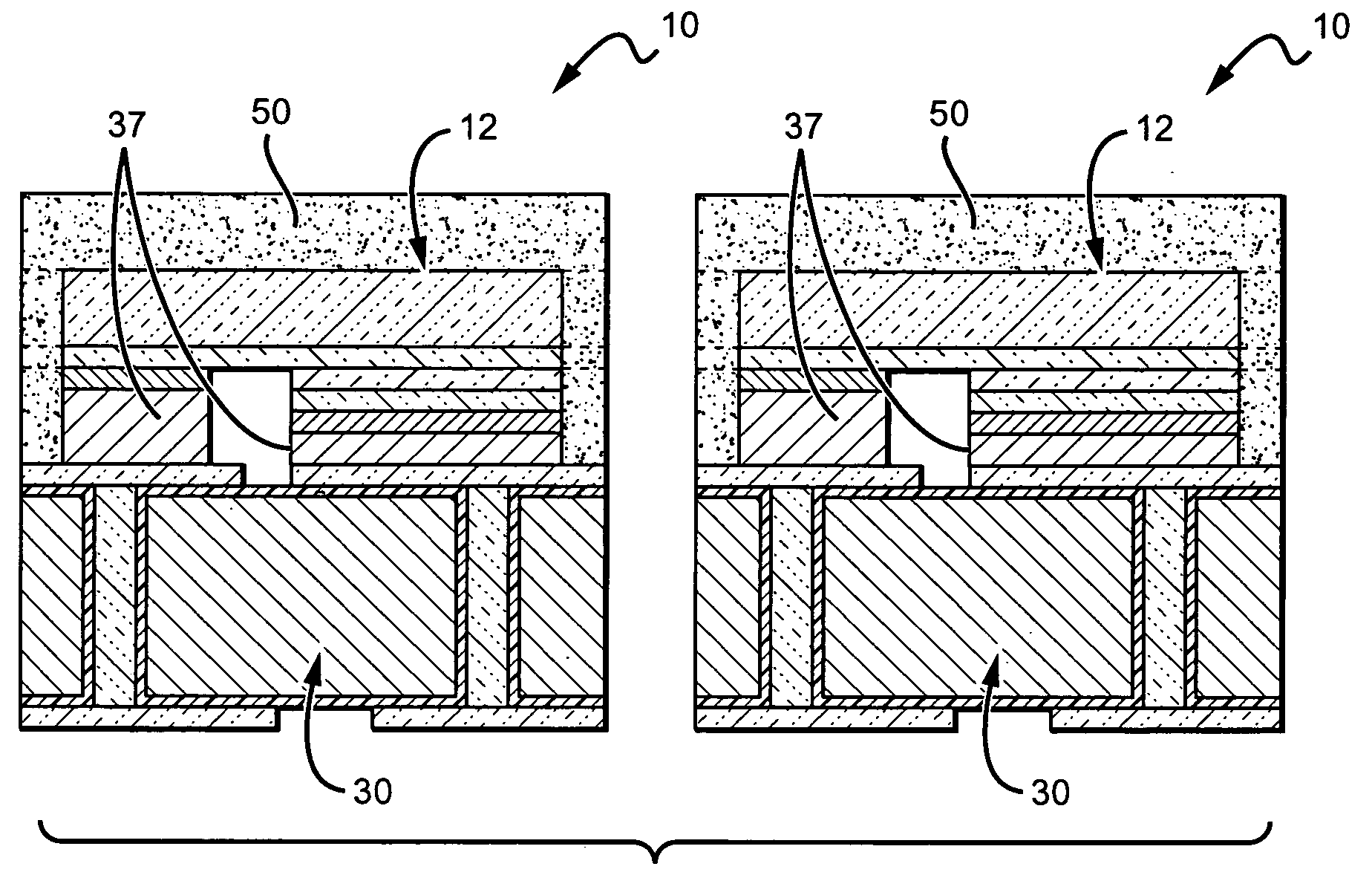
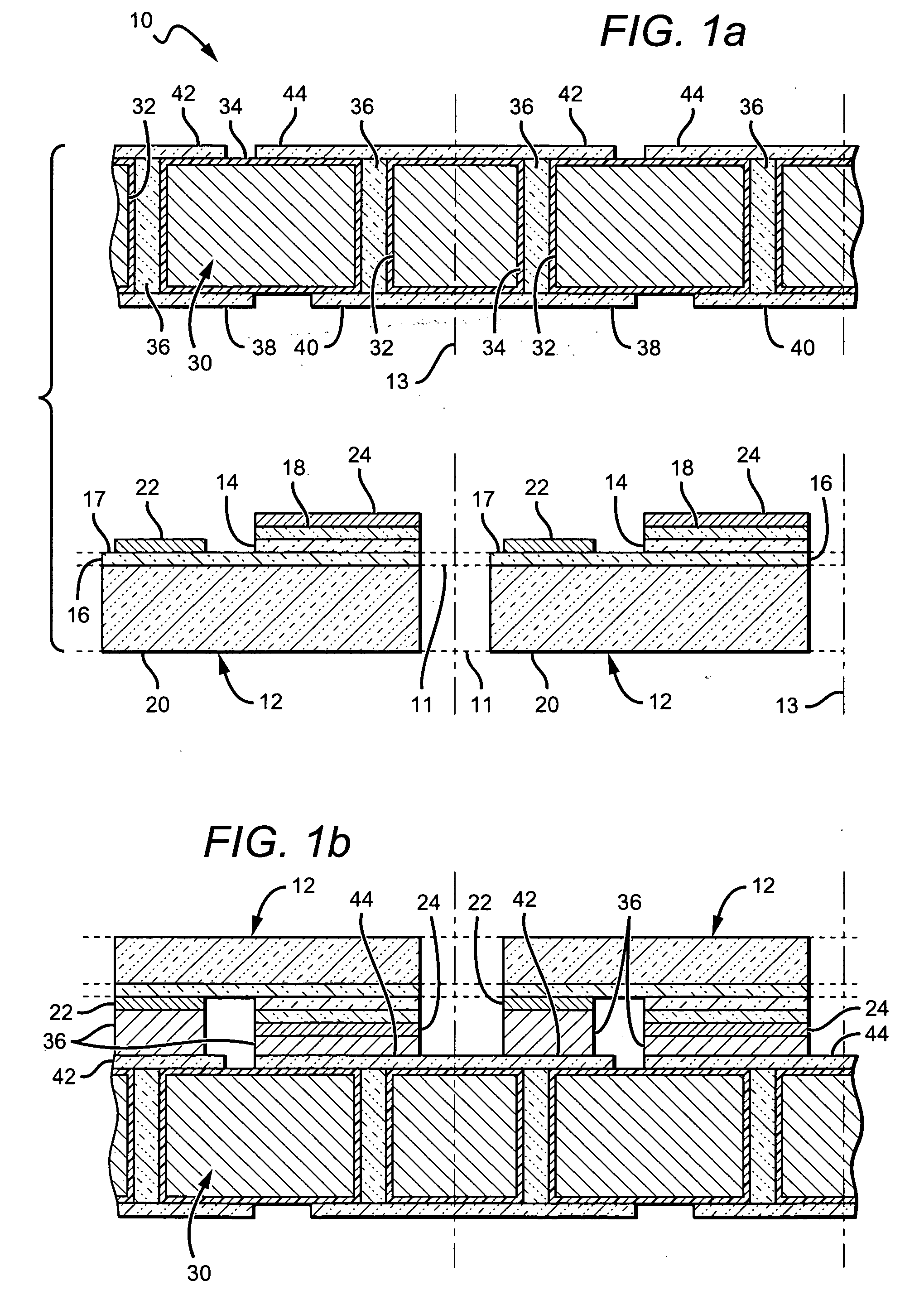
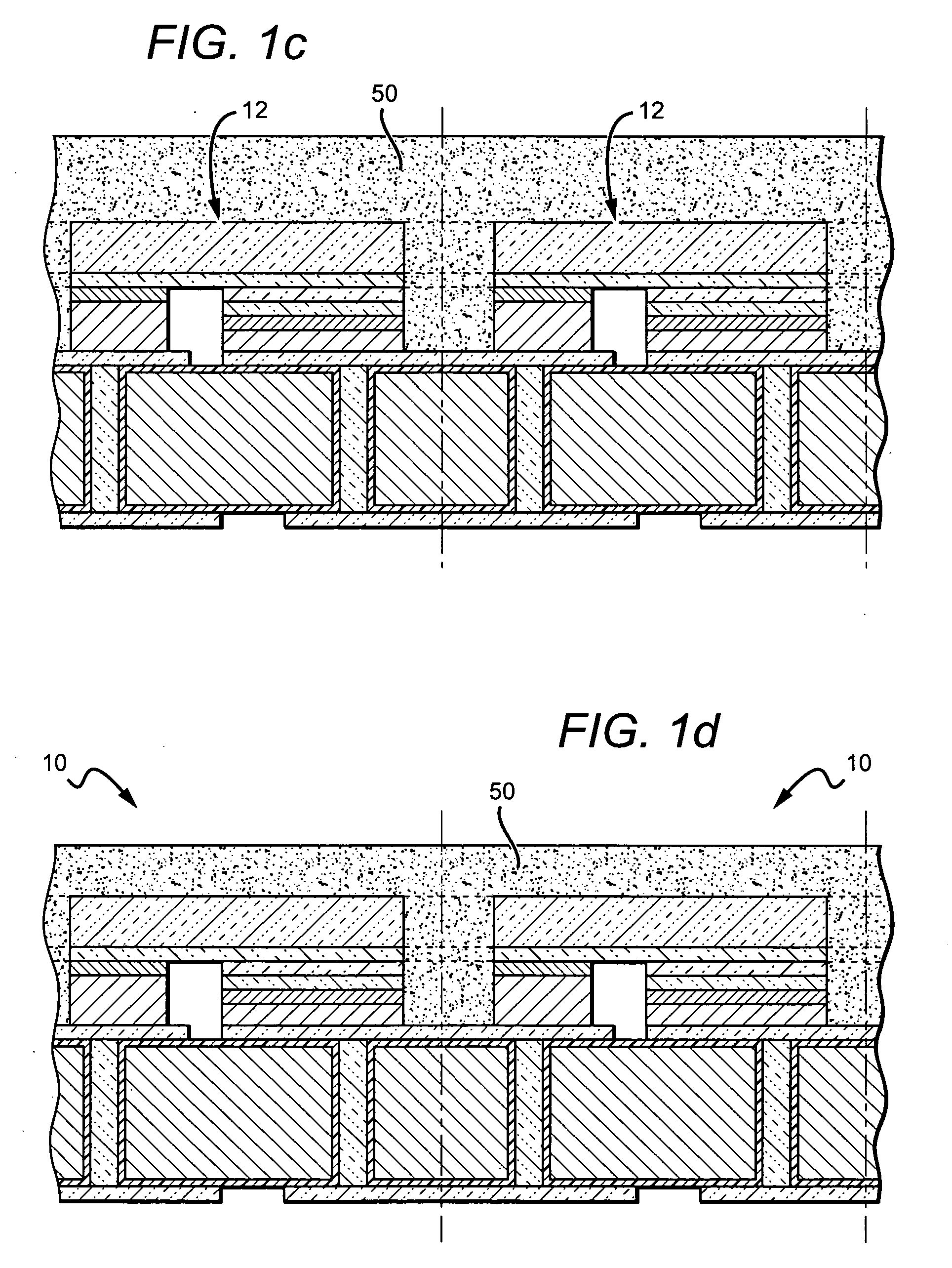
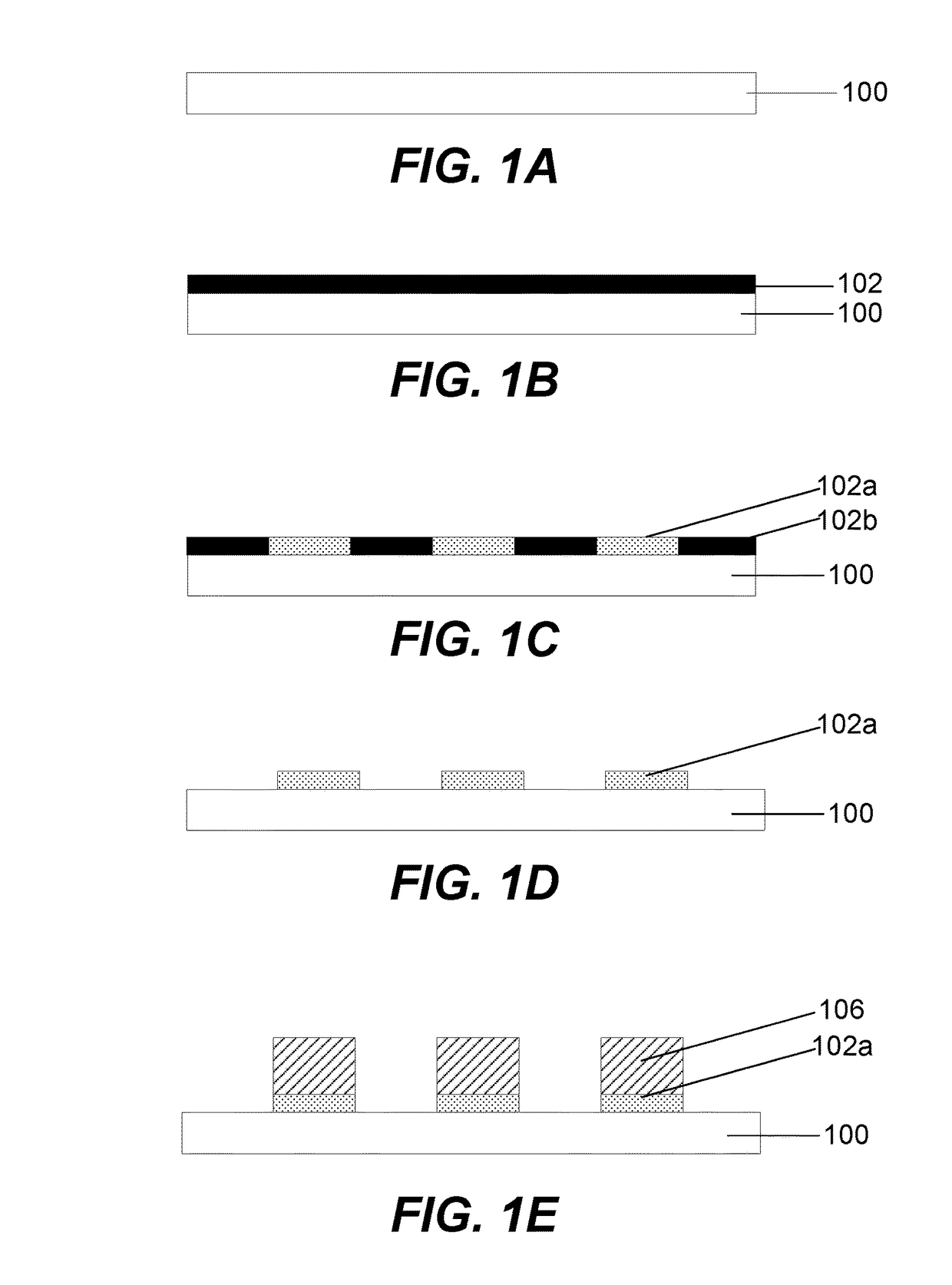
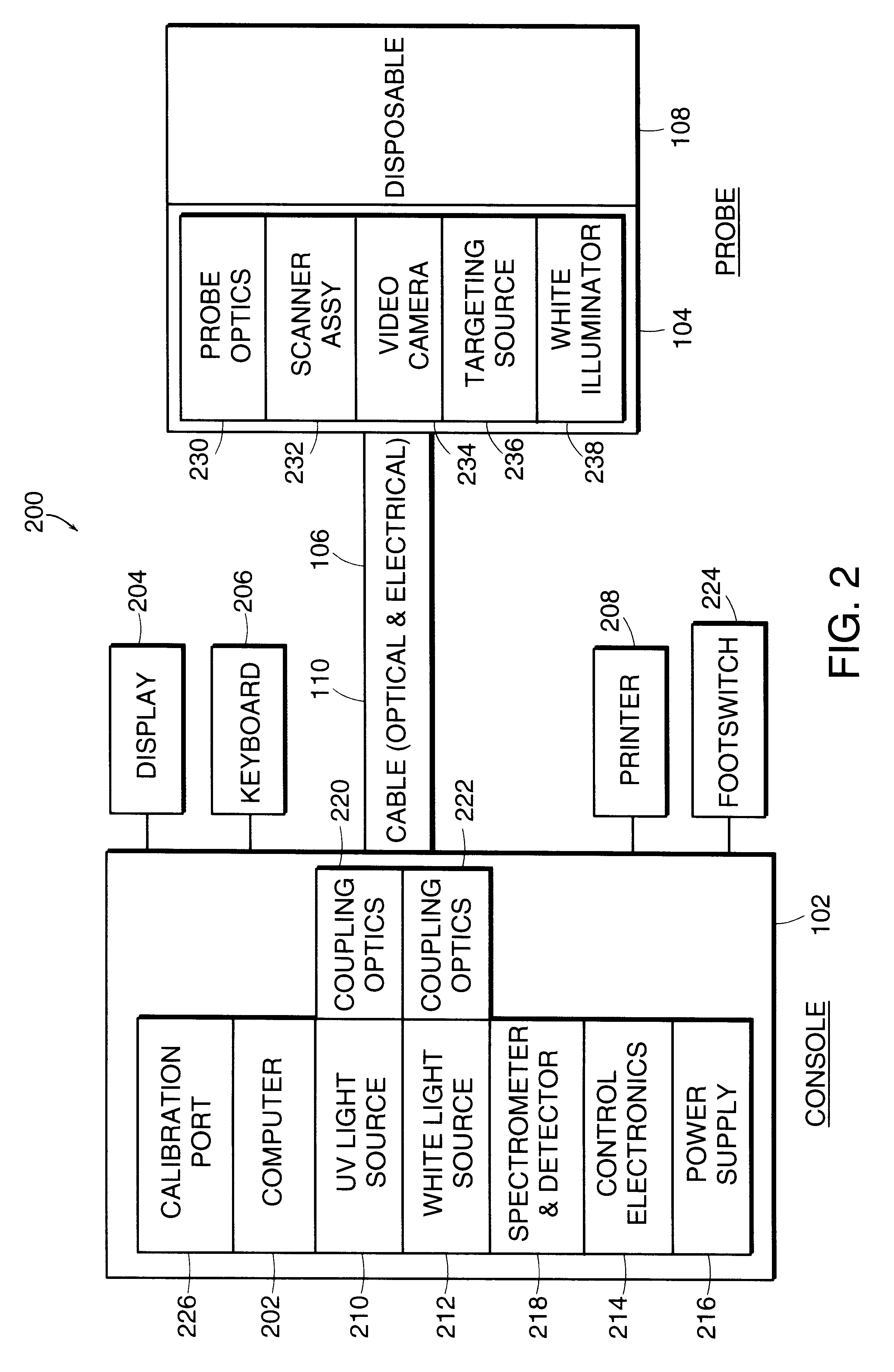
Patents
Literature
14840 results about "Wavelength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
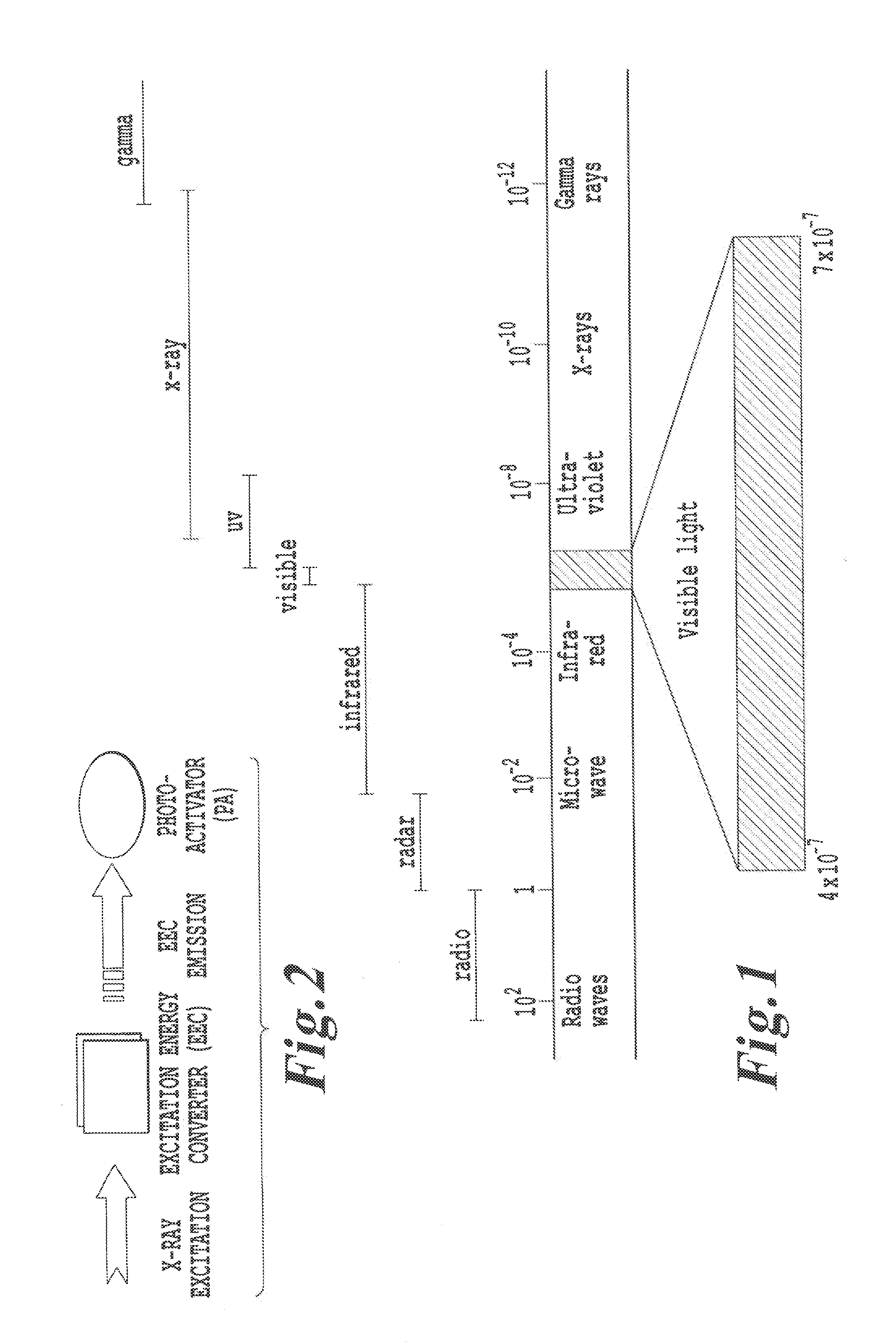
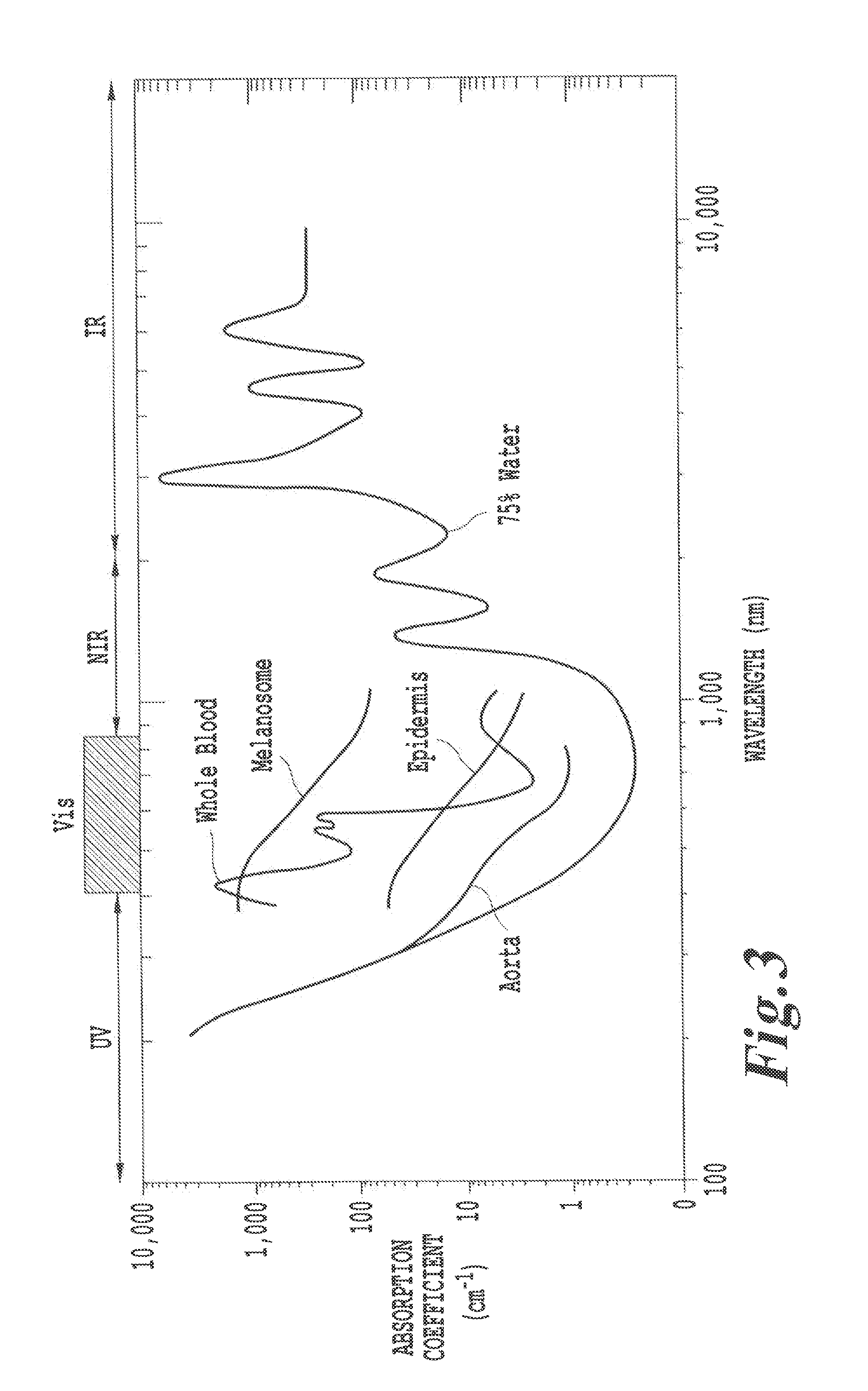
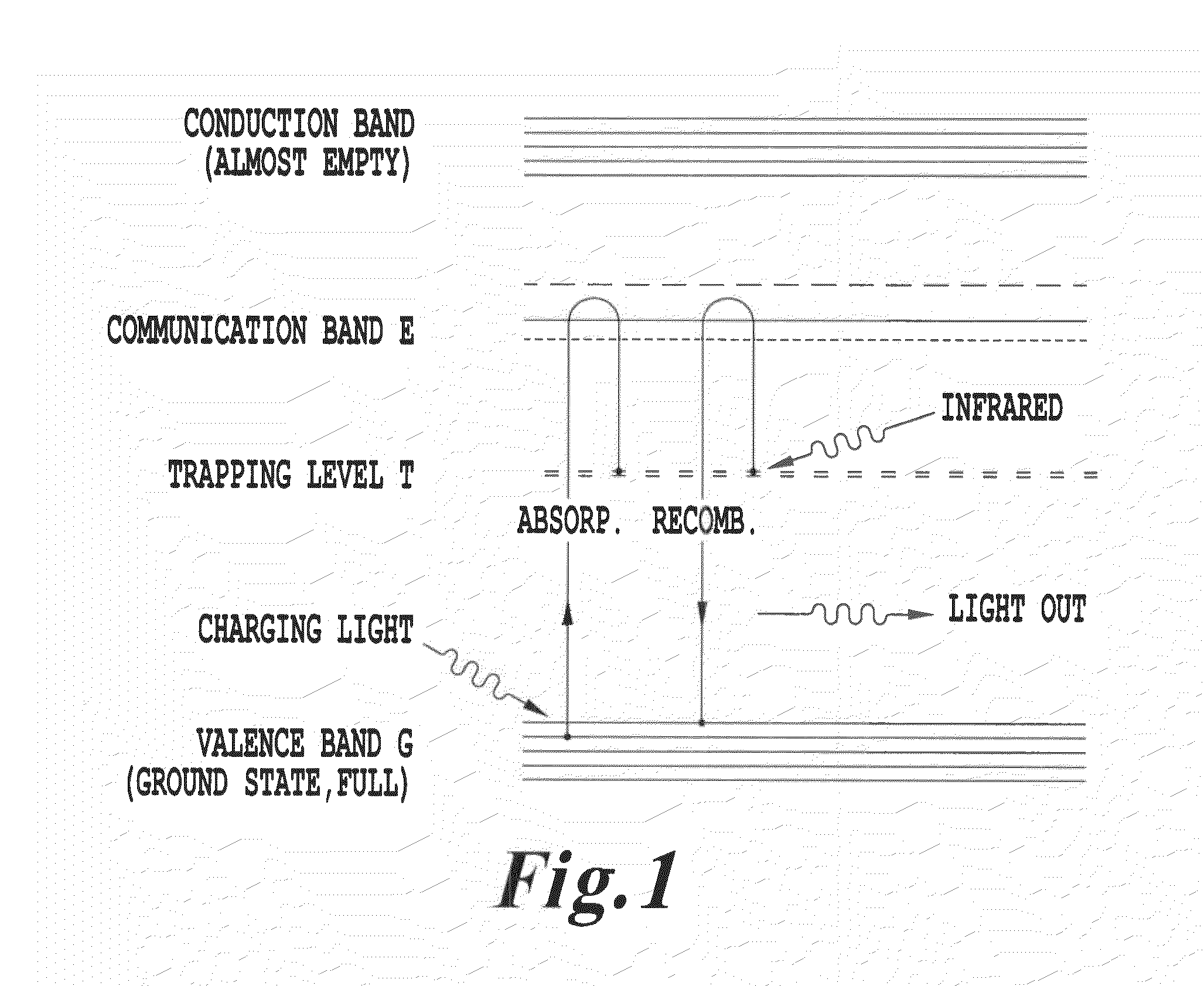
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (λ). The term wavelength is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids.
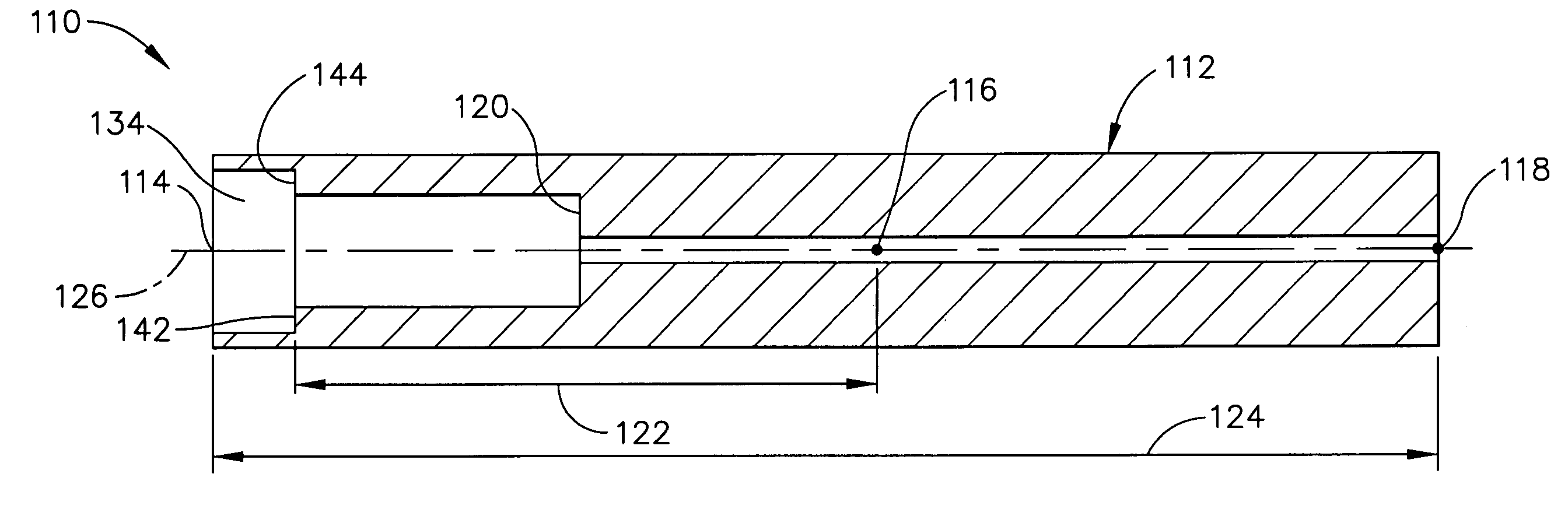
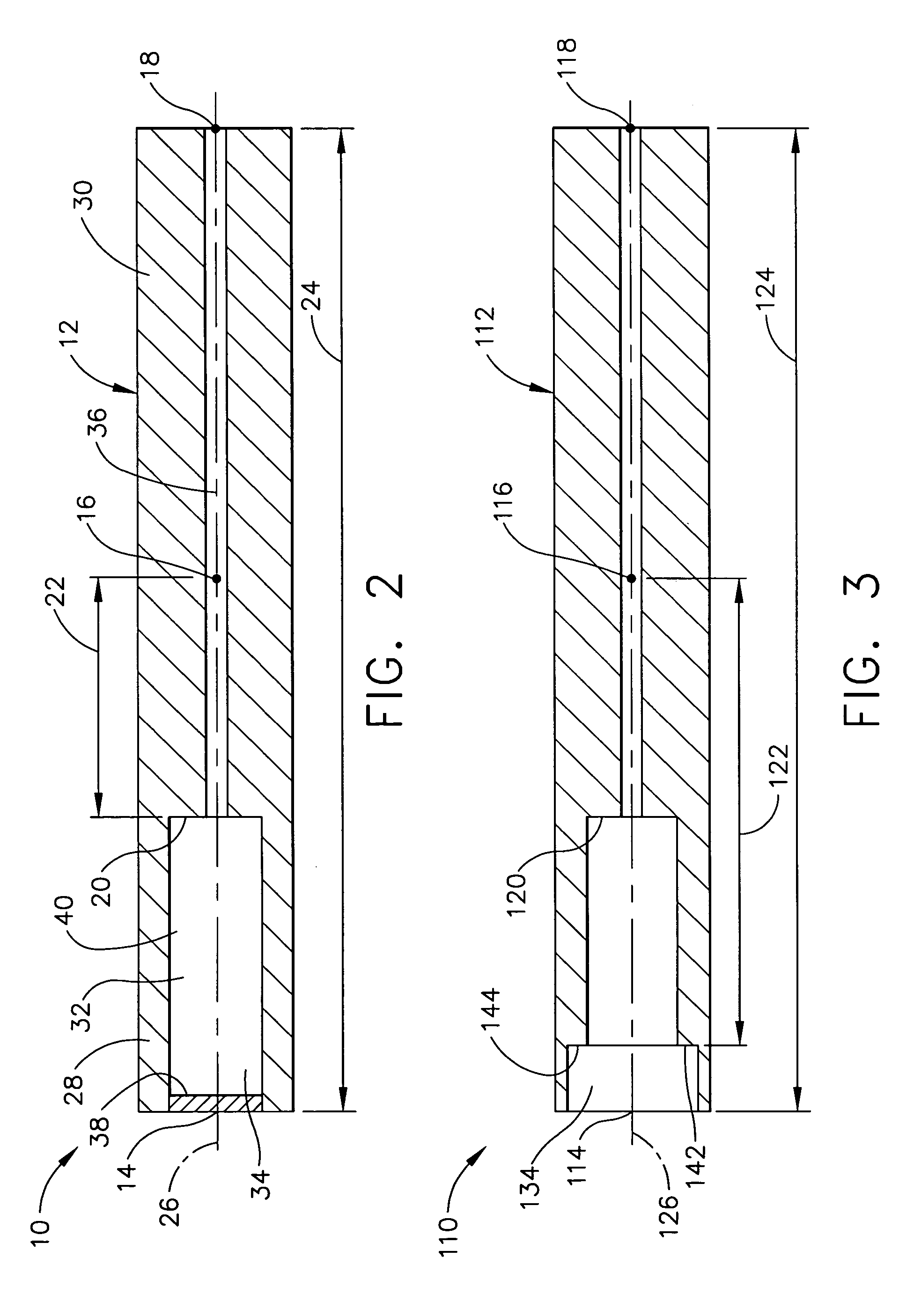
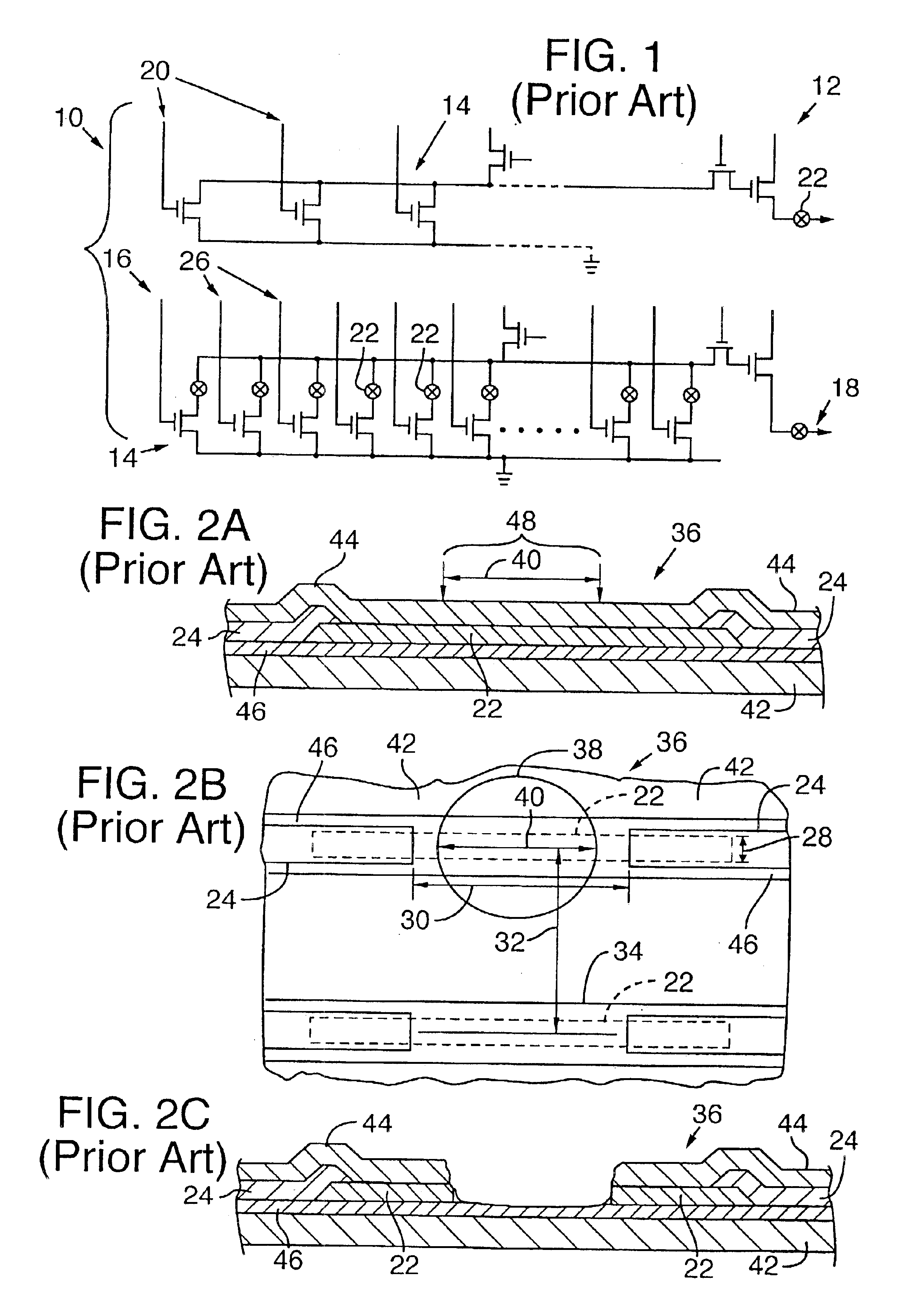
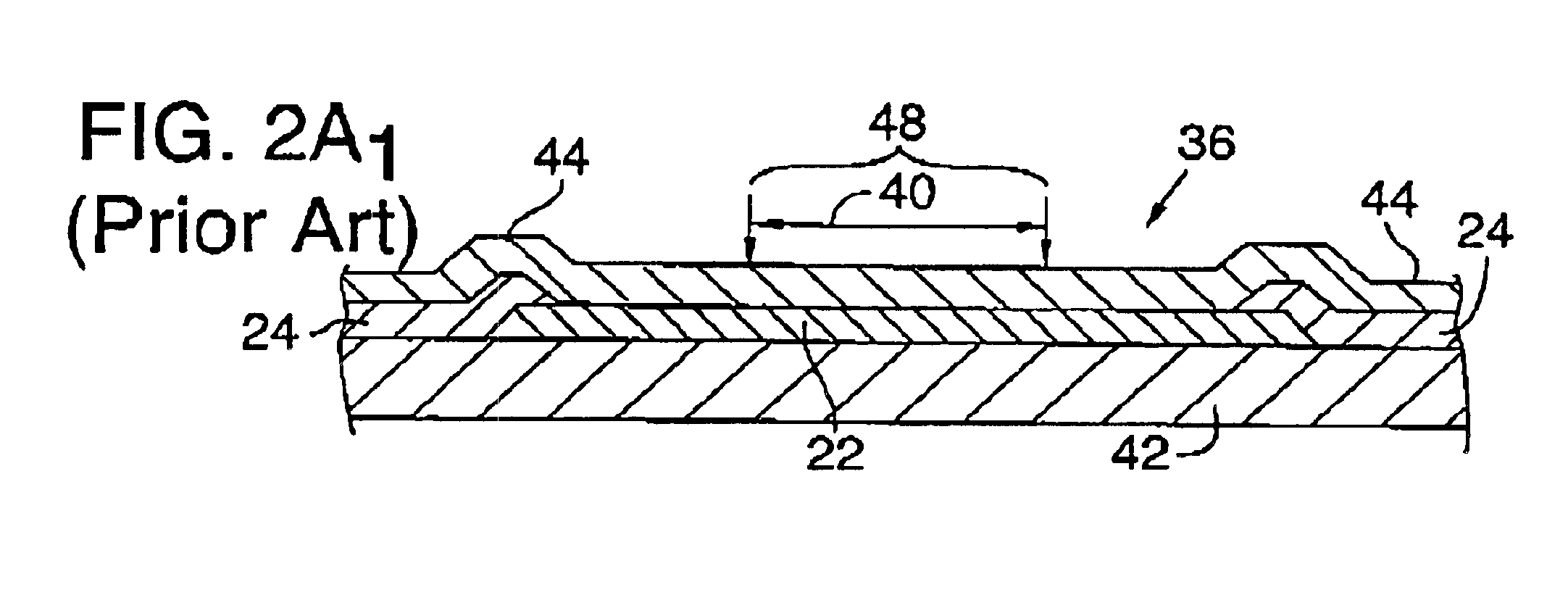
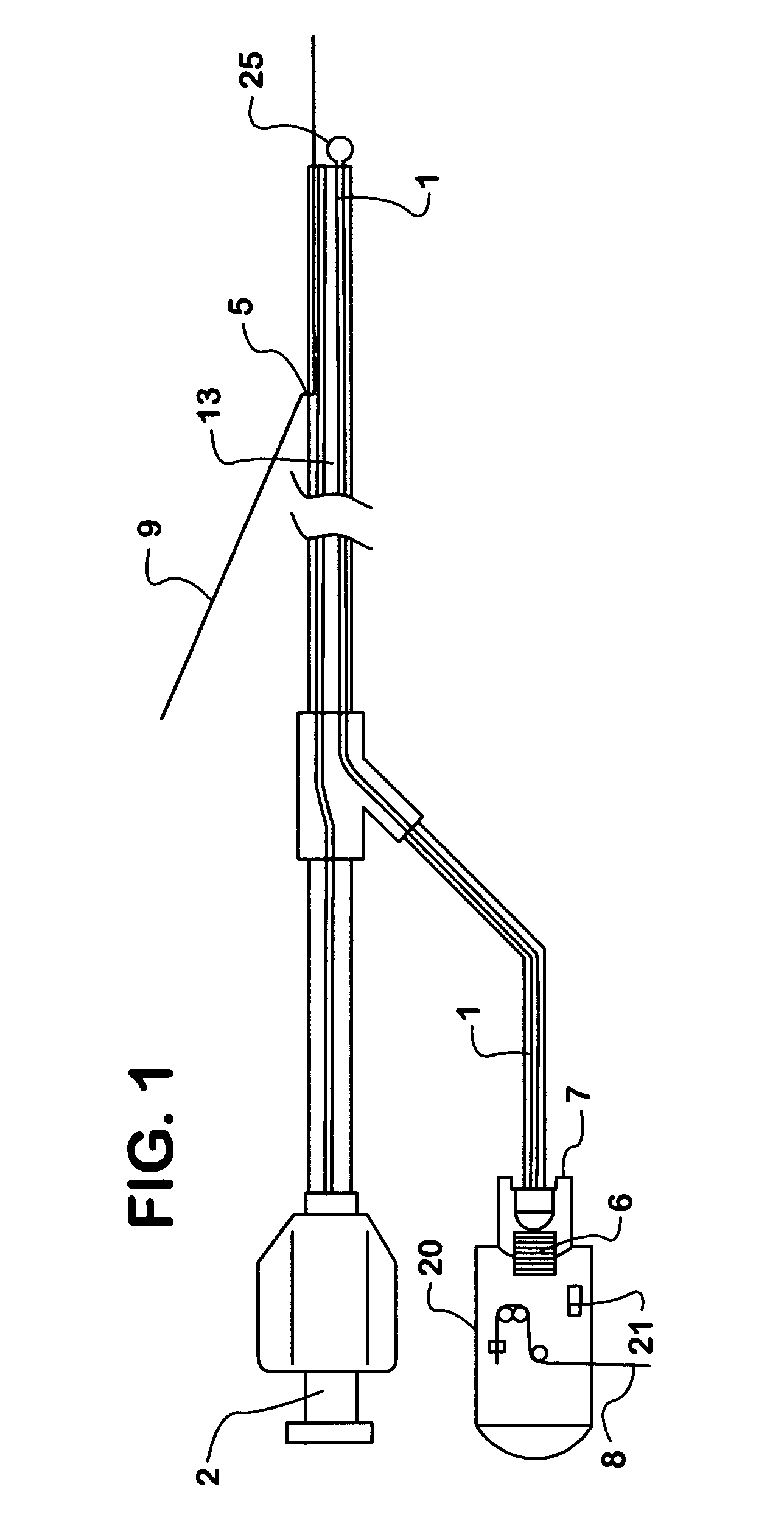
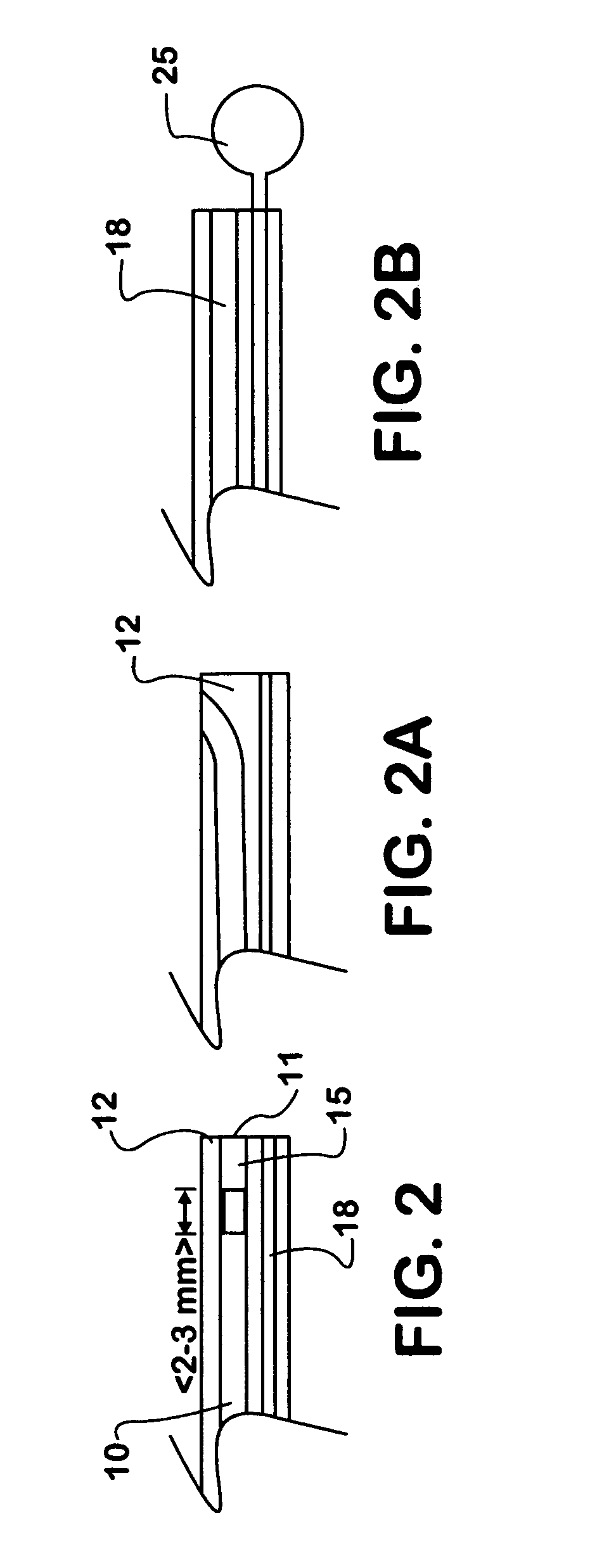
Ultrasonic surgical blade and instrument having a gain step
ActiveUS7163548B2Increase the lengthShorten half wave lengthCannulasTooth pluggers/hammersSurgical bladeWavelength
An ultrasonic surgical blade, and an instrument, having a gain step. The blade body has, in any half wave length of the ultrasonic-surgical-blade body, a first vibration antinode, a vibration node, a second vibration antinode, and a gain step. The gain step is located between the second vibration antinode and the first vibration antinode. The gain step is spaced apart from the vibration node by a gain-step distance greater than 5% of the distance between the second vibration antinode and the first vibration antinode. The instrument includes the blade, a handpiece having an ultrasonic transducer, and an ultrasonic transmission rod whose proximal end is operatively connected to the ultrasonic transducer and whose distal end activates the blade. In one option, the first vibration antinode is the distal tip, and the gain step is located between the vibration node and the distal tip, resulting in an increased active length of the blade.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
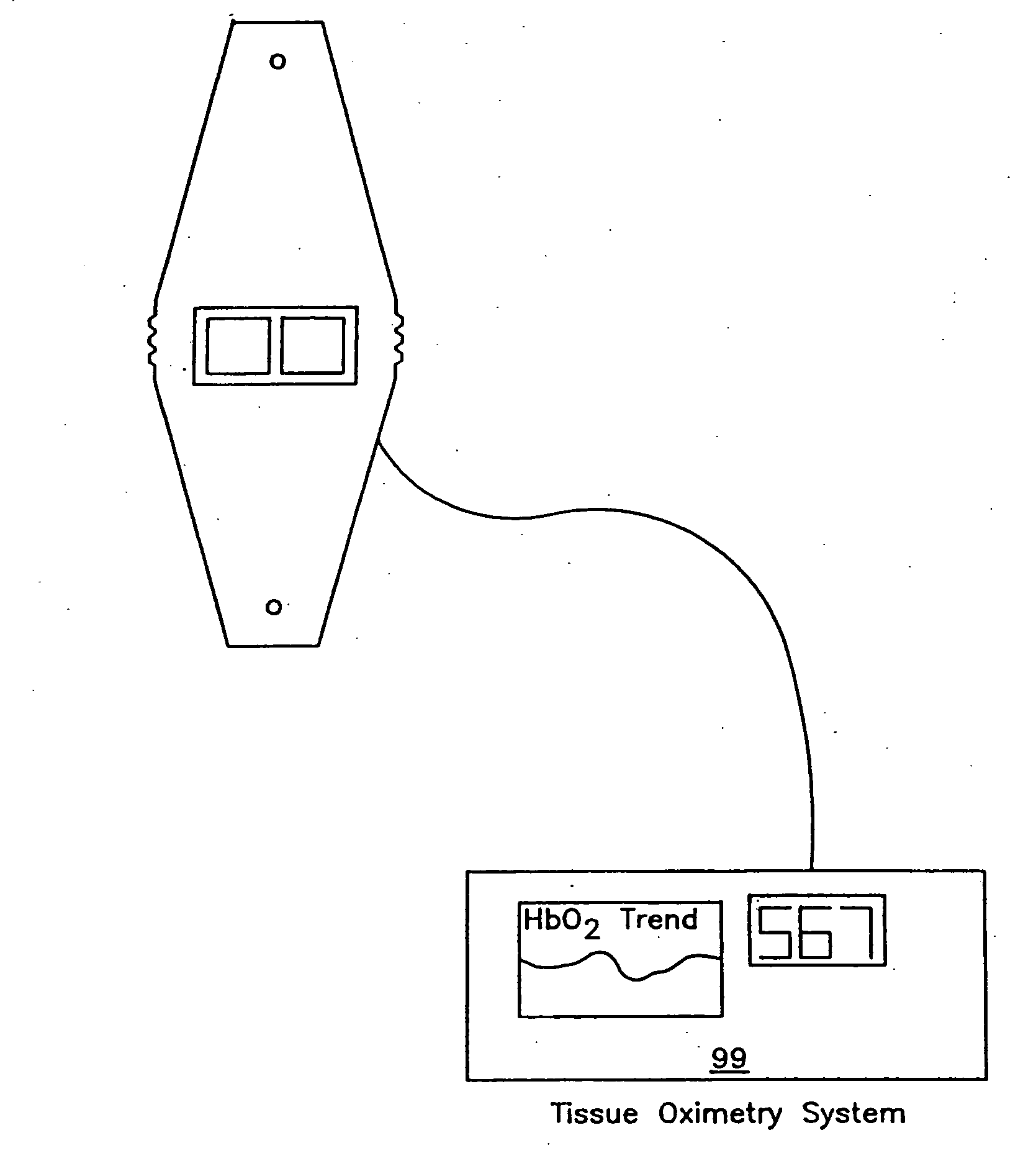
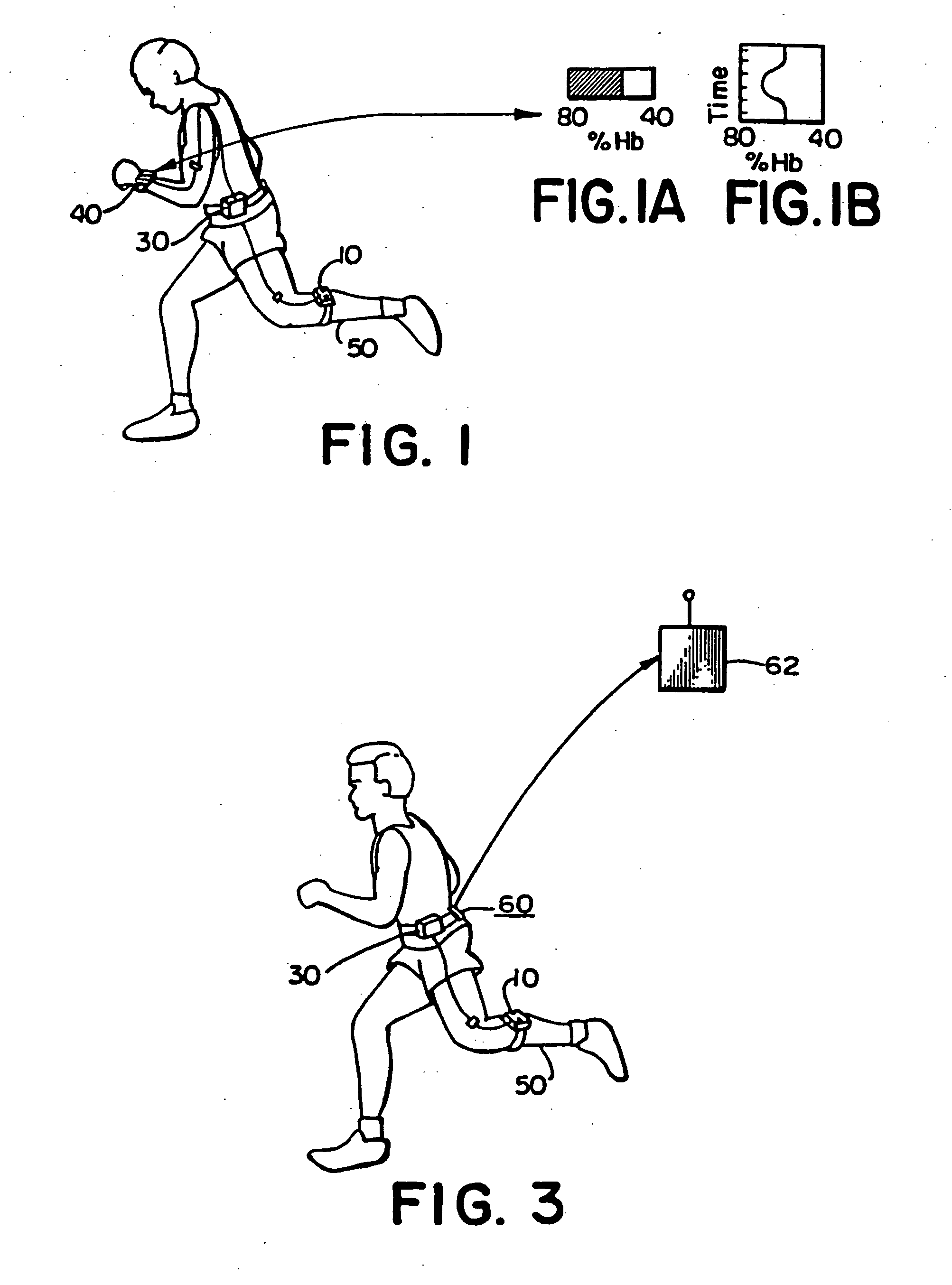
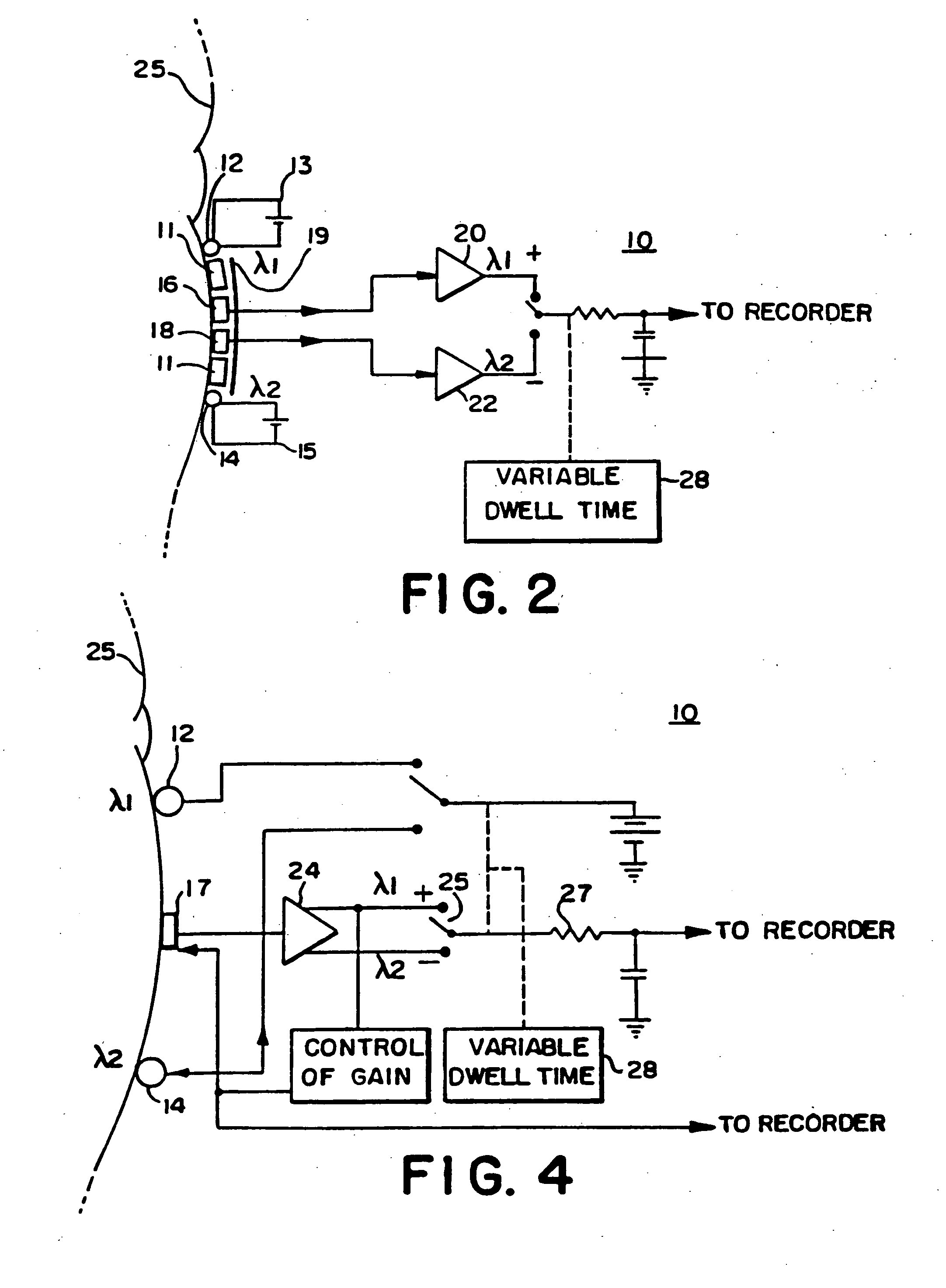
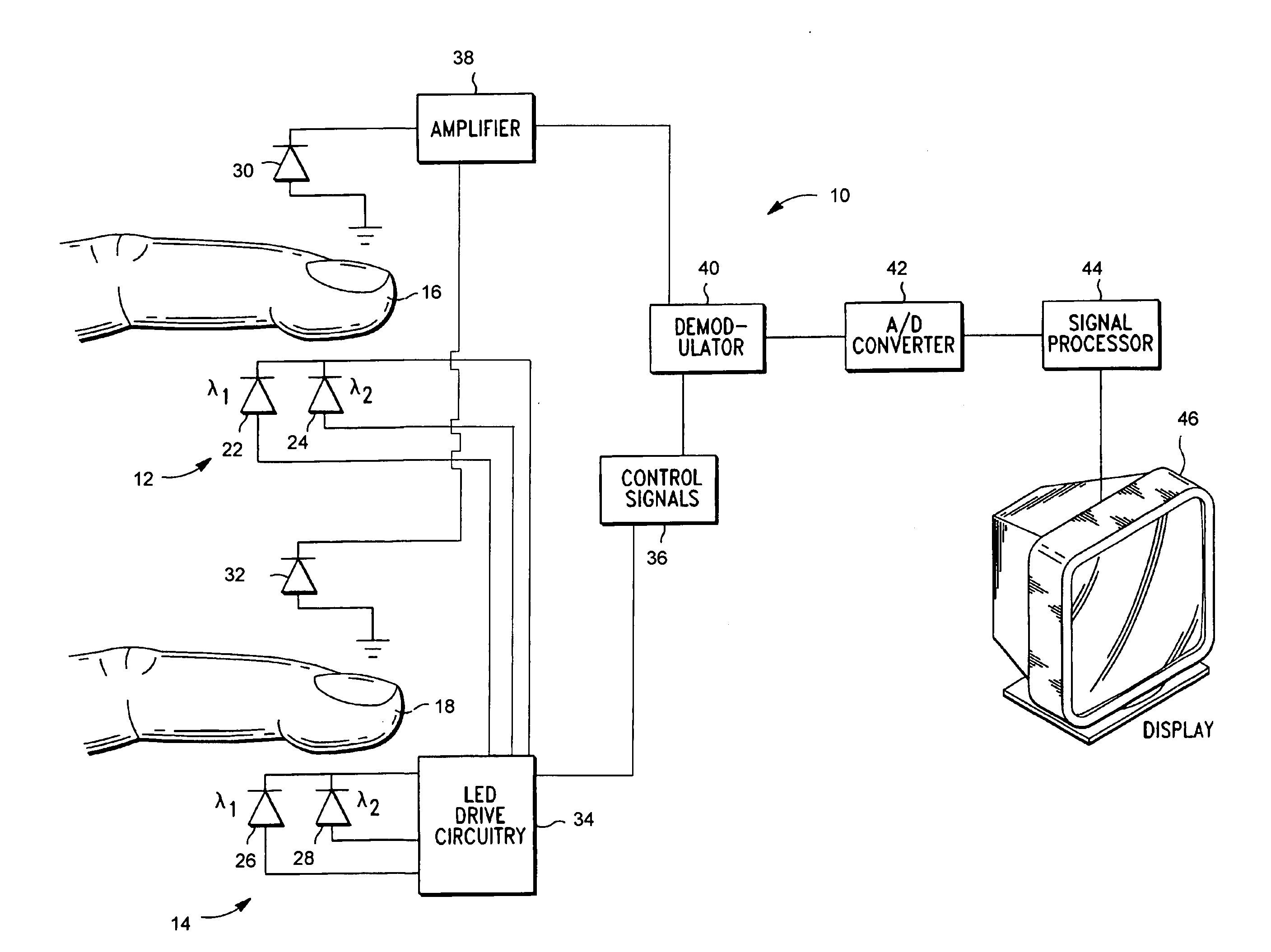
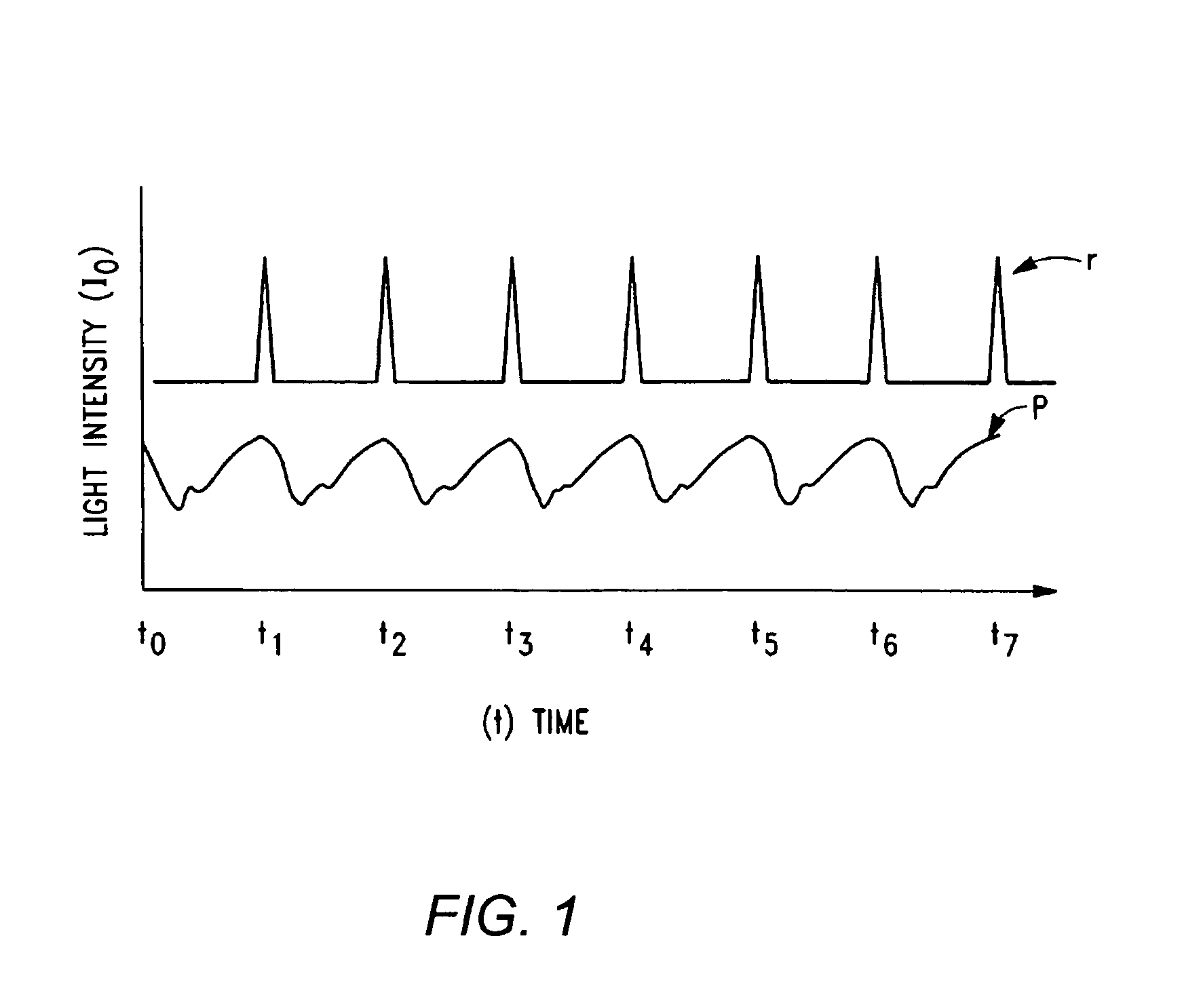
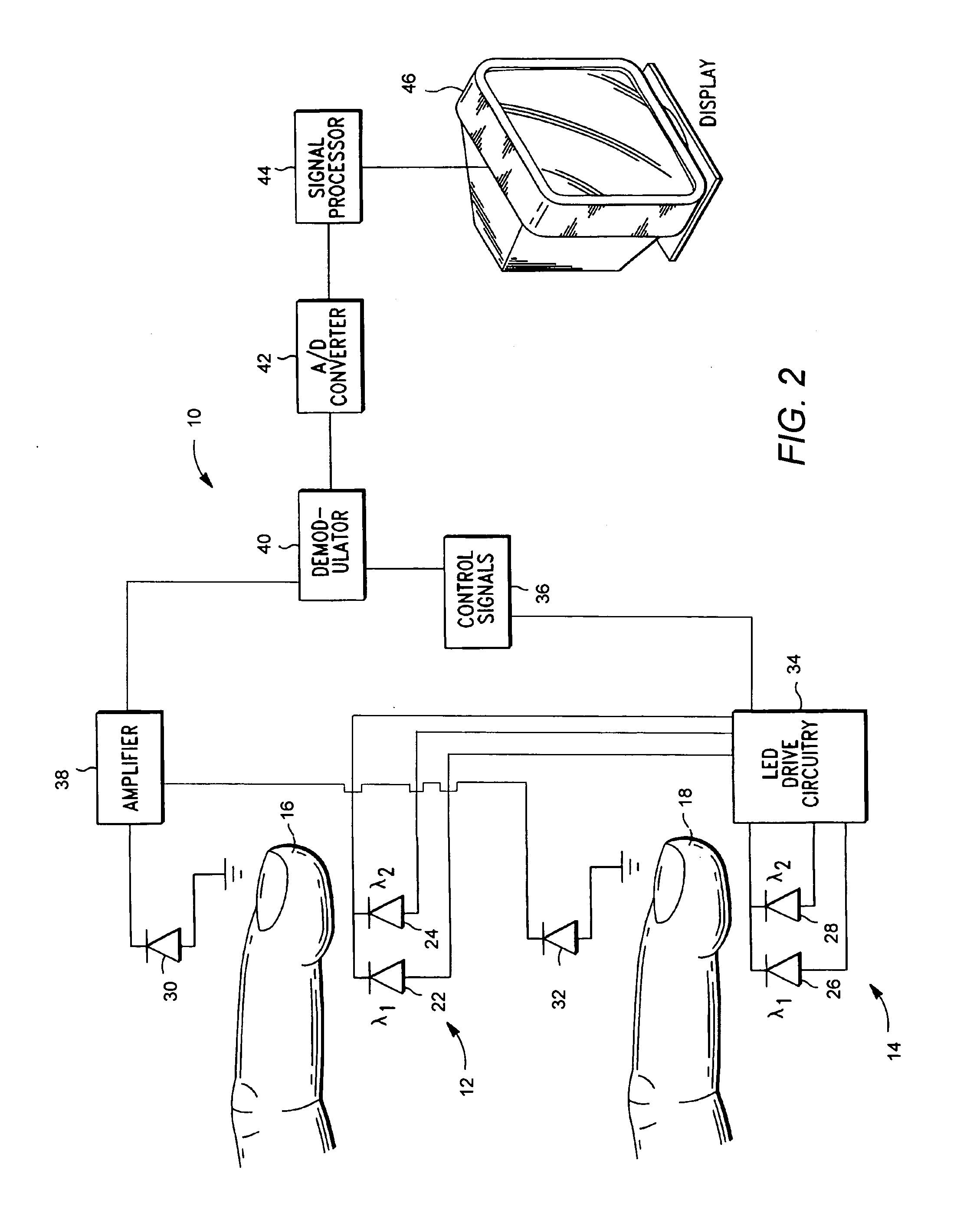
Hemoglobinometers and the like for measuring the metabolic condition of a subject
InactiveUS20050113656A1Performance of was minimizedEfficient couplingCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringSkin surfaceContinuous wave
The present invention discloses a novel, user-wearable system for monitoring the oxygen concentration, or oxygenation trend, in the tissue of a subject undergoing aerobic stress. The system comprises a lightweight detector, worn against the skin surface of the subject, at the site being monitored. The system further includes wearable power pack and display means for displaying information indicative of the metabolic condition of the region being monitored. The detector preferably employs a continuous wave spectrophotometer having one or more sources of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between about 760 and 800 nanometers directed into the tissue of the subject. The detector utilizes photon migration to detect the portion of the transmitted radiation arriving at an adjacent skin region. The present invention also discloses methods for displaying the aerobic metabolic condition of a subject.
Owner:CHANCE BRITTON
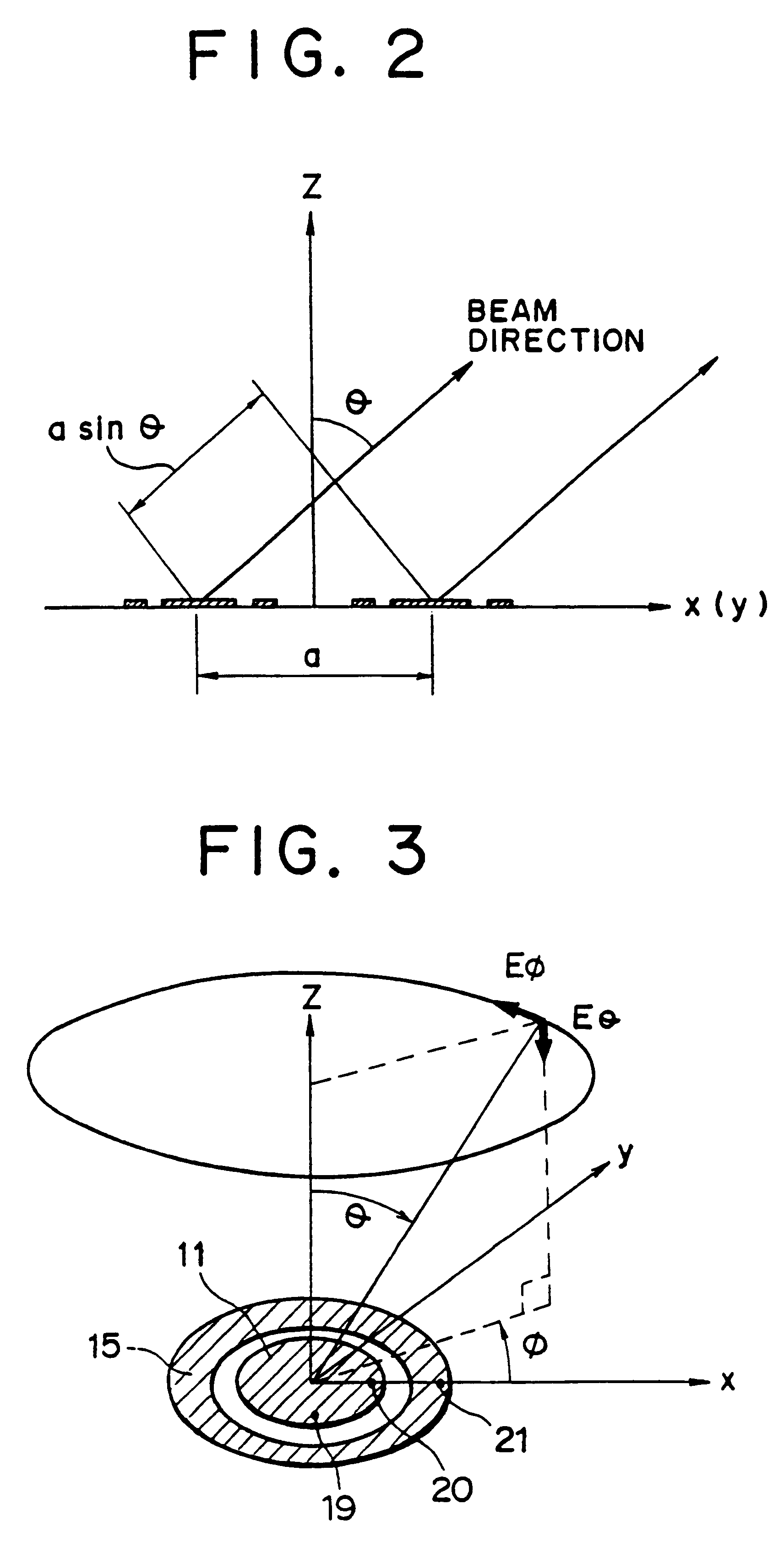
Beam scanning antennas with plurality of antenna elements for scanning beam direction
An array antenna is formed of a plurality of antenna elements, each of which scans a beam in the direction of an angle theta to a boresight of the antenna and electrically varies the direction of a rotation angle phi of the beam. The antenna elements are disposed so that the optical path difference of radio waves transmitted or received by two adjacent antenna elements in the directions of a plurality of direction angles phi on the plane tilted for an angle theta to the boresight of the antenna is nearly a multiple of the wave length of the radio waves.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for processing signals reflecting physiological characteristics from multiple sensors
InactiveUS20070260132A1Improve accuracyEnhanced signalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineMultiple sensor
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for processing signals reflecting a physiological characteristic by performing an error minimizing mathematical combination between signals from at least two independent sensors. For example, the intensity of light is detected following tissue absorption at two wavelengths and the signals are corrected. Preferably, corrected intensity signals are derived by orthogonal regression. In one embodiment, the method and apparatus are used to determine arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:WOOLSTHORPE TECH
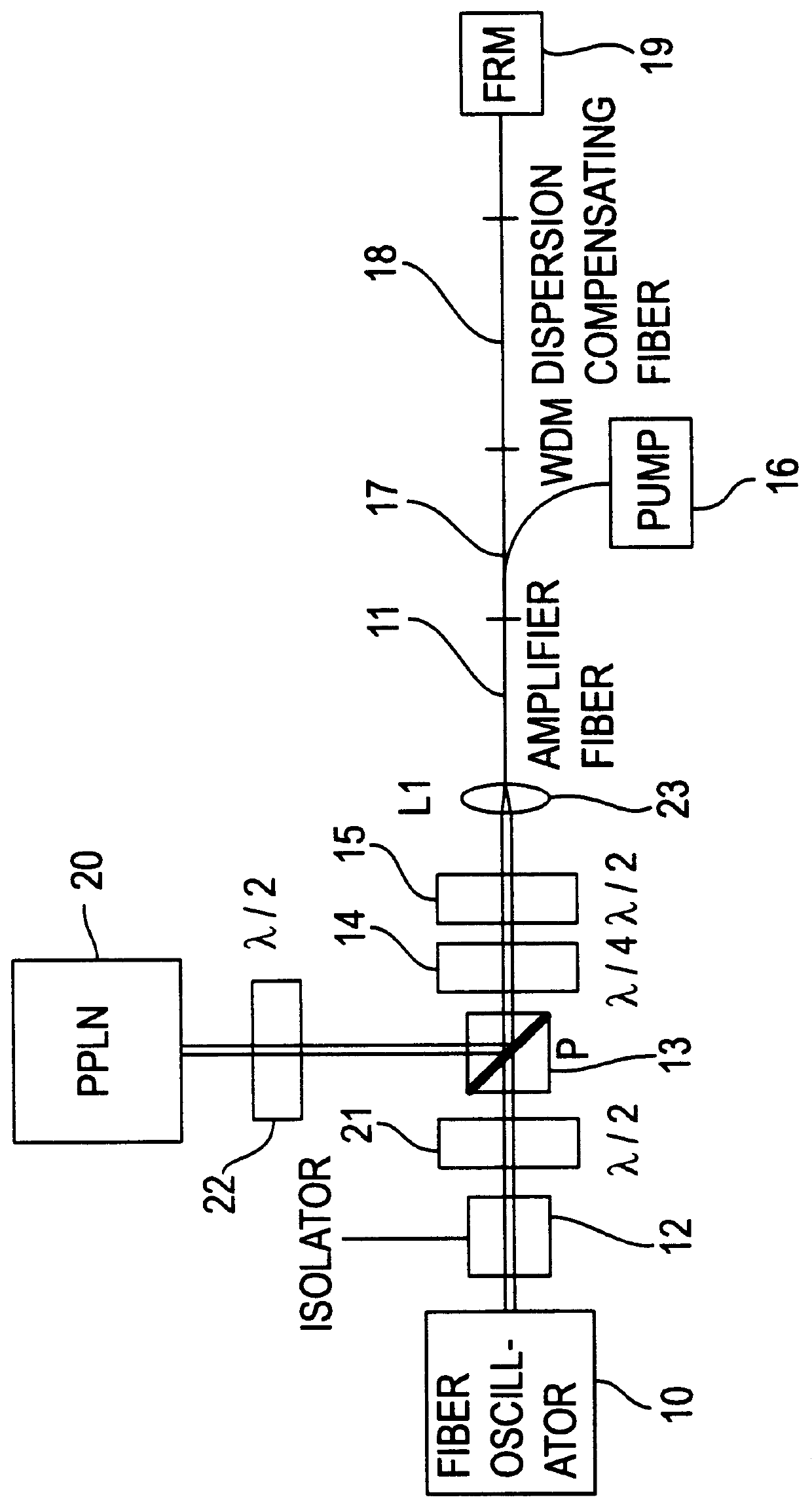
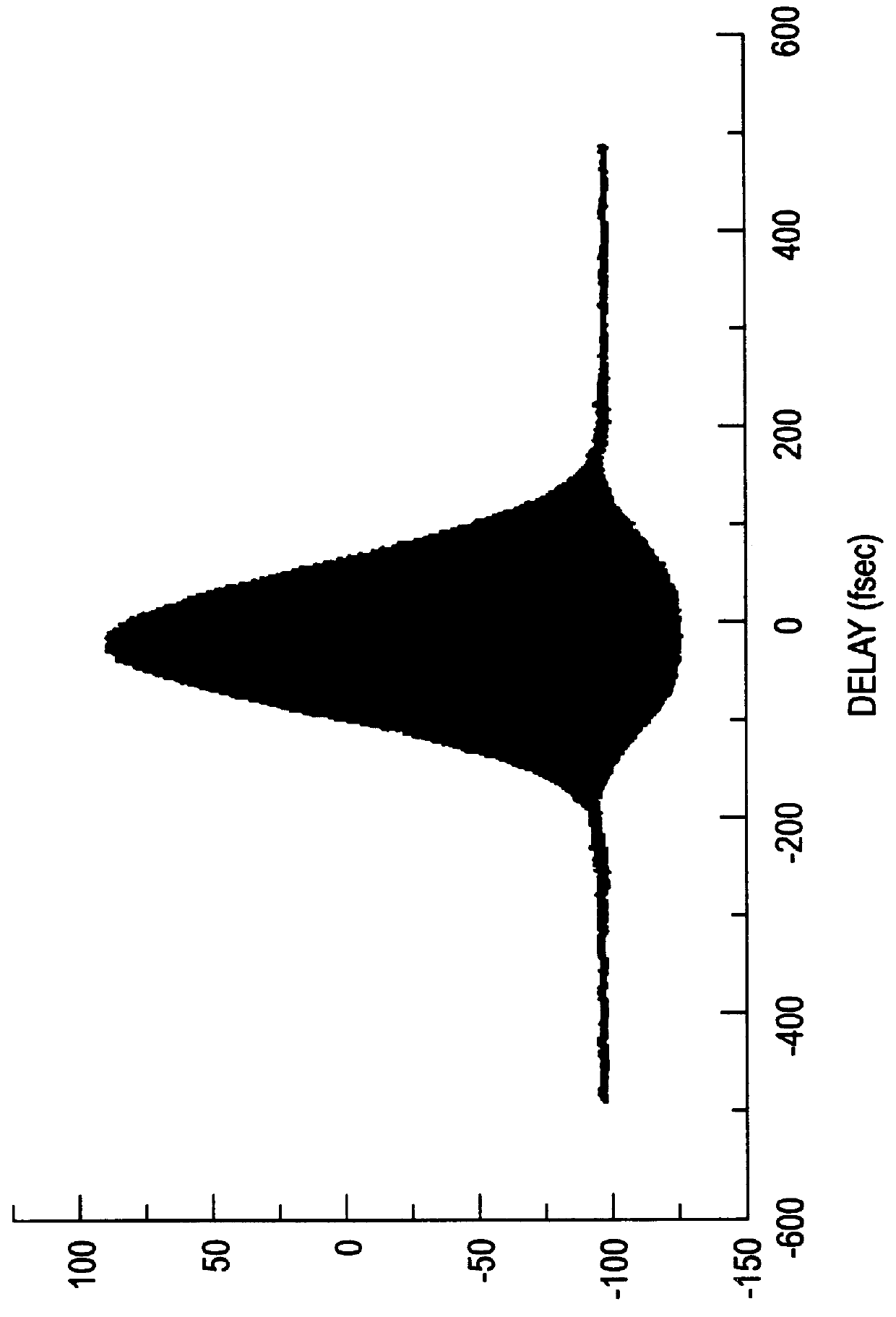
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
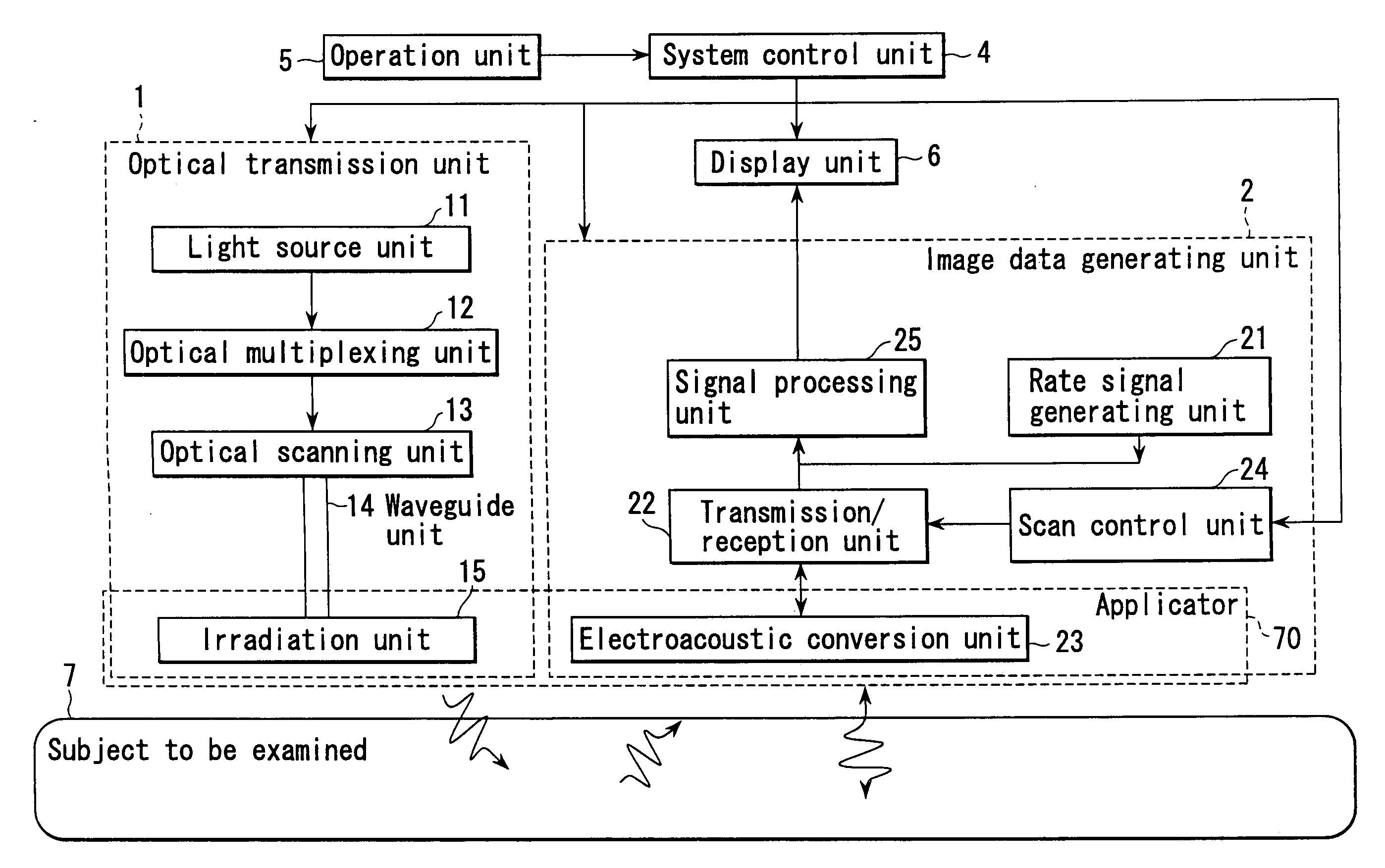
Method and apparatus for forming an image that shows information about a subject
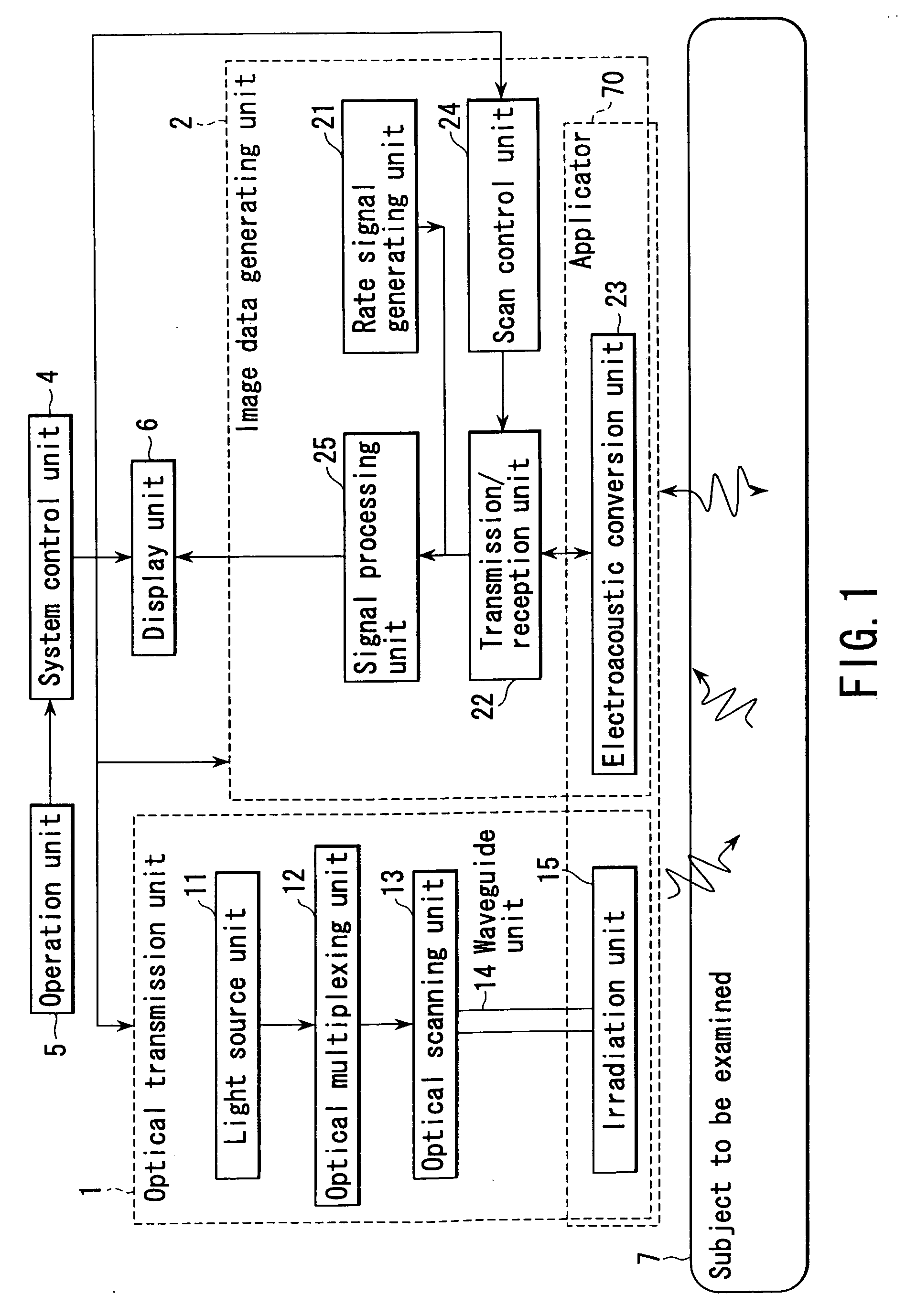
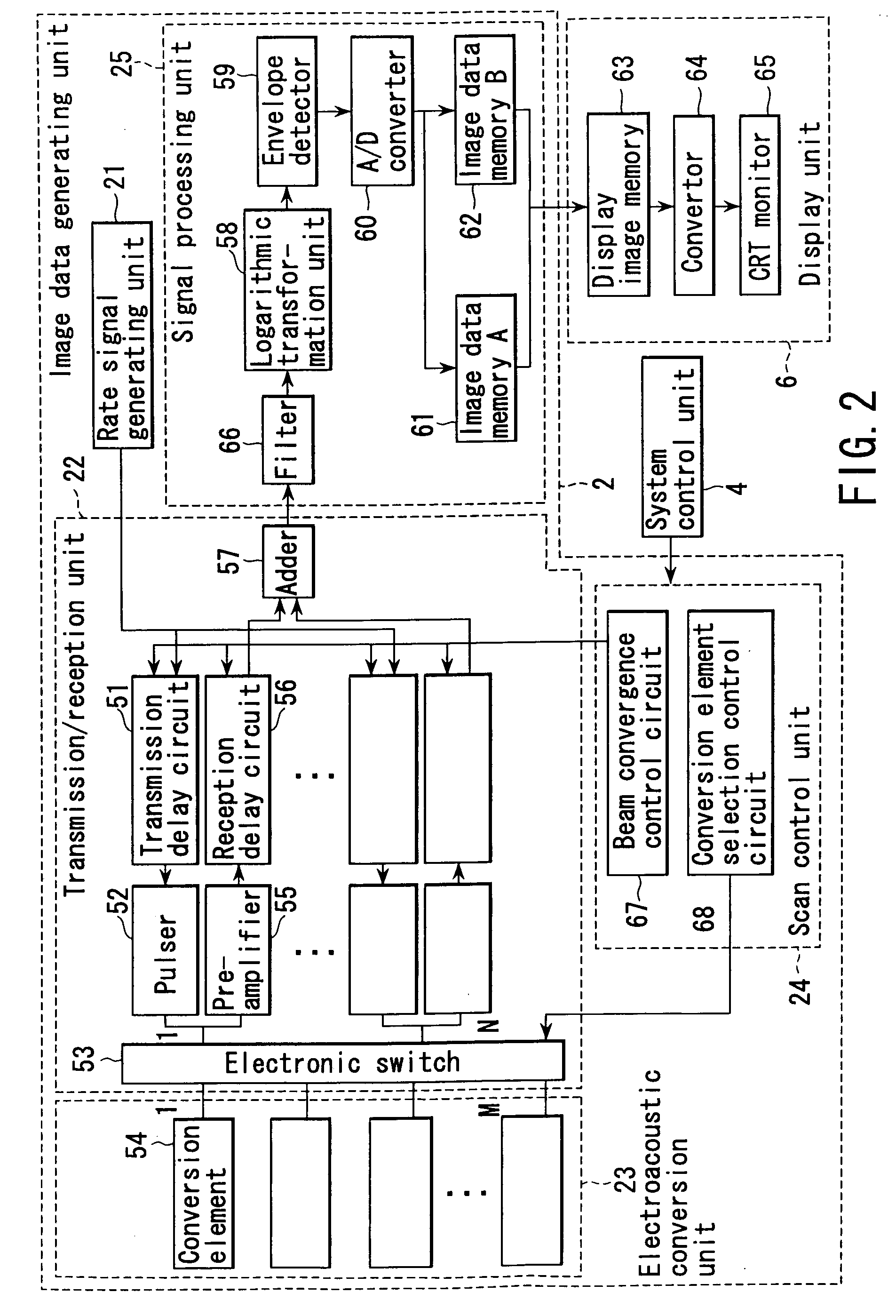
ActiveUS20050004458A1Easy to operateImprove spatial resolutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionAcoustic waveLength wave
An apparatus includes an optical transmission unit which irradiates a subject to be examined with light containing a specific wavelength component, an electroacoustic conversion unit which receives acoustic waves generated inside the subject by the light radiated by the optical transmission unit and converts them into electrical signals, an image data generating unit which generates first image data on the basis of the reception signals obtained by the electroacoustic conversion unit, an electroacoustic conversion unit which receives ultrasonic reflection signals obtained by transmitting ultrasonic waves to the subject and converts them into electrical signals, an image data generating unit which generates second image data on the basis of the reception signals obtained by the electroacoustic conversion unit, and a display unit which combines the first and second image data and displays the resultant data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Illumination system particularly for microlithography
InactiveUS6438199B1Reduced beam diameterReduce the overall diameterNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionExit pupilGrating
The invention concerns an illumination system, particularly for microlithography with wavelengths <=193 nm, comprising a light source, a first optical component, a second optical component, an image plane and an exit pupil. The first optical component transforms the light source into a plurality of secondary light sources being imaged by the second optical component in said exit pupil. The first optical component comprises a first optical element having a plurality of first raster elements, which are imaged into said image plane producing a plurality of images being superimposed at least partially on a field in said image plane. The first raster elements deflect incoming ray bundles with first deflection angles, wherein at least two of the first deflection angles are different. The first raster elements are preferably rectangular, wherein the field is a segment of an annulus. To transform the rectangular images of the first raster elements into the segment of the annulus, the second optical component comprises a first field mirror for shaping the field to the segment of the annulus.
Owner:CARL-ZEISS-STIFTUNG TRADING AS CARL ZEISS
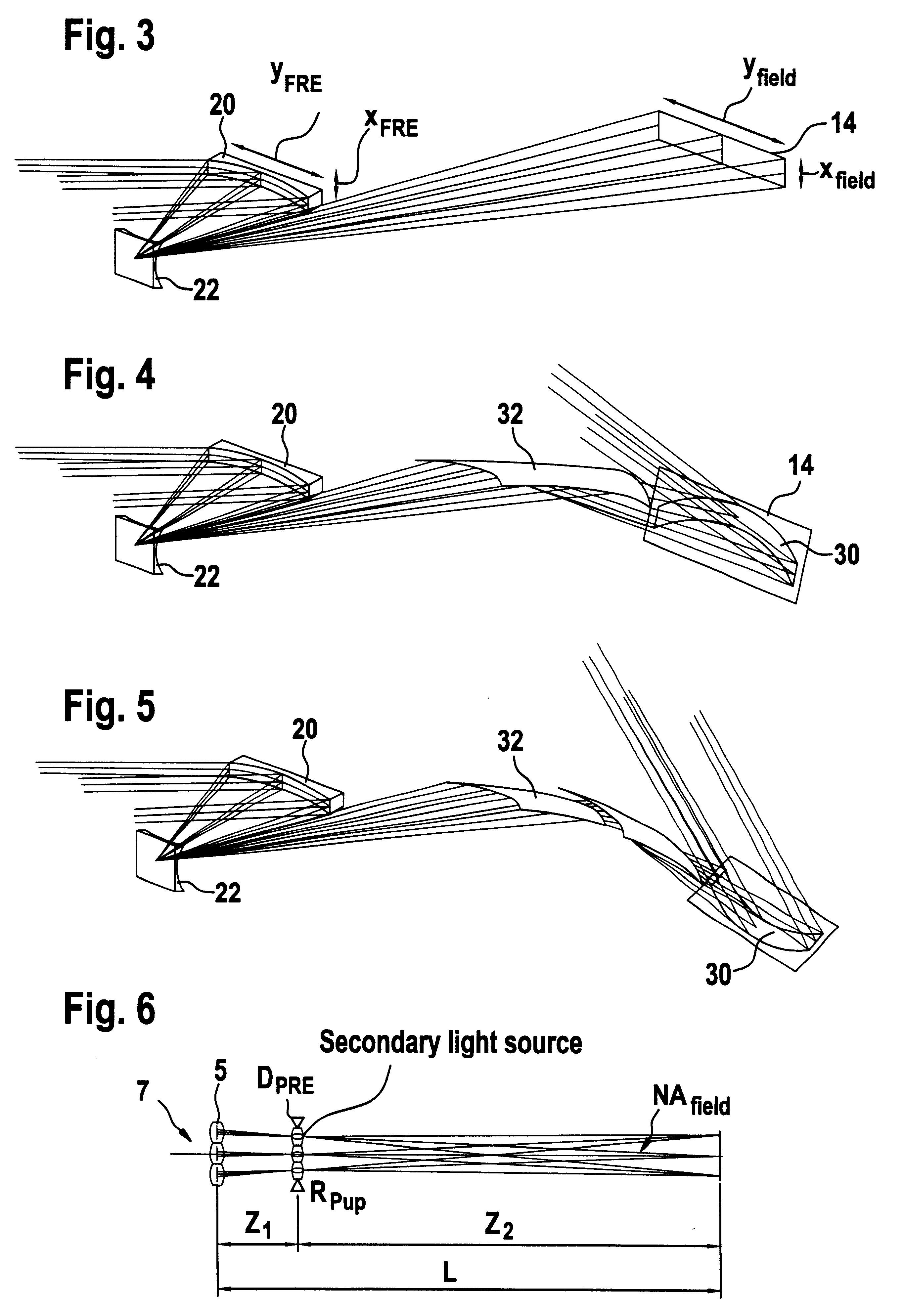
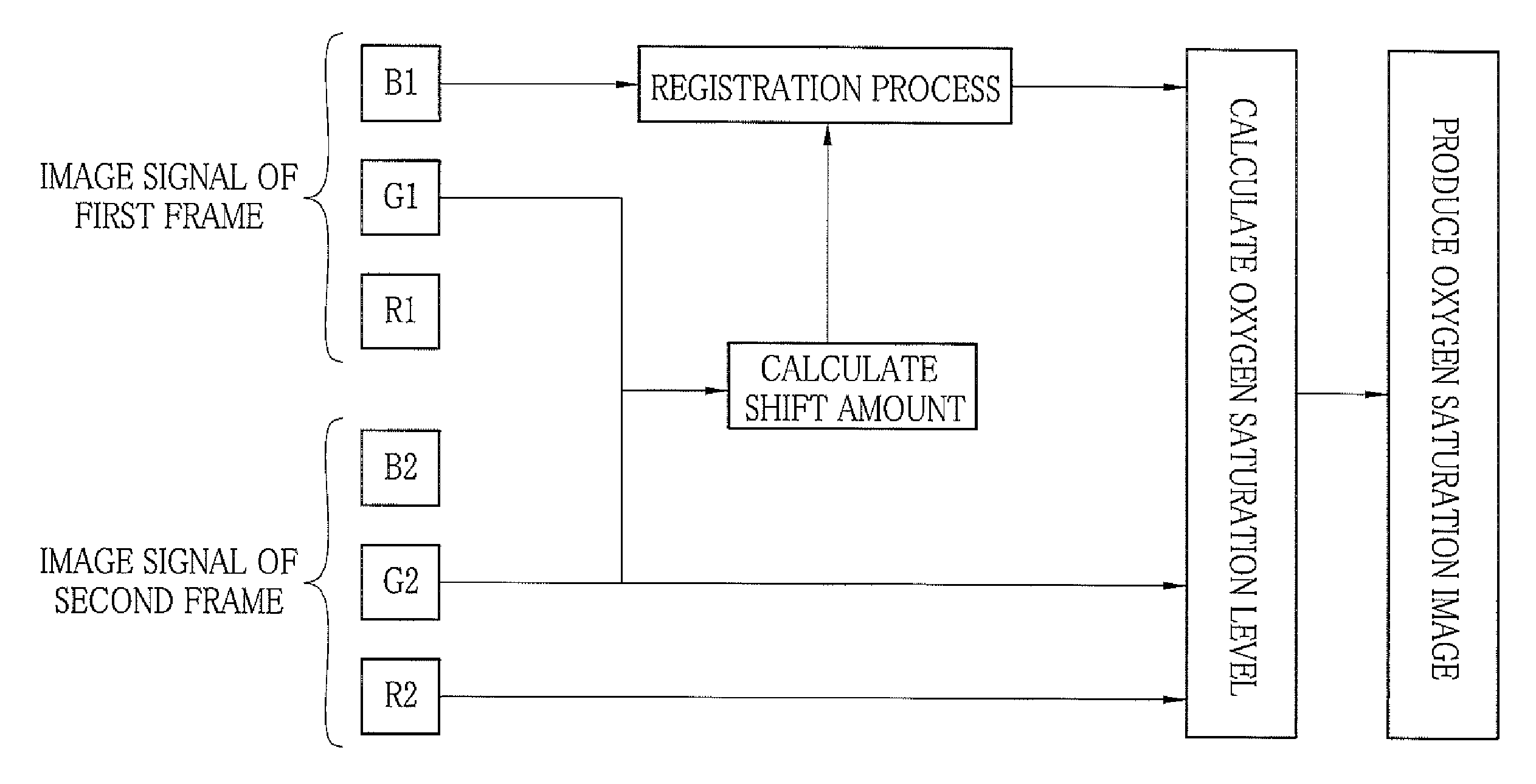
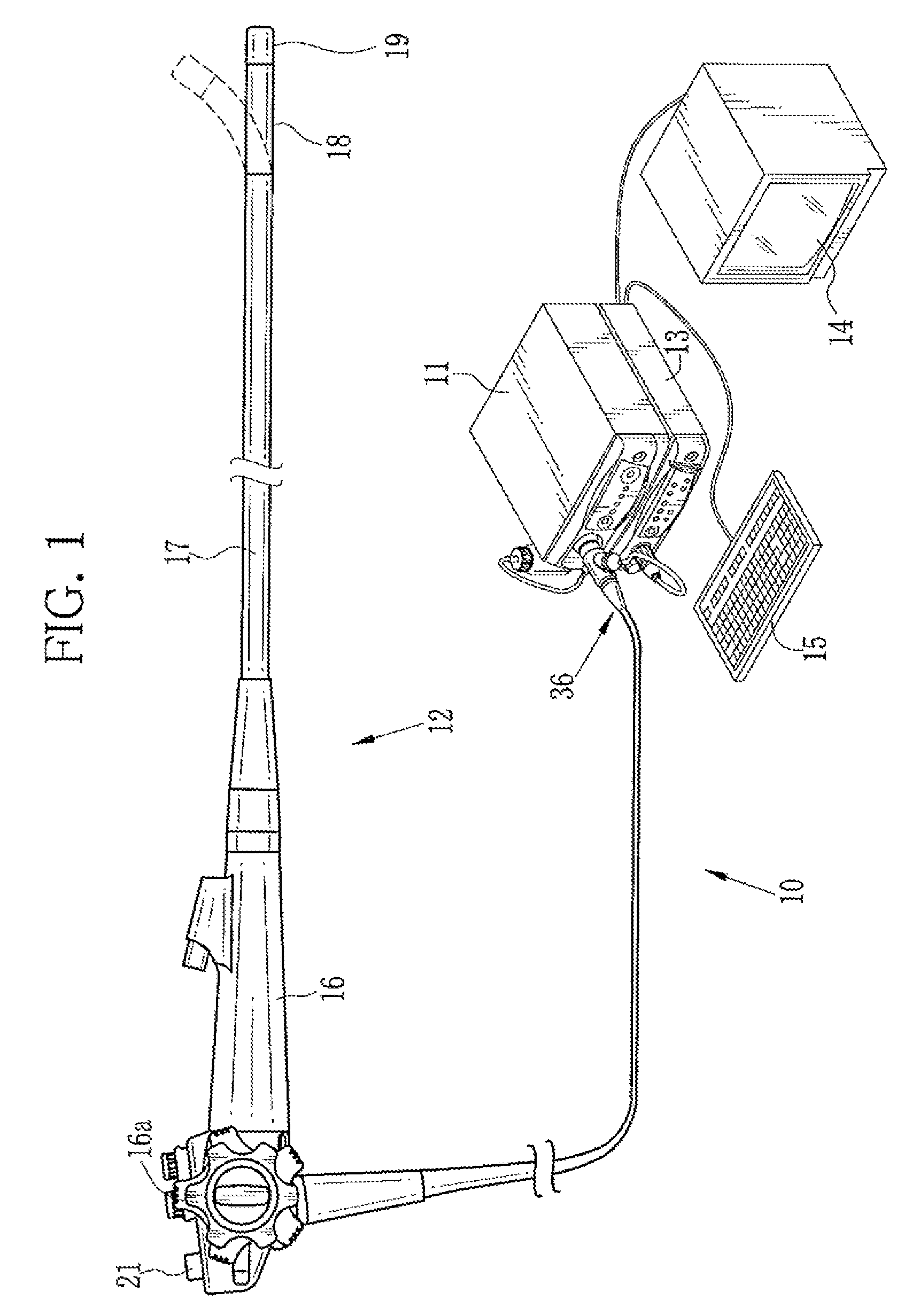
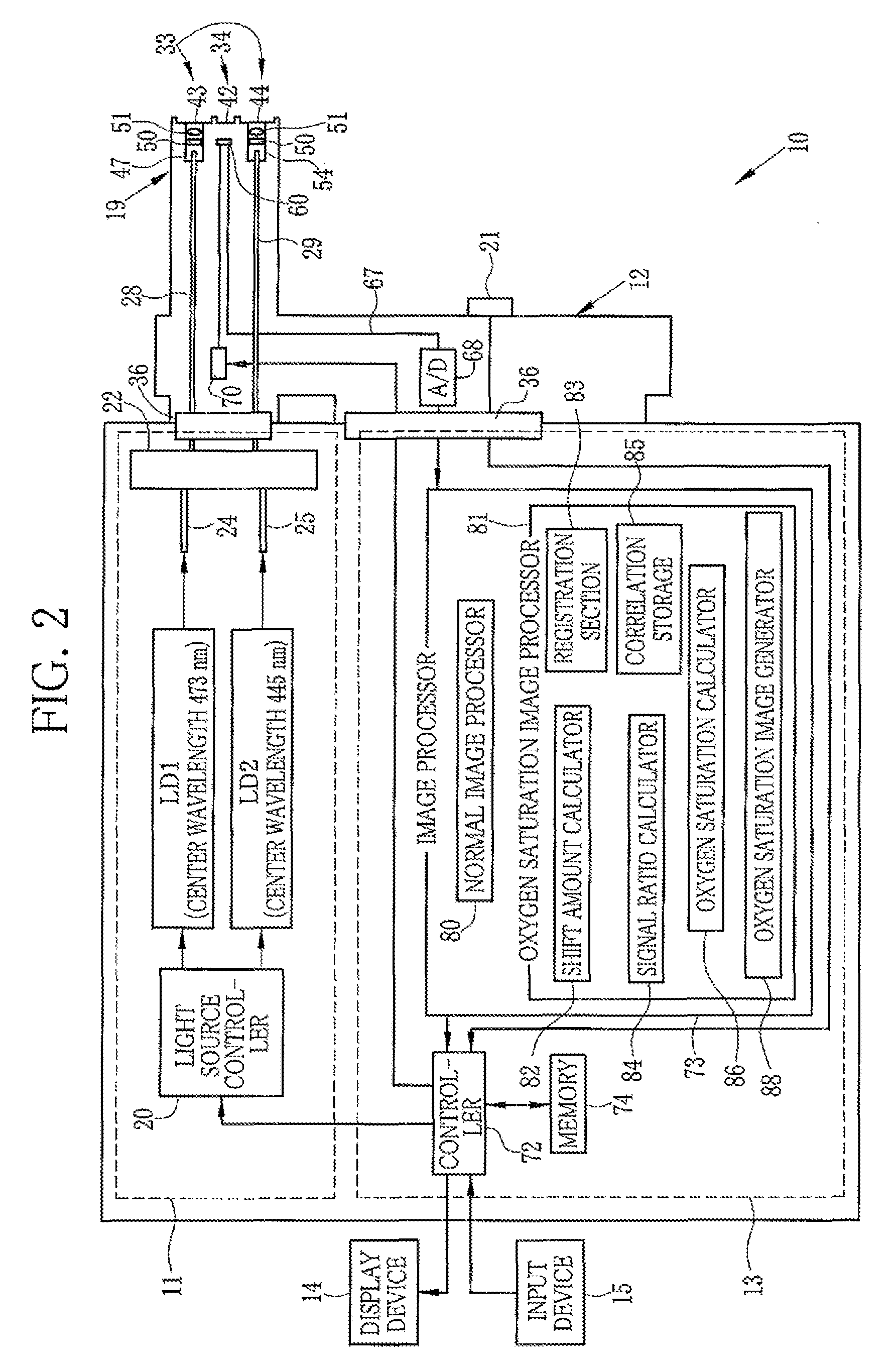
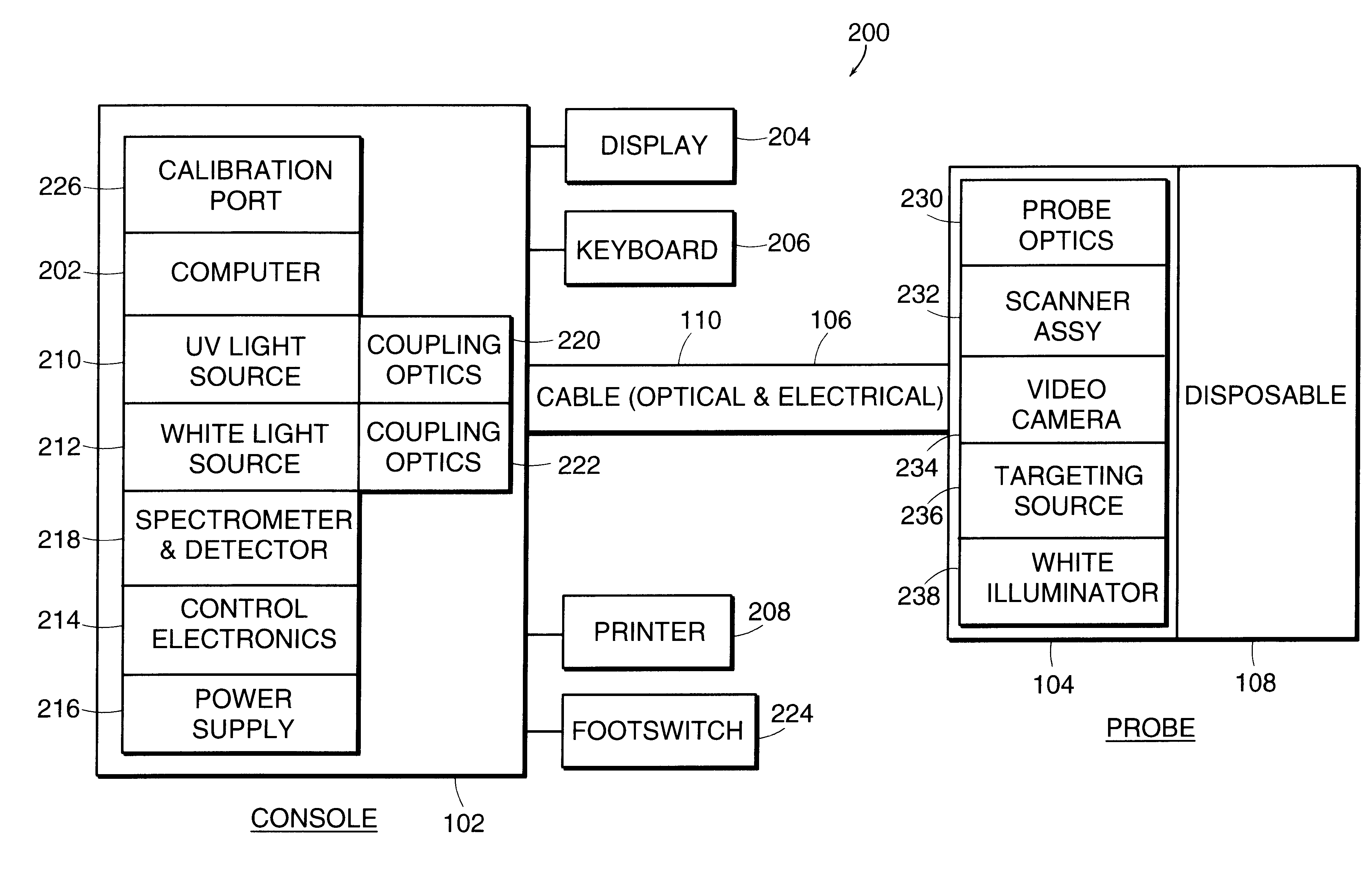
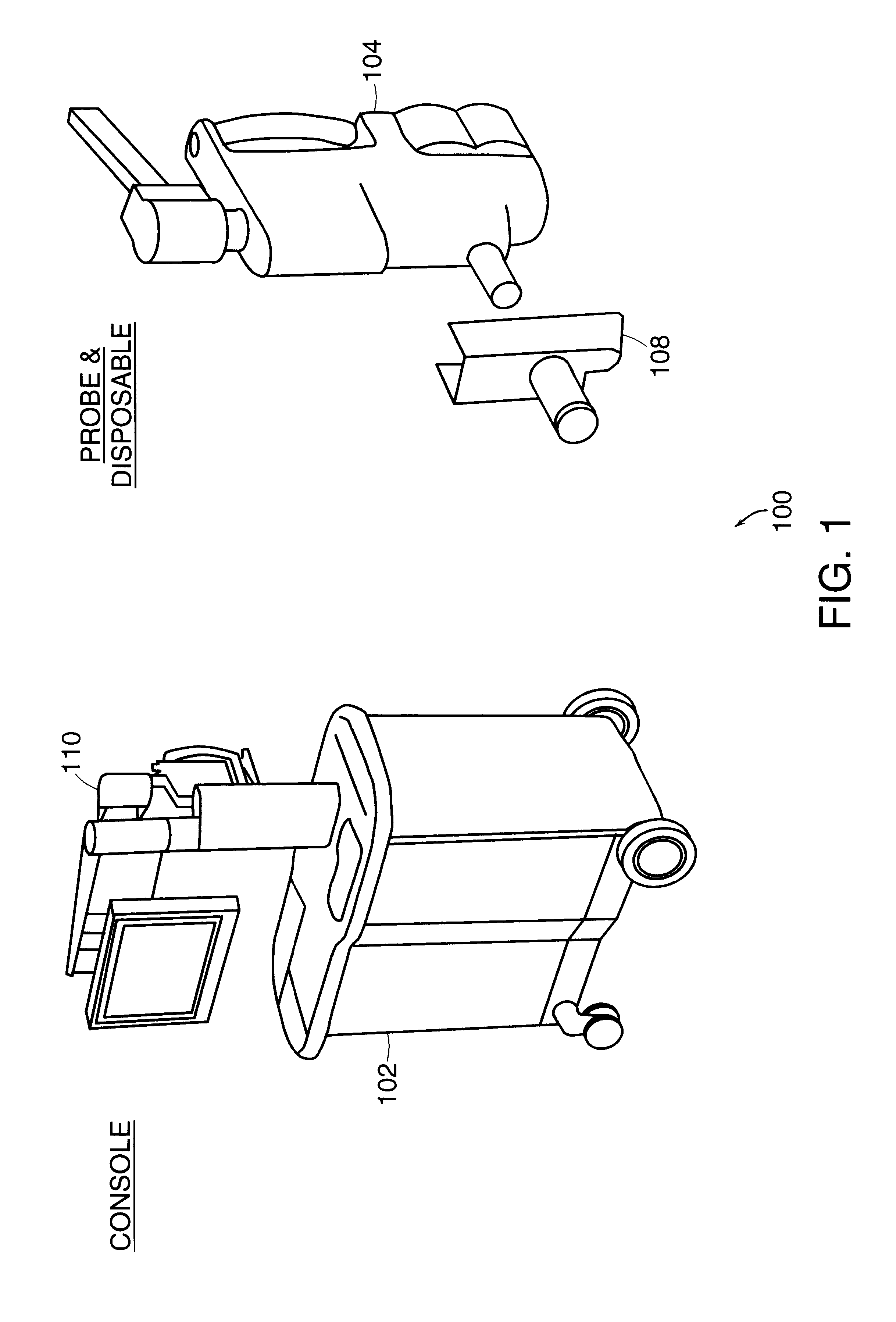
Endoscope system, processor device thereof, and image producing method
First and second white light is generated by excitations of phosphors with first and second laser beams having center wavelengths of 473 nm and 445 nm, respectively. The first and second white light is applied, in respective frames, sequentially to a region of interest in a subject. A color image sensor images the region of interest in the each frame. Based on a shift amount, calculated from green signals of first and second frames, between images, an image of a blue signal of the first frame is moved to be aligned with an image of a green signal and an image of a red signal of the second frame. After the alignment, an oxygen saturation image representing an oxygen saturation level of hemoglobin in blood is produced from the blue signal of the first frame and green and red signals of the second frame.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
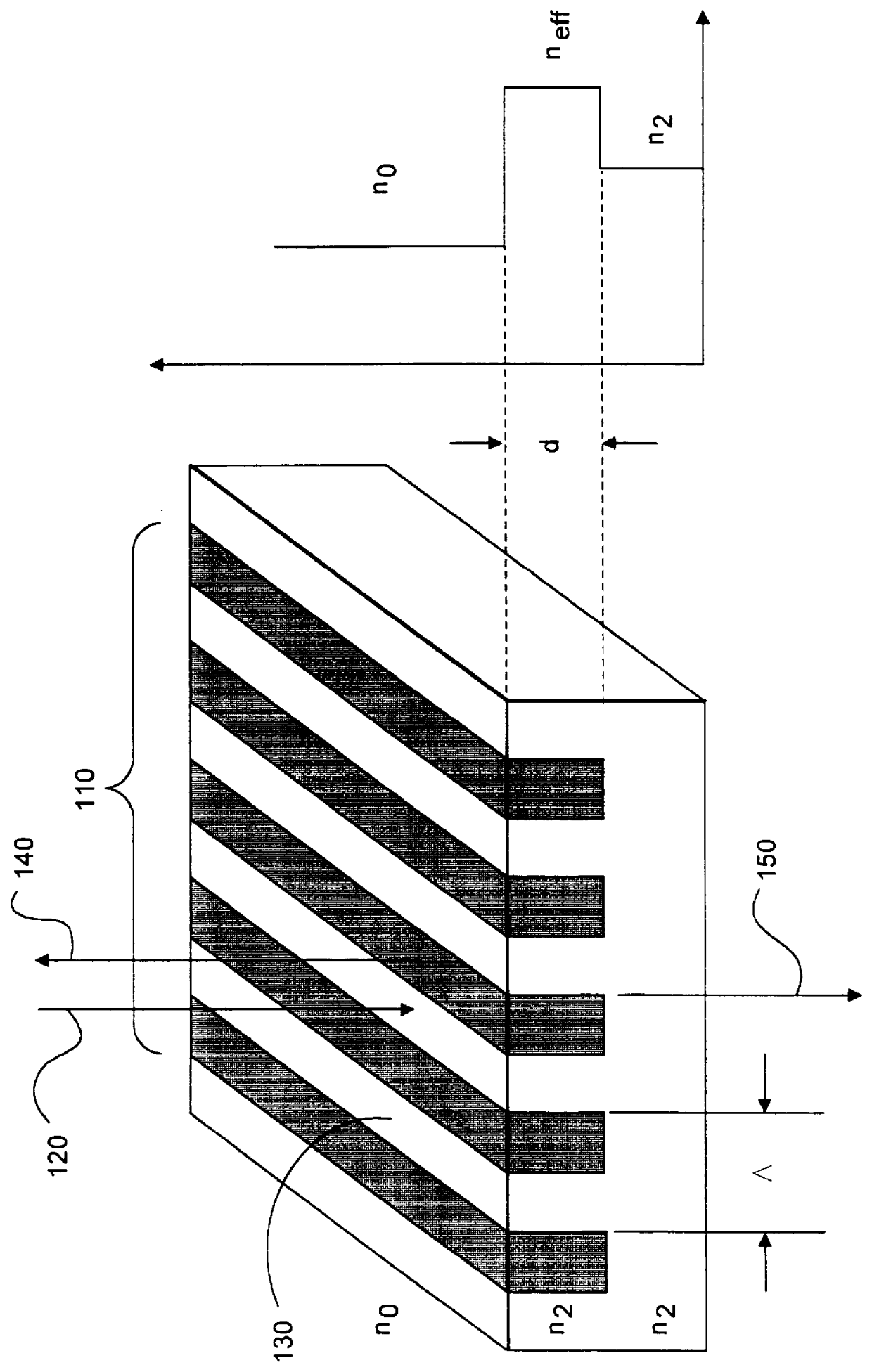
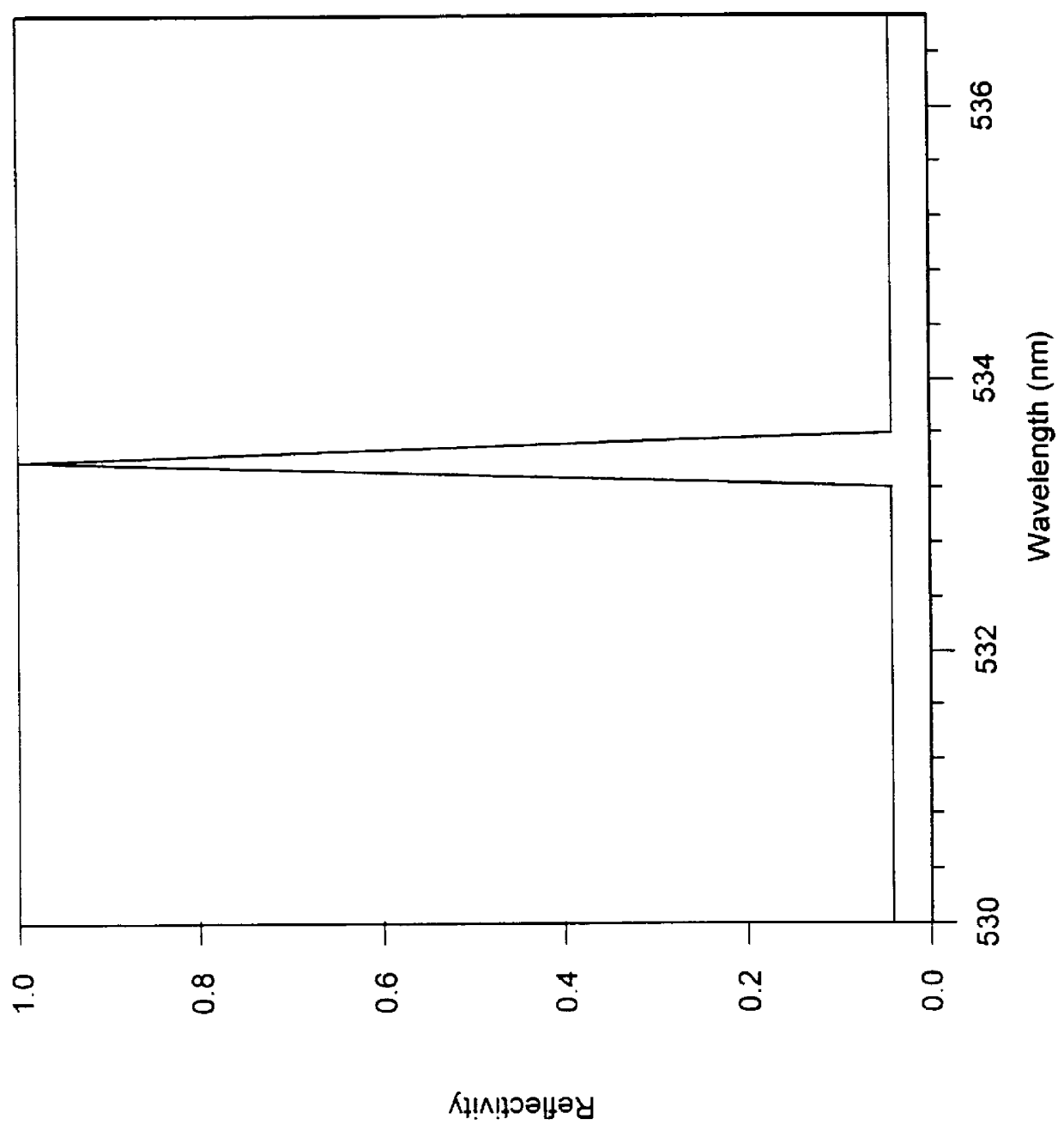
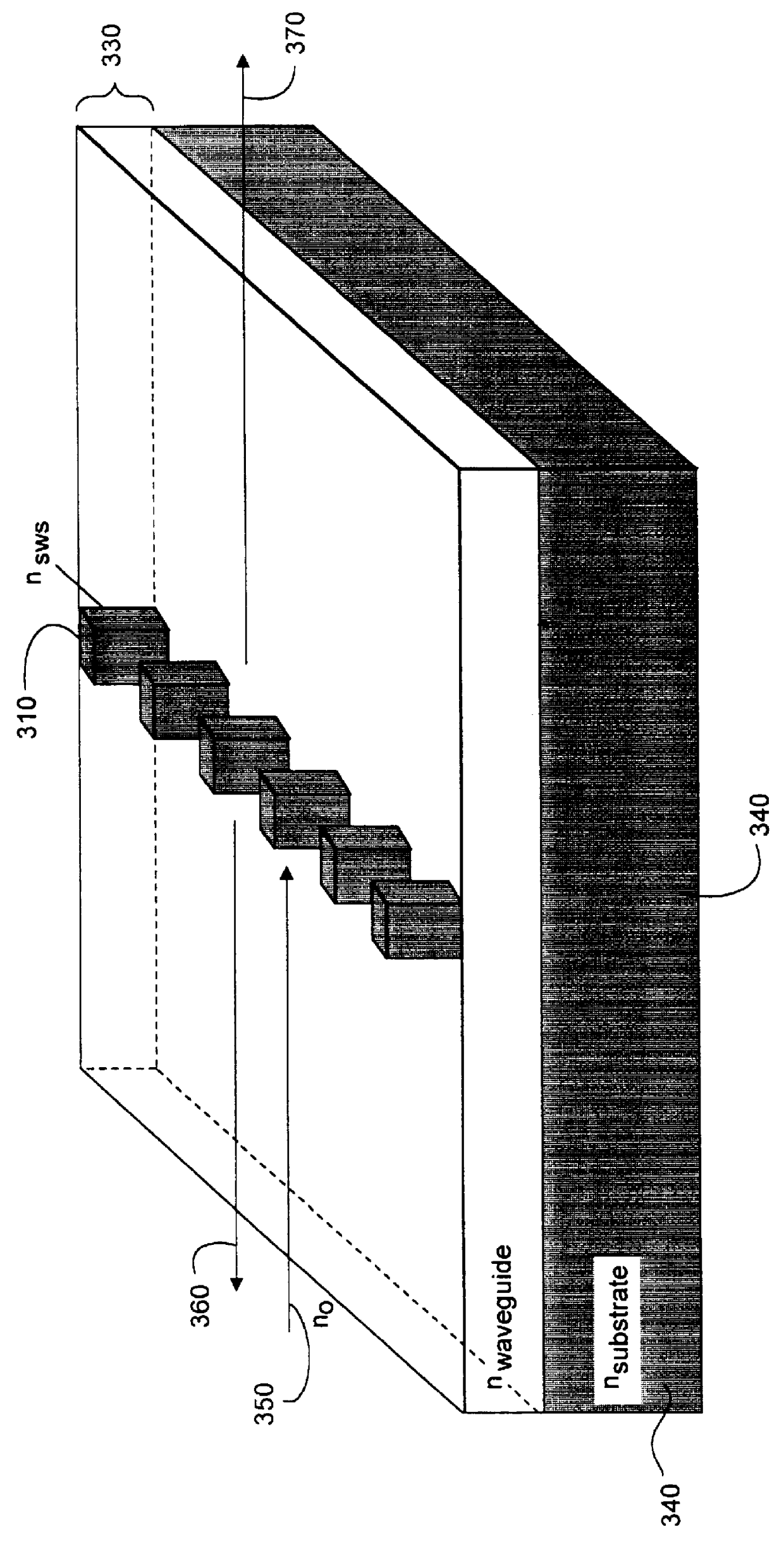
Integrated narrowband optical filter based on embedded subwavelength resonant grating structures
InactiveUS6035089ACost effectiveMinimal reflectionOptical filtersOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingWavelength
A resonant grating structure in a waveguide and methods of tuning the performance of the grating structure are described. An apparatus includes a waveguide; and a subwavelength resonant grating structure embedded in the waveguide. The systems and methods provide advantages including narrowband filtering capabilities, minimal sideband reflections, spatial control, high packing density, and tunability.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
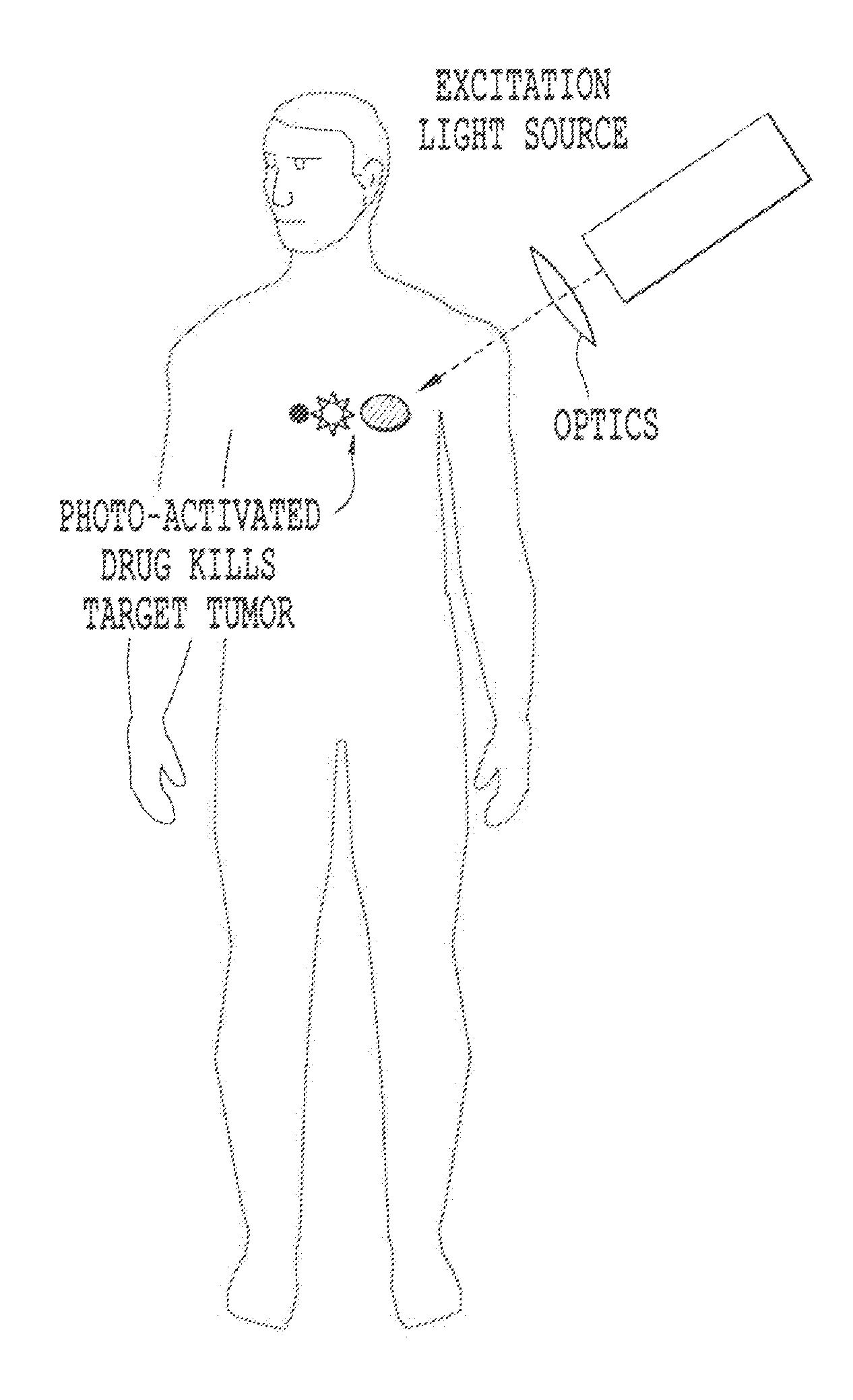
Non-invasive energy upconversion methods and systems for in-situ photobiomodulation
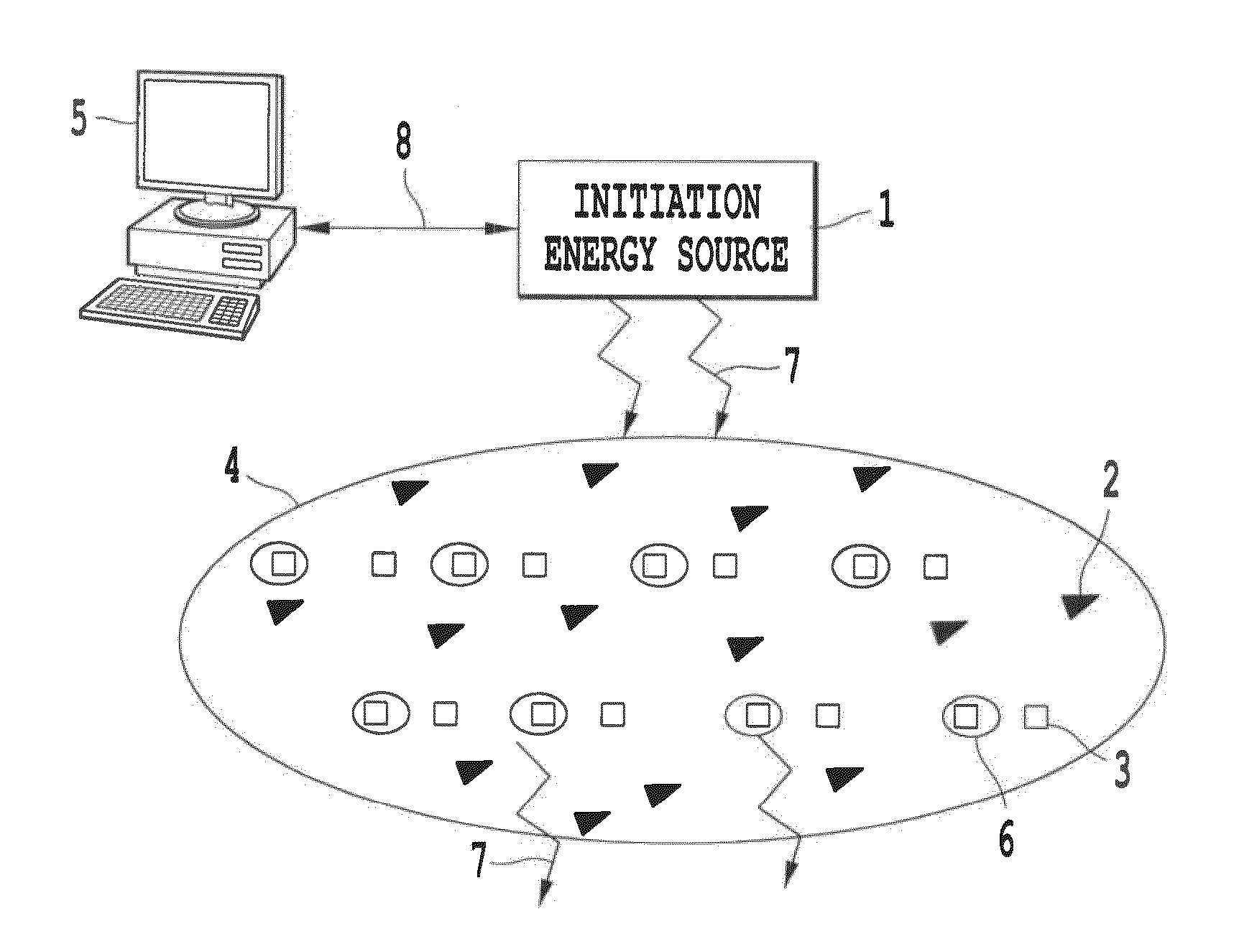
ActiveUS20110021970A1High selectivityAvoid the needAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseHigh energy
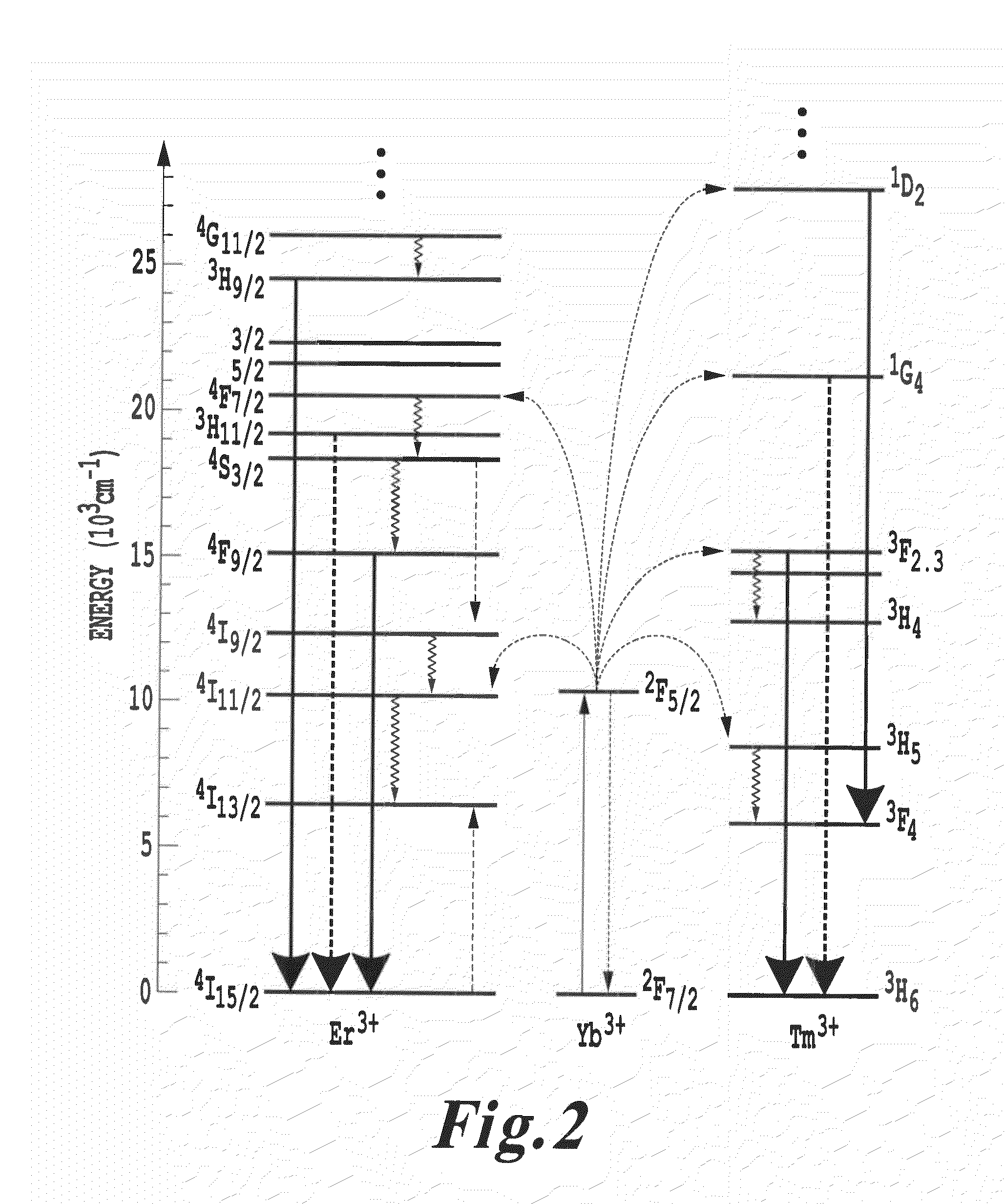
Products, compositions, systems, and methods for modifying a target structure which mediates or is associated with a biological activity, including treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases mediated by or associated with a target structure, such as a virus, cell, subcellular structure or extracellular structure. The methods may be performed in situ in a non-invasive manner by placing a nanoparticle having a metallic shell on at least a fraction of a surface in a vicinity of a target structure in a subject and applying an initiation energy to a subject thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure directly or via a modulation agent. The nanoparticle is configured, upon exposure to a first wavelength λ1, to generate a second wavelength λ2 of radiation having a higher energy than the first wavelength λ1. The methods may further be performed by application of an initiation energy to a subject in situ to activate a pharmaceutical agent directly or via an energy modulation agent, optionally in the presence of one or more plasmonics active agents, thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure. Kits containing products or compositions formulated or configured and systems for use in practicing these methods.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Scannable barcode display and methods for using the same
InactiveUS6877661B2Facilitates redemptionClear wellCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesData centerData acquisition
A system and method for implementing a wireless data transmission scheme through the use of a display capable of displaying symbolic information, a data acquisition device capable of identifying and capturing said displayed information and a mitigation device adapted to allow the data acquisition device to capture the symbolic information. The symbolic information may be a barcode displayed on an LCD outputting linearly polarized light. The data acquisition device may be a laser scanner, and the mitigation device may be a quarter wave retarder located between the display and the scanner. A larger system may utilize this wireless system or a different front end in a more generalized backend information transfer system. The backend system may include a centralized data center adapted to be used with retail couponing, ticketing, digital receipts, or a plurality of other information systems in which data is used separately from its storage location.
Owner:WEBB RICHARD M +4
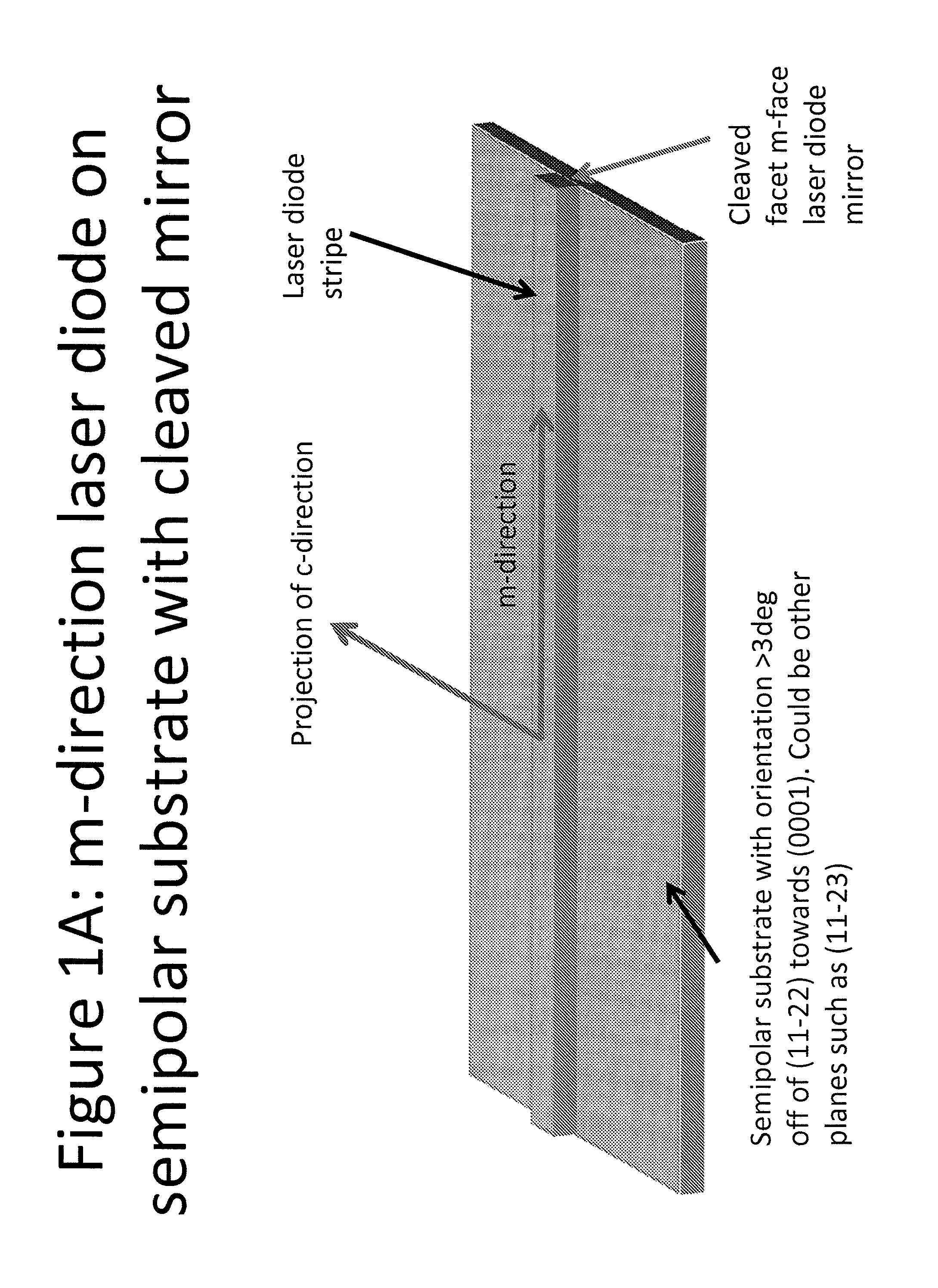
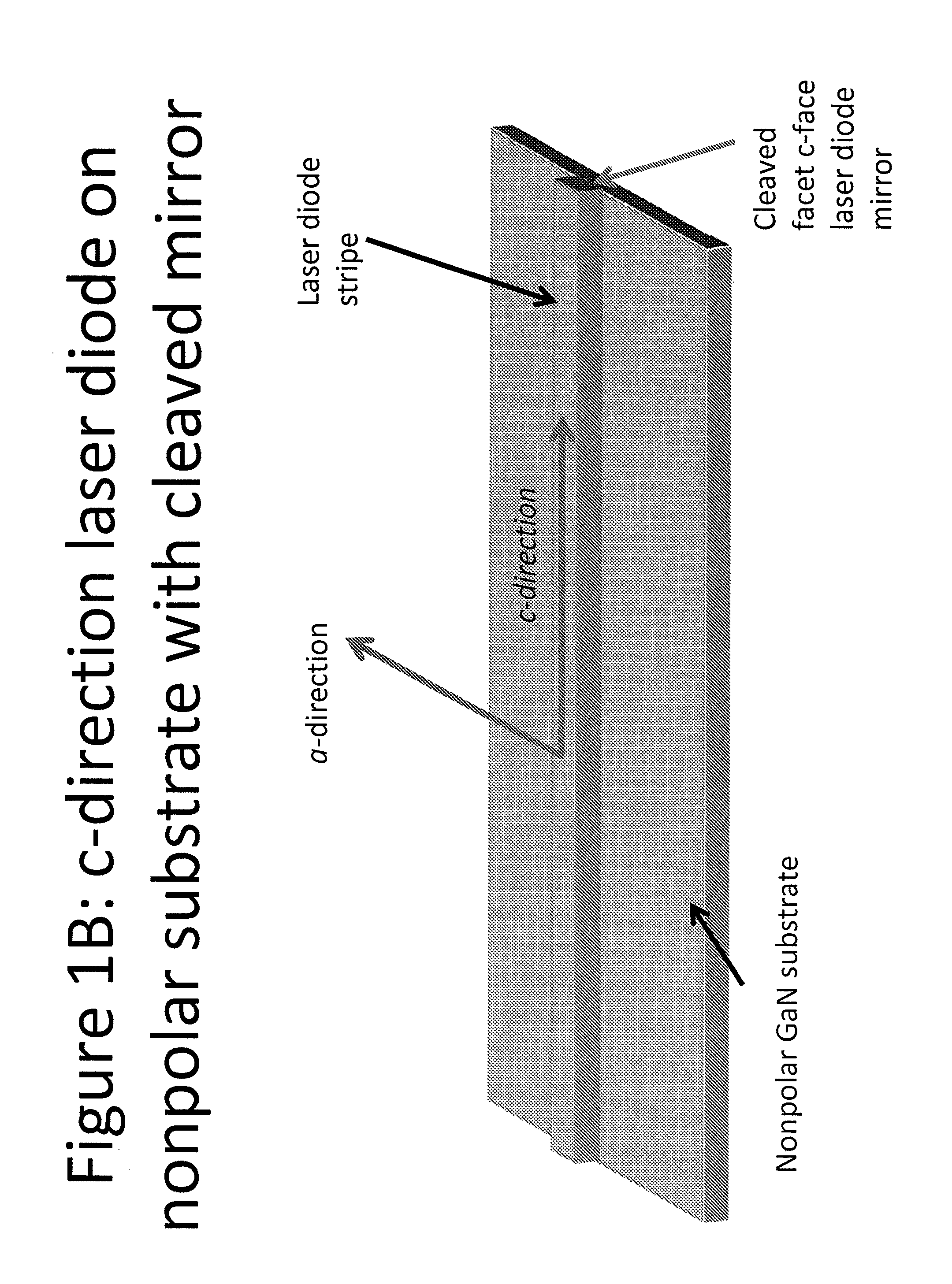
Growth structures and method for forming laser diodes on {30-31} or off cut gallium and nitrogen containing substrates
ActiveUS8351478B2Improved cleavesCost-effectiveLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenGallium
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Arrangements, systems and methods capable of providing spectral-domain polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20070038040A1Improve measurement reliabilityHigh sensitivityPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsSpectral domainTomography
Systems, arrangements and methods for separating an electromagnetic radiation and obtaining information for a sample using an electromagnetic radiation are provided. In particular, the electromagnetic radiation can be separated into at least one first portion and at least one second portion according to at least one polarization and at least one wave-length of the electromagnetic radiation. The first and second separated portions may be simultaneously detected. Further, a first radiation can be obtained from the sample and a second radiation may be obtained from a reference, and the first and second radiations may be combined to form a further radiation, with the first and second radiations being associated with the electro-magnetic radiation. The information is provided as a function of first and second portions of the further radiations that have been previously separated and can be analyzed to extract birefringent information characterizing the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Functionalized matrixes for dispersion of nanostructures
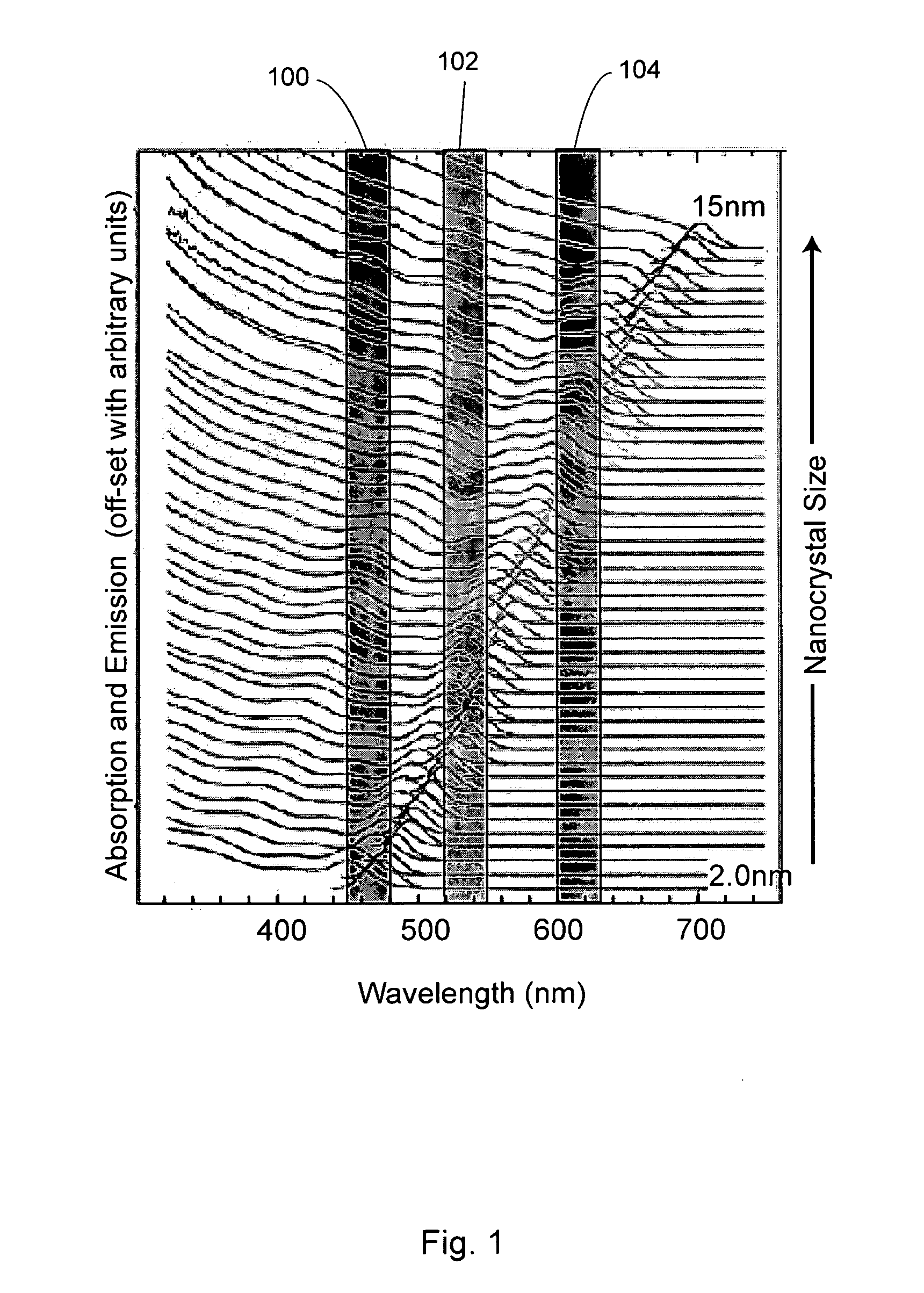
ActiveUS20100276638A1High quantum yieldFacilitate device fabricationMaterial nanotechnologyGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsAnti-reflective coatingVolumetric Mass Density
Matrixes doped with semiconductor nanocrystals are provided. In certain embodiments, the semiconductor nanocrystals have a size and composition such that they absorb or emit light at particular wavelengths. The nanocrystals can comprise ligands that allow for mixing with various matrix materials, including polymers, such that a minimal portion of light is scattered by the matrixes. The matrixes are optionally formed from the ligands. The matrixes of the present invention can also be utilized in refractive index matching applications. In other embodiments, semiconductor nanocrystals are embedded within matrixes to form a nanocrystal density gradient, thereby creating an effective refractive index gradient. The matrixes of the present invention can also be used as filters and antireflective coatings on optical devices and as down-converting layers. Processes for producing matrixes comprising semiconductor nanocrystals are also provided. Nanostructures having high quantum efficiency, small size, and / or a narrow size distribution are also described, as are methods of producing indium phosphide nanostructures and core-shell nanostructures with Group II-VI shells.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
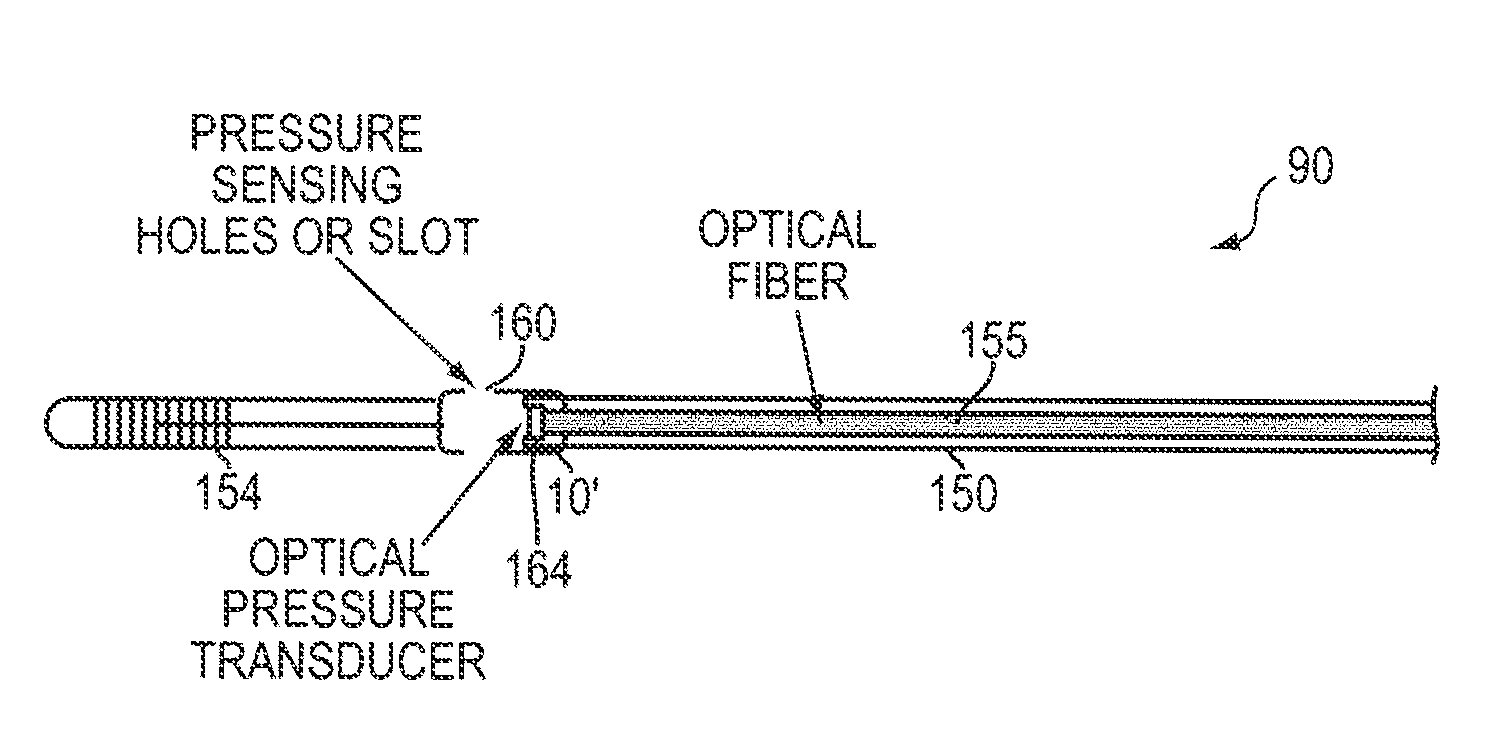
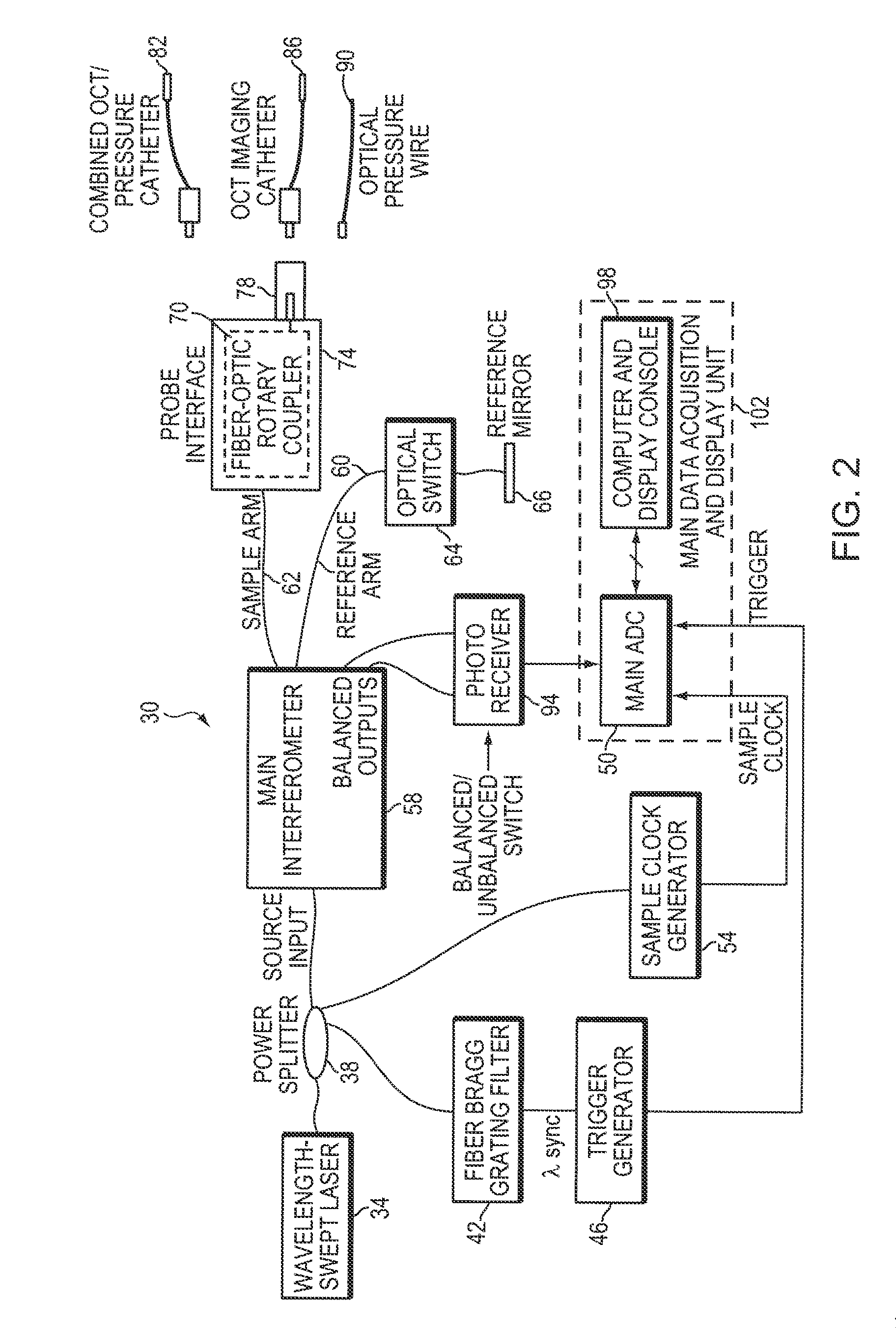
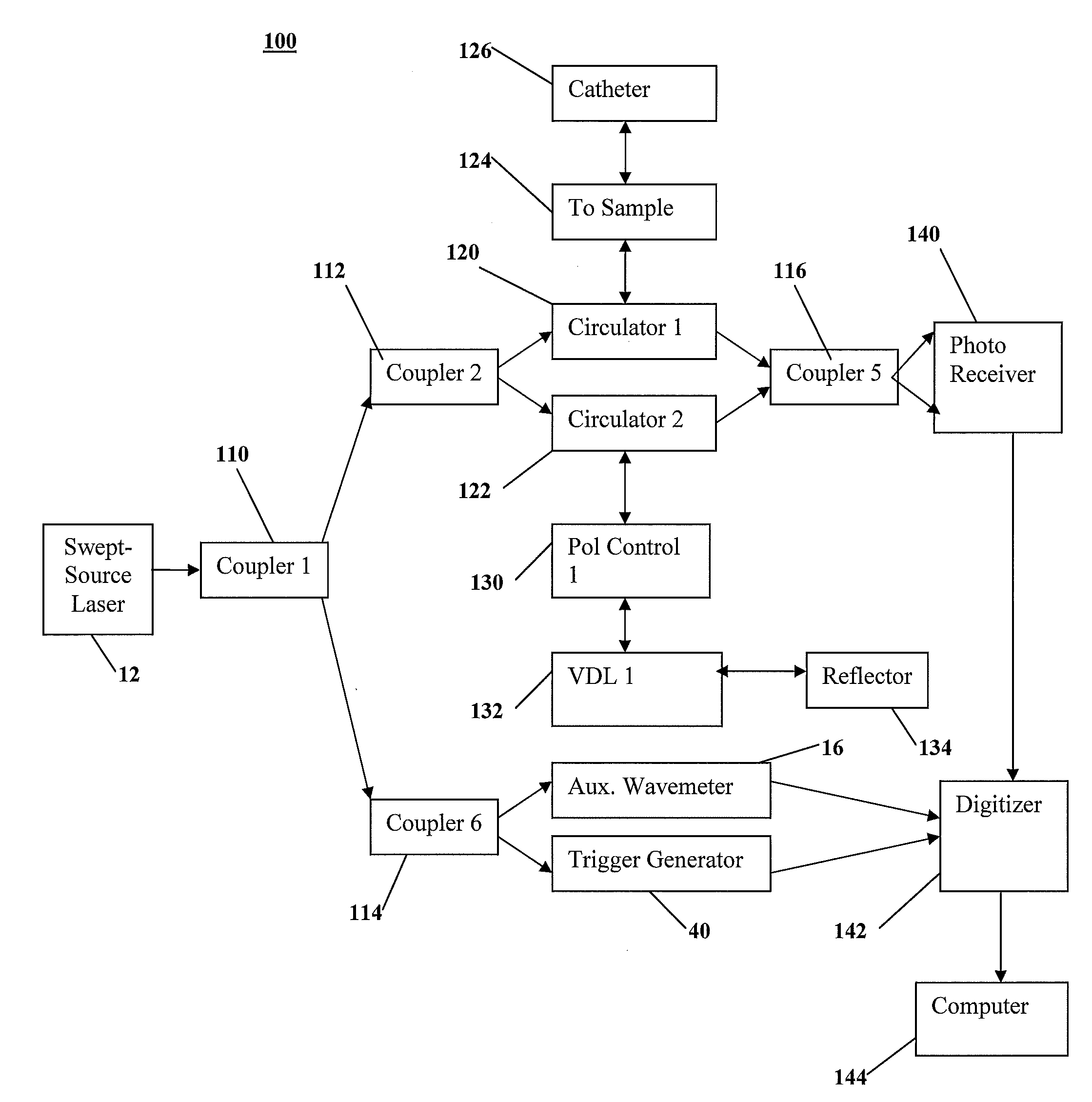
Intravascular Optical Coherence Tomography System with Pressure Monitoring Interface and Accessories
ActiveUS20120238869A1PressureEasy to useDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical coherence tomography system and method with integrated pressure measurement. In one embodiment the system includes an interferometer including: a wavelength swept laser; a source arm in communication with the wavelength swept laser; a reference arm in communication with a reference reflector; a first photodetector having a signal output; a detector arm in communication with the first photodetector, a probe interface; a sample arm in communication with a first optical connector of the probe interface; an acquisition and display system comprising: an A / D converter having a signal input in communication with the first photodetector signal output and a signal output; a processor system in communication with the A / D converter signal output; and a display in communication with the processor system; and a probe comprising a pressure sensor and configured for connection to the first optical connector of the probe interface, wherein the pressure transducer comprises an optical pressure transducer.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Antenna with a conductive layer and a two-band transmitter including the antenna
InactiveUS20020003499A1Improve matchSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual modeTwo band
The antenna of said transmitter is a microstrip antenna. A rear edge of its patch is provided with a short circuit by means of which a quarter-wave primary resonance can be excited by a coplanar line formed by two coupling slots in an area. Separator slots separate said area from another area in which a secondary resonance can be established at twice the frequency of the primary resonance from a slotted line extending one slot of the coplanar line. The invention applies in particular to the production of a dual-mode mobile telephone to the GSM and DCS standards.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
White light devices using non-polar or semipolar gallium containing materials and phosphors
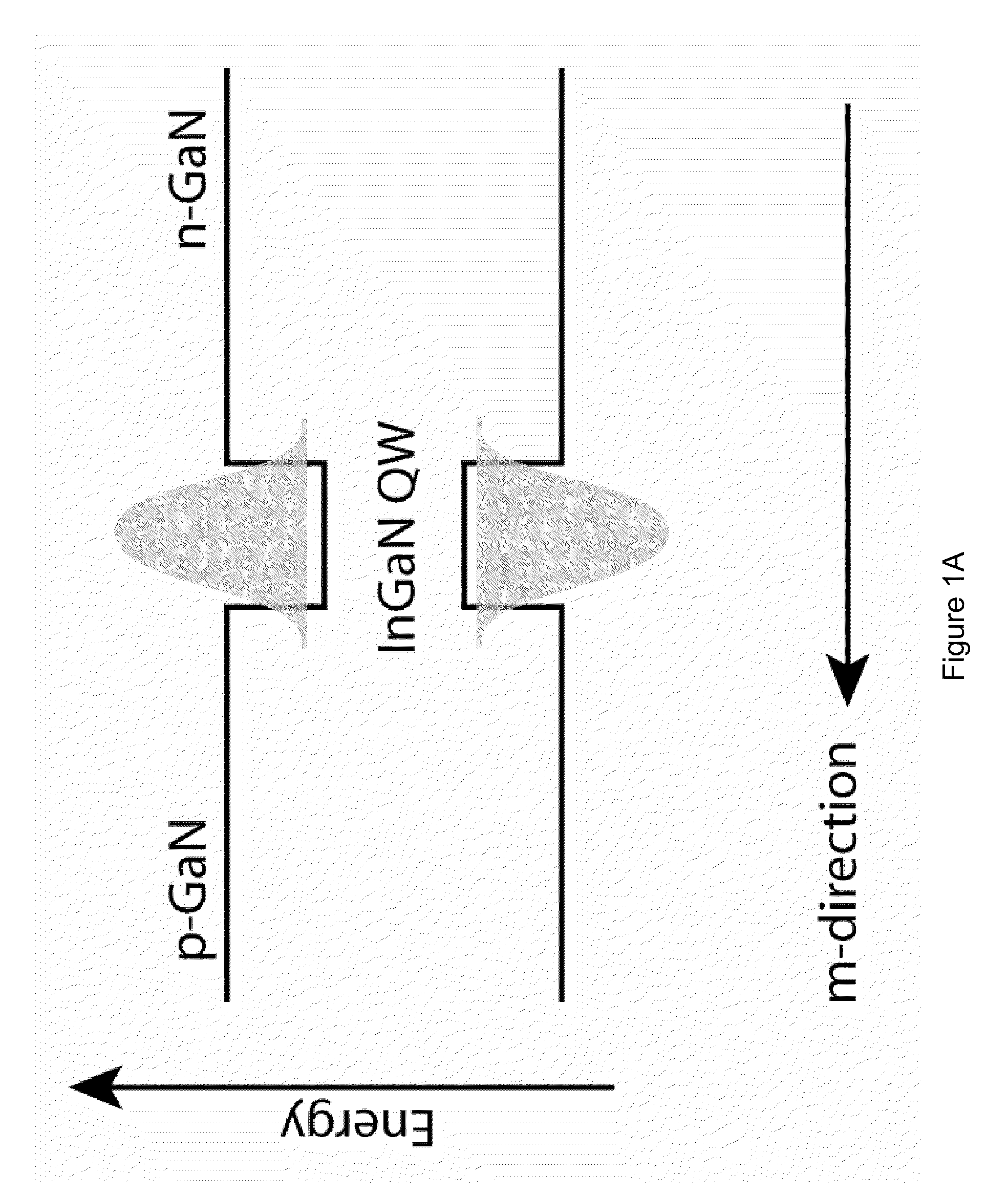
ActiveUS8124996B2Easy to implementImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorQuantum well
A packaged light emitting device. The device includes a substrate member comprising a surface region and one or more light emitting diode devices overlying the surface region. In a specific embodiment, at least one of the light emitting diode device is fabricated on a semipolar or nonpolar GaN containing substrate. The one or more light emitting diode devices are fabricated on the semipolar or nonpolar GaN containing substrate emits substantially polarized emission of one or more first wavelengths. At least at least one of the light emitting diode devices comprise a quantum well region, which is characterized by an electron wave function and a hole wave function. In a specific embodiment, the electron wave function and the hole wave function are substantially overlapped within a predetermined spatial region of the quantum well region. In a specific embodiment, the device has a thickness of one or more entities formed overlying the one or more light emitting diode devices. The one or more entities are excited by the substantially polarized emission and emitting electromagnetic radiation of one or more second wavelengths.
Owner:SLT TECH
Passivation processing over a memory link
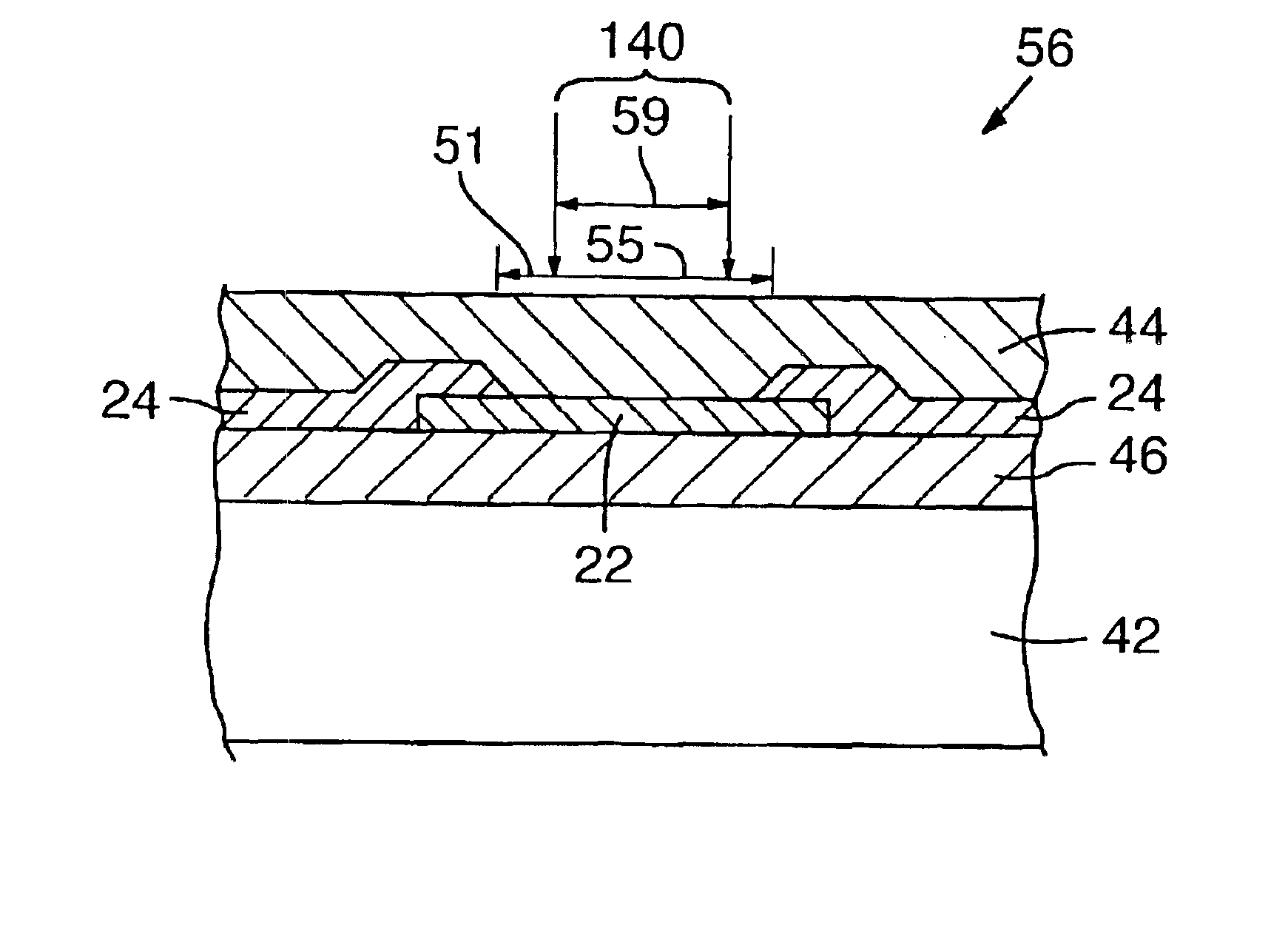
InactiveUS6887804B2Improve processing qualityAvoid and minimize substrate damage and undesirable damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEtchingHarmonic
A set (50) of one or more laser pulses (52) is employed to remove passivation layer (44) over a conductive link (22). The link (22) can subsequently be removed by a different process such as chemical etching. The duration of the set (50) is preferably shorter than 1,000 ns; and the pulse width of each laser pulse (52) within the set (50) is preferably within a range of about 0.05 ps to 30 ns. The set (50) can be treated as a single “pulse” by conventional laser positioning systems (62) to perform on-the-fly material removal without stopping whenever the laser system (60) fires a set (50) of laser pulses (52) at each target area (51). Conventional wavelengths in the IR range or their harmonics in the green or UV range can be employed.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
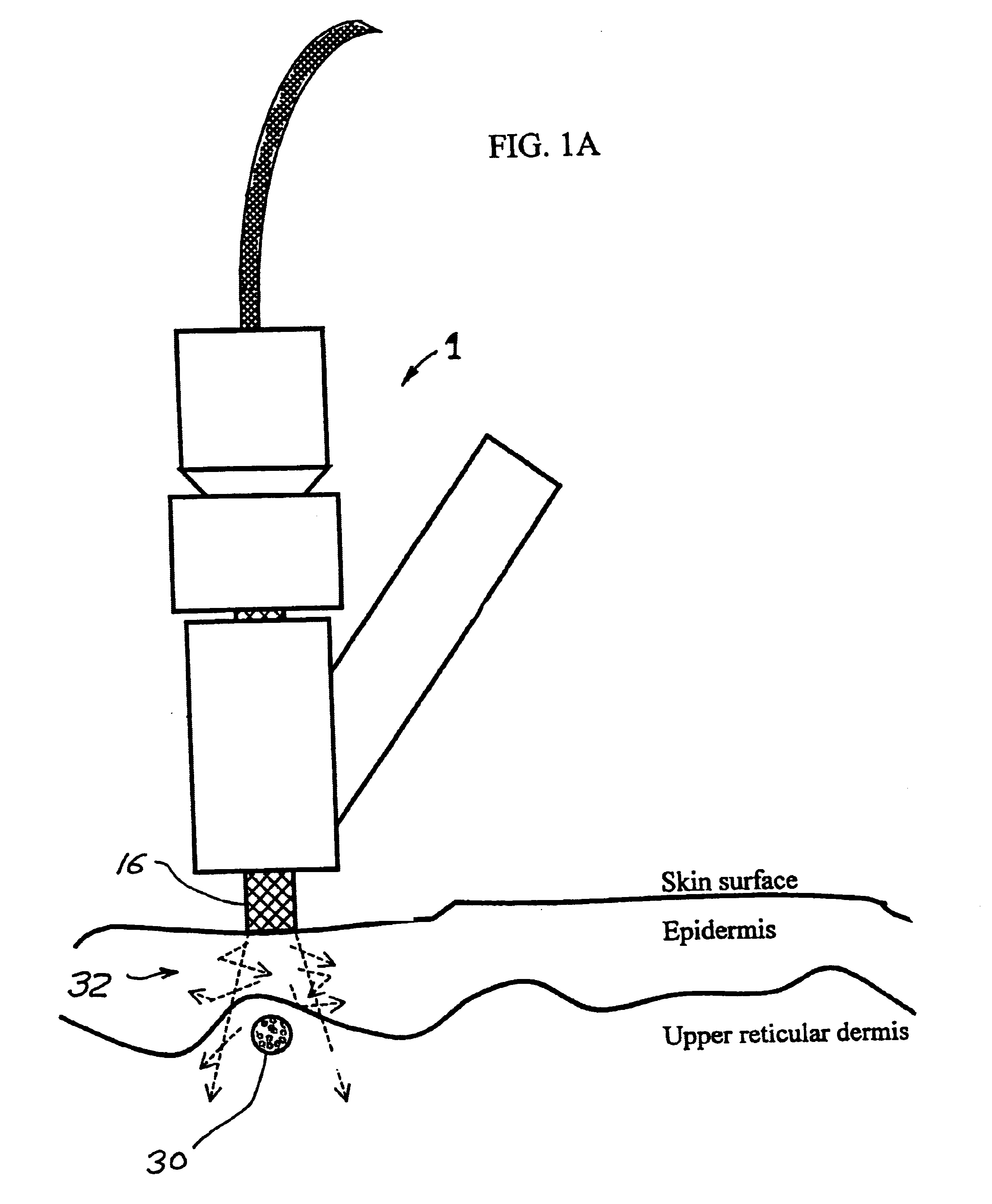
Tissue cooling rod for laser surgery
A laser treatment device and process with controlled cooling. The device contains a cooling element with high heat conduction properties, which is transparent to the laser beam. A surface of the cooling element is held in contact with the tissue being treated while at least one other surface of the cooling element is cooled by the evaporation of a cryogenic fluid. The cooling is coordinated with the application of the laser beam so as to control the temperatures of all affected layers of tissues. In a preferred embodiment useful for removal of wrinkles and spider veins, the cooling element is a sapphire plate. A cryogenic spray cools the top surface of the plate and the bottom surface of the plate is in contact with the skin. In preferred embodiments the wavelength of the laser beam is chosen so that absorption in targeted tissue is low enough so that substantial absorption occurs throughout the targeted tissue. In a preferred embodiment for treating large spider veins with diameters in the range of 1.5 mm, Applicants use an Er:Glass laser with a wavelength of 1.54 microns.< / PTEXT>
Owner:RELIANT TECH INC
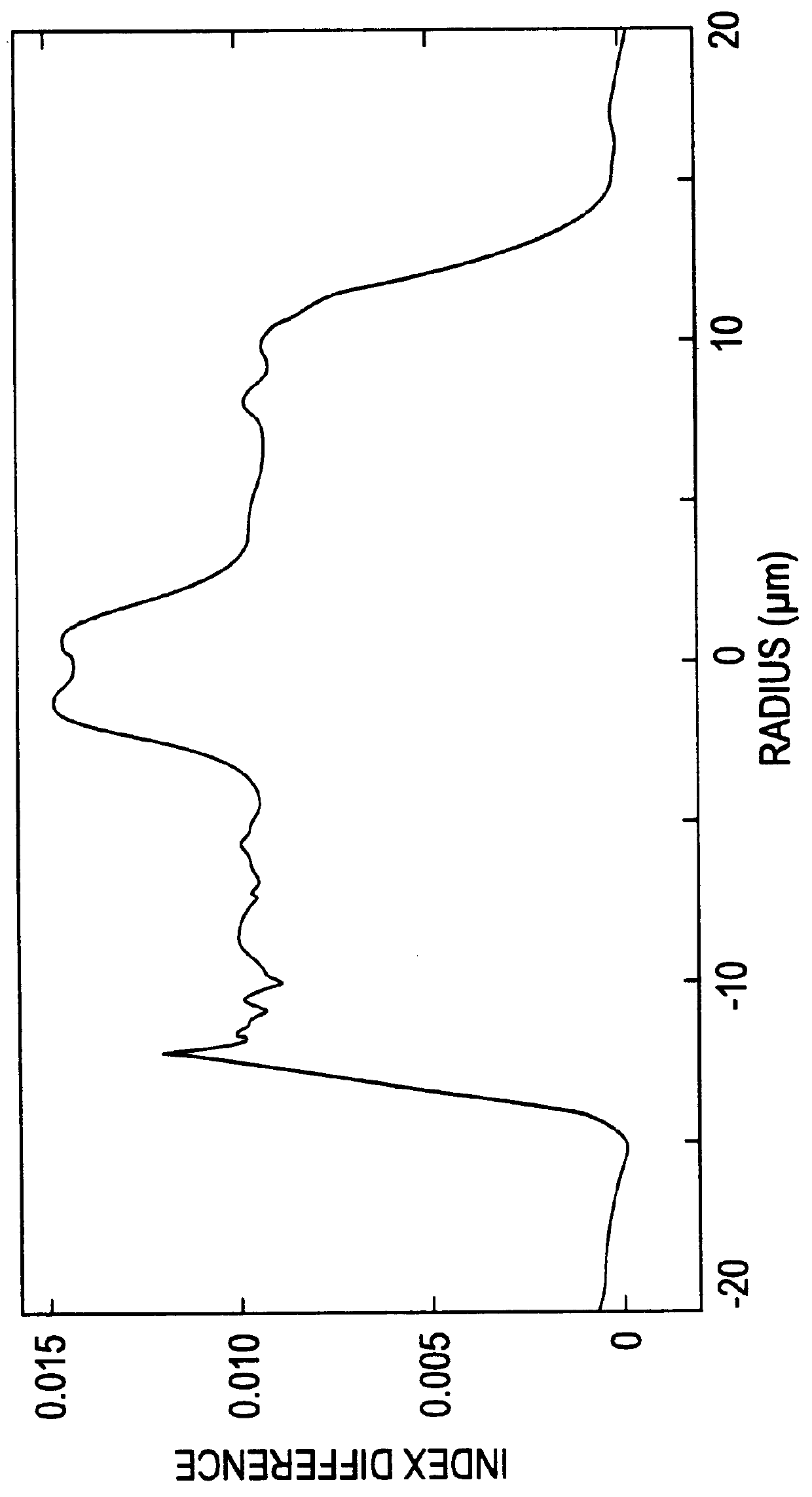
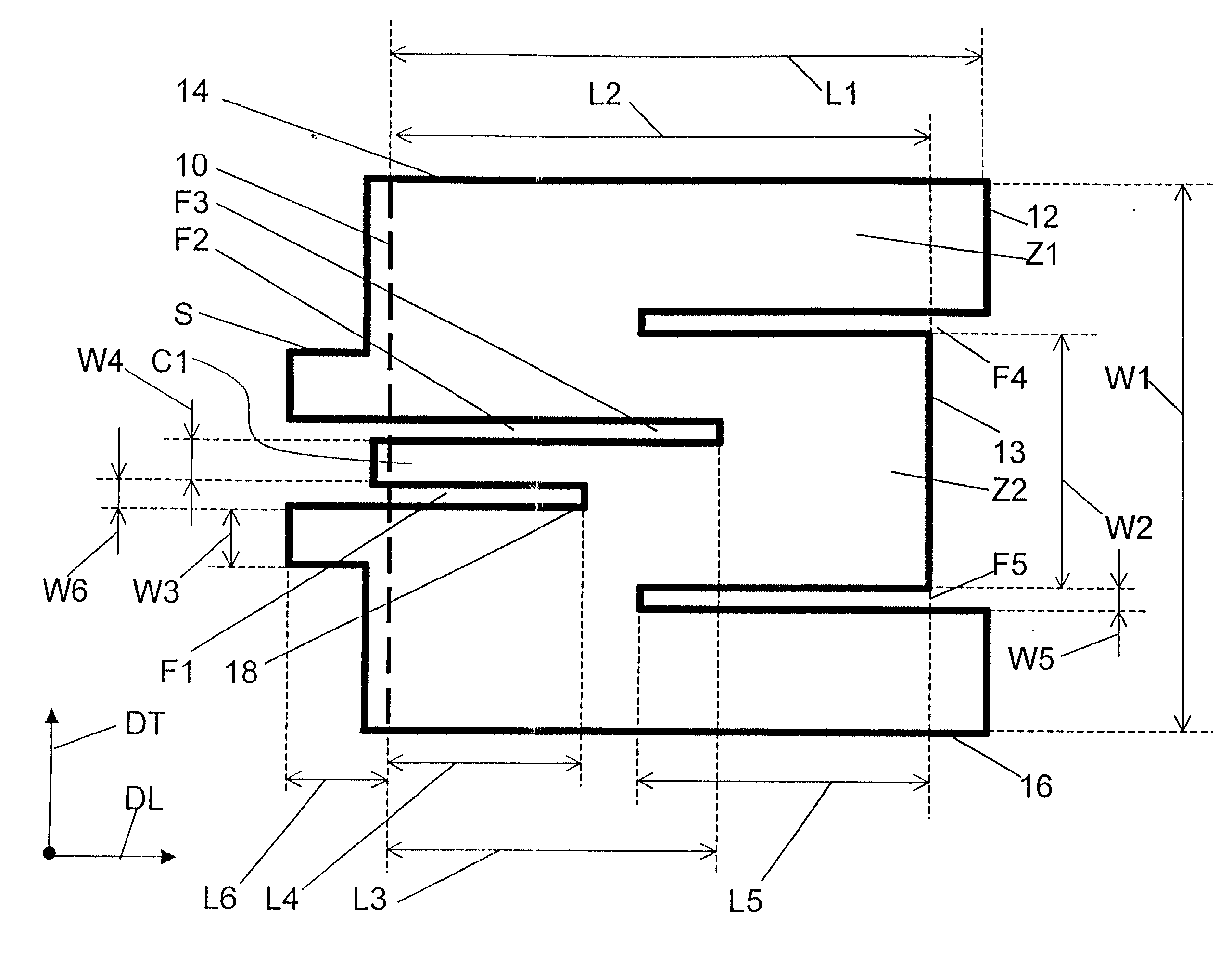
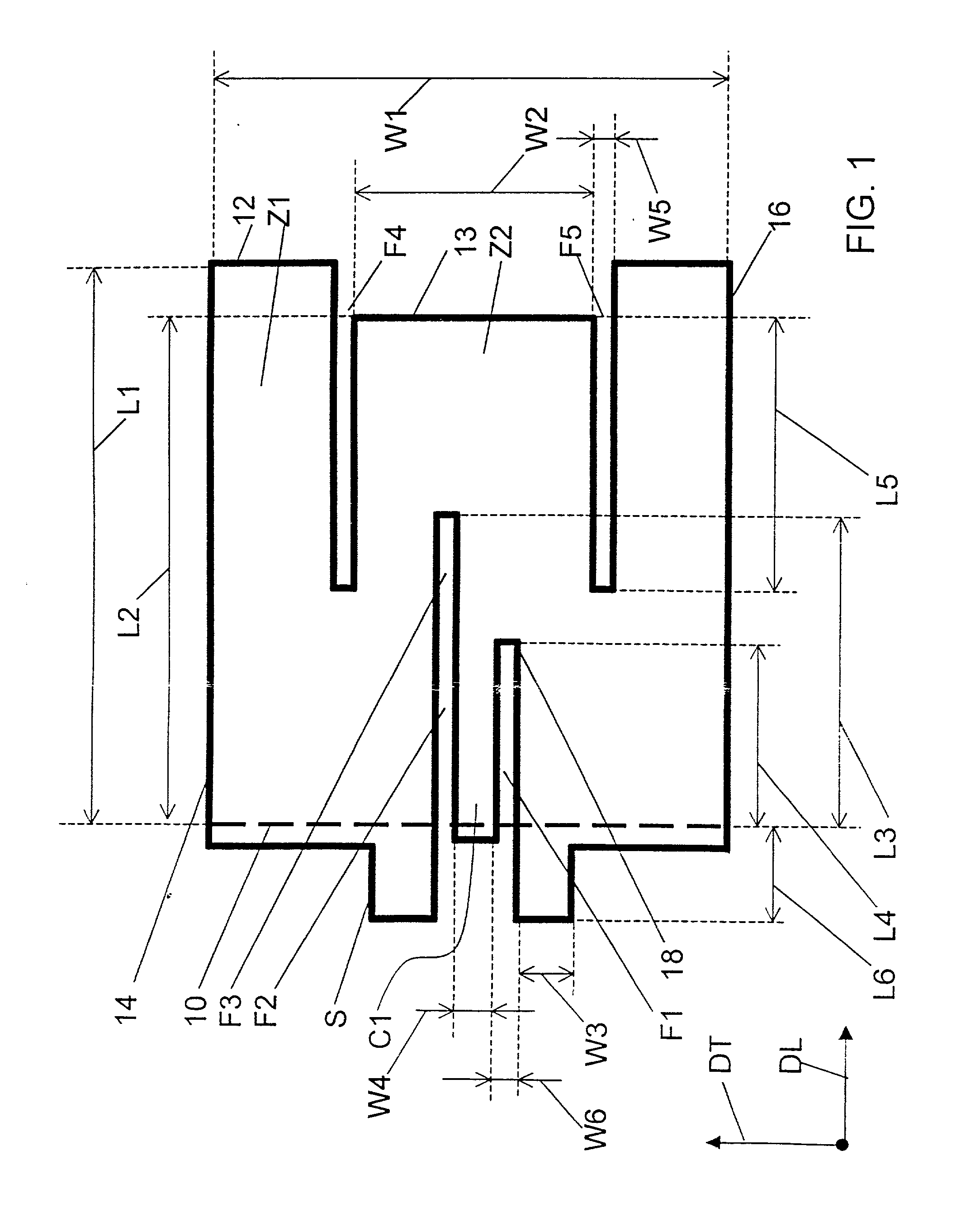
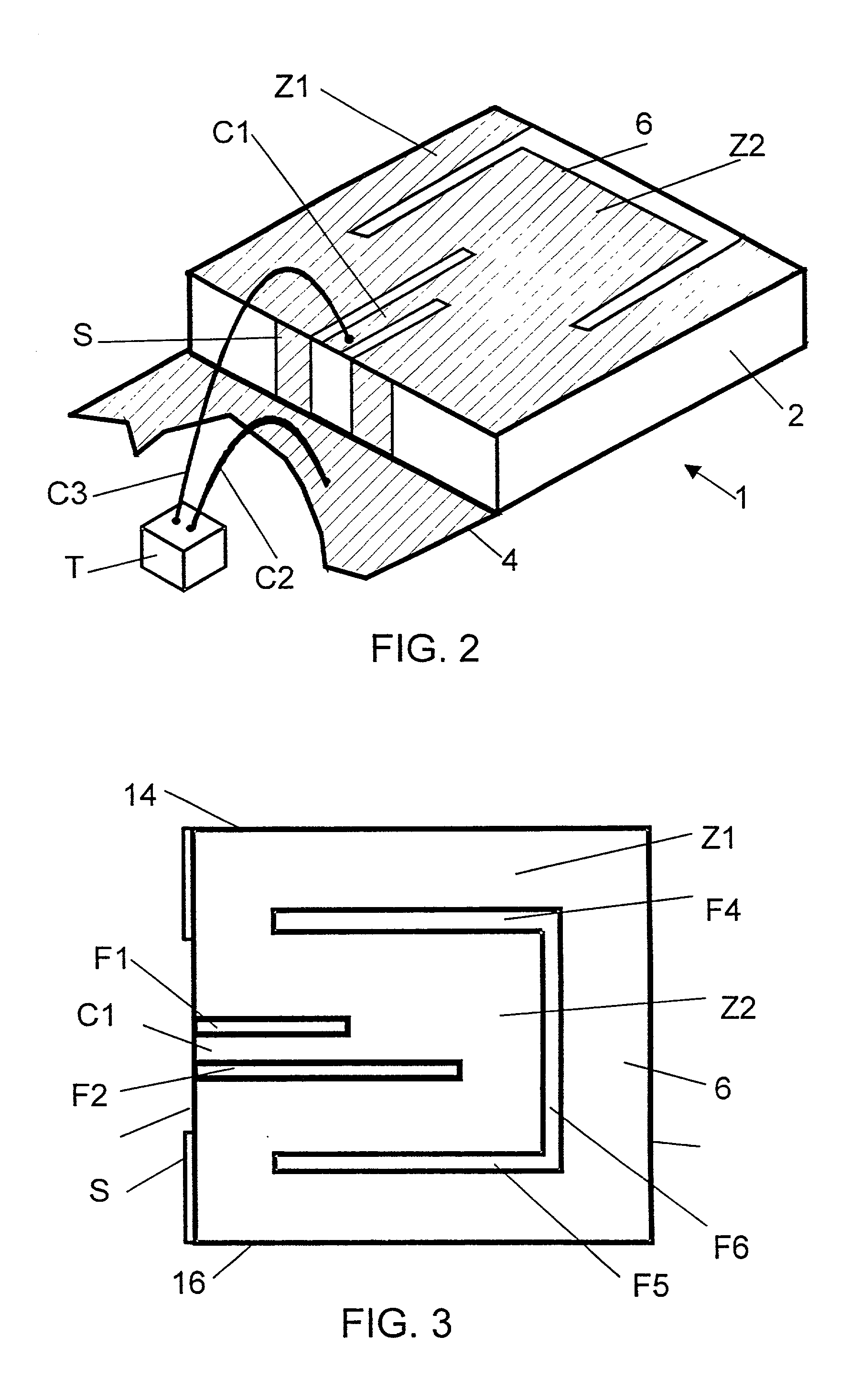
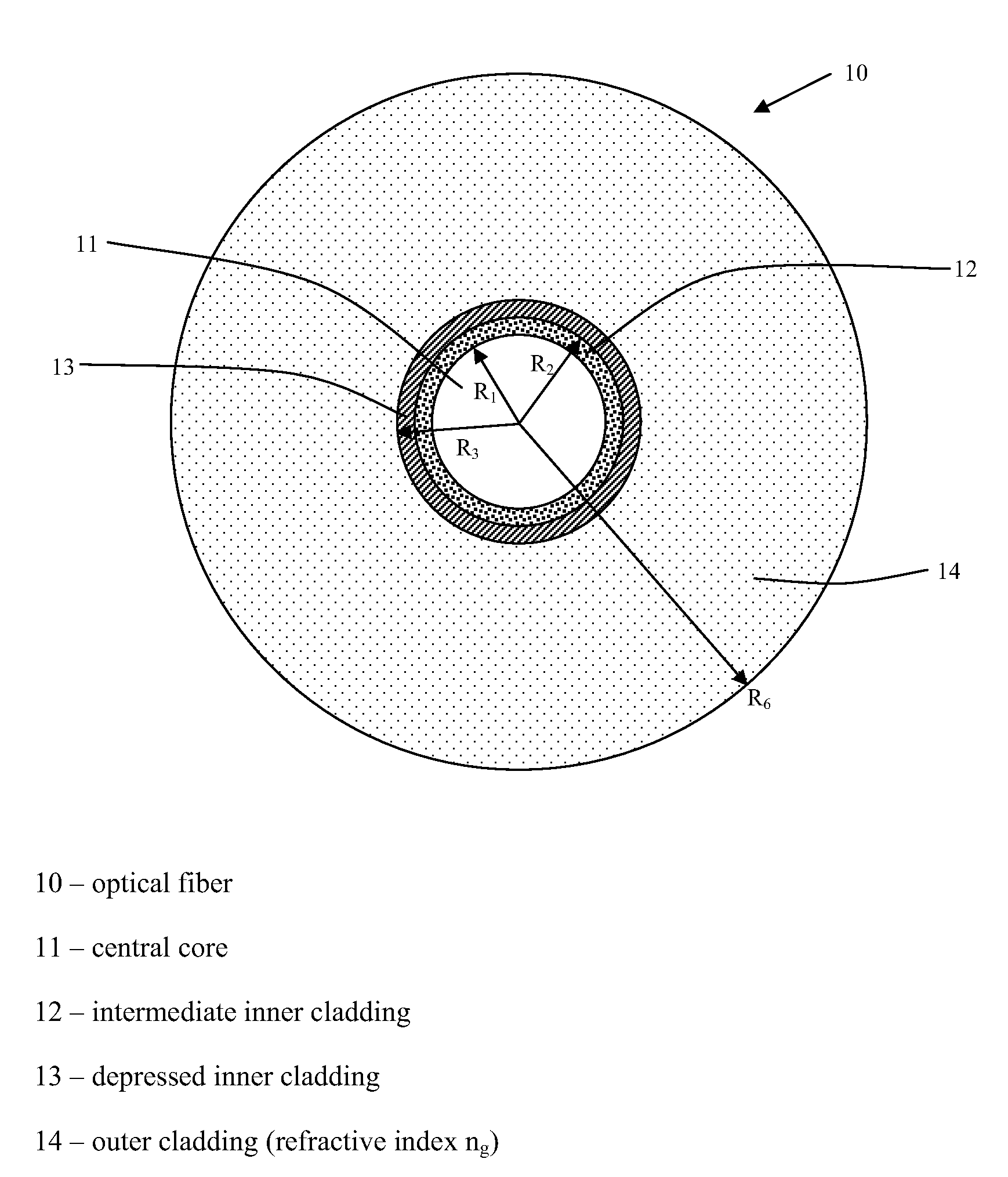
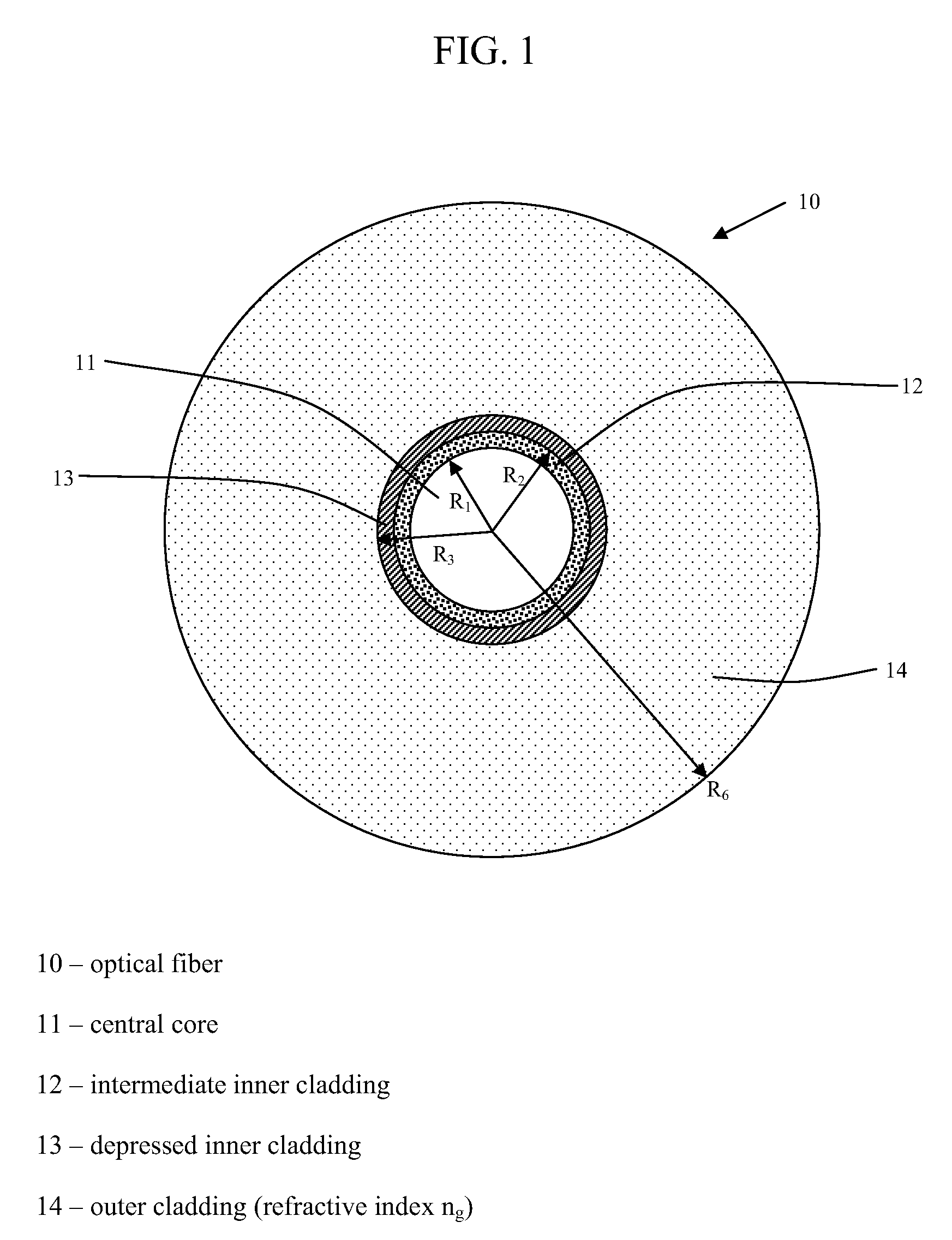
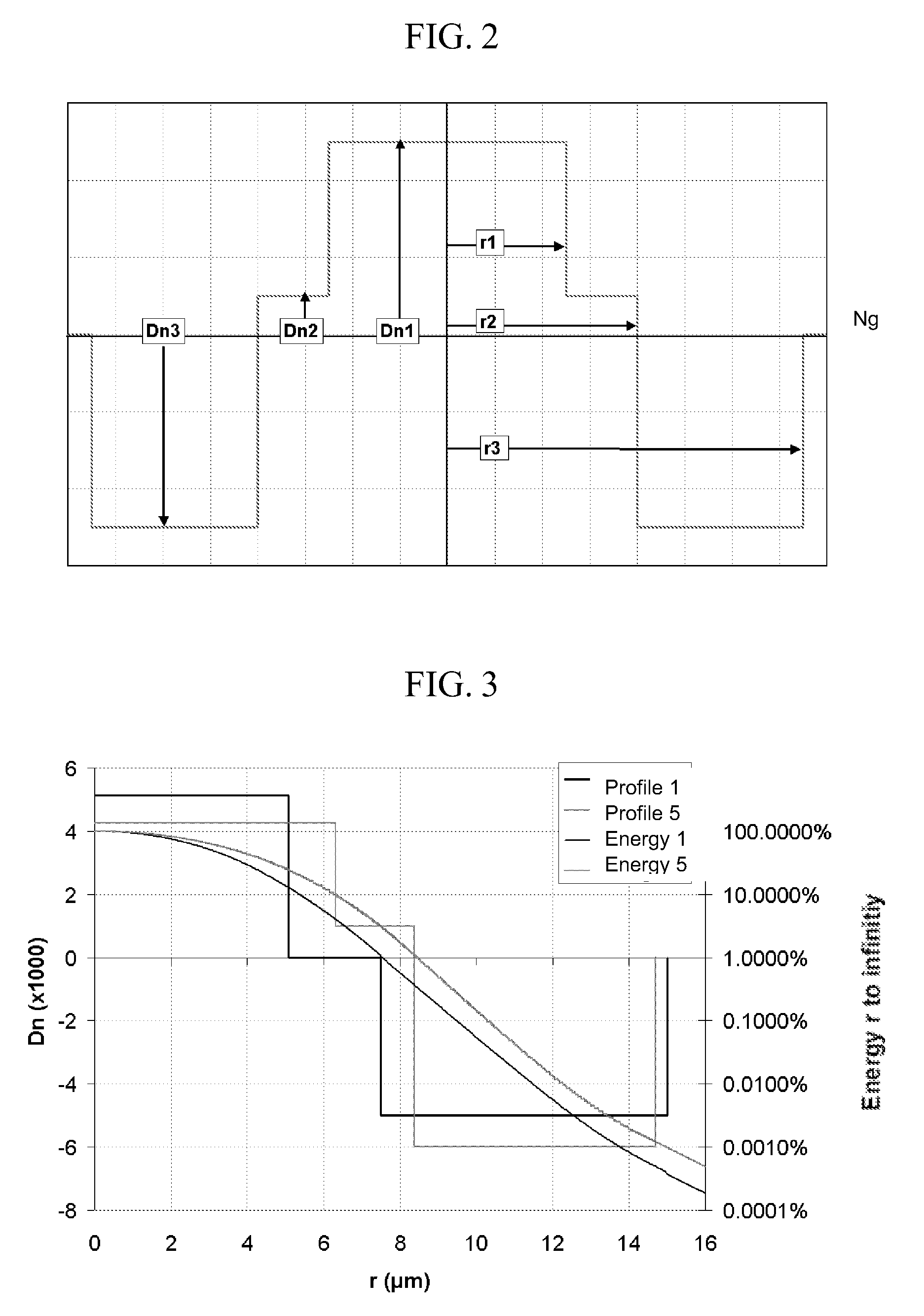
Chromatic dispersion compensating fiber
ActiveUS7356234B2Improved FOM valueLimited bending and micro-bending lossesOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideOptical ModuleRefractive index
Disclosed is a chromatic dispersion compensating optical fiber comprising a central core, an intermediate cladding having a width (r2−r1) of 2.0 microns or greater, and a depressed inner cladding having a refractive index difference Dn3 with the external optical cladding of −3.0×10−3 or lower. At a wavelength of 1550 nm, the optical fiber exhibits a positive chromatic dispersion of 21 ps / (nm·km) or higher and a ratio of mode radius to intermediate cladding radius of (W02 / r2) of 0.7 or less. The present optical fiber has a good figure of merit value and limited bending and microbending losses. The optical fiber can be rolled up in a housing of reduced size in a chromatic dispersion compensating optical module having limited insertion losses and reduced polarization mode dispersion.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
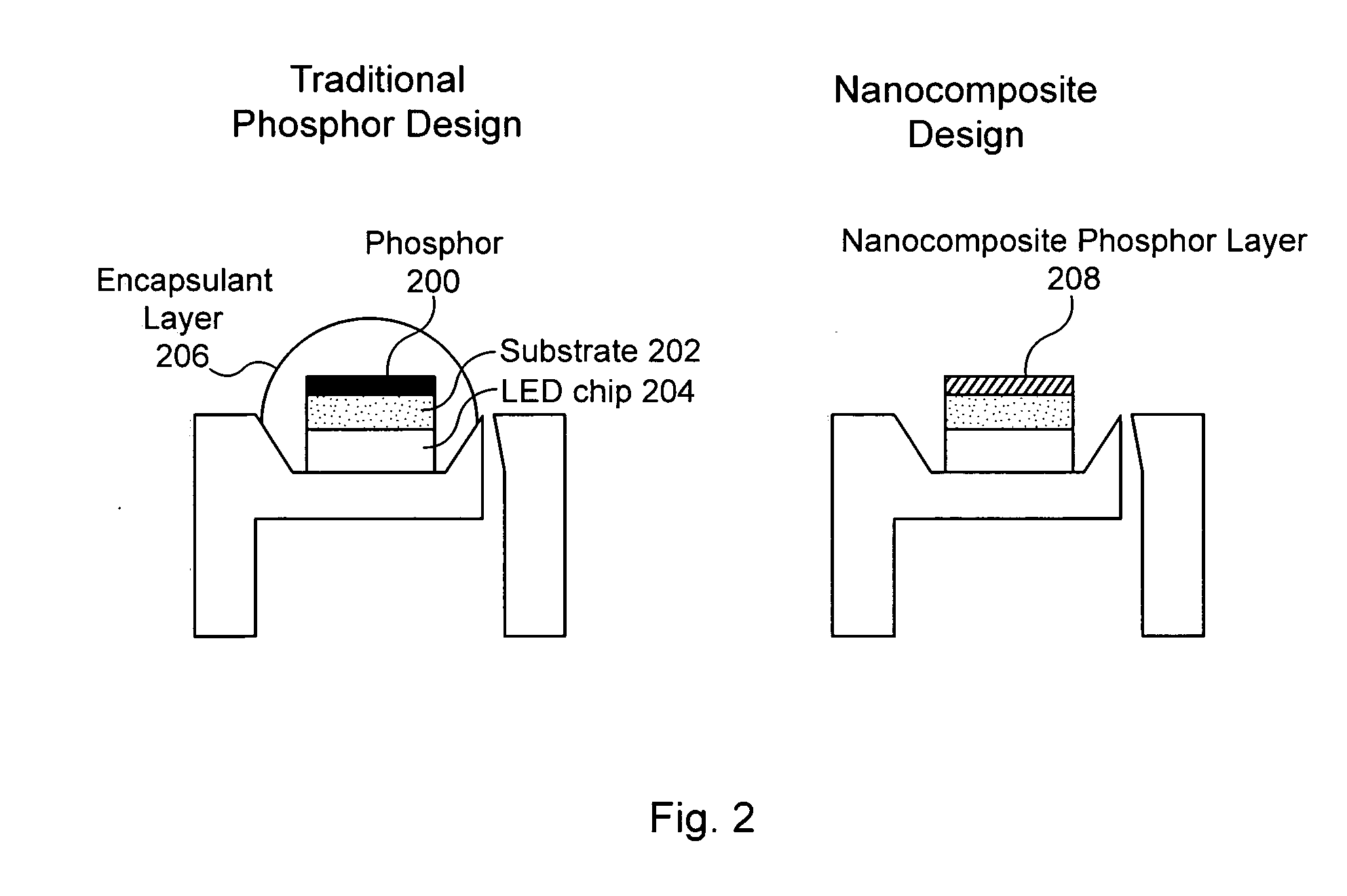
Flip-chip phosphor coating method and devices fabricated utilizing method
ActiveUS20090179207A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorEngineering
Methods for fabricating light emitting diode (LED) chips one of which comprises flip-chip mounting a plurality of LEDs on a surface of a submount wafer and forming a coating over said LEDs. The coating comprising a conversion material at least partially covering the LEDs. The coating is planarized to the desired thickness with the coating being continuous and unobstructed on the top surface of the LEDs. The LEDs chips are then singulated from the submount wafer. An LED chip comprising a lateral geometry LED having first and second contacts, with the LED flip-chip mounted to a submount by a conductive bonding material. A phosphor loaded binder coats and at least partially covers the LED. The binder provides a substantially continuous and unobstructed coating over the LED. The phosphor within the coating absorbs and converts the wavelength of at least some of the LED light with the coating planarized to achieve the desired emission color point of the LED chip.
Owner:CREELED INC
Vacuum-integrated hardmask processes and apparatus
ActiveUS9778561B2Improve performanceReduced line edge roughnessVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesImage resolutionWavelength
Vacuum-integrated photoresist-less methods and apparatuses for forming metal hardmasks can provide sub-30 nm patterning resolution. A metal-containing (e.g., metal salt or organometallic compound) film that is sensitive to a patterning agent is deposited on a semiconductor substrate. The metal-containing film is then patterned directly (i.e., without the use of a photoresist) by exposure to the patterning agent in a vacuum ambient to form the metal mask. For example, the metal-containing film is photosensitive and the patterning is conducted using sub-30 nm wavelength optical lithography, such as EUV lithography.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Lighting device and lighting method
ActiveUS20080304261A1Excellent color renditionEffective limitDischarge tube luminescnet screensLighting support devicesEffect lightWavelength
A lighting device comprising one or more solid state light emitters which emit near ultraviolet light and one or more lumiphors which emit light having a wavelength in the range of from 490 nm to 555 nm, which in the absence of other light would produce a mixture of light within an area defined by x, y coordinates (0.32, 0.40), (0.36, 0.48), (0.43, 0.45), (0.42, 0.42), and (0.36, 0.38). The lighting device may further comprise one or more 600 nm to 630 nm light emitters, and a mixture of light emitted from the lighting device may be within ten MacAdam ellipses of the blackbody locus. Also, packaged solid state light emitters and methods of lighting.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
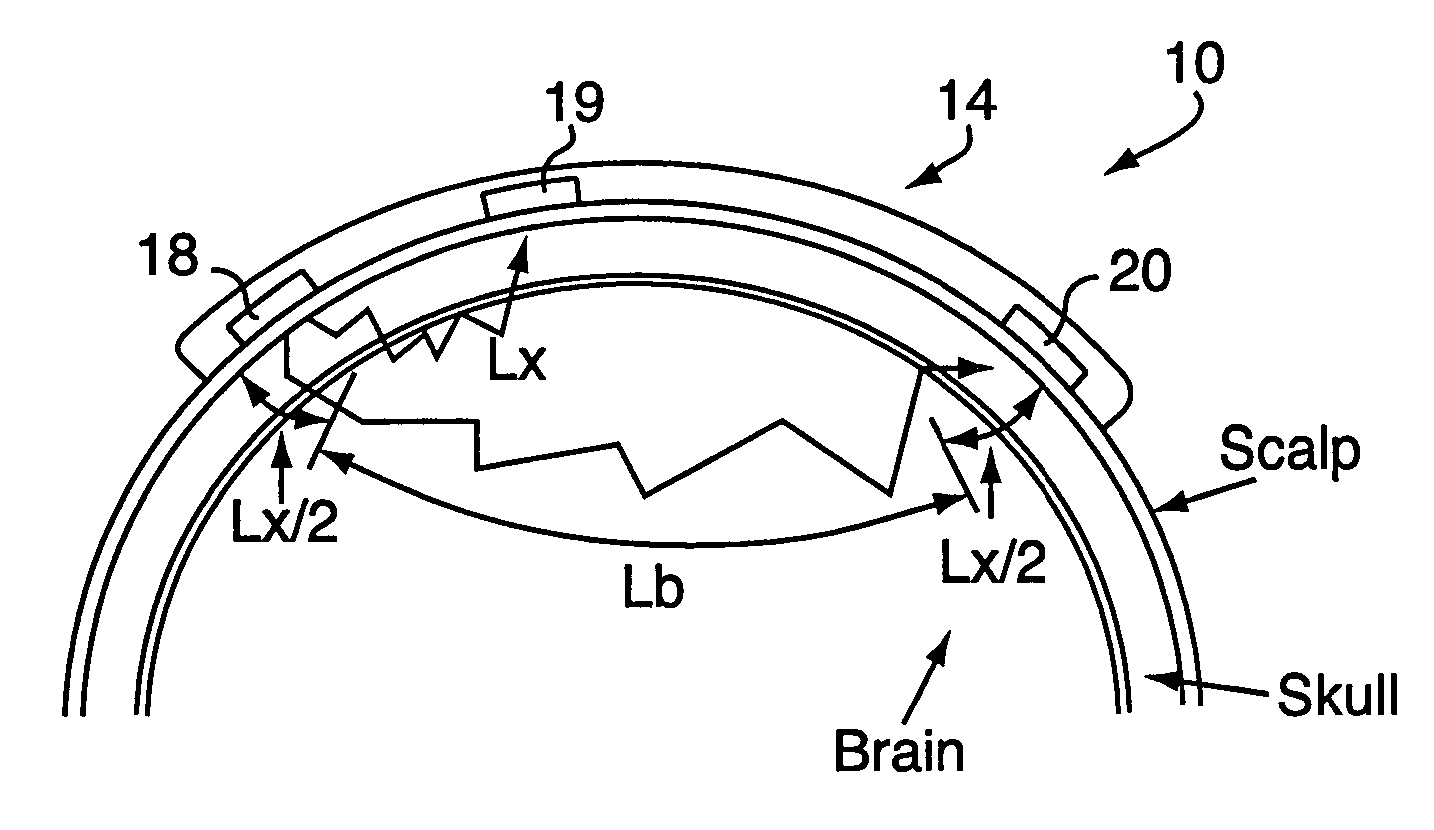
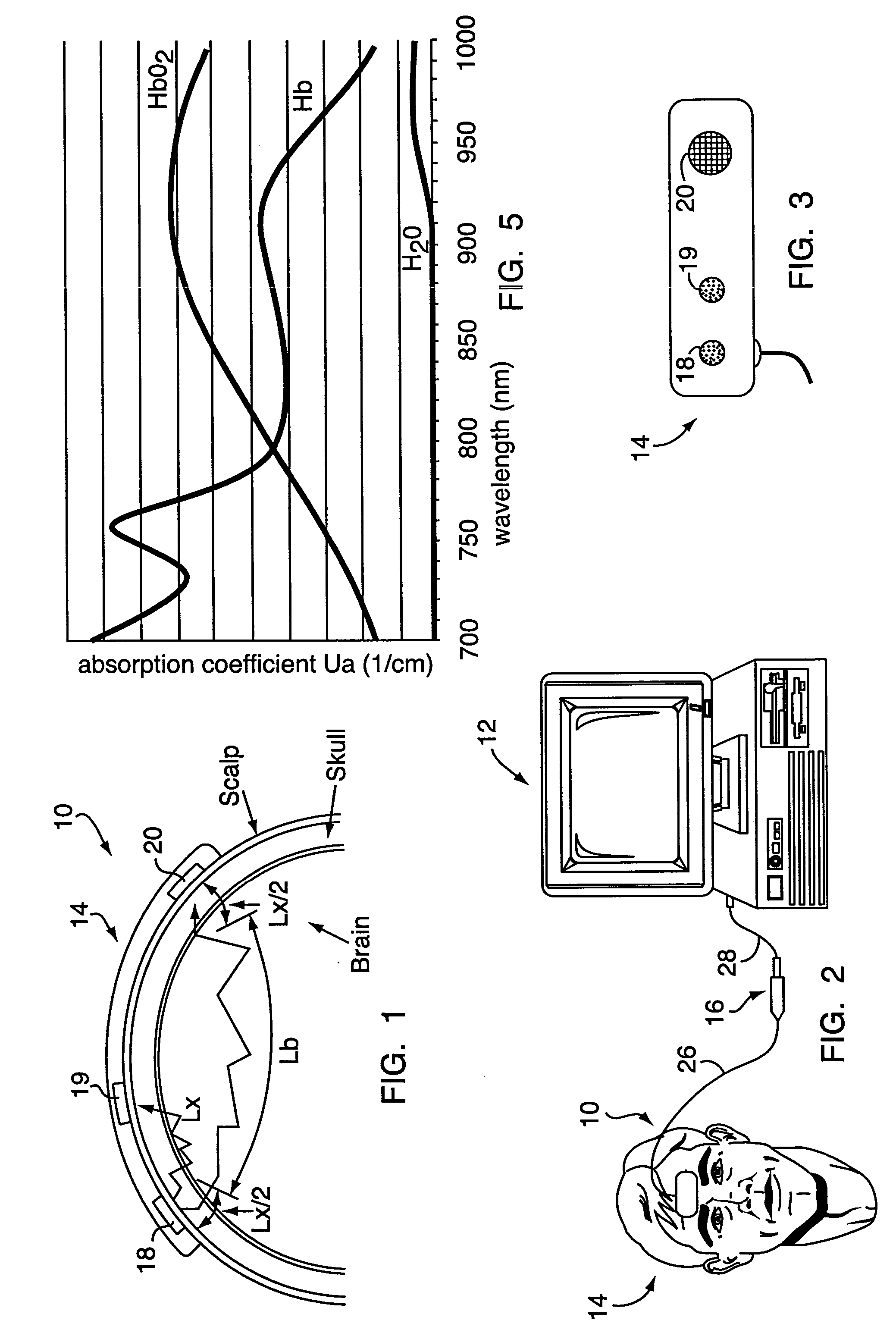
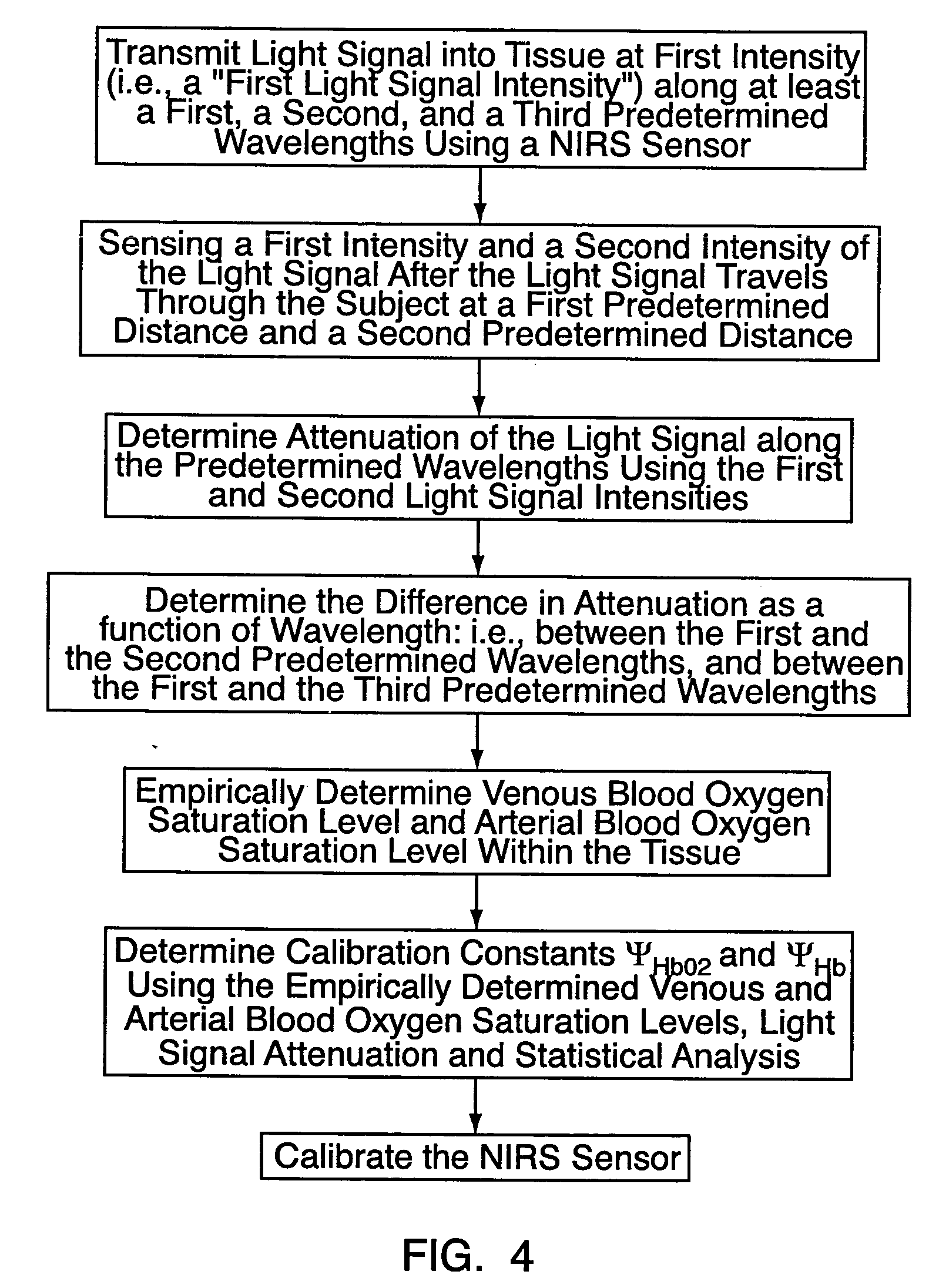
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
ActiveUS20040024297A1Inhibition effectNon-invasive determinationSensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsBlood oxygenationNon invasive
A method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided that utilizes a near infrared spectrophotometric (NIRS) sensor capable of transmitting a light signal into the tissue of a subject and sensing the light signal once it has passed through the transmitting a light signal into the subject's tissue, wherein the transmitted light signal includes a first wavelength, a second wavelength, and a third wavelength; (2) sensing a first intensity and a second intensity of the light signal, along the first, second, and third wavelengths after the light signal travels through the subject at a first and second predetermined distance; (3) determining an attenuation of the light signal for each of the first, second, and third wavelengths using the sensed first intensity and sensed second intensity of the first, second, and third wavelengths; (4) determining a difference in attenuation of the light signal between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and between the first wavelength and the third wavelength; and (5) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the third wavelength.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Electromagnetic photonic catheter for reducing restenosis
InactiveUS6962584B1Reduce spreadImprove scalabilitySurgical instrument detailsCatheterPhotonicsPercent Diameter Stenosis
The method of vascular treatment for restenosis or vulnerable plaque after an invasive procedure, such as for example angioplasty, stenting with or without drug coating, or drug delivery, comprises: inserting a catheter or hollow guide wire to the treatment location; delivering light through the catheter in the wavelength range of about 700–2500 nm; and moving the light to treat the affected region.
Owner:STONE GREGG W +5
Spectral data classification of samples
A system and method for classifying tissue by application of discriminant analysis to spectral data. Spectra are recorded as amplitudes at a series of discrete wavelengths. Pluralities of reference spectra are recorded for specimens having known conditions. The reference spectra are subjected to discriminant analysis to determine wavelength regions of interest for the analysis. A plurality of amplitudes are selected for the analysis, and are plotted in an N-dimensional space. For each plurality of reference spectra corresponding to a specific known condition, a characteristic point is determined and plotted, the characteristic point representative of the known condition. A test spectrum is recorded from a test specimen, and the plurality of amplitudes corresponding in wavelength to the wavelength regions of interest are selected. A characteristic point in N-dimensional space is determined for the test spectrum. The distance of the characteristic point of the test spectrum from each of the plurality of characteristic points representative of known conditions is determined. The test specimen is assigned the condition corresponding to the characteristic point of a plurality of reference spectra, based on a distance relationship with at least two distances, provided that at least one distance is less than a pre-determined maximum distance. In some embodiments, the test specimen can comprise human cervical tissue, and the known conditions can include normal health, metaplasia, CIN I and CIN II / III.
Owner:LUMA IMAGING CORP
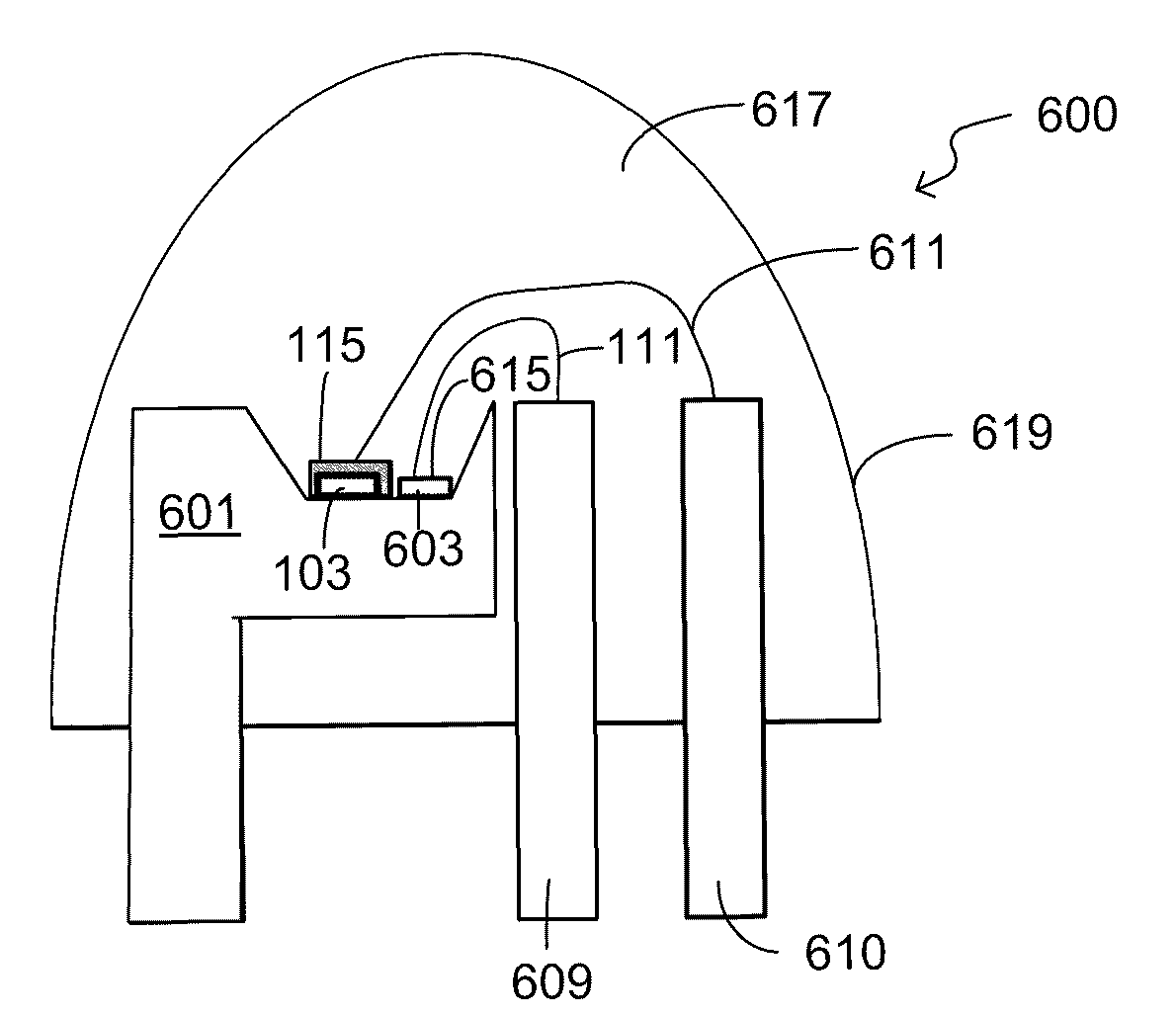
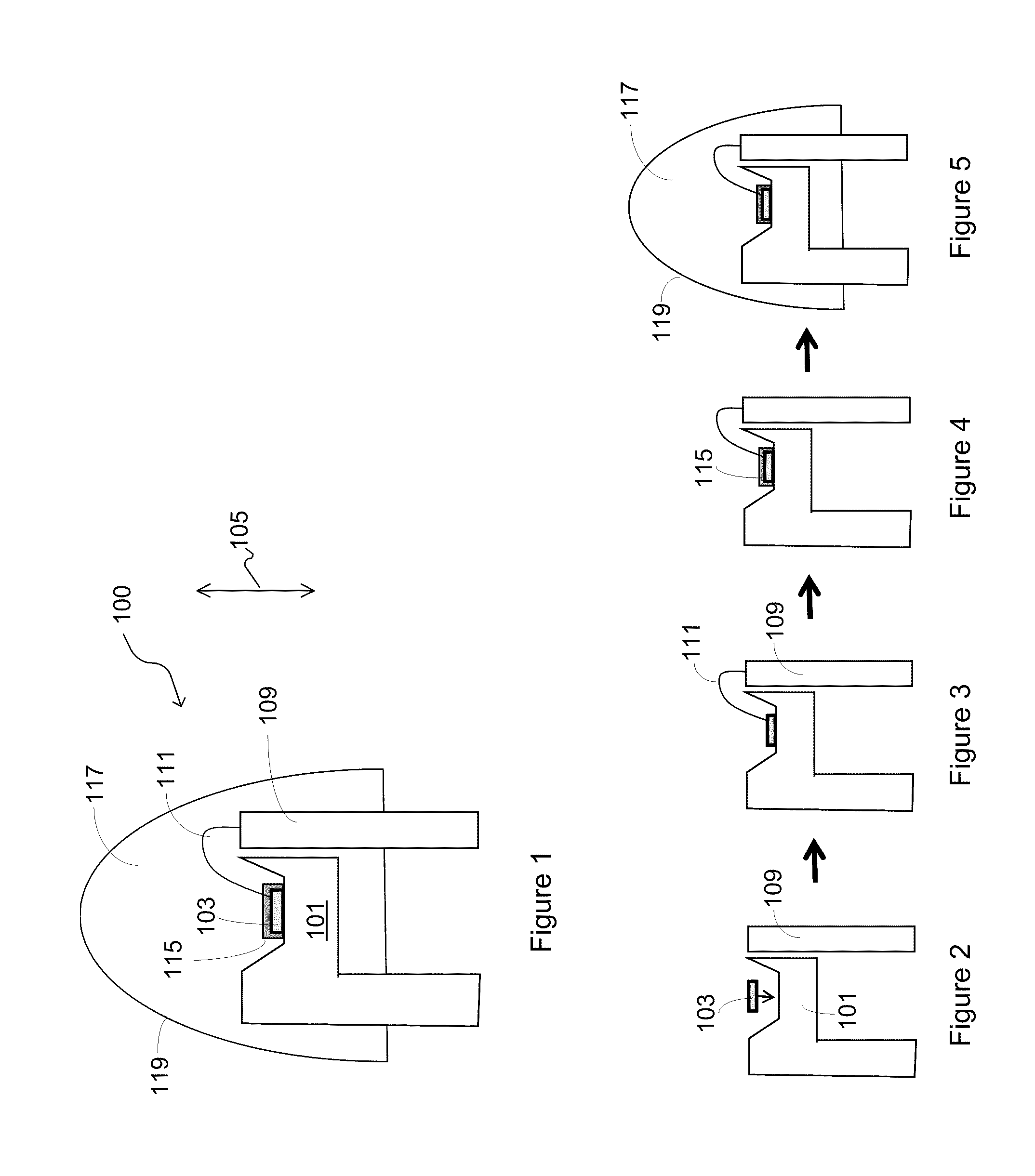
Optical device structure using GaN substrates and growth structures for laser applications
ActiveUS8294179B1Simple and cost-effectiveCost-effectiveOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsWavelengthLight emission
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Up and down conversion systems for production of emitted light from various energy sources
ActiveUS20100261263A1Enhance upconversionOptical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologyHigh energyRadiation
A system for energy upconversion and / or down conversion and a system for producing a photostimulated reaction in a medium. These systems include 1) a nanoparticle configured, upon exposure to a first wavelength λ1 of radiation, to generate a second wavelength λ2 of radiation having a higher energy than the first wavelength λ1 and 2) a metallic structure disposed in relation to the nanoparticle. A physical characteristic of the metallic structure is set to a value where a surface plasmon resonance in the metallic structure resonates at a frequency which provides a spectral overlap with either the first wavelength λ1 or the second wavelength λ2, or with both λ1 and λ2. The system for producing a photostimulated reaction in a medium includes a receptor disposed in the medium in proximity to the nanoparticle which, upon activation by the second wavelength λ2, generates the photostimulated reaction.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
High powered light emitting diode photobiology compositions, methods and systems
InactiveUS20150112411A1Increase light intensityLight therapySleep inducing/ending devicesMedicineLight treatment
Devices with high-power light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for use in human and / or animal phototherapy applications are disclosed. The phototherapy device includes a number of select LEDs for emitting a desired range or ranges of wavelengths of high intensity light for use in treatment. Additionally, the phototherapy treatment includes one or more methods for providing a treatment appropriate to the condition desired to be treated. The phototherapy device provides a diversity of high power light settings, intensity levels, and selectable time intervals.
Owner:BECKMAN FRANCES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com