Patents
Literature
1570 results about "Surface plasmon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface plasmons (SPs) are coherent delocalized electron oscillations that exist at the interface between any two materials where the real part of the dielectric function changes sign across the interface (e.g. a metal-dielectric interface, such as a metal sheet in air). SPs have lower energy than bulk (or volume) plasmons which quantise the longitudinal electron oscillations about positive ion cores within the bulk of an electron gas (or plasma).
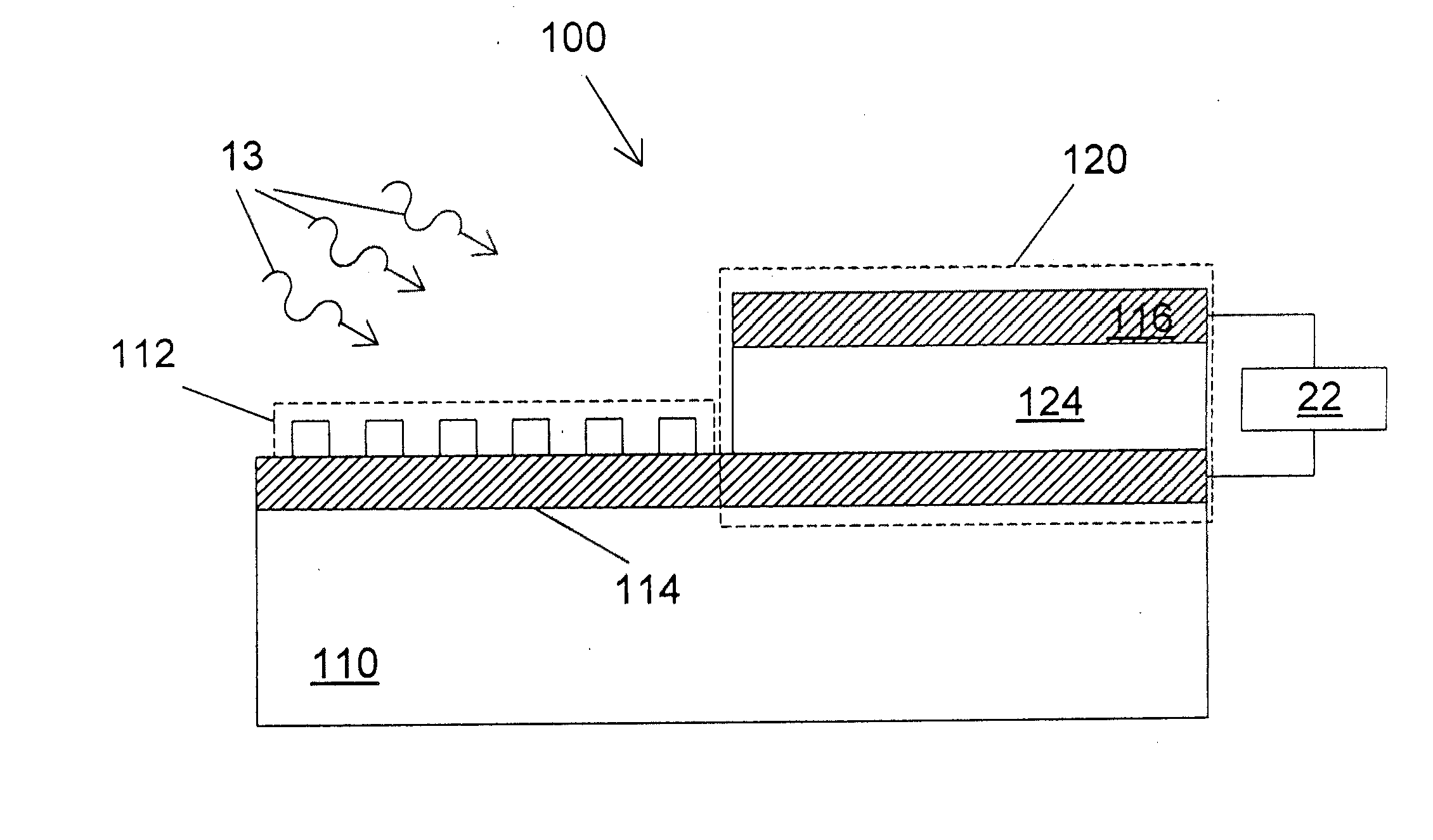
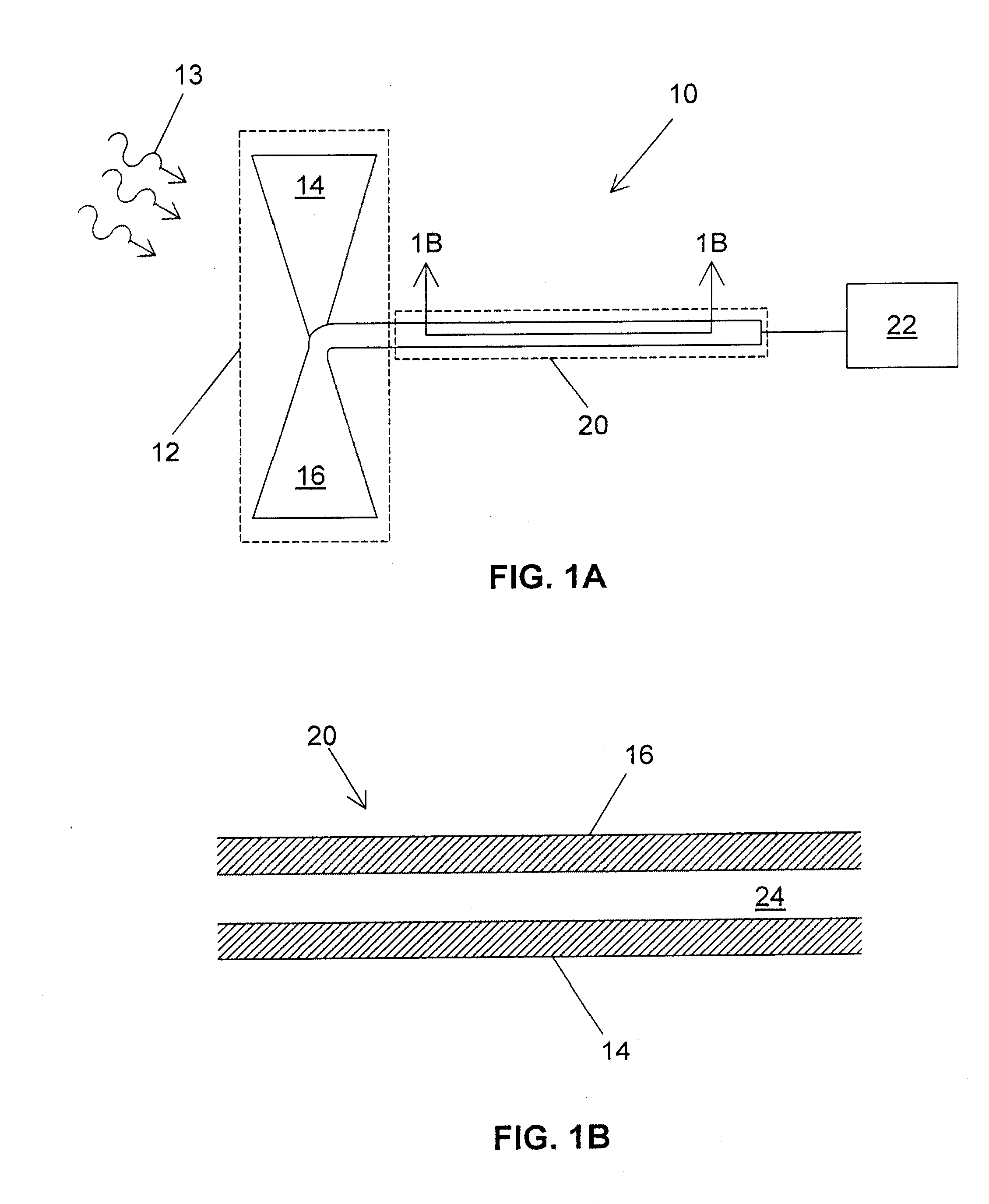
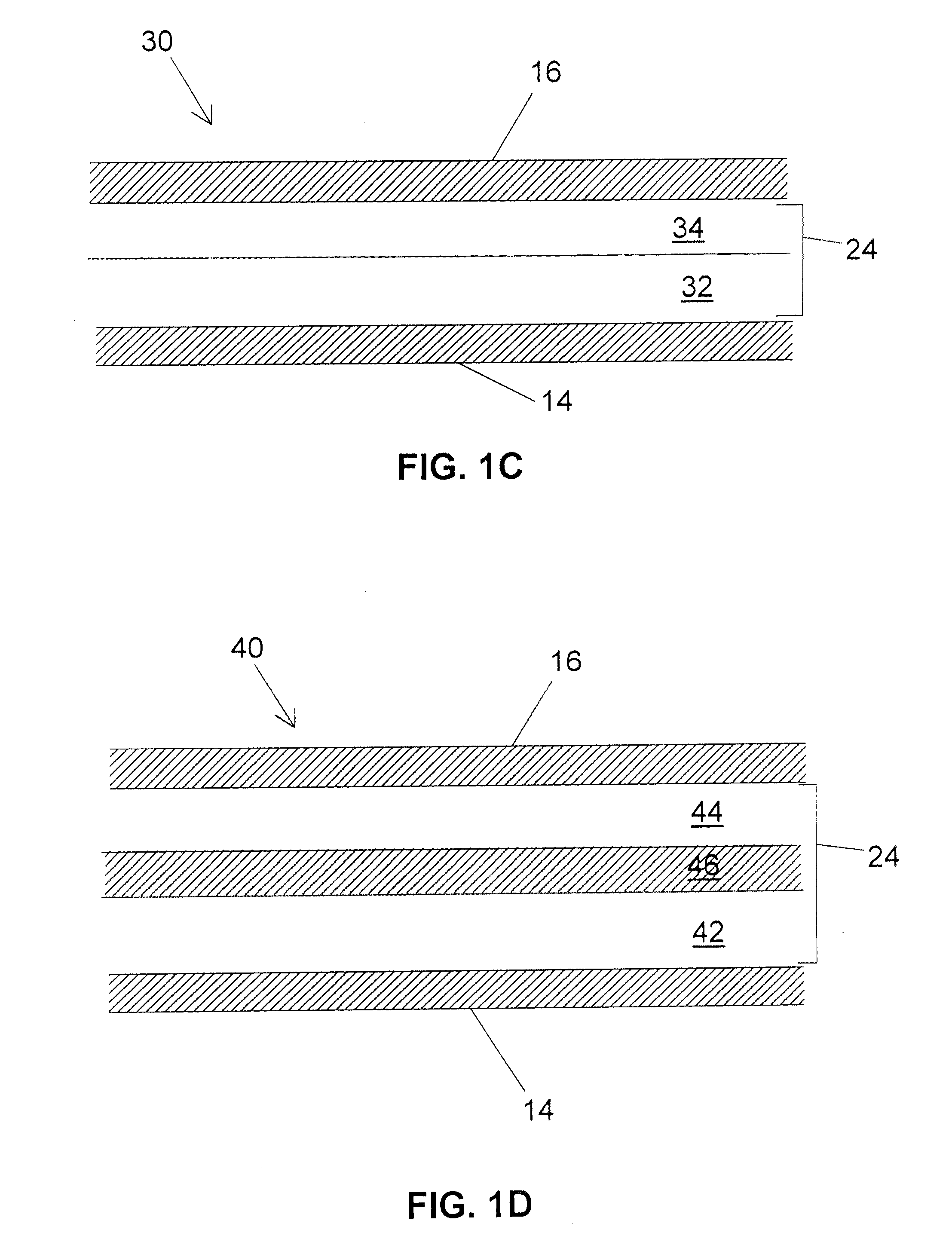
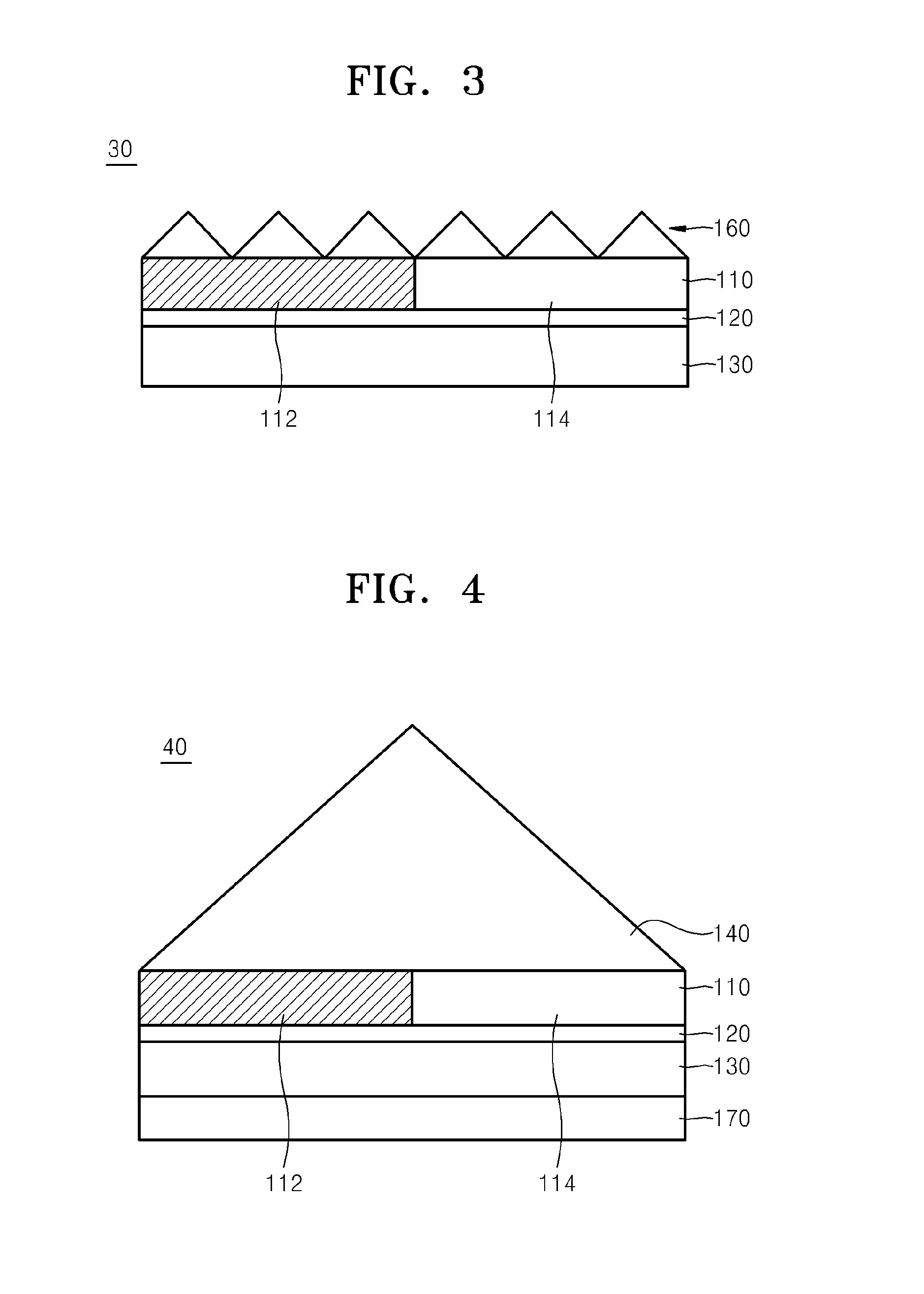
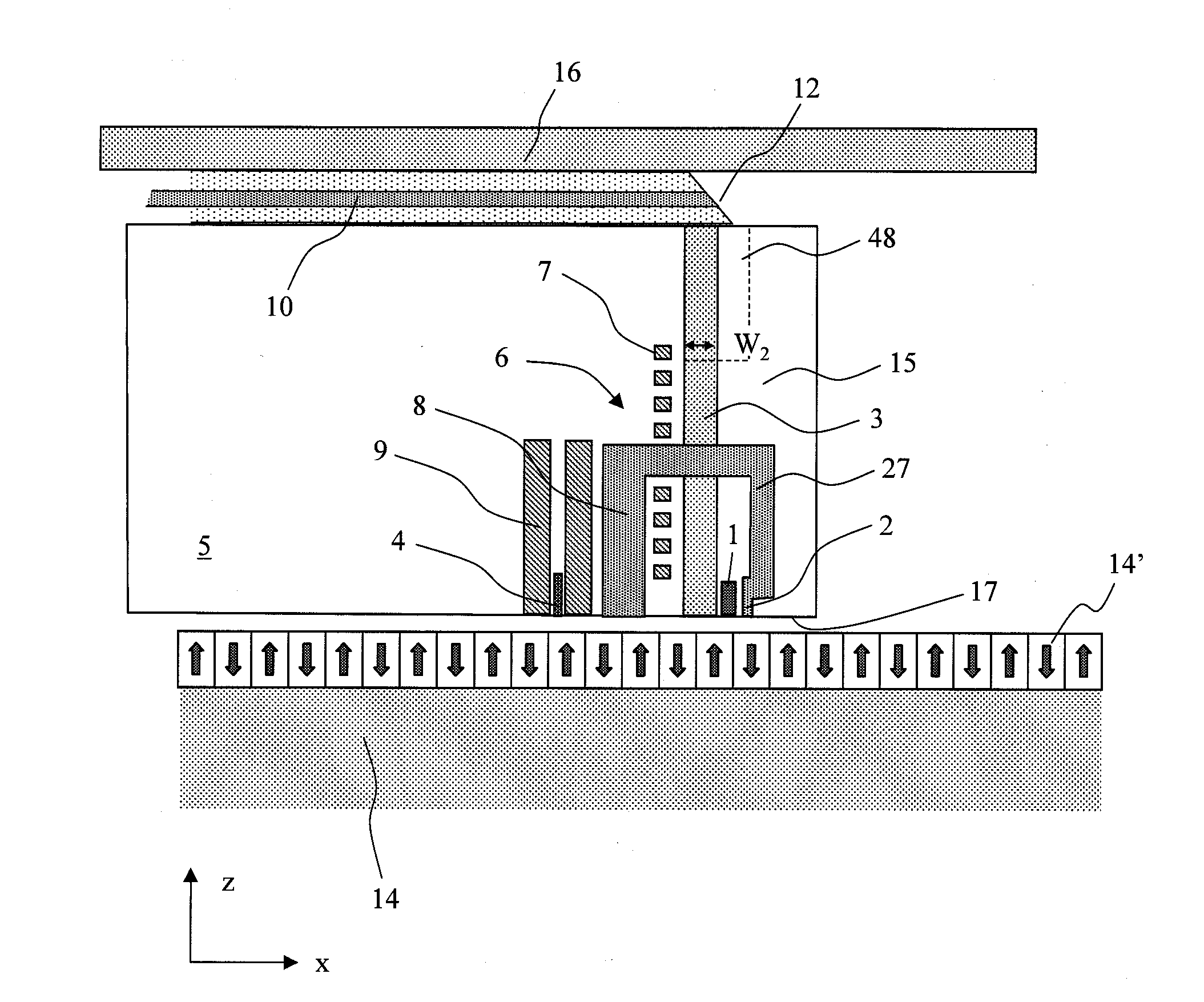
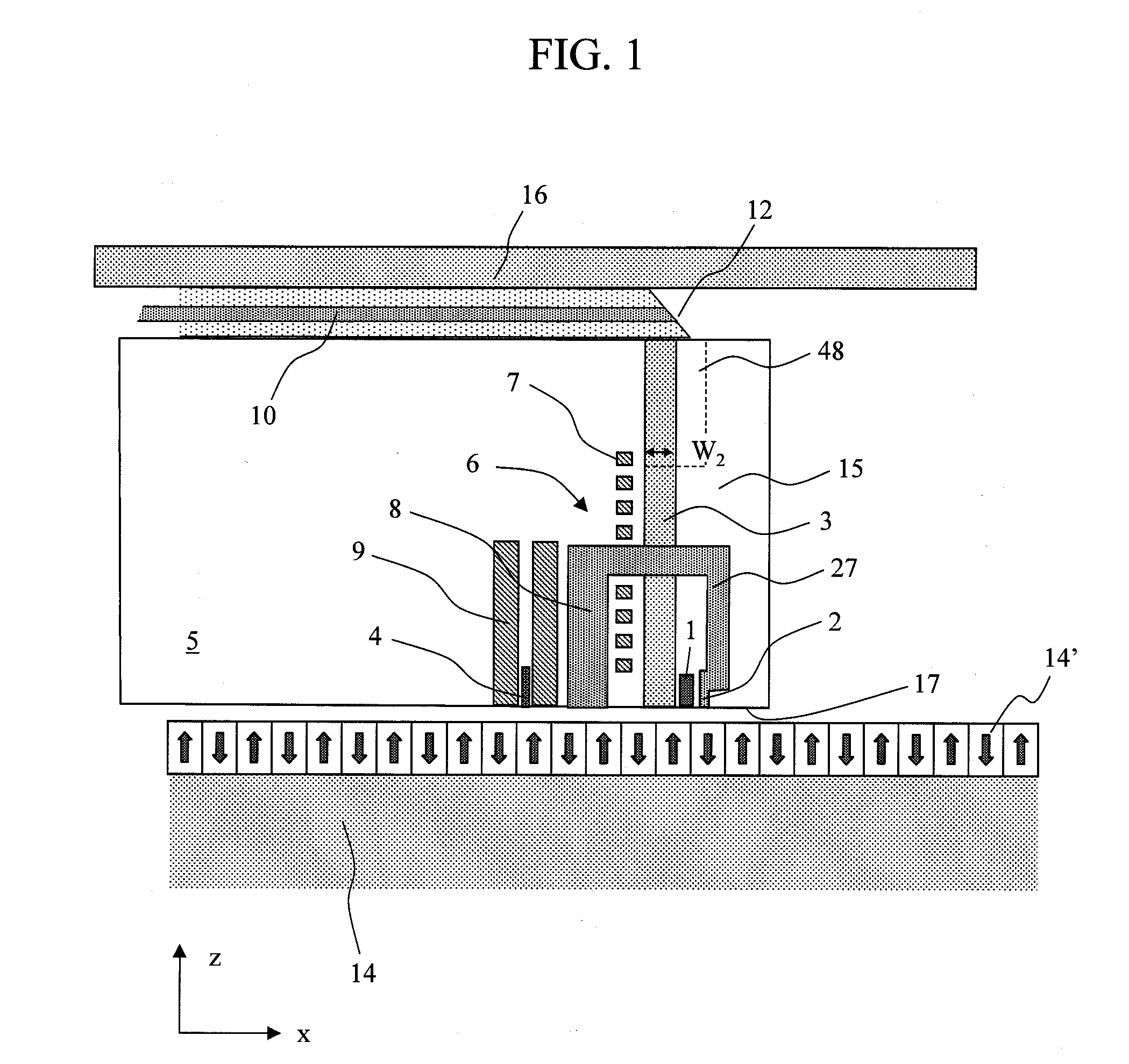
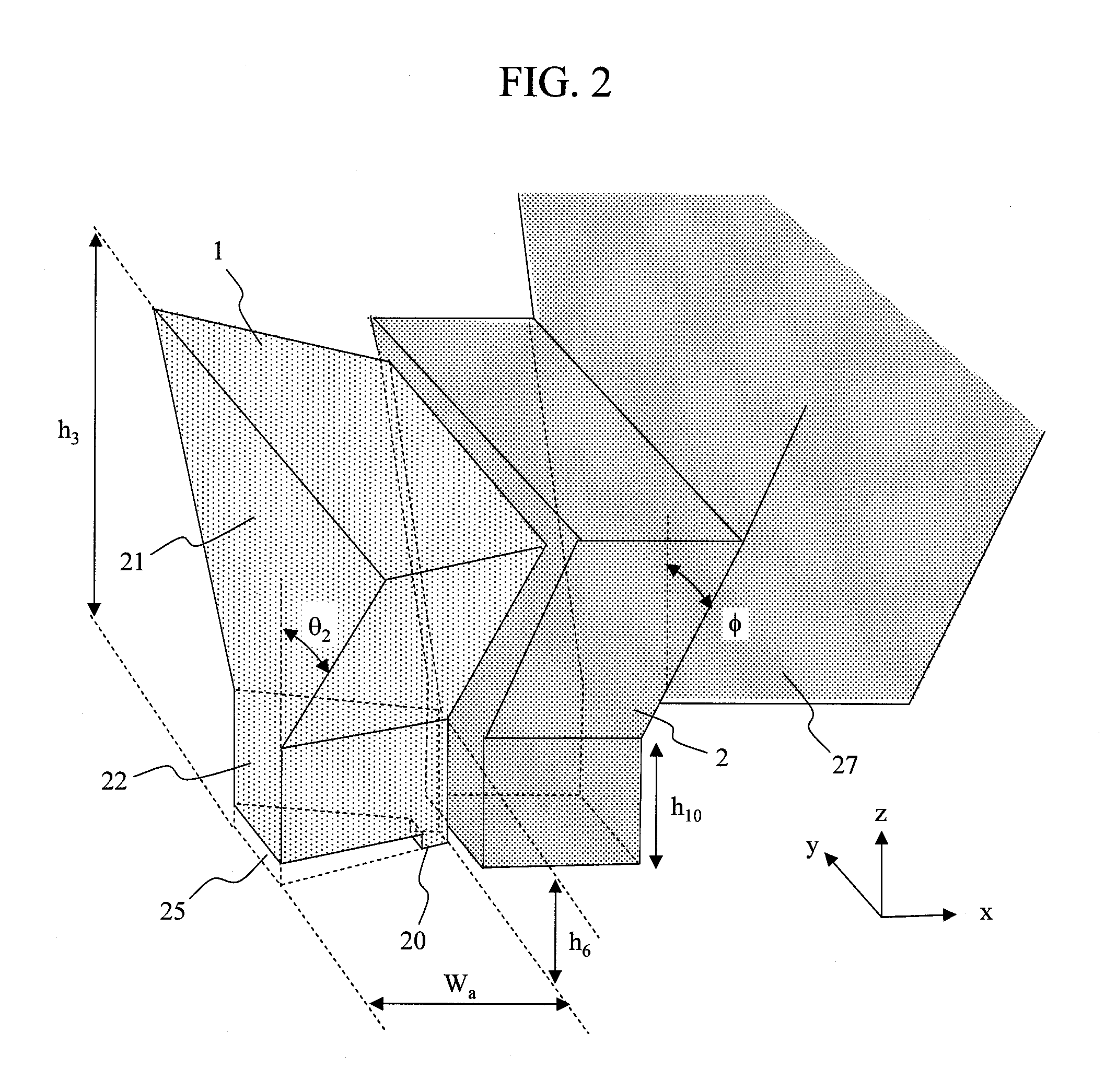
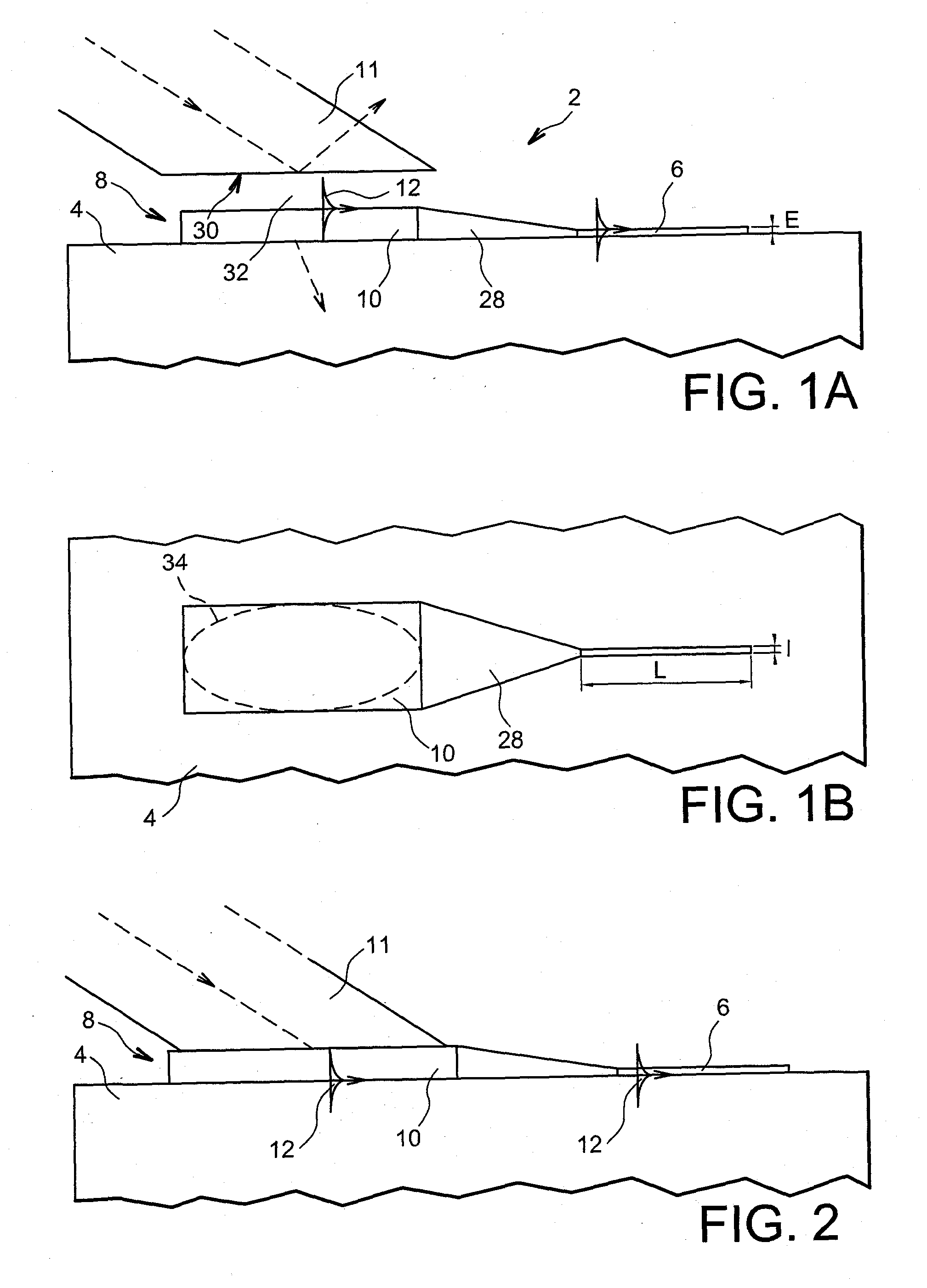
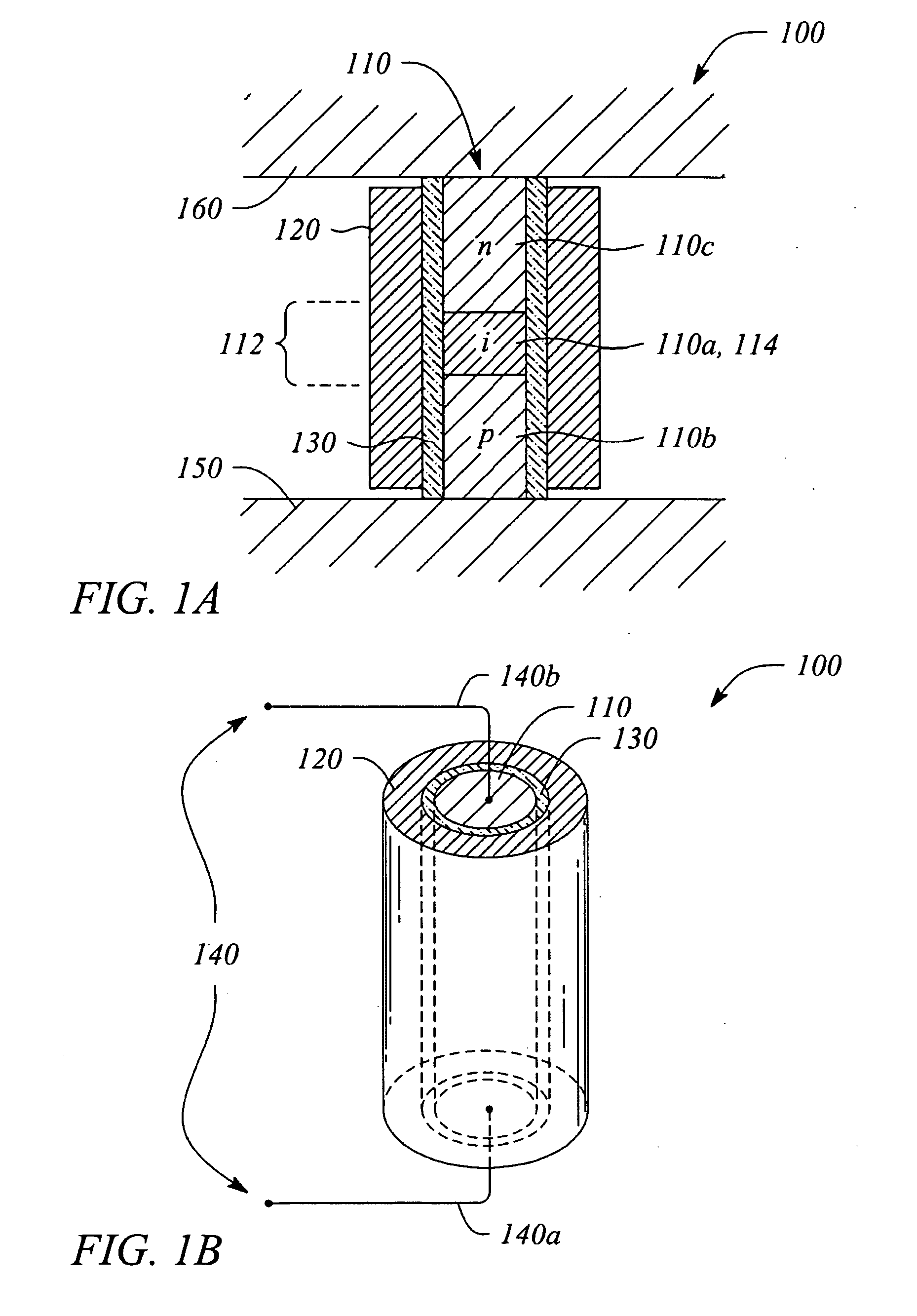
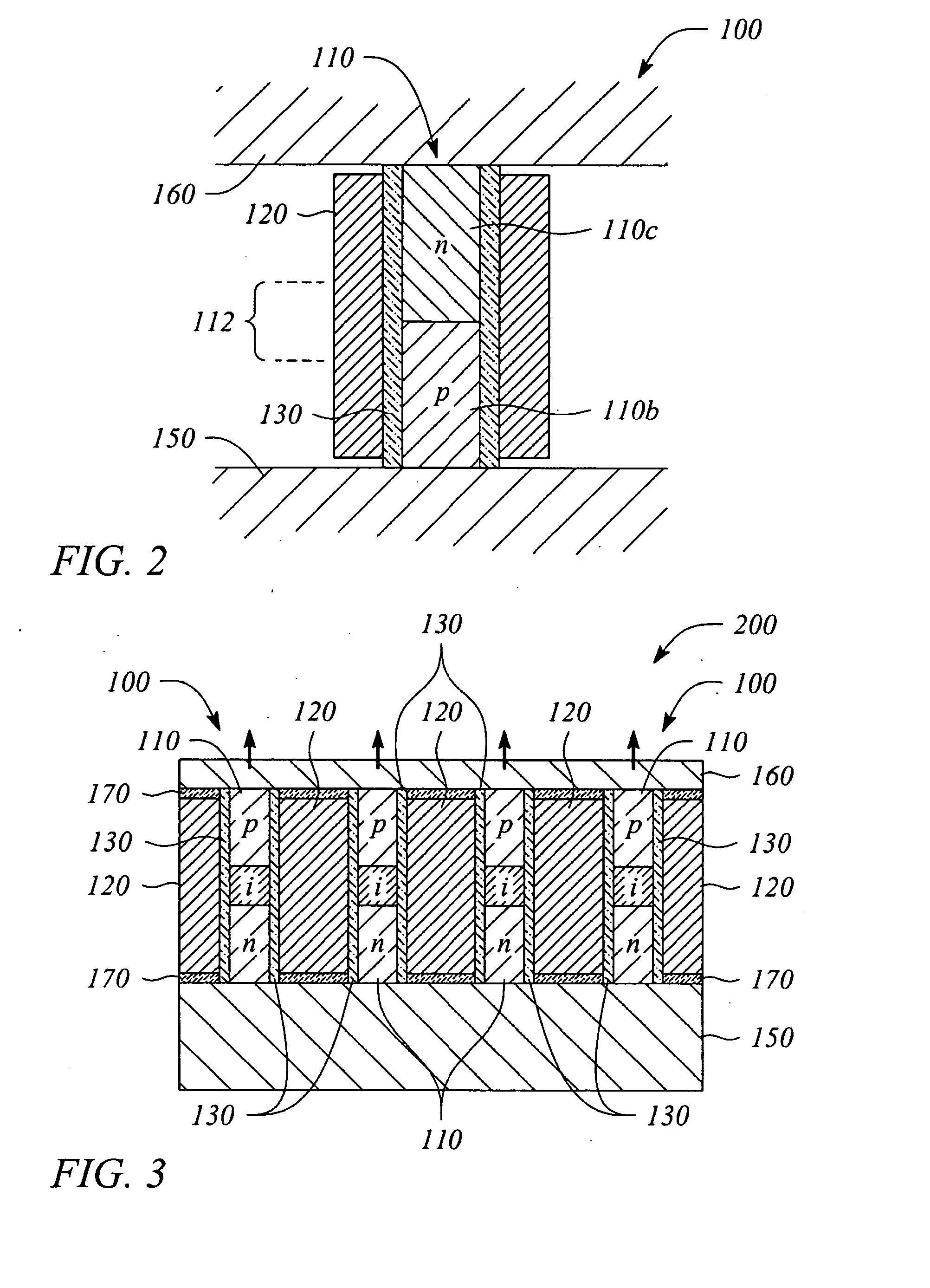
Surface plasmon light emitter structure and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050285128A1Increased formationSolve the lack of spaceSemiconductor devicesElectron holeCoupling
A method (and resulting structures) for manufacturing light emitting semiconductor devices. The method includes providing a substrate comprising a surface region and forming a metal layer overlying the surface region of the substrate. In a specific embodiment, the metal layer and the surface region are characterized by a spatial spacing between the metal layer and the substrate to cause a coupling between electron-hole pairs generated in the substrate and a surface plasmon mode at an interface region between the metal layer and the surface region. Additionally, the interface region has a textured characteristic between the surface region and the metal layer. The textured characteristics causes emission of electromagnetic radiation through the surface plasmon mode or like mechanism according to a specific embodiment.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
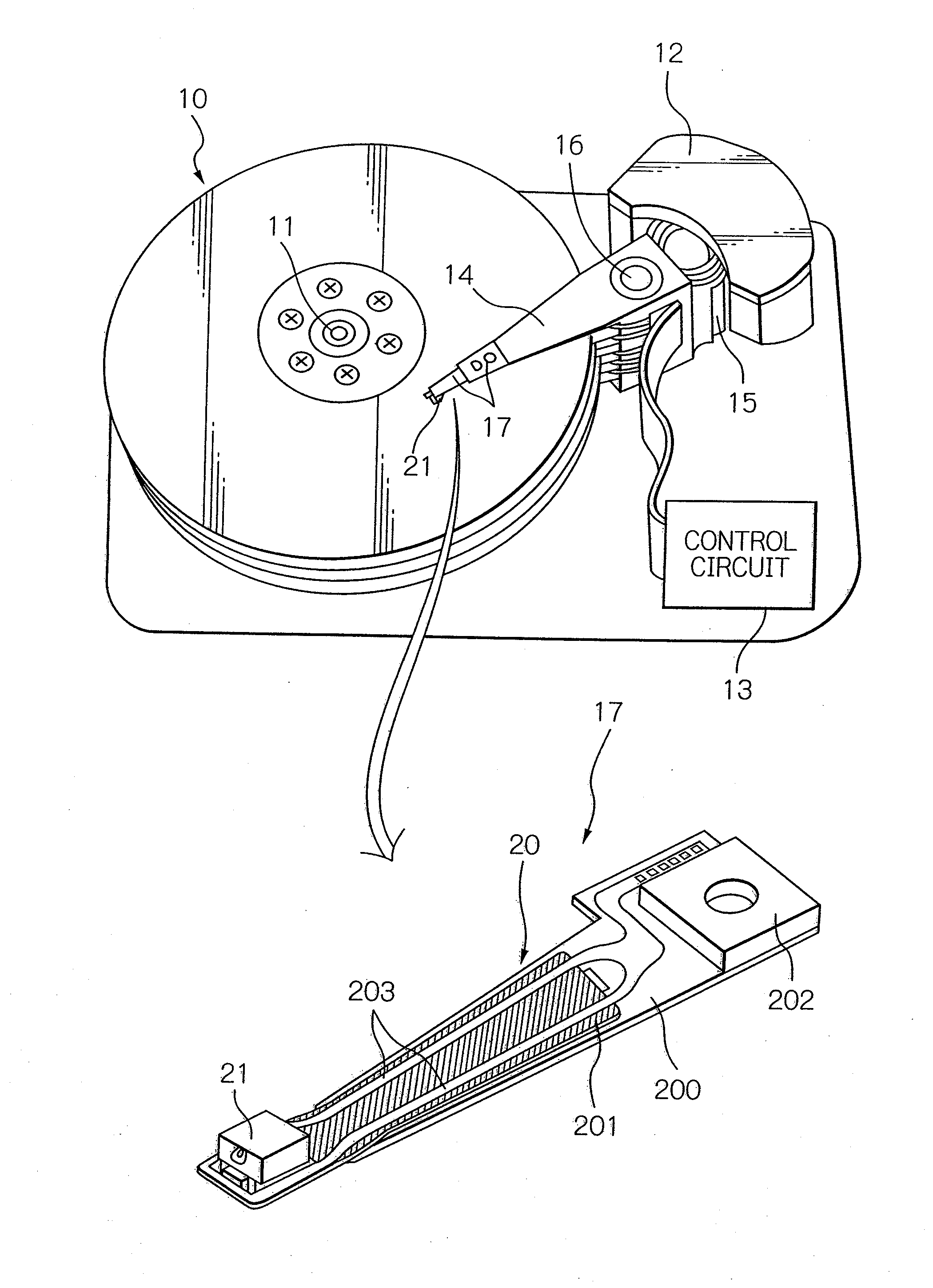
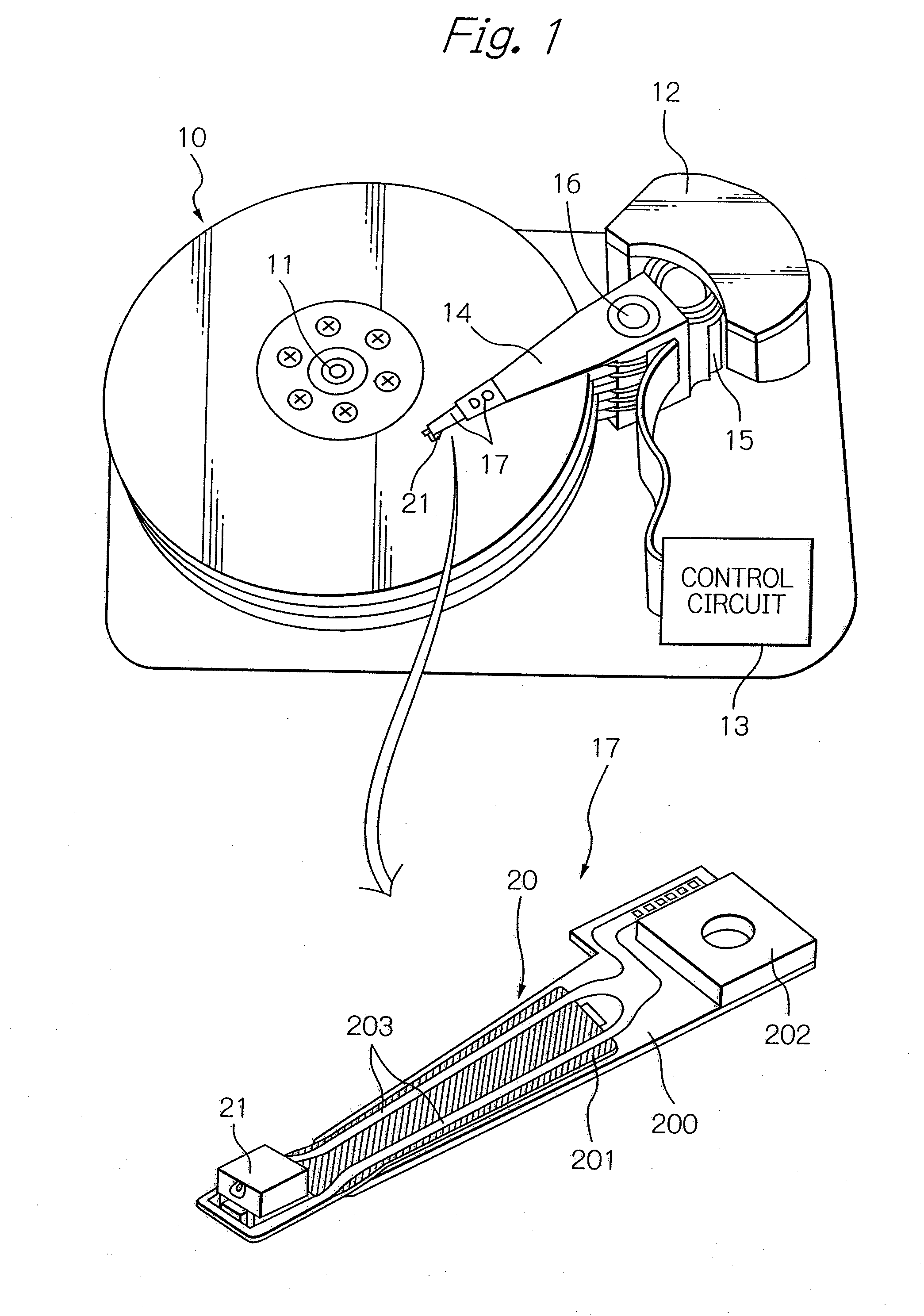
Near-field optical transducers for thermal assisted magnetic and optical data storage
ActiveUS7330404B2Recording by magnetic meansRecord information storageSurface plasmonRefractive index
An optical transducer comprises an optical element for directing an electromagnetic wave to a focal region and a metallic nano-structure having a longitudinal axis substantially parallel to an electric field of the electromagnetic wave, the metallic nano-structure being positioned outside of the optical element, wherein the electromagnetic wave produces surface plasmons on the metallic nano-structure. A cladding material having a refractive index differing from the refractive index of the optical element can be positioned adjacent to a surface of the metallic nano-structure. Magneto-optical recording heads that include the transducers and disc drives that include the magneto-optical recording heads are also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
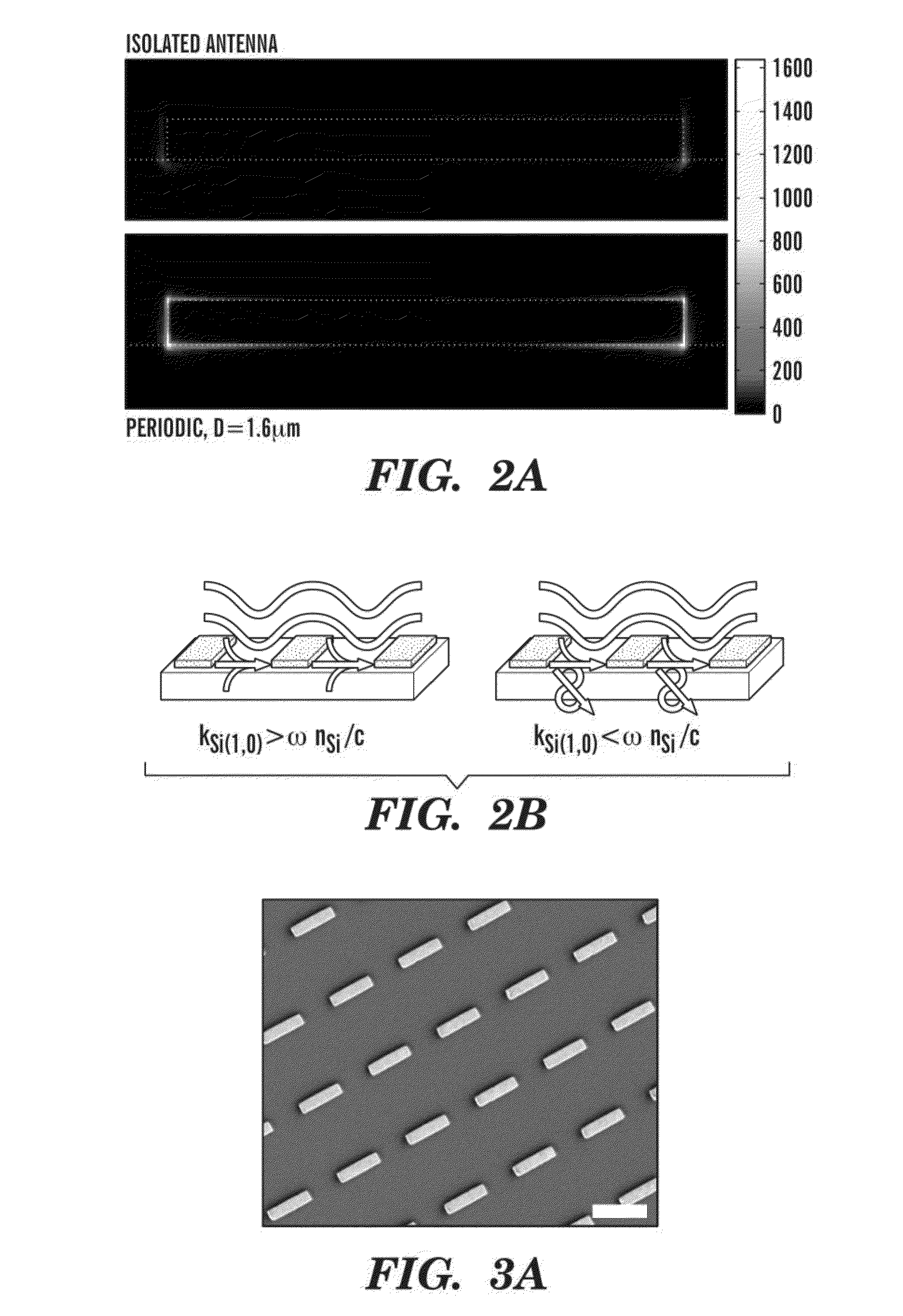
Nanoantenna arrays for nanospectroscopy, methods of use and methods of high-throughput nanofabrication
ActiveUS20130148194A1Large scaleStrong and enhanced couplingMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLithographic artistSurface plasmon
The present invention generally relates to nanoantenna arrays and methods of their fabrication. In particular, one aspect relates to nanoantenna arrays comprising nanostructures of predefined shapes in predefined patterns, which results in collective excitement of surface plasmons. In some embodiments the nanoantenna arrays can be used for spectroscopy and nanospectroscopy. Another aspects of the present invention relate to a method of high-throughput fabrication of nanoantenna arrays includes fabricating a reusable nanostencil for nanostensil lithography (NSL) which provides a mask to deposit materials onto virtually any support, such as flexible and thin-film stretchable supports. The nanostencil lithography methods enable high quality, high-throughput fabrication of nanostructures on conducting, non-conducting and magnetic supports. The nanostencil can be prepared by etching nanoapertures of predefined patterns into a waffer or ceramic membrane. In some embodiments, a nanoantenna array comprises plasmonic nanostructures or non-plasmonic nanostructures.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
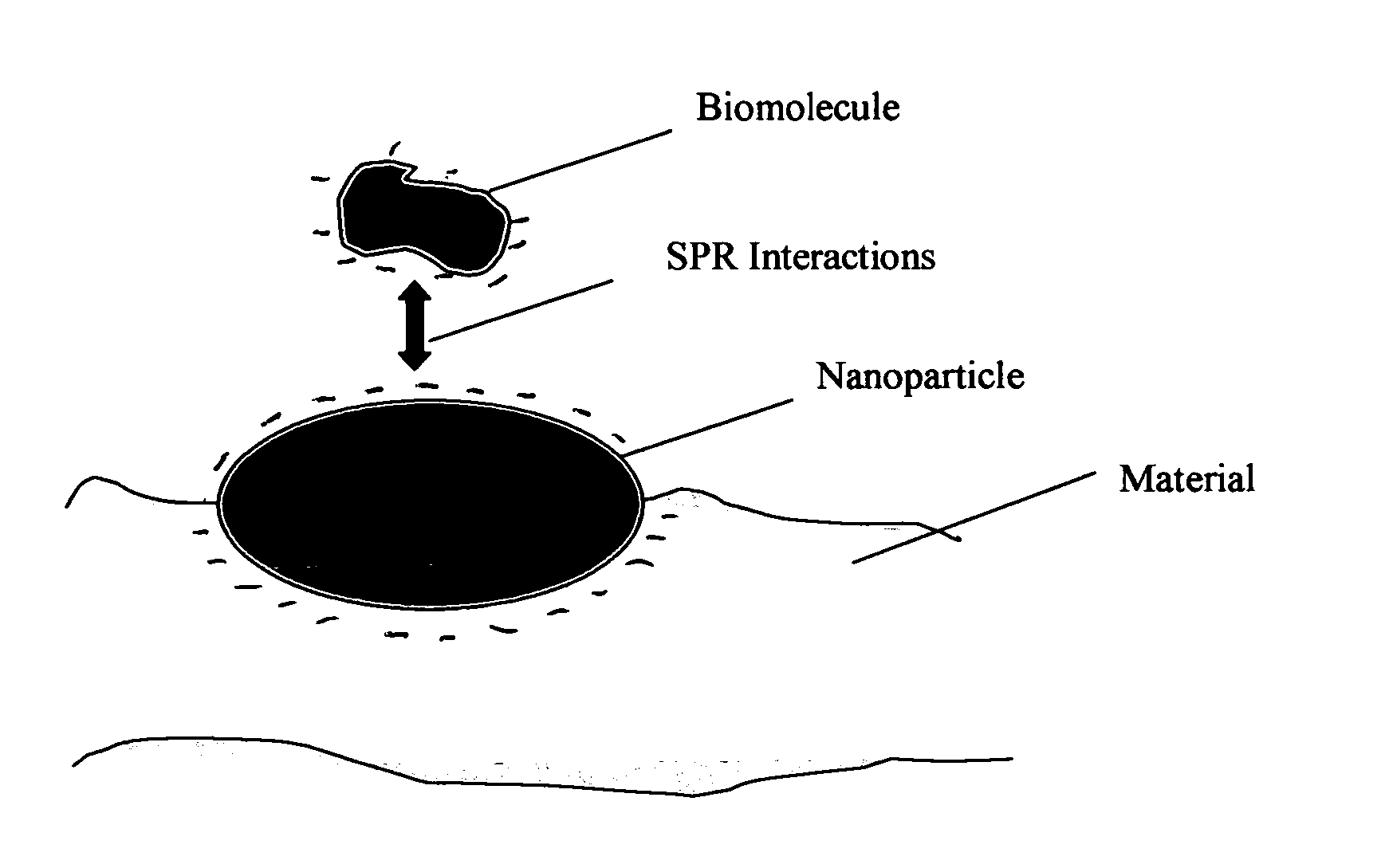
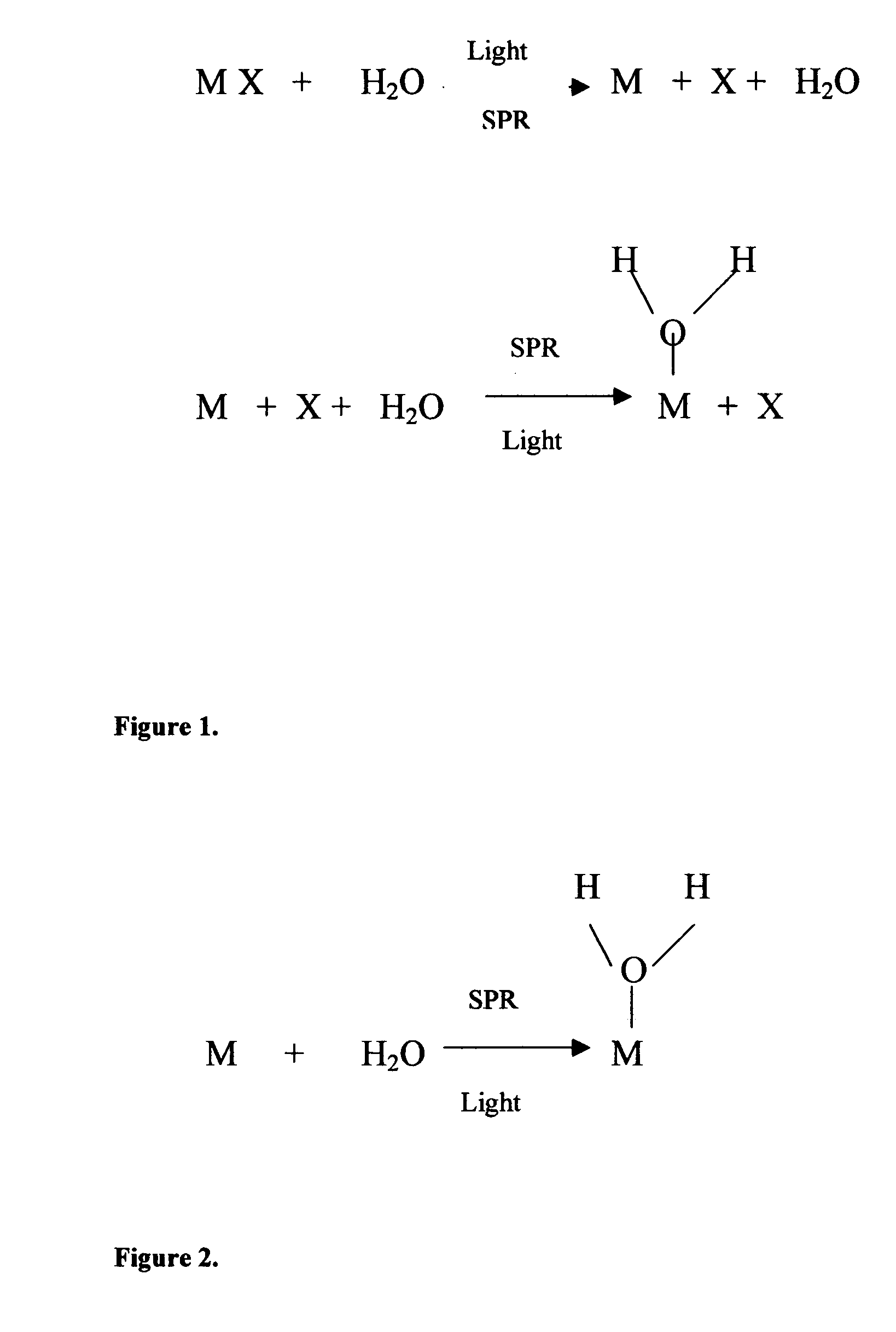
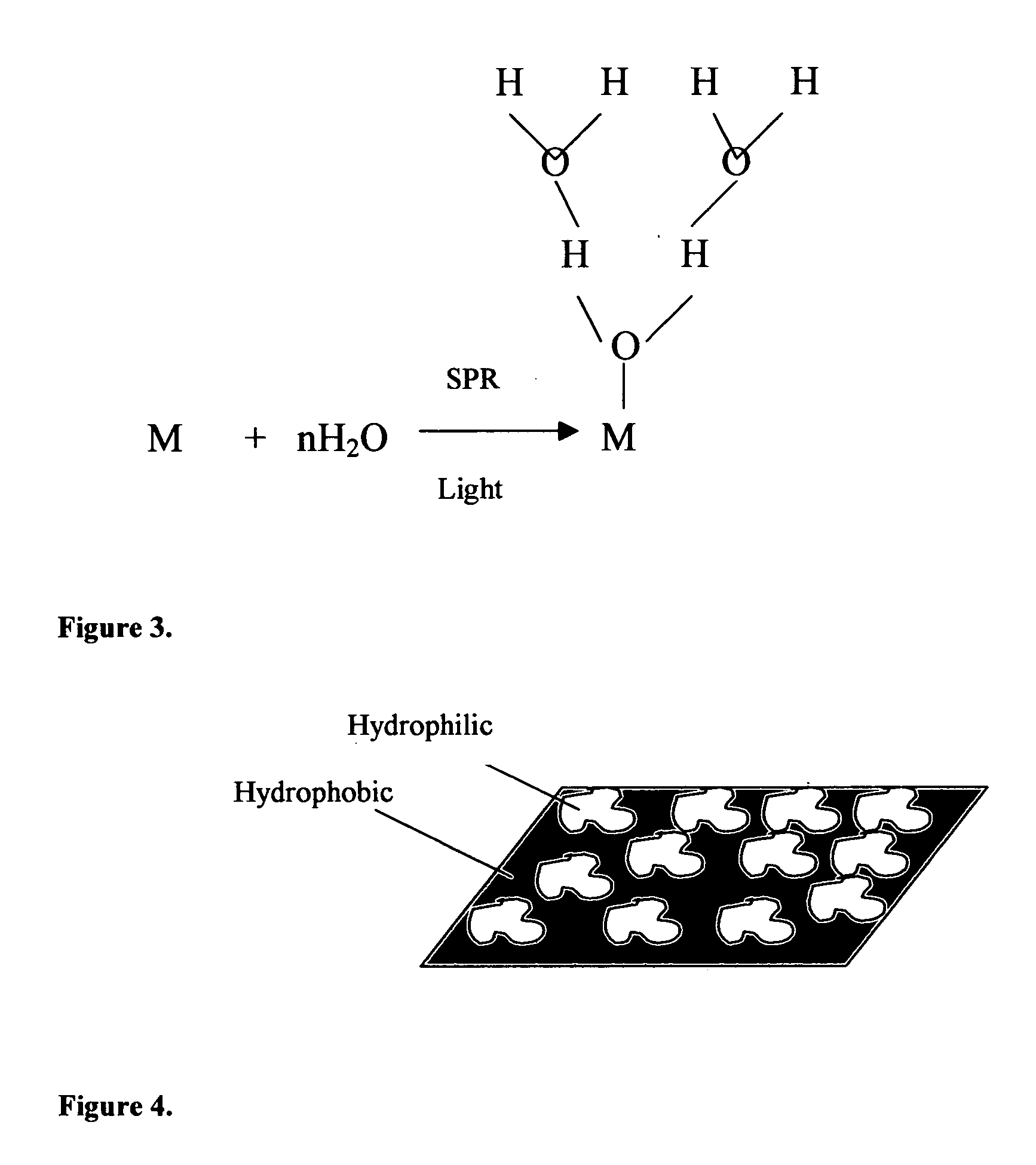
Method of plasmon-enhanced properties of materials and applications thereof
InactiveUS20050164169A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyInfraredThermochromism
Methods and applications of surface plasmon resonance-enhanced antibacterial, anti-adhere, adhere, catalytic, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, spectral change, biological and chemical decomposition properties of materials with embedded nanoparticles are disclosed. A method of the nonlinear generation of surface plasmon resonance enables the use of light with wavelengths from X-Ray to IR to enhance properties of materials by several orders of magnitude. The nanoparticle size is crucial for the enhancement and their size is considered to be in the proposed methods and applications within a range of 0.1 nm to 200,000 nm. The nanoparticles preferably are made of noble metals and / or semiconductor oxides. The invention describes a very broad spectrum of applications of surface plasmon resonance-enhanced properties of materials with embedded nanoparticles, from environmental cleanup by road pavement and construction materials, self-cleaning processes of surface materials, thermochromic effects on heat blocking materials, corrosion preventing paint, to sanitization by antibacterial textile fabrics, filters, personal clothing, contact lenses and medical devices.
Owner:SPR ADVANCED TECH INC
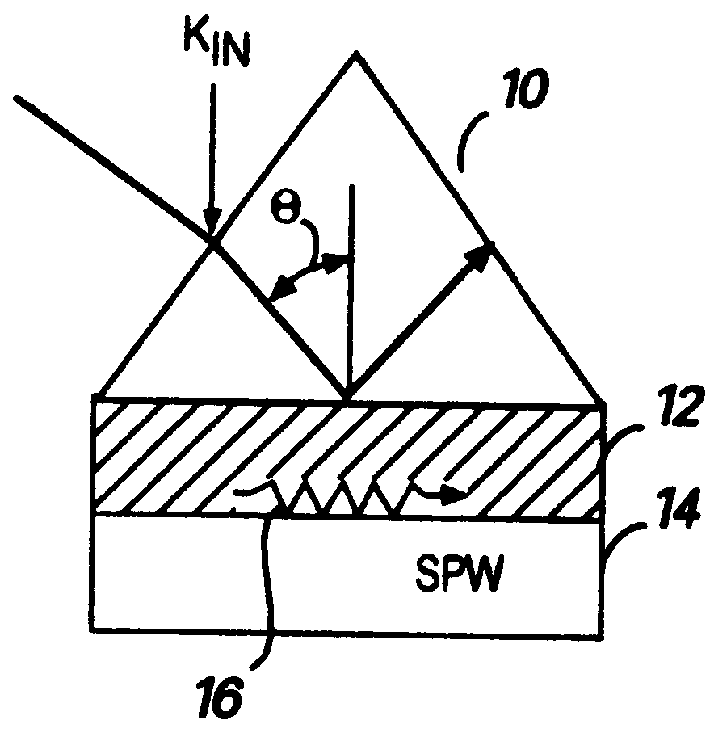
Surface plasmon devices
A device including an input port configured to receive an input signal is described. The device also includes an output port and a structure, which structure includes a tunneling junction connected with the input port and the output port. The tunneling junction is configured in a way (i) which provides electrons in a particular energy state within the structure, (ii) which produces surface plasmons in response to the input signal, (iii) which causes the structure to act as a waveguide for directing at least a portion of the surface plasmons along a predetermined path toward the output port such that the surface plasmons so directed interact with the electrons in a particular way, and (iv) which produces at the output port an output signal resulting from the particular interaction between the electrons and the surface plasmons.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
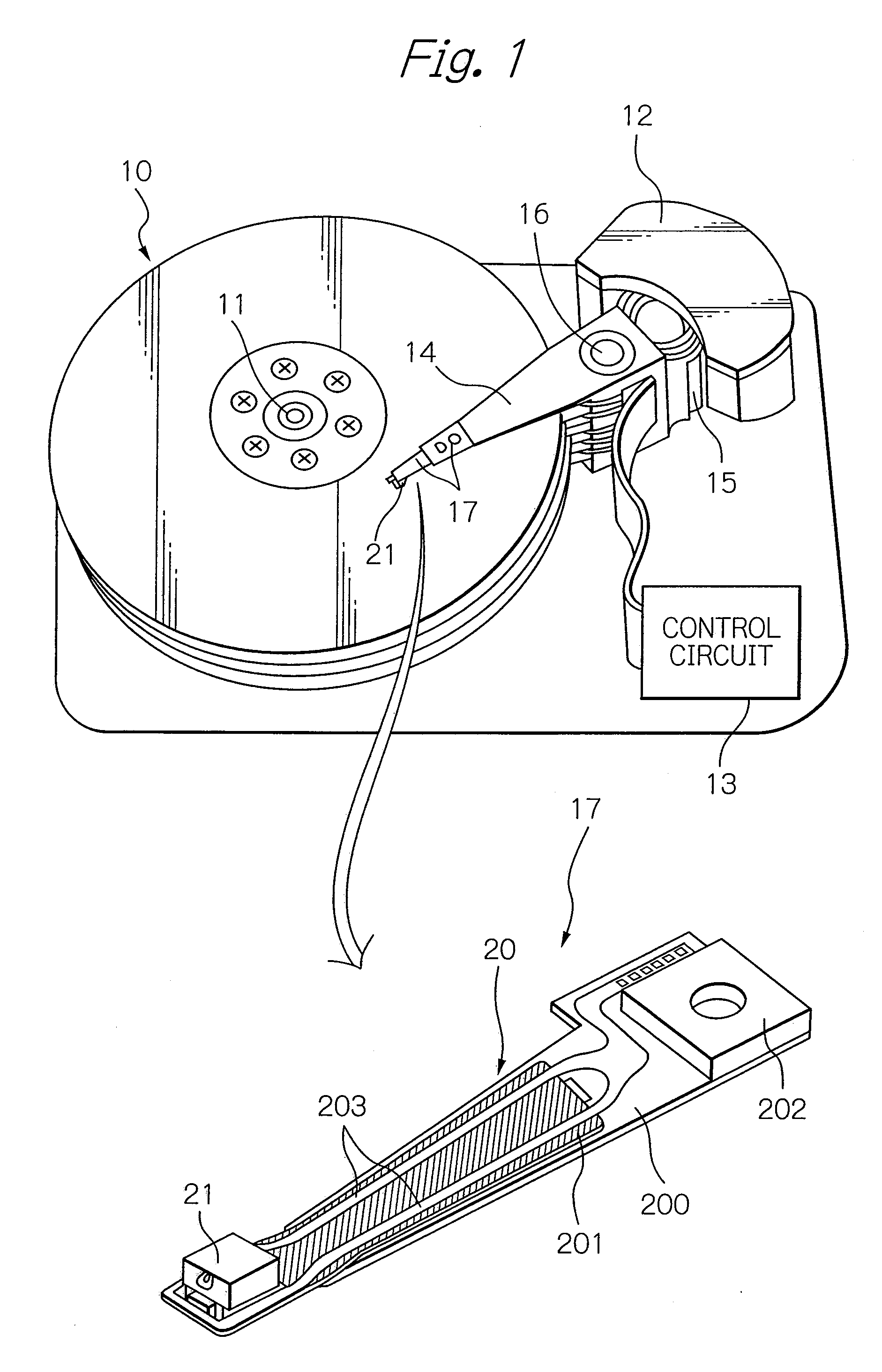
Surface plasmon antenna with propagation edge and near-field light generating element
ActiveUS20100103553A1Avoid excessive heatAppropriate heatCombination recordingArm with optical waveguideSurface plasmonMagnetic poles
Provided is a surface plasmon antenna that can be set so that the emitting position on the end surface of the plasmon antenna where near-field light is emitted is located sufficiently close to the end of a magnetic pole. The surface plasmon antenna comprises an edge having a portion for coupling with a light in a surface plasmon mode. The edge is provided for propagating surface plasmon excited by the light and extends from the portion to a near-field light generating end surface that emits near-field light. The edge for propagating surface plasmon is a very narrow propagation region. Therefore, the near-field light generating end surface, which appears as a polished surface processed through polishing in the manufacturing of the plasmon antenna, can be made a shape with a very small size, and further can be set so that surface plasmon propagates to reach the end surface reliably.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
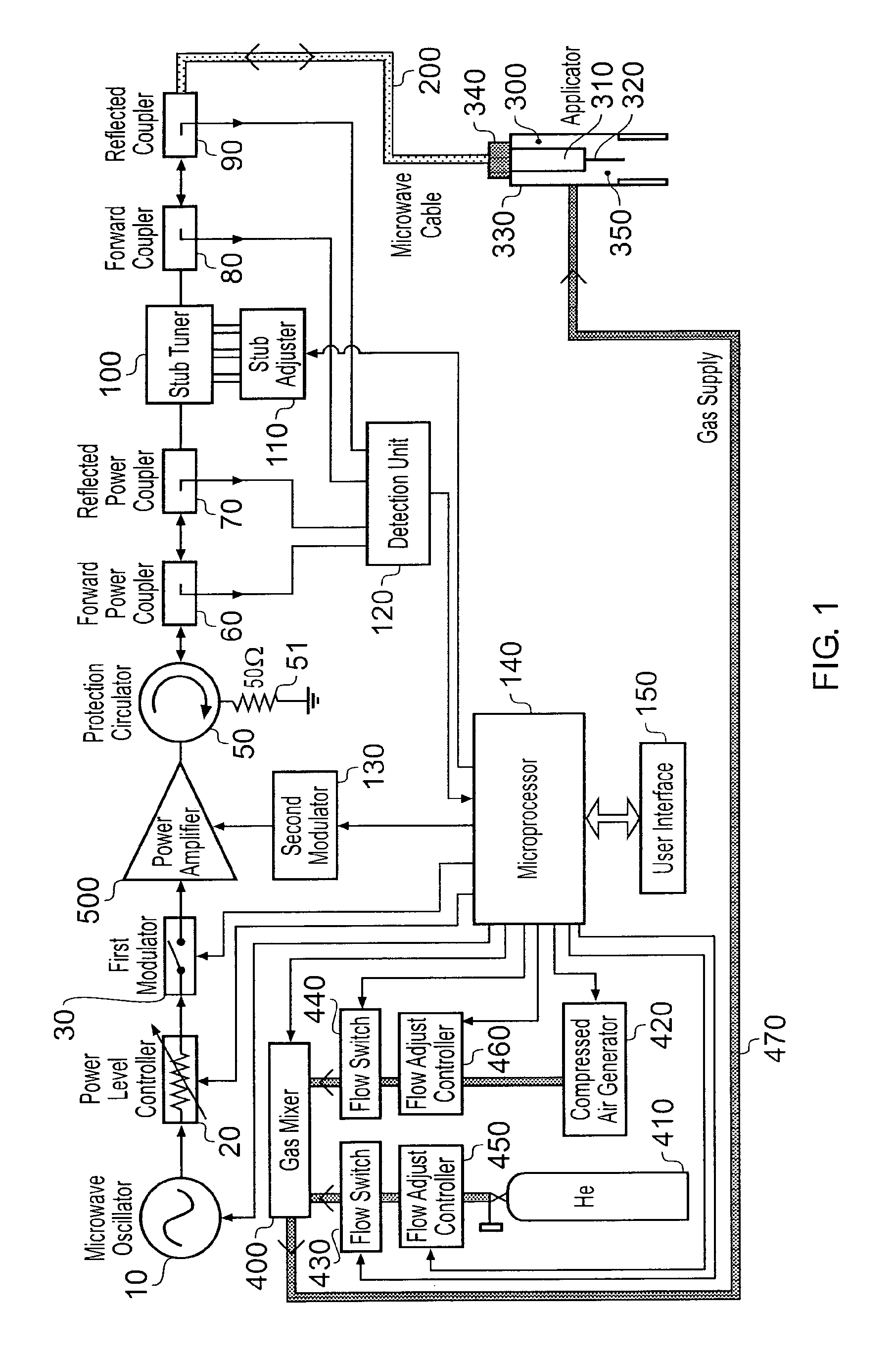
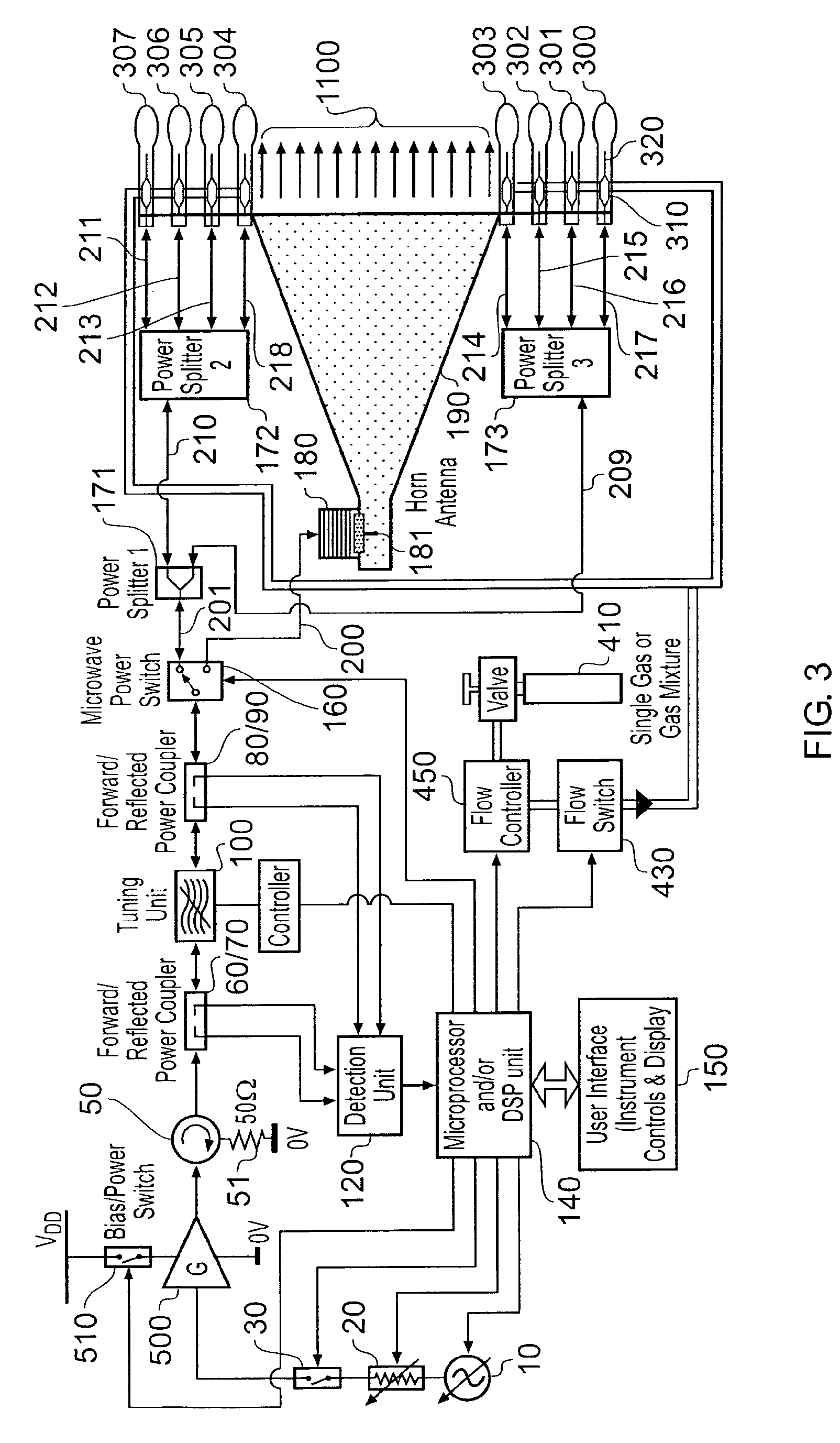
Microwave plasma sterilisation system and applicators therefor
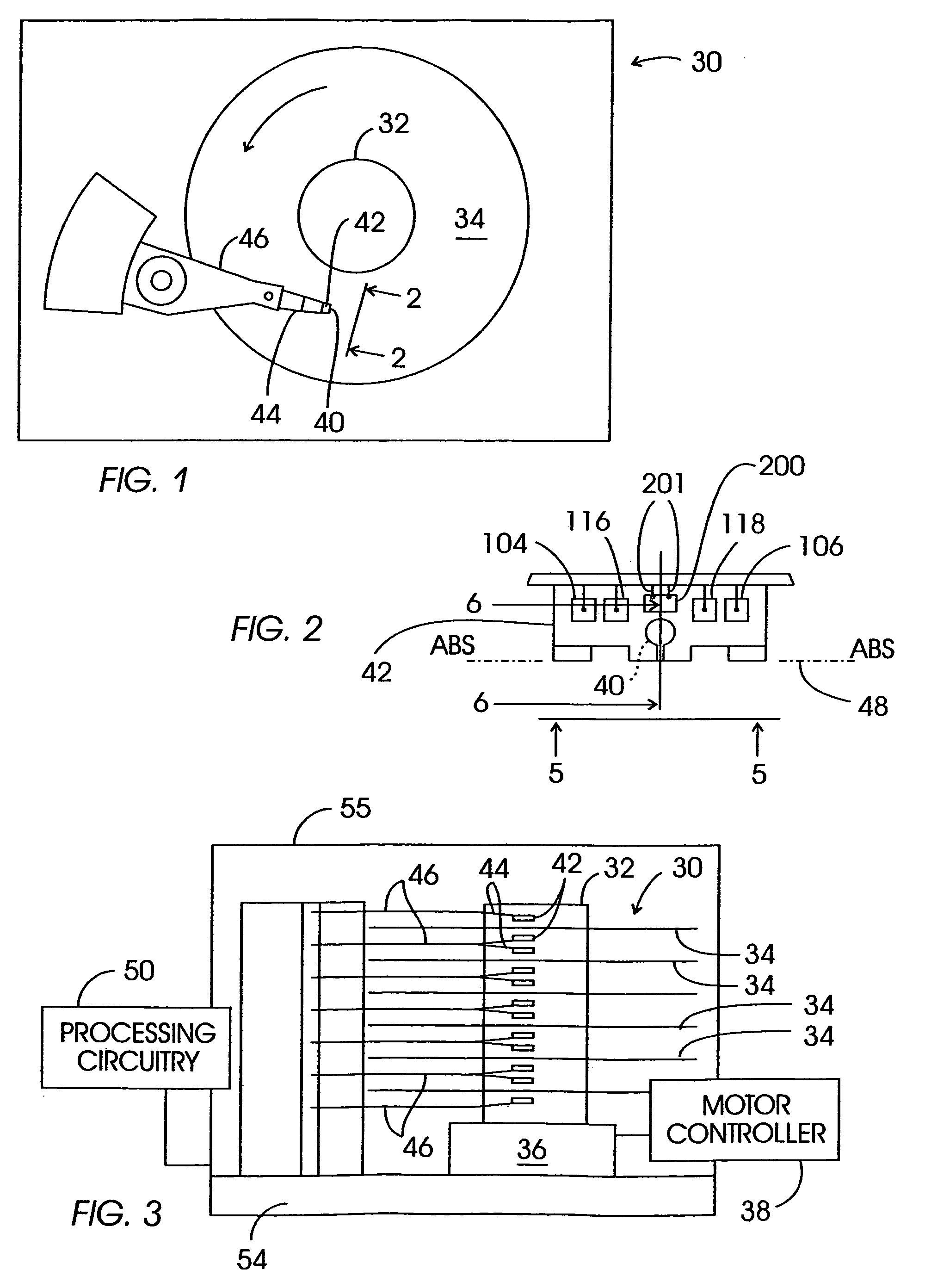
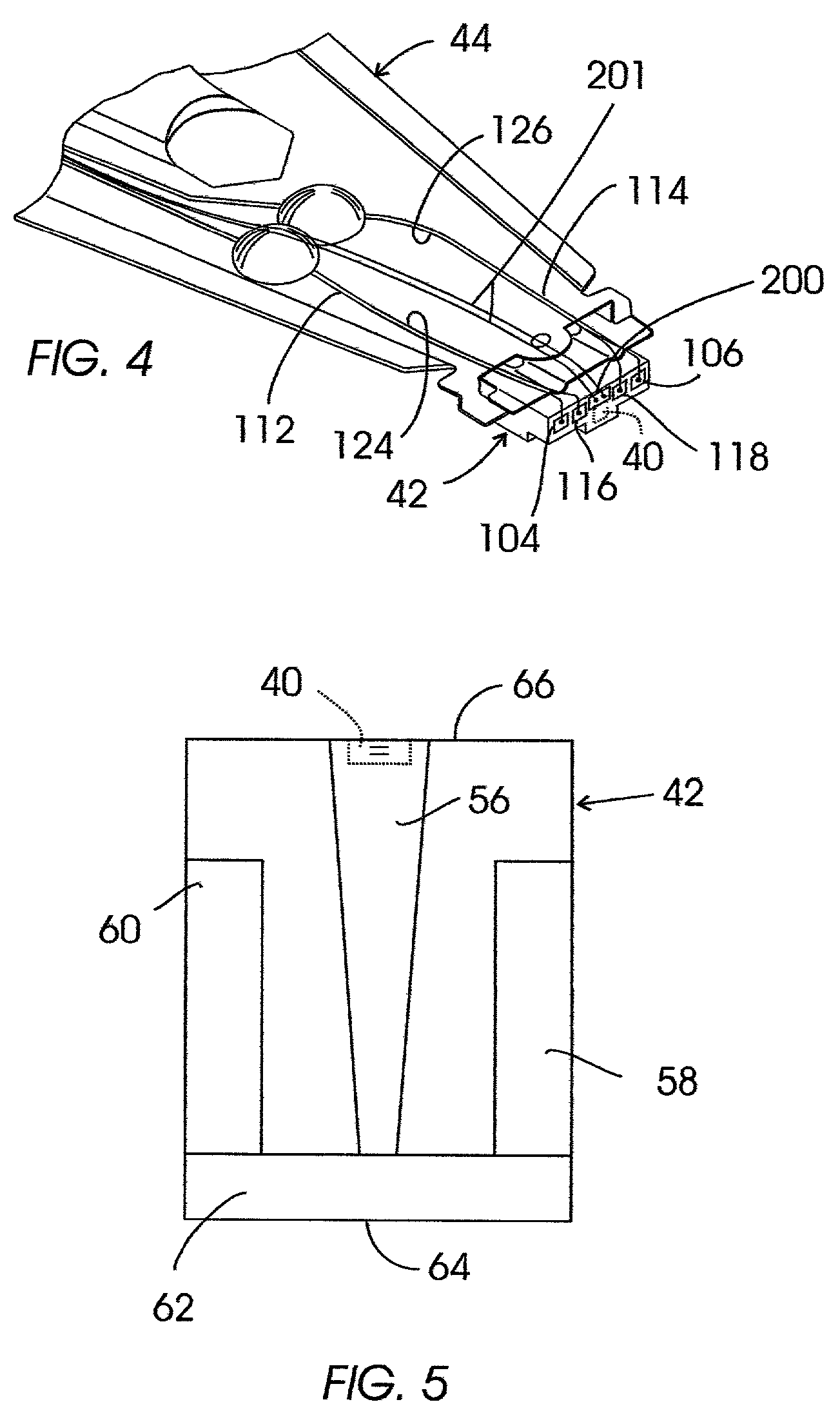
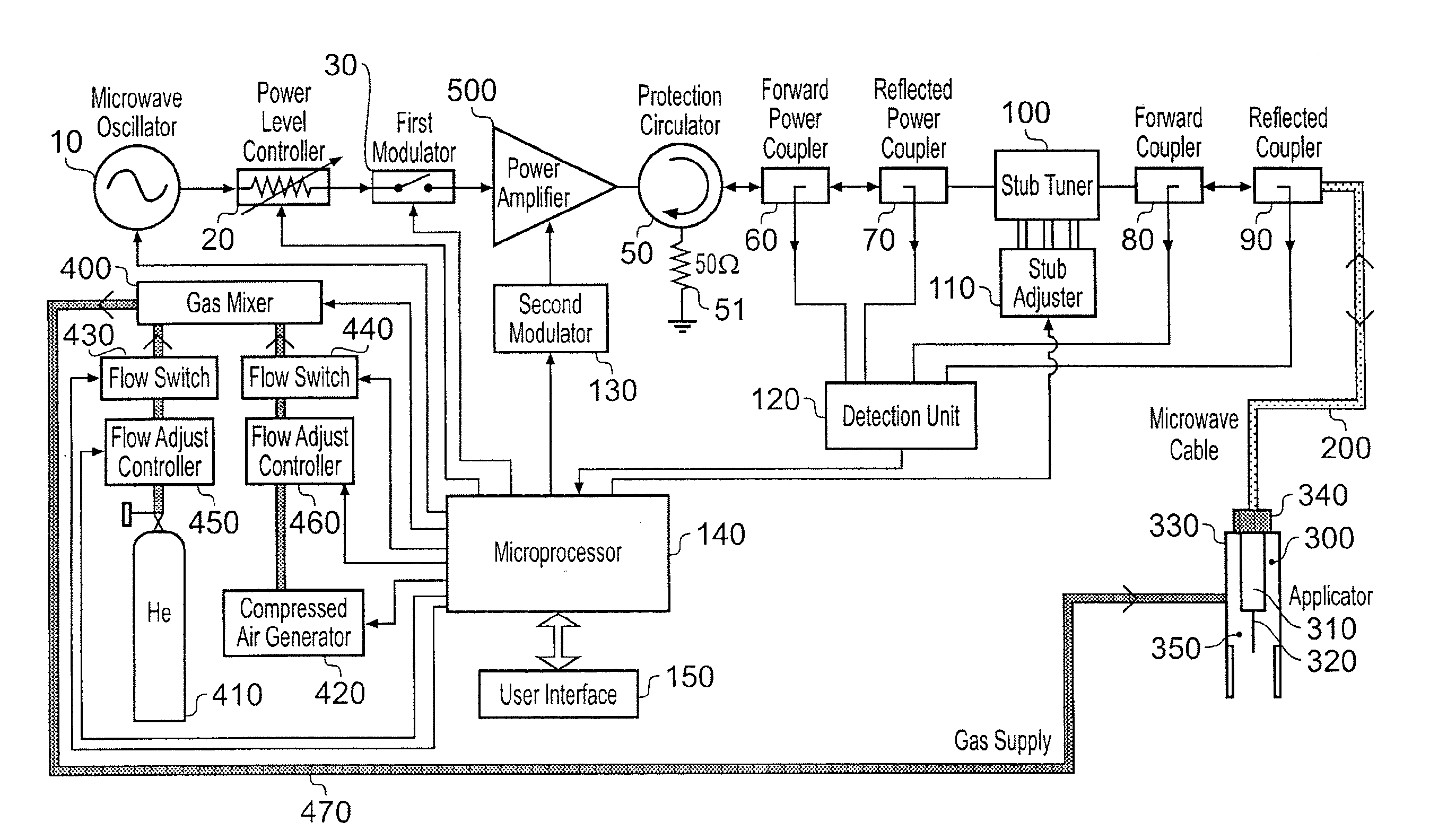
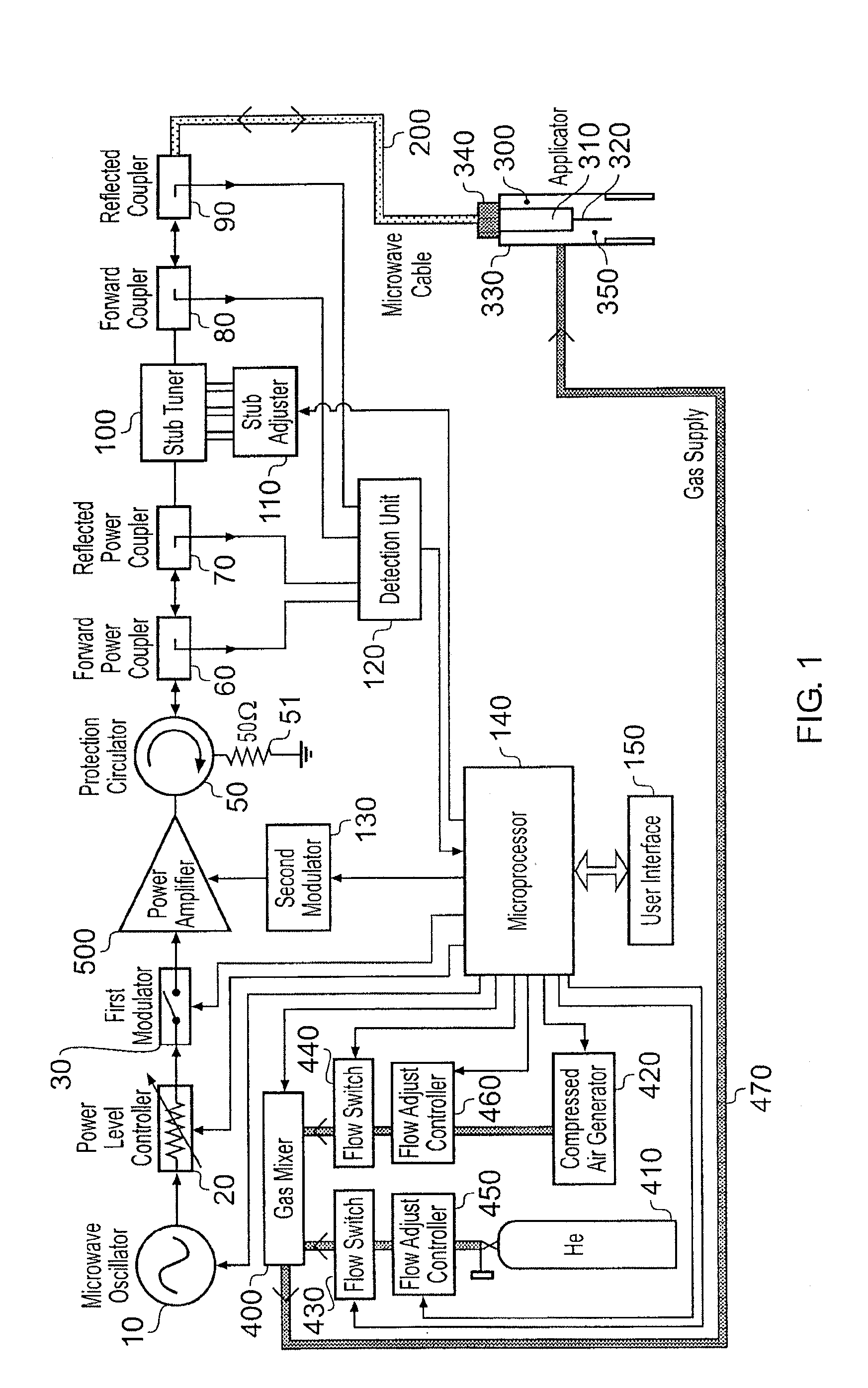
ActiveUS20100296977A1Avoid damageEasy to operateDisinfectionEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMicrowaveSurface plasmon
A sterilisation system having a controllable (e.g. adjustably modulatable) non-ionising microwave radiation source for providing microwave energy for combining with a gas (e.g. an inert gas or a mixture of inert gases) to produce atmospheric low temperature plasma for sterilising biological tissue surfaces or the like. A plasma generating region may be contained in a hand held plasma applicator. The system may include an impedance adjustor e.g. integrated in the plasma applicator arranged to set a plasma strike condition and plasma sustain condition. The gas and microwave energy may be transported to a plasma generating region along an integrated cable assembly. The integrated cable assembly may provide a two way gas flow arrangement to permit residual gas to be removed from the surface. Invasive surface plasma treatment is therefore possible. The plasma applicator may have multiple plasma emitters to produce a line or blanket of plasma.
Owner:CREO MEDICAL LTD
Vertical LED with conductive vias
ActiveUS20100213485A1Maximizing light extractionLight extraction efficiency can be improvedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface plasmonHigh reflectivity
A light emitting device comprises a novel low-loss array of conductive vias embedded in a dielectric multilayer stack, to act as an electrically-conductive, low-loss, high-reflectivity reflector layer (CVMR). In one example the CVMR stack is employed between a reflective metal bottom contact and a p-GaN semiconductor flip chip layer. The CVMR stack comprises at least (3) layers with at least (2) differing dielectric constants. The conductive vias are arranged such that localised and propagating surface plasmons associated with the structure reside within the electromagnetic stopband of the CVMR stack, which in turn inhibits trapped LED modes coupling into these plasmonic modes, thereby increasing the overall reflectivity of the CVM R. This technique improves optical light extraction and provides a vertical conduction path for optimal current spreading in a semiconductor light emitting device. A light emitting module and method of manufacture are also described.
Owner:LUMILEDS HLDG BV
Surface Plasmon Devices
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
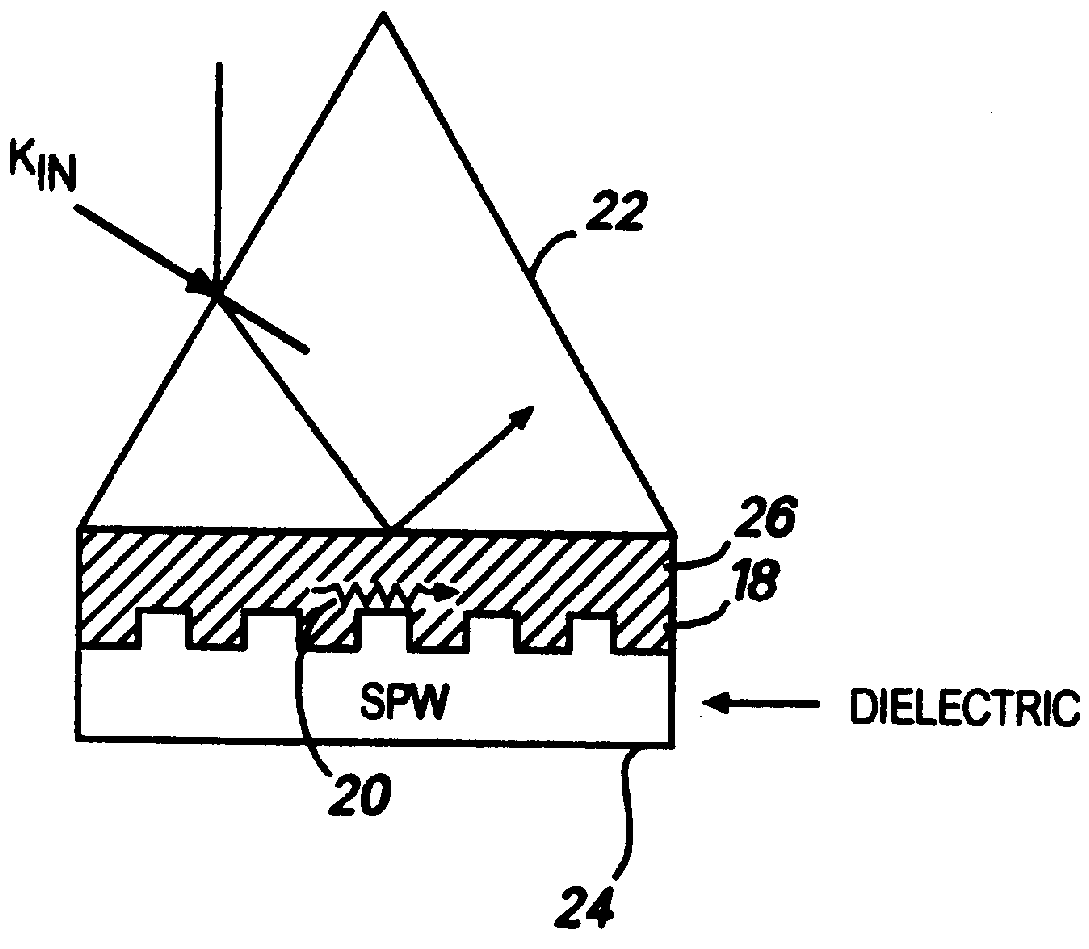
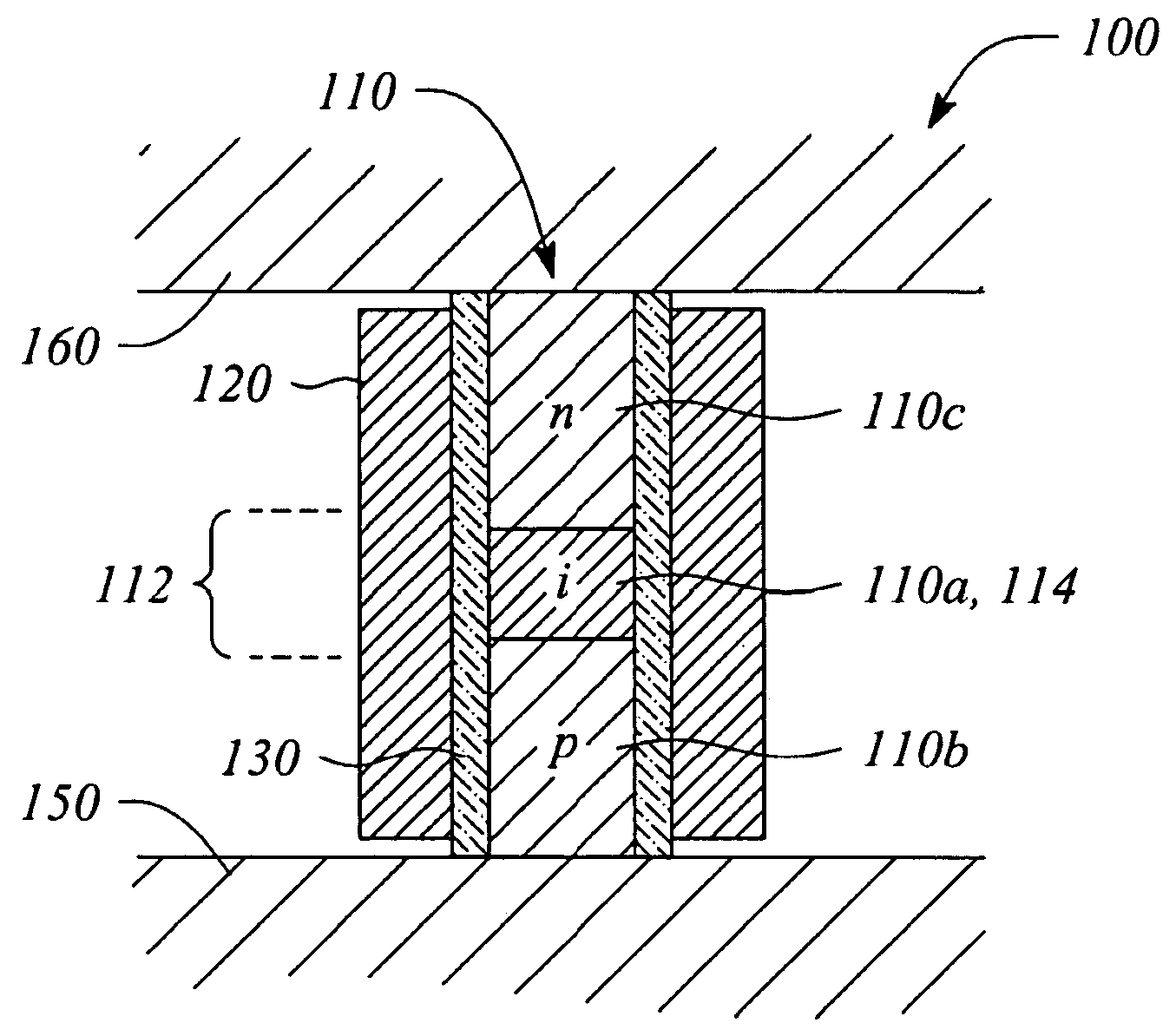
Optical plasmon-wave structures
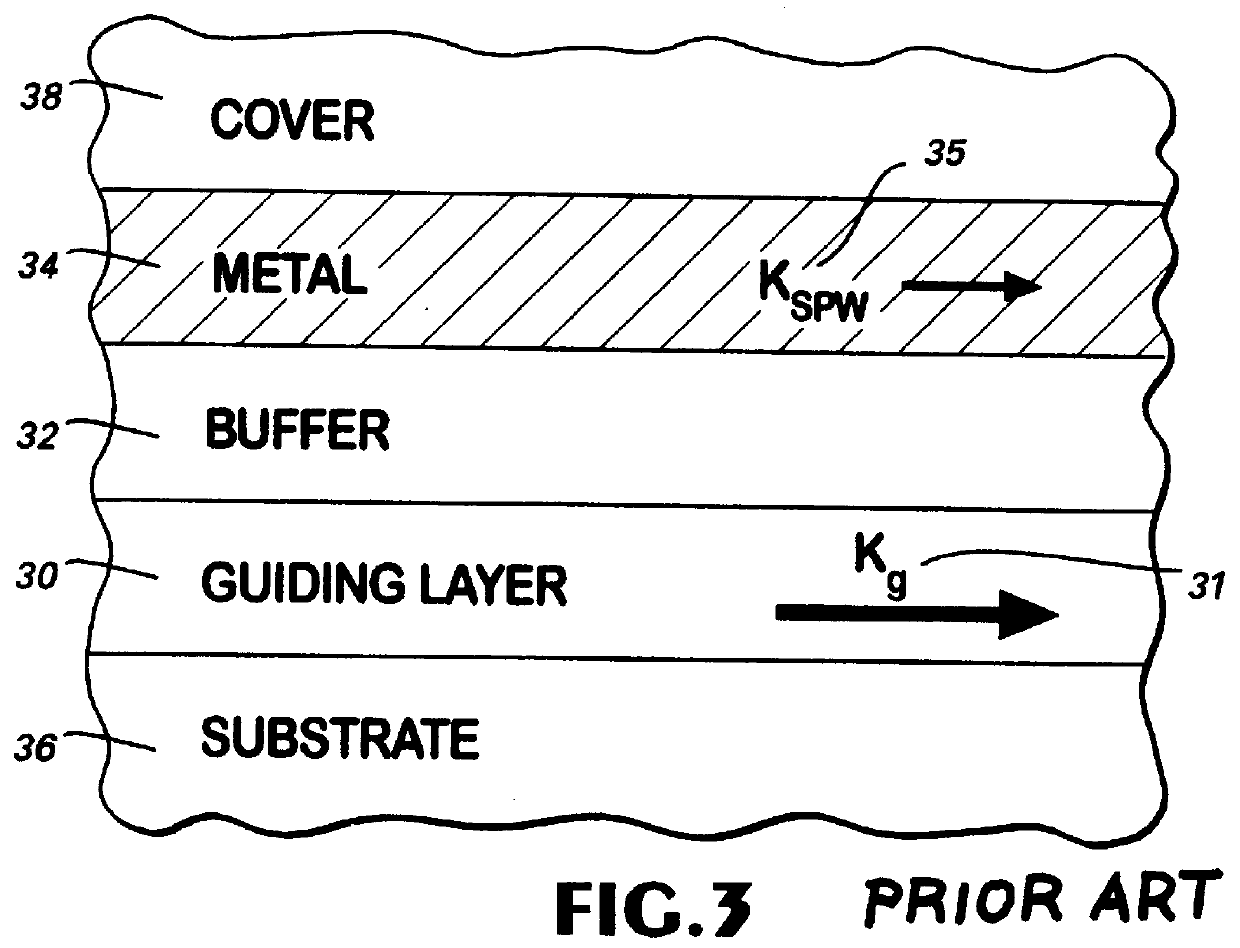
Optical plasmon-wave attenuator and modulator structures for controlling the amount of coupling between an guided optical signal and a surface plasmon wave. Optical power coupled to the plasmon wave mode is dissipated in varying amounts producing an intensity modulation effect on the optical signal. For electrical modulation, an additional dielectric (or polymer) layer with variable refractive index in optical contact with a metal layer supporting at least one plasmon wave mode is used to perturb or vary the propagation constant of plasmon wave. Propagation constant variation results in the power coupling variation between the surface plasmon wave and the optical wave. The refractive index variation of the dielectric (or polymer) layer can be accomplished via an electro-optic traveling-wave, a lump-element, or any other integrated optics modulator configuration situated to affect the layer, thereby permitting data rates into tens of GHz. Because of the extremely small interaction lengths needed, the optical plasmon-wave modulator is a very compact device which can be implemented on the top of a fiber or as an integrated optical planar structure.
Owner:VERIFIBER TECH
Spatial light modulators, holographic 3-dimensional display apparatuses including the spatial light modulators, and methods of modulating spatial light
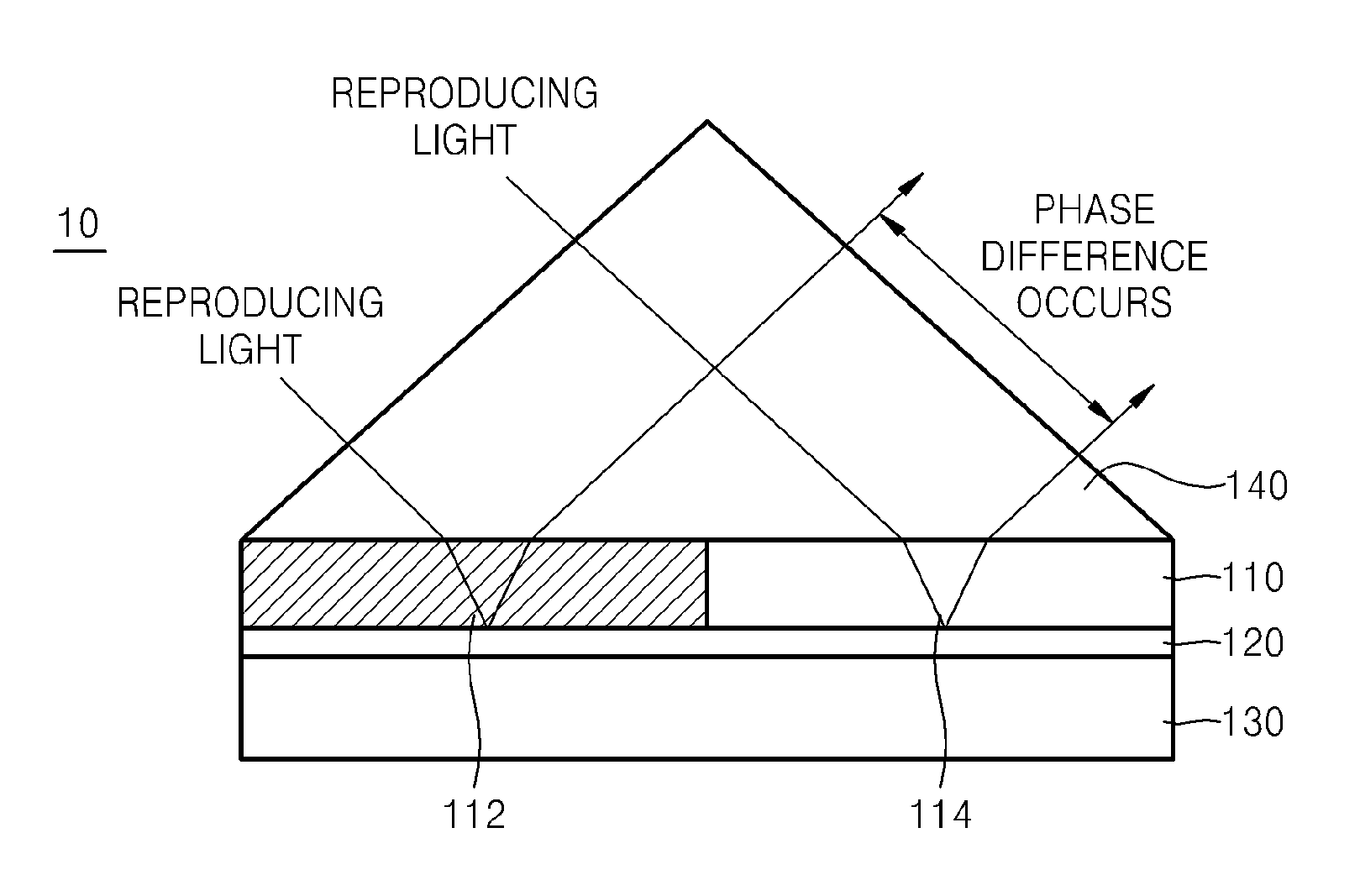
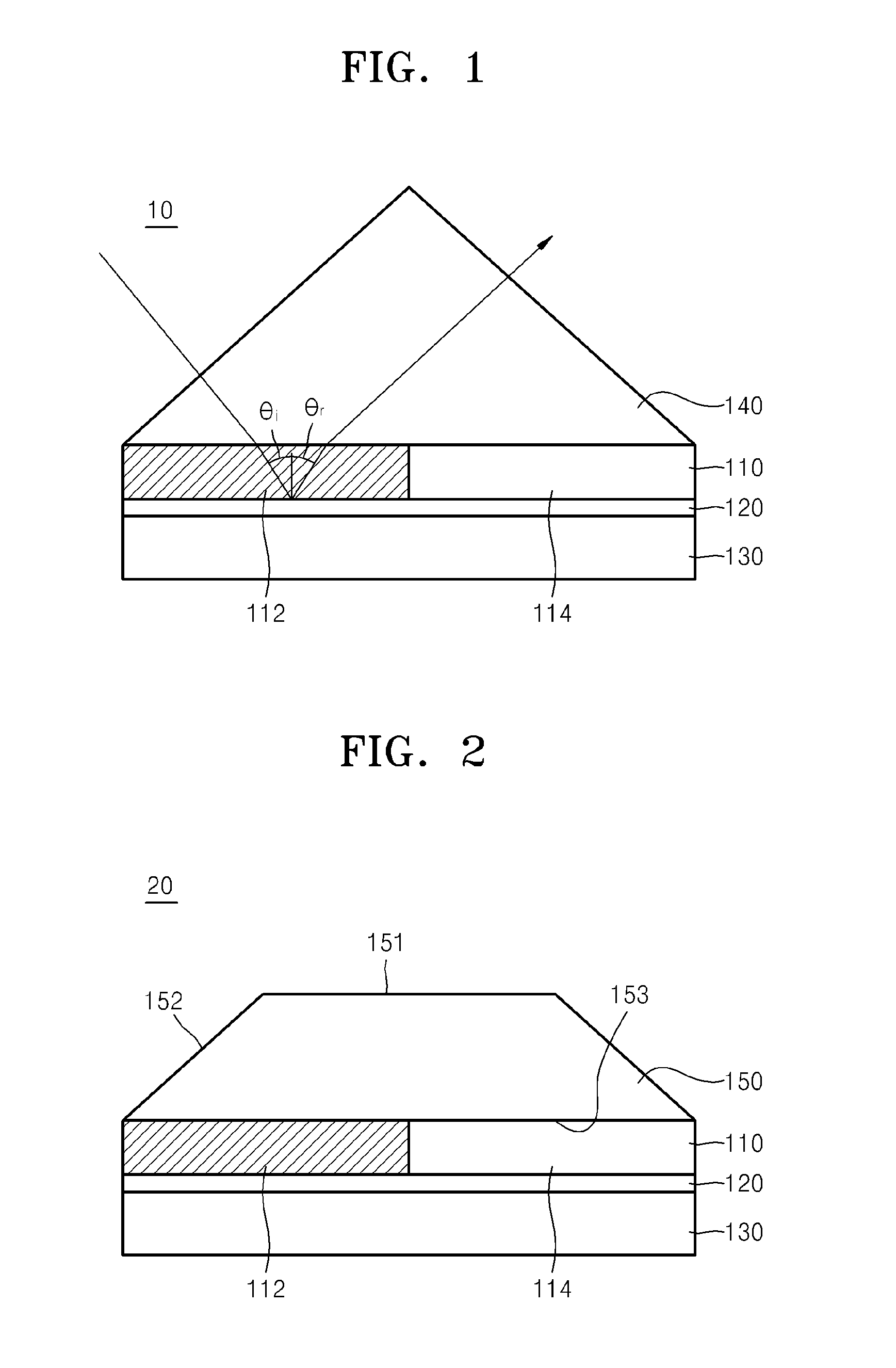
ActiveUS20130094069A1Active addressable light modulatorNon-linear opticsSpatial light modulatorPhase difference
A spatial light modulator may include a refraction layer including first and second regions with refractive indices different from each other; and / or a metal thin film on a lower face of the refraction layer configured to generate surface plasmons due to light incident on the metal thin film via the refraction layer. When first light is incident on the refraction layer, a phase difference between light reflected by the first and second regions may occur. A spatial light modulator may include a metal thin film and a refraction layer on the metal thin film. The refraction layer may include a first region with a first refractive index and a second region with a second refractive index different from the first refractive index. When first light is incident on the refraction layer, there may be a phase difference between light reflected from the first and second regions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
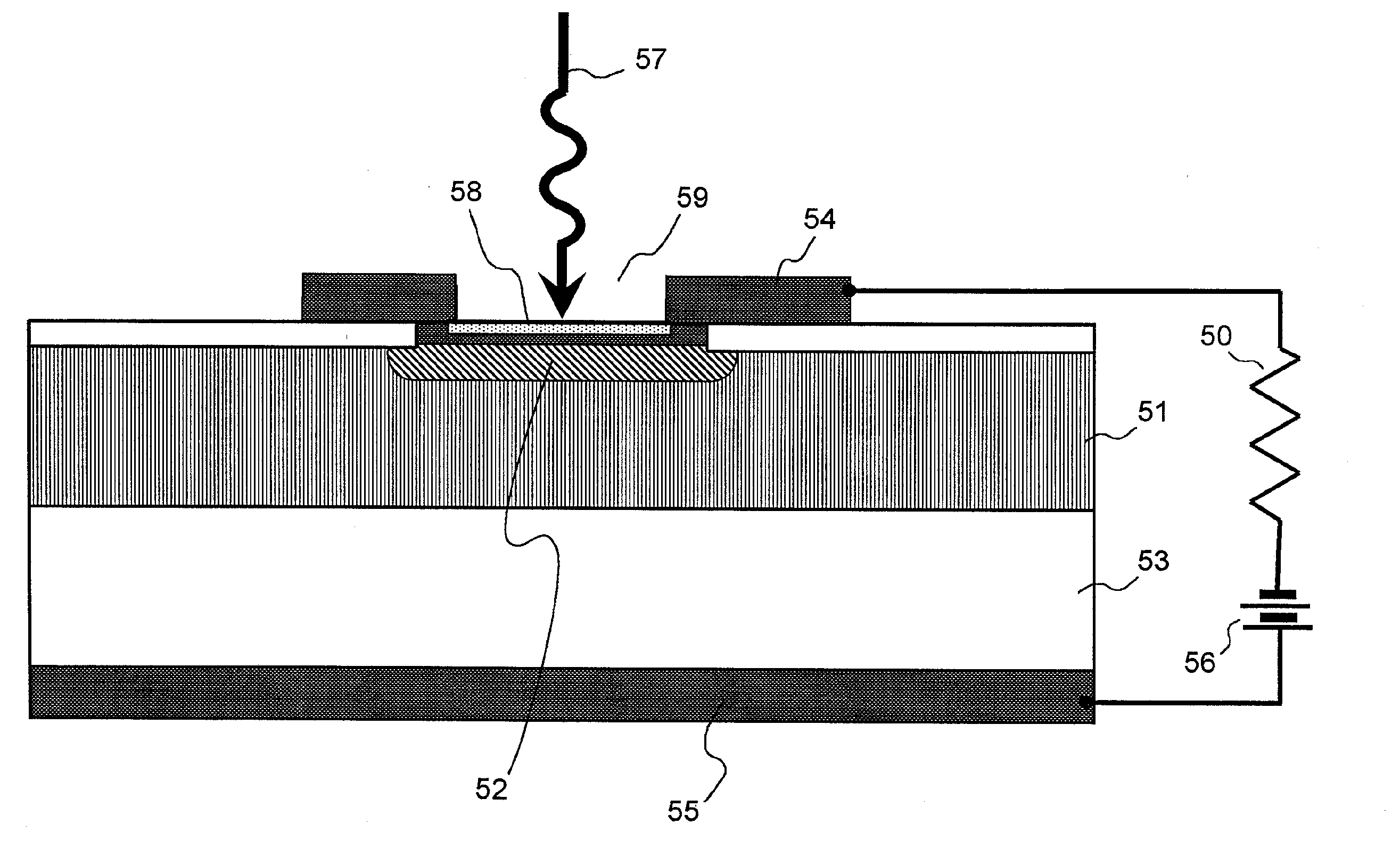
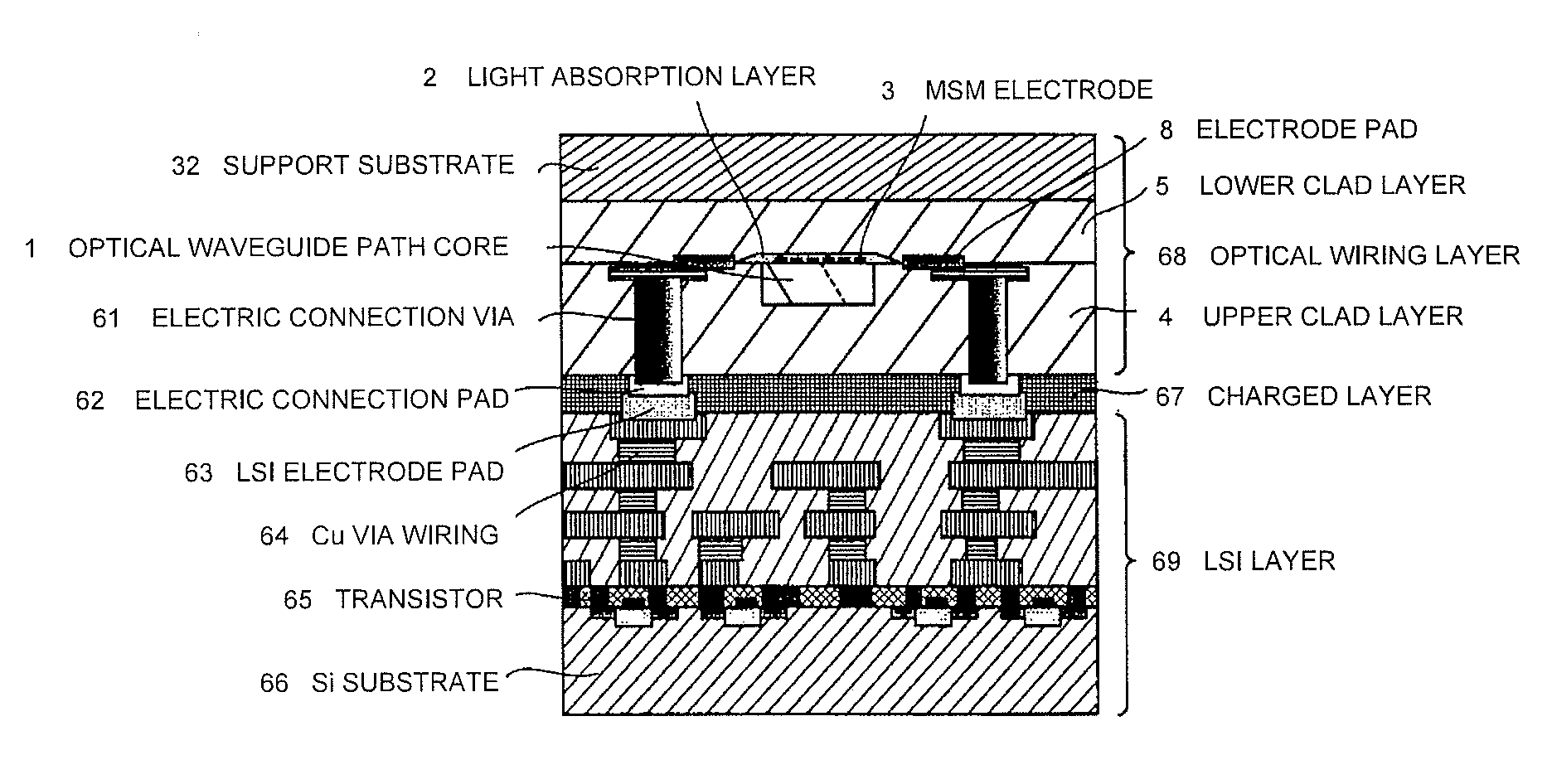
Photodiode and method for fabricating same
InactiveUS20070194357A1High speed responseImprove load resistanceSemiconductor devicesSurface plasmonSchottky photodiode
A Schottky photodiode includes a semiconductor layer and a conductive film provided in contact with the semiconductor layer. The conductive film has an aperture and a periodic structure provided around said aperture for producing a resonant state by an excited surface plasmon in a film surface of the conductive film by means of the incident light to the film surface. The photodiode detects near-field light that is generated by at the interface between the conductive film and semiconductor layer the excited surface plasmon. The aperture has a diameter smaller than the wavelength of the incident light.
Owner:NEC CORP
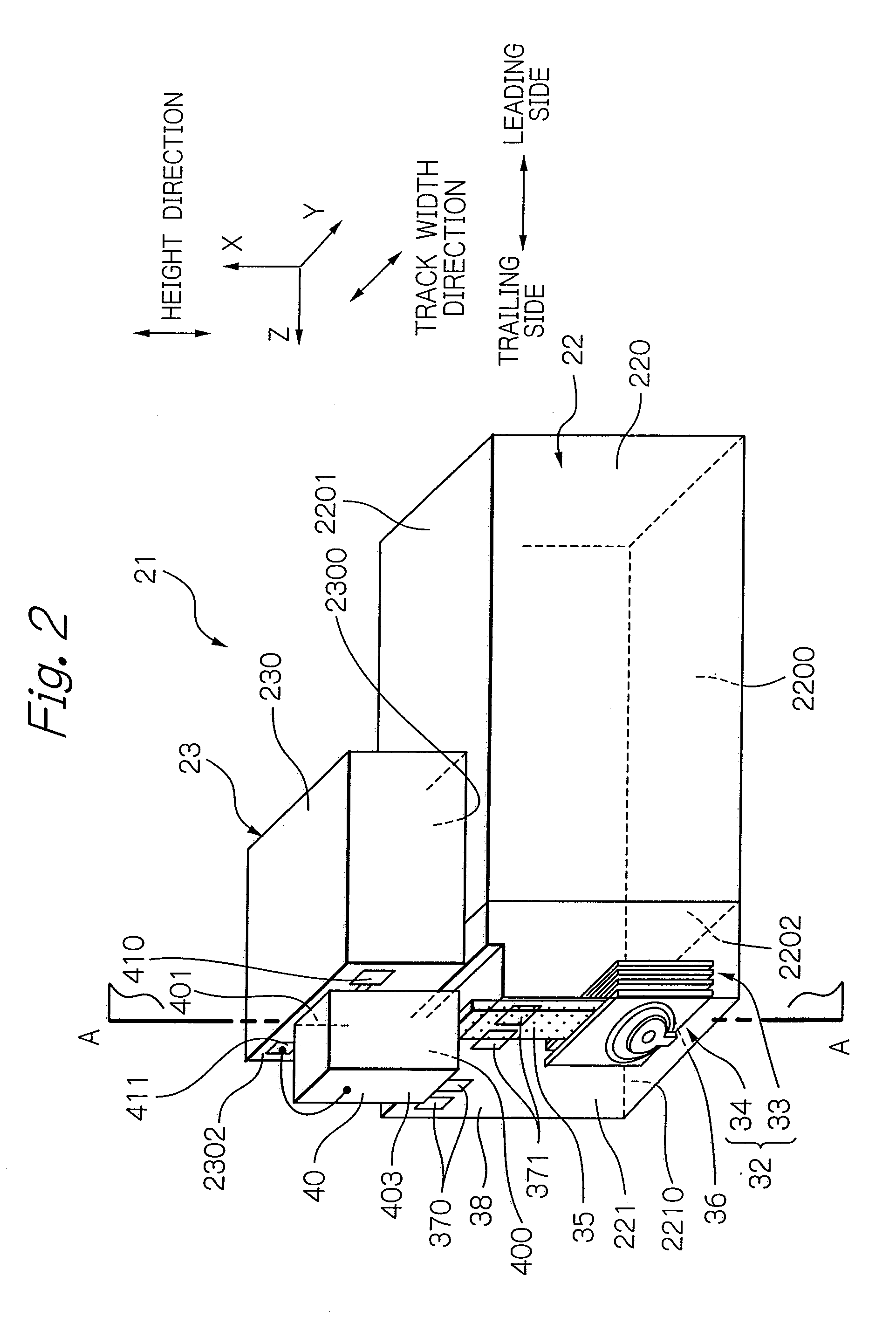
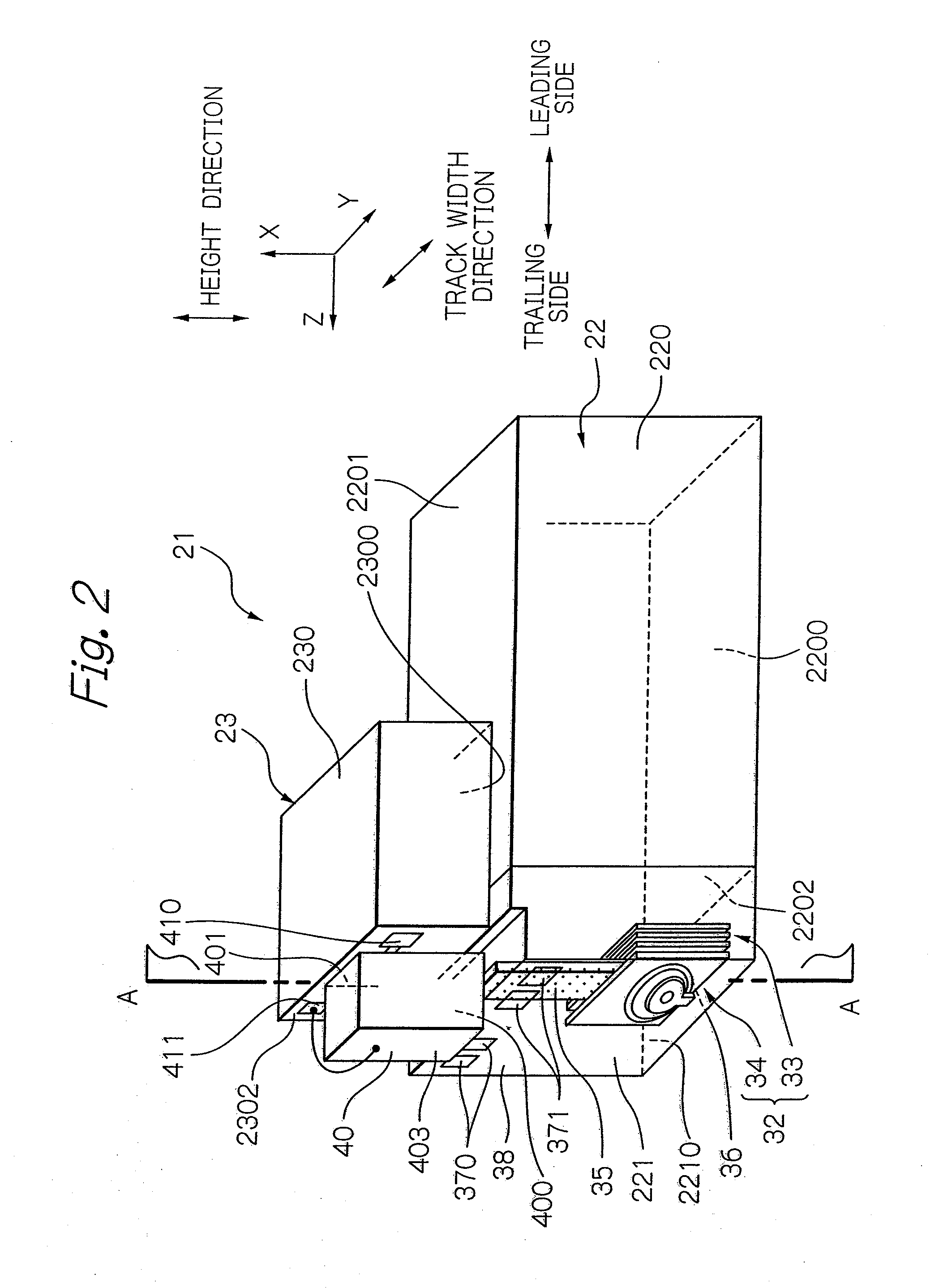
Head for thermal assisted magnetic recording device, and thermal assisted magnetic recording device
InactiveUS20110170381A1Improve performanceInhibit temperature riseCombination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingSurface plasmon
An optical near-field generating efficiency of an optical near-field generating element is improved and a temperature rise of the element is suppressed. An optical near-field is generated using a conductive structure having a cross-sectional shape whose width in a direction perpendicular to a polarization direction of incident light transmitted through a waveguide gradually becomes shorter toward a vertex where an optical near-field is generated and having a shape whose width gradually, or in stages, becomes smaller in a traveling direction of the incident light toward the vertex where an optical near-field is generated. The waveguide is arranged beside the conductive structure and an optical near-field is generated via a surface plasmon generated on a lateral face of the conductive structure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
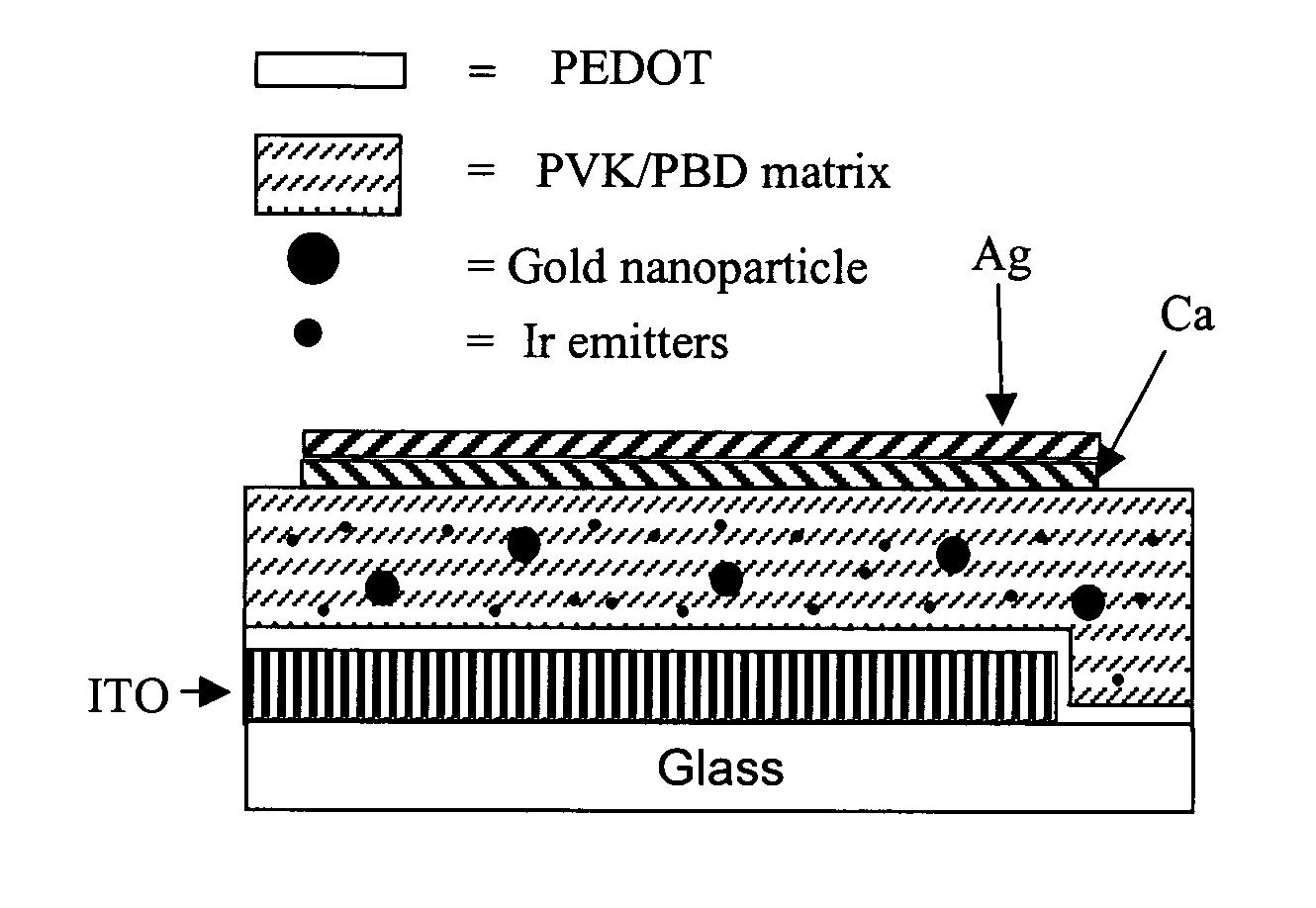
Plasmon assisted enhancement of organic optoelectronic devices
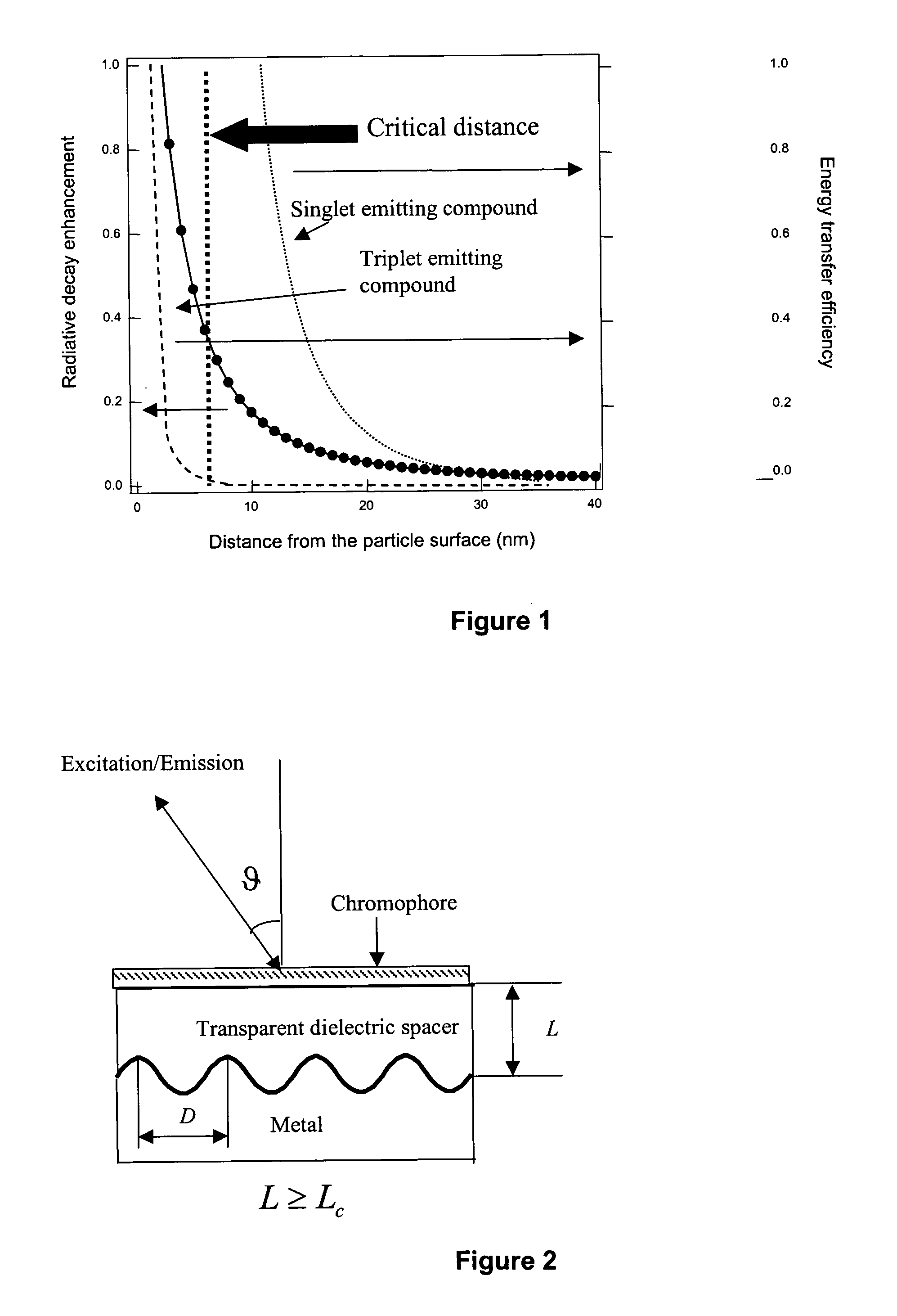
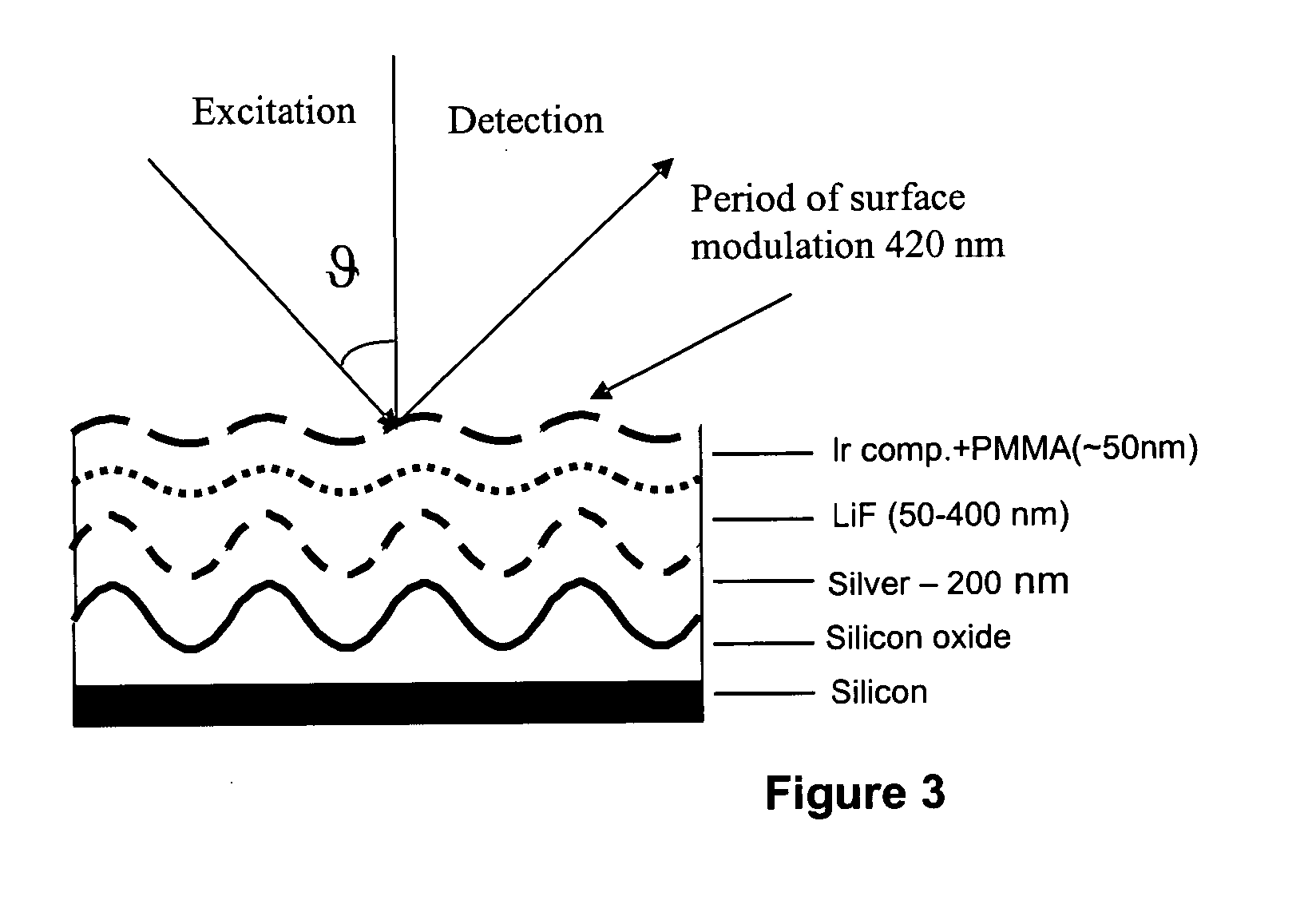
InactiveUS20050035346A1Enhanced and controllable rate of radiative relaxationImprove launch performanceMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesOscillator strengthLight emitter
Optoelectronic devices and methods for their fabrication having enhanced and controllable rates of the radiative relaxation of triplet light emitters are provided exemplified by organic light emitting devices based on phosphorescent materials with enhanced emission properties. Acceleration of the radiative processes is achieved by the interaction of the light emitting species with surface plasmon resonances in the vicinity of metal surfaces. Non-radiative Förster-type processes are efficiently suppressed by introducing a transparent dielectric or molecular layer between the metal surface and the chromophore. For materials with low emission oscillator strengths (such as triplet emitters), the optimal separation distance from the metal surface is determined, thus suppressing energy transfer and achieving a significant acceleration of the emission rate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
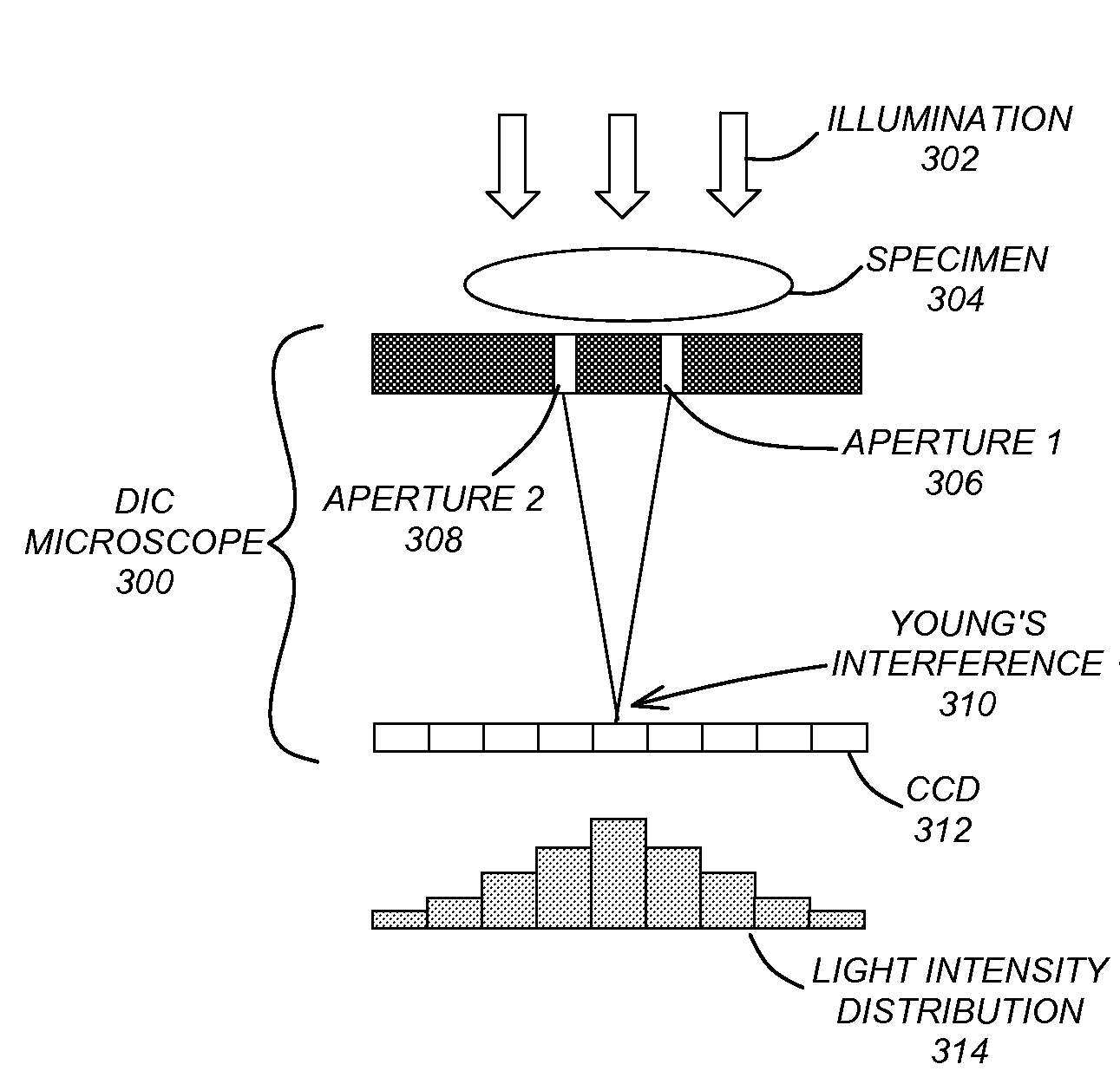
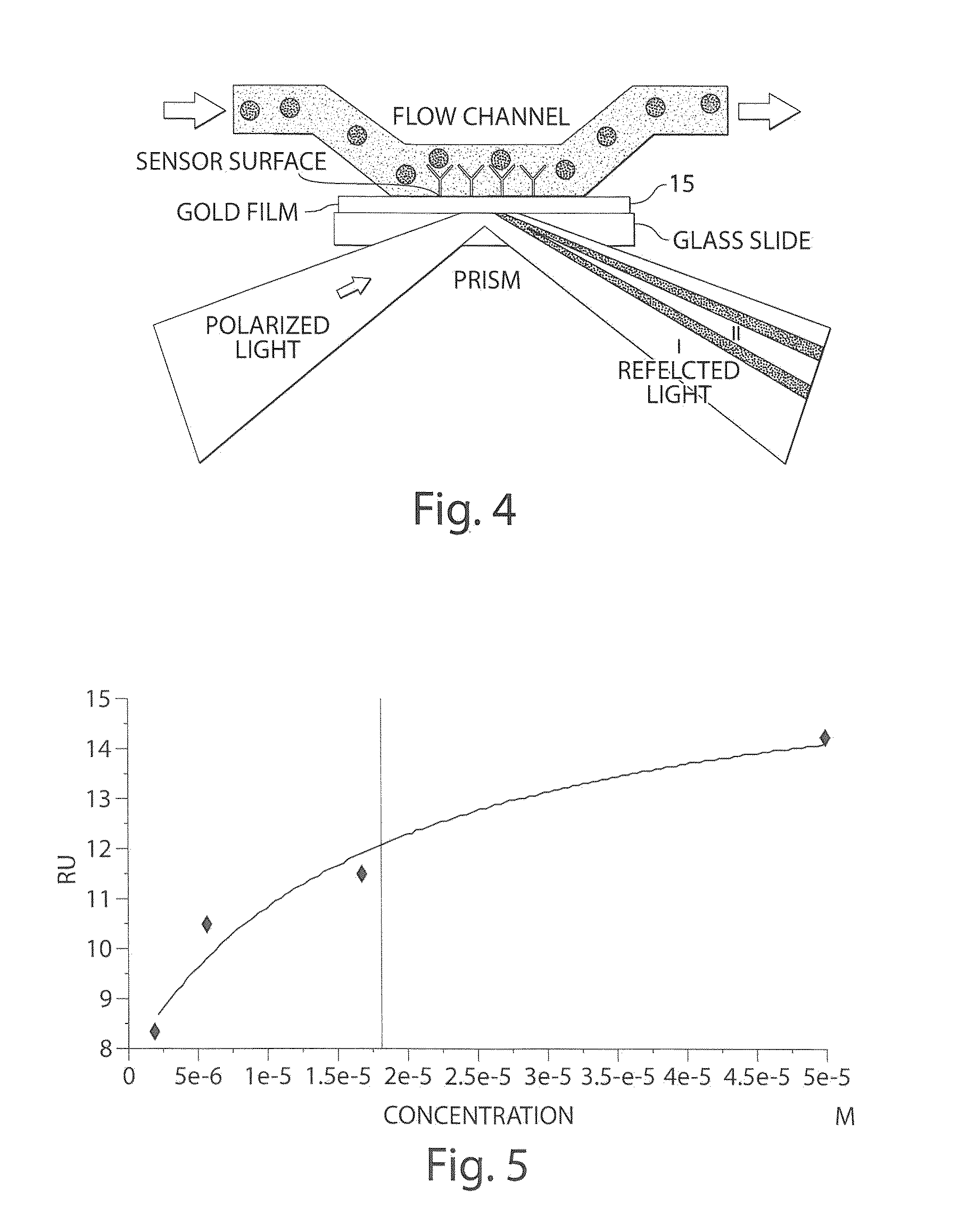
On-chip phase microscope/beam profiler based on differential interference contrast and/or surface plasmon assisted interference
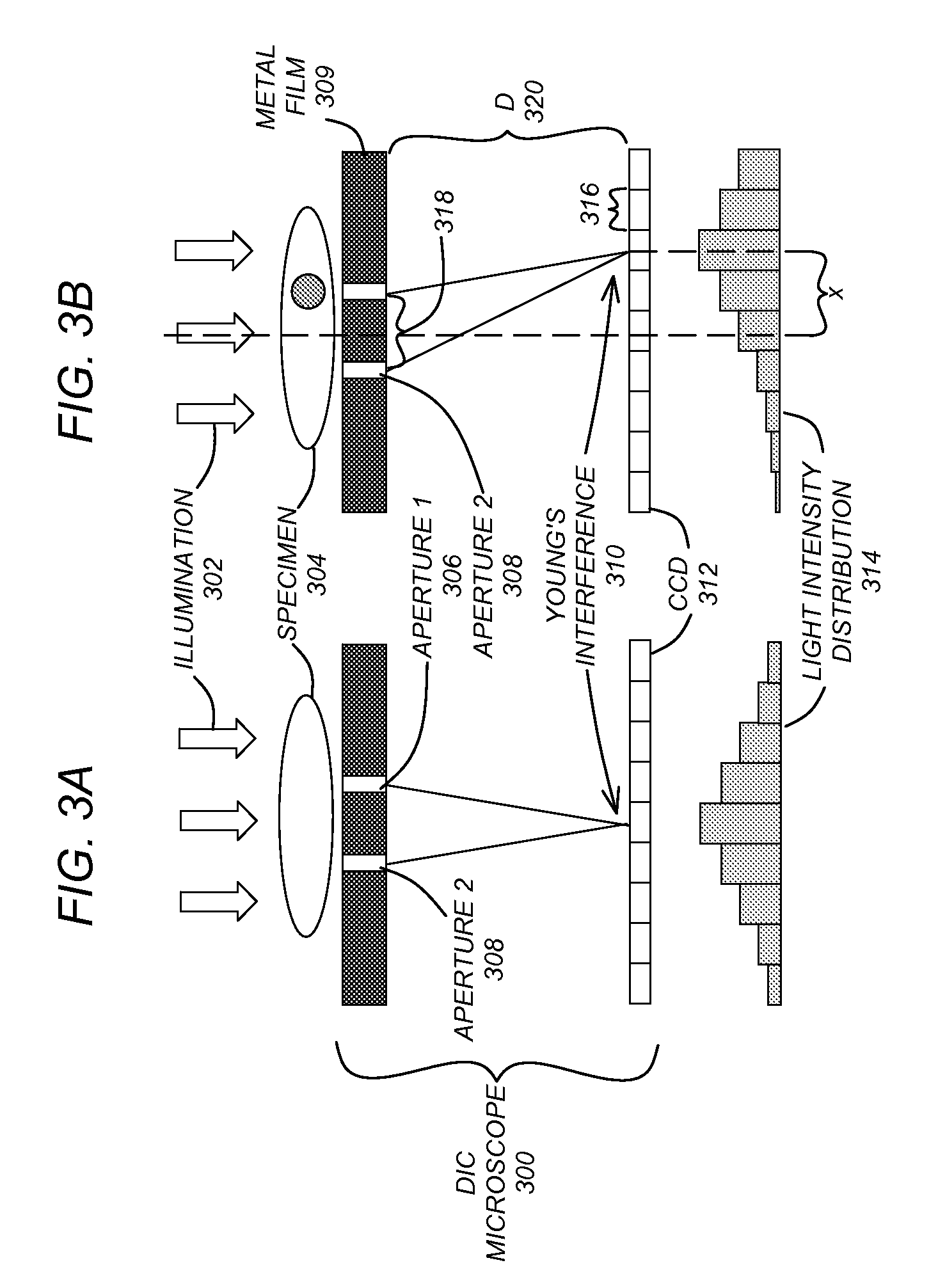
InactiveUS20070258096A1Image is limitedEasy to integrateMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A differential interference contrast (DIC) determination device and method utilizes an illumination source, a layer having a pair of two apertures that receive illumination from the illumination source, and a photodetector to receive Young's interference from the illumination passing through the pair of two apertures. In addition, a surface plasmon assisted optofluidic microscope and method utilize an illumination source, a fluid channel having a layer with at least one aperture as a surface, and a photodetector that receives a signal based on the illumination passing through the aperture. The layer is corrugated (e.g., via fabrication) and parameters of the corrugation optimize the signal received on the photodetector.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Surface plasmon wavelength converter
InactiveUS20100126566A1Light demodulationPhotovoltaic energy generationSurface plasmonElectromagnetic radiation
A surface plasmon wavelength converter device includes a metallic film which has a plurality of nanofeatures. A wavelength conversion layer having a plurality of centers is disposed adjacent to the metallic film. The surface plasmon wavelength converter device is configured to respond to an incident electromagnetic radiation having a first wavelength by radiating away from the surface plasmon wavelength converter device an electromagnetic radiation having a second wavelength. A surface plasmon wavelength converter device having a metallic film and at least one center disposed in at least one of a plurality of nanofeatures of the metallic film is also described. A surface plasmon wavelength converter device having a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) film having a plurality of metallic nanofeatures, adjacent to a wavelength conversion layer, and a TCO film having a plurality of metallic nanofeatures with at least one center disposed therein is also described.
Owner:LIGHTWAVE POWER
Efficient color display using low-absorption in-pixel color filters
InactiveUS6097456AImprove efficiencyTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesSurface plasmonLight beam
A display system having a non-absorbing and reflective color filtering array and a reflector to improve light utilization efficiency. One implementation of the color filtering array uses a surface plasmon filter having two symmetric metal-dielectric interfaces coupled with each other to produce a transmission optical wave at a surface plasmon resonance wavelength at one interface from a p-polarized input beam on the other interface. Another implementation of the color filtering array uses a metal-film interference filter having two dielectric layers and three metallic films.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
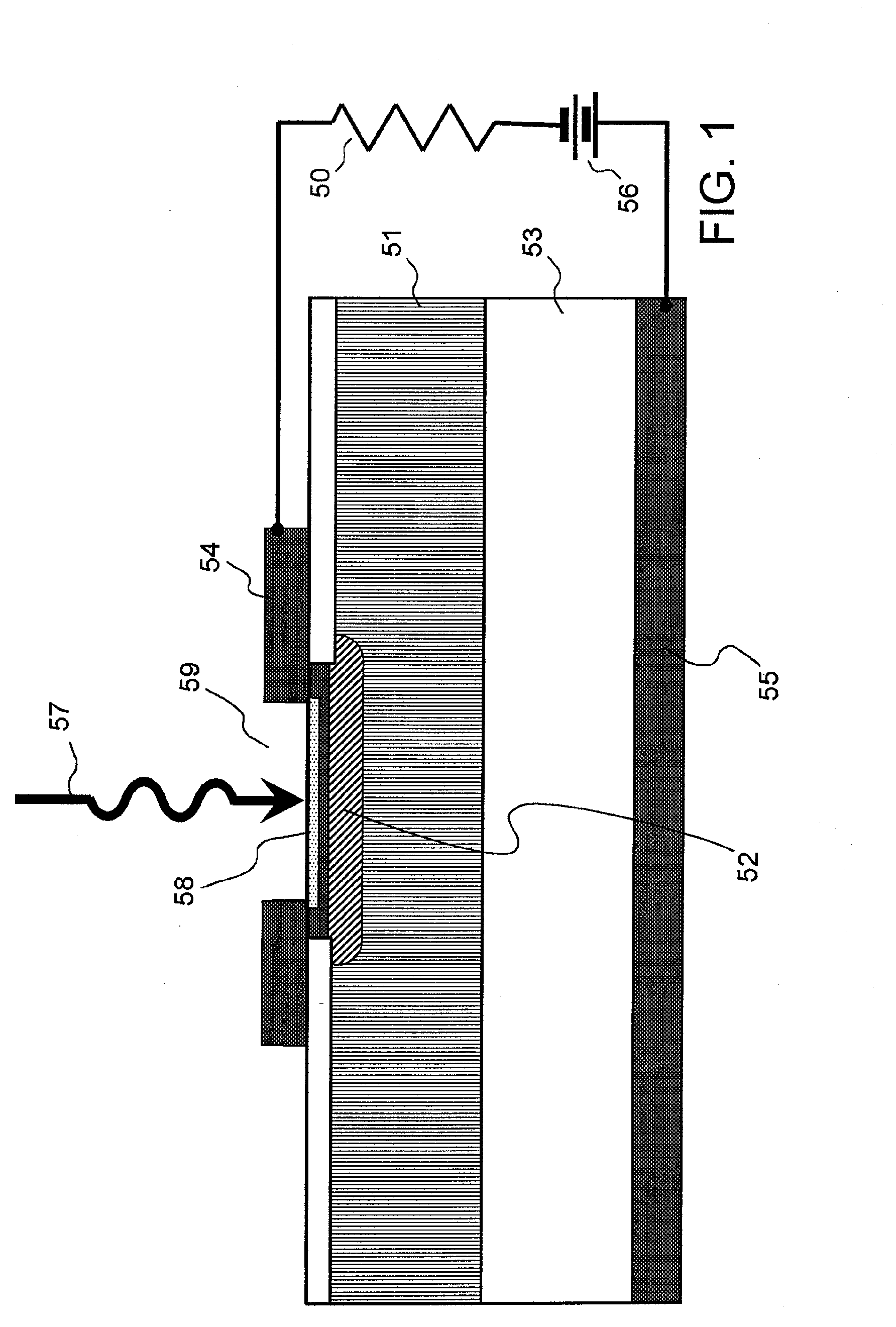
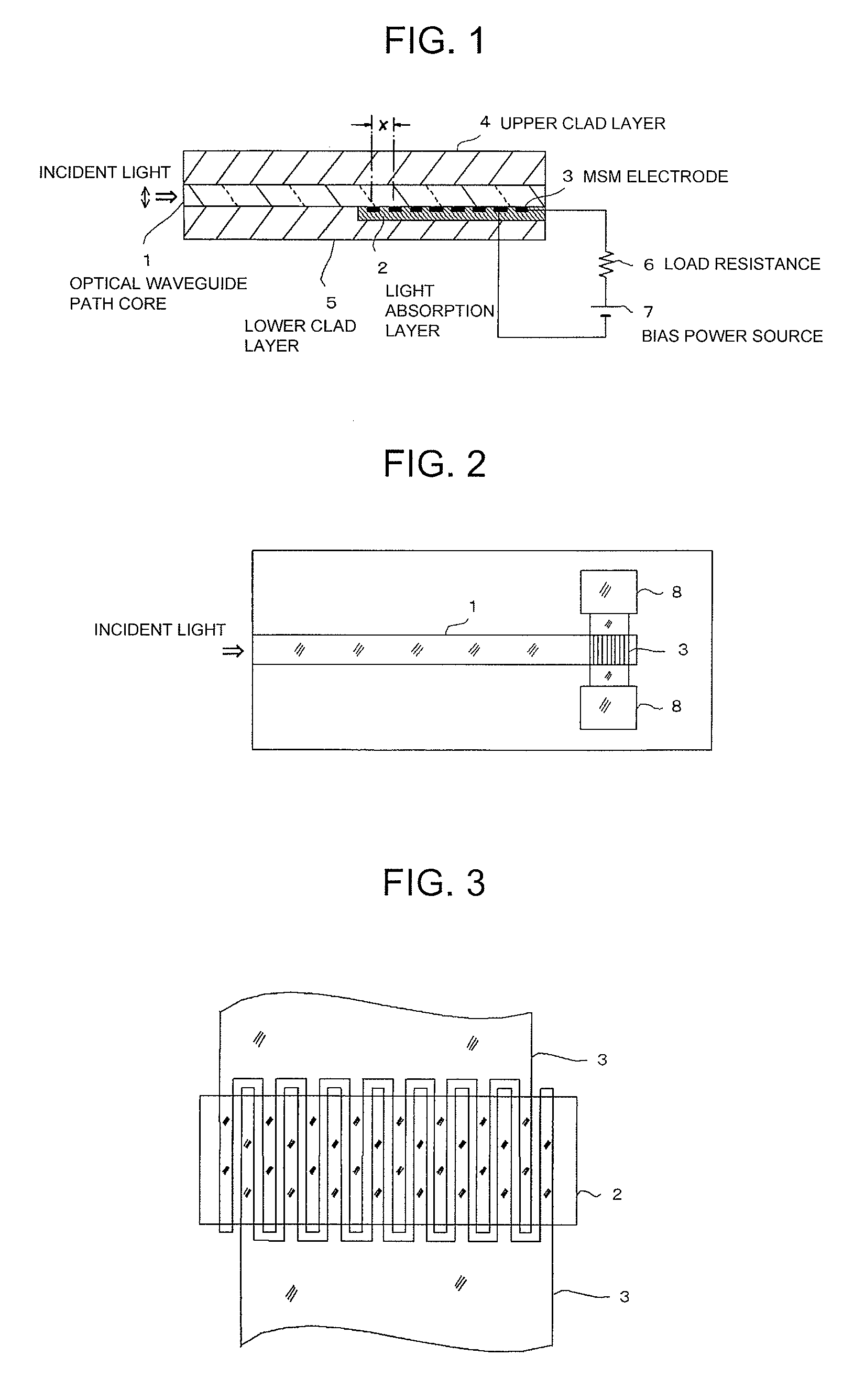
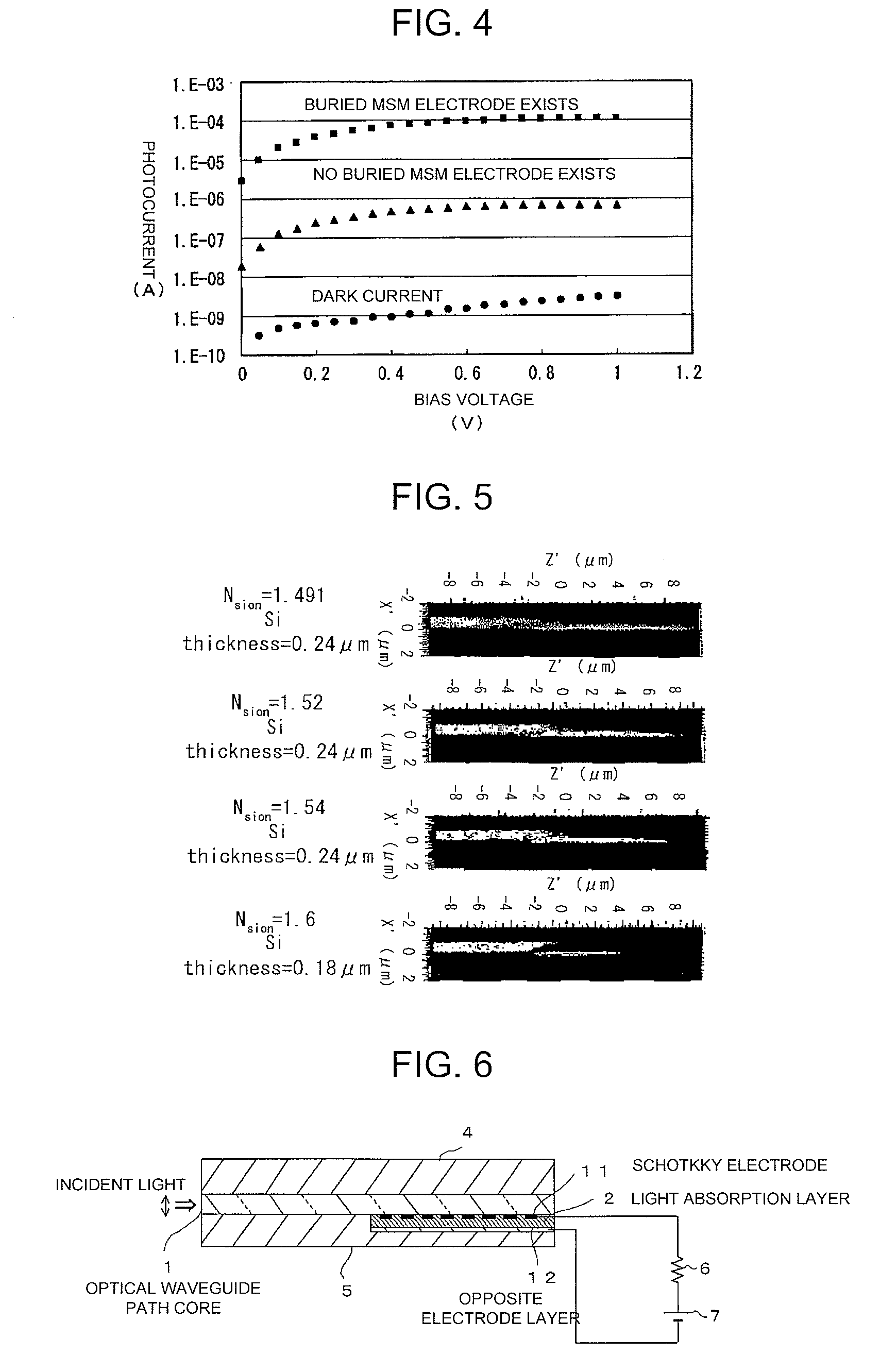
Photodiode, method for manufacturing such photodiode, optical communication device and optical interconnection module
InactiveUS20090134486A1Valid conversionLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSurface plasmonRefractive index
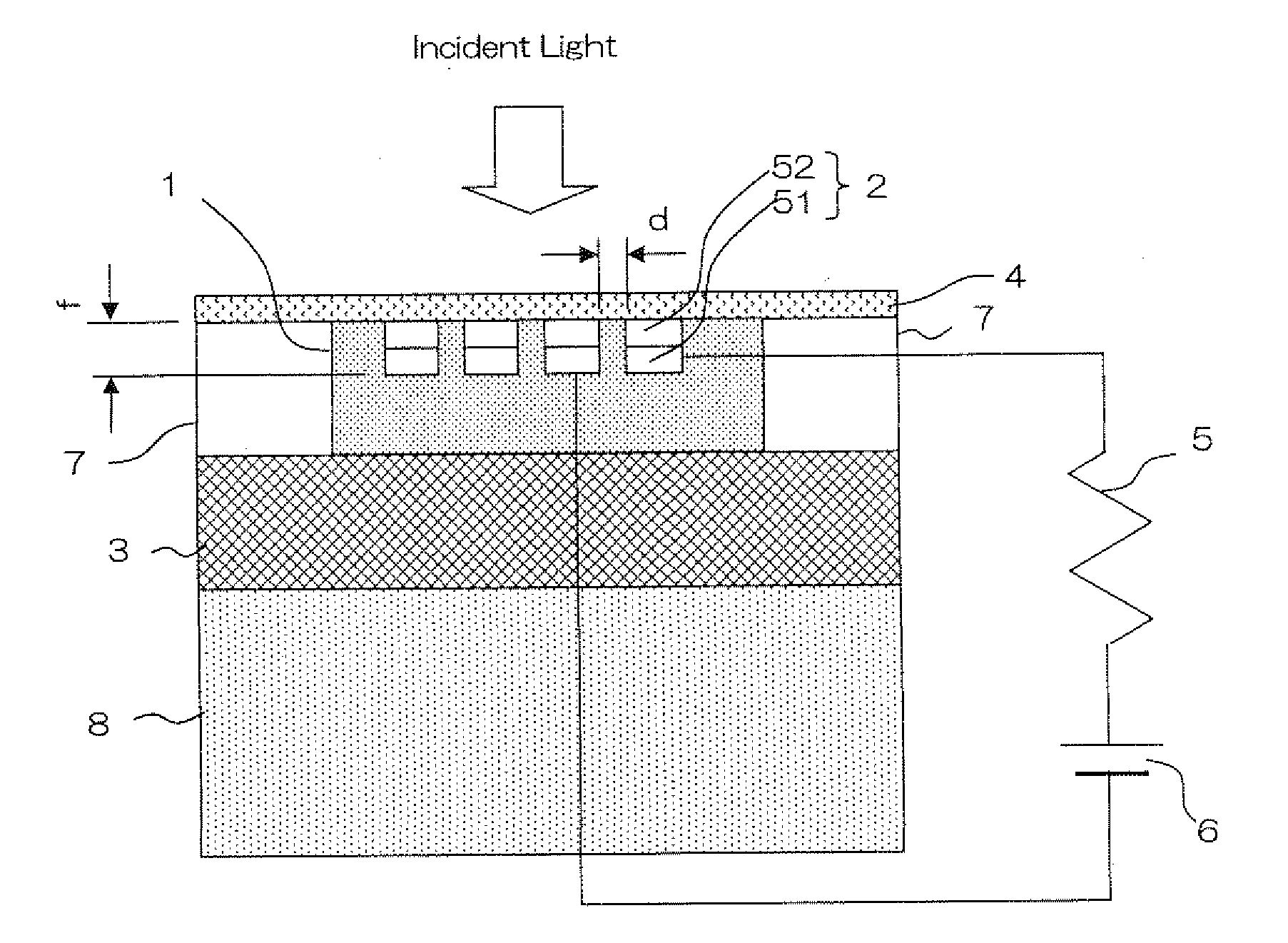
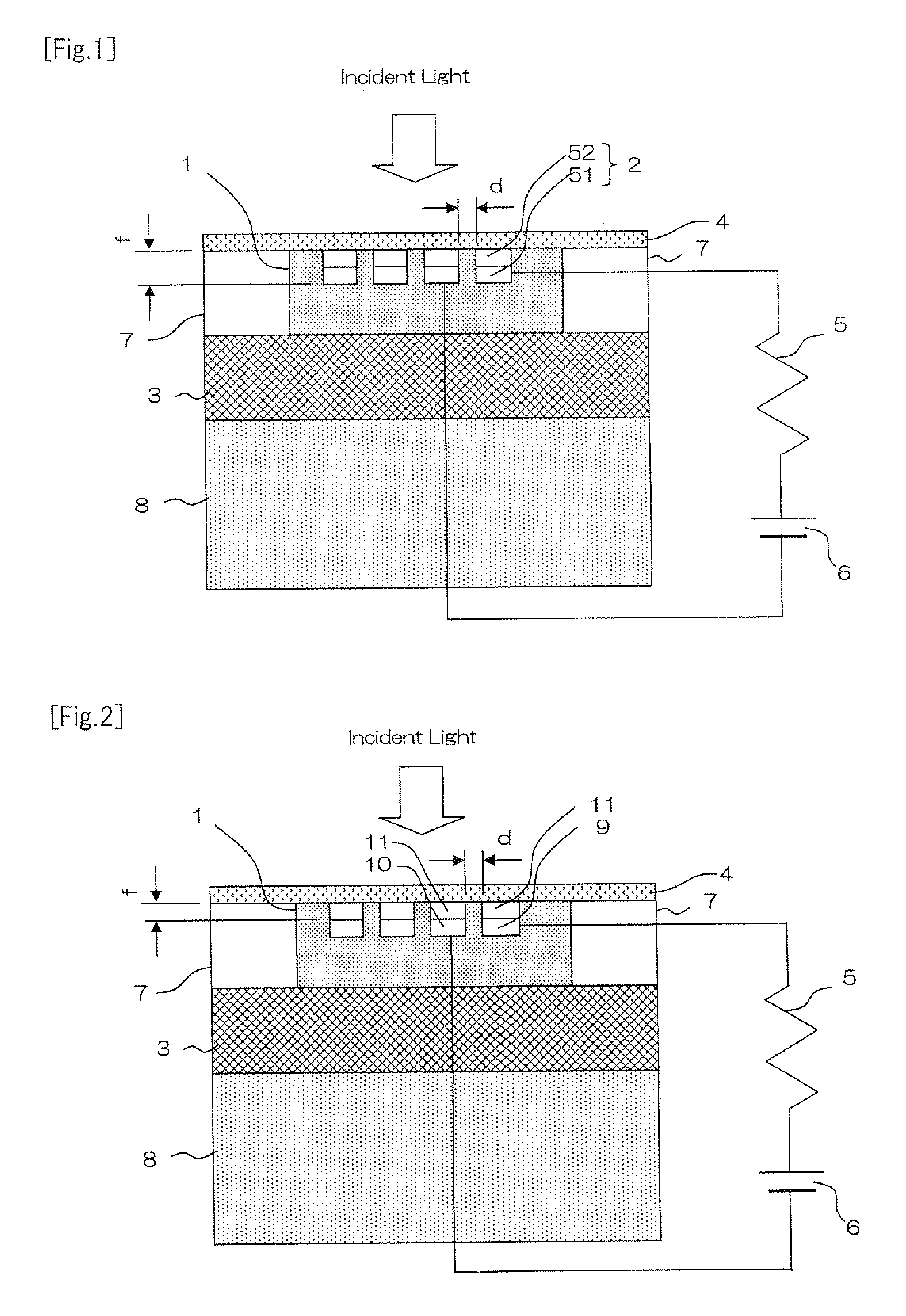
Both high light receiving sensitivity and high speed of a photodiode are achieved at the same time. The photodiode is provided with a semiconductor layer (1) and a pair of metal electrodes (2) which are arranged on the surface of the semiconductor layer (1) at an interval (d) and form an MSM junction. The interval (d) satisfies the relationship of λ>d>λ100, where λ is the wavelength of incident light. The metal electrodes (2) can induce surface plasmon. At least one of the electrodes forms a Schottky junction with the semiconductor layer (1), and a low end portion is embedded in the semiconductor layer (1) to a position at a depth less than λ / 2n, where n is the refractive index of the semiconductor layer (1).
Owner:NEC CORP
Vertical tri-color sensor
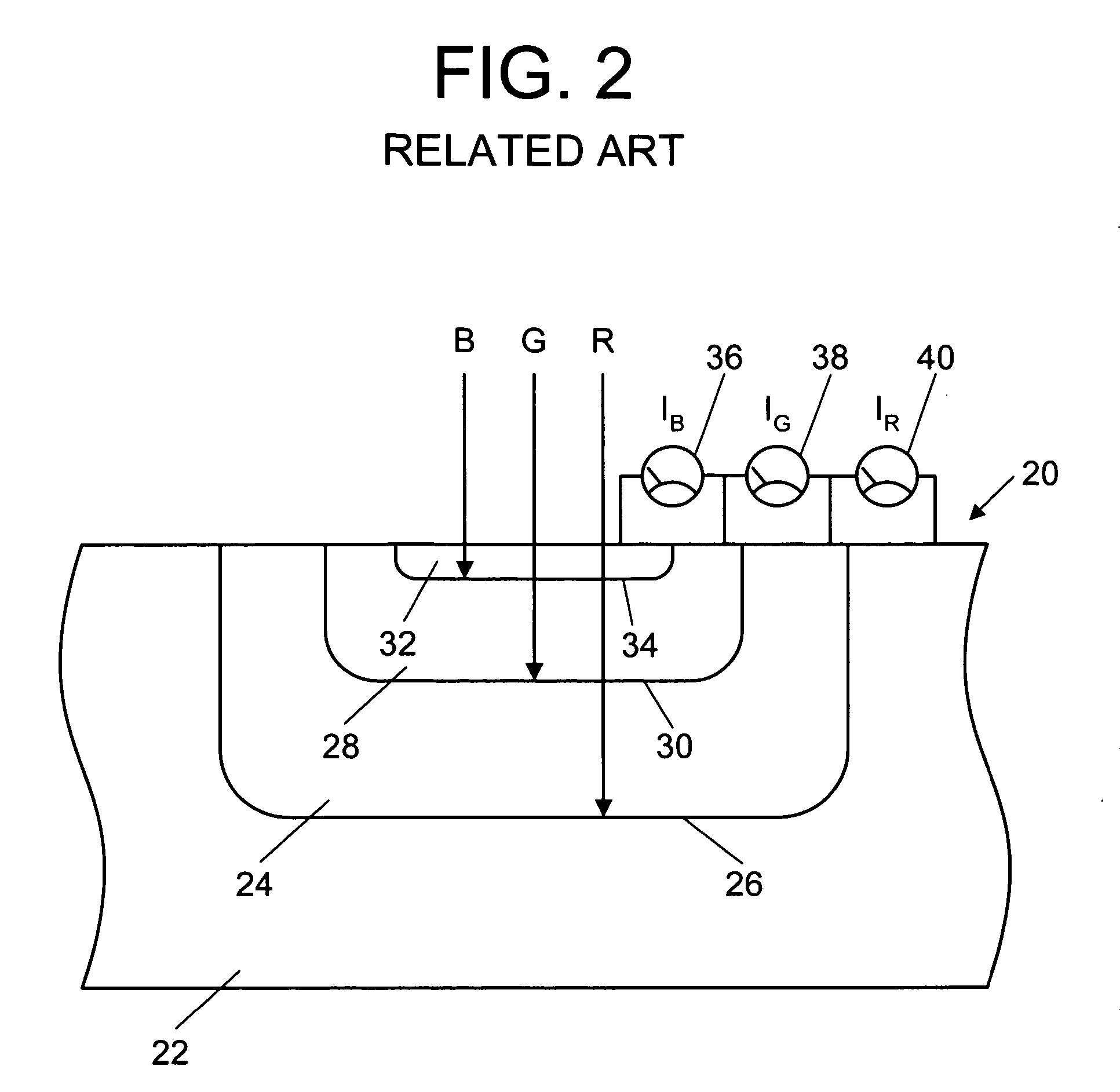
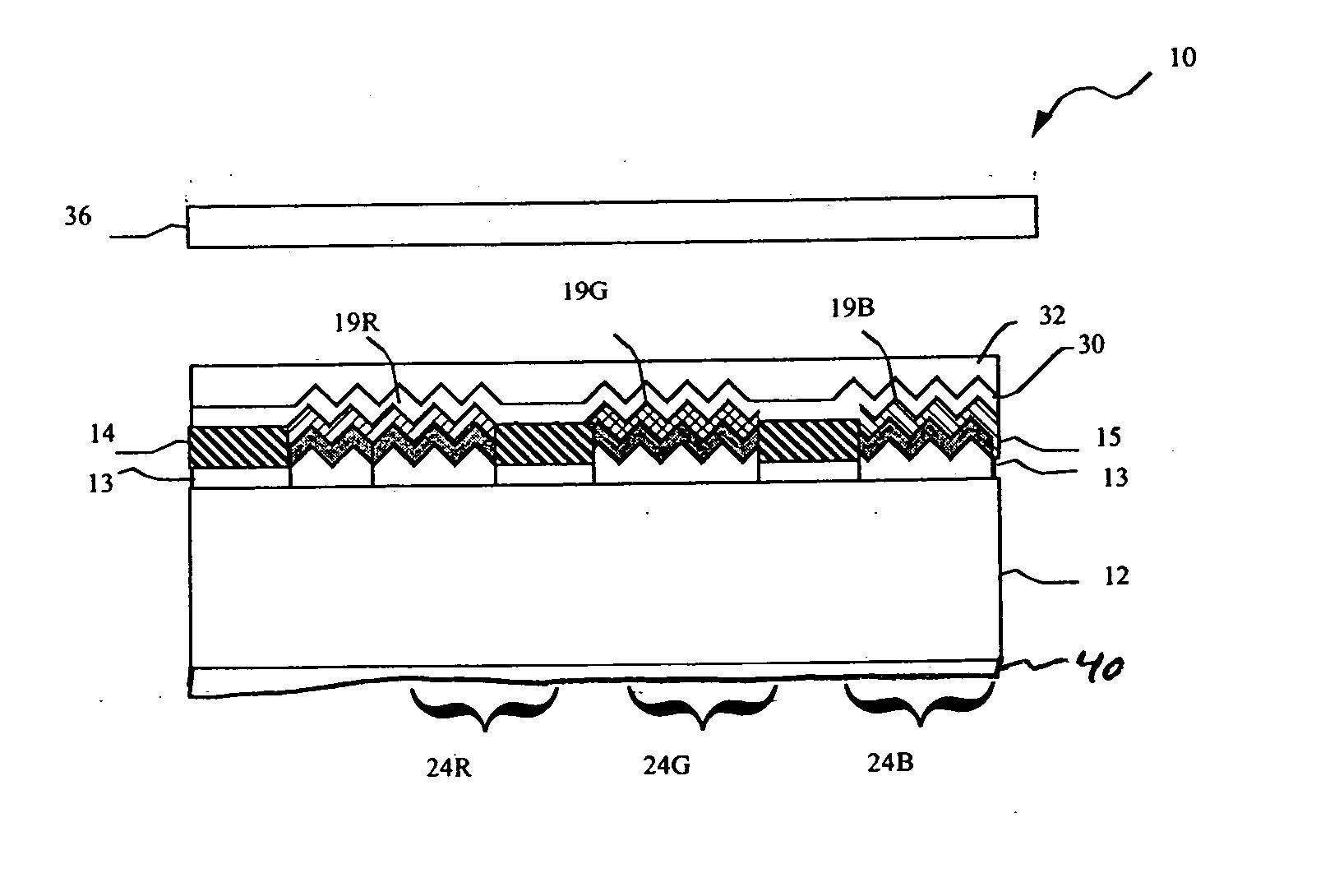
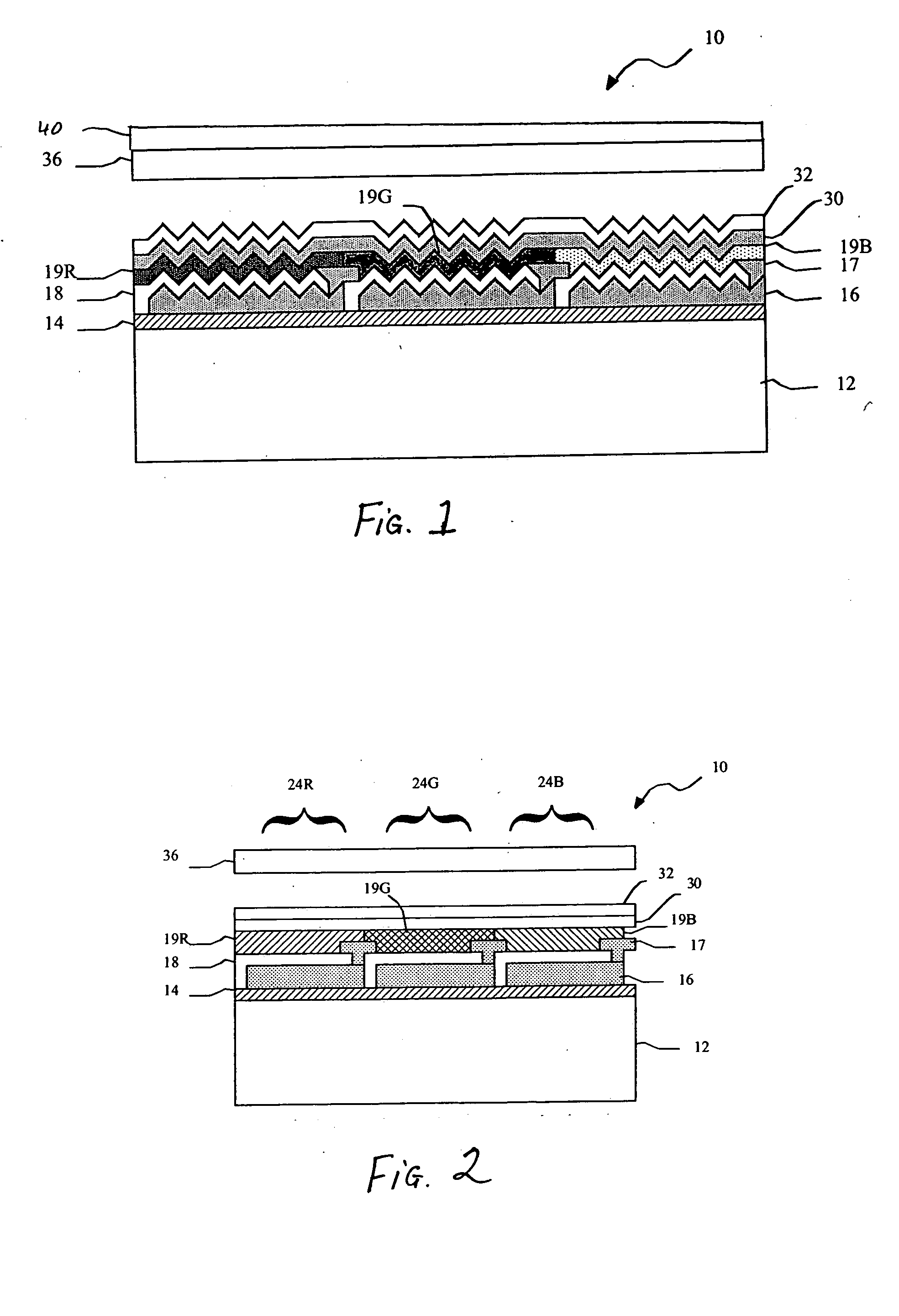
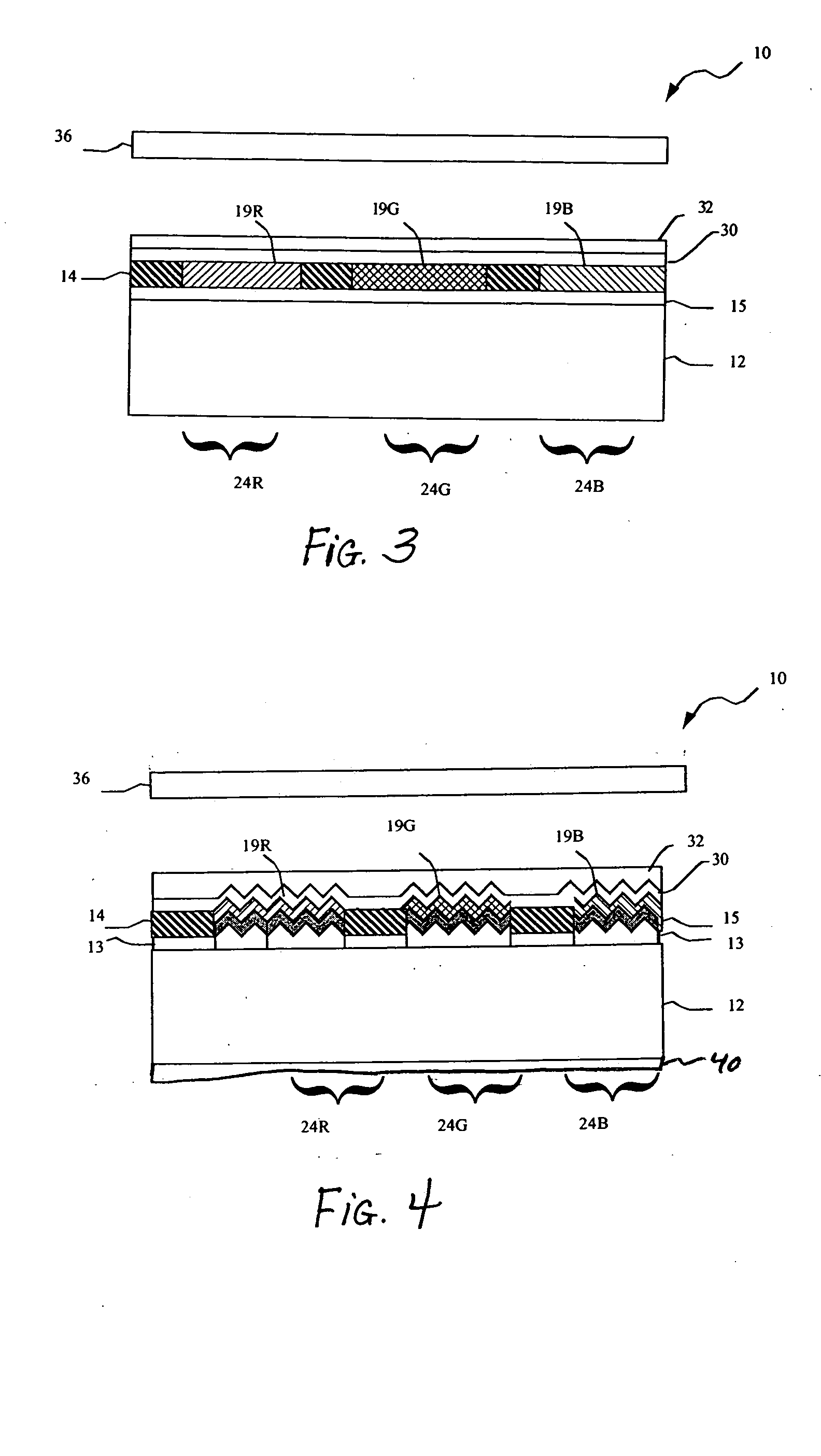
InactiveUS20070200940A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSurface plasmonOptoelectronics
A vertical tri-color sensor having vertically stacked blue, green, and red pixels detects at least blue and green components of incident light by converting the blue and green components to surface plasmons.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Organic polarized light emitting diode display with polarizer
InactiveUS20050088084A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesMetallic electrodeLED display
An organic light emitting diode display includes a substrate; a plurality of OLEDs formed on the substrate, the OLEDs emitting polarized light wherein the OLEDs comprise a layer defining a periodic grating structure; a first electrode layer conforming to the grating structure; an OLED material layer formed over the first electrode layer and conforming to the grating structure; and a second electrode layer formed over the OLED material layer and conforming to the grating structure, wherein the first and / or second electrode layers are metallic layers, whereby the periodic grating structure induces surface plasmon cross coupling in the metallic electrode layer(s) to emit polarized light; and a polarizer located over the substrate through which the polarized light is emitted.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
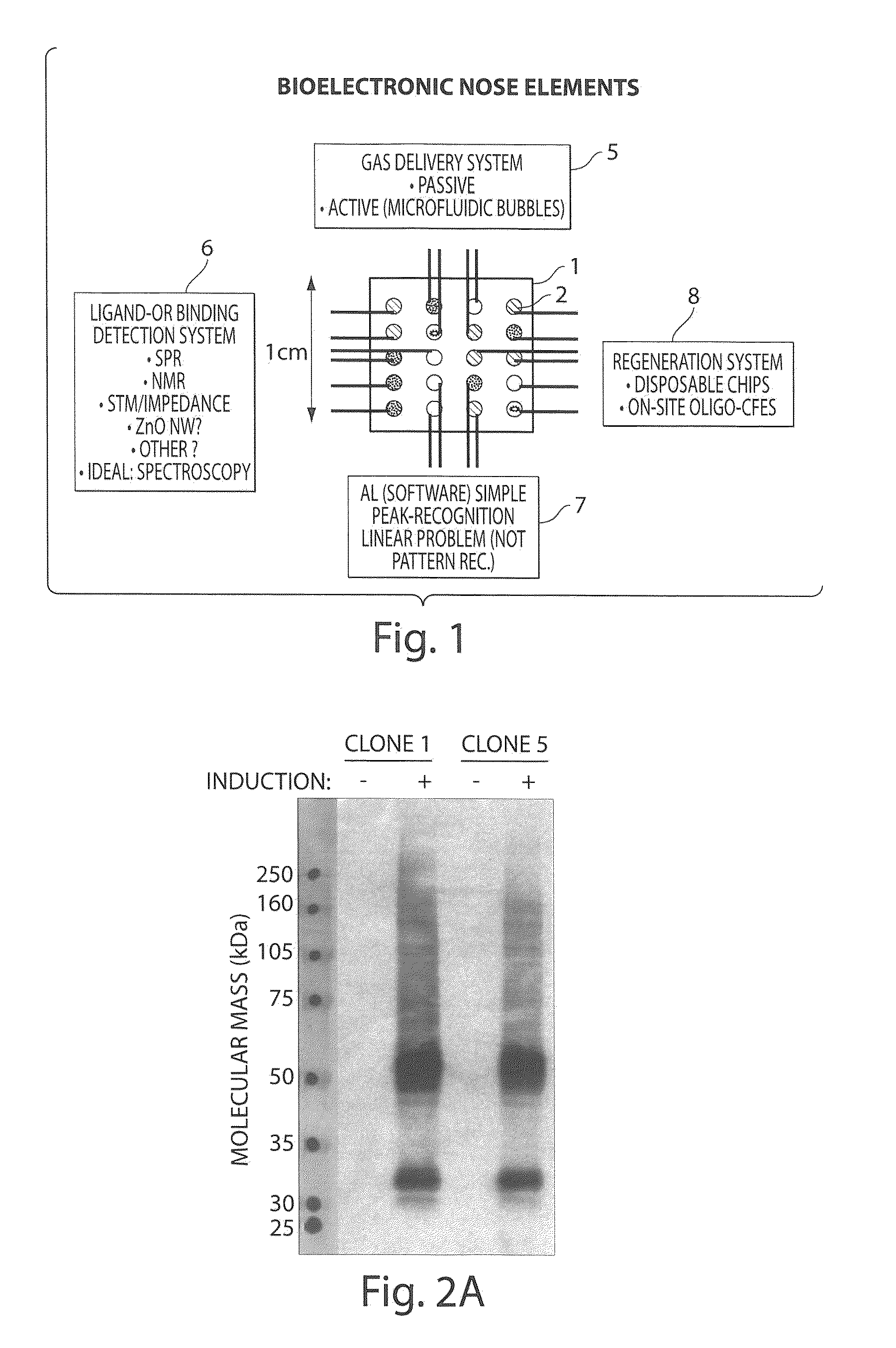
Multiplexed Olfactory Receptor-Based Microsurface Plasmon Polariton Detector
InactiveUS20120021932A1Reducing agentEasy to measureMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide librariesG protein-coupled receptorSurface plasmon
The invention provides a bio-sensing nanodevice comprising: a stabilized G-protein coupled receptor on a support, a real time receptor-ligand binding detection method, a test composition delivery system and a test composition recognition program. The G-protein coupled receptor can be stabilized using surfactant peptide. The nanodevice provides a greater surface area for better precision and sensitivity to odorant detection. The invention further provides a microfluidic chip containing a stabilized G-protein coupled receptor immobilized on a support, and arranged in at least two dimensional microarray system. The invention also provides a method of delivering odorant comprising the step of manipulating the bubbles in complex microfluidic networks wherein the bubbles travel in a microfluidic channel carrying a variety of gas samples to a precise location on a chip. The invention further provides method of fabricating hOR17-4 olfactory receptor.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
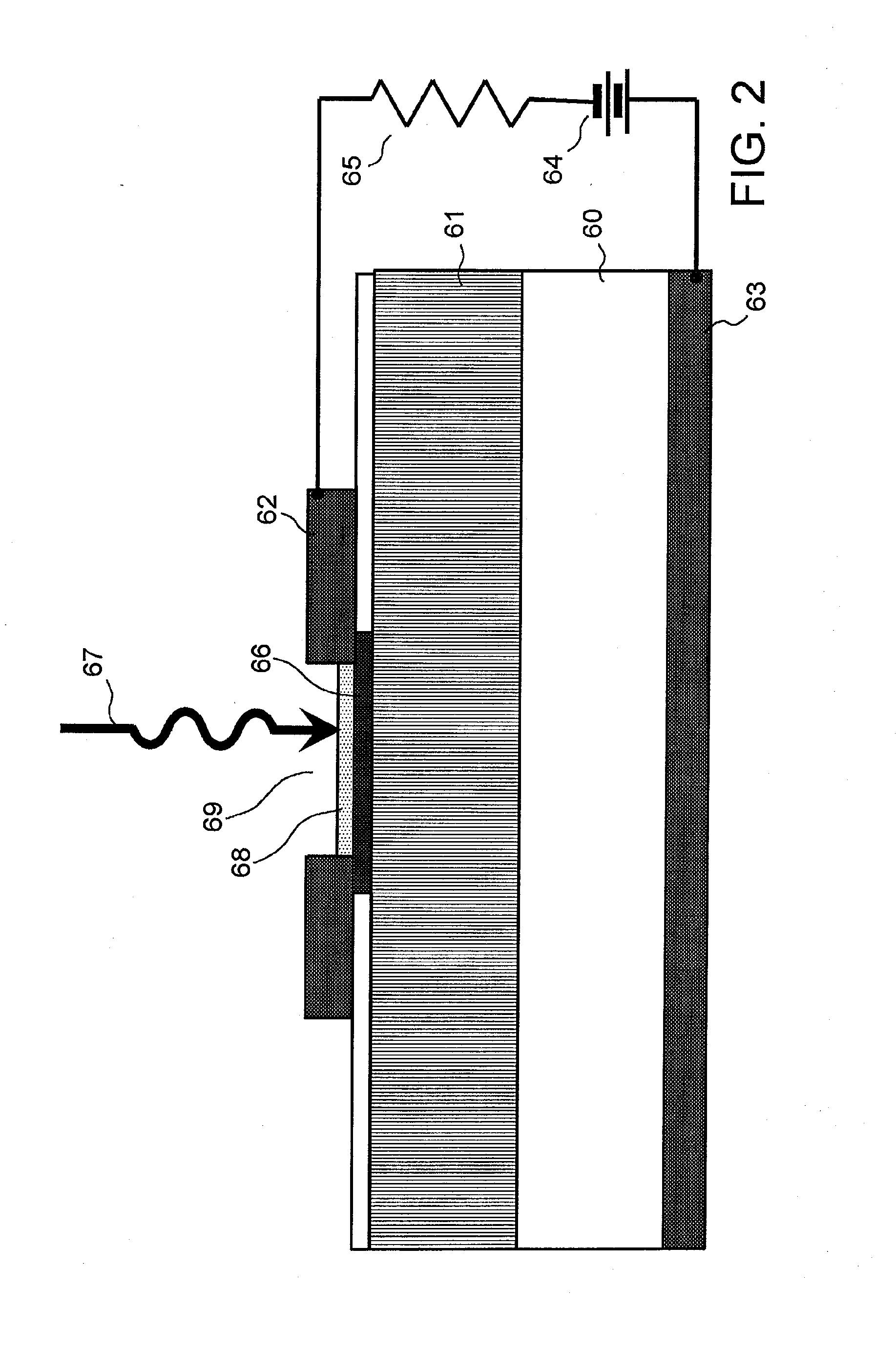
Ultra-Sensitive Optical Detector With High Time Resolution
InactiveUS20080272302A1Increase valueLess phase noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSurface plasmonCoupling
An ultra-sensitive optical detector with large time resolution, using a surface plasmon. The optical detector is configured to detect at least one photon, and including a dielectric substrate, and on the substrate, at least one bolometric detection component, that generates an electrical signal from the energy of received photon(s). Additionally, at least one coupling component is formed on the substrate, distinct from the detection component and including a metal component, and generates a surface plasmon by interaction with the photon(s) and guiding the plasmon right up to the detection component, which then absorbs the energy of the surface plasmon.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
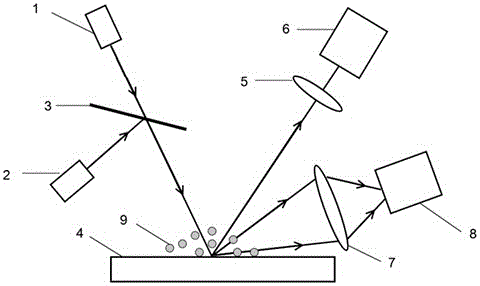
Surface Raman and infrared spectroscopy double-enhanced detecting method based on graphene and nanogold compounding
ActiveCN105699358ARealize measurementComplete measurementMaterial nanotechnologyRaman scatteringPlasma effectComposite substrate
Provided is a surface Raman and infrared spectroscopy double-enhanced detecting method based on graphene and nanogold compounding.According to the method, light sources, a lens, a graphene nanobelt and gold nanoparticle composite substrate, an infrared Fourier spectrograph and a Raman spectrometer are included.Infrared light waves and visible light waves emitted by the infrared light source and the laser light source respectively pass through a beam combiner and then irradiate the graphene nanobelt and gold nanoparticle composite substrate, after the light waves and trace molecules adsorbed on the substrate interact, reflected light is gathered by the focusing lens to enter the infrared Fourier spectrograph, and meanwhile scattered light is gathered into the Raman spectrometer.Raman scattering signals of the trace molecules can be enhanced through the local area plasma effect of the gold nanoparticles, and meanwhile infrared absorption spectrum signals of the trace molecules can be dynamically enhanced through the graphene surface plasma effect within the broadband range.According to the method, double enhancement of surface Raman and broadband infrared spectroscopy signals is achieved on the same substrate, and the advantages of being wide in enhancement wave band, high in detecting sensitivity, wide in detected matter variety range, good in stability and the like are achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Imaging SPR apparatus
InactiveUS6862094B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsColor imageConductive materials
Owner:SPRING SYST
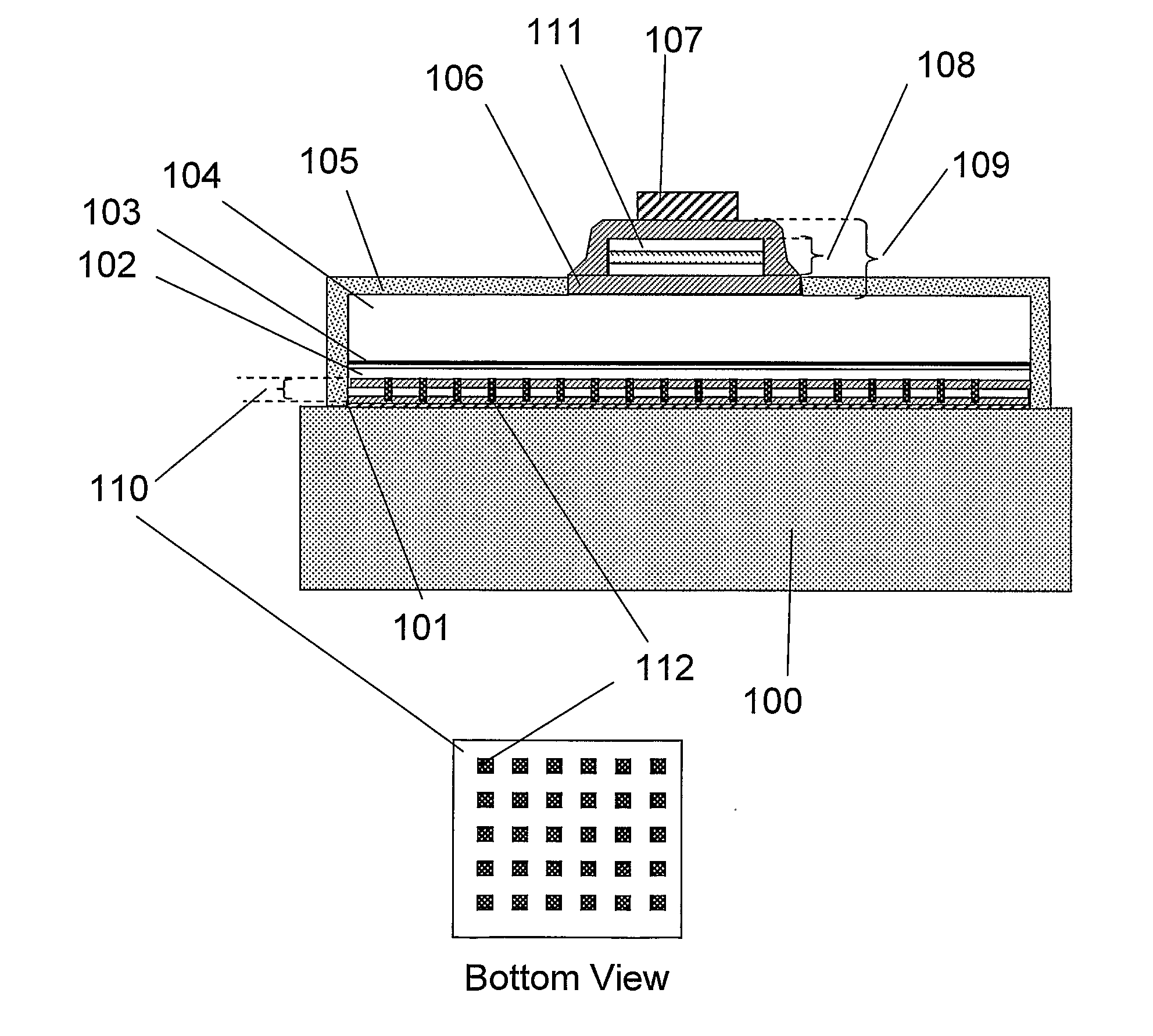
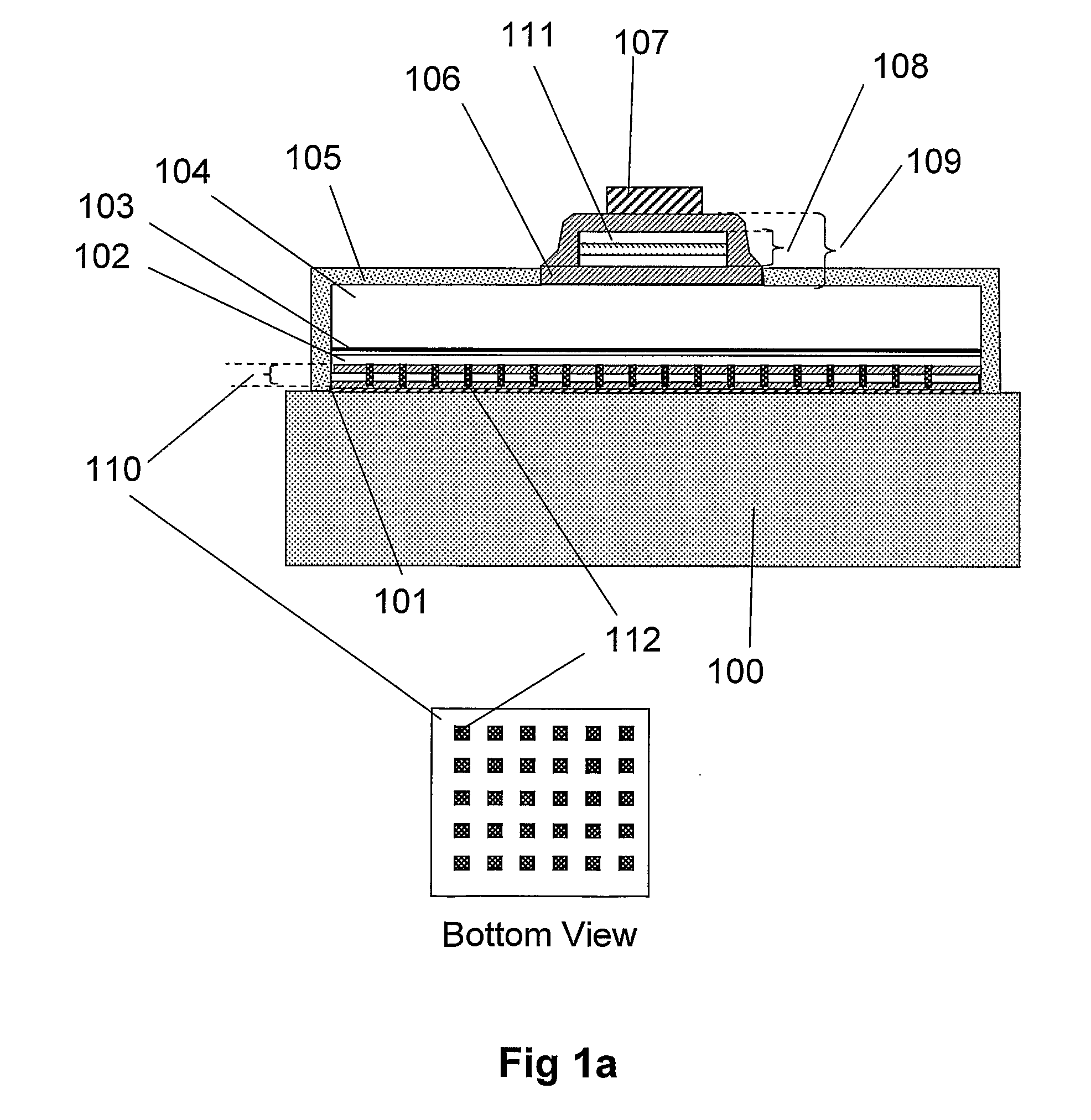
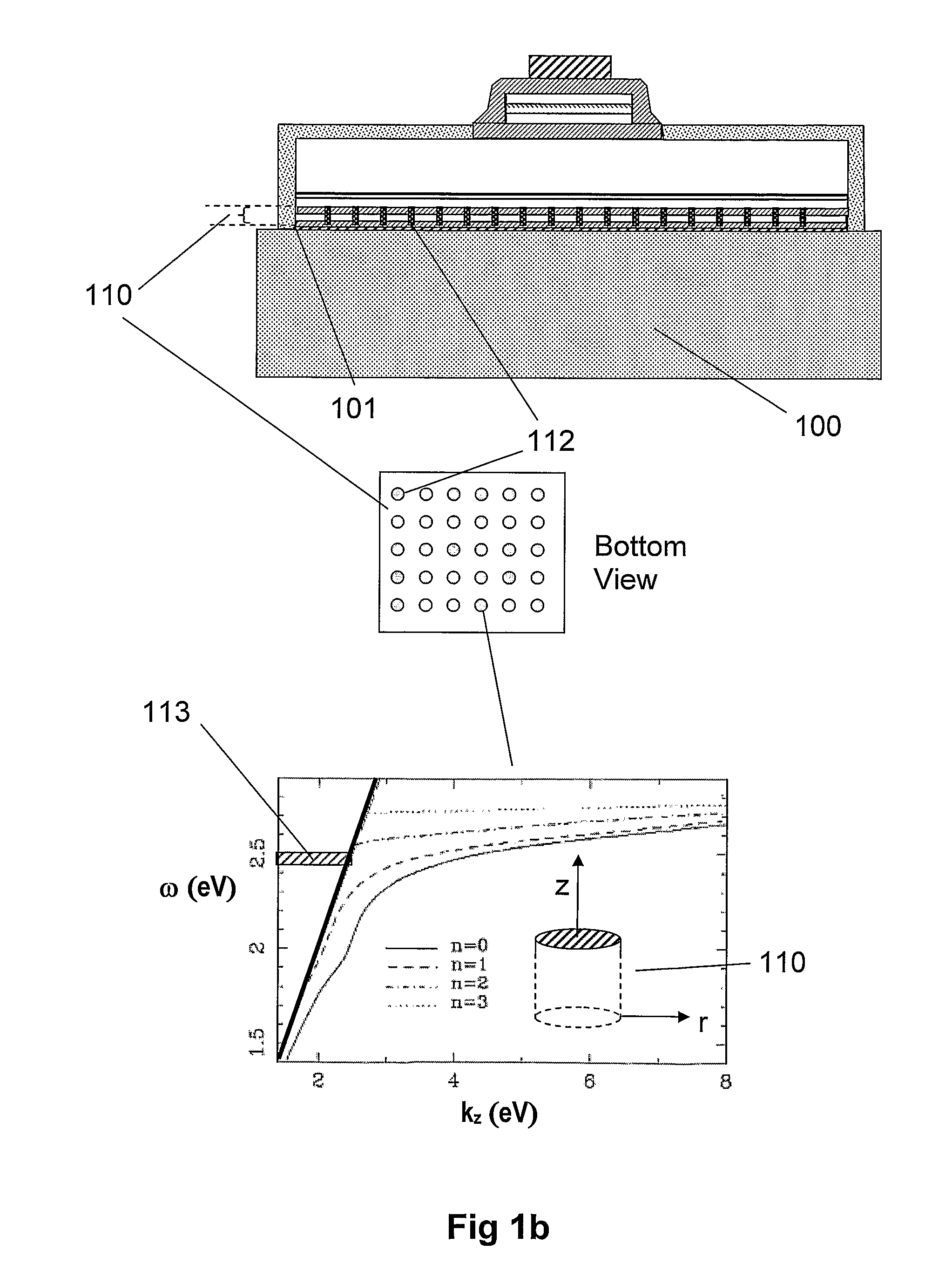
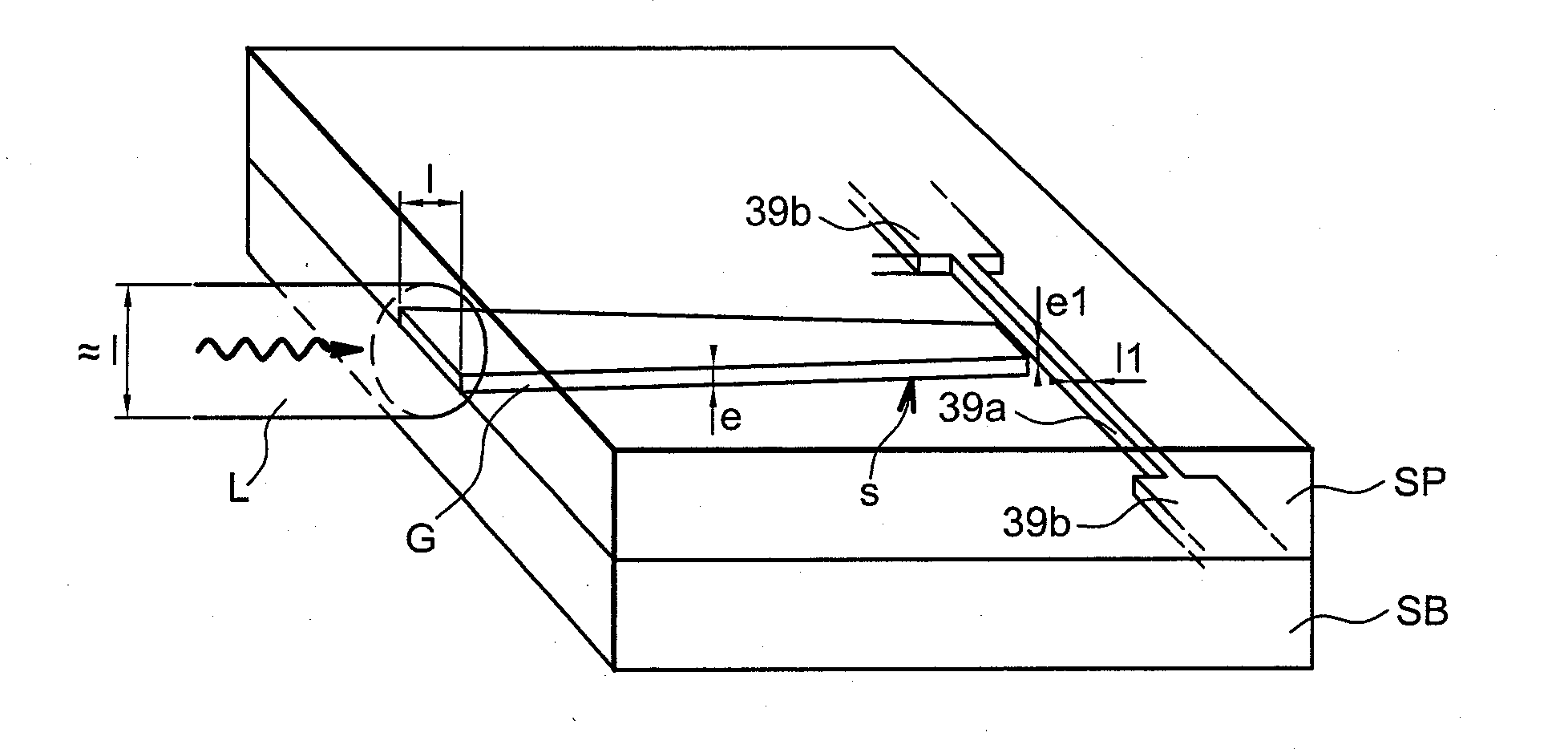
Near-Field Light Generator Comprising Waveguide With Inclined End Surface
ActiveUS20110002199A1InhibitionAvoid noiseCombination recordingRecord information storageSurface plasmonWaveguide
Provided is a near-field light generator capable of avoiding a noise to the generated near-field light. The generator comprises a waveguide and a plasmon antenna comprising a propagation surface or edge, for propagating surface plasmon, extending to a near-field light generating end. A portion of one side surface of the waveguide is opposed to a portion of the propagation surface or edge, so as for the waveguide light to be coupled with the plasmon antenna. And an end surface of the waveguide is inclined in such a way as to become away from the plasmon antenna toward the near-field light generating end side. The light that propagates through the waveguide and is not transformed into surface plasmon is refracted or totally reflected in the inclined end surface, does not come close to the generated near-field light, thus does not become a noise for the generated near-field light.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
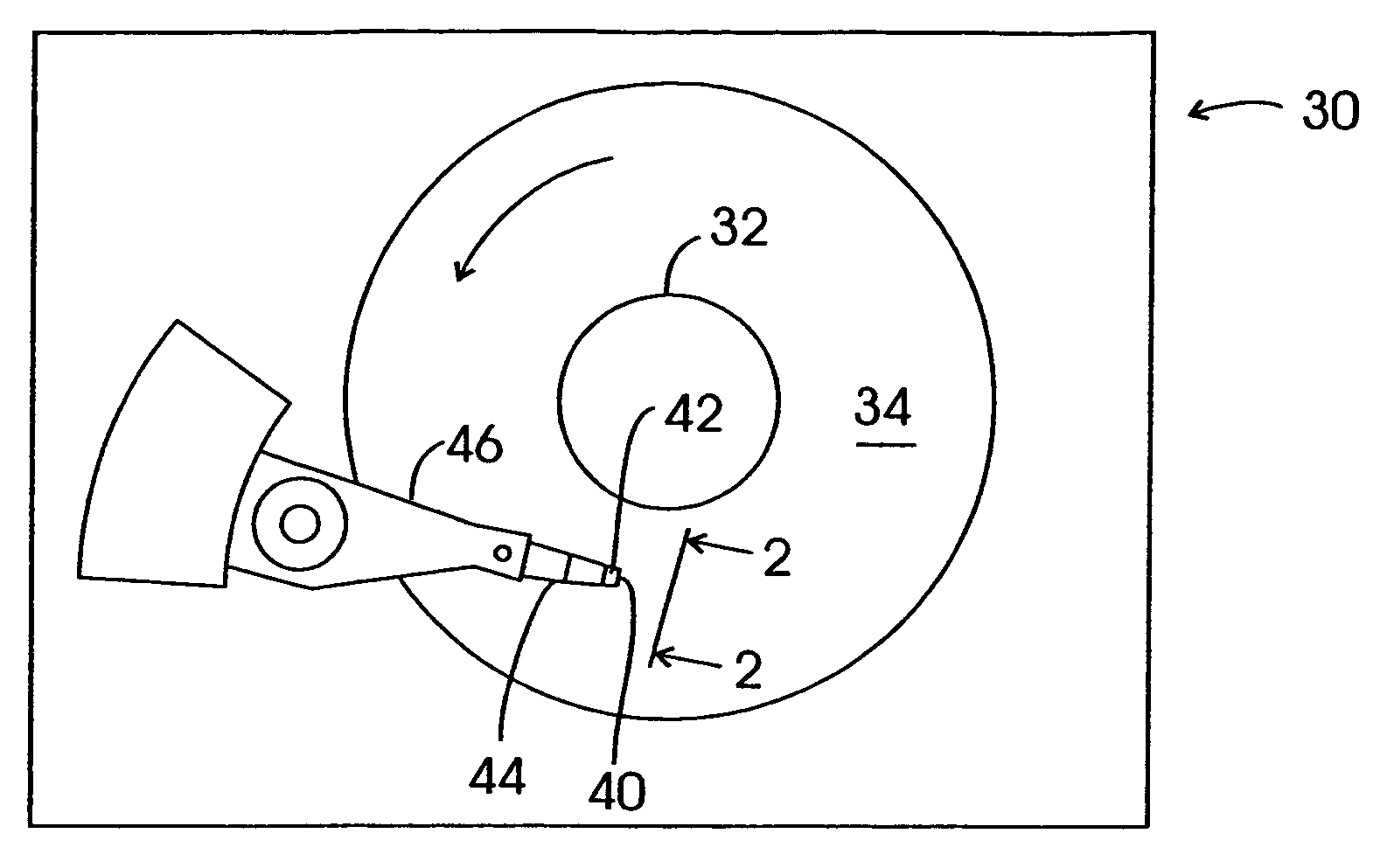
Optical aperture for data recording having transmission enhanced by surface plasmon resonance
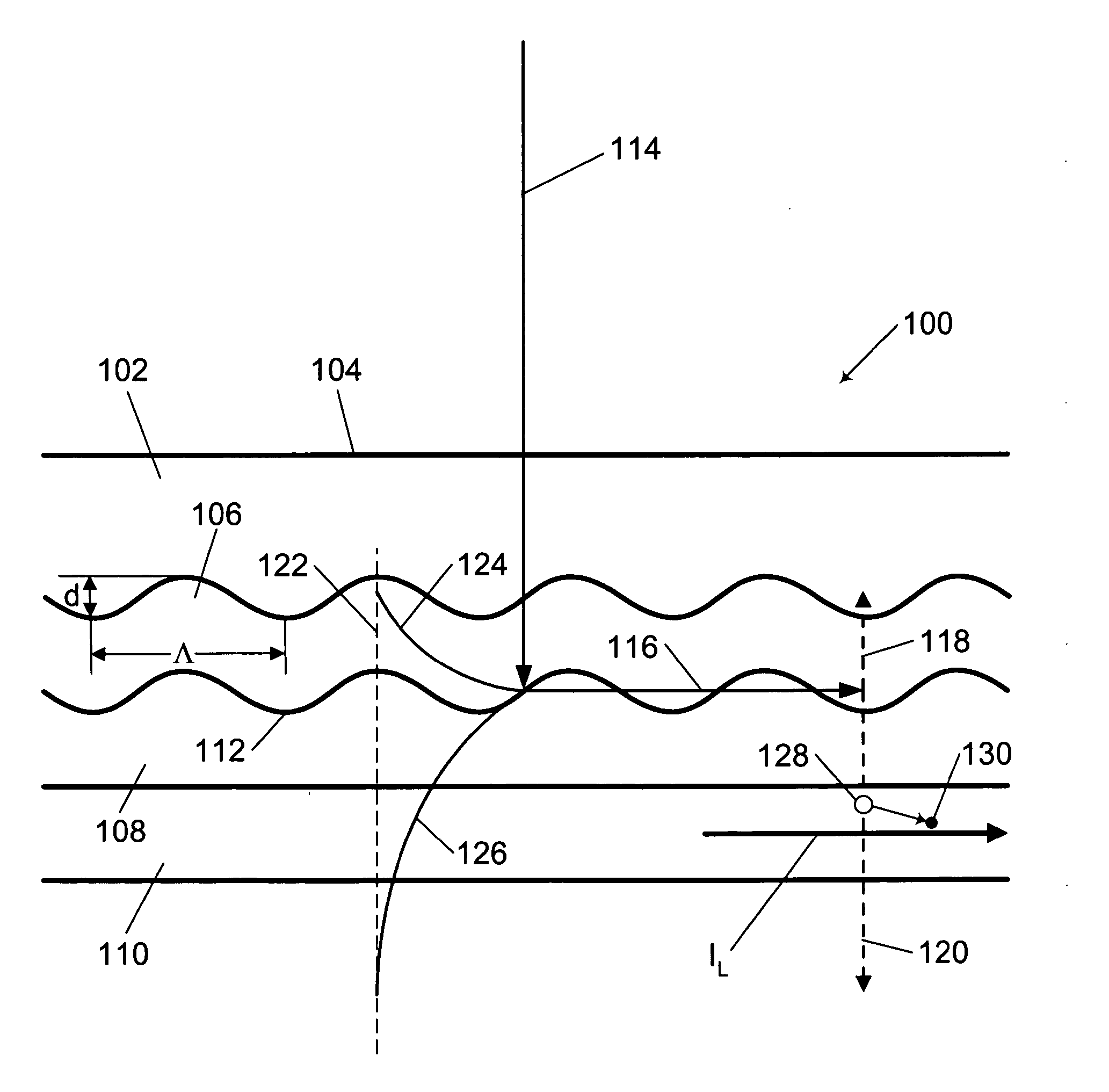
InactiveUS6982844B2Enhanced couplingSave energyCombination recordingHeads using thin filmsSurface plasmonElectromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation from an optical source is directed onto a metallic structure. The metallic structure in turn emits optical output from an emission region in the structure and onto a recording medium (e.g., a magnetic recording disk), thereby heating the medium. The output from the emission region is enhanced due to surface plasmons in the metallic structure. The surface plasmons are generated by an array of features (such as ridges or trenches) in the metallic structure and act to increase the emitted optical output from the emission region beyond what the emitted optical output from the emission region would be in the absence of these features. The apparatus and associated method are useful for data recording, e.g., thermally assisted data recording.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
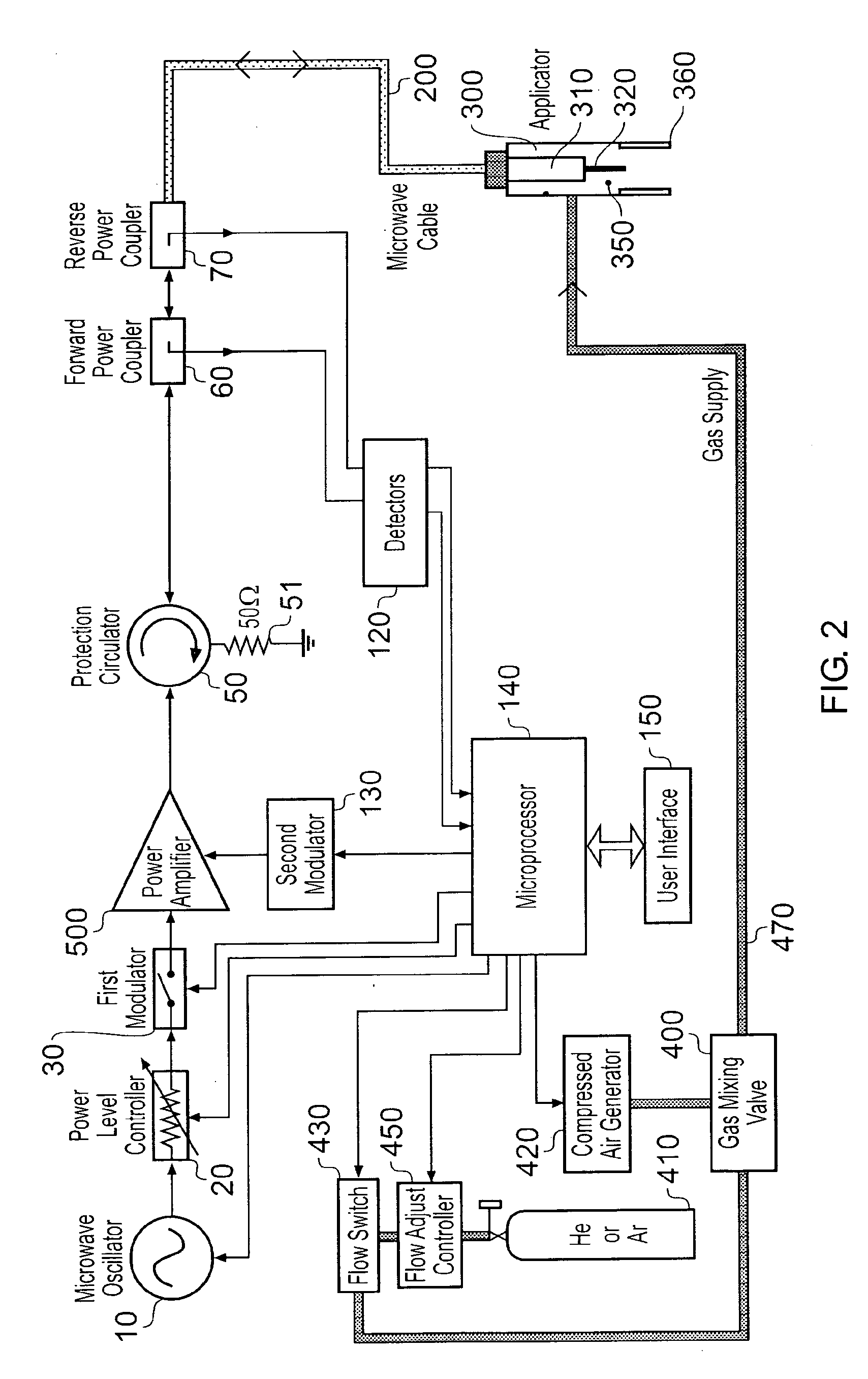
Microwave plasma sterilisation system and applicators therefor
ActiveUS20140066838A1Easy to operateSufficient magnitudeMedical devicesLavatory sanitoryMicrowaveSurface plasmon
Owner:CREO MEDICAL LTD
Electromagnetic wave detector and electromagnetic wave detector array
ActiveUS20140319357A1High-sensitivity photodetectionImprove absorption rateSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansInter layerSurface plasmon
An electromagnetic wave detector that detects incident light by converting the incident light into an electric signal includes a flat metal layer formed on a supporting substrate, an intermediate layer formed on the metal layer, a graphene layer formed on the intermediate layer, isolated metals periodically formed on the graphene layer, and electrodes arranged oppositely on both sides of the isolated metals. Depending on a size of a planar shape of each of the isolated metals, light having a predetermined wavelength at which surface plasmon occurs is determined out of the incident light, and the light having the predetermined wavelength is absorbed to detect a change in the electric signal generated in the graphene layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Waveguide path coupling-type photodiode
ActiveUS20100119192A1Efficient optoelectric conversionEasy to integrateNanoopticsCoupling light guidesSurface plasmonCoupling
In a waveguide path coupling-type photodiode, a semiconductor light absorbing layer and an optical waveguide path core are adjacently arranged. An electrode formed of at least one layer is installed in a boundary part of the semiconductor light absorbing layer and the optical waveguide path core. The electrodes are arranged at an interval of (1 / 100)λ to λ [λ: wavelength of light transmitted through optical waveguide path core]. At least a part of the electrodes is embedded in the semiconductor light absorbing layer. Embedding depth from a surface of the semiconductor light absorbing layer is a value not more than λ / (2ns) [ns: refractive index of semiconductor light absorbing layer]. At least one layer of the electrode is constituted of a material which can surface plasmon-induced.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Plasmon Enhanced Nanowire Light Emitting Diode
ActiveUS20090267049A1Light emission efficiencyRate of light emission of light emitting is enhancedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNanowireCoupling
A nanowire light emitting diode (LED) and method of emitting light employ a plasmonic mode. The nanowire LED includes a nanowire having a semiconductor junction, a shell layer coaxially surrounding the nanowire, and an insulating layer, which is plasmonically thin, isolating the shell layer from the nanowire. The shell layer supports a surface plasmon that couples to the semiconductor junction by an evanescent field. Light is generated in a vicinity of the semiconductor junction and the surface plasmon is coupled to the semiconductor junction during light generation. The coupling enhances one or both of an efficiency of light emission and a light emission rate of the LED. A method of making the nanowire LED includes forming the nanowire, providing the insulating layer on the surface of the nanowire, and forming the shell layer on the insulating layer in the vicinity of the semiconductor junction.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com