Patents
Literature
568 results about "Output coupler" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
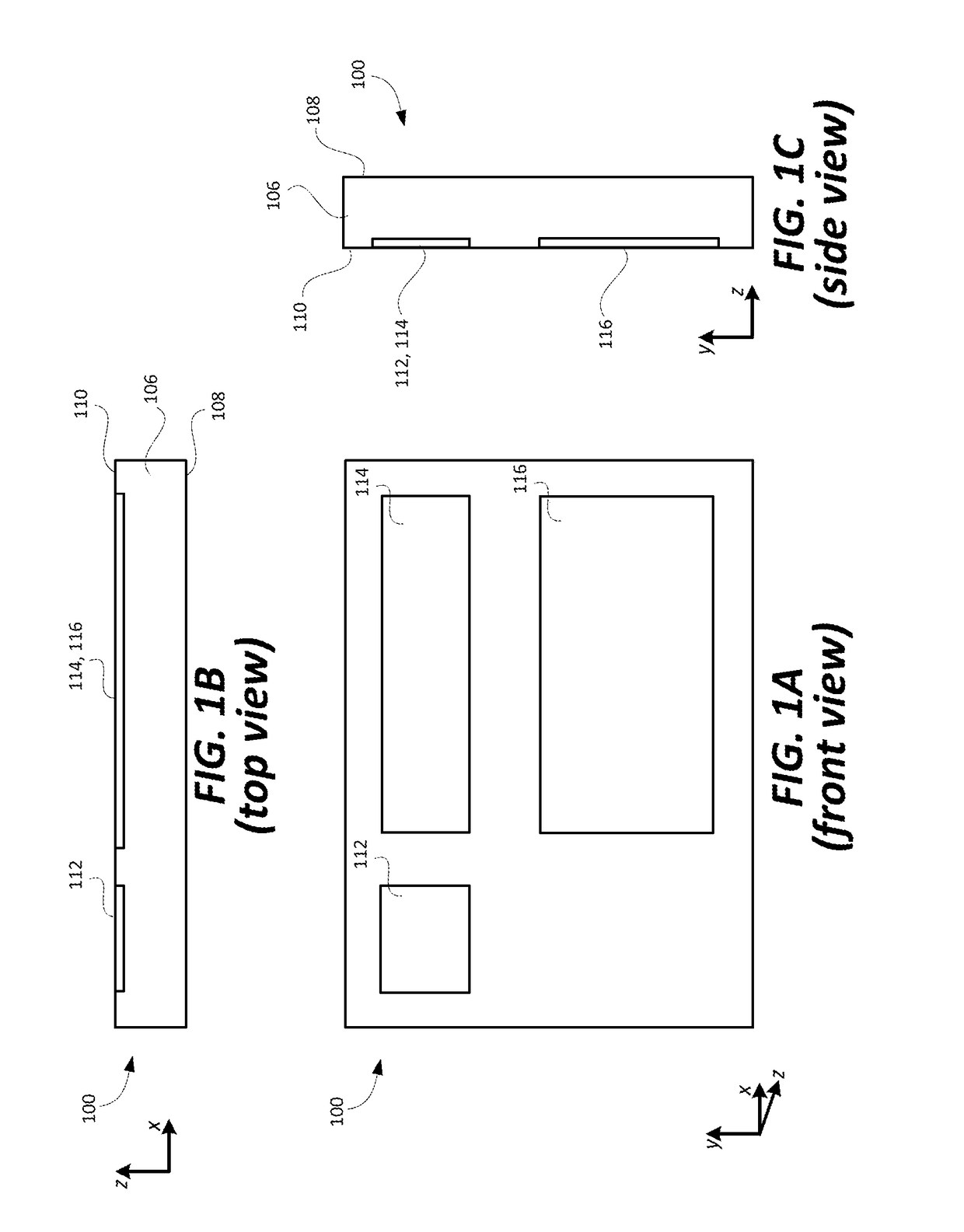
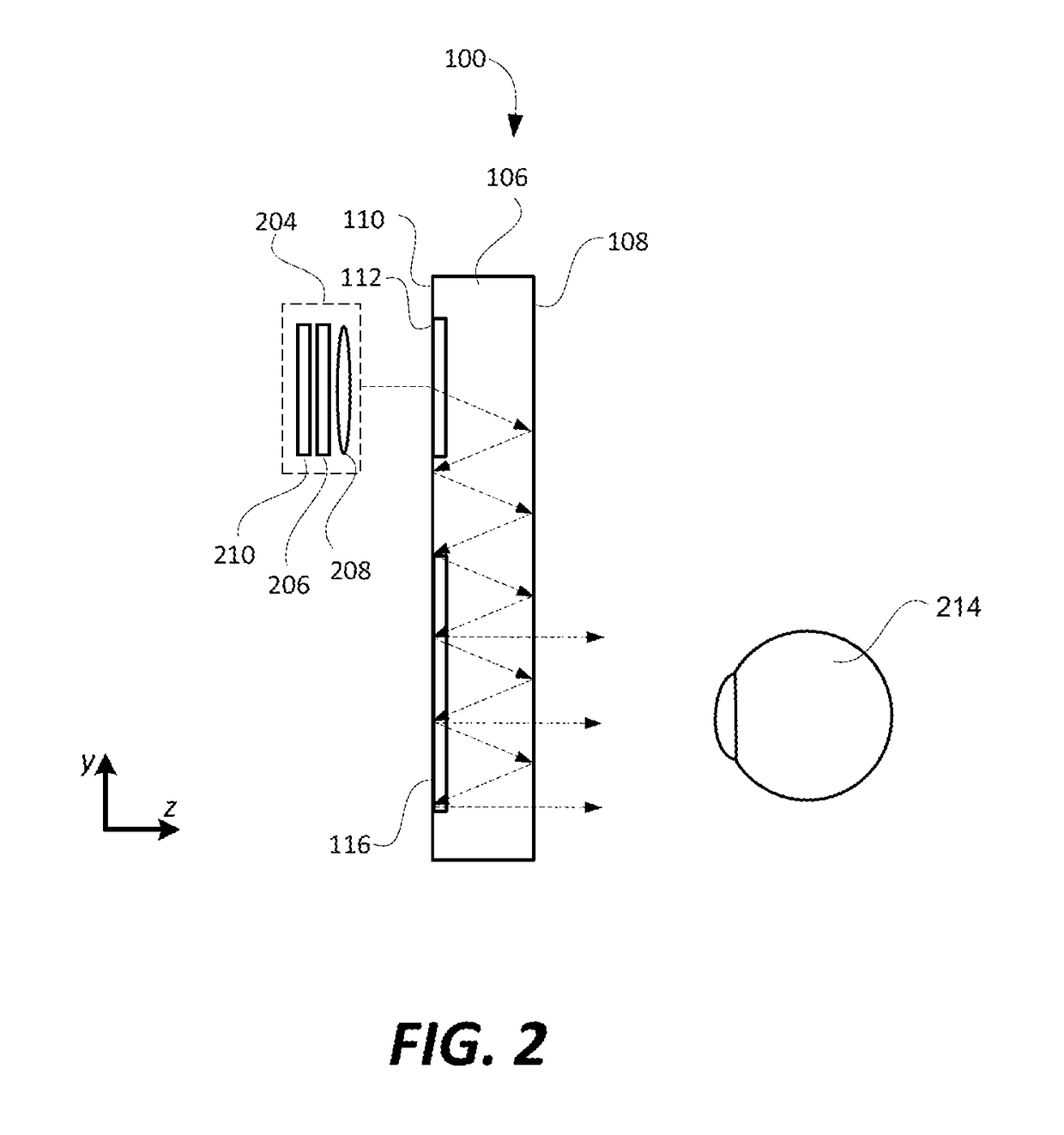
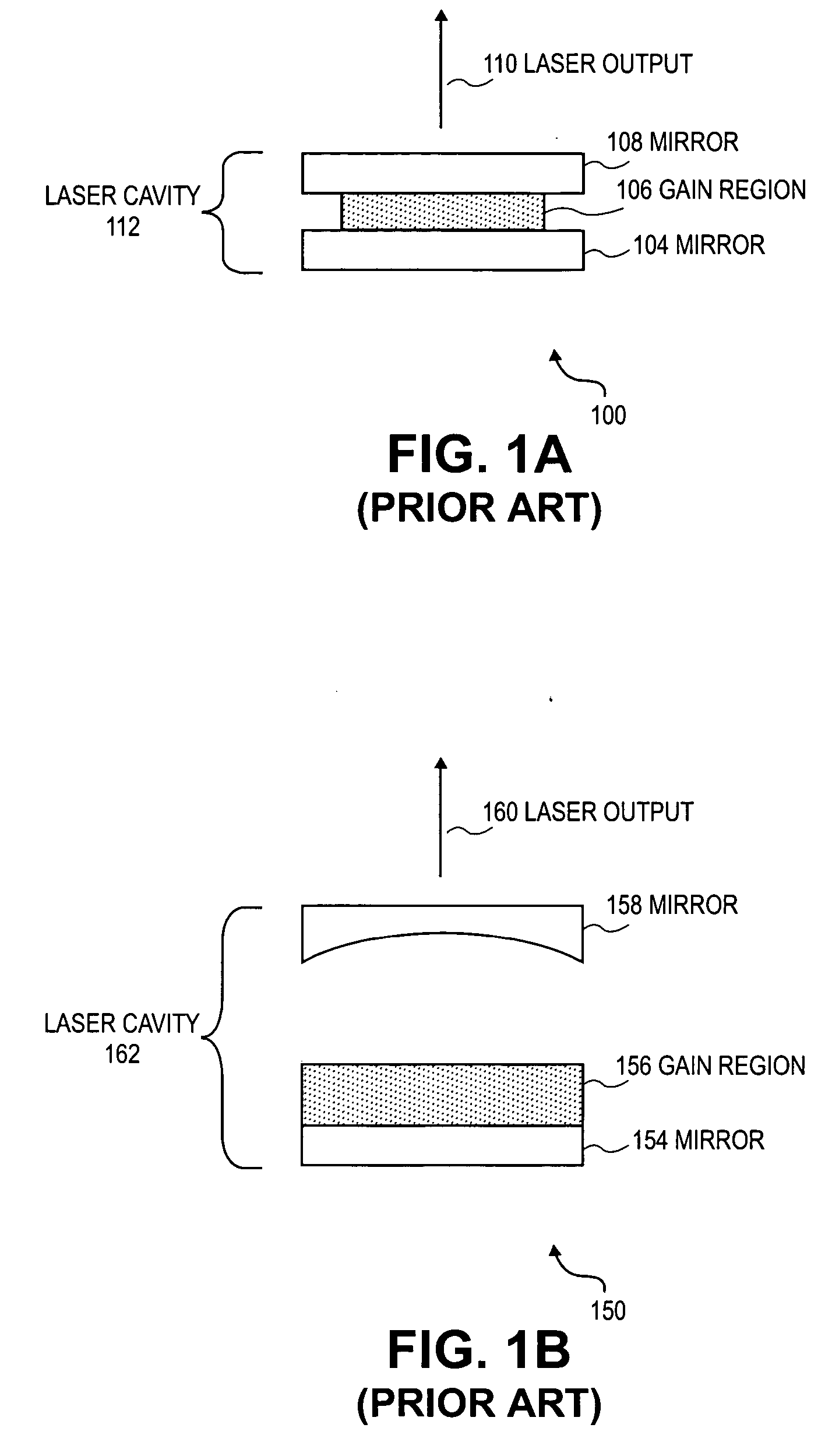
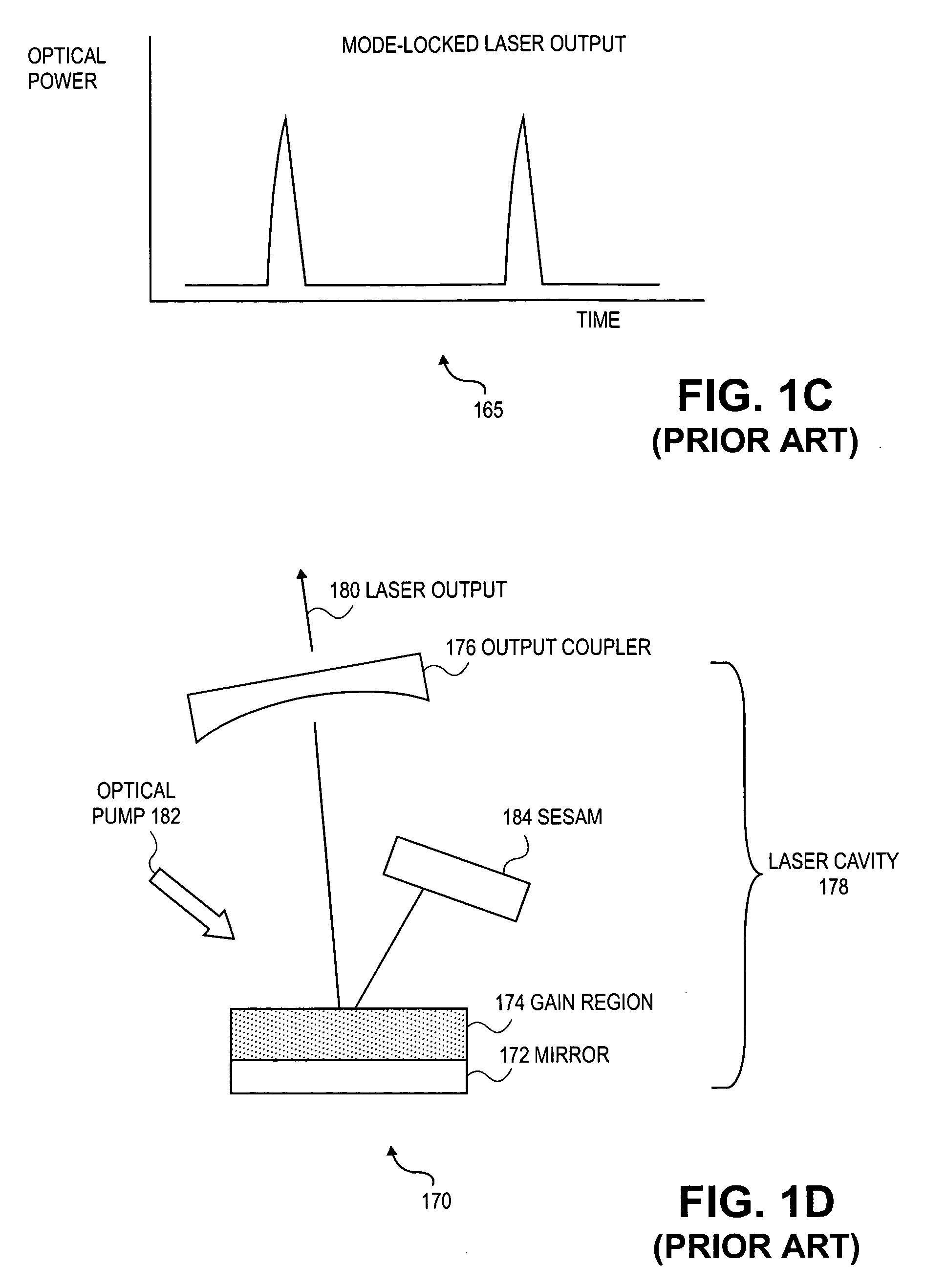
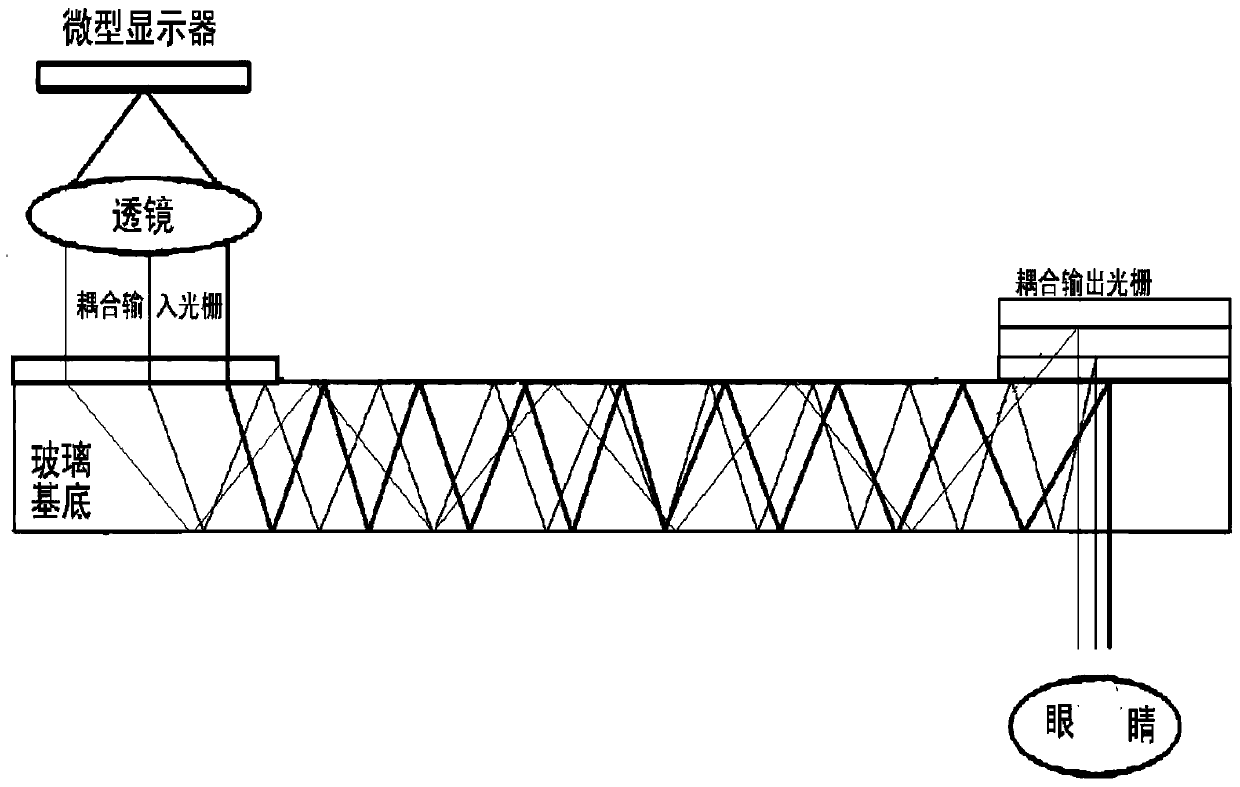
An output coupler (OC) is the component of an optical resonator that allows the extraction of a portion of the light from the laser's intracavity beam. An output coupler most often consists of a partially reflective mirror, allowing a certain portion of the intracavity beam to transmit through. Other methods include the use of almost-totally reflective mirrors at each end of the cavity, emitting the beam either by focusing it into a small hole drilled in the center of one mirror, or by redirecting through the use of rotating mirrors, prisms, or other optical devices, causing the beam to bypass one of the end mirrors at a given time.
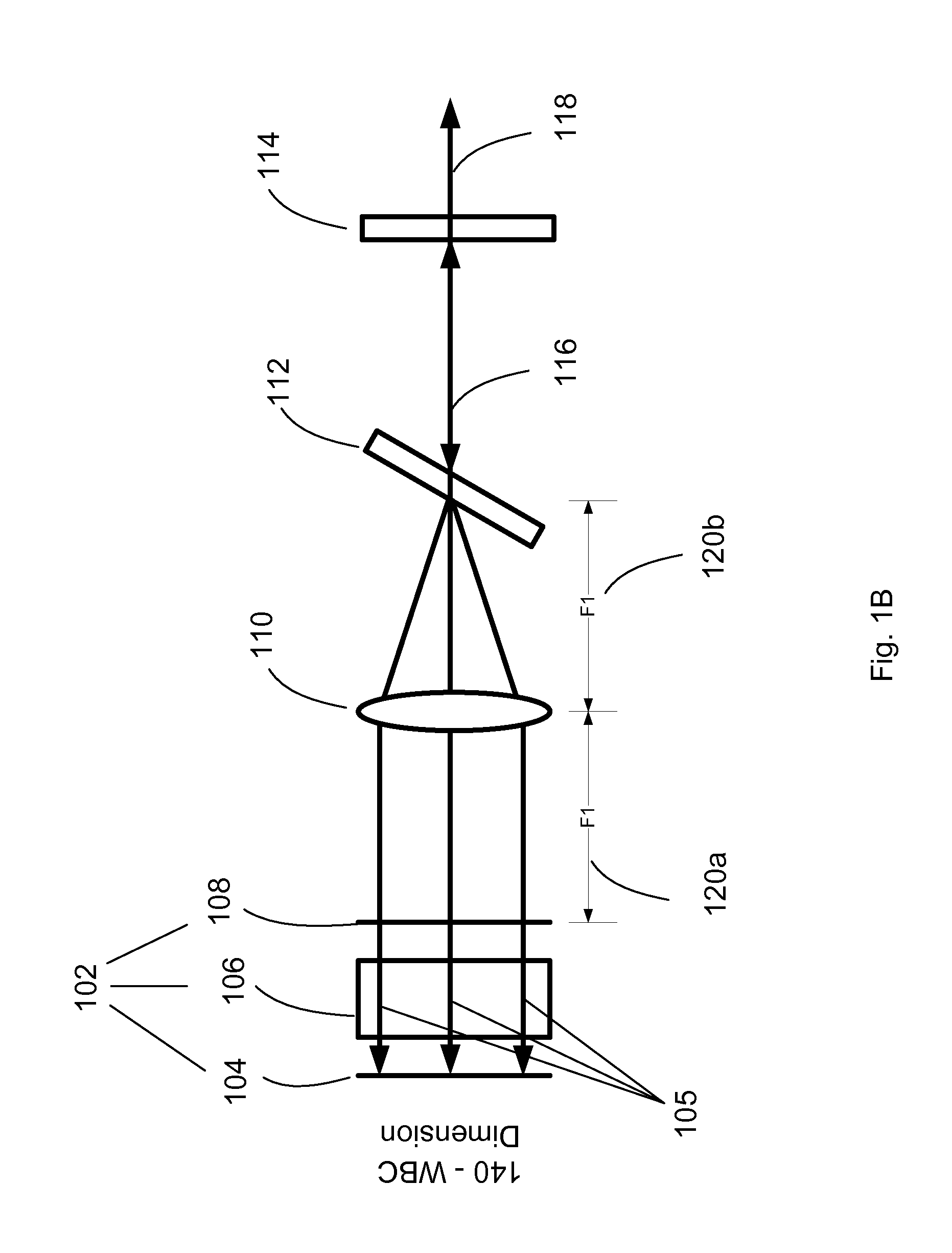
System for and method of extending vertical field of view in head up display utilizing a waveguide combiner
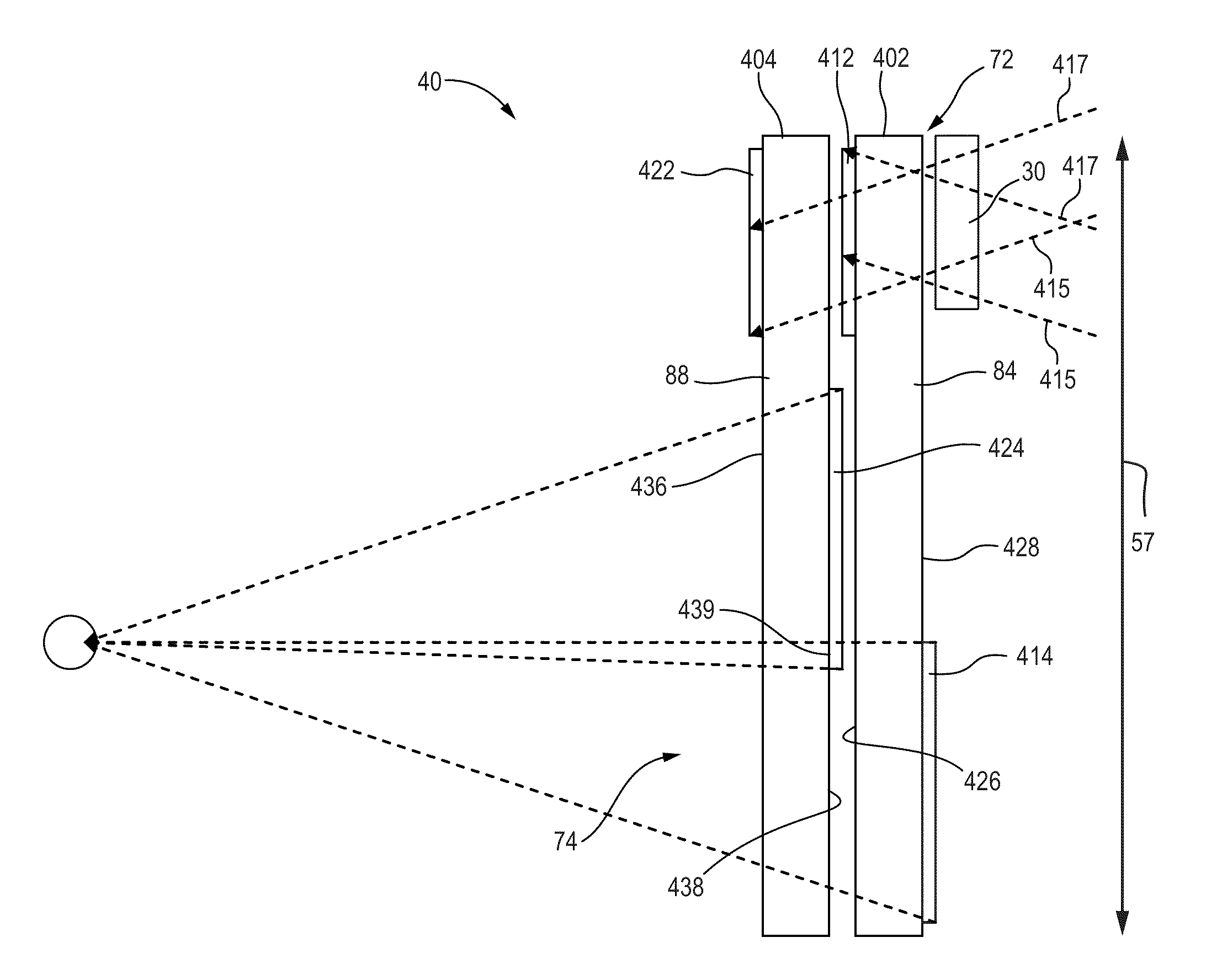
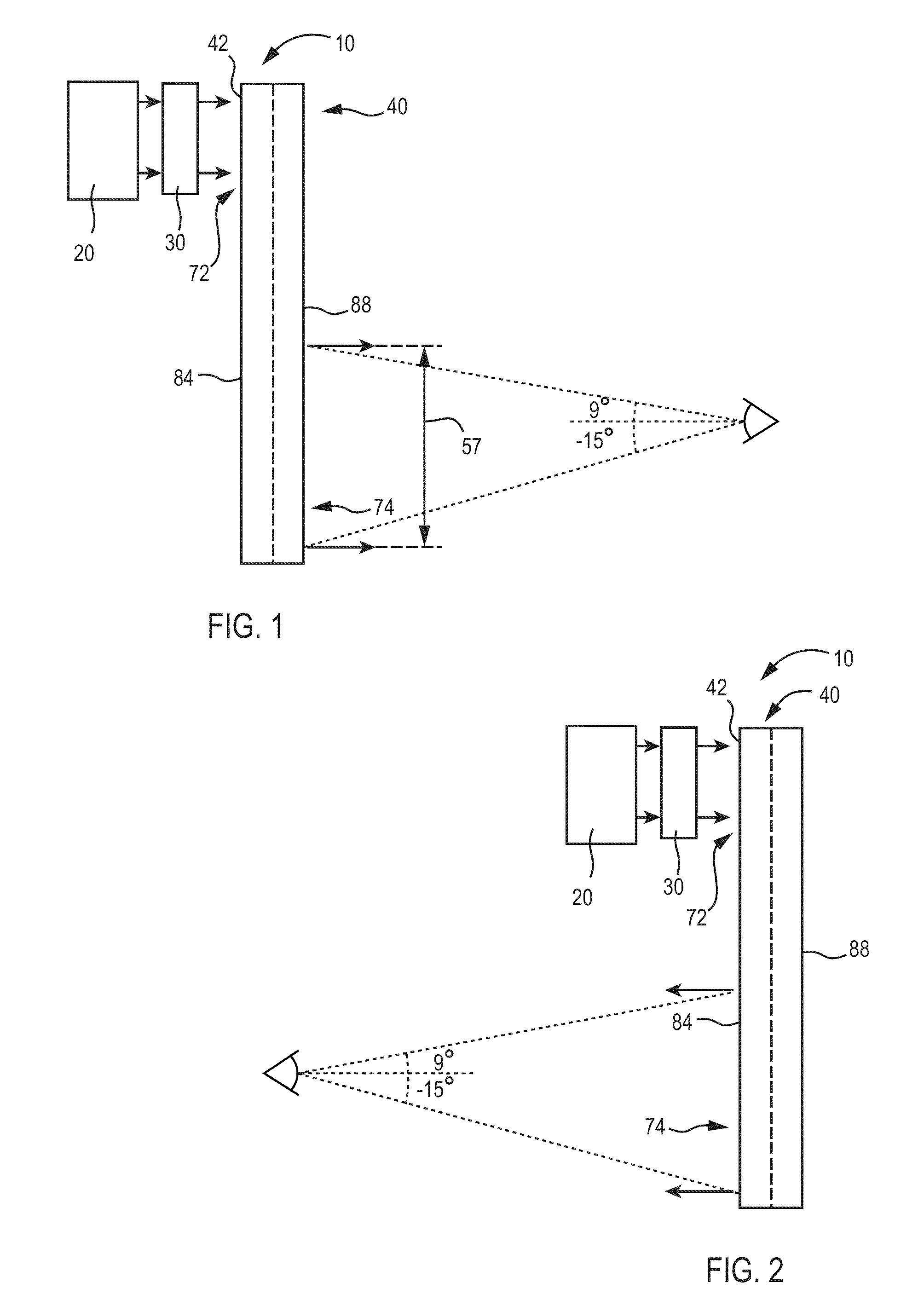
A Head Up Display can be utilized to find light from an energy source. The Head Up Display includes a first waveguide having a first input coupler and a first output coupler. The Head Up Display can also include a second waveguide having a second input coupler and a second output coupler. The first waveguide has a first major surface and the second waveguide has a second major surface, which are disposed approximately parallel to each other. The first waveguide and the second waveguide are positioned as a combiner and allowing viewing an outside feed and information from an image source. The first input coupler diffracts light in the first field of view into the first waveguide and light in a second field of view reaches the second input coupler and is diffracted into the second waveguide.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
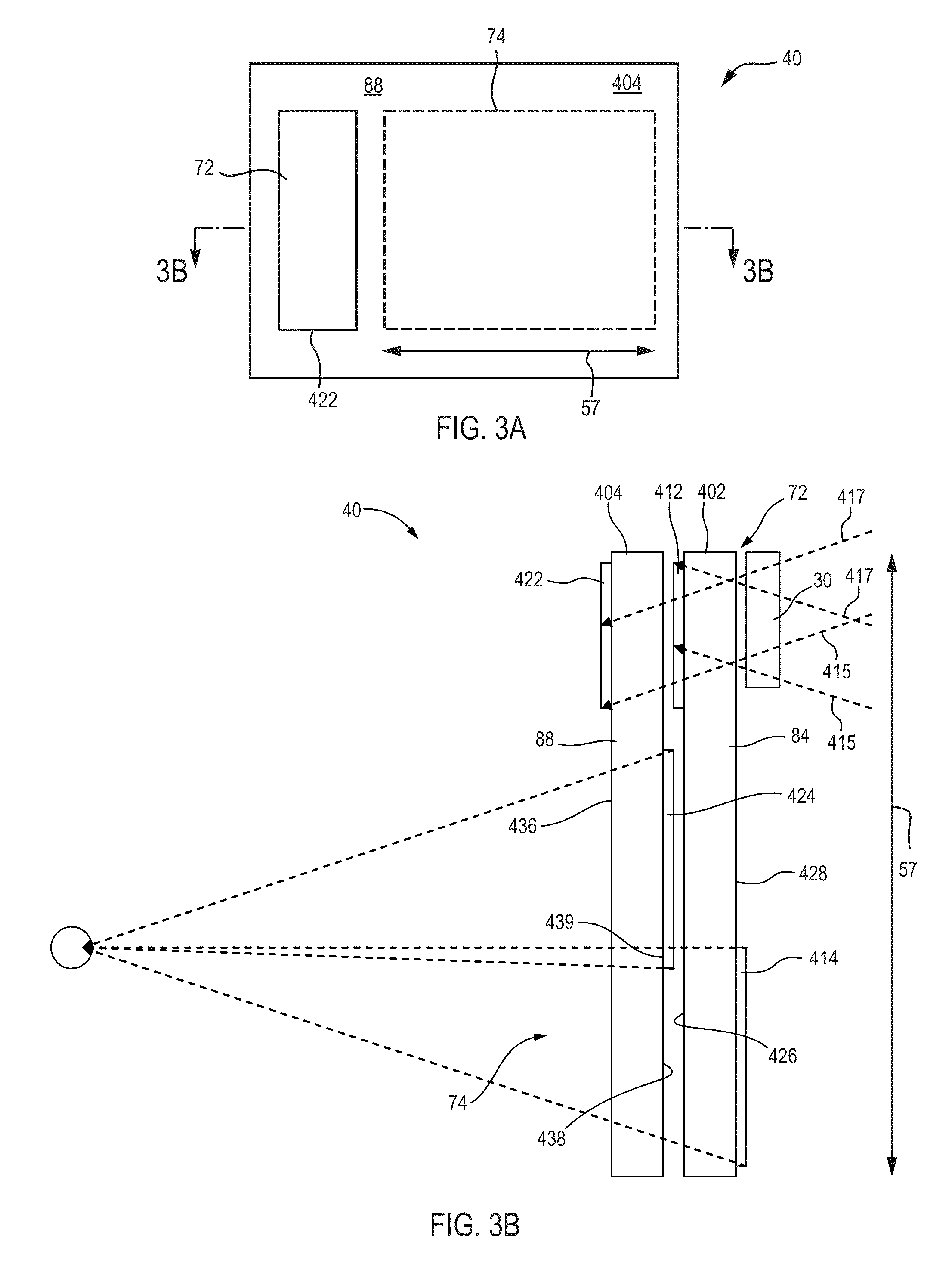
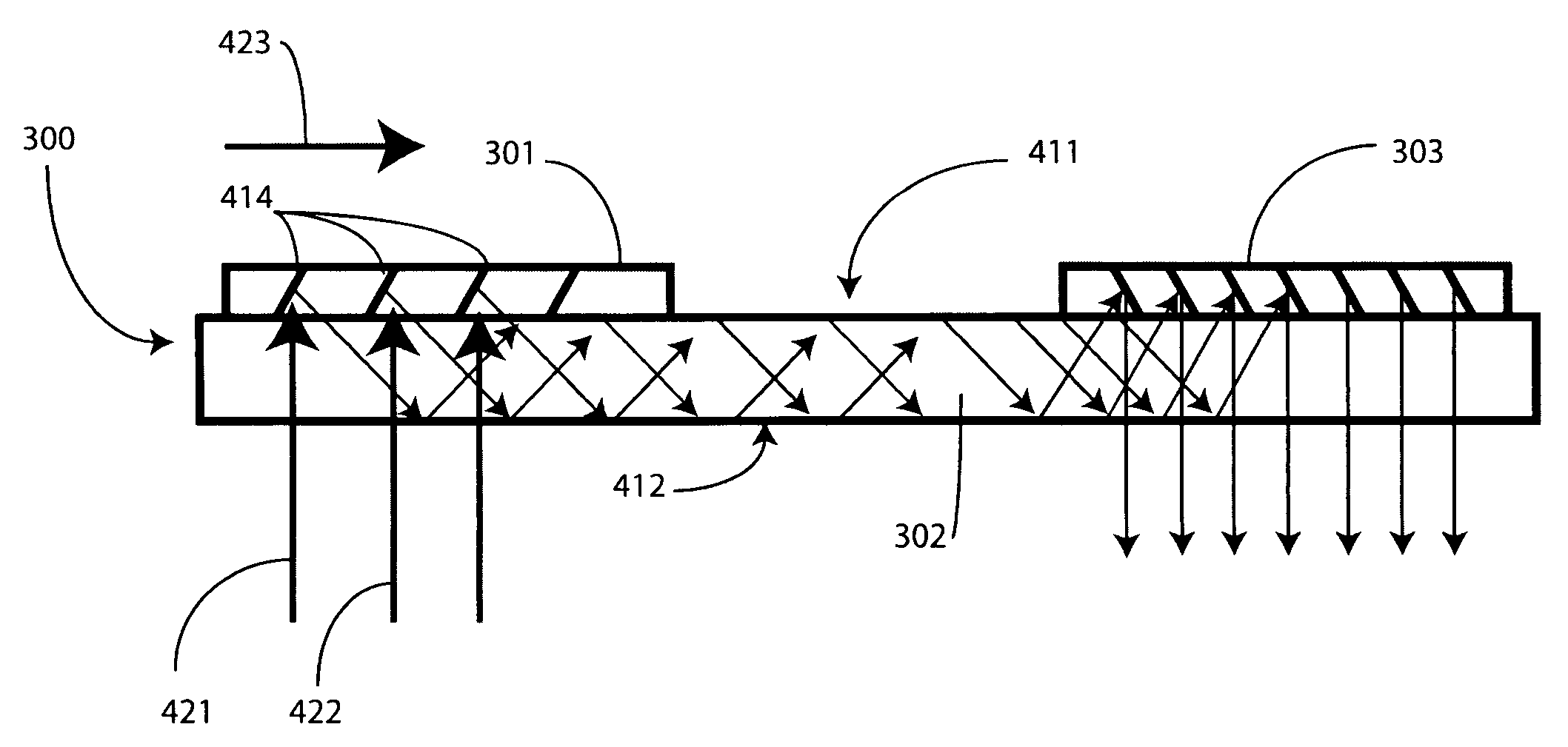
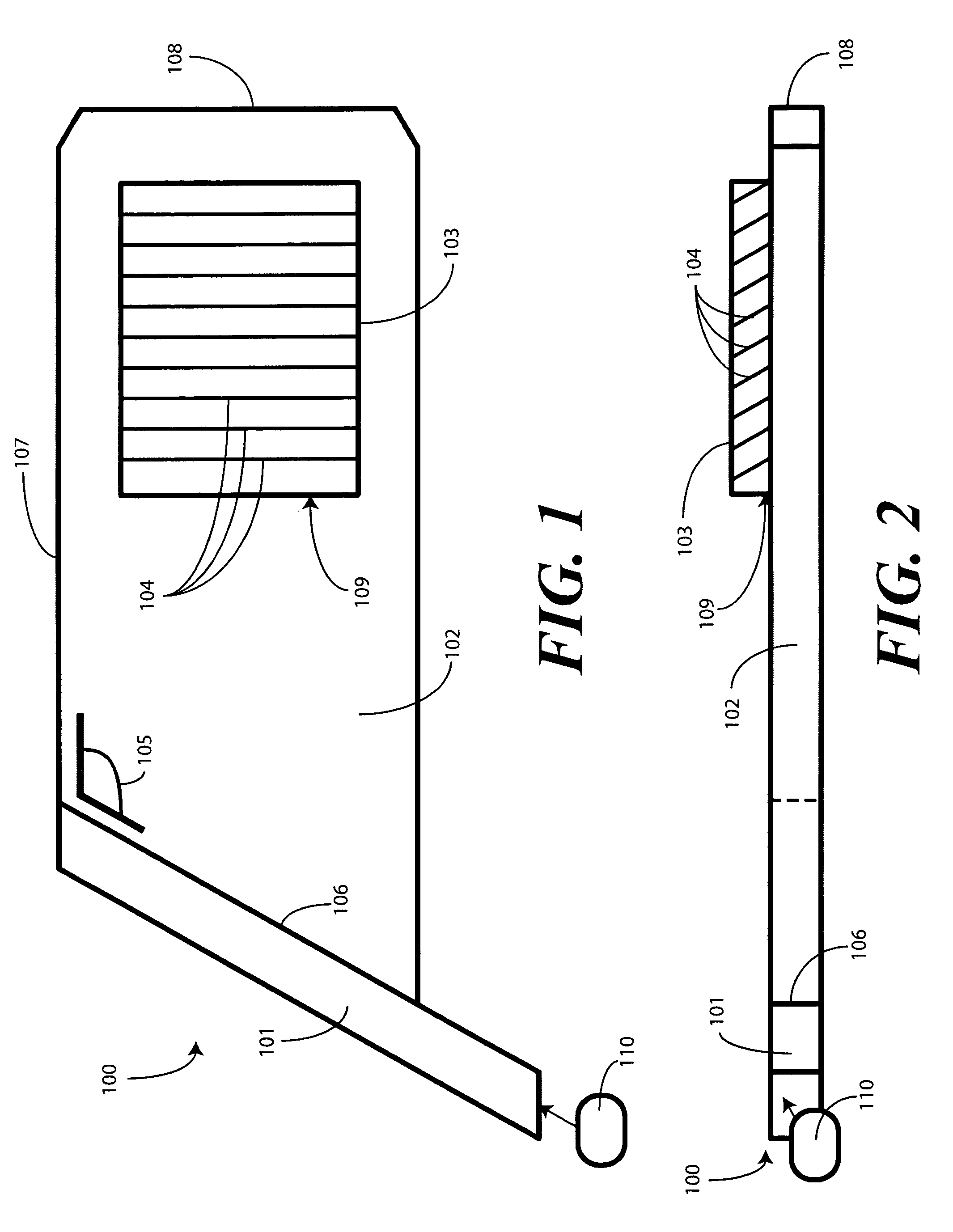
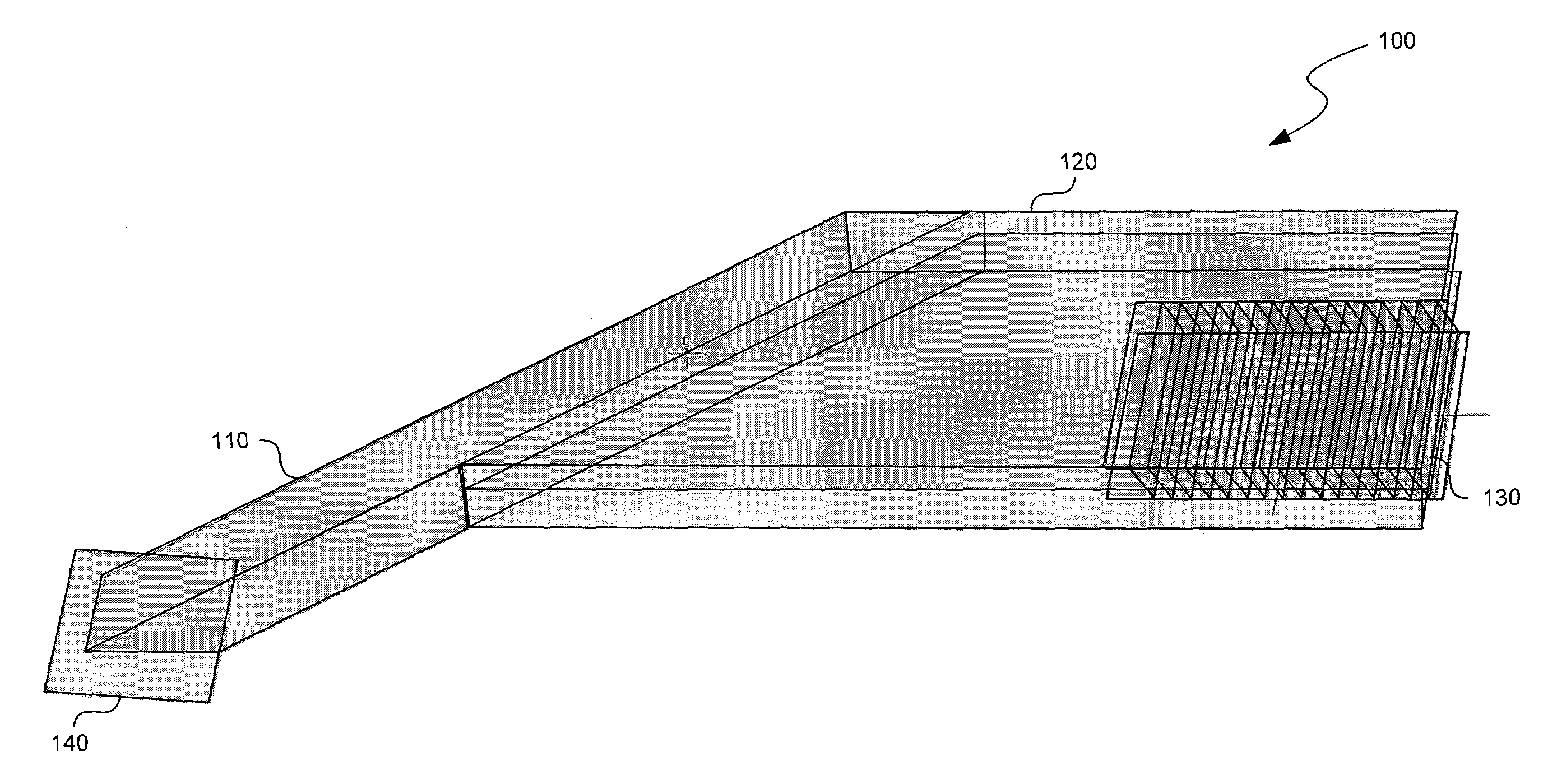
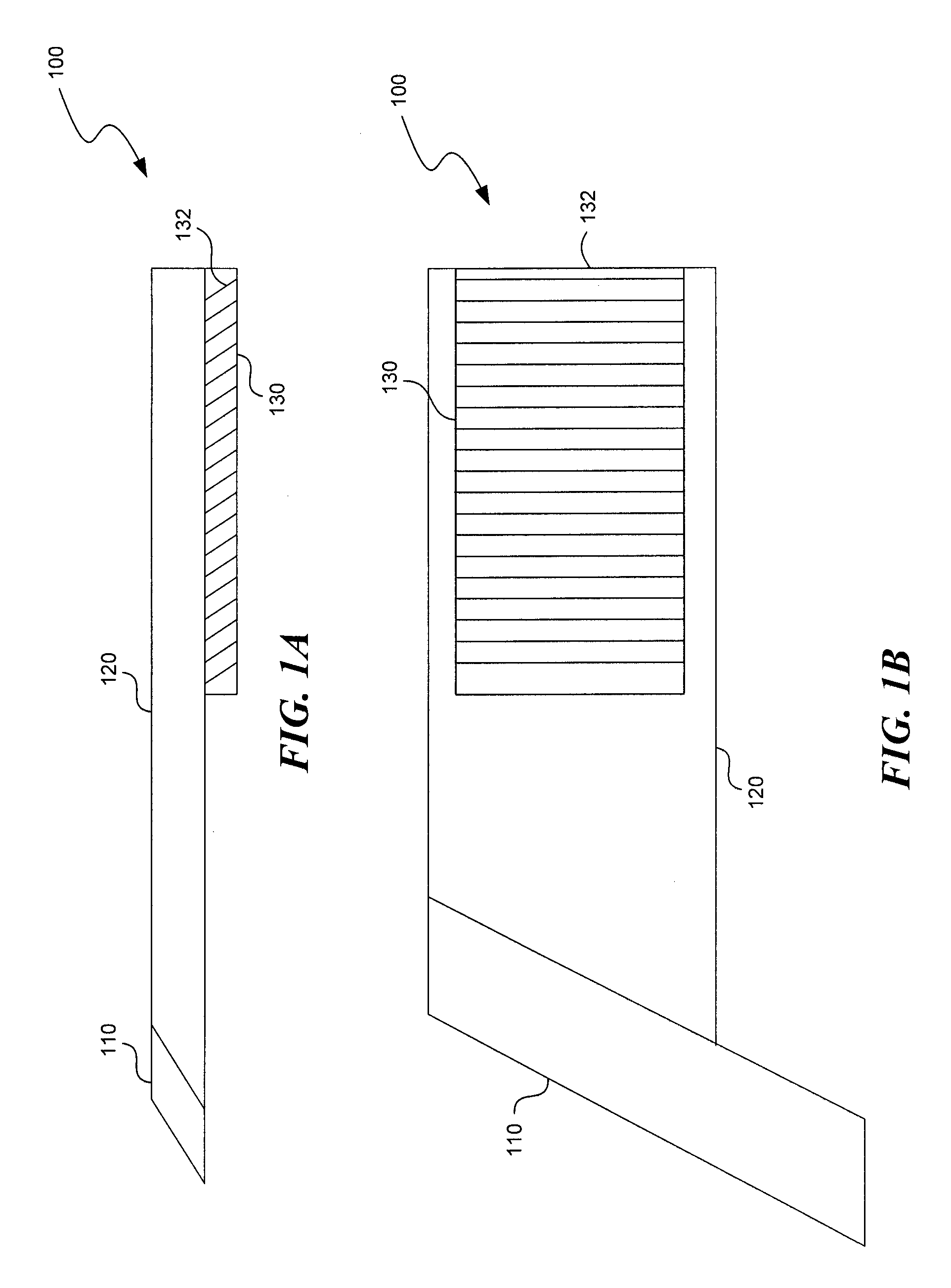
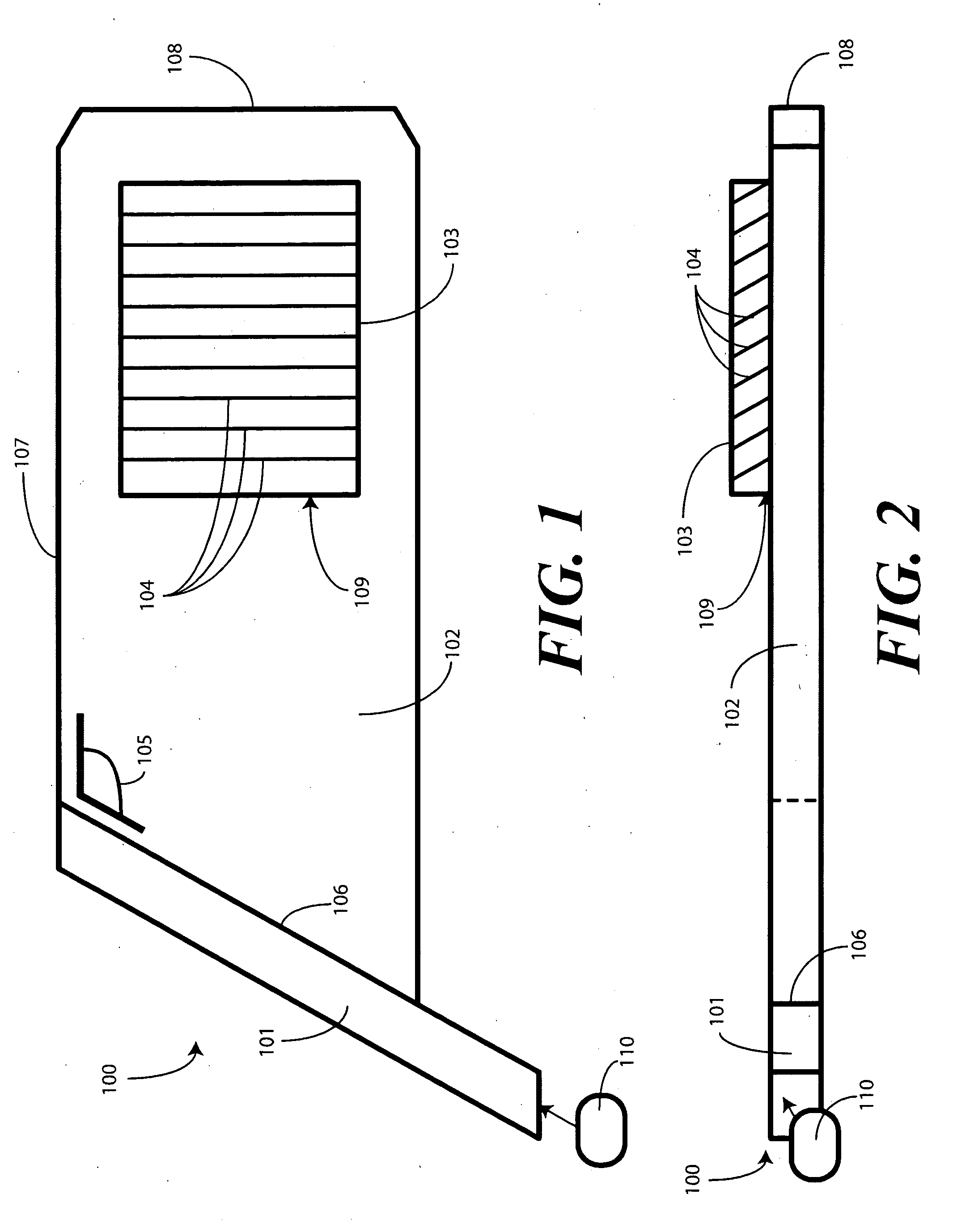
Substrate guided relay with pupil expanding input coupler
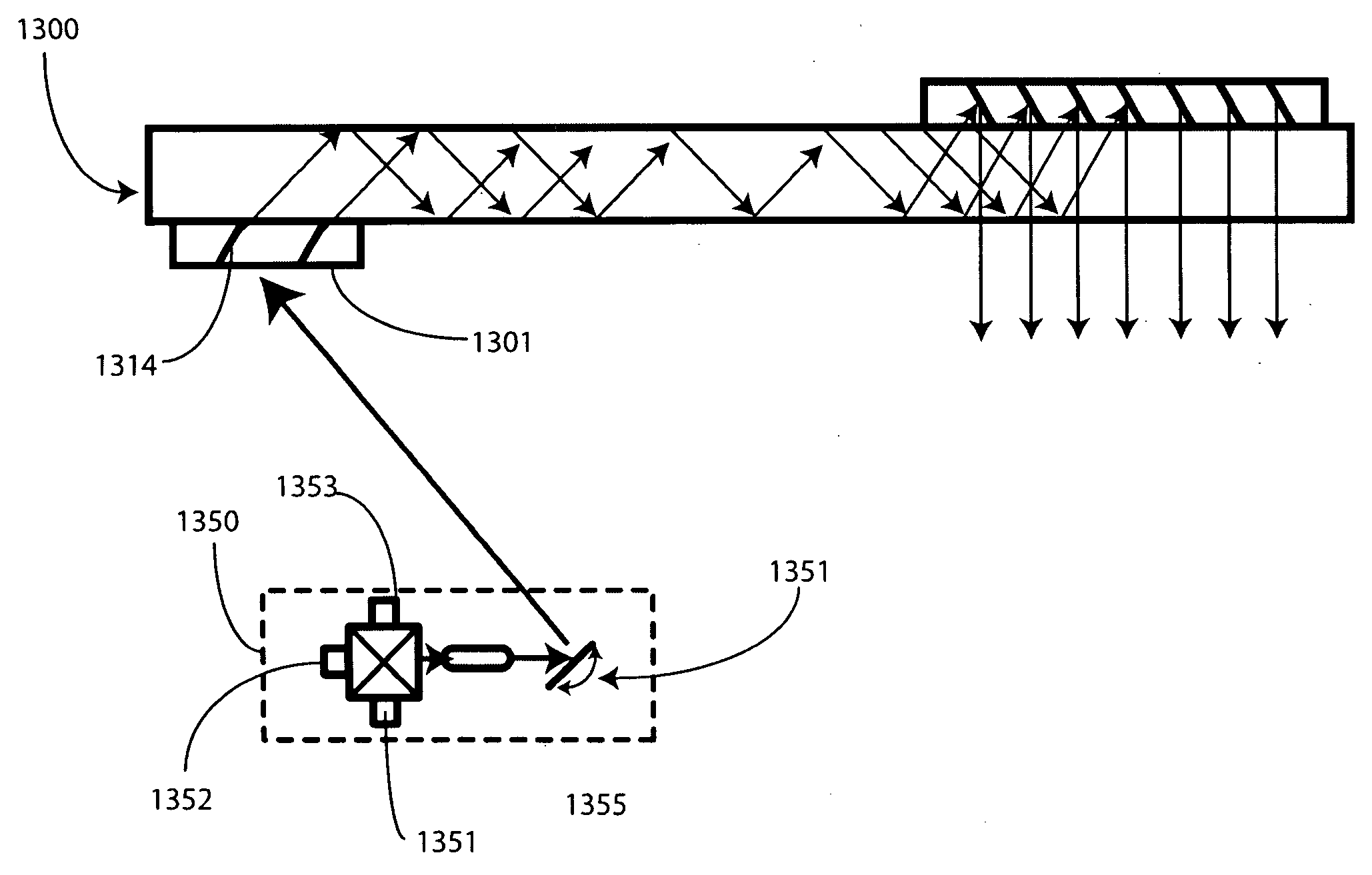
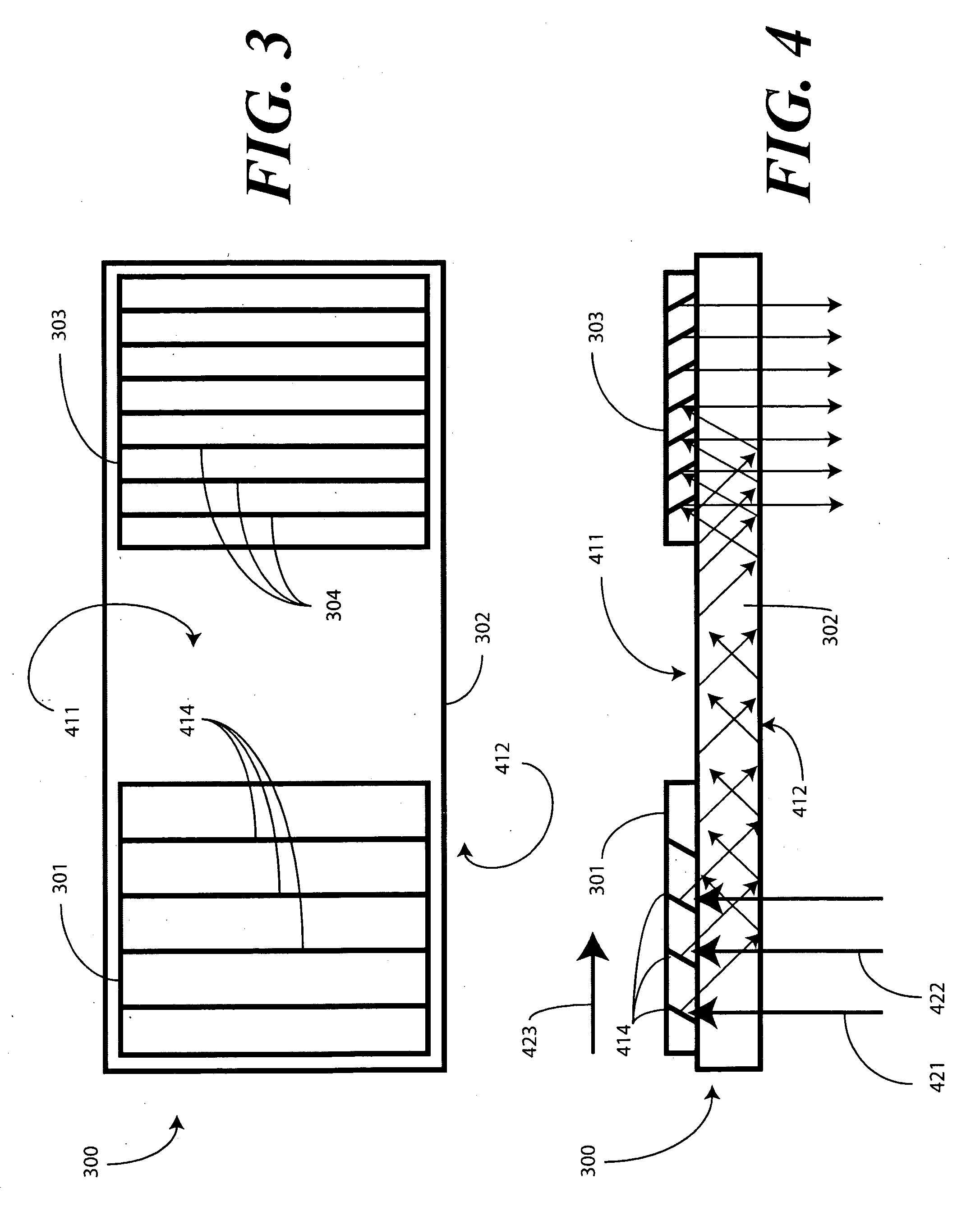
An optical substrate guided relay (300) includes an optical substrate (302) having at least one major face (411), an output coupler (303) coupled to a major face (411,412), and an input coupler (301) coupled to a major face (411,412). The input coupler (301) is configured to reflect, via internal layers (414), portions of received light to the optical substrate 302. The input coupler (301) includes either one or more internal layers (414) or a contoured face (1040) with surfaces configured as reflectors that expand the received light and direct it into the optical substrate (302). The output coupler (303) expands a pupil of light in one direction and directs the expanded light away from the optical substrate guided relay.
Owner:MICROVISION
Substrate-guided relays for use with scanned beam light sources
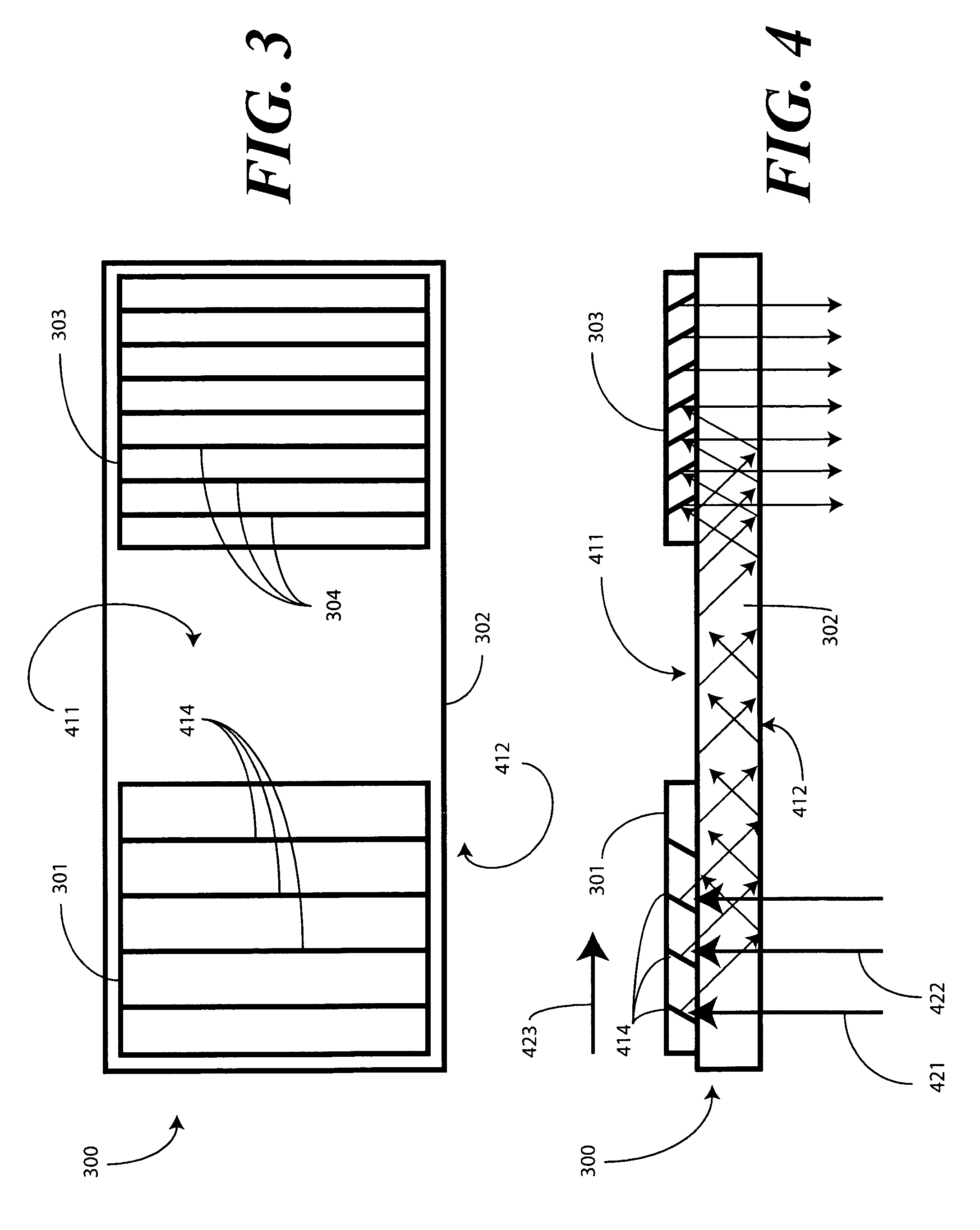
Substrate-guided relays that employ light guiding substrates to relay images from sources to viewers in optical display systems. The substrate-guided relays are comprised of an input coupler, an intermediate substrate, and an output coupler. In some embodiments, the output coupler is formed in a separate substrate that is coupled to the intermediate substrate. The output coupler may be placed in front of or behind the intermediate substrate, and may employ two or more partially reflective surfaces to couple light from the coupler. In some embodiments, the input coupler is coupled to the intermediate substrate in a manner that the optical axis of the input coupler intersects the optical axis of the intermediate substrate at a non-perpendicular angle.
Owner:MICROVISION
Computer program product configured to control modular transmission system components
A computer program product is configured to control a modular transmission system having a control processor and at least N power amplifier modules, each having a controller submodule, wherein the system receives an input signal which may be a single carrier or multiple carriers. The signal is passed to a one-by-N divider which divides the signal N ways. Each of the N divided signals are independently amplified by the power amplifier (PA) modules "slices" (i.e., PA modules) that includes an RF amplifier module, a microcontroller module, and a power supply module, all of which are tightly coupled via a plurality of signal, power, control, and status connections. Each the PA slices amplifies its respective input signal and outputs a respective radio frequency output signal at a predetermined power level as controlled by the microcontrol module, the driver, and the system controller, or a network manager via a system input / output interface. The output coupler provides power coupling and status monitoring via feedback lines to support control at a module-level, a system-level, and a network-level.
Owner:THALES BROADCAST & MULTIMEDIA
Substrate Guided Relay with Pupil Expanding Input Coupler
An optical substrate guided relay (300) includes an optical substrate (302) having at least one major face (411), an output coupler (303) coupled to a major face (411,412), and an input coupler (301) coupled to a major face (411,412). The input coupler (301) is configured to reflect, via internal layers (414), portions of received light to the optical substrate 302. The input coupler (301) includes either one or more internal layers (414) or a contoured face (1040) with surfaces configured as reflectors that expand the received light and direct it into the optical substrate (302). The output coupler (303) expands a pupil of light in one direction and directs the expanded light away from the optical substrate guided relay.
Owner:MICROVISION
Laser ignition
InactiveUS6676402B1Durable and reliable and economical ignitionEliminate needLaser detailsPulsating combustionResonant cavityLight beam
Sequenced pulses of light from an excitation laser with at least two resonator cavities with separate output couplers are directed through a light modulator and a first polarzing analyzer. A portion of the light not rejected by the first polarizing analyzer is transported through a first optical fiber into a first ignitor laser rod in an ignitor laser. Another portion of the light is rejected by the first polarizing analyzer and directed through a halfwave plate into a second polarization analyzer. A first portion of the output of the second polarization analyzer passes through the second polarization analyzer to a second, oscillator, laser rod in the ignitor laser. A second portion of the output of the second polarization analyzer is redirected by the second polarization analyzer to a second optical fiber which delays the beam before the beam is combined with output of the first ignitor laser rod. Output of the second laser rod in the ignitor laser is directed into the first ignitor laser rod which was energized by light passing through the first polarizing analyzer. Combined output of the first ignitor laser rod and output of the second optical fiber is focused into a combustible fuel where the first short duration, high peak power pulse from the ignitor laser ignites the fuel and the second long duration, low peak power pulse directly from the excitation laser sustains the combustion.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Method and apparatus for generating high power visible and near-visible laser light
ActiveUS20090225793A1Efficient and reliableIncrease light outputLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor lasersOptical radiationFiber
A multimode-fiber Raman laser includes a pump source configured to provide optical radiation centered at a pump wavelength and characterized by a spectral bandwidth greater than 100 MHz and an oscillator resonant at an emission wavelength greater than the pump wavelength. The oscillator includes an input coupler optically aligned with the pump source and a multimode optical fiber optically coupled to the input coupler. The multimode optical fiber includes an input section having a fiber Bragg grating, an intracavity section of a predetermined length optically coupled to the input section, and an output section having a fiber Bragg grating. The oscillator also includes an output coupler optically coupled to the multimode optical fiber and configured to provide a laser output at the emission wavelength.
Owner:RAM PHOTONICS IND LLC
Beam generation and steering with integrated optical circuits for light detection and ranging
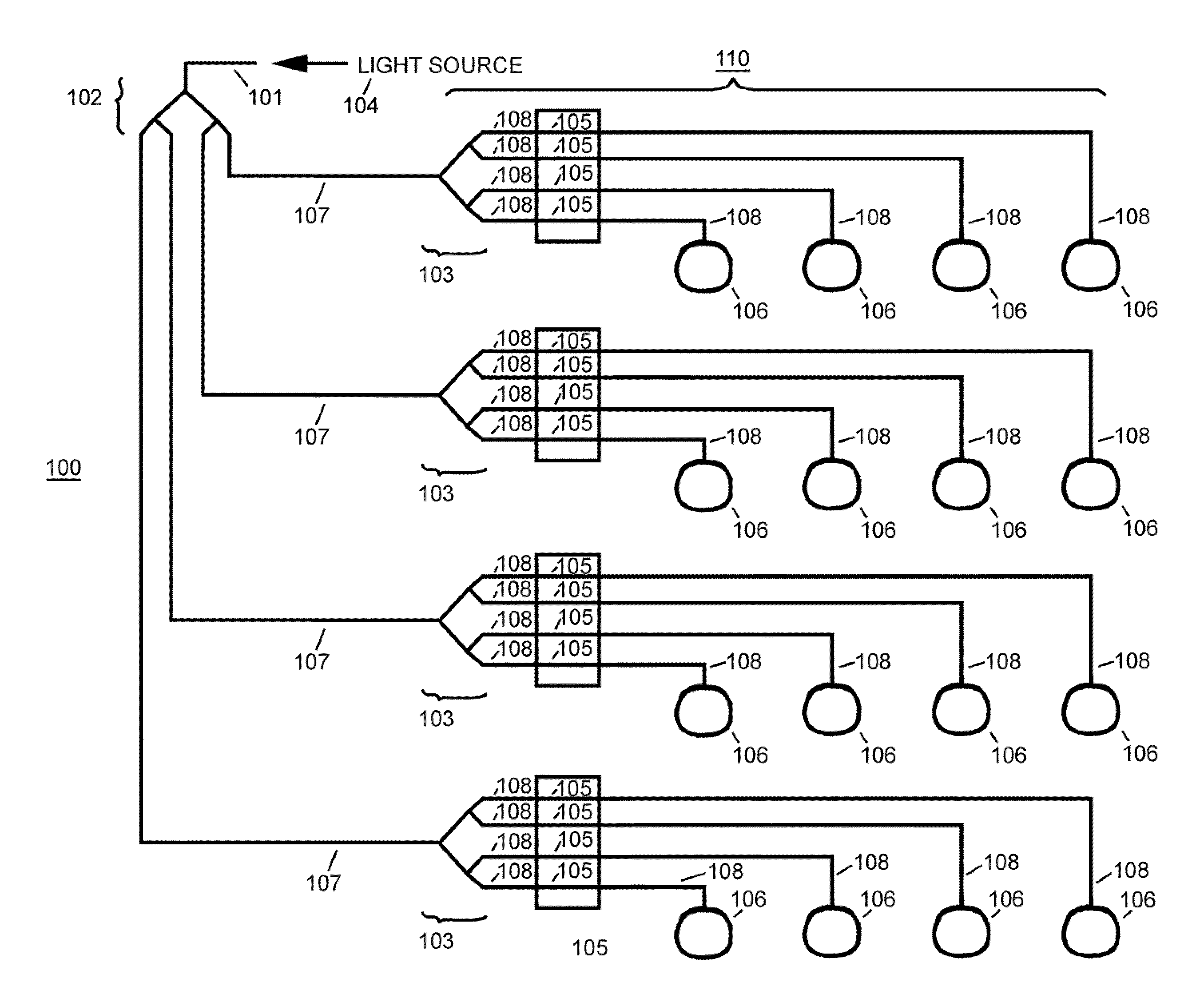
An integrated photonic beam steering device includes a planar photonic substrate. An input waveguide is configured to accept an electromagnetic energy from a source of electromagnetic energy radiation. A first splitter is configured to split the electromagnetic radiation into one or more paths. One or more phased array rows are optically coupled to each of the one or more paths. Each phased array row includes a row splitter configured to split the each of the one or more paths into two or more row paths. Two or more phase modulators are each optically coupled respectively to each of the two or more row paths. Two or more output couplers are optically coupled respectively to each phase modulator output of the two or more phase modulators. The two or more output couplers are configured to radiate a steered photonic beam away from the integrated photonic beam steering device.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Switchless combining system and method
A switchless combiner for high-power broadcast signals incorporates a circular waveguide configured as an orthogonal mode transducer to provide a coherent signal and a phase rotator to steer the combined signal to an output coupler. Out-of-phase RF is absorbed by a station load. The phase rotator is capable of redirecting the output from either of the sources or all of the combined output to the station load. Switching between destinations for the RF components may be made with power applied. The input and output characteristics and mechanical configuration permit the switchless combiner to be integrated with other high-power RF broadcast signal manipulation devices.
Owner:SPX CORP
Hybrid vertical-cavity laser
InactiveUS20120008658A1Decrease unwanted scattering lossImprove routing efficiencyLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionIn planeCMOS
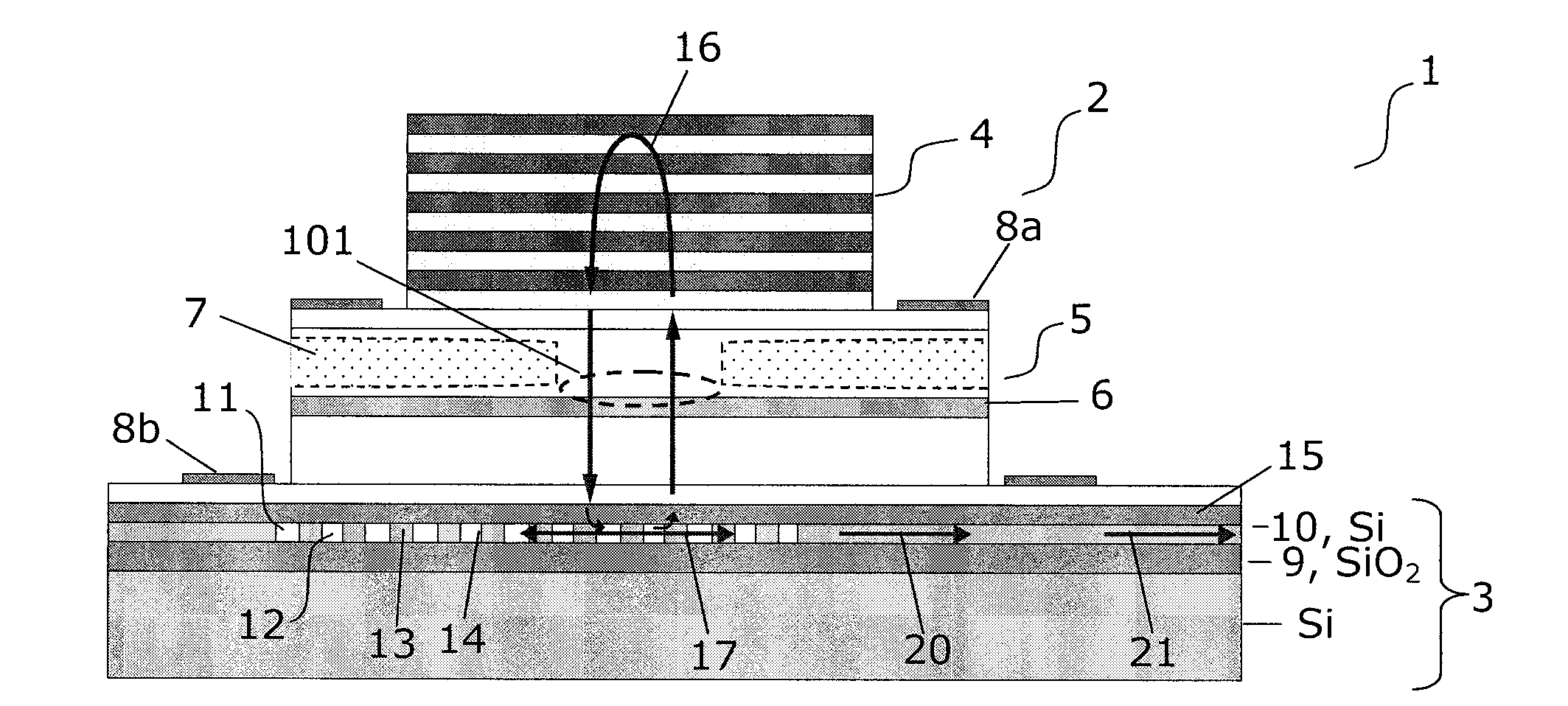
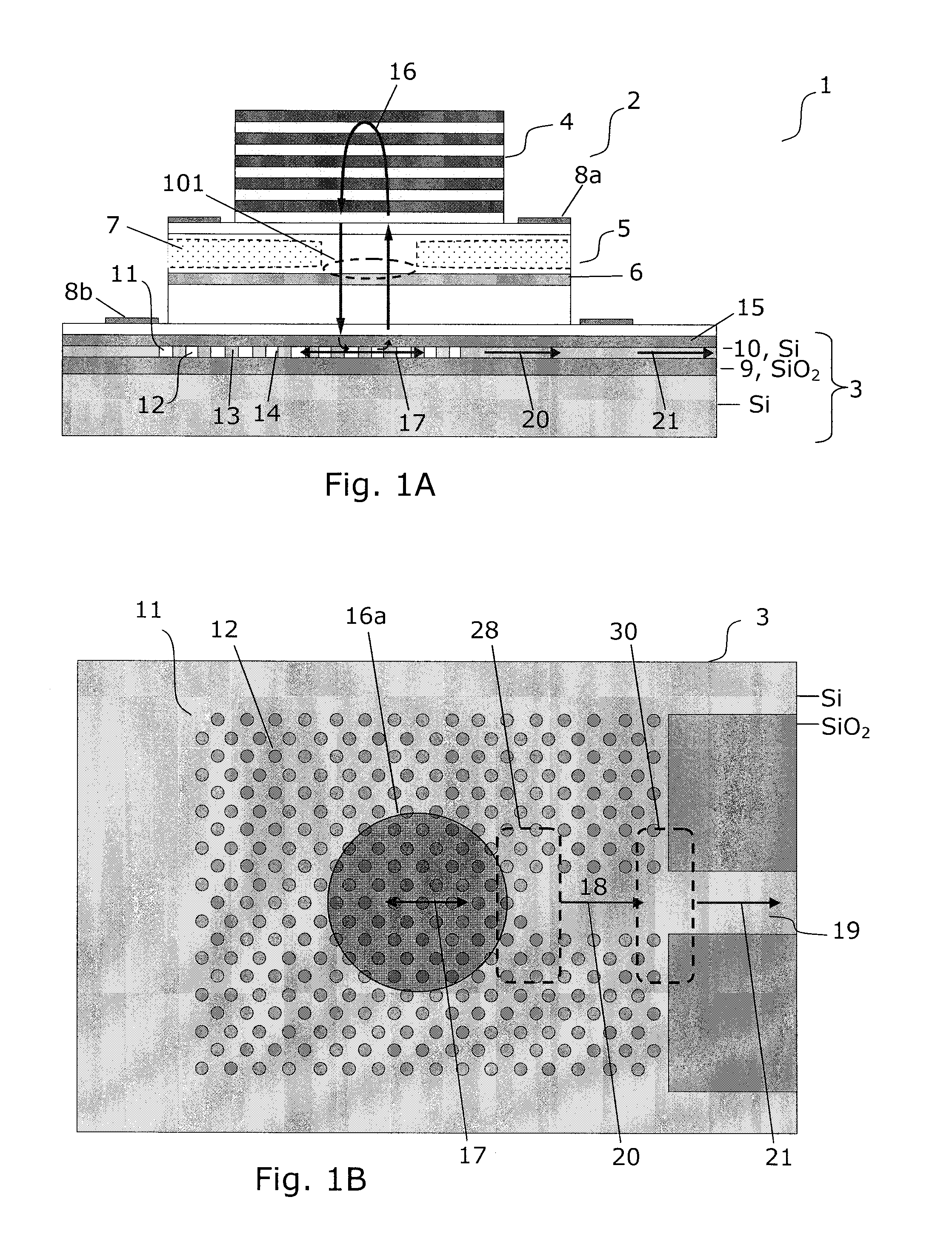
The present invention provides a light source (2) for light circuits on a silicon platform (3). A vertical laser cavity is formed by a gain region (101) arranged between a top mirror (4) and a bottom grating-mirror (12) in a grating region (11) in a silicon layer (10) on a substrate. A waveguide (18, 19) for receiving light from the grating region (11) is formed within or to be connected to the grating region, and functions as an 5 output coupler for the VCL. Thereby, vertical lasing modes (16) are coupled to lateral in-plane modes (17, 20) of the in-plane waveguide formed in the silicon layer, and light can be provided to e.g. photonic circuits on a SOI or CMOS substrate in the silicon.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Contact image sensor using switchable bragg gratings
ActiveUS20180120669A1High resolutionSolid-state devicesPrint image acquisitionContact image sensorGrating
Owner:DIGILENS
Method and Apparatus for Providing a Polarization Selective Holographic Waveguide Device
A waveguide apparatus, comprises: disposed in at least one layer: an input coupler; a first fold grating; a second fold grating; an output coupler; and a source of light optically coupled to the waveguide providing at least first and second polarizations of the light and at least one wavelength. The input coupler is configured to cause the first polarization light to travel along a first total internal reflection (TIR) path and the second polarization light to travel along a second TIR path.
Owner:DIGILENS
Beam generation and steering with integrated optical circuits for light detection and ranging
An integrated photonic beam steering device includes a planar photonic substrate. An input waveguide is configured to accept an electromagnetic energy from a source of electromagnetic energy radiation. A first splitter is configured to split the electromagnetic radiation into one or more paths. One or more phased array rows are optically coupled to each of the one or more paths. Each phased array row includes a row splitter configured to split the each of the one or more paths into two or more row paths. Two or more phase modulators are each optically coupled respectively to each of the two or more row paths. Two or more output couplers are optically coupled respectively to each phase modulator output of the two or more phase modulators. The two or more output couplers are configured to radiate a steered photonic beam away from the integrated photonic beam steering device.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
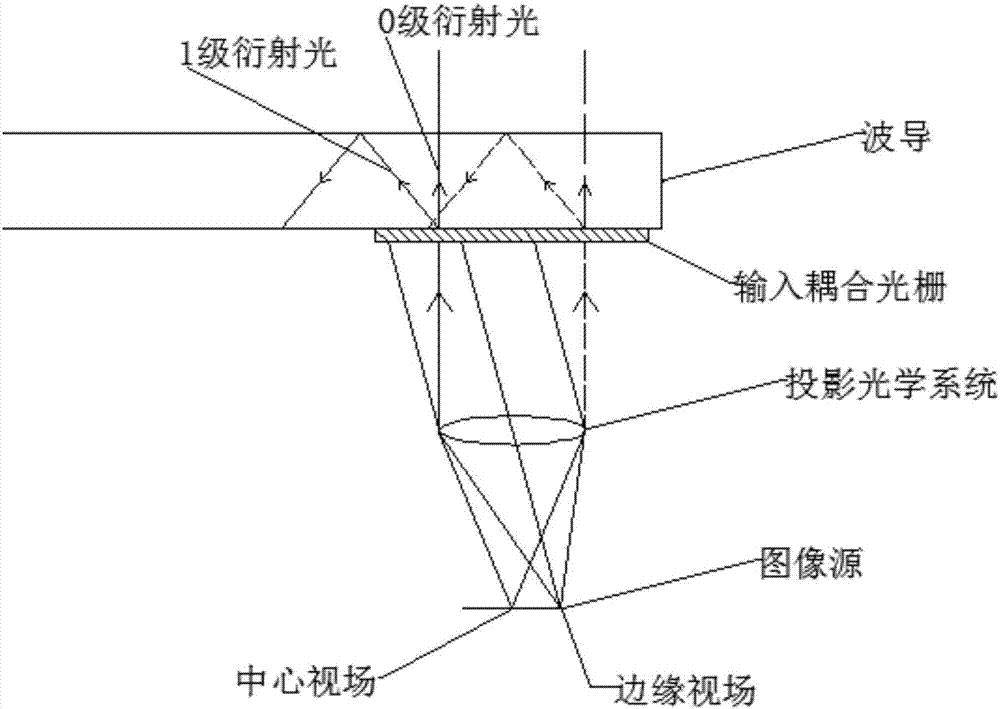
Waveguides with extended field of view
An input-coupler of an optical waveguide couples light corresponding to the image and having a corresponding FOV into the optical waveguide, and the input-coupler splits the FOV of the image coupled into the optical waveguide into first and second portions by diffracting a portion of the light corresponding to the image in a first direction toward a first intermediate-component, and diffracting a portion of the light corresponding to the image in a second direction toward a second intermediate-component. An output-coupler of the waveguide combines the light corresponding to the first and second portions of the FOV, and couples the light corresponding to the combined first and second portions of the FOV out of the optical waveguide so that the light corresponding to the image and the combined first and second portions of the FOV is output from the optical waveguide. The intermediate-components and the output-coupler also provide for pupil expansion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
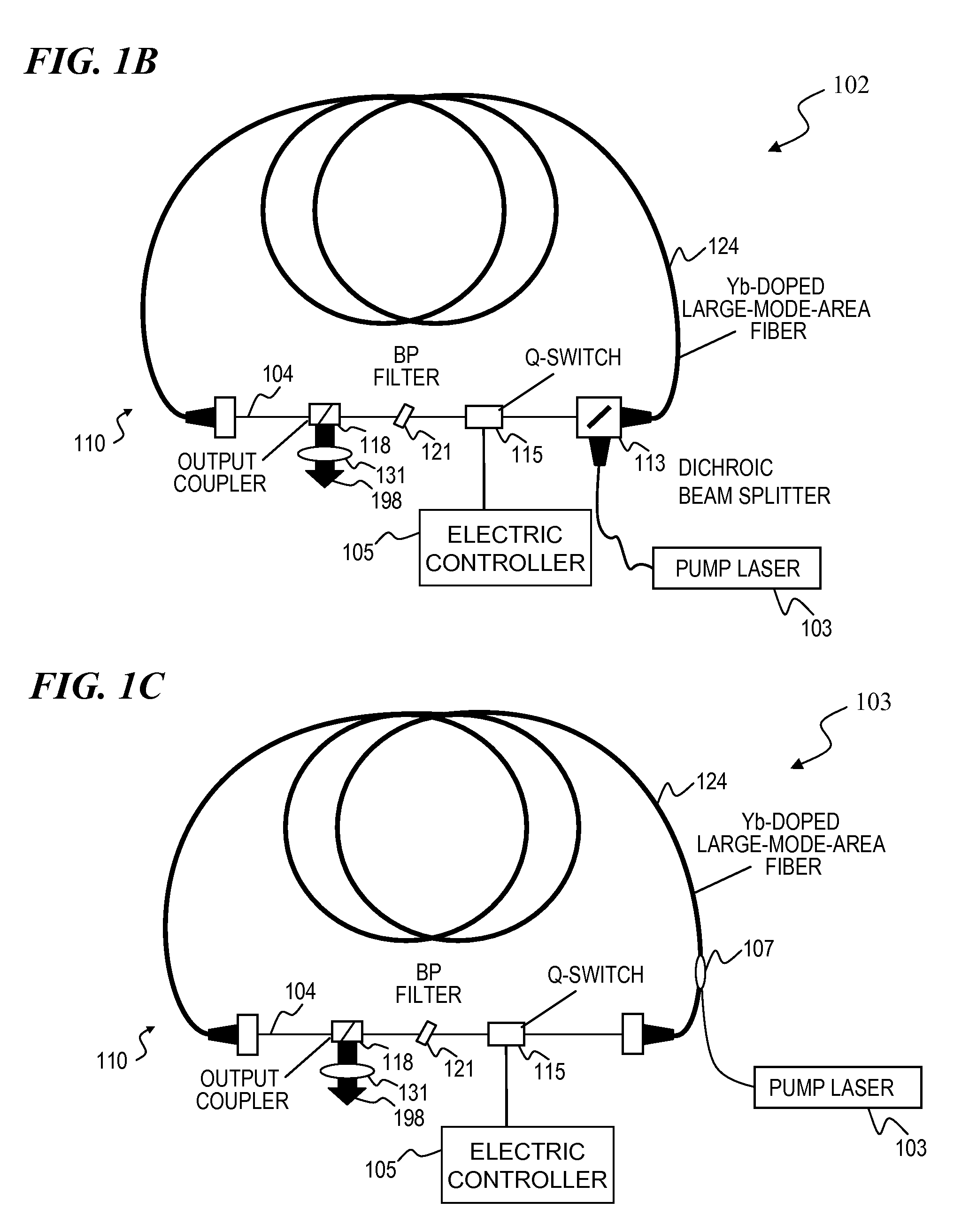
High-power, pulsed ring fiber oscillator and method
InactiveUS7876803B1Low costSmall footprintLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsBand-pass filterUltraviolet
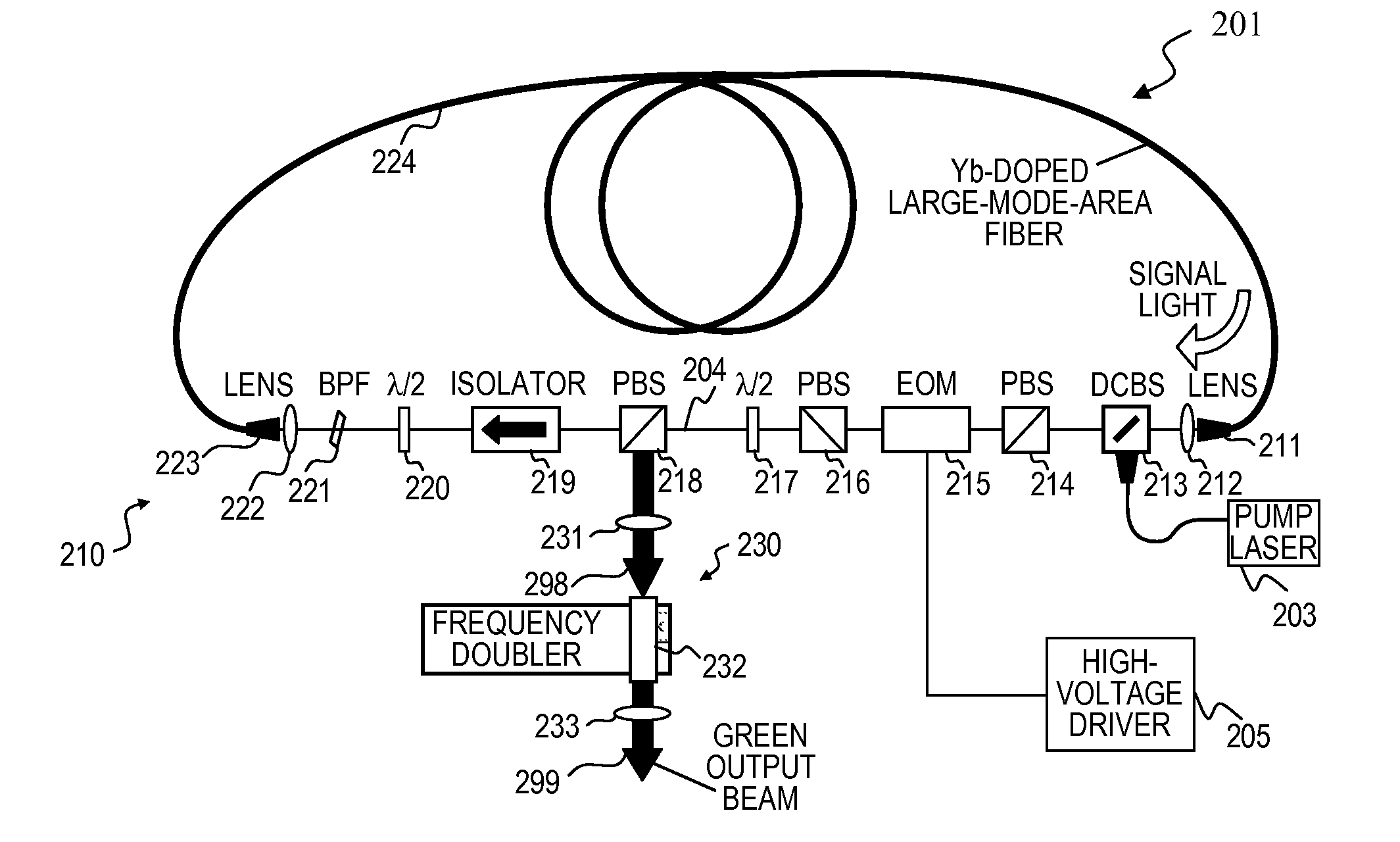
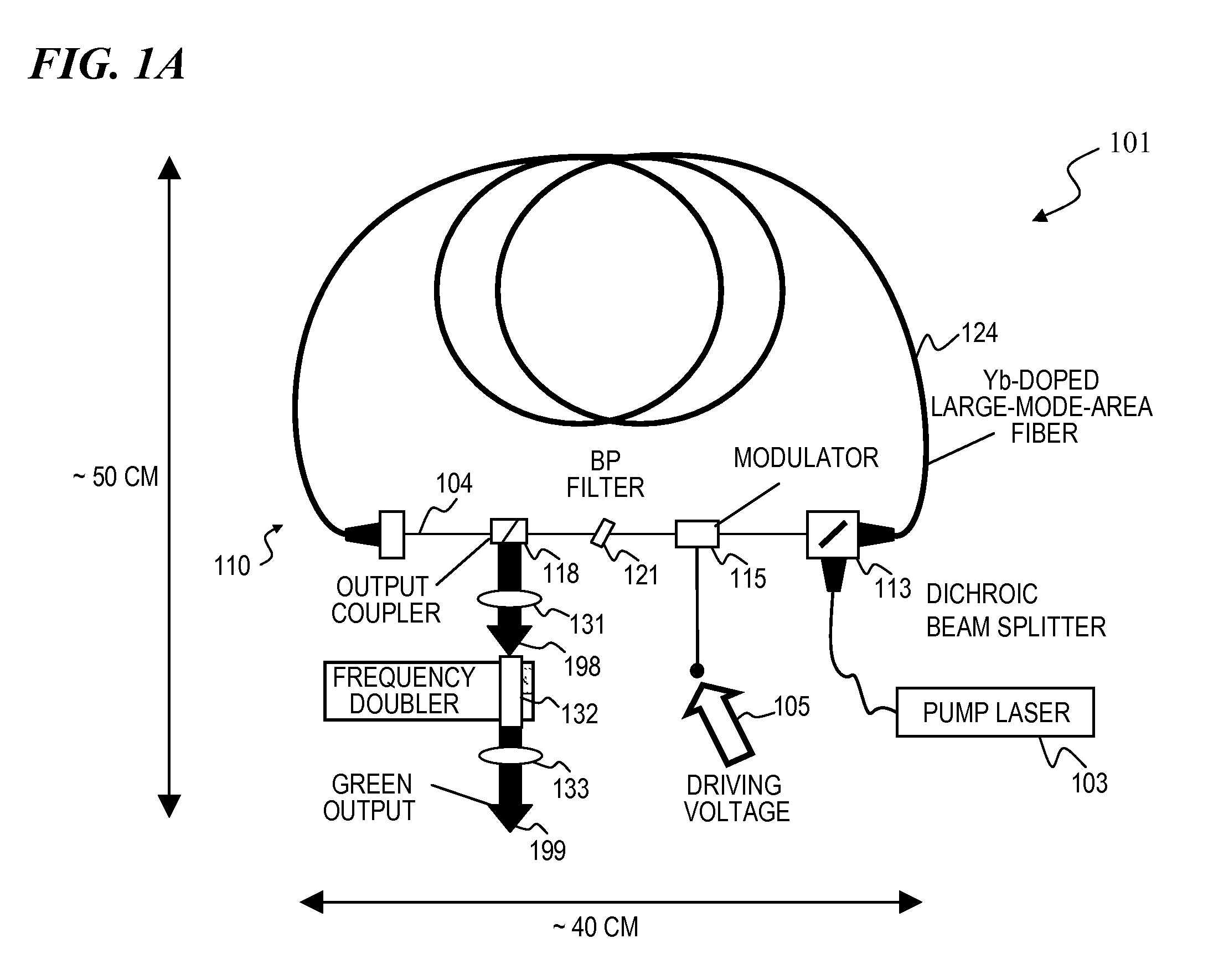
A ring laser includes a large-core rare-earth-doped fiber ring-connected with a free-space path having an electro-optic switch, output coupler, and intracavity band-pass filter to enforce lasing operation in narrow wavelength range. In some cavity-dumped modes, the laser is configured in a similar manner, except that an output coupler is omitted since the optical power is extracted from the laser cavity by the electro-optic switch itself. The same laser can be configured to operate in Q-switched and / or cavity-dumping modes as well as in hybrid modes (e.g., partial Q-switch, followed by cavity dumping, or even CW). In some embodiments, the laser can be used as, or inject laser light into, a regenerative solid-state amplifier, or a Raman laser, or can be also used to generate visible, ultra-violet, mid-infrared, and far-infrared (THz) radiation via nonlinear wavelength conversion processes. The various embodiments can use a power oscillator or seed-plus-amplifier MOPA configuration.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
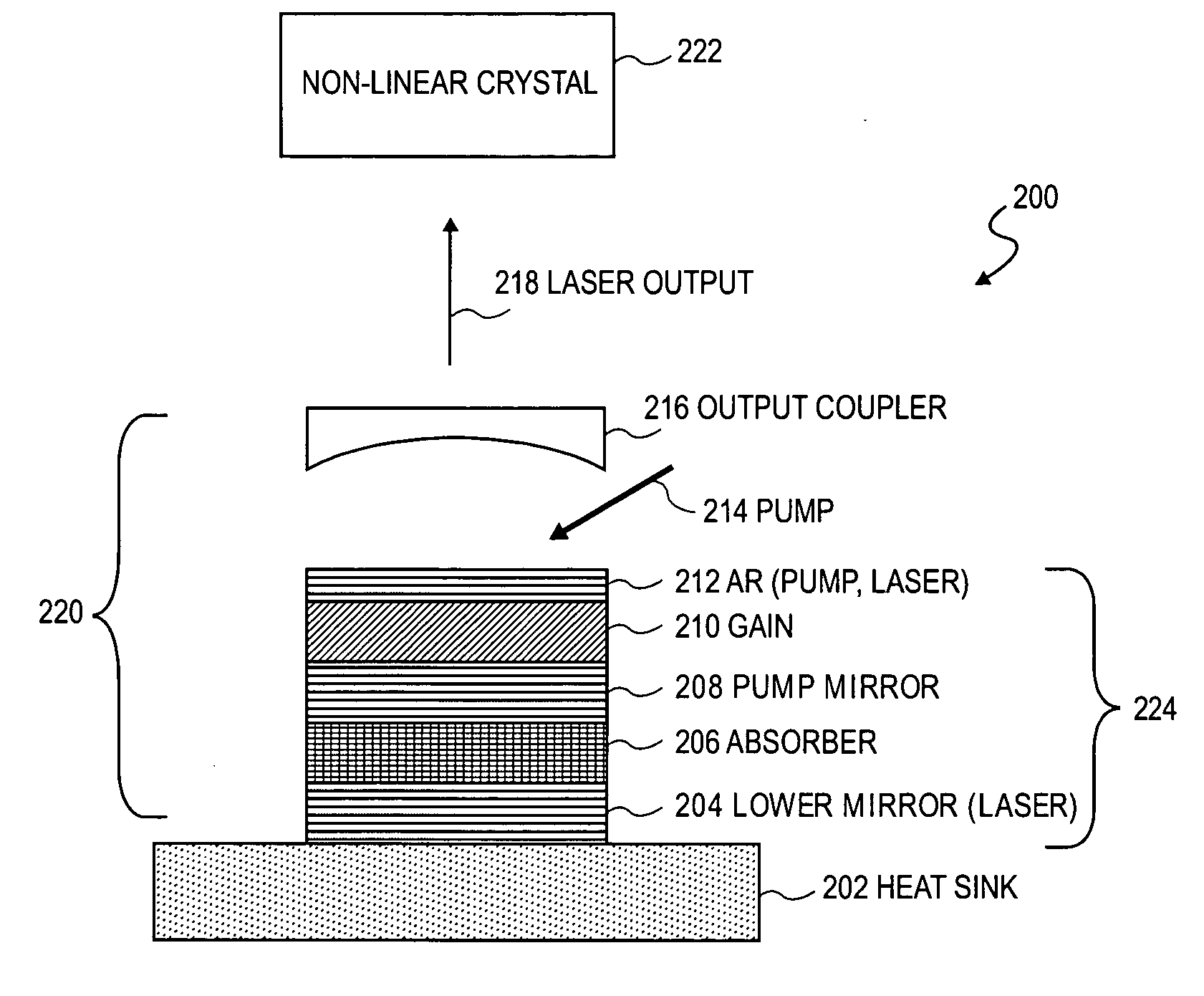
Surface emitting laser with an integrated absorber
InactiveUS20060029112A1Laser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionOutput couplerOptoelectronics
A surface emitting laser (SEL) with an integrated absorber. A lower mirror and an output coupler define a laser cavity of the SEL. A monolithic gain structure positioned in the laser cavity includes a gain region and an absorber, wherein a saturation fluence of the absorber is less than a saturation fluence of the gain region.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
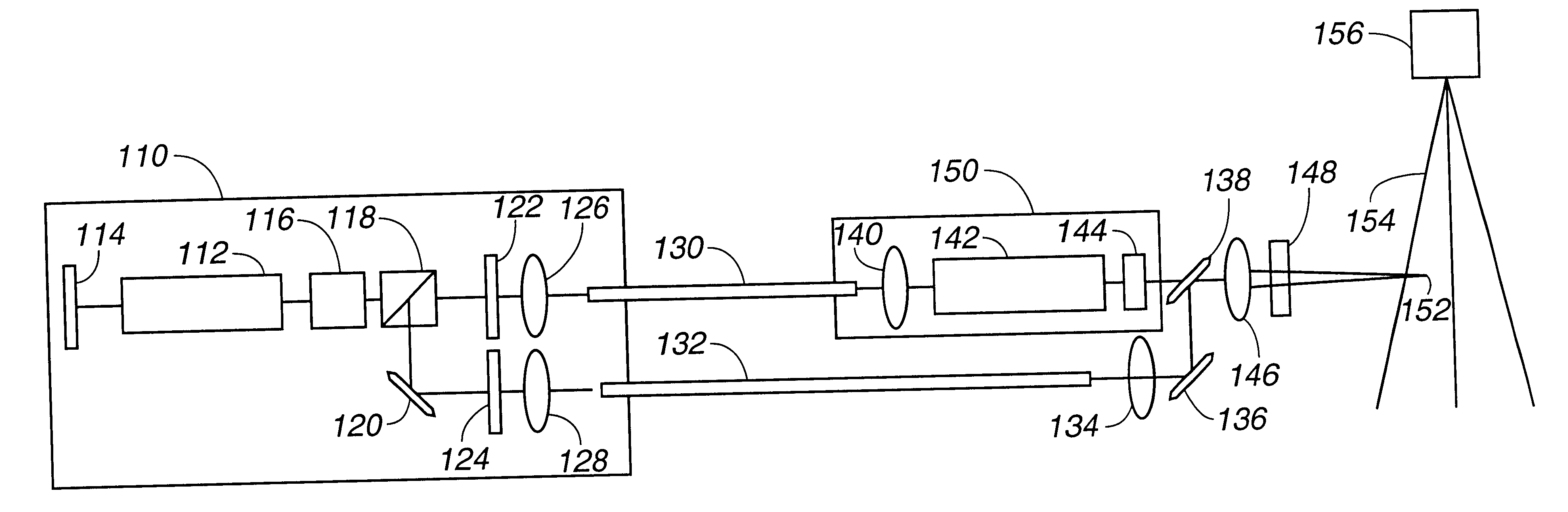
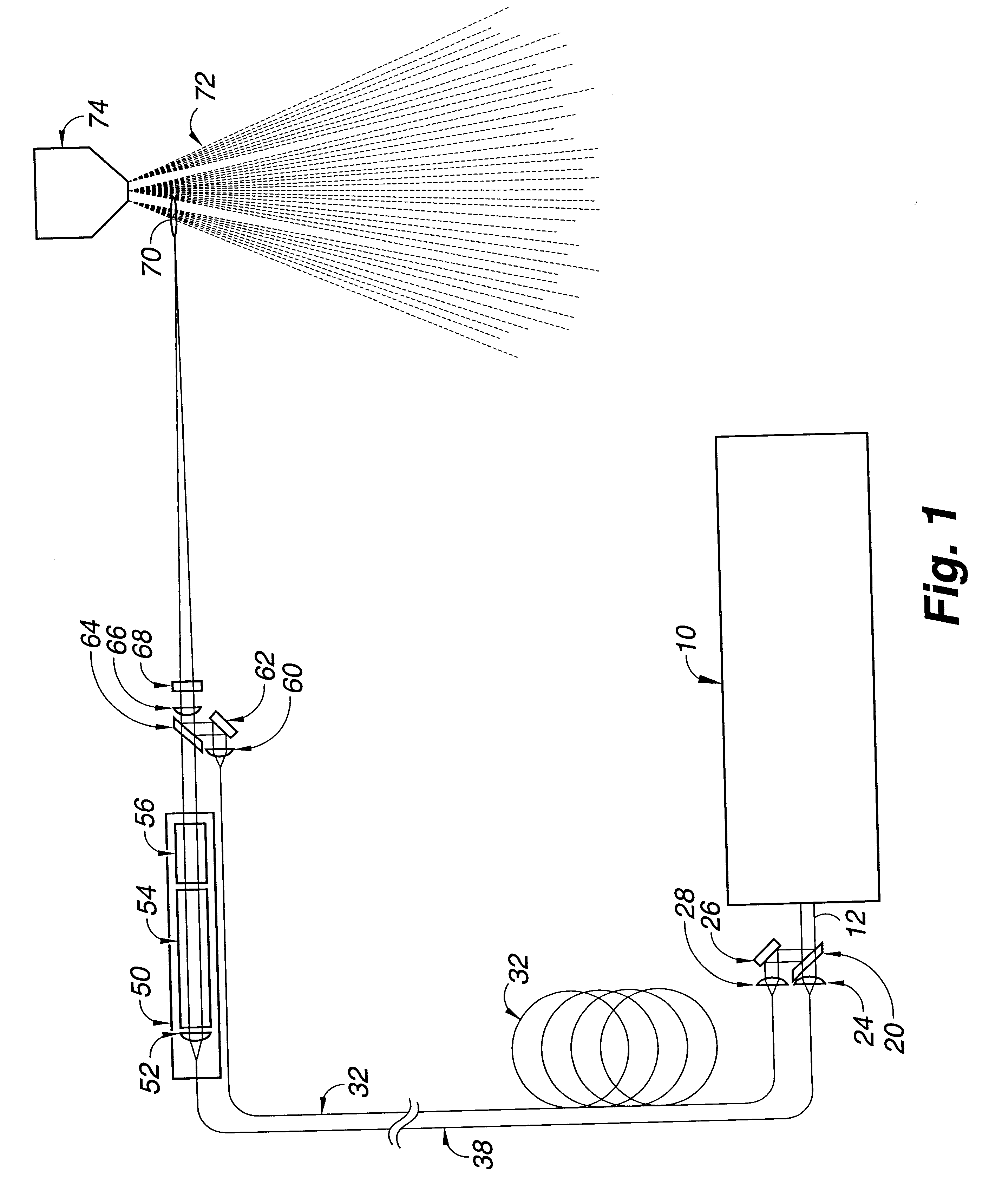
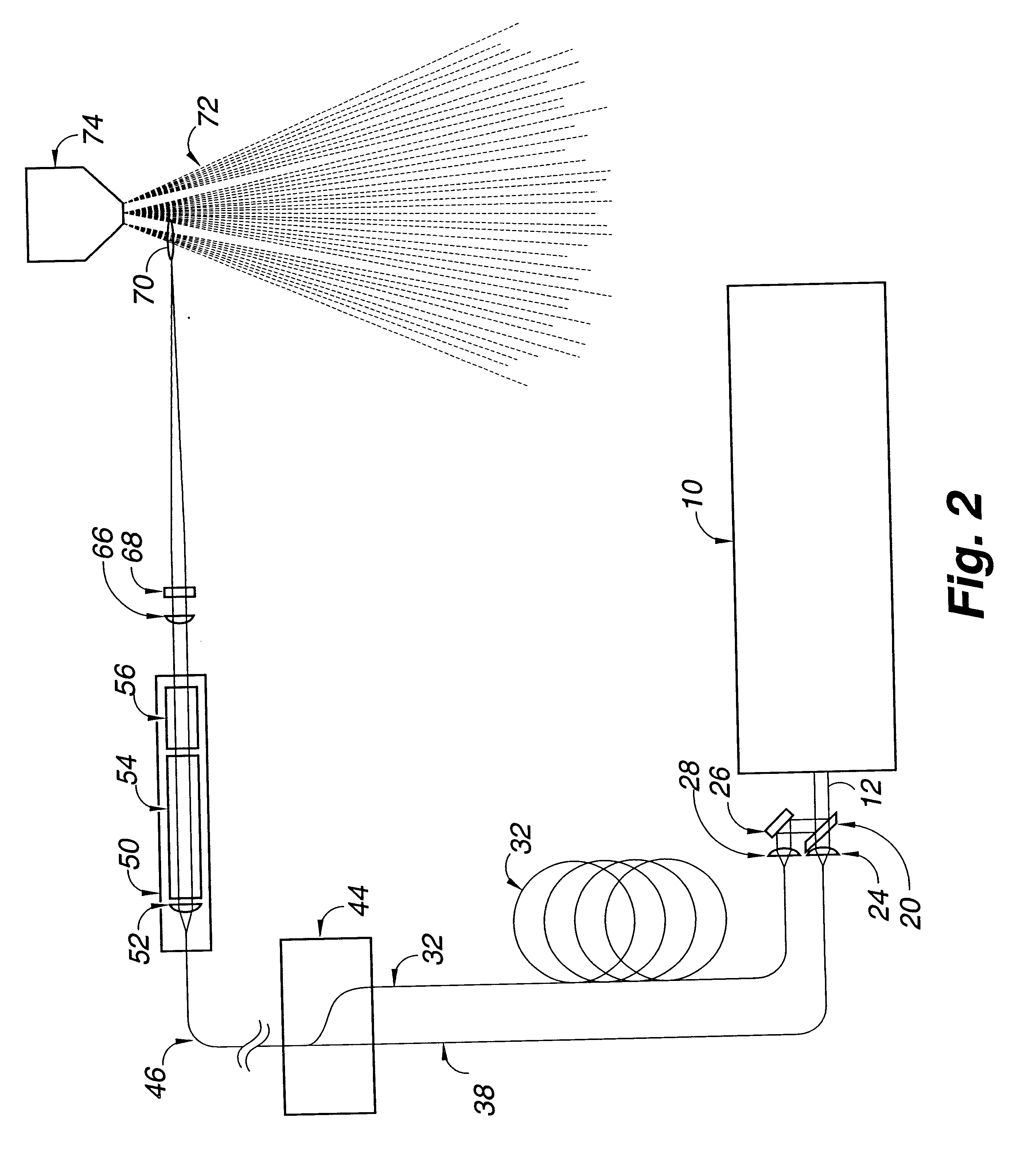
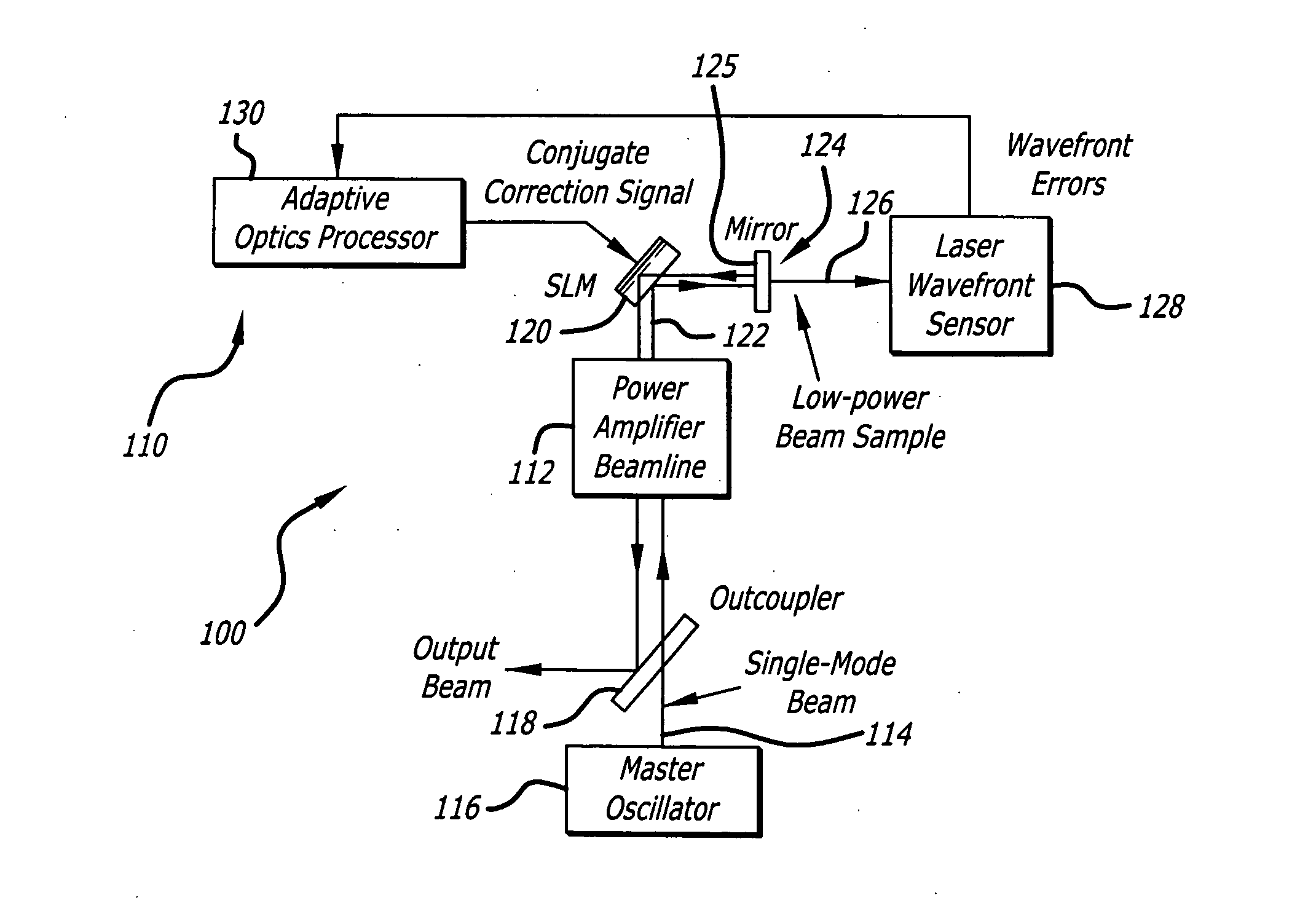
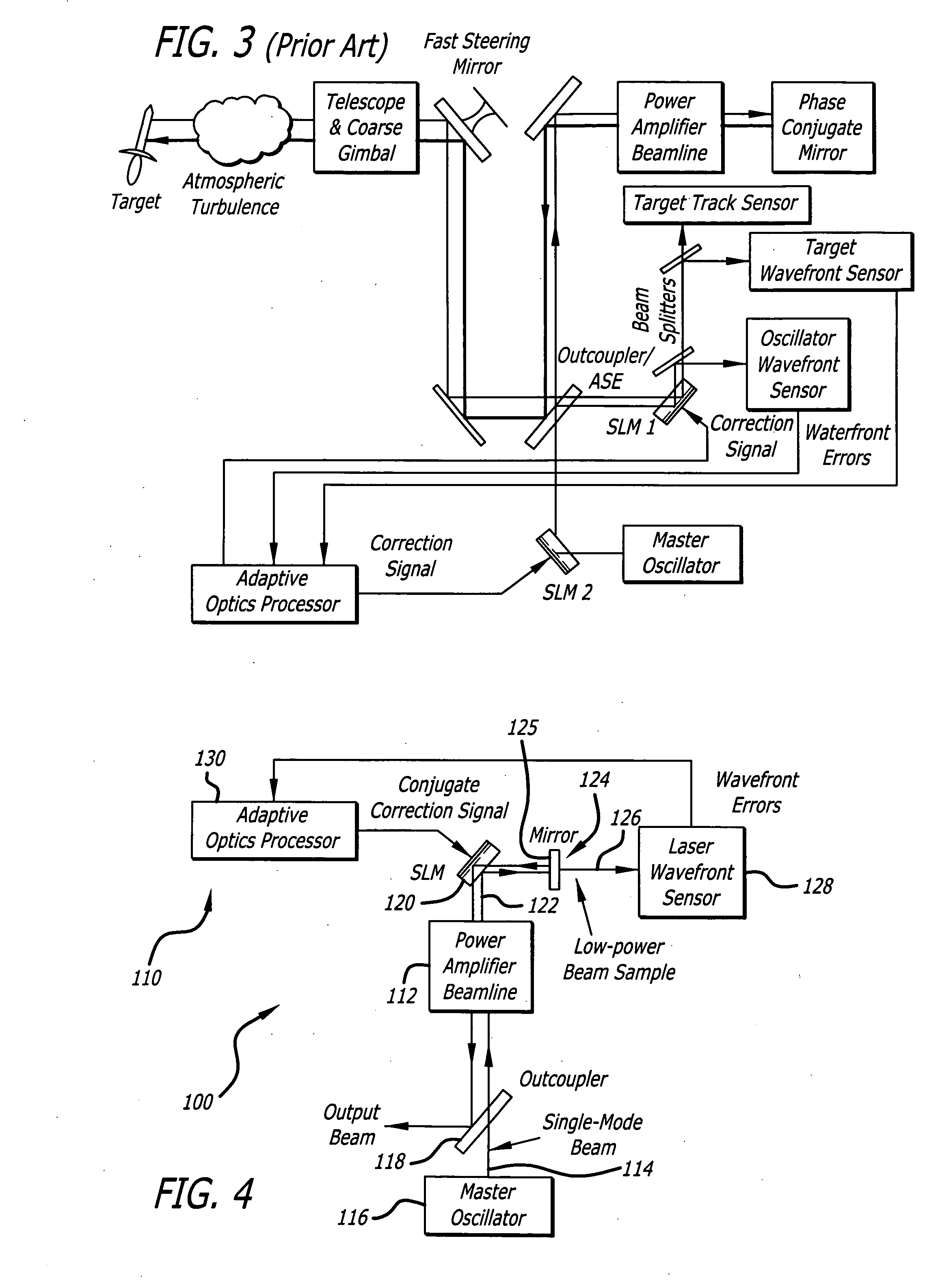
Linear adaptive optics system in low power beam path and method
InactiveUS20100232007A1Aberration correctionDirection controllersDirected energy weaponsDielectricWavefront sensor
A system and method for providing a wavefront corrected high-energy beam of electromagnetic energy. In the illustrative embodiment, the system includes a source of a first beam of electromagnetic energy; an amplifier for amplifying said beam to provide a second beam; a sensor for sensing aberration in said second beam and providing an error signal in response thereto; a processor for processing said error signal and providing a correction signal in response thereto; and a spatial light modulator responsive to said correction signal for adjusting said beam to facilitate a correction of said aberration thereof. In more specific embodiments, the source is a laser and the sensor is a laser wavefront sensor. A mirror is disposed between said modulator and said sensor for sampling said beam. The mirror has an optical thin-film dielectric coating on at least one optical surface thereof. The coating is effective to sample said beam and transmit a low power sample thereof to said means for sensing aberration. The processor is an adaptive optics processor. The spatial light modulator may be a micro electro-mechanical system deformable mirror or an optical phased array. In the illustrative embodiment, the source is a master oscillator and the amplifier is a power amplifier beamline. An outcoupler is disposed between the oscillator and the amplifier.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
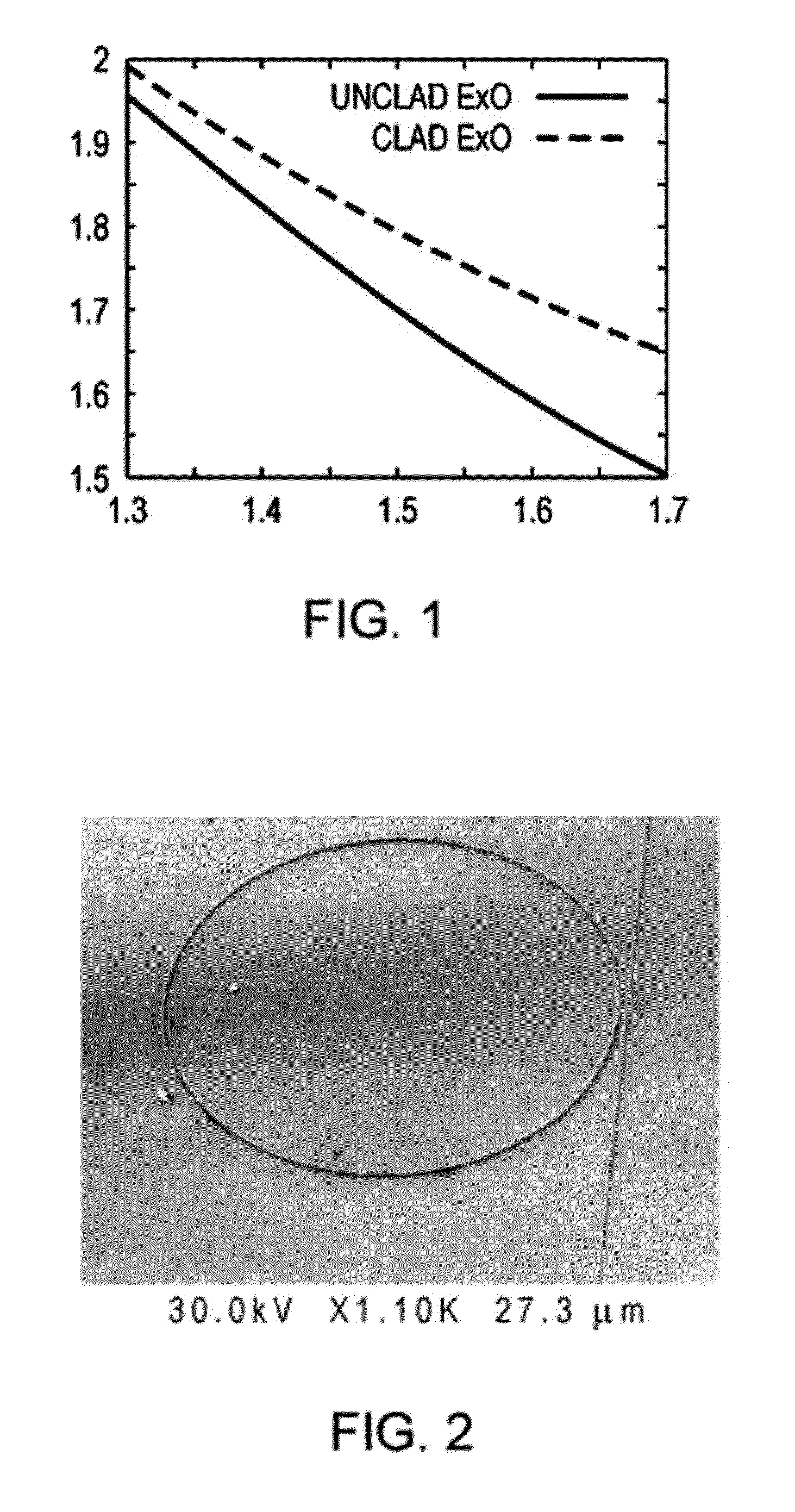
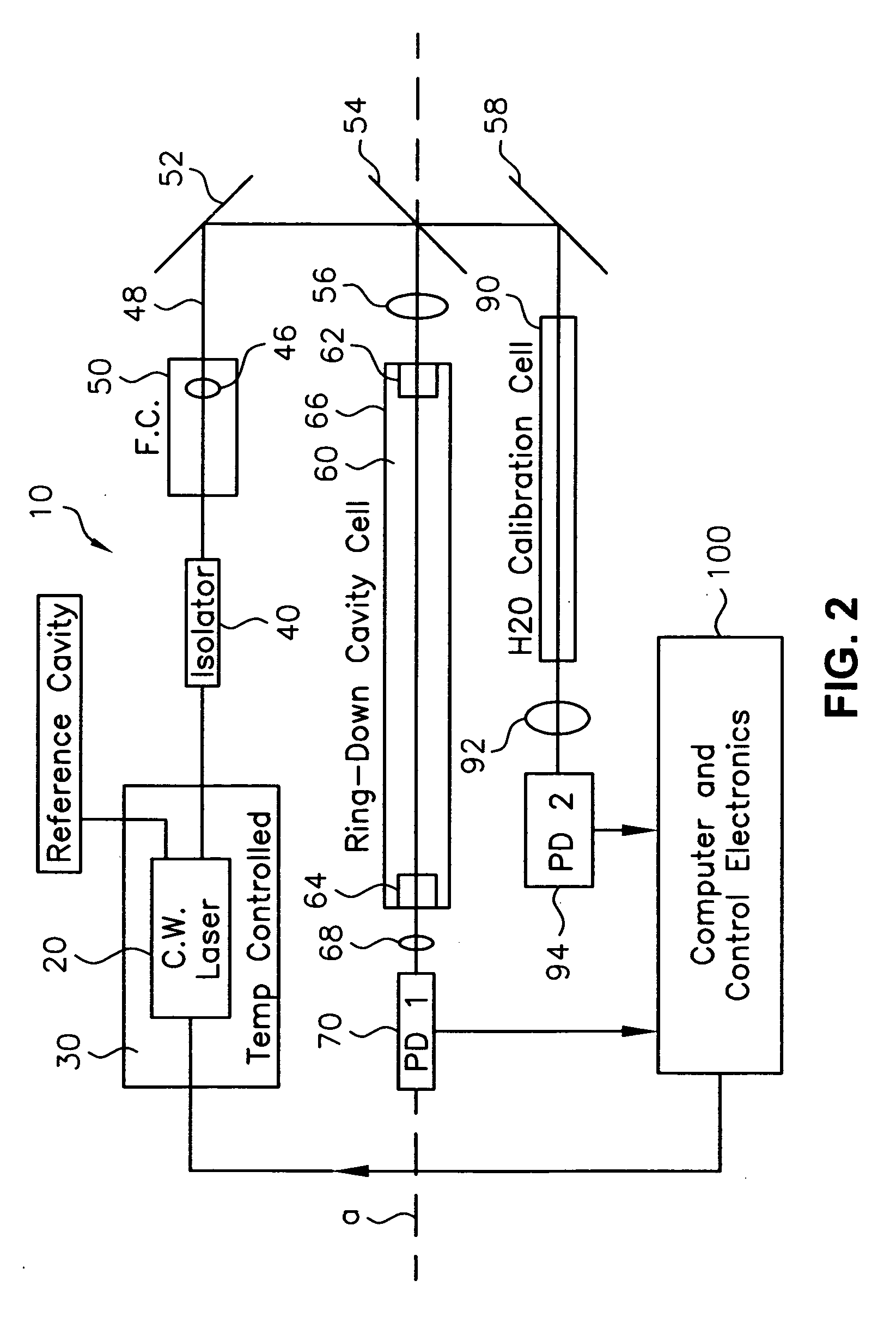
Apparatus for enhanced evanescent field exposure in an optical fiber resonator for spectroscopic detection and measurement of trace species
InactiveUS20060183241A1Increase reduction rateIncrease exposureAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFiberRing down
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
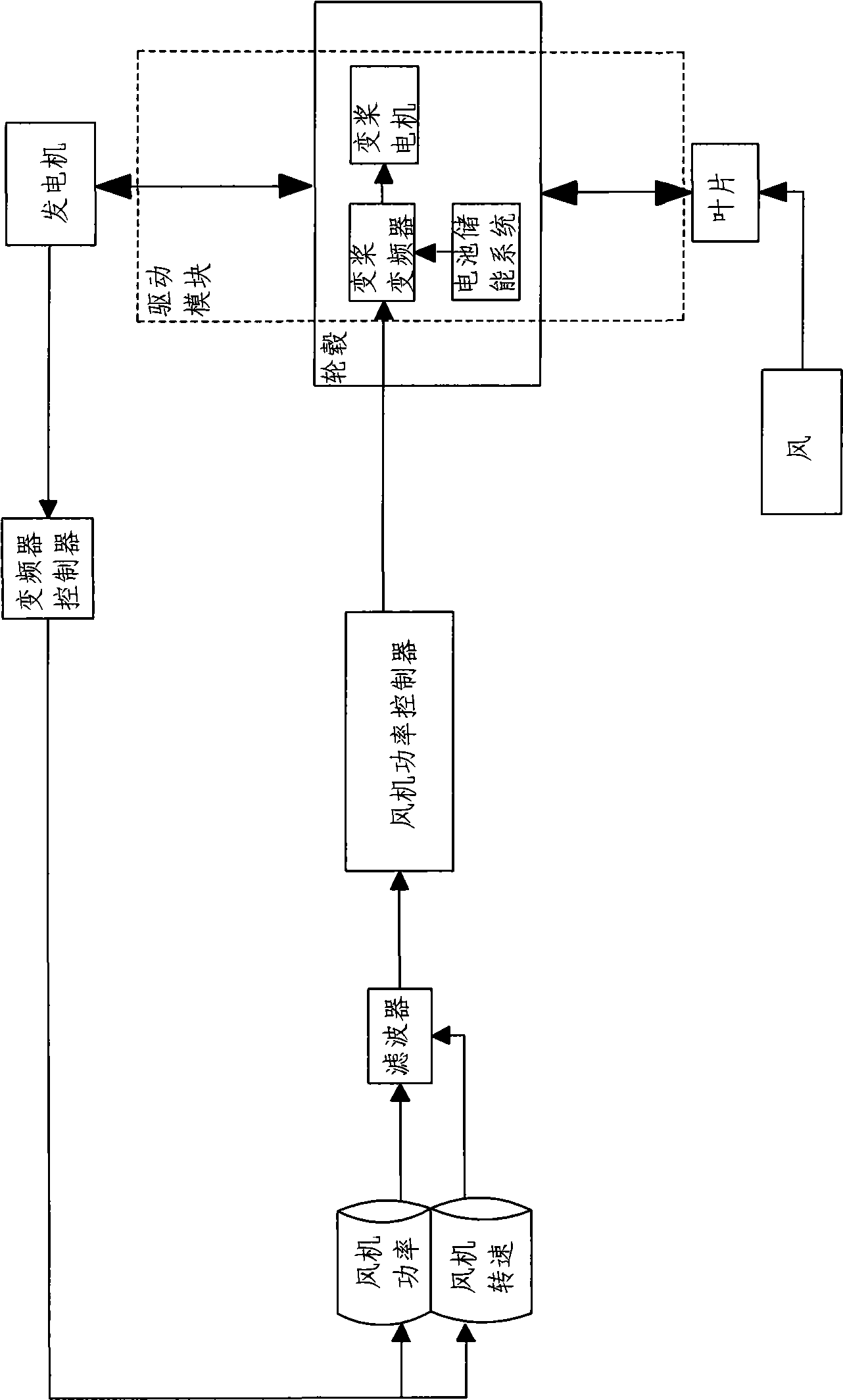
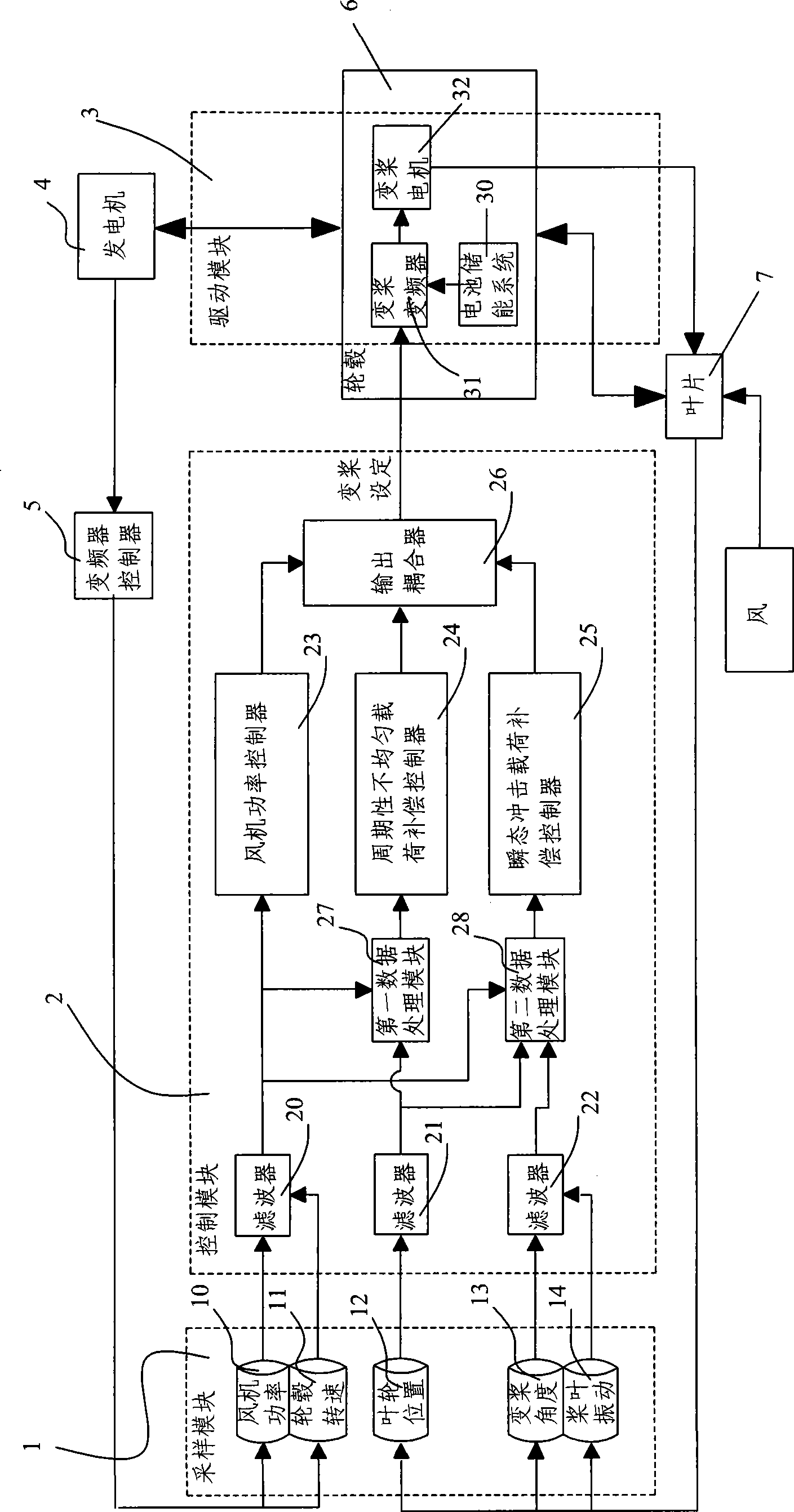
Independent variable oar control system and control method for wind generator set
ActiveCN101476541AIncreased fatigue loadLow mechanical requirementsWind motor controlMachines/enginesWind drivenReduction drive
The invention relates to an independent feathering control system and a control method for a wind driven generating set, wherein the control system comprises a sampling module, a control module and a driving module. A feathering motor in the driving module is connected with the blades of the wind driven generating set through a speed reducer. The sampling module is used to acquire the signals such as the wind driven generating set power, the boss rotating speed, the impeller position, the feathering angle, the paddle vibration, and the like, and to respectively send the acquired signals to the control module. The control module comprises a wind machine power controller for processing the wind driven generating set power signal and the boss rotating speed signal, a periodic unbalanced load compensation controller for processing the impeller position signal, the wind machine power signal and the boss rotating speed signal, a transient state impact load compensation controller for processing the feathering angle signal, the paddle vibration signal, the impeller position signal, the wind machine power signal and the boss rotating speed signal, and an output coupler for processing the signals outputted from the three controllers and comprehensively outputting the signals to the driving module.
Owner:SINOVEL WIND GRP
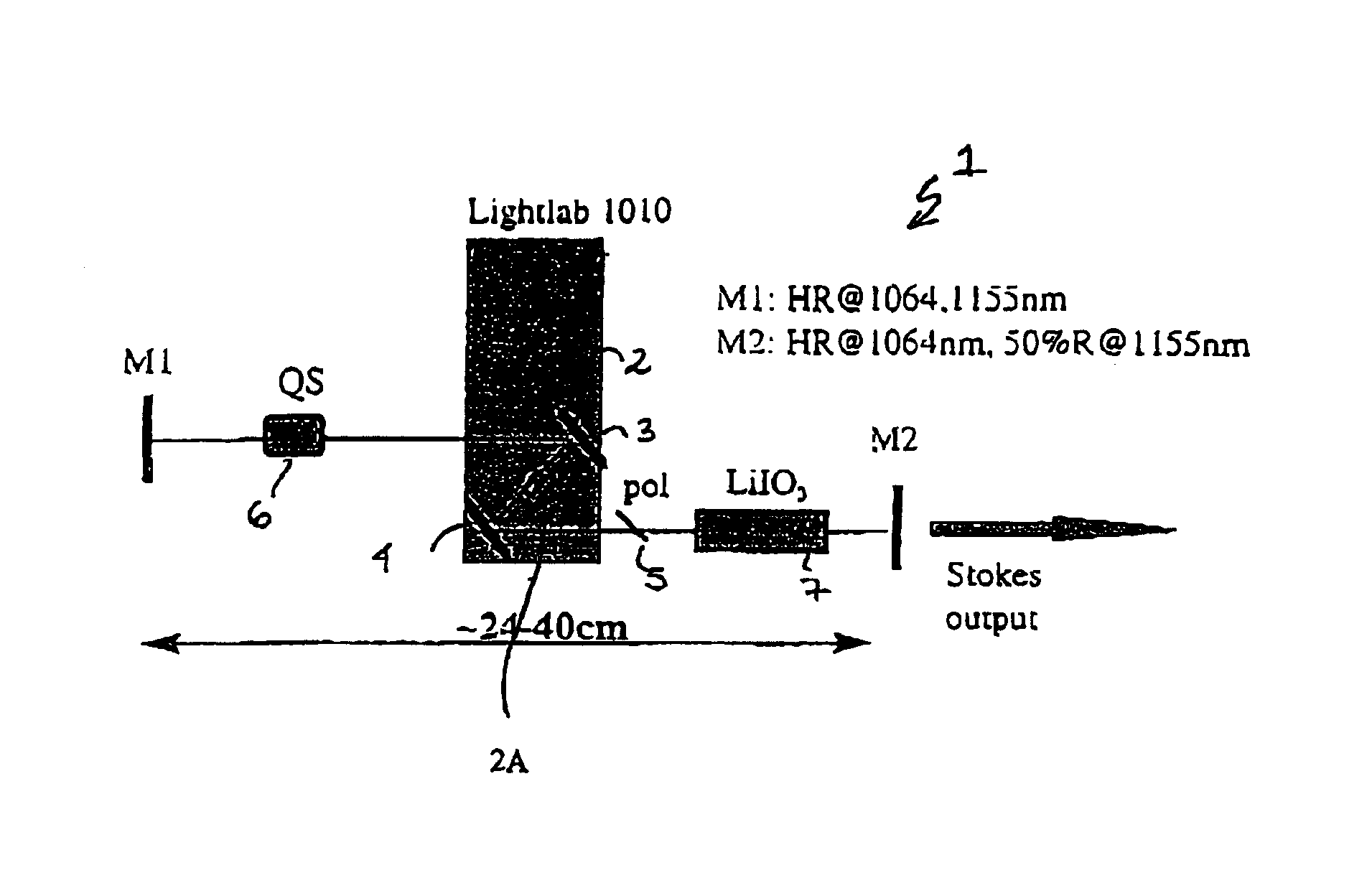
Stable solid state raman laser and method of operating same
InactiveUS20040028090A1Effective approachLimited scalabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSolid massInstability
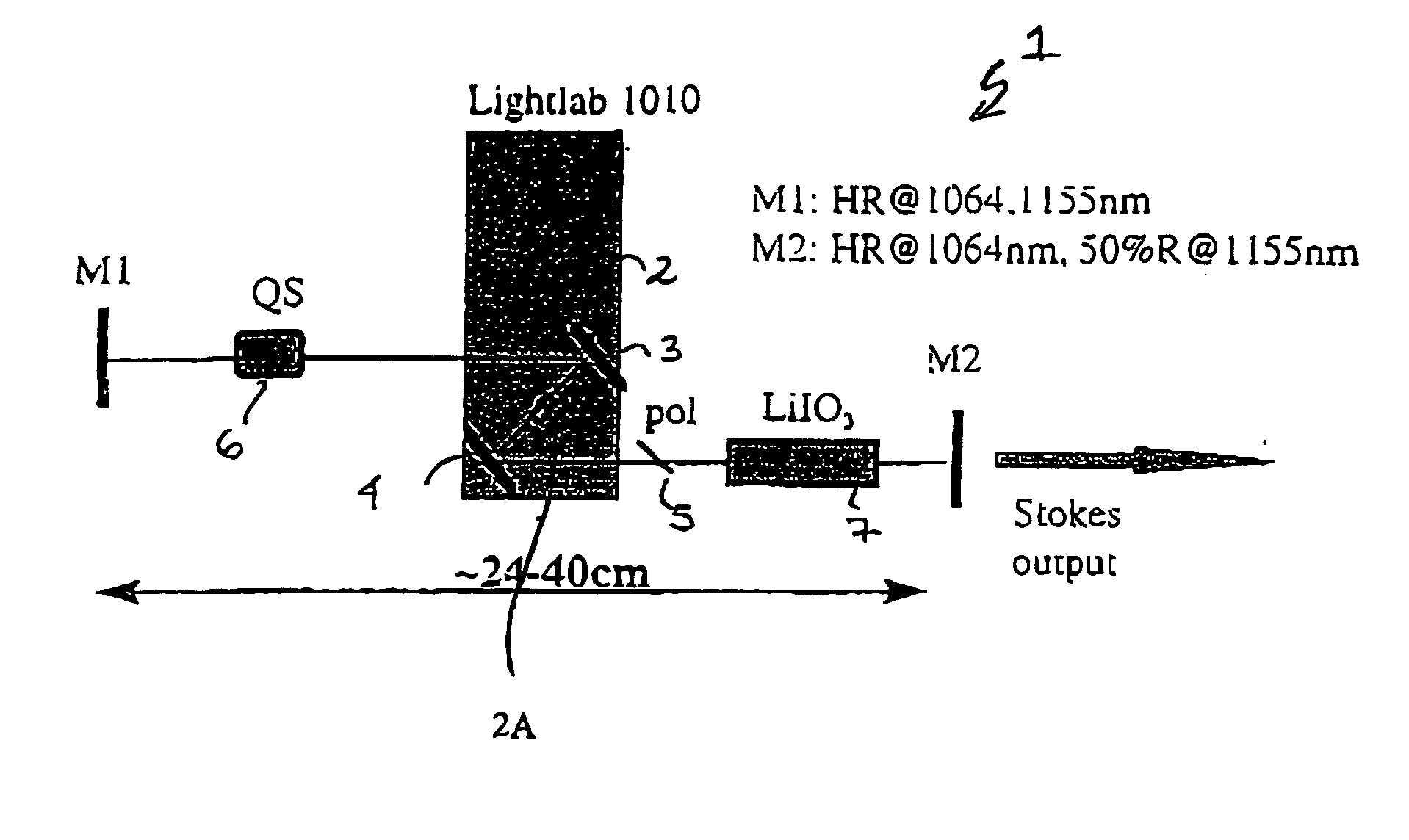
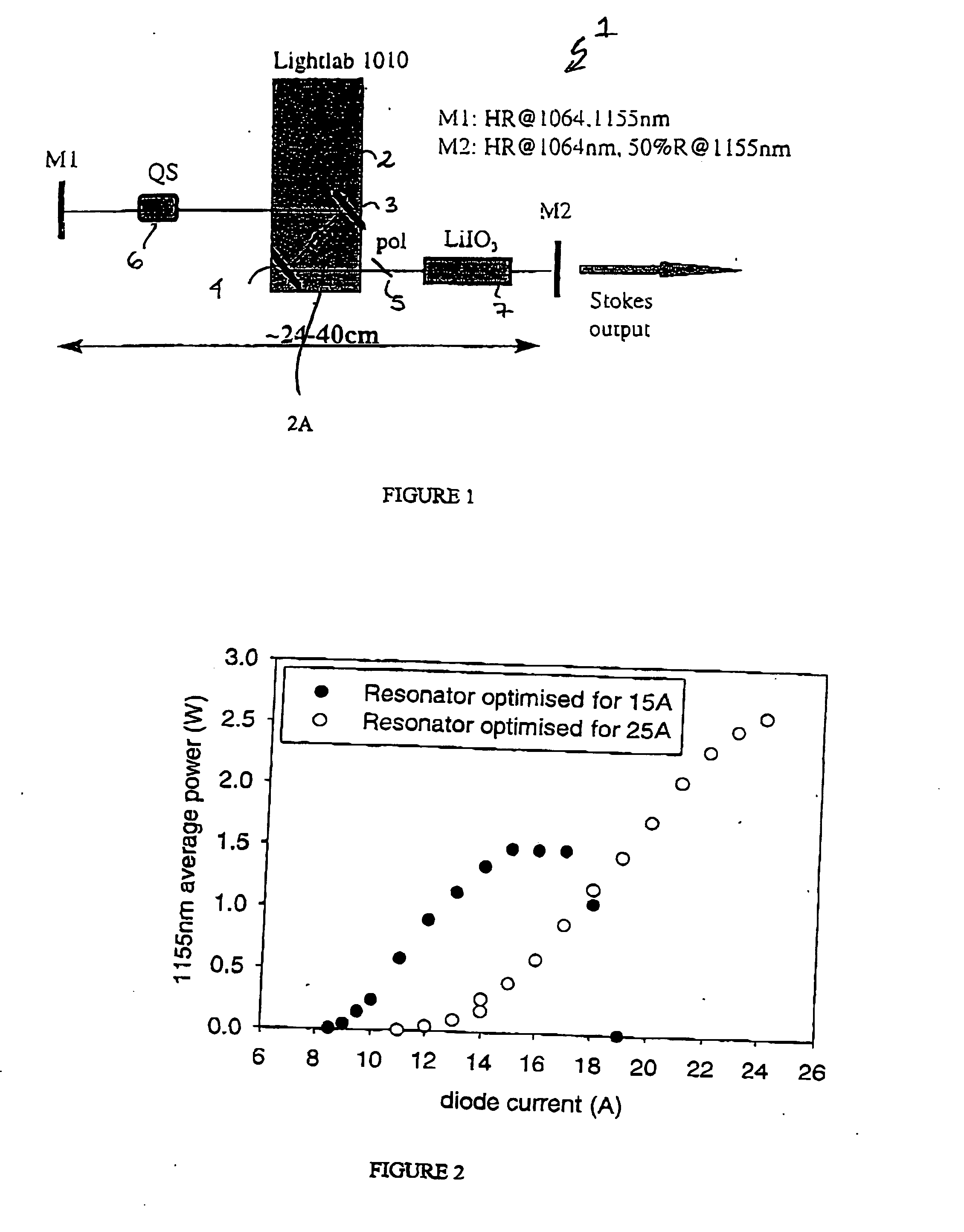
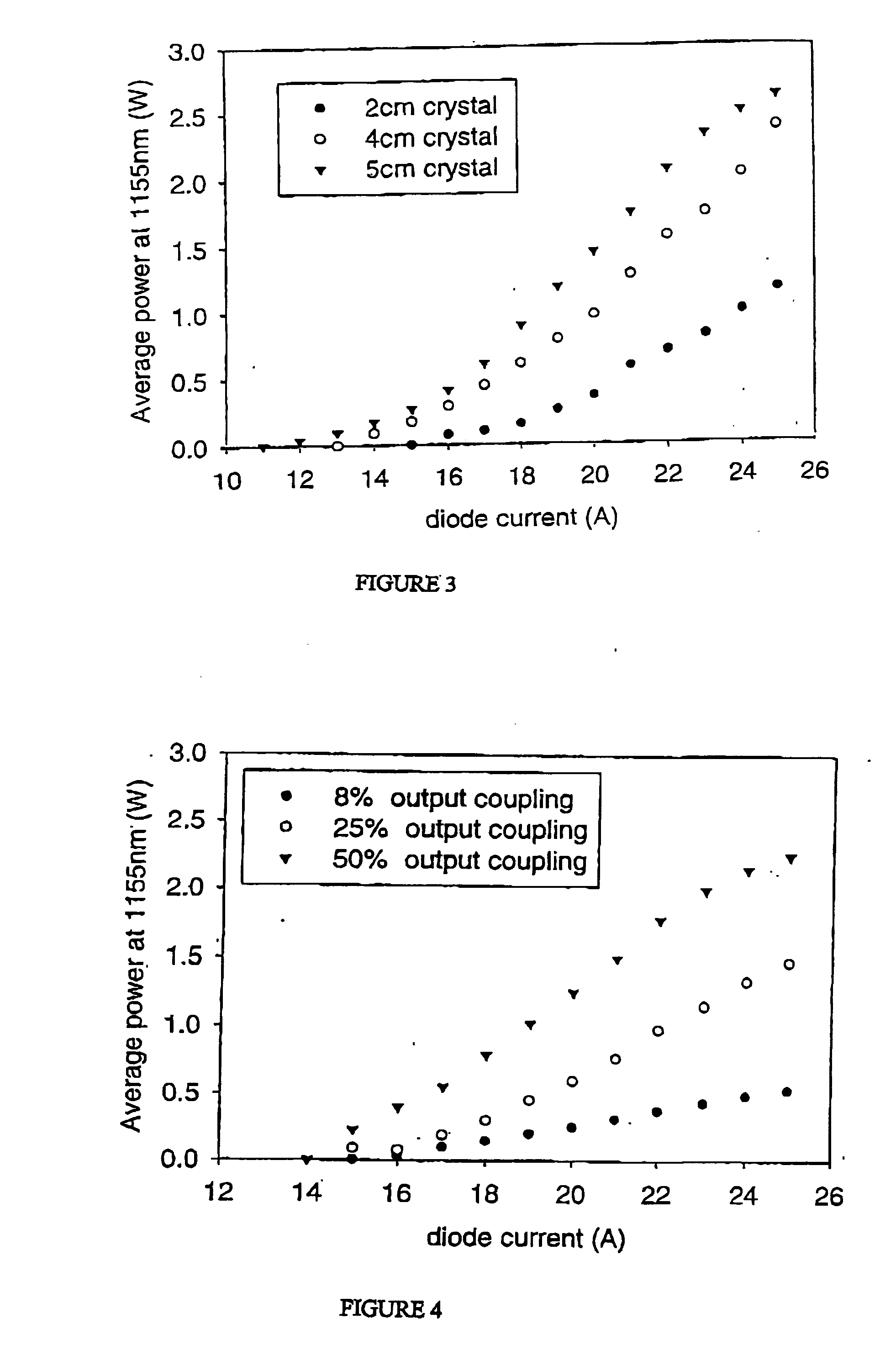
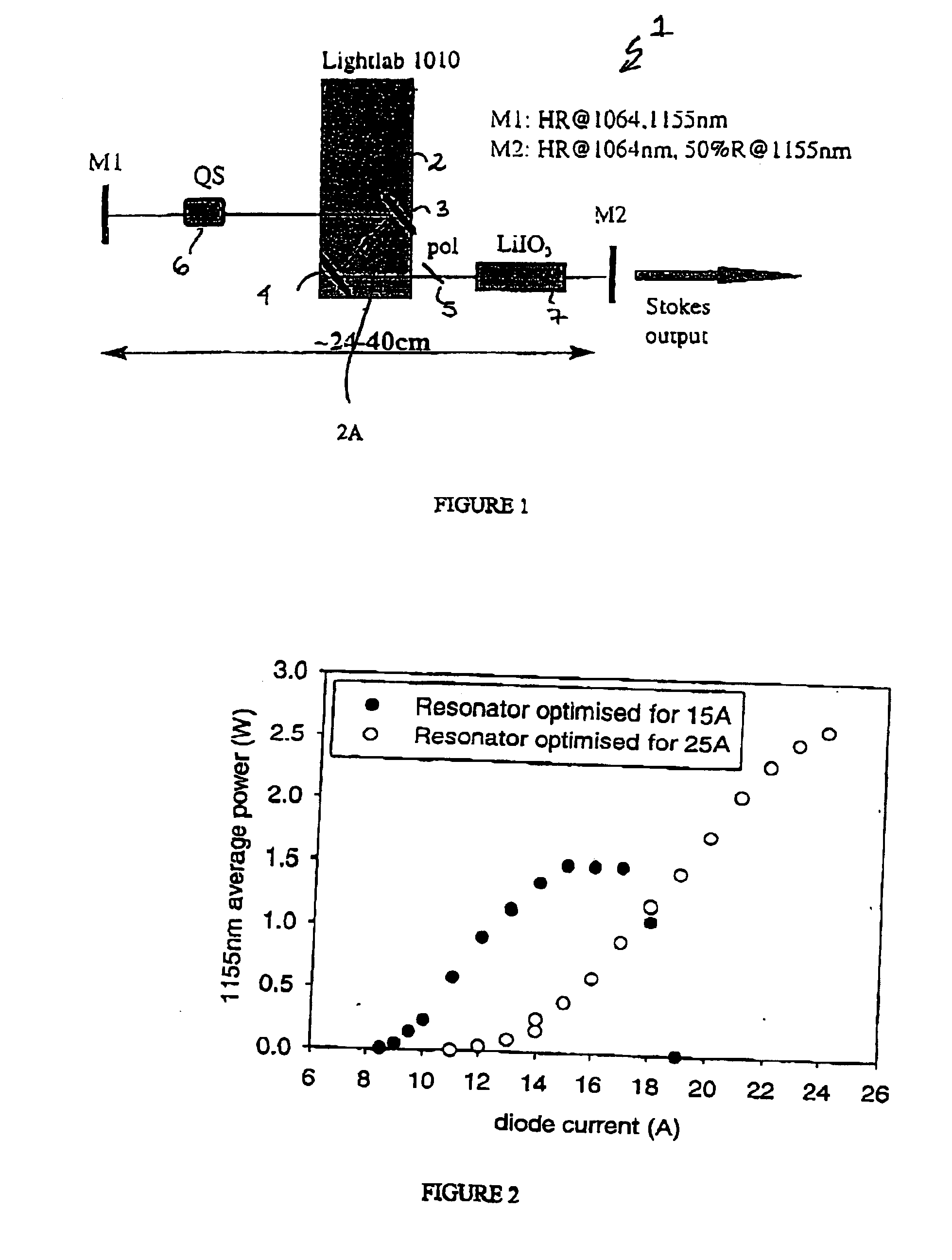
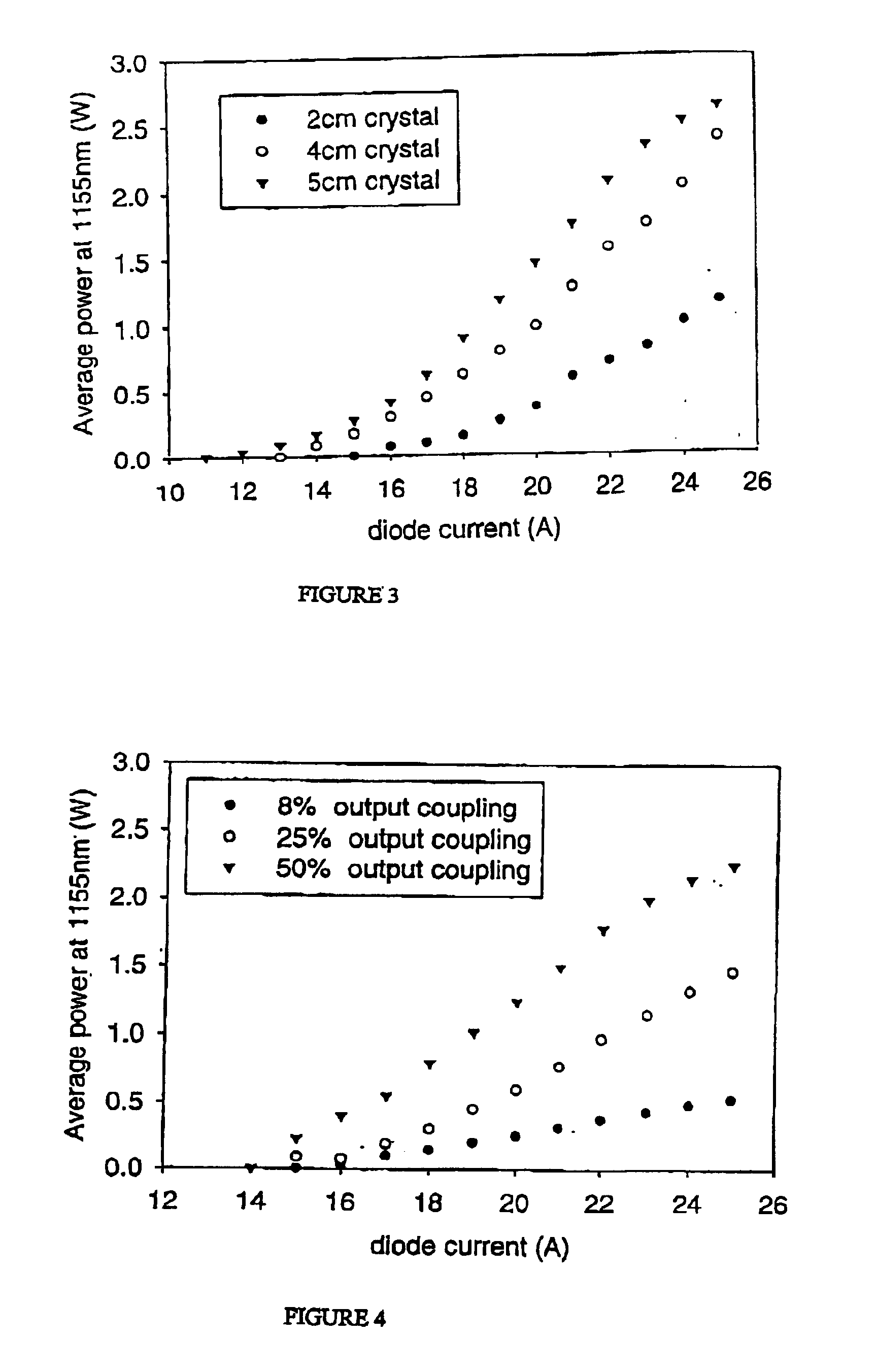
The present invention relates to a stable solid-state Raman laser (1), the solid-state Raman laser including: (a) a resonator cavity defined by at least two reflectors (M1 and M2), (b) a laser material (2A) located in the resonator cavity and capable of generating a cavity laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity, (c) a solid Raman medium (7) located in the resonator cavity for shifting the frequency of the cavity laser beam to produce a Raman laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity; and (d) an output coupler (M2) for coupling and outputting the Raman laser beam from the resonator cavity, wherein at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of (i) the position of the laser material (2A) relative to the position of the Raman medium (7) in the cavity, (ii) the length of the cavity and (iii) the curvature of at least one of the reflectors (M1 or M2), is selected such that changes in the focal lengths of both the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) as a result of thermal effects in the laser material (2A) and the Raman medium (7) during operation of the laser do not substantially cause instability in the power of the output Raman laser beam. A method of maintaining stable operation of a solid state Raman laser is also described.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Reliable, modular, production quality narrow-band high rep rate F2 laser
InactiveUSRE38054E1Improve product qualityFast chargingVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEngineeringHigh pressure
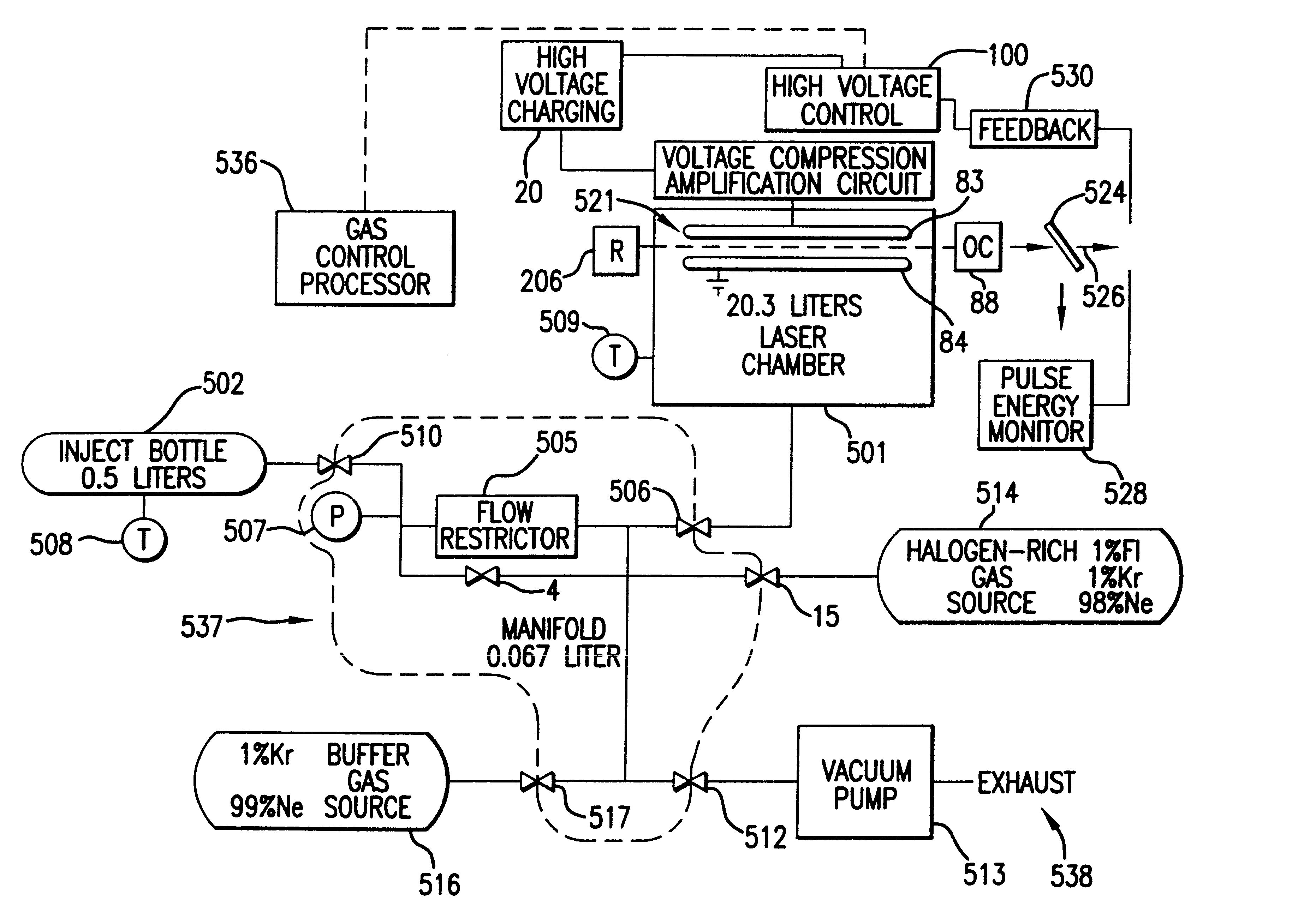
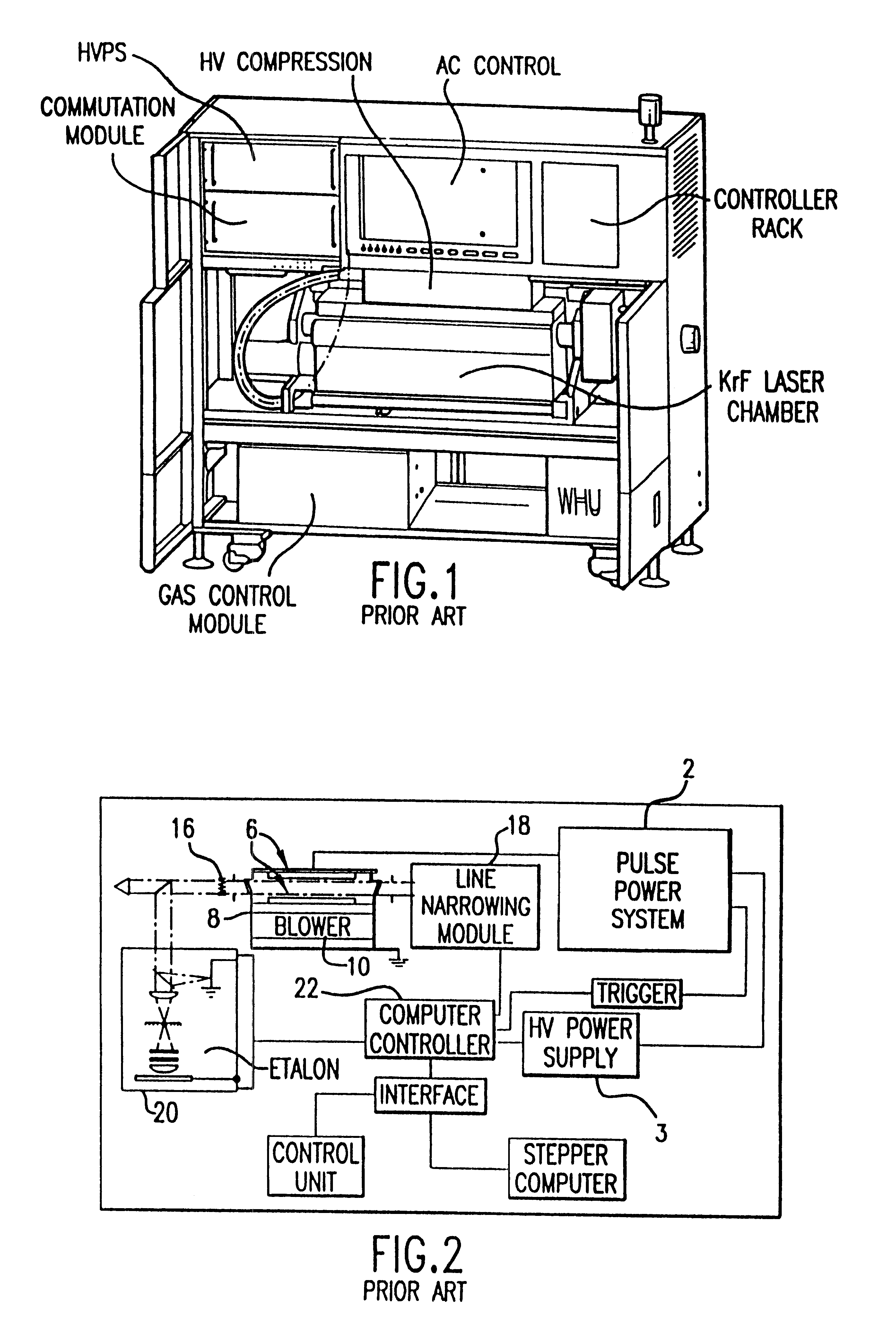
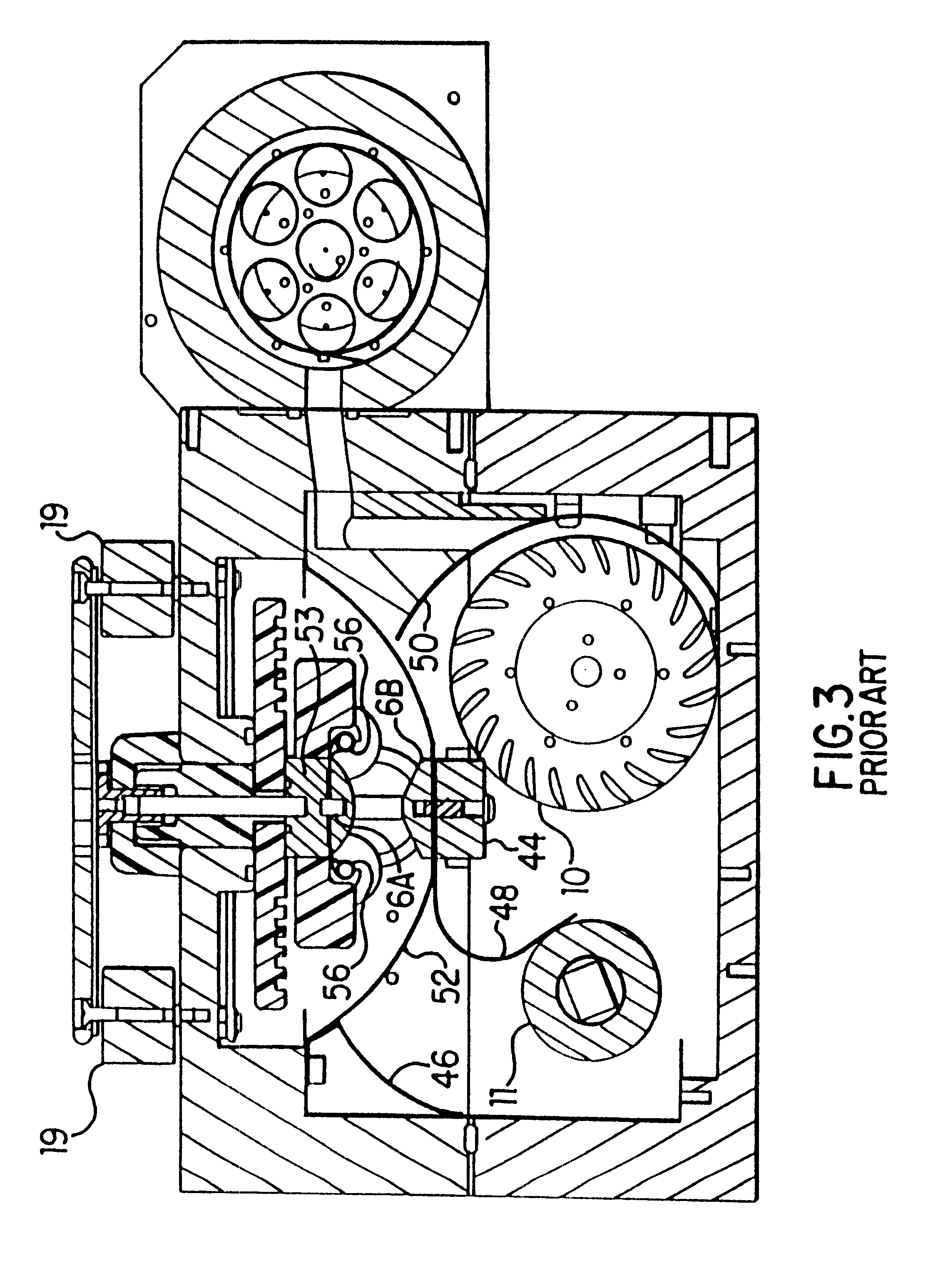
The present invention provides a reliable modular production quality excimer laser capable of producing 10 mJ laser pulses in the range of 1000 Hz to 2000 Hz or greater. Replaceable modules include a laser chamber; a pulse power system comprised of three modules; an optical resonator comprised of a line narrowing module and an output coupler module; a wavemeter module, an electrical control module, a cooling water module and a gas control module. Important improvements have been provided in the pulse power unit to produce faster rise time and improved pulse energy control. These improvements include an increased capacity high voltage power supply with a voltage bleed-down circuit for precise voltage trimming, an improved communication module that generates a high voltage pulse from the capacitors charged by the high voltage power supply and amplifies the pulse voltage 23 times with a very fast voltage transformer having a secondary winding consisting of a single four-segment stainless steel rod. A novel design for the compression head saturable inductor greatly reduces the quantity of transformer oil required and virtually eliminates the possibility of oil leakage which in the past has posed a hazard.
Owner:CYMER INC
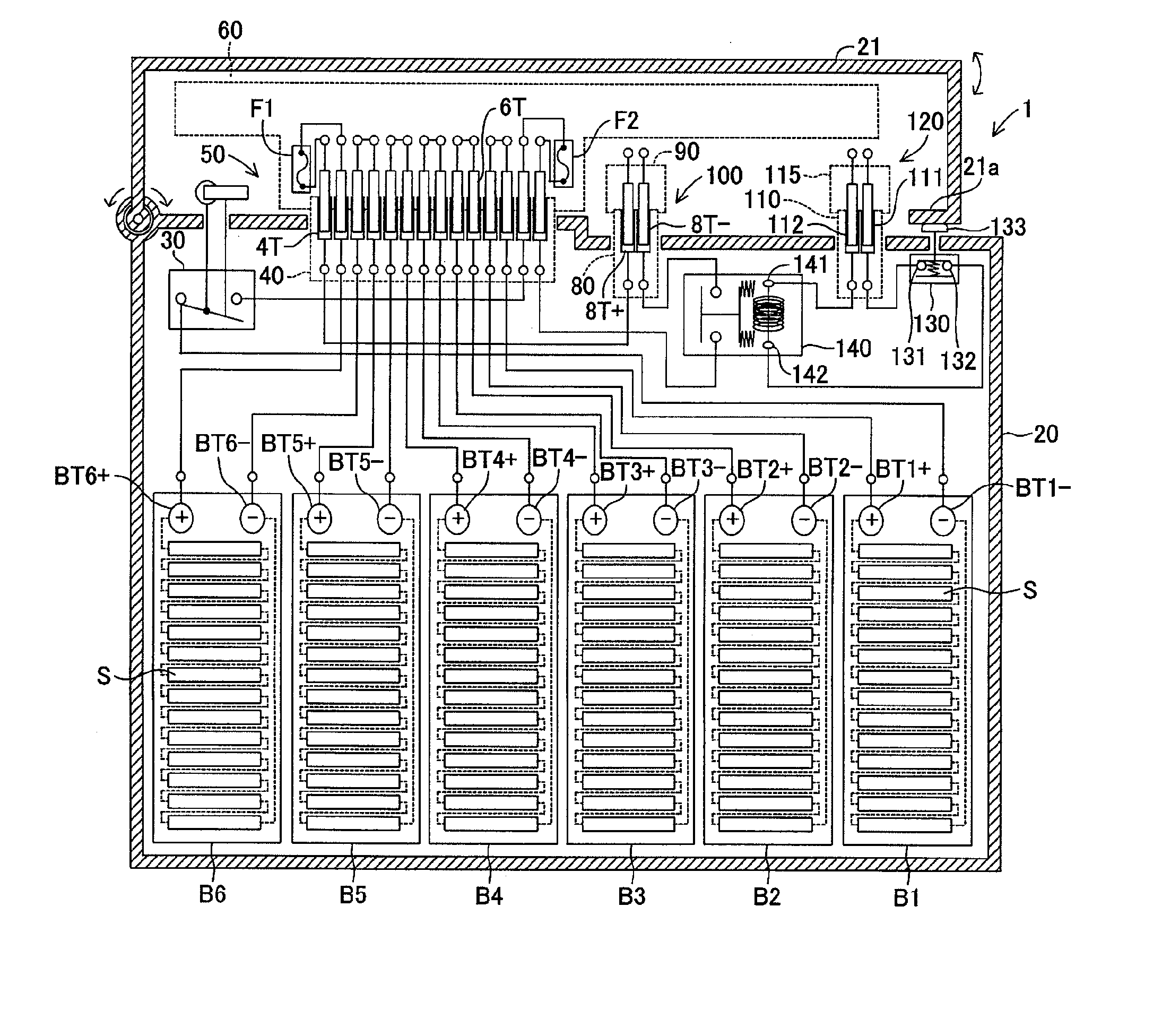
Power supply device for a vehicle
A high voltage power supply device has a plurality of battery modules connected to each other in series by coupling a safety plug unit to a safety plug unit connecting base to output a series voltage from a power supply output coupler. The safety plug unit connects / disconnects electrode terminals of all the battery modules to each other. Female electrode bodies electrically connected to power supply terminals of the respective battery modules are collectively positioned in a limited area and are arranged at equal intervals on the safety plug unit connecting base. An output voltage of each battery module is set to be lower than 50V to reduce the risk of injury during use, inspection or maintenance of the high voltage power supply device and to downsize the device.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Waveguide display system for eliminating chromatic aberration and based on based holographic diffraction optical element
ActiveCN103995354ANo reduction in diffraction efficiencyReduce volumeOptical elementsOutput couplerWaveguide
The invention relates to a waveguide display system for eliminating chromatic aberration and based on a holographic diffraction optical element. The waveguide display system comprises an input coupler, a waveguide and an output coupler. When color light is irradiated on a transmission-type plane grating serving as the input coupler after passing a collimating lens, the plane grating exerts the dispersion characteristic and disperses the light into the light waves in different colors, the light waves enter the waveguide by different angles, and then the light continues to be transmitted in the waveguide, and when the light is transmitted to a reflection-type volume grating serving as the output coupler, the light waves are modulated through the volume grating, the light waves in which dispersion occurs are reflected out of the waveguide in the same direction and enter the eyes of people, people can see color pictures with the eyes, and therefore the chromatic aberration can be eliminated. Meanwhile, according to the waveguide display system for eliminating chromatic aberration and based on the holographic diffraction optical element, the negative effects of reduction of diffraction efficiency, the increase of the size and the weight of the system and the like cannot be caused, and the waveguide display system can be widely applied to the field of display systems.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Substrate guided relay with homogenizing input relay
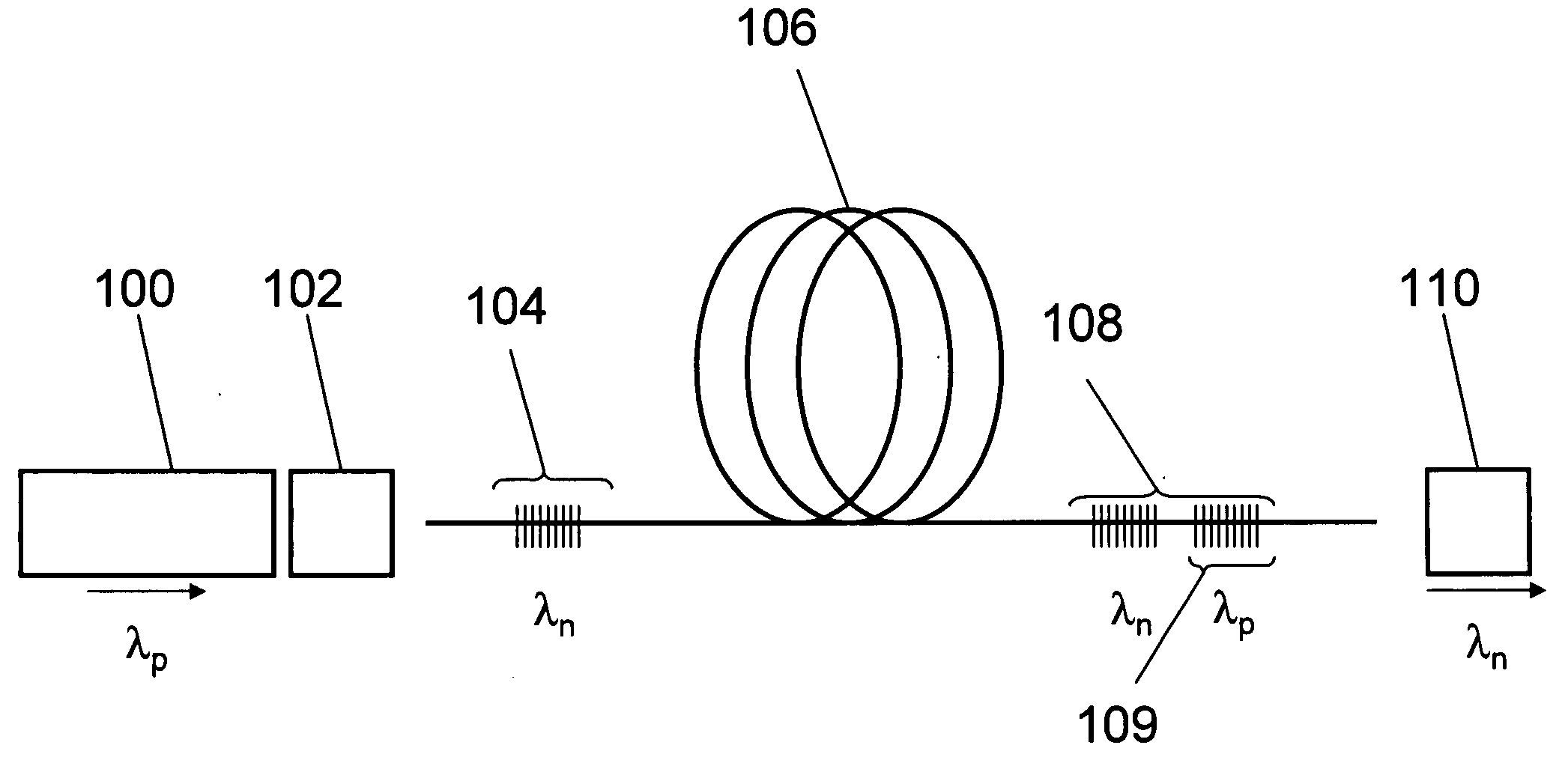
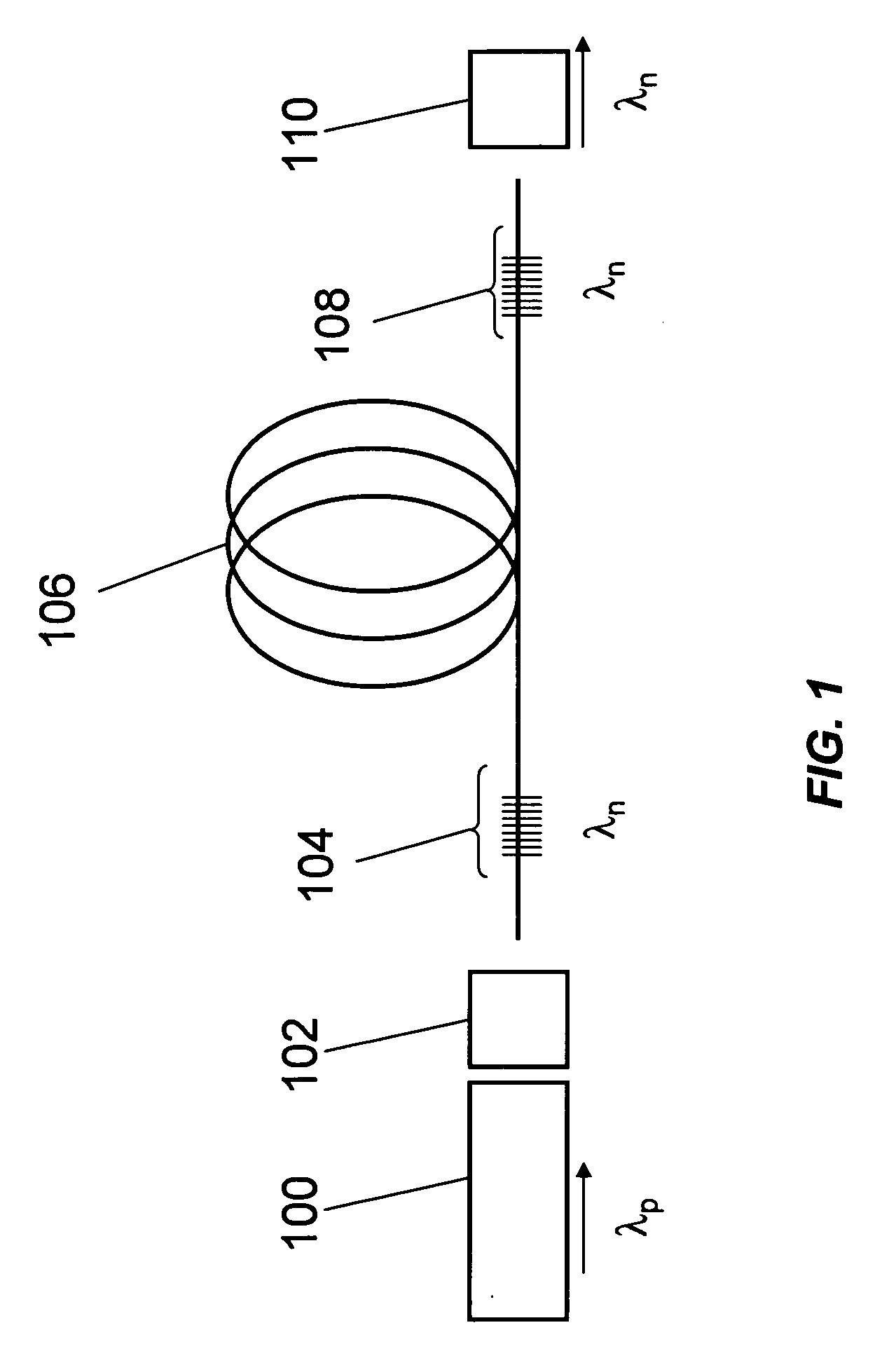
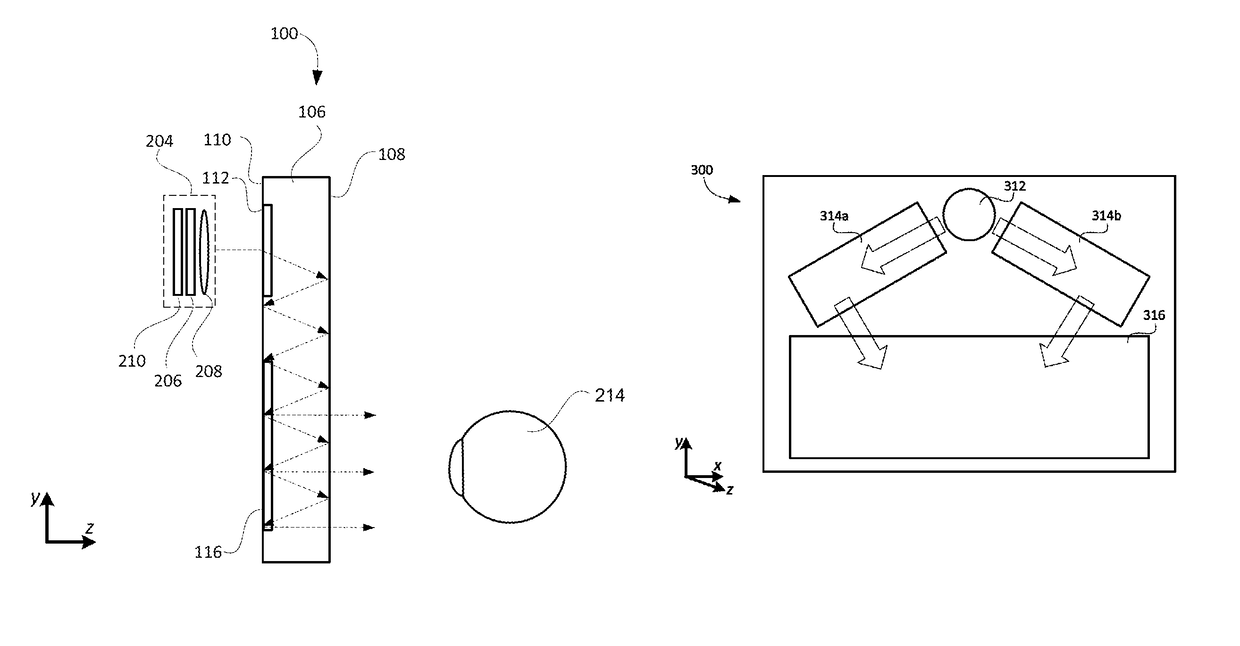
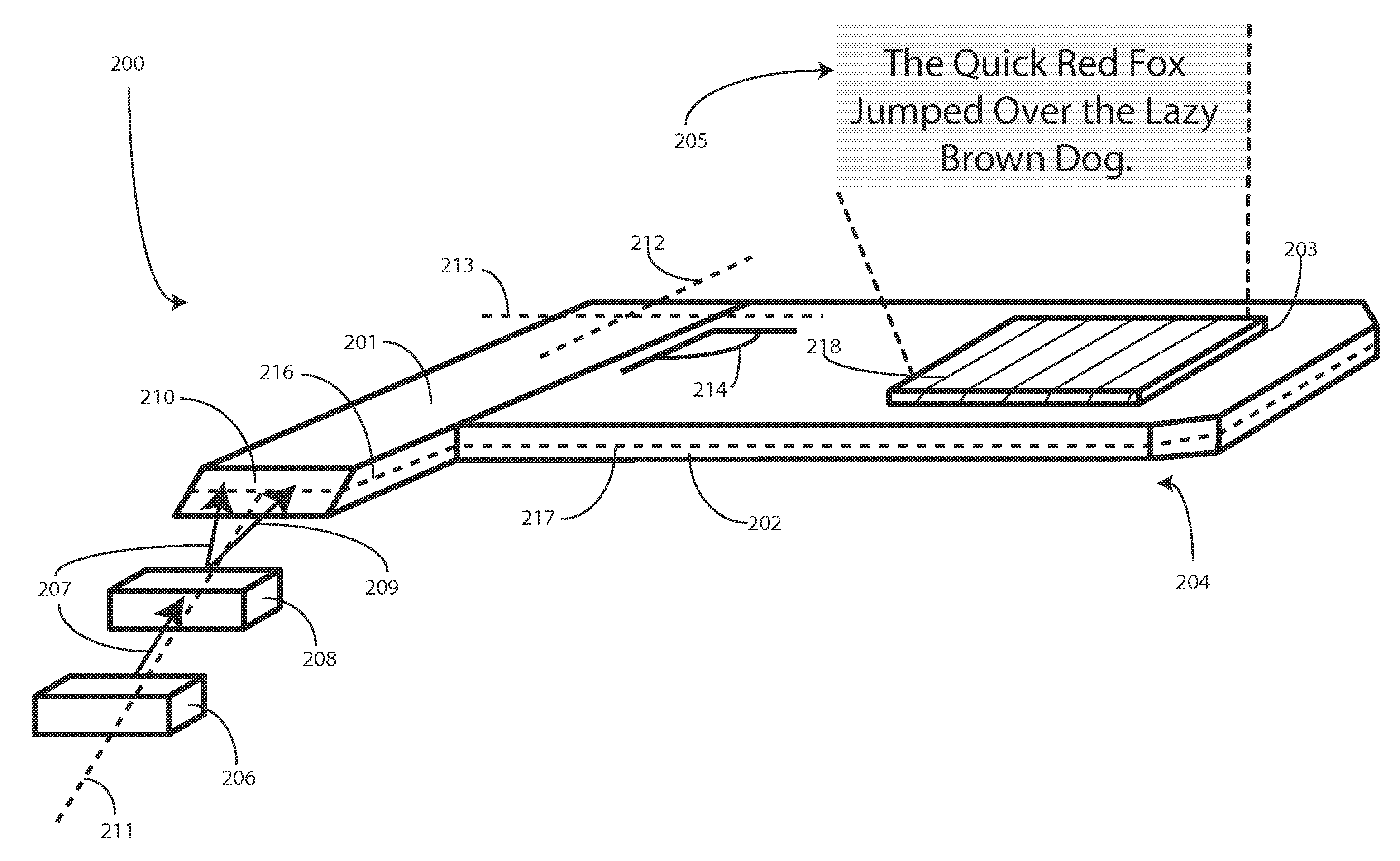
An optical relay system (200) includes a scanned light source (206) and a substrate guided relay (204). The substrate guided relay (204) includes an input coupler (201), an output coupler (203), and an optical substrate (202) disposed therebetween. A light homogenizing relay device (208) is disposed between the scanned light source (206) and the substrate guided relay (204). The light homogenizing relay device (208) is configured to receive a light beam (207) from the scanned light source (206). The light homogenizing relay device (208) makes at least one copy (209) of the light beam (207), and delivers the light beam (207) and the at least one copy (209) to a light receiving surface (210) of the input coupler (201), thereby effectively creating a larger input beam while retaining the angular spread of the initial light beam (207).
Owner:MICROVISION
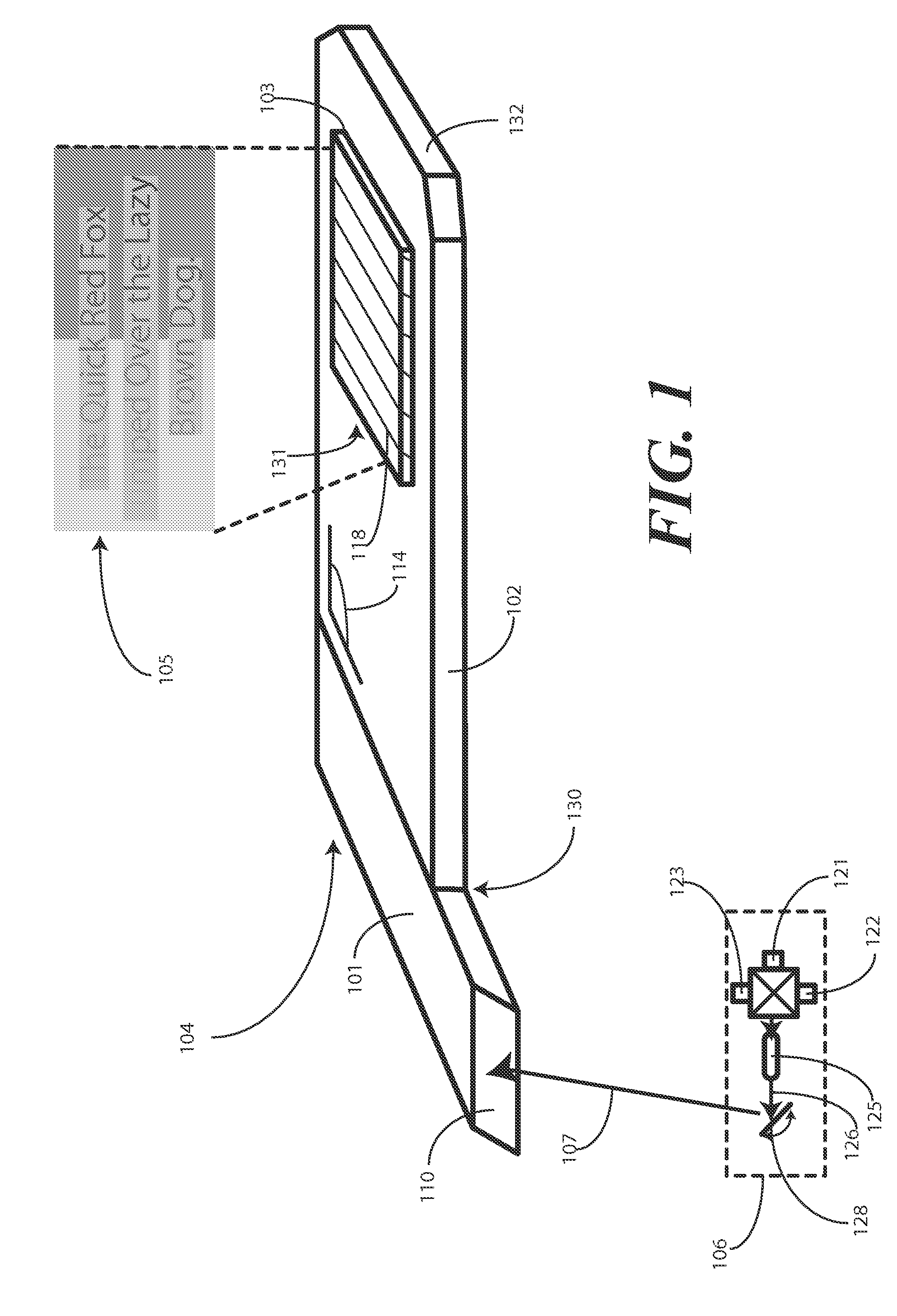
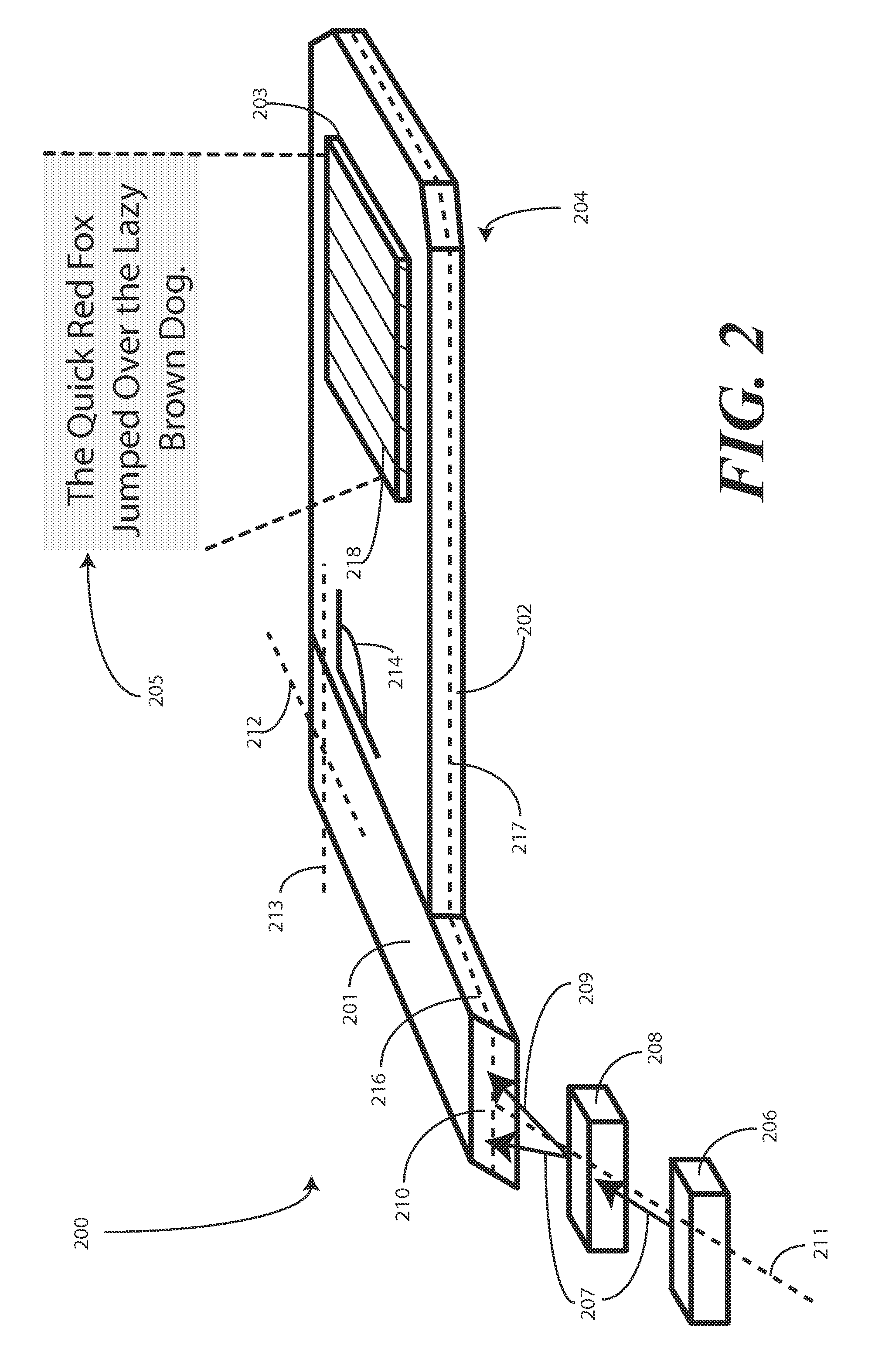
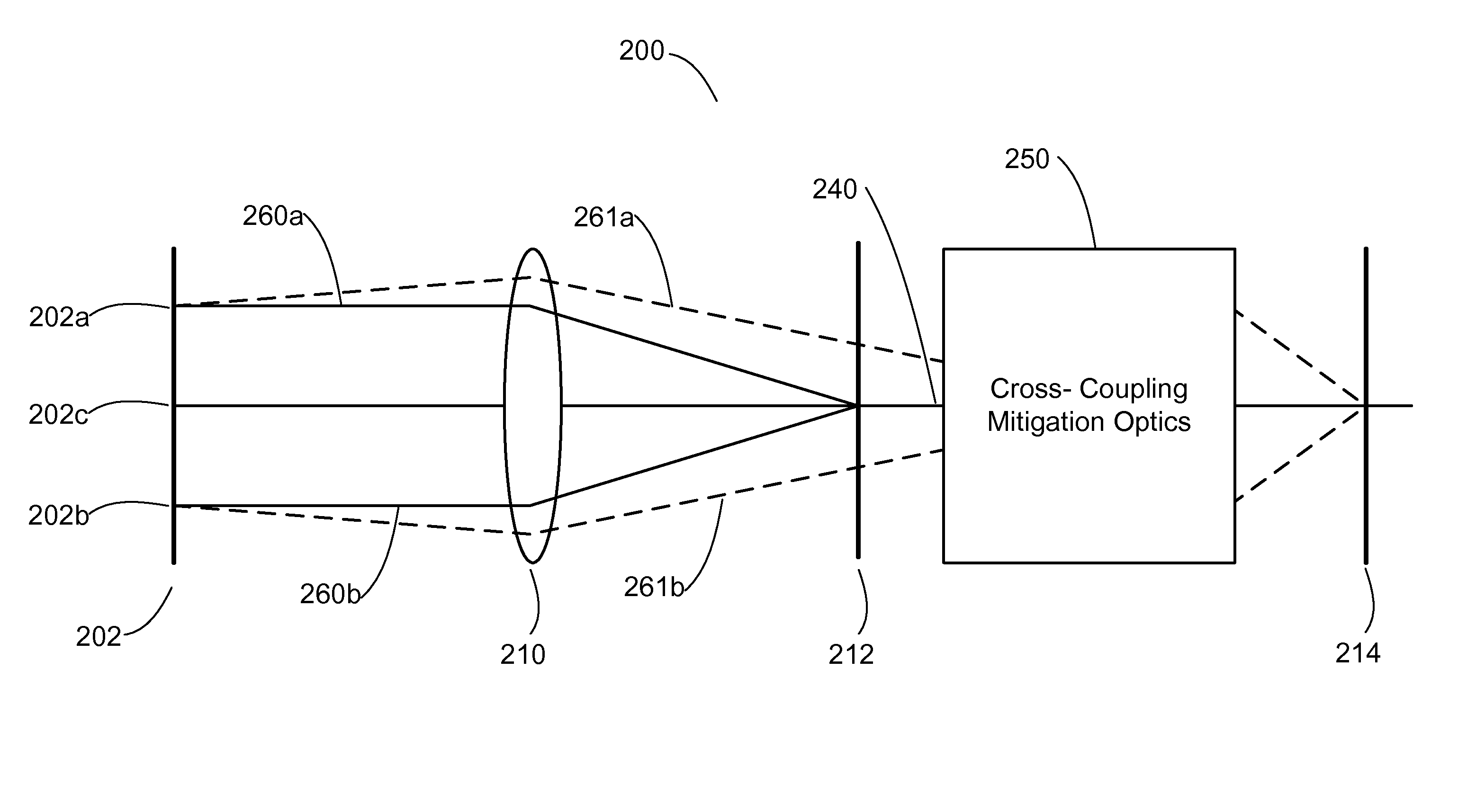
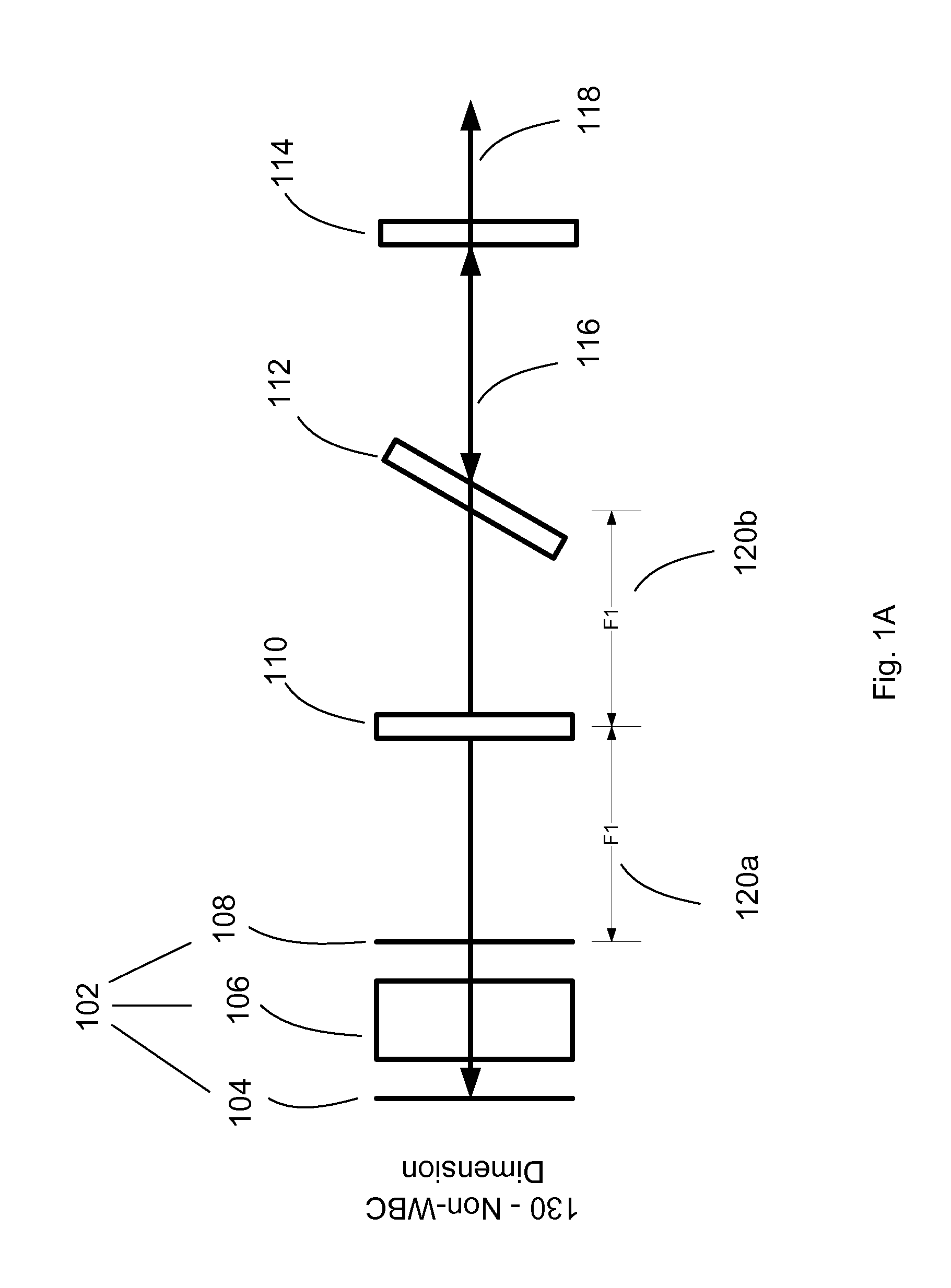
Optical cross-coupling mitigation system for multi-wavelength beam combining systems
A system and method for increasing efficiency and power output of a multi-wavelength beam combining system through providing a common output coupler to reflect feedback that stabilizes or individually seeds each emitter, and wherein the individual feedback is preserved by mitigating cross-coupling, wherein a multi-wavelength beam comprised of radiation having a plurality of wavelengths, high brightness and power.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA
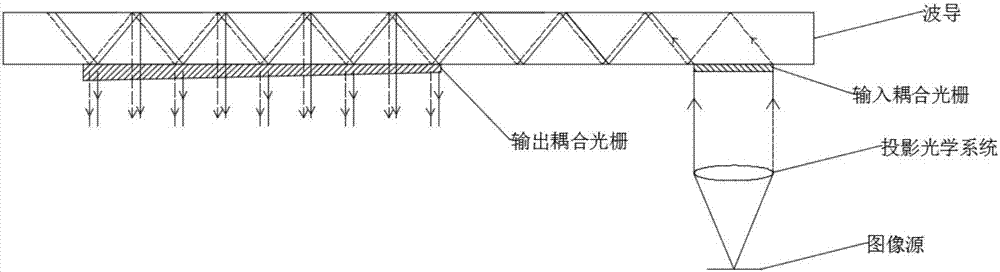
Waveguide display device
InactiveCN107966819AImprove Field of View Brightness UniformityExpand field of viewOptical elementsDisplay deviceOutput coupler
The invention discloses a waveguide display device, which relates to the technical field of optics. A first image source is used for generating an S-polarized light image. A second image source is used for generating a P-polarized light image. A first projection optical system is used for projecting the S-polarized light image generated by the first image source to a first input coupler. A secondprojection optical system is used for projecting the P-polarized light image generated by the second image source to a second input coupler. The first input coupler is used for coupling the S-polarized light emitted by the first projection optical system into a waveguide. The second input coupler is used for coupling the P-polarized light emitted by the second projection optical system into the waveguide. A first output coupler is used for coupling out the S-polarized light propagated in the waveguide. A second output coupler is used for coupling out the P-polarized light propagated in the waveguide. The brightness uniformity of the field of view of the display image and the field angle of the system can be improved.
Owner:JOURNEY TECH LTD
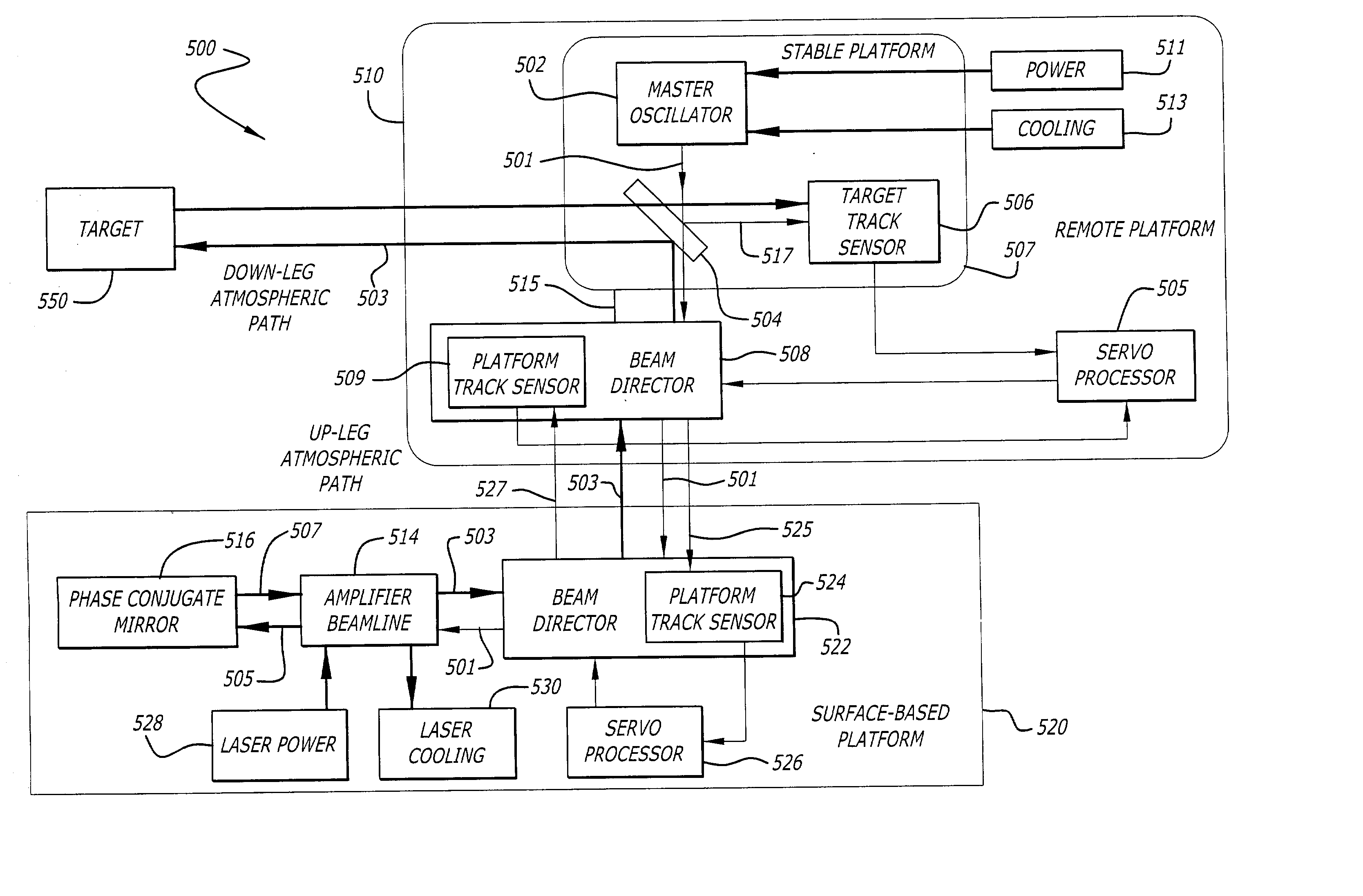
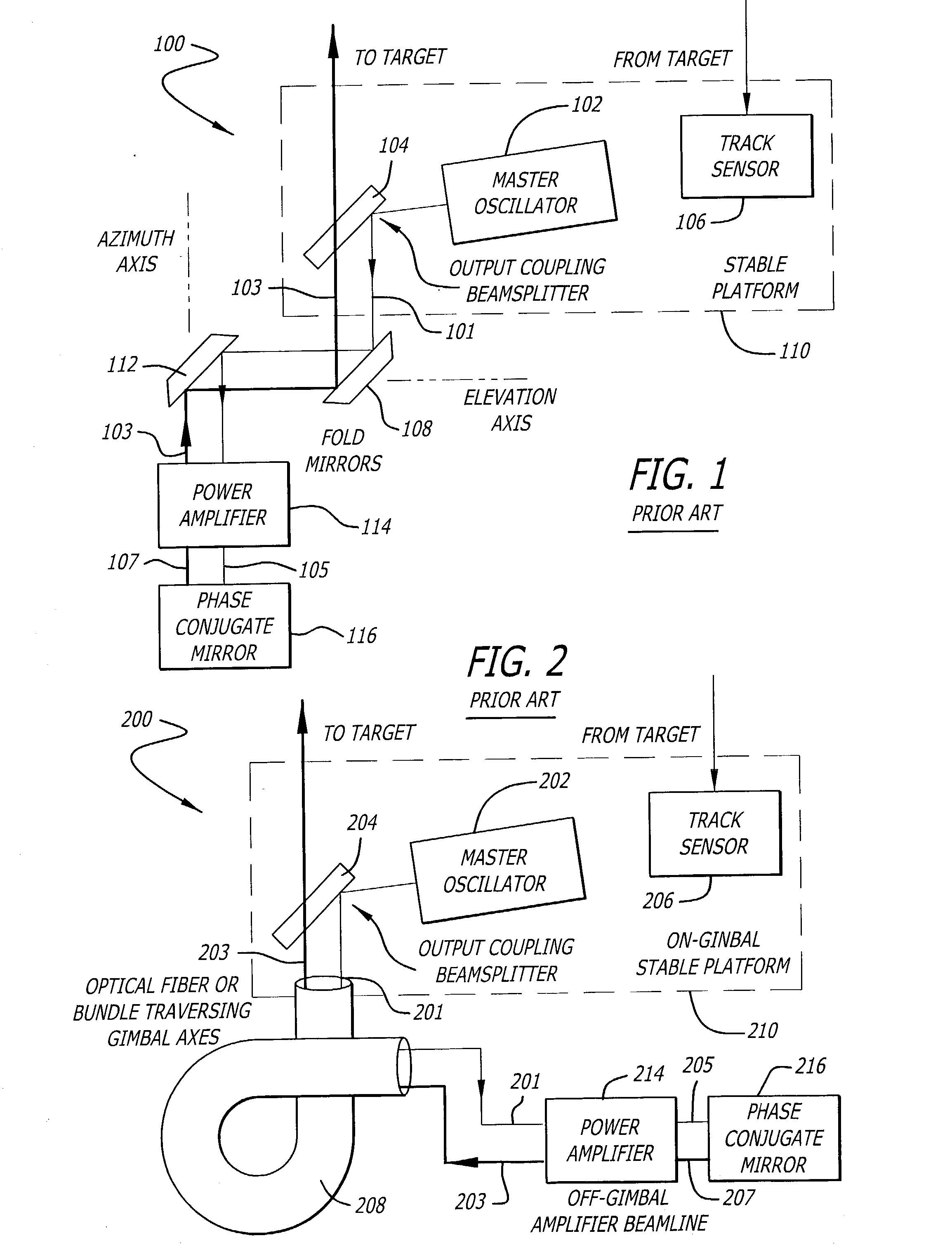
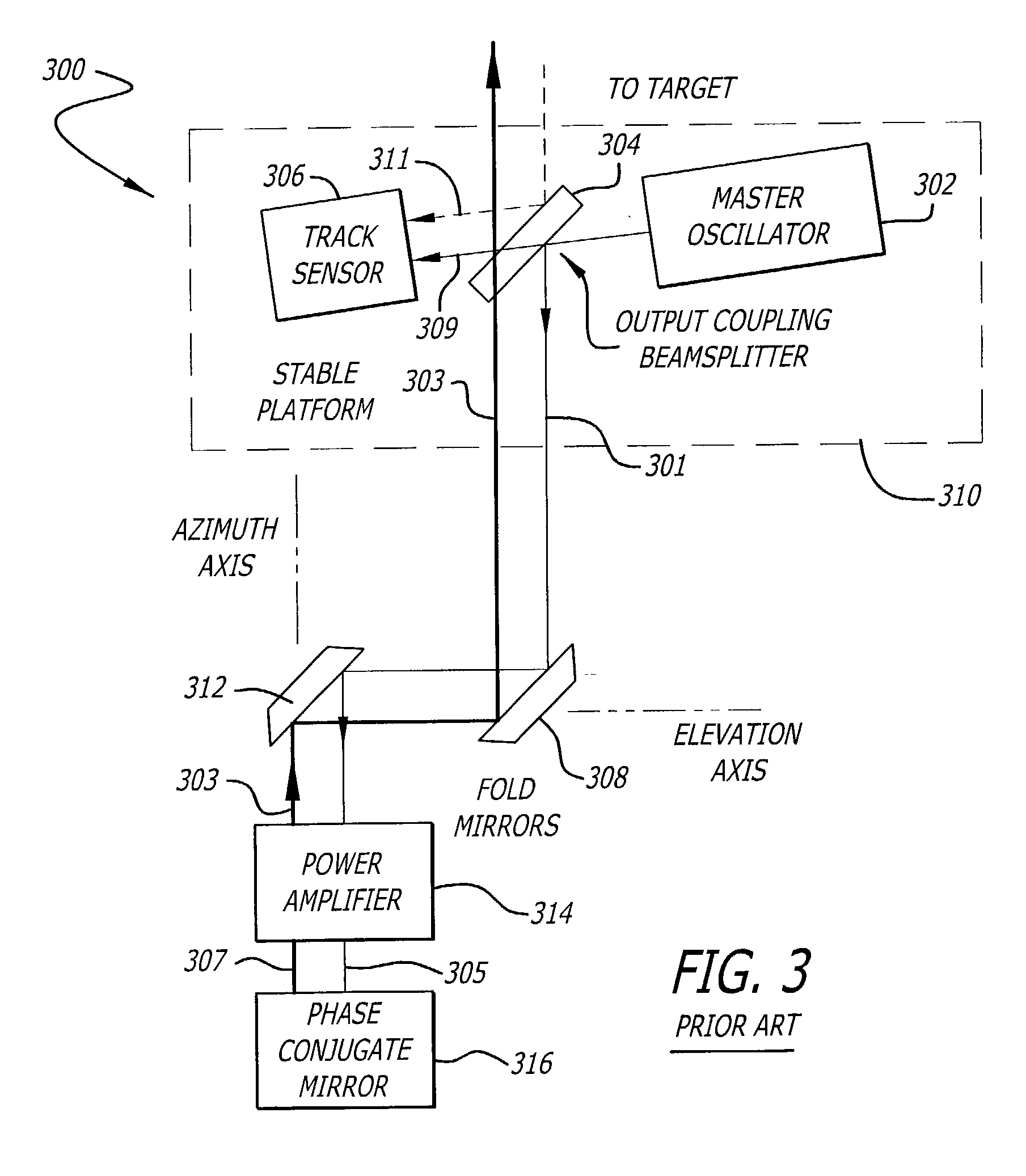
Phase conjugate relay mirror apparatus for high energy laser system and method
A system for directing electromagnetic energy. The inventive system includes a first subsystem mounted on a first platform for transmitting a beam of the electromagnetic energy through a medium and a second subsystem mounted on a second platform for redirecting the beam. In accordance with the invention, the second platform is mobile relative to the first platform. In the illustrative embodiment, the beam is a high-energy laser beam. The first subsystem includes a phase conjugate mirror in optical alignment with a laser amplifier. The first subsystem further includes a beam director in optical alignment with the amplifier and a platform track sensor coupled thereto. In the illustrative embodiment, the second subsystem includes a co-aligned master oscillator, outcoupler, and target track sensor which are fixedly mounted to a stabilized platform, a beam director, and a platform track sensor. In the best mode, the stable platform is mounted for independent articulation relative to the beam director. A first alternative embodiment of the second subsystem includes first and second beam directors. The first beam director is adapted to receive the transmitted beam and the second beam director is adapted to redirect the received beam. In accordance with a second alternative embodiment, an optical fiber is provided for coupling the beam between the first platform and the second platform.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Stable solid state raman laser and a method of operating same
InactiveUS6901084B2Avoid optical damageCavity stabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionResonant cavitySolid mass
The present invention relates to a stable solid-state Raman laser, the solid-state Raman laser including a resonator cavity defined by at least two reflectors, a laser material located in the resonator cavity and capable of generating a cavity laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity, a solid Raman medium located in the resonator cavity for shifting the frequency of the cavity laser beam to produce a Raman laser beam which propagates within the resonator cavity; and an output coupler for coupling and outputting the Raman laser beam from the resonator cavity, wherein at least one parameter selected from the group consisting of the position of the laser material relative to the position of the Raman medium in the cavity, the length of the cavity and the curvature of at least one of the reflectors, is selected such that changes in the focal lengths of both the laser material and the Raman medium as a result of thermal effects in the laser material and the Raman medium during operation of the laser do not substantially cause instability in the power of the output Raman laser beam. A method of maintaining stable operation of a solid state Raman laser is also described.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
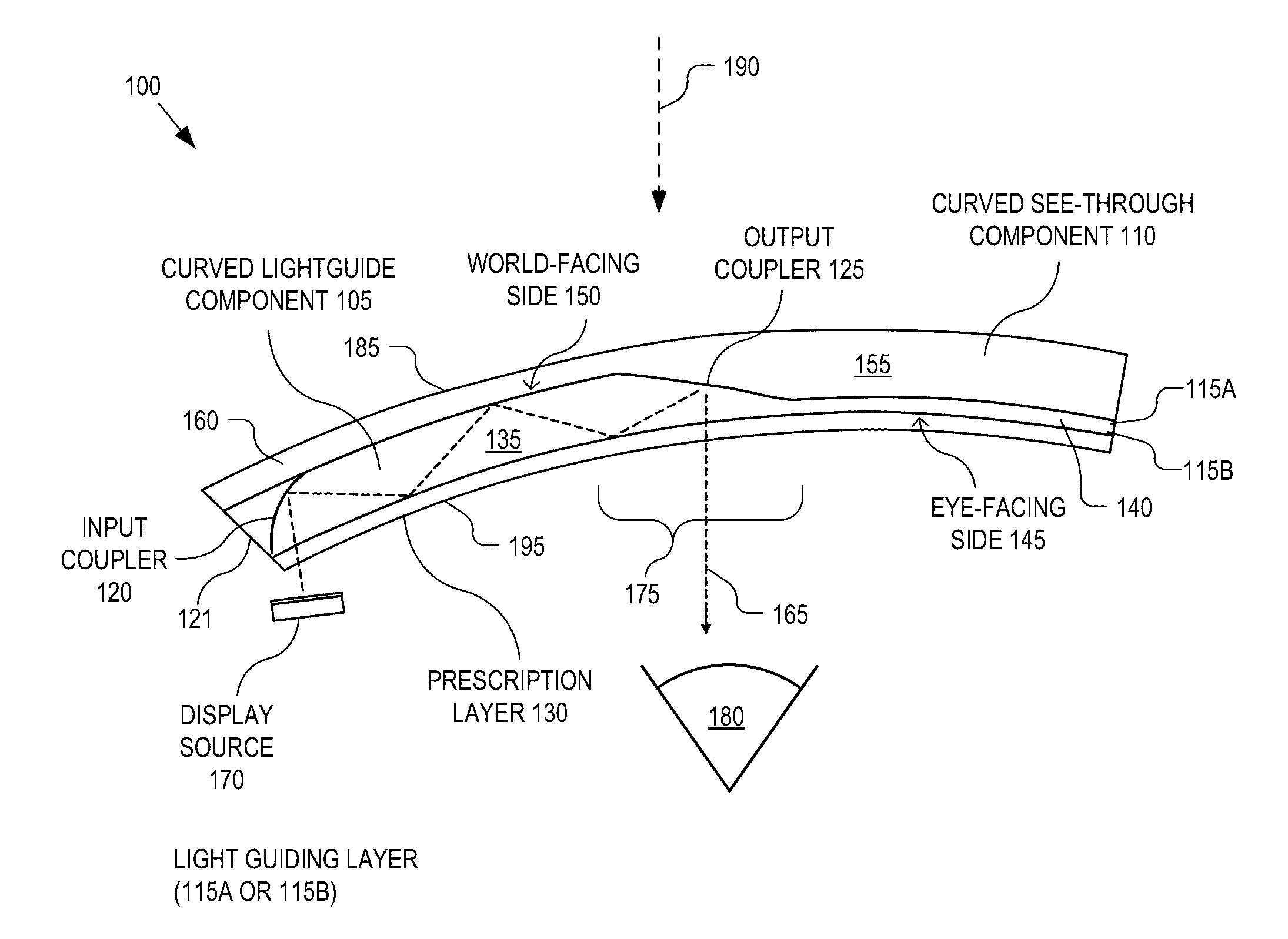
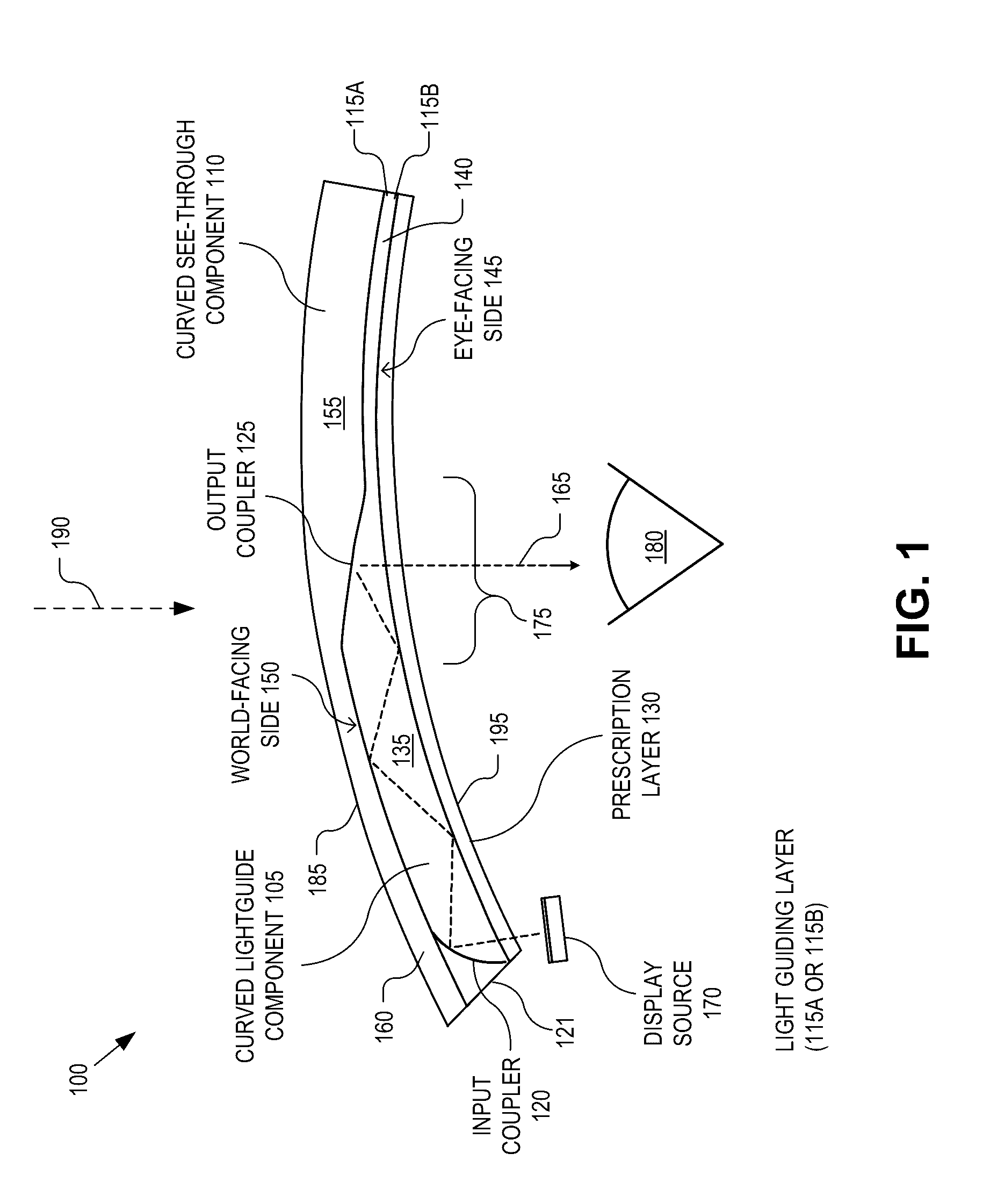
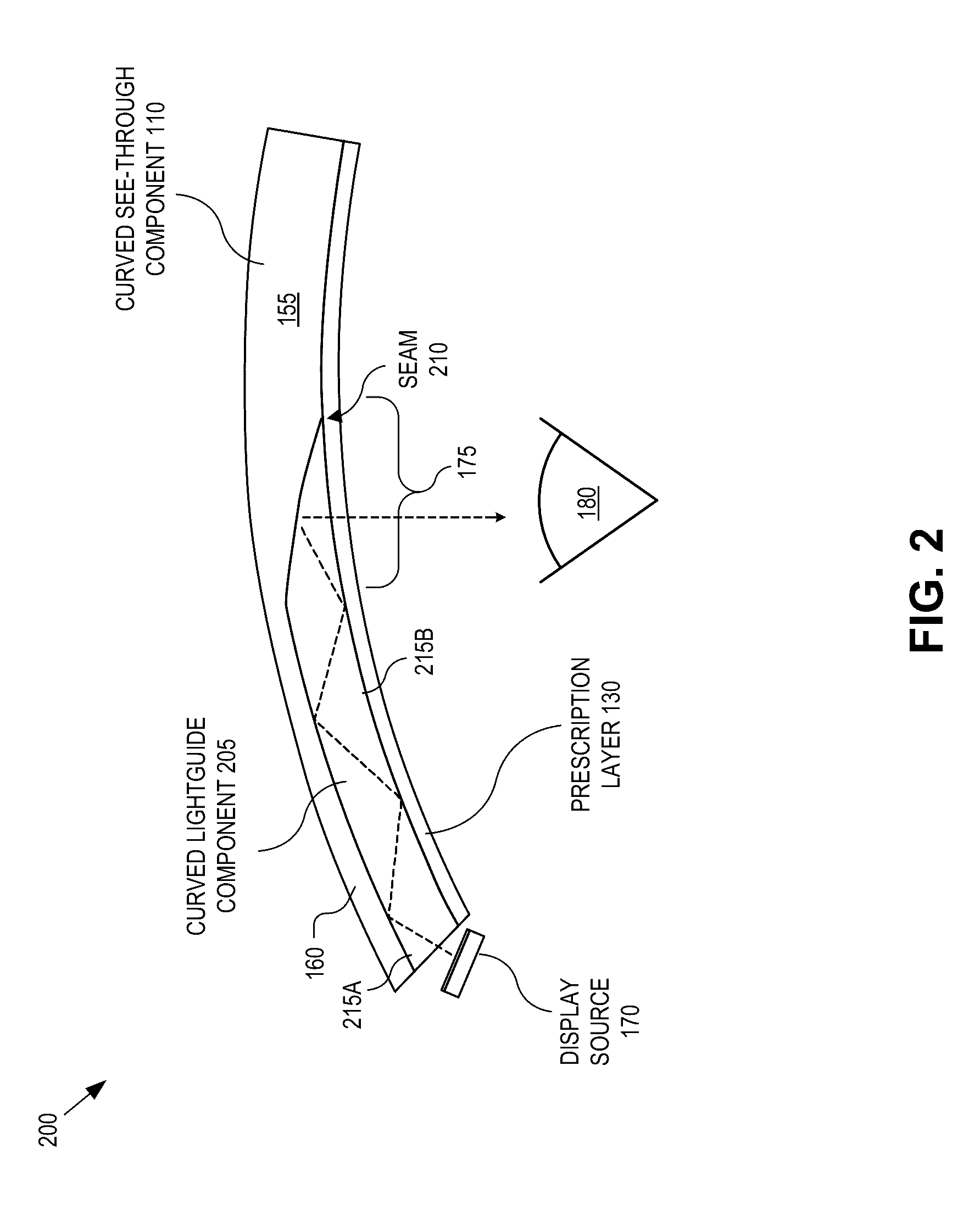
Adding prescriptive correction to eyepieces for see-through head wearable displays
An eyepiece for a head wearable display includes a curved lightguide component, a curved see-through component, an output coupler, and a prescription layer. The curved lightguide component guides display light received at an input region and releases the display light along an eye-ward direction in a viewing region. The output coupler is disposed at the viewing region to redirect the display light towards the eye-ward direction for output from the curved lightguide component. The output coupler is at least partially transmissive to ambient light incident through a world-facing side such that the viewing region is see-through. The curved see-through component is mated to the world-facing side of the curved lightguide component. The prescription layer has a first side mated to an eye-facing side of the curved lightguide component and a second side having a curvature that introduces prescriptive lensing to both the ambient light and the display light.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
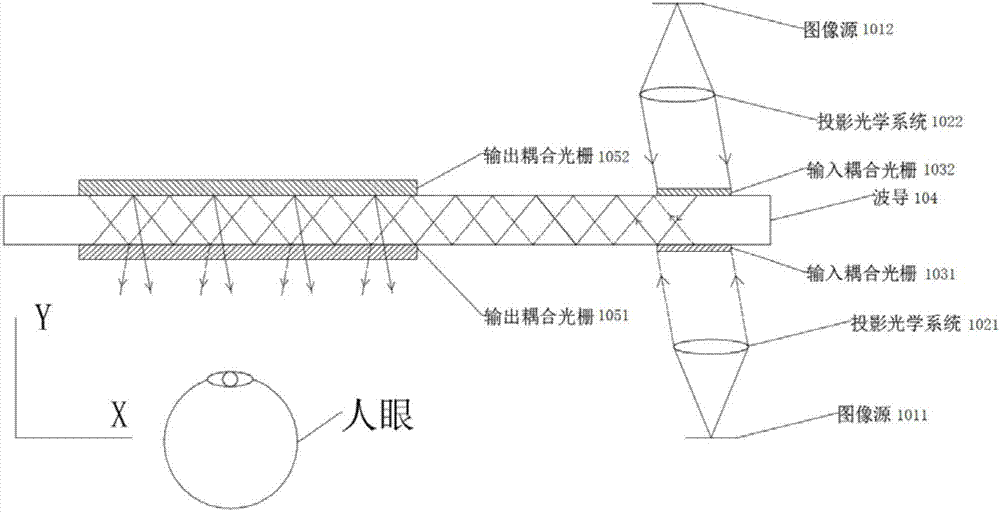
Waveguide display device
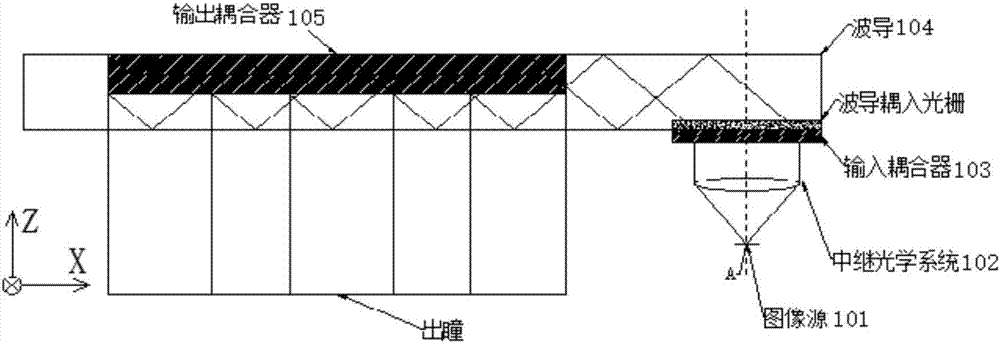
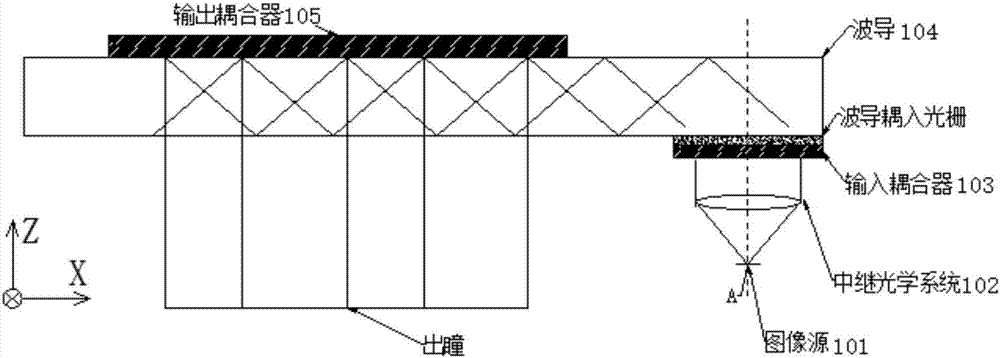
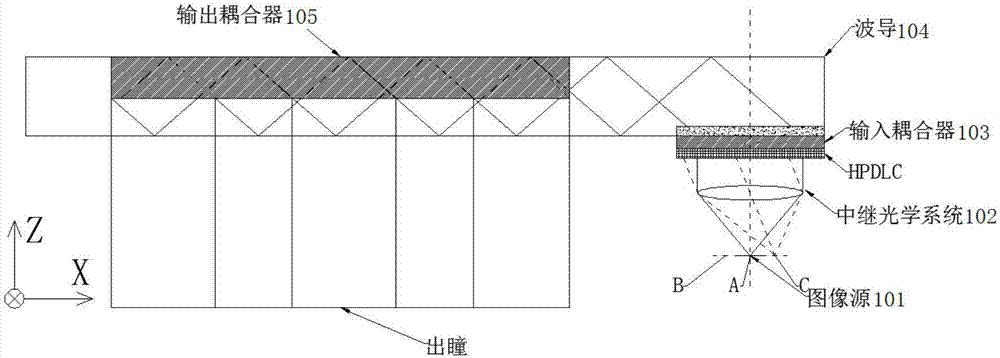
The invention discloses a waveguide display device, which relates to the technical field of optics. The waveguide display device comprises an image source, a relay optical system, an input coupler, a waveguide and an output coupler, wherein the image source is used for displaying an image; the relay optical system is used for emitting the image displayed by the image source to the input coupler; the input coupler is used for coupling emergent light of the relay optical system to the waveguide; and the output coupler is used for coupling out light propagated in the waveguide. The optical device can use the small-sized image source, and the design difficulty and the complexity degree of the relay optical system can be reduced.
Owner:JOURNEY TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com