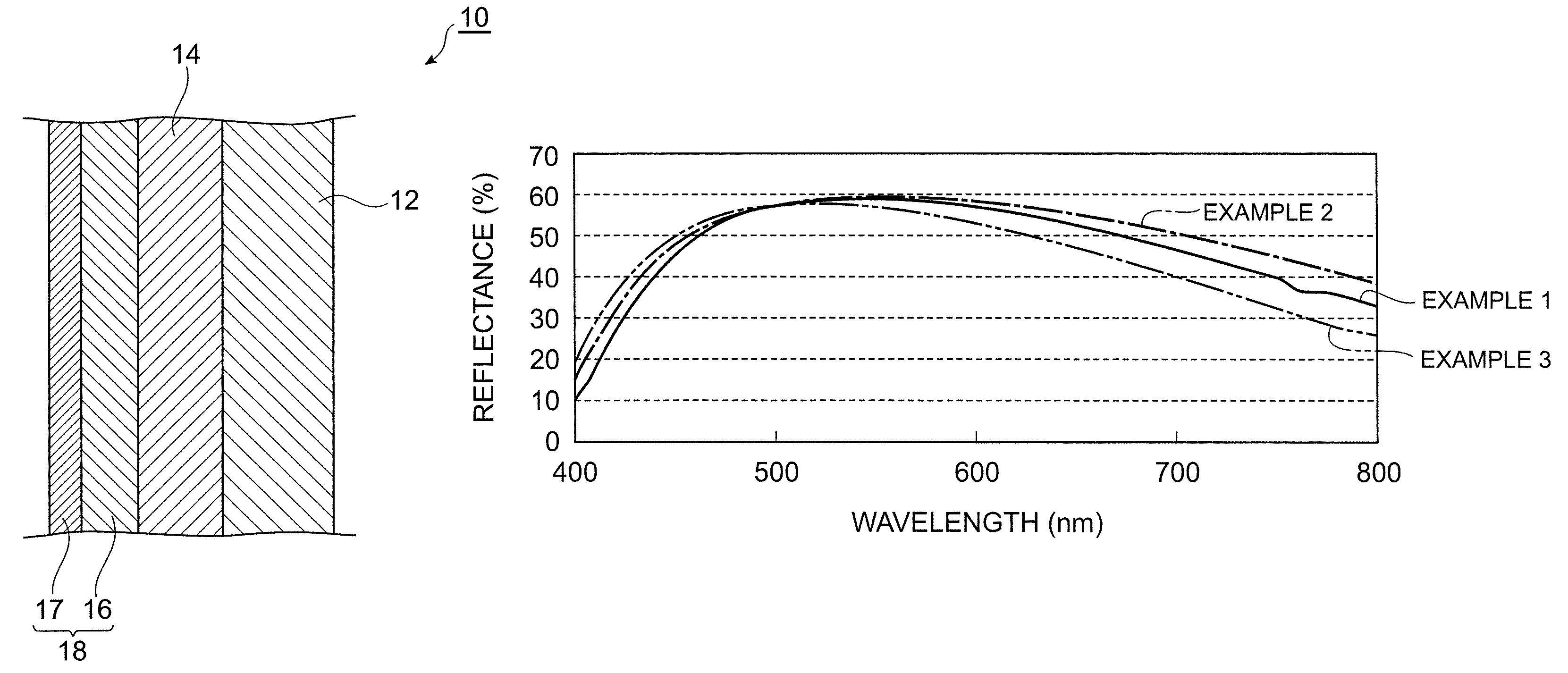
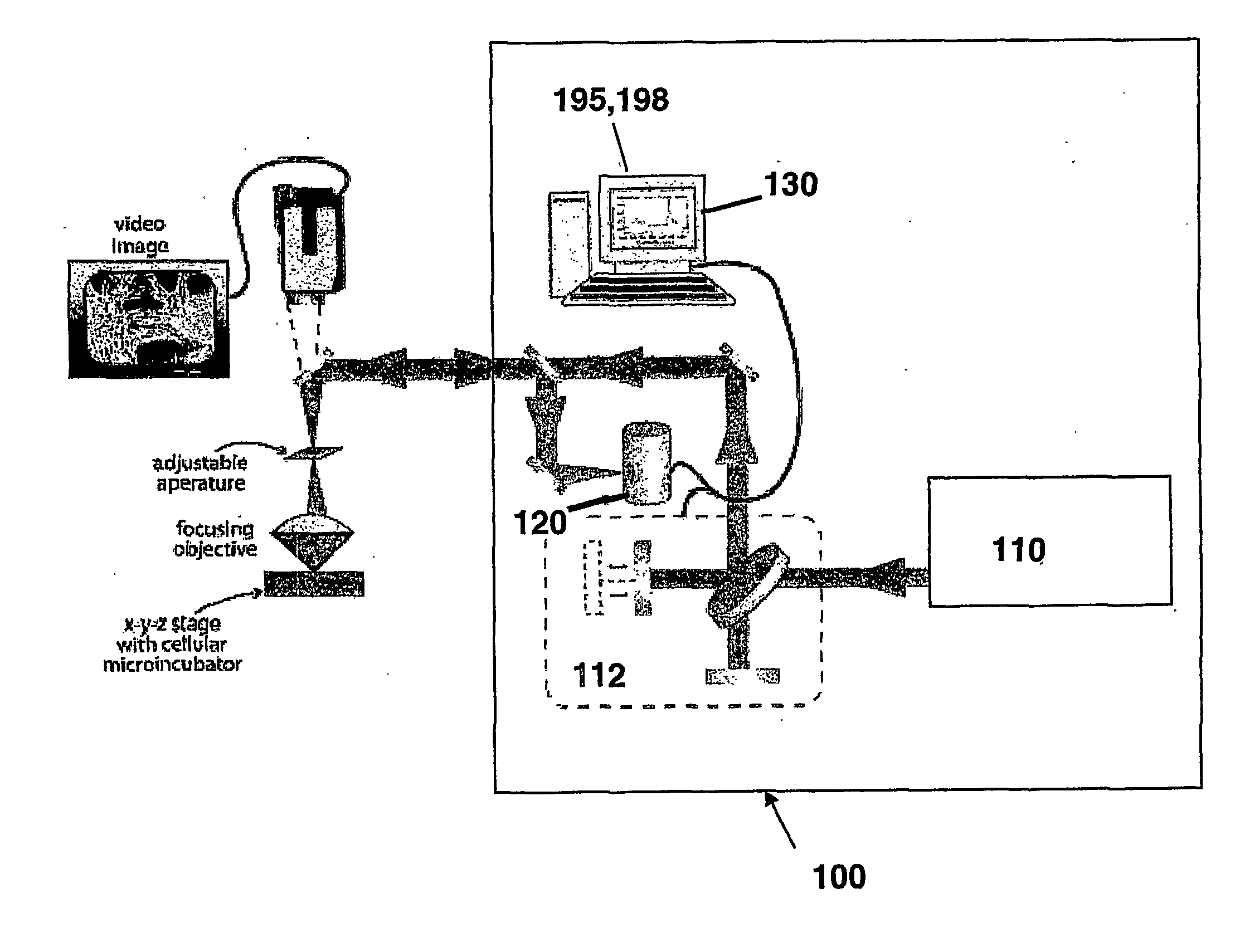
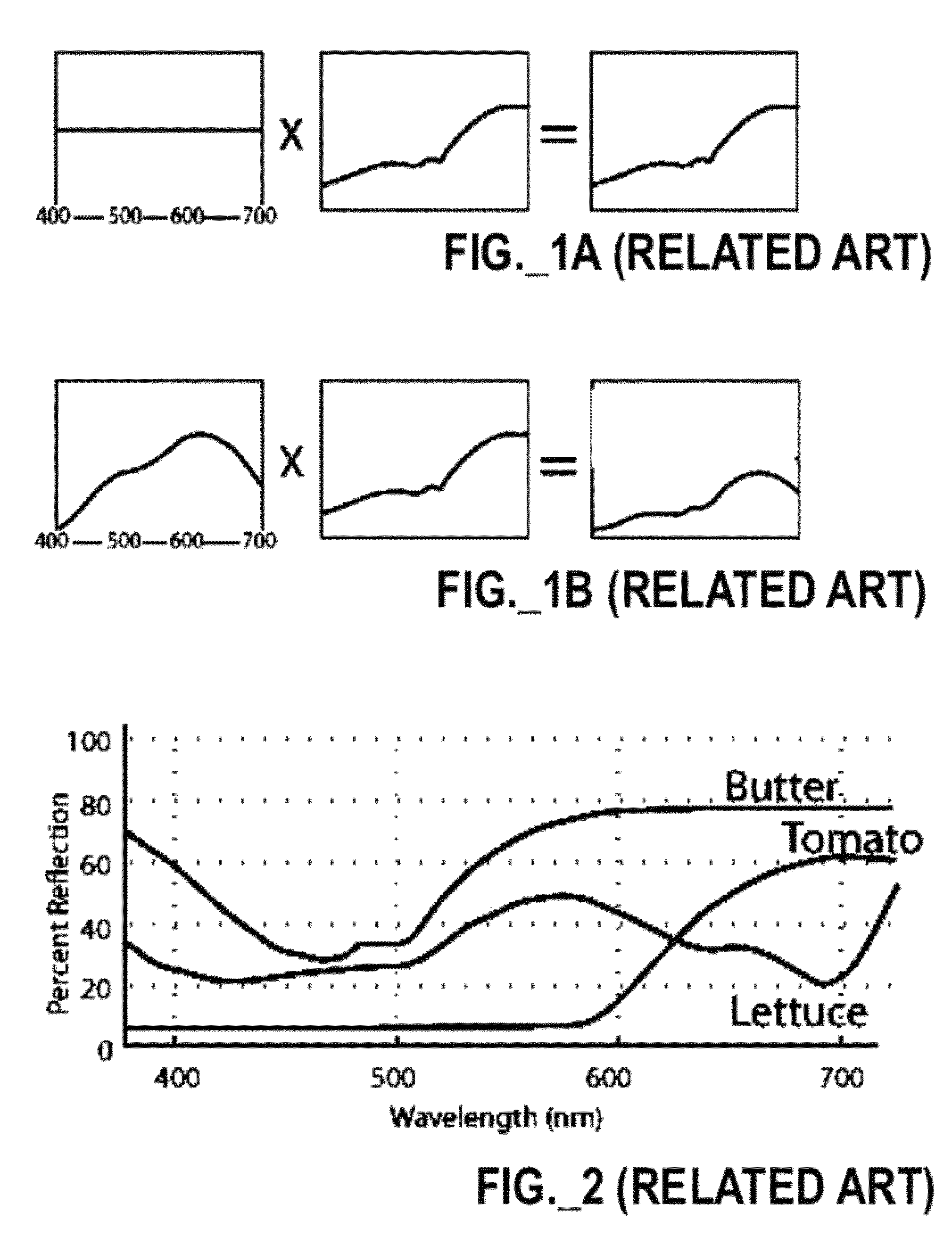
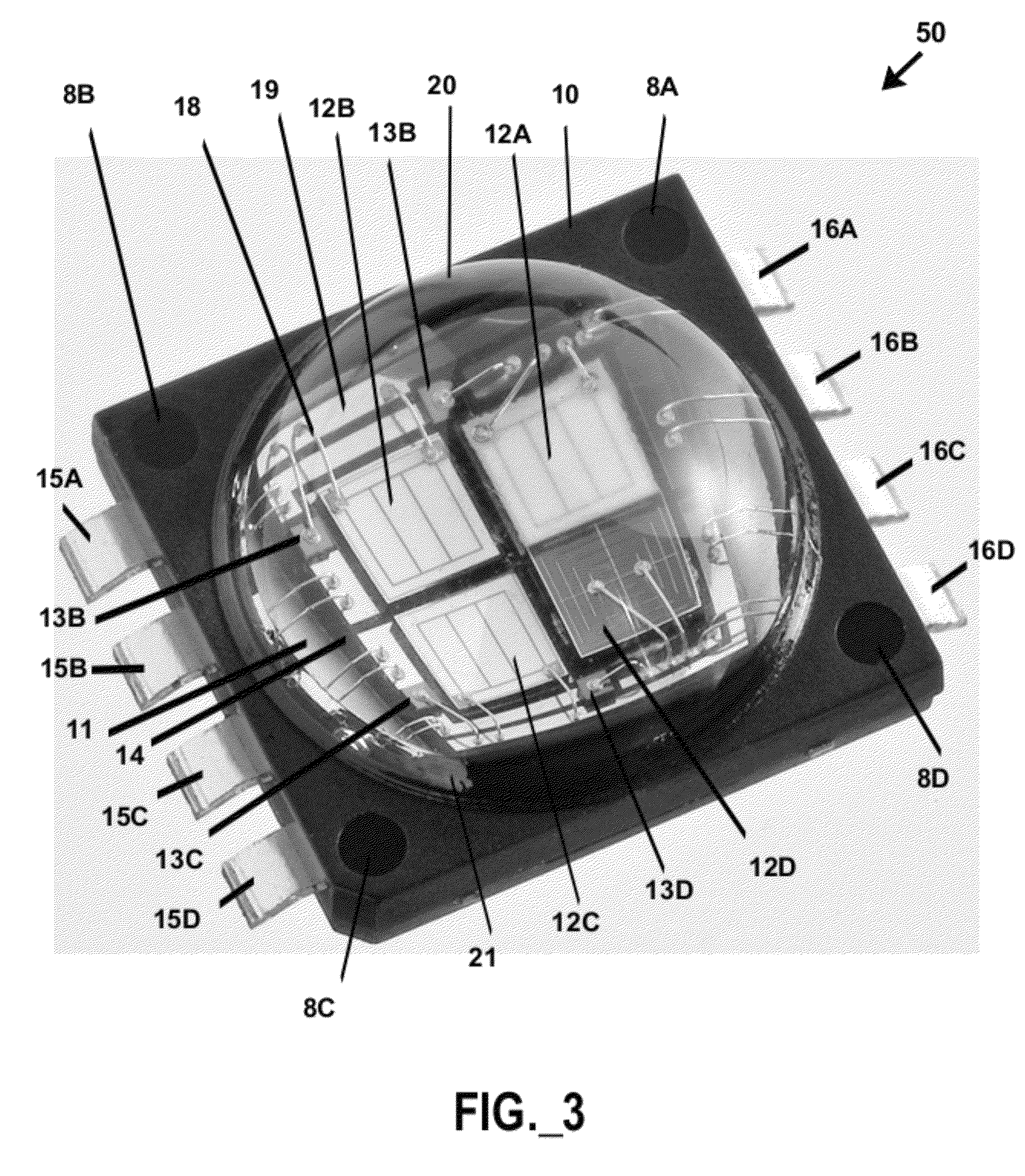
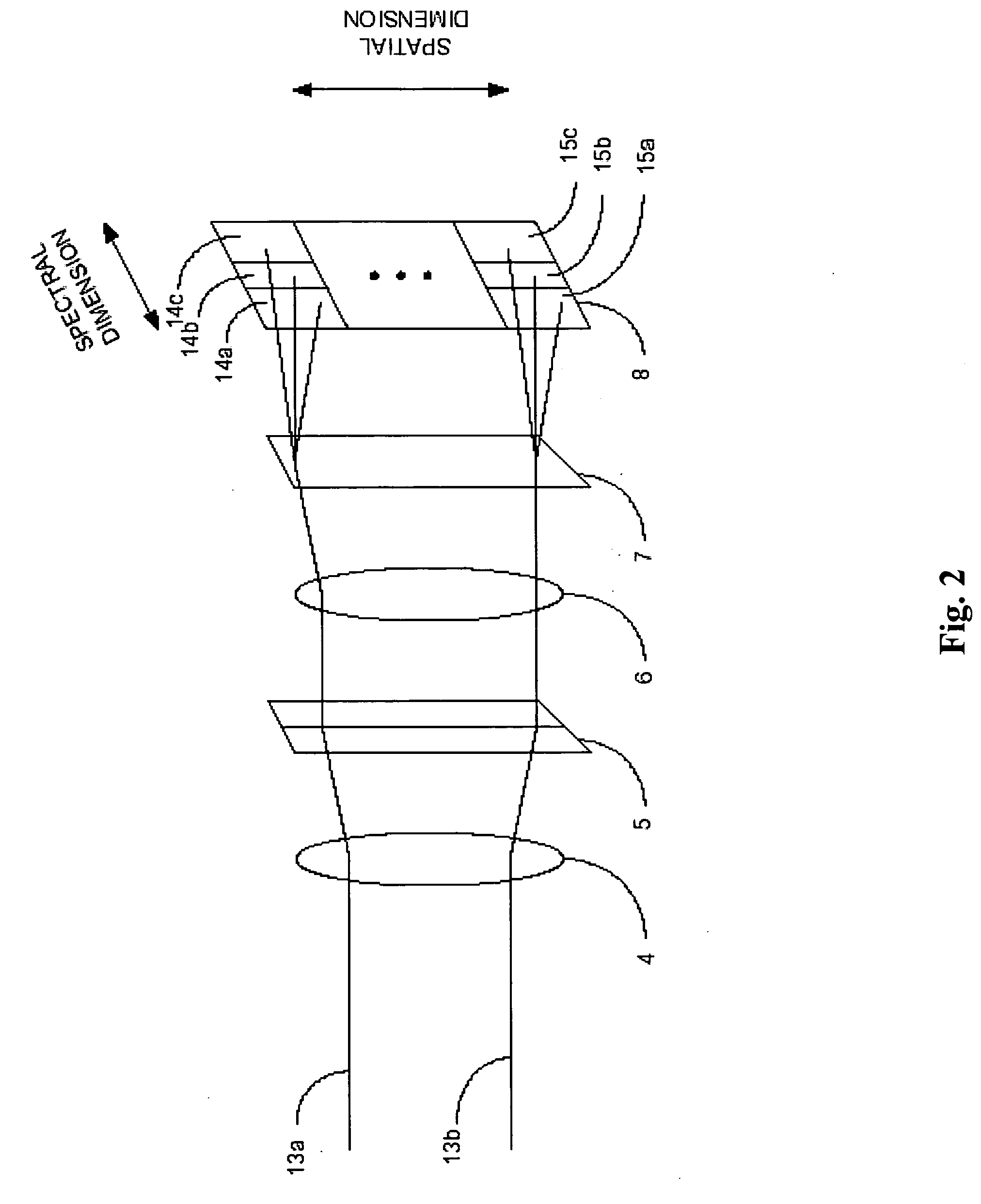
Patents
Literature
1114 results about "Reflection spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
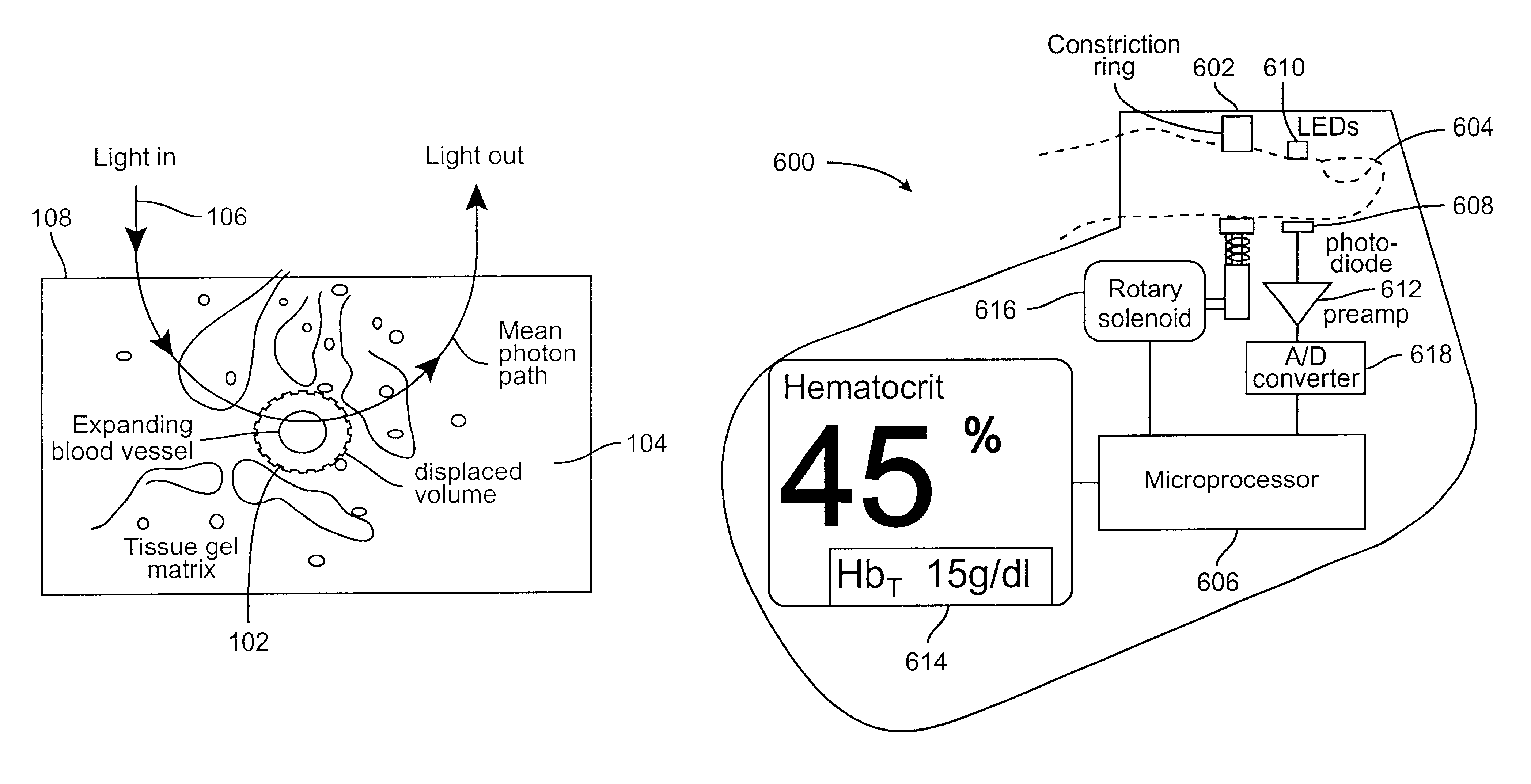
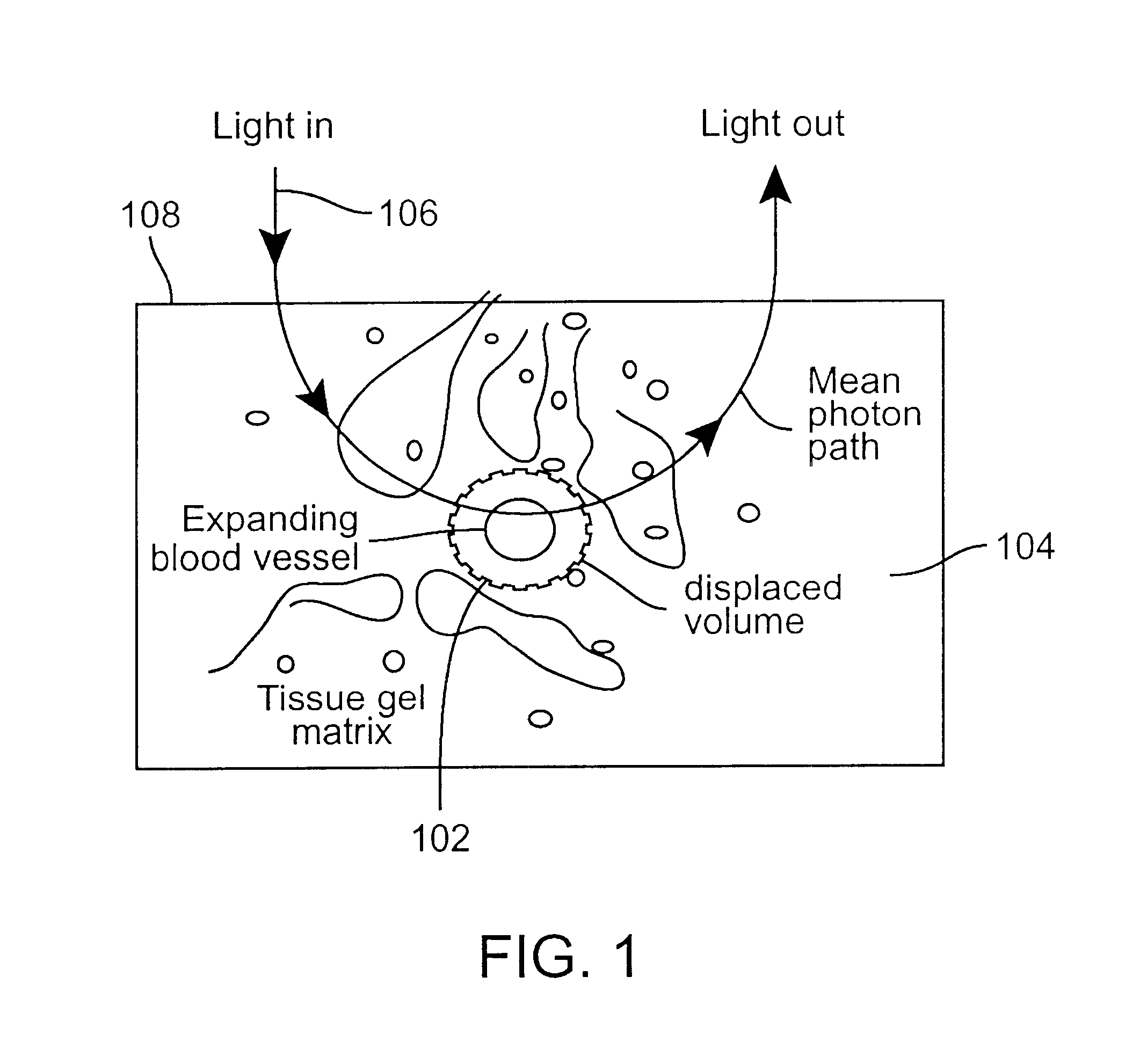
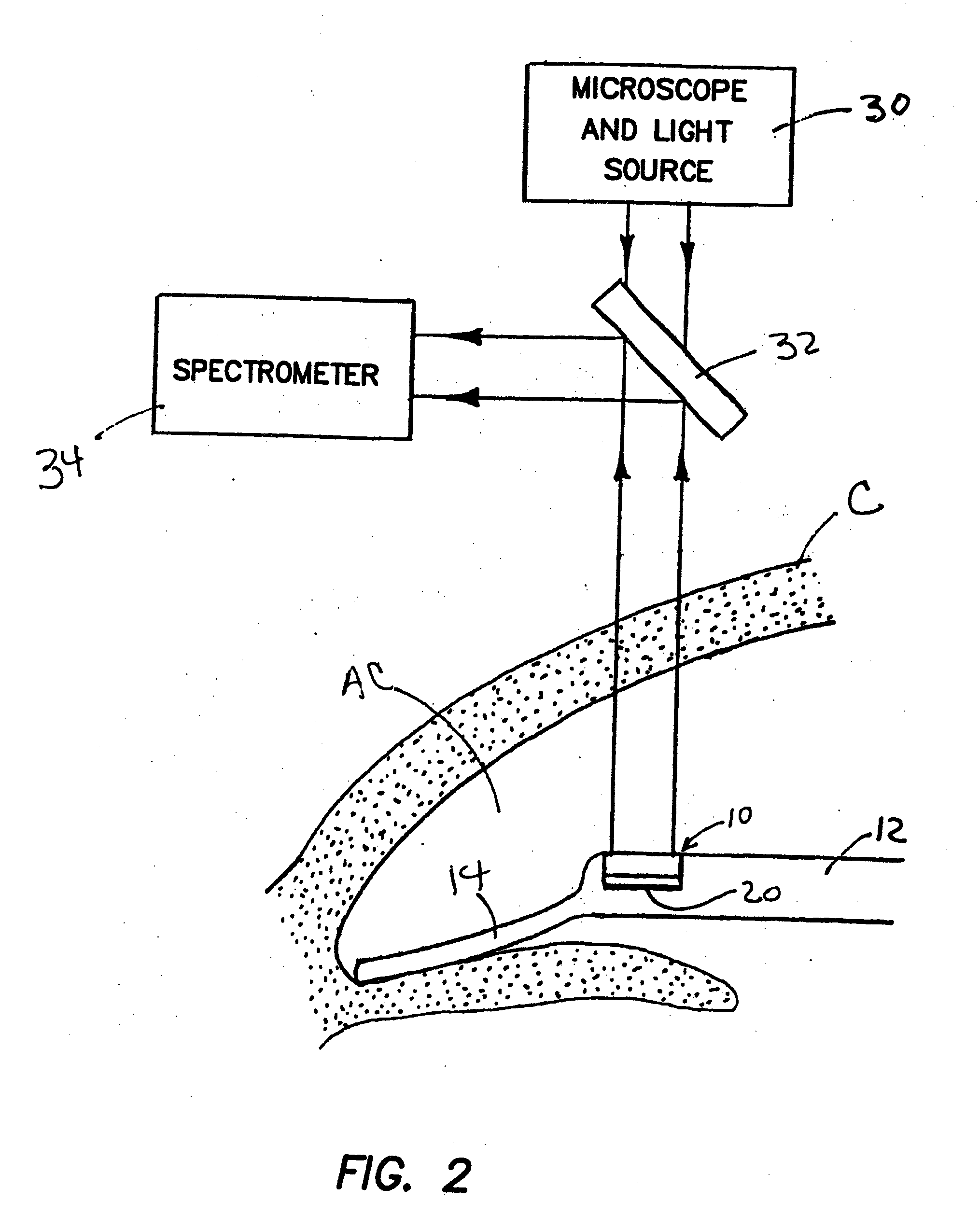
Method and apparatus for improving the accuracy of noninvasive hematocrit measurements
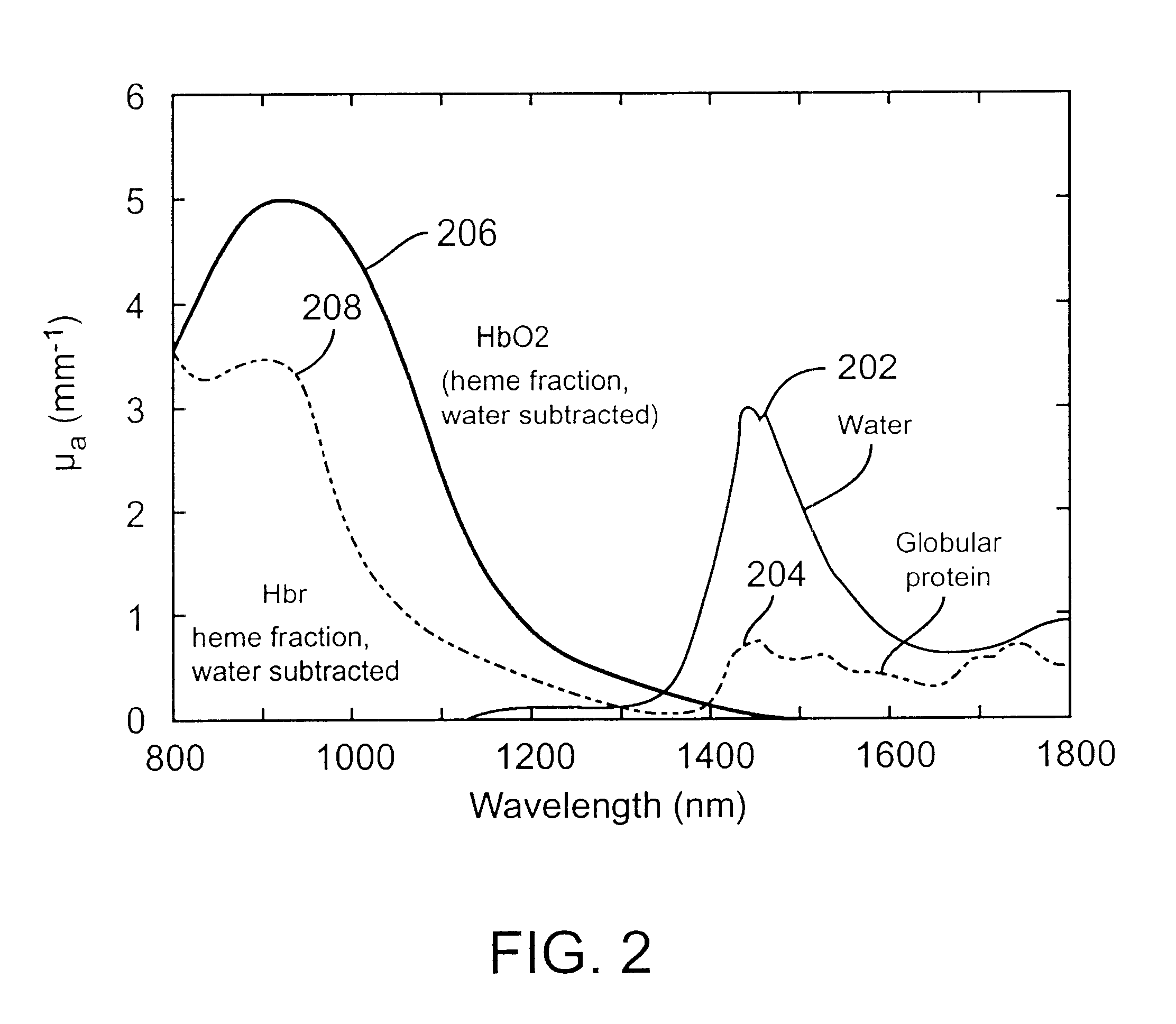
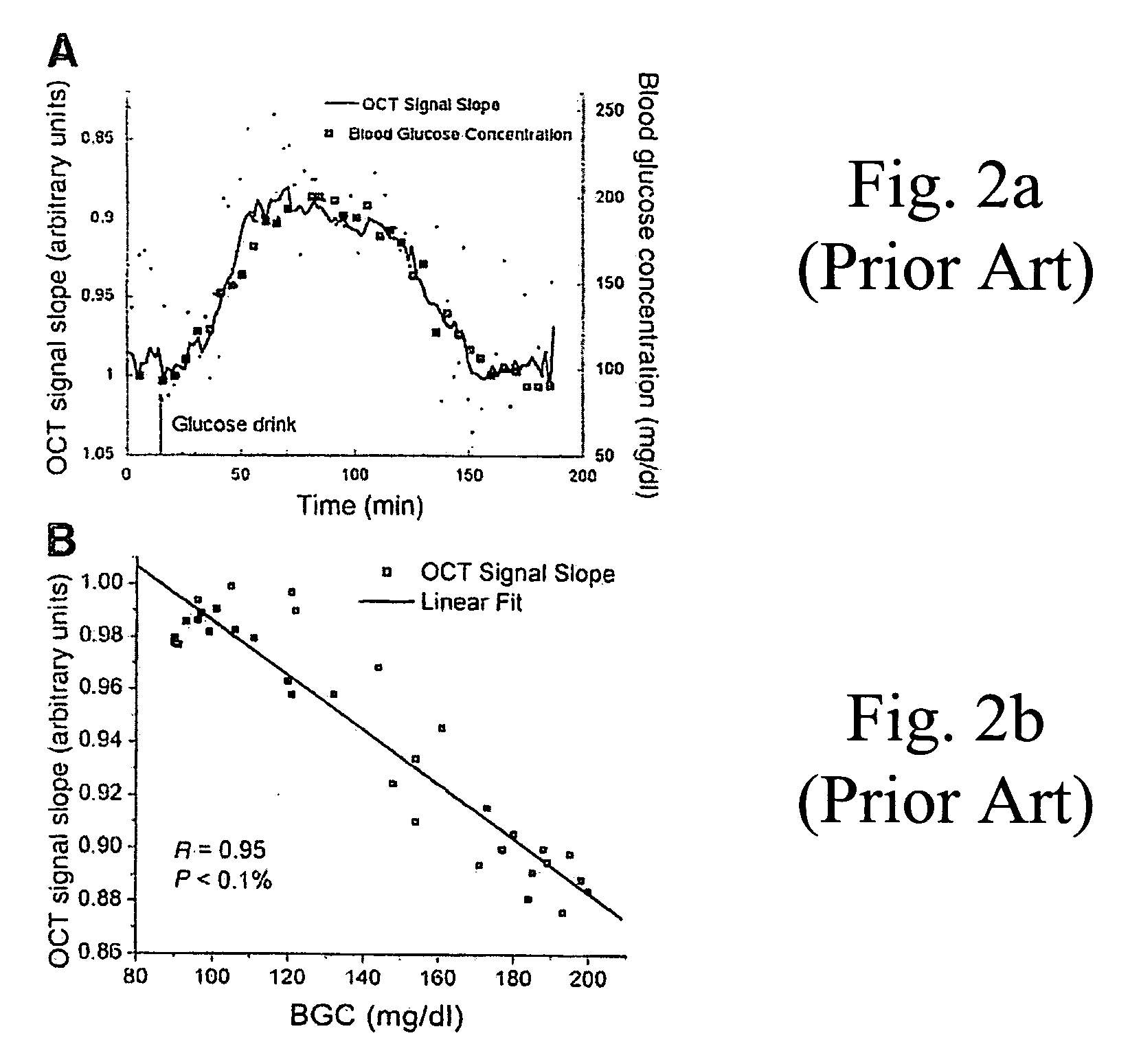
A device and a method to provide a more reliable and accurate measurement of hematocrit (Hct) by noninvasive means. The changes in the intensities of light of multiple wavelengths transmitted through or reflected light from the tissue location are recorded immediately before and after occluding the flow of venous blood from the tissue location with an occlusion device positioned near the tissue location. As the venous return stops and the incoming arterial blood expands the blood vessels, the light intensities measured within a particular band of near-infrared wavelengths decrease in proportion to the volume of hemoglobin in the tissue location; those intensities measured within a separate band of wavelengths in which water absorbs respond to the difference between the water fractions within the blood and the displaced tissue volume. A mathematical algorithm applied to the time-varying intensities yields a quantitative estimate of the absolute concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. To compensate for the effect of the unknown fraction of water in the extravascular tissue on the Hct measurement, the tissue water fraction is determined before the occlusion cycle begins by measuring the diffuse transmittance or reflectance spectra of the tissue at selected wavelengths.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
System and method for functional brain mapping and an oxygen saturation difference map algorithm for effecting same
A method of functional brain mapping of a subject is disclosed. The method is effected by (a) illuminating an exposed cortex of a brain or portion thereof of the subject with incident light; (b) acquiring a reflectance spectrum of each picture element of at least a portion of the exposed cortex of the subject; (c) stimulating the brain of the subject; (d) during or after step (c) acquiring at least one additional reflectance spectrum of each picture element of at least the portion of the exposed cortex of the subject; and (e) generating an image highlighting differences among spectra of the exposed cortex acquired in steps (b) and (d), so as to highlight functional brain regions. Algorithms for calculating oxygen saturation and blood volume maps which can be used to practice the method are also disclosed. Systems for practicing the method are also disclosed.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Sub-wavelength grating integrated VCSEL
InactiveUS20070153860A1Good optical performanceEasy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is described using a sub-wavelength grating (SWG) structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity. The grating comprises segments of high and low refractive index materials with an index differential between the high and low index materials. By way of example, a SWG reflective structure is disposed over a low index cavity region and above another reflective layer (either SWG or DBR). In one embodiment, the SWG structure is movable, such as according to MEMS techniques, in relation to the opposing reflector to provide wavelength selective tuning. The SWG-VCSEL design is scalable to form the optical cavities for a range of SWG-VCSELs at different wavelengths, and wavelength ranges.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
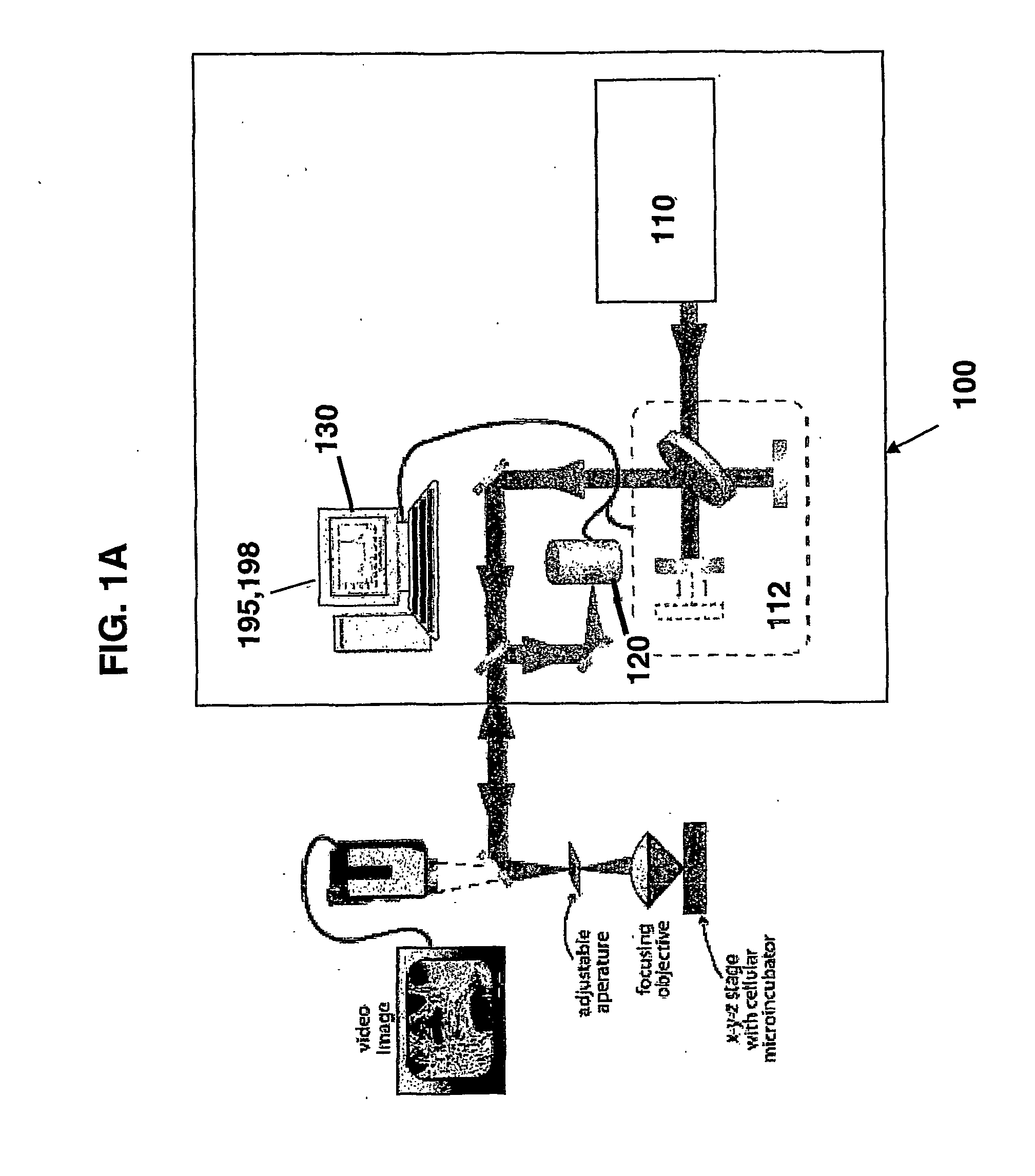
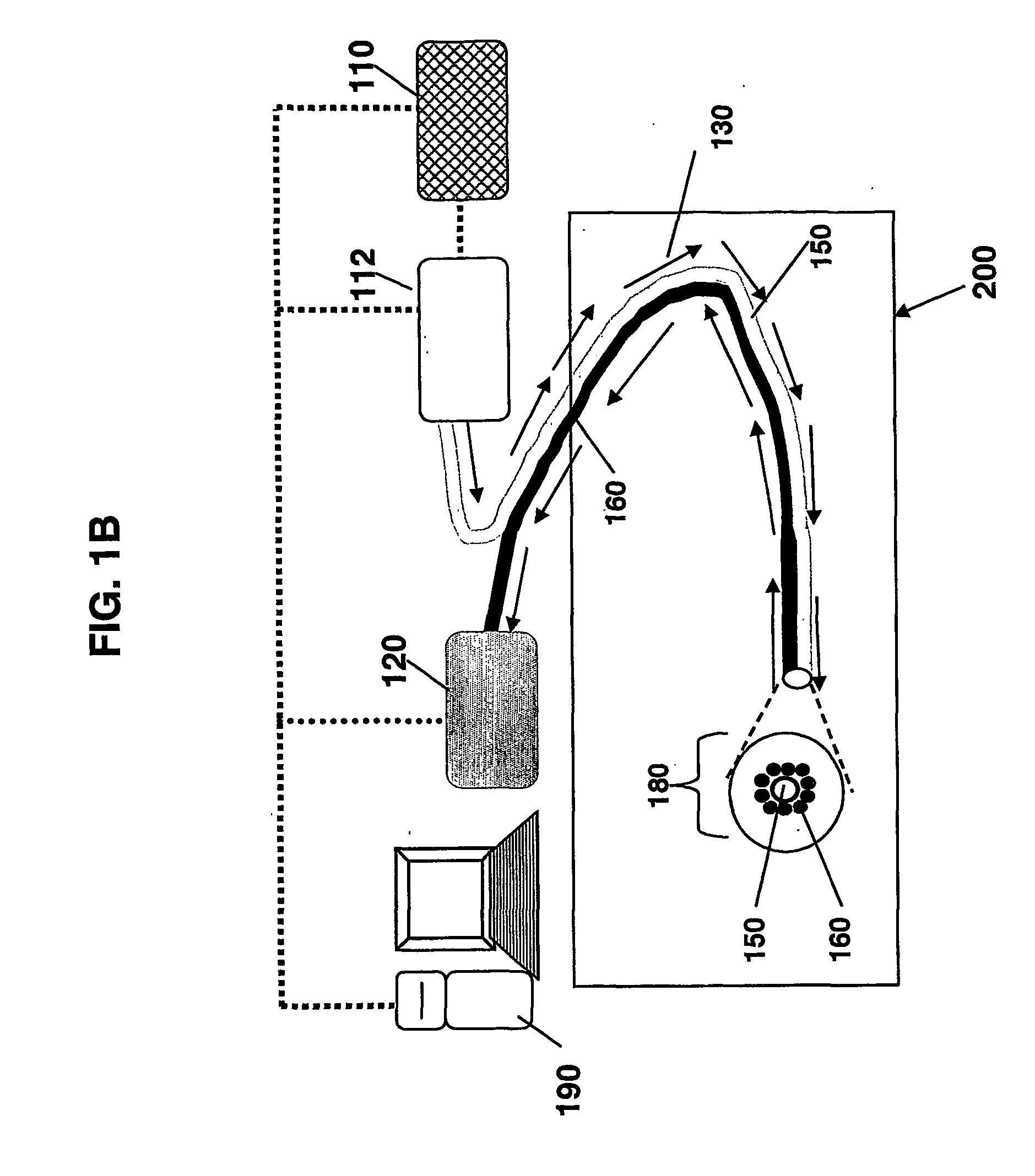
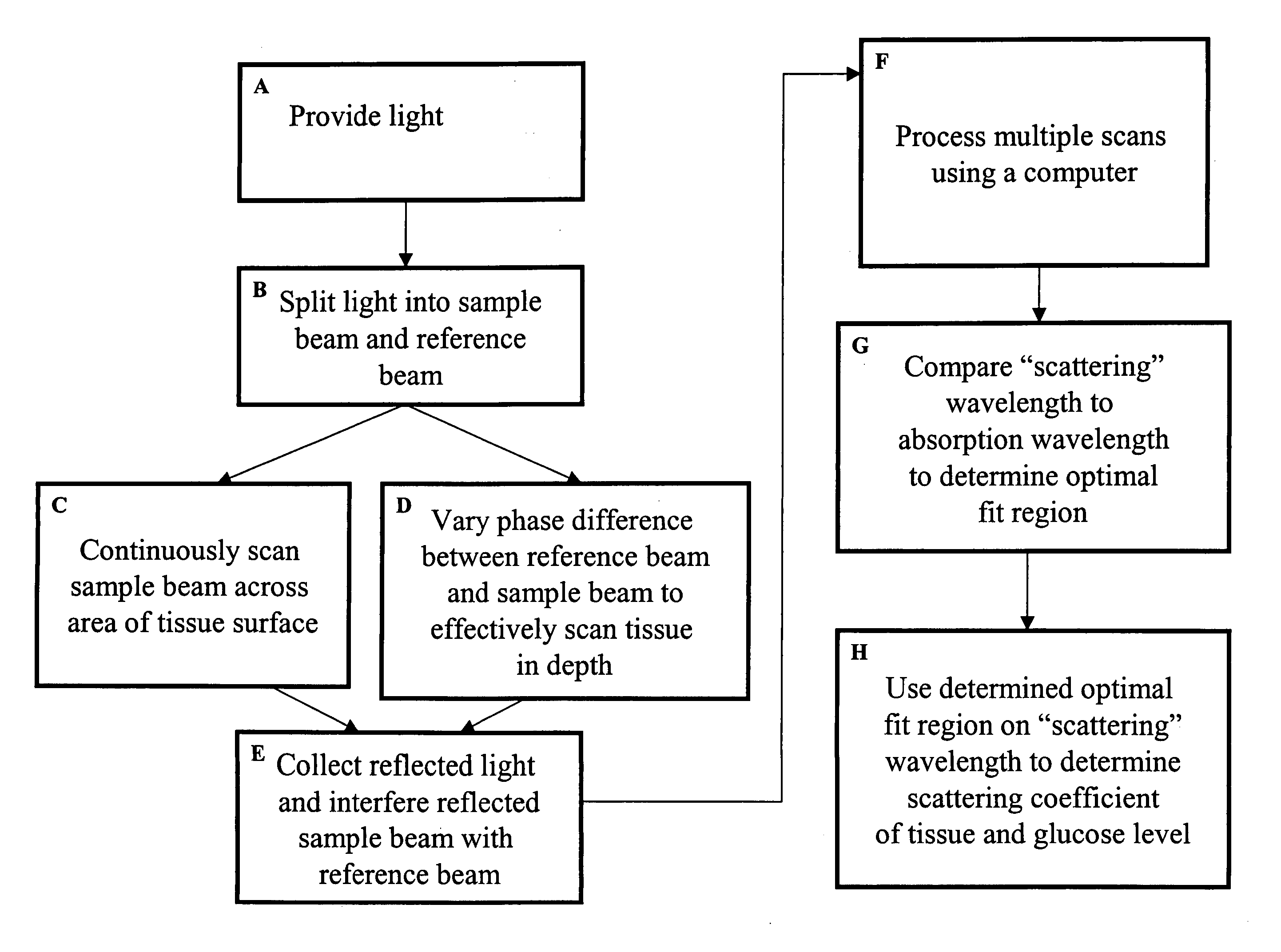
Method and apparatus for monitoring glucose levels in a biological tissue
ActiveUS20080021293A1Convenient amountLow lightDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBLOOD FILLEDConcentrations glucose
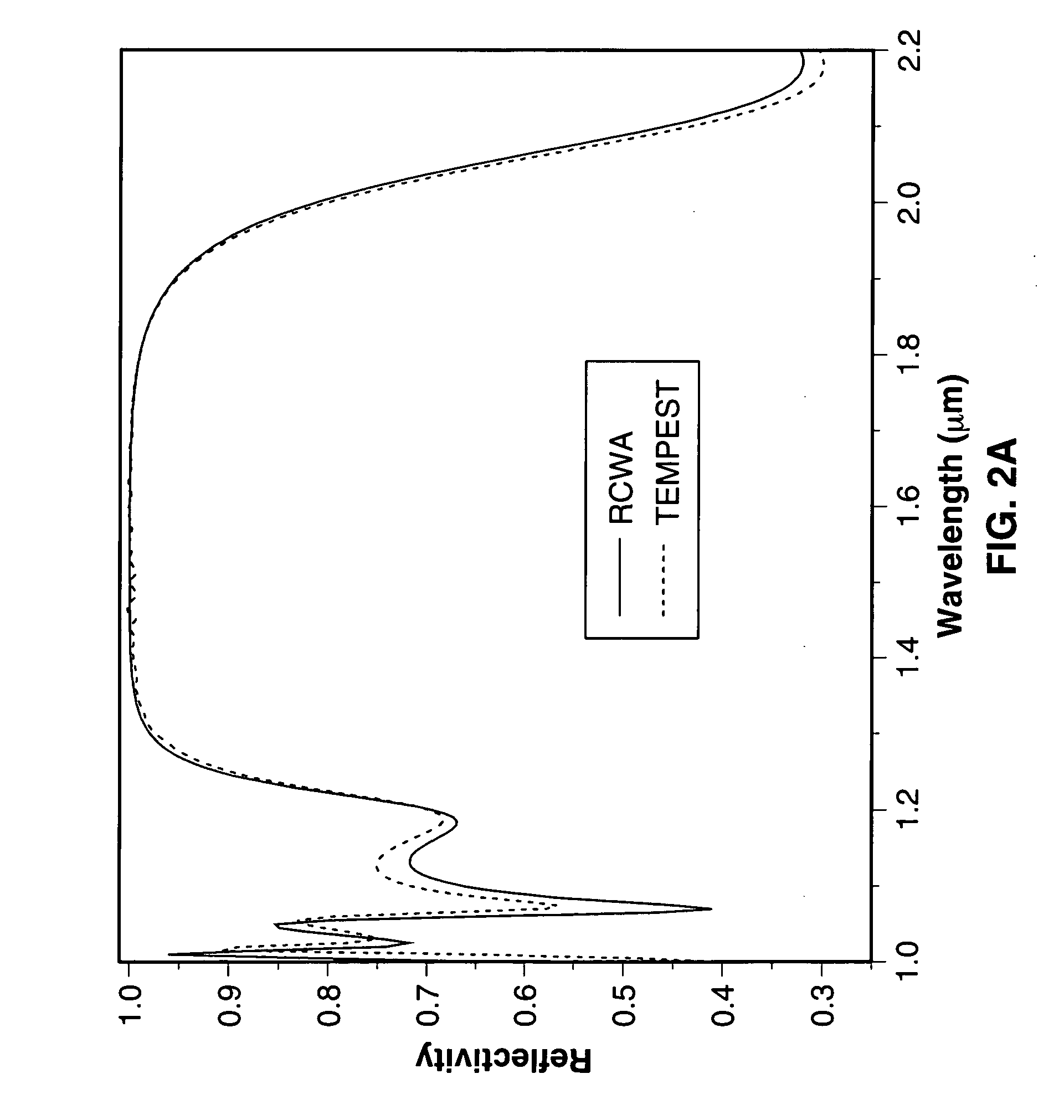
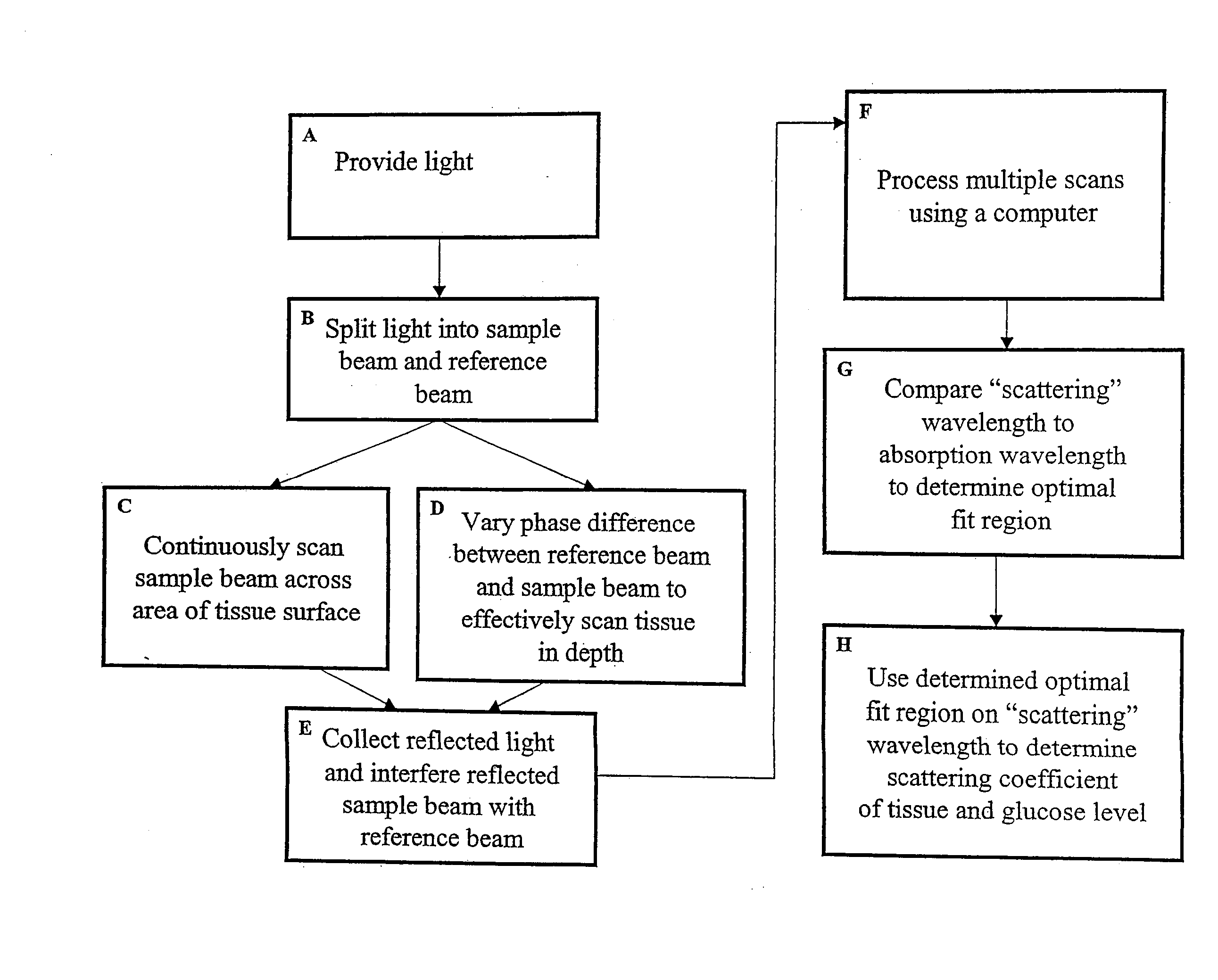
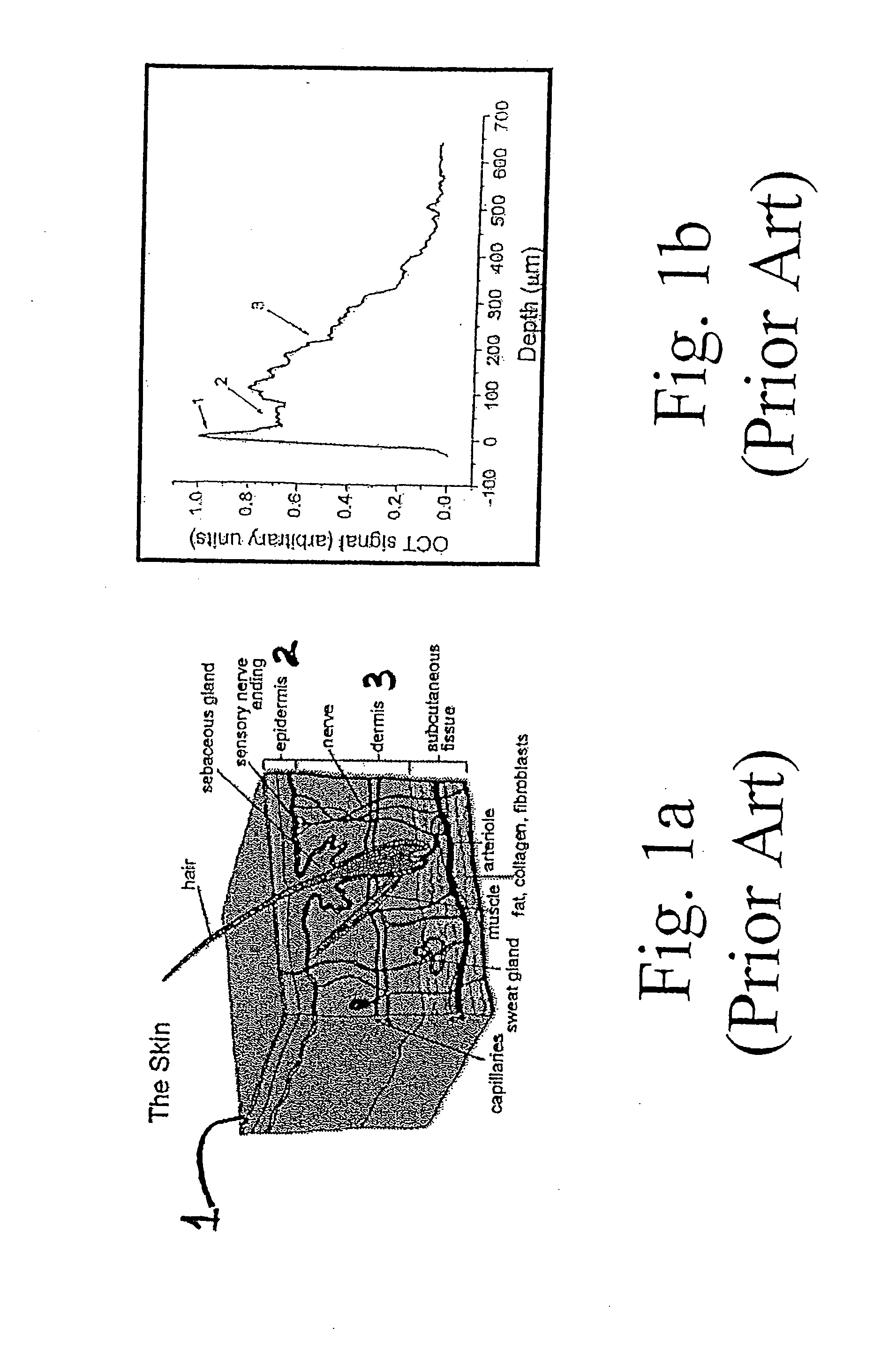
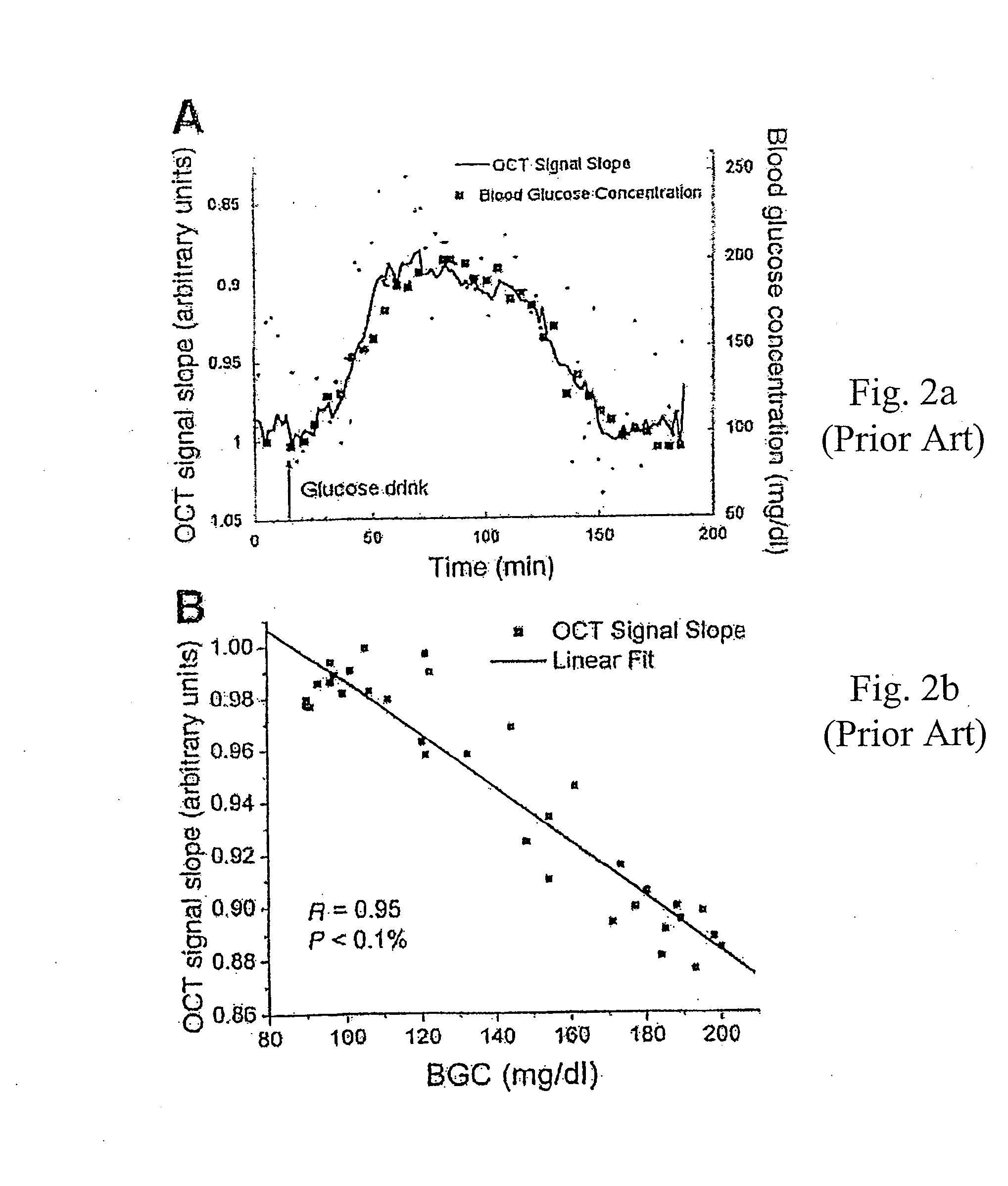
In accordance with the invention, a low coherence interferometer is used to non-invasively monitor the concentration of glucose in blood by shining a light over a surface area of human or animal tissue, continuously scanning the light over a two dimensional area of the surface, collecting the reflected light from within the tissue and constructively interfering this reflected light with light reflected along a reference path to scan the tissue in depth. Since the reflection spectrum is sensitive to glucose concentration at particular wavelengths, measurement and analysis of the reflected light provides a measure of the level of glucose in the blood. The measurement of glucose is taken from multiple depths within blood-profused tissue, and sensitivity is preferably enhanced by the use of multiple wavelengths. Noise or speckle associated with this technique is minimized by continuously scanning the illuminated tissue in area and depth.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Colored anti-fog mirror
A colored anti-fog mirror that emits reflected light in response to incident light, the colored anti-fog mirror comprising a substrate, a hydrophilic functional layer containing a photocatalytic substance, and a metallic reflecting film provided between the substrate and the hydrophilic functional layer, wherein a material of the metallic reflecting film and a thickness of the hydrophilic functional layer are set such that the reflected light has a spectral reflection spectrum having a maximum reflectance in the visible region over 510 nm and not more than 600 nm.
Owner:MURAKAMI CORP
Catheter-based mid-infrared reflectance and reflectance generated absorption spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070078348A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove reflectivityDiagnostics using spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsDiseasePhysiological markers
A catheter based method and apparatus for reflectance generated absorption spectral analysis of chronic inflammatory vascular conditions such as seen with atherosclerotic plaque within a blood vessel or other body cavity or compartment. The use of a bright mid range infrared light (mid-IR) source yields detectable reflected optical signals that may be sampled from an area smaller or larger than the typical diameter of a mammalian cell. The mid-IR light is delivered at selected mid-infrared wavenumbers. Using the apparatus and methods, the reflectance spectra and reflectance generated absorption spectra of a target tissue can be compared to reference spectra to identify and distinguish normal epithelium from tissue containing physiological markers indicative of vascular disease or other inflammatory conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for monitoring glucose levels in a biological tissue
ActiveUS20060063988A1Different scattering propertyReduce noiseDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsContinuous scanningConcentrations glucose
In accordance with the invention, a low coherence interferometer is used to non-invasively monitor the concentration of glucose in blood by shining a light over a surface area of human or animal tissue, continuously scanning the light over a two dimensional area of the surface, collecting the reflected light from within the tissue and constructively interfering this reflected light with light reflected along a reference path to scan the tissue in depth. Since the reflection spectrum is sensitive to glucose concentration at particular wavelengths, measurement and analysis of the reflected light provides a measure of the level of glucose in the blood. The measurement of glucose is taken from multiple depths within blood-profused tissue, and sensitivity is preferably enhanced by the use of multiple wavelengths. Noise or speckle associated with this technique is minimized by continuously scanning the illuminated tissue in area and depth.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
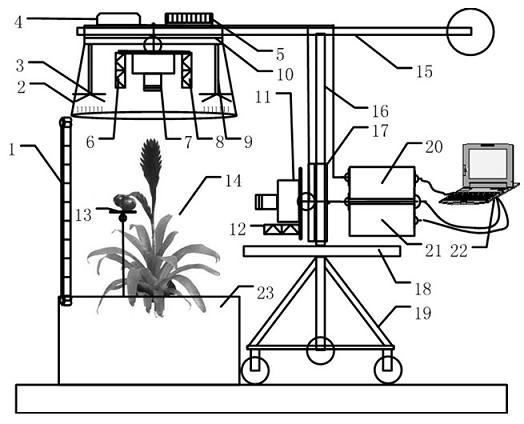
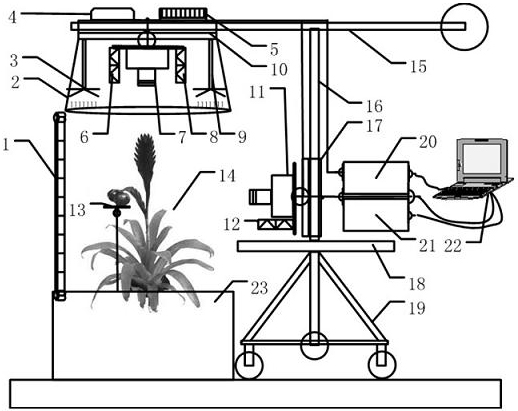
Nondestructive detection device and method for facility crop growth information
ActiveCN102384767AGrasp the state of growthImprove acquisitionMeasurement devicesPotassiumCharacteristic space
The invention discloses a nondestructive detection device and a nondestructive detection method for facility crop growth information, and belongs to the technical field of monitoring of facility crops. The device comprises a growth information sensing system, an electric control mechanical rocker arm and a control computer; the control computer drives the electric control mechanical rocker arm to be positioned at a detection position, and controls the growth information sensing system; reflection spectrums of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and moisture of crops, multispectral images, canopy temperature characteristic, multispectral morphological characteristics of canopies, stalks, plants and fruits, fruit quality information, and information of environmental illumination, temperature and humidity are acquired by using a multispectral imager and sensors of infrared temperature, irradiance, environmental temperature and humidity and load; nutrient and moisture characteristic spaces are acquired by optimizing and compensating the nutrient and moisture characteristics of the crops; and growth vigor information of canopy area, stalk thickness, fruit quality, plant height and the like is acquired by extracting the multispectral morphological characteristics of the crops, and comprehensive acquisition and nondestructive detection of the growth information of the crops are realized by combining nutrient, moisture and growth vigor characteristics.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Hyperspectral polarization profiler for remote sensing
InactiveUS6052187AMinimize healthMinimize problemsRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyFluorescenceLarge range
A device to provide hyperspectral reflection spectrum, hyperspectral depolarization, and hyperspectral fluorescence spectrum data in a portable, remote sensing instrument. The device can provide a large range of remotely-sensed optical property data, presently only obtainable in laboratories, in a low-cost field instrument. Among its many uses, the present invention can be used by farmers as a tool for determining the nitrogen content of crops to optimize fertilizer laydown.
Owner:CONTAINERLESS RES
Implantable Devices and Methods for Measuring Intraocular, Subconjunctival or Subdermal Pressure and/or Analyte Concentration
Methods, apparatus and systems for measuring pressure and / or for quantitative or qualitative measurement of analytes within the eye or elsewhere in the body. Optical pressure sensors and / or optical analyte sensors are implanted in the body and light is cast from an extracorporeal light source, though the cornea, conjunctiva or dermis, and onto a reflective element located within each pressure sensor or analyte sensor. The position or configuration of each sensor's reflective element varies with pressure or analyte concentration. Thus, the reflectance spectra of light reflected by the sensors' reflective elements will vary with changes in pressure or changes in analyte concentration. A spectrometer or other suitable instrument is used to process and analyze the reflectance spectra of the reflected light, thereby obtaining an indication of pressure or analyte concentration adjacent to the sensor(s). The wavelength of the interrogating beam of light may vary to control out potential interference or inaccuracies in the system.
Owner:BCC ENTERPRISE
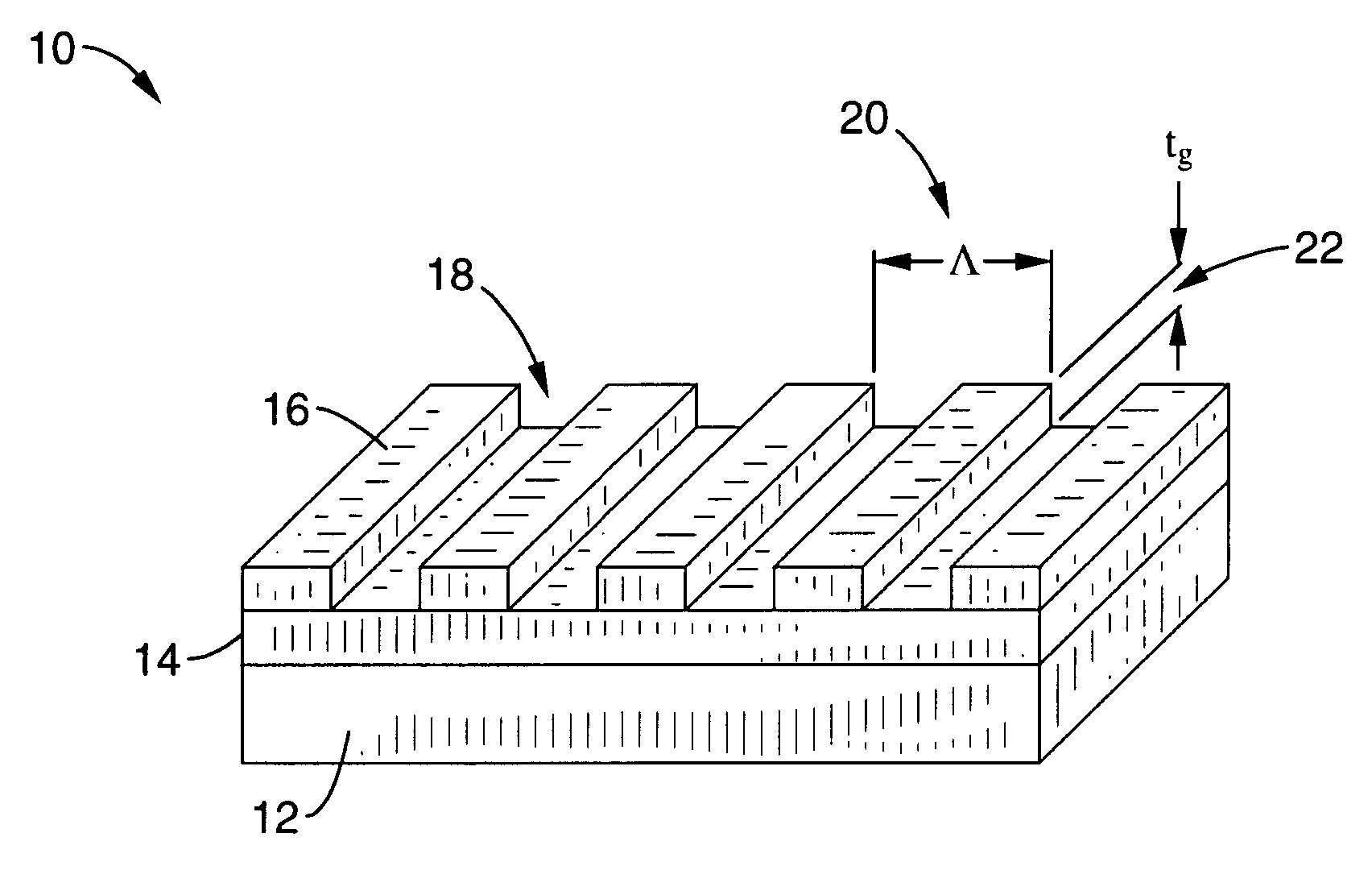
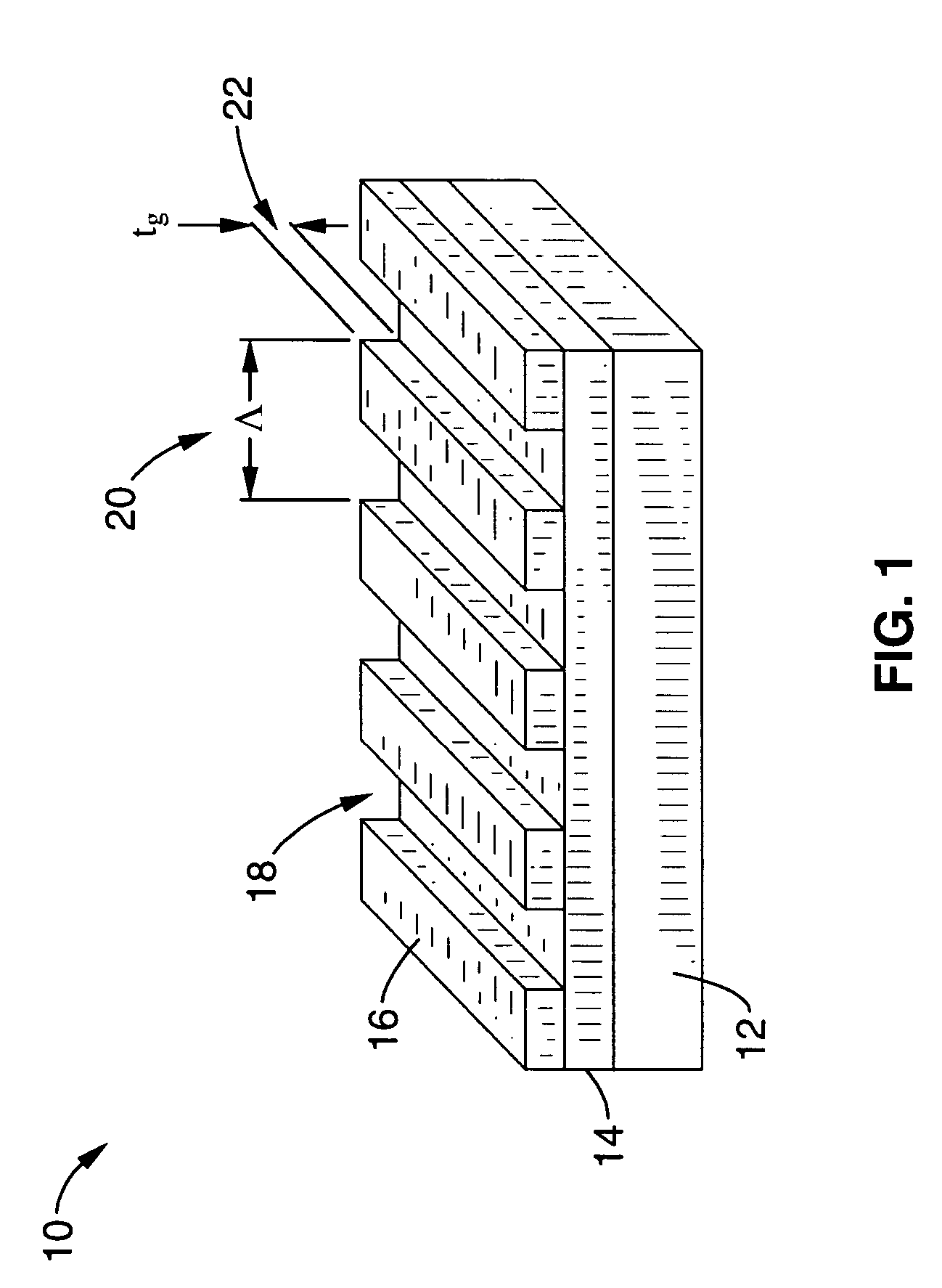
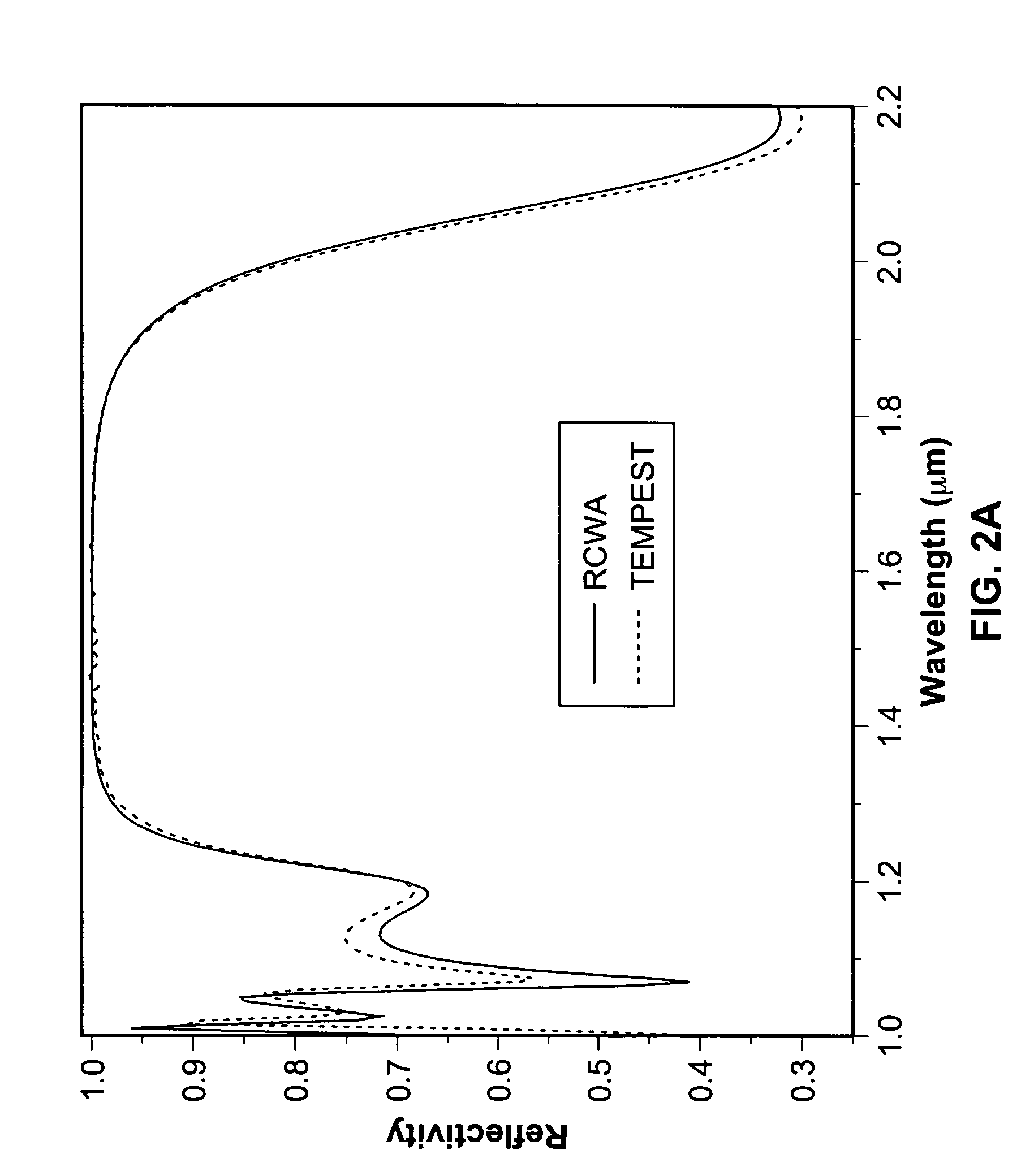
Ultra broadband mirror using subwavelength grating
ActiveUS20070115553A1Broad reflection spectrumImprove reflectivityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingRefractive index
A sub-wavelength grating structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity comprising segments made of high refractive index material disposed on a layer of low refractive index material and a low refractive index material disposed above and between the segments. The index differential between the high and low index materials determines the bandwidth and modulation depth. The larger difference in refractive indices gives rise to wider reflection bands. The reflection is sensitive to parameters such as the grating period, the grating thickness, the duty cycle of the grating, the refractive index and the thickness of the low index layer underneath the grating. The design is scalable for different wavelengths, and facilitates monolithic integration of optoelectronic devices at a wide range of wavelengths from visible to far infrared. The sub-wavelength grating reflectors may be used in a variety of settings such as tunable etalon filters and as a replacement for conventional distributed Bragg reflectors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-stability optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor packaged without glue and manufacturing method
ActiveCN102384809AEliminate the effects ofEasy to achieve airtightFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsOptical light guidesEngineeringCo2 laser
The invention provides a high-stability optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor packaged without glue and a manufacturing method. The sensor comprises a sensor head, a sensor body with a through-hole in middle, and an optical fiber, wherein a four-layer structure (comprising a first monocrystalline silicon piece, a first Pyrex sheet glass, a second monocrystalline silicon piece and a second Pyrex sheet glass) is adopted by the sensor head; a first reflecting surface of a Fabry-Perot cavity is formed by the back surface of the first monocrystalline silicon piece; the second monocrystalline silicon piece is used for providing a second reflecting surface of the Fabry-Perot cavity; the second Pyrex sheet glass is in butt fusion with the sensor body; and the optical fiber is fixedly arrangedin the sensor body by adopting a CO2 laser, and thereby non-glue packaging is realized. When the first layer of monocrystalline silicon piece is deformed by external pressure changes, the length of the optical fiber Fabry-Perot cavity is changed; and after a broadband light source is accessed to the sensor, the change of the cavity length can be extracted through collecting a reflection spectrum of the sensor or extracting low-coherence interference fringes of the sensor, and thereby pressure information is obtained. By adopting the structure, the influences of environmental changes such as the temperature, the humidity, and the like can be effectively eliminated, and the measurement accuracy can be greatly improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
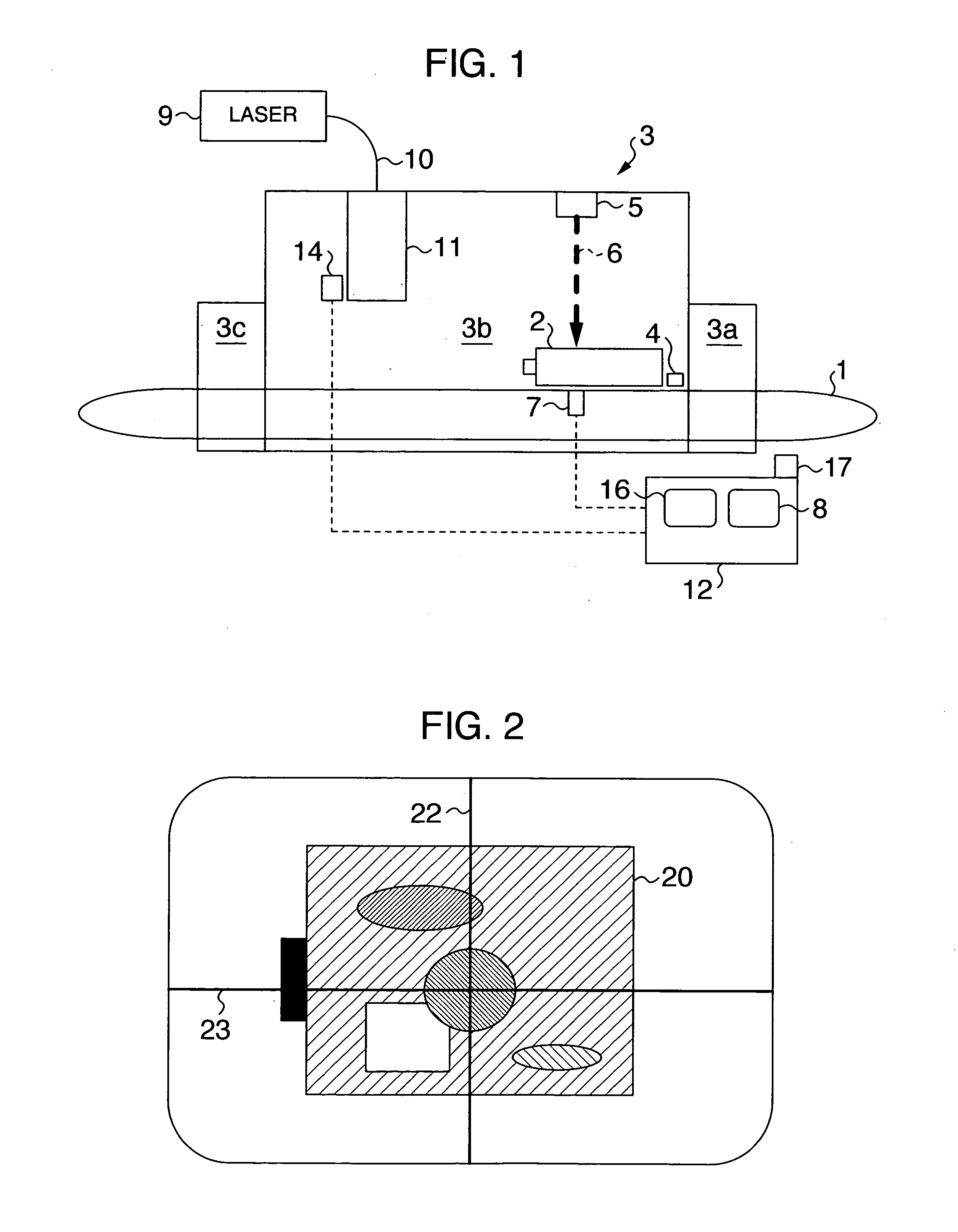
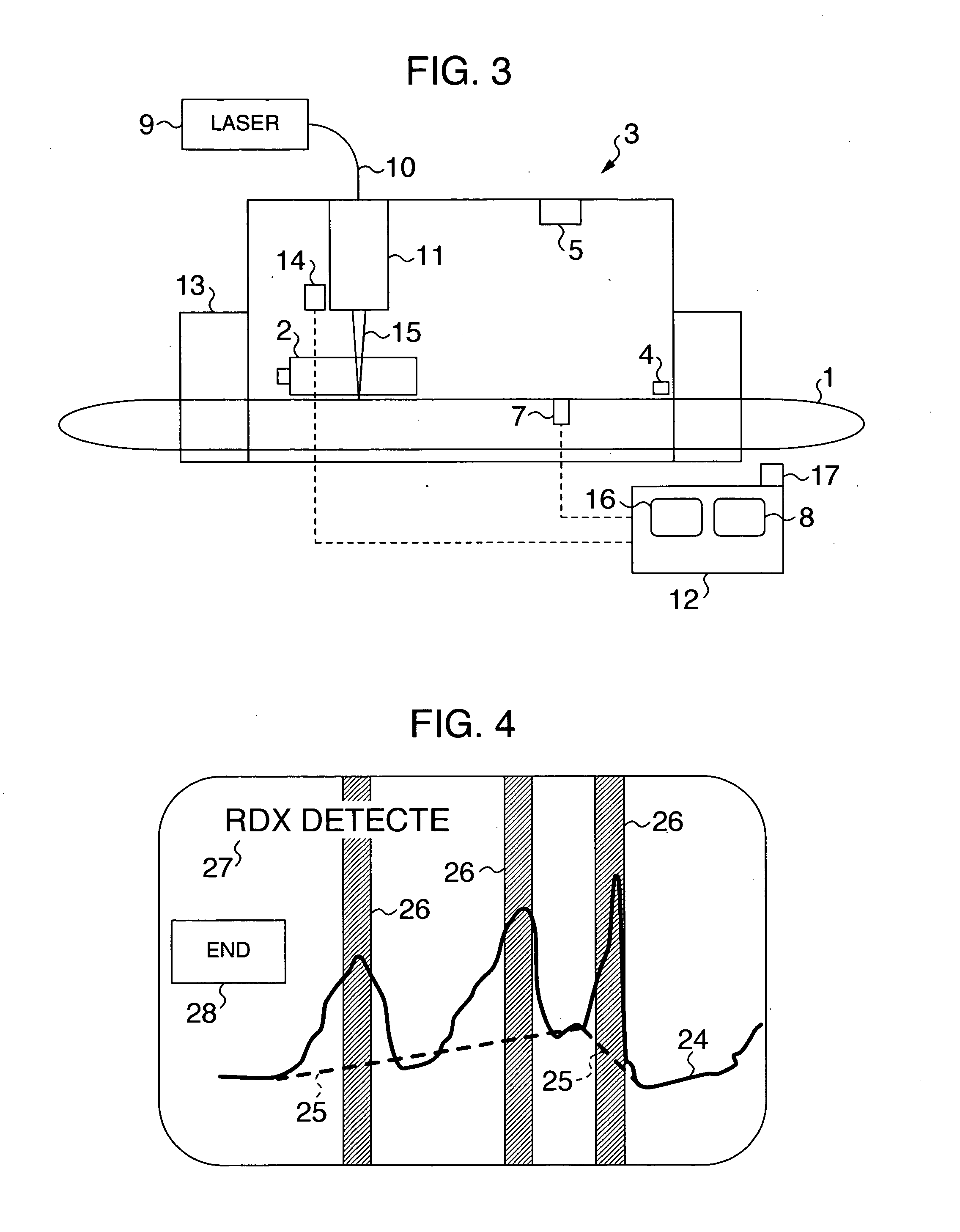
Method and equipment for detecting explosives, etc.
InactiveUS20060056586A1Short inspection timeImprove the delivery effectElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by optical meansX-rayX ray image
A method and equipment for detecting an explosive, etc. are disclosed. A specified portion highly likely to contain an explosive, etc. is extracted based on the X-ray image obtained by radiating an X ray on an object to be inspected. An electromagnetic wave containing the terahertz wave is radiated on the specified portion thus extracted. The presence or absence of the explosive, etc. is determined based on at least one of the absorption spectrum and the reflection spectrum of the electromagnetic wave at the specified portion.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
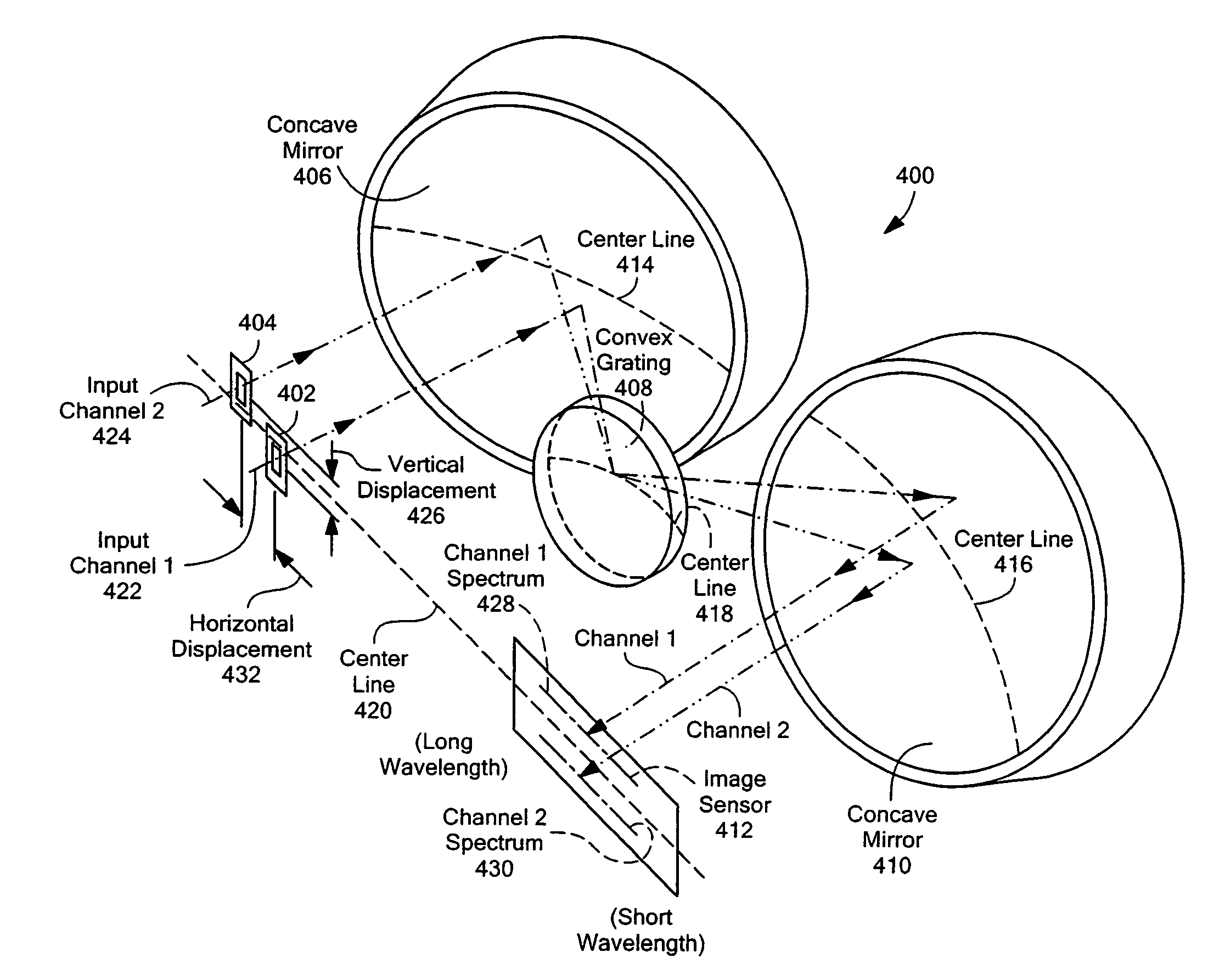
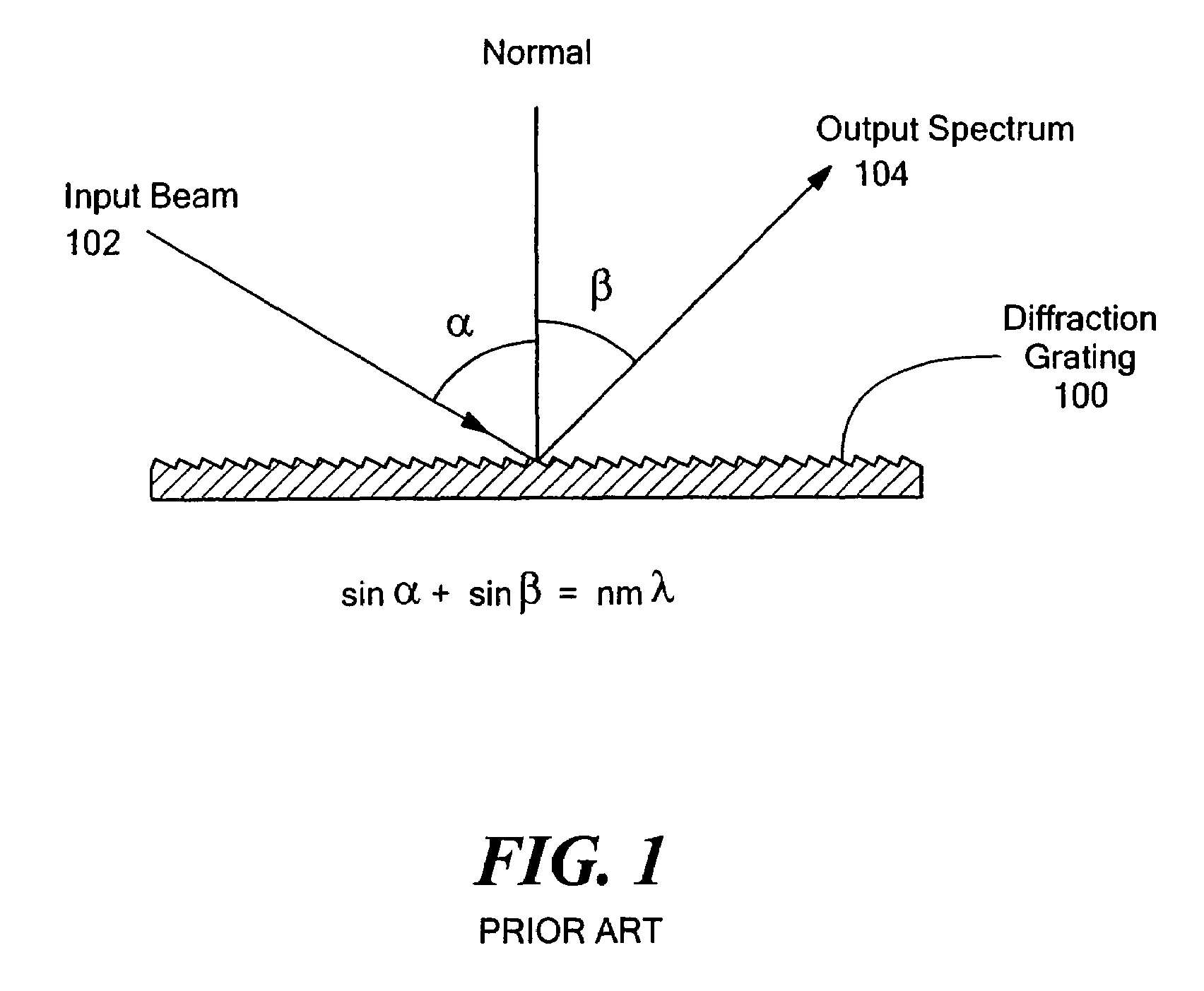
Multi-channel, multi-spectrum imaging spectrometer
Owner:HEADWALL PHOTONICS
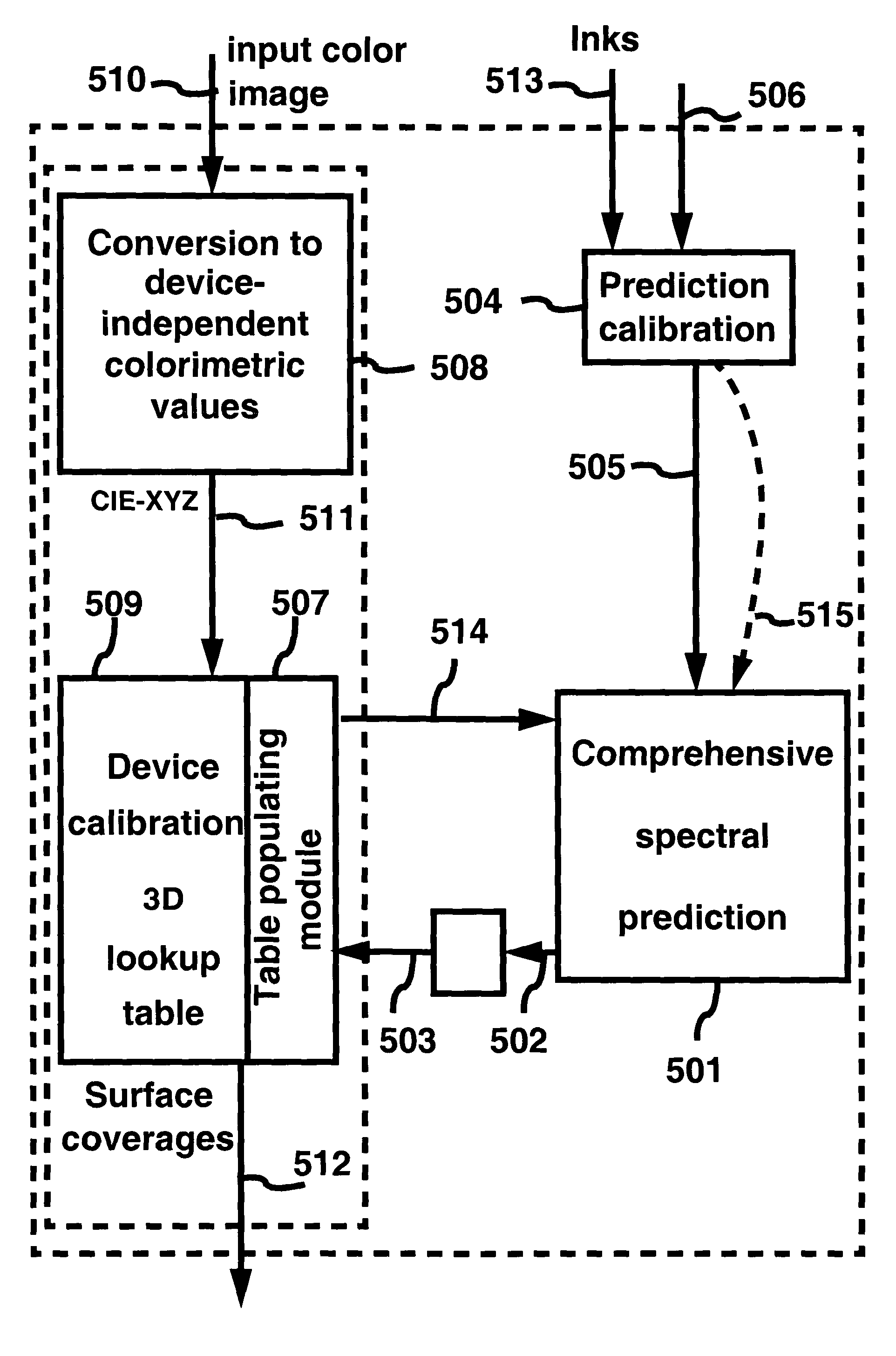
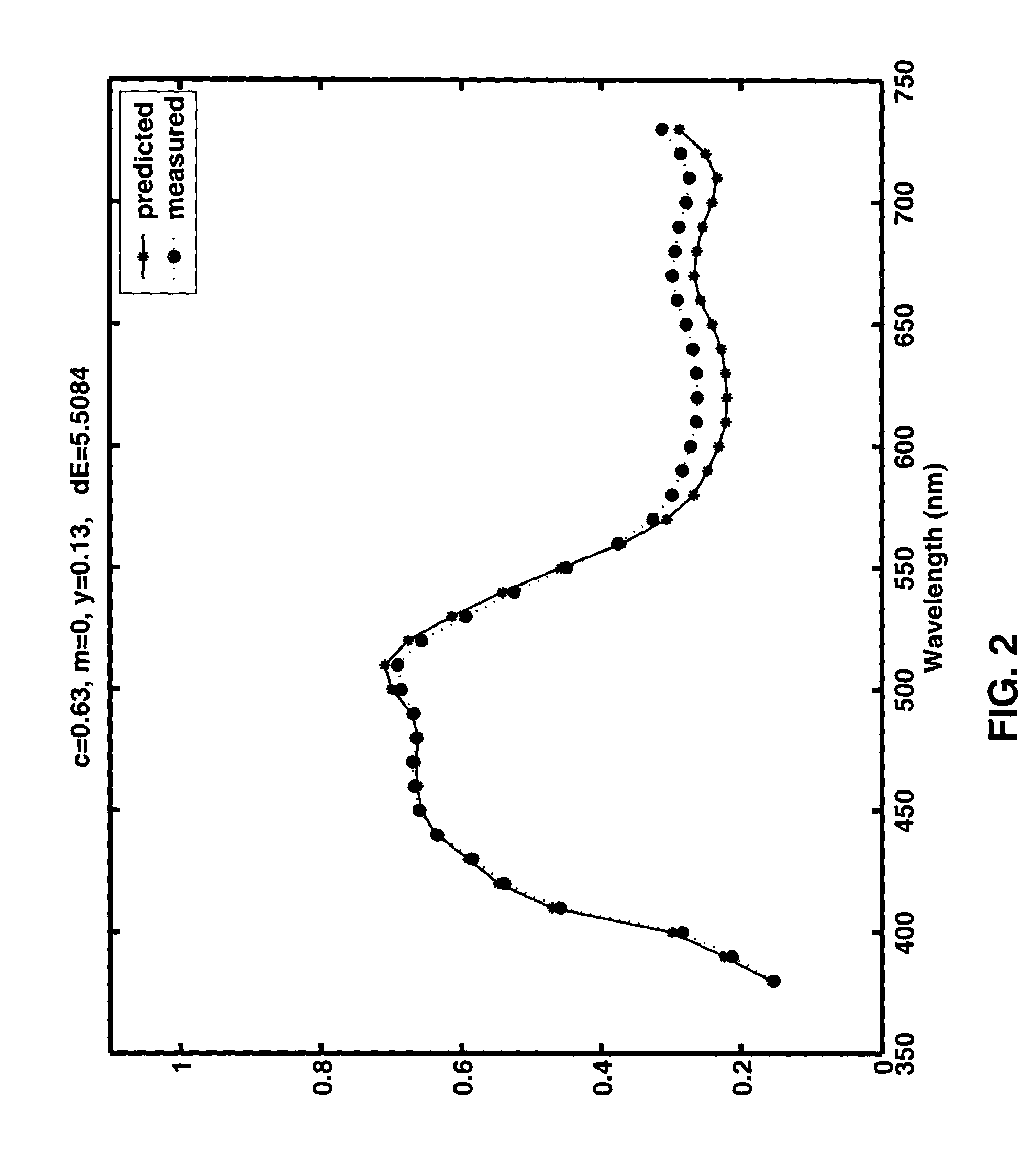
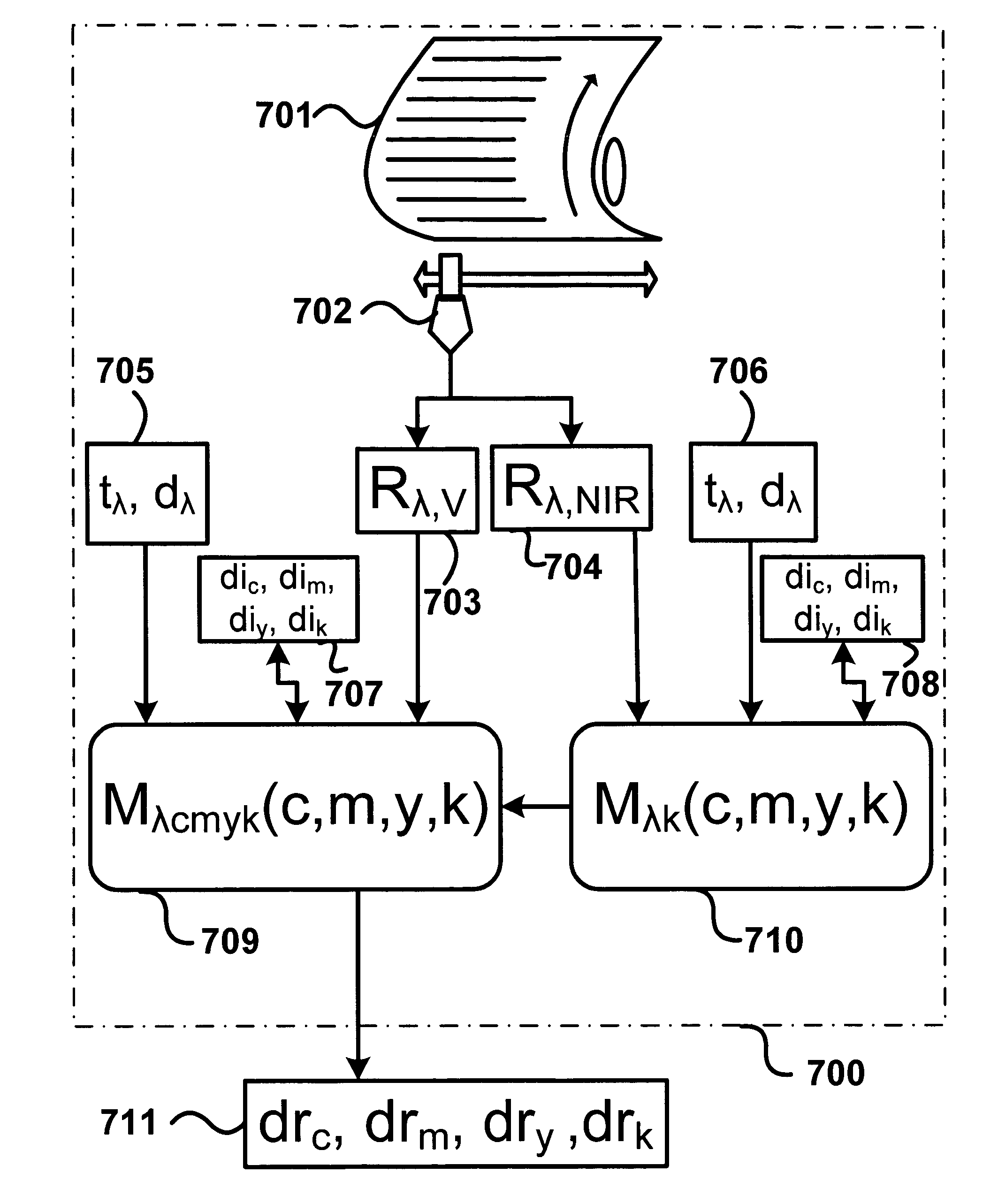
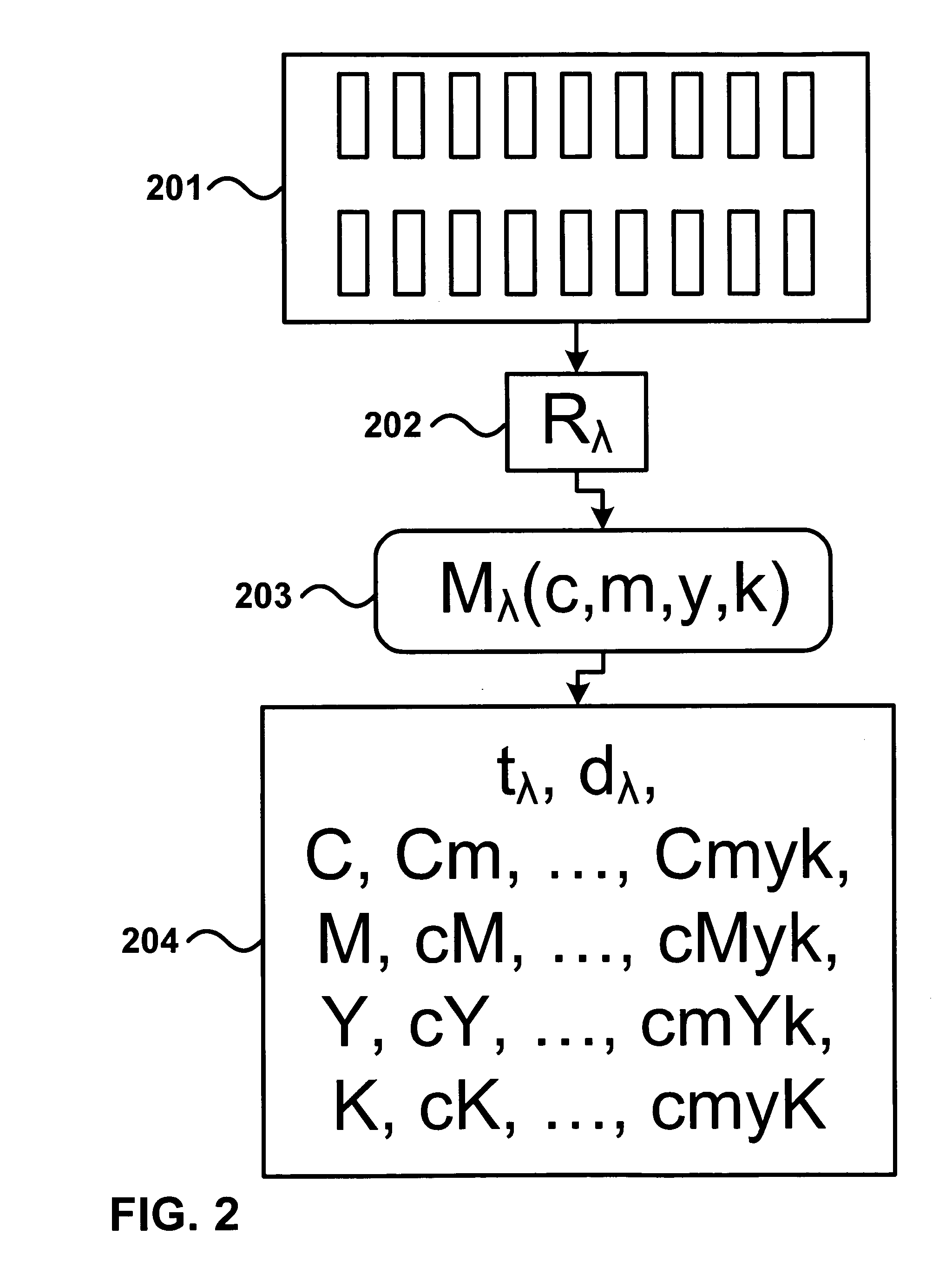
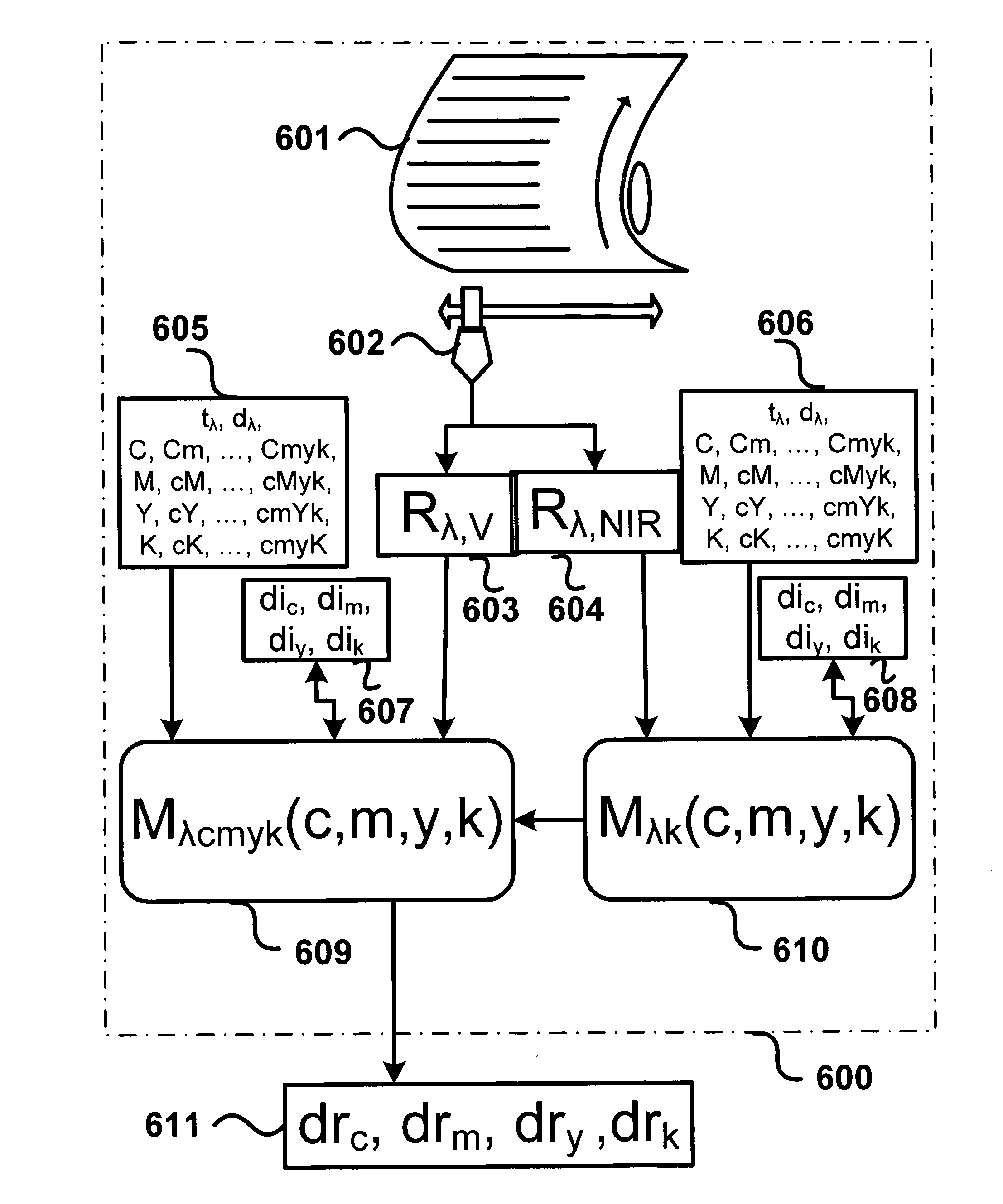
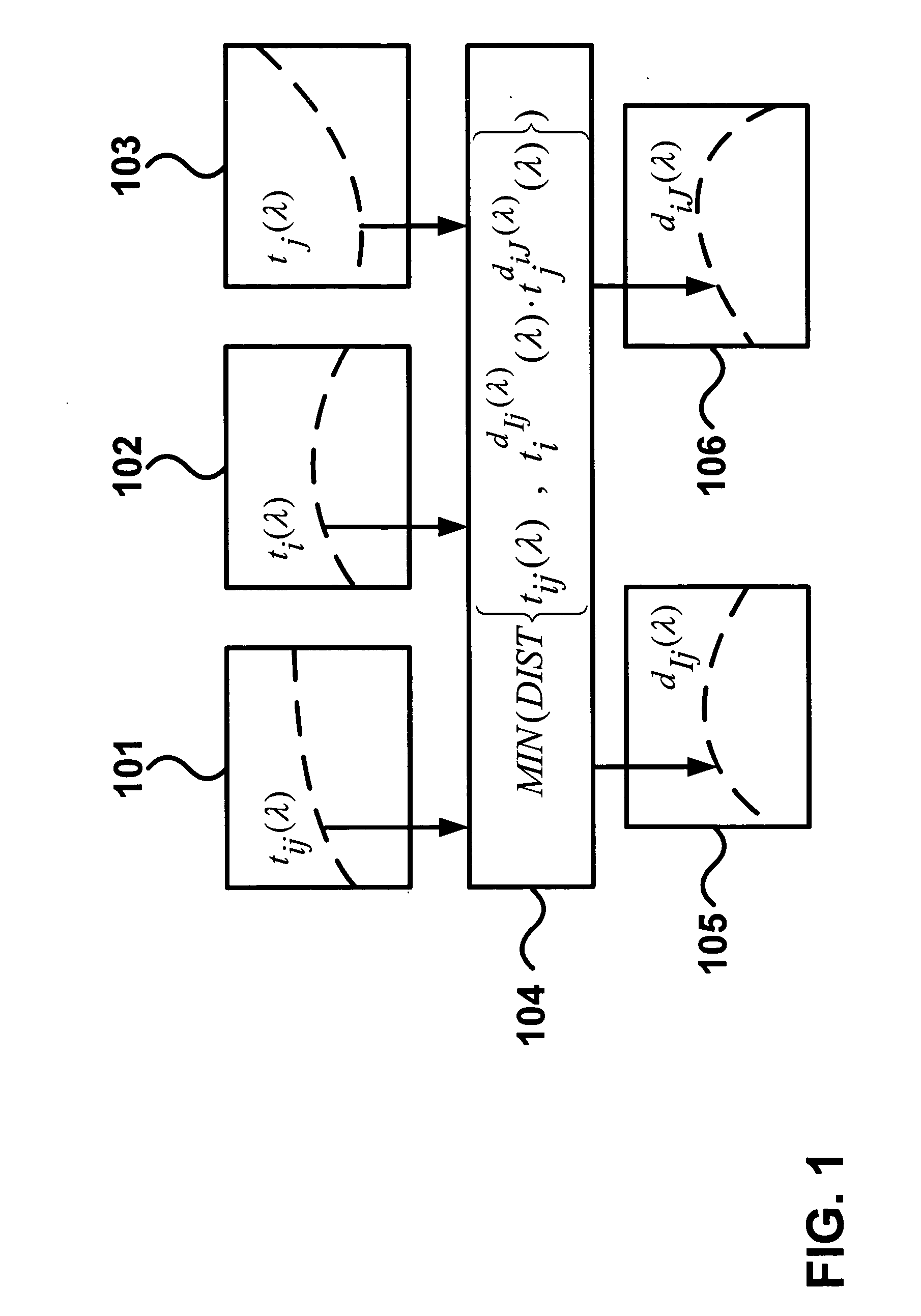
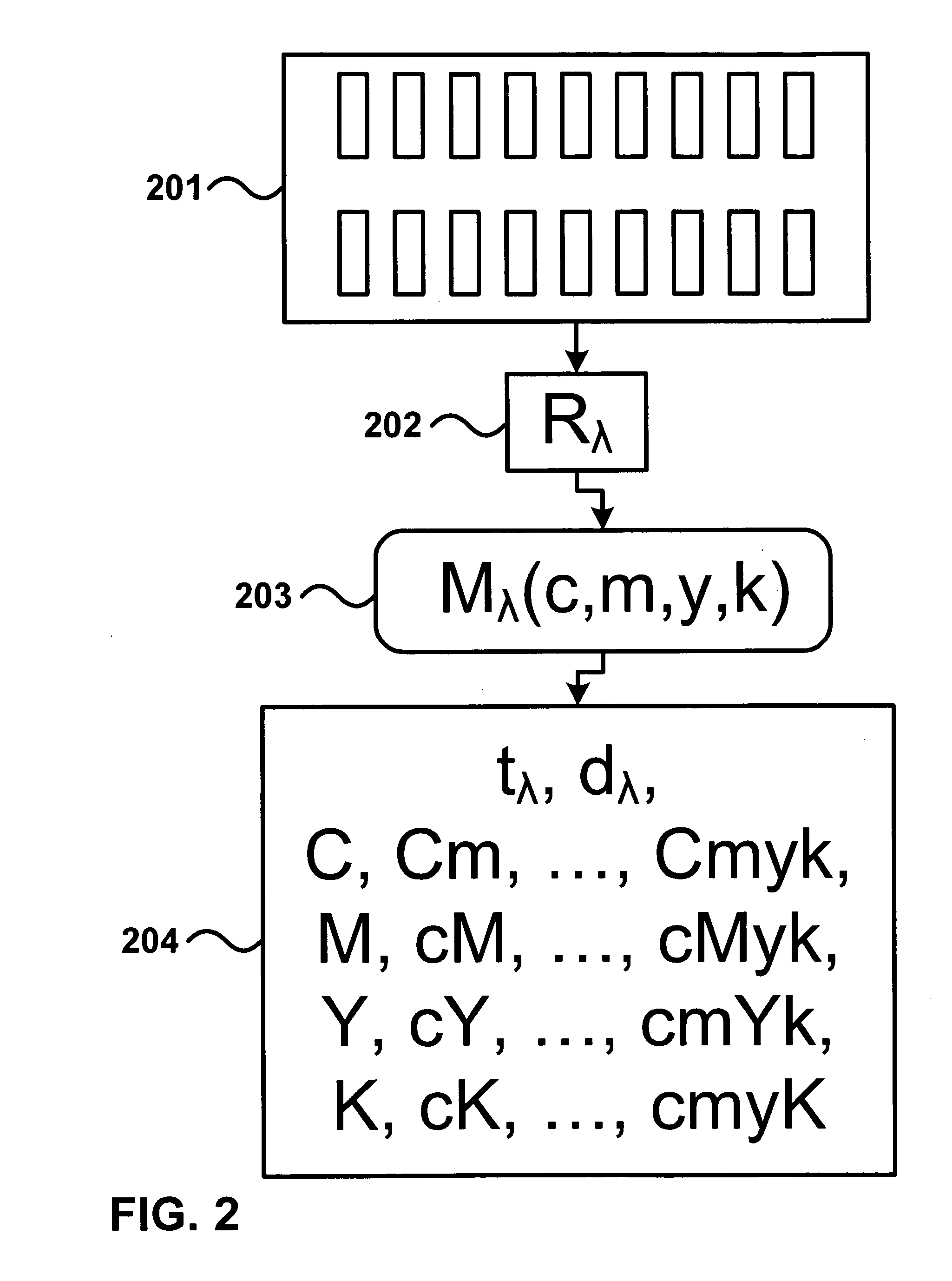
Prediction model for color separation, calibration and control of printers
InactiveUS20050083540A1Easy CalibrationImprove accuracyDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsEffective surfaceHue
The present invention facilitates the calibration of printers and the color separation of input images into a set of inks by disclosing methods and systems for populating device-calibration lookup tables. The disclosed methods and systems rely on a comprehensive spectral prediction model which is capable of predicting at a high accuracy the reflectance spectra of halftone ink patches. The comprehensive spectral prediction model is composed of a first part predicting the reflection spectra as a function of physical (mechanical) surface coverages and of a second part comprising functions mapping nominal surface coverages to effective surface coverages. These mapping functions are calibrated by halftone patch wedges printed alone and by half-tone patch wedges printed in superposition with one or several solid inks. The part of the comprehensive spectral prediction model predicting the reflection spectra relies on a weighted average between one component behaving according to the Clapper-Yule model and another component behaving as the spectral Neugebauer model, extended to include multiple internal reflections at the paper-air boundary. The disclosed methods and systems can perform the color separation as well as the calibration of printers printing with standard cyan, magenta, and yellow inks as well as with inks comprising standard and non-standard inks such as Pantone inks (custom inks). They are also used for performing precise undercolour removal in order to carry out the color separation of images into cyan, magenta, yellow and black inks. They can further be used to carry out the color separation of images into cyan, magenta, yellow, black, light cyan and light magenta inks. In addition, the disclosed methods and systems can be used for printer control, i.e. to control printer actuation parameters in different types of printers e.g. liquid ink professional printers (offset, gravure, letterpress), electrophotographic printers, ink-jet printers, thermal transfer printers and in dye-sublimation printers.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
On-line measurement method and device for micro/nano deep trench structure
ActiveCN101393015ARealize onlineQuick measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUsing optical meansWidth ratioArtificial neural network
The invention discloses an online measuring method and an online measuring device for a micro-nano deep groove structure. The method comprises the following steps: linearly polarized infrared beams are projected to the surface of a sample piece which is provided with the deep groove structure, and measured reflection spectra are obtained after interference signals which are formed by reflected light on various interfaces of the groove structure are subjected to filtration and so on; an equivalent optical model of the deep groove structure is established by the polarization-based equivalent medium theory, and theoretic reflection spectra of the equivalent optical model of the deep groove structure are calculated; and the width and the depth of the groove are quickly extracted by the quick parameter extraction method of combination of an artificial neural network and a local search algorithm and through fitting of the theoretic reflection spectra and the measured reflection spectra, and precise online measurement of geometrical shape parameters of the deep groove is realized. The device comprises an infrared source, an infrared polaroid sheet, an interferometer, a plane mirror, two off-axis parabolic mirrors and an infrared detector. The device can realize online measurement of the depth and the width of the deep groove structure with high depth-width ratio in a field effect tube and a dynamic RAM during the manufacturing procedure, and has the characteristics of nondestructiveness, quickness and low cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
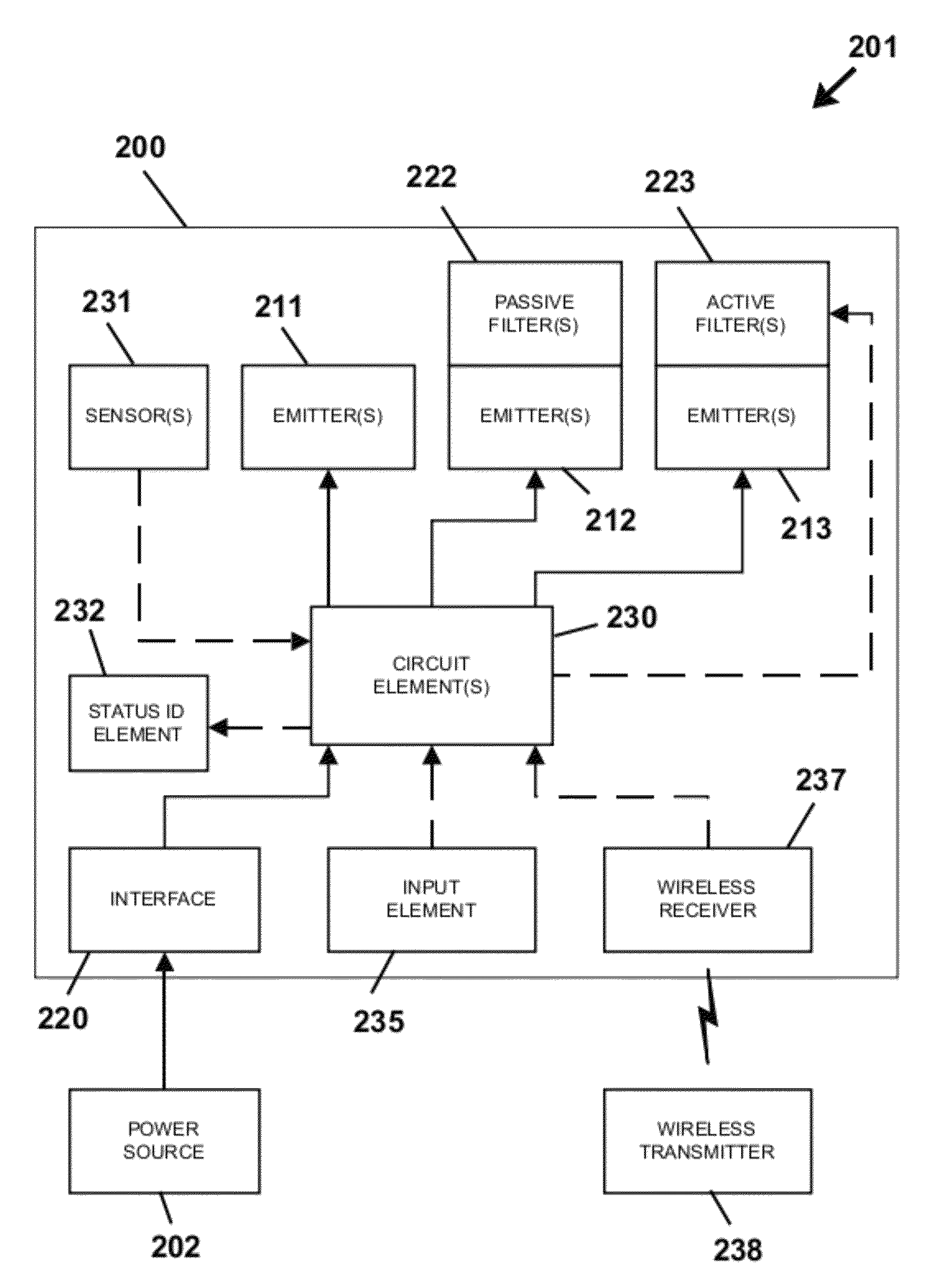
Lighting device with defined spectral power distribution
Solid state lighting devices and illumination methods involve use of multiple solid state emitters of different colored outputs (optionally including at least one white or near-white emitter). Operation of the solid state emitters is controlled with at least one circuit element to emphasize and / or deemphasize perception of at least one color of a target surface based upon a reflectance spectral distribution of the target surface. At least one emitter may have an associated passive or active filter; the filterable emitter and / or active filter may be operated to deemphasize perception of at least one color of a target surface. Activation and / or alteration of emphasis or deemphasis of perception of color of a target surface may be selected by a user or automatically controlled.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
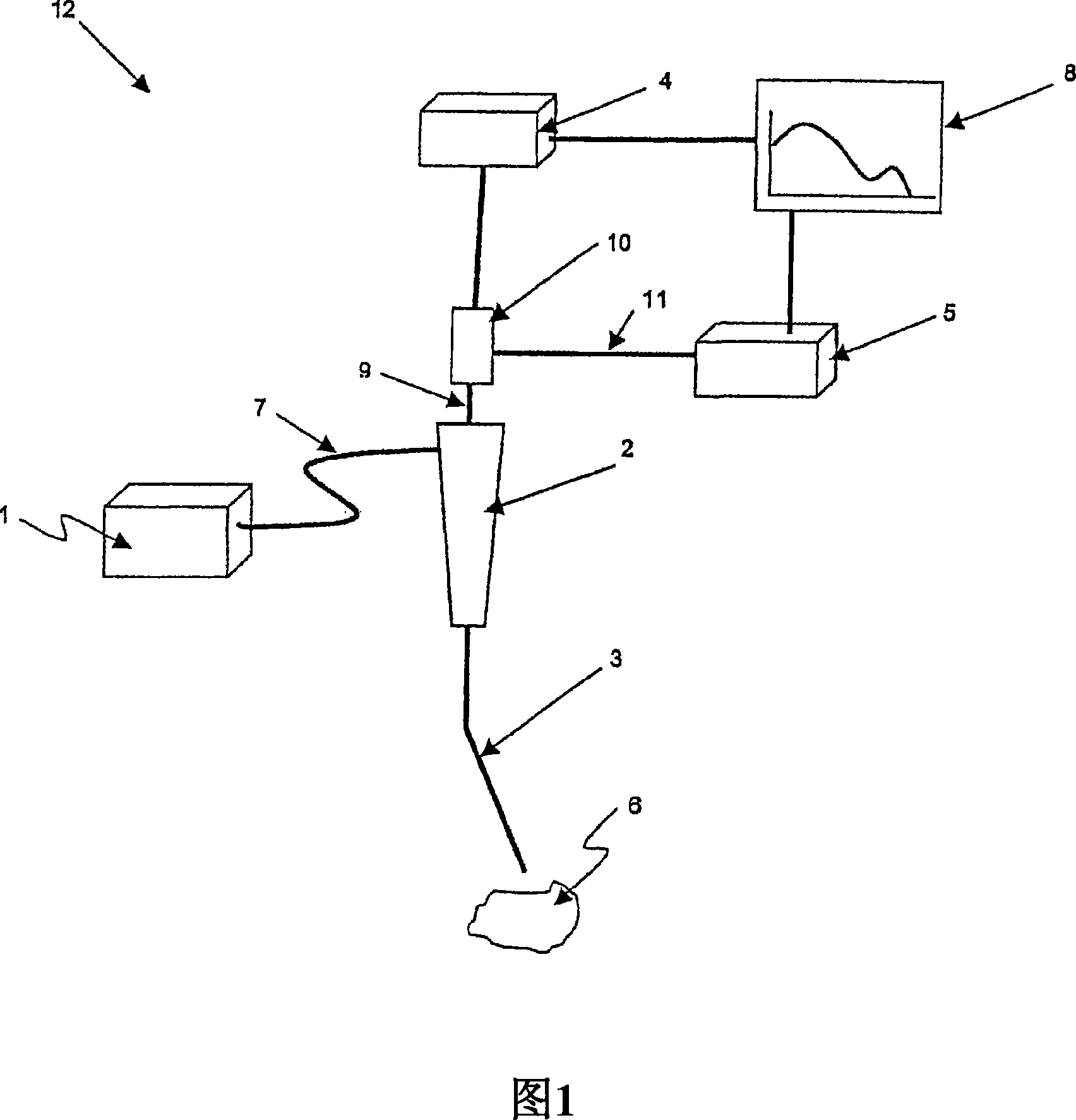
Optical sensing system for determining the position and/or shape of an associated object
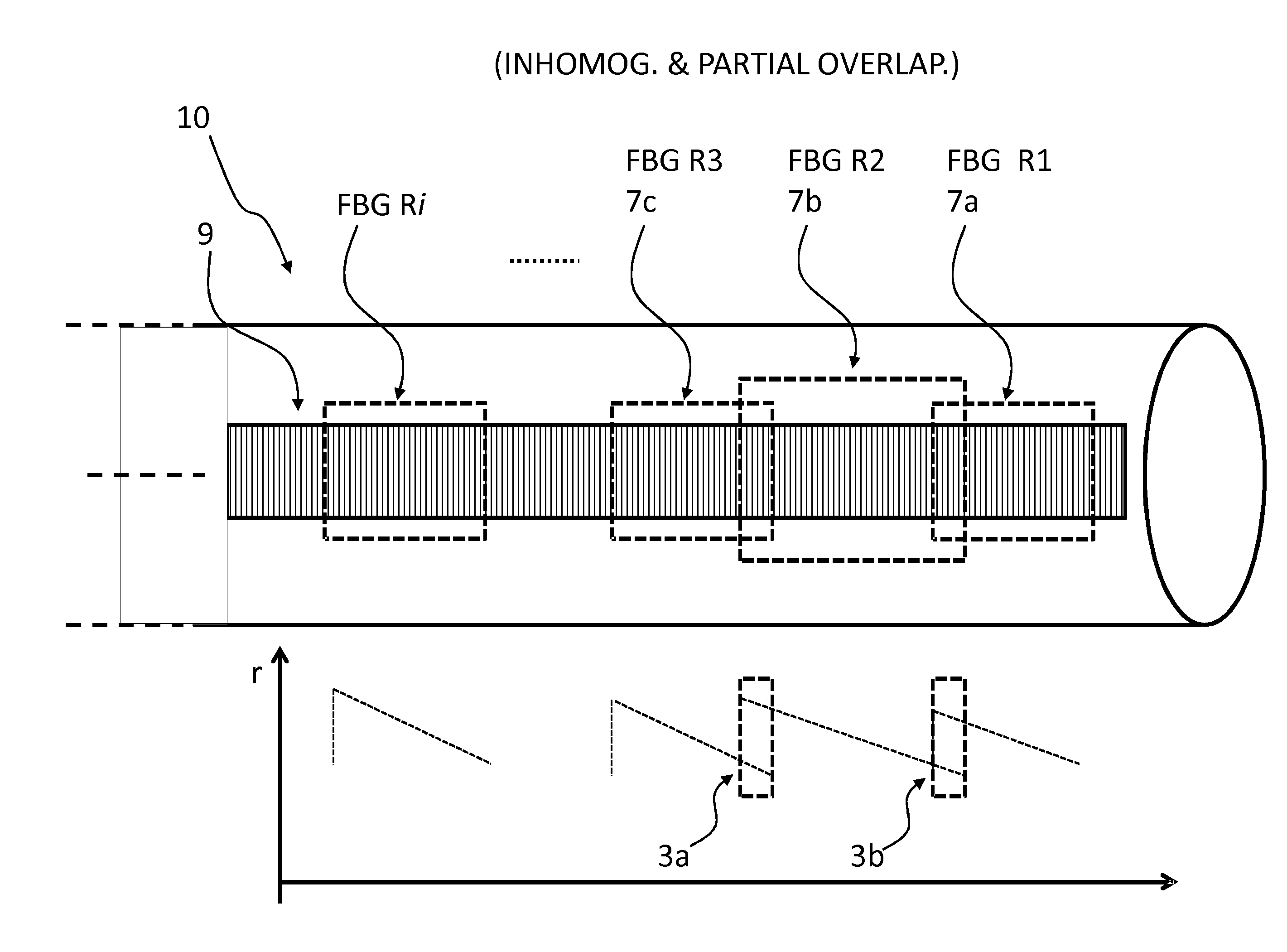
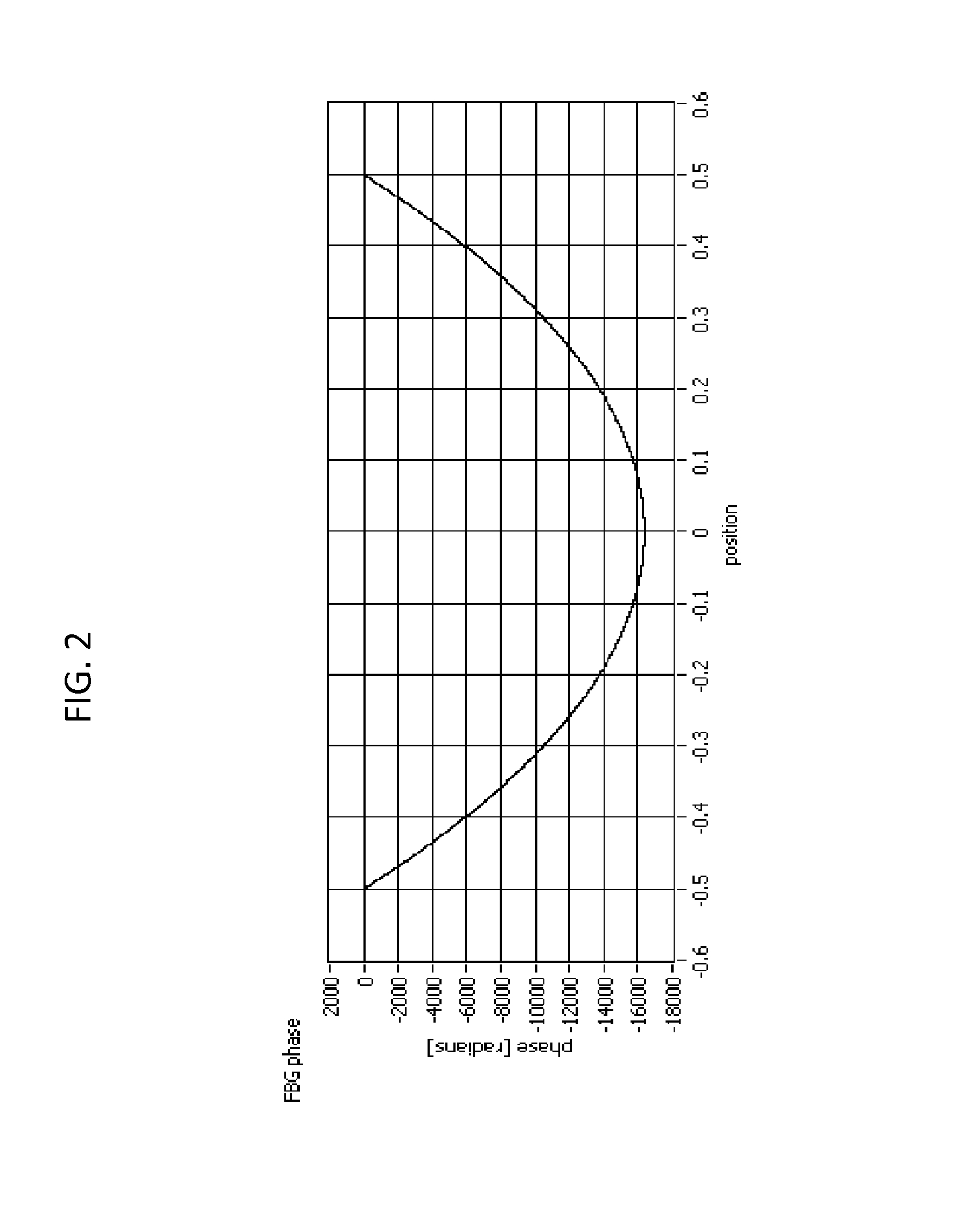
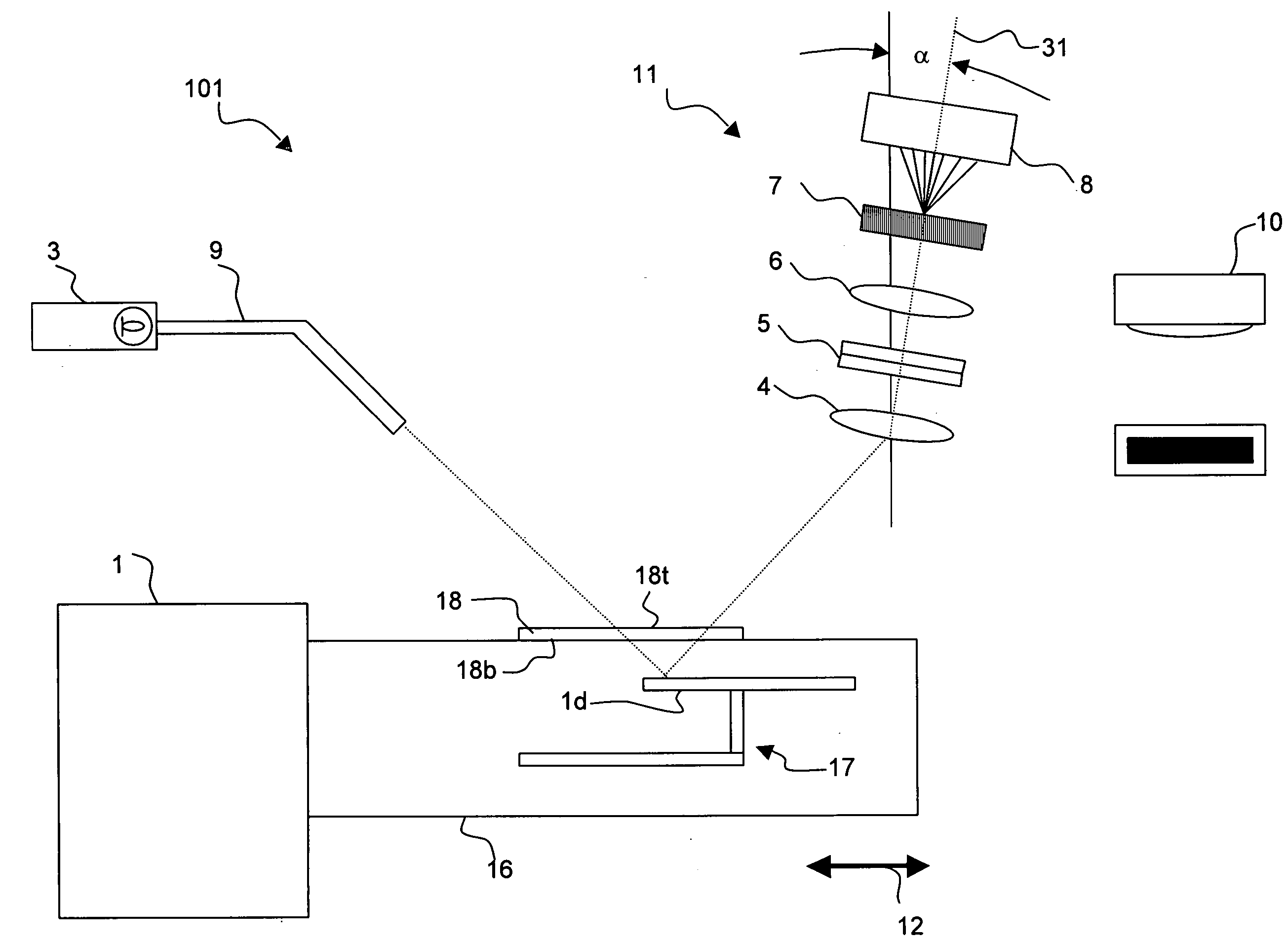
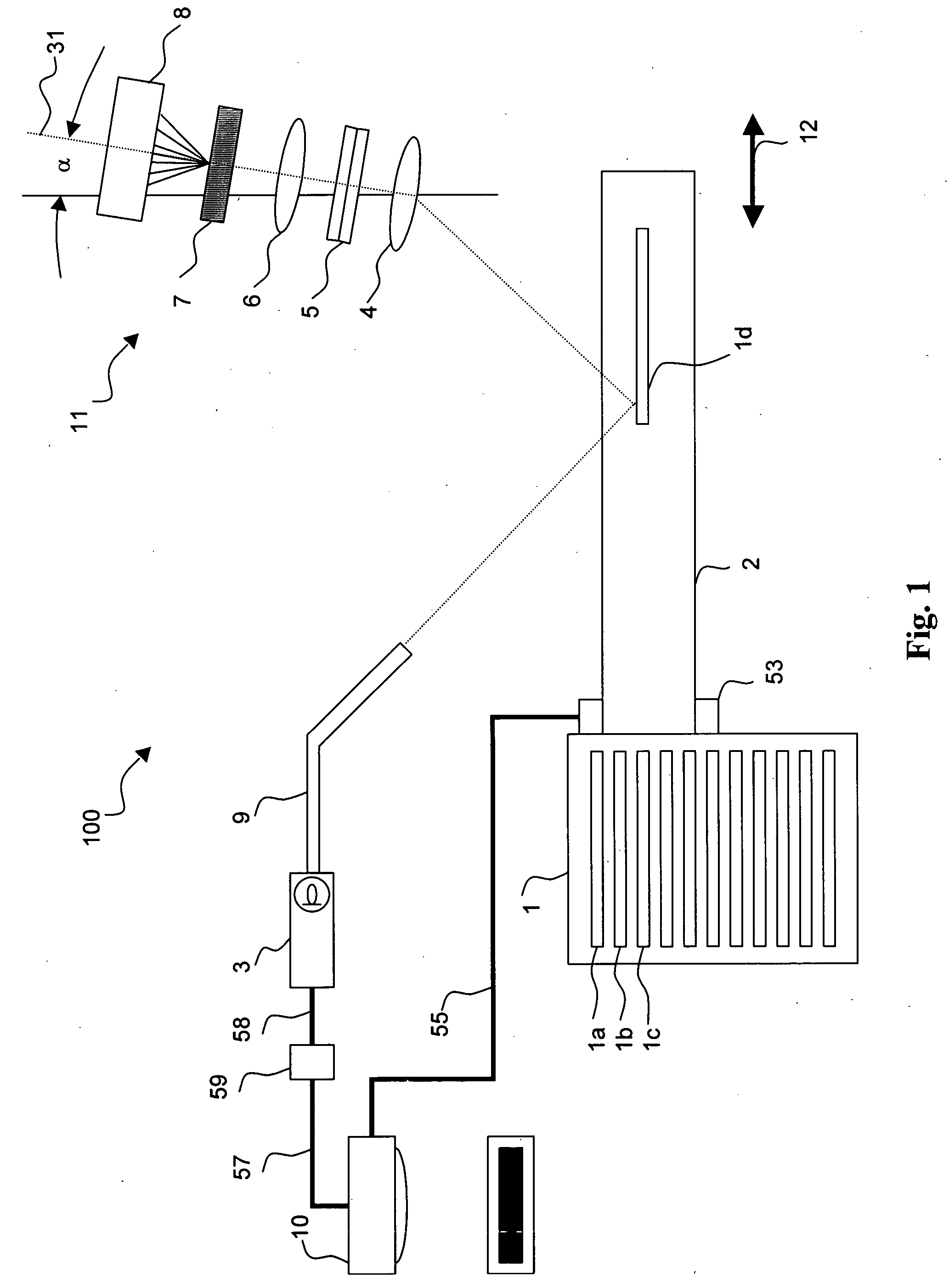
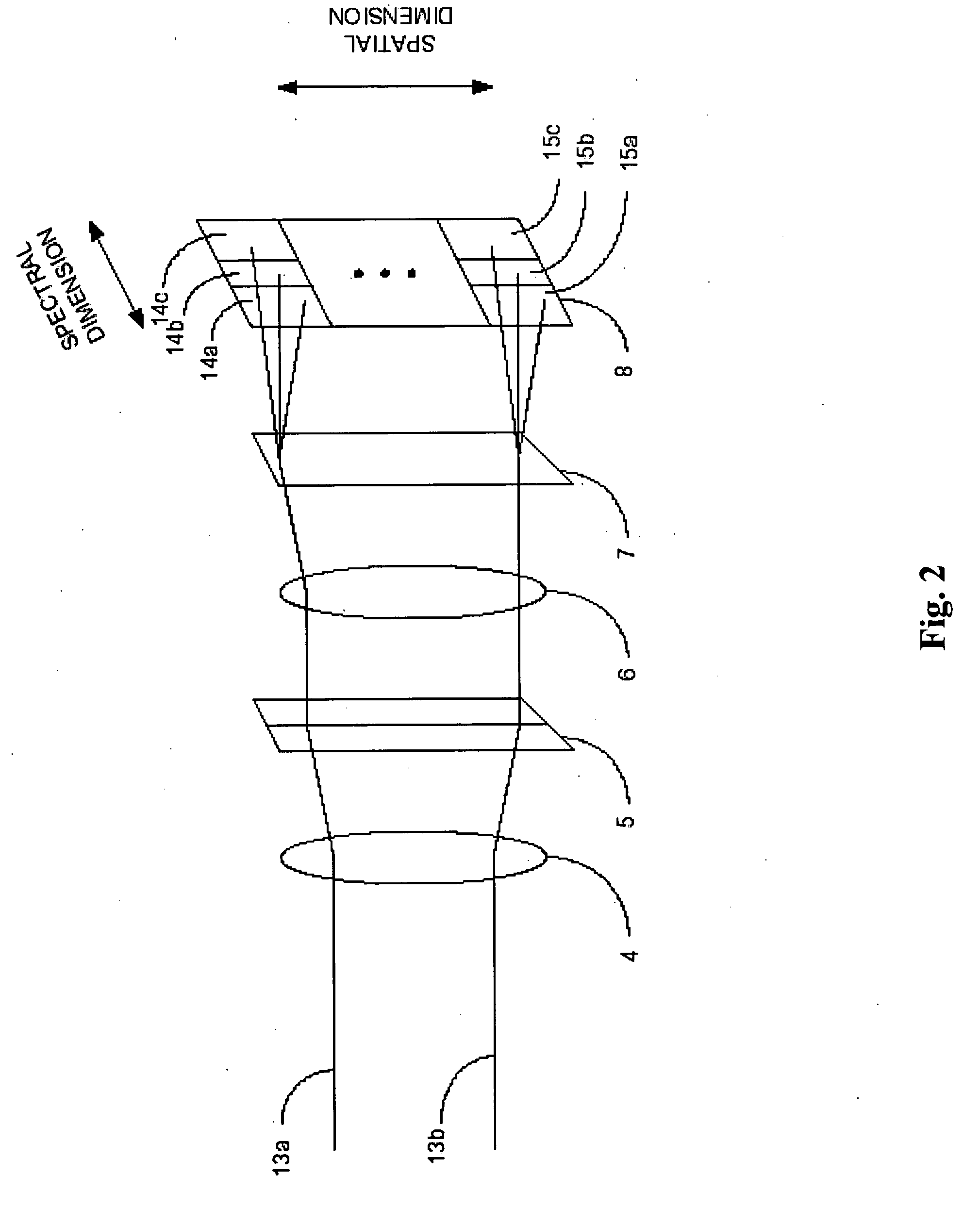
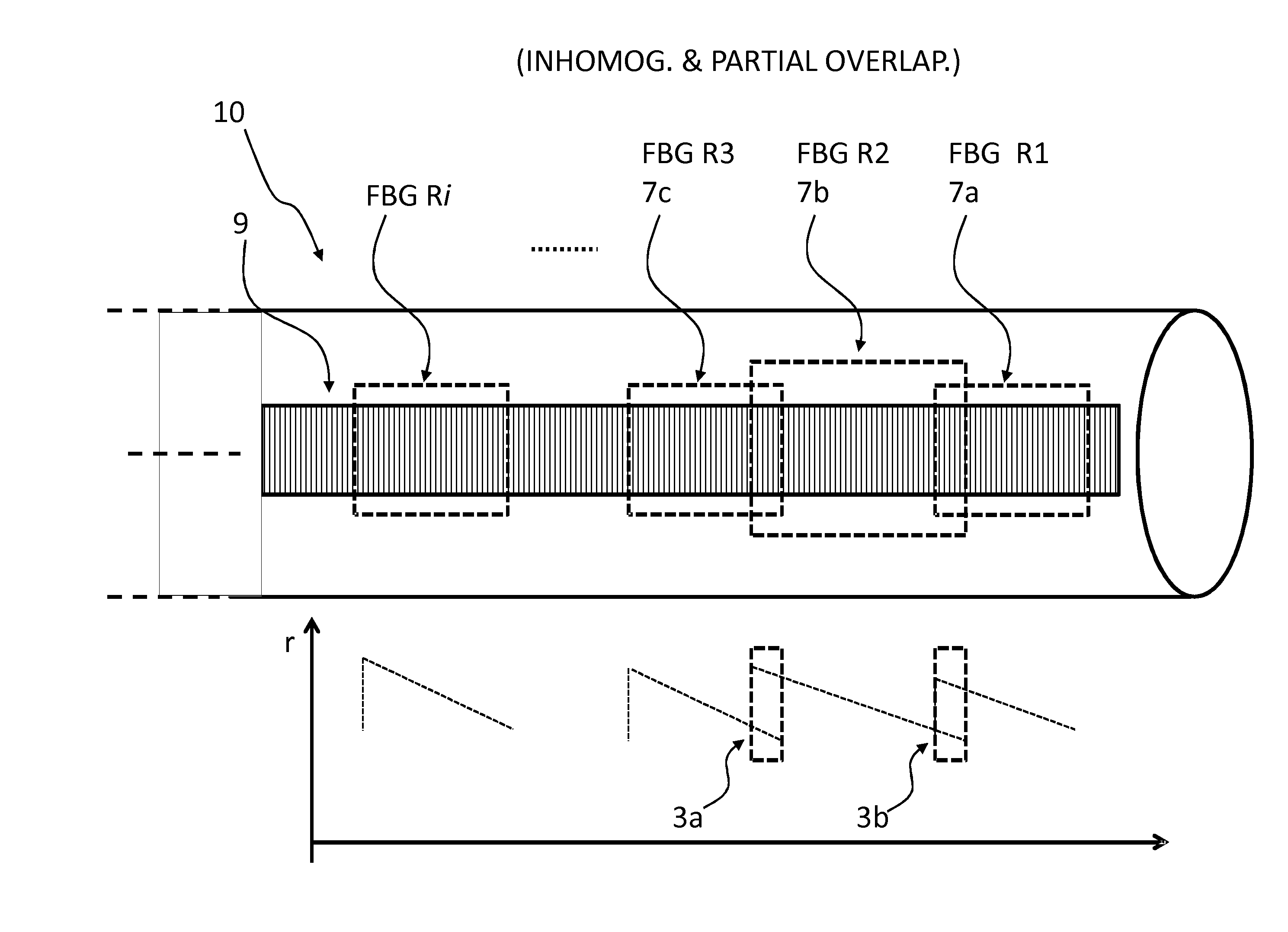
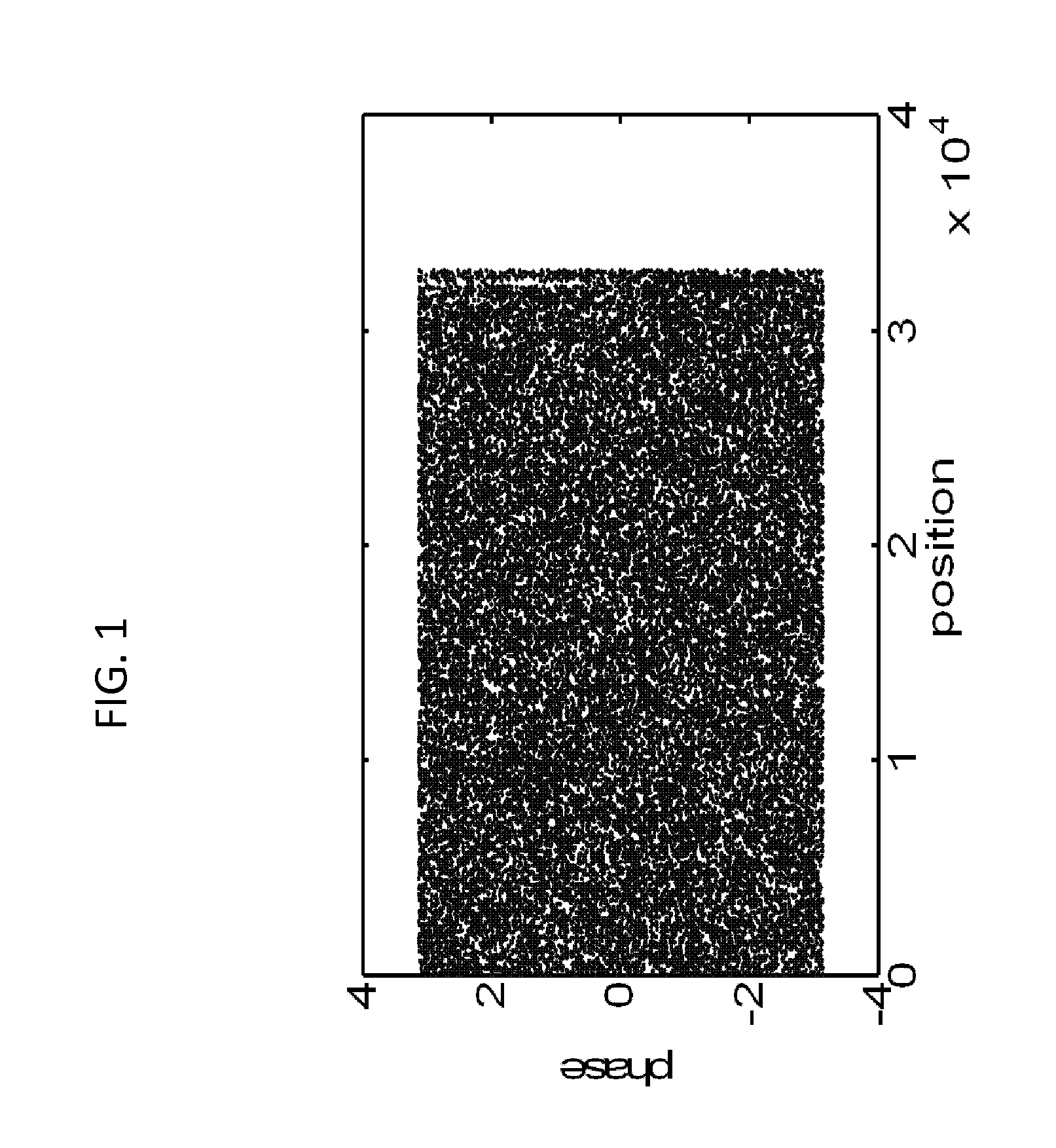
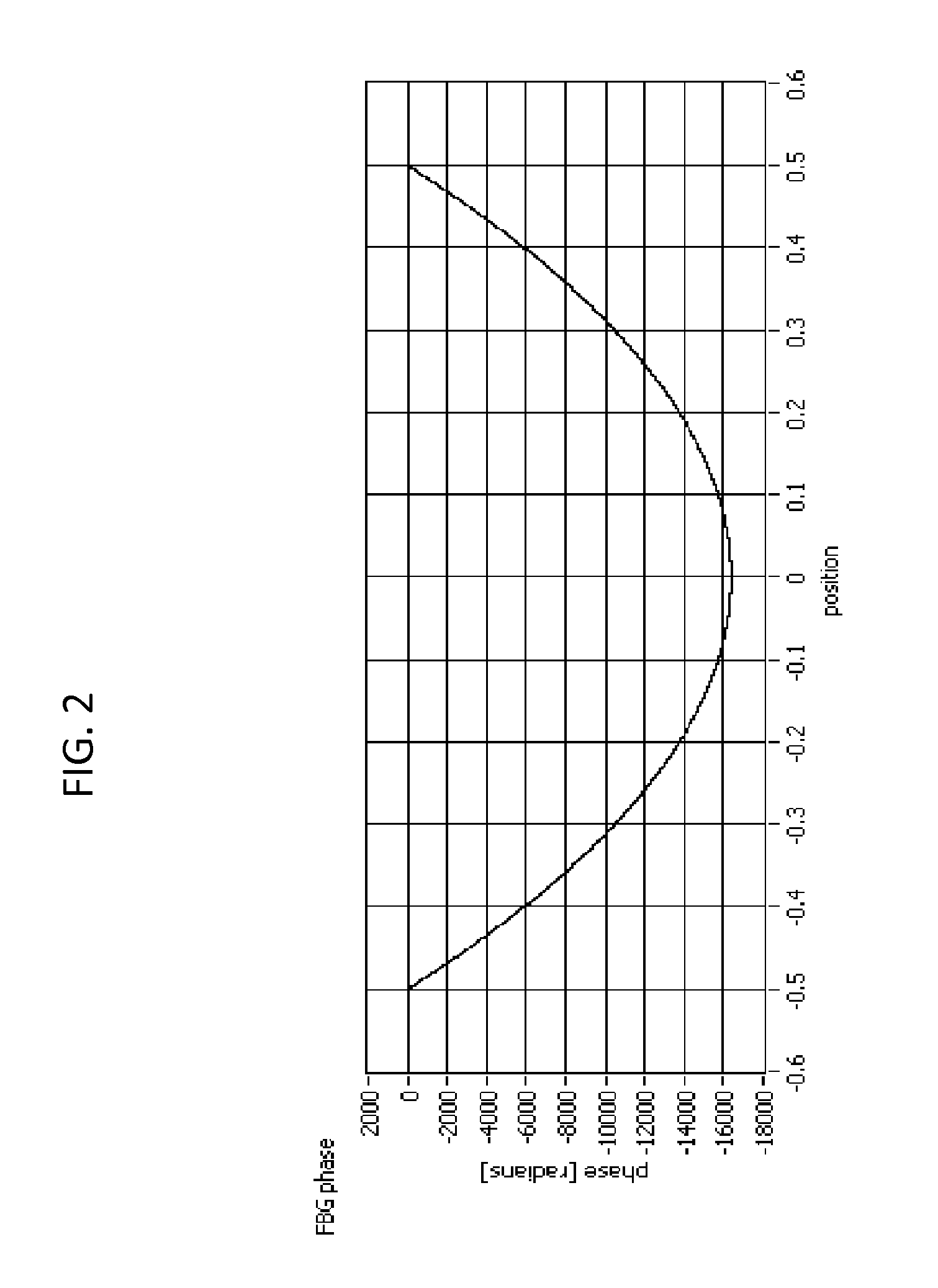
The present invention relates to an optical sensing system (1) for determining the position and / or shape of an associated object (O), the system comprises an optical fibers (10) having one or more optical fiber cores (9) with one or more fiber Bragg gratings (FBG, 8) extending along the full length where the position and / or shape is be to determined of said object (O). A reflectometer (REFL, 12) measures strain at a number of sampling points along the optical fiber cores, and a processor (PROC, 14) determines the position and / or shape based on said measured strains from the plurality of optical fiber cores. The fiber Bragg grating(s) (FBG, 8) extends along the full length of said optical fiber cores (9), the fiber core having a spatially modulated reflection (r) along the said full length of the optical fiber core so that the corresponding reflection spectrum is detectable in said wavelength scan. Thus, the fiber Bragg grating(s) may be effectively continuous along the optical fiber leaving no gaps so that every position gives rise to a detectable reflection, and achieving that the reflection spectrum may encompass a wavelength span equaling the wavelength scan, or ‘sweep’, of an optical source in the reflectometer.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
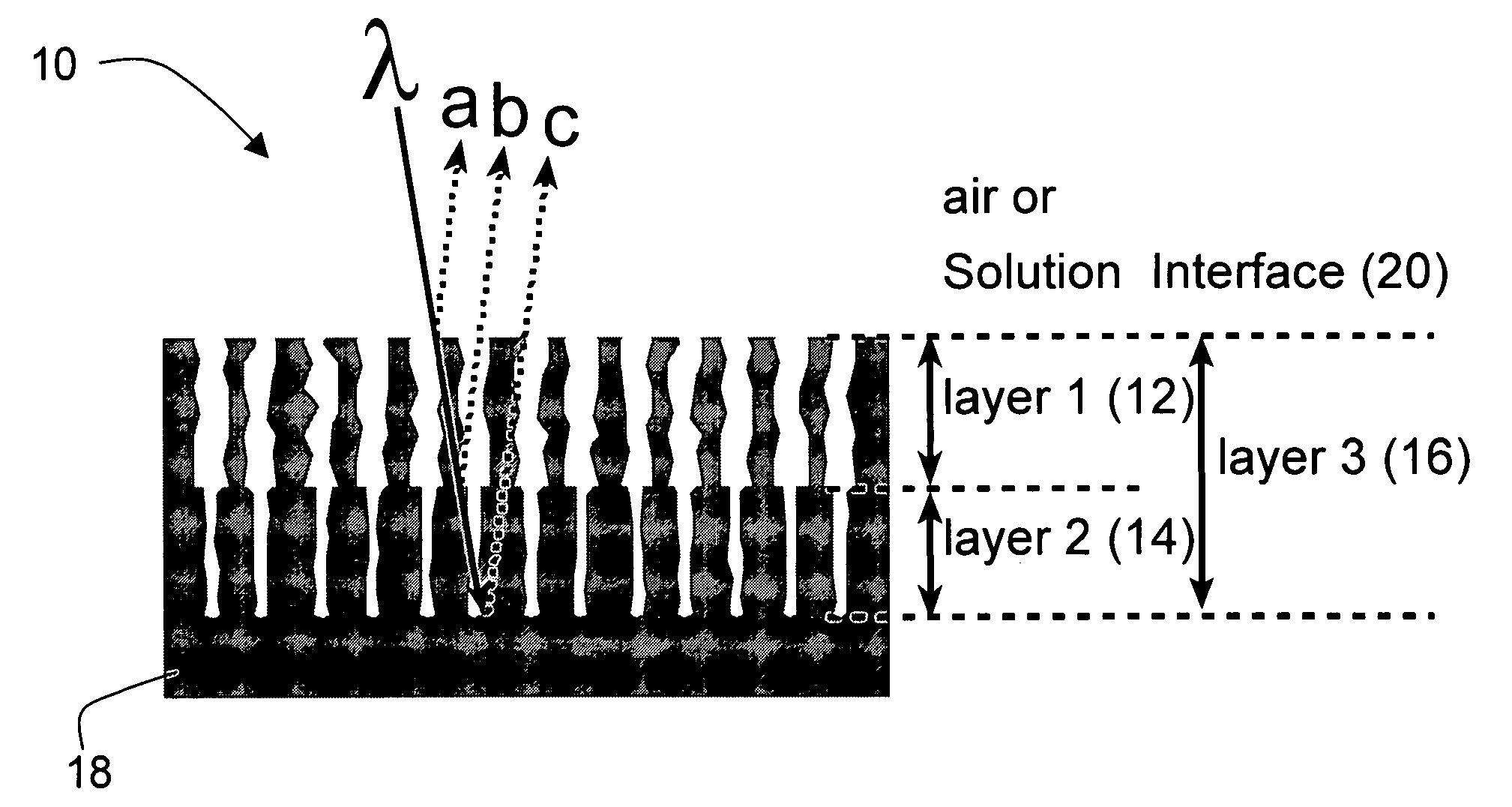
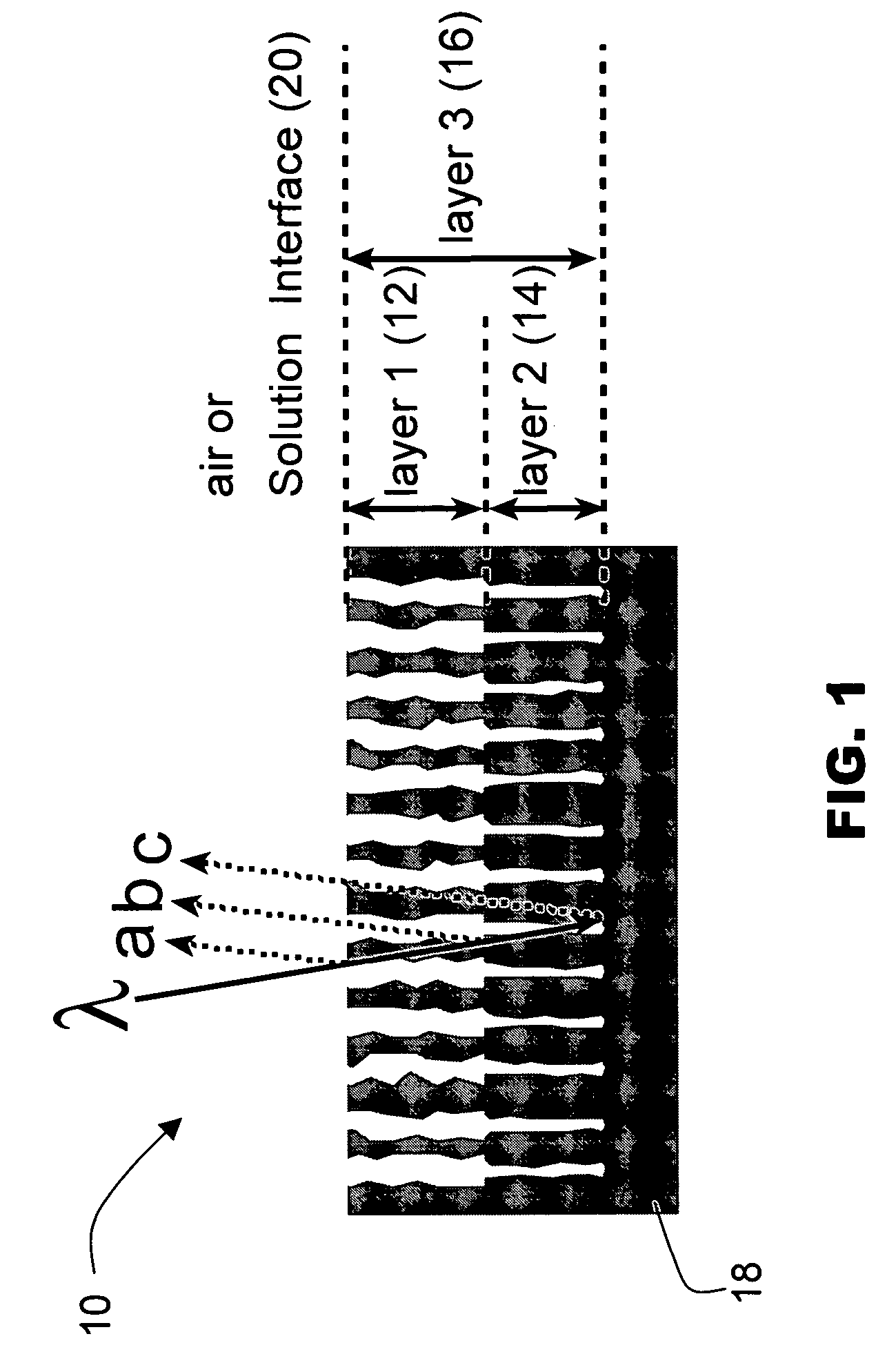
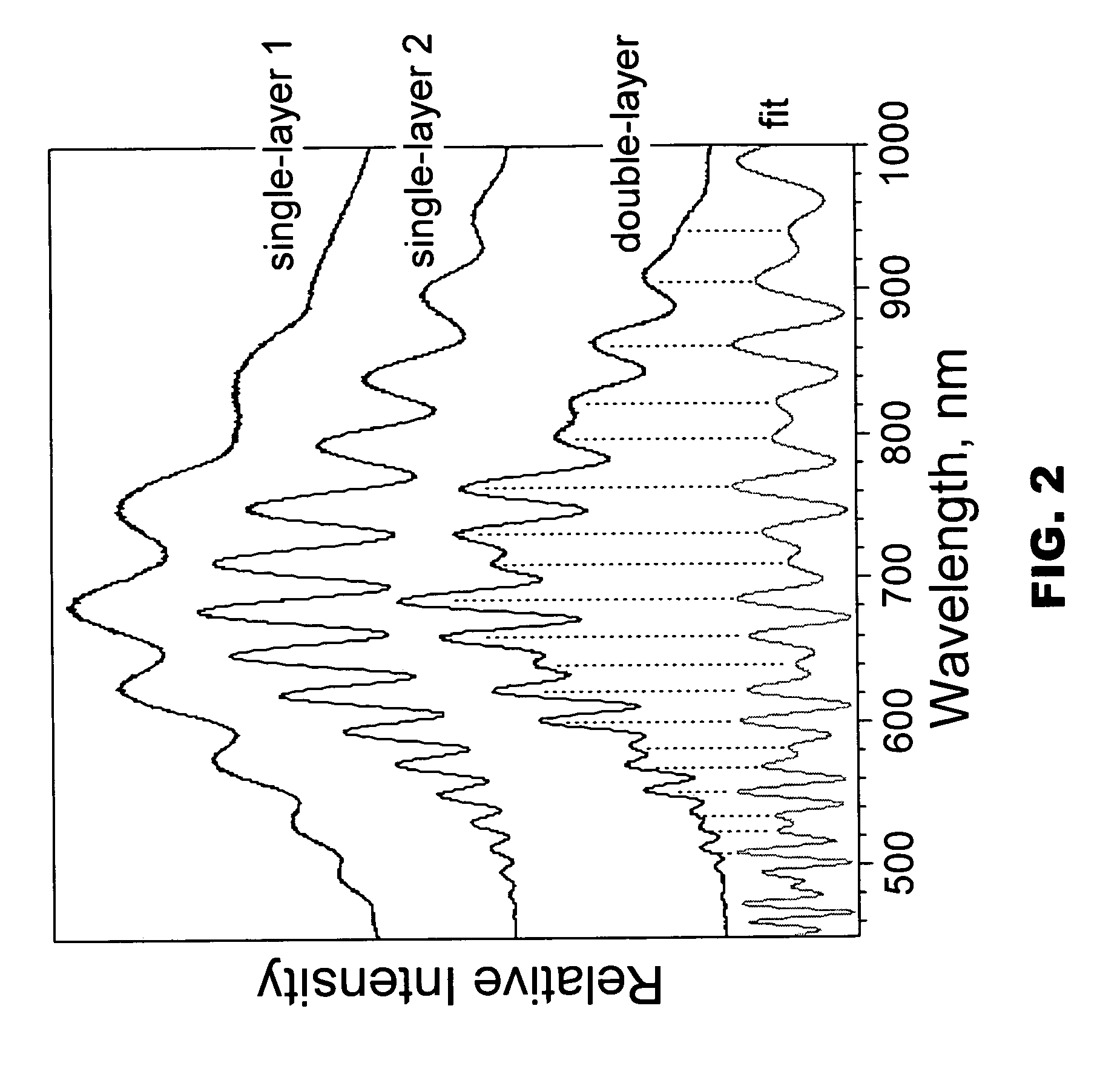
Porous microstructure multi layer spectroscopy and biosensing
InactiveUS20070108465A1Scattering properties measurementsSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionSpectroscopyPorous silicon
A preferred embodiment biosensor is a multi-layer micro-porous thin film structure. Pores in a top layer of the micro-porous thin film structure are sized to accept a first molecule of interest. Pores in a second layer of the micro-porous thin film structure are smaller than the pores in the top layer and are sized to accept a second molecule of interest that is smaller than the first molecule of interest. The pores in the second layer are too small to accept the first molecule of interest. The pores in the top layer and the pores in the second layer are sized and arranged such that light reflected from the multi-layer micro-porous thin film structure produces multiple superimposed interference patterns that can be resolved. In preferred embodiments, the multi-layer micro-porous thin film structure is a porous silicon thin film multi-layer structure formed on a silicon substrate, such as a silicon wafer. Specific and nonspecific binding can be detected with biosensors of the invention. The position of peaks in the Fourier transform of the reflection spectrum and the shift in peak amplitudes can be used to determine the presence and quantity of targeted biological molecules of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for high-speed thickness mapping of patterned thin films
InactiveUS20050174584A1Reduce distanceImprove image qualityScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationWaferingOptical spectrometer
An apparatus or method captures reflectance spectrum for each of a plurality of spatial locations on the surface of a patterned wafer. A spectrometer system having a wavelength-dispersive element receives light reflected from the locations and separates the light into its constituent wavelength components. A one-dimensional imager scans the reflected light during translation of the wafer with respect to the spectrometer to obtain a set of successive, spatially contiguous, one-spatial dimension spectral images. A processor aggregates the images to form a two-spatial dimension spectral image. One or more properties of the wafer, such as film thickness, are determined from the spectral image. The apparatus or method may provide for relatively translating the wafer at a desired angle with respect to the line being imaged by the spectrometer to enhance measurement spot density, and may provide for automatic focusing of the wafer image by displacement sensor feedback control. The spectrometer system may include an Offner optical system configured to twice pass light reflected from the wafer and received by the imager.
Owner:FILMETRICS
Optical sensing system for determining the position and/or shape of an associated object
ActiveUS9417057B2Improve stabilityPossible gapForce measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansFiberGrating
The present invention relates to an optical sensing system (1) for determining the position and / or shape of an associated object (O), the system comprises an optical fibers (10) having one or more optical fiber cores (9) with one or more fiber Bragg gratings (FBG, 8) extending along the full length where the position and / or shape is be to determined of said object (O). A reflectometer (REFL, 12) measures strain at a number of sampling points along the optical fiber cores, and a processor (PROC, 14) determines the position and / or shape based on said measured strains from the plurality of optical fiber cores. The fiber Bragg grating(s) (FBG, 8) extends along the full length of said optical fiber cores (9), the fiber core having a spatially modulated reflection (r) along the said full length of the optical fiber core so that the corresponding reflection spectrum is detectable in said wavelength scan. Thus, the fiber Bragg grating(s) may be effectively continuous along the optical fiber leaving no gaps so that every position gives rise to a detectable reflection, and achieving that the reflection spectrum may encompass a wavelength span equaling the wavelength scan, or ‘sweep’, of an optical source in the reflectometer.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
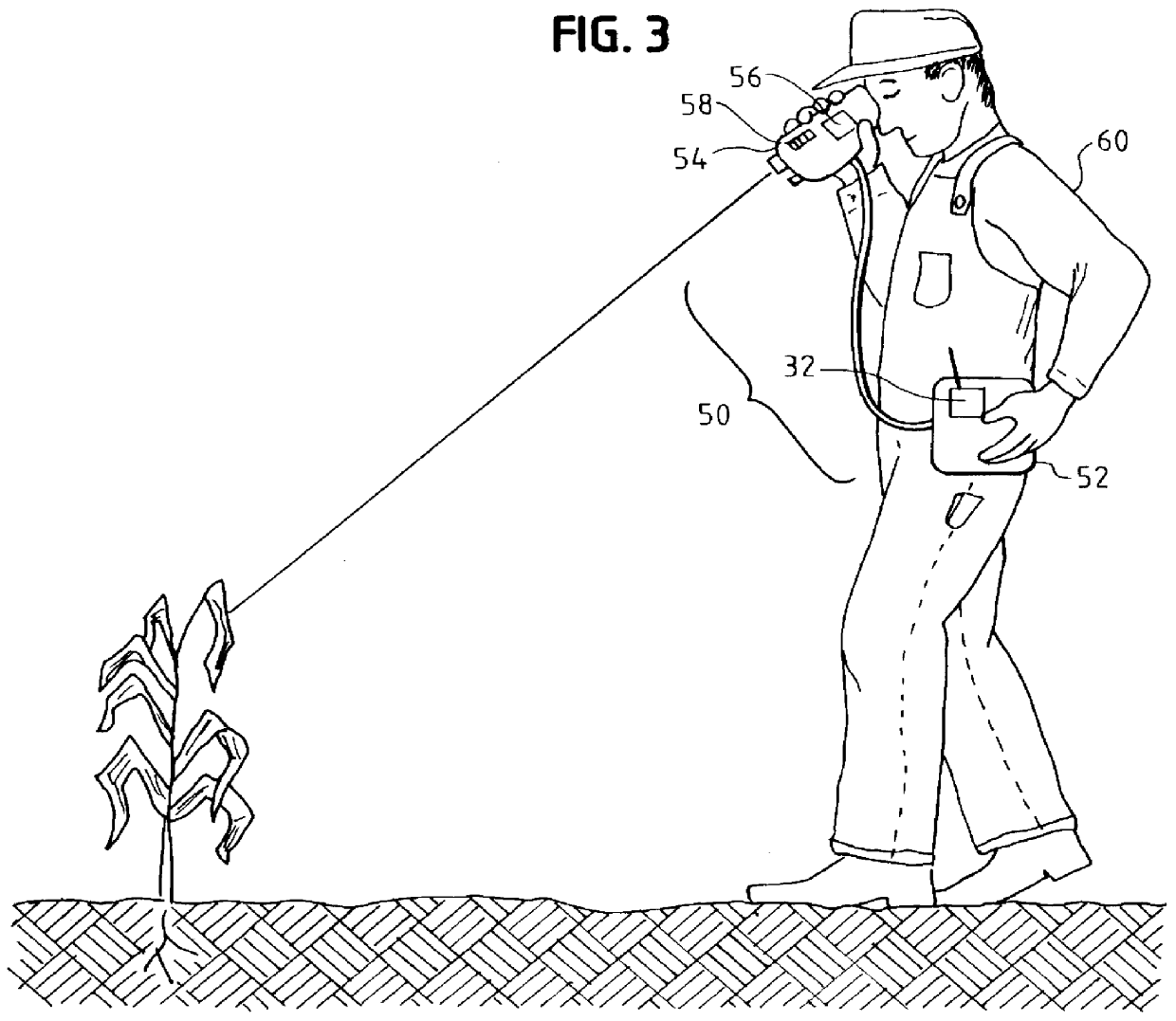
Portable multiway crop leaf nitrogen nutrient index nondestructive monitoring device
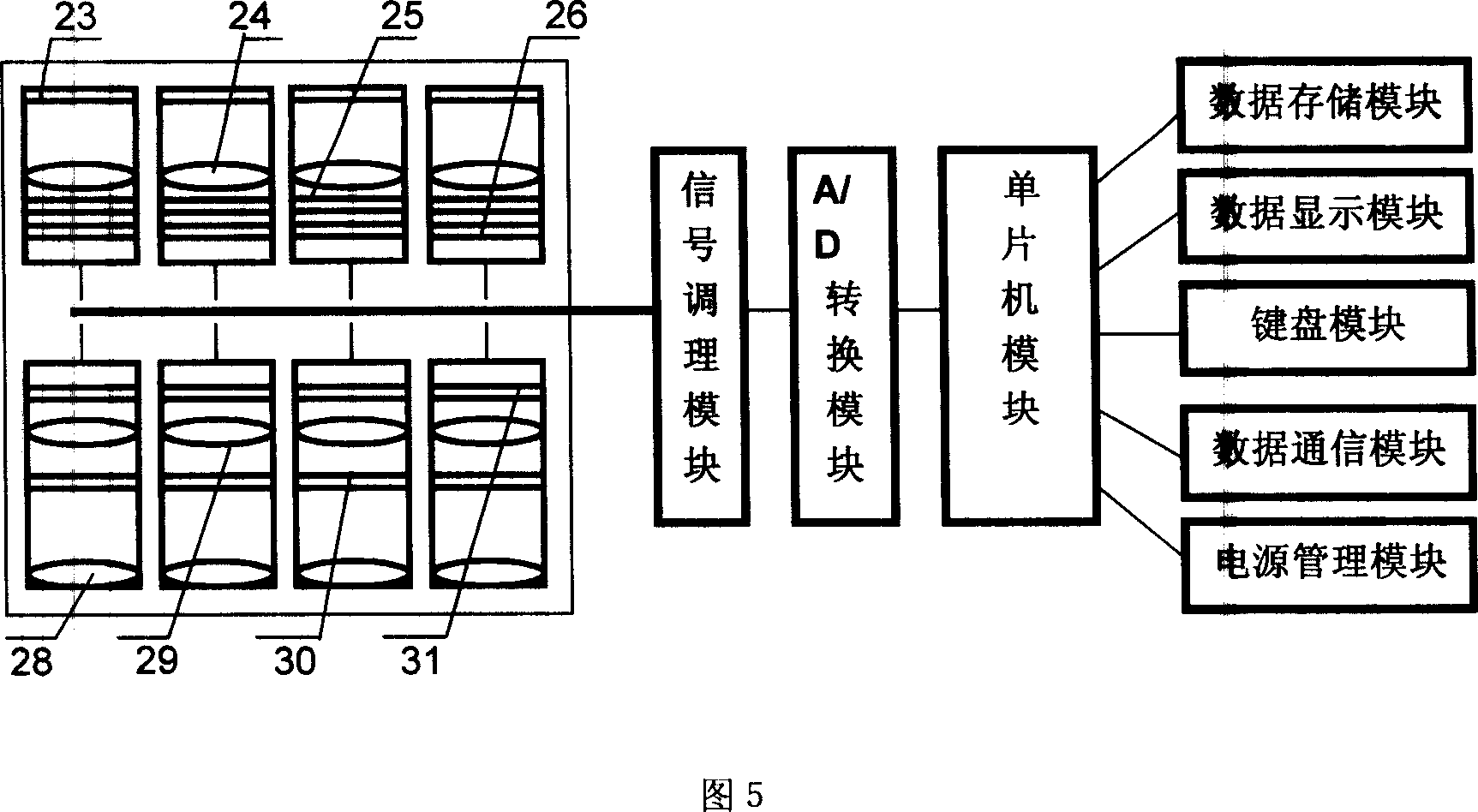
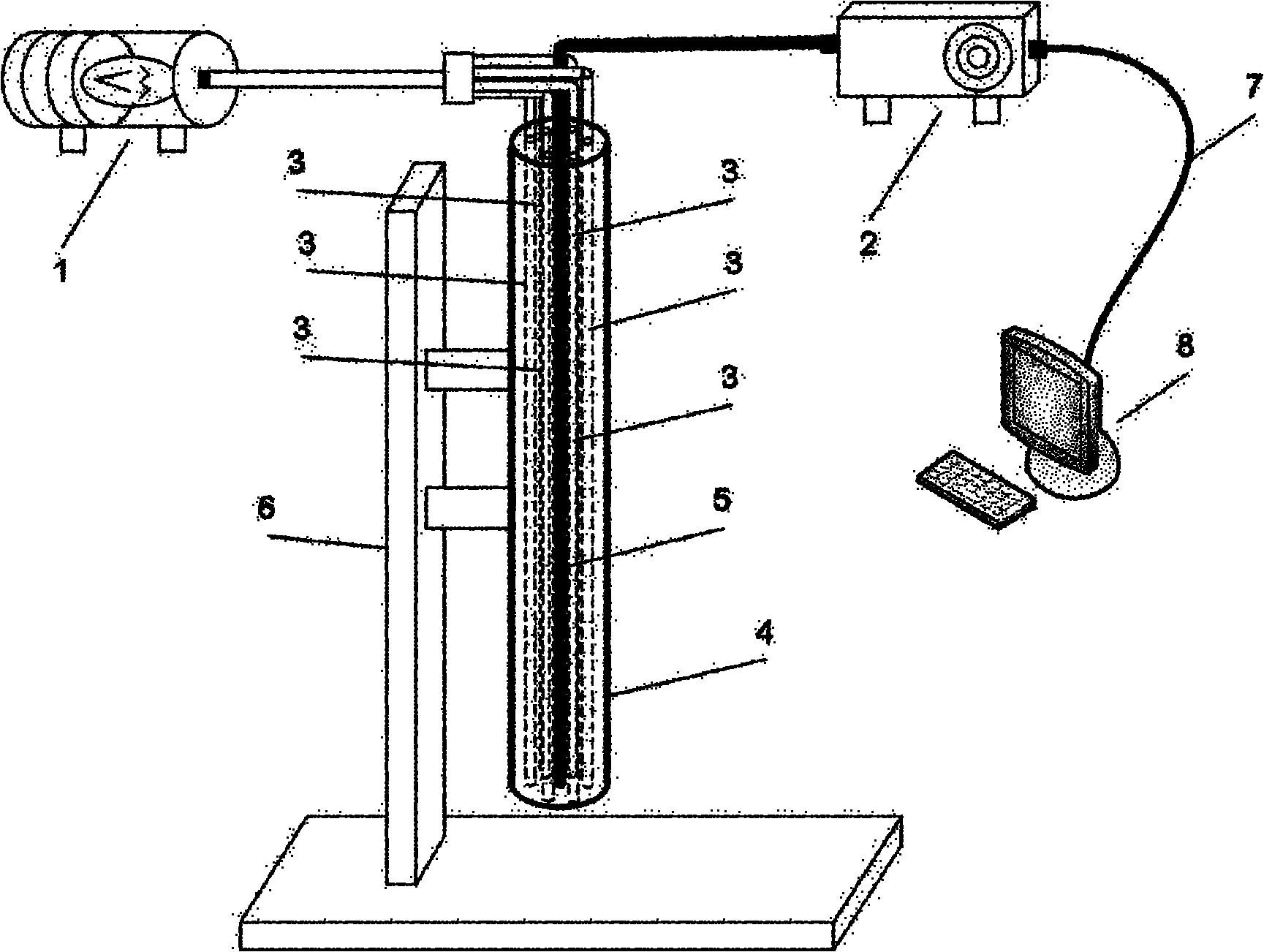
InactiveCN101021472AReduce pollutionEasy to monitor on siteColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsAgricultural scienceNitrogen accumulation
The invention relates to a lossless testing device for nitrogen nutritive index of crop leaves based on canopy reflection spectrum. It belongs to technology field of crop production, which is specially used in online detecting and precious fertilizing guidance of crop field production. It is mainly composed of bracket, spectrum signal collection and host computer. Spectrum signal collection adopts design of 4 waveband and 8 channels. Hardware system is composed of analog signals conditioning module, A / D transfer module, chip module, memory module, display module, keyboard module, communication module and power management module. Software system is programmed by C51 chip language. Detection of nitrogen content, nitrogen accumulation and leaf area index of canopy not only ensures high detecting precision, but also provides three data indexes of different facets to analyze nitrogen nutritive level of crop, which guarantees reliability and stability of detecting results. It can be applied in field operation, online lossless detecting, field online manage and guidance for agricultural production personnel.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for measuring kin physiology parameters and optical property parameters based on reflective spectral measurement
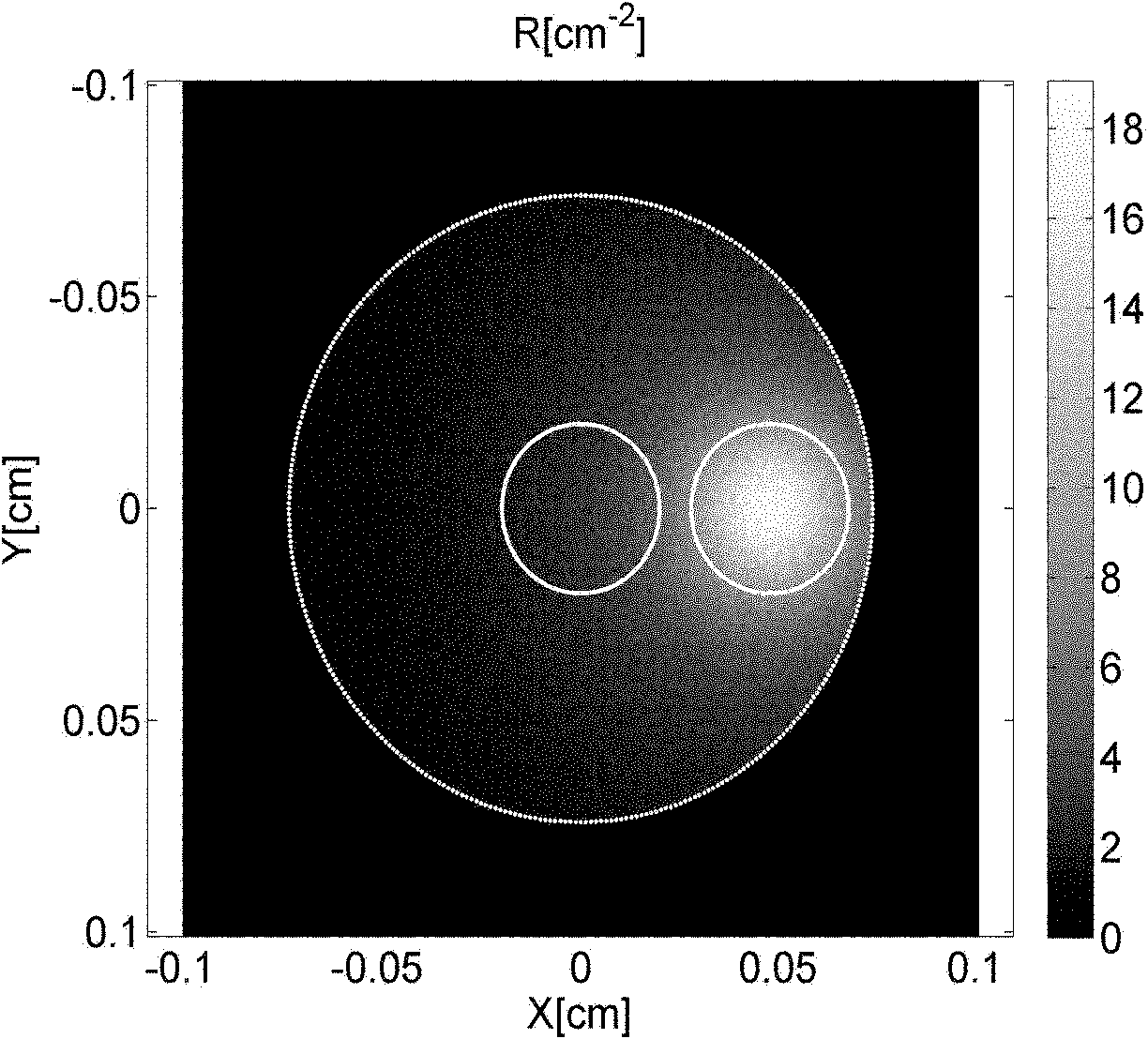
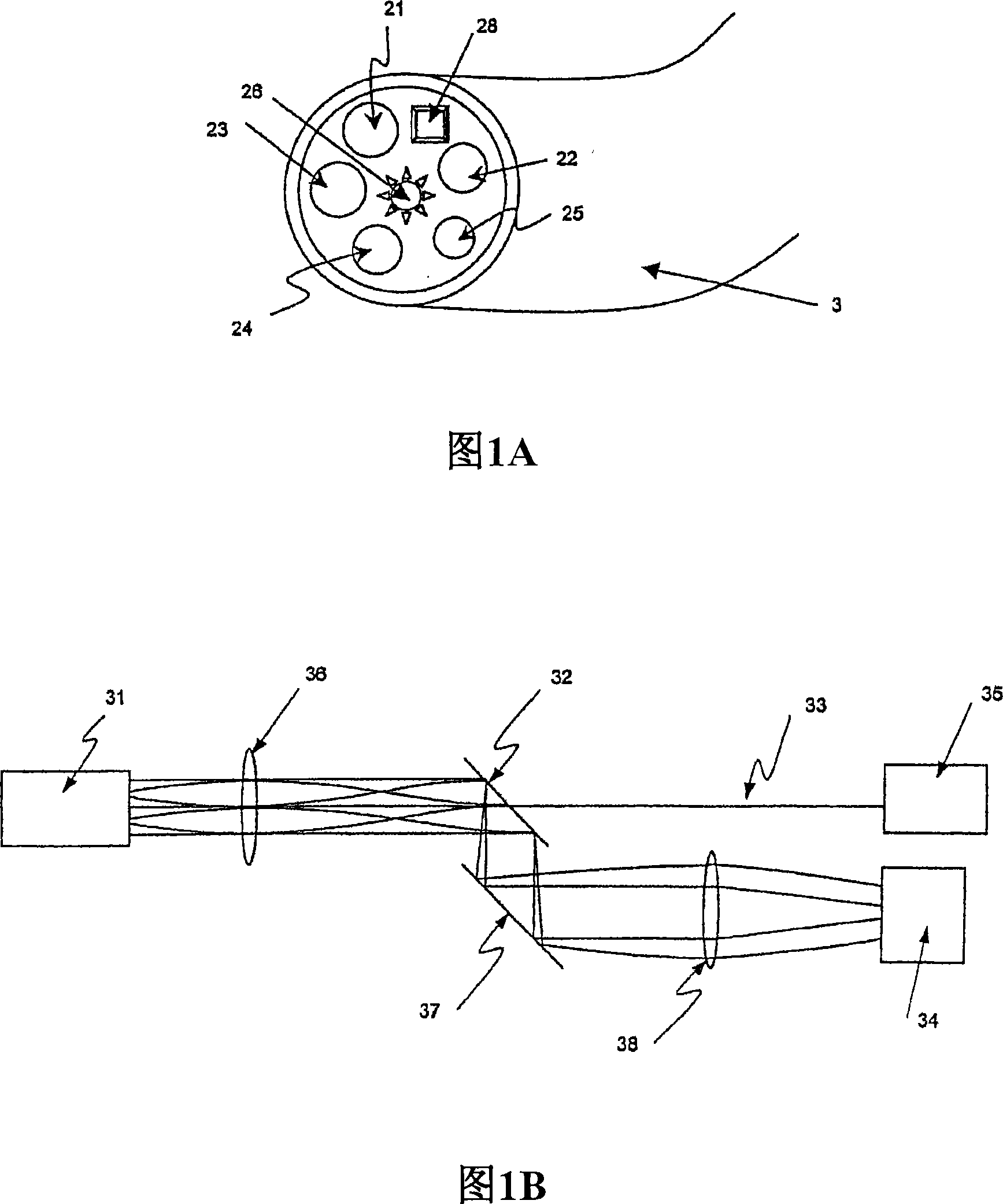
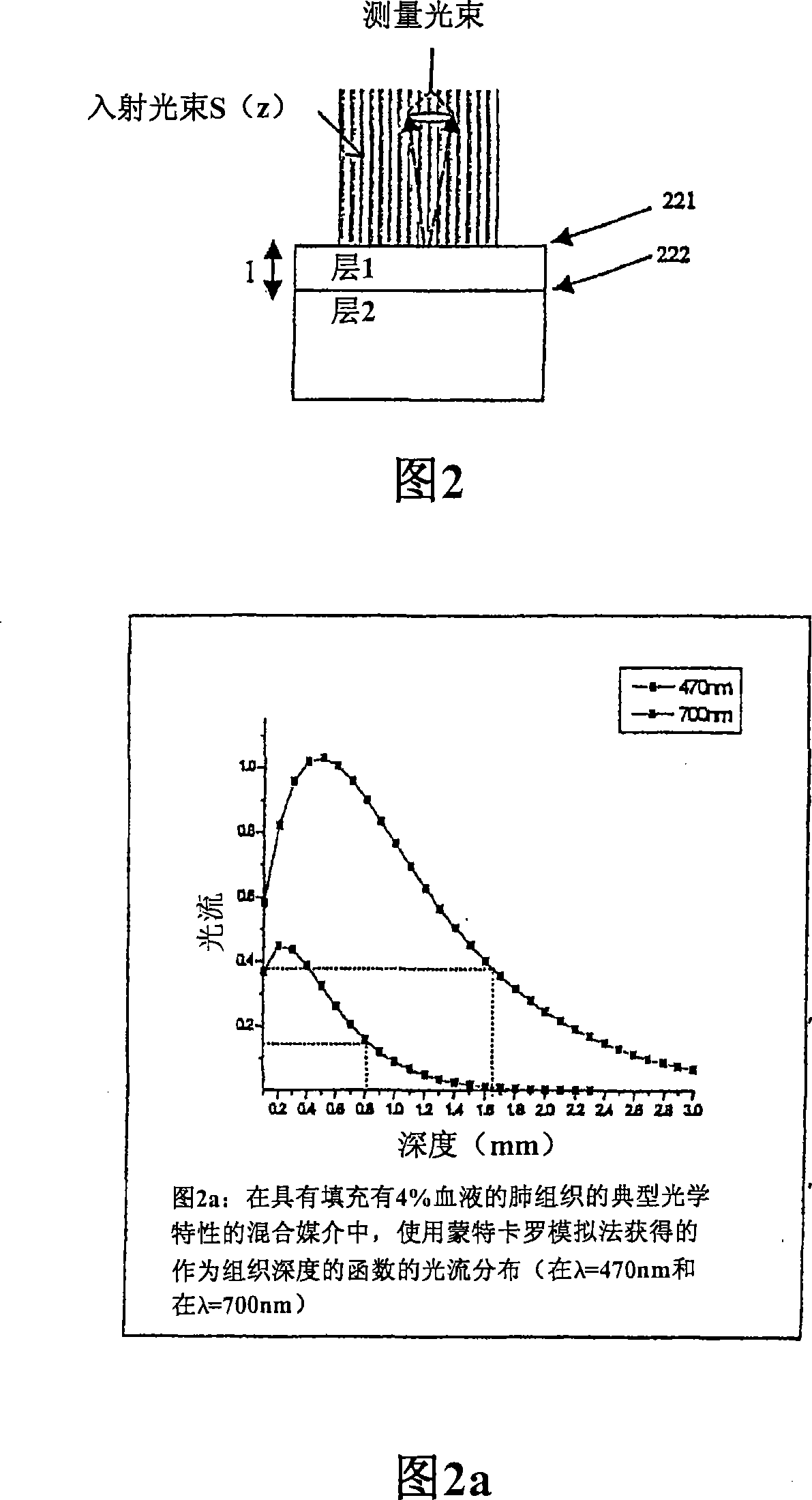
The invention provides a method and system for measuring skin physiology parameters and optical property parameters based on reflective spectral measurement. The measuring system is composed of measuring equipment for a skin reflection spectrum and a computation and display device. By utilizing an analysis method of combining experimental data with the Monte Carlo simulation, the measuring system provides more accurate corresponding data of reflection light intensity and skin optical property; during the practical measurement of sample skin, on the basis of a practically measured reflection spectrum, the data and more physiology parameters are calculated and fit to obtain the skin physiology parameters and the optical property parameters based on reflective spectral measurement; finally, the optical property parameters of the skin adsorption coefficient mu a, a reduction scattering coefficient mu s' and the like as well as physiological information, such as melanin content, deoxygenated haemoglobin content, oxygenated haemoglobin content, moisture content and the like are also measured are measured in real time in a non-invasive and lossless mode.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Anti-reflection film and polarization plate containing the same
InactiveCN101900841AExcellent rainbow effectReduce reflectivityCellulosic plastic layered productsPolarising elementsAngle of incidencePolyvinyl alcohol
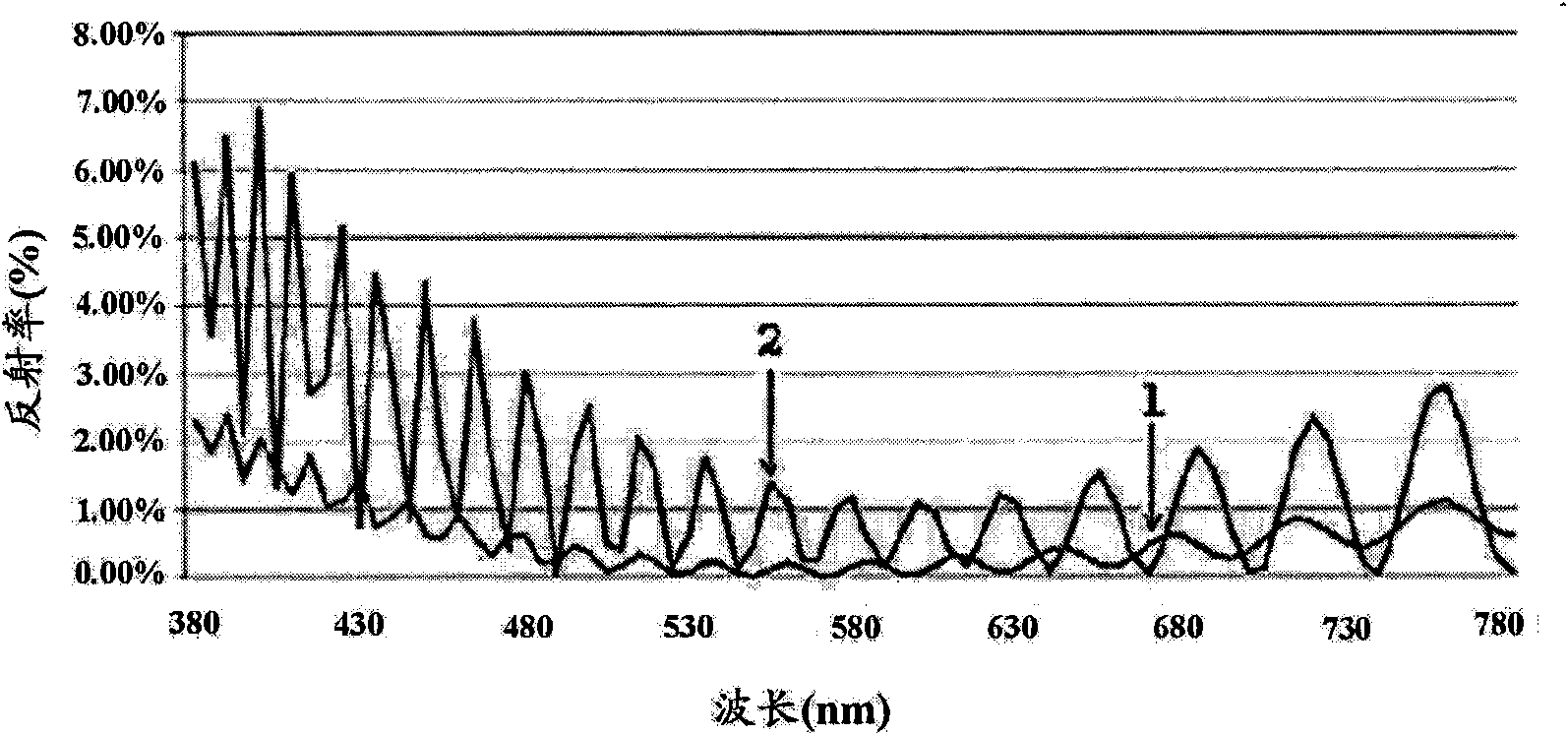
The present invention generally relate to an anti-reflection film and a polarization plate containing the same, particularly relate to the anti-reflection film having an excellent rainbow effect and low reflectivity by reducing amplitude of reflection spectrum, and the polarization plate containing the anti-reflection film. The anti-reflection film includes a cellulose triacetate (TAC) transparent base for protecting a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) polaroid sheet; a high-hardness layer coated on the transparent base and having a high refractivity of 1.50-1.60 as well as antistatic function; and a low refractivity layer coated on the high-hardness layer by a wet method and having a refractivity of 1.31-1.40, wherein the anti-reflection film has an average specular reflectance of 0.1-1.40% in a wavelength range from 480-680nm at an incidence angle of 5 DEG.
Owner:TORAY ADVANCED MATERIALS KOREA
Method and apparatus for high-speed thickness mapping of patterned thin films
An apparatus or method captures reflectance spectrum for each of a plurality of spatial locations on the surface of a patterned wafer. A spectrometer system having a wavelength-dispersive element receives light reflected from the locations and separates the light into its constituent wavelength components. A one-dimensional imager scans the reflected light during translation of the wafer with respect to the spectrometer to obtain a set of successive, spatially contiguous, one-spatial dimension spectral images. A processor aggregates the images to form a two-spatial dimension spectral image. One or more properties of the wafer, such as film thickness, are determined from the spectral image. The apparatus or method may generate a wavelength-dependent correction factor to correct for diffraction errors introduced in reflectance spectra by the wavelength-dispersive element. The invention provides for automatic rotation of a patterned wafer to determine Goodness of Alignment during a measurement process. The invention may include a dual Offner optical system disposed between the wafer and imager.
Owner:FILMETRICS
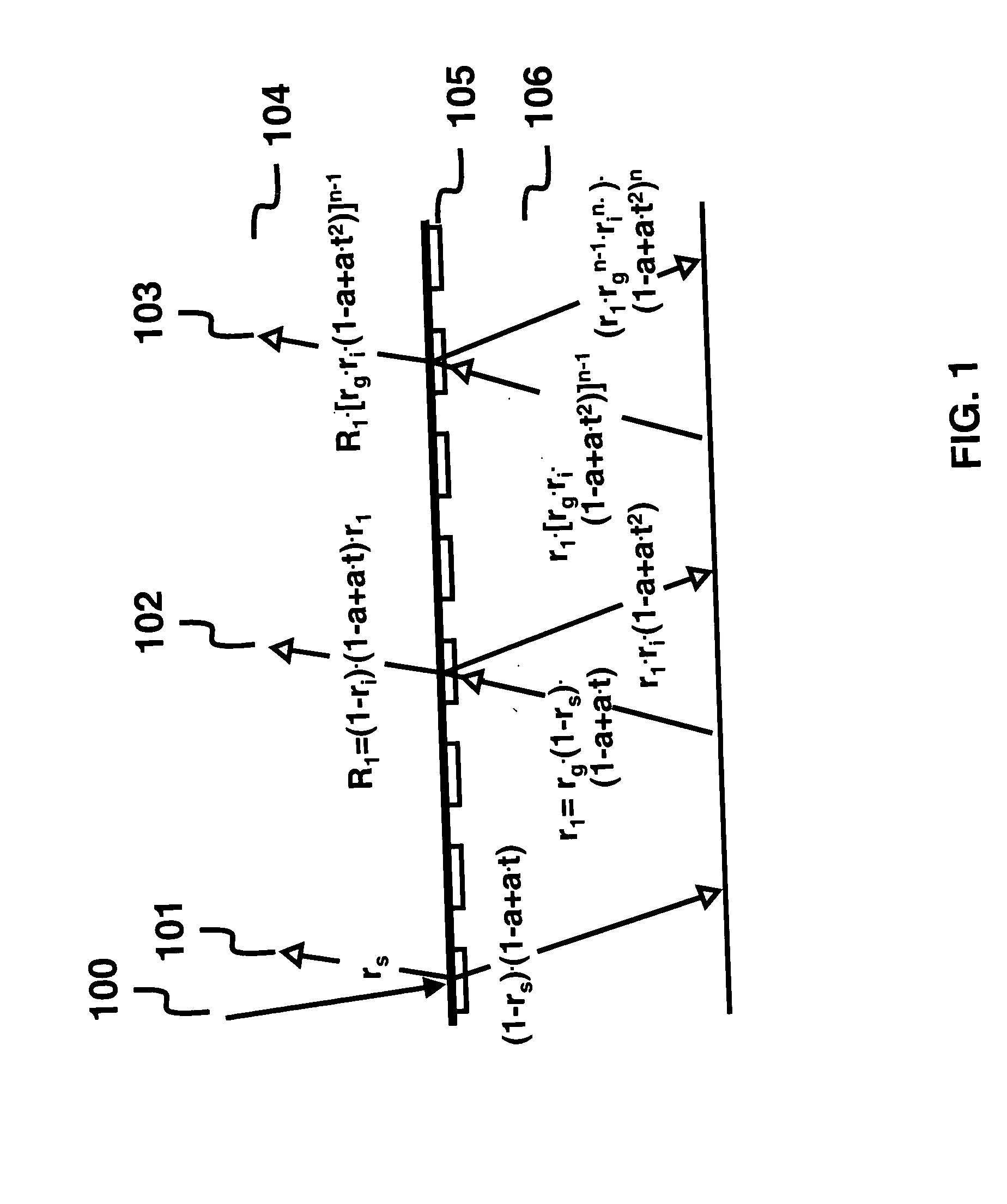
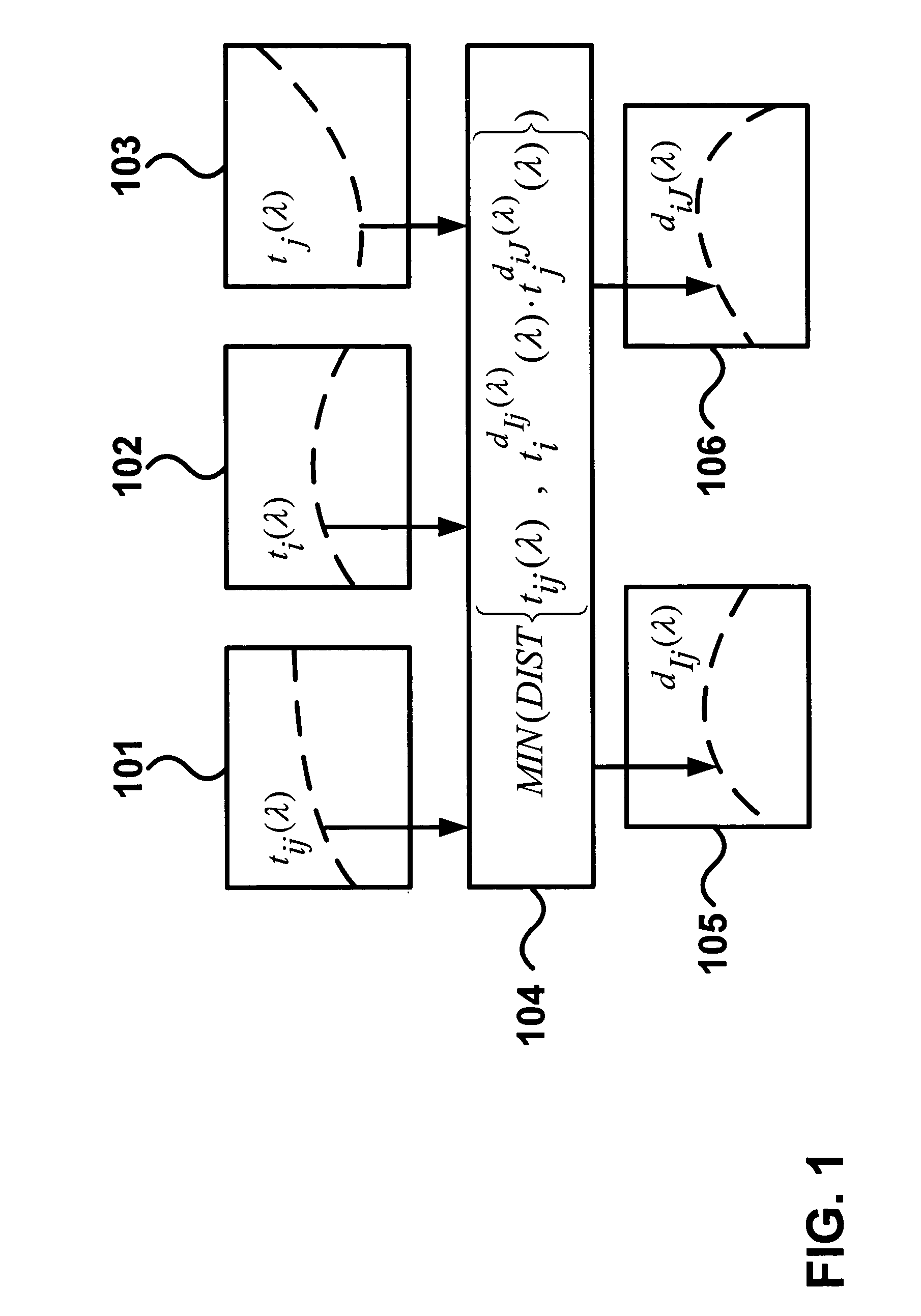
Ink thickness variations for the control of color printers
The present invention proposes a method and a computing system for deducing ink thickness variations from spectral reflectance measurements performed on a printing press or on a printer. The computed ink thickness variations enable controlling the ink deposition and therefore the color accuracy, both in the case of high-speed printing presses and of network printers. Ink thickness variations are expressed as ink thickness variation factors incorporated into a spectral prediction model. The method for computing ink thickness variations comprises both calibration and ink thickness variation computation steps. The calibration steps comprise the calculation of ink transmittances from measured reflectances and the computation of possibly wavelength-dependent ink thicknesses of solid superposed inks. Wavelength-dependent ink thicknesses account for the scattering behavior of non-transparent inks or of inks partly entering into the paper bulk. The ink thickness variation factors are fitted by minimizing a distance metric between the reflection spectrum predicted according to the thickness variation enhanced spectral prediction model and the measured reflection spectrum. The ink thickness variation enhanced spectral prediction model can be applied both in the visible wavelength range and in the near-infrared wavelength range. This enables computing unambiguously the thickness variations of the cyan, magenta, yellow and black inks. Furthermore, a spectral reflection may be measured over a stripe of a printed page and used to predict the ink thickness variations occurring within that stripe. This enables the real-time control of the ink deposition process on a printing press.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Ink thickness variations for the control of control of color printers
InactiveUS20070091138A1High color accuracyAvoid time-consuming setupOther printing apparatusPrinting press partsEngineeringPaper sheet
The present invention proposes a method and a computing system for deducing ink thickness variations from spectral reflectance measurements performed on a printing press or on a printer. The computed ink thickness variations enable controlling the ink deposition and therefore the color accuracy, both in the case of high-speed printing presses and of network printers. Ink thickness variations are expressed as ink thickness variation factors incorporated into a spectral prediction model. The method for computing ink thickness variations comprises both calibration and ink thickness variation computation steps. The calibration steps comprise the calculation of ink transmittances from measured reflectances and the computation of possibly wavelength-dependent ink thicknesses of solid superposed inks. Wavelength-dependent ink thicknesses account for the scattering behavior of non-transparent inks or of inks partly entering into the paper bulk. The ink thickness variation factors are fitted by minimizing a distance metric between the reflection spectrum predicted according to the thickness variation enhanced spectral prediction model and the measured reflection spectrum. The ink thickness variation enhanced spectral prediction model can be applied both in the visible wavelength range and in the near-infrared wavelength range. This enables computing unambiguously the thickness variations of the cyan, magenta, yellow and black inks. Furthermore, a spectral reflection may be measured over a stripe of a printed page and used to predict the ink thickness variations occurring within that stripe. This enables the real-time control of the ink deposition process on a printing press.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
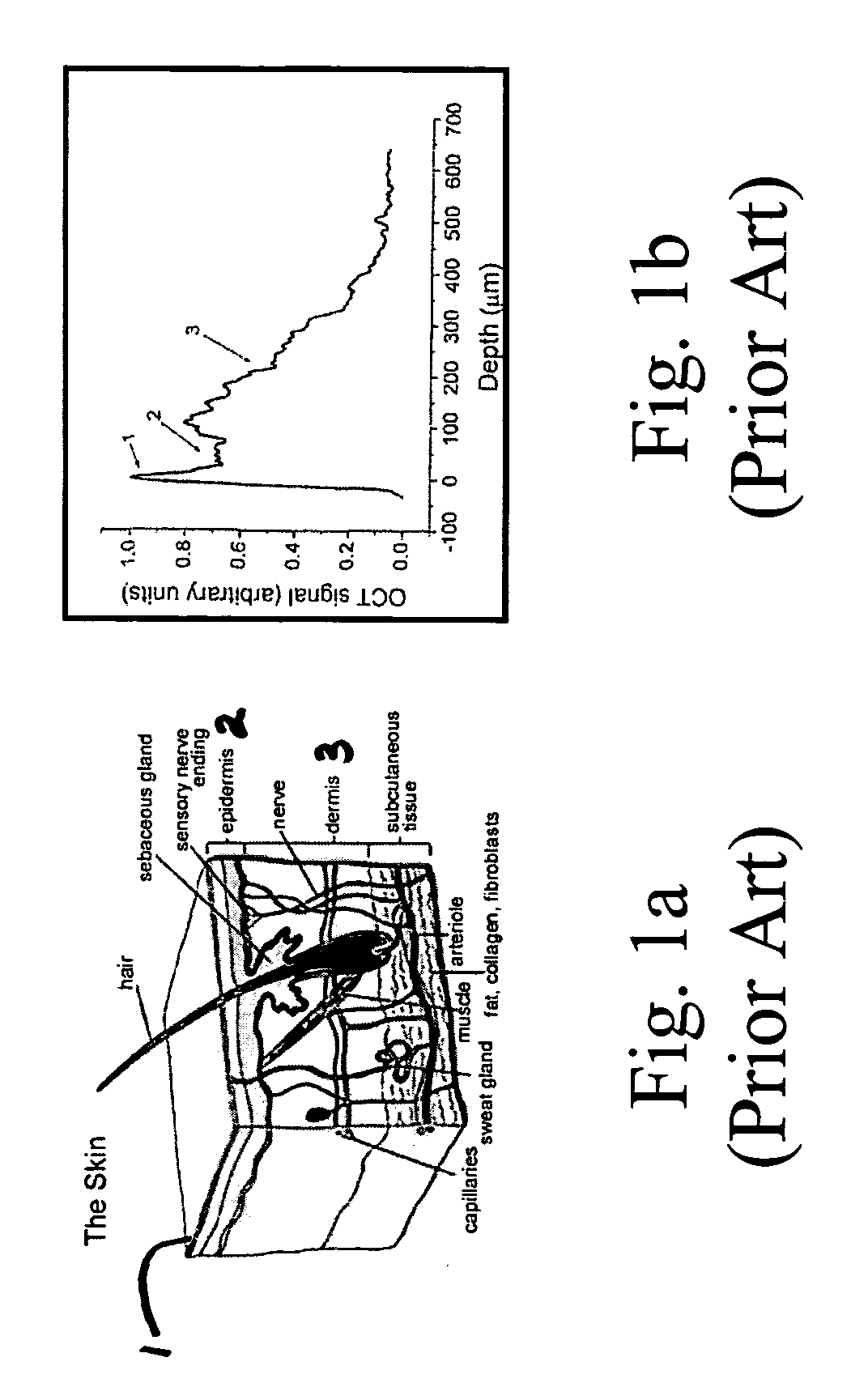
Method and apparatus for measuring cancerous changes from reflectance spectral measurements obtained during endoscopic imaging
The present invention provides a new method and device for disease detection, more particularly cancer detection, from the analysis of diffuse reflectance spectra measured in vivo during endoscopic imaging. The measured diffuse reflectance spectra are analyzed using a specially developed light-transport model and numerical method to derive quantitative parameters related to tissue physiology and morphology. The method also corrects the effects of the specular reflection and the varying distance between endoscope tip and tissue surface on the clinical reflectance measurements. The model allows us to obtain the absorption coefficient ([mu]a) and further to derive the tissue micro-vascular blood volume fraction and the tissue blood oxygen saturation parameters. It also allows us to obtain the scattering coefficients ([mu]s and g) and further to derive the tissue micro-particles volume fraction and size distribution parameters.
Owner:维利桑特技术公司 +1
Single longitudinal-mode optical fiber laser with low noise, narrow linewidth and high power
ActiveCN101447637AOptimizing Doping ConcentrationReduce noiseActive medium shape and constructionLow noiseHigh concentration
The invention discloses a single longitudinal-mode optical fiber laser with low noise, narrow linewidth and high power. Polarization maintaining optical fiber is rare-earth-doped phosphate single-mode glass optical fiber, the component of a fiber core is phosphate glass which consists of 70P2O5-8Al2O3-15BaO-4La2O3-3Nd2O3, the fiber core of the polarization maintaining optical fiber is doped with high-concentration luminous ions, the luminous ions are one or combination of more than one of lanthanide ions and transition metal ions, the doping density of the luminous ions is greater than 1*10<19>ions / cm<3> and the luminous ions are evenly doped in the fiber core. A polarization maintaining fiber Bragg grating with the narrow linewidth and a dichroscope form a front cavity mirror and a rear cavity mirror of the optical fiber laser, a centimeter-sized erbium-ytterbium co-doped phosphate glass polarization maintaining optical fiber is taken as a laser working substance, and polarization maintaining output laser generated by a single-mode semiconductor laser is taken as a pumping source, thus achieving the single longitudinal-mode laser output by designing and manufacturing the reflection spectrum width of the polarization maintaining fiber Bragg grating and controlling the cavity length of the whole laser cavity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain
The invention provides a method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain. In order to solve the technical problems that as fiber grating sensors are bonded to the surface of a structure through polyimide resin or epoxy resin commonly used in the prior engineering, optic fiber in service is easily destroyed; the optic fiber can get encapsulation protection but cause the concentration of surrounding stress / strain thereof if the optic fiber is directly embedded in a composite-material structure; and thermal residual stress produced in a material-curing process can cause chirp phenomena of fiber grating reflection spectrum to affect the measurement accuracy of grating strain, and the like, the invention provides the method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain. In the method, the fiber grating sensors are embedded in composite-material layers to replace resistance strain gauges commonly used in the field of monitoring structural health; by applying prestress to embedded fiber gratings, the influence of the curing residual stress of composite material on the fiber grating reflection spectrum is reduced so as to avoid the chirp phenomena; and the stability and repeatability of the sensors are improved. In addition, the composite material plays a good role in encapsulating and protecting bare fiber gratings, and meets engineering construction requirement on sensor sensitivity.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AERONAUTICAL ENG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com