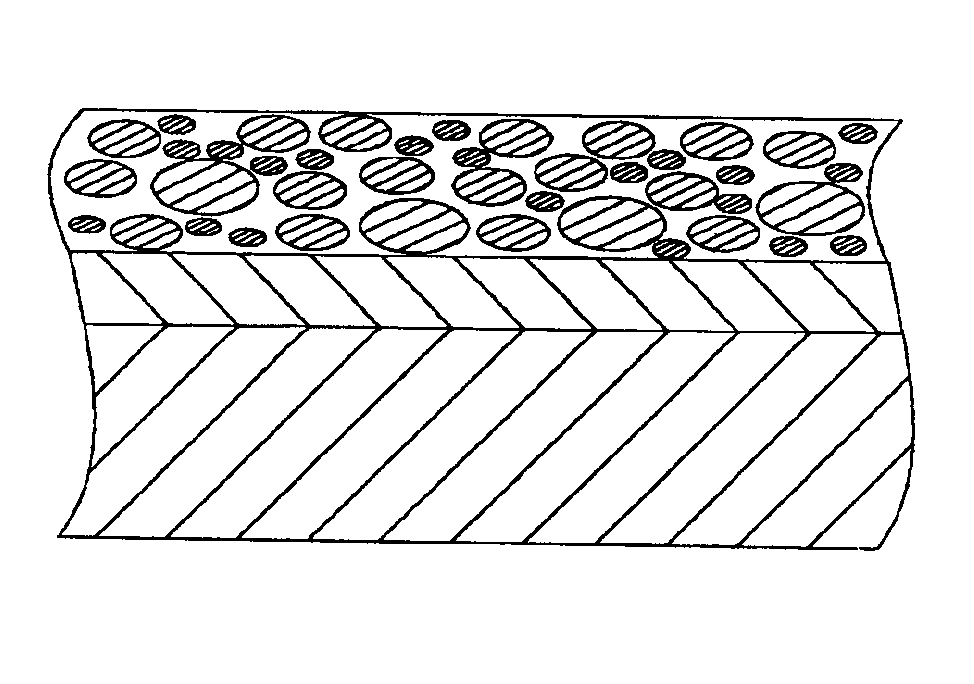
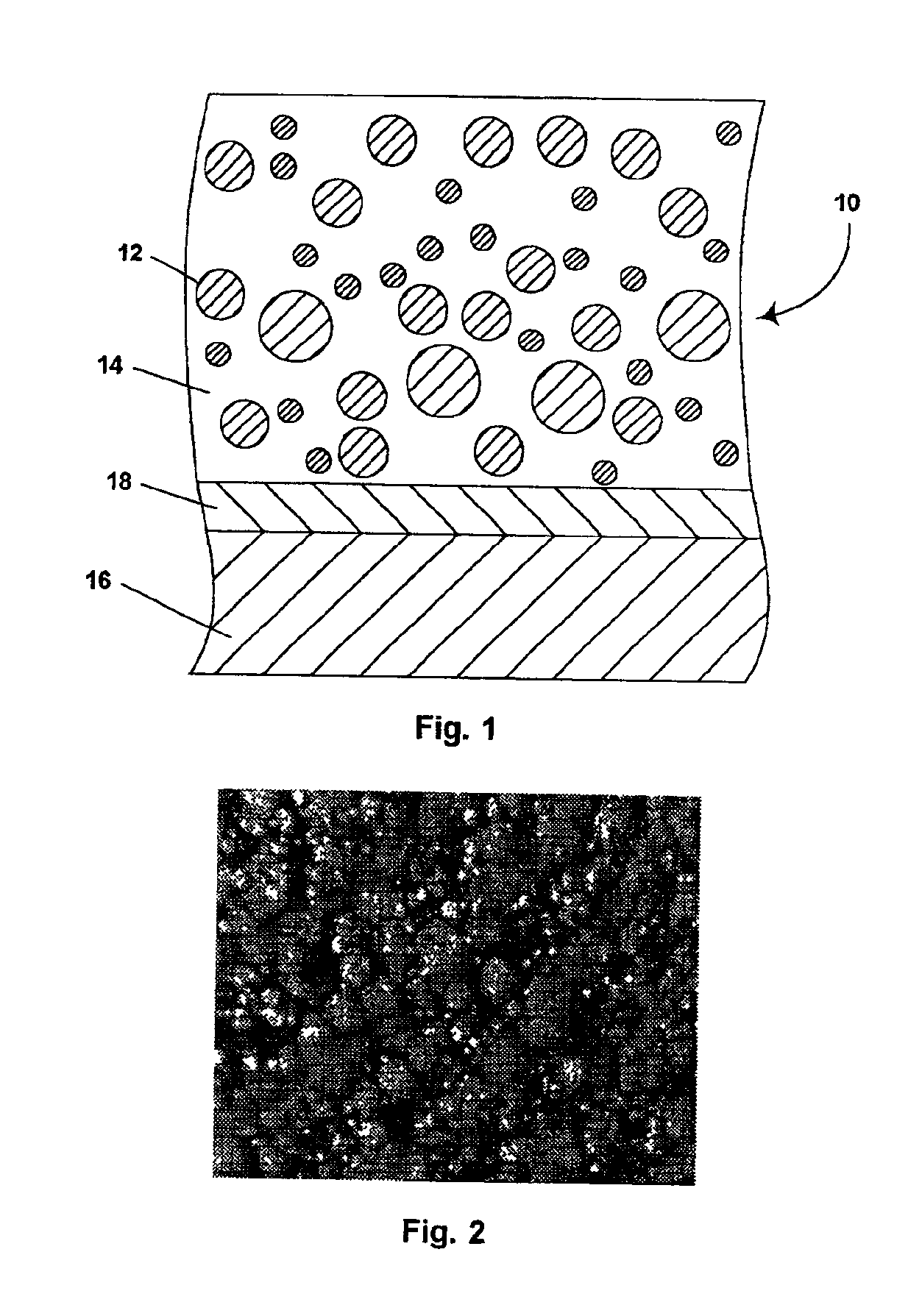
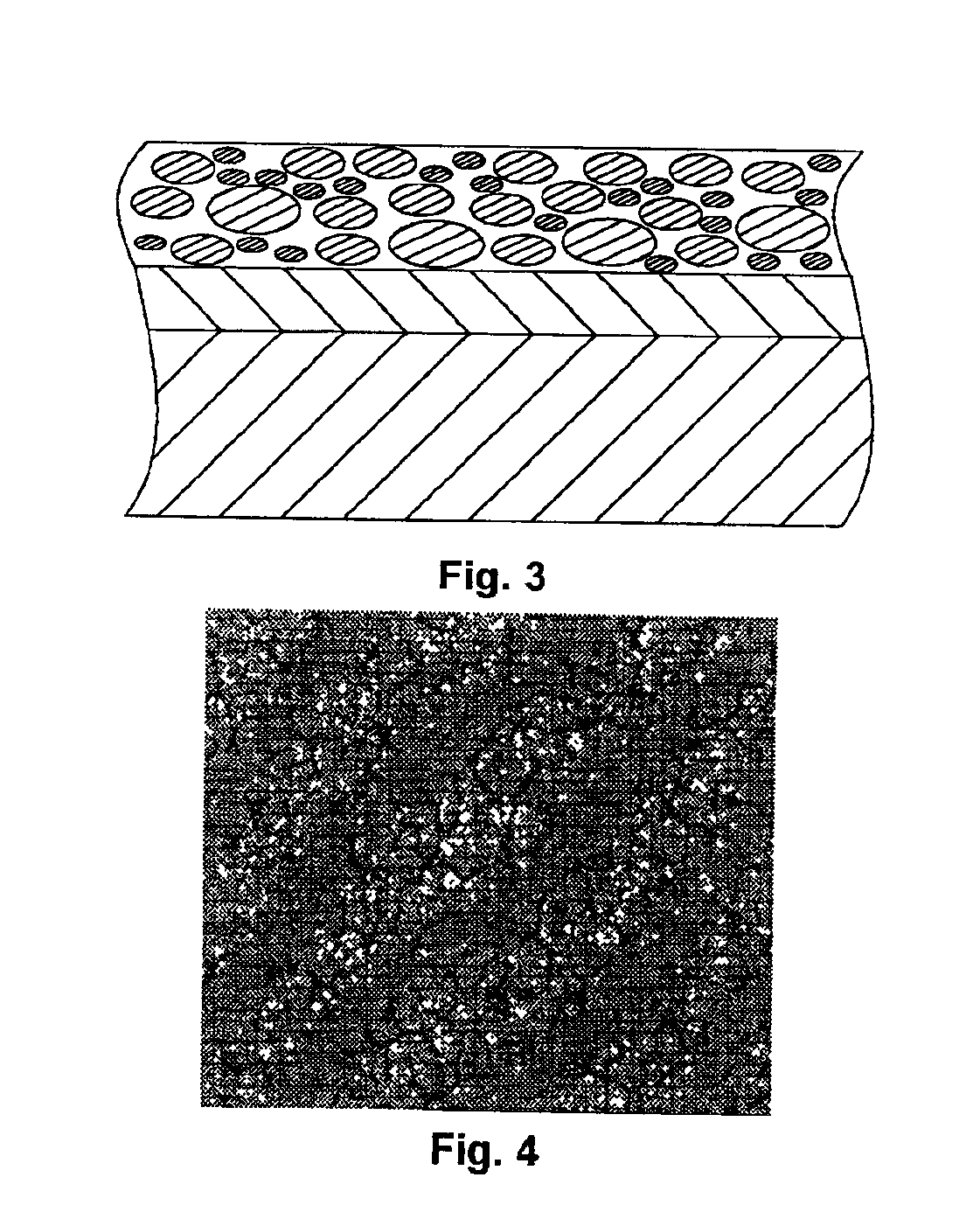
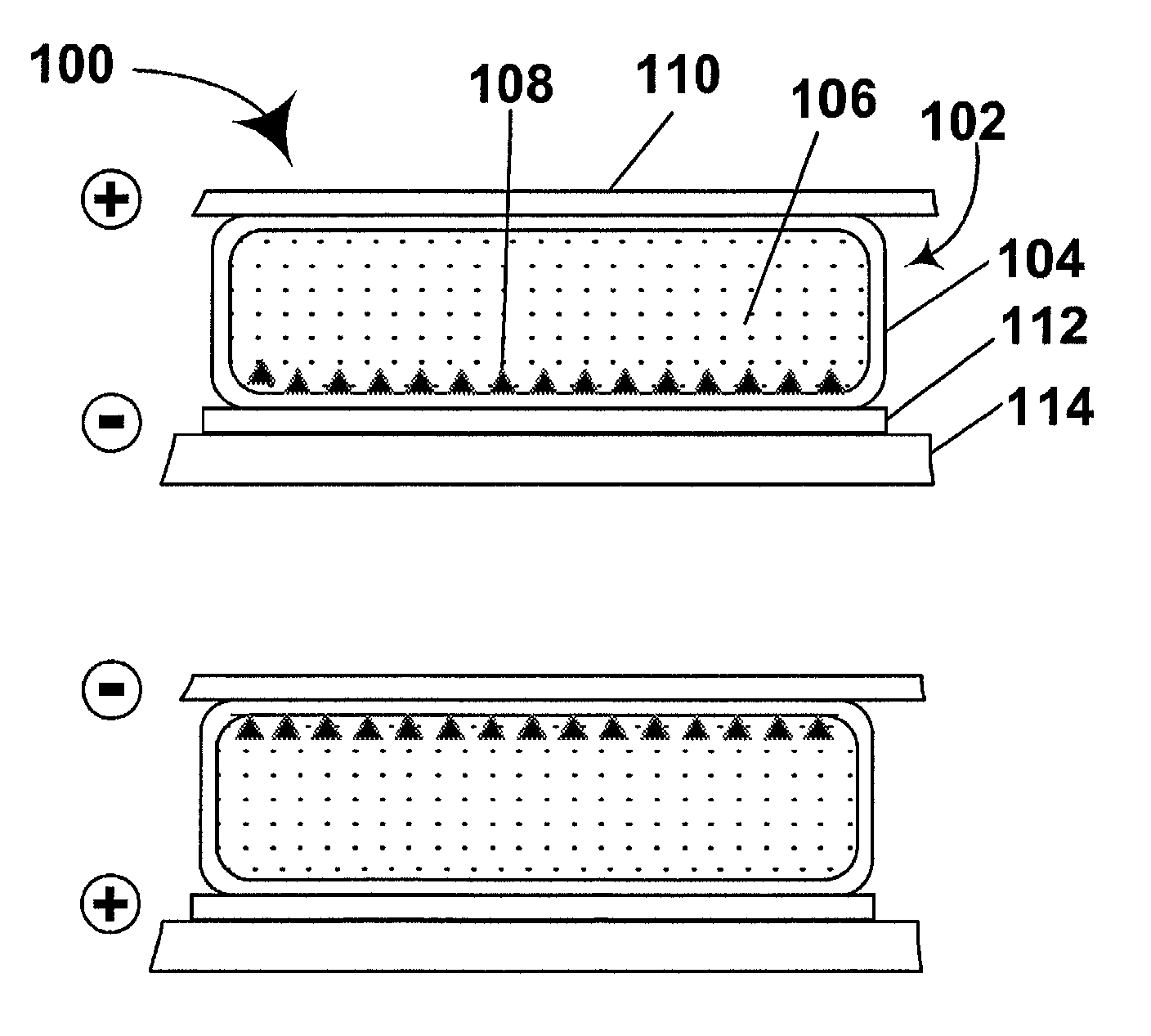
Patents
Literature
38510 results about "Electric field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
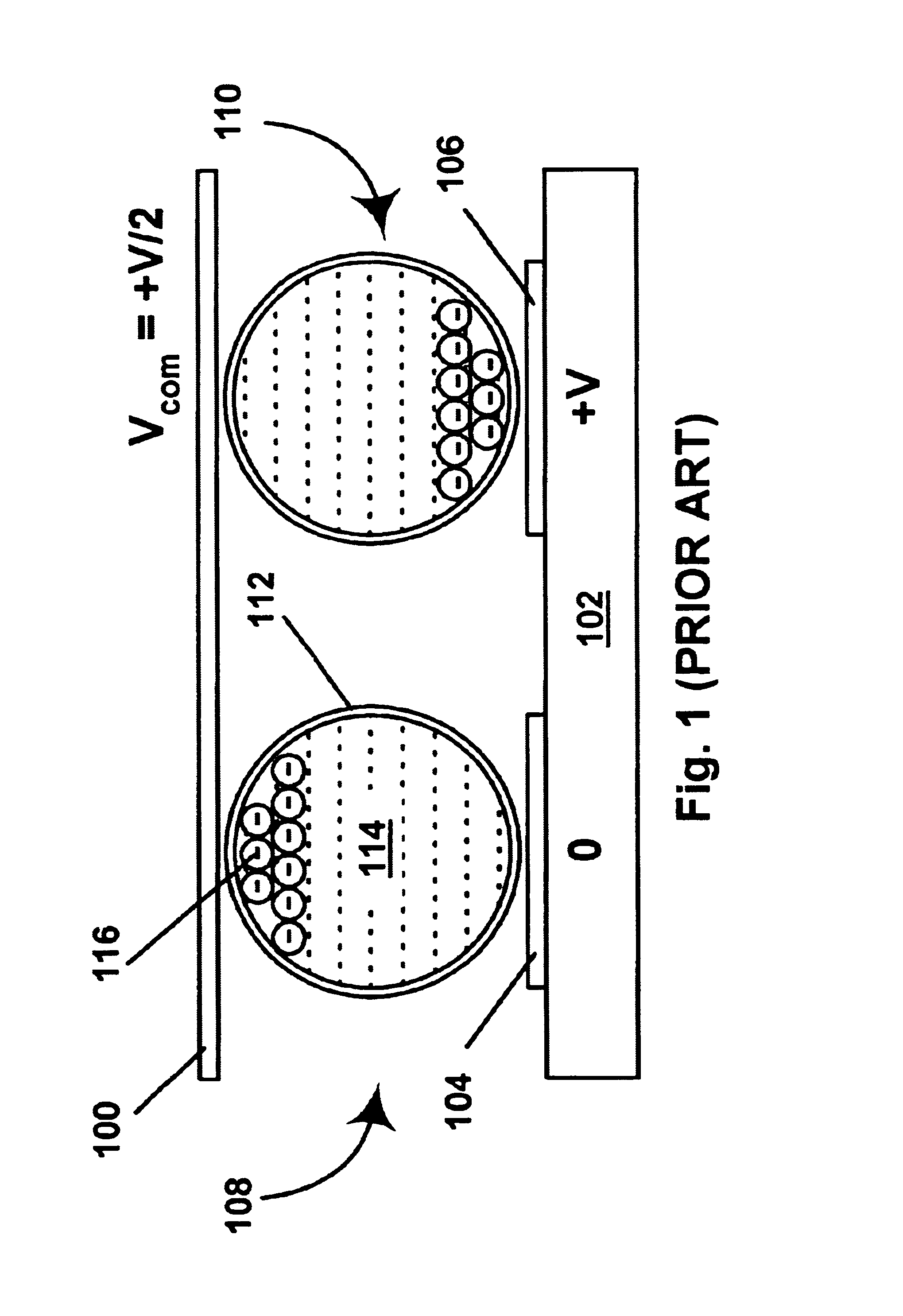
An electric field surrounds an electric charge, and exerts force on other charges in the field, attracting or repelling them. Electric field is sometimes abbreviated as E-field. The electric field is defined mathematically as a vector field that associates to each point in space the (electrostatic or Coulomb) force per unit of charge exerted on an infinitesimal positive test charge at rest at that point. The SI unit for electric field strength is volt per meter (V/m). Newtons per coulomb (N/C) is also used as a unit of electric field strength. Electric fields are created by electric charges, or by time-varying magnetic fields. Electric fields are important in many areas of physics, and are exploited practically in electrical technology. On an atomic scale, the electric field is responsible for the attractive force between the atomic nucleus and electrons that holds atoms together, and the forces between atoms that cause chemical bonding. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces (or interactions) of nature.
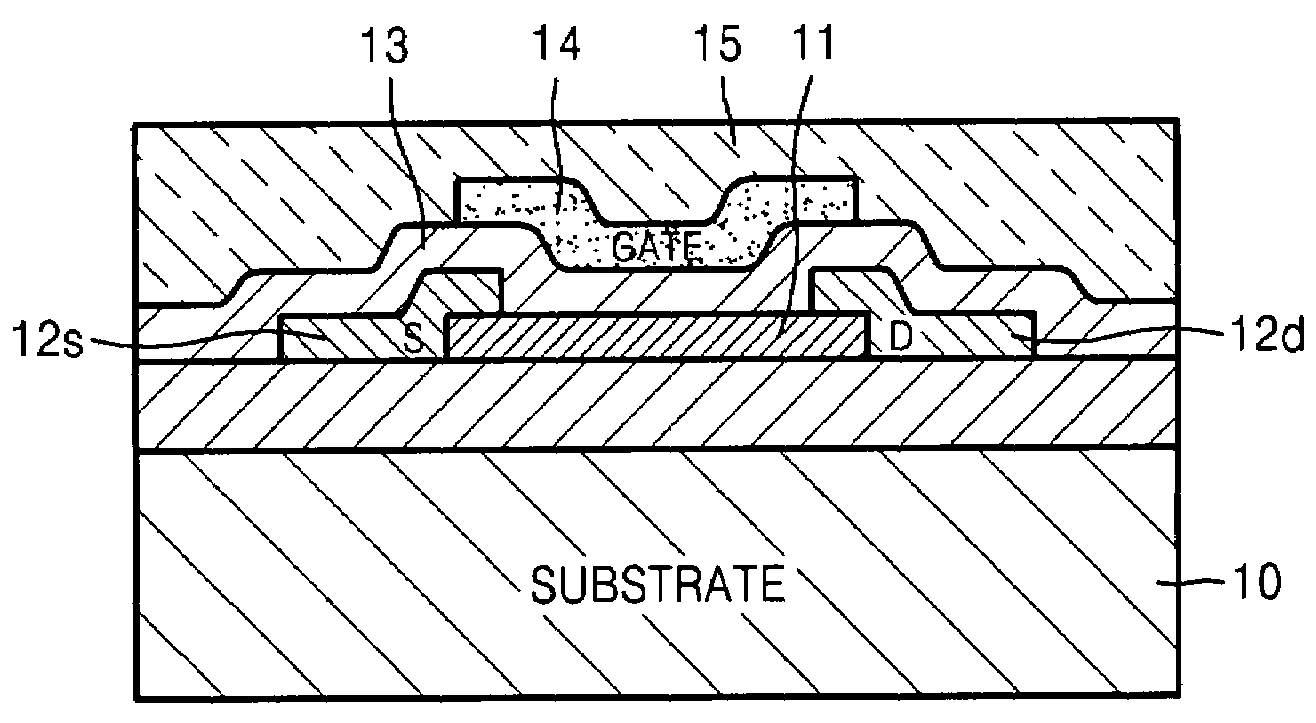
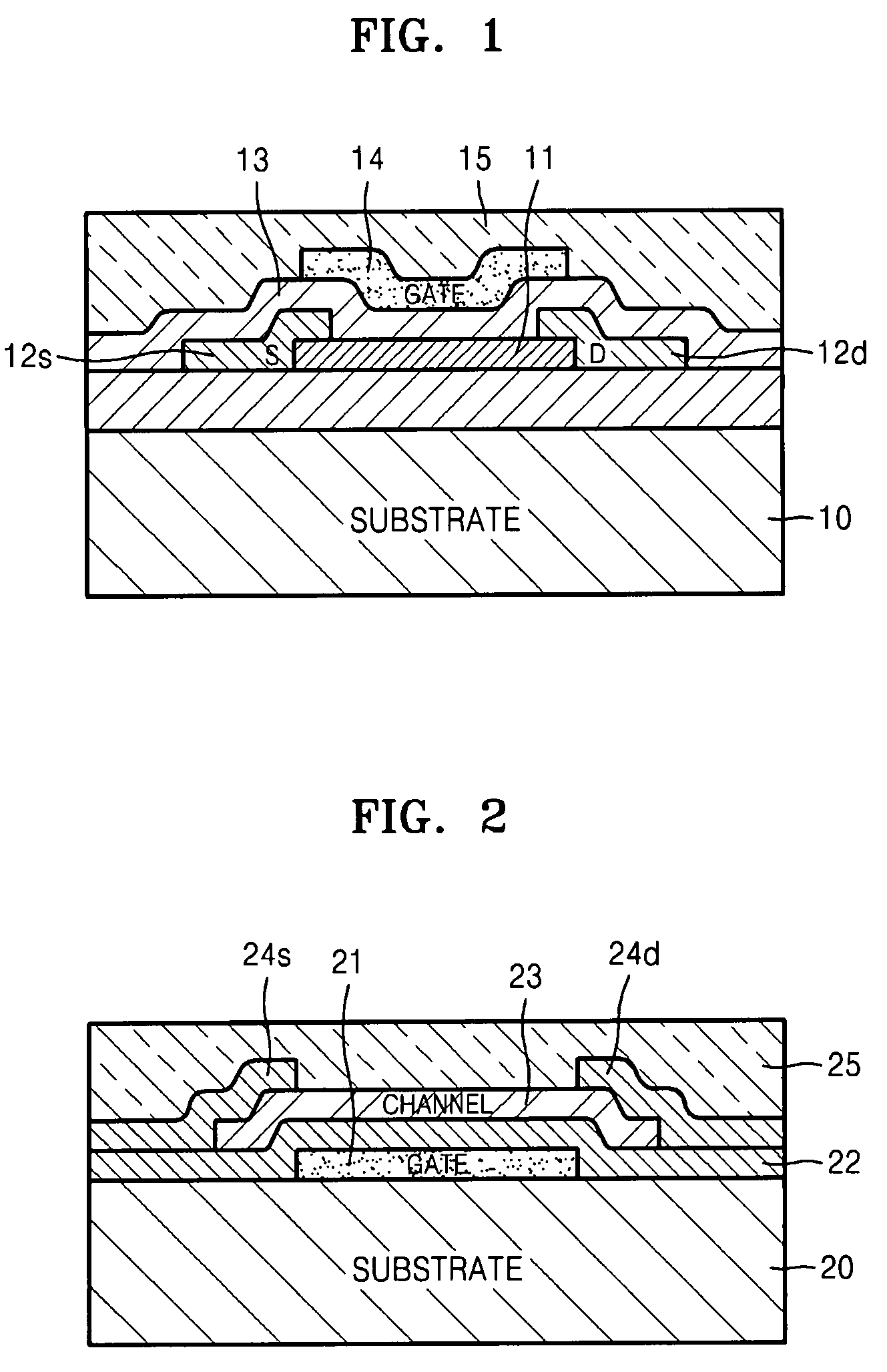
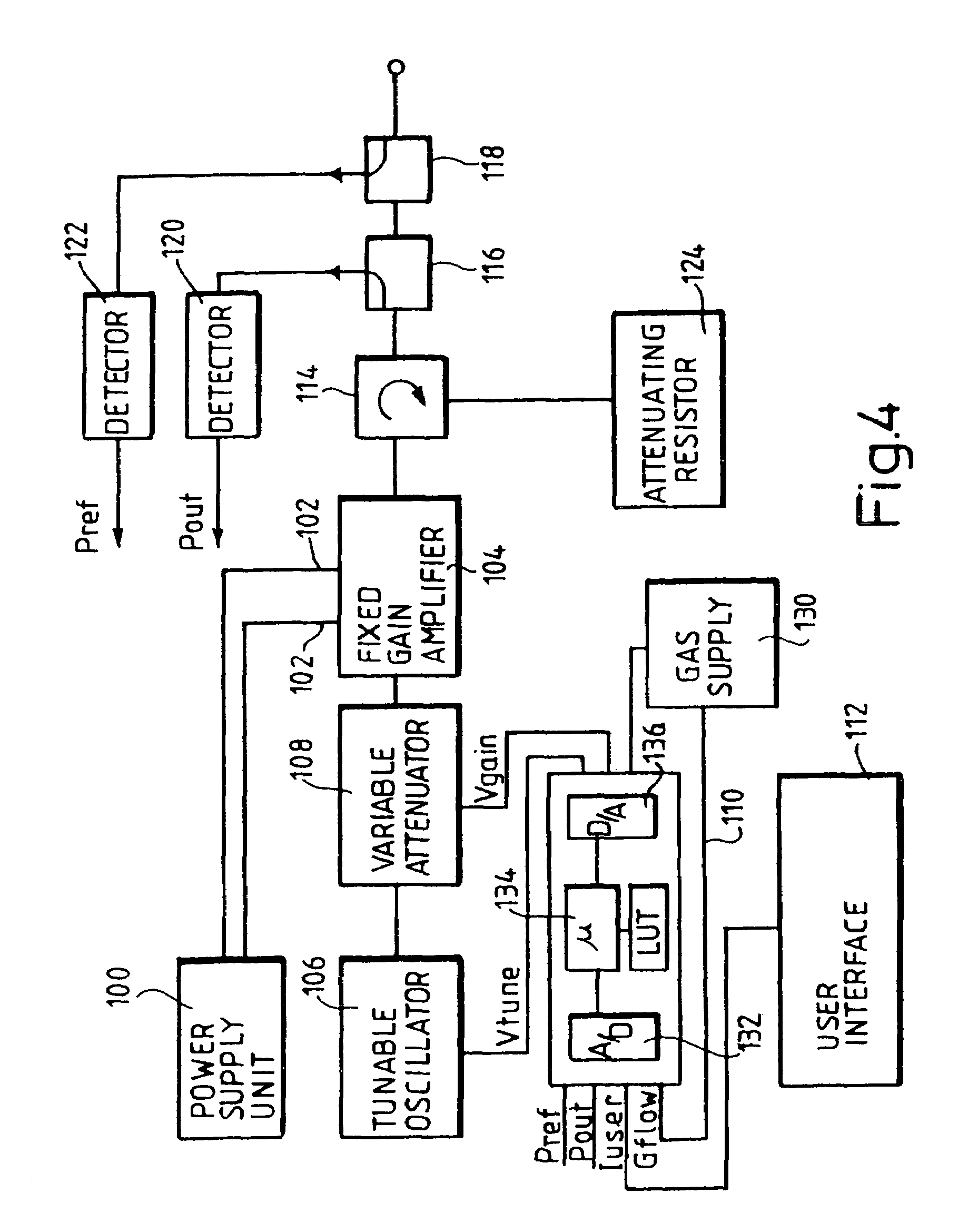
ZnO thin film transistor and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20070272922A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate insulatorEngineering
A zinc oxide (ZnO) thin film transistor (TFT) and method of forming the same are provided. The ZnO may include a ZnO semiconductor channel, a conductive ZnO gate forming an electric field around the ZnO semiconductor channel, an ZnO gate insulator interposed between the conductive ZnO gate and the ZnO semiconductor channel and an insulating ZnO passivation layer on the ZnO semiconductor channel, the conductive ZnO gate and the ZnO gate insulator to protect the ZnO semiconductor channel, the conductive ZnO gate, and the ZnO gate insulator. A thin film transistor (TFT) may be formed by forming a semiconductor channel, forming a conductive gate having an electric field around the semiconductor channel, forming a gate insulator between the conductive gate and the semiconductor channel, and forming an insulating passivation layer on the semiconductor channel, the conductive gate and the gate insulator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
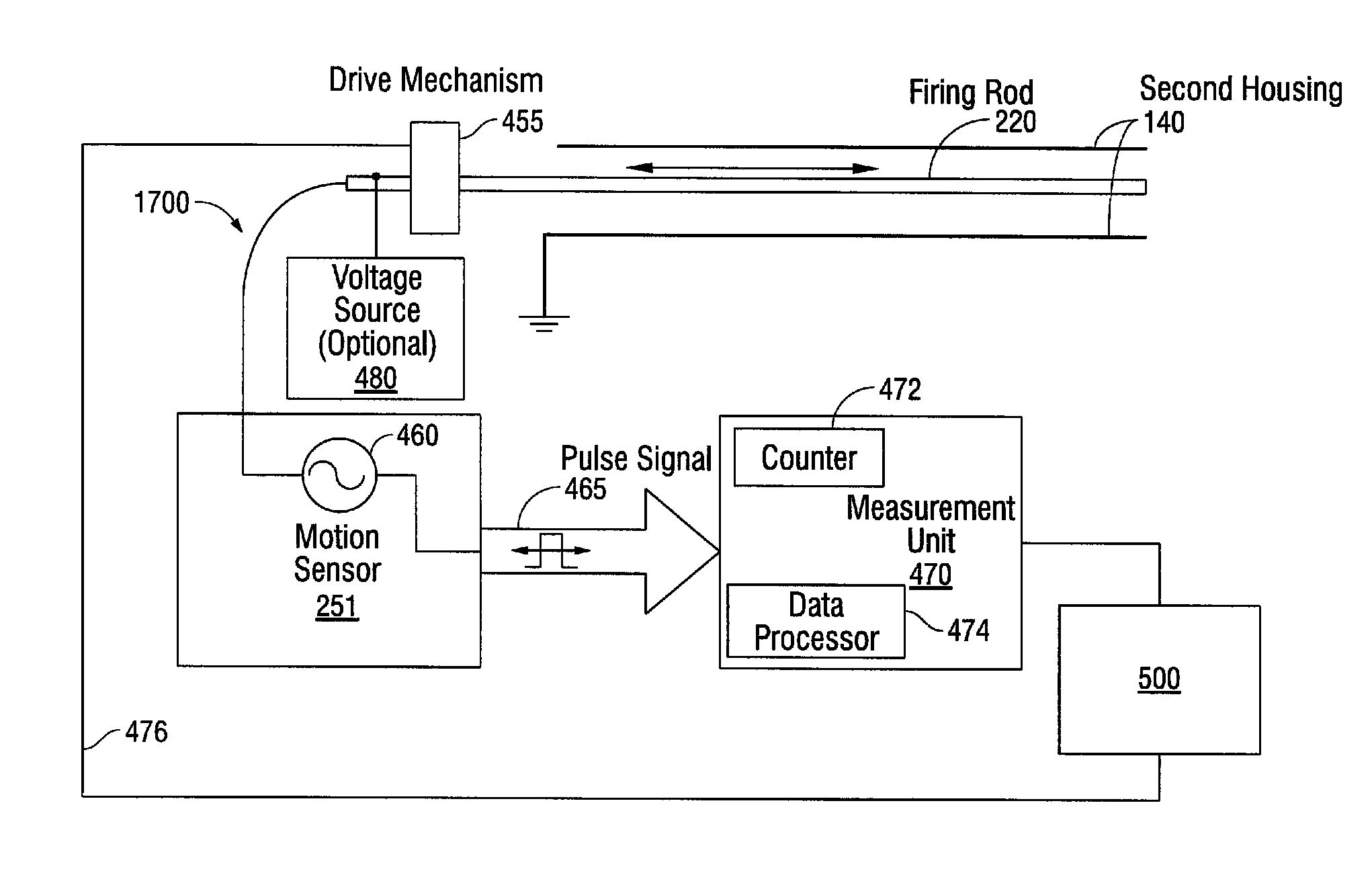
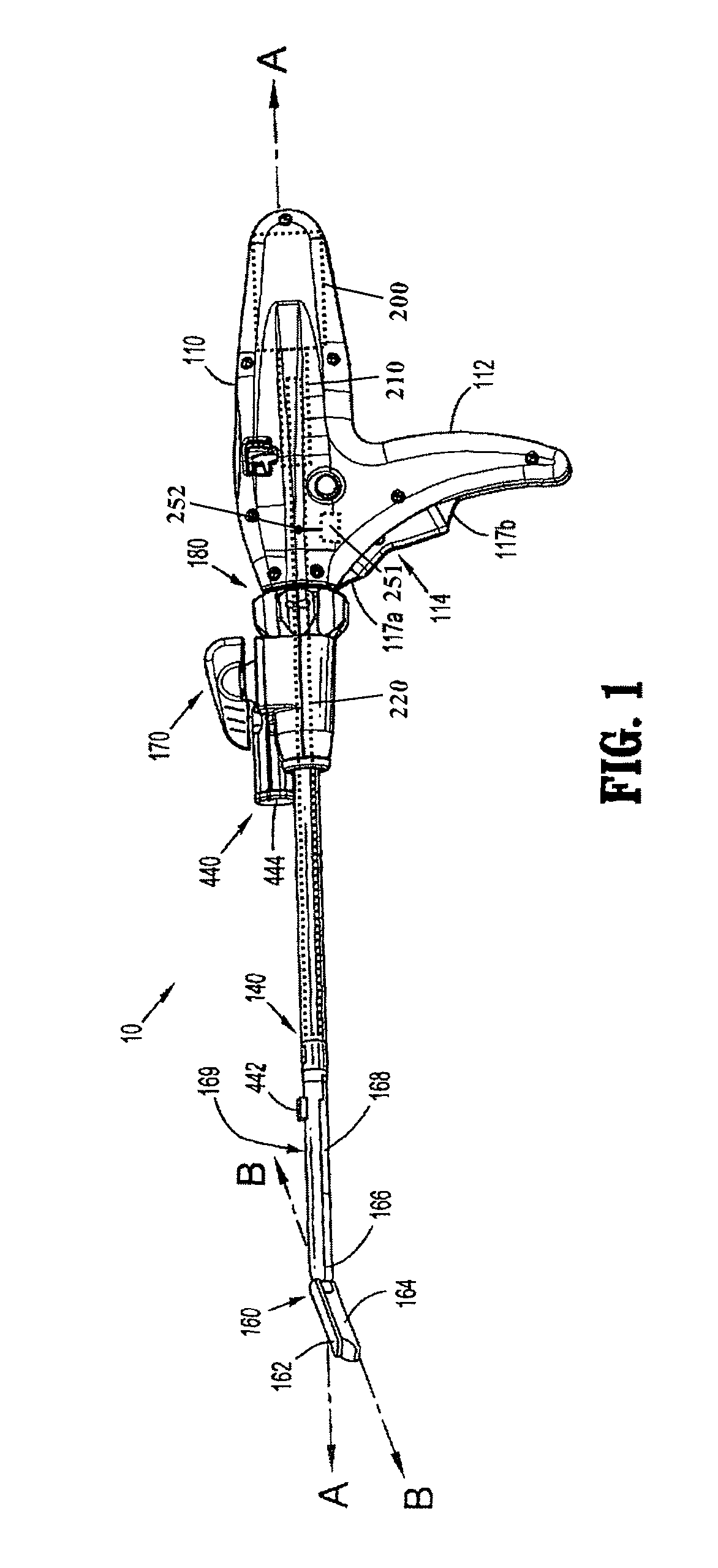
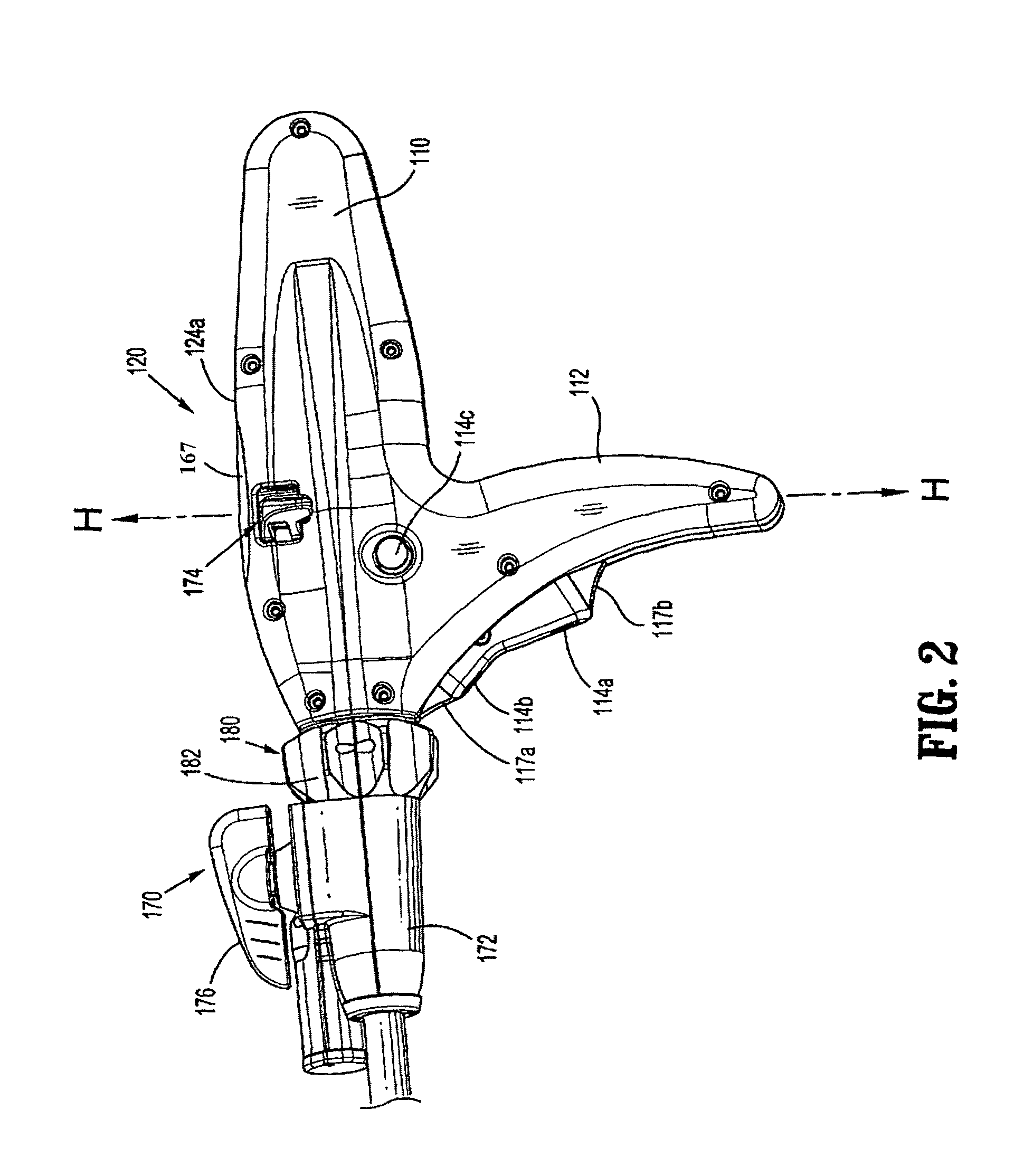
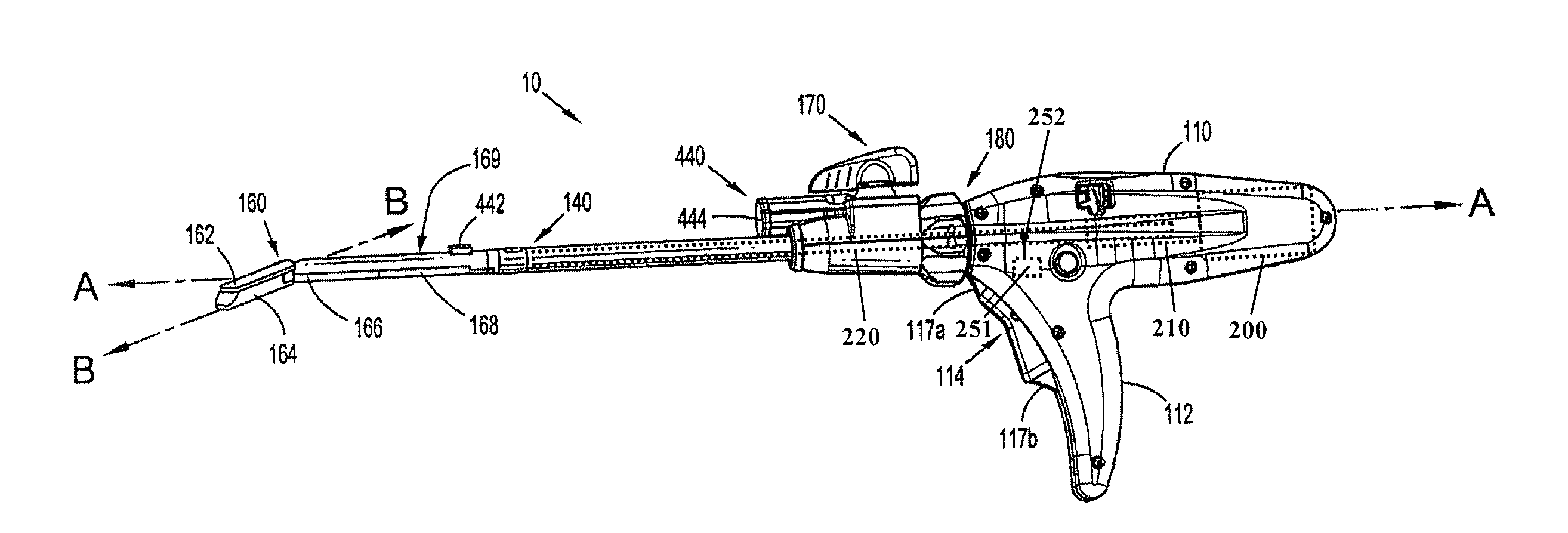
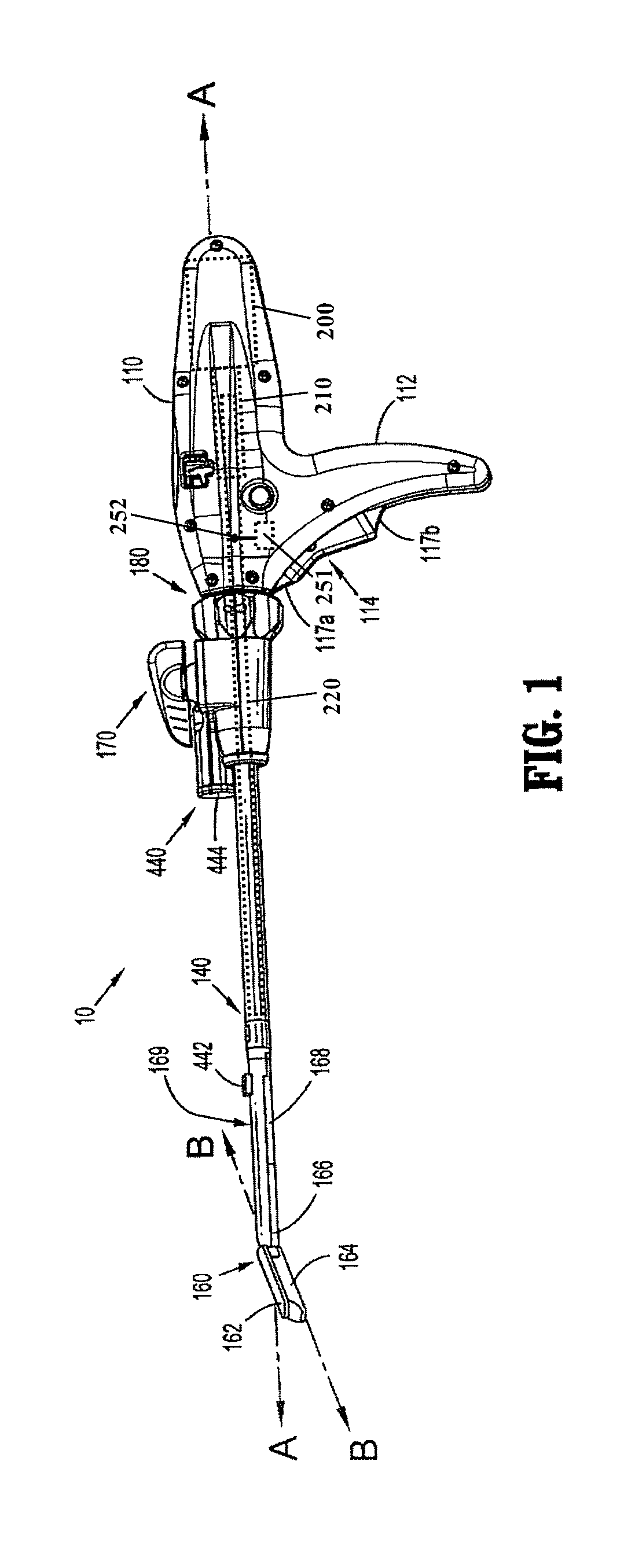
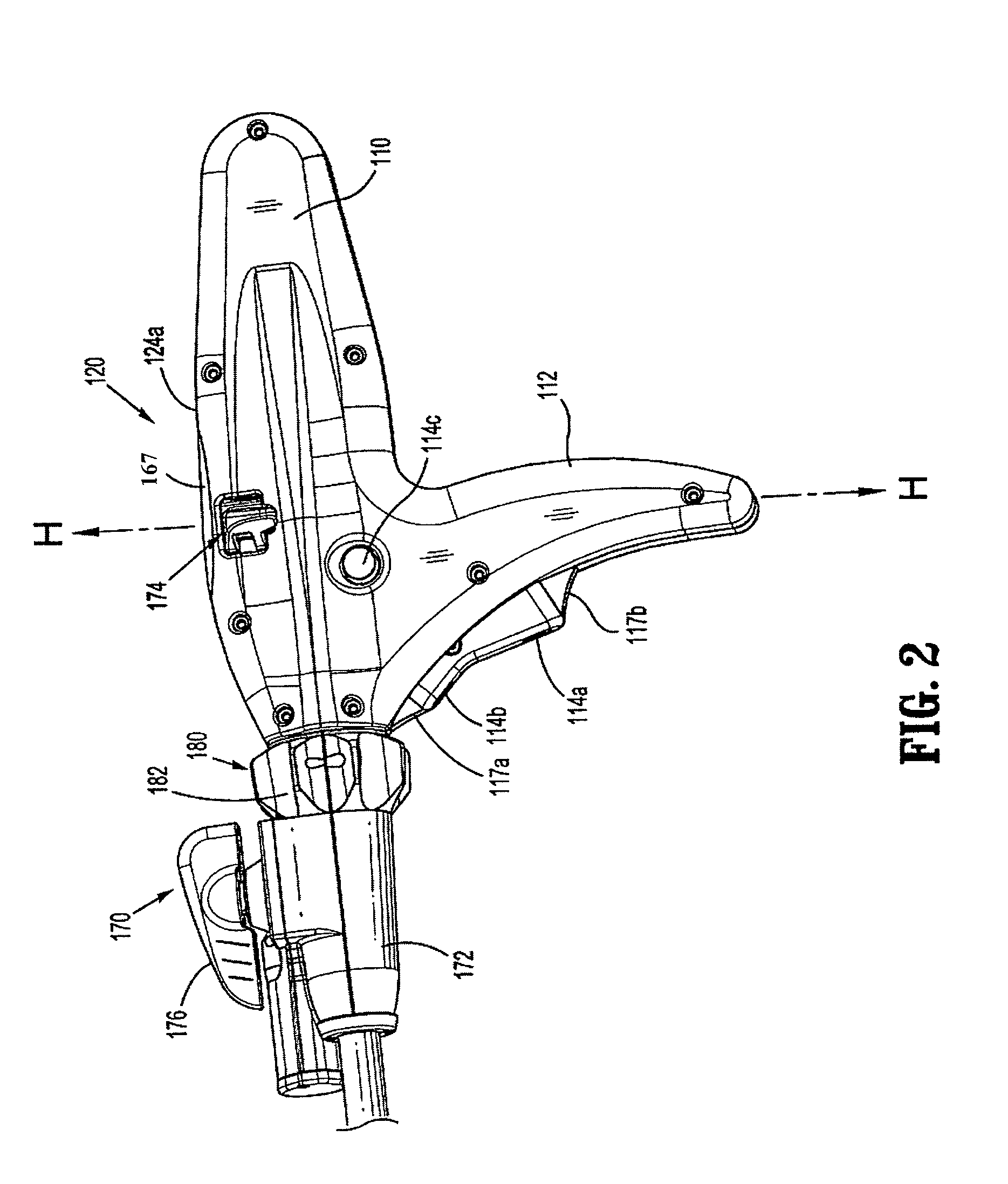
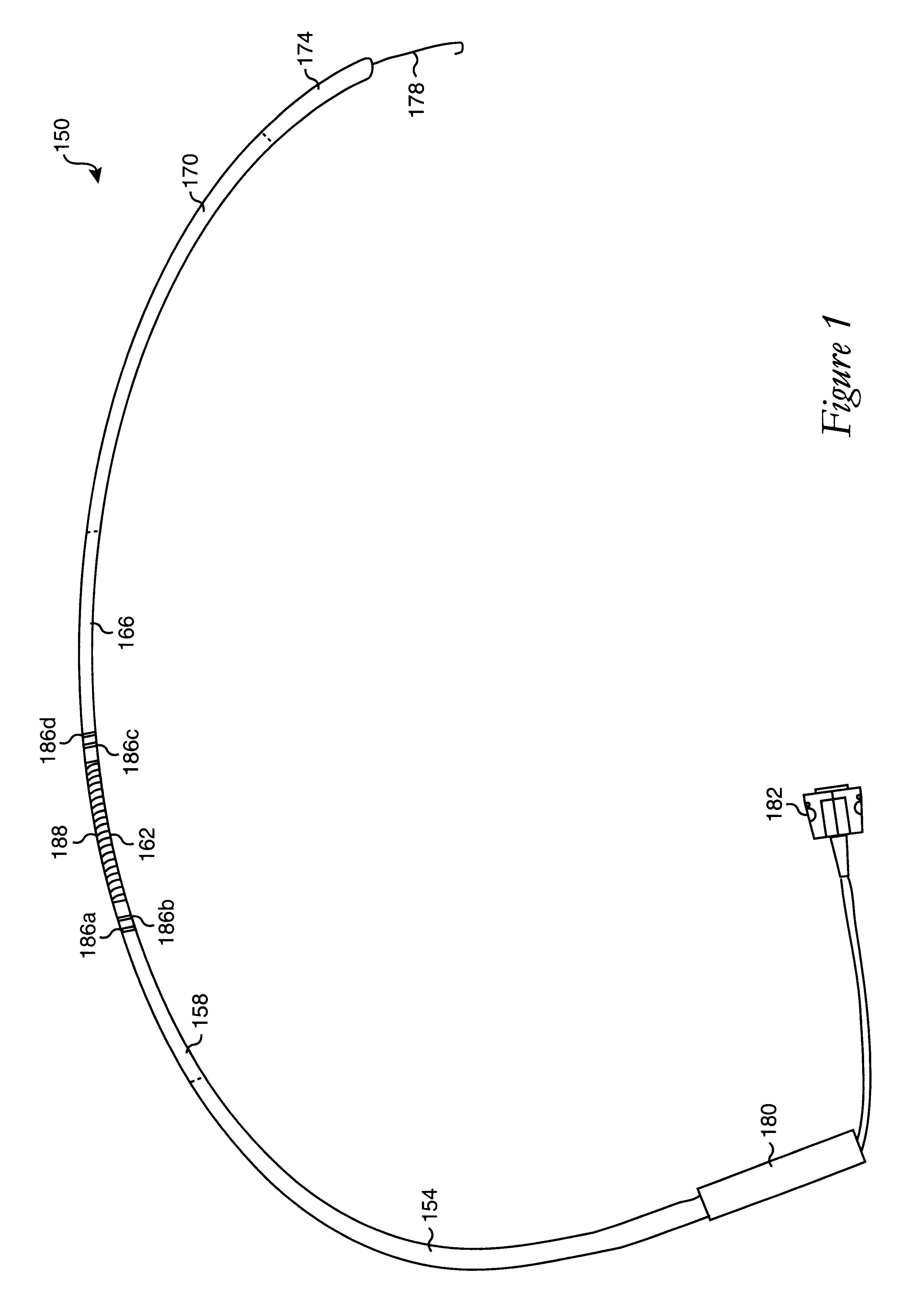
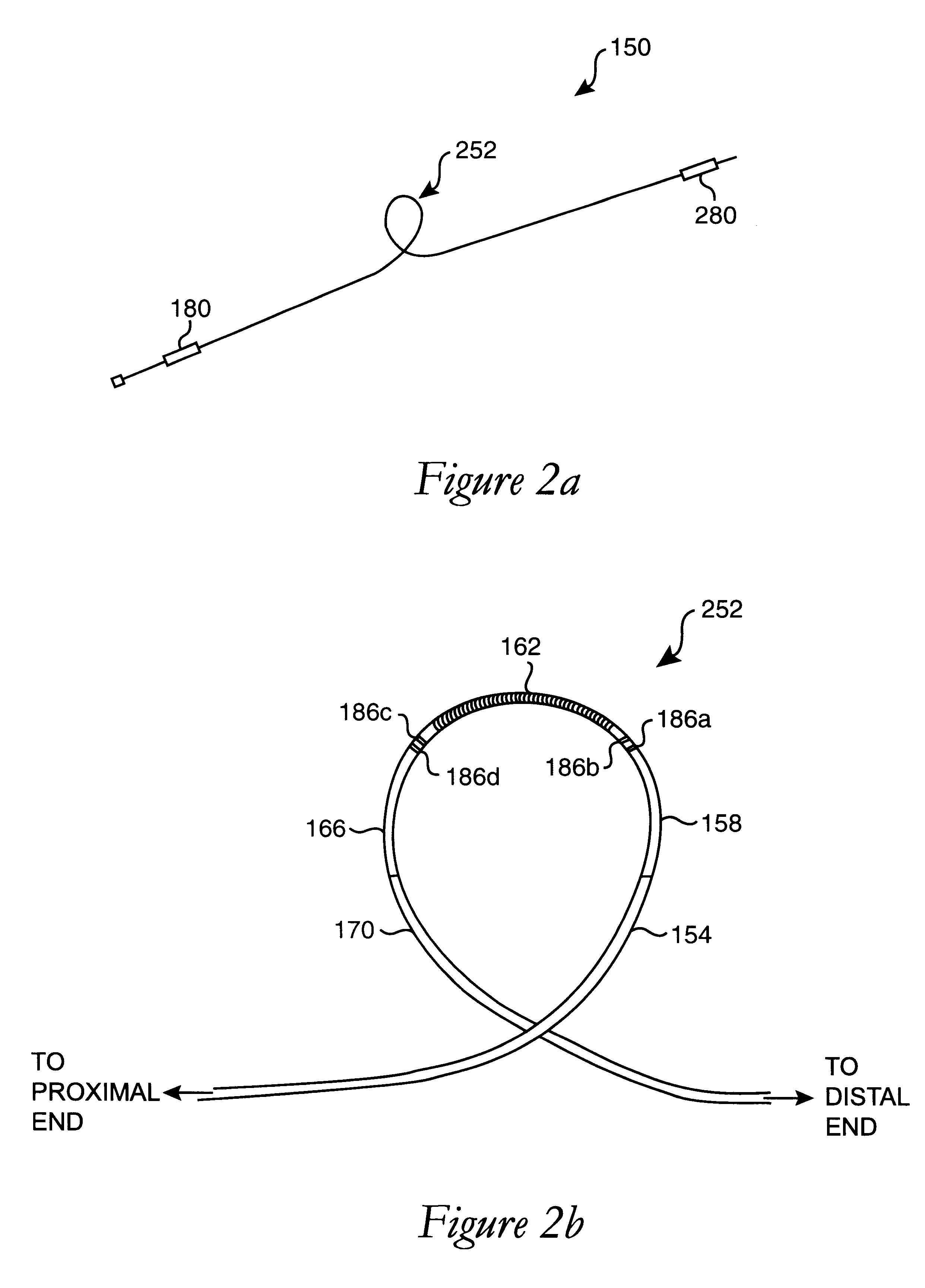
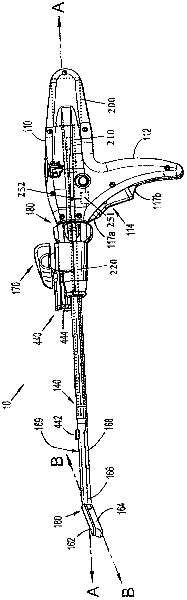
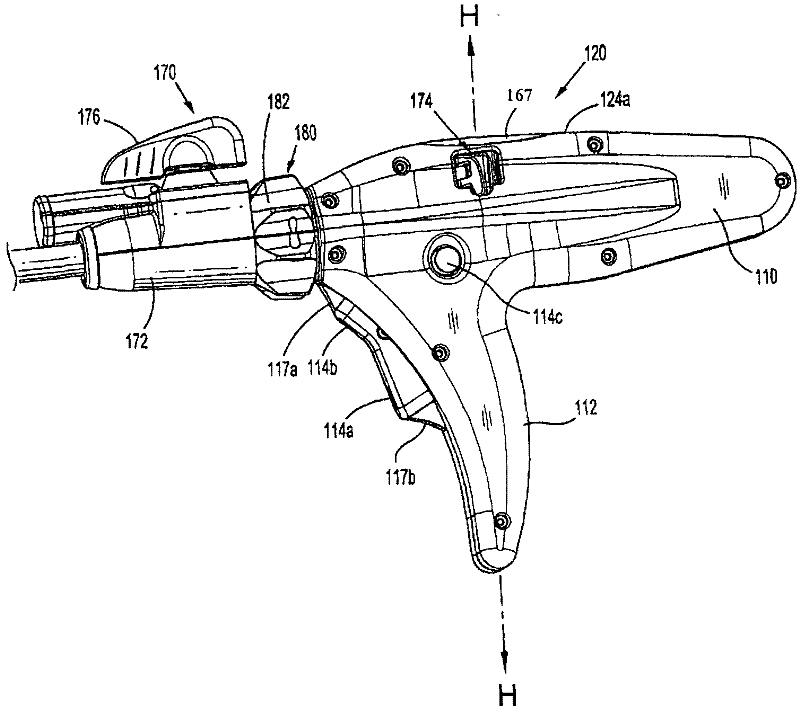
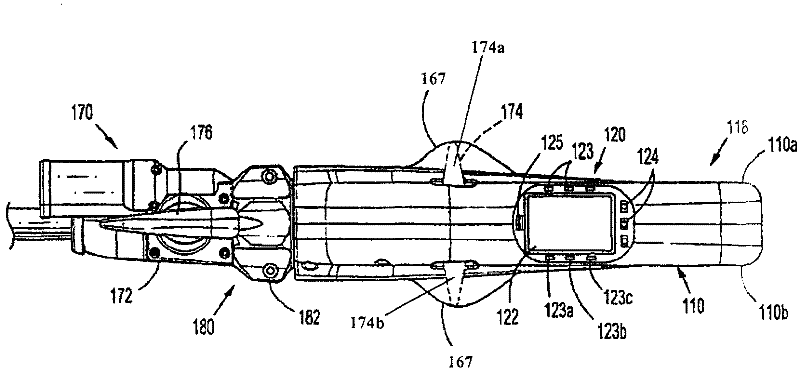
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS8960520B2Reduce mechanical wearMinimized in sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsCapacitanceLinear motion
A surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument are disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A motion sensor senses a change in the electric field (e.g., capacitance, impedance, or admittance) between the firing rod and the elongated shaft. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position, speed, and direction of the firing rod, based on the sensed change in the electric field. A controller uses the measured parameter of the motion of the firing rod to control the drive mechanism.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Tissue resurfacing
InactiveUS7335199B2Easy to getRapid treatment at the tissue surfaceInstrument handpiecesSurgical instruments for heatingSkin treatmentsSkin surface
Owner:ENERGIST
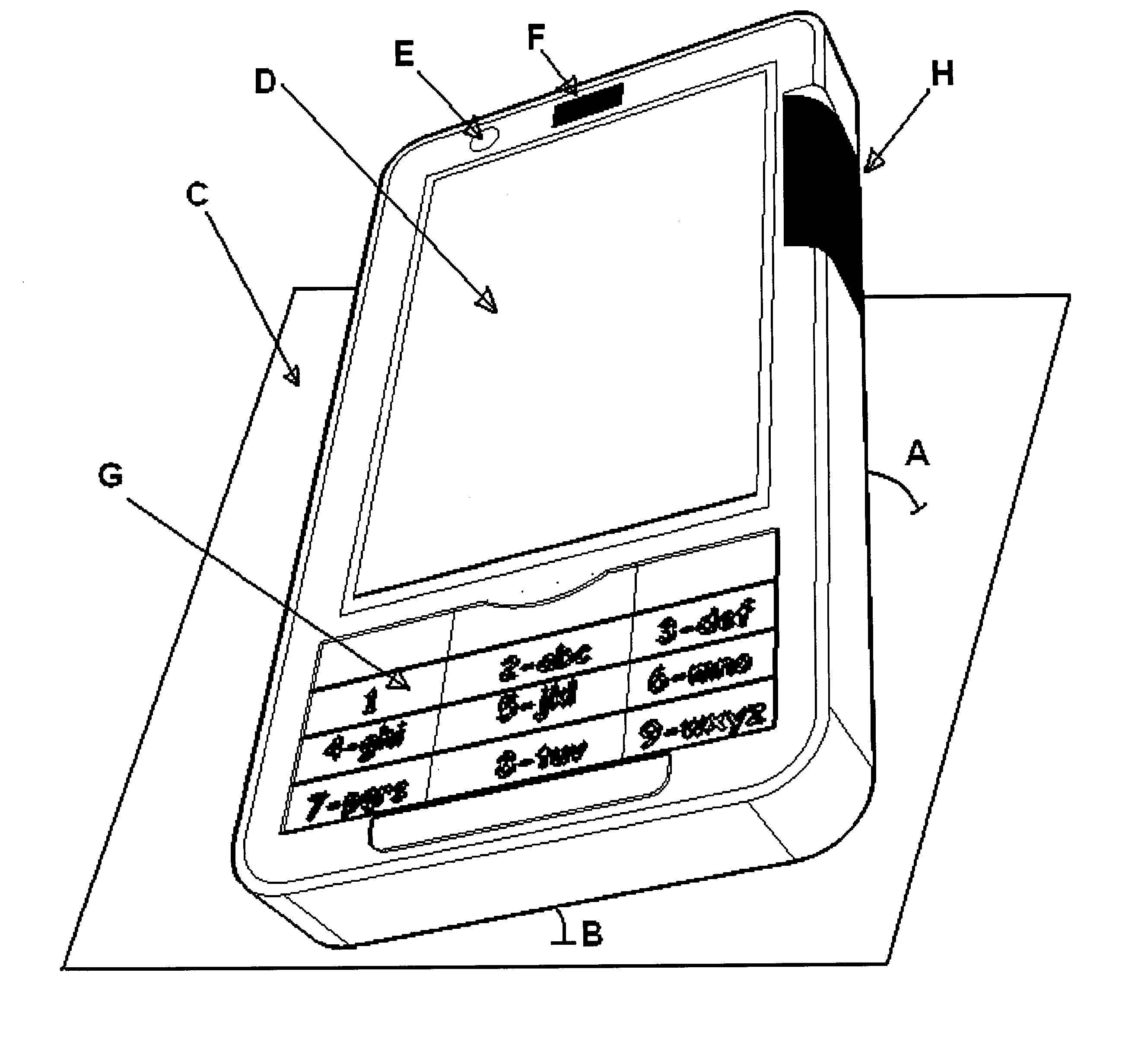
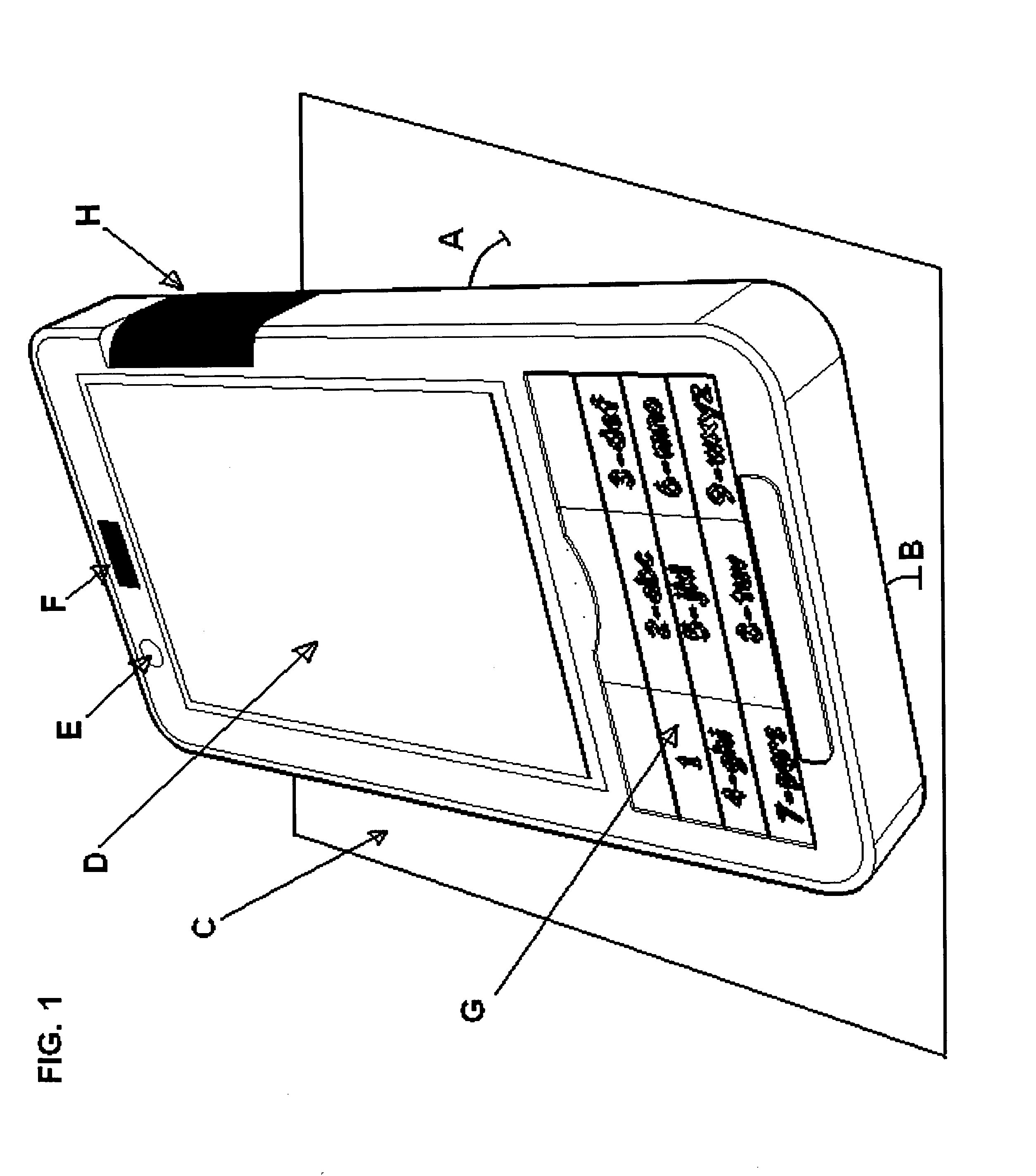
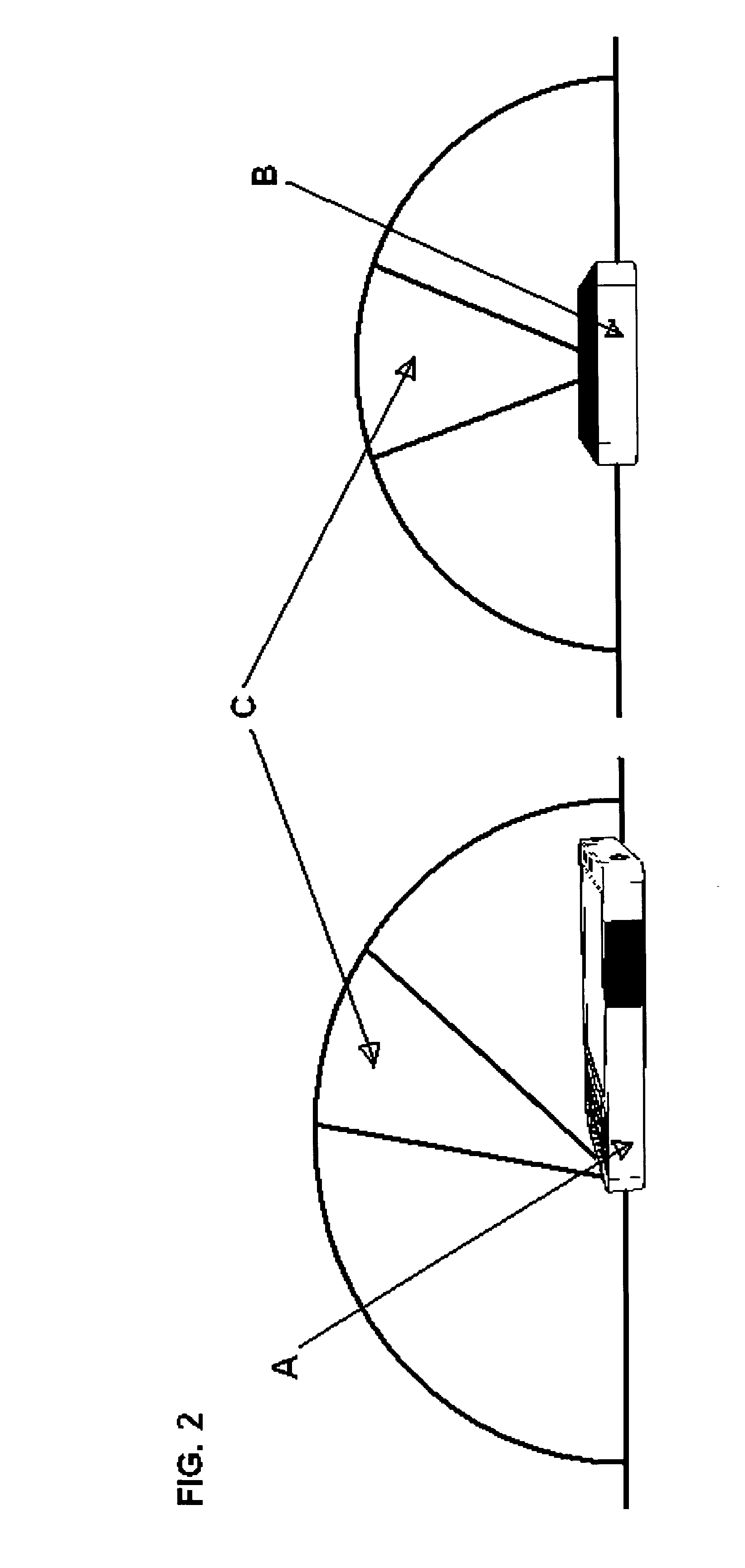
Cellular phone with special sensor functions
InactiveUS20090262078A1Input/output for user-computer interactionUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionProximity sensorDisplay device
Specific ambient and user behaviour sensing systems and methods are presented to improve friendliness and usability of electronic handheld devices, in particular cellular phones, PDAs, multimedia players and similar.The improvements and special functions include following components:a. The keypad is locked / unlocked (disabled / enabled) and / or the display activated based on the device inclination relative to its longitudinal and / or lateral axes.b. The keypad is locked if objects are detected above the display (for example the boundary of a bag or pursue).c. The keypad is locked / unlocked (disabled / enabled) and / or the display activated based on electric field displacement or bio-field sensing systems recognizing the user hand in any position behind the handheld device.d. The electric response signal generated by an electric field through the user hand in contact with a receiver plate is used to identify the user and in negative case lock the device.e. Connection with incoming calls is automatically opened as soon as a hand is detected behind the device and the device is put close to the ear (proximity sensor).f. The profile (ring-tone mode, volume and silent mode) can be changed just putting the device in a specific verse (upside up or upside down).g. Has a lateral curved touchpad with tactile markings over more surfaces to control a mouse pointer / cursor or selection with the thumb finger.
Owner:PIZZI DAVID
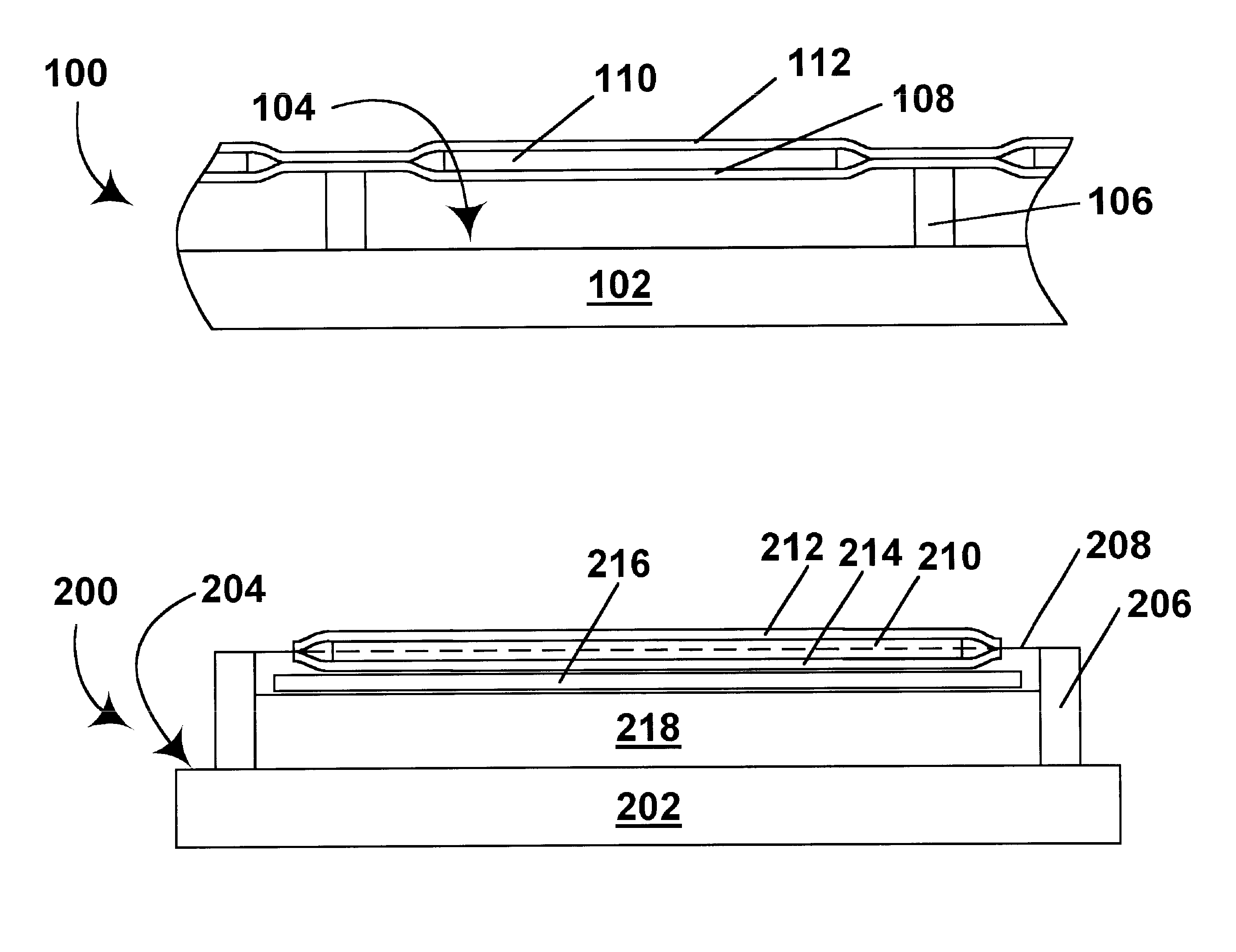
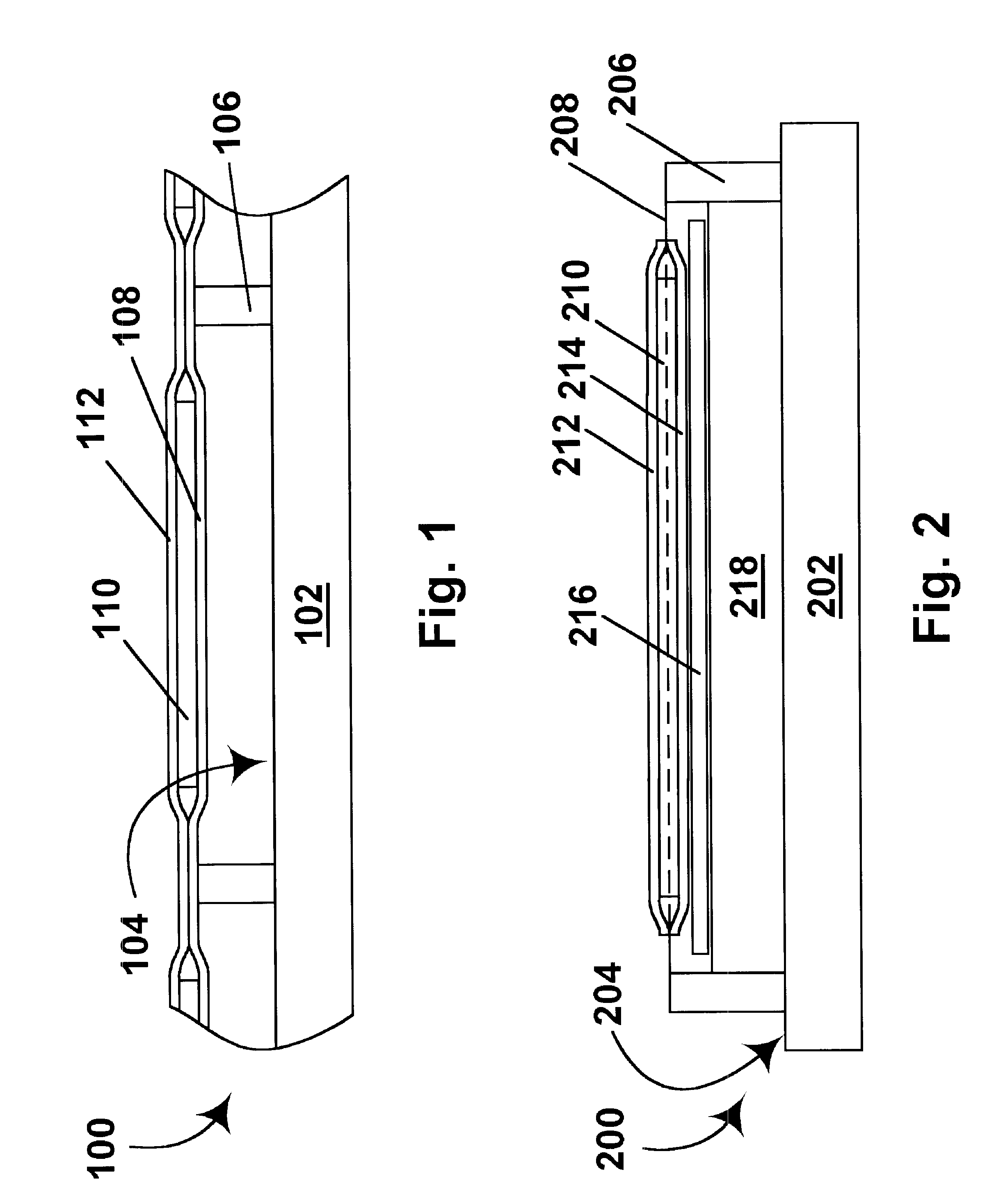
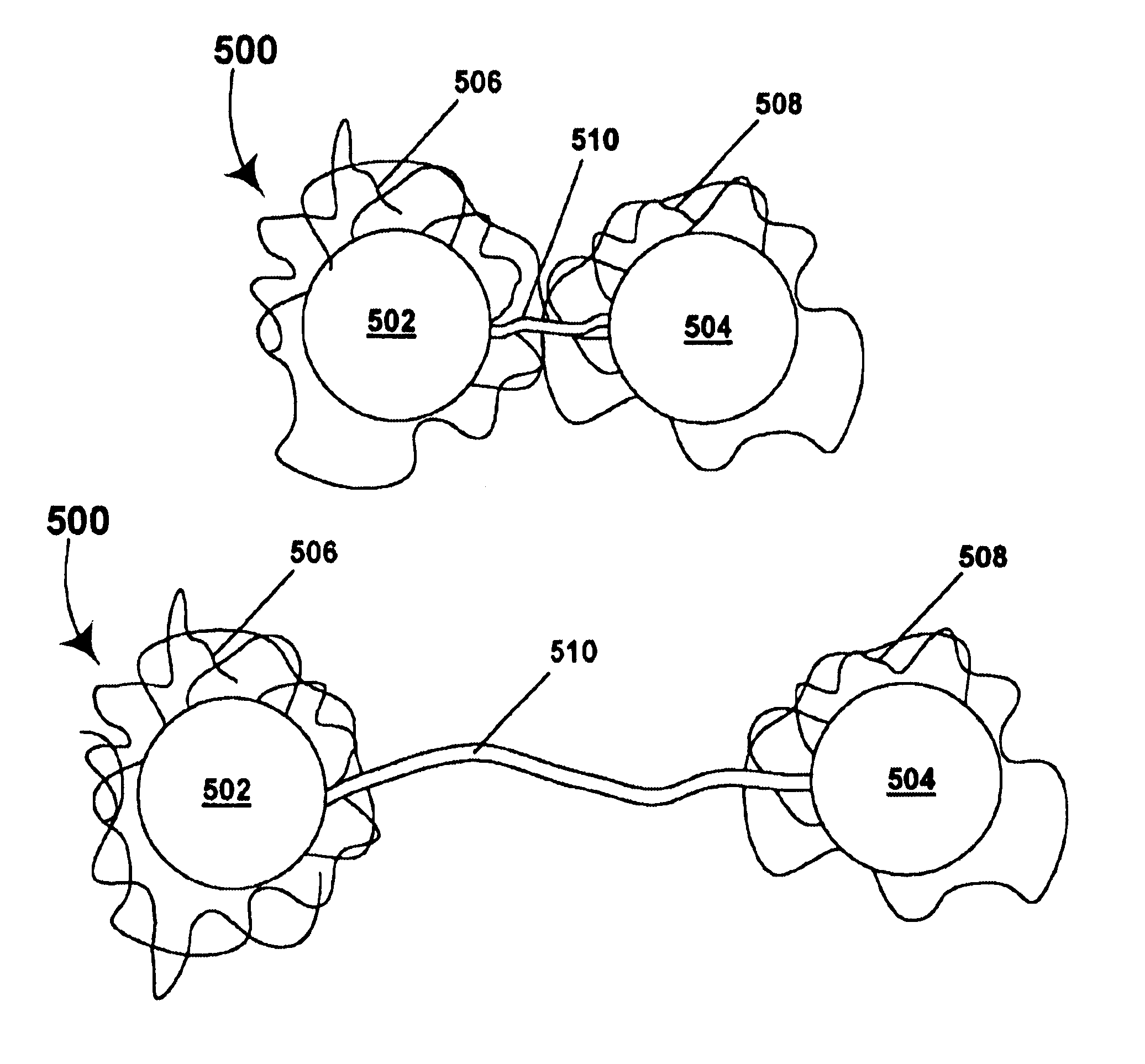
Electrophoretic medium and process for the production thereof
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Electrophoretic medium and display with improved image stability
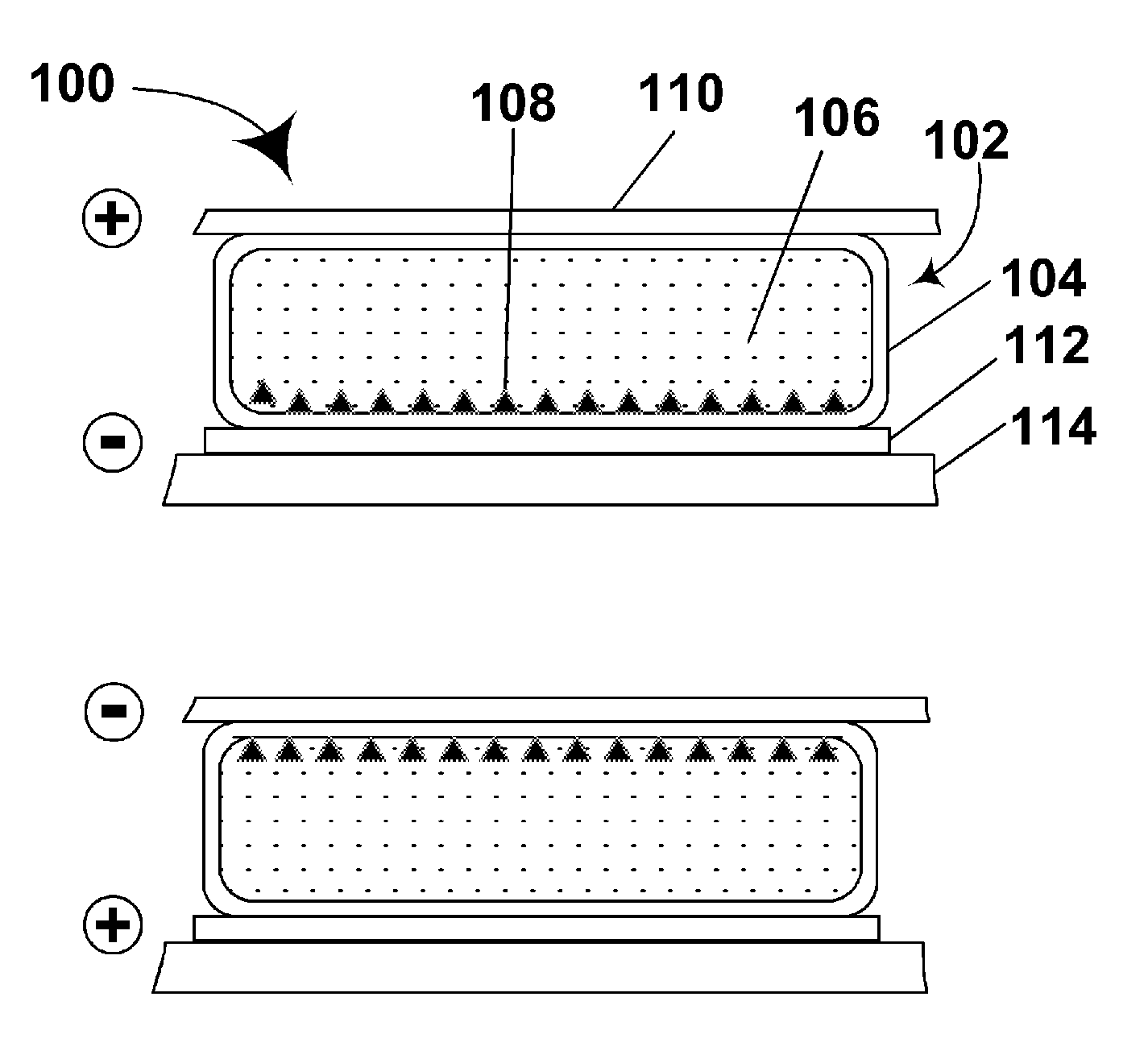
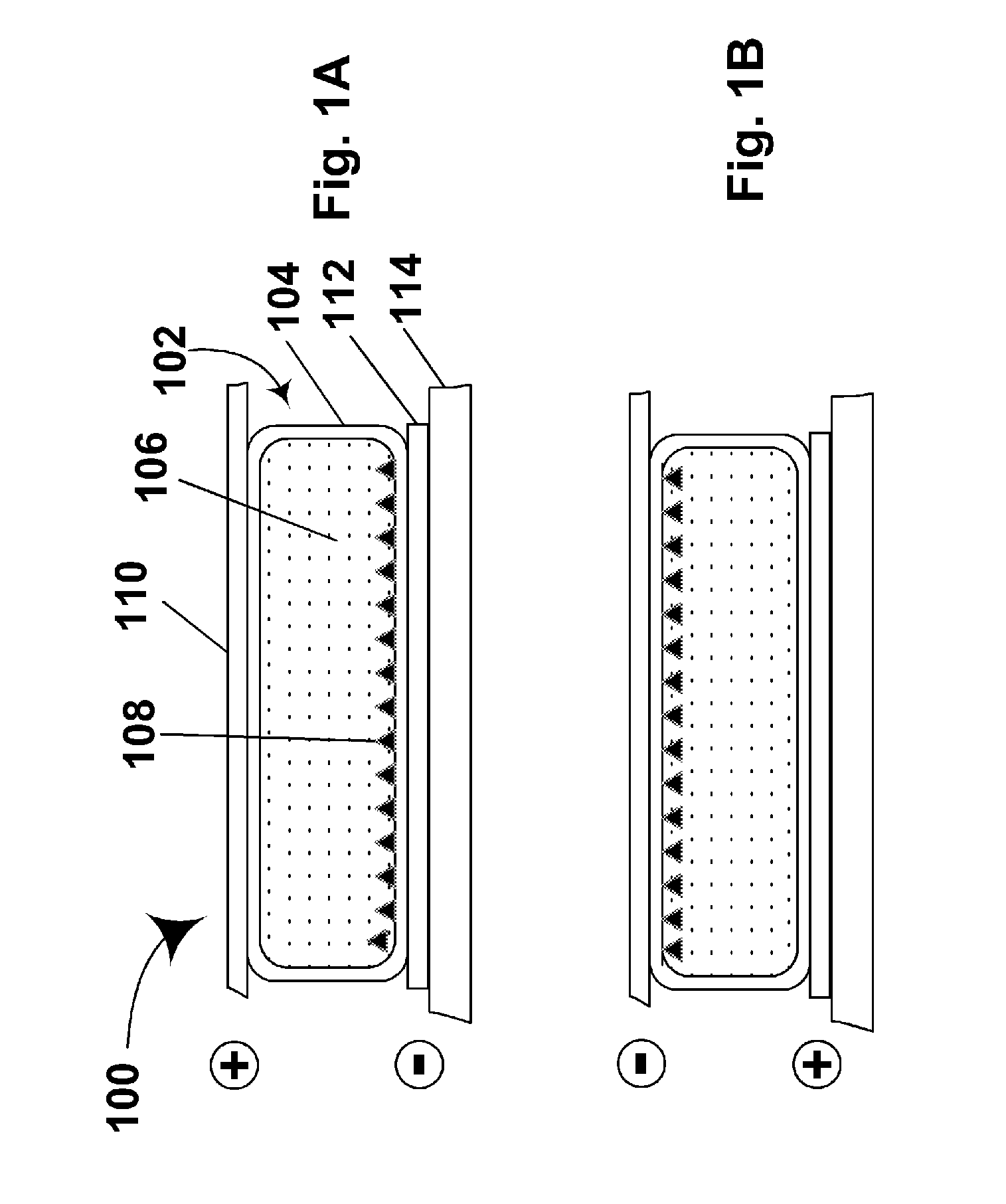
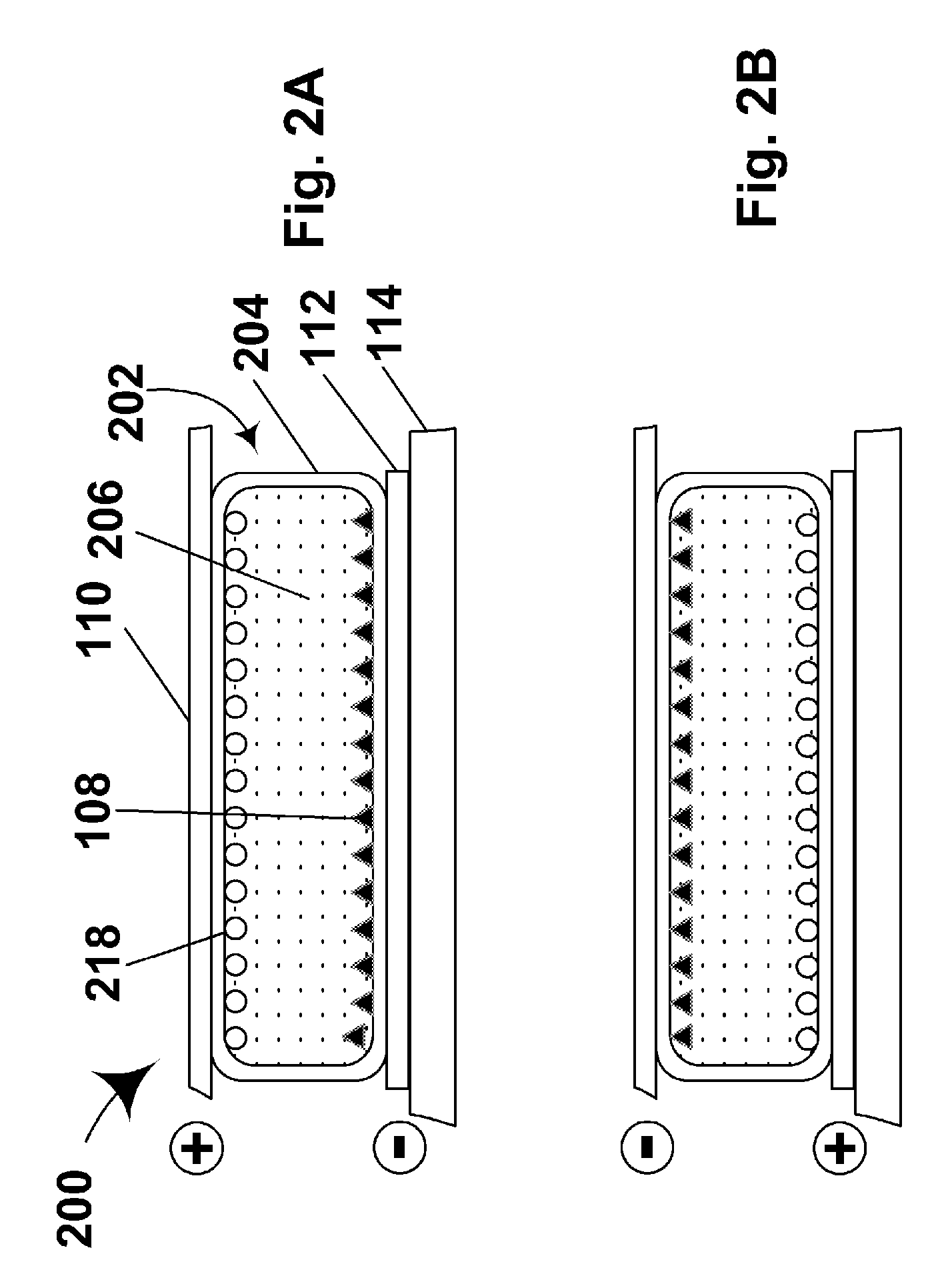
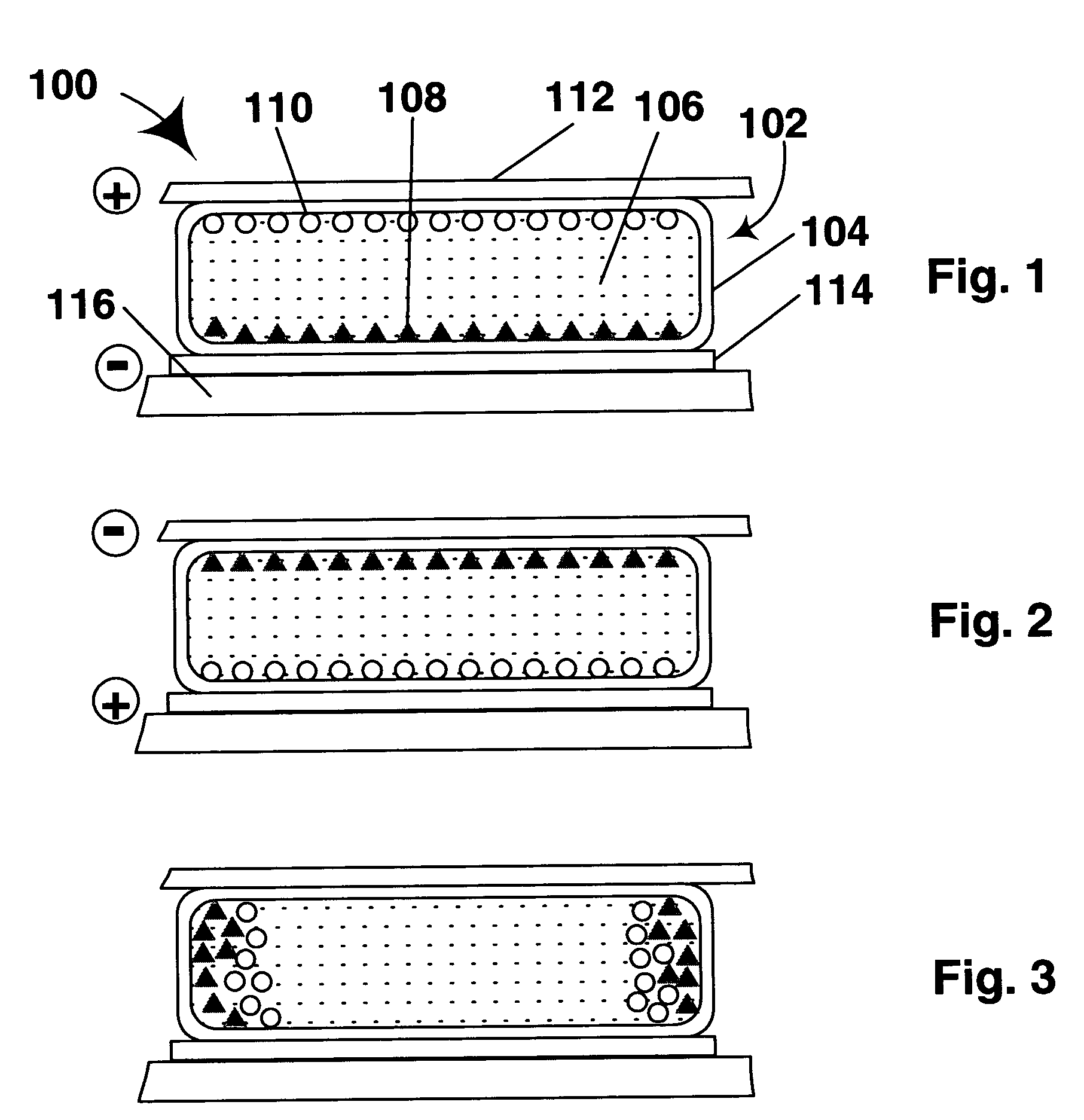
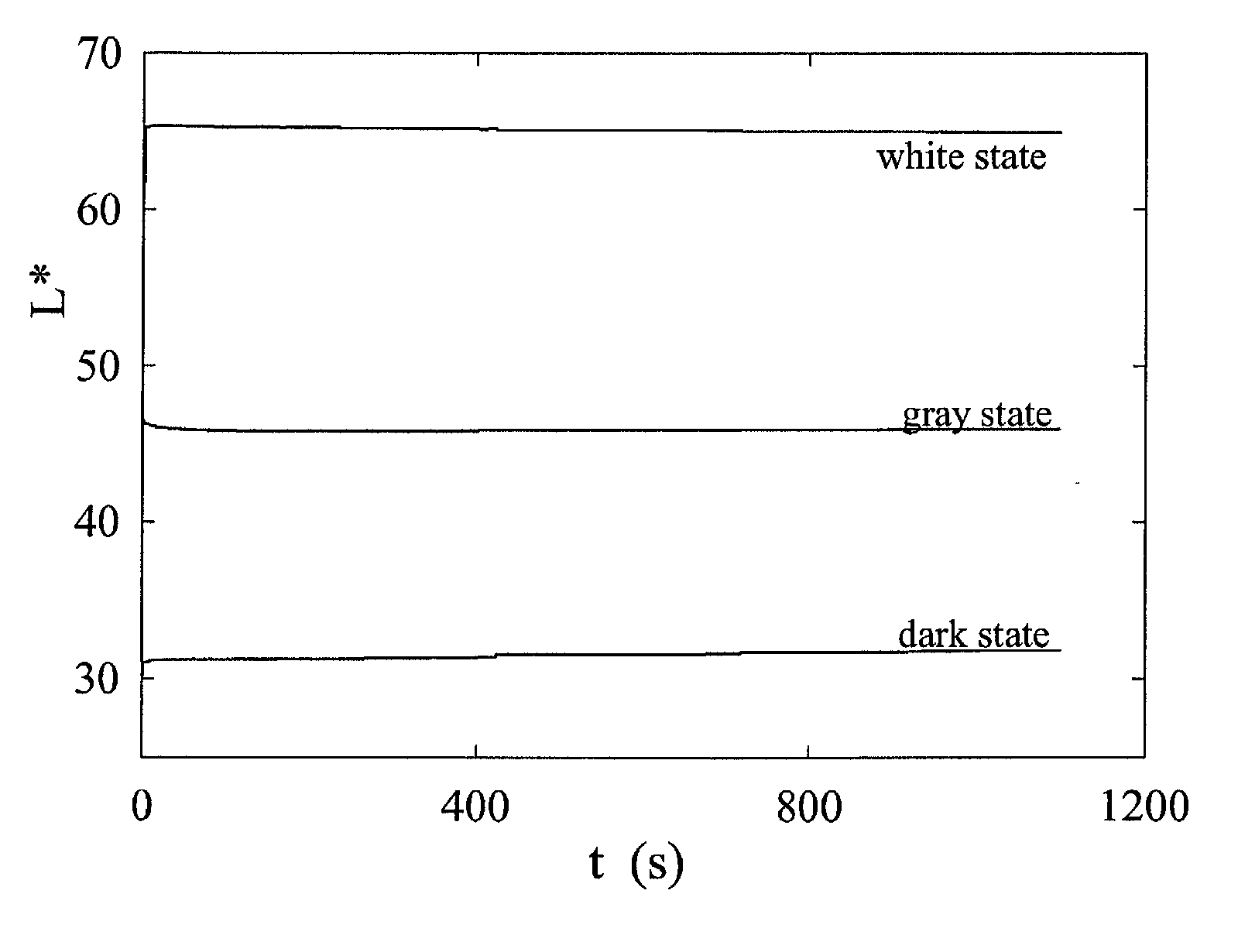
An electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of particles suspended in a suspending fluid, the particles being capable of moving through the fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium, the fluid having dissolved or dispersed therein a polymer having a number average molecular weight in excess of about 20,000, the polymer being essentially non-absorbing on the particles. The polymer improves the bistability of the display (i.e., the period for which a written image persist without the display being refreshed) but does not greatly increase the viscosity of the suspending fluid, thus keeping the switching time of the display within reasonable limits. The medium may be encapsulated, or may be in the form a polymer-dispersed electrophoretic medium.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
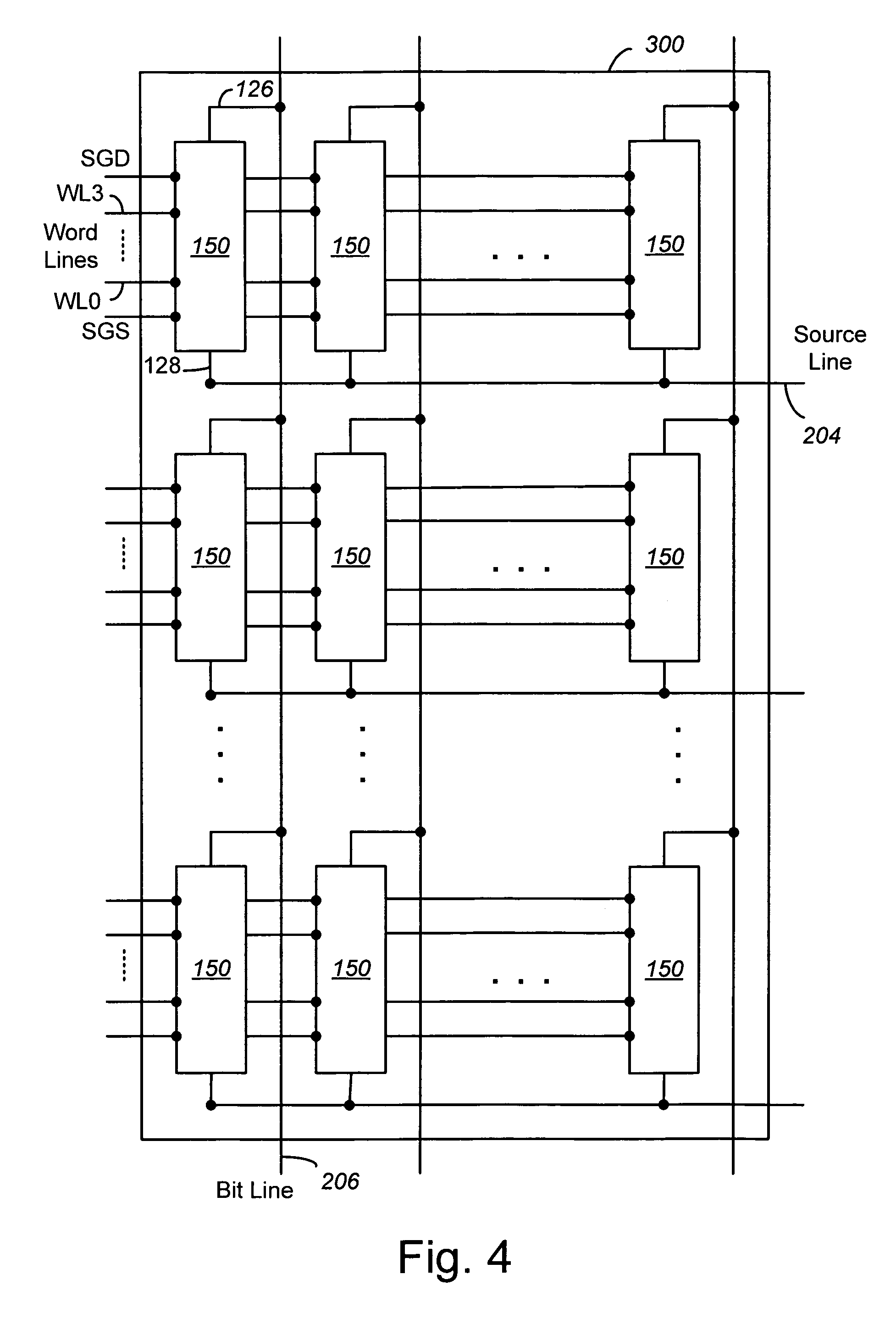
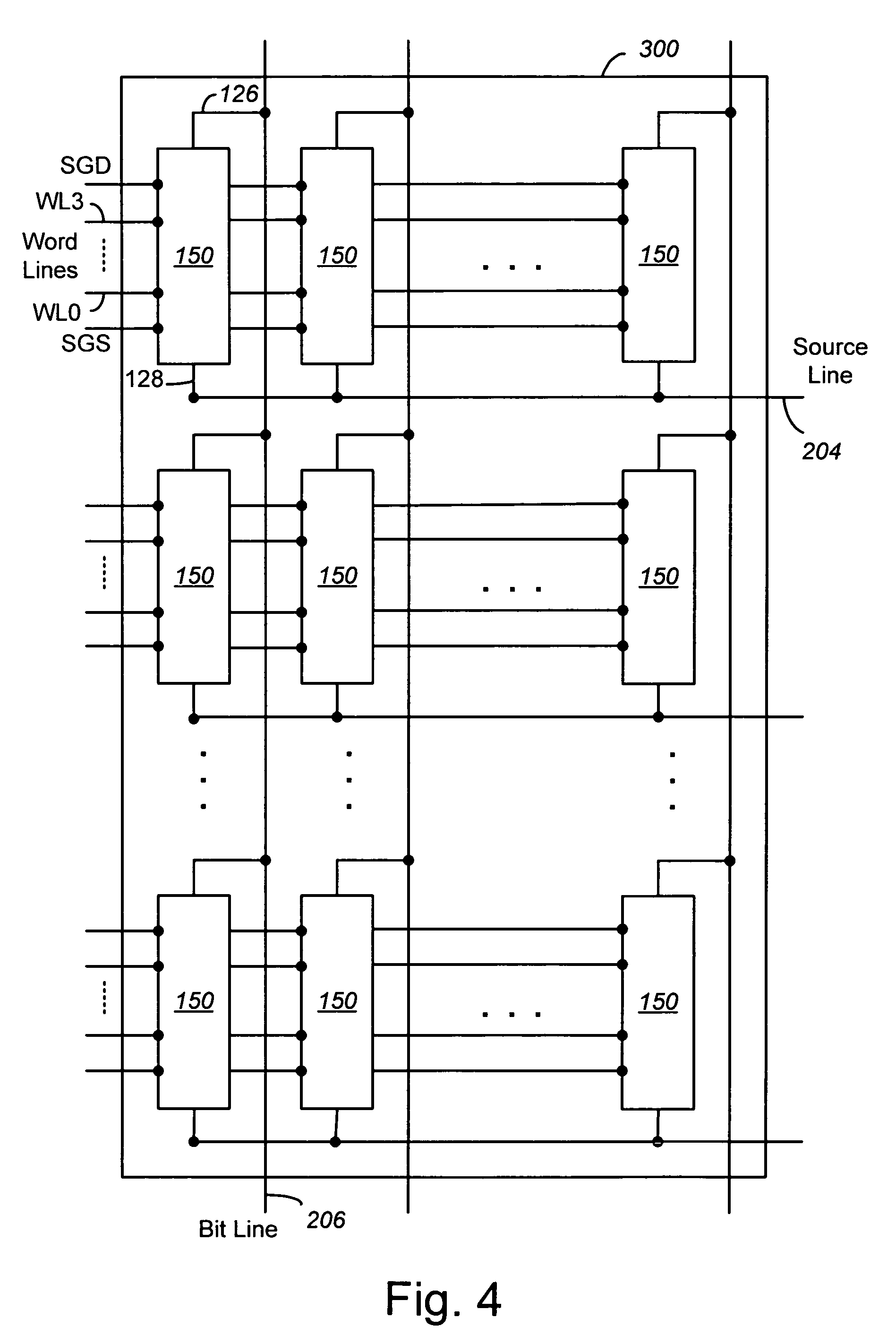
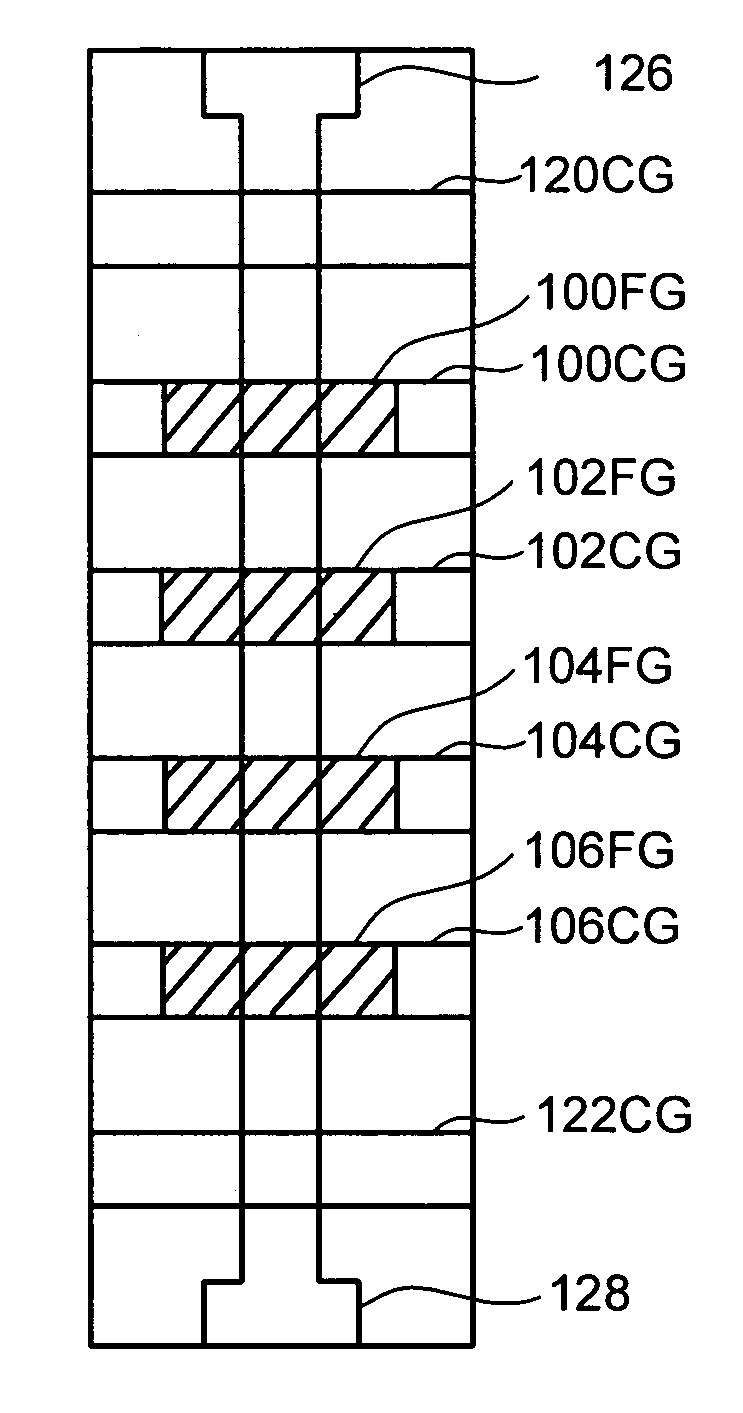
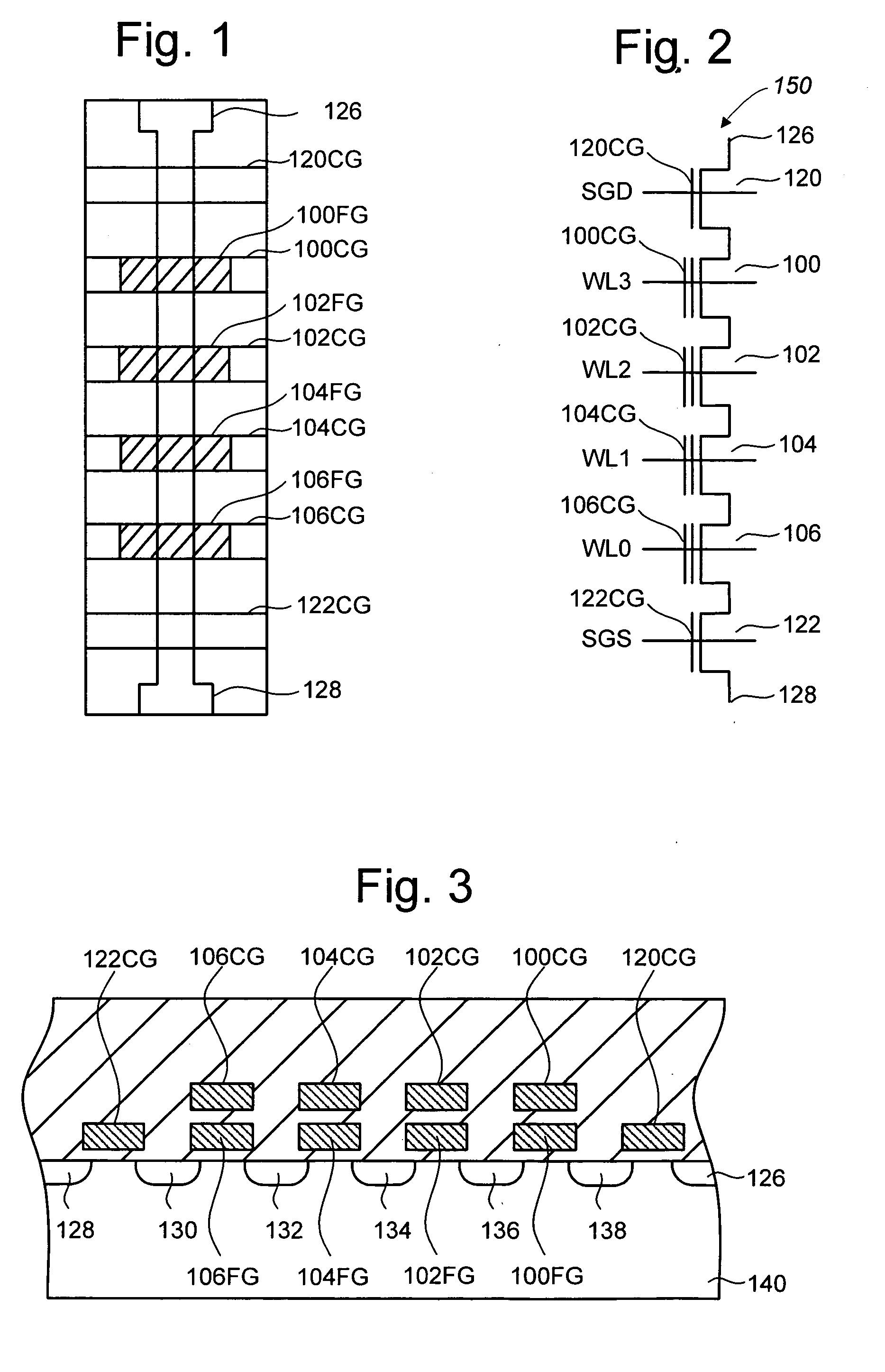
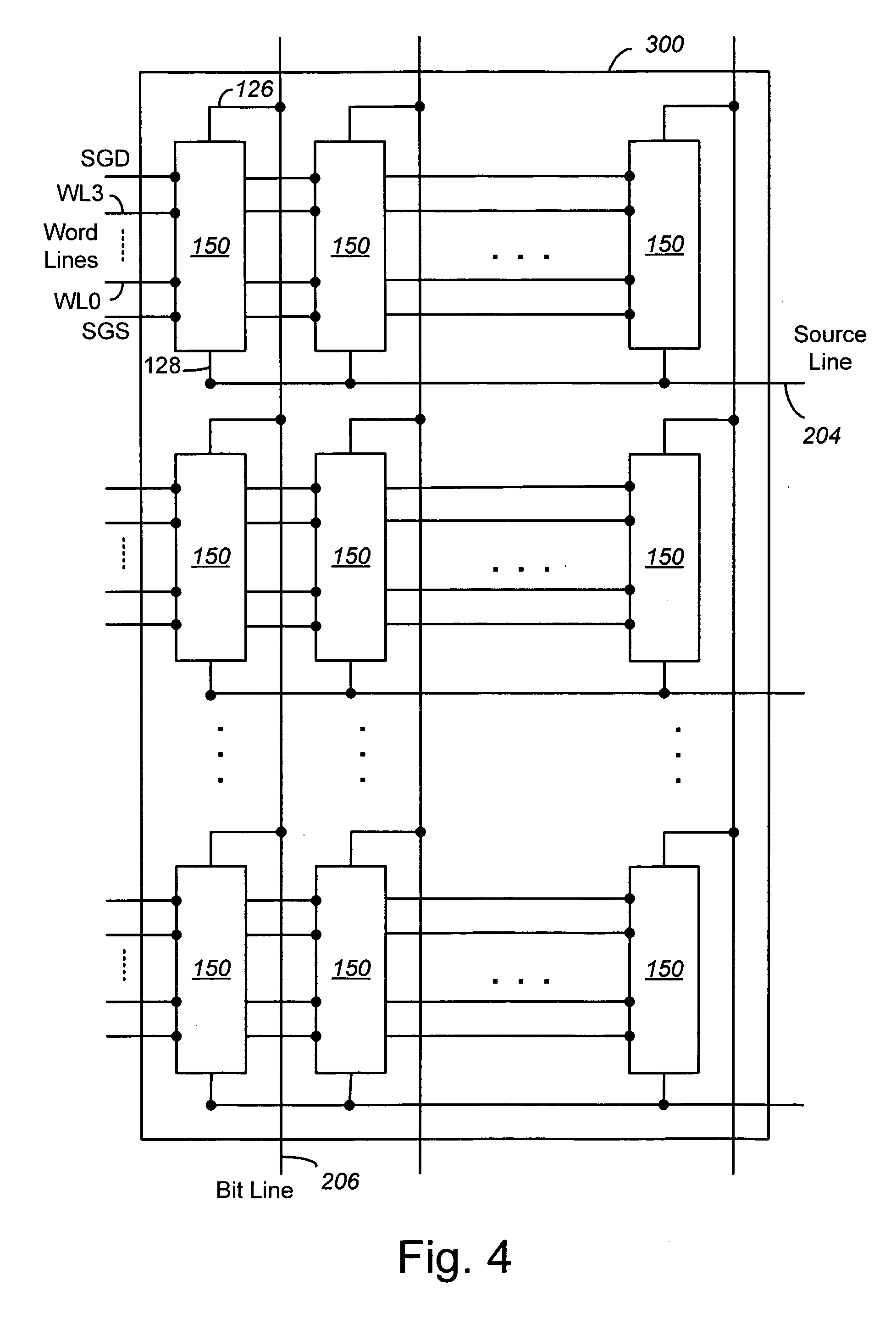
Compensating for coupling during read operations of non-volatile memory
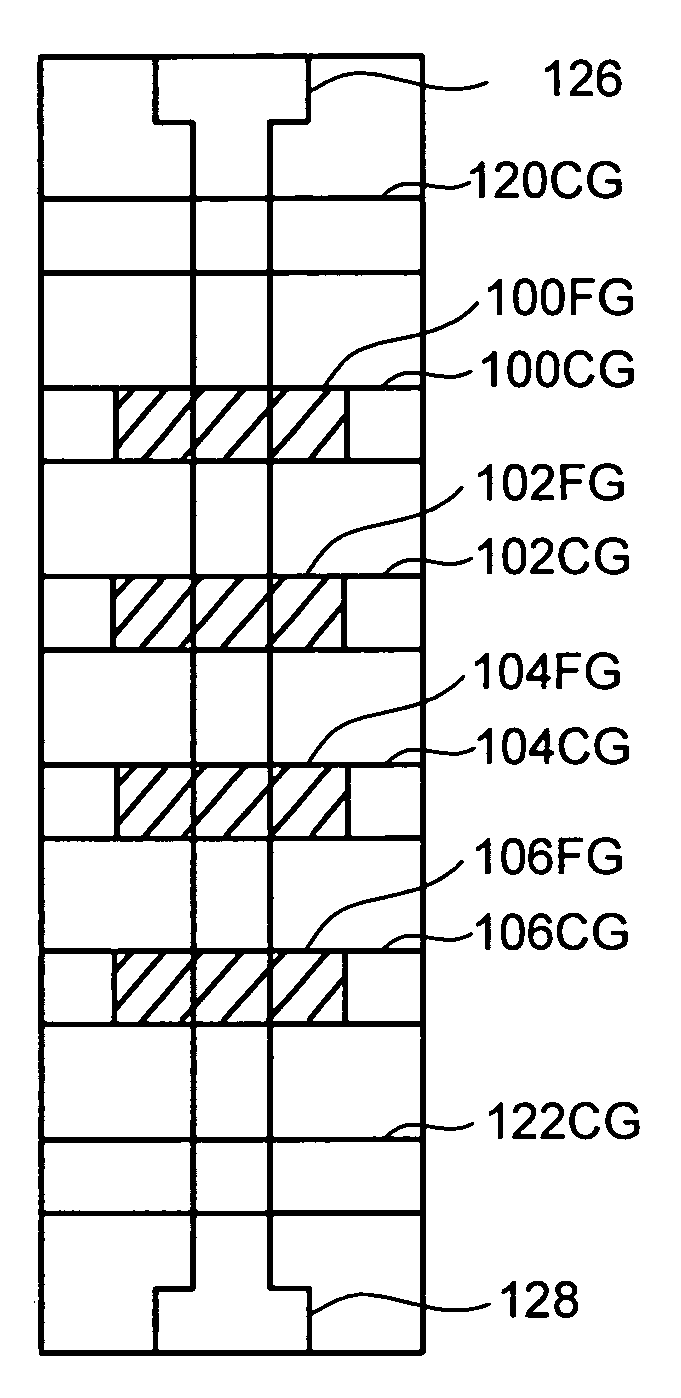
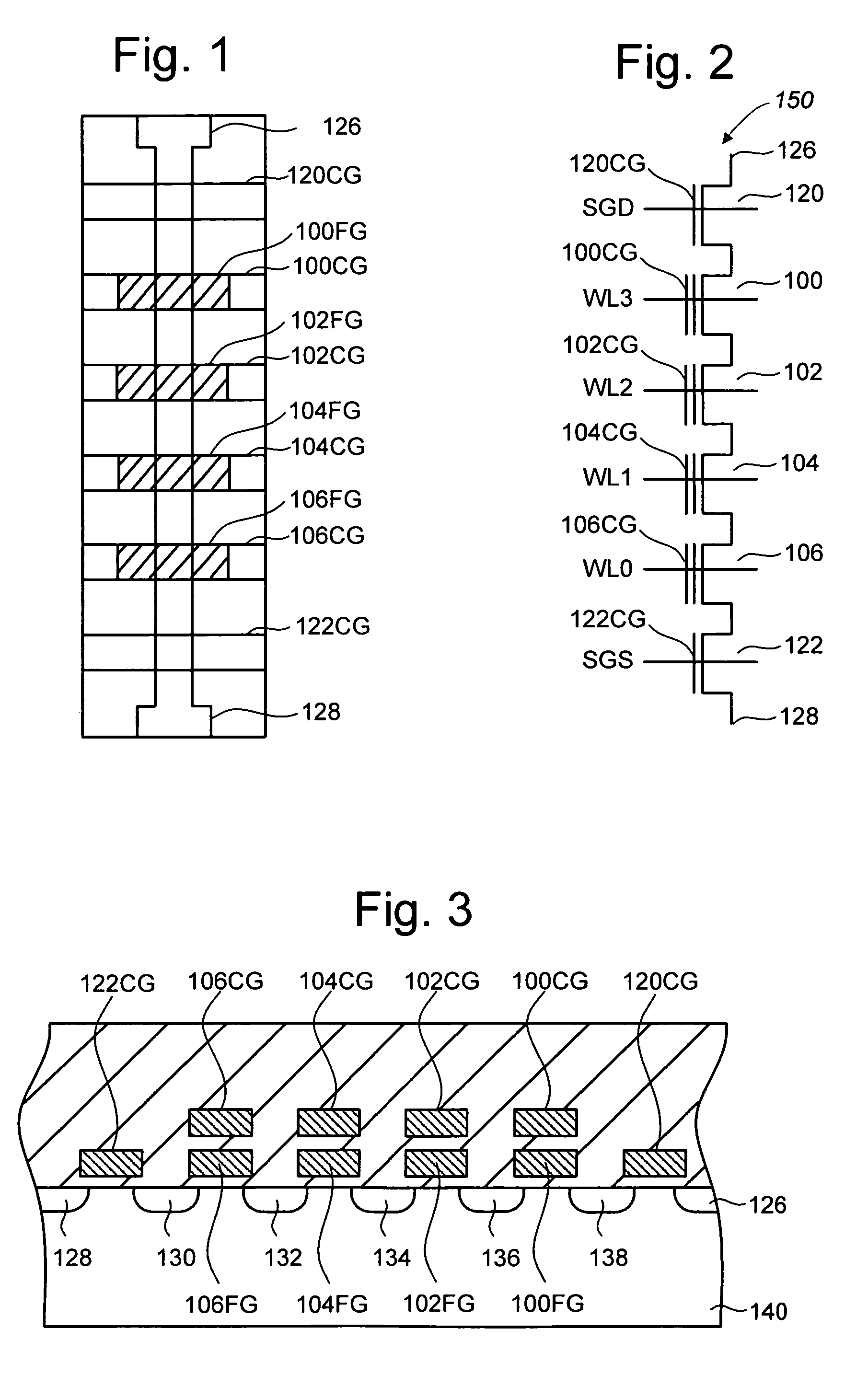
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Flexible electro-optic displays
An encapsulated electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of capsules dispersed in a polymeric binder, each of the capsules comprising a capsule wall, a suspending fluid contained within the capsule wall, and a plurality of electrically charged particles suspended in the suspending fluid and capable of moving therethrough upon application of an electric field to the medium, the polymeric binder having a shear modulus of at least about 10 mPa at 20° C., and preferably over the range of 10-50° C.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Electrophoretic medium and process for the production thereof
InactiveUS7411719B2Static indicating devicesElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisElectrophoresisElectric field
A two-phase electrophoretic medium comprises a continuous phase and a discontinuous phase. The discontinuous phase comprises a plurality of droplets, each of which comprises a suspending fluid and at least one particle disposed within the suspending fluid and capable of moving through the fluid upon application of an electric field to the electrophoretic medium. The continuous phase surrounds and encapsulates the discontinuous phase. To reduce the humidity sensitivity of the medium, a non-ionizable or crystalline polymer may be used as the continuous phase.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS6993384B2Sure easySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
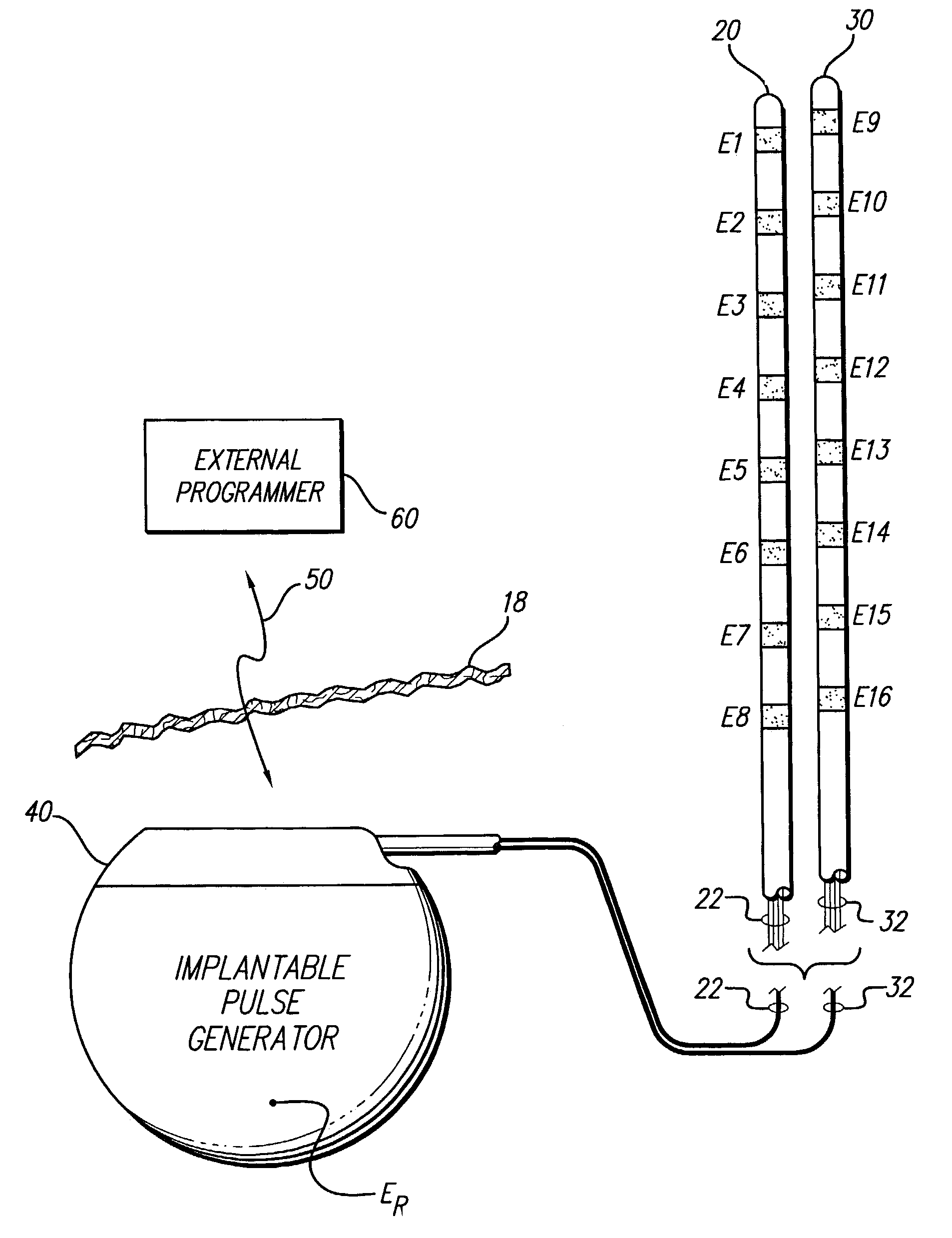
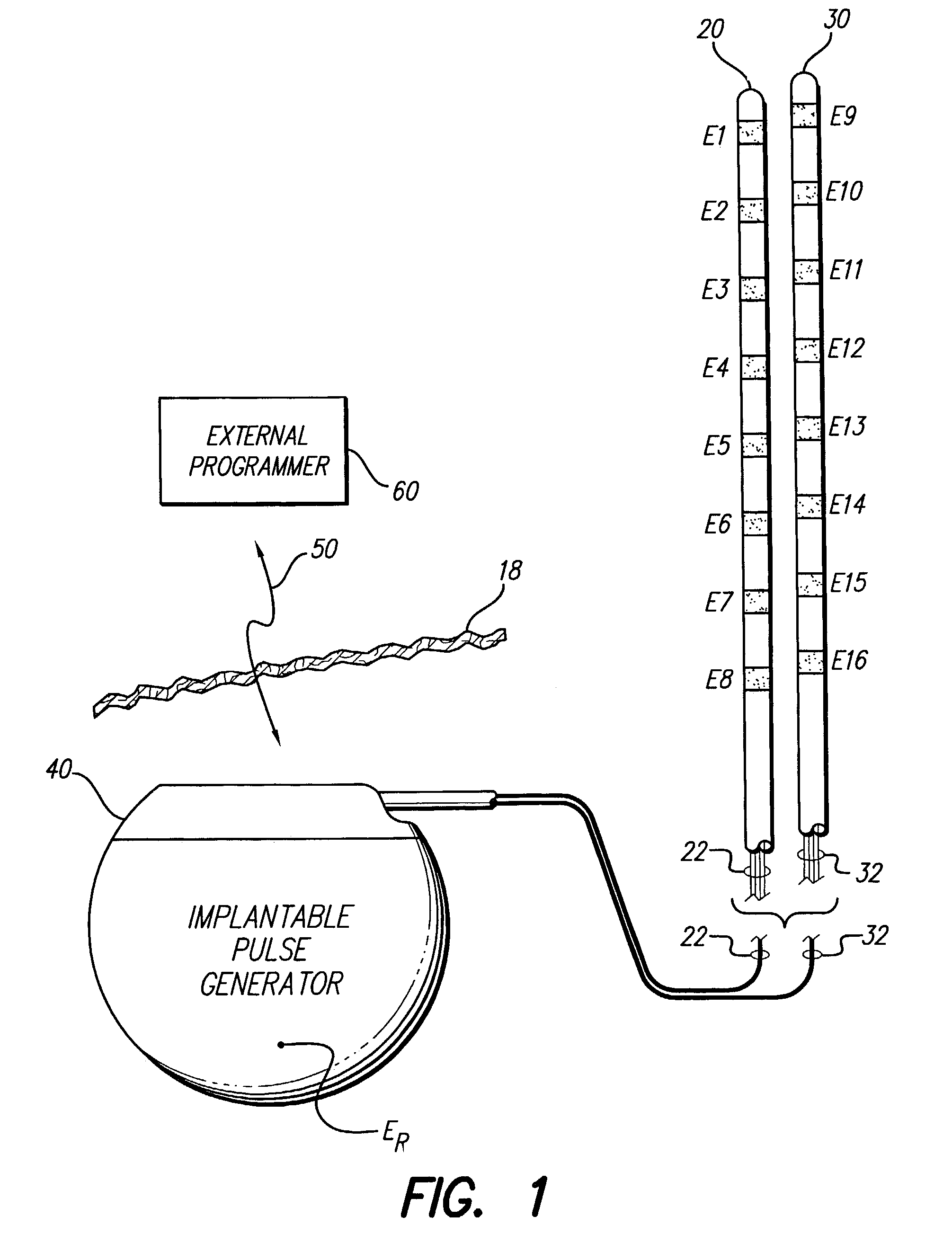
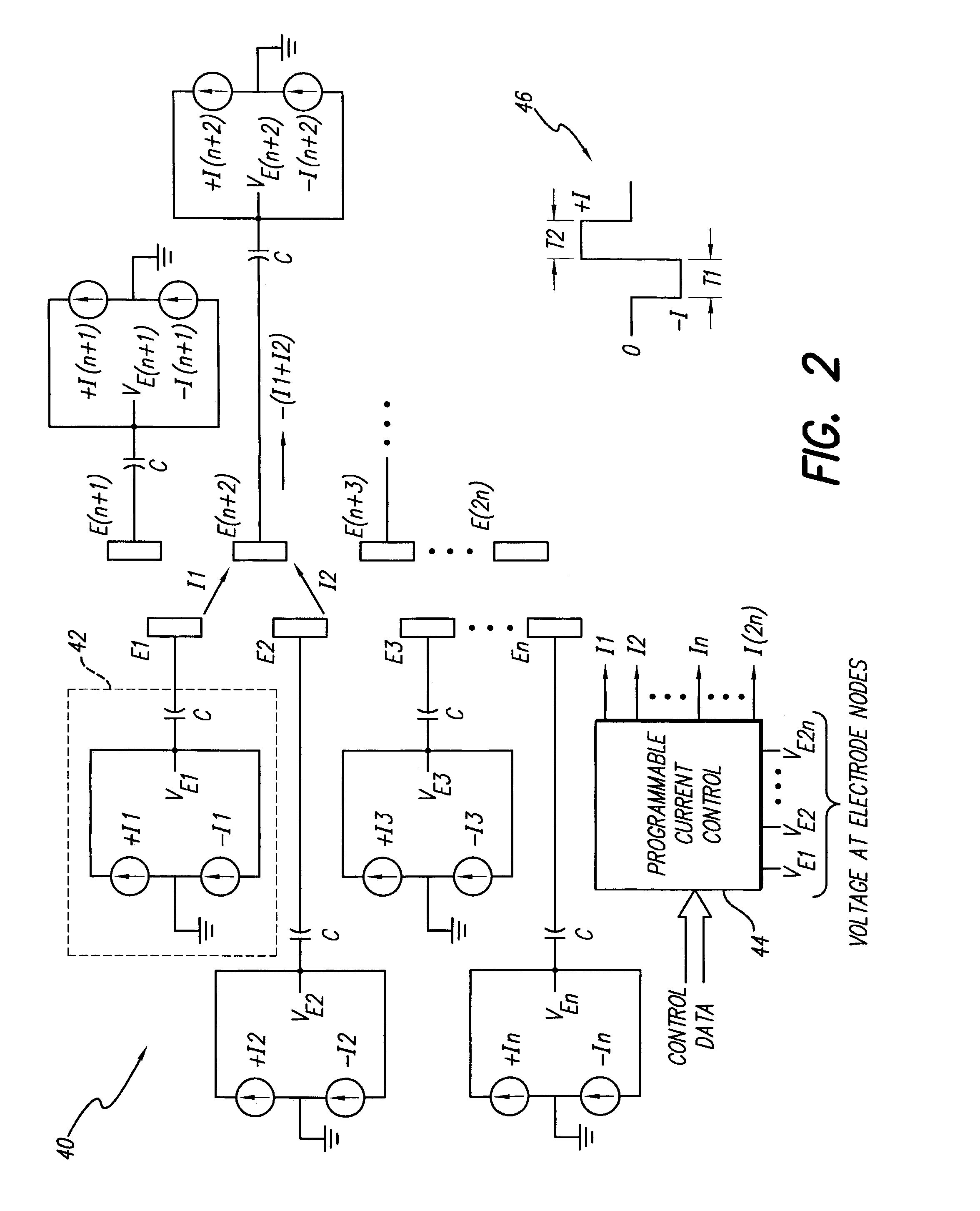
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
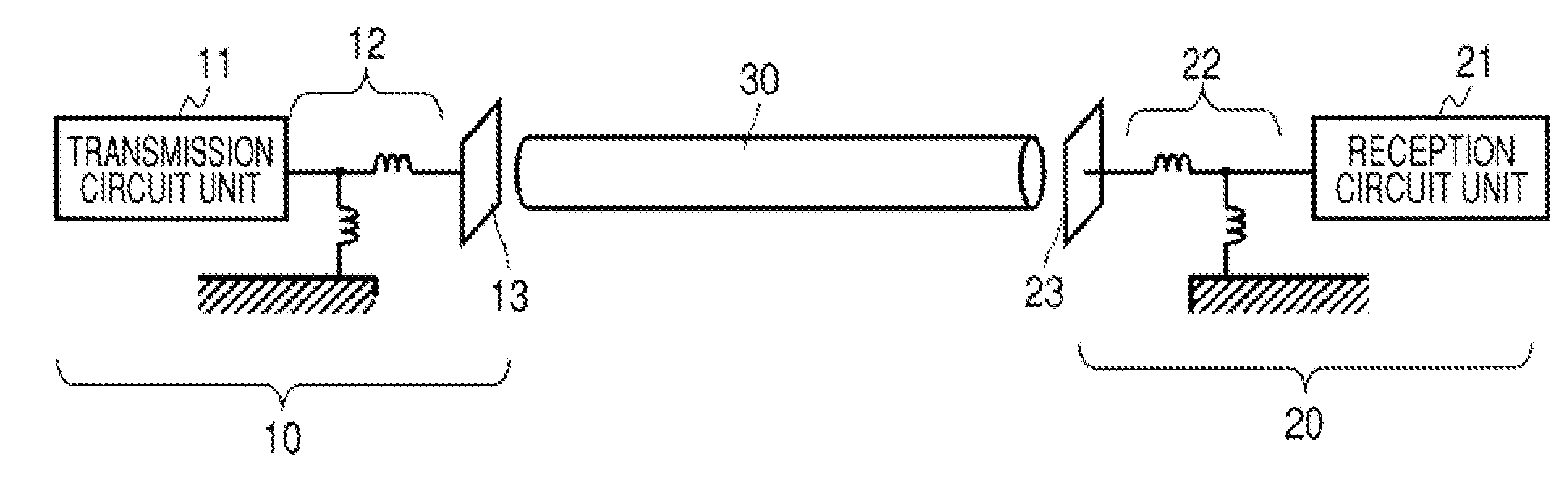
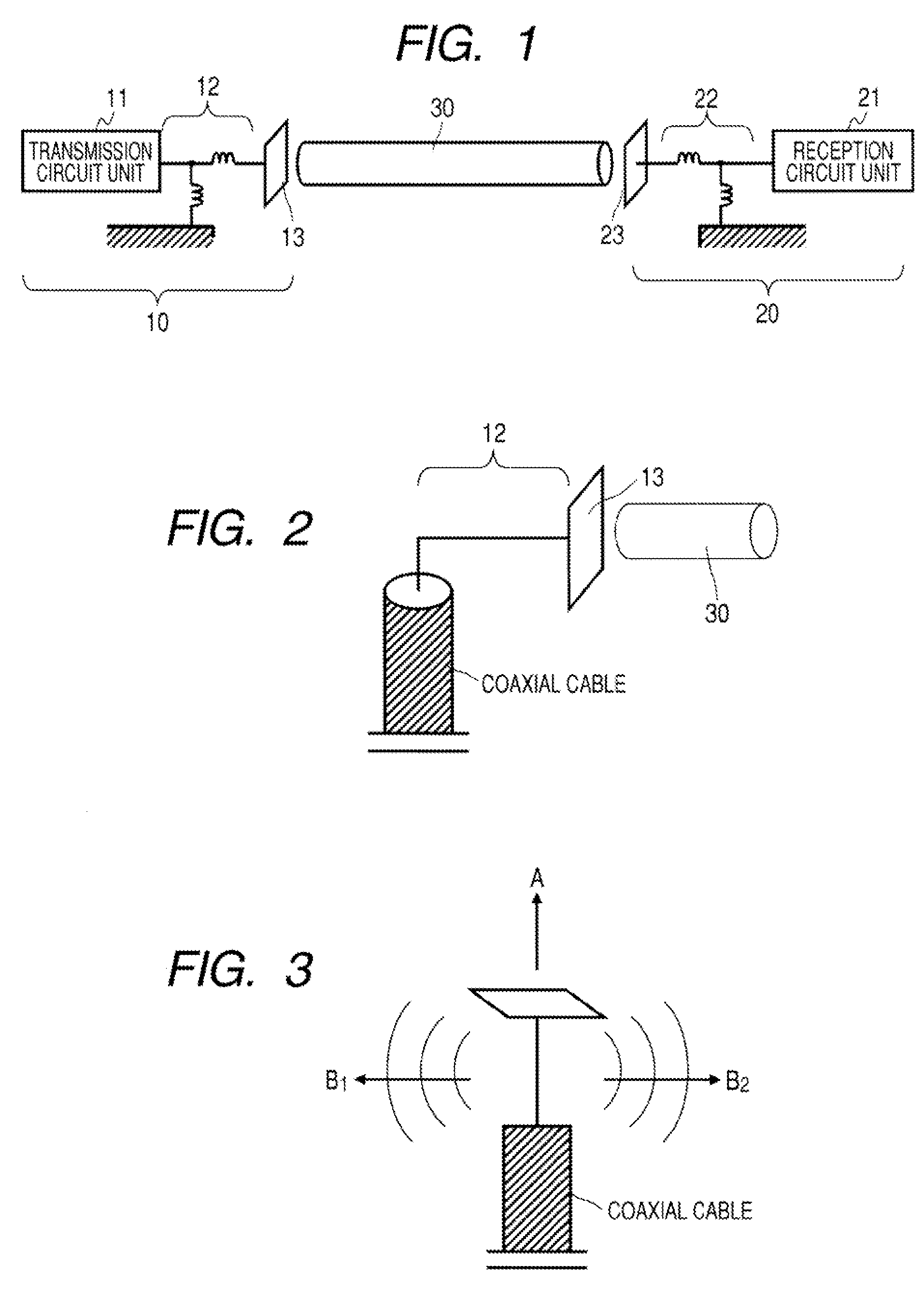
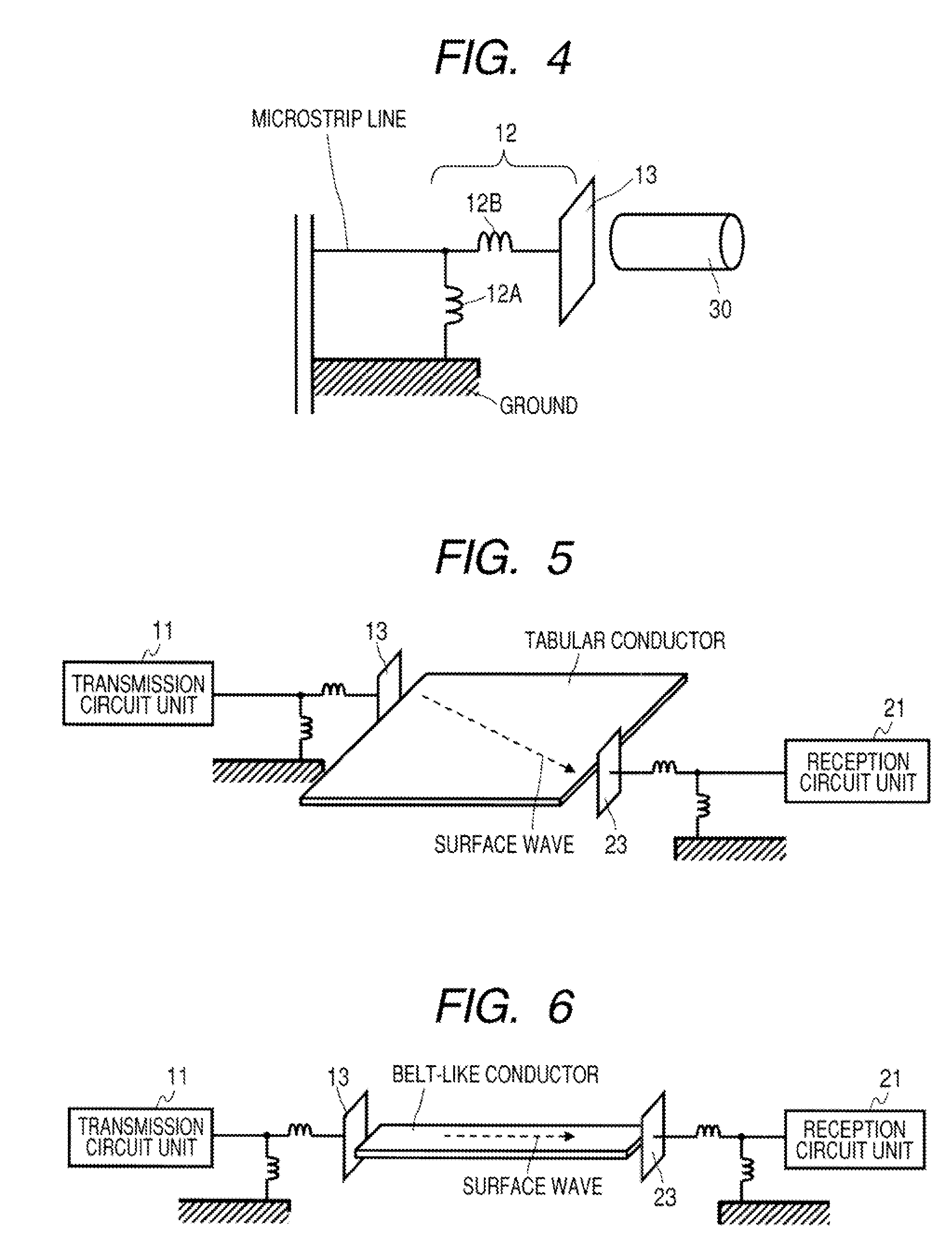
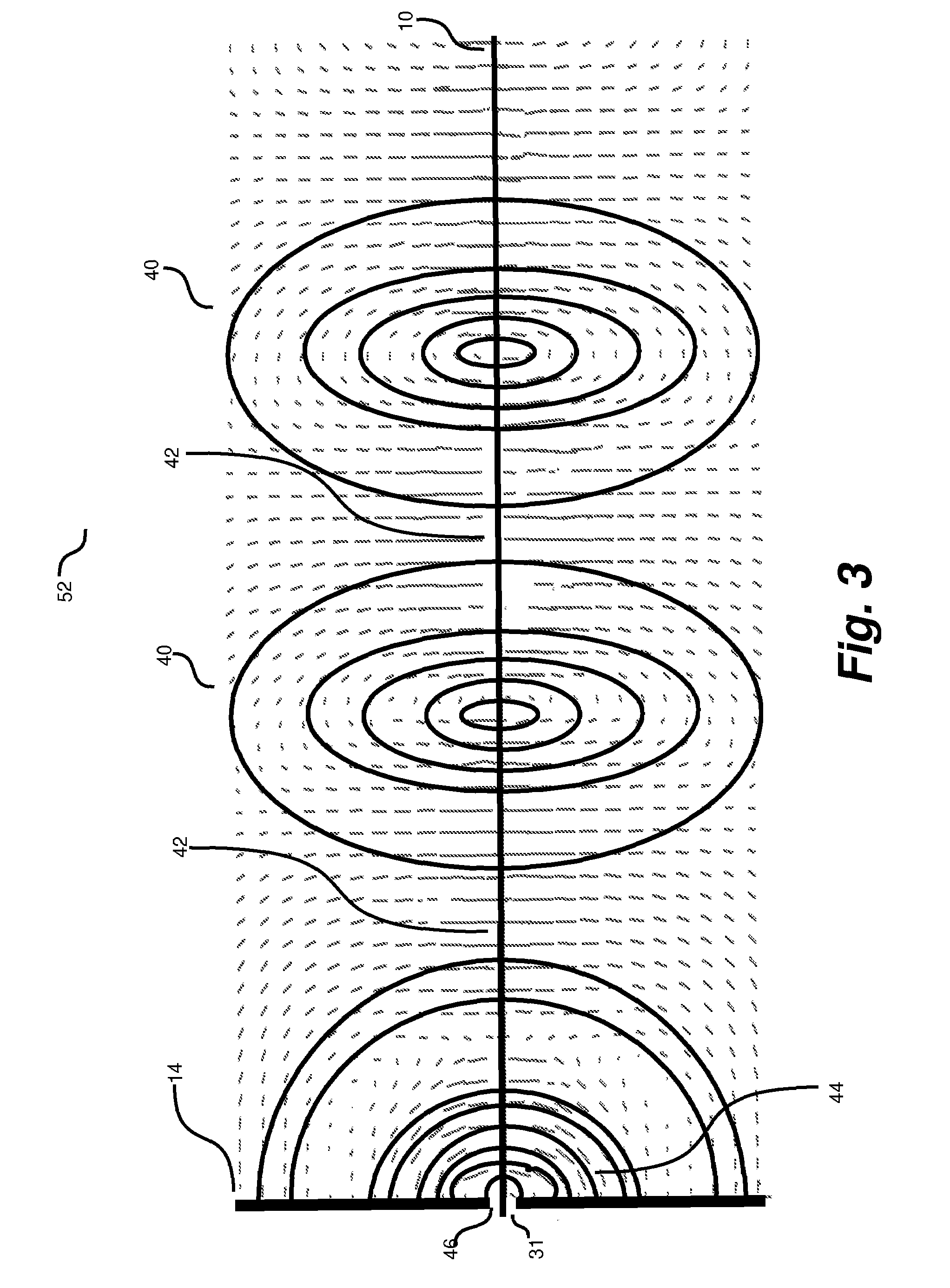
Communication System
A communication system includes a transmitter including a transmission circuit unit that generates an RF signal for transmitting data and an electric-field-coupling antenna that transmits the RF signal as an electrostatic field, a receiver including an electric-field-coupling antenna and a reception circuit unit that subjects an RF signal received by the electric-field-coupling antenna to reception processing, and a surface-wave propagating means for providing a surface wave transmission line made of a conductor that propagates a surface wave radiated from the electric-field-coupling antenna of the transmitter along a surface of the surface wave transmission line.
Owner:SONY CORP
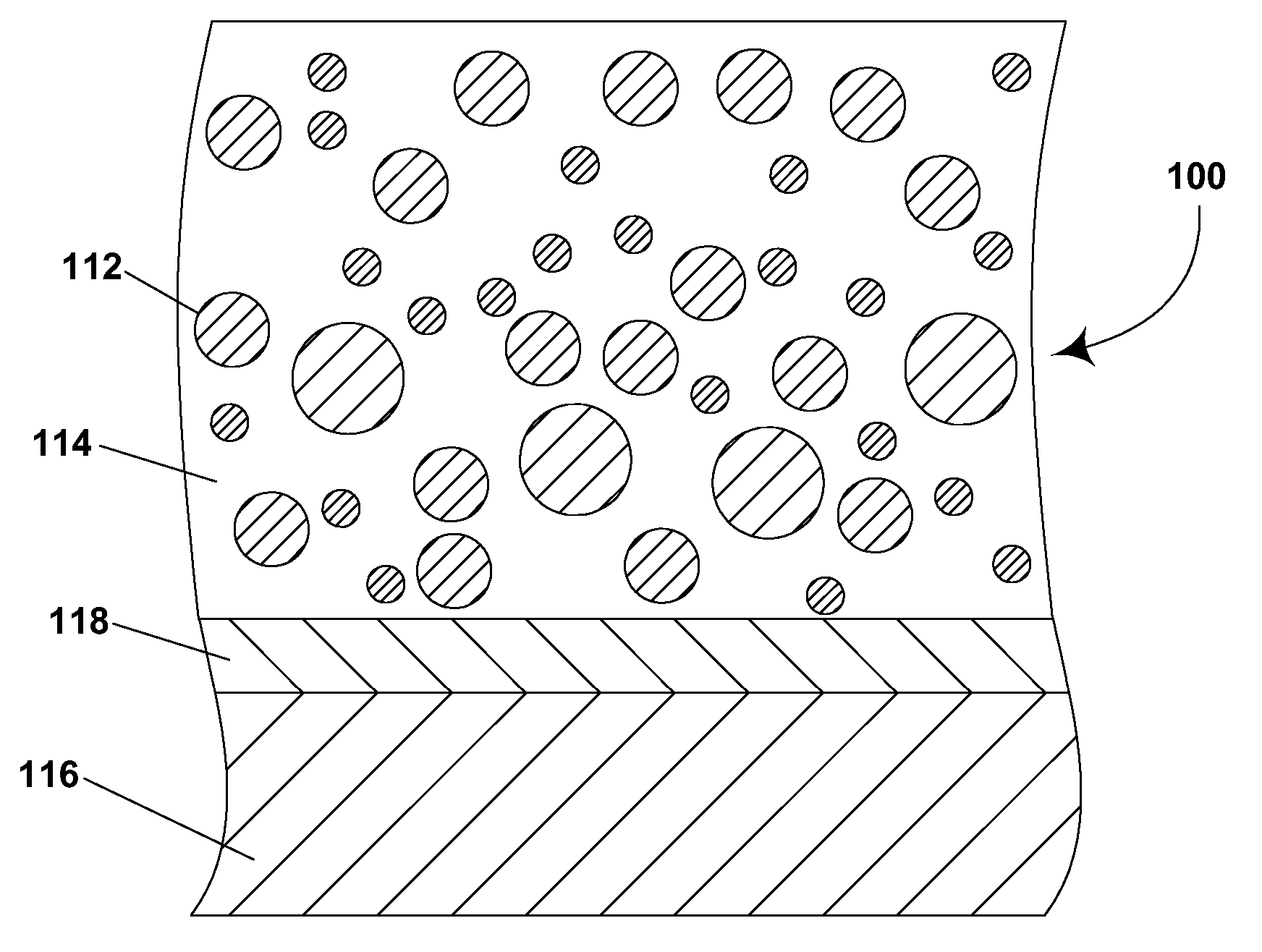
Electrophoretic displays using nanoparticles
InactiveUS6721083B2Less wavelengthIncrease volumeMechanical clocksSolid-state devicesChemical compoundElectrophoresis
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
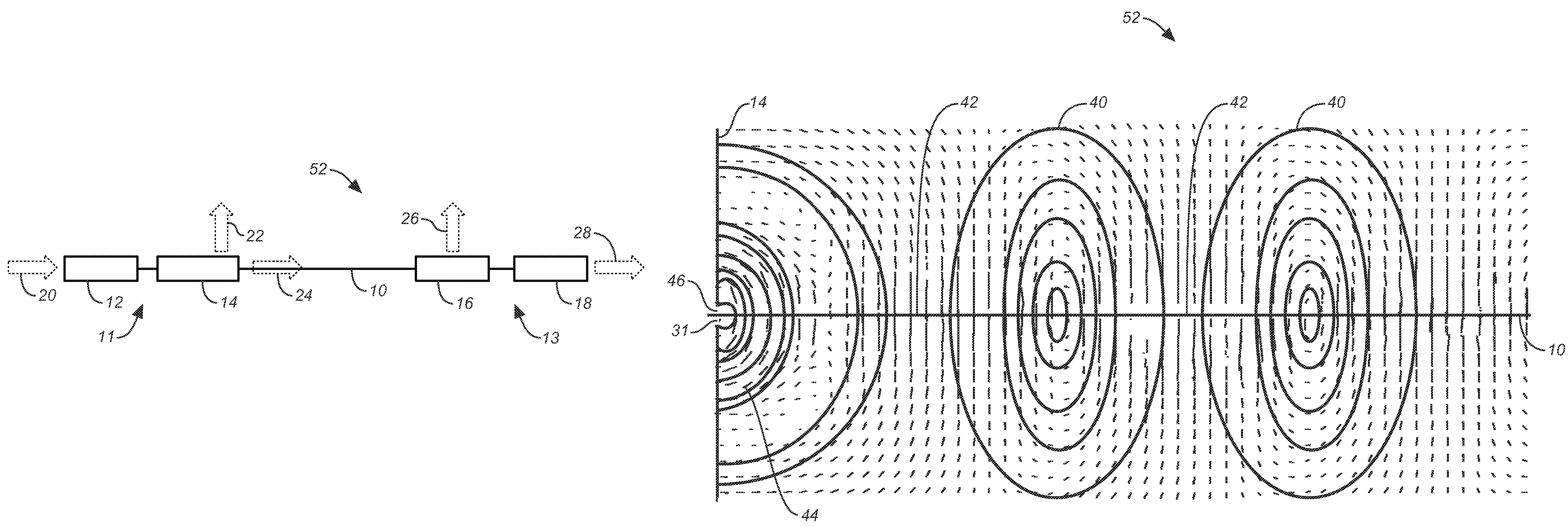
Surface wave transmission system over a single conductor having E-fields terminating along the conductor
ActiveUS7567154B2Reduce energy costsEnable economicMultiple-port networksWaveguidesElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
A low attenuation surface wave transmission line system for launching surface waves on a bare and unconditioned conductor, such as are found in abundance in the power transmission lines of the existing power grids. The conductors within the power grid typically lack dielectric and special conditioning. Accordingly, the present invention includes a first launcher, preferably including a mode converter and an adapter, for receiving an incident wave of electromagnetic energy and propagating a surface wave longitudinally on the power lines. The system includes at least one other launcher, and more likely a number of other launchers, spaced apart from one another along the constellation of transmission lines. The system and associated electric fields along any given conductor are radially and longitudinally symmetrical.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
System and apparatus for transmitting a surface wave over a single conductor
ActiveUS20080211727A1Reduce radiationSmall sizeWaveguide hornsMultiple-port networksElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
A low attenuation surface wave transmission line system for launching surface waves on a bare and unconditioned conductor, such as are found in abundance in the power transmission lines of the existing power grids. The conductors within the power grid typically lack dielectric and special conditioning. Accordingly, the present invention includes a first launcher, preferably including a mode converter and an adapter, for receiving an incident wave of electromagnetic energy and propagating a surface wave longitudinally on the power lines. The system includes at least one other launcher, and more likely a number of other launchers, spaced apart from one another along the constellation of transmission lines. The system and associated electric fields along any given conductor are radially and longitudinally symmetrical.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
Materials for use in electrophoretic displays
The image stability of electrophoretic media, comprising a plurality of particles disposed in a fluid and capable of moving through the fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium, can be improved by including in the fluid either a polystyrene or an aggregating diblock copolymer which forms micelle-like structures in the fluid, the diblock copolymer having a first block soluble in the fluid and a second block not swellable by the fluid. In variable transmission electrophoretic media, haze can be reduced by using as the fluid a mixture of a partially hydrogenated aromatic hydrocarbon and a terpene.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS20110204119A1Reduce mechanical wearMinimized in sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsLinear motionCapacitance
A surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument are disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A motion sensor senses a change in the electric field (e.g., capacitance, impedance, or admittance) between the firing rod and the elongated shaft. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position, speed, and direction of the firing rod, based on the sensed change in the electric field. A controller uses the measured parameter of the motion of the firing rod to control the drive mechanism.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
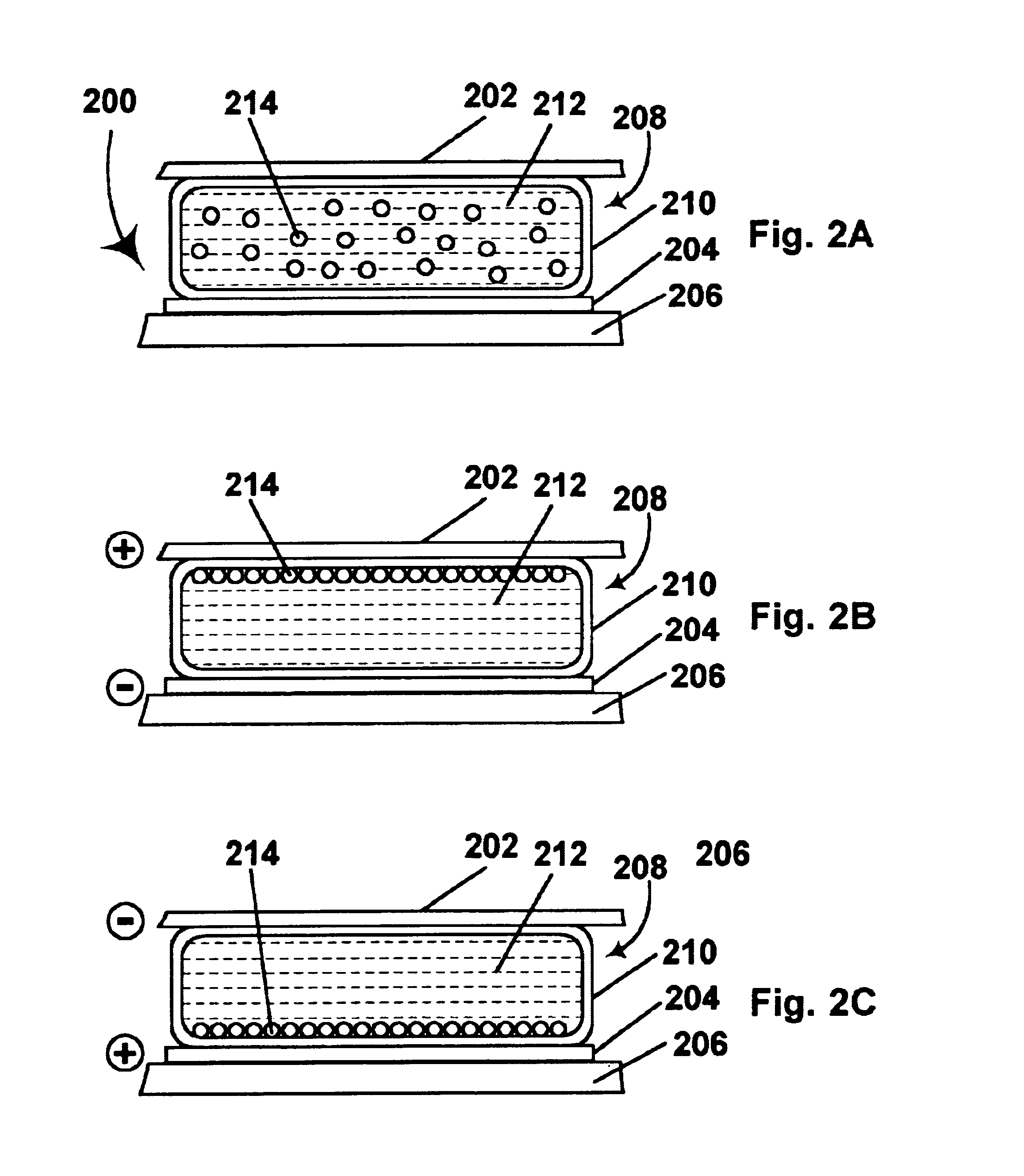
Dielectrophoretic displays
A dielectrophoretic display comprises a substrate having walls defining at least one cavity, the cavity having a viewing surface and a side wall inclined to the viewing surface; a suspending fluid contained within the cavity; a plurality of at least one type of particle suspended within the suspending fluid; and means for applying to the substrate an electric field effect effective to cause dielectrophoretic movement of the particles to the side wall of the cavity.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Read operation for non-volatile storage that includes compensation for coupling
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
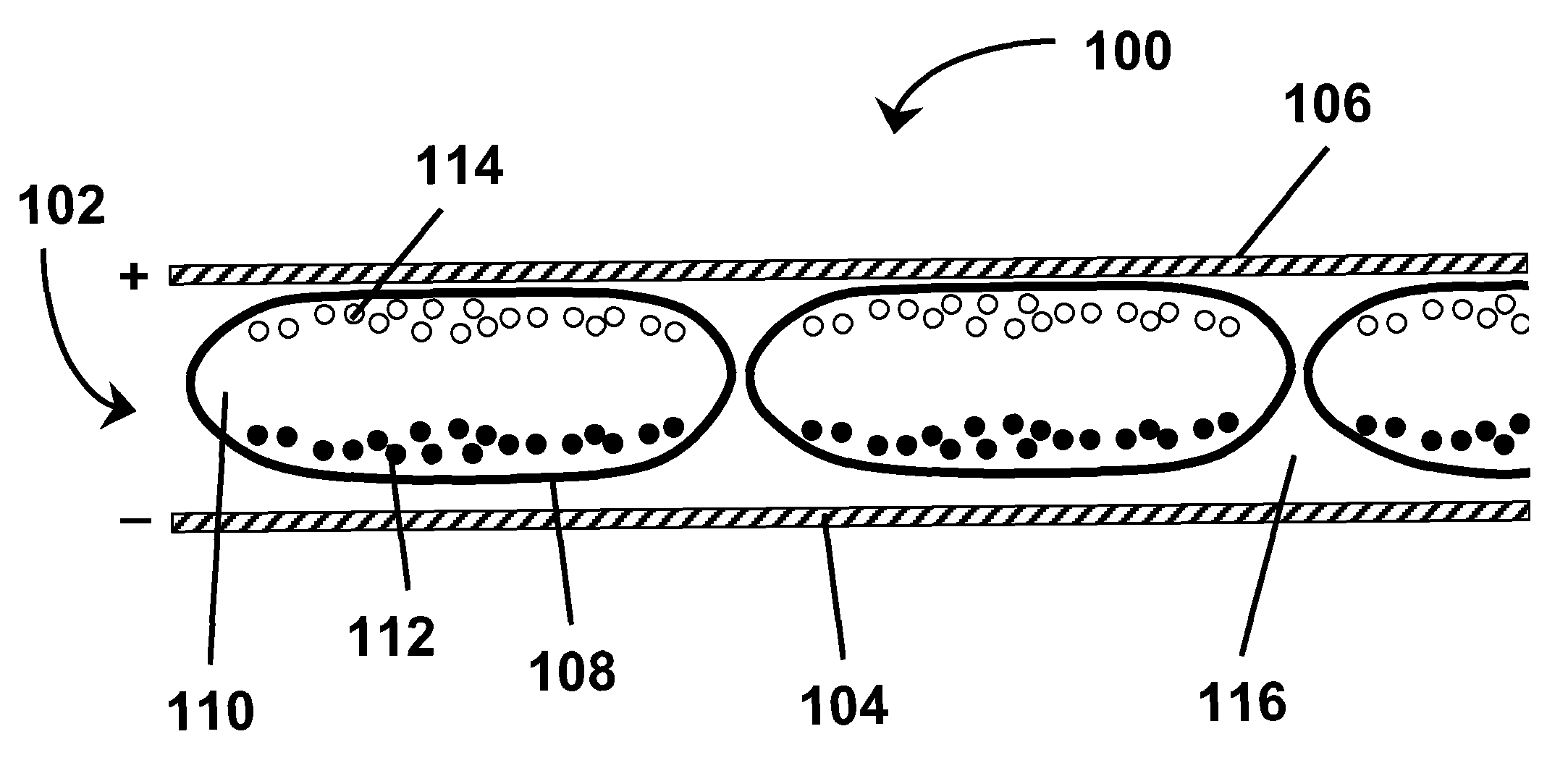
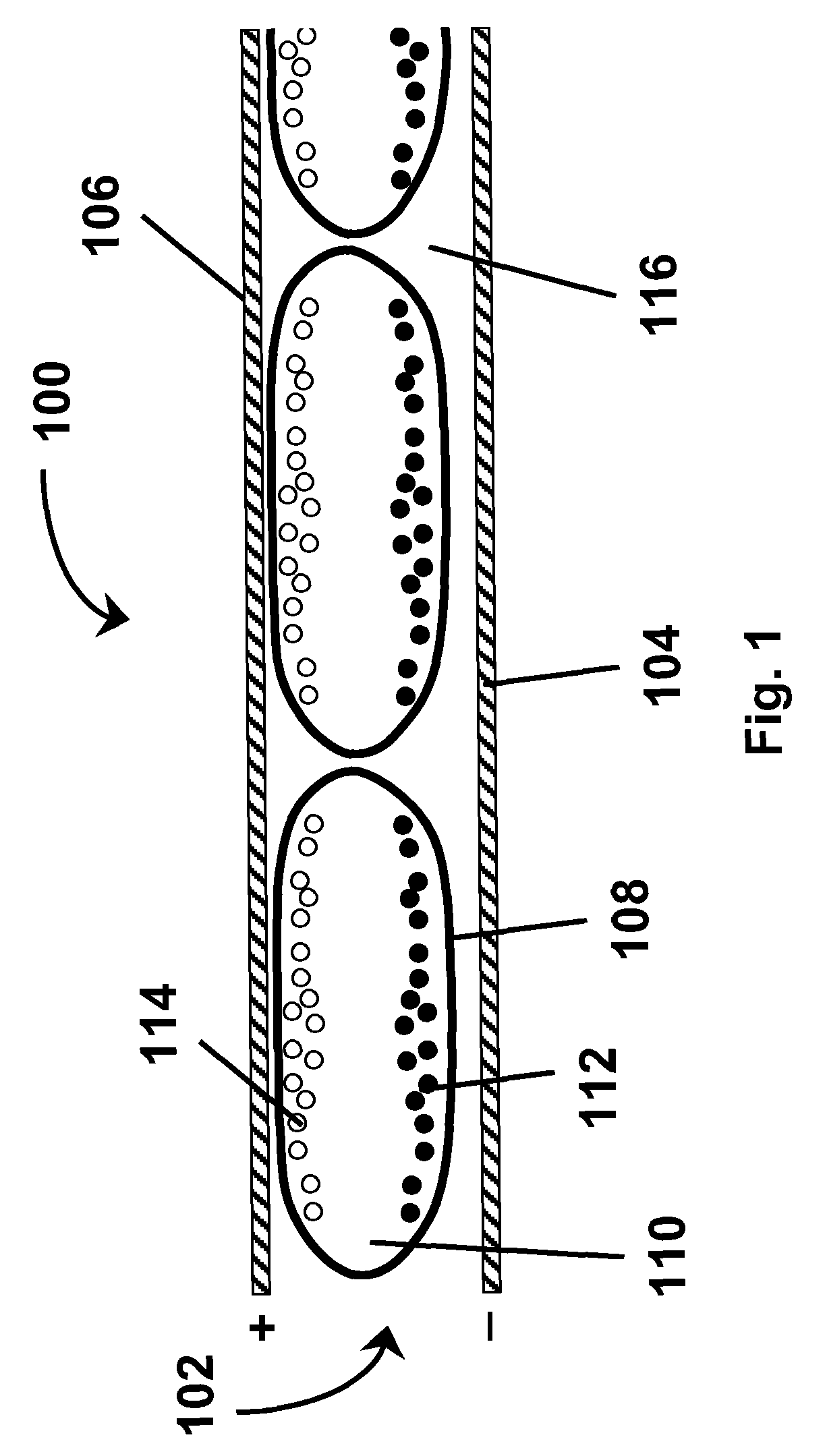
Electrophoretic displays containing magnetic particles
InactiveUS6870661B2Easy to fallImprove stabilitySludge treatmentStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisDisplay device
An electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of one or more types of particles suspended in a suspending fluid. The particles include at least one electrically charged, electrophoretically mobile particle capable of translating through the suspending fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium and at least one magnetic particle. A magnet is disposed adjacent the electrophoretic medium to introduce a threshold resistance to magnetic particle movement.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Power transmission network
ActiveUS7844306B2Augment an internal batteryEliminate needBatteries circuit arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsElectric power transmissionWireless transmission
A network for power transmission to a receiver that converts the power into current includes a first node for transmitting power wirelessly in a first area. The first area has a minimum electric or magnetic field strength. The network includes a second node for transmitting power wirelessly in a second area. The second area has a minimum electric or magnetic field strength and overlaps the first area to define an overlap area. In another embodiment, the network includes a source in communication with the first and second nodes which provides power to them. Also disclosed are methods for power transmission to a receiver that converts the power into current.
Owner:POWERCAST
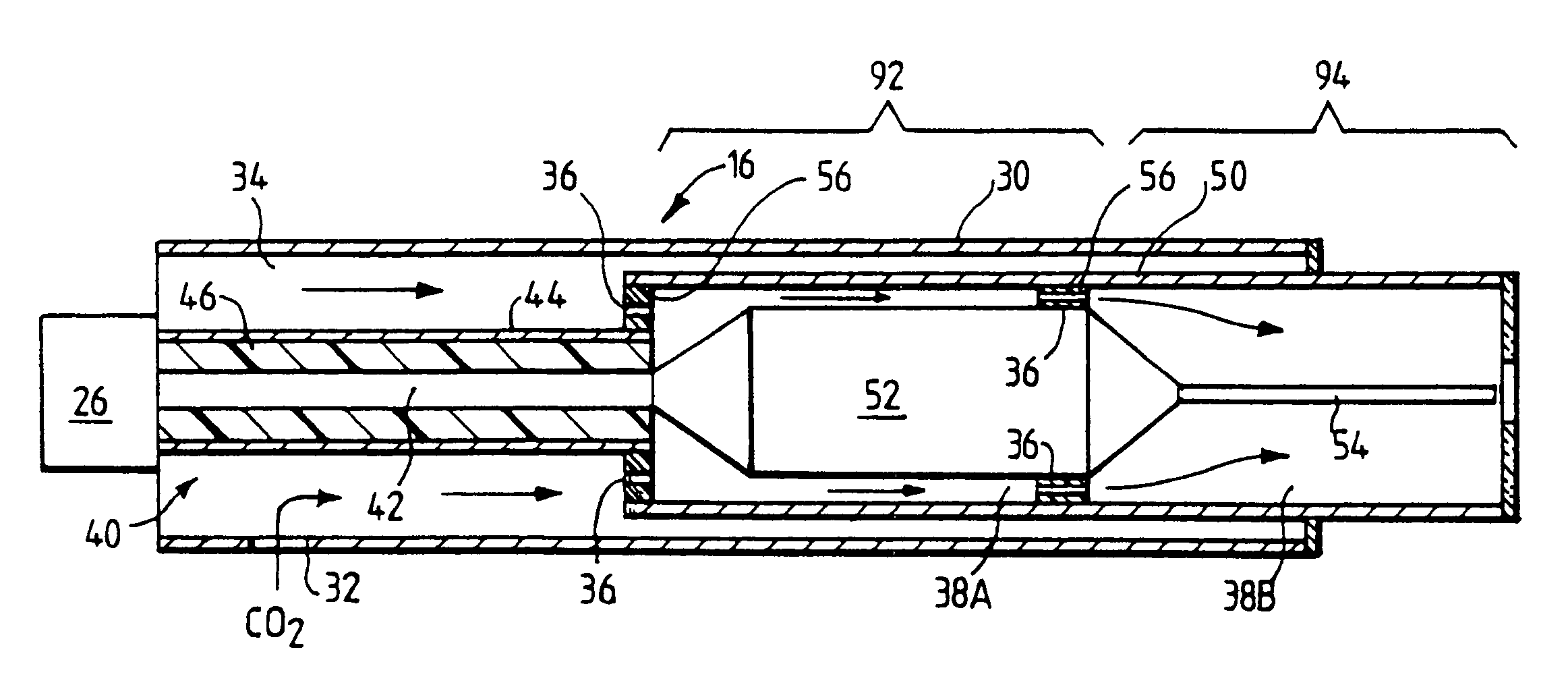
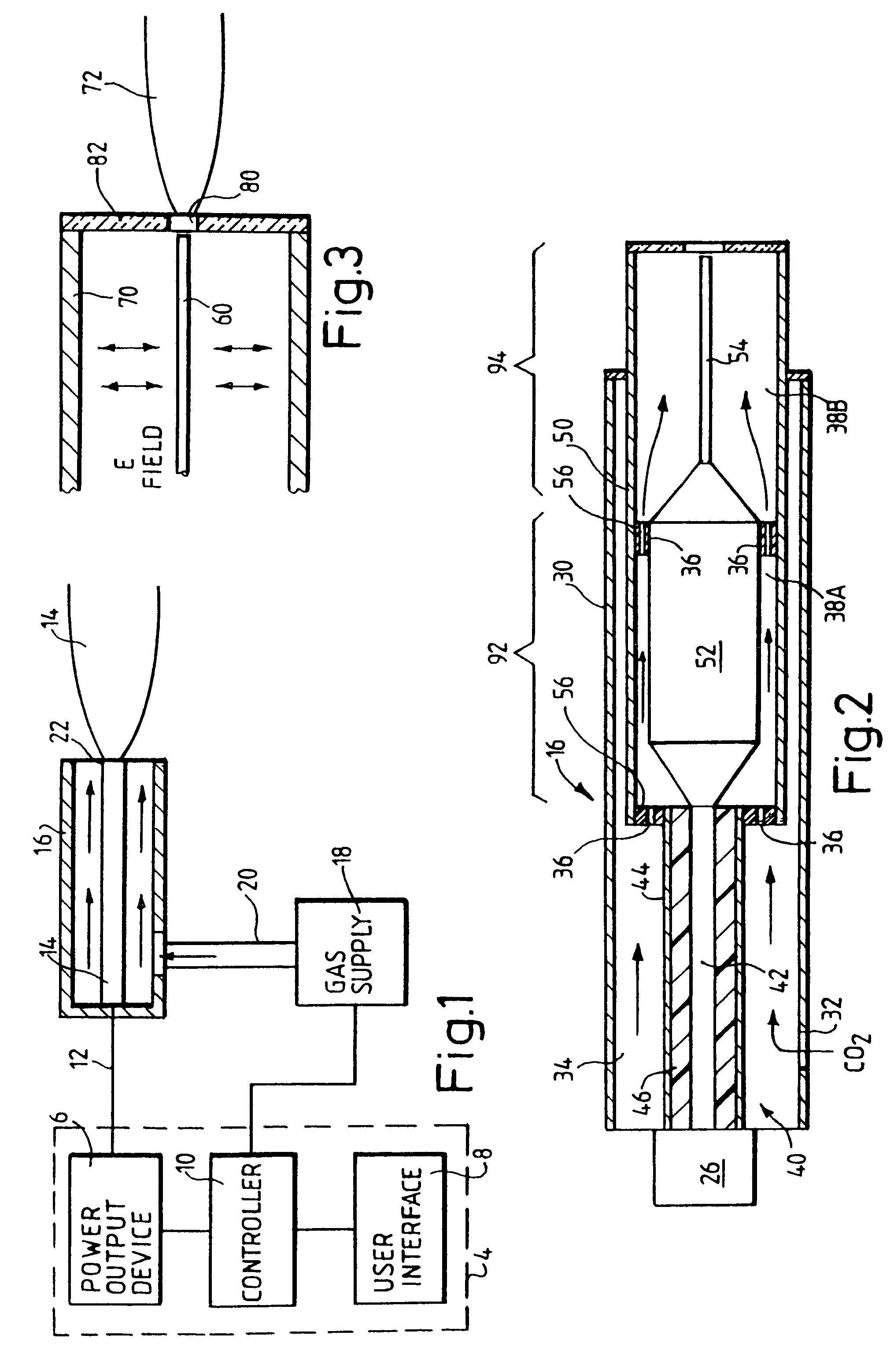
Dynamic heating method and radio frequency thermal treatment
A method and system for the delivery of radiofrequency energy to the tissue, particularly, the prostate, to alleviate the symptoms of BPH is disclosed. The system incorporates a bipolar or multipolar electrode array to create an electric field where the heat created is confined solely to a specific volume of the prostate gland and therefore the heated tissue is defined only by the electrode geometry. The bipolar electrode array provides a variety of three dimensional, symmetric heating patterns within the prostatic tissue depending on the relative electrode lengths and angular separation. The system provides precision tissue temperature and impedance measurements thereby enabling the surgeon to accurately predict heating pattern performance and tissue response to RF heating.
Owner:KASEVICH RAYMOND S
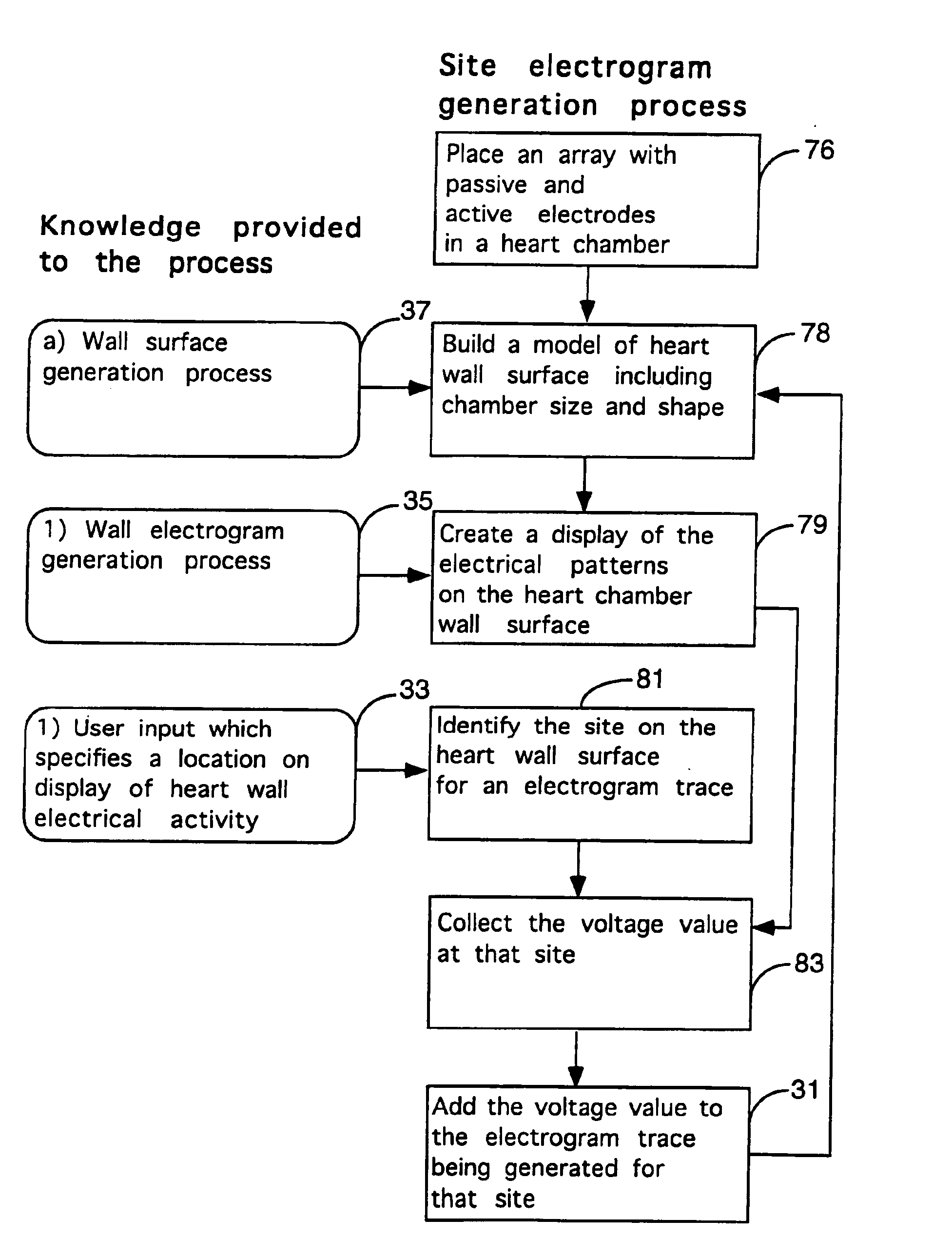
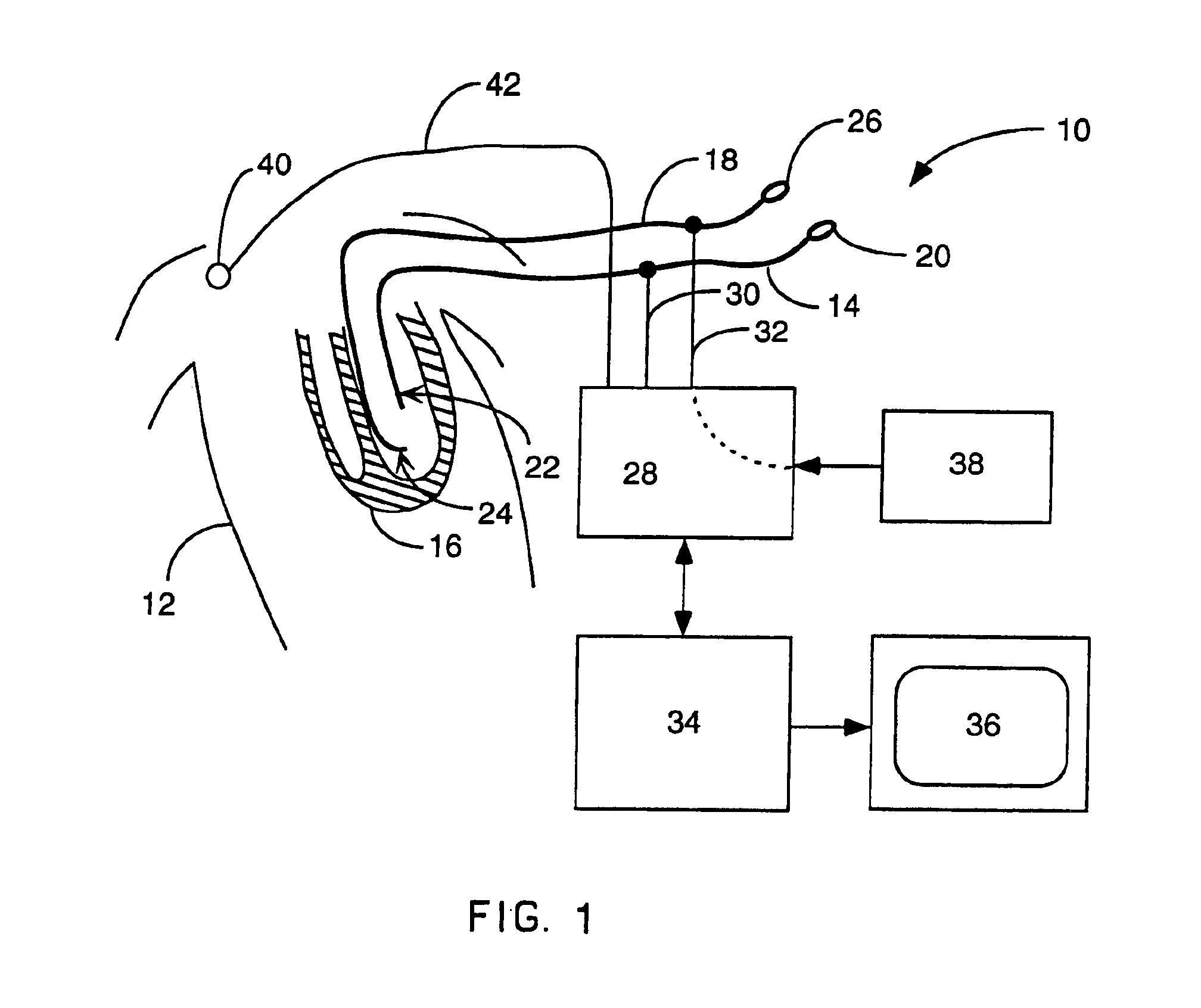
Method for mapping heart electrophysiology
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Semiconductor device
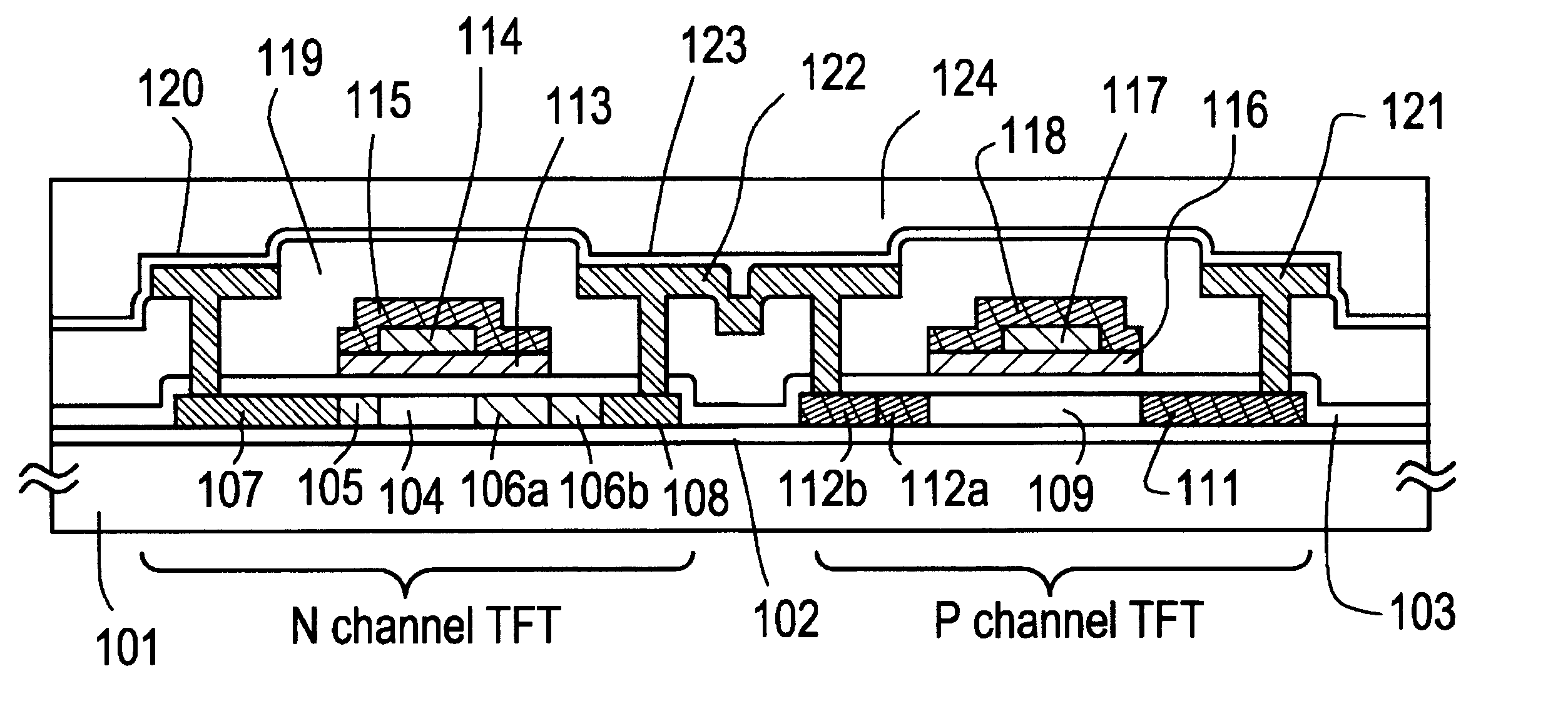
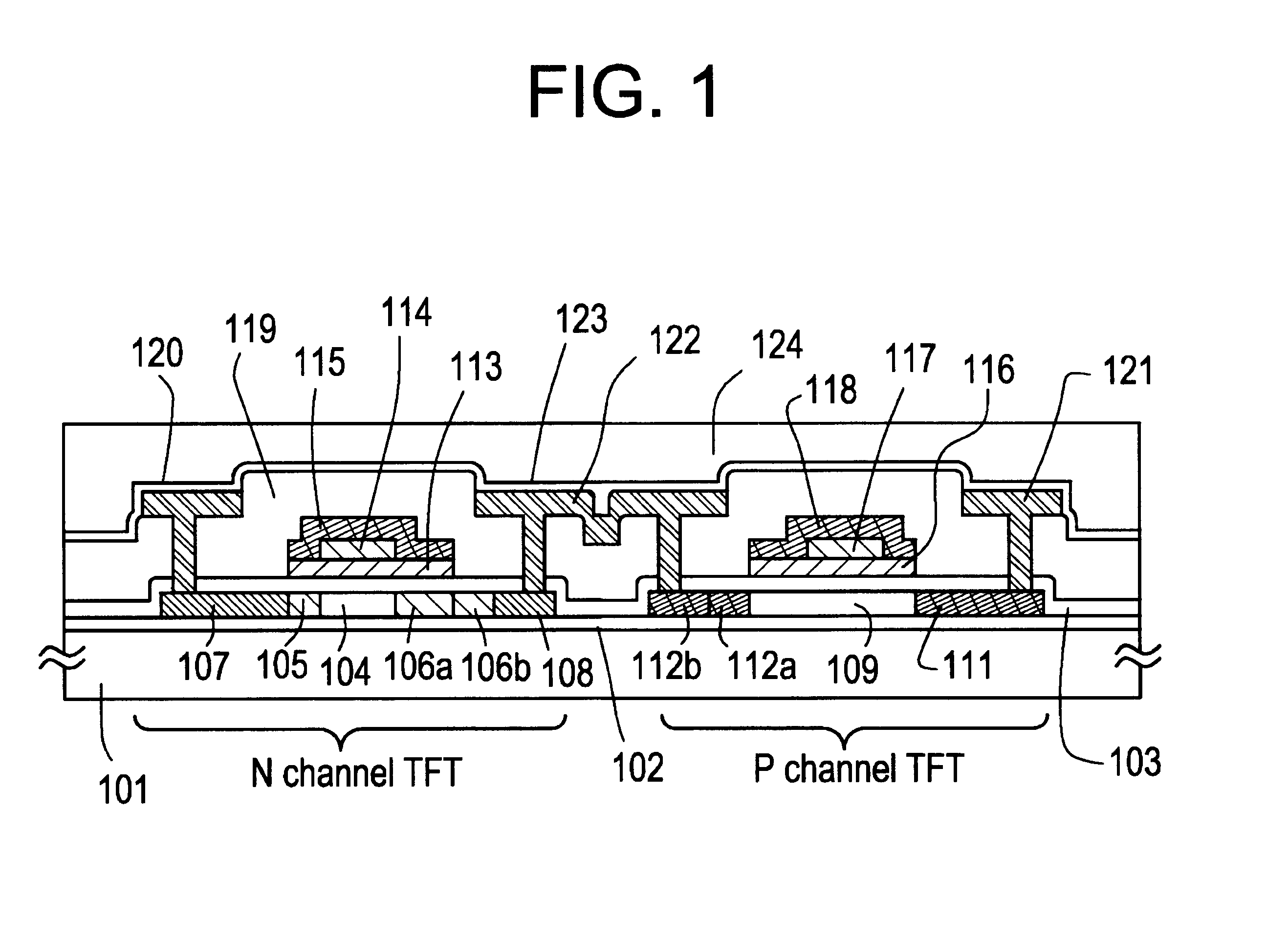
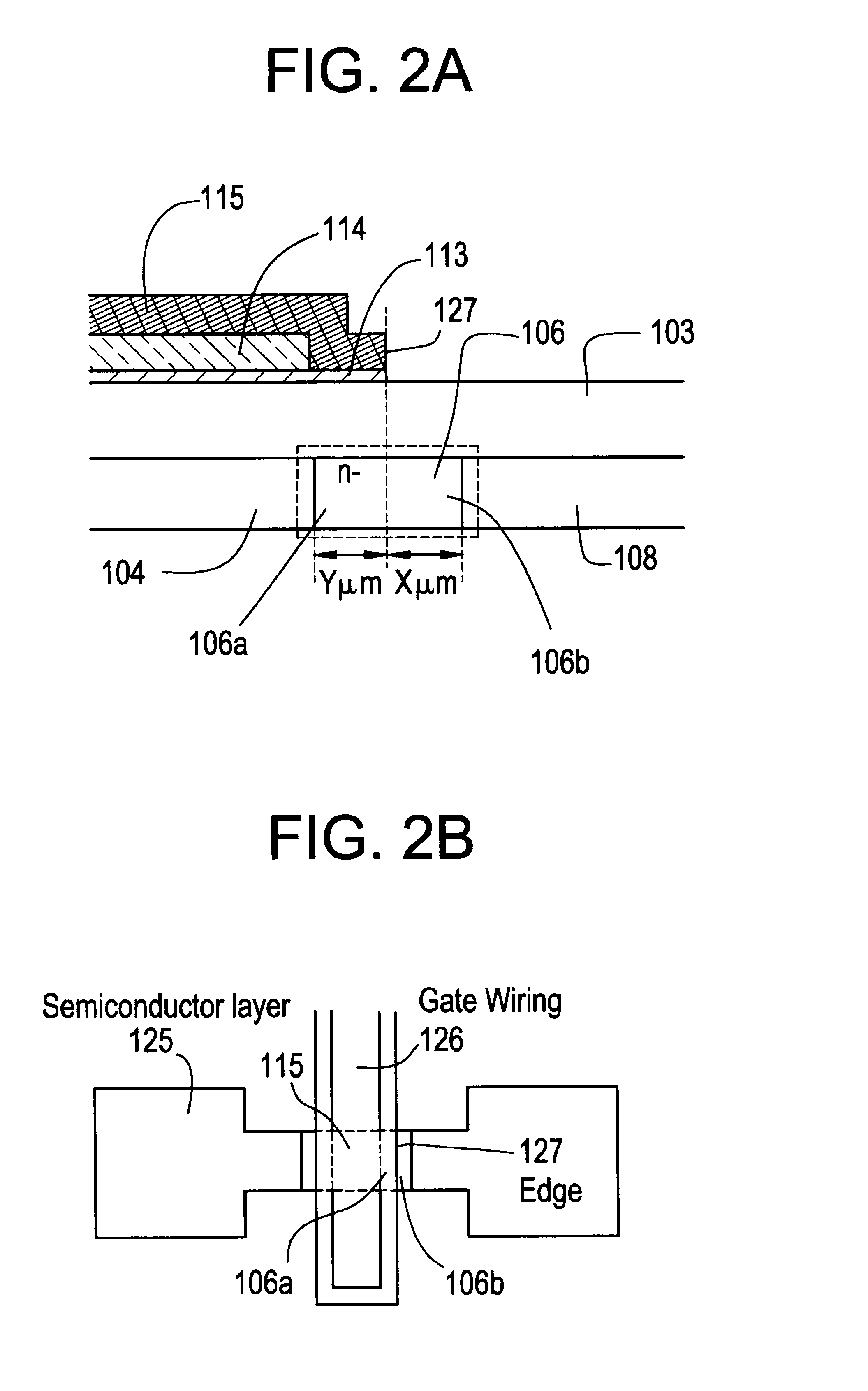
The gate electrode of a crystalline TFT is constructed as a clad structure which consists of a first gate electrode, a second gate electrode and a third gate electrode, thereby to enhance the thermal resistance of the gate electrode. Besides, an n-channel TFT is provided with a low-concentration impurity region which adjoins a channel forming region, and which includes a subregion overlapped by the gate electrode and a subregion not overlapped by the gate electrode, thereby to mitigate a high electric field near the drain of the TFT and to simultaneously prevent the OFF current of the TFT from increasing.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Compensating for coupling during read operations on non-volatile memory
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Microwave ablation catheter with loop configuration
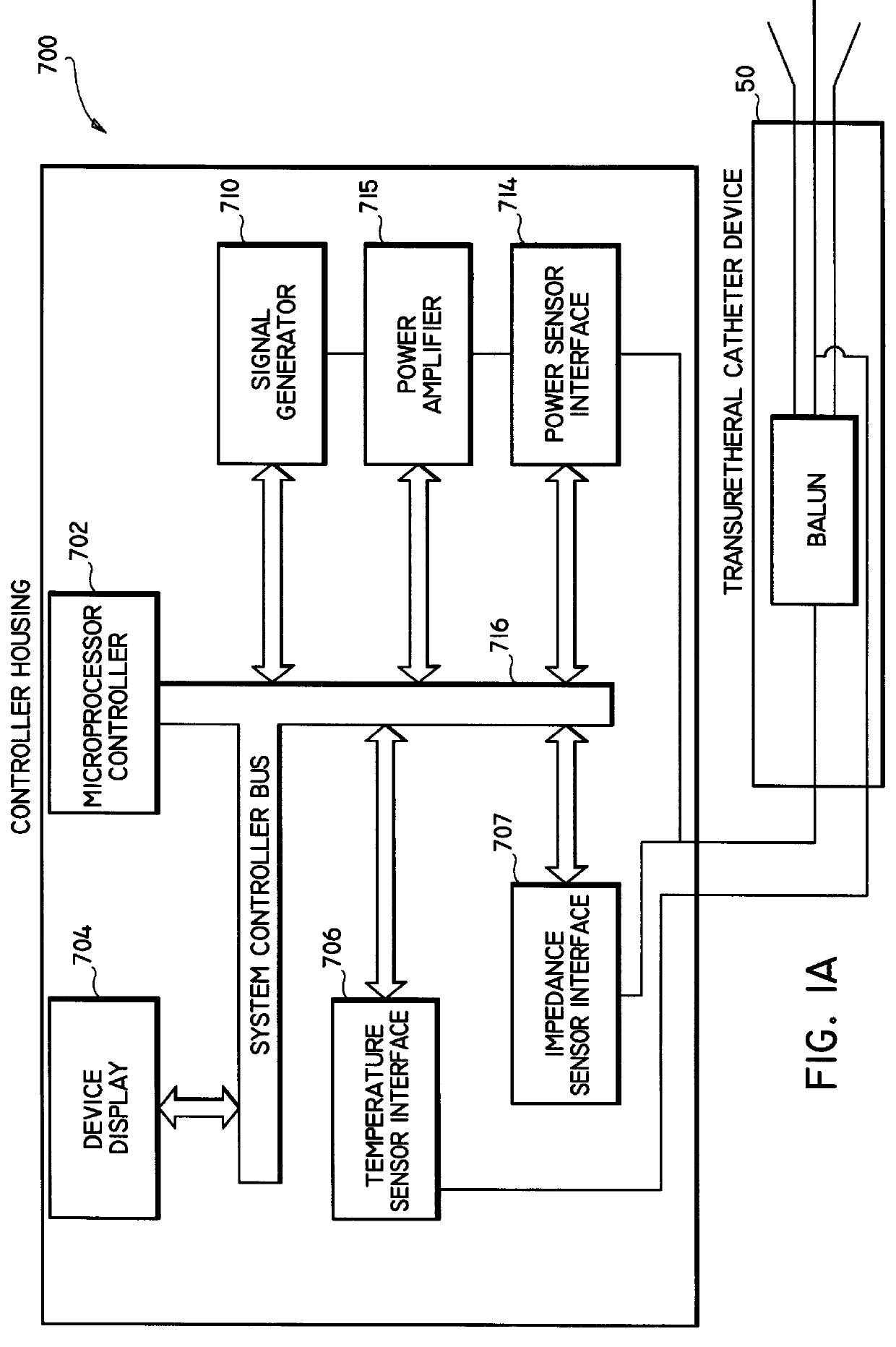
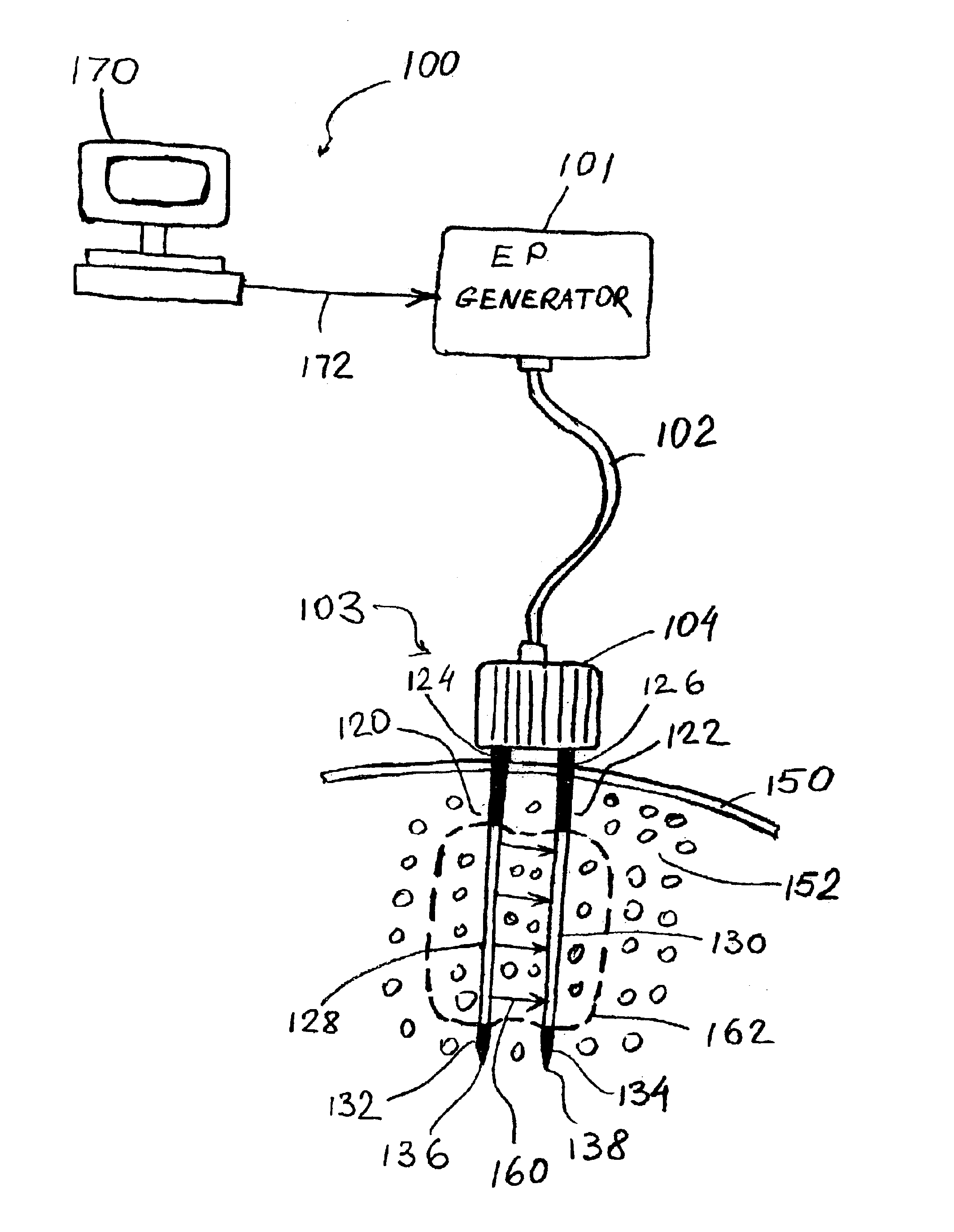
A catheter which may be configured as a loop during an ablation procedure, and a method of use for such a catheter, are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, an ablation catheter includes a flexible distal member arranged to inserted into a first vessel in the body of a patient, and an elongated flexible tubular member with a distal portion which is coupled to a proximal portion of the flexible distal member. The elongated flexible tubular member has a flexibility that is greater than or equal to the flexibility of the flexible distal member. The catheter also includes a transmission line which is at least partially disposed within the elongated flexible tubular member. A proximal end of the transmission line is suitable for connection to an electromagnetic energy source. The catheter further includes a transducer that is coupled to the transmission line, and is arranged to generate an electric field sufficiently strong to cause tissue ablation. In one embodiment, a distal portion of the flexible distal member is arranged to protrude from a second vessel of the body of the patient while at least part of the elongated flexible tubular member is located in a cardiac chamber of the heart of the patient.
Owner:AFX
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveCN102217961AFrequency increase or decreaseDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsLinear motionCapacitance
The invention discloses a surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument, especially discloses a method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A motion sensor senses a change in the electric field (e.g., capacitance, impedance, or admittance) between the firing rod and the elongated shaft. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position, speed, and direction of the firing rod, based on the sensed change in the electric field. A controller uses the measured parameter of the motion of the firing rod to control the drive mechanism.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Acrylic microchannels and their use in electrophoretic applications
Microchannels having at least an acrylic inner surface and methods of their use in electrophoretic applications are provided. The subject microchannels may be in the form of a variety of configurations suitable for holding an electrophoretic medium. The subject microchannels give rise to substantially reduced EOF and / or adsorption as compared to fused silica under conditions of electrophoresis and find use in a variety of electrophoretic applications in which charged entities are moved through a medium under the influence of the an applied electric field.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Electrophoretic medium and display with improved image stability
InactiveUS20020180687A1Improve imaging stabilityExtend switching timeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsPolymer scienceElectrophoresis
An electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of particles suspended in a suspending fluid, the particles being capable of moving through the fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium, the fluid having dissolved or dispersed therein a polymer having a number average molecular weight in excess of about 20,000, the polymer being essentially non-absorbing on the particles. The polymer improves the bistability of the display (i.e., the period for which a written image persist without the display being refreshed) but does not greatly increase the viscosity of the suspending fluid, thus keeping the switching time of the display within reasonable limits. The medium may be encapsulated, or may be in the form a polymer-dispersed electrophoretic medium.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
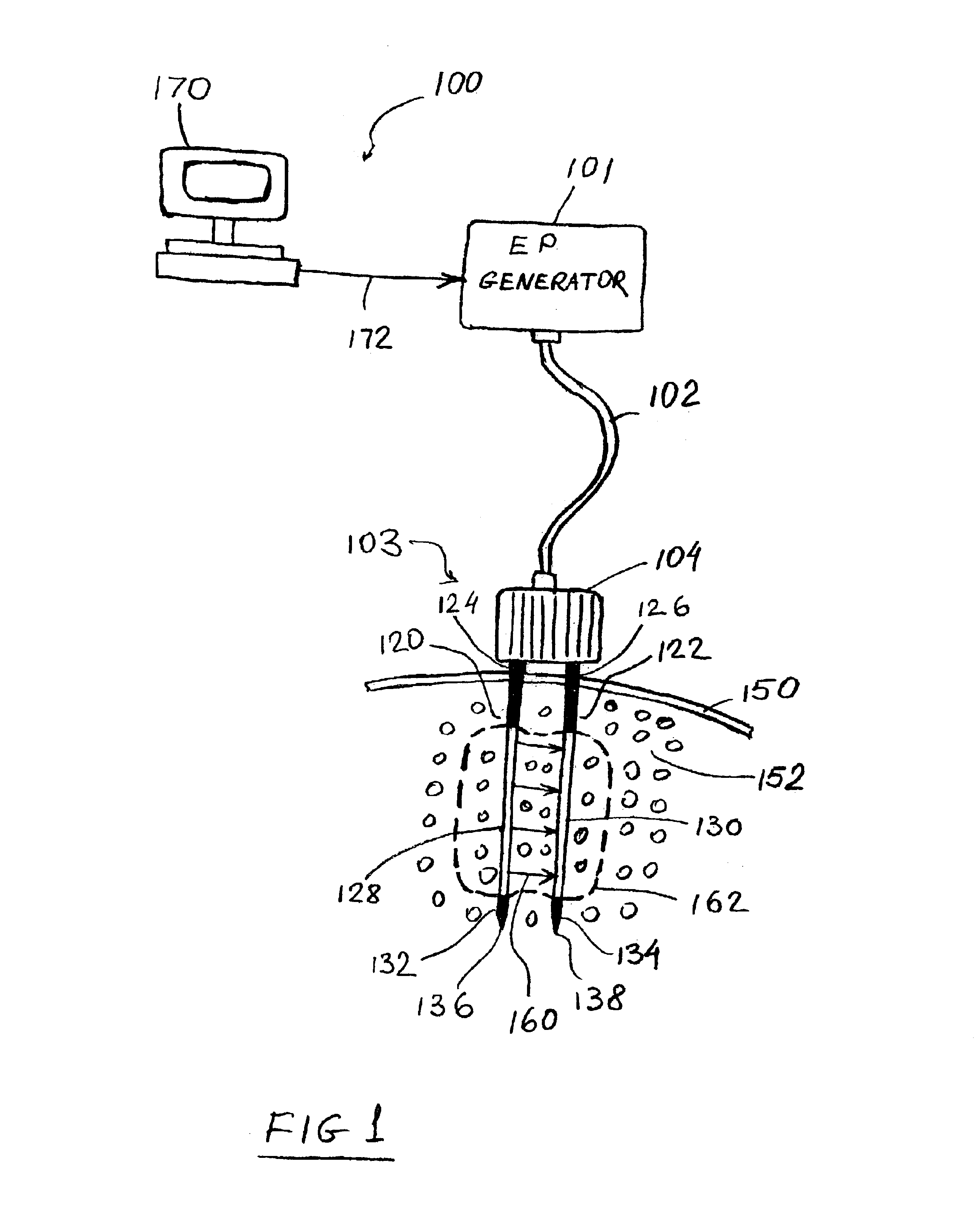
Apparatus and method for reducing subcutaneous fat deposits by electroporation
InactiveUS6795728B2Surgical instrument detailsSkin piercing electrodesReduced subcutaneous fatInvasive treatments
An apparatus and method for minimally invasive treatment of deep subcutaneous fat deposits in lieu of cosmetic surgery is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a high voltage pulse generator connected to two or more needle electrodes at least one of which is configured for placement deeply under the skin in a treatment site of the patient's body. High voltage pulses, delivered to the electrodes, create an electric field that kills subcutaneous fat cells.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Methods for driving electrophoretic displays using dielectrophoretic forces
InactiveUS7999787B2Static indicating devicesLight protection screensElectrophoresisDielectrophoretic force
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com