Patents
Literature
276 results about "Radiant flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
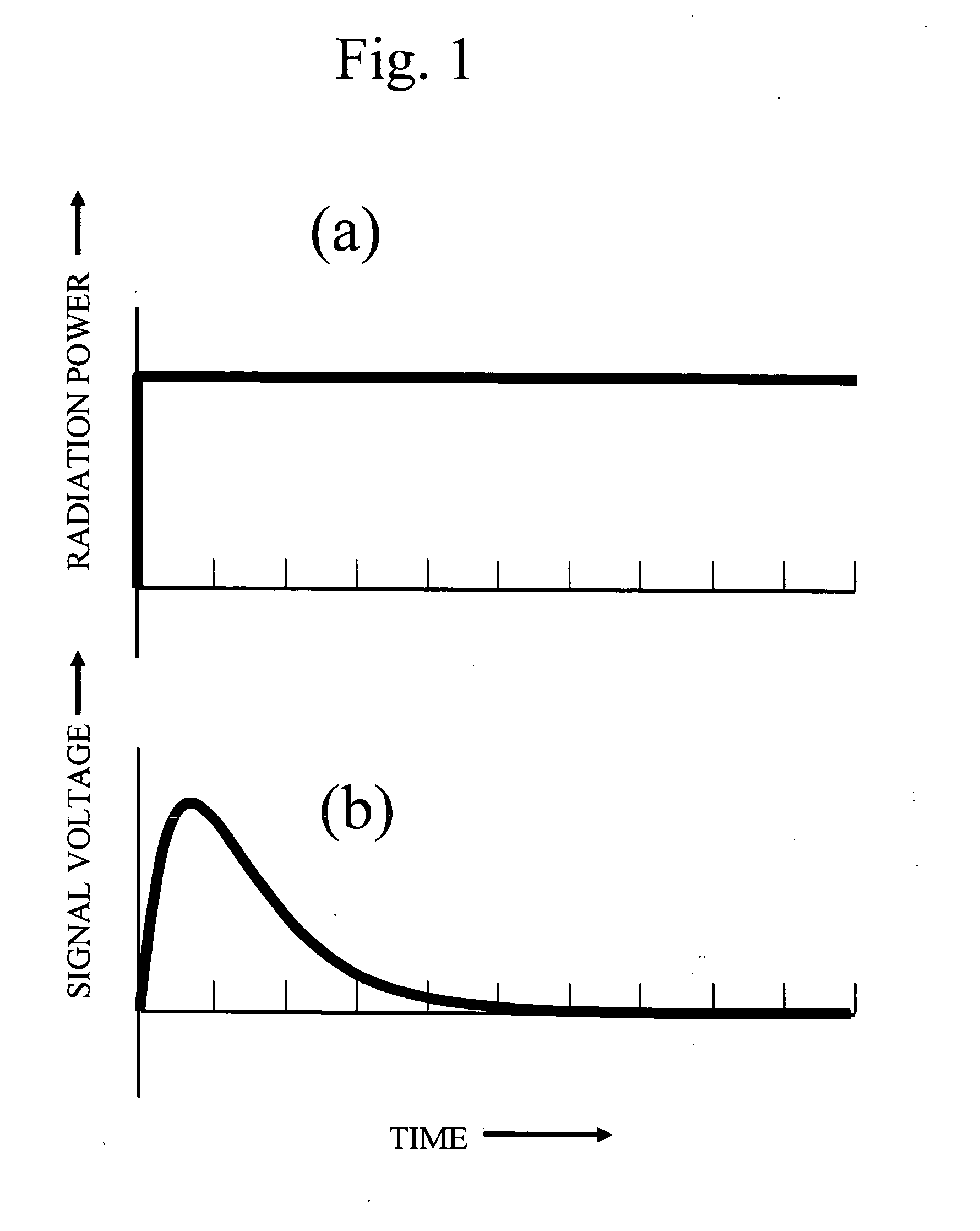
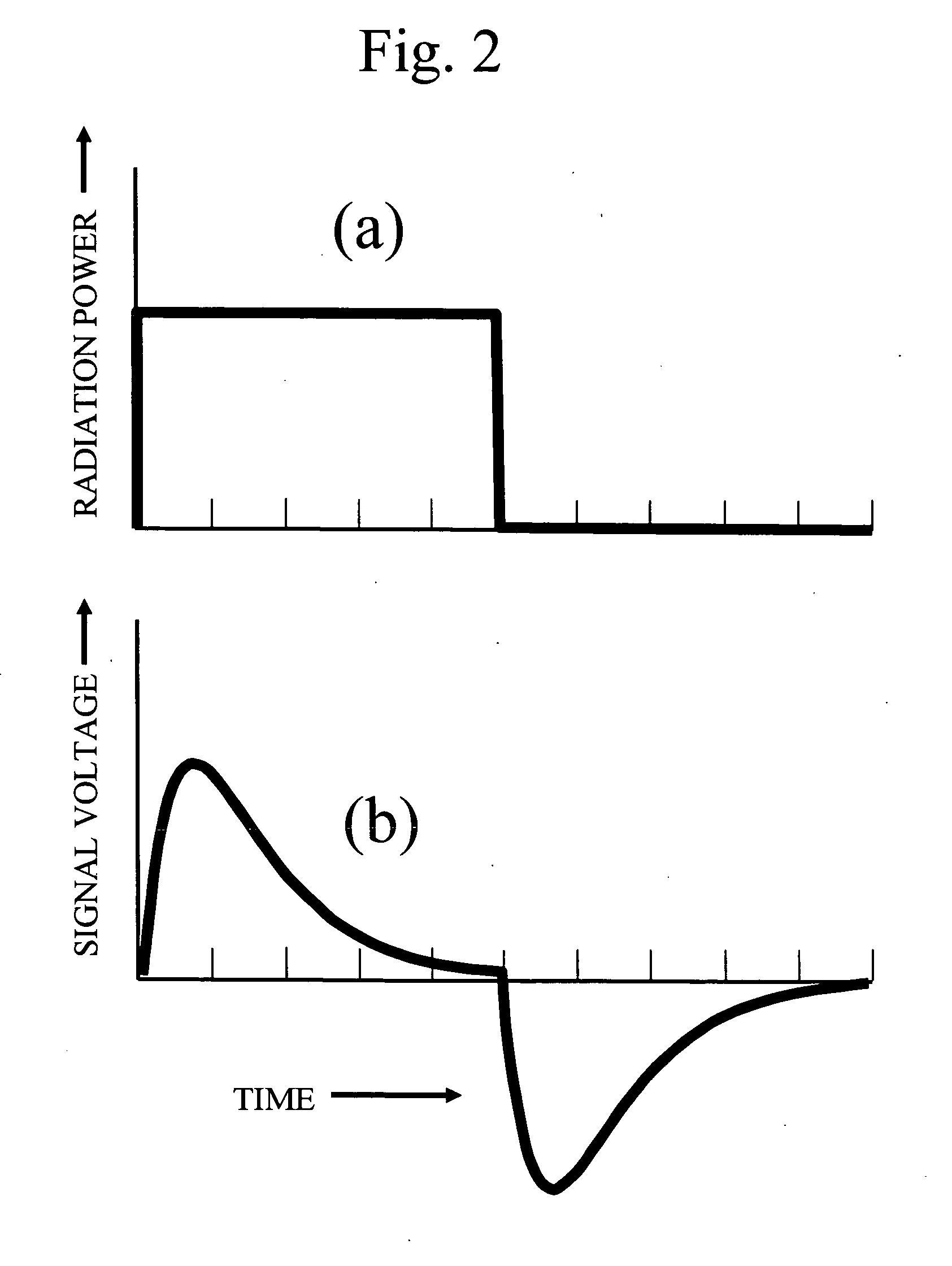
In radiometry, radiant flux or radiant power is the radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit time, and spectral flux or spectral power is the radiant flux per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. The SI unit of radiant flux is the watt (W), that is the joule per second (J/s) in SI base units, while that of spectral flux in frequency is the watt per hertz (W/Hz) and that of spectral flux in wavelength is the watt per metre (W/m)—commonly the watt per nanometre (W/nm).
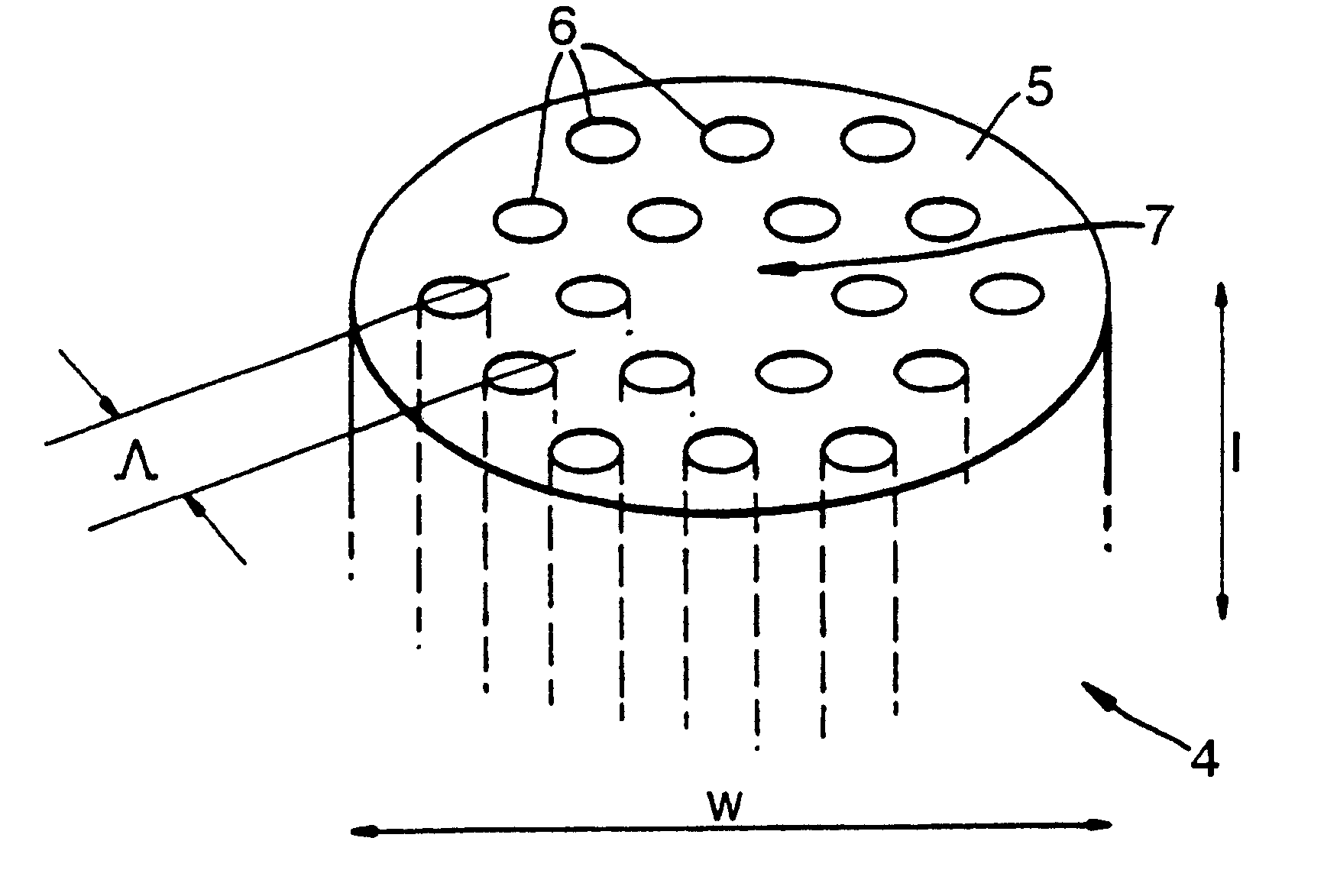
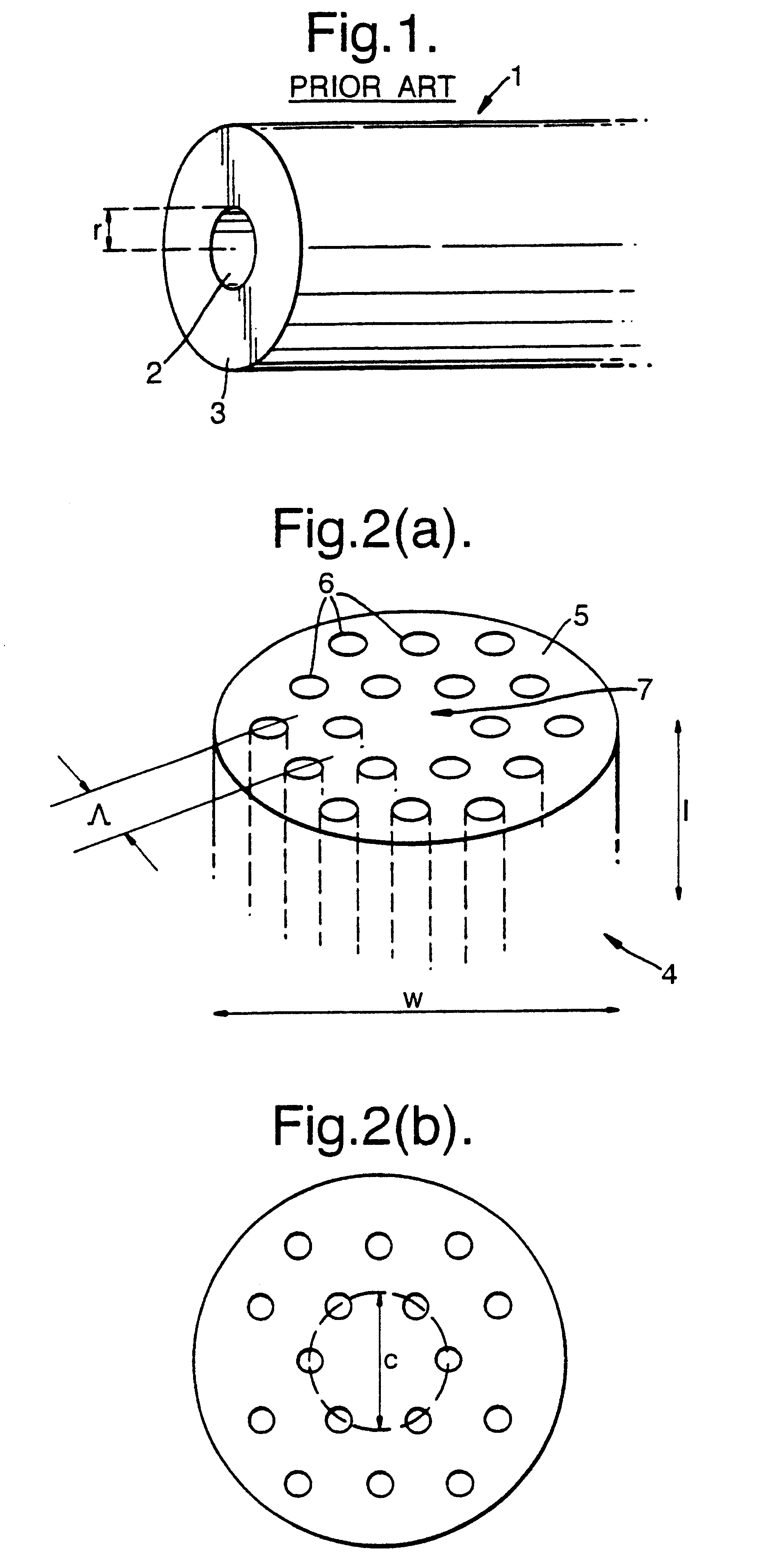
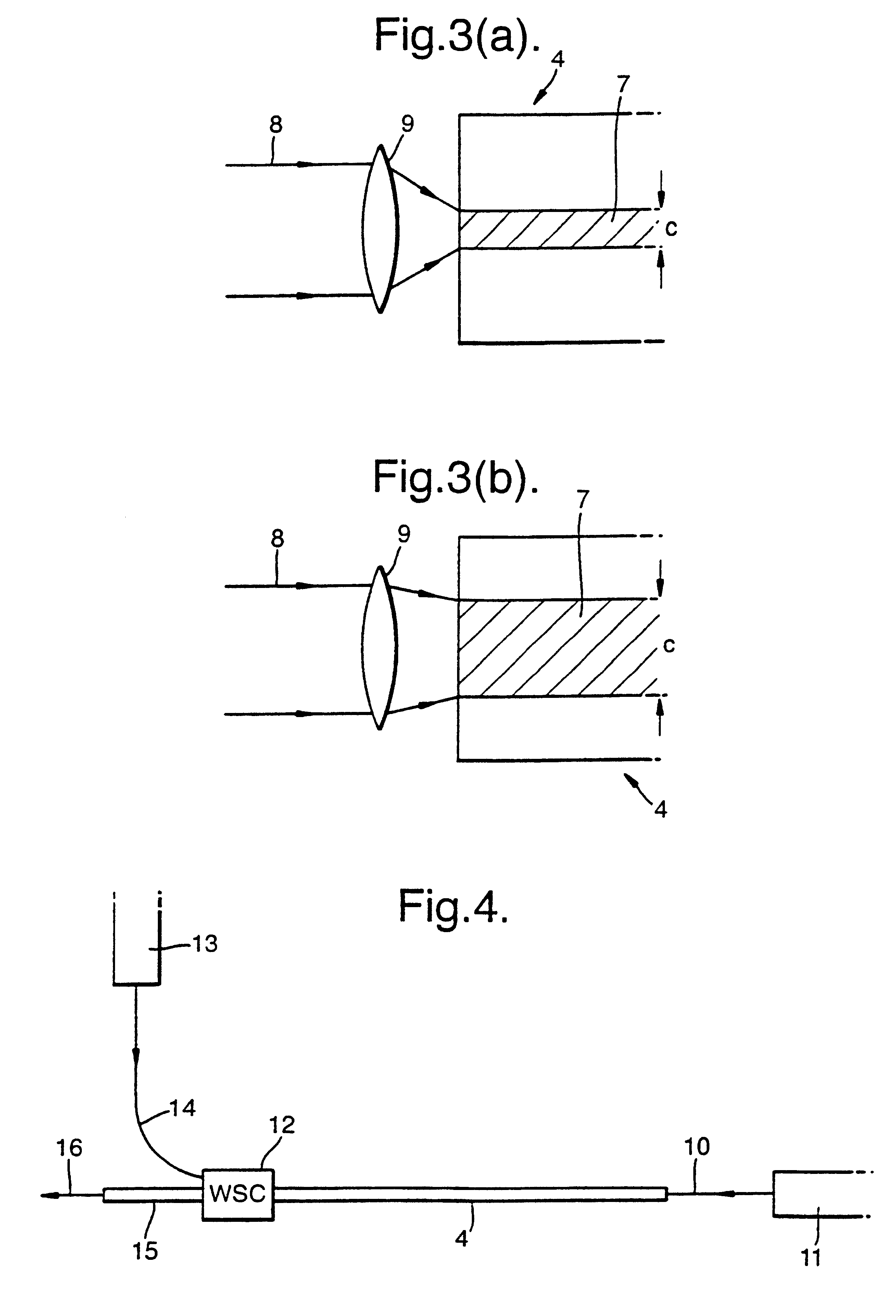
Single mode optical fiber
InactiveUS6334019B1High refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexFiber disk laser
A large core photonic crystal fiber for transmitting radiation having a core comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core diameter of at least 5 mu. The fiber also comprises a cladding region surrounding the length of core material, wherein the cladding region comprises a first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, and wherein the first substantially transparent cladding material has embedded along its length a substantially periodic array of holes, wherein the holes are filled with a second cladding material having a second refractive index less than the first refractive index, such that radiation input to the optical fiber is transmitted along the length of the core material in a single mode of propagation. In a preferred embodiment, the core diameter may be at least 20 mu, and may be as large as 50 mu. The fiber is capable of transmitting higher power radiation than conventional fibres, whilst maintaining propagation in a single mode. The core material may be doped with a material capable of providing amplification under the action of pump radiation input to the fiber. The invention also relates to a fiber amplifier and a fiber laser comprising a doped large core photonic crystal fiber. The fiber may also be used in a system for transmitting radiation comprising a plurality of lengths of large core photonic crystal fiber, separated by large core photonic crystal fiber amplifiers, such that the power of radiation transmitted through the system is maintained above a predetermined threshold power.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
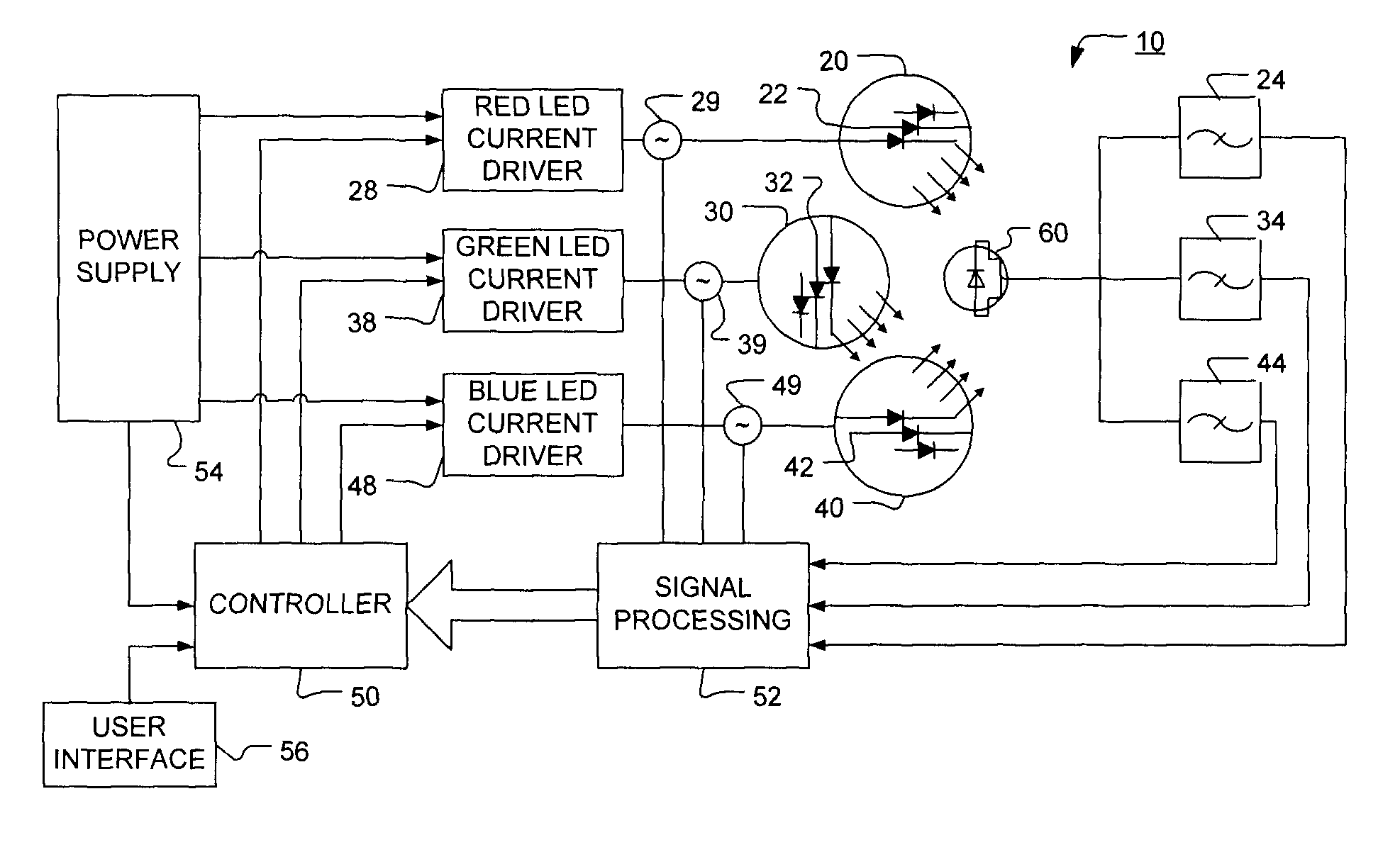
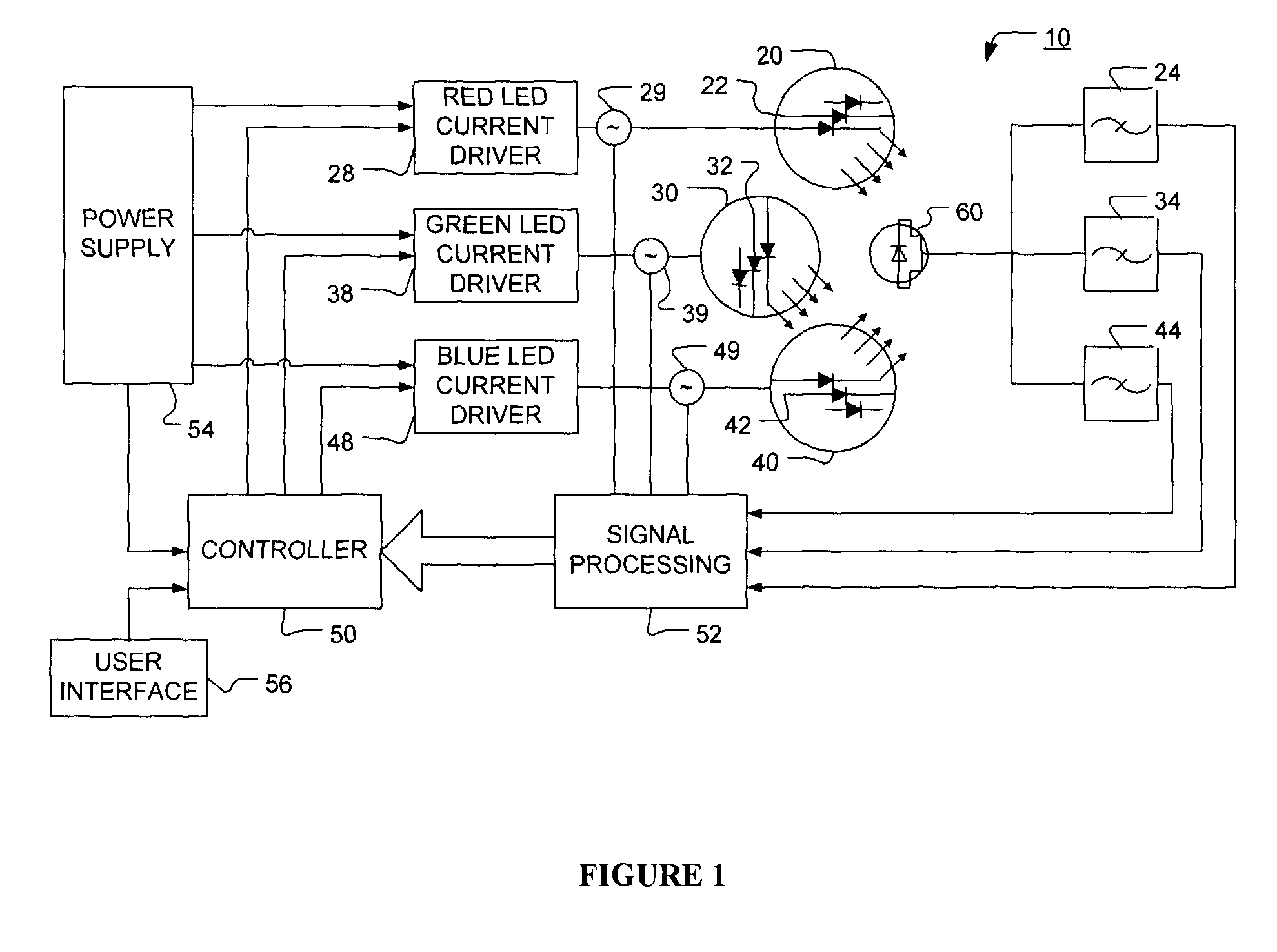
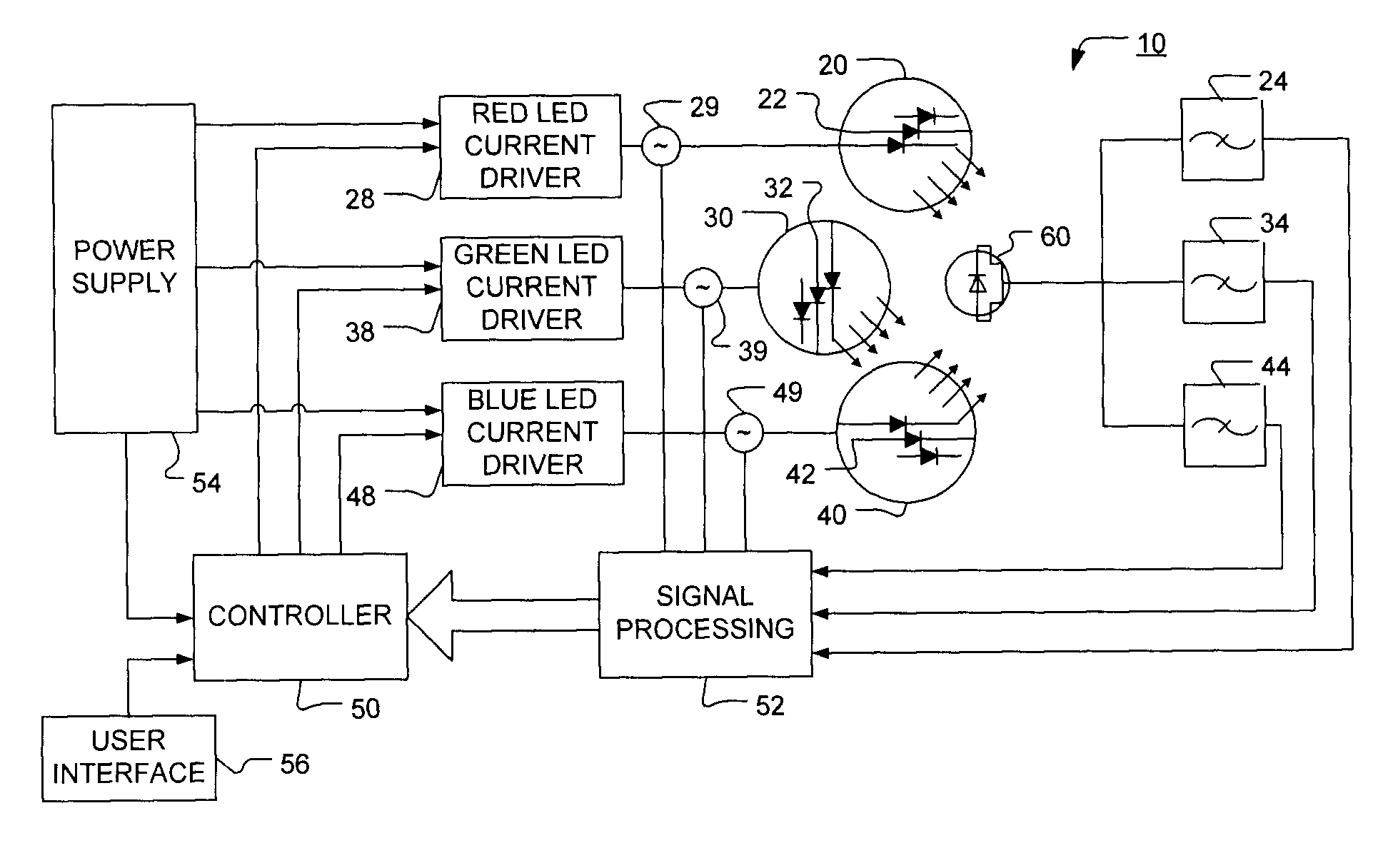
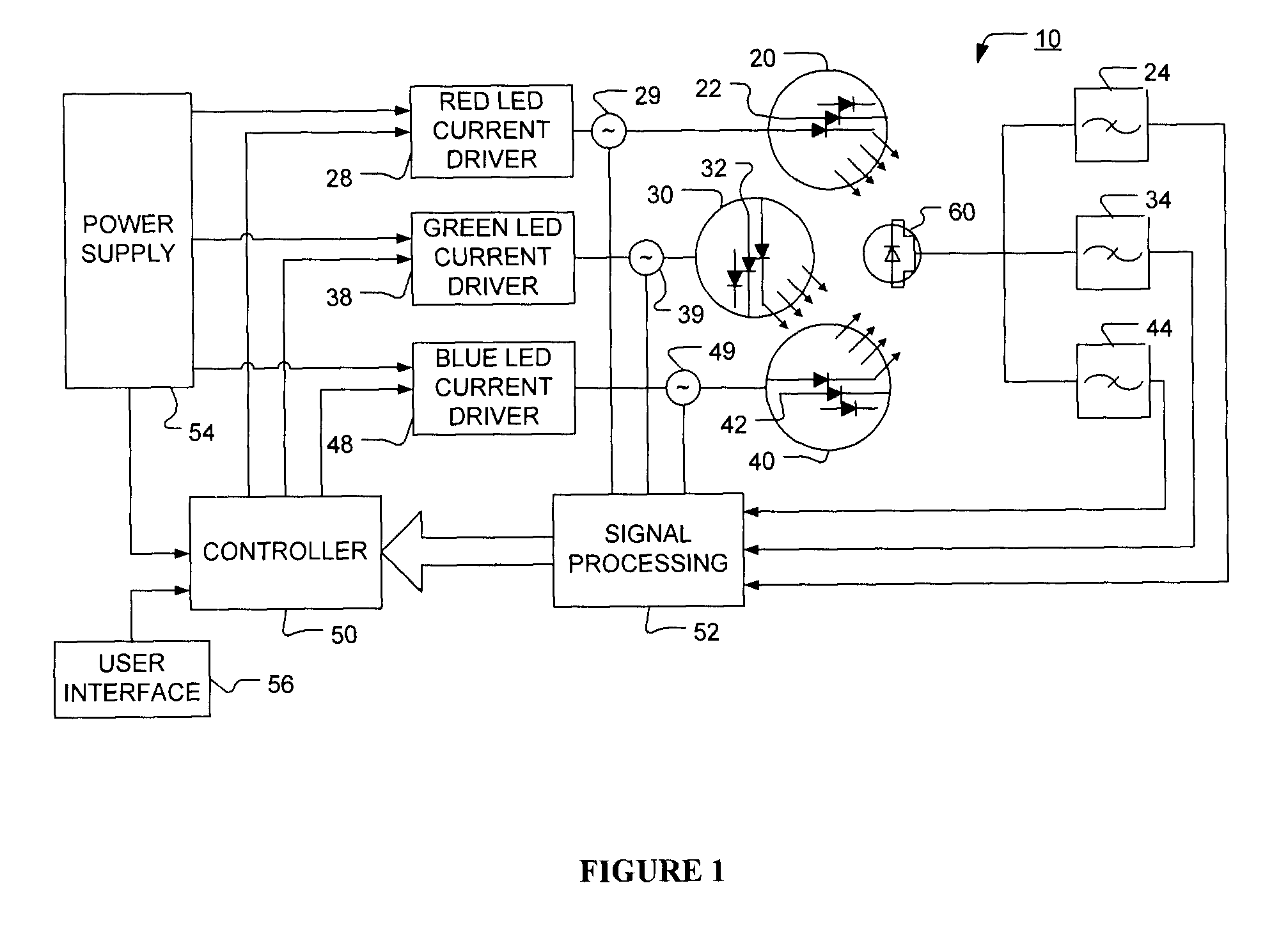
Method and apparatus for light intensity control
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical feedback control for an illumination device, wherein the control signal for each array of one or more light-emitting elements corresponding to a particular color, is independently configured using a modification signal whose frequency is different for each color. Electronic filters whose center frequencies are substantially equal to the modification signal frequencies of the drive currents for the light-emitting elements are used to discriminate between the radiant flux corresponding to each of the different colors of light-emitting elements, from a sample of the mixed radiant flux output collected by one or more optical sensors. The output of an individual electronic filter is substantially directly proportional to the radiant flux output of the light-emitting elements of the associated color, which together with the desired luminous flux and chromaticity of the output light, the controller can use to adjust the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
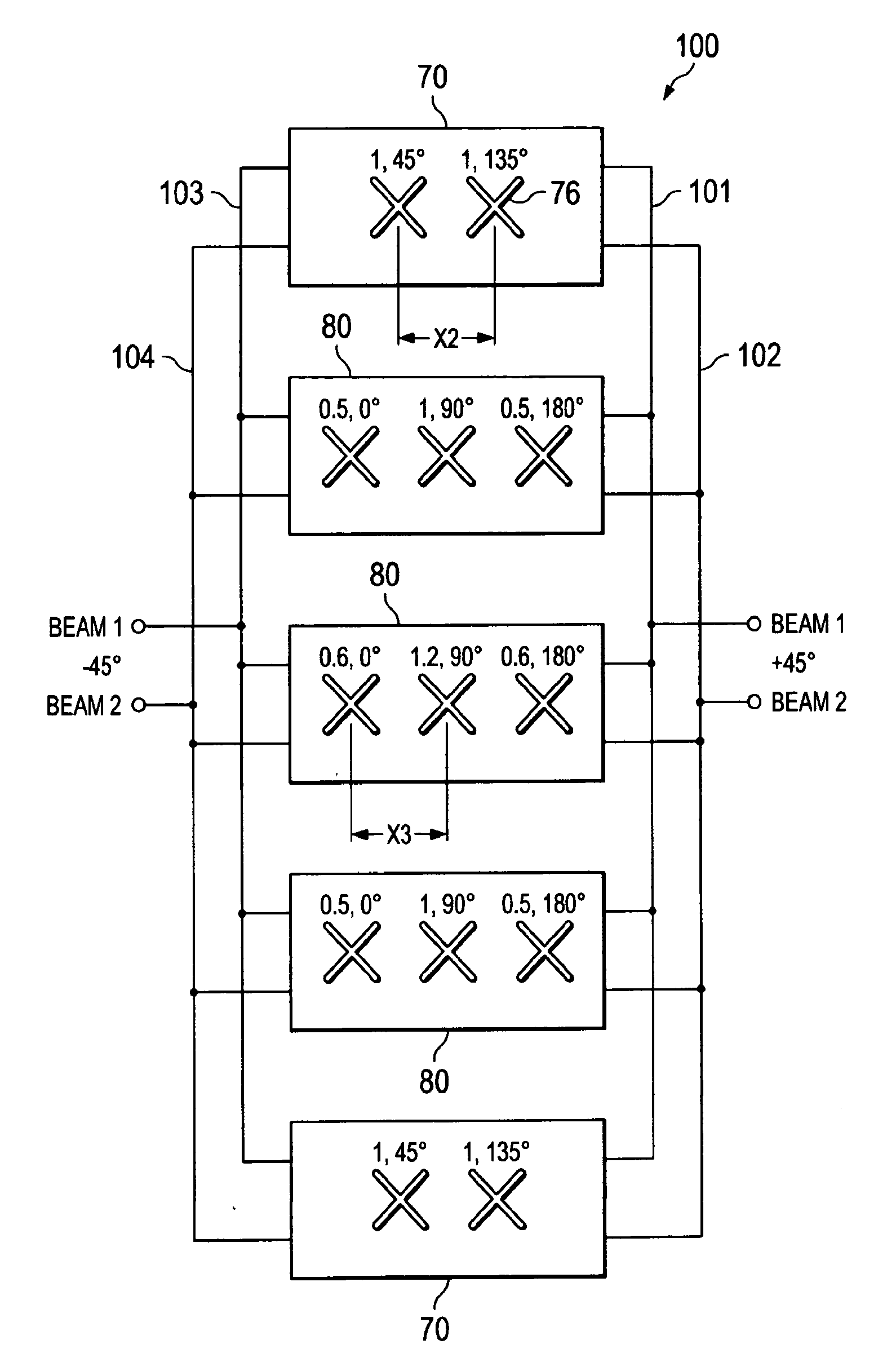
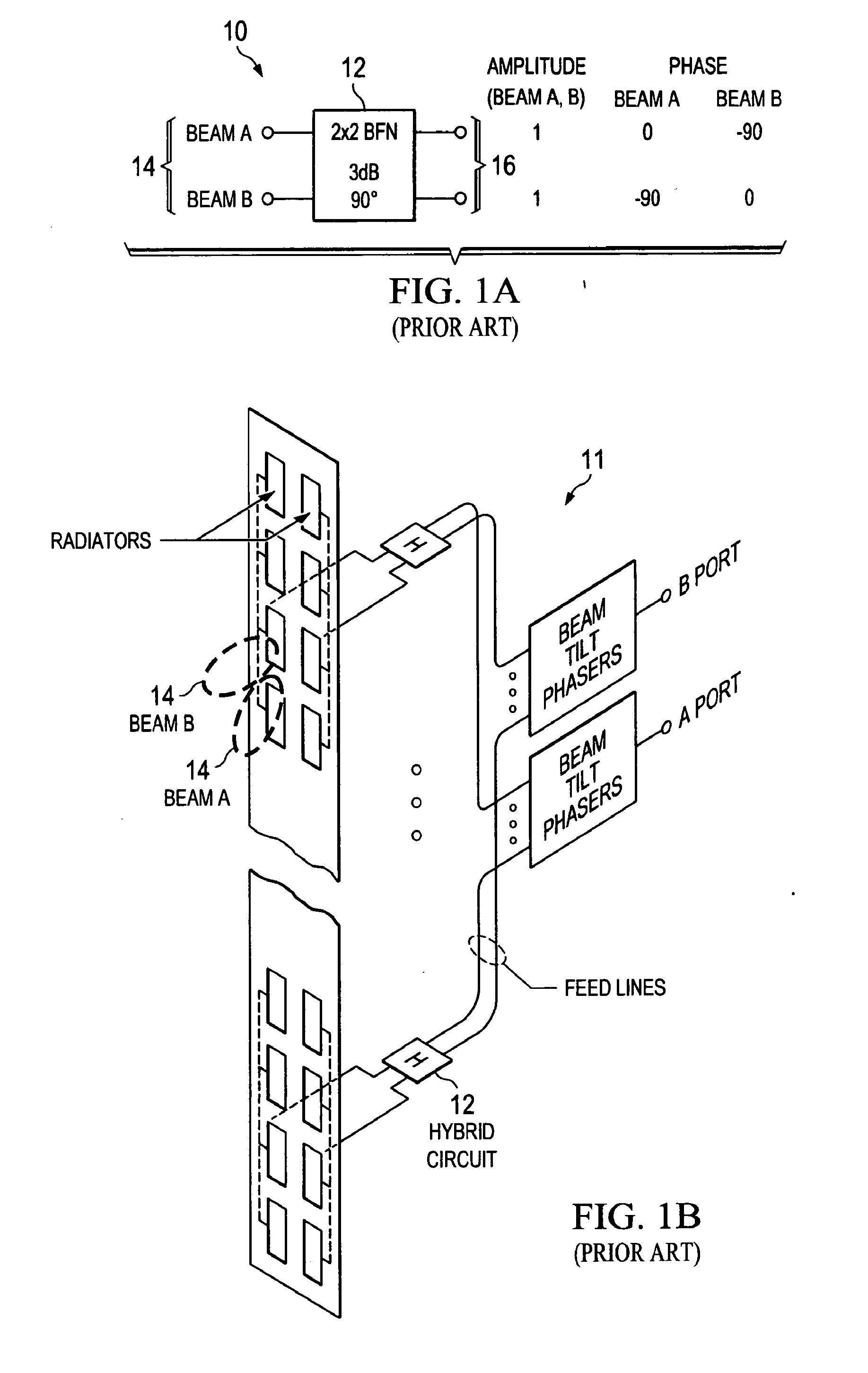
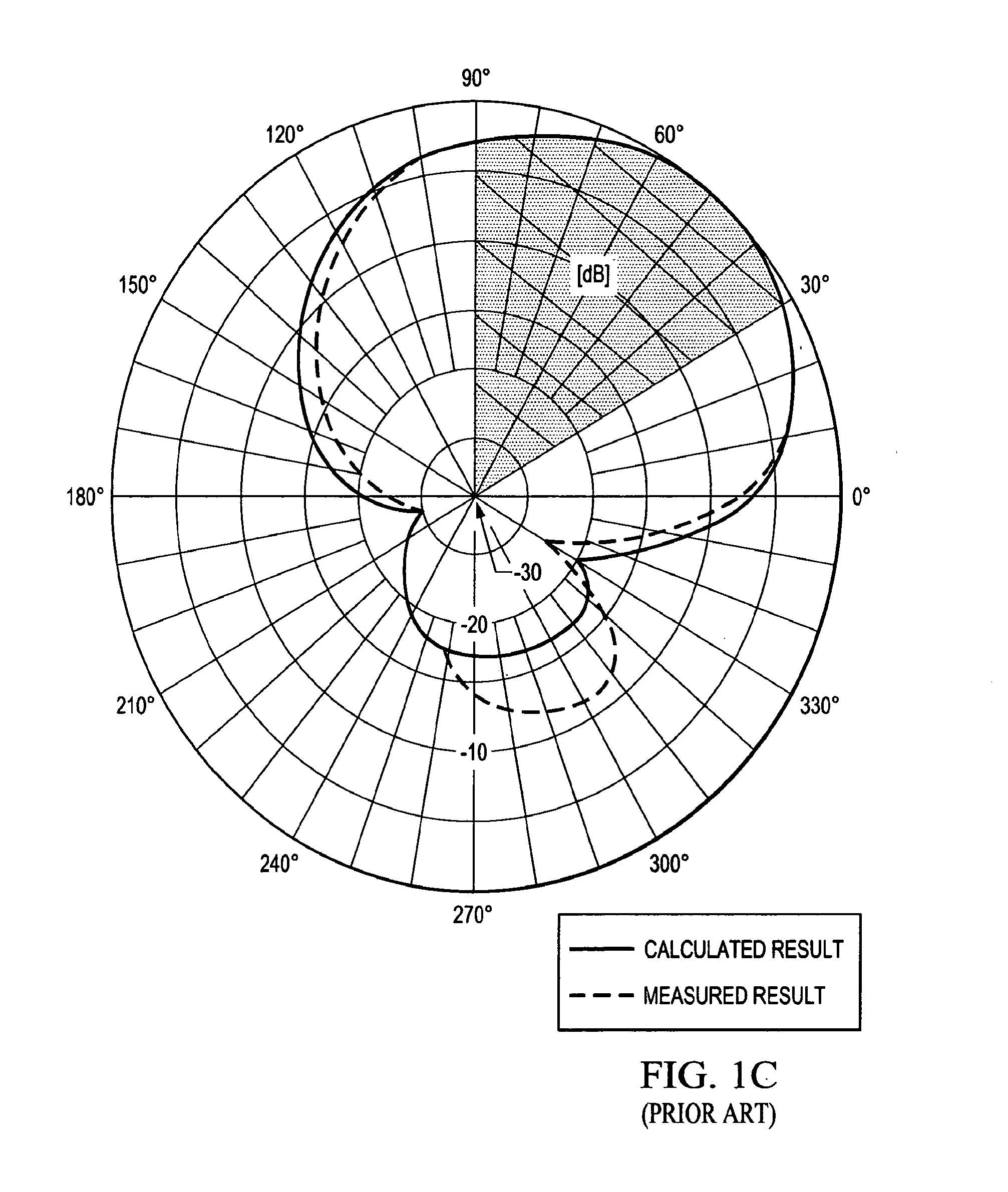
Dual-Beam Sector Antenna and Array
ActiveUS20110205119A1Less interferenceBetter cell efficiencyAntenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysDual beamSide lobe
A low sidelobe beam forming method and dual-beam antenna schematic are disclosed, which may preferably be used for 3-sector and 6-sector cellular communication system. Complete antenna combines 2-, 3- or -4 columns dual-beam sub-arrays (modules) with improved beam-forming network (BFN). The modules may be used as part of an array, or as an independent 2-beam antenna. By integrating different types of modules to form a complete array, the present invention provides an improved dual-beam antenna with improved azimuth sidelobe suppression in a wide frequency band of operation, with improved coverage of a desired cellular sector and with less interference being created with other cells. Advantageously, a better cell efficiency is realized with up to 95% of the radiated power being directed in a desired cellular sector.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Multispectral therapeutic light source
ActiveUS20140288351A1High cost-effectiveHigh quantum-efficiencyElectrotherapySurgeryUltravioletPeak value
A light source apparatus including light spectrum-converting materials that emit light primarily over large portions of the 360 nm-480 nm and the 590-860 nm spectral range is provided. This apparatus provides a cooled, high-luminance, high-efficiency light source that can provide a broader spectrum of light within these spectral ranges than has been cost-practical by using many different dominant peak emission LEDs. Up to 15% of the output radiant power may be in the spectral range 350-480 nm in one embodiment of this device, unless a specific separate source and lamp operating mode is provided for the violet and UV. Control methods for light exposure dose based on monitoring and controlling reflected or backscattered light from the illuminated surface and new heat management methods are also provided. This flexible or rigid light source may be designed into a wide range of sizes or shapes that can be adjusted to fit over or around portions of the bodies of humans or animals being treated, or mounted in such a way as to provide the special spectrum light to other materials or biological processes. This new light source can be designed to provide a cost-effective therapeutic light source for photodynamic therapy, intense pulsed light, for low light level therapy, diagnostics, medical and other biological applications as well as certain non-organic applications.
Owner:JONES GARY W
Method and apparatus for light intensity control
InactiveUS20090189530A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentControl signal
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical feedback control for an illumination device, wherein the control signal for each array of one or more light-emitting elements corresponding to a particular colour, is independently configured using a modification signal whose frequency is different for each colour. Electronic filters whose center frequencies are substantially equal to the modification signal frequencies of the drive currents for the light-emitting elements are used to discriminate between the radiant flux corresponding to each of the different colours of light-emitting elements, from a sample of the mixed radiant flux output collected by one or more optical sensors. The output of an individual electronic filter is substantially directly proportional to the radiant flux output of the light-emitting elements of the associated colour, which together with the desired luminous flux and chromaticity of the output light, the controller can use to adjust the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
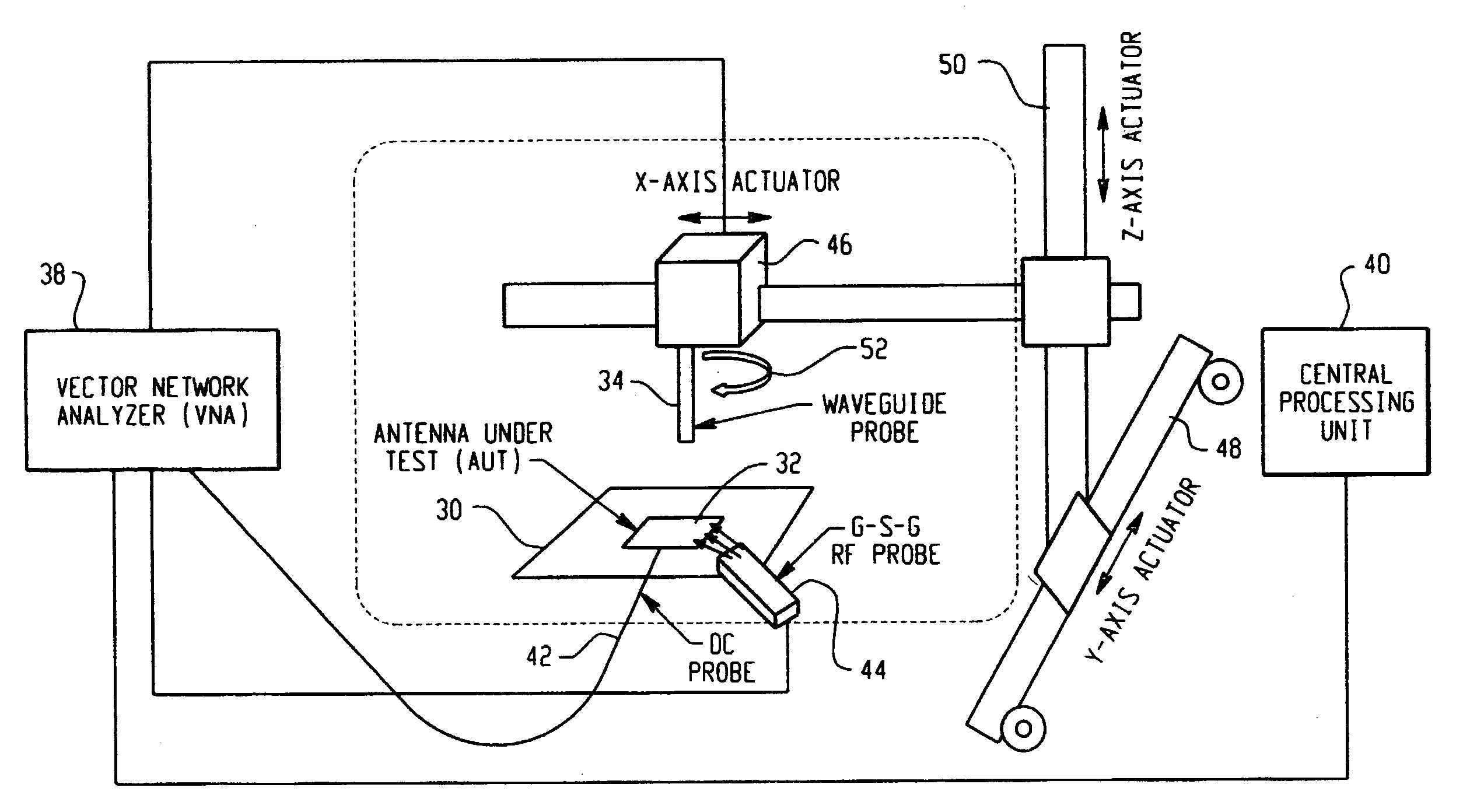
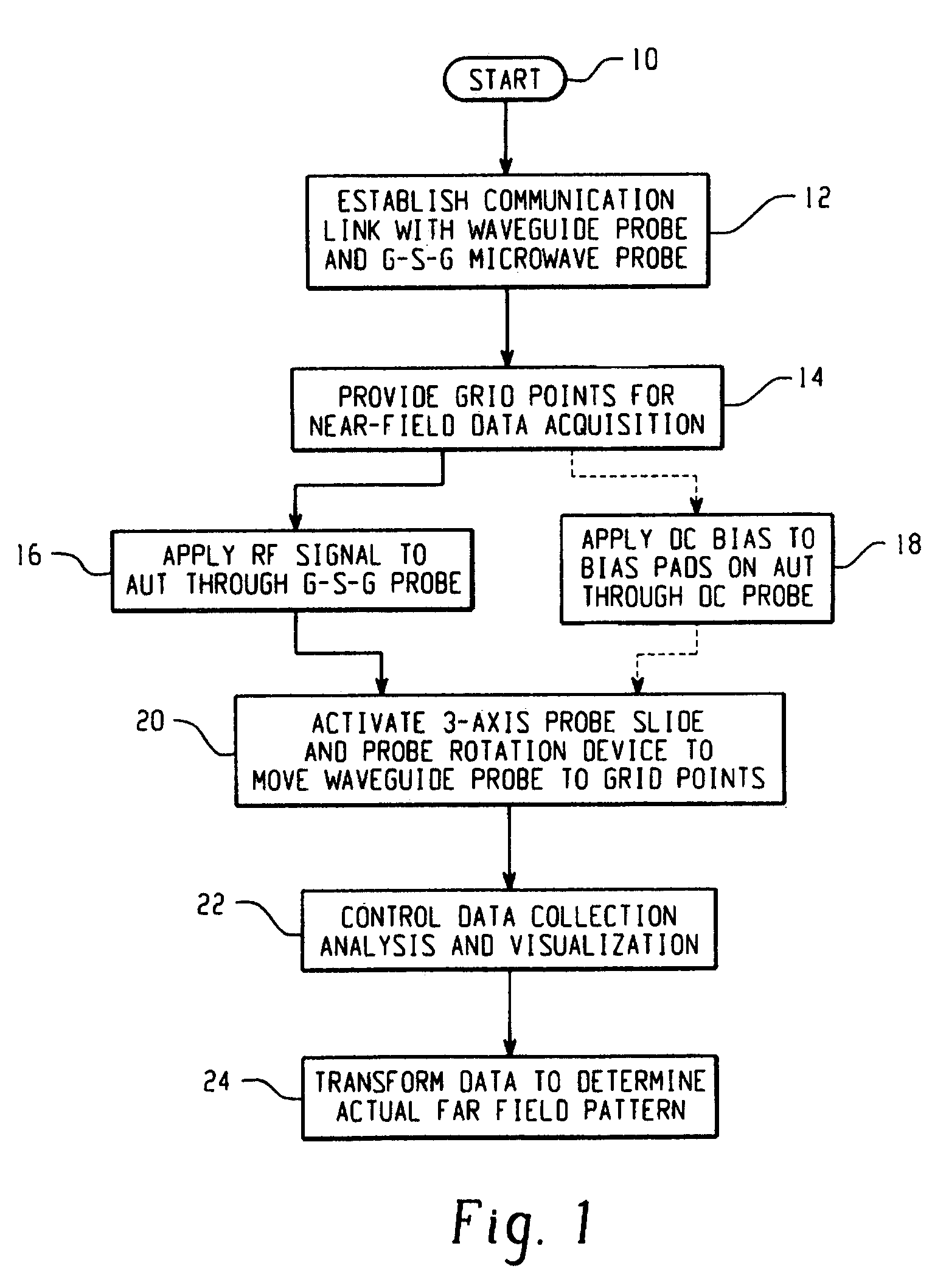
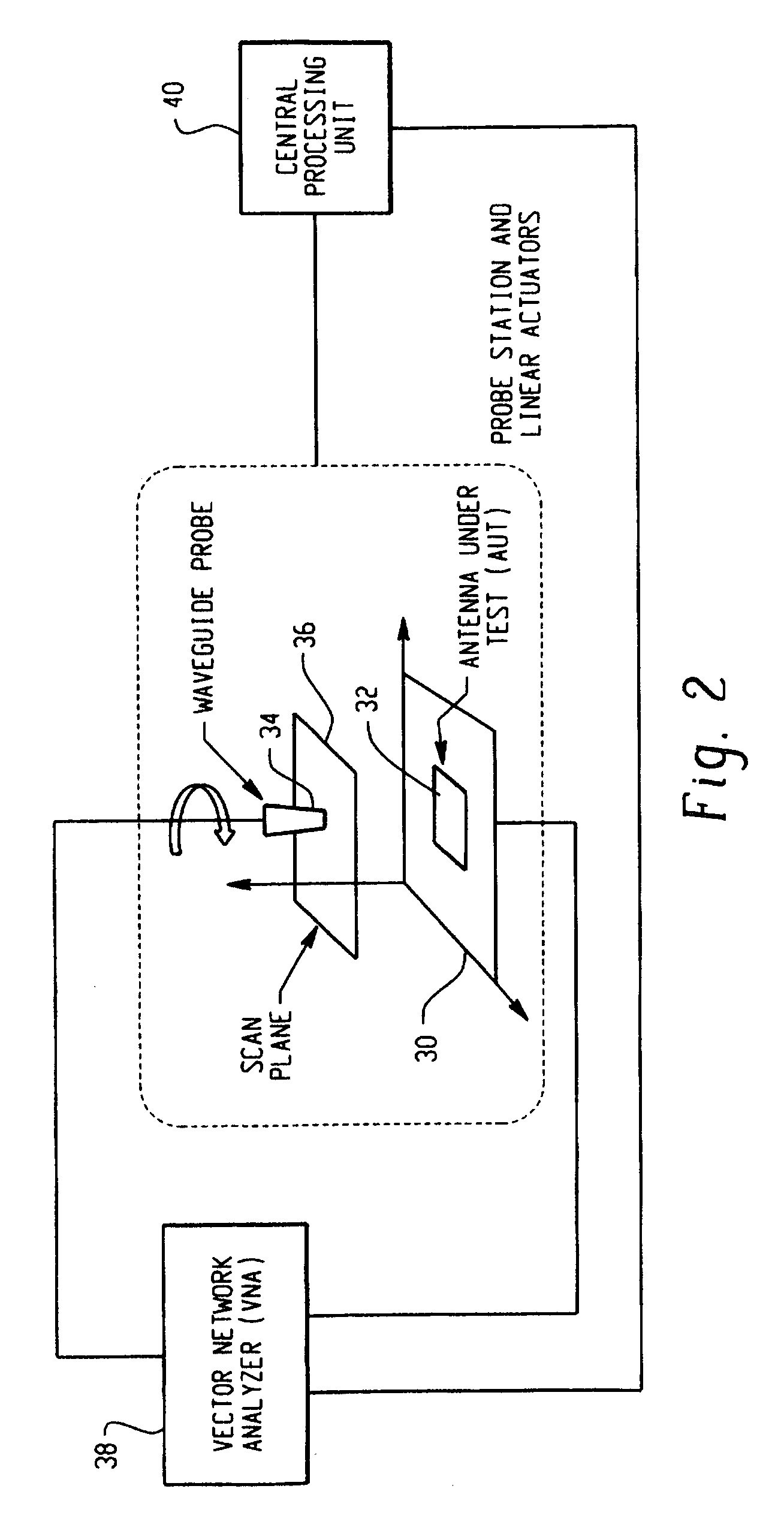
Antenna near-field probe station scanner
A miniaturized antenna system is characterized non-destructively through the use of a scanner that measures its near-field radiated power performance. When taking measurements, the scanner can be moved linearly along the x, y and z axis, as well as rotationally relative to the antenna. The data obtained from the characterization are processed to determine the far-field properties of the system and to optimize the system. Each antenna is excited using a probe station system while a scanning probe scans the space above the antenna to measure the near field signals. Upon completion of the scan, the near-field patterns are transformed into far-field patterns. Along with taking data, this system also allows for extensive graphing and analysis of both the near-field and far-field data. The details of the probe station as well as the procedures for setting up a test, conducting a test, and analyzing the resulting data are also described.
Owner:ADMINISTATOR OF NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE +1
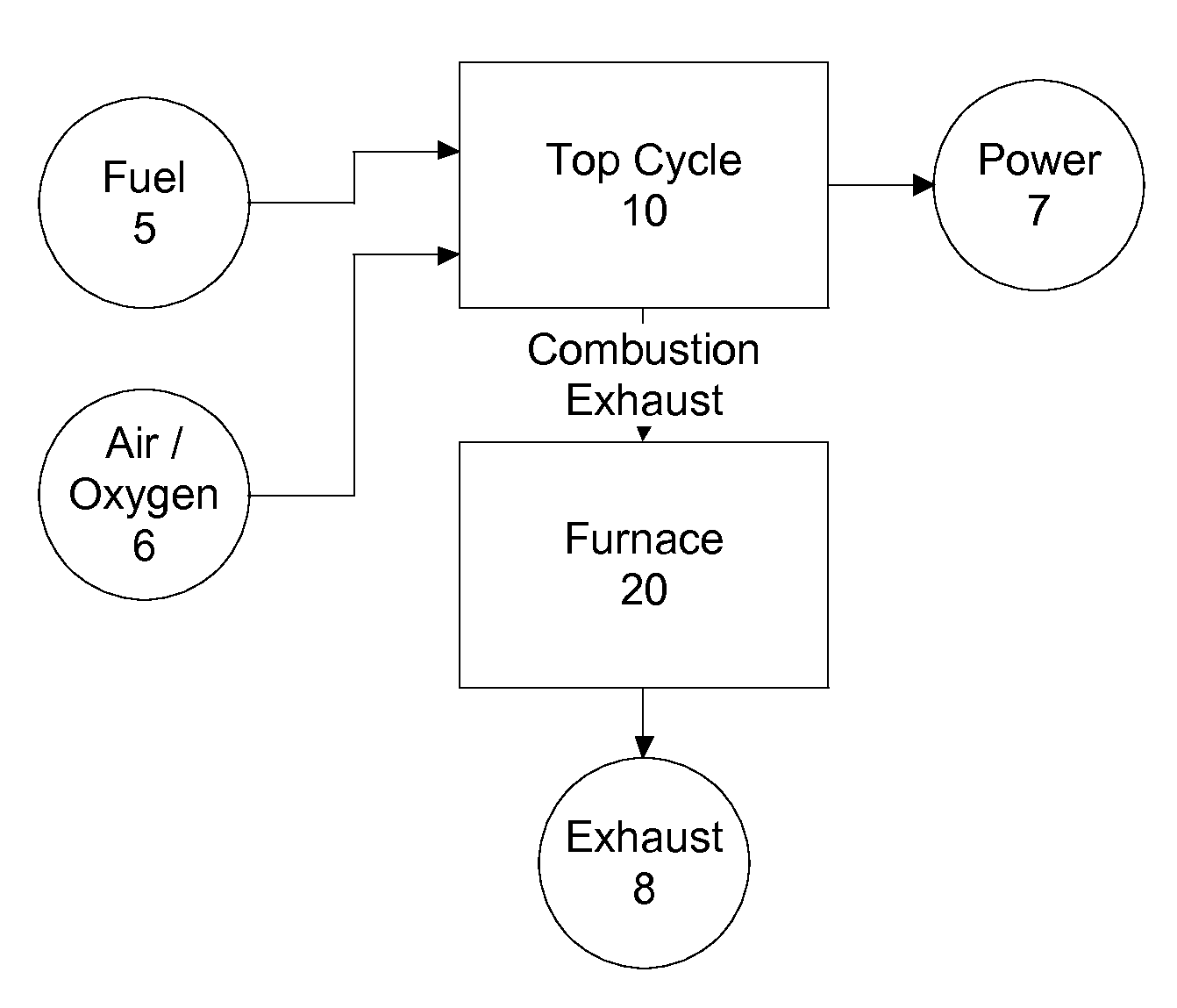
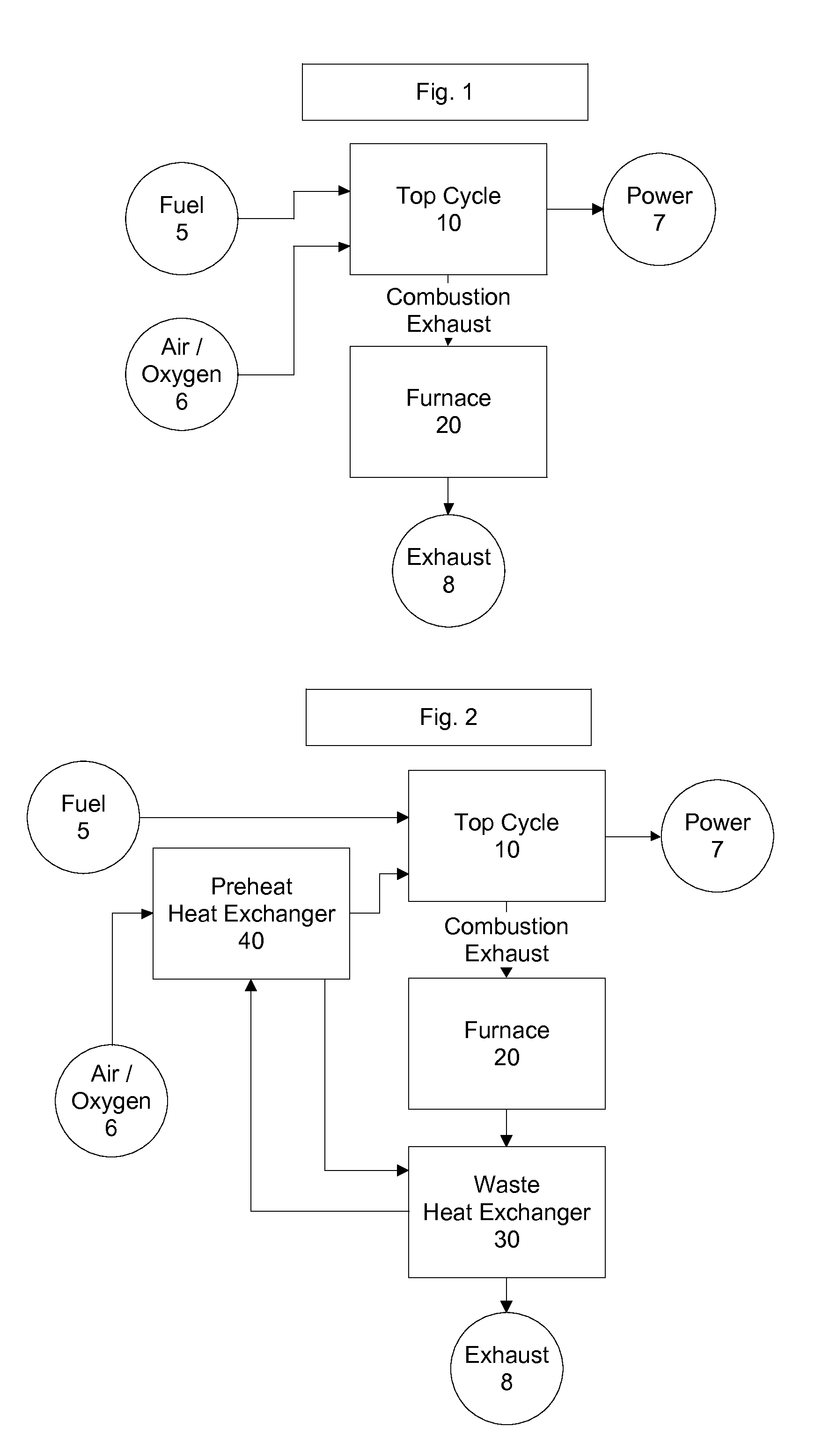
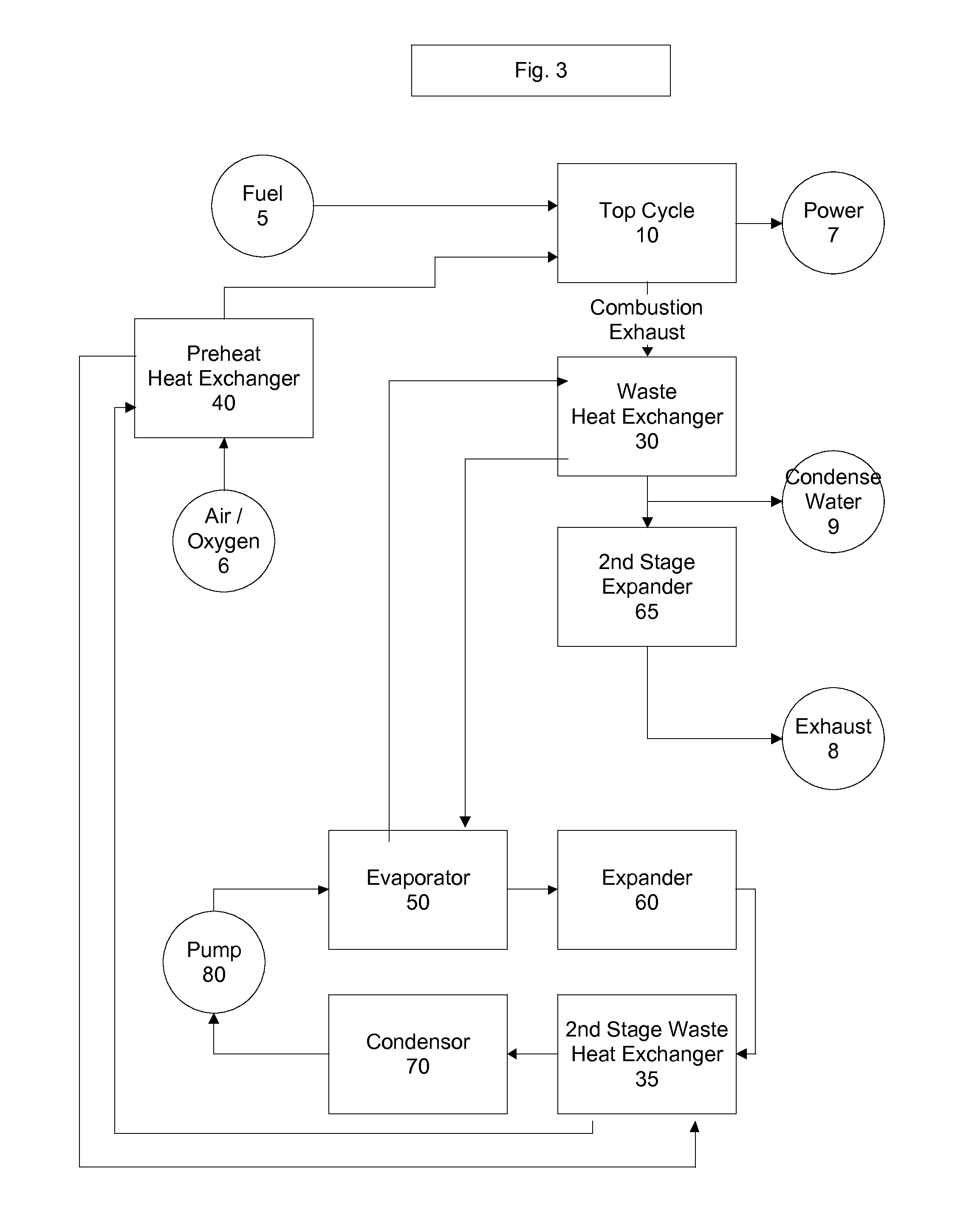
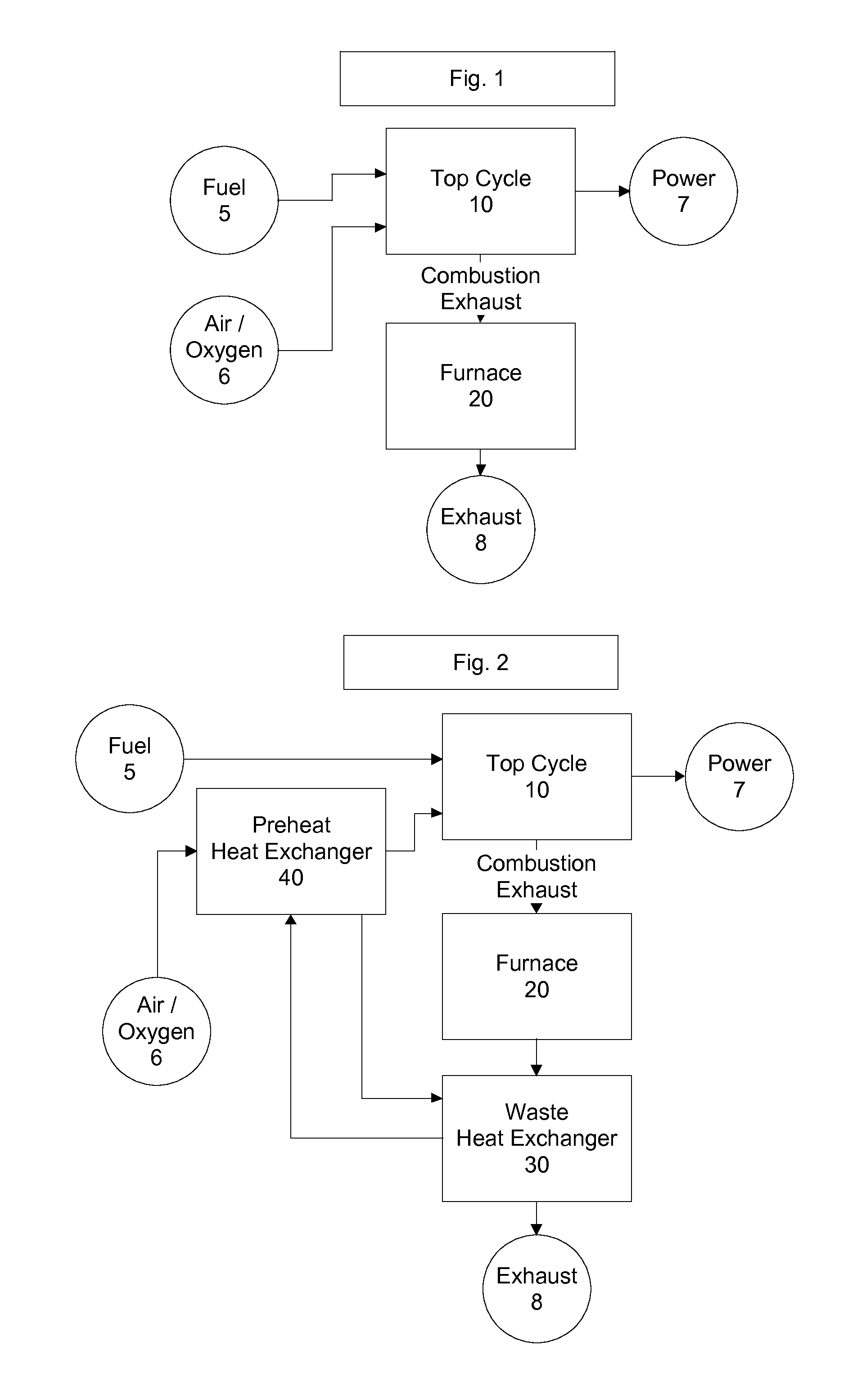
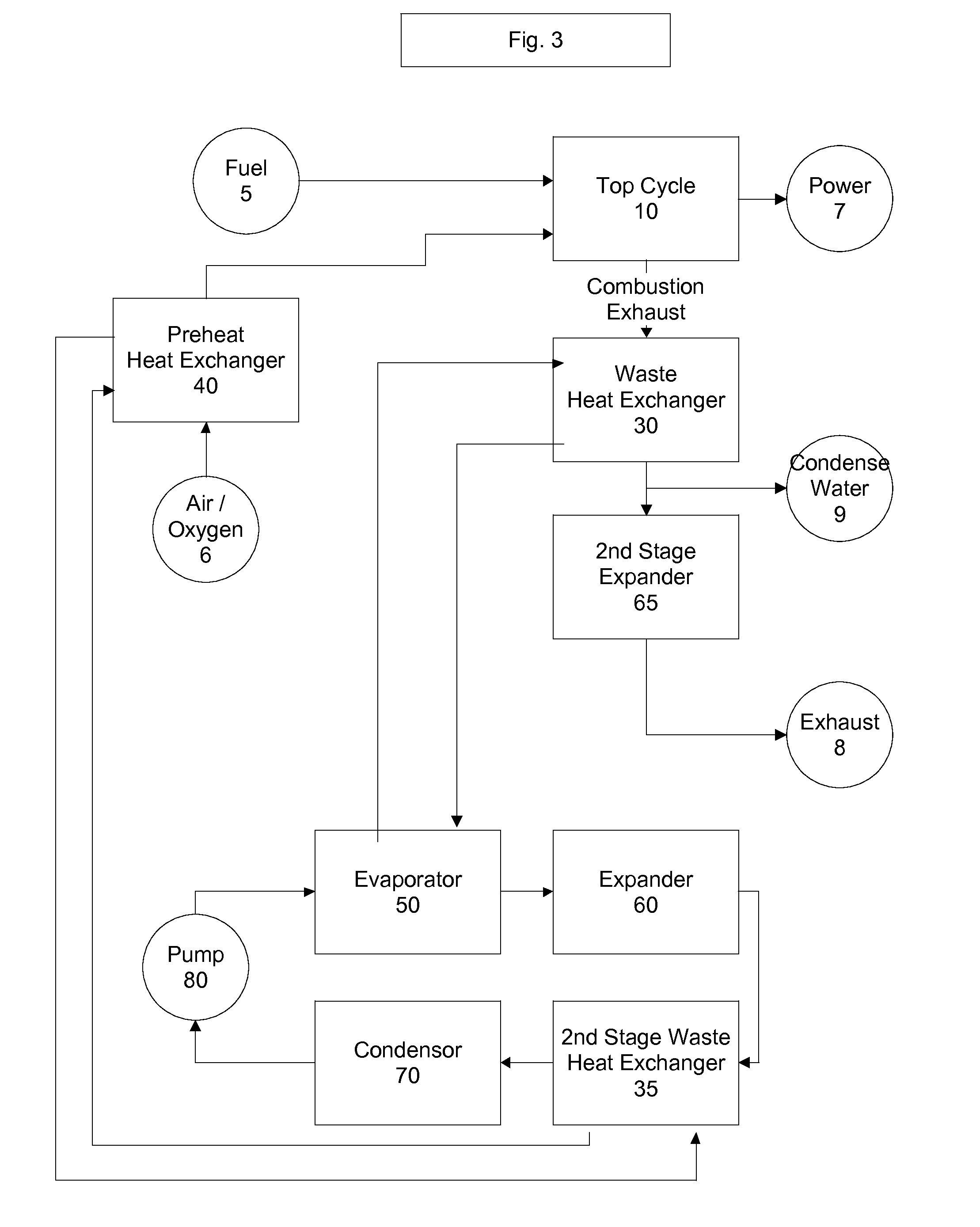
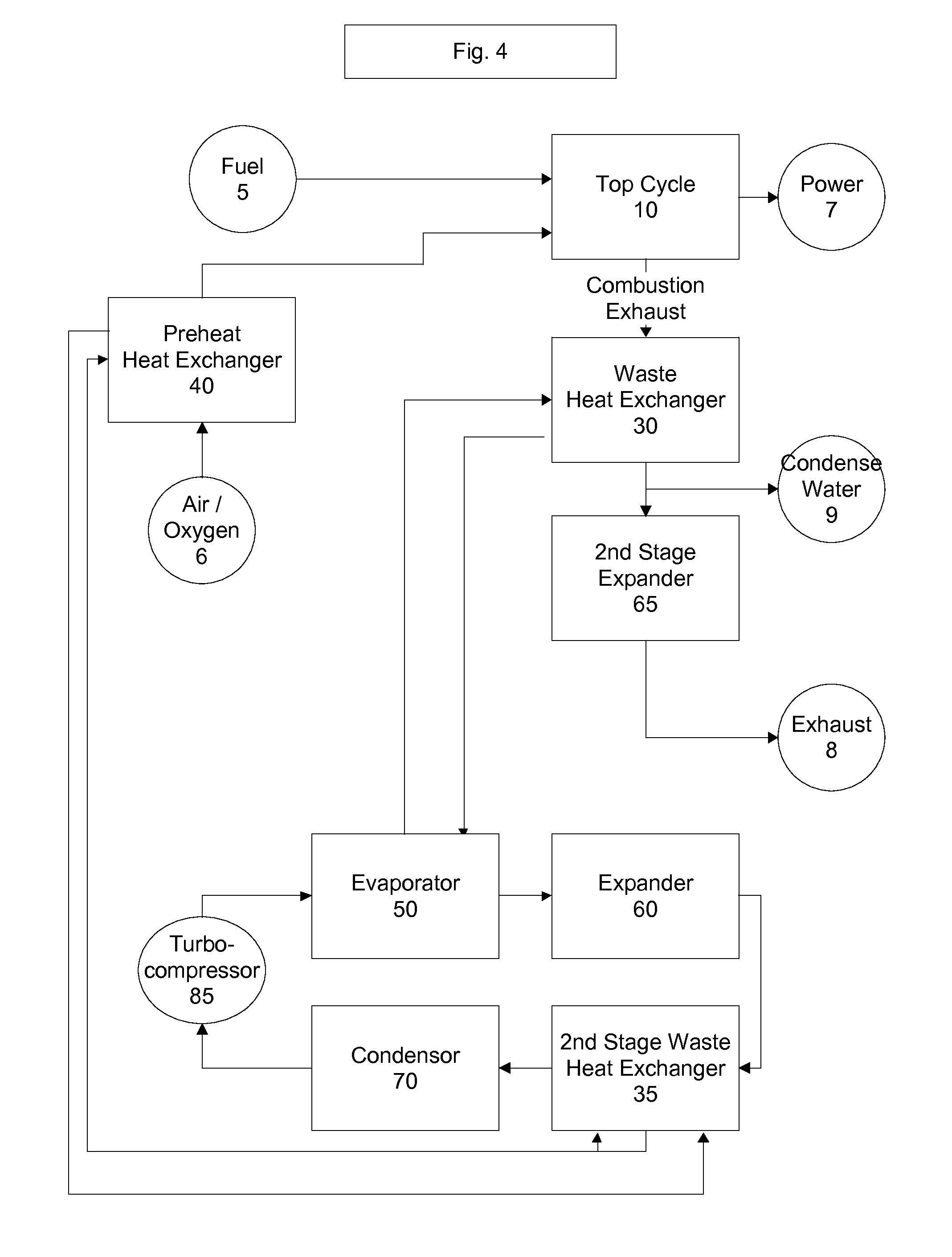
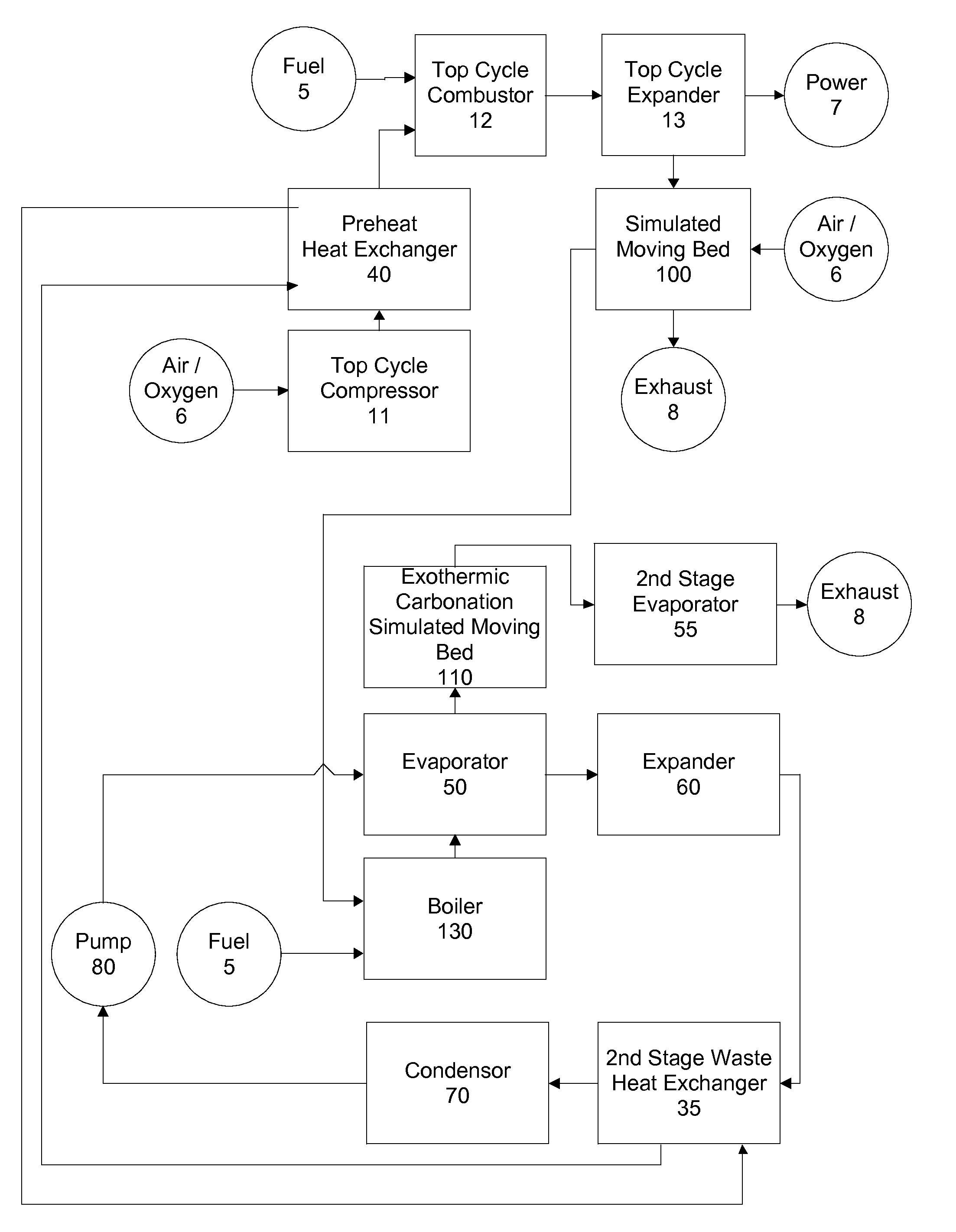
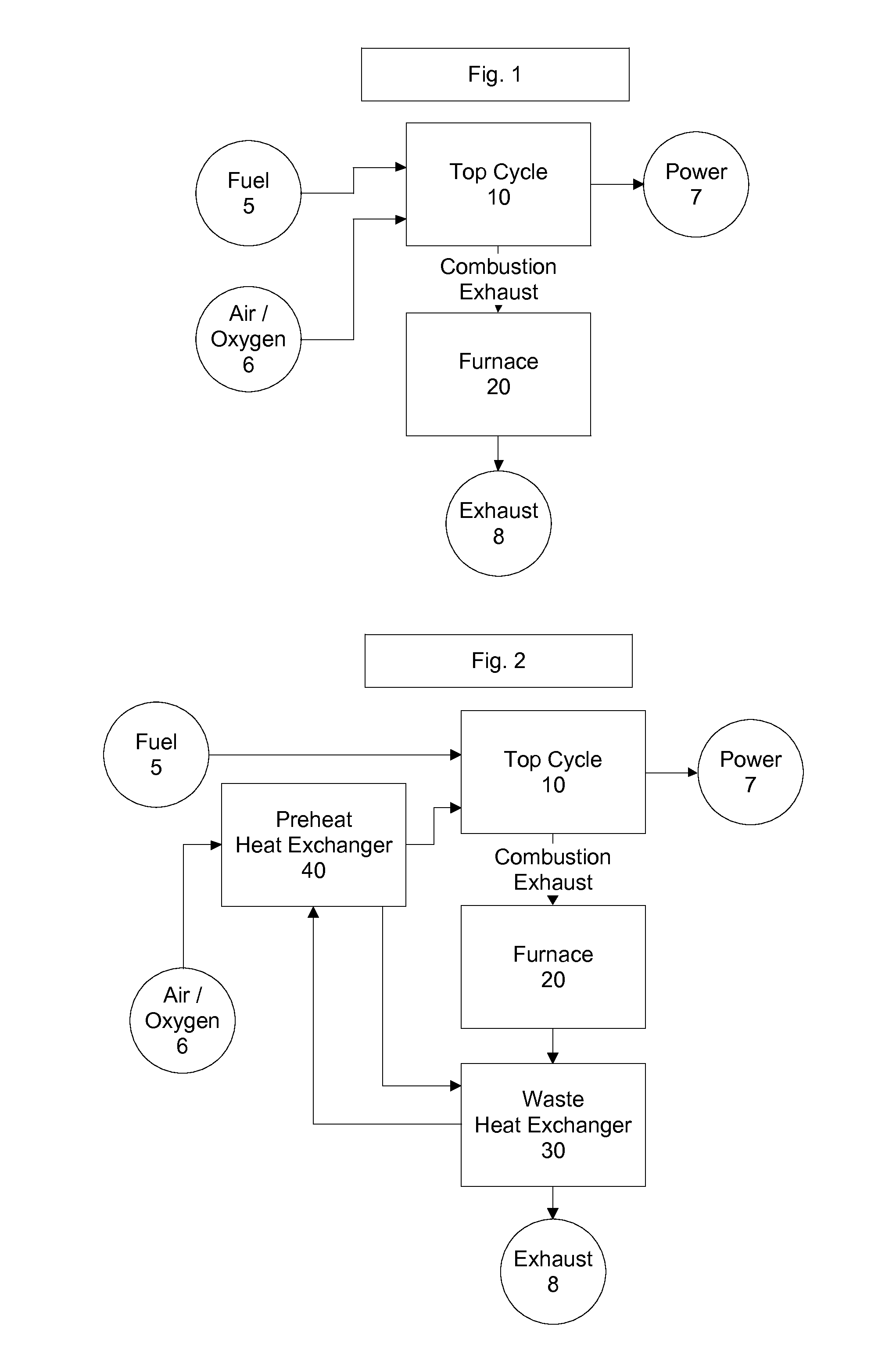
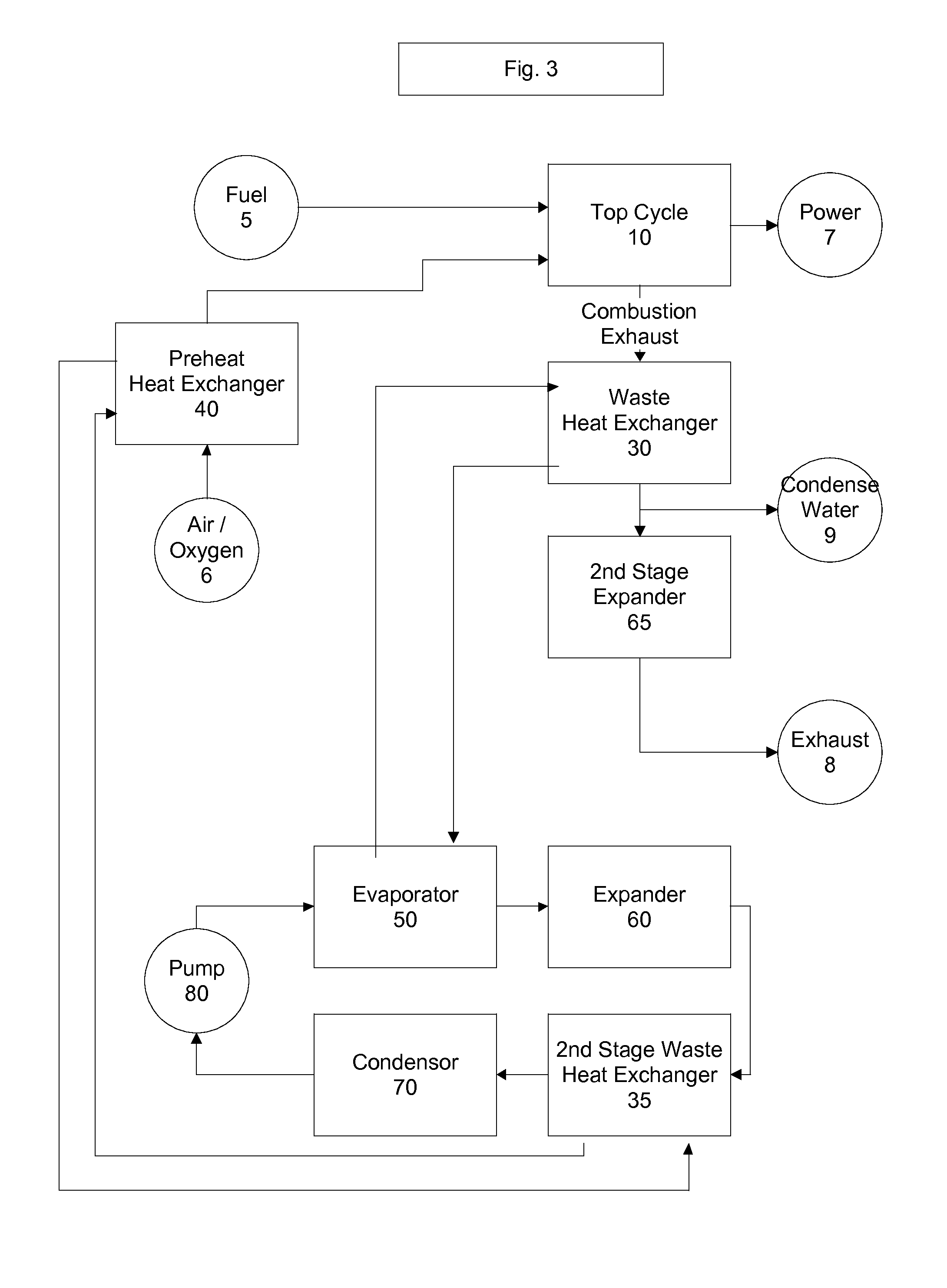
Top cycle power generation with high radiant and emissivity exhaust
The present invention generally relates to power generation methods and secondary processes requiring high radiant and emissivity homogeneous combustion to maximize production output. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to a top cycle power generator with combustion exhaust modified to have radiant flux in excess of 500 kW per square meter and emissivity greater than 0.90, and supercritical CO2 power generating cycle to maximize exergy efficiency.
Owner:GURIN MICHAEL
Polychromatic solid-state light sources for the control of colour saturation of illuminated surfaces
InactiveUS20140167646A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLuminophoreLight-emitting diode
Polychromatic light sources of white light are composed of at least two different coloured emitters, such as groups of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Disclosed are the spectral power distributions and relative partial radiant fluxes of the coloured emitters that allow controlling the colour saturating ability of the generated light, namely, the ability to render colours with increased saturation and the ability to render colours with decreased saturation. Also disclosed is a method for dynamical tailoring the colour saturating ability of the generated light.
Owner:VILNIUS UNIV
Wave interrogated near field arrays system and method for detection of subwavelength scale anomalies
InactiveUS20060065856A1Retaining convenienceRetaining speedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsImaging processingOptical frequencies
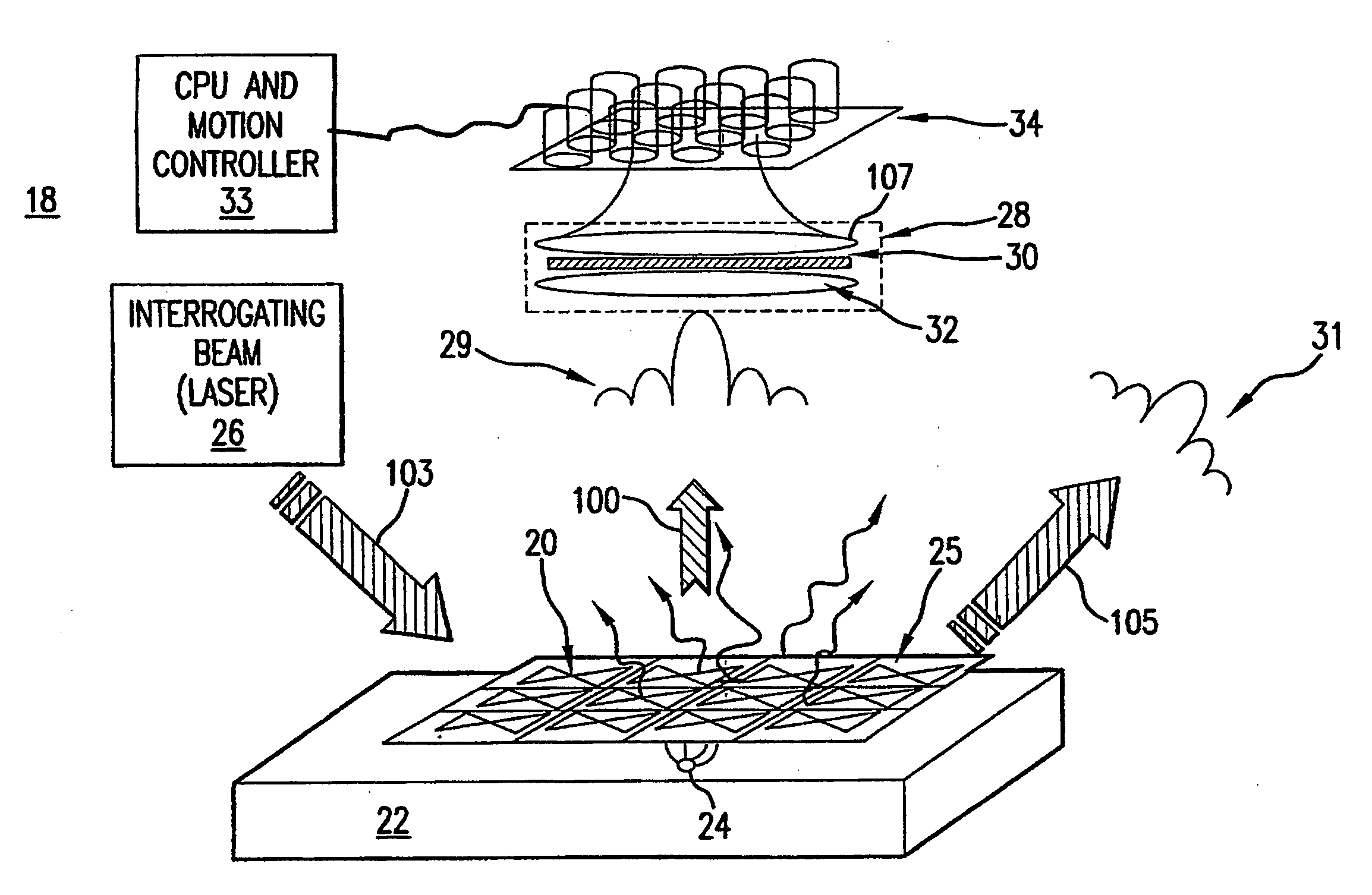
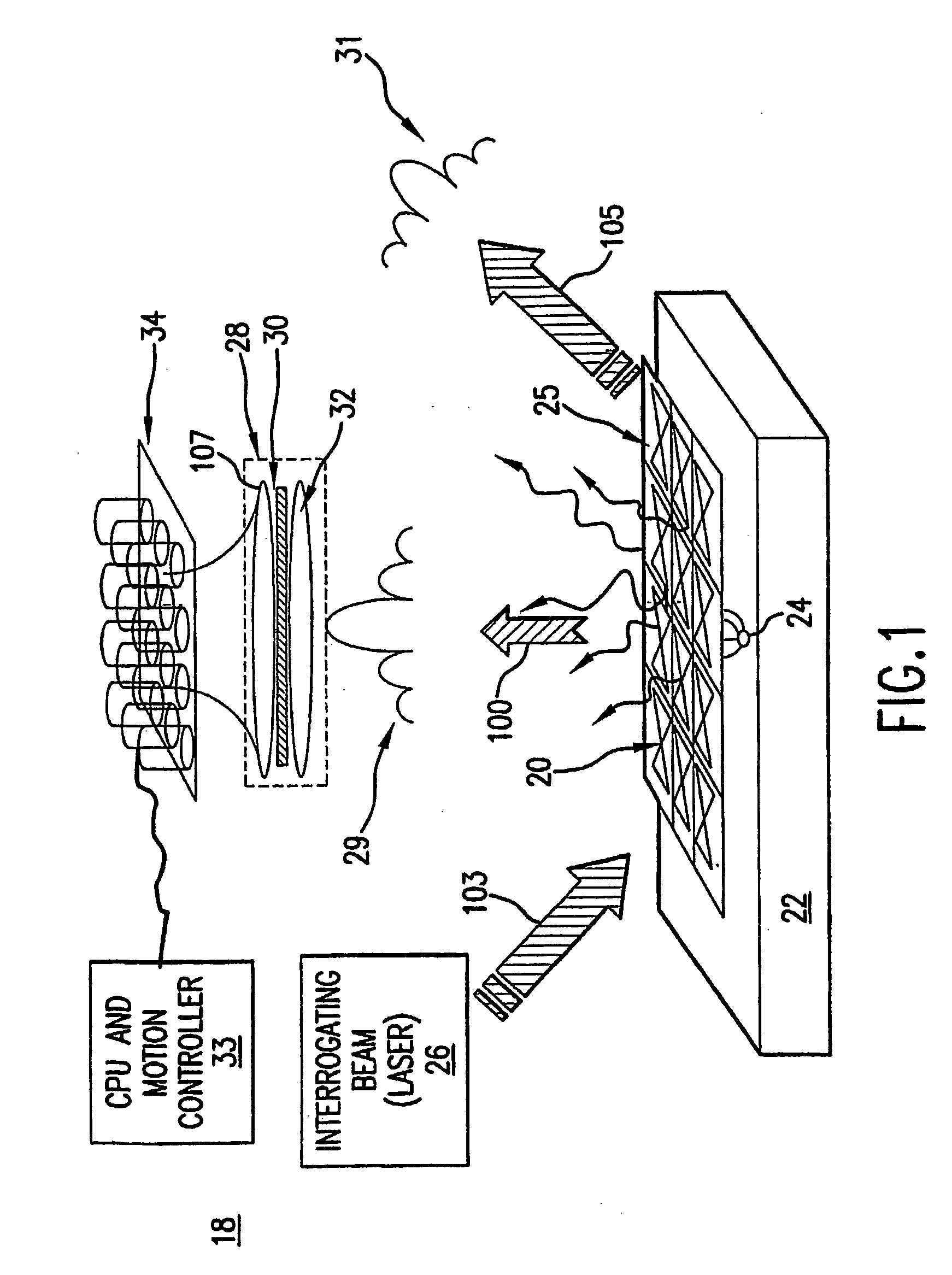
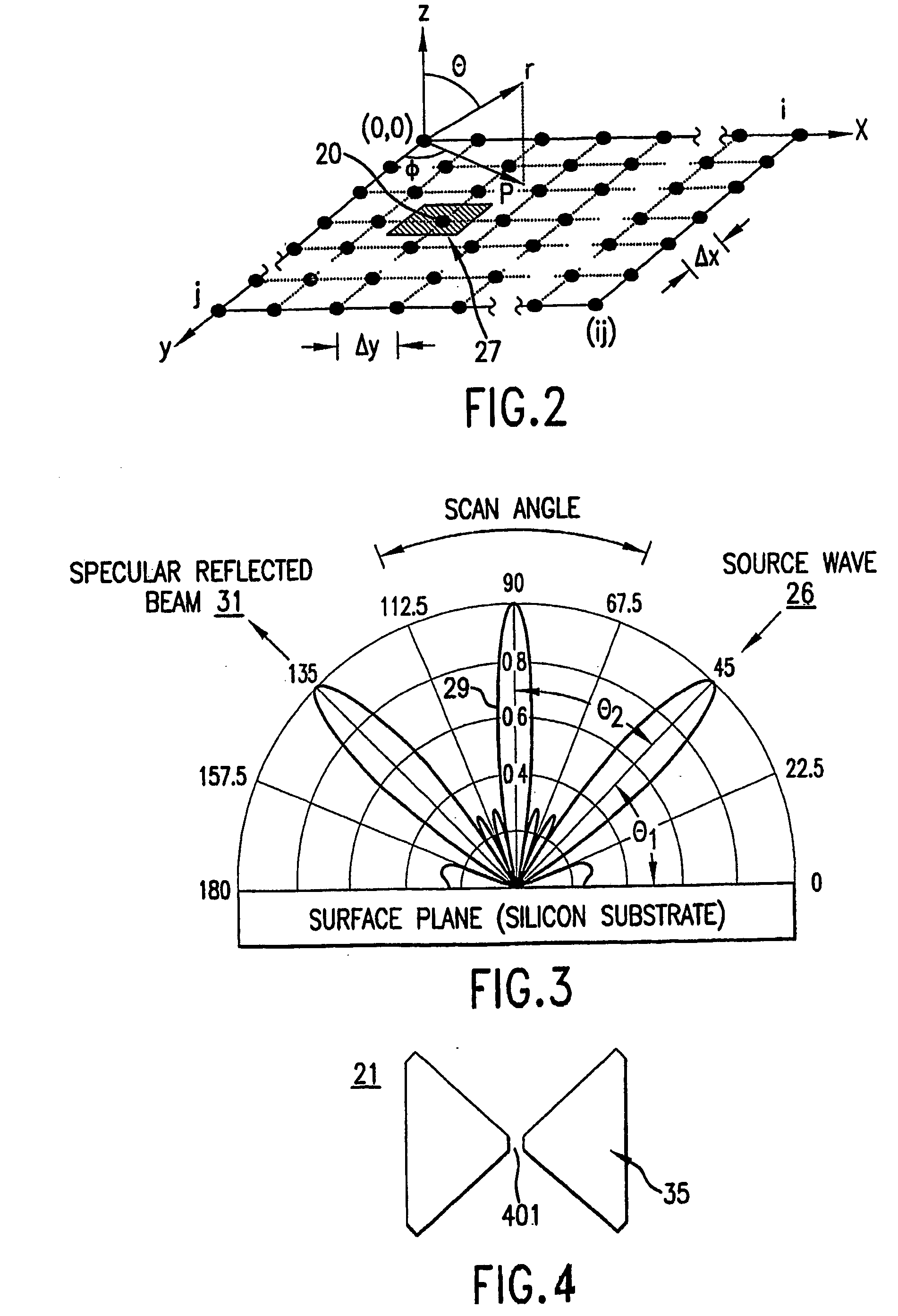
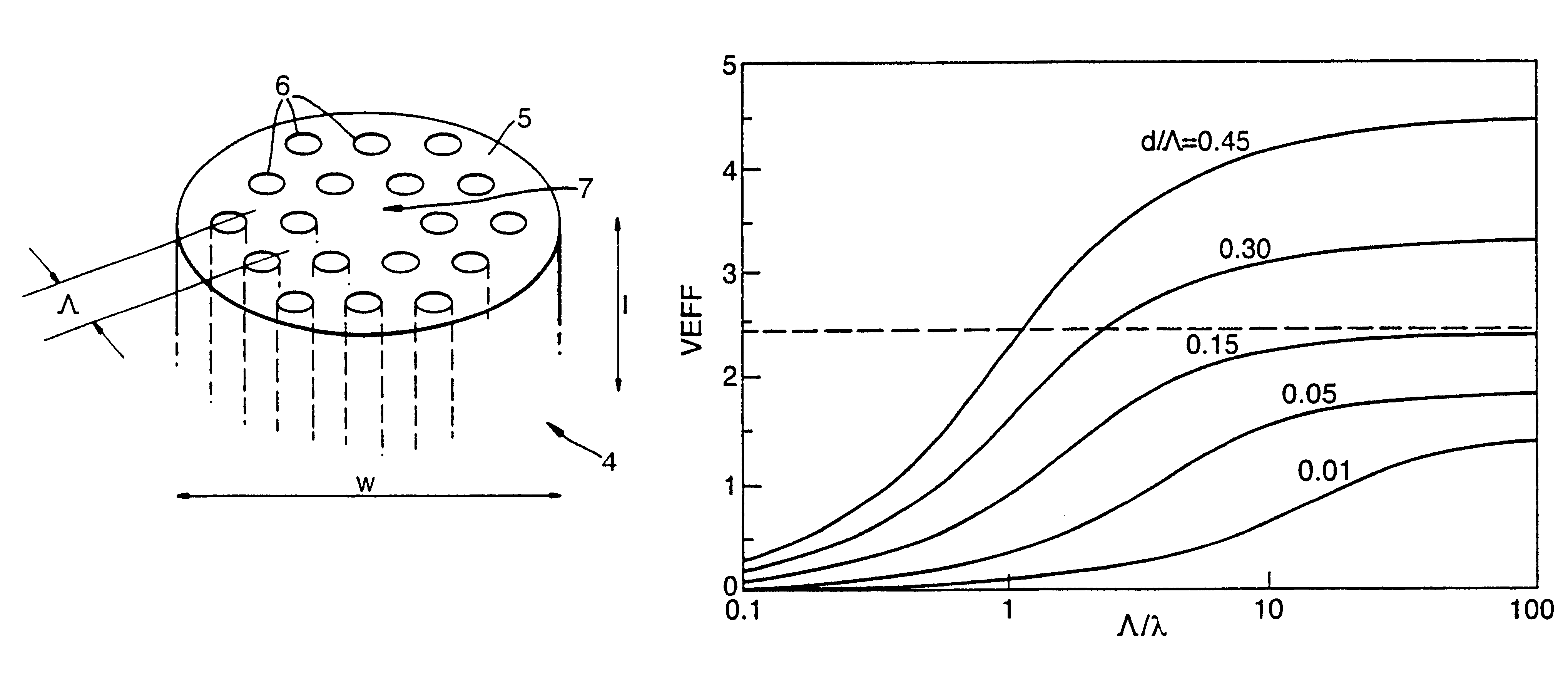
An array of antenna elements (20) can be used to detect subwavelength sized anomalies on a surface below the array. An array (20) is illuminated at optical frequencies by a coherent optical energy source (26). The change in reactance and radiated power of the antenna elements that results from the proximity of the anomaly to the near field of the antenna element's open-circuited is detected and holographically filtered to eliminate the radiation caused by the antenna array itself. Image processing is performed on the detected scattered radiation (100) to determine whether an anomaly is present and to locate the anomaly and its characteristics.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Single mode optical fibre having a large cone photonic crystal
InactiveUS6603912B2High refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexFiber disk laser
A large core photonic crystal fiber for transmitting radiation having a core comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core diameter of at least 5mu. The fiber also comprises a cladding region surrounding the length of core material, wherein the cladding region comprises a first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, and wherein the first substantially transparent cladding material has embedded along its length a substantially periodic array of holes, wherein the holes are filled with a second cladding material having a second refractive index less than the first refractive index, such that radiation input to the optical fiber is transmitted along the length of the core material in a single mode of propagation. In a preferred embodiment, the core diameter may be at least 20mu, and may be as large as 50mu. The fiber is capable of transmitting higher power radiation than conventional fibers, whilst maintaining propagation in a single mode. The core material may be doped with a material capable of providing amplification under the action of pump radiation input to the fiber. The invention also relates to a fiber amplifier and a fiber laser comprising a doped large core photonic crystal fiber. The fibre may also be used in a system for transmitting radiation comprising a plurality of lengths of large core photonic crystal fiber, separated by large core photonic crystal fiber amplifiers, such that the power of radiation transmitted through the system is maintained above a predetermined threshold power.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
Apparatus and method for classifying and sorting articles
InactiveUS7768643B1Polarisation-affecting propertiesInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsElectricityControl circuit
An apparatus for classifying articles may include a frame connected to (1) transport means for directing articles to create a product stream, (2) an emitter section having a radiation source and (3) a detection section for detecting a portion of radiation reflected by articles. The detection section may include first detection means for converting radiant power of reflected radiation having a first polarization state into a first electrical signal, second detection means for converting radiant power of reflected radiation having a second polarization state into a second electrical signal, and third detection means for converting radiant power of reflected radiation into a third electrical signal. Control circuitry, which may receive the electrical signals, may include decision means for generating a selection signal. Selection means may separate an article from the product stream according to the received selection signal from the control circuitry.
Owner:KII TEKU INC
Method and system for radiated power control for short range RFID tag reading
ActiveUS20090021374A1Electric signal transmission systemsMemory record carrier reading problemsUltrasound attenuationControl power
A method and system for power control for Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tag reading is provided. The system includes a power amplifier for providing an RF transmit signal for the RFID tag reading. The RF transmit signal is provided to an antenna for radiating the transmit signal. The power of the radiated transmit signal defining a read range for the RFID tag reading. The system includes an attenuator provided between the power amplifier and the antenna for controlling the power of the radiated transmit signal to adjust the read range. A handheld RFID reader may include the system. The method includes calibrating the output power of a reader having a power amplifier and an attenuator provided between the power amplifier and an antenna. The step of calibrating includes at least one of controlling power of the power amplifier in its linear region, and controlling attenuation level of the attenuator.
Owner:PSION
Method of reducing a wave front aberration, and computer program product
ActiveUS20070296938A1Reduce optical effectsReduce decreasePhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansPupilProjection system
A method of reducing a wave front aberration is provided for a lithographic process whereby the reducing is based on the selected pattern to be printed and the selected illumination mode used for exposure. Wave front aberrations of a projection system of a lithographic apparatus are measured and reduced by calculating adjustments of optical elements of the projection system and applying the calculated adjustments to the projection system. The calculation of adjustments is based on information on a spatial distribution of radiant intensity in a pupil of the projection system as present during exposing the radiation sensitive layer, and is limited to aberrations in projection lens pupil areas of relative high radiant flux.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Top cycle power generation with high radiant and emissivity exhaust
The present invention generally relates to power generation methods and secondary processes requiring high radiant and emissivity homogeneous combustion to maximize production output. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to a top cycle power generator with combustion exhaust modified to have radiant flux in excess of 500 kW per square meter and emissivity greater than 0.90, and supercritical CO2 power generating cycle to maximize energy efficiency.
Owner:GURIN MICHAEL
Top cycle power generation with high radiant and emissivity exhaust
The present invention generally relates to power generation methods and secondary processes requiring high radiant and emissivity homogeneous combustion to maximize production output. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to a top cycle power generator with combustion exhaust modified to have radiant flux in excess of 500 kW per square meter and emissivity greater than 0.90, and supercritical CO2 power generating cycle to maximize exergy efficiency.
Owner:GURIN MICHAEL
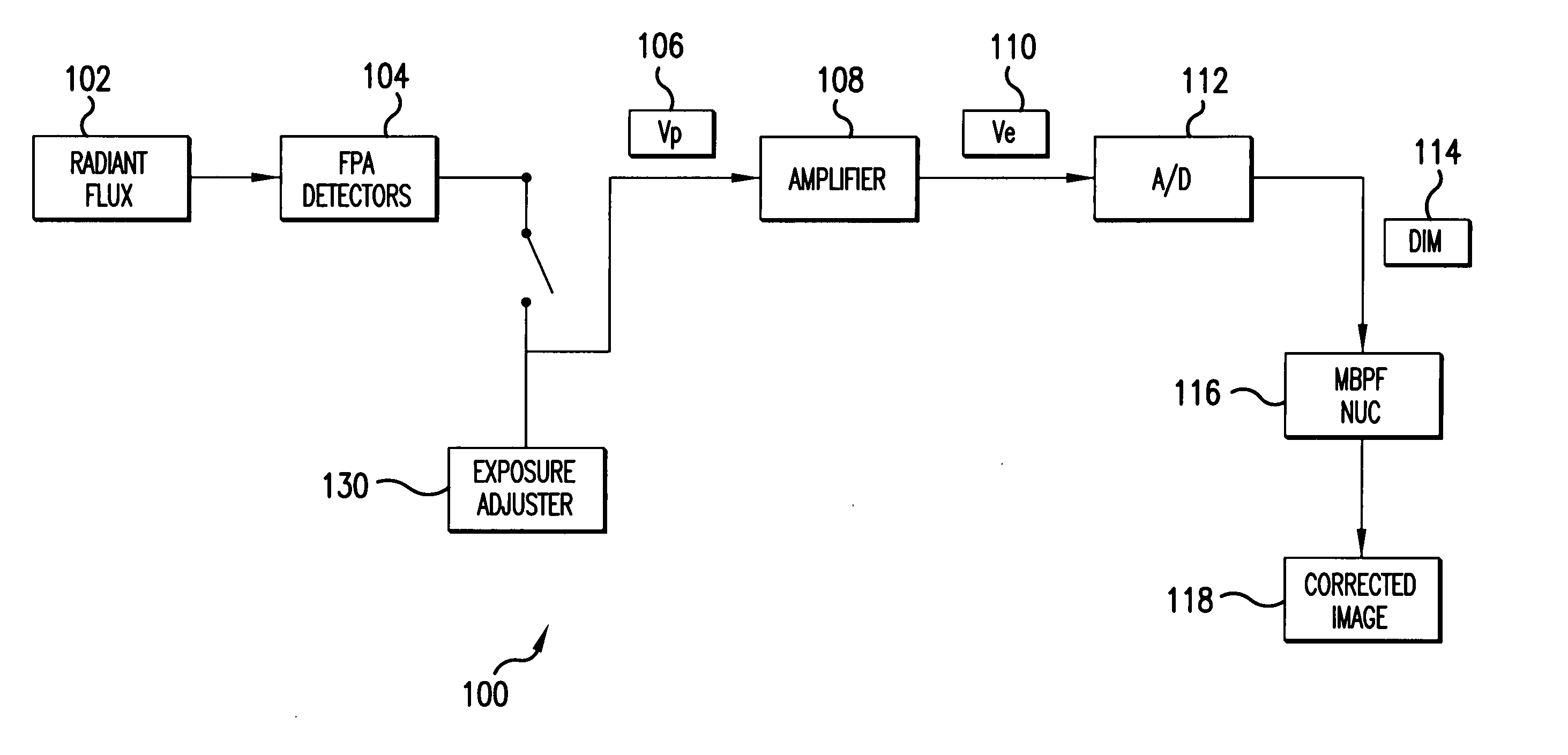
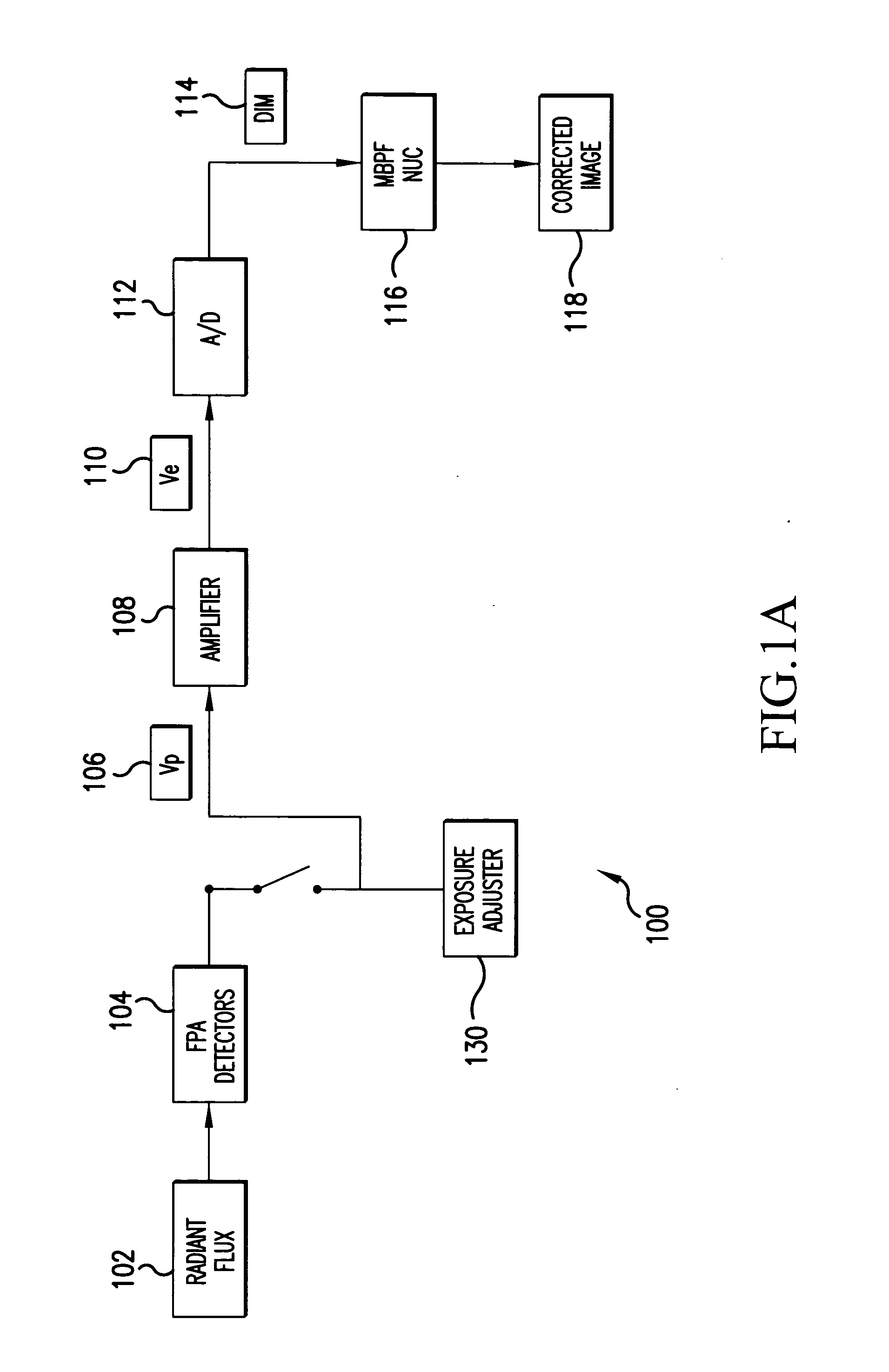
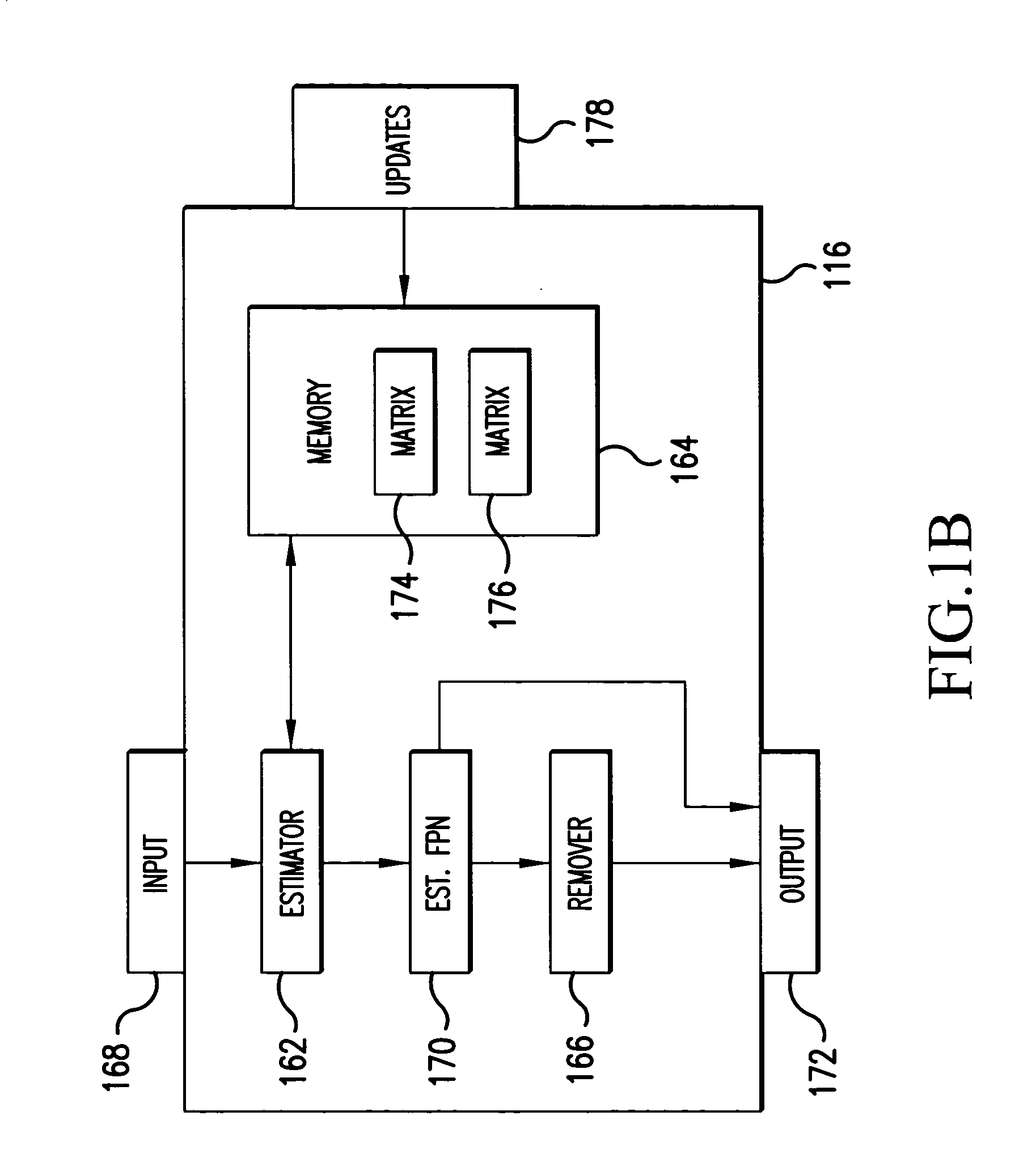
System and method for estimating noise using measurement based parametric fitting non-uniformity correction
InactiveUS20050157942A1Solve the deficienciesSolves shortcomingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDigital imageComputer science
A system and method for estimating noise using measurement based parametric fitting non-uniformity correction is disclosed. Fixed pattern noise (“FPN”) is estimating from an overall noise component within a detection system to enhance candidate target detection and tracking. A sensor in the detection system receives energy, such as radiant flux, that is converted to a digital image. A non-uniformity correction device generates an estimated FPN according to an applicable temperate range and integration time. A memory storing an array of coefficients is accessed to determine the estimated FPN. The valves within the array of coefficients are based on actual FPN measurements that are parametrically fitted.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN MISSILES & FIRE CONTROL
Methods and Apparatus for Coded Time-of-Flight Camera
ActiveUS20150120241A1Accurate measurementDepth accurateOptical rangefindersMechanical depth measurementsWiener deconvolutionMultipath interference
In illustrative implementations, a time-of-flight camera robustly measures scene depths, despite multipath interference. The camera emits amplitude modulated light. An FPGA sends at least two electrical signals, the first being to control modulation of radiant power of a light source and the second being a reference signal to control modulation of pixel gain in a light sensor. These signals are identical, except for time delays. These signals comprise binary codes that are m-sequences or other broadband codes. The correlation waveform is not sinusoidal. During measurements, only one fundamental modulation frequency is used. One or more computer processors solve a linear system by deconvolution, in order to recover an environmental function. Sparse deconvolution is used if the scene has only a few objects at a finite depth. Another algorithm, such as Wiener deconvolution, is used is the scene has global illumination or a scattering media.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multiple Aperture Hand-Held Laser Therapy Apparatus
ActiveUS20130317571A1Easy to changeIncrease the areaLaser detailsControlling energy of instrumentHigh energyHand held
A hand-held therapeutic laser apparatus with a special opto-mechanical construction, which enables changeability of a front collimating lens to create different effective laser apertures. A smaller effective aperture has a comparatively higher radiant flux density for treatment of a small area that requires a higher energy dose, while a larger effective aperture facilitates treatment of a large area at a relatively reduced radiant intensity.
Owner:MEDICAL COHERENCE
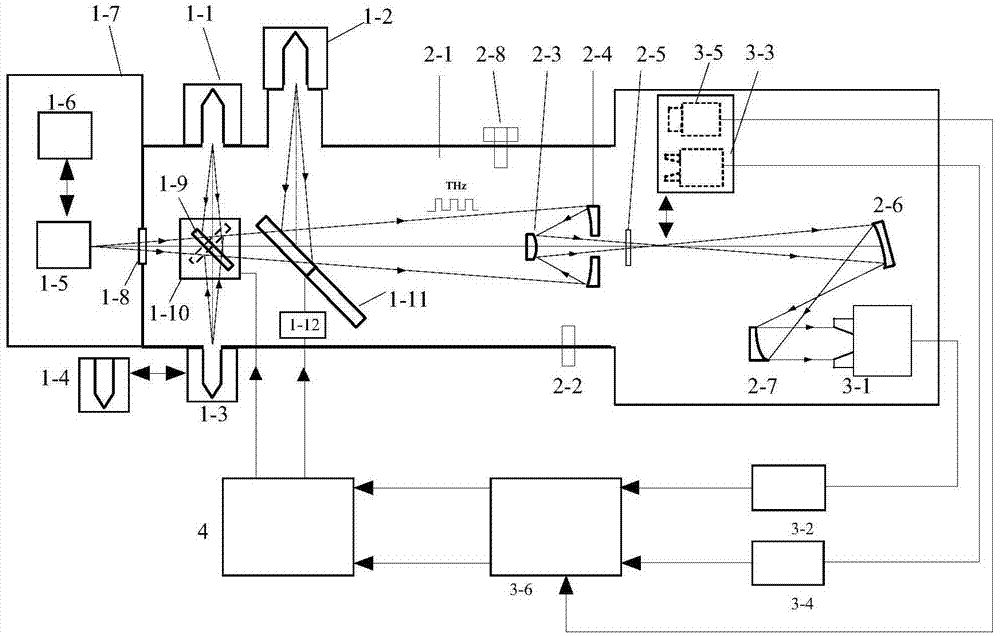
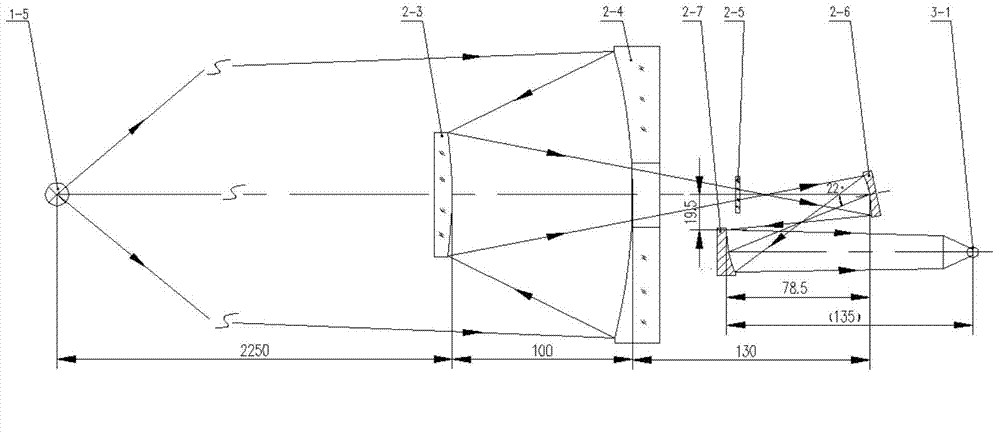
Broadband terahertz source radiant power calibration device and method
ActiveCN104713641AAchieve calibrationImprove measurement accuracyPhotometry using reference valueBroadbandPower correction
The invention provides a broadband terahertz source radiant power calibration device and method. A terahertz source capable of being tested is a terahertz source with a light beam divergence angle larger than 1.732 degree and the spectral region ranging from 30 micrometer to 3000 micrometer. According to the broadband terahertz source radiant power calibration device and method, the measurement method that radiation parameters of a standard terahertz source are compared with radiation parameters of the to-be-tested terahertz source is adopted; after radiation of the standard terahertz source or the to-be-tested terahertz source enters a low temperature vacuum background channel through a terahertz transmission window, the radiation and background radiation of a liquid nitrogen refrigeration black body are alternatively modulated through a light chopper sheet into periodically-changed terahertz radiation signals, are gathered through a Cassegrain system, income a terahertz detector through a terahertz spectrum light filter, are converted into periodically-changed voltage signals, and are processed through a lock-in amplifier to obtain stable measuring voltage signals. The radiant power of the to-be-tested terahertz source is obtained through calculation according to the radiant power correction factors obtained by measuring a weak radiation source or a strong radiation source, and meanwhile the radiation luminance of the to-be-tested terahertz source can be obtained through calculation.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
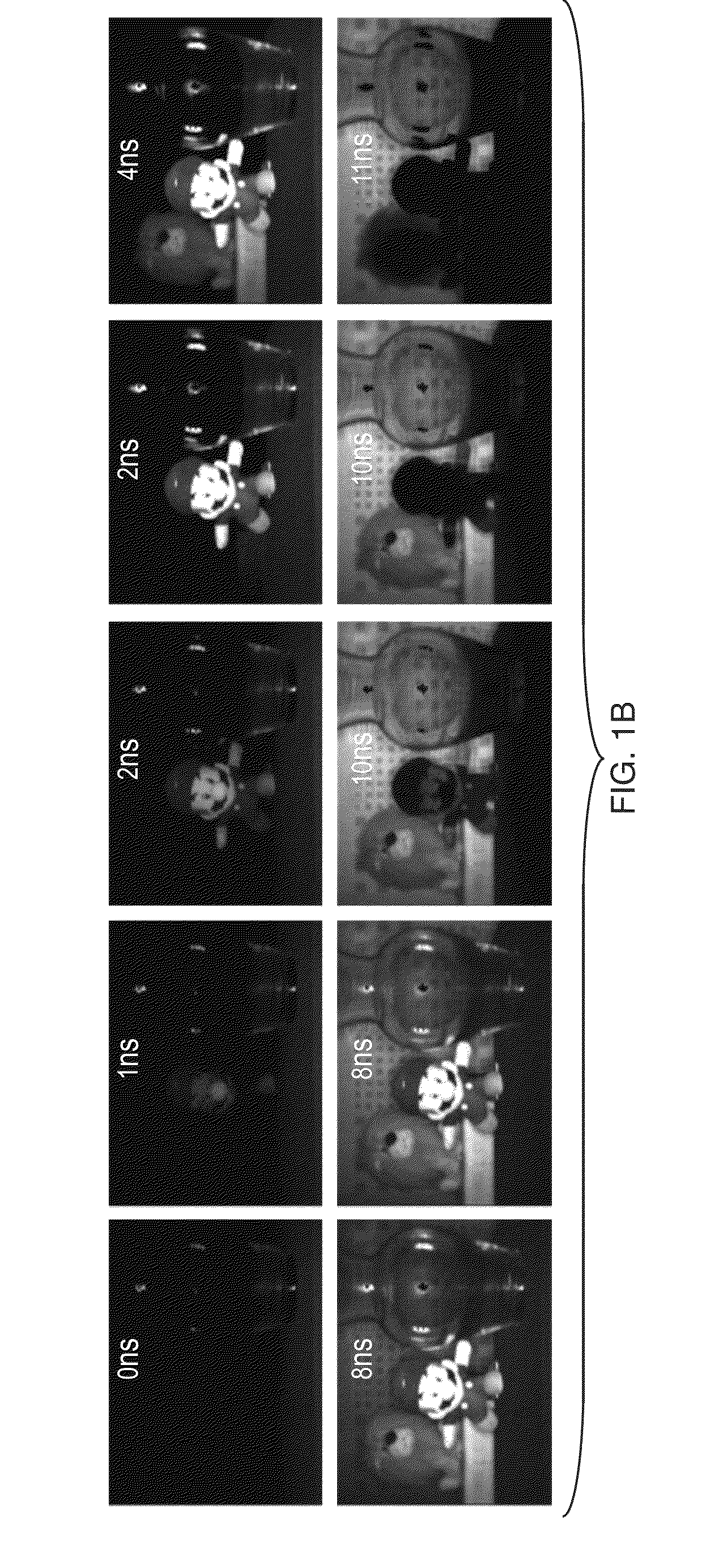
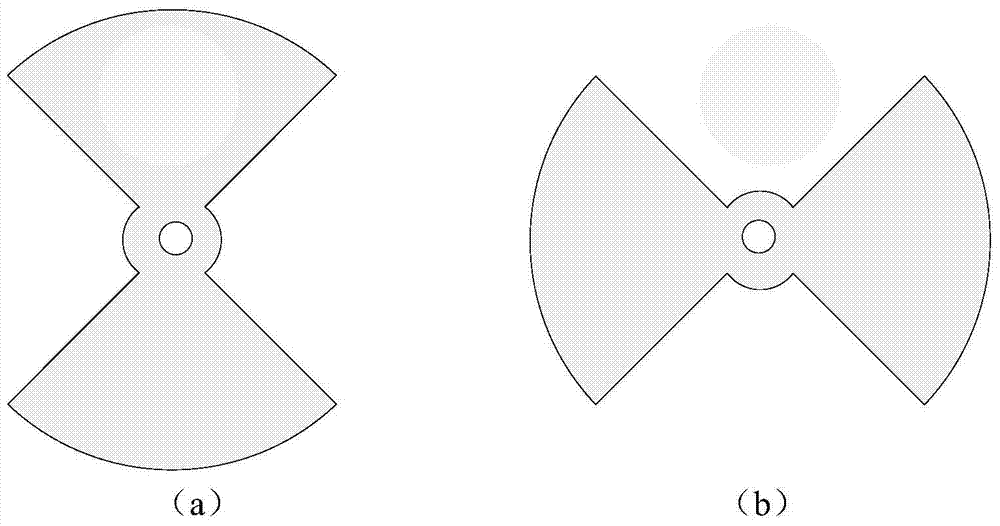
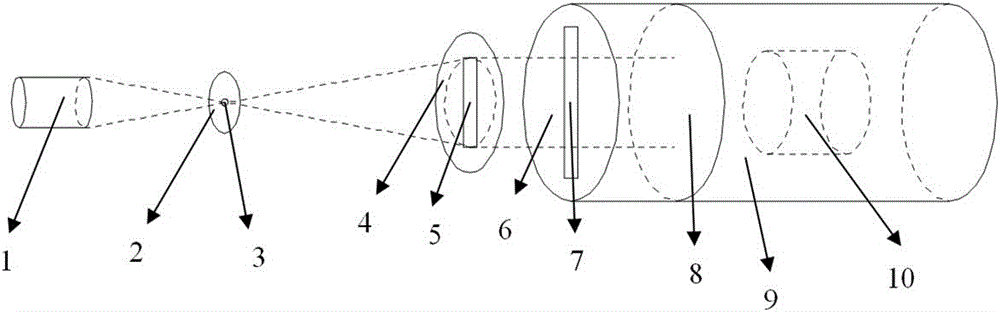
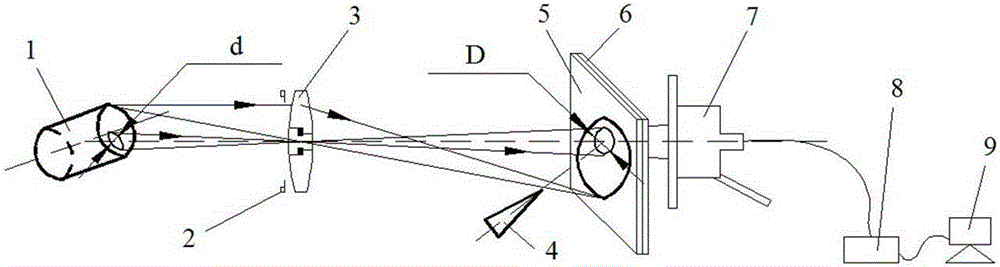
Temporal-spatial resolution radiant flux diagnosis system
ActiveCN106526654AImprove time resolutionHigh spatial resolution measurementX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentTemporal resolutionMicrometer
The invention provides a temporal-spatial resolution radiant flux diagnosis system, which is used for conducting precise diagnosis on the temporal and spatial evolution process of an X-ray radiant flux in a hohlraum. The hohlraum emits X-rays which undergo imaging by means of a pinhole in a pinhole plate, a portion of the X-rays is imaged onto an imaging plate; the other portion of the X-ray passes through a slit I in the imaging plate and then passes through a slit II in a time resolution plate to irradiate on an X-ray photocathode, further passes through a streak camera focusing deflection system and is recorded in a streak camera. According to the recorded signal, the temporal and spatial evolution process of the X-ray radiant flux emitted at a specified position of the hohlraum can be obtained. The temporal-spatial resolution radiant flux diagnosis system has time resolution with picosecond magnitude and temporal resolution with dozens of micrometer magnitude, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Spatial distinguishing radiant flux detection apparatus
ActiveCN105158789AQuantitative detection of radiation flowX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentX-rayX ray image
The invention provides a spatial distinguishing radiant flux detection apparatus, which comprises a pinhole lens assembly, a camera, an aperture-limiting imaging plate, an aperture-limiting plate and a flat response X-ray detector F-XRD; a black chamber inlet emits visible light; a lens produces image onto the aperture-limiting imaging plate; the X-ray emitted from the black chamber inlet passes through the pinhole after determining the position relation of the aperture and the visible light image in the inlet; only part of the X-ray passes through the aperture-limiting imaging plate and the aperture of the aperture-limiting plate and gets to a sensitive surface of the flat response X-ray detector F-XRD to trigger response; that X-ray energy flow is correspond to a radiant flux of part area inside the inlet; at the same time, the aperture-limiting imaging plate records the position relation between X-ray image and the aperture after passing though the pin hole of the inlet so as to realize spatial distinguishing radiant flux detection. According to the invention, the X-ray radiant flux quantitative detection can be distinguished in time and space without being influenced by extra X-ray generated at the edge of the black chamber inlet of laser; and a wide application prospect is provided.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
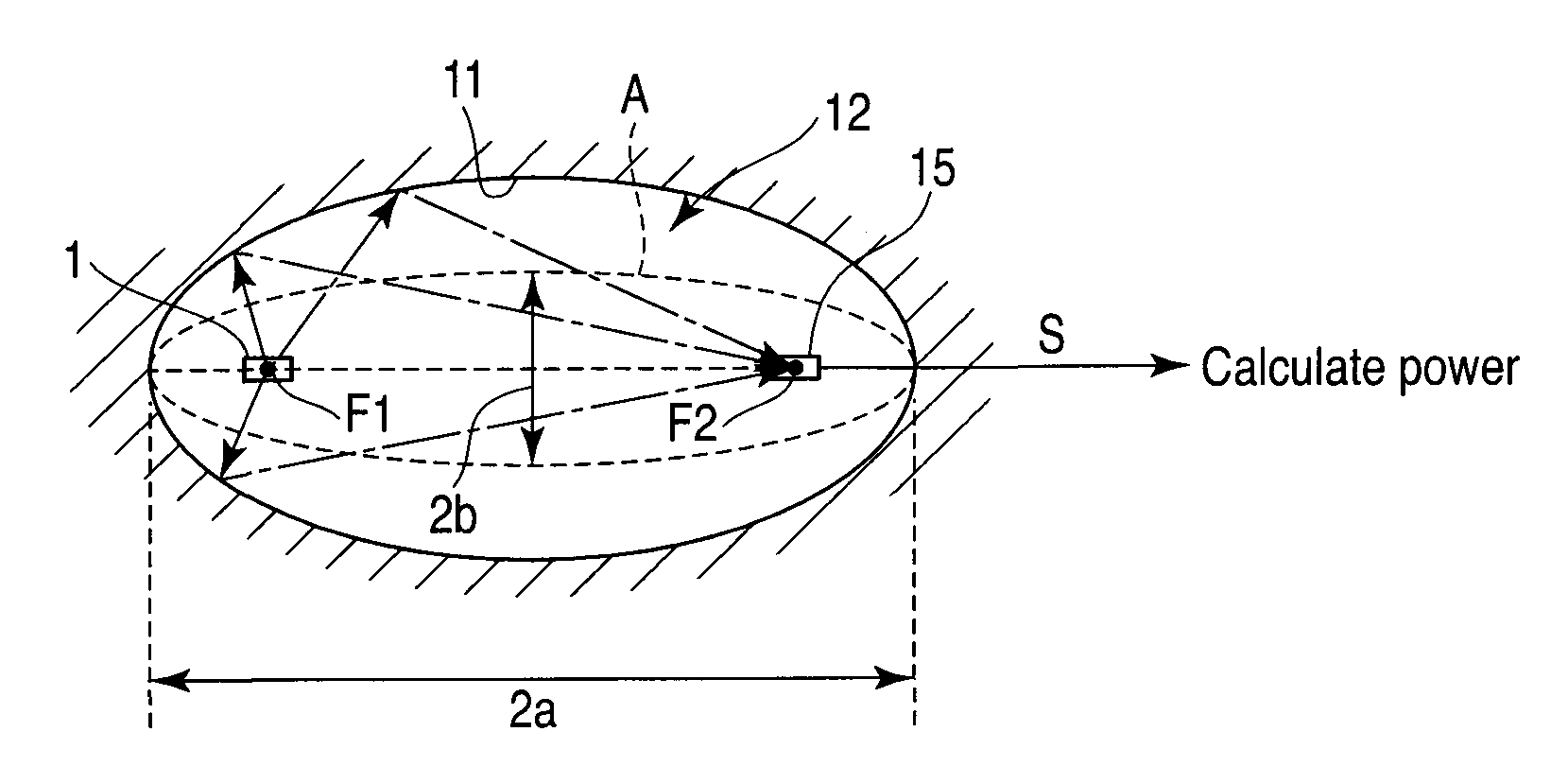
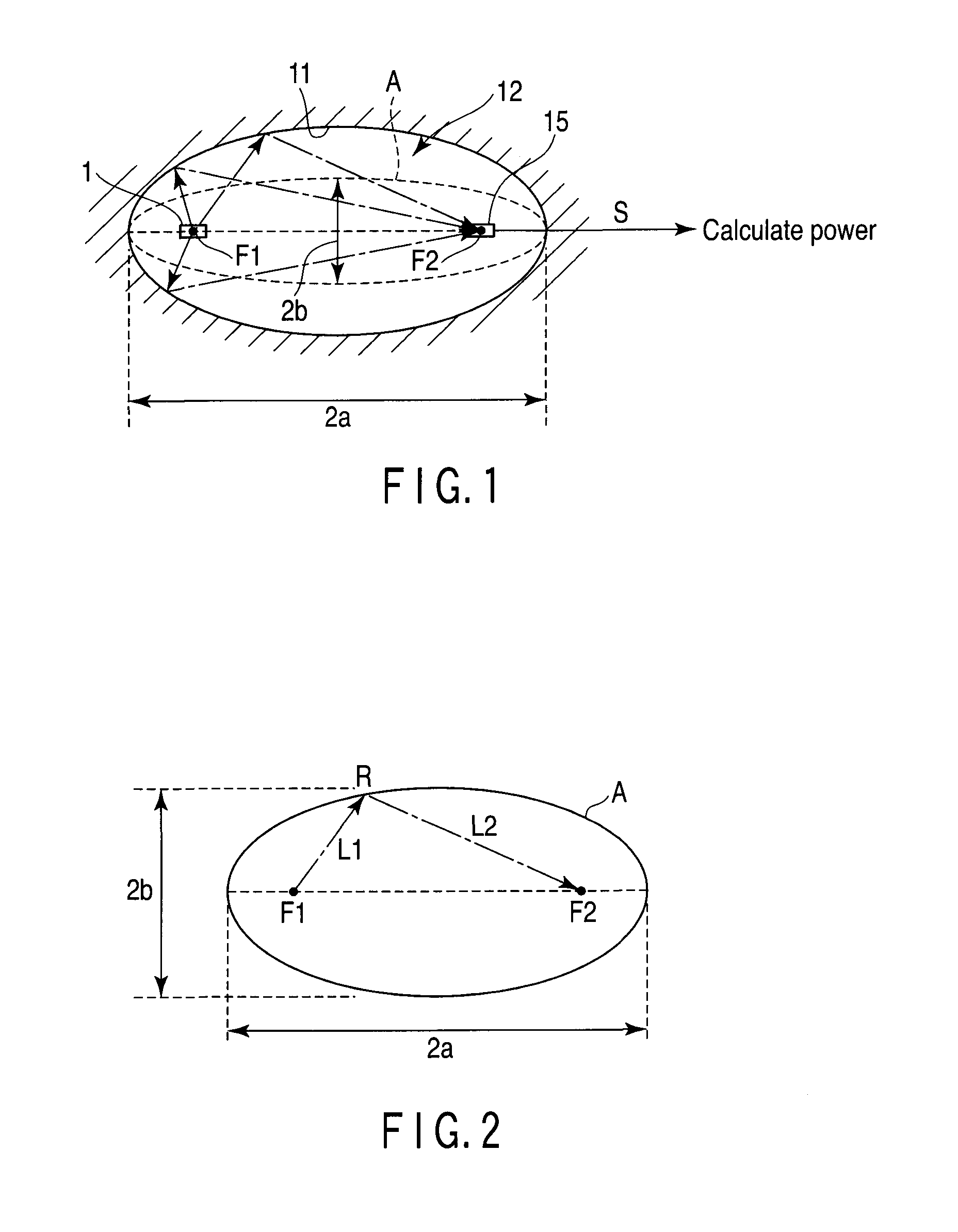
Radiated power measurement method, radiated power measurement coupler and radiated power measurement apparatus
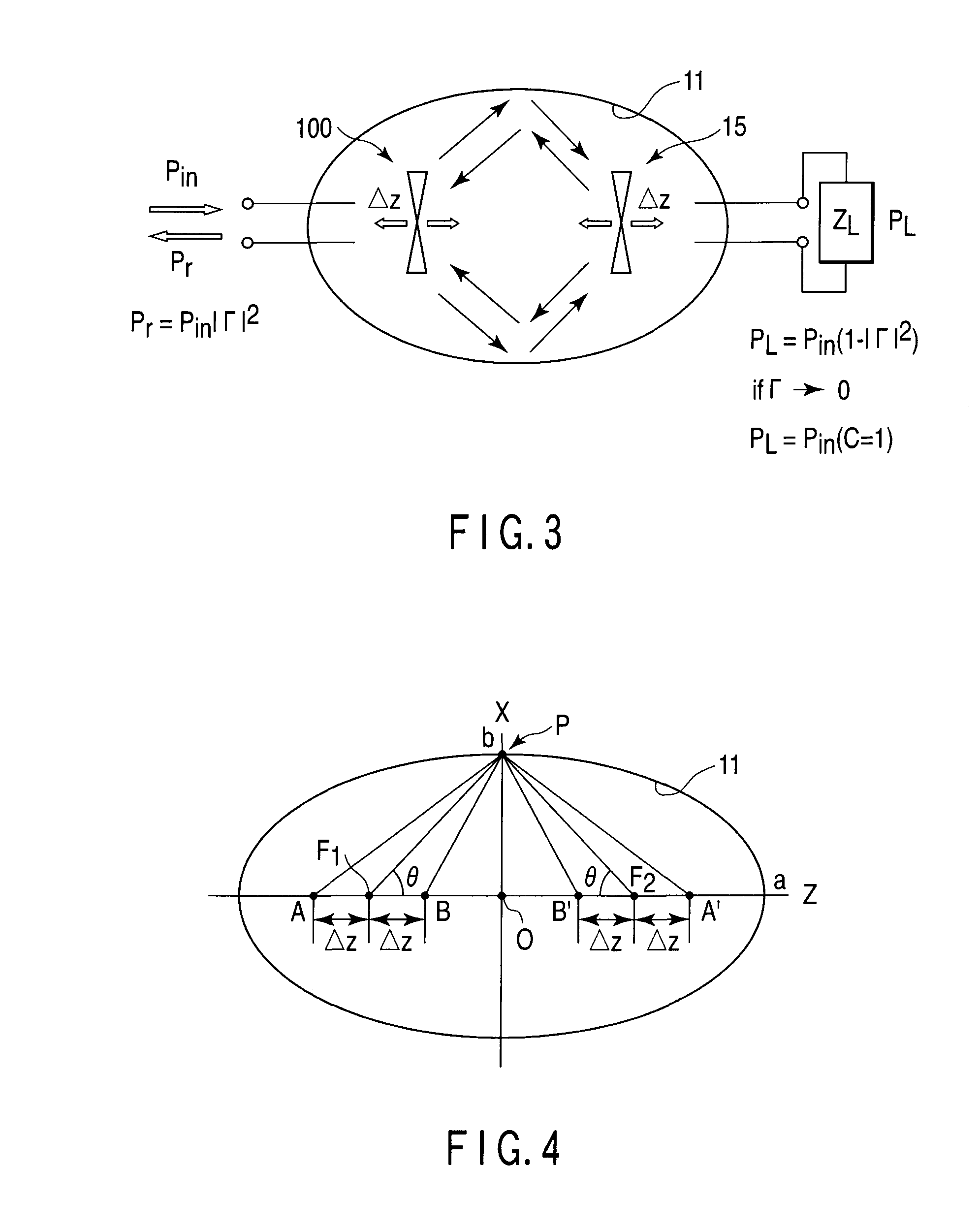
ActiveUS20110043418A1Accurate measurementEnhanced couplingReceivers monitoringElectromagentic field characteristicsRadiant fluxRadio wave
In a method of measuring a radiation power generated from a DUT from an output of a measurement antenna, wherein the DUT is arranged in an ellipsoid enclosed space such that a radiation center of the radio wave is substantially coincided with the neighborhood of a first focal point. The radio wave radiated from the DUT and reflected from the wall surface is received by a receiving antenna arranged in the neighborhood a second focal point thereby to measure the total radiated power of the DUT from the output signal of the receiving antenna. One of the DUT and the receiving antenna is moved along the axis passing through the first and second focal points, and based on the measurement value maximizing the output signal power of the receiving antenna, calculating the total radiated power of the DUT.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Equipment and method for quick-speed image-forming checking mobile target
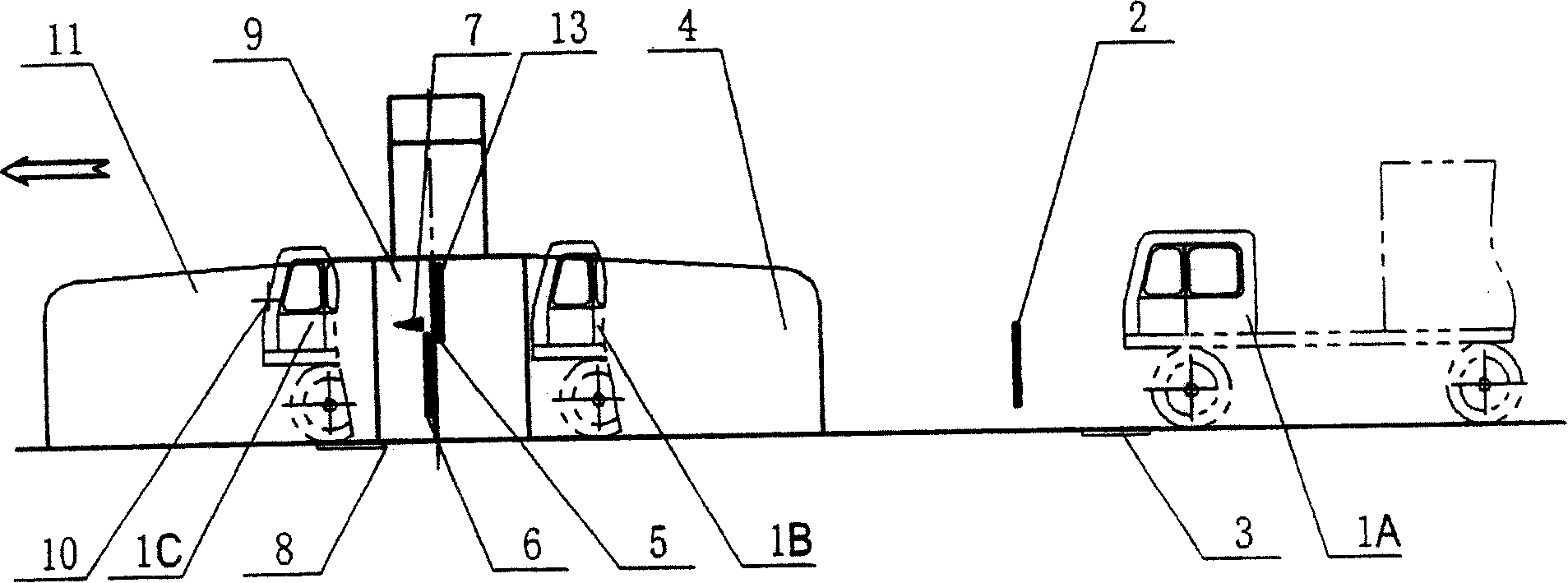
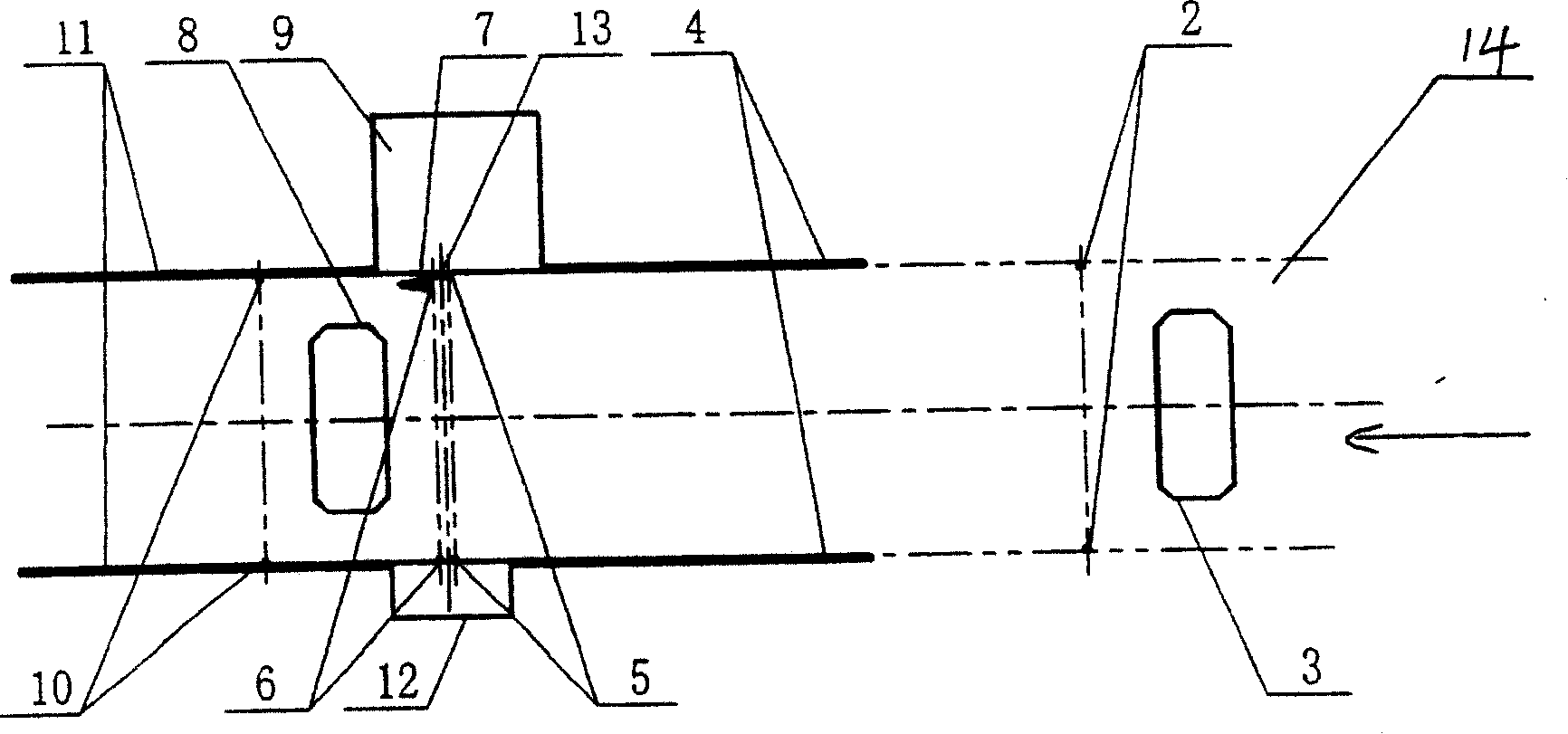
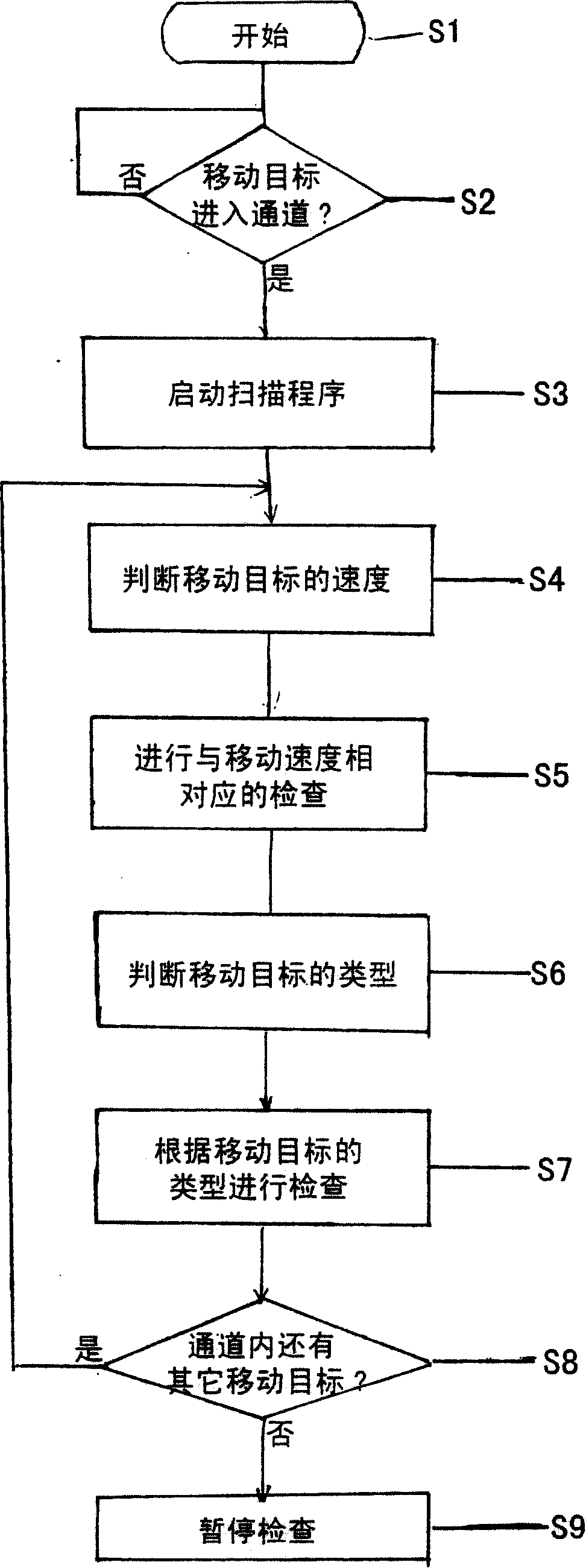
ActiveCN101162209AImprove pass rateShorten inspection timeX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRapid imagingComputer science
The invention discloses a device used for the imaging and checking to a moving target rapidly, comprising a channel for the moving target to pass through; a scan imaging device which images the moving target by emitting radiant flux to the moving target passing through the channel and then checks the moving target; a first detecting unit which is used for judging whether the moving target enters the channel and counting the number of the moving target entering the channel; a second detecting unit which is used for measuring the moving speed of the moving target in the channel; and a control unit which controls the second detecting unit to detect the moving speed of the moving target according to the detecting signals received from the first detecting unit about the moving target entering the channel, and controls the scan imaging device according to the measuring result of the second detecting unit, so that the scan imaging device emits radiant flux at a frequency corresponding to the speed of the moving target, thereby checking the moving target.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Light delivery device with improved conversion element
ActiveUS20090244923A1Maintain normalChange color temperaturePrintersSurgeryLight deliveryOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a light delivery device comprising a conversion element and one or several LEDs, which emit light into the conversion element. The light is then converted and emitted with a high radiant flux.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and device for obstacle detection and distance measurement by infrared radiation
The invention concerns a method for measuring distance between a first object (1) and a second object (2) which consists in: a) emitting an infrared wave radiation (3) from an emitter (4) fixed on the first object (1), said radiation (3) being emitted towards said second object (2); and b) detecting the return of said radiation after it has been reflected by said second object (2) on a receiver (5) fixed on said first object (1) proximate to said emitter (4). The inventive method is characterised in that it consists in: 1 / gradually varying the power of the infrared radiation emitted by said emitter (1) until it reaches a detection power (Ps) corresponding to the power of the wave emitted as from which the radiation reflected by said second object is detected by said receiver; and 2 / calculating the distance (D) between said first object (1) and said second object (2) from the value of said detection power, by establishing an equating correlation between said distance (D) and said detection power. The invention also concerns a device for detection and distance measurement.
Owner:威尼
Exposure apparatus and exposing method and method of manufacturing a printed wiring board
ActiveUS20060215143A1Low costImprove stabilityPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLight irradiationUltraviolet
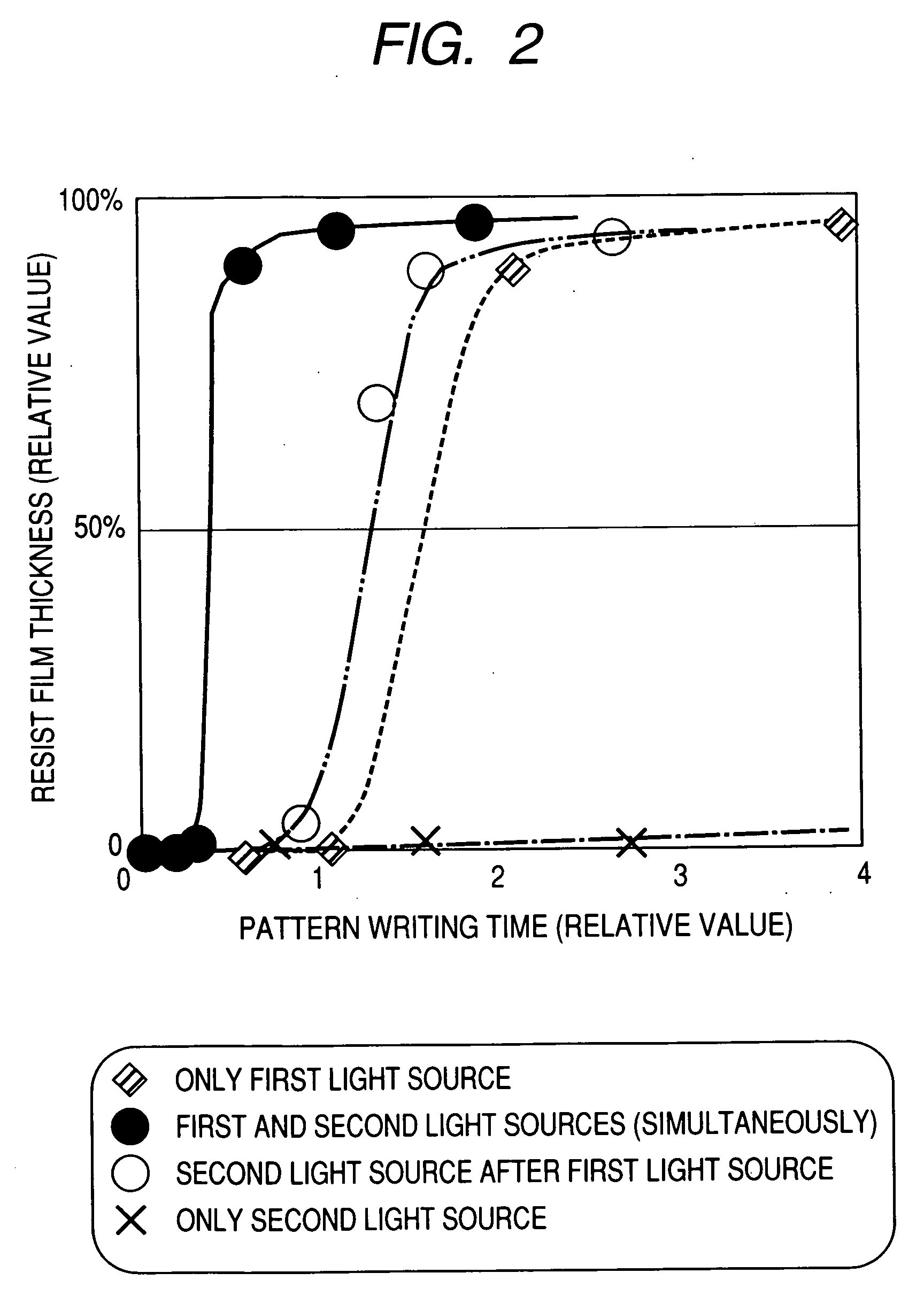
The mask-less exposure apparatus includes: a stage which moves with the substrate having a photosensitive resin layer with sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation formed thereon; a first light source for emitting light containing a wavelength component in the wavelength range of 300 to 410 nm; a first light irradiation optical system for modulating a radiant flux emitted from the first light source based on data of a desired exposure pattern to image a pattern on the photosensitive resin layer; a second light source for emitting light containing a wavelength component in the wavelength range of 450 to 2500 nm; and a second light irradiation optical system for guiding a radiant flux emitted from the second light source to a second light irradiation area that is set so as to include at least a first light irradiation area.
Owner:ADTEC ENG
Backlighting system for liquid crystal displays
InactiveUS20050099791A1The process is simple and effectiveSimple methodIlluminated signsNon-linear opticsOperating pointLiquid-crystal display
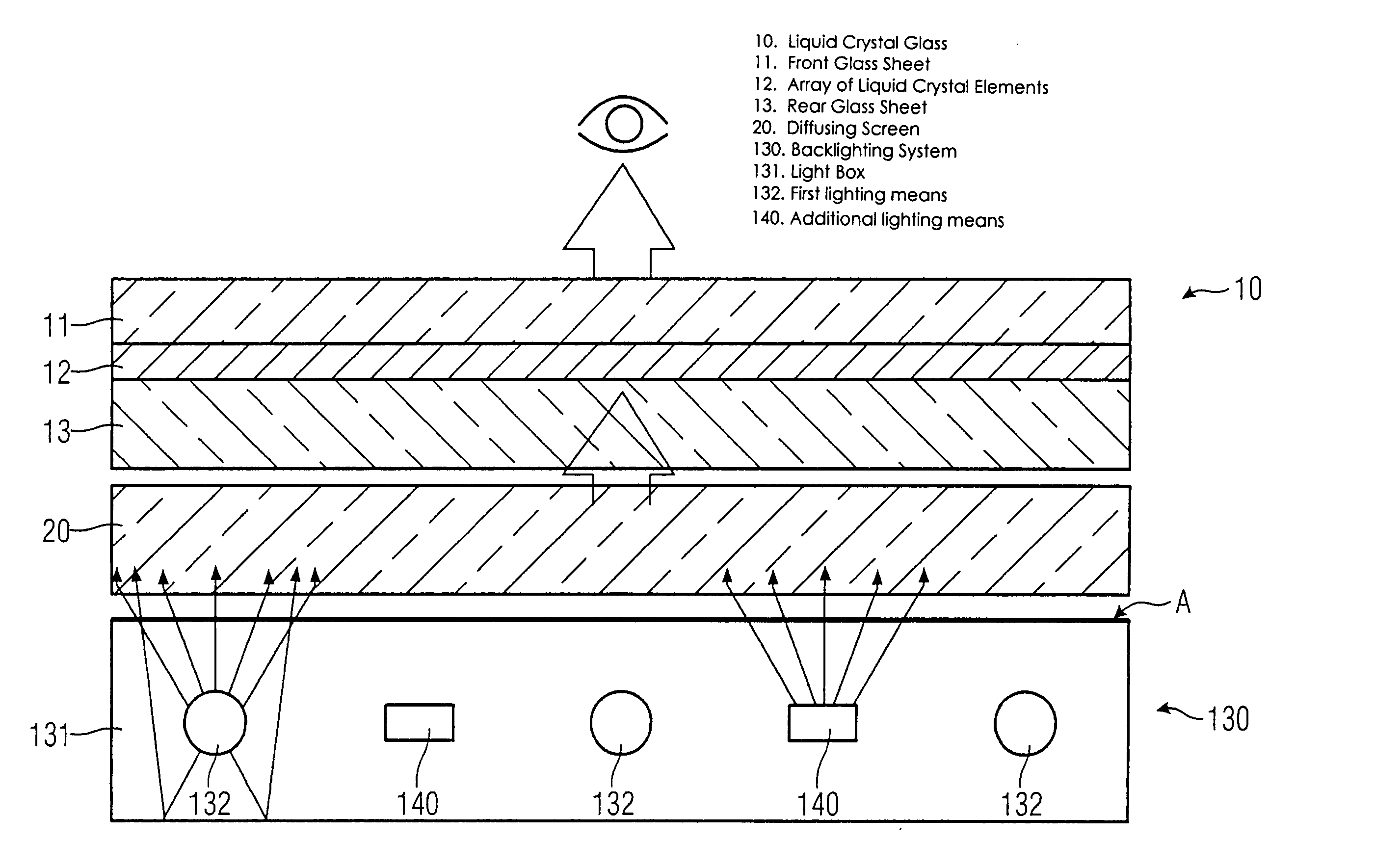
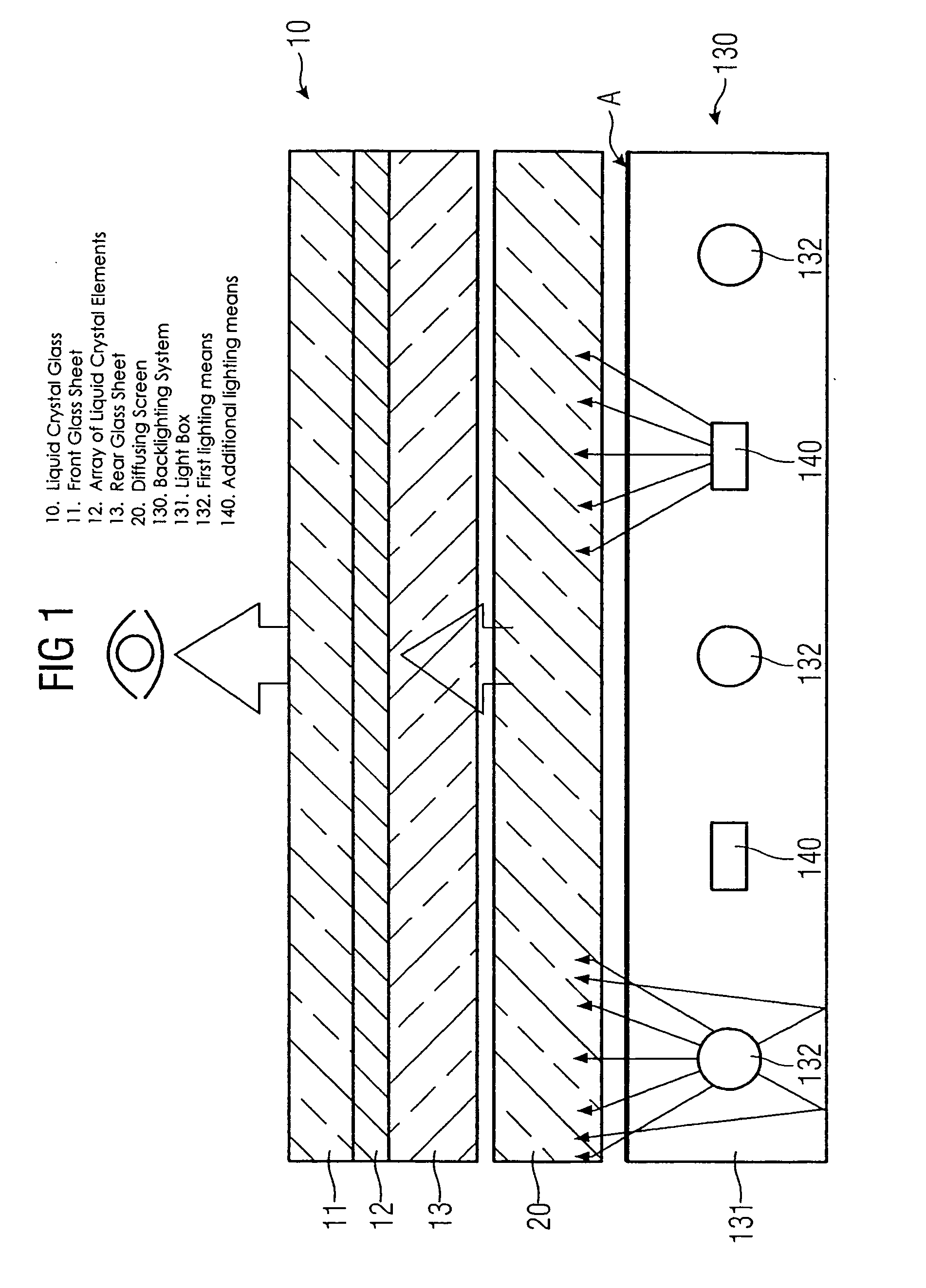
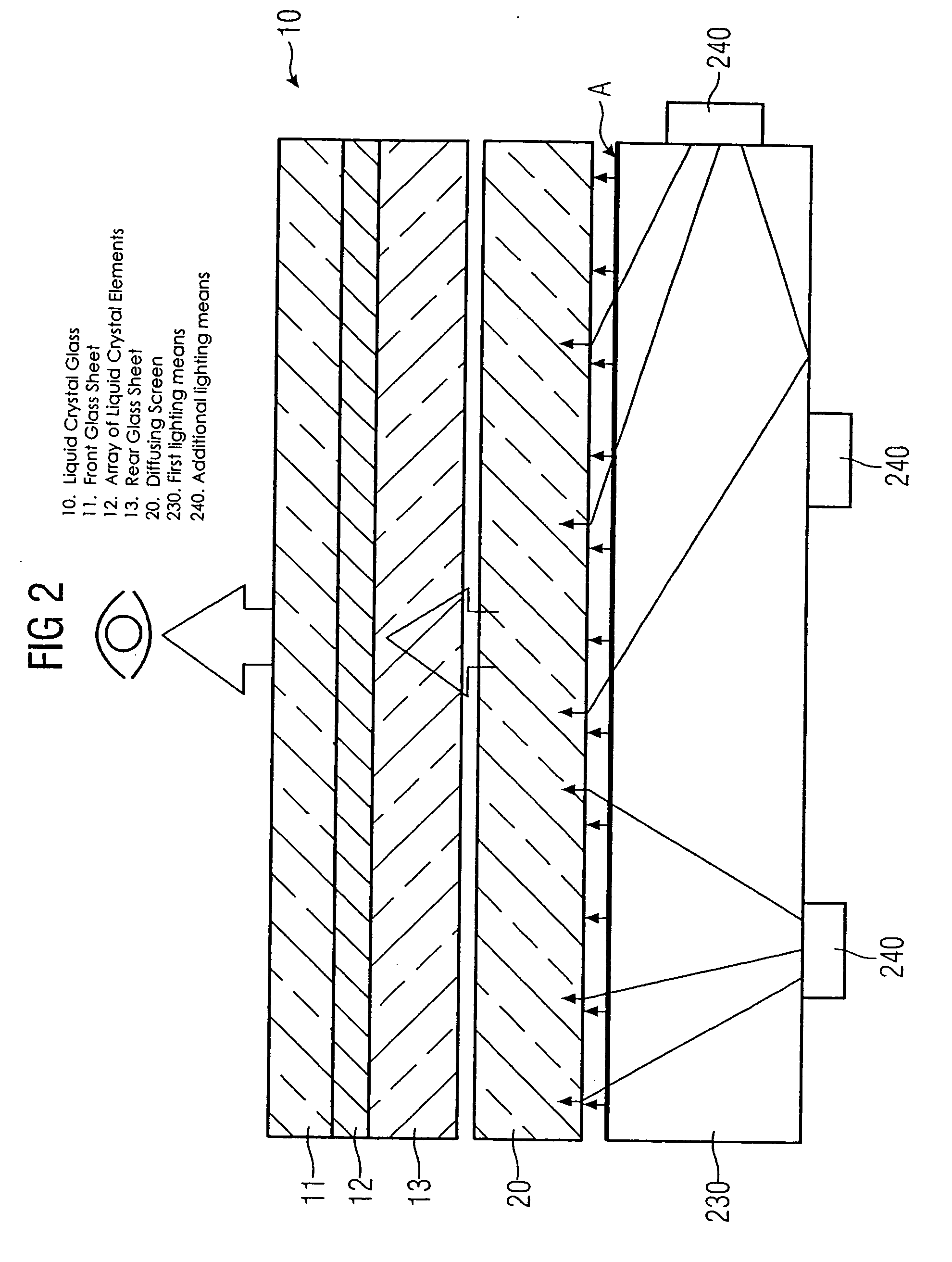
A backlighting system for liquid crystal displays includes one or more first lighting structure (130, 230), which has a defined radiant flux with spectral color components at one operating point. The radiant flux output from the first lighting structure (130, 230) exits across a radiant surface (A) of the backlighting system and thus provides a defined luminous flux with spectral color components on a liquid crystal glass (10) that can be arranged in front of this radiant surface (A). Also, the backlighting system has one or more additional lighting structure (140, 240, 340). The radiant flux of the additional lighting structure varies. This additional lighting structure (140, 240, 340) is arranged such that the spectral color components of the luminous flux change when the radiant flux of the additional lighting structure (140, 240, 340) is changed. The liquid crystal display is used for controlling and monitoring in an automation system.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
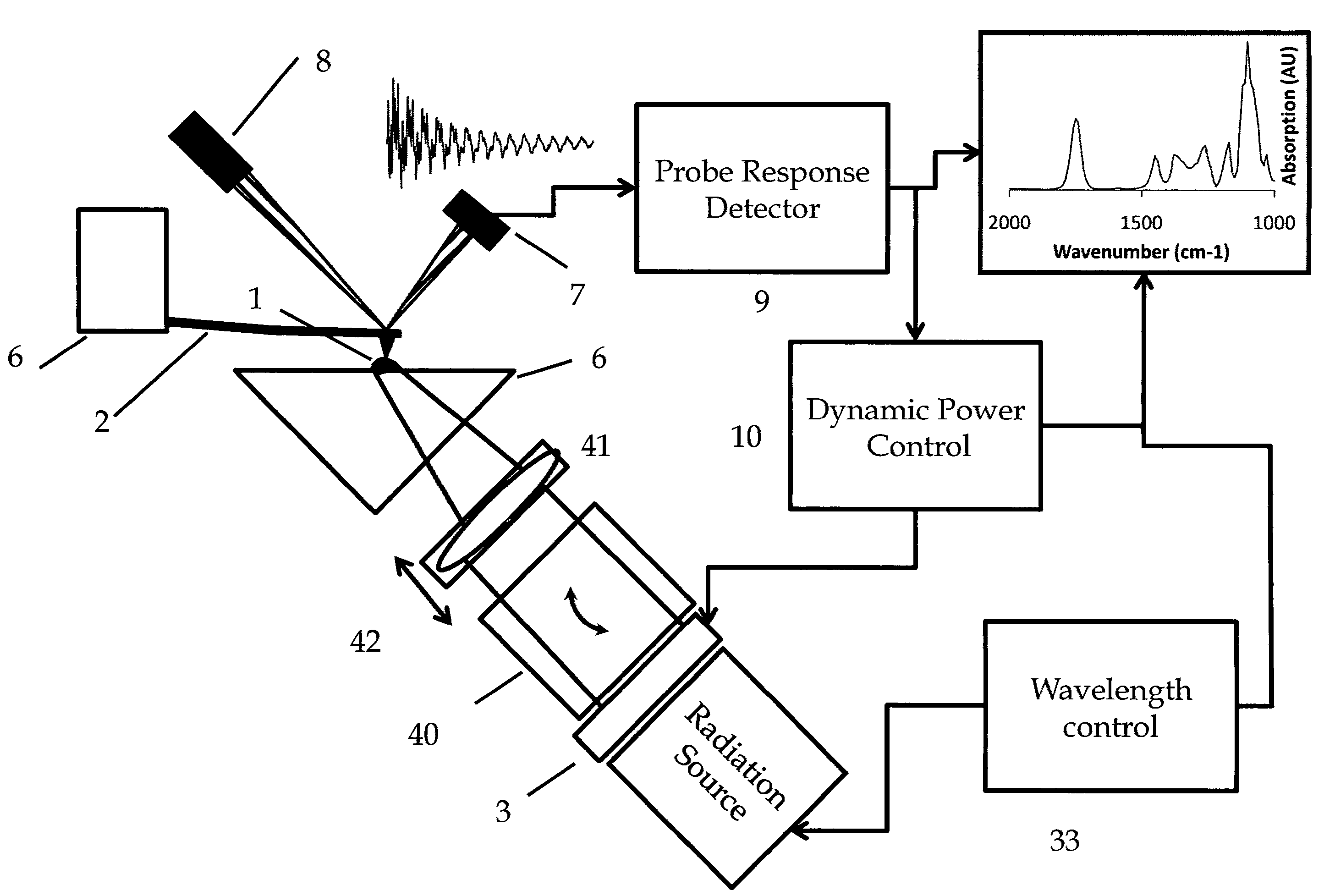
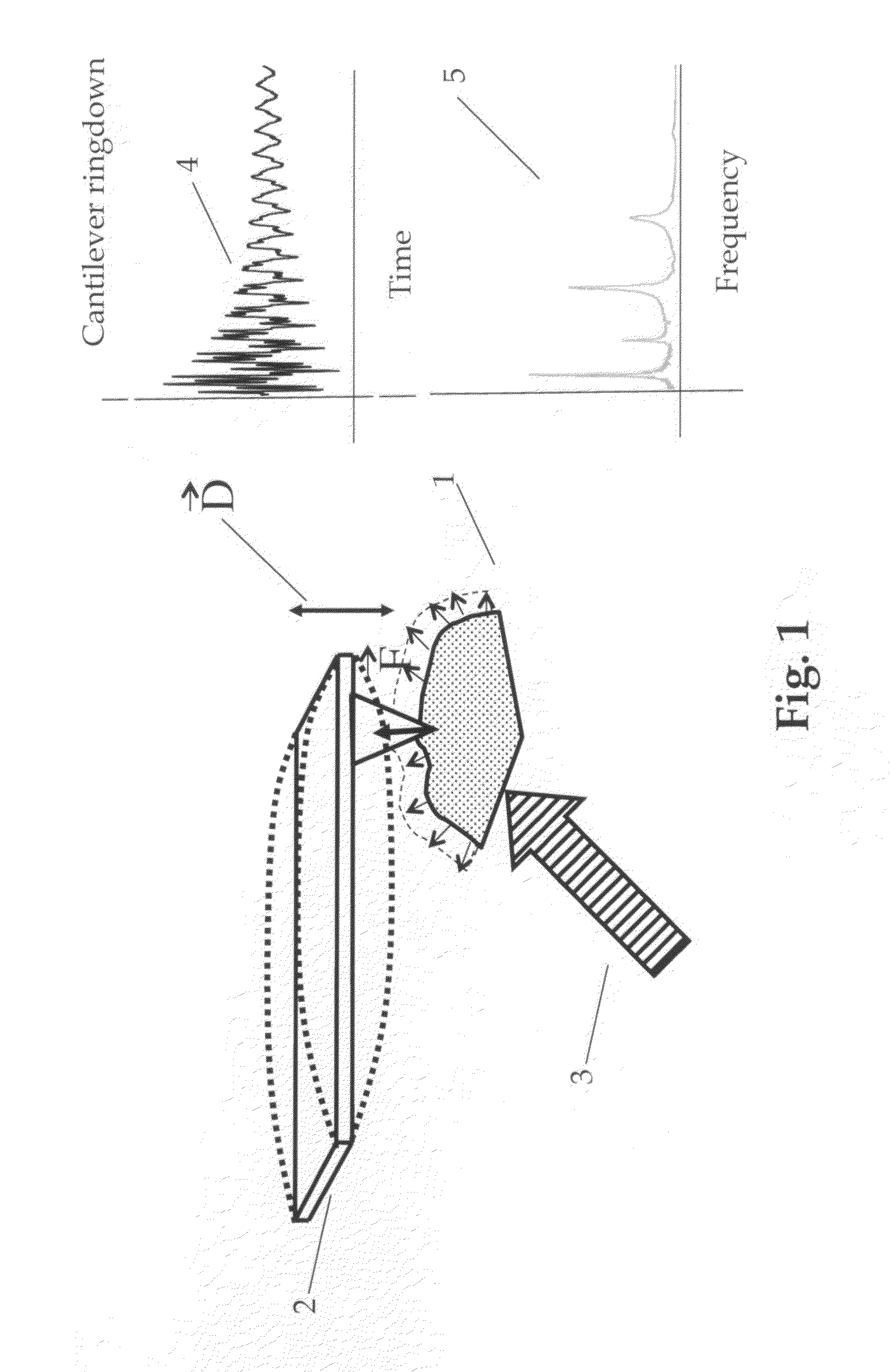
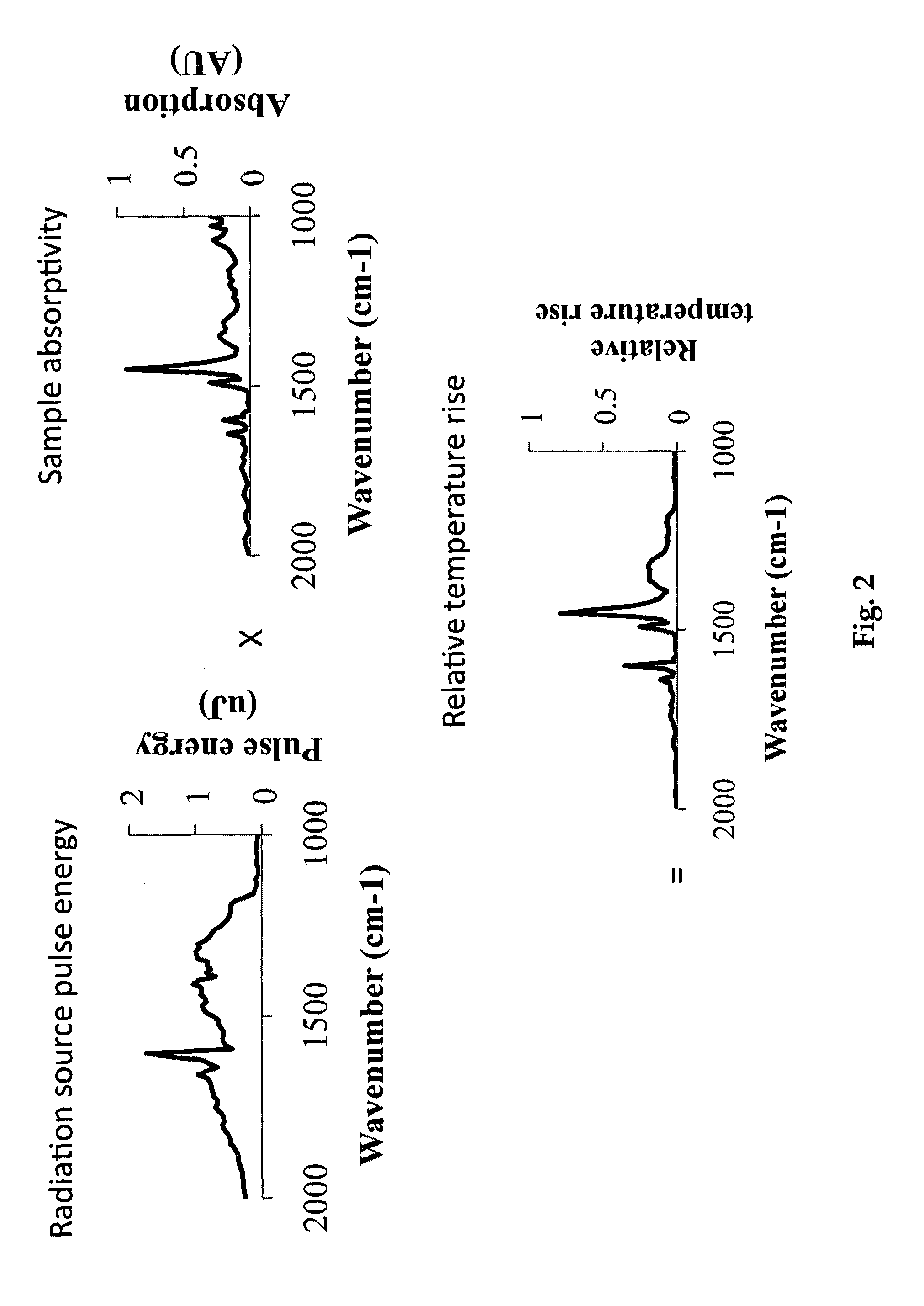
Dynamic power control, beam alignment and focus for nanoscale spectroscopy
ActiveUS8242448B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Light beam
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
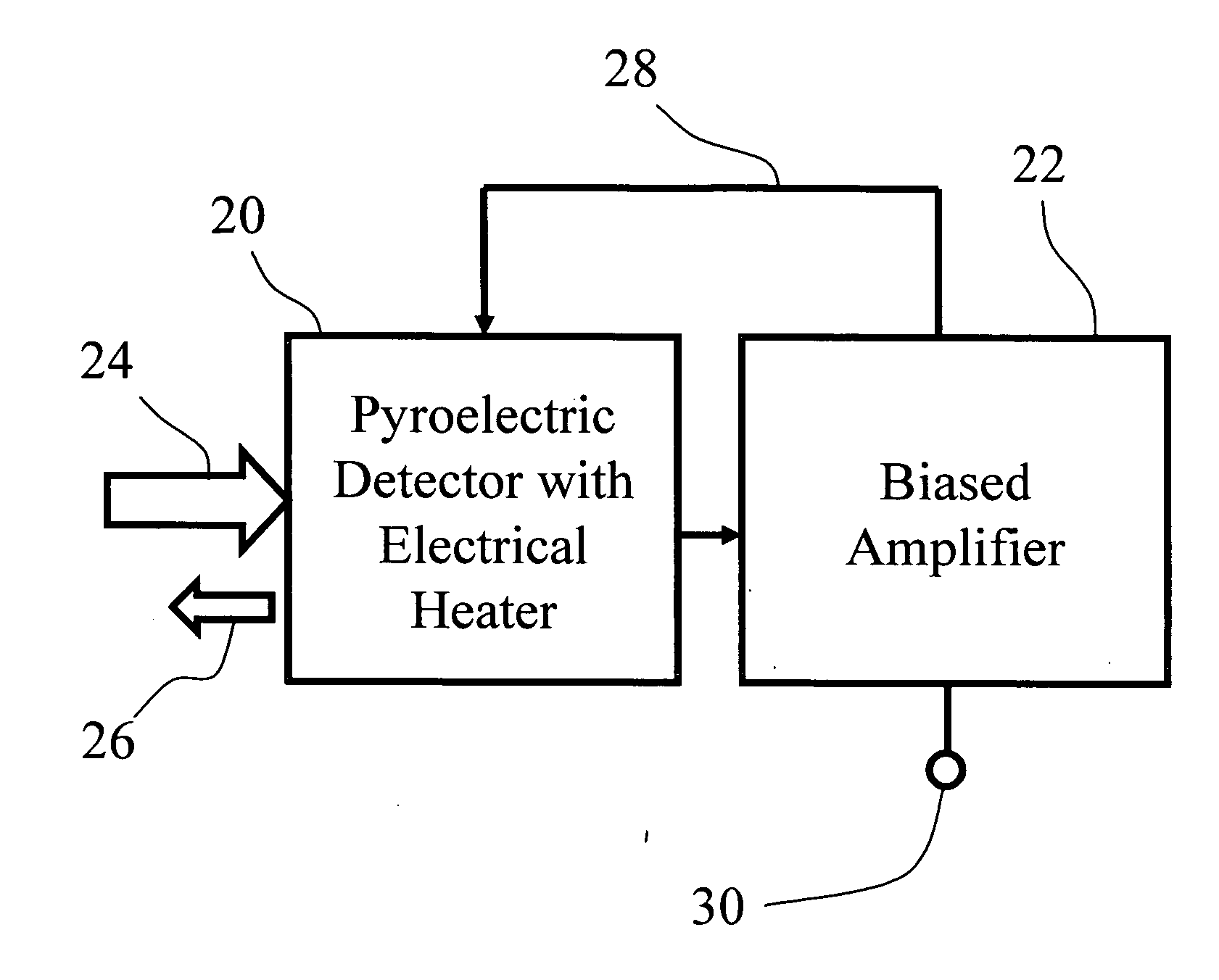
High fidelity electrically calibrated pyroelectric radiometer
InactiveUS20060266943A1Improve fidelityAccurate CalibrationMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsPhase noisePyroelectric detectors
Using biased, electrical power feedback to an electrical heater, the output signal from a pyroelectric detector is made to follow the waveform of incident electromagnetic radiation. The feedback power is applied to the detector to reduce the rate of change of the detector temperature that would otherwise be caused by the absorbed radiation. The combined signals from the radiation and feedback power produce a response that follows the radiation waveform with a fast rise time and with substantially less droop than previously reported. The high fidelity of the response waveform allows for a substantial simplification of the optical chopper designs and electronics needed to implement electrical calibration. In contrast to previous electrical calibration with pyroelectrics that needed very specialized electronics, with this method a variety instruments can be used for reading pyroelectric signals. The method allows for signal processing that reduces phase noise and yields very accurate radiation power measurements.
Owner:PHELAN JR ROBERT JOSEPH
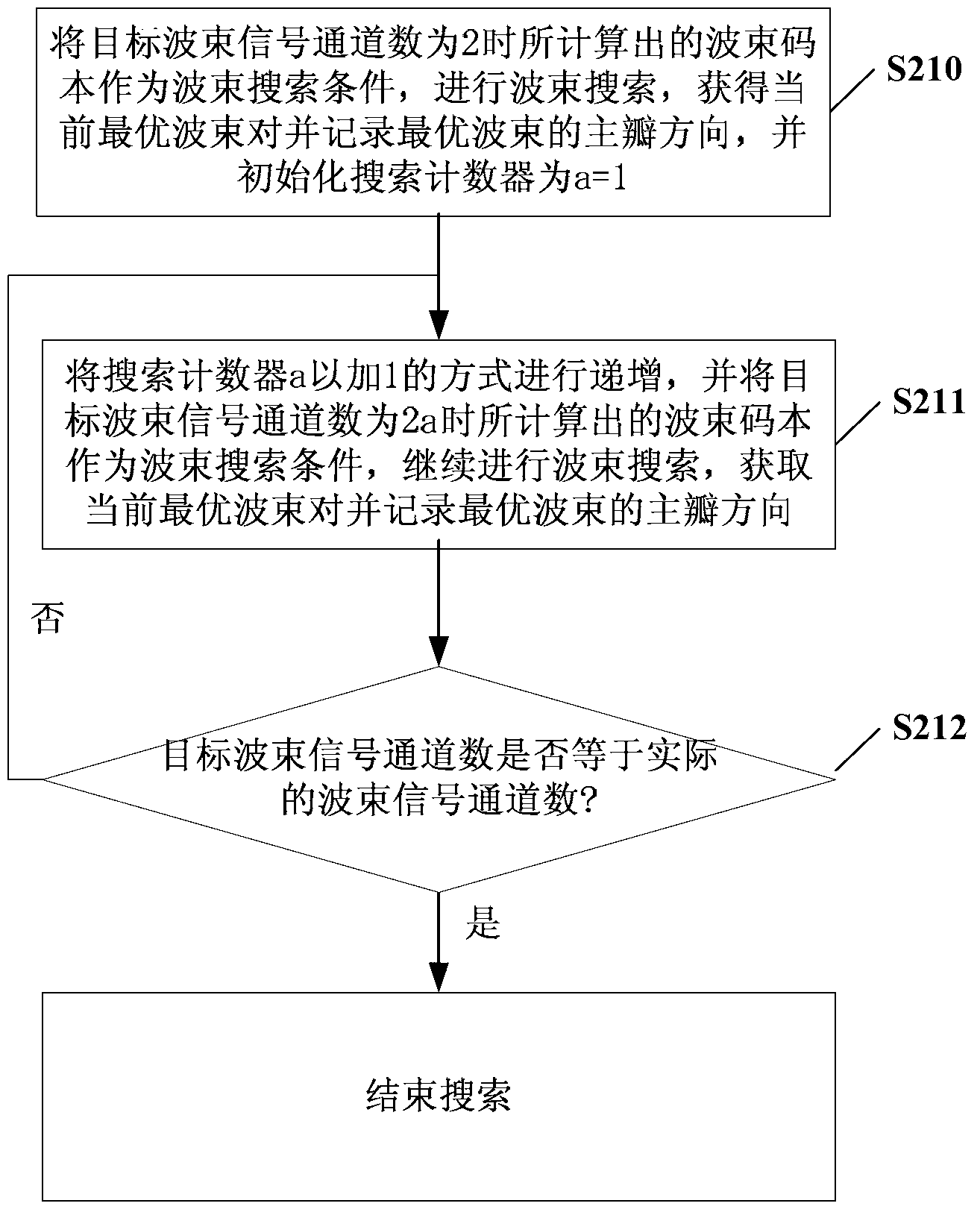
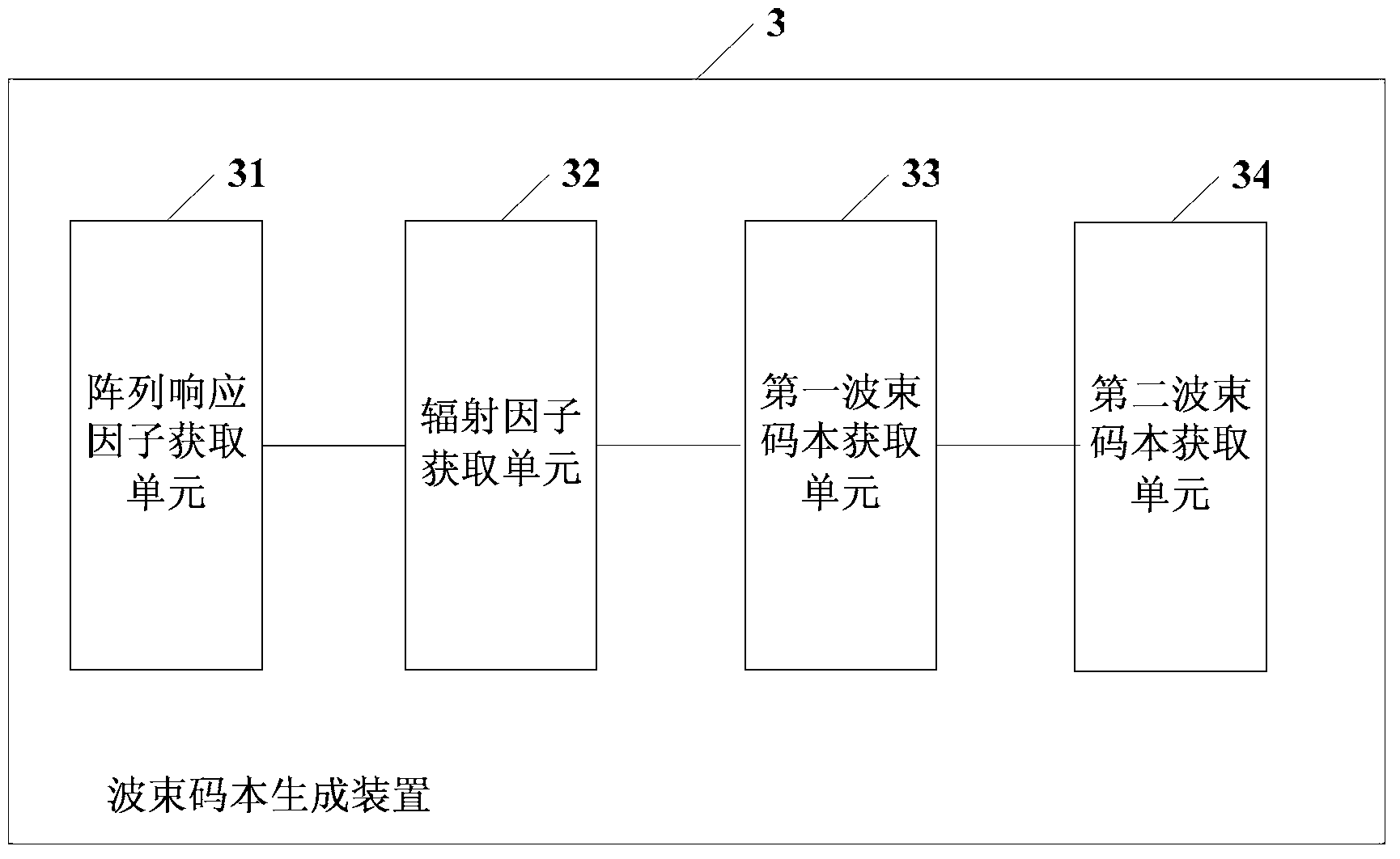
Beam codebook generating method, beam searching method and relevant device
InactiveCN102801455AReduce the difficulty of implementationSpatial transmit diversityBaseband systemsResponse factorBeam search
The embodiment of the invention discloses a beam codebook generating method, a beam searching method and a relevant device. The beam codebook generating method comprises the following steps of: calculating a first array response factor of a standard beam according to the quantity of actually-generated beam signal channels, and calculating a second array response factor of the standard beam according to the quantity of pre-set target beam signal channels; carrying out radiation power normalization on the first array response factor so as to obtain a first radiation factor of the standard beam, and carrying out the radiation power normalization on the second array response factor so as to obtain a second radiation factor of the standard beam; normalizing the first radiation factor and the second radiation factor, so as to obtain a beam codebook of the standard beam; and rotating the obtained beam codebook of the standard beam, so as to obtain a beam codebook of the other beam except the standard beam in the target beams. With the adoption of the beam codebook generating method provided by the invention, all the beam channels can be used, and the realization difficulty of hardware can be reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com