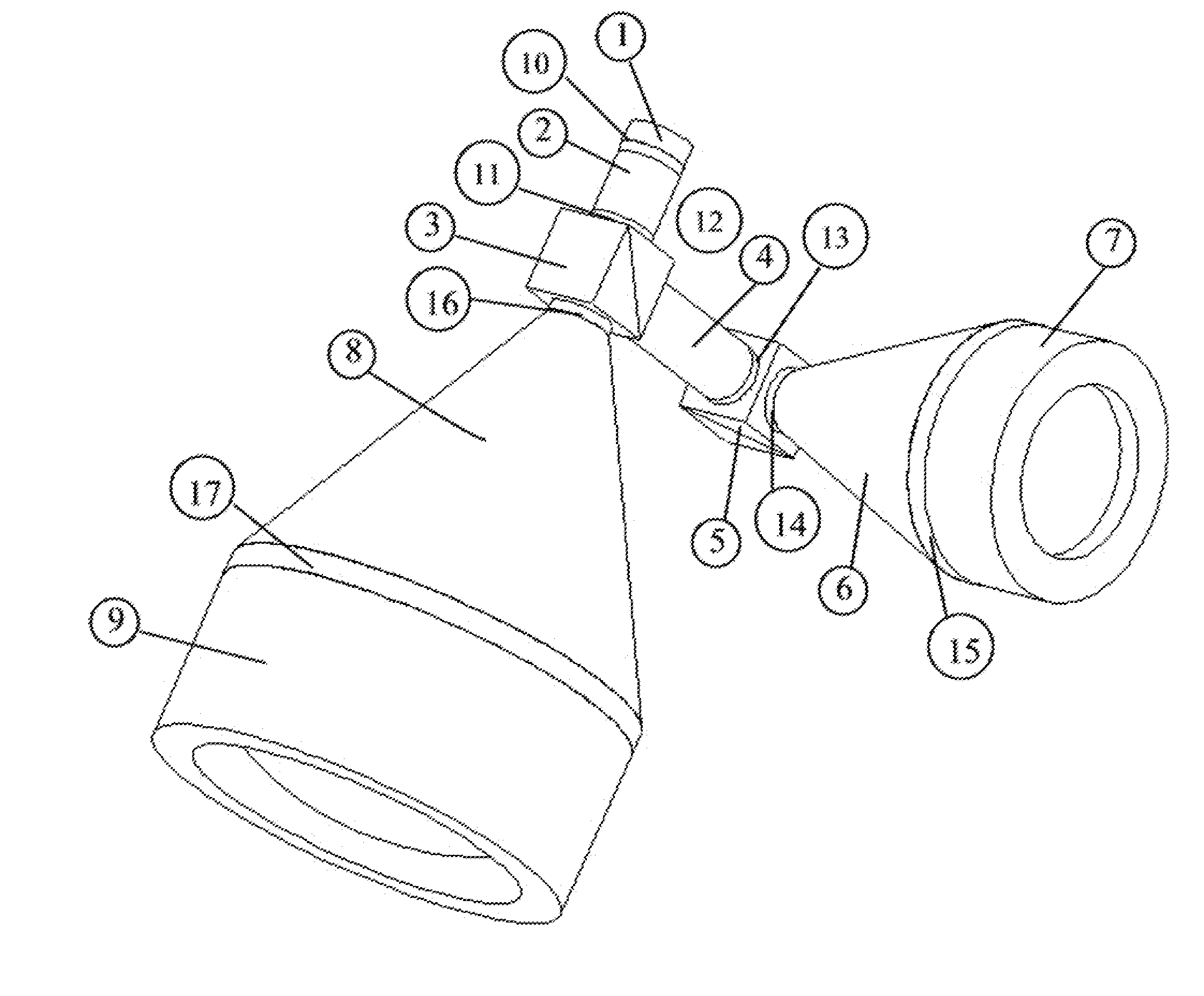
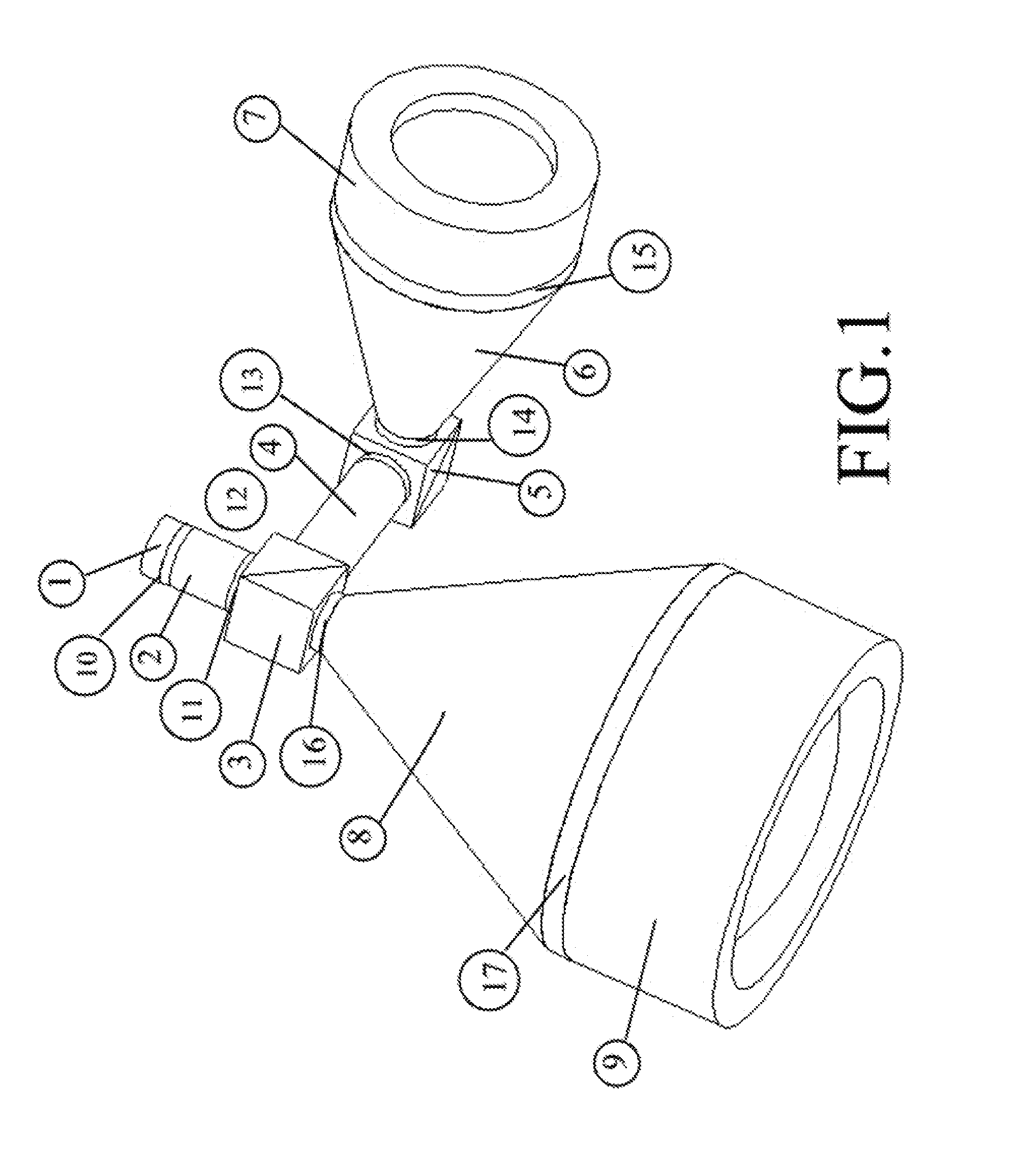
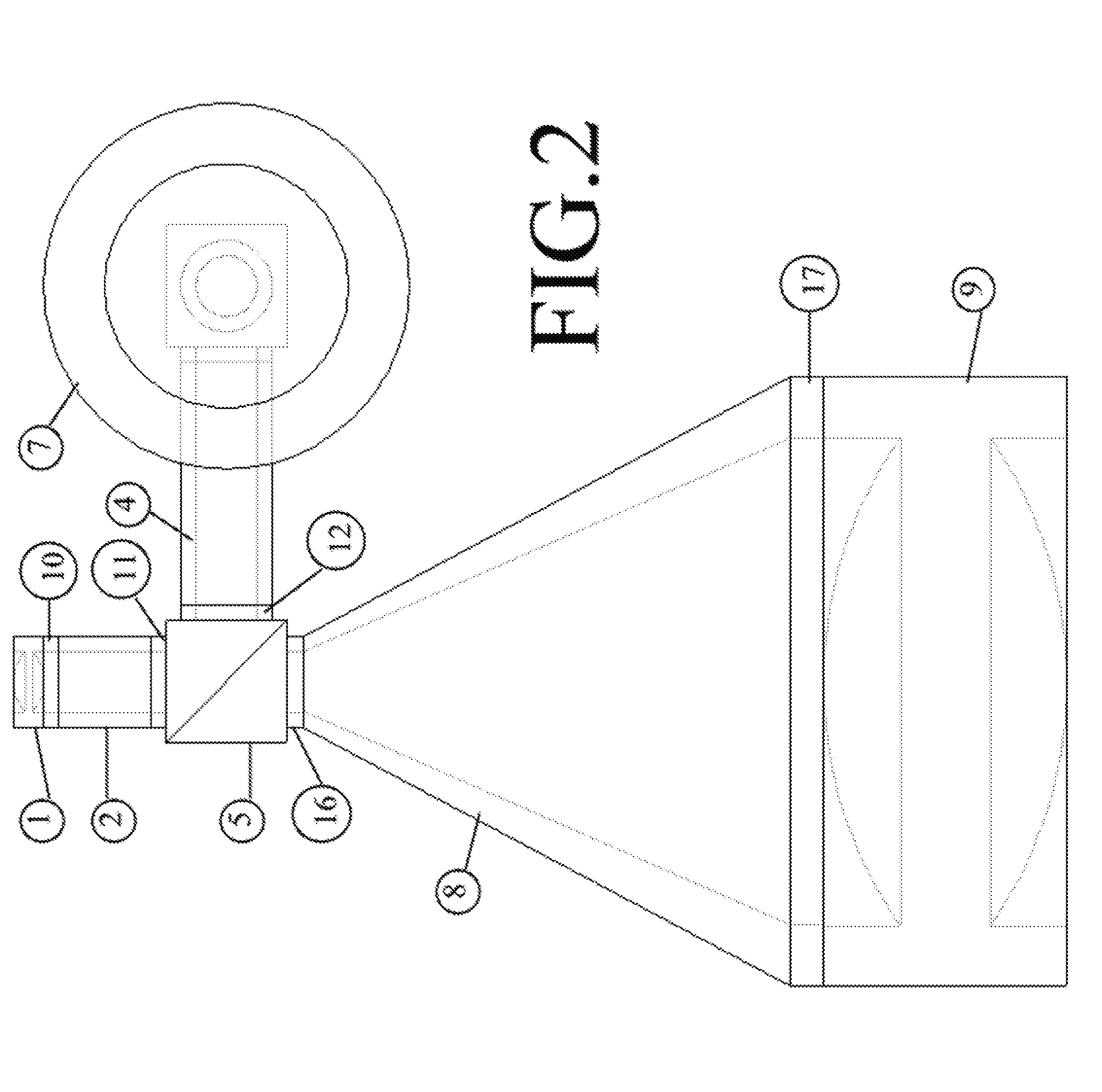
Patents
Literature
5805 results about "Internal stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Internal stress. [in′tərn·əl ′stres] (mechanics) A stress system within a solid that is not dependent on external forces. Also known as residual stress.
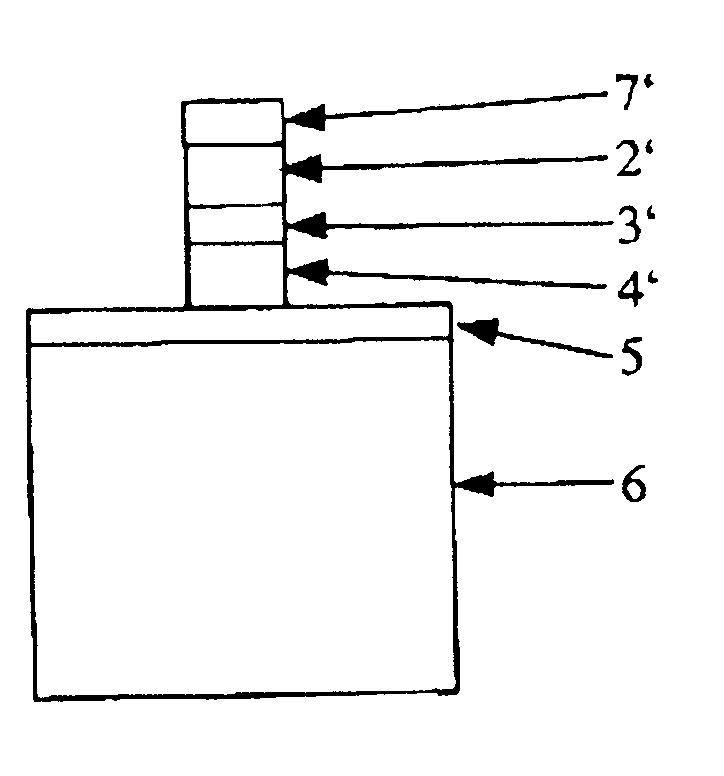
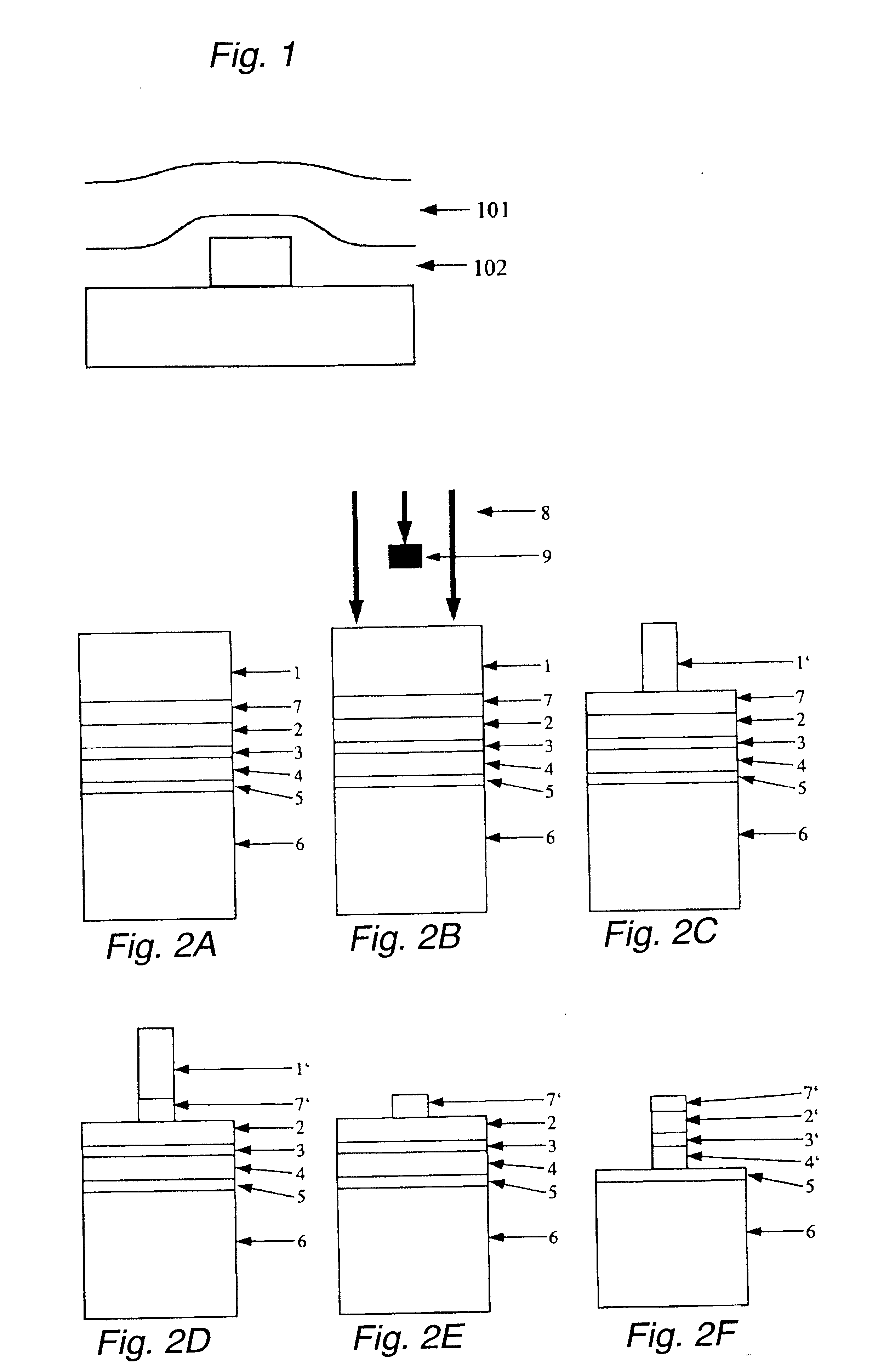
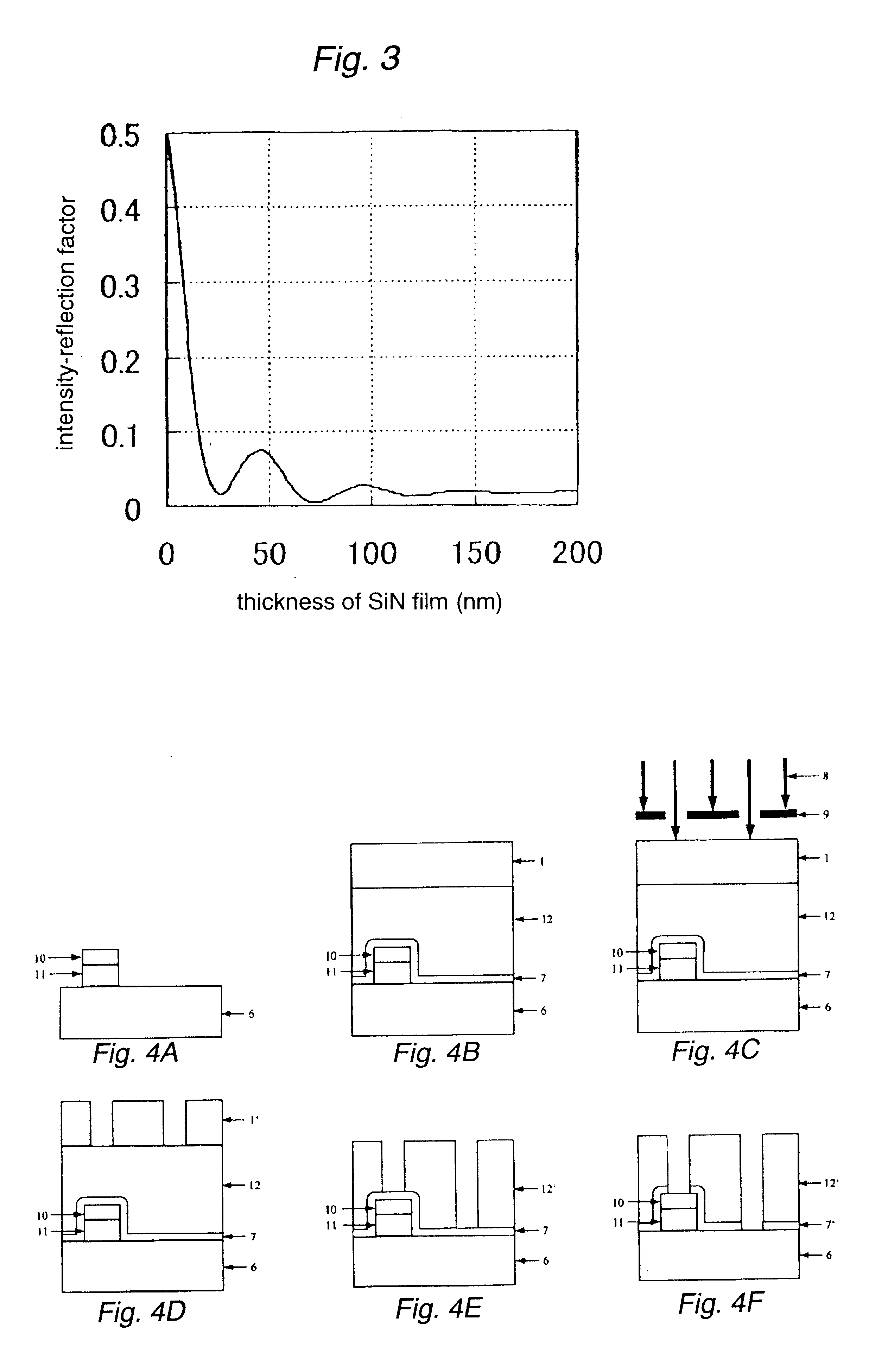
Method of forming fine pattern
InactiveUS6586163B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistSilicon oxide
There is described a method of forming a fine pattern aimed at depositing a silicon-nitride-based anti-reflection film which is stable even at high temperature and involves small internal stress. The method is also intended to preventing occurrence of a footing pattern (a rounded corner) in a boundary surface between a photoresist and a substrate at the time of formation of a chemically-amplified positive resist pattern on the anti-reflection film. The method includes the steps of forming a silicon-nitride-based film directly on a substrate or on a substrate by way of another layer; and forming a photoresist directly on the silicon-nitride-based film or on the silicon-nitride-based film by way of another layer. The silicon-nitride-based film is deposited while the temperature at which the substrate is to be situated is set so as to fall within the range of 400 to 700° C., through use of a plasma CVD system. The method further includes a step of depositing a silicon-oxide-based film immediately below the photoresist. The silicon-oxide-based film is deposited while the temperature at which the substrate is to be situated is set so as to fall within the range of 400 to 700° C., through use of a plasma CVD system.
Owner:ASM JAPAN +1
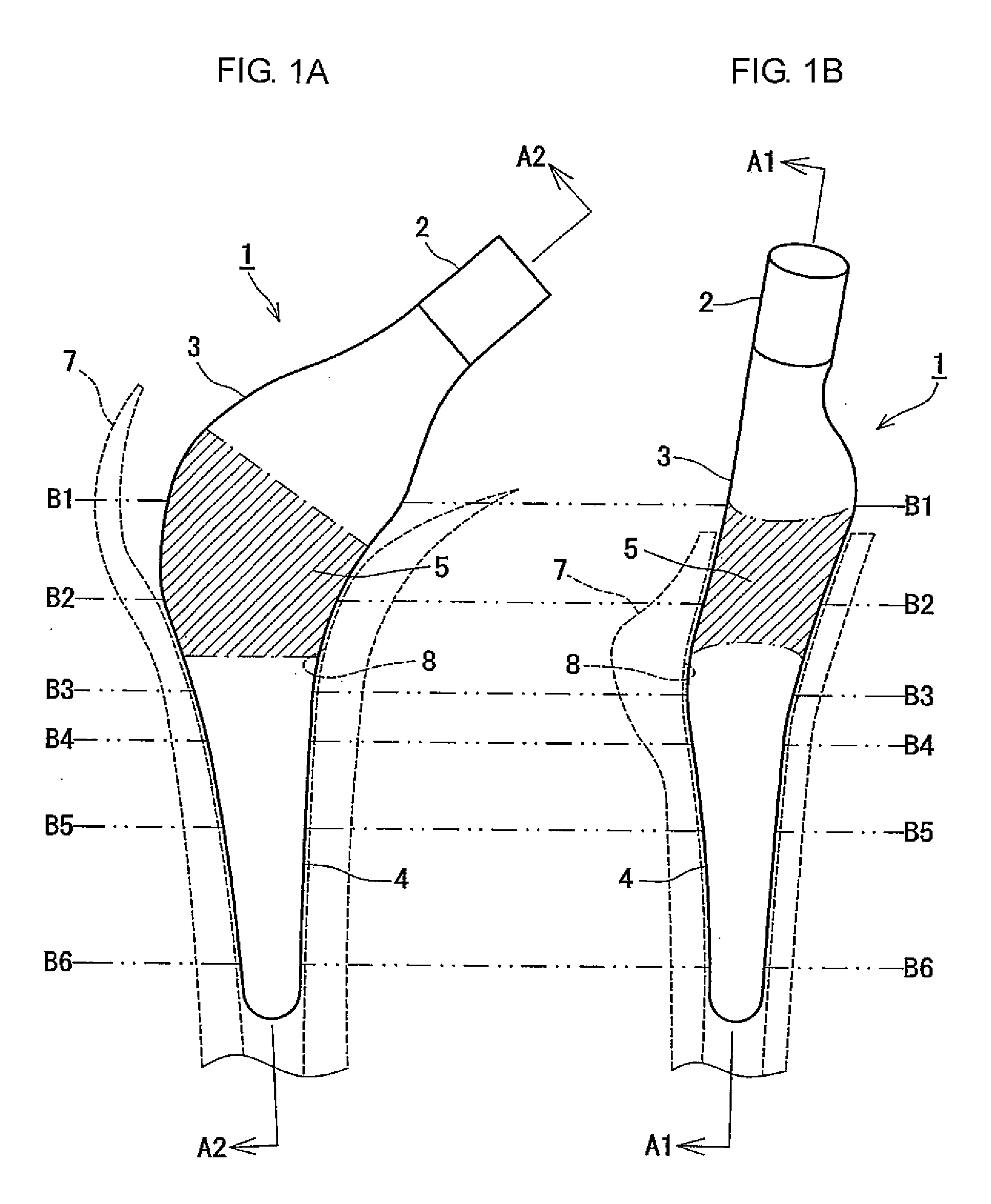
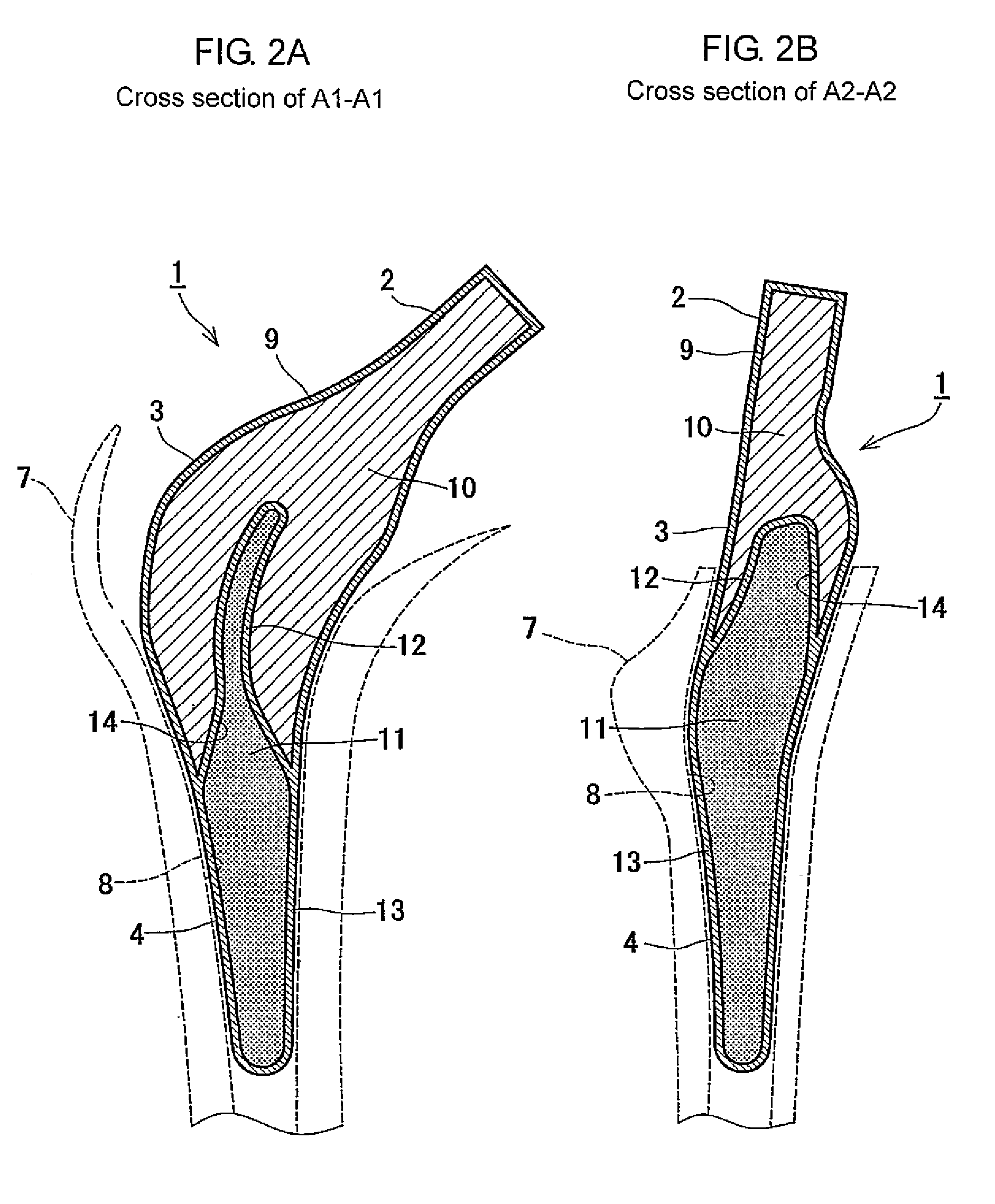
Method of Designing and Manufacturing Artificial Joint Stem with Use of Composite Material
InactiveUS20080234833A1Low costIncreased durabilityJoint implantsTomographyArtificial jointsEngineering
The method of designing and manufacturing the artificial joint stem, comprising steps of performing analysis of the internal stress of the artificial joint stem and bone and the adhesive stress of the artificial stem and bone, using the computer, based on the three dimension data indicating the structure of the bone formed by using plural tomographic images of the bone, the design condition involving the form and stiffness of the artificial joint stem configured by using at least one of the tomographic images and the three dimension data, wherein if the result of the analysis does not satisfy the design condition, the condition is changed to have the computer reanalyze and if the result of the analysis satisfies the design condition, the artificial joint stem is designed and manufactured with the stem data based on the result of analysis and the design condition.
Owner:B I TEC
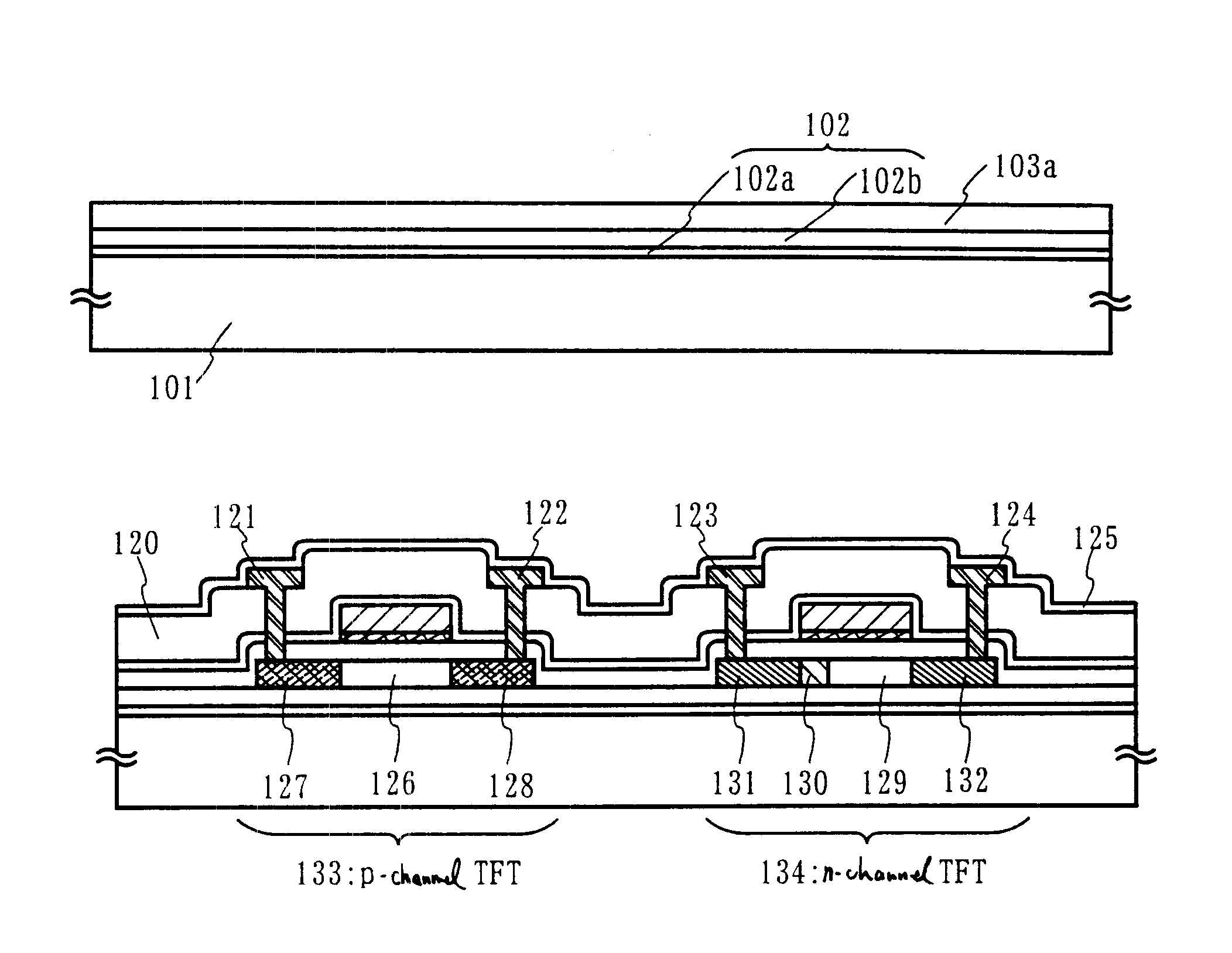
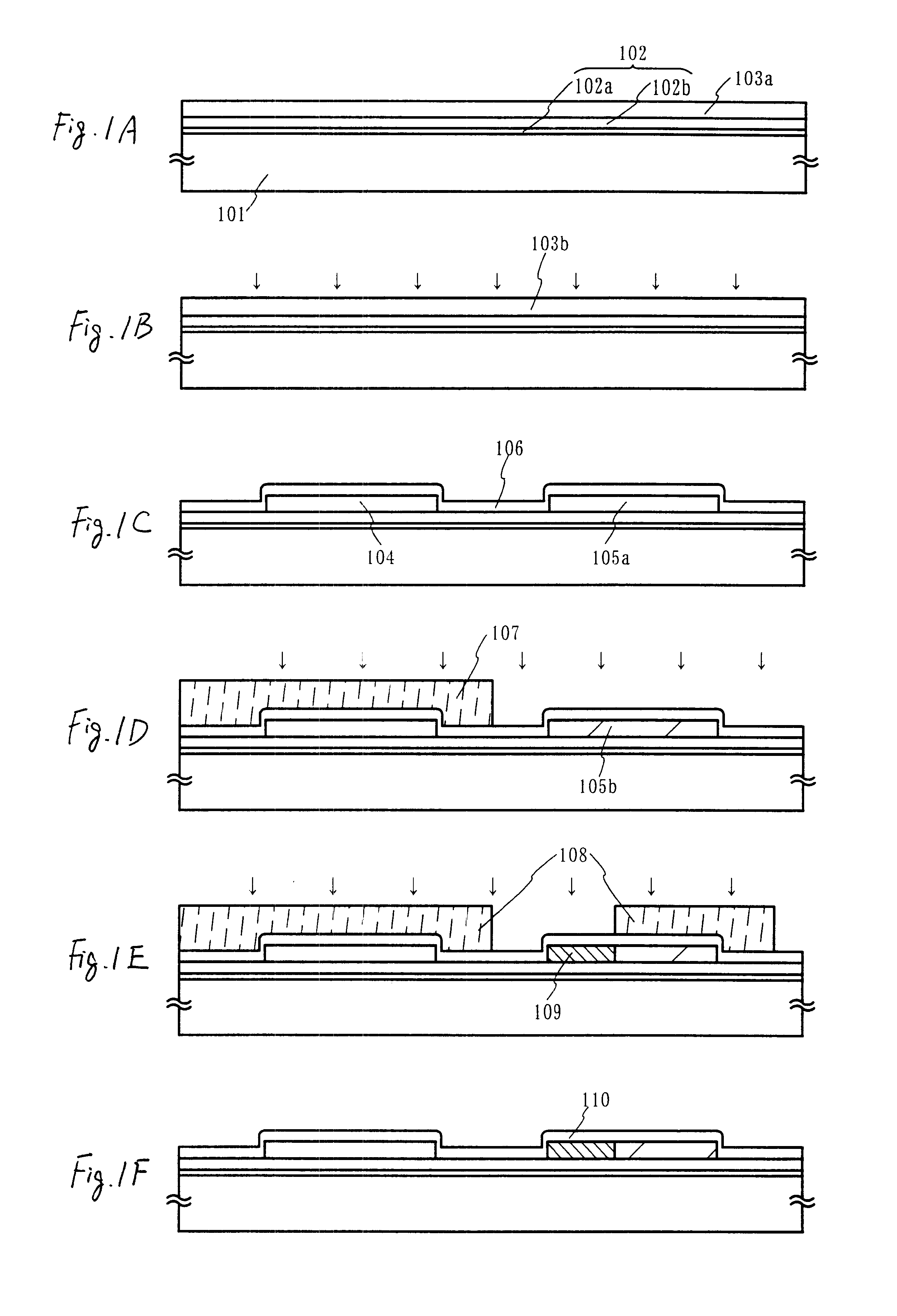
Oxynitride laminate "blocking layer" for thin film semiconductor devices
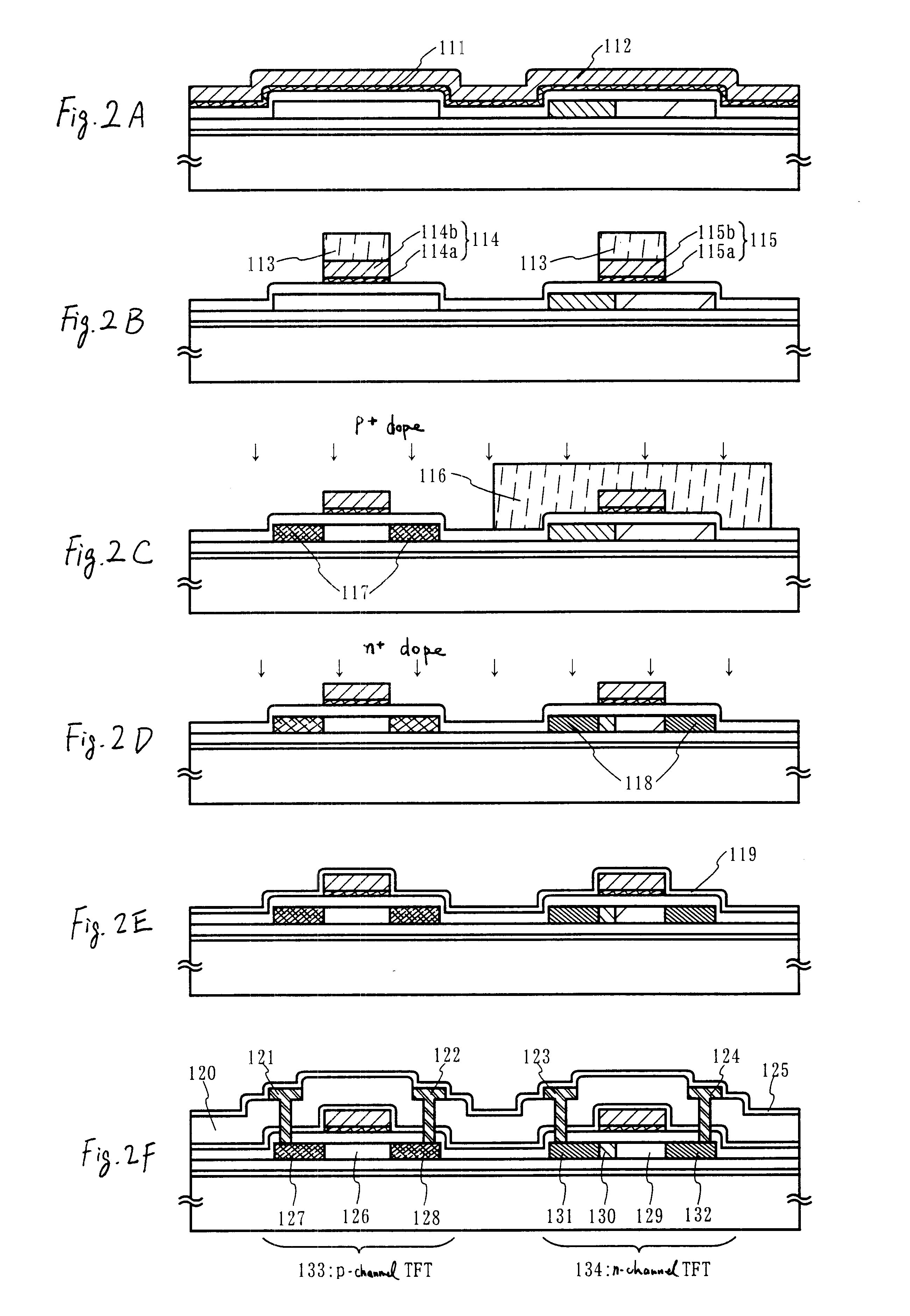
Channel doping is an effective method for controlling Vth, but if Vth shifts to the order of -4 to -3 V when forming circuits such as a CMOS circuit formed from both an n-channel TFT and a P-channel TFT on the same substrate, then it is difficult to control the Vth of both TFTs with one channel dope. In order to solve the above problem, the present invention forms a blocking layer on the back channel side, which is a laminate of a silicon oxynitride film (A) manufactured from SiH4, NH3, and N2O, and a silicon oxynitride film (B)manufactured from SiH4and N2O. By making this silicon oxynitride film laminate structure, contamination by alkaline metallic elements from the substrate can be prevented, and influence by stresses, caused by internal stress, imparted to the TFT can be relieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
MEMS device and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveUS20070190680A1Relaxation stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingForming microstructural systemsEngineeringWafer bonding
MEMS devices require special cavity formation and sealing steps such as wafer bonding which reduce the yield and increase the cost. In addition, it is difficult to form a cavity of a large area by the LSI process owing to a residual stress of a sealing film which will be a lid. This leads to a difficulty of realizing an integrated MEMS having a MEMS and a high-performance LSI mounted on one substrate. The lid (or diaphragm) covering therewith a cavity is equipped with slits or beams. During the formation of the cavity, the slits are deformed to absorb and relax the internal stress of the thin sealing film. Then, the cavity is sealed by filling the open portions of the film overlying the cavity between the inside and outside of the cavity. The cavity is formed by removing a portion of the interlayer film of LSI multilevel interconnects and the lid is made of a LSI-process thin film.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
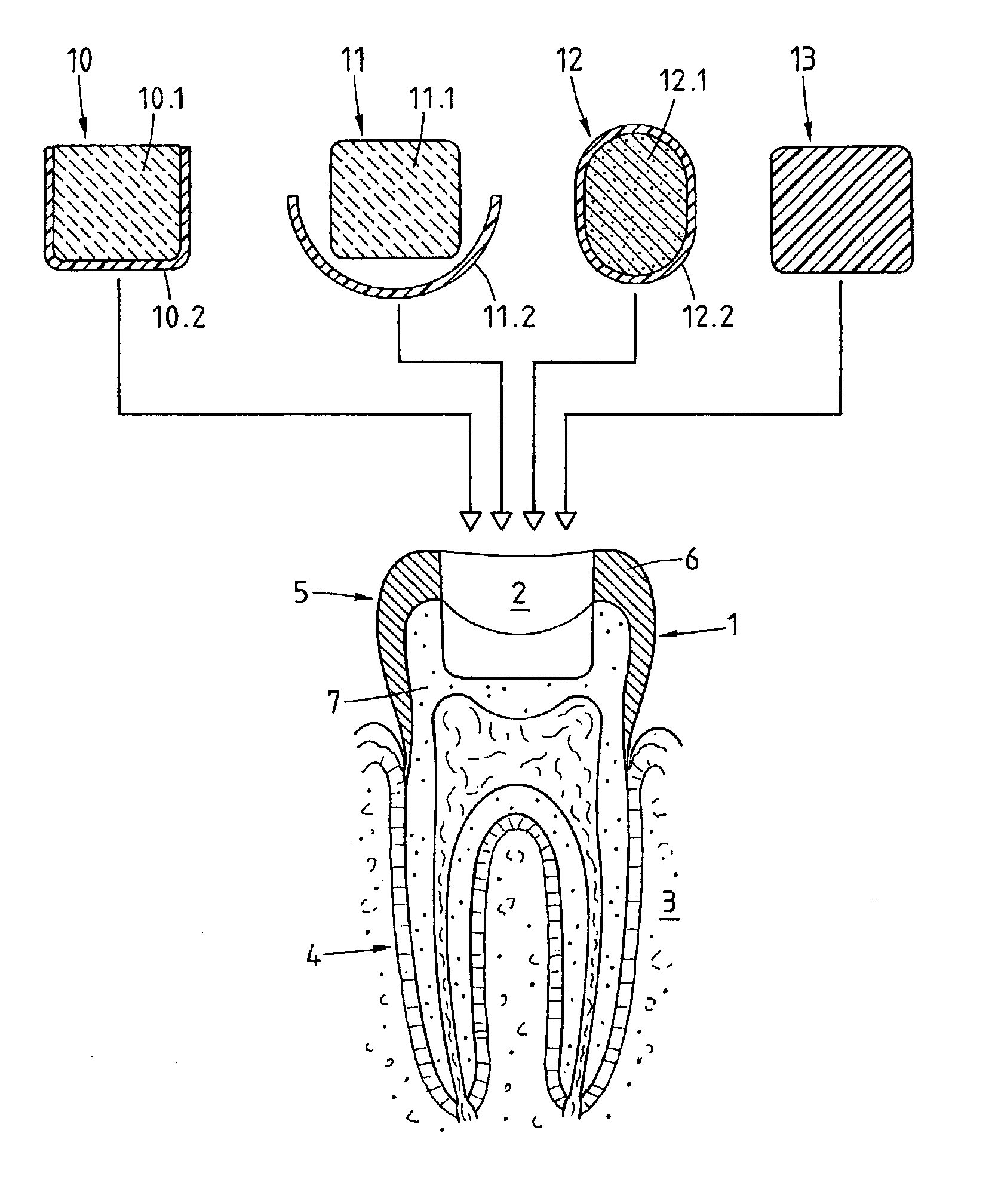
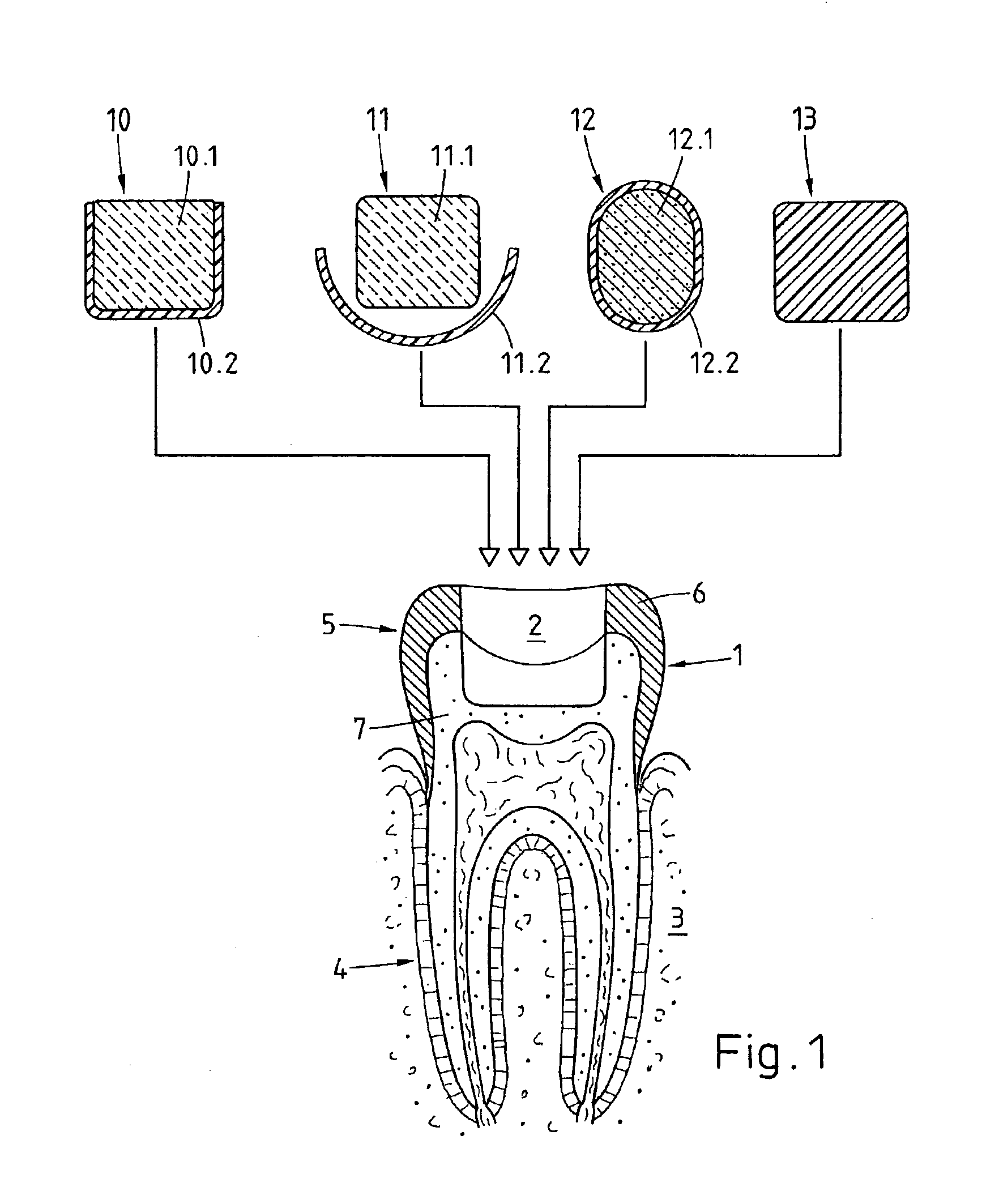
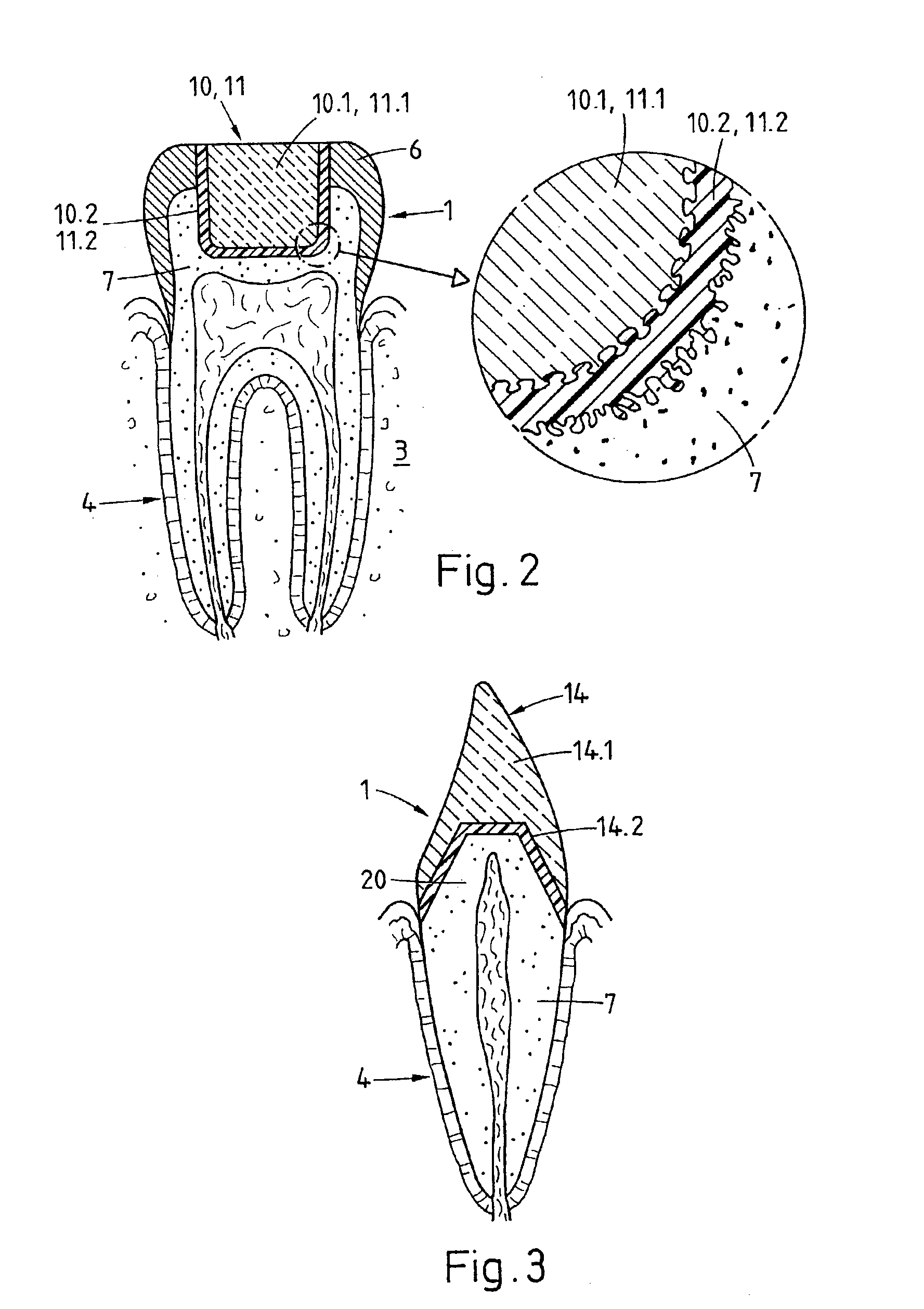
Preparation for being fastened on a natural tooth part or tooth and corresponding fastening method
ActiveUS6955540B2Reduce Shrinkage ProblemsRelieve stressDental implantsImpression capsStress concentrationNatural tooth
A preparation (10, 11,12,13) to be fixed to a natural tooth part or tooth, in particular for the replacement of a load-bearing tooth part, is for example a filling for a drilled-out tooth (1), a crown, bridge or prosthesis to be placed on a tooth stub, or a tooth pin to be fixed in a tooth root for fastening an artificial tooth, a bridge or a prosthesis. The preparation has surface regions which consist of a material with thermoplastic properties. The preparation (10, 11, 12,13) is designed in a manner such that it has oscillation properties with such low damping losses that for a liquefaction of the material with thermoplastic properties by way of oscillations there are local stress concentrations required, and in a manner such that such stress concentrations only occur in the region of the preparation surface. The preparation is positioned on a suitably prepared natural tooth part in a manner such that the material with the thermoplastic properties is in contact or may be brought into contact with the dentin surface and / or enamel surface. The preparation is then made to mechanically oscillate and is simultaneously pressed against the natural tooth part, whereby the material with the thermoplastic properties is at least partly liquefied and brought into intimate contact with the dentin or enamel surface in a manner such that after solidification it forms a positive fit and / or material fit connection. Teeth restored with such preparations have a high stability and a long life, which in particular is attributed to the fact that the thermoplastic material, in contrast to cements used for the same purpose, shrinks less and has the ability to relieve internal stress by creeping.
Owner:WOODWELDING
High surface quality GaN wafer and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS6951695B2Improve surface qualityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface roughnessHigh surface
AlxGayInzN, wherein 0≦x≦1, 0≦y≦1, 0≦z≦1, and x+y+z=1, characterized by a root mean square surface roughness of less than 1 nm in a 10×10 μm2 area. The AlxGayInzN may be in the form of a wafer, which is chemically mechanically polished (CMP) using a CMP slurry comprising abrasive particles, such as silica or alumina, and an acid or a base. High quality AlxGayInzN wafers can be fabricated by steps including lapping, mechanical polishing, and reducing internal stress of said wafer by thermal annealing or chemical etching for further enhancement of its surface quality. CMP processing may be usefully employed to highlight crystal defects of an AlxGayInzN wafer.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Fast forming method of fusion of metal powder of three beams of laser compound scanning
The invention discloses a fast manufacturing method of three-beam laser compound scanning. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly utilizing long-wavelength laser (CO2 laser) for preheating the metal powder, then utilizing short-wavelength laser (YAG or optical fiber laser) for fusing the metal powder and finally utilizing long-wavelength laser (CO2 laser) to carry out heat treatment to the frozen metal. The fast manufacturing method uses the three beams of laser to carry out compound scanning, namely uses long-wavelength laser to preheat, short-wavelength laser to fuse and then long-wavelength laser to carry out heat treatment, can realize the compound process of preheating, fusion and heat treatment of the metal powder. The three beams of laser compound scanning mode can reduce internal stress of the metal part, avoid warping and cracking, improve organization and improve performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
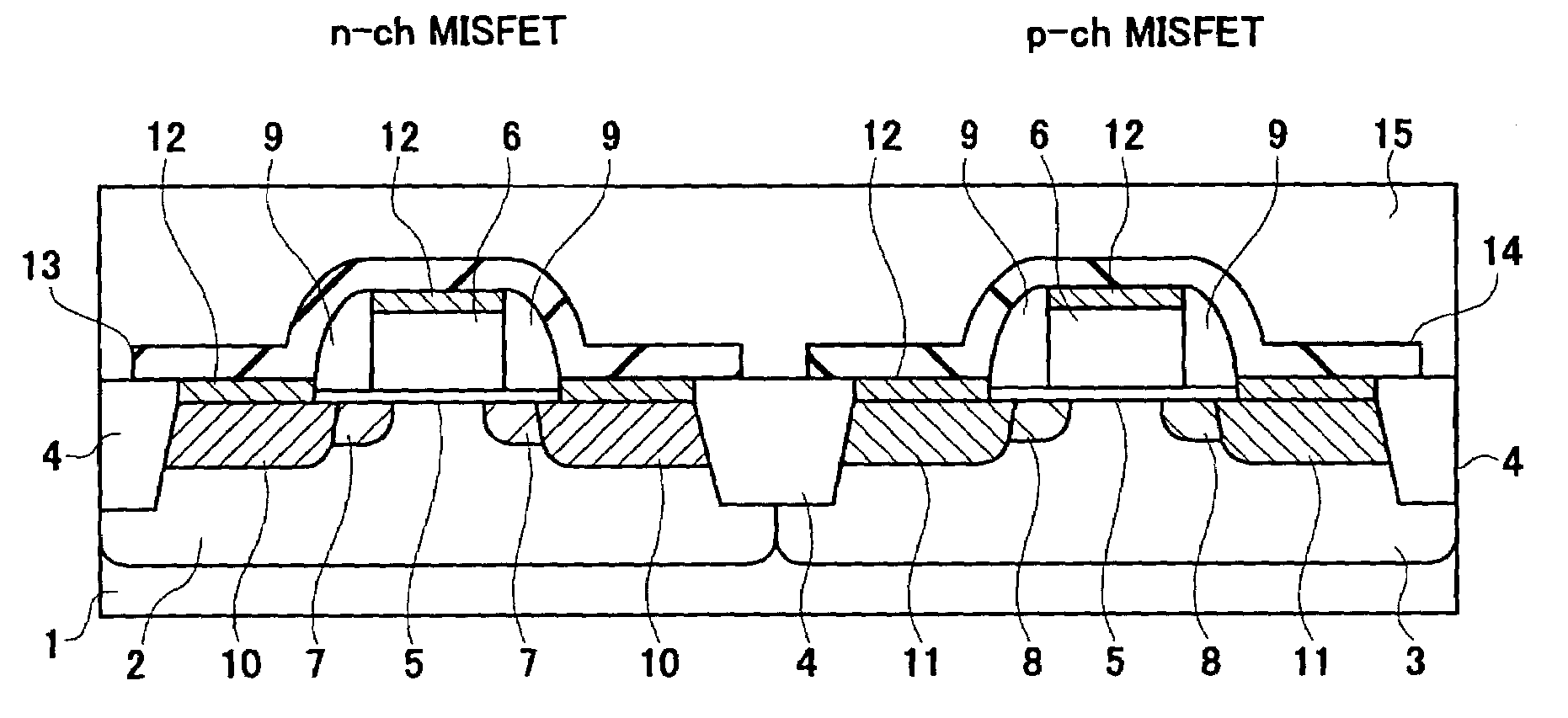
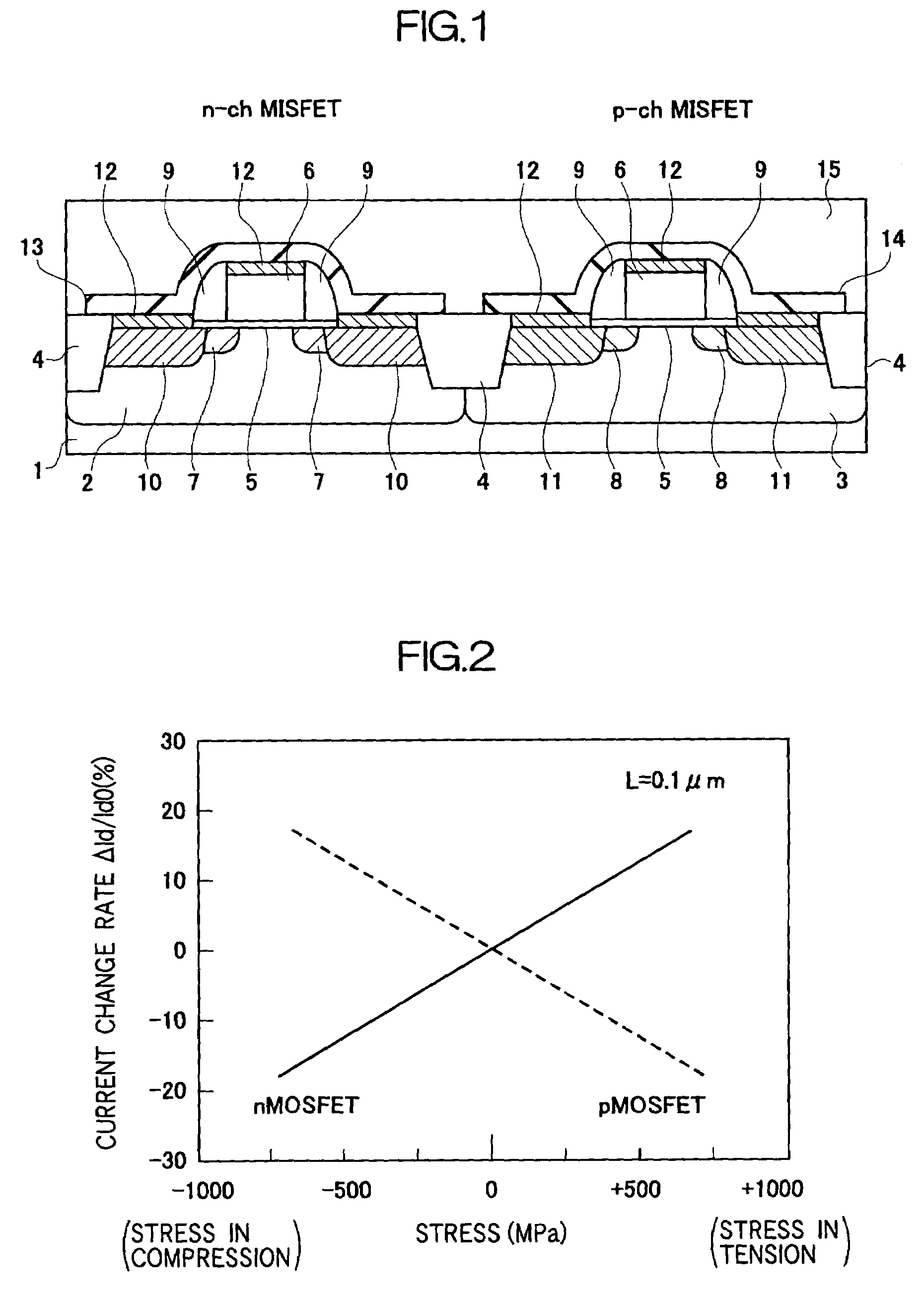
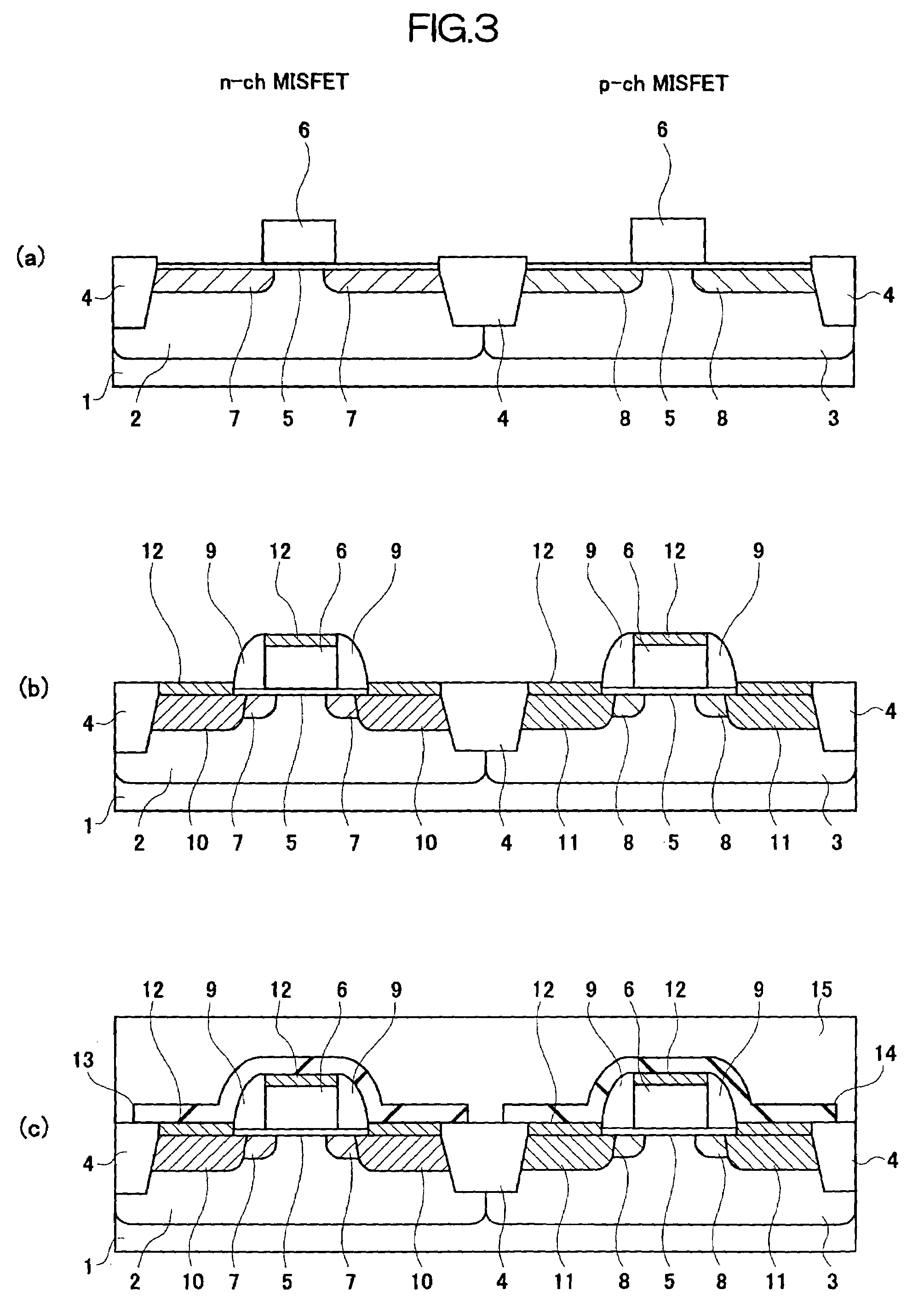
Semiconductor device including stress inducing films formed over n-channel and p-channel field effect transistors and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7115954B2Improve driving abilityImprove current drive capabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStress inducedField-effect transistor
A semiconductor device has an n channel conductivity type field effect transistor having a channel formation region formed in a first region on one main surface of a semiconductor substrate and a p channel conductivity type field effect transistor having a channel formation region formed in a second region on the main surface of the semiconductor substrate, which second region is different from the first region. An internal stress generated in the channel formation region of the n channel conductivity type field effect transistor is different from an internal stress generated in the channel formation region of the p channel conductivity type field effect transistor. The internal stress generated in the channel formation region of the n channel conductivity type field effect transistor is a tensile stress, while the internal stress generated in the channel formation region of the p channel conductivity type field effect transistor is a compressive stress.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Medical instrument for fluid injection and related method
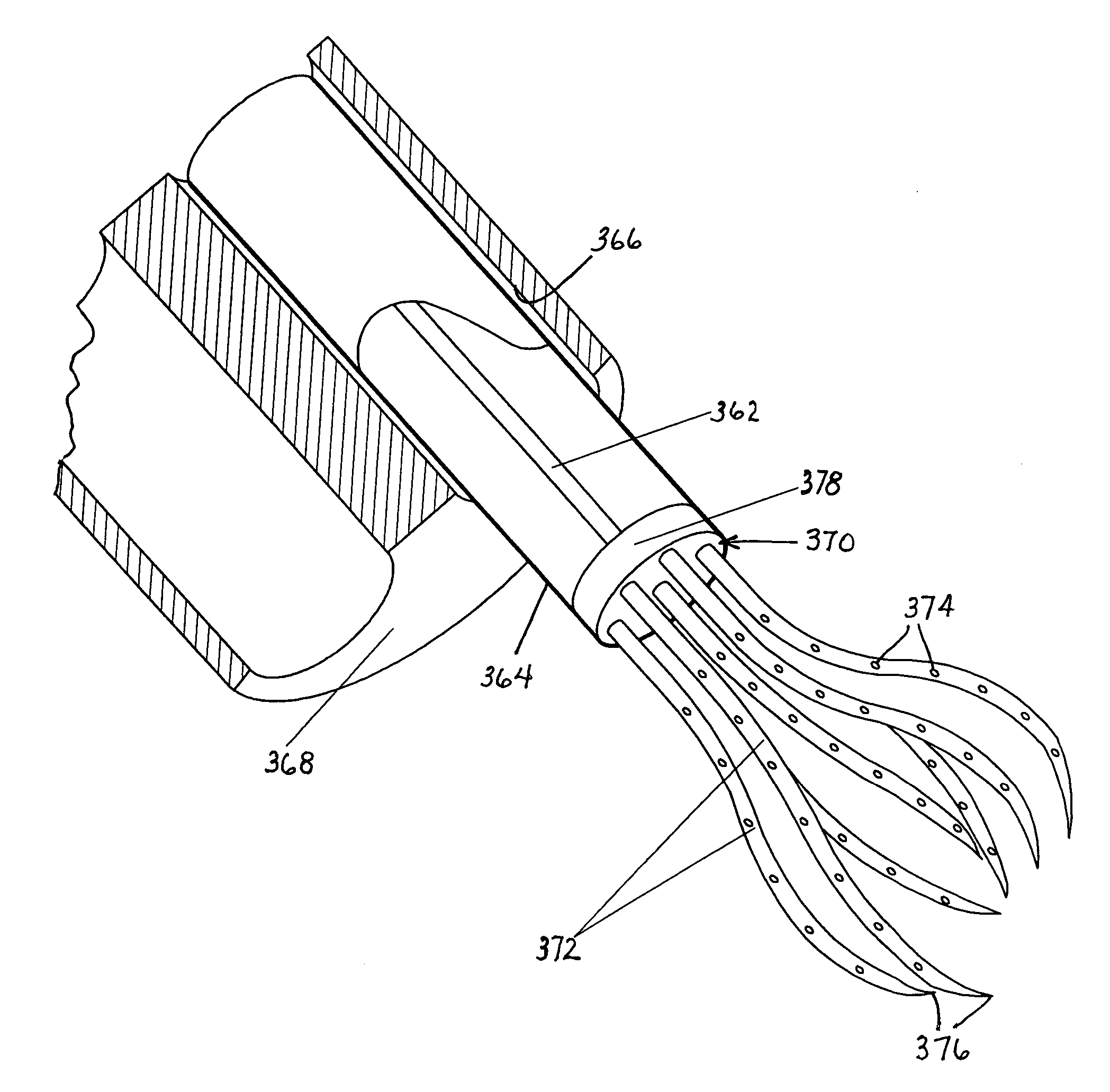
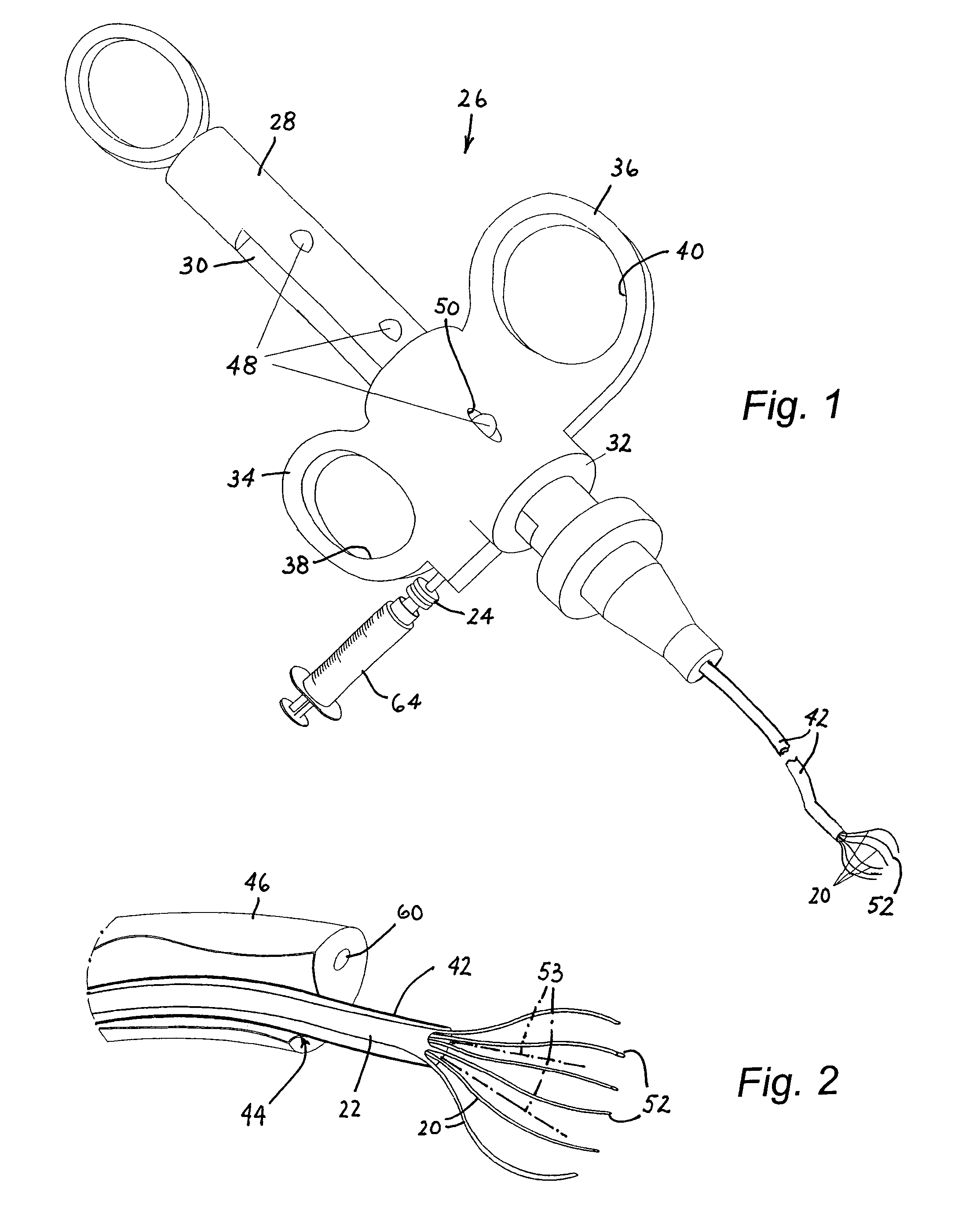
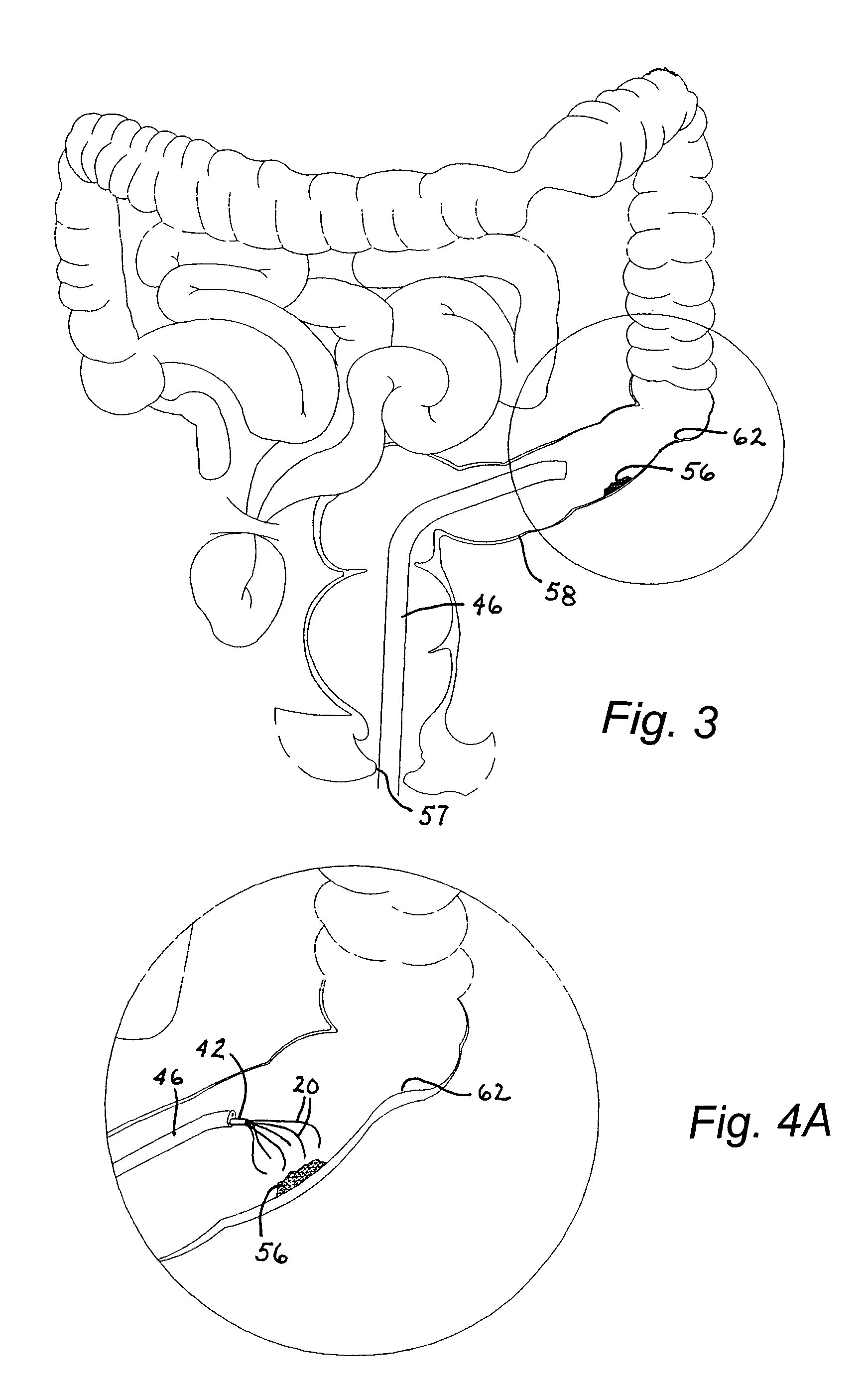
InactiveUS7588557B2Without risk of perforationSaving painInfusion syringesSurgical needlesInternal stressBiomedical engineering
A medical instrument for fluid injection includes a tubular member and a plurality of hollow needle elements connected to one end of the tubular member. Generally, the tubular member has a lumen and all the needle elements communicate with the lumen to enable a distribution of a diagnostic or therapeutic fluid to various points in a predetermined region. The tubular member is provided with a fluid introduction port at an end of the tubular member opposite the needle elements, the fluid introduction port communicating with the lumen. The needle elements are disposed in a predetermined configuration adapted to carry out a desired function. The needle elements are at least partially made of resilient material with a memory so that the needle elements are biased by their internal stresses towards a predetermined rest configuration and are alternately disposable in the rest configuration and at least one stressed or loaded configuration.
Owner:GRANIT MEDICAL INNOVATION
Fin field effect transistor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060118876A1Stay in shapeAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIsolation layerInternal stress
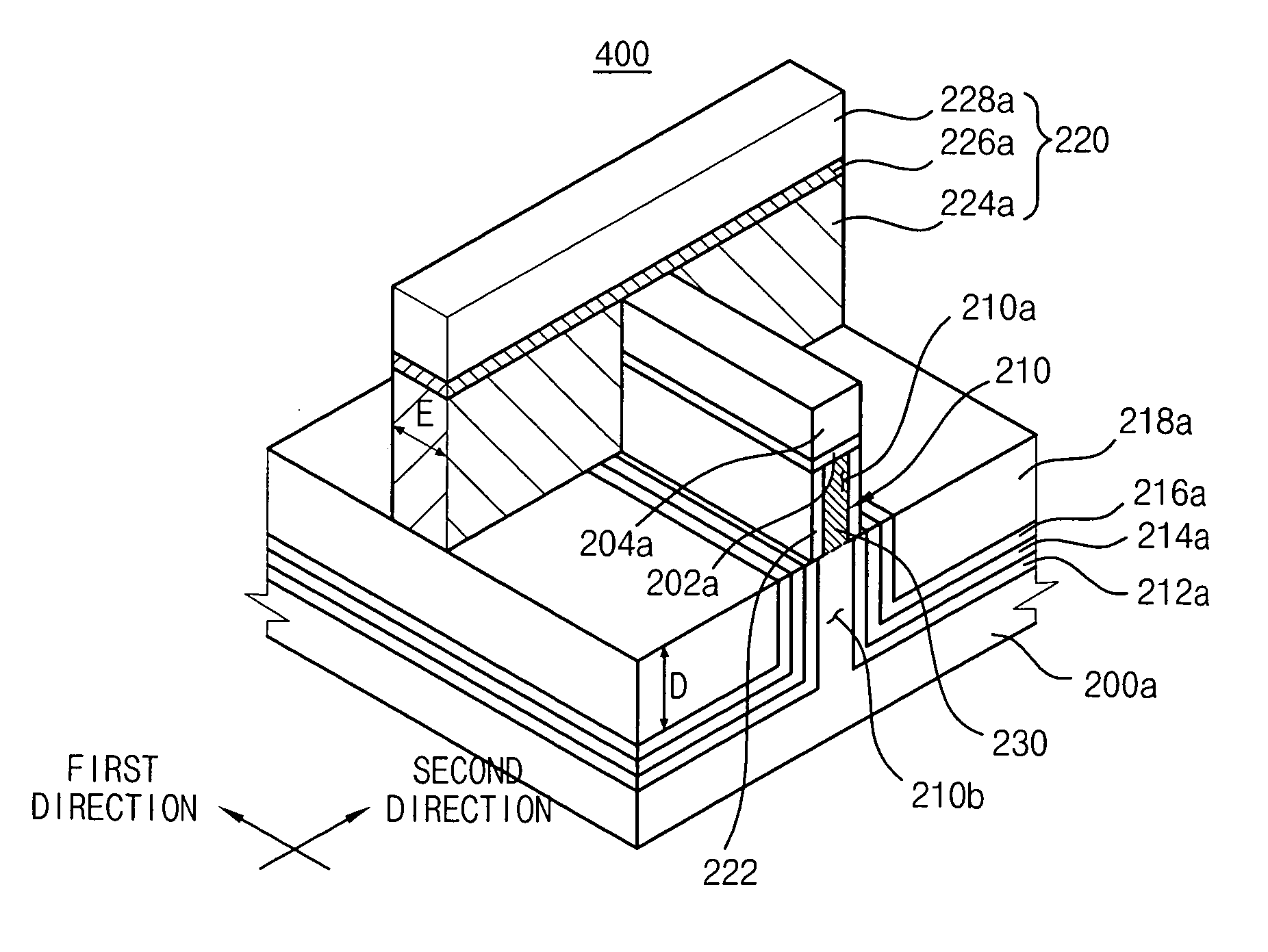
In a fin field effect transistor (FET), an active pattern protrudes in a vertical direction from a substrate and extends across the substrate in a first horizontal direction. A first silicon nitride pattern is formed on the active pattern, and a first oxide pattern and a second silicon nitride pattern are sequentially formed on the substrate and on a sidewall of a lower portion of the active pattern. A device isolation layer is formed on the second silicon nitride pattern, and a top surface of the device isolation layer is coplanar with top surfaces of the oxide pattern and the second silicon nitride pattern. A buffer pattern having an etching selectivity with respect to the second silicon nitride pattern is formed between the first oxide pattern and the second silicon nitride pattern. Internal stresses that can be generated in sidewalls of the active pattern are sufficiently released and an original shape of the first silicon nitride pattern remains unchanged, thereby improving electrical characteristics of the fin FET.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Laser system and method for non-destructive bond detection and evaluation
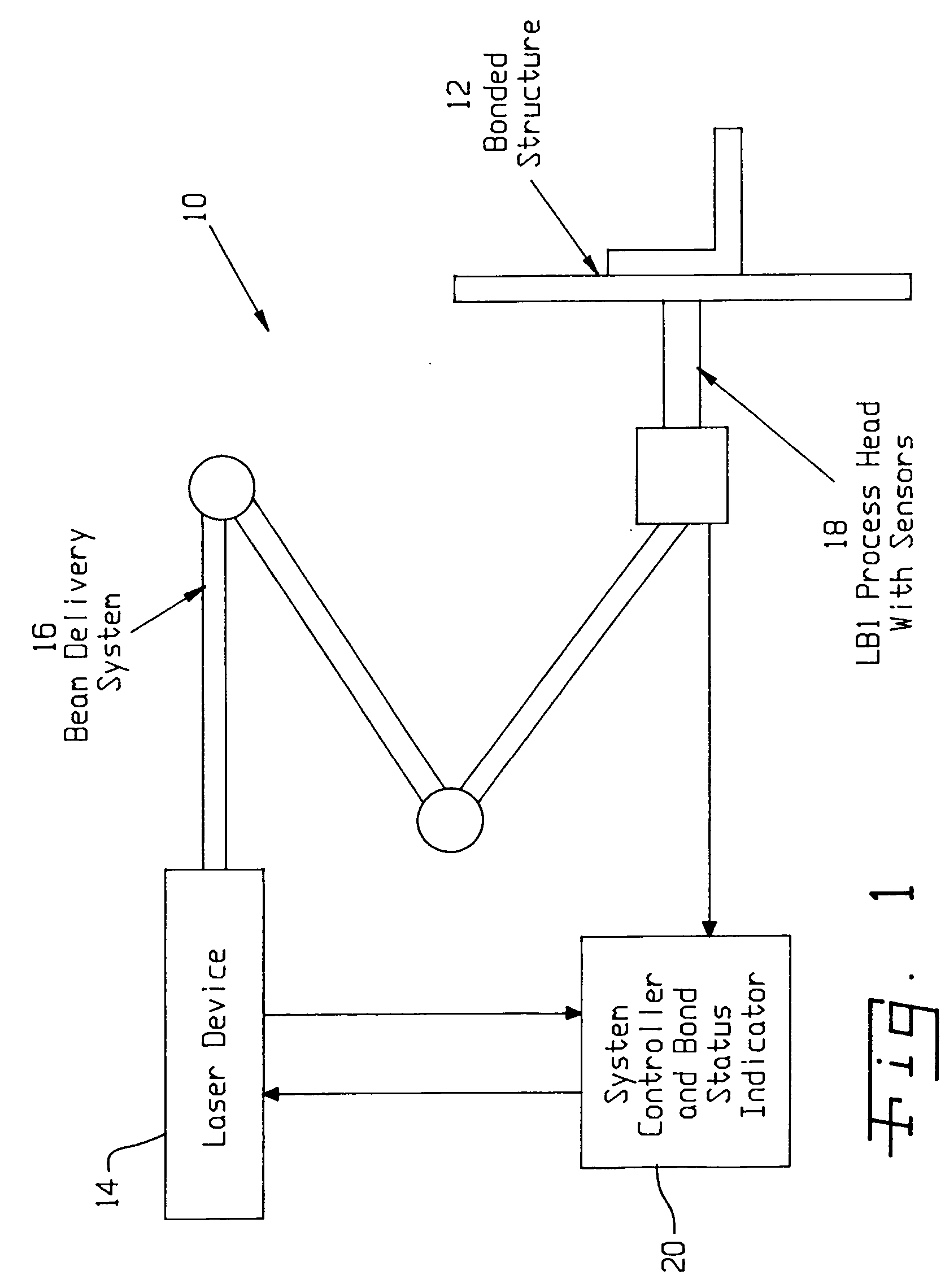
ActiveUS20050120803A1Easy to collectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesNon destructiveLight beam
A system for evaluating the integrity of a bonded joint in an article includes a laser configured in a laser shock processing arrangement to perform a laser shock processing treatment on the article. A beam delivery system employs an articulated arm assembly to communicate the radiant energy emitted by the laser to a process head proximate the article. The laser shock processing treatment causes the formation of shockwaves that propagate through the article, inducing internal stress wave activity that characteristically interacts with the bonded joint. A sensor detects a stress wave signature emanating from the article, which is indicative of the integrity of the bond. A detector such as a non-contact electromagnetic acoustic transducer provides a measure of the stress wave signature in the form of surface motion measurements.
Owner:LSP TECH INC
Normal force gradient/shear force sensors and method of measuring internal biological tissue stress
InactiveUS7201063B2Small sizeStretchable conformabilityForce measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayElectrical conductor
A normal force gradient / shear force sensor device and measurement method for measuring internal stresses in tissues of a person supported by a chair or bed includes a planar matrix array of peripheral normal force sensors radially spaced from central shear force sensors, comprising an electrically conductive disk located within a circular opening bordered by circumferentially spaced apart electrodes. The disk and electrodes are located between upper and lower cover sheets made of a stretchable material such as polyurethane; one cover sheet is adhered to the disk and the other sheet is adhered to a support sheet for the electrodes. Motion between the cover sheets in response to shear forces exerted on the array causes the disk to press more or less tightly against the electrodes varying electrical conductance between the disk and electrodes proportionally to the magnitude and direction of the shear force. Each normal force sensor includes an electrically conductive film pressed between row and column conductors. Measurements of conductance values of pairs of sensor, which vary proportionally to normal forces exerted on the sensor, are used to calculate a gradient vector of normal forces exerted by a body part on the sensor array, which is combined with the shear force vectors in an algorithm to calculate internal reaction shear forces, e.g., on flesh near a bony prominence.
Owner:VISTA MEDICAL
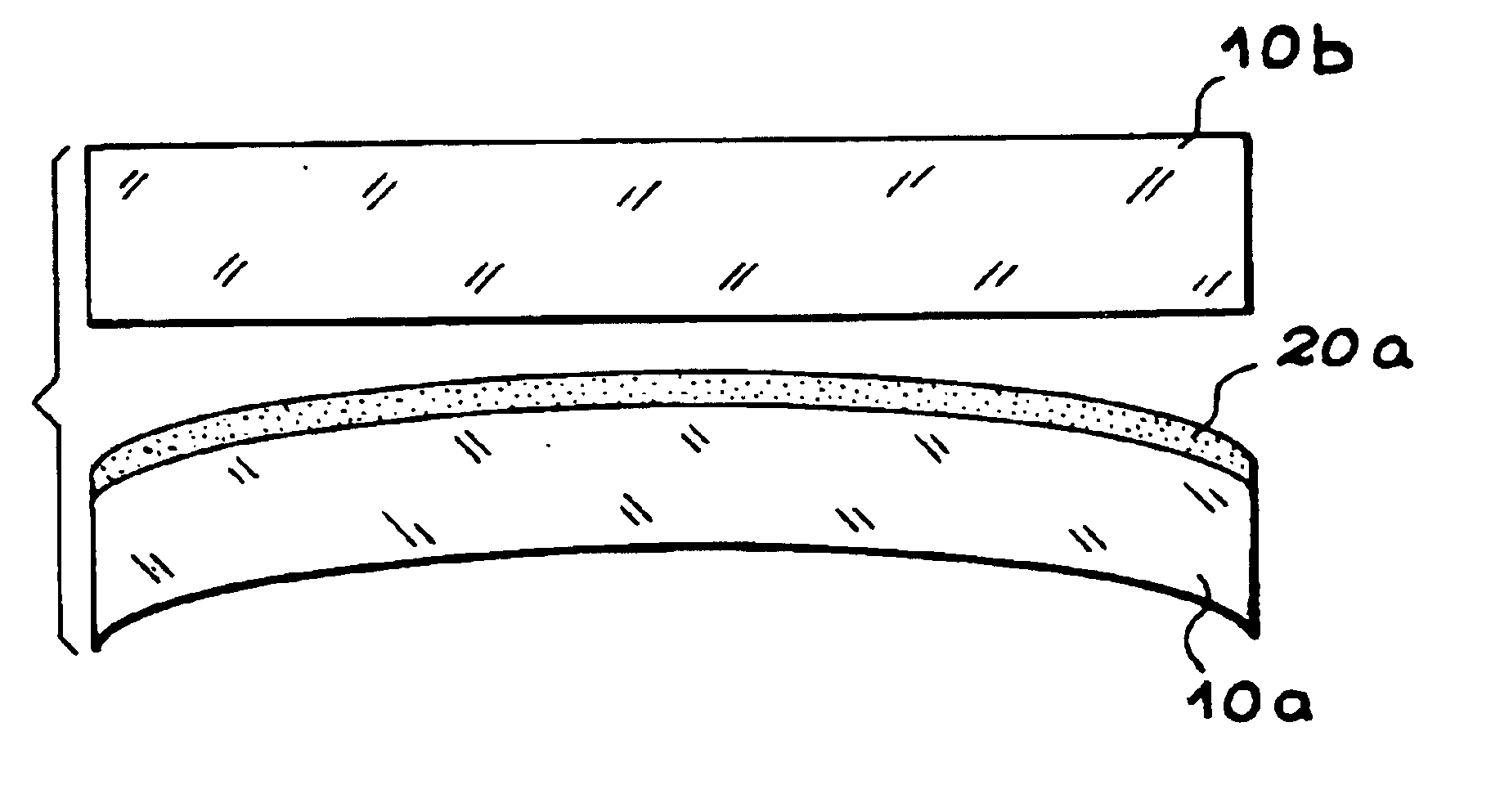
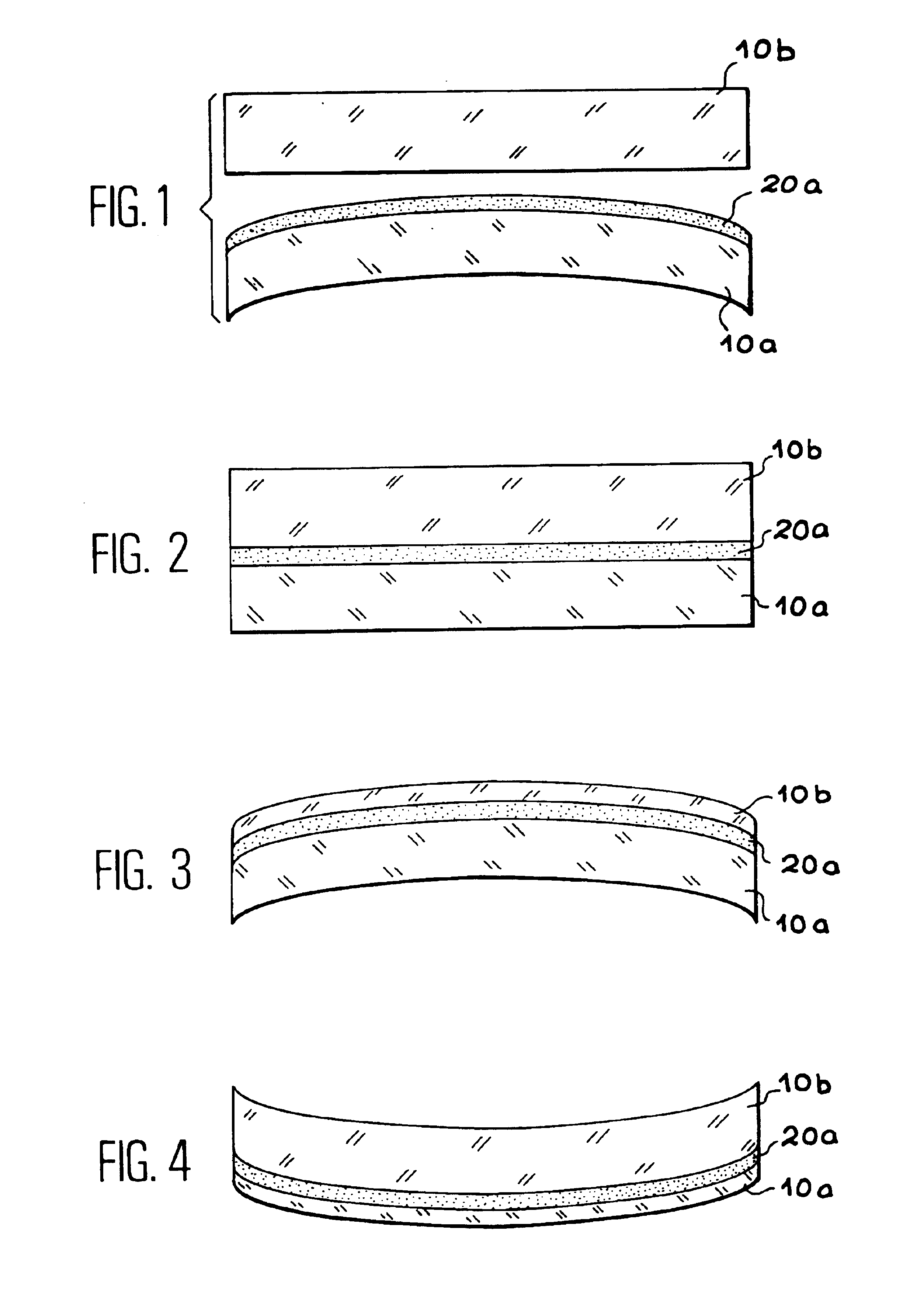
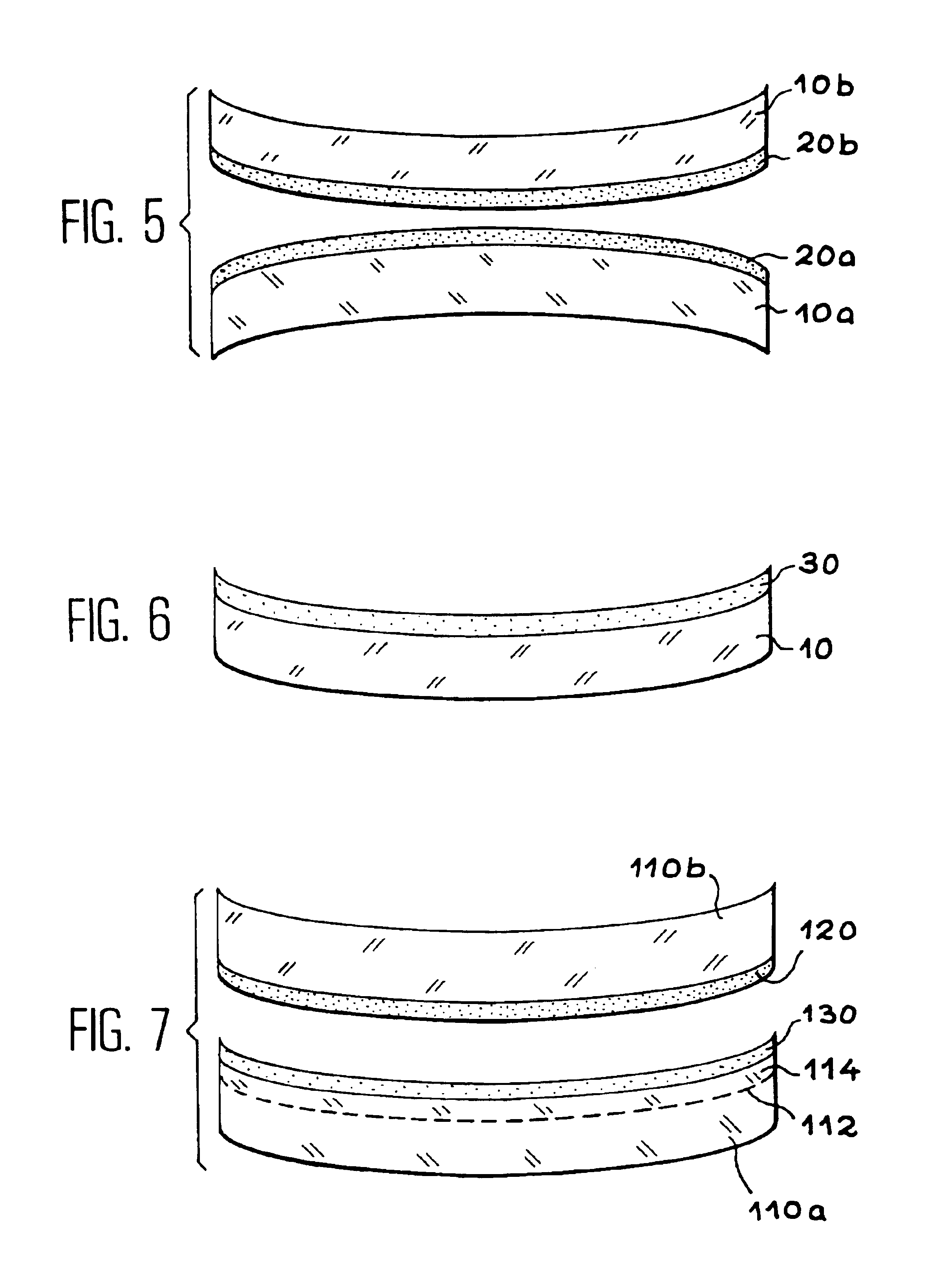
Multilayer structure with controlled internal stresses and making same
A multilayer structure with controlled internal stresses comprising, in this order, a first main layer (110a), at least a first constraint adaptation layer (130) in contact with the first main layer, at least a second stress adaptation layer (120) put into contact by adhesion with said first stress adaptation layer, and a second main layer (110b) in contact with the second stress adaptation layer, the first and second stress adaptation layers having contact stresses with the first and second main layers.Application to the realization of electronic circuits and membrane devices.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Multi-mode bending-resistant fiber and production method thereof
ActiveUS20110044596A1High mechanical reliabilityEasy to useOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical articlesMedicineRelative refractive index
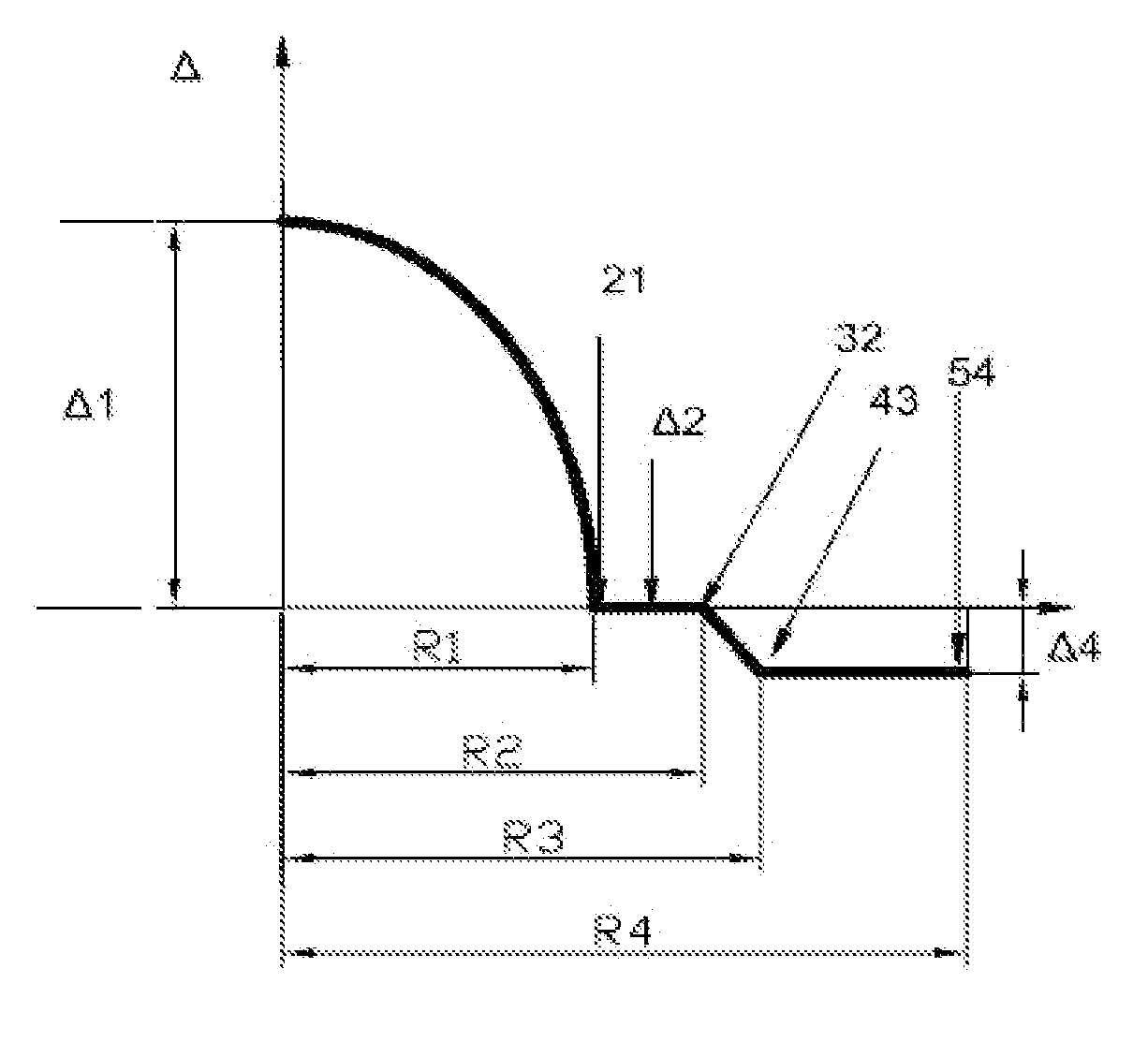
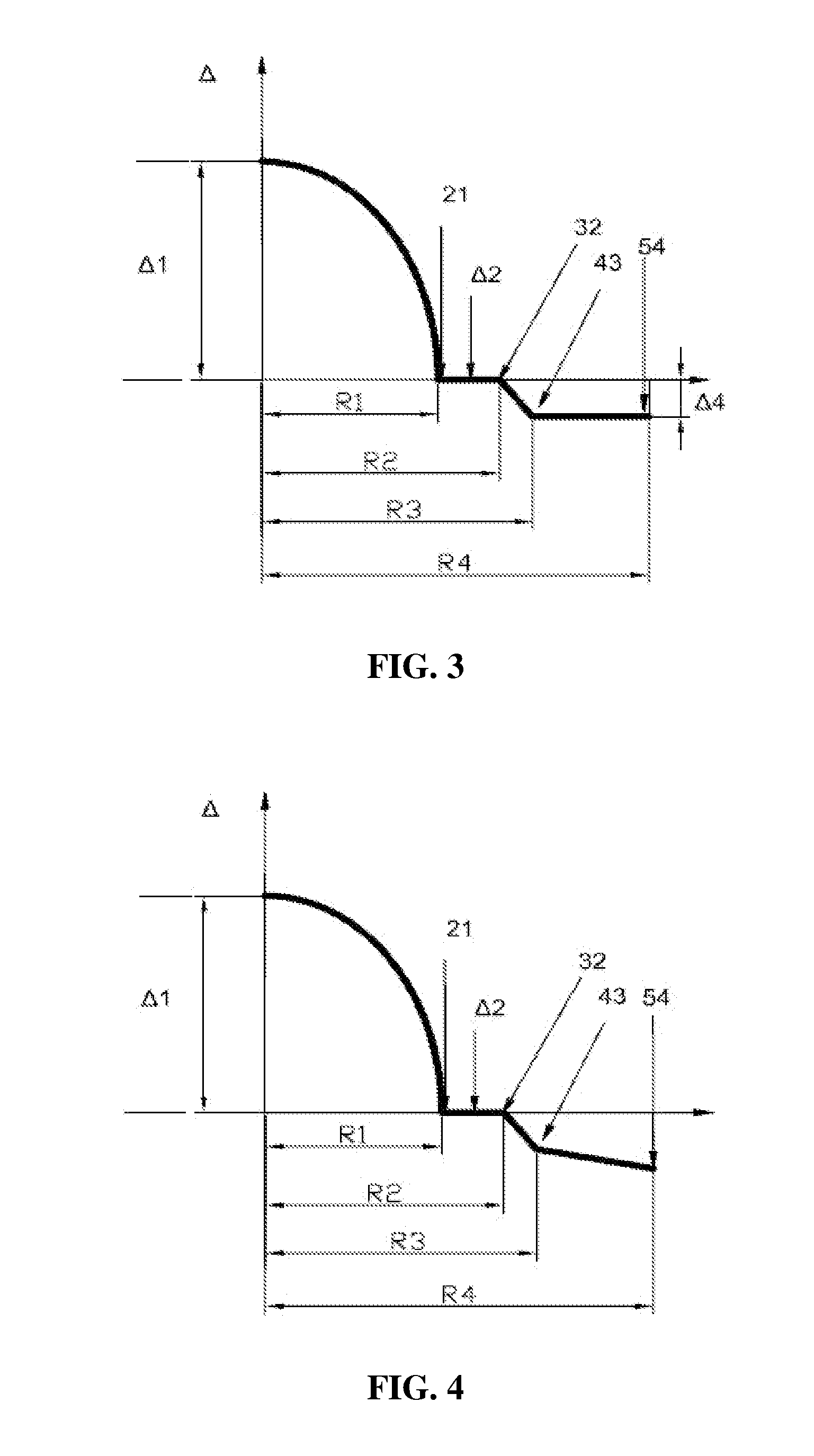
A multimode fiber including a core and a cladding. The core has a radius (R1) of 24-26 μm, the refractive index profile thereof is a parabola, and the maximum relative refractive index difference (Δ1) is 0.9-1.1%. The cladding surrounds the core and includes from inside to outside an inner cladding, a middle cladding, and an outer cladding; a radius (R2) of the inner cladding is 1.04-1.6 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference (Δ2) thereof is −0.01-0.01%; the middle cladding is a graded refractive index cladding whose radius (R3) is 1.06-1.8 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference thereof is decreased from Δ2 to Δ4; and a radius (R4) of the outer cladding is 2.38-2.63 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference (Δ4) thereof is between −0.20 and −0.40%. The invention reduces the additional bending loss of the fiber, improves the bending resistance and mechanical properties, basically eliminates the internal stress, and ensures the service life even working for a long term under the condition of low radius. The method for producing the fiber is simple, effective, and suitable for mass production.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Wearable compound layer material for machine parts and manufacturing method and equipment thereof
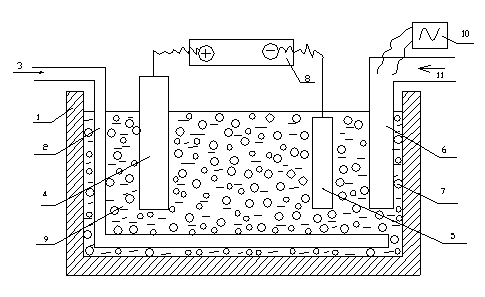
The invention relates to a wearable compound layer material for machine parts and a manufacturing method and equipment thereof. The wearable compound layer material is a metal-based wearable compound layer material which is composed of a matrix metal and lots of particles or fibers dispersed and distributed in the matrix metal, thereby having a multi-phase structure. The wearable compound layer material is manufactured by a direct-current electroplating or pulse electroplating method. The direct-current electroplating or pulse electroplating equipment is composed of parts such as an electroplating power source, an electroplating tank, a metal anode or a metal alloy anode, a machine part substrate cathode, a stirring device, a solution circulating device, a heating and temperature control device, an additive supplementing device and the like. The wearable compound layer material for machine parts provided by the invention is obviously superior in performance to good-quality cast iron wearable parts, good-quality cast steel wearable parts and wearable parts for surface heat treatment of common steel and good-quality steel commonly employed in the present product. The wearable compound layer also has high-temperature abrasive resistance and excellent corrosion resistance while having excellent abrasive performance; and the internal stress of the coating is very low.
Owner:肖云捷
Coefficient of thermal expansion adaptor
InactiveUS20080160274A1Improve accuracyAfter-treatment detailsLamination ancillary operationsBond interfaceThermal expansion
In designing a precision monolithic structure having all discrete components with different Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) permanently bonded together, to avoid internal stress caused by changing of temperature: The Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) Adaptor must be bonded between two components having different Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE); the Bonding Interfaces must be parallel; the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) Adaptor is made of material having varied CTE, the variation must be gradual and in only one direction, which is perpendicular to the said Bonding Interfaces; at each Bonding Interface, the CTE of the CTE Adaptor must match the CTE of bonding component in certain degree.
Owner:DANG CHI HUNG
High surface quality GaN wafer and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS20060029832A1Improve surface qualityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface roughnessCompound (substance)
Owner:XU XUEPING +1
Semiconductor device having an external electrode
InactiveUS20030025202A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSolder ball
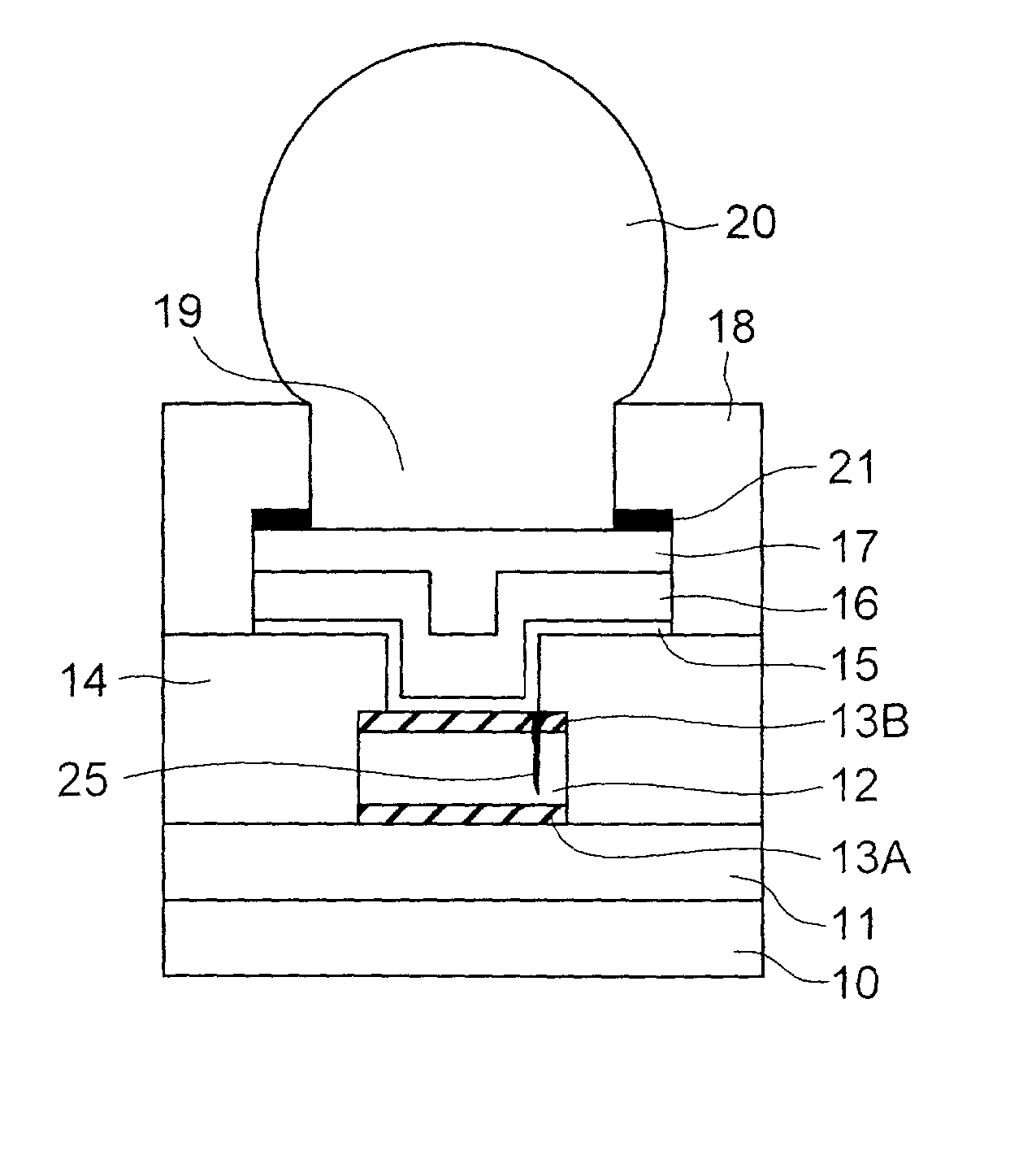
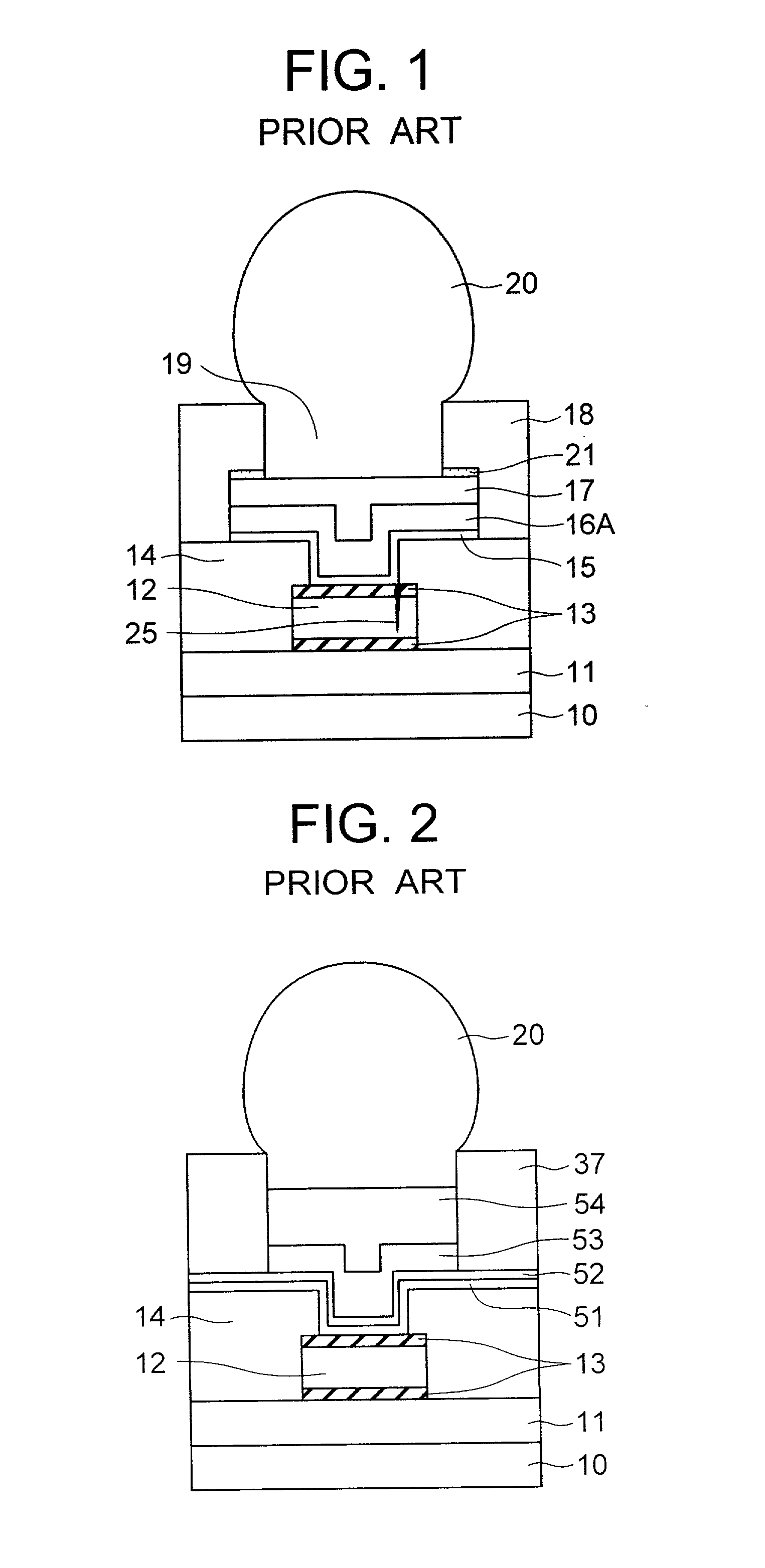
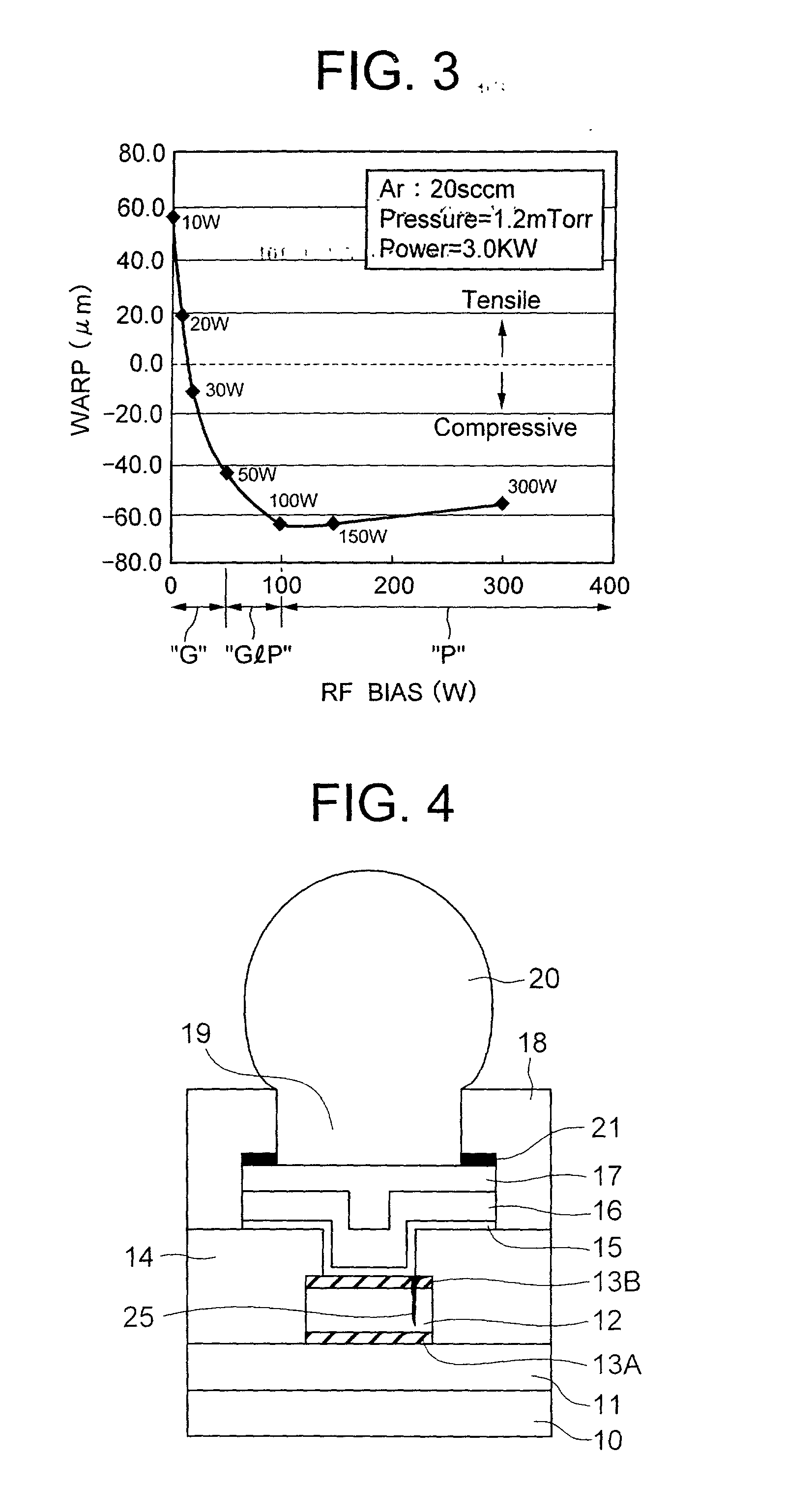
An external electrode in a semiconductor device includes, from the bottom of a wafer, a wiring pad, first and second barrier metal layers, a solder-wetting film and a solder ball. The first barrier metal layer has a tensile internal stress and a granular crystalline structure, whereas the second barrier metal layer has a compressive internal stress and a pillar crystalline structure. The two-layer structure of the barrier metal film has an excellent barrier function against Sn diffusion from the solder ball and reduces the internal stress of the barrier metal film.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical multilayer structure material and process for producing the same, light switching device, and image display apparatus
InactiveUS20020126387A1Stable fast responseImprove support strengthPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesFlexible microstructural devicesOptical thin filmOptoelectronics
An optical multilayer structure material has a structure such that, on a substrate, a conductive layer in contact with the substrate, a gap portion having a size that enables an interference phenomenon to occur and can be changed, and an optical thin film are formed in this order. The circumference of a movable portion in the optical thin film is uniformly supported by supporting portions, suppressing generation of strain due to an internal stress. Through holes are formed in the movable portion to allow an etchant to easily reach a sacrifice layer when forming a gap portion by etching for sacrifice layer. There is provided an optical multilayer structure material having a simple construction, which can suppress generation of strain due to an internal stress and can be advantageously used in an image display apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Low-cost, user-friendly hardcoating solution, process and coating
InactiveUS6265029B1Excellent abrasion resistanceArticle accumulatePretreated surfacesCoatingsColloidal silicaSilanes
An improved, user-friendly silane / silica sol copolymer hardcoating composition for protecting optical plastic and other substrates (including wood, metals, glass, plastics and most coated articles) from scratching is able to be manufactured at lower costs and to provide much-improved ease of use in transportation, storage, dipbath (or other coating tank) stability, and blush resistance in ordinary cleanroom atmospheres. The silane / silica sol copolymer is formed as a direct reaction product of an acidic silica sol and monomethyltrialkoxysilane, preferably substantially monomethyltriethoxysilane, in ratios of 30:70 to 70:30, most preferably about 40:60. A tail solvent aids blush resistance, reduces internal stress and permits adhesion to unprimed polycarbonate. Optionally, colloidal silica sol dissolved in water-miscible solvent may be reacted in a second stage with acidic aqueous colloidal silica sol earlier silanized with monomethyltrialkoxysilane.
Owner:LEWIS WILLIAM
Substrate inspection apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060038980A1Improve accuracyEasy to operateRadiation pyrometrySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementManufacturing technologyMeasurement point
The present invention provides a method and substrate examining device that sequentially and automatically measures at least the thickness and the internal stress of the thin film at a predetermined measurement point on the surface of every manufactured semiconductor substrate to perform quality control on each substrate, and reliably recognizes the cause of defects to improve productivity. The examining device and method accurately analyzes the correlation between film thickness and stress to establish the manufacturing processes necessary for manufacturing a semiconductor substrate of higher performance, and measures the distribution of a physical quantity such as internal stress, index of refraction, and composition of the semiconductor substrate in the film thickness direction, without being influenced by change in ambient environmental temperature thereby further improving examination precision.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
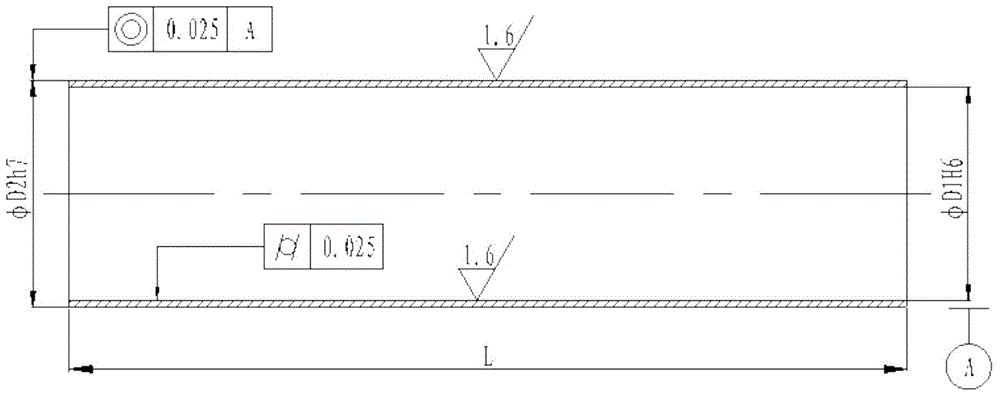
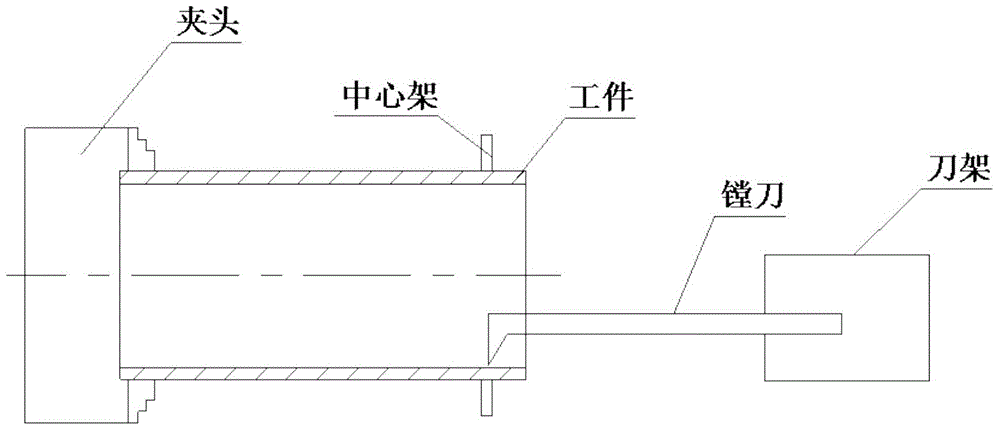
Processing method of aluminum alloy thin-wall cylindrical part
The invention discloses a processing method of an aluminum alloy thin-wall cylindrical part. The method comprises the following steps of blanking, tool selection, rough machining, excircle semi-finish machining, aging treatment, internal-hole semi-finish machining, internal-hole finish machining, excircle finish machining and the like. According to the method, as a special clamp is adopted to guarantee clamping precision, the clamping deformation is reduced and the internal stress of part processing is eliminated; moreover, the method is simple to operate; for a workpiece, procedures of keeping a technological chuck and removing the technological chuck are omitted, so that the material and the processing time are saved; meanwhile, the aluminum alloy thin-wall cylindrical part processed by using the method is stable in quality, low in processing cost and high in efficiency; in addition, the influence that a product generates deformation due to directly suffering three-point clamping force can also be avoided, the rotation heat stress deformation and the pressure damage can be reduced, the flexible deformation of the tools can be reduced, the raw material consumption of the product can be reduced, and the qualification rate and the production efficiency of the workpiece can be improved; moreover, the processing cost can be lowered.
Owner:贵州凯星液力传动机械有限公司
Low-loss magnetic powder core, and switching power supply, active filter, filter, and amplifying device using the same
InactiveUS6897718B2Reduced core lossLess distortionDc-dc conversionInorganic material magnetismMetallurgyAlloy
A magnetic powder core comprises a molded article of a mixture of a glassy alloy powder and an insulating material. The glassy alloy comprises Fe and at least one element selected from Al, P, C, Si, and B, and has a texture primarily composed of an amorphous phase. The glassy alloy exhibits a temperature difference ΔTx, which is represented by the equation ΔTx=Tx−Tg, of at least 20 K in a supercooled liquid, wherein Tx indicates the crystallization temperature and Tg indicates the glass transition temperature. The magnetic core precursor is produced mixing the glassy alloy powder with the insulating material, compacting the mixture to form a magnetic core precursor, and annealing the magnetic core precursor at a temperature in the range between (Tg−170) K and Tg K to relieve the internal stress of the magnetic core precursor. The glassy alloy exhibits low coercive force and low core loss.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Reinforced battery electrodes
ActiveUS9362551B2Avoid strainMaintain electrical continuityElectrode carriers/collectorsActive material electrodesElectrical batteryShape-memory alloy
The gravimetric and volumetric efficiency of lithium ion batteries may be increased if high capacity materials like tin and silicon may be employed as the lithium-accepting host in the negative electrode of the battery. But both tin and silicon, when fully charged with lithium, undergo expansions of up to 300% and generate appreciable internal stresses which have potential to spall off material from the electrode on each discharge-charge cycle, resulting in a progressive reduction in battery capacity, also known as battery fade. A method of reinforcing such electrode materials by incorporating within them fiber reinforcements or shaped, elongated reinforcements fabricated of shape memory alloy is described. Electrode materials incorporating such reinforcements are less prone to damage under applied stress and so less prone to battery fade.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Skinless sausage or frankfurter manufacturing method and apparatus utilizing reusable deformable support
InactiveUS6326039B1Reduce manufacturing costLow costDough treatmentConfectioneryEngineeringConveyor belt
In a method for the manufacture of frankfurters, hot dogs and other skinless sausage products, a meat emulsion is extruded onto a flexible conveyor belt which is then conveyed through a tube whose internal diameter is equal to the desired diameter of the sausage product plus twice the thickness of the conveyor belt. In a camming type process, the conveyor belt is caused, upon its entry into the tube, to temporarily form a cylinder containing the meat emulsion. The temporary belt cylinder together with the surrounded meat emulsion extrudate is then conveyed through an ultrasonic waveform generator to cook an outer layer of the meat emulsion. The outer layer may be part of the meat emulsion or a thermoset gelling material deposited on the extruded meat emulsion. At the exit end of the tube, the conveyor belt naturally opens under internal stresses from its cylindrical shape to a flattened belt. The at least partially cooked sausage is then removed from the belt for further processing or packaging. The conveyor belt acts as a temporary skin to hold the meat emulsion during its ultrasonic processing.
Owner:MISONIX INC
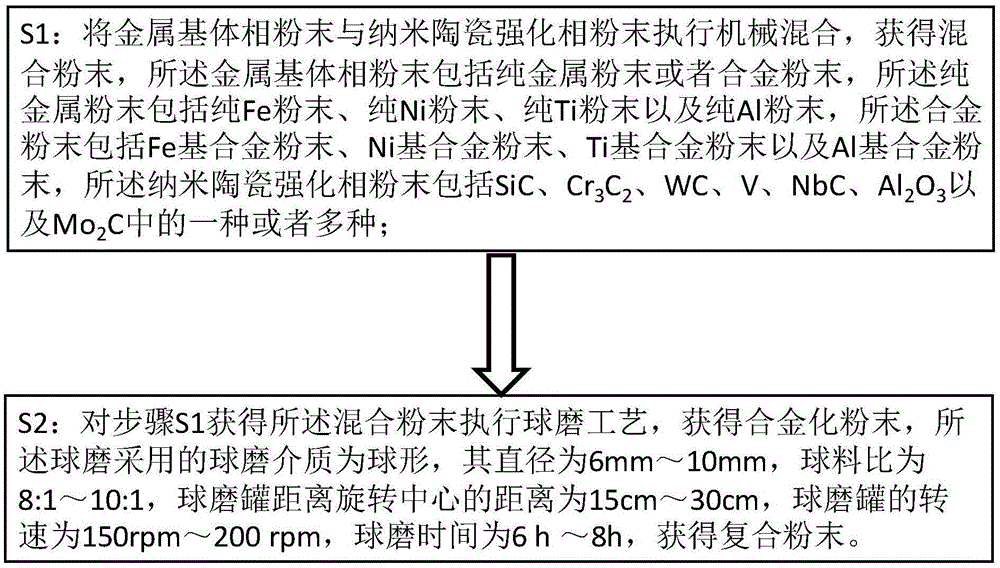
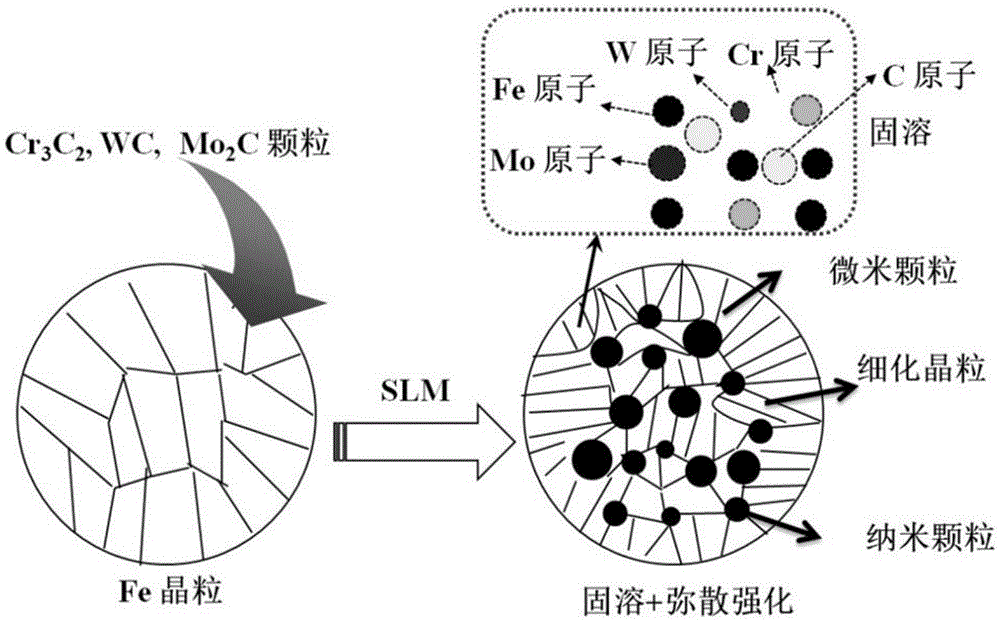
Method for preparing composite powder for 3D printing, product and application
ActiveCN105583401ANo microscopic cracksSuper full noAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingSupersaturated solid solution
The invention discloses a method for preparing a composite powder for 3D printing, and belongs to the technical field of material additive manufacturing. The method comprises the following steps: S1, executing mechanical mixing on a metal matrix phase powder and a nano-ceramic strengthening phase powder to obtain a mixed powder; and S2, executing a ball-milling process on the mixed powder to obtain an alloyed powder, wherein a ball-milling medium used in ball-milling is spherical and has a diameter of 6-10mm, a ball-to-powder ratio is 8: 1 to 10: 1, a distance from a ball-milling tank to a rotary centre is 15-30cm, a rotational speed is 150-200rpm, a ball-milling time is 6-8h, and the composite powder is obtained. The invention further provides a method for using the composite powder prepared by the above-mentioned method for 3D printing forming for parts. The composite powder prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is free from micro-cracks and the problem of supersaturated solid solution, and has no high internal stress; and the parts prepared by virtue of the composite powder disclosed by the invention through a selective laser melting forming method have good comprehensive performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
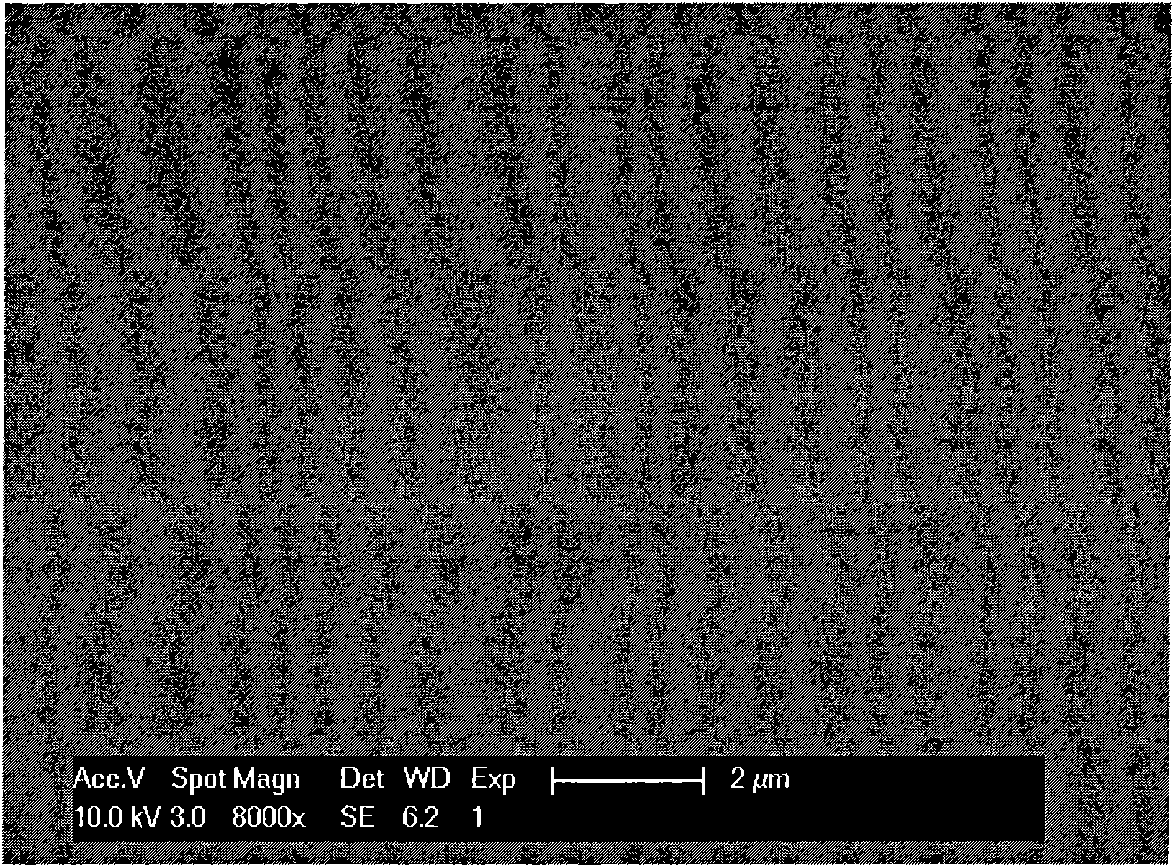
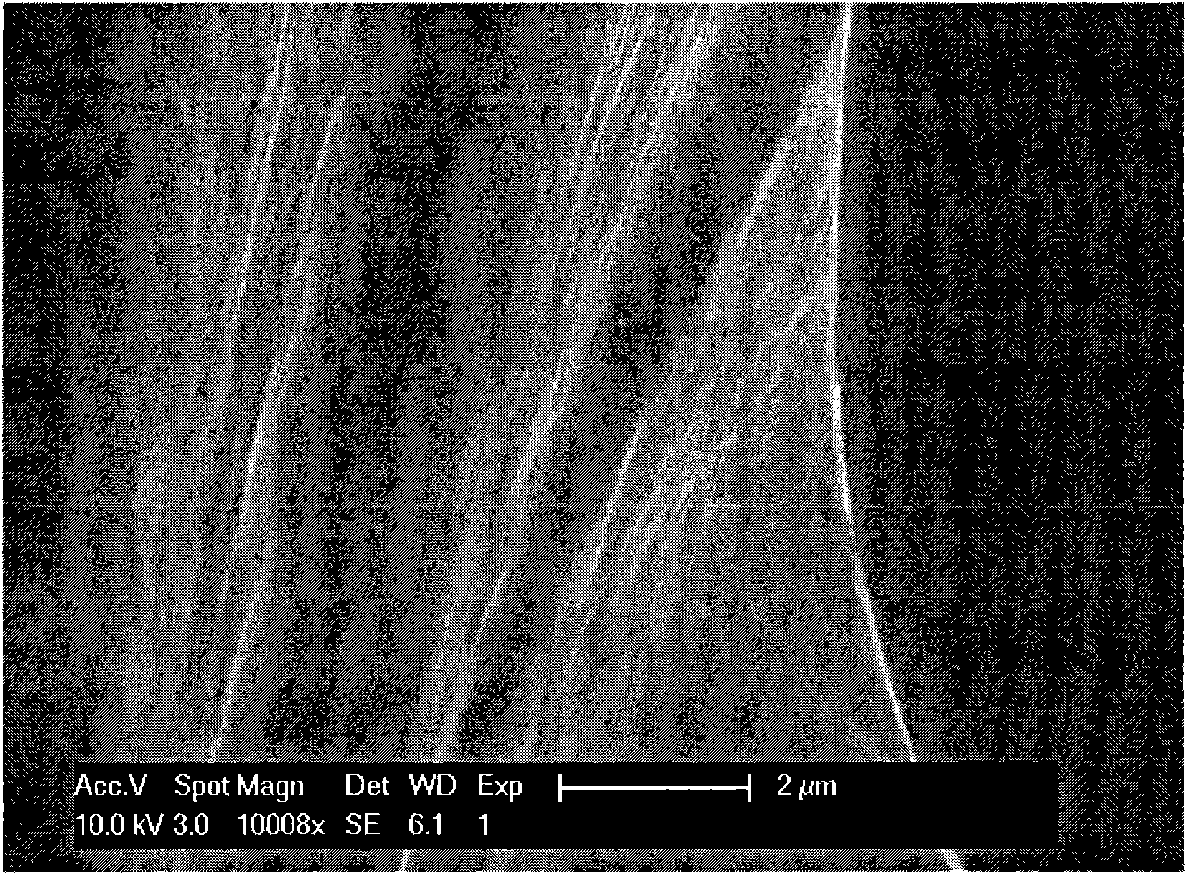
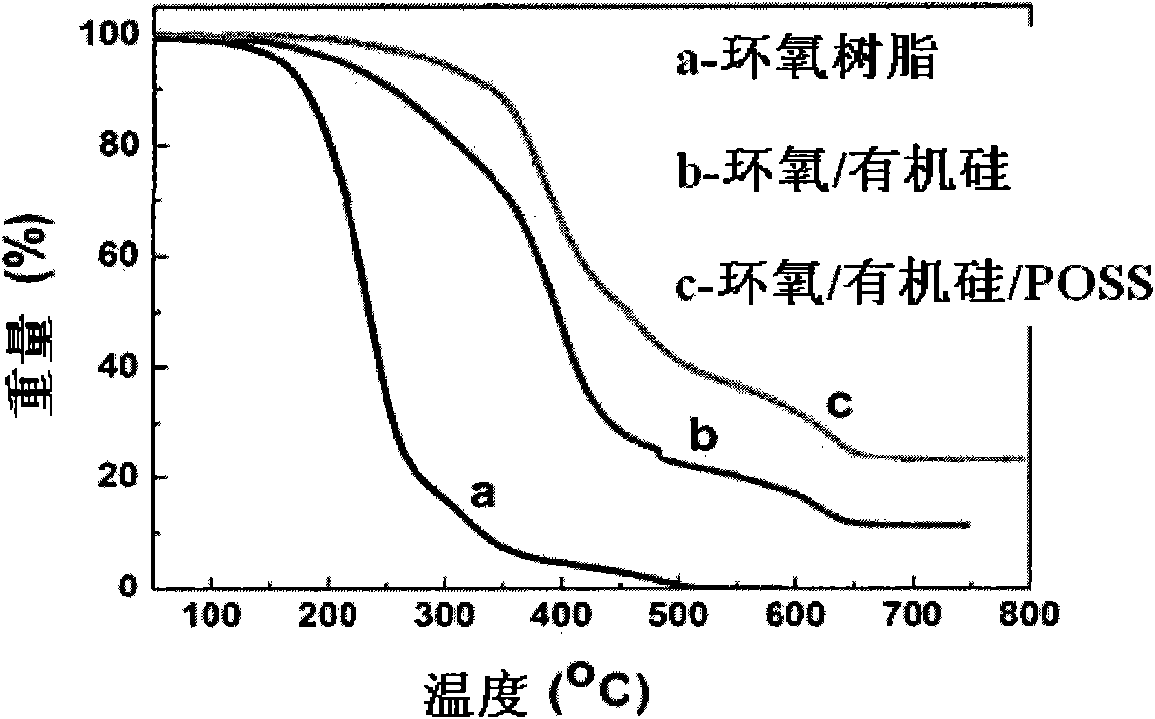
Low-stress epoxy/organic silicon/POSS nano hybrid material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101974227AImprove thermal stabilityHigh light transmittanceEpoxy resin adhesivesEpoxy resin coatingsChemical industryEpoxy
The invention relates to the technical fields of photoelectricity and chemical industry, in particular to a low-stress epoxy / organic silicon / POSS nano hybrid material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The epoxy / organic silicon / POSS nano hybrid material comprises (a) an epoxy resin, (b) a polyorganosiloxane, (c) a cage-type polysilsesquioxane (POSS), (d) an epoxy hardener, (e) non-essential silane oxycompound and (f) non-essential assistants, wherein the polyorganosiloxane contains epoxy groups and silane oxygen groups. The cured nano hybrid system has excellent reticular cross-linked structure and does not have microphase separation. The epoxy / organic silicon / POSS nano hybrid material has the advantages of high mechanical strength, favorable heat resistance, favorable cohesive property, high chemical stability, favorable ultraviolet aging resistance, favorable optical transparency and other excellent properties, has the functions of low internal stress and pressure buffer, and can be used as an LED packaging material, optical protection material, circuit protection coating material, adhesive paint and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
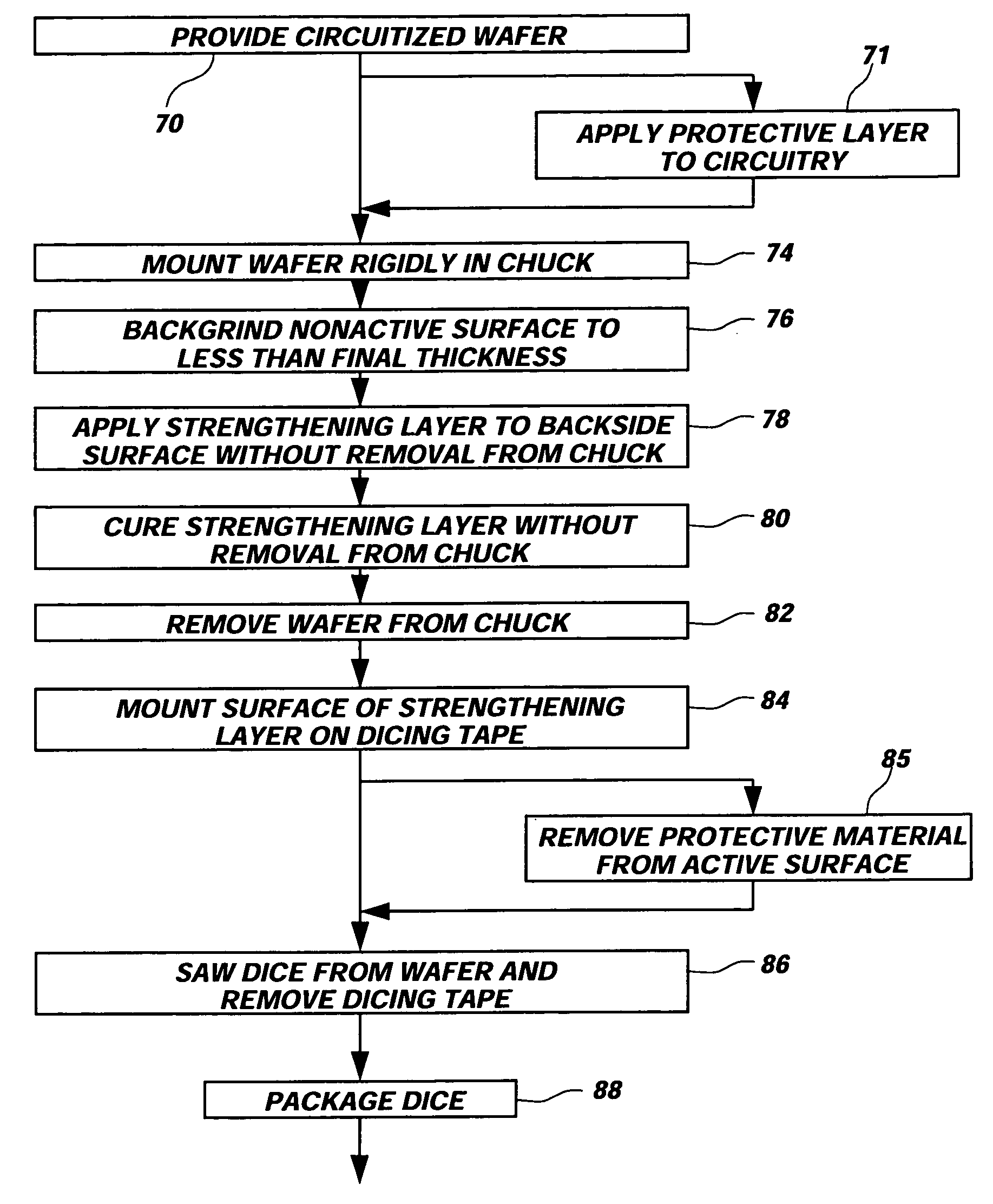
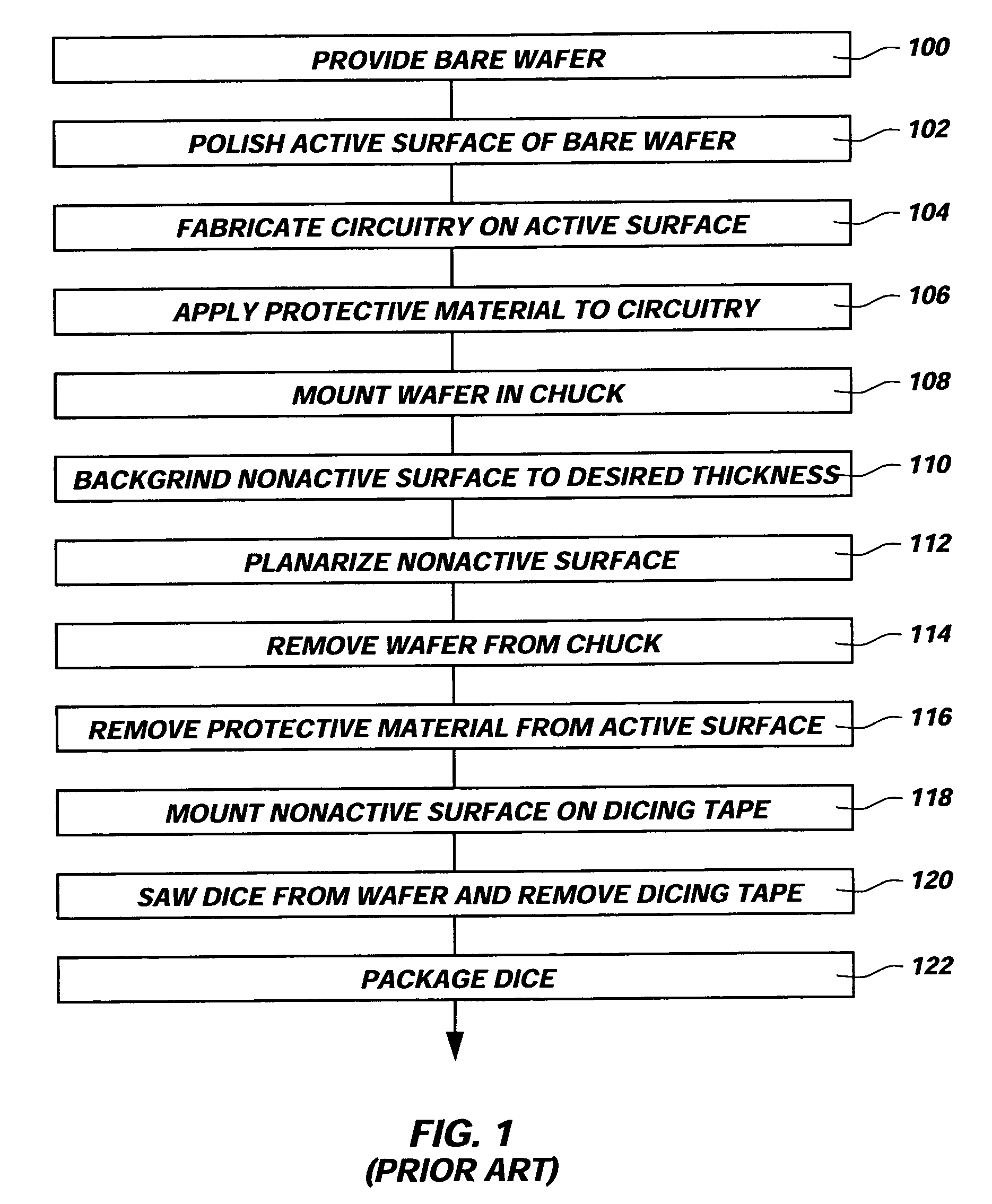
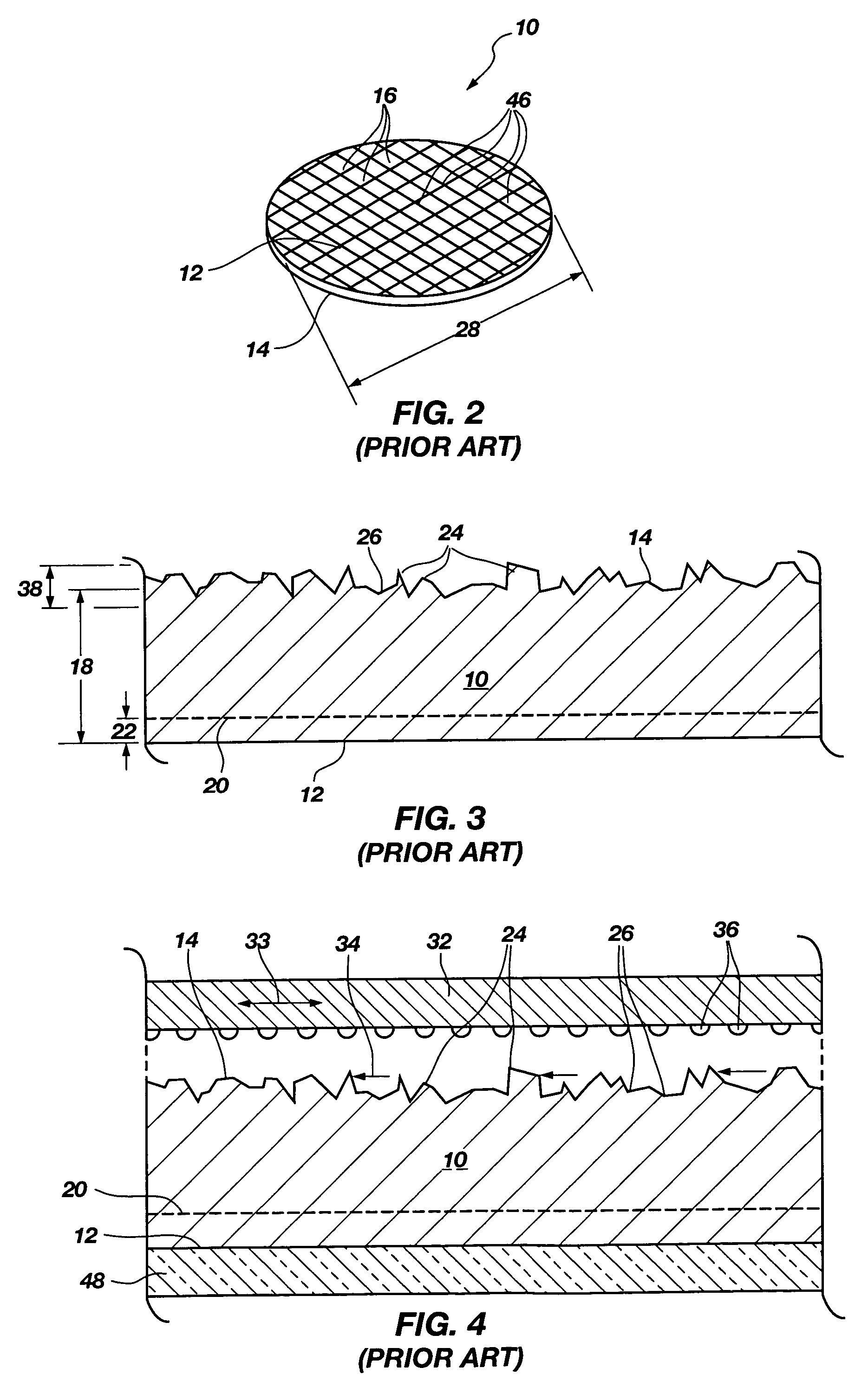
Process for strengthening semiconductor substrates following thinning
ActiveUS20050085008A1Improve adhesionProvide ionic barrierDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface layerLattice defects
A semiconductor wafer having a high degree of thinness and exhibiting an enhanced strength state. A layer of tenacious reinforcement material is disposed over a back side of the wafer while in a rough state from backgrinding, without prior, conventional polishing or plasma etching of the back side. The thin layer or film of reinforcement material fills grooves, fractures and scratches in the back side of the wafer, enhance the rigidity of the wafer and provide a planar, smooth, back side surface layer. The reinforcement material counteracts internal stresses of the wafer tending to warp, crack and propagate lattice defects in the wafer. The reinforcement material may also be configured to act as a die attach adhesive, may provide an ionic barrier, and may remain as part of the packaging for semiconductor dice singulated from the wafer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Current collector for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, electrode for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, production methods thereof, and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveUS20110111277A1Increase flexibilityAvoid problemsFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsMetal foilEngineering
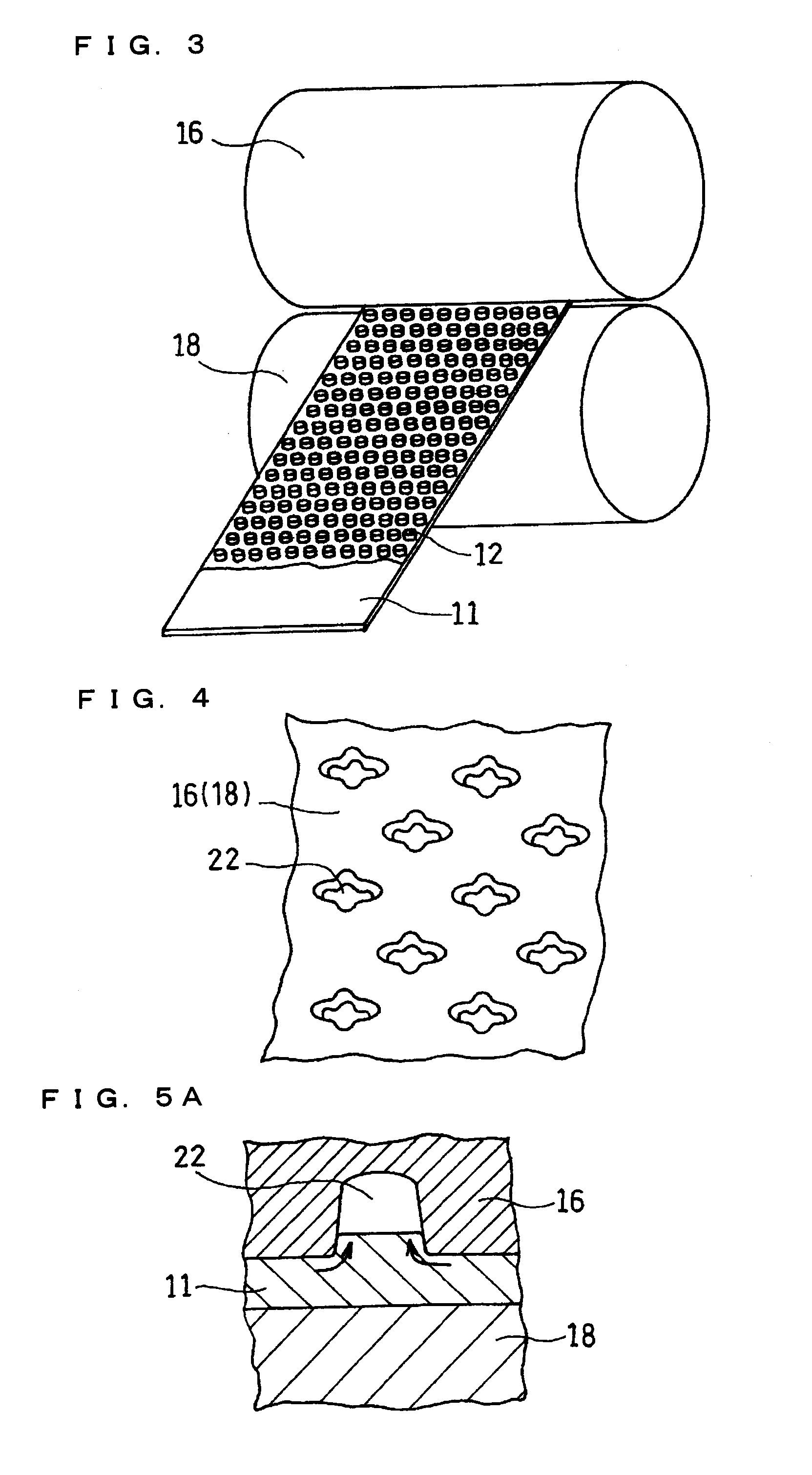
A current collector includes a metal foil and protrusions formed on one face or both faces of the metal foil in a predetermined arrangement. The protrusions are substantially rhombic and aligned in a zigzag. Also, both end portions of each protrusion in each of two orthogonal axial directions protrude outward. Middle portions between the end portions are recessed inward. When columnar blocks of an active material are formed on the protrusions to form an active material layer, the gaps between the protrusions can be increased at portions where the interval between the protrusions is the smallest. As a result, internal stress of the active material layer created by charge / discharge of the battery can be alleviated, and the battery life can be increased.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
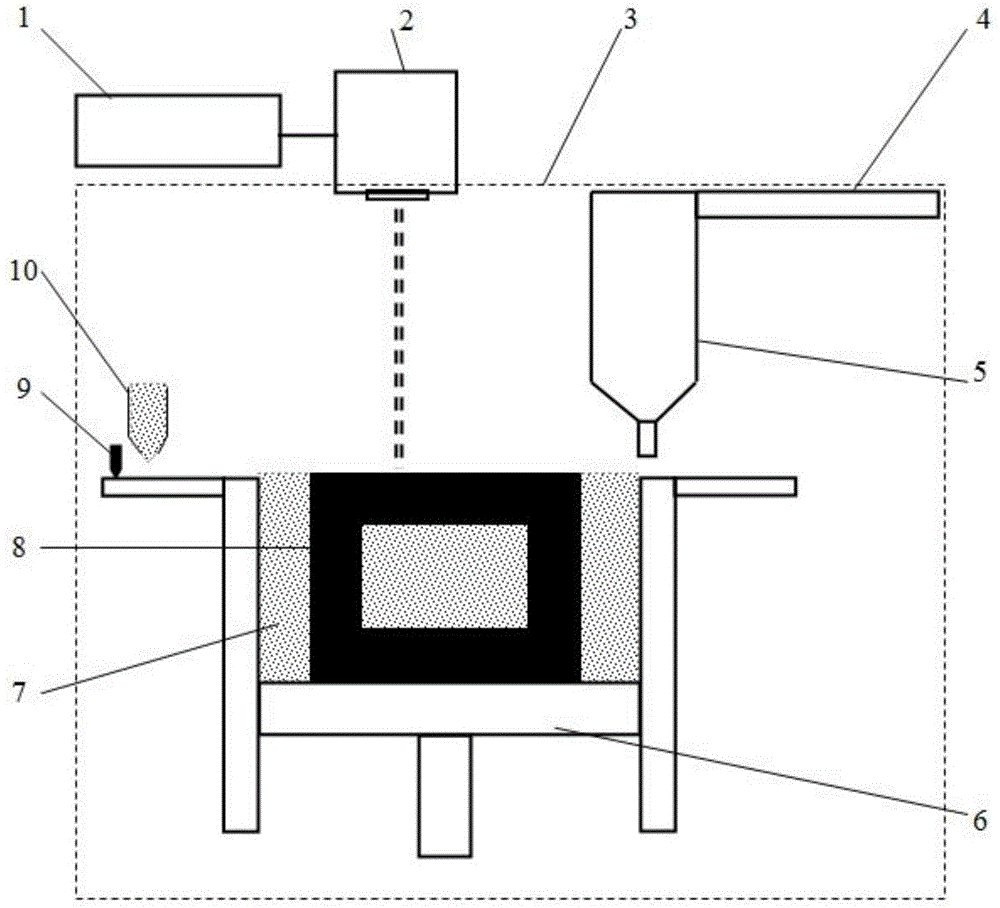
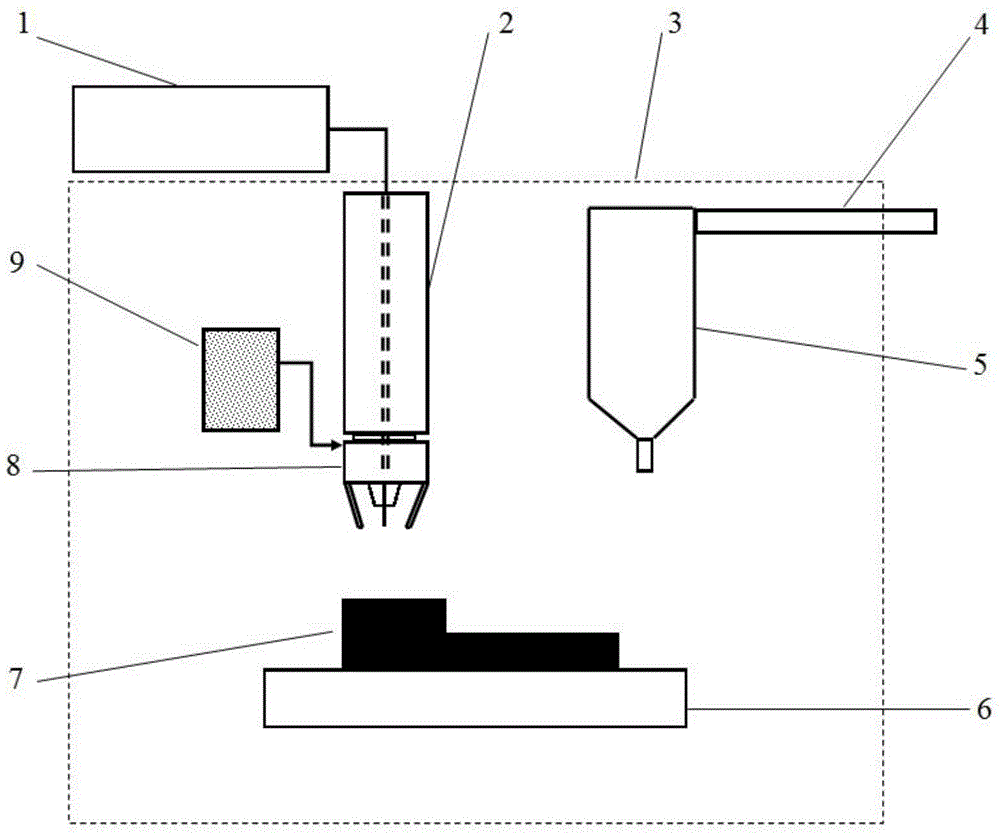
High-energy beam-ultrasonic composite additive manufacturing method for metal materials
InactiveCN104525944AHigh dimensional accuracyHigh performance controlIncreasing energy efficiencyHigh energyMechanical property
The invention discloses a high-energy beam-ultrasonic composite additive manufacturing method for metal materials and belongs to the field of additive manufacturing (3D printing) of metal materials. The method comprises the steps that based on the technical principle of layer-by-layer accumulation of additive manufacturing, metal forming materials are melted through high-energy beams; after the metal forming materials are melted / solidified layer by layer to accumulate to a certain number of layers, the solidified layers are subjected to ultrasonic peening to have compressive plastic deformation, so the internal stress and the internal defects of formed parts are eliminated, and crystalline grains are refined; afterwards, the process of layer-by-layer melting / solidifying accumulation and the process of ultrasonic peening are continued until the whole forming process of metal members is completed. According to the method, real-time layer-by-layer treatment is performed on the solidified layers through ultrasonic peening, so the internal stress and the internal defects can be effectively reduced or eliminated, the crystalline grains can be refined, and the mechanical property of the metal members through additive manufacturing can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com