Patents
Literature
1651 results about "Partial reflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
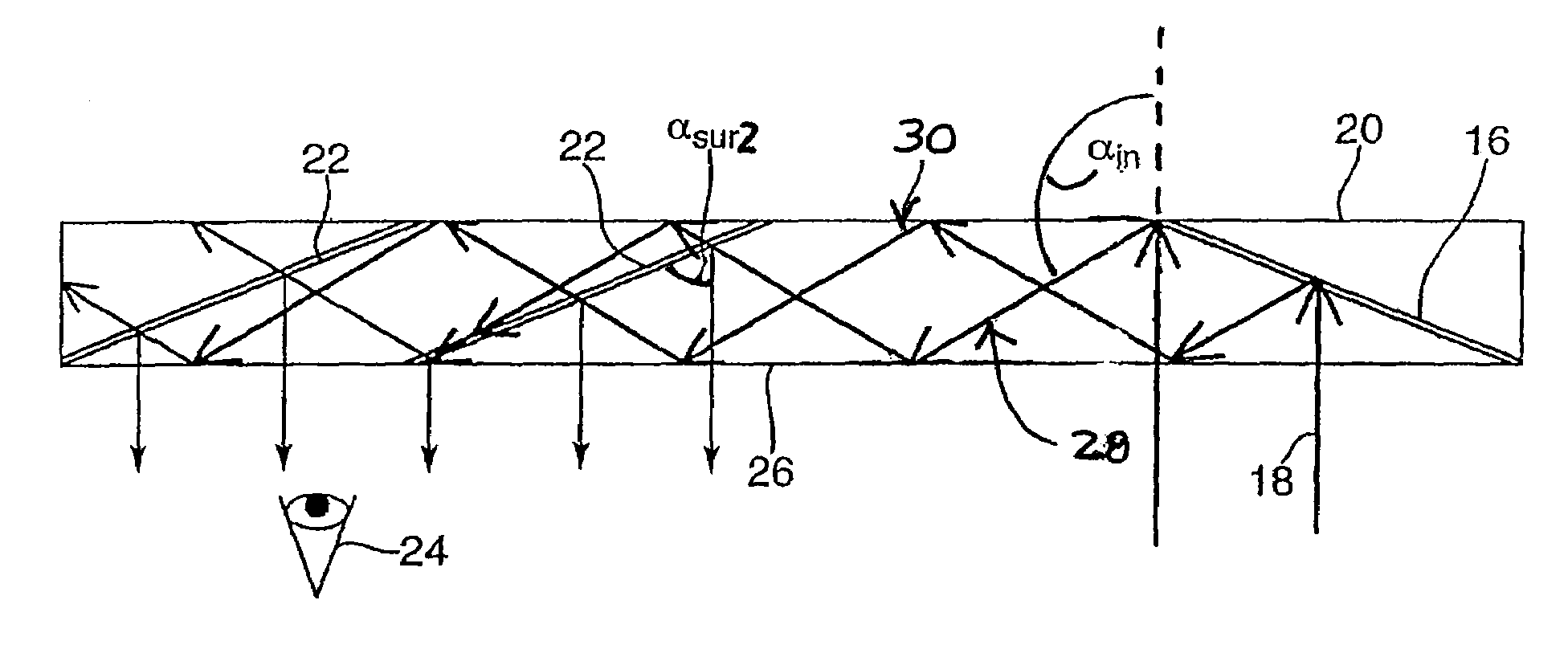
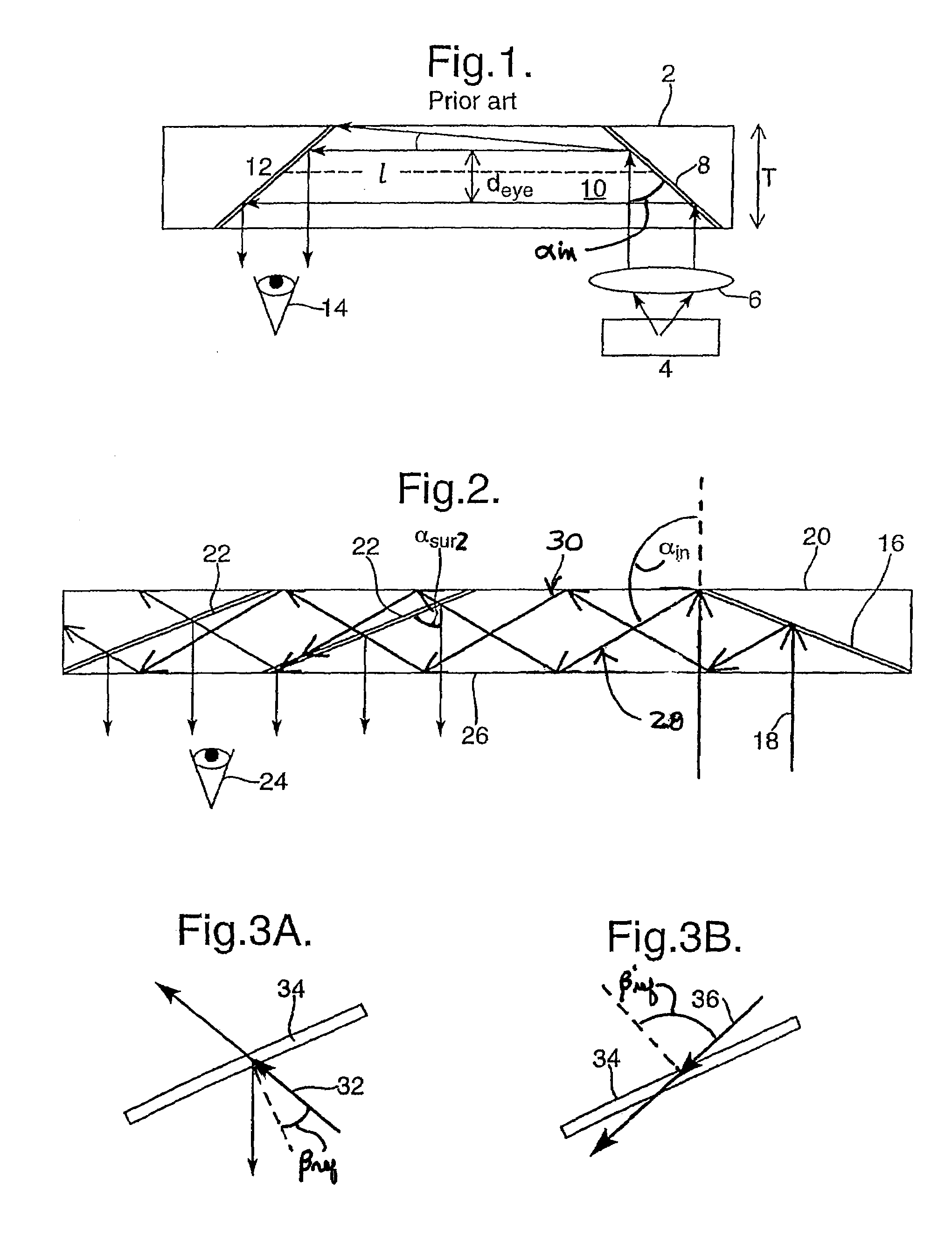
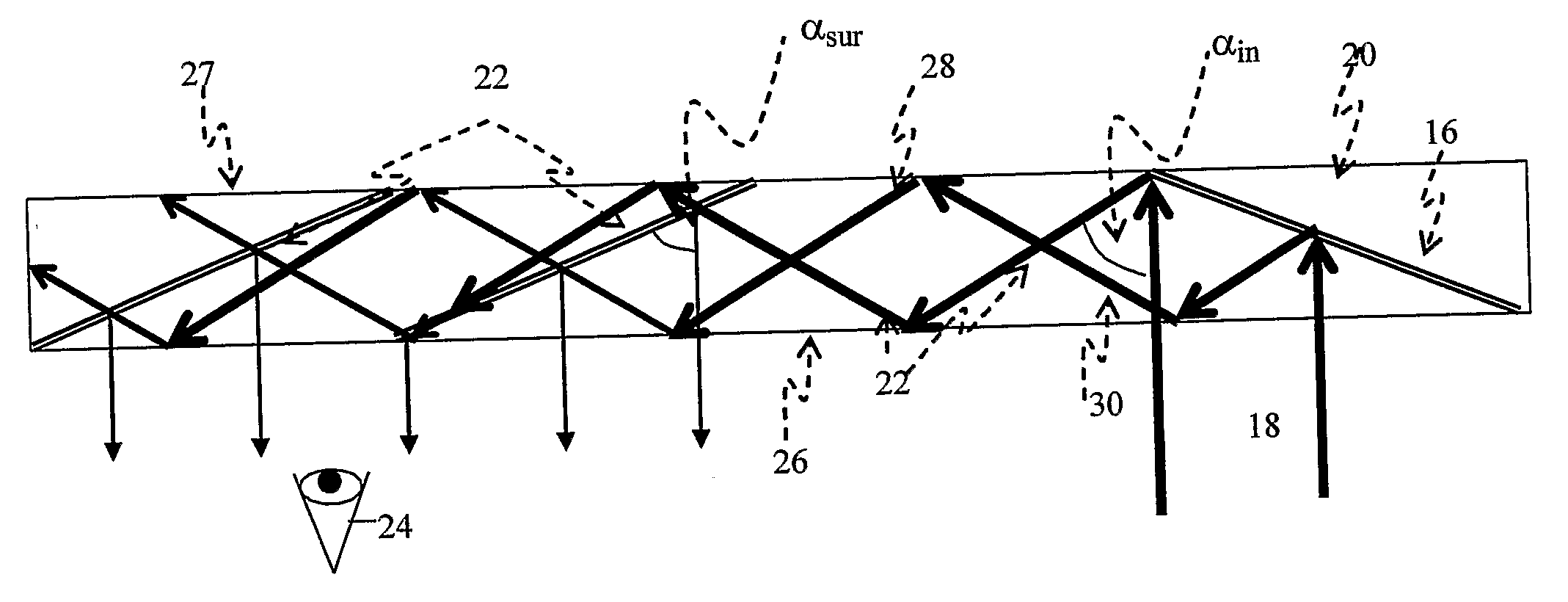
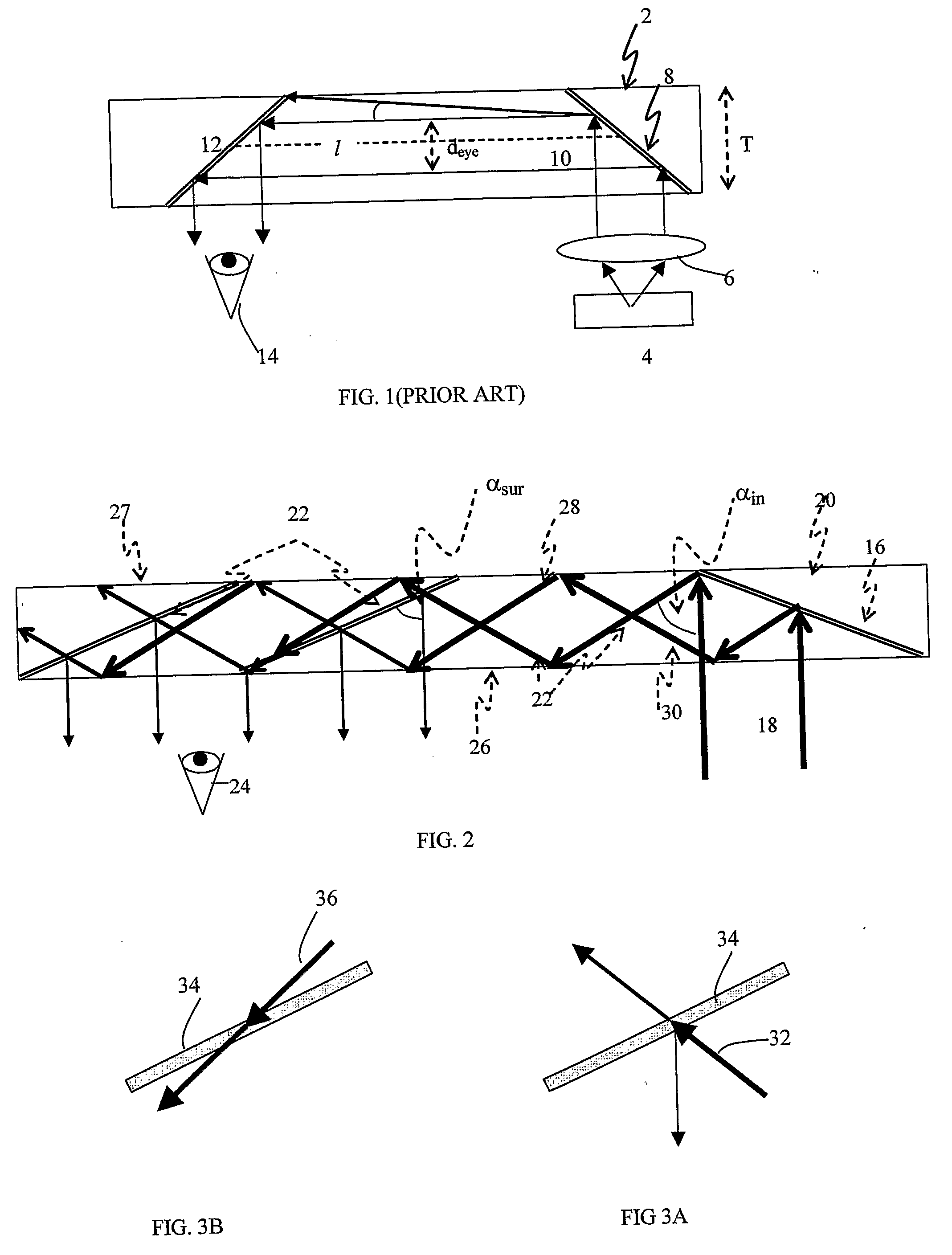
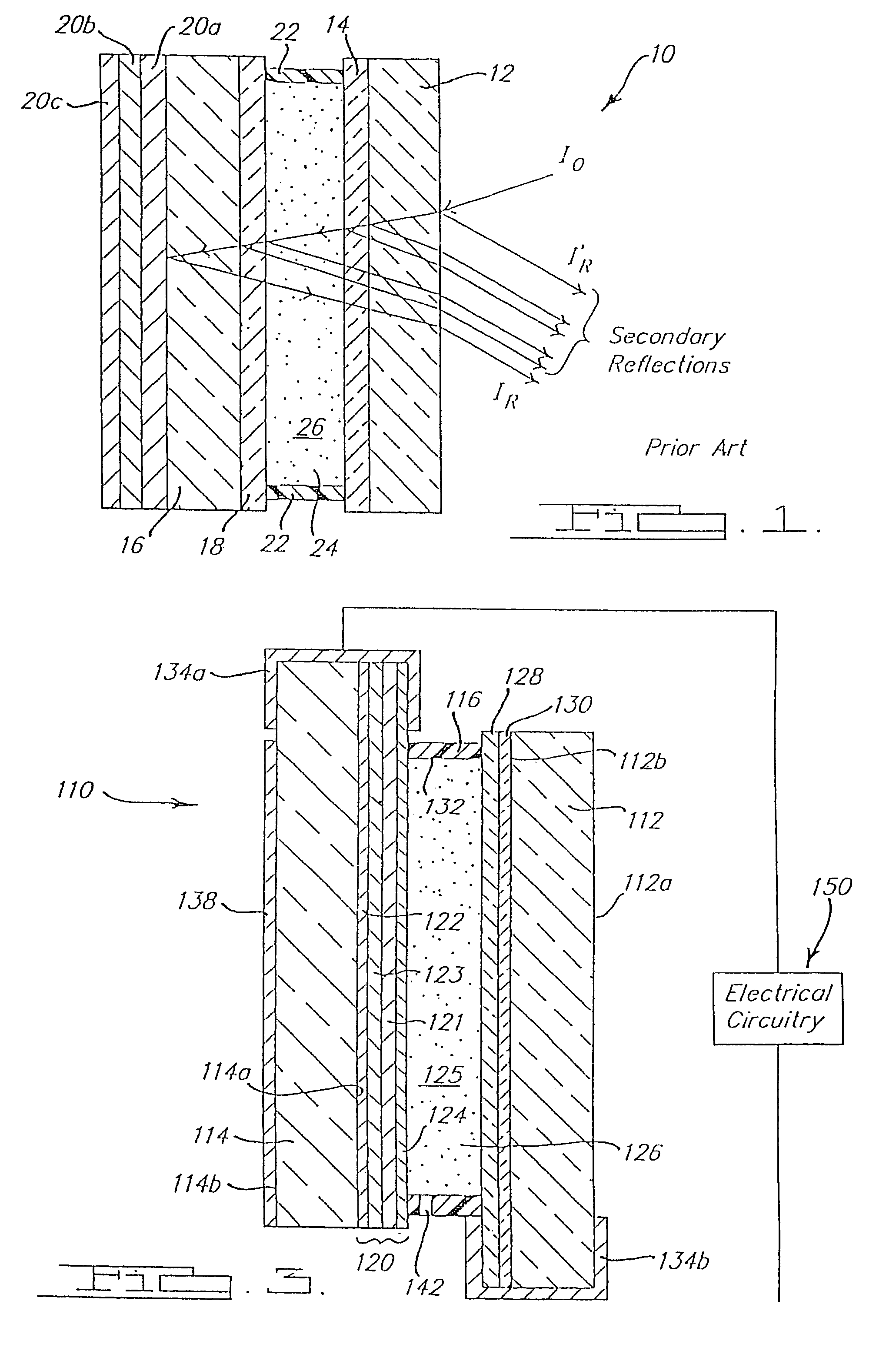
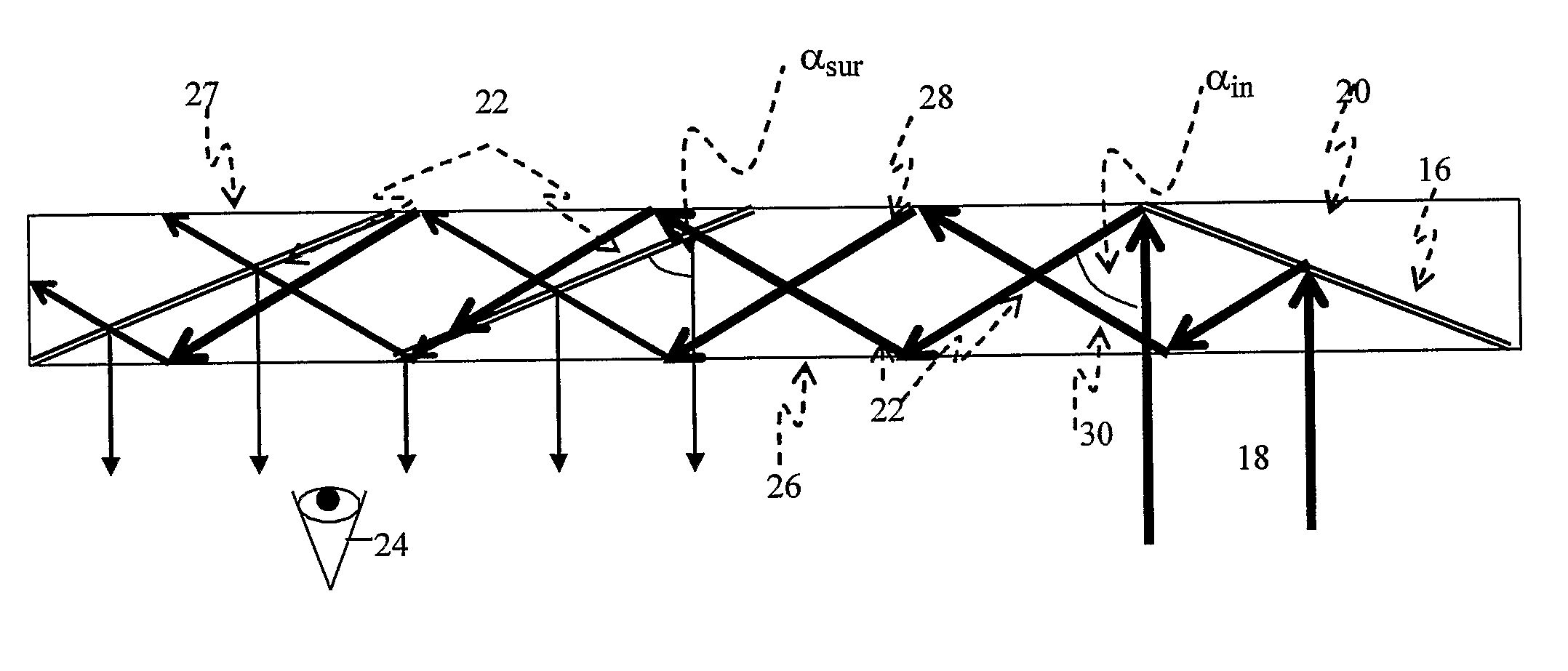
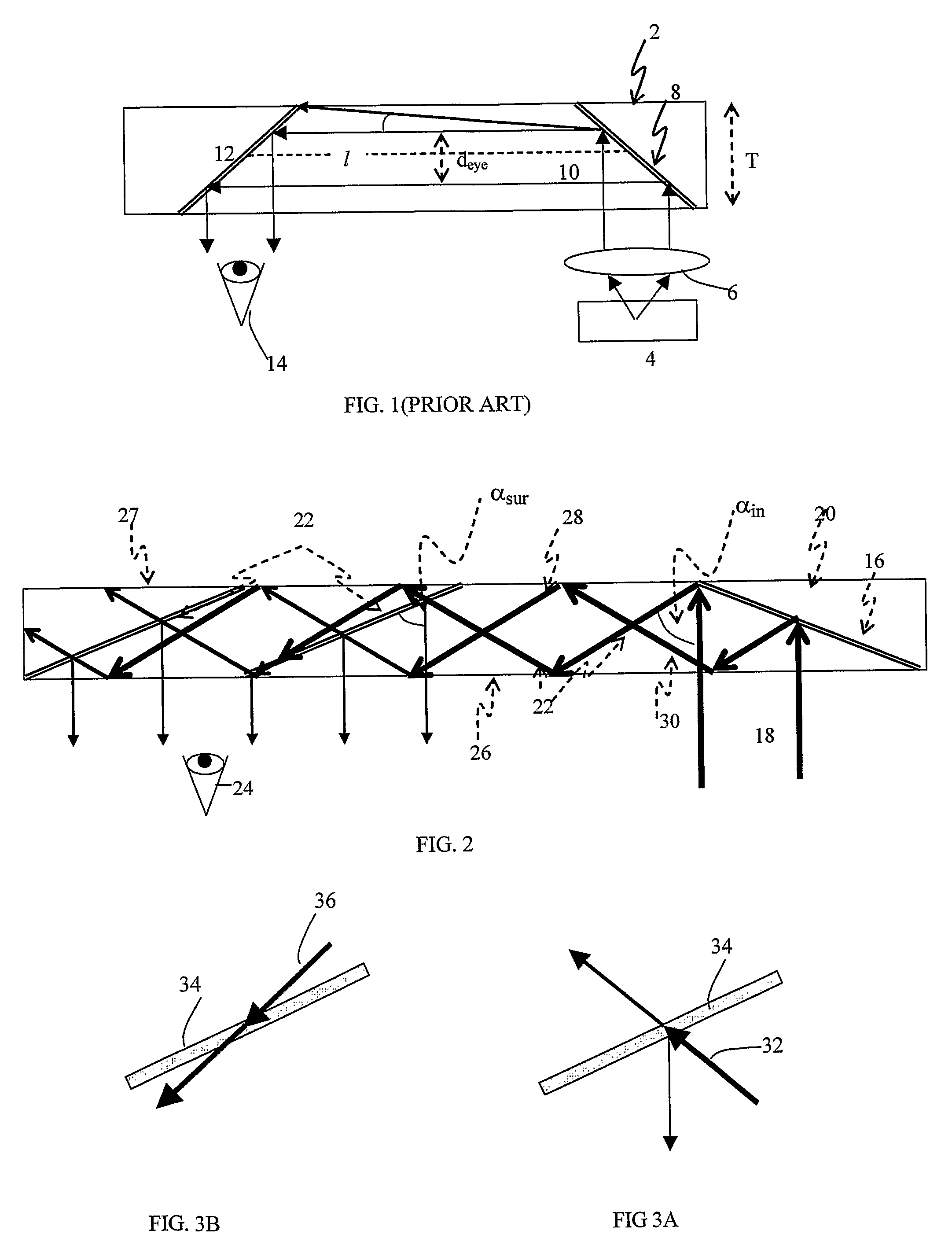
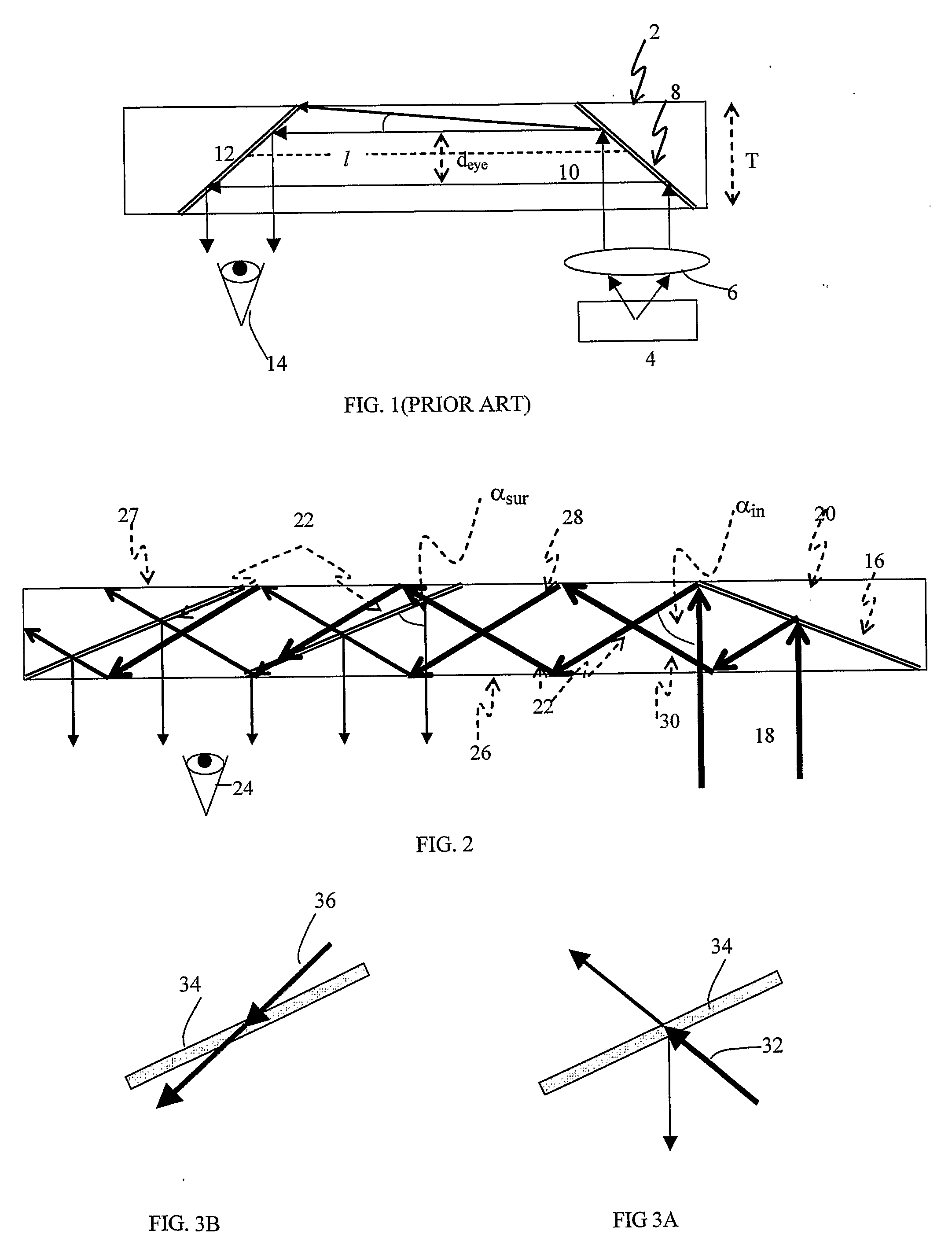
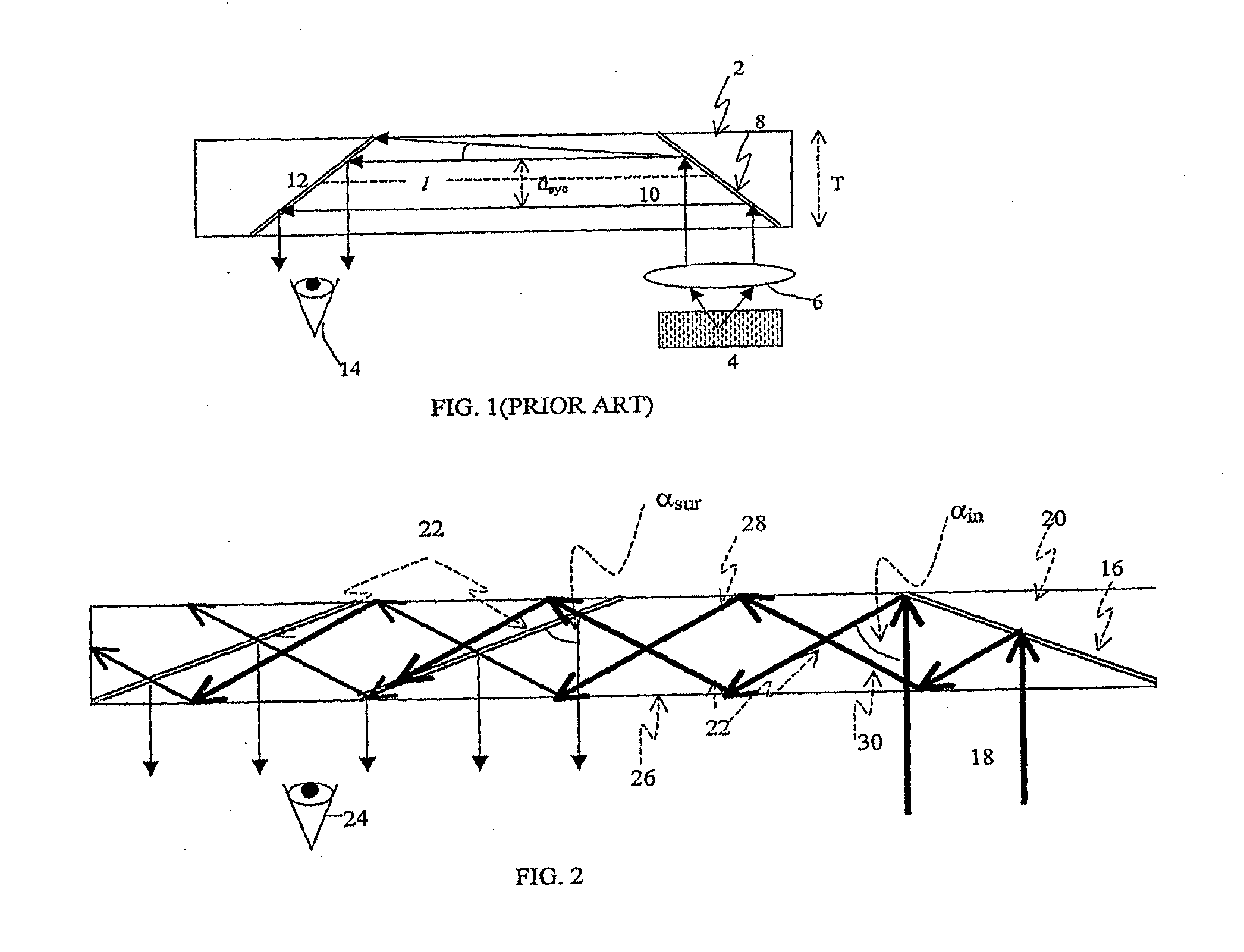
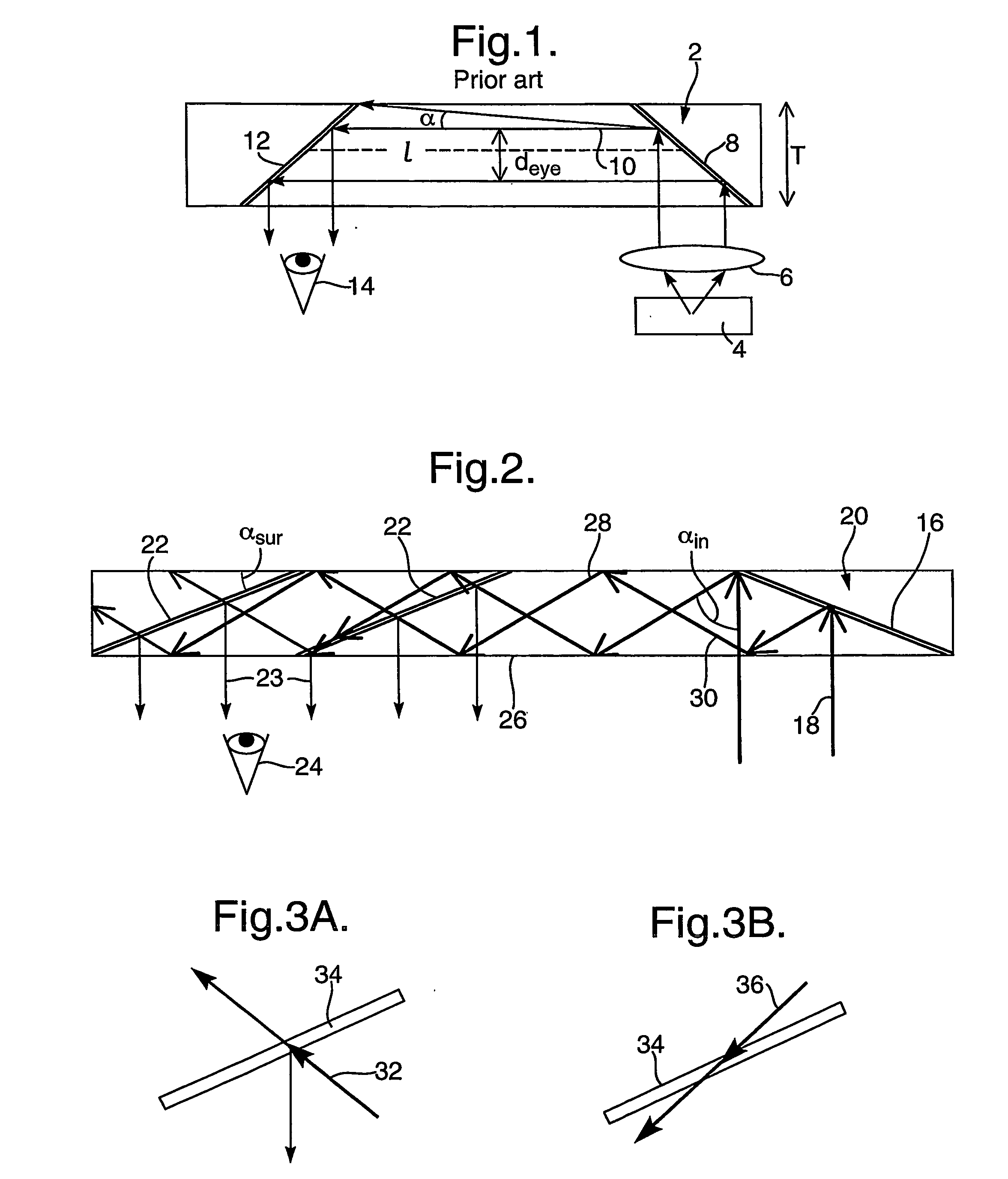
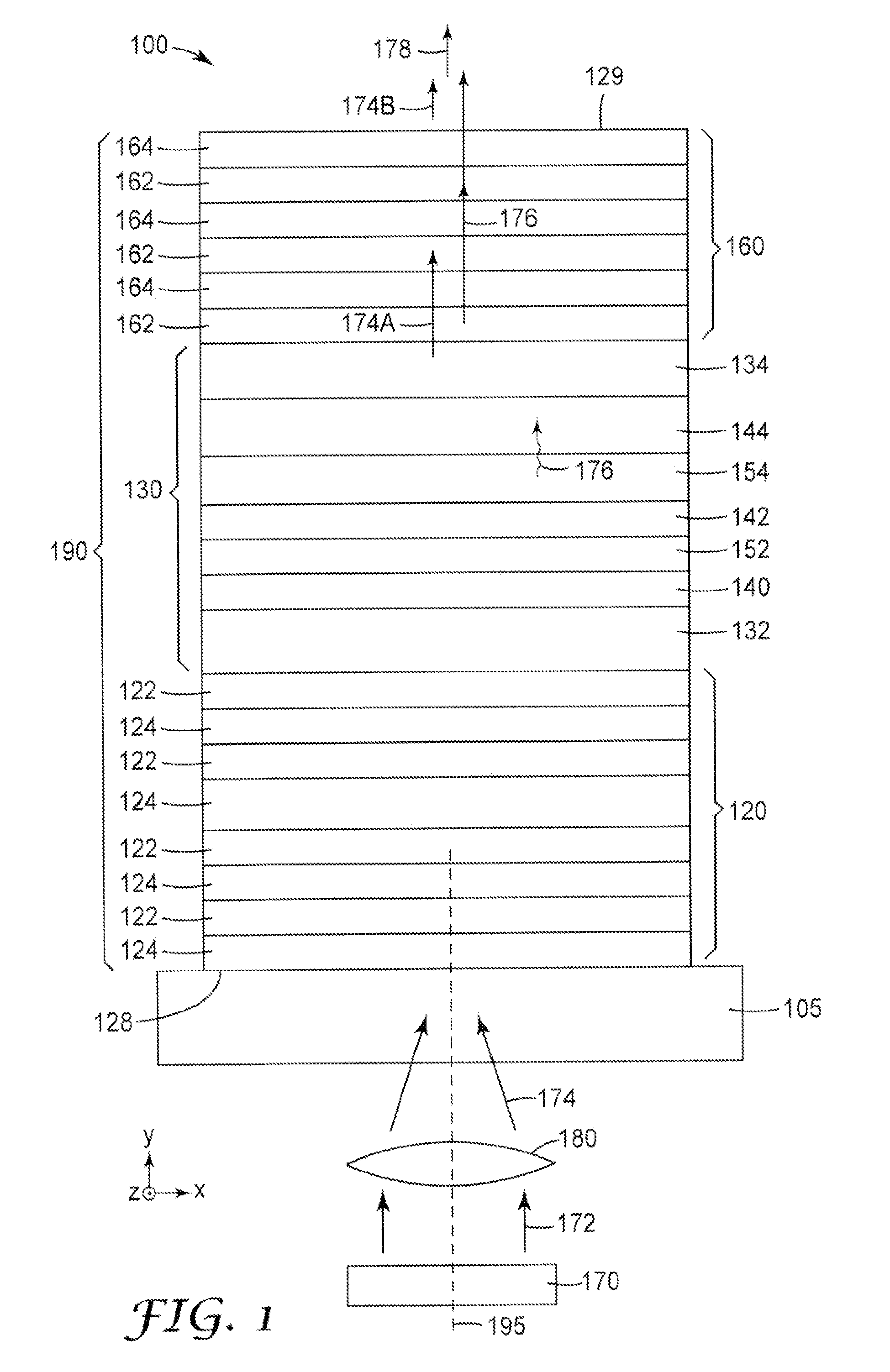
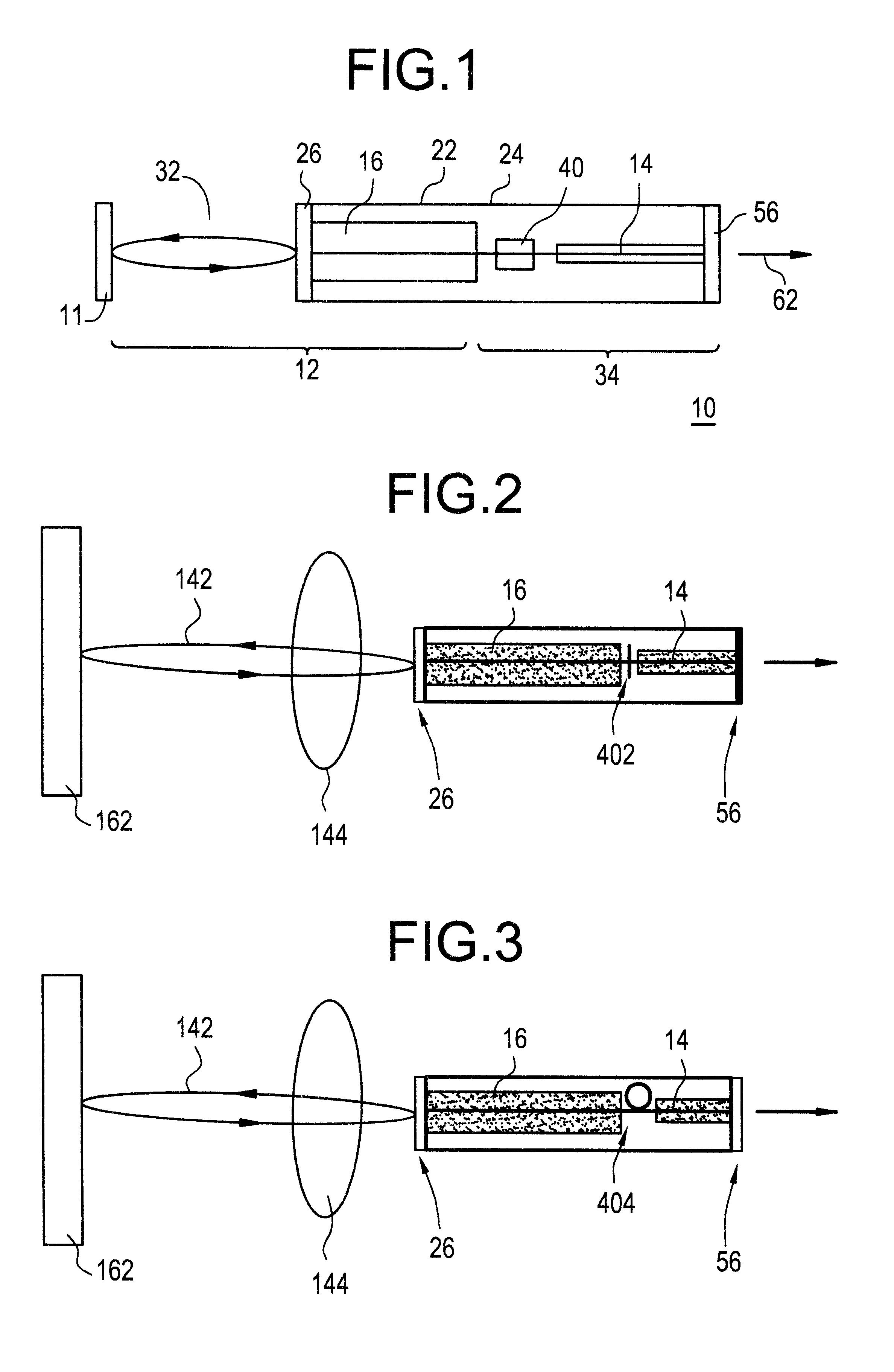
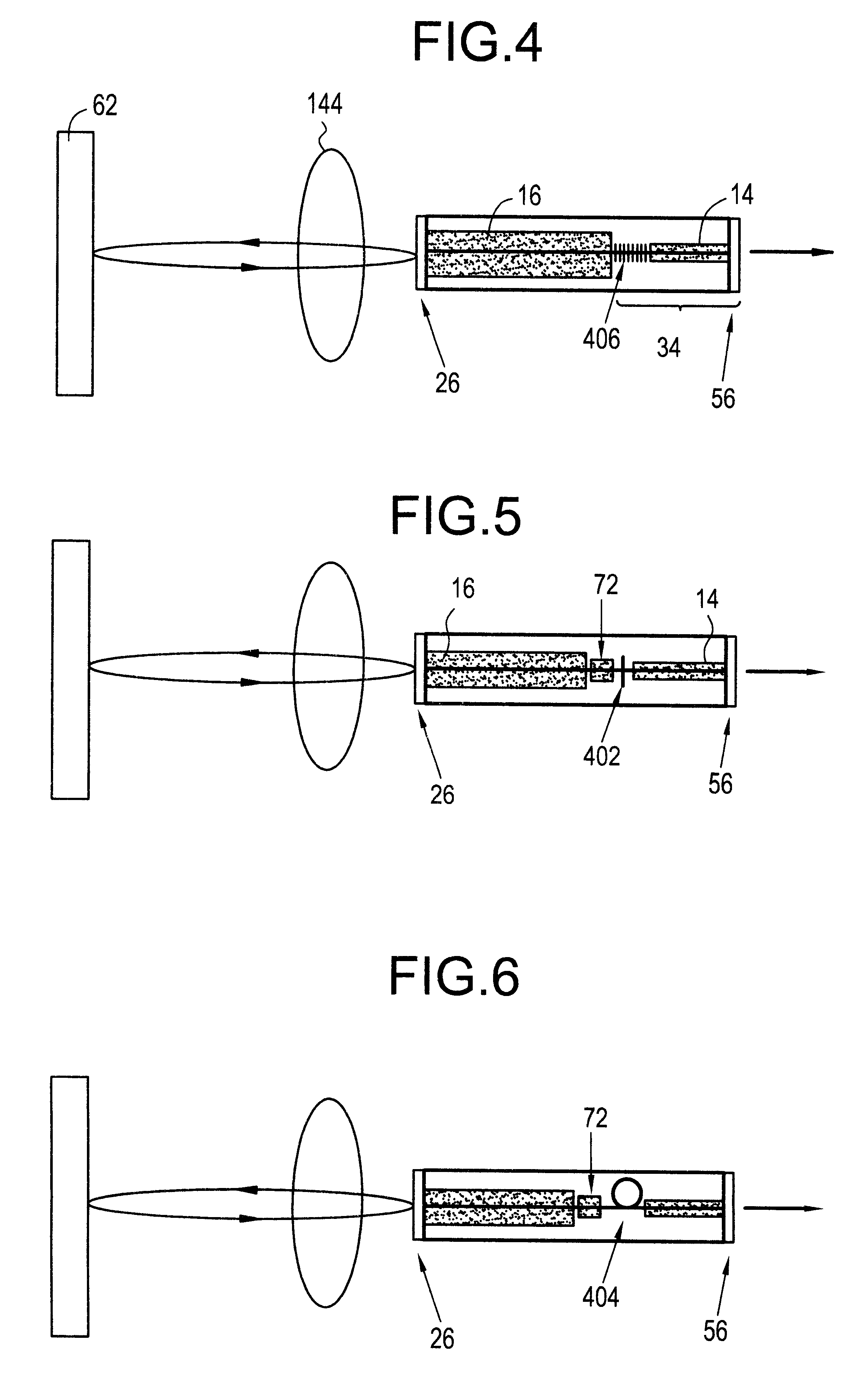
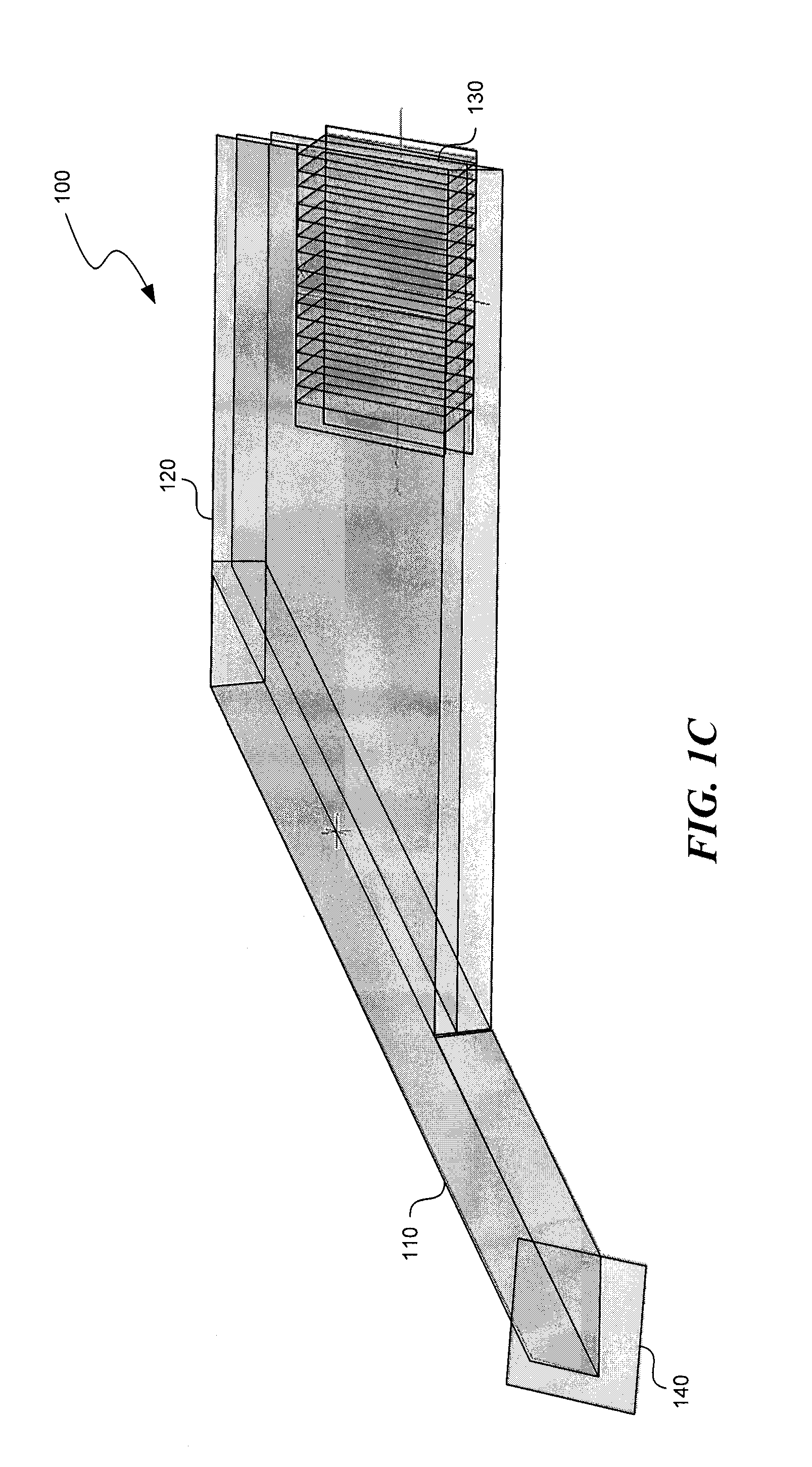
Light guide optical device
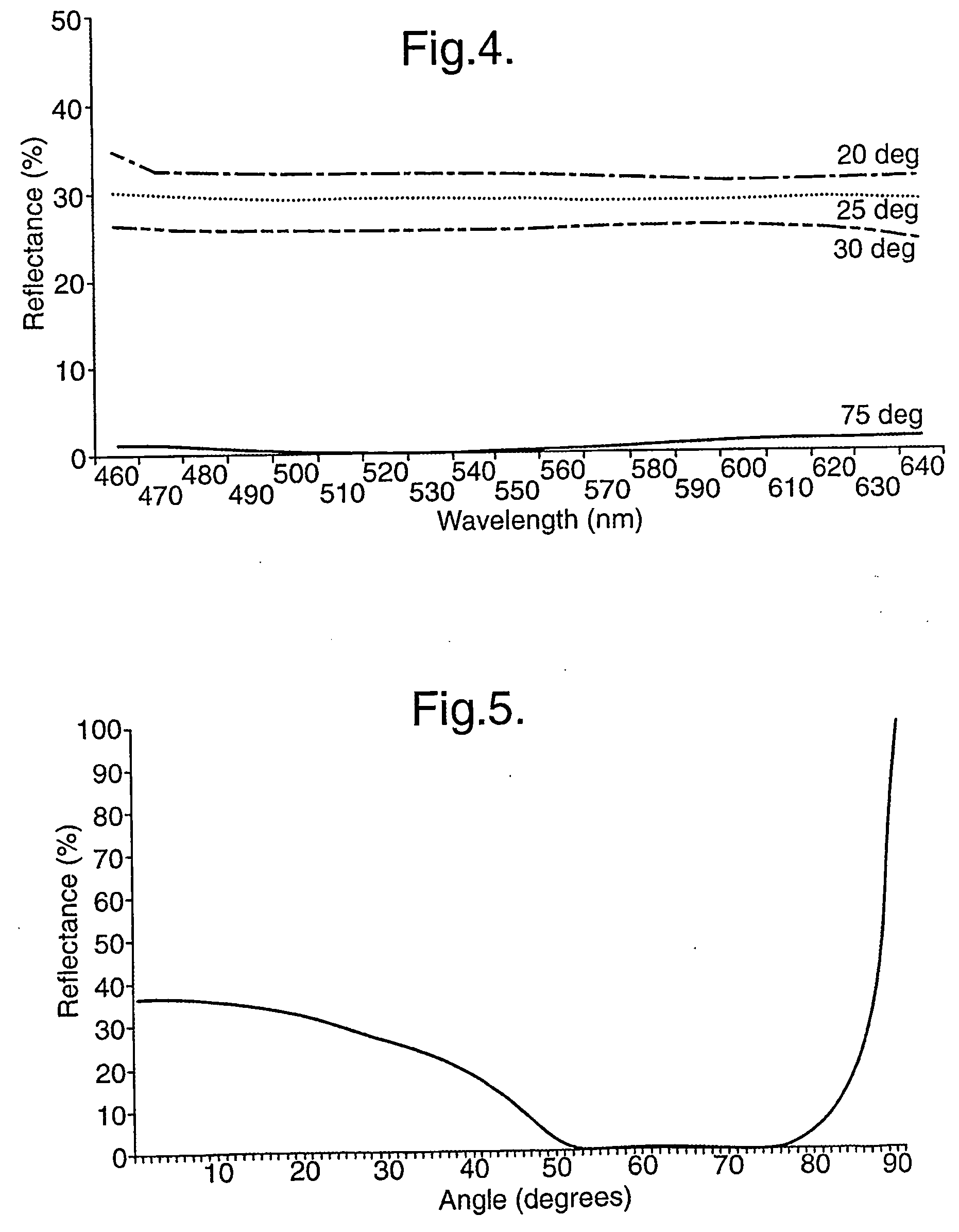
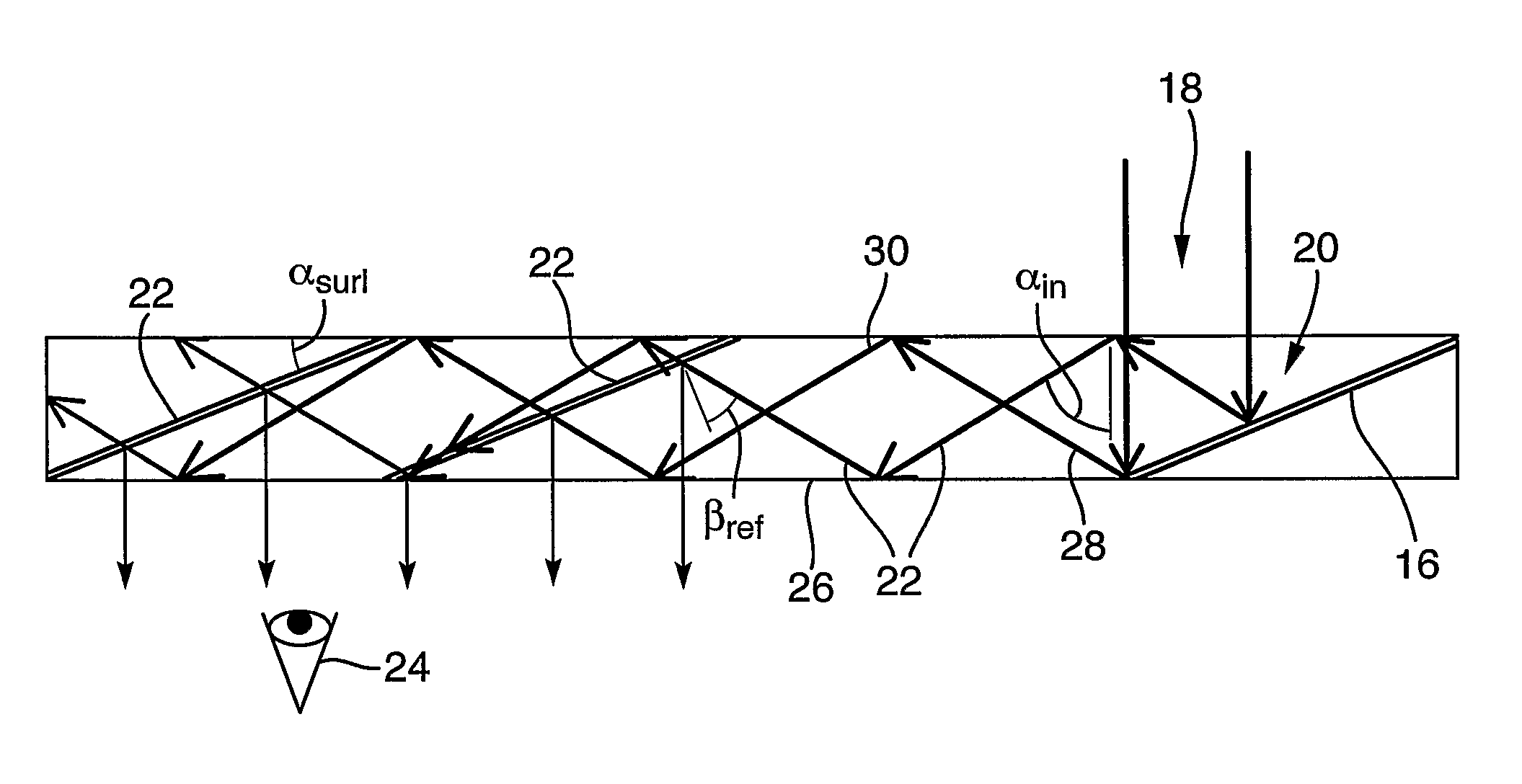
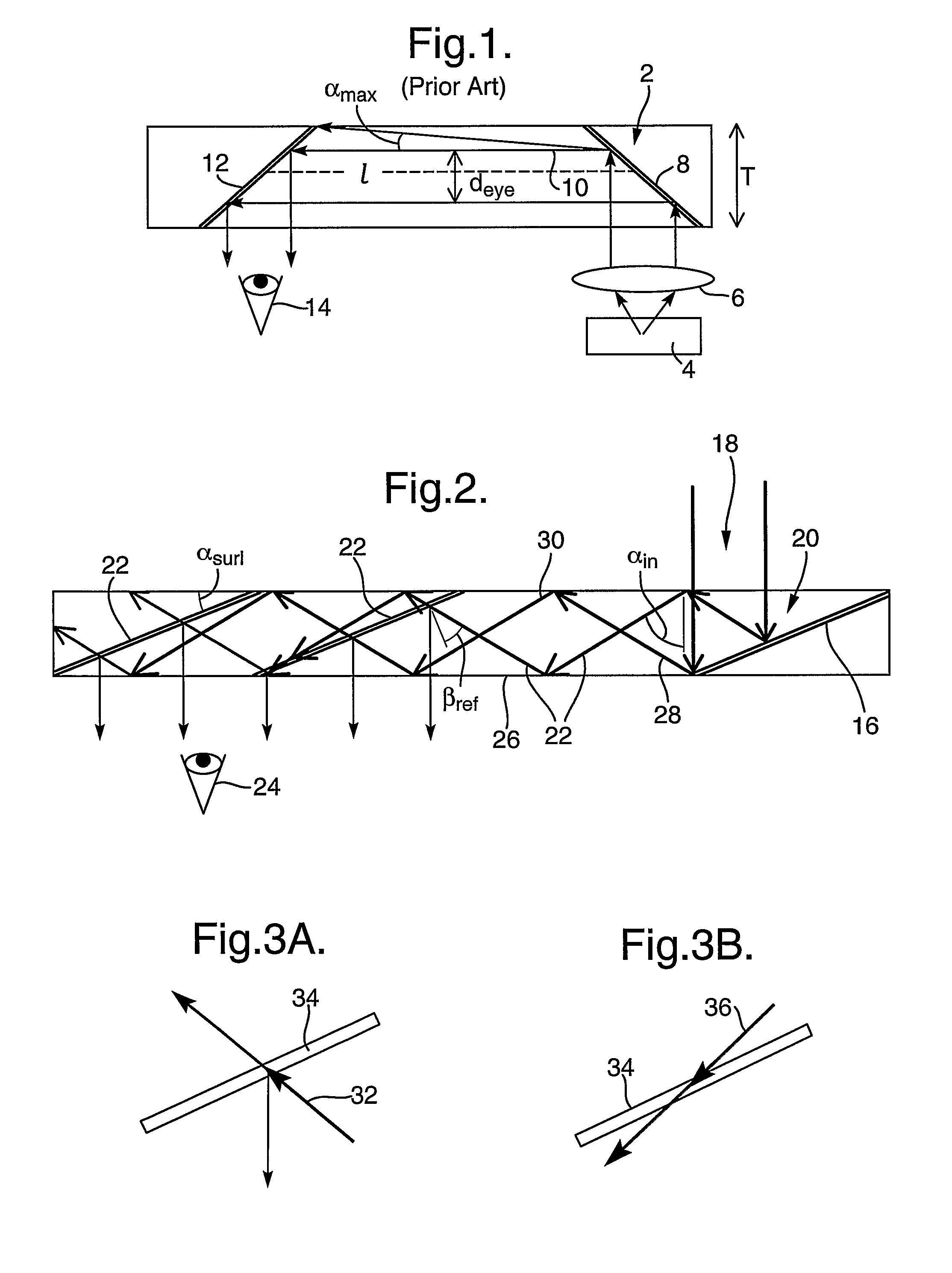
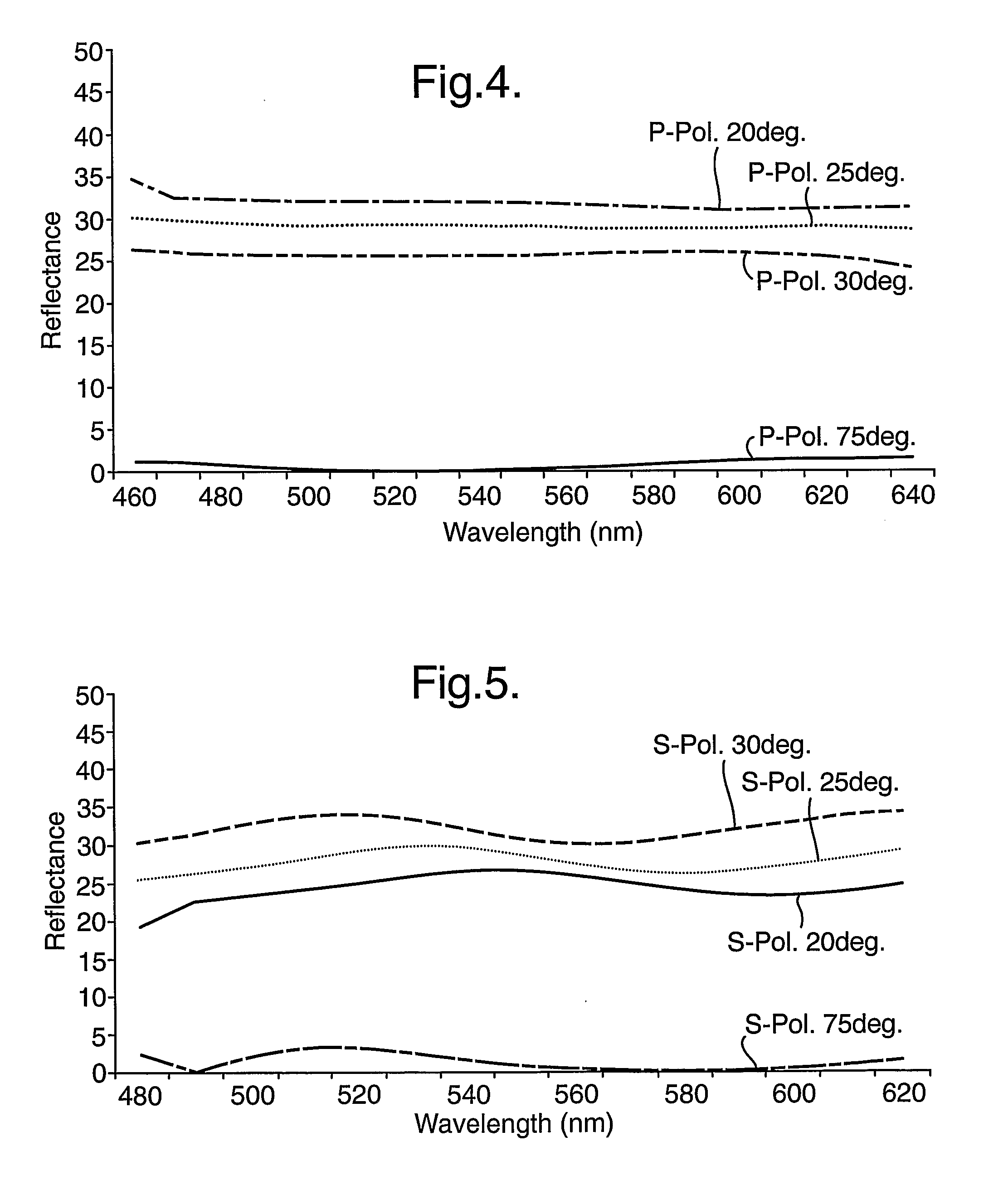
InactiveUS7457040B2Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to mergeMechanical apparatusMirrorsTotal internal reflectionLight guide
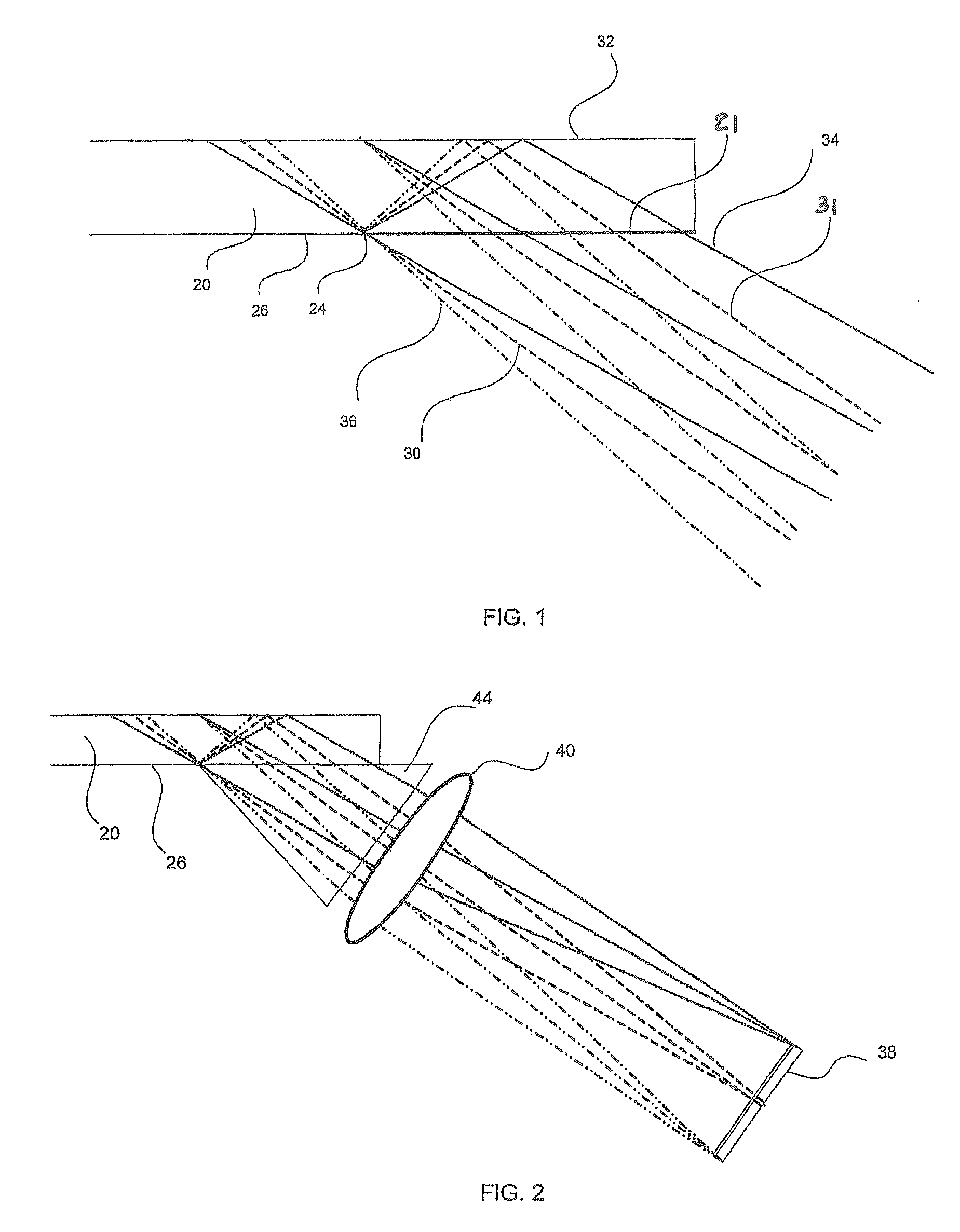
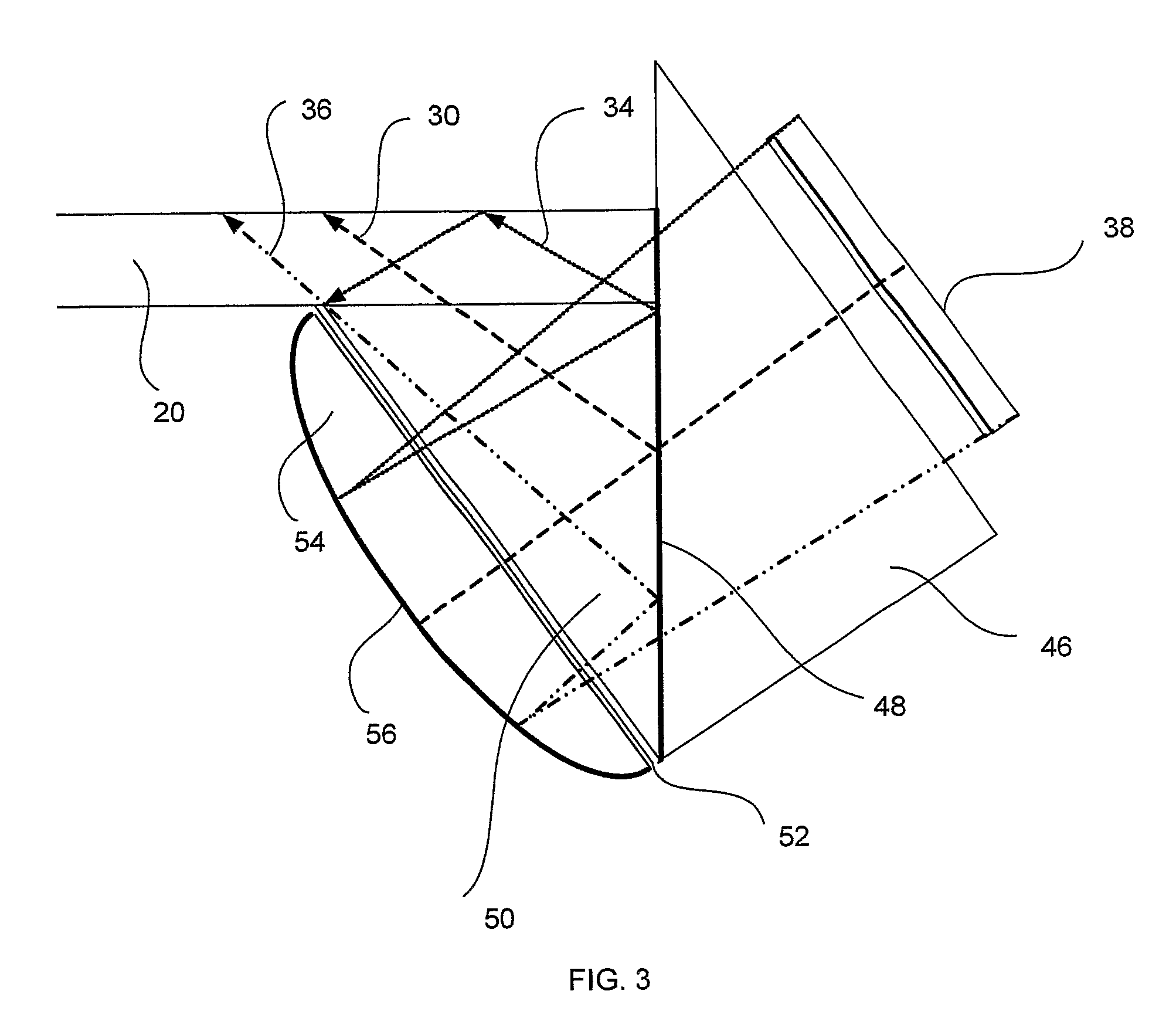
There is provided an optical device including a light-transmitting substrate having at least two major surfaces and edges, optical means for coupling light into the substrate by total internal reflection and at least one partially reflecting surface located in the substrate.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Method and apparatus for histological and physiological biometric operation and authentication
InactiveUS6483929B1Improve securityLow profileElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisProcess moduleComputer science
The present invention is directed toward a device for biometric authentication. The device comprises an infra red signal transmitter, signal receiver, memory module, and processing module. The signal transmitter transmits infrared energy toward a user. The infrared energy is partly absorbed and partly reflected by the user's body. The infra red signal receiver collects partly reflected infrared energy. The memory module stores the data, and the processing module processes and compares the reflected infrared energy and stored data for use in biometric authentication.
Owner:HALO WEARABLES LLC
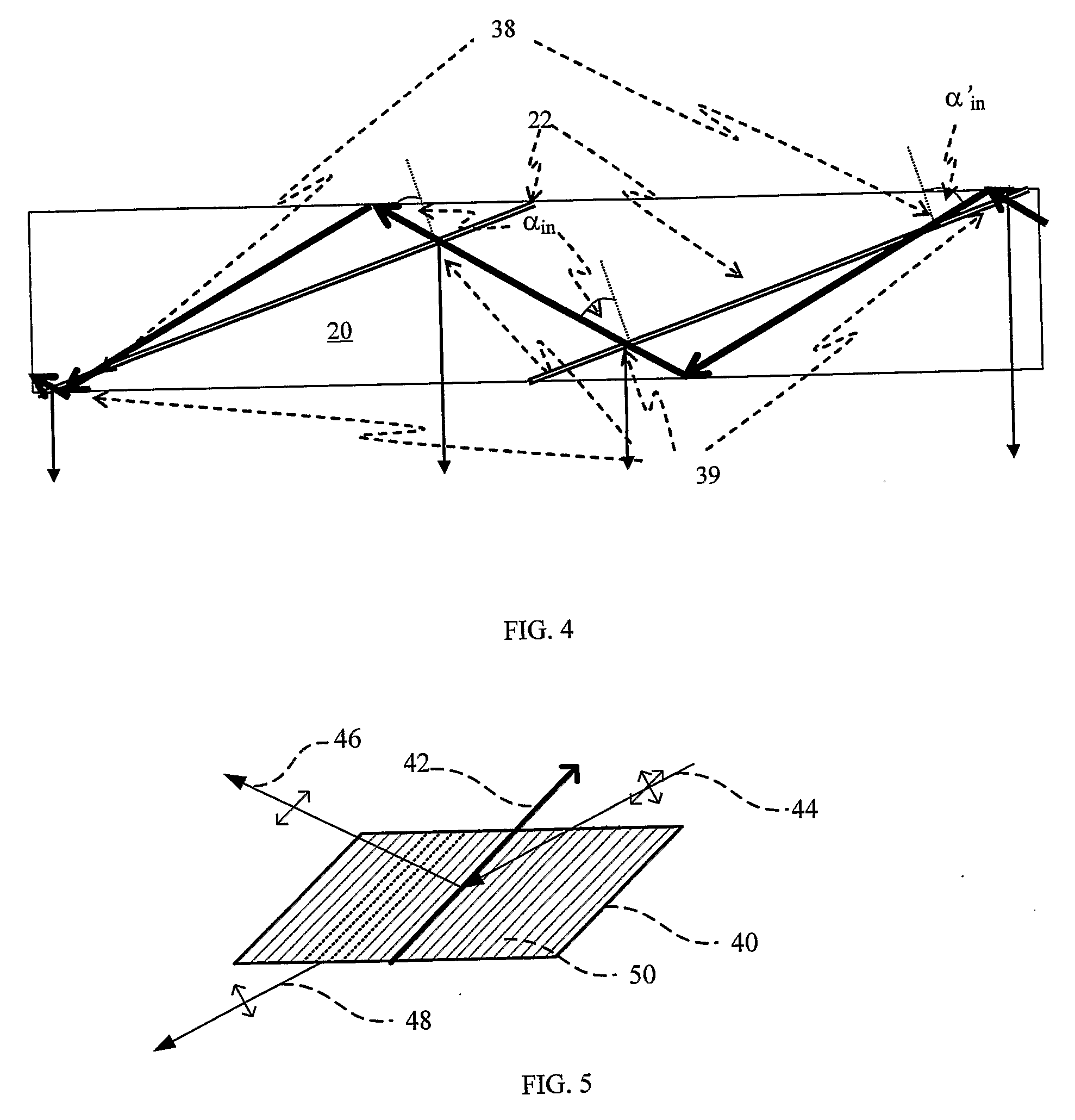
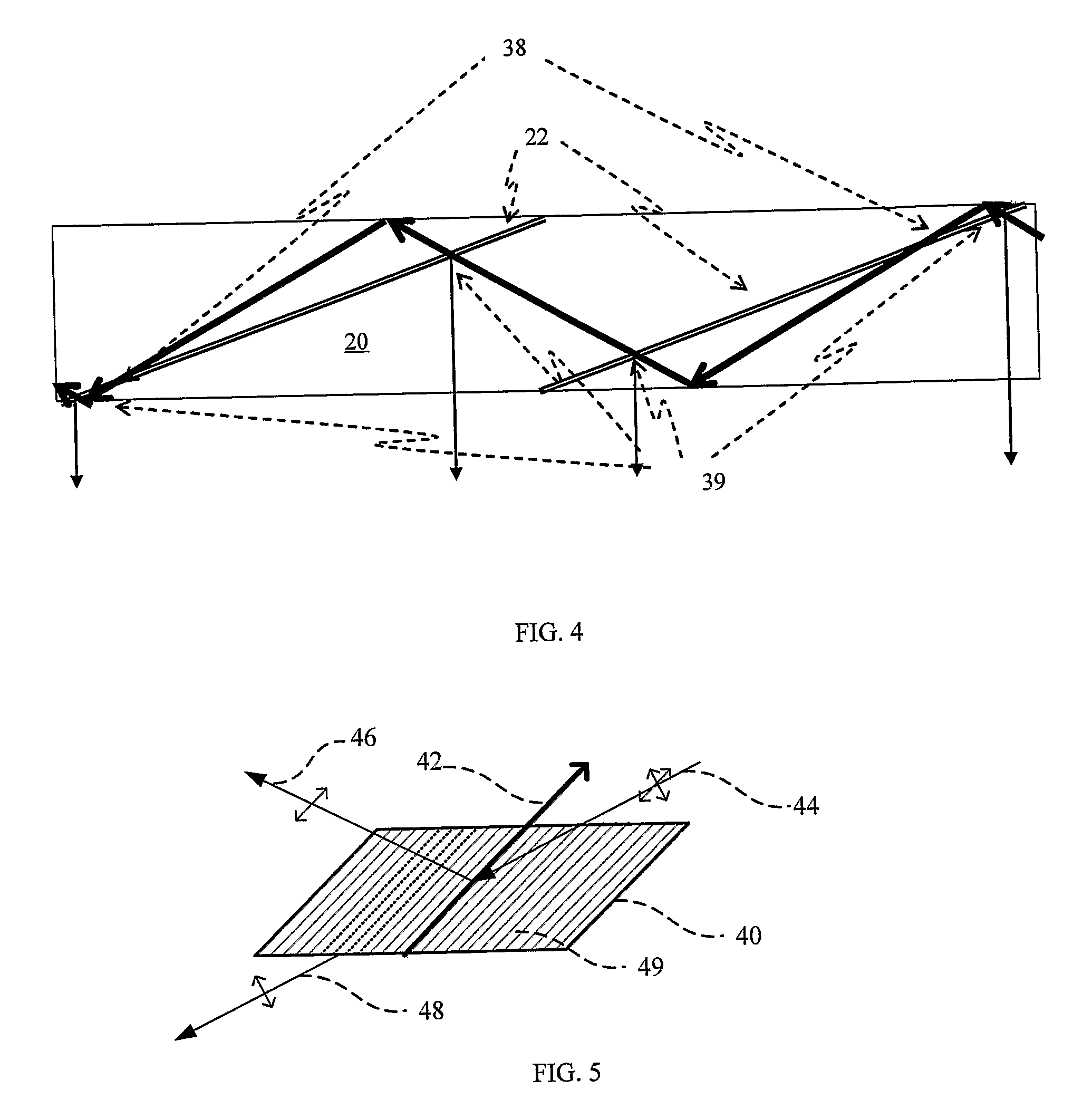
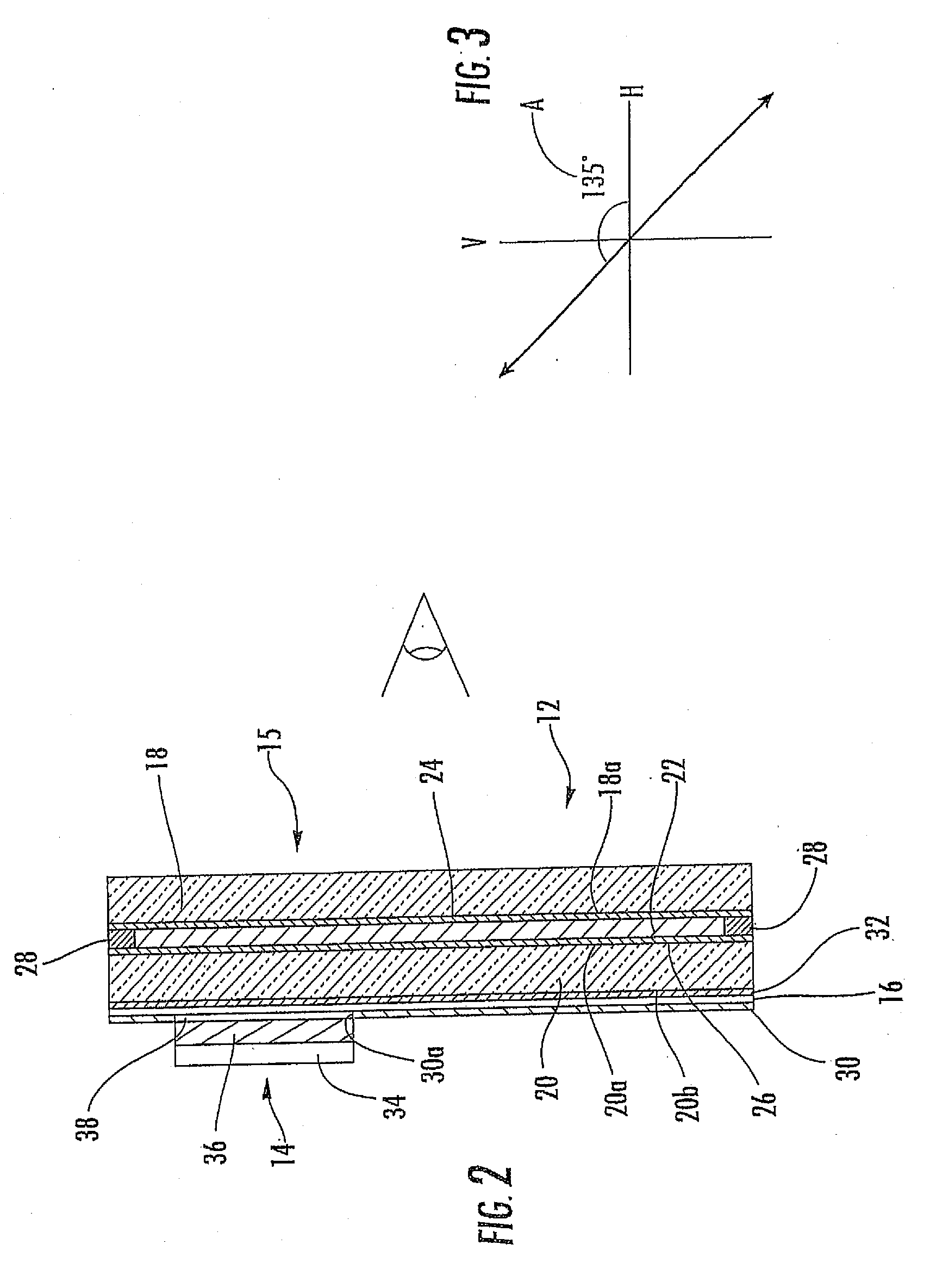
Substrate-guided optical device with wide aperture
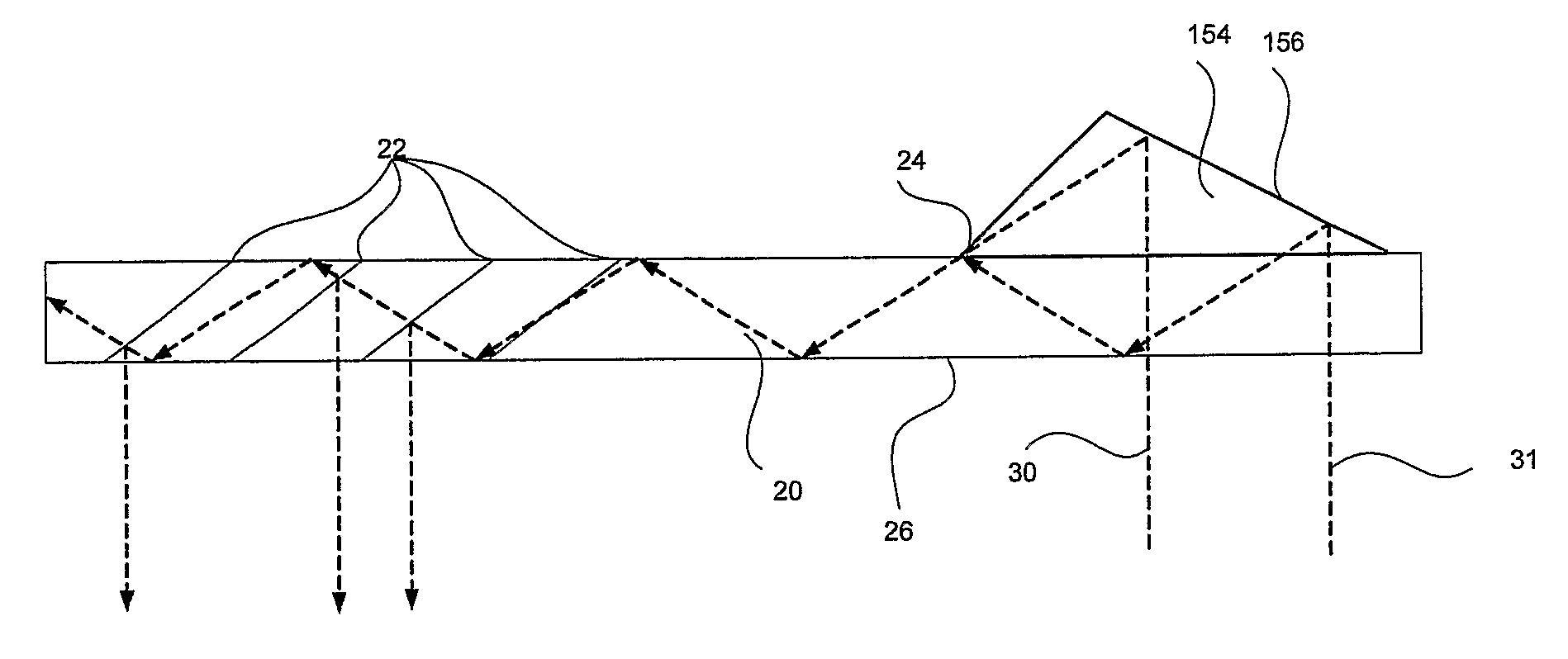
ActiveUS7643214B2Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to mergePolarising elementsCoupling light guidesOptoelectronicsPartial reflection
There is provided an optical device, having a light transmitting substrate (20) including at least two major surfaces parallel to each other and edges; optical means (16) for coupling light into the substrate by internal reflection and at least one reflecting, surface (22) located in the substrate which is non-parallel to the major surfaces of the substrate (20) characterized in that the optical means (16) for coupling light into the substrate is a partially reflecting surface, wherein part of the light coupled into the substrate (20) passes through the partially reflecting surface (16) out of the substrate and part of the light is reflected into the substrate (20).
Owner:LUMUS LTD
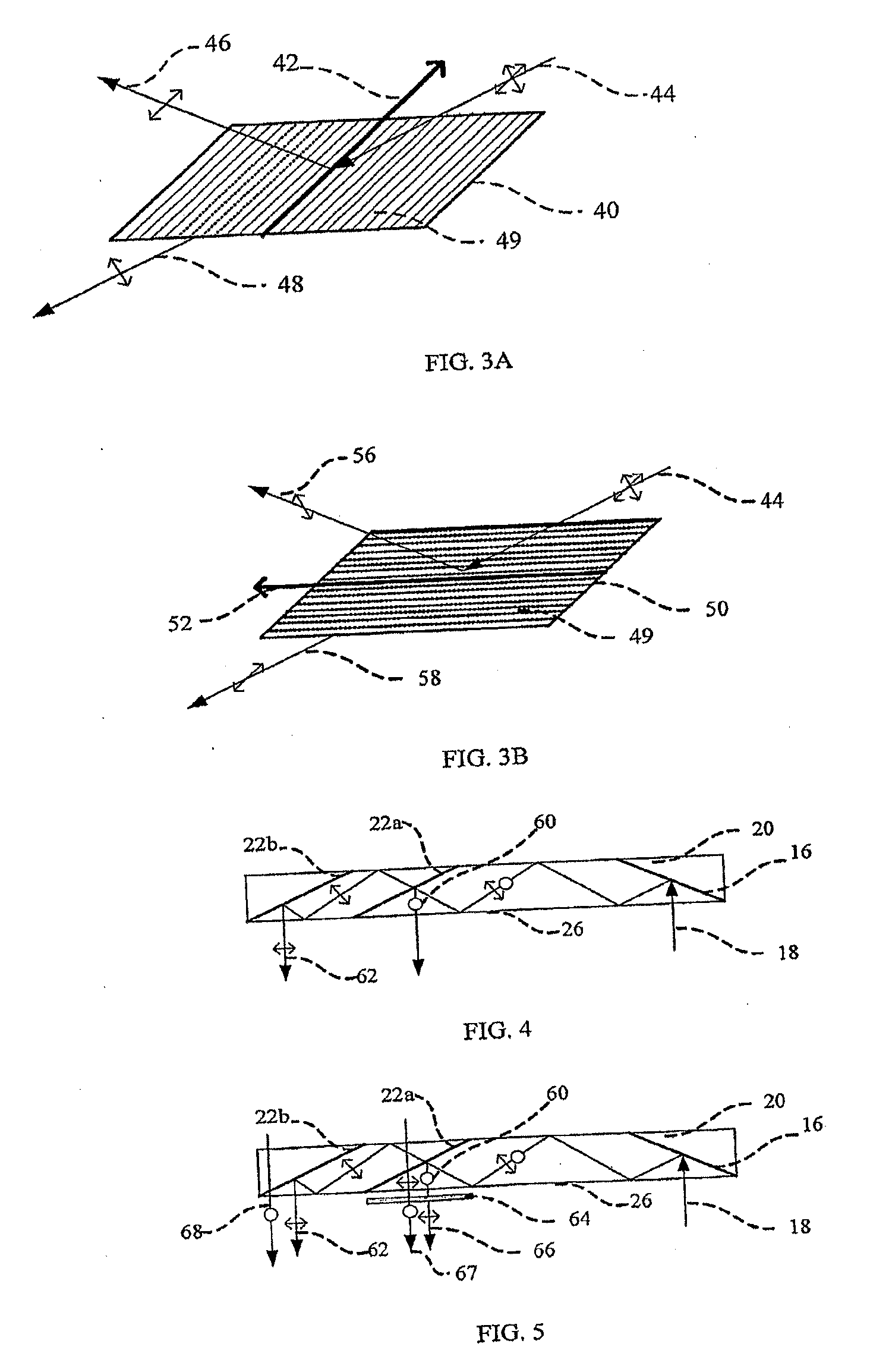
Substrate-Guide Optical Device Utilizing Polarization Beam Splitters
ActiveUS20080151379A1Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to mergeNon-optical adjunctsPolarising elementsTotal internal reflectionLight beam
There is provided an optical device, including a light waves-transmitting substrate having two major surfaces and edges, optical means for coupling light into the substrate by total internal reflection, and a plurality of partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) carried by the substrate wherein the partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) are parallel to each other and are not parallel to any of the edges of the substrate, and wherein one or more of the partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) is an anisotropic surface.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Substrate-Guided Optical Device Utilzing Thin Transparent Layer
ActiveUS20090122414A1Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to mergePolarising elementsOptical light guidesClear LayerTotal internal reflection
There is provided an optical device, including a light-transmitting substrate having two major surfaces and edges, an optical element (16) for coupling light waves into the substrate by total internal reflexion, and a plurality of partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b, 22c) carried by the substrate. The partially reflecting surfaces are parallel to each other and are not parallel to any of the edges of the substrate. At least one of the partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b, 22c) does not intersect with at least one of the two major surfaces, and the optical element (16) intersects with at least one of the two major surfaces.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
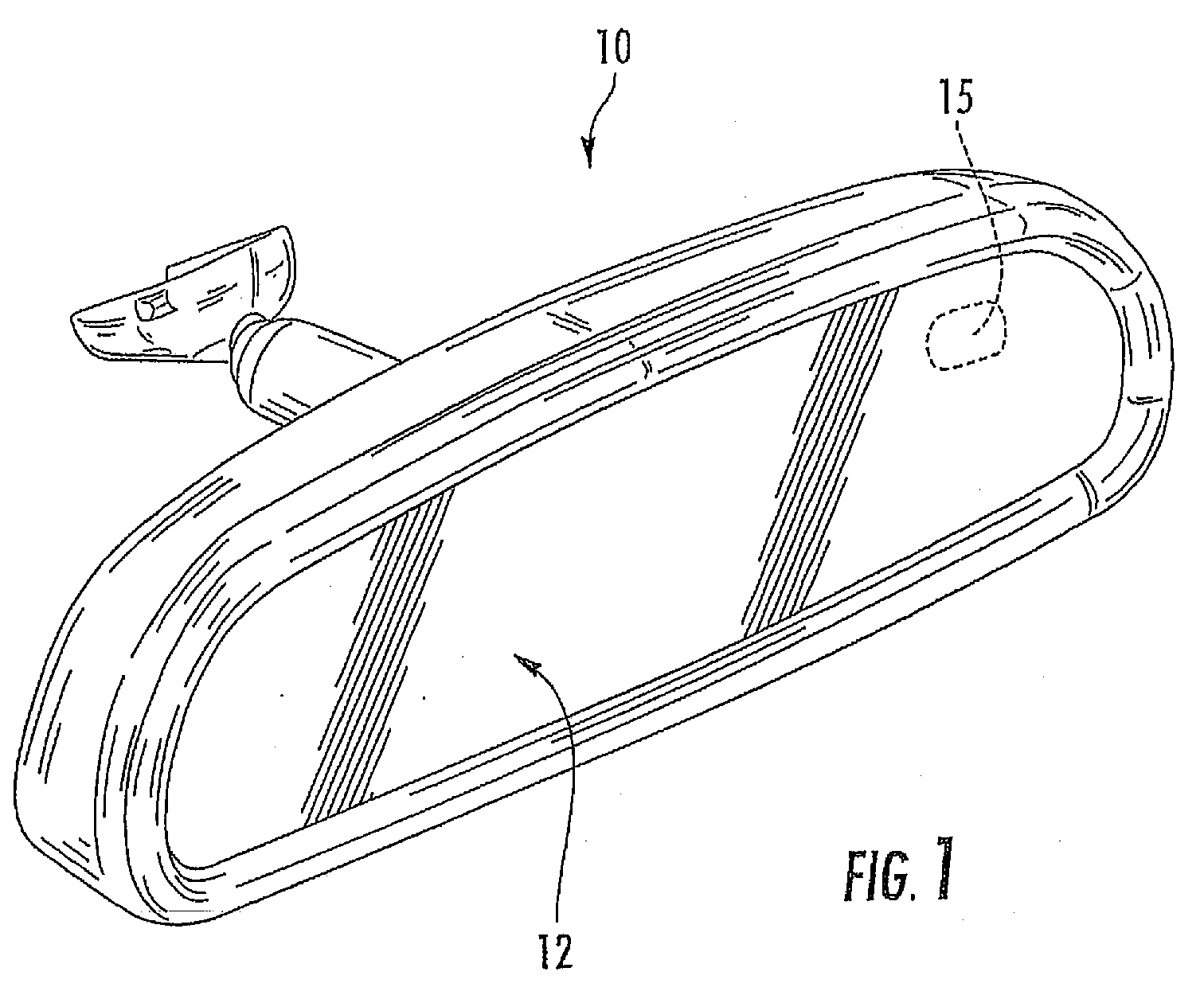
Electrochromic rearview mirror assembly incorporating a display/signal light
According to one embodiment of the present invention, an electrochromic rearview mirror assembly for a vehicle includes an electrochromic mirror having a variable reflectivity, a glare sensor for sensing levels of light directed towards the front element from the rear of the vehicle, an ambient sensor for sensing levels of ambient light, a display positioned behind the partially transmissive, partially reflective portion of the reflector for displaying information therethrough; and a control circuit coupled to the sensors and the display. The control circuit determines whether daytime or nighttime conditions are present as a function of the ambient light level sensed by the ambient sensor. During daytime conditions, the control circuit responds to light levels sensed by the glare sensor to control a contrast ratio of light originating from the display and light reflecting from the partially transmissive, partially reflective area of the reflector.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Light guide optical device
ActiveUS20050180687A1Simple designFabrication facilitatedMechanical apparatusMirrorsTotal internal reflectionLight guide
There is provided an optical device including a light-transmitting substrate having at least two major surfaces and edges, optical means for coupling light into the substrate by total internal reflection and at least one partially reflecting surface located win the substrate.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Substrate-Guided Optical Device with Wide Aperture
ActiveUS20080198471A1Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to mergePolarising elementsCoupling light guidesOptoelectronicsPartial reflection
There is provided an optical device, having a light-transmitting substrate (20) including at least two major surfaces parallel to each other and edges; optical means (16) for coupling light into the substrate by internal reflection, and at least one reflecting, surface (22) located in the substrate which is non-parallel to the major surfaces of the substrate (20) characterized in that the optical means (16) for coupling light into the substrate is a partially reflecting surface, wherein part of the light coupled into the substrate (20) passes through the partially reflecting surface (16) out of the substrate and part of the light is reflected into the substrate (20).
Owner:LUMUS LTD
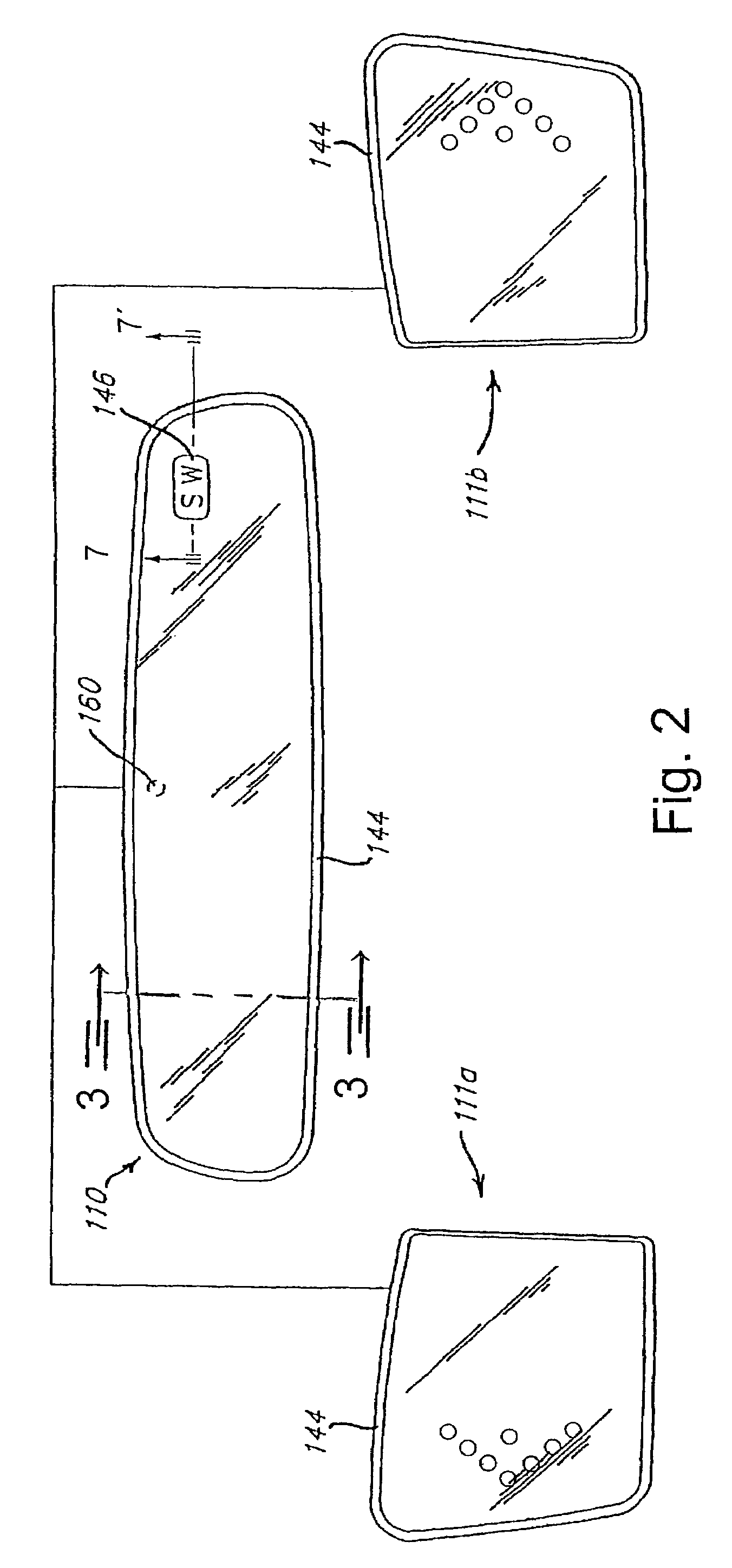
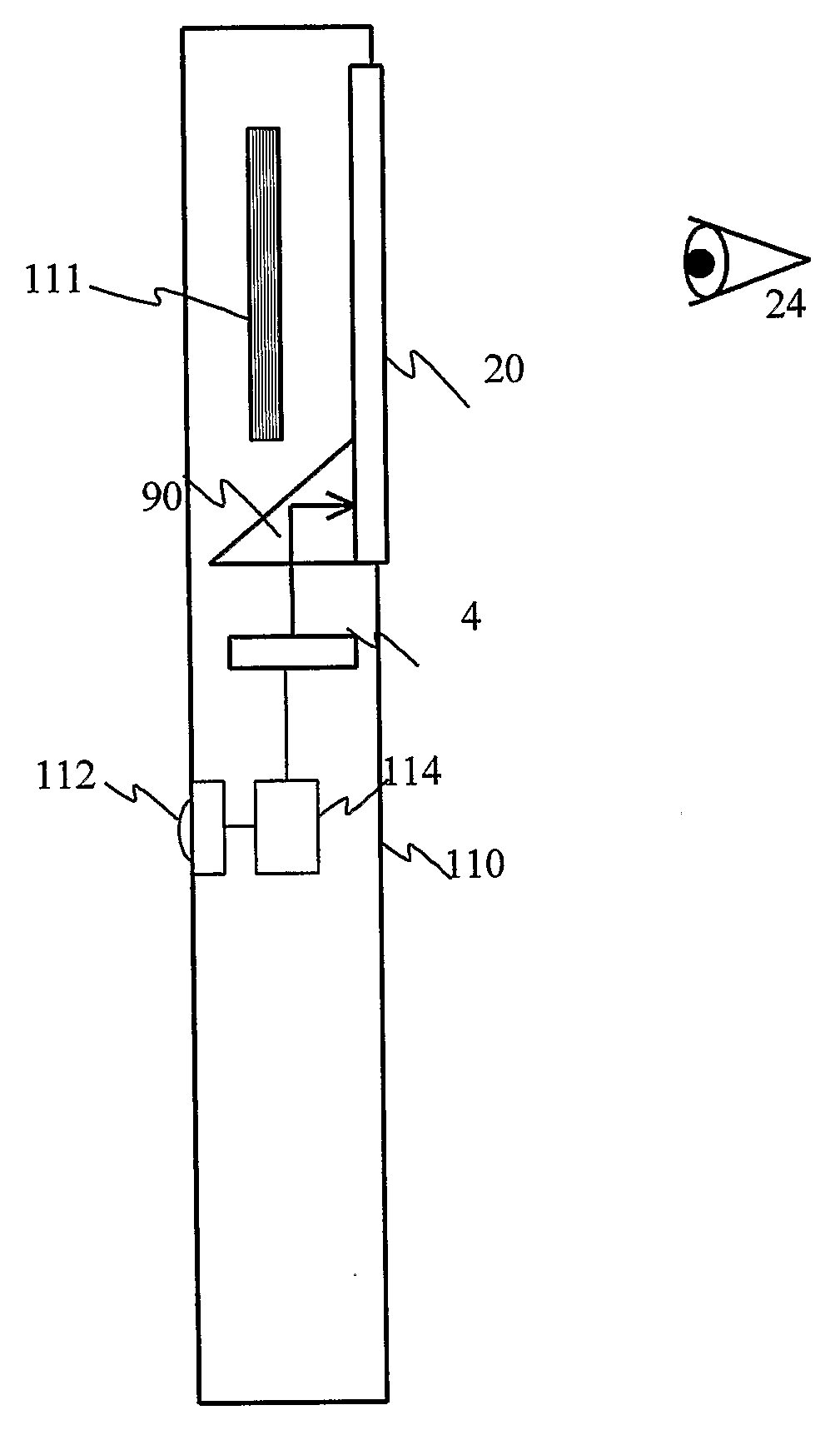
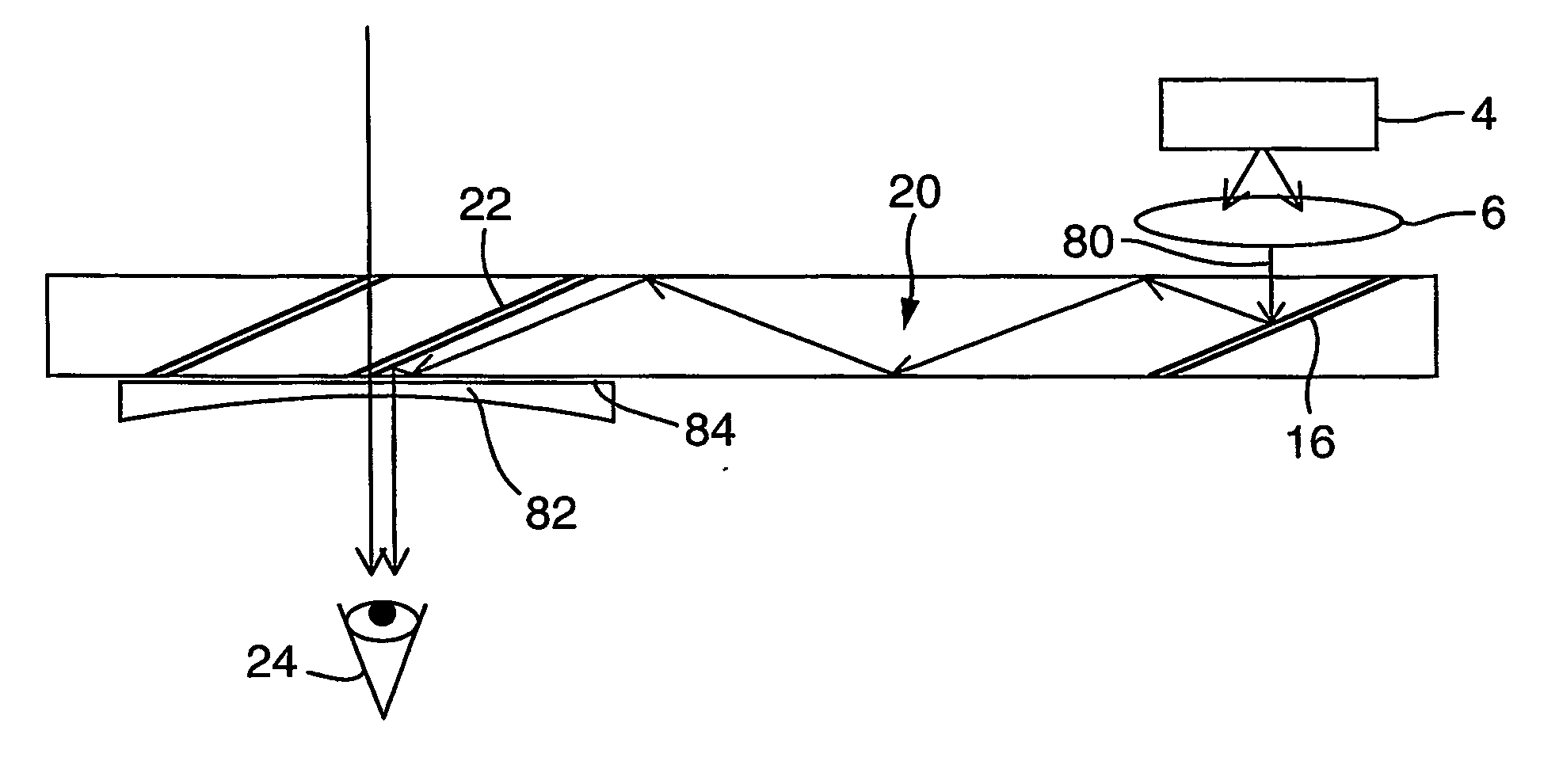
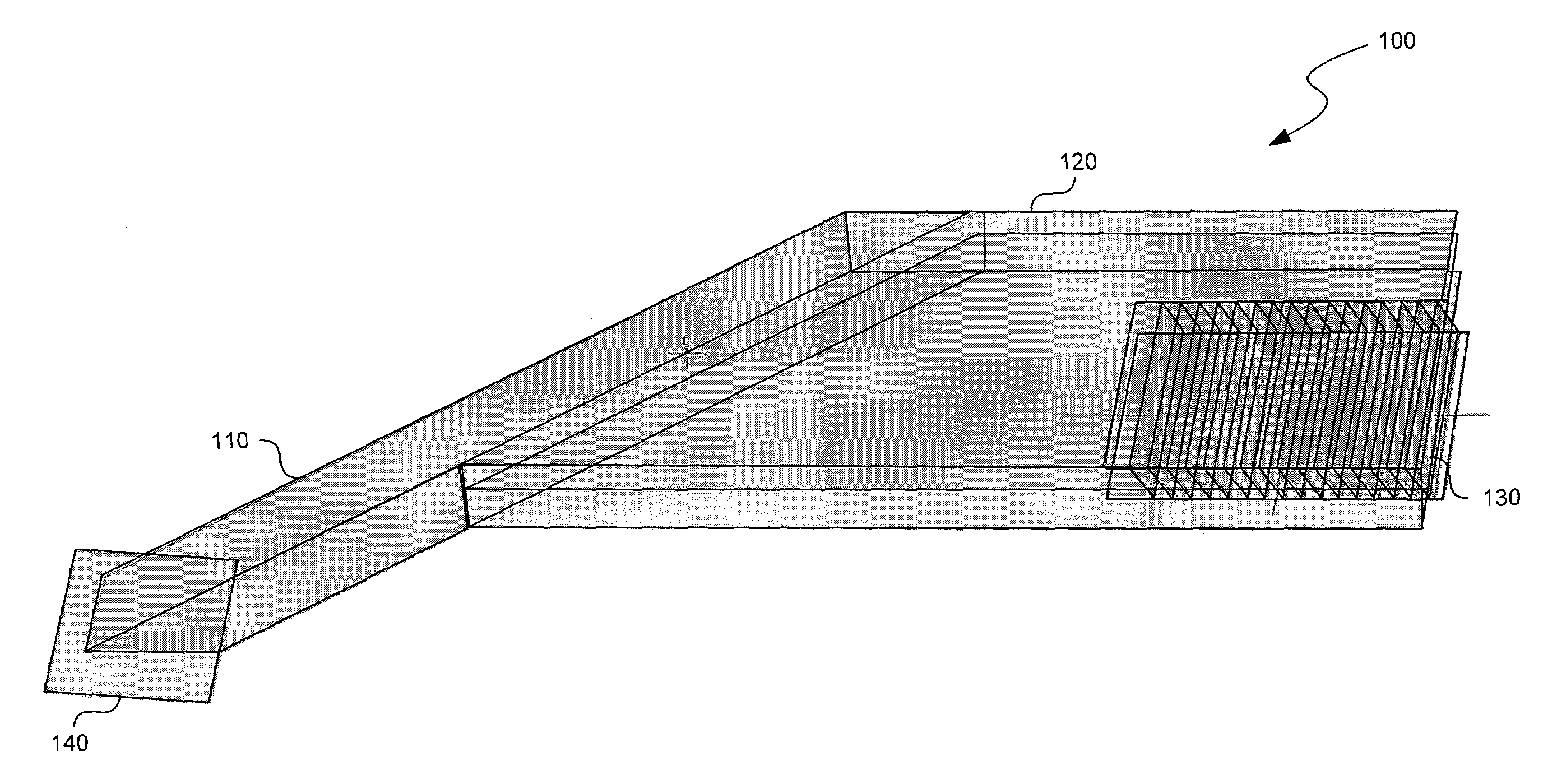
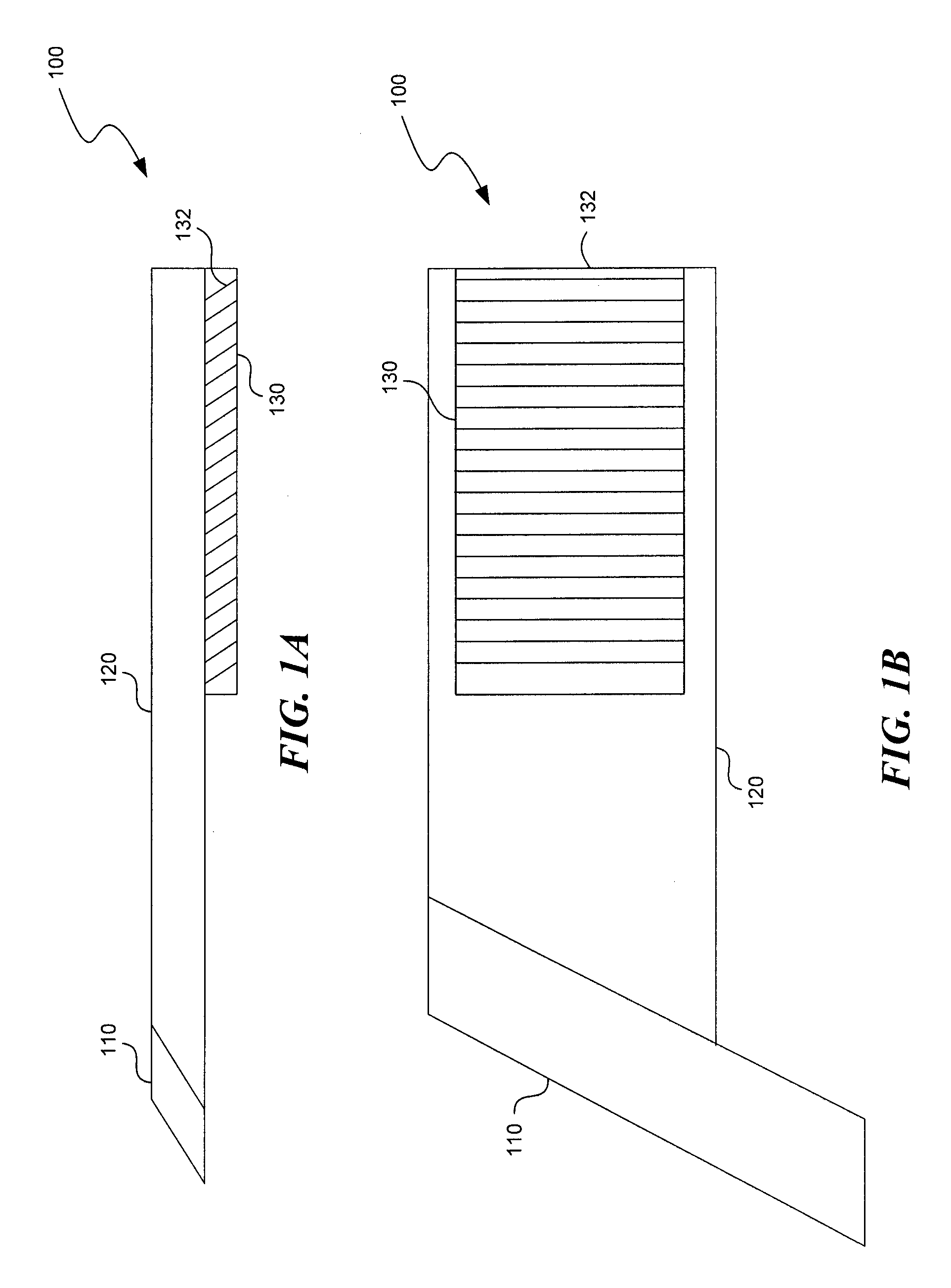
Substrate-guided optical device particularly for vision enhanced optical systems
ActiveUS7751122B2Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to mergeMirrorsMountingsTotal internal reflectionImaging processing
There is provided an optical system, including a mechanical body (110), a light-transmitting substrate (20) having two major surfaces and edges, embedded in the mechanical body, an optical element (90) for coupling light into the substrate by total internal reflection and a plurality of partially reflecting surfaces (22) carried by the substrate, wherein the partially reflecting surfaces are parallel to each other and are not parallel to any of the edges of the substrate. The system also includes an image capturing device (112), a display source (4), and an image-processing unit (114). The image-capturing device (112) is connected via the image-processing unit (114) to the display source (4).
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Rearview assembly with display
InactiveUS20090201137A1Spread the wordDegradation of display imageMirrorsOptical signallingDisplay deviceControl circuit
A rearview assembly for a vehicle includes a mirror element having a partially reflective, partially transmissive coating and a video display positioned behind the mirror element such that a display image is viewable through the partially reflective, partially transmissive coating. The video display may generate a viewable display image that has an intensity of at least 250 cd / m2. The video display may generate a display image that extends along and abuts at least a portion of curved edges of a housing. The assembly may include a forward facing light sensor for sensing a first light level forward of the vehicle, a rearward facing light sensor sensing a second light level to the rear of the vehicle, and a control circuit for comparing the first and second light levels and generating a warning signal when the second light level exceeds the first light level by at least threshold amount.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS INC
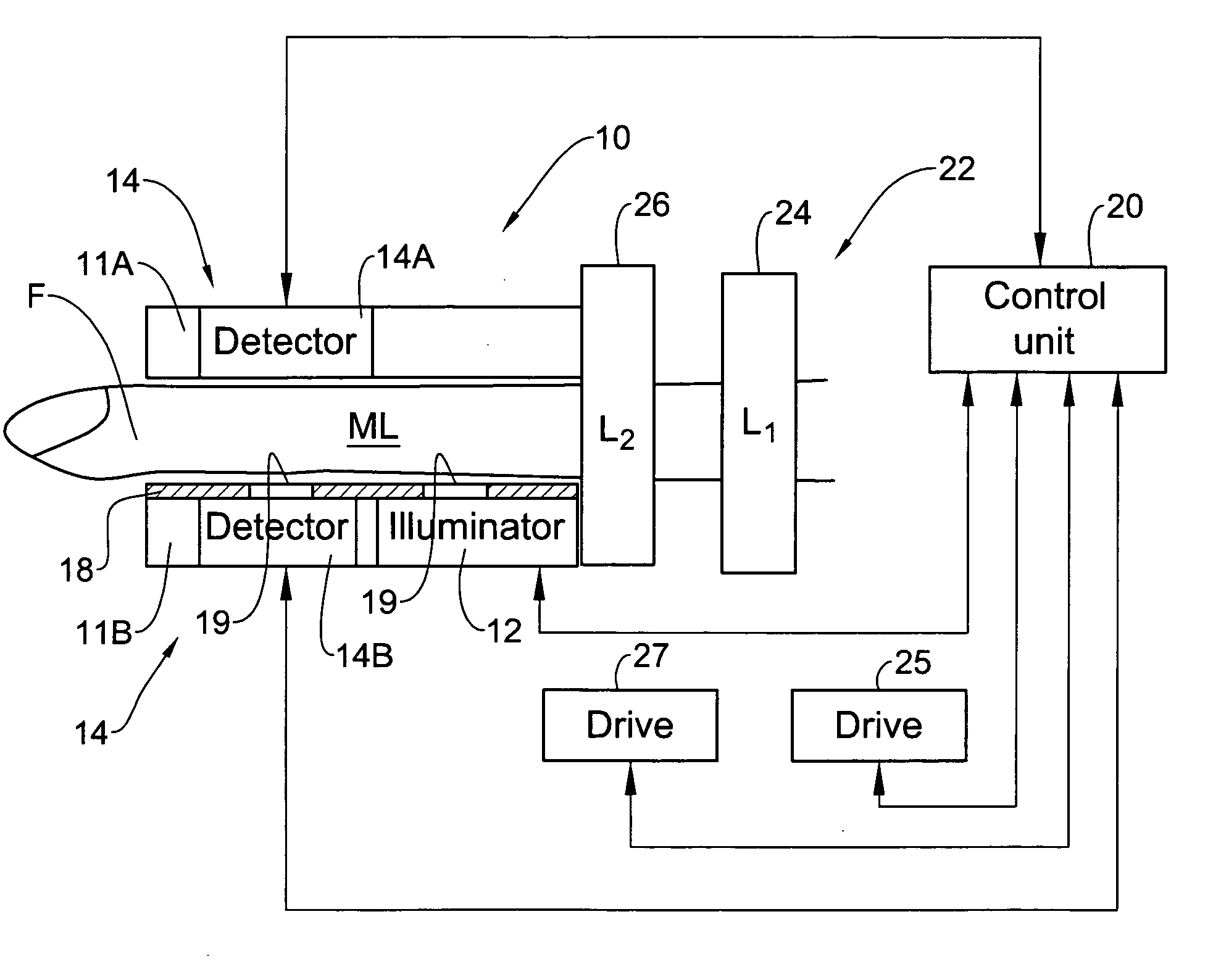
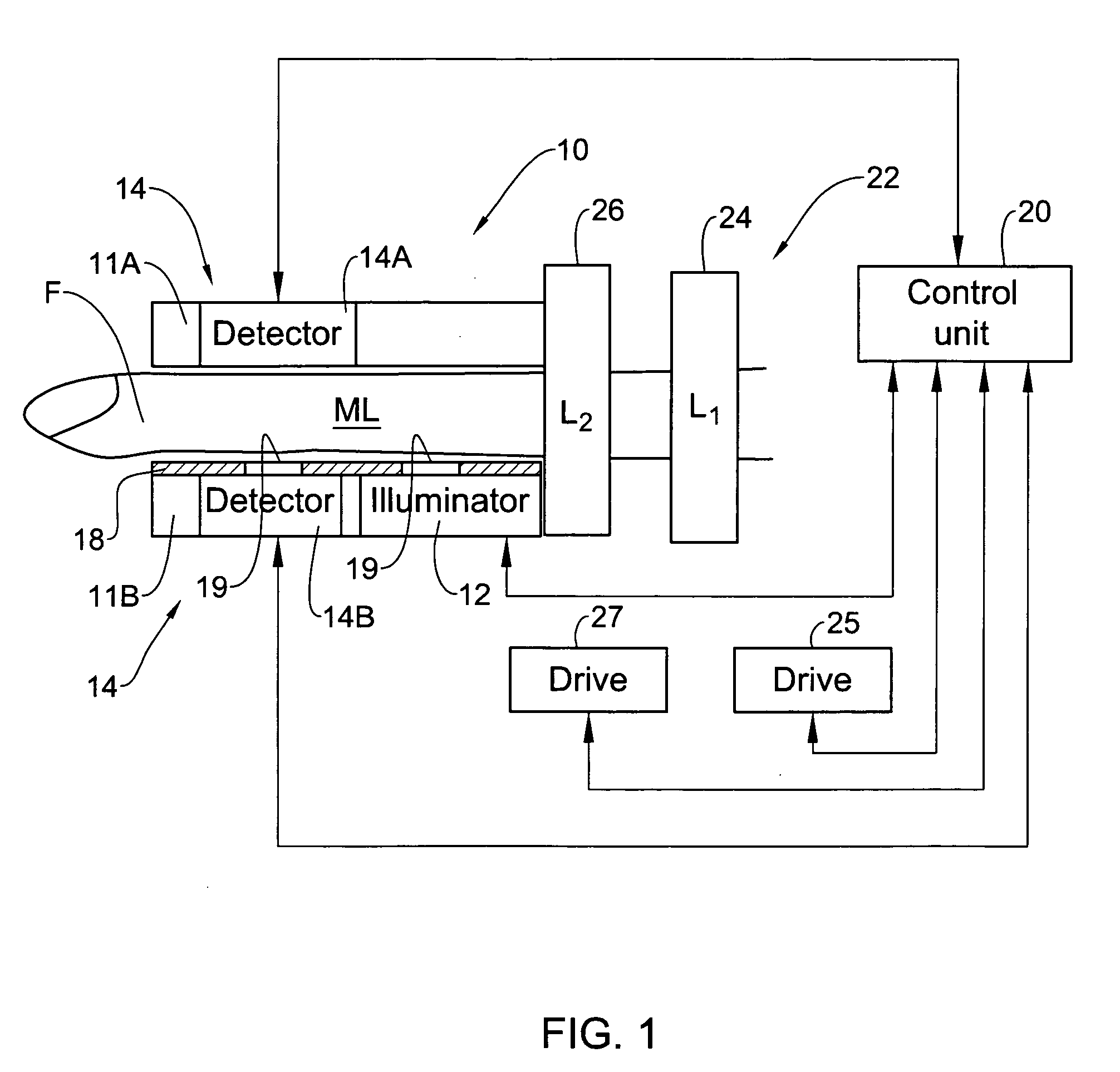
Device and method for non-invasive optical measurements
ActiveUS20060009685A1Facilitate non-invasive optical measurementStabilizing optical responseDiagnostics using pressureSensorsOptical measurementsLight signal
An optical measurement device and method are presented for use in non-invasive measurements on a patient's body. The device comprises an illumination assembly configured and operable to generate illuminating light of a predetermined wavelength range; a detection assembly; and a light directing assembly. The detection assembly comprises a first detector unit for detecting a first light signal transmitted through an illuminated body portion and generating first measured data indicative of the detected transmitted light, and a second detector unit for detecting a second light signal reflected from the illuminated body portion and generating second measured data indicative of the detected reflected light. The light directing assembly comprises a light diffuser for scattering back light incident thereto, to thereby direct the illuminating light or the light coming from the body portion back towards the body portion. This technique provides for increasing the amount of light reaching a region of interest inside the body portion and maximizing homogeneity of the first and second detected light signals.
Owner:ORSENSE LTD
Method and device for detecting touch pad input
InactiveUS20050128190A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLight beamPartial reflection
A method and system for determining the location of an object touching a touch pad. A light source is used to provide a light beam and a plurality of reflecting surfaces are disposed along an edge of the touch pad to partially reflect the light beam in order to provide a light sheet over the touch pad, such that the reflected intensity varies monotonously along the edge. A detector structure is disposed on the opposite edge to measure the light intensity of the light sheet, part of which is blocked when the object touches the touch pad. The reduction in the measured light intensity is used to calculate the location of the touching object in one direction. A second light sheet and a corresponding detector structure can be used to determine the location of the touching object in a different direction.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
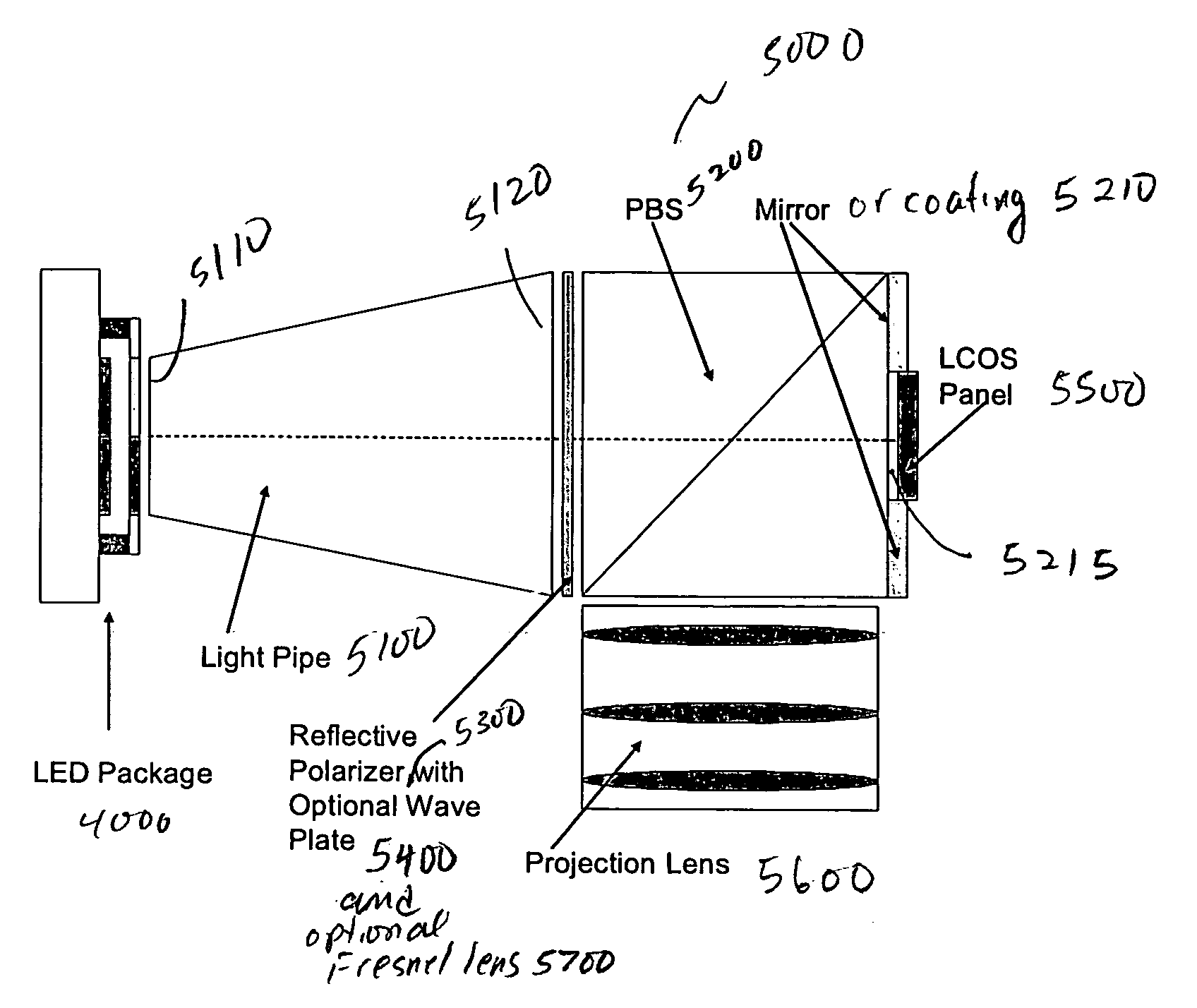
LED multiplexer and recycler and micro-projector incorporating the Same
InactiveUS20090128781A1Increase brightnessEasy to mergeCosmonautic condition simulationsLaser using scattering effectsMultiplexerLight pipe
A micro-projector comprises an LED layer, a light pipe coupled to the LED, a LCOS panel, a projection lens, a PBS, an aperture layer coupled to the output end of the light pipe which has a transmissive opening for transmitting a portion of the light output and a reflective surface for reflecting the remaining portion of the light output toward the input end of the light pipe. Thus, the remaining portion of the light output is recycled back to the LED to increase the brightness of the light output of the LED. The micro-projector also comprises a reflective polarizer disposed between the light pipe and the aperture layer for transmitting the light output of a predetermined polarization and reflecting other polarization of the light output, thereby recycling unused polarization of the light output back to the LED to increase the brightness of the light output of the LED.
Owner:WAVIEN
Substrate-Guided Optical Device Particularly for Vision Enhanced Optical Systems
ActiveUS20080186604A1Simple designFabrication facilitatedMirrorsMountingsTotal internal reflectionImaging processing
There is provided an optical system, including a mechanical body (110), a light-transmitting substrate (20) having two major surfaces and edges, embedded in the mechanical body, an optical element (90) for coupling light into the substrate by total internal reflection and a plurality of partially reflecting surfaces (22) carried by the substrate, wherein the partially reflecting surfaces are parallel to each other and are not parallel to any of the edges of the substrate. The system also includes an image capturing device (112), a display source (4), and an image-processing unit (114). The image-capturing device (112) is connected via the image-processing unit (114) to the display source (4).
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Optical disk-based assay devices and methods
InactiveUS6342349B1Strong specificityReduce nonspecific bindingSequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesAnalyteLaser light
Optical disk-based assay devices and methods are described, in which analyte-specific signal elements are disposed on an optical disk substrate. In preferred embodiments, the analyte-specific signal elements are disposed readably with the disk's tracking features. Also described are cleavable signal elements particularly suitable for use in the assay device and methods. Binding of the chosen analyte simultaneously to a first and a second analyte-specific side member of the cleavable signal element tethers the signal-responsive moiety to the signal element's substrate-attaching end, despite subsequent cleavage at the cleavage site that lies intermediate the first and second side members. The signal responsive moiety reflects, absorbs, or refracts incident laser light. Described are nucleic acid hybridization assays, nucleic acid sequencing, immunoassays, cell counting assays, and chemical detection. Adaptation of the assay device substrate to function as an optical waveguide permits assay geometries suitable for continuous monitoring applications.
Owner:VINDUR TECH
Optical beam tilt for offset head mounted display
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Dual axis internal optical beam tilt for eyepiece of an HMD
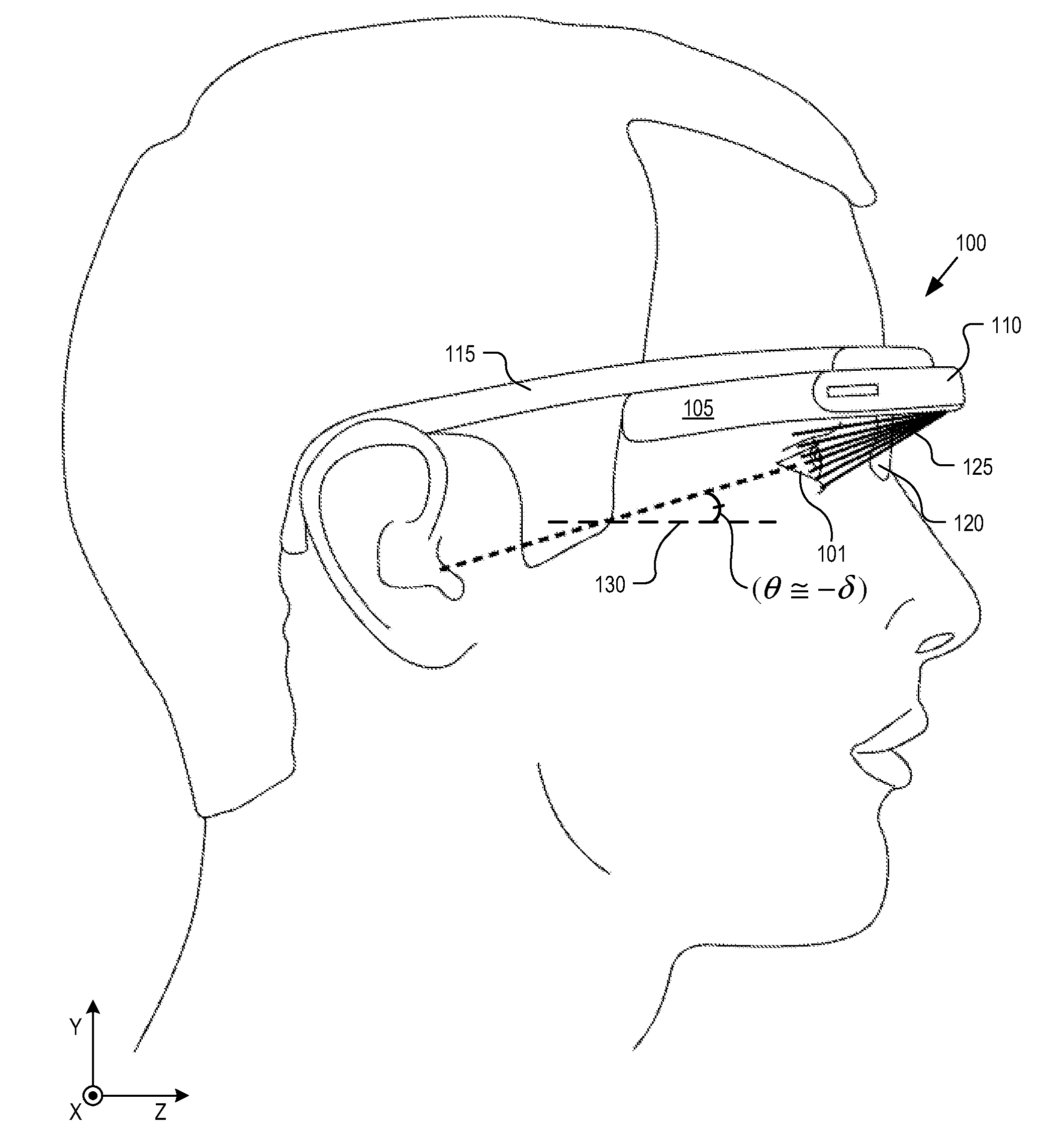
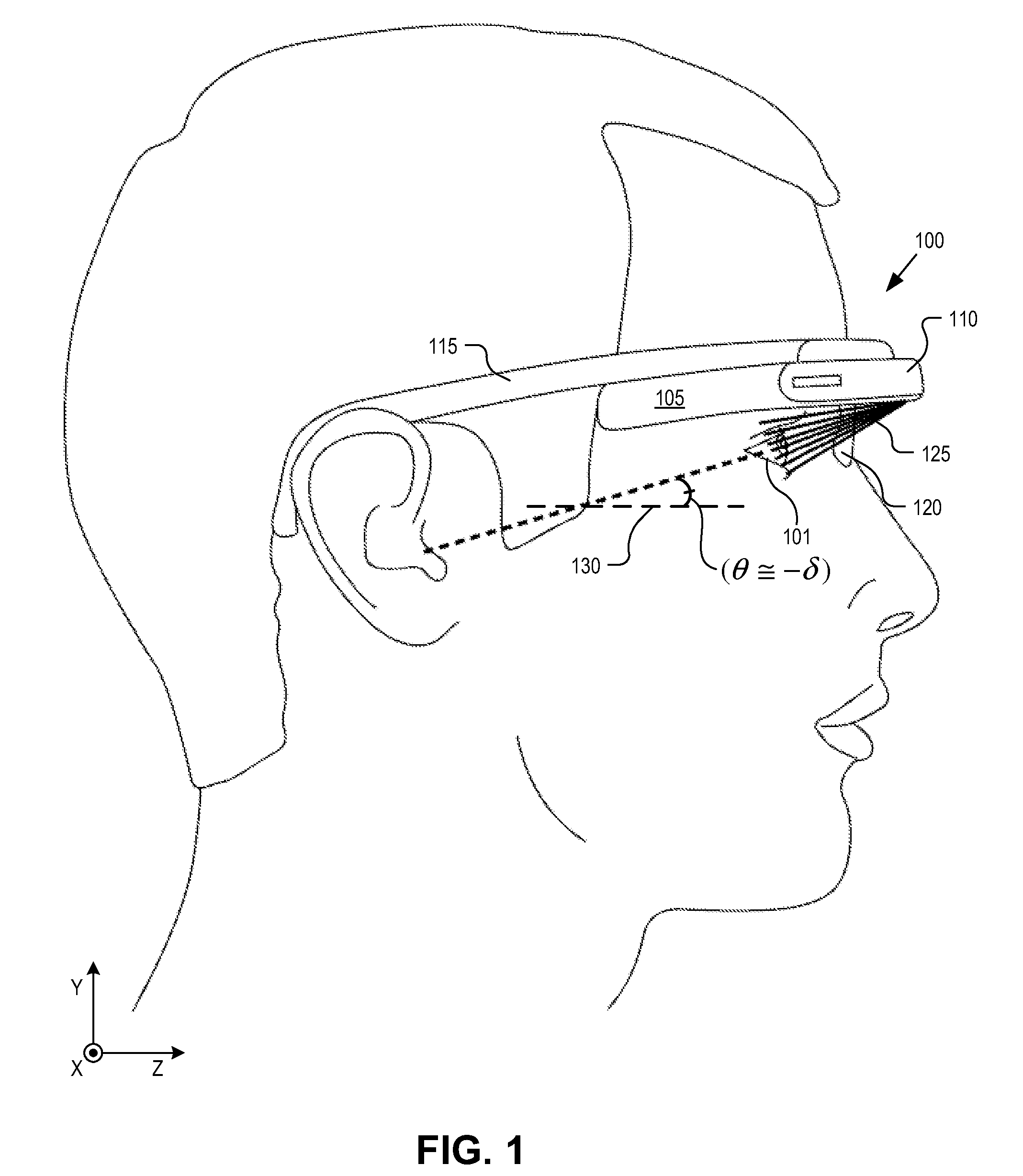
InactiveUS8867139B2Polarising elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPartially reflective surfaceEyepiece
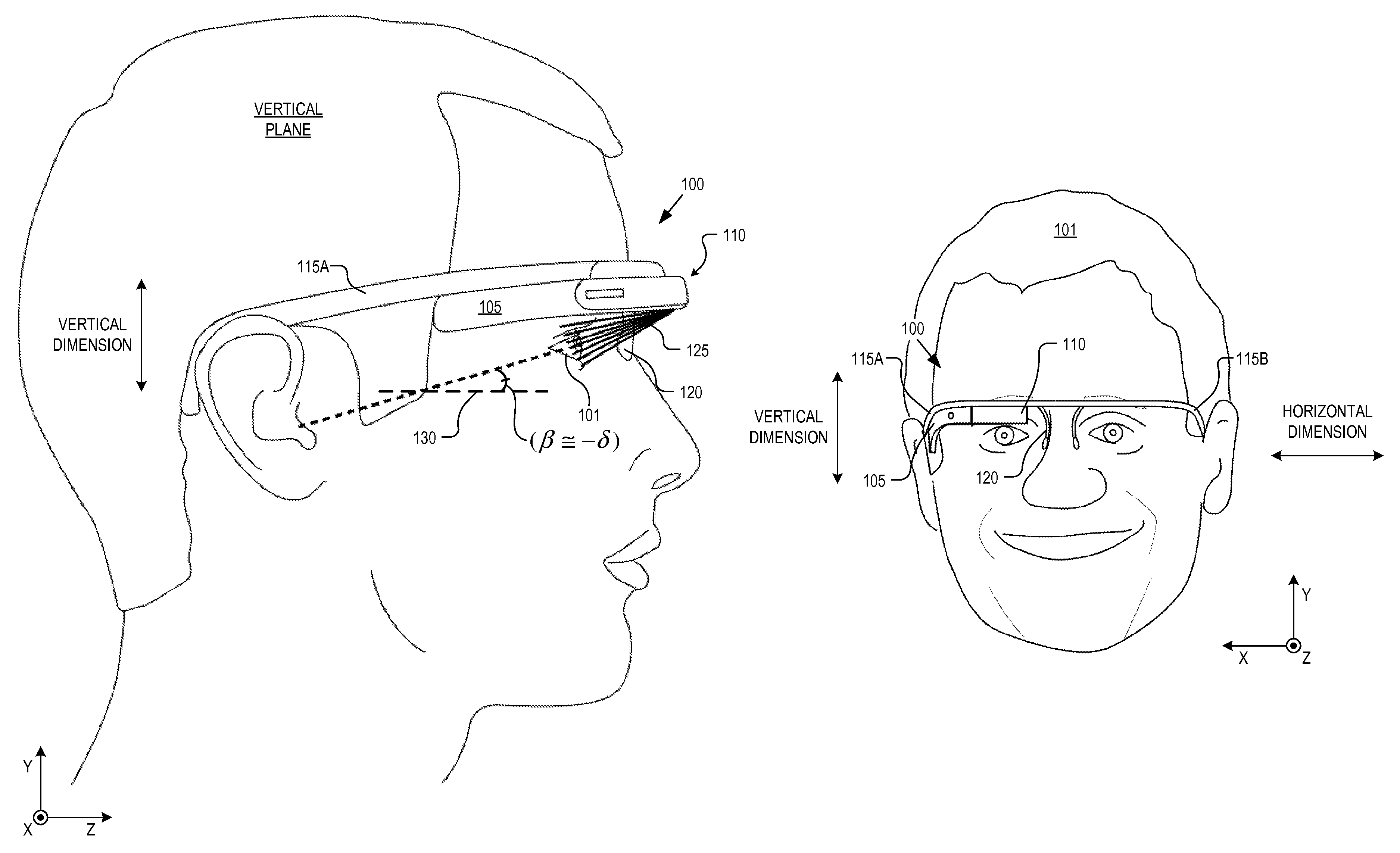
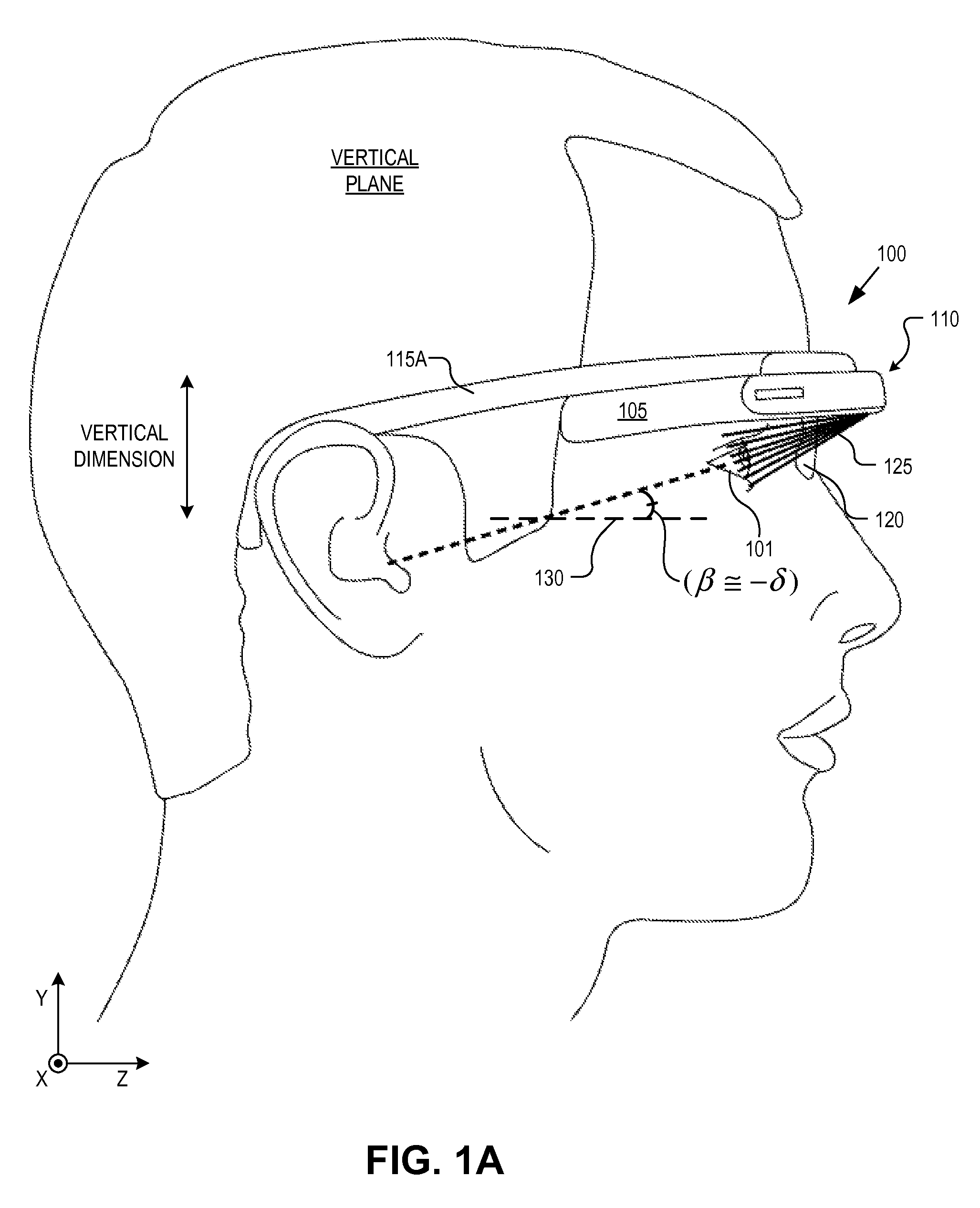
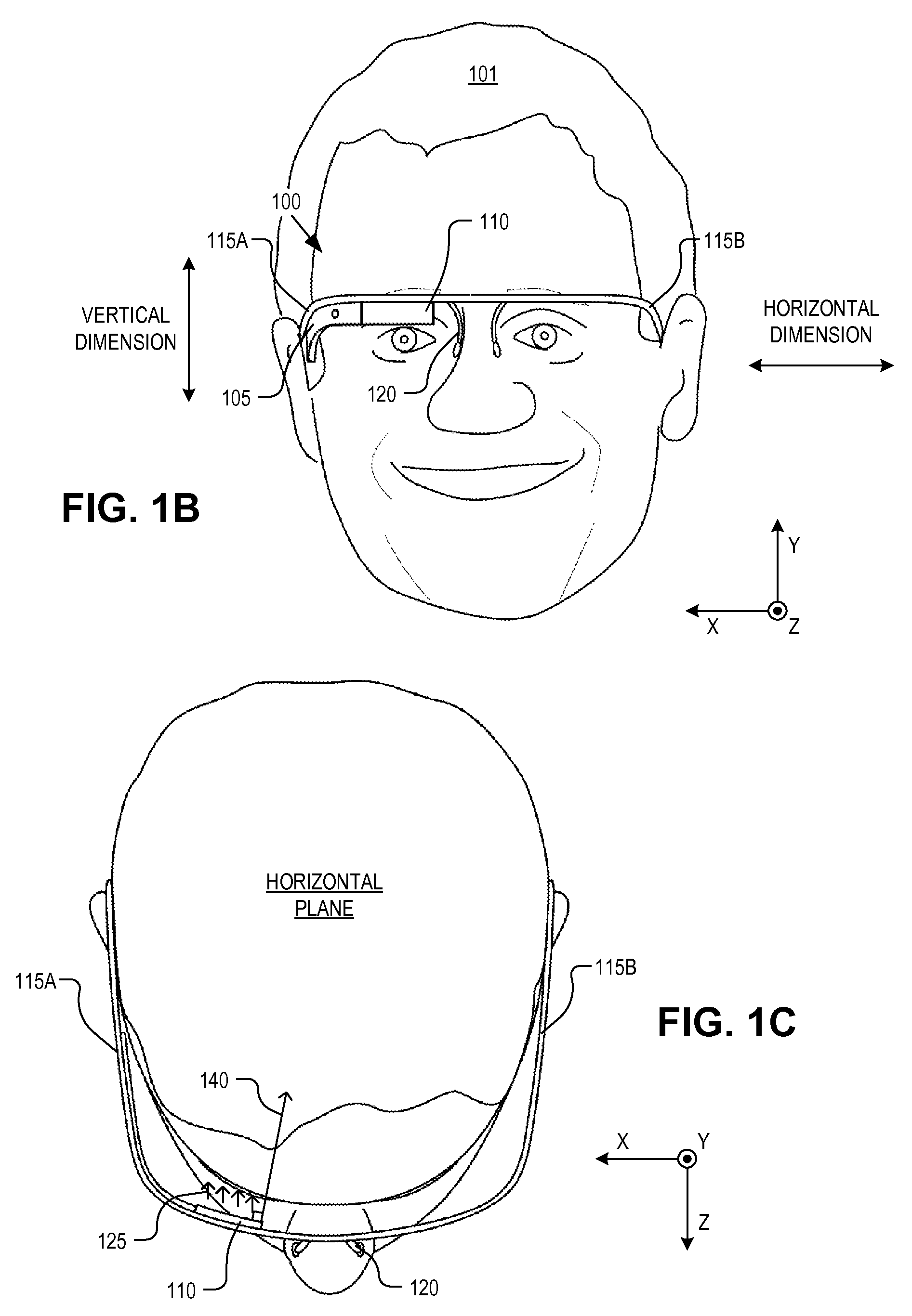
An eyepiece includes a display module for providing display light, a concave end reflector, and a viewing region including a partially reflective surface to redirect at least a portion of the display light out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece along an emission path. The partially reflective surface is obliquely angled with an offset from 45 degrees relative to the eye-ward side to cause the emission path to have a first oblique angle in a horizontal dimension relative to a first normal vector of the eye-ward side. The concave end reflector is tilted such that a second normal vector from a center point of the concave end reflector is obliquely angled relative to a top or bottom surface of the eyepiece to cause the emission path to have a second oblique angle in a vertical dimension relative to the first normal vector of the eye-ward side.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
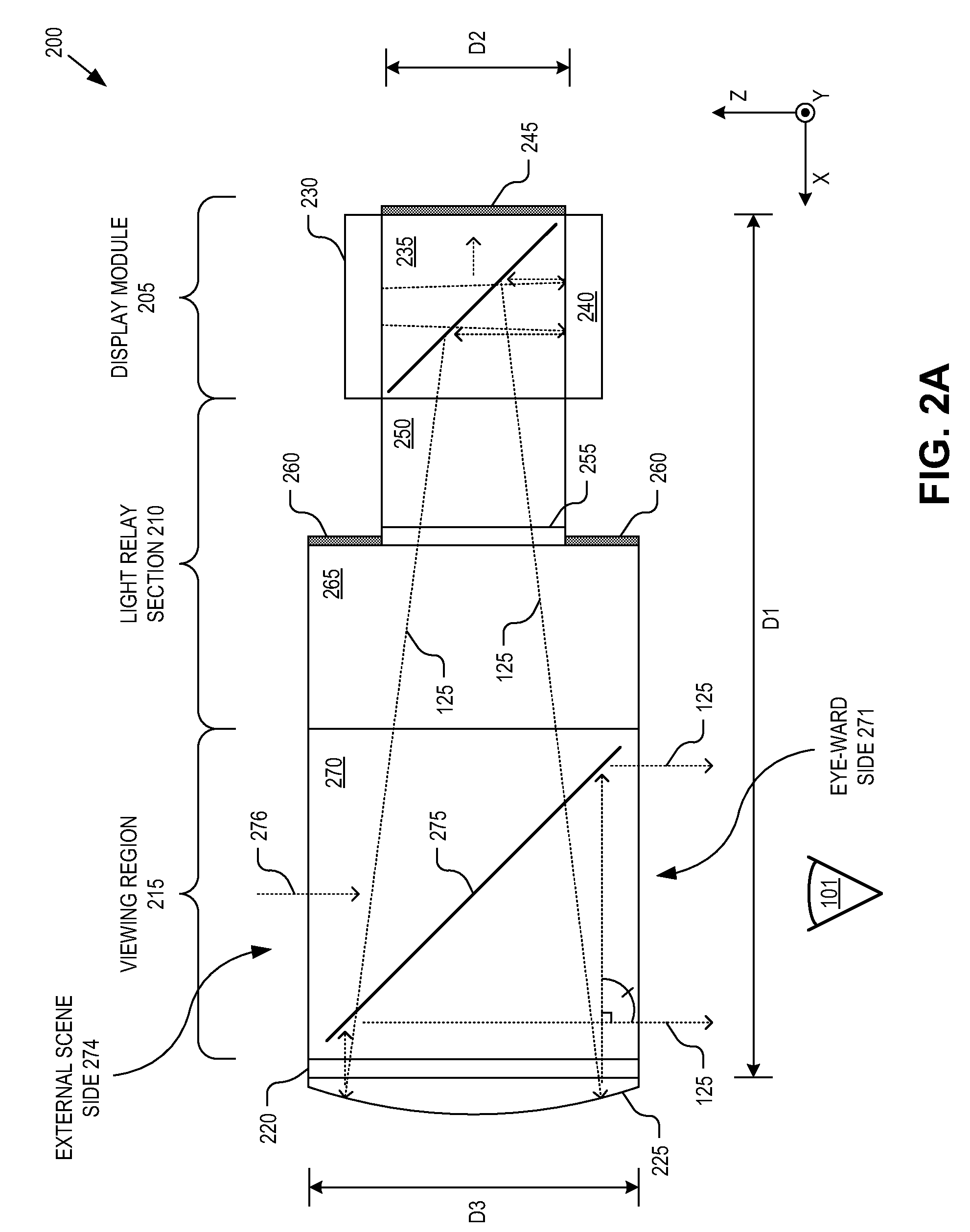
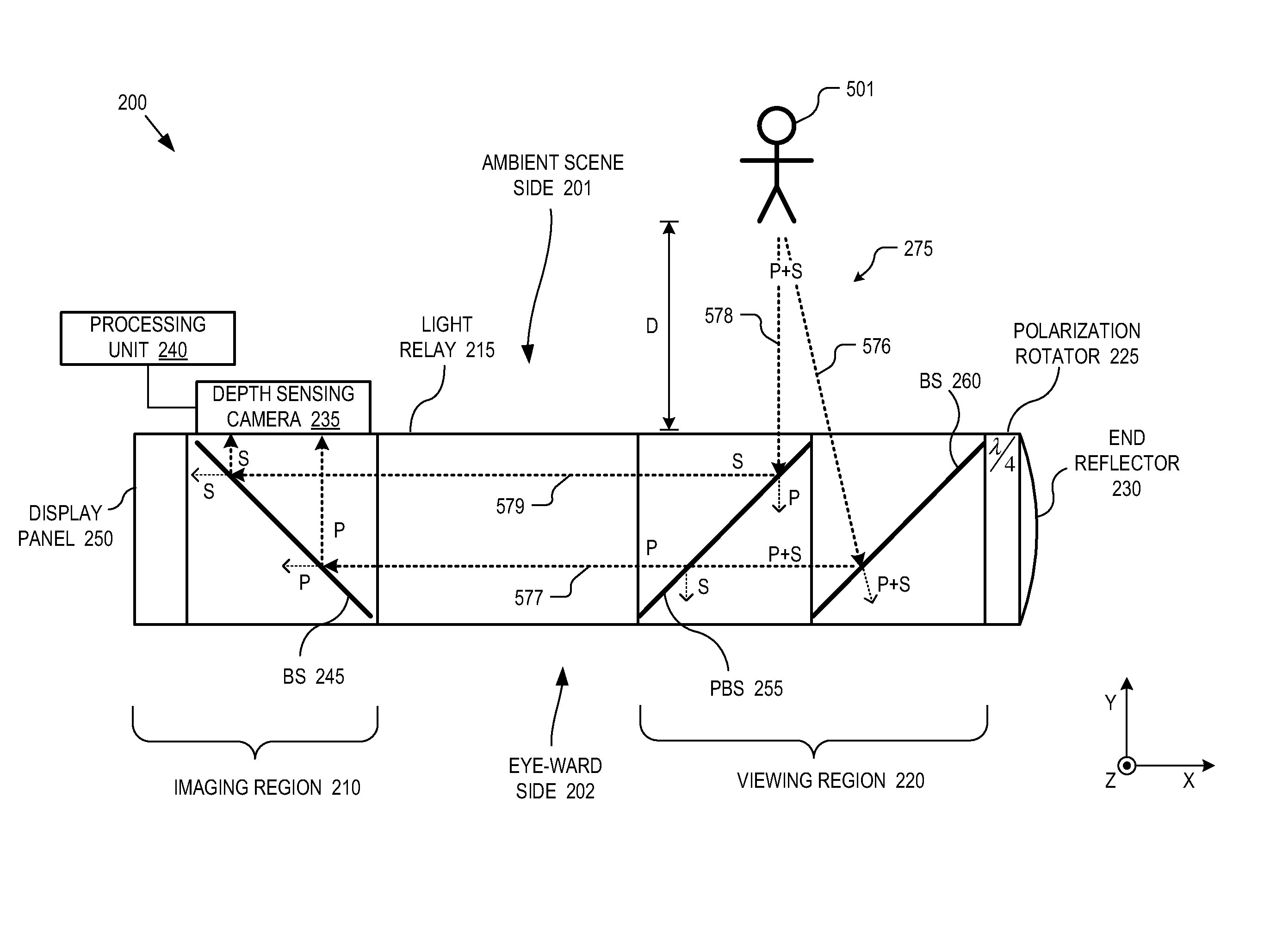
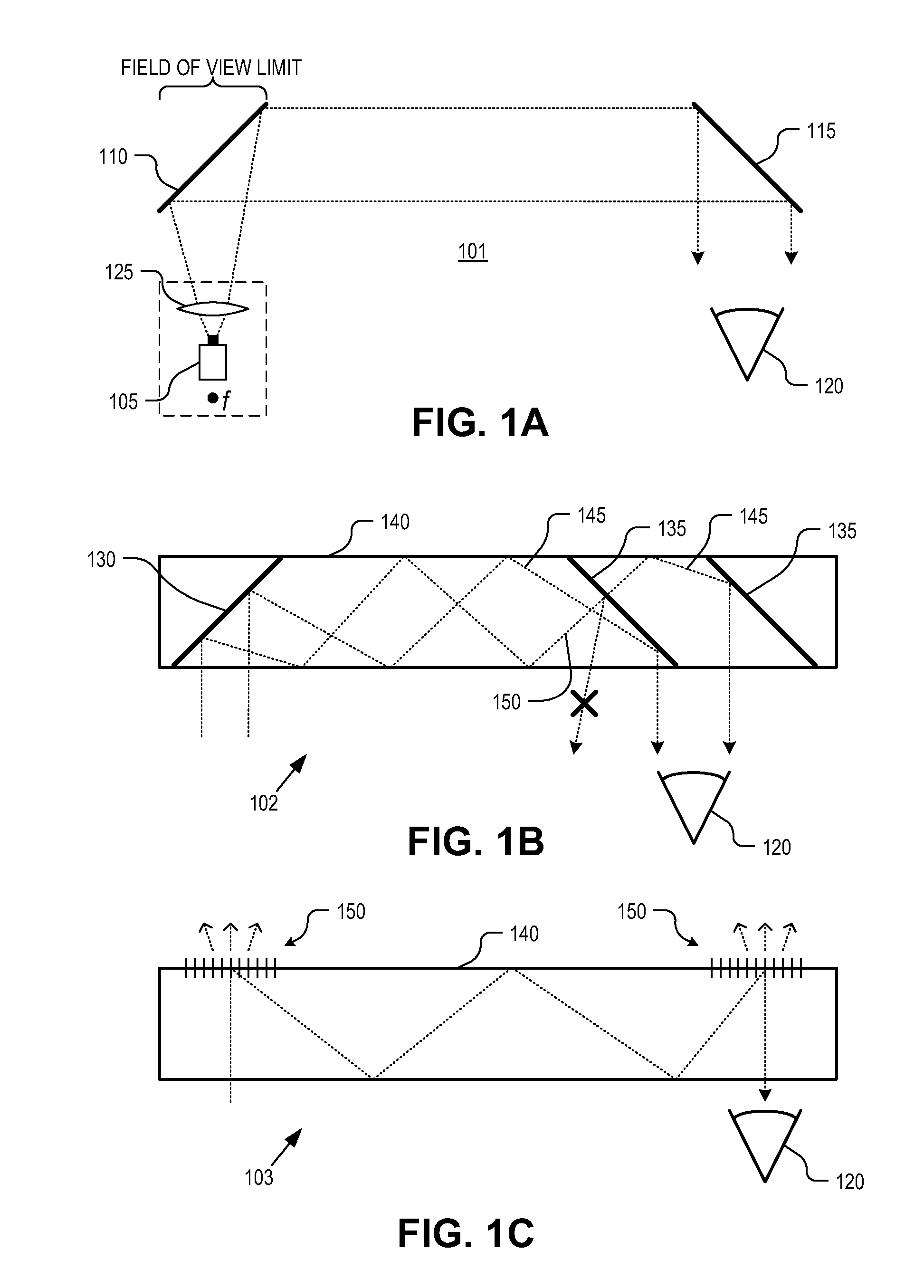
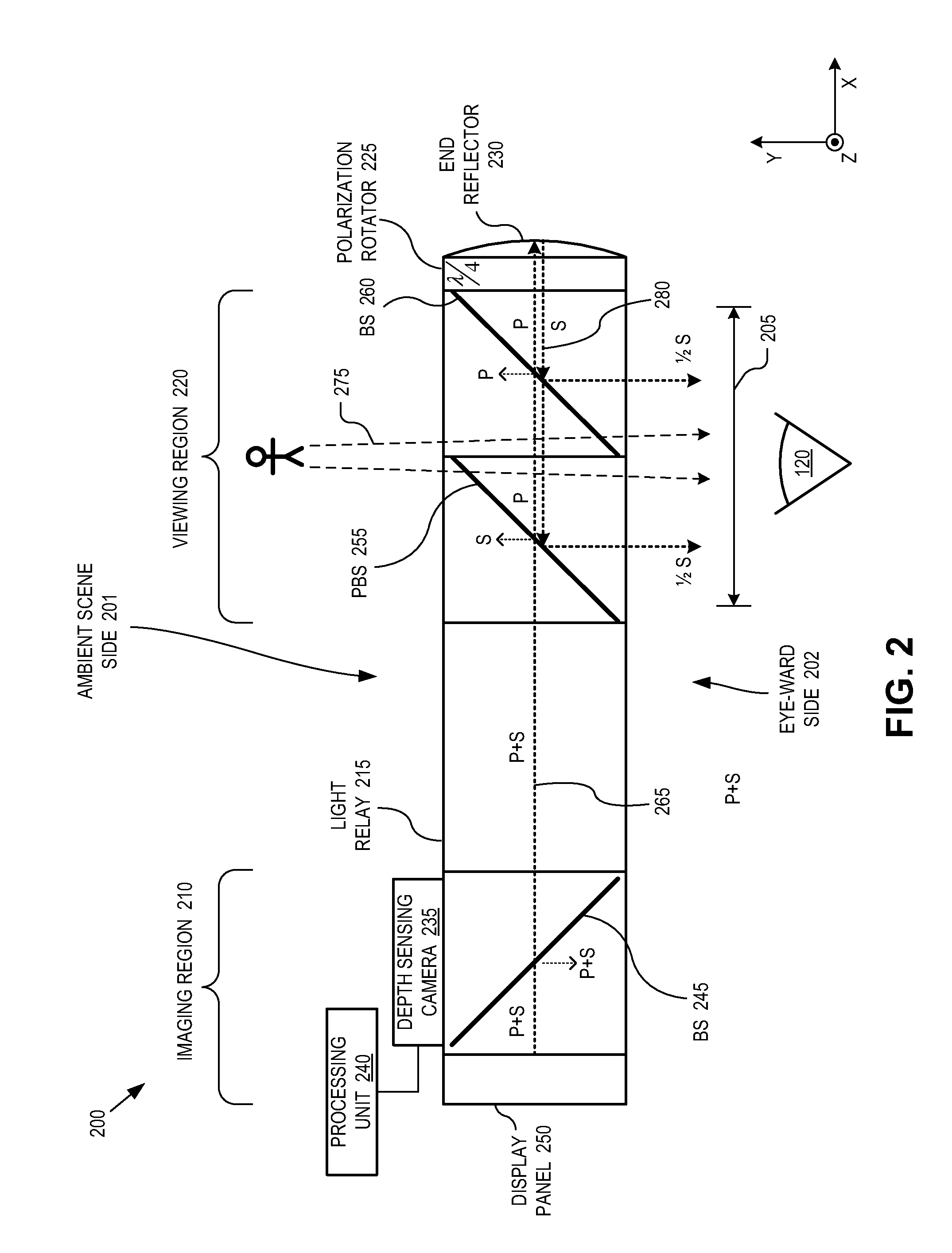
Head mounted display eyepiece with integrated depth sensing
An eyepiece for a head mounted display includes an imaging region and a viewing region. The imaging region includes a camera. The viewing region is aligned with an eye of a user and includes a first beam splitter and a second beam splitter. The viewing region is partially transparent to pass a first portion of ambient scene light received through an ambient scene side of the eyepiece out an eye-ward side of the eyepiece. The first BS and the second BS are partially reflective and oriented to redirect offset portions of the ambient scene light received through the ambient scene side along the eyepiece towards the imaging region. The camera is positioned to capture both of the offset portions of the ambient scene light redirected by the first beam splitter and the second beam splitter.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
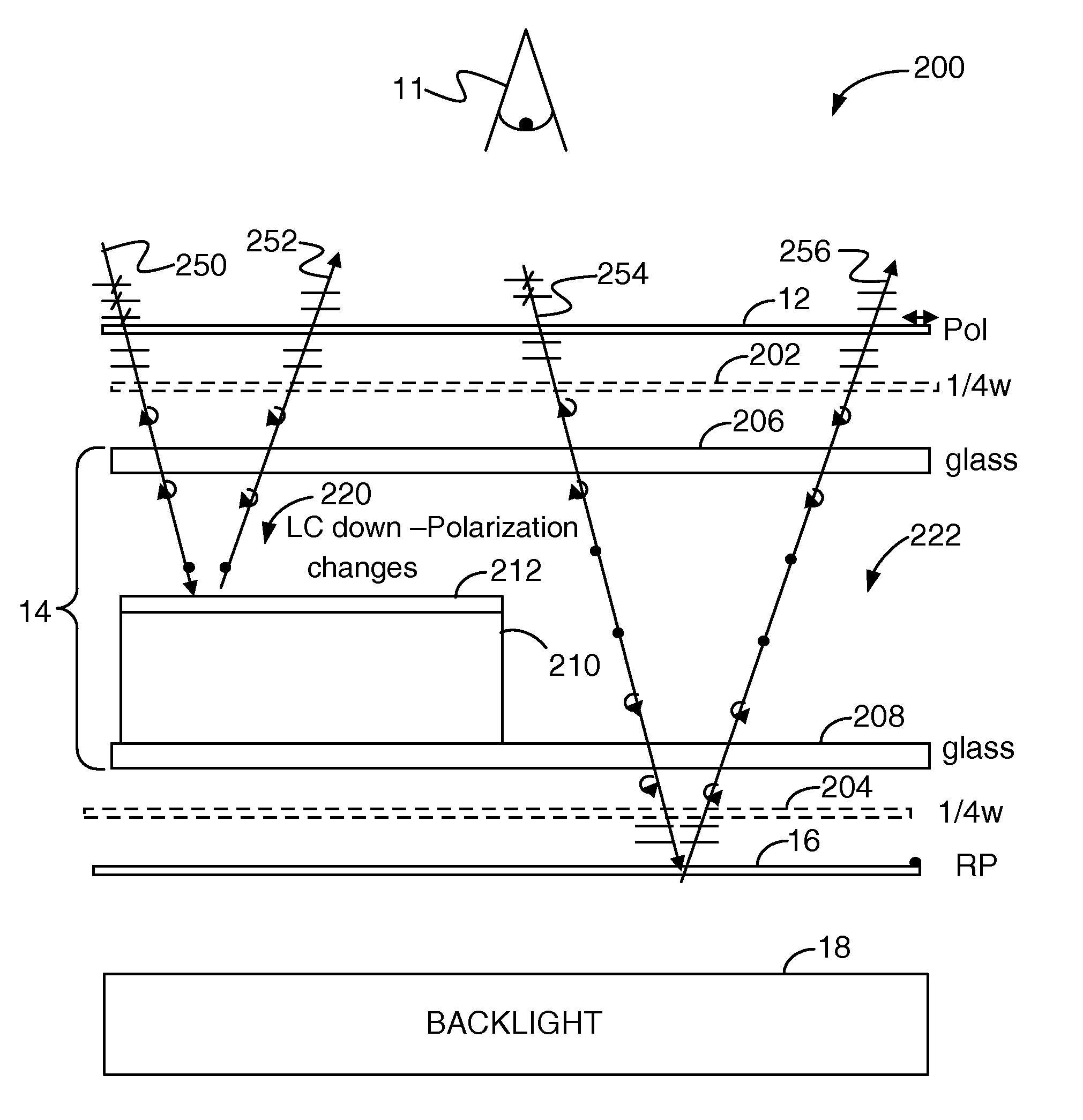
Transflective LC display with internal reflector and reflective polarizer
A transflective display having a reflective viewing mode and a transmissive viewing mode is provided. The transflective display includes a liquid crystal (LC) panel having an array of partially reflective pixels. The reflective portions of the array of partially reflective pixels include metal positioned on a viewer side of the LC panel to reflect light back toward the viewer. The display also includes a reflective polarizer, in place of a conventional rear polarizer, positioned behind the LC panel on a side of the LC panel opposite the viewer side. The reflective polarizer is also oriented to reflect ambient light back toward the viewer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Optical system and display
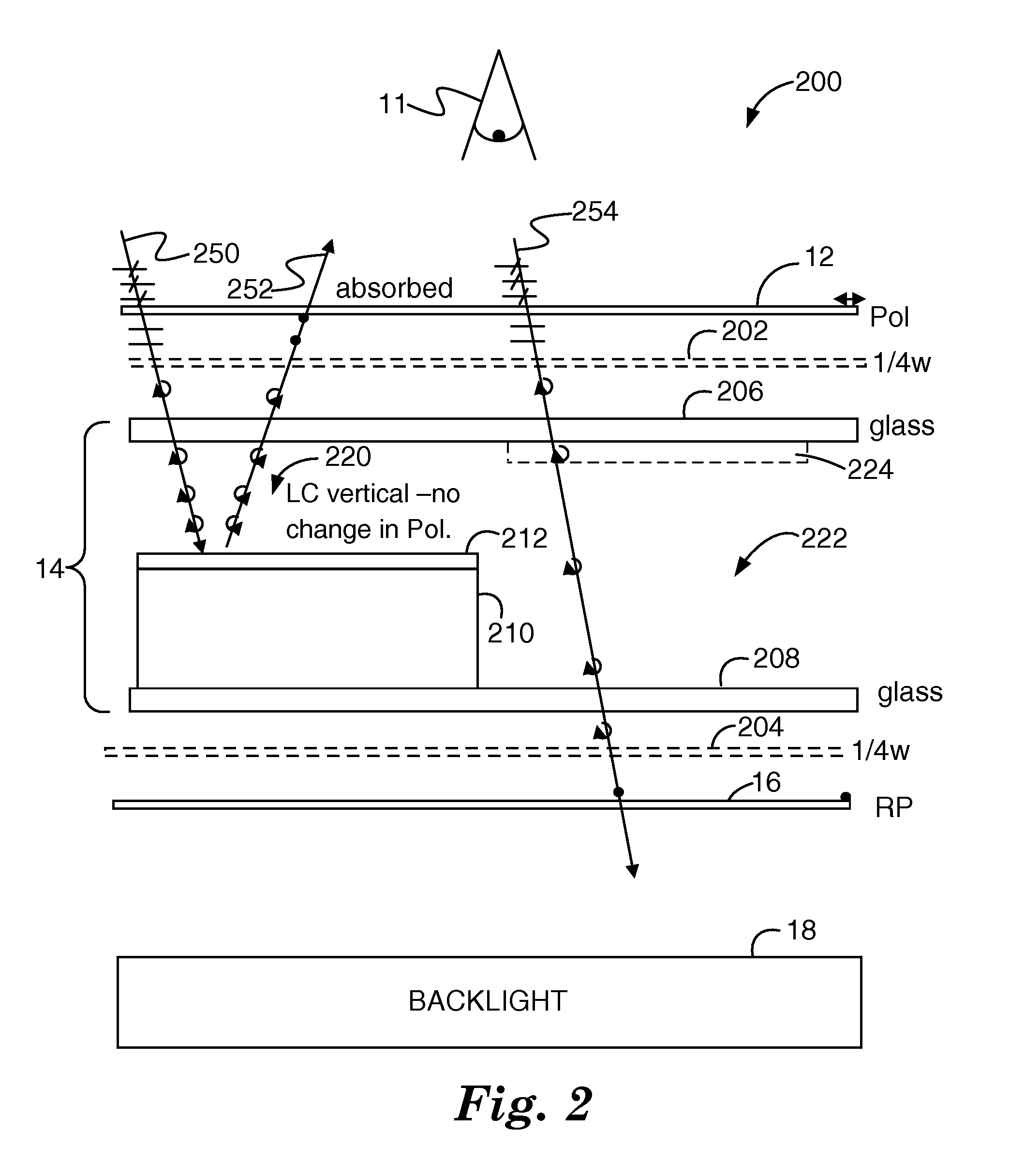
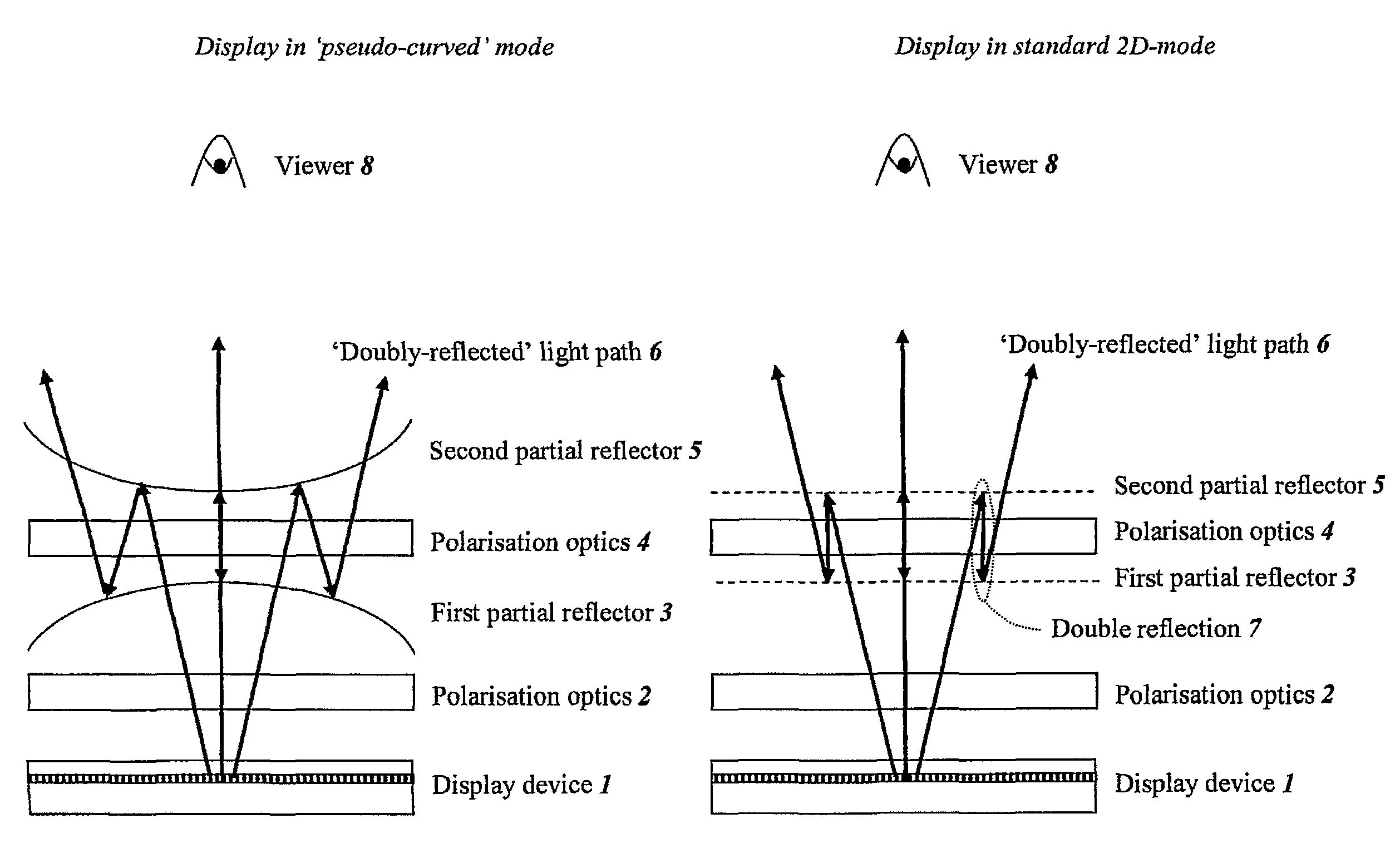
InactiveUS8780039B2Avoid emissionsImprove aestheticsStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceOptic system
An optical system is provided, for example for use with a display device, for varying the shape of a surface in which an image displayed by the display device is perceived. The optical system comprises first and second spaced-apart partial reflectors, at least one of which is switchable between a first non-flat shape and a second different shape, which may be flat or non-flat. The reflectors, together with polarisation optics, provide a light path such that light from the display is at least partially transmitted by the first reflector, partially reflected by the second reflector, partially reflected by the first reflector and partially transmitted by the second reflector. Light which does not follow the light path is prevented from leaving the optical system.
Owner:SHARP KK
Compact optical system with improved contrast uniformity
ActiveUS20160216516A1Increase contrastLow costElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceOptic system
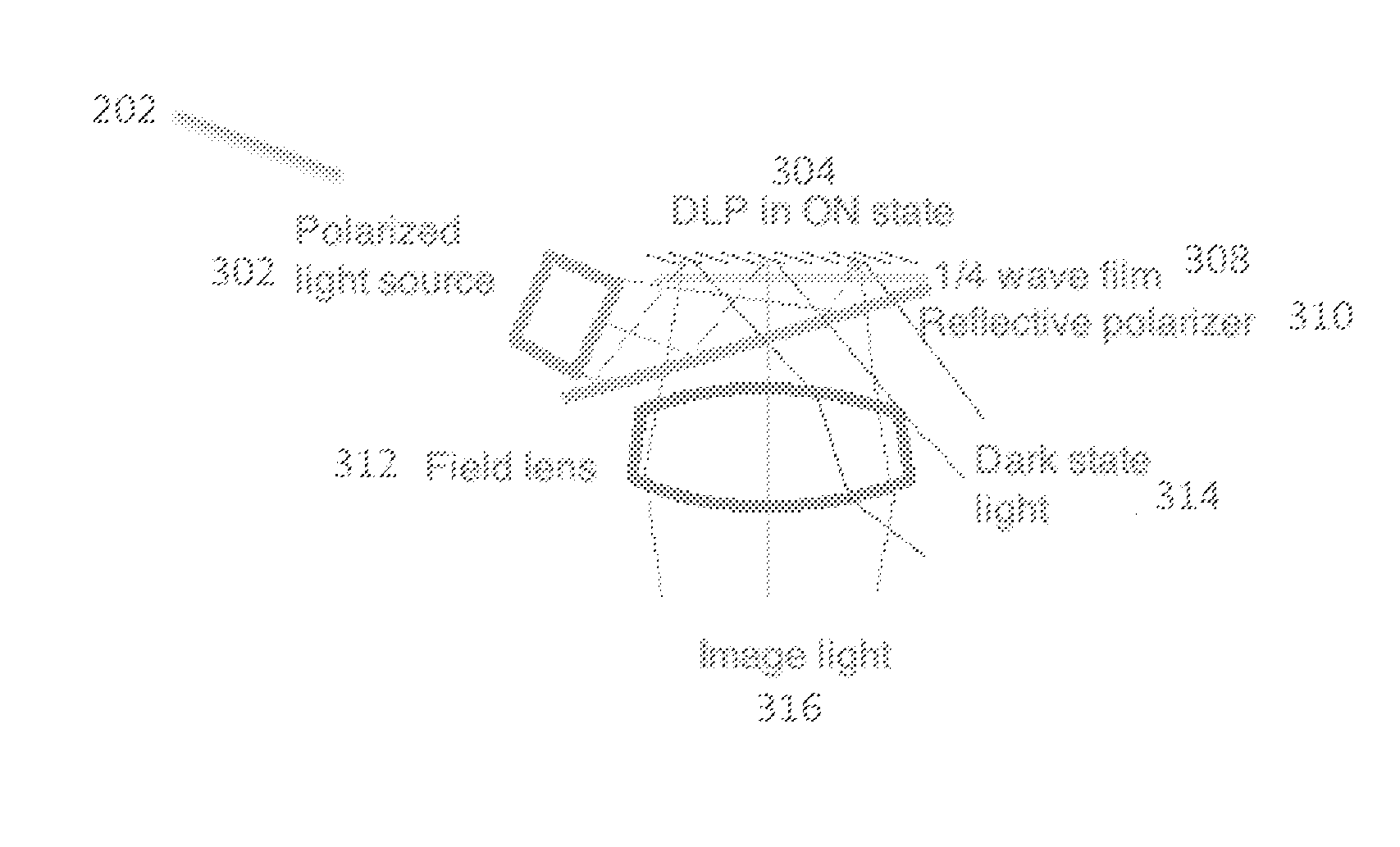
An optical system for a head-worn computer may include a light source positioned within the head-worn computer and adapted to project non-polarized illuminating light towards a partially reflective partially transmissive surface such that the illuminating light reflects through a field lens and towards a reflective display and a polarizing film adjacent to a surface of the reflective display that polarizes the illuminating light after it passes through the field lens. The illuminating light reflects off a surface of the reflective display, forming image light which is then analyzed by the polarizing film prior to being transmitted through the field lens and then through the partially reflective partially transmissive surface to a non-polarizing lower display optical system adapted to present the image light to an eye of a user wearing the head-worn computer.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
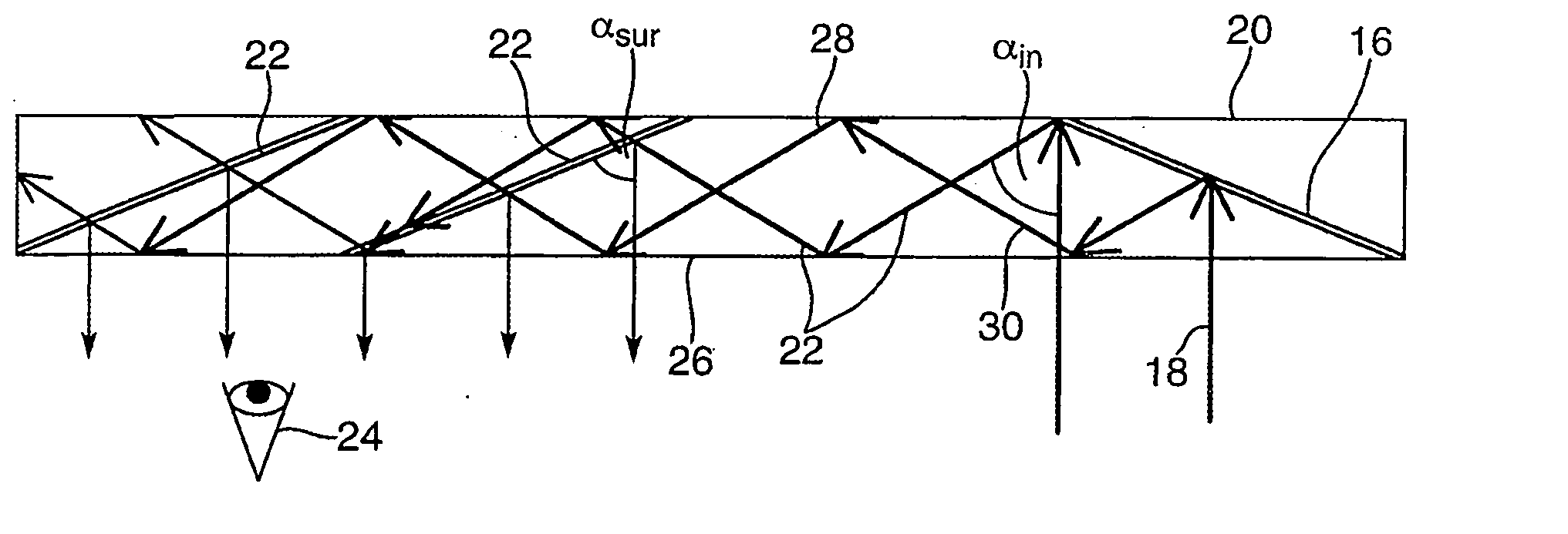
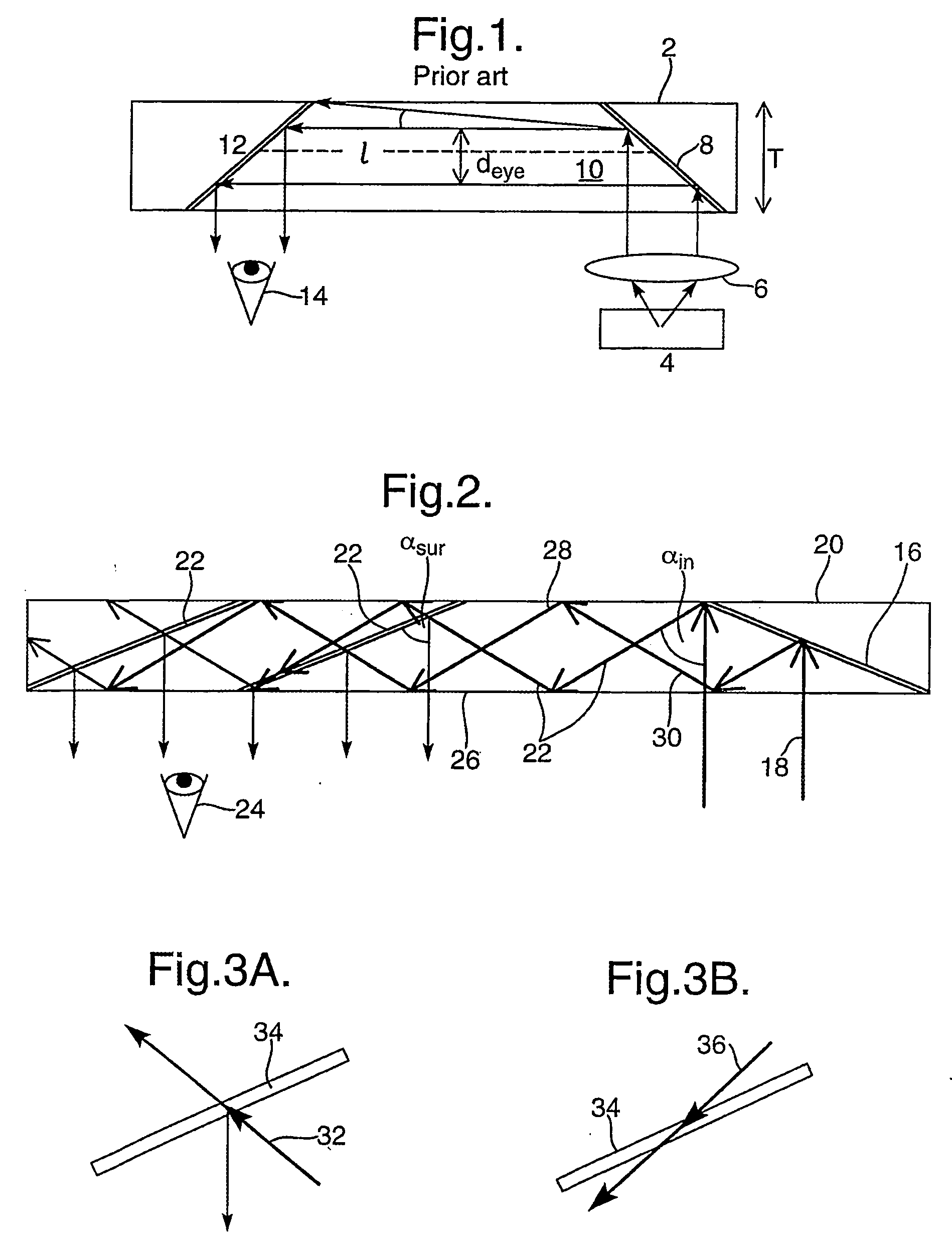
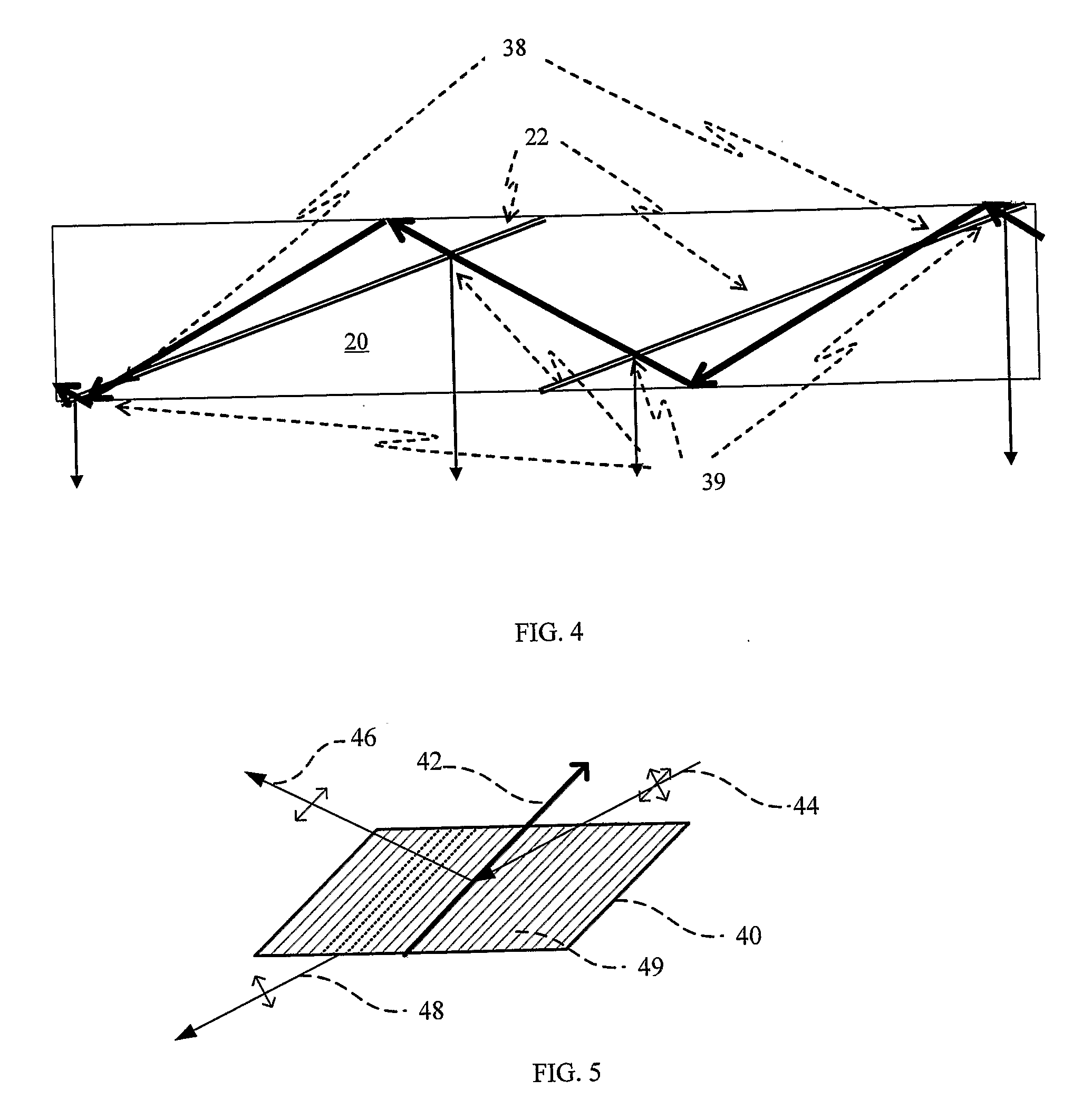
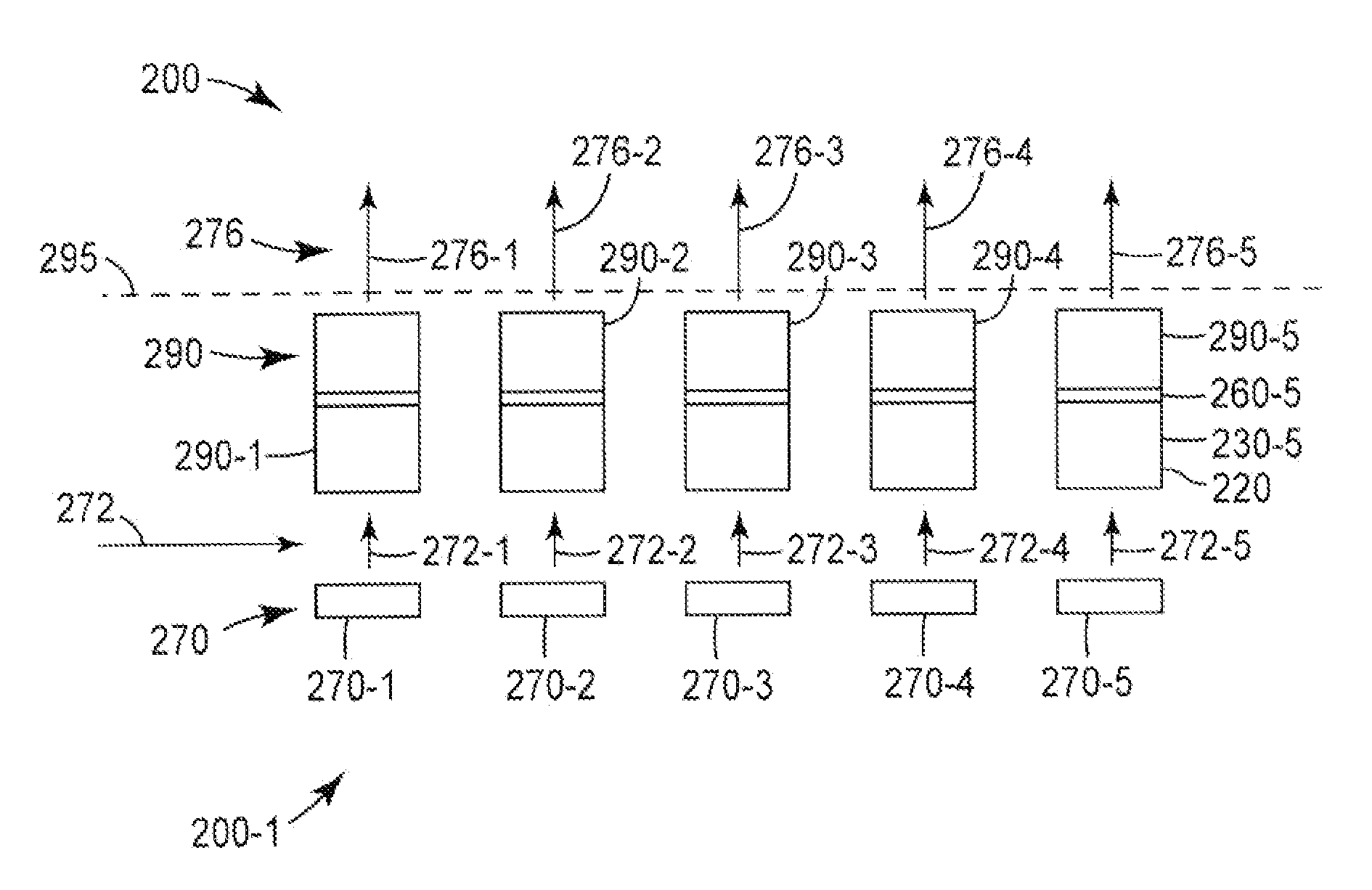
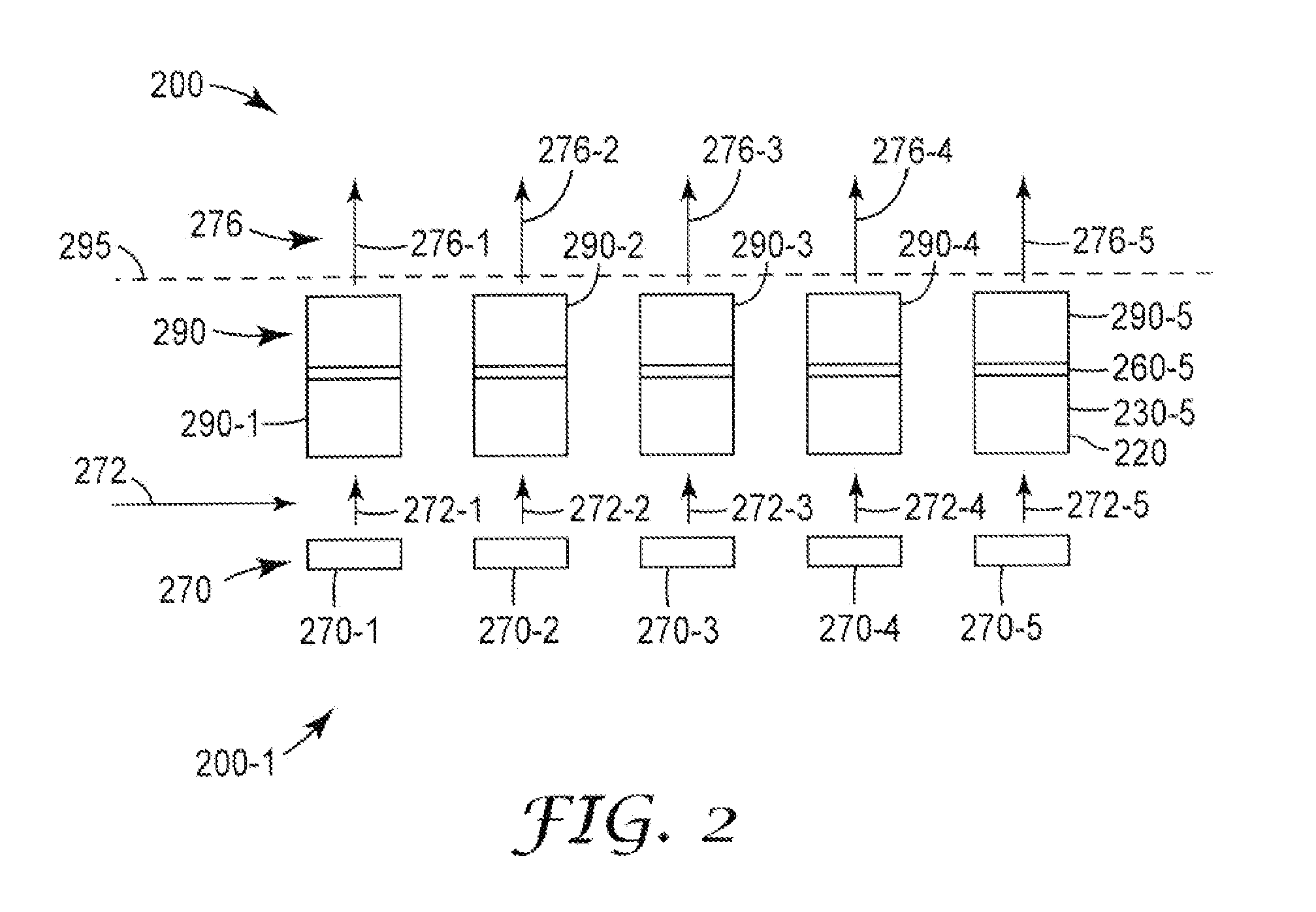
Substrate-guide optical device
ActiveUS20160341964A1Simple designFabrication facilitatedSpectales/gogglesInput/output for user-computer interactionTotal internal reflectionPartial reflection
An optical device, including a light waves-transmitting substrate has two major surfaces and edges, optical means for coupling light into the substrate by total internal reflection, and a plurality of partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) carried by the substrate. The partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) are parallel to each other and are not parallel to any of the edges of the substrate, one or more of the partially reflecting surfaces (22a, 22b) being an anisotropic surface. The optical device has dual operational modes in see-through configuration. In a first mode, light waves are projected from a display source through the substrate to an eye of a viewer. In a second mode, the display source is shut off and only an external scene is viewable through the substrate.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Substrate-guided optical devices
ActiveUS20070091445A1Simple structureFacilitates fabricationMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsImage resolutionAngular deviation
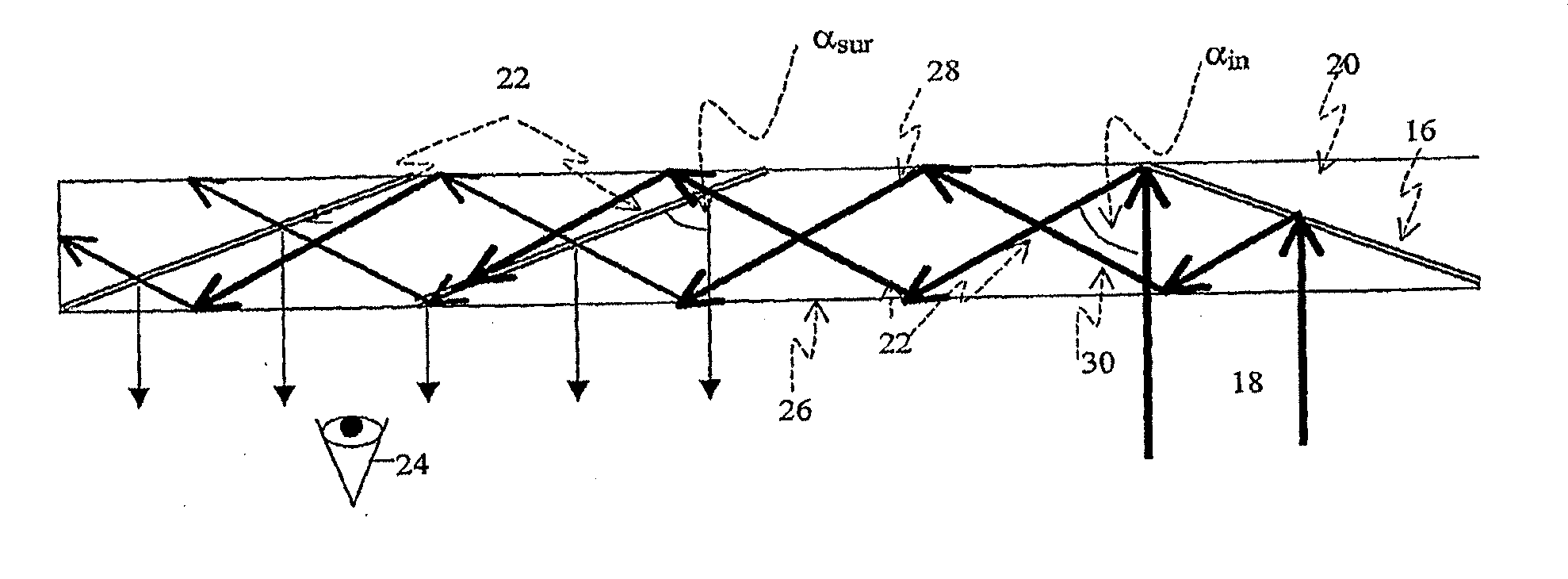
There is provided an optical device, having a light-transmitting substrate (20) having at least two major surfaces parallel to each other and edges; a display light source; optical means for coupling light from the light source into the substrate (20) by internal reflection, and at least one partially reflecting surface (22) located in the substrate (20) which is non-parallel to the major surfaces of the substrate wherein the source emits light waves located in a given field-of-view, that the light waves are collimated, that an angular resolution is defined for the optical device, and wherein the angular deviation between any two different rays located in one of the collimated light waves, is smaller than the angular resolution.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Diffractive imaging system and method for the reading and analysis of skin topology
ActiveUS20060119837A1High resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arraySkin contact
An apparatus and a method for acquiring an image of skin topology. The apparatus comprises at least one light source, configured to form a source beam; at least one illuminating diffractive optical element (DOE) disposed in the optical path of the source beam, configured to diffract the source beam, thereby forming an illuminating beam; a skin contact surface, disposed in the optical path of the illuminating beam, configured to at least partially reflect the illuminating beam at regions of the boundary between the skin contact surface and skin that are not in contact with skin, thereby forming a reflected beam; at least one imaging diffractive optical element (DOE), disposed in the optical path of the reflected beam, configured to diffract the reflected light beam, thereby forming an image beam; and a sensor array, configured to receive at least a portion of the image beam and thereby to detect the acquired image.
Owner:APRILIS
Ii-vi mqw vscel on a heat sink optically pumped by a GAN ld
InactiveUS20110150020A1Improved light emissionSuppress luminescenceLaser optical resonator constructionNanoopticsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserOptical cavity
Light sources are disclosed. A disclosed light source includes a III-V based pump light source (170) that includes nitrogen and emits light at a first wavelength. The light source further includes a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) that converts at least a portion of the first wavelength light (174) emitted by the pump light source (170) to at least a partially coherent light at a second wavelength (176). The VCSEL includes first and second mirrors (120, 160) that form an optical cavity for light at the second wavelength. The first mirror (120) is substantially reflective at the second wavelength and includes a first multilayer stack. The second mirror (160) is substantially transmissive at the first wavelength and partially reflective and partially transmissive and the second wavelength. The second mirror includes a second multilayer stack. The VCSEL further includes a semiconductor multilayer stack (130) that is disposed between the first and second mirrors and converts at least a portion of the first wavelength light to the second wavelength light. The semiconductor multilayer stack (130) includes a quantum well that includes a Cd(Mg)ZnSe alloy.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
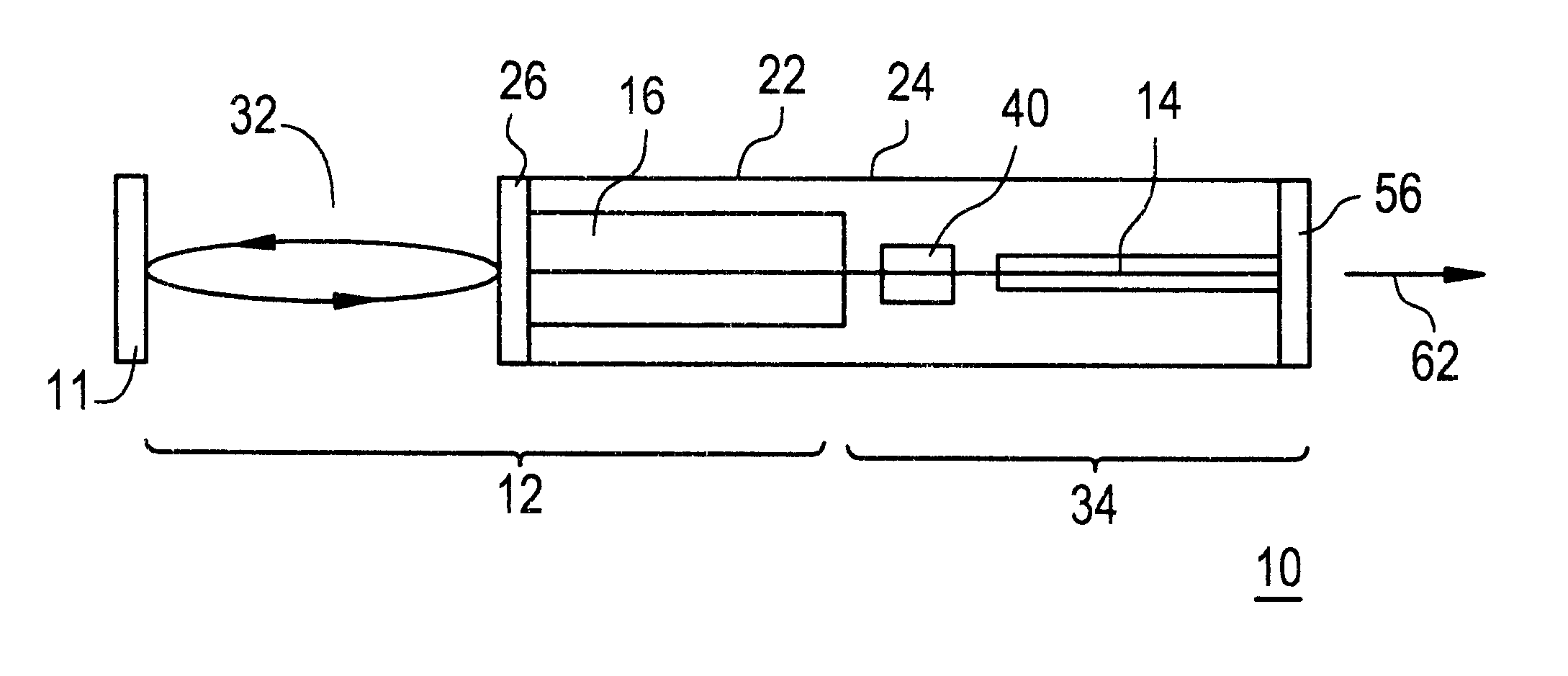
Wavelength-locked external cavity lasers with an integrated modulator
InactiveUS6295308B1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionExternal cavity laserLength wave
An optical transmitter providing the benefits of both filter-locked and wavelength-locked lasers is disclosed by modifying an external cavity (32) for the integration of an optical modulator (14). The external cavity (32) provides a round-trip path for light travel. A substrate (24) is connected to the external cavity (32) where at least one gain element (16) and the optical modulator (14) are integral with the substrate (24). A partial reflector (40) is also integral with the substrate (24) and couples the at least one gain element (16) with the optical modulator (14).
Owner:OCLARO NORTH AMERICA
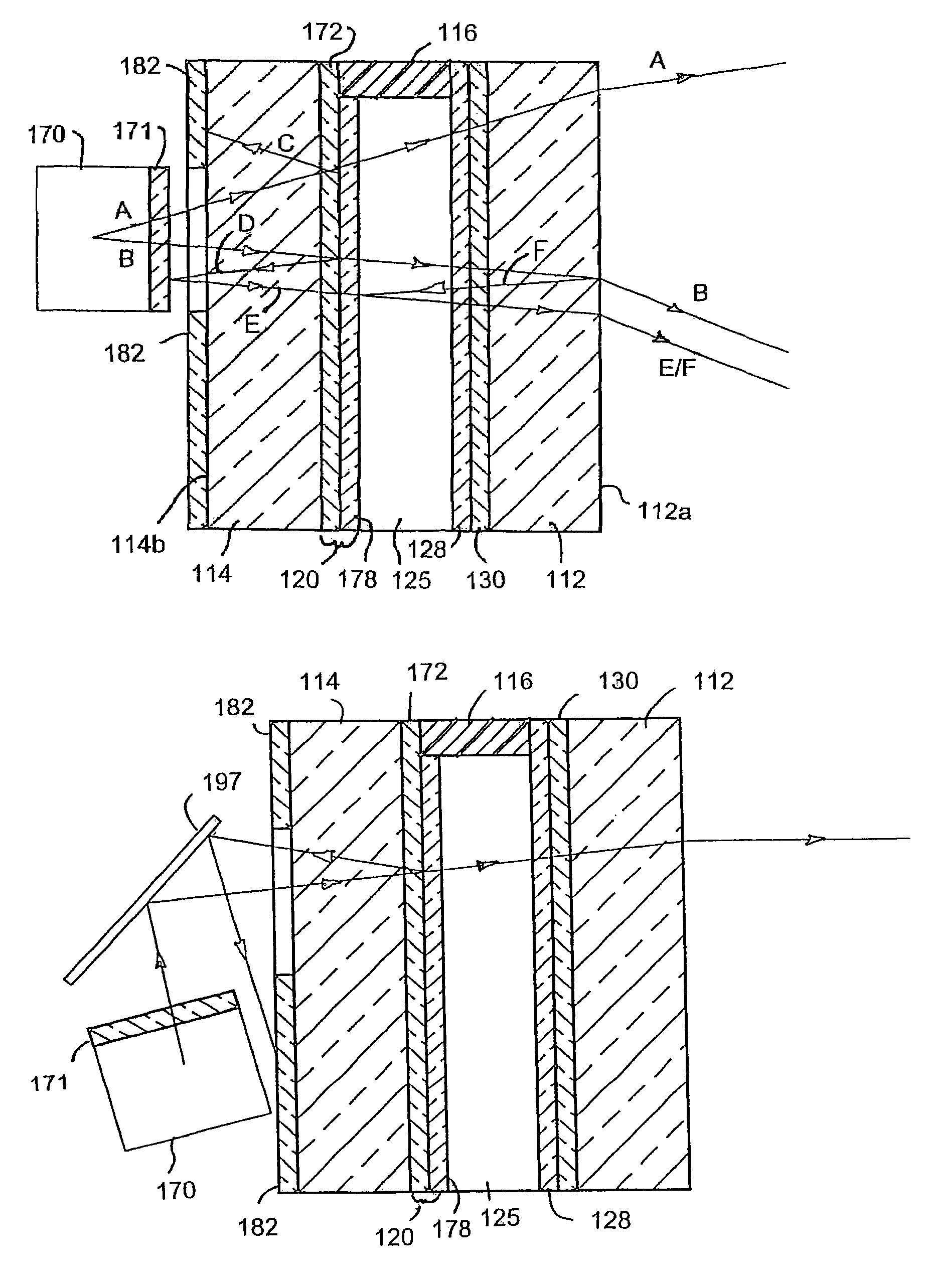
Substrate-guided relays for use with scanned beam light sources
Substrate-guided relays that employ light guiding substrates to relay images from sources to viewers in optical display systems. The substrate-guided relays are comprised of an input coupler, an intermediate substrate, and an output coupler. In some embodiments, the output coupler is formed in a separate substrate that is coupled to the intermediate substrate. The output coupler may be placed in front of or behind the intermediate substrate, and may employ two or more partially reflective surfaces to couple light from the coupler. In some embodiments, the input coupler is coupled to the intermediate substrate in a manner that the optical axis of the input coupler intersects the optical axis of the intermediate substrate at a non-perpendicular angle.
Owner:MICROVISION
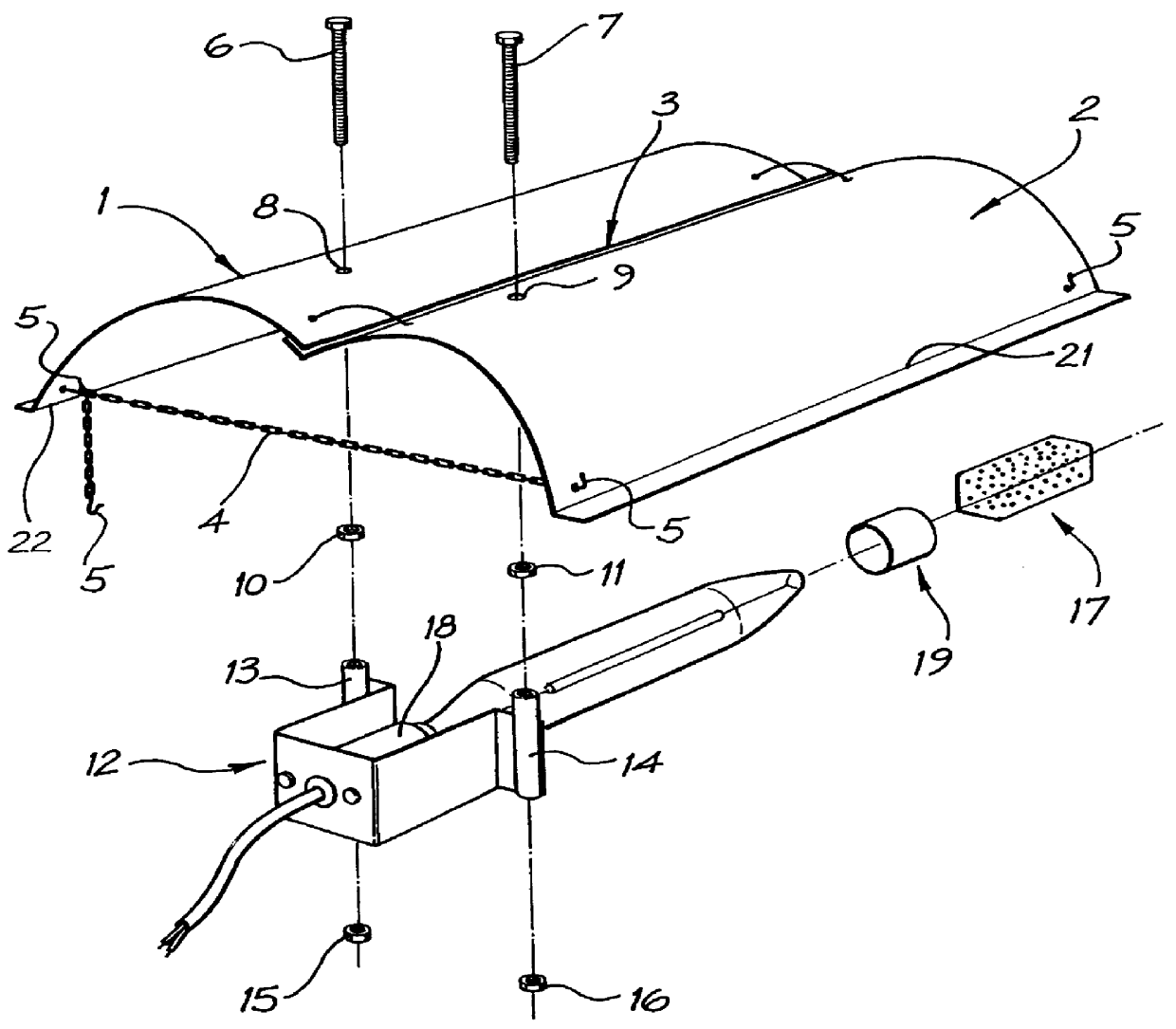
Lamp reflector with adjustable curvature
InactiveUS6053624AElongate light sourcesLighting heating/cooling arrangementsLight headPartial reflection
PCT No. PCT / AU95 / 00303 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 10, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 10, 1998 PCT Filed May 24, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 37732 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 28, 1996An adjustable reflector device is disclosed. The device consists of an adjustable double parabolic reflective skin (1,2) with an adjustable lamp mount (12), incorporating a V-shaped perforated heat shield (17), attached. The two part reflective skin (1,2) forms a double parabolic shape when flexed back against a reinforced spine (3). This flexible shape is secured by lengthwise adjustable chain retainers (4) attached at both ends of the skin (1,2). The lamp mount (12) slides onto a pair of threaded bolts (6,7) secured to the skin and adjustment is achieved by tightening or loosening the appropriate nuts (15,16). The heat shield (17) slides onto the lamp fitting (18) and is positioned appropriately to deflect incident heat and light. This device can be used to provide variable conditions of artificial illumination.
Owner:CRONK PAUL ANDREW
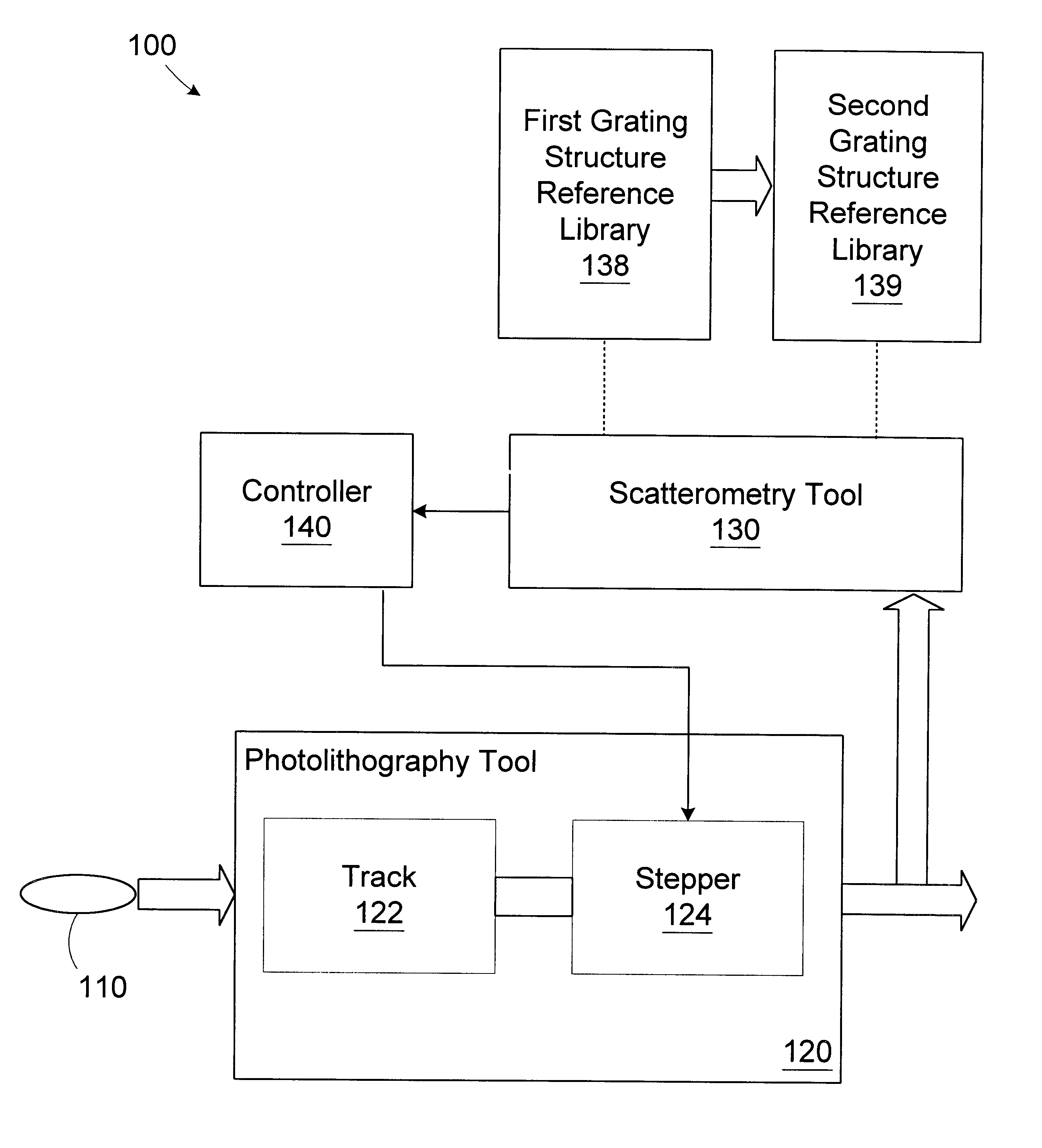
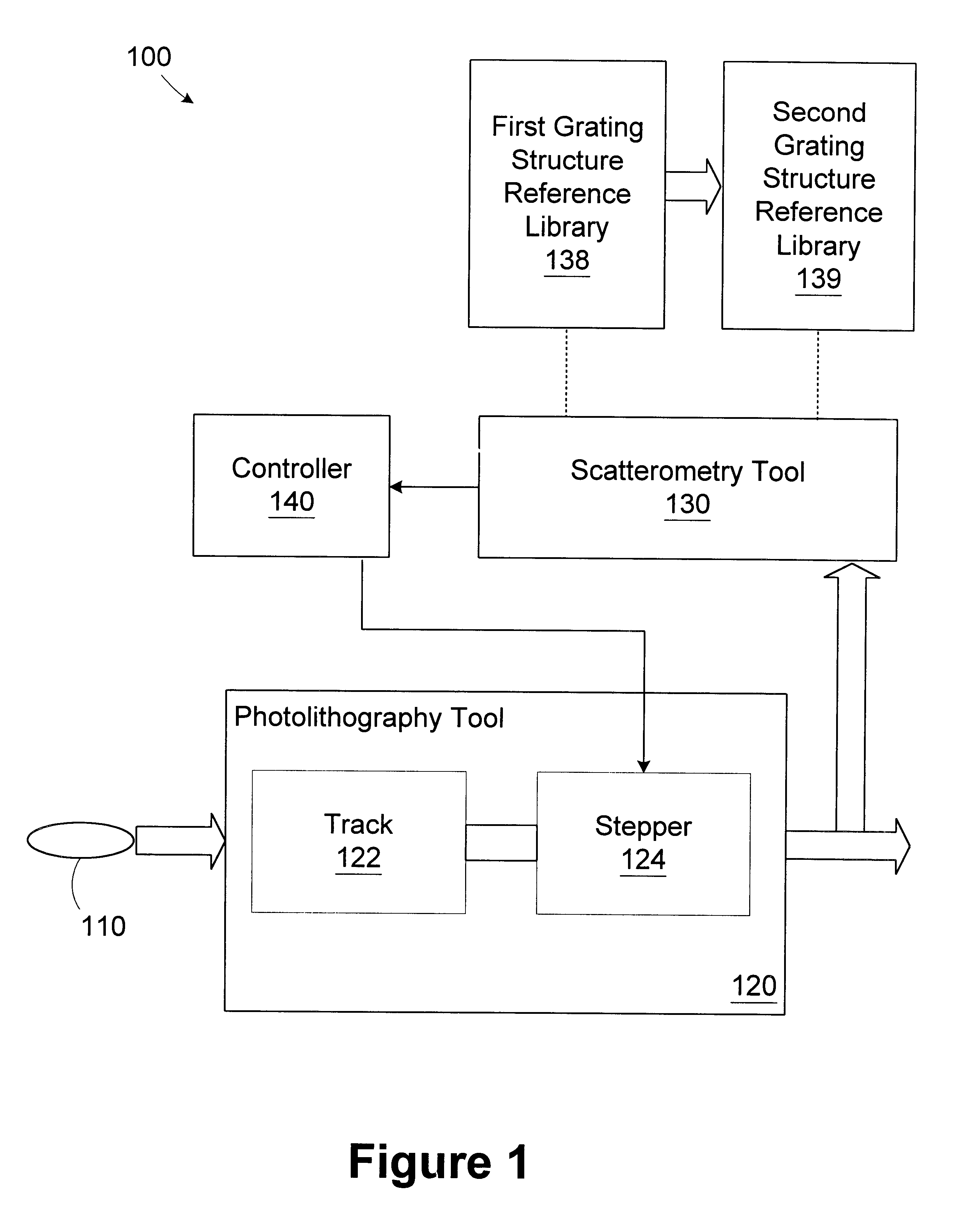
Method and apparatus for controlling photolithography overlay registration
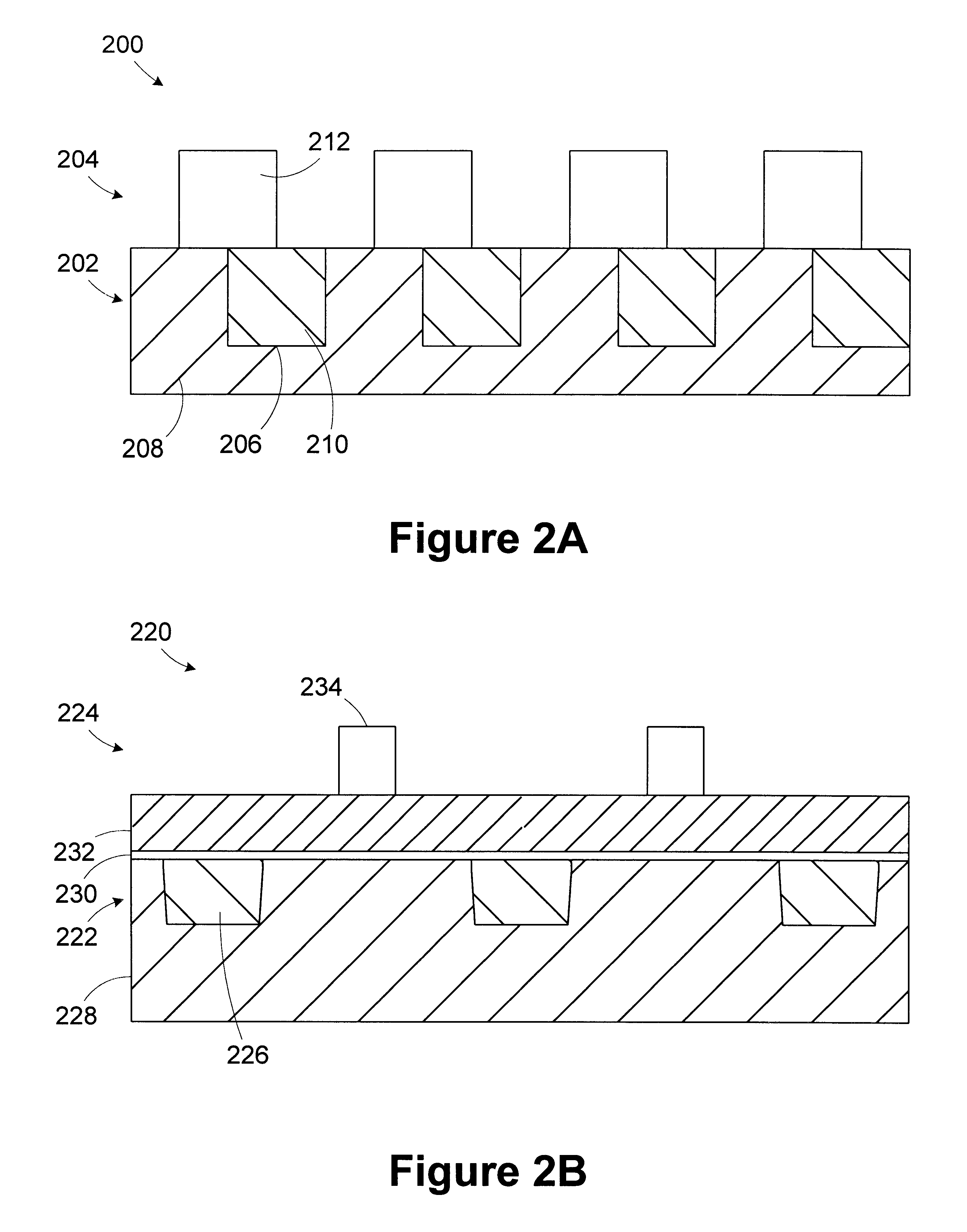
InactiveUS6458605B1Electrolytic capacitorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingMetrology
A method for controlling a photolithography process includes providing a wafer having a first grating structure and a second grating structure overlying the first grating structure; illuminating at least a portion of the first and second grating structures with a light source; measuring light reflected from the illuminated portion of the first and second grating structures to generate a reflection profile; determining an overlay error between the first and second grating structures based on the reflection profile; and determining at least one parameter of an operating recipe for a photolithography stepper based on the determined overlay error. A processing line includes a photolithography stepper, a first metrology tool, and a controller. The photolithography stepper is adapted to process wafers in accordance with an operating recipe. The first metrology tool is adapted to receive a wafer having a first grating structure and a second grating structure overlying the first grating structure. The metrology tool includes a light source, a detector, and a data processing unit. The light source is adapted to illuminate at least a portion of the first and second grating structures. The detector is adapted to measure light reflected from the illuminated portion of the first and second grating structures to generate a reflection profile. The data processing unit is adapted to determine an overlay error between the first and second grating structures based on the reflection profile. The controller is adapted to determine at least one parameter of the operating recipe of the photolithography stepper based on the determined overlay error.
Owner:FULLBRITE CAPITAL PARTNERS
Optical device having a light transmitting substrate with external light coupling means
ActiveUS9025253B2Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to mergePrismsProjectorsTotal internal reflectionCoupling
An optical device, includes a light-transmitting substrate (20) having an input aperture and first and second major surfaces (26, 32) parallel to each other and edges, one partially reflecting surface located in the substrate which is non-parallel to the major surfaces of the substrate and an external optical arrangement having an output aperture for coupling light into the substrate by total internal reflection. The optical arrangement for coupling light having an output aperture optically attached to the input aperture of the substrate with the part of the substrate located next to the substrate input aperture, being substantially transparent.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com