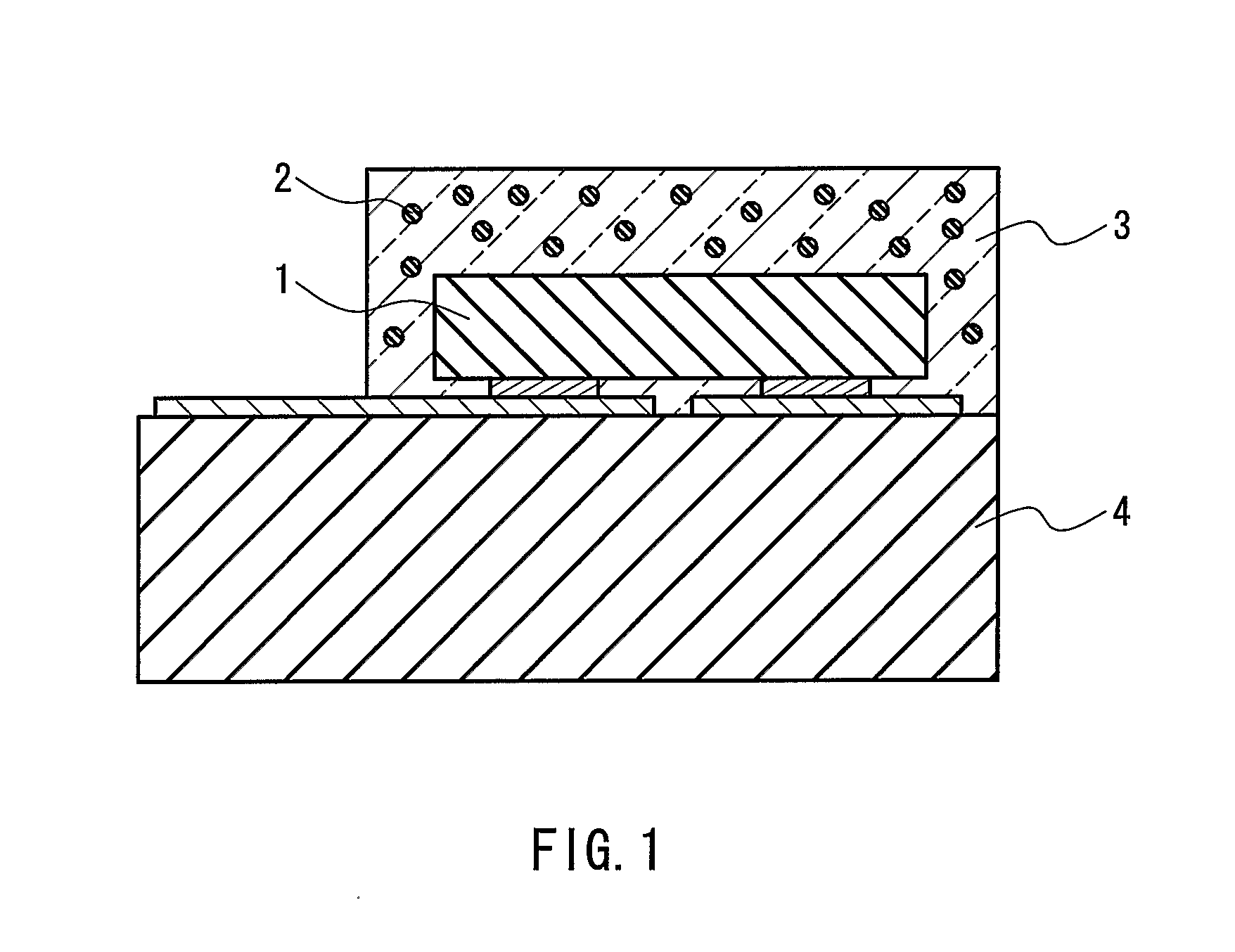
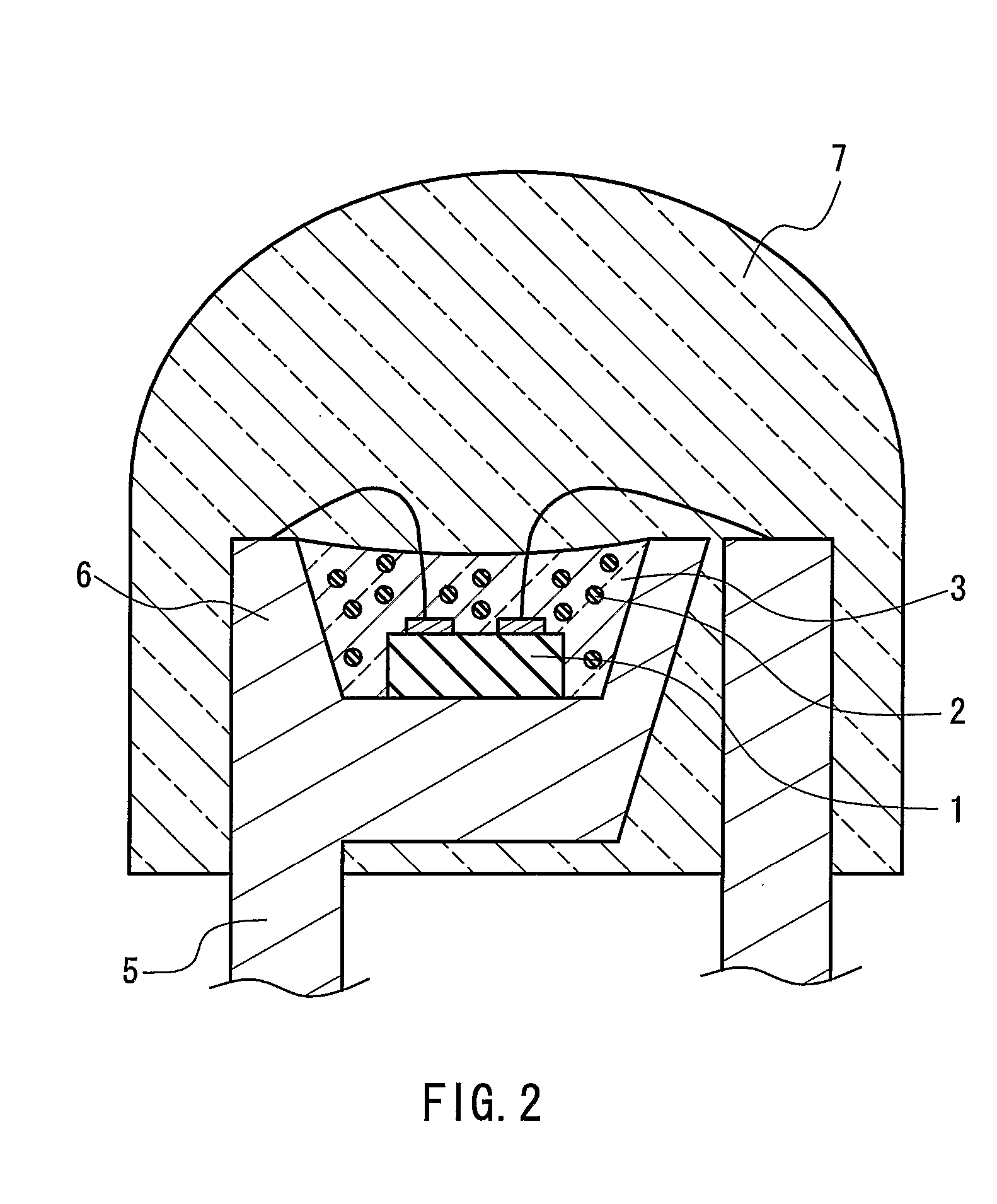
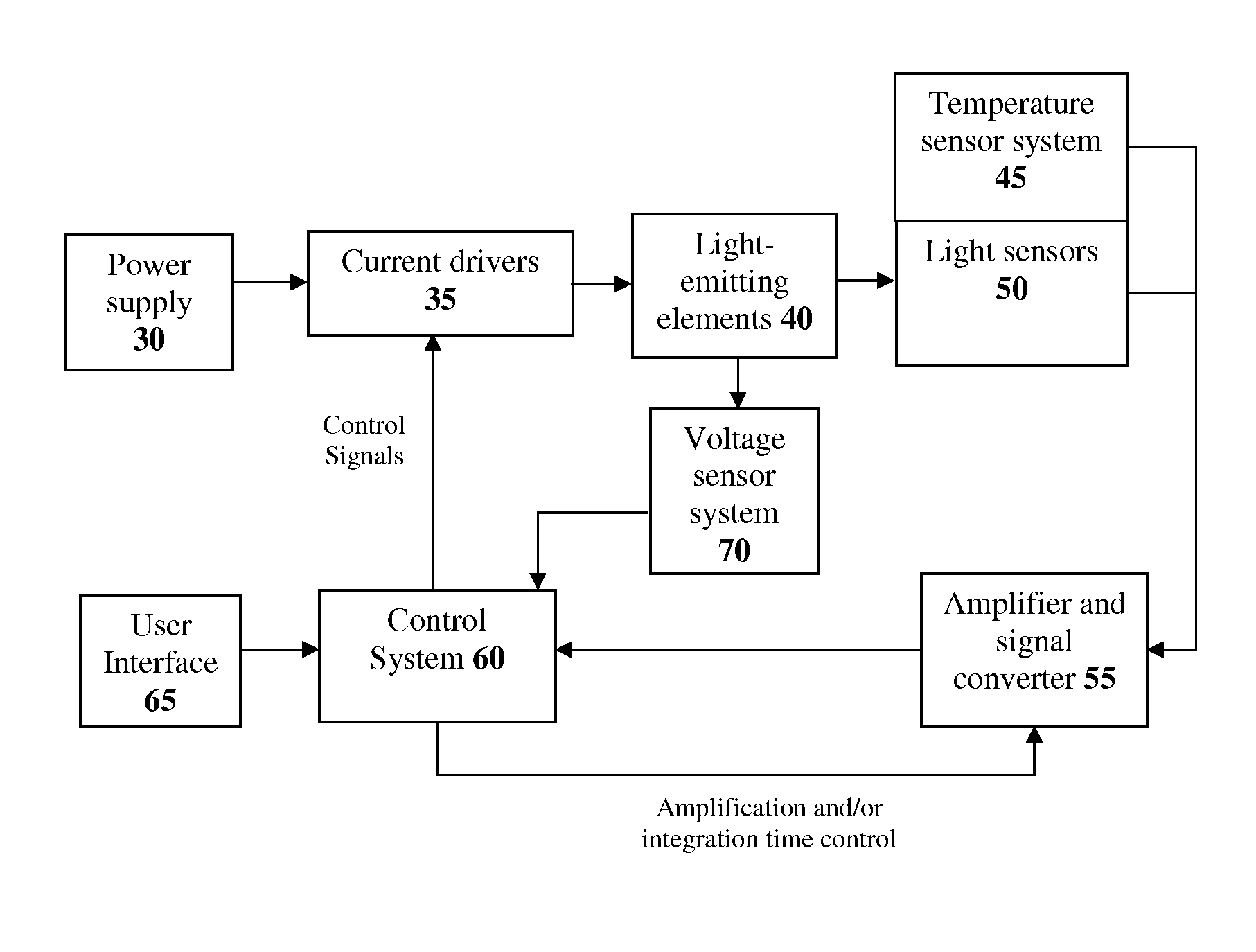
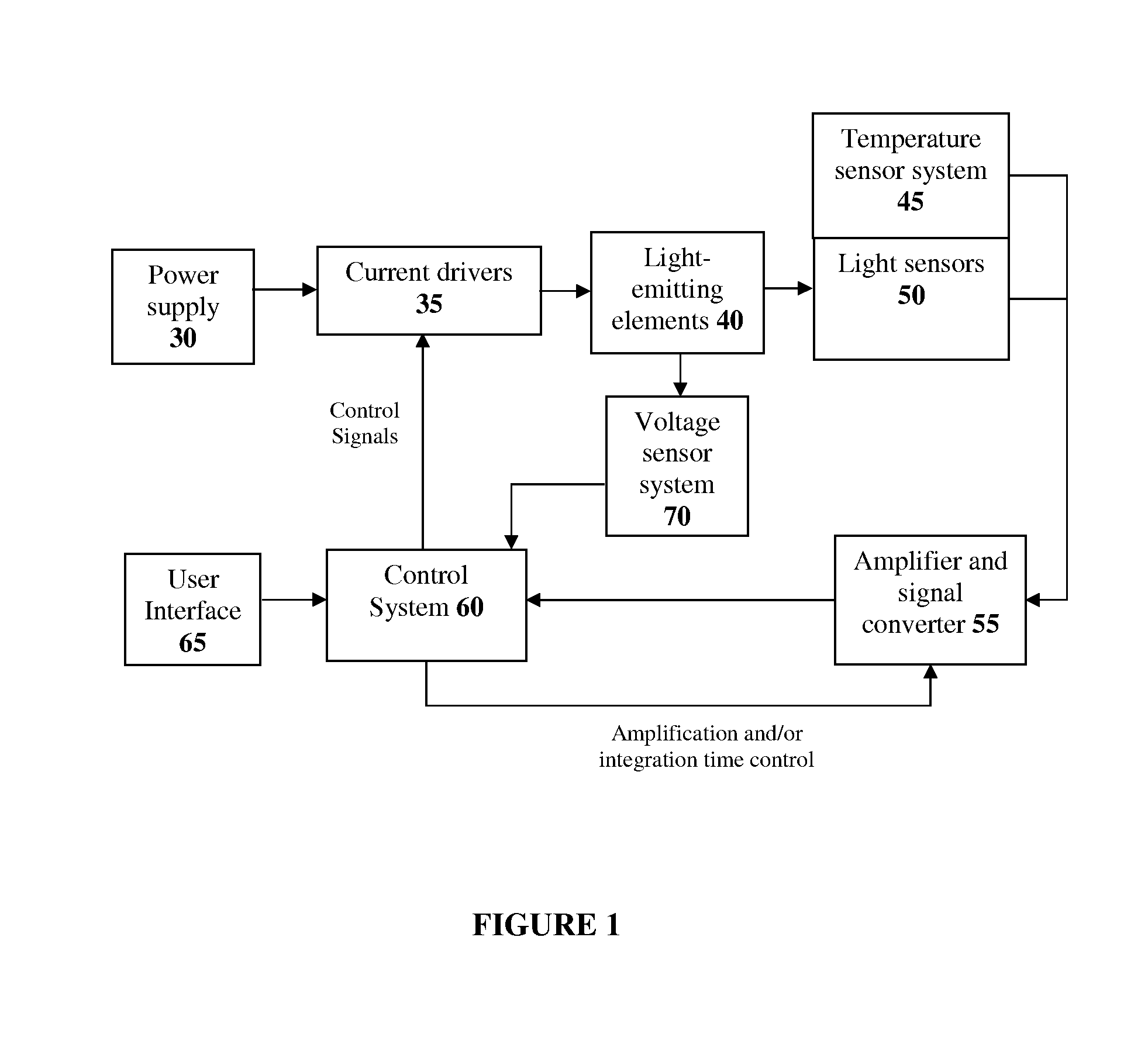
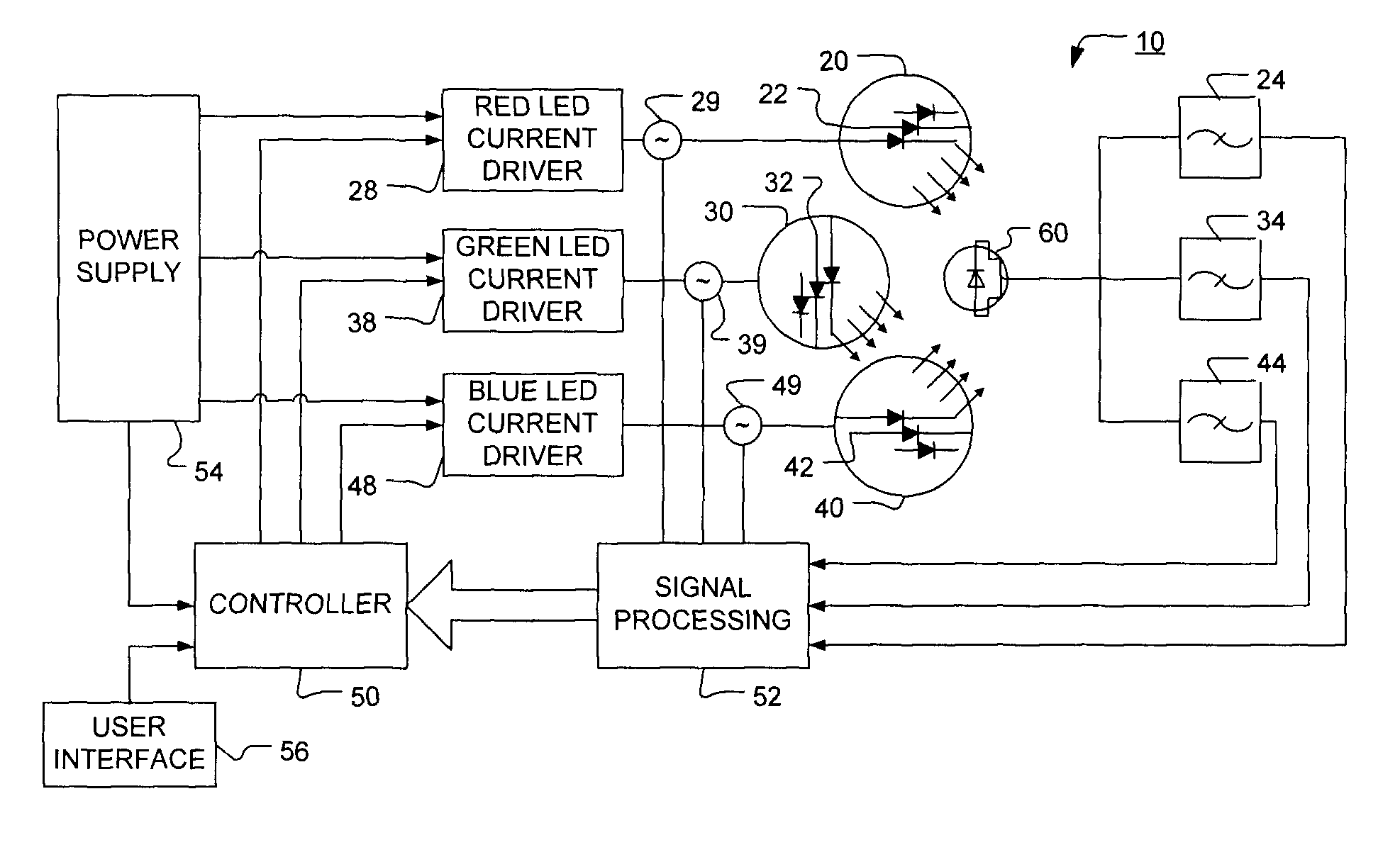
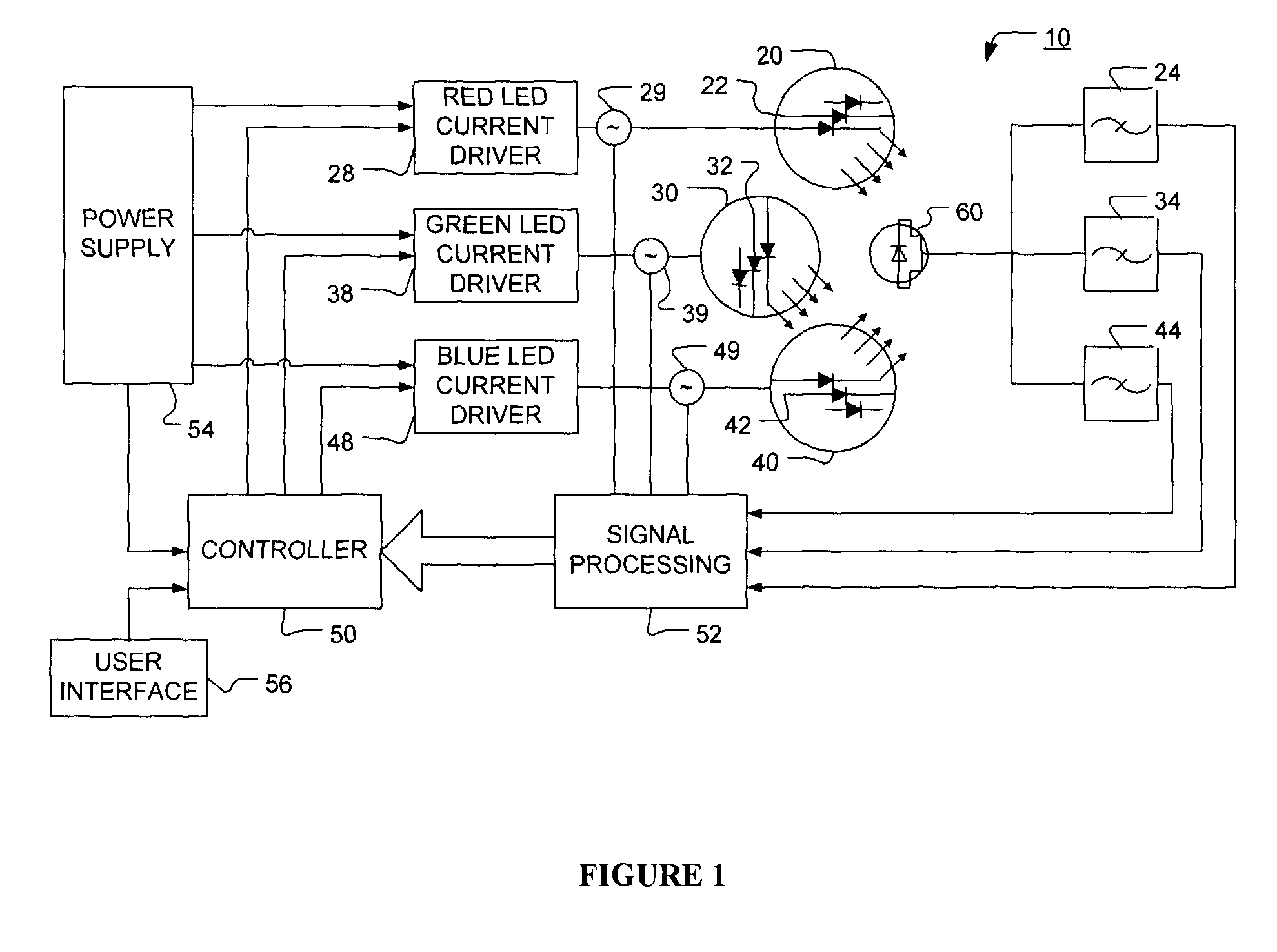
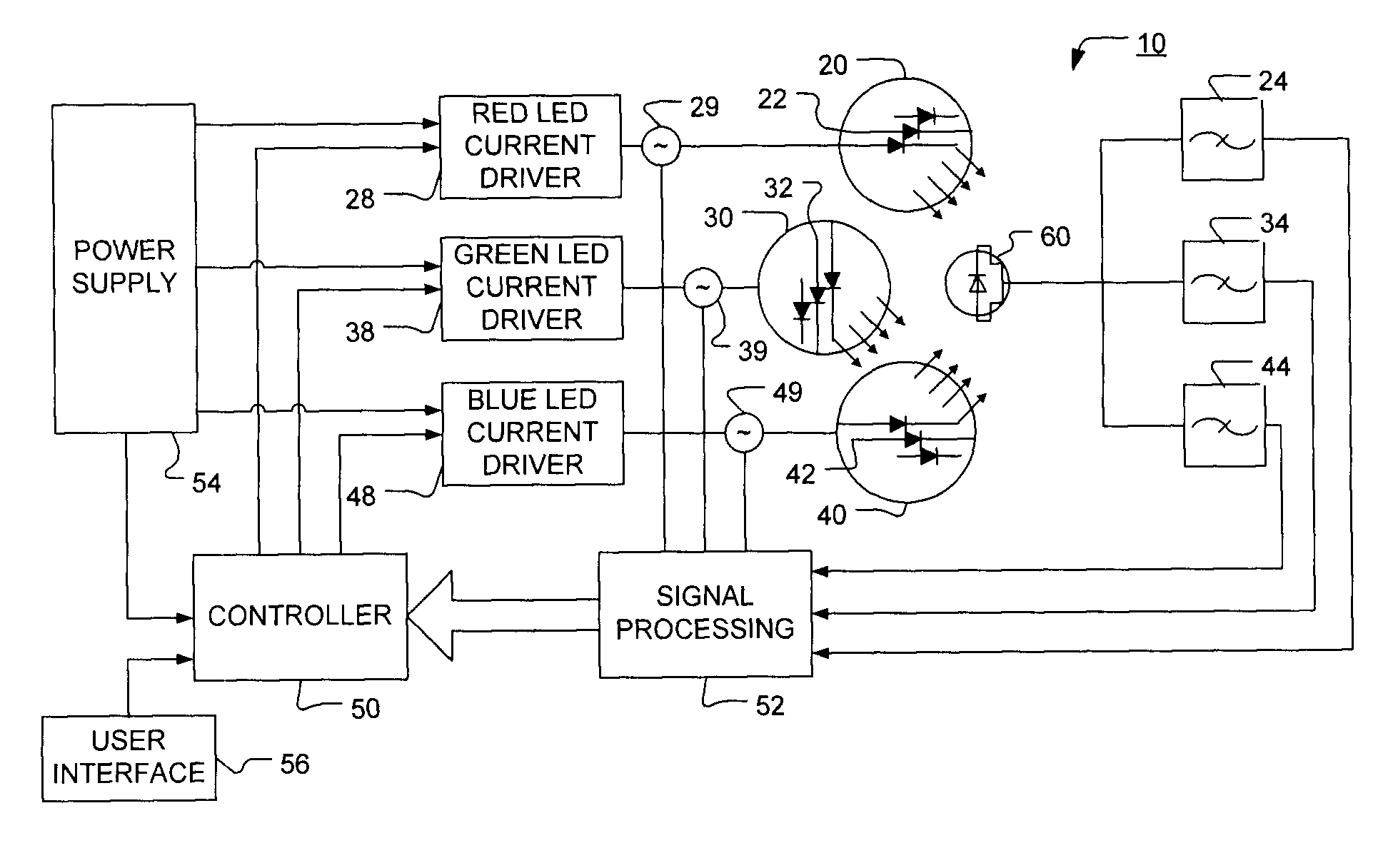
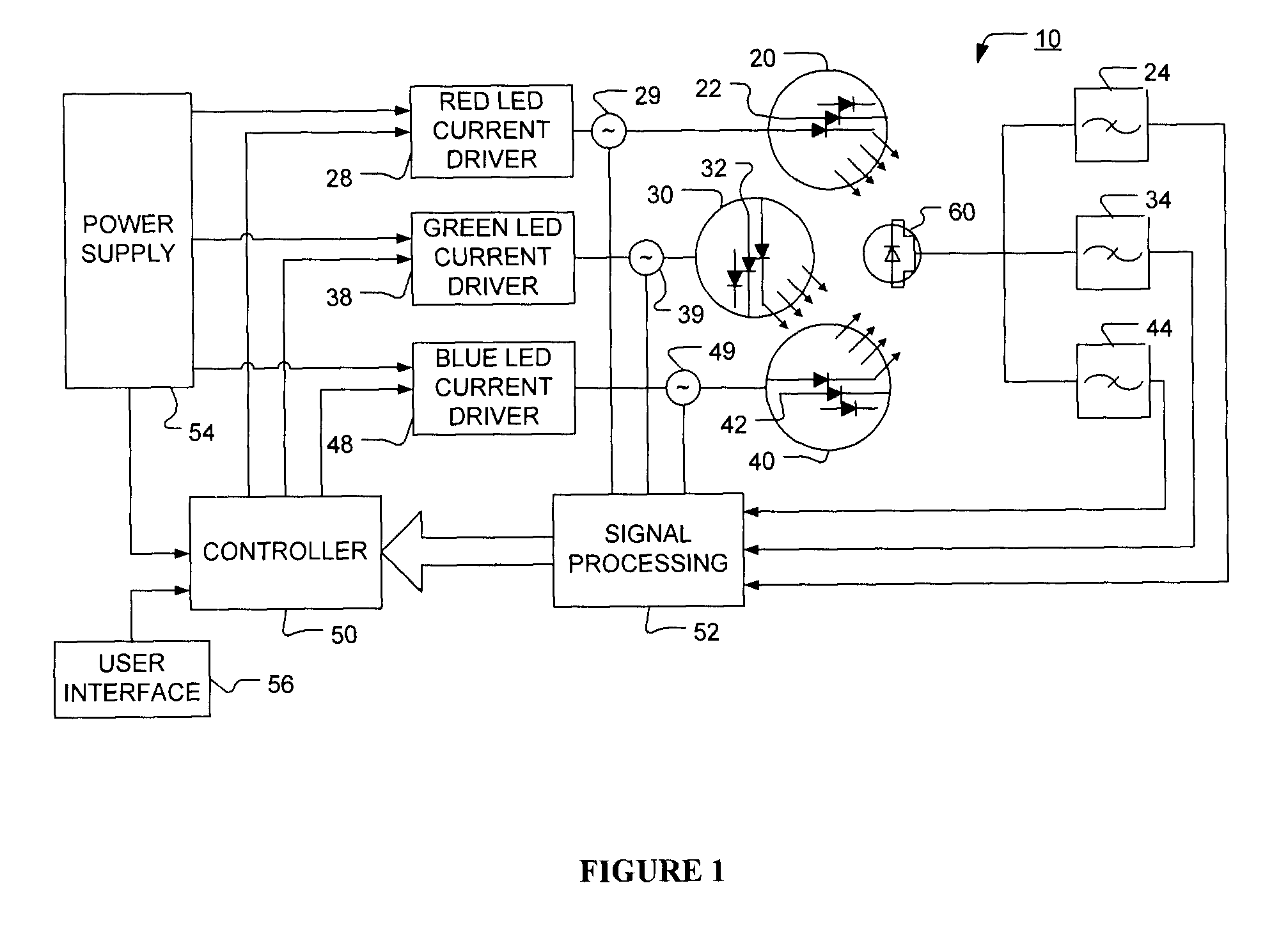
The present invention provides a luminaire system capable of generating light of a desired chromaticity and luminous flux output during continuous operation with varying ambient operating temperature. The luminaire system can be further capable of maintaining a desired correlated colour temperature during dimming of the luminaire. The luminaire system comprises one or more arrays of light-emitting elements for generating light with a current driver system coupled thereto for selectively supplying electrical drive current to each of the arrays, wherein the current driver system is responsive to drive signals received from a controller. The luminaire system further comprises an optical sensor system for generating optical signals representative of chromaticity and luminous flux output of the light. A heat sensing system is operatively coupled to the one or more arrays for generating signals representative of the junction temperatures of arrays of light-emitting elements during operation. The luminaire system further comprises a controller that is operatively connected to the current driver system, the optical sensor system and the heat sensing system for receiving the signals generated by each of these systems and is configured to generate one or more drive signals for transmission to the current driver system in response to the optical signals and thermal signals received from the optical system and the heat sensing system, respectively, thereby enabling a desired level of control of the output light.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Digitally controlled luminaire system
InactiveUS7319298B2Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsJunction temperatureLuminous flux
The present invention provides a luminaire system capable of generating light of a desired chromaticity and luminous flux output during continuous operation with varying ambient operating temperature. The luminaire system can be further capable of maintaining a desired correlated colour temperature during dimming of the luminaire. The luminaire system comprises one or more arrays of light-emitting elements for generating light with a current driver system coupled thereto for selectively supplying electrical drive current to each of the arrays, wherein the current driver system is responsive to drive signals received from a controller. The luminaire system further comprises an optical sensor system for generating optical signals representative of chromaticity and luminous flux output of the light. A heat sensing system is operatively coupled to the one or more arrays for generating signals representative of the junction temperatures of arrays of light-emitting elements during operation. The luminaire system further comprises a controller that is operatively connected to the current driver system, the optical sensor system and the heat sensing system for receiving the signals generated by each of these systems and is configured to generate one or more drive signals for transmission to the current driver system in response to the optical signals and thermal signals received from the optical system and the heat sensing system, respectively, thereby enabling a desired level of control of the output light.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method and system for feedback and control of a luminaire
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
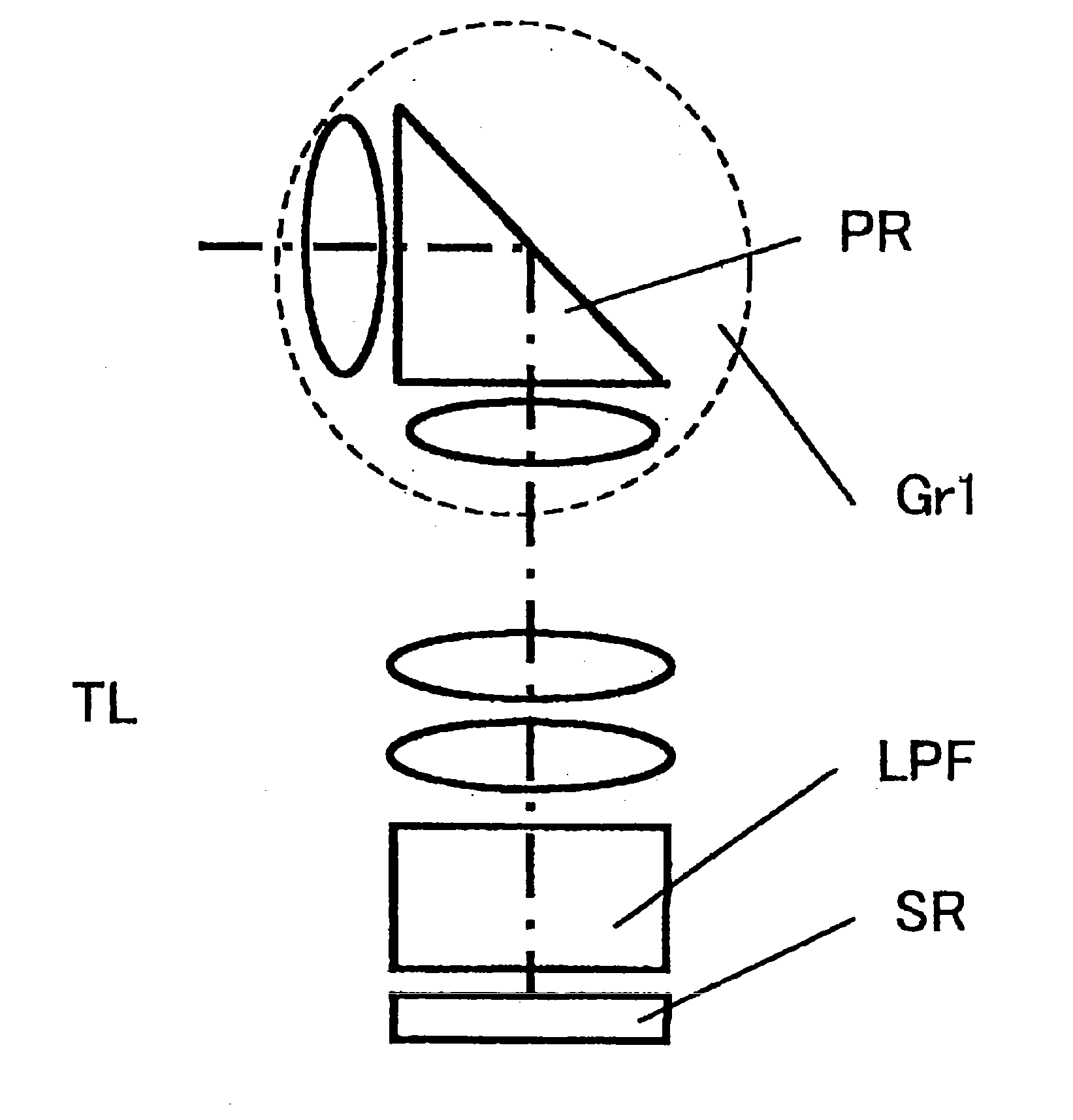
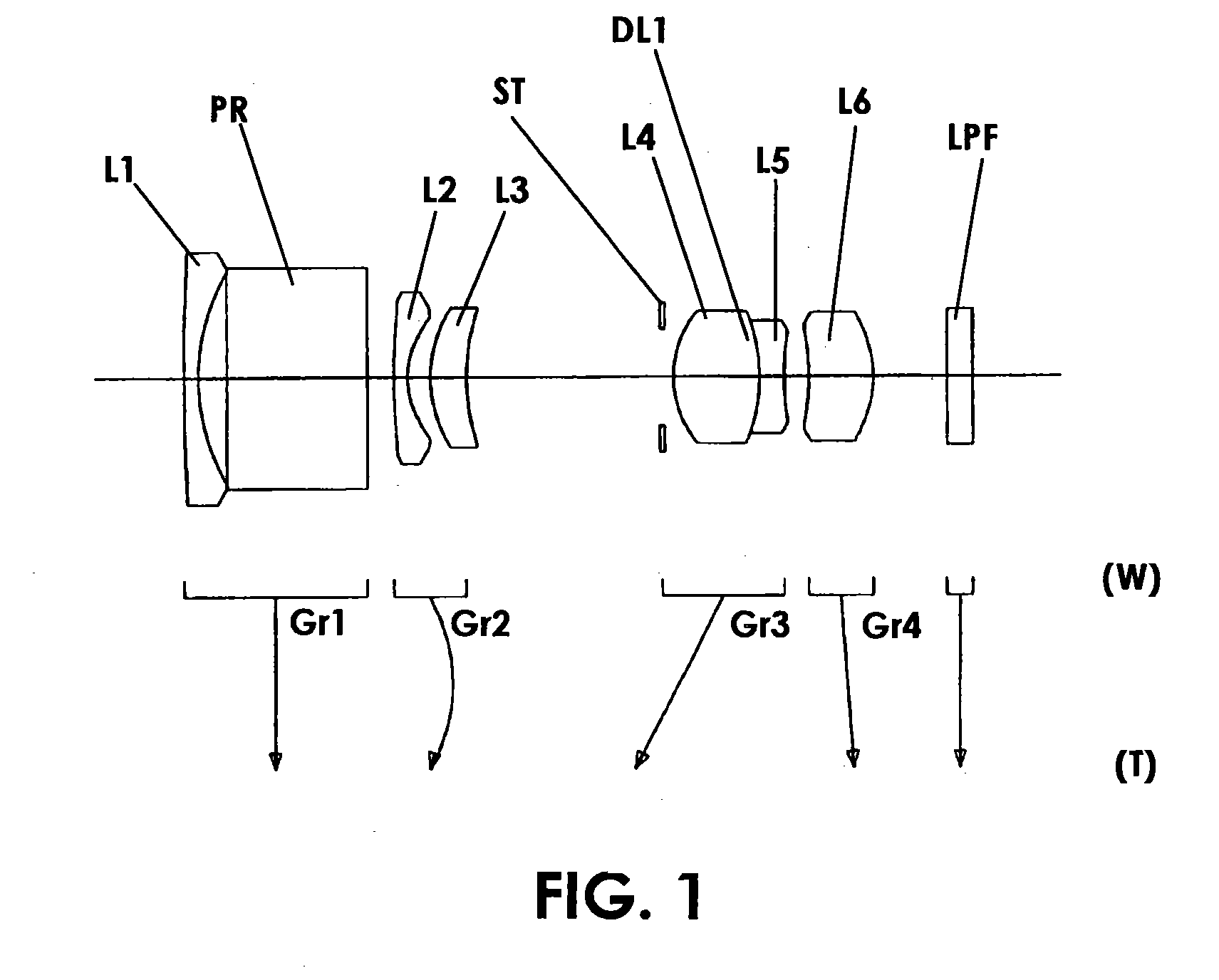
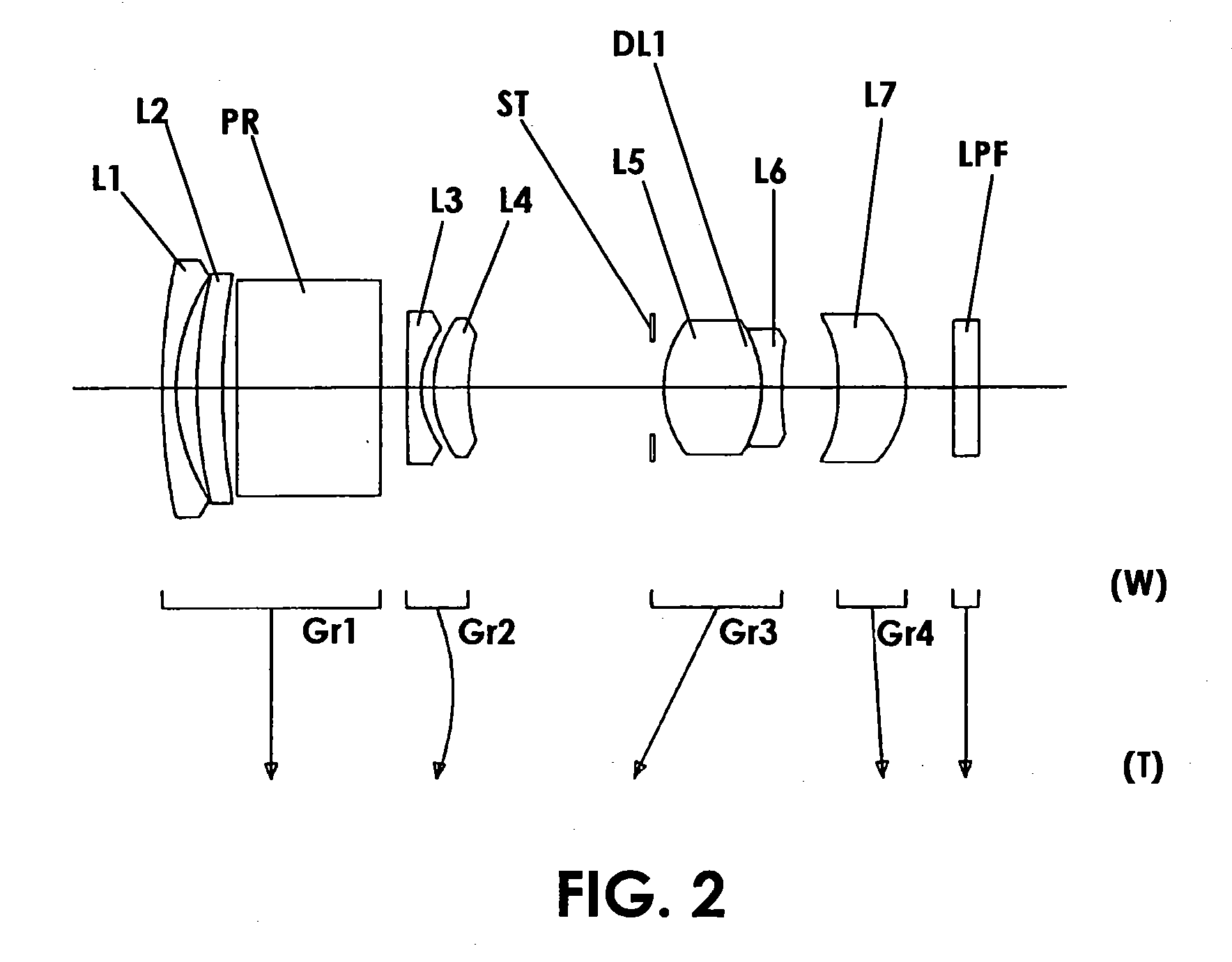
Imaging device and digital camera using the imaging device
InactiveUS20040008271A1Solve the thickerLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical power
An imaging device has a zoom lens system having a plurality of lens units and forming an optical image of an object so as to continuously optically zoom by varying distances between the lens unit; and an image sensor converting the optical image formed by the zoom lens system to an electric signal. The zoom lens system has from an object side, a first lens unit being overall negative and including a reflecting surface that bends a luminous flux substantially 90 degrees; and a second lens unit disposed with a variable air distance from the first lens unit, and having an optical power, and wherein at least one lens element made of resin is included in the entire lens system.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
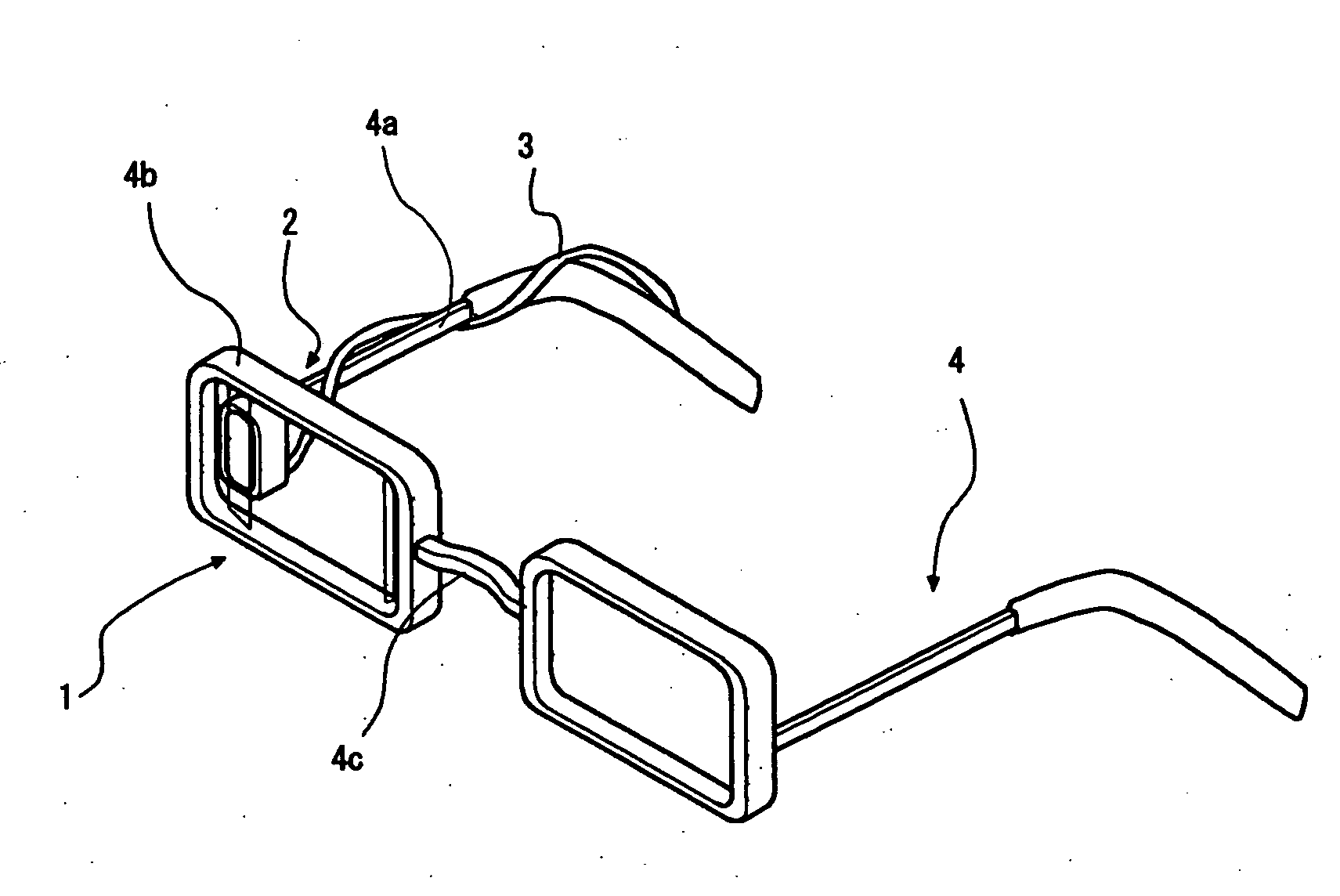
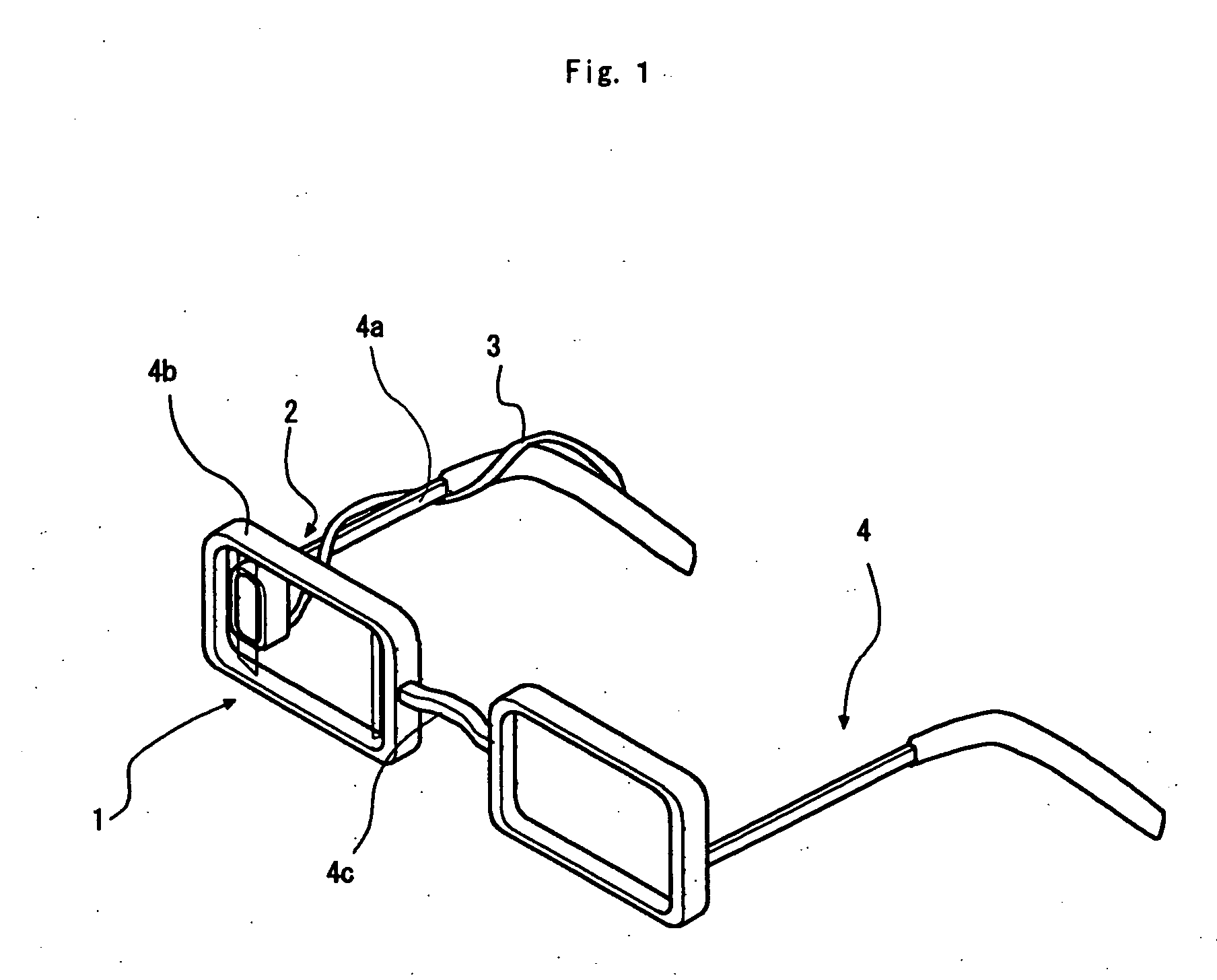
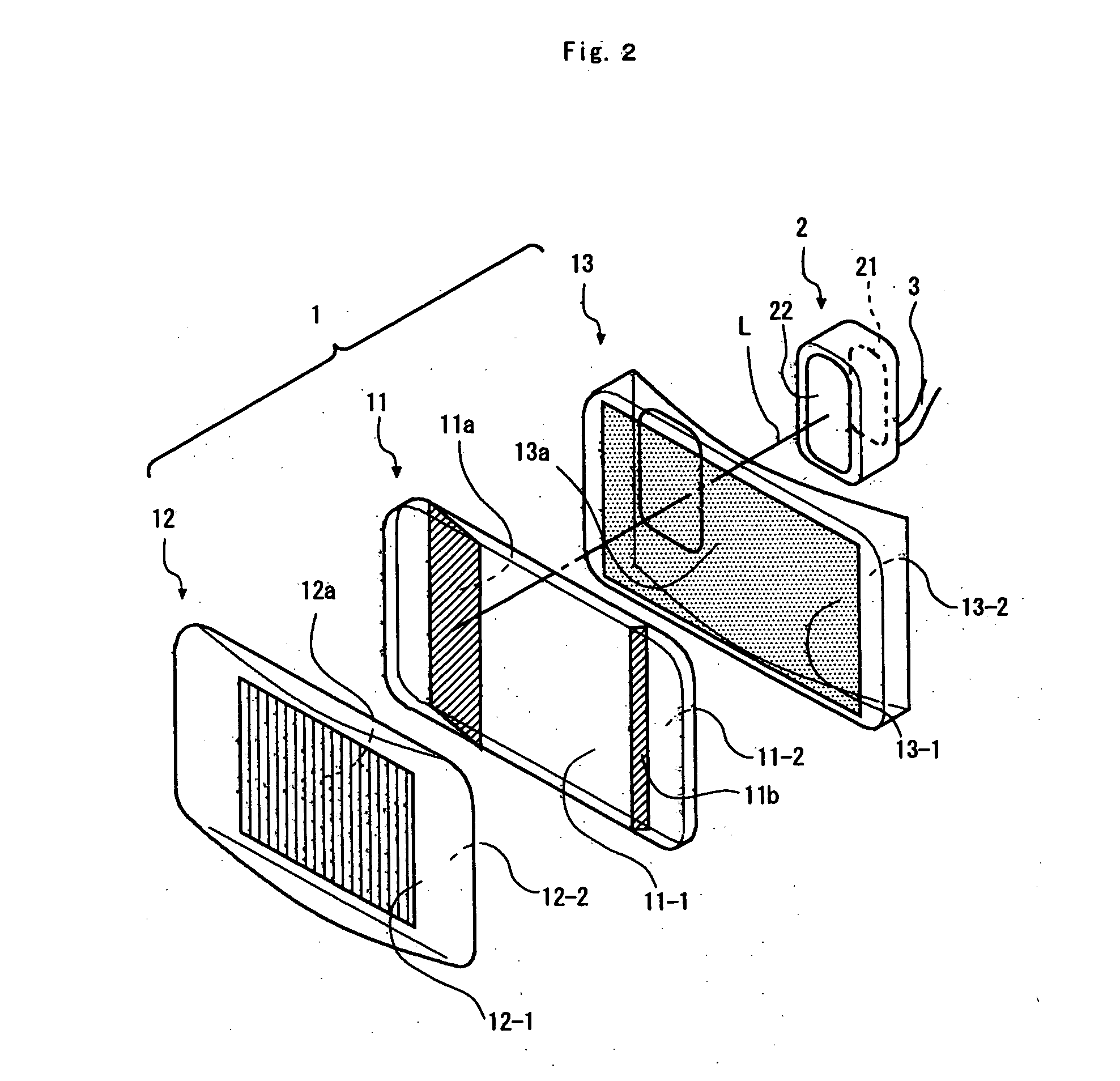
Phosphor Composition and Method for Producing the Same, and Light-Emitting Device Using the Same
A light-emitting device is produced using a phosphor composition containing a phosphor host having as a main component a composition represented by a composition formula: aM3N2.bAlN.cSi3N4, where“M” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Zn, and “a”, “b”, and “c” are numerical values satisfying 0.2≦a / (a+b)≦0.95, 0.05≦b / (b+c)≦0.8, and 0.4≦c / (c+a)≦0.95. This enables a light-emitting device emitting white light and satisfying both a high color rendering property and a high luminous flux to be provided.
Owner:SHENZHEN JUFEI OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for feedback and control of a luminaire
The present invention comprises a method and system for controlling the chromaticity and luminous flux output of a digitally controlled luminaire. The luminaire comprises one or more light-emitting elements and one or more light sensors which can provide optical feedback, wherein this optical feedback is filtered to remove undesired frequencies. The method and system comprises a control system which can sample the filtered signals from the light sensors according to a predetermined feedback sampling frequency scheme, wherein this scheme is specifically configured to provide sufficient iterations of the feedback loop to be performed for adjustment of the chromaticity and luminous flux output of the light-emitting elements, without perceptible visual flicker or momentary chromaticity shifts.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Display device, display method and head-up display
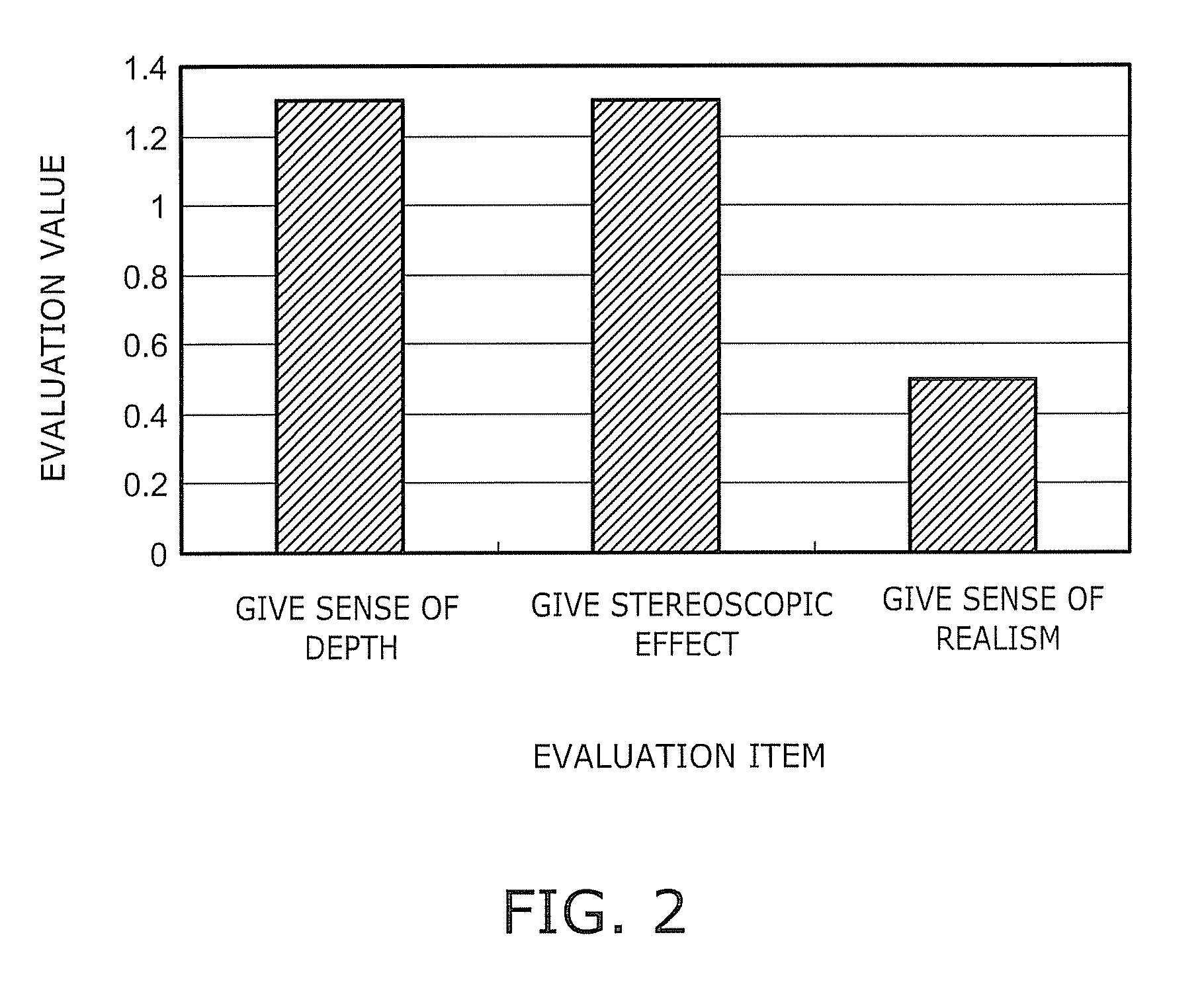
InactiveUS20100214635A1Enhance the sense of depthImprove realismPrismsMountingsHead-up displayDisplay device
A display device, generating light flux containing image information and making the light flux incident to one-eye of an image viewer by controlling an angle of divergence of the light flux is provided. The device includes a first lens, a second lens and an angle of divergence control device provided between the first lens and the second lens, the angle of divergence control device being configured to control the angle of divergence of the light flux.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical image display system and image display unit
InactiveUS20070008624A1Simple structureLarge exit pupilTelevision system detailsPolarising elementsExit pupilLight beam
Optical-image display systems are disclosed having simple structure and a large exit pupil. An exemplary system includes a transmissive plate having inside an optical path of light flux from a display at each angular field of view of an image-display element. The light flux is internally reflected repeatedly in the transmissive plate. An optical-deflection member is provided in close contact with a predetermined region of one surface of the plate used for internal reflection. The optical-deflection member emits to the outside of the plate a portion of each of the light fluxes from the display having reached the predetermined region, and deflects a portion of each light flux in a predetermined direction by reflection. Thus, a virtual image is formed of the display screen of the image-display element.
Owner:NIKON CORP
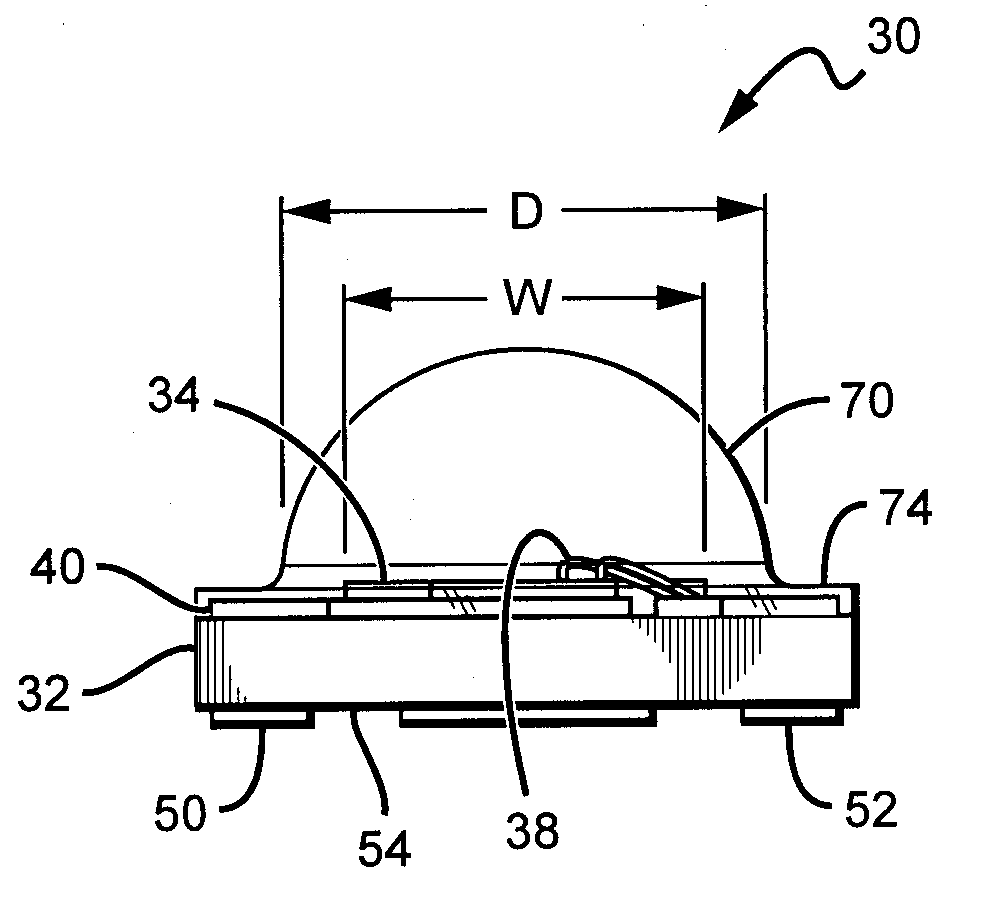
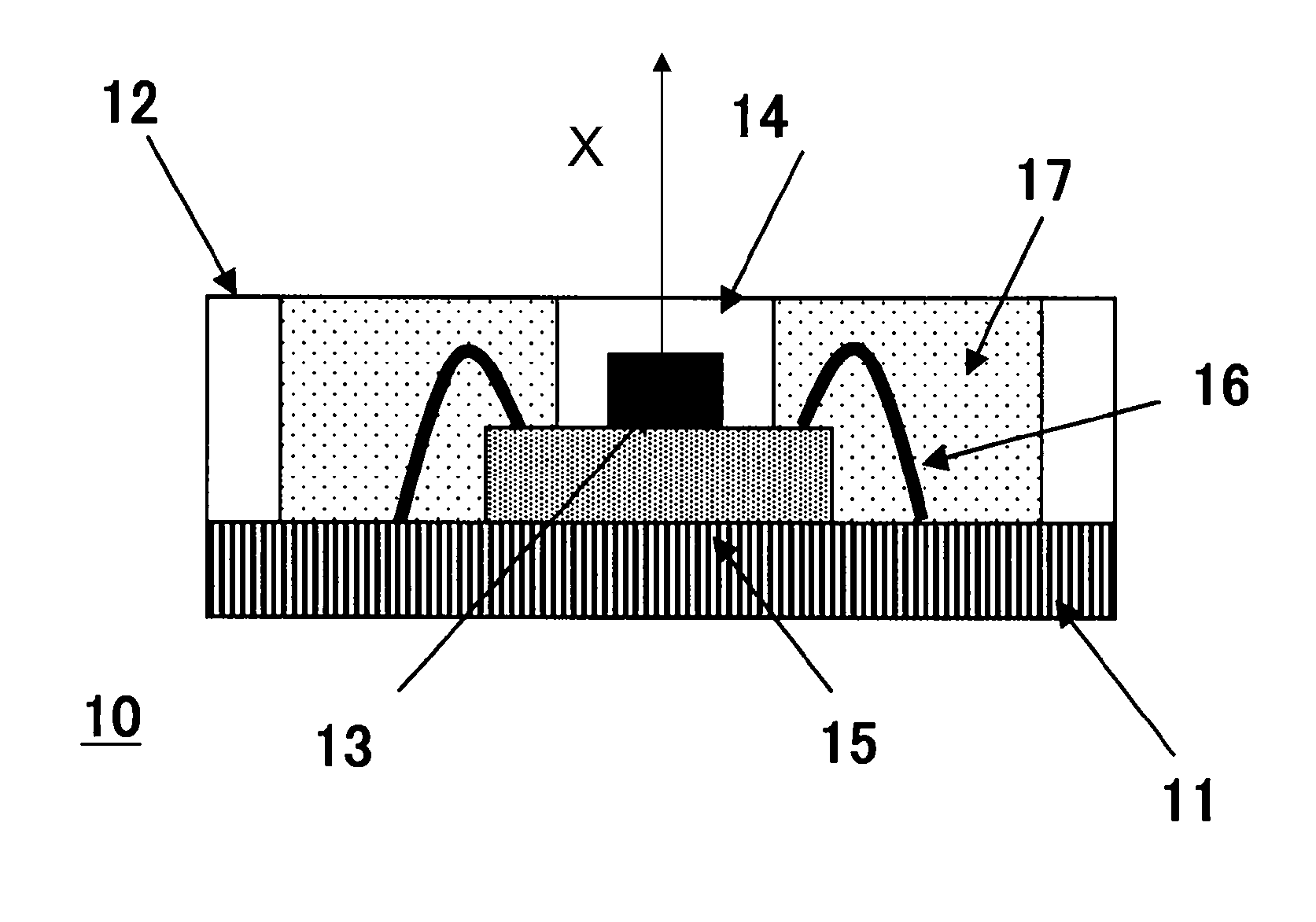
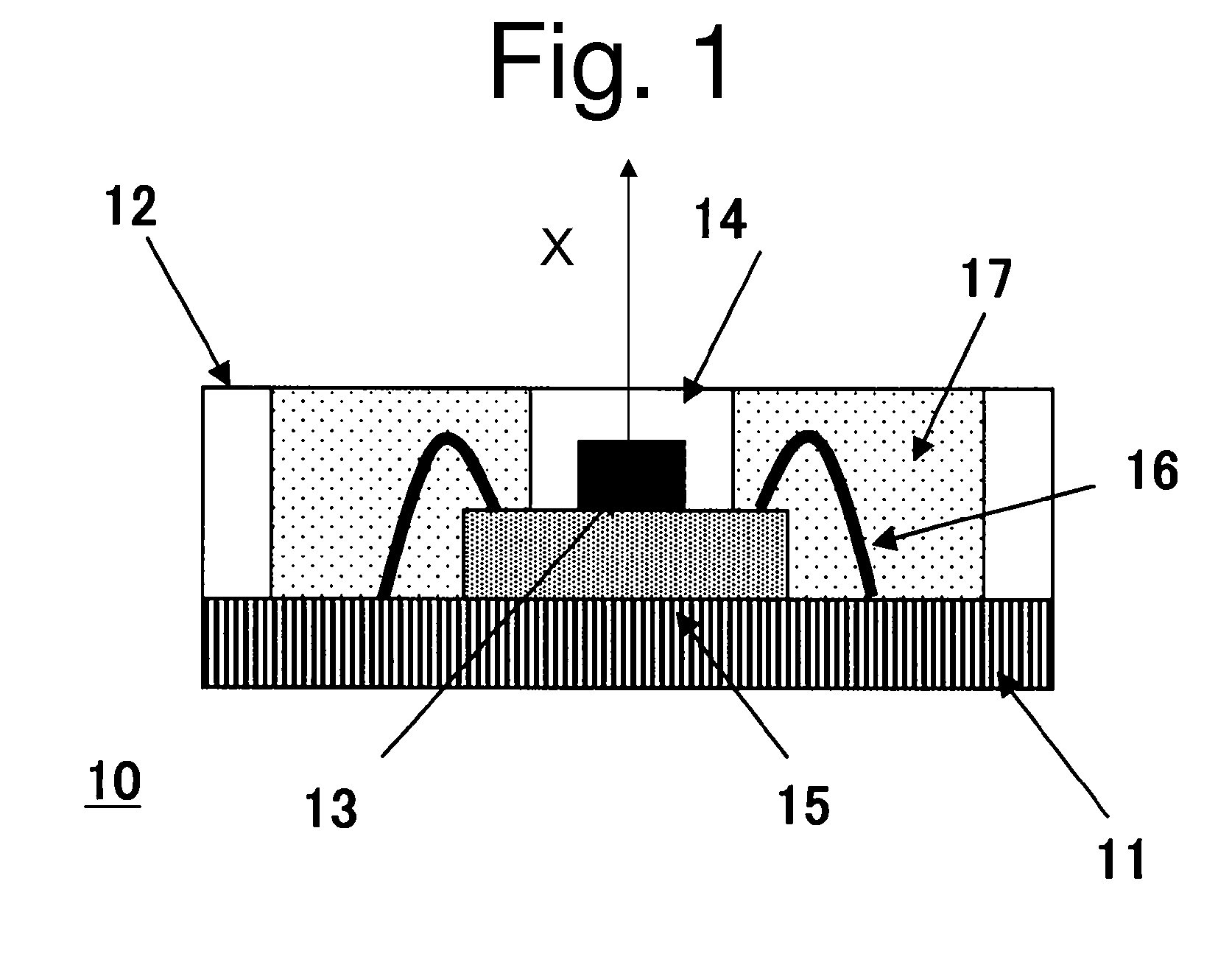
LED package with increased feature sizes
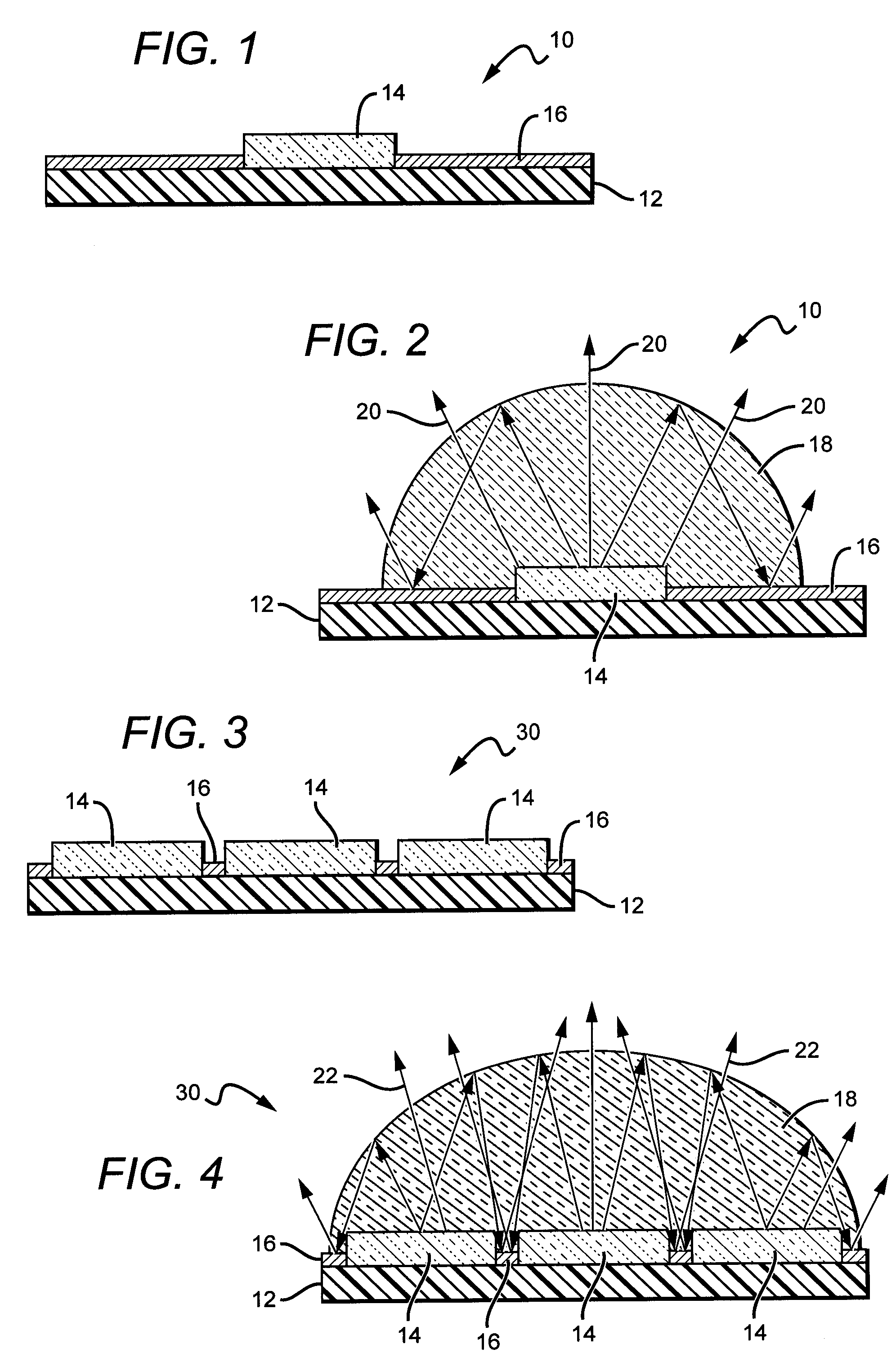
A light emitter package having increased feature sizes for improved luminous flux and efficacy. An emitter chip is disposed on a submount with a lens that covers the emitter chip. In some cases, the ratio of the width of the light emitter chip to the width of said lens in a given direction is 0.5 or greater. Increased feature sizes allow the package to emit light more efficiently. Some packages include submounts having dimensions greater than 3.5 mm square used in conjunction with larger emitter chips. Materials having higher thermal conductivities are used to fabricate the submounts, providing the package with better thermal management.
Owner:CREELED INC
Phosphor composition and method for producing the same, and light-emitting device using the same
A light-emitting device is produced using a phosphor composition containing a phosphor host having as a main component a composition represented by a composition formula: aM3N2.bAlN.cSi3N4, where “M” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Zn, and “a”, “b”, and “c” are numerical values satisfying 0.2≦a / (a+b)≦0.95, 0.05≦b / (b+c)≦0.8, and 0.4≦c / (c+a)≦0.95. This enables a light-emitting device emitting white light and satisfying both a high color rendering property and a high luminous flux to be provided.
Owner:SHENZHEN JUFEI OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Virtual image display apparatus
InactiveUS20160124223A1Change in luminanceSuppressing image degradationMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight beamDisplay device
A virtual image display apparatus includes a first light guide that not only causes a display light flux incident through a first light incident surface to repeatedly undergo internal reflection to travel in a first direction away from the first light incident surface but also causes part of the display light flux to exit to the outside through areas of a first light exiting surface that is at least one of interfaces with the outside and extends in the first direction, a first light-incident-side diffraction grating that diffracts light incident thereon to cause the diffracted light to enter the first light guide, and a first light-exiting-side diffraction grating that diffracts light incident from the first light guide.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Semiconductor light-emitting device, lighting module, lighting device and method for manufacturing semiconductor light-emitting device
ActiveUS7420221B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorFluorescence
A semiconductor light-emitting device includes: a semiconductor multilayer film, a substrate supporting the semiconductor multilayer film; and a phosphor layer formed on the substrate so as to cover the semiconductor multilayer film. The phosphor layer has an outer edge of a cross section taken in a direction parallel to the principal surface of the substrate having a substantially circular shape or a substantially regular polygonal shape having five or more sides. An outer edge of the principal surface of the substrate is formed in a substantially circular shape or a substantially regular polygonal shape having five or more sides. With this configuration, light obtained therefrom has less non-uniformity in color and a high luminous flux can be realized.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image display apparatus
ActiveUS20050237488A1Improve efficiencyIncreasing amount of passageTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight beamLuminous flux
A technique is provided that improves the usage ratio of light in the illumination optical system of an image display apparatus. The cross-sectional size or shape of the flux of light that has formed a light source image of an LED-based light-emitting section is converted by anamorphic optics, such as collimator lens, into a size or shape appropriate for an aperture in the portion that permits the flux of the light source image to pass through, in an optical system leading to an image display element(s), and thus the quantity of fluxes of light passed through the aperture is increased.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Semiconductor light emitting device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100140648A1Increase brightnessInhibitionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesHigh luminanceLuminous flux
A semiconductor light emitting device can be configured to maintain high luminance and to suppress the possibility of the occurrence of wire breakage with high quality and reliability. A method for producing such a semiconductor light emitting device with a high process yield is also disclosed. The semiconductor light emitting device can include a sealing member into which a reflective filler can be mixed in such an amount (concentration) range that luminous flux with a predetermined amount can be maintained and the possibility of the occurrence of wire breakage can be lowered. Various sealing members containing a reflective filler with a plurality of concentrations within this range can be prepared in advance. By taking advantage of the phenomenon where chromaticity shifts depending on the concentration of the reflective filler, a semiconductor light emitting device with less chromaticity variation can be produced utilizing a sealing member with a particular concentration in accordance with the chromaticity of a particular semiconductor light emitting element that is used and which may be varied during fabrication.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Scalable LED with improved current spreading structures
InactiveUS6885036B2Increase power outputIncreased luminous fluxSemiconductor devicesLuminous fluxEngineering
An LED with improved current spreading structures that provide enhanced current injection into the LED's active layer, improving its power and luminous flux. The current spreading structures can be used in LEDs larger than conventional LEDs while maintaining the enhanced current injection. The invention is particularly applicable to LEDs having insulating substrates but can also reduce the series resistance of LEDs having conductive substrates. The improved structures comprise conductive fingers that form cooperating conductive paths that ensure that current spreads from the p-type and n-type contacts into the fingers and uniformly spreads though the oppositely doped layers. The current then spreads to the active layer to uniformly inject electrons and holes throughout the active layer, which recombine to emit light.
Owner:CREE INC
Illumination apparatus providing longitudinal illumination
InactiveUS20060269213A1Improve reflectivityUniform lightLighting and heating apparatusOptical signallingLight equipmentLight guide
An illumination device using an innovative design to provide a uniform, highly concentrated and substantially longitudinal illumination. The device includes, at least one light source unit, a compound light guide with a built-in light-extracting feature and a reflective envelope. The compound light guide comprises two optically coupled sub-guides. A first sub-guide has a constant cross-section area with a profile optimized for an integral light-concentrating optics, and a second sub-guide has a varying cross-section area for controlling local light flux density inside the light guide and providing assembly means. Said light extracting feature having variable light extraction efficiency improves illumination uniformity at an area close to a light input end of the light guide without displacing a light source from the central normal line of a light-extracting feature. The extracted light from the light-extracting feature forms an effective light-emitting object with a constant width for the integral light-concentrating optics and therefore, the width of the light-extracting feature can be modulated to improve illumination uniformity without affecting the width of illumination. The reflective envelope recycles all light leaked out of the light guide and protects the light guide from environmental contamination and provides mechanical interface between the device and the application assembly.
Owner:BRIGHT VIEW ELECTRONICS
LED lighting system
ActiveUS8436556B2Reduce impactElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentEffect light
A system and method involving lighting fixtures, a control network, a controller and other devices such as light sensors, input devices and network adapters for coordinating precise brightness and color schedules among the lighting fixtures while maintaining a high color reliability including provisions for managing a plurality of lighting fixtures. The lighting fixtures contain lighting elements selected such that when controlled properly, operating along a daytime locus, the resultant light output closely resembles sunlight on a cloudless day in spectral characteristics, and wherein the total flux of blue light can be adjusted from a relative level of 1-100% the maximum blue flux of the lighting fixture by controlling individual lighting elements.
Owner:DELOS LIVING LLC
Passive collimating tubular skylight
InactiveUS6363667B2Convenient lightingImproved passive tubular skylightsBuilding roofsCeilingsEngineeringSpecular reflection
A passive collimating tubular skylight consisting of a radiant energy-collecting aperture, a radiant energy-delivering aperture, and a radiant energy passageway between these two apertures, the passageway having a specularly reflective interior surface and a configuration to improve the collimation of the radiant energy passing therethrough. The skylight can be configured with the radiant energy-collecting aperture located above the roof of a building, oriented to collect sunlight; and equipped with a sealed weatherproof glazing, with the radiant energy-delivering aperture, or luminaire, located at ceiling level within the building, and equipped with a diffusing glazing; and with the reflective tubular light passageway constructed with a larger cross sectional area near the radiant energy-delivering aperture than near the radiant energy-collecting aperture. In complete accord with the second law of thermodynamics, and as proven by experimental results, the new passive collimating tubular skylight provides significant advantages over the prior art, including better solar energy collection, higher throughput optical efficiency, improved radiant energy collimation, enhanced interior illumination levels, and more precise positional control of the interior illumination.
Owner:ENTECH INC
Method and apparatus for light intensity control
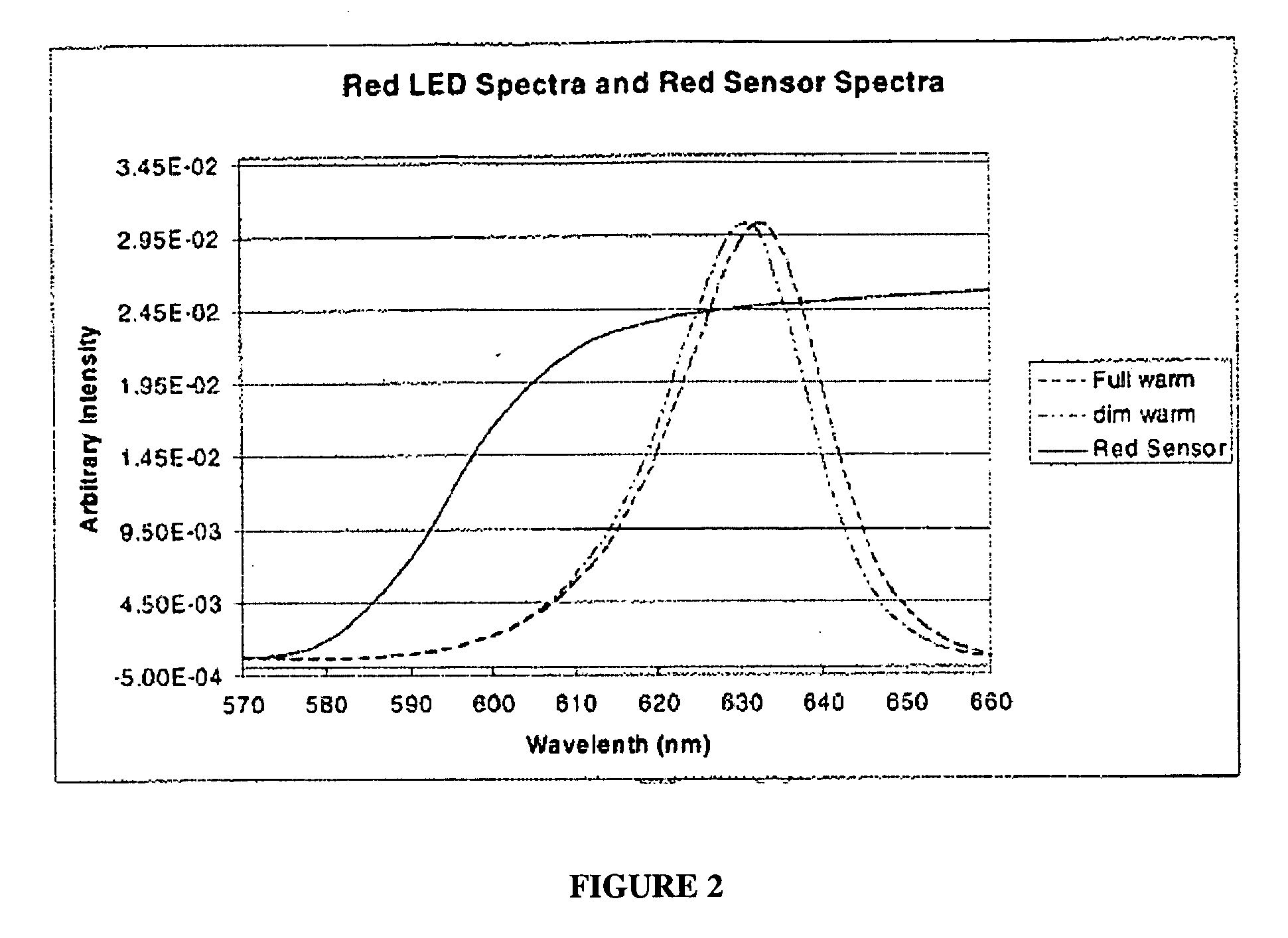
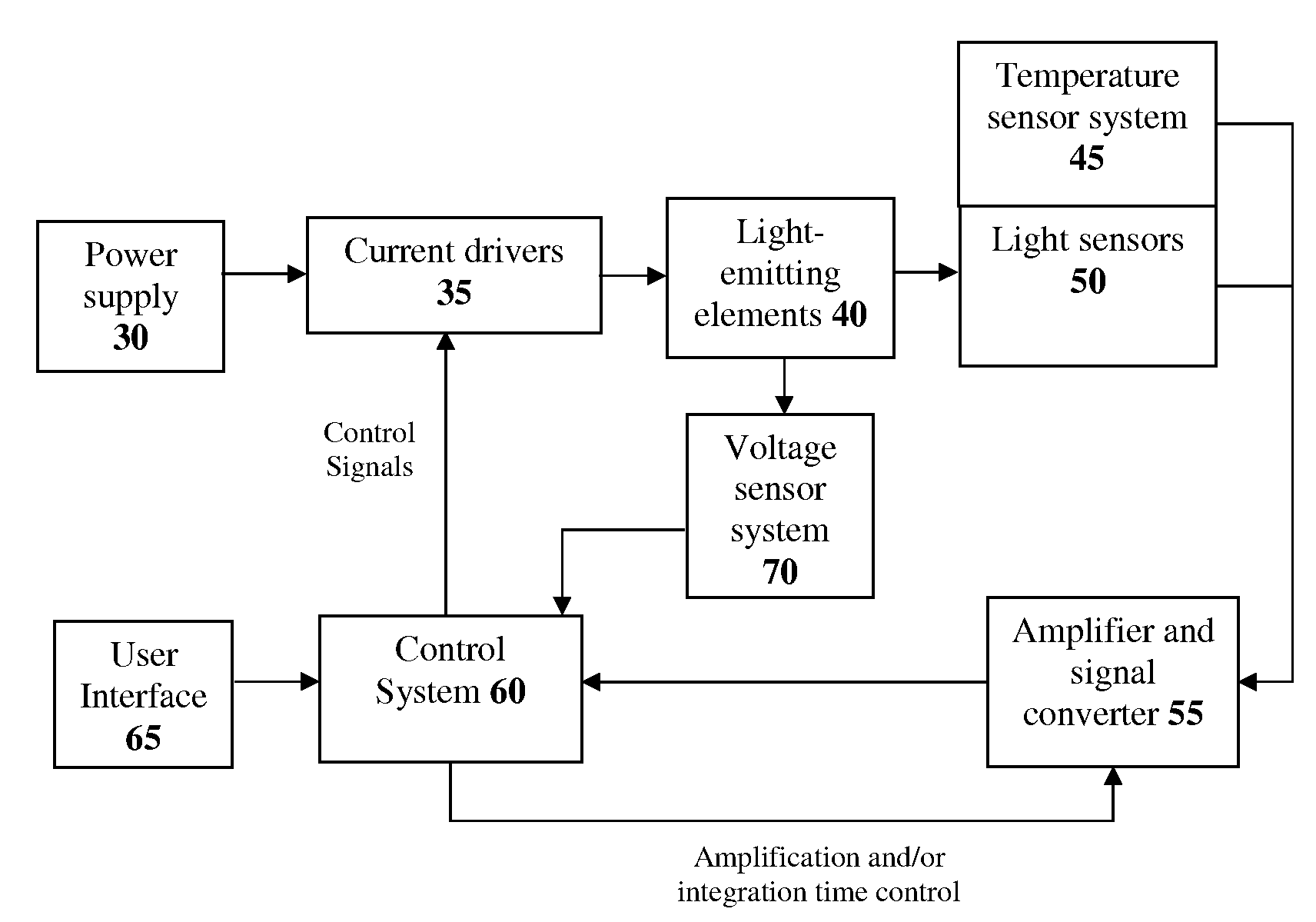
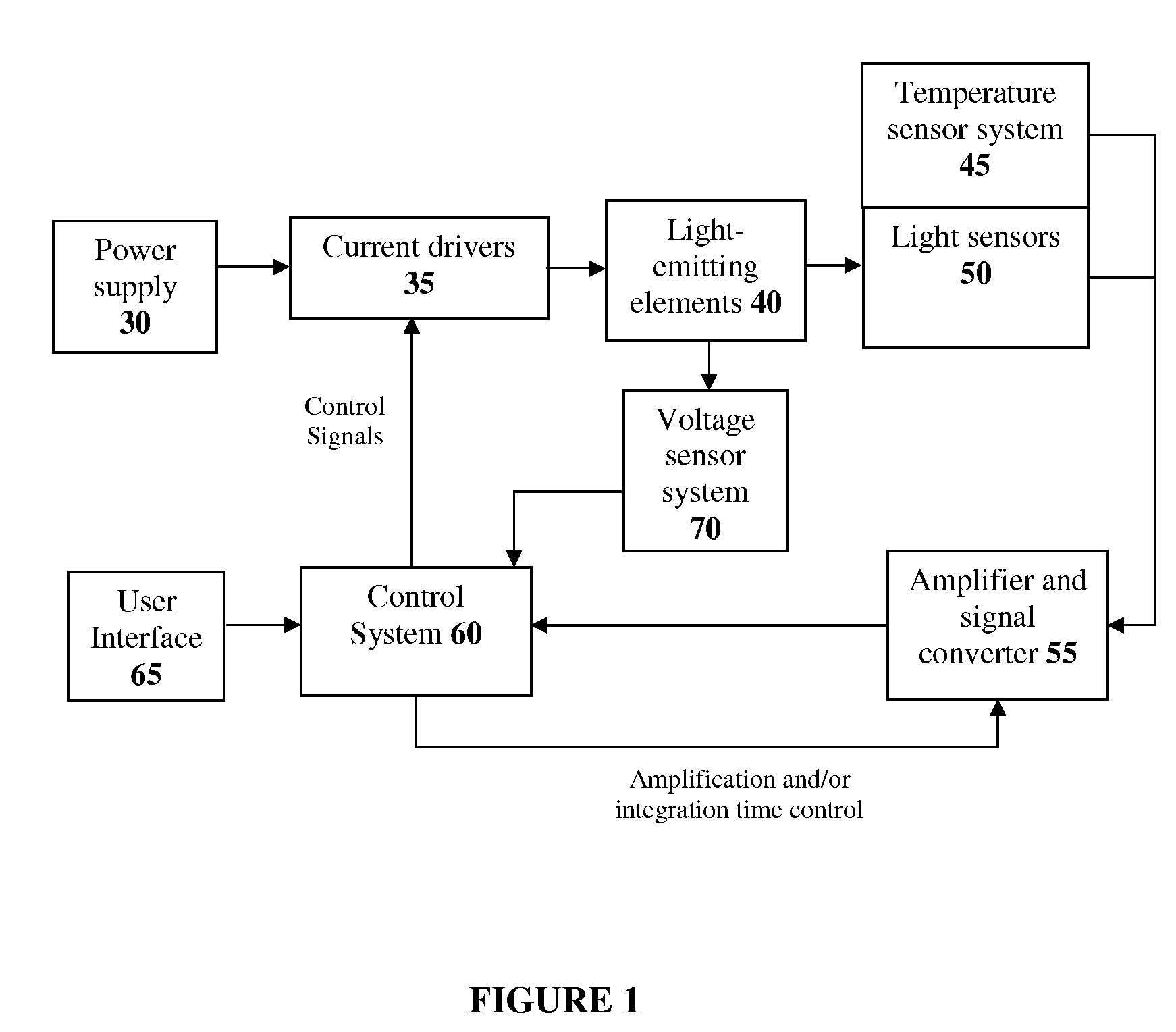
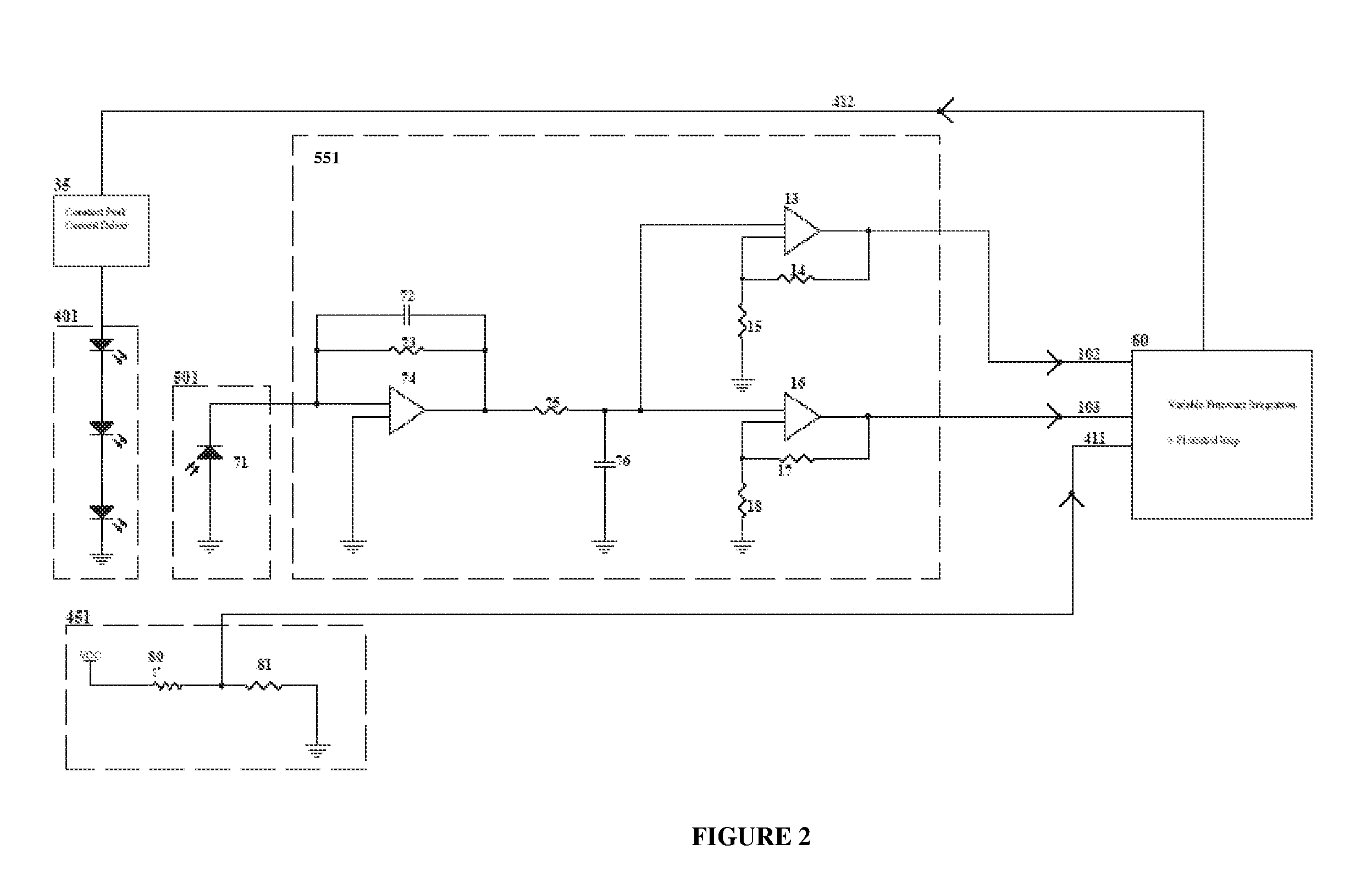
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical feedback control for an illumination device, wherein the control signal for each array of one or more light-emitting elements corresponding to a particular color, is independently configured using a modification signal whose frequency is different for each color. Electronic filters whose center frequencies are substantially equal to the modification signal frequencies of the drive currents for the light-emitting elements are used to discriminate between the radiant flux corresponding to each of the different colors of light-emitting elements, from a sample of the mixed radiant flux output collected by one or more optical sensors. The output of an individual electronic filter is substantially directly proportional to the radiant flux output of the light-emitting elements of the associated color, which together with the desired luminous flux and chromaticity of the output light, the controller can use to adjust the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Controlling light sources of a directional backlight
InactiveUS20140009508A1Viewing comfortReduce power consumptionMechanical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsLuminous intensityImaging quality
Disclosed is an imaging directional backlight including an array of light sources, and a control system arranged to provide variable distribution of luminous fluxes, scaled inversely by the width associated with the respective light sources in the lateral direction, across the array of light sources. The luminous intensity distribution of output optical windows may be controlled to provide desirable luminance distributions in the window plane of an autostereoscopic display, a directional display operating in wide angle 2D mode, privacy mode and low power consumption mode. Image quality may be improved and power consumption reduced.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
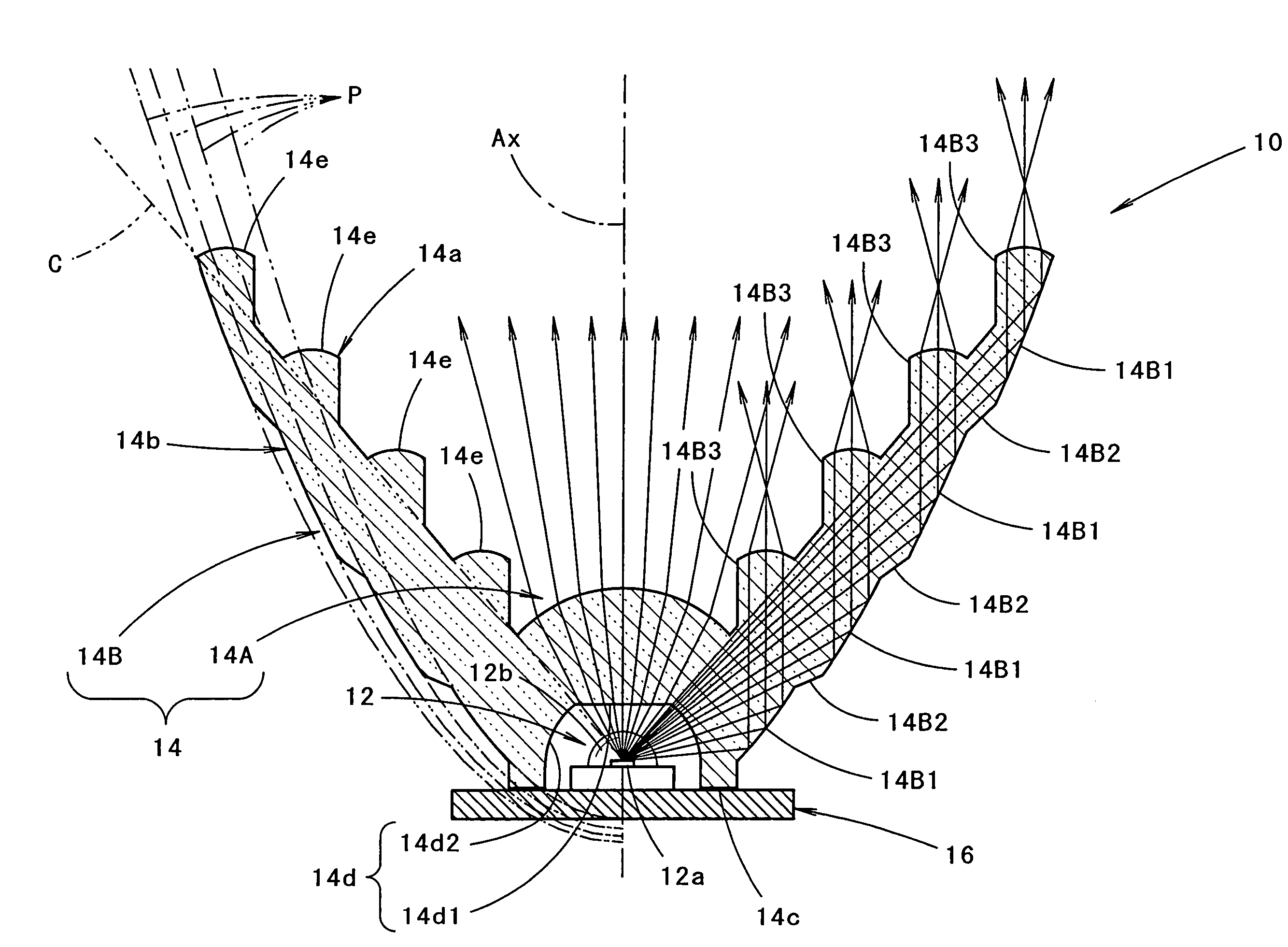
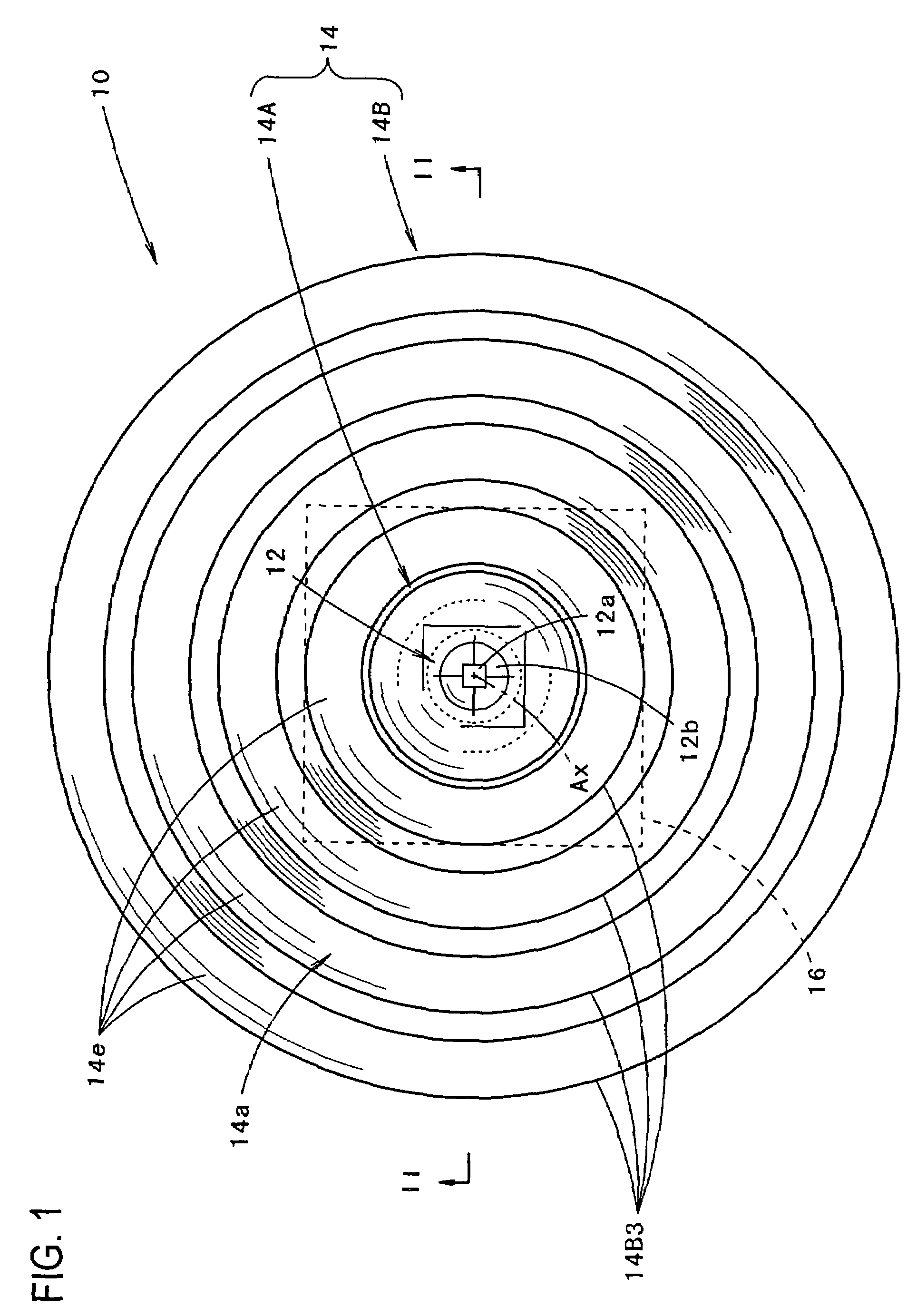
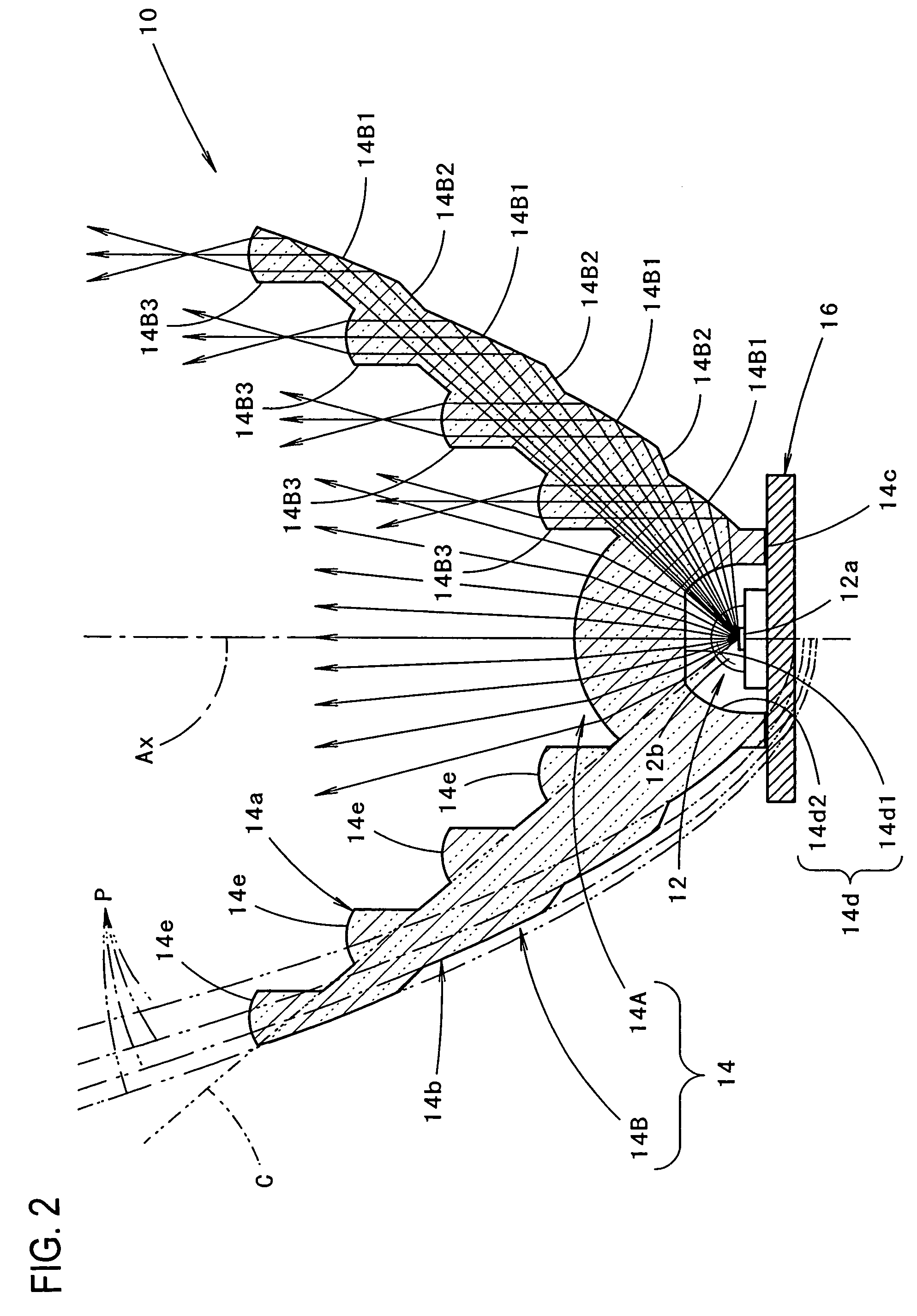
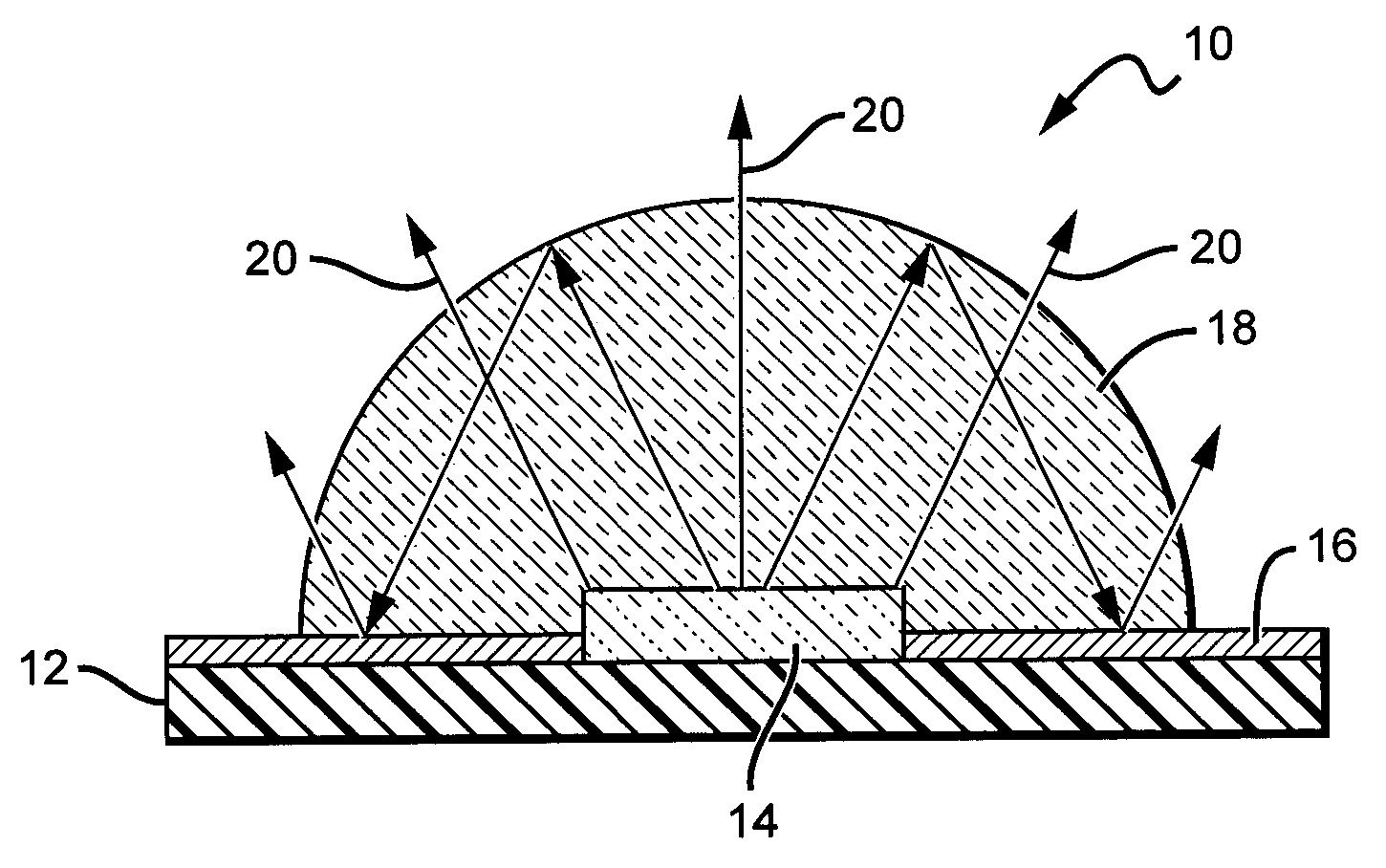
Vehicular lamp
ActiveUS7270454B2Attractive appearanceLuminous flux utilization factor for light from the light-emitting element is enhancedMeasurement apparatus componentsPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLuminous flux
A vehicular lamp in which a luminous flux utilization factor is enhanced by a structure of a light-emitting element that is disposed to face forward with respect to a vehicular lamp and covered from its front side with a translucent member. The circumferential region of the translucent member forms a reflected light control portion that allows light from the light-emitting element which has impinged on the translucent member to be internally reflected by the rear face of the translucent member and turned into parallel light which travels forward, and the reflected light control portion further allows the parallel light to emit forward from the front face of the reflected light control portion.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
High reflective substrate of light emitting devices with improved light outpput
ActiveUS20110248287A1Improve light outputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrosphereLuminous flux
Apparatuses and methods for producing light emitting devices maximizing luminous flux output are disclosed. In one possible embodiment, a light emitting device comprises a substrate and a reflective layer at least partially covering the substrate. The reflective layer is non-yellowing, and may be substantially light transparent. One or more light emitting diode (LED) chips are disposed on the substrate. The light emitting device may emit white light. The reflective layer may comprise a silicone carrier with light reflective particles dispersed in the silicone carrier. A light diffusion lens may also be disposed on the substrate and surrounding the LED chips. Furthermore, one or more microspheres, light scattering particles, and / or phosphor particles may be dispersed in the lens. In one possible method for producing a light emitting device, a substrate is provided. One or more LED chips are coupled with the substrate, and a high reflective, non-yellowing coating is applied on at least a portion of the top surface of the substrate. The coating comprises a carrier with reflective particles dispersed throughout.
Owner:CREELED INC
Illuminated electric toothbrushes emitting high luminous intensity toothbrush
An illuminated electric toothbrush comprising a light emitting diode emitting light having a flux density of at least about 30 mW / cm2. An illuminated electric toothbrush having this level of flux density can result in an oral care benefit such as whitening. When this toothbrush is used within the oral cavity the heat generated by the toothbrush remains low enough that the surface temperature of the teeth remains below about 43° C. The flux density of at least about 30 mW / cm2 can be achieved by overpowering the light emitting diode, by using a light emitting diode having at least about two dices, and by providing a pulsed or non-continuous current to the LED which results in a pulsing or non-continuous light.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Vehicular lamp
ActiveUS20050152153A1Attractive appearanceImprove accuracyPoint-like light sourceMeasurement apparatus componentsEngineeringLuminous flux
A vehicular lamp in which a luminous flux utilization factor is enhanced by a structure of a light-emitting element that is disposed to face forward with respect to a vehicular lamp and covered from its front side with a translucent member. The circumferential region of the translucent member forms a reflected light control portion that allows light from the light-emitting element which has impinged on the translucent member to be internally reflected by the rear face of the translucent member and turned into parallel light which travels forward, and the reflected light control portion further allows the parallel light to emit forward from the front face of the reflected light control portion.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Multi-chip light emitting diode modules
ActiveUS20100117099A1Increased luminous flux outputImprove cooling effectLight absorption dielectricsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLuminous fluxReflective layer
A multi-chip lighting module is disclosed for maximizing luminous flux output and thermal management. In one embodiment, a multi-chip module device comprises a substantially thermally dissipative substrate with a dark insulating layer deposited on a surface of the substrate. A plurality of light emitting devices is also provided. An electrically conductive layer is applied to a surface of the substrate, with the conductive layer comprising a plurality of chip carrier parts each having a surface for carrying at least one of the light emitting devices. Each light emitting device has a first and a second electrical terminal. A reflective layer is also provided that at least partially covers the conductive layer.
Owner:CREELED INC
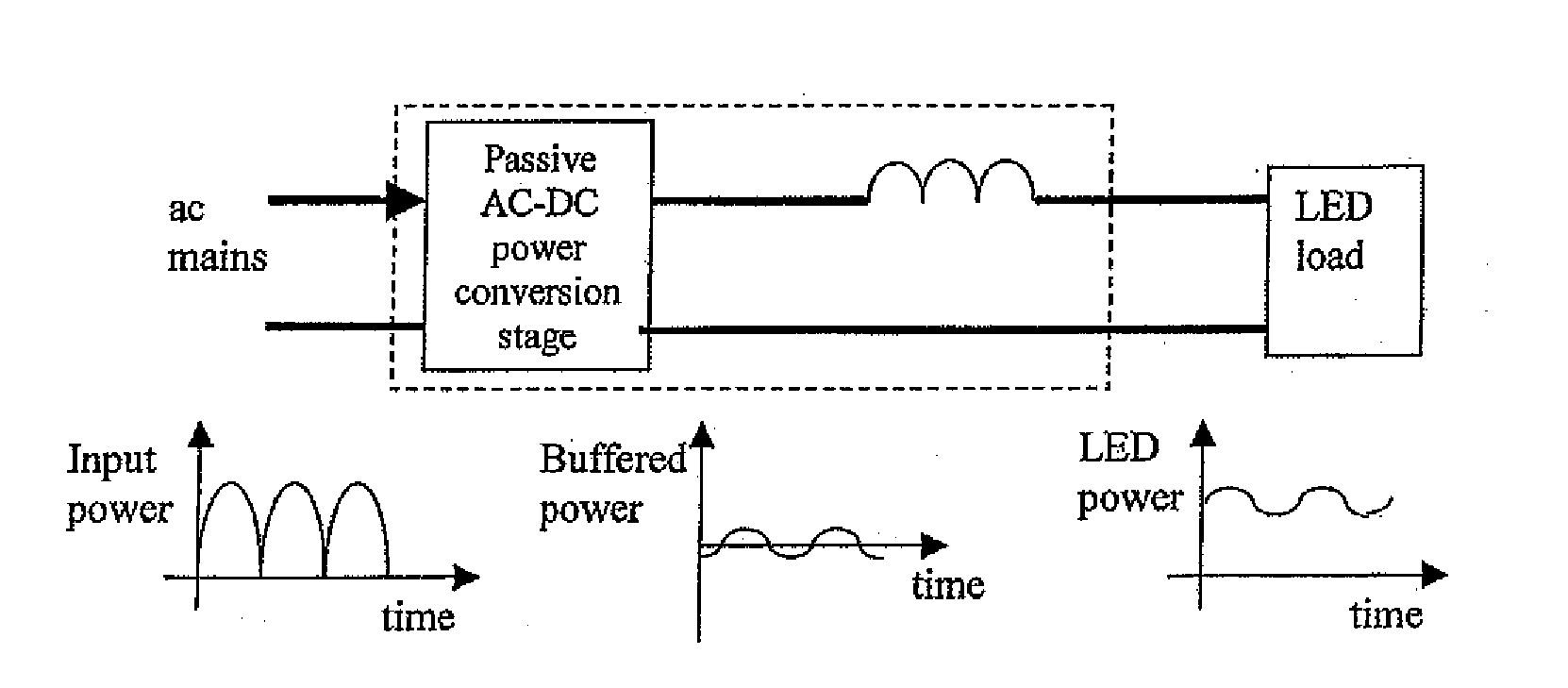
Apparatus and methods of operation of passive LED lighting equipment
ActiveUS20100270942A1Reduce voltage rippleReduce sensitivityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPower factorEffect light
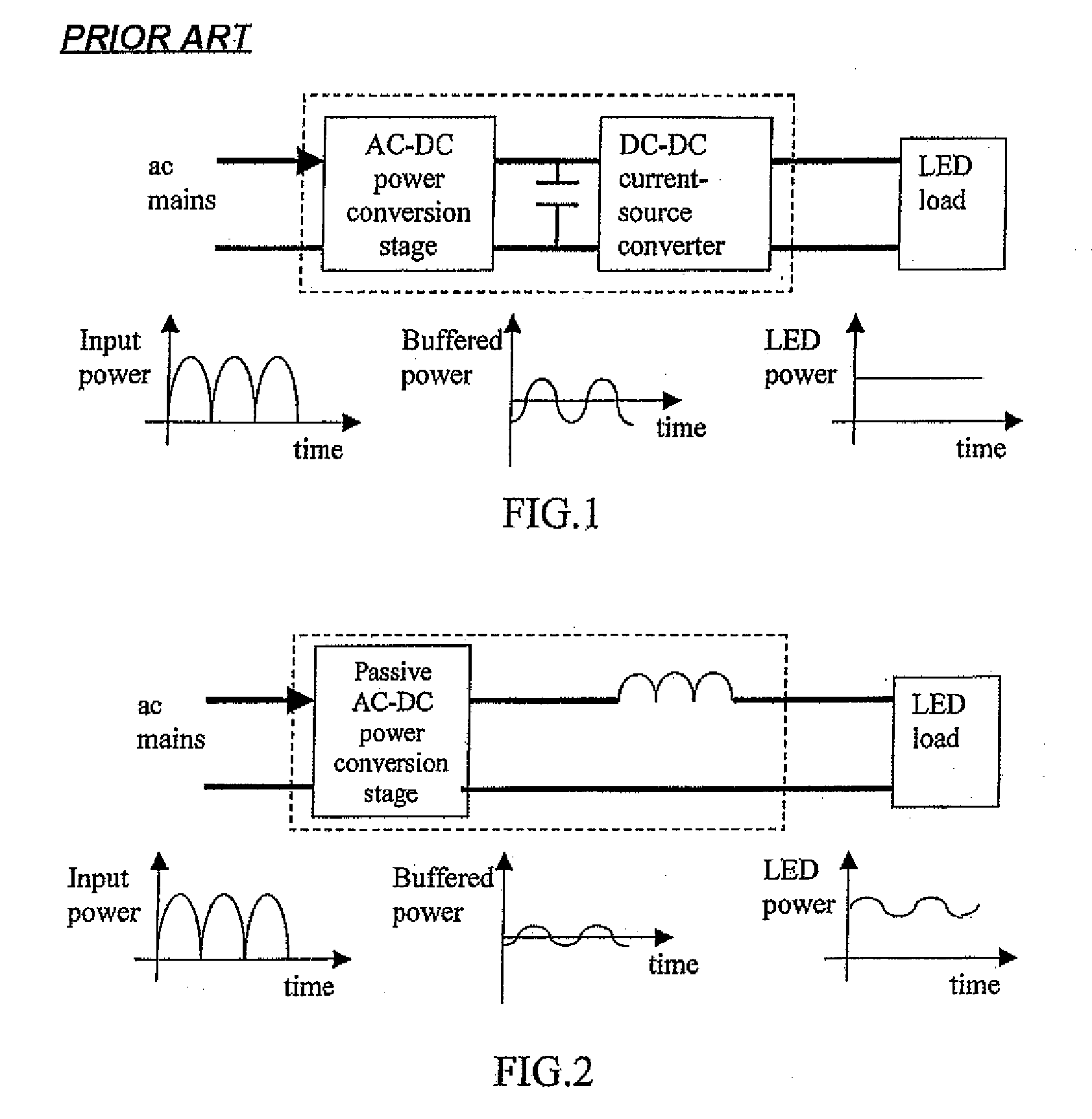
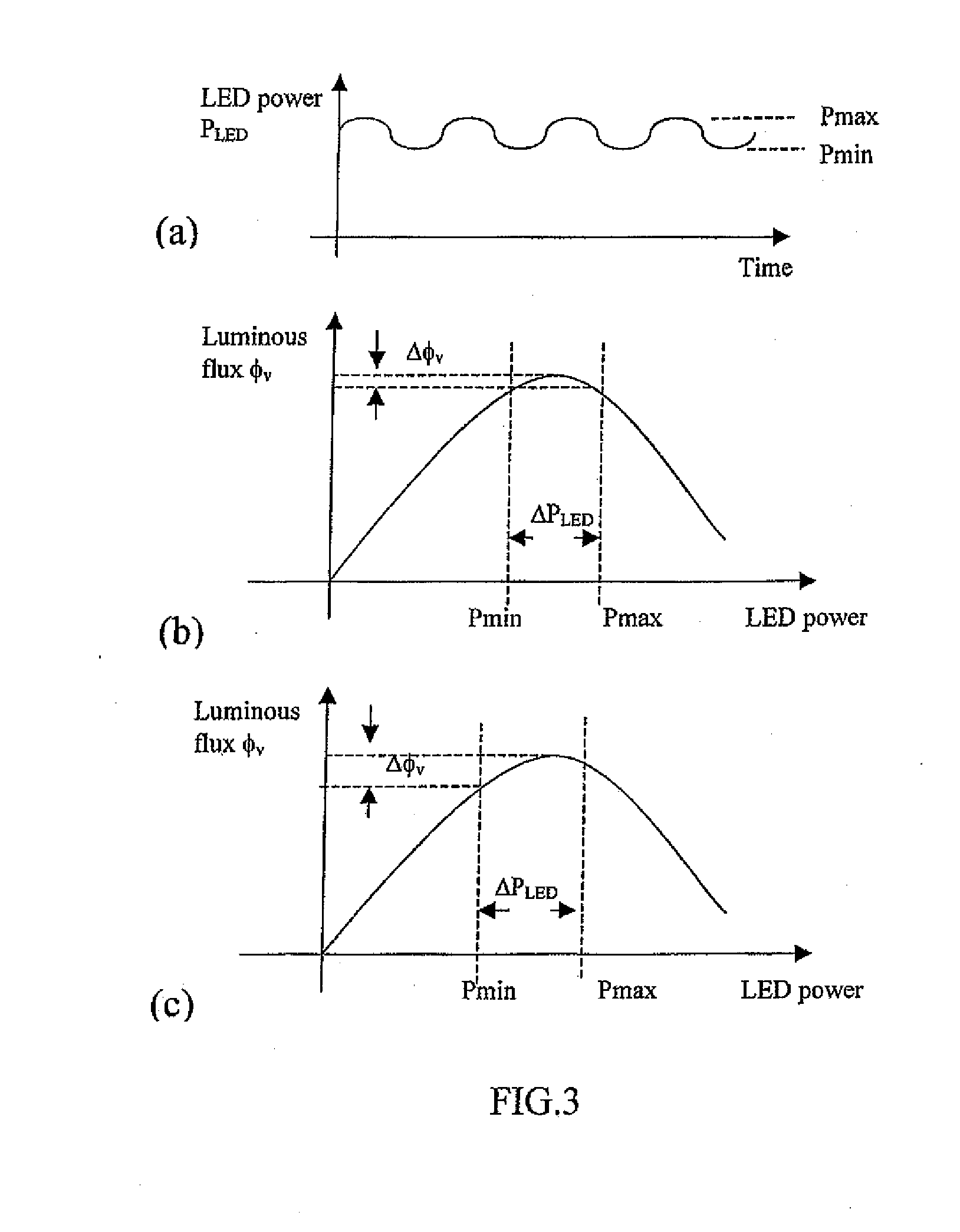
This invention is concerned with the control and design of a LED lighting system that does not need electrolytic capacitors in the entire system and can generate light output with reduced luminous flux fluctuation. The proposal is particularly suitable, but not restricted to, off-line applications in which the lighting system is powered by the ac mains. By eliminating electrolytic capacitors which have a limited lifetime of typically 15000 hours, the proposed system can be developed with passive and robust electrical components such as inductor and diode circuits, and it features long lifetime, low maintenance cost, robustness against extreme temperature variations and good power factor. No extra electronic control board is needed for the proposed passive circuits, which can become dimmable systems if the ac input voltage can be adjusted by external means.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
In-pavement directional LED luminaire
InactiveUS6902291B2Point-like light sourcePortable electric lightingThermoelectric coolingElectricity infrastructure
An in-pavement high intensity LED-based luminaire includes a housing, a power controller, a light module and a thermoelectric cooling device. The housing includes a generally flat top surface having at least one transparent window for output light passage. The power controller has an input and an output, wherein the input is electrically connected to an airfield power infrastructure and the output is electrically connected to a light module. The light module includes multiple high flux LEDs and a non-imaging light transformer. The non-imaging light transformer includes an input end opposite an output end, a refractive member located around the LED optical axis, and a total internal reflection member. The thermoelectric cooling device provides LED temperature control for emitted luminous flux, color and spatial intensity distribution stabilization, and is electrically connected to the power controller.
Owner:FARLIGHT
Method and apparatus for light intensity control
InactiveUS20090189530A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentControl signal
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical feedback control for an illumination device, wherein the control signal for each array of one or more light-emitting elements corresponding to a particular colour, is independently configured using a modification signal whose frequency is different for each colour. Electronic filters whose center frequencies are substantially equal to the modification signal frequencies of the drive currents for the light-emitting elements are used to discriminate between the radiant flux corresponding to each of the different colours of light-emitting elements, from a sample of the mixed radiant flux output collected by one or more optical sensors. The output of an individual electronic filter is substantially directly proportional to the radiant flux output of the light-emitting elements of the associated colour, which together with the desired luminous flux and chromaticity of the output light, the controller can use to adjust the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optical device and projector
An optical device includes: a light modulation element that modulates a luminous flux emitted from a light source; a casing that houses the light modulation element; a holding member that holds the light modulation element and exposes a part thereof to outside; a refrigerant housed in a housing space surrounded by the casing, the holding member and the light modulation element; and a convection start unit that is provided in the casing and causes convection of refrigerant.
Owner:COLUMBIA PEAK VENTURES LLC
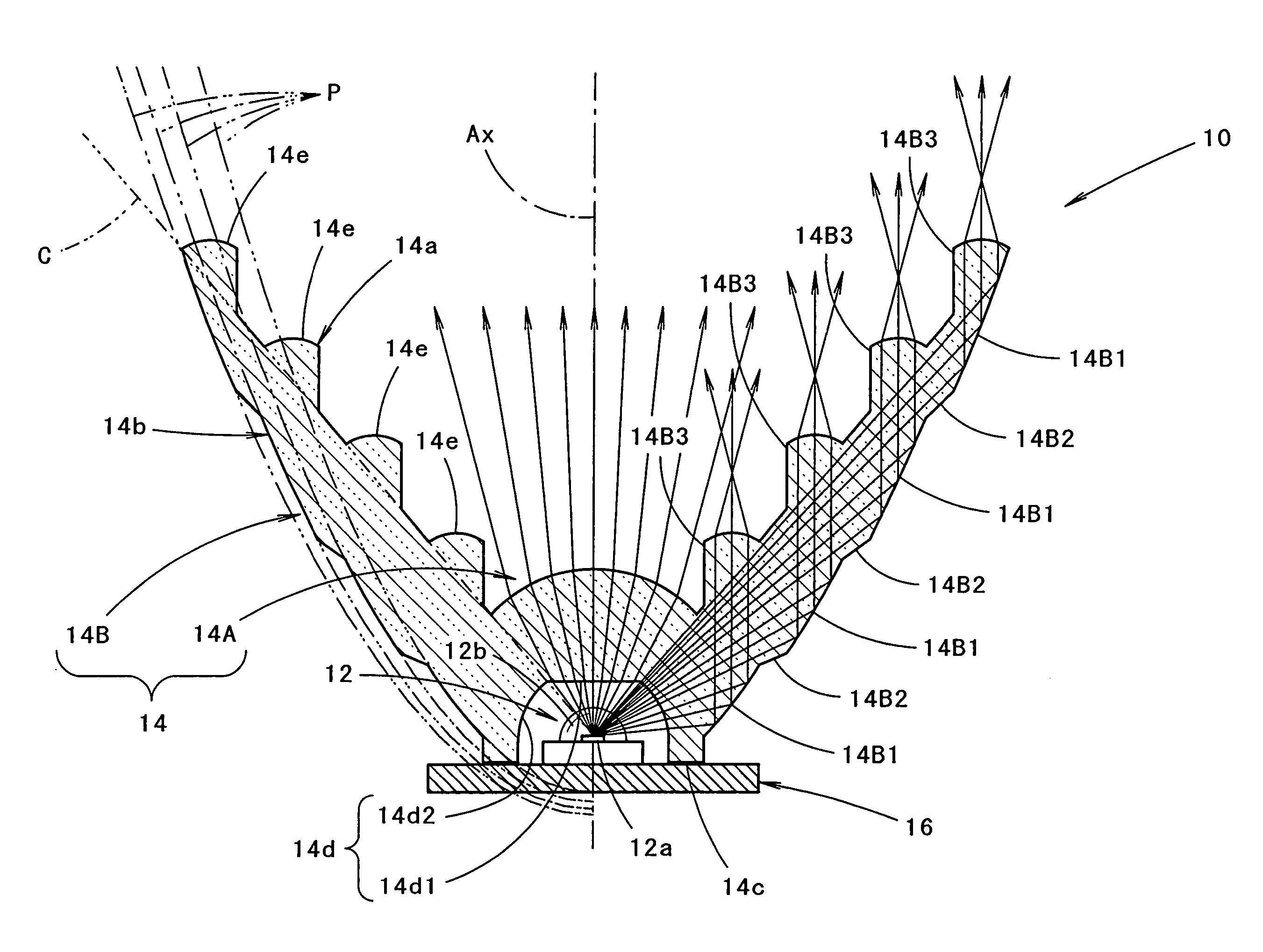
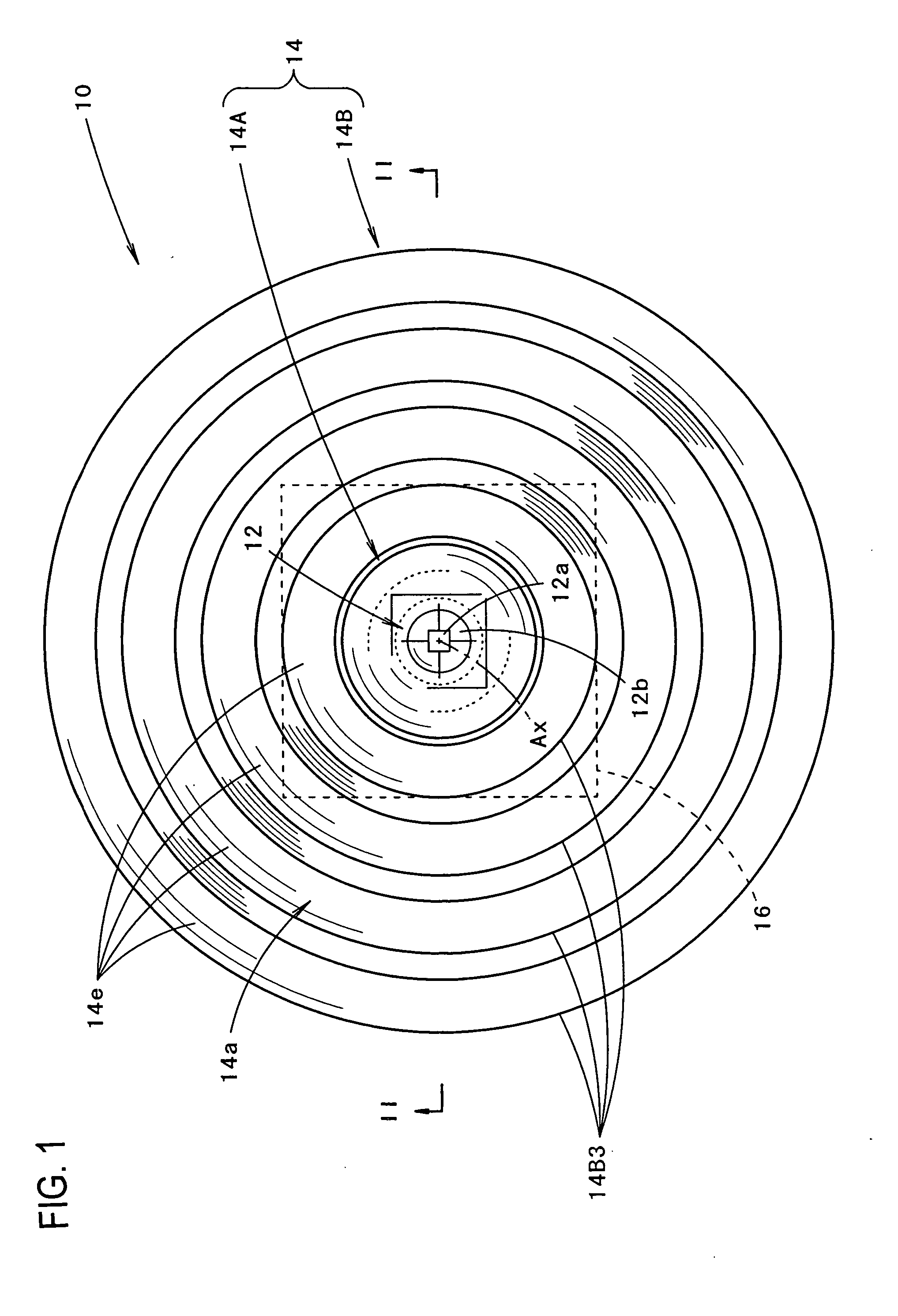
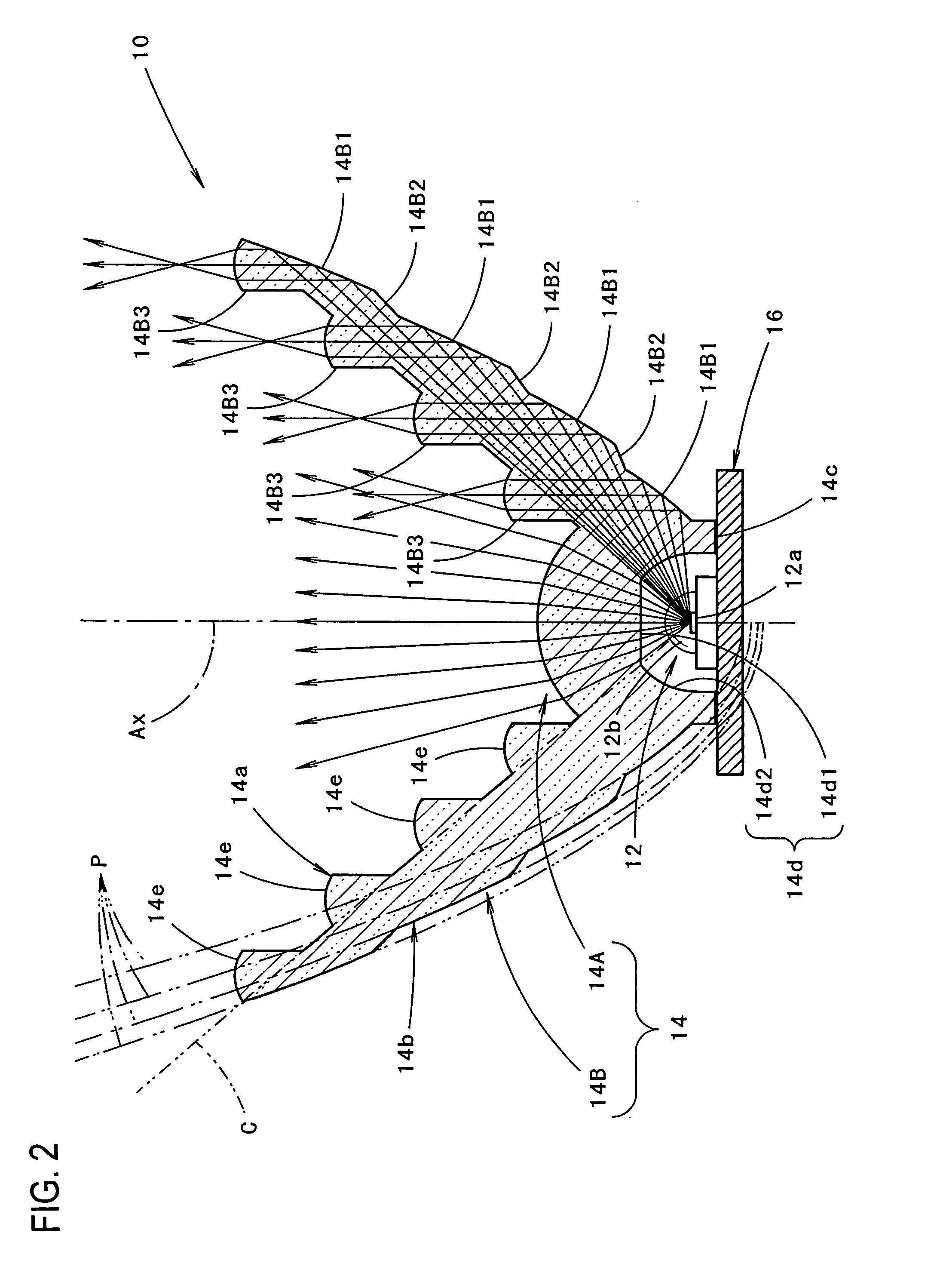
Indicator lamp comprising an optical device for recovering and distributing the light flux towards an annular reflector
The invention proposes an indicator lamp comprising an optical axis oriented from the rear to the front, on which there is a light source which is provided for emitting a light flux towards the front, and of the type comprising an optical device for recovering and distributing the rays of light emitted by the source, with a view to providing an indicating faction that meets the regulations, wherein the optical device comprises a coaxial annular reflector and, in front of the light source a central optical part known as the light engine which is provided for distributing the rays of light emitted by the source in directions that are generally transverse about the optical axis, towards the coaxial annular reflector that is provided for distributing the rays of light axially towards the front.
Owner:VALEO VISION SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com