Patents
Literature
324 results about "Large core" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
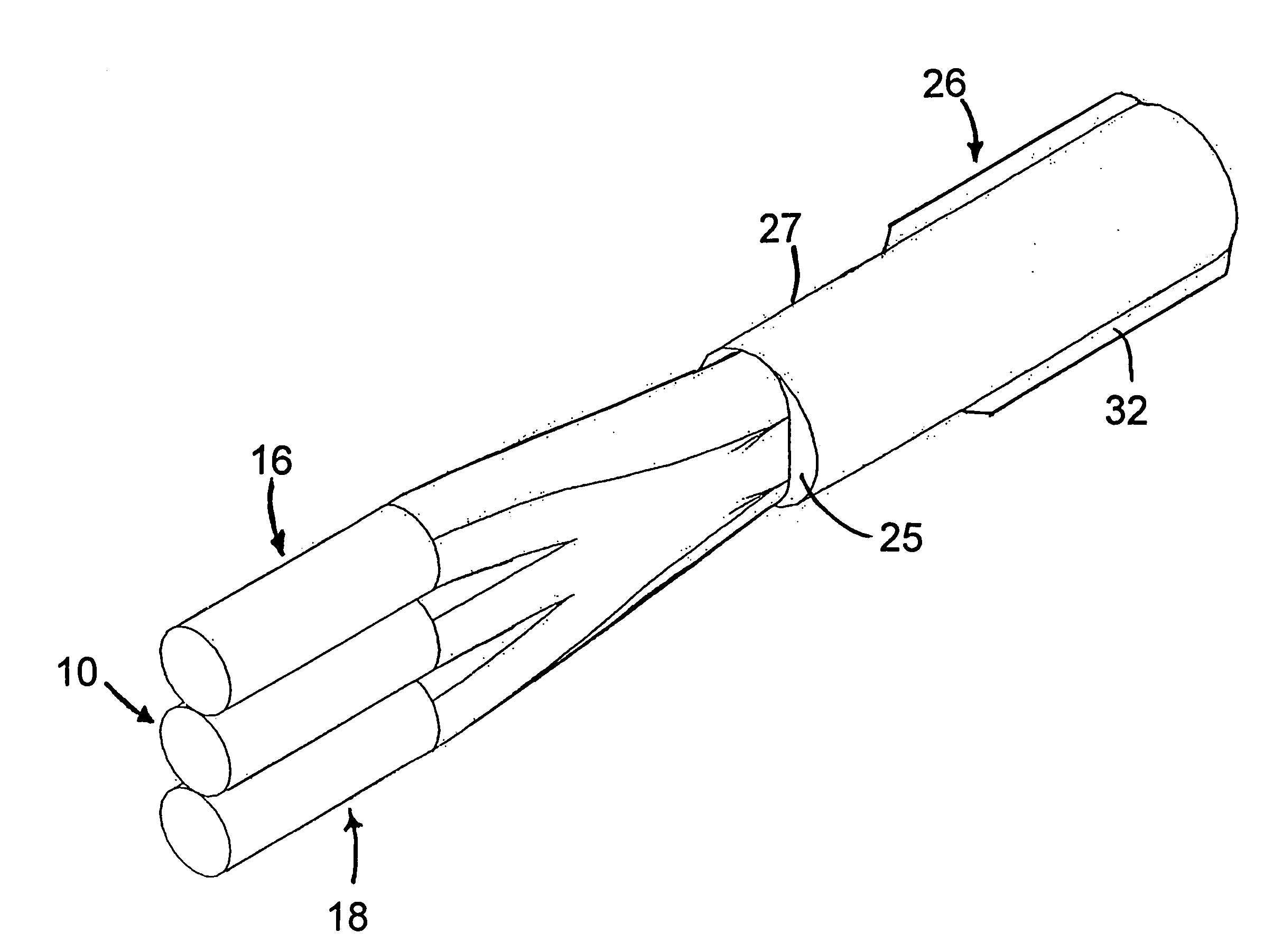
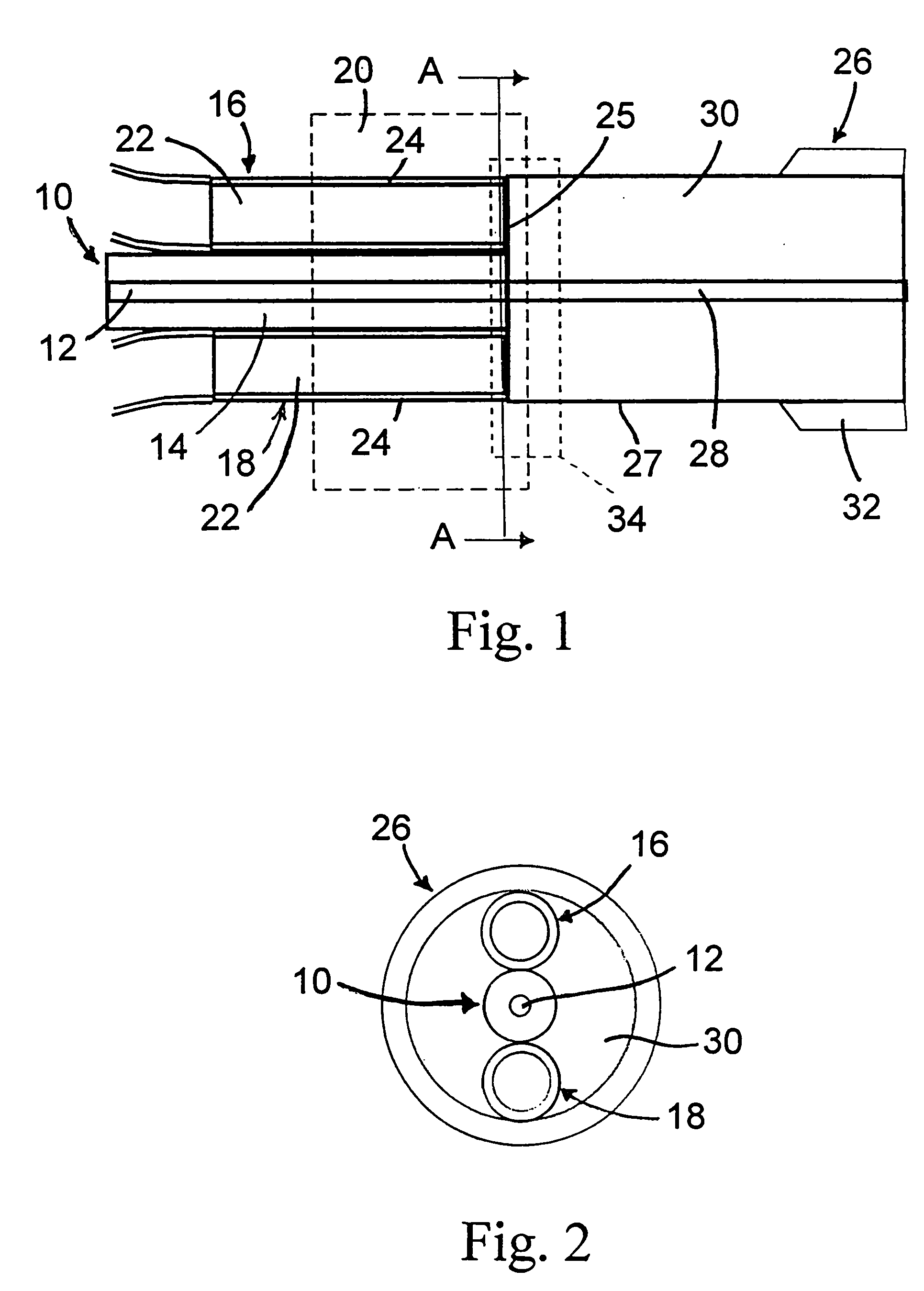
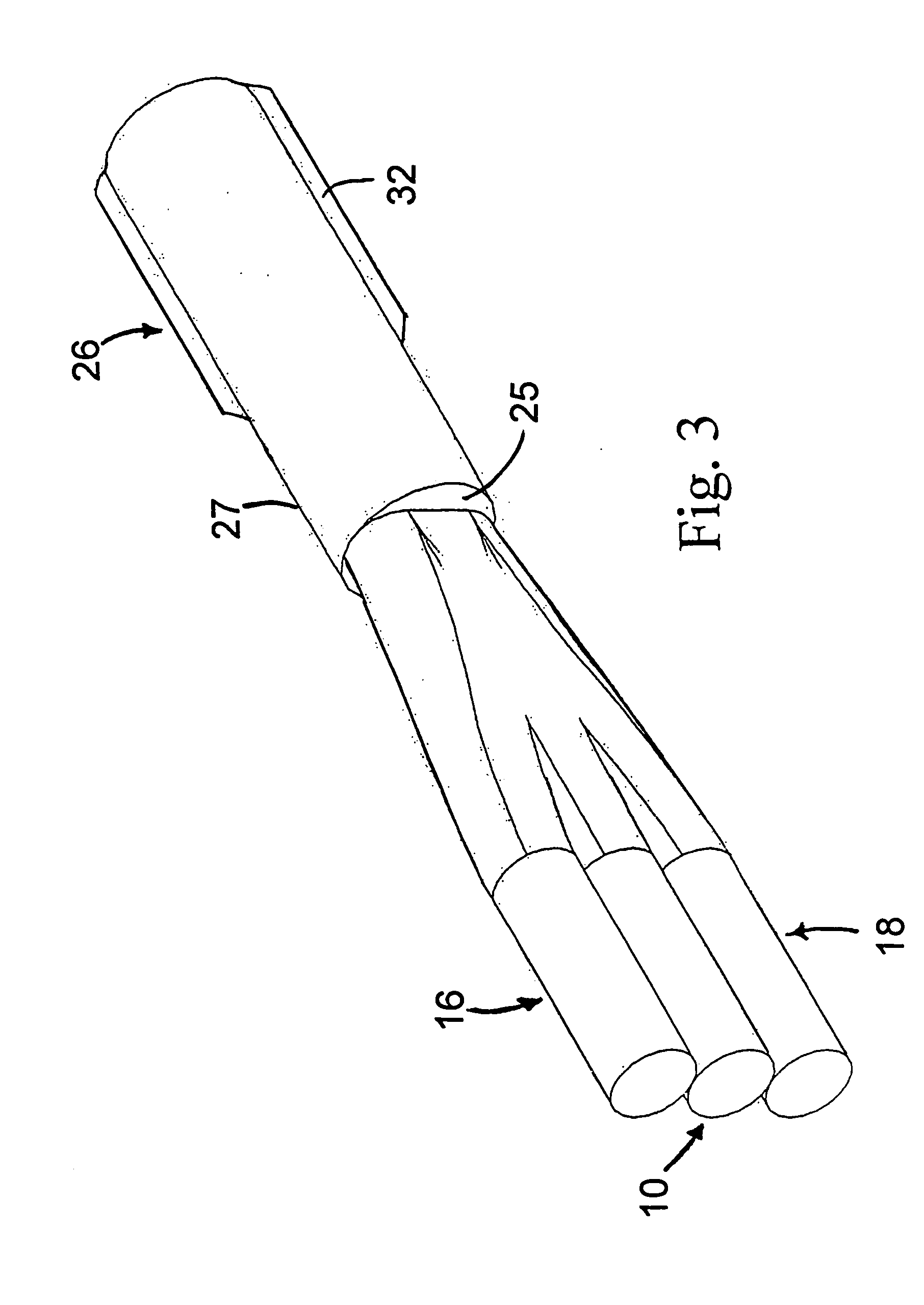
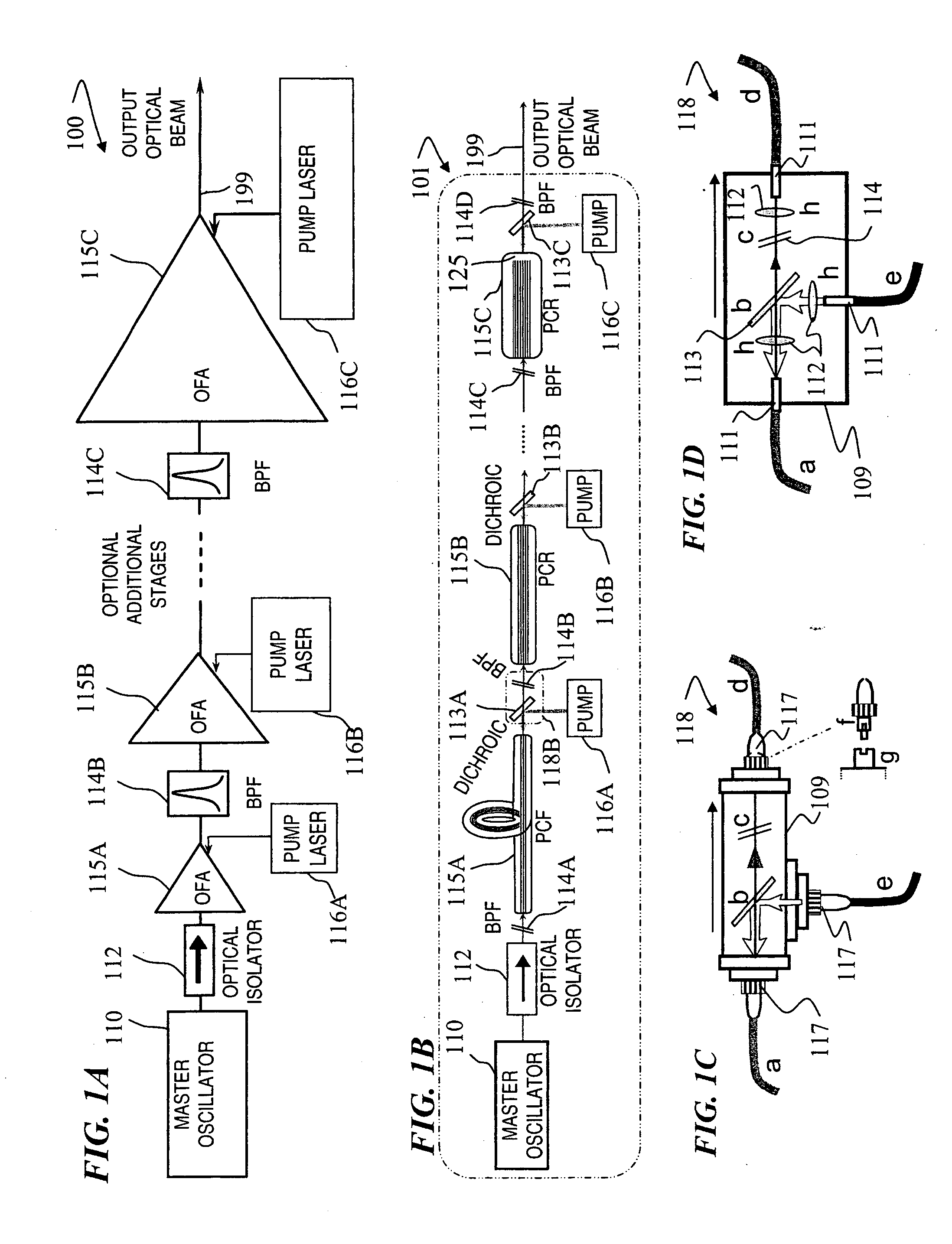
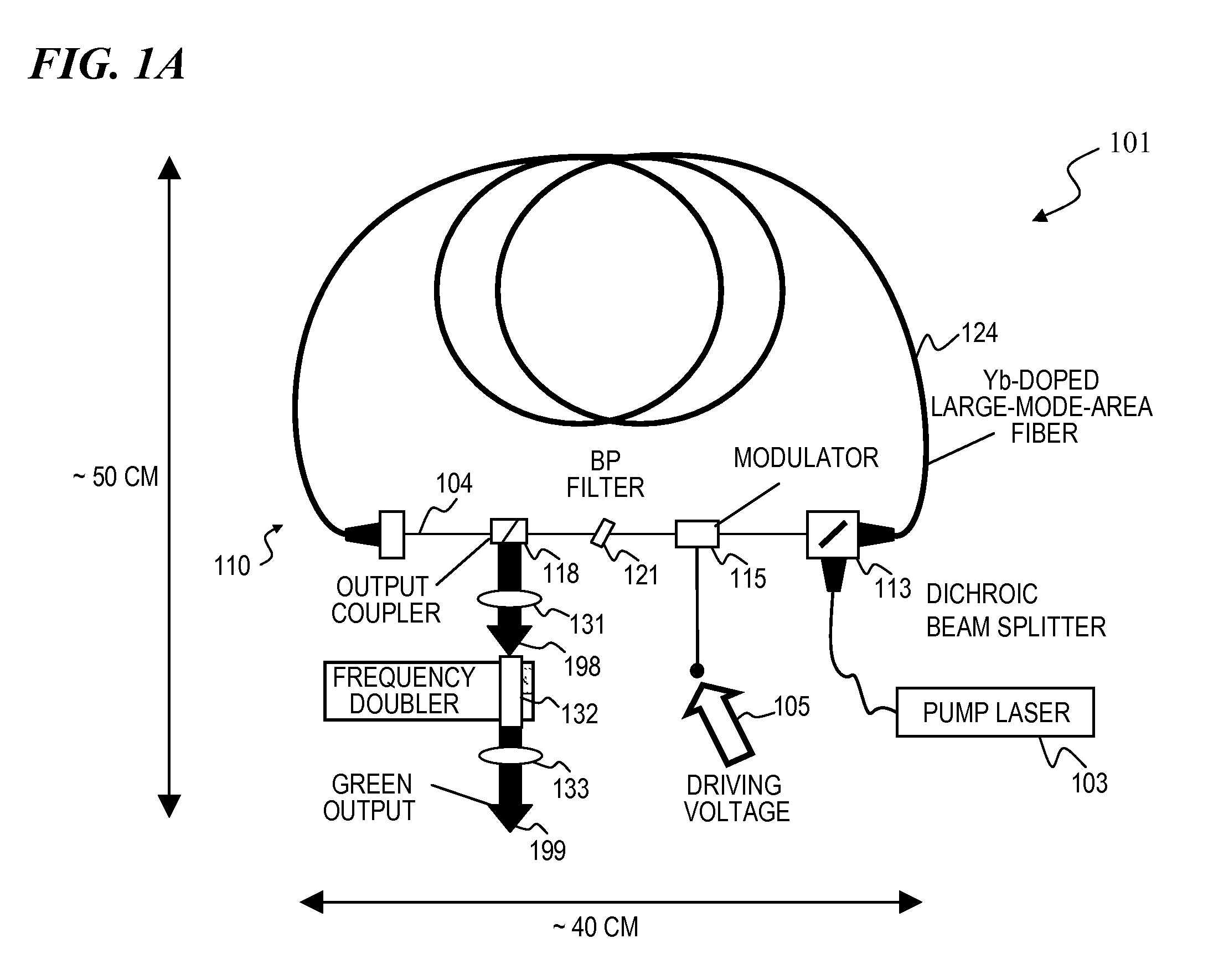
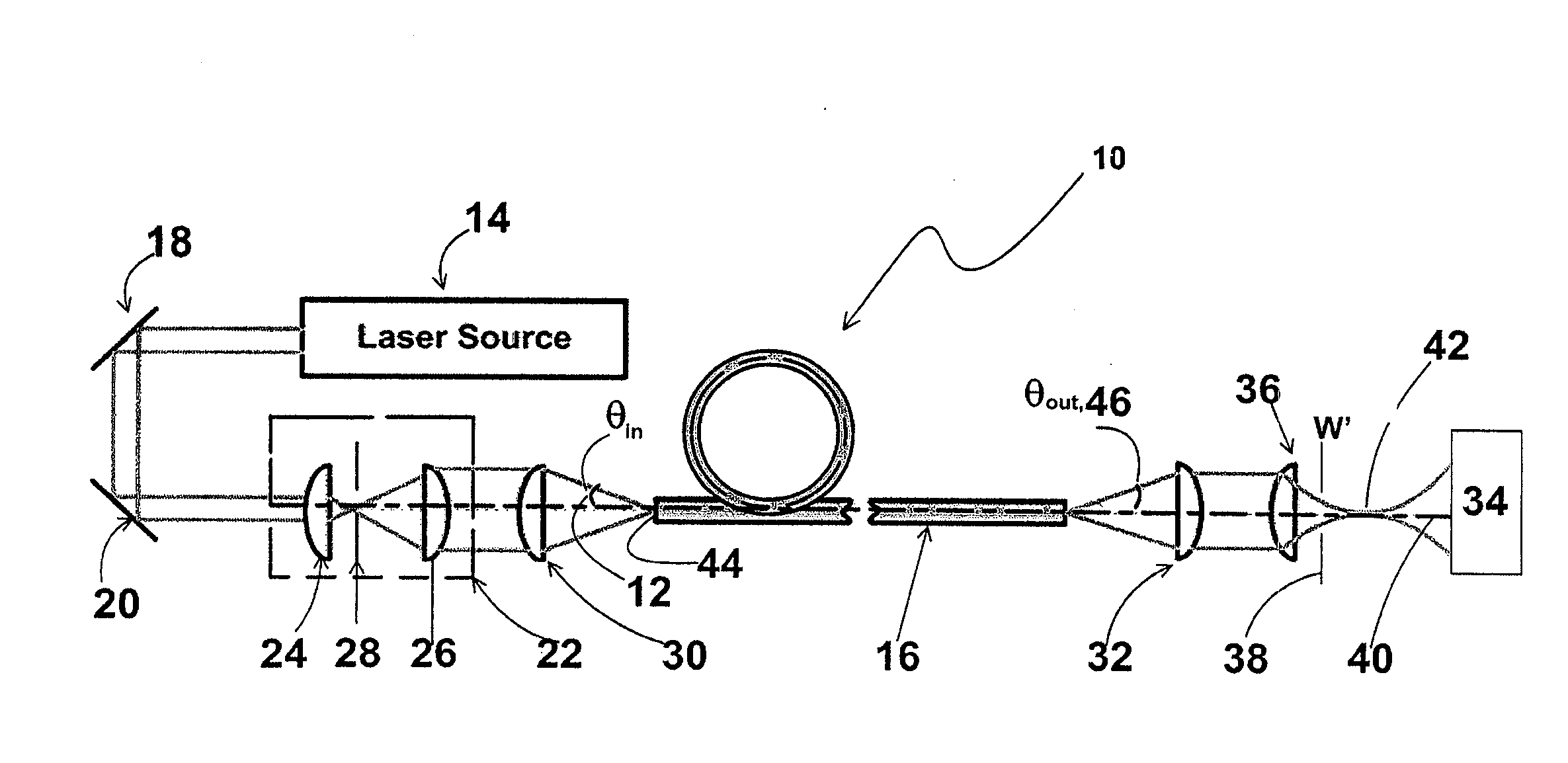
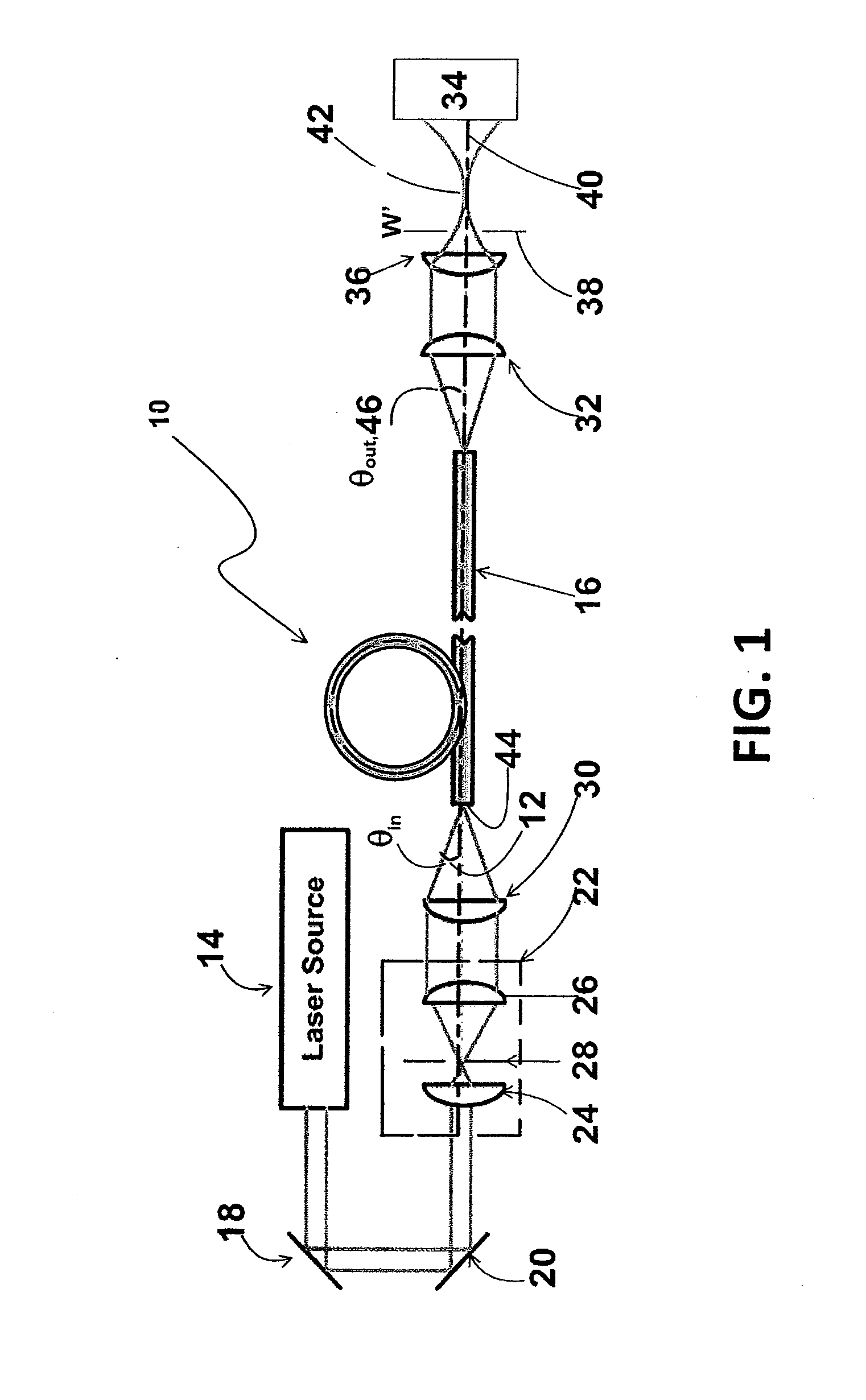
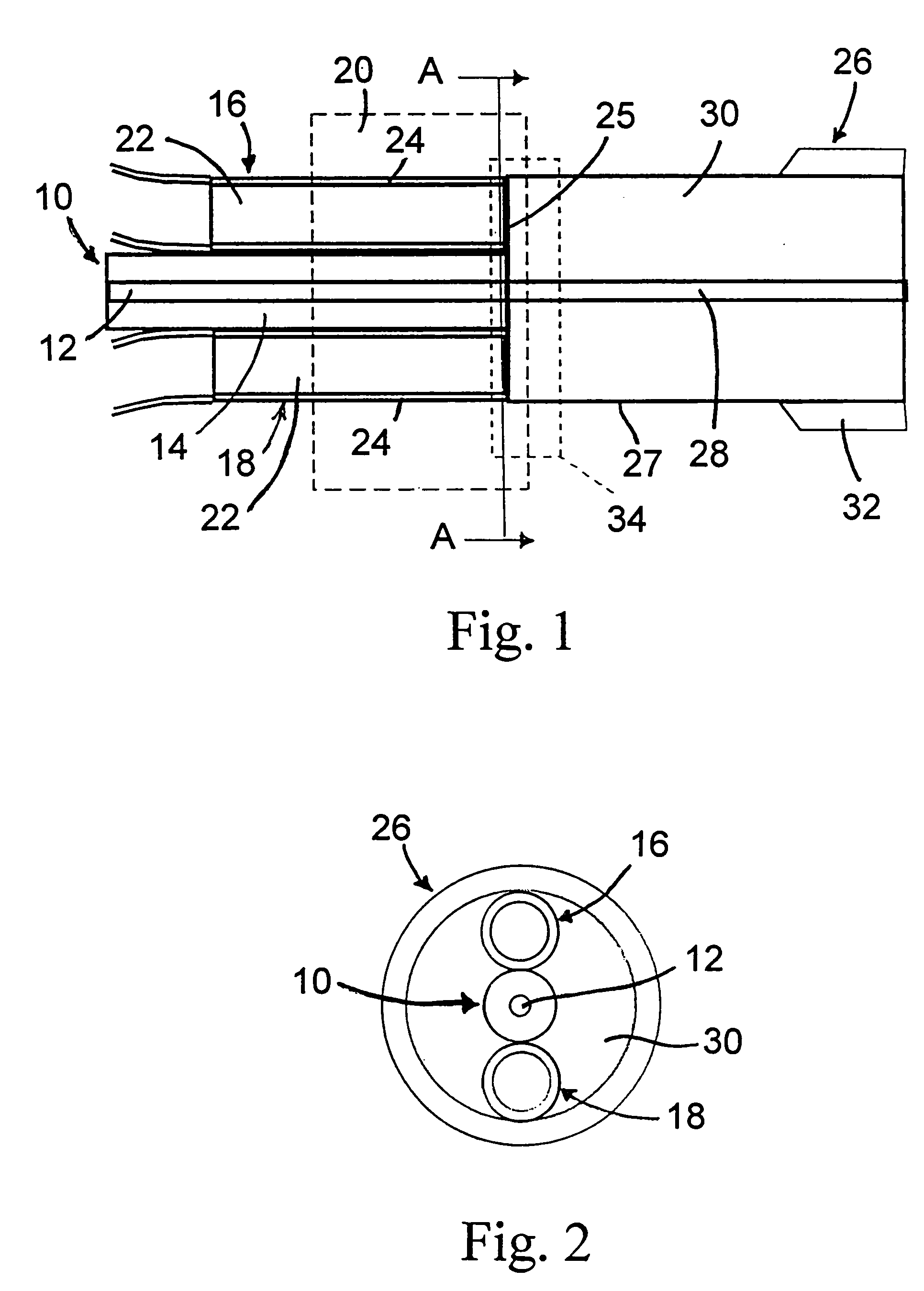
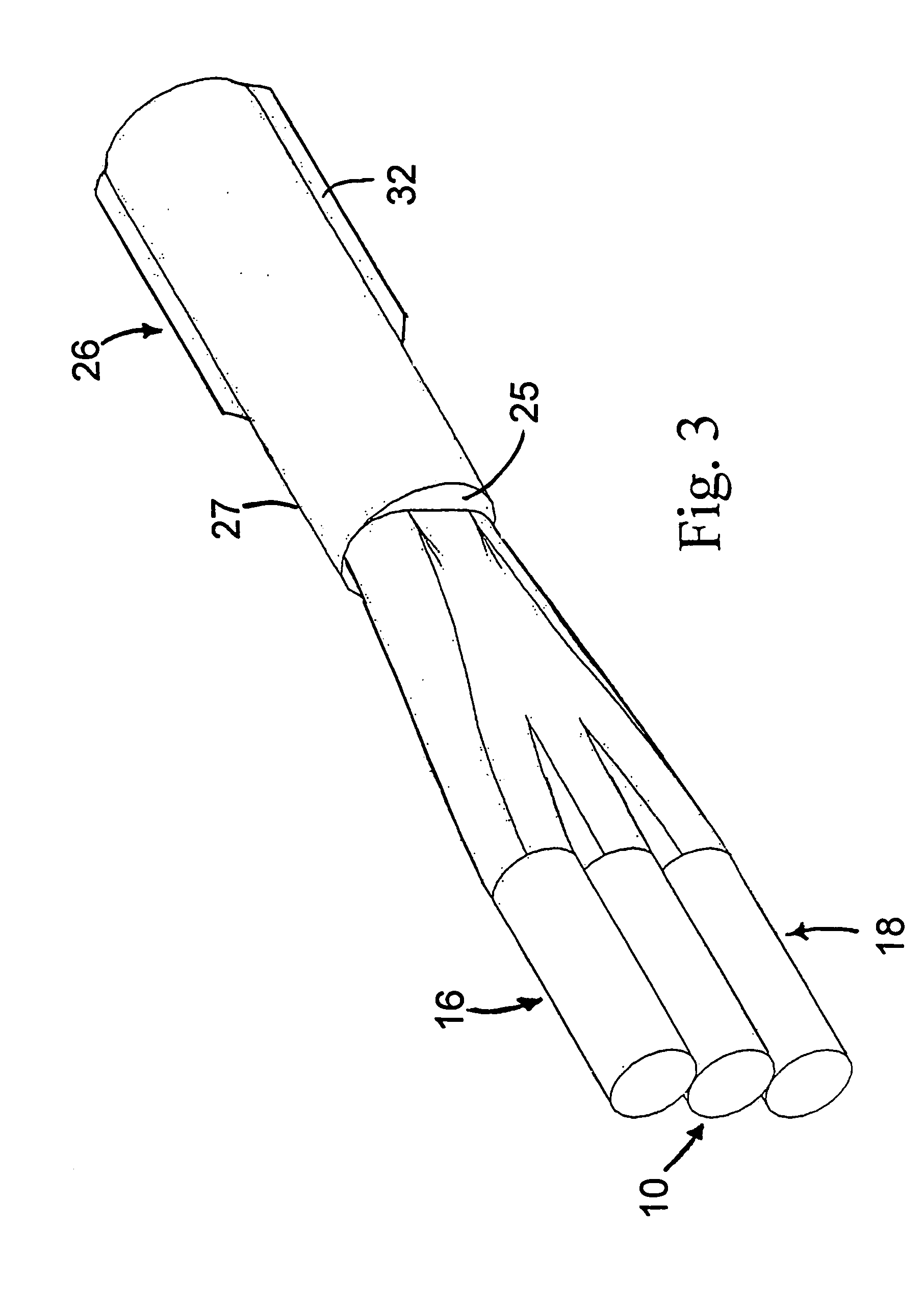
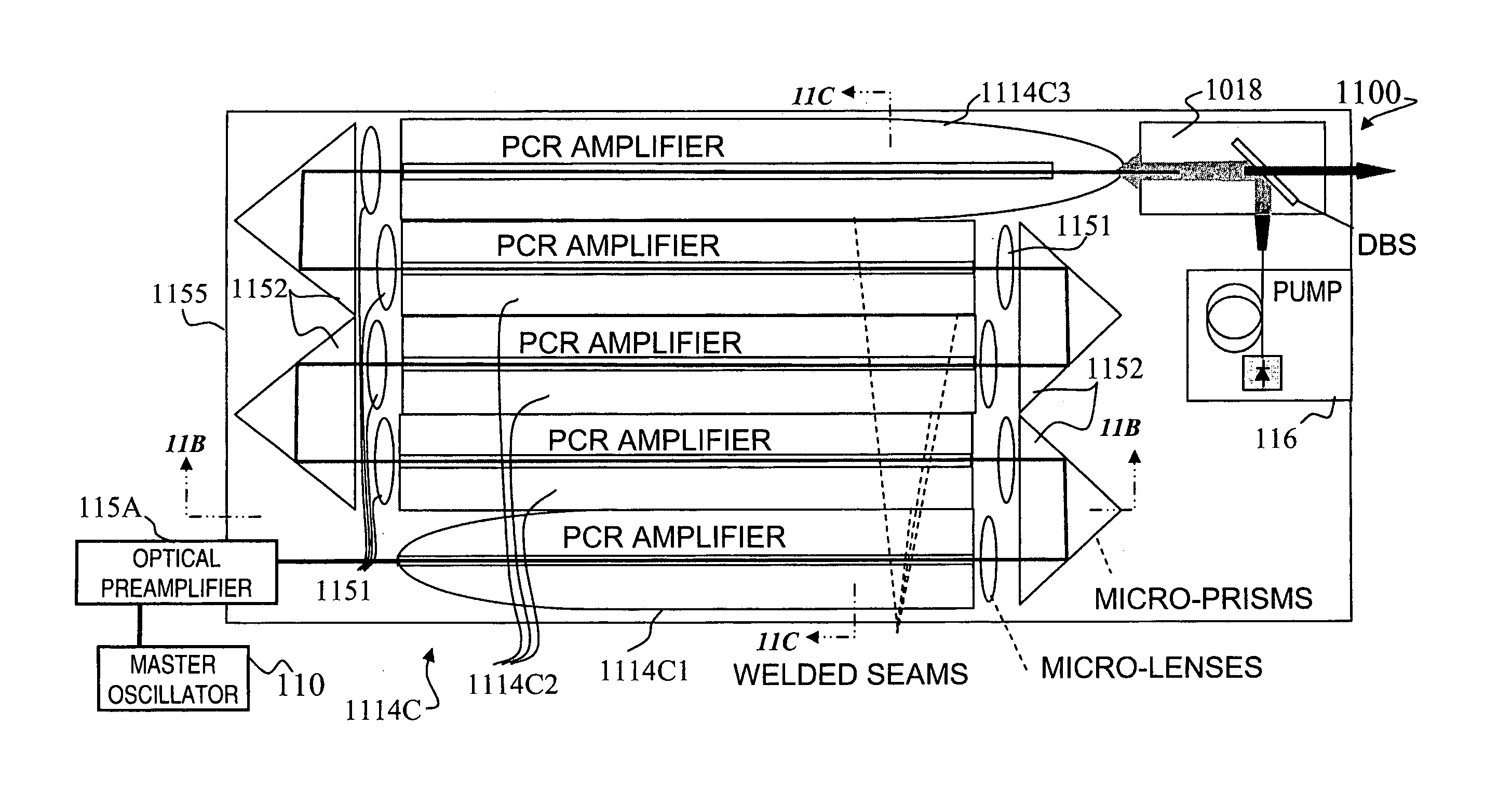
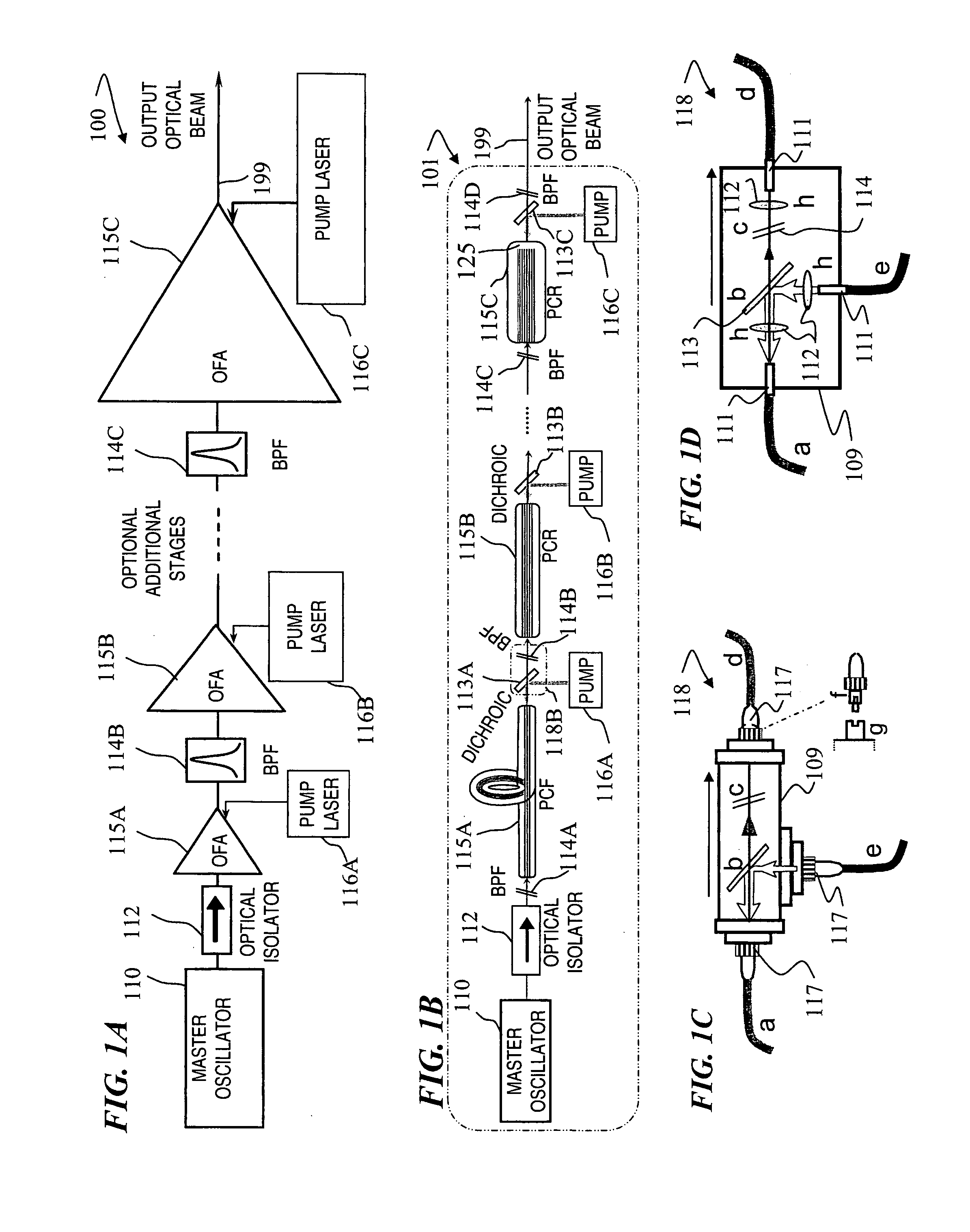
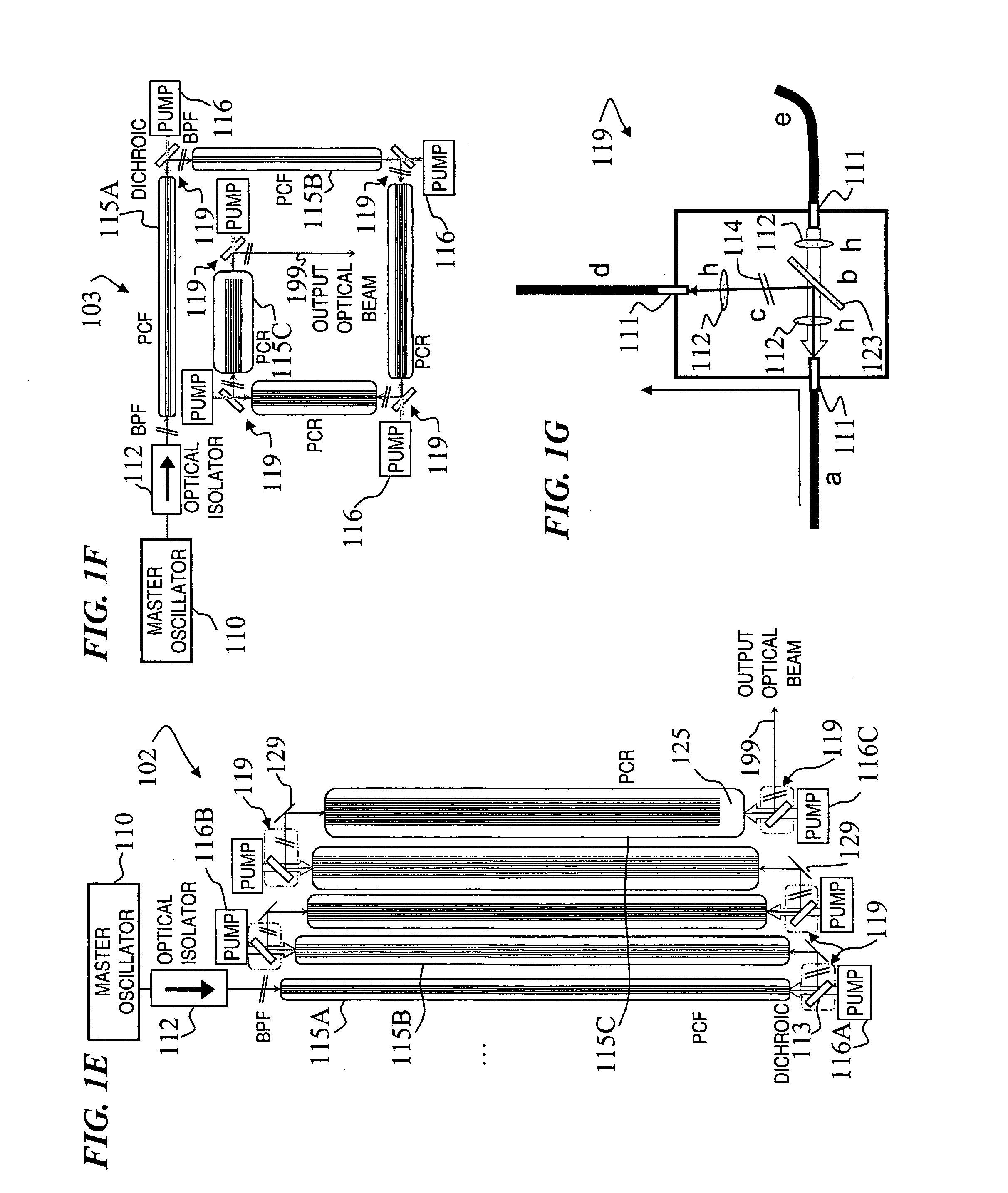
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
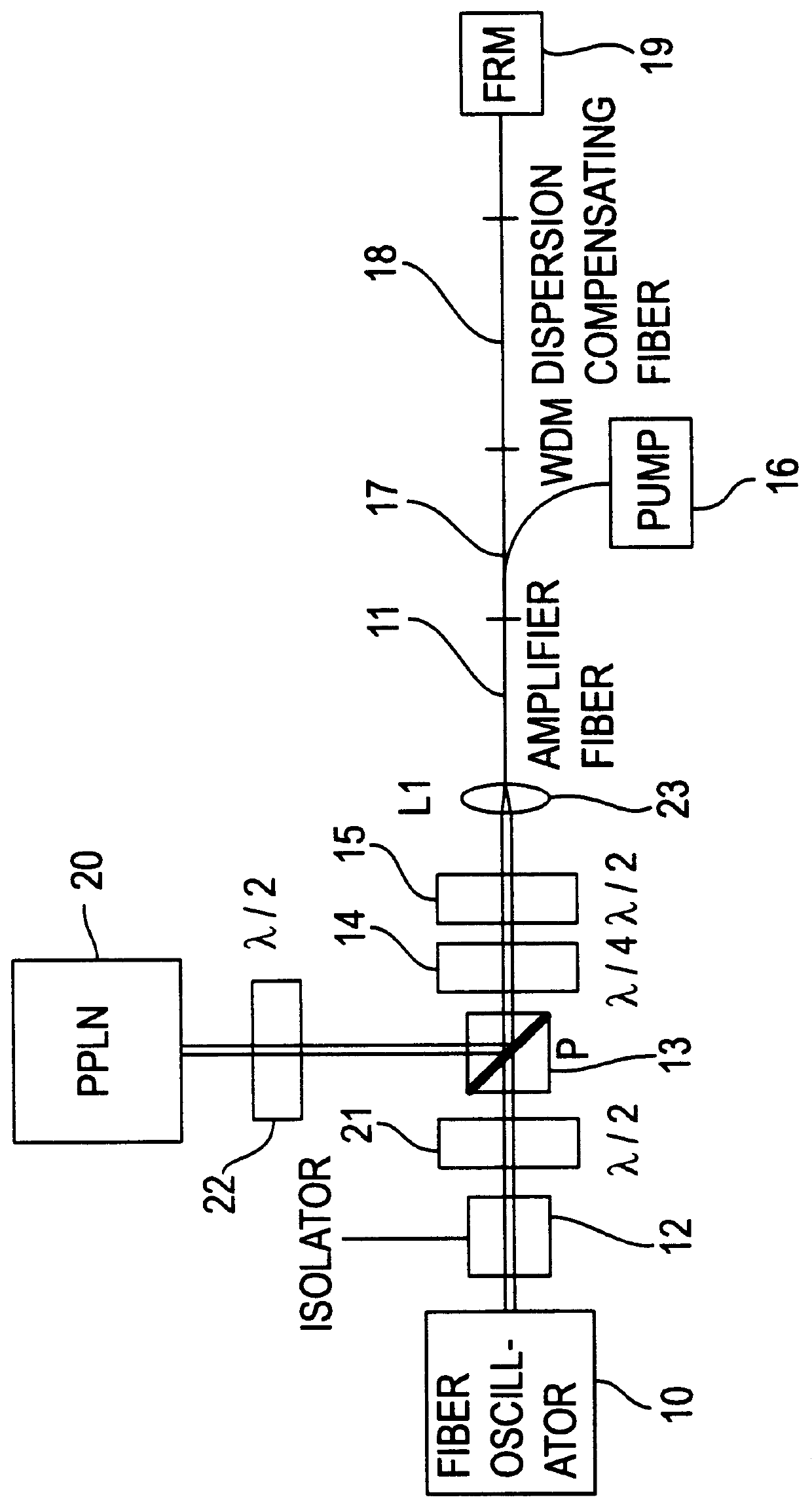
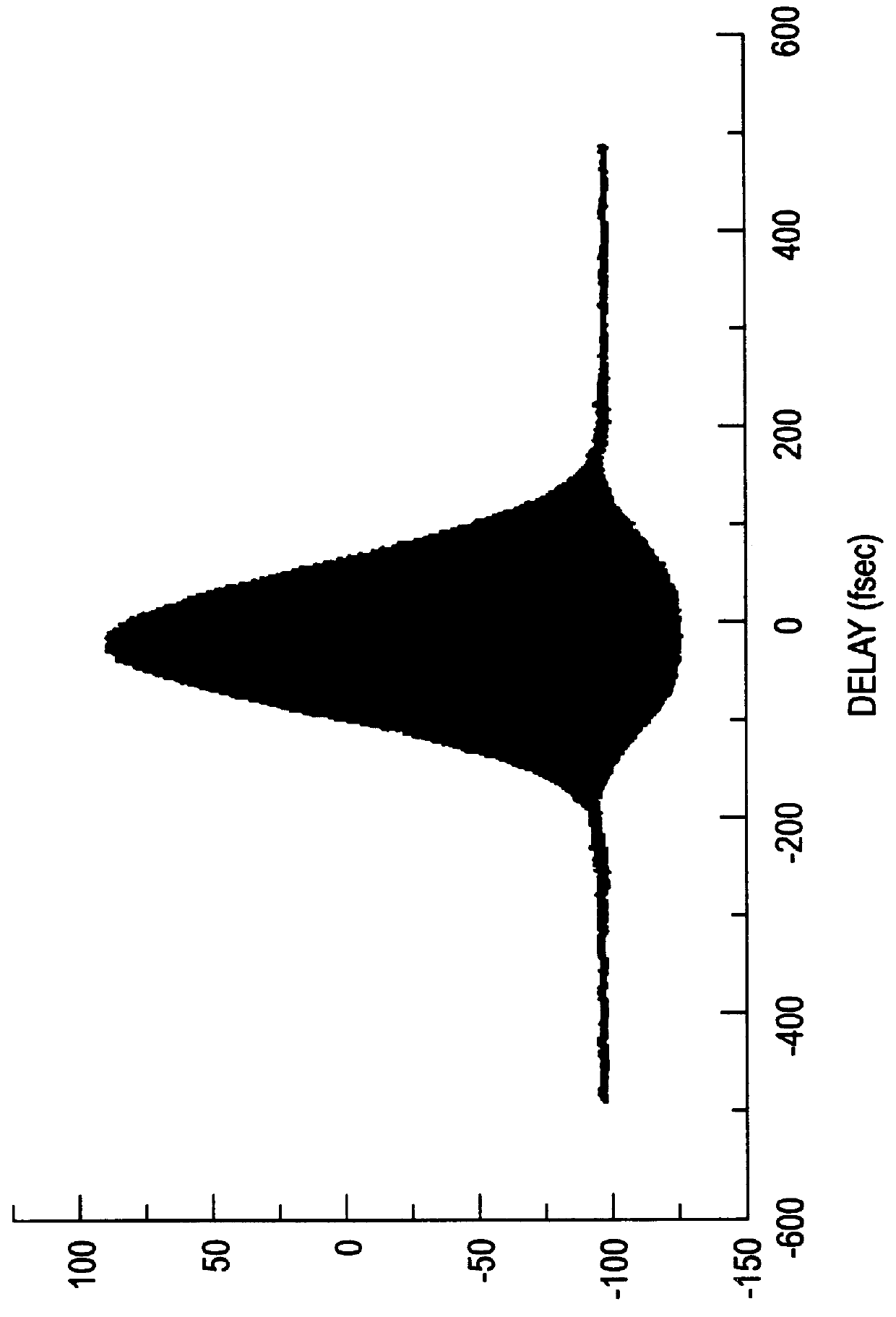
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
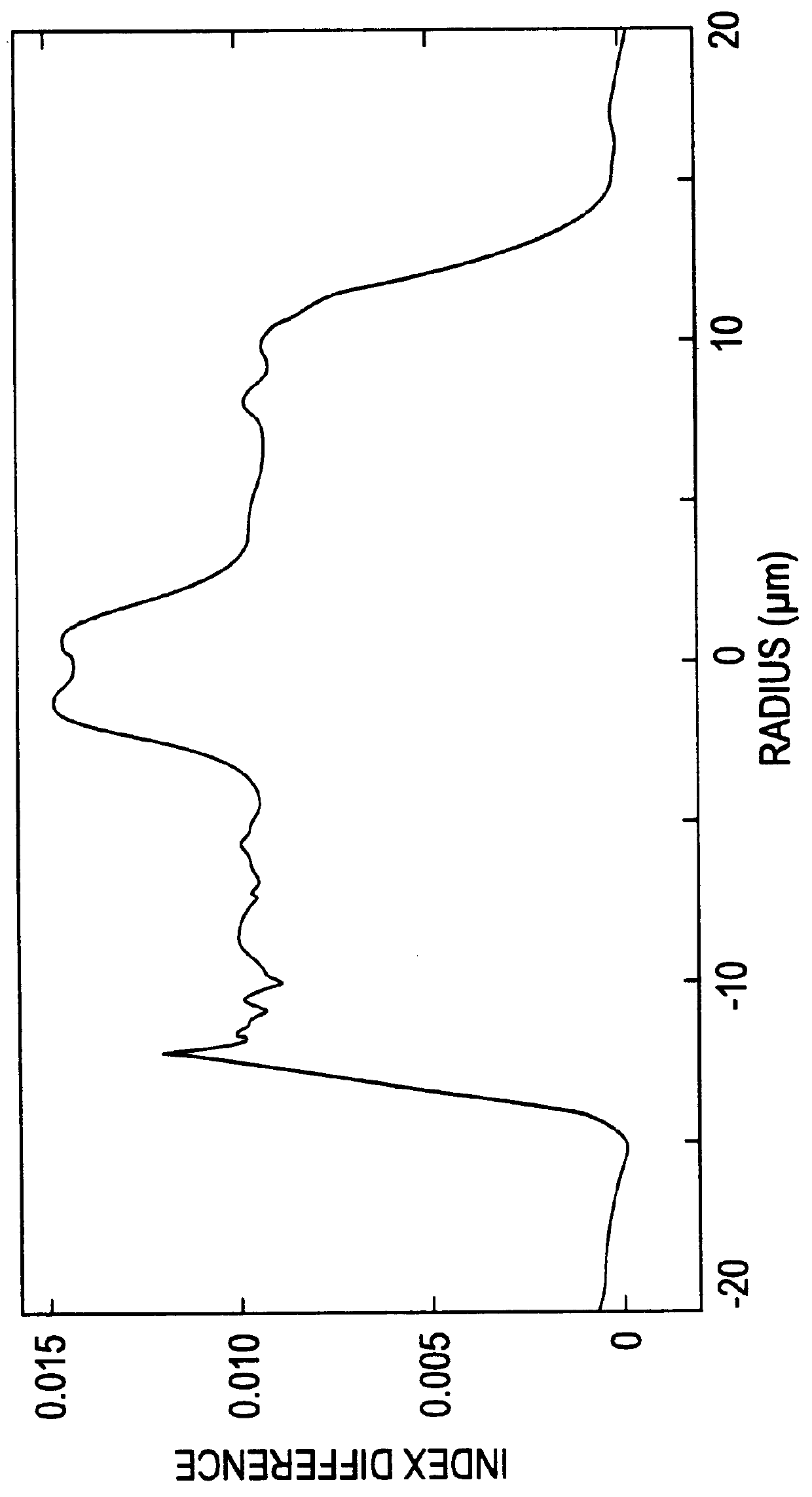
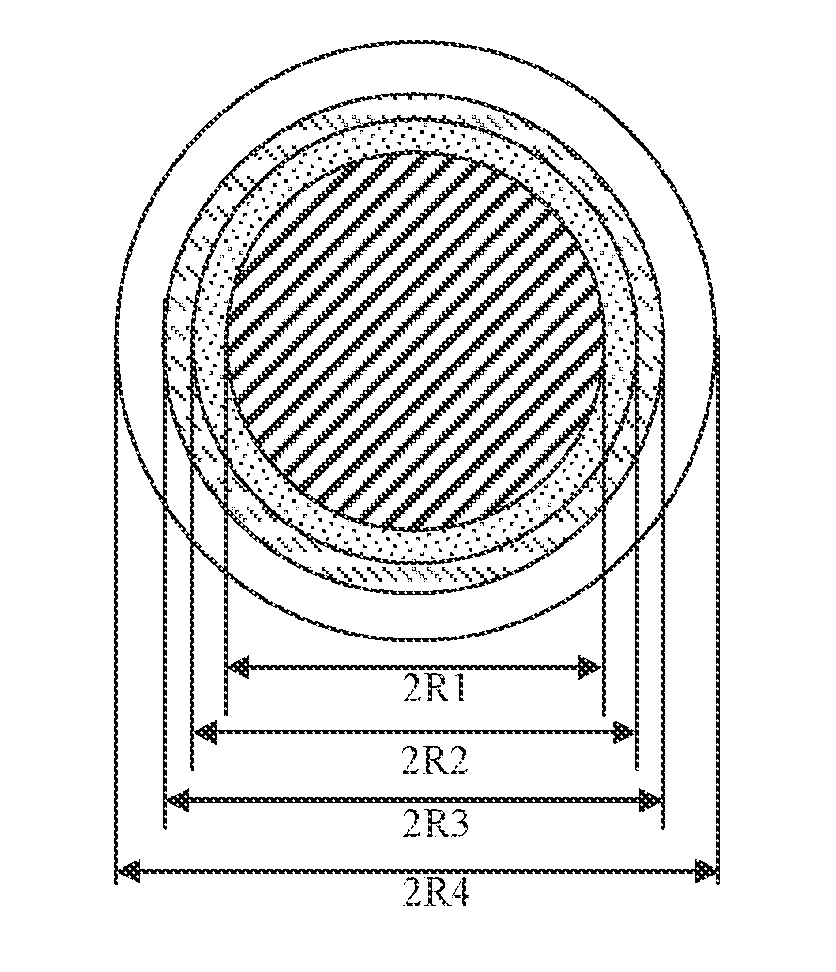
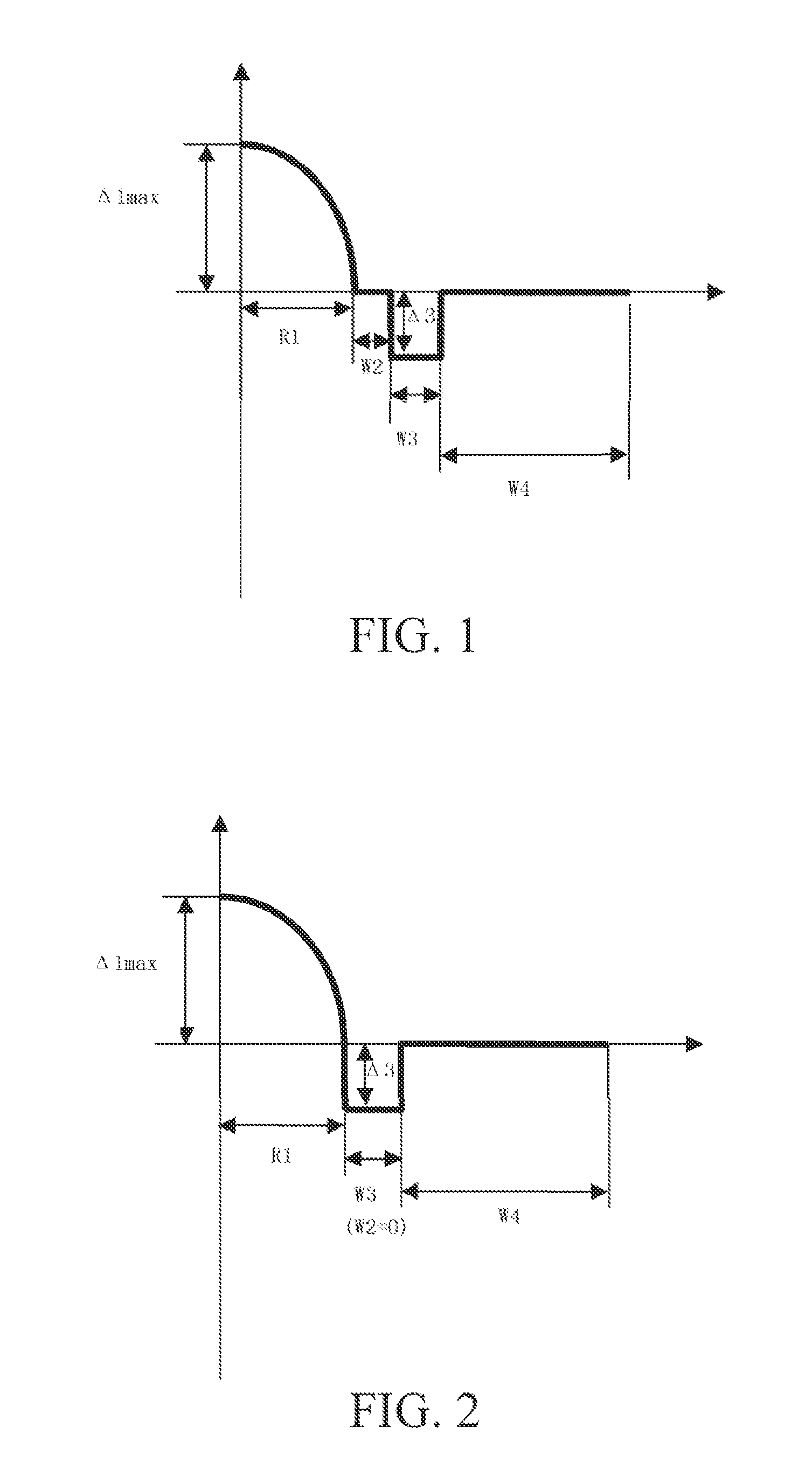
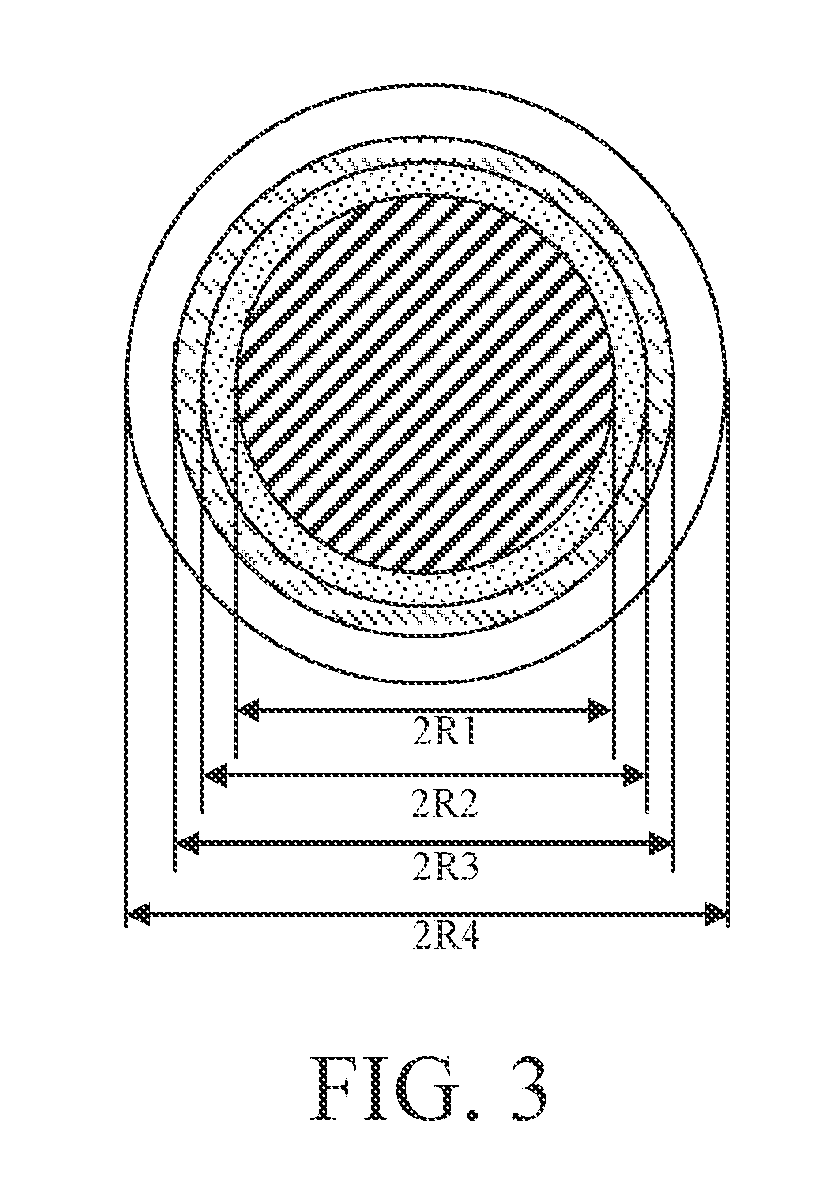
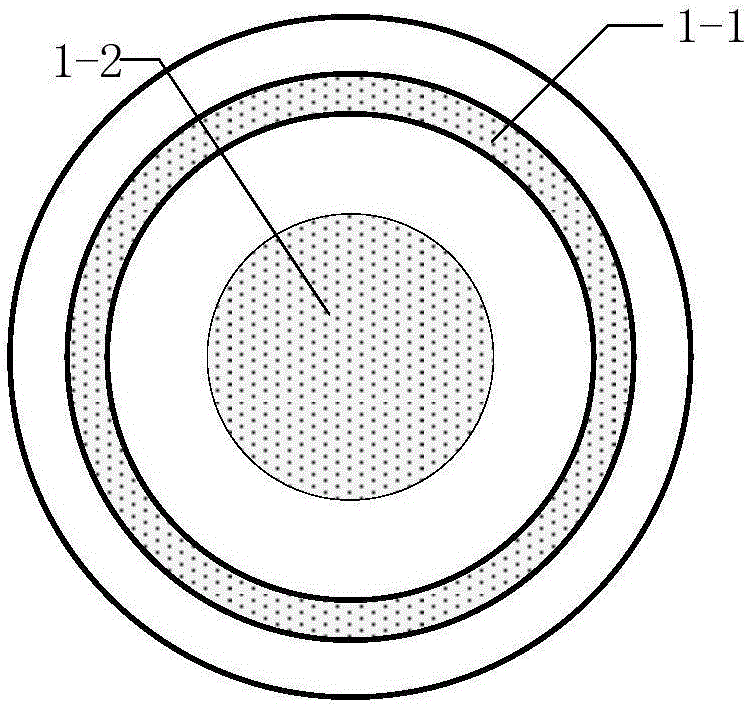
Bending-resistant large core diameter high numerical aperture multimode fiber
ActiveUS20130279868A1Convenient lightingReduce configuration costsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideHigh numerical apertureRelative refractive index
A bending-resistant large core diameter high numerical aperture multimode fiber includes a core and a cladding surrounding the core. The core has a radius R1 in a range of 28 to 50 microns, a refractive index profile of a parabola shape with α being in a range of 1.9 to 2.2, and a maximum relative refractive index difference Δ1% max being in a range of 1.9% to 2.5%. The cladding includes an inner cladding and / or a trench cladding, and an outer cladding disposed from the inner to the outer in sequence. The radius R2 of the inner cladding is in a range of 28 to 55 microns, and the relative refractive index difference Δ2% is −0.1% to 0.1%. The radius R3 of the trench cladding is in a range of 28 to 60 microns, and the relative refractive index difference Δ3% is in a range of −0.15% to −0.8%.
Owner:EVERPRO TECH COMPANY
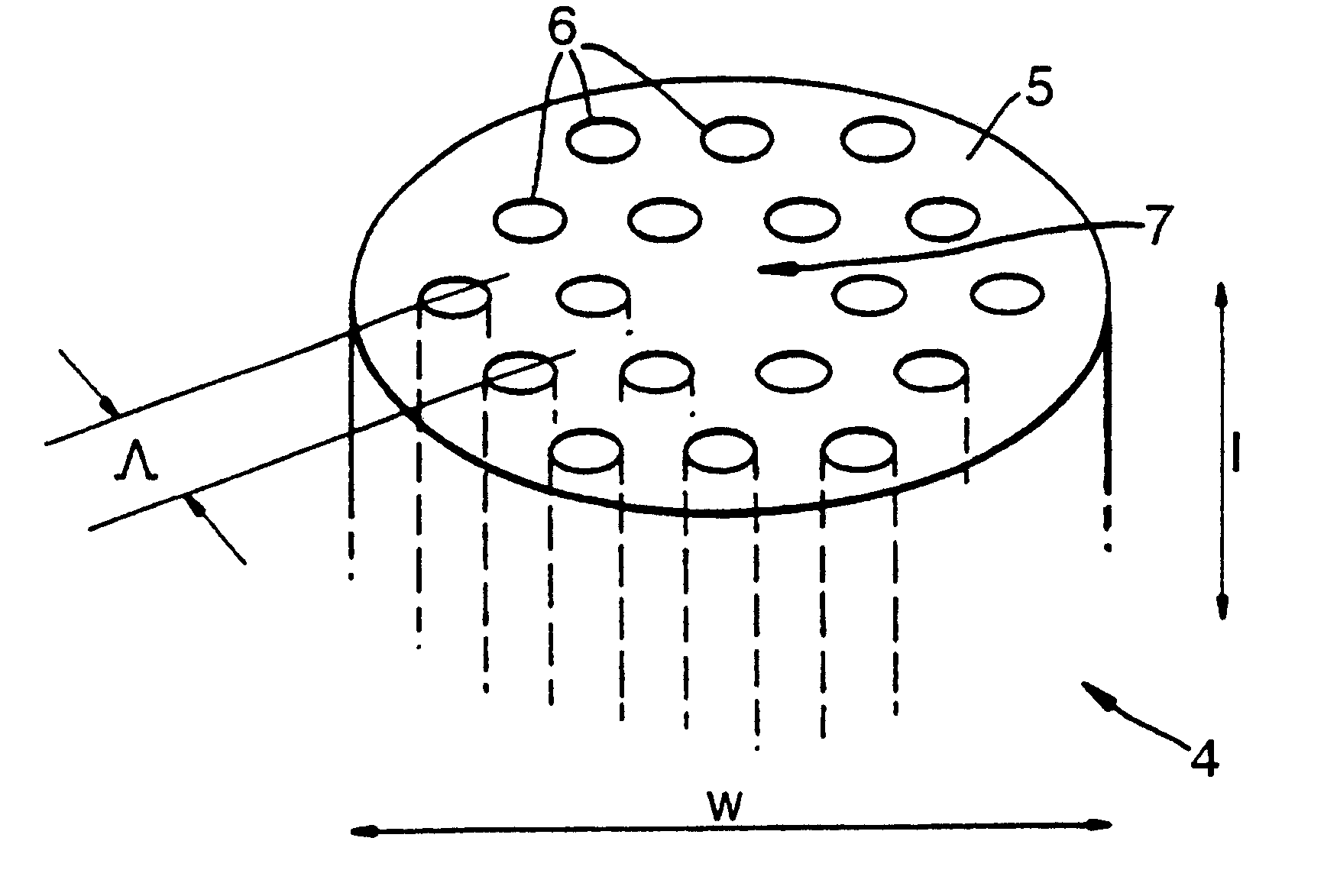
Single mode optical fiber
InactiveUS6334019B1High refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexFiber disk laser
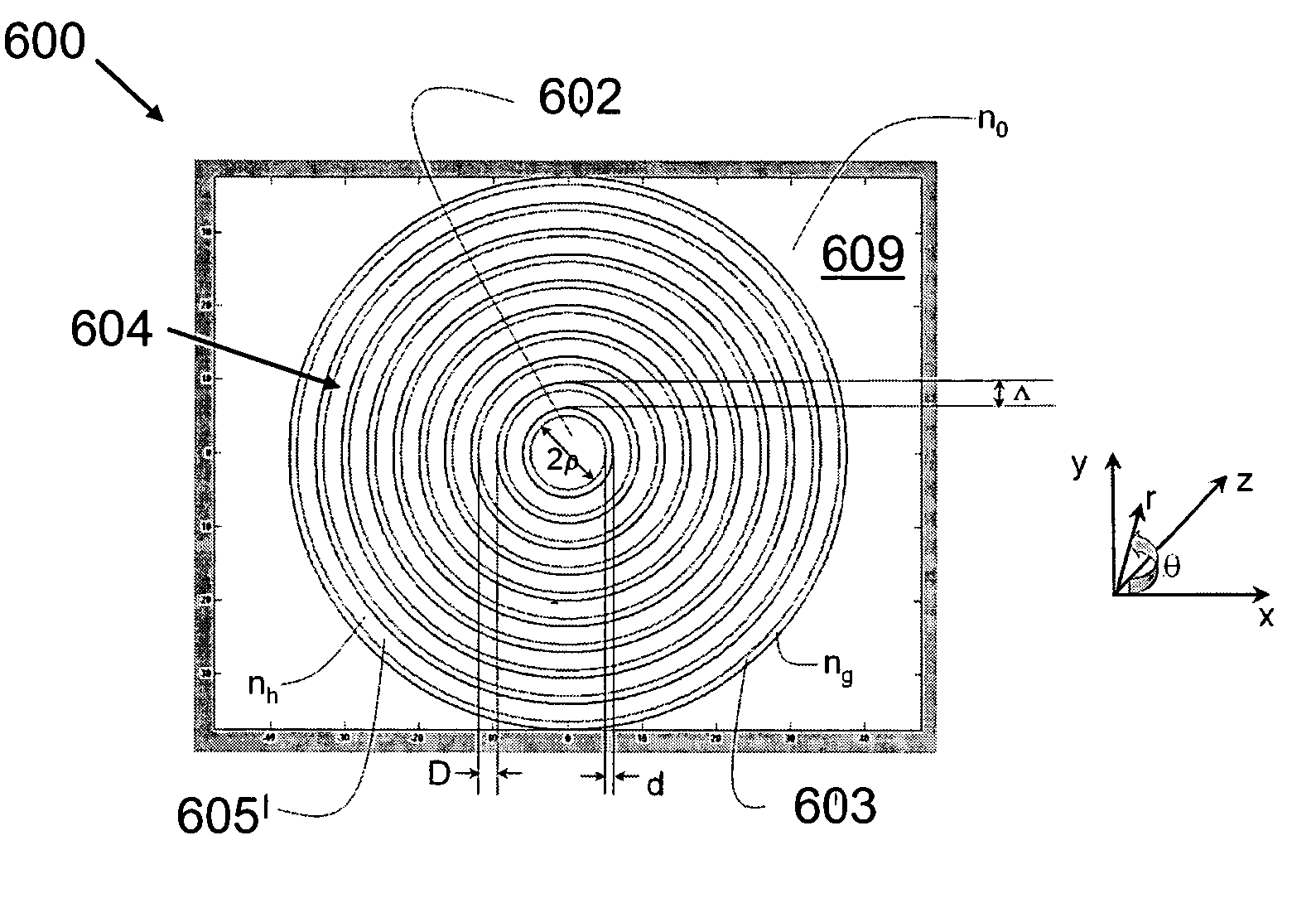
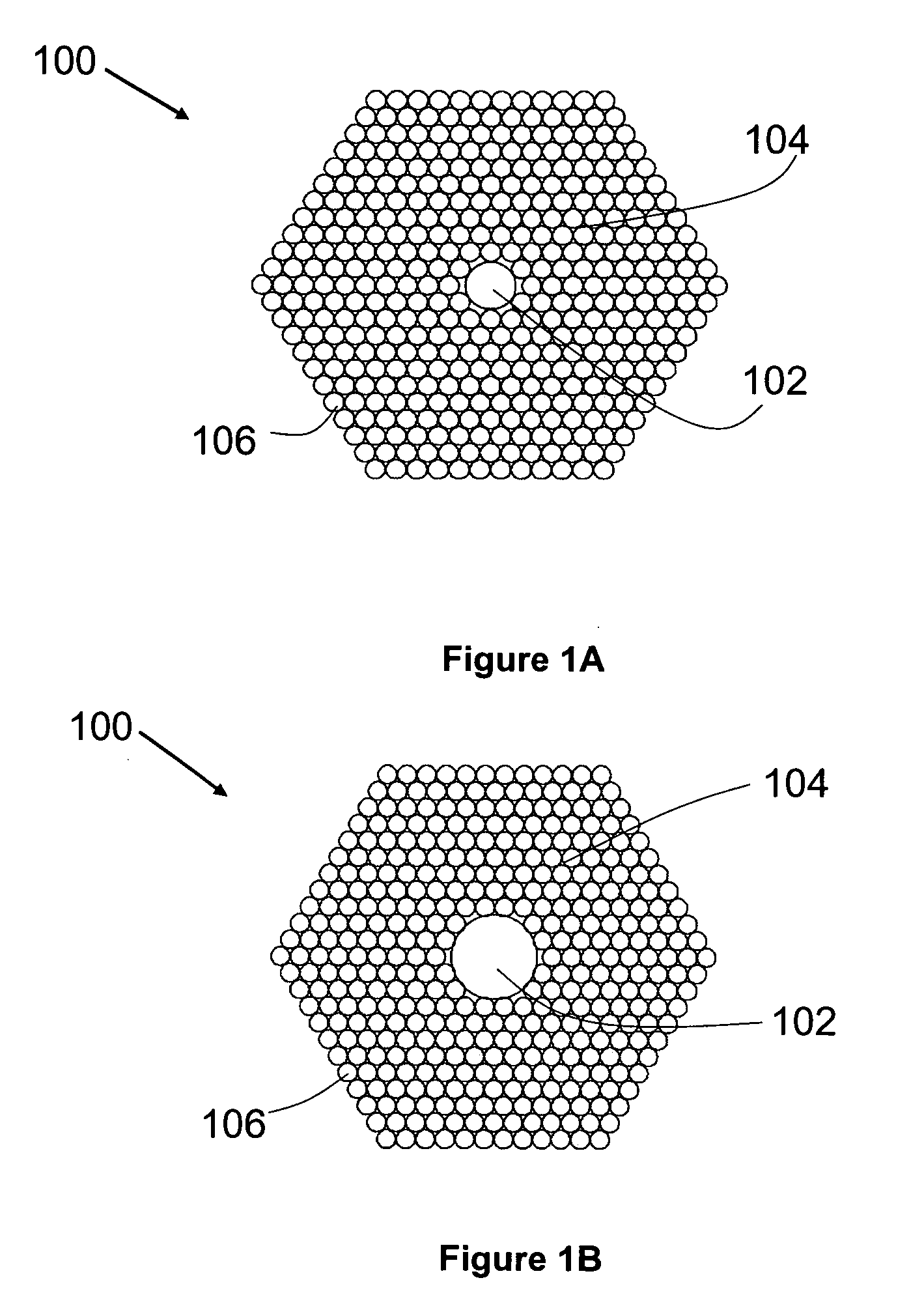
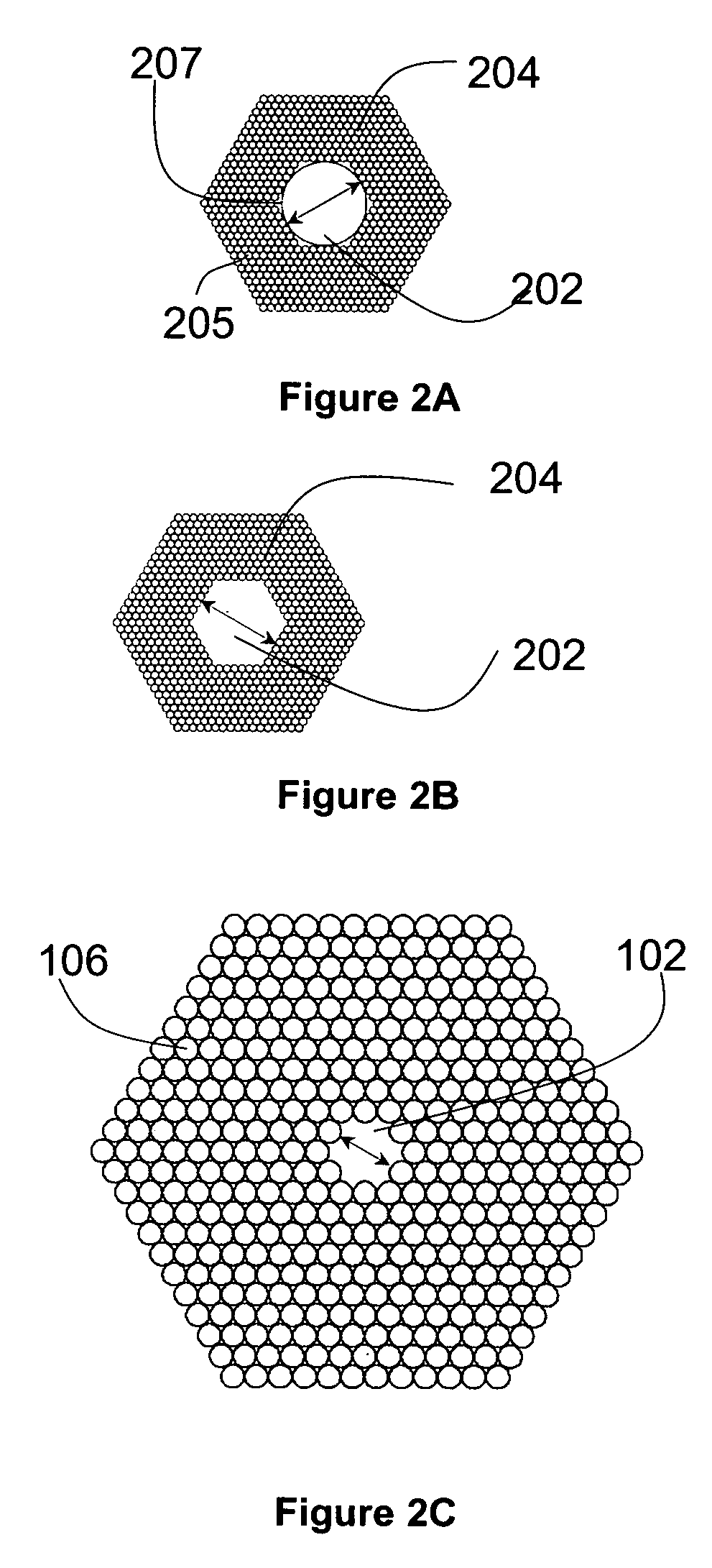
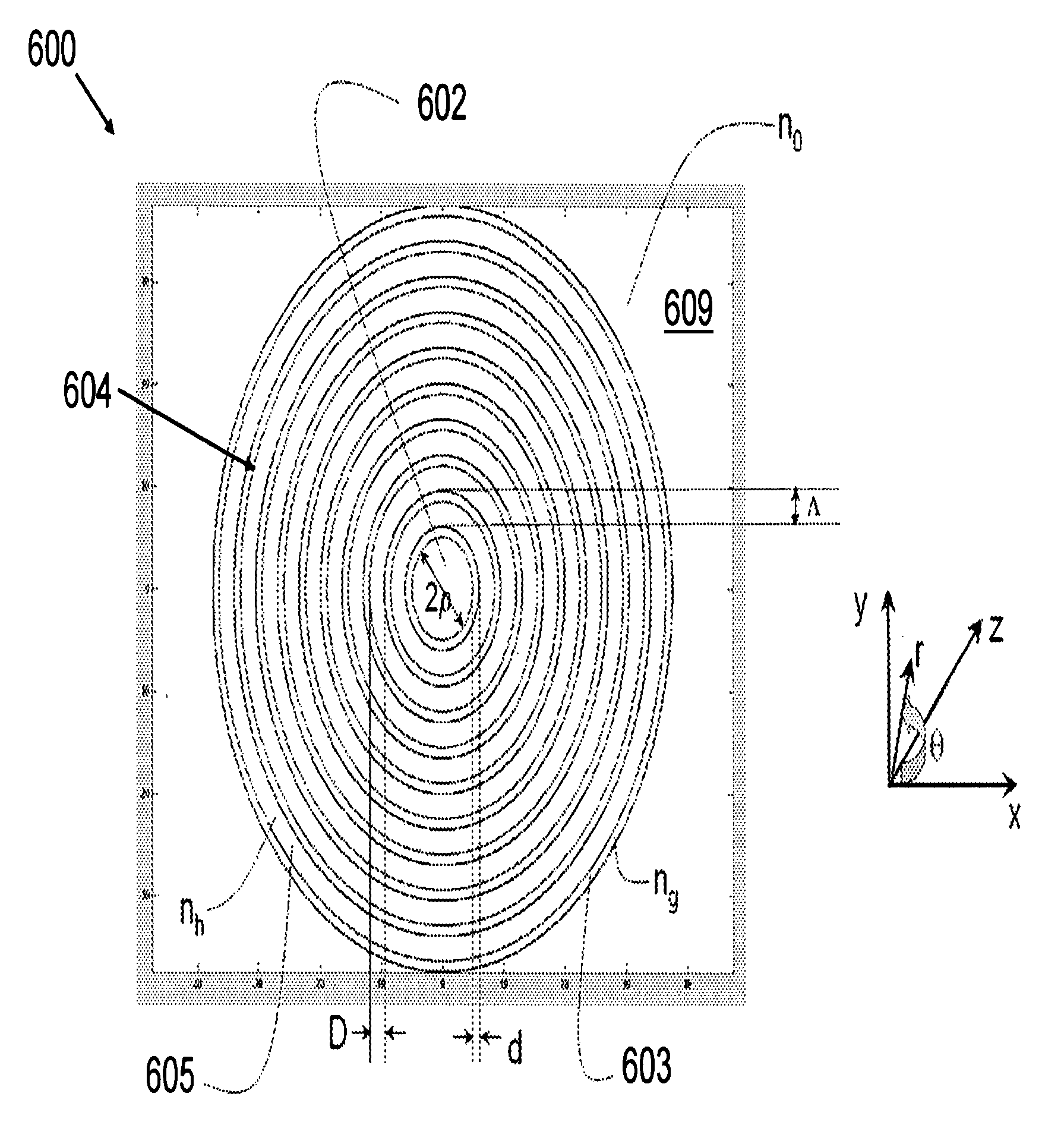
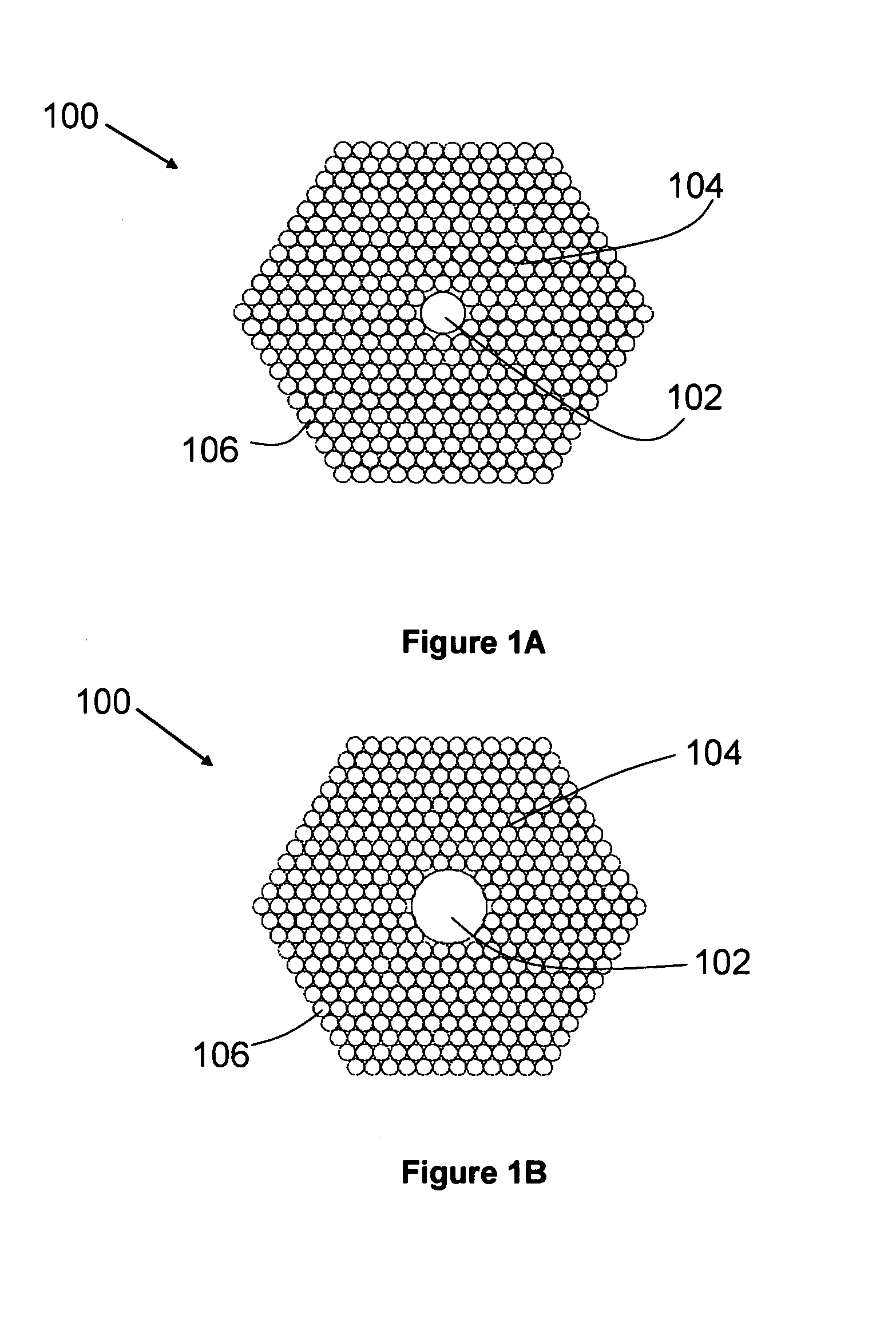
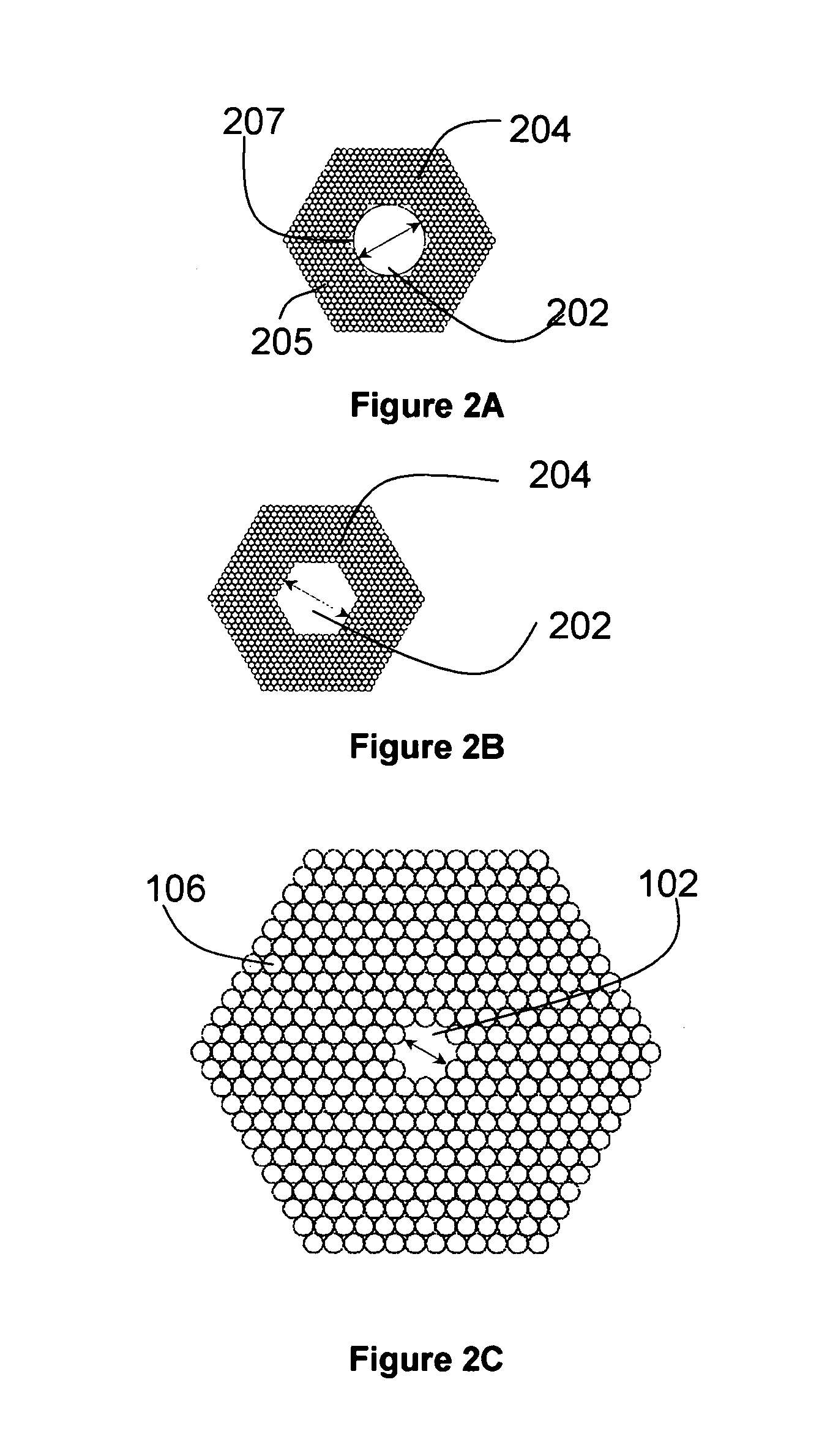
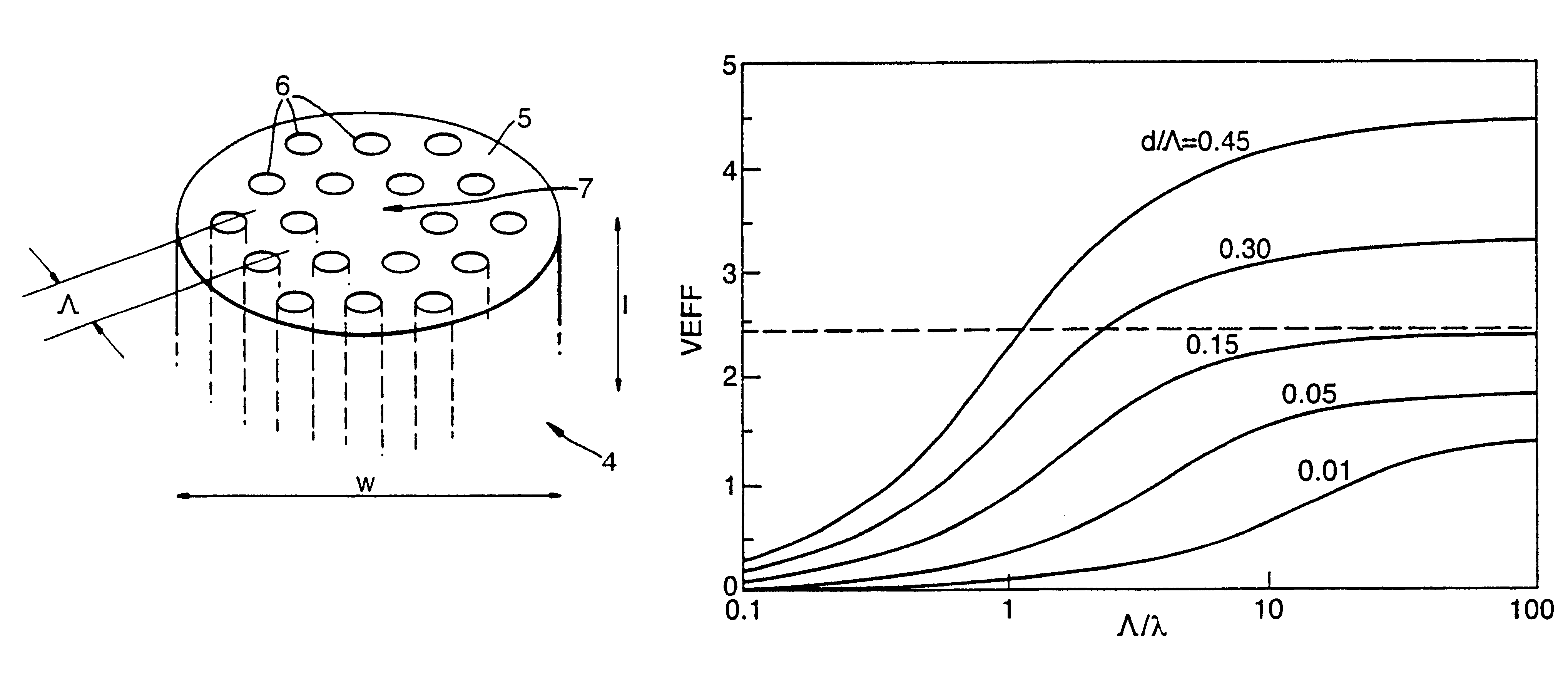
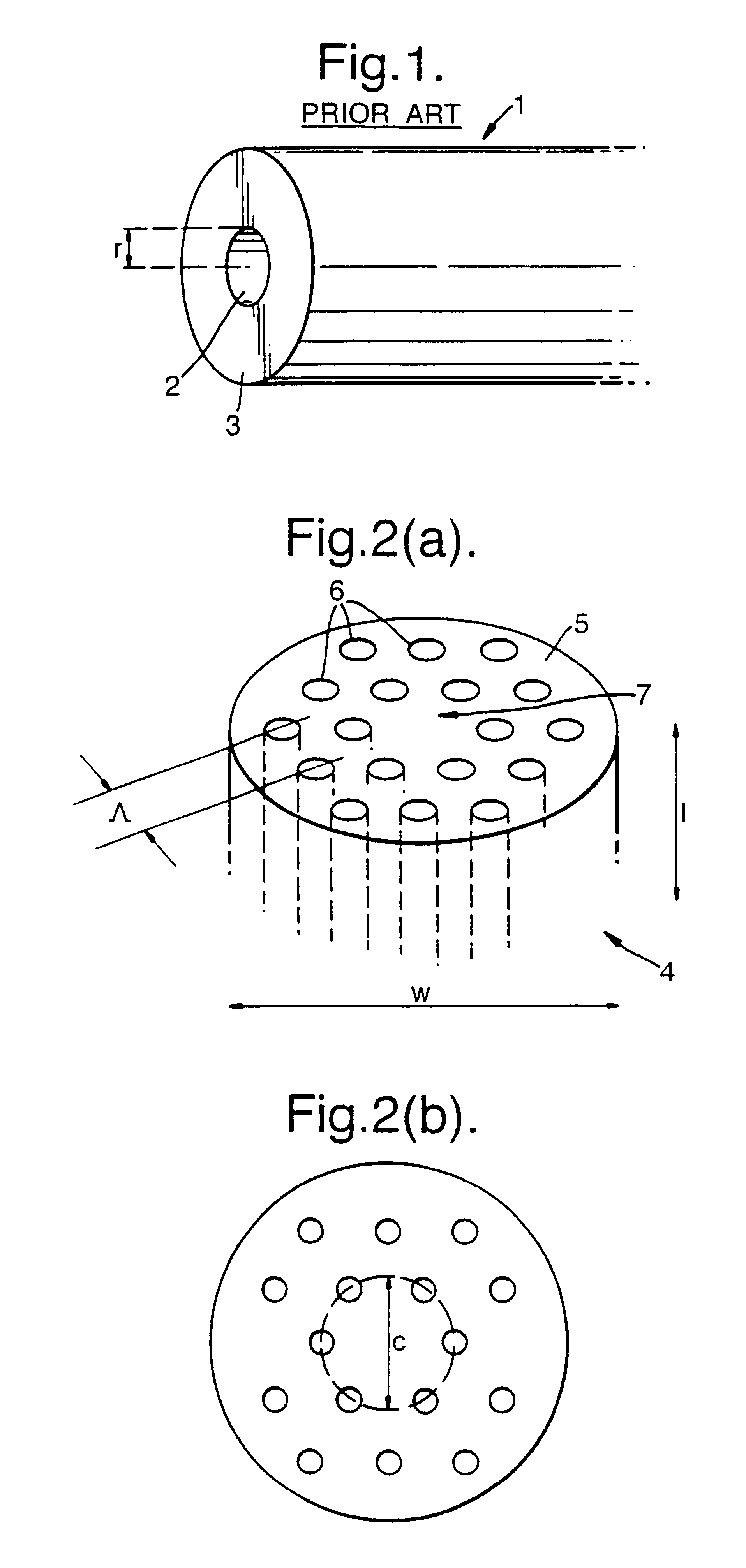
A large core photonic crystal fiber for transmitting radiation having a core comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core diameter of at least 5 mu. The fiber also comprises a cladding region surrounding the length of core material, wherein the cladding region comprises a first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, and wherein the first substantially transparent cladding material has embedded along its length a substantially periodic array of holes, wherein the holes are filled with a second cladding material having a second refractive index less than the first refractive index, such that radiation input to the optical fiber is transmitted along the length of the core material in a single mode of propagation. In a preferred embodiment, the core diameter may be at least 20 mu, and may be as large as 50 mu. The fiber is capable of transmitting higher power radiation than conventional fibres, whilst maintaining propagation in a single mode. The core material may be doped with a material capable of providing amplification under the action of pump radiation input to the fiber. The invention also relates to a fiber amplifier and a fiber laser comprising a doped large core photonic crystal fiber. The fiber may also be used in a system for transmitting radiation comprising a plurality of lengths of large core photonic crystal fiber, separated by large core photonic crystal fiber amplifiers, such that the power of radiation transmitted through the system is maintained above a predetermined threshold power.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
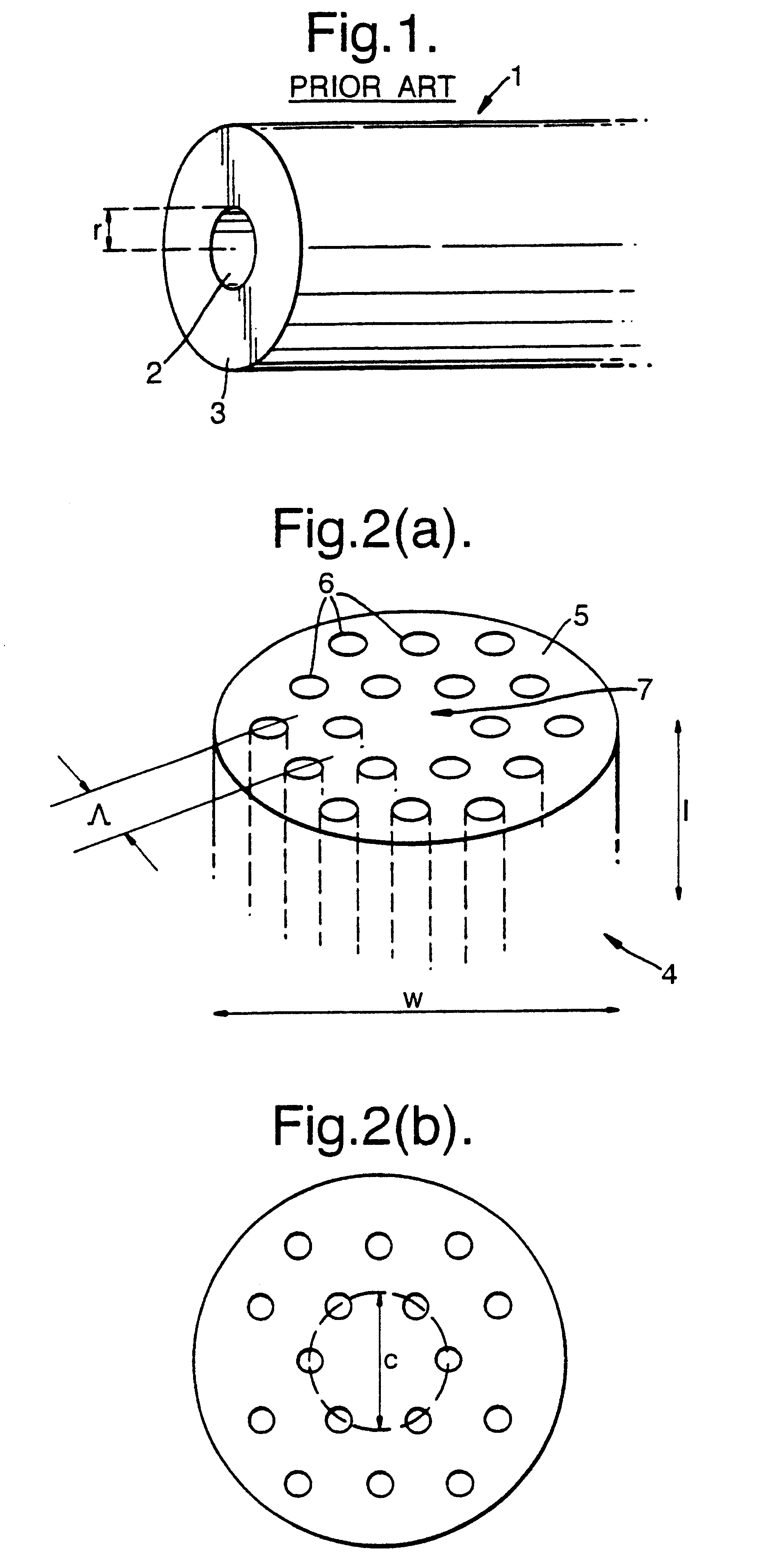
Large core holey fibers
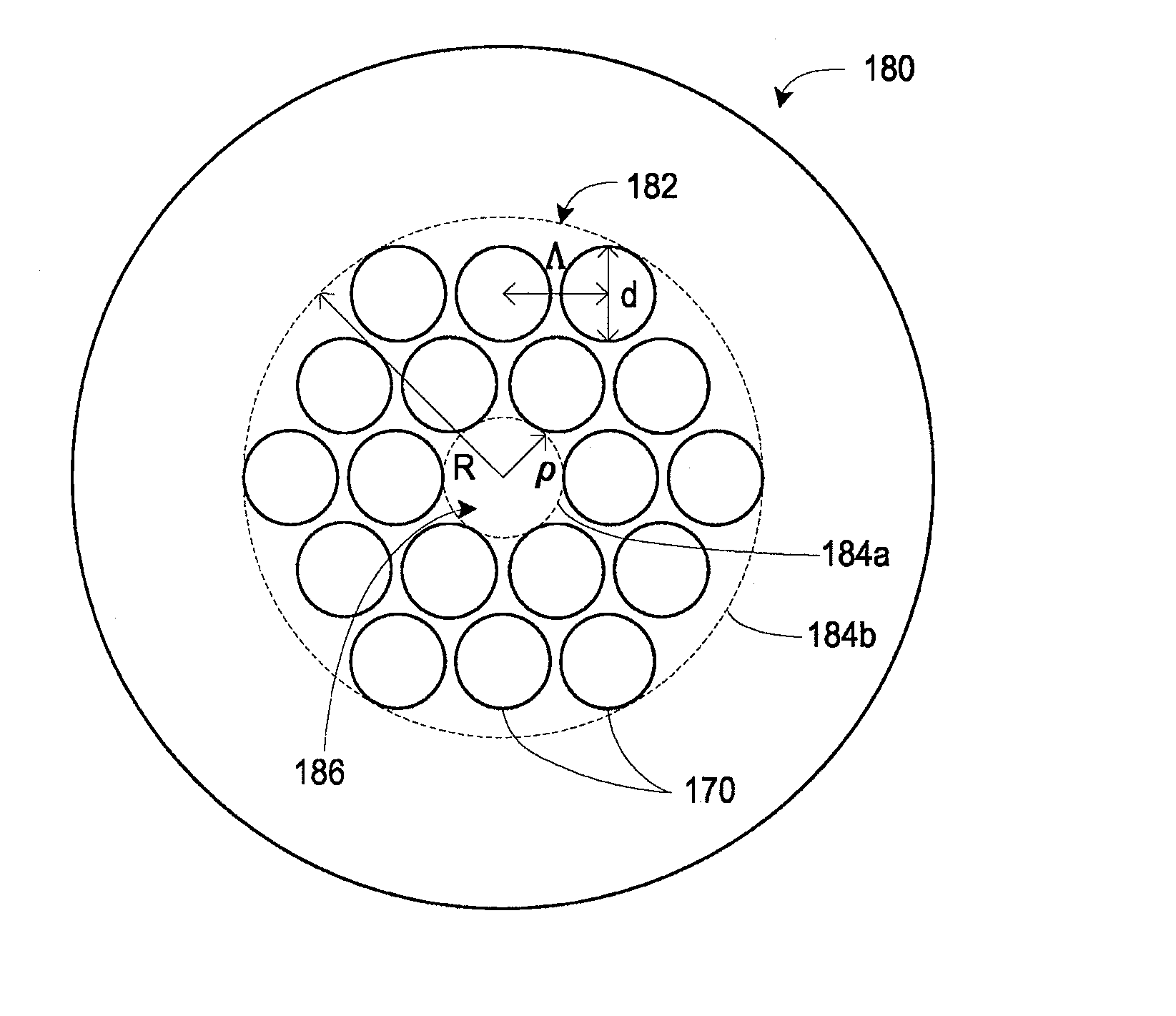
Various types of holey fiber provide optical propagation. In various embodiments, for example, a large core holey fiber comprises a cladding region formed by large holes arranged in few layers. The number of layers or rows of holes about the large core can be used to coarse tune the leakage losses of the fundamental and higher modes of a signal, thereby allowing the non-fundamental modes to be substantially eliminated by leakage over a given length of fiber. Fine tuning of leakage losses can be performed by adjusting the hole dimension and / or the hole spacing to yield a desired operation with a desired leakage loss of the fundamental mode. Resulting holely fibers have a large hole dimension and spacing, and thus a large core, when compared to traditional fibers and conventional fibers that propagate a single mode. Other loss mechanisms, such as bend loss and modal spacing can be utilized for selected modes of operation of holey fibers. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
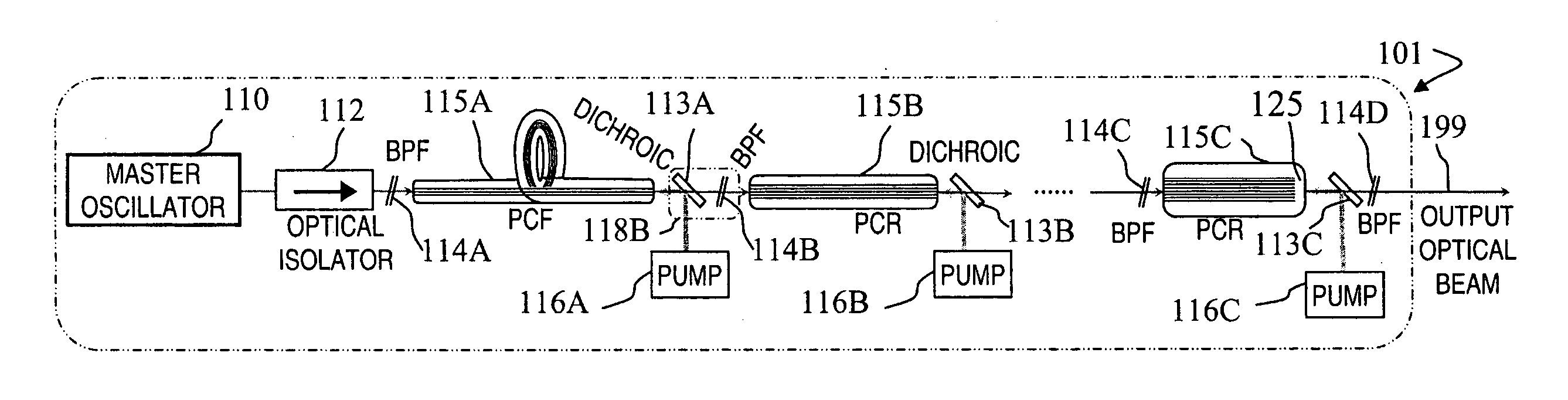
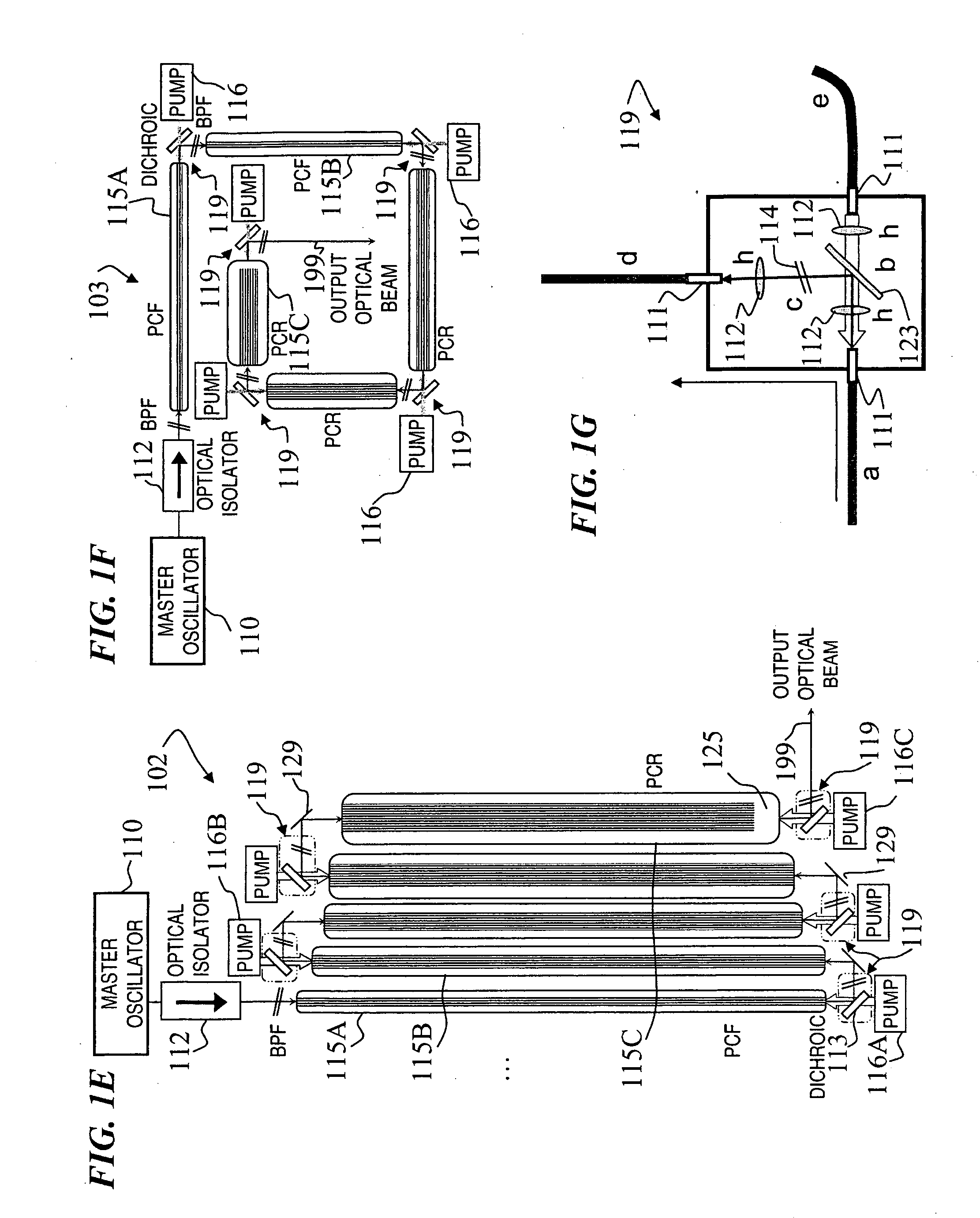
Fiber- or rod-based optical source featuring a large-core, rare-earth-doped photonic-crystal device for generation of high-power pulsed radiation and method
ActiveUS20070041083A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRare earthEngineering
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
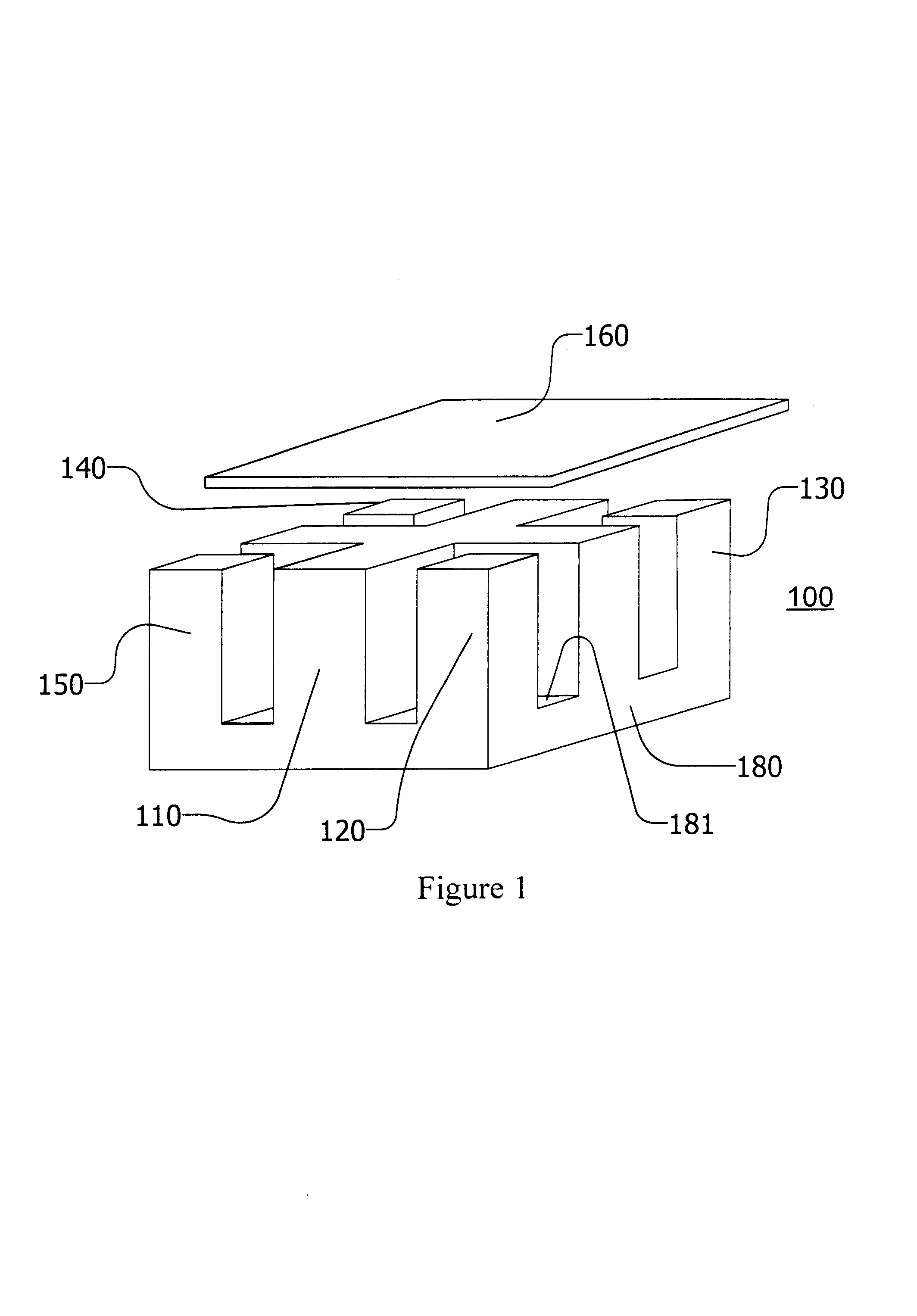
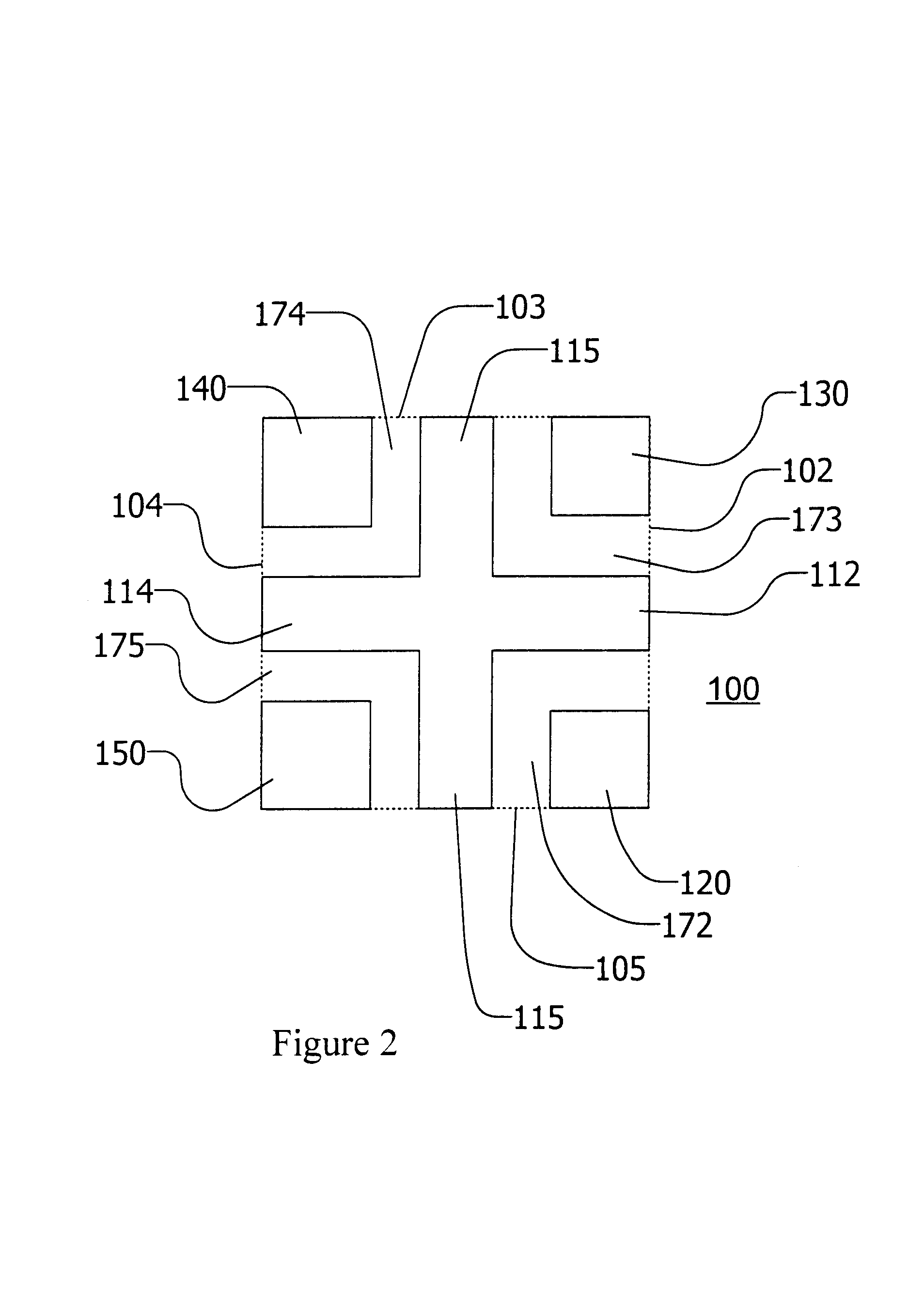
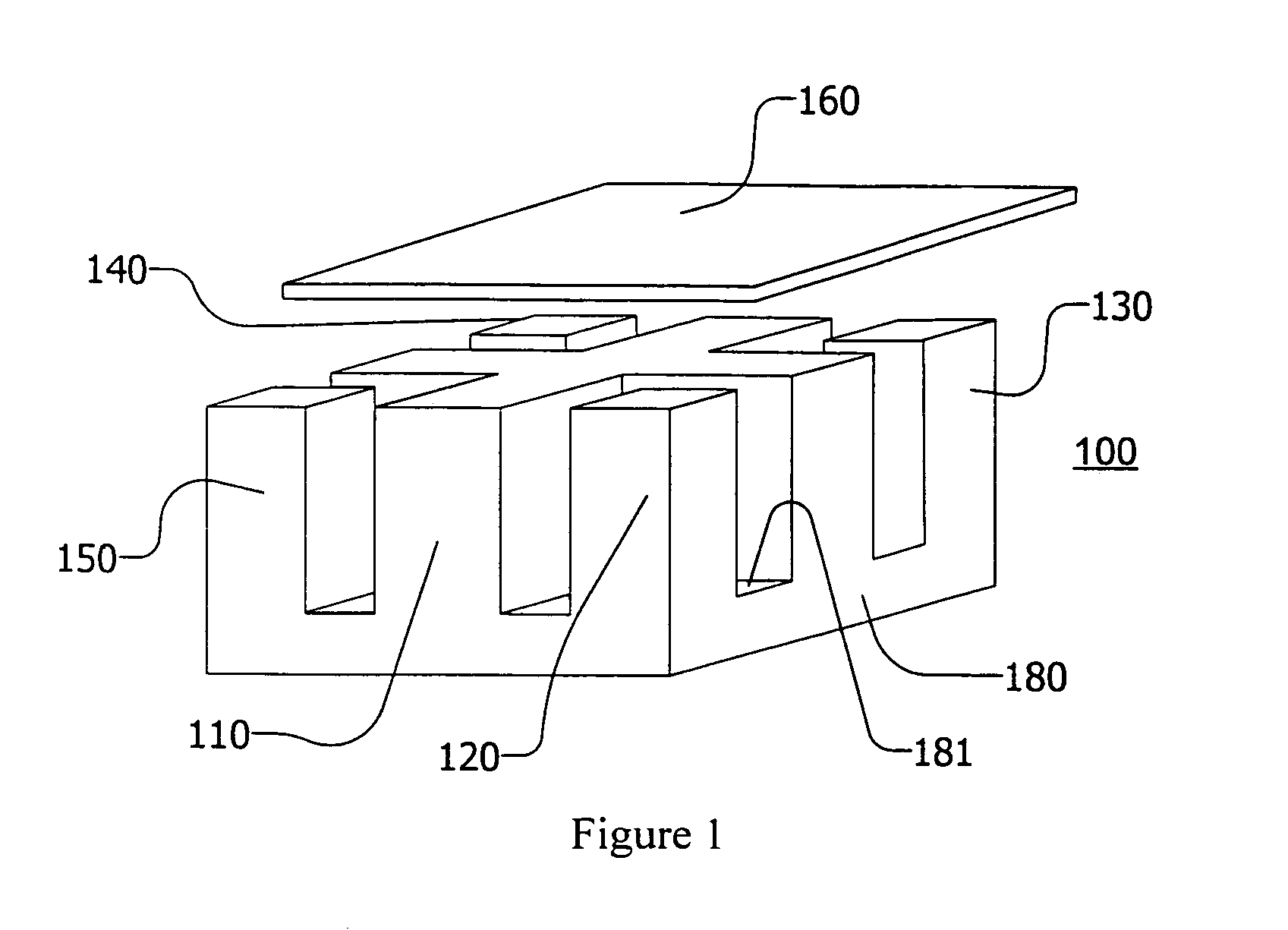
Core structure
InactiveUS6873237B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalTransformers/inductances casingsHigh power densityLarge core
There is disclosed a core structure with a very low profile, high power density and lower losses. Higher core surface area and improved core utilization in terms of flux density are other desirable feature in the disclosed design. The disclosed design also allowed for a larger core area where the DC fluxes are added, thereby reducing the air-gap requirements in the cores derived from low saturation density materials such as ferrites. The cellular nature of the design can also be effectively employed in vertically packaged power converters and modules.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
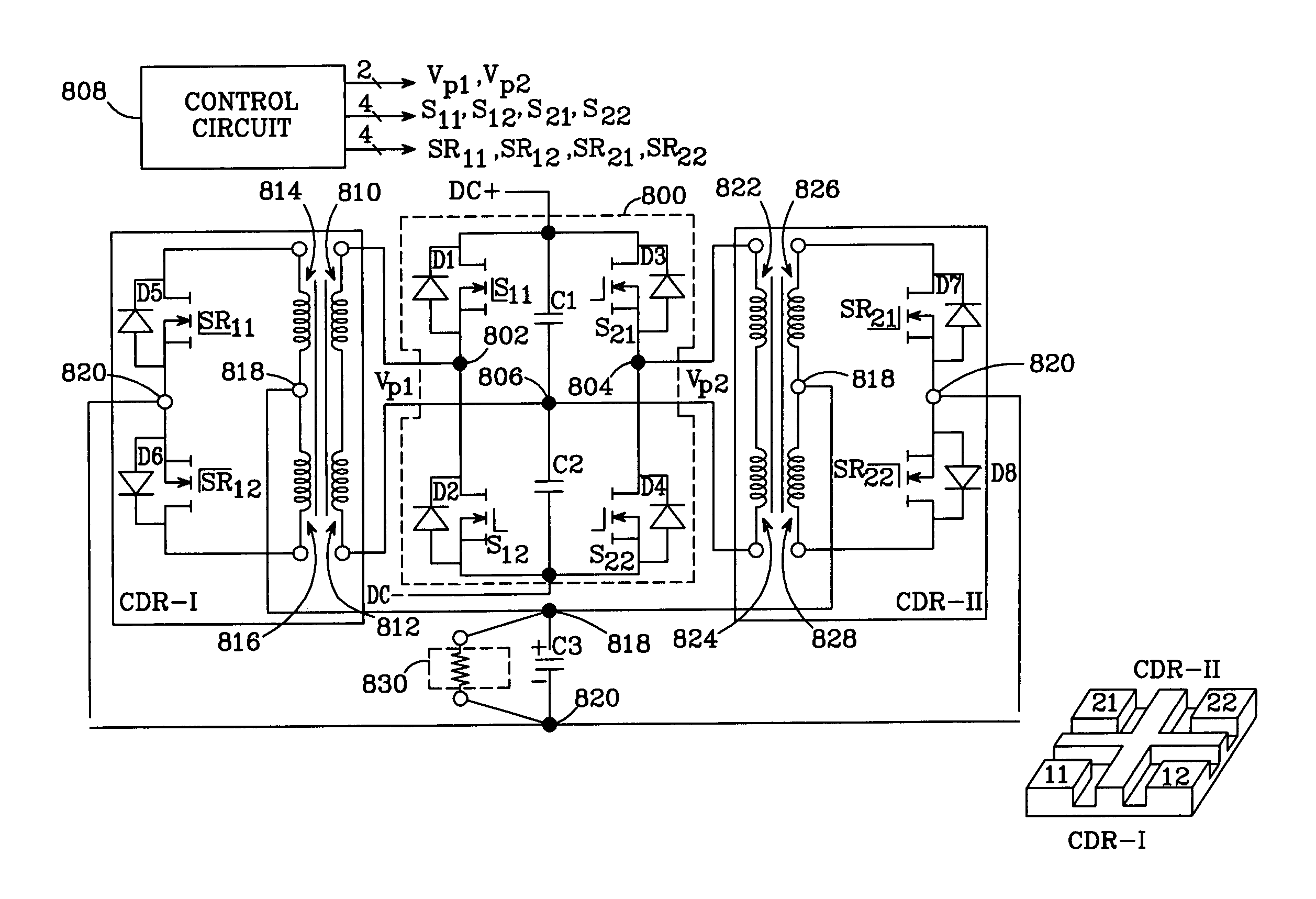
Core structure and interleaved DC-DC converter topology
ActiveUS7046523B2Reduced output voltage rippleReduce outputAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc dc converterPhase shifted
There is disclosed a core structure with a very low profile, high power density and lower losses. The disclosed design allows for a larger core area where the DC fluxes are added, thereby reducing the air-gap requirements in the cores derived from low saturation density materials such as ferrites. The cellular nature of the design can be effectively employed in vertically packaged power converters and modules. Also disclosed is a DC-DC converter topology which preferably employs the disclosed core. N AC drive voltages drive N current doubler rectifiers (CDRs) in accordance with the symmetric modulation scheme; each CDR provides two rectified output currents to an output node. Each AC drive voltage has a switching period Ts. The drive voltages are phase-shifted by Ts / (2*N), such that the rectified output currents of the CDRs are interleaved, thereby reducing output voltage ripple.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Optical coupler comprising multimode fibers and method of making the same
ActiveUS20050094952A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFew mode fiberDouble-clad fiber
An optical coupler is provided. It has a bundle of multimode fibers with a few-mode fiber in its centre. Such bundle is fused at one end which is the output end for the signal that is transmitted by the few-mode fiber. To make the coupler, this output end of the bundle is aligned and spliced with a large area core double clad fiber while preserving the modal content of the feed-through. A method for making such optical coupler is also provided. It includes the steps of bundling a central few-mode fiber with a plurality of multimode fibers and then fusing one end of such bundle and aligning it and splicing with a large core double clad fiber, while preserving fundamental mode transmission from one to the other.
Owner:ITF TECH +1
Multi-segment photonic-crystal-rod waveguides for amplification of high-power pulsed optical radiation and associated method
InactiveUS20070104431A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreOptical radiationPromiscuous behaviour
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
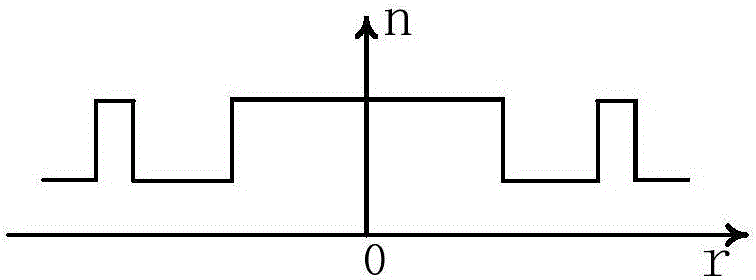
Photonic bandgap fibers
InactiveUS20060193583A1Reduce transmission lossWide transmission bandAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
Included among the many structures described herein are photonic bandgap fibers designed to provide a desired dispersion spectrum. Additionally, designs for achieving wide transmission bands and lower transmission loss are also discussed. For example, in some fiber designs, smaller dimensions of high index material in the cladding and large core size provide small flat dispersion over a wide spectral range. In other examples, the thickness of the high index ring-shaped region closest to the core has sufficiently large dimensions to provide negative dispersion or zero dispersion at a desired wavelength. Additionally, low index cladding features distributed along concentric rings or circles may be used for achieving wide bandgaps.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Large core holey fibers
Various types of holey fiber provide optical propagation. In various embodiments, for example, a large core holey fiber comprises a cladding region formed by large holes arranged in few layers. The number of layers or rows of holes about the large core can be used to coarse tune the leakage losses of the fundamental and higher modes of a signal, thereby allowing the non-fundamental modes to be substantially eliminated by leakage over a given length of fiber. Fine tuning of leakage losses can be performed by adjusting the hole dimension and / or the hole spacing to yield a desired operation with a desired leakage loss of the fundamental mode. Resulting holey fibers have a large hole dimension and spacing, and thus a large core, when compared to traditional fibers and conventional fibers that propagate a single mode. Other loss mechanisms, such as bend loss and modal spacing can be utilized for selected modes of operation of holey fibers. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Fiber amplifier system for suppression of modal instabilities and method
ActiveUS20150138630A1Avoids and minimizes modal instabilitySame performanceLaser detailsFibre transmissionInstabilitySignal beam
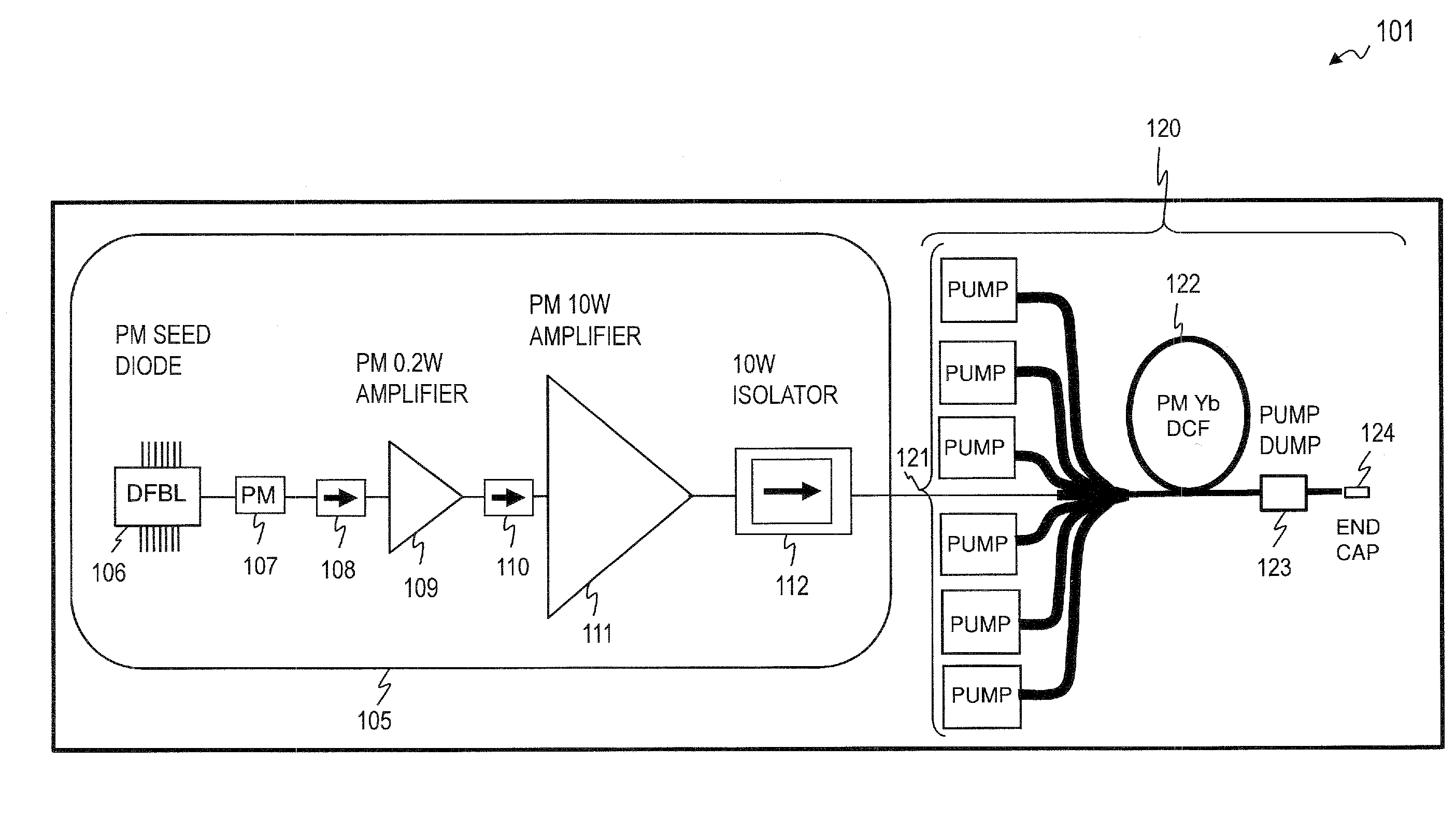
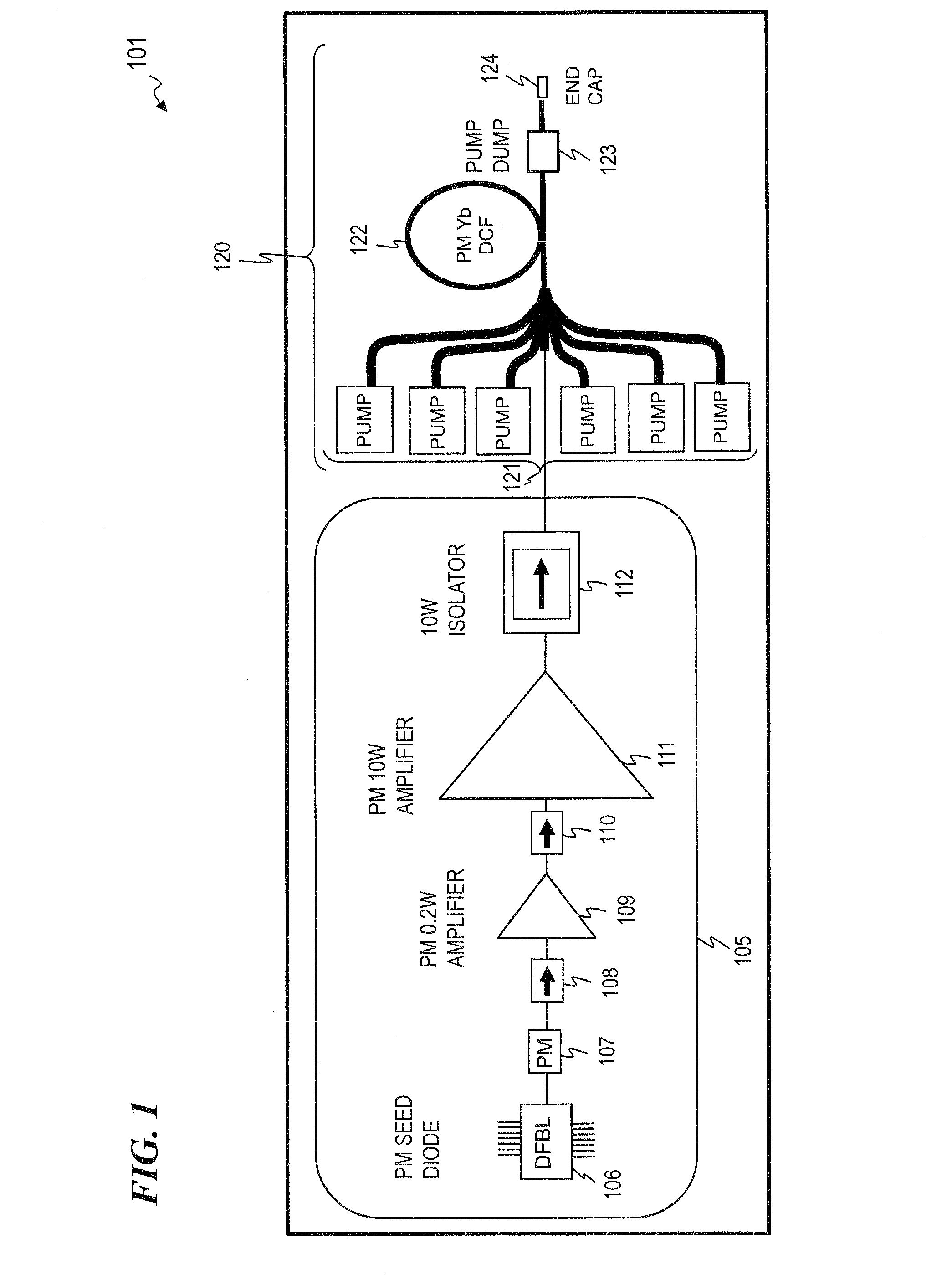
Apparatus and method for suppressing modal instabilities (MI) in fiber-amplifier systems. In some embodiments, thermal effects drive the MI process, and in some such embodiments, the present invention provides a plurality of options for mitigating these thermal effects. In some embodiments, the present invention provides a hybrid fiber with a smaller core in the initial length where the thermal loads are highest, followed by a larger-core fiber. In some embodiments the length of the smaller-core section is chosen to keep the core heat-per-unit-length of the second section below a critical value for the onset of MI. In some embodiments, the hybrid fiber of the present invention avoids modal instabilities while yielding almost the same performance as compared to conventional fibers with regard to minimizing fiber nonlinearities such as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering (SBS). In some embodiments, the hybrid fiber outputs a signal beam with at least 1 kW of power.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
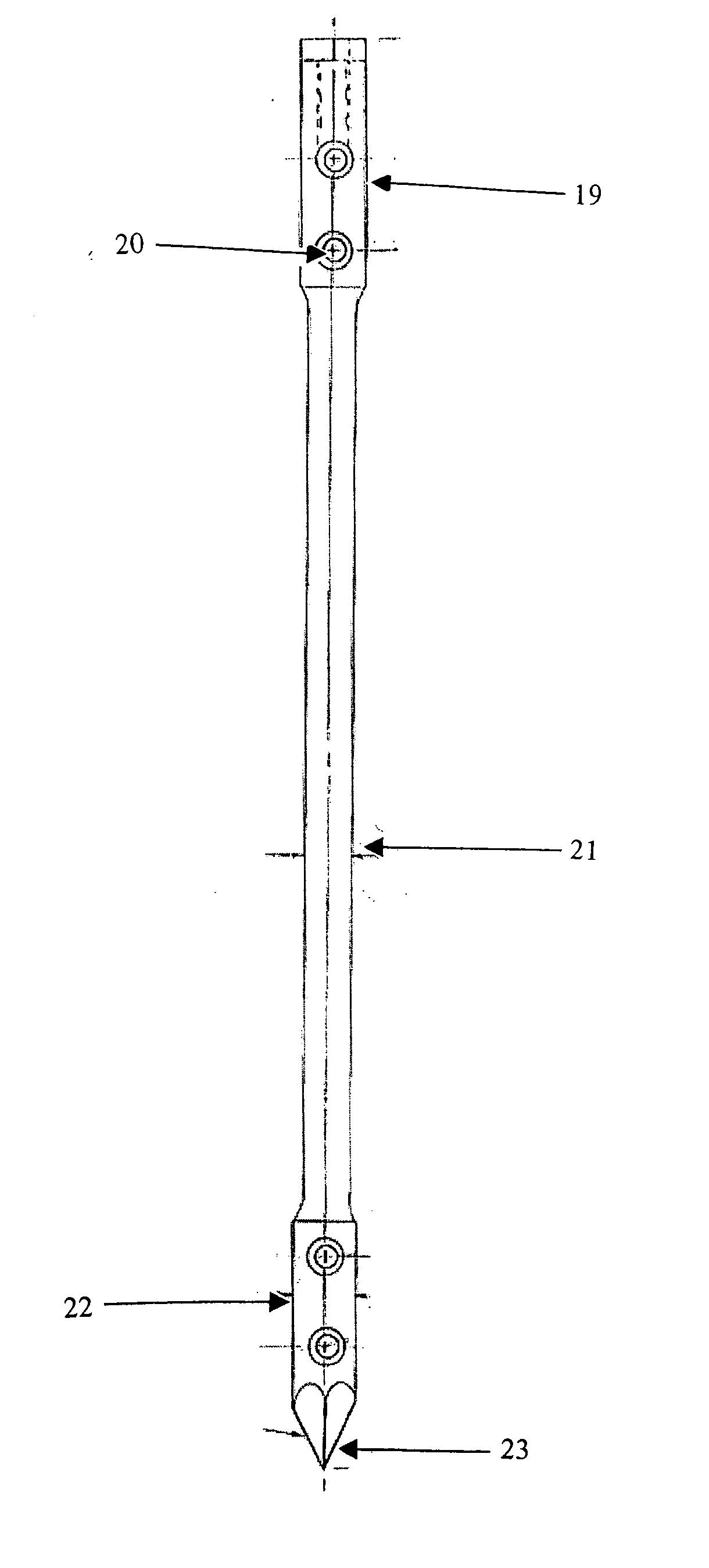
Devices and methods for interlocking surgical screws and nails
ActiveUS20060084997A1Advancing screwSimple methodInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgeryIliac screw
The present invention demonstrates and improved interlocking nail and screw combination to repair fracture bones. The preferred combination uses an hourglass shaped intramedullary nail wherein the larger ends of the nail have holes capable of receiving screws. The holes may, or may not be conical. Further, the holes may or may not be threaded. The surgical screws have a variety of thread patterns, or lack threads. A non-threaded end is believed to improve healing because of a larger core diameter as compared to a comparably sized threaded screw end.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Photonic bandgap fibers
InactiveUS7209619B2Reduce transmission lossSmall sizeAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
Included among the many structures described herein are photonic bandgap fibers designed to provide a desired dispersion spectrum. Additionally, designs for achieving wide transmission bands and lower transmission loss are also discussed. For example, in some fiber designs, smaller dimensions of high index material in the cladding and large core size provide small flat dispersion over a wide spectral range. In other examples, the thickness of the high index ring-shaped region closest to the core has sufficiently large dimensions to provide negative dispersion or zero dispersion at a desired wavelength. Additionally, low index cladding features distributed along concentric rings or circles may be used for achieving wide bandgaps.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
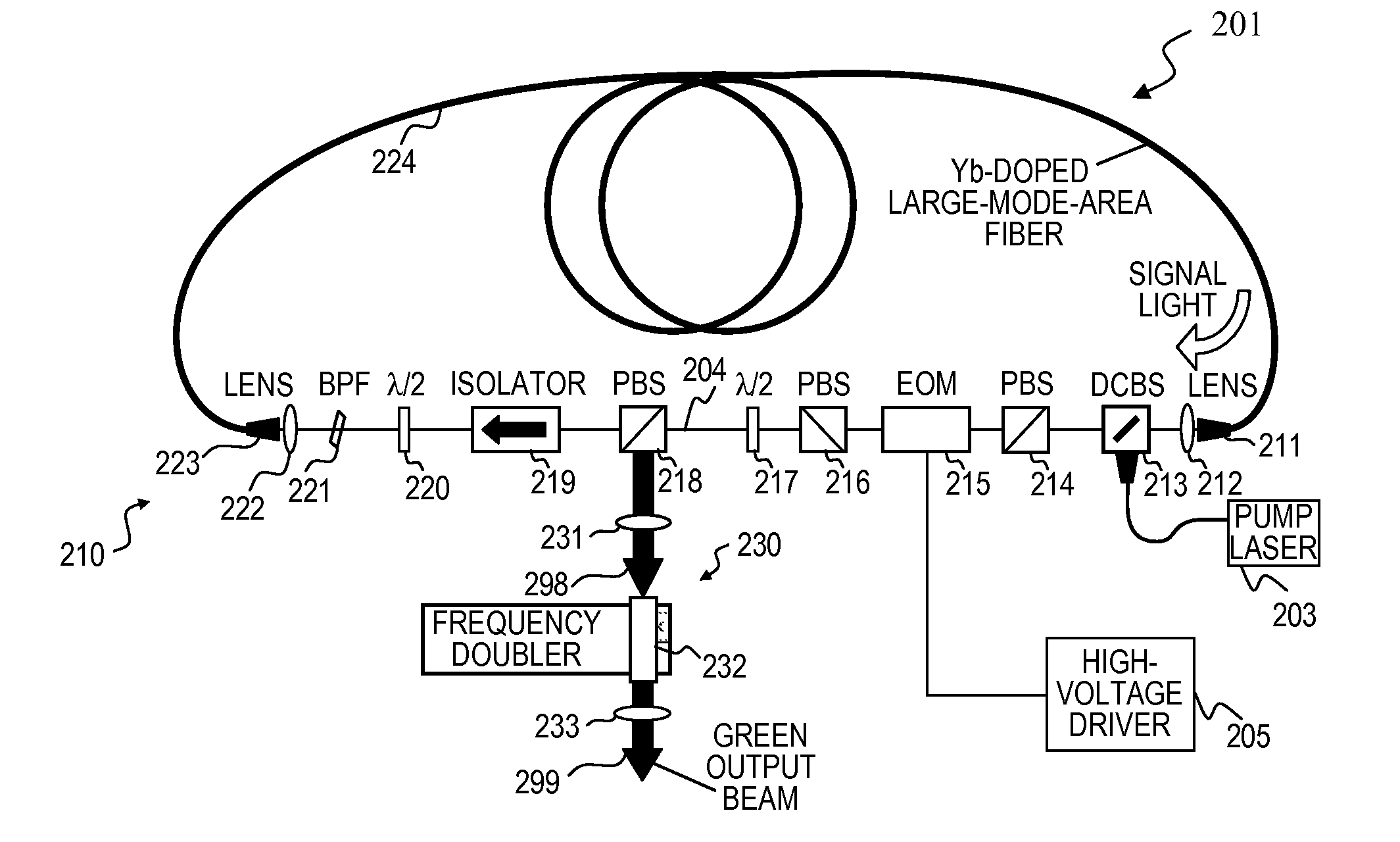
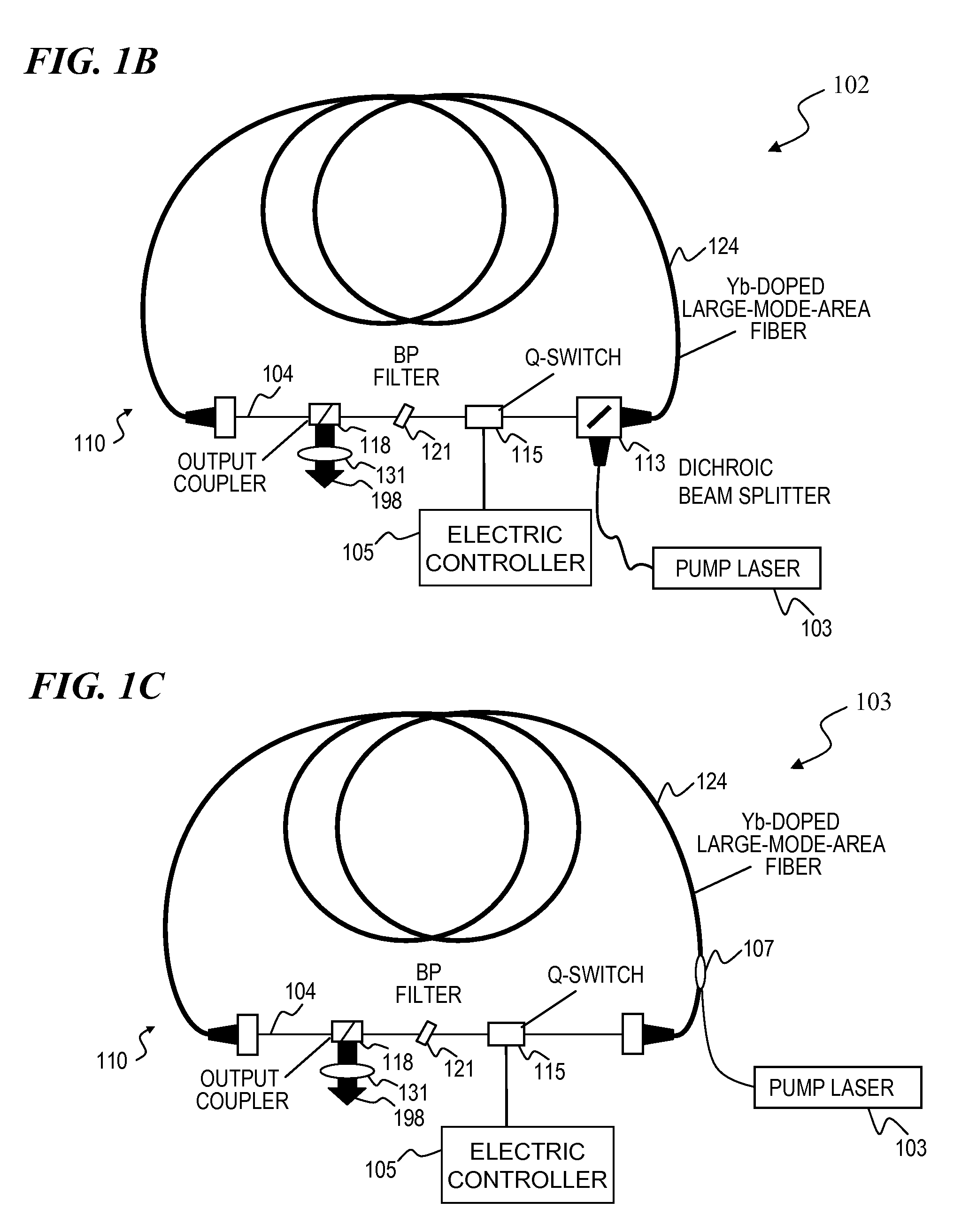
High-power, pulsed ring fiber oscillator and method
InactiveUS7876803B1Low costSmall footprintLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsBand-pass filterUltraviolet
A ring laser includes a large-core rare-earth-doped fiber ring-connected with a free-space path having an electro-optic switch, output coupler, and intracavity band-pass filter to enforce lasing operation in narrow wavelength range. In some cavity-dumped modes, the laser is configured in a similar manner, except that an output coupler is omitted since the optical power is extracted from the laser cavity by the electro-optic switch itself. The same laser can be configured to operate in Q-switched and / or cavity-dumping modes as well as in hybrid modes (e.g., partial Q-switch, followed by cavity dumping, or even CW). In some embodiments, the laser can be used as, or inject laser light into, a regenerative solid-state amplifier, or a Raman laser, or can be also used to generate visible, ultra-violet, mid-infrared, and far-infrared (THz) radiation via nonlinear wavelength conversion processes. The various embodiments can use a power oscillator or seed-plus-amplifier MOPA configuration.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
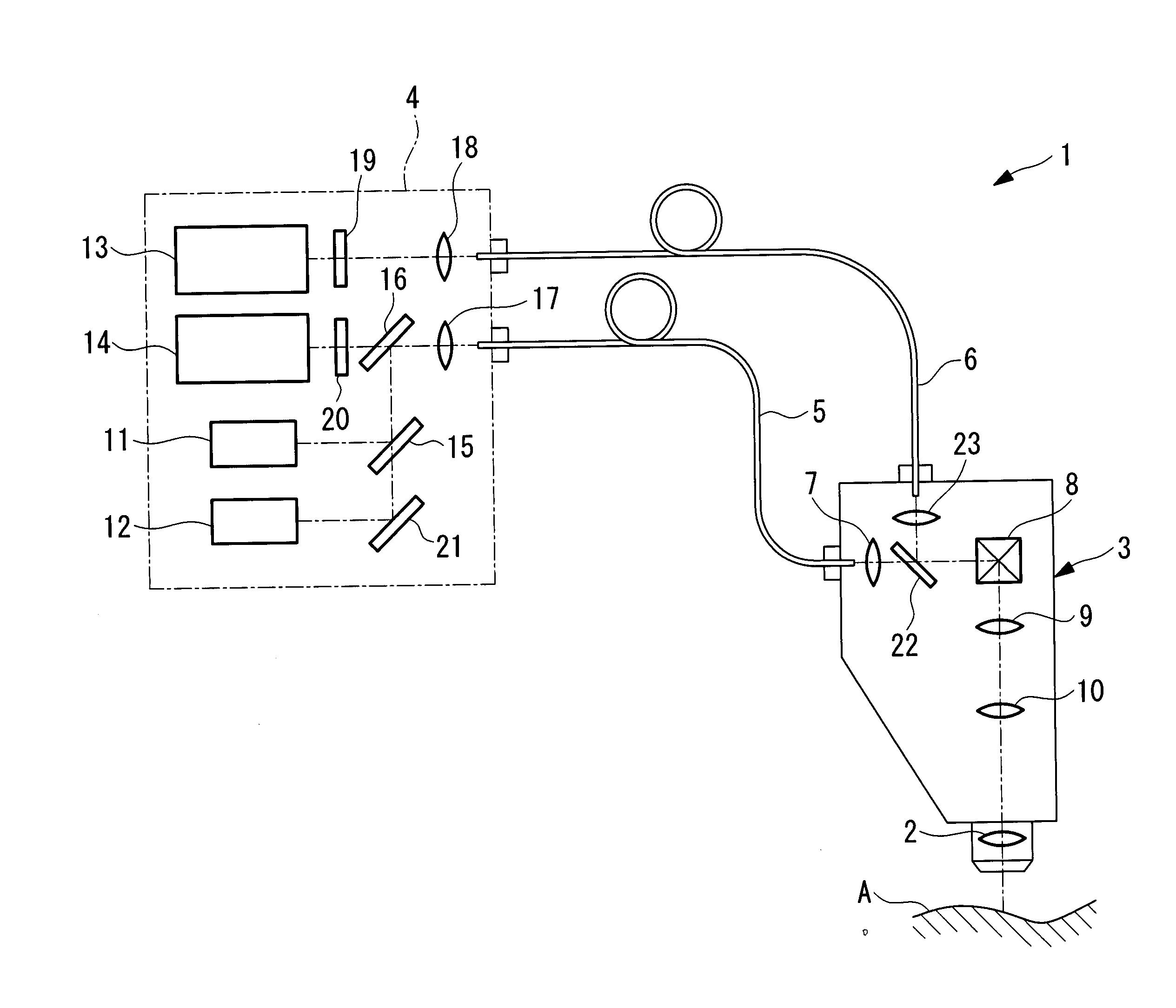
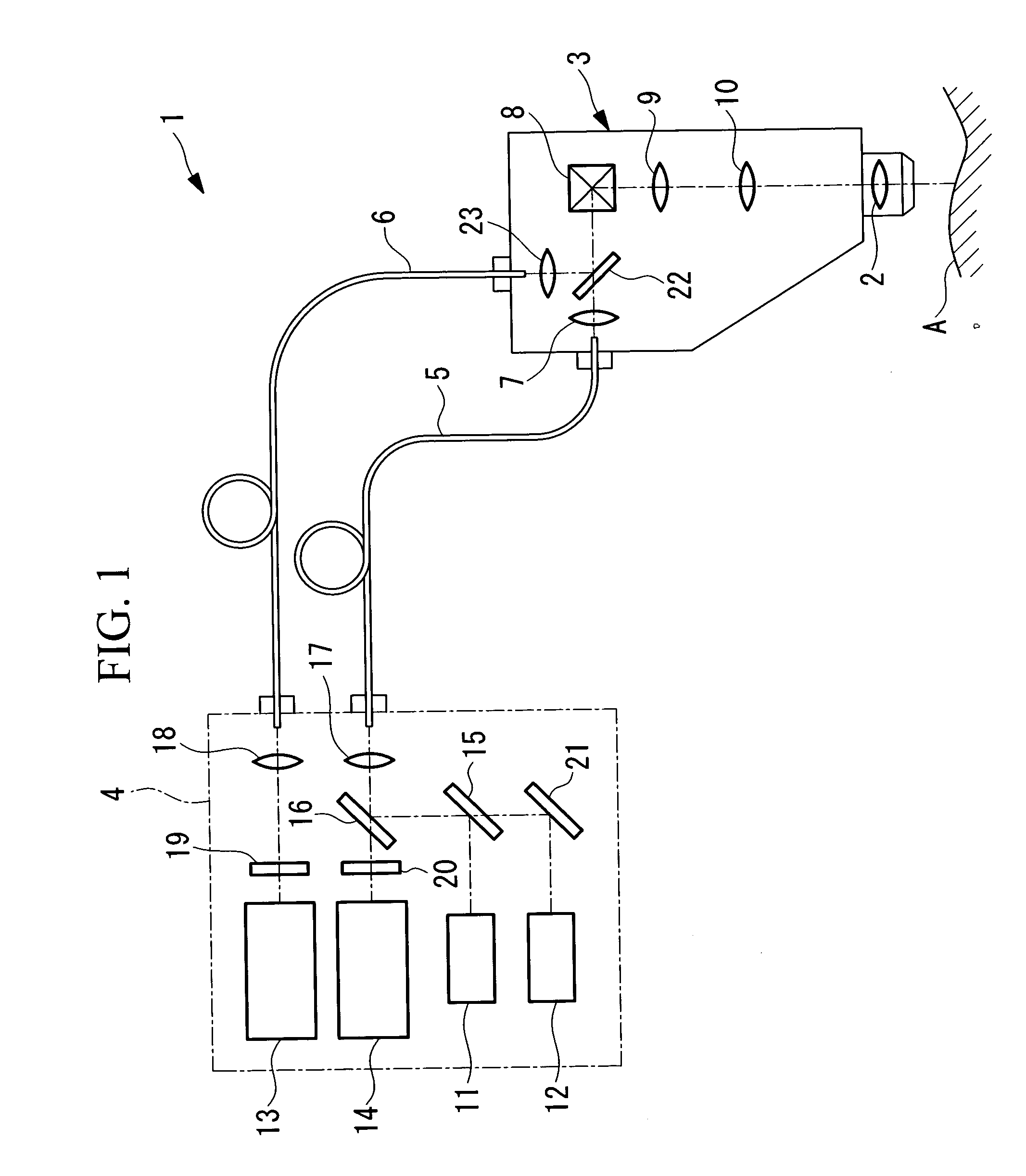
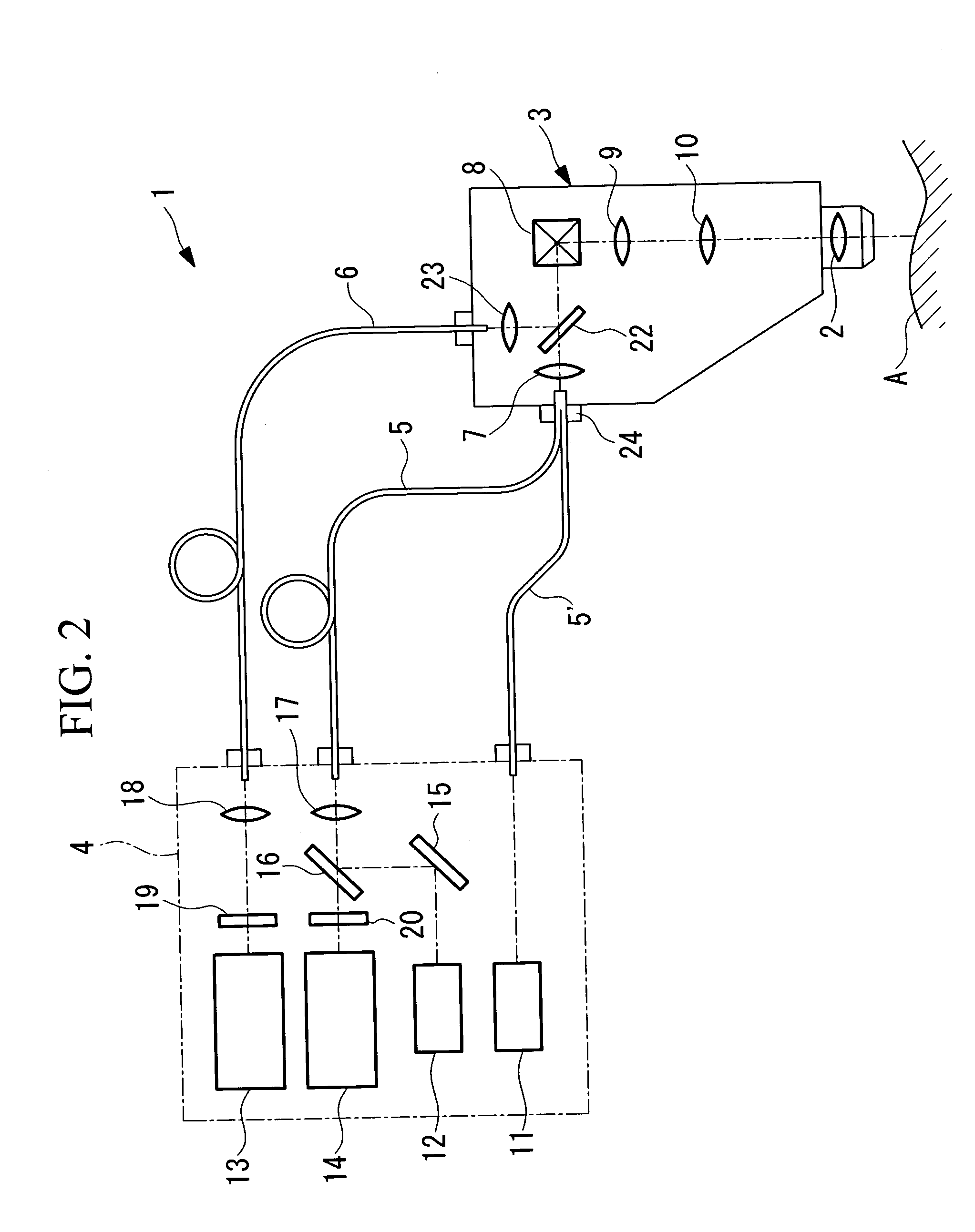
Laser-scanning examination apparatus
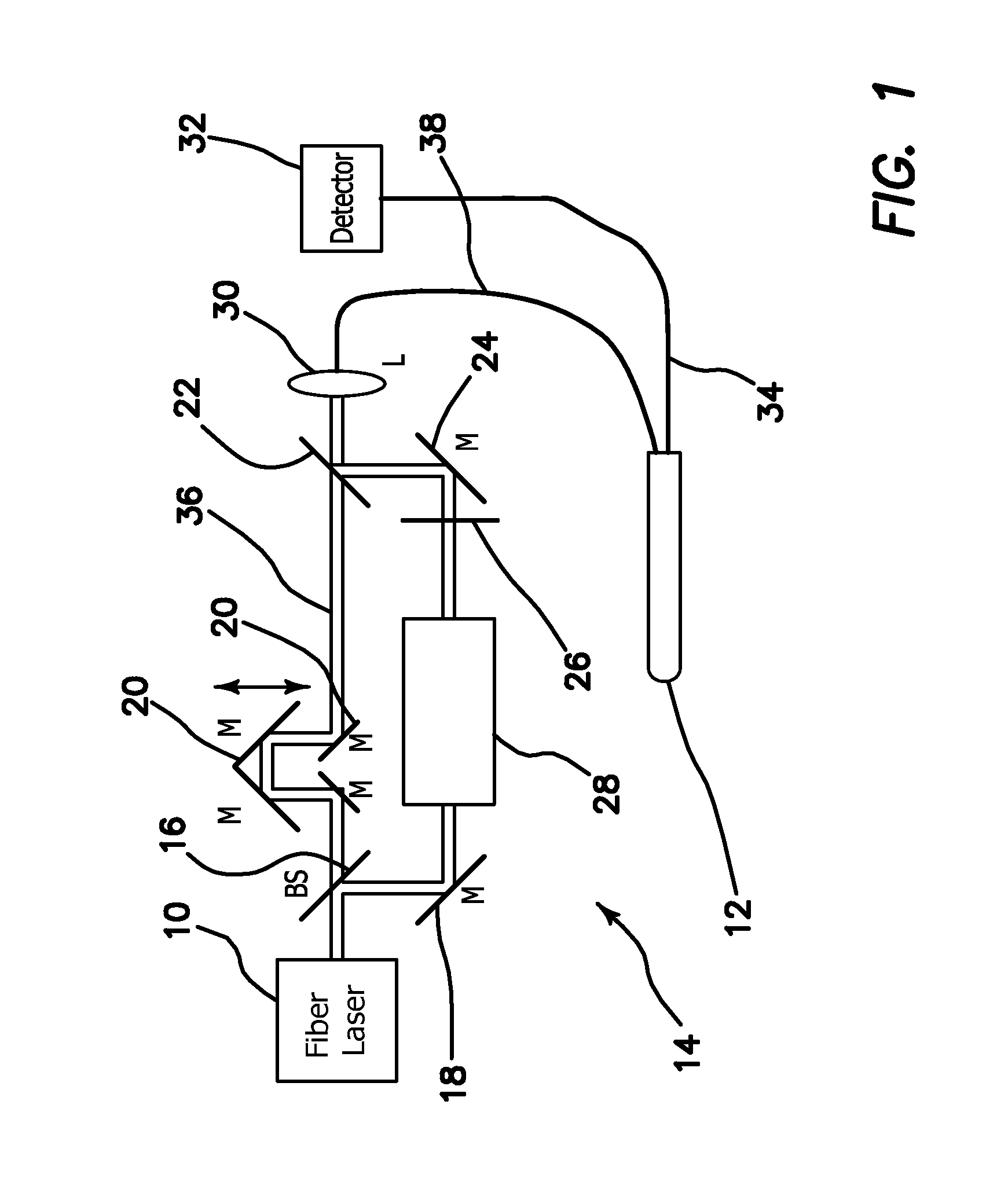
InactiveUS20060017920A1Reduce lossesCompact configurationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLaser scanningLaser light
The invention reduces the loss of fluorescence intensity obtained from a specimen to acquire clear fluorescence images when irradiating the specimen with ultrashort-pulse laser light produced by a laser light source. The invention provides a laser-scanning examination apparatus including a laser light source for producing ultrashort-pulse laser light; a laser light source for producing continuous-wave laser light; a measurement head including an optical scanning unit for scanning the laser light on a specimen and an objective optical system; an imaging unit for detecting return light from the specimen in response to the ultrashort-pulse laser light; and an imaging unit for detecting return light from the specimen in response to the continuous-wave laser light. The laser light sources and one imaging unit are connected to the measurement head by an optical fiber, and the other imaging unit is connected to the measurement head by another optical fiber with a larger core diameter.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Transmission of laser pulses with high output beam quality using step-index fibers having large cladding
InactiveUS20120051084A1Reduce couplingTighter focusingCosmonautic condition simulationsMechanical apparatusForming gasSilicon dioxide
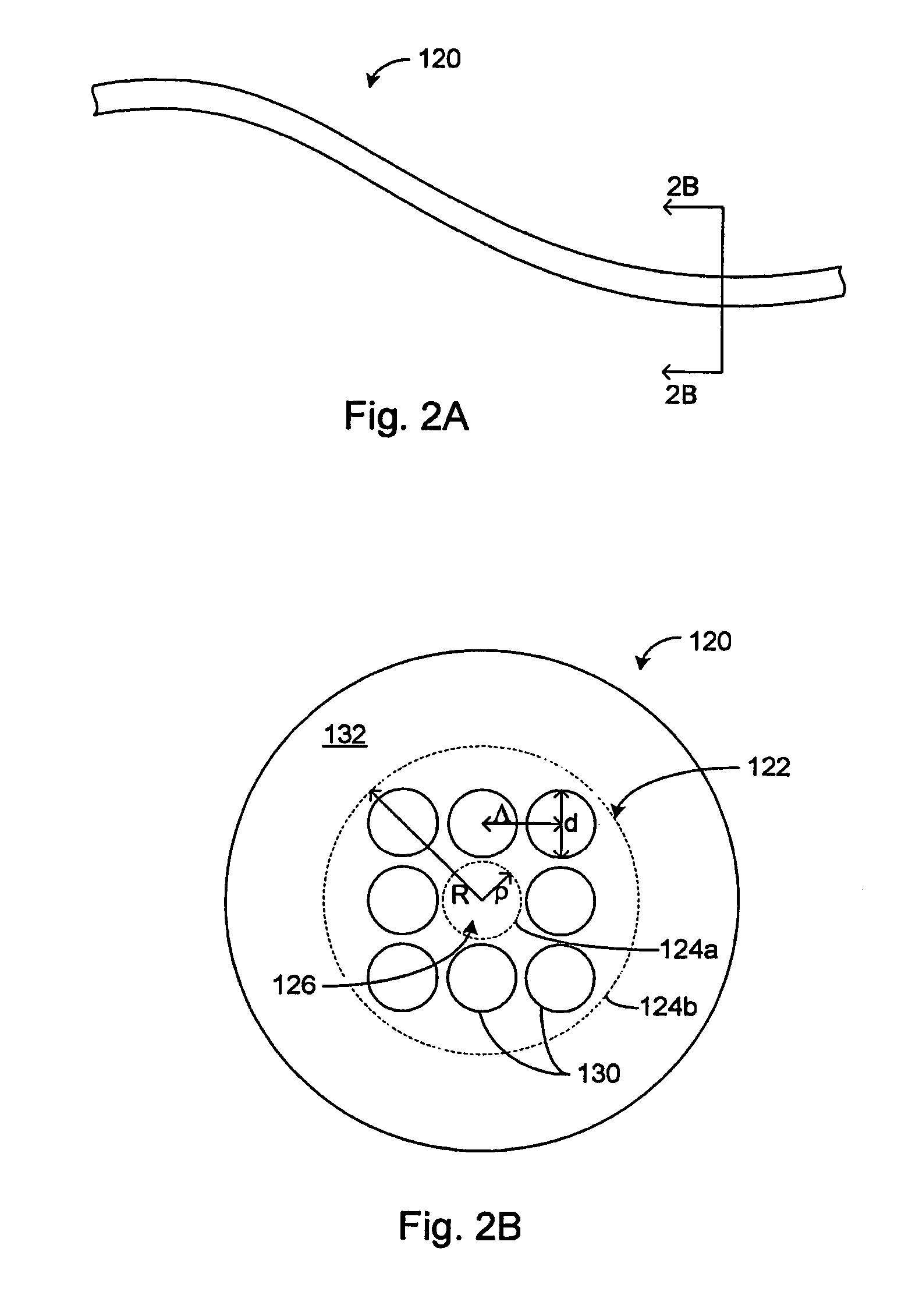
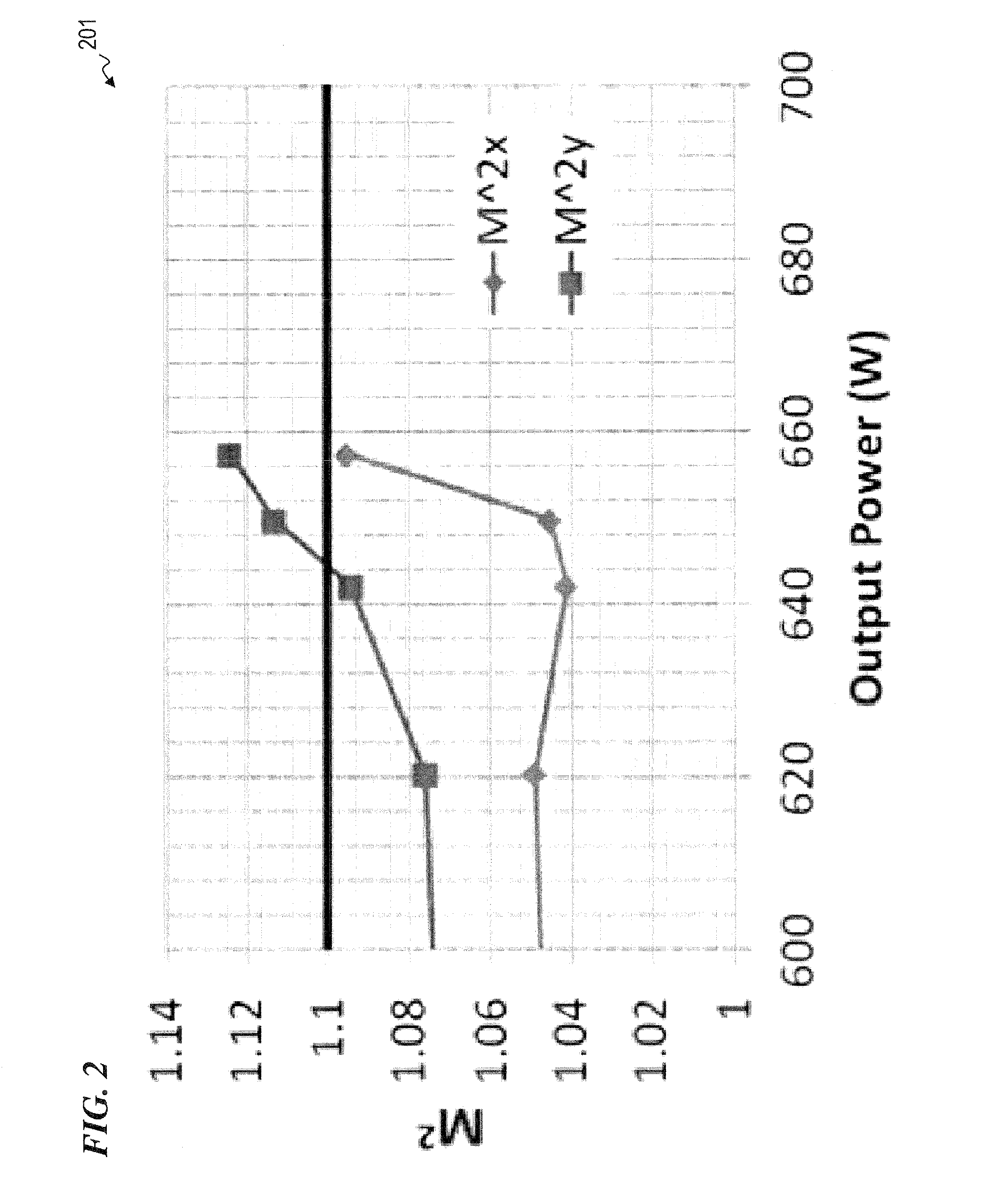
An apparatus and method for transmission of laser pulses with high output beam quality using large core step-index silica optical fibers having thick cladding, are described. The thick cladding suppresses diffusion of modal power to higher order modes at the core-cladding interface, thereby enabling higher beam quality, M2, than are observed for large core, thin cladding optical fibers. For a given NA and core size, the thicker the cladding, the better the output beam quality. Mode coupling coefficients, D, has been found to scale approximately as the inverse square of the cladding dimension and the inverse square root of the wavelength. Output from a 2 m long silica optical fiber having a 100 μm core and a 660 μm cladding was found to be close to single mode, with an M2=1.6. Another thick cladding fiber (400 μm core and 720 μm clad) was used to transmit 1064 nm pulses of nanosecond duration with high beam quality to form gas sparks at the focused output (focused intensity of >100 GW / cm2), wherein the energy in the core was <6 mJ, and the duration of the laser pulses was about 6 ns. Extending the pulse duration provided the ability to increase the delivered pulse energy (>20 mJ delivered for 50 ns pulses) without damaging the silica fiber.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
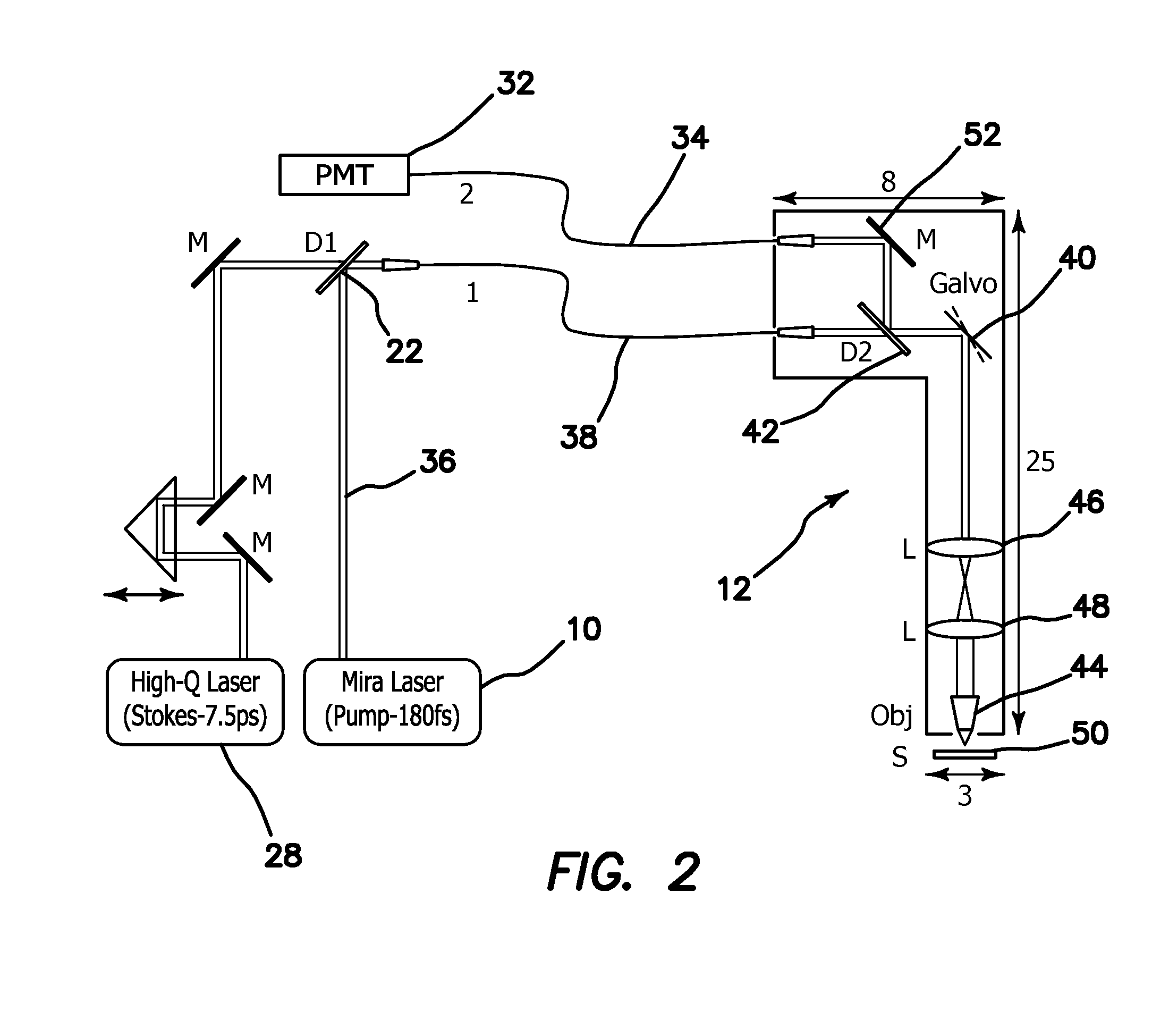
System and Method for Efficient Coherence Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Endoscopic and Intravascular Imaging and Multimodal Imaging
ActiveUS20110282166A1Complicate interpretationEliminate the problemRadiation pyrometryEndoscopesFiberStokes component
A fiber-delivered probe suitable for CARS imaging of thick tissues is practical. The disclosed design is based on two advances. First, a major problem in CARS probe design is the presence of a very strong anti-Stokes component in silica delivery fibers generated through a FWM process. Without proper spectral filtering, this component affects the CARS image from the tissue sample. The illustrated embodiments of the invention efficiently suppress this spurious anti-Stokes component through the use of a separate fiber for excitation delivery and for signal detection, which allows the incorporation of dichroic optics for anti-Stokes rejection. Second, the detection of backscattered CARS radiation from the sample is optimized by using a large core multi mode fiber in the detection channel. This scheme produces high quality CARS images free of detector aperture effects. Miniaturization of this fiber-delivered probe results in a practical handheld probe for clinical CARS imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Single mode optical fibre having a large cone photonic crystal
InactiveUS6603912B2High refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexFiber disk laser
A large core photonic crystal fiber for transmitting radiation having a core comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core diameter of at least 5mu. The fiber also comprises a cladding region surrounding the length of core material, wherein the cladding region comprises a first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, and wherein the first substantially transparent cladding material has embedded along its length a substantially periodic array of holes, wherein the holes are filled with a second cladding material having a second refractive index less than the first refractive index, such that radiation input to the optical fiber is transmitted along the length of the core material in a single mode of propagation. In a preferred embodiment, the core diameter may be at least 20mu, and may be as large as 50mu. The fiber is capable of transmitting higher power radiation than conventional fibers, whilst maintaining propagation in a single mode. The core material may be doped with a material capable of providing amplification under the action of pump radiation input to the fiber. The invention also relates to a fiber amplifier and a fiber laser comprising a doped large core photonic crystal fiber. The fibre may also be used in a system for transmitting radiation comprising a plurality of lengths of large core photonic crystal fiber, separated by large core photonic crystal fiber amplifiers, such that the power of radiation transmitted through the system is maintained above a predetermined threshold power.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
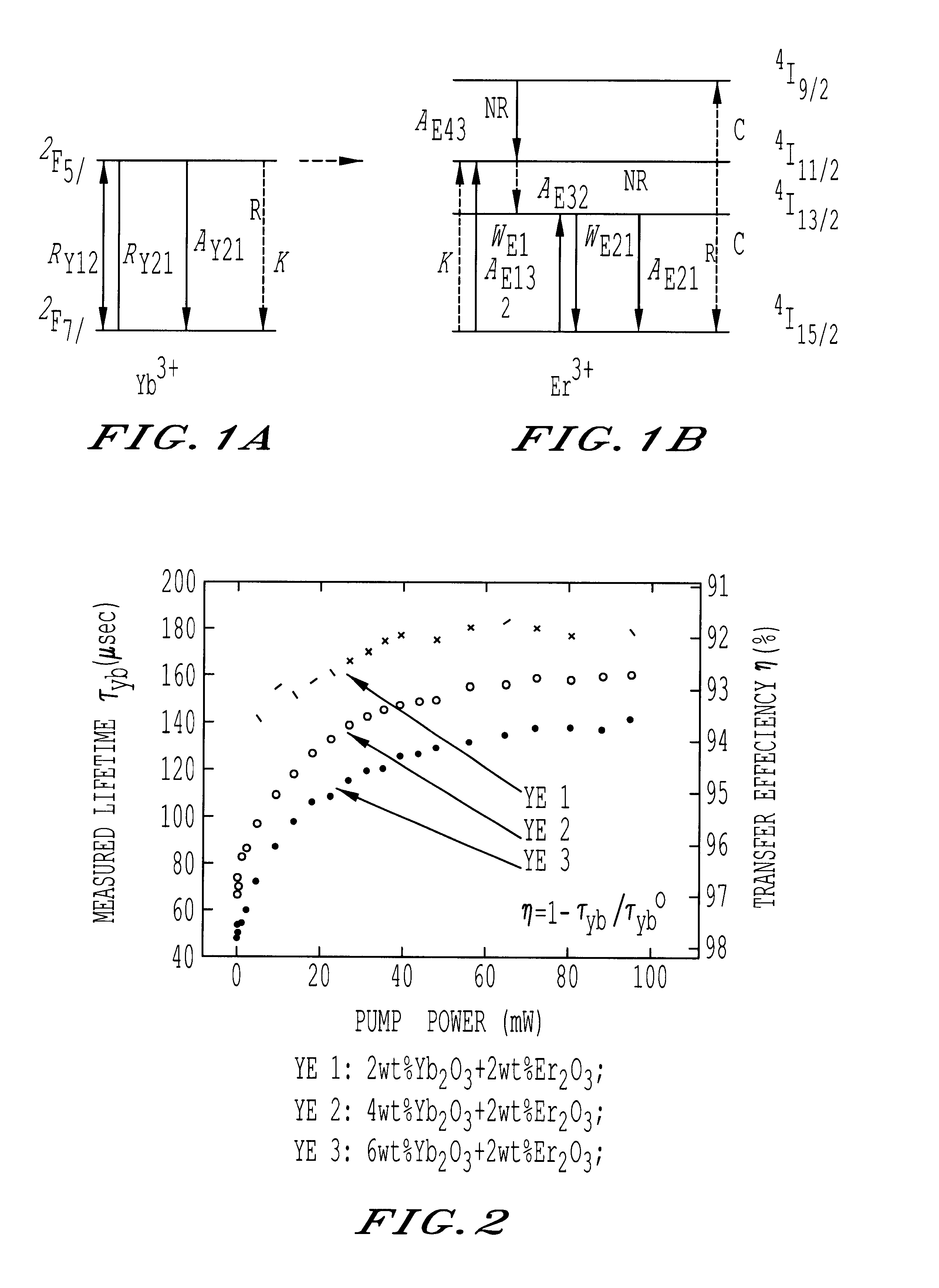
Erbium and ytterbium co-doped phosphate glass optical fiber amplifiers using short active fiber length
InactiveUS6611372B1High gain per unit lengthHigh gain amplificationLaser arrangementsActive medium materialErbium dopingPhosphate glass
An optical fiber amplifier utilizing a phosphate glass optical fiber highly doped with rare-earth ions such as erbium to exhibit high gain per unit length, enabling the use of short fiber strands to achieve the needed gain in practical fiber optical communication networks. The high-gain phosphate optical glass fiber amplifiers are integrated onto substrates to form an integrated optics amplifier module. An optical pump such as a semiconductor laser of suitable wavelength is used to promote gain inversion of erbium ions and ultimately provide power amplification of a given input signal. Gain inversion is enhanced in the erbium doped phosphate glass fiber by co-doping with ytterbium. A phosphate fiber amplifier or an integrated optics amplifier module utilizing this power amplification can be combined with other components such as splitters, combiners, modulators, or arrayed waveguide gratings to form lossless or amplified components that do not suffer from insertion loss when added to an optical network. The fiber amplifier can be a single fiber or an array of fibers. Further, the phosphate glass fibers can be designed with a temperature coefficient of refractive index close to zero enabling proper mode performance as ambient temperatures or induced heating changes the temperature of the phosphate glass fiber. Large core 50-100 .mu.m fibers can be used for fiber amplifiers. The phosphate glass composition includes erbium concentrations of at least 1.5 weight percentage, preferably further including ytterbium at 1.5 weight percentage, or greater.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
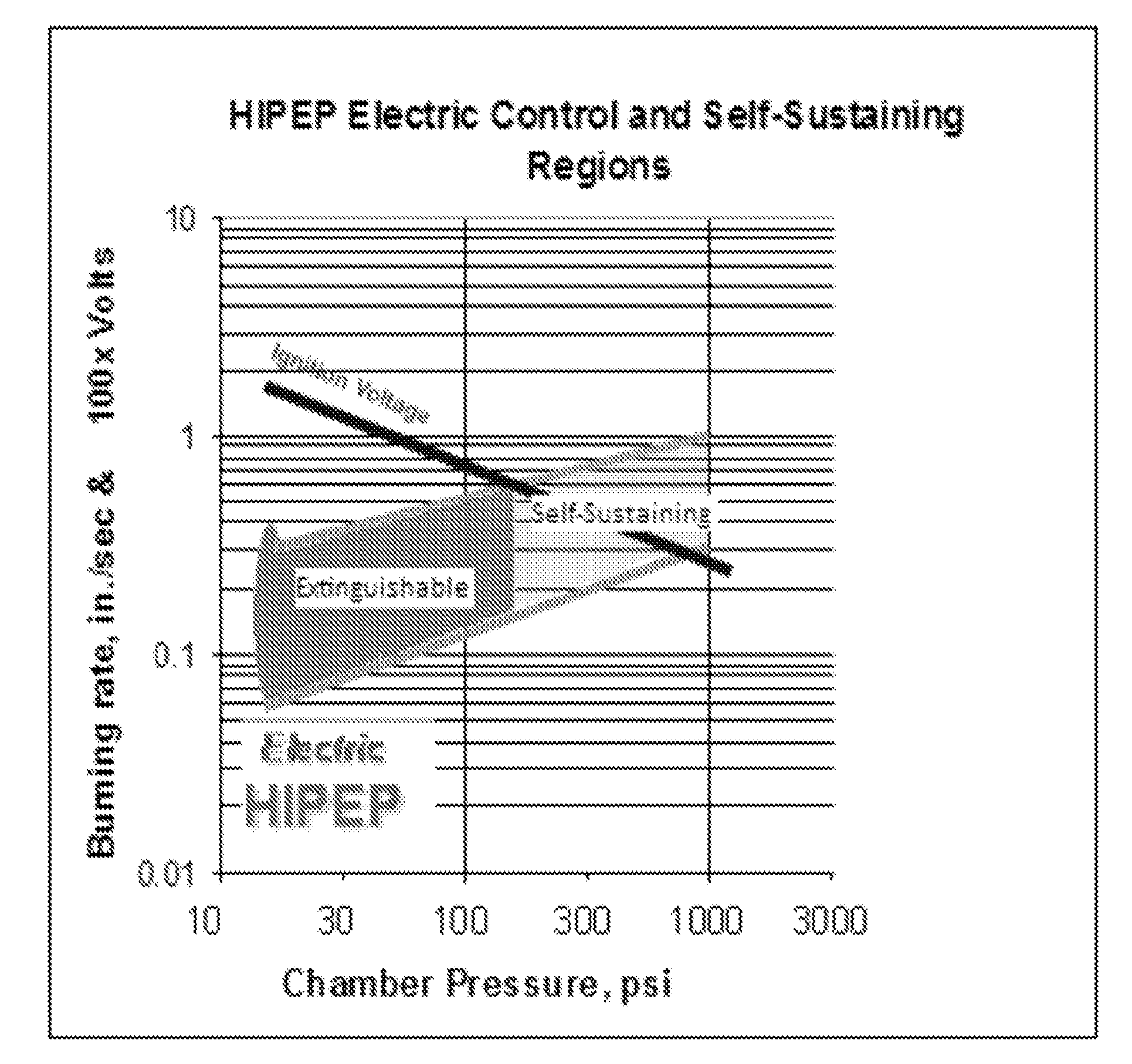
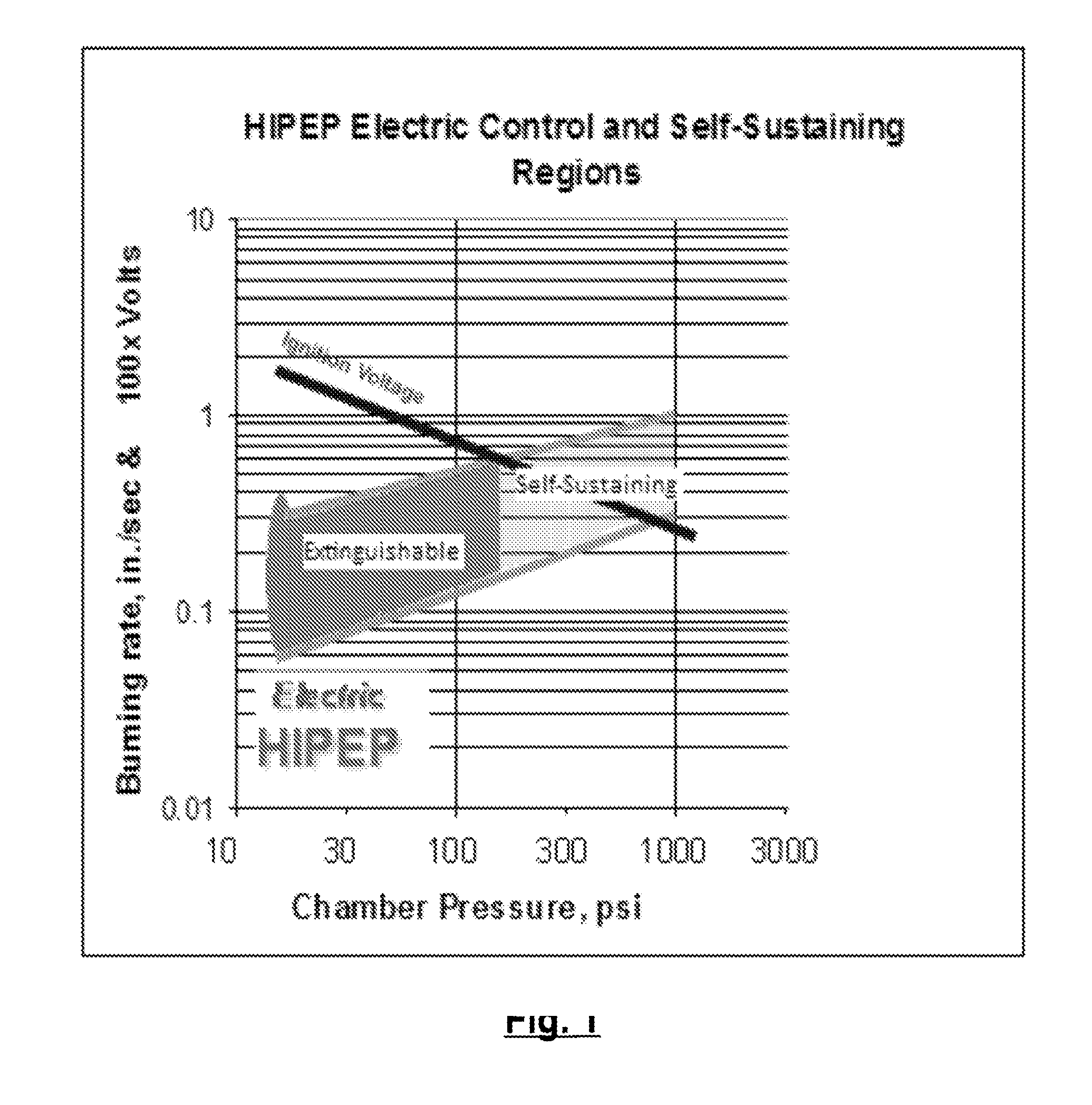
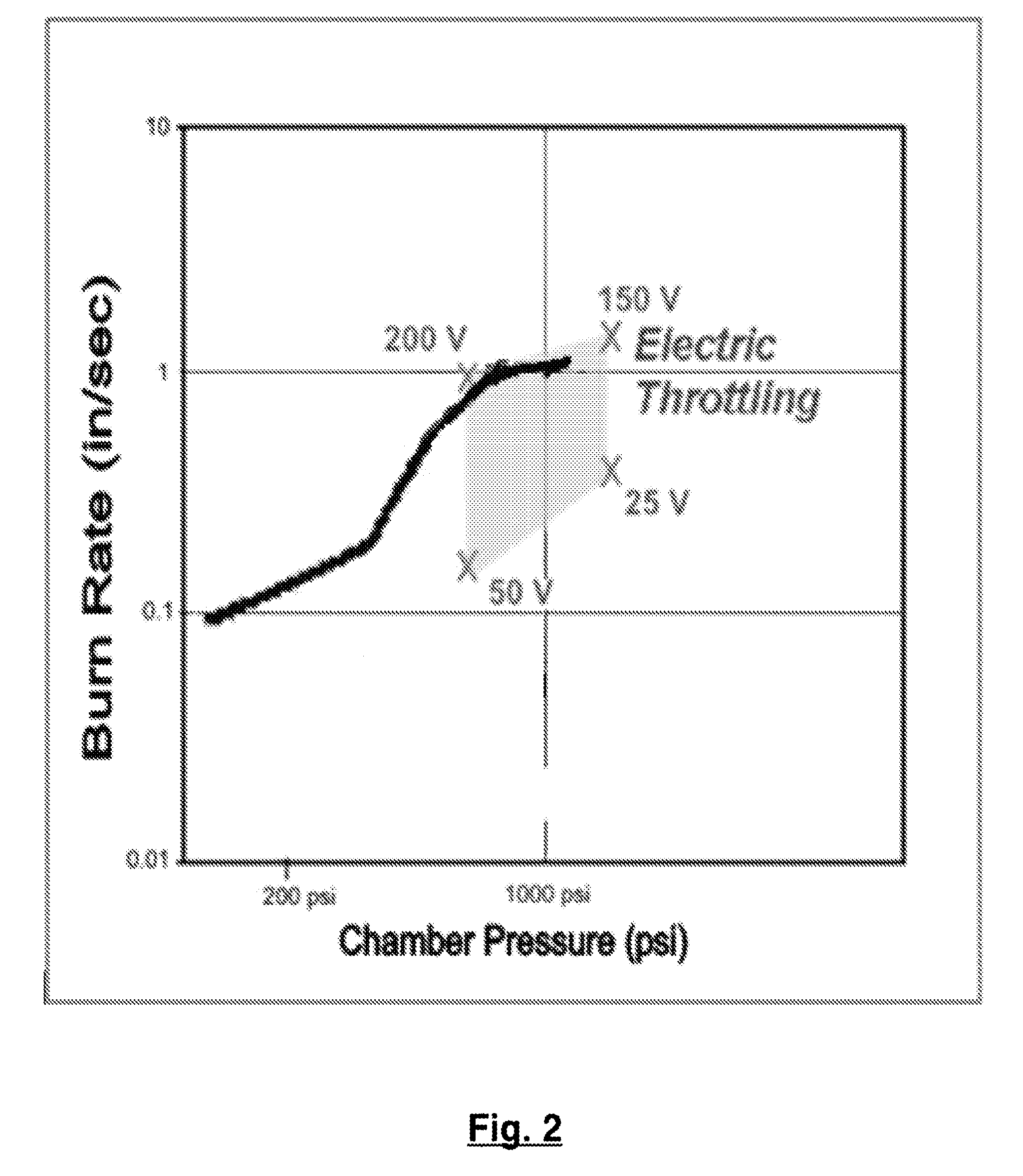
Family of Modifiable High Performance Electrically Controlled Propellants and Explosives
ActiveUS20110067789A1Improve simplicityLow costNon-explosive stabilisersNon-explosive fillers/gelling/thickening agentsElectricityAmbient pressure
A composition capable of producing either solid propellant grains, liquid or gel monopropellants, all of which are electrically ignitable and capable of sustained controllable combustion at ambient pressure. Additional compositions capable of sustained controllable combustion at elevated pressures are described. Applications for the compositions disclosed herein are provided, and include among other applications use in small micro thrusters, large core-burning solid propellant gains, shaped explosives charges for military application, and pumpable liquids and gel monopropellants or explosives for military, commercial mining or gas and oil recovery. In alternative embodiments the above compositions may also incorporate an energetic nitrate polymer, bum rate modifiers, and / or metal fuel(s). The HIPEP formulation makes it possible to ignite and sustain combustion at ambient and vacuum conditions (a) without continuous electrical power and (b) while providing faster bum rates.
Owner:DIGITAL SOLID STATE PROPULSION
Optical tweezers type optical fiber Raman microprobe and manufacturing method
The invention provides an optical tweezers type optical fiber Raman microprobe and a manufacturing method. The probe has two optical channels which are coaxial, wherein an annular optical fiber core provides a Raman exciting light channel and a channel in the coaxial center is used for receiving Raman probe light; and by performing fine taper angle grinding on the fiber ends of coaxial dual waveguide channel optical fibers, a rotary symmetrical plane (or chambered surface) structure is formed. The structure can converge Raman exciting light transmitted by the annular core in a micron order, and on the one hand, the converged exciting light has an ability of capturing micron-order and nanoscale particles and on the other hand, the converged exciting light interacts with the particles, so that a back scattering Raman optical signal generated by the exciting light converged by the Raman scattering light can be collected and transmitted to a Raman spectrometer through an intermediate large-core fire cores. The microprobe provided by the invention can capture micro living matters of cell living bodies to effectively excite the Raman spectrum of the matters in cells and to obtain the Raman spectrum so as to achieve Raman measurement of micro liquids, single cells in living bodies and inner substances thereof.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Modular, cleanable tactile switch mechanism for use in electronic pipes and other "heirloom" electromechanical applications
InactiveUS20160020048A1Ease manual pivotingReduce manufacturing costPermanent magnet reed switchesSnap-action arrangementsLocking mechanismModularity
A modular, cleanable, tactile switch mechanism is developed for use in an electronic pipe style personal vaporizer. The mechanism includes magnets and a pivoting arm of magnetically active material along with a customizable base that supports and guides these interacting parts. In the electronic pipe implementation of this mechanism, guiding niches of the base are integrated with a larger core support structure, demonstrating its versatility and ability to reduce overall enclosure footprint under some circumstances. Additionally, the pipe system features a locking mechanism which allows easy disassembly and repair of hand carved or otherwise fragile devices without risk of damage.The present invention relates primarily to the field of magnetic or mechanical switches, particularly those capable of providing tactile feedback in a compact, durable configuration. Additionally, the invention relates to miscellaneous spring devices as well as tobacco substitute products and components thereof.
Owner:WARE KENNETH LATHAM
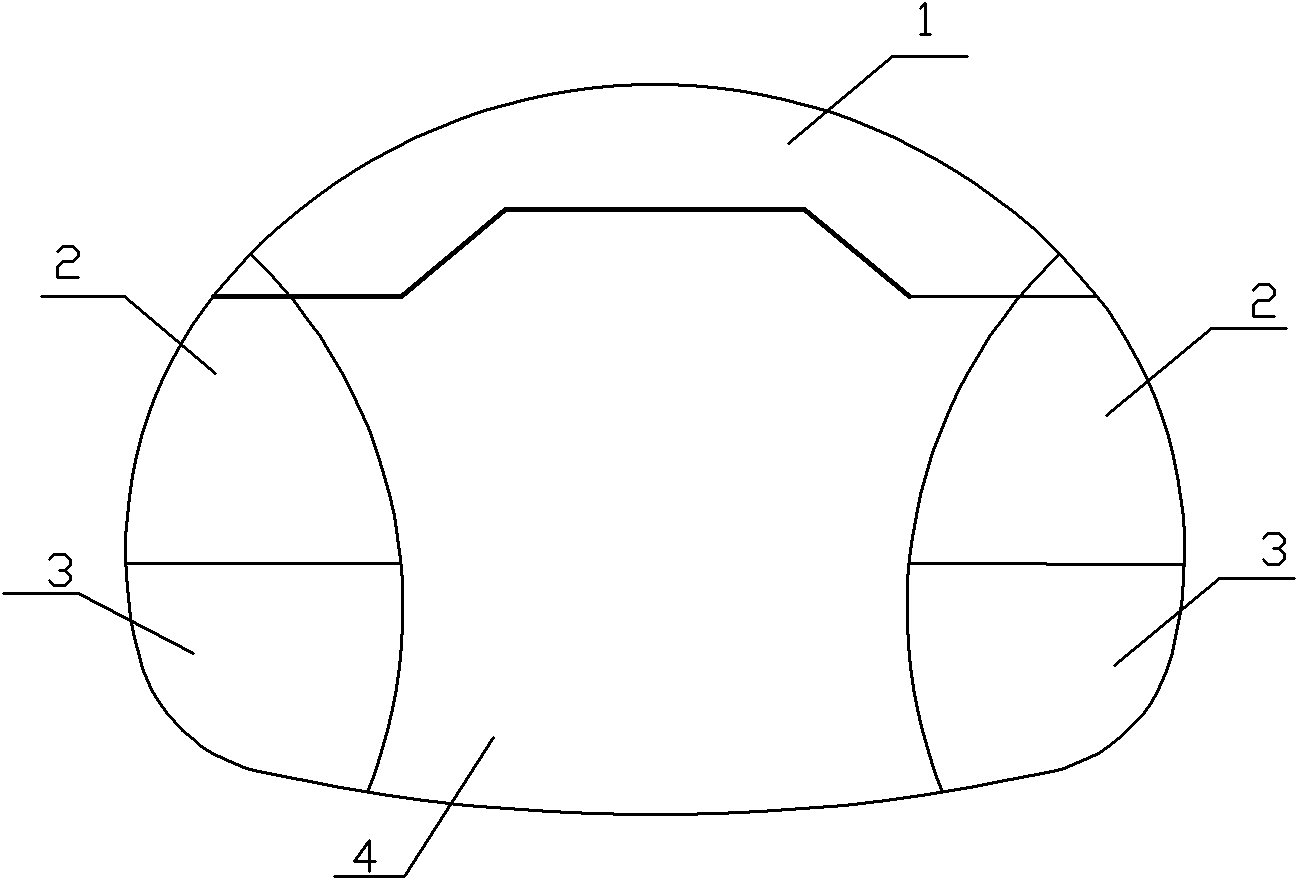
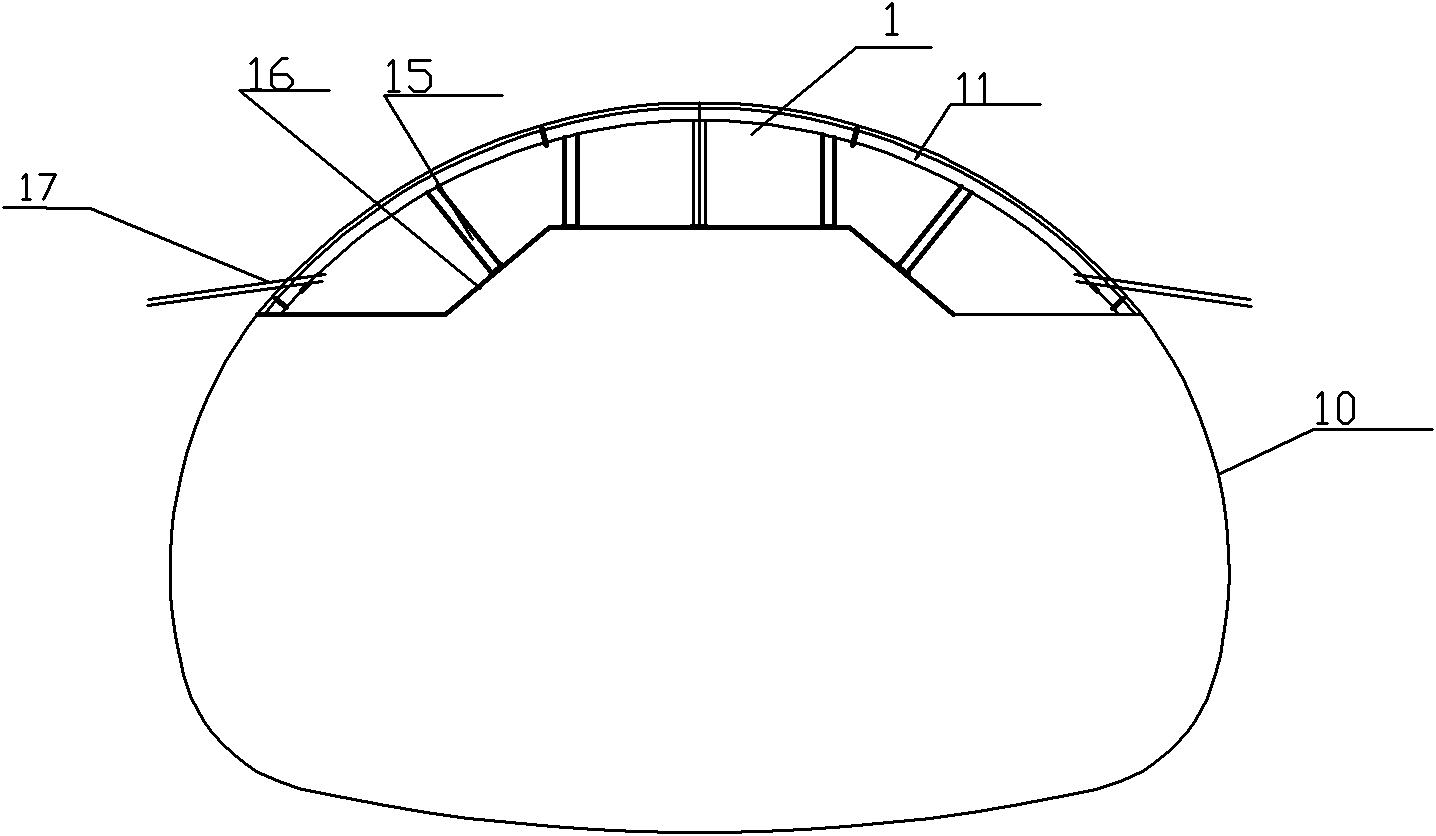
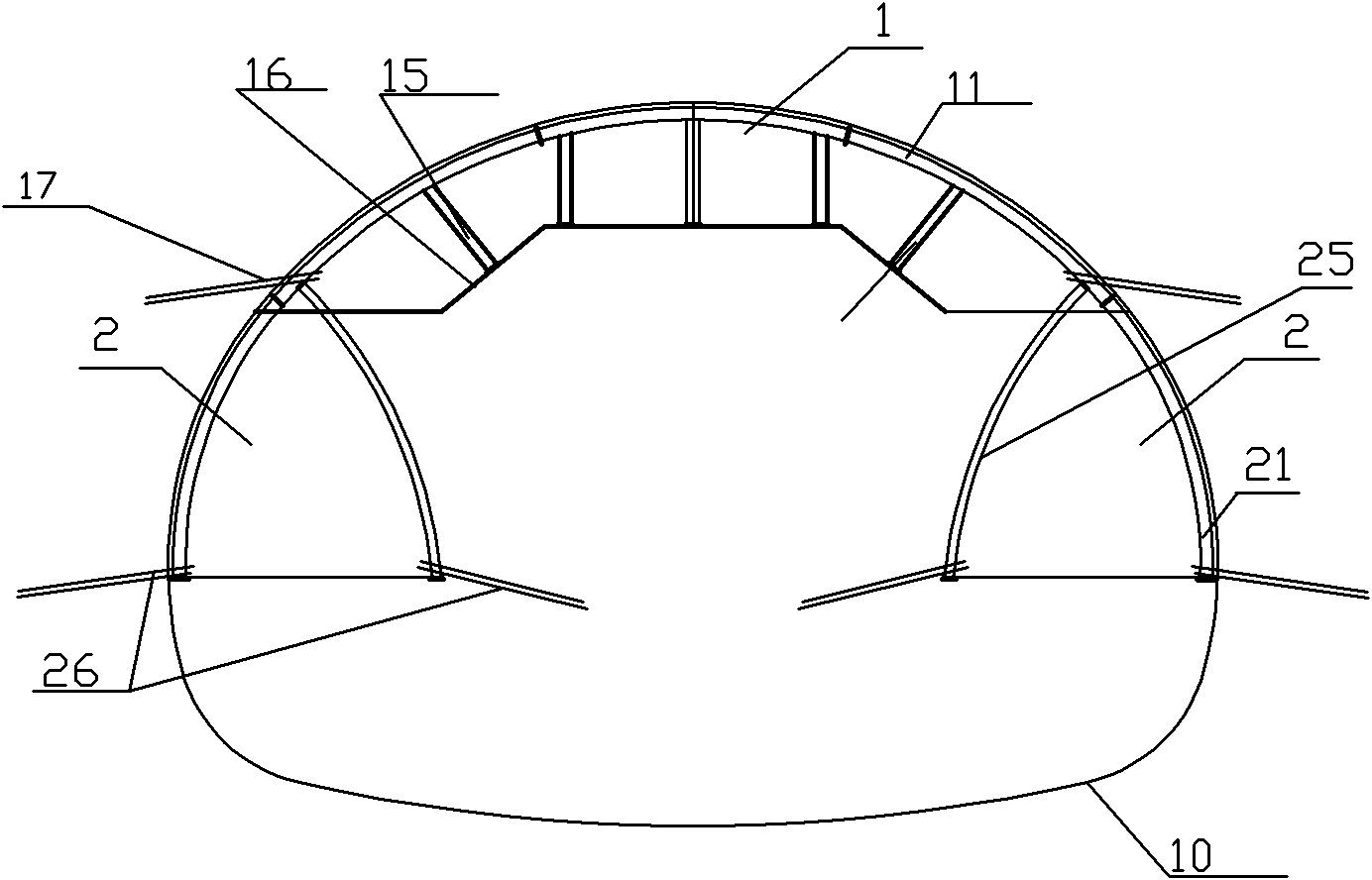
Construction method for soft surrounding rock section of large-span tunnel portal
ActiveCN102071947AAvoid advanced sideAvoid progressUnderground chambersTunnel liningSteel frameLarge core
The invention discloses a construction method for a soft surrounding rock section of a large-span tunnel portal. The construction method comprises the following steps of: excavating an arc-shaped pilot tunnel on the top of a tunnel section; performing initial support in time after the excavation process is finished and performing temporary support at the same time; excavating upper pilot tunnels on the left side wall and the right side wall at the same time; performing initial support in time after the excavation process is finished and performing temporary support on the core soil side wallsat the same time; excavating lower pilot tunnels on the left side wall and the right side wall at the same time, wherein the depth of circulation drilling for each time is 0.5 m; performing initial support in time after the excavation process is finished and performing temporary support on the lower parts of the core soil side walls at the same time; performing large core soil excavation; reserving core soil steps; installing inverted arch steel frames and injecting C25 concrete in time, so that the initial support of the whole tunnel forms a closed ring as soon as possible; and dismantling the temporary support. By the top arc side wall pilot tunnel construction method, vault subsidence can be favorably controlled; and the method is applicable to tunneling excavation construction for strongly differentiating a surrounding rock portal when the tunnel portal is under the protection of a large pipe roof section.
Owner:THE FIRST ENG OF CCCC FOURTH HARBOR ENG
Rare earth doped and large effective area optical fibers for fiber lasers and amplifiers
InactiveUS7450813B2Reduce formationIncrease in sizeGlass making apparatusLaser detailsAudio power amplifierRare earth
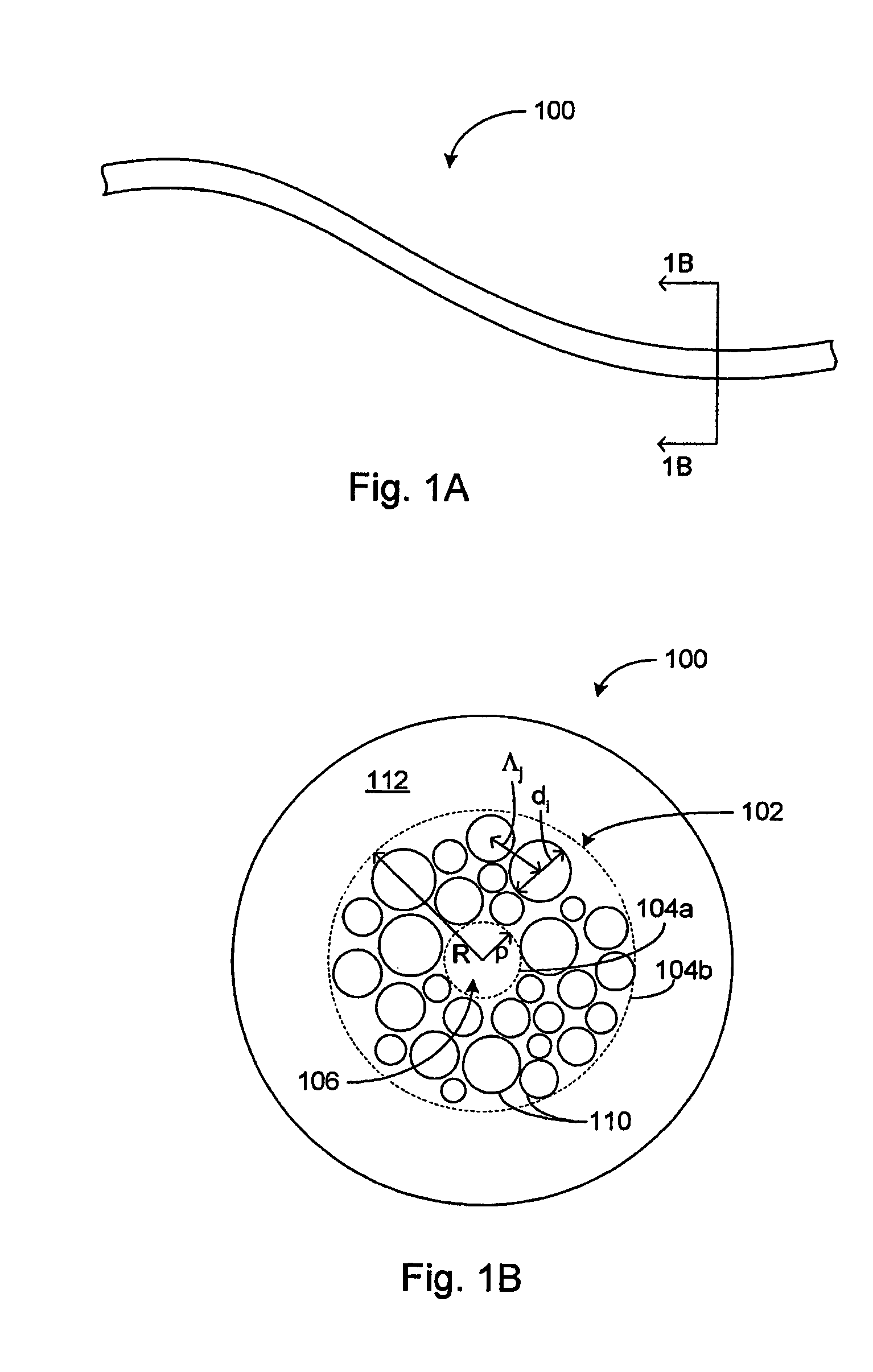
Various embodiments described herein include rare earth doped glass compositions that may be used in optical fiber and rods having large core sizes. Such optical fibers and rods may be employed in fiber lasers and amplifiers. The index of refraction of the glass may be substantially uniform and may be close to that of silica in some embodiments. Possible advantages to such features include reduction of formation of additional waveguides within the core, which becomes increasingly a problem with larger core sizes.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Optical coupler comprising multimode fibers and method of making the same
ActiveUS7046875B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFew mode fiberDouble-clad fiber
An optical coupler is provided. It has a bundle of multimode fibers with a few-mode fiber in its centre. Such bundle is fused at one end which is the output end for the signal that is transmitted by the few-mode fiber. To make the coupler, this output end of the bundle is aligned and spliced with a large area core double clad fiber while preserving the modal content of the feed-through. A method for making such optical coupler is also provided. It includes the steps of bundling a central few-mode fiber with a plurality of multimode fibers and then fusing one end of such bundle and aligning it and splicing with a large core double clad fiber, while preserving fundamental mode transmission from one to the other.
Owner:ITF TECH +1
Cold box molding core maker
ActiveCN101347820AMeet the needs of stylingEasy maintenanceFoundry mouldsMoulding machinesEngineeringLarge core
The invention discloses a cold core box forming core-making machine, comprising a stander part, a sand adding device, a movable ejection head, an upper pressure head and a sand ejection mechanism, a gas bag and a pipeline connection, a movable blowing cover with the function of an upper top core, a tray dolly, an upper core box lifting mechanism and a core box dolly with the function of a lower top core. When the equipment is provided with two sets of core boxes, core sand with two different process characteristics are added through a sand adding mouth as well as cut into ejection heads of two sand ejection areas, blowing covers of two blowing areas and a relatively independent sand ejection mechanism and a relatively independent blowing mechanism in a matched way, thus realizing the synchronous production of sand type or sand core in the same equipment and the independently adjustable process parameters. When the equipment is provided with a set of large core box, the mechanisms can be used in combination, thus being capable of preparing large sand types or sand cores.
Owner:SUZHOU MINGZHI TECH
Buried dual taper waveguide for passive alignment and photonic integration
InactiveUS8000565B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling light guidesFiberPhotonic integrated circuit
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and system for a quasi longitudinal mode electro optic sensor for high power microwave testing
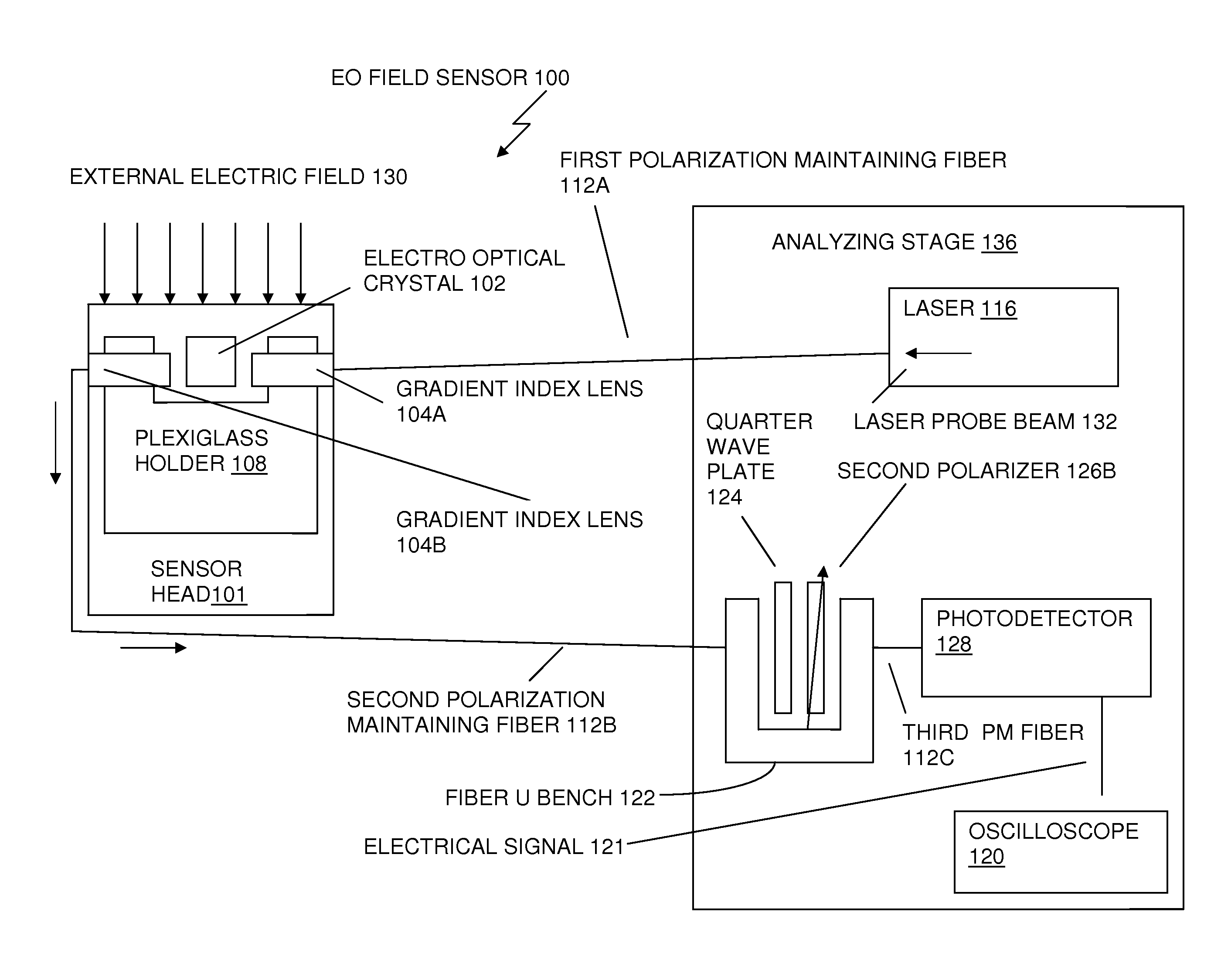
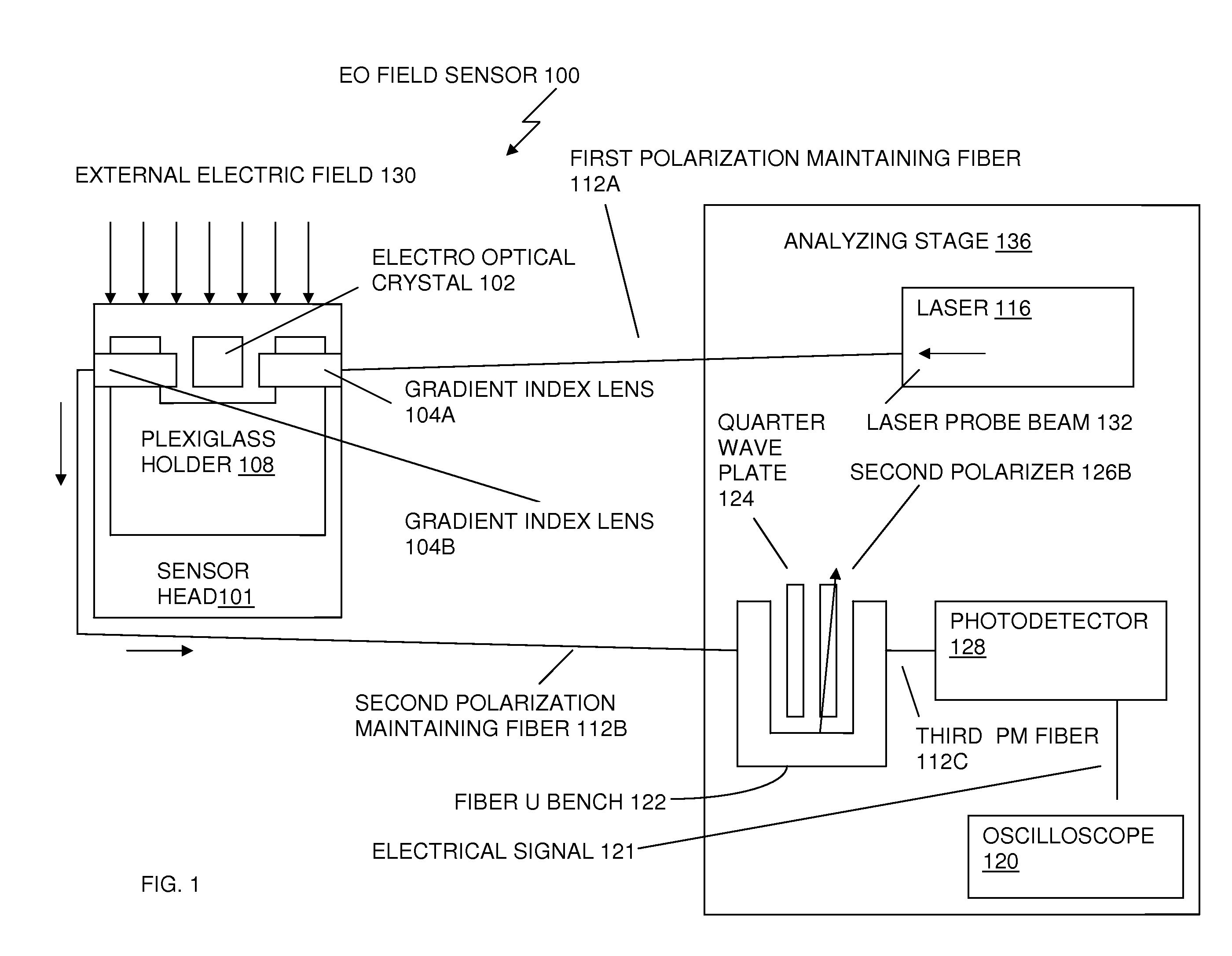
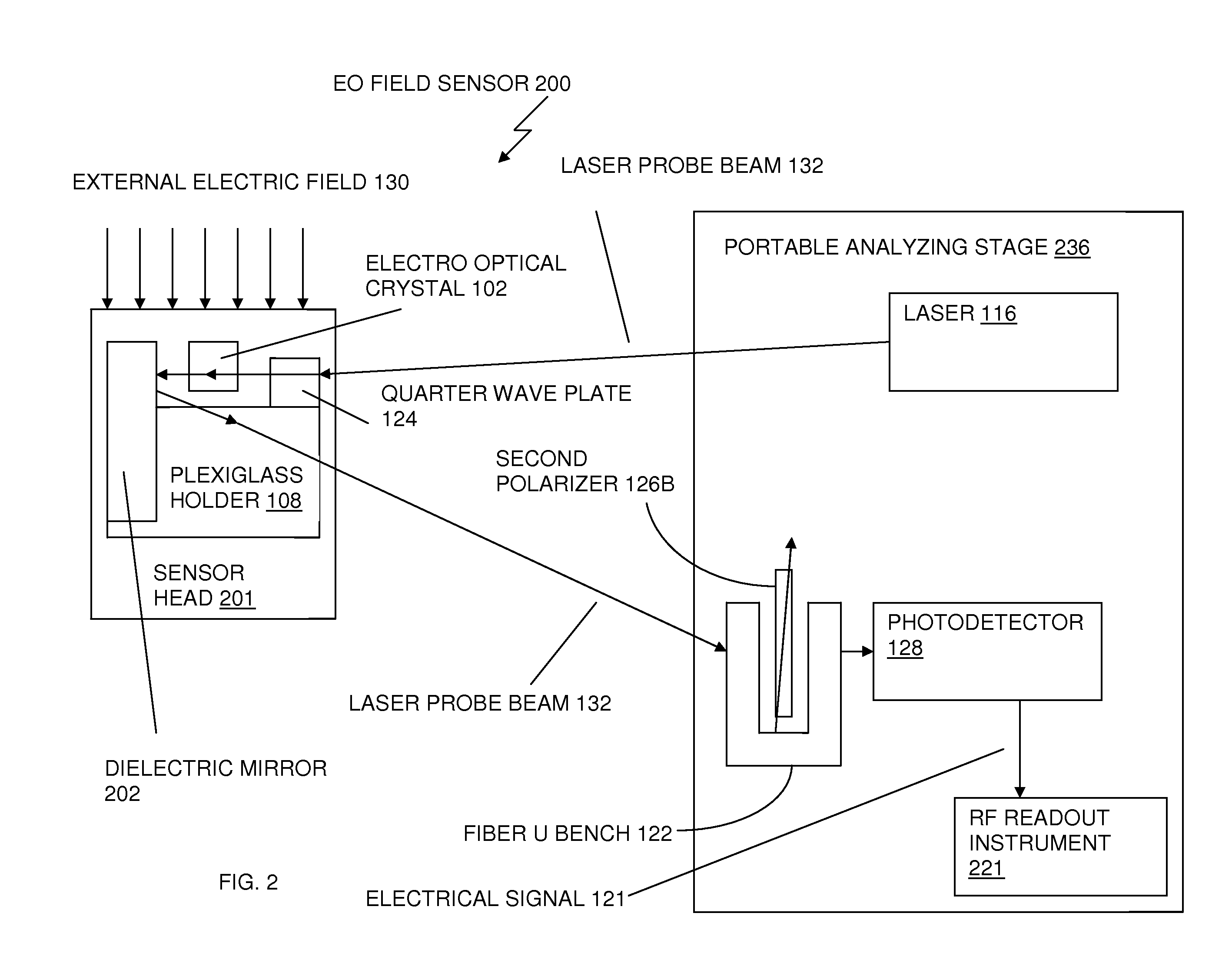
ActiveUS20100264904A1Reduce disturbanceImprovement in EO signal stabilityDigital variable/waveform displayLight polarisation measurementFiberElectrical field strength
An apparatus, for measuring an applied electrical field and for reducing perturbation to the electrical field being measured, includes a laser integrated into an electro optic crystal sensor head prior to the output fiber. A probe beam is passed along the crystal direction of low birefringence of nearly circular optical indicatrix, rather than one of high EO modulation. The EO crystal is placed between two crossed polarizers and oriented such that a small tilt angle is subtended between its optic axis and the path of the probe beam. Improved optical coupling is achieved by using a large core multimode fiber at the output, to reduce optical insertion losses. A collimating lens emits the intensity modulated laser beam back to a photodetector, where the intensity modulated laser beam is converted to an electrical signal representing both field strength and phase of the electrical field applied to the sensor head.
Owner:US GOVT REPRESENTED BY SEC OF NAVY CHIEF OF NAVAL RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com