Patents
Literature
2711 results about "Low temperature plasma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low temperature plasmas are gasiform plasmas with electron temperature under 10 eV, electron density typically from 10 14 to 10 24 m -3. In general, low temperature plasmas have a low degree of ionization at low densities.
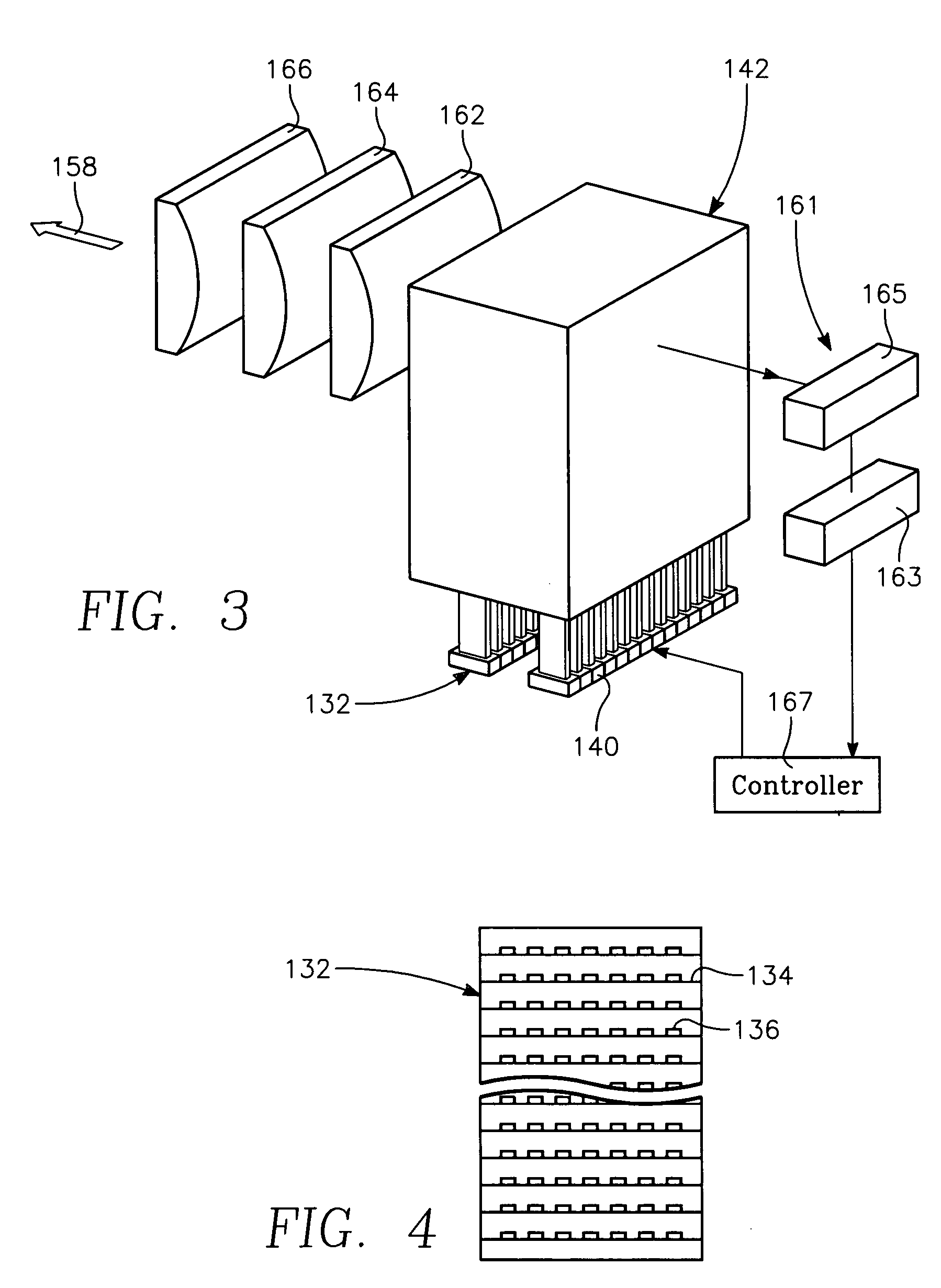
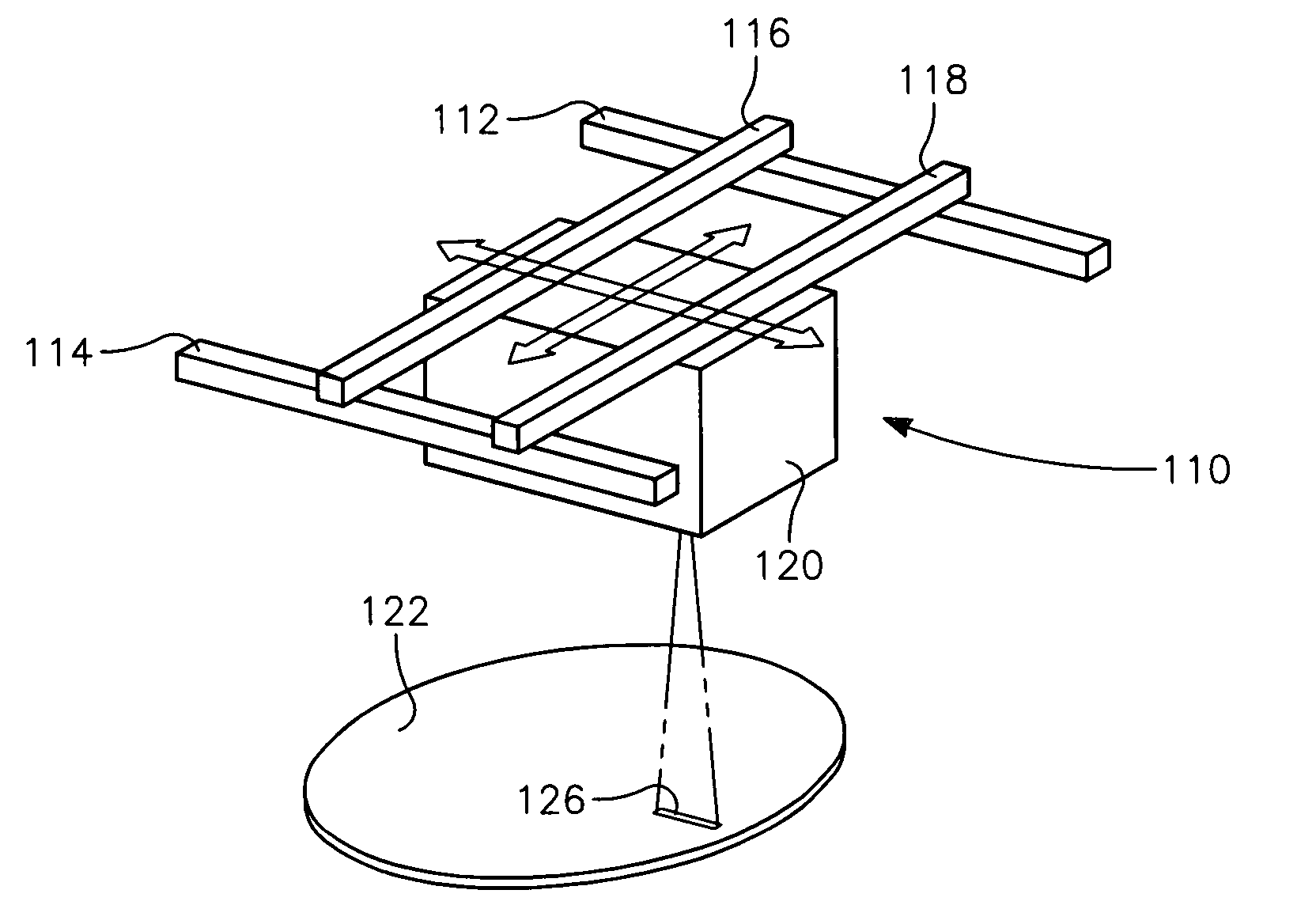
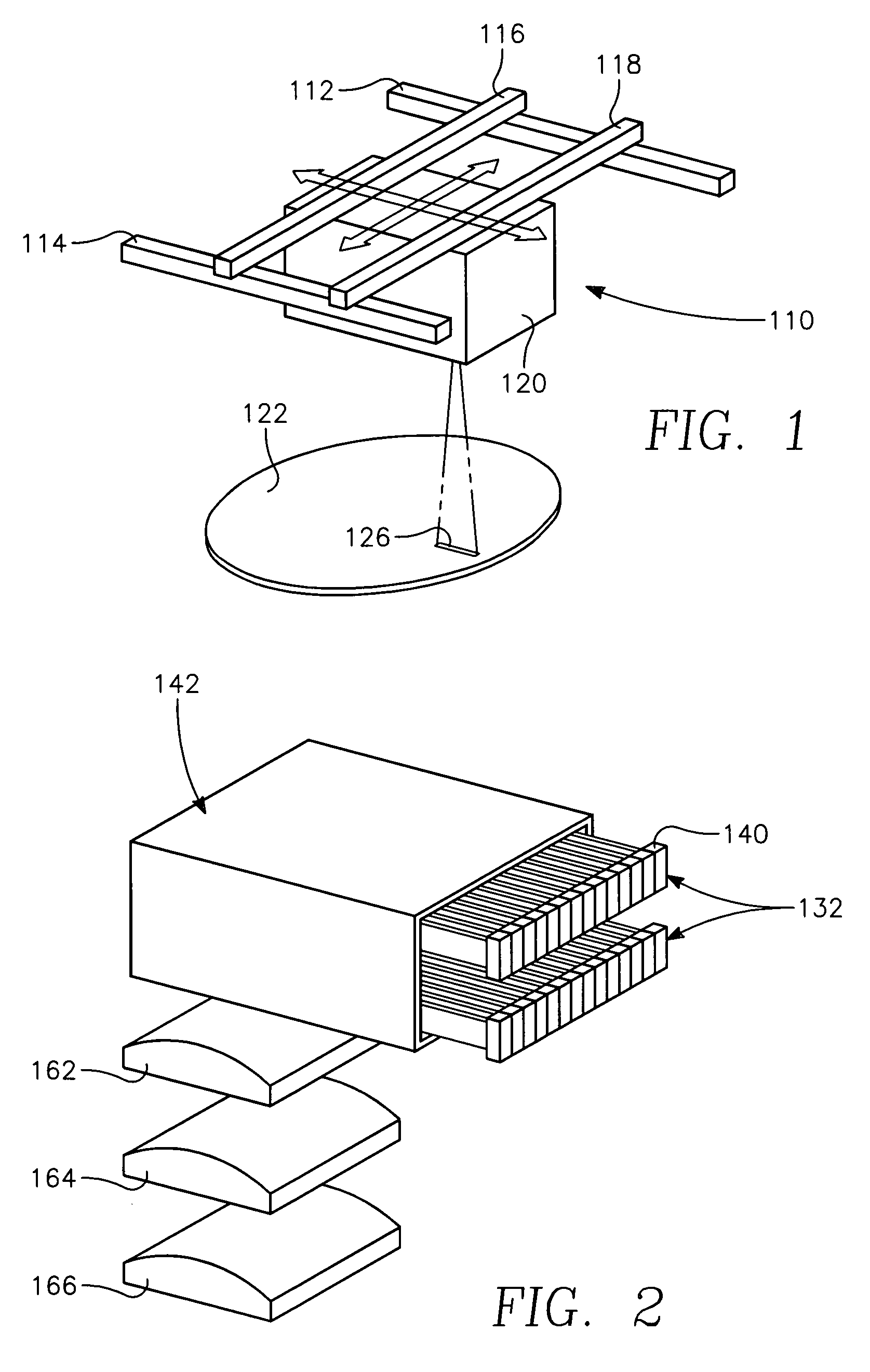
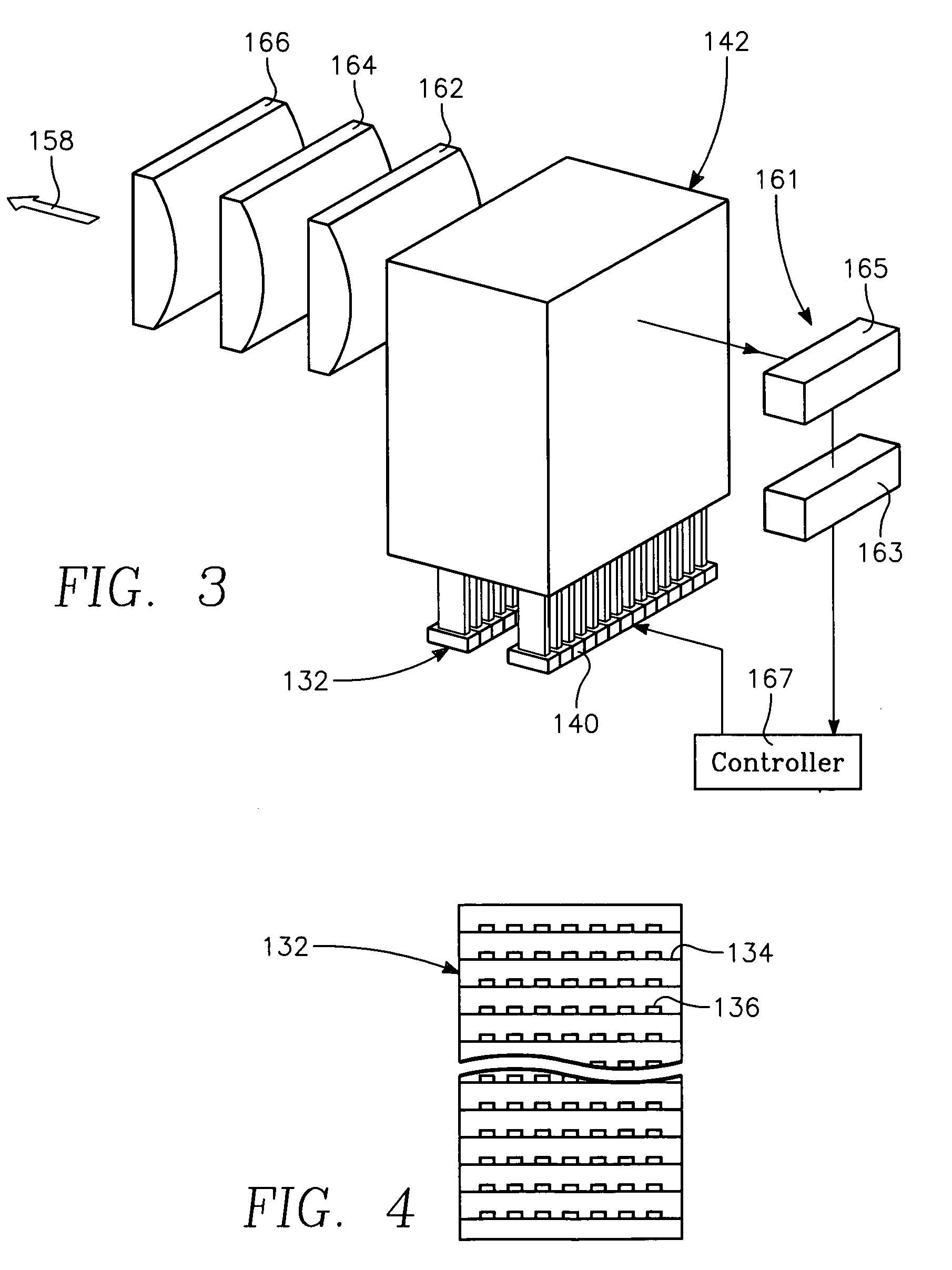
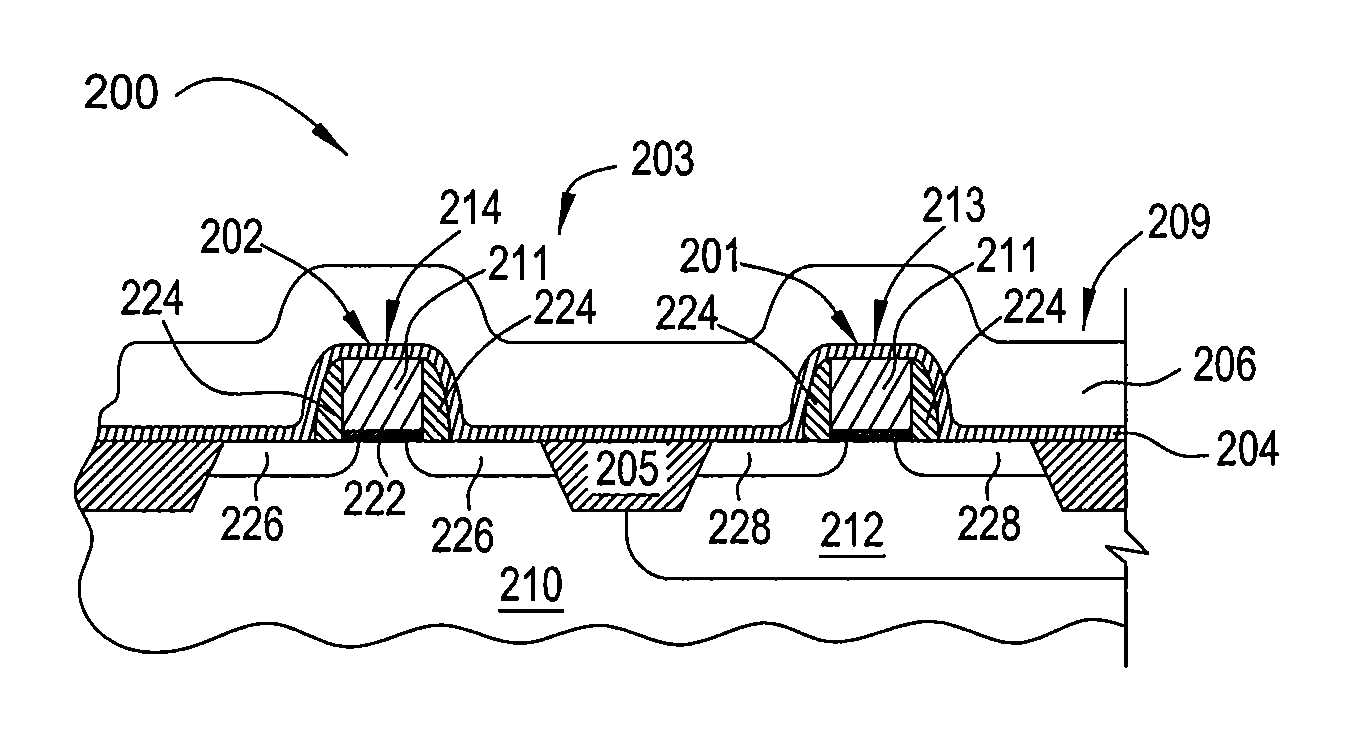
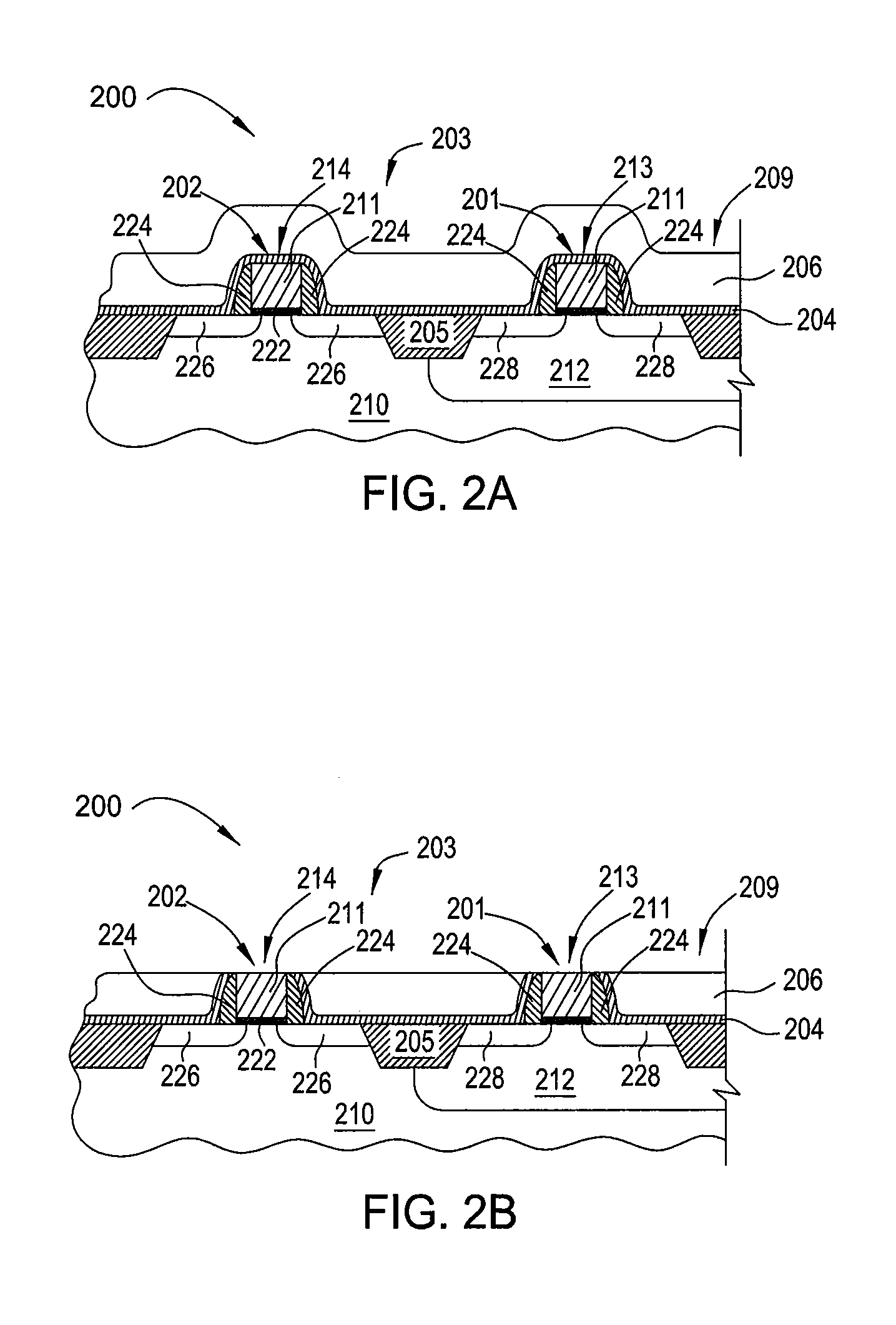
Low temperature plasma deposition process for carbon layer deposition
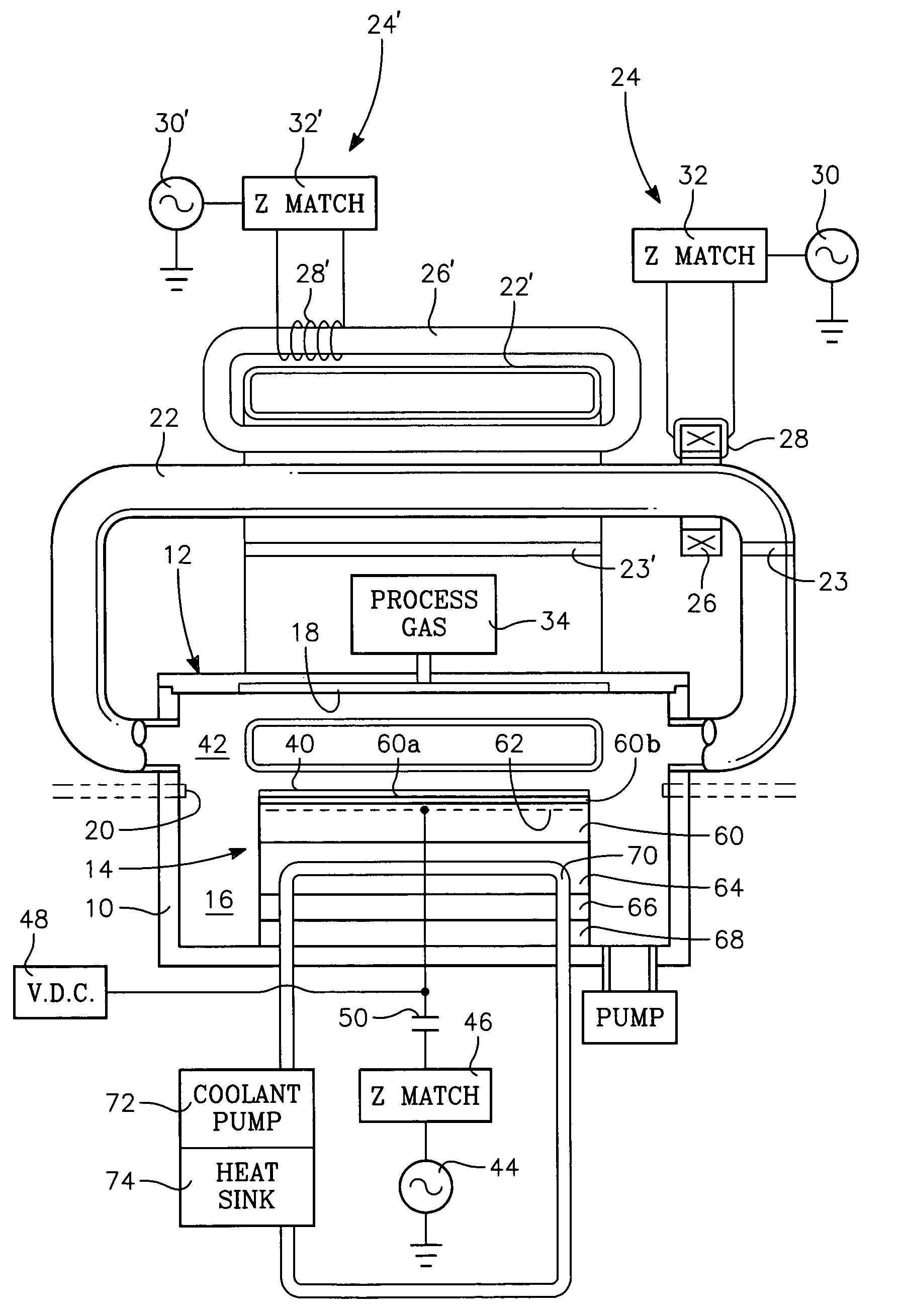
InactiveUS7312162B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerPlasma current
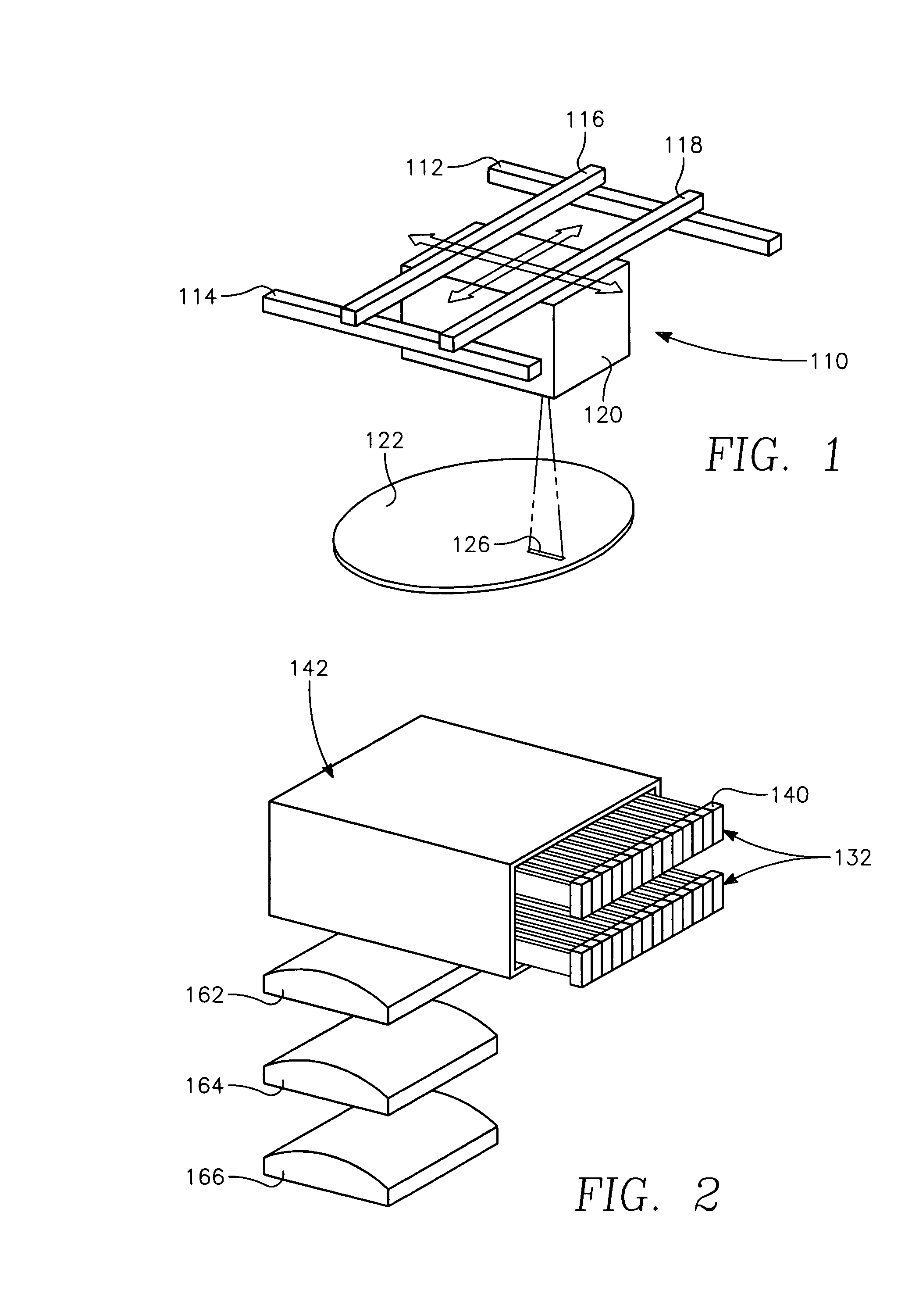
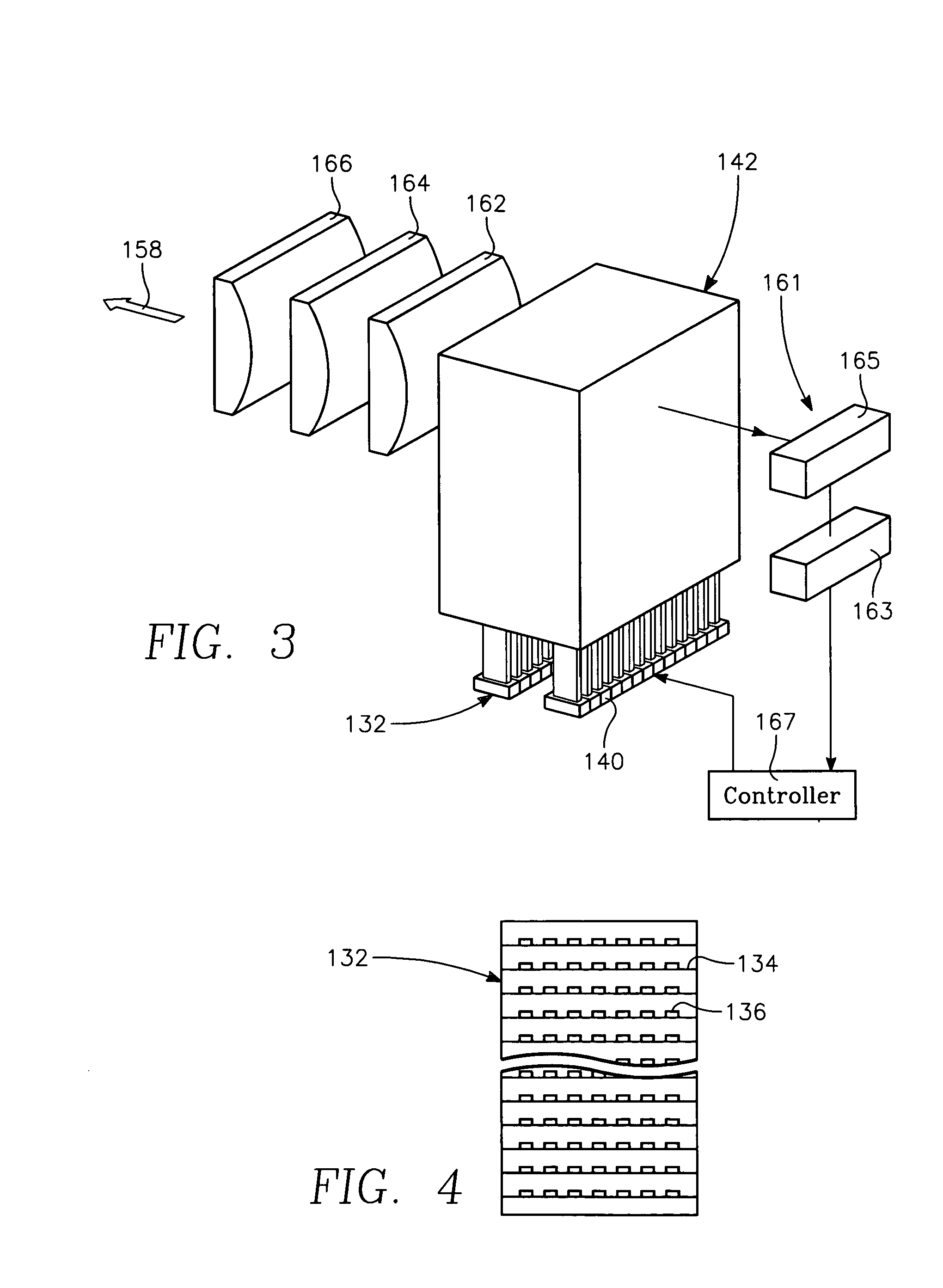
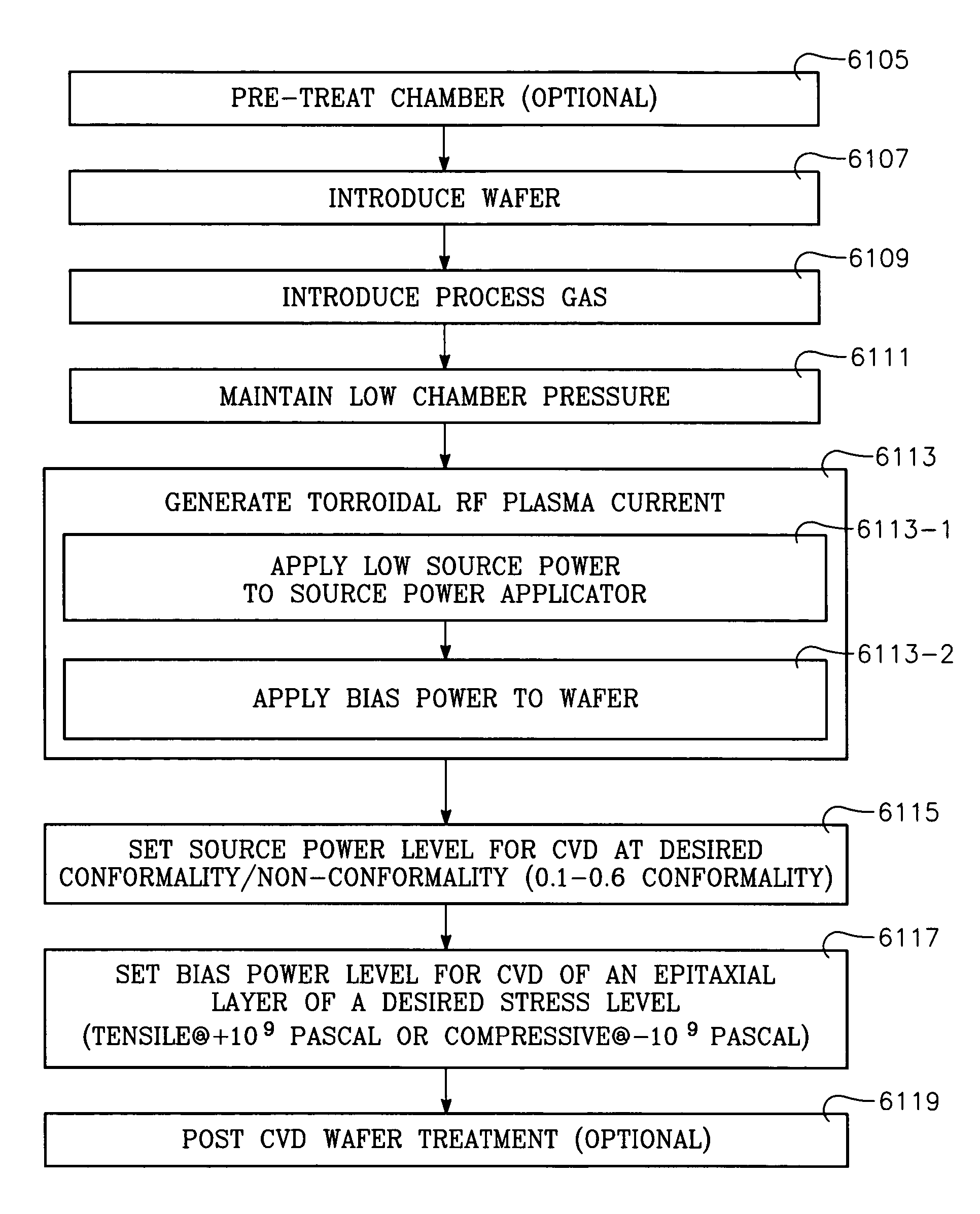
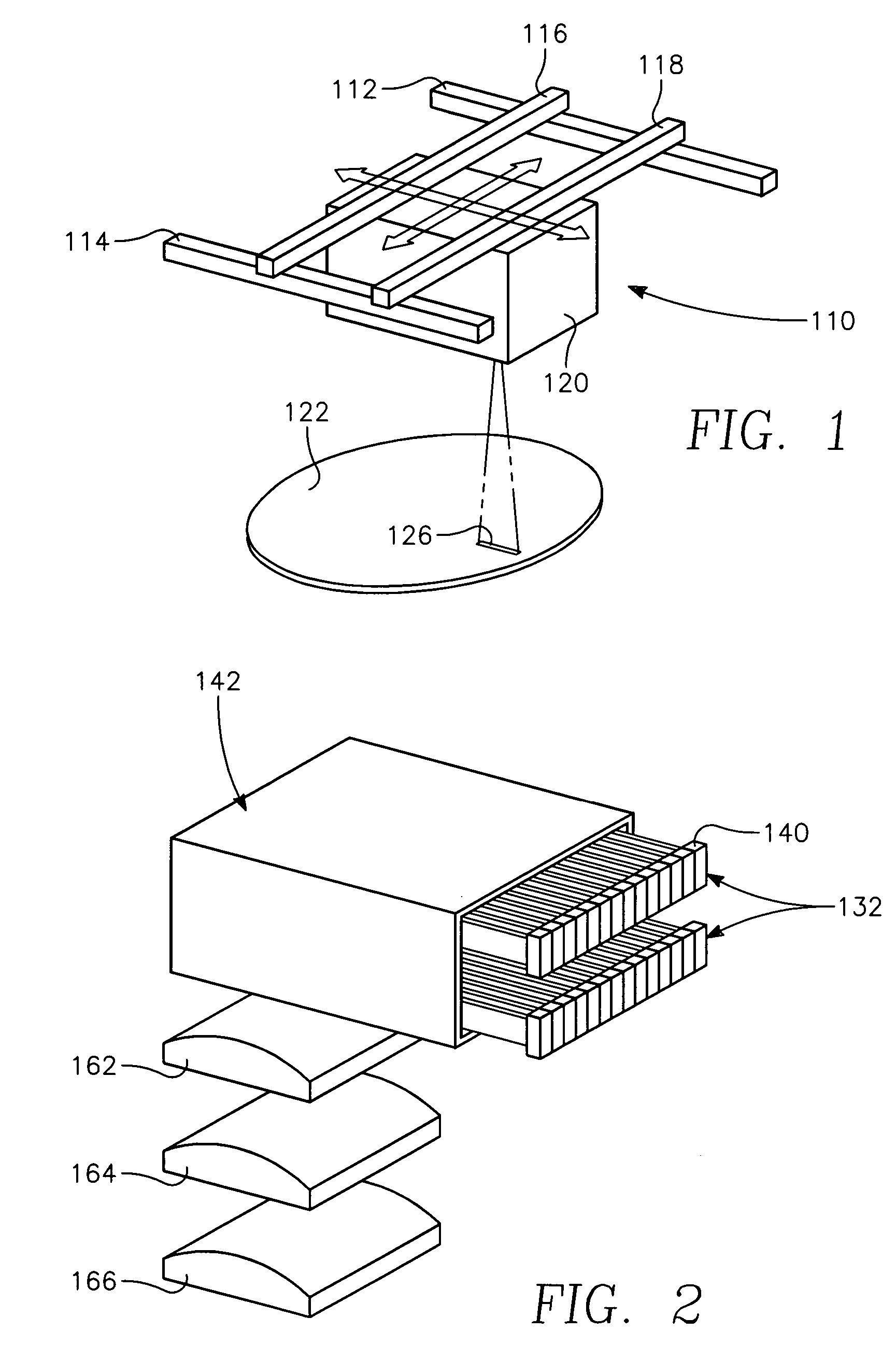
A method of depositing a carbon layer on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber, introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor junction formation process including low temperature plasma deposition of an optical absorption layer and high speed optical annealing
A method of forming semiconductor junctions in a semiconductor material of a workpiece includes ion implanting dopant impurities in selected regions of the semiconductor material, introducing an optical absorber material precursor gas into a chamber containing the workpiece, generating an RF oscillating toroidal plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by applying RF source power, so as to deposit a layer of an optical absorber material on the workpiece, and optically annealing the workpiece so as to activate dopant impurities in the semiconductor material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low temperature plasma deposition process for carbon layer deposition
InactiveUS20060264060A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerPlasma current
A method of depositing a carbon layer on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber, introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Process for low temperature plasma deposition of an optical absorption layer and high speed optical annealing
A method of processing a workpiece includes introducing an optical absorber material precursor gas into a chamber containing the workpiece, generating an RF oscillating toroidal plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by applying RF source power, so as to deposit a layer of an optical absorber material on the workpiece, and exposing the workpiece to optical radiation that is at least partially absorbed in the optical absorber layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of Depositing Silicon Oxide Film by Plasma Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition at Low Temperature
ActiveUS20100255218A1Increase deposition rateInhibition is effectiveLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistDeposition temperature
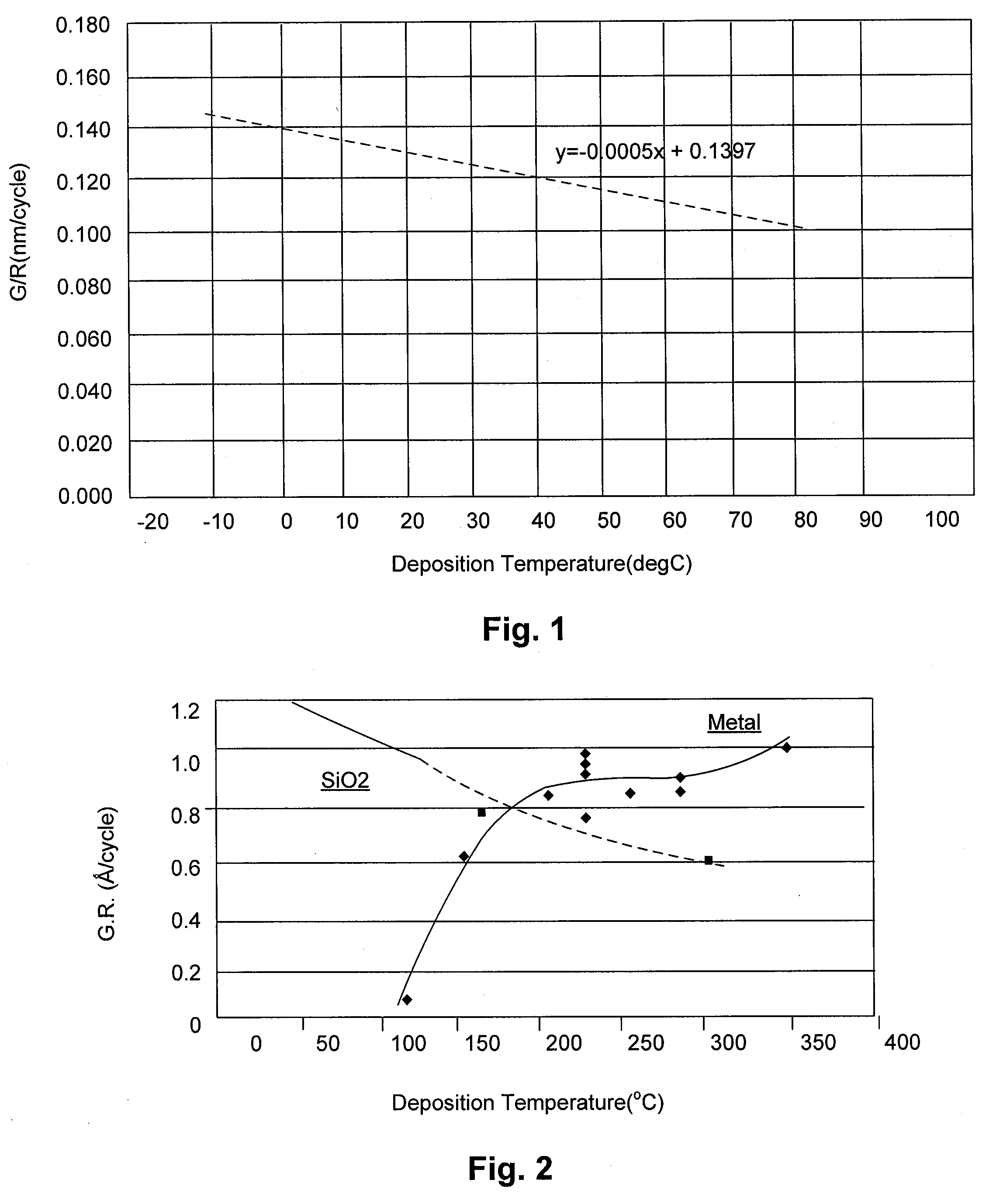
A method of depositing a silicon oxide film on a resist pattern or etched lines formed on a substrate by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) includes: providing a substrate on which a resist pattern or etched lines are formed in a PEALD reactor; controlling a temperature of a susceptor on which the substrate is placed at less than 50° C. as a deposition temperature; introducing a silicon-containing precursor and an oxygen-supplying reactant to the PEALD reactor and applying RF power therein in a cycle, while the deposition temperature is controlled substantially or nearly at a constant temperature of less than 50° C., thereby depositing a silicon oxide atomic layer on the resist pattern or etched lines; and repeating the cycle multiple times substantially or nearly at the constant temperature to deposit a silicon oxide atomic film on the resist pattern or etched lines.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
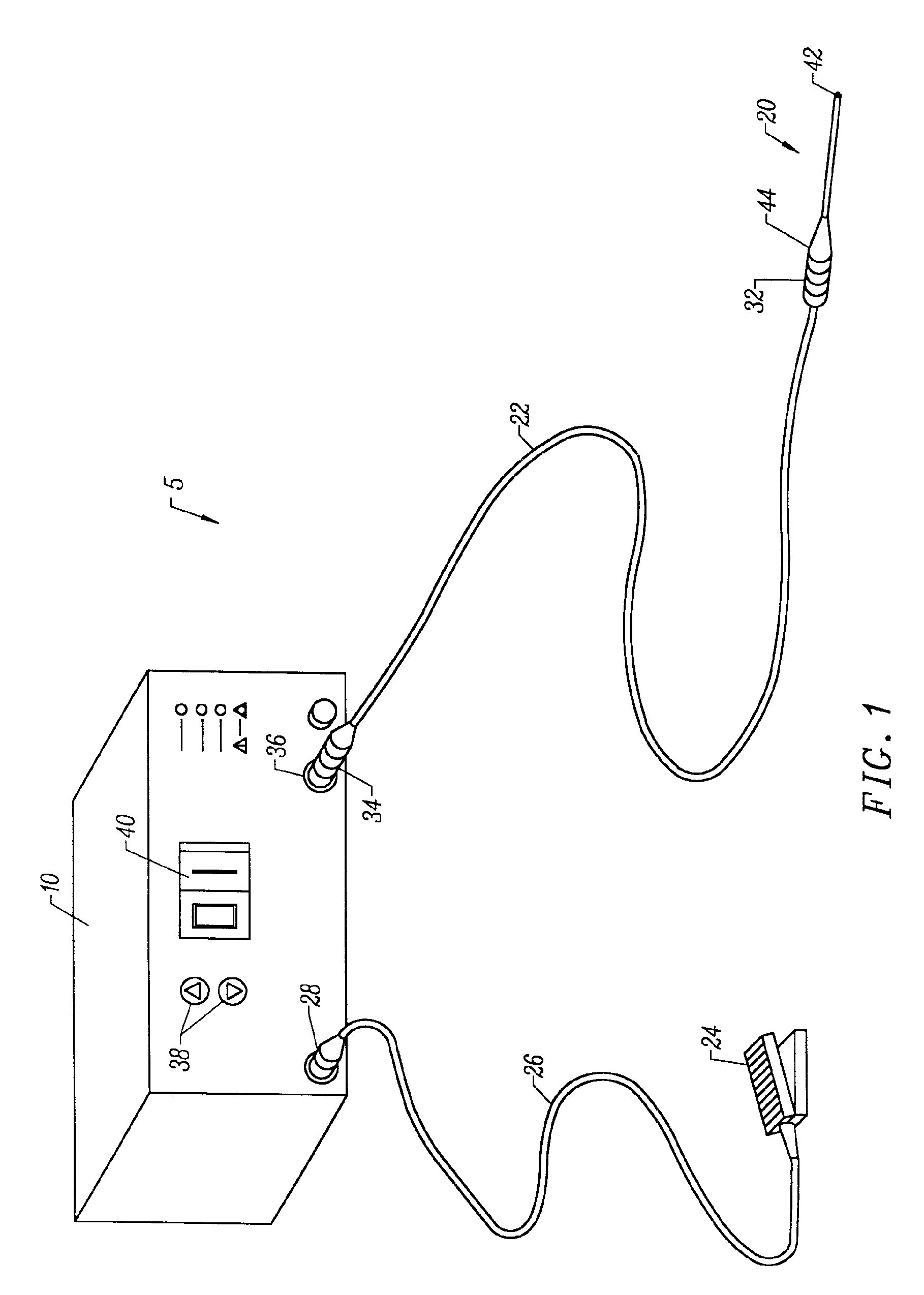
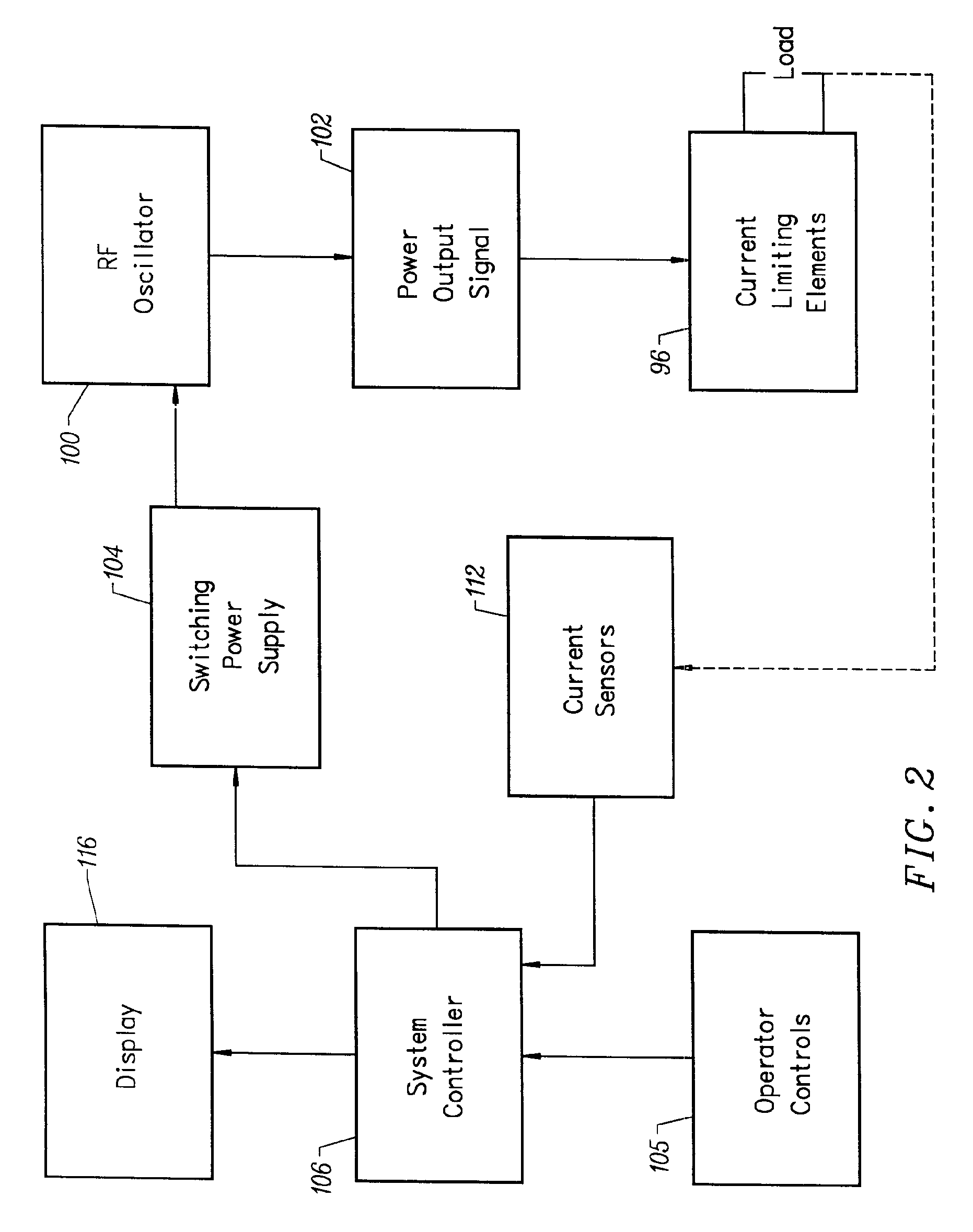
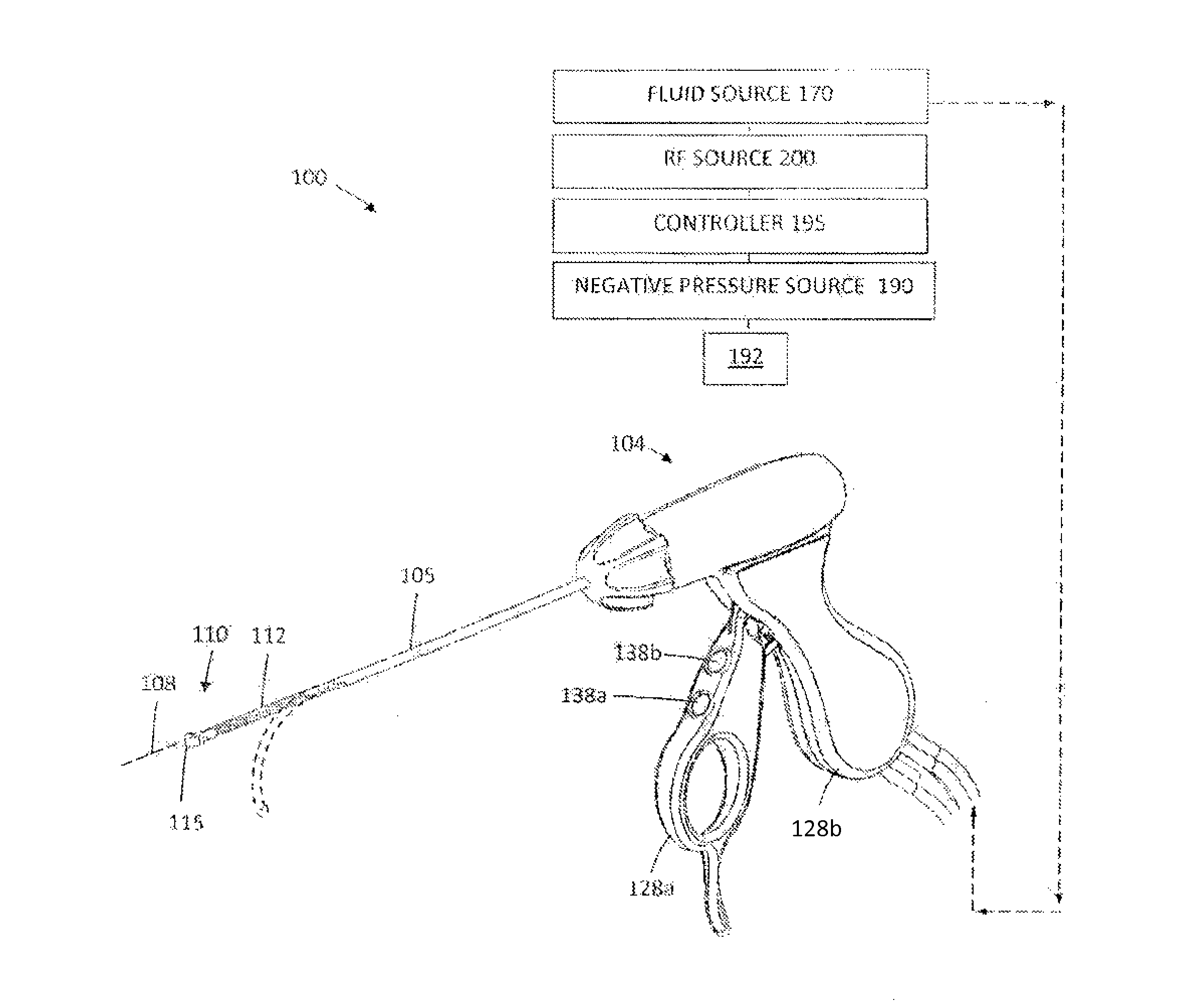
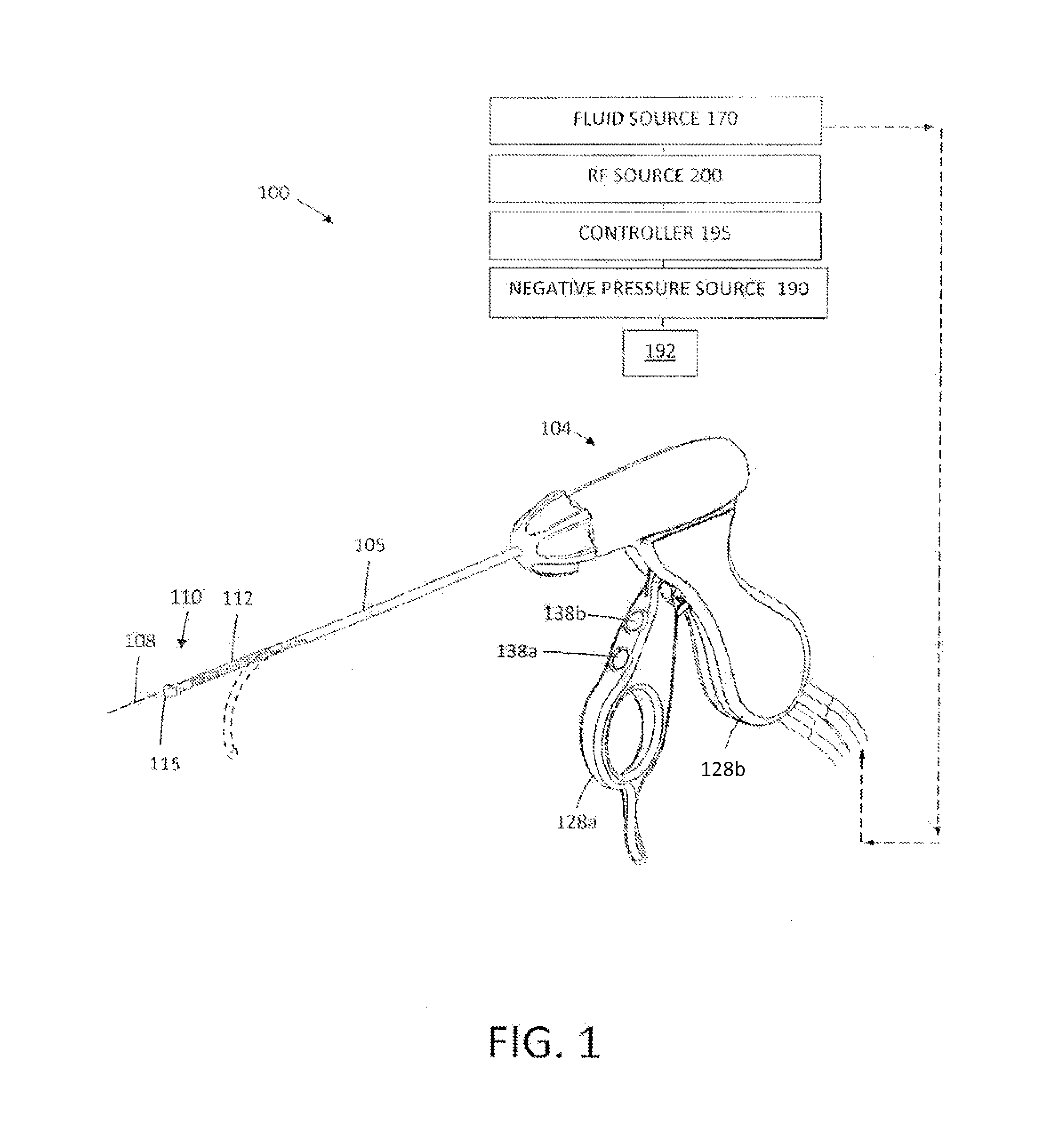
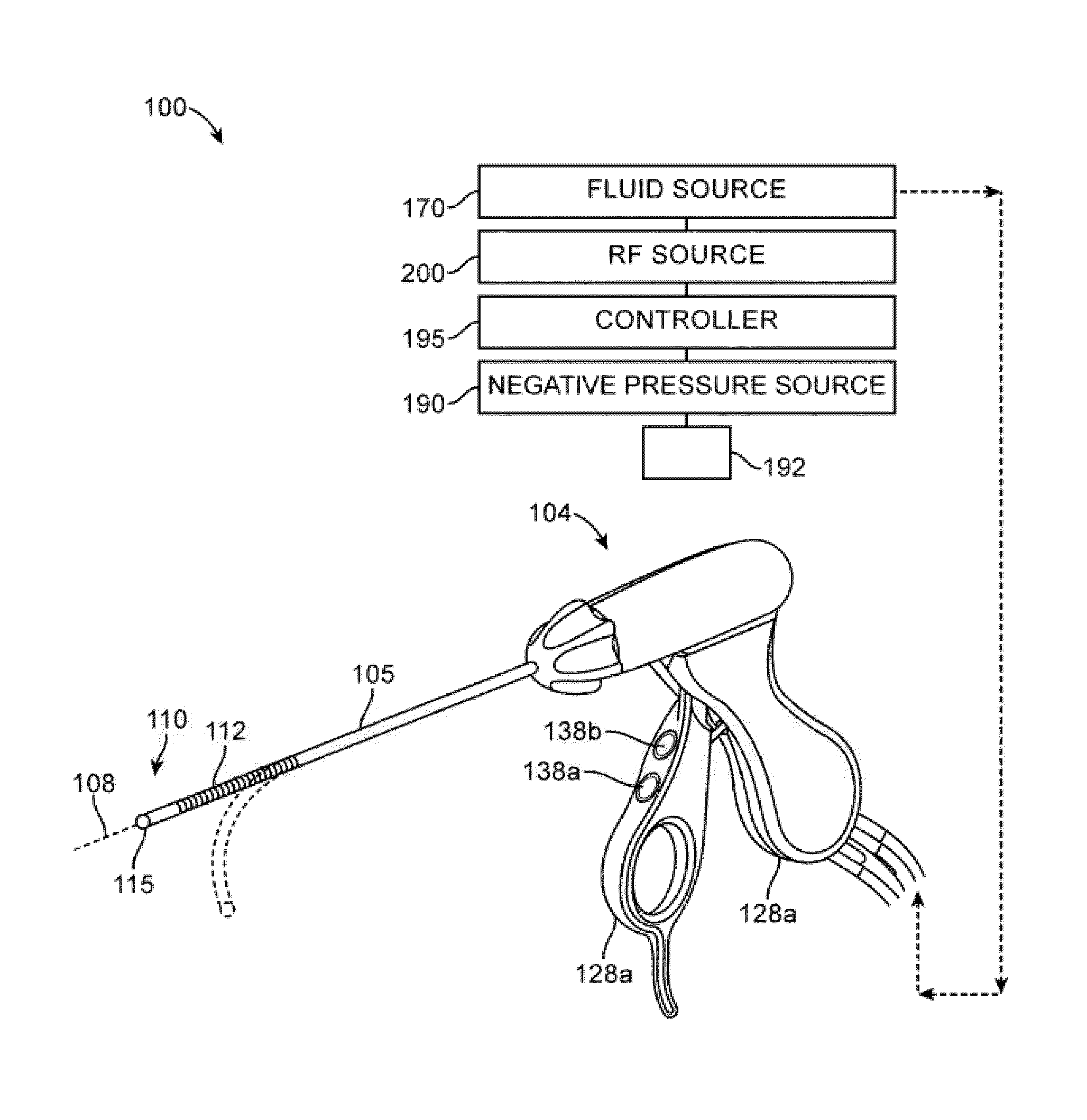
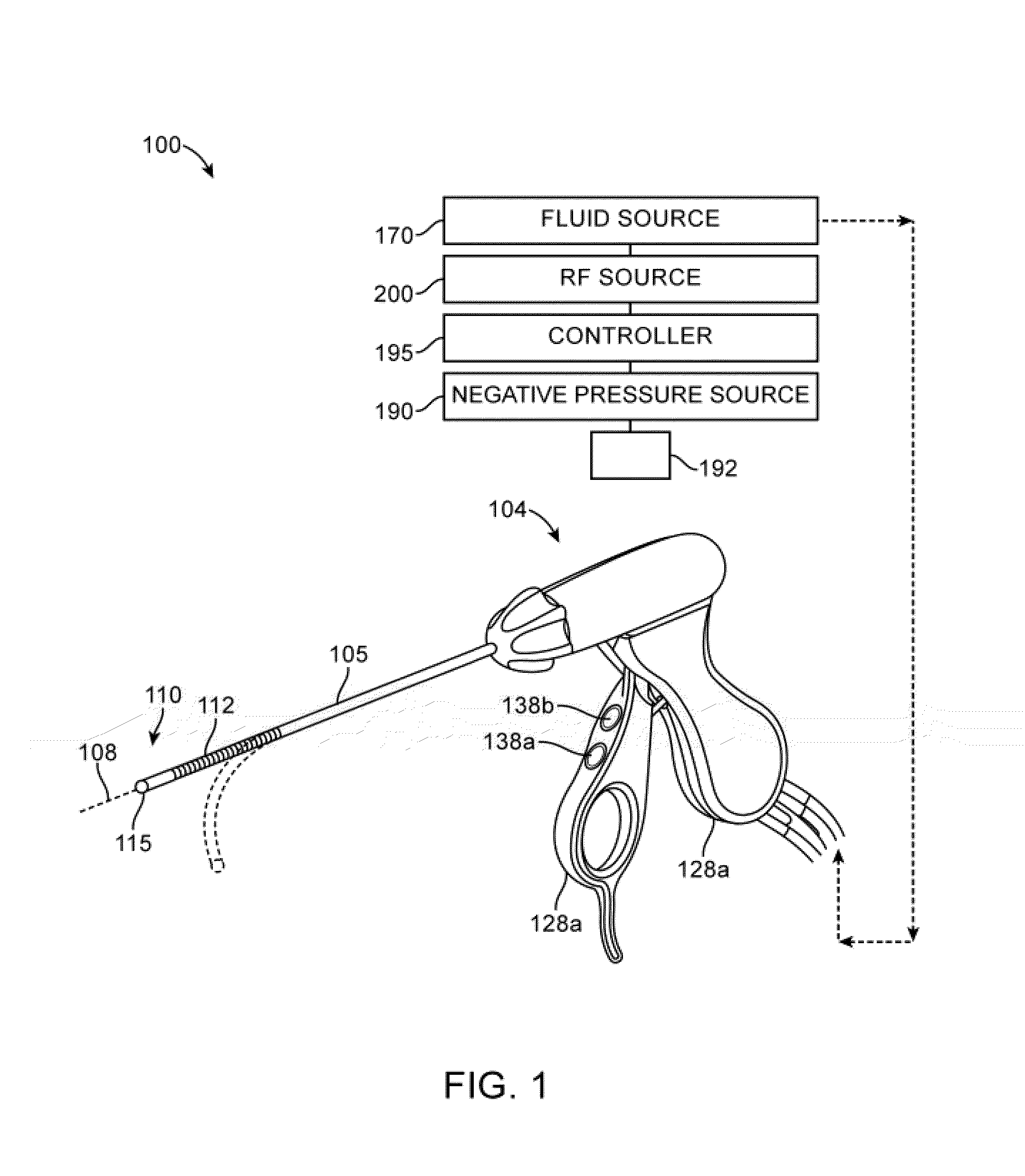
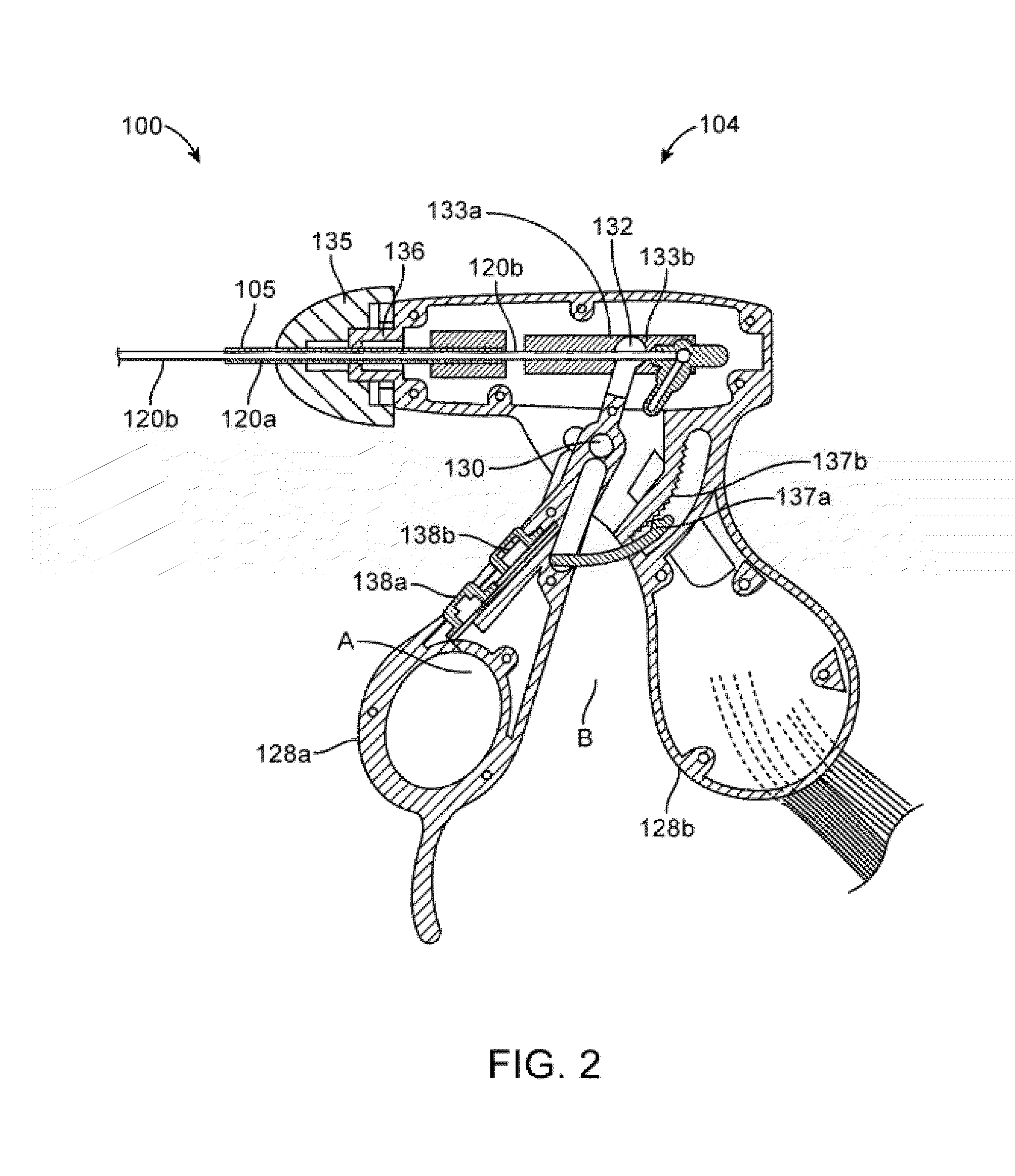
System for electrosurgical tissue treatment in the presence of electrically conductive fluid
InactiveUS7678069B1Quantity minimizationReduce the temperatureCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the electrode terminal(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
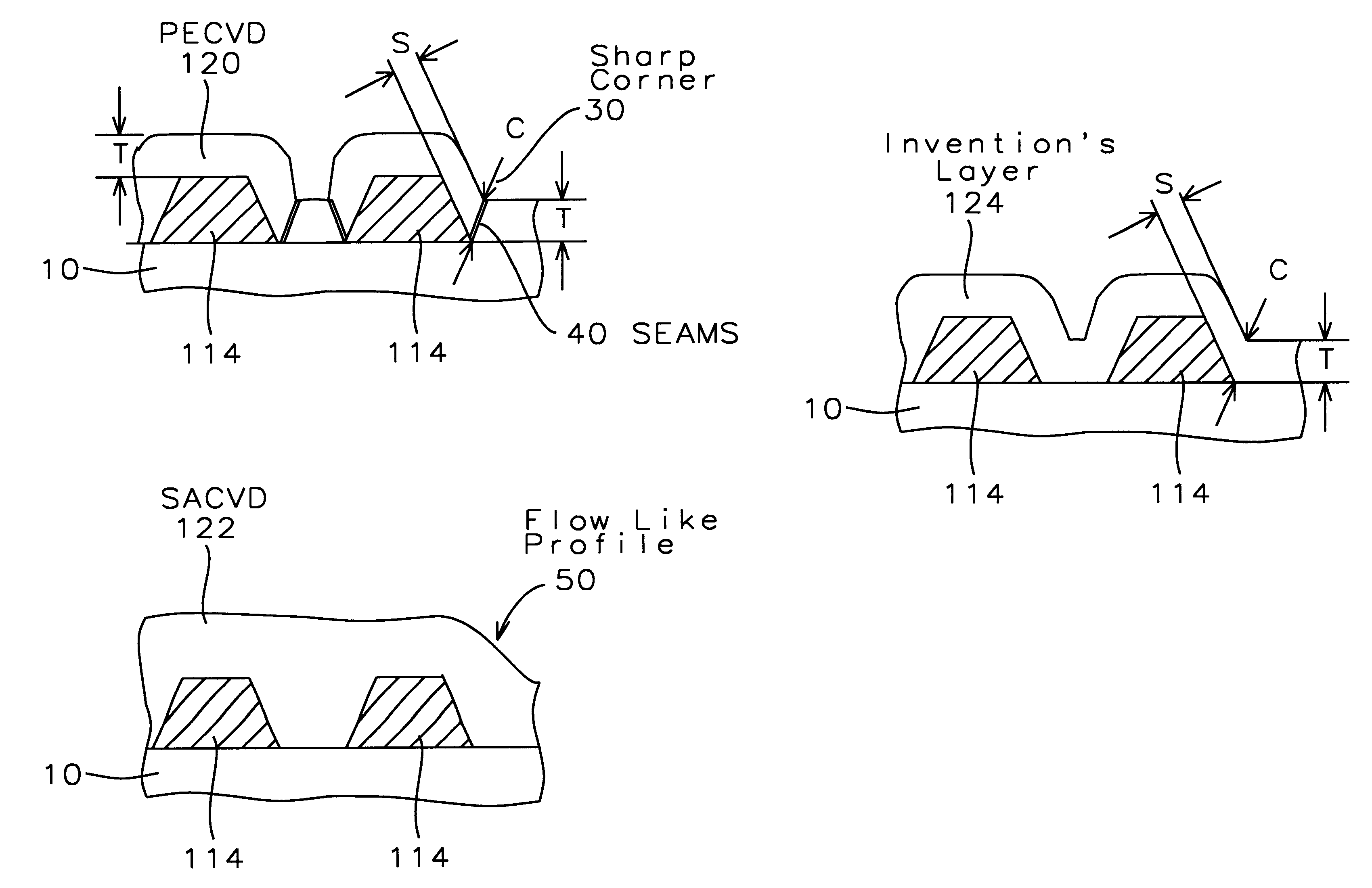
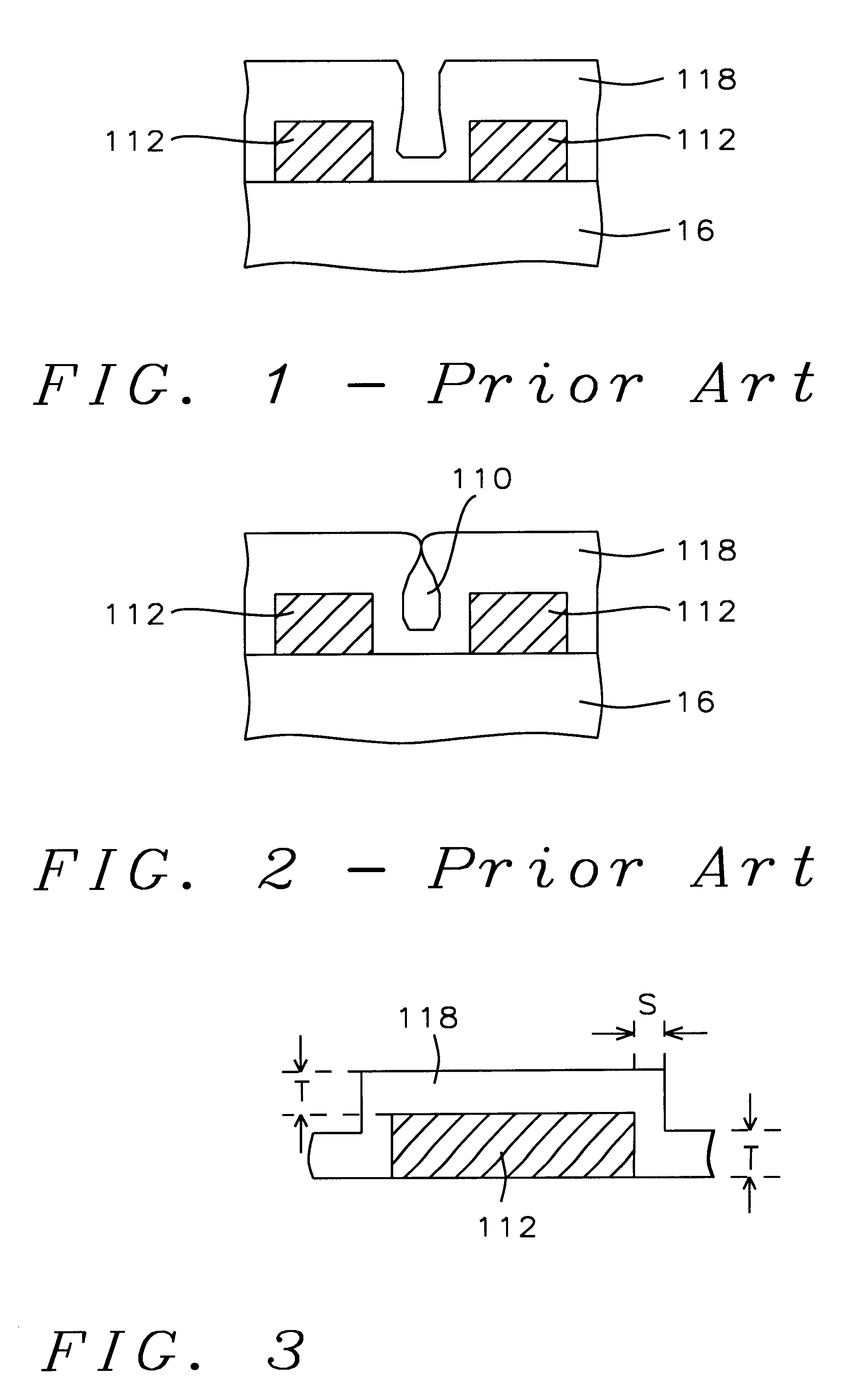
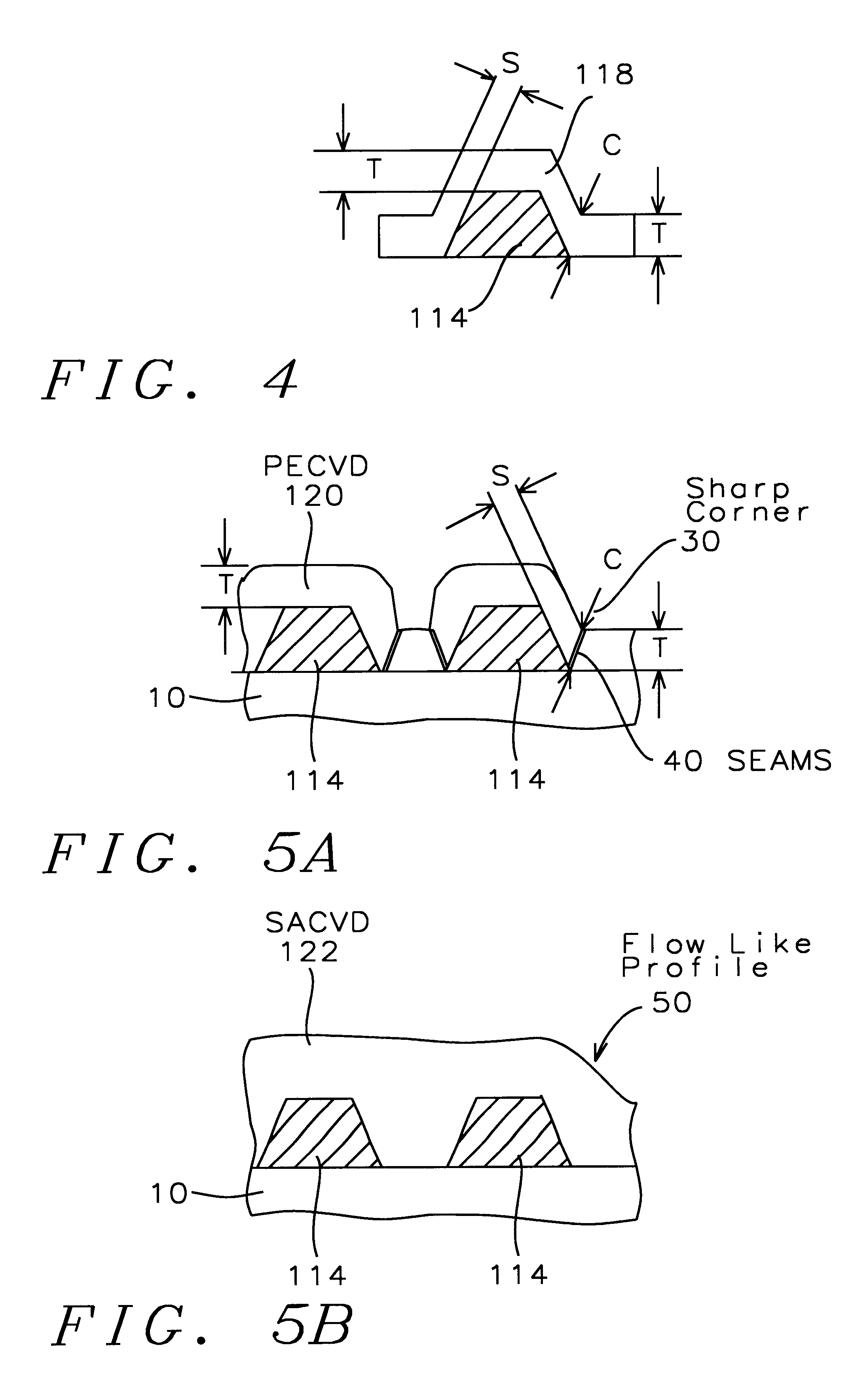
Method of silicon oxide and silicon glass films deposition
InactiveUS6197705B1Good step coverageImprove integrityPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricPlasma density
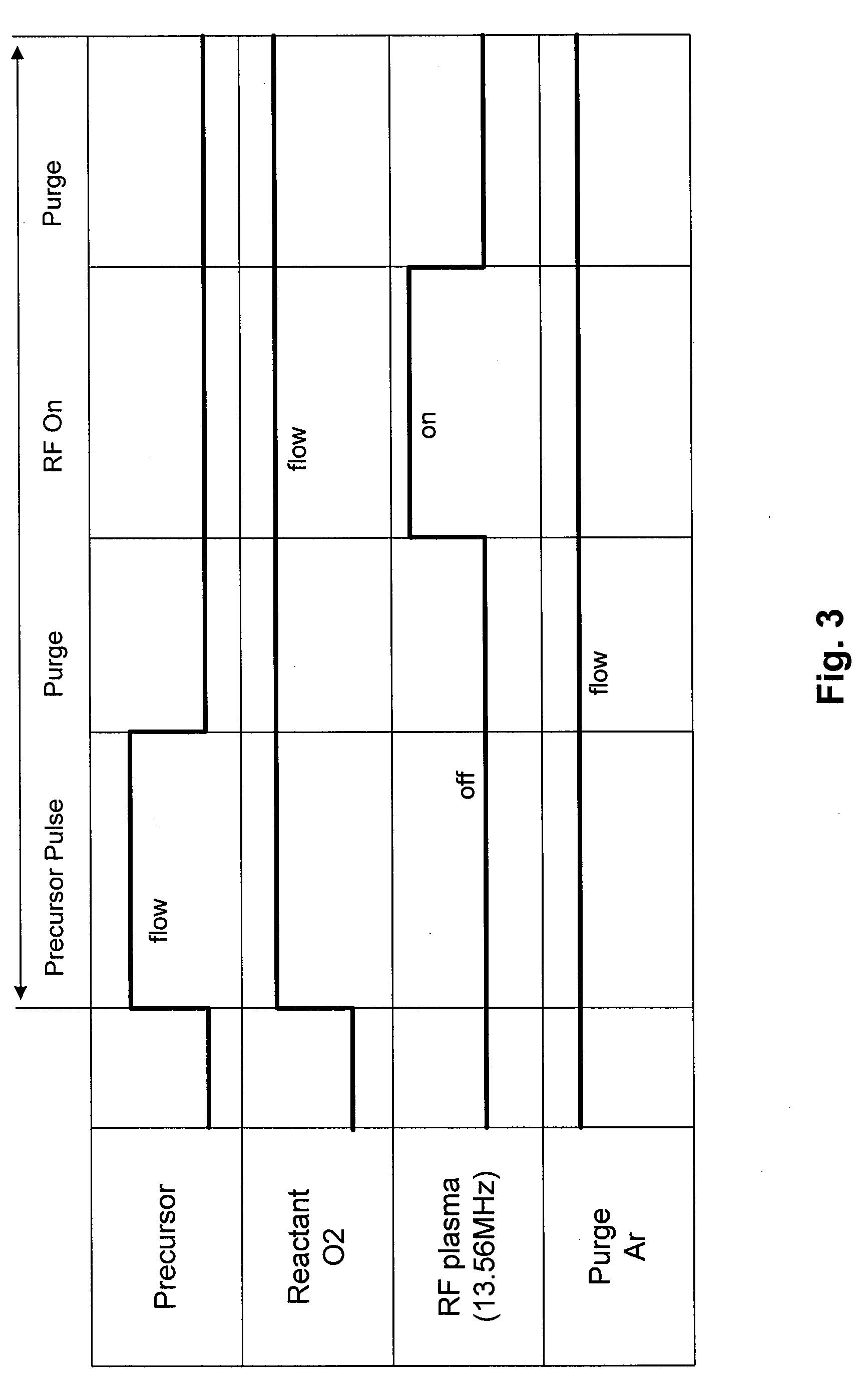
A method for fabricating a silicon oxide and silicon glass layers at low temperature using soft power-optimized Plasma-Activated CVD with a TEOS-ozone-oxygen reaction gas mixture (TEOS O3 / O2 PACVD) is described. It combines advantages of both low temperature Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) and TEOS-ozone Sub-Atmospheric Chemical Vapor Deposition (SACVD) and yields a coating of silicon oxide with stable and high deposition rate, no surface sensitivity, good film properties, conformal step coverage and good gap-fill. Key features of the invention's O3 / O2 PACVD process are: a plasma is maintain throughout the entire deposition step in a parallel plate type reactor chamber, the precise RF plasma density, ozone concentration in oxygen and the deposition temperature. These features provide the reaction conditions for the proper O3 / O2 reaction mechanism that deposits a conformal silicon oxide layer. The process has significant implication for semiconductor device manufacturing involving the deposition of a dielectric over a conducting non-planar surface.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
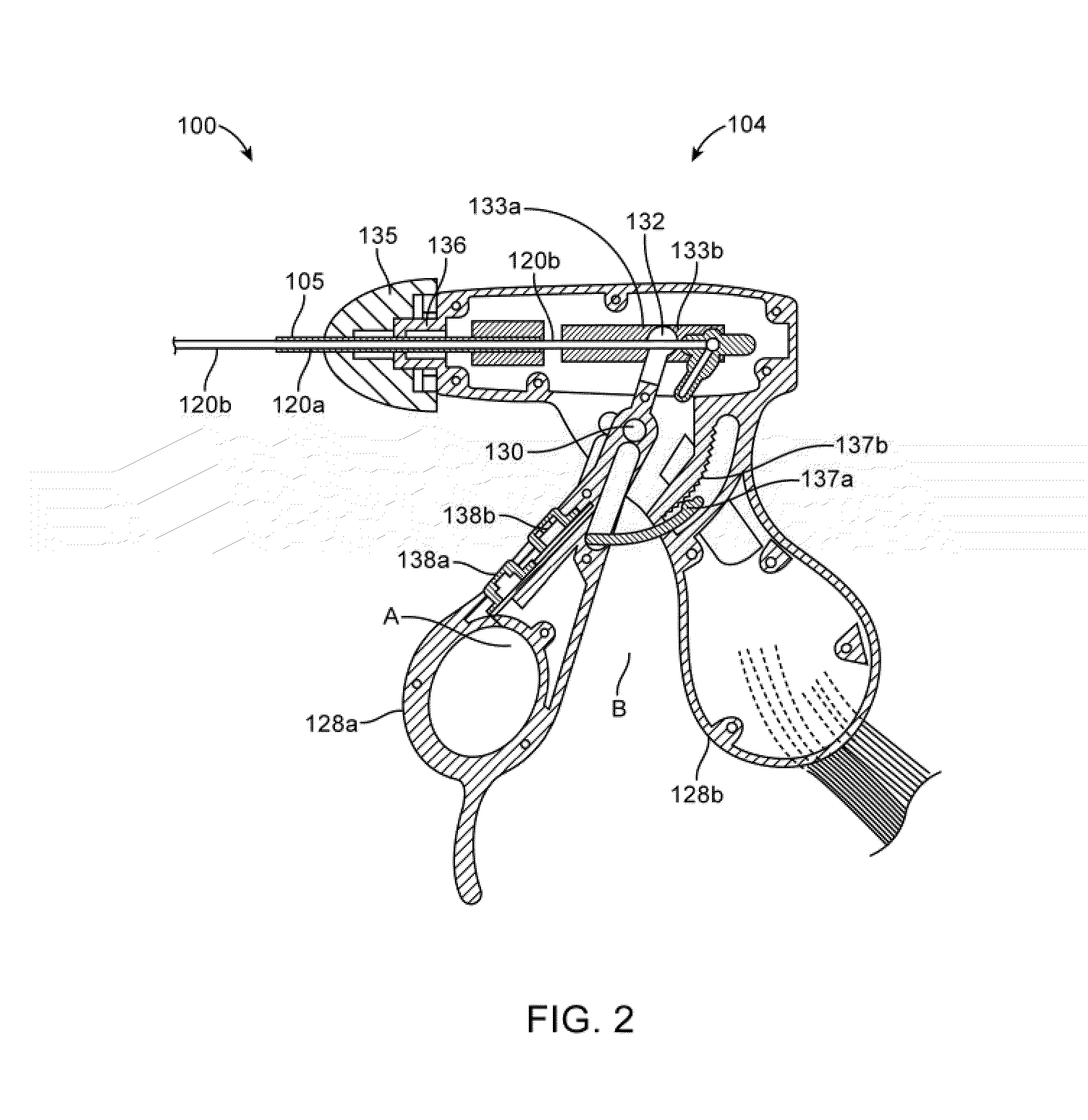
Instrument for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS7276063B2Low resistivityMinimizes production of heatSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to non-thermally generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Medical ablation system and method of use
ActiveUS9204918B2DiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingLow temperature plasmaBiomedical engineering
A probe for ablating tissue comprises an electrosurgical working end configured to provide a first plasma about a first surface location and a second plasma about a second surface location, the first plasma having first ablation parameters and the second plasma having second ablation parameters. The probe has a working end with a thickness below 3 mm and produces a low temperature plasma.
Owner:RELIGN CORP
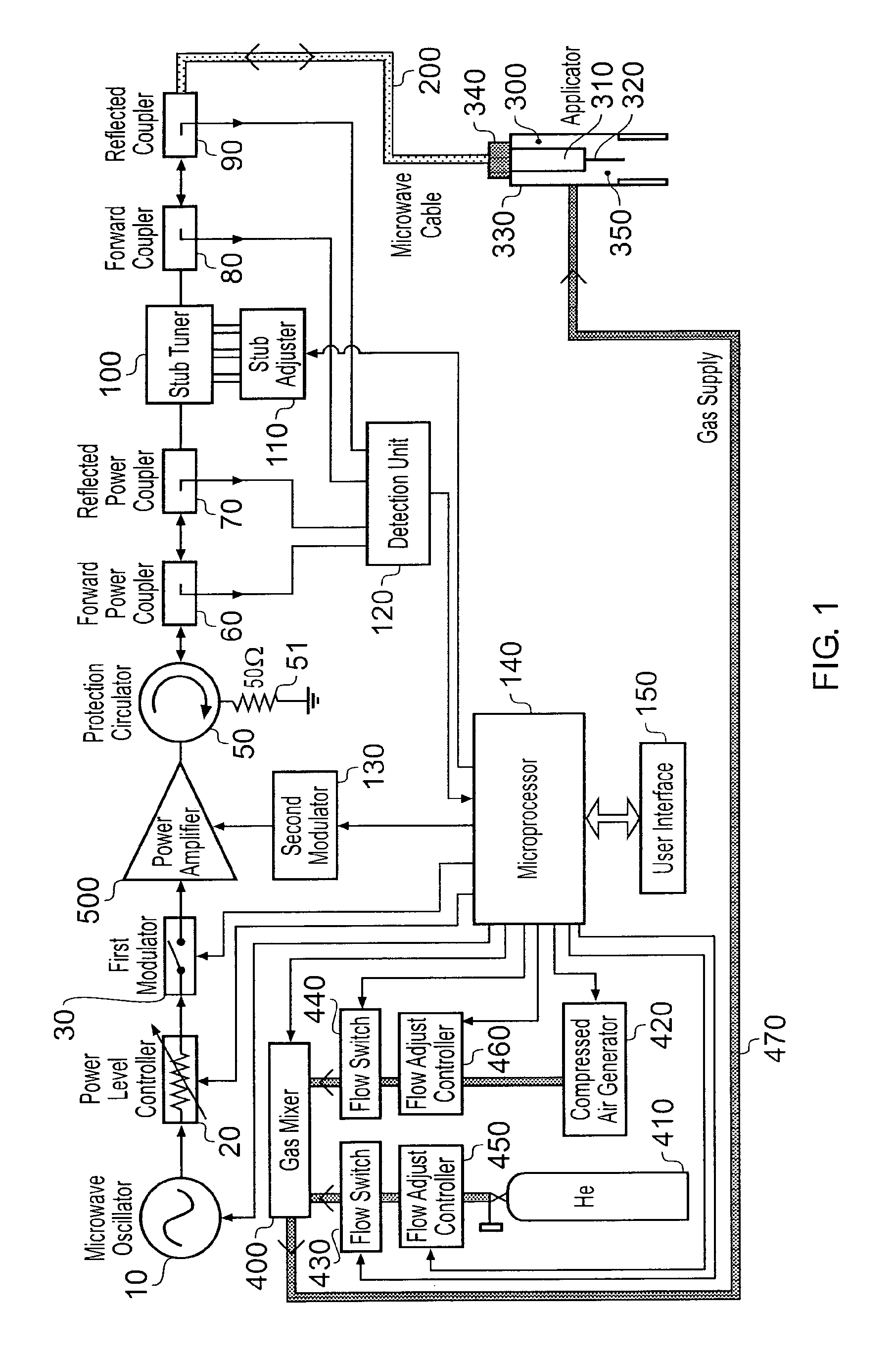
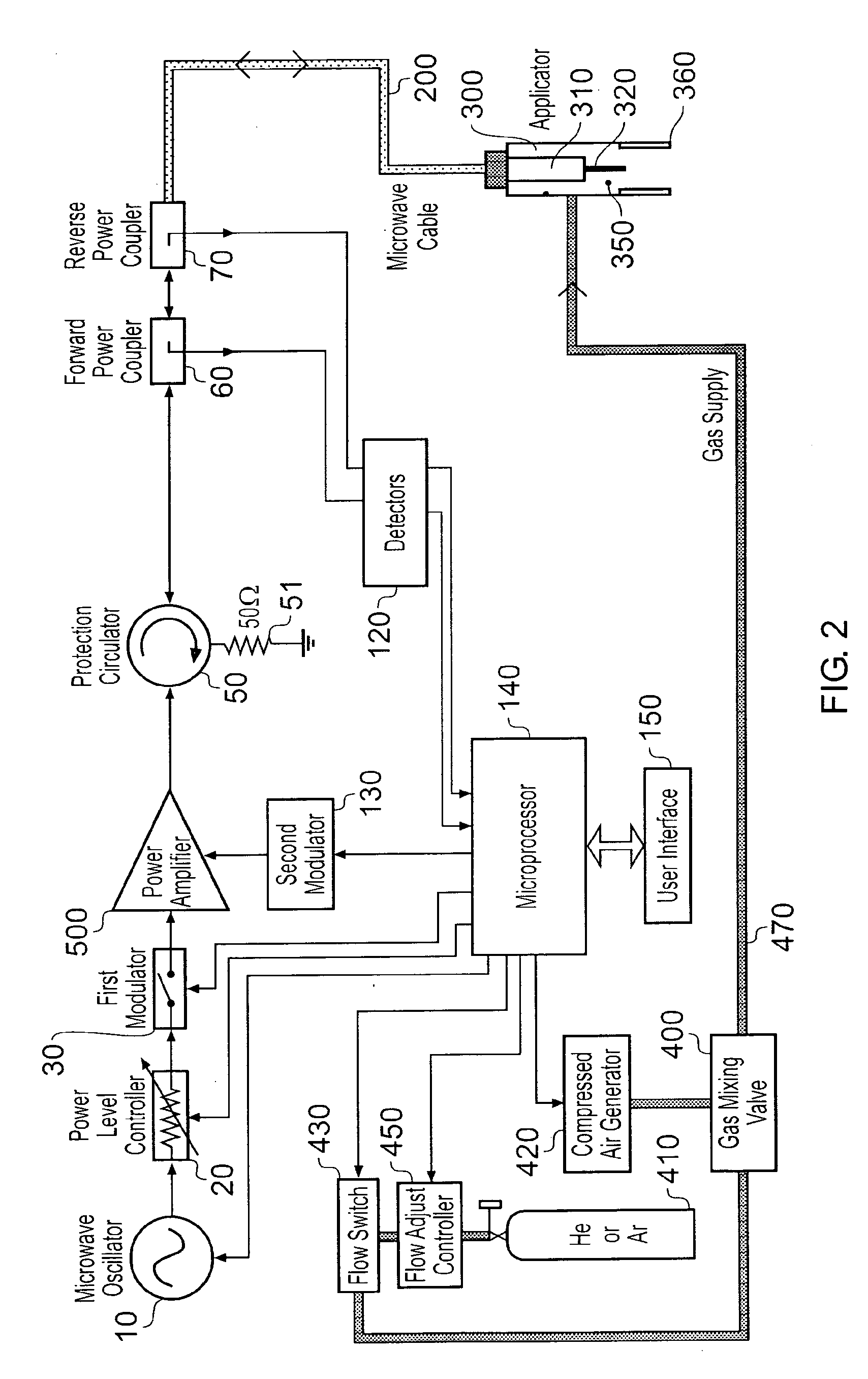
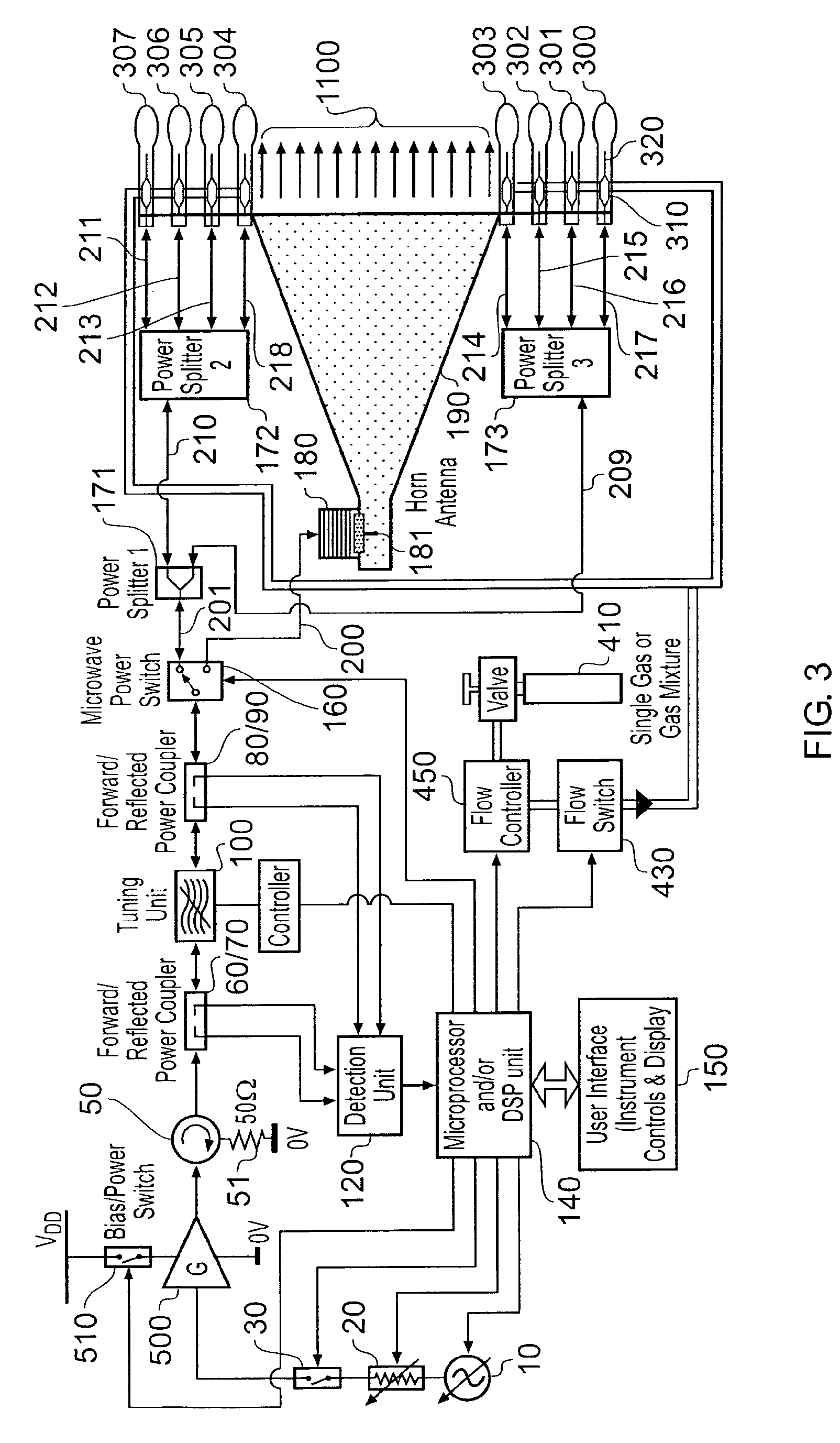
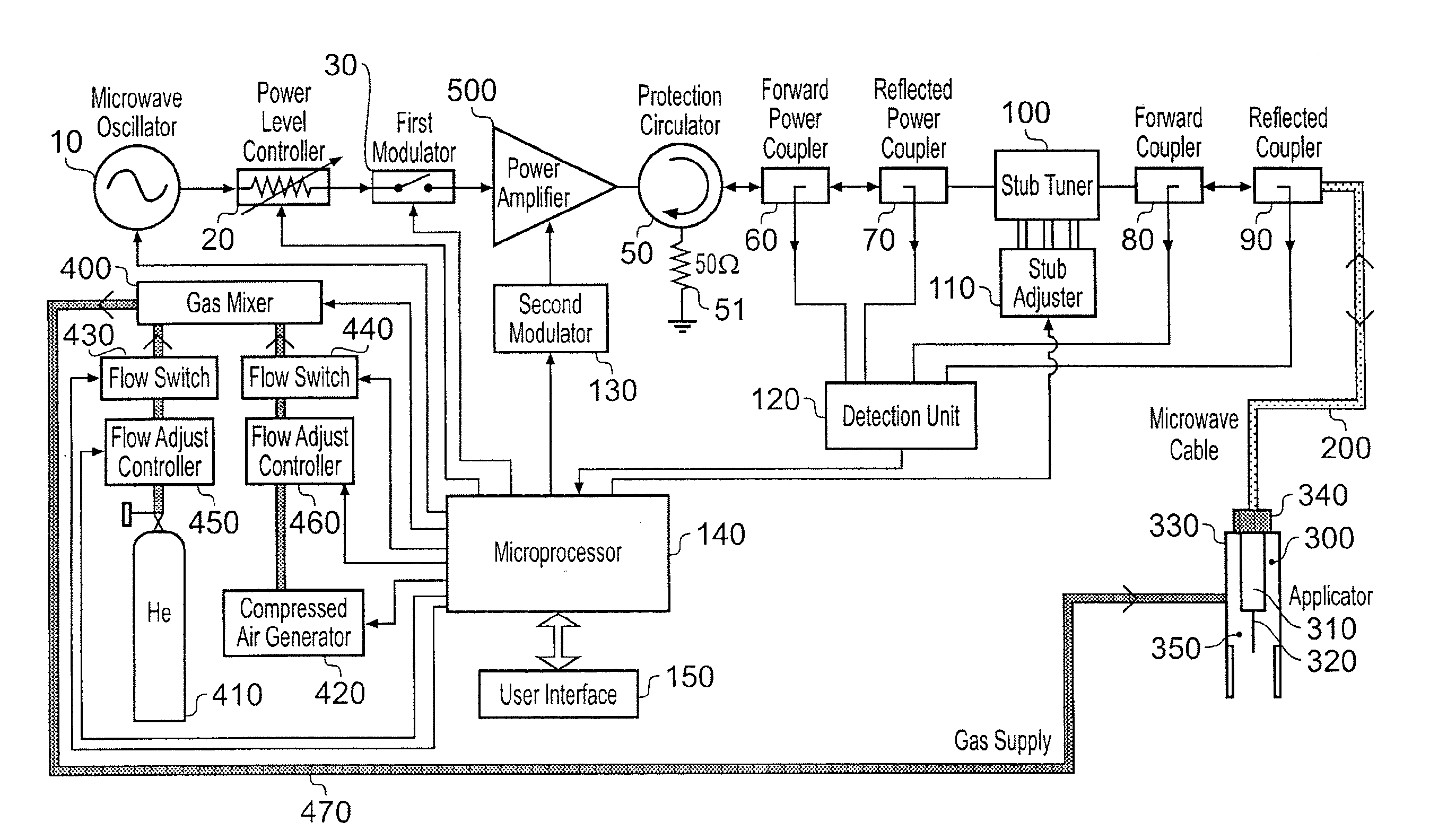
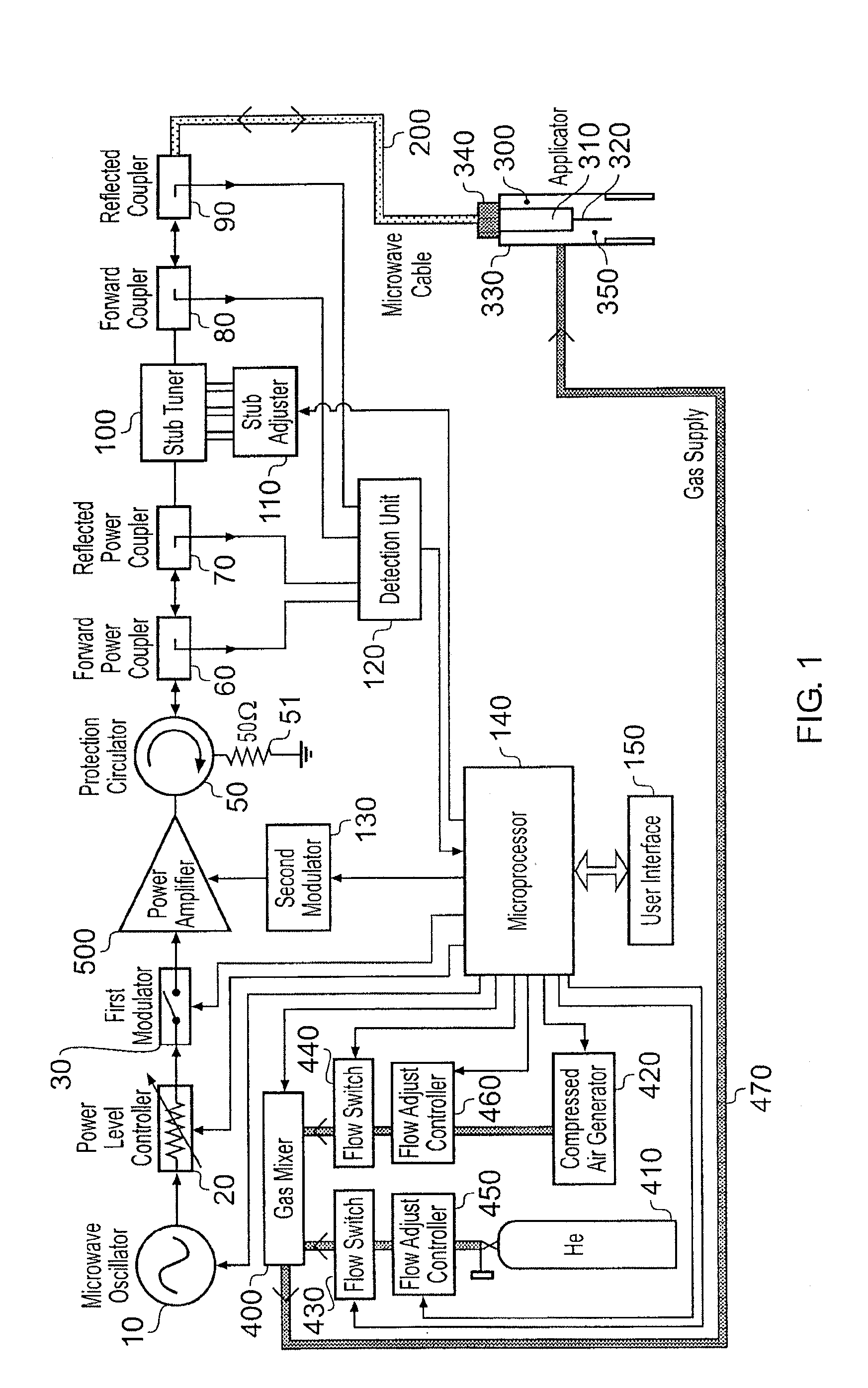
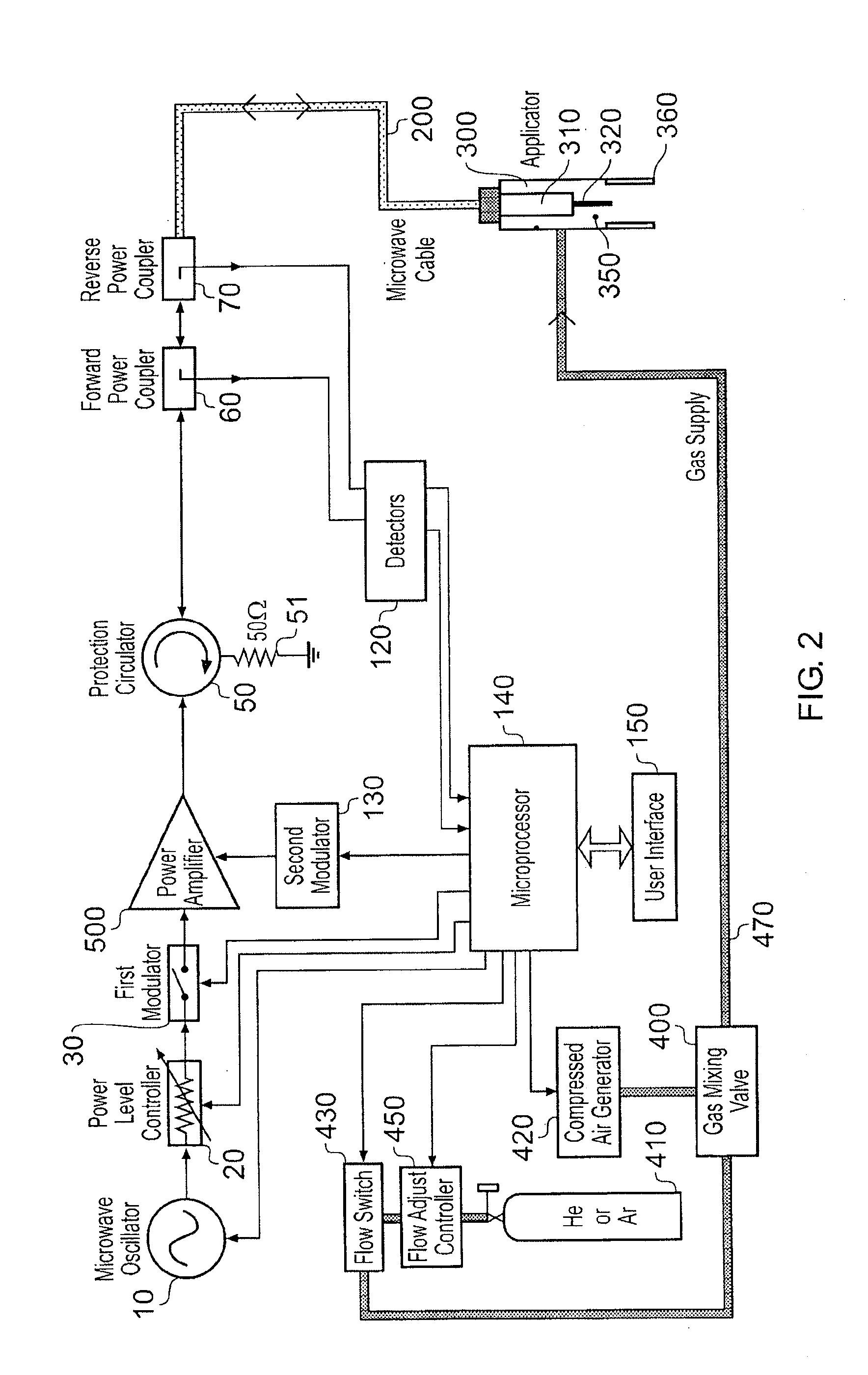
Microwave plasma sterilisation system and applicators therefor
ActiveUS20100296977A1Avoid damageEasy to operateDisinfectionEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMicrowaveSurface plasmon
A sterilisation system having a controllable (e.g. adjustably modulatable) non-ionising microwave radiation source for providing microwave energy for combining with a gas (e.g. an inert gas or a mixture of inert gases) to produce atmospheric low temperature plasma for sterilising biological tissue surfaces or the like. A plasma generating region may be contained in a hand held plasma applicator. The system may include an impedance adjustor e.g. integrated in the plasma applicator arranged to set a plasma strike condition and plasma sustain condition. The gas and microwave energy may be transported to a plasma generating region along an integrated cable assembly. The integrated cable assembly may provide a two way gas flow arrangement to permit residual gas to be removed from the surface. Invasive surface plasma treatment is therefore possible. The plasma applicator may have multiple plasma emitters to produce a line or blanket of plasma.
Owner:CREO MEDICAL LTD
Instrument for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS20080021447A1Efficient ionizationLess heatSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to non-thermally generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
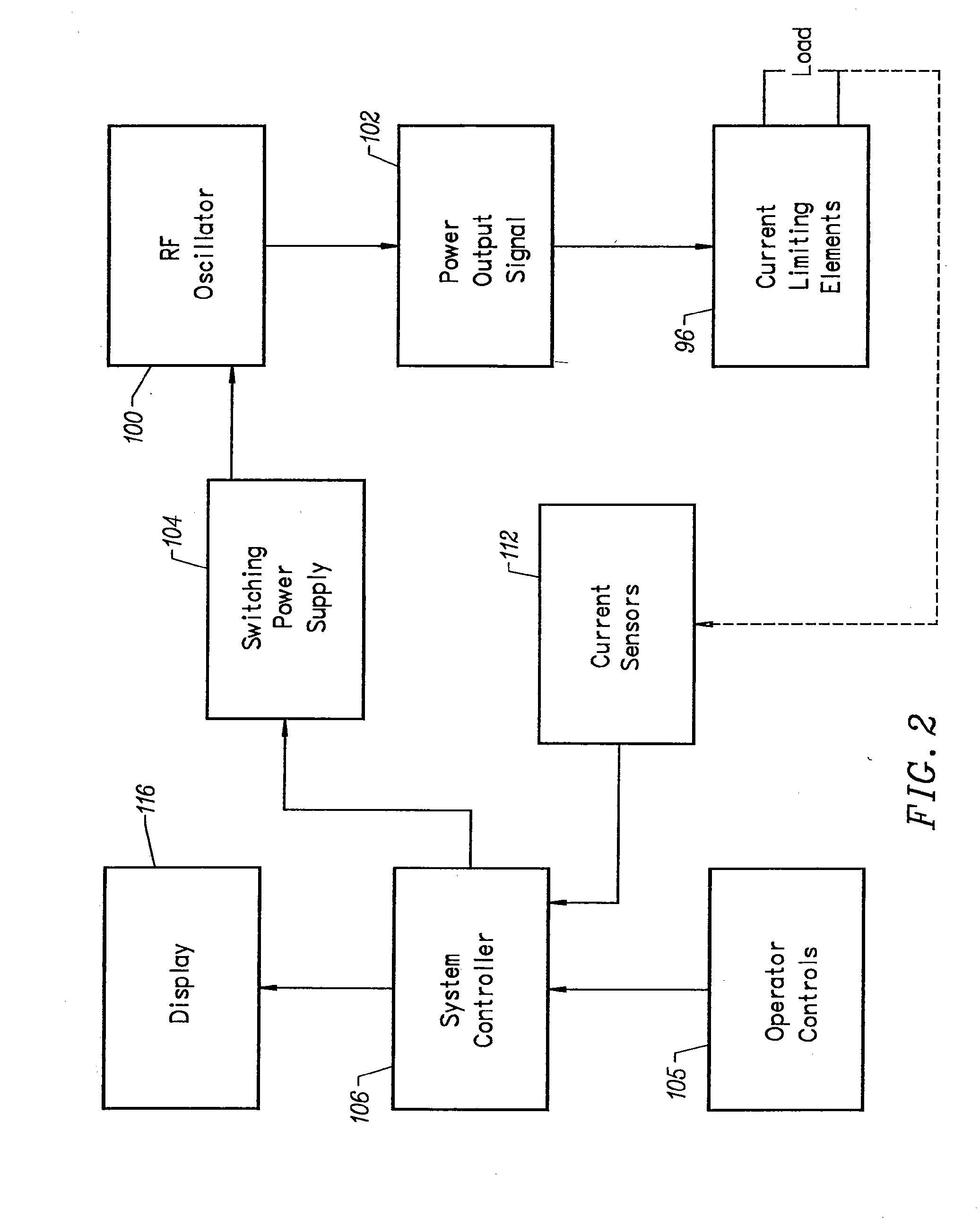
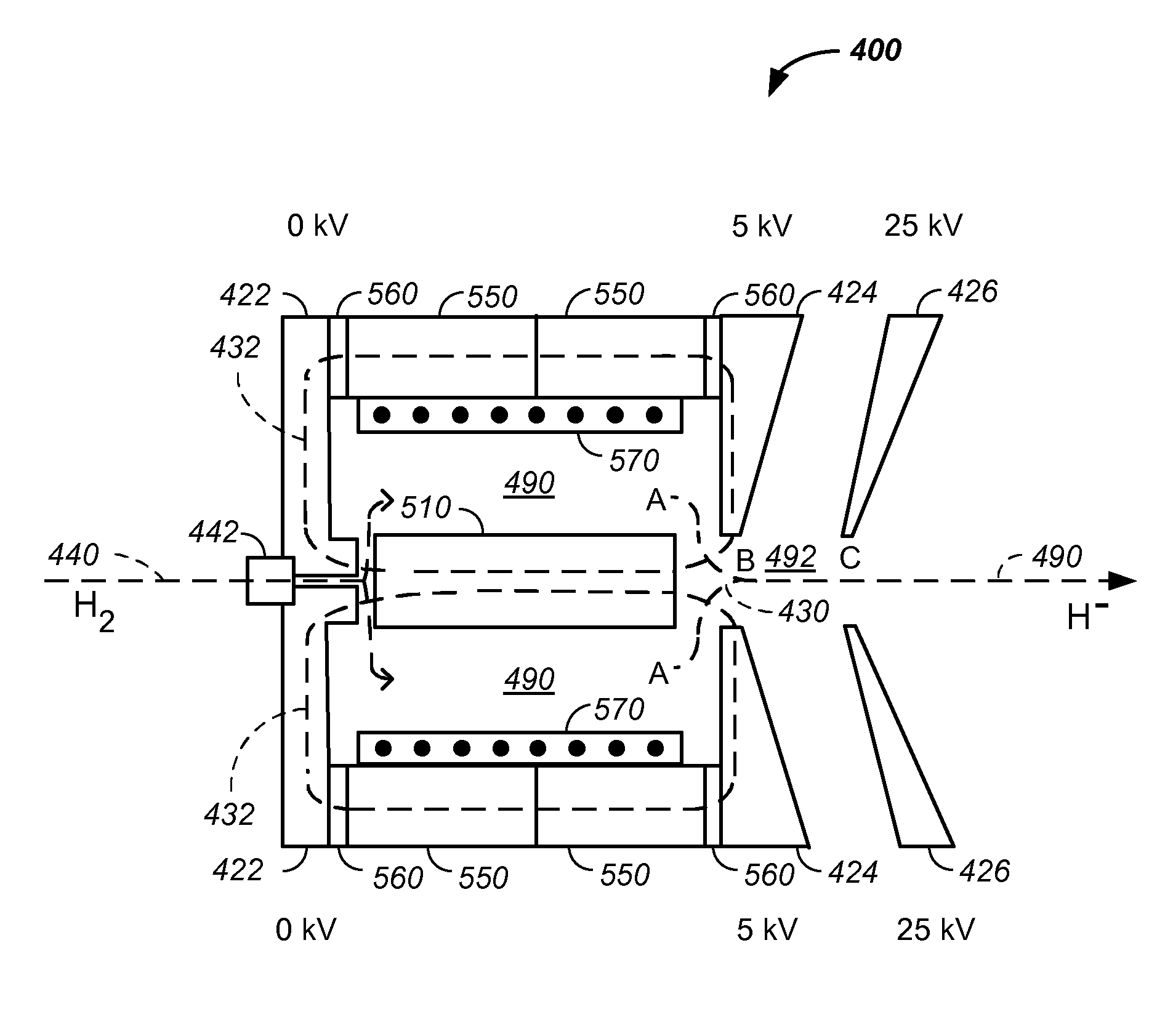
Negative ion source method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS7943913B2Material analysis by optical meansMagnetic resonance acceleratorsTandem acceleratorSynchrotron
The invention comprises a negative ion source method and apparatus used as part of an ion beam injection system, which is used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle or proton beam radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. The negative ion source preferably includes an inlet port for injection of hydrogen gas into a high temperature plasma chamber. In one embodiment, the plasma chamber includes a magnetic material, which provides a magnetic field barrier between the high temperature plasma chamber and a low temperature plasma region on the opposite side of the magnetic field barrier. An extraction pulse is applied to a negative ion extraction electrode to pull the negative ion beam into a negative ion beam path, which proceeds through a first partial vacuum system, through an ion beam focusing system, into the tandem accelerator, and into a synchrotron.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
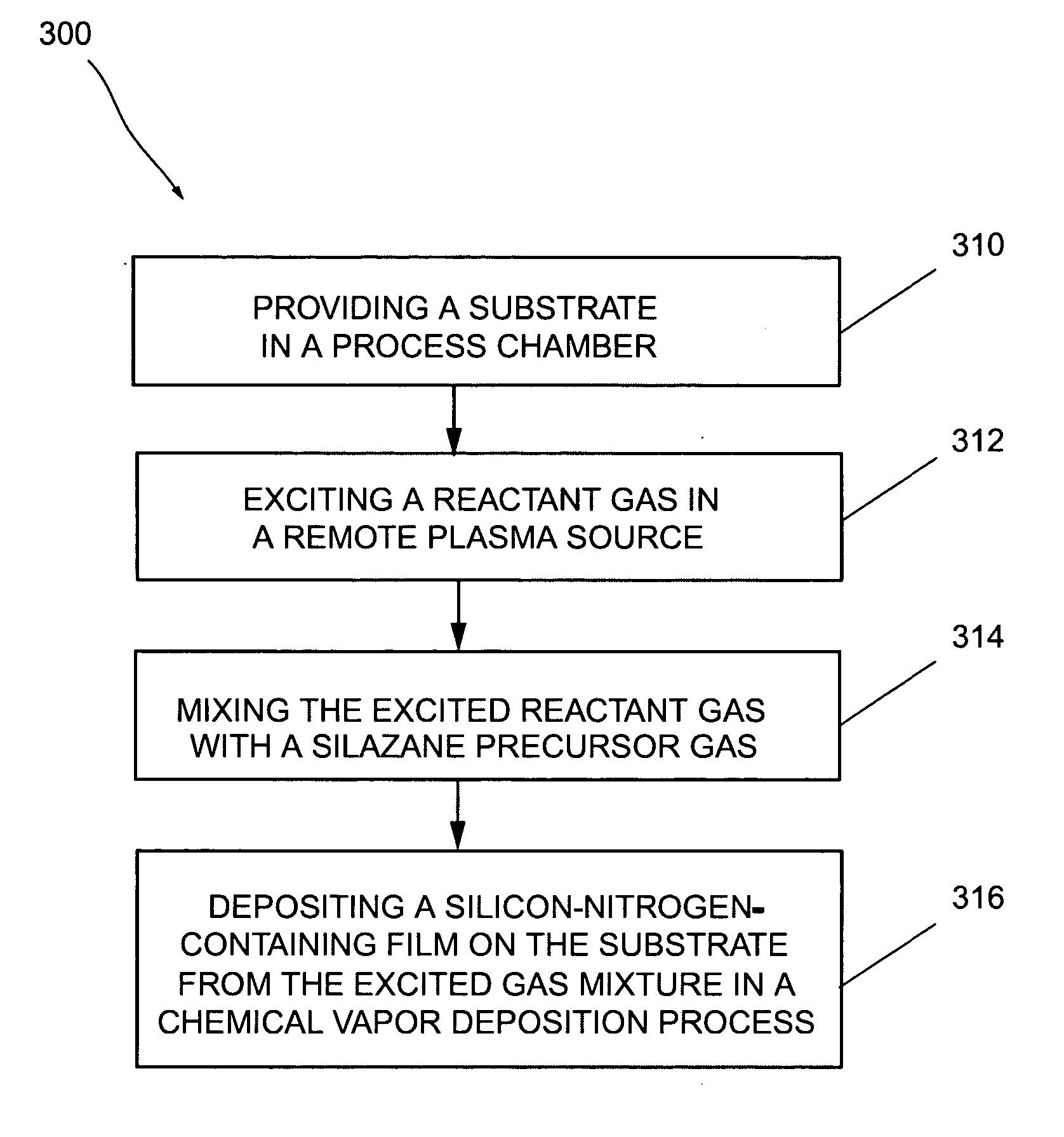
Low-temperature plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition of silicon-nitrogen-containing films
InactiveUS20060014399A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilazaneRemote plasma
A method for low-temperature plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition of a silicon-nitrogen-containing film on a substrate. The method includes providing a substrate in a process chamber, exciting a reactant gas in a remote plasma source, thereafter mixing the excited reactant gas with a silazane precursor gas, and depositing a silicon-nitrogen-containing film on the substrate from the excited gas mixture in a chemical vapor deposition process. In one embodiment of the invention, the reactant gas can contain a nitrogen-containing gas to deposit a SiCNH film. In another embodiment of the invention, the reactant gas can contain an oxygen-containing gas to deposit a SiCNOH film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for using low-temperature plasma to prepare supported metal sulfide catalyst
InactiveCN103495427AGood dispersionAvoid exposureMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsDispersityReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for using low-temperature plasma to prepare a supported metal sulfide catalyst and belongs to the technical field of material science. The method is characterized by including: allowing ionization of hydrogen sulfide gas or gas containing hydrogen sulfide through gas discharge to form the low-temperature plasma distributed evenly, and using the low-temperature plasma to interact with supported metal salt precursor to generate metal sulfide. Due to the fact that the catalyst is avoided from being exposed in excessively high temperature, the prepared catalyst is free of thermal agglomeration, so that the catalyst is smaller in particle size and higher in dispersity. The method is suitable for preparation of various sulfide catalysts, metal sulfide can be supported on different materials to prepare various supported catalysts. The method has the advantages of low reaction temperature, low energy consumption, short preparation time and the like. In addition, processing objects are common metal salt, wide involve range is achieved, and the prepared catalyst is applicable to various common heterogeneous reactions.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS7572251B1Reduce ionic strengthFacilitate initiationCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to non-thermally generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
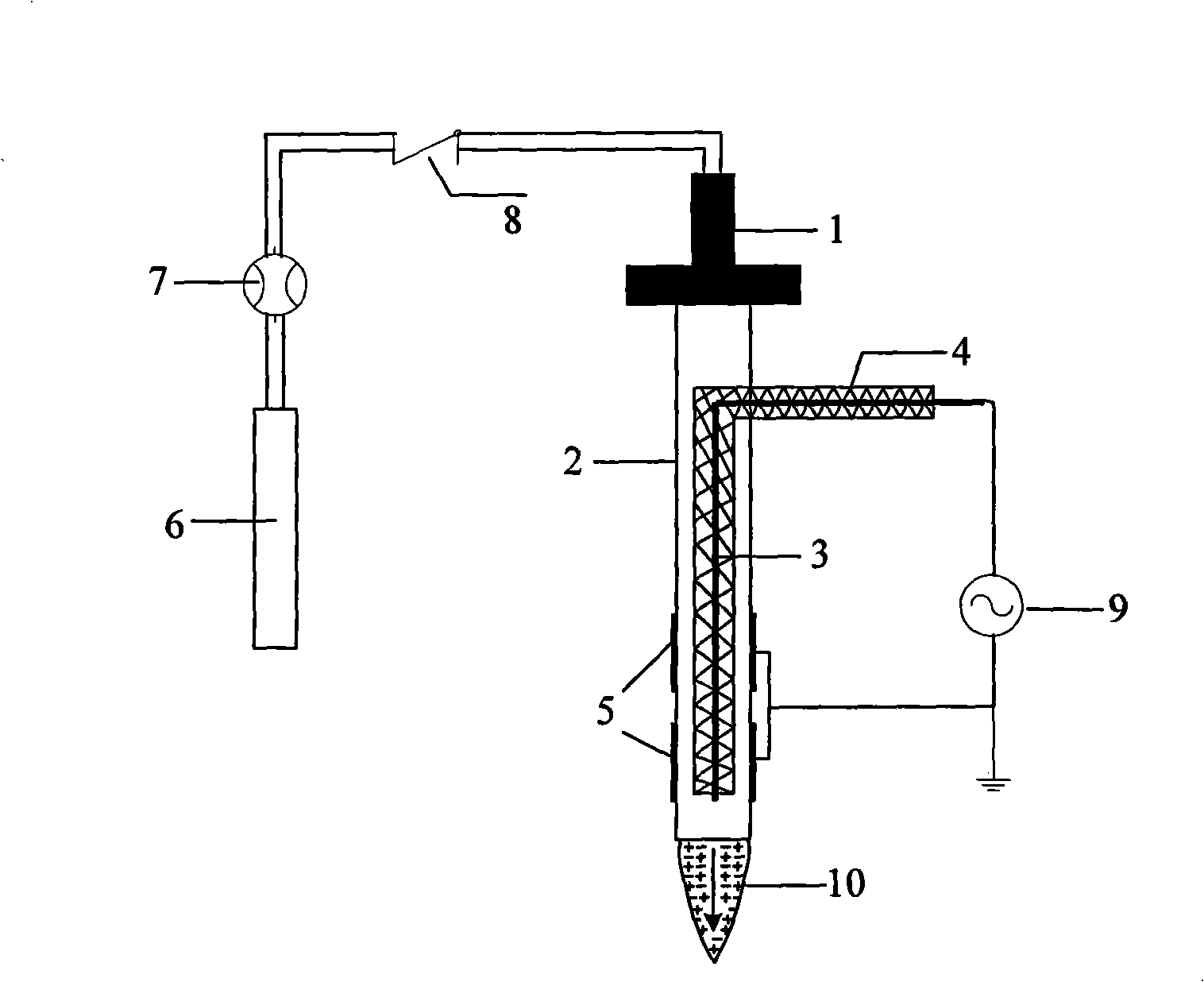
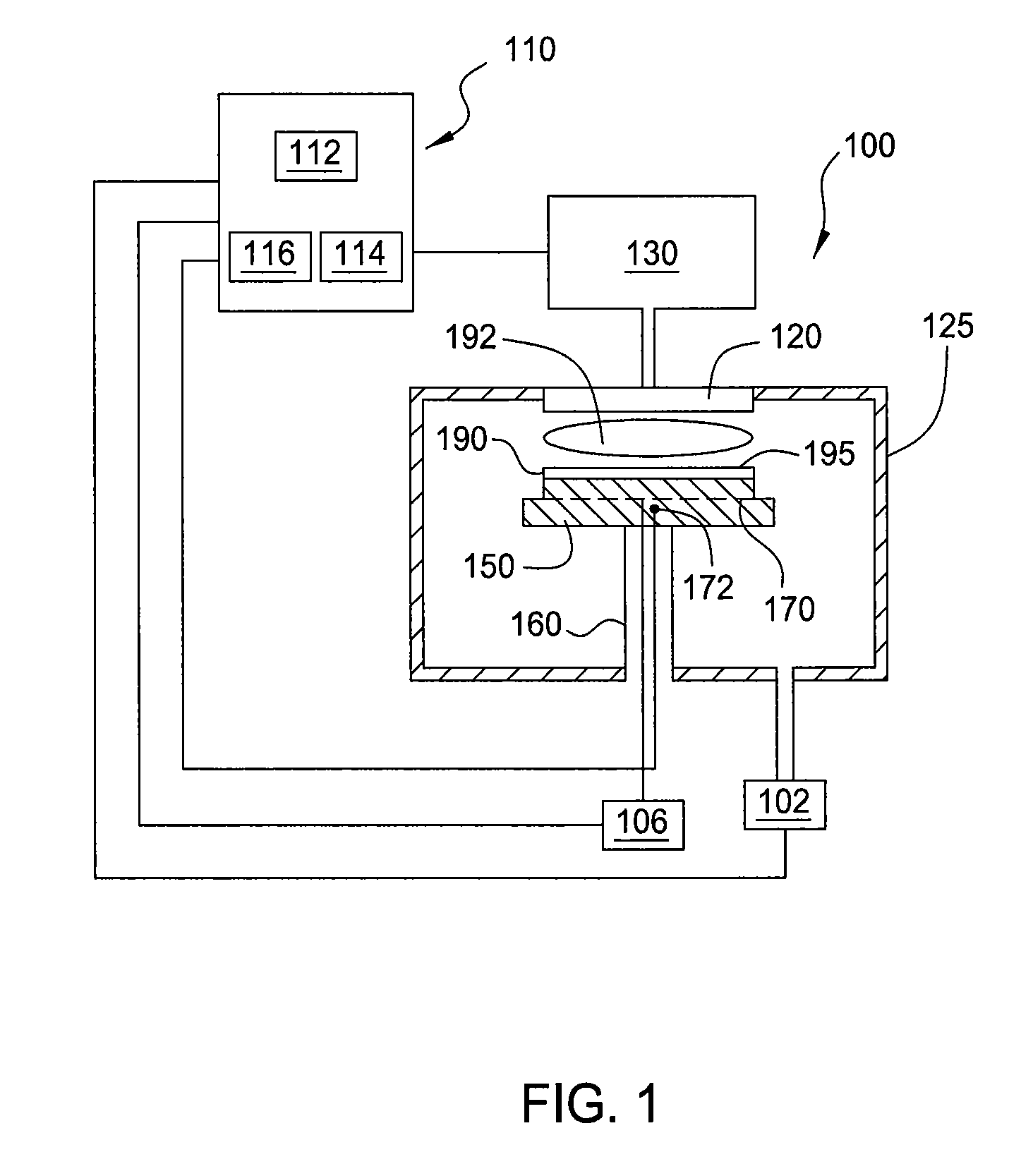
Apparatus for generating low temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS6441554B1Reduce discharge voltageReduce operating and installment cost and electricity consumptionElectric discharge tubesWater treatment compoundsDielectricElectrical conductor
Owner:SE PLASMA
Changing surface properties by functionalized nanoparticles
InactiveUS20100178512A1Strong and durable adhesionMaterial nanotechnologyPretreated surfacesFunctionalized nanoparticlesUltraviolet
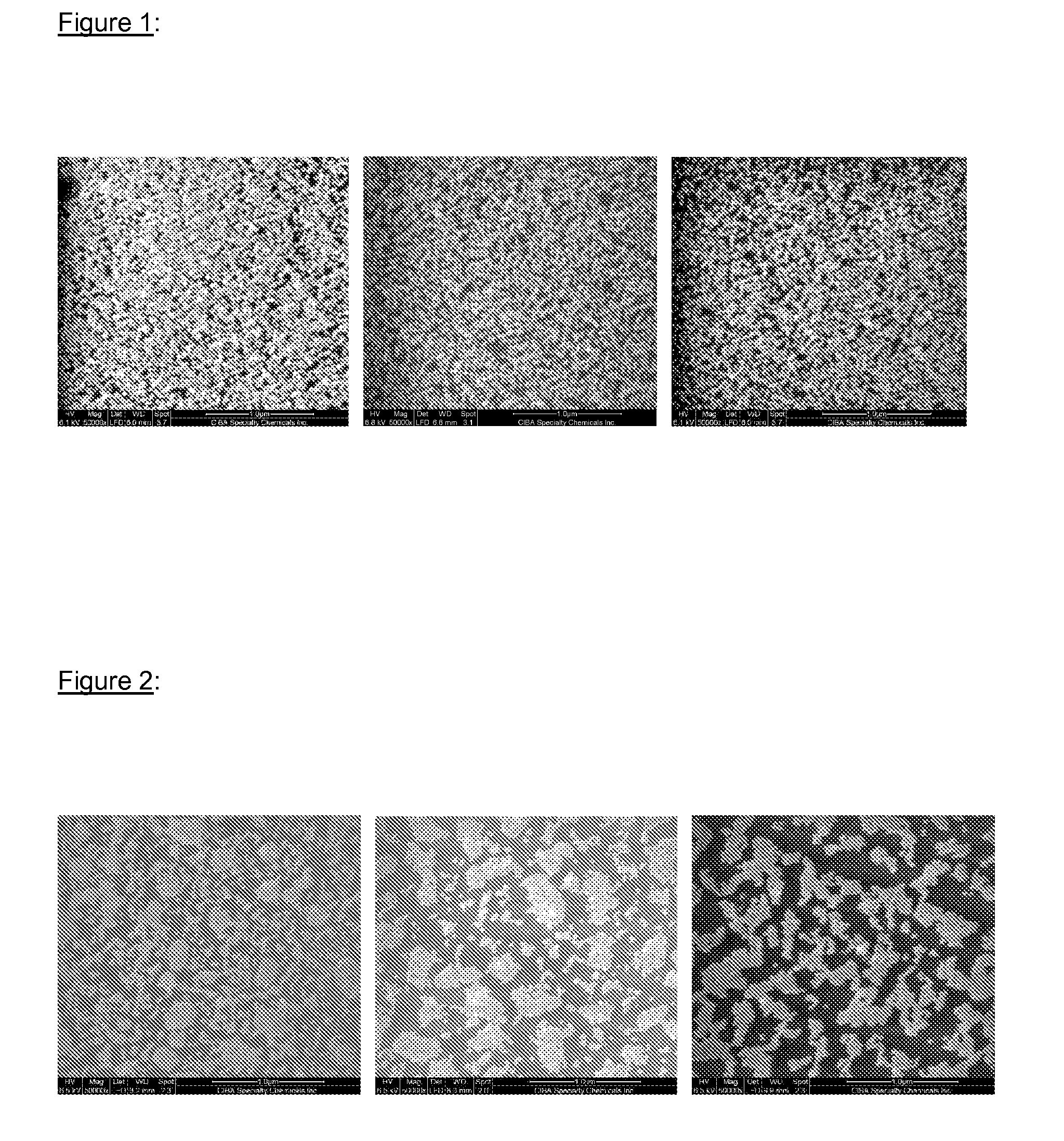
A process for modifying the surface of an inorganic or organic substrate with strongly adherent nanoparticles is described, providing to the surface modified substrate durable effects like hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, electrical conductivity, magnetic properties, flame retardance, color, adhesion, roughness, scratch resistance, UV-absorbance, antimicrobial properties, antifouling properties, antiprotein properties, antistatic properties, antifog properties, release properties. In this process, an optional first step a) a low-temperature plasma, ozonization, high energy irradiation, corona discharge or a flame is caused to act on the inorganic or organic substrate, and in a second step b) one or more defined nanoparticles or mixtures of defined nanoparticles with monomers, containing at least one ethylenically unsaturated group, or solutions, suspensions or emulsions of the afore-mentioned substances, are applied, preferably at normal pressure, to the inorganic or organic substrate. In a third step c) suitable methods are applied to dry or cure those afore-mentioned substances and, optionally, in a fourth step d) a further coating is applied on the substrate so pretreated.
Owner:CIBA CORP
Method of producing nanoparticles, nanoparticles, and lithium battery comprising electrode comprising the nanoparticles
ActiveUS20090253037A1Material nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleLow temperature plasma
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Medical ablation system and method of use
ActiveUS20130253498A1Reduce the temperatureDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingLow temperature plasmaBiomedical engineering
A probe for ablating tissue comprises an electrosurgical working end configured to provide a first plasma about a first surface location and a second plasma about a second surface location, the first plasma having first ablation parameters and the second plasma having second ablation parameters. The probe has a working end with a thickness below 3 mm and produces a low temperature plasma.
Owner:RELIGN CORP
Method for reducing loaded metal catalyst using low temperature plasma
InactiveCN1647858ARestore quickly and efficientlyGood dispersionCatalyst activation/preparationOxygenLow temperature plasma
The method of reducing loaded metal catalyst with low temperature plasma includes the steps of: 1) dissolving active metal salt component in deionized water or distilled water to form solution with metal component content of 0.01-20 wt%, filling solution into catalyst carrier, letting stand at room temperature for 8-24 hr and drying at 40-110 deg.c for 2-10 hr; and 2) setting the catalyst between two electrodes of plasma apparatus, introducing inert gas, air or oxygen as plasma discharge gas into discharge tube of pressure of 50-10000 Pa, and applying DC or AC voltage of 100-20000 V across the electrodes to process for 5-200 min. The low temperature plasma contains great amount of electrons, has powerful reducing capacity to reduce metal ion into metal simple substance and has no negative reaction appearing at high temperature. The process is simple, short in reduction time, without need of chemical reductant and environment friendly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Microwave plasma sterilisation system and applicators therefor
ActiveUS20140066838A1Easy to operateSufficient magnitudeMedical devicesLavatory sanitoryMicrowaveSurface plasmon
Owner:CREO MEDICAL LTD
Method for preparing light metal super-hydrophobic surface
InactiveCN101423945AExcellent superhydrophobic propertiesWear-resistantAnodisationOther chemical processesLow temperature plasmaWear resistance
The invention relates to a preparation method for a light metal superhydrophobic surface, in particular to a light metal surface with a superhydrophobic property and corrosion and wear resistance. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a layer of porous oxidation film is formed on the surface through anodic oxidation of the light metal surface first; the surface is modified by a low-temperature plasma treatment technique; and at last, the superhydrophobic surface is formed on the surface of the oxidation film through chemical modification. The method does not require complex and expense equipment and has a simple process, good repetitiveness, a contact angle of the surface and water up to 153 to 170 degrees as well as good corrosion and wear resistance.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
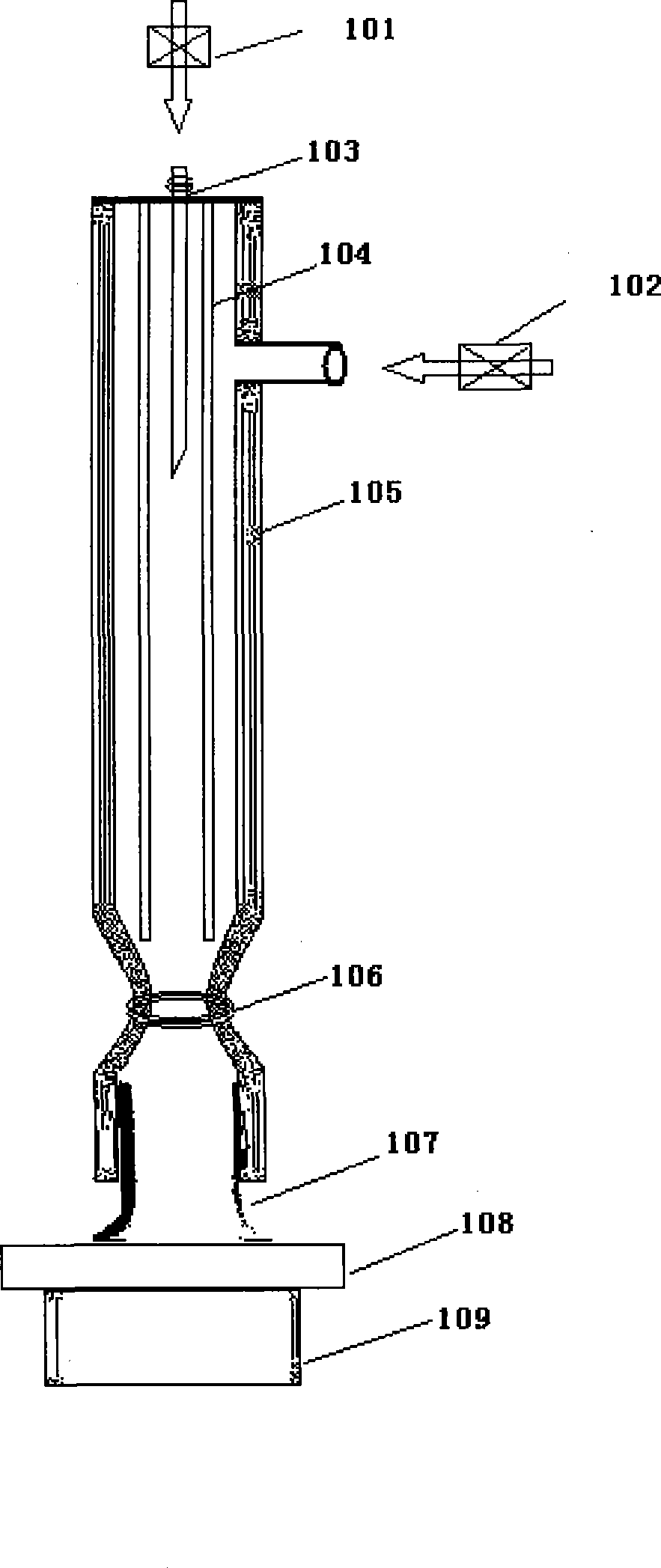
Jet apparatus capable of blocking discharging from generating low temperature plasma by atmos medium
InactiveCN101330794ASolve the problem of limited application rangeEasy to modifyPlasma techniquePlasma jetParallel plate
A jetting device for a low-temperature plasma generated by the atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge relates to the technical field of the application of gas discharge plasma. Inert gas and air are used as working gas; the plasma generated in a discharge area is blown out in the form of jet; the problem of limited application range caused by the narrow parallel-plate dielectric barrier discharge area and a high plasma macroscopic temperature can be solved. The device has the structural characteristics that a hollow pipe-shaped connector is connected with a hollow dielectric pipe; an electrode coated with insulation dielectric is fixed at the center of the dielectric pipe; an annular electrode is closely attached to the outer wall of the dielectric pipe; the working gas enters the dielectric pipe from a flow meter and a retaining valve through the connector; the plasma is blown out to form the plasma jetting. The jetting device has the advantages of low plasma macroscopic temperature, large electron energy, wide expanded range, low cost, low energy consumption and high reliability; furthermore, the jetting device can used in the fields of sterilization and disinfection, the surface modification of complex-shaped material, waste gas treatment, ozone synthesis, as well as the physical and chemical fields of the discharge light source plasma.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preionization atmos low-temperature plasma jet generator
InactiveCN101466194AReduce breakdownIncrease discharge powerElectric discharge tubesPlasma techniquePlasma jetHigh concentration
The invention relates to an atmospheric pressure low-temperature plasma jet reactor with preionization structure, which belongs to plasma discharge reactor technical field, and the reactor is characterized in that: the device main body is a millimeter magnitude main silica tube with one open end; a part is arranged above the open end at the lower part with 15 to 25mm, and the part becomes the thinnest at 20mm part, and a ring-shaped electrode is wound on the part; a thin silica tube is connected at the closed end arranged in the inner part thereof through the closed end arranged at the upper part of the silica tube; and a needle electrode is arranged in the thin silica tube. An earthing electrode is arranged below the open end of the main silica tube; and the argon gas is filled into the needle electrode, and the oxygen gas is filled into the main silica tube. The needle electrode and the ring-shaped electrode can be exerted with the same high voltage; the needle electrode discharge can supply the seed electrons for the ring-shaped electrode discharge, and a stable glowing discharge plasma jet is arranged between the ring-shaped electrode and the earthing electrode. The reactor has the beneficial effects that the obtained plasma jet can generate high-concentration chemical activity species, and the reactor has practical value.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Low temperature plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition of conformal silicon carbon nitride and silicon nitride films
ActiveUS20130183835A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseCarbon nitride
Methods and apparatus for forming conformal silicon nitride films at low temperatures on a substrate are provided. The methods of forming a silicon nitride layer include performing a deposition cycle including flowing a processing gas mixture into a processing chamber having a substrate therein, wherein the processing gas mixture comprises precursor gas molecules having labile silicon to nitrogen, silicon to carbon, or nitrogen to carbon bonds, activating the precursor gas at a temperature between about 20° C. to about 480° C. by preferentially breaking labile bonds to provide one or more reaction sites along a precursor gas molecule, forming a precursor material layer on the substrate, wherein the activated precursor gas molecules bond with a surface on the substrate at the one or more reaction sites, and performing a plasma treatment process on the precursor material layer to form a conformal silicon nitride layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
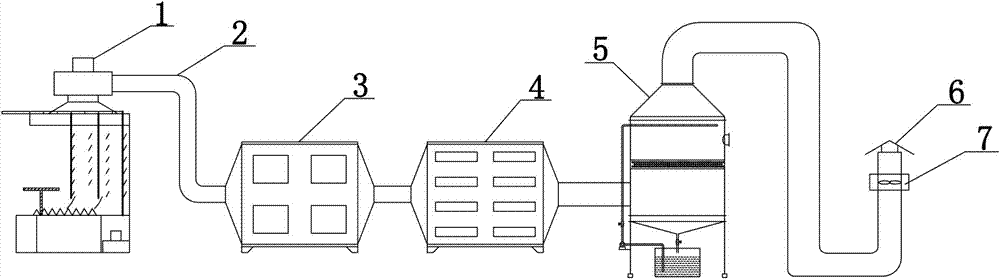
System for treatment of spraying organic waste gas by circulating liquid curtain
InactiveCN102784550AReasonable designEnsure up-to-standard purificationLiquid surface applicatorsUsing liquid separation agentDual stageGas phase
The invention relates to a system for treatment of spraying organic waste gas by a circulating liquid curtain, in particular to a device for treatment of sticky paint and coating particles and organic waste gas during construction of coating industry. The system comprises a circulating liquid curtain type spraying table, an organic waste gas low-temperature plasma and photocatalyst waste gas treatment device, an organic waste gas active carbon treatment device, and an organic waste gas treatment device with a gas phase oxidation process. The system is characterized in that: the sticky paint particles, which are not adhered to a coated object during painting construction, are treated by using the circulating liquid curtain, so that the sticky paint particles are no longer sticky and become powder, and also baffle paint coating dust; organic waste gas enters the organic waste gas low-temperature plasma and photocatalyst waste gas treatment device, the organic waste gas active carbon adsorption device and the organic waste gas treatment device with the gas phase oxidation process, through splitting action of low-temperature plasmas, organic waste gas molecular groups are oxidized by ozone to generate carbon dioxide and water, and then enters a photolytic purification stage to form dual-stage purification of carbon dioxide and water, in this way, spraying organic waste gas is guaranteed to reach the standard of purification and also reach the national emission standard.
Owner:孙金魁
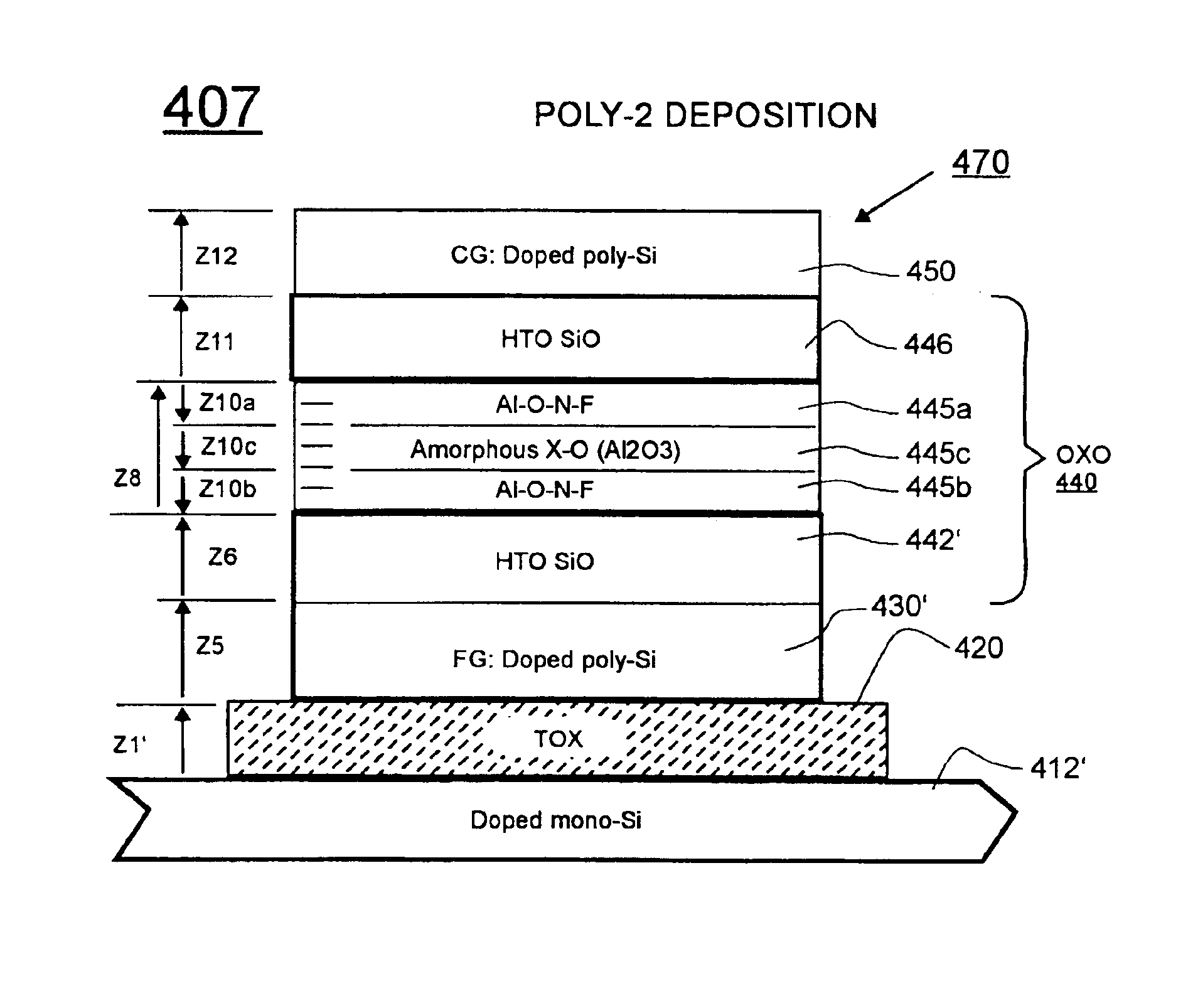
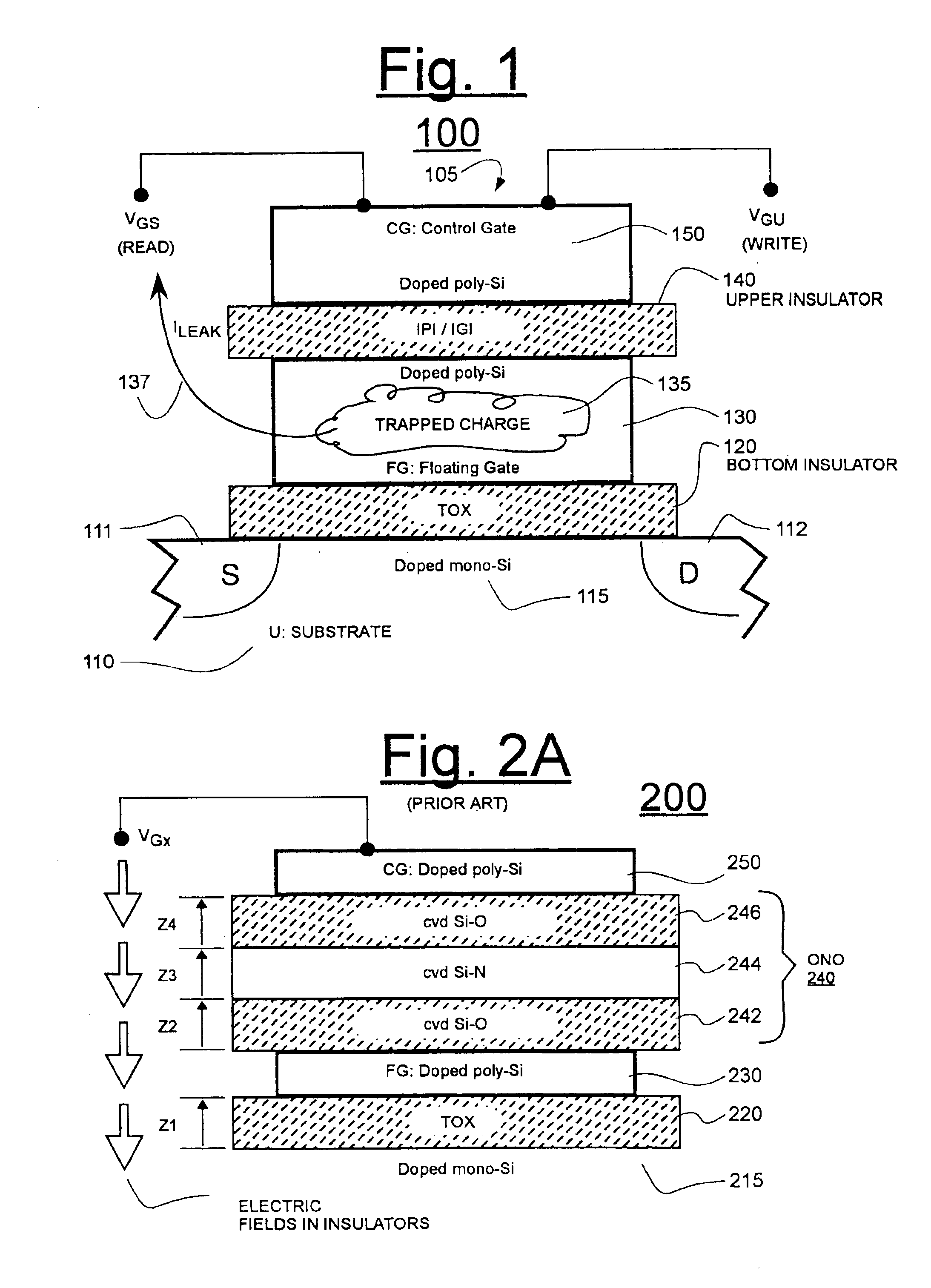
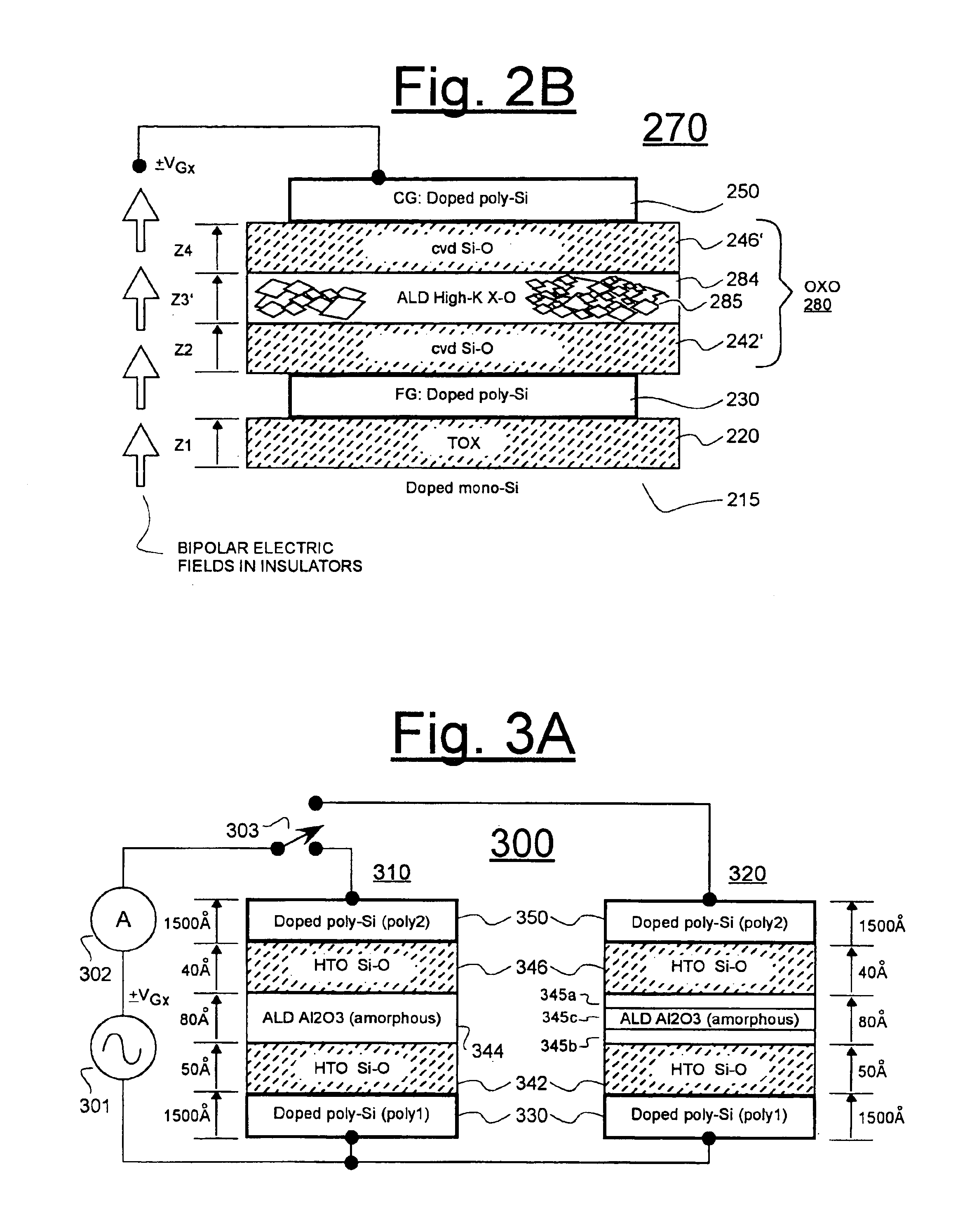
Low temperature nitridation of amorphous high-K metal-oxide in inter-gates insulator stack
ActiveUS6933218B1Improve leakagePromote voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideSilicon oxideLow temperature plasma
An OXO-type inter-poly insulator (where X is a high-K metal oxide and O is an insulative oxide) is defined by forming an amorphous metal oxide layer on a silicon-based insulator (e.g., a silicon oxide layer) and then nitridating at least upper and lower sub-layers of the amorphous metal oxide with a low temperature plasma treatment that maintains temperature below the recrystallization temperature of the amorphous material. Such a plasma treatment has been found to improve breakdown voltage characteristics of the insulator. In one embodiment, the metal oxide includes aluminum oxide and it is fluorinated with low temperature plasma prior to nitridation.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
Anti-flaming ceramic modified size and lithium ion battery membrane coated with same
InactiveCN106519742AGood dispersionNot easy to reuniteFireproof paintsCell component detailsPolyolefinCeramic coating
The invention discloses anti-flaming ceramic modified size and a lithium ion battery membrane coated with same. A preparation method of the anti-flaming ceramic modified size comprises the following steps: carrying out surface pretreatment on inorganic particles and a flame retardant by utilizing a silane coupling agent, thus forming anti-flaming ceramic modified powder; then uniformly stirring in a solvent, and carrying out ball milling; sequentially adding a binding agent and a thickening agent, and stirring at high speed, thus forming the anti-flaming ceramic modified size. The lithium ion battery membrane is formed by coating a polyolefin microporous membrane, which is subjected to low-temperature plasma surface modification treatment, with the anti-flaming ceramic modified size. According to the anti-flaming ceramic modified size disclosed by the invention, the problems that a ceramic coating layer is easy to fall off from a membrane and the coating thickness or the surface density is non-uniform are effectively solved; meanwhile, the inorganic particles and the flame retardant in the ceramic coating layer take a synergistic effect, the inorganic particles are used for supporting the lithium ion battery membrane not to shrink when the lithium ion battery membrane is in over-charge heating, and the security of a battery is improved.
Owner:XUCHENG FUJIAN SCI & TECH
Enhanced-type capillary-needle discharging plasma water treatment device
ActiveCN102897892AAvoid problems with limited depth of actionAvoid lostWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsCapillary TubingEngineering
The invention relates to an enhanced-type capillary-needle discharging plasma water treatment device, which belongs to the technical field of the application of low-temperature plasma, and relates to a constant-pressure plasma discharging reaction device for water treatment, and the enhanced-type capillary-needle discharging plasma water treatment device is characterized by comprising a reaction container and a discharging device, wherein the discharging device consists of a metal capillary power electrode, an insulation medium pipe, a metal end cover suspension electrode and an air chamber and is arranged inside the reaction container; working gas enters the metal capillary and the insulation medium pipe through the air chamber, gas discharging plasma is generated inside the insulation medium pipe between a needle-shaped pipe orifice on the lower end of the metal capillary and a metal end cap under the effect of high-voltage power supply, a generated product enters solution to be treated through small holes on the metal end cap, and solution inside the reaction container is purified; and the enhanced-type capillary-needle discharging plasma water treatment device has advantages that the utilization rate of active substances is high, the universality for different solutions to be treated is strong, the stability is good, easiness in integration is realized, and the exciting source requirement of the plasma is reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of cellulose-based water absorbent material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cellulose-based water absorbent material. The method comprises the main operation steps: grinding a natural cellulose material, washing with distilled water and ethanol, and drying; performing low-temperature plasma treatment on the conditions that the treatment voltage is 50-210V, the vacuum degree is 800-1500Pa and the discharge time is 30-250s;and then placing cellulose in a 10-50wt% monomer solution, then adding an initiator and a crosslinking agent in the mixed solution of monomer and cellulose, injecting nitrogen for protection, performing a graft copolymerization reaction at 40-80 DEG C for 10-40min, and then drying to obtain the cellulose-based water absorbent material. The prepared cellulose-based water absorbent material can be used in disposable diapers for babies, sanitary towels, napkins, handkerchiefs, bandages, absorbent cotton, operation liners and the like; and by utilizing the slow release effect of resin, the material can be used as a carrier material of the scenting agent and the deodorant to realize the effects of deodorizing.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com