Patents
Literature
1421 results about "Optical cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors that forms a standing wave cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric oscillators and some interferometers. Light confined in the cavity reflects multiple times producing standing waves for certain resonance frequencies. The standing wave patterns produced are called modes; longitudinal modes differ only in frequency while transverse modes differ for different frequencies and have different intensity patterns across the cross section of the beam.
Lighting device
ActiveUS20070274080A1Non-electric lightingDischarge tube luminescnet screensOptical cavityEffect light
A first lighting device comprises at least one plural cavity element and a plurality of solid state light emitters. A second lighting device comprises at least one plural cavity element, a plurality of solid state light emitters and at least one encapsulant region, at least a portion of the plural cavity element being surrounded by the encapsulant region. Each plural cavity element has at least two optical cavities. Each optical cavity comprises a concave region in the plural cavity element. At least one solid state light emitter is present in each of at least two of the optical cavities.
Owner:CREELED INC
Electrically-pumped (Ga,In,Al)N vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
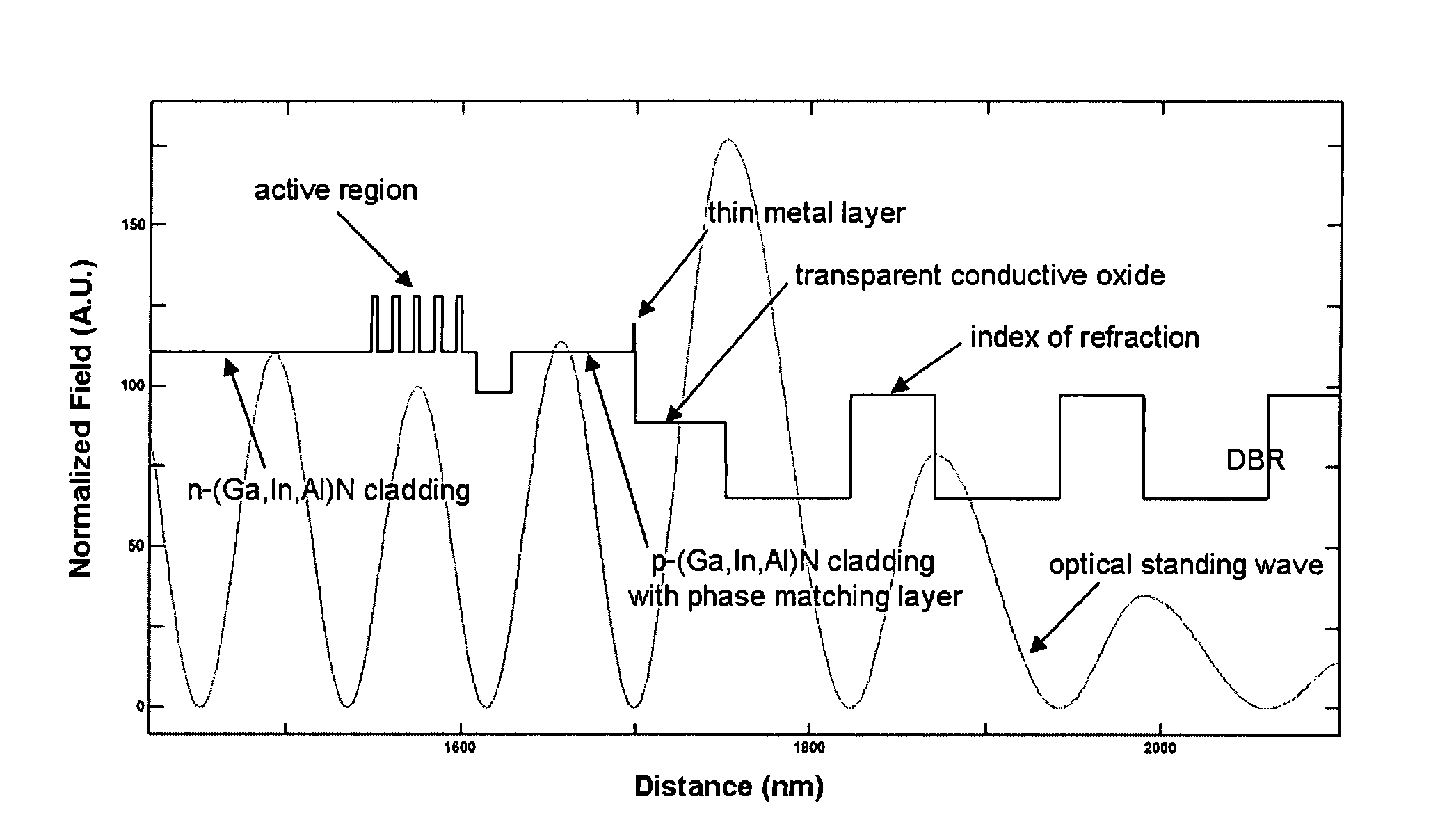
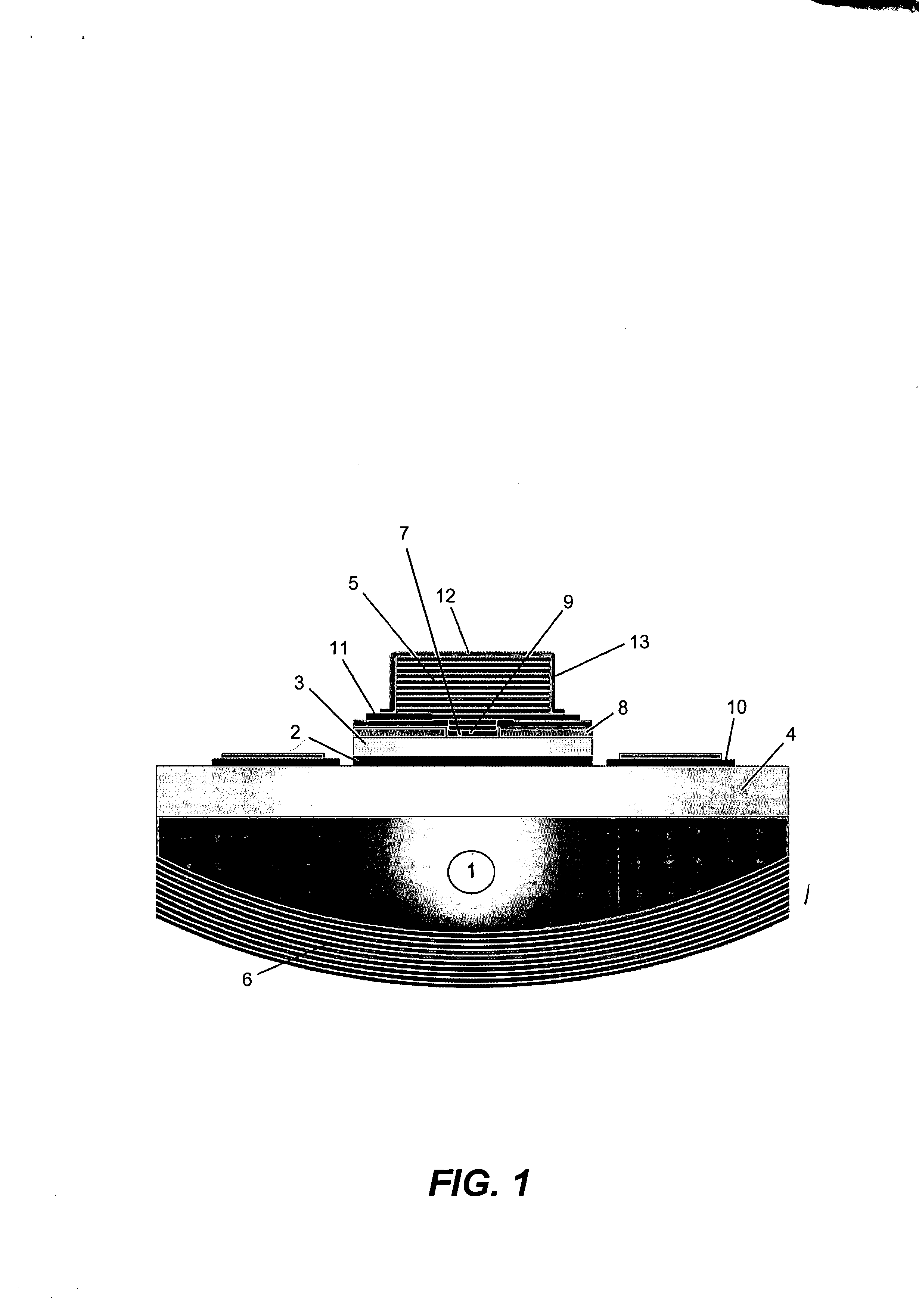
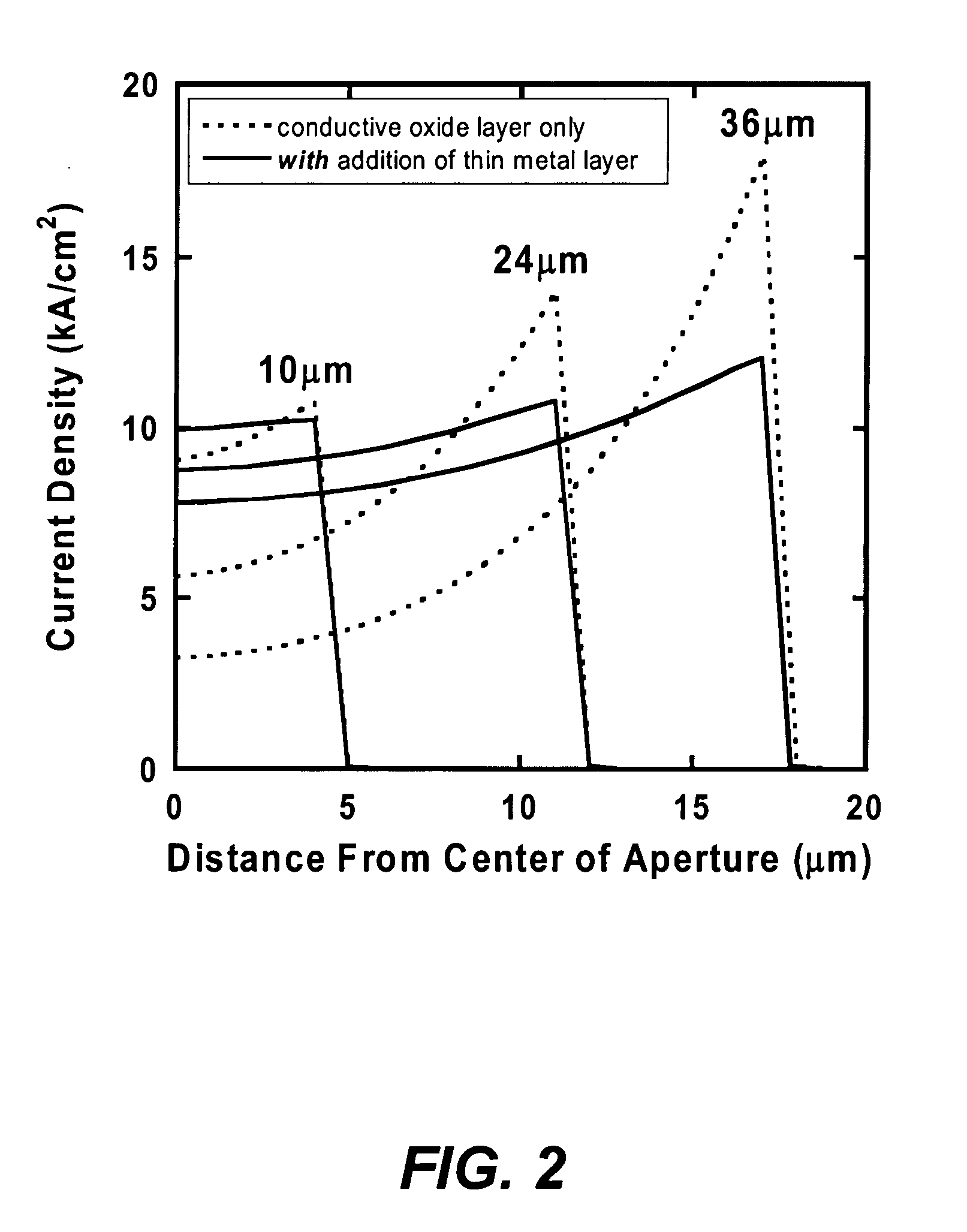
InactiveUS20070280320A1Good ohmic contactOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersThin metalVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
A vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) comprising a low-loss thin metal contact and current spreading layer within the optical cavity that provides for improved ohmic contact and lateral current distribution, a substrate including a plano-concave optical cavity, a (Ga,In,Al)N multiple quantum well (MQW) active region contained within the optical cavity that generates light when injected by an electrical current, and an integrated micromirror fabricated onto the substrate that provides for optical mode control of the light generated by the active region. A relatively simple process is used to fabricate the VCSEL.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
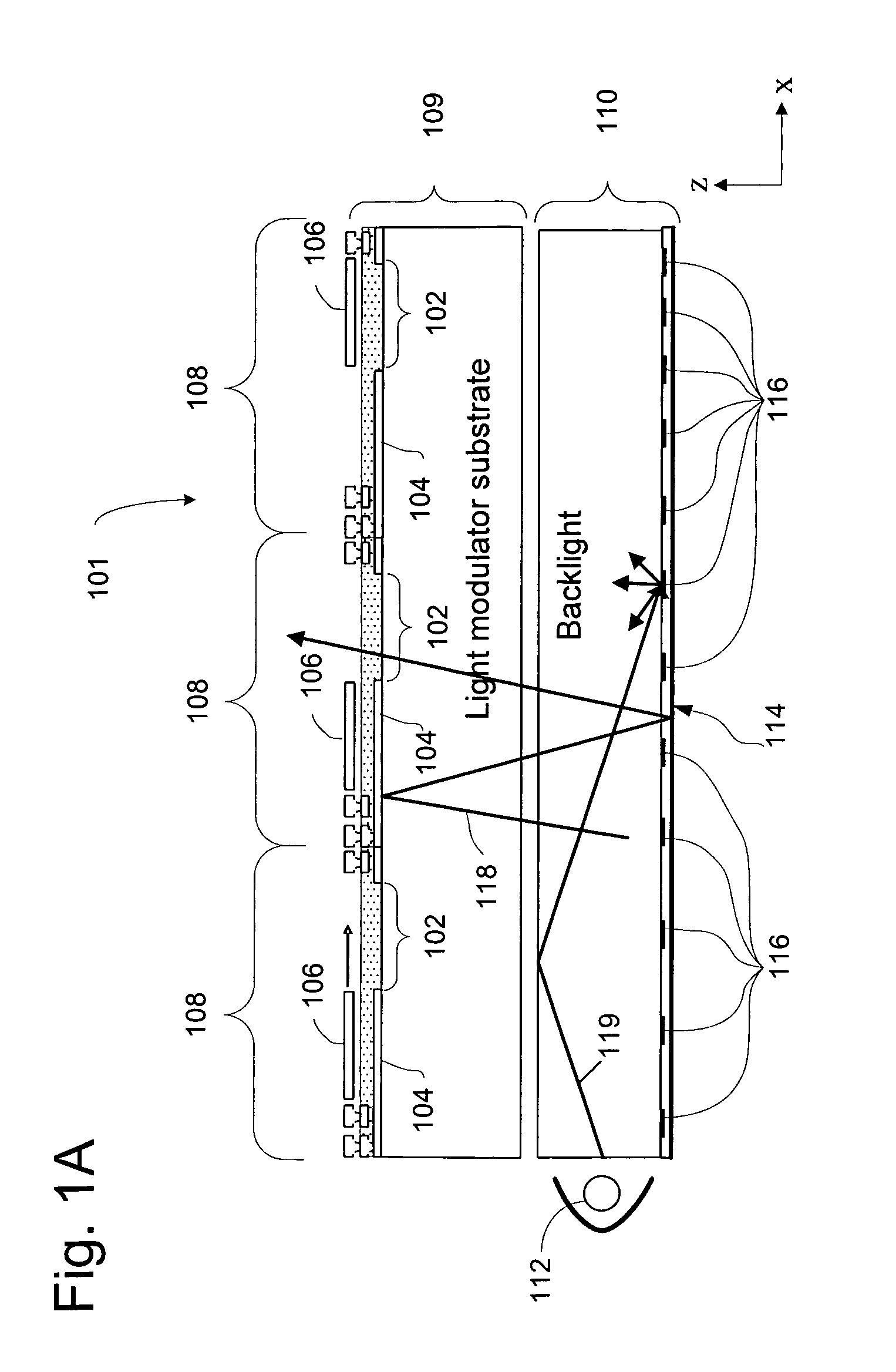
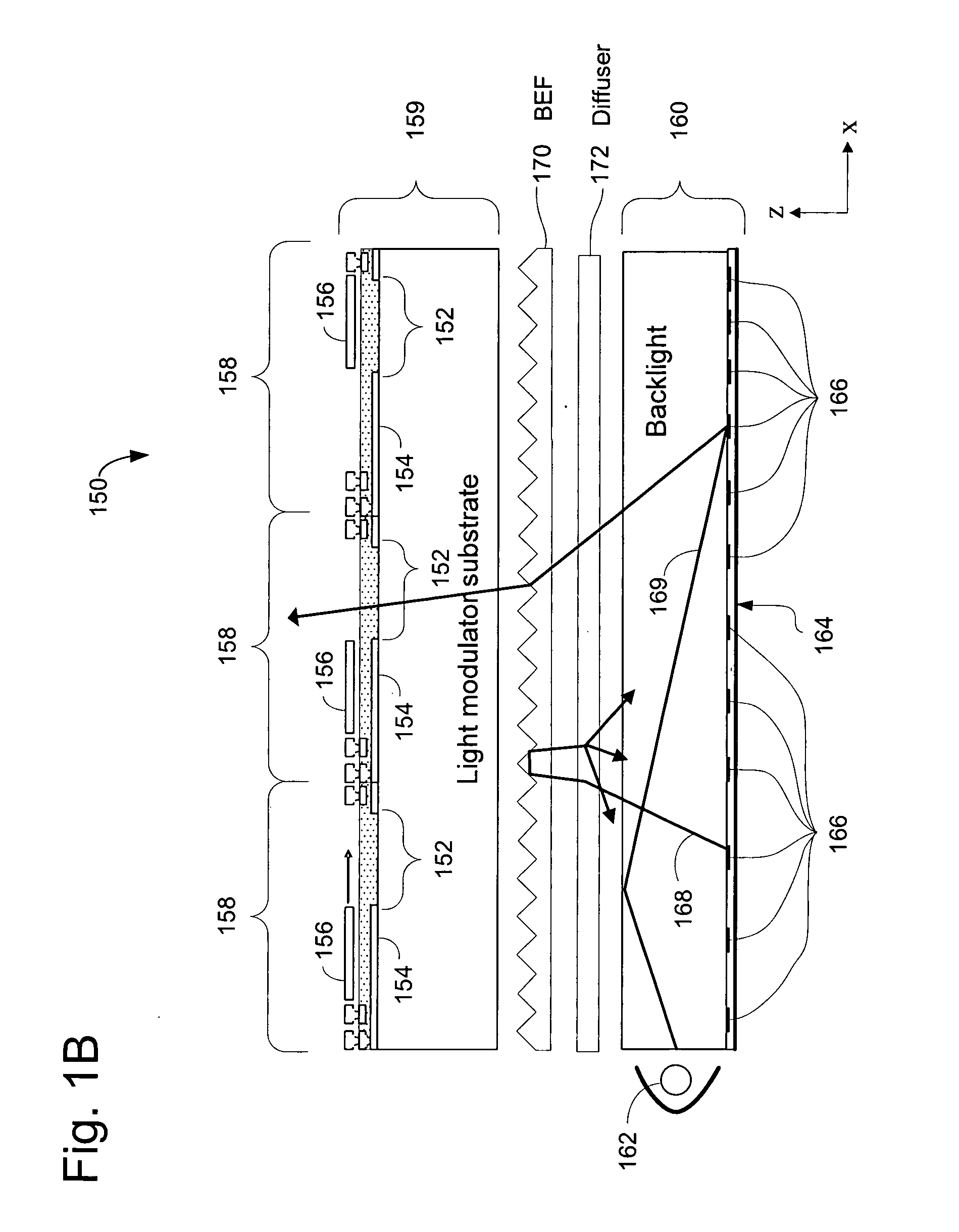
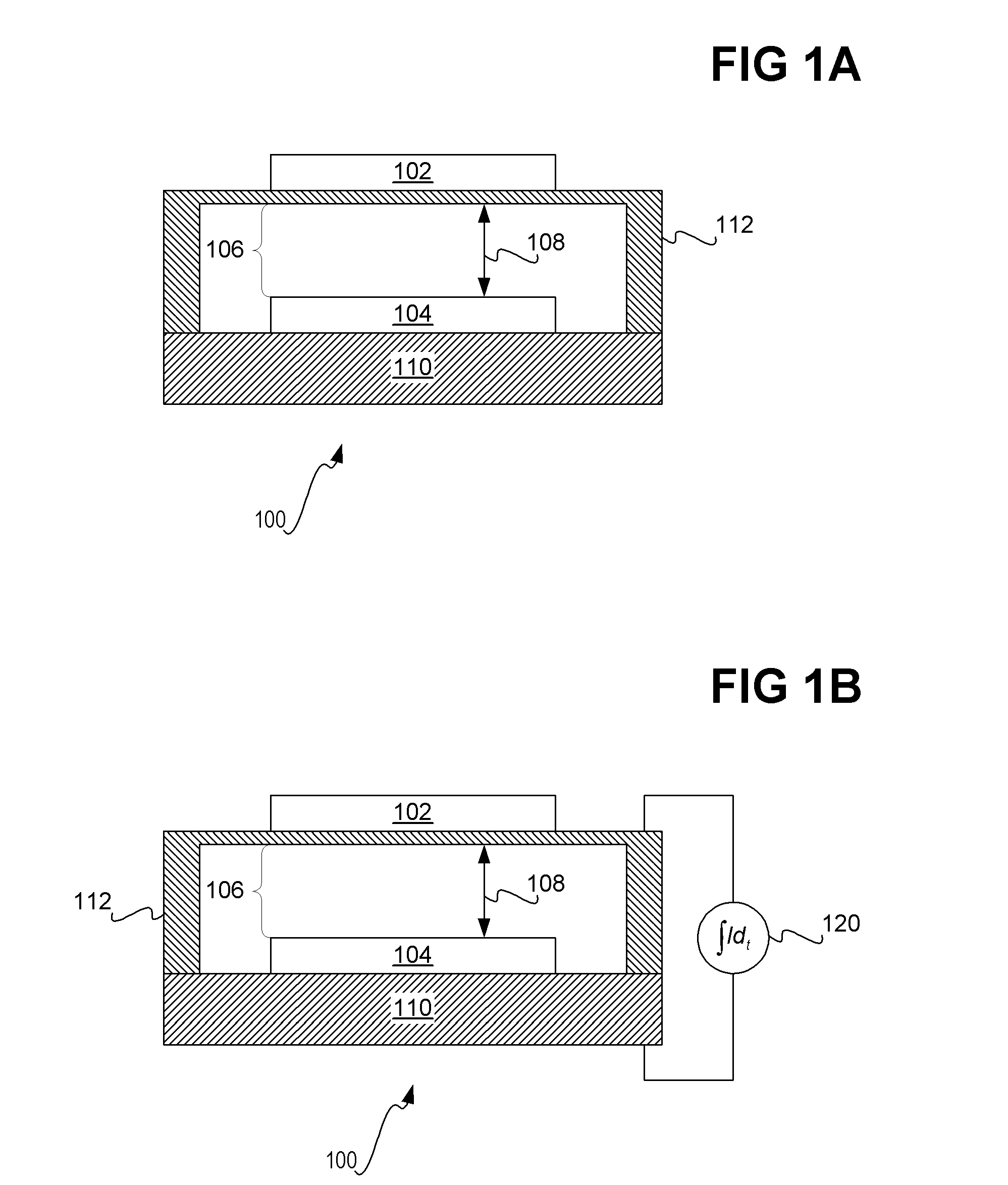
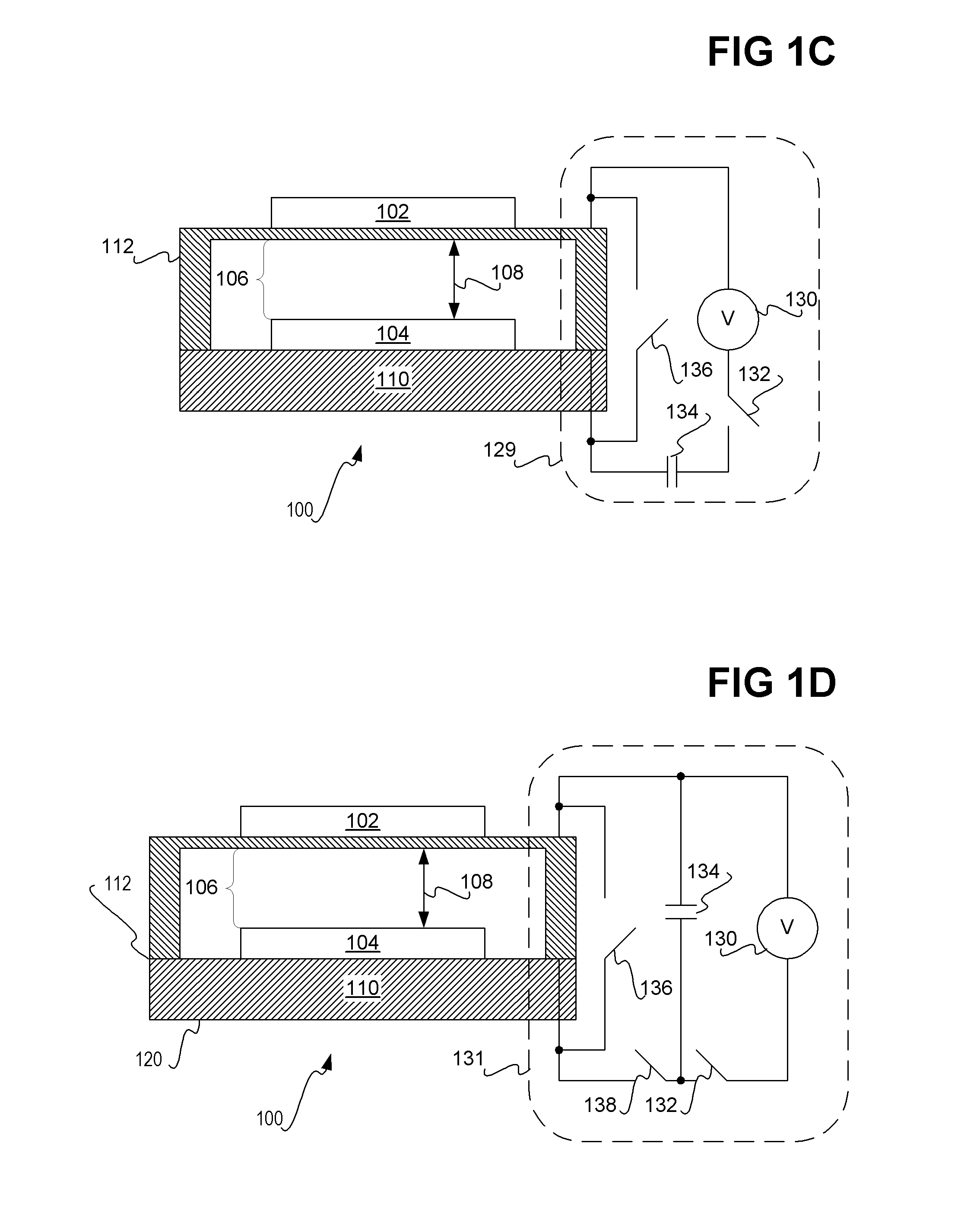
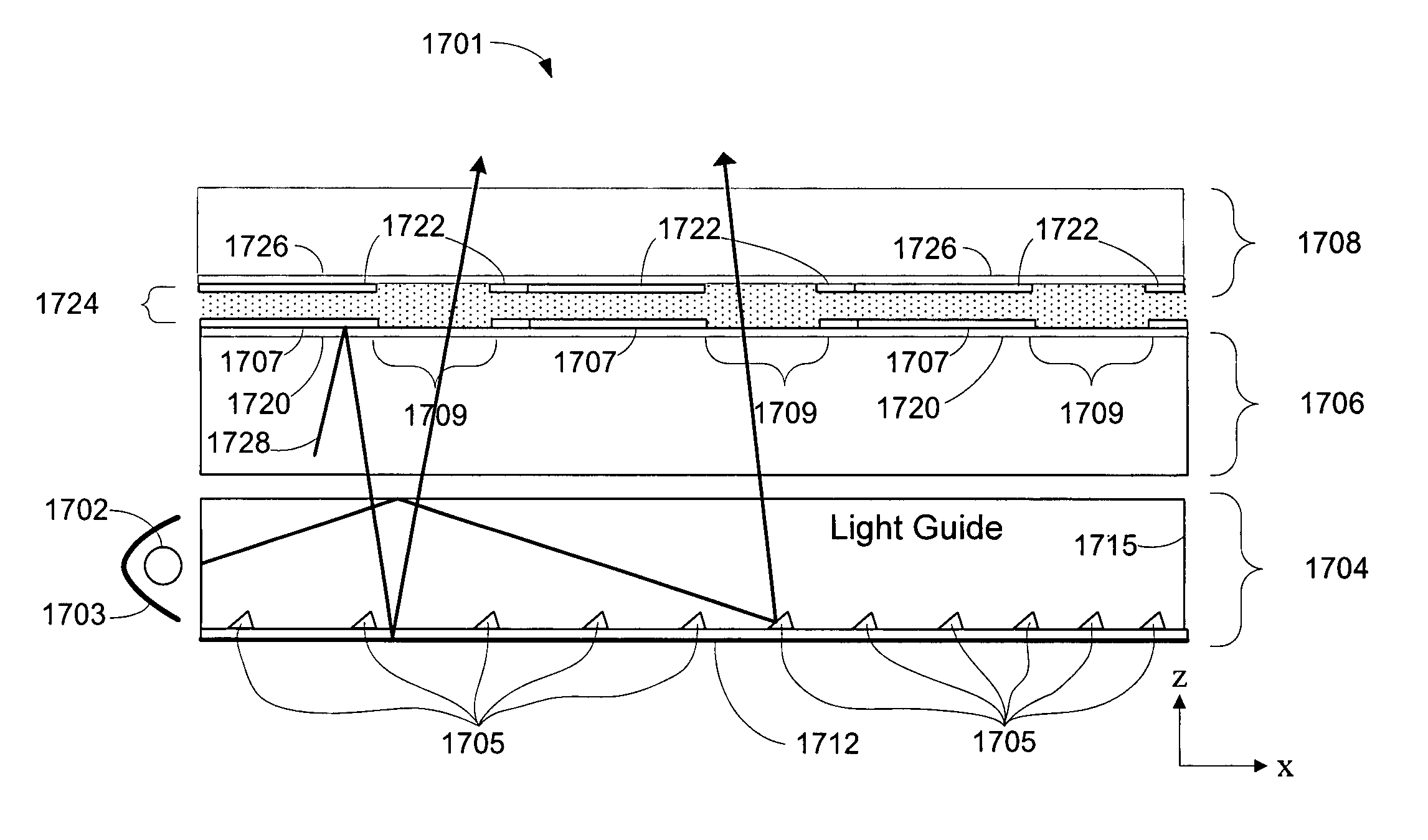
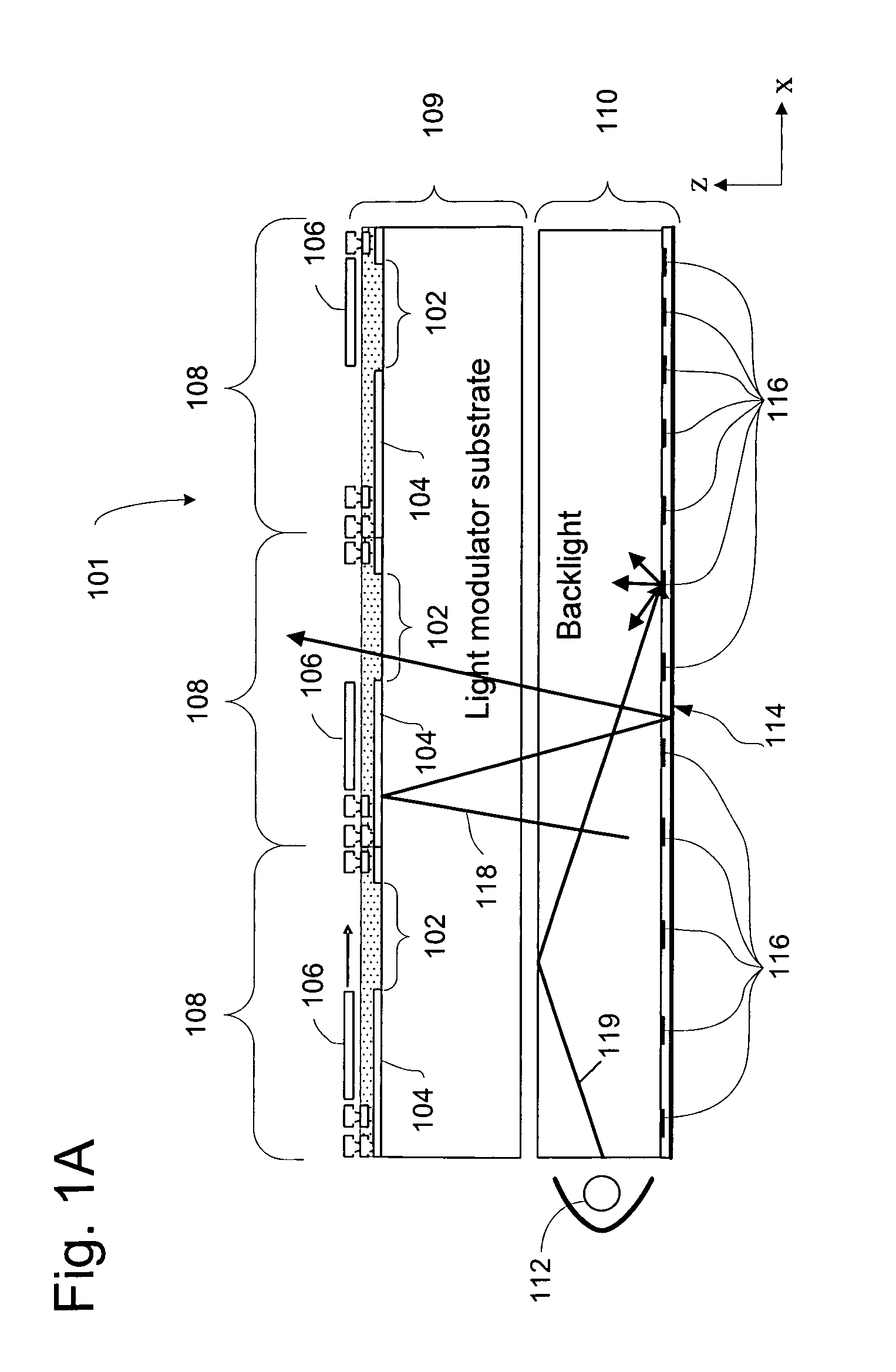
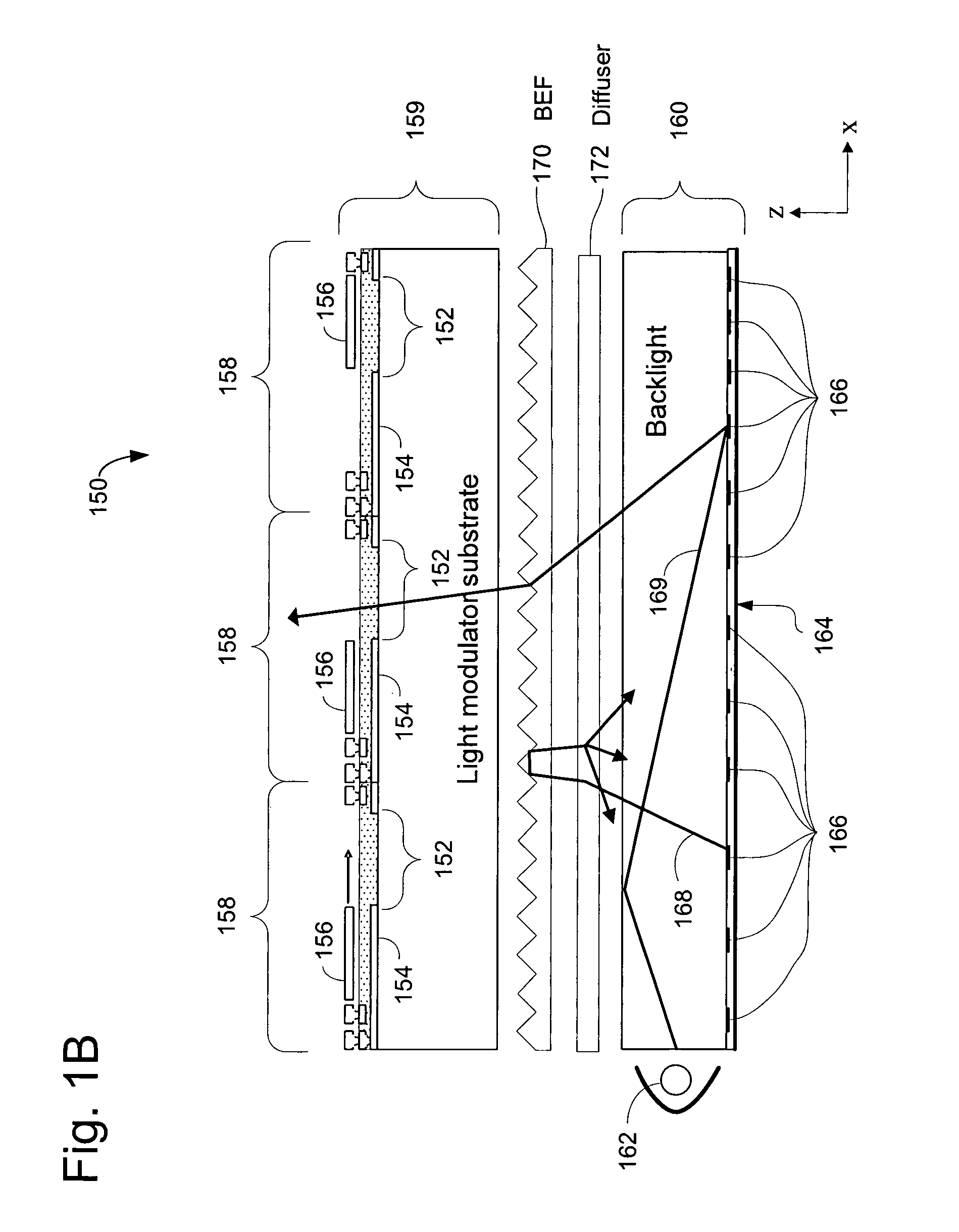
Display apparatus with optical cavities
A display includes an array of light modulators that define a display plane, a light guide and front- and rear-facing reflective surfaces. The light guide includes a plurality of geometric light redirectors, and at least 50% of the light guide's rear surface is parallel to the display plane. The rear-facing reflective surface is parallel to the display plane and includes a plurality of apertures.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Light emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090078944A1High gainSimple stepsOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOptical cavityLight emitting device
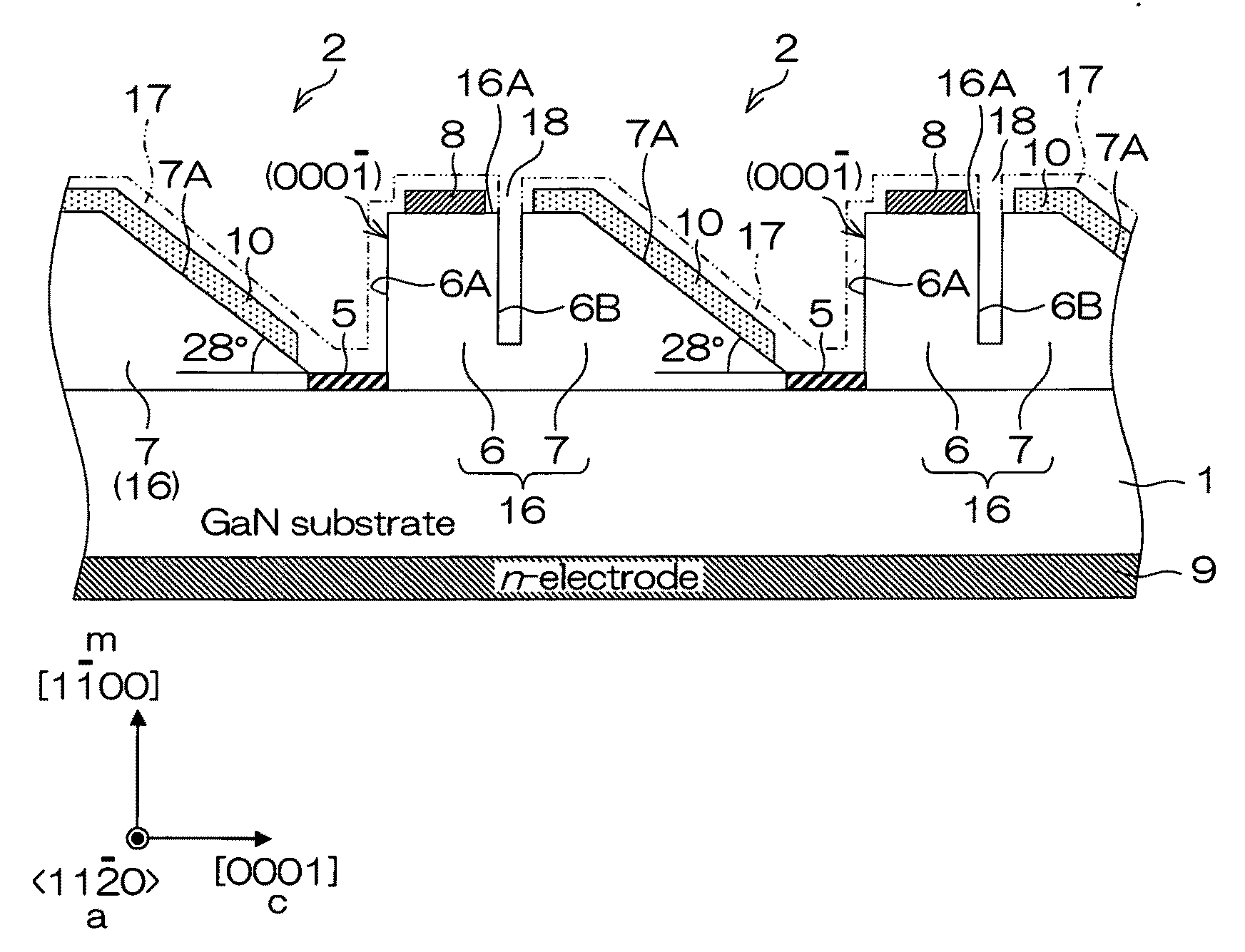
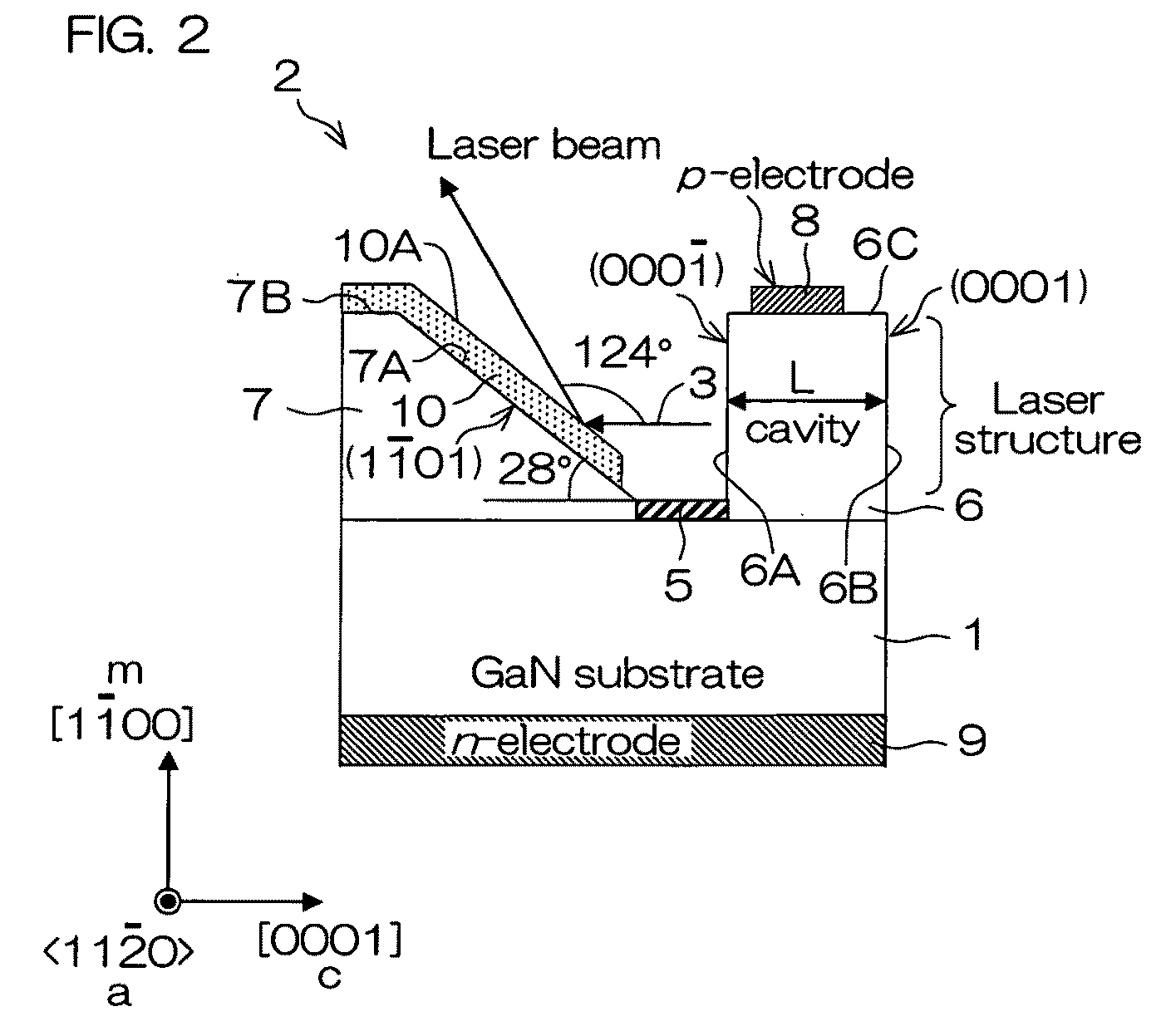
This semiconductor light emitting device includes an optical cavity made of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major growth surface defined by a nonpolar plane and including a pair of cavity end faces parallel to c-planes, and a reflecting portion made of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major growth surface defined by a nonpolar plane and having a reflective facet opposed to one of the pair of cavity end faces and inclined with respect to a normal of the major growth surface. The optical cavity and the reflecting portion may be crystal-grown from the major surface of the substrate. The substrate is preferably a group III nitride semiconductor substrate having a major surface defined by a nonpolar plane.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Optical interference pixel display with charge control
An electronic device of an embodiment of the invention is for at least partially displaying a pixel of a displayable image. The electronic device includes a first reflector and a second reflector that define an optical cavity therebetween, and which is selective of a visible wavelength at an intensity by optical interference. The electronic device also includes a charge-controlling mechanism to allow optical properties of the optical cavity to be varied by controlling a predetermined amount of charge stored on the first and the second reflectors. The visible wavelength and / or the intensity are thus variably selectable in correspondence with the pixel of the displayable image.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Aperiodic dielectric multilayer stack
A structure is provided that includes an aperiodic dielectric stack. The structure may include a substrate, a device disposed over the substrate, and a first dielectric stack disposed between the substrate and the device. The first dielectric stack includes a plurality of layers comprising a first dielectric material, wherein at least two of the layers comprising a first dielectric material have substantially different thicknesses, as well as a plurality of layers comprising a second dielectric material. The average outcoupling efficiency into air of the device over a bandwidth of at least 300 nm may be at least 40% greater than that of an otherwise identical device disposed in a structure without the first dielectric stack. The substrate may have a treated surface such that light that may otherwise be waveguided in the substrate is outcoupled into air, and the average outcoupling efficiency into air of the device over a bandwidth of at least 300 nm may be at least 10% greater than that of an otherwise identical device disposed in a structure without the first dielectric stack. The structure may include an optical cavity defined by a first end layer and a second end layer, where the first end layer further comprising a first dielectric stack having a plurality of layers comprising a first dielectric material, wherein at least two of the layers comprising a first dielectric material have substantially different thicknesses, and a plurality of layers comprising a second dielectric material. An optoelectronic device having a first active layer may be disposed within the optical cavity.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Optical heterodyne detection in optical cavity ringdown spectroscopy
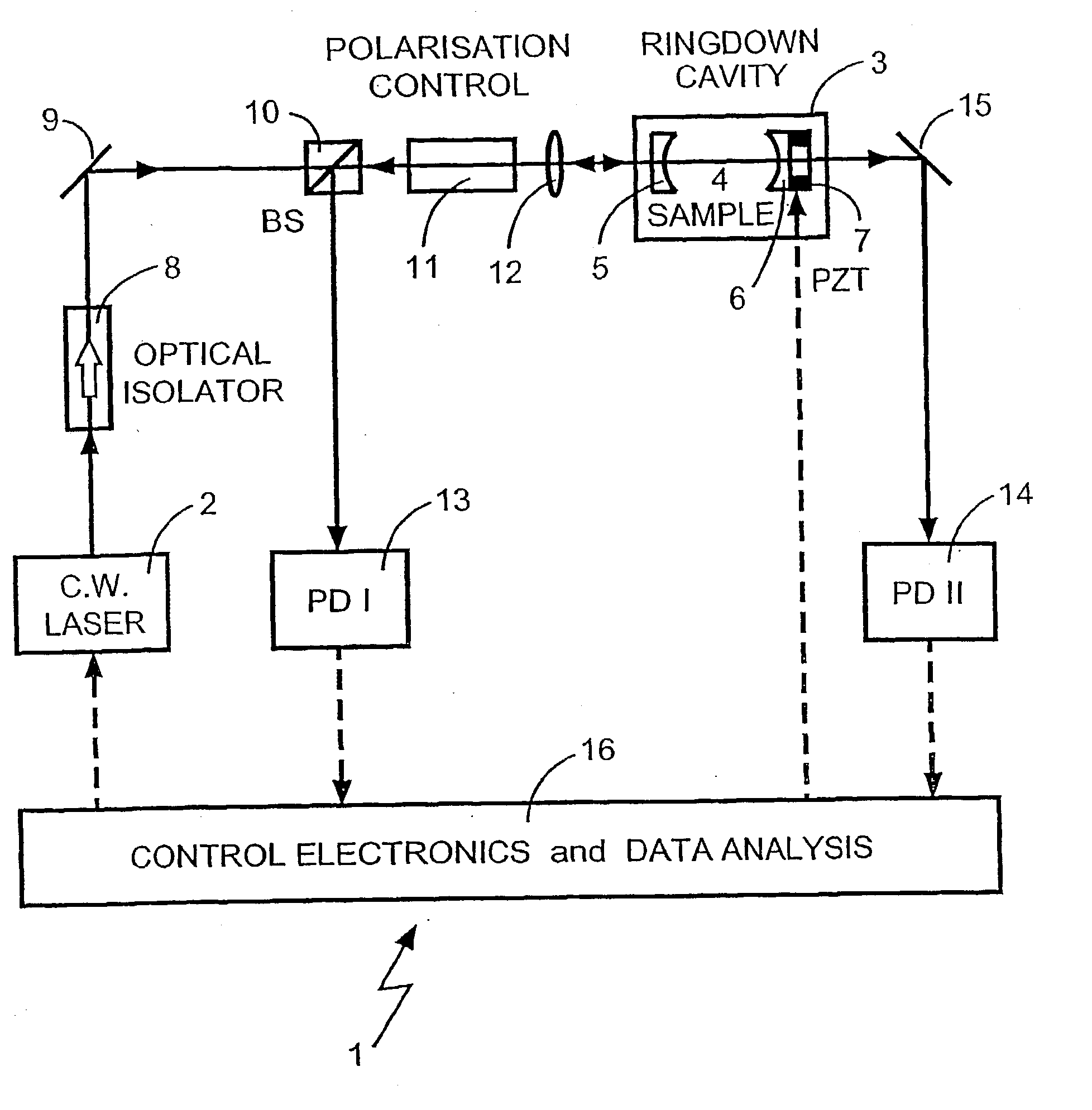
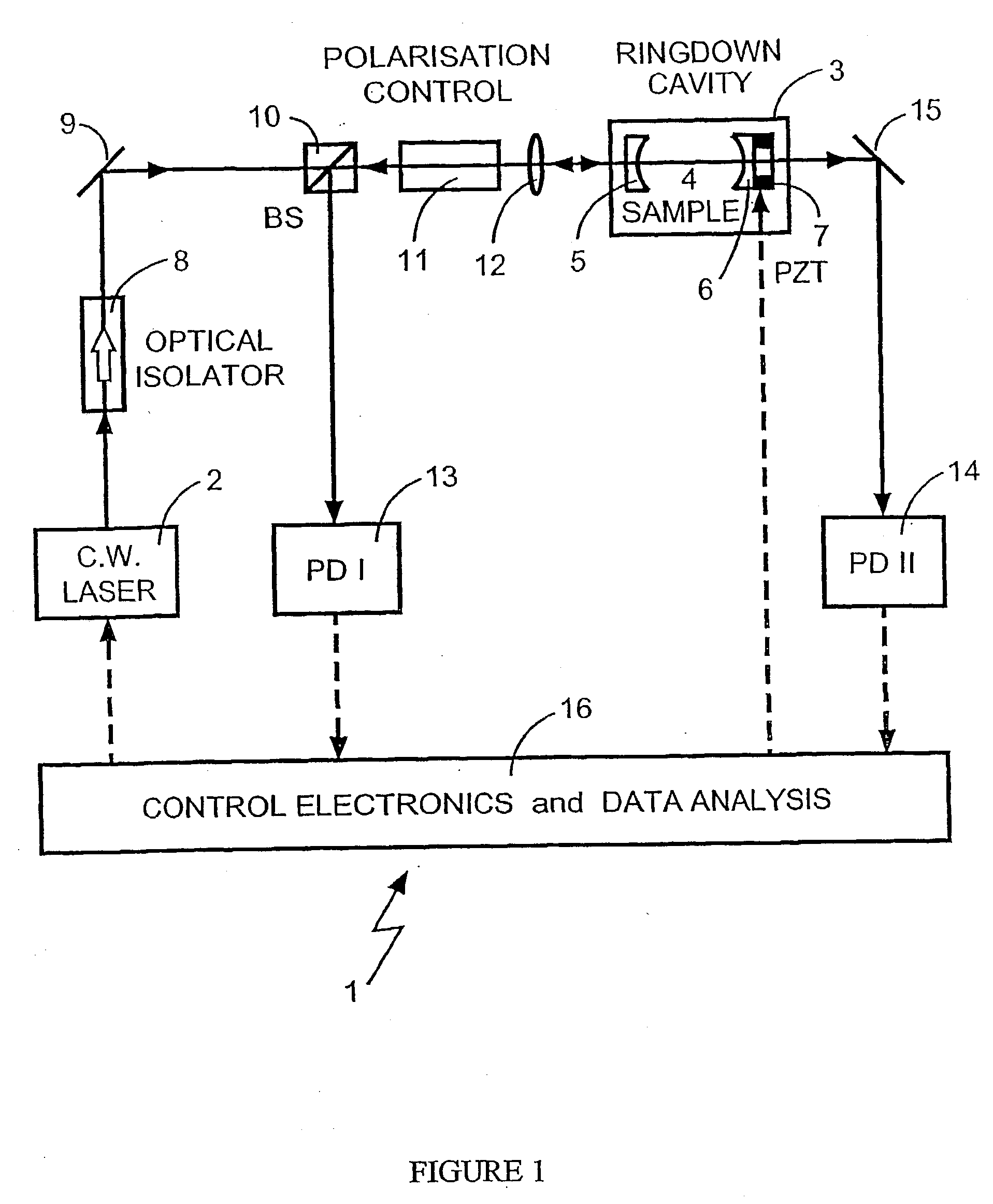
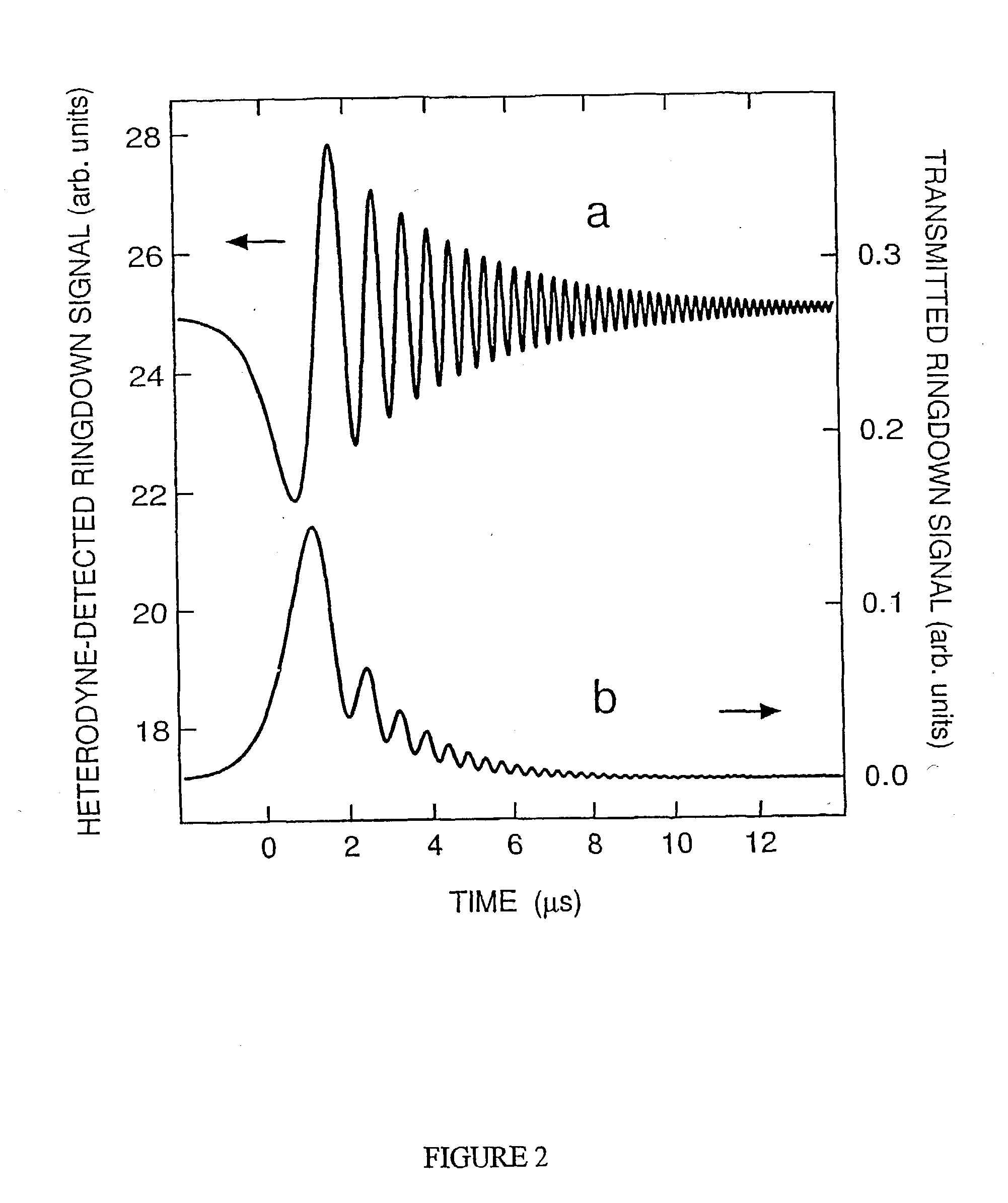
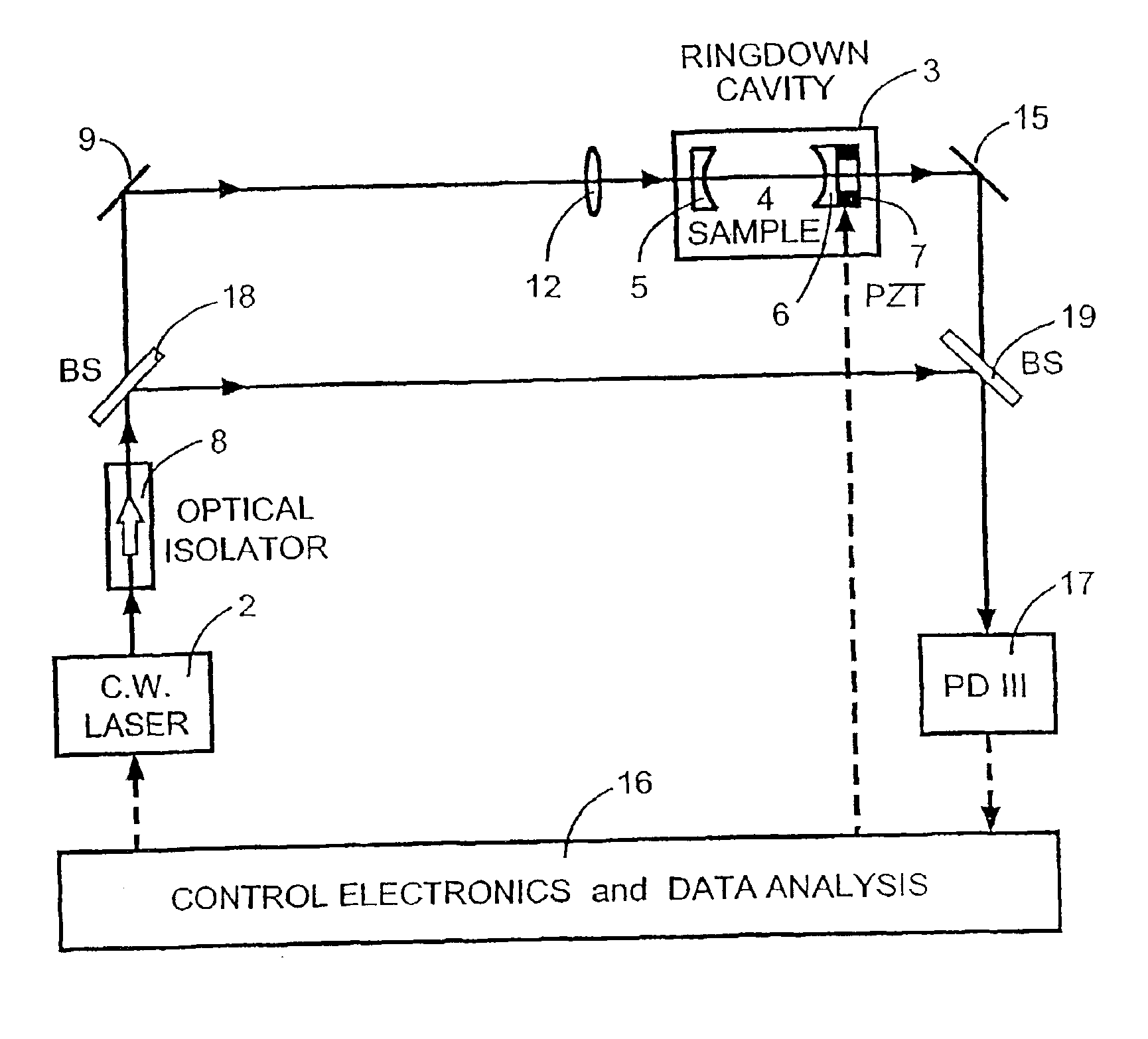
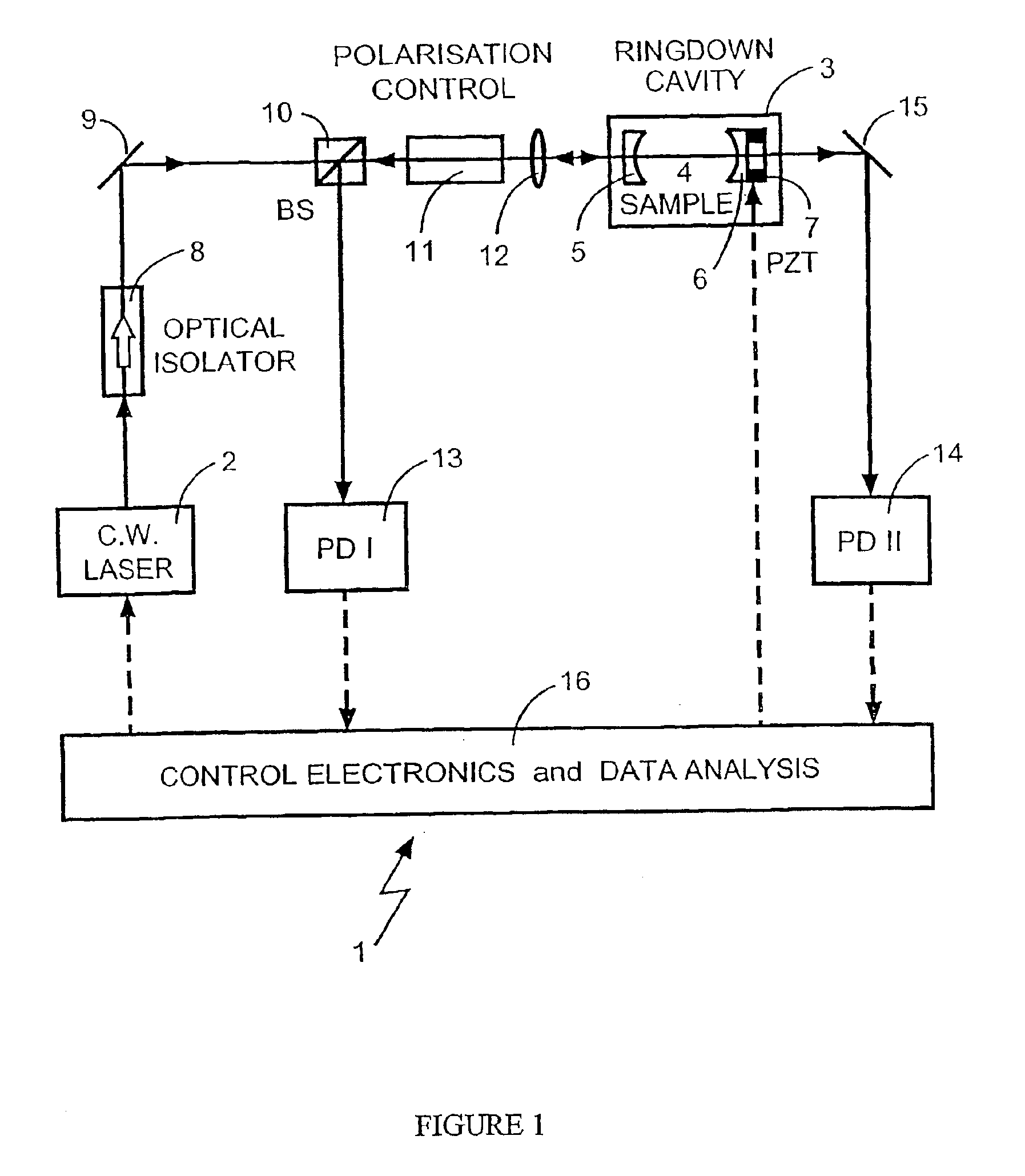
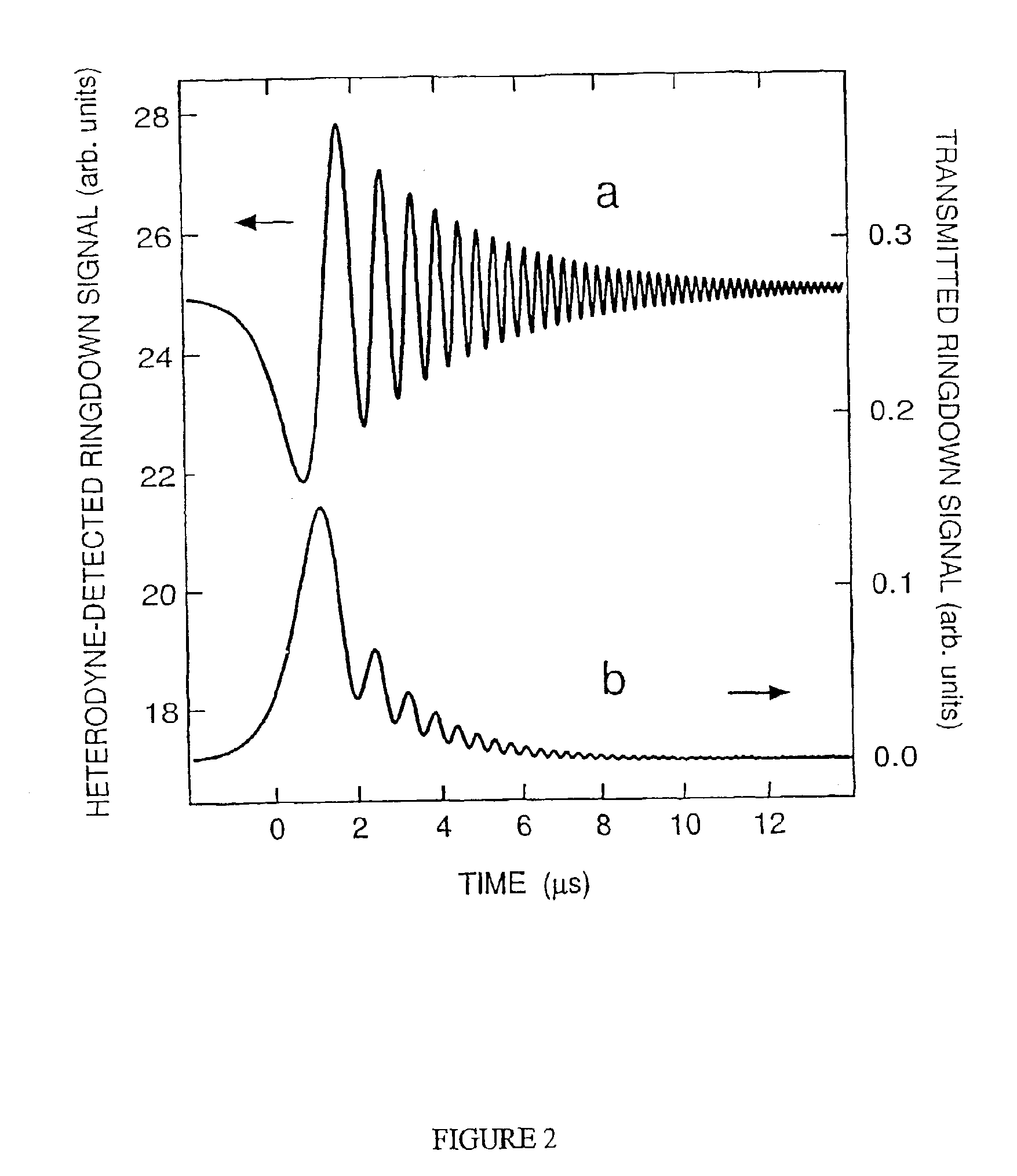
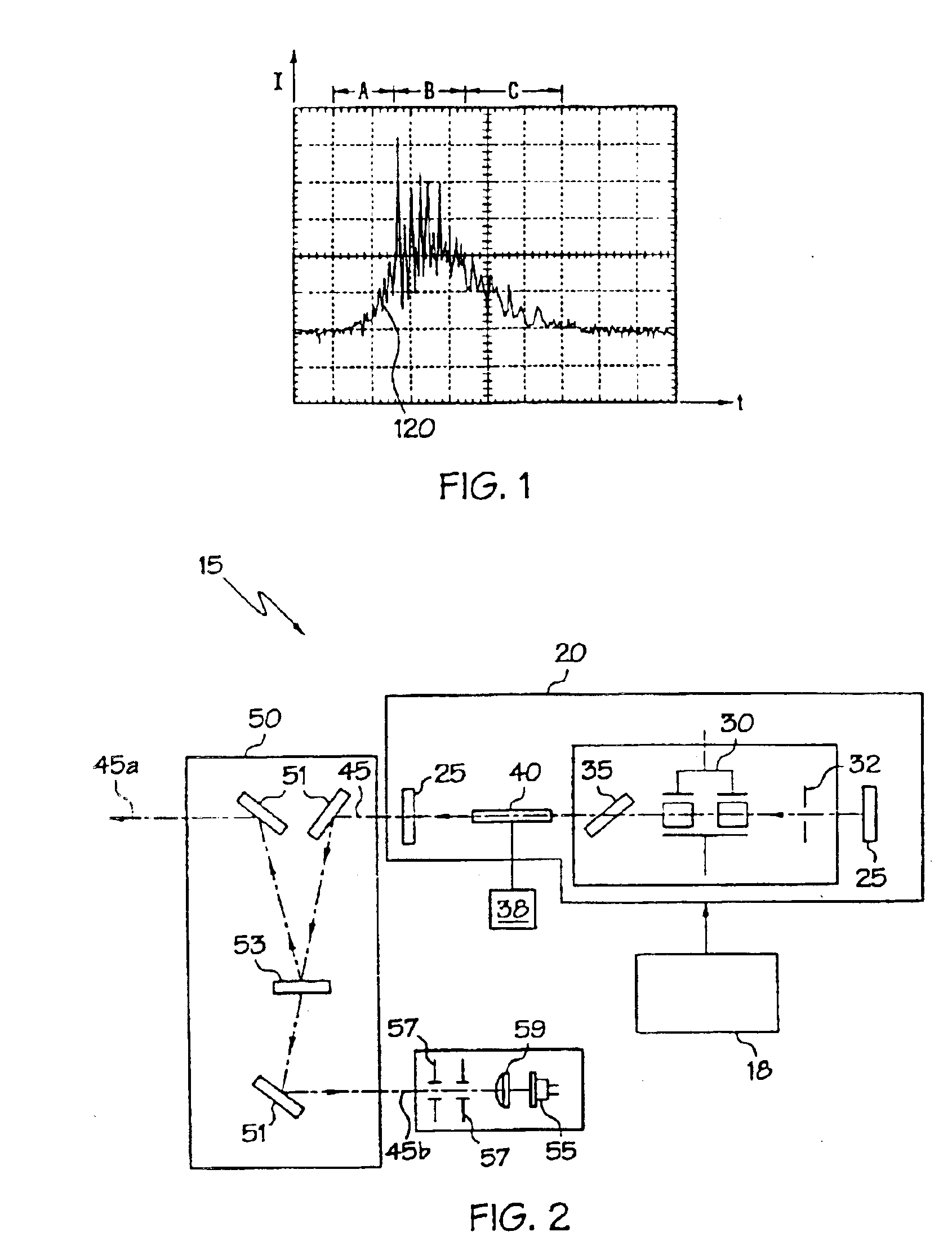
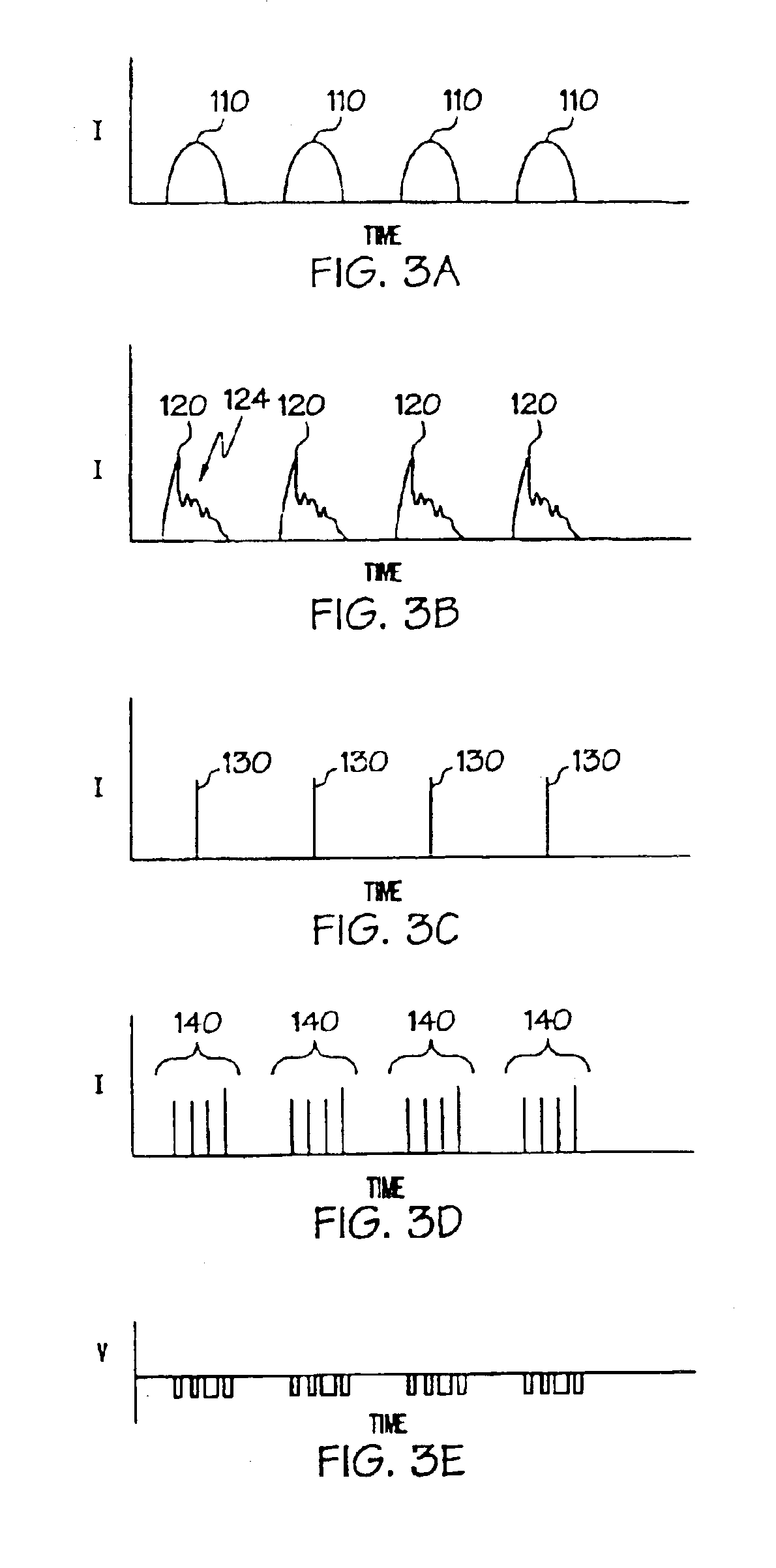
The present invention relates to optical heterodyne detection cavity ringdown spectroscopy. In one aspect the invention relates to an optical system (1) comprising a ring-down cavity cell (3) defining a resonant optical cavity, means for directing coherent light selected from the group consisting of continuous or quasi-continuous light into said optical cavity (8, 9, 10, 11, and 12), means for altering the resonant optical cavity so as to generate a frequency shift of the coherent light in the optical cavity (6, 7), means for coupling said coherent light into the optical cavity and means for decoupling the frequency shifted coherent light out of said optical cavity (5, 6, 7), means for optically combining (10, 11, 12) said decoupled frequency shifted coherent light with another portion of coherent light not in optical communication with the optical cavity and means for optical heterodyne detection (13) of the intensity of said combined light. A method for optical detection is also described as well as methods and apparatus for detecting a parameter of a sample.
Owner:MACQUARIE RES
Optical heterodyne detection in optical cavity ringdown spectroscopy
InactiveUS7012696B2Efficient couplingImprove skillsRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsContinuous lightOptical cavity
Owner:MACQUARIE RES
Sub-wavelength grating integrated VCSEL
InactiveUS20070153860A1Good optical performanceEasy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is described using a sub-wavelength grating (SWG) structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity. The grating comprises segments of high and low refractive index materials with an index differential between the high and low index materials. By way of example, a SWG reflective structure is disposed over a low index cavity region and above another reflective layer (either SWG or DBR). In one embodiment, the SWG structure is movable, such as according to MEMS techniques, in relation to the opposing reflector to provide wavelength selective tuning. The SWG-VCSEL design is scalable to form the optical cavities for a range of SWG-VCSELs at different wavelengths, and wavelength ranges.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Self-packaged optical interference display device having anti-stiction bumps, integral micro-lens, and reflection-absorbing layers
InactiveUS20070020948A1Reduce reflectionStatic indicating devicesVolume/mass flow measurementOptical propertyOptical cavity
An electronic device of an embodiment of the invention is disclosed that at least partially displays a pixel of a display image. The device includes a first reflector and a second reflector defining an optical cavity therebetween that is selective of a visible wavelength at an intensity. The device includes a mechanism to allow optical properties of the cavity to be varied such that the visible wavelength and / or the intensity are variably selectable in correspondence with the pixel of the displayable image. The device also includes one or more transparent deposited films, one or more absorbing layers, an integral micro-lens, and / or one or more anti-stiction bumps. The deposited films are over one of the reflectors, for self-packaging of the device. The absorbing layers are over one of the reflectors, to reduce undesired reflections. The integral micro-lens is over one of the reflectors, and the anti-stiction bumps are between the reflectors.
Owner:PIEHL ARTHUR +3
Display apparatus with optical cavities
A display includes an array of light modulators that define a display plane, a light guide and front- and rear-facing reflective surfaces. The light guide includes a plurality of geometric light redirectors, and at least 50% of the light guide's rear surface is parallel to the display plane. The rear-facing reflective surface is parallel to the display plane and includes a plurality of apertures.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
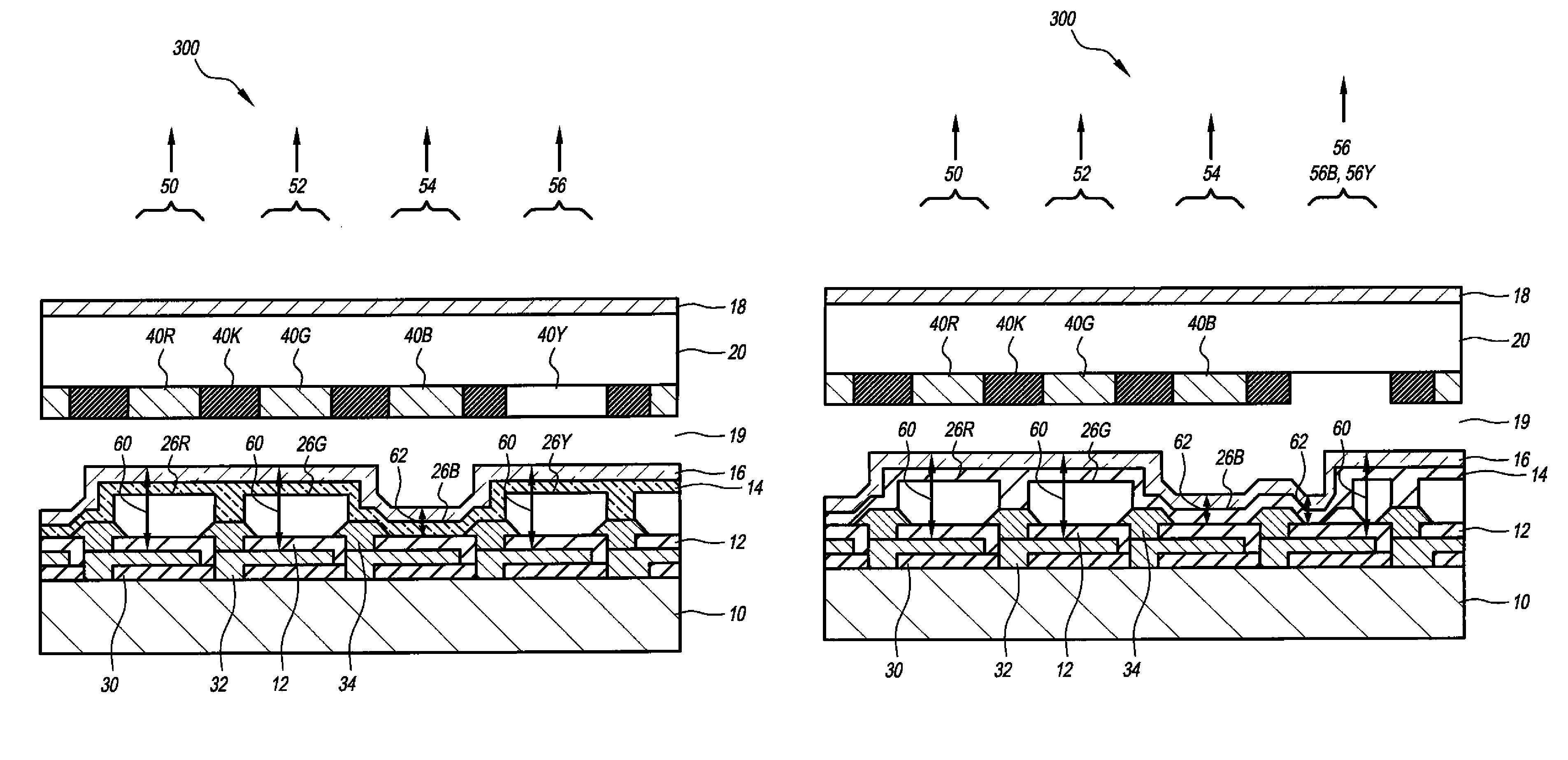
LED device having improved light output
ActiveUS7893612B2Incadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensOptical cavityLight-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode device that includes a first group of sub-pixels each subpixel comprising a reflective electrode and a second electrode formed over a substrate with an unpatterned light-emitting layer formed between the reflective electrode and the second electrode, thus forming a first optical cavity having a first cavity length. Either the reflective or second electrode is patterned to form two or more independently-controllable, light-emitting sub-pixels. A second group of sub-pixels, each comprising a reflective electrode and a second electrode formed over the substrate. An unpatterned light-emitting layer is formed between the reflective electrode and the second electrode to comprise a second optical cavity having a second cavity length different from the first cavity length of the first optical cavity. Either the reflective or second electrode is patterned to form one or more independently-controllable, light-emitting sub-pixels.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Optoelectronic device incorporating an interference filter
InactiveUS20050117623A1Optical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical cavityResonance
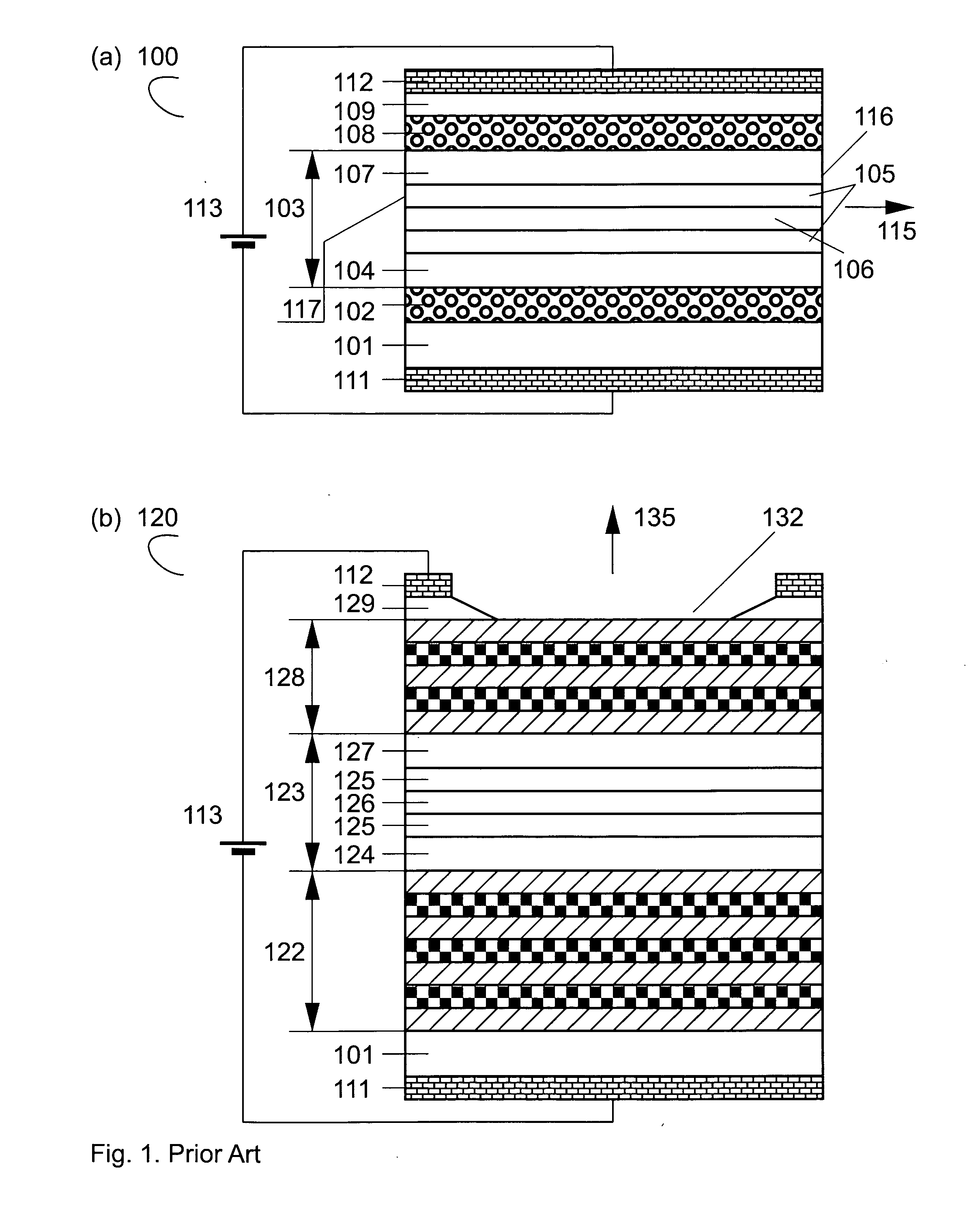
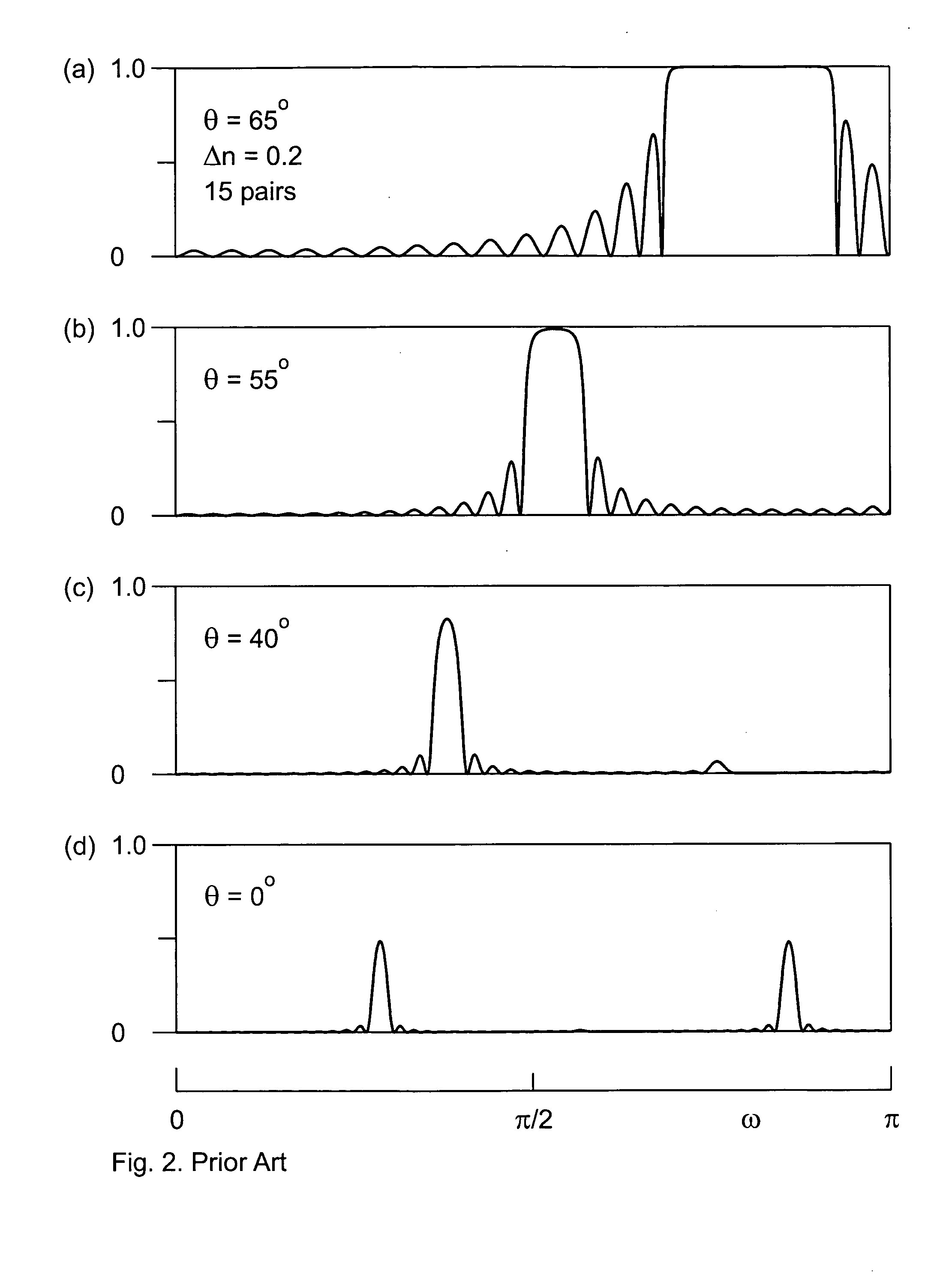
A novel class of optoelectronic devices incorporate an interference filter. The filter includes at least two optical cavities. Each of the cavities localizes al least one optical mode. The optical modes localized at two cavities are at resonance only at one or at a few discrete selective wavelengths. At resonance, the optical eigenmodes contain one mode having a zero intensity at a node position between the two cavities, where this position shifts as a function of the wavelength. A non-transparent element, which is preferably an absorbing element, a scatterer, or a reflector, is placed between two cavities. At a discrete selective wavelength, when the node of the optical mode matches with the non-transparent element, the filter is transparent for light. At other wavelengths, the filter is not transparent for light. This allows for the construction of various optoelectronic devices showing a strongly wavelength-selective operation.
Owner:INNOLUME
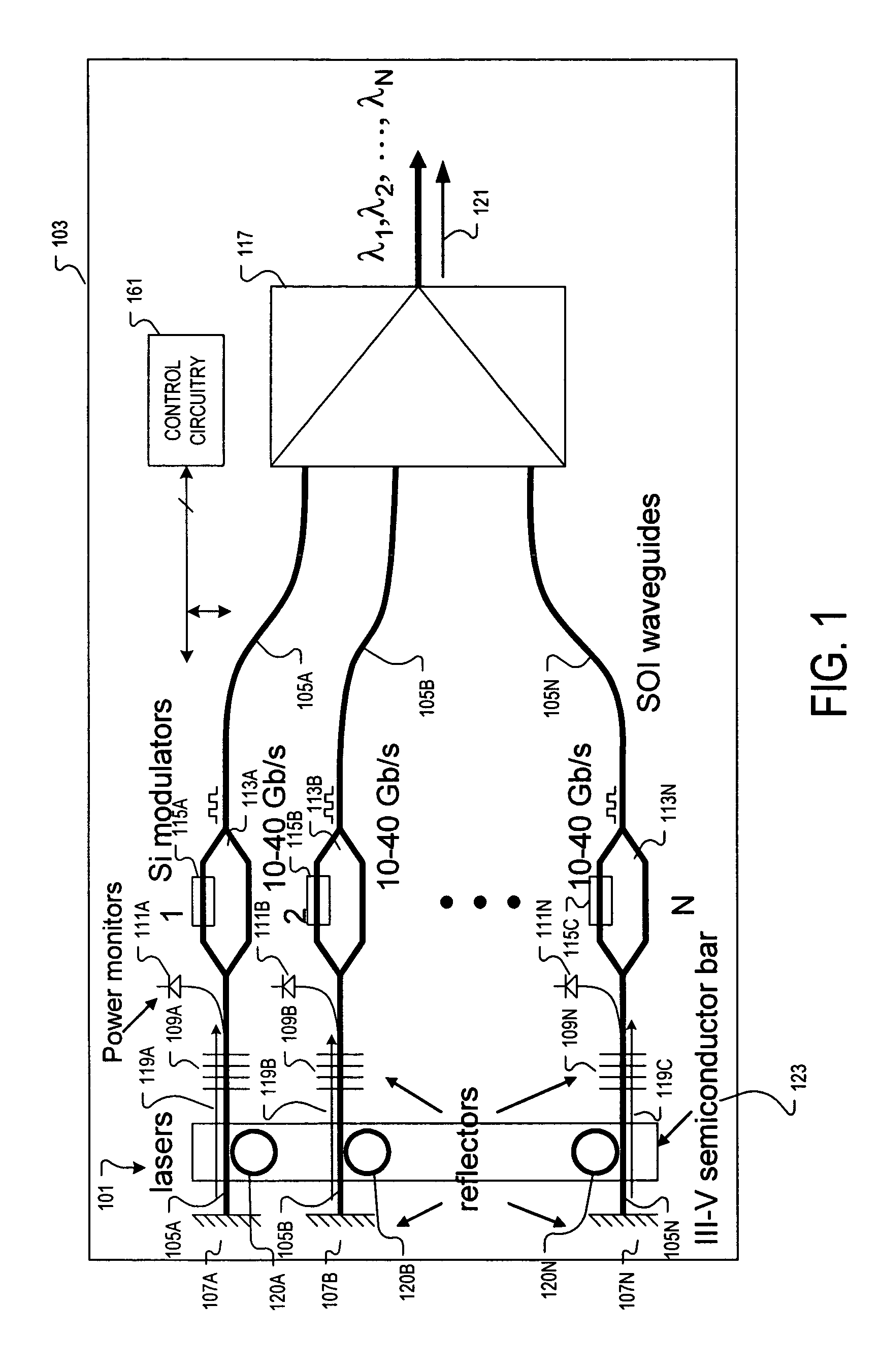
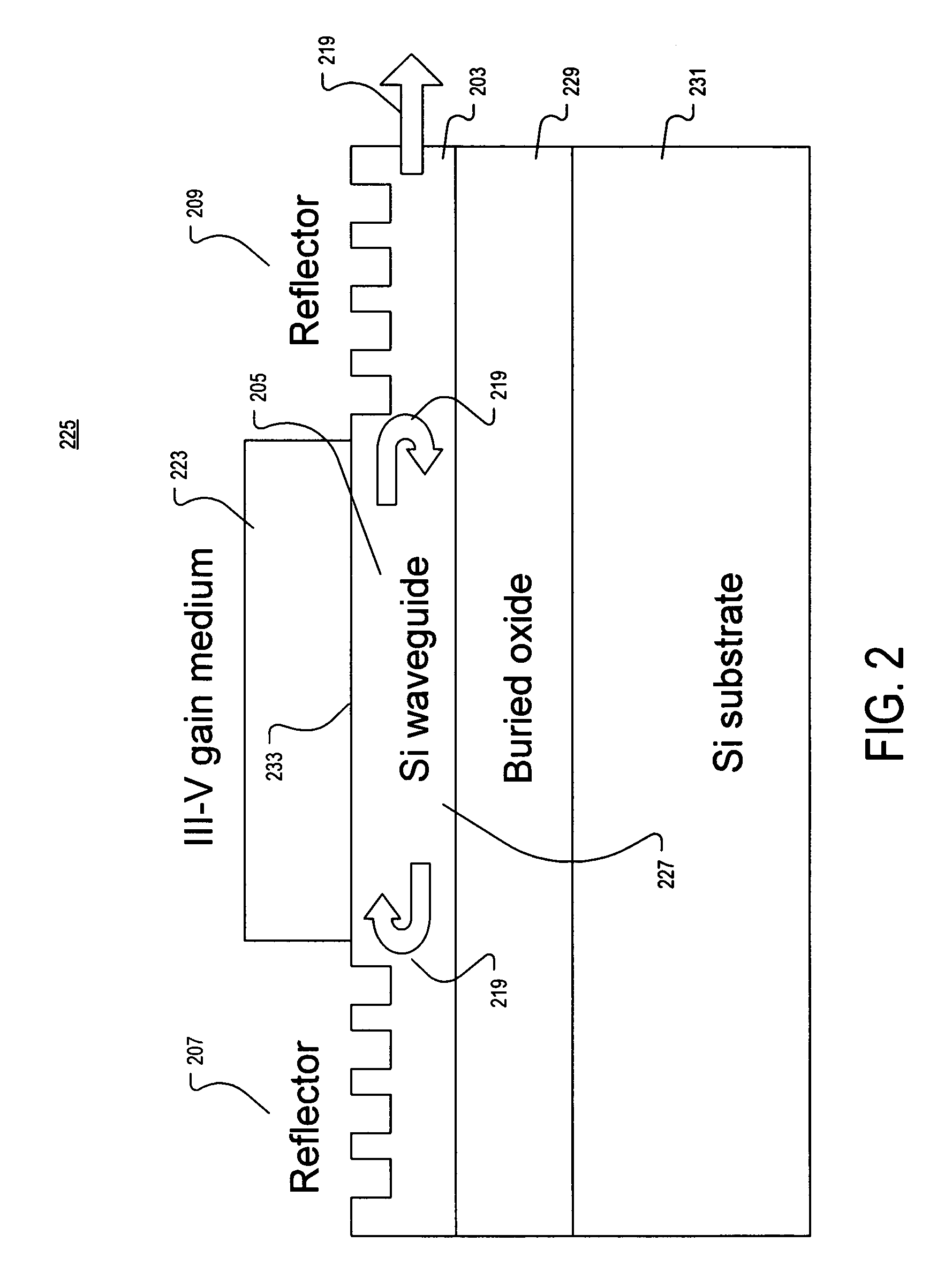
Transmitter-receiver with integrated modulator array and hybrid bonded multi-wavelength laser array
InactiveUS7257283B1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSemiconductor materialsOptical cavity
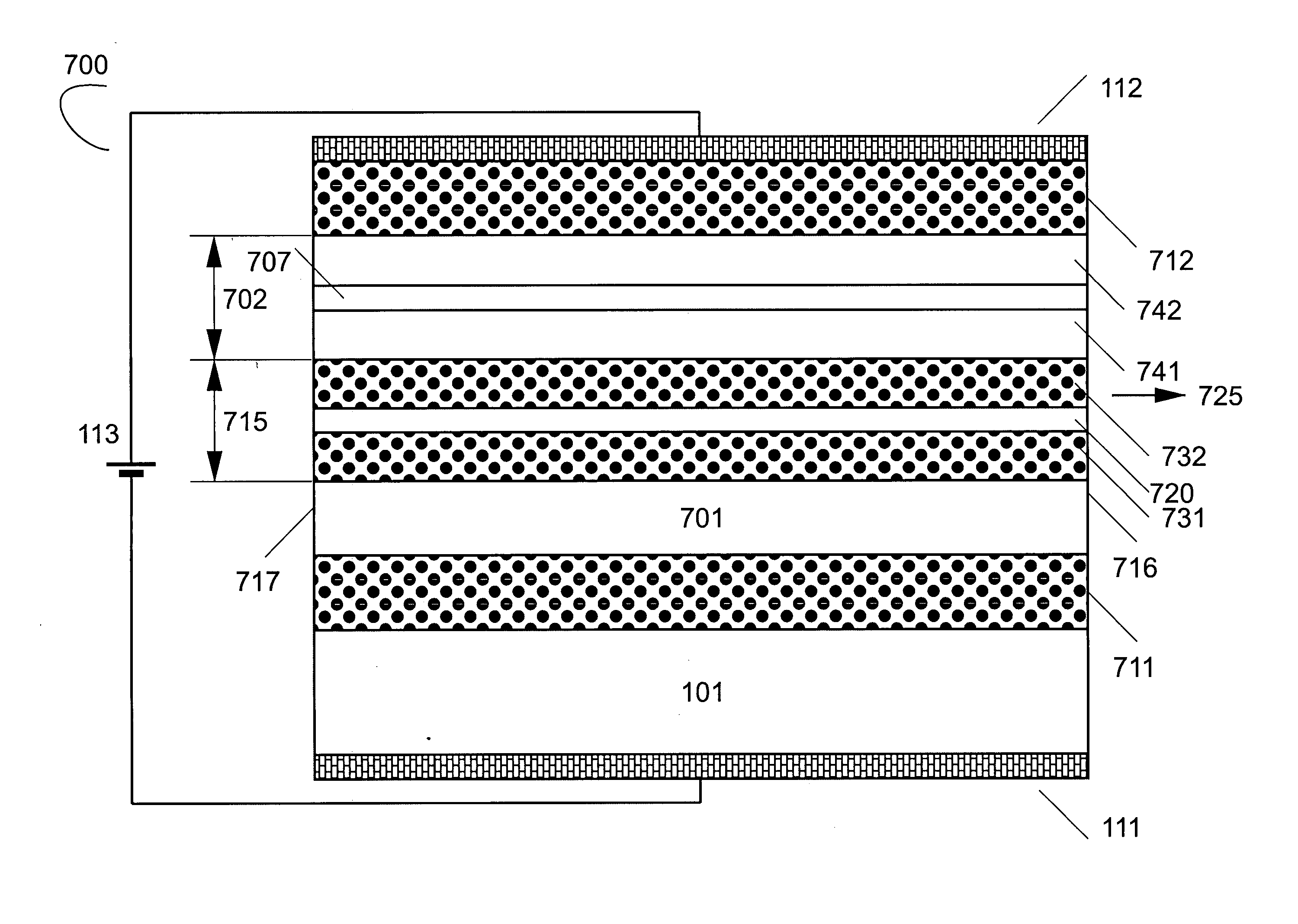
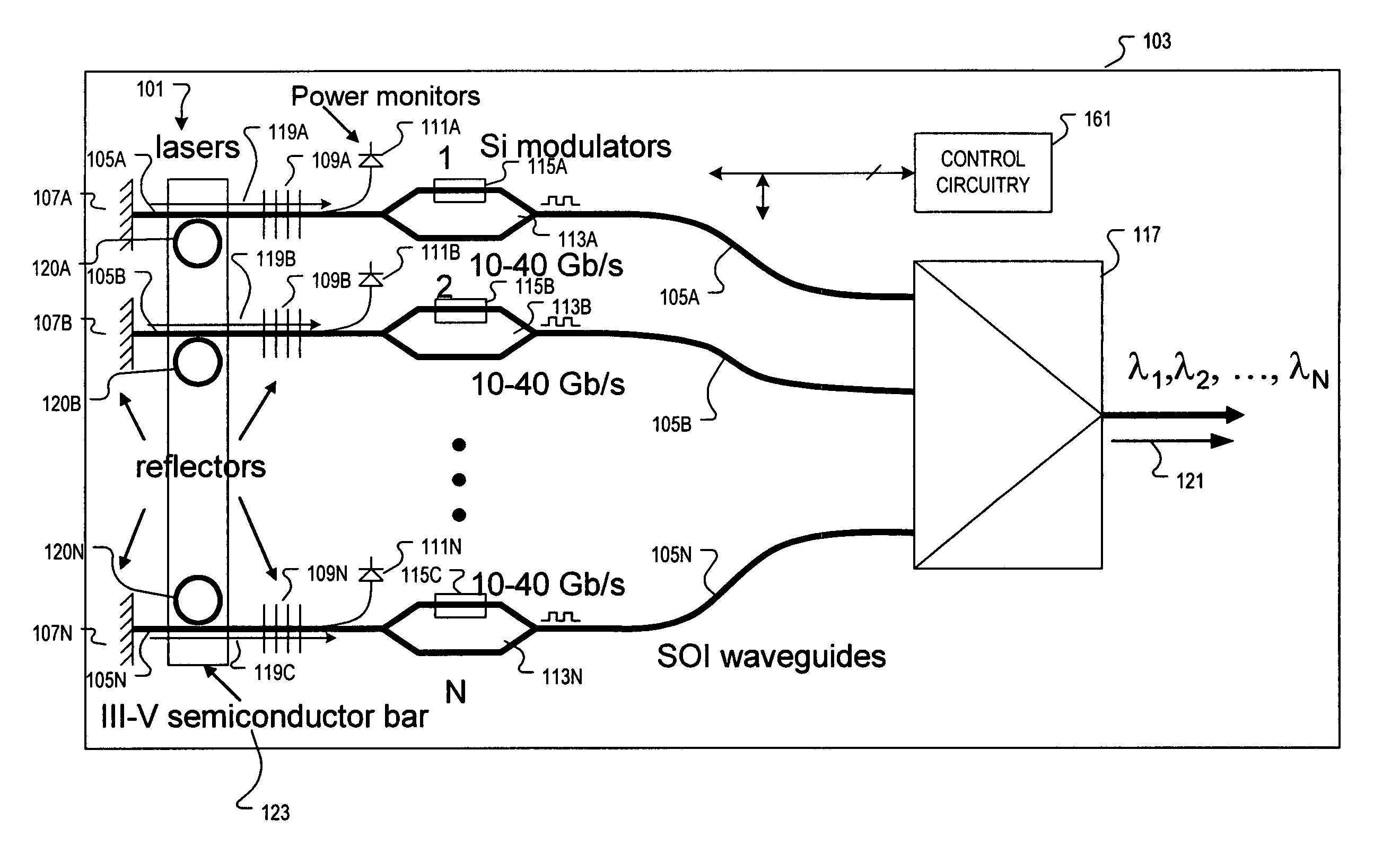
An apparatus and method providing a plurality of modulated optical beams from a single layer of semiconductor material. For one example, an apparatus includes a plurality of optical waveguides disposed in a single layer of semiconductor material. Each one of the plurality of optical waveguides includes an optical cavity defined along the optical waveguide. A single bar of gain medium material adjoining the single layer of semiconductor material across the plurality of optical waveguides is included. The gain medium-semiconductor material interface is defined along each of the plurality of optical waveguides. A plurality of optical modulators is disposed in the single layer of semiconductor material. Each one of the plurality of optical modulators is optically coupled to a respective one of the plurality of optical waveguides to modulate a respective optical beam directed from the optical cavity.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Ii-vi mqw vscel on a heat sink optically pumped by a GAN ld
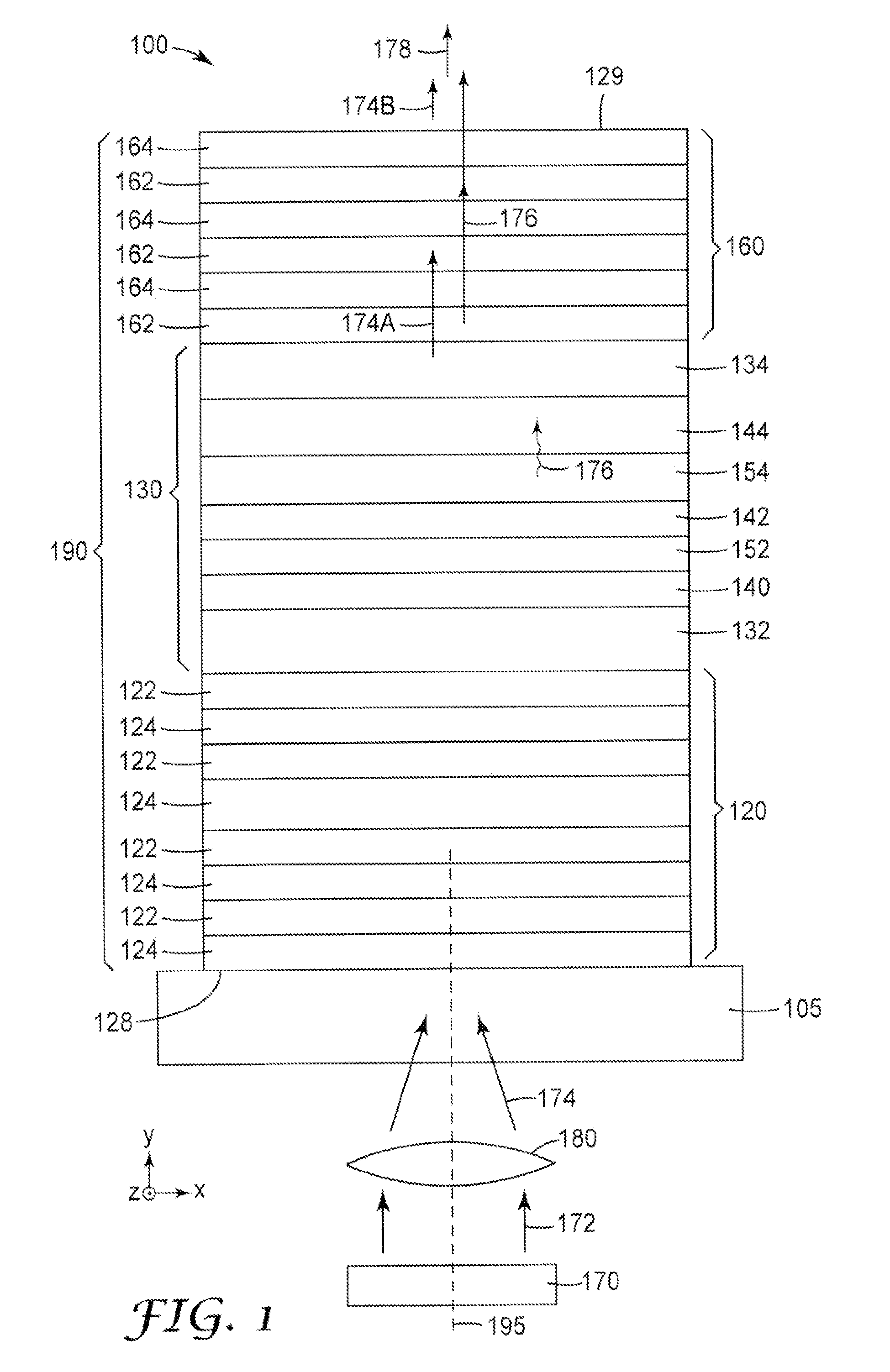
InactiveUS20110150020A1Improved light emissionSuppress luminescenceLaser optical resonator constructionNanoopticsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserOptical cavity
Light sources are disclosed. A disclosed light source includes a III-V based pump light source (170) that includes nitrogen and emits light at a first wavelength. The light source further includes a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) that converts at least a portion of the first wavelength light (174) emitted by the pump light source (170) to at least a partially coherent light at a second wavelength (176). The VCSEL includes first and second mirrors (120, 160) that form an optical cavity for light at the second wavelength. The first mirror (120) is substantially reflective at the second wavelength and includes a first multilayer stack. The second mirror (160) is substantially transmissive at the first wavelength and partially reflective and partially transmissive and the second wavelength. The second mirror includes a second multilayer stack. The VCSEL further includes a semiconductor multilayer stack (130) that is disposed between the first and second mirrors and converts at least a portion of the first wavelength light to the second wavelength light. The semiconductor multilayer stack (130) includes a quantum well that includes a Cd(Mg)ZnSe alloy.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
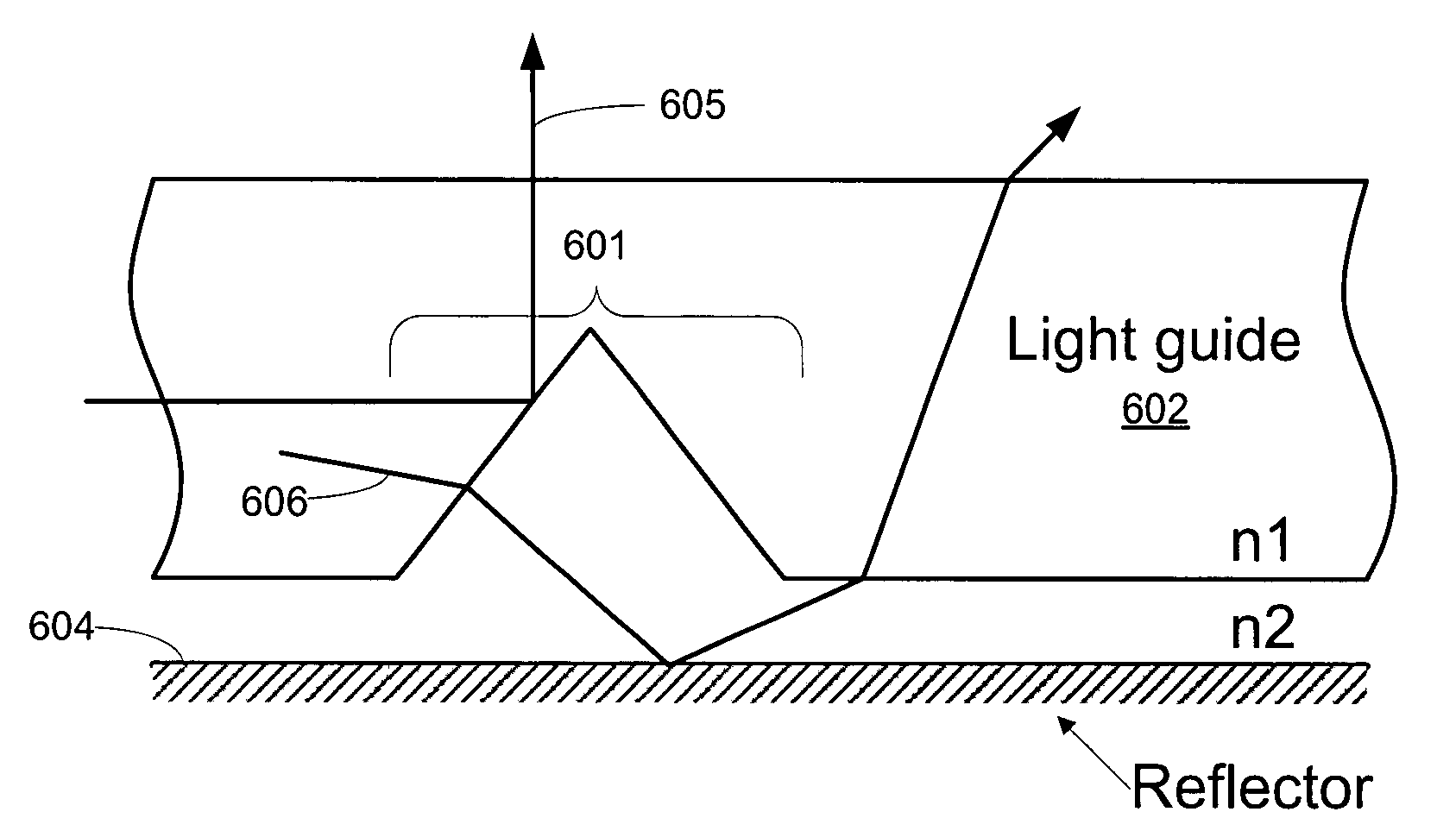
Methods and apparatus for spatial light modulation
ActiveUS20060187528A1Improve luminous efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical cavityOptoelectronics
Improved apparatus and methods for spatial light modulation are disclosed which utilize optical cavities having both front and rear reflective surfaces. Light-transmissive regions are formed in the front reflective surface for spatially modulating light.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
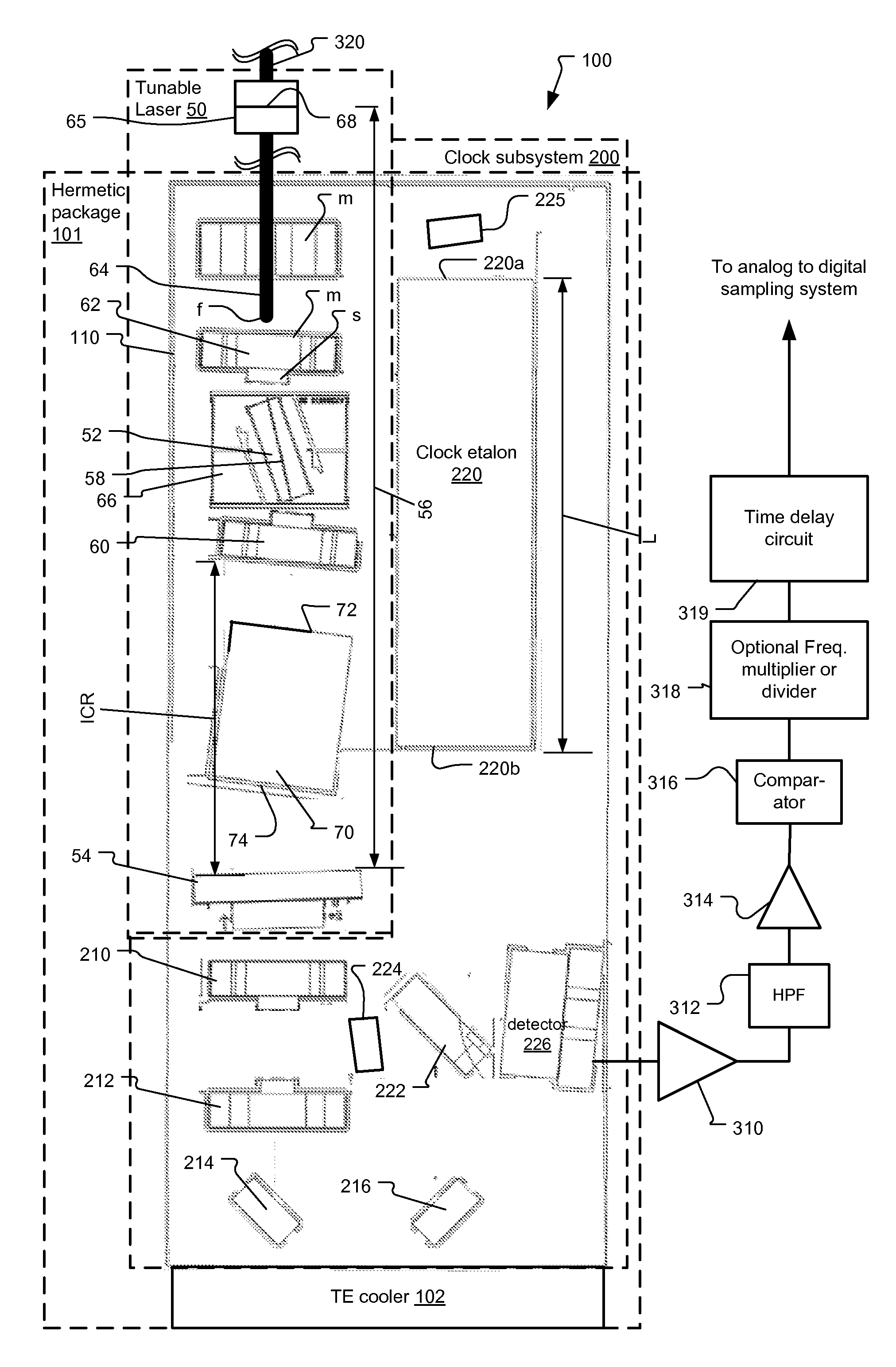
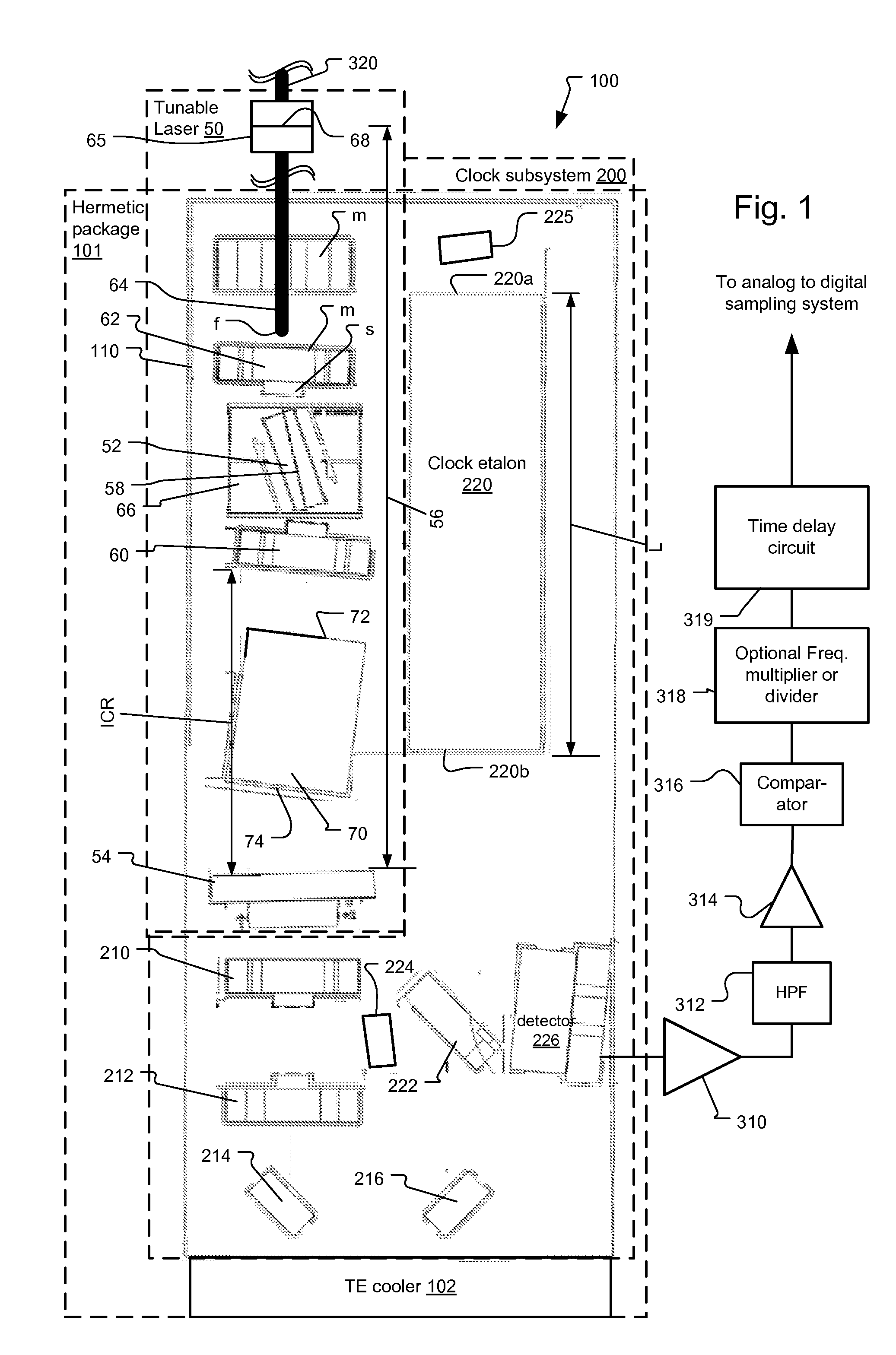
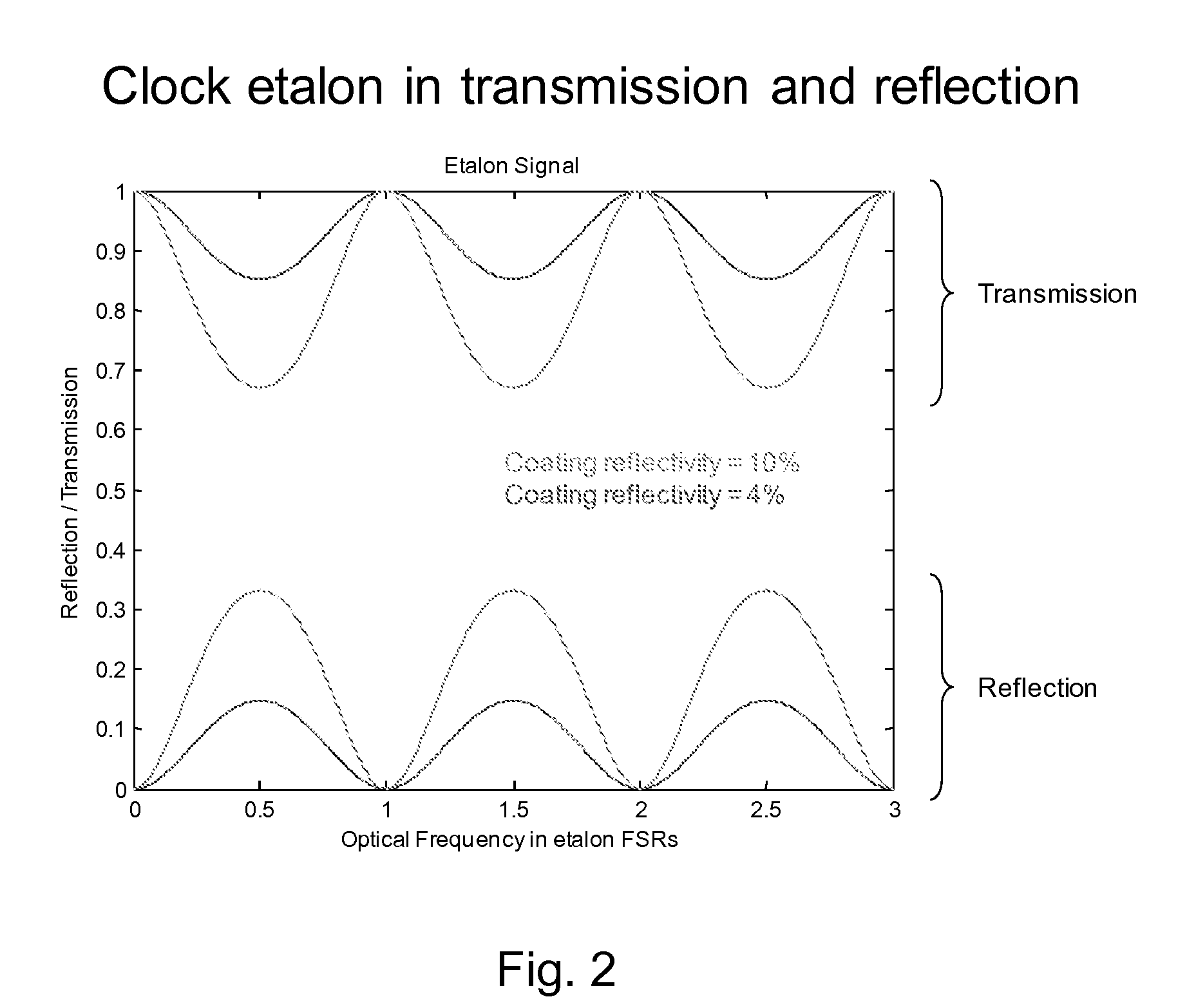
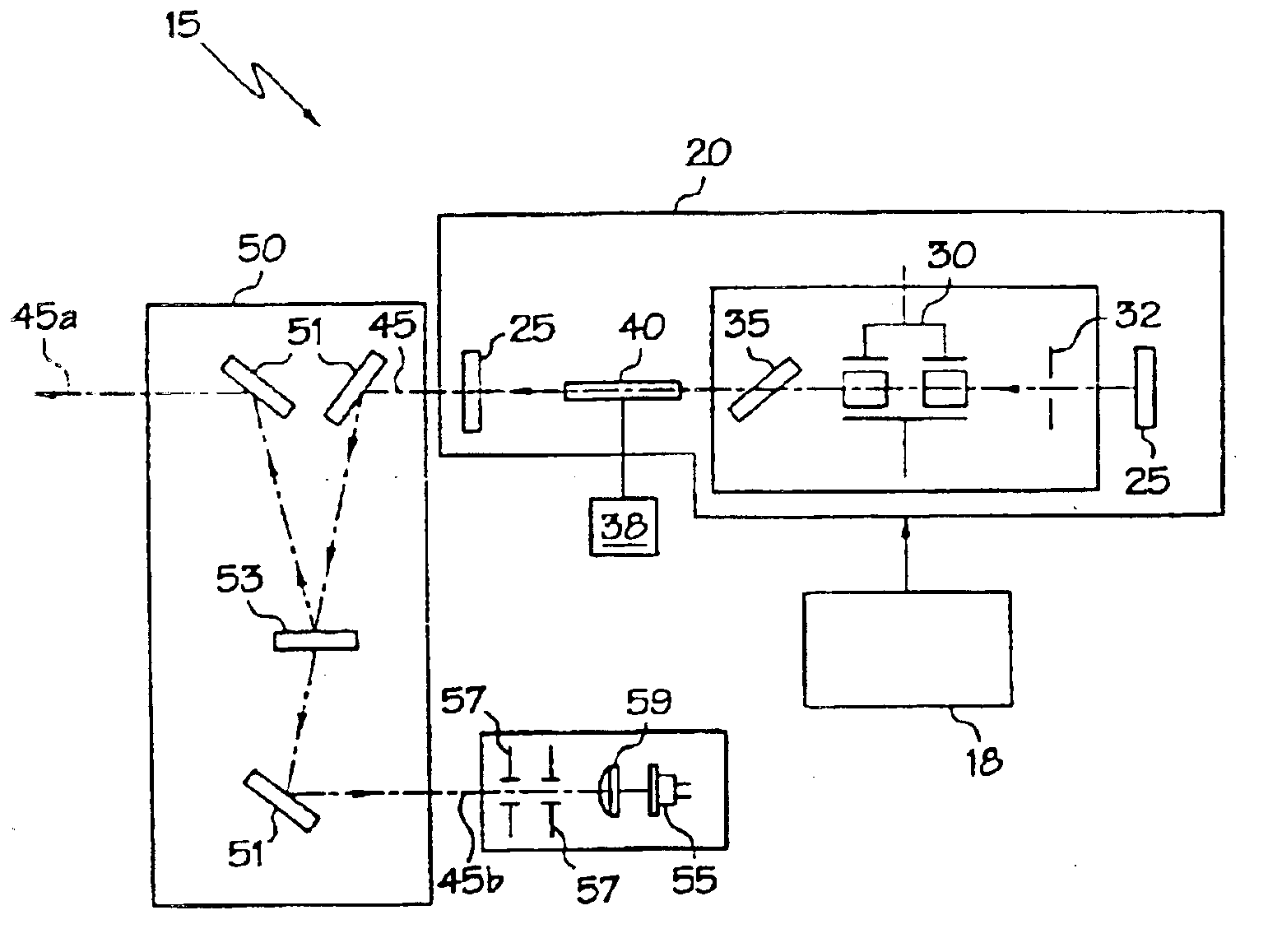
Optical Coherence Tomography Laser with Integrated Clock
A frequency swept laser source for TEFD-OCT imaging includes an integrated clock subsystem on the optical bench with the laser source. The clock subsystem generates frequency clock signals as the optical signal is tuned over the scan band. Preferably the laser source further includes a cavity extender in its optical cavity between a tunable filter and gain medium to increase an optical distance between the tunable filter and the gain medium in order to control the location of laser intensity pattern noise. The laser also include a fiber stub that allows for control over the cavity length while also controlling birefringence in the cavity.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Laser cutting of stents and other medical devices
A desired pattern may be cut into a stent preform by impinging a laser beam onto the stent preform. The laser beam is formed using a laser system comprising a resonator cavity for resonating laser radiation, a gain medium contained in the resonator cavity, a pump for periodically pumping the gain medium and an electro-optical modulator in communication with the resonator cavity. The laser system produces a radiation pulse for each pump period. Each radiation pulse is conditioned by suppressing at least a portion of the pulse. The pulse may also be modulated with an electro-optical modulator to produce a pulse train of ordered pulses of radiation. Each pulse train is output from the optical cavity as an output laser beam which is directed at the stent preform to cut a desired pattern in the stent preform.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Surface emitting semiconductor laser
InactiveUS6052398AImprove reflectivityLower resistanceLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersOptical cavitySemiconductor package
Two semiconductor layers of the laser form a tunnel junction enabling an electrical current for pumping the laser to pass from an N doped semiconductor Bragg mirror to a P doped injection layer belonging to the light-amplifying structure. The Bragg mirror co-operates with another mirror of the same type having the same doping to include said structure in an optical cavity of the laser. In a variant, the tunnel junction may be buried and located so as to constitute confinement means for said pumping current. The laser can be used in an optical fiber communications network.
Owner:II VI LASER ENTERPRISE
OLED display and touch screen
InactiveUS7202856B2Easy to manufactureLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionCarbon compoundsOptical cavityDisplay device
An OLED display and touch screen system includes a substrate; an OLED display including an array of individually addressable OLEDs formed on the substrate; and a touch screen including an OLED light emitter formed on the substrate the OLED light emitter defining an optical cavity for reducing the angle of emission of light from the OLED light emitter and a light sensor formed on the substrate across the display from the OLED light emitter, and optics located around the display above the OLED light emitter and the light sensor for directing light emitted from the OLED light emitter across the display to the light sensor.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
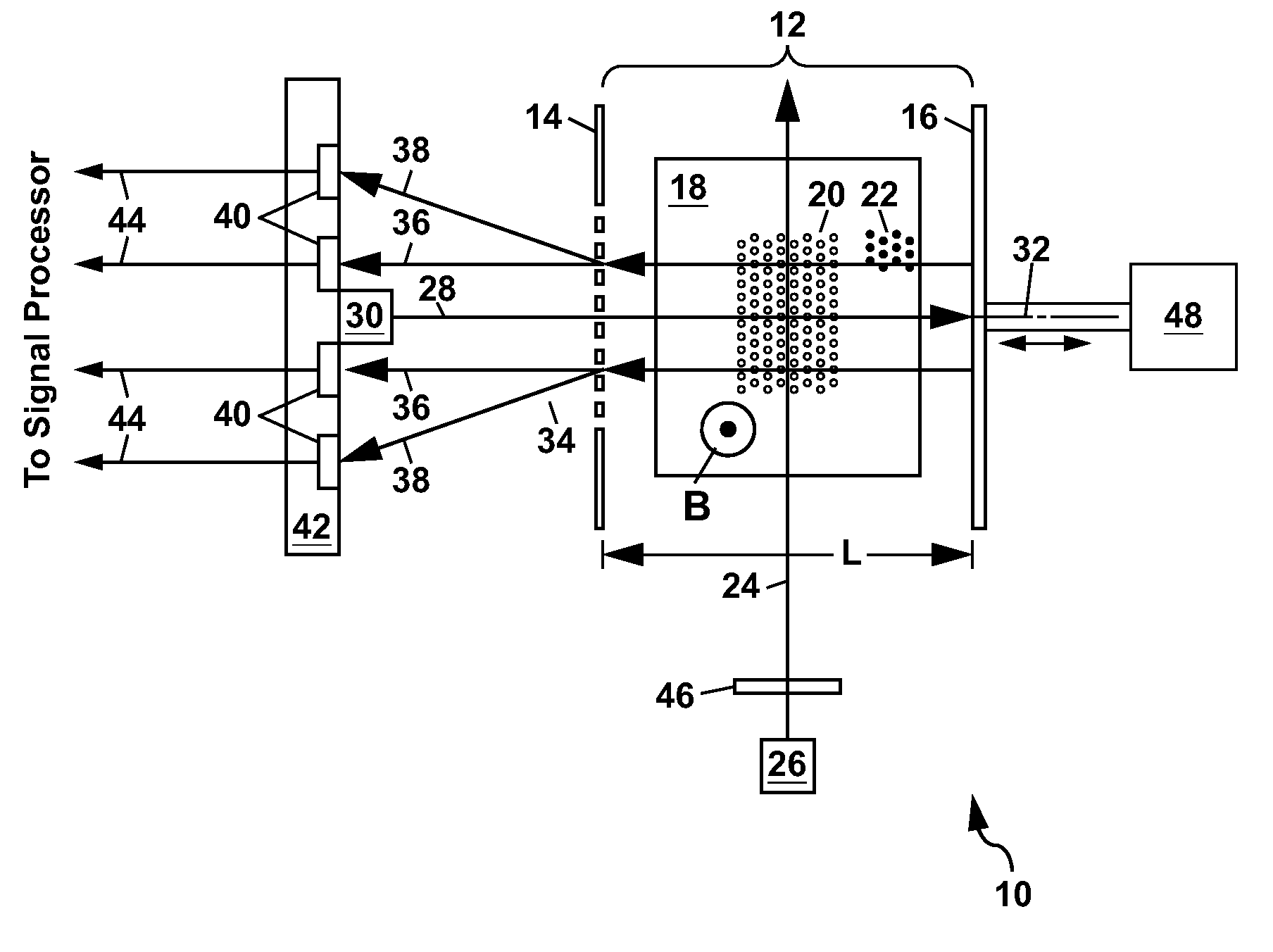
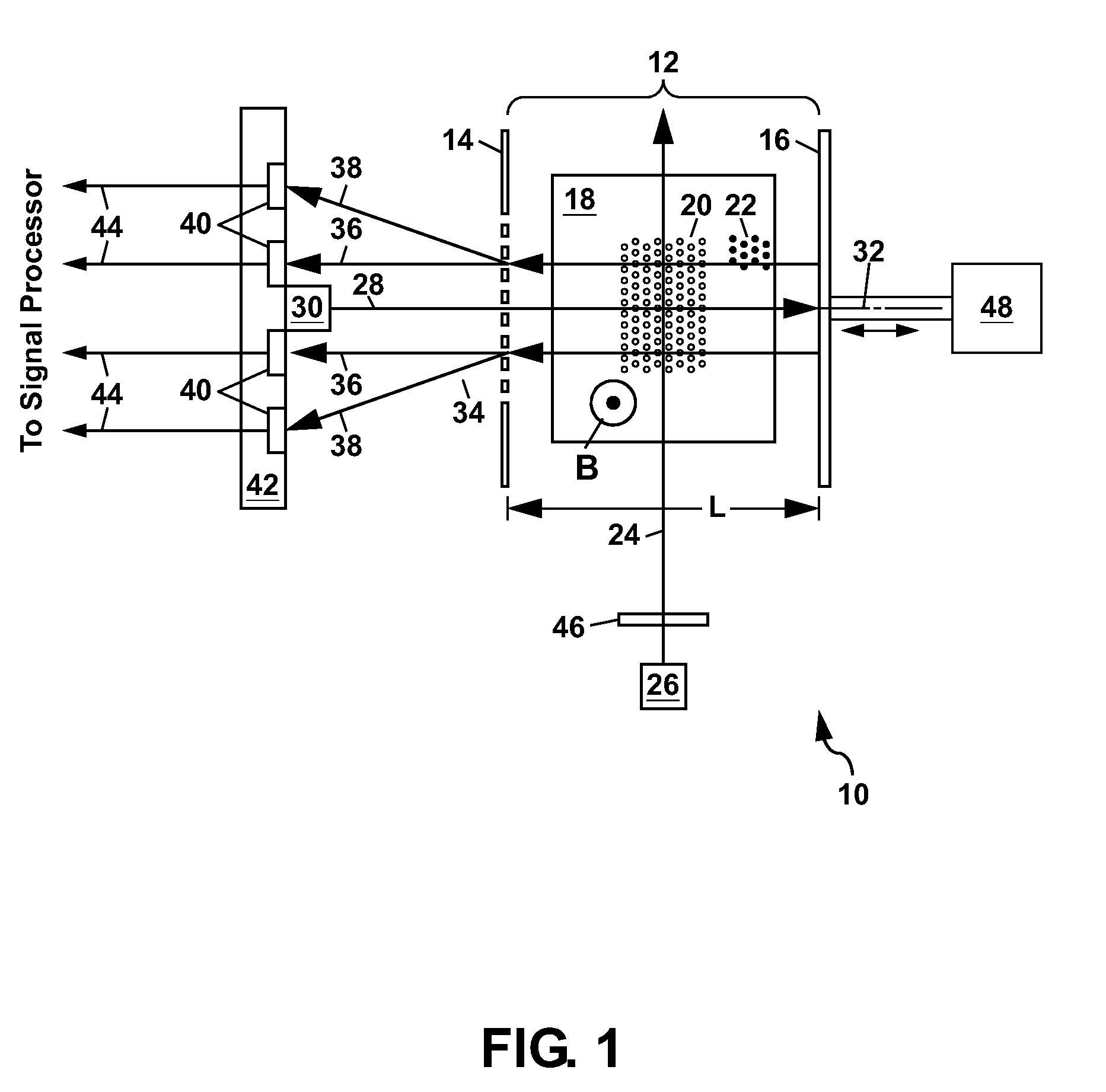
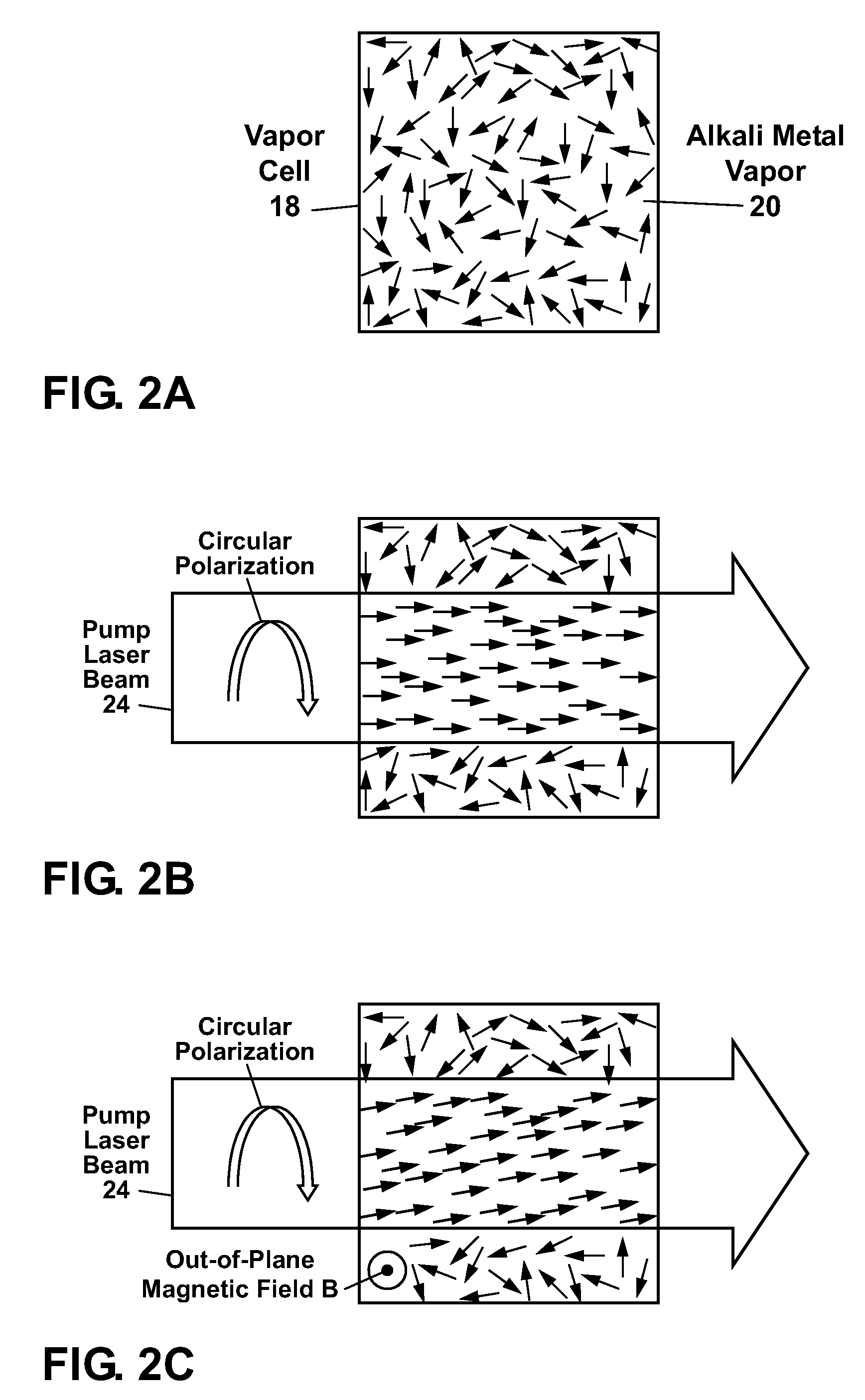
Tuned optical cavity magnetometer
An atomic magnetometer is disclosed which utilizes an optical cavity formed from a grating and a mirror, with a vapor cell containing an alkali metal vapor located inside the optical cavity. Lasers are used to magnetically polarize the alkali metal vapor and to probe the vapor and generate a diffracted laser beam which can be used to sense a magnetic field. Electrostatic actuators can be used in the magnetometer for positioning of the mirror, or for modulation thereof. Another optical cavity can also be formed from the mirror and a second grating for sensing, adjusting, or stabilizing the position of the mirror.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
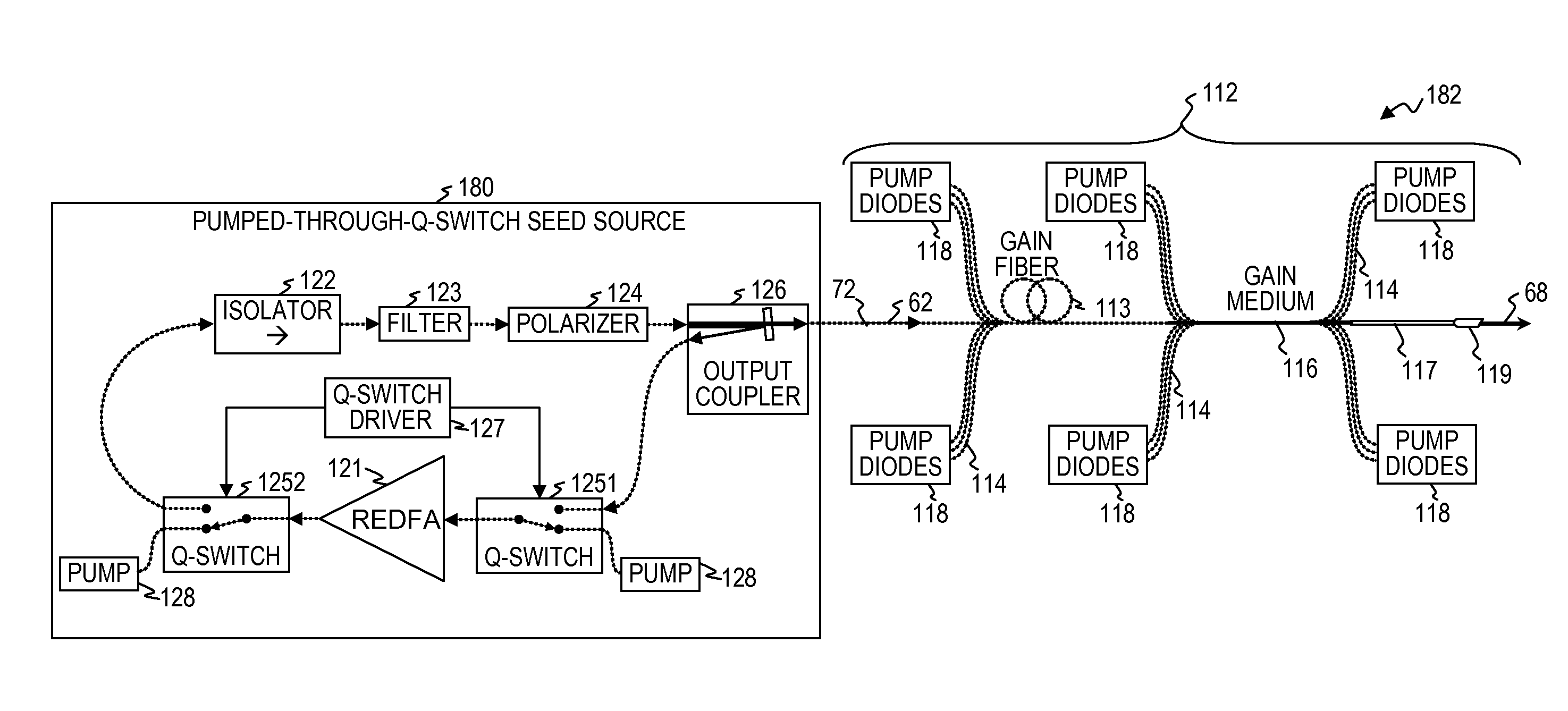
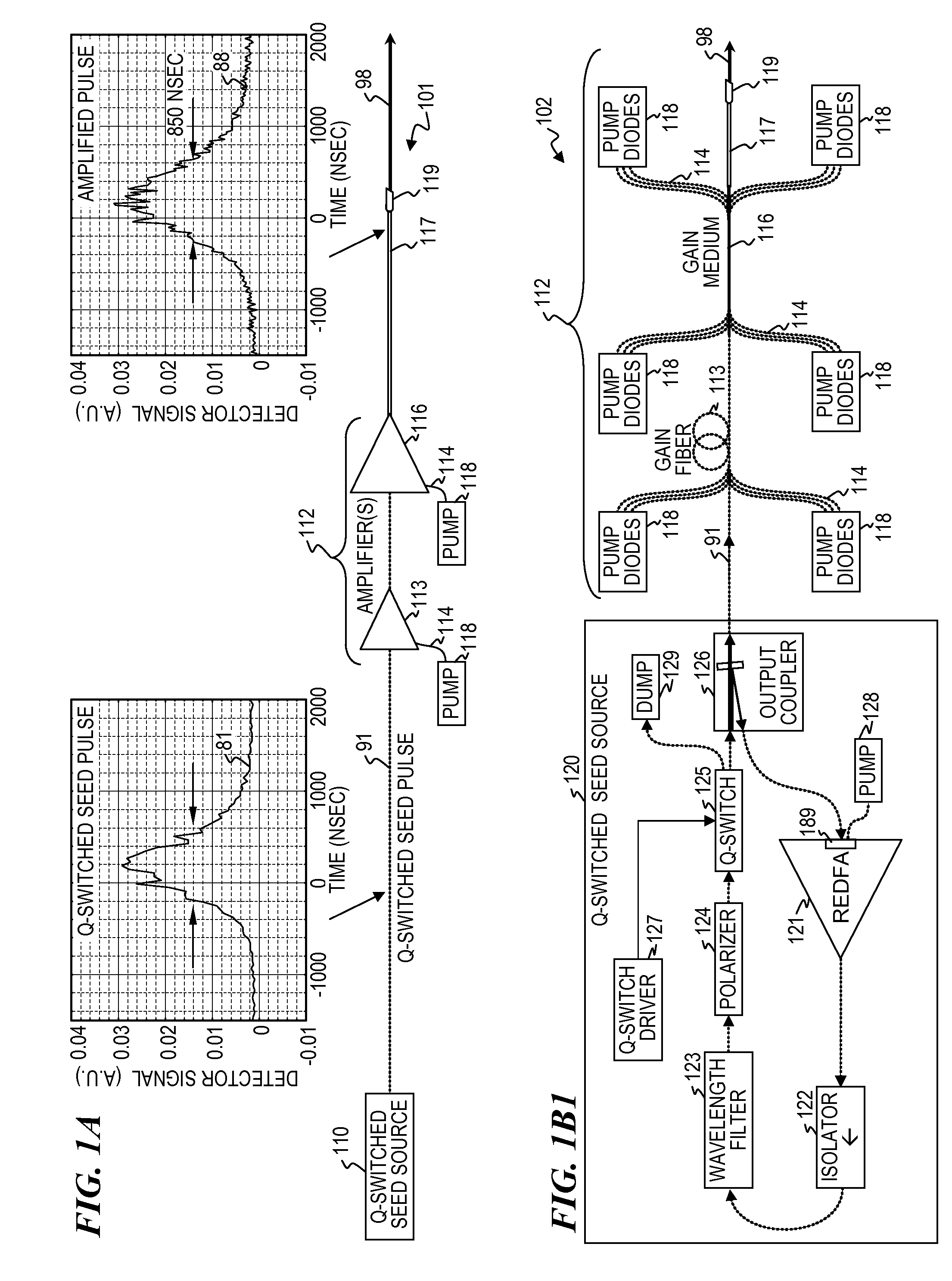
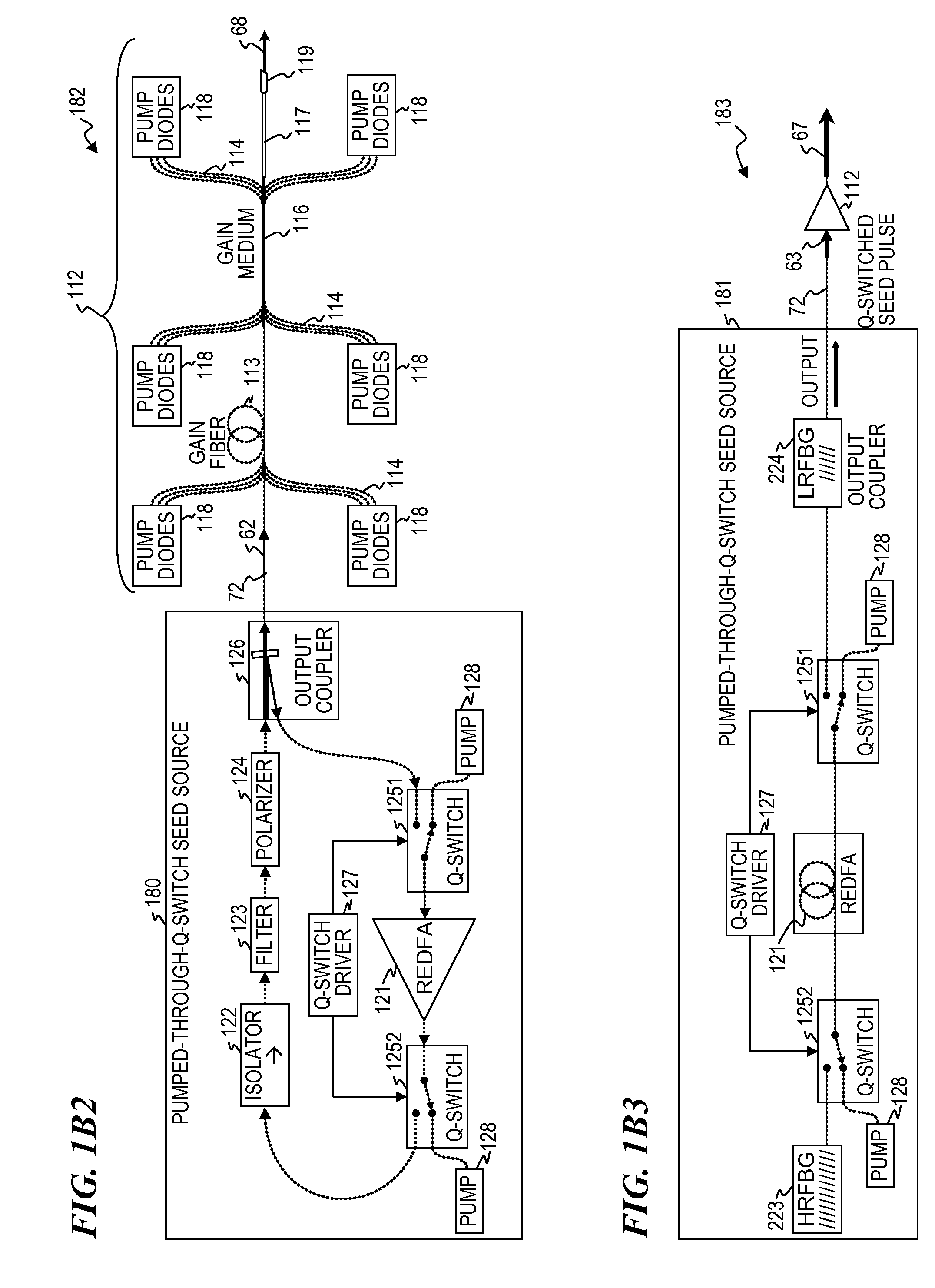
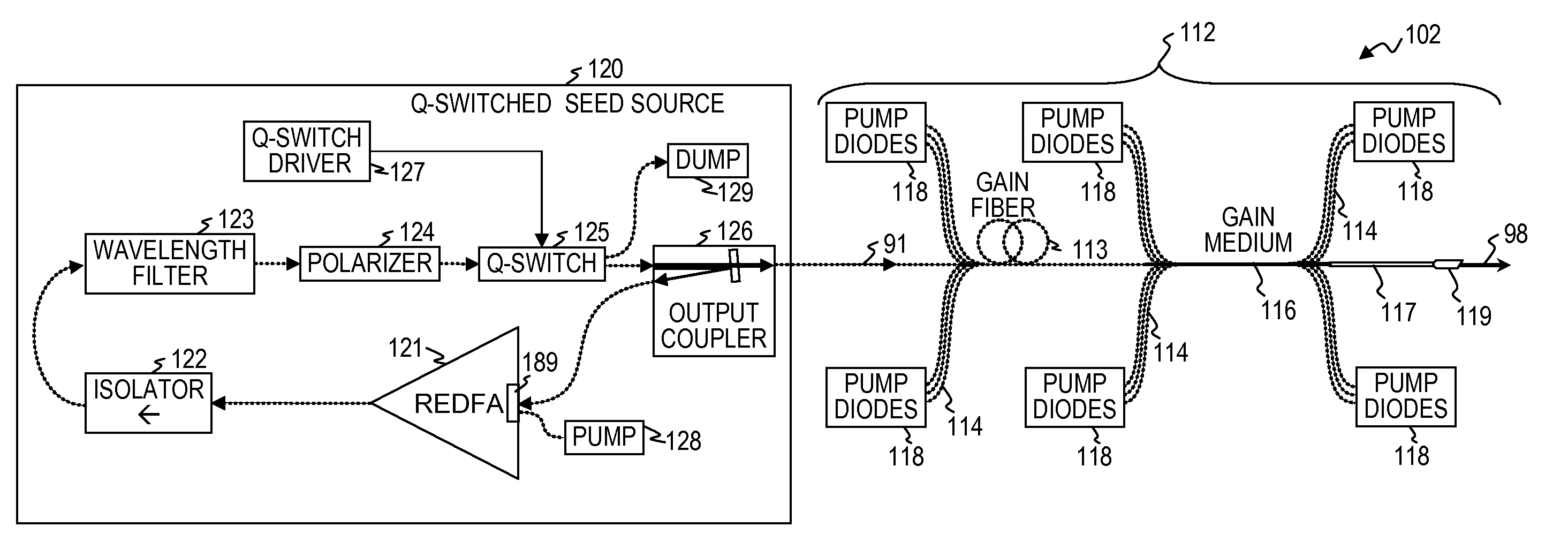
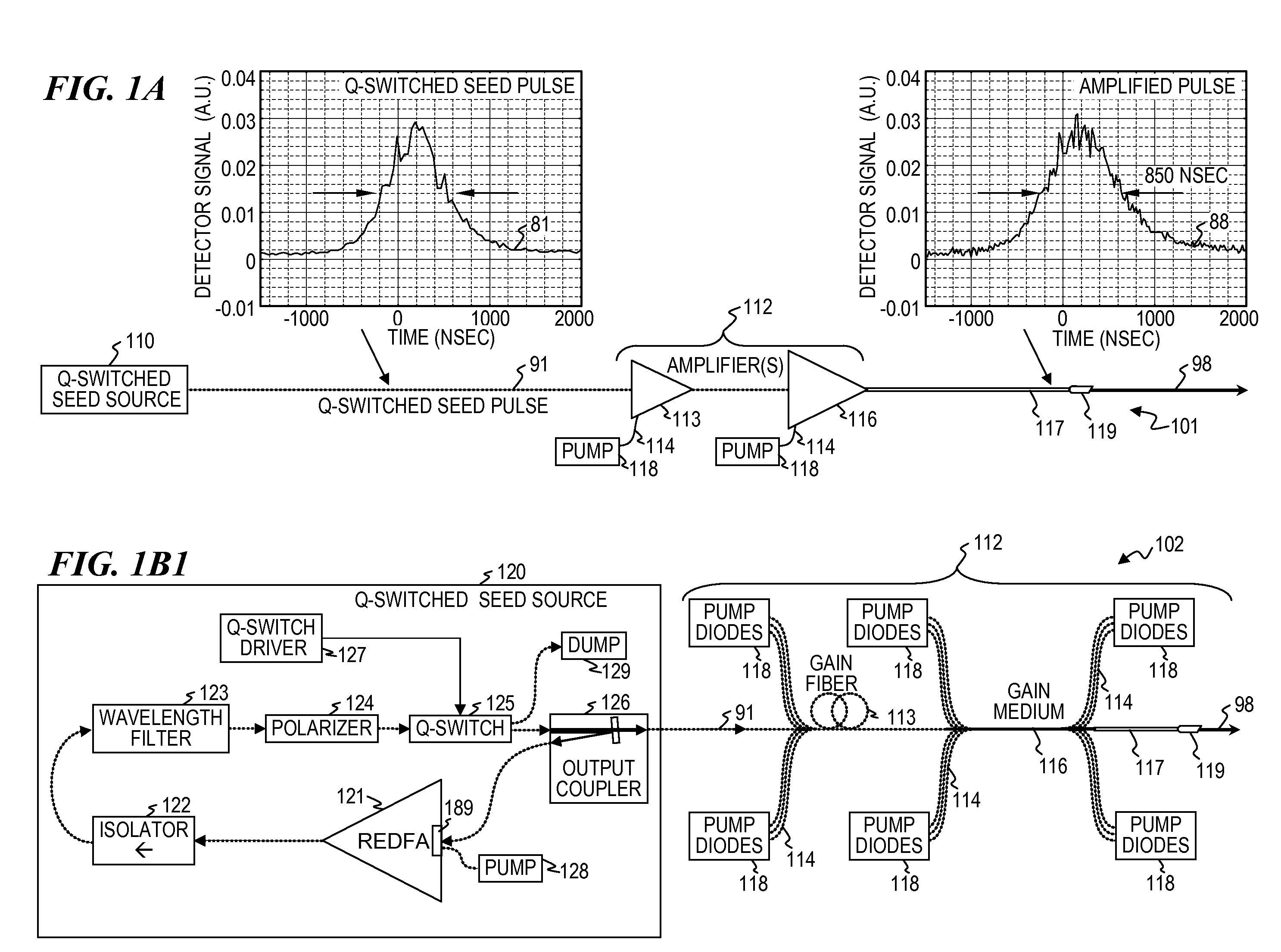
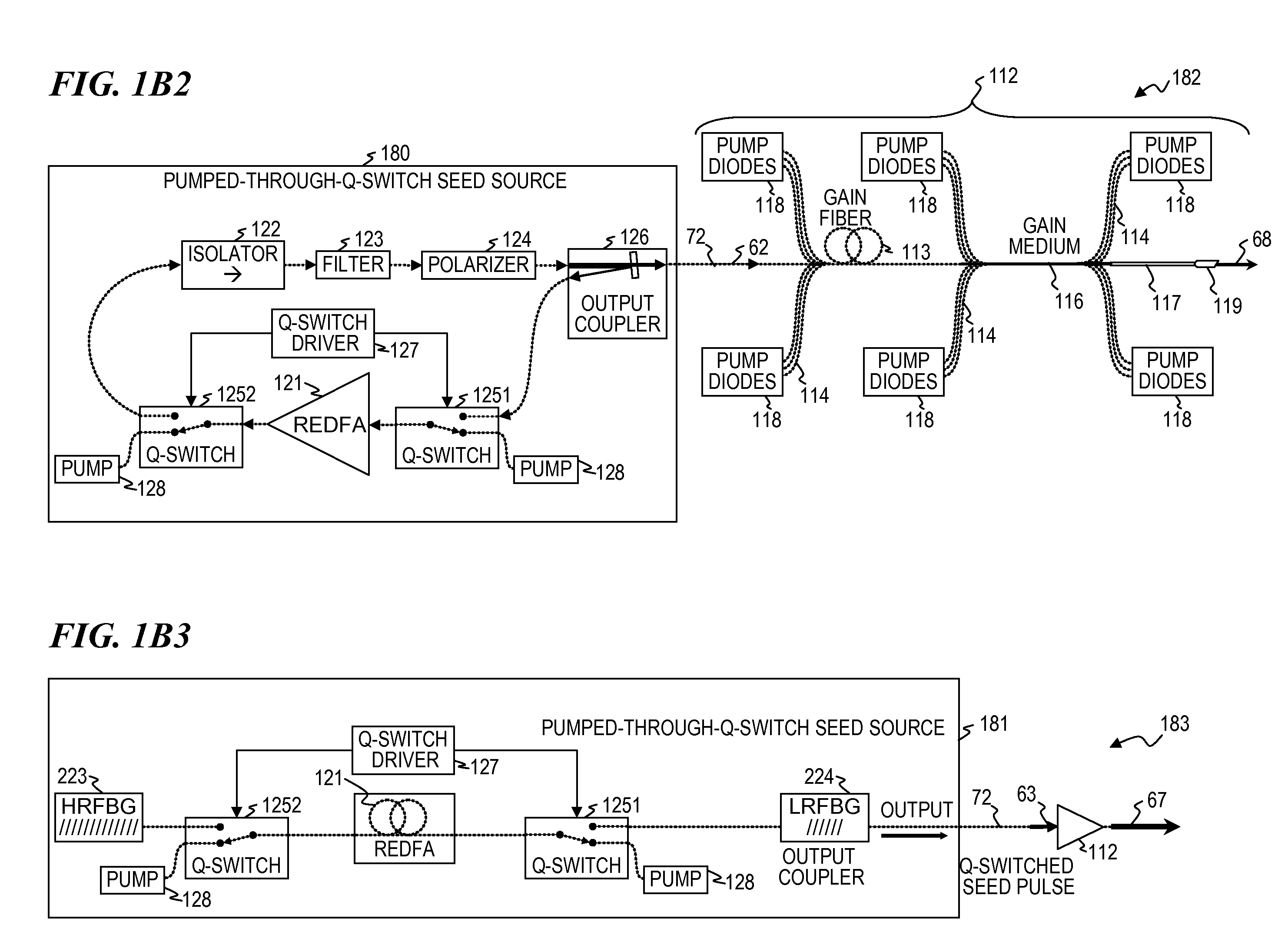
Q-switched oscillator seed-source for MOPA laser illuminator method and apparatus
ActiveUS8934509B2Wide dynamicAccelerate buildingLaser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionFrequency spectrumLine width
An apparatus, method and system that uses a Q-switched laser or a Q-seed source for a seed pulse signal having a controlled high-dynamic-range amplitude that avoids and / or compensates for pulse steepening in high-gain optical-fiber and / or optical-rod amplification of optical pulses. Optionally, the optical output is used for LIDAR or illumination purposes (e.g., for image acquisition). In some embodiments, well-controlled pulse shapes are obtained having a wide dynamic range, long duration, and not-too-narrow linewidth. In some embodiments, upon the opening of a Q-switch in an optical cavity having a gain medium, the amplification builds relatively slowly, wherein each round trip through the gain medium increases the amplitude of the optical pulse. Other embodiments use quasi-Q-switch devices or a plurality of amplitude modulators to obtain Q-seed pulses. These configurations provide optical pulses having wide dynamic ranges that ameliorate problems of pulse steepening, non-linear spectral broadening and the like in very-high-power MOPA devices.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
System and method for gas analysis using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy
ActiveUS20060123884A1Increase productionReduce equipment downtimeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis using microwave meansGas analysisGas detector
A method for analyzing gas concentration using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy, and a doubly resonant photaoacoustic gas detector comprising: i) a continuous wave light beam whose wavelength coincides with an absorption wavelength of a gaseous analyte; ii) a closed path optical cavity having at least two reflective surfaces; iii) an acoustic resonator chamber contained within said optical cavity, and comprising an acoustic sensor for detecting sound waves generated by a gaseous analyte present within said chamber, the light beam passing sequentially into, through and out of said chamber, and being repeatedly reflected back and forth through said chamber, and being modulated at a frequency which is equal to or equal to one-half of an acoustic resonance frequency of said acoustic resonator chamber.
Owner:LI COR
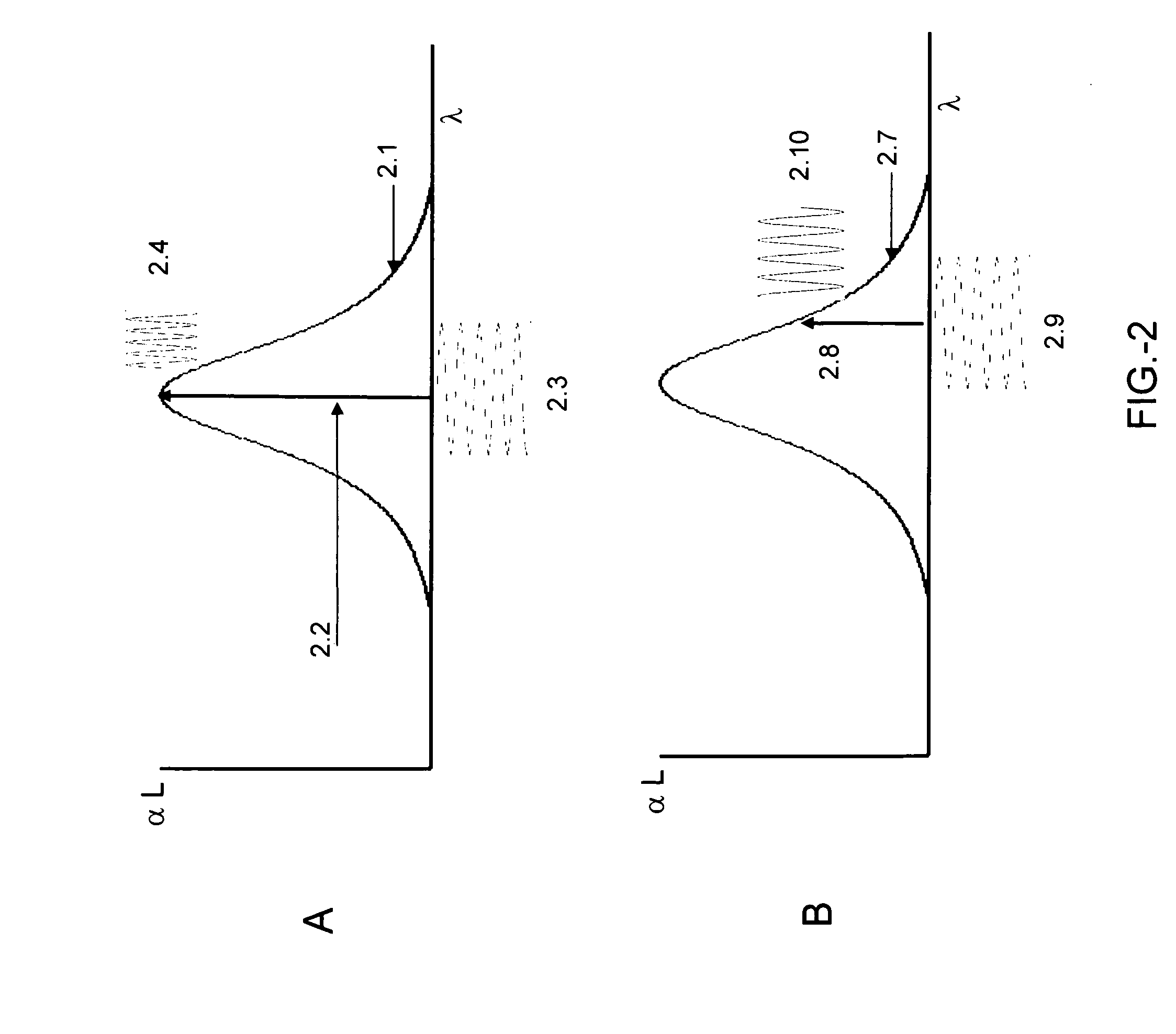
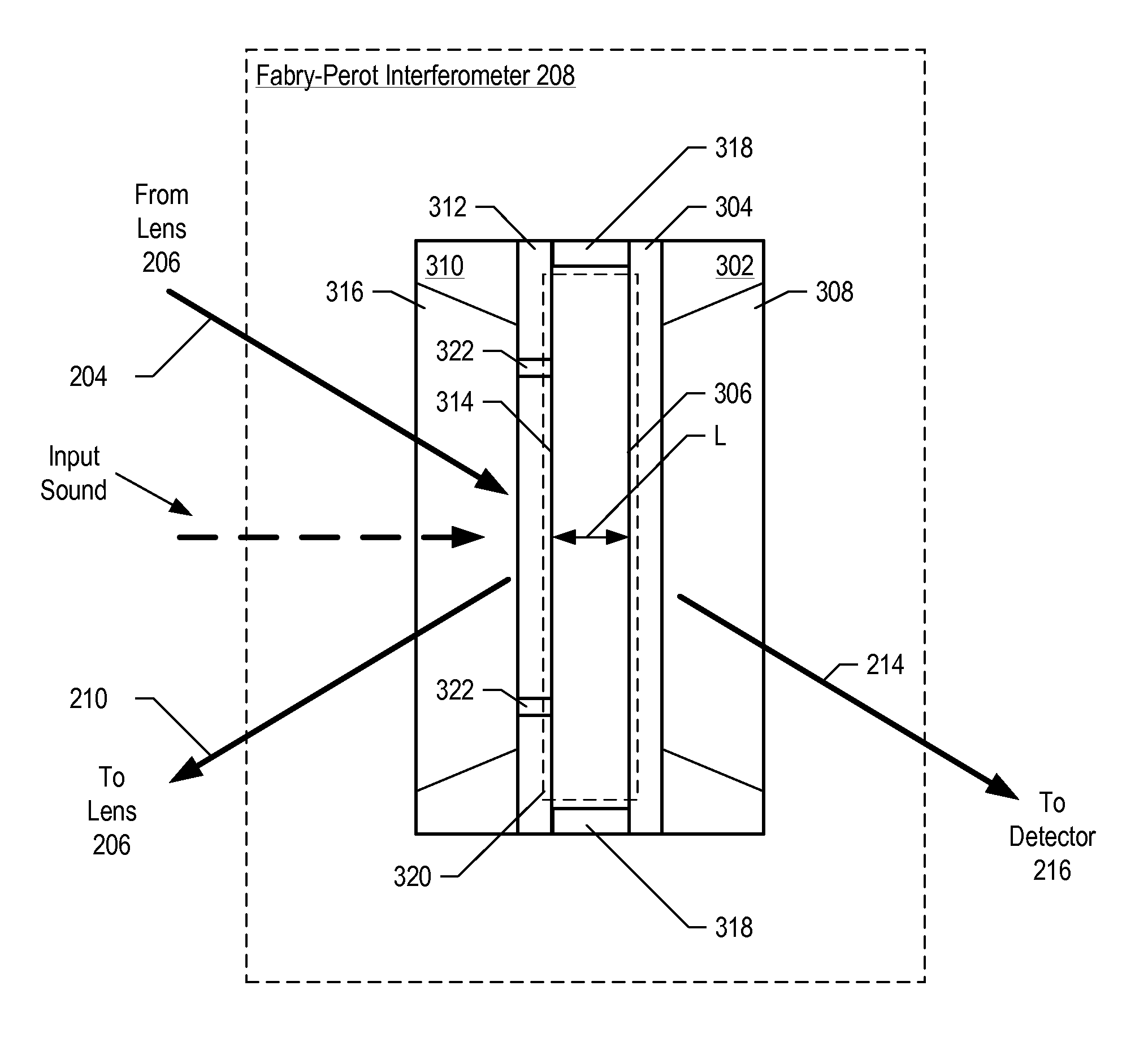
Optical Displacement Sensor Comprising a Wavelength-tunable Optical Source
InactiveUS20070236704A1Optical signal transducersFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsResonant cavityOptical cavity
An optical displacement sensor is disclosed that provides a optical displacement sensor that includes a optically-resonant cavity tuned to an operating wavelength without some of the disadvantages for doing so in the prior art. An embodiment of the present invention tunes an operating wavelength used with a Fabry-Perot interferometer to develop a desired relationship between the wavelength and the Fabry-Perot interferometer's initial cavity length.
Owner:SYMPHONY ACOUSTICS
Three-level air-clad rare-earth doped fiber laser/amplifier
InactiveUS6987783B2Facilitates dopingLower effective refractive indexOptical wave guidanceLaser using scattering effectsThree levelAudio power amplifier
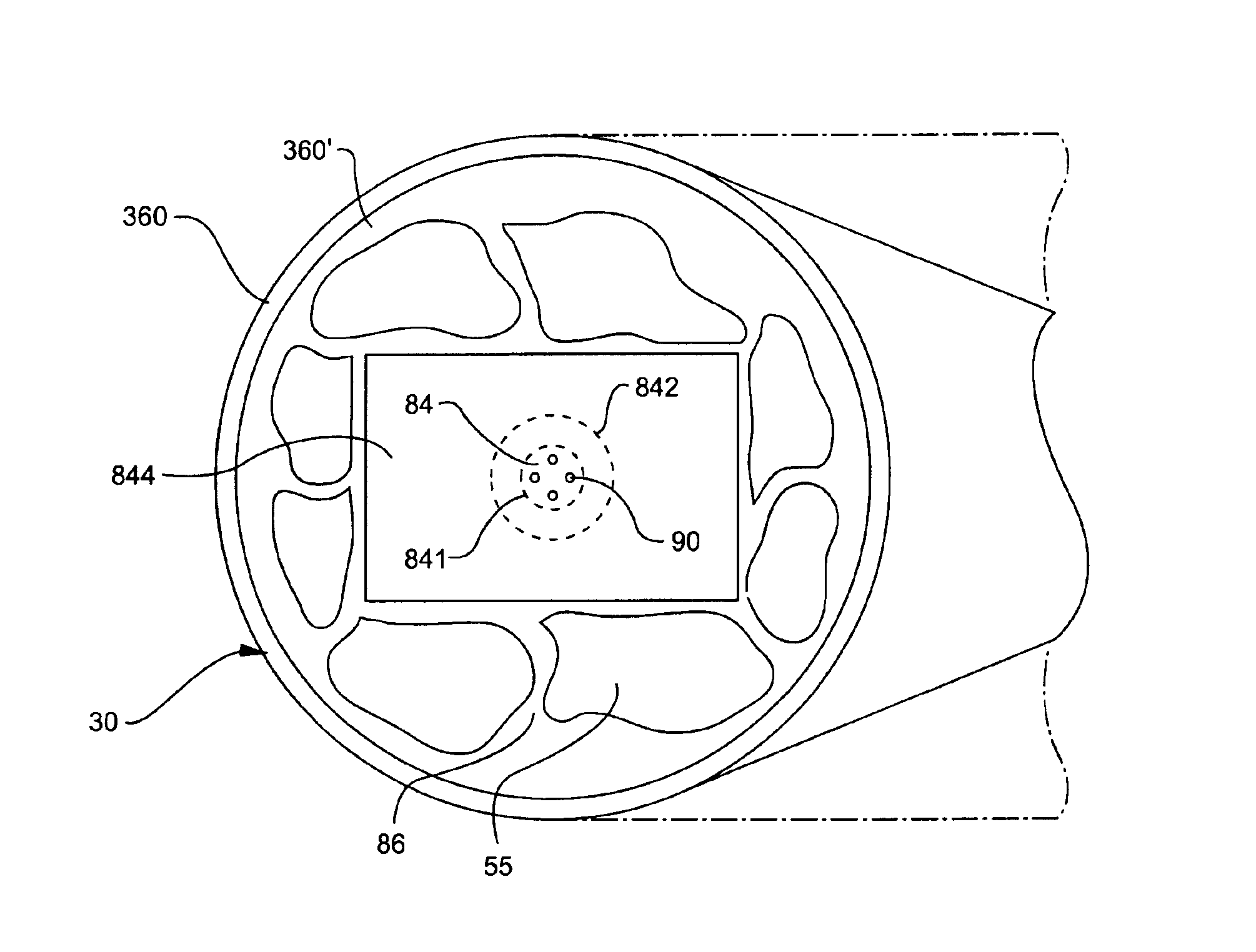
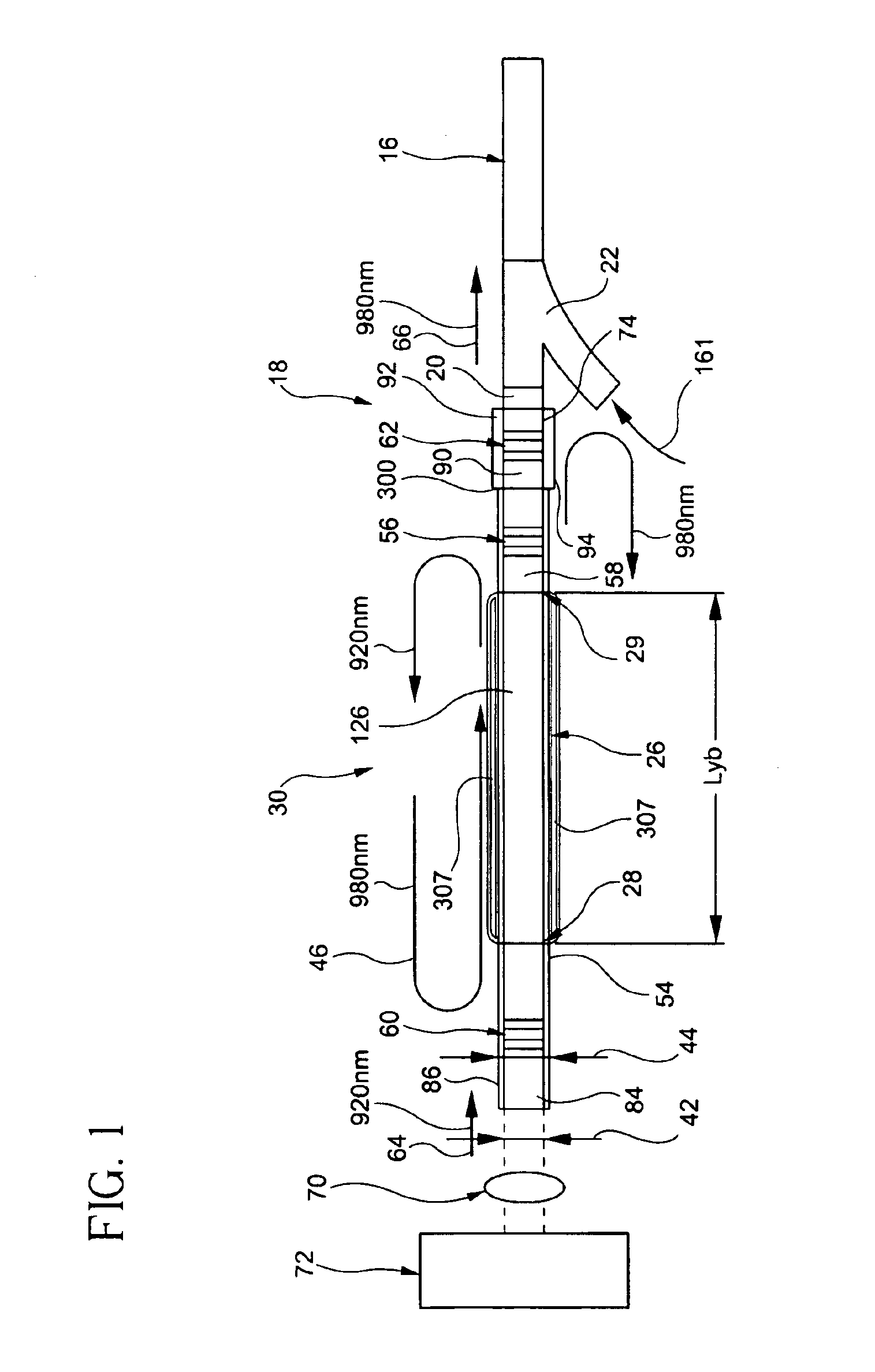
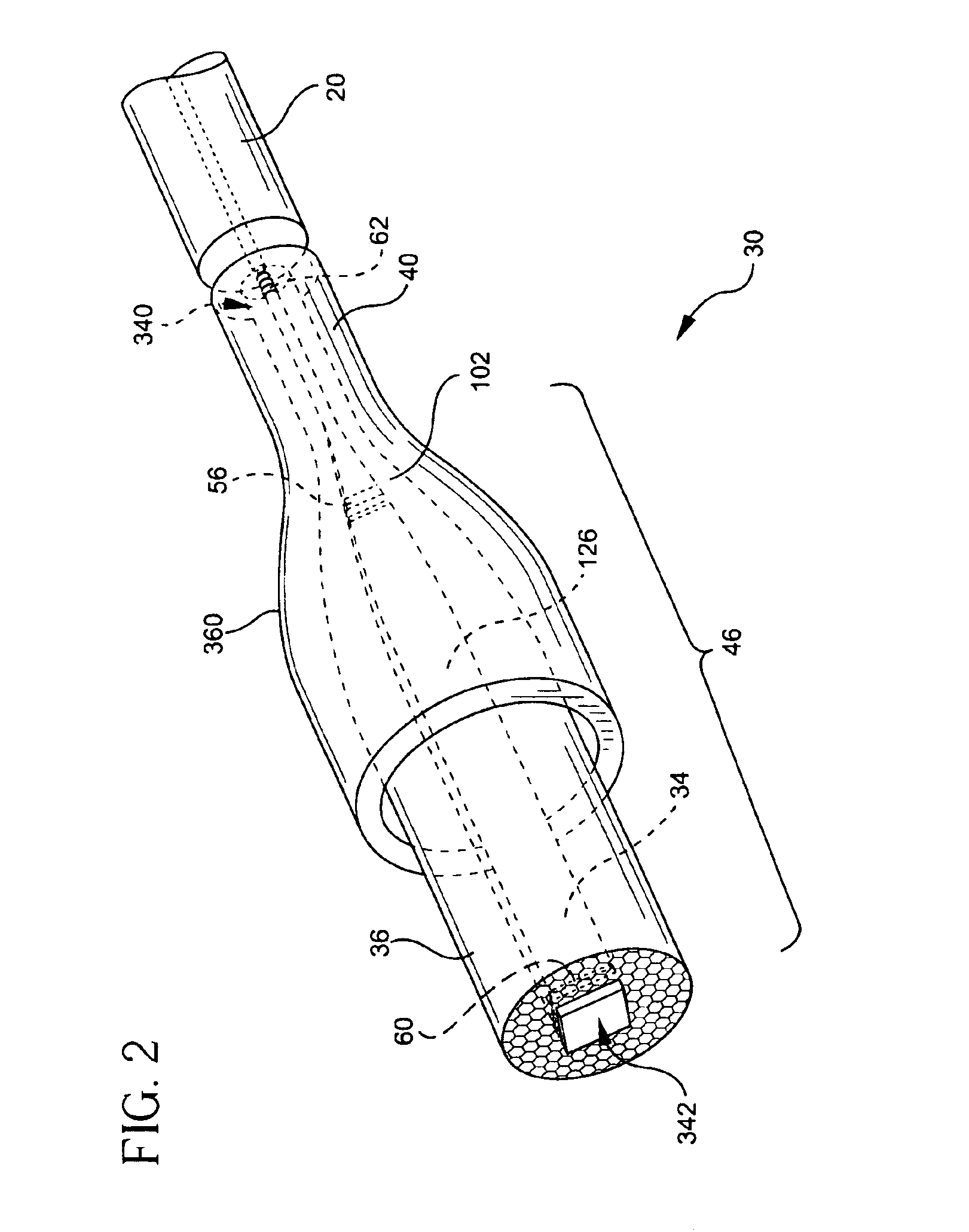
An optically-active air-clad fiber (30) includes a core (34, 84) that facilitates doping with an ion optically excitable and having a three-level optical transition when pumped at a first end (28) of an optical cavity (46) by a multimode pump source (72) at a pump wavelength (64) for lasing at a signal wavelength (66) different than the pump wavelength (64) at a second end (29) of the optical cavity (46), the core (34, 84) having a refractive index, wherein the core (34, 84) is transformed from the first end to proximate the second end (29) thereof such that the optically-active fiber (30) is multimode at the pump wavelength proximate to the first end (28), and is single-mode at the signal wavelength proximate to the second end (29). An air-clad (36, 86) surrounds at least one portion of the core (34, 84) and has a lower effective refractive index than the refractive index of the core (34, 84).
Owner:CORNING INC
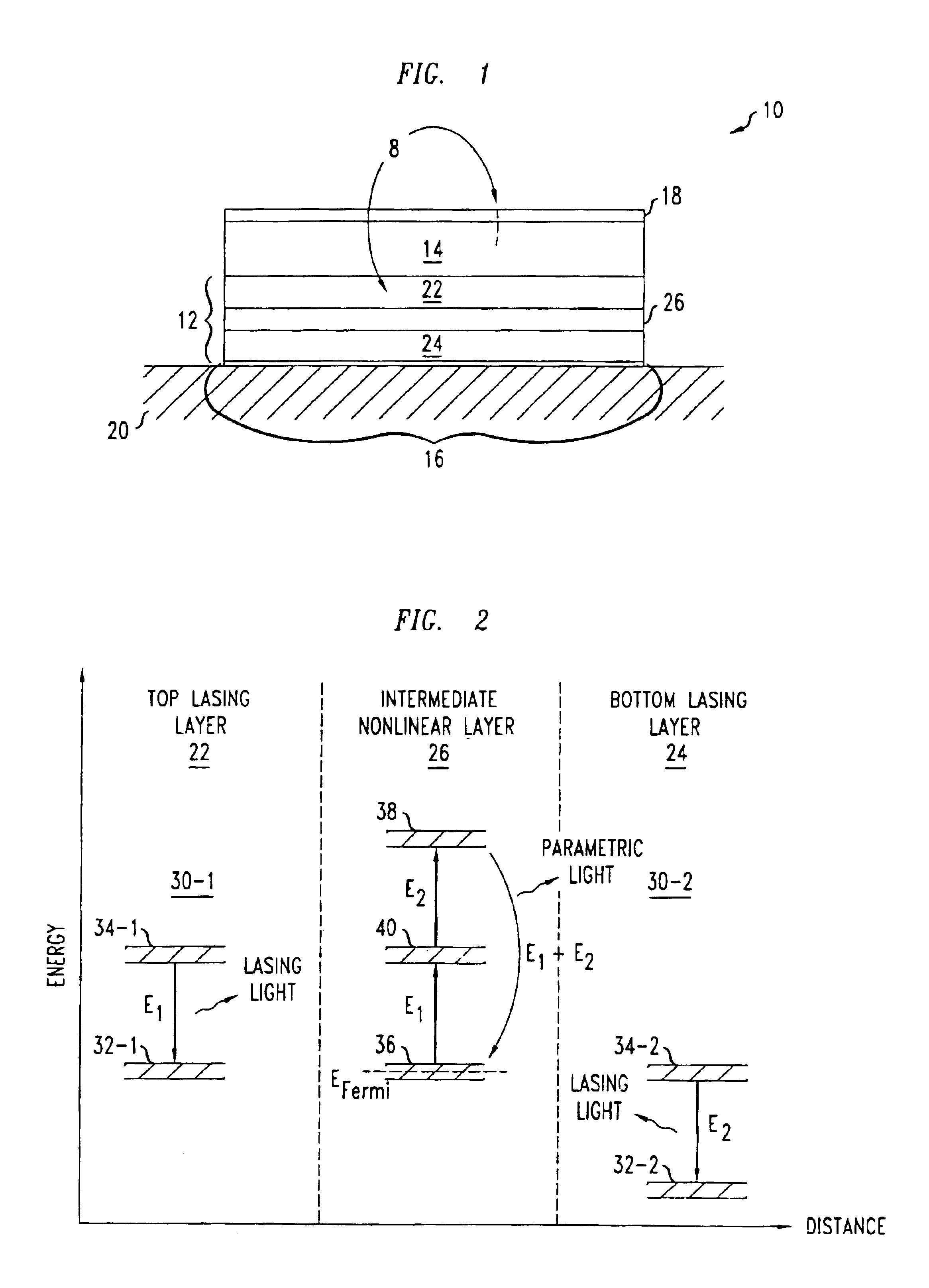
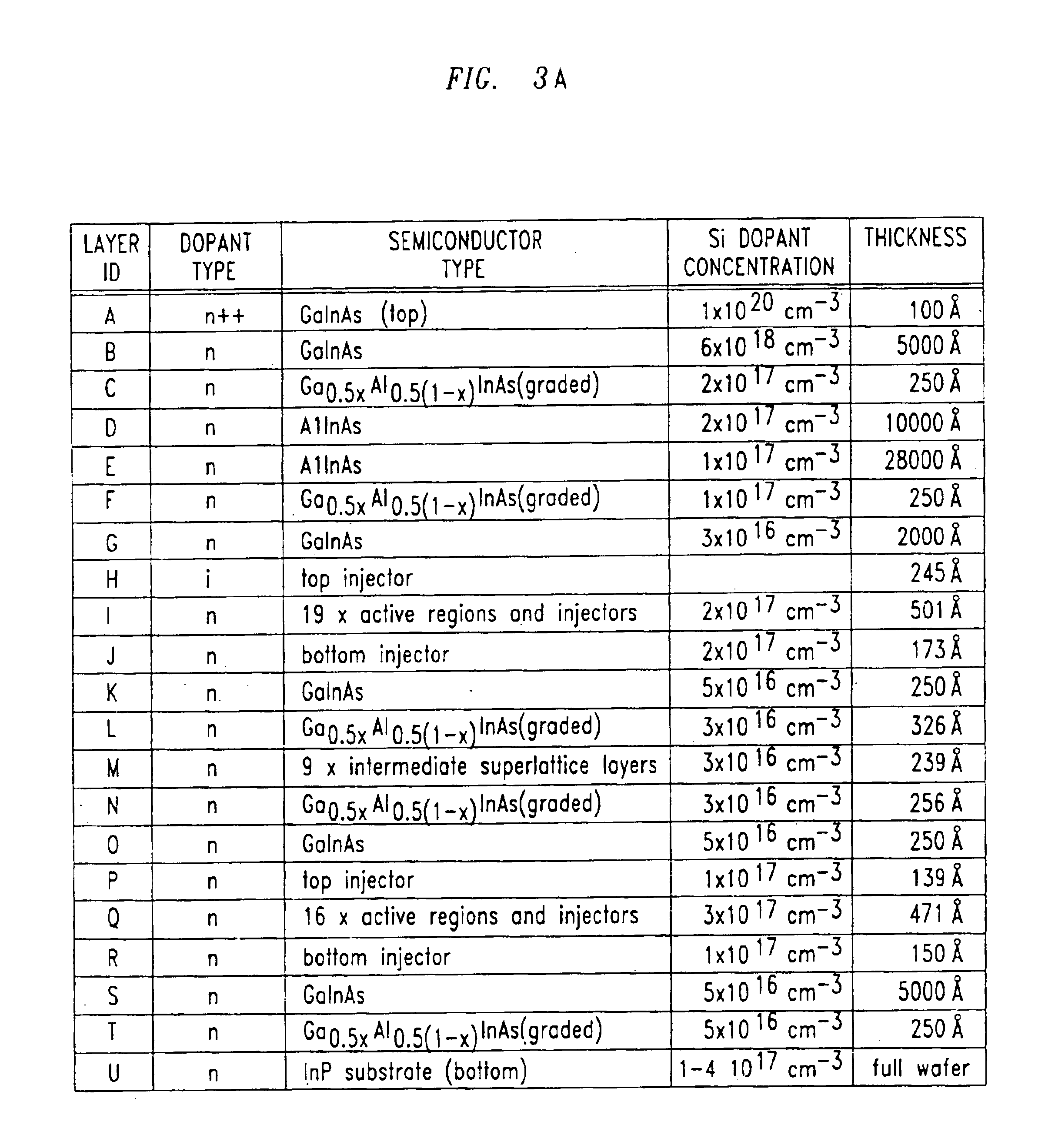
Nonlinear semiconductor light sources
InactiveUS6816530B2Laser active region structureOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical cavityQuantum well
A monolithic apparatus has a laser optical cavity. The laser optical cavity has a multi-layer structure that includes a first active semiconductor multi-layer and a second semiconductor multi-layer. The second semiconductor multi-layer is located laterally adjacent to the first active semiconductor multi-layer. The first active semiconductor multi-layer includes a sequence of quantum well structures that produce light of a lasing frequency in response to being electrically pumped. The second semiconductor multi-layer includes a sequence of quantum well structures and is configured to both absorb light of the lasing frequency and produce one of parametric light and harmonic light in response to absorbing light of the lasing frequency.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
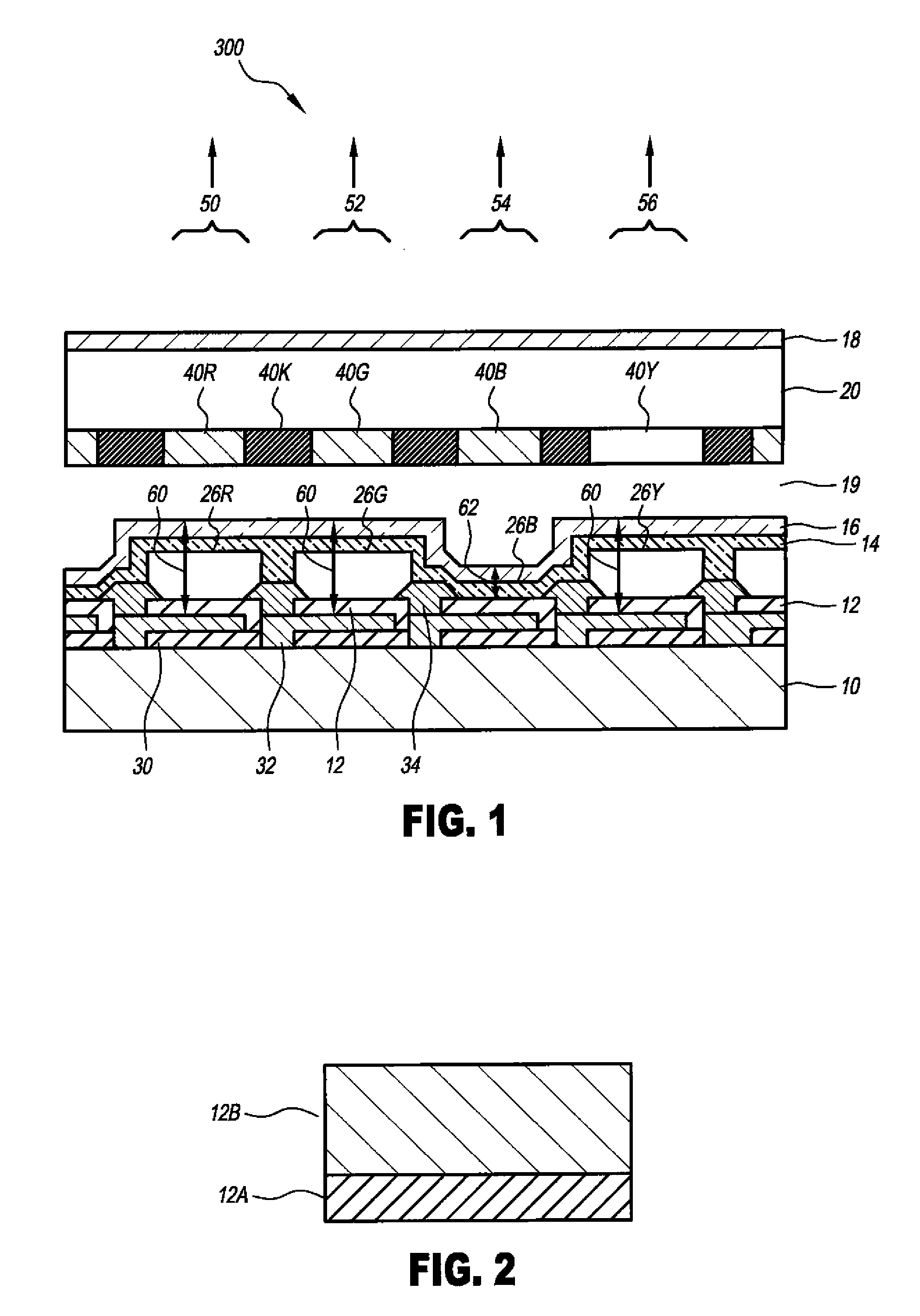
LED device having improved light output
ActiveUS20090102352A1Improve light outputReduces any angular color changeDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesOptical cavityRefractive index
A light-emitting optical cavity light-emitting diode device, comprising:a) a substrate;b) a reflective electrode formed over the substrate;c) an unpatterned light-emitting layer formed over the reflective electrode;d) a transparent electrode formed over the unpatterned light-emitting layer;e) one or more different optical spacers, defining at least two different optical path lengths, are formed in different locations over the substrate, between the reflective electrode and the transparent electrode; andf) a low-index layer formed over the transparent electrode.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Oxygen sensor for aircraft fuel inerting systems
ActiveUS20050286054A1Transmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsFuel tankEngineering
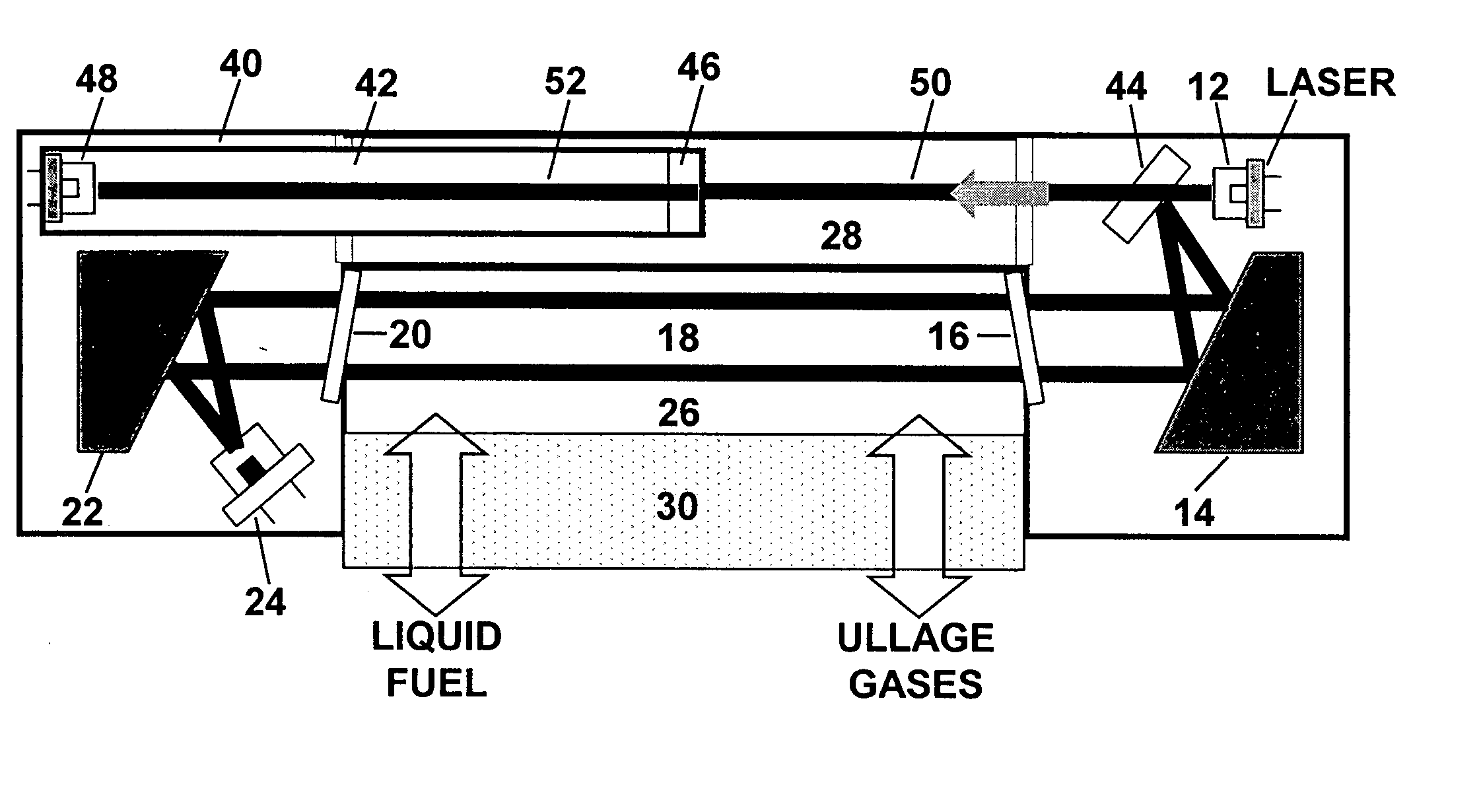
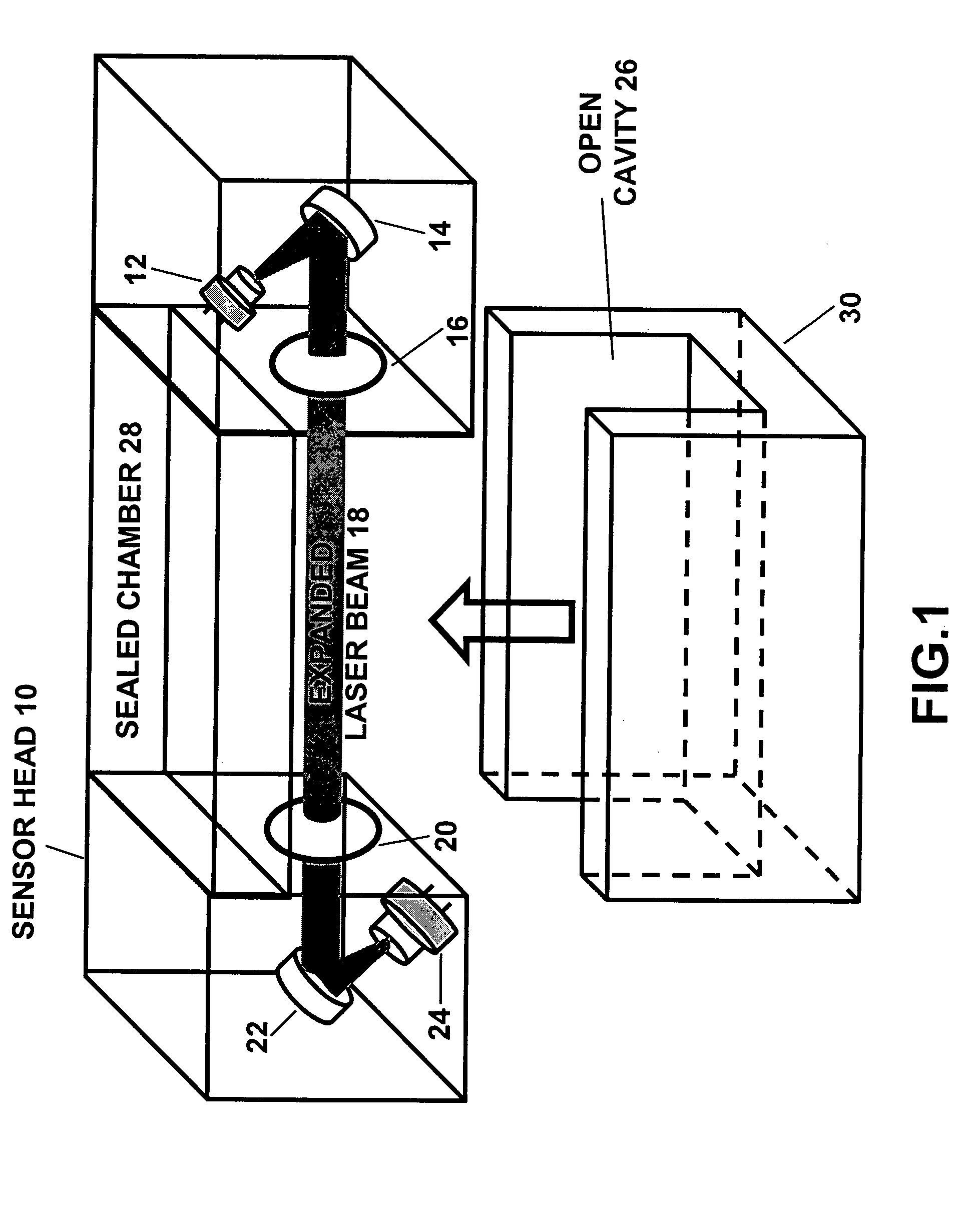
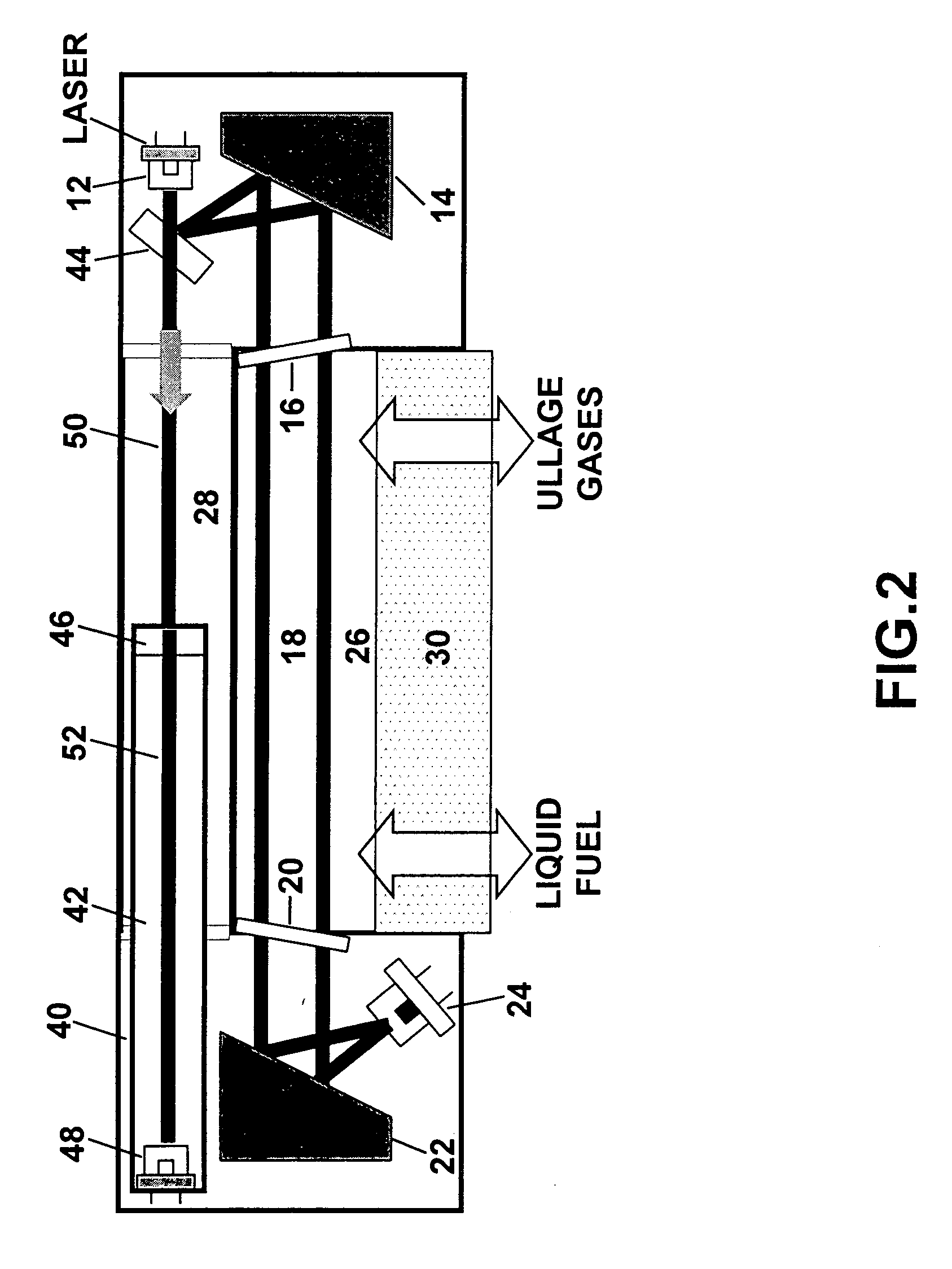
An apparatus and method for monitoring oxygen concentrations in fuel tank ullage comprising providing a sensor head comprising an optical cavity, exposing the optical cavity to an ambient gaseous environment of a fuel tank or air separation module, via a laser light source emitting wavelength modulated light through the cavity, and receiving the wavelength modulated light with a detector.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI
Q-switched oscillator seed-source for MOPA laser illuminator method and apparatus
ActiveUS20110122895A1Wide dynamic rangeAccelerate buildingLaser detailsOptical signallingLine widthWide dynamic range
An apparatus, method and system that uses a Q-switched laser or a Q-seed source for a seed pulse signal having a controlled high-dynamic-range amplitude that avoids and / or compensates for pulse steepening in high-gain optical-fiber and / or optical-rod amplification of optical pulses. Optionally, the optical output is used for LIDAR or illumination purposes (e.g., for image acquisition). In some embodiments, well-controlled pulse shapes are obtained having a wide dynamic range, long duration, and not-too-narrow linewidth. In some embodiments, upon the opening of a Q-switch in an optical cavity having a gain medium, the amplification builds relatively slowly, wherein each round trip through the gain medium increases the amplitude of the optical pulse. Other embodiments use quasi-Q-switch devices or a plurality of amplitude modulators to obtain Q-seed pulses. These configurations provide optical pulses having wide dynamic ranges that ameliorate problems of pulse steepening, non-linear spectral broadening and the like in very-high-power MOPA devices.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
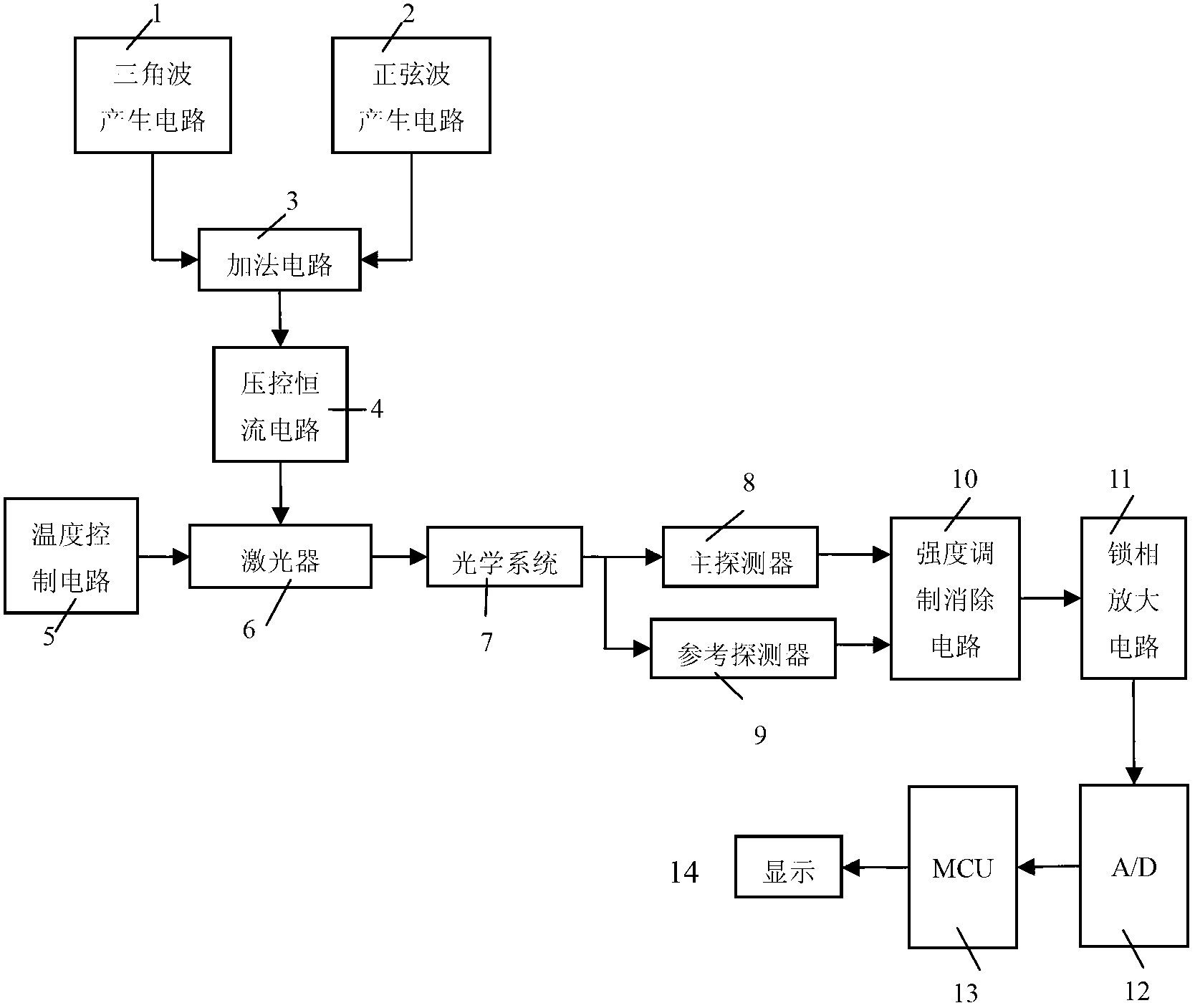
Laser infrared gas analyzer based on TDLAS-WMS (tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy-wavelength modulation spectroscopy)
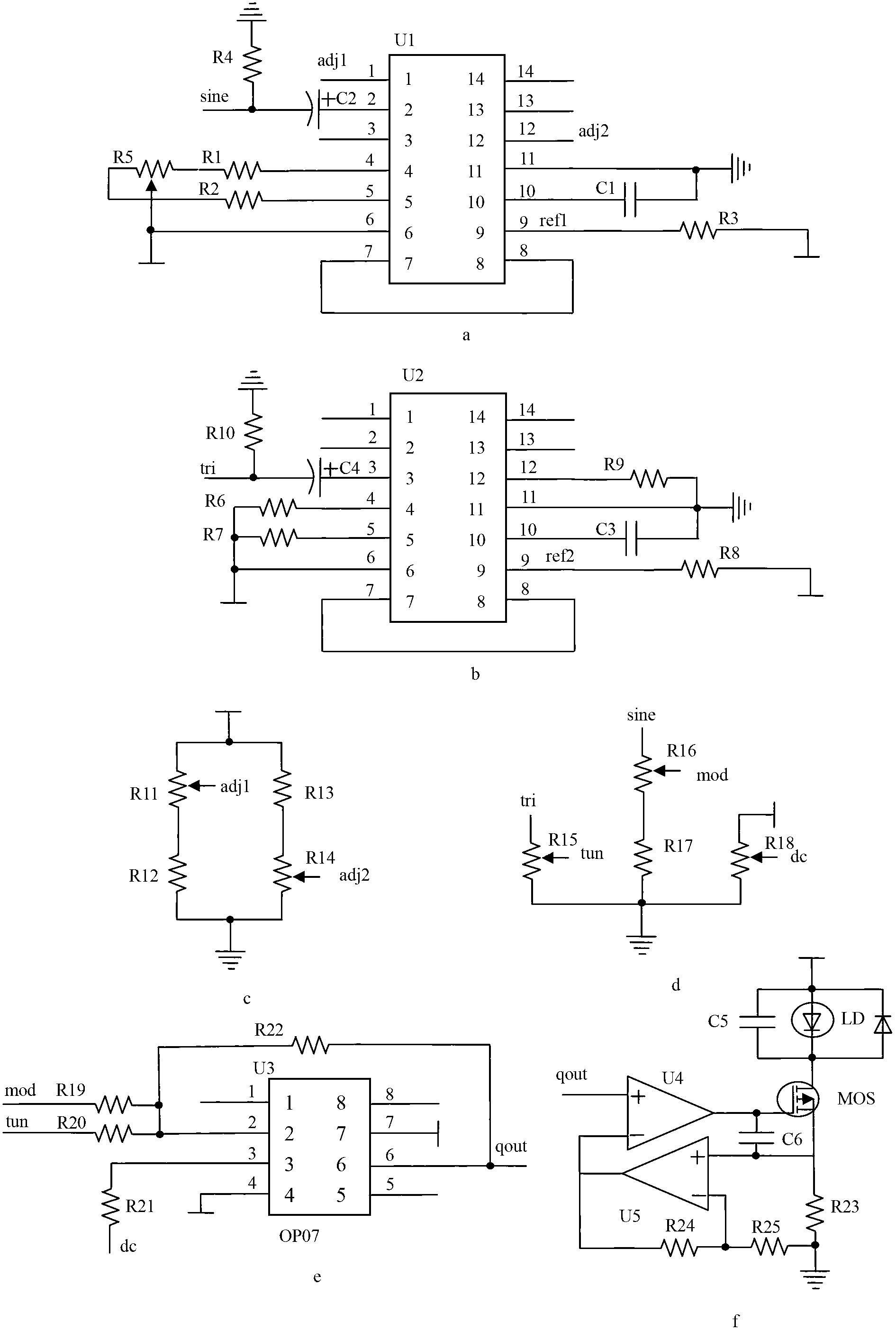
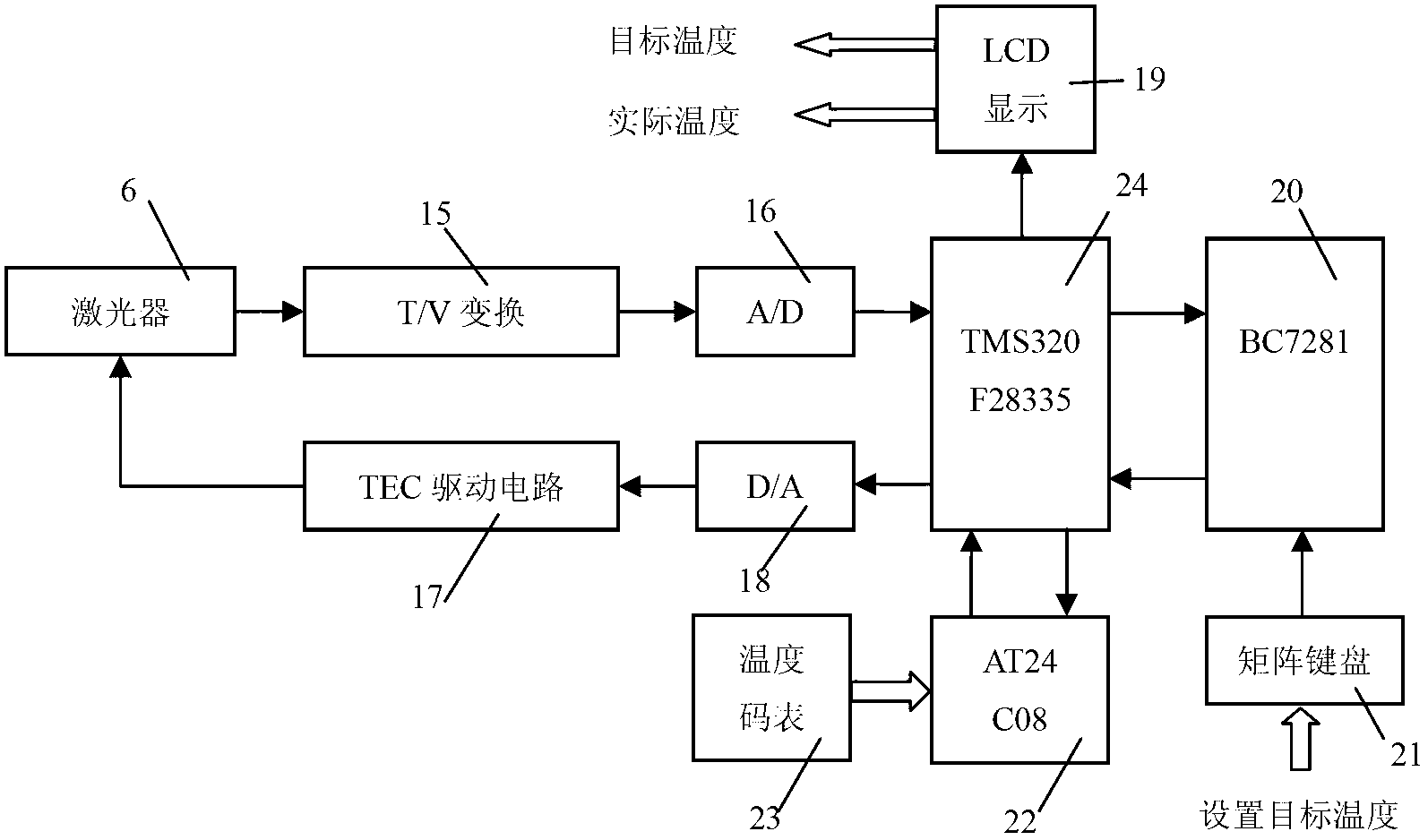
ActiveCN102706832AAdjustable temperatureAvoid damageColor/spectral properties measurementsWater vaporData acquisition
The invention belongs to the technical field of gas detection and relates to a laser infrared gas analyzer based on TDLAS-WMS (tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy-wavelength modulation spectroscopy) for detecting hydrogen chloride, methane, carbon monoxide, water vapor and other gases. The laser infrared gas analyzer comprises a laser, a laser driving circuit, a temperature control circuit, an optical system with an optical cavity, a main detector, a reference detector, an intensity modulation and canceling circuit, a phase-locking and amplification circuit and a data acquisition and display circuit, wherein the laser driving circuit and the temperature control circuit are used for controlling the laser to emit light, the two ends of the optical system are respectively connected with the laser and the detector, the intensity modulation and canceling circuit is used for canceling the influence of intensity modulation in the system, the phase-locking and amplification circuit is used for extracting harmonic signals, and the data acquisition and display circuit is used for displaying the concentration of the gas to be detected. Compared with other detection instruments, the laser infrared gas analyzer has the advantages that division operation is introduced into the intensity modulation and canceling circuit, and the laser infrared gas analyzer is combined with a space double-optical path differential detection method, so that the influence of the intensity modulation can be fundamentally canceled.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com