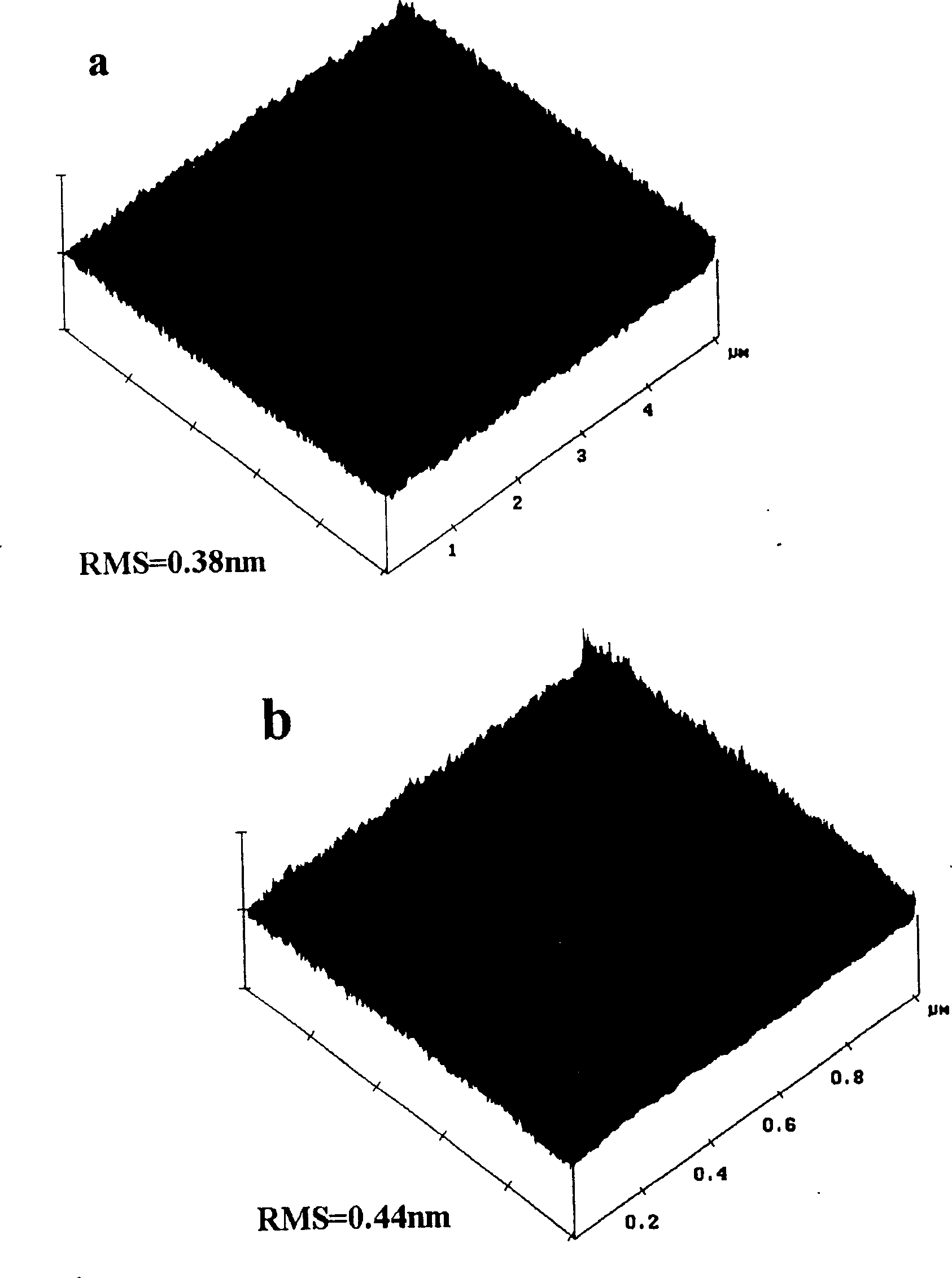
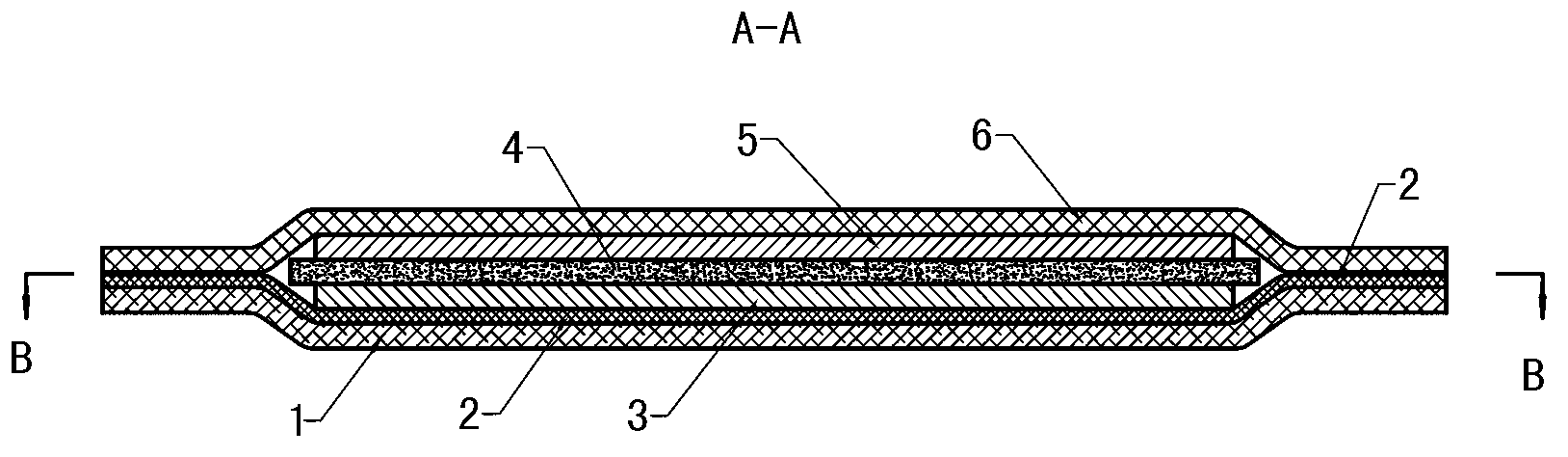
Patents
Literature
125 results about "Ion deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
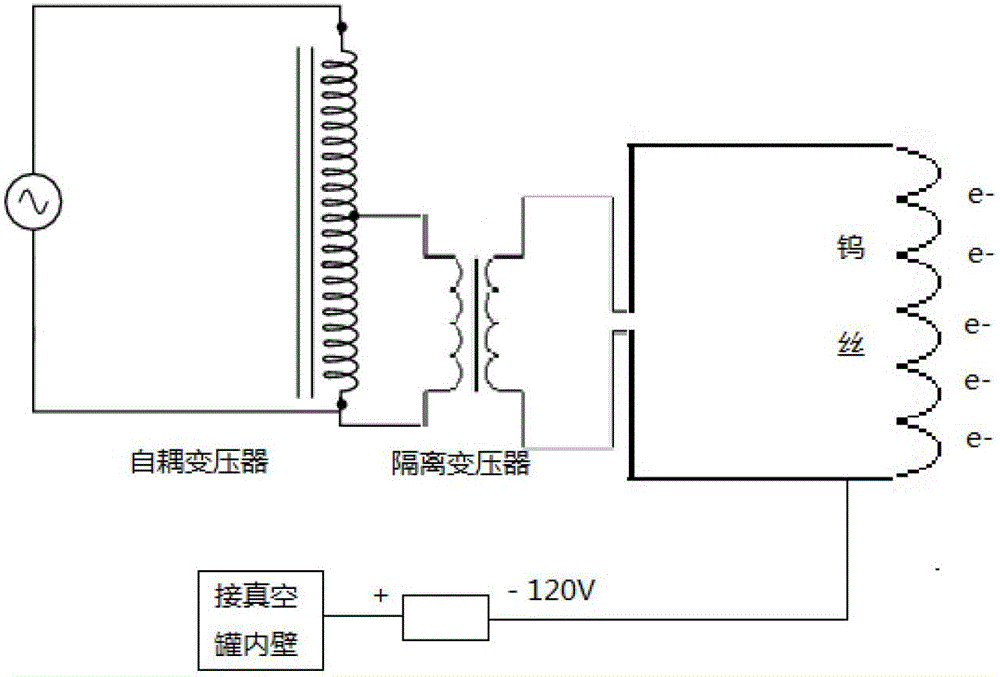
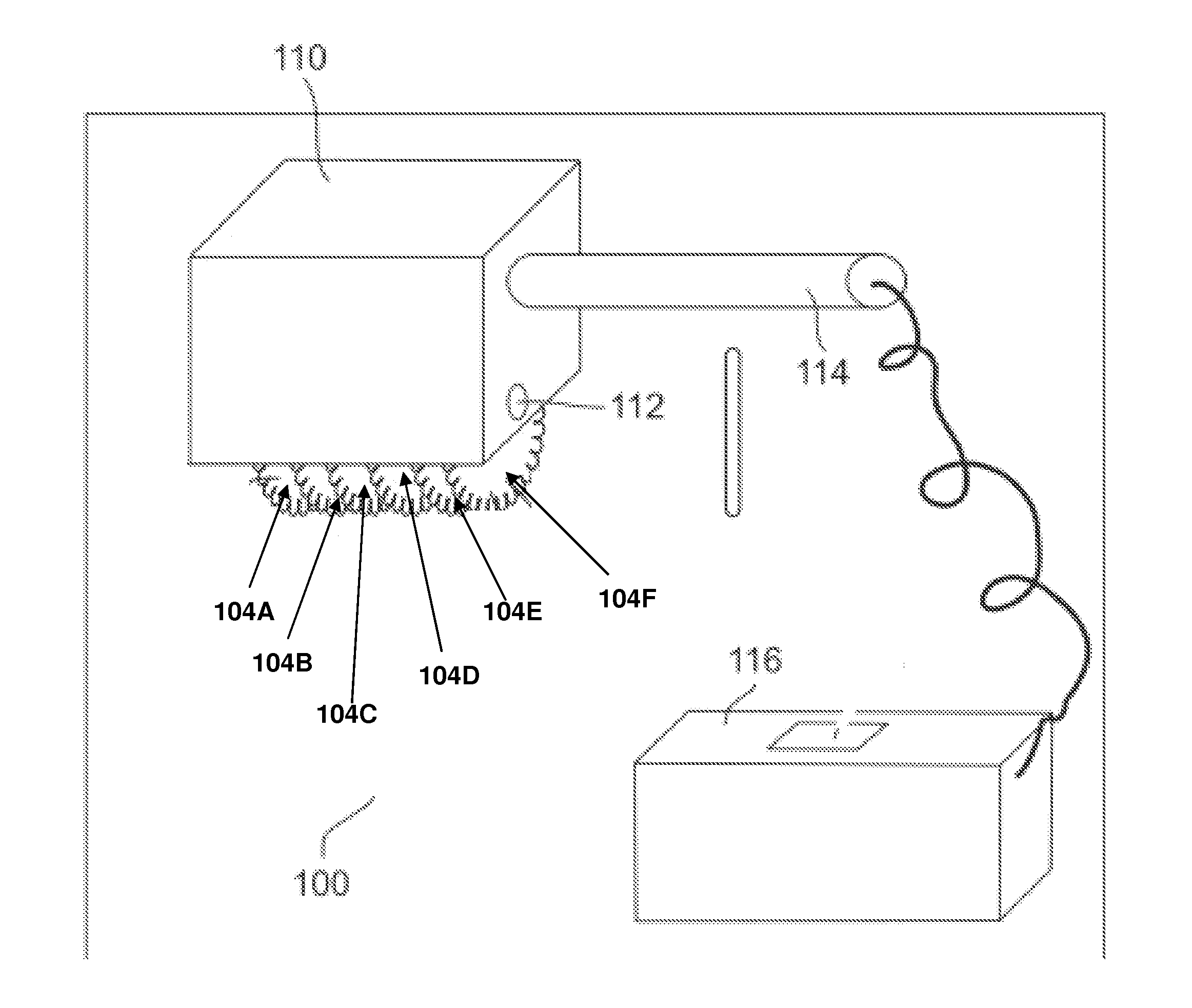
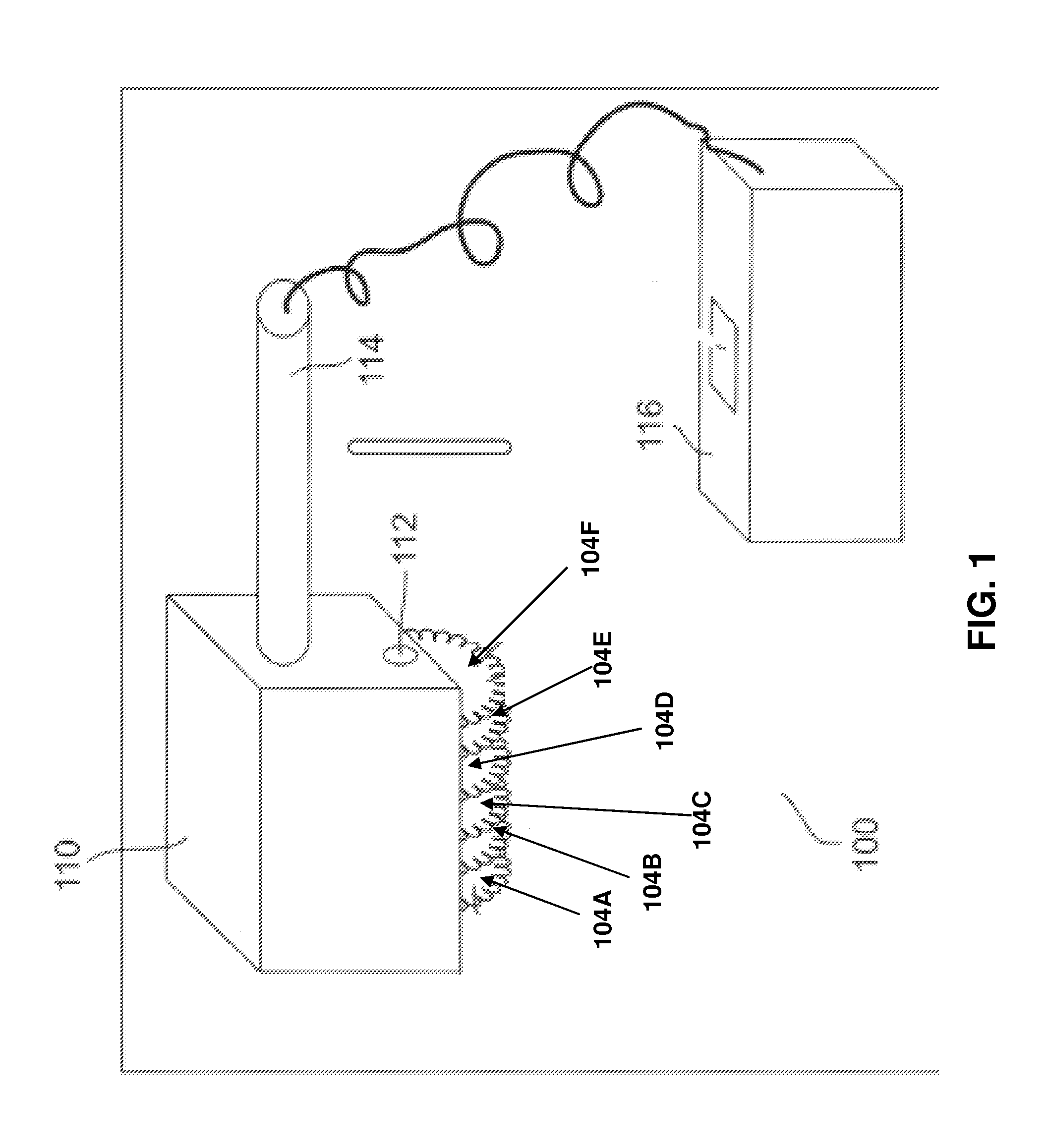
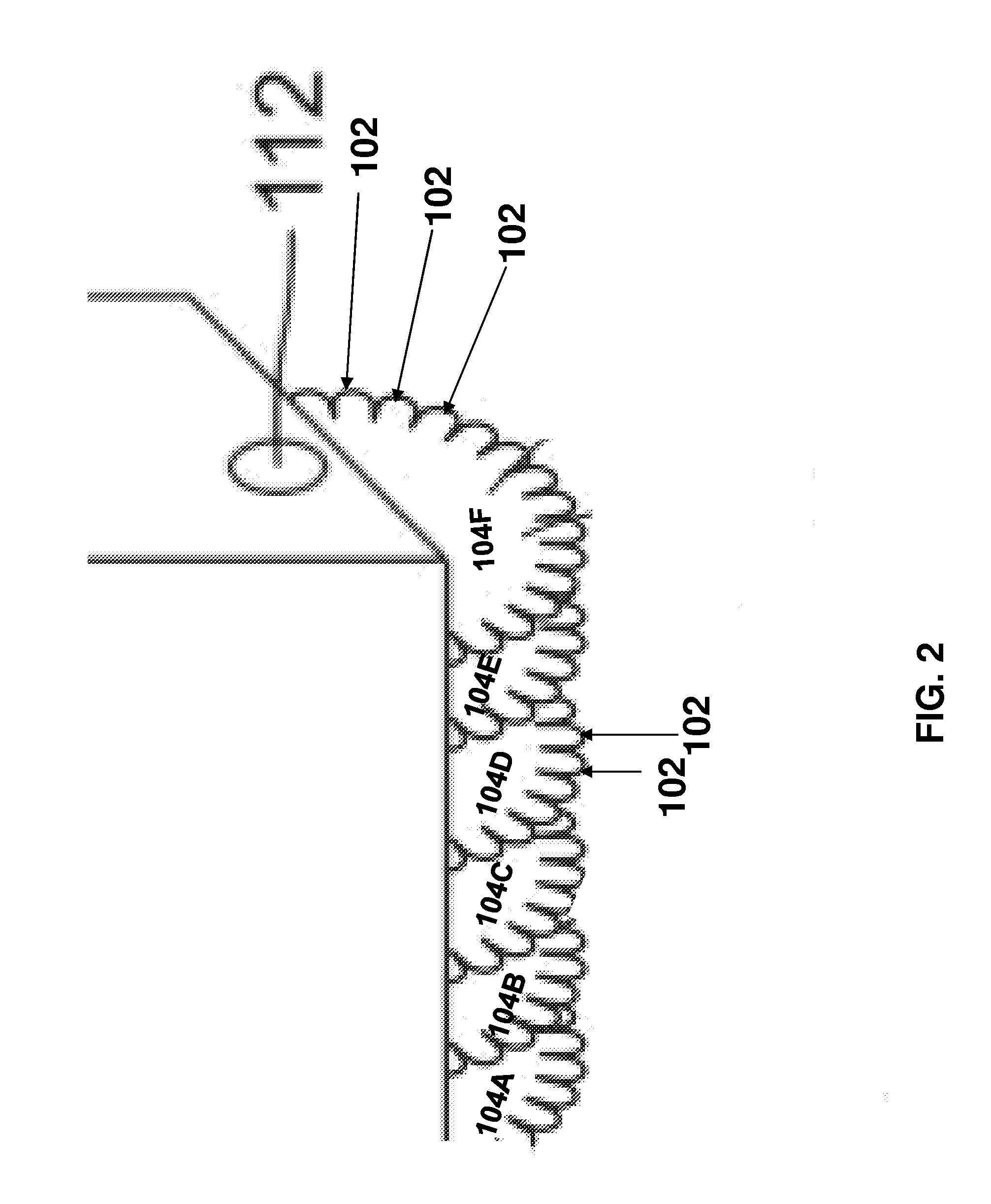
Ion deposition. A printing technology used in high-speed page printers. Ion deposition is similar to laser printing, except instead of using light to create a charged image on a drum, it uses a printhead that deposits positive ions.
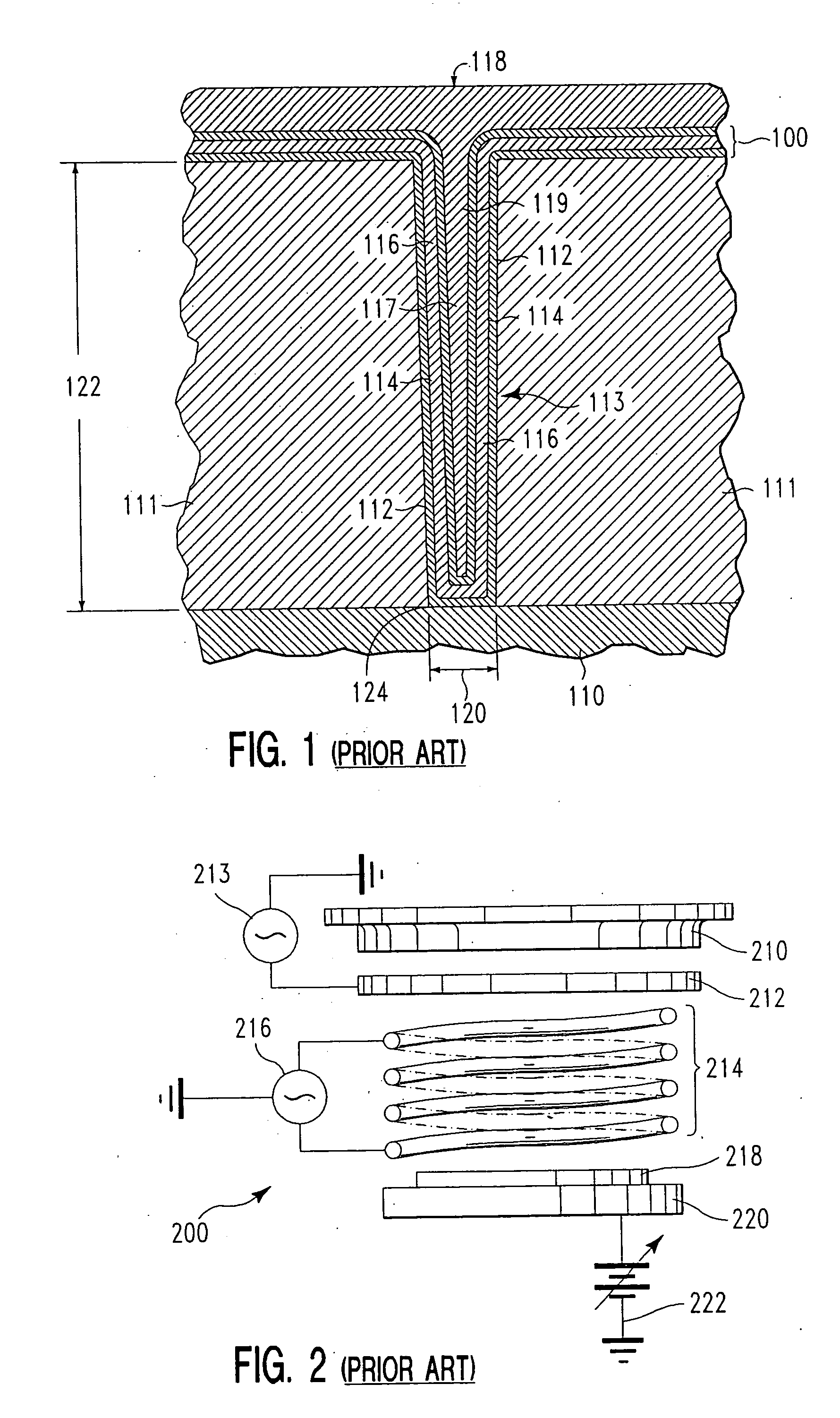
Low temperature plasma deposition process for carbon layer deposition
InactiveUS7312162B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerPlasma current
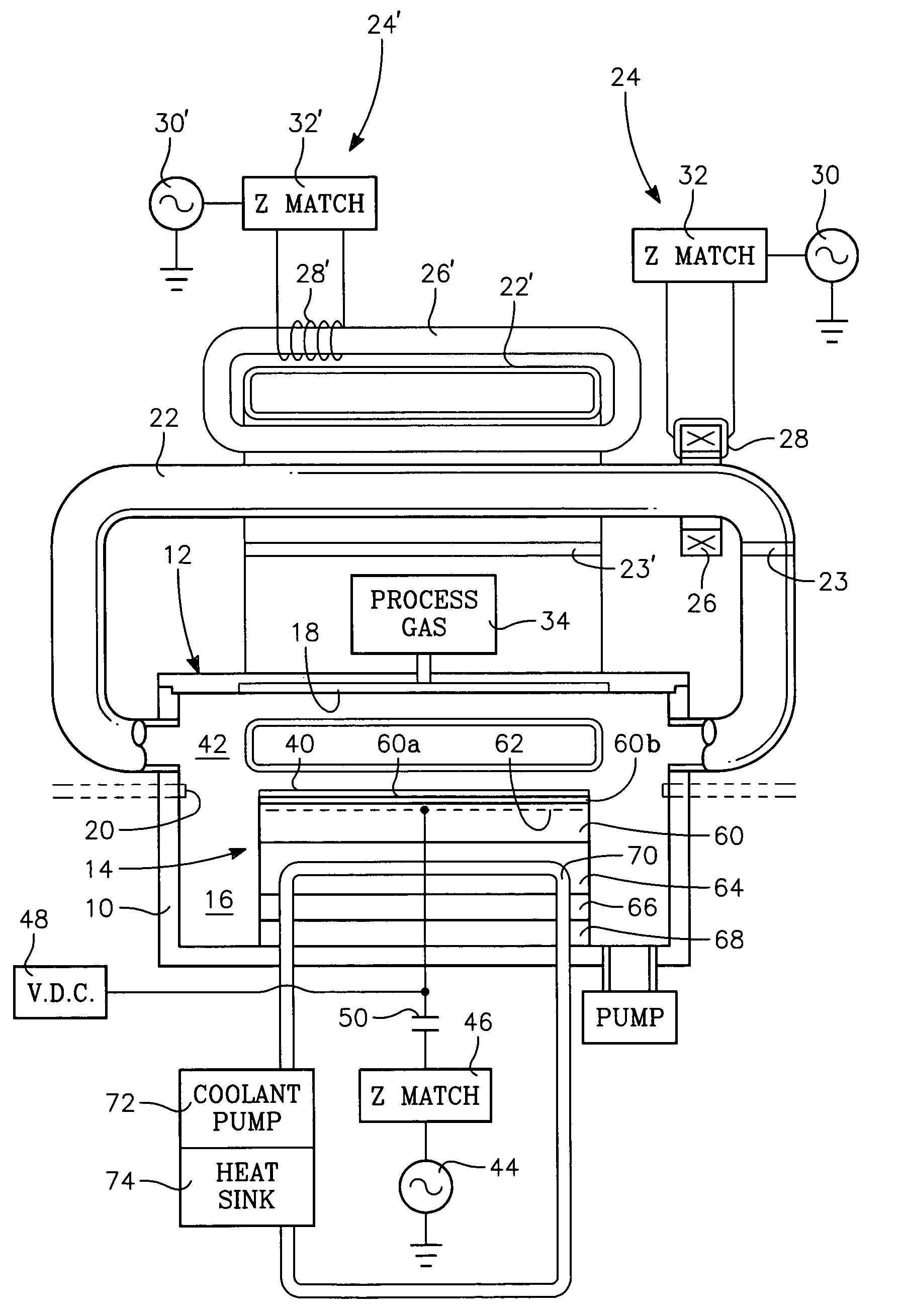
A method of depositing a carbon layer on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber, introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low temperature plasma deposition process for carbon layer deposition
InactiveUS20060264060A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerPlasma current
A method of depositing a carbon layer on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber, introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method to form electrostatic discharge protection on flexible circuits
ActiveUS20050117257A1Avoid noisePreventing ESD damageSubstation/switching arrangement detailsRecord information storageFlexible circuitsIon deposition
Techniques for preventing electrostatic discharge (ESD) and circuit noise are provided. More particularly, the present invention provides a method to prevent ESD damage during the assembly of computer disk commonly called a hard disk for memory applications. The coating mainly involves a ion-deposition process. Merely by way of example, the present invention is implemented by using filtered cathodic vacuum arc (FCVA) with a dissipative crystalline and / or amorphous carbon base thin film coating on a flexible circuit to drain the potential electrostatic charges during circuit assembly and interconnect processes, yet it would be recognized that the invention has a much broader range of applicability on any electronic apparatus that is susceptible to electrostatic damage and static noise.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
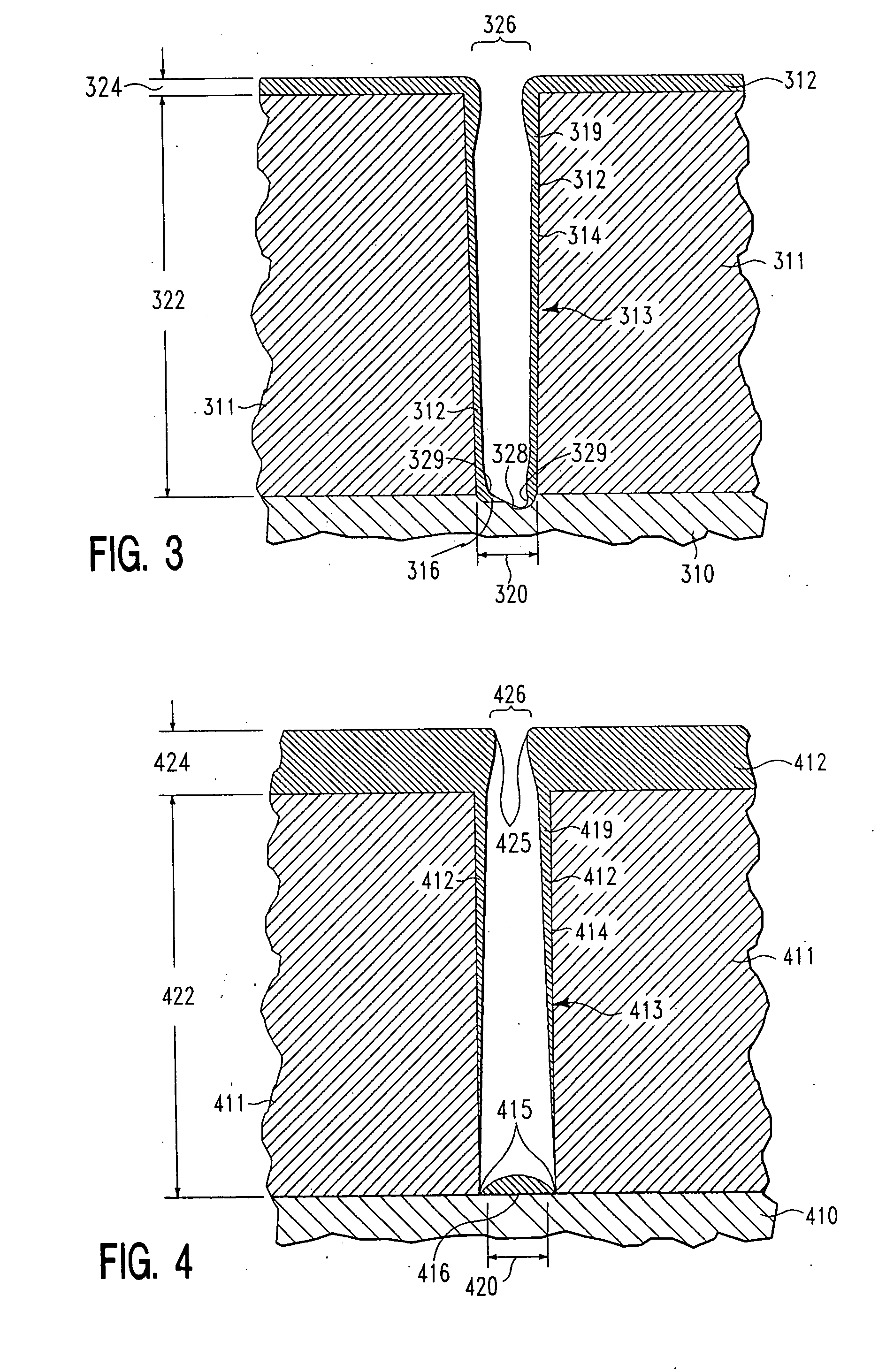
Damage-free sculptured coating deposition
We disclose a method of applying a sculptured layer of material on a semiconductor feature surface using ion deposition sputtering, wherein a surface onto which the sculptured layer is applied is protected to resist erosion and contamination by impacting ions of a depositing layer. A first protective layer of material is deposited on a substrate surface using traditional sputtering or ion deposition sputtering, in combination with sufficiently low substrate bias that a surface onto which the layer is applied is not eroded away or contaminated during deposition of the protective layer. Subsequently, a sculptured second layer of material is applied using ion deposition sputtering at an increased substrate bias, to sculpture a shape from a portion of the first protective layer of material and the second layer of depositing material. The method is particularly applicable to the sculpturing of barrier layers, wetting layers, and conductive layers upon semiconductor feature surfaces.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Damage-free sculptured coating deposition
We disclose a method of applying a sculptured layer of material on a semiconductor feature surface using ion deposition sputtering, wherein a surface onto which the sculptured layer is applied is protected to resist erosion and contamination by impacting ions of a depositing layer, said method comprising the steps of: a) applying a first portion of a sculptured layer with sufficiently low substrate bias that a surface onto which said sculptured layer is applied is not eroded away or contaminated in an amount which is harmful to said semiconductor device performance or longevity; and b) applying a subsequent portion of said sculptured layer with sufficiently high substrate bias to sculpture a shape from said the first portion, while depositing additional layer material. The method is particularly applicable to the sculpturing of barrier layers, wetting layers, and conductive layers upon semiconductor feature surfaces and is especially helpful when the conductive layer is copper. In the application of a barrier layer, a first portion of barrier layer material is deposited on the substrate surface using standard sputtering techniques or using an ion deposition plasma, but in combination with sufficiently low substrate bias voltage (including at no applied substrate voltage) that the surfaces impacted by ions are not sputtered in an amount which is harmful to device performance or longevity. Subsequently, a second portion of barrier material is applied using ion deposition sputtering at increased substrate bias voltage which causes resputtering (sculpturing) of the first portion of barrier layer material, while enabling a more anisotropic deposition of newly depositing material. A conductive material, and particularly a copper seed layer applied to the feature may be accomplished using the same sculpturing technique as that described above with reference to the barrier layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus and method for metal plasma immersion ion implantation and metal plasma immersion ion deposition
InactiveUS20050061251A1Large-scale processingReduce pressureElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingIon depositionPlasma deposition
This invention is a method for metal plasma ion implantation and metal plasma ion deposition, comprising: providing a vacuum chamber with at least one workpiece having a surface positioned on a worktable within the vacuum chamber; reducing the pressure in the vacuum chamber; generating a plasma of metal ions within the vacuum chamber, applying a negative bias to the worktable to thereby accelerate metal ions from the plasma toward at least one workpiece to thereby either implant metal ions into or deposit metal ions onto the workpiece or both. This invention includes an apparatus for metal ion implantation and metal ion plasma deposition, comprising: a vacuum chamber, a metal plasma generator within the vacuum chamber, and at least one worktable within the vacuum chamber.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
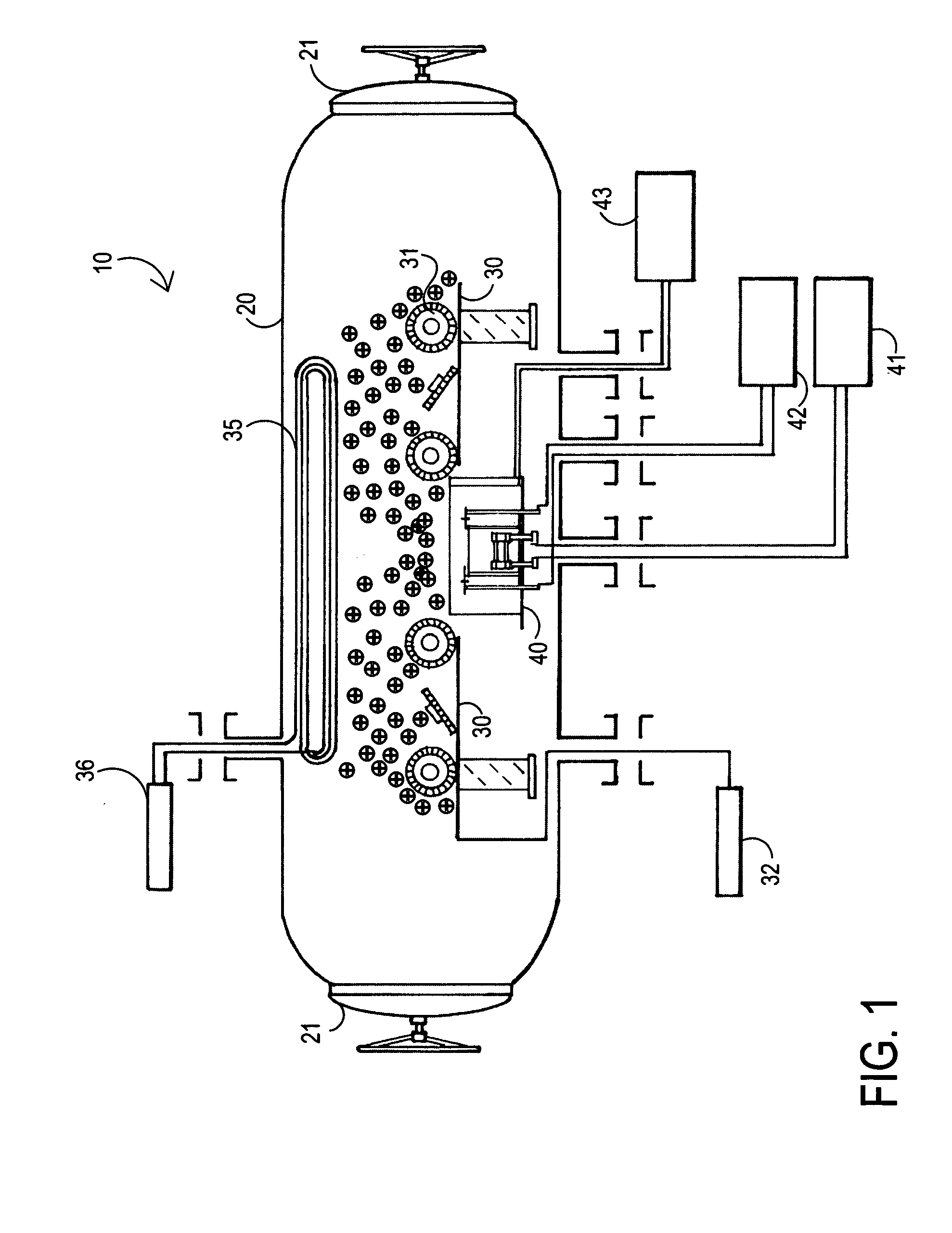
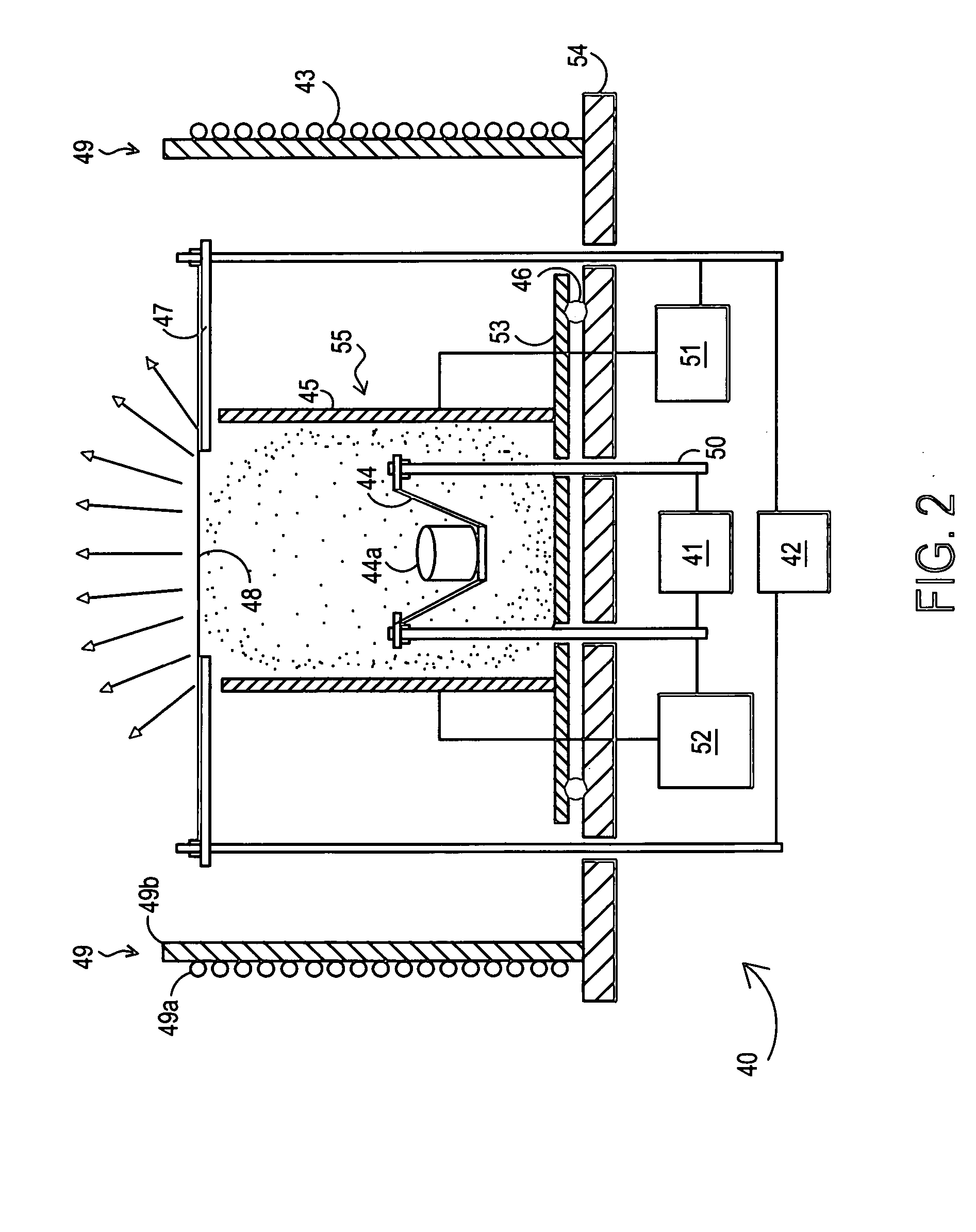
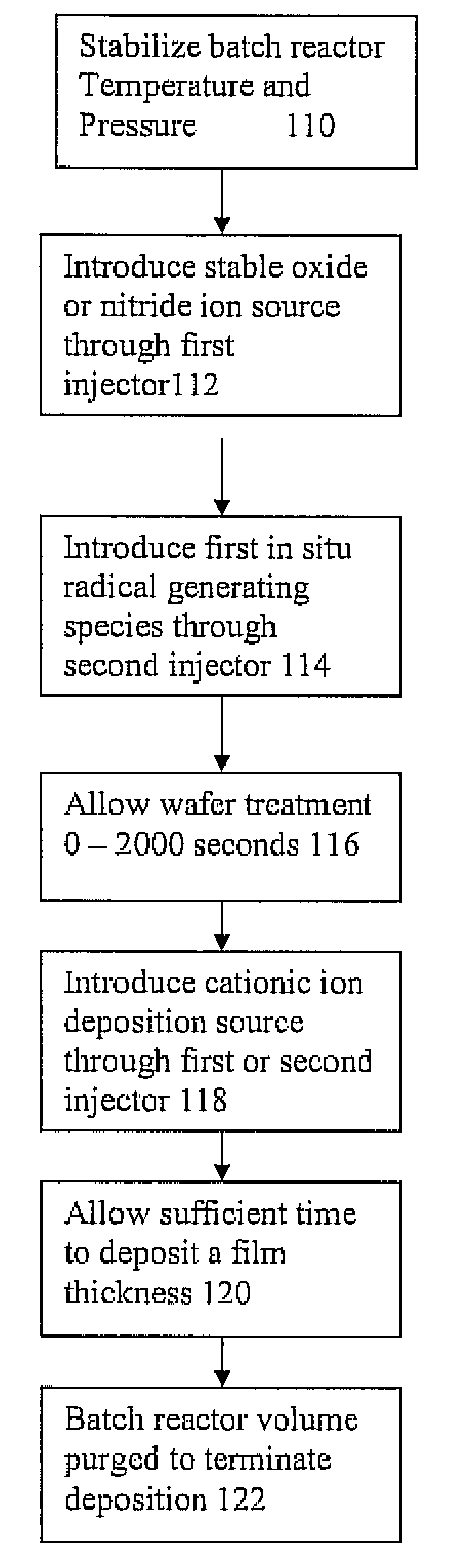
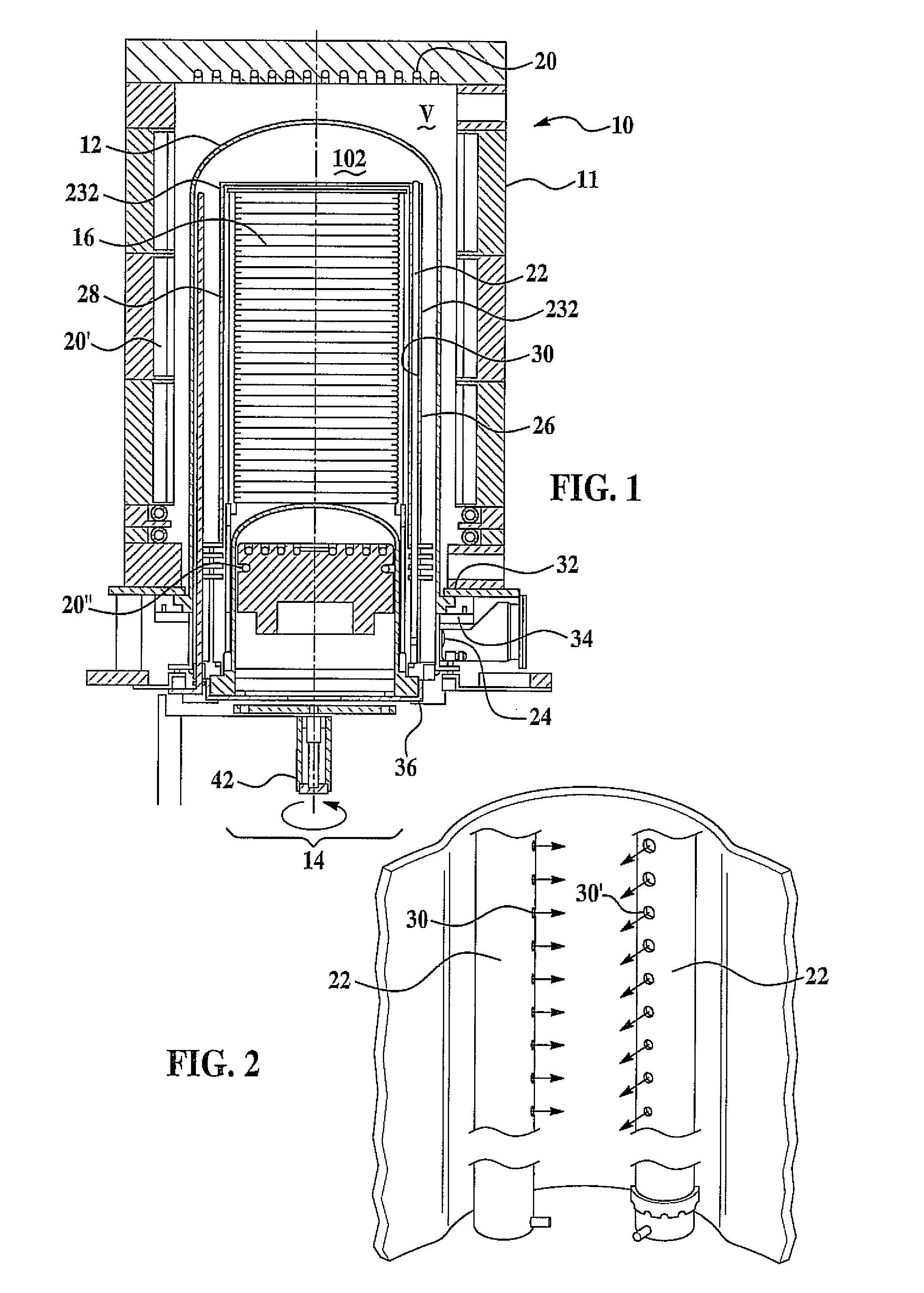
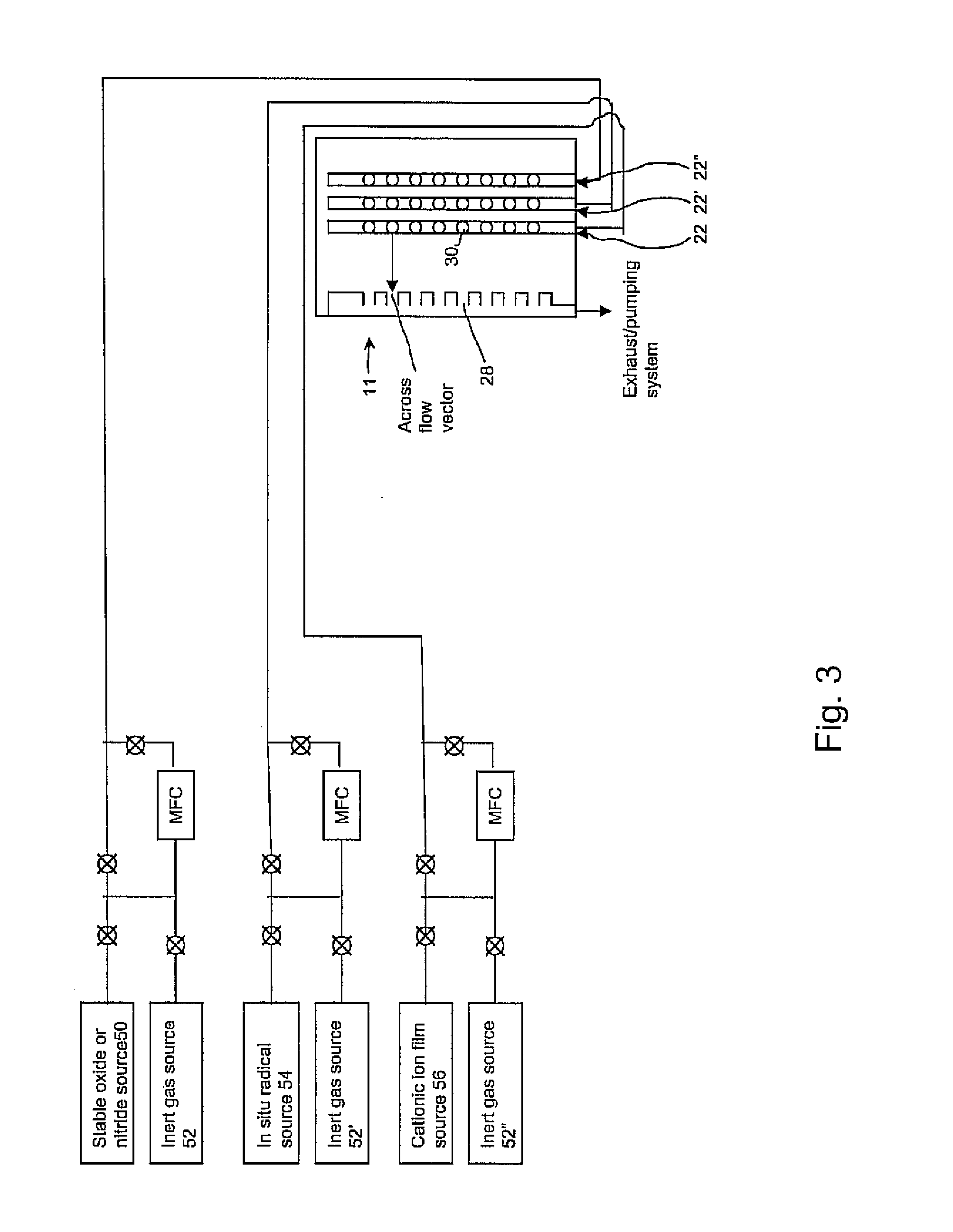
Radical Assisted Batch Film Deposition
InactiveUS20080038486A1High degreeEasy to produceSolid state diffusion coatingChemical vapor deposition coatingVertical tubeChemical vapor deposition
A process for radical assisted film deposition simultaneously on multiple wafer substrates is provided. The multiple wafer substrates are loaded into a reactor that is heated to a desired film deposition temperature. A stable species source of oxide or nitride counter ion is introduced into the reactor. An in situ radical generating reactant is also introduced into the reactor along with a cationic ion deposition source. The cationic ion deposition source is introduced for a time sufficient to deposit a cationic ion-oxide or a cationic ion-nitride film simultaneously on multiple wafer substrates. Deposition temperature is below a conventional chemical vapor deposition temperature absent the in situ radical generating reactant. A high degree of wafer-to-wafer uniformity among the multiple wafer substrates is obtained by introducing the reactants through elongated vertical tube injectors having vertically displaced orifices, injectors surrounded by a liner having vertically displaced exhaust ports to impart across flow of movement of reactants simultaneously across the multiple wafer substrates. With molecular oxygen as a stable species source of oxide, and hydrogen as the in situ radical generating reactant, oxide films of silicon are readily produced with a silicon-containing precursor introduced into the reactor.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC
Ni Co Cr Al Y Si B coating layer capable of resisting thermal corrosion and its preparation method
InactiveCN1536033AExcellent thermal corrosion resistanceCorrosion weight gain is smallCoatingsHigh resistanceIon deposition
The present invention relates to coating technology, in the concrete, it discloses a NICoCrAlYSiB hot corrosion resisting high-temp. protection coating and its preparation method. Its element content composition includes: Co 28-35 wt%, Cr 17-23 wt%, Al 5-12 wt%, Y 0.1-0.6 wt%, Si 0.9-1.1 wt%, B 0.02-0.04 wt% and the rest is Ni. Said invention adopts electric arc ion deposition technique to prepare said protection coating, and as compared with existent technology said invented protection coating has highest resistance to hot corrosion and high temp. oxidative property, and its preparation process is low in cost.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
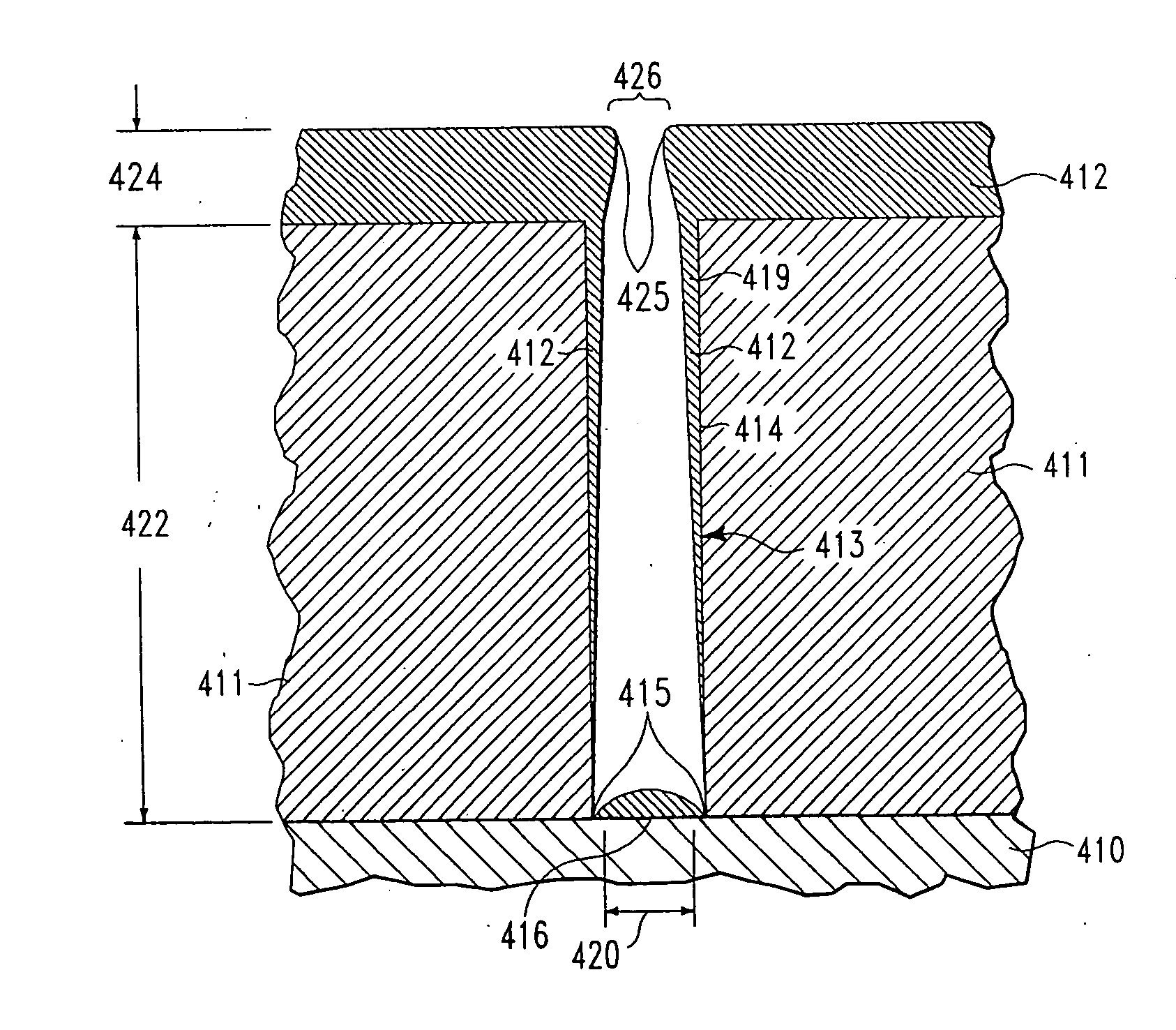
Method of preventing diffusion of copper through a tantalum-comprising barrier layer
InactiveUS20040171250A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDevice materialConductive materials
We disclose a method of applying a sculptured layer of material on a semiconductor feature surface using ion deposition sputtering, wherein a surface onto which the sculptured layer is applied is protected to resist erosion and contamination by impacting ions of a depositing layer, said method comprising the steps of: a) applying a first portion of a sculptured layer with sufficiently low substrate bias that a surface onto which said sculptured layer is applied is not eroded away or contaminated in an amount which is harmful to said semiconductor device performance or longevity; and b) applying a subsequent portion of said sculptured layer with sufficiently high substrate bias to sculpture a shape from said the first portion, while depositing additional layer material. The method is particularly applicable to the sculpturing of barrier layers, wetting layers, and conductive layers upon semiconductor feature surfaces and is especially helpful when the conductive layer is copper. In the application of a barrier layer, a first portion of barrier layer material is deposited on the substrate surface using standard sputtering techniques or using an ion deposition plasma, but in combination with sufficiently low substrate bias voltage (including at no applied substrate voltage) that the surfaces impacted by ions are not sputtered in an amount which is harmful to device performance or longevity. Subsequently, a second portion of barrier material is applied using ion deposition sputtering at increased substrate bias voltage which causes resputtering (sculpturing) of the first portion of barrier layer material, while enabling a more anisotropic deposition of newly depositing material. A conductive material, and particularly a copper seed layer applied to the feature may be accomplished using the same sculpturing technique as that described above with reference to the barrier layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
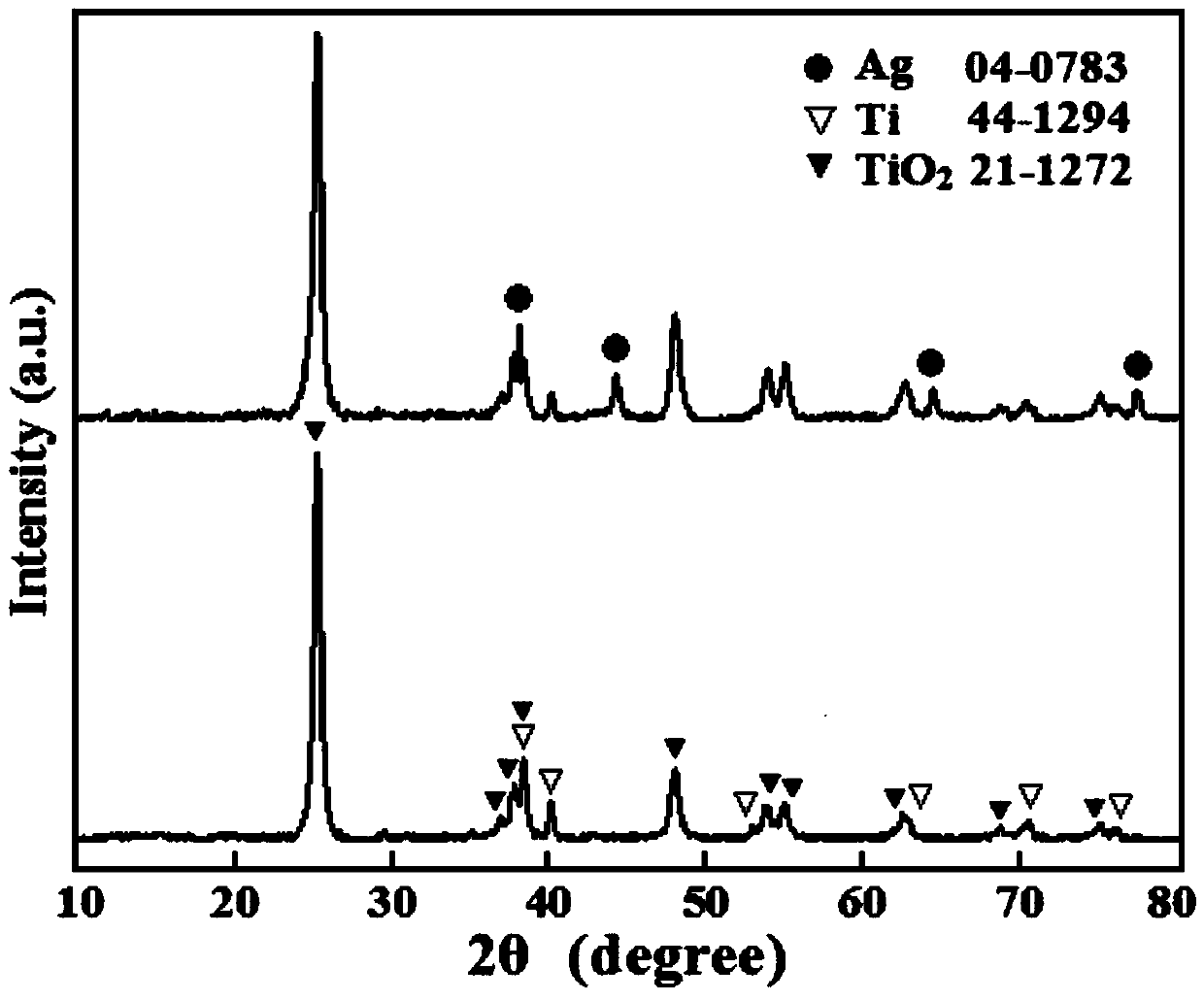
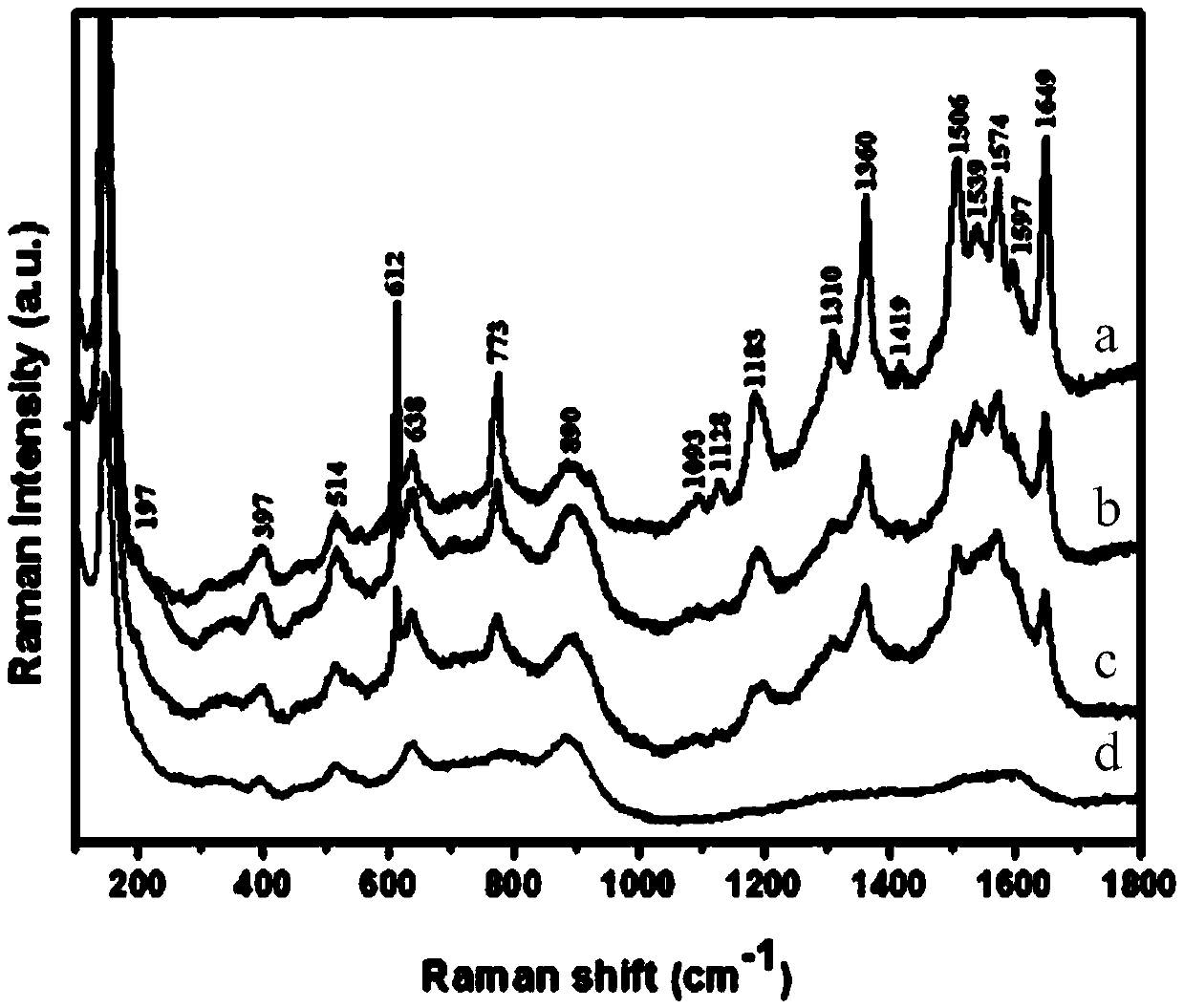
Ag/TiO2 flexible SERS substrate capable of being repeatedly utilized and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105372223ANot easy to fall offTo achieve the function of "detoxification"Raman scatteringLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSynthesis methodsIon deposition
The invention discloses a preparation method of an Ag / TiO2 flexible SERS substrate capable of being repeatedly utilized. A thin Ti sheet is adopted as a Ti source, a TiO2 nanobelt array with Ti as a substrate is prepared through a hydro-thermal synthesis method, an SERS substrate material of Ag / TiO2 is prepared through a continuous ion deposition method, the Ti sheet can be cut to be of any shape and size according to test requirements, the large-area SERS substrate material can be prepared according to the size of the Ti sheet, and potential industrial production prospects are achieved. In addition, the number of silver nanoparticles on the surface of an Ag / TiO2 film is controllable, the silver nanoparticles are firm and not likely to fall off, an organic tested objected adsorbed on the surface of the material can be degraded and decomposed under the irradiation of a xenon lamp light source, the function of detoxicating the SERS material is achieved, and therefore a sample can be used repeatedly and cyclically.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
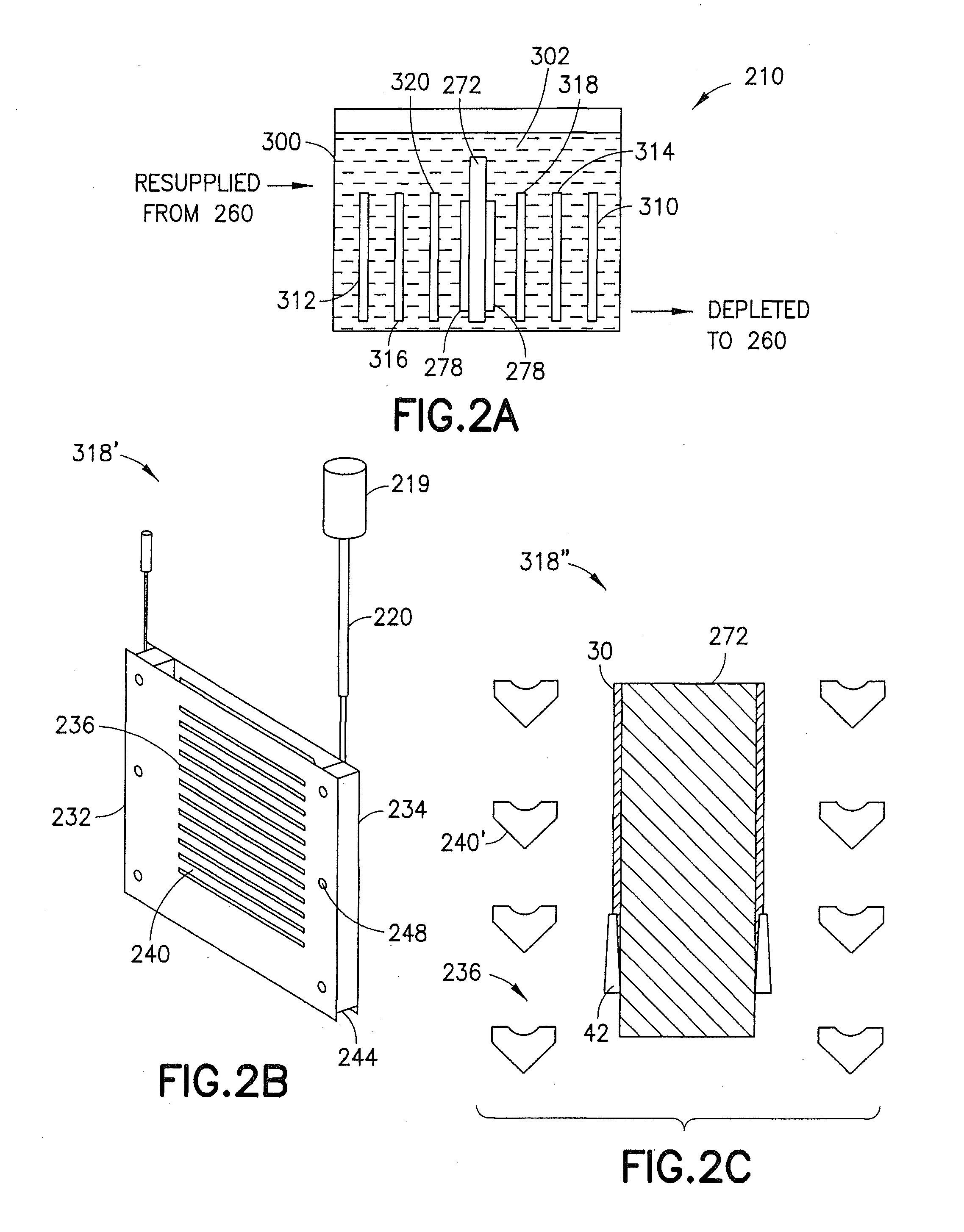
Electro chemical deposition and replenishment apparatus
An electrochemical deposition apparatus adapted to deposit metal onto a surface of a substrate, the apparatus has a frame configured for holding a process electrolyte. A substrate holder is removably coupled to the frame, the substrate holder supporting the substrate in the process electrolyte. An anode fluid compartment is removably coupled to the frame and containing an anolyte and having an anode facing the surface of the substrate, the anode fluid compartment further having a ion exchange membrane disposed between the anode and the surface of the substrate, the anode fluid compartment removable from the frame as a unit with the ion exchange membrane and the anode. The holder, the anode and the membrane are arranged in the frame so that ions from the anode pass through the ion exchange membrane into and primarily replenish ions in the process electrolyte depleted by ion deposition onto the surface of the substrate.
Owner:ASMPT NEXX INC
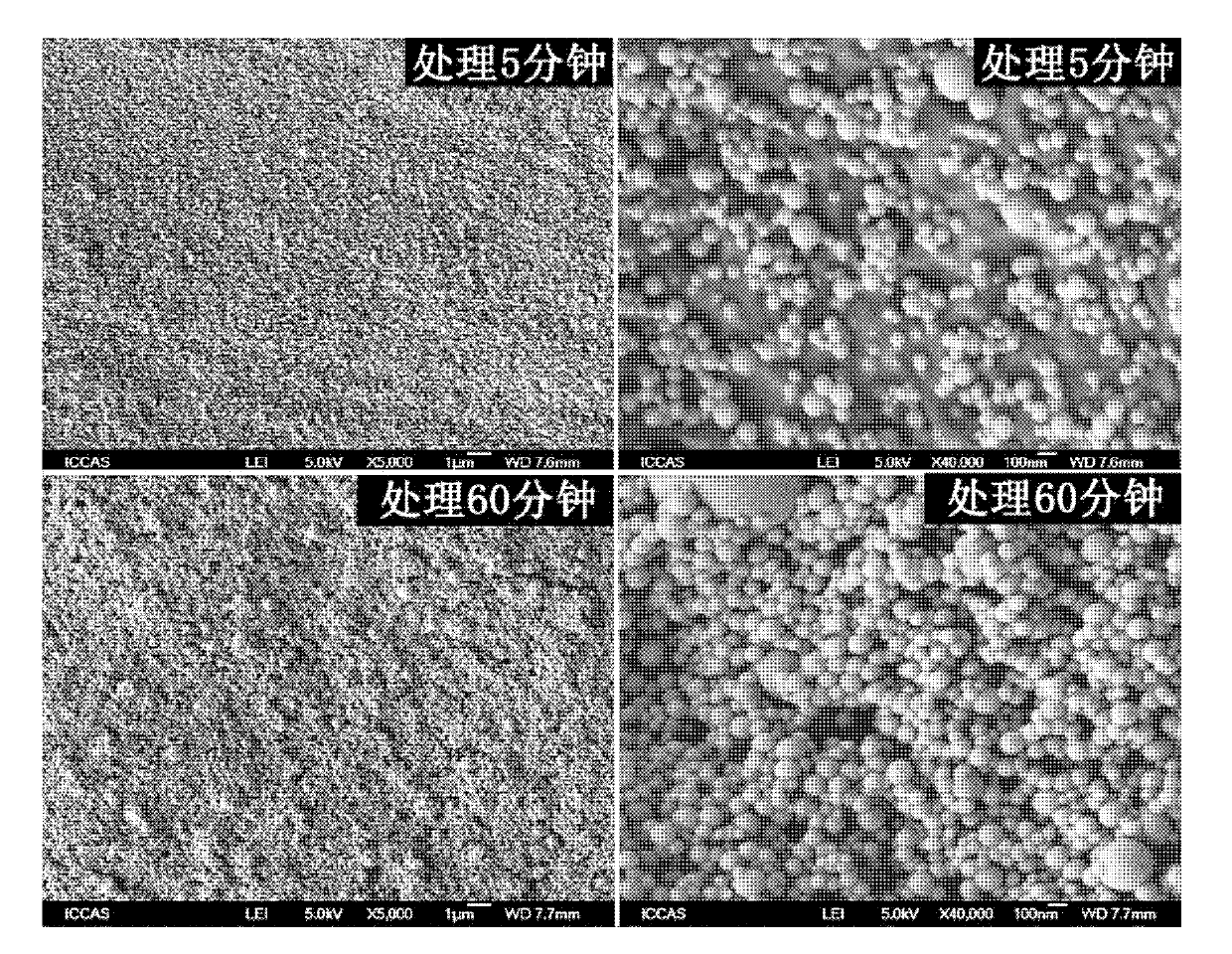
Hydroxyapatite/biodegradable polyester composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103319696AGood biocompatibilityImprove biological activityProsthesisApatiteIn situ polymerization
The invention discloses a hydroxylapatite / biodegradable polyester composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the following steps: under conditions of no water, no oxygen, and argon protection, the composite material is obtained by carrying out an in-situ polymerization reaction of hydroxyapatite and an aliphatic cyclic monomer under catalysis of stannous octoate; the aliphatic cyclic monomer is selected form at least one of lactide, epsilon-caprolactone and glycolide; and the composite material provided by the invention comprises hydroxylapatite and a biodegradable polyester. The composite material provided by the invention has the surface enriched with a hydroxylapatite layer having a biological activity, and has an excellent biological compatibility and the biological activity; an biological activity interface can rapidly induce calcium ion deposition in a physiological environment so as to induce nucleation and growth of apatite, and imitates inorganic / organic components of a natural bone matrix in composition; based on the above characteristics, the modified hydroxylapatite / biodegradable polyester composite material is a good support material for repairing bone defects, and has good application prospects in the fields of cell expansion and bone tissue engineering.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
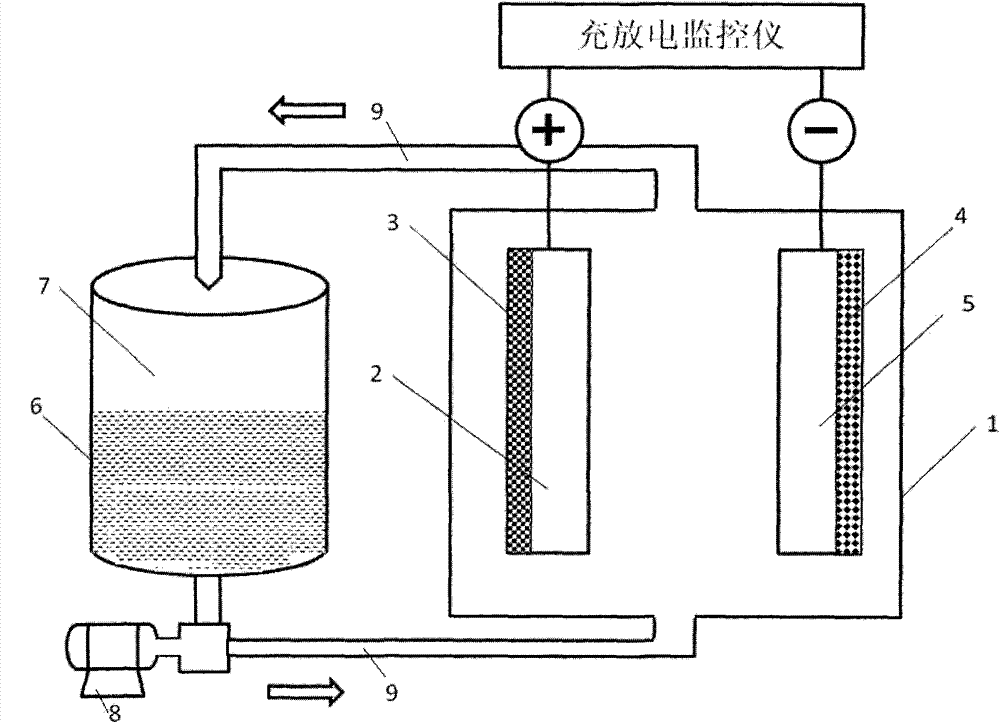
Aqueous lithium ion flow battery
InactiveCN104716372AImprove cycle lifeHigh specific capacityCell electrodesRegenerative fuel cellsEnvironmental resistanceHigh energy
The invention relates to a novel aqueous lithium ion flow battery with high performances and low cost. A lithium ion intercalation-deintercalation mechanism and a flow battery metal ion deposition-dissolution mechanism are optically combined in an energy storage device. A positive electrode adopts a lithium ion intercalatable-deintercalatable solid oxide material, a negative electrode adopts a deposition type metal electrode material deposited-dissolved on an inert electrode, an electrolyte is an aqueous electrolyte containing lithium ions and capable of depositing and dissolving metal ions, and the separation of positive electrode and the negative electrode by a diaphragm is not needed. In the charge and discharge process, the electrolyte is promoted by a liquid pump to go through a pipeline and continuously circularly flow between a storage tank and a battery main body. The aqueous lithium ion flow battery has the characteristics of long cycle life, high energy efficiency, safety, low cost, less maintenance, environmental protection, high utilization rate and energy density of active substances, and large specific capacity, and is especially suitable for large scale power storage of off-grid renewable energy power generation and distributed power supply.
Owner:NO 63971 TROOPS PLA
Film temperature sensor for turbine blades of aero-engine
ActiveCN109338290ASolve insulation problemsSolve sheddingMolten spray coatingThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThin film sensorSputtering
The invention discloses a film temperature sensor for turbine blades of an aero-engine. The film temperature sensor comprises a transition layer, a thermal growing layer, an insulating layer and a thermocouple layer which are sequentially connected, wherein the thermocouple layer is formed by lapping a first thermocouple and a second thermocouple through one end part, and the lapping part forms athermal connecting point which is a measuring end; an outgoing conductor is a fine wire which has the same quality as the first thermocouple and the second thermocouple; and the outgoing conductor iscorrespondingly connected to the other end part of each of the first thermocouple and the second thermocouple through high-temperature conductive glue. According to the film temperature sensor for theturbine blades of the aero-engine, a film layer structure of the sensor is specially designed for the aero-engine in a high-temperature severe environment; the film sputtering, annealing and other preparation technologies are optimized; the ion deposition technology is carried out to directly deposit a plurality of layers of films on the surfaces of the turbine blades, and thus the function and structure integrated film sensor is obtained; the adhesion strength of the film layers is improved; the problems such as high-temperature insulating of the film layer, separating and signal exporting can be solved; and the total thickness of the film sensor is less than 25 microns, and the maximum measurement temperature is 1100 DEG C.
Owner:AVIC SHANGHAI AERONAUTICAL MEASUREMENT CONTROLLING RES INST
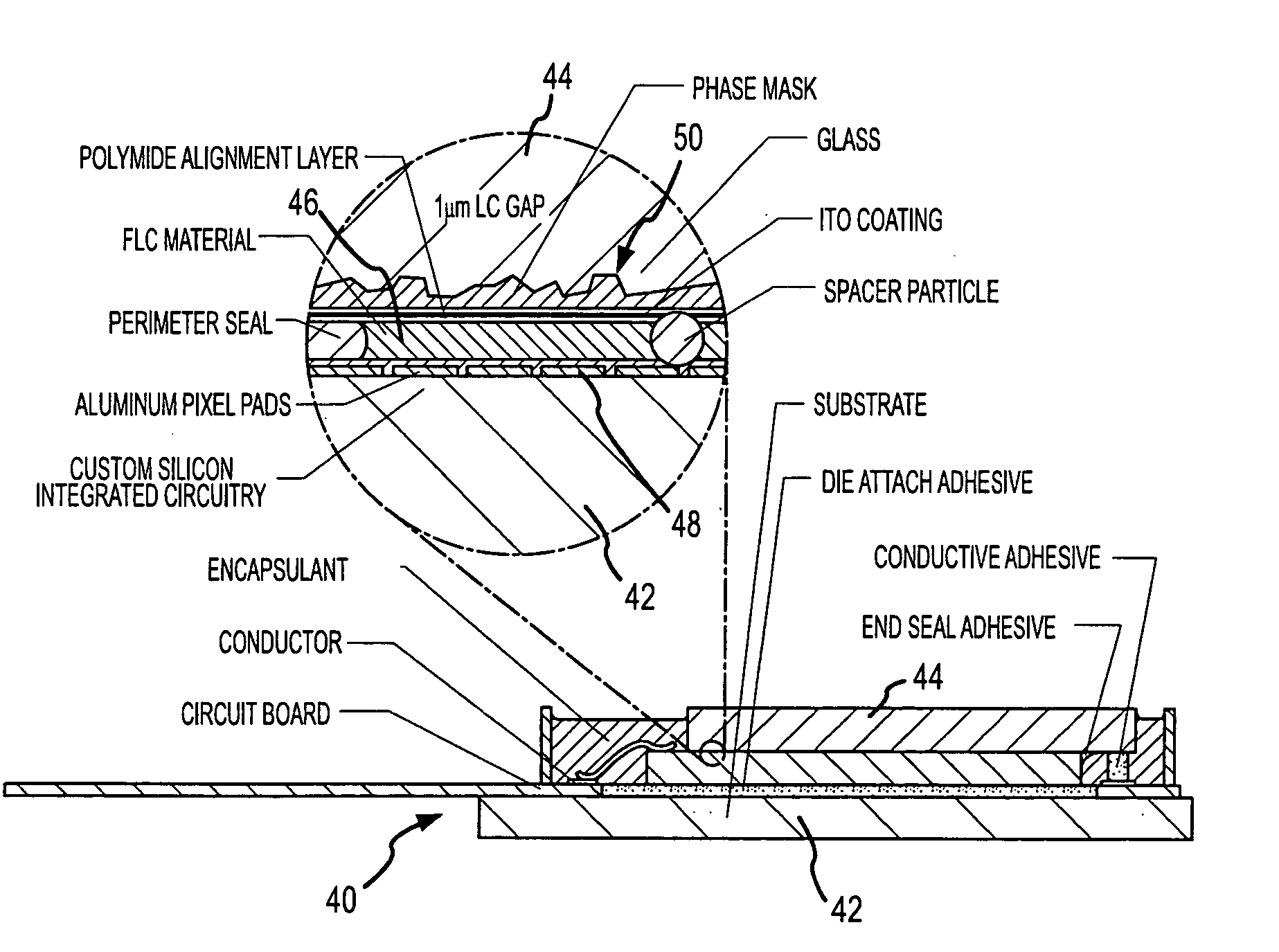
Phase masks for use in holographic data storage
InactiveUS20050207313A1Optical beam sourcesHolographic optical componentsSpatial light modulatorRefractive index
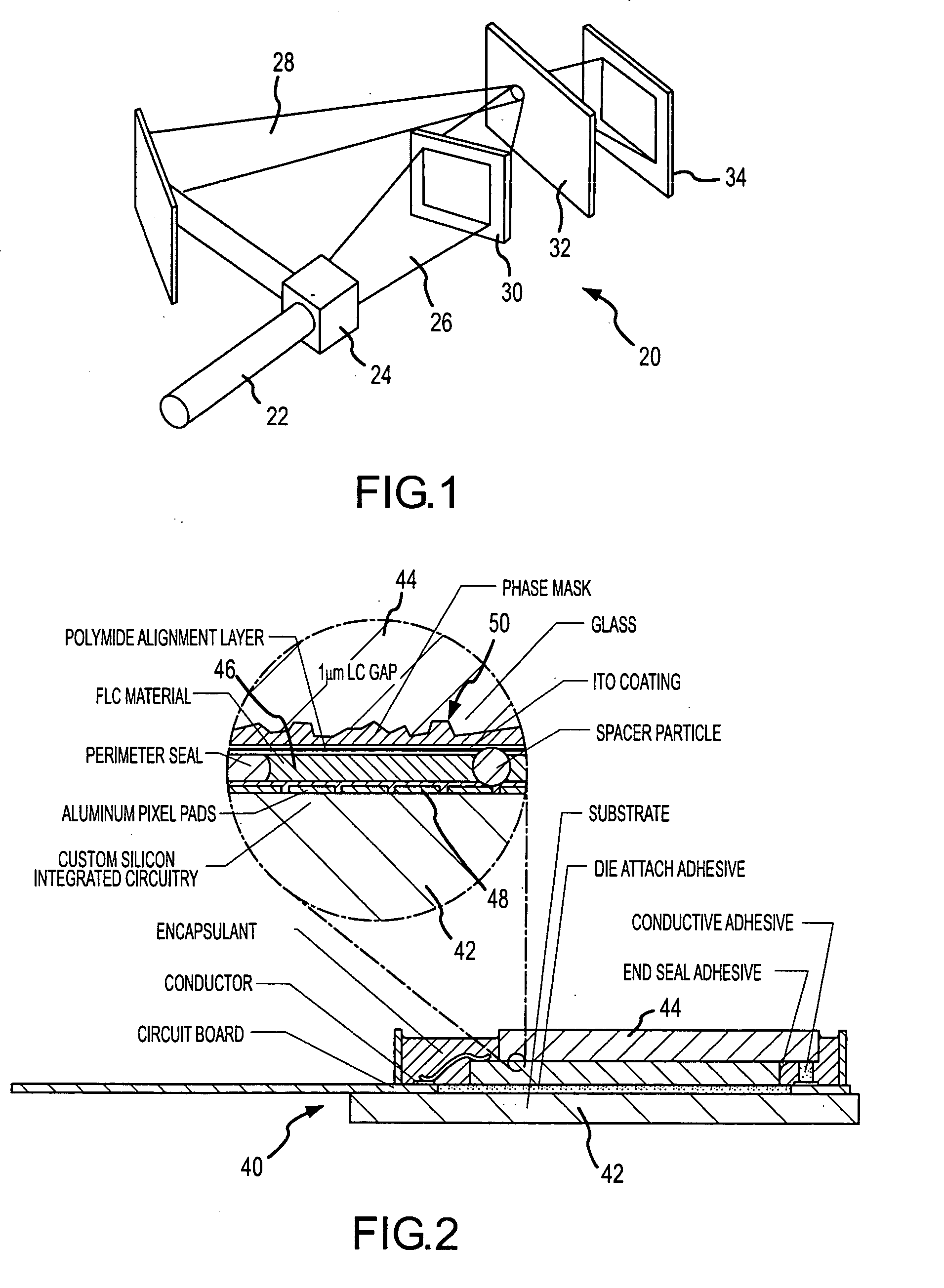
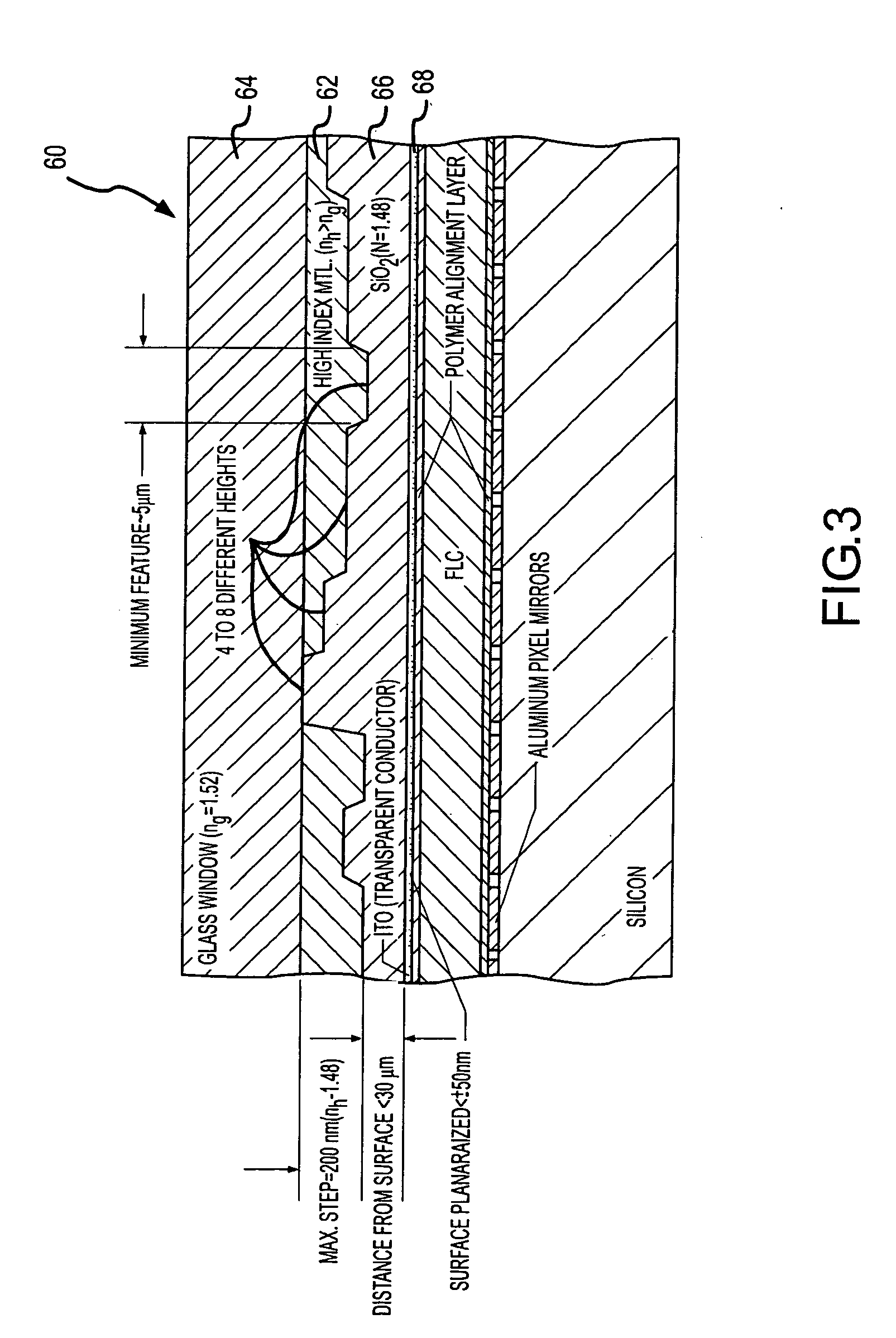
A spatial light modulator (SLM) having a phase mask that is provided as an internal component thereof. The phase mask can be provided as a multilevel surface of relatively higher index of refraction material on an inner surface of a transmissive cover window or as a separate transmissive window between the cover window and the pixels of the SLM. If the phase mask is to be used with a liquid crystal SLM, then it may be desirable to planarize the surface of the cover window contacting the liquid crystal by providing a layer of relatively lower index of refraction material adjacent the multilevel surface. The phase mask can also be provided on the transmissive cover window by patterned ion deposition, exposing patterned light to a photopolymeric material, or in some other suitable fashion. Arranging for the pixel electrodes to be at one of multiple levels rather than lying in an exactly planar relationship can also effectively create the phase mask.
Owner:CITIZEN FINETECH MIYOTA CO LTD
Method for manufacturing a tunnel junction magnetic sensor using ion beam deposition
InactiveUS20080152834A1Avoids target poisoningQuality improvementNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsOxygen ionsIon deposition
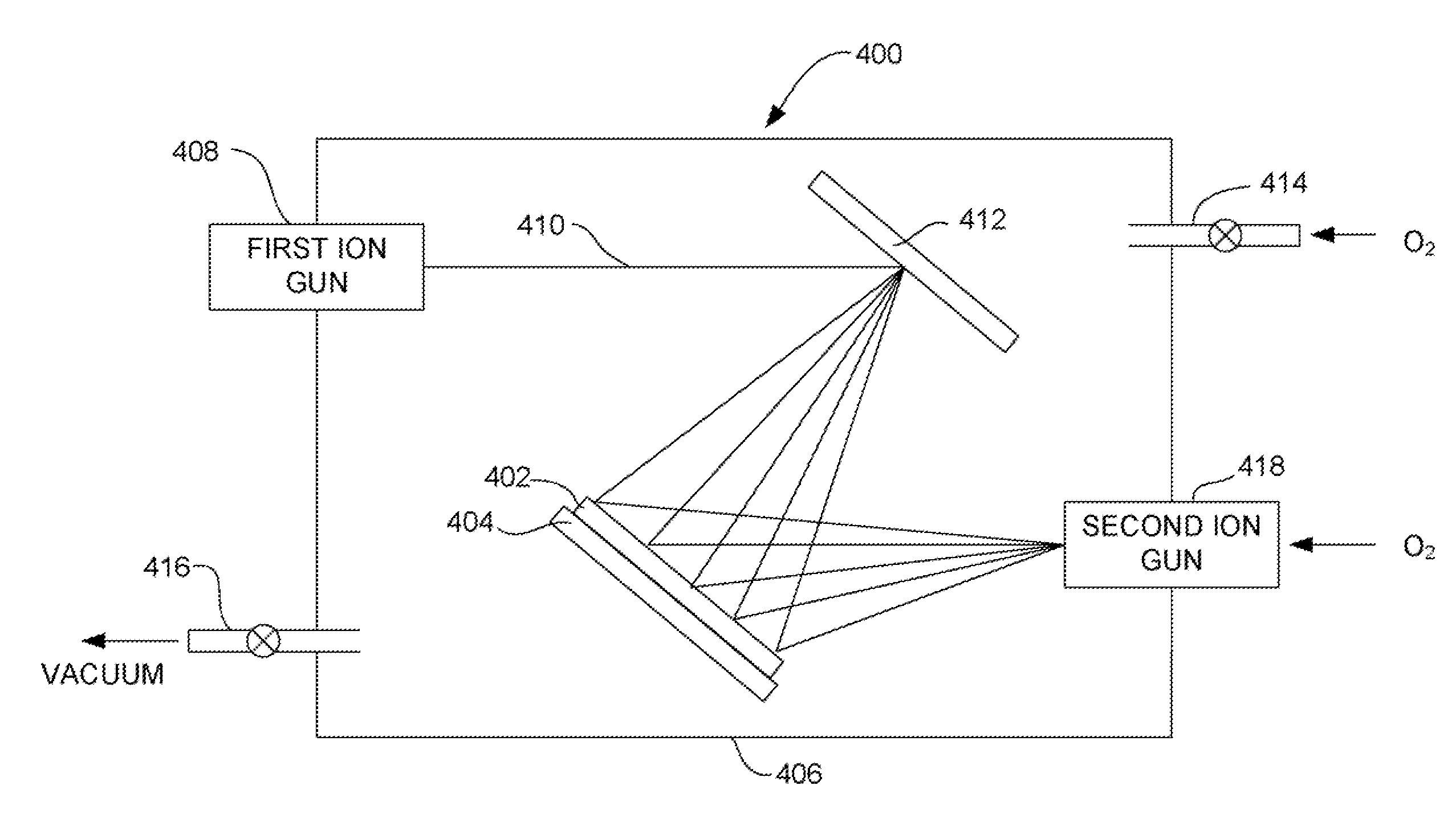
A method for forming a MgO barrier layer in a tunnel junction magnetoresistive sensor (TMR). The MgO barrier layer is deposited by an ion beam deposition process that results in a MgO barrier layer having exceptional, uniform properties and a well controlled oxygen content. The ion beam deposition of the barrier layer includes placing a wafer into an ion deposition chamber and placing Mg target into the chamber. An ion beam from an ion beam gun is directed at the target thereby dislodging Mg atoms from the target for deposition onto the wafer. Oxygen is introduced into the chamber by one or both of pumping molecular oxygen (O2) into the chamber and / or introducing oxygen ions into the chamber from a second ion beam gun. The use of ion beam deposition avoids oxygen poisoning of the Mg target, such as would occur using a more conventional plasma vapor deposition technique.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Coating process for lotus leaf-like diamond film
InactiveCN103469205AReduce stressToo much dopingSolid state diffusion coatingChemical vapor deposition coatingWear resistantGas phase
The invention relates to a coating process for a lotus leaf-like diamond film. According to the process, gases such as octafluorocyclobutane, monomethylsilane and dimethylsilane are introduced into a vacuum tank, denpending on plasma immersion ion deposition equipment; and the lotus leaf-like diamond film is coated on a workpiece surface by a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition method. The coating process mainly comprises five steps of plasma cleaning, plasma nitriding, transition layer plating, diamond-like plating and lotus leaf-like film plating. The lotus leaf-like diamond film has very high hardness. Since the lotus leaf-like diamond film has a structure similar to the surface of the lotus leaf, the lotus leaf-like diamond film has extremely low surface energy. In consideration of high wear-resistant and hydrophobic properties of the lotus leaf-like diamond film, the lotus leaf-like diamond film can be successfully applied in the fields such as coal mine screen meshes, metal molds, aerospace aircraft wings and oil pipelines.
Owner:HEFEI YONGXIN PLASMA TECH
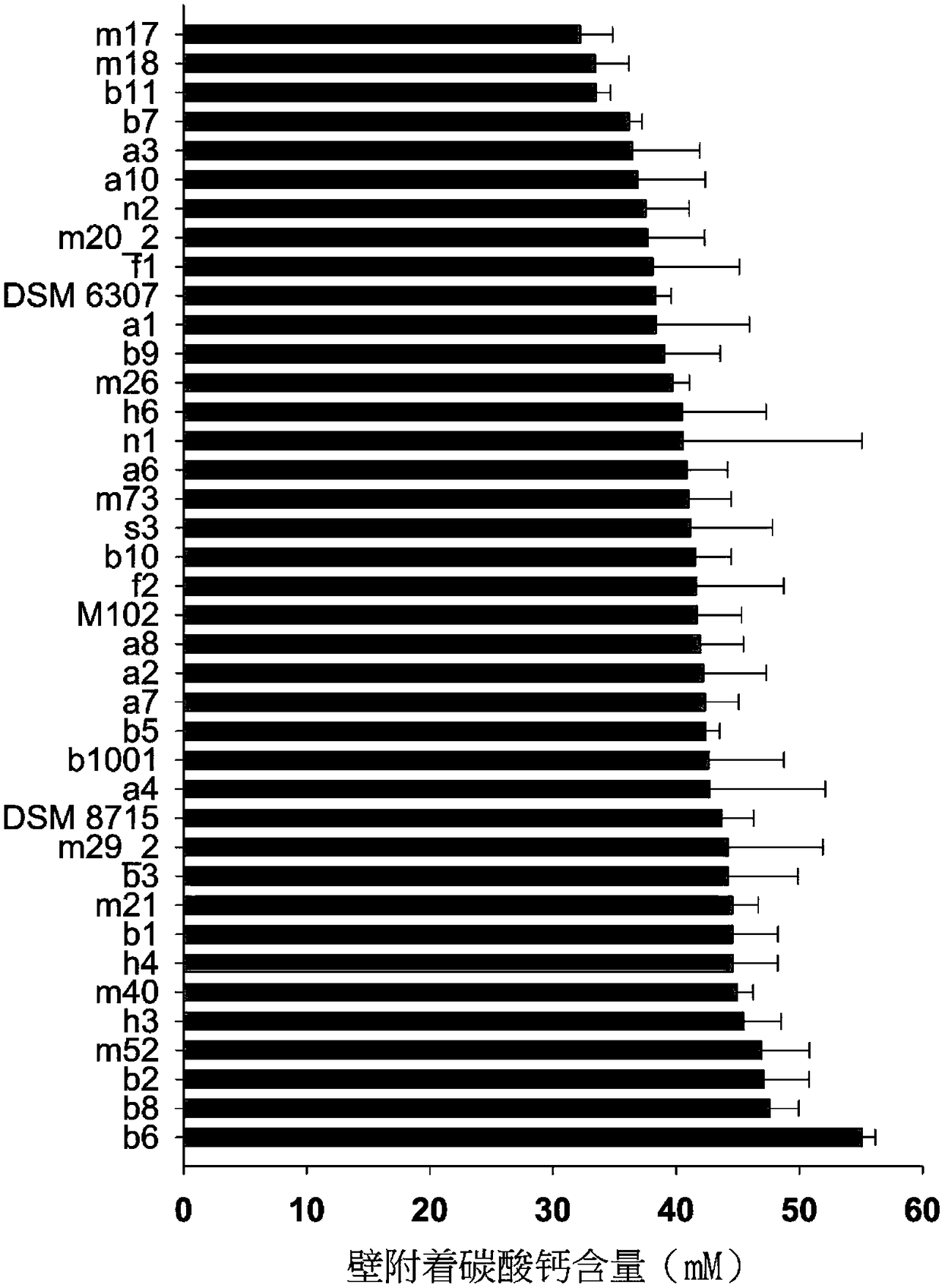
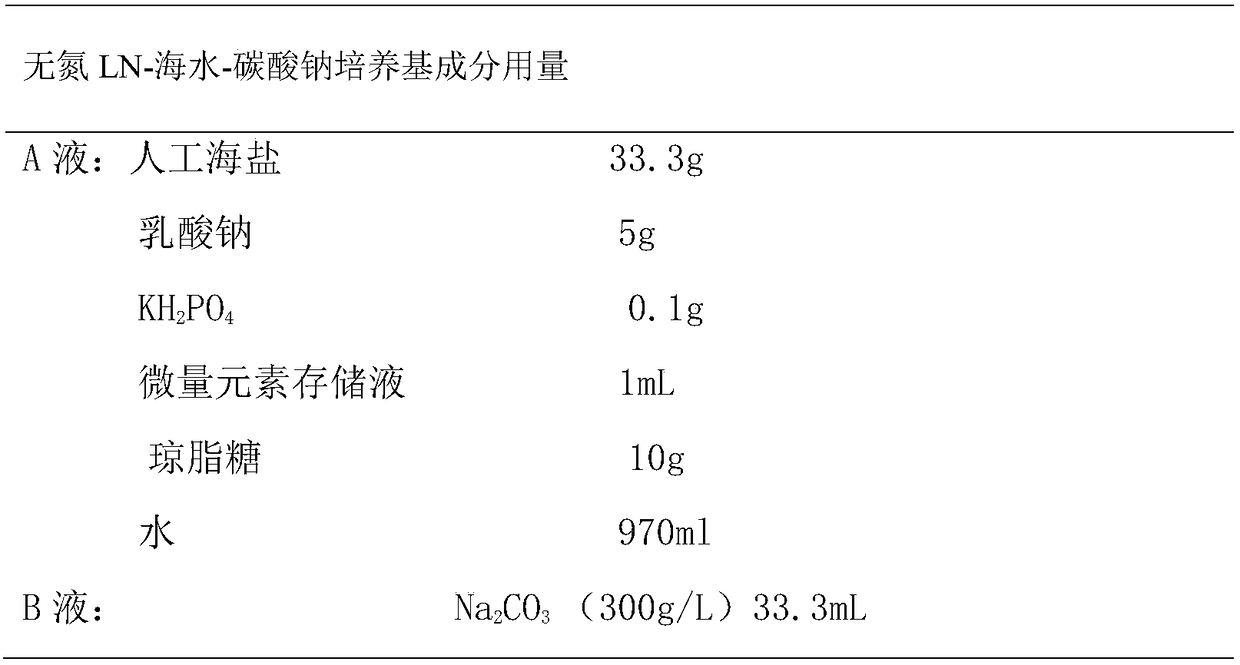
Aerobic type high-efficiency calcium mineralized bacillus and application thereof in concrete repair
The invention discloses an aerobic type high-efficiency calcium mineralized bacillus and application thereof in concrete repair. The Latin name of the strain of the high-efficiency calcium mineralizedbacillus is Bacillus sp.B6, and is identified as Bacillus, and is preserved in China Centre for Type Culture Collection; the preservation number is CGMCC NO.13360; the bacterium has high-efficiency calcium ion deposition activity; under the condition that calcium peroxide provides oxygen and calcium ions in a water environment, the yield of calcium carbonate formed on the wall of a glass test pipe is up to 54 mmol / L through 30 days of culture when initial cell concentration is 1*10<9> cells / ml; and the bacterium has good reproductive capacity and capacity of inducing calcium carbonate deposition in a strong alkaline environment, and can be used for repairing a concrete crack.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Ion film-plating device and ion film-plating method
ActiveCN104131258AAchieve depositionAvoid influenceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringTarget surface
The invention discloses an ion film-plating device and an ion film-plating method. In the ion film-plating device, a magnetic-control target is designed into a cylinder shape, all sputtering is completed inside the cylindrical target source, a bias power supply is adopted to lead out an ion beam flow to be deposited on a workpiece, therefore, ions which are electrically neutral or are not ionized cannot be attracted out by an electric field, and thus ion deposition can achieve 100%. In addition, as sputtering of the magnetic-control sputtering target source is carried out in the cylinder, even through arcing is generated, generation is carried out just inside the cylinder, and the film plated workpiece cannot be affected, and the arcing is avoided from affecting film plating. Furthermore, the target source ions are led out of the cylinder by the bias power supply, target voltage attraction on the ions after leading out is weakened, and at the same time, the area of the led-out beam flow is far smaller than the target surface area, so that the led-out beam flow density is greatly improved, and the deposition rate is effectively improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
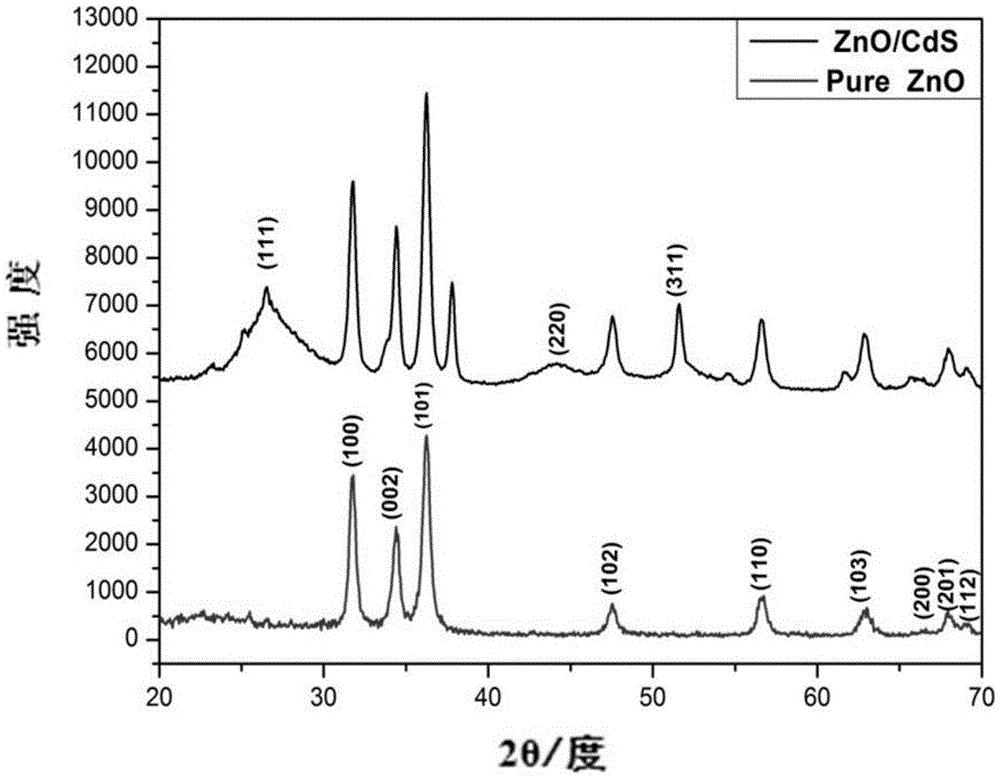
Cadmium sulfide and zinc oxide core-shell multilayer nanorod array photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105642314AStable growthSize is easy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsLight energyQuantum dot
The invention discloses a cadmium sulfide and zinc oxide core-shell multilayer nanorod array photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof. A zinc oxide nanorod is prepared through a sol-hydrothermal method, a continuous ionic depositing method is combined, CdS quantum dots are deposited on the zinc oxide nanorod surface, the related method is simple and few in side reaction, and quantum dot bear loads are controllable; the steps of ZnO nanorod array generation and CdS quantum dot deposition are repeated, preparation of the zinc oxide core-shell multilayer nanorod array photocatalytic material can be achieved, and the load rate of the quantum dots is effectively increased. The cadmium sulfide and zinc oxide core-shell multilayer nanorod array photocatalytic material can effectively control the quantum dot bear loads, and the problems that the photocatalytic material is high in photon-generated carrier compound probability, few in surface activity site and the like are solved; a multilayer nanorod structure can have refraction on sunlight, and improvement of the utilization rate on light energy is facilitated; the related preparation method is simple and suitable for application and promotion.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for environment-friendly utilization of copper-nickel-tungsten alloy
InactiveCN101525692ANo pollution in the processProcess efficiency improvementEtchingEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a method for environment-friendly utilization of copper-nickel-tungsten alloy. Sodium chloride and acid waste etching solution containing copper ions are added into alloy scraps; indissoluble tungsten and copper ion deposition is recycled after scraps are dissolved to recycle copper; the iron and manganese ions are removed, and nickel is recycled from nickel ion deposition, thereby the precious copper, nickel, tungsten are recycled from alloy scraps and copper is recycled from waste etching solution, and the environment-friendly treatment of waste etching solution is realized. The invention has the advantages that the precious copper, nickel and tungsten are recycled from copper-nickel-tungsten alloy scraps, and the acid waste etching solution containing copper ions from the treatment of electronic products scraps can be utilized without environment pollution; furthermore, the production process is environment-friendly, therefore the invention has high social and economic benefits.
Owner:丁四宜 +1
Preparation method of negative electrode of metal lithium secondary battery
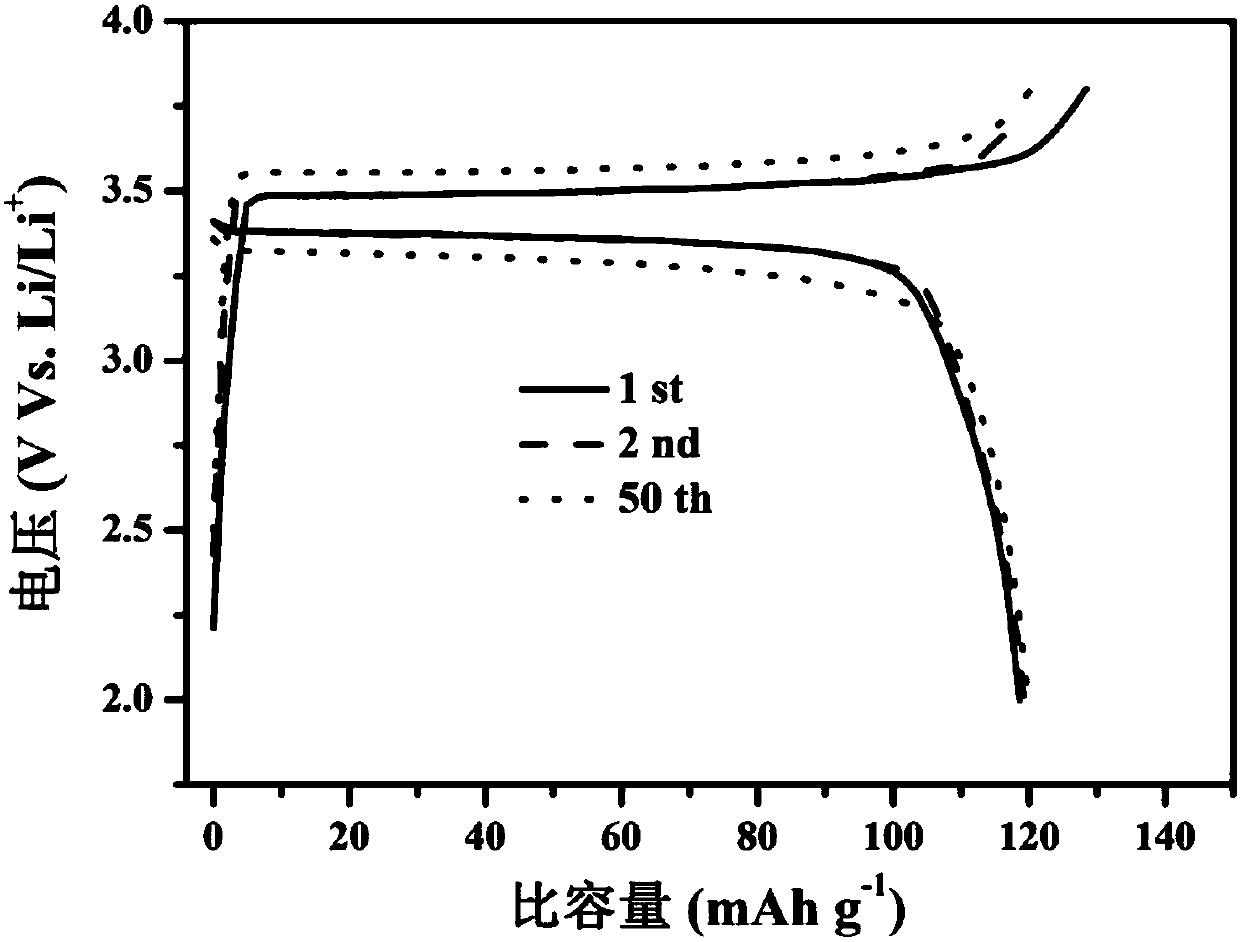
ActiveCN107565088AImprove cycle lifeReduce adverse reactionsElectrode manufacturing processesElectrode carriers/collectorsLithiumIon deposition
The invention discloses a preparation method of a negative electrode of a metal lithium secondary battery. According to the method, the surface of the original metal lithium negative electrode is coated with a layer of aluminum foil with thickness of about 600nm; and in a battery assembling process, an electrolyte is dropwise added to the aluminum foil, and the electrolyte and the aluminium foil react quickly to form lithium aluminium alloy. By virtue of the preparation method, an adverse reaction generated by direct contact between metal lithium with overhigh activity and the electrolyte canbe prevented, and lithium dendrites formed by the uneven lithium ion deposition process can be reduced, thereby greatly relieving the problem of constant electrolyte consumption and severe lithium negative electrode corrosion to a certain degree, and further prolonging the cycle life of the battery.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing film material of metal hafnium
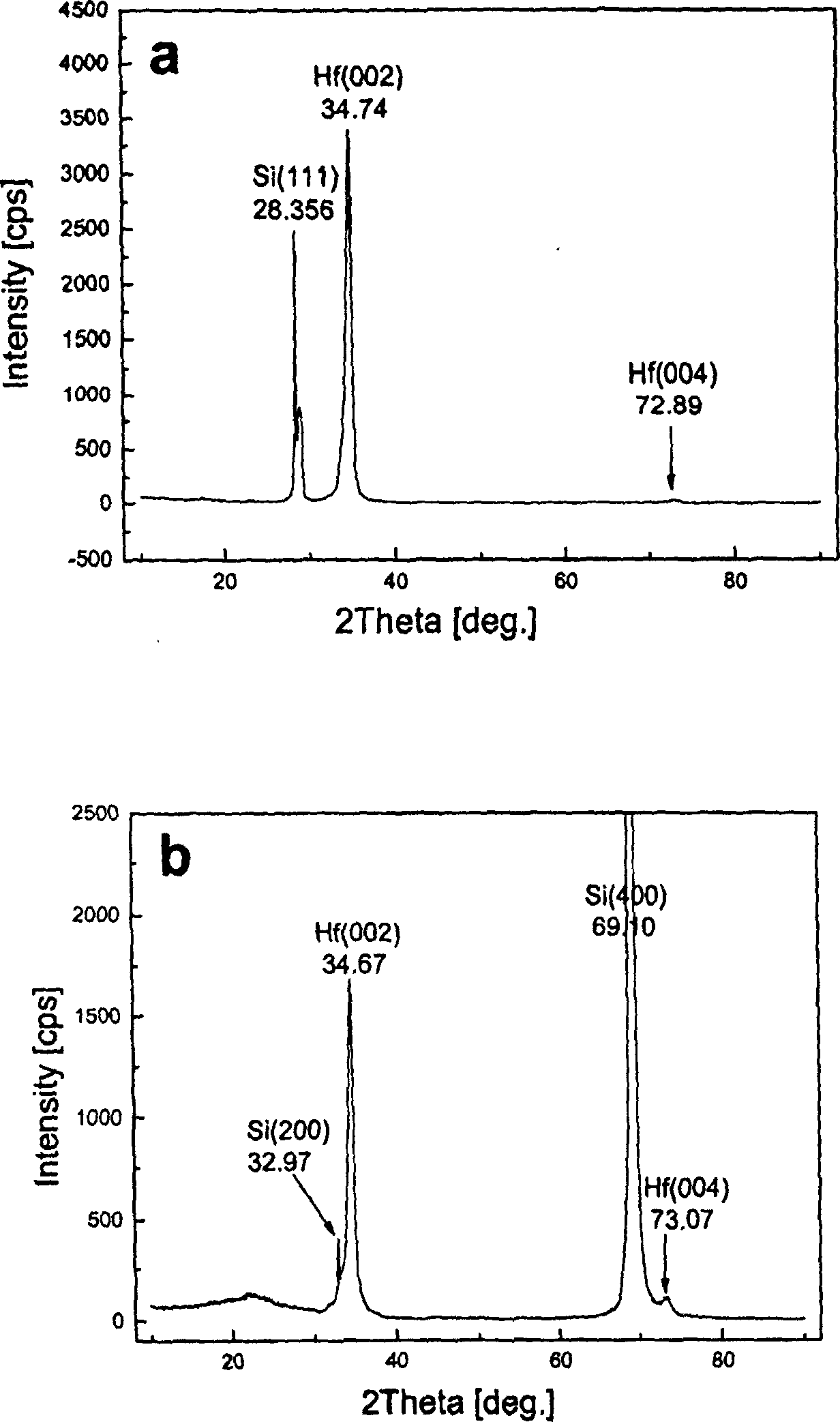
InactiveCN1796593AHigh purityImprove crystal qualityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingUltra-high vacuumFilm material
This invention provides a preparation method for hafnium thin film materials. A dual ion beam epitaxy apparatus with the function of mass separation and characteristics of energetic ion deposition is adopted, and in the condition of low purity requirement, low-cost hafnium chloride serves as raw materials is sputtered onto a sanitized substrate with single beam of pure isotopic low-energy argon ions. First, a thin film of hafnium nitride as block layer and buffer layer preventing reactions between substrate and hafnium ion is prepared from consequent pure isotopic low-energy hafnium ion beam and nitrogen ion beam. Next, hafnium film is deposited by means of single pure isotopic low-energy hafnium ion beam epitaxy. By exactly controlling the energy of hafnium ion beam, the amount of deposition agent, beam density, beam shape and deposition temperature, low-cost deposition and low-temperature epitaxy of hafnium which has a high melting point and is difficult to purify can be realized with high purity and high crystallization quality in ultravacuum cultivation room. The preparation method in this invention is convenient to modulate and optimized and is economical for manufacturing hafnium thin films used in semiconductor technology.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of ion induction patch
ActiveCN103006381AReasonable material selectionUnique designElectrotherapyAdhesive dressingsInfraredMetal foil
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ion induction patch. The method comprises the following steps of: blending and mixing organic high polymer fine powder with nanometer far infrared powder, pressing a film, drying and sizing to obtain a film; performing ion transformation deposition micro-treatment on the film to form an ion deposition layer; placing metal foils onto both sides of the ion deposition layer respectively to obtain a metal foil ion deposition layer; and sticking one side of the metal foil ion deposition layer to a sticking base layer and covering a surface gloss paper support layer on the other side of the metal foil ion deposition layer to obtain an ion induction patch. According to a prepared product, the principle of the biological stimulation effects of a high-voltage electrostatic field, far infrared rays and microcurrent on human bodies is utilized comprehensively, and electrostatic ion induction directly acts on afflicted parts, so that the proliferation of abnormal cells is suppressed effectively, normal growth of benign cells is activated, local blood circulation is facilitated in combination with far infrared rays, blood acidity is lowered, metabolism is facilitated, and the immunity is enhanced; and the product has the effects of rapidly relieving pain, diminishing inflammation and subsiding swelling.
Owner:GUANGDONG TAIBAO MEDICAL SCI TECH
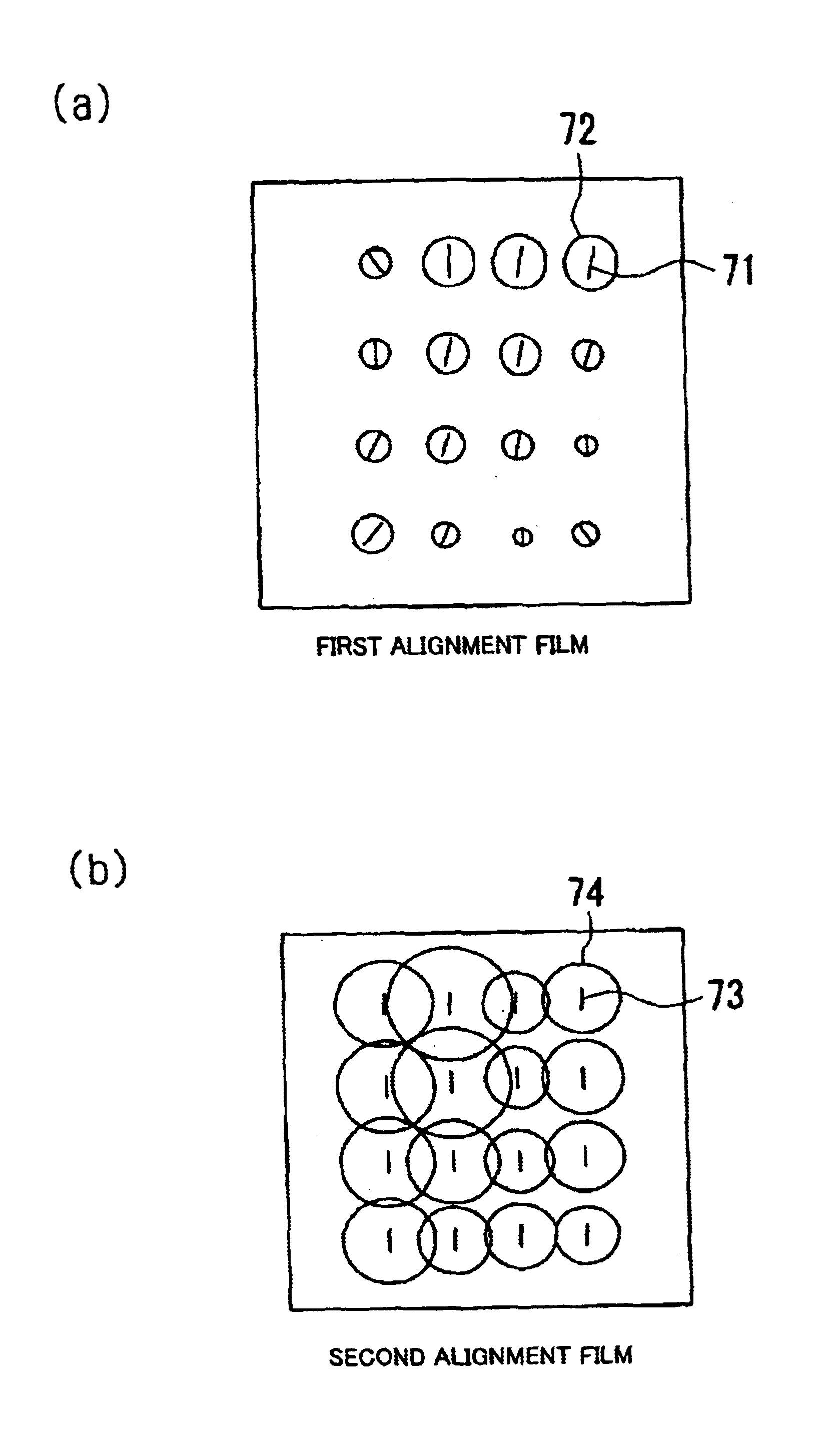
Alignment film, method for fabricating the alignment film, liquid crystal device, and projection type display device
InactiveUS6844905B2Conveniently obtainHigh liquid crystal alignment control forceLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesIn planeDisplay device
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Plasma omnibearing ion deposition equipment
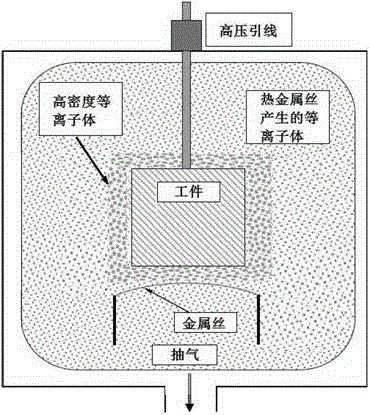
InactiveCN102719788AHigh densityImprove compactnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDlc coatingDirect-current discharge
The invention discloses plasma omnibearing ion deposition equipment which comprises a vacuum plating chamber, an air extracting system, a man-machine control system and an inflation system, wherein the vacuum plating chamber is internally provided with a support for supporting a to-be-plated workpiece. The plasma omnibearing ion deposition equipment is characterized in that the equipment is further provided with a plasma enhancing device and a DLC (diamond like carbon) coating doping device, wherein the enhancing device consists of a metal wire in the vacuum plating chamber, an auto-transformer, an isolation transformer and a direct current discharge power supply, and the DLC coating doping device consists of an external air source input device and an internal metal vapor source high-frequency induction heating device. According to the equipment disclosed by the invention, in the plating process, due to the improvement of density of plasma, more ions with positive charges are deposited on the surface of the workpiece, and thus the plating rate is improved. Moreover, due to a great amount of ions perform bombardment, the consistency and bonding force of the DLC are improved. In addition, internal stress of the DLC coating can be significantly reduced after the doping of metal elements.
Owner:HEFEI YONGXIN PLASMA TECH
Apparatus and method for stimulating hair growth and/or preventing hair loss
InactiveUS20160001073A1Promote cell growthCombating baldnessExternal electrodesArtificial respirationPower flowIon deposition
A method of treating or preventing a hair-condition of a user comprising: subjecting the user's scalp to at least 200 distinct electrode-scalp contact events during a time-interval of at most one minute and dividable into 5 non-overlapping equal-duration sub-intervals covering the time-interval, method performed such that i. for at least a majority of the electrode-scalp contact events, no electrode of the event enters into the dermis; ii. a duration of each electrode contact event is at most 100 milliseconds; and iii. for each electrode contact event, an electrical current flows between the electrode and the scalp so as to deposit electrode-released ions of a first metal or of a second metal on the scalp, thereby forming a respective metal-ion-deposition island on the user's scalp.
Owner:PILOGICS LP
Lithium ion battery electrolyte and lithium ion battery
InactiveCN105742710AAvoid depositionRaise the thermodynamic energy barrierSecondary cellsOrganic electrolytesOrganic solventPhysical chemistry
The invention is applicable to the field of the lithium ion battery, and provides a lithium ion battery electrolyte. The electrolyte comprises a lithium salt, an organic solvent and a functional additive, wherein the functional additive is TAC; and the concentration of the functional additive in the electrolyte is 0.01-0.1mol / L. The invention also provides a lithium ion battery, including the electrolyte. According to the lithium ion battery, the TAC is added in the electrolyte; a coordination compound formed by the TAC and the metal ions in the battery restrains metal ion deposition, so that the high temperature performance and the safety performance of the battery are obviously improved. In addition, the TAC is used as the functional additive, so that an obvious effect can be achieved by only requiring a small dosage.
Owner:OPTIMUM BATTERY CO LTD
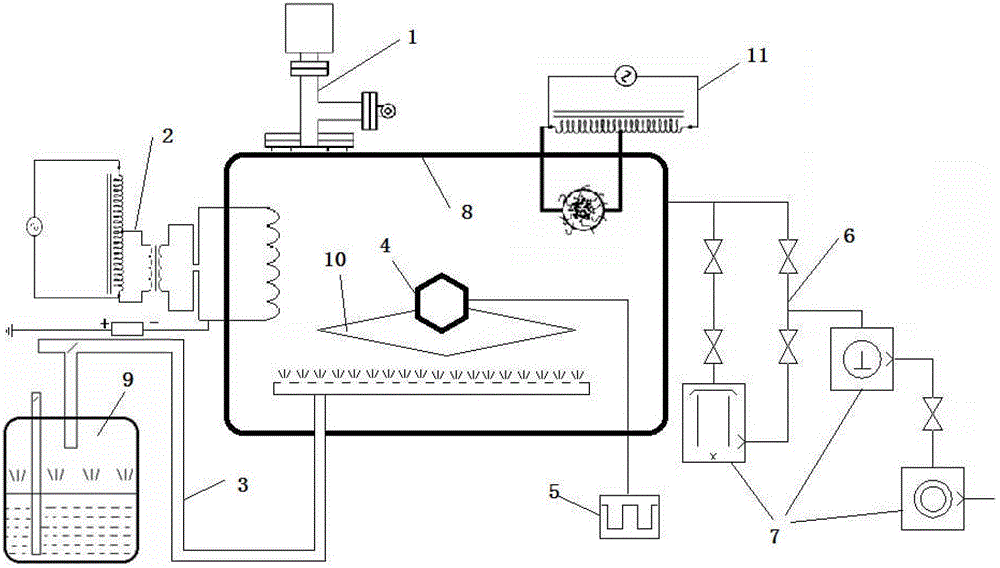
Arc evaporation source actively controlling arc spot and equipment using same
InactiveCN101928922AImprove overall utilizationIncrease profitVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEvaporation (deposition)Ion deposition
The invention relates to an arc evaporation source actively controlling an arc spot and vacuum arc ion deposition equipment using the same. The arc evaporation source comprises an arc initiating mechanism, a target fixed link, a small coil, an outer insulating sleeve, a target seat, a big coil, a target material, a small magnetic field polar axis and the like. The vacuum arc ion deposition equipment comprises a rack, a vacuum chamber, the arc evaporation source and a vacuum acquisition system. By using the arc evaporation source and the vacuum arc ion deposition equipment, the number of large particles in a coat can be greatly reduced, and the diameter of the largest particle can be greatly reduced. Therefore, by using the equipment, the service life of manufacture workpieces can be improved by 3 to 10 times, the production cost is remarkably reduced, and the production efficiency and the product quality are improved.
Owner:姜文
Method for realizing metallization of back of indium tin oxide (ITO) target material by ion deposition
ActiveCN103031524AIncrease profitImprove bindingVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndiumMetal impurities
The invention relates to a method for realizing metallization of the back of an indium tin oxide (ITO) target material by ion deposition. The method comprises the following steps: preparing indium into an indium target; after ultrasonically cleaning and drying the ITO target material, mounting and fixing the ITO target material on a workpiece rest of a multi-arc ion plating machine; after cleaning under biasing, starting the multi-arc ion plating function and depositing one layer of metal indium film on the surface of the ITO, wherein in the plating process, the temperature is 100 to 150 DEG C, the voltage is 20 to 80 V, the current is 0.1 to 0.6 A, the time is 5 to 15 minutes and the argon pressure intensity is 0.3 to 1 Pa; and cooling, taking out and cleaning the target material to obtain the ITO target material with the surface subjected to uniform metallization. The method is simple; the back of the ITO target material can be metalized through multi-arc ion deposition and then production of components can be realized by braze welding; the metalized layer has a high binding force and a high speed; and pollution is avoided, other metal impurities are not introduced, and recovery of the target material is promoted.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com