Patents
Literature
5205results about "After-treatment details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
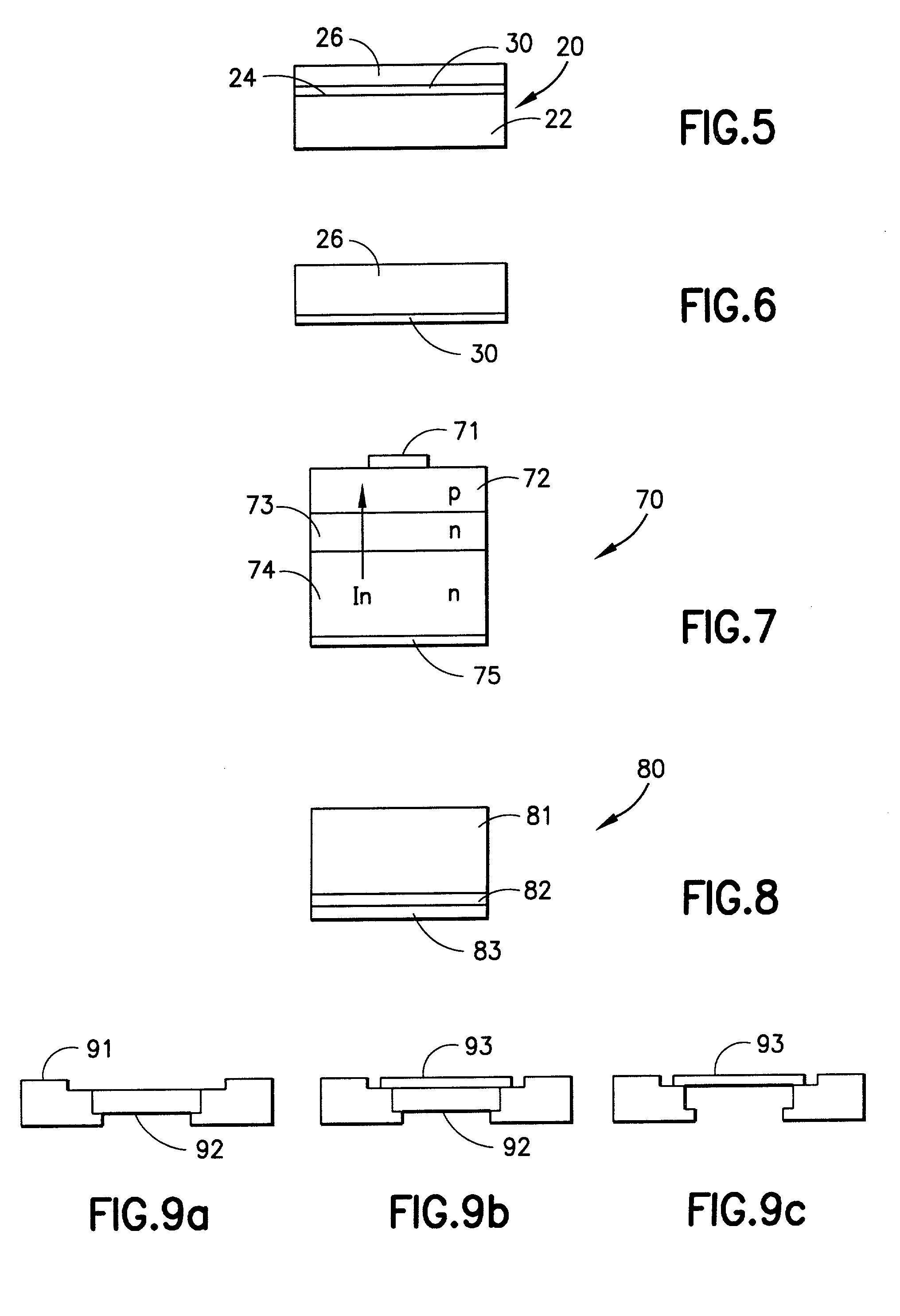
Nanowires-based transparent conductors
ActiveUS20070074316A1Improve drawing legibilityMaterial nanotechnologyFrom normal temperature solutionsElectrical conductorNanowire
Owner:CHAMP GREAT INTL
Semi-insulating silicon carbide without vanadium domination
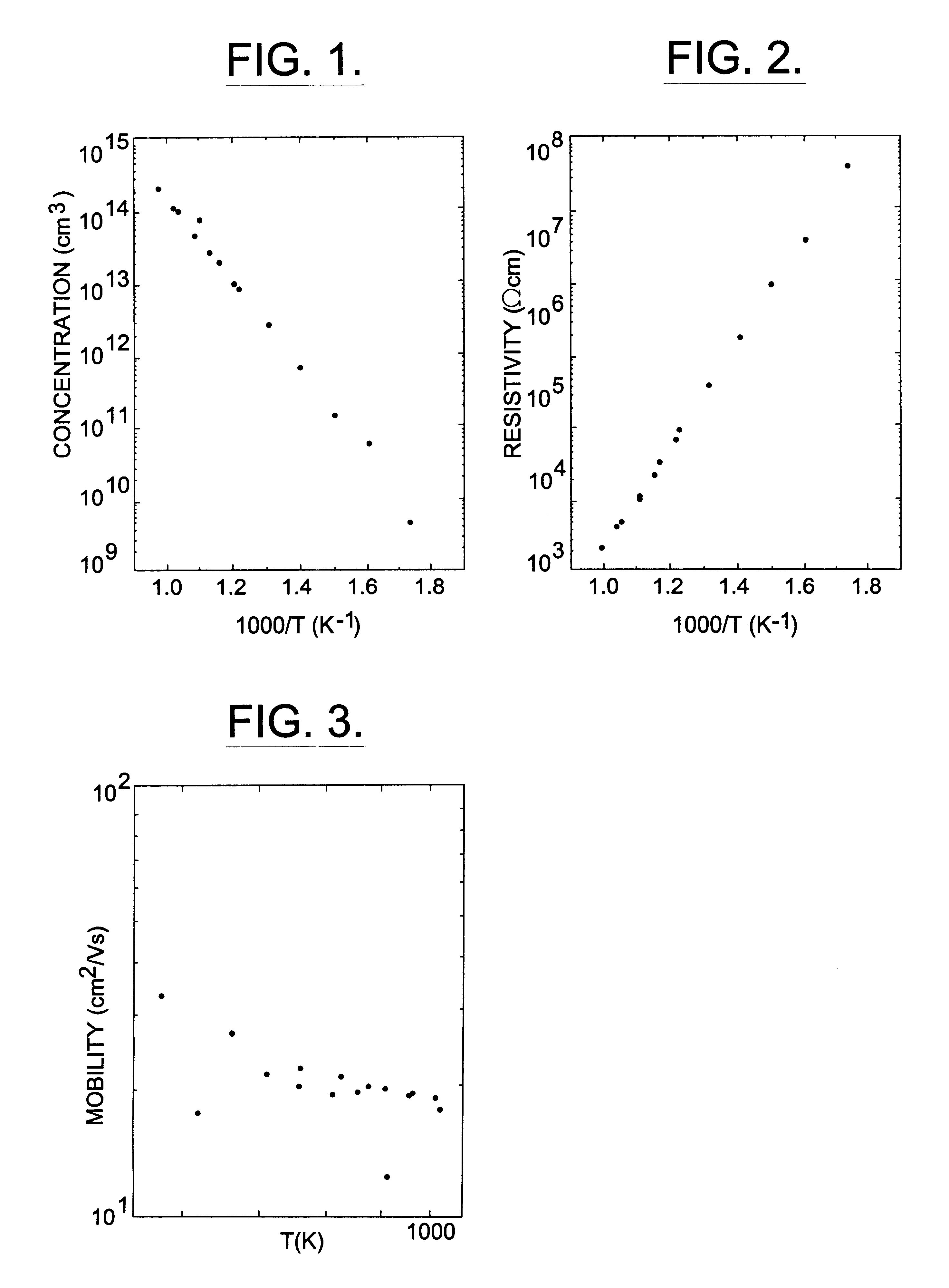
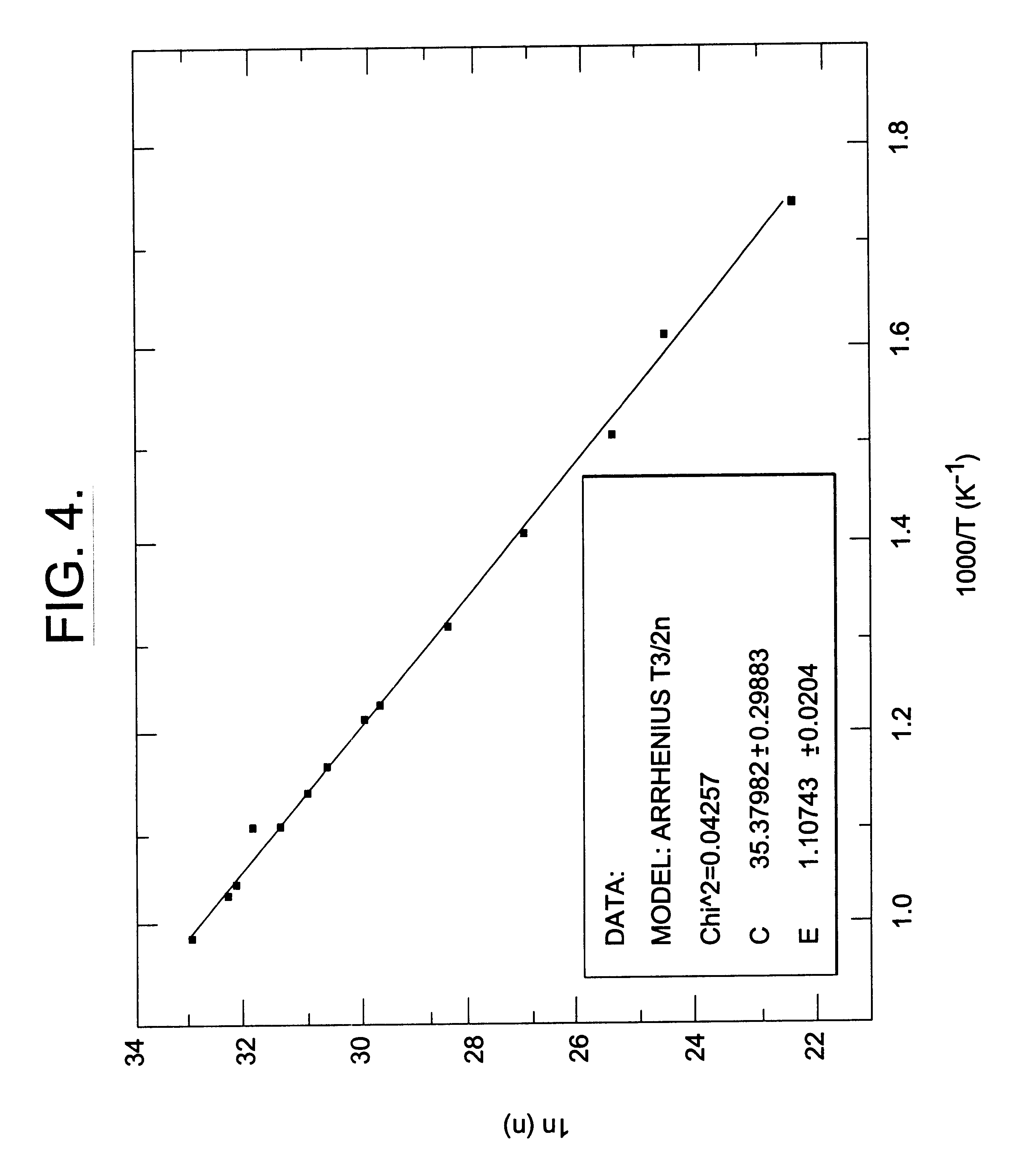
InactiveUS6218680B1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease the number ofPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDevice formTrapping
Owner:CREE INC
Method and apparatus for treating article to be treated
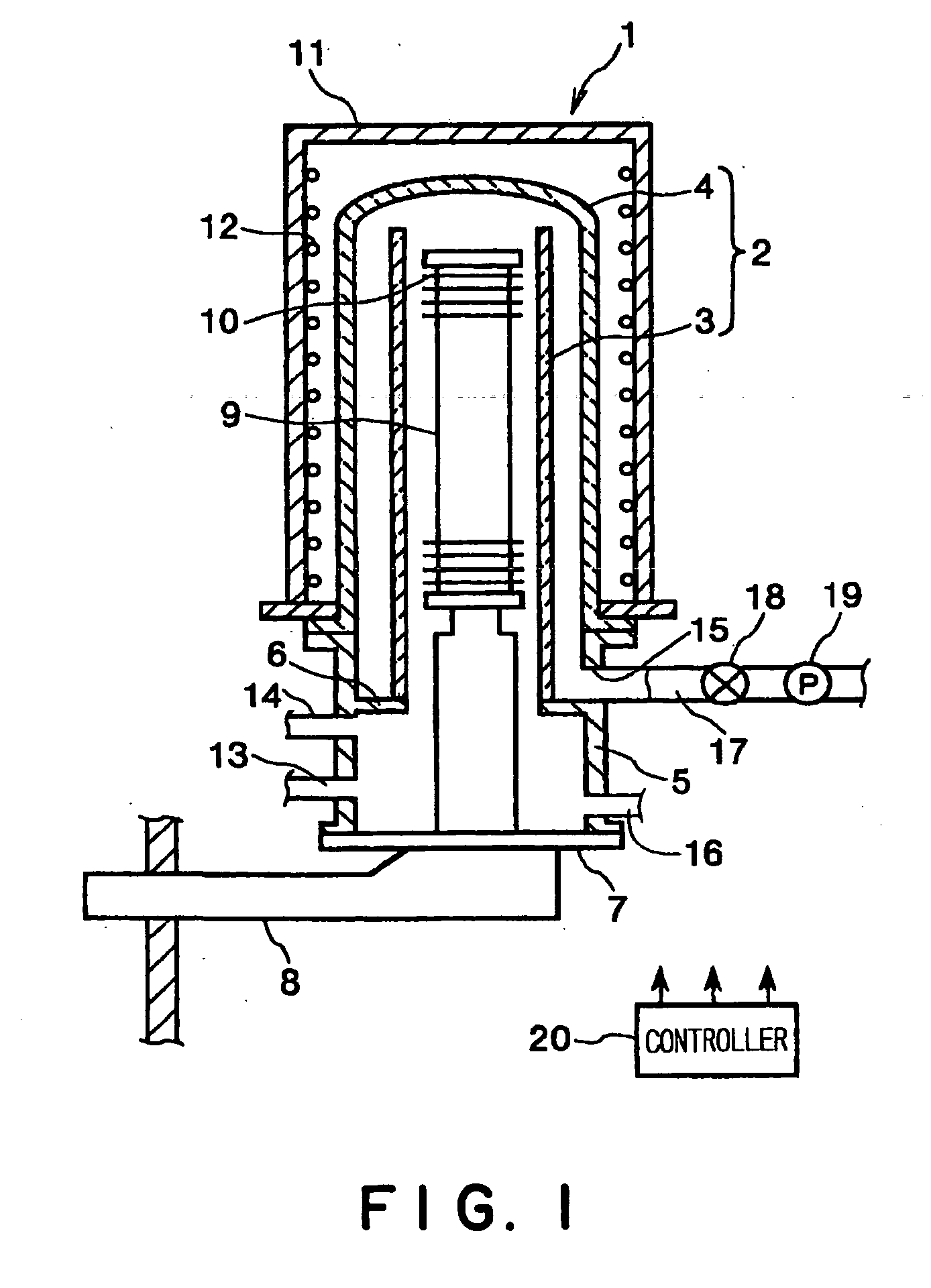
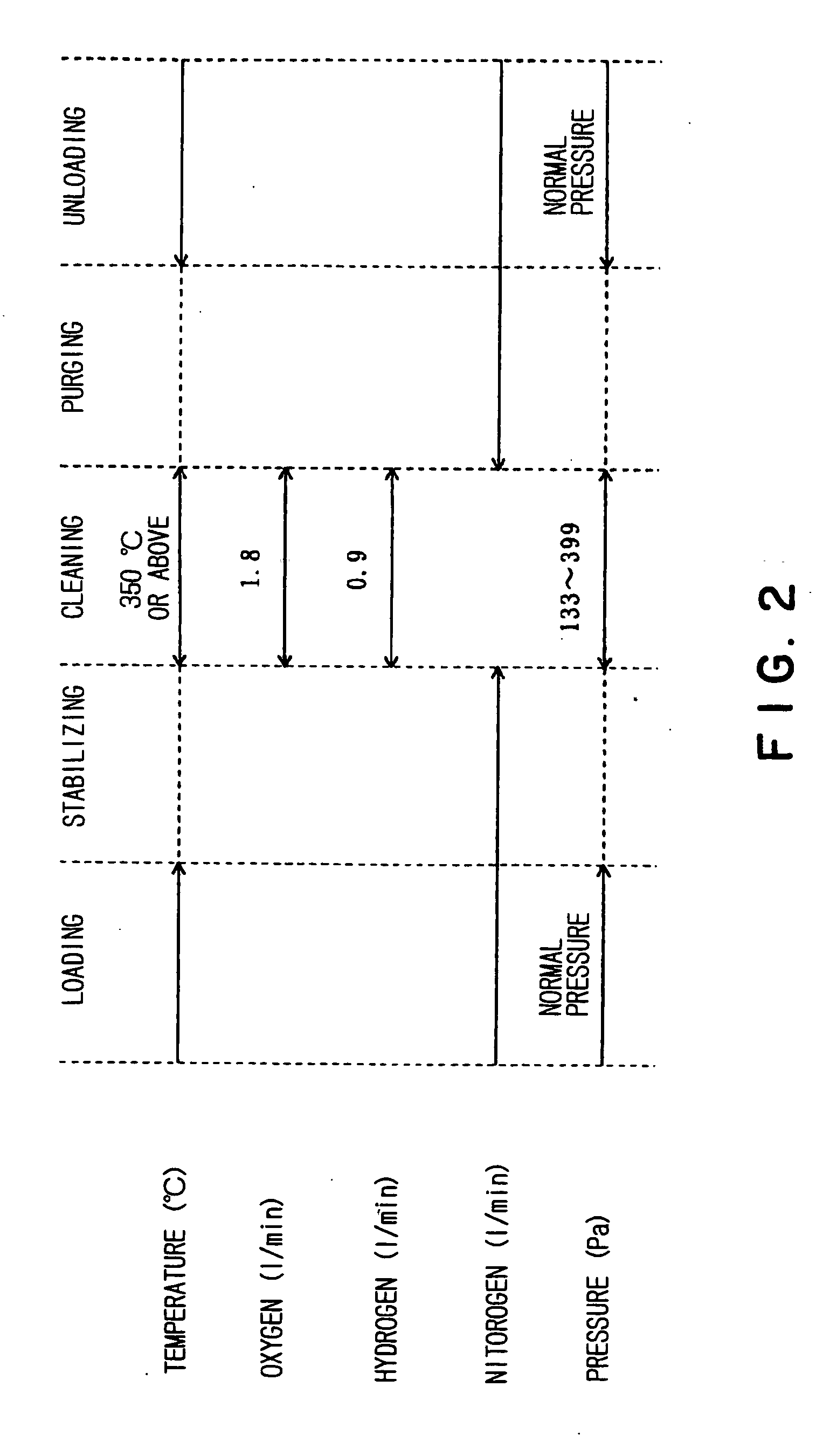
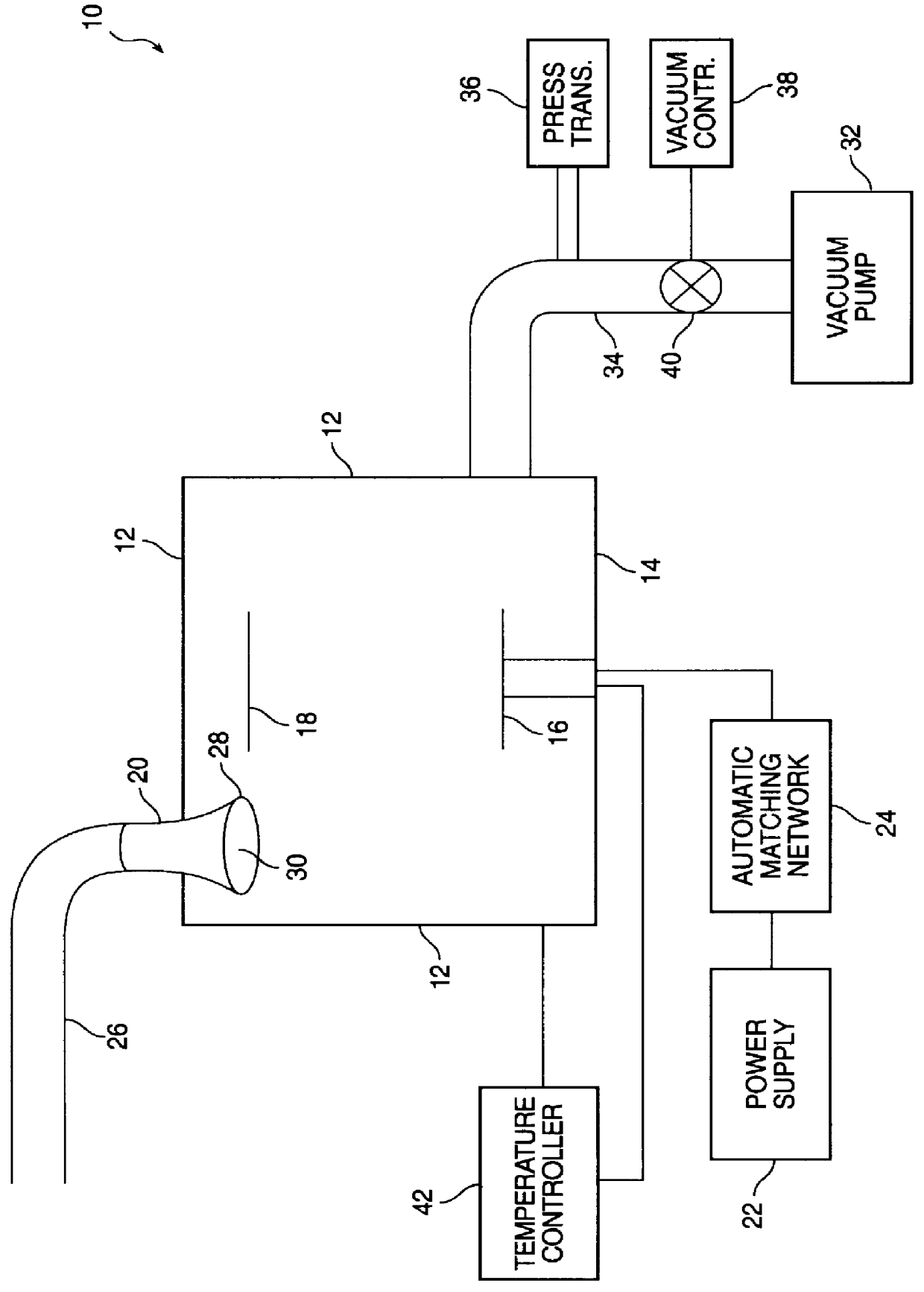
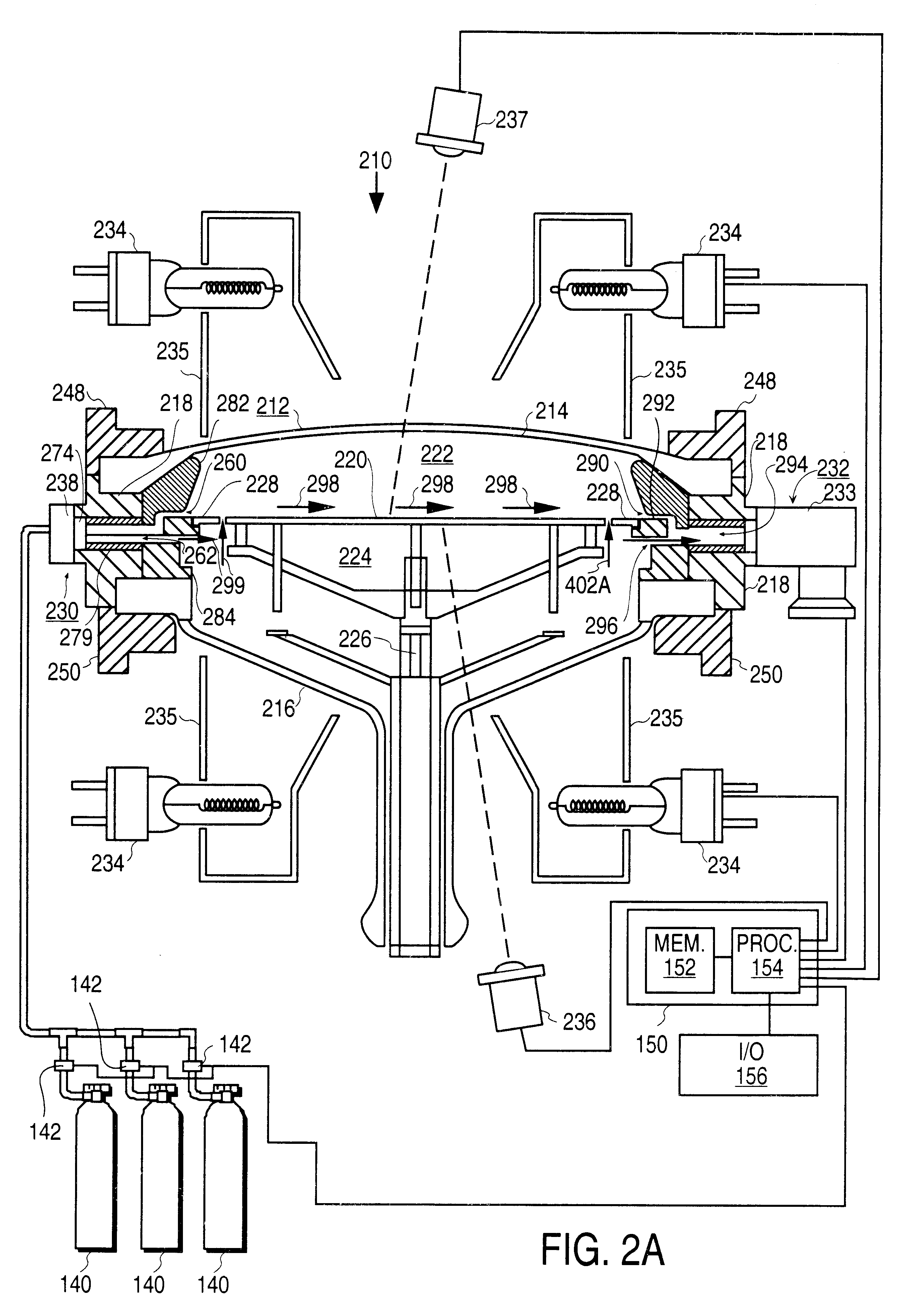
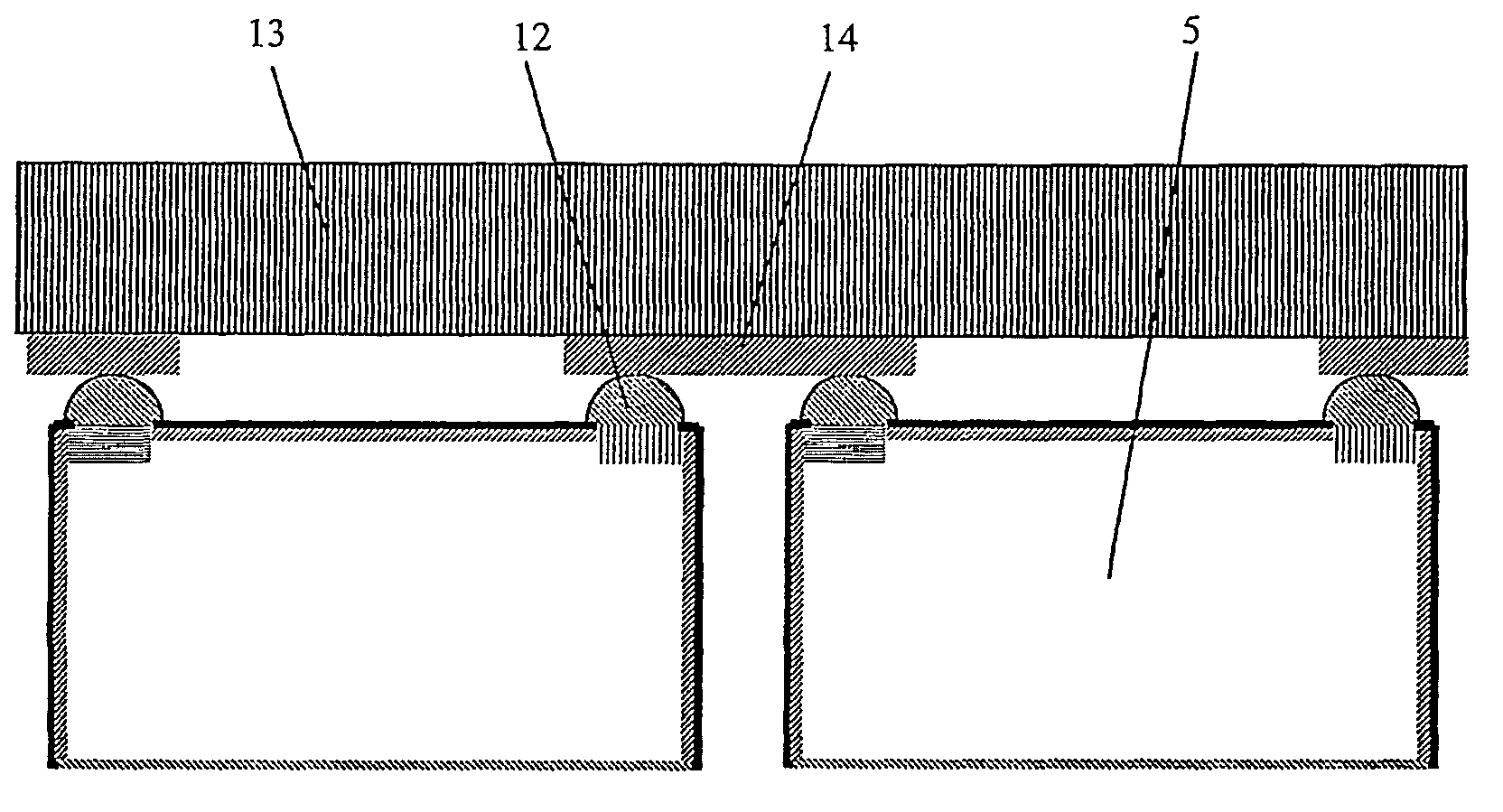
InactiveUS20040219793A1Efficient removalShort timeAfter-treatment detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCombustionHydrogen
A thermal treatment apparatus 1 includes a reaction tube 2 for containing wafers 10 contaminated with organic substances having a heater 12 capable of heating the reaction tube; a first gas supply pipe 13 for carrying oxygen gas into the reaction tube 2; and a second gas supply pipe 14 for carrying hydrogen gas into the reaction tube 2. Oxygen gas and hydrogen gas are supplied through the first gas supply pipe 13 and the second gas supply pipe 14, respectively, into the reaction tube 2, and the heater 12 heats the reaction tube 2 at a temperature capable of activating oxygen gas and hydrogen gas. A combustion reaction occurs in the reaction tube 2 and thereby the organic substances adhering to the wafers 10 are oxidized, decomposed and removed.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method of semiconductor film stabilization
InactiveUS20130330911A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsMetallurgySemiconductor
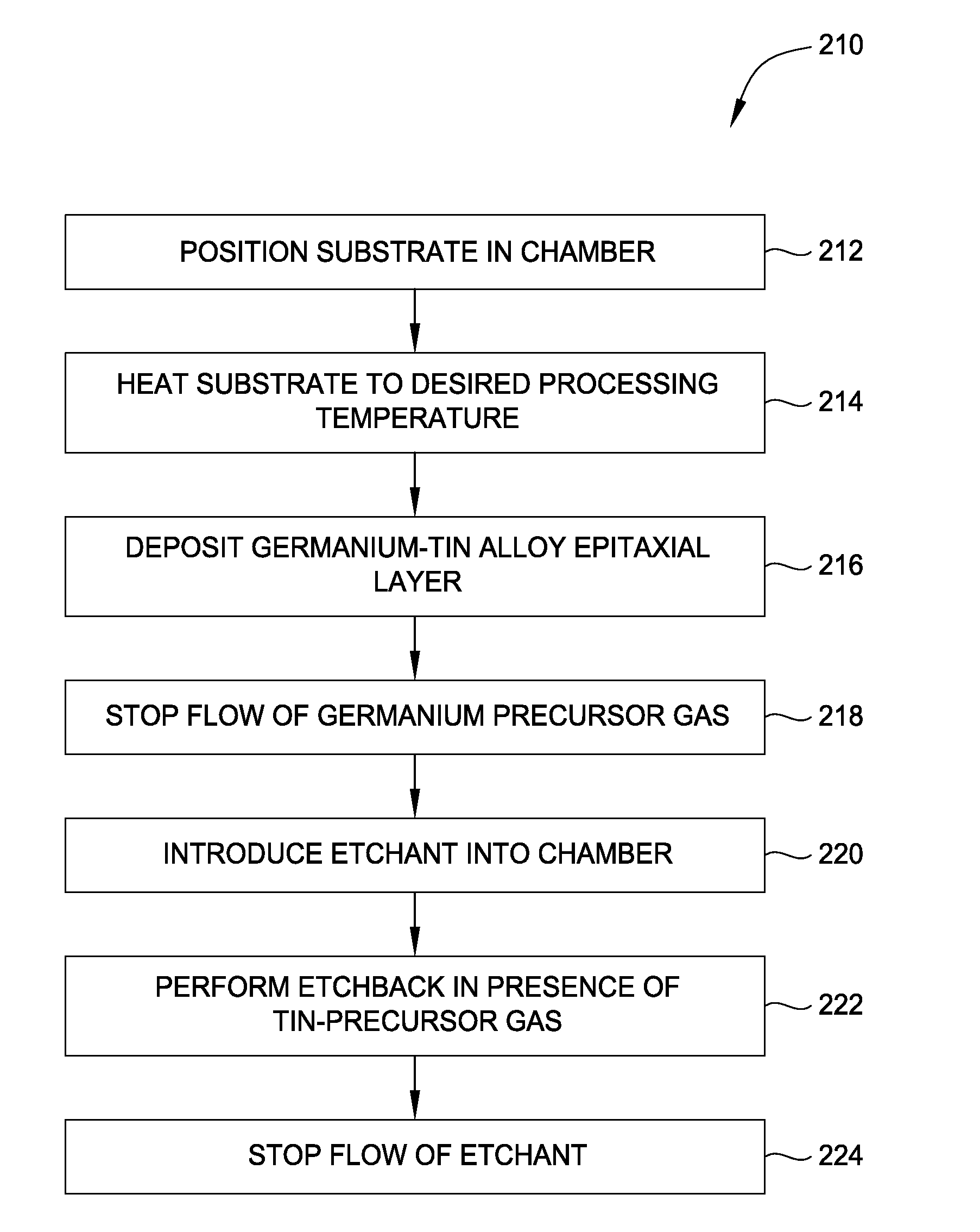
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to methods for forming silicon-germanium-tin alloy epitaxial layers, germanium-tin alloy epitaxial layers, and germanium epitaxial layers that may be doped with boron, phosphorus, arsenic, or other n-type or p-type dopants. The methods generally include positioning a substrate in a processing chamber. A germanium precursor gas is then introduced into the chamber concurrently with a stressor precursor gas, such as a tin precursor gas, to form an epitaxial layer. The flow of the germanium gas is then halted, and an etchant gas is introduced into the chamber. An etch back is then performed while in the presence of the stressor precursor gas used in the formation of the epitaxial film. The flow of the etchant gas is then stopped, and the cycle may then be repeated. In addition to or as an alternative to the etch back process, an annealing processing may be performed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for fabricating optical interference display cell
InactiveUS20050003667A1Easily reorganized and consolidatedLow costDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesRemote plasmaOptoelectronics
A method for fabricating an optical interference display cell is described. A first electrode and a sacrificial layer are sequentially formed on a transparent substrate and at least two openings are formed in the first electrode and the sacrificial layer to define a position of the optical interference display cell. An insulated heat-resistant inorganic supporter is formed in each of the openings. A second electrode is formed on the sacrificial layer and the supporters. Finally, a remote plasma etching process is used for removing the sacrificial layer.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Method for achieving improved epitaxy quality (surface texture and defect density) on free-standing (aluminum, indium, gallium) nitride ((al,in,ga)n) substrates for opto-electronic and electronic devices
A III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structure comprising a III-V nitride homoepitaxial epi layer on a III-V nitride material substrate, e.g., of freestanding character. Various processing techniques are described, including a method of forming a III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer on a corresponding III-V nitride material substrate, by depositing the III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer by a VPE process using Group III source material and nitrogen source material under process conditions including V / III ratio in a range of from about 1 to about 105, nitrogen source material partial pressure in a range of from about 1 to about 103 torr, growth temperature in a range of from about 500 to about 1250 degrees Celsius, and growth rate in a range of from about 0.1 to about 500 microns per hour. The III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structures are usefully employed in device applications such as UV LEDs, high electron mobility transistors, and the like.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Flat sic semiconductor substrate
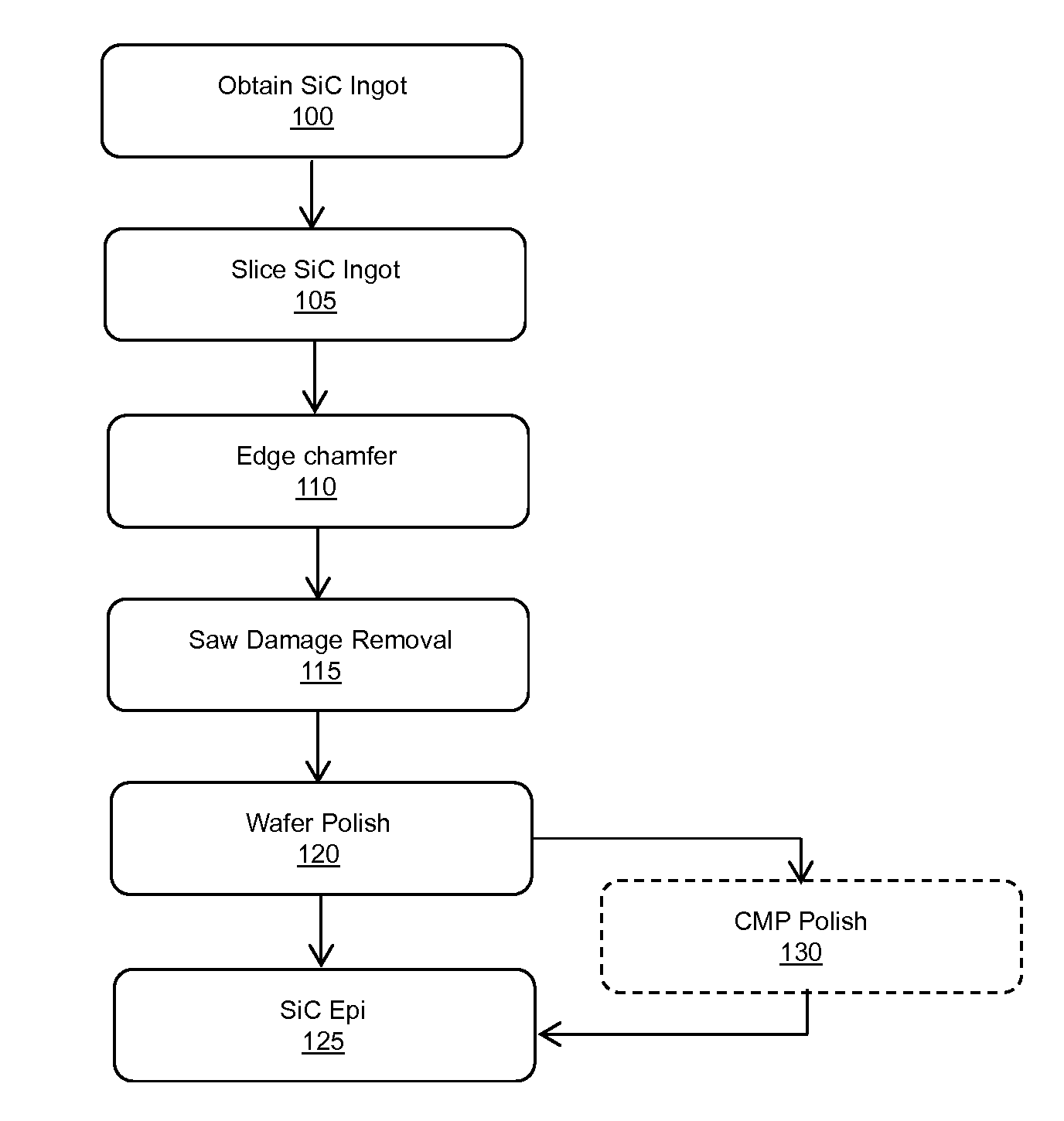
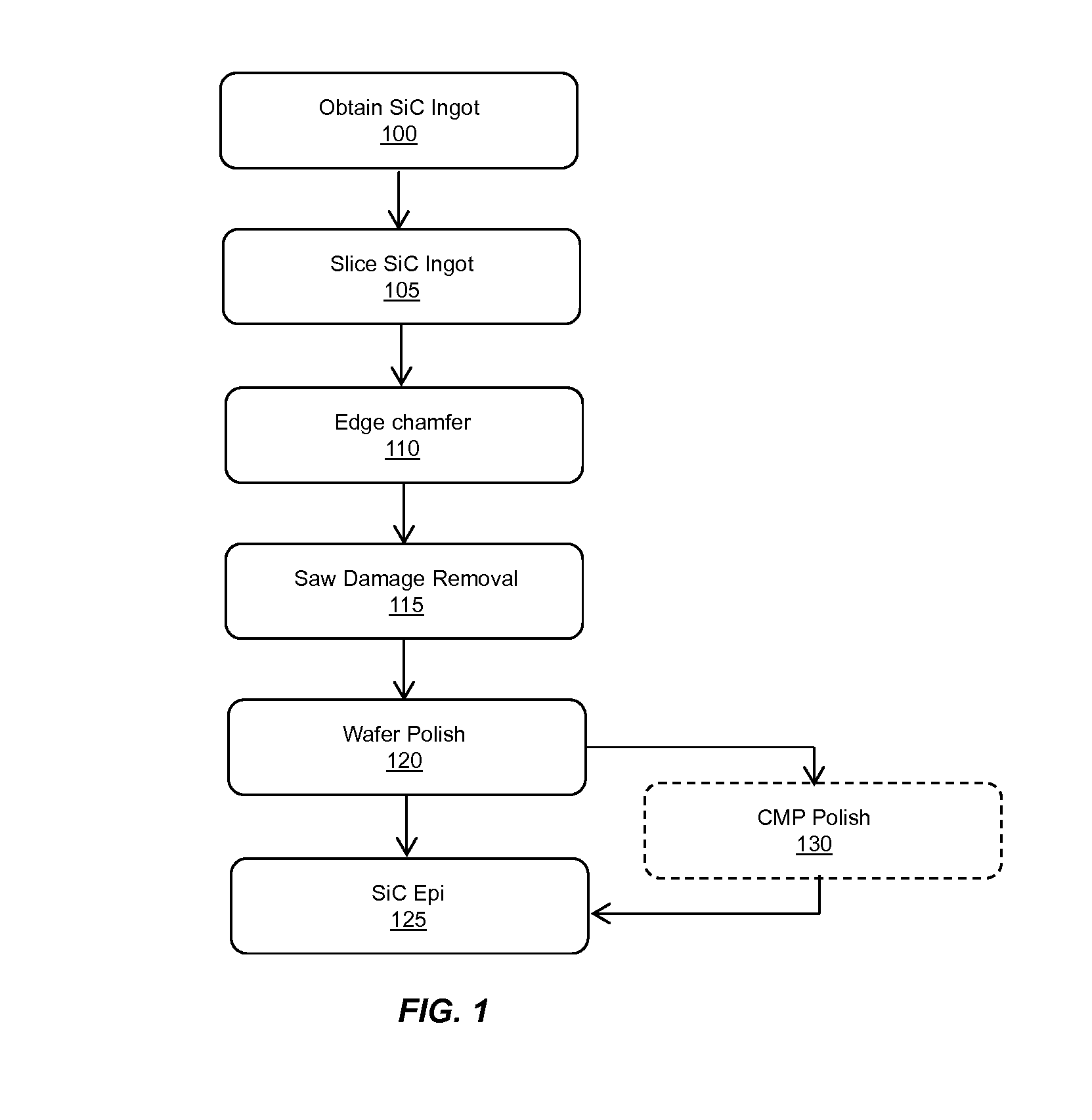
ActiveUS20140117380A1Efficient polishingImprove performanceEdge grinding machinesPolycrystalline material growthCrystallographyWafering
Methods for manufacturing silicon carbide wafers having superior specifications for bow, warp, total thickness variation (TTV), local thickness variation (LTV), and site front side least squares focal plane range (SFQR). The resulting SiC wafer has a mirror-like surface that is fit for epitaxial deposition of SiC. The specifications for bow, warp, total thickness variation (TTV), local thickness variation (LTV), and site front side least squares focal plane range (SFQR) of the wafer are preserved following the addition of the epitaxy layer.
Owner:SK SILTRON CSS LLC
Method of polishing CVD diamond films by oxygen plasma
InactiveUS6013191APolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsFluorinated gasesOxygen plasma
A method for polishing the surface of a diamond film with a low power density plasma in a reactor which comprises disposing O2 gas and a fluorinated gas such as SF6, NF3, and C2F6 in the reactor, providing power to the reactor so that the power density in the reactor is between about 1.0 watts / cm2 and about 1.1 watts / cm2 for a first duration, and maintaining temperature in the reactor at between about 200 DEG to about 400 DEG . The method may alternatively comprise disposing a sputter gas such as Ar,O2 or N2 in the reactor, providing power to the reactor so that the power density in the reactor is between about 3.0 watts / cm2 and about 7.5 watts / cm2 for a first duration, and performing a sputter etch, disposing O2 gas and a fluorinated gas such as SF6, NF3, and C2F6 in the reactor, and providing power to the reactor so that the power density in the reactor is between about 1.5 watts / cm2 and about 3.0 watts / cm2 for a second duration.
Owner:ADVANCED REFRACTORY TECH INC
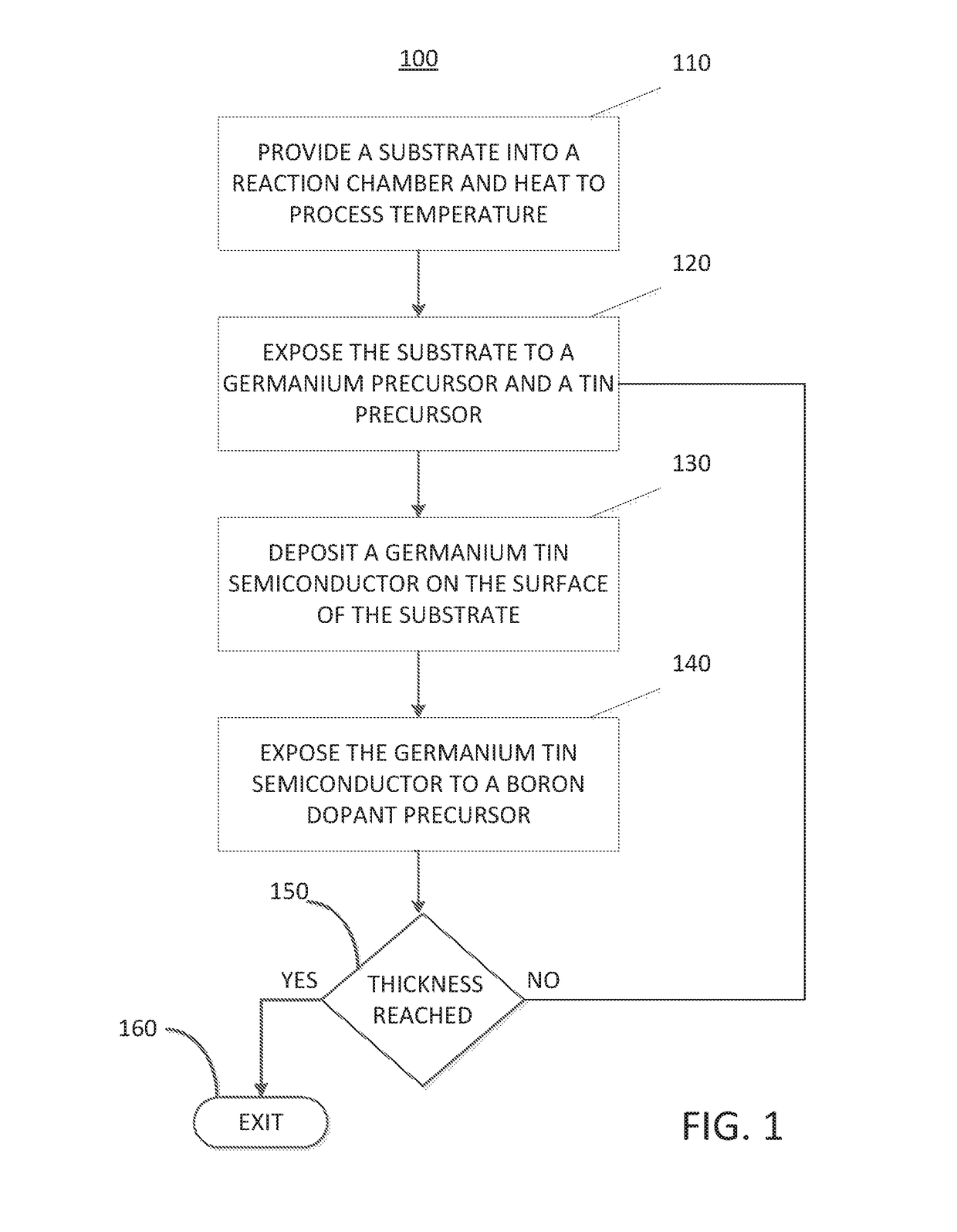
Methods for depositing a doped germanium tin semiconductor and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS10236177B1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantDeposition temperature
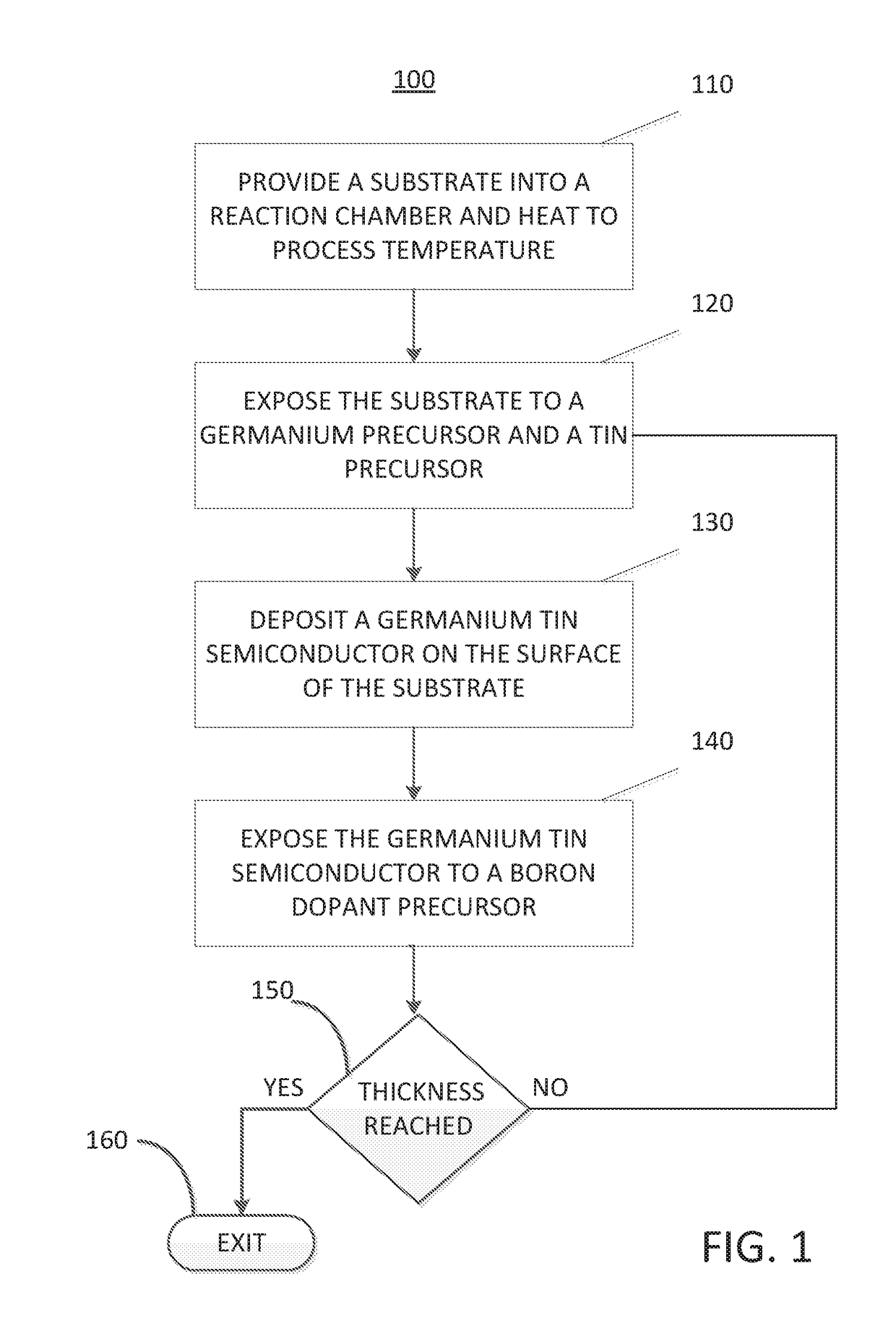
A method for depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor is disclosed. The method may include; providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature and exposing the substrate to a germanium precursor and a tin precursor. The method may further include; depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor on the surface of the substrate, and exposing the germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor to a boron dopant precursor. Semiconductor device structures including a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor formed by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
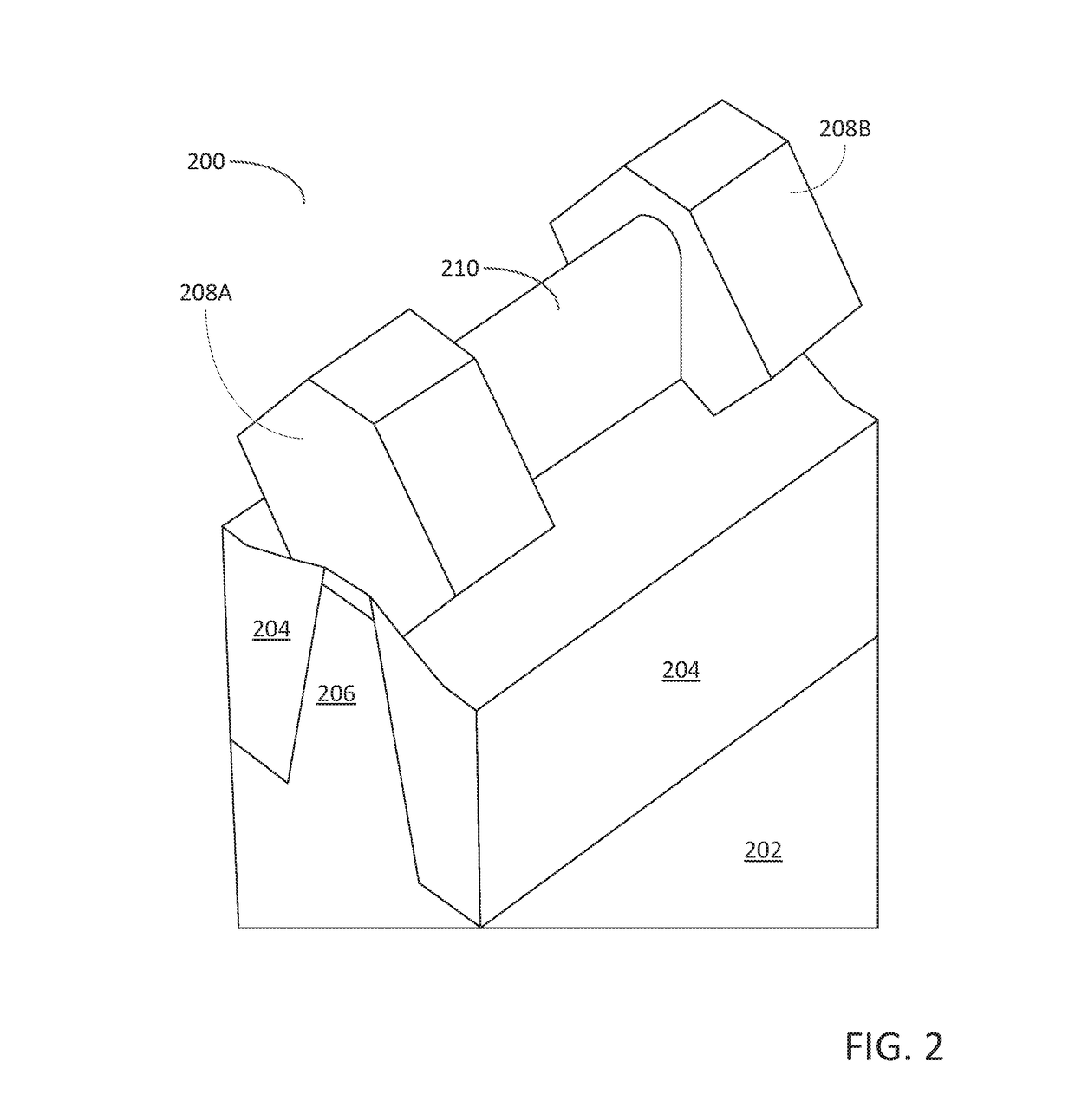
Non-contact etch annealing of strained layers
InactiveUS20070051299A1Reduce misalignmentReduce dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantElectrical conductor
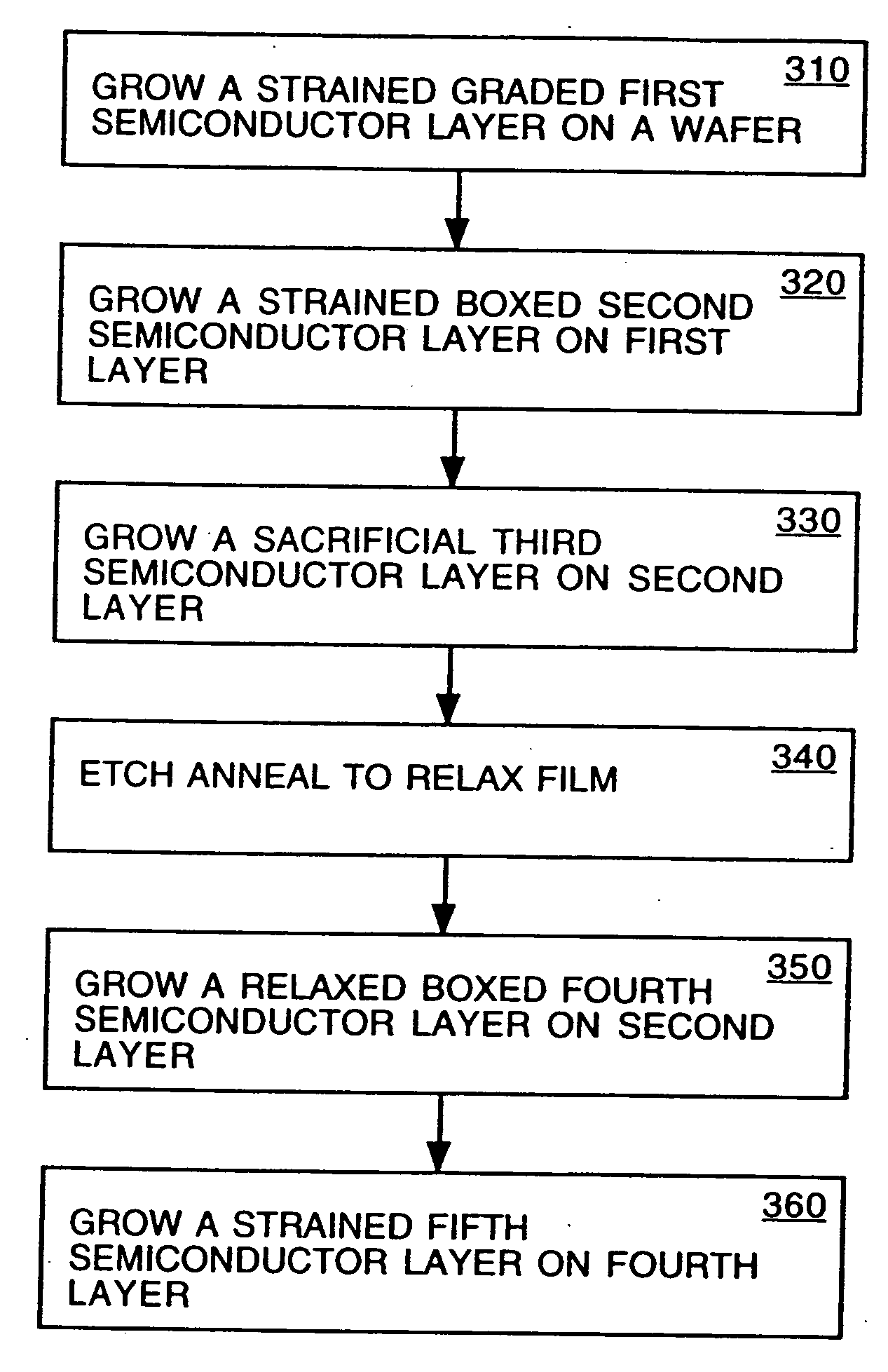
The present invention provides a method of forming a strained semiconductor layer. The method comprises growing a strained first semiconductor layer, having a graded dopant profile, on a wafer, having a first lattice constant. The dopant imparts a second lattice constant to the first semiconductor layer. The method further comprises growing a strained boxed second semiconductor layer having the second lattice constant on the first semiconductor layer and growing a sacrificial third semiconductor layer having the first lattice constant on the second semiconductor layer. The method further comprises etch annealing the third and second semiconductor layer, wherein the third semiconductor layer is removed and the second semiconductor layer is relaxed. The method may further comprises growing a fourth semiconductor layer having the second lattice constant on the second semiconductor layer, wherein the fourth semiconductor layer is relaxed, and growing a strained fifth semiconductor layer having the first semiconductor lattice constant on the fourth semiconductor layer. The method controls the surface roughness of the semiconductor layers. The method also has the unexpected benefit of reducing dislocations in the semiconductor layers.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
Methods for depositing a doped germanium tin semiconductor and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20190067004A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantDeposition temperature
A method for depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor is disclosed. The method may include; providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature and exposing the substrate to a germanium precursor and a tin precursor. The method may further include; depositing a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor on the surface of the substrate, and exposing the germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor to a boron dopant precursor. Semiconductor device structures including a germanium tin (Ge1-xSnx) semiconductor formed by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Nanowires-based transparent conductors
ActiveUS20080286447A1Material nanotechnologyFrom normal temperature solutionsNanowireElectrical conductor
Owner:CHAMP GREAT INTL
High efficiency solar cells utilizing wafer bonding and layer transfer to integrate non-lattice matched materials
ActiveUS20060185582A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSemiconductor materialsEngineering
A method of making a virtual substrate includes providing a donor substrate comprising a single crystal donor layer of a first material over a support substrate, wherein the first material comprises a ternary, quaternary or penternary semiconductor material or a material which is not available in bulk form, bonding the donor substrate to a handle substrate, and separating the donor substrate from the handle substrate such that a single crystal film of the first material remains bonded to the handle substrate.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
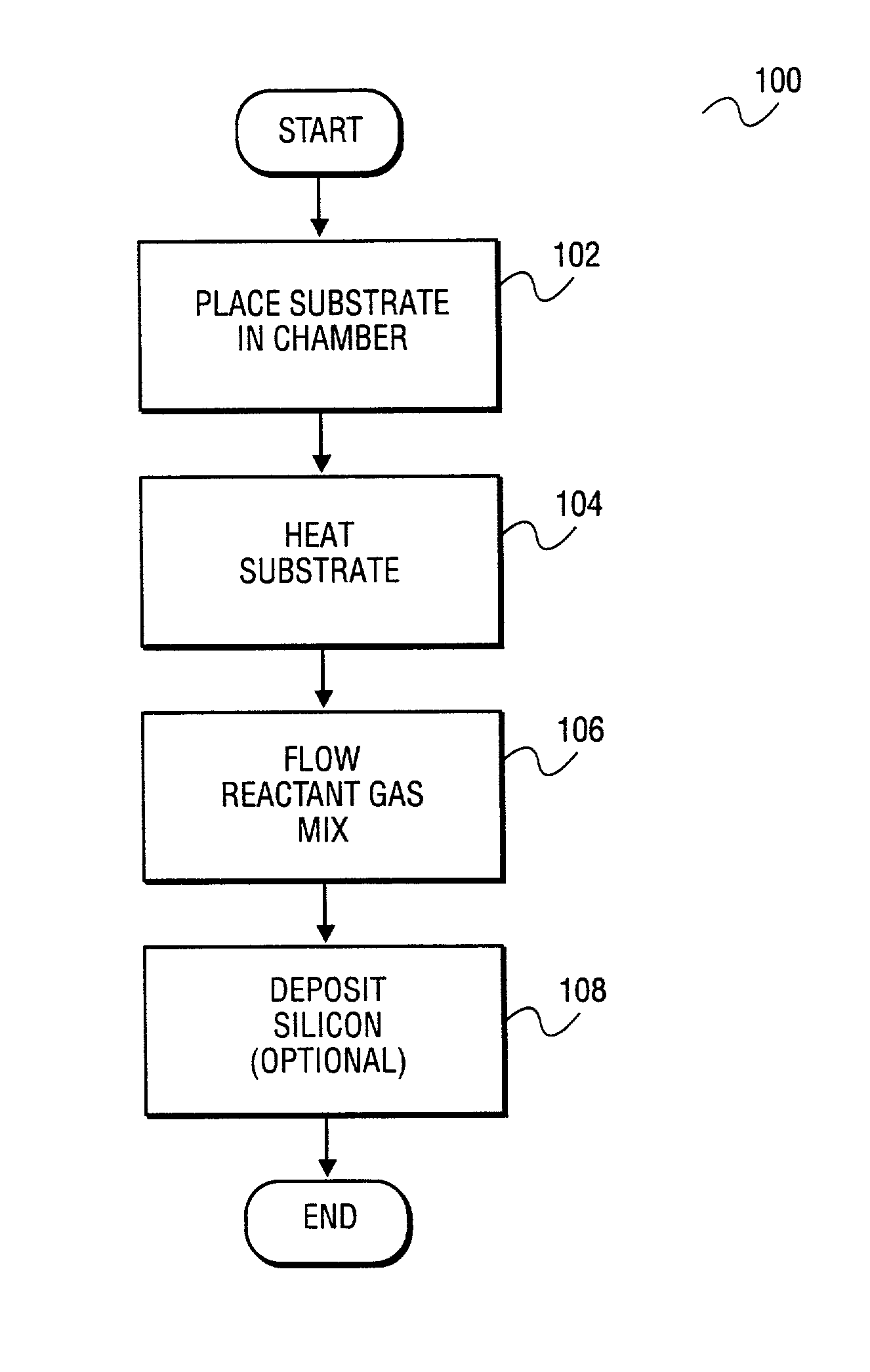
Low-temperature selective epitaxial growth of silicon for device integration
InactiveUS20150247259A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDeposition temperaturePhysical chemistry
An epitaxy method includes providing an exposed crystalline region of a substrate material. Silicon is epitaxially deposited on the substrate material in a low temperature process wherein a deposition temperature is less than 500 degrees Celsius. A source gas is diluted with a dilution gas with a gas ratio of dilution gas to source gas of less than 1000.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for preparing epitaxial-substrate and method for manufacturing semiconductor device employing the same
InactiveUS6627552B1Improve convenienceImprove surface morphologyPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSingle crystalSemiconductor
The present invention provides a method for preparing epitaxial-substrate, for growing a multilayered structure of GaN based semiconductor layers on the epitaxial-substrate so as to construct a semiconductor device such as blue-emitting laser diode and LED. The method for preparing the epitaxial-substrate encompasses (a) growing a first GaN based semiconductor layer on a bulk-substrate; (b) growing an InGaN based semiconductor layer on the first GaN based semiconductor layer; (c) growing a second GaN based semiconductor layer on the InGaN based semiconductor layer; and (d) separating the second GaN based semiconductor layer from the first GaN based semiconductor layer to provide the epitaxial-substrate. The epitaxial-substrate having a high crystallographic perfection and an excellent surface morphology is obtained simply and in a short time. The defect density of the single crystalline GaN based semiconductor layer film grown on the epitaxial-substrate is greatly reduced.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High surface quality GaN wafer and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS6951695B2Improve surface qualityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface roughnessHigh surface
AlxGayInzN, wherein 0≦x≦1, 0≦y≦1, 0≦z≦1, and x+y+z=1, characterized by a root mean square surface roughness of less than 1 nm in a 10×10 μm2 area. The AlxGayInzN may be in the form of a wafer, which is chemically mechanically polished (CMP) using a CMP slurry comprising abrasive particles, such as silica or alumina, and an acid or a base. High quality AlxGayInzN wafers can be fabricated by steps including lapping, mechanical polishing, and reducing internal stress of said wafer by thermal annealing or chemical etching for further enhancement of its surface quality. CMP processing may be usefully employed to highlight crystal defects of an AlxGayInzN wafer.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Bulk single crystal gallium nitride and method of making same
InactiveUS20010008656A1Enhance crystallinity and other characteristicAvoid etchingEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsElectronic structureSingle crystal
A single crystal M*N article, which may be made by a process including the steps of: providing a substrate of material having a crystalline surface which is epitaxially compatible with M*N; depositing a layer of single crystal M*N over the surface of the substrate; and removing the substrate from the layer of single crystal M*N, e.g., with an etching agent which is applied to the substrate to remove same, to yield the layer of single crystal M*N as said single crystal M*N article. The bulk single crystal M*N article is suitable for use as a substrate for the fabrication of microelectronic structures thereon, to produce microelectronic devices comprising bulk single crystal M*N substrates, or precursor structures thereof.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
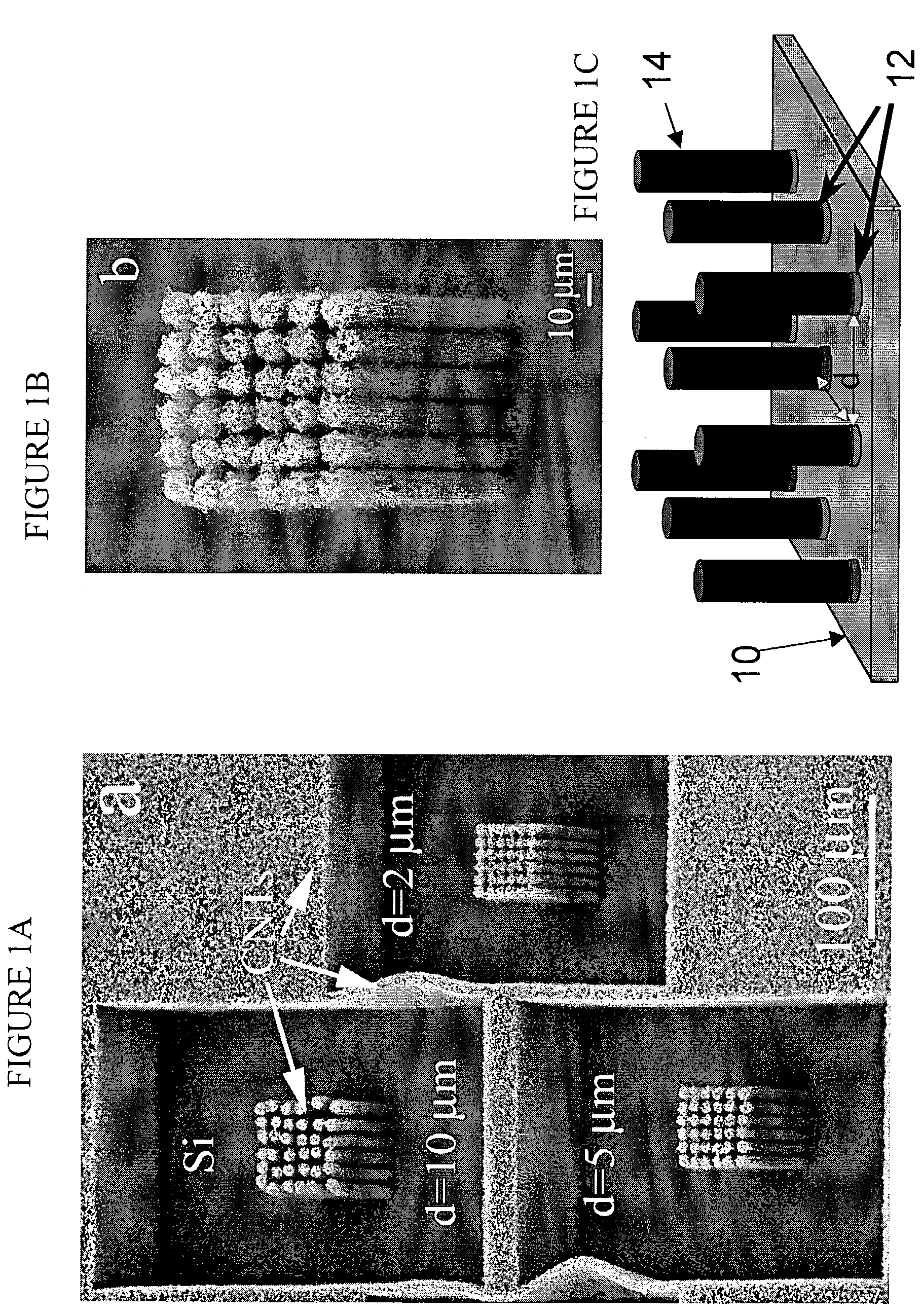
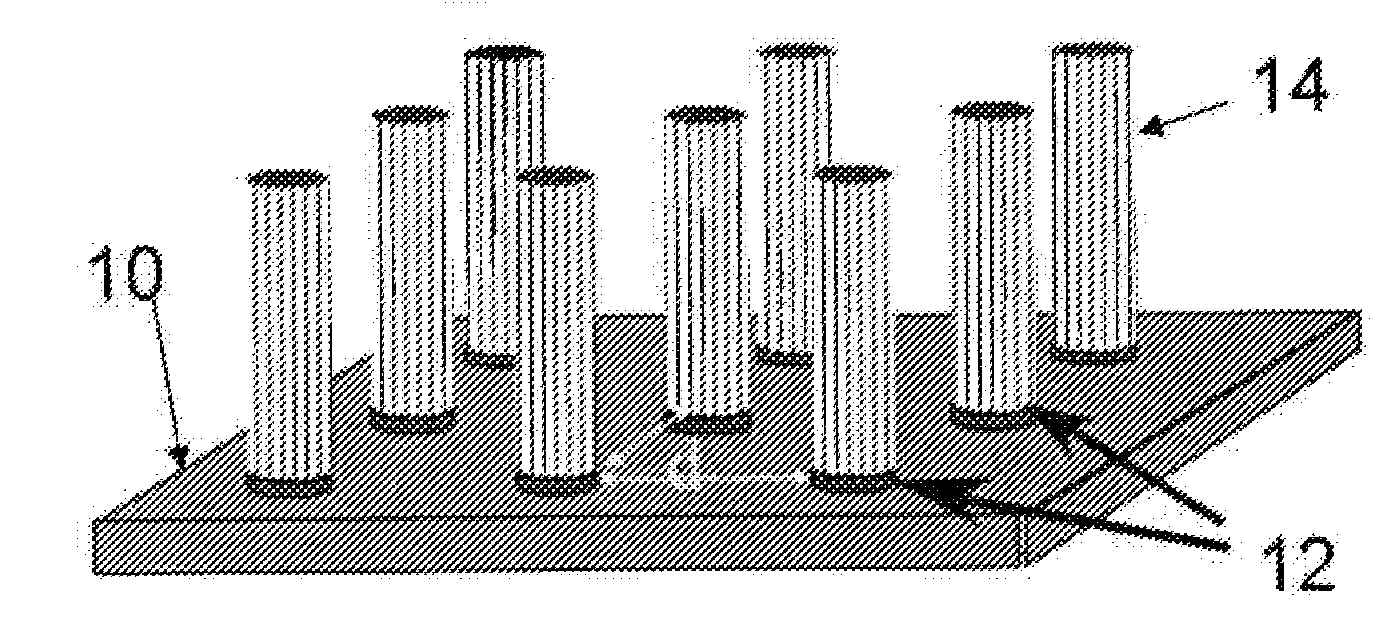
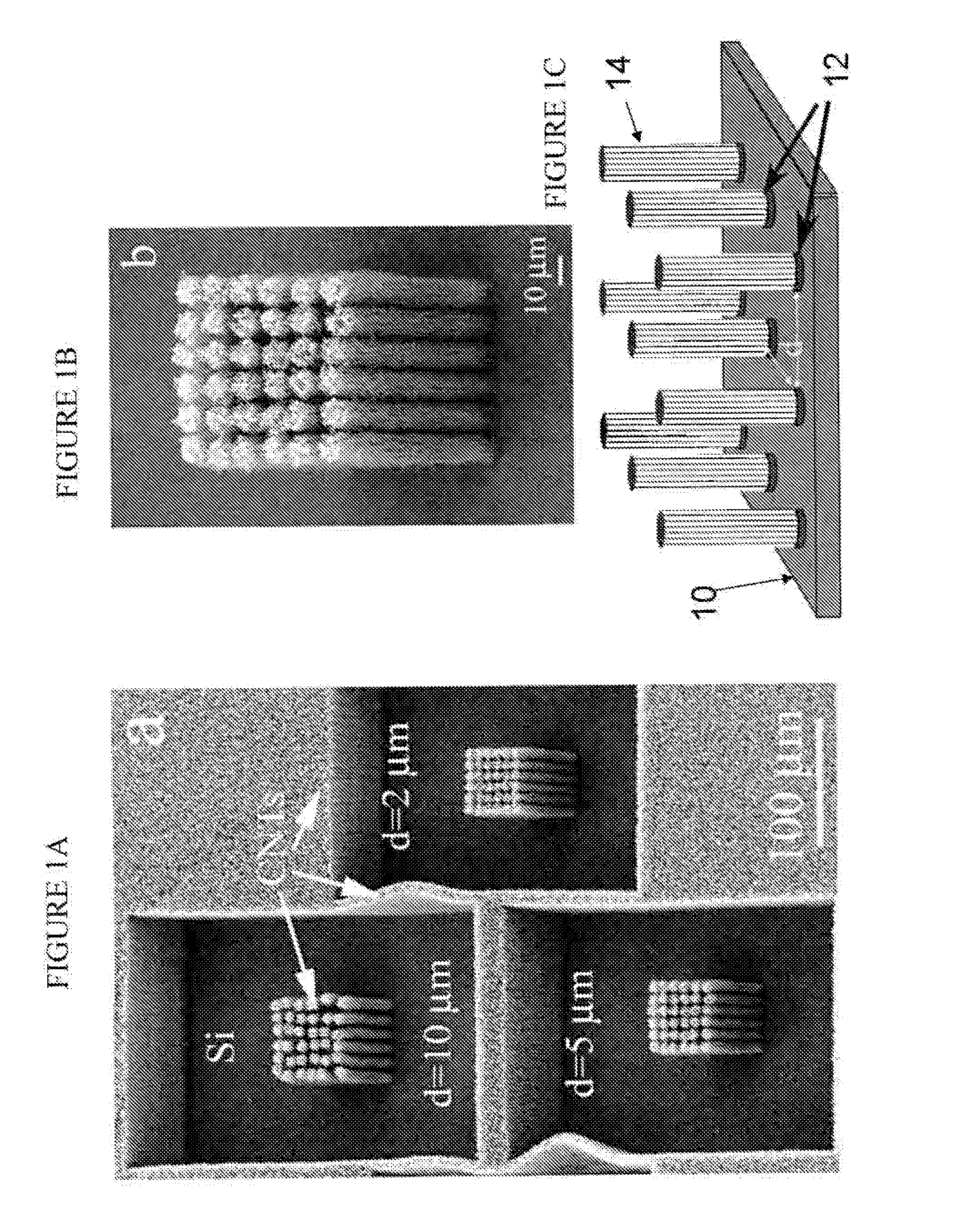
Directed assembly of highly-organized carbon nanotube architectures
A method of controllably aligning carbon nanotubes to a template structure to fabricate a variety of carbon nanotube containing structures and devices having desired characteristics is provided. The method allows simultaneous, selective growth of both vertically and horizontally controllably aligned nanotubes on the template structure but not on a substrate in a single process step.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
III-V Nitride homoepitaxial material of improved MOVPE epitaxial quality (surface texture and defect density) formed on free-standing (Al,In,Ga)N substrates, and opto-electronic and electronic devices comprising same
InactiveUS20030213964A1Improve material qualityReduce dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCelsius DegreeSource material
A III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structure comprising a III-V nitride homoepitaxial epi layer of improved epitaxial quality deposited on a III-V nitride material substrate, e.g., of freestanding character. Various processing techniques are described, including a method of forming a III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer on a corresponding III-V nitride material substrate, by depositing the III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer by a VPE process using Group III source material and nitrogen source material under process conditions including V / III ratio in a range of from about 1 to about 10<5>, nitrogen source material partial pressure in a range of from about 1 to about 10<3 >torr, growth temperature in a range of from about 500 to about 1250 degrees Celsius, and growth rate in a range of from about 0.1 to about 10<2 >microns per hour. The III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structures are usefully employed in device applications such as UV LEDs, high electron mobility transistors, and the like.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Nitride Single Crystal Seeded Growth in Supercritical Ammonia with Alkali Metal Ion
ActiveUS20080156254A1Increase in sizeShorten the timePolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsDissolutionSingle crystal
The present invention is related to a process for obtaining a larger area substrate of mono-crystalline gallium-containing nitride by making selective crystallization of gallium containing nitride on a smaller seed under a crystallization temperature and / or pressure from a supercritical ammonia-containing solution made by dissolution of gallium-containing feedstock in a supercritical ammonia-containing solvent with alkali metal ions, comprising: providing two or more elementary seeds, and making selective crystallization on the two or more separate elementary seeds to get a merged larger compound seed. The merged larger compound seed is used for a seed in a new growth process and then to get a larger substrate of mono-crystal gallium-containing nitride.
Owner:AMMONO SP Z O O (PL) +1
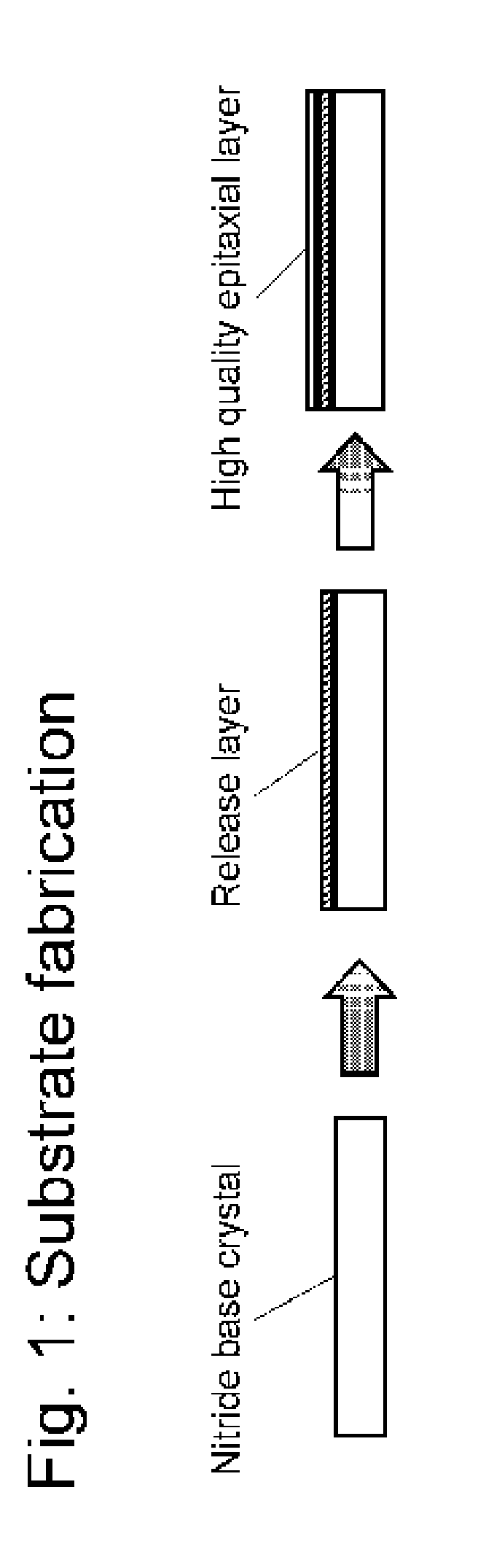
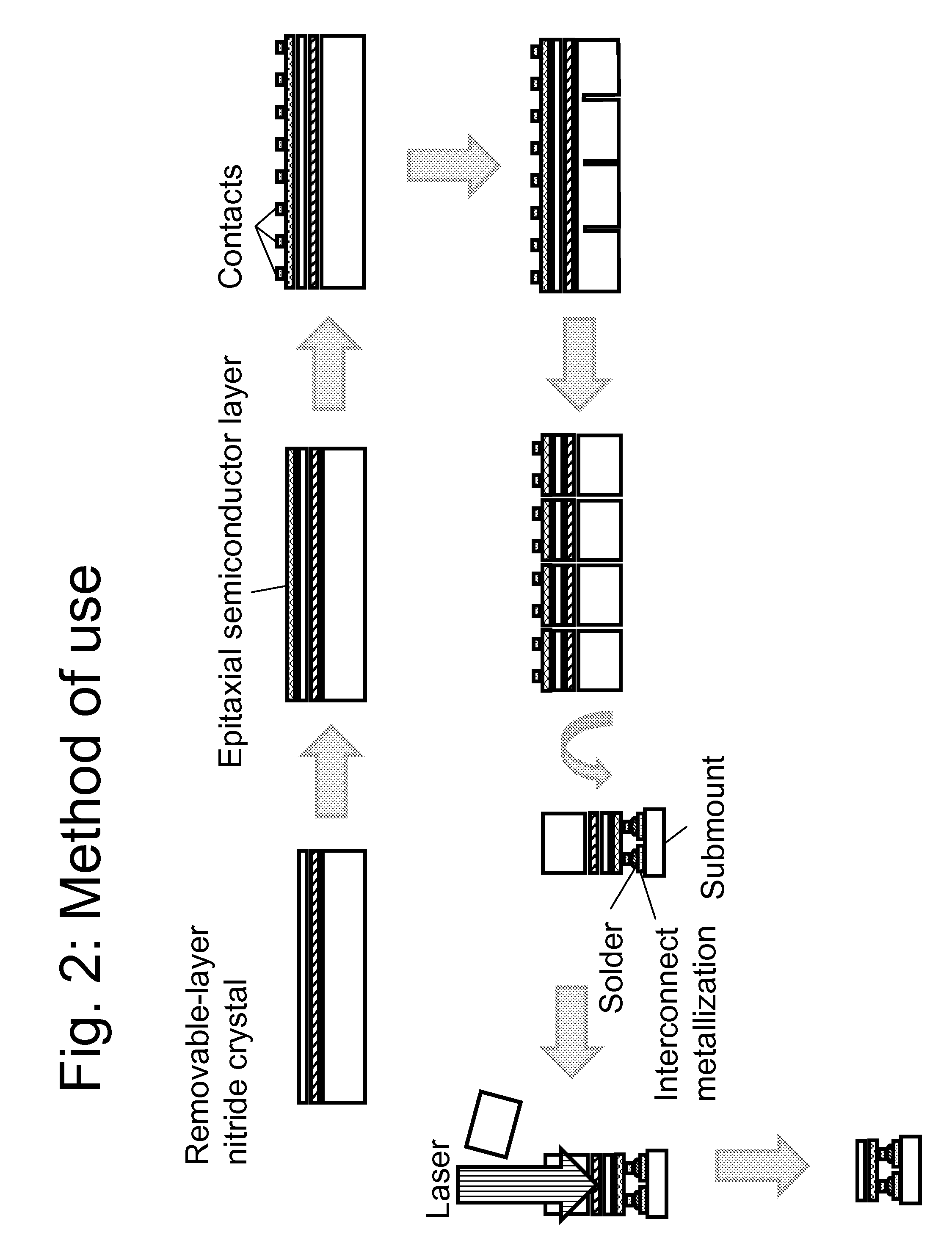
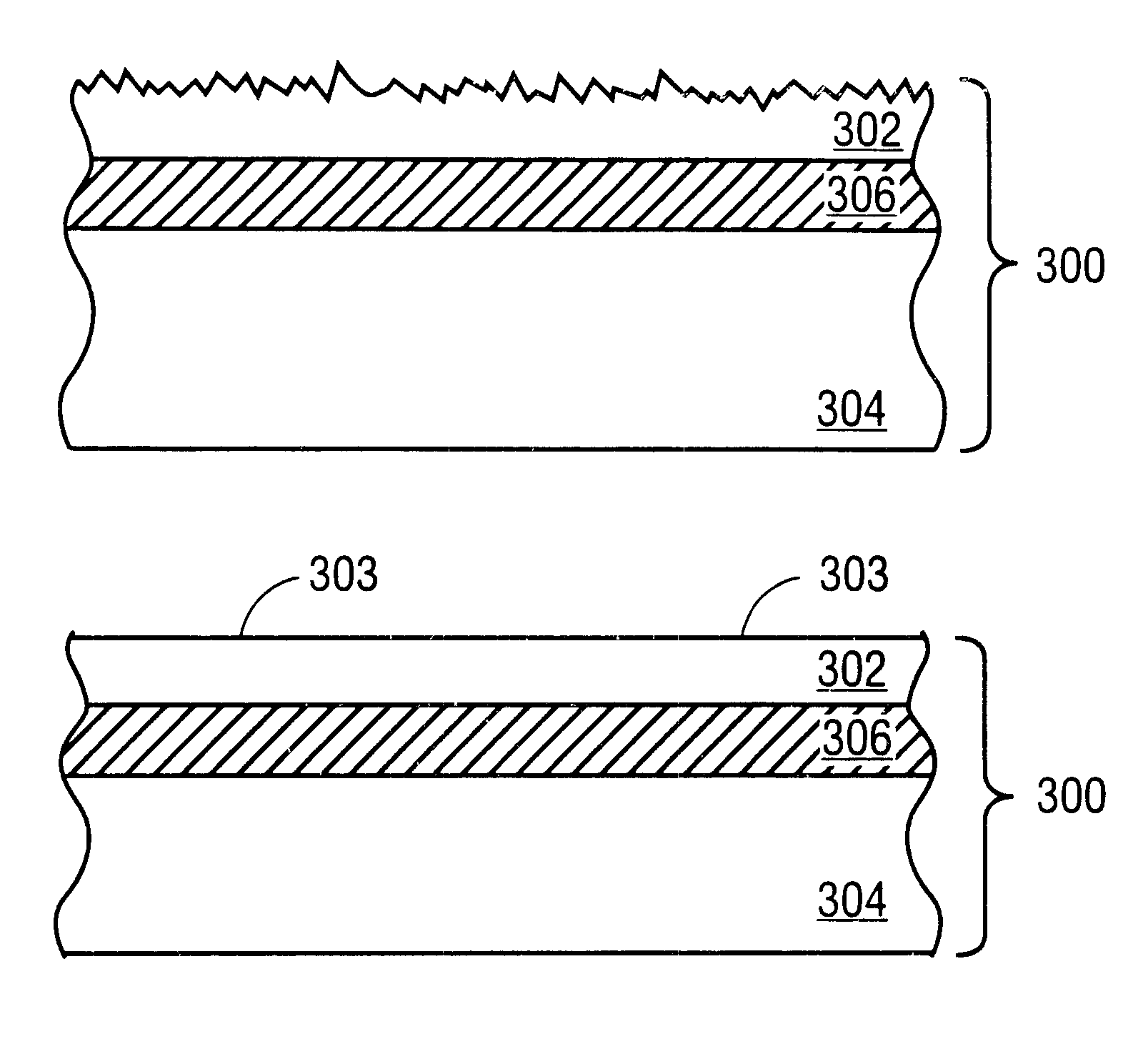
Nitride crystal with removable surface layer and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS8148801B2Quality improvementSimple and cost-effectivePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotodetectorSolar cell
Owner:SLT TECH
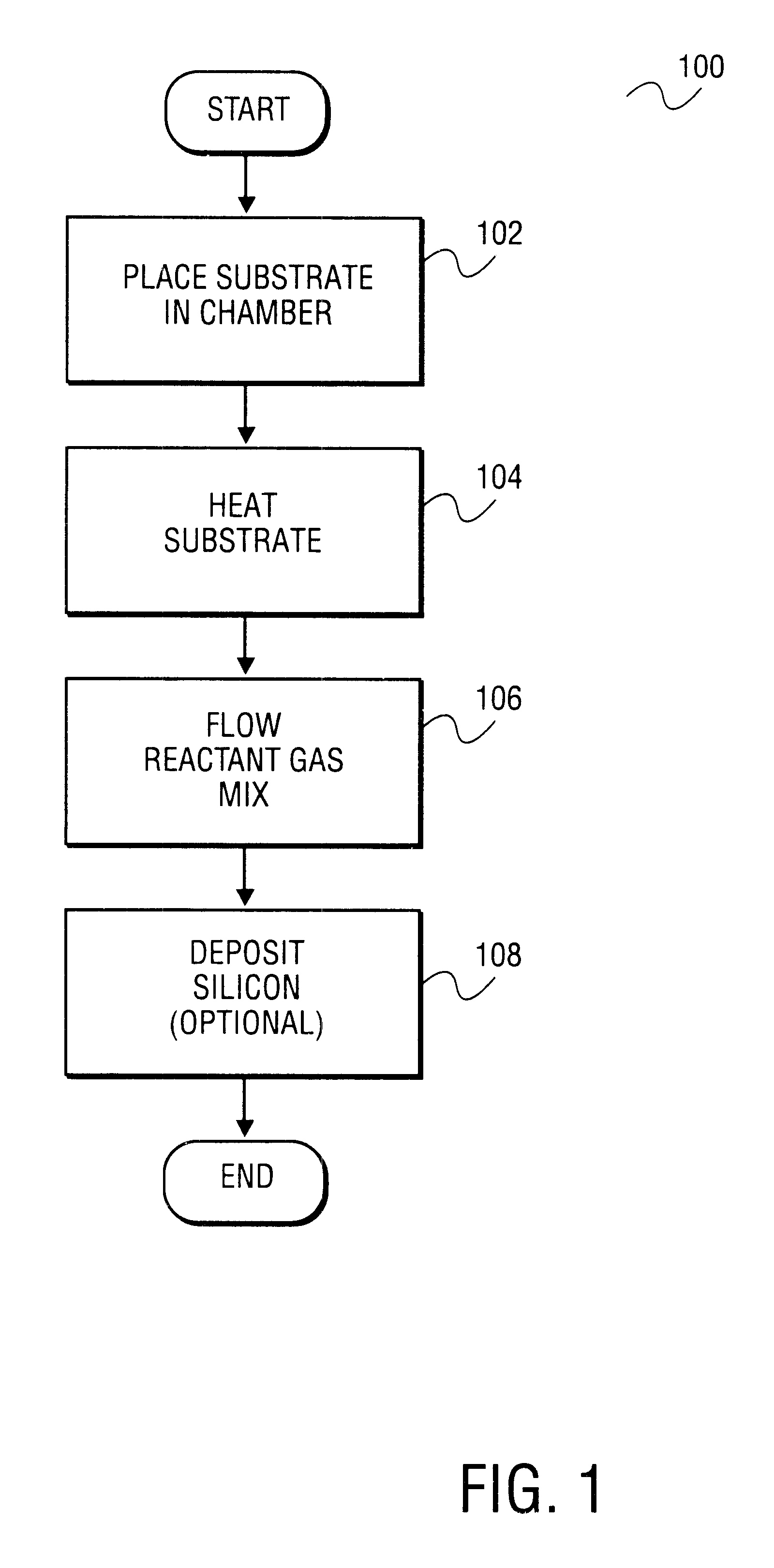
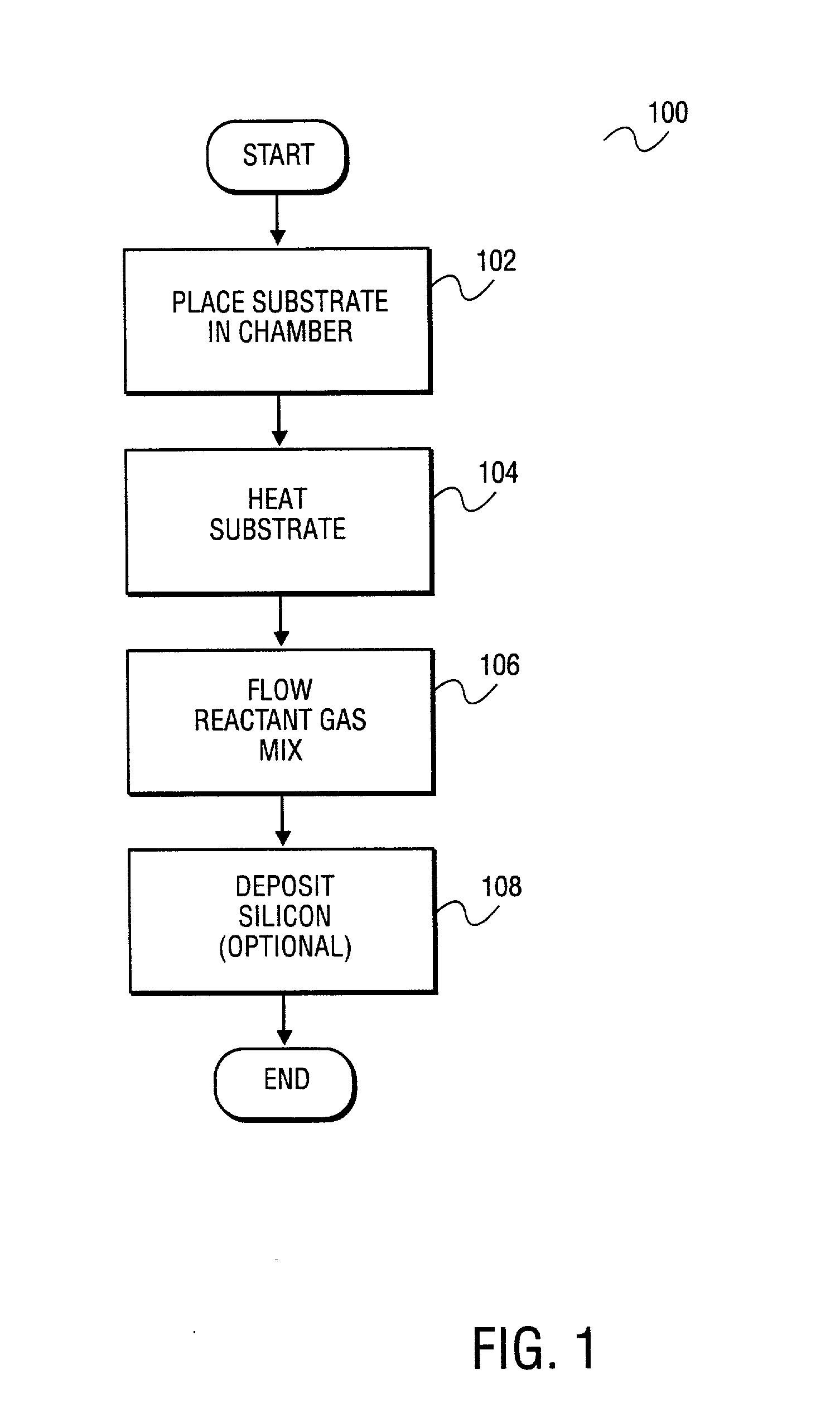
Apparatus and method for surface finishing a silicon film
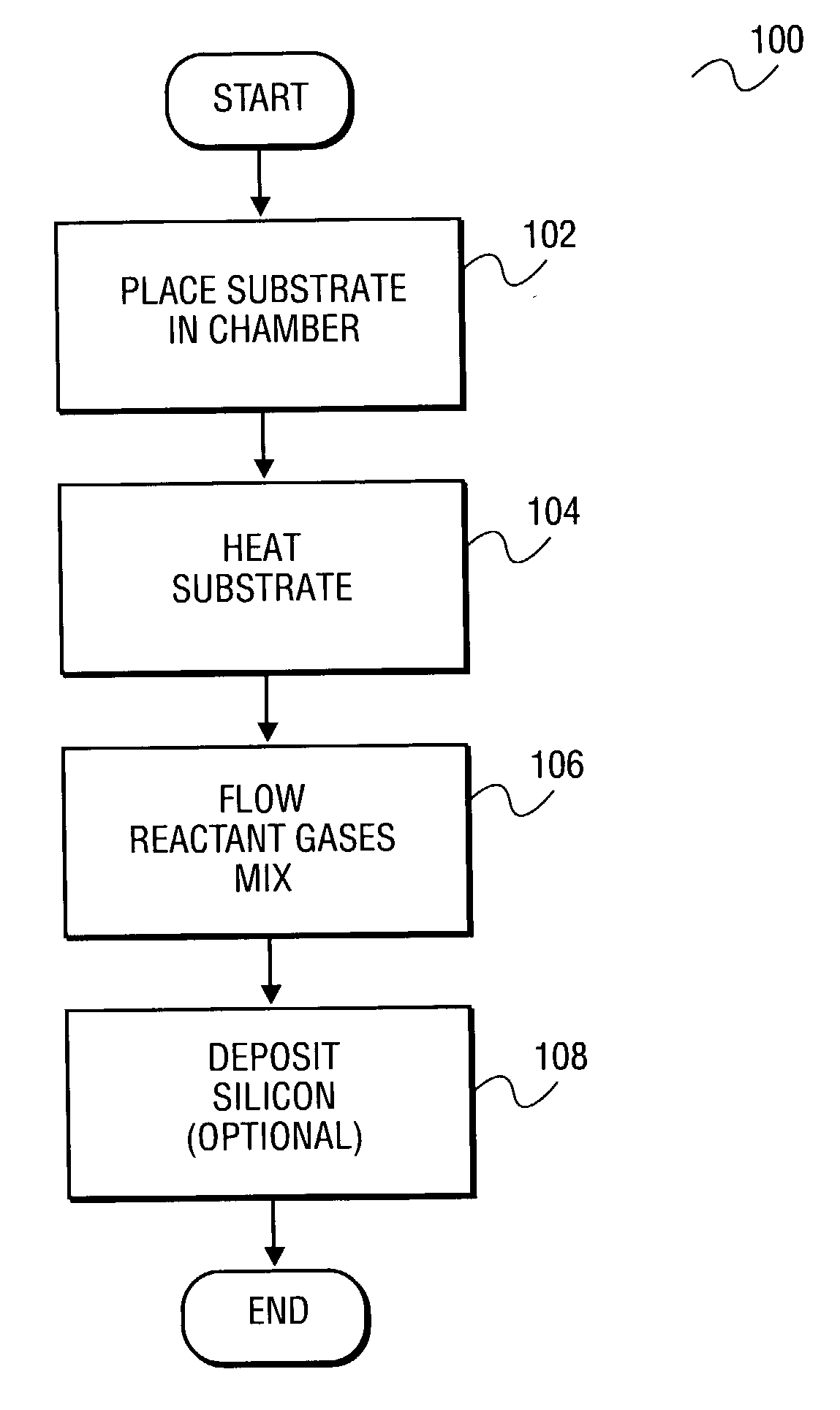
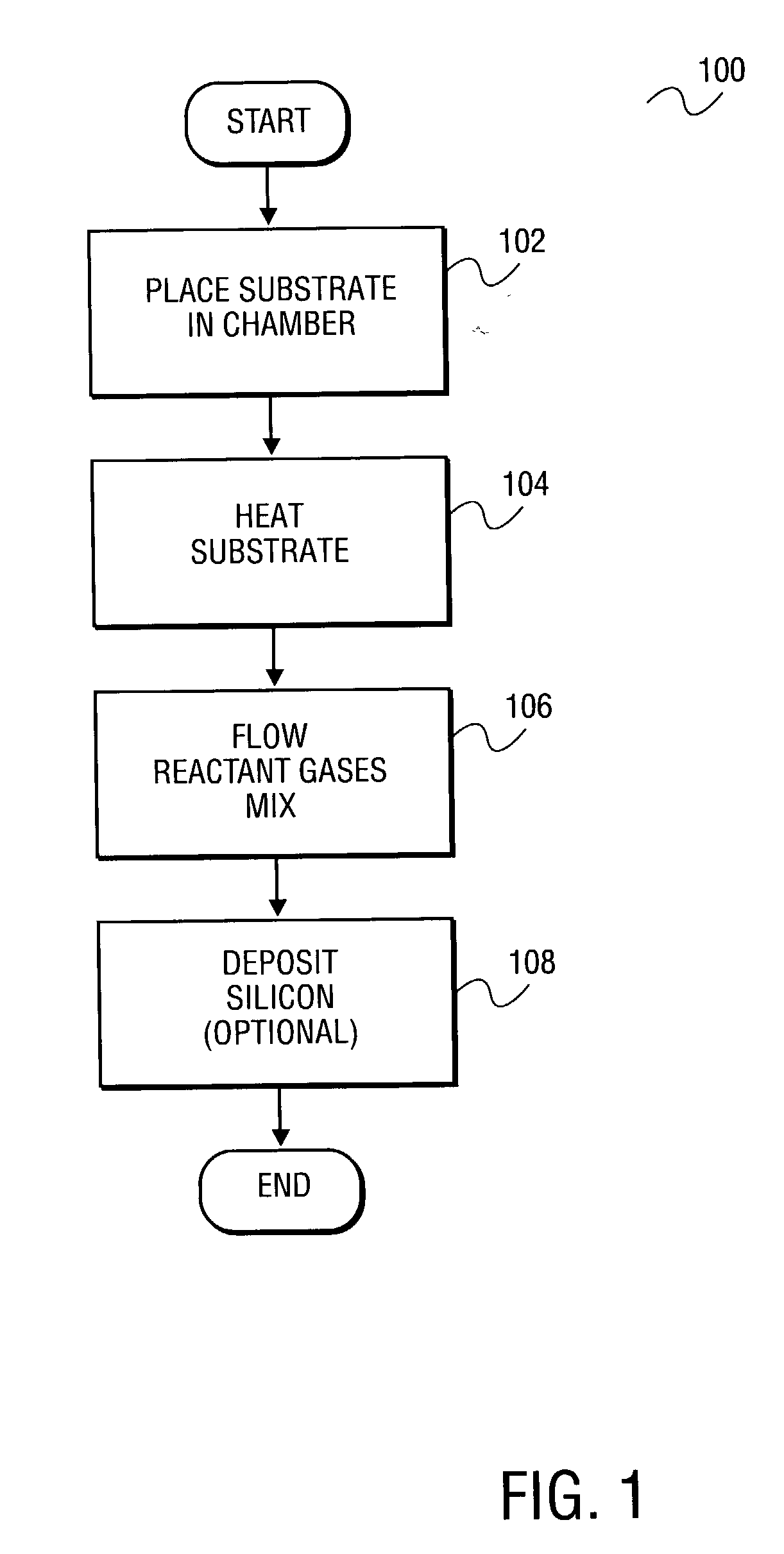
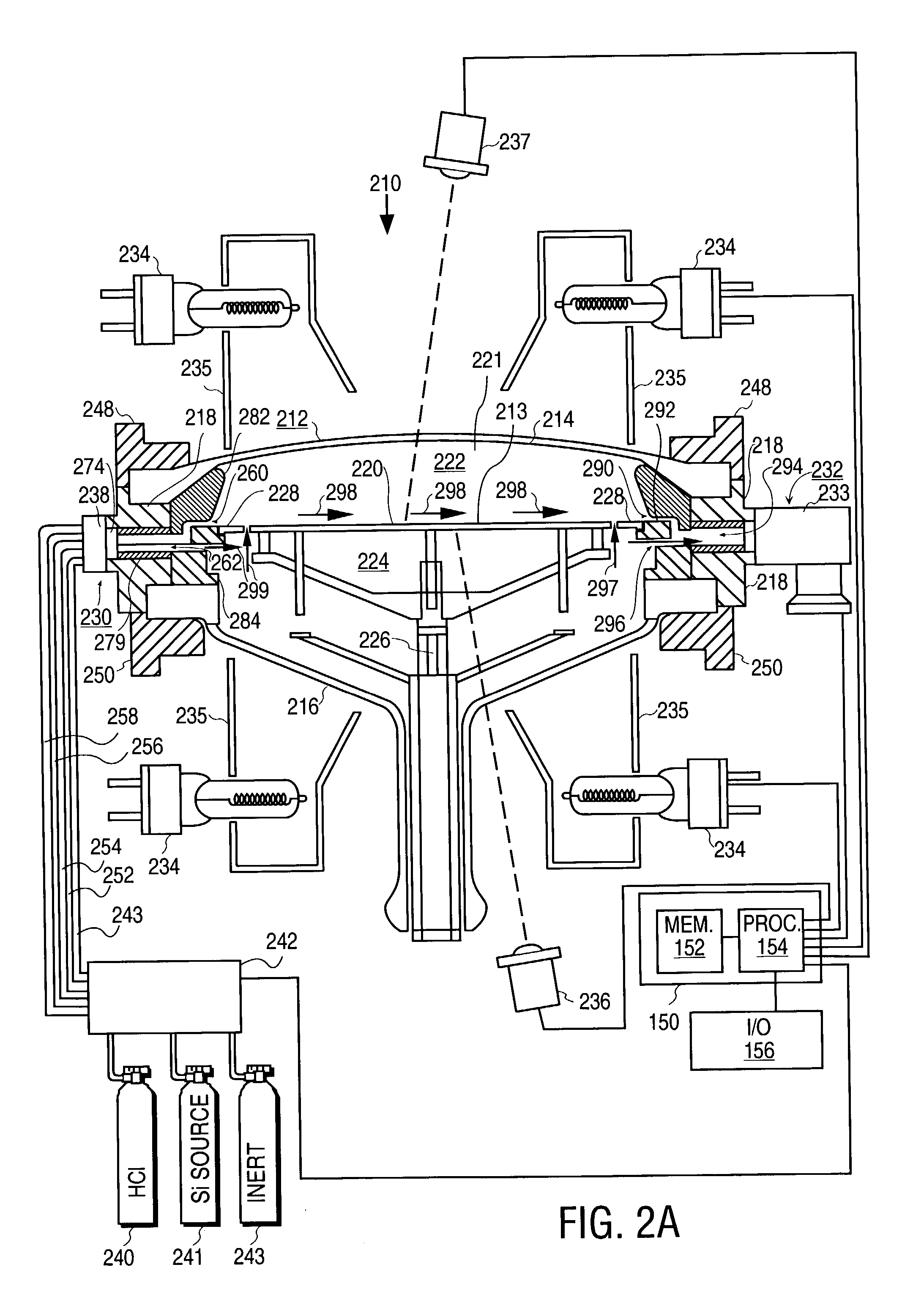
A method of smoothing a silicon surface formed on a substrate. According to the present invention a substrate having a silicon surface is placed into a chamber and heated to a temperature of between 1000°-1300° C. While the substrate is heated to a temperature between 1000°-1300° C., the silicon surface is exposed to a gas mix comprising H2 and HCl in the chamber to smooth the silicon surface.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION +1
Method and apparatus for destroying dividing cells
InactiveUS7333852B2Eliminate growthAccurate and effectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyPresent methodDividing cell
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for selectively destroying dividing cells in living tissue formed of dividing cells and non-dividing cells. The dividing cells contain polarizable intracellular members and during late anaphase or telophase, the dividing cells are connected to one another by a cleavage furrow. According to the present method the living tissue is subjected to electric field conditions sufficient to cause movement of the polarizable intracellular members toward the cleavage furrow in response to a non-homogenous electric field being induced in the dividing cells. The non-homogenous electric field produces an increased density electric field in the region of the cleavage furrow. The movement of the polarizable intracellular members towards the cleavage furrow causes the break down thereof which results in destruction of the dividing cells, while the non-dividing cells of the living tissue remain intact.
Owner:NOVOCURE GMBH
Method of making thin silicon sheets for solar cells
InactiveUS7169669B2Reduce wasteReduce thicknessPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsThin layerSolar cell
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Apparatus and method for surface finishing a silicon film
InactiveUS20020090818A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface finishSilicon membrane
A method of smoothing a silicon surface formed on a substrate. According to the present invention a substrate having a silicon surface is placed into a chamber and heated to a temperature of between 1000°-1300° C. While the substrate is heated to a temperature between 1000°-1300° C., the silicon surface is exposed to a gas mix comprising H2 and HCl in the chamber to smooth the silicon surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
Large area nitride crystal and method for making it
Techniques for processing materials in supercritical fluids including processing in a capsule disposed within a high-pressure apparatus enclosure are disclosed. The disclosed techniques are useful for growing crystals of GaN, AlN, InN, and their alloys, including InGaN, AlGaN, and AlInGaN for the manufacture of bulk or patterned substrates, which in turn can be used to make optoelectronic devices, lasers, light emitting diodes, solar cells, photoelectrochemical water splitting and hydrogen generation devices, photodetectors, integrated circuits, and transistors.
Owner:SLT TECH
Semi-insulating silicon carbide without vanadium domination
InactiveUS6396080B2High-frequency operationReduce complicationsPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDevice formRoom temperature
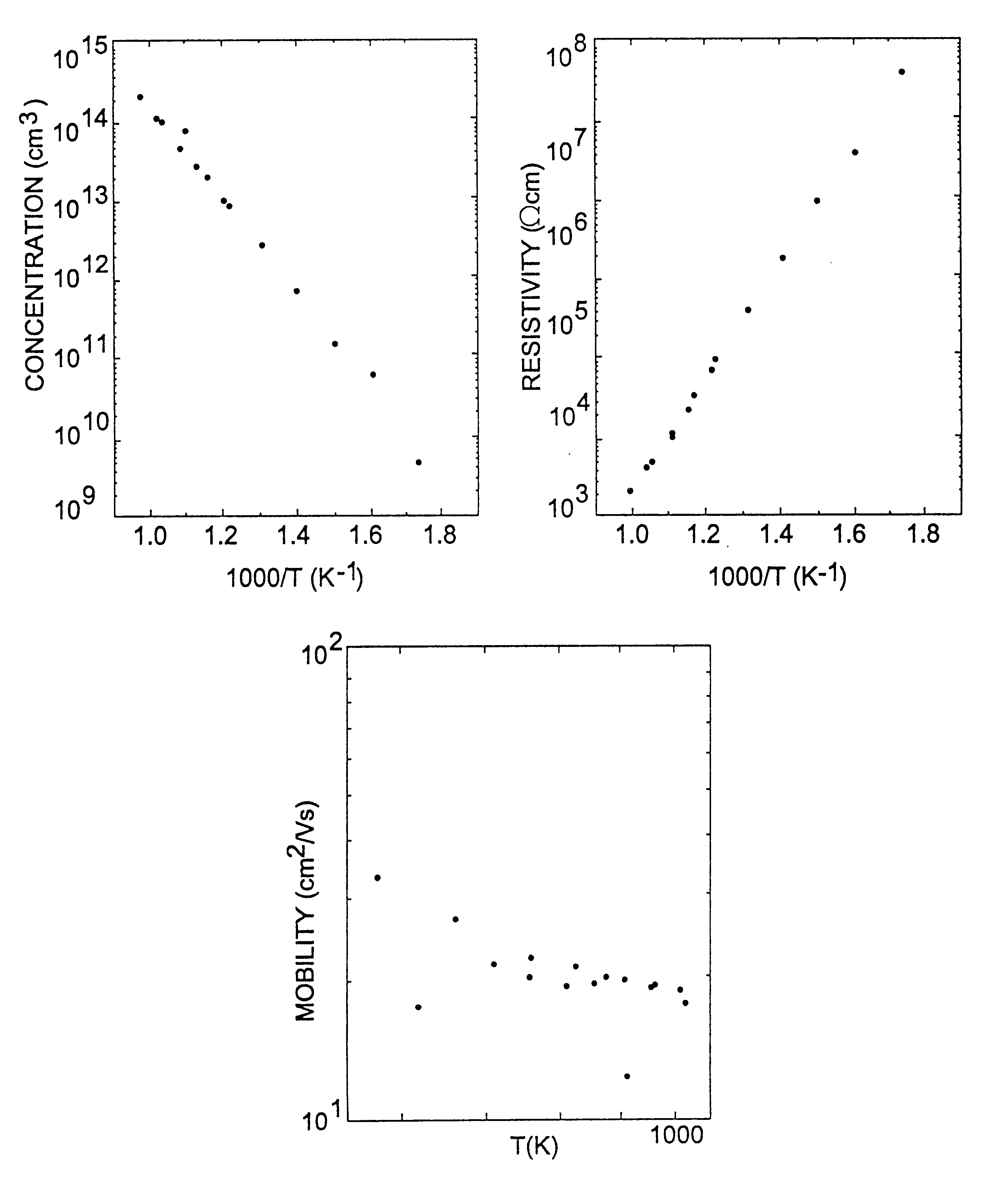
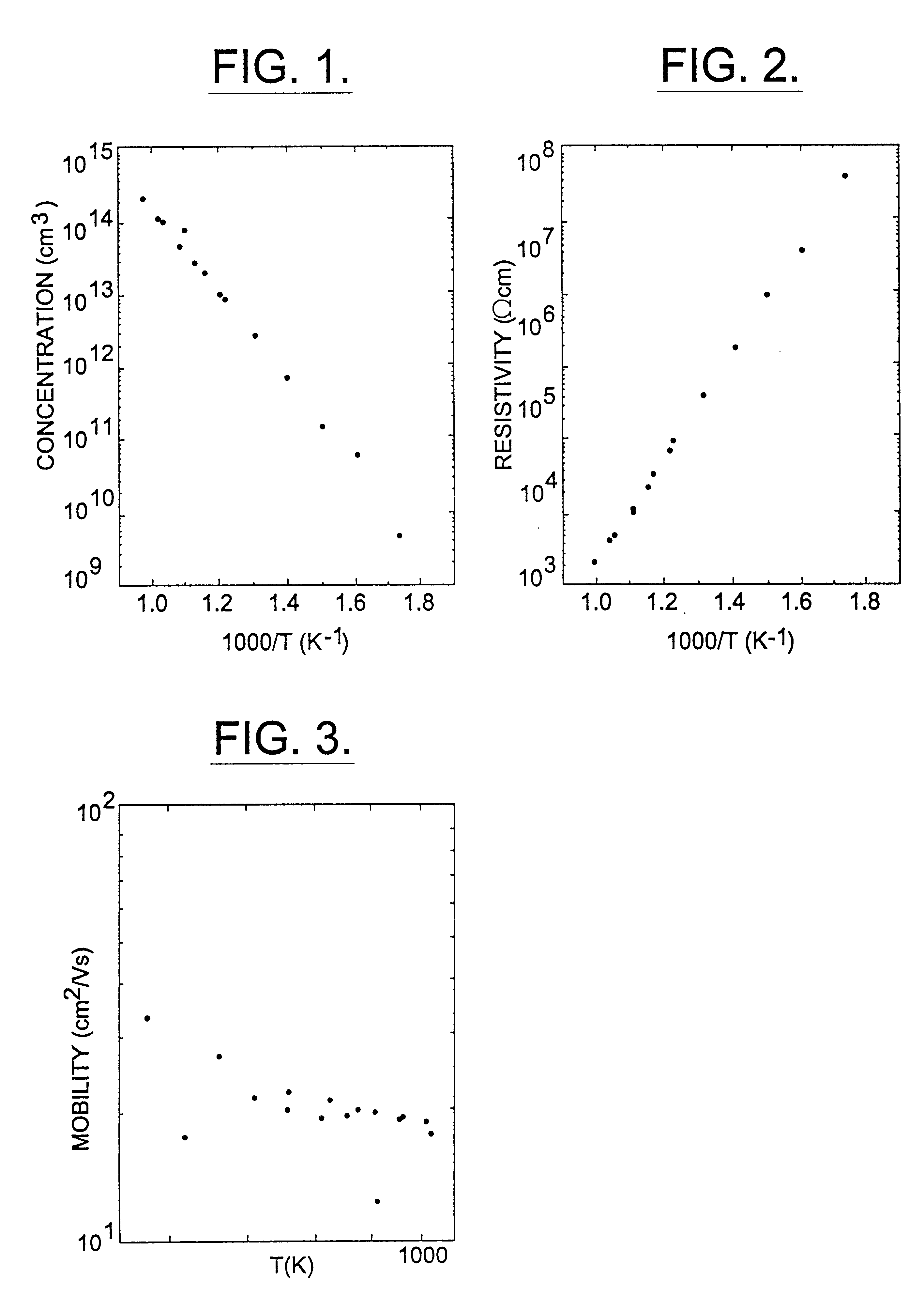
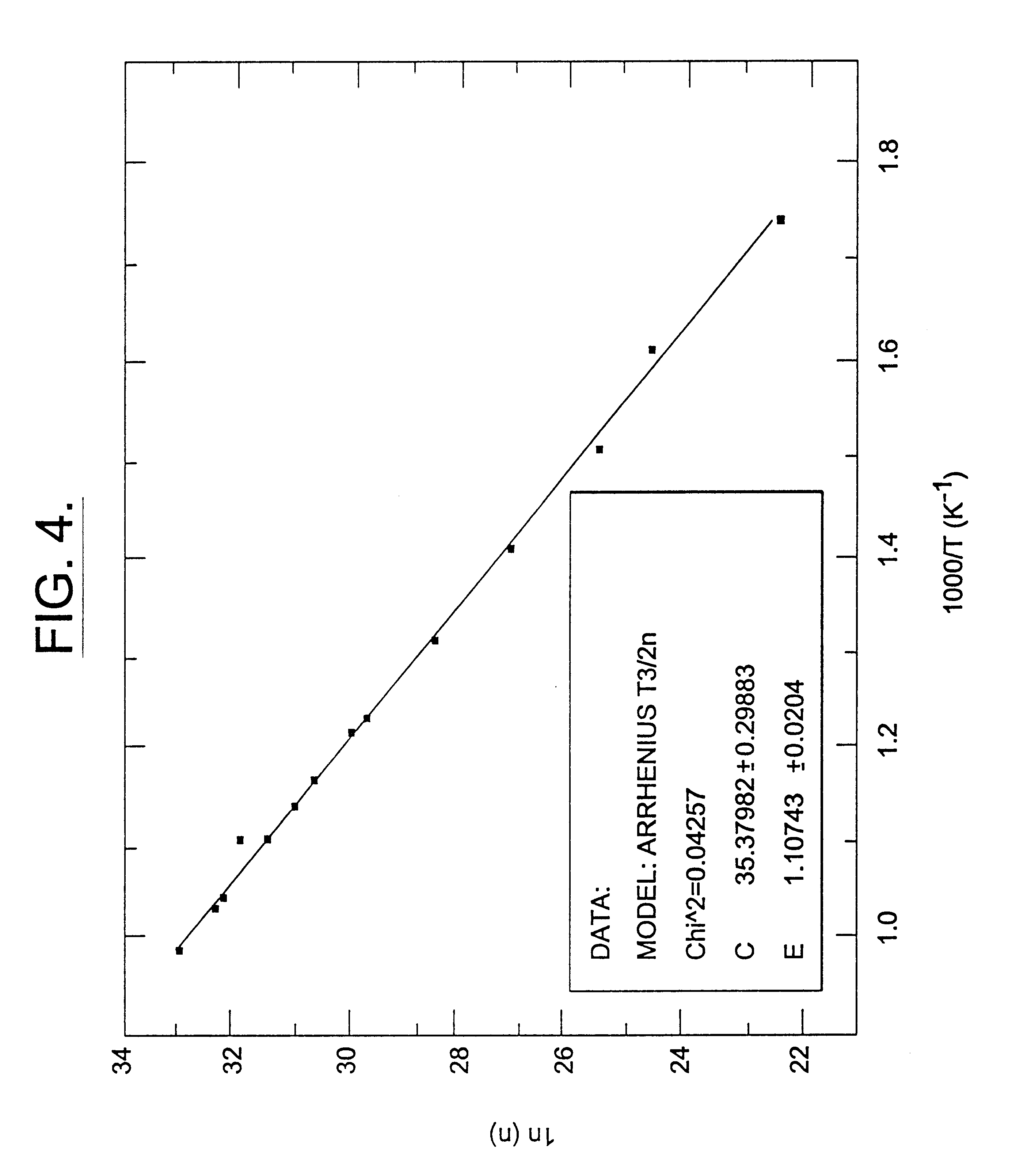
A semi-insulating bulk single crystal of silicon carbide is disclosed that has a resistivity of at least 5000 OMEGA-cm at room temperature and a concentration of trapping elements that create states at least 700 meV from the valence or conduction band that is below the amounts that will affect the resistivity of the crystal, preferably below detectable levels. A method of forming the crystal is also disclosed, along with some resulting devices that take advantage of the microwave frequency capabilities of devices formed using substrates according to the invention.
Owner:CREE INC
Apparatus and method for surface finishing a silicon film
InactiveUS20040053515A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface finishSilicon membrane
A method of treating a silicon surface of a substrate that includes heating the substrate in a process chamber to a temperature, exposing a first area adjacent to the silicon surface to a first gas mixture comprising an etchant, a silicon source gas, and a carrier, exposing a second area adjacent to the silicon surface to a second gas mixture, wherein the second gas mixture is different from the first gas mixture.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for reducing defect concentrations in crystals
InactiveUS7175704B2Polycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSufficient timeDiamond crystal
A method for removing defects at high pressure and high temperature (HP / HT) or for relieving strain in a non-diamond crystal commences by providing a crystal, which contains defects, and a pressure medium. The crystal and the pressure medium are disposed in a high pressure cell and placed in a high pressure apparatus, for processing under reaction conditions of sufficiently high pressure and high temperature for a time adequate for one or more of removing defects or relieving strain in the single crystal.
Owner:DIAMOND INNOVATIONS INC
Directed assembly of highly-organized carbon nanotube architectures
A method of controllably aligning carbon nanotubes to a template structure to fabricate a variety of carbon nanotube containing structures and devices having desired characteristics is provided. The method allows simultaneous, selective growth of both vertically and horizontally controllably aligned nanotubes on the template structure but not on a substrate in a single process step.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com