Anti-reflection film and polarization plate containing the same
An anti-reflection film, polarizing plate technology, applied in polarizing elements, chemical instruments and methods, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of reflected light damage to display quality, insufficient anti-reflection performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0078] 1. Preparation of high hardness layer with high refractive index
[0079] 1.1 High hardness layer with high refractive index
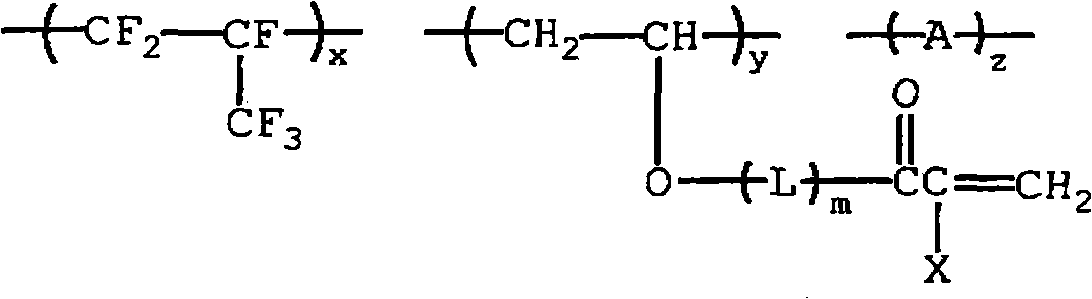
[0080] As described above, the high-refractive high-hardness layer, which is an essential thin layer of the antireflection film of the present invention, has a refractive index of 1.50 to 1.60, more preferably 1.52 to 1.56. In order to produce a high-refractive-index high-hardness layer, although it is possible to use transparent thin layers of inorganic oxides formed by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD), especially vacuum deposition or sputtering classified as PVD techniques , but thin layers formed by all-wet coating are preferred.
[0081] The high-refractive-index high-hardness layer is preferably formed by the following method: coating a coating composition, the coating composition comprising: titanium (Ti), zirconium (Zr), indium (In), Inorganic fine particles of at least one metal oxide among oxides of...
Embodiment 1
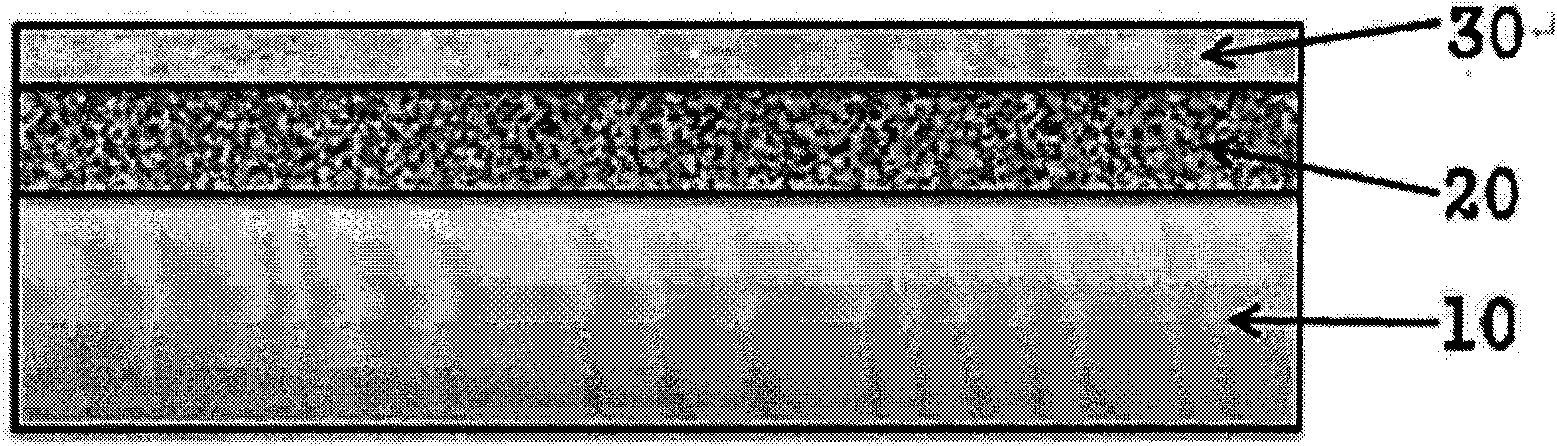
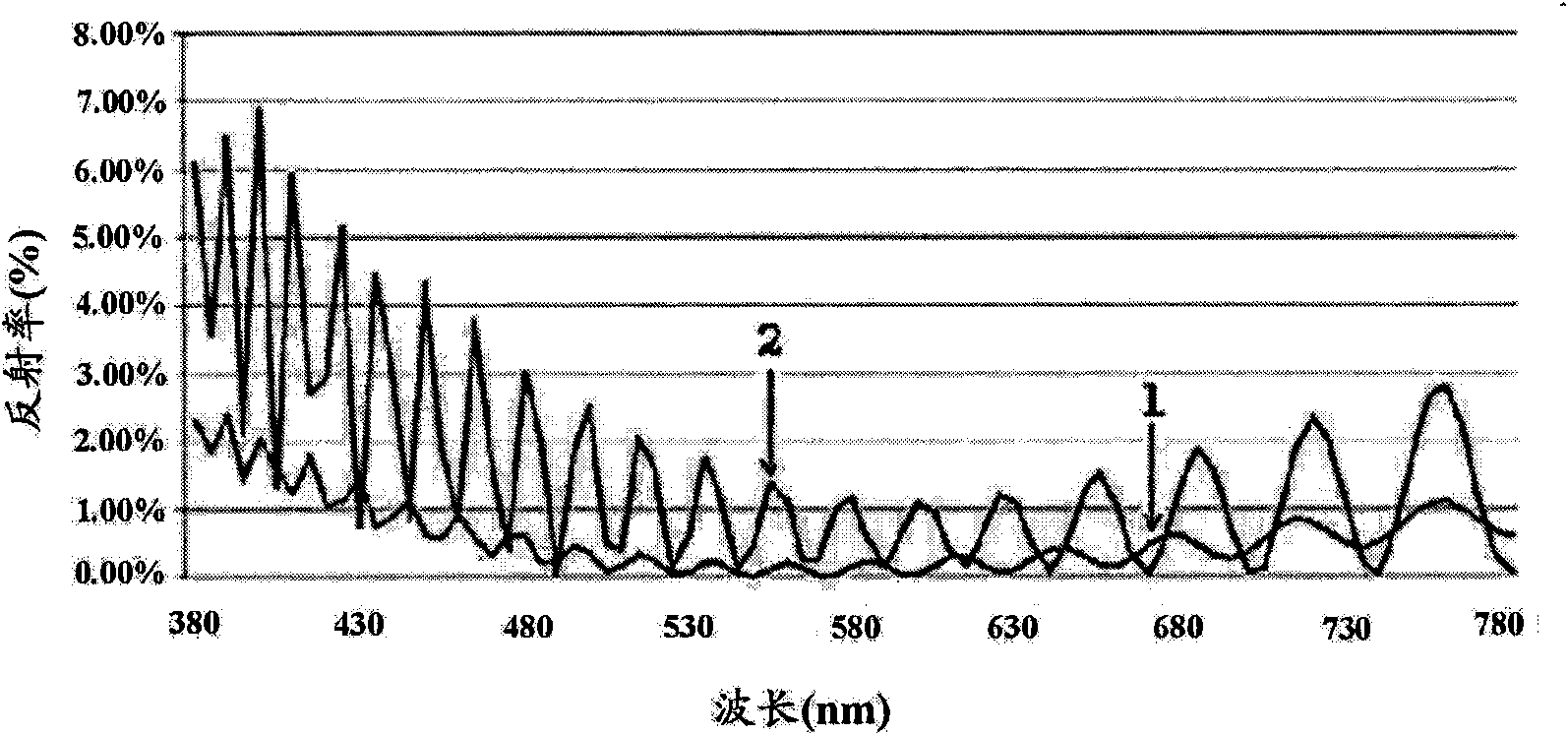
[0206] A 110-mesh gravure coater (gravure coater) was used to coat the coating composition for a high-refractive-index high-hardness layer on a triacetate cellulose substrate (TAC-TD80U, refractive index: 1.49, manufactured by Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd.), dried at 100° C. for 2 minutes, and cured by irradiating with ultraviolet rays to form a high-refractive-index high-hardness layer having a thickness of 4.2 μm and a refractive index of 1.51.
[0207] Next, a coating composition for a low-refractive index layer was coated on the high-refractive-index high-hardness layer using a 180-mesh gravure coater, dried at 100° C. for 2 minutes, and cured by UV irradiation to A low refractive index layer having a thickness of 110 nm and a refractive index of 1.36 was formed. Thus the antireflection film of the present invention was obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0209] The coating composition for a high-hardness layer with a high refractive index was coated on a cellulose triacetate substrate (TAC-TD80U, refractive index: 1.49, manufactured by Fuji Photo Film Co. , Ltd.), dried at 100° C. for 2 minutes, and cured by irradiating with ultraviolet rays to form a high-refractive-index high-hardness layer having a thickness of 4.5 μm and a refractive index of 1.54.
[0210] Next, a coating composition for a low-refractive index layer was coated on the high-refractive-index high-hardness layer using a 180-mesh gravure coater, dried at 100° C. for 2 minutes, and cured by UV irradiation to A low refractive index layer having a thickness of 110 nm and a refractive index of 1.36 was formed. Thus the antireflection film of the present invention was obtained. The obtained antireflection film was evaluated according to the following method.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com